
Easy as 1-2-3!
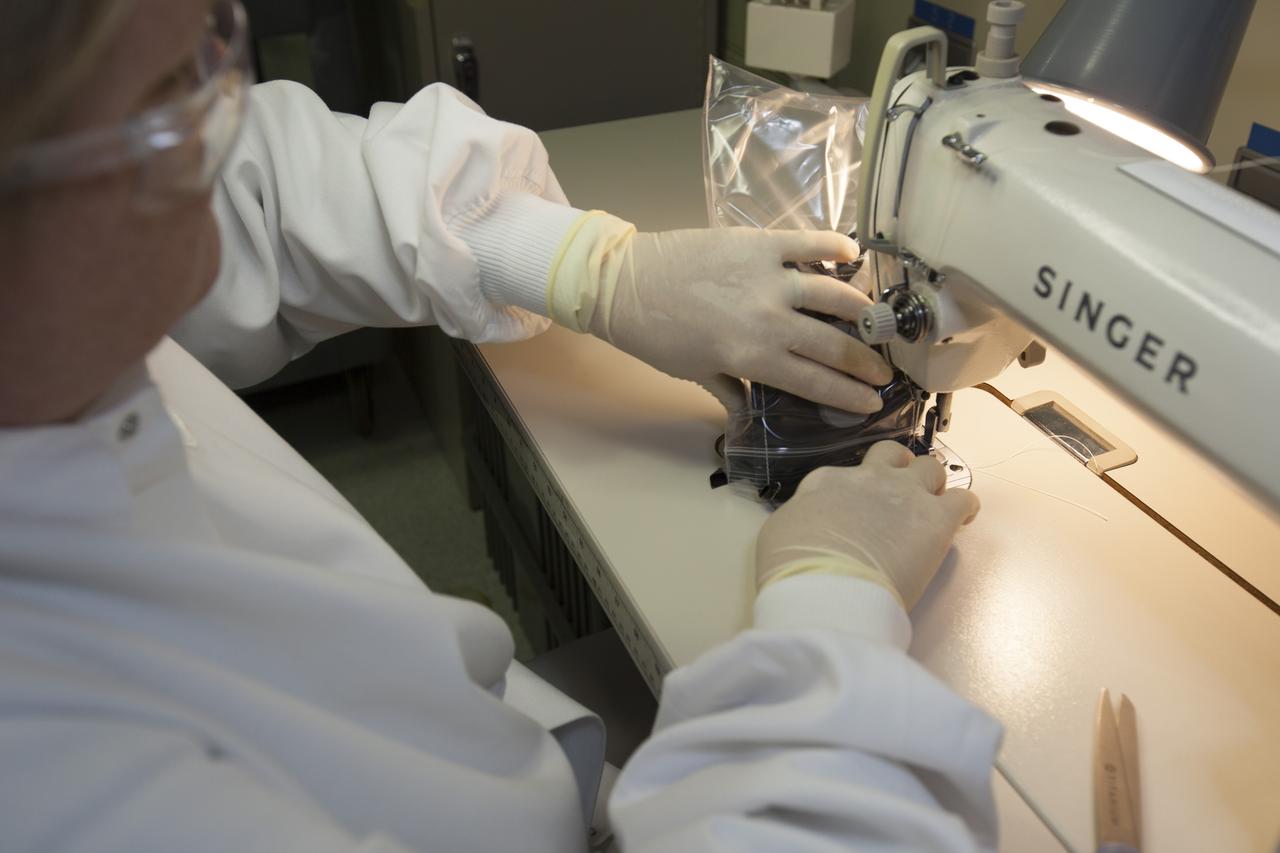

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Michele Koralewicz, a mechanical technician with EASI on the Engineering Services Contract, sews up the end of a bag that contains one of the Veg-03 plant pillows. The Veg-03 experiment will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard the eighth SpaceX Dragon commercial resupply mission. The Veg-03 plant pillows will contain ‘Tokyo Bekana’ cabbage seeds and lettuce seeds for NASA’s third Veggie plant growth system experiment. The experiment will continue NASA’s deep space plant growth research to benefit the Earth and the agency’s journey to Mars.

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Michele Koralewicz, a mechanical technician with EASI on the Engineering Services Contract, sews up the end of a bag that contains one of the Veg-03 plant pillows. The Veg-03 experiment will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard the eighth SpaceX Dragon commercial resupply mission. The Veg-03 plant pillows will contain ‘Tokyo Bekana’ cabbage seeds and lettuce seeds for NASA’s third Veggie plant growth system experiment. The experiment will continue NASA’s deep space plant growth research to benefit the Earth and the agency’s journey to Mars.
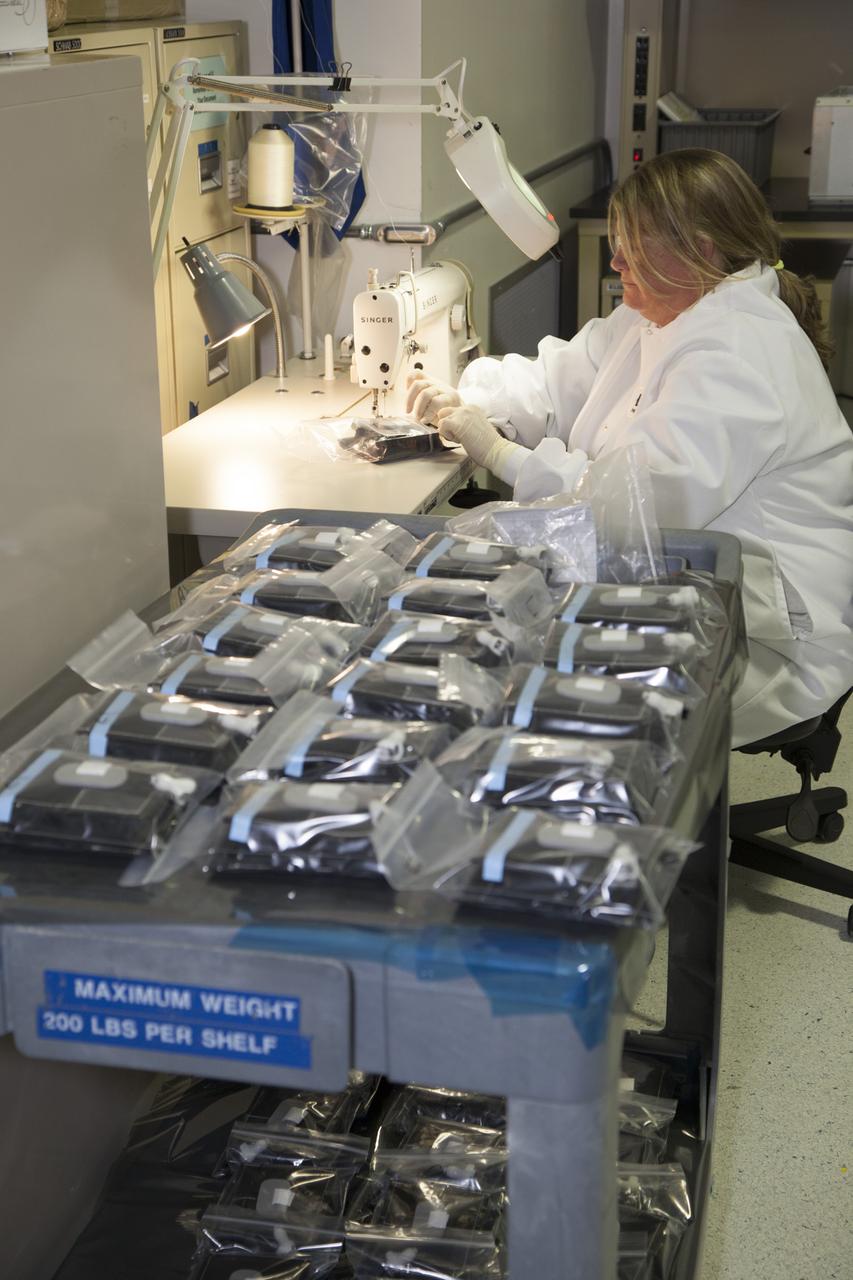

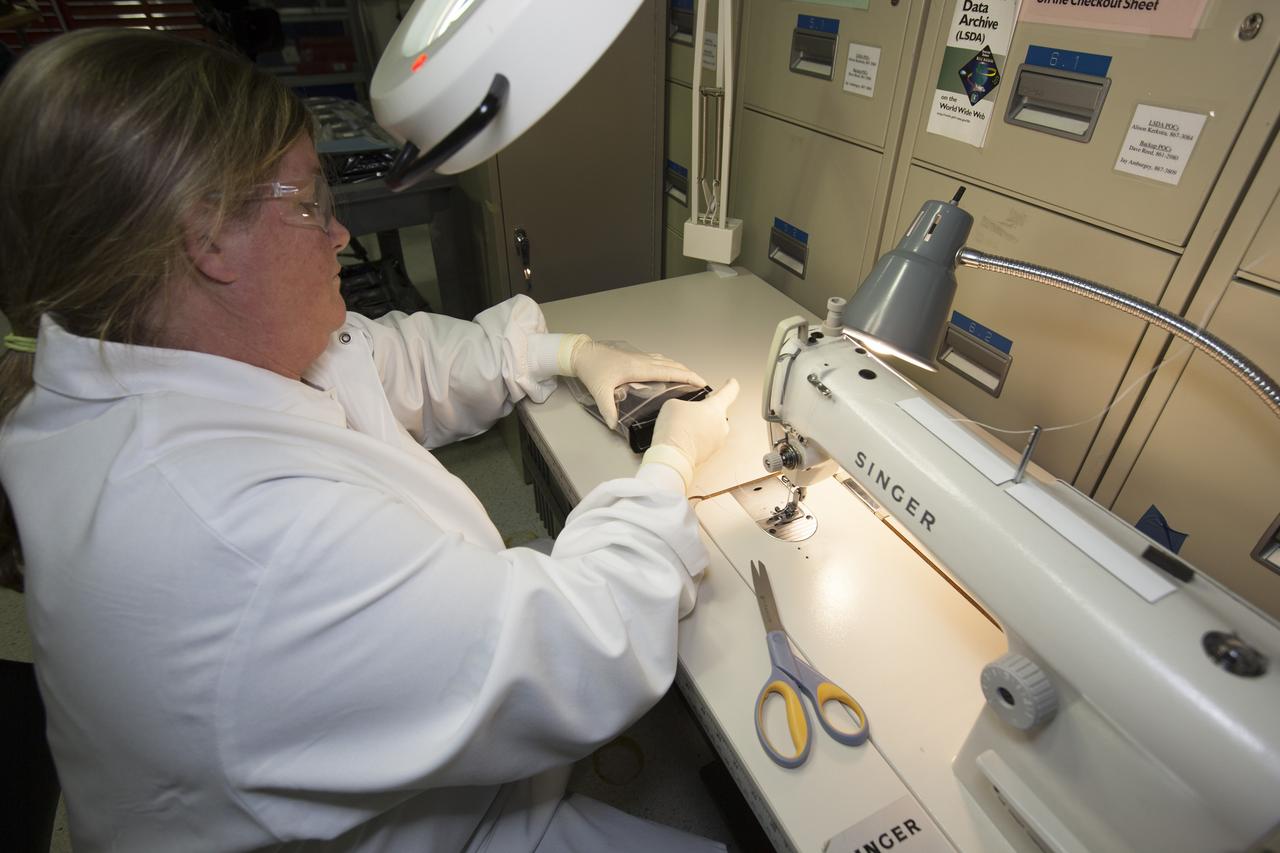
Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Michele Koralewicz, a mechanical technician with EASI on the Engineering Services Contract, prepares to sew up the end of a bag that contains one of the Veg-03 plant pillows. In the foreground are all of the other plant pillows that need to be sealed. The Veg-03 experiment will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard the eighth SpaceX Dragon commercial resupply mission. The Veg-03 plant pillows will contain ‘Tokyo Bekana’ cabbage seeds and lettuce seeds for NASA’s third Veggie plant growth system experiment. The experiment will continue NASA’s deep space plant growth research to benefit the Earth and the agency’s journey to Mars.
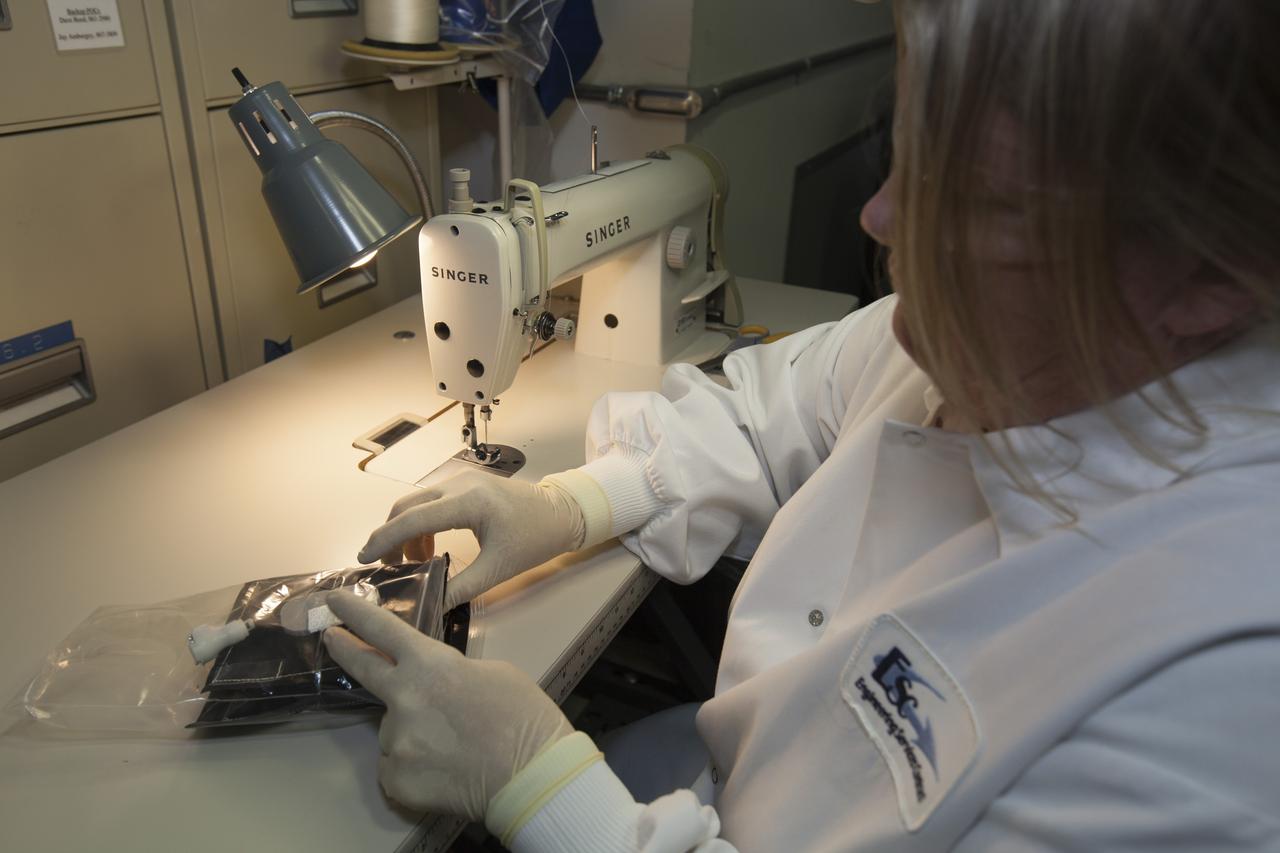

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Michele Koralewicz, a mechanical technician with EASI on the Engineering Services Contract, prepares to sew the end of a bag that contains one of the Veg-03 plant pillows. The Veg-03 experiment will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard the eighth SpaceX Dragon commercial resupply mission. The Veg-03 plant pillows will contain ‘Tokyo Bekana’ cabbage seeds and lettuce seeds for NASA’s third Veggie plant growth system experiment. The experiment will continue NASA’s deep space plant growth research to benefit the Earth and the agency’s journey to Mars.

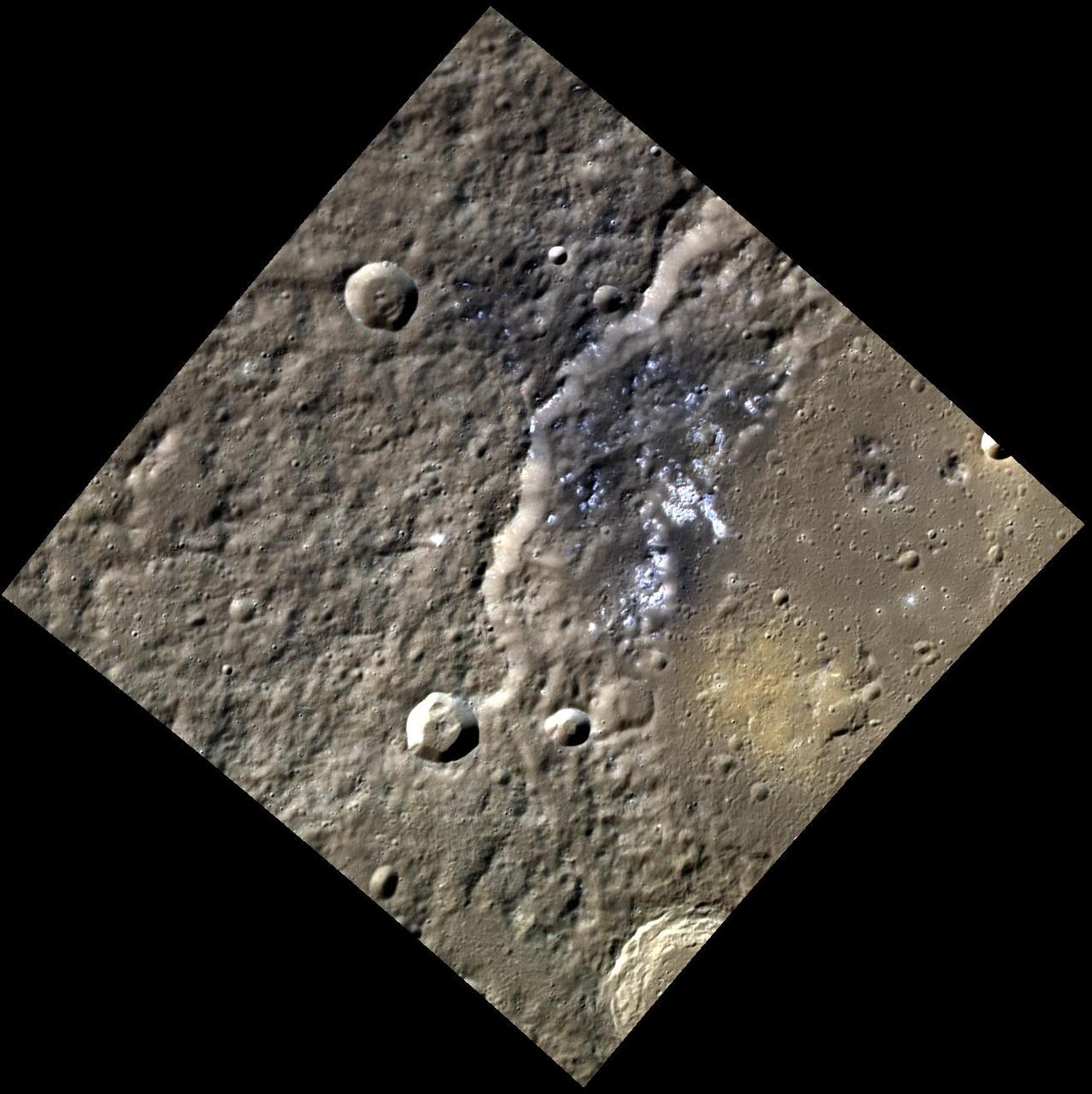
Layering in south polar ice is easy to see in this outlier of the main polar cap. This image was captured by NASA Mars Odyssey.

Rhea displays a marked color contrast from north to south that is particularly easy to see in the extreme color-enhanced Cassini spacecraft view presented here
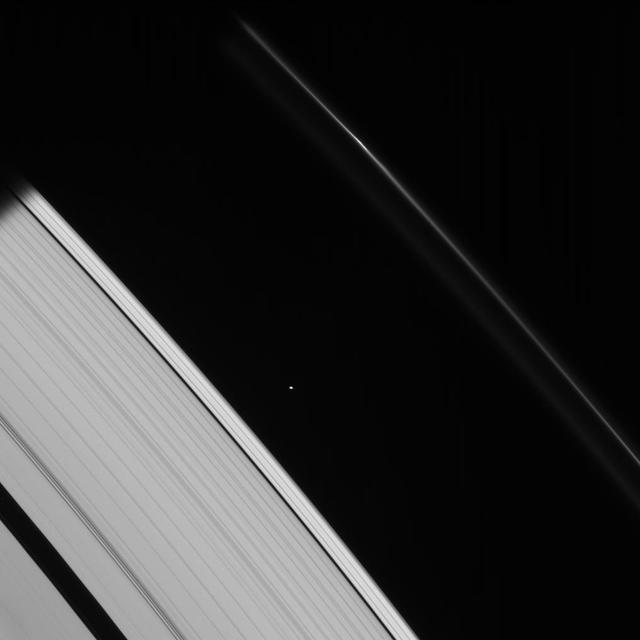

This strikingly crisp view shows Atlas heading into Saturn shadow at upper left. The moon basic, elongated shape is easy to detect here
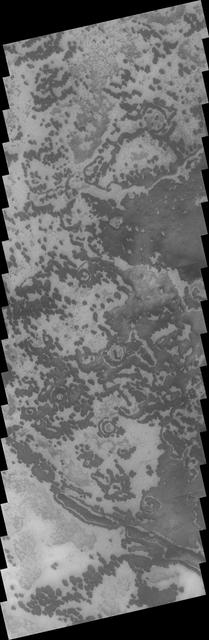
This VIS image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft of the south polar region was collected during the summer season. The markings of the pole are very diverse and easy to see after the winter frost has been removed.

With Saturn terminator as a backdrop, this view of the unlit face of the rings makes it easy to distinguish between areas that are actual gaps, where light passes through essentially unimpeded, and areas where the rings block or scatter light

It no easy task getting NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter ready for launch. Workers stabilize the crane holding one of the enormous billboard-sized solar panels temporarily removed from the spacecraft prior to rigorous testing.

The bizarre patterns on the floor of this crater in Nilosyrtis Mensae imaged by NASA Mars Odyssey defy an easy explanation. It is possible that some form of periglacial process combined with the vaporization of ground ice to form these patterns.
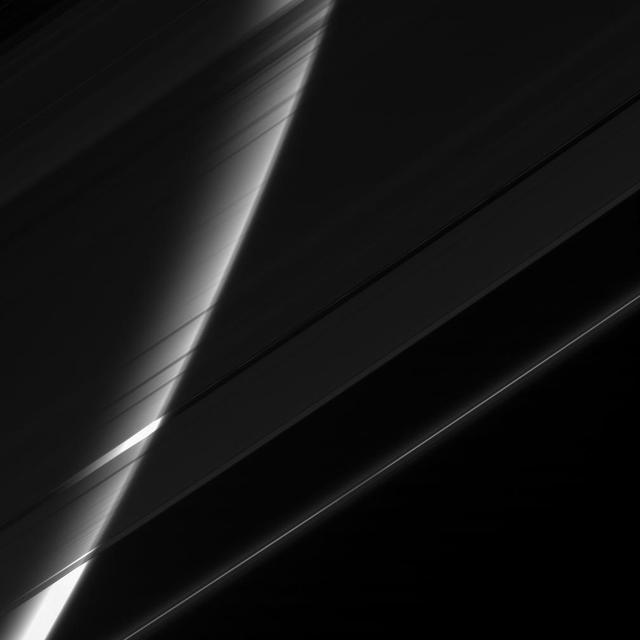
The Cassini spacecraft stares toward Saturn through its gauzy veil of rings. The great ice-particle screen acts like a filter here, attenuating the glare from the planet and making its high altitude haze easy to see
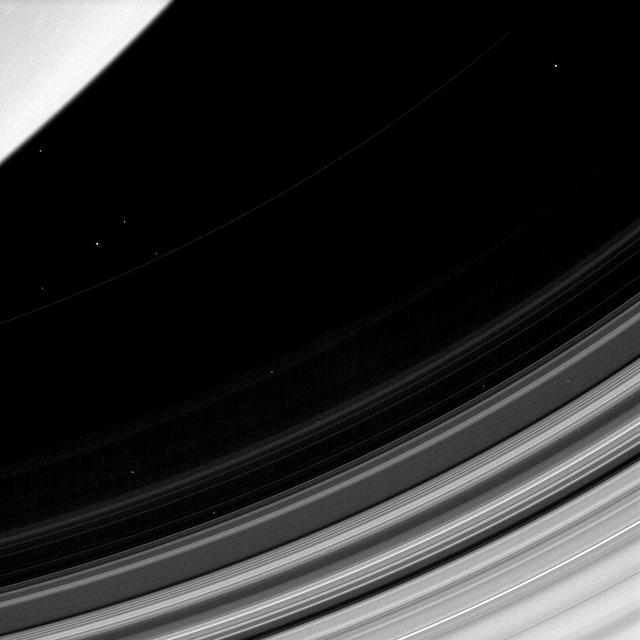

Saturn D ring is easy to overlook since it trapped between the brighter C ring and the planet itself. In this view from NASA Cassini spacecraft, all that can be seen of the D ring is the faint and narrow arc as it stretches from top right of the ima
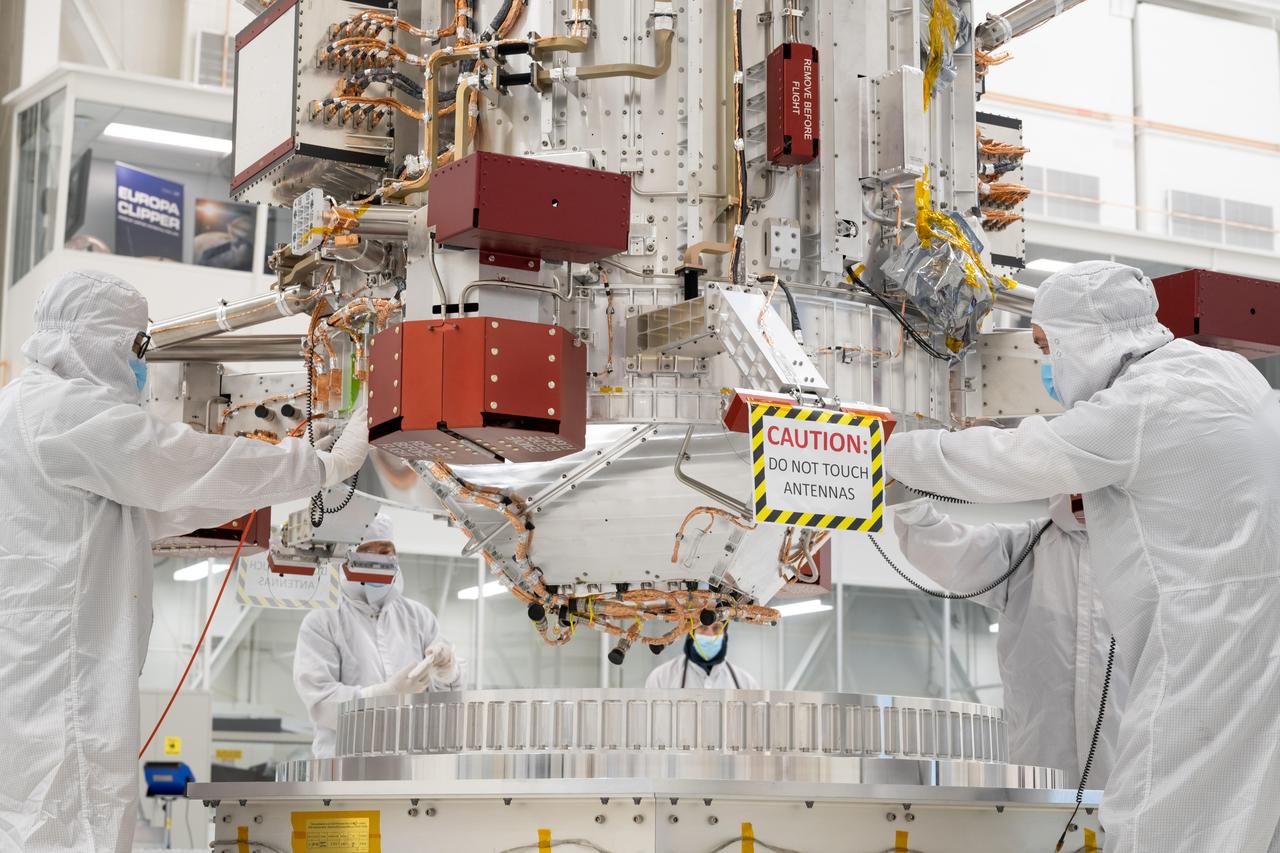
Engineers and technicians use a crane to lower the main body of NASA's Europa Clipper spacecraft into position in the High Bay 1 clean room of the Spacecraft Assembly Facility at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Standing 10 feet (3 meters) high and 5 feet (1.5 meters) wide, the core will be the focus of attention as the spacecraft is assembled for its launch to Jupiter's moon Europa in October 2024.This image was taken on Aug. 9, 2022. Europa Clipper will conduct nearly 50 flybys of the icy Jovian moon Europa, which scientists are confident harbors an internal ocean containing twice as much water as Earth's oceans combined. The moon may currently have conditions suitable for supporting life. The spacecraft's nine science instruments, plus a gravity science investigation, will gather data on the moon's atmosphere, surface, and interior – information that scientists will use to gauge the depth and salinity of the ocean, the thickness of the ice crust, and potential plumes that may be venting subsurface water into space. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25492

