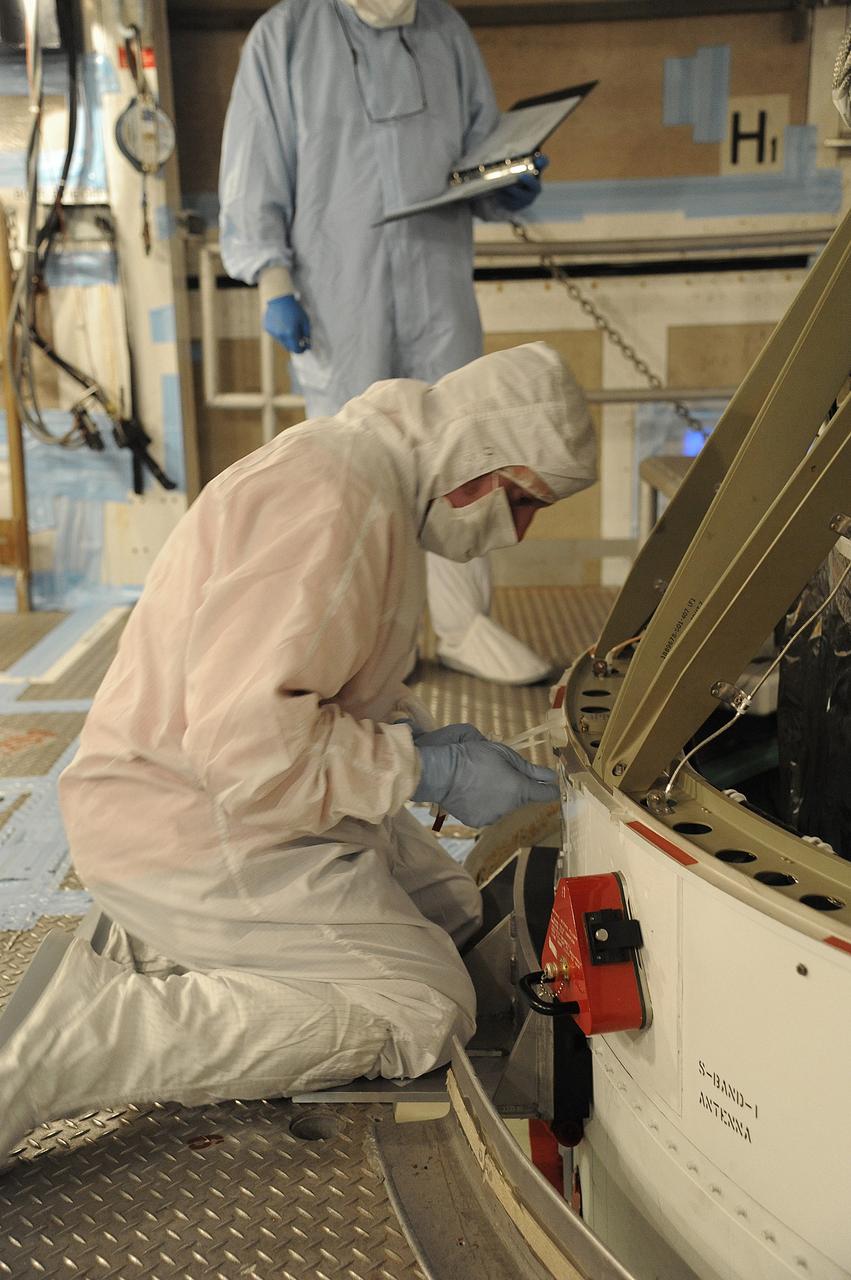

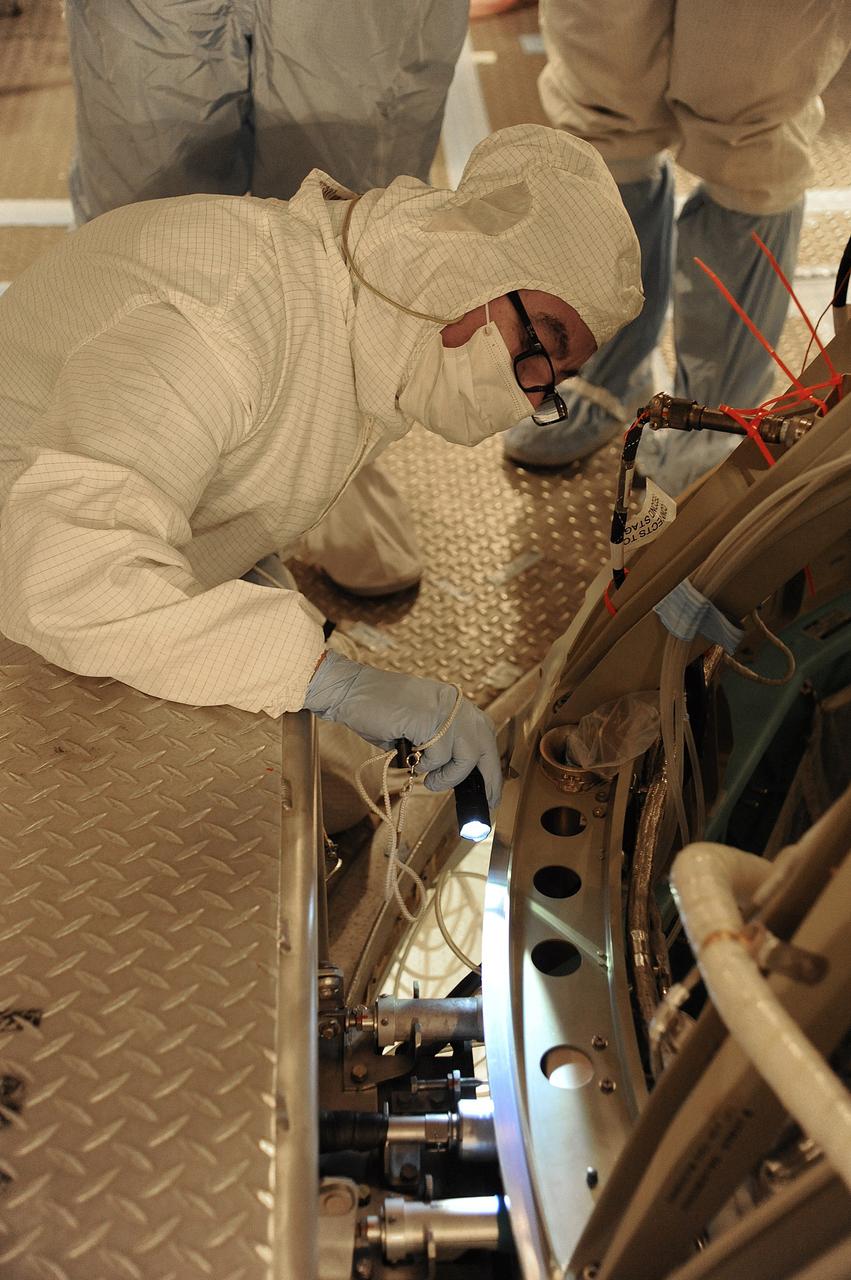
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The task is taking place prior to encapsulation in its payload fairing atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
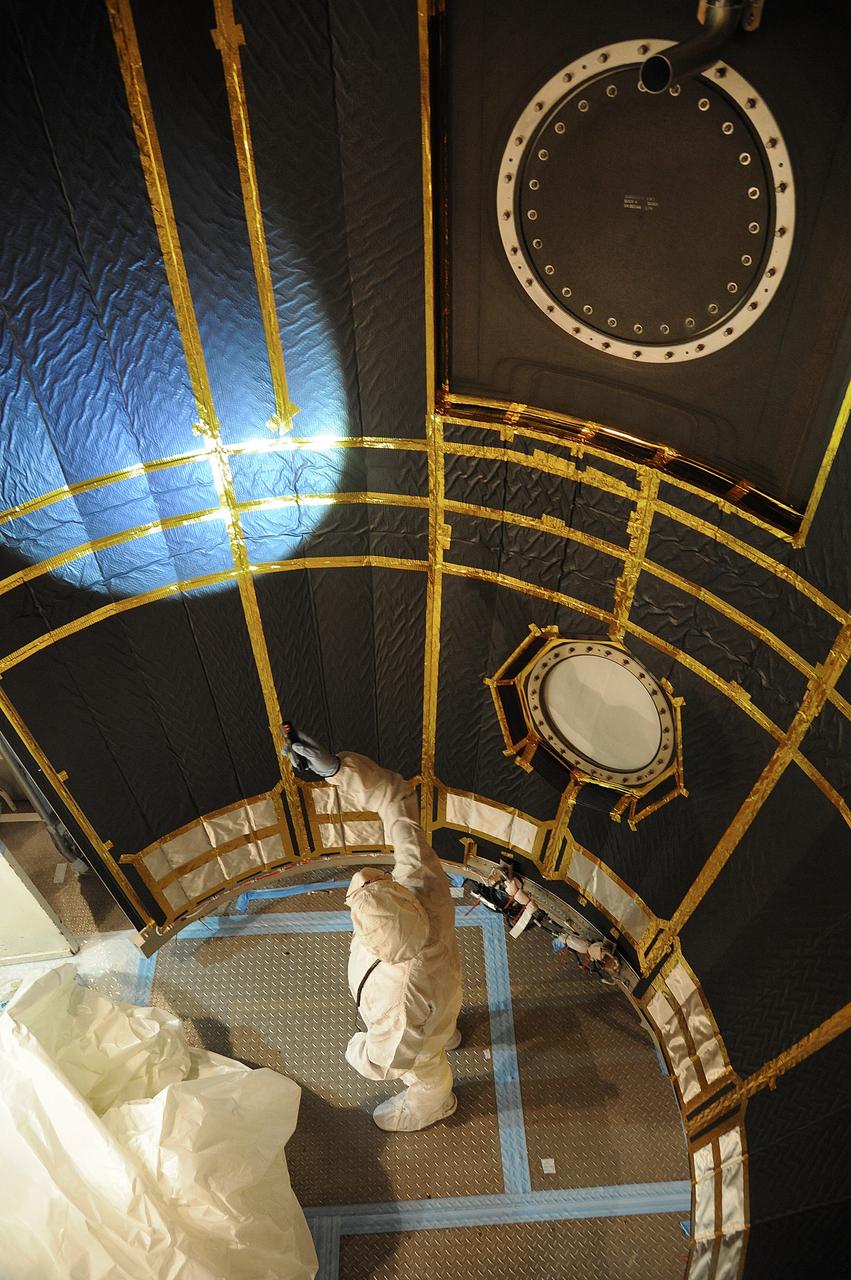

