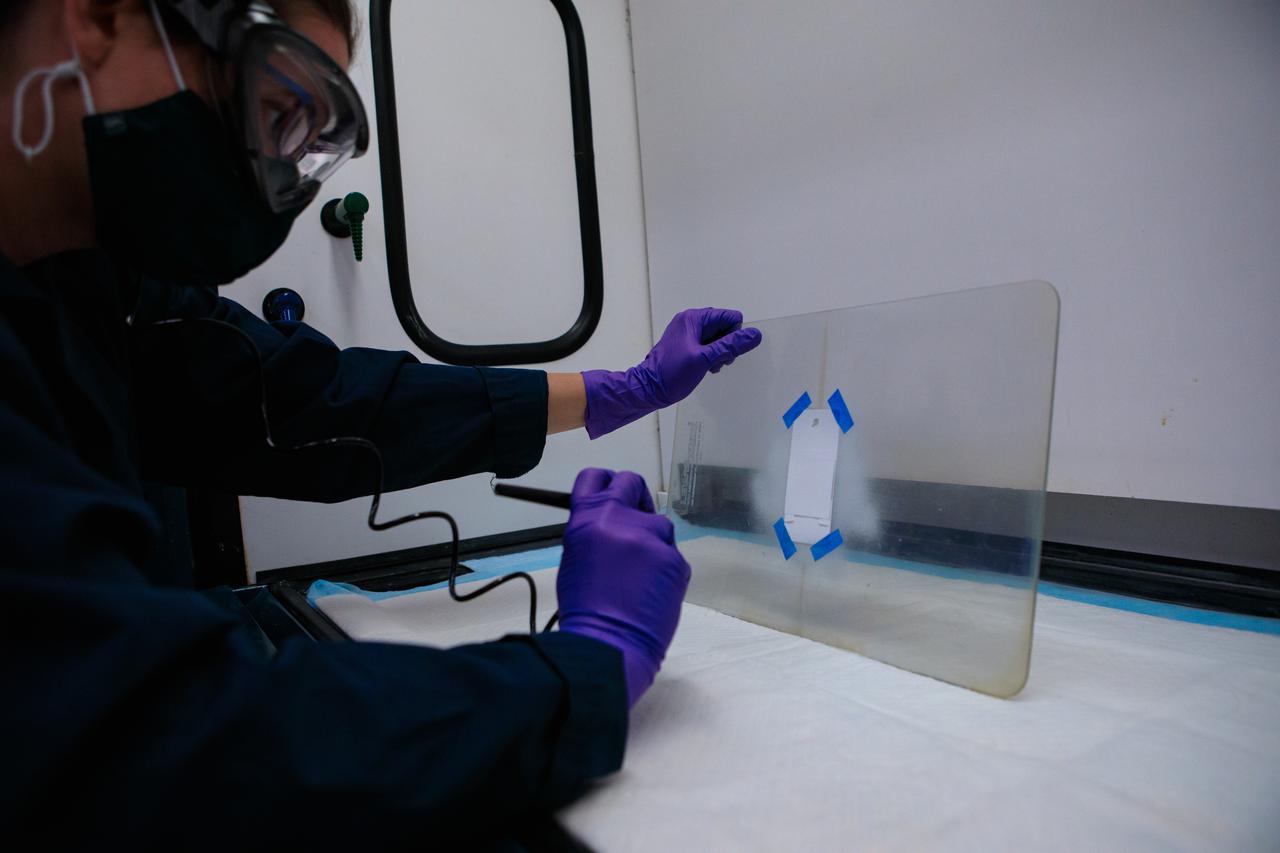

Inside a laboratory at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, research scientist Sarah Snyder applies a selective surface coating to an Electrodynamic Dust Shield (EDS) on March 31, 2021. This is one of several concurrent activities preparing dust shield samples for testing in space. Dust mitigation technologies could one day be applied to diminish dust hazards on lunar surface systems such as cameras, solar panels, spacesuits, and instrumentation, enabling sustainable exploration of the Moon under the Artemis program.
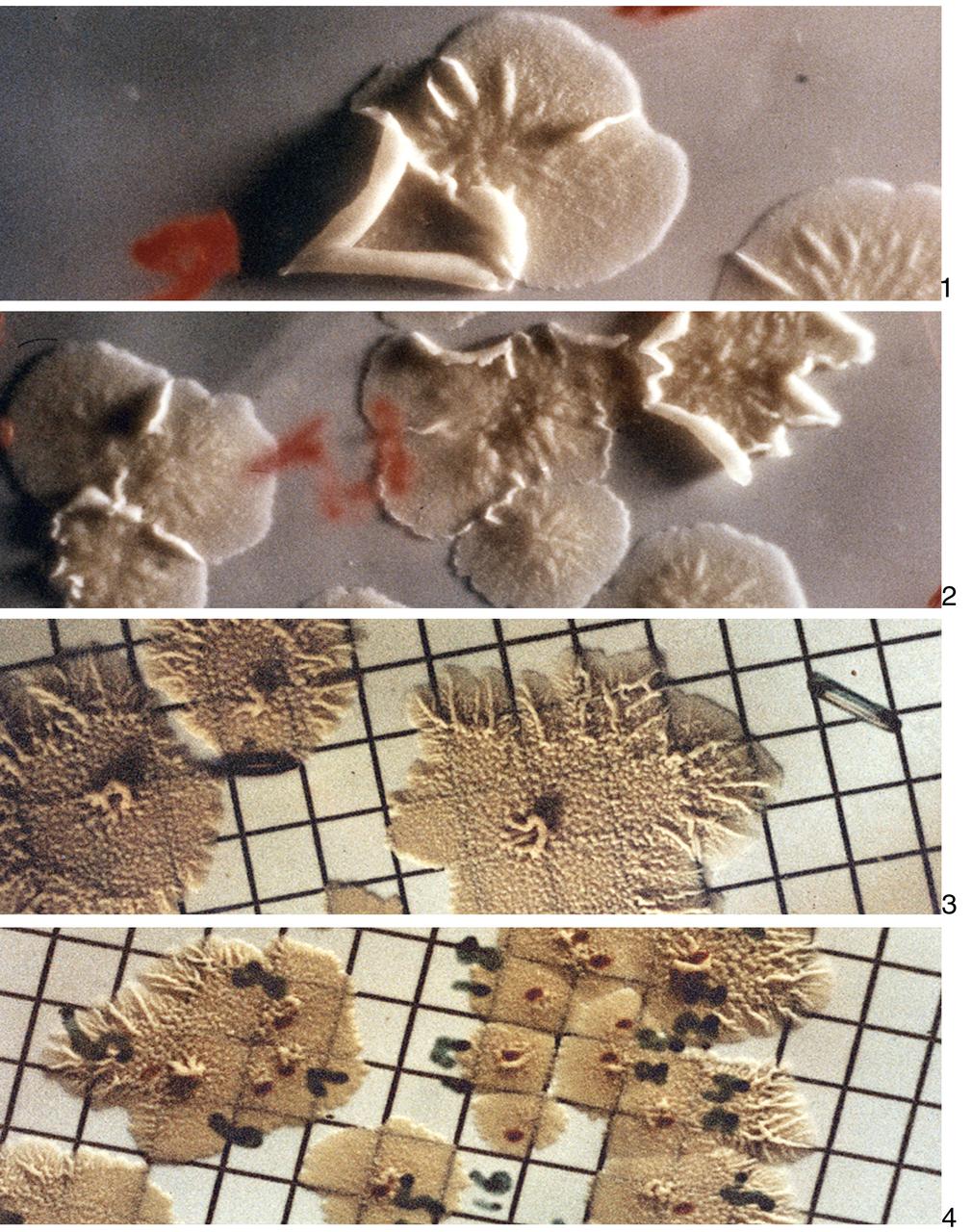
Pictures 1 and 2 show samples of Bacillus Subtillus grown during the first performance of Robert Staehle's experiment (ED-31) aboard Skylab. Pictures 3 and 4 show colonies of the same bacteria that developed during the second performance of the experiment. The experiment ED-31 was proposed by Robert L. Staehle of Rochester, New York to determine the effect of the Skylab environment (particularly weightlessness) on the survival, growth rates, and mutations of certain bacteria and spores.