What's up and what's down? This image covers mesas, or high-standing plateaus, to the north and pits, or low-standing, depressions to the south. If it looks the other way around, then you are not seeing the topography correctly. Remember that the Sun is coming from the left (west) at MRO's imaging time of about 3 p.m. What formed these mesas and pits is a question that is not so easy to answer. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20812
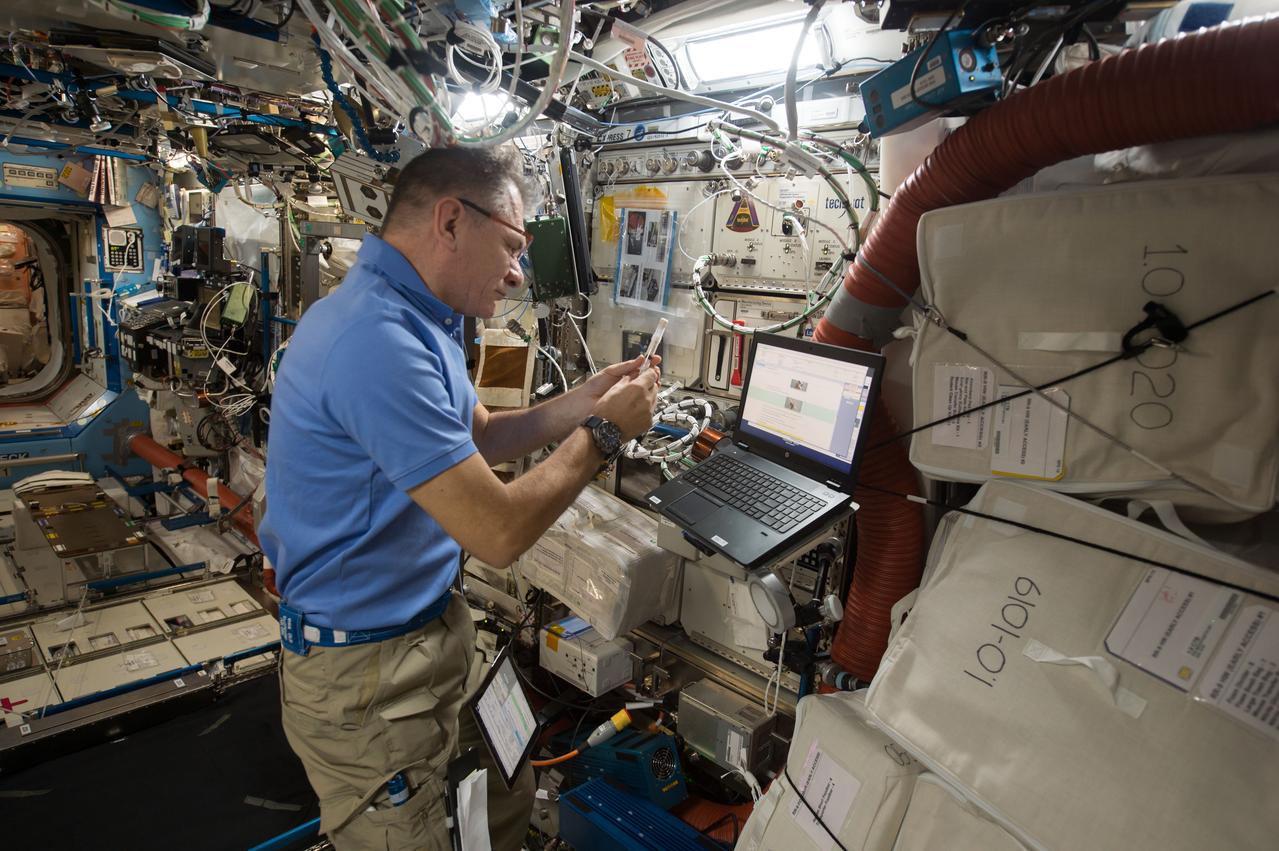

iss052e058828(8/18/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Paolo Nespoli collects and processes saliva samples in the bioanalyzer for the ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and Results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (In Situ). Crew on the International Space Station (ISS) are continually monitored for health changes, and as part of these measurements, they take saliva samples that are stored and returned to Earth later. The ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (IN SITU) bioanalysis is a portable device that can check crew members’ saliva on board, enabling direct real-time analysis. The device’s first uses are to monitor stress levels and appetites among crew members
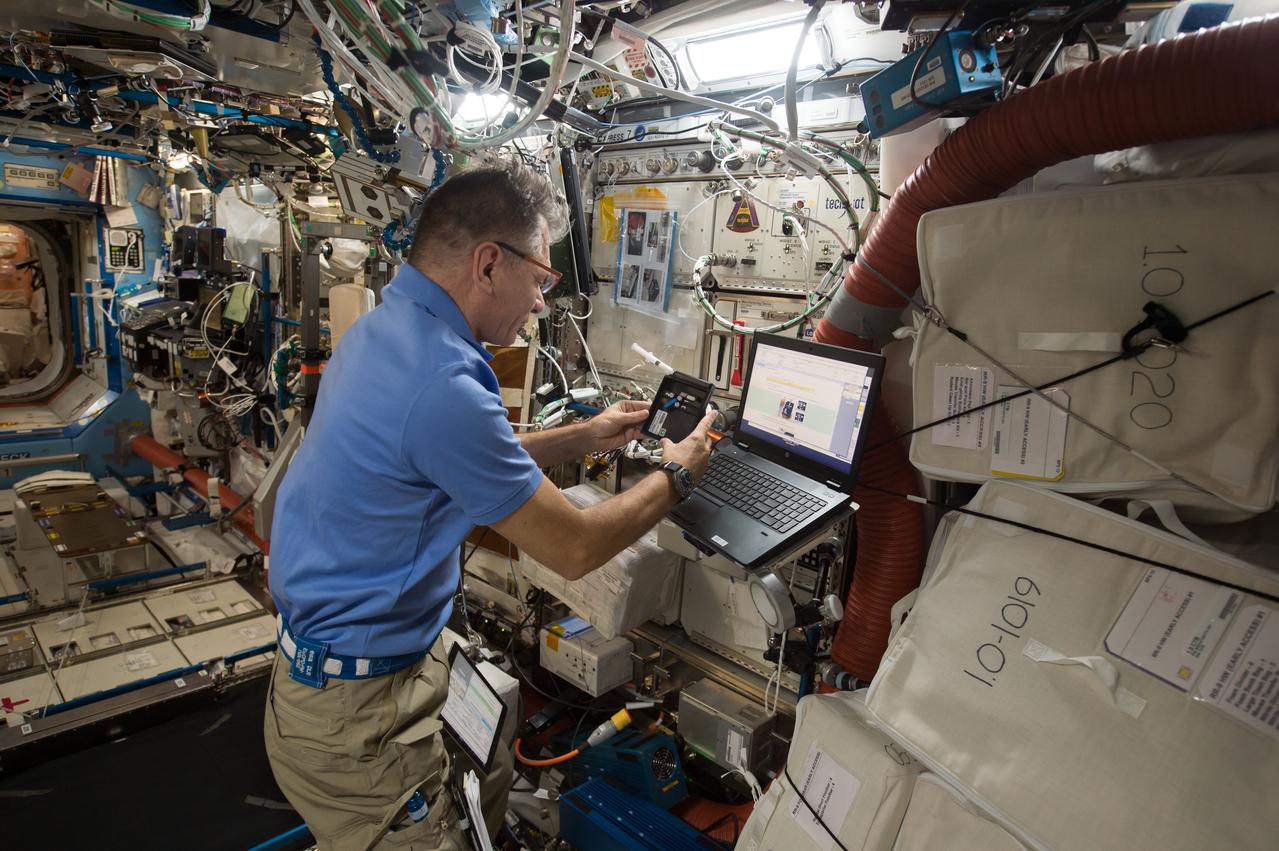

iss052e058906 (8/18/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Paolo Nespoli collects and processes saliva samples in the bioanalyzer for the ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and Results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (In Situ). Crew on the International Space Station (ISS) are continually monitored for health changes, and as part of these measurements, they take saliva samples that are stored and returned to Earth later. The ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (IN SITU) bioanalysis is a portable device that can check crew members’ saliva on board, enabling direct real-time analysis. The device’s first uses are to monitor stress levels and appetites among crew members
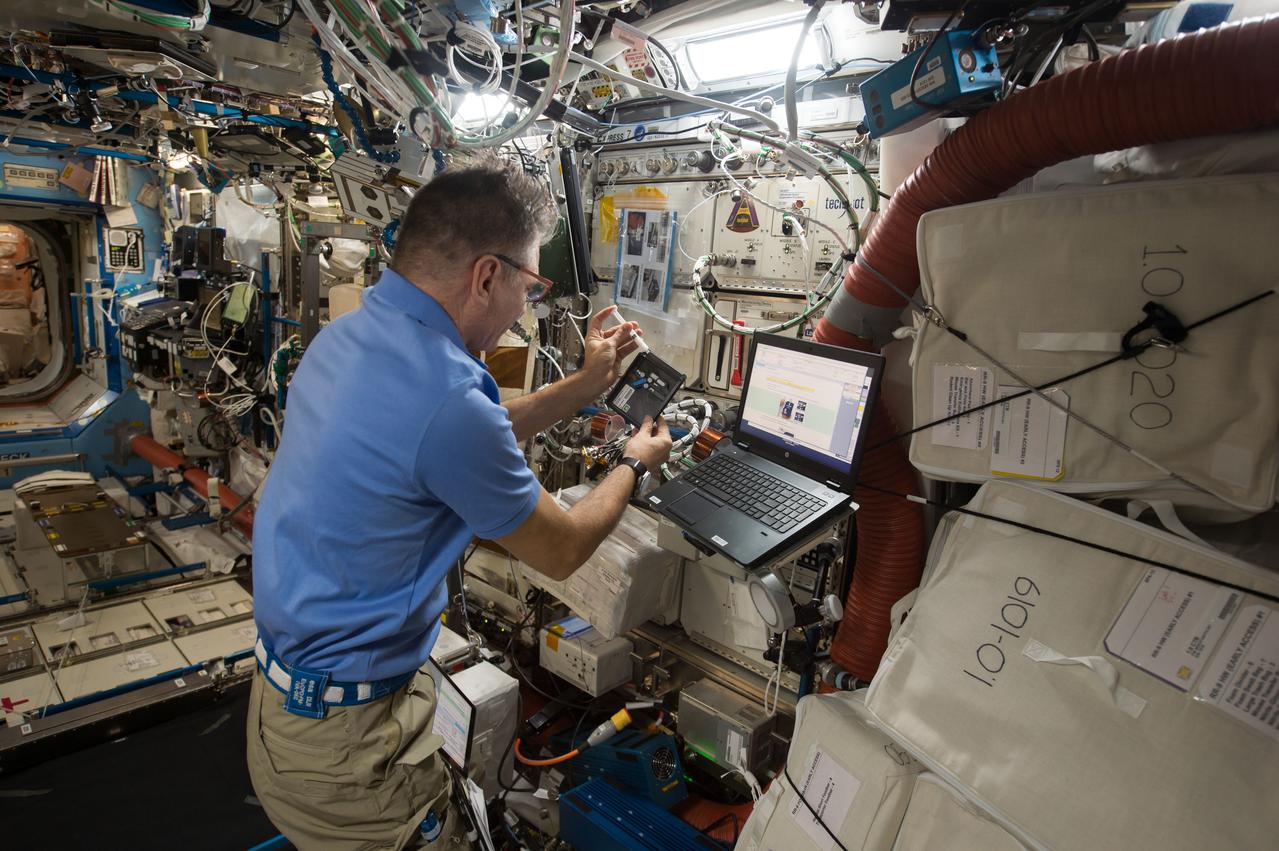

iss052e058893 (8/18/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Paolo Nespoli collects and processes saliva samples in the bioanalyzer for the ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and Results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (In Situ). Crew on the International Space Station (ISS) are continually monitored for health changes, and as part of these measurements, they take saliva samples that are stored and returned to Earth later. The ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (IN SITU) bioanalysis is a portable device that can check crew members’ saliva on board, enabling direct real-time analysis. The device’s first uses are to monitor stress levels and appetites among crew members
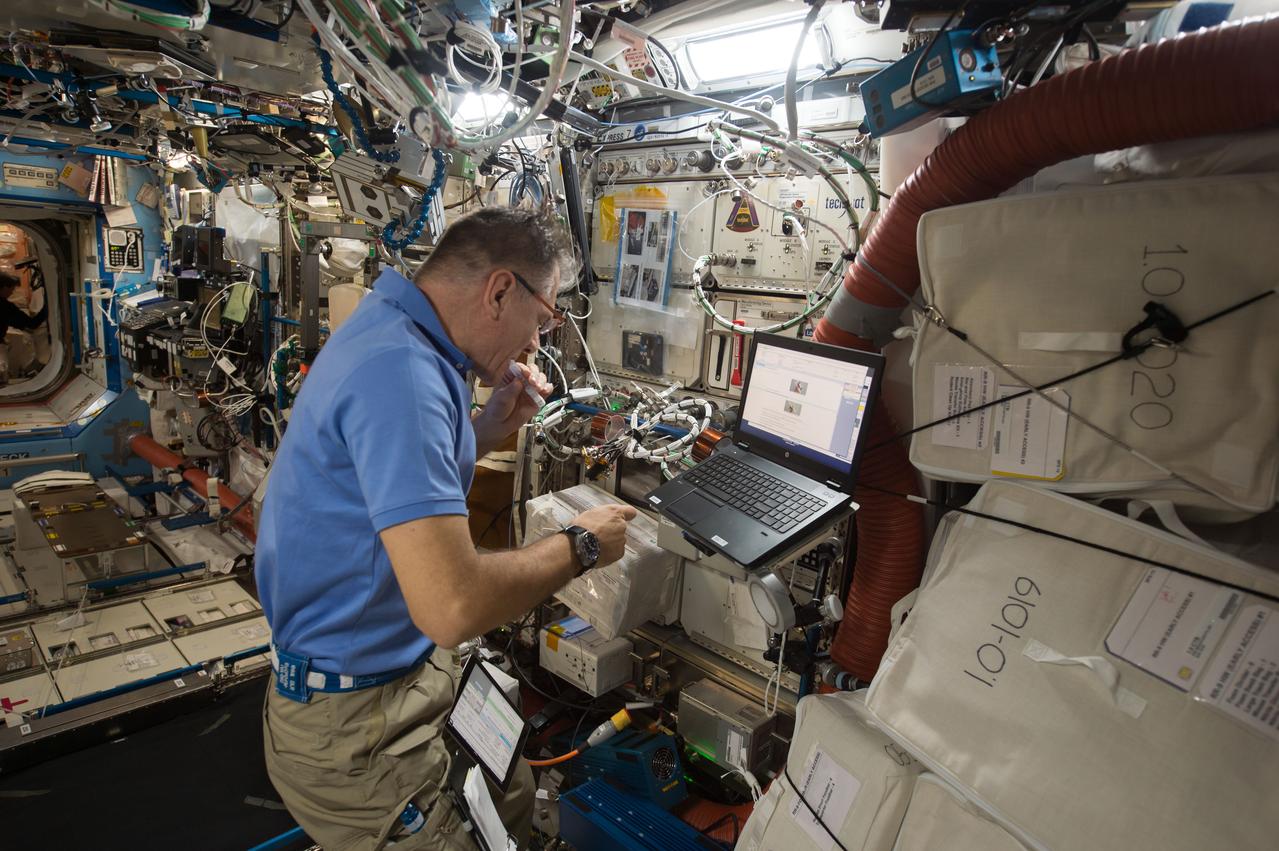

iss052e058815 (8/18/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Paolo Nespoli collects and processes saliva samples in the bioanalyzer for the ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and Results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (In Situ). Crew on the International Space Station (ISS) are continually monitored for health changes, and as part of these measurements, they take saliva samples that are stored and returned to Earth later. The ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (IN SITU) bioanalysis is a portable device that can check crew members’ saliva on board, enabling direct real-time analysis. The device’s first uses are to monitor stress levels and appetites among crew members
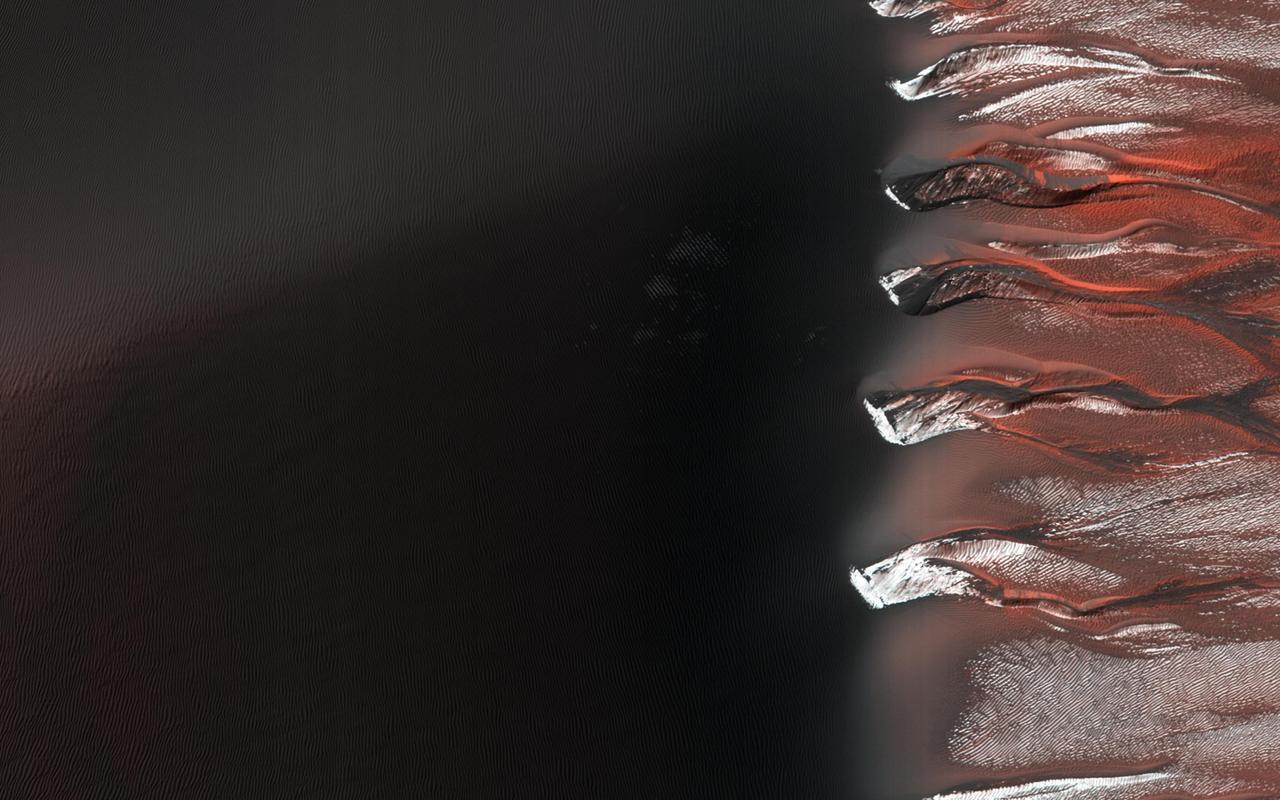
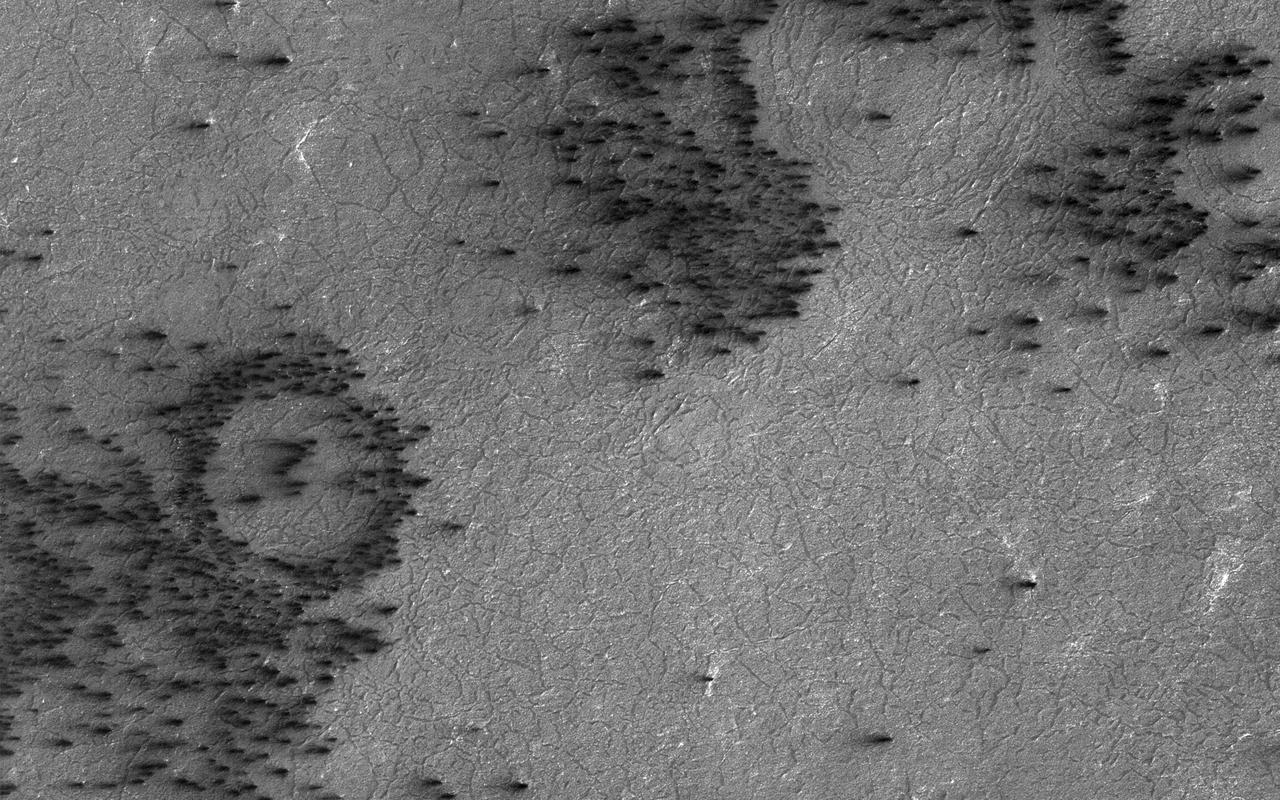
Kaiser Crater hosts a large field of sand dunes. Every winter the dunes are covered with a layer of seasonal carbon dioxide ice (dry ice). In early spring the ice begins to sublimate (going directly from solid ice to gas). In this image, the dunes are partially free of seasonal ice, with the contrast making it easy to see the ripples. Deep alcoves have been carved at the crest of the dune. We hypothesize that this is the result of the gas coming from the dry ice, destabilizing the sand at the crest. As blocks of ice protected in the cold shadows of the alcove break off they slide downslope, carving the channels we see. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21038
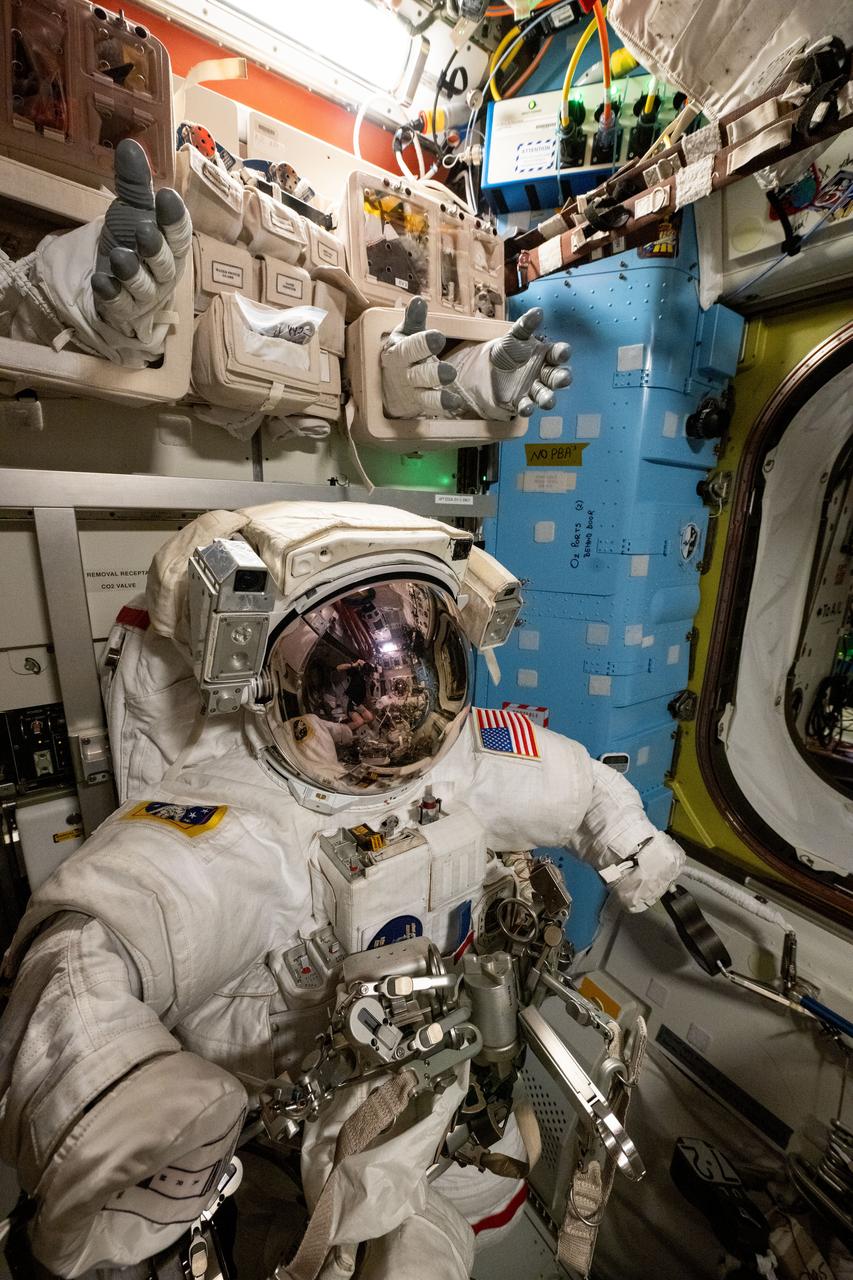

iss072e518461 (Jan. 23, 2025) --- A spacesuit is pictured staged inside the International Space Station's Quest airlock ahead of a spacewalk planned for NASA astronauts Suni Williams and Butch Wilmore. The two spacewalkers are scheduled to exit the Quest airlock on Jan. 30 to remove a radio frequency group antenna assembly and search for microbes outside the orbital outpost. At top, spacesuit gloves are stowed above the spacesuits for easy access when astronauts are preparing to begin a spacewalk.
![“Discipline is one of the things that they instill with you [in the military.] All the way starting in boot camp, [the goal] is doing the right thing when nobody's looking. Integrity. Whenever you're in boot camp, they always say, ‘it's too easy.’ It's just too easy to follow the rules, read the book, read the regulations, and that's probably why I enjoy contracting. I like reading the regulations and following the regulations. …[Now that I work for Safety and Mission Assurance,] it's really cool to read everything about the different types of the scenarios. I always get to see the task orders and the type of work that is going on to keep people safe on the ground and in the air.” NASA Contract Specialist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC), Miranda Meyer, poses for a portrait, Wednesday, Feb. 7, 2024 at GSFC in Greenbelt, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Thalia Patrinos)](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/NHQ202402070015/NHQ202402070015~medium.jpg)
“Discipline is one of the things that they instill with you [in the military.] All the way starting in boot camp, [the goal] is doing the right thing when nobody's looking. Integrity. Whenever you're in boot camp, they always say, ‘it's too easy.’ It's just too easy to follow the rules, read the book, read the regulations, and that's probably why I enjoy contracting. I like reading the regulations and following the regulations. …[Now that I work for Safety and Mission Assurance,] it's really cool to read everything about the different types of the scenarios. I always get to see the task orders and the type of work that is going on to keep people safe on the ground and in the air.” NASA Contract Specialist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC), Miranda Meyer, poses for a portrait, Wednesday, Feb. 7, 2024 at GSFC in Greenbelt, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Thalia Patrinos)
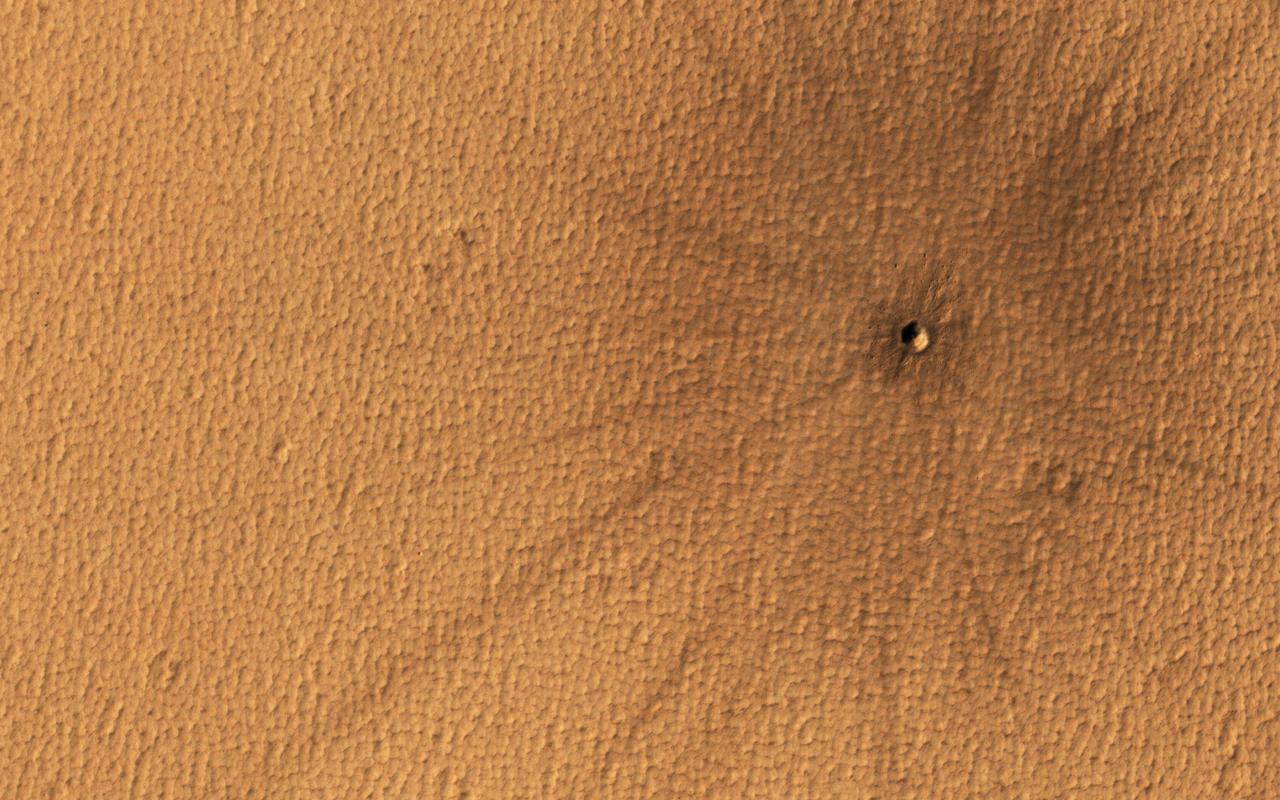

Mars and the Earth run into debris in space regularly, and on our planet, meteors usually vaporize in the atmosphere. On Mars however, with a surface pressure 1/100th that of the Earth, the impactors generally make it to the surface. This particular impact took place on Mars sometime in the last 5 years. Although the crater is small, the rays of ejecta thrown out by the impact are easy to spot, stretching out almost a kilometer. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24694

ISS032-E-012070 (4 Aug. 2012) --- This night time image of Valencia on the Mediterranean coast of Spain was captured with a digital still camera by one of the Expedition 32 crew members aboard the International Space Station on Aug. 4, 2012. The nocturnal lighting of the city make it easy to locate numerous features within the metropolitan area, which, with a population exceeding two million, is the country's third largest.