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the payload fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The fairing will soon be used to encapsulate the satellite atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
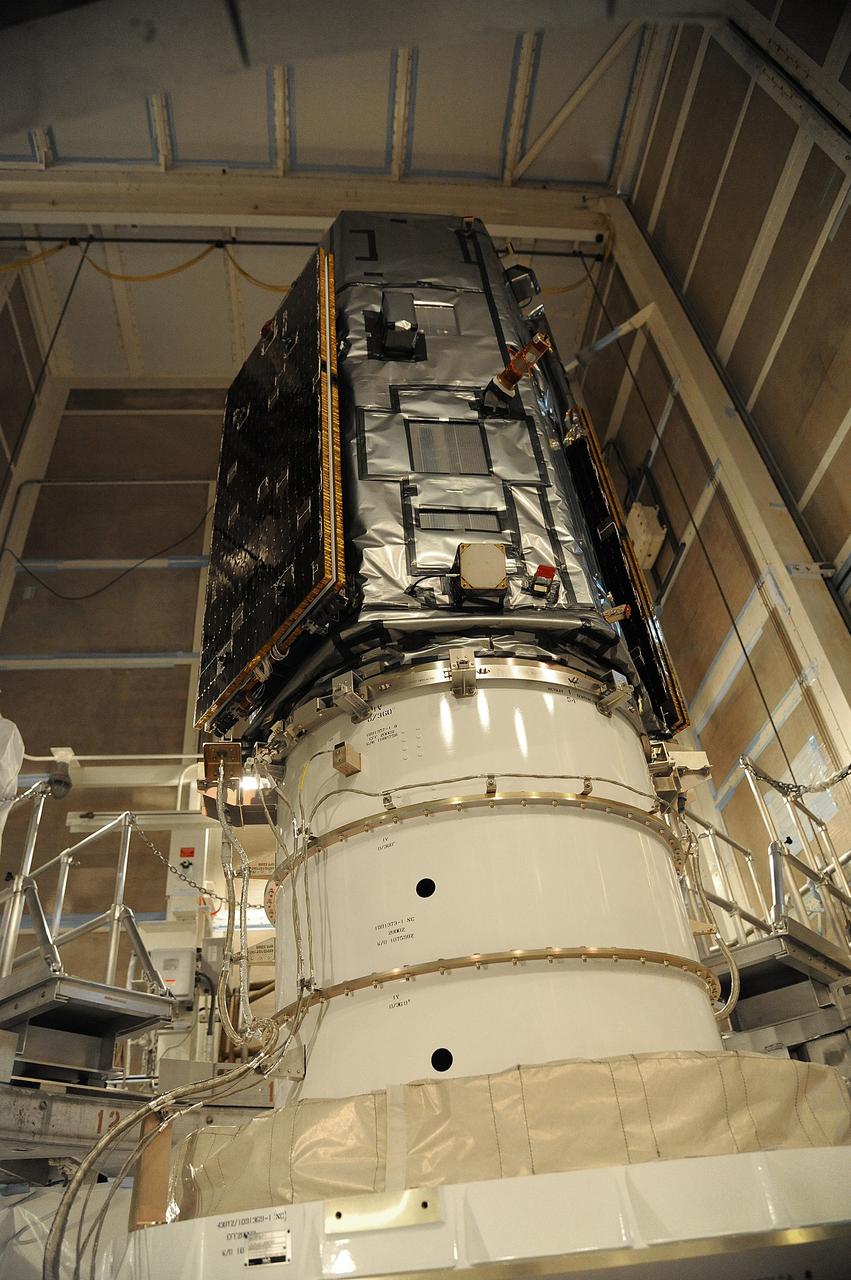
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite sits atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket prior to encapsulation in its payload fairing at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The task is taking place prior to encapsulation in its payload fairing atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
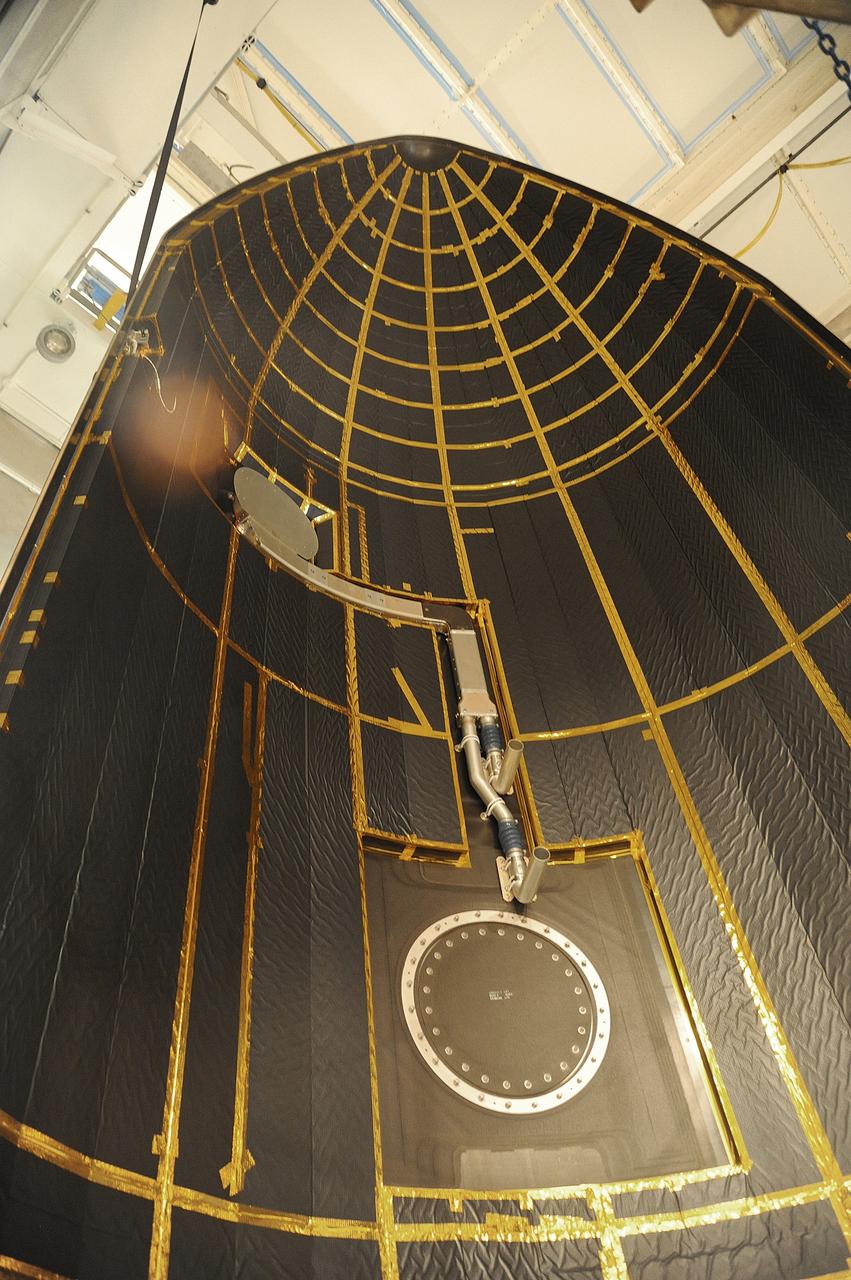