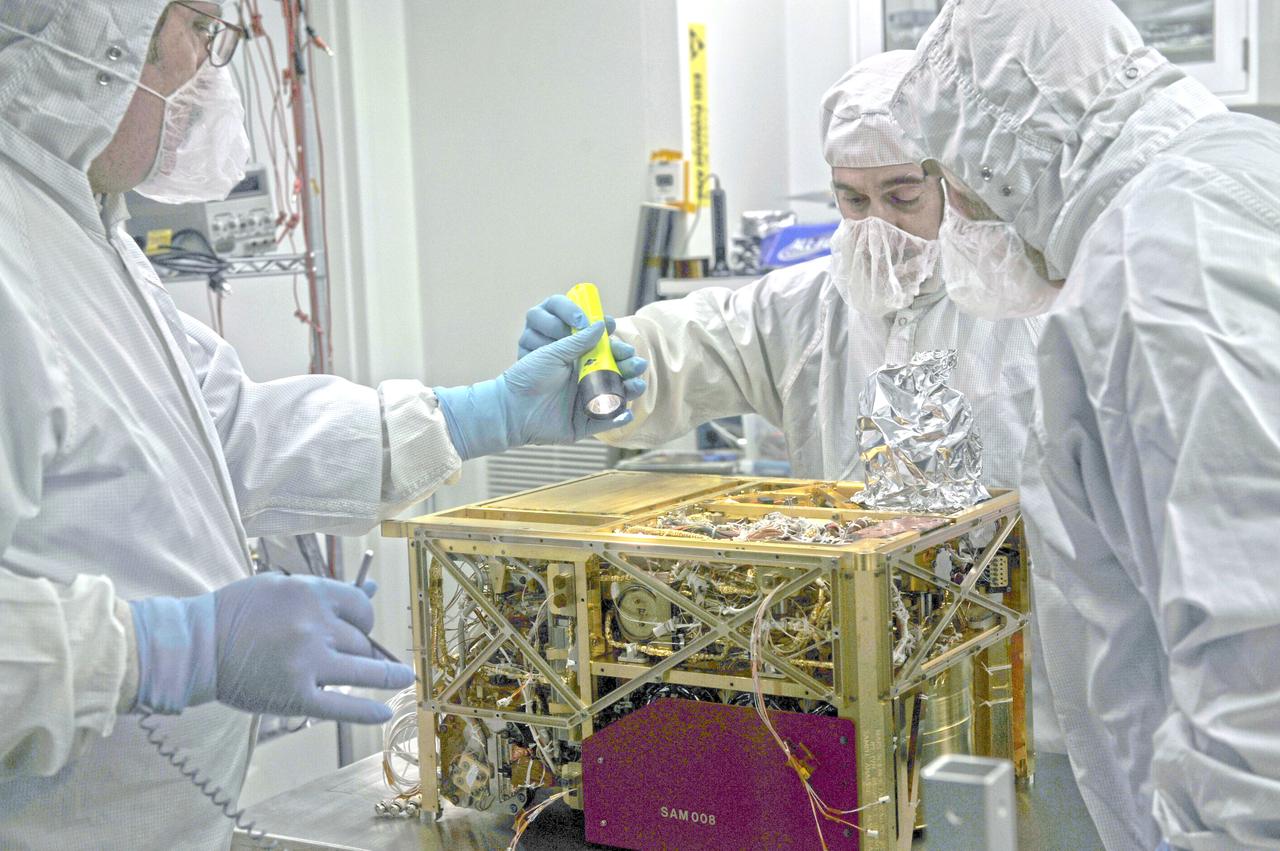

On Saturday, November 26, NASA is scheduled to launch the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission featuring Curiosity, the largest and most advanced rover ever sent to the Red Planet. The Curiosity rover bristles with multiple cameras and instruments, including Goddard's Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) instrument suite. By looking for evidence of water, carbon, and other important building blocks of life in the Martian soil and atmosphere, SAM will help discover whether Mars ever had the potential to support life. Curiosity will be delivered to Gale crater, a 96-mile-wide crater that contains a record of environmental changes in its sedimentary rock, in August 2012. ----- NASA image November 18, 2010 The Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) instrument is considered one of the most complicated instruments ever to land on the surface of another planet. Equipped with a gas chromatograph, a quadruple mass spectrometer, and a tunable laser spectrometer, SAM will carry out the initial search for organic compounds when the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover lands in 2012. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Ed Campion <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>