STS009-05-0153 (28 Nov. - 8 Dec. 1983) --- Though STS-9 was the space shuttle Columbia's sixth spaceflight, it was the first opportunity for an onboard galley, some of the results of which are shown in this 35mm scene on the flight deck. The metal tray makes for easy preparation and serving of in-space meals for crew members. This crewman is seated at the pilot's station on the flight deck. The actual galley is located in the middeck. Photo credit: NASA
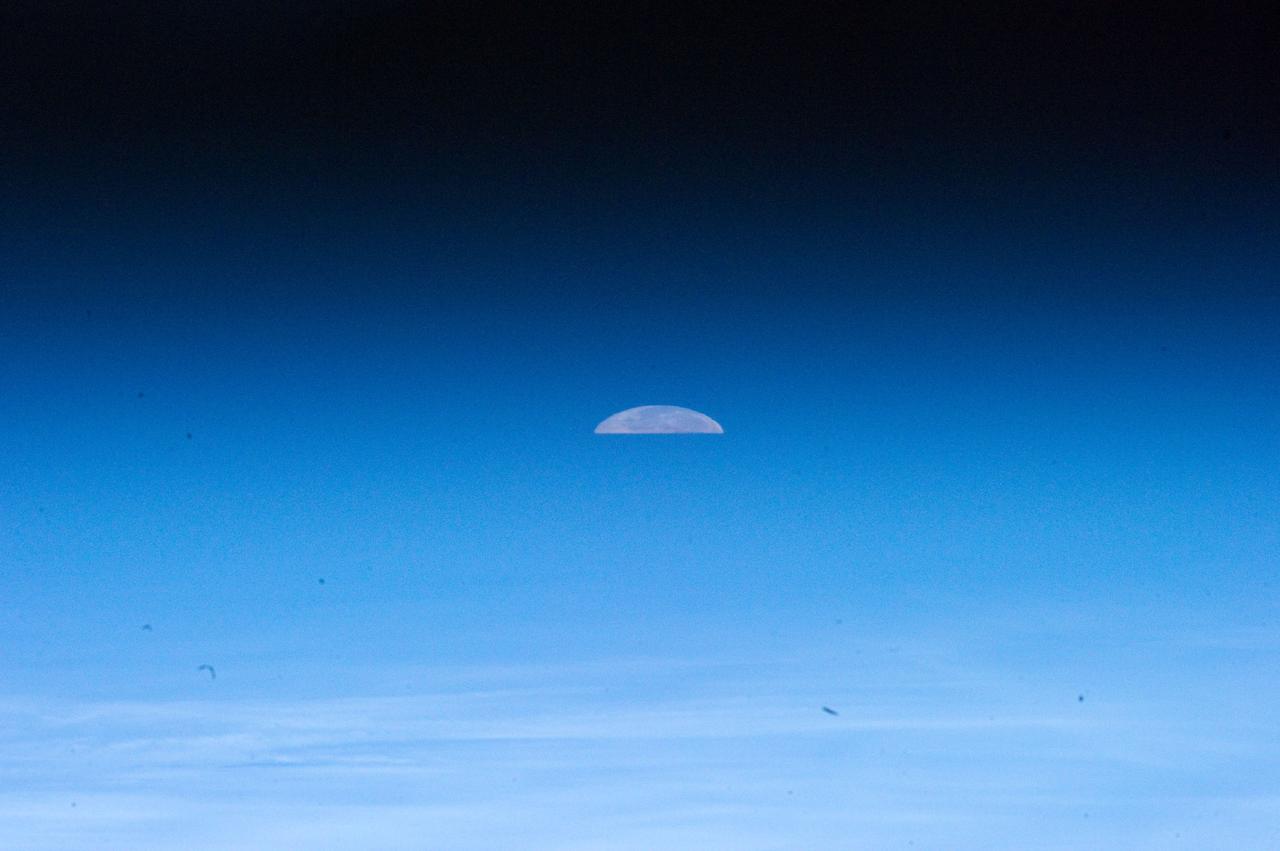

ISS032-E-011478 (1 Aug. 2012) --- One of the Expedition 32 crew members aboard the Earth-orbiting International Space Station captured this image of the full moon on Aug. 1, 2012. Because of the home planet's atmosphere, it is not easy at first sighting to recognize the slice as the full moon. Another picture in this series depicts a totally different image of Earth's natural satellite because of the lack of distortion caused by the atmosphere.
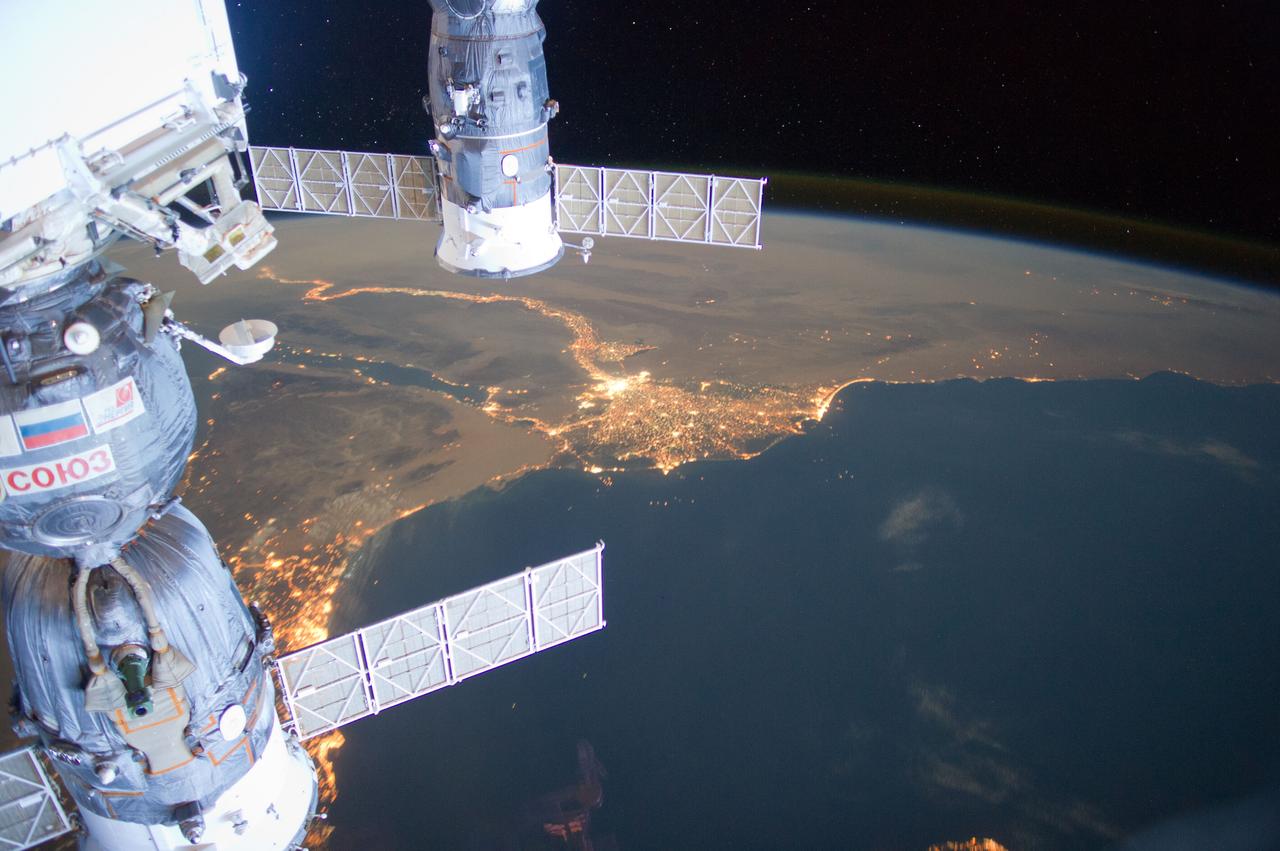

ISS031-E-095276 (4 June 2012) --- Much of the Middle East is seen in this night time image photographed by one of the Expedition 31 crew members aboard the International Space Station as it flew some 240 miles above the Mediterranean Sea on June 4, 2012. The Nile River Delta is easily recognizable in center frame, and city lights make it easy to see both Cairo and Alexandria, Egypt near the Delta. Two Russian spacecraft -- a Soyuz (left) and a Progress -- appear in the frame while they are docked to the station.
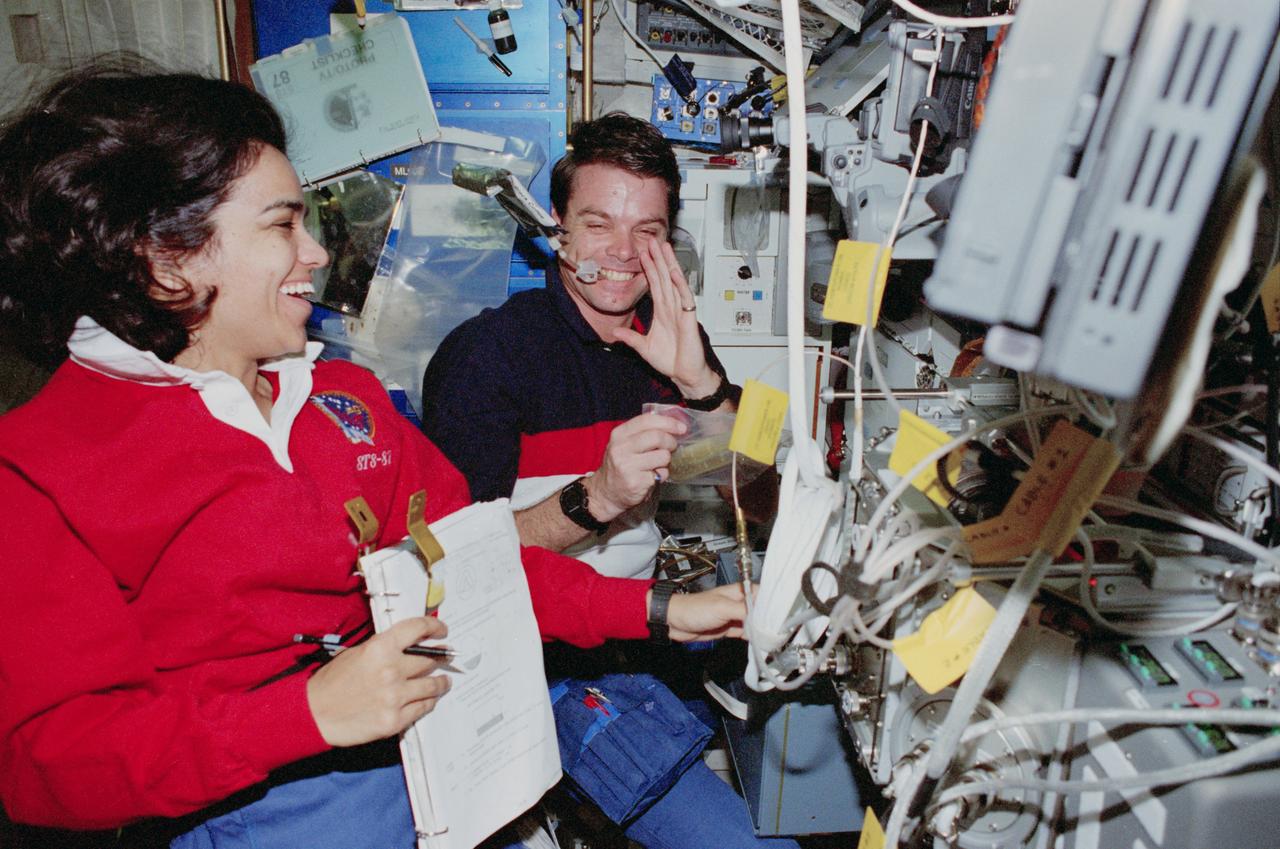

STS087-332-010 (19 November – 5 December 1997) --- Astronaut Kevin R. Kregel doesn't bother to "break" for coffee as he enjoys a serving while sharing work at the Space Shuttle Columbia's microgravity glove box with astronaut Kalpana Chawla. The glove box's (right edge of frame) proximity to the galley (partially obscured behind the mission commander) makes the time economy measure an easy task for the three-time space veteran. Chawla, mission specialist, is making her initial space flight.
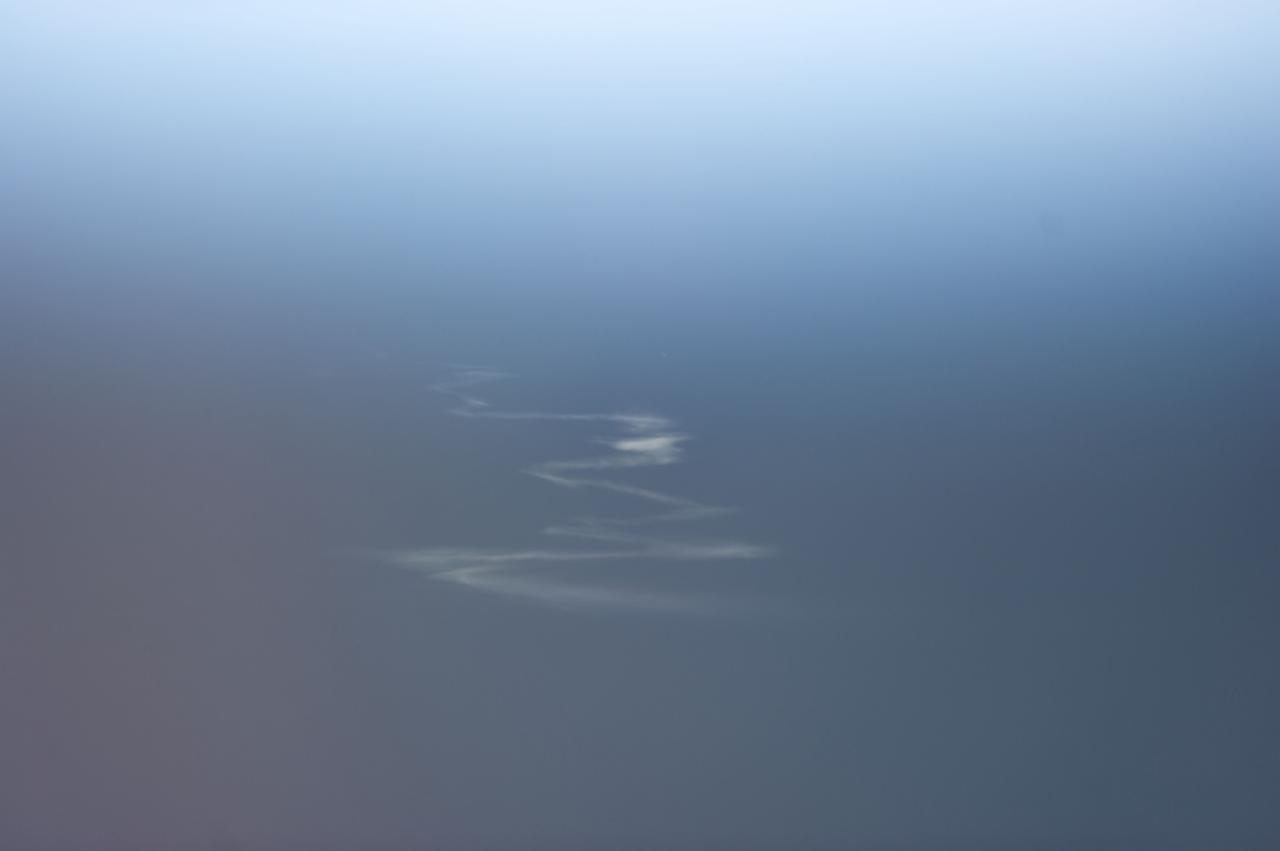

ISS034-E-009486 (19 Dec. 2012) --- Though somewhat faint, the contrails from the launch of the Expedition 34/35 crew onboard the Soyuz TMA-07M on Dec. 19 are recognizable while the International Space Station and its three-man Expedition 34 crew were over the Caspian Sea. The skies were clear over the Baikonur Cosmodrome at this time, making it possible that these contrail "clouds" would be easy to spot.
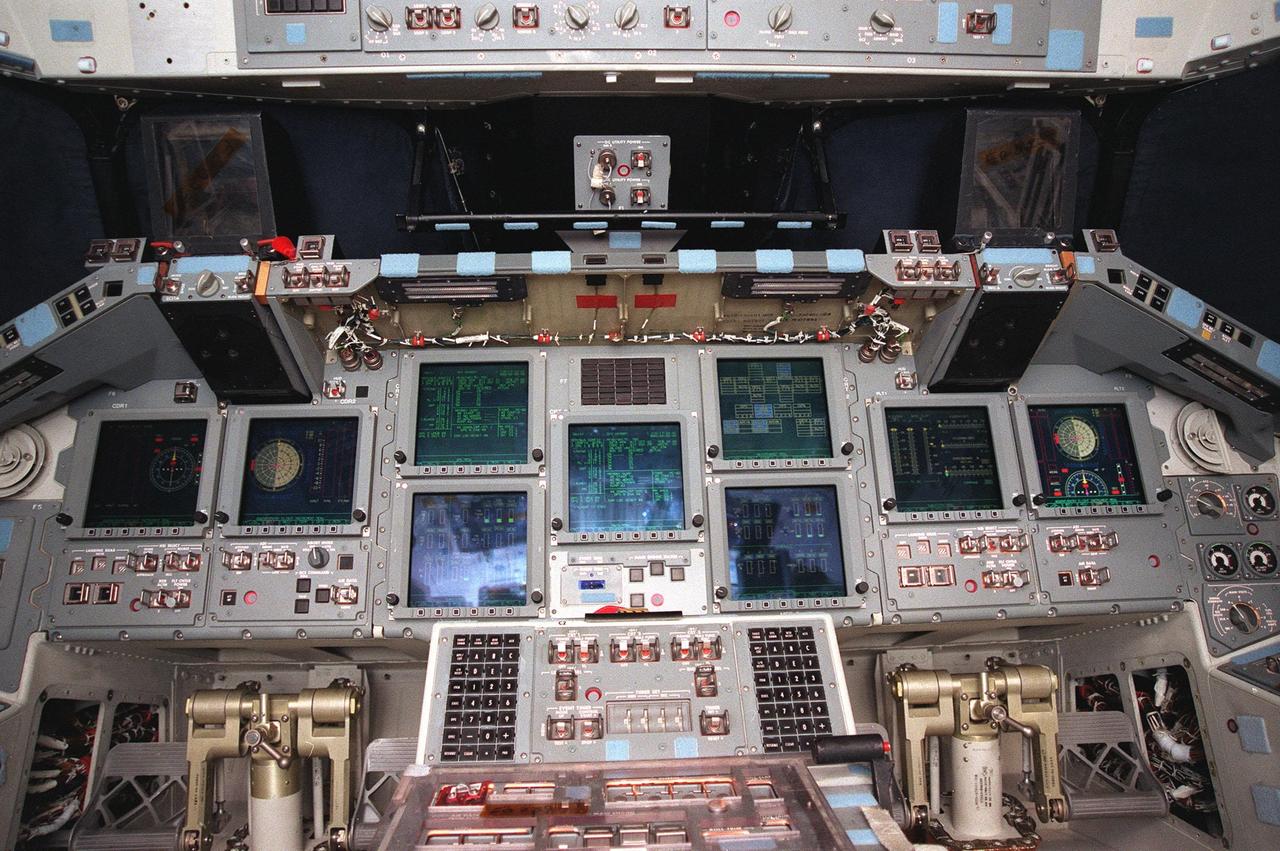

In this broad view, the new full-color, flat panel Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS) is shown in the cockpit of the orbiter Atlantis. It is often called the "glass cockpit." The recently installed MEDS upgrade improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed. The installation makes Atlantis the most modern orbiter in the fleet and equals the systems on current commercial jet airliners and military aircraft. Atlantis is scheduled to fly on mission STS-101 in early December

STS79-E-5370 (24 September 1996)--- During off-duty time in the Spacehab Module, astronaut Shannon W. Lucid uses the microgravity of space to fabricate her own kind of easy chair as the days of her lengthy Russian Mir Space Station stay as a cosmonaut guest researcher come to a close. The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC) during Flight Day 9.

Gas under pressure will choose an easy escape route. In this image, the terrain is covered with a seasonal layer of dry ice. The weak spots, for gas sublimating from the bottom of the seasonal ice layer to escape, appear to be around craters, where the surface was broken and pulverized by an impact. Fans of surface material deposited on top of the seasonal ice layer show where the escape vents are. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21271

STS081-E-05144 (13 Jan. 1997) --- Making sure everything is in its place is no easy task as witnessed by the serious countenance of astronaut John M. Grunsfeld, mission specialist. Grunsfeld communicates with ground controllers as he checks progress of item transfers in the Spacehab Double Module (DM). This image was recorded with an Electronic Still Camera (ESC) and was later downlinked to flight controllers in Houston, Texas. Grunsfeld and five astronaut crew mates are preparing for a scheduled mid-week docking with Russia's Mir Space Station.
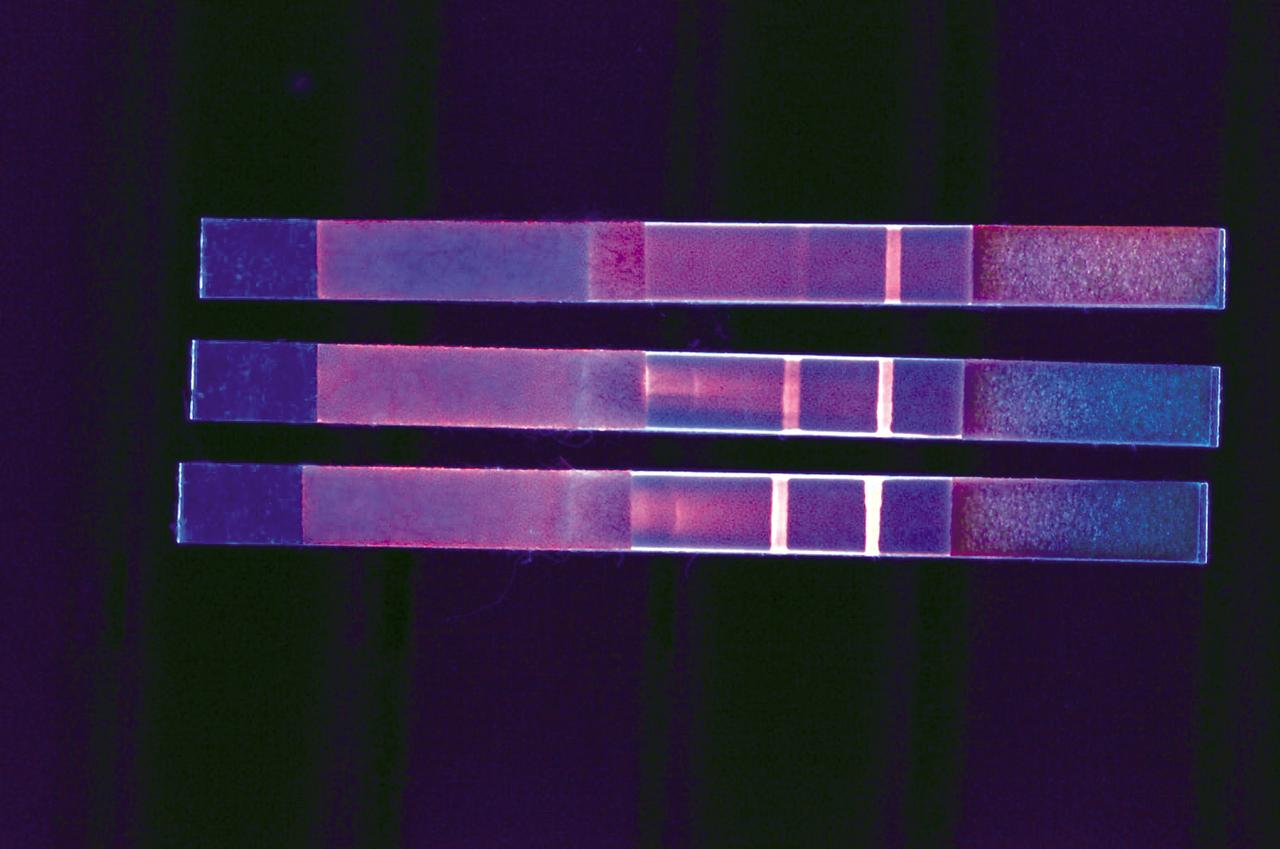
As easy to read as a home pregnancy test, three Quantifiable Lateral Flow Assay (QLFA) strips used to test water for E. coli show different results. The brightly glowing control line on the far right of each strip indicates that all three tests ran successfully. But the glowing test line on the middle left and bottom strips reveal their samples were contaminated with E. coli bacteria at two different concentrations. The color intensity correlates with concentration of contamination.
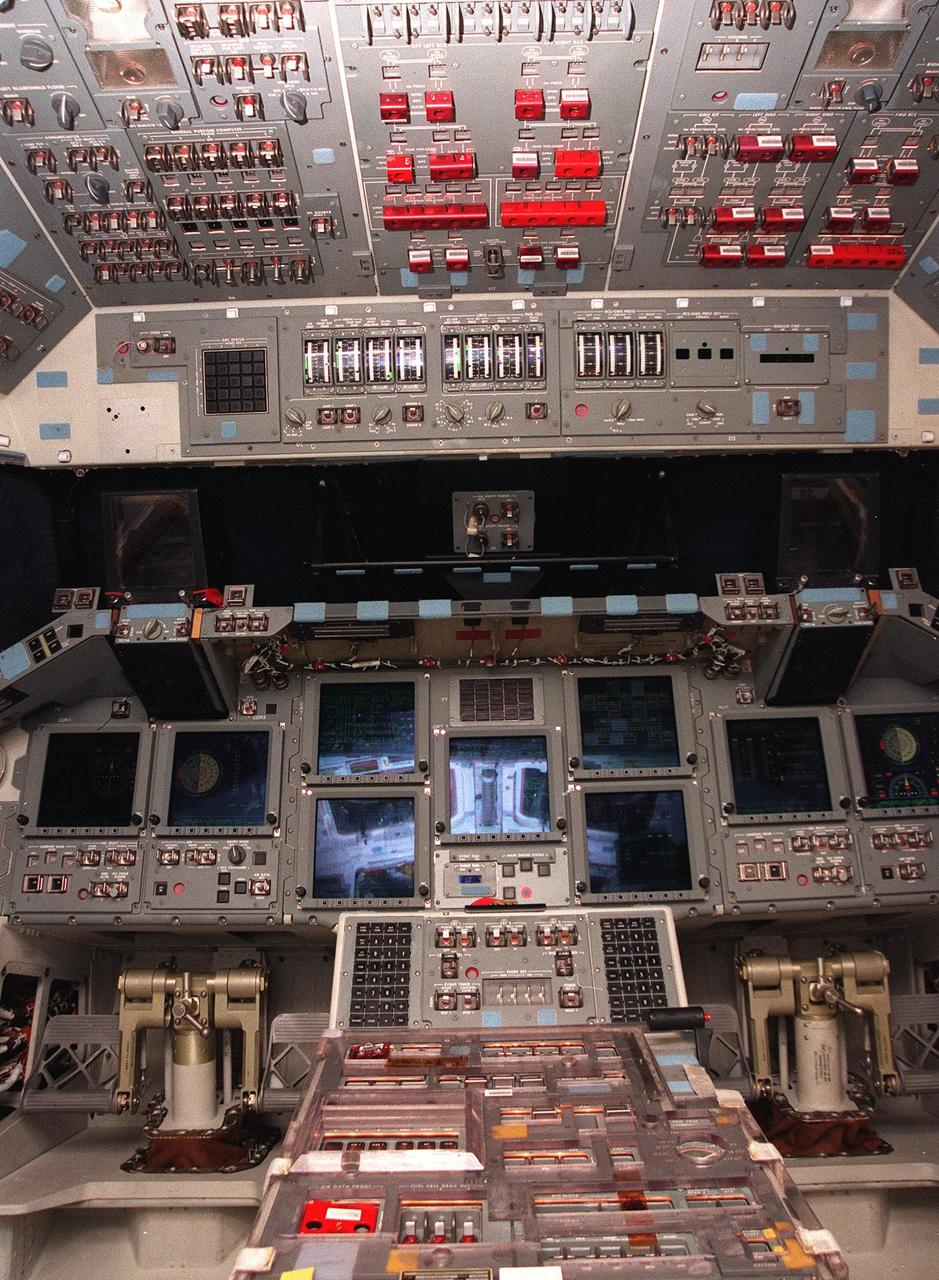
The cockpit of the orbiter Atlantis is revealed with its new full-color, flat panel Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS), also called the "glass cockpit." The recently installed MEDS upgrade improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed. The installation makes Atlantis the most modern orbiter in the fleet and equals the systems on current commercial jet airliners and military aircraft. Atlantis is scheduled to fly on mission STS-101 in early December
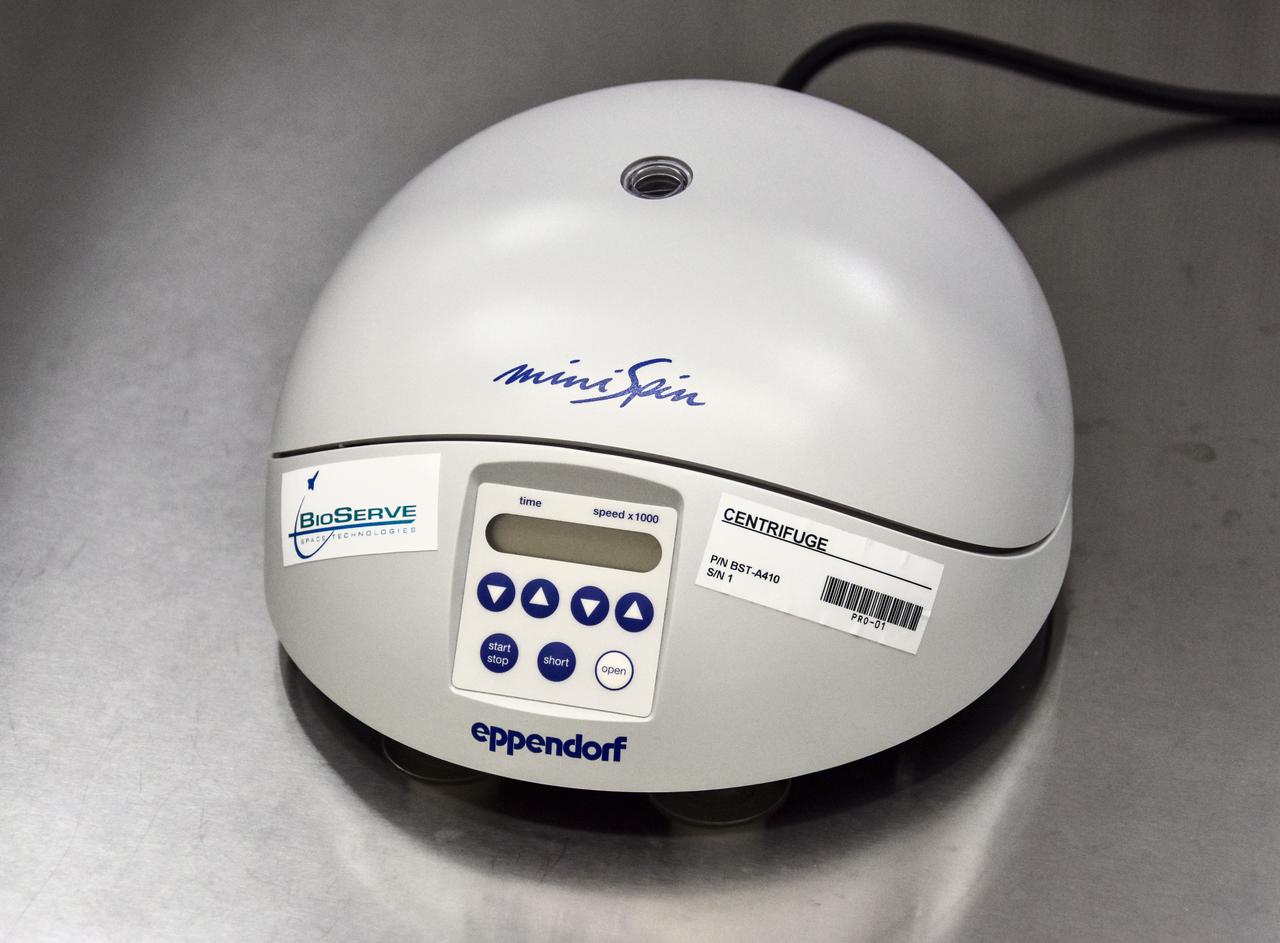

jsc2022e031229 (8/13/2021) --- A preflight view of the The BioServe Centrifuge facility supports a wide variety of life, physical, and materials science research. The Centrifuge is compatible with BioServe’s extensive array of investigation-specific hardware. Small, portable, and easy to set up, the facility further enhances the International Space Station’s scientific capabilities. Image courtesy of BioServe Space Technologies.
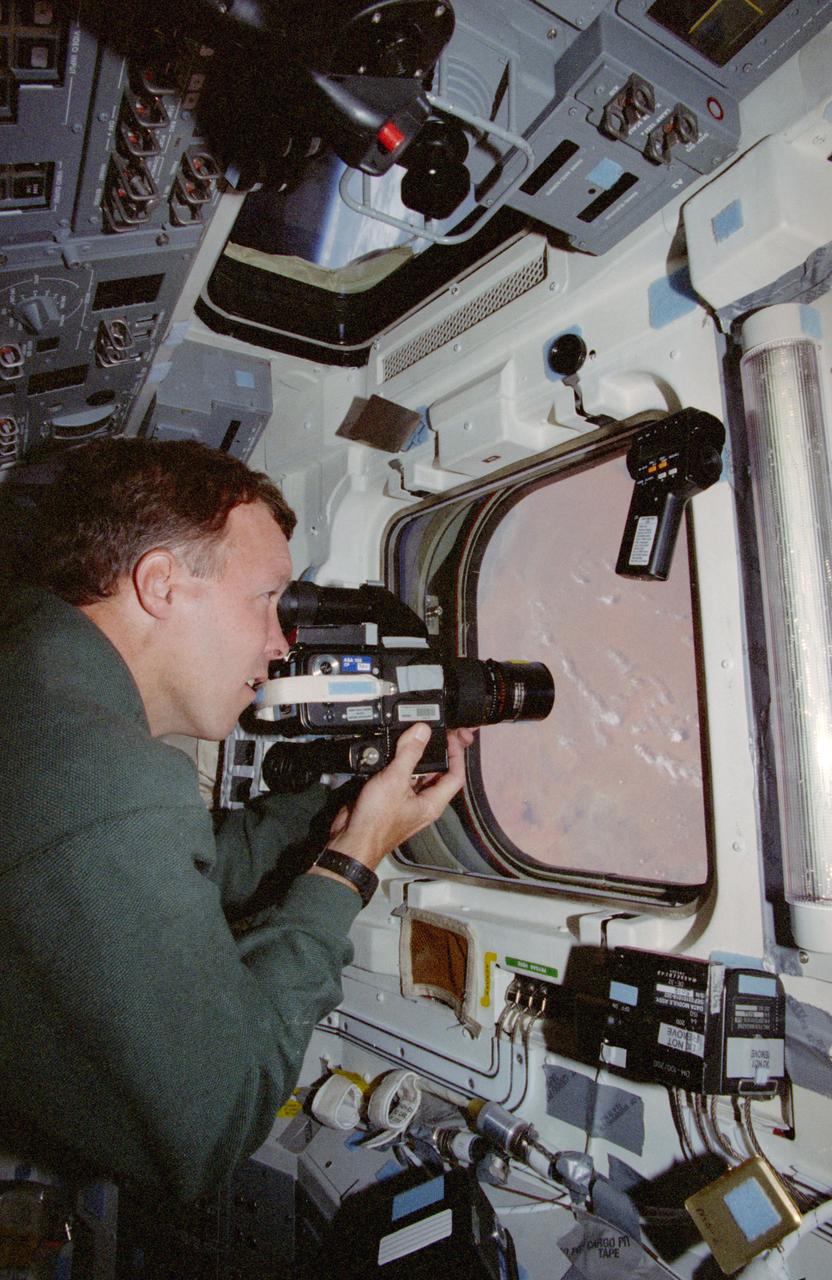