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the payload fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite is being prepared for encapsulation atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
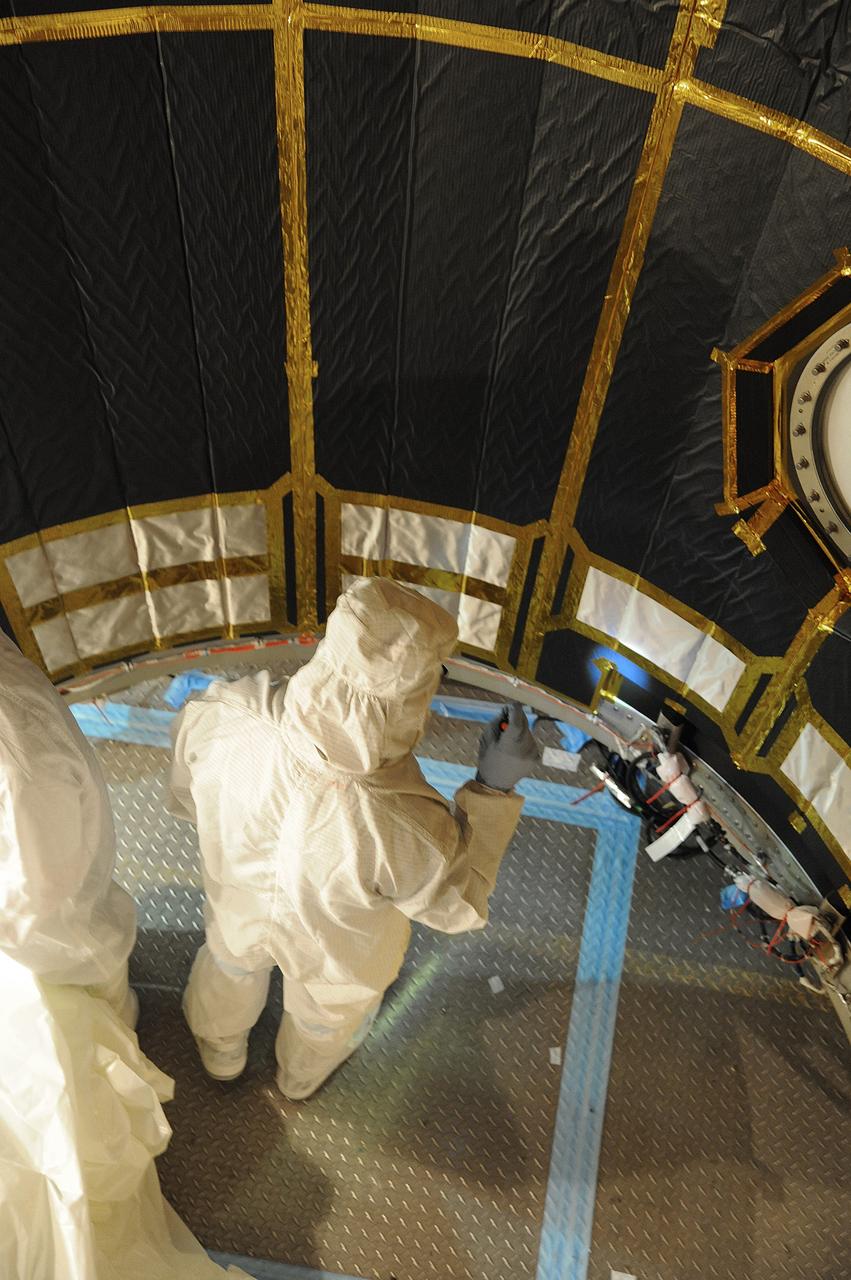

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the payload fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The fairing will soon be used to encapsulate the satellite atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
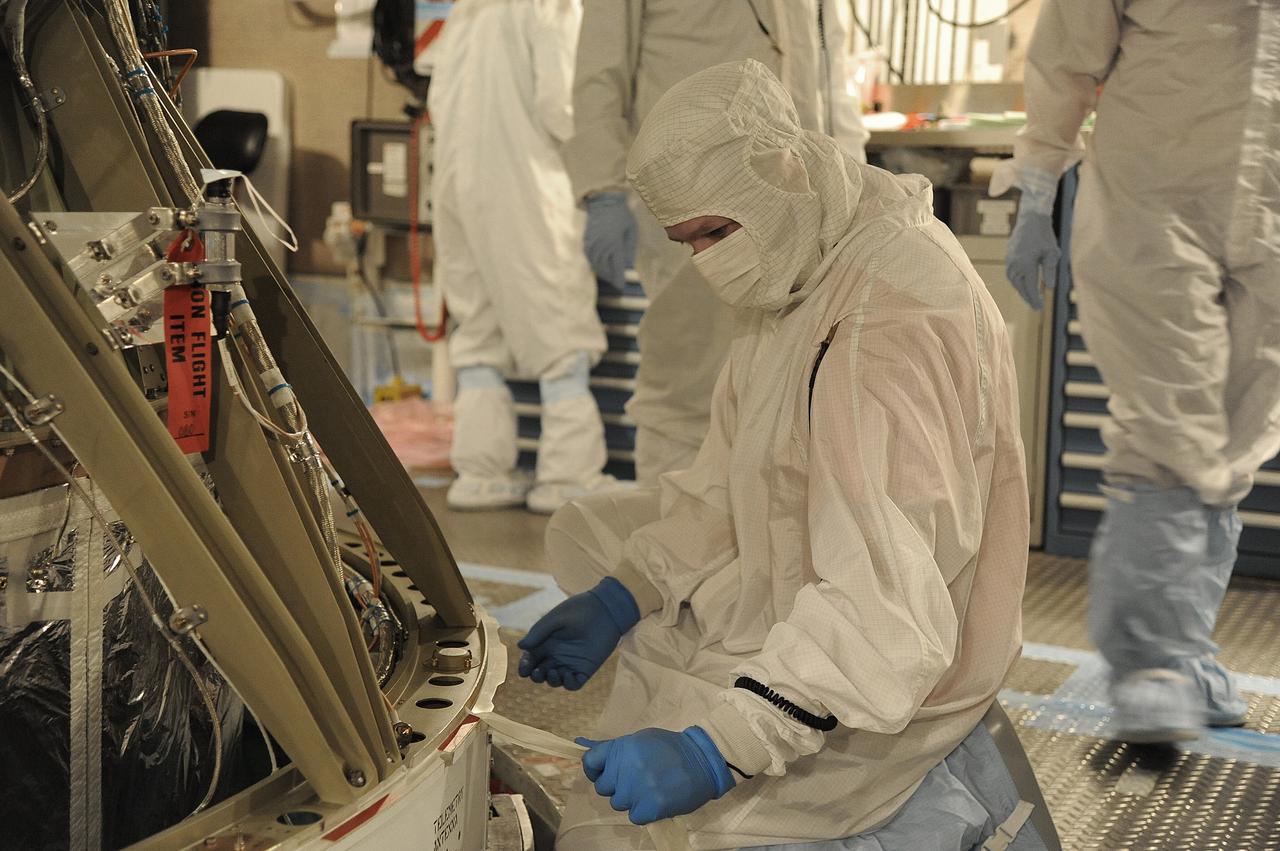