STS091-391-033 (2-12 June 1998) --- On Discovery's aft flight deck, astronaut Dominic C. Gorie, pilot, uses a 70mm handheld camera to record images of Africa. Two overhead and two head-level windows, located on the aft flight deck, afford an easy means for astronauts-turned-photographers to take pictures of targets of opportunity on the home planet.
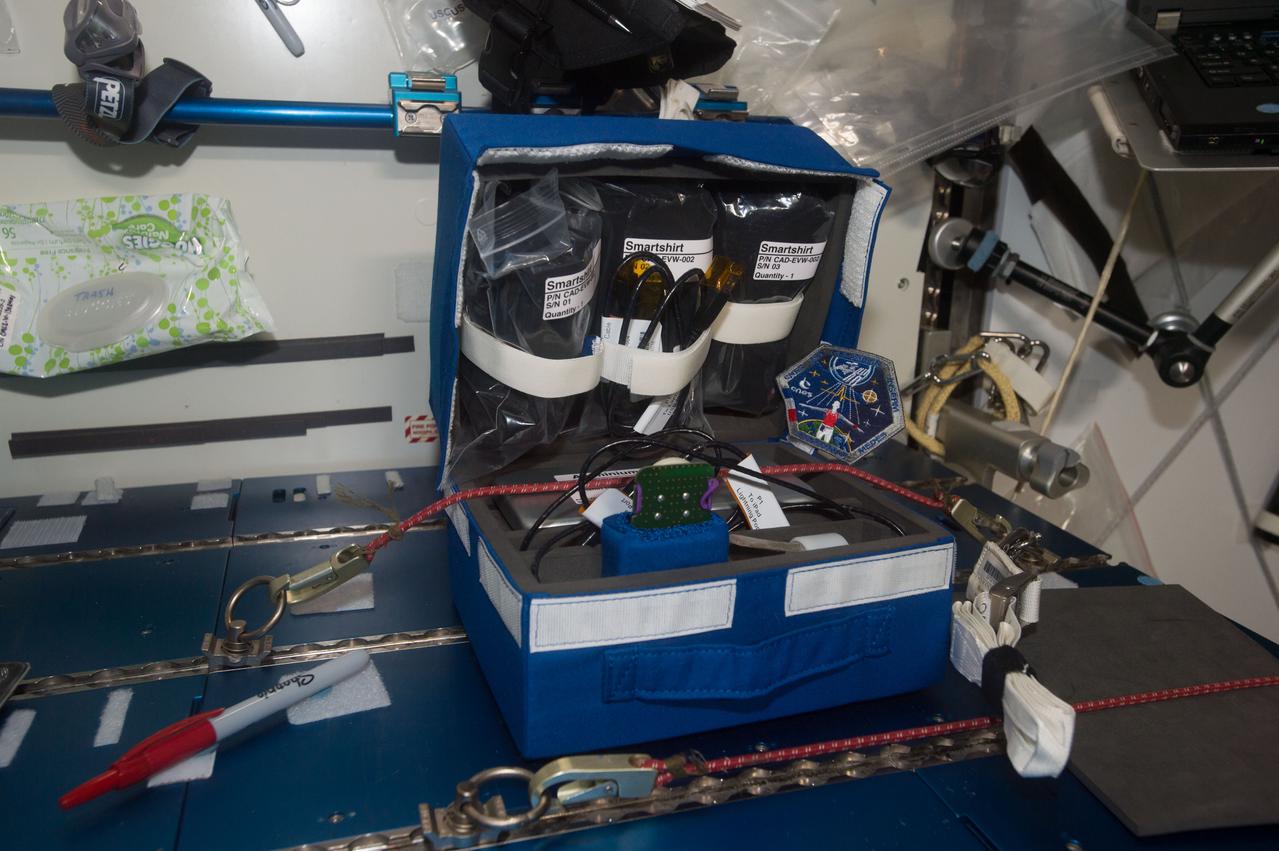

iss050e014794 (12/6/2016) --- View of Smartshirts within Cargo Transfer Bag (CTB). The EveryWear system is an ambulatory data collection system making use of wearable sensors connected to a station iPad itself wirelessly synchronized with ground. This easy-use system should demonstrate extensive physiology data collection for both science and medical follow-up purpose by improving usability for the astronauts.
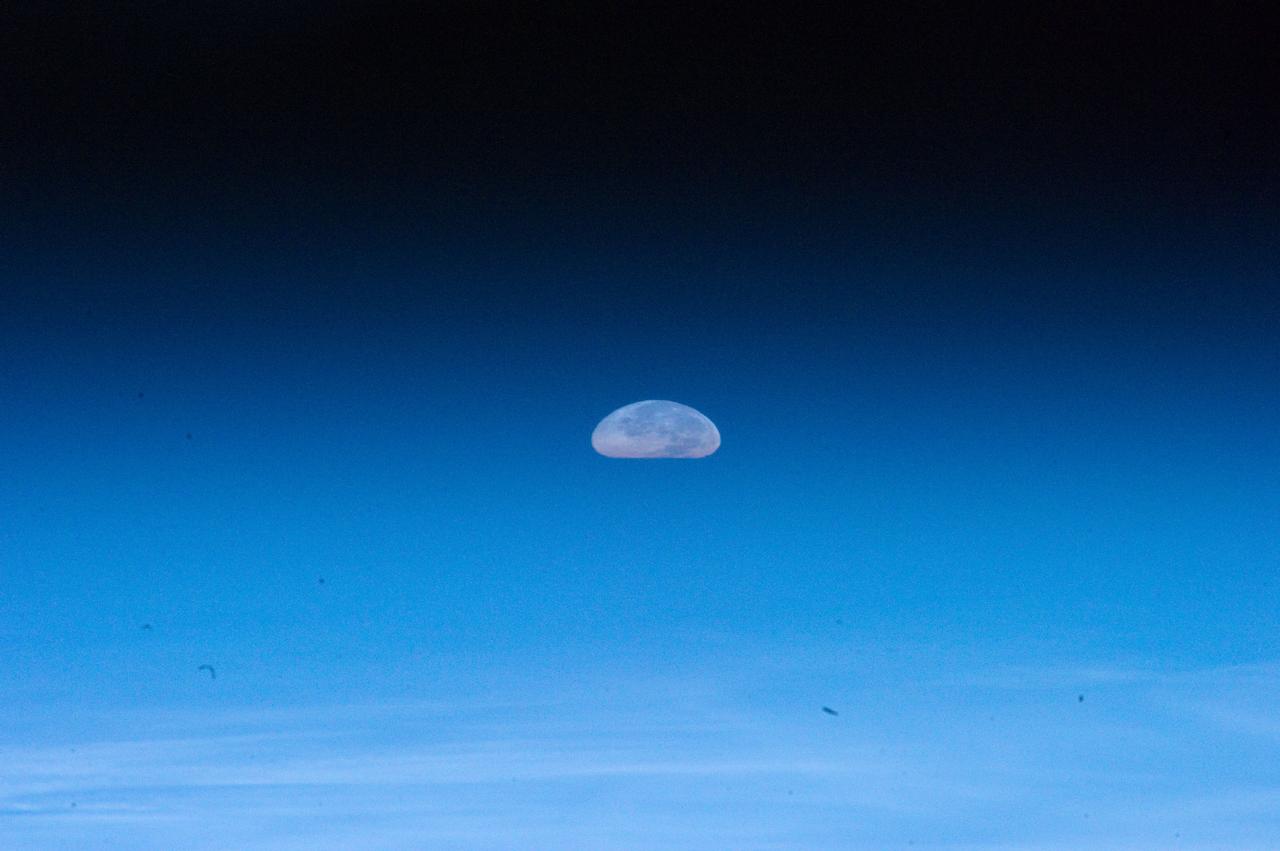

ISS032-E-011477 (1 Aug. 2012) --- One of the Expedition 32 crew members aboard the Earth-orbiting International Space Station captured this image of the full moon on Aug. 1, 2012. Because of the home planet's atmosphere, it is not easy at first sighting to recognize the heavenly body as the full moon. Another picture in this series depicts a totally different image of Earth's natural satellite because of the lack of distortion caused by the atmosphere.

Today's VIS image shows a small part of the south polar cap. The layering of the cap is easy to see. The layers record the seasonal deposition of dust and ice over the course of 1000's of years. This image was taken during summer at the pole. Orbit Number: 74904 Latitude: -85.4168 Longitude: 184.015 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2018-11-02 20:21 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22990
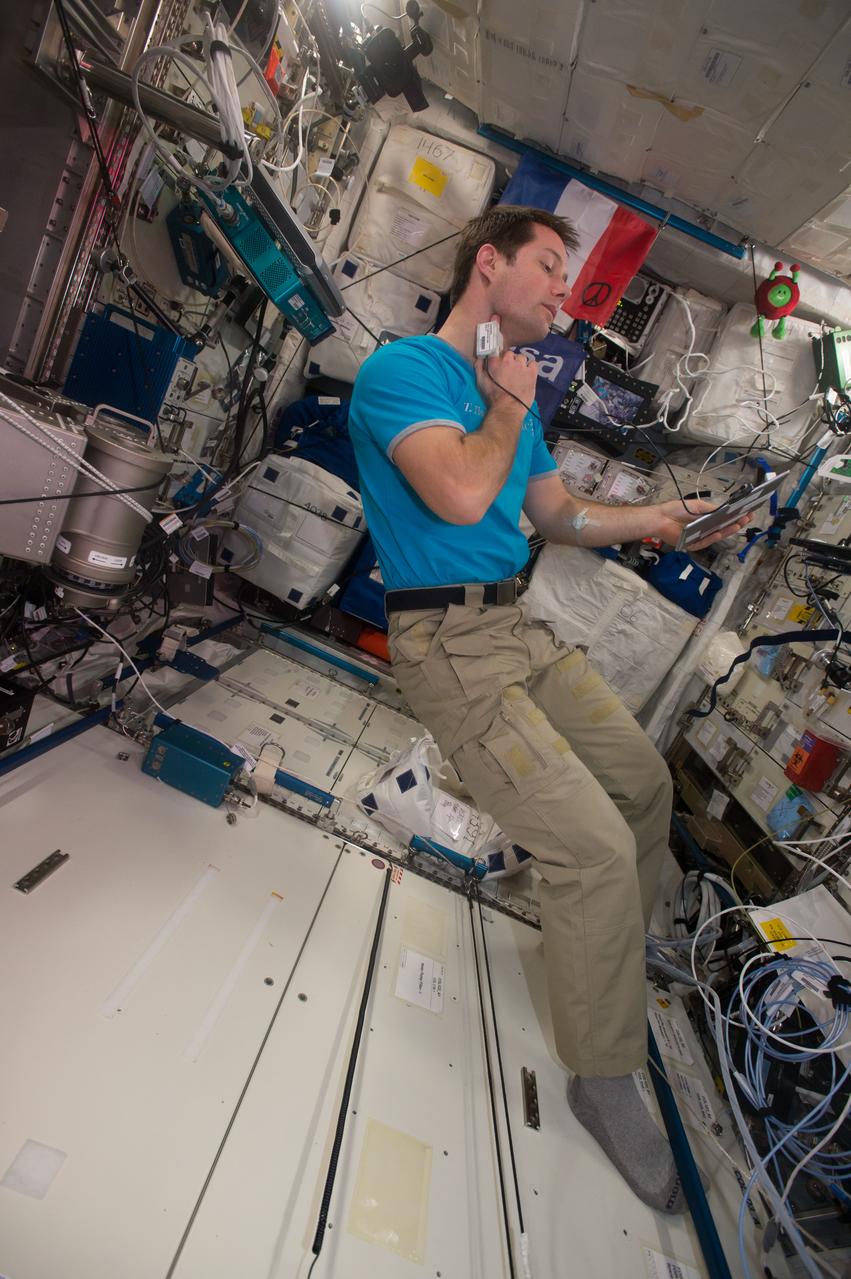

iss050e014804 (12/7/2016) --- European Space Agency (ESA) Thomas Pesquet wearing sensor (Tonometer) connected to iPad during EVERYWEAR experiment, in the Columbus Module. The EveryWear system is an ambulatory data collection system making use of wearable sensors connected to a station iPad itself wirelessly synchronized with ground. This easy-use system should demonstrate extensive physiology data collection for both science and medical follow-up purpose by improving usability for the astronauts.

ISS026-E-028375 (22 Feb. 2011) --- Having enjoyed a clear sky nocturnal photo opportunity over New Orleans earlier (Jan. 26) in their mission, Expedition 26 crew members aboard the International Space Station had another window on Feb. 22 to capture images of the Crescent City or Big Easy from 220 miles above Earth. The Mississippi River is visible winding its way through the city. A 200-mm lens was used to take the picture.
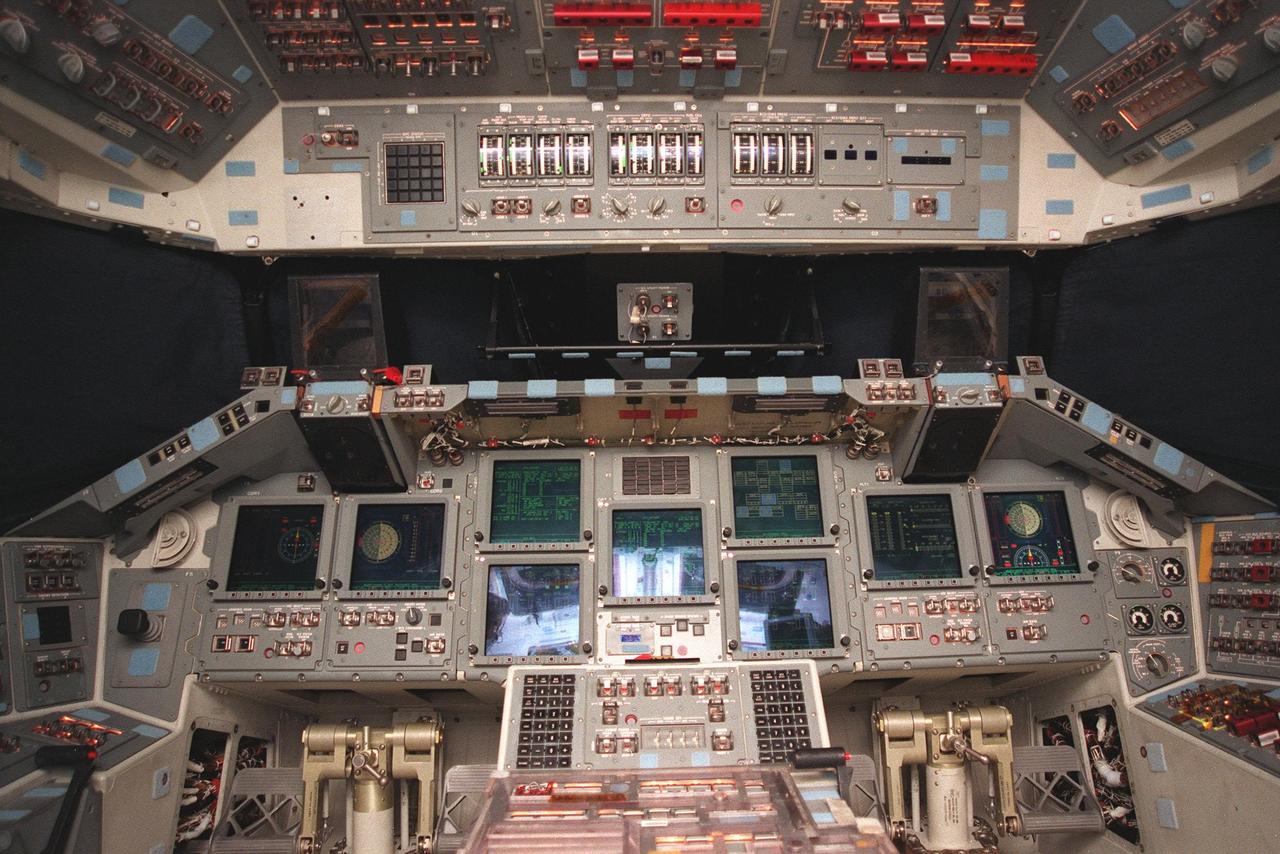

A new full-color, flat panel Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS) is shown in the cockpit of the orbiter Atlantis. It is often called the "glass cockpit." The recently installed MEDS upgrade improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed. The installation makes Atlantis the most modern orbiter in the fleet and equals the systems on current commercial jet airliners and military aircraft. Atlantis is scheduled to fly on mission STS-101 in early December
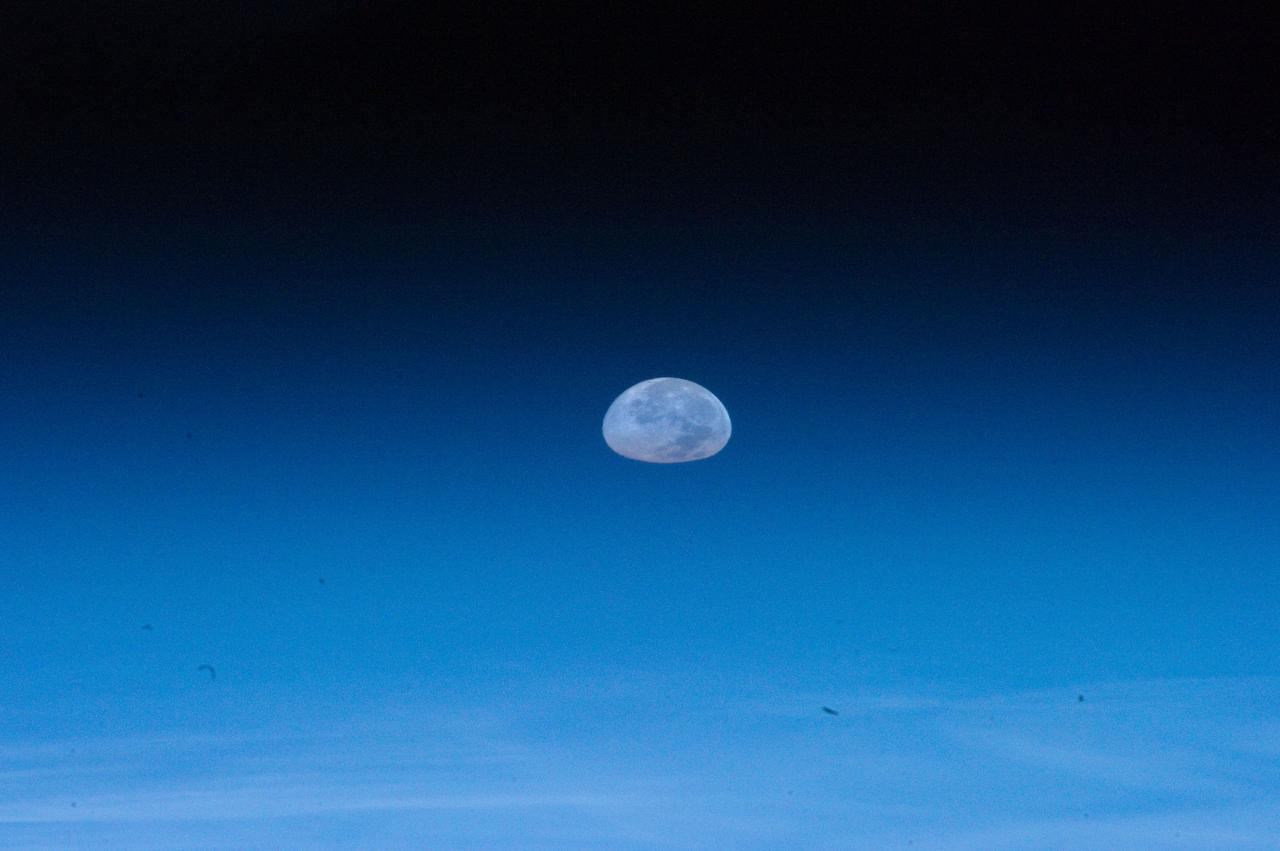

ISS032-E-011476 (1 Aug. 2012) --- One of the Expedition 32 crew members aboard the Earth-orbiting International Space Station captured this image of the full moon on Aug. 1, 2012. Because of the home planet's atmosphere, it is not easy at first sighting to recognize the heavenly body as the full moon. Another picture in this series depicts a totally different image of Earth's natural satellite because of the lack of distortion caused by the atmosphere.
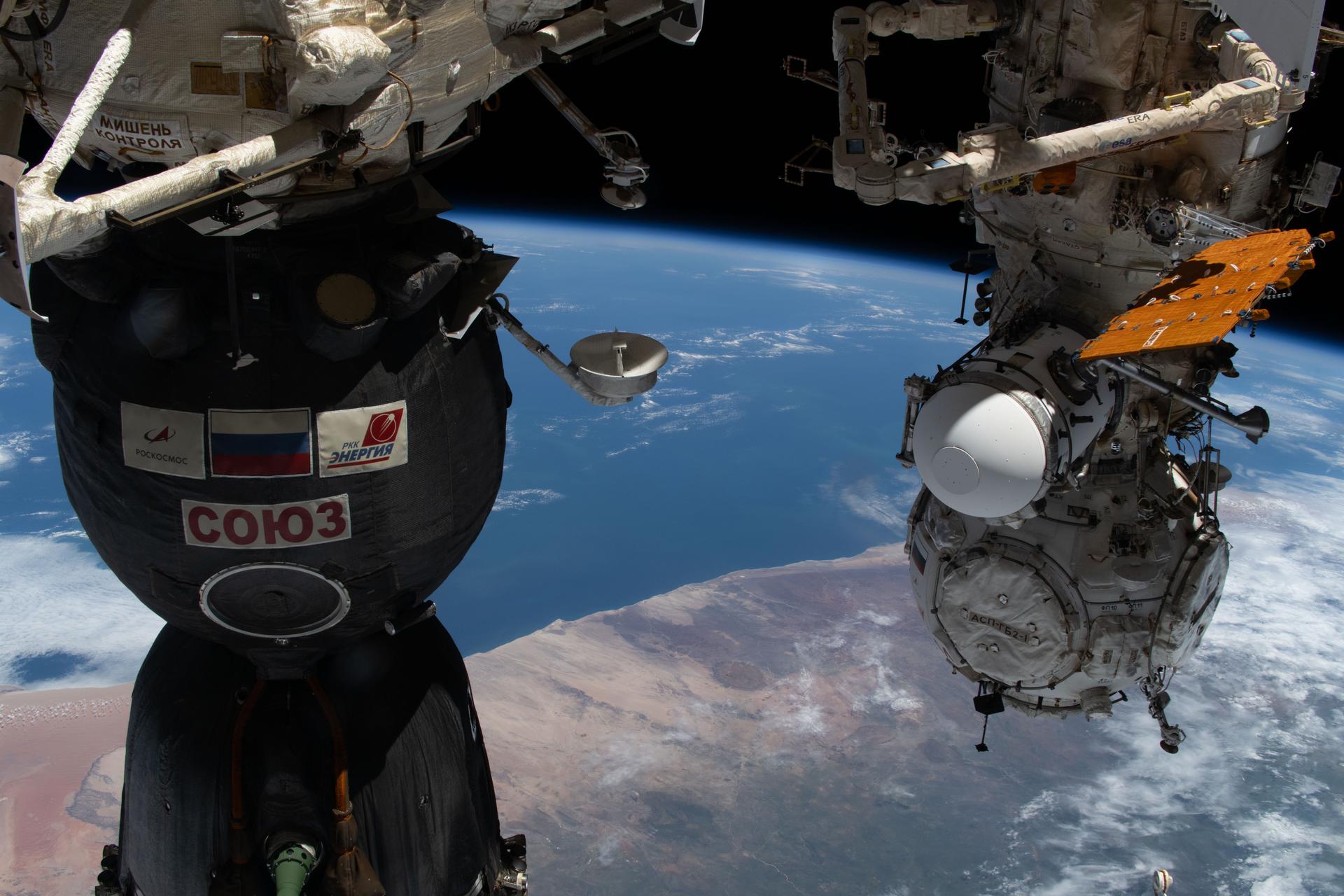

iss074e0325203 (Feb. 24, 2026) --- Namibia's Brandberg Massif, near the center of the photograph, appears as a nearly perfect circular formation just inland from the Atlantic coast, and easy to mistake for a meteorite impact crater when seen from space. At left, is the Soyuz MS-28 crew spacecraft docked to the Rassvet module. At right, the Prichal docking module is attached to the Nauka science module. The International Space Station was orbiting 266 miles above southern Africa at the time of this photograph. Credit: NASA/Jessica Meir
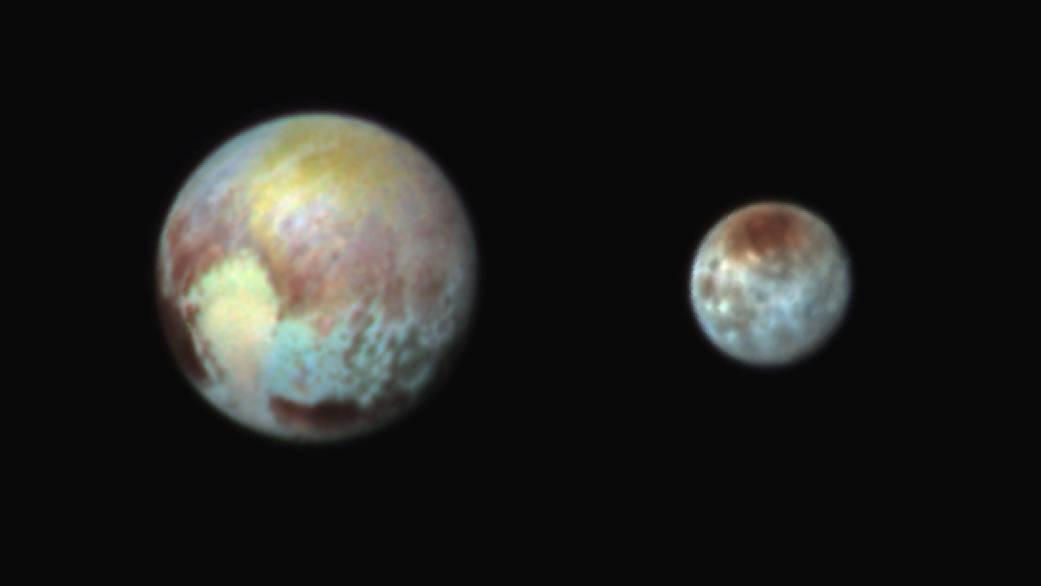