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The task is taking place prior to encapsulation in its payload fairing atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
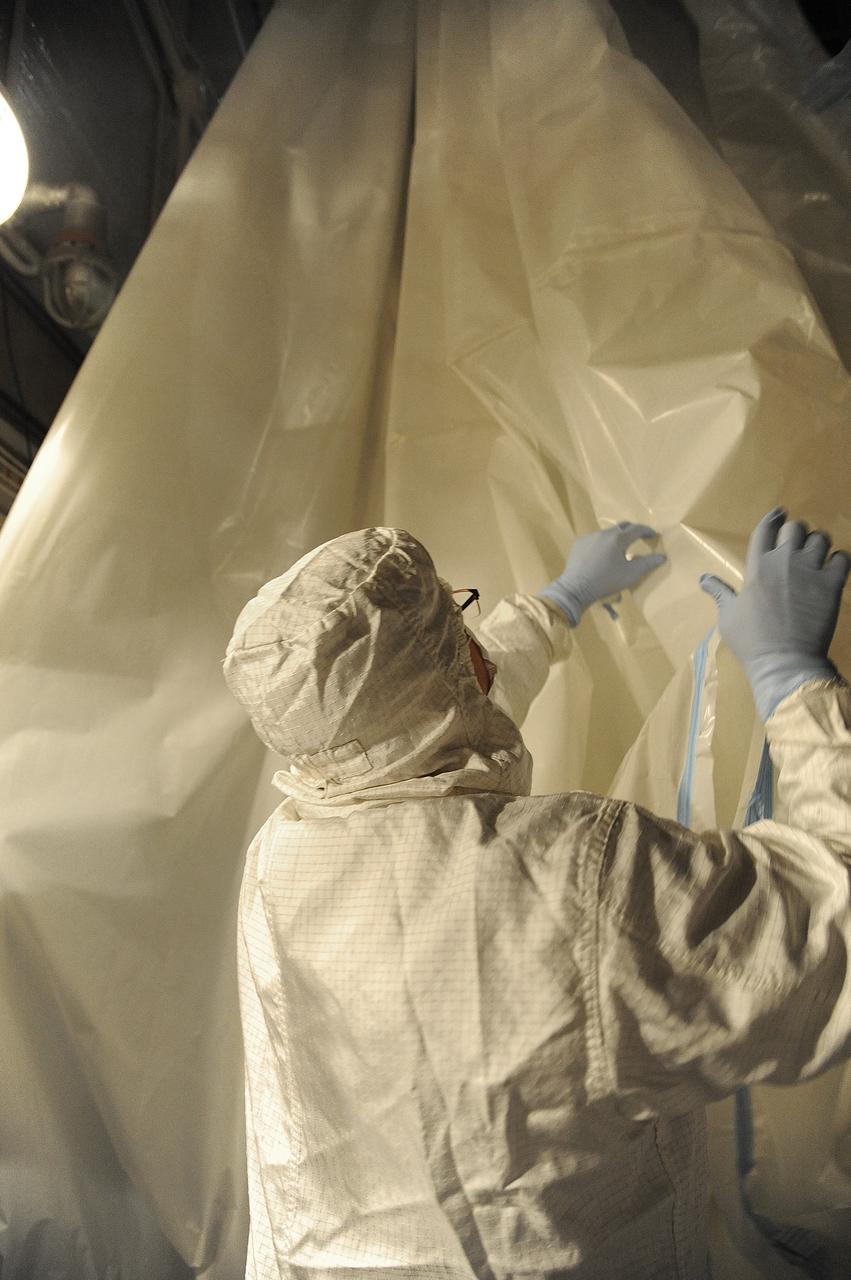

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The task is taking place prior to encapsulation in its payload fairing atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
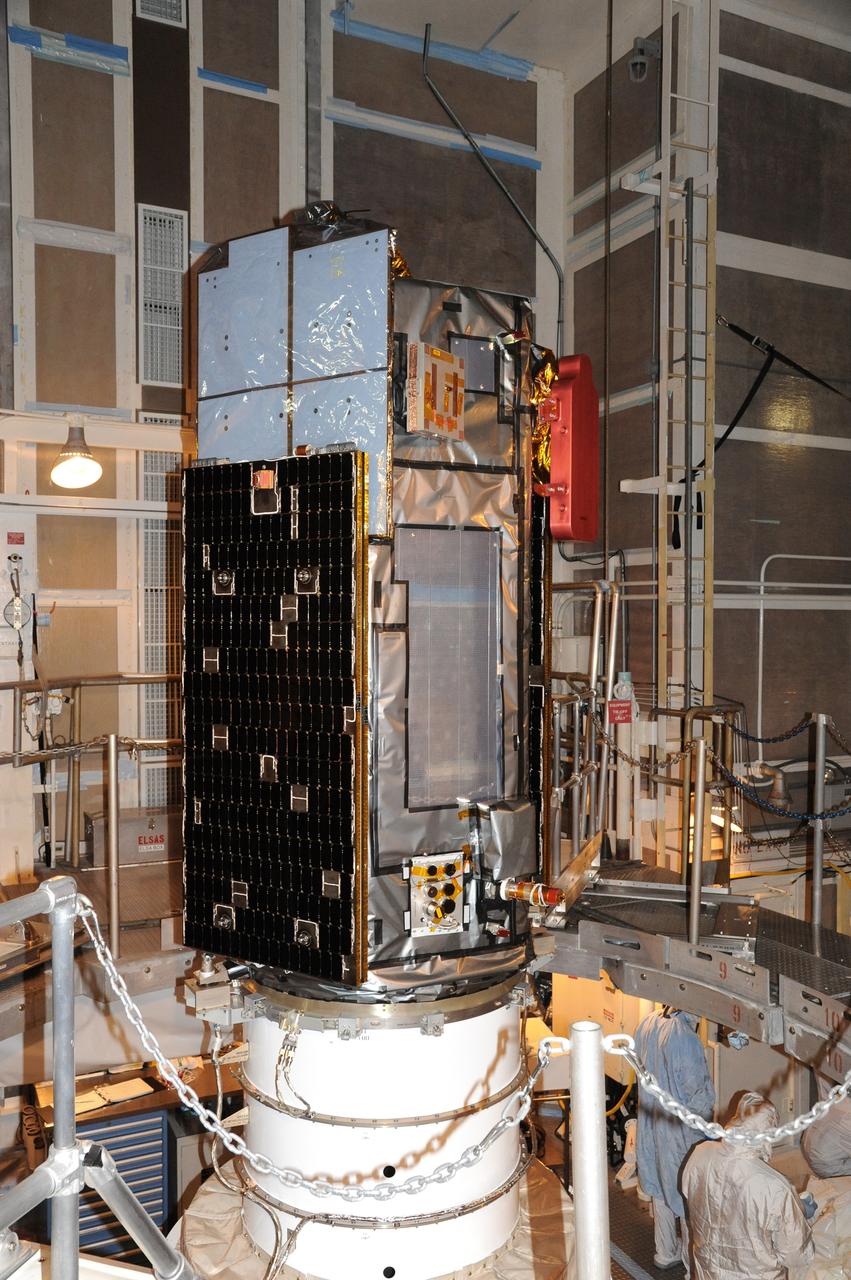

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite sits atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket prior to encapsulation in its payload fairing at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
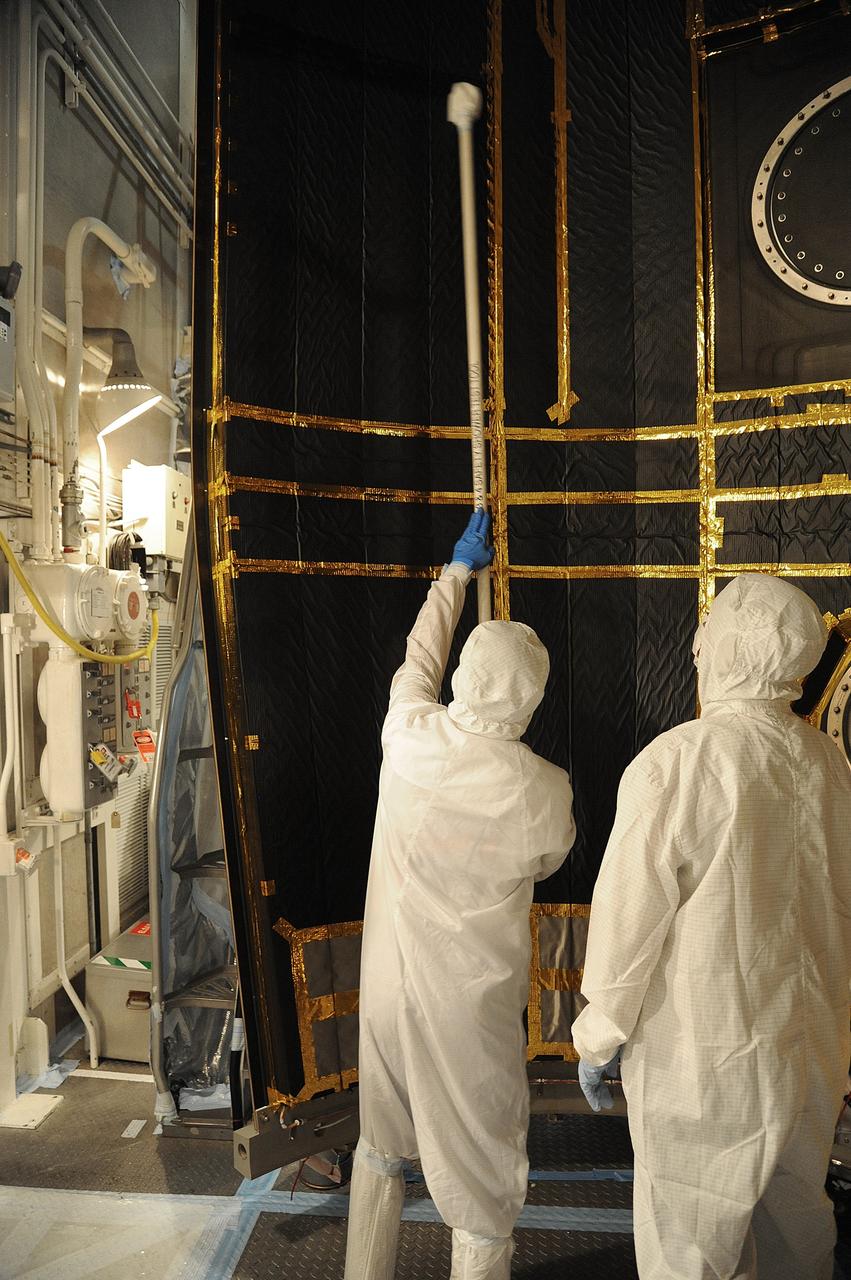