This July 13, 2015, image of Pluto and Charon is presented in false colors to make differences in surface material and features easy to see. It was obtained by the Ralph instrument on NASA's New Horizons spacecraft, using three filters to obtain color information, which is exaggerated in the image. These are not the actual colors of Pluto and Charon, and the apparent distance between the two bodies has been reduced for this side-by-side view. The image reveals that the bright heart-shaped region of Pluto includes areas that differ in color characteristics. The western lobe, shaped like an ice-cream cone, appears peach color in this image. A mottled area on the right (east) appears bluish. Even within Pluto's northern polar cap, in the upper part of the image, various shades of yellow-orange indicate subtle compositional differences. The surface of Charon is viewed using the same exaggerated color. The red on the dark northern polar cap of Charon is attributed to hydrocarbon materials including a class of chemical compounds called tholins. The mottled colors at lower latitudes point to the diversity of terrains on Charon. This image was taken at 3:38 a.m. EDT on July 13, one day before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19707
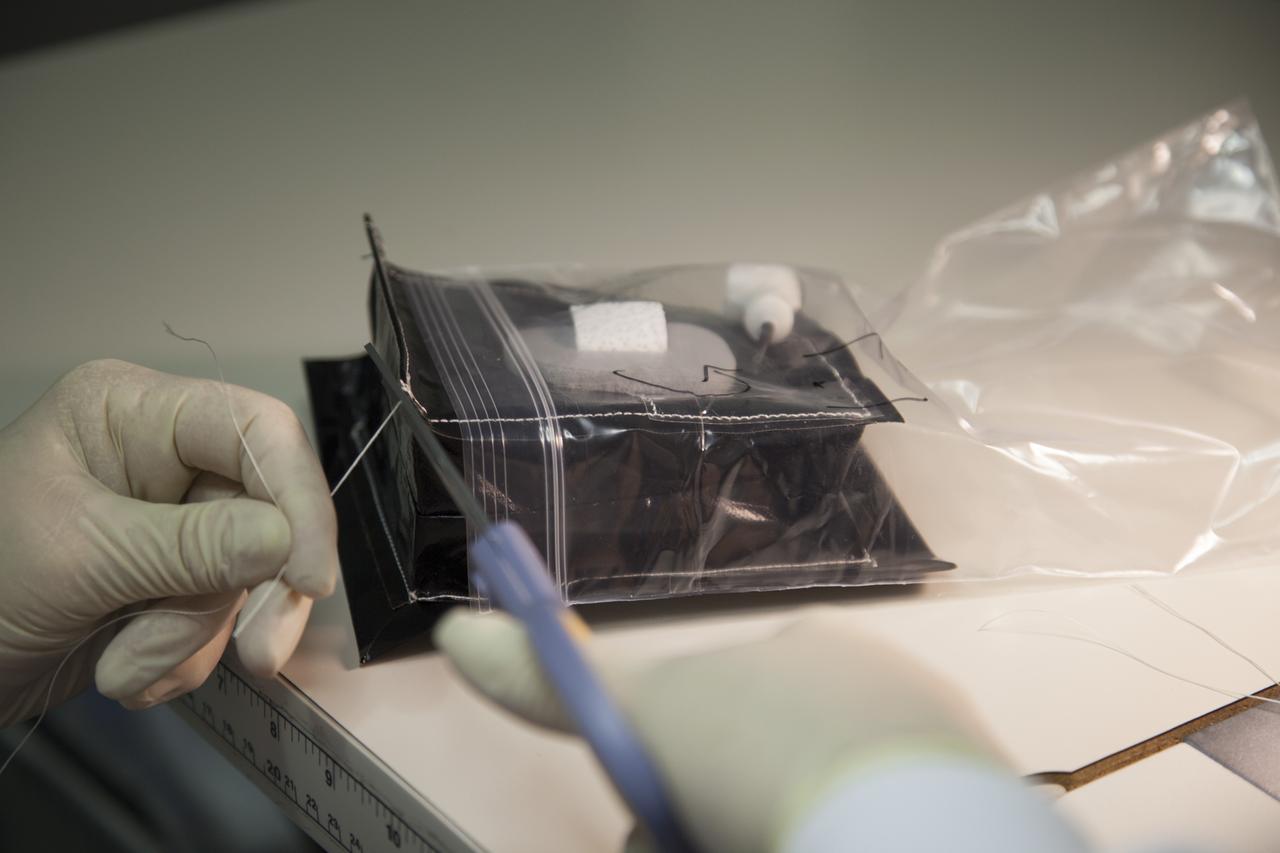
Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Michele Koralewicz, a mechanical technician with EASI on the Engineering Services Contract, sews up the end of a bag that contains one of the Veg-03 plant pillows. The Veg-03 experiment will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard the eighth SpaceX Dragon commercial resupply mission. The Veg-03 plant pillows will contain ‘Tokyo Bekana’ cabbage seeds and lettuce seeds for NASA’s third Veggie plant growth system experiment. The experiment will continue NASA’s deep space plant growth research to benefit the Earth and the agency’s journey to Mars.
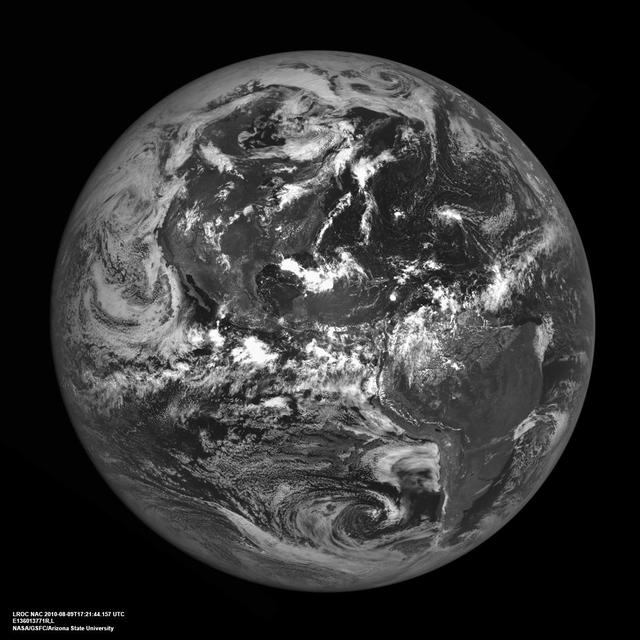
The western hemisphere of our home planet Earth. North (upper left), Central, and South America (lower right) were nicely free of clouds when LRO pointed home on 9 August 2010 to acquire this beautiful view. LROC NAC E136013771. As LRO orbits the Moon every two hours sending down a stream of science data, it is easy to forget how close the Moon is to the Earth. The average distance between the two heavenly bodies is just 384,399 km (238,854 miles). Check your airline frequent flyer totals, perhaps you have already flown the distance to the Moon and back on a single airline. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA13519
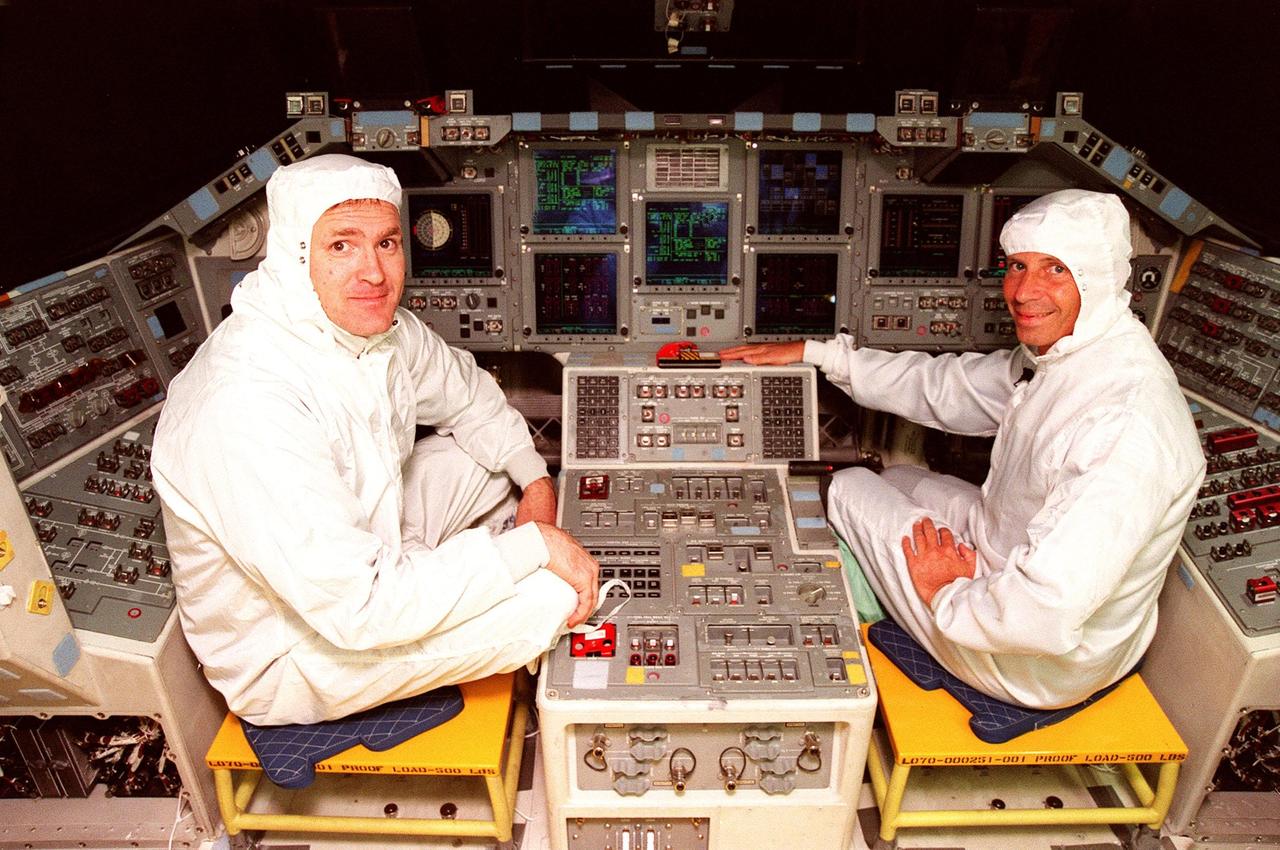

STS-101 Commander James Halsell (left) and STS-98 Commander Ken Cockrell (right) pause for a photo while looking over the recently installed Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS) in the cockpit of the orbiter Atlantis. The new full-color, flat panel MEDS improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed. The installation makes Atlantis the most modern orbiter in the fleet and equals the systems on current commercial jet airliners and military aircraft. The first flight of the upgraded Atlantis is STS-101, scheduled for launch in December 1999; the second flight, STS-98, is scheduled for launch in April 2000
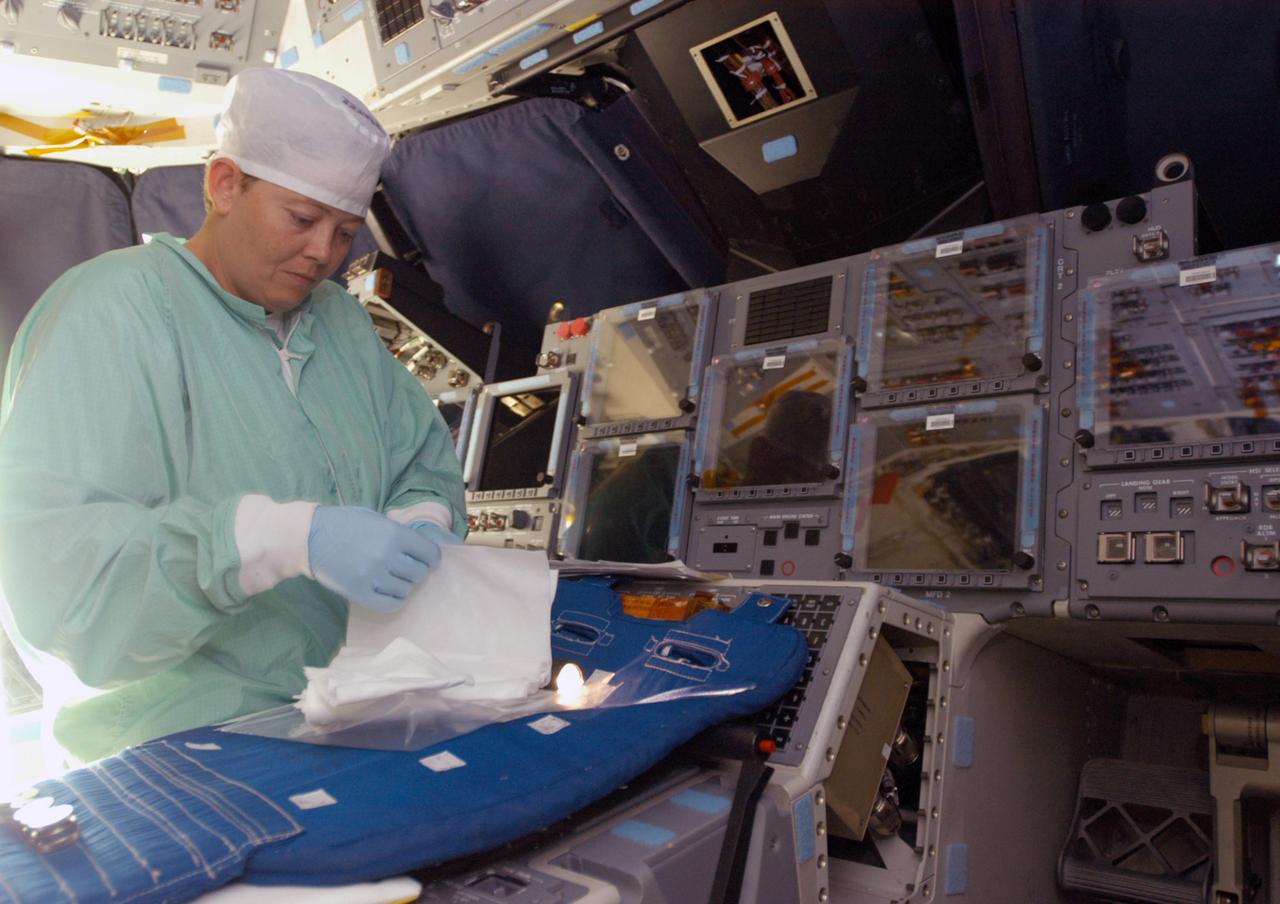
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Carmen Prater, with United Space Alliance, works on the flight deck of the orbiter Endeavour in bay 2 of the Orbiter Processing Facility. She wears a “bunny suit,” clean room attire required for anyone coming in close proximity to the orbiter. Endeavour is undergoing major modifications, which include inspecting more than 150 miles of wiring, bonding 1,000 thermal tiles, and installing the Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem - a state-of-the-art “glass cockpit.” The full-color, flat-panel MEDS upgrade improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed.
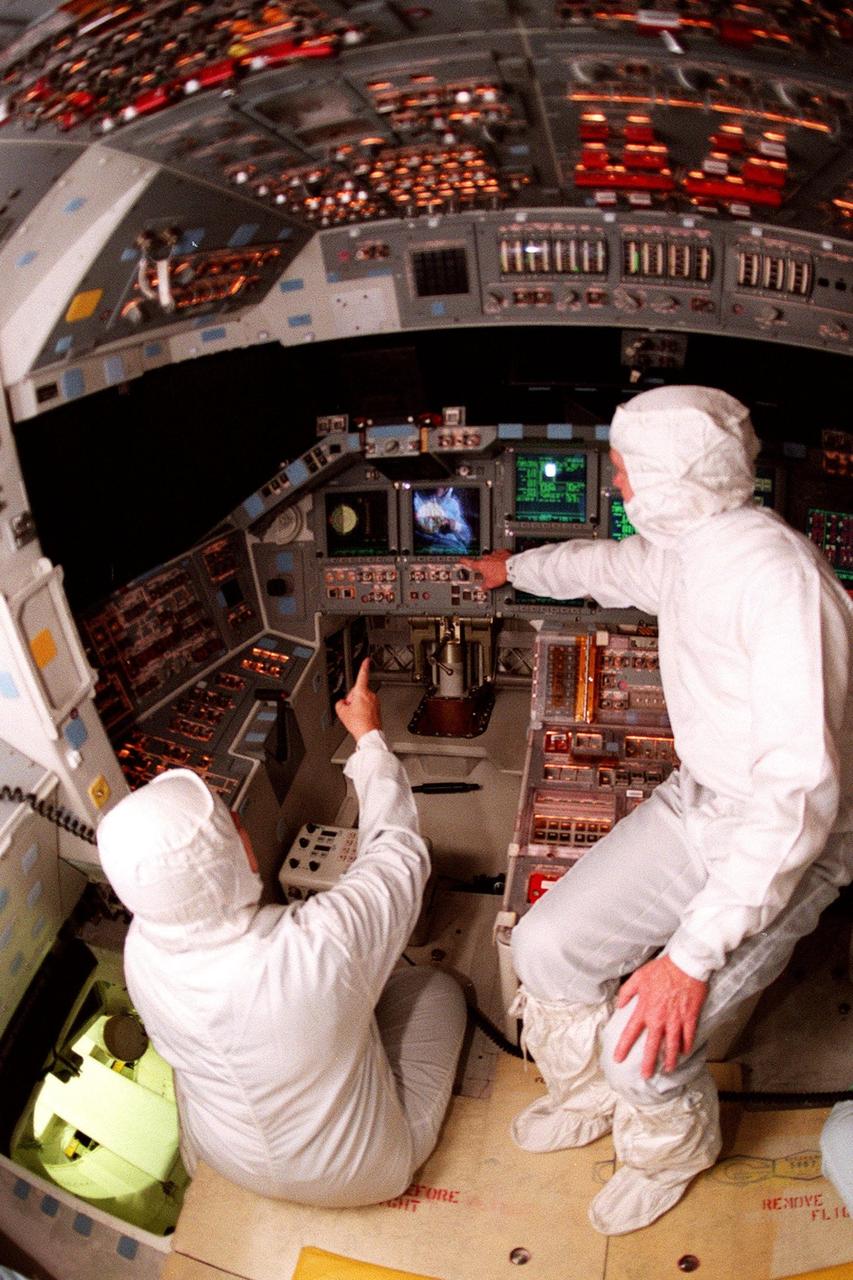

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the orbiter Atlantis, JoAnn Morgan, Associate Director for Advanced Development and Shuttle Upgrades, and Roy Bridges Jr., Center Director, get a closeup view of the new full-color flat panel Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS), also called the "glass cockpit." The MEDS upgrade improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed. The installation makes Atlantis the most modern orbiter in the fleet and equals the systems on current commercial jet airliners and military aircraft. Atlantis is scheduled to fly on mission STS-101 in early December

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Carmen Prater, with United Space Alliance, cleans a screen on the flight deck of the orbiter Endeavour in bay 2 of the Orbiter Processing Facility. She wears a “bunny suit,” clean room attire required for anyone coming in close proximity to the orbiter. Endeavour is undergoing major modifications, which include inspecting more than 150 miles of wiring, bonding 1,000 thermal tiles, and installing the Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem - a state-of-the-art “glass cockpit.” The full-color, flat-panel MEDS upgrade improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed.
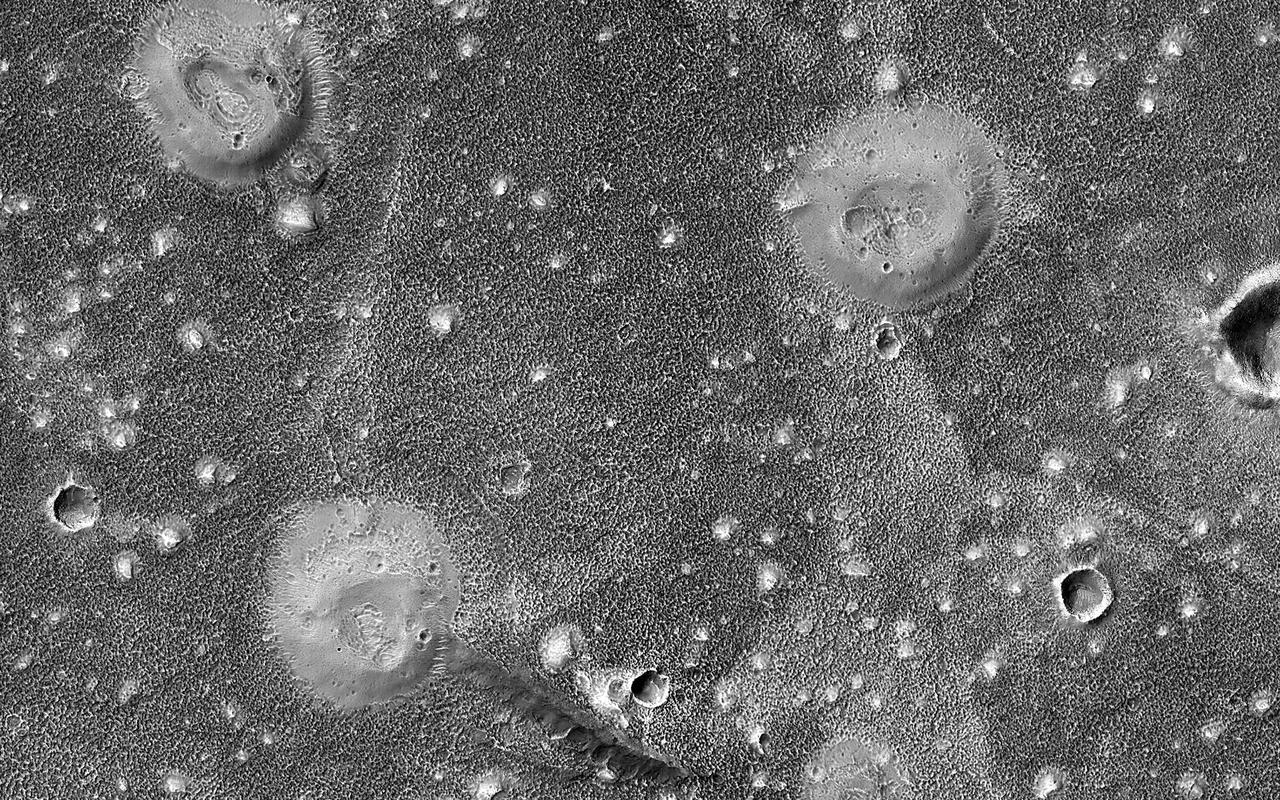

The northern lowlands of Mars in this location are stippled with mounds, such as those visible throughout this image. These lighter-toned circular mounds with bowl-shaped depressions are easy to spot against the darker-toned floor. Scientists think these landforms are similar to mud volcanoes that are also found here on Earth. Mud volcanoes form as gas and liquid-rich sediment interacts underground. Over time, this slurry of mud is brought to the surface and forms a rounded mound. Scientists are interested in studying mud volcanoes on Mars because the material forming the mound has the potential to be organic in nature and would give insight into possible microbial life below the surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25987
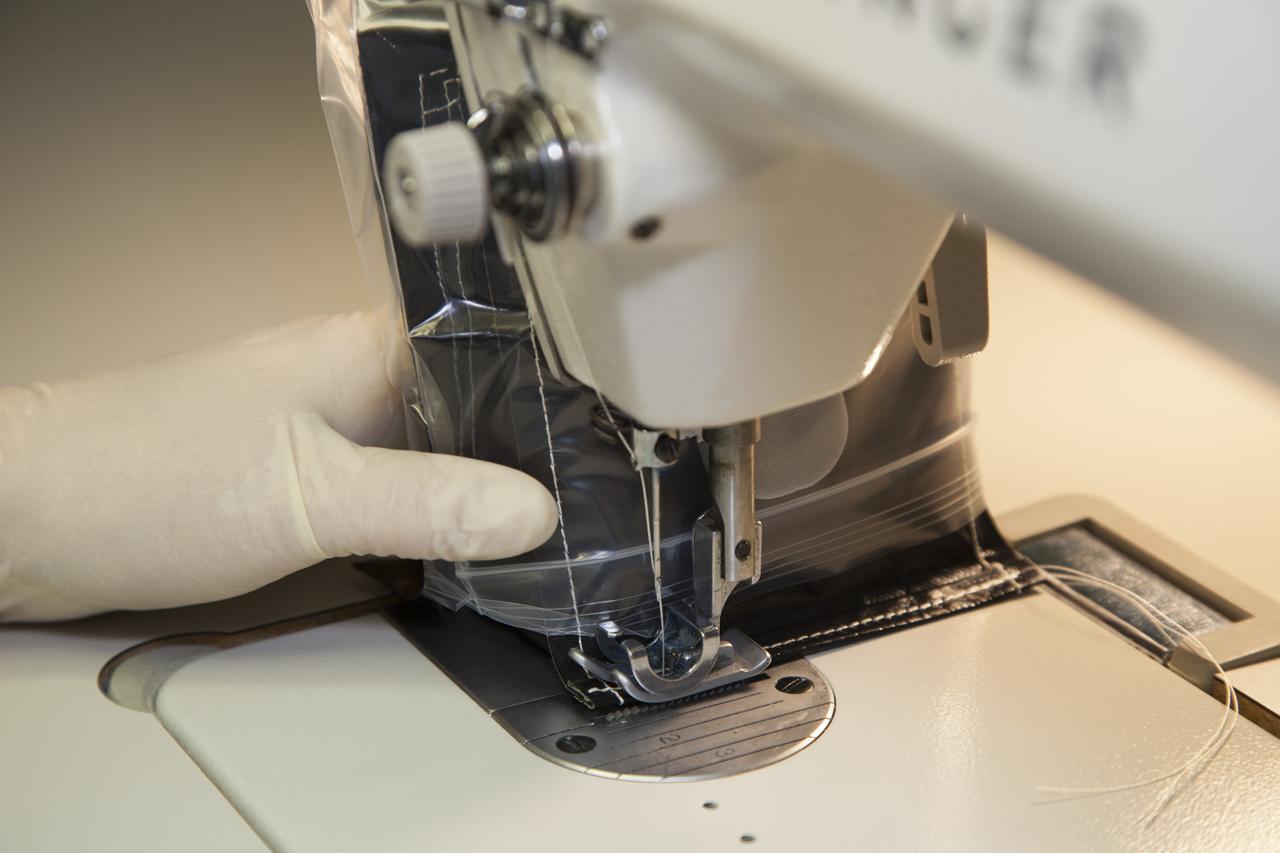

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Michele Koralewicz, a mechanical technician with EASI on the Engineering Services Contract, precisely sews up the end of a bag that contains one of the Veg-03 plant pillows. The Veg-03 experiment will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard the eighth SpaceX Dragon commercial resupply mission. The Veg-03 plant pillows will contain ‘Tokyo Bekana’ cabbage seeds and lettuce seeds for NASA’s third Veggie plant growth system experiment. The experiment will continue NASA’s deep space plant growth research to benefit the Earth and the agency’s journey to Mars.
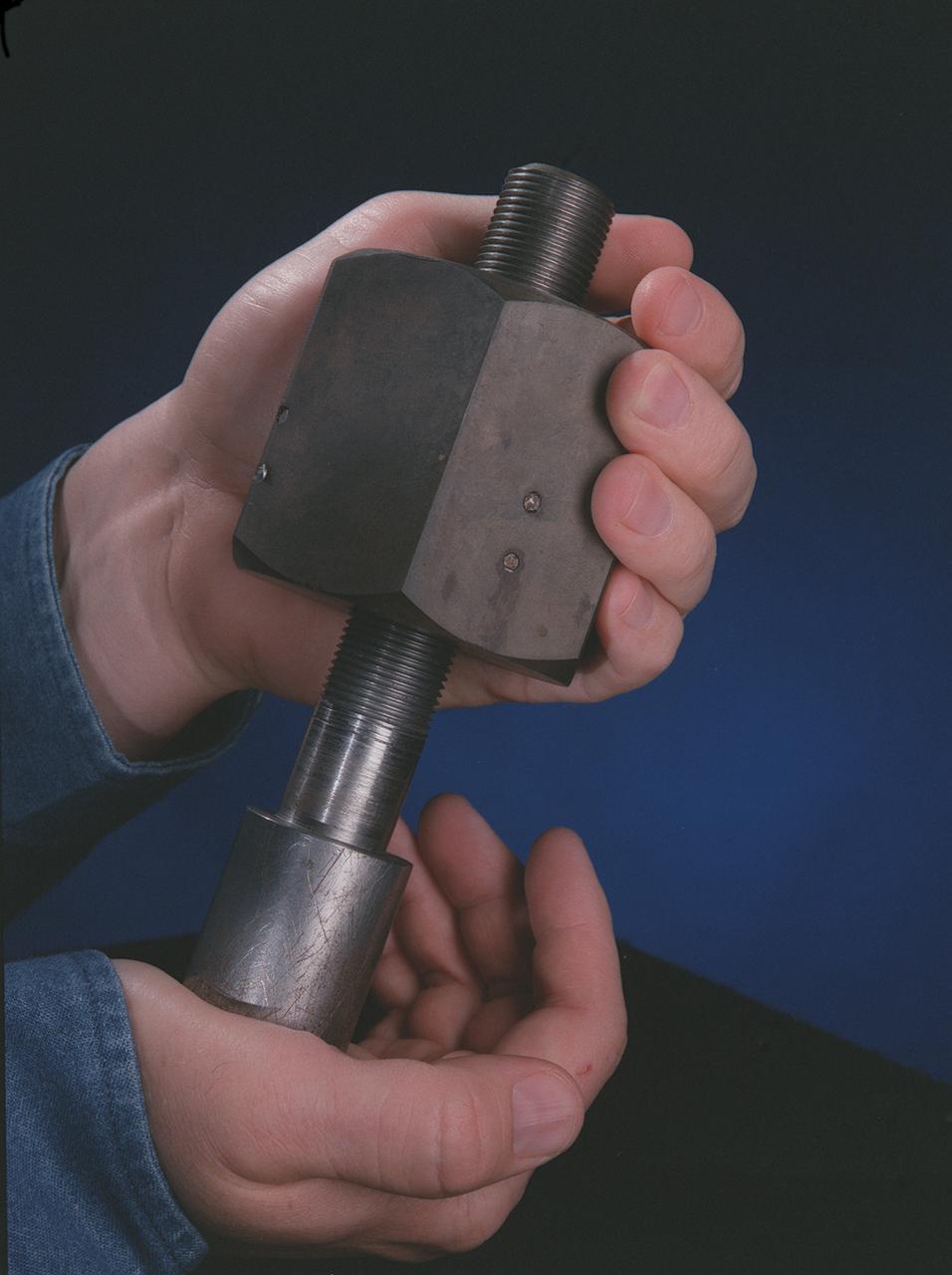

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) has developed a specially-designed nut, called the Quick-Connect Nut, for quick and easy assembly of components in the harsh environment of space, as in assembly of International Space Station. The design permits nuts to be installed simply by pushing them onto standard bolts, then giving a quick twist. To remove, they are unscrewed like conventional nuts. Possible applications include the mining industry for erecting support barriers, assembling underwater oil drilling platforms, fire-fighting equipment, scaffolding, assembly-line machinery, industrial cranes, and even changing lug nuts on race cars. The speed of assembly can make the difference between life and death in different aspects of life on Earth.
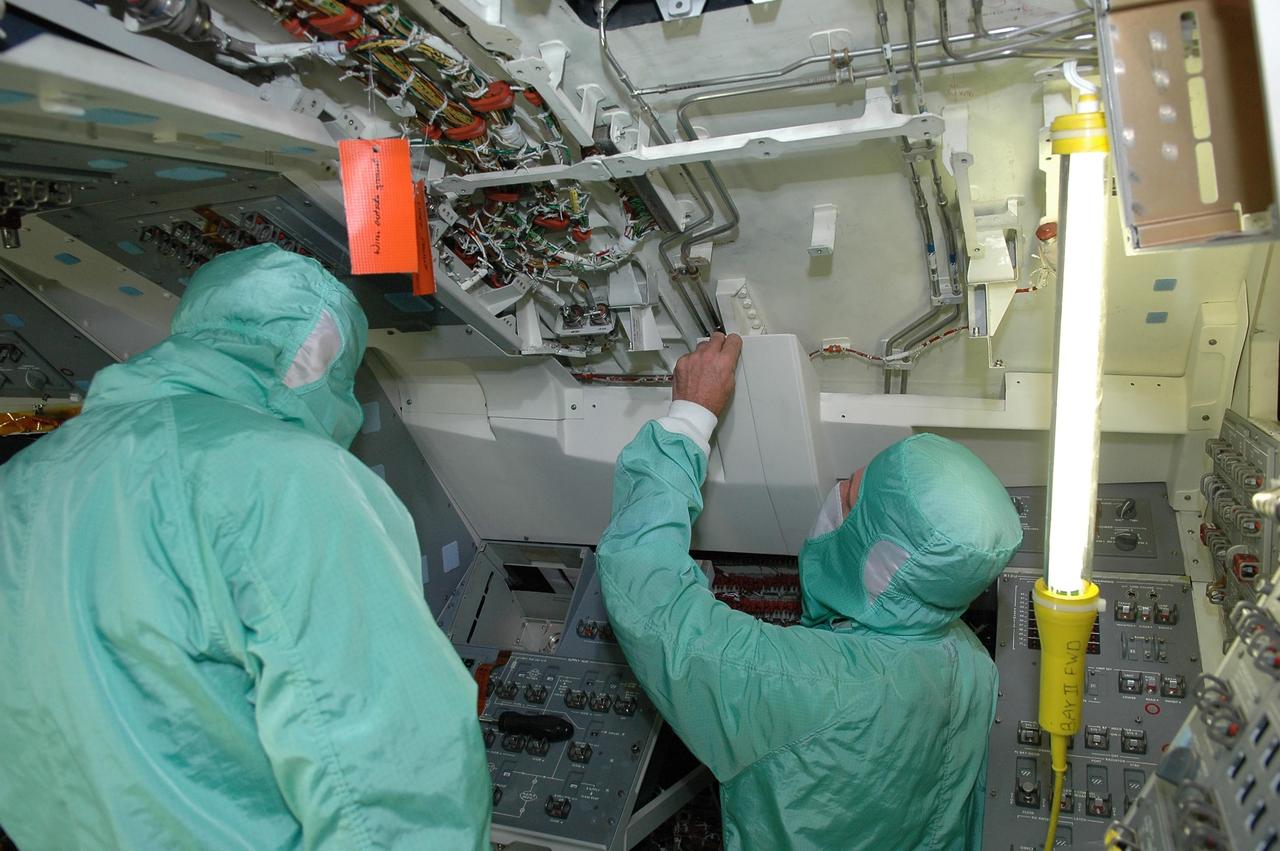

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In bay 2 of the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers are installing the Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem - a state-of-the-art “glass cockpit” - on the orbiter Endeavour. The “bunny suits” they are wearing are clean room attire required for anyone coming in close proximity to the orbiter. The full-color, flat-panel MEDS upgrade improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed. Endeavour is undergoing major modifications, which include inspecting more than 150 miles of wiring and bonding 1,000 thermal tiles, along with installing the display system.
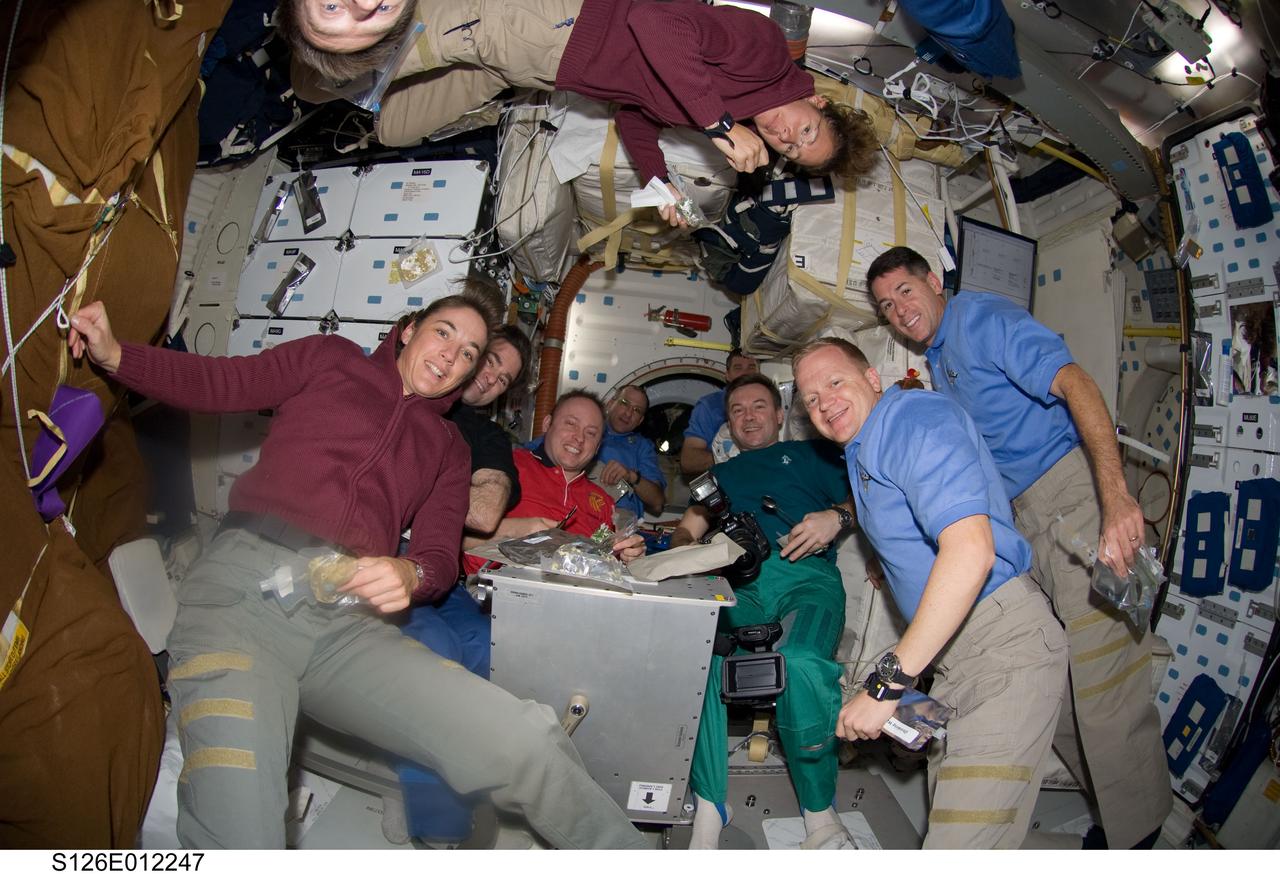

S126-E-012247 (27 Nov. 2008) --- Getting all ten members of an aggregation consisting of seven Endeavour astronauts and three Expedition 18 crewmembers into a single photo wasn't easy as the two crews shared a Thanksgiving meal on the middeck of the orbiter. Astronaut Sandra Magnus, Expedition 18 flight engineer, appears at top center. Clockwise from her position are astronauts Shane Kimbrough and Eric Boe, along with cosmonaut Yury Lonchakov, and astronauts Steve Bowen (partially visible behind Lonchakov), Donald Pettit, Michael Fincke, Gregory Chamitoff, Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper and Chris Ferguson (partially visible at top right). Ferguson is STS-126 commander, and Fincke is commander for the station crew.
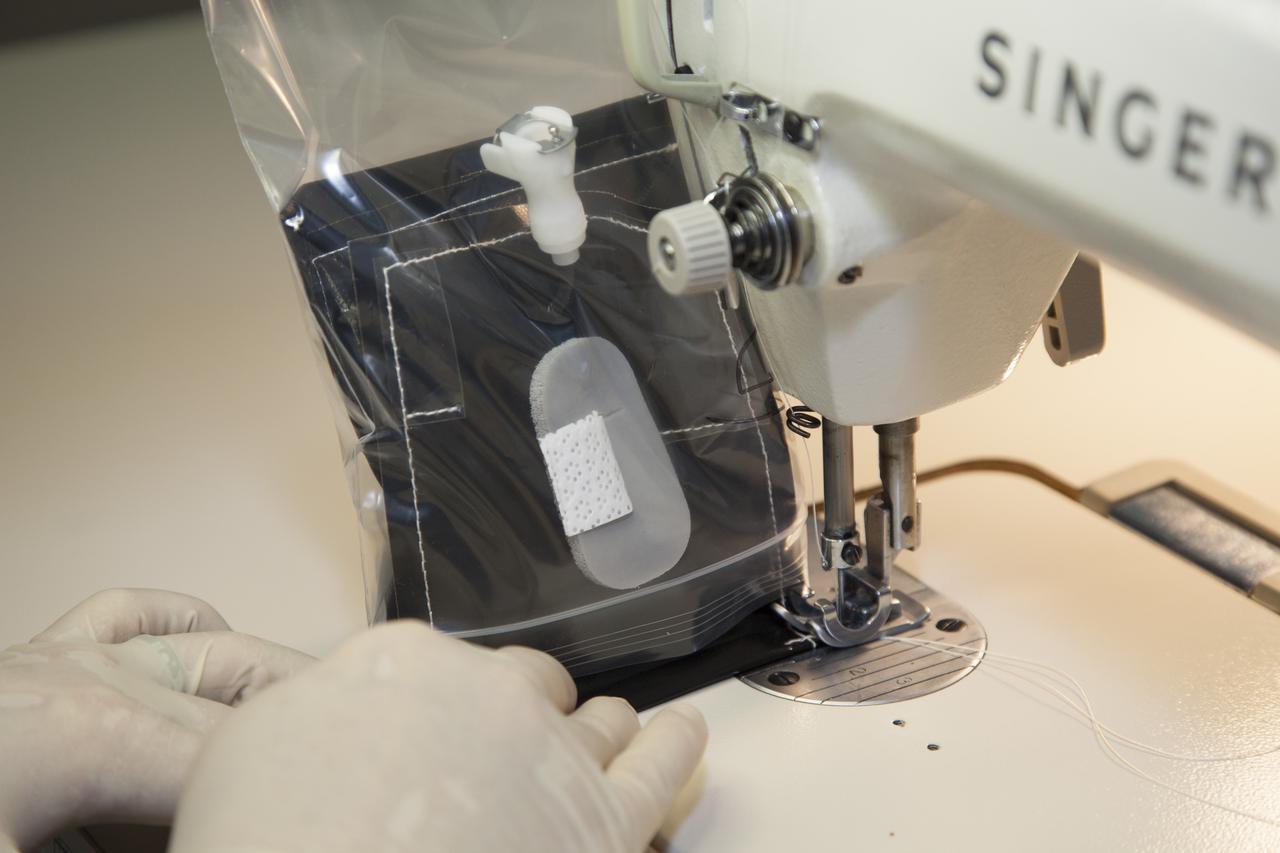

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Michele Koralewicz, a mechanical technician with EASI on the Engineering Services Contract, sews up the end of a bag that contains one of the Veg-03 plant pillows. The Veg-03 experiment will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard the eighth SpaceX Dragon commercial resupply mission. The Veg-03 plant pillows will contain ‘Tokyo Bekana’ cabbage seeds and lettuce seeds for NASA’s third Veggie plant growth system experiment. The experiment will continue NASA’s deep space plant growth research to benefit the Earth and the agency’s journey to Mars.

Magnetic arcs of solar material spewing from our favorite sphere of hot plasma, the sun. Magnetic arcs of solar material held their shapes fairly well as they spiraled above two solar active regions over 18 hours on Jan. 11-12, 2017. The charged solar material, called plasma, traces out the magnetic field lines above the active regions when viewed in wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light, captured here by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory. Extreme ultraviolet light is typically invisible to our eyes, but is colorized here in gold for easy viewing. Credit: NASA/SDO
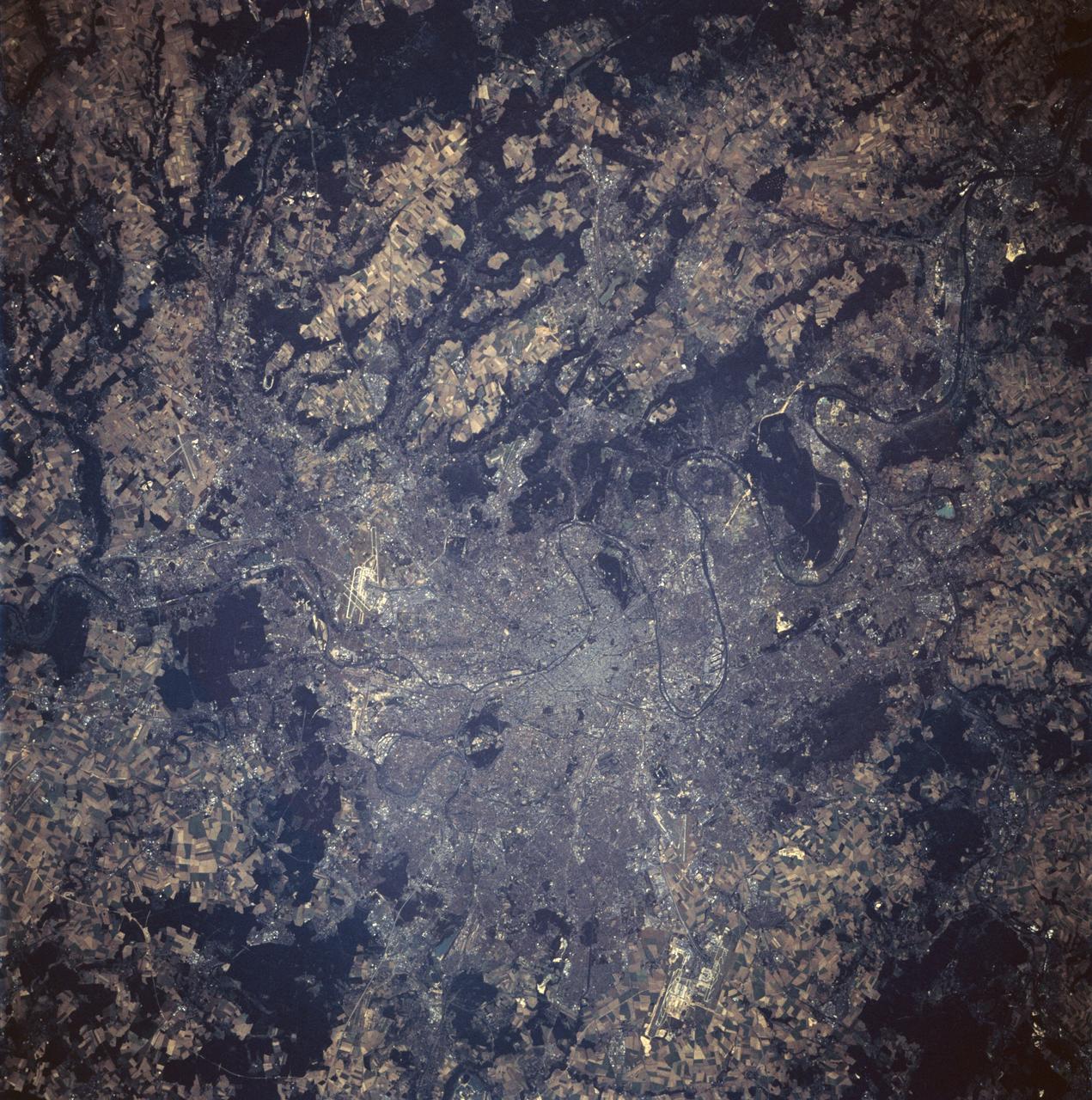

STS047-94-010 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- This 250mm Hasselblad color photo of Paris, France recorded during this mission, shows urban land uses in great detail. Several airports are clear, including the two major international airports of Orly and Le Bourget. Paris was founded in pre-Roman times on an island in the Seine River and continued as a Roman outpost. The easily defensible location was one of the keys to the growth of this island city. The city expanded from its island state to become a major urban center in Europe because of its location, its easy access by river traffic, and its productive hinterland.

Solar material repeatedly bursts from the sun in this close-up captured on July 9-10, 2016, by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. The sun is composed of plasma, a gas in which the negative electrons move freely around the positive ions, forming a powerful mix of charged particles. Each burst of plasma licks out from the surface only to withdraw back into the active region – a dance commanded by complex magnetic forces above the sun. SDO captured this video in wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light, which are typically invisible to our eyes. The imagery is colorized here in red for easy viewing. Credit: NASA/SDO/Goddard Space Flight Center/Joy Ng
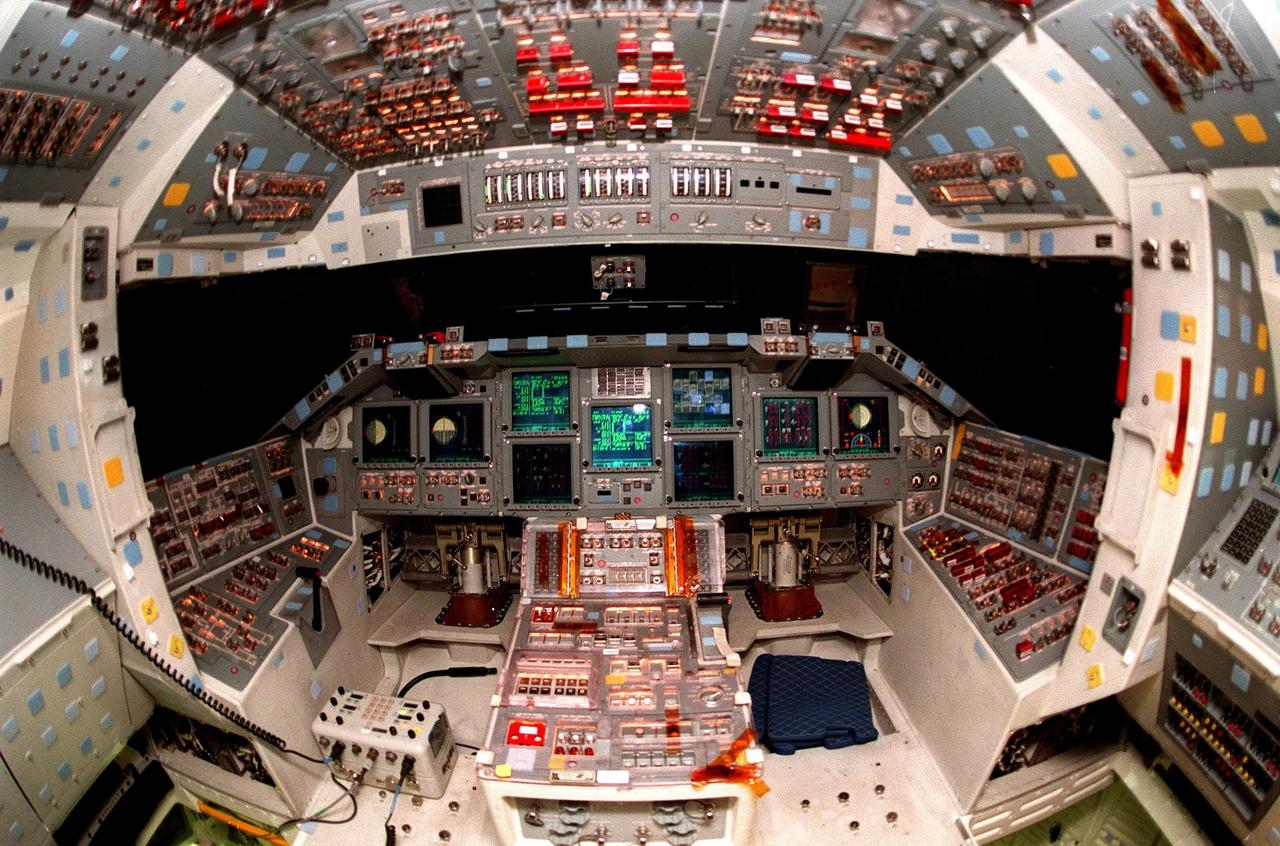

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The cockpit of the orbiter Atlantis is seen in the round, revealing the new full-color flat panel Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS), also called the "glass cockpit." The recently installed MEDS upgrade improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed. The installation makes Atlantis the most modern orbiter in the fleet and equals the systems on current commercial jet airliners and military aircraft. Atlantis is scheduled to fly on mission STS-101 in early December
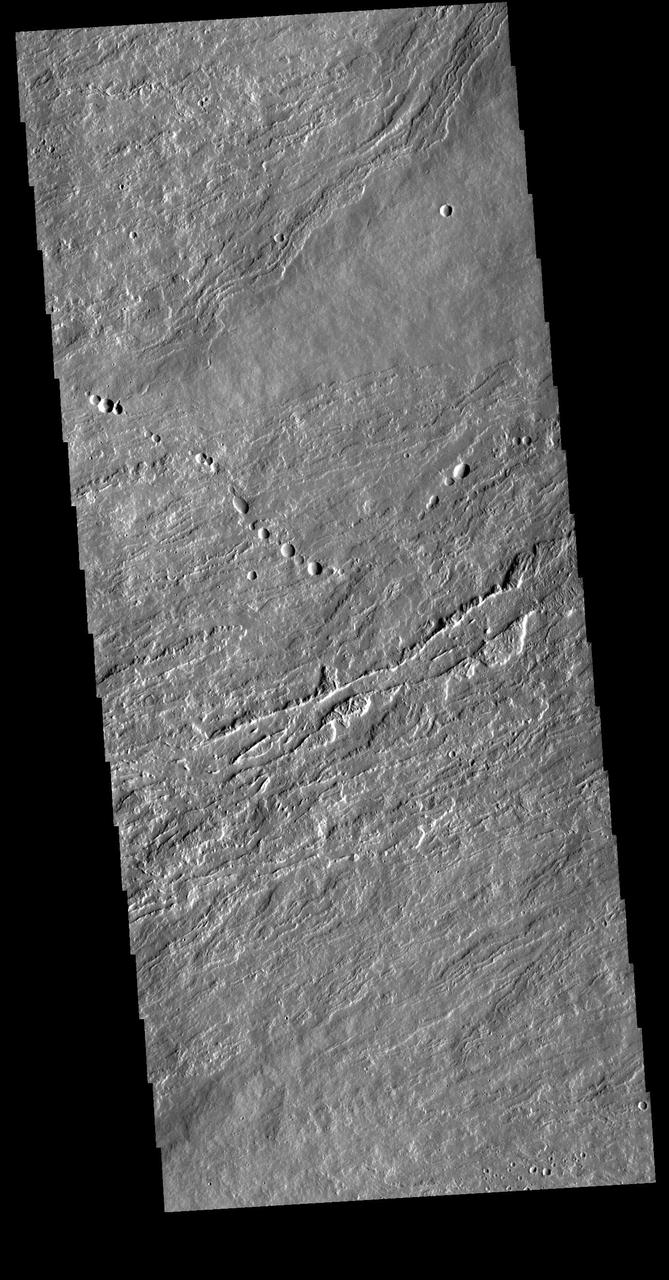

Today's VIS image shows flank flows on the east side of Olympus Mons. Olympus Mons stands 26 km (16 miles) above the surrounding plains, which is three times taller than Mt. Everest, and is the tallest volcano in the solar system. Olympus Mons is also wider (585 km, 363 miles) than the state of Arizona. Although these are impressive dimensions an astronaut would find walking these slopes easy, as they are typically only 2 to 5 degrees. This image contains numerous lava flows, leveed lava channels, and a series of round depressions thought to be where the roof of a lava tube has collapsed into the underlying void. Orbit Number: 81077 Latitude: 19.9207 Longitude: 231.287 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-03-25 04:51 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23928

SL4-137-3579 (13 Dec. 1973) --- A near vertical view of the Melbourne, State of Victoria, Australia area as seen from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. This picture was taken by one of the Skylab 4 crewmen using a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera. Included in this view are Port Phillip Bay, Ninety-Mile Beach and the Australian Alps. This view is not in sunglint. Compare this view with that of SL4-137-3578 which is in sunglint. Colors are not easy to distinguish in sunglint, but are without it. There are surface features visible in the first photograph which are not visible in the second. Similarly, some water colors are evident in the second photograph which are not seen in the first. Port Phillip Bay is the best sample. The bay opens to the south. Photo credit: NASA
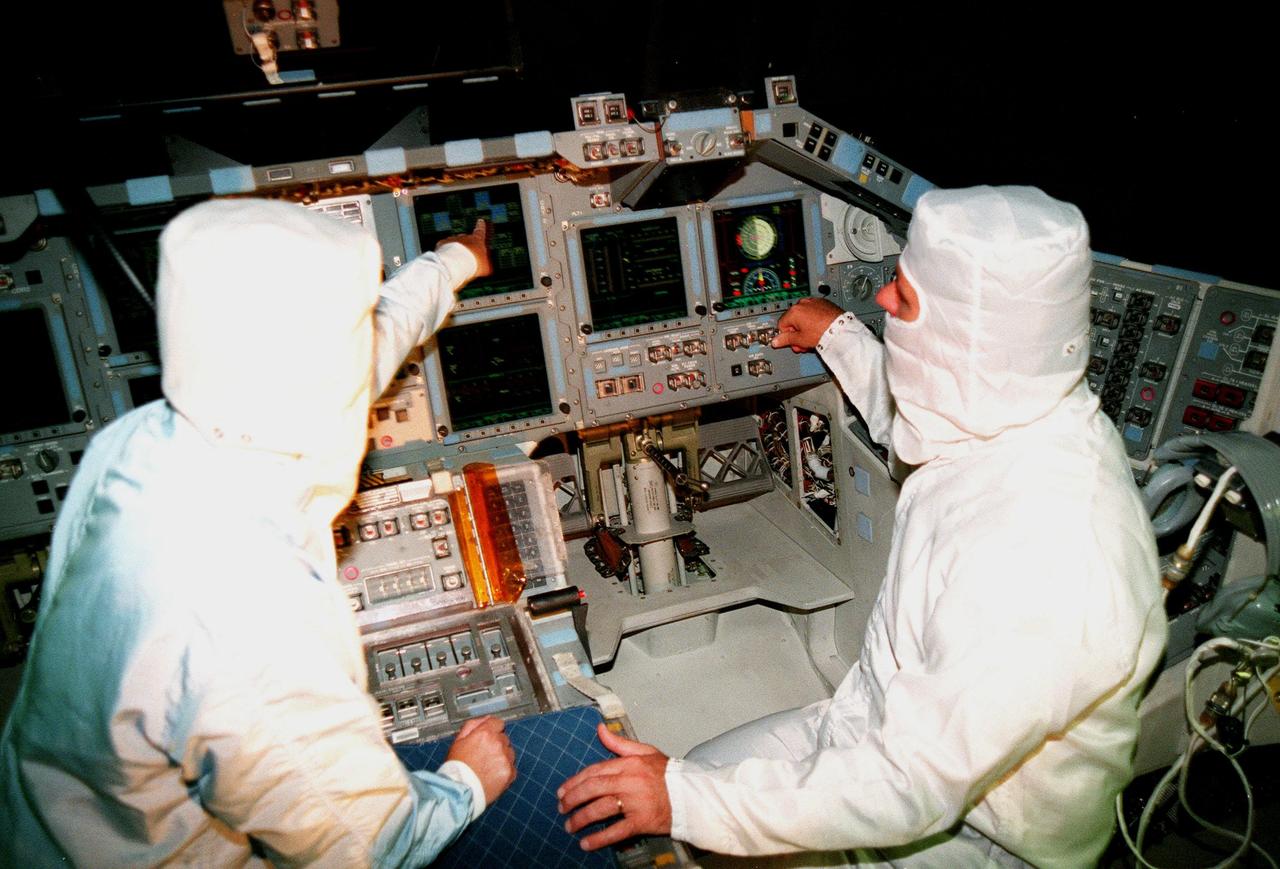

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the cockpit of the orbiter Atlantis, which is in the Orbiter Processing Facility, Laural Patrick (left), a systems engineer with MEDS, points out a feature of the newly installed Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS), known as the "glass cockpit," to U.S. Rep. Dave Weldon. The congressman is on the House Science Committee and vice chairman of the Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee. He was in Palmdale, Calif., when Atlantis underwent the modification and he wanted to see the final product. The full-color, flat-panel MEDS upgrade improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed. The installation makes Atlantis the most modern orbiter in the fleet and equals the systems on current commercial jet airliners and military aircraft. Atlantis is scheduled to fly on mission STS-101 in early December

STS-101 Commander James Halsell (left) and STS-98 Commander Ken Cockrell (right) look over the recently installed Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS) in the cockpit of the orbiter Atlantis, which each will command on their upcoming respective missions. The new full-color, flat panel MEDS improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed. The installation makes Atlantis the most modern orbiter in the fleet and equals the systems on current commercial jet airliners and military aircraft. . The first flight of the upgraded Atlantis is STS-101, scheduled for launch in December 1999; the second flight, STS-98, is scheduled for launch in April 2000
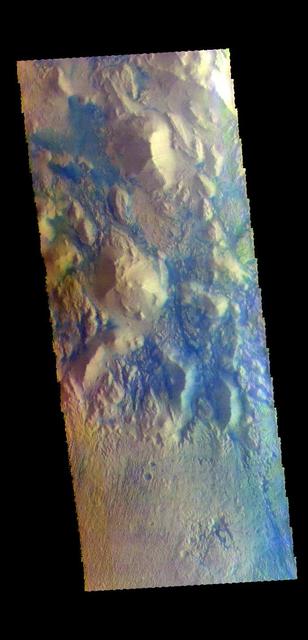
The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of the region between Terra Cimmeria and Aeolis Planum. The bottom half of the image is a surface that has been etched by wind action. To form the fine scale grooves, the surface material must be easy to erode. In the hills at the top of the image the same fine scale groove features don't exist. In this region the hills are partially surrounded by material that is blue in this false color combination. Dark blue is interpreted to be basaltic sand. It is possible that the sand in the top of the image was scoured from the surface in the bottom of the image. Orbit Number: 68393 Latitude: -7.61871 Longitude: 150.994 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-05-15 11:31 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24077

SL4-137-3578 (13 Dec. 1973) --- A near vertical view of the Melbourne, State of Victoria, Australia area as seen from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. Note sunglint. This picture was taken by one of the Skylab 4 crewmen using a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera. Included in this view are Port Phillip Bay, Ninety-Mile Beach and the Australian Alps. In general, sunglint allows best viewing of ocean surface features. Compare this view with that of SL4-137-3579 which is not in sunglint. Colors are not easy to distinguish in sunglint, but are without it. There are surface features visible in the first photograph which are not visible in the second. Similarly, some water colors are evident in the second photograph which are not seen in the first. Port Phillip is the best sample. The bay opens to the south. Photo credit: NASA
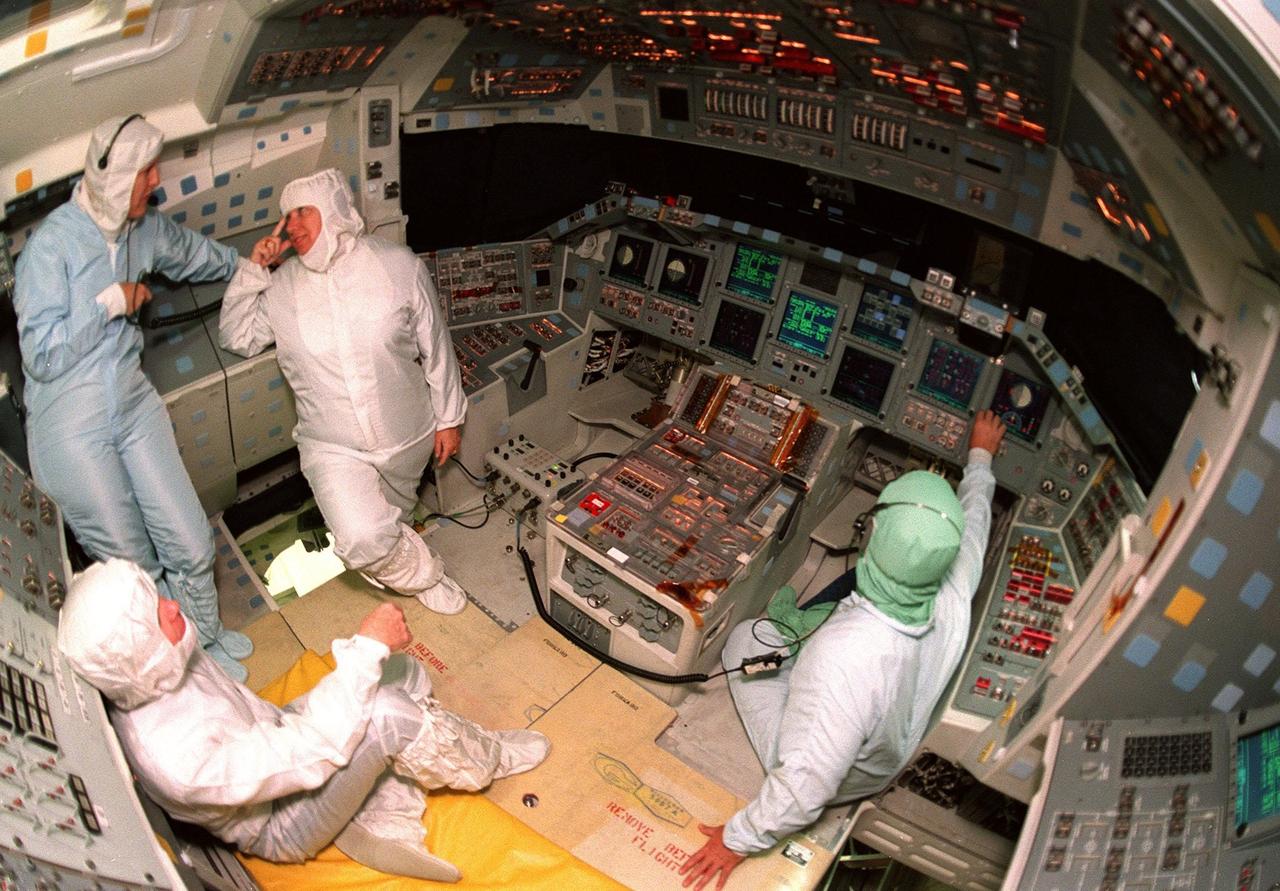

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the orbiter Atlantis, Center Director Roy Bridges (seated at bottom left) and Associate Director for Advanced Development and Shuttle Upgrades JoAnn Morgan (standing second from left) learn about the new Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS) from Laural Patrick (standing left), a systems engineer with MEDS, and George Selina (at right), with United Space Alliance. Also called the "glass cockpit," the new full-color flat panel MEDS upgrade improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed. The installation makes Atlantis the most modern orbiter in the fleet and equals the systems on current commercial jet airliners and military aircraft. Atlantis is scheduled to fly on mission STS-101 in early December
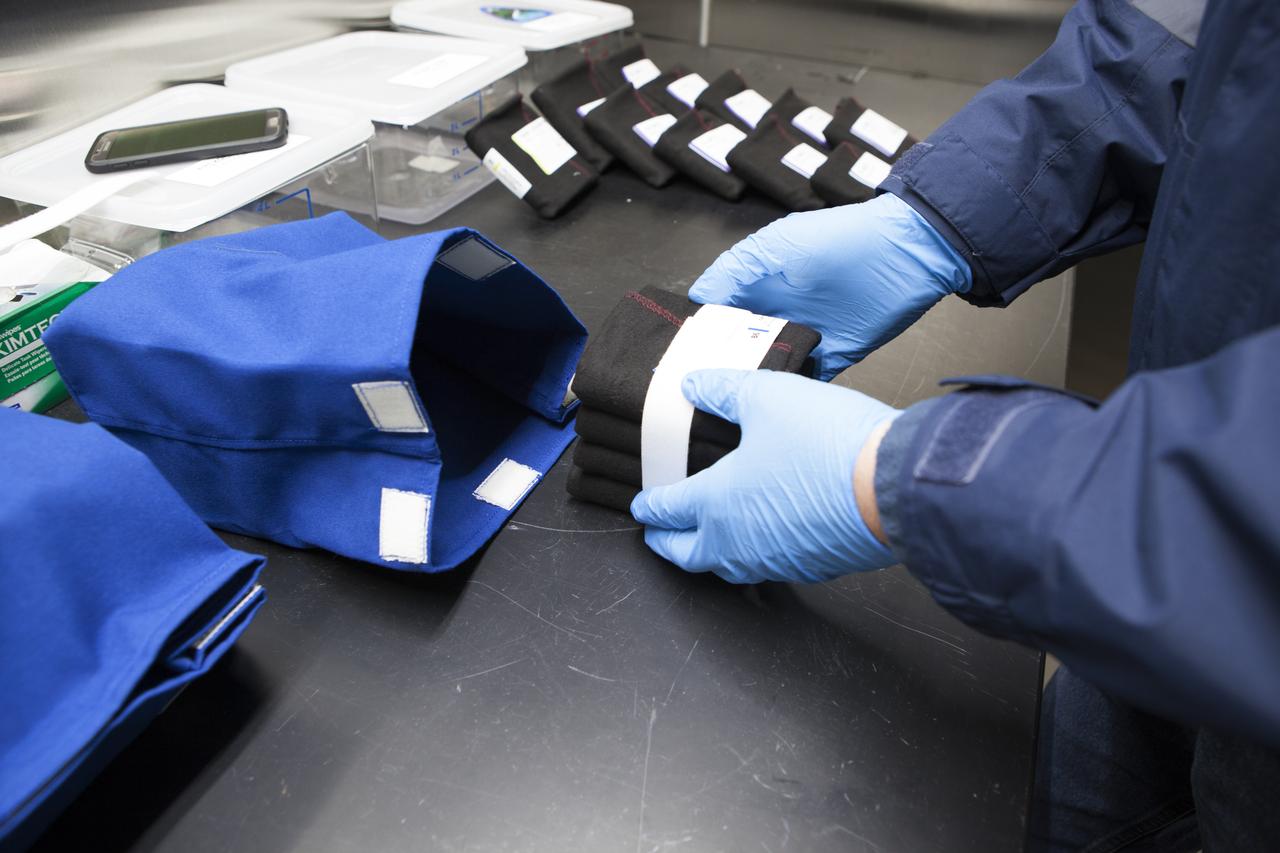