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the payload fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The fairing will soon be used to encapsulate the satellite atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
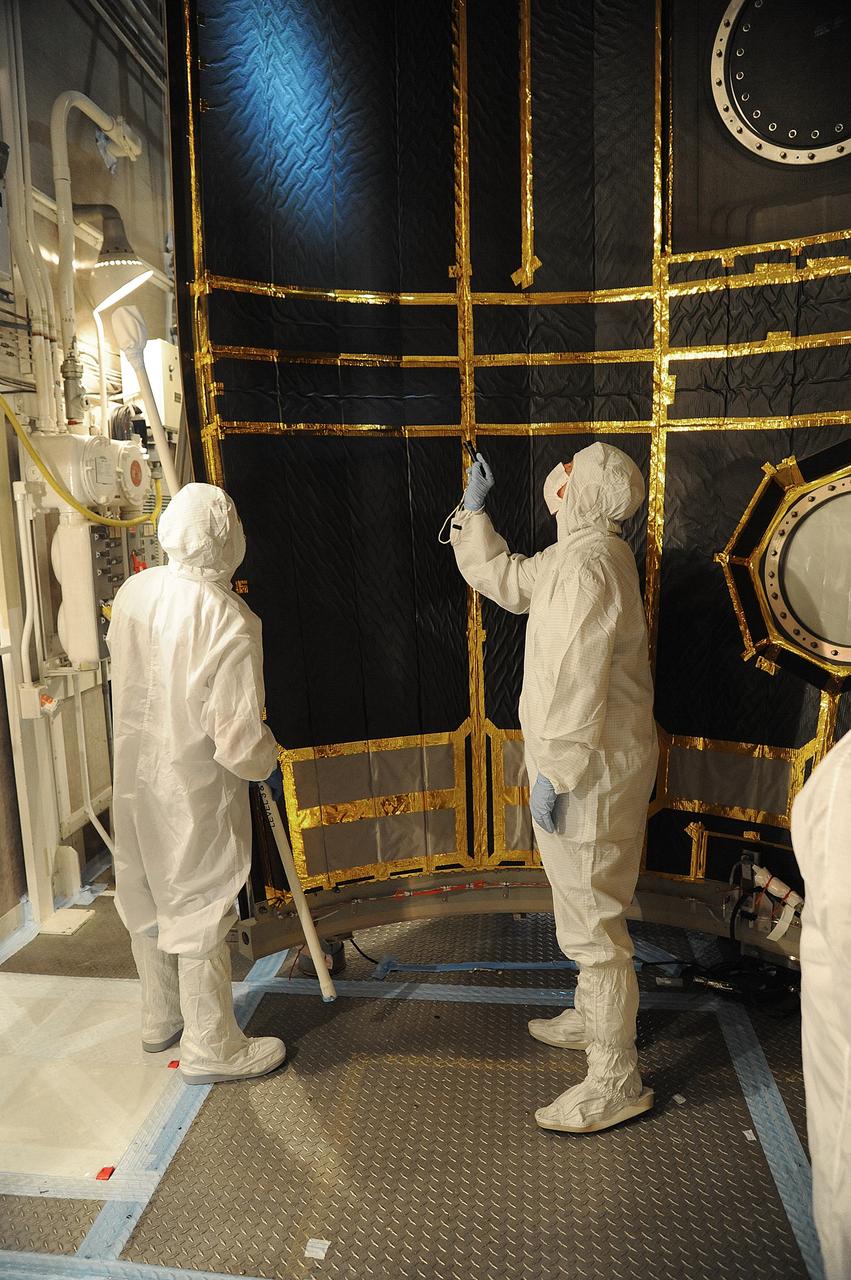

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the payload fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The fairing will soon be used to encapsulate the satellite atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
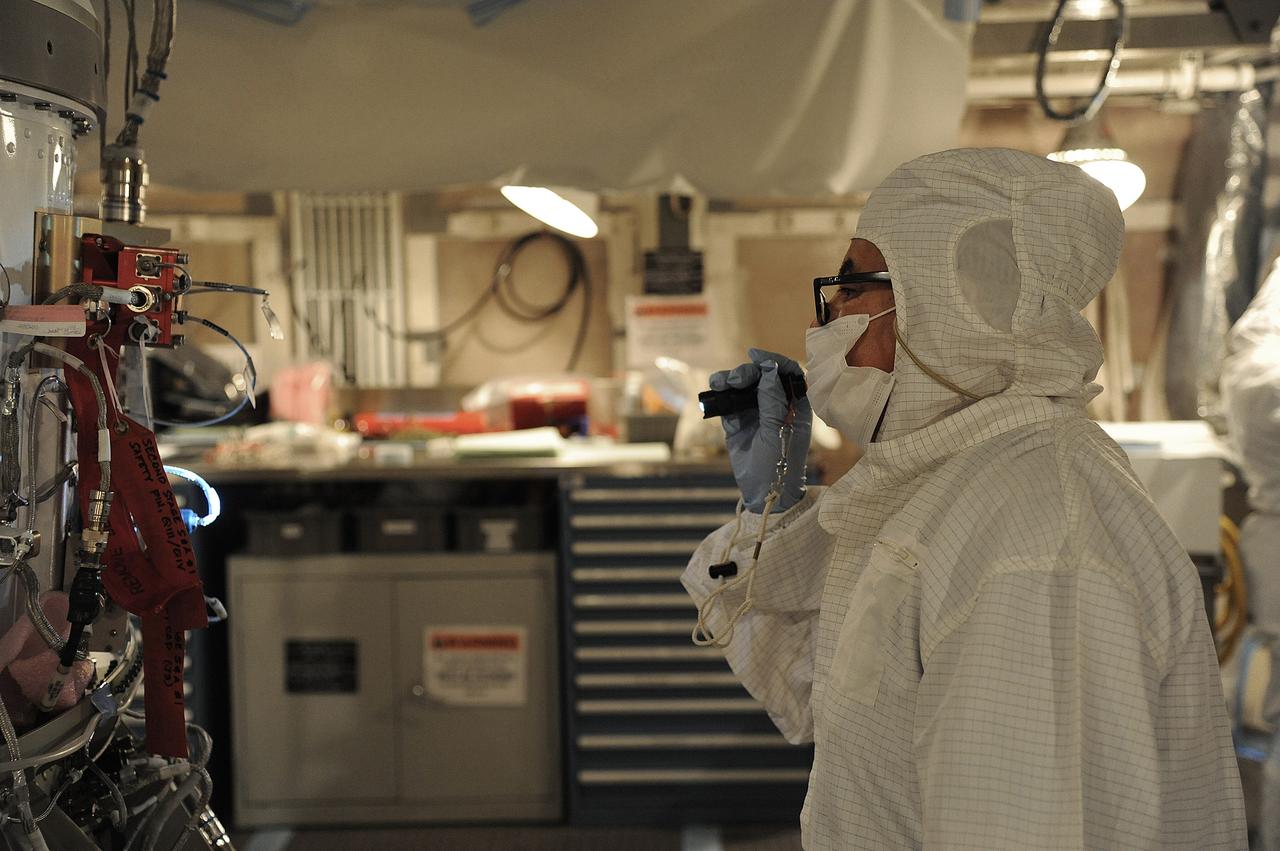

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The task is taking place prior to encapsulation in its payload fairing atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
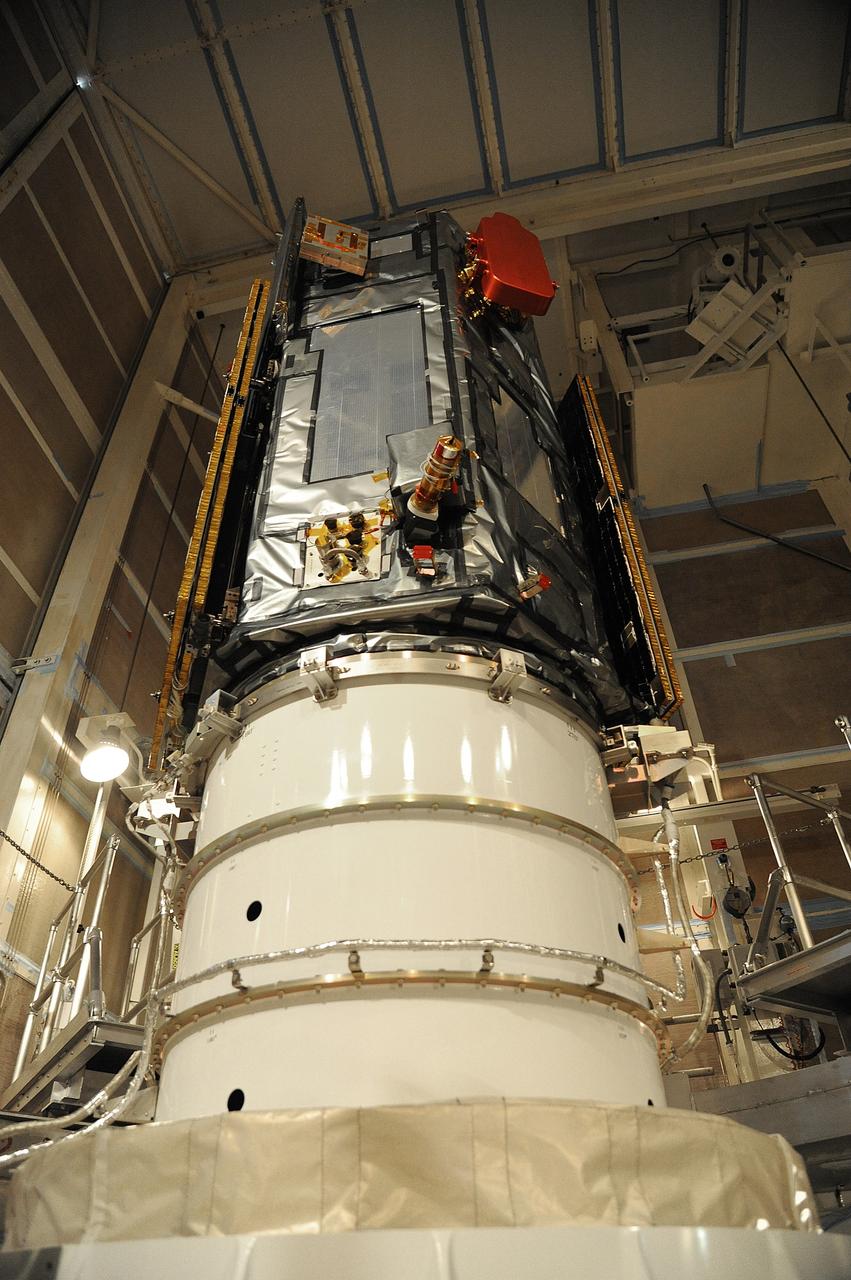

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite sits atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket prior to encapsulation in its payload fairing at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
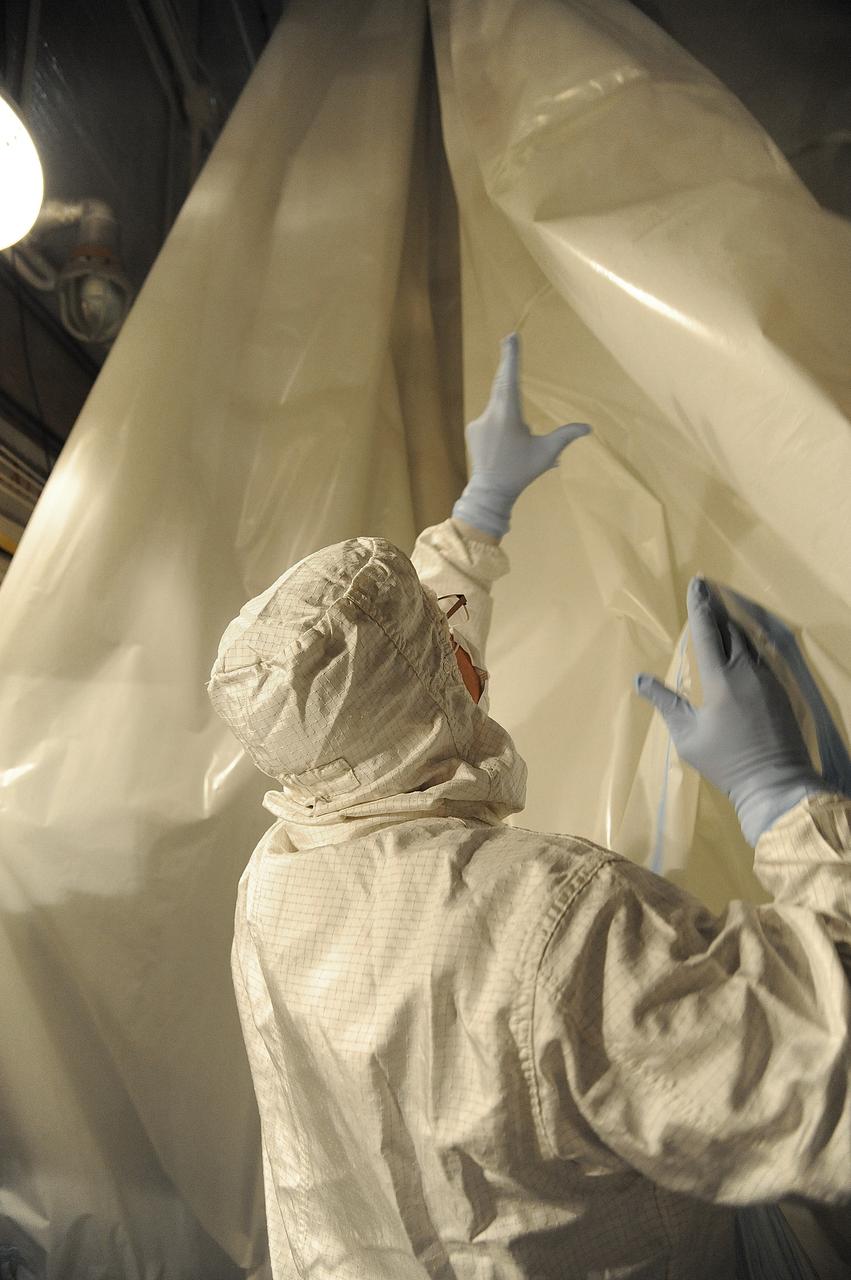