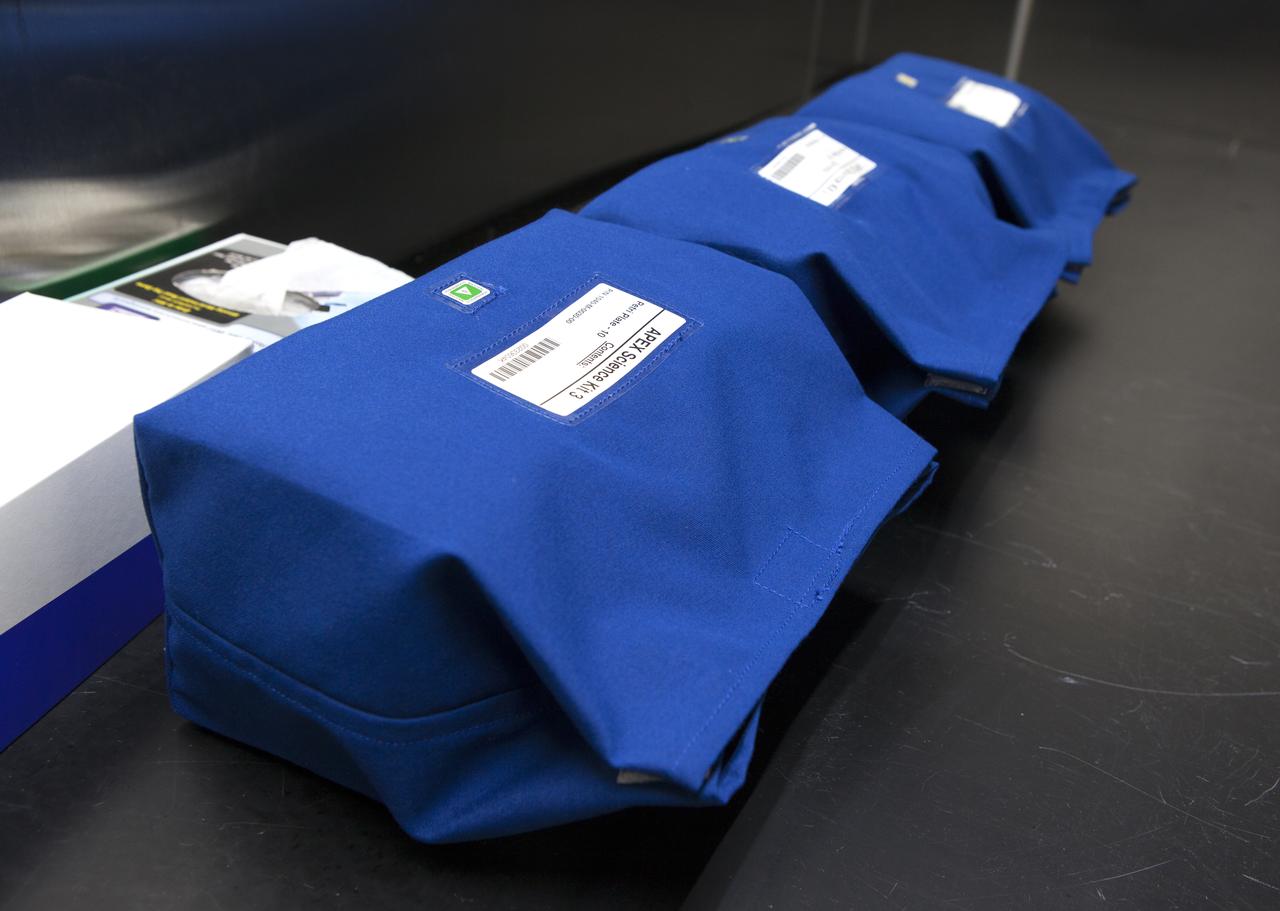
APEX-04, or Advanced Plant EXperiments-04, is being prepared in a cold room in the Kennedy Space Center Processing Facility for SpaceX-10. The 30 petri plates are bundled into groups of 10 and placed into one of three science kits. The science kits allow easy handling when the crew removes the plates from cold stowage on station. Dr. Anna Lisa Paul of the University of Florida is the principal investigator for APEX-04. Apex-04 is an experiment involving Arabidopsis in petri plates inside the Veggie facility aboard the International Space Station. Since Arabidopsis is the genetic model of the plant world, it is a perfect sample organism for performing genetic studies in spaceflight. The experiment is the result of a grant from NASA’s Space Life and Physical Sciences division.
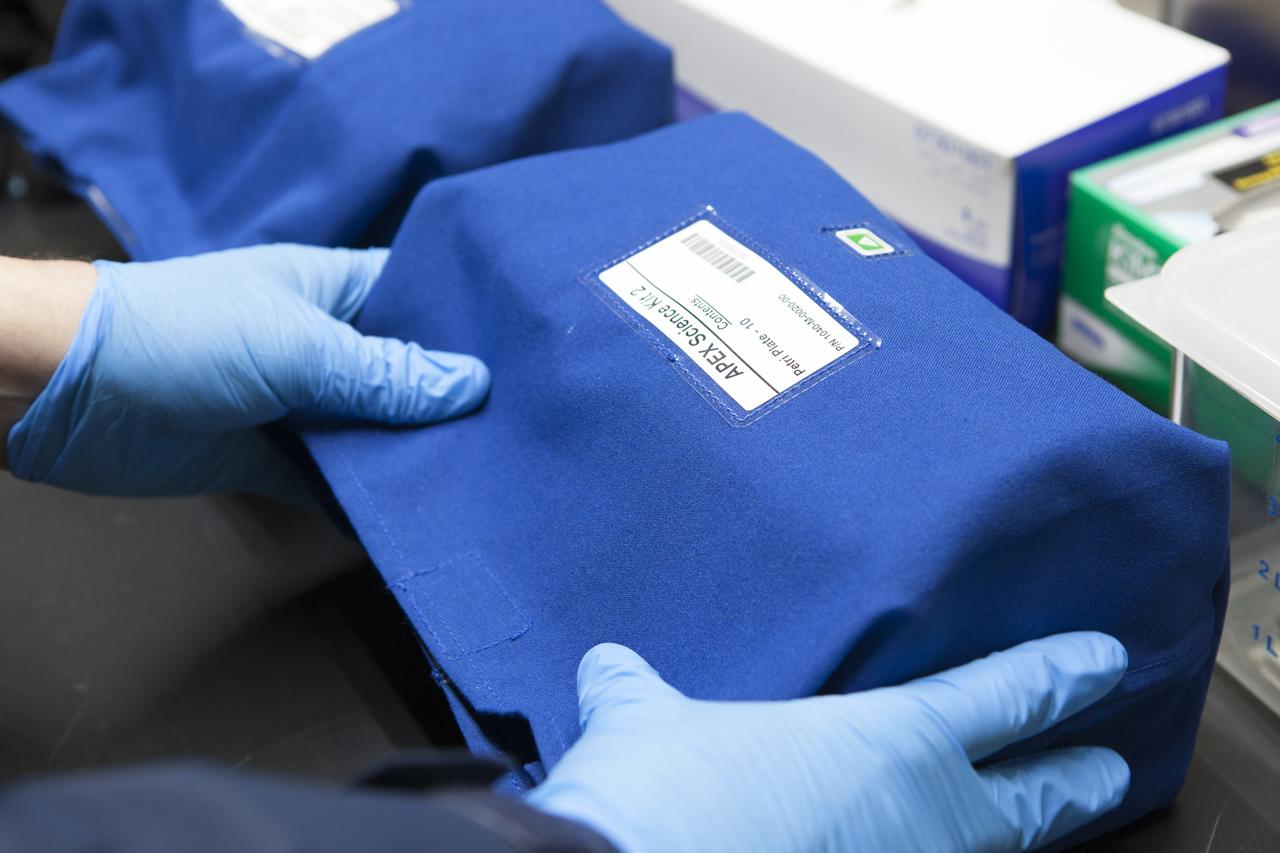

APEX-04, or Advanced Plant EXperiments-04, is being prepared in a cold room in the Kennedy Space Center Processing Facility for SpaceX-10. The 30 petri plates are bundled into groups of 10 and placed into one of three science kits. The science kits allow easy handling when the crew removes the plates from cold stowage on station. Dr. Anna Lisa Paul of the University of Florida is the principal investigator for APEX-04. Apex-04 is an experiment involving Arabidopsis in petri plates inside the Veggie facility aboard the International Space Station. Since Arabidopsis is the genetic model of the plant world, it is a perfect sample organism for performing genetic studies in spaceflight. The experiment is the result of a grant from NASA’s Space Life and Physical Sciences division.
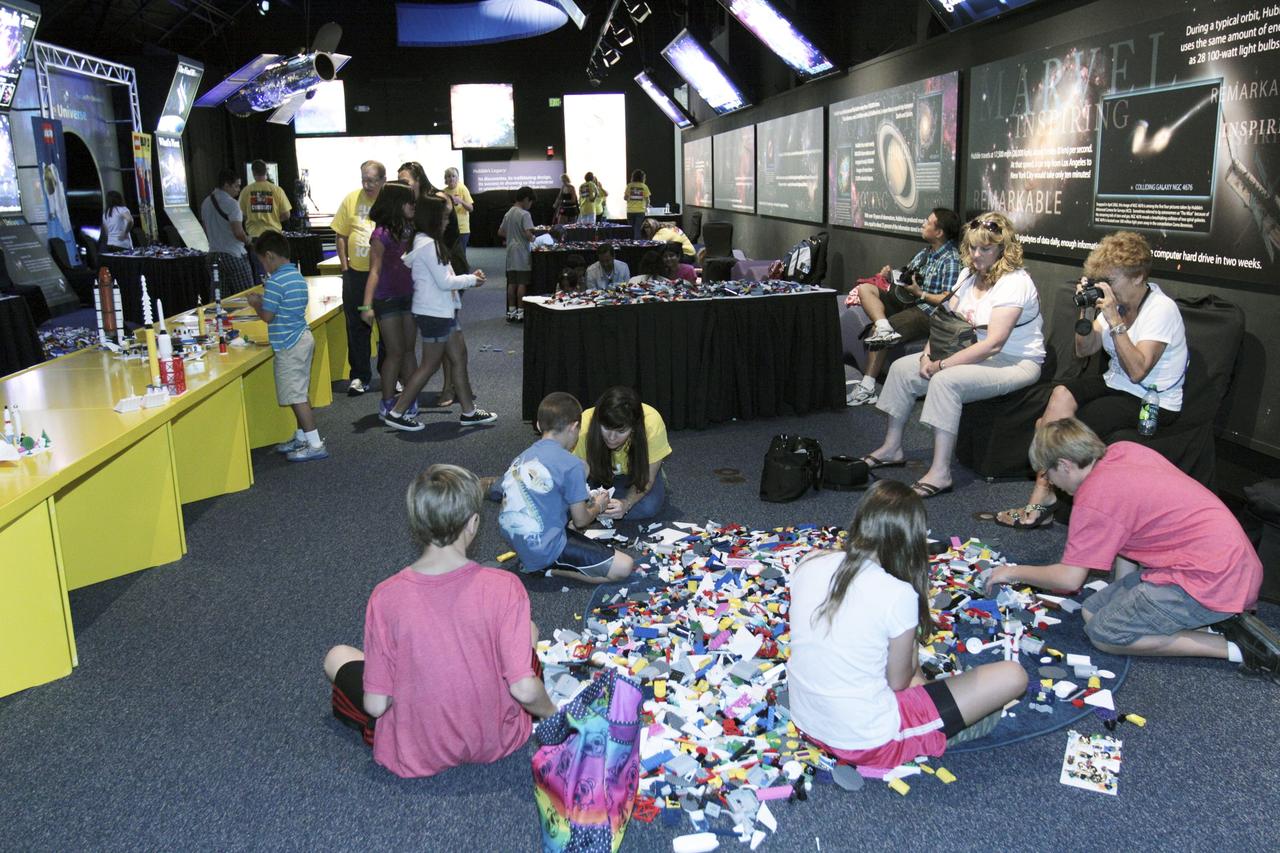

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – LEGO blocks are spread out on the floor of an exhibition hall at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida for easy access during the LEGO "Build the Future" event. The festivities coincide with the launch of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), carrying a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, to the red planet. Part of the Space Act Agreement between NASA and LEGO A/S, the activities are designed to inspire students of every age to consider an education and careers in the science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, disciplines. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/audience/foreducators/nasa-lego-partnership.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
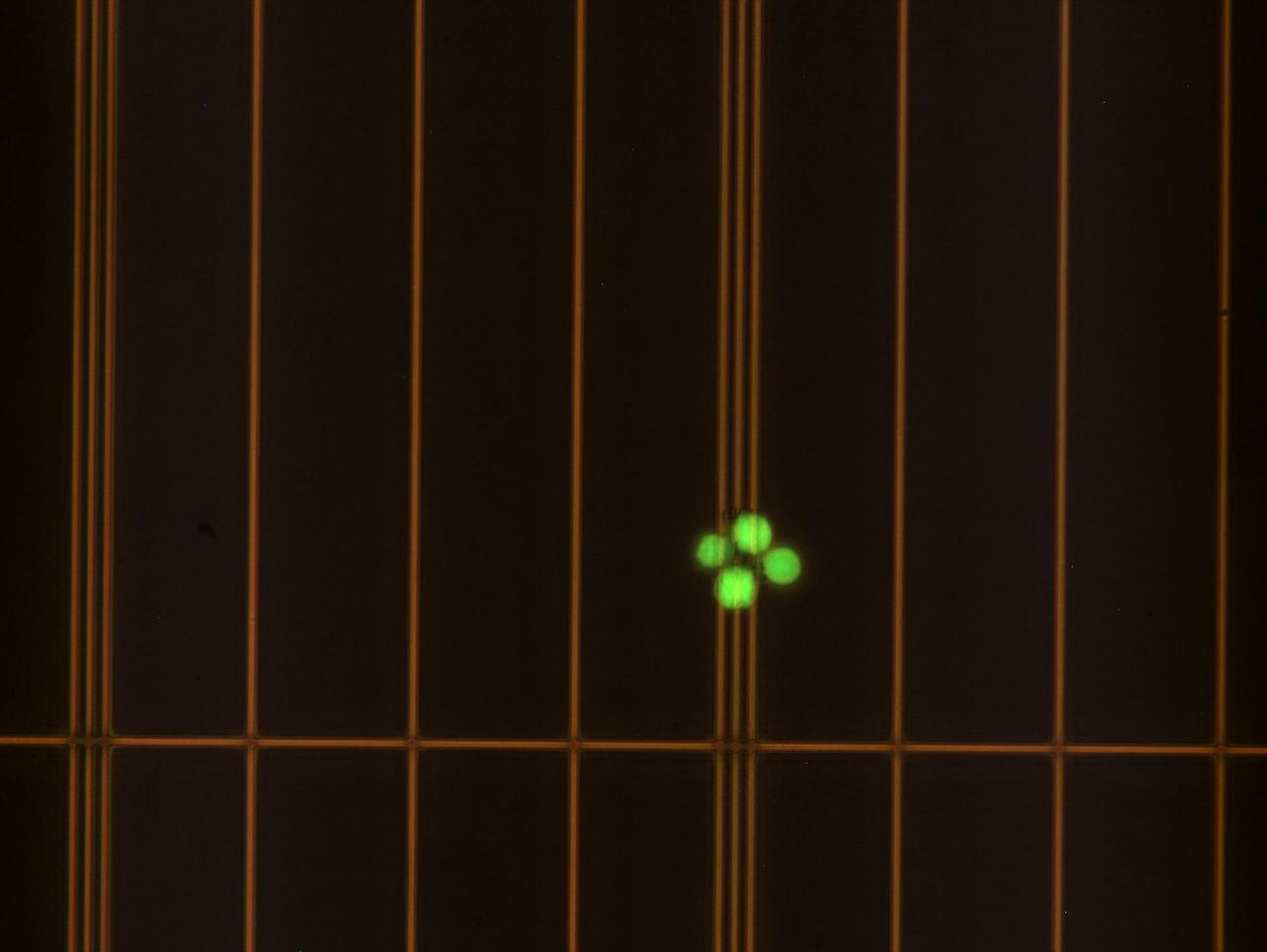
jsc2024e043914 (7/10/2024) --- In-Space Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells for Clinical Application (InSPA-StemCellEX-H1) continues tests of a technology to produce human hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in space. In this image, HSCs were incubated with a fluorescent probe that identifies living cells. Dead cells would fluoresce green. The cells have been loaded into a device called a hemocytometer that provides a grid to make it easy to obtain an accurate count of cells. Astronauts will use a similar technique in space to help determine the rate of HSC expansion over time. Expanding HSC production has the potential to improve patient outcomes and reduce overall mortality for thousands of people diagnosed and living with blood cancer every year. Image courtesy of University of Colorado Boulder.
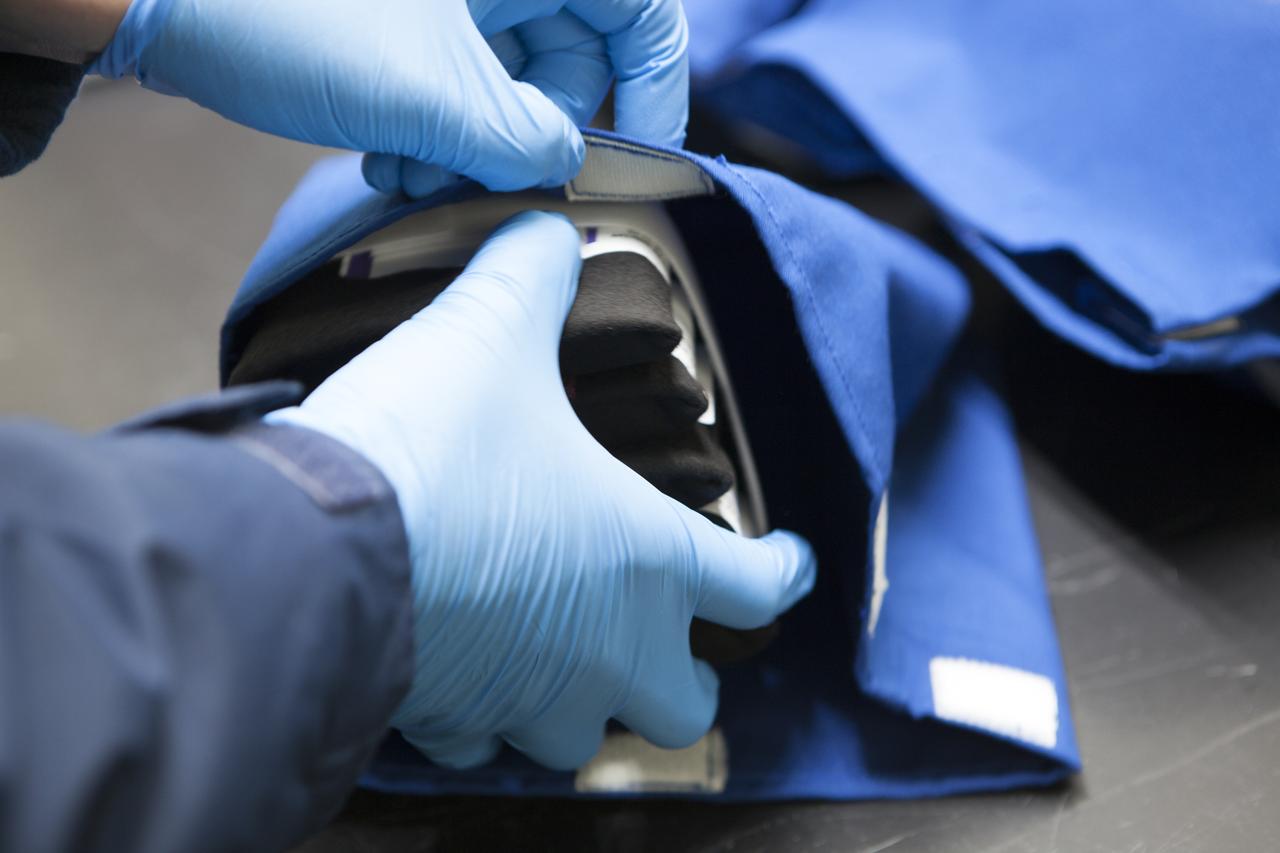

APEX-04, or Advanced Plant EXperiments-04, is being prepared in a cold room in the Kennedy Space Center Processing Facility for SpaceX-10. The 30 petri plates are bundled into groups of 10 and placed into one of three science kits. The science kits allow easy handling when the crew removes the plates from cold stowage on station. Dr. Anna Lisa Paul of the University of Florida is the principal investigator for APEX-04. Apex-04 is an experiment involving Arabidopsis in petri plates inside the Veggie facility aboard the International Space Station. Since Arabidopsis is the genetic model of the plant world, it is a perfect sample organism for performing genetic studies in spaceflight. The experiment is the result of a grant from NASA’s Space Life and Physical Sciences division.

APEX-04, or Advanced Plant EXperiments-04, is being prepared in a cold room in the Kennedy Space Center Processing Facility for SpaceX-10. The 30 petri plates are bundled into groups of 10 and placed into one of three science kits. The science kits allow easy handling when the crew removes the plates from cold stowage on station. Dr. Anna Lisa Paul of the University of Florida is the principal investigator for APEX-04. Apex-04 is an experiment involving Arabidopsis in petri plates inside the Veggie facility aboard the International Space Station. Since Arabidopsis is the genetic model of the plant world, it is a perfect sample organism for performing genetic studies in spaceflight. The experiment is the result of a grant from NASA’s Space Life and Physical Sciences division.
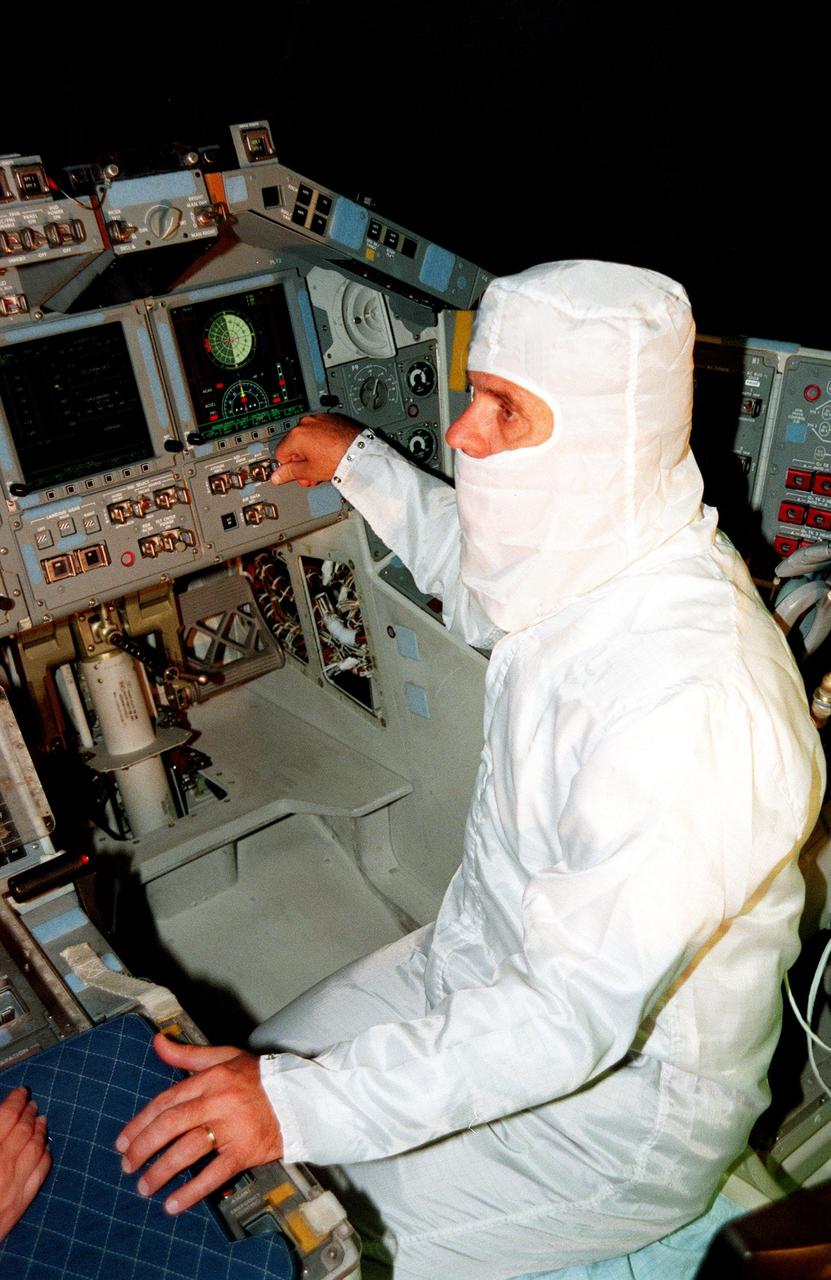

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the cockpit of the orbiter Atlantis, which is in the Orbiter Processing Facility, U.S. Rep. Dave Weldon looks at the newly installed Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS), known as the "glass cockpit." Weldon is on the House Science Committee and vice chairman of the Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee. He was in Palmdale, Calif., when Atlantis underwent the modification and he wanted to see the final product. The full-color, flat-panel MEDS upgrade improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed. The installation makes Atlantis the most modern orbiter in the fleet and equals the systems on current commercial jet airliners and military aircraft. Atlantis is scheduled to fly on mission STS-101 in early December
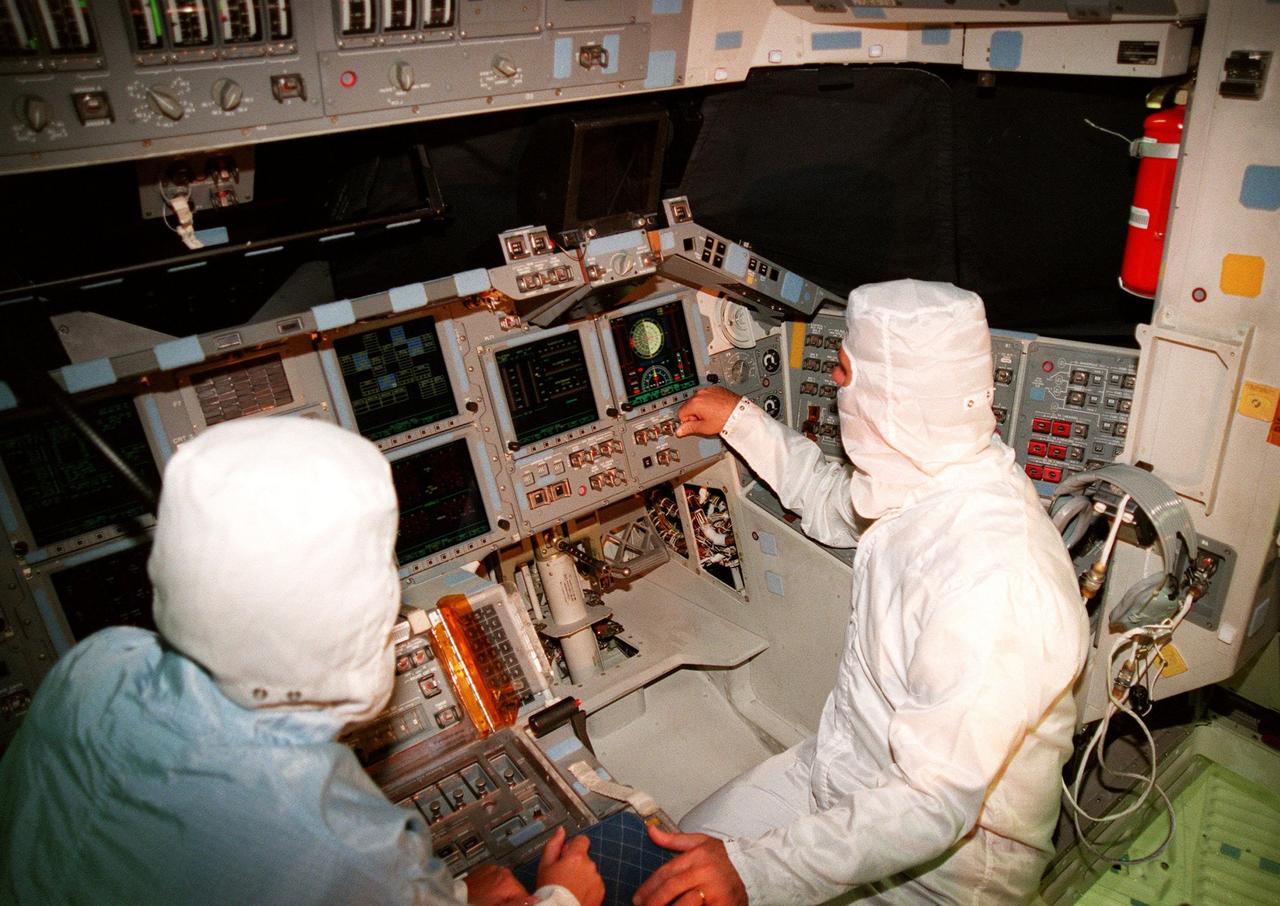

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the cockpit of the orbiter Atlantis, which is in the Orbiter Processing Facility, U.S. Rep. Dave Weldon (right) looks at the newly installed Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS), known as the "glass cockpit." At left is Laural Patrick, a systems engineer with MEDS. Weldon is on the House Science Committee and vice chairman of the Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee. He was in Palmdale, Calif., when Atlantis underwent the modification and he wanted to see the final product. The full-color, flat-panel MEDS upgrade improves crew/orbiter interaction with easy-to-read, graphic portrayals of key flight indicators like attitude display and mach speed. The installation makes Atlantis the most modern orbiter in the fleet and equals the systems on current commercial jet airliners and military aircraft. Atlantis is scheduled to fly on mission STS-101 in early December
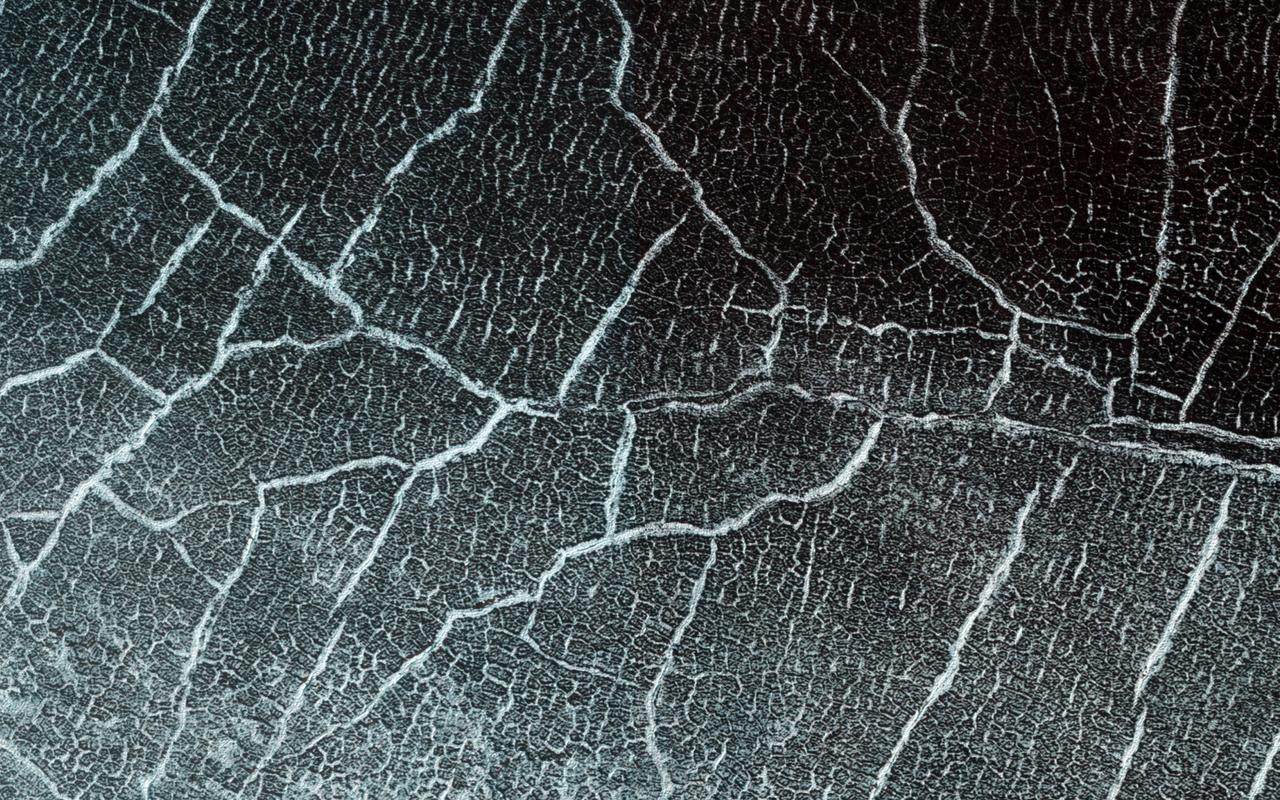

Many impact craters on Mars were filled with ice in past climates. Sometimes this ice flows or slumps down the crater walls into the center and acquires concentric wrinkles as a result. This image shows an example of this. There are other ways that scientists know the material in the crater is icy. Surface cracks that form polygonal shapes cover the material in the crater. They are easy to see in this spring-time image because seasonal frost hides inside the cracks, outlining them in bright white. These cracks form because ice within the ground expands and contracts a lot as it warms and cools. Scientists can see similar cracks in icy areas of the Earth and other icy locations on Mars. If you look closely, you'll see small polygons inside larger ones. The small polygons are younger and the cracks shallower while the large ones are outlined with cracks that penetrate more deeply. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21215
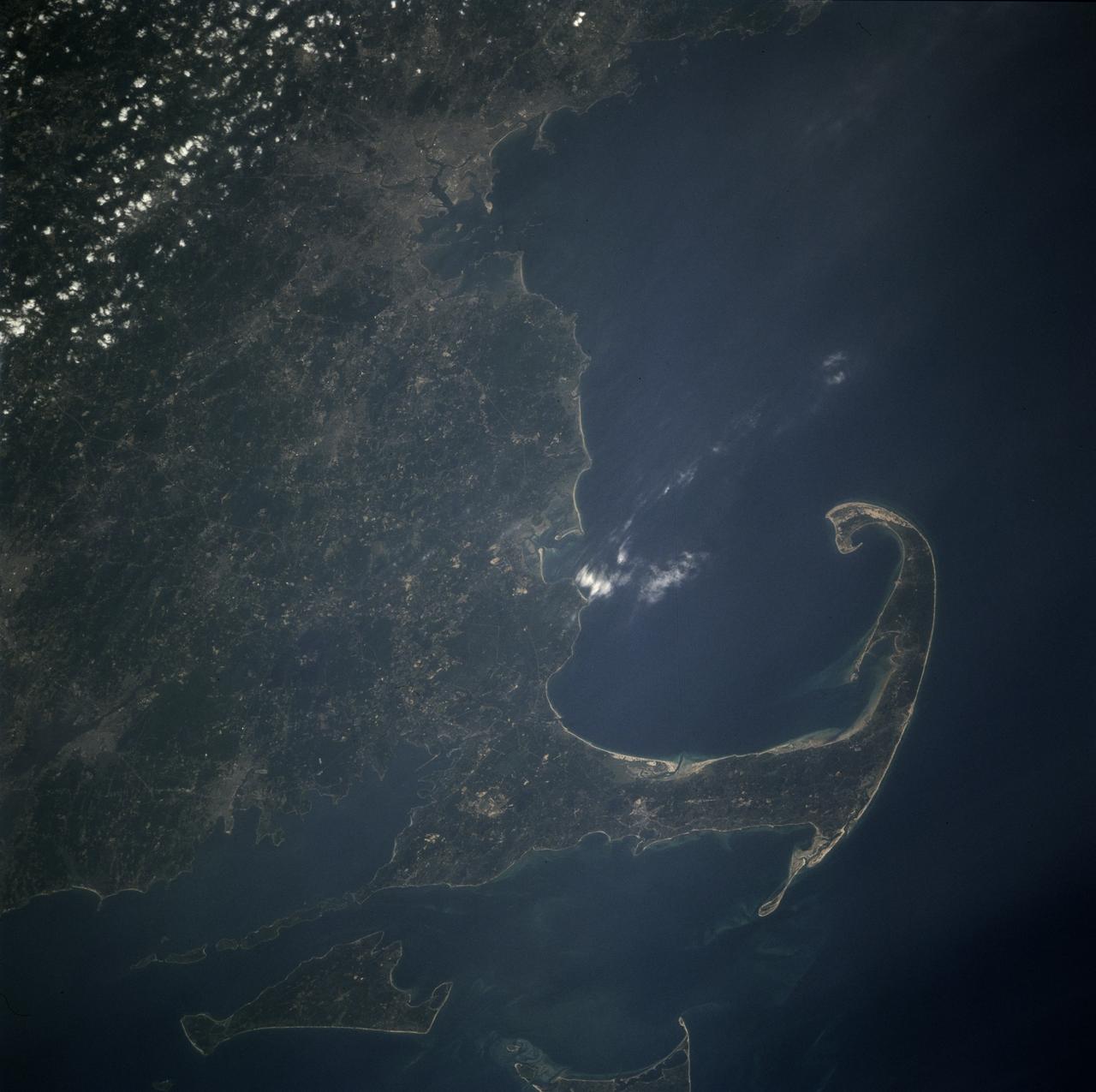

STS071-708-040 (27 June-7 July 1995) --- This view shows Cape Cod in some detail in the center right of the view. Provincetown lies on the inside of the hook of Cape Cod. Other larger cities are unusually easy to see on this frame. The Boston metropolitan area is the large gray area at the top (north), with a smaller gray patch immediately south indicating Brockton, Massachusetts. Other smaller patches in southern Massachusetts (bottom left) indicate Fall River (far left) and New Bedford in the coast on the north side of Buzzard's Bay. The outskirts of Providence, Rhode Island appear half way up the left edge of the frame. The islands at the bottom of the frame are Martha's Vineyard (bottom left) and Nantucket Island (partial view). Shoals (near-surface sand bars) appear as light-blue swirls on the shallow sea bottom between Cape Cod and these islands. The distance from Boston to Nantucket is almost 100 miles.
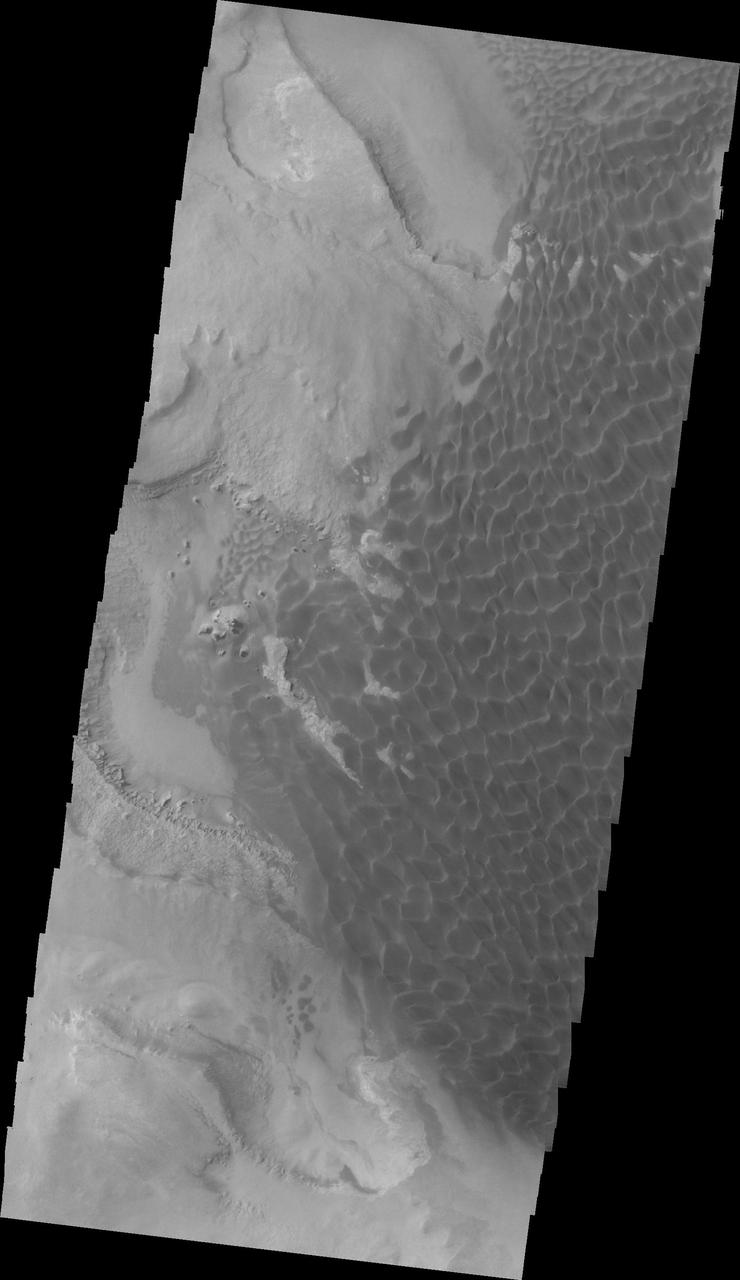

In this VIS image of the floor of Rabe Crater the step down into the pit is visible in the sinuous ridges on the left side of the image. The appearance of the exposed side of the cliffs does not look like a volcanic, difficult to erode material, but rather an easy to erode material such as layered sediments. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 34456 Latitude: -43.7164 Longitude: 34.4056 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2009-09-20 09:38 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22140
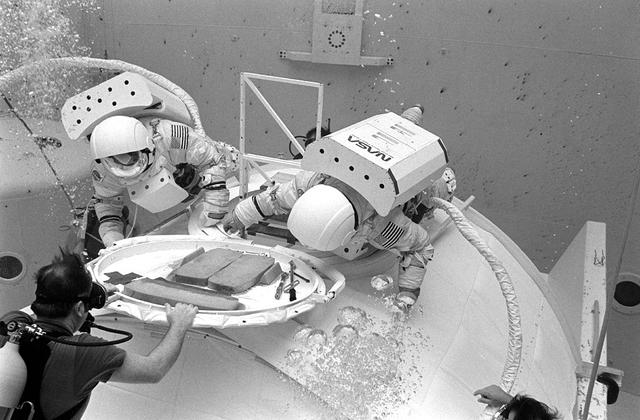
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. Pictured is Astronaut Paul Weitz training on a mock-up of Spacelab's airlock-hatch cover. Training was also done on the use of foot restraints which had recently been developed to help astronauts maintain their positions during space walks rather than having their feet float out from underneath them while they tried to perform maintenance and repair operations. Every aspect of every space mission was researched and demonstrated in the NBS. Using the airlock hatch cover and foot restraints were just a small example of the preparation that went into each mission.
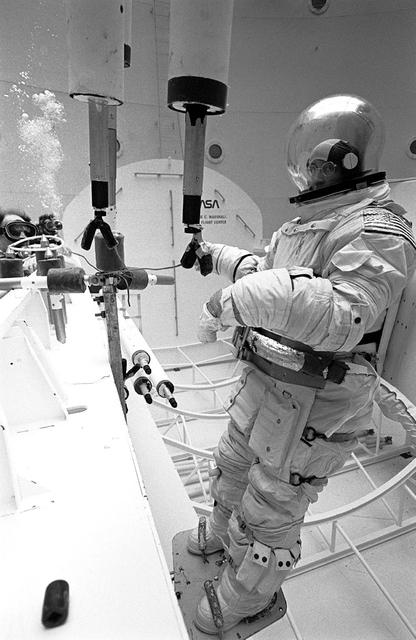

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Pictured is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) student working in a spacesuit on the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project which was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and MIT. The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle. The MIT student in this photo is assembling two six-beam tetrahedrons.
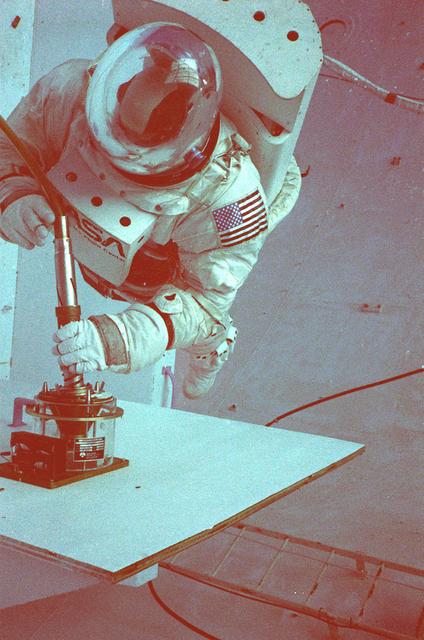

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Another facet of the space station would be electrical cornectors which would be used for powering tools the astronauts would need for construction, maintenance and repairs. Shown is an astronaut training during an underwater electrical connector test in the NBS.
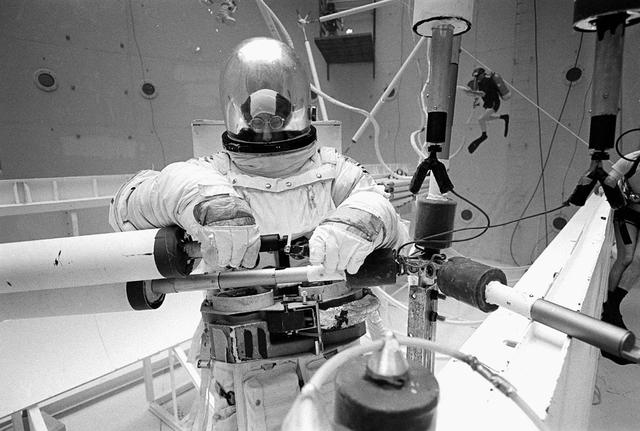
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Pictured is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) student working in a spacesuit on the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project which was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and MIT. The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle. The MIT student in this photo is assembling two six-beam tetrahedrons.
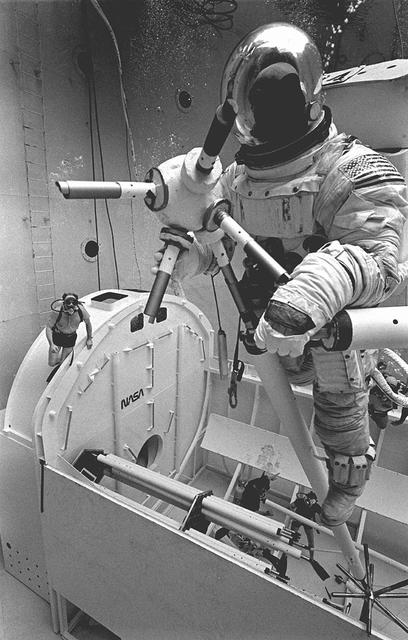

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Pictured is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) student working in a spacesuit on the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project which was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and MIT. The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle. The MIT student in this photo is assembling two six-beam tetrahedrons.
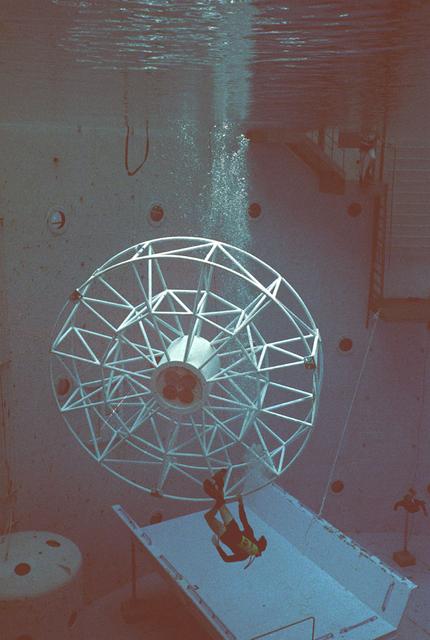
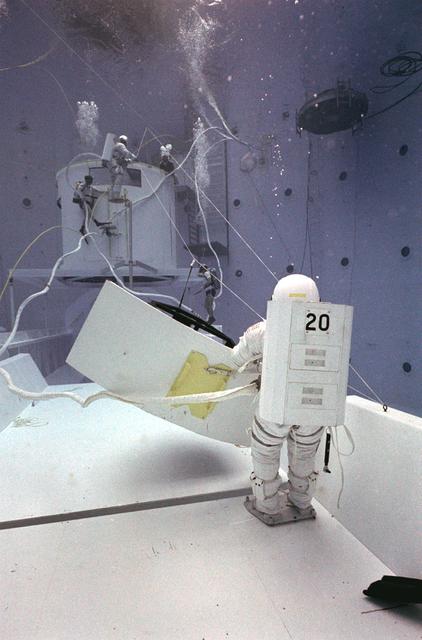
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Included in the plans for the space station was a space telescope. This telescope would be attached to the space station and directed towards outerspace. Astronomers hoped that the space telescope would provide a look at space that is impossible to see from Earth because of Earth's atmosphere and other man made influences. Pictured is a large structure that is being used as the antenna base for the space telescope.
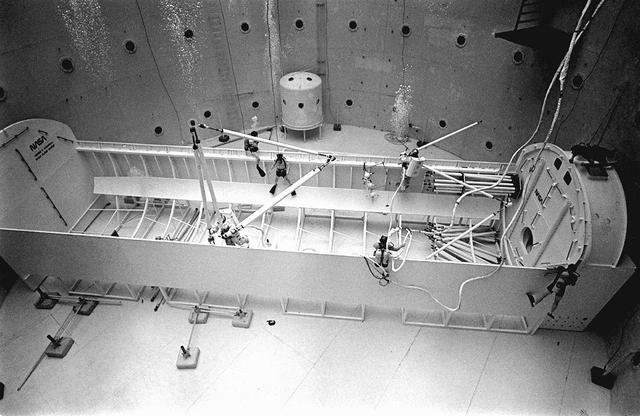
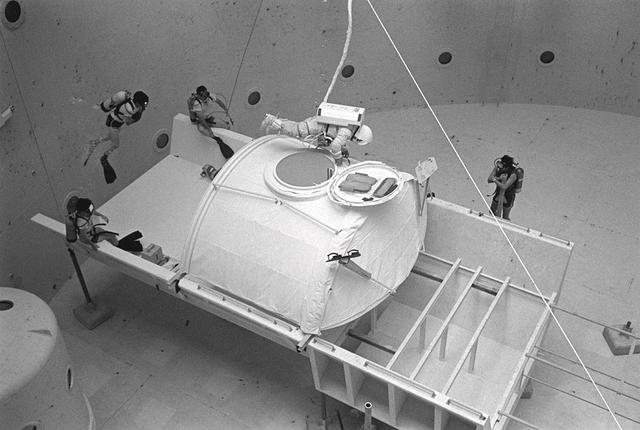
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. As part of this experimentation, the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle. Pictured is an entire unit that has been constructed and is sitting in the bottom of a mock-up shuttle cargo bay pallet.
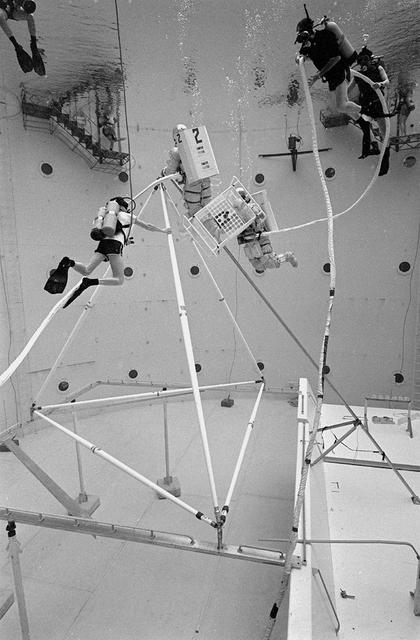

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA and MSFC, the Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures (ACCESS) was developed and demonstrated at MSFC's NBS. The primary objective of this experiment was to test the ACCESS structural assembly concept for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction. Pictured is a demonstration of ACCESS.
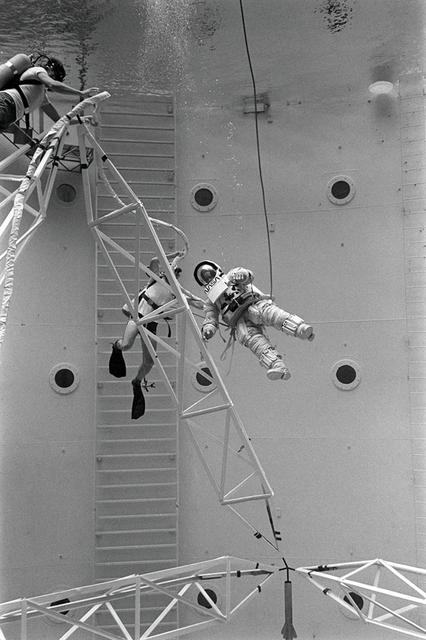

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA and MSFC, the Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures (ACCESS) was developed and demonstrated at MSFC's NBS. The primary objective of this experiment was to test the ACCESS structural assembly concept for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction. Pictured is a demonstration of ACCESS.
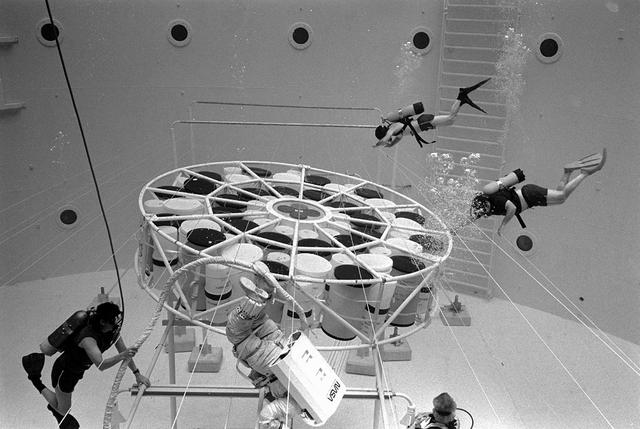

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built.Pictured is an experiment where the astronaut is required to move a large object which weighed 19,000 pounds. It was moved with realitive ease once the astronaut became familiar with his environment and his near weightless condition. Experiments of this nature provided scientists with the information needed regarding weight and mass allowances astronauts could manage in preparation for building a permanent space station in the future.
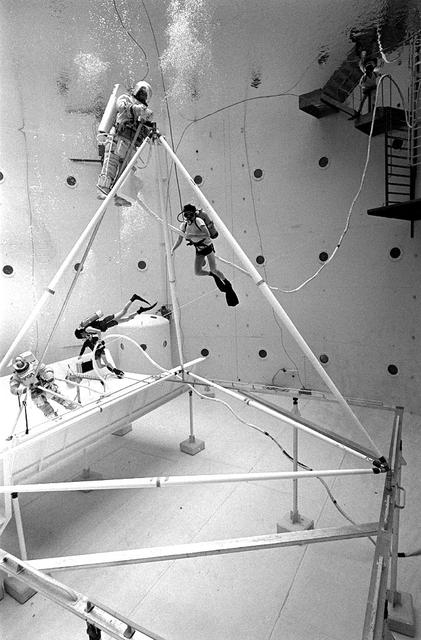
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA and MSFC, the Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures (ACCESS) was developed and demonstrated at MSFC's NBS. The primary objective of this experiment was to test the ACCESS structural assembly concept for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction. Pictured is a demonstration of ACCESS.

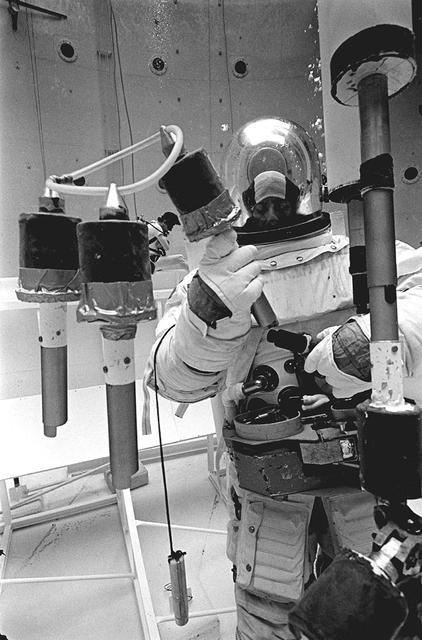
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Included in the plans for the space station was a space telescope. This telescope would be attached to the space station and directed towards outerspace. Astronomers hoped that the space telescope would provide a look at space that is impossible to see from Earth because of Earth's atmosphere and other man made influences. In an effort to make replacement and repairs easier on astronauts the space telescope was designed to be modular. Practice makes perfect as demonstrated in this photo: an astronaut practices moving modular pieces of the space telescope in the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) at MSFC. The space telescope was later deployed in April 1990 as the Hubble Space Telescope.

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, theprospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Pictured is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) student working in a spacesuit on the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project which was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and MIT. The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle. The MIT student in this photo is assembling two six-beam tetrahedrons.

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. Pictured is Astronaut Paul Weitz training on a mock-up of Spacelab's airlock-hatch cover. Training was also done on the use of foot restraints which had recently been developed to help astronauts maintain their positions during space walks rather than having their feet float out from underneath them while they tried to perform maintenance and repair operations. Every aspect of every space mission was researched and demonstrated in the NBS. Using the airlock hatch cover and foot restraints were just a small example of the preparation that went into each mission.
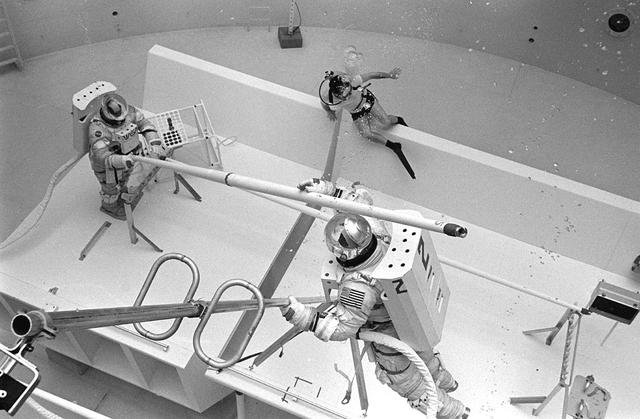
Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA and MSFC, the Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures (ACCESS) was developed and demonstrated at MSFC's NBS. The primary objective of this experiment was to test the ACCESS structural assembly concept for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction. Pictured is a demonstration of ACCESS.
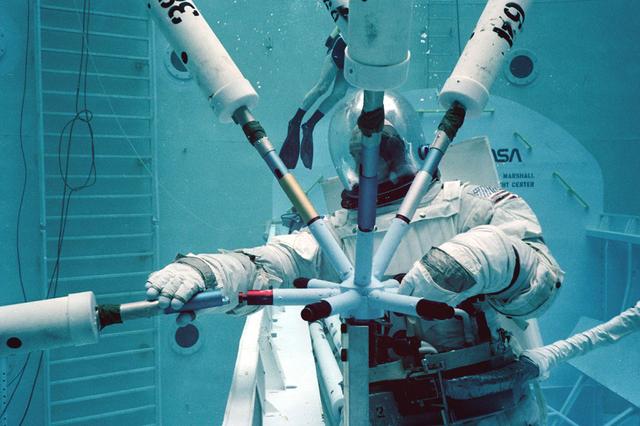

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Pictured is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) student working in a spacesuit on the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project which was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and MIT. The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle.
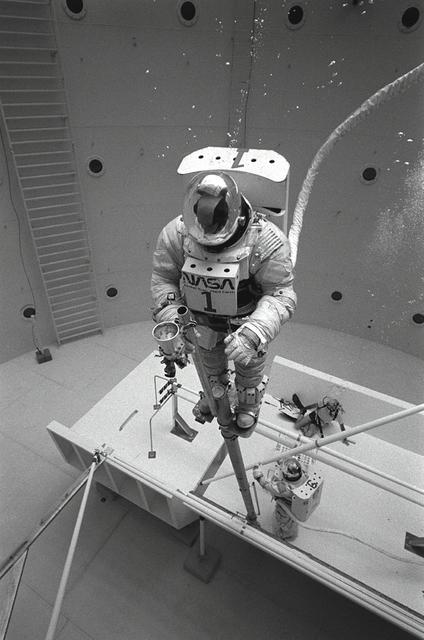

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. Construction methods had to be efficient due to the limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. With the help of the NBS, building a space station became more of a reality. In a joint venture between NASA/Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia and the MSFC, the Assembly Concept for Construction of Erectable Space Structures (ACCESS) was developed and demonstrated at MSFC's NBS. The primary objective of this experiment was to test the ACCESS structural assembly concept for suitability as the framework for larger space structures and to identify ways to improve the productivity of space construction. Pictured is a demonstration of ACCESS.

Janus (111 miles or 179 kilometers across) seems to almost stare off into the distance, contemplating deep, moonish thoughts as the F ring stands by at the bottom of this image. From this image, it is easy to distinguish Janus' shape from that of a sphere. Many of Saturn's smaller moons have similarly irregular shapes that scientists believe may give clues to their origins and internal structure. Models combining the dynamics of this moon with its shape imply the existence of mass inhomogeneities within Janus. This would be a surprising result for a body the size of Janus. By studying more images of Janus, scientists may be able confirm this finding and determine just how complicated the internal structure of this small body is. This image is roughly centered on the side of Janus which faces away from Saturn. North on Janus is up and rotated 3 degrees to the right. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on March 28, 2012. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 54,000 miles (87,000 kilometers) from Janus. Image scale is 1,700 feet (520 meters) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18299

ISS006-E-33736 (25 February 2003) --- The boot of Italy crosses the image in this southwest-looking view taken by an Expedition Six crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS). The spine of Italy is highlighted with snow and the largely cloud-covered Mediterranean Sea is at the top. The Adriatic Sea transverses most of the bottom of the image and Sicily appears top left beyond the toe of the boot. The heel lies out of the left side of the image. Corsica and Sardinia appear right of center partly under cloud. The floor of the Po River valley, lower right, is obscured by haze. Experience gained from similar haze events, in which atmospheric pressure, humidity and visibility and atmospheric chemistry were known, suggests that the haze as industrial smog. Industrial haze from the urban region of the central and upper Po valley accumulates to visible concentrations under conditions of high atmospheric pressure and the surrounding mountains prevent easy dispersal. This view illustrates the markedly different color and texture of cloud versus industrial aerosol haze.