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The task is taking place prior to encapsulation in its payload fairing atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
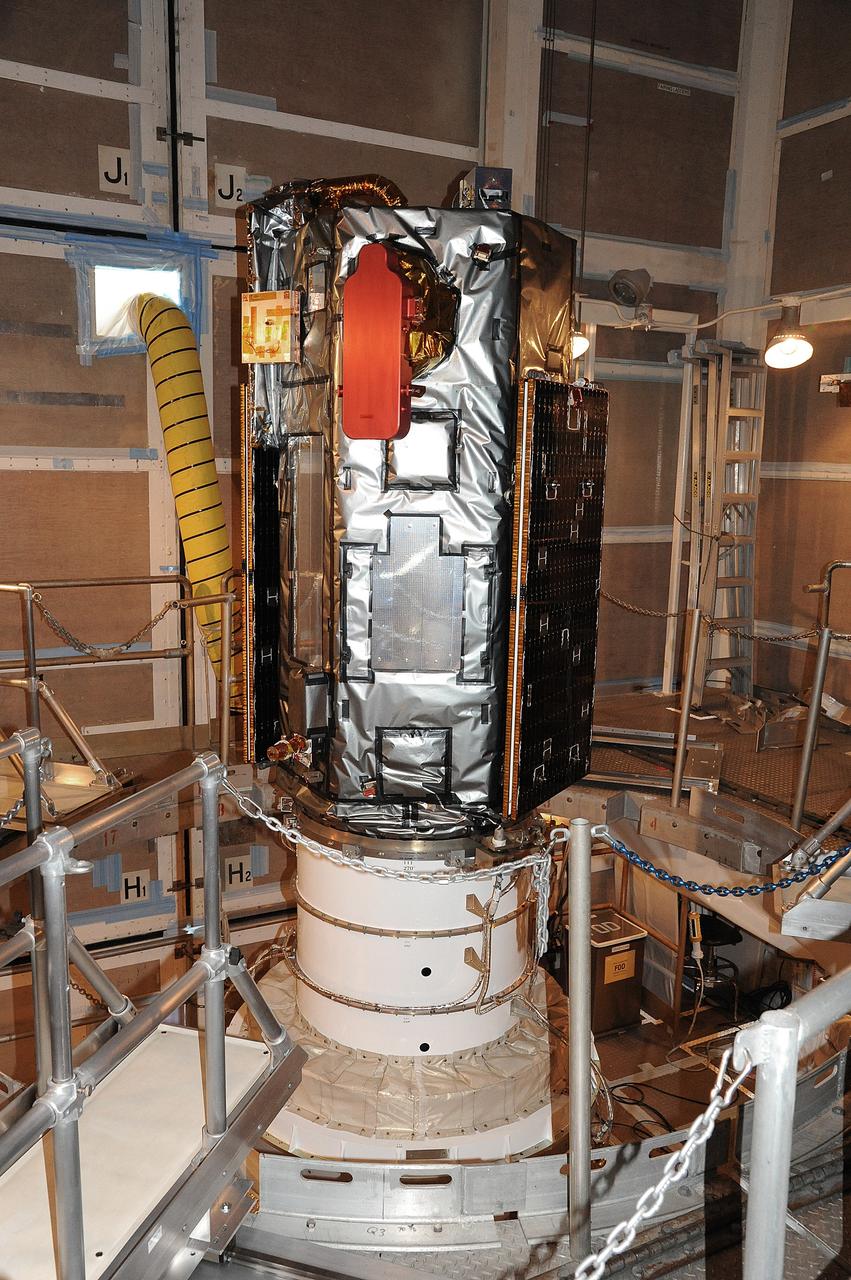

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite sits atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket prior to encapsulation in its payload fairing at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
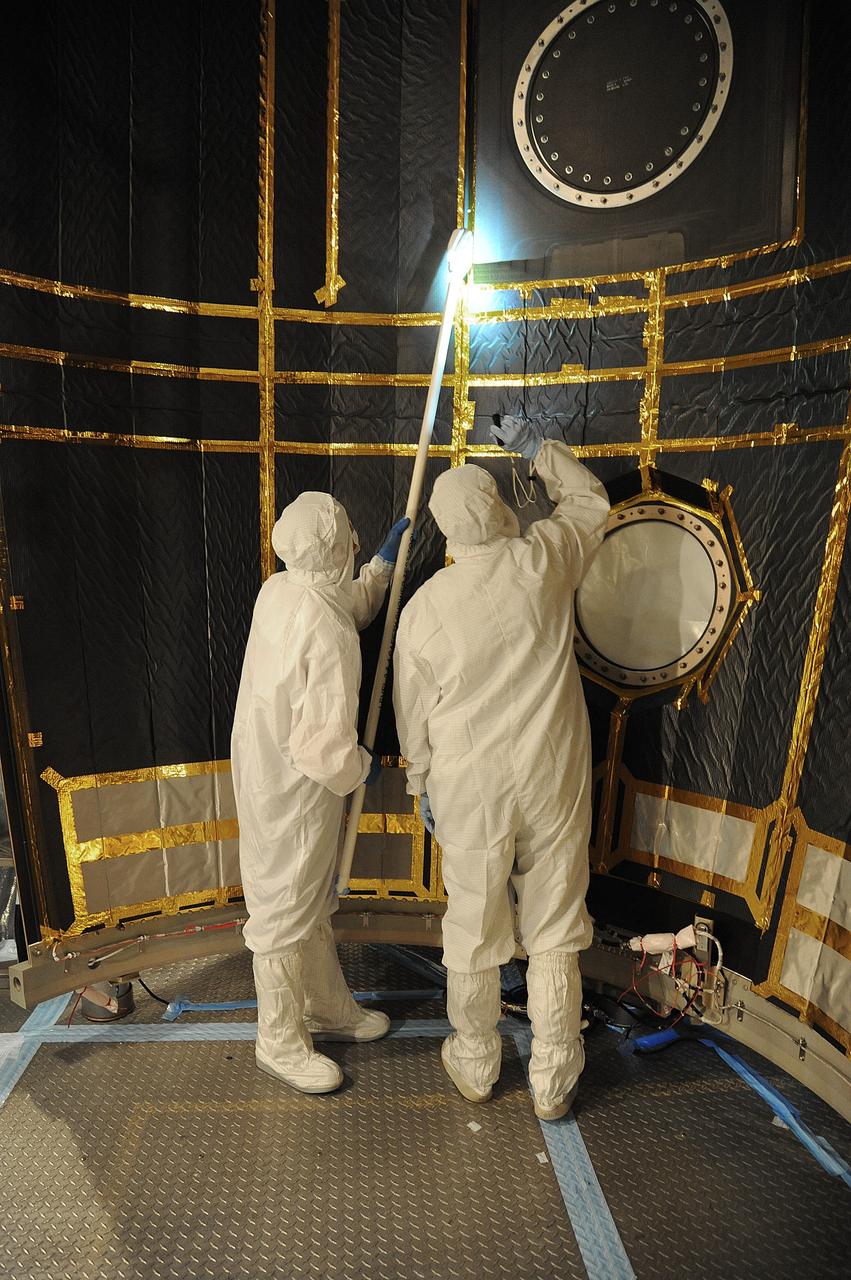

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the payload fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The fairing will soon be used to encapsulate the satellite atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
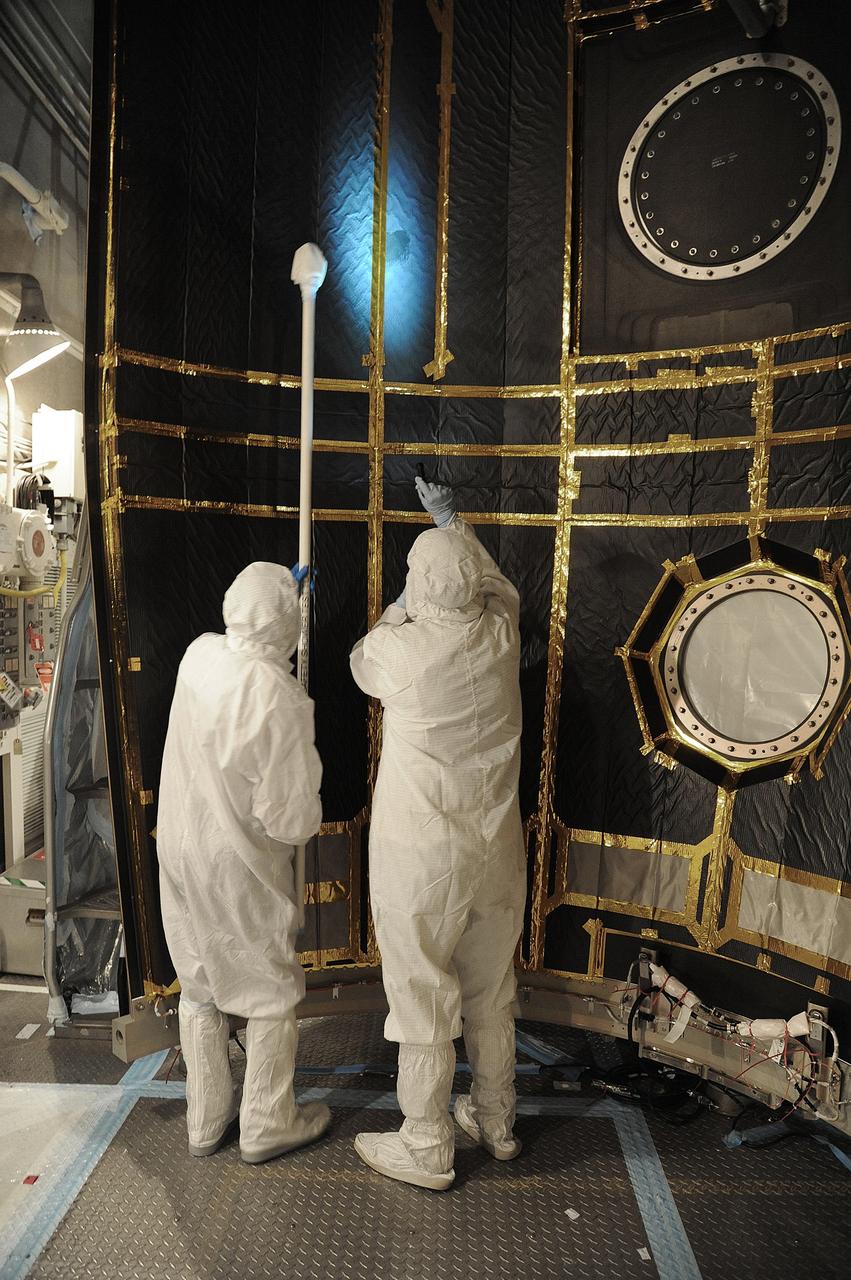

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the payload fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The fairing will soon be used to encapsulate the satellite atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
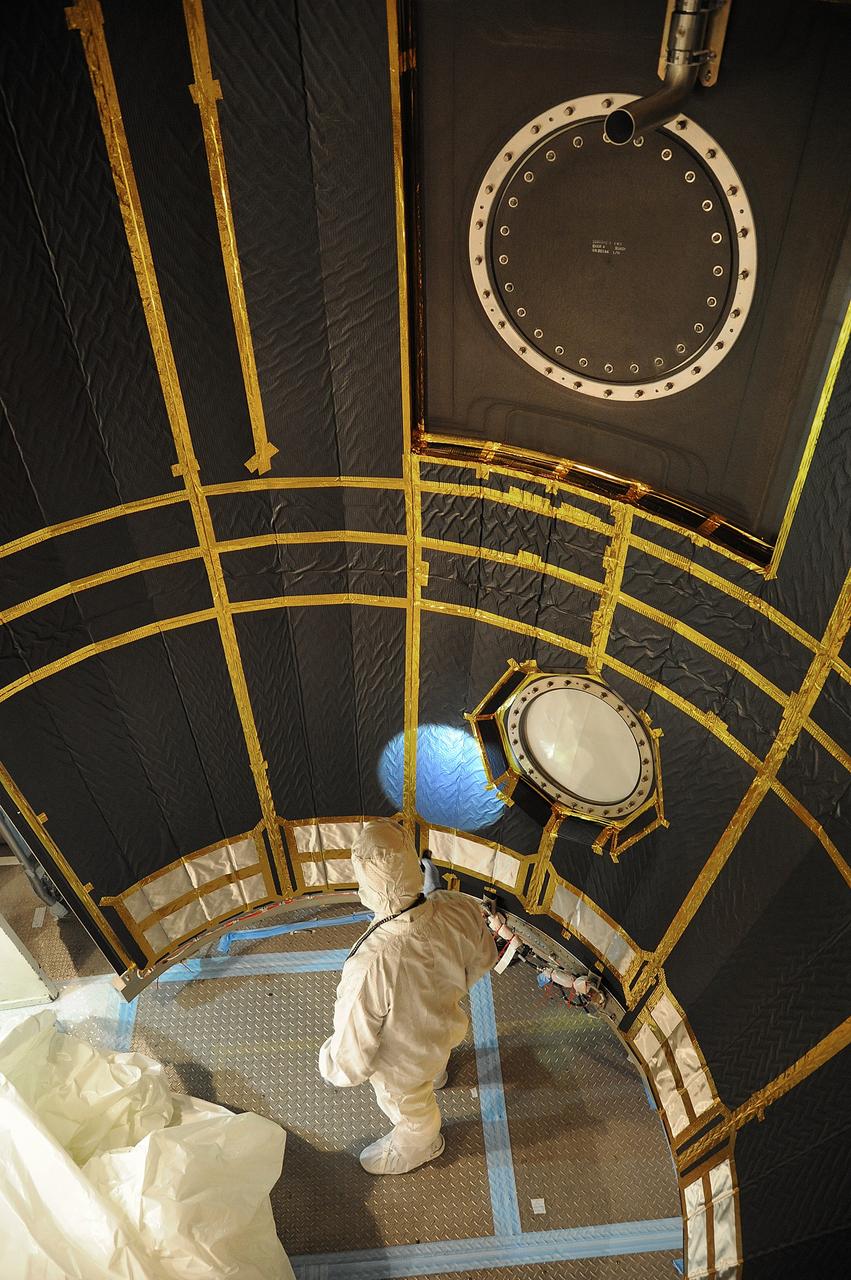

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the payload fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The fairing will soon be used to encapsulate the satellite atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley
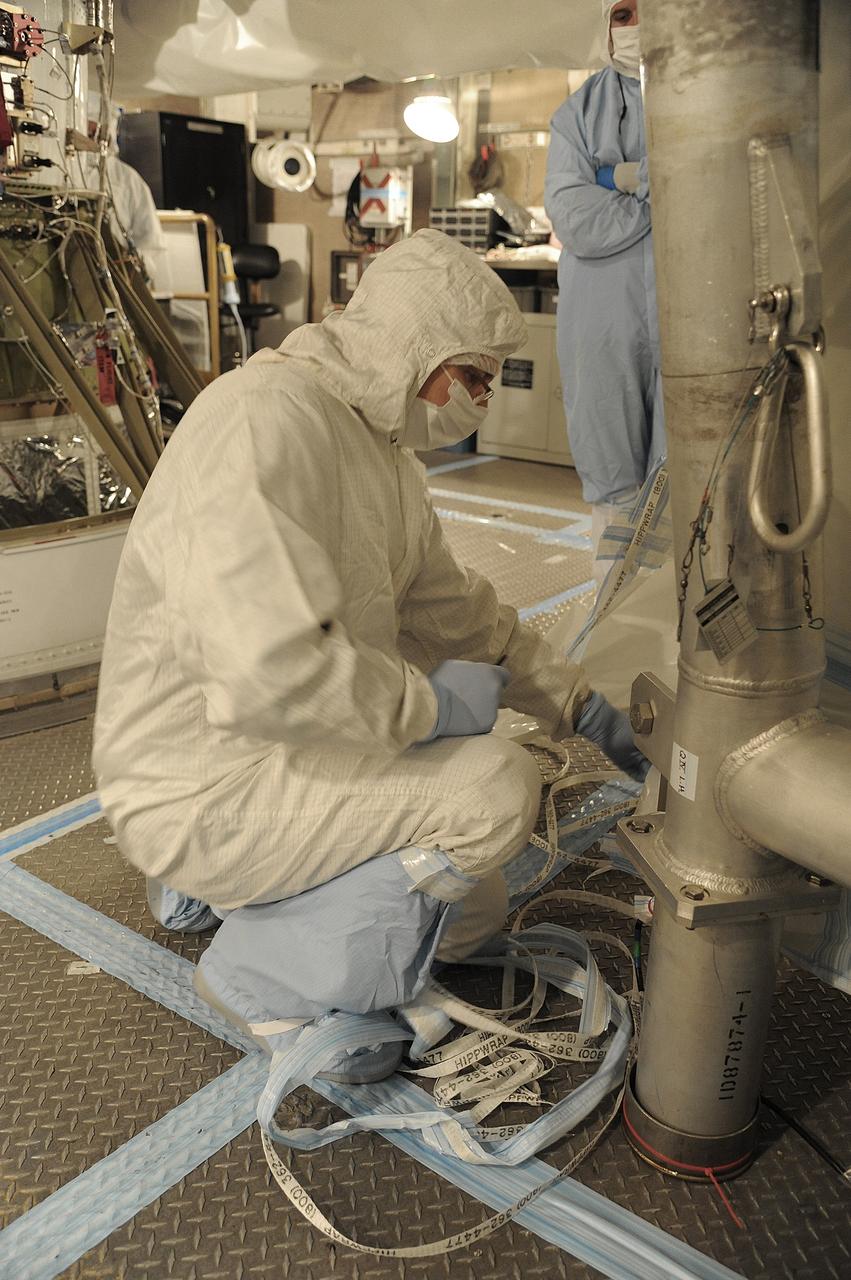

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians are inspecting the NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, satellite. The task is taking place prior to encapsulation in its payload fairing atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for 2:56 a.m. PDT 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackley