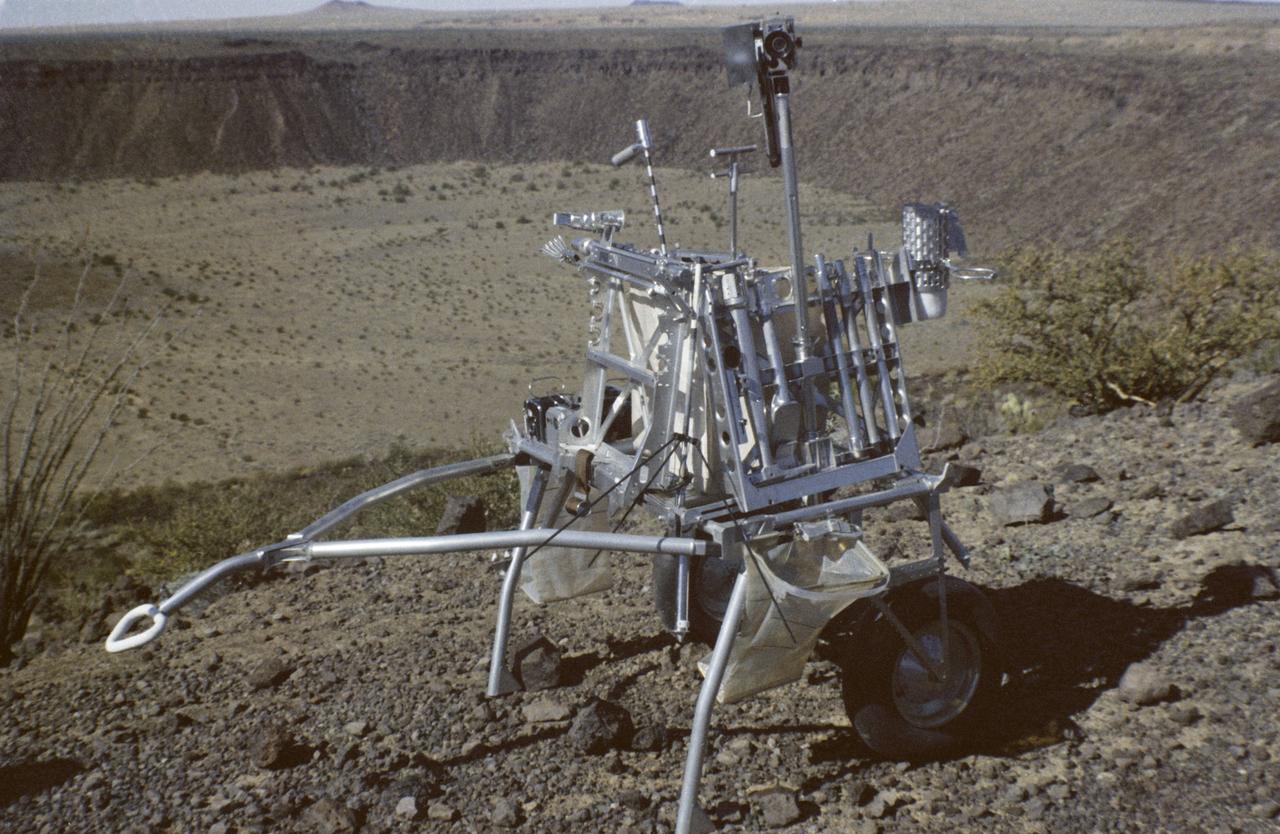

S70-29505 (13-18 Feb. 1970) --- A prototype of the modular equipment transporter (MET), nicknamed the "Rickshaw" after its shape and method of propulsion. This equipment was used by the Apollo 14 astronauts during their geological and lunar surface simulation training in the Pinacate volcanic area of northwestern Sonora, Mexico. The Apollo 14 crew will be the first one to use the MET. It will be a portable workbench with a place for the lunar hand tools and their carrier, three cameras, two sample container bags, a special environmental sample container, spare film magazines, and a lunar surface Penetrometer.
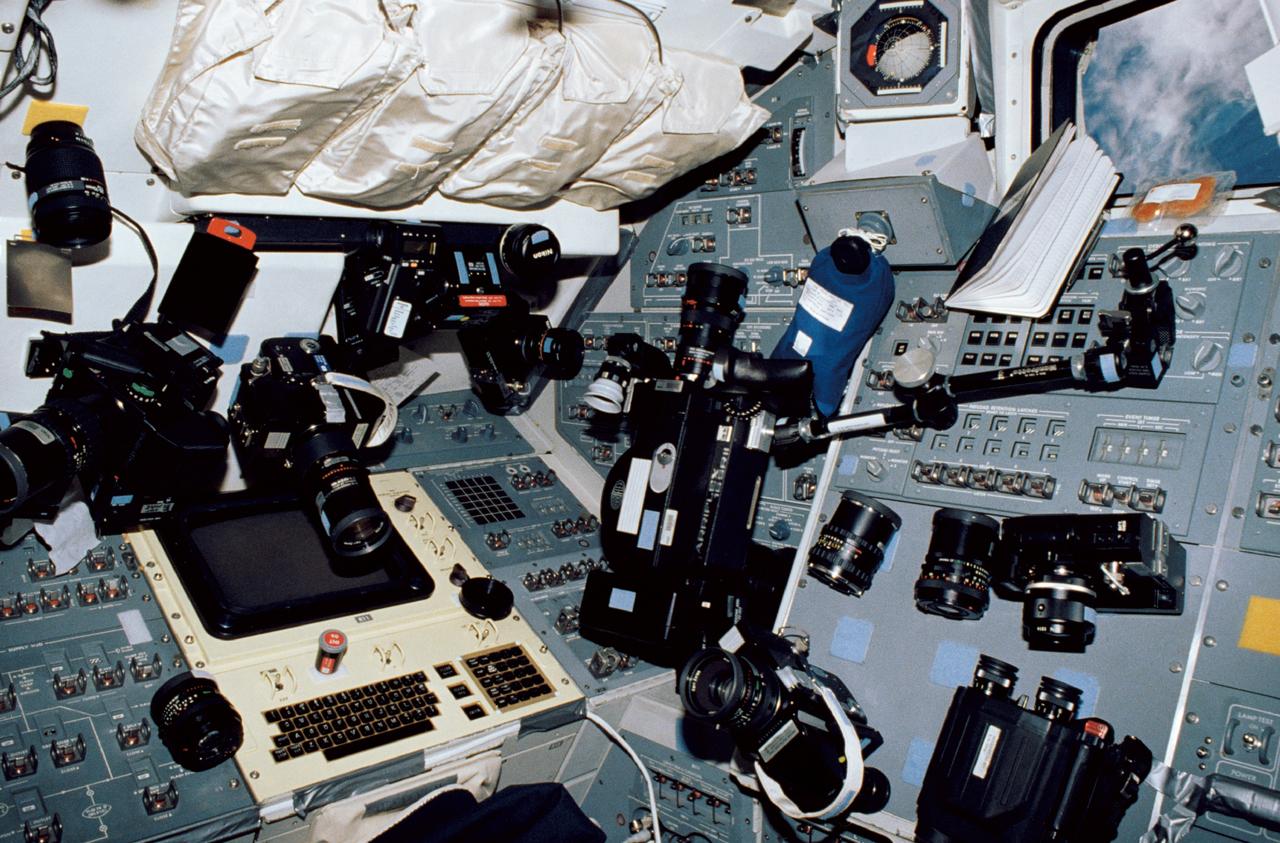

STS035-10-015 (2-10 Dec 1990) --- This busy scene shows cameras and supportive photographic gear temporarily stowed on Space Shuttle Columbia's aft flight deck. It was photographed with a 35mm camera by astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, mission specialist, who called the cluster a "camera forest." The seven STS-35 crewmembers trained to record a wide variety of imagery with an equally broad range of equipment. In addition to cameras, a spot meter, film, a pair of binoculars, a bracket, lenses, lens cleaner and other photographic equipment are in the scene. Clouds over ocean waters are framed by an aft flight deck window at upper right.
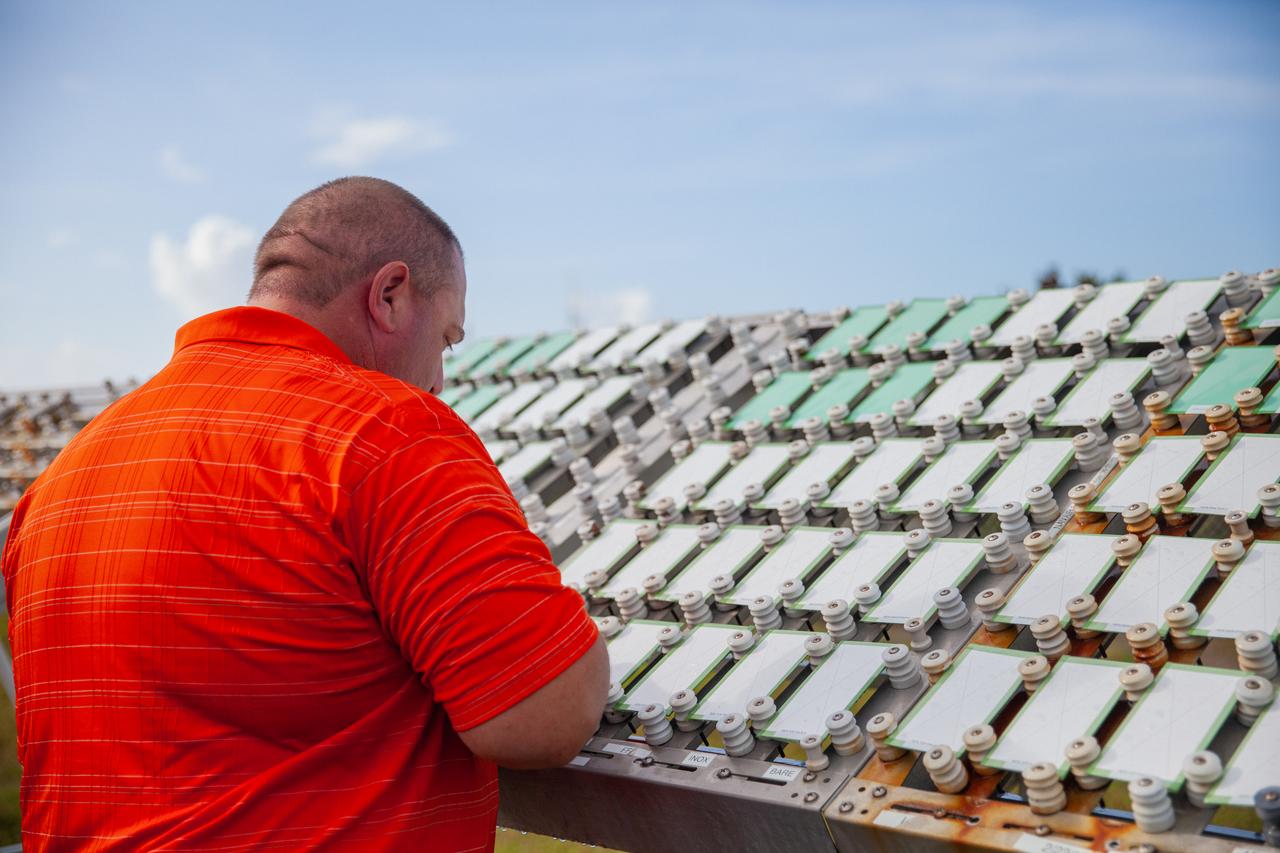

A Mechanical and Environmental Testing Lab engineer examines samples at the corrosion engineering test site at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 6, 2020. The corrosion lab is a network of people, equipment, and facilities that provides engineering services and technical innovations in all areas of corrosion for NASA and external customers.
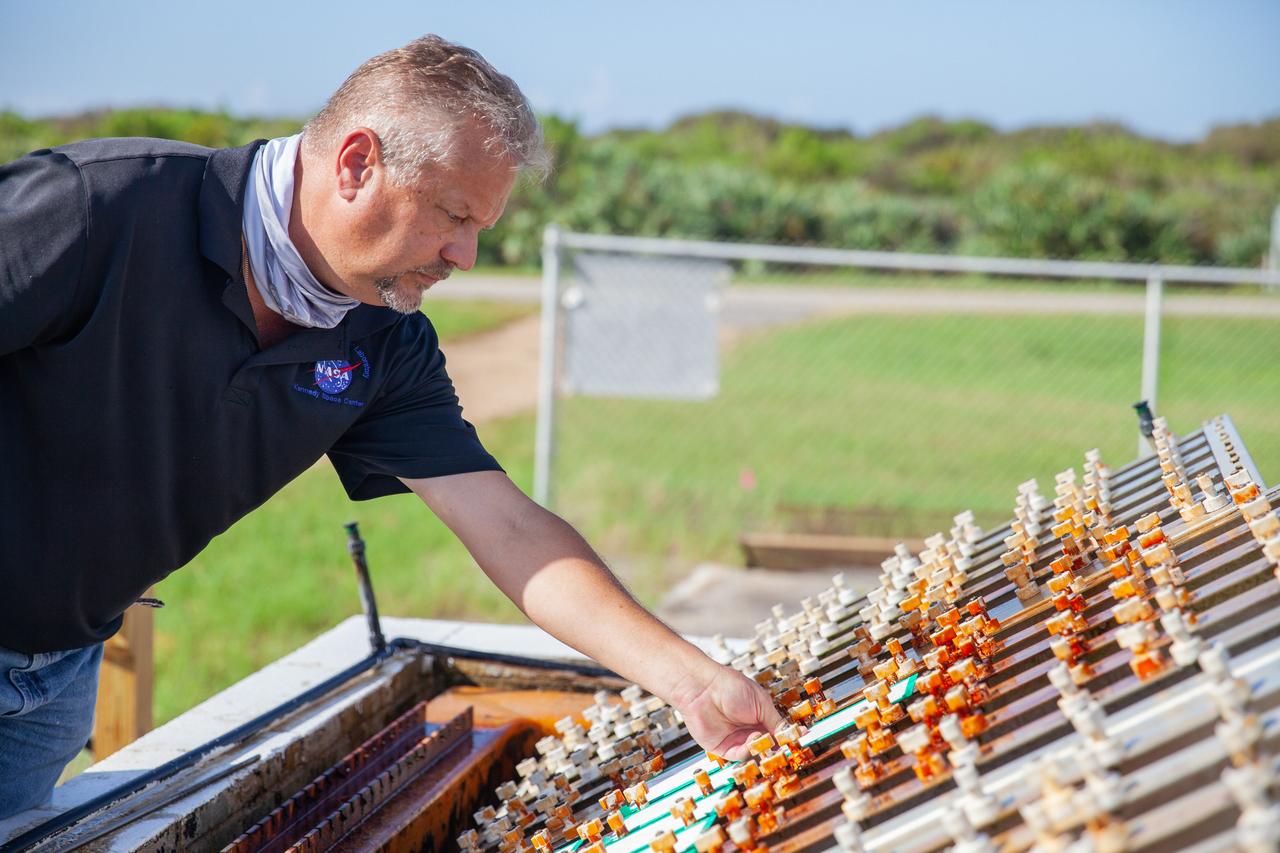

A Mechanical and Environmental Testing Lab engineer examines samples at the corrosion engineering test site on Oct. 6, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The corrosion lab is a network of people, equipment, and facilities that provides engineering services and technical innovations in all areas of corrosion for NASA and external customers.
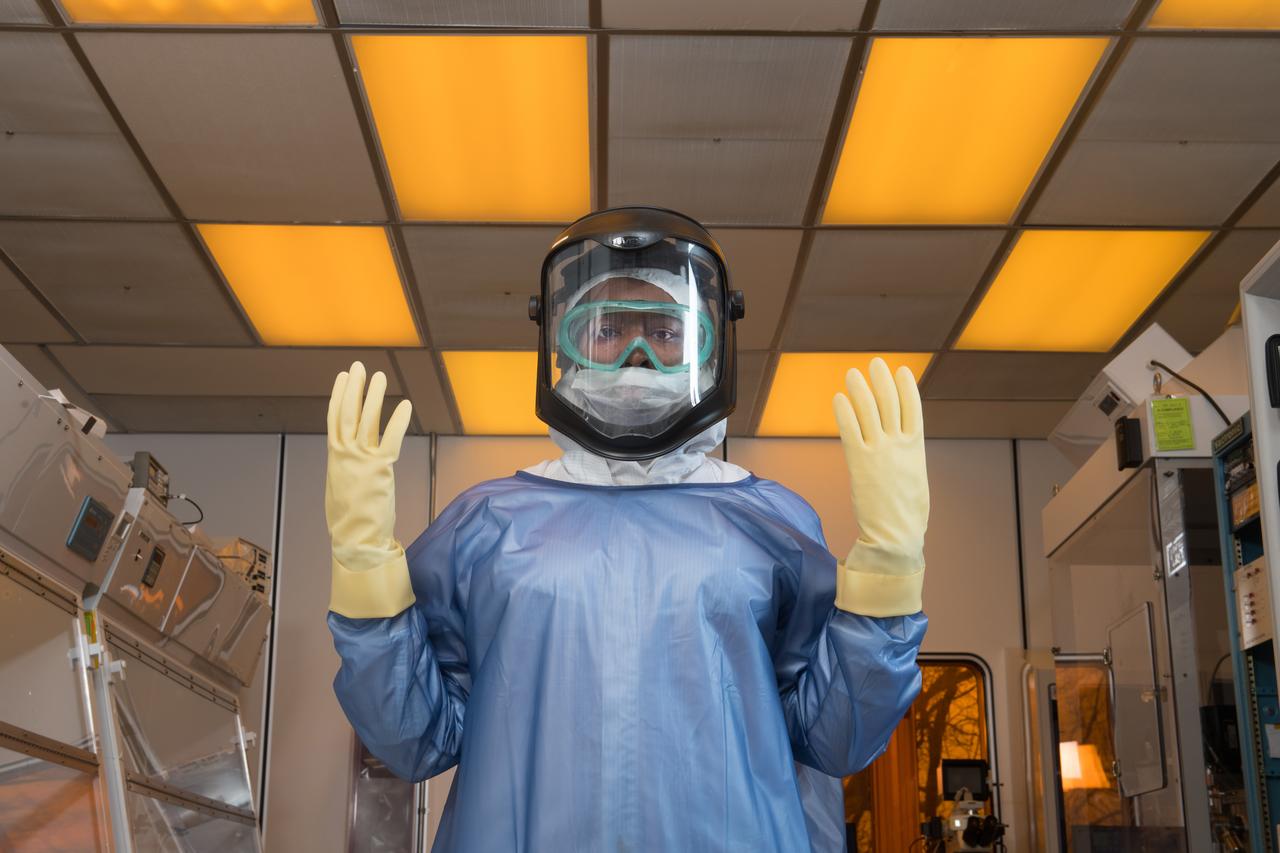
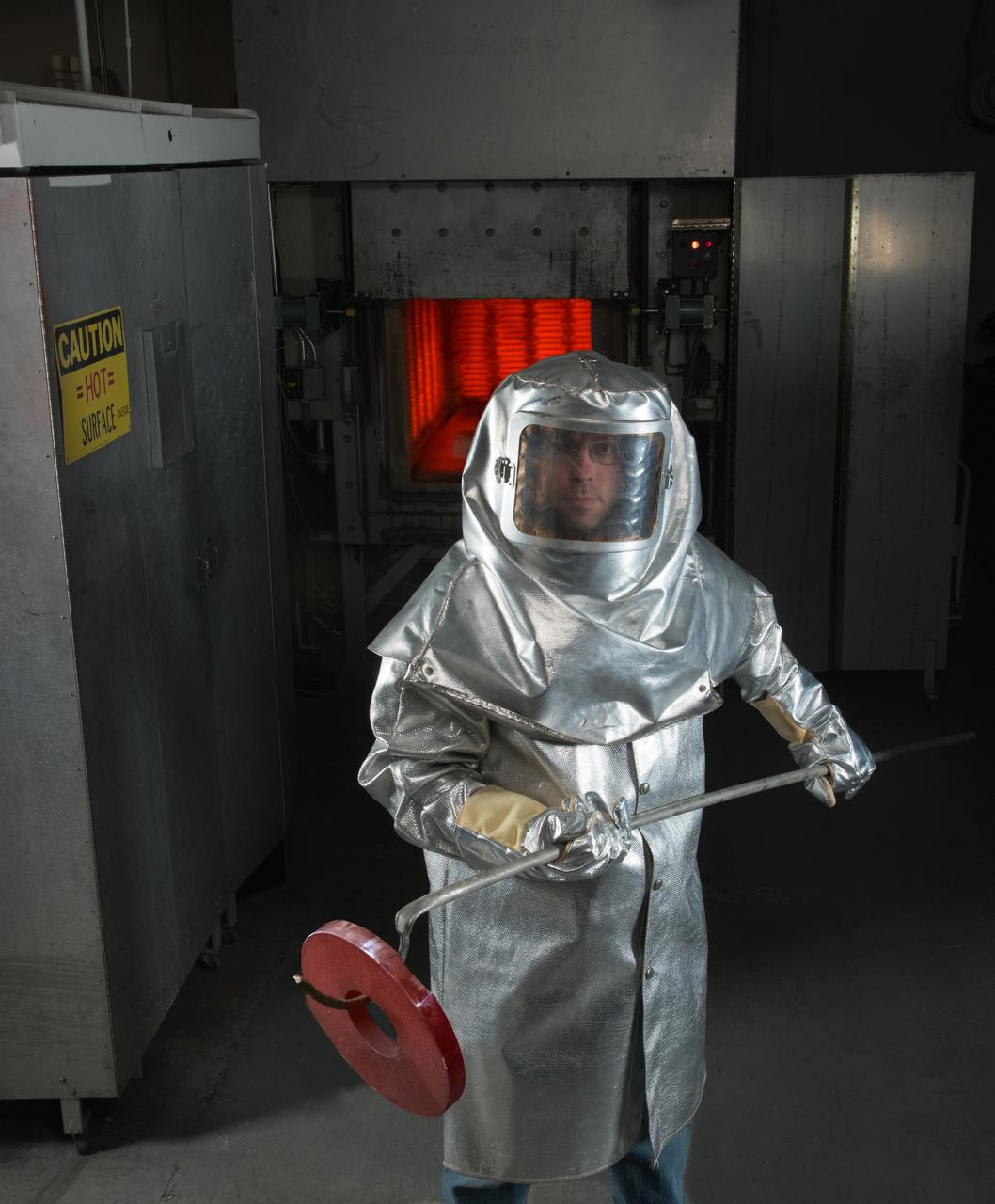
Laboratory researcher suits up for work in a research clean room. Personal Protective Equipment, PPE, Portait Series
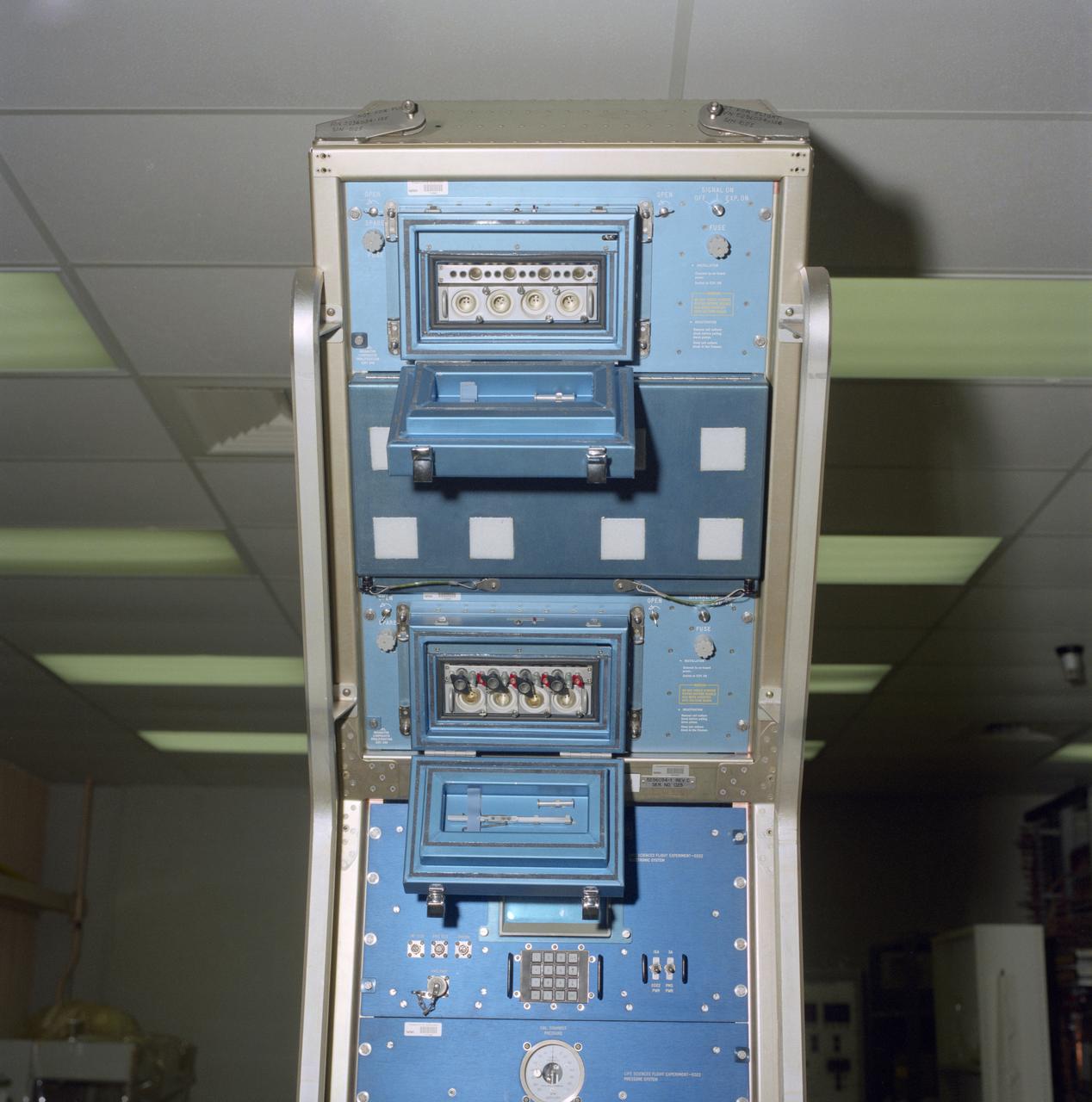

S84-43683 (26 Nov 1984) --- This vertically positioned rectangular piece of hardware, scheduled to fly on the science module of Spacelab Life Sciences-1, is important to the immunology investigation on the mission. Called Lymphocyte Proliferation in Weightlessness (Experiment 240), the test was developed by Dr. Augosto Cogoli of the Institute of Biotechnology, Gruppe Weltraum Biologie, in Zurich, Switzerland. It represents a continuation of previous Spacelab experiments by examining the effects of weightlessness on lymphocyte activation. Cultures will be grown in the microgravity incubators on the pictured hardware.
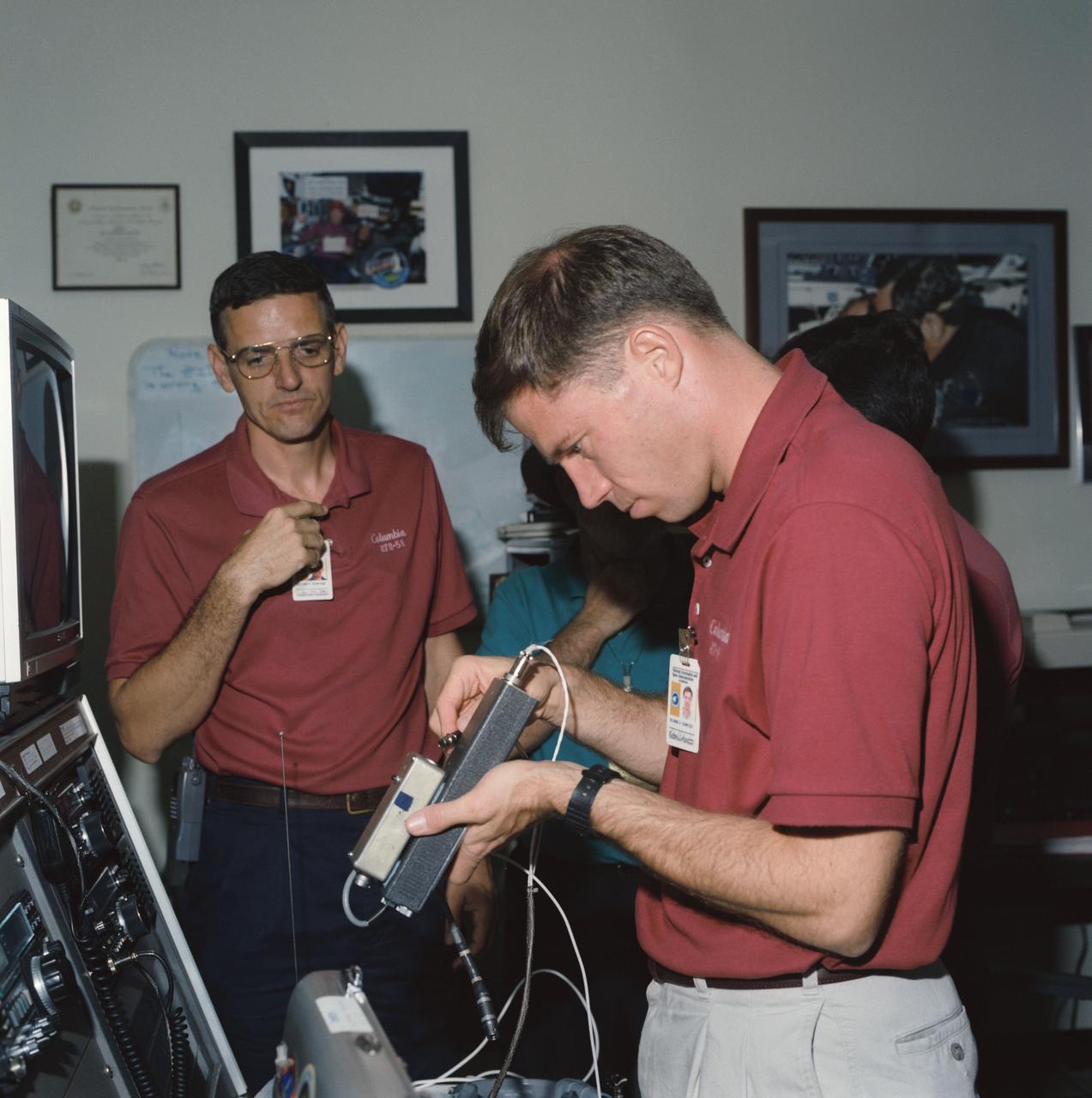

S93-45068 (22 Sept 1993) --- Two members of the STS-58 Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-2) crew, train with amateur radio equipment at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). They are William S. McArthur (left), mission specialist, and Richard A. Searfoss, pilot. The STS-58 flight will carry the Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX) payload, configuration C, which includes FM voice and packet. Three of the seven crewmembers are licensed amateur radio operators. Searfoss' call letters are KC5CKM; McArthur, KC5ACR; and payload specialist Martin J. Fettman, KC5AXA. Licensed students at a number of schools around the country will have the opportunity to talk directly with the astronauts during the 14-day flight.
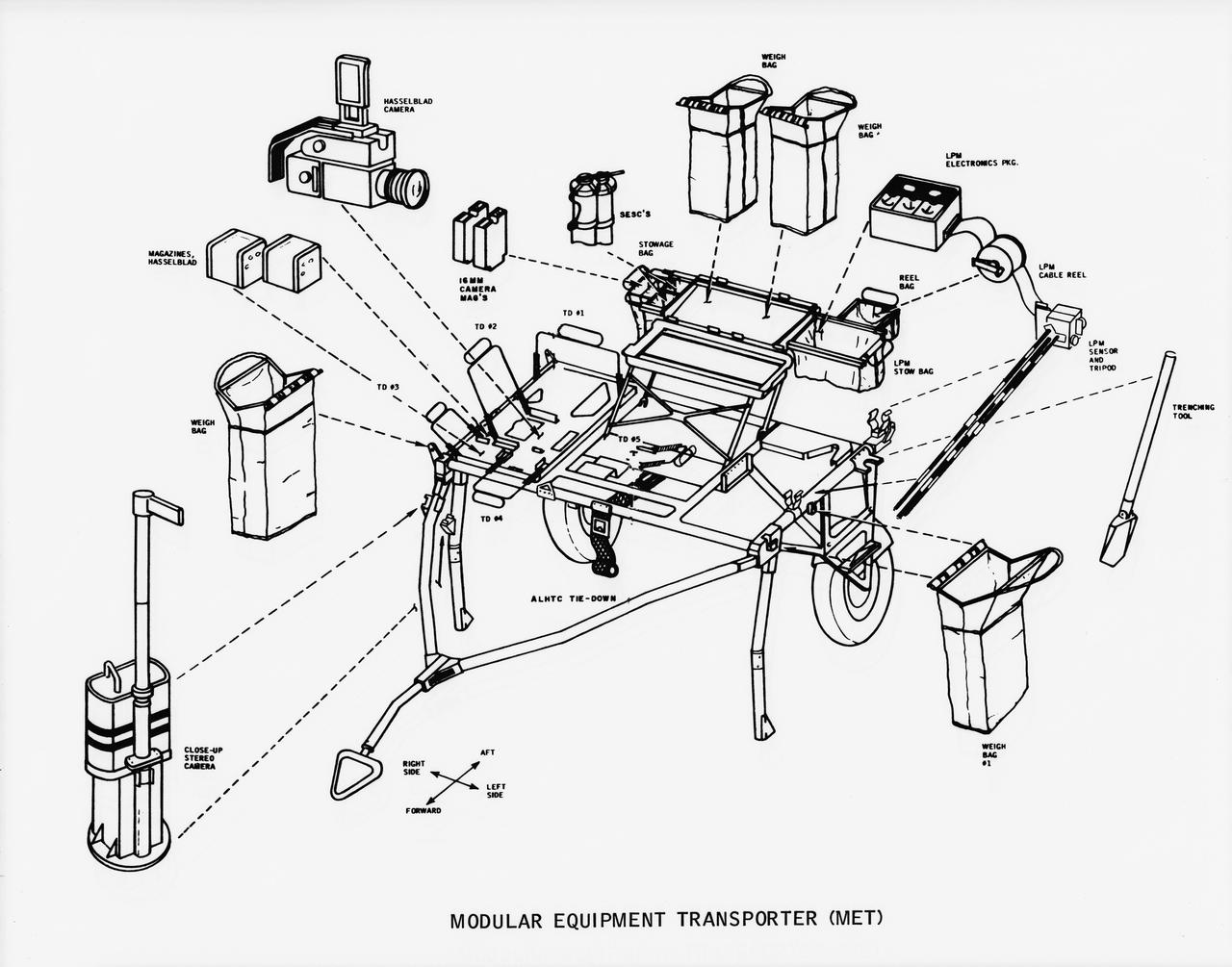
S70-50762 (November 1970) --- A line drawing illustrating layout view of the modular equipment transporter (MET) and its equipment. A MET (or Rickshaw, as it has been nicknamed) will be used on the lunar surface for the first time during the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. The Rickshaw will serve as a portable workbench with a place for the Apollo lunar hand tools (ALHT) and their carrier, three cameras, two sample container bags, a special environment sample container (SESC), a lunar portable magnetometer (LPM) and spare film magazines.

The prototype Flexible Damage Detection System stands in a laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The system uses circuits printed on thin thermal film and specialized software. The system is designed to show where damage to a surface occurs and how severe it may be. It could offer astronauts a real-time update on their spacecraft's condition during a mission without requiring a spacewalk.
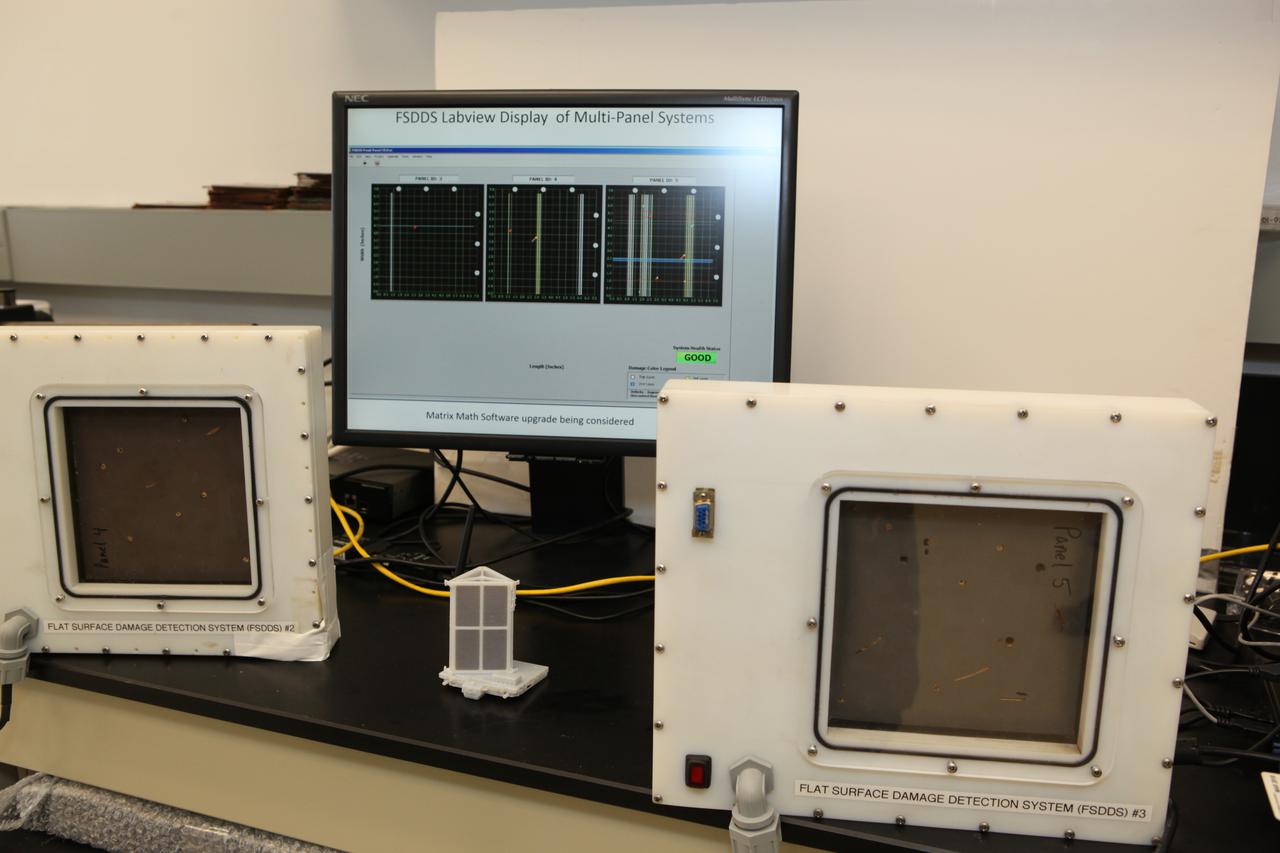

The complete prototype Flexible Damage Detection System stands in a laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The system uses circuits printed on thin thermal film and specialized software. The system is designed to show where damage to a surface occurs and how severe it may be. It could offer astronauts a real-time update on their spacecraft's condition during a mission without requiring a spacewalk. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
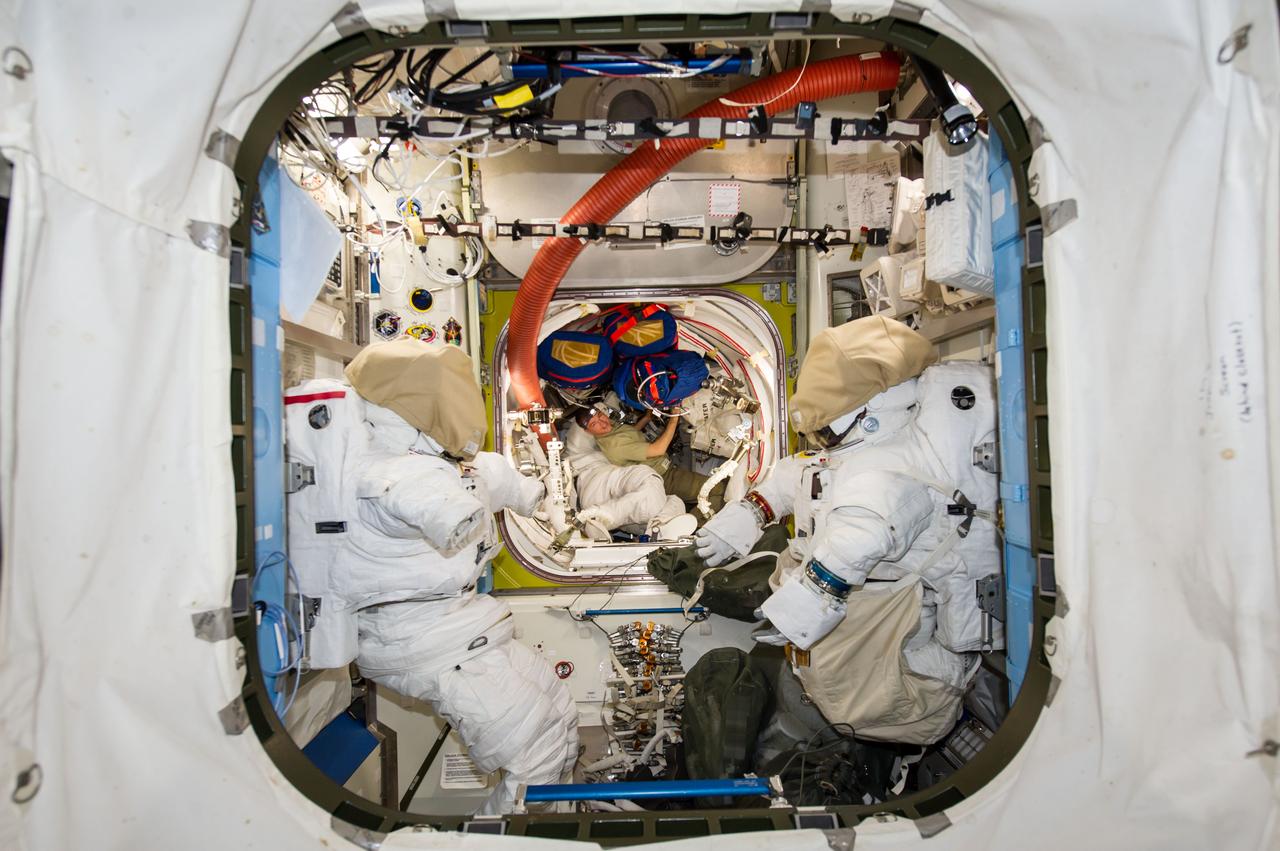

ISS041-E-016637 (16 Sept. 2014) --- NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman (center background), Expedition 41 flight engineer, works among stowed equipment in the Quest airlock of the International Space Station. Two Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuits are visible in the foreground.
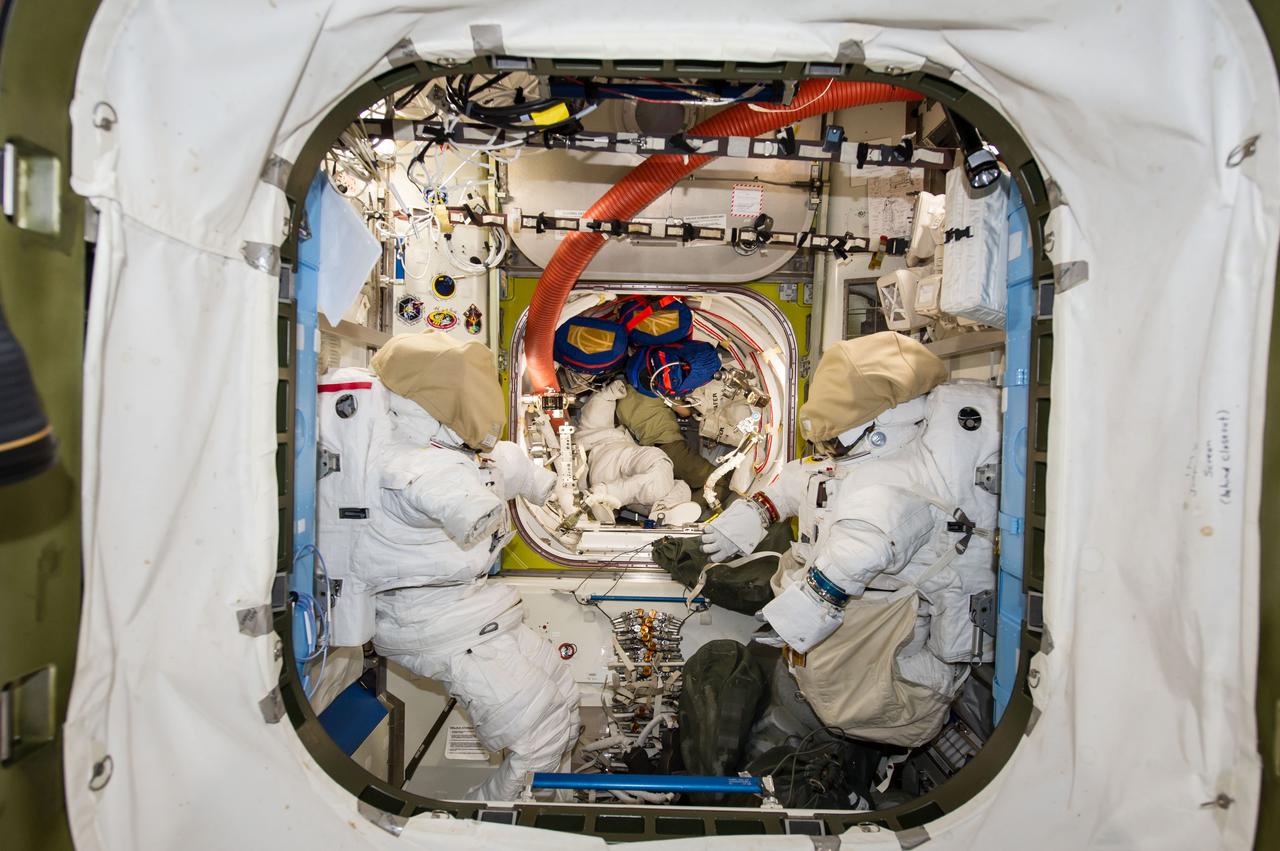

ISS041-E-016635 (16 Sept. 2014) --- NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman (center background), Expedition 41 flight engineer, works among stowed equipment in the Quest airlock of the International Space Station. Two Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuits are visible in the foreground.
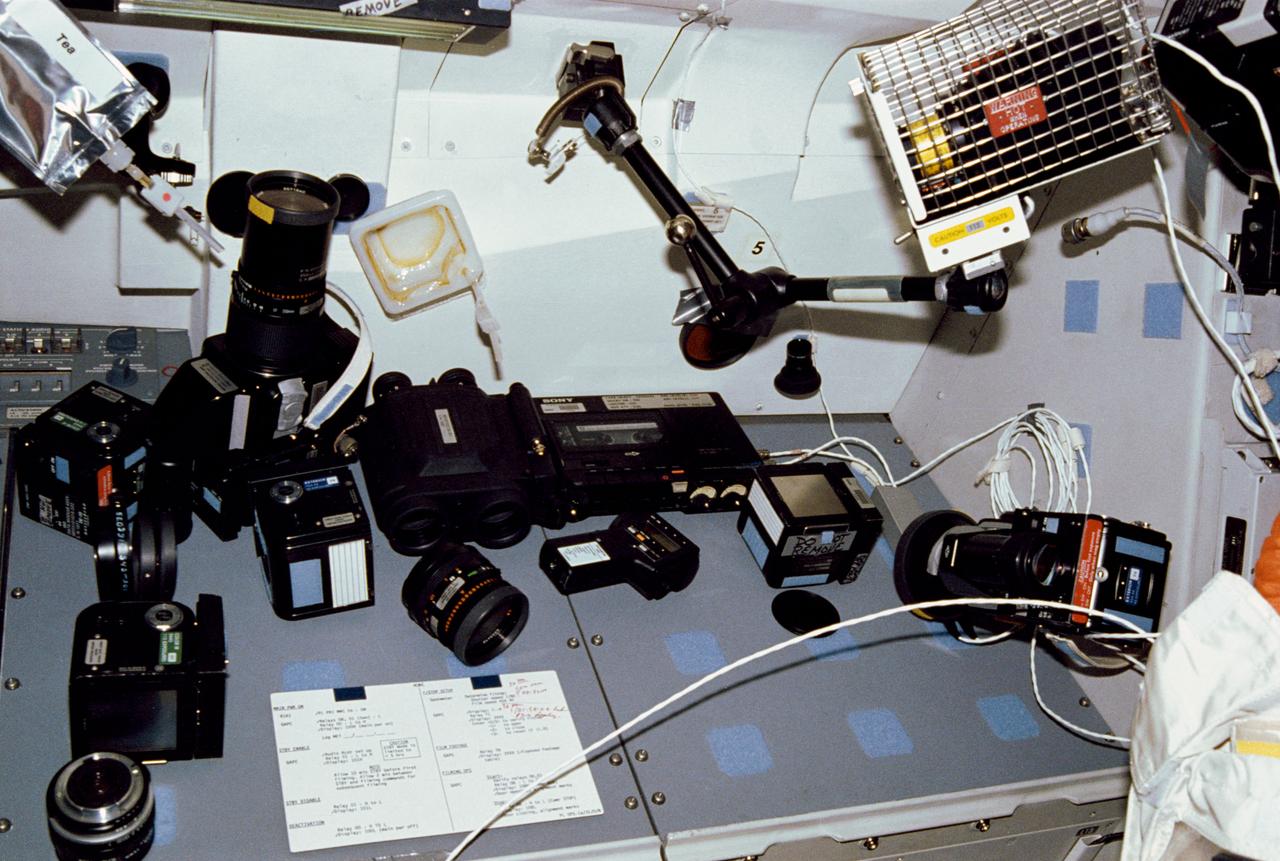

This array of photographic equipment, displayed on the aft flight deck payload station, represents just a part of the imaging and recording hardware which was carried aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, for STS-31's five day mission. Lenses, film magazines, cassettes, recorders, camera chassis, a pair of binoculars, spot meter, tape recorder, and a bracket-mounted light fixture are included among the array.

Personal Protective Equipment, PPE, Portrait Series, Welch_503059, Shape memory alloys, Shape memory alloy, Welch-Bey-503059, Glen Bigelow,

STS-34 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, crewmembers listen to trainer Bill Bowers explain ARRIFLEX camera equipment during briefing at JSC. Across the table from Bowers are (left to right) Pilot Michael J. McCulley, Mission Specialist (MS) Ellen S. Baker, Commander Donald E. Williams, MS Shannon W. Lucid, and MS Franklin R. Chang-Diaz.
AS17-162-24063 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- A close-up view of the equipment used for the Heat Flow and Convection Experiment, an engineering and operational test and demonstration carried out aboard the Apollo 17 command module during the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. Three test cells were used in the demonstration for measuring and observing fluid flow behavior in the absence of gravity in space flight. Data obtained from such demonstrations will be valuable in the design of future science experiments and for manufacturing processes in space.

Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, uses the lunar equipment conveyer (LEC) at the Lunar Module during the Apollo 12 extravehicular activity on the lunar surface. This photograph was taken by Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot.

S66-54590 (13 Sept. 1966) --- Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., Gemini-11 pilot, prepares to open spacecraft hatch to jettison used equipment. Photo credit: NASA

S66-62999 (13 Nov. 1966) --- Jettison of the extravehicular life support system (ELSS) and other equipment from the Gemini-12 spacecraft during its rendezvous mission in space. The nose of the Gemini-12 spacecraft is clearly visible at right edge of photo. Photo credit: NASA
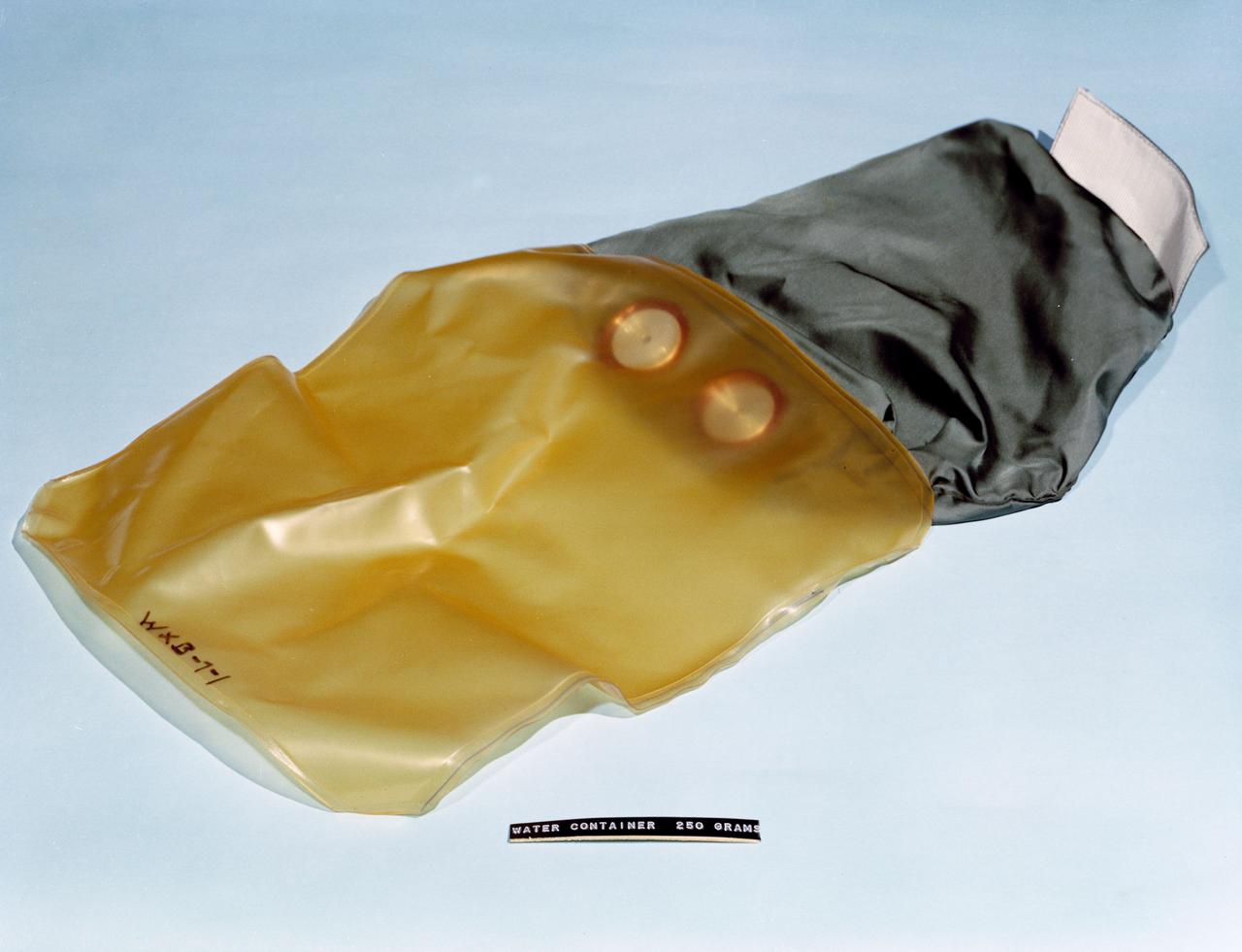
S62-06783 (1962) --- Component of Mercury astronauts survival equipment backpack - water container holding 250 grams when full. Photo credit: NASA
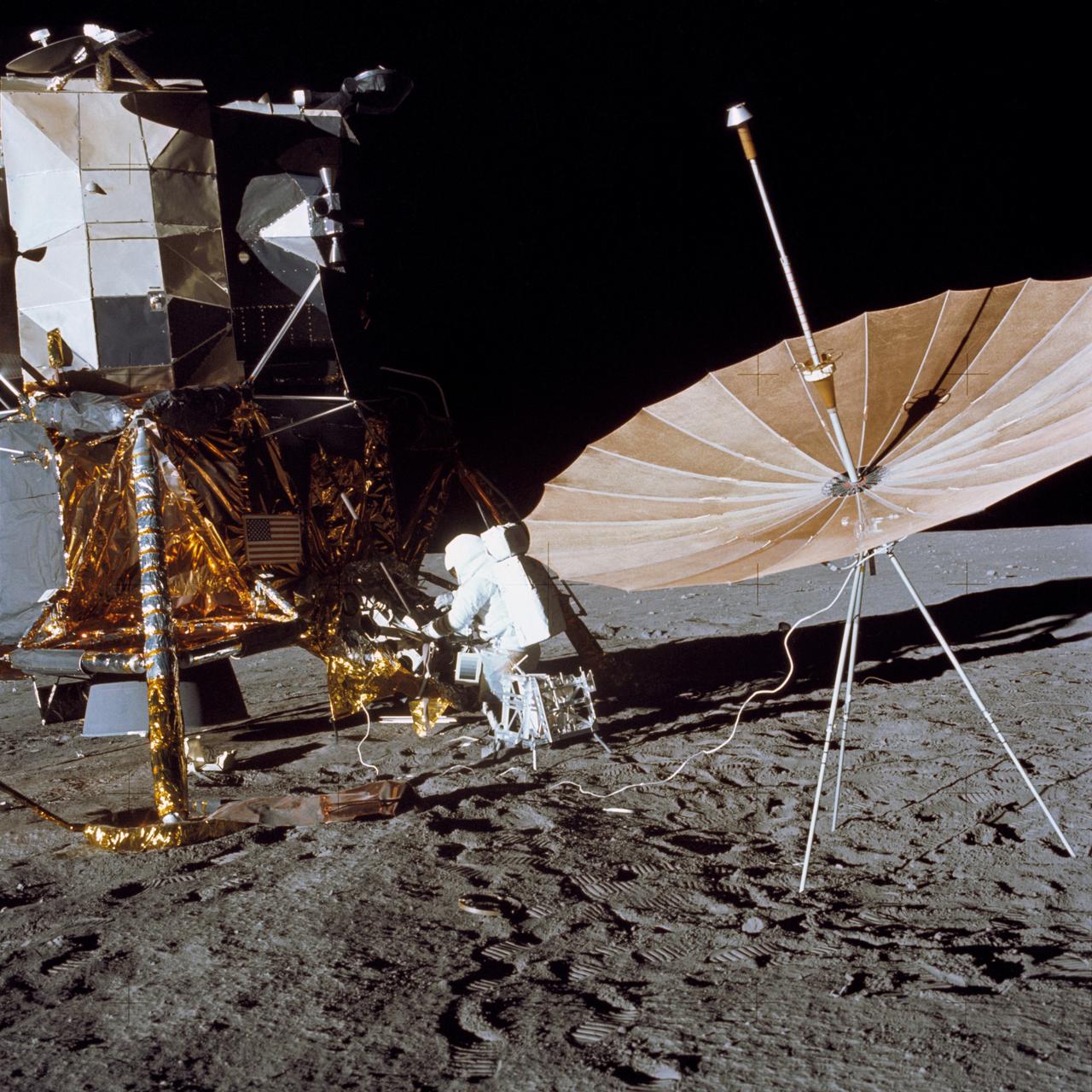

AS12-47-6988 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, stands at the Module Equipment Stowage Assembly (MESA) on the Lunar Module (LM) following the first Apollo 12 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The erectable S-band antenna is already deployed at right. The carrier for the Apollo Lunar Hand Tools (ALHT) is near Conrad. While astronauts Conrad and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
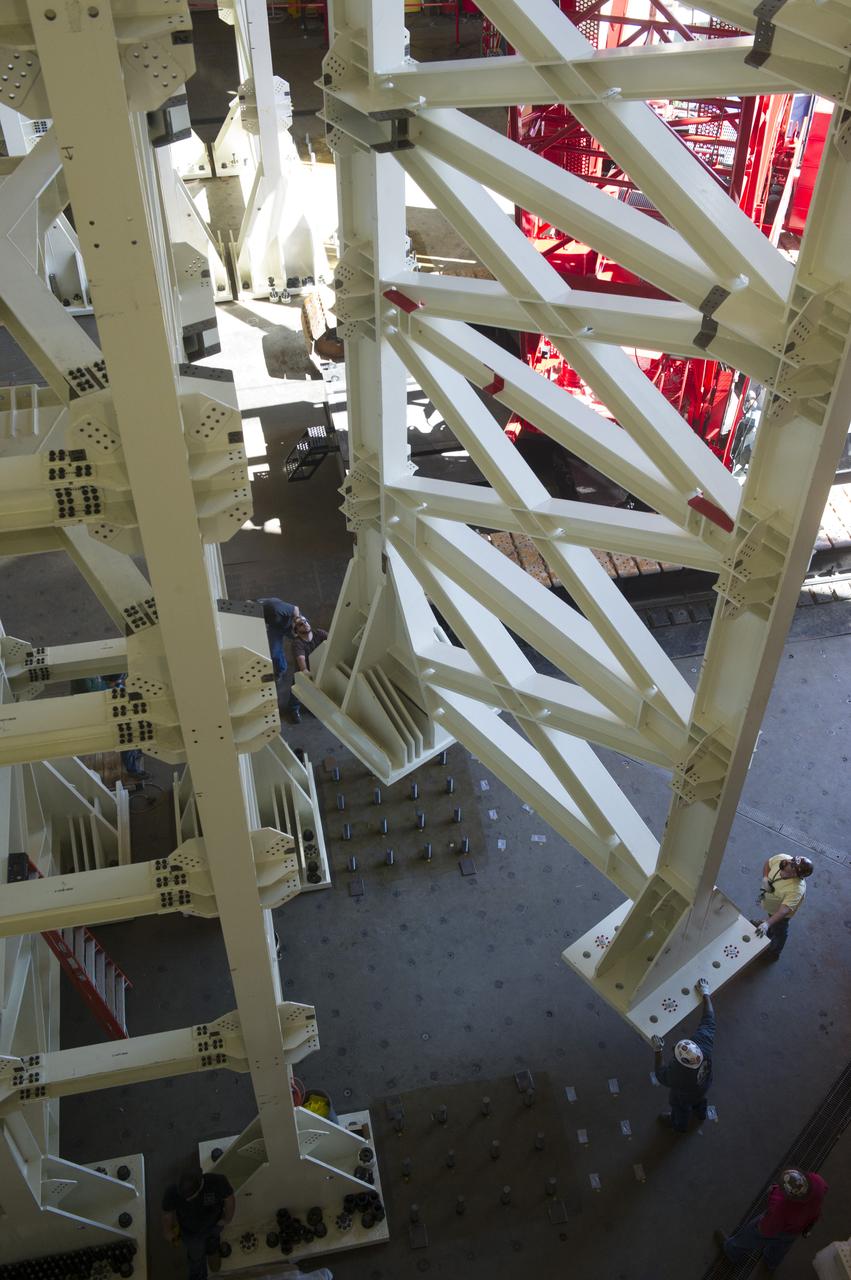
ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
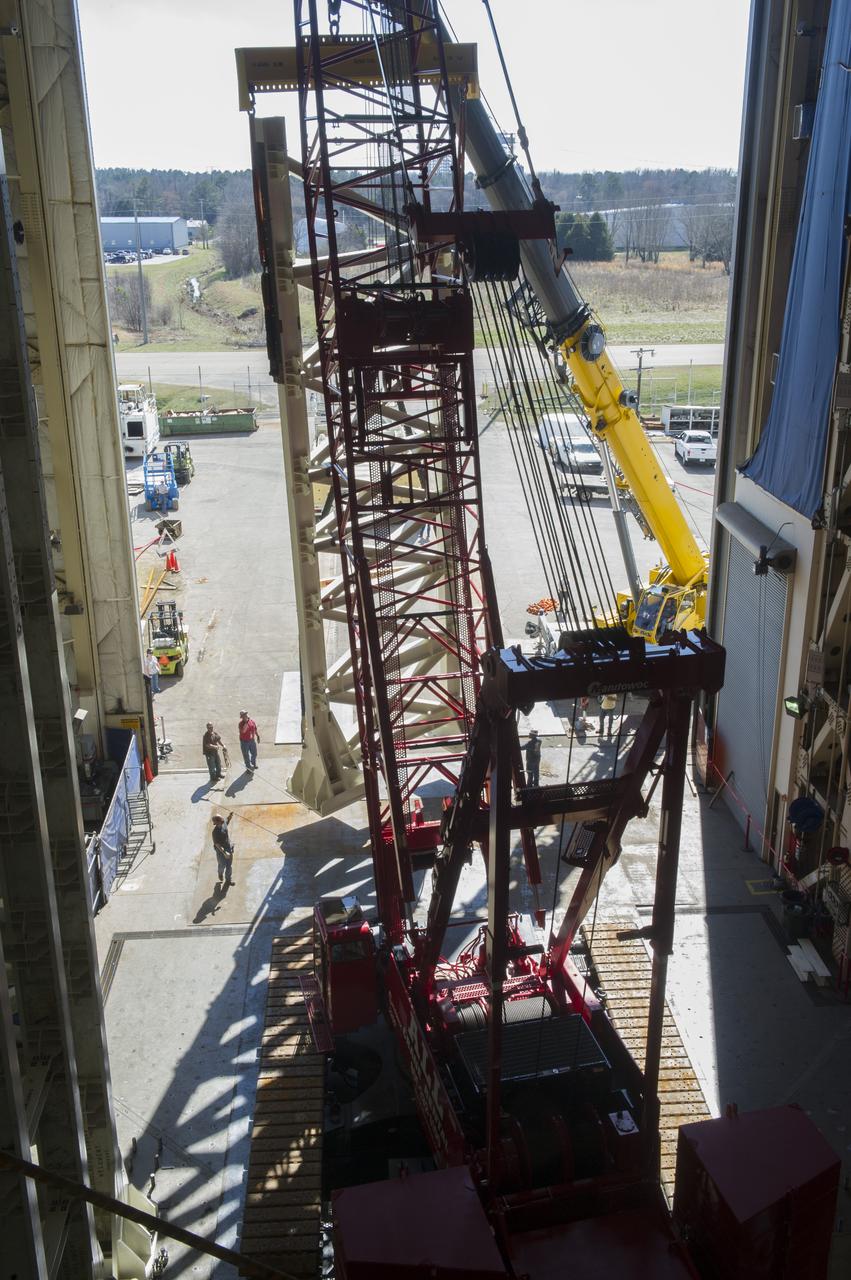

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
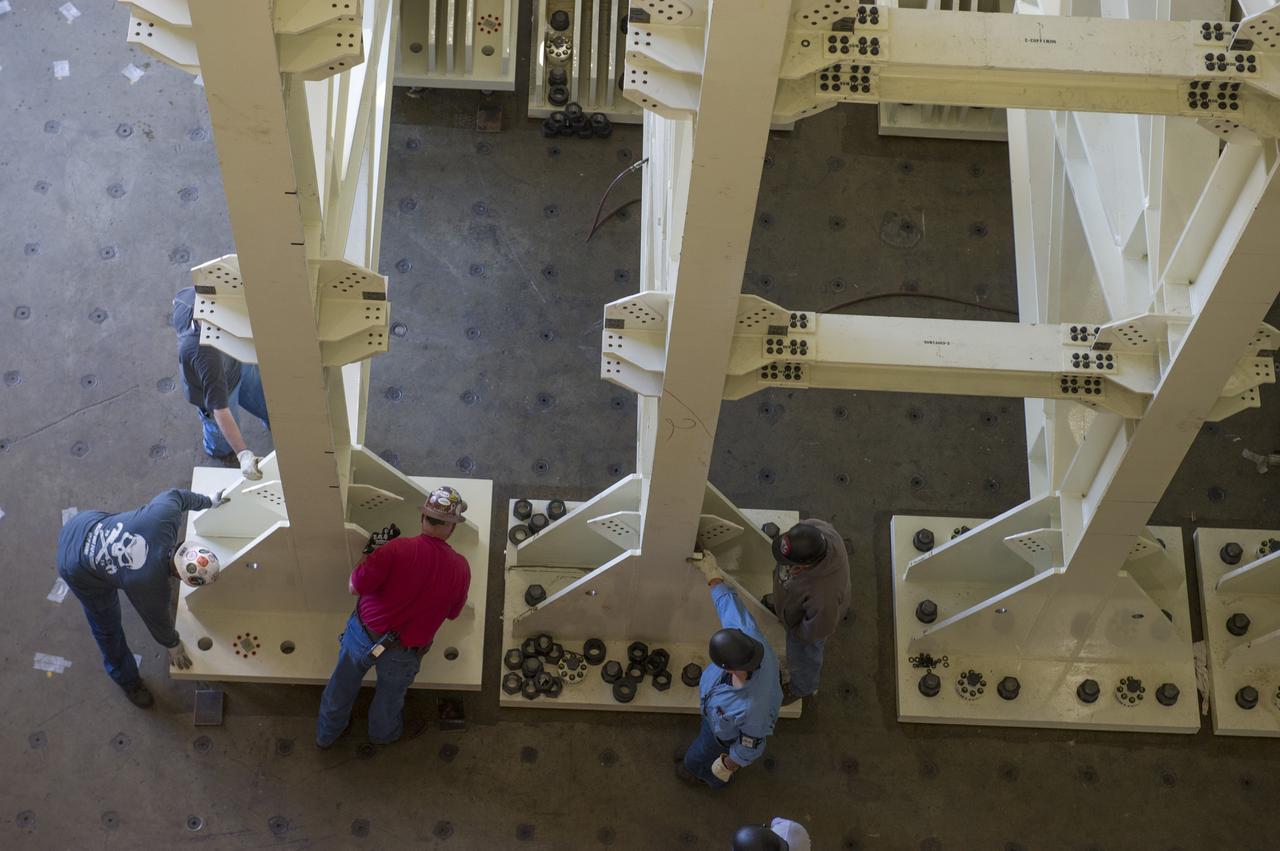

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
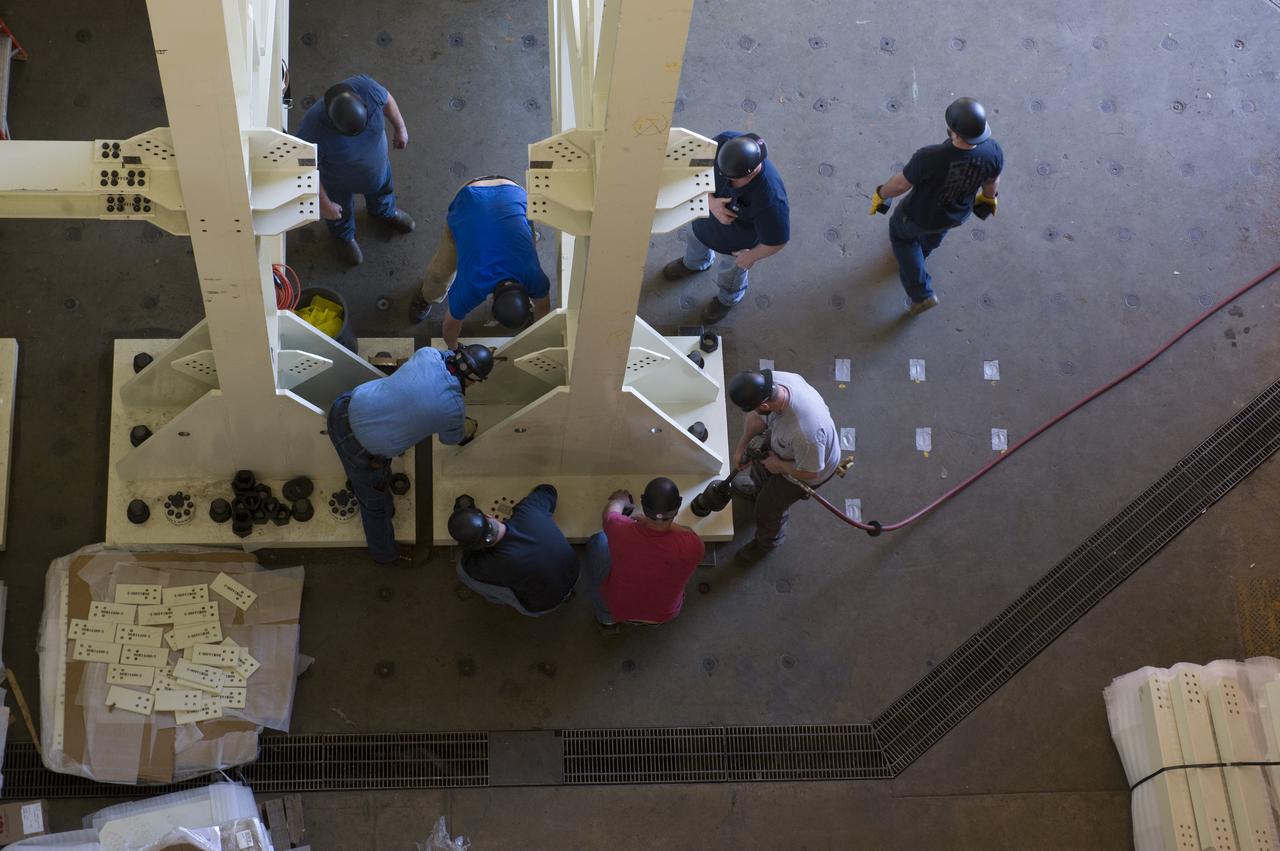

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
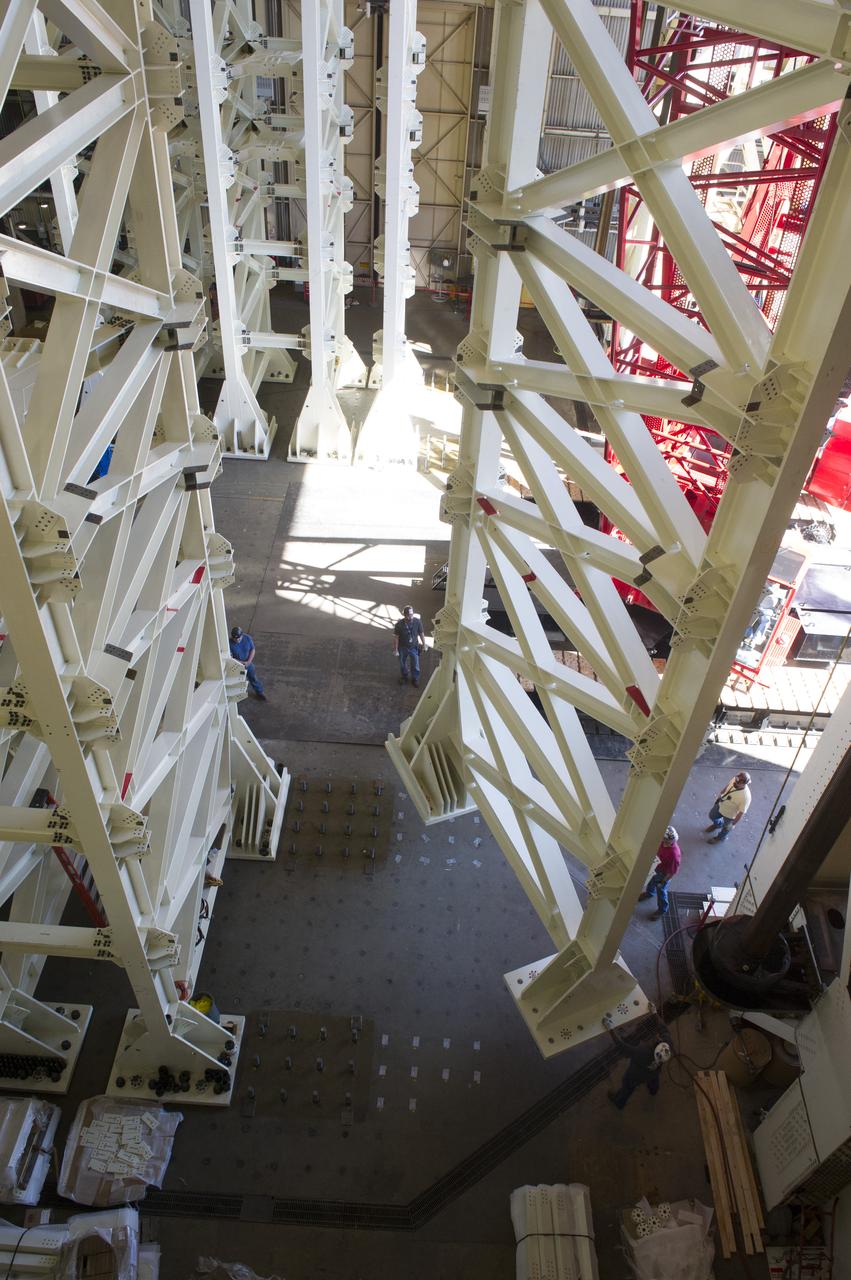

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
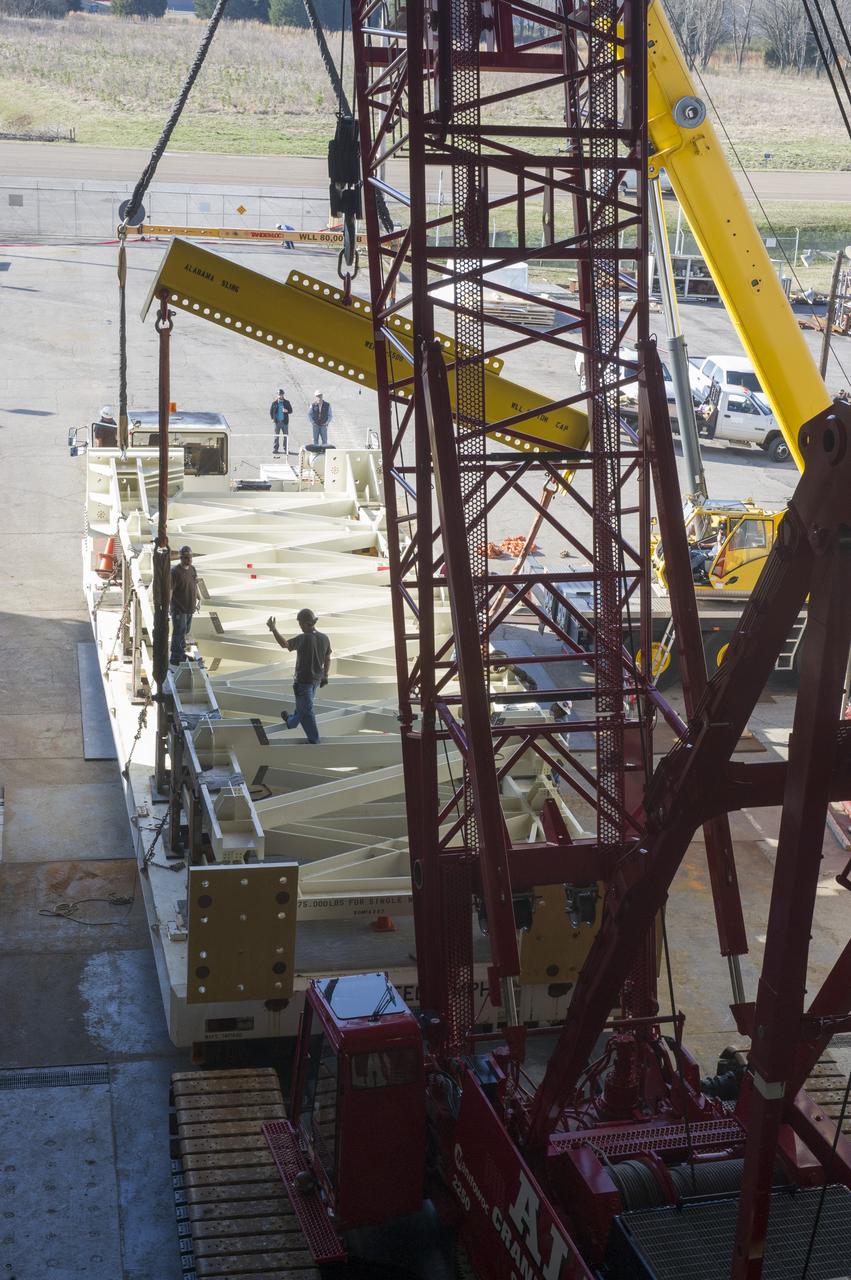

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
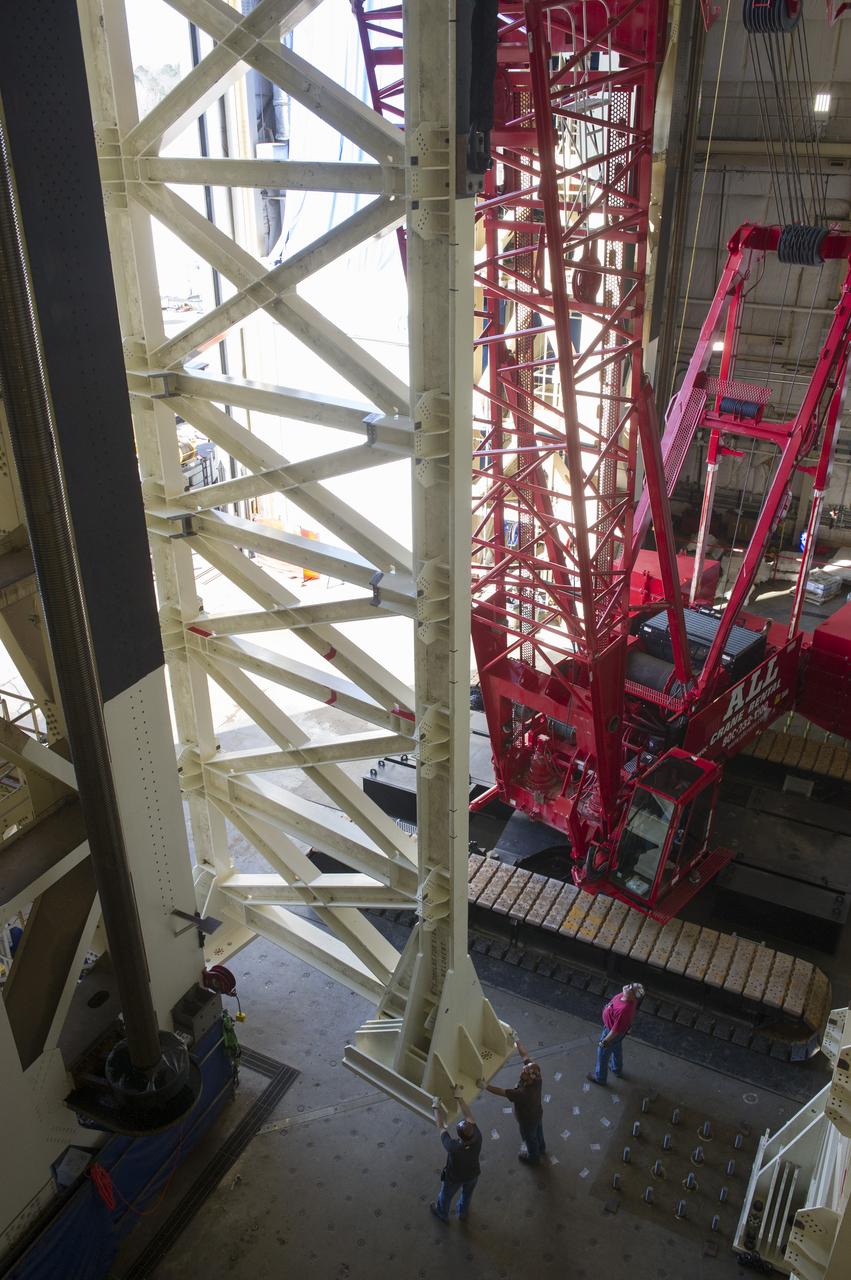

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
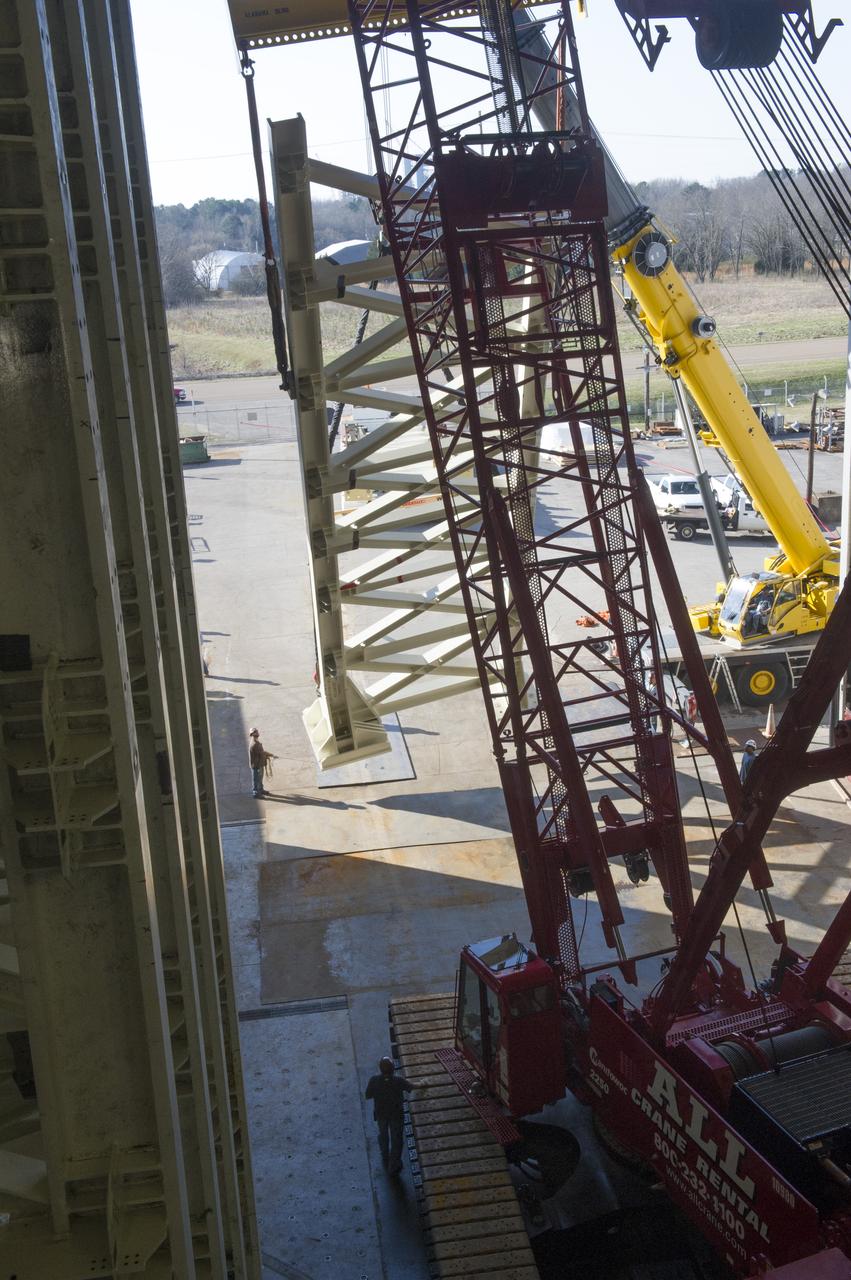

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
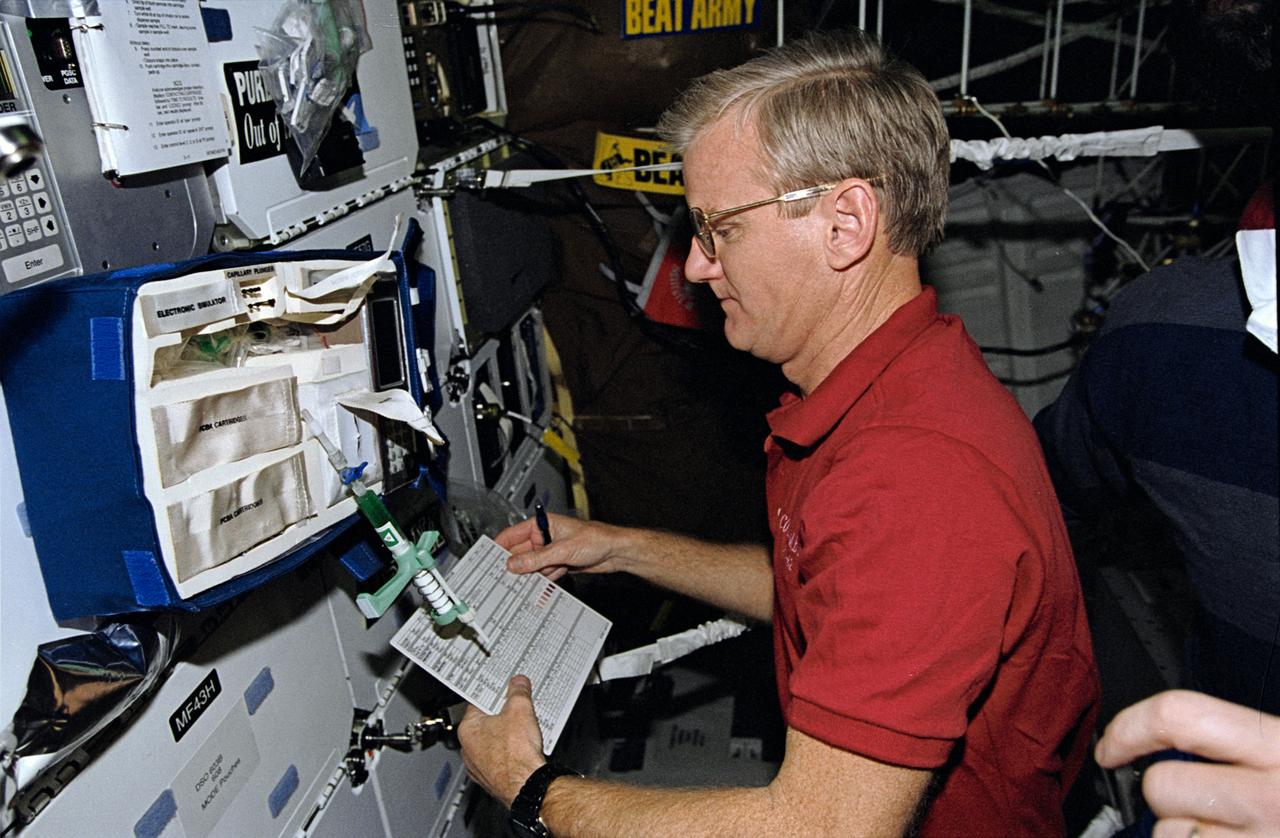

STS062-10-010 (4-18 March 1994) --- Astronaut John H. Casper, mission commander, takes stock of paraphenalia used to support medical testing onboard Columbia's middeck. Casper was poind by four other veteran astronauts for 14 days of variegated research in earth orbit.
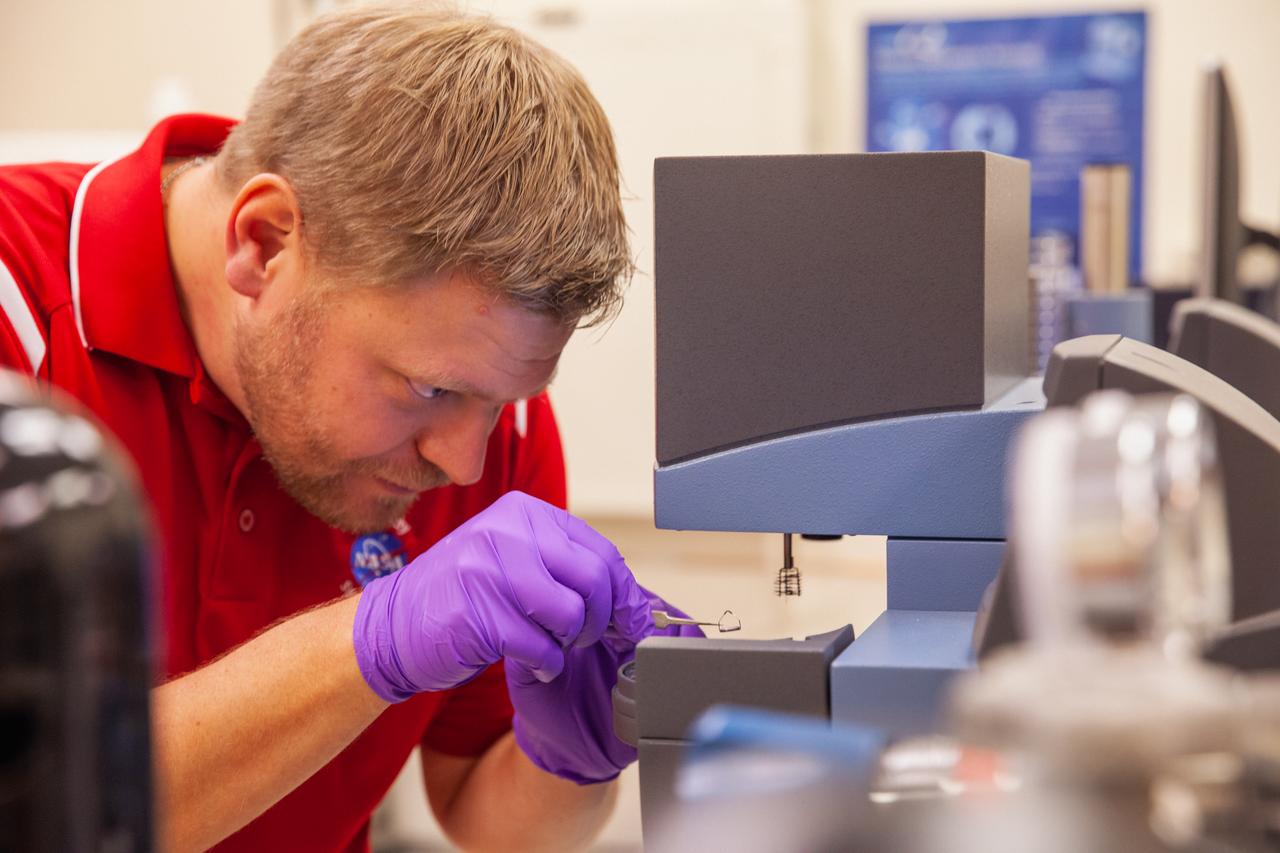

Jerry Buhrow, an engineer in the Materials Analysis Lab, places a sample on a thermal testing unit inside a lab at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 6, 2020.
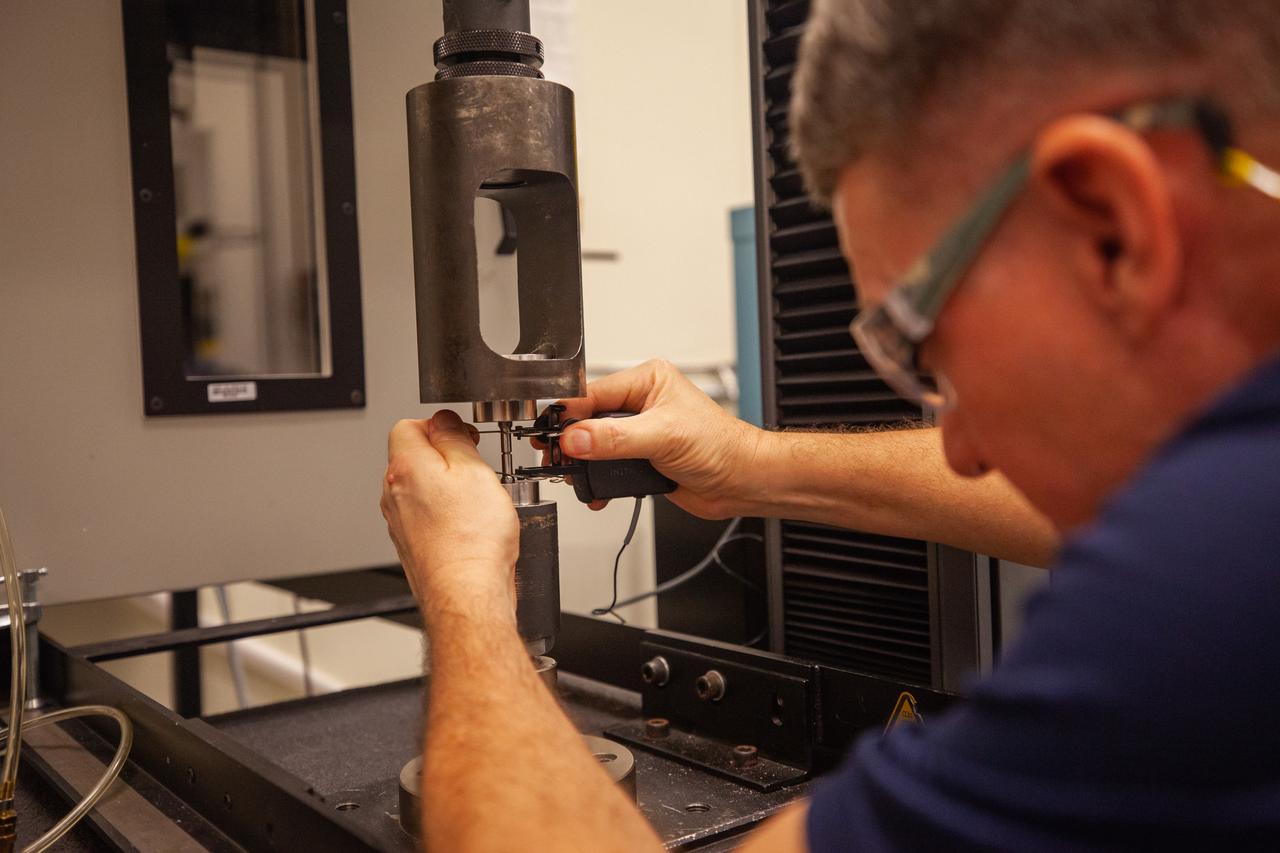

Brian Cheshire, an engineer in the Mechanical and Environmental Testing Lab at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, works in front of an Instron inside a lab at the Florida spaceport’s Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 6, 2020.
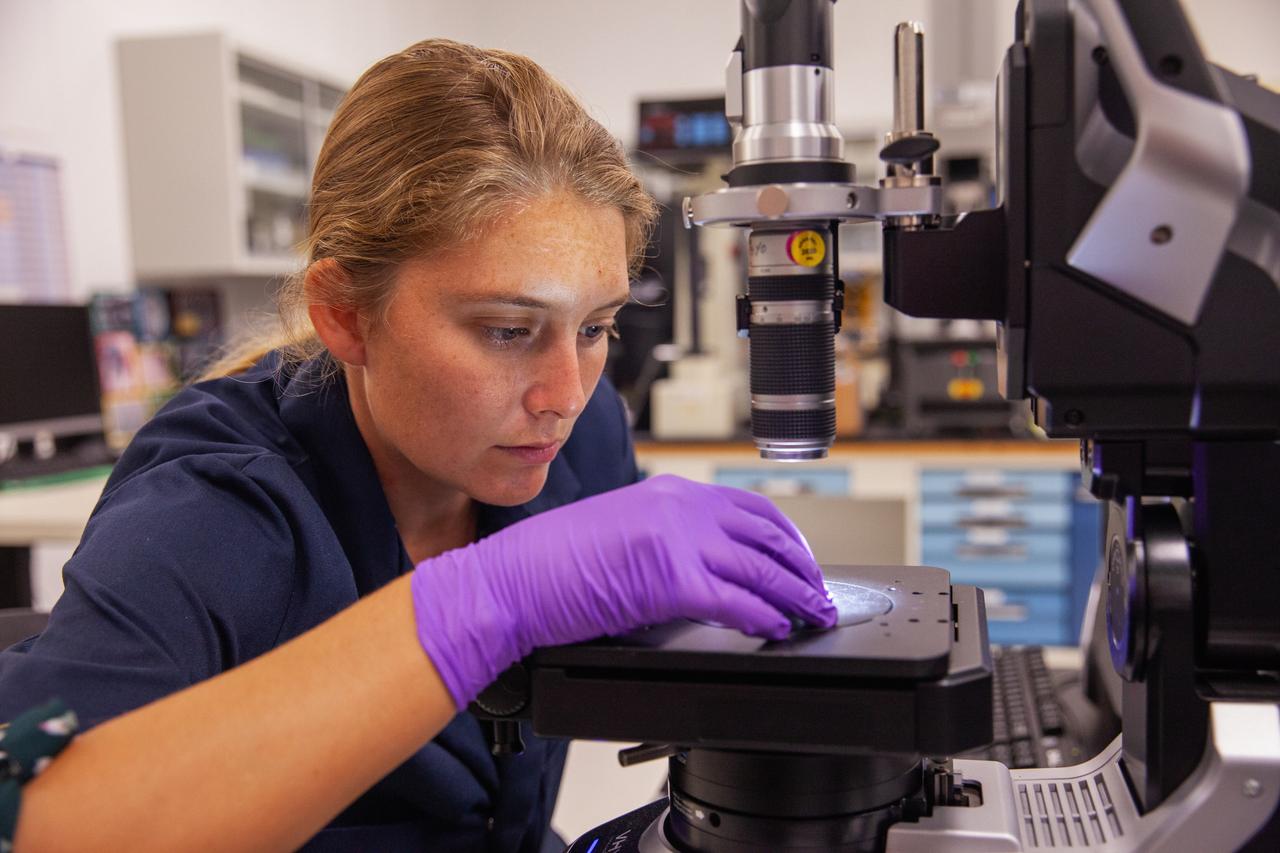

Liz Tomsik, an engineer in the Materials Analysis Lab, examines a sample placed on a digital microscope inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 6, 2020.
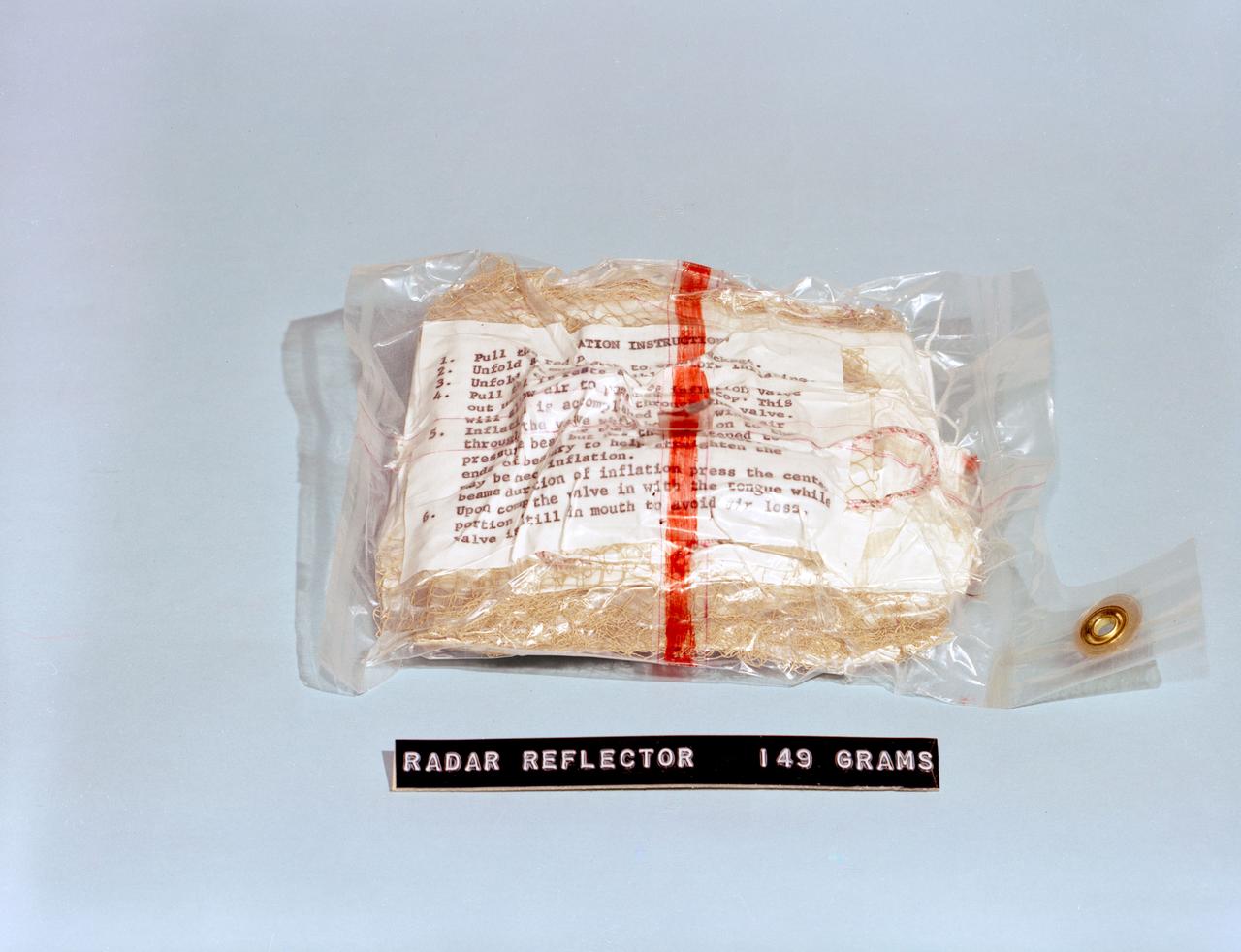

S62-06767 (1962) --- A radar reflector, survival equipment for the Mercury astronauts. Photo credit: NASA
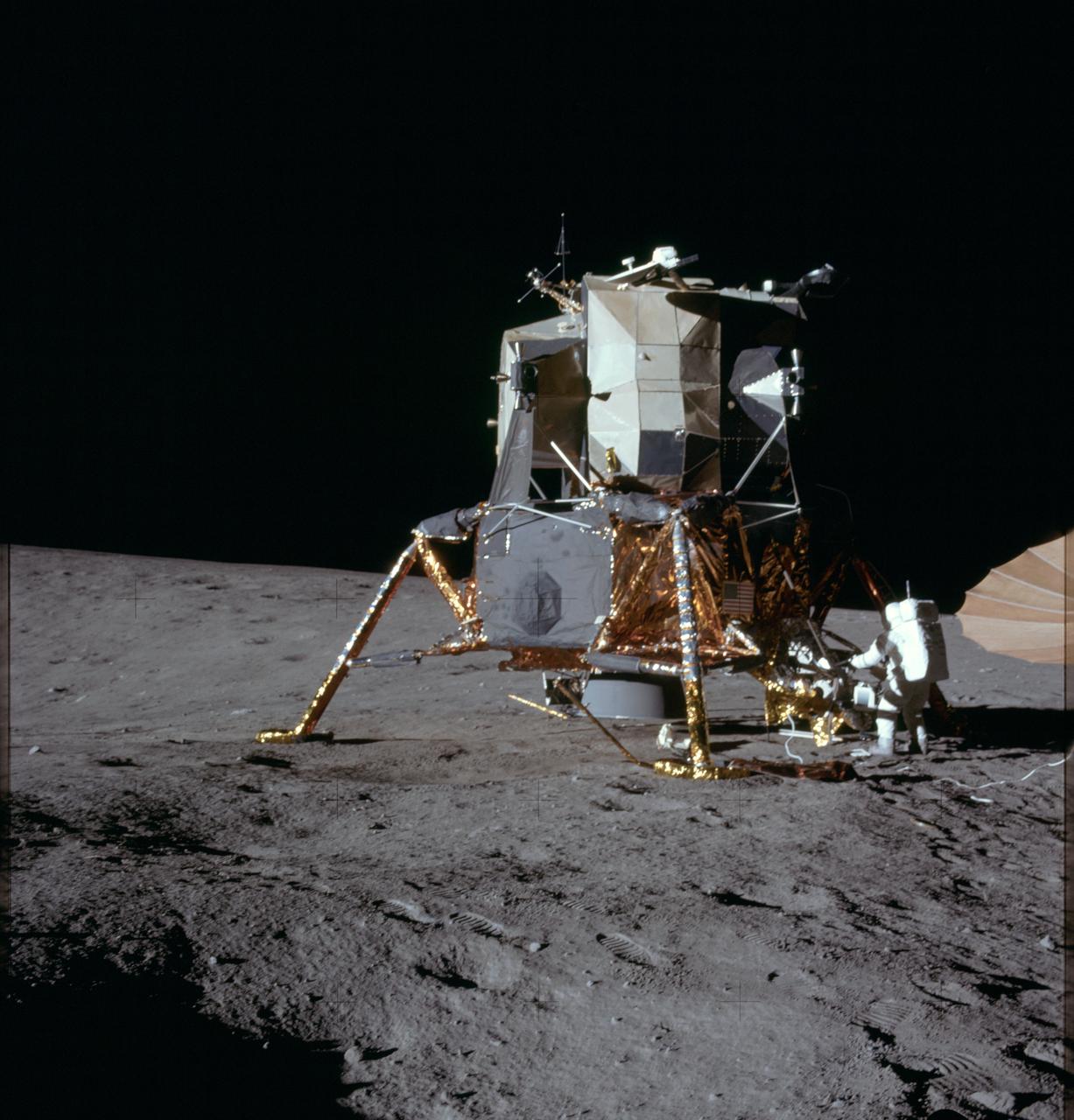

AS12-46-6749 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot for the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, works at the Modular Equipment Stowage Assembly (MESA) on the Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM) during the mission's first extravehicular activity, (EVA) on Nov. 19, 1969. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Bean descended in the Apollo 12 LM to explore the moon while astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
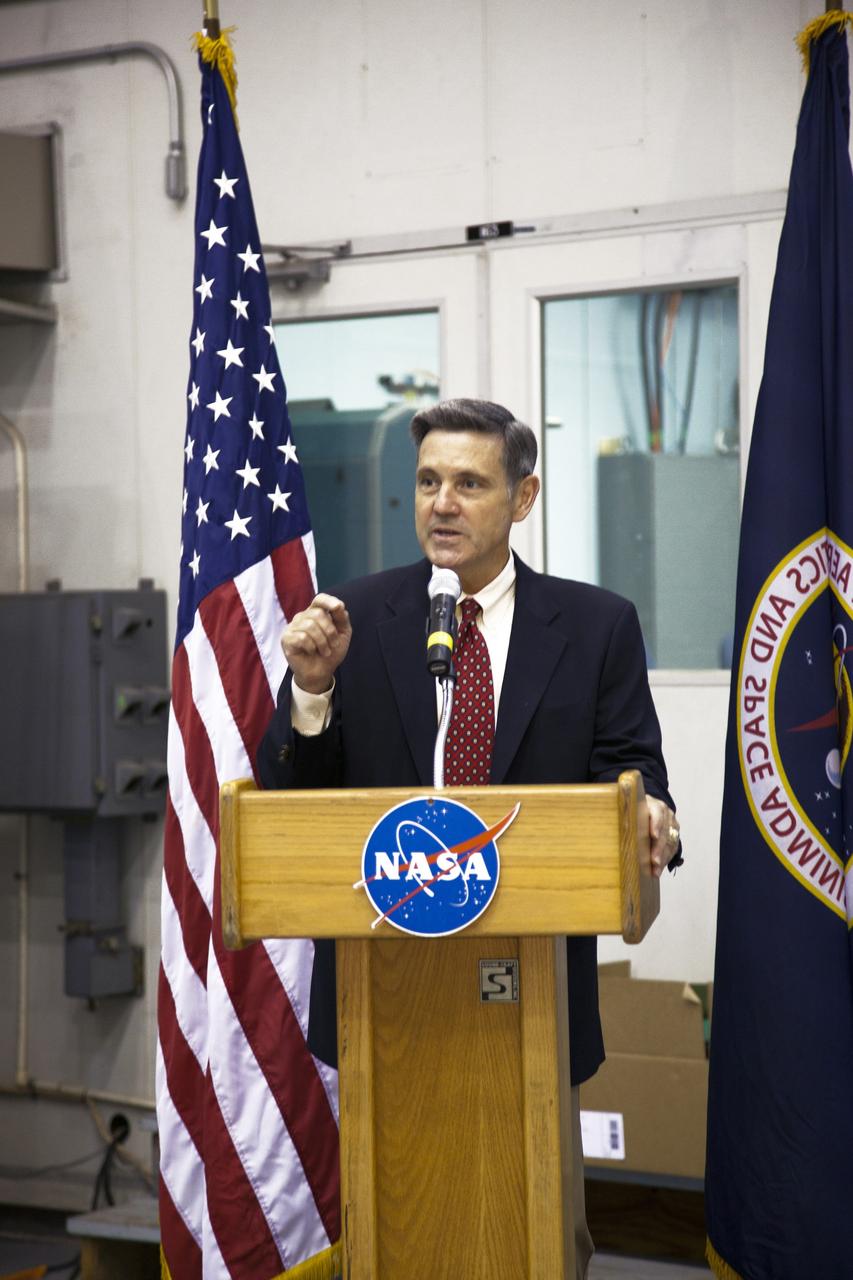

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Center Director Bob Cabana talks to workers at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF), which recently underwent a $35 million comprehensive upgrade that lasted four years. The LETF was established in the 1970s to support the qualification of the Space Shuttle Program’s umbilical and T-0 mechanisms. Throughout the years, it has supported the development of systems for shuttle and the International Space Station, Delta and Atlas rockets, and various research and development programs. The LETF has unique capabilities to evolve into a versatile test and development area that supports a wide spectrum of programs. For information on NASA's future plans, visit www.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
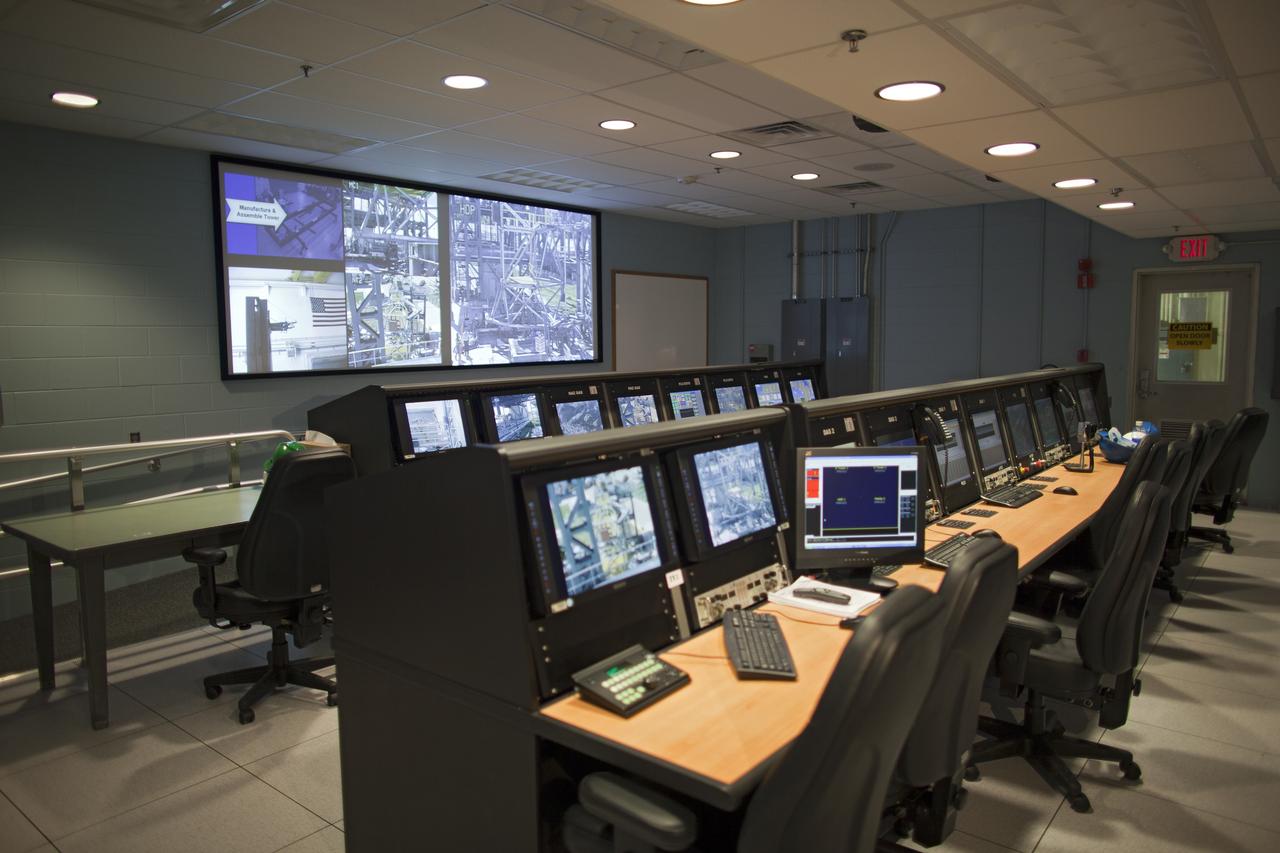

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is the control room of the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF). The LETF recently underwent a $35 million comprehensive upgrade that lasted four years. The LETF was established in the 1970s to support the qualification of the Space Shuttle Program’s umbilical and T-0 mechanisms. Throughout the years, it has supported the development of systems for shuttle and the International Space Station, Delta and Atlas rockets, and various research and development programs. The LETF has unique capabilities to evolve into a versatile test and development area that supports a wide spectrum of programs. For information on NASA's future plans, visit www.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
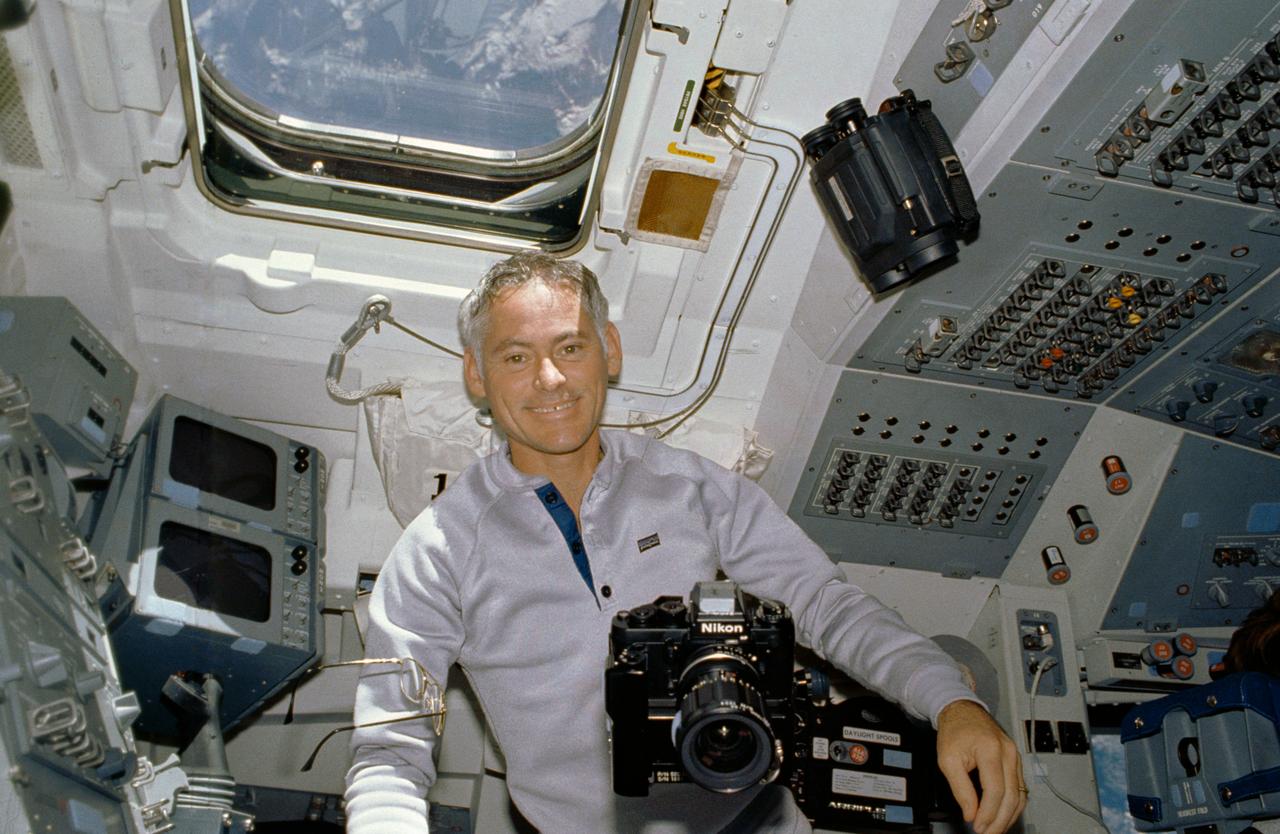

STS027-10-021 (2-6 Dec. 1988) --- Astronaut Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, STS-27 mission specialist, is able to handle a number of cameras with the aid of the microgravity in the shirt sleeve environment of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Atlantis. Photo credit: NASA
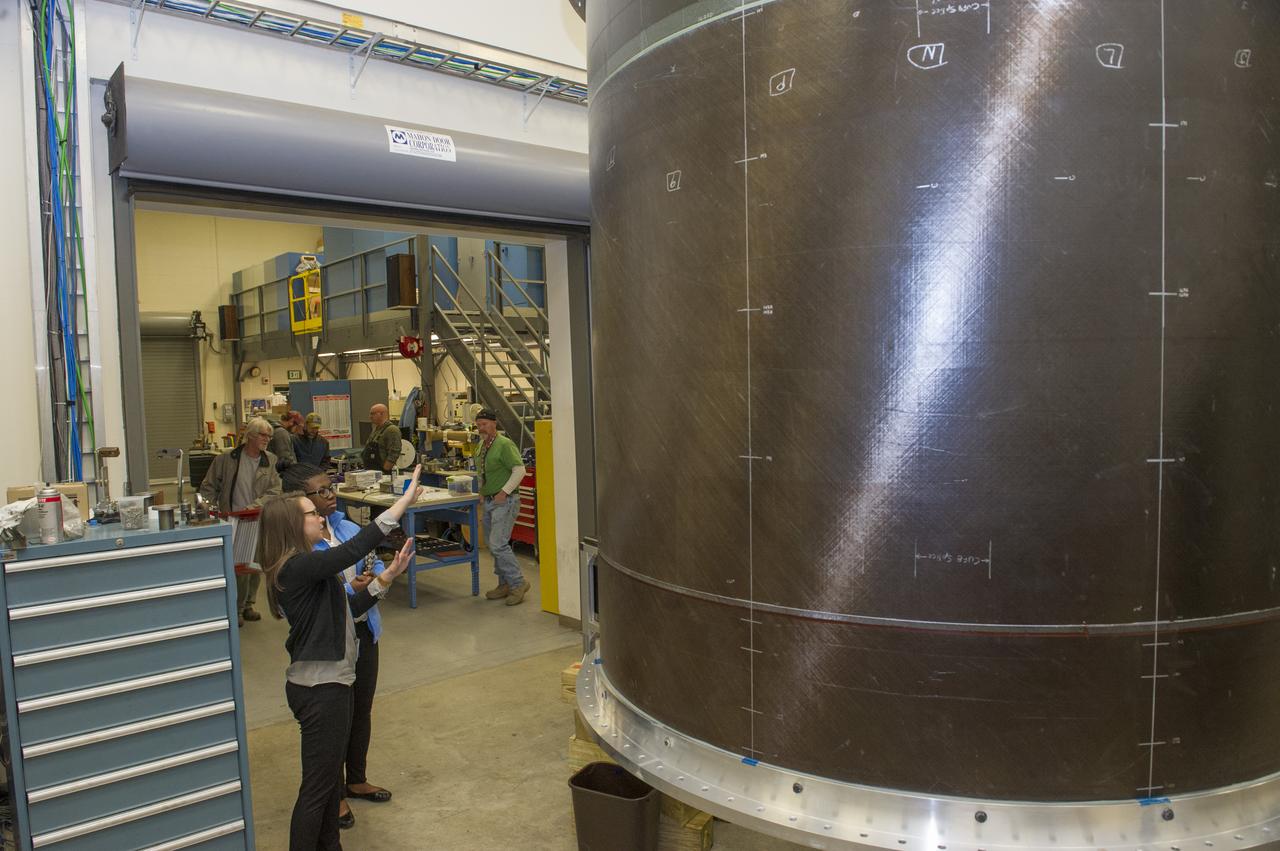

MICHELLE TILLOTSON, AN ENGINEER AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER, SHOWS KALYN HOPKINS A STUDENT AT THE MIAMI VALLEY SCHOOL, DAYTON OHIO, NEW EQUIPMENT THAT WILL BE USED TO TEST THE PROPELLANT TANKS FOR THE SLS
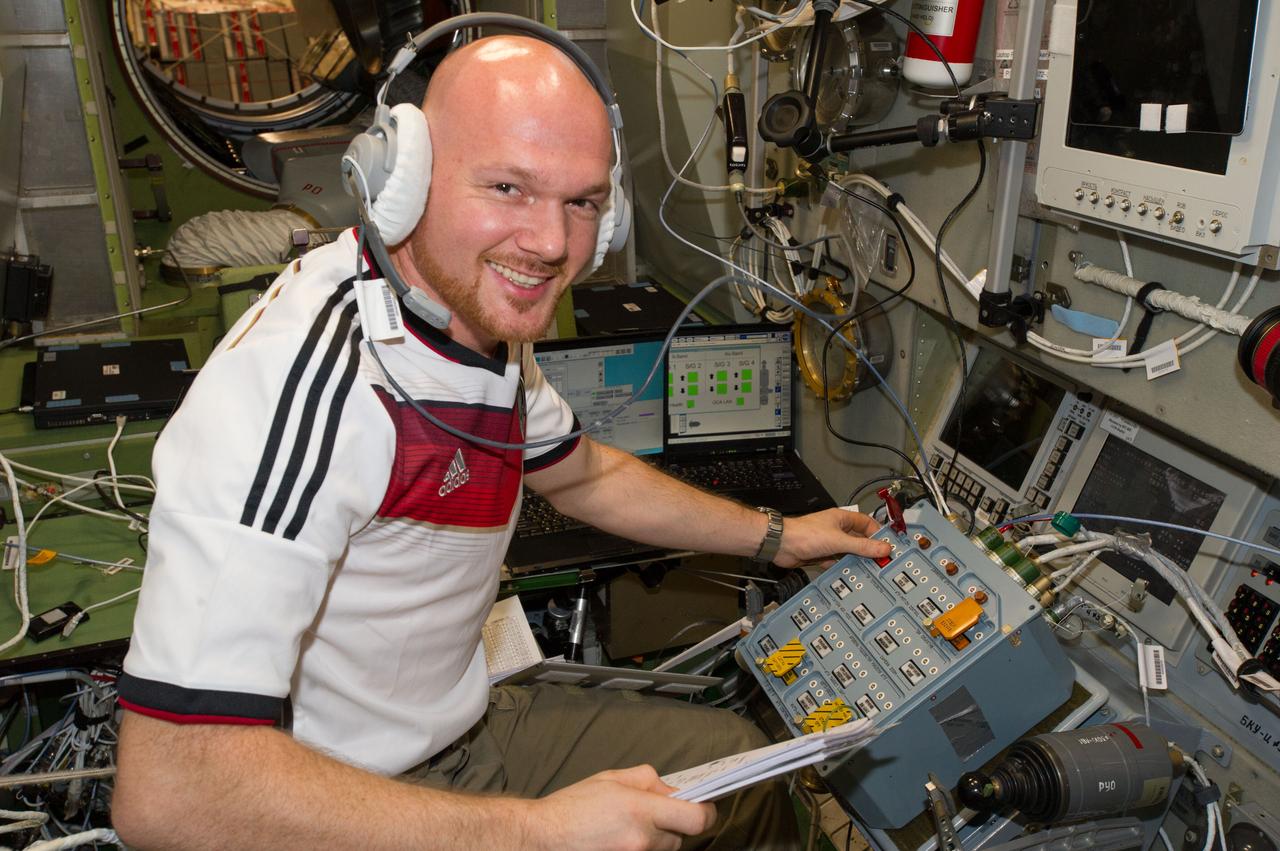

ESA astronaut Alexander Gerst, Expedition 40 flight engineer (wearing soccer shirt), is photographed during ATV equipment preparation in the Service Module (SM) prior to ATV launch.
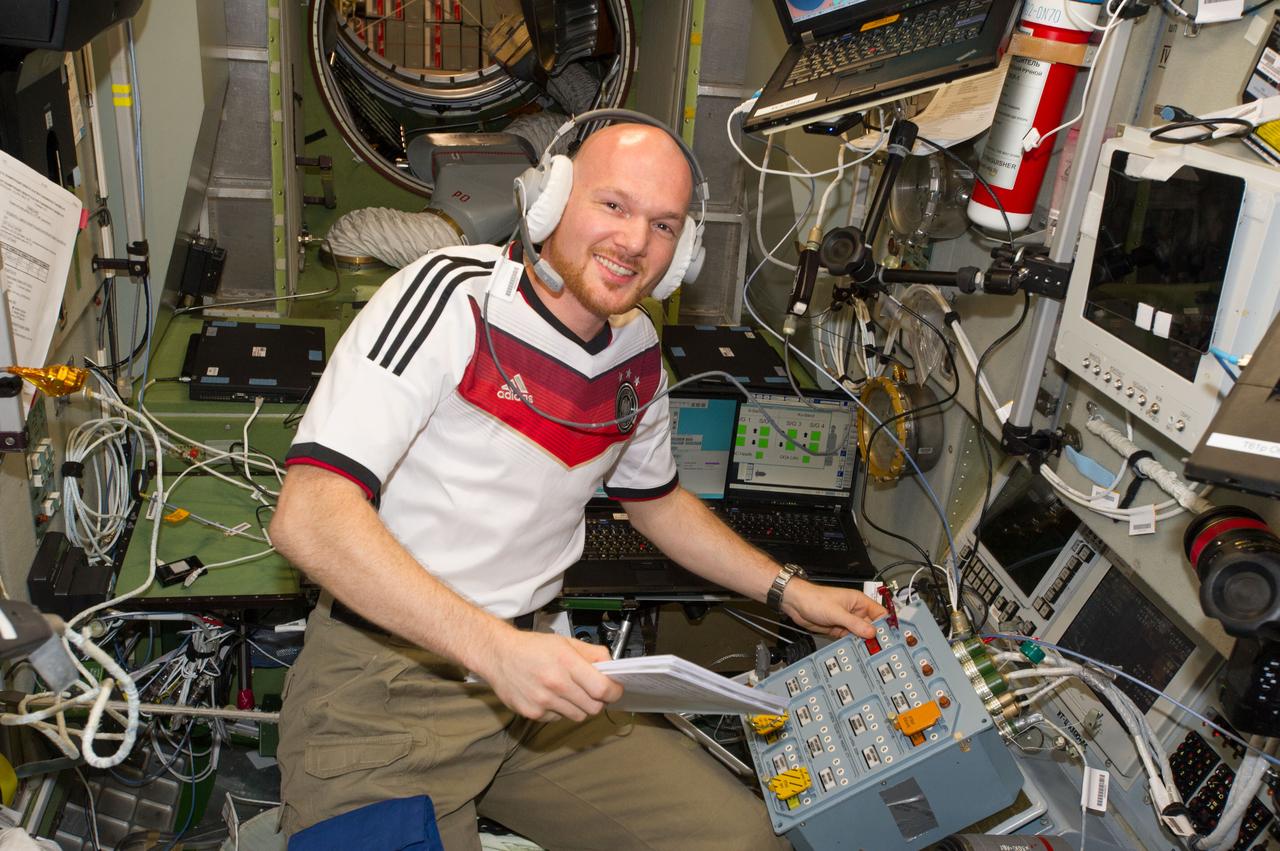

ESA astronaut Alexander Gerst, Expedition 40 flight engineer (wearing soccer shirt), is photographed during ATV equipment preparation in the Service Module (SM) prior to ATV launch.
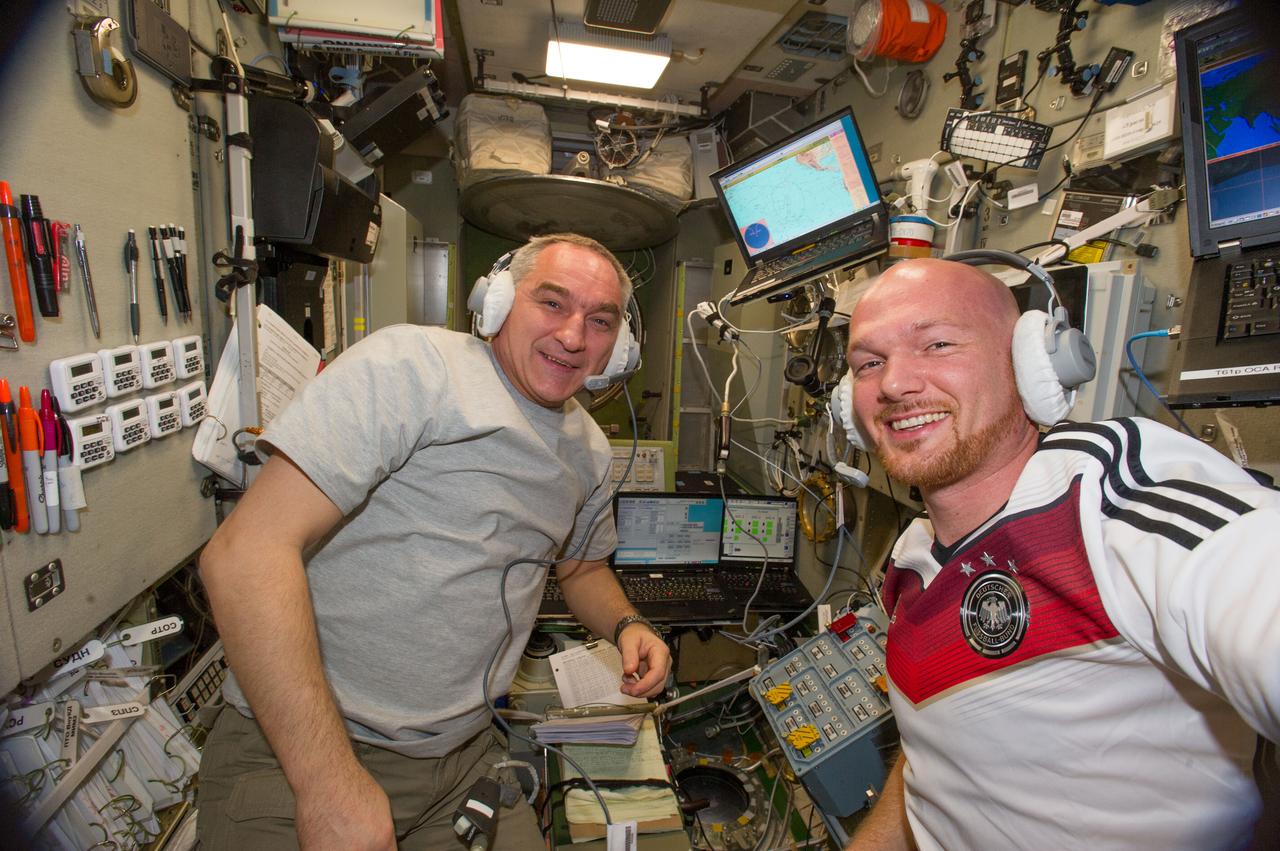

Cosmonaut Alexander Skvortsov and ESA Astronaut Alexander Gerst, Expedition 40 flight engineers, are photographed during ATV equipment preparation in the Service Module (SM) prior to ATV launch.
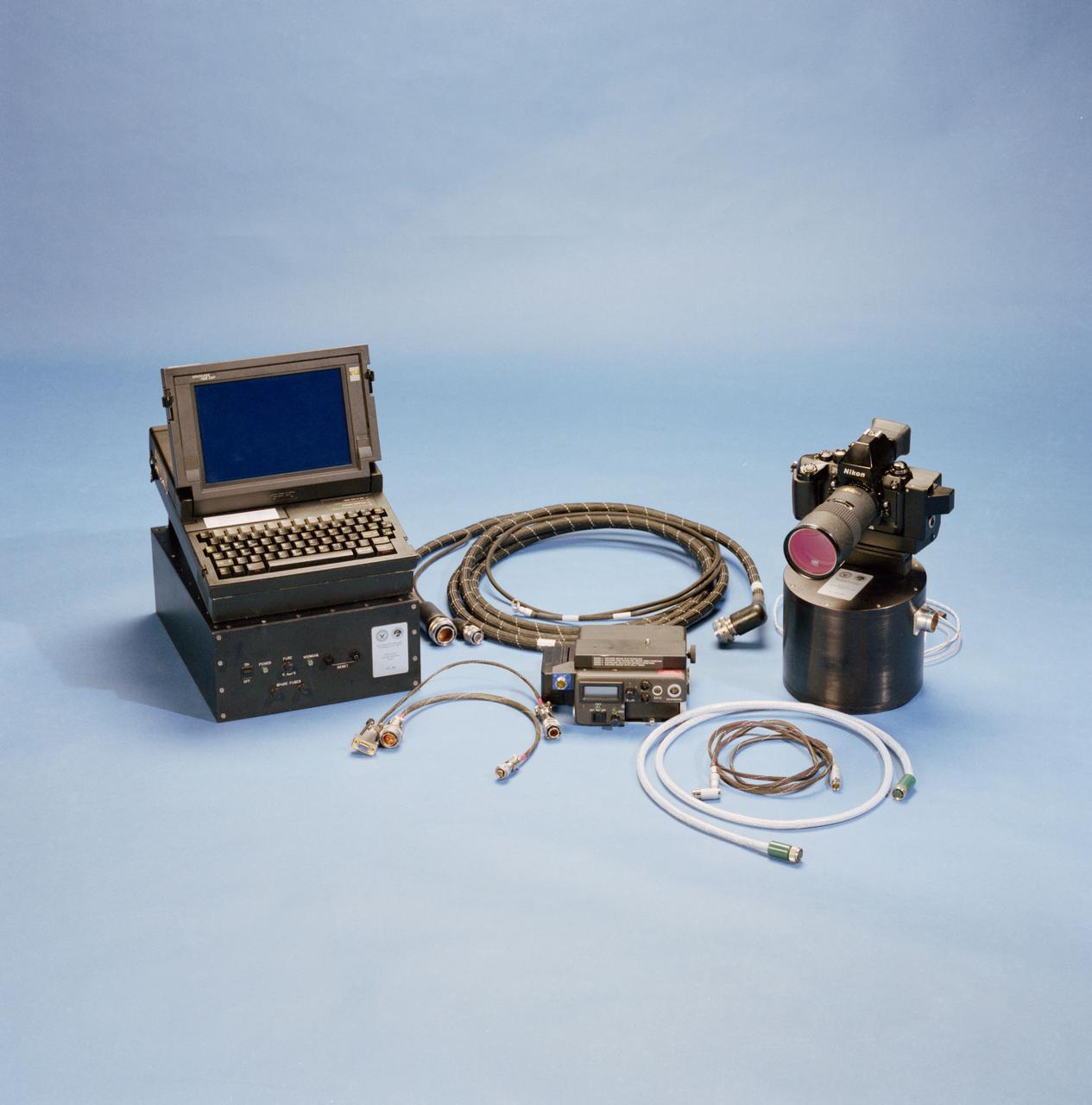

STS-53 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, Department of Defense (DOD) mission Hand-held Earth-oriented Real-time Cooperative, User-friendly, Location, targeting, and Environmental System (Hercules) spaceborne experiment equipment is documented in this table top view. HERCULES is a joint NAVY-NASA-ARMY payload designed to provide real-time high resolution digital electronic imagery and geolocation (latitude and longitude determination) of earth surface targets of interest. HERCULES system consists of (from left to right): a specially modified GRID Systems portable computer mounted atop NASA developed Playback-Downlink Unit (PDU) and the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) developed HERCULES Attitude Processor (HAP); the NASA-developed Electronic Still Camera (ESC) Electronics Box (ESCEB) including removable imagery data storage disks and various connecting cables; the ESC (a NASA modified Nikon F-4 camera) mounted atop the NRL HERCULES Inertial Measurement Unit (HIMU) containing the three-axis ring-laser gyro.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers check out the 6,000-square-foot high bay of the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF). The LETF recently underwent a $35 million comprehensive upgrade that lasted four years. The LETF was established in the 1970s to support the qualification of the Space Shuttle Program’s umbilical and T-0 mechanisms. Throughout the years, it has supported the development of systems for shuttle and the International Space Station, Delta and Atlas rockets, and various research and development programs. The LETF has unique capabilities to evolve into a versatile test and development area that supports a wide spectrum of programs. For information on NASA's future plans, visit www.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers watch the vehicle motion simulator, or VMS, simulate all of the movements a space vehicle could experience from rollout to launch. The VMS is part of the Launch Equipment Test Facility's (LETF) $35 million comprehensive upgrade that lasted four years. The LETF was established in the 1970s to support the qualification of the Space Shuttle Program’s umbilical and T-0 mechanisms. Throughout the years, it has supported the development of systems for shuttle and the International Space Station, Delta and Atlas rockets, and various research and development programs. The LETF has unique capabilities to evolve into a versatile test and development area that supports a wide spectrum of programs. For information on NASA's future plans, visit www.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers watch the vehicle motion simulator, or VMS, simulate all of the movements a space vehicle could experience from rollout to launch. The VMS is part of the Launch Equipment Test Facility's (LETF) $35 million comprehensive upgrade that lasted four years. The LETF was established in the 1970s to support the qualification of the Space Shuttle Program’s umbilical and T-0 mechanisms. Throughout the years, it has supported the development of systems for shuttle and the International Space Station, Delta and Atlas rockets, and various research and development programs. The LETF has unique capabilities to evolve into a versatile test and development area that supports a wide spectrum of programs. For information on NASA's future plans, visit www.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
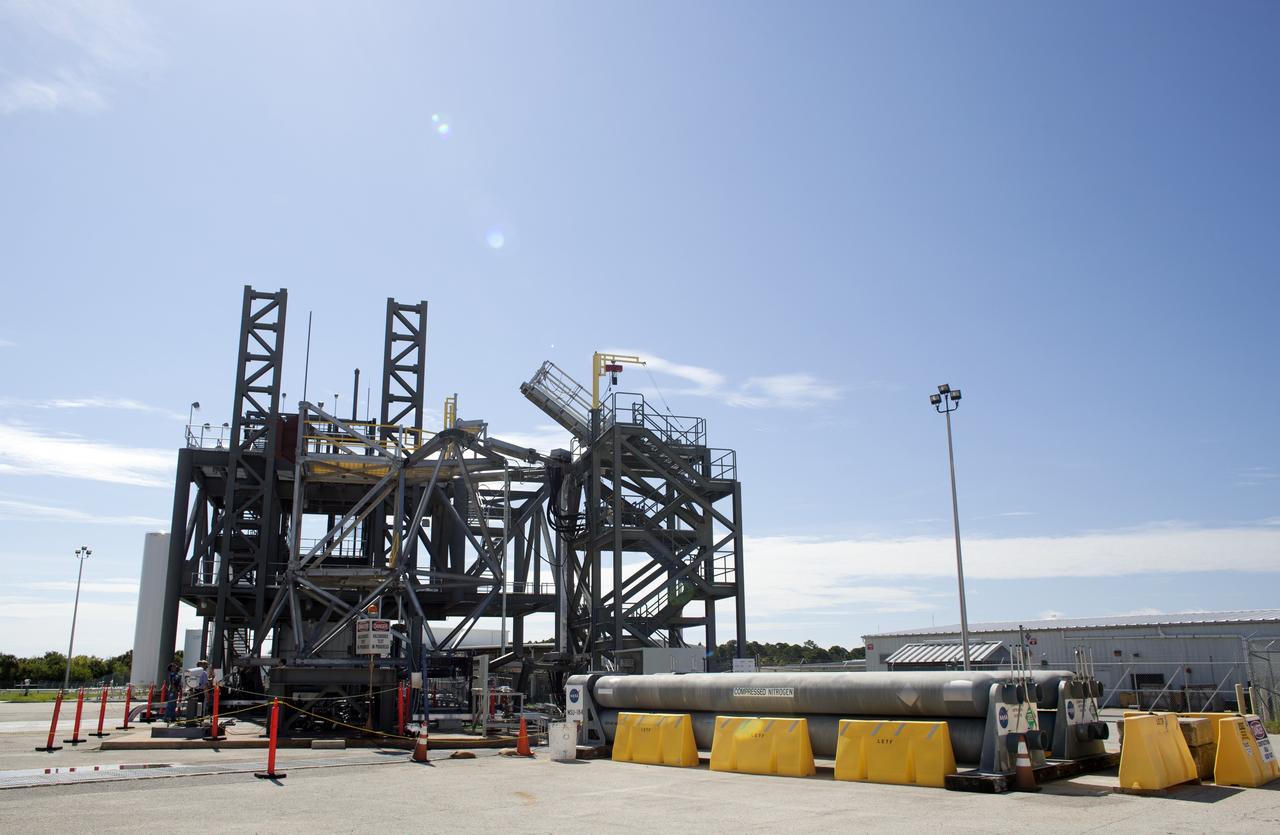

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is the vehicle motion simulator, or VMS, which simulates all of the movements a space vehicle could experience from rollout to launch. The VMS is part of the Launch Equipment Test Facility's (LETF) $35 million comprehensive upgrade that lasted four years. The LETF was established in the 1970s to support the qualification of the Space Shuttle Program’s umbilical and T-0 mechanisms. Throughout the years, it has supported the development of systems for shuttle and the International Space Station, Delta and Atlas rockets, and various research and development programs. The LETF has unique capabilities to evolve into a versatile test and development area that supports a wide spectrum of programs. For information on NASA's future plans, visit www.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
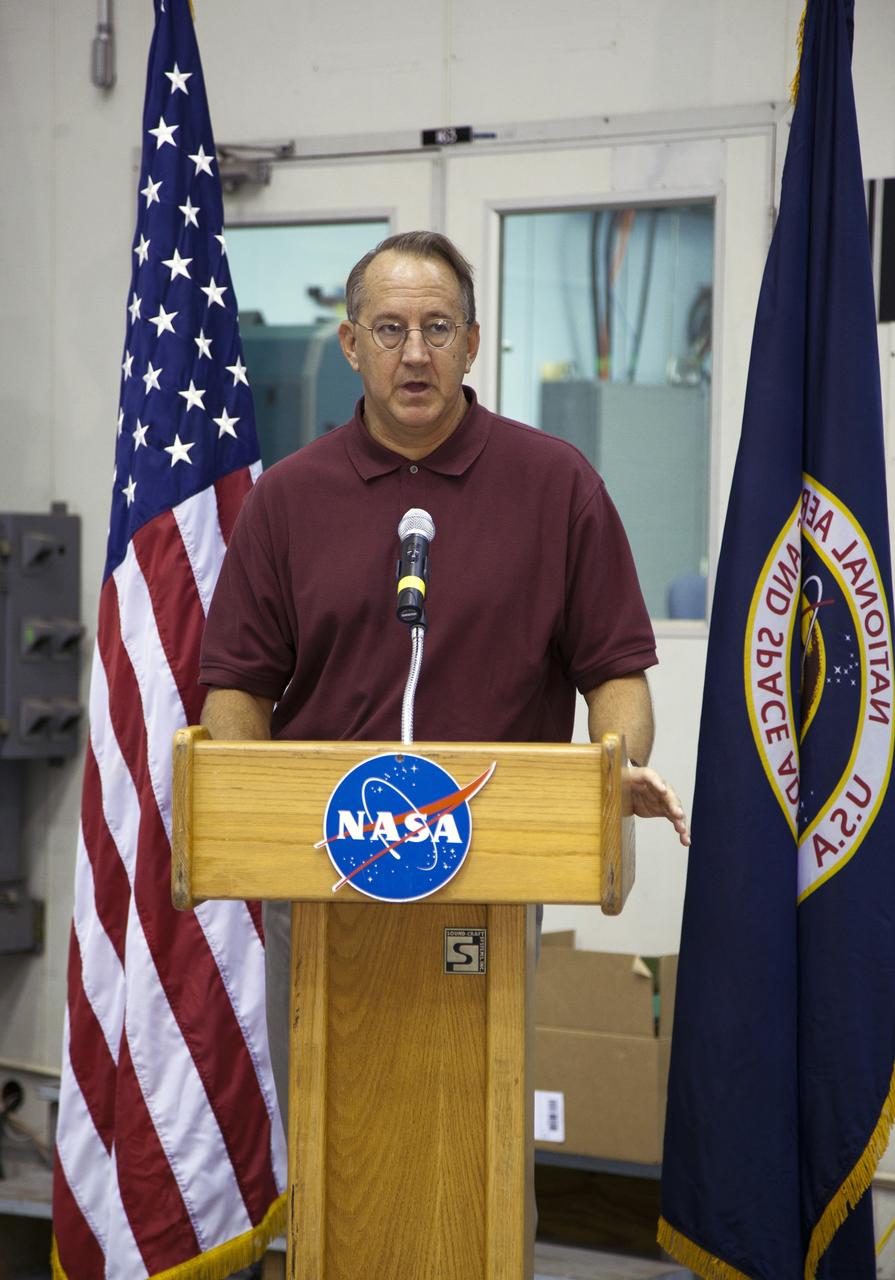

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Director of the center's Engineering Directorate Pat Simpkins talks to workers at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF), which recently underwent a $35 million comprehensive upgrade that lasted four years. The LETF was established in the 1970s to support the qualification of the Space Shuttle Program’s umbilical and T-0 mechanisms. Throughout the years, it has supported the development of systems for shuttle and the International Space Station, Delta and Atlas rockets, and various research and development programs. The LETF has unique capabilities to evolve into a versatile test and development area that supports a wide spectrum of programs. For information on NASA's future plans, visit www.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
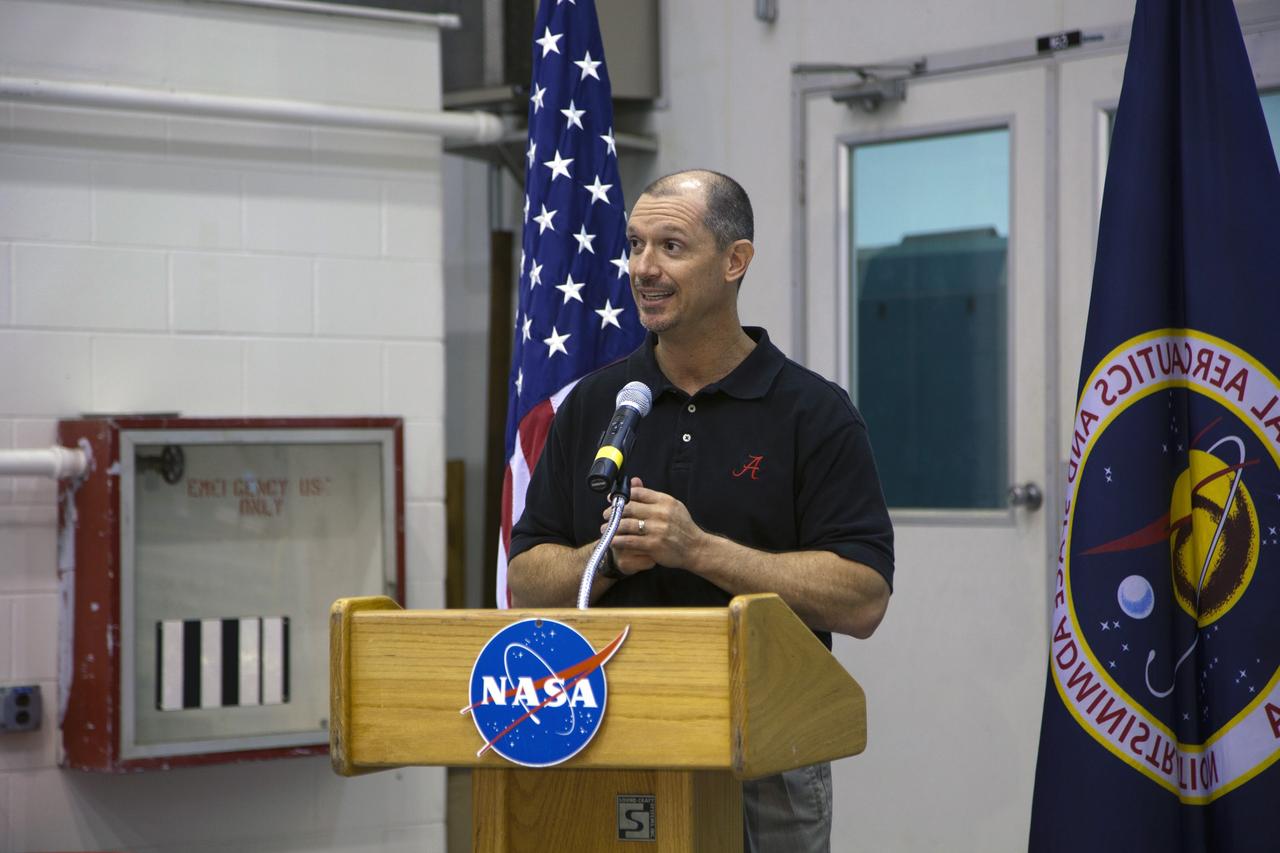

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Director of the center's Constellation Project Office Pepper Phillips talks to workers at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF), which recently underwent a $35 million comprehensive upgrade that lasted four years. The LETF was established in the 1970s to support the qualification of the Space Shuttle Program’s umbilical and T-0 mechanisms. Throughout the years, it has supported the development of systems for shuttle and the International Space Station, Delta and Atlas rockets, and various research and development programs. The LETF has unique capabilities to evolve into a versatile test and development area that supports a wide spectrum of programs. For information on NASA's future plans, visit www.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
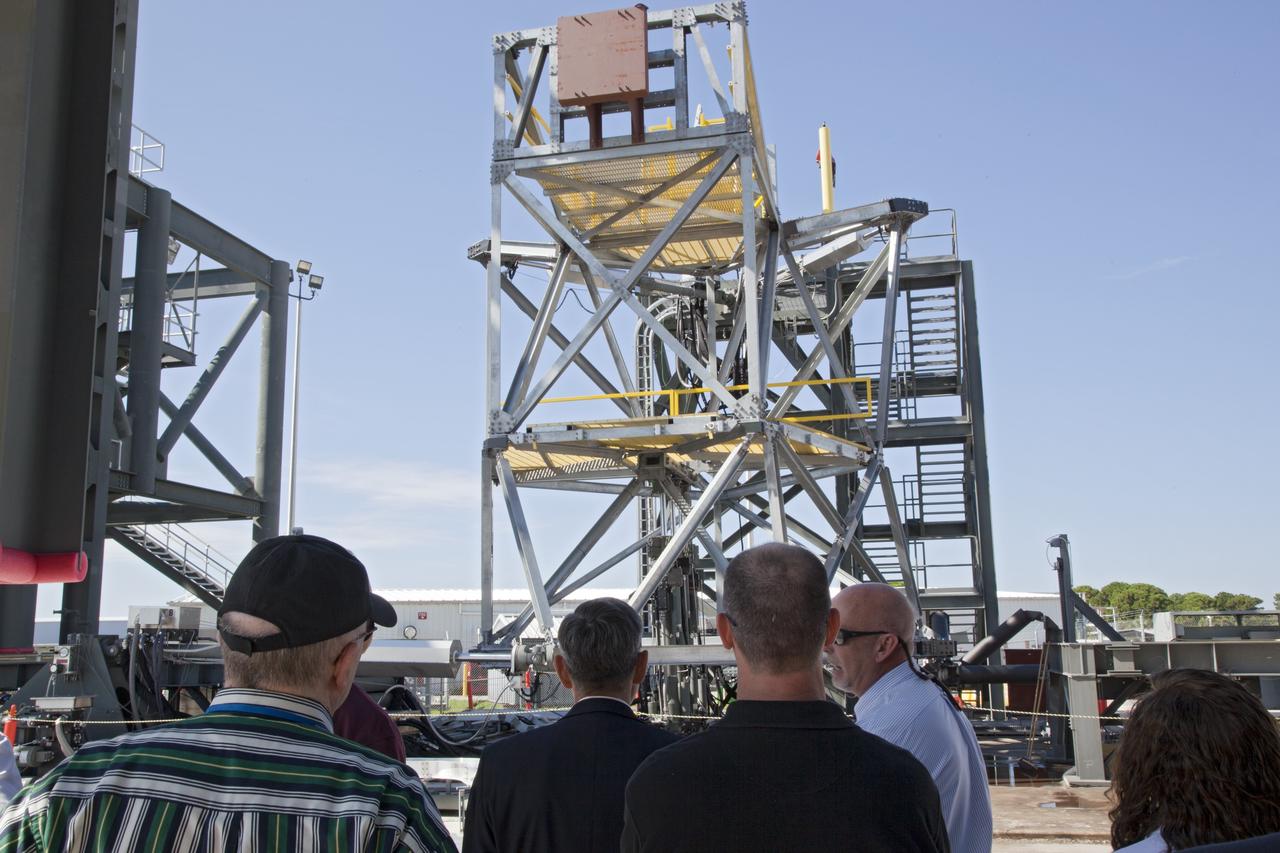

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers watch the vehicle motion simulator, or VMS, simulate all of the movements a space vehicle could experience from rollout to launch. The VMS is part of the Launch Equipment Test Facility's (LETF) $35 million comprehensive upgrade that lasted four years. The LETF was established in the 1970s to support the qualification of the Space Shuttle Program’s umbilical and T-0 mechanisms. Throughout the years, it has supported the development of systems for shuttle and the International Space Station, Delta and Atlas rockets, and various research and development programs. The LETF has unique capabilities to evolve into a versatile test and development area that supports a wide spectrum of programs. For information on NASA's future plans, visit www.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
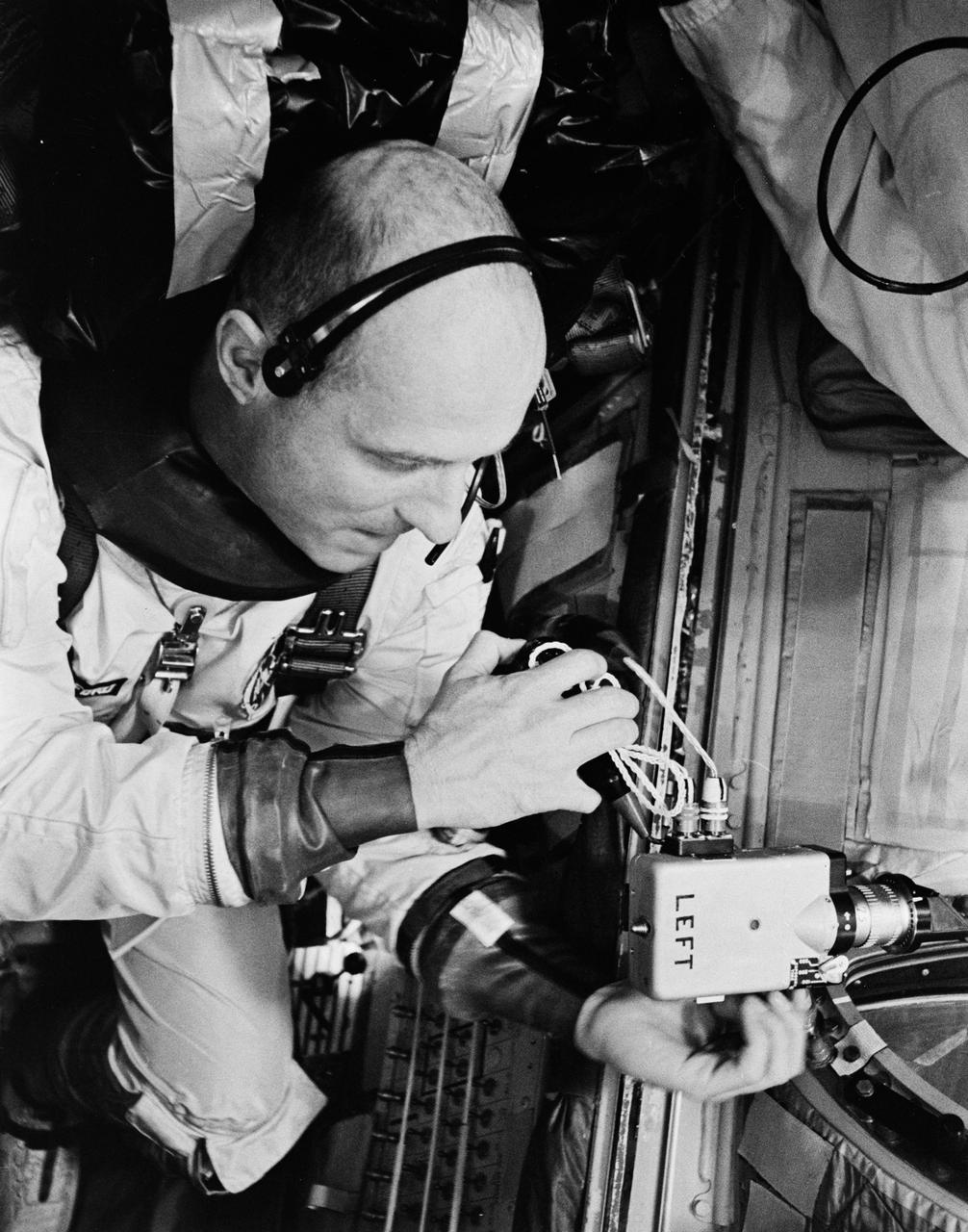

S66-33728 (10 May 1966) --- Astronaut Thomas P. Stafford, command pilot of the Gemini-9 spaceflight, checks the 16mm Mauer camera which will be used in space. The camera will record and document the exterior of the spacecraft and the Agena target vehicle in the docked configuration during the Gemini-9/Agena rendezvous and docking mission. Photo credit: NASA

STS-34 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, Pilot Michael J. McCulley squints while looking through ARRIFLEX camera eye piece during camera briefing at JSC. McCulley rests part of the camera on his shoulder as he operates it.
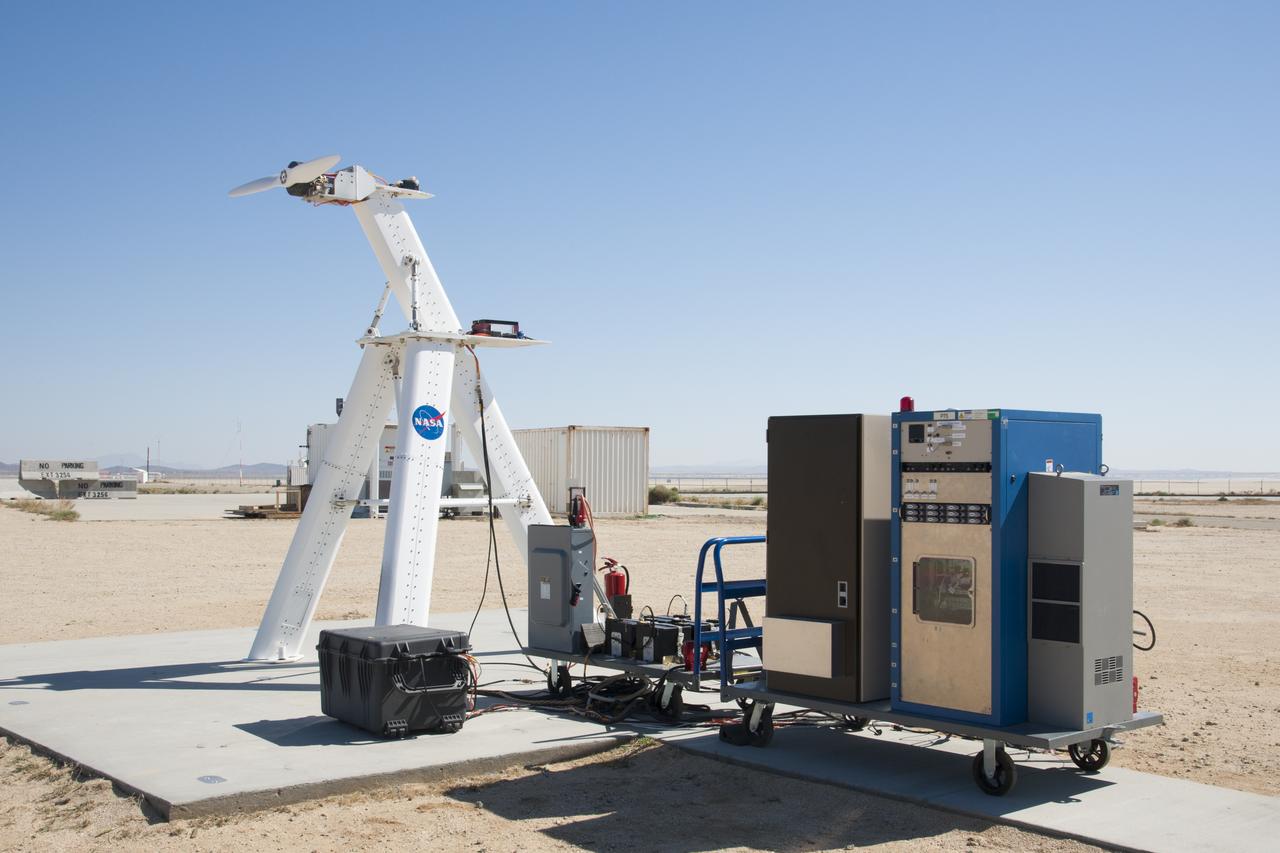

The equipment required for an electric propulsion test is ready for research.
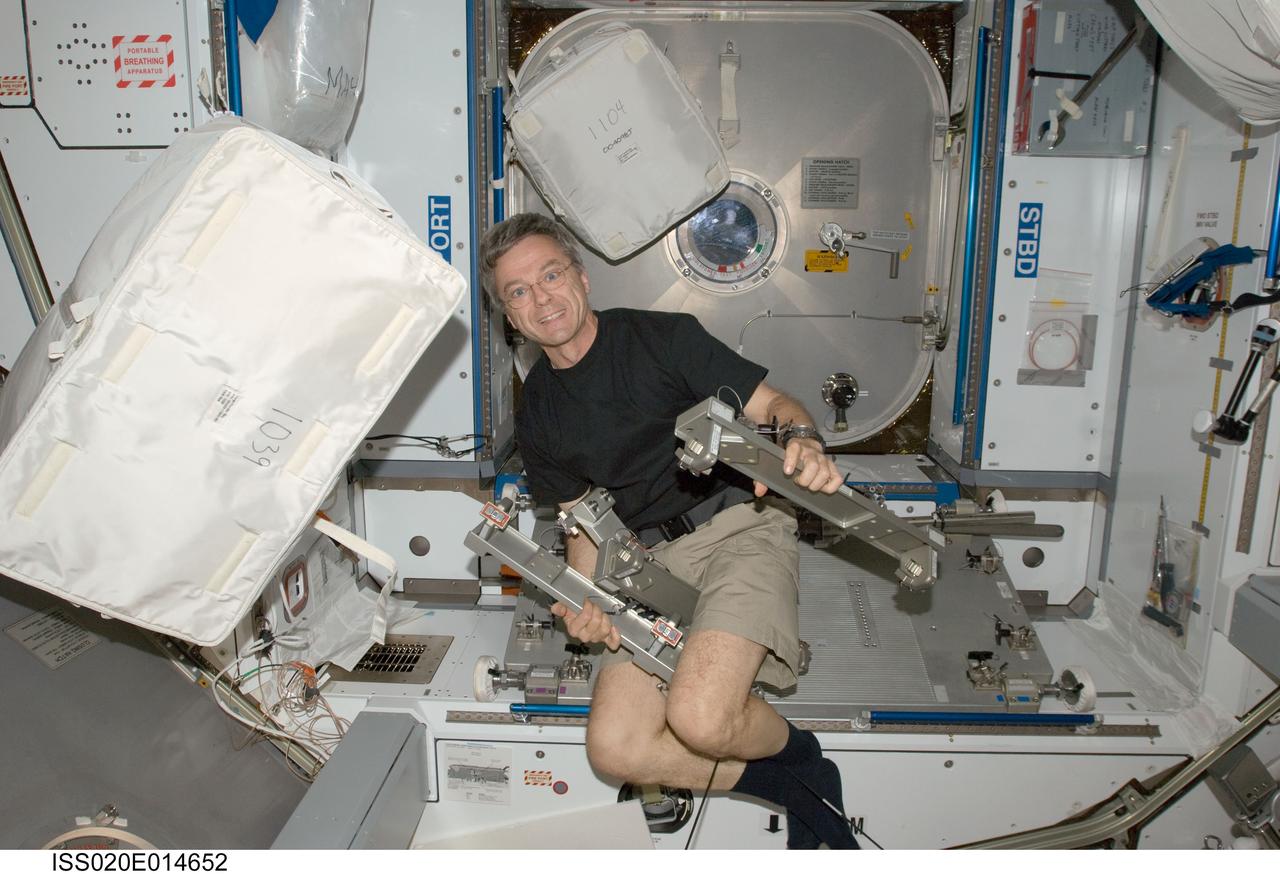

ISS020-E-014652 (26 June 2009) --- Canadian Space Agency astronaut Robert Thirsk, Expedition 20 flight engineer, installs the Interim Resistive Exercise Device (IRED) equipment in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
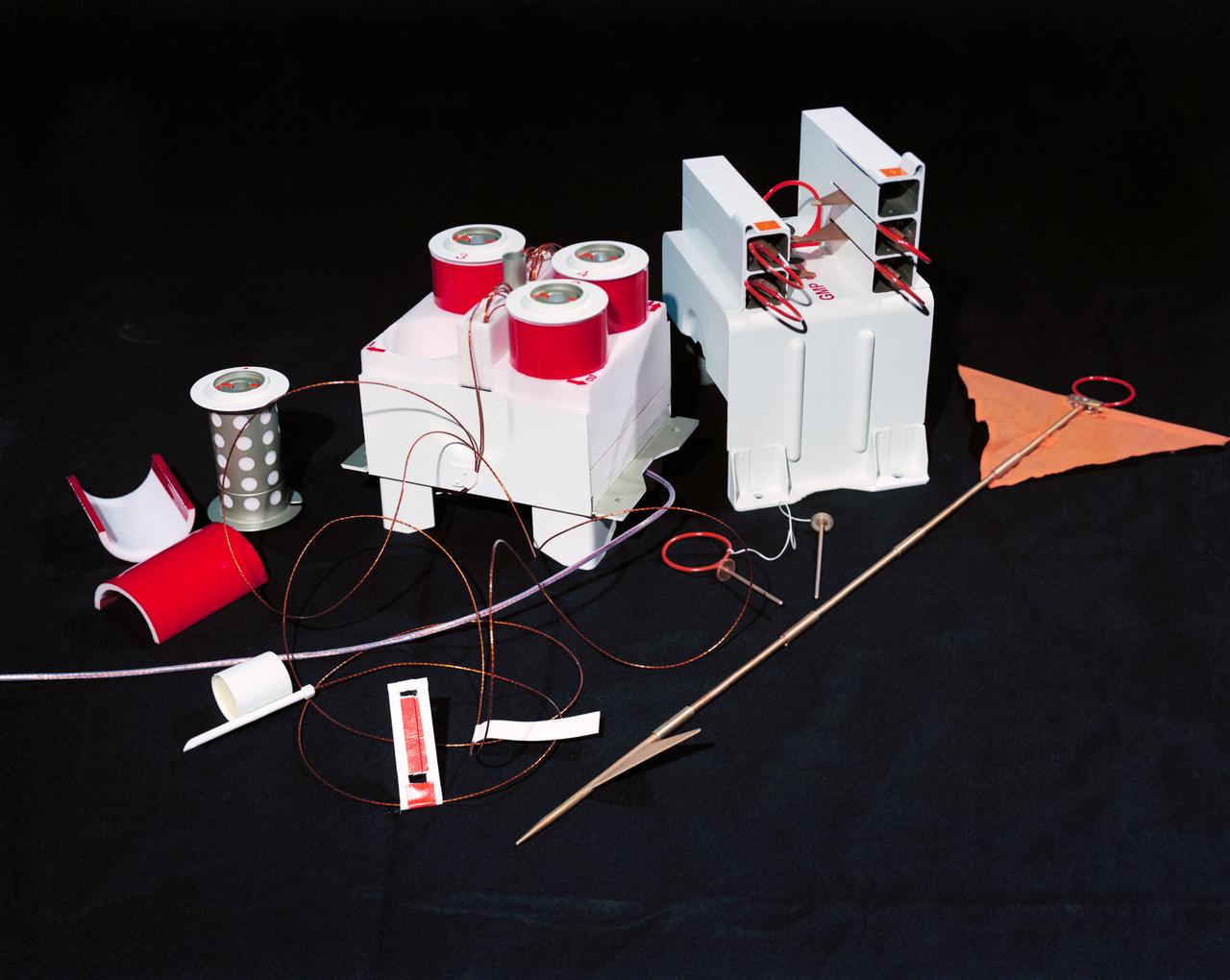
S72-37259 (November 1972) --- The Geophone Module and Cable Reels of the Lunar Seismic Profiling Experiment (S-203), a component of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package which will be carried on the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. LSPE components are four geophones similar to those used in an earlier active seismic experiment, an electronics package in the ALSEP central station, and eight explosive packages which will be deployed during the geology traverse. The four geophones will be placed one in the center and one at each corner of a 90-meter equilateral triangle. Explosive charges placed on the surface will generate seismic waves of varying strengths to provide data on the structural profile of the landing site. After the charges have been fired by ground command, the experiment will settle down into a passive listening mode, detecting moonquakes, meteorite impacts and the thump caused by the Lunar Module ascent stage impact.
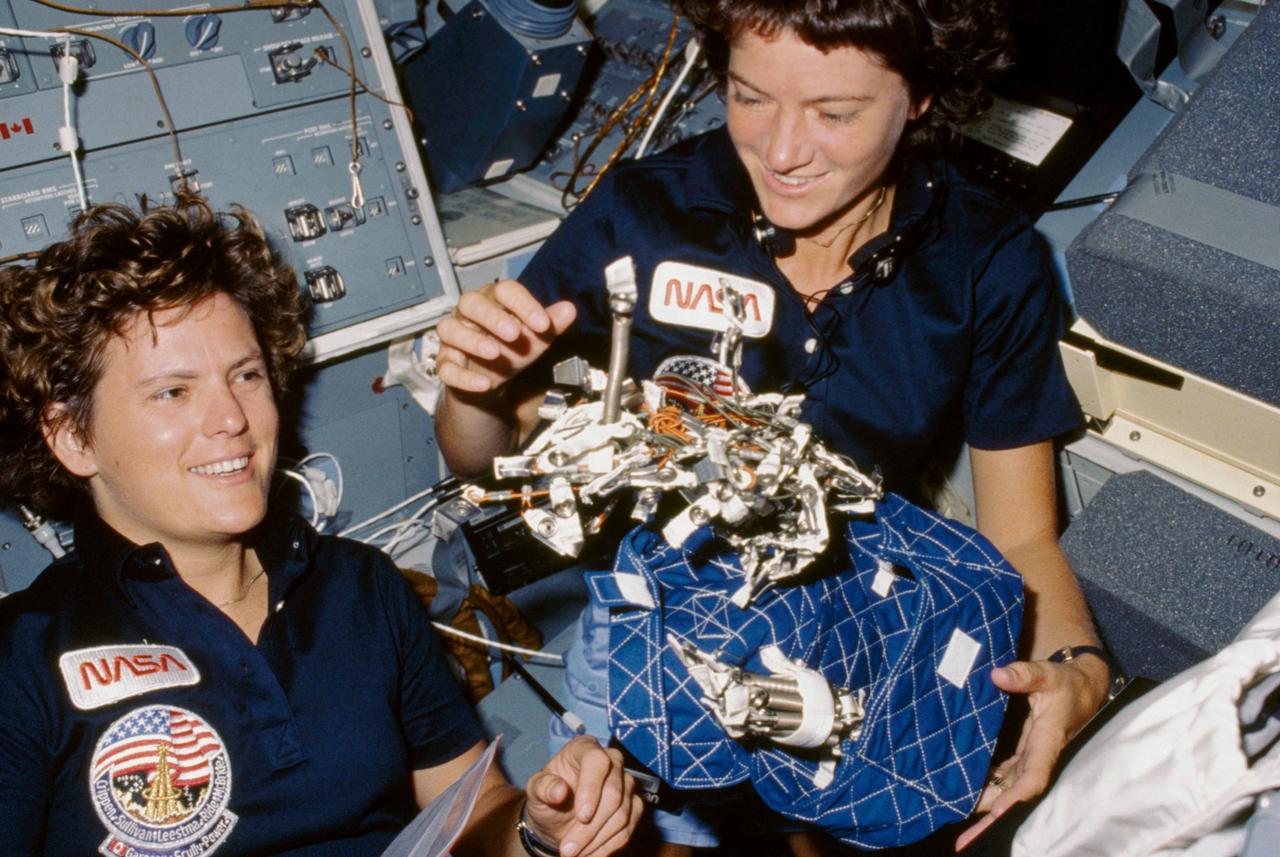

41G-07-021 (5-13 October 1984) --- Astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan, left, and Sally K. Ride show off what appears to be a "bag of worms", a product of their creativity. The "bag" is a sleep restraint and the majority of the "worms" are springs and clips used with the sleep restraint in its normal application. Clamps, a bungee cord and Velcro strips are other recognizable items in the "creation".
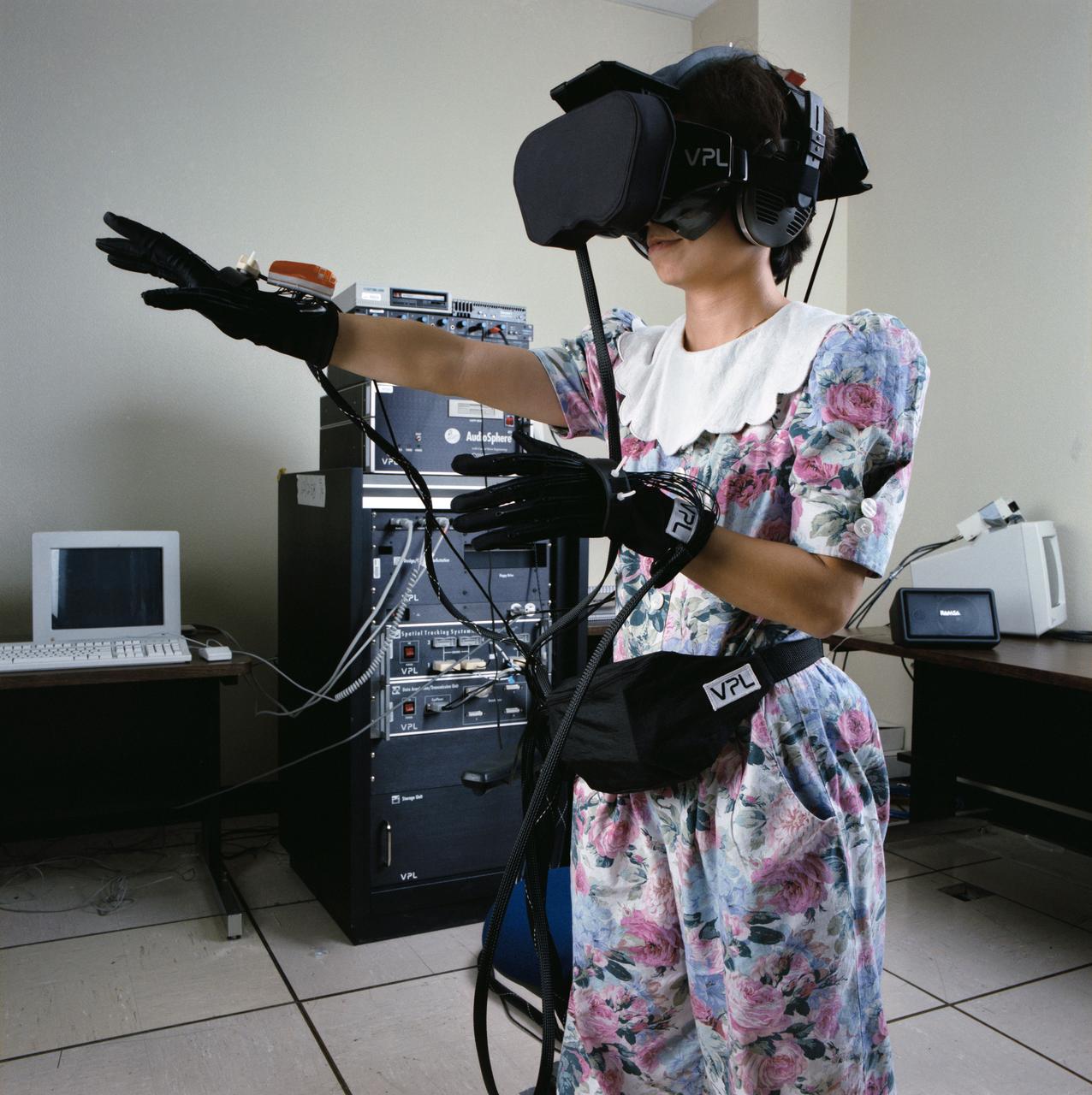

S91-50404 (1 Nov 1991) --- Bebe Ly of the Information Systems Directorate's (ISD) Software Technology Branch at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) gives virtual reality a try. The stereo video goggles and head[phones allow her to see and hear in a computer-generated world and the gloves allow her to move around and grasp objects. Ly is a member of the team that developed the C Language Integrated production System (CLIPS) which has been instrumental in developing several of the systems to be demonstrated in an upcoming Software Technology Exposition at JSC.
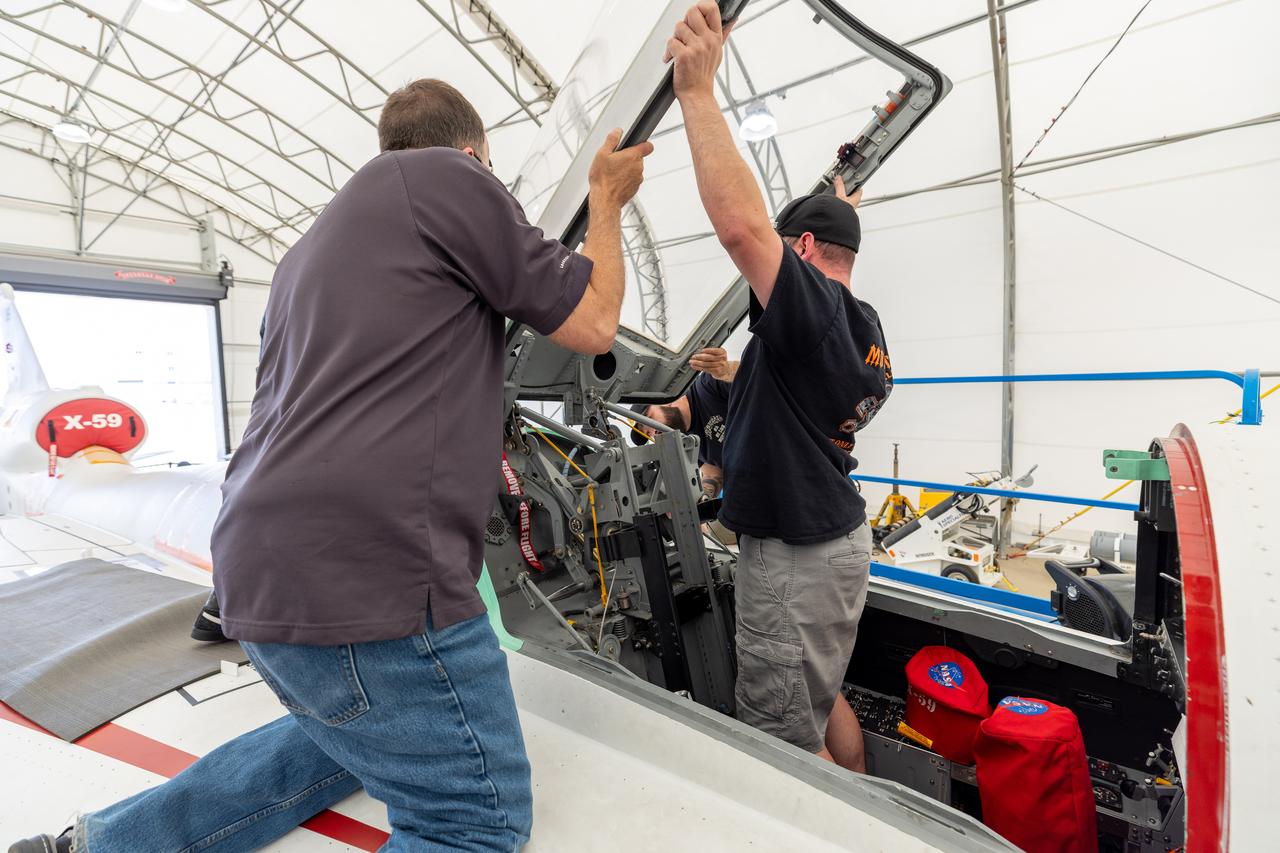

Lockheed Martin technicians temporarily remove the canopy from the X-59 in preparation for final installation of the ejection seat into the aircraft.
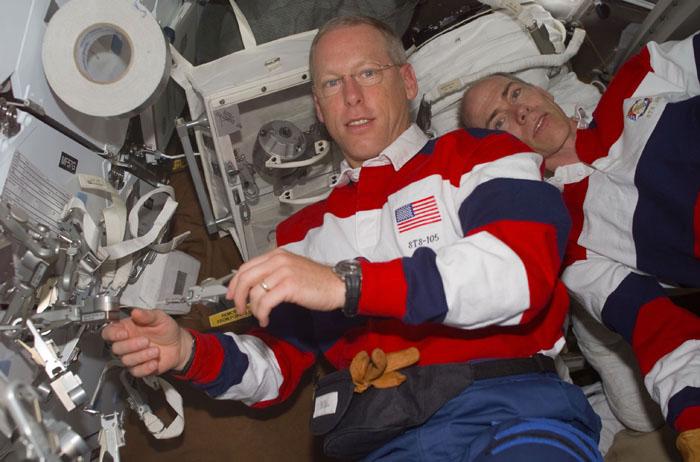

STS105-E-5217 (15 August 2001) --- Onboard the Space Shuttle Discovery, astronauts Patrick G. Forrester (left) and Daniel T. Barry check out some of the equipment they will be working with on their scheduled space walk in less than 24 hours. The image was recorded with a digital still camera.
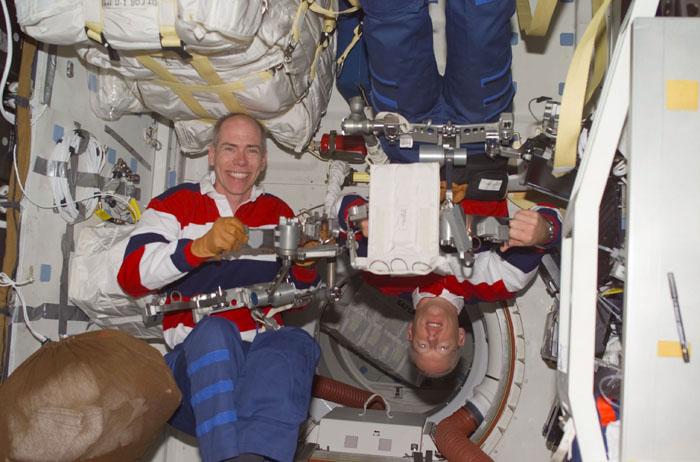

STS105-E-5214 (15 August 2001) --- Astronauts Daniel T. Barry (left) and Patrick G. Forrester check out some of the equipment they will be working with on their scheduled space walk in less than 24 hours. The image was recorded with a digital still camera.
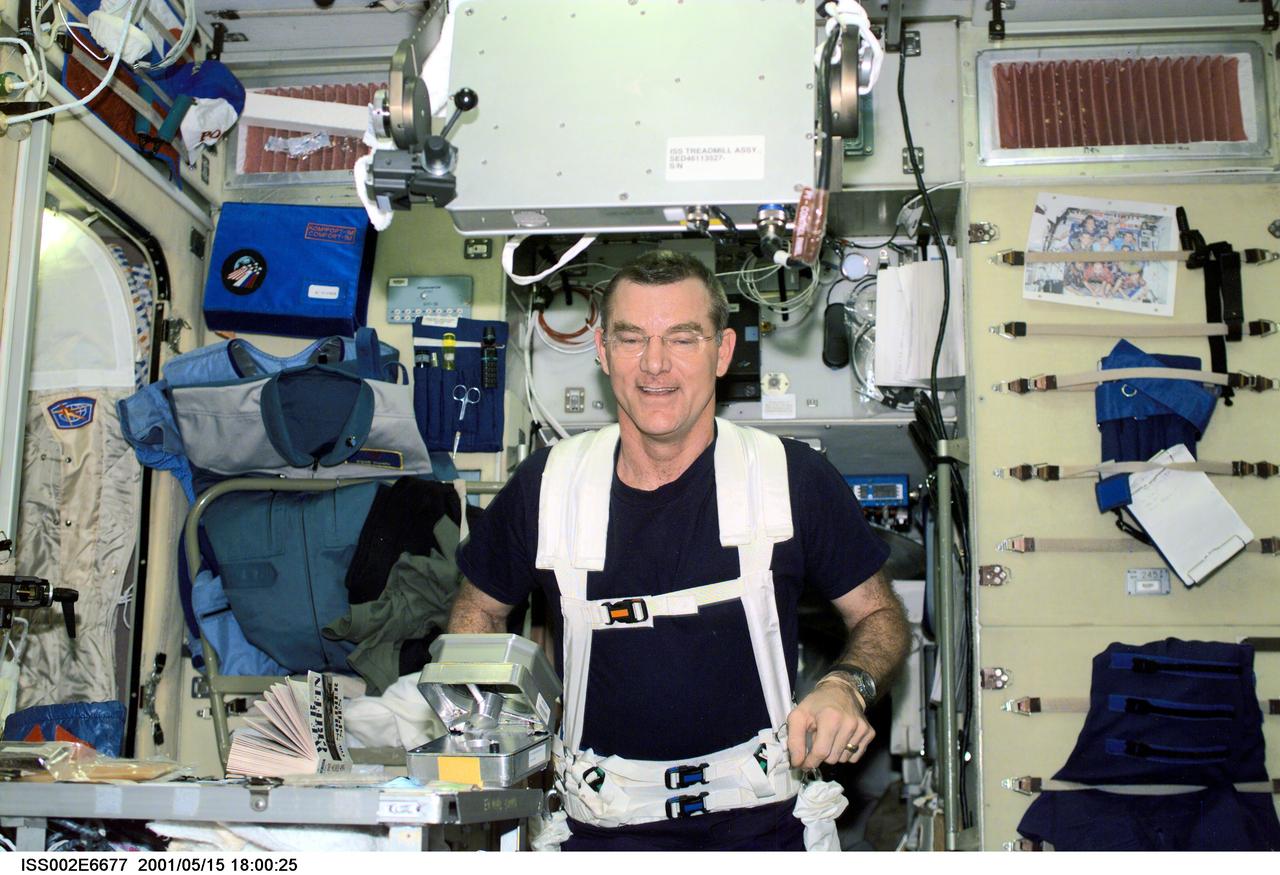

ISS002-E-06677 (15 May 2001) --- James S. Voss, Expedition Two flight engineer, wearing a safety harness, exercises on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) equipment in the Zvezda Service Module. This image was taken with a digital still camera.
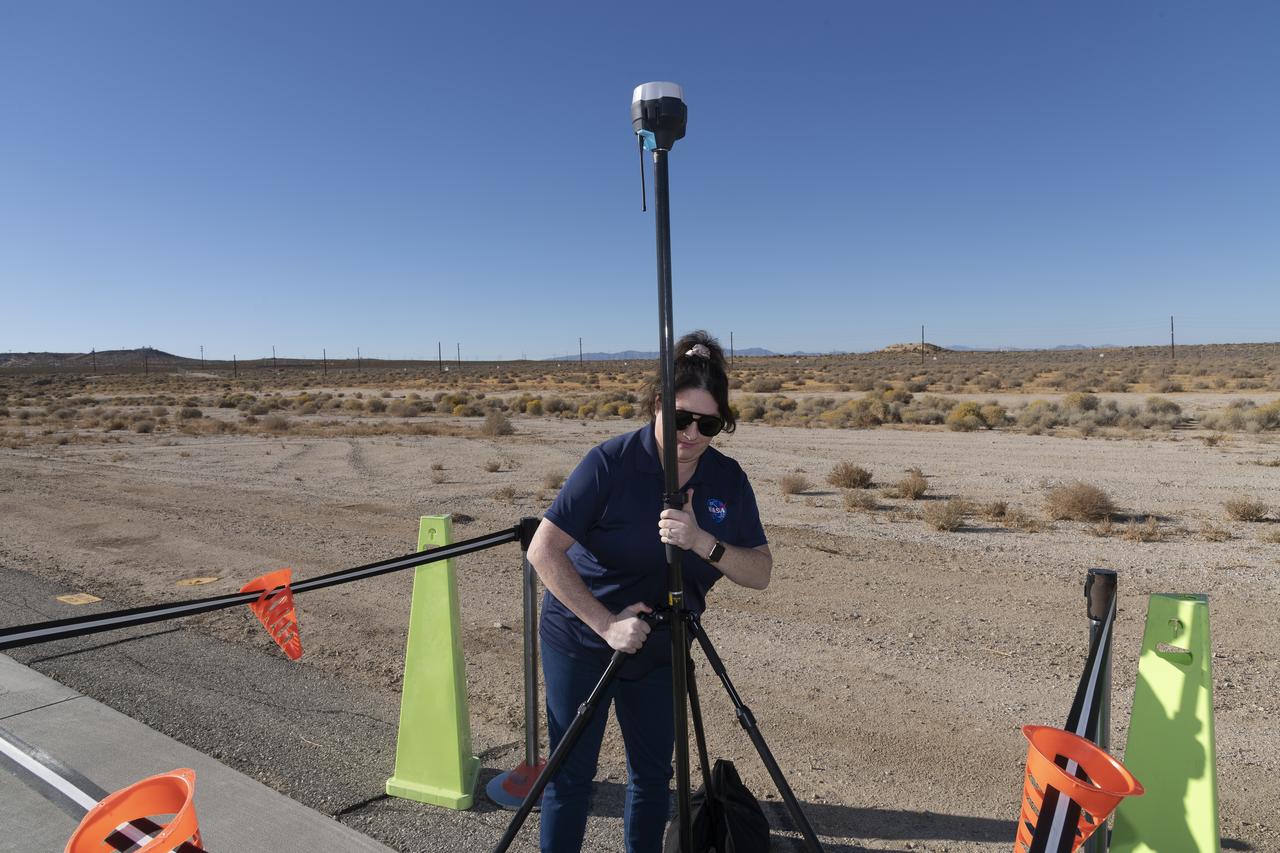

Saré Culbertson, NASA Pathways intern at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, adjusts the Emlid Reach RS2+ receiver equipment that connects with GPS and global navigation satellite systems on Nov. 7, 2024, in preparation for future air taxi test flight research.
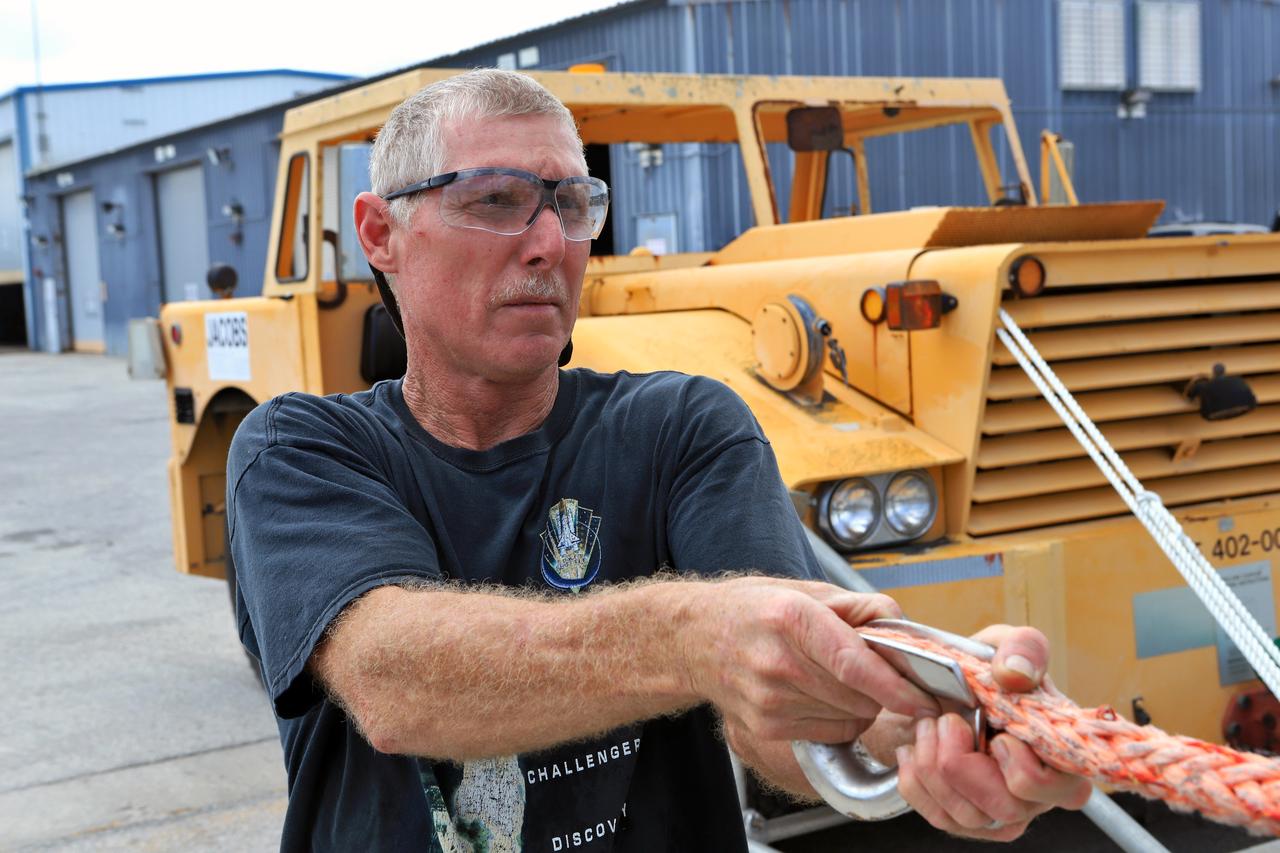

Orion Landing and Recovery team member John Stirling, with Jacobs, practices using a winch to prepare for Underway Recovery Test 7 ( URT-7) on Sept. 5, 2018, in the heavy equipment yard at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. During URT-7, the recovery team, including Exploration Ground Systems and the U.S. Navy, will practice recovering a test version of the Orion crew module in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of California, and guiding it into the well deck of a ship. Over several days, the team will demonstrate and evaluate new recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to deep space destinations, including the Moon and on to Mars. Orion will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.
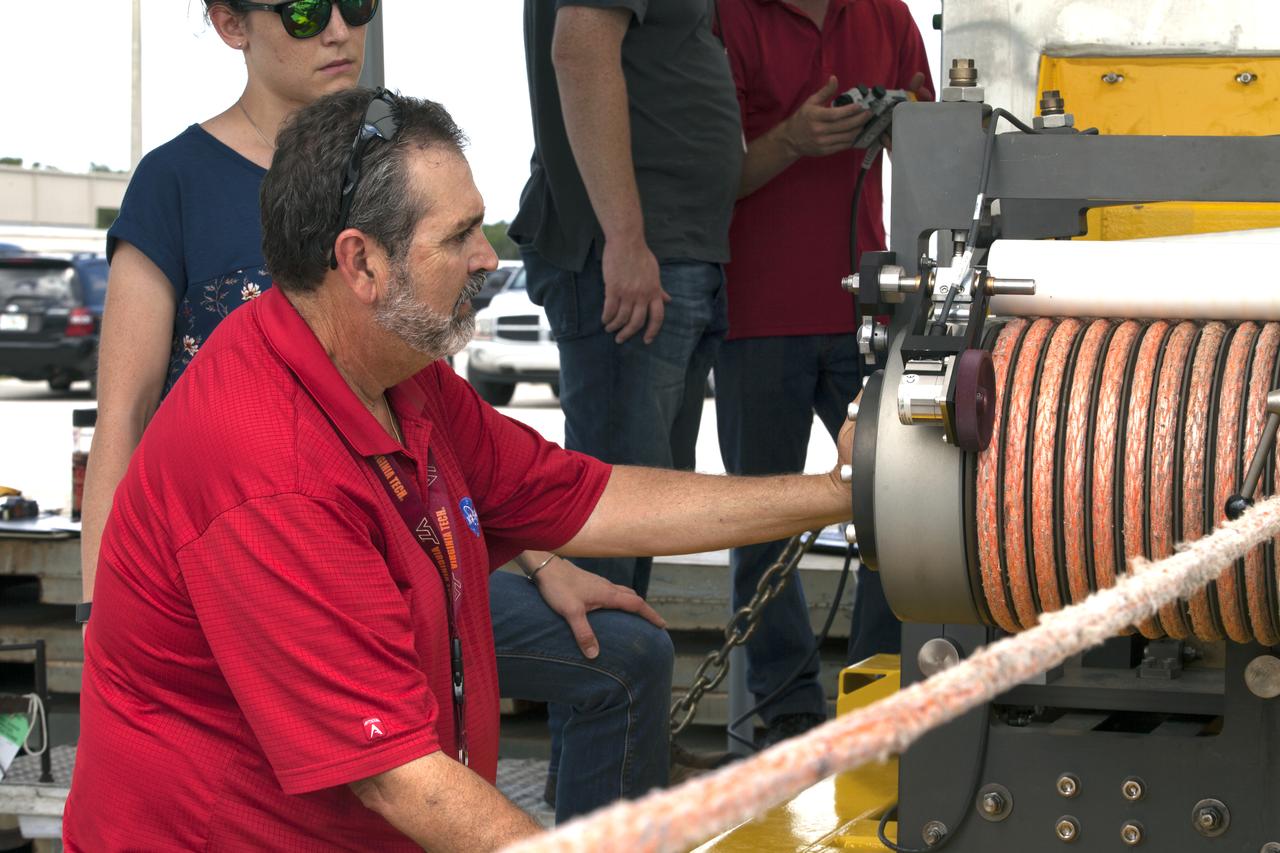

Orion Landing and Recovery team members with Jacobs practice using a winch to prepare for Underway Recovery Test 7 (URT-7) on Sept. 5, 2018, in the heavy equipment yard at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In front is Pete Ruett. Behind him is Amy Hein. Both are handling and access engineers. During URT-7, the recovery team, including Exploration Ground Systems and the U.S. Navy, will practice recovering a test version of the Orion crew module in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of California, and guiding it into the well deck of a ship. Over several days, the team will demonstrate and evaluate new recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to deep space destinations, including the Moon and on to Mars. Orion will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.
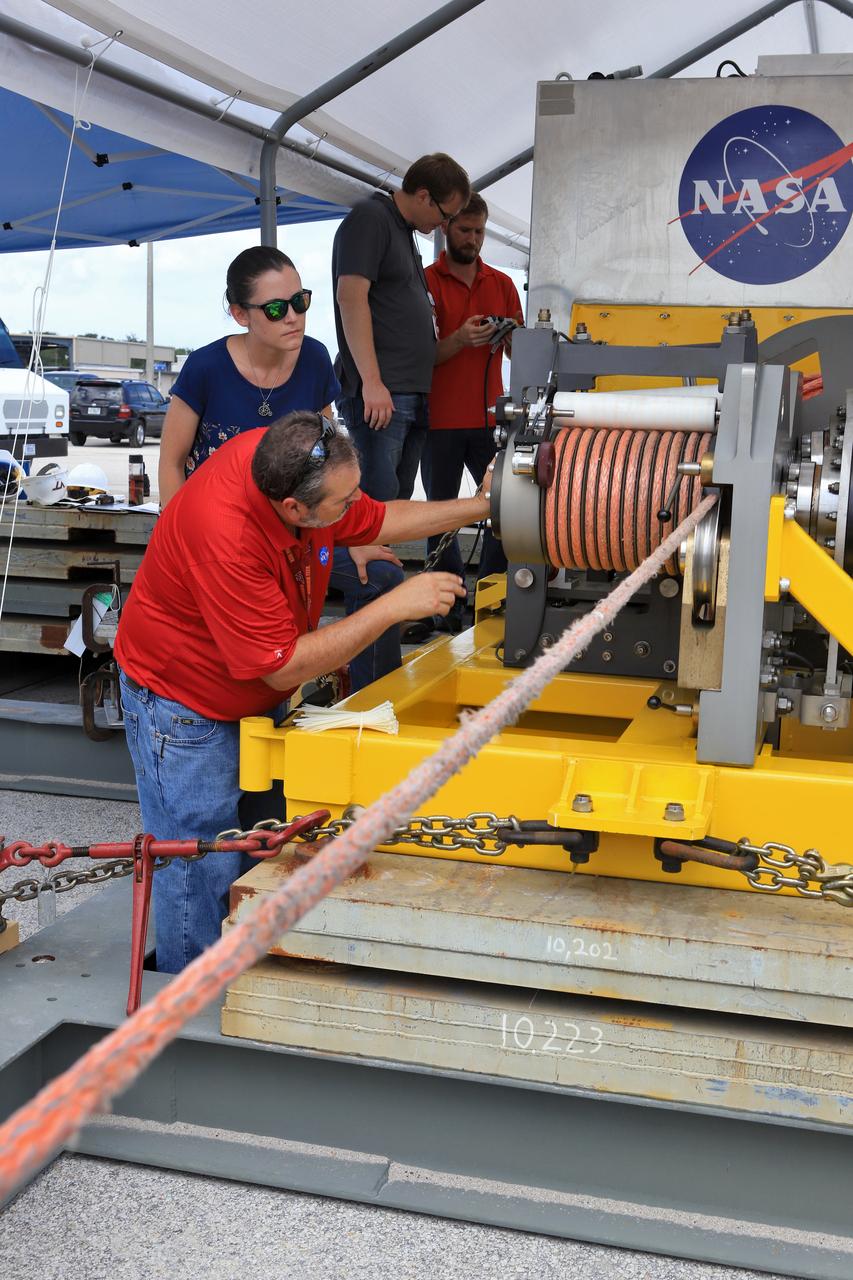

Orion Landing and Recovery team members with Jacobs, practice using a winch to prepare for Underway Recovery Test 7 (URT-7) on Sept. 5, 2018, in the heavy equipment yard at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left, are handling and access engineers Pete Ruett, Amy Hein, Peter Thorn and Eric Hernandez. During URT-7, the recovery team, including Exploration Ground Systems and the U.S. Navy, will practice recovering a test version of the Orion crew module in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of California, and guiding it into the well deck of a ship. Over several days, the team will demonstrate and evaluate new recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to deep space destinations, including the Moon and on to Mars. Orion will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.
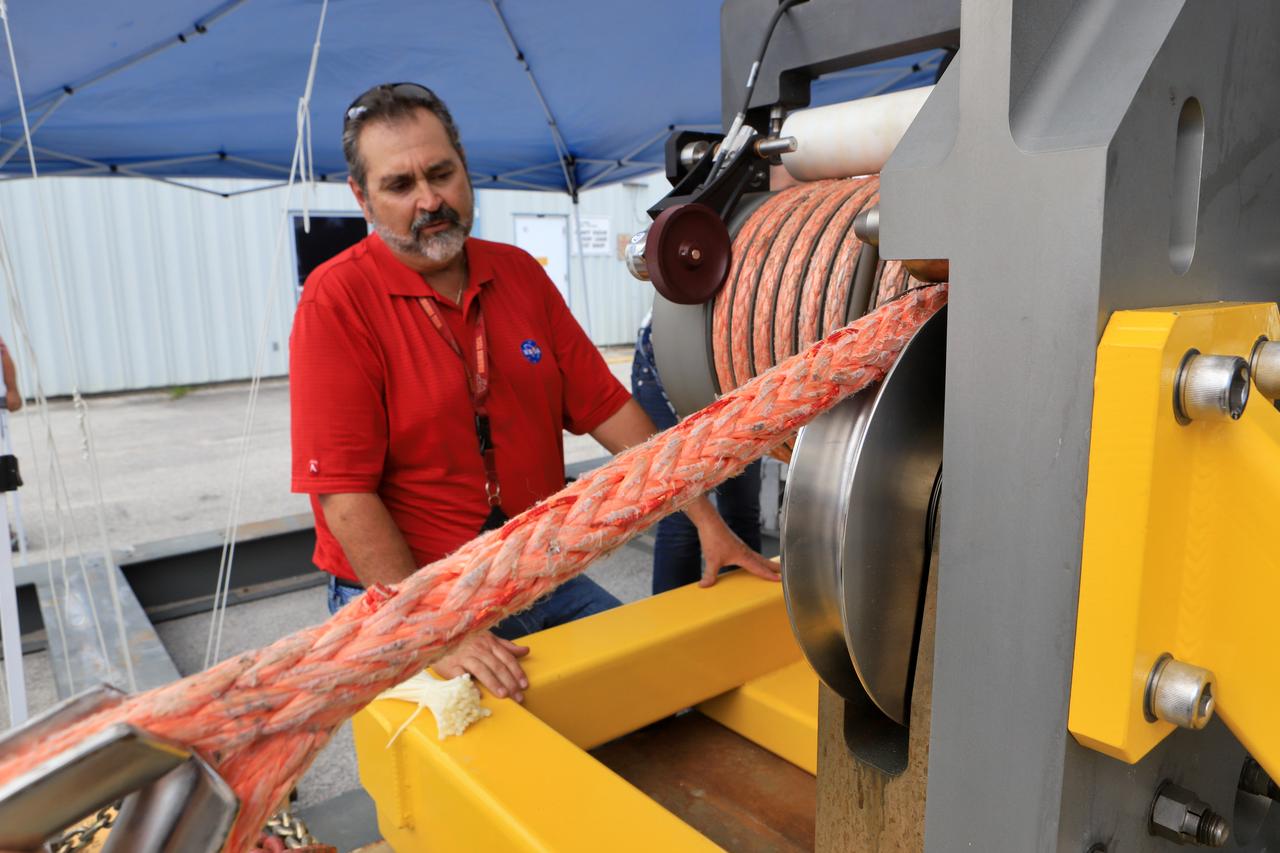

Orion Landing and Recovery team member Pete Ruett, with Jacobs, practices using a winch to prepare for Underway Recovery Test 7 (URT-7) on Sept. 5, 2018, in the heavy equipment yard at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ruett is a handling and access engineer. During URT-7, the recovery team, including Exploration Ground Systems and the U.S. Navy, will practice recovering a test version of the Orion crew module in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of California, and guiding it into the well deck of a ship. Over several days, the team will demonstrate and evaluate new recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to deep space destinations, including the Moon and on to Mars. Orion will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.
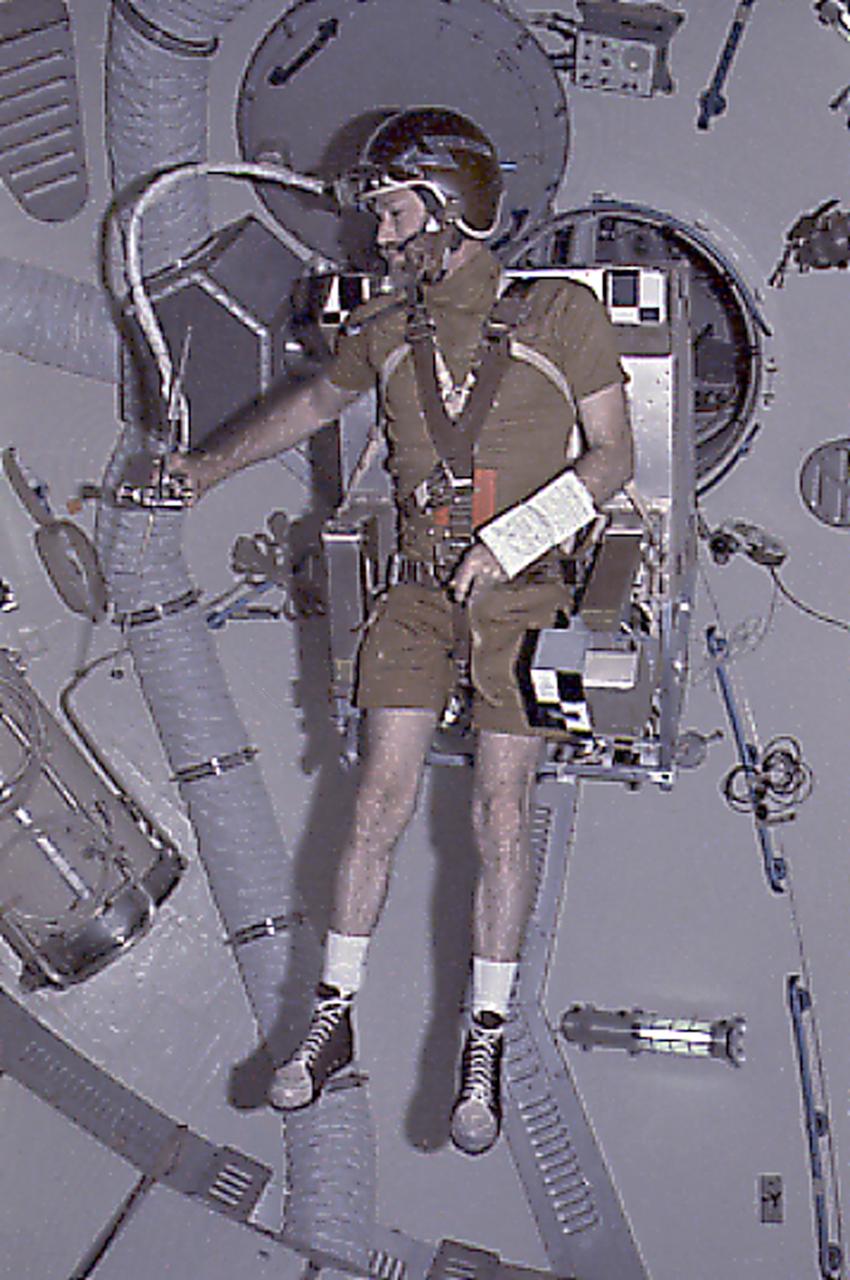
This Skylab-4 onboard photograph depicts Astronaut Gerald Carr testing Astronaut Maneuvering Equipment (M509) by flying it around under weightless conditions in the Orbital Workshop. The M509 experiment was an operational study to evaluate and conduct an in-orbit verification of the utility of various maneuvering techniques to assist astronauts in performing tasks that were representative of future extravehicular activity requirements.
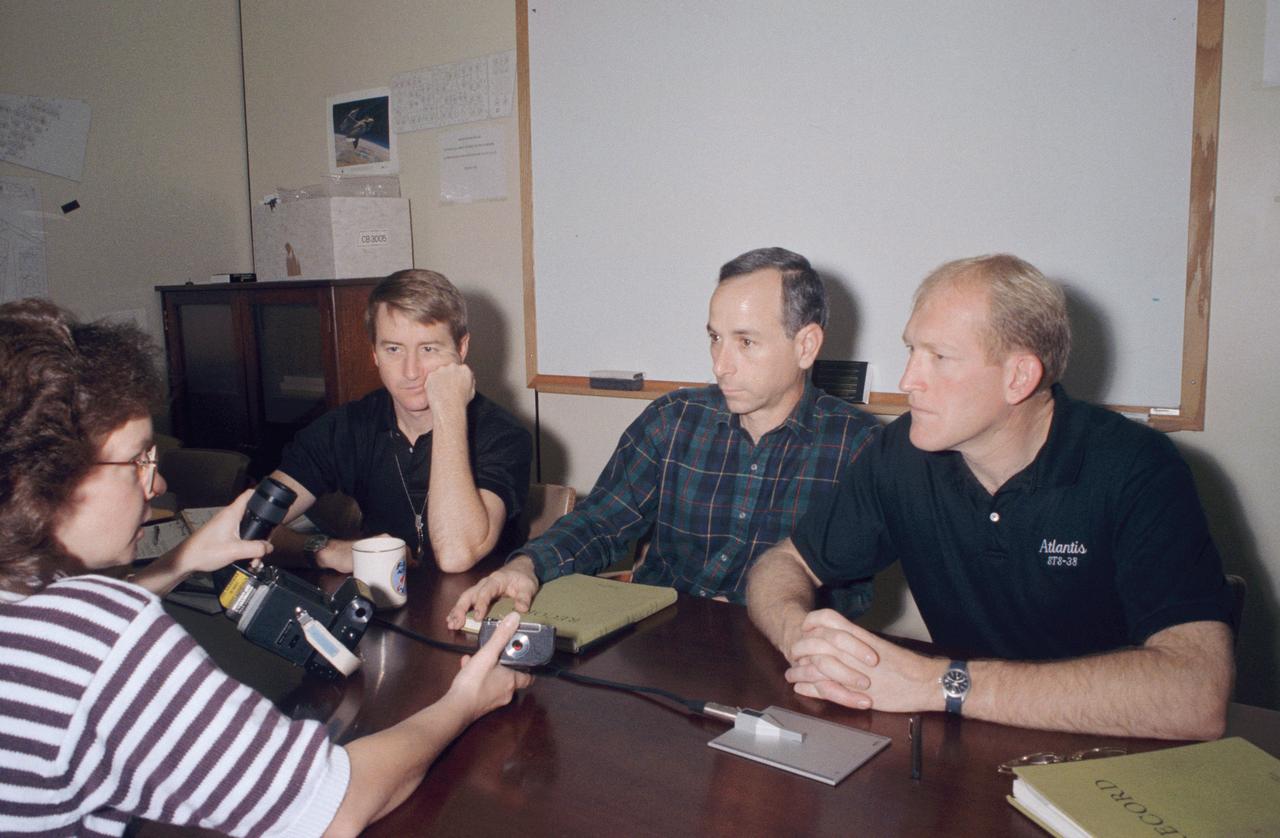

STS-38 crewmembers listen as RSOC-JSC crew trainer M. Judy Alexander explains the camera equipment they will be using on their upcoming Department of Defense (DOD) mission. Left to right are Pilot Frank L. Culbertson, Mission Specialist (MS) Carl J. Meade, and MS Charles D. Gemar. Alexander is holding a training version of the 70mm handheld HASSELBLAD camera.
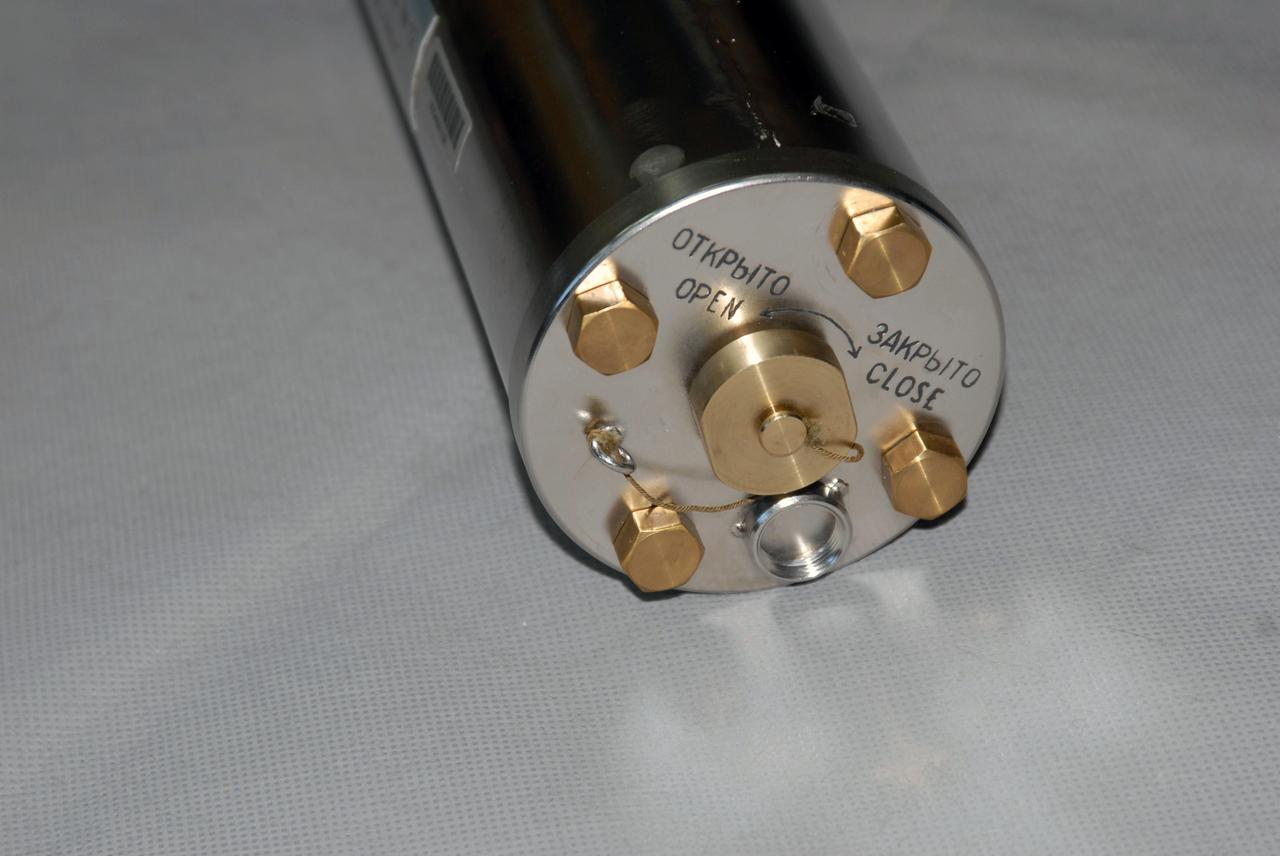

jsc2008e152662 (12/10/2008) --- A preflight view of connectors on a Biorisk-MSV container, part of the Biorisk experiment equipment to be delivered to the ISS during the 31P flight. The Influence of Factors of the Space Environment on the Condition of the System of Microorganisms-Hosts Relating to the Problem of Environmental Safety of Flight Techniques and Planetary Quarantine (Biorisk) investigation aims to obtain new data on physical and genetic changes in bacteria and fungi typically found on spacecraft equipment, and also in various biological test objects (higher plant seeds, dormant forms of lower crustaceans) under exposure in the interior ISS compartments and on the exterior ISS surfaces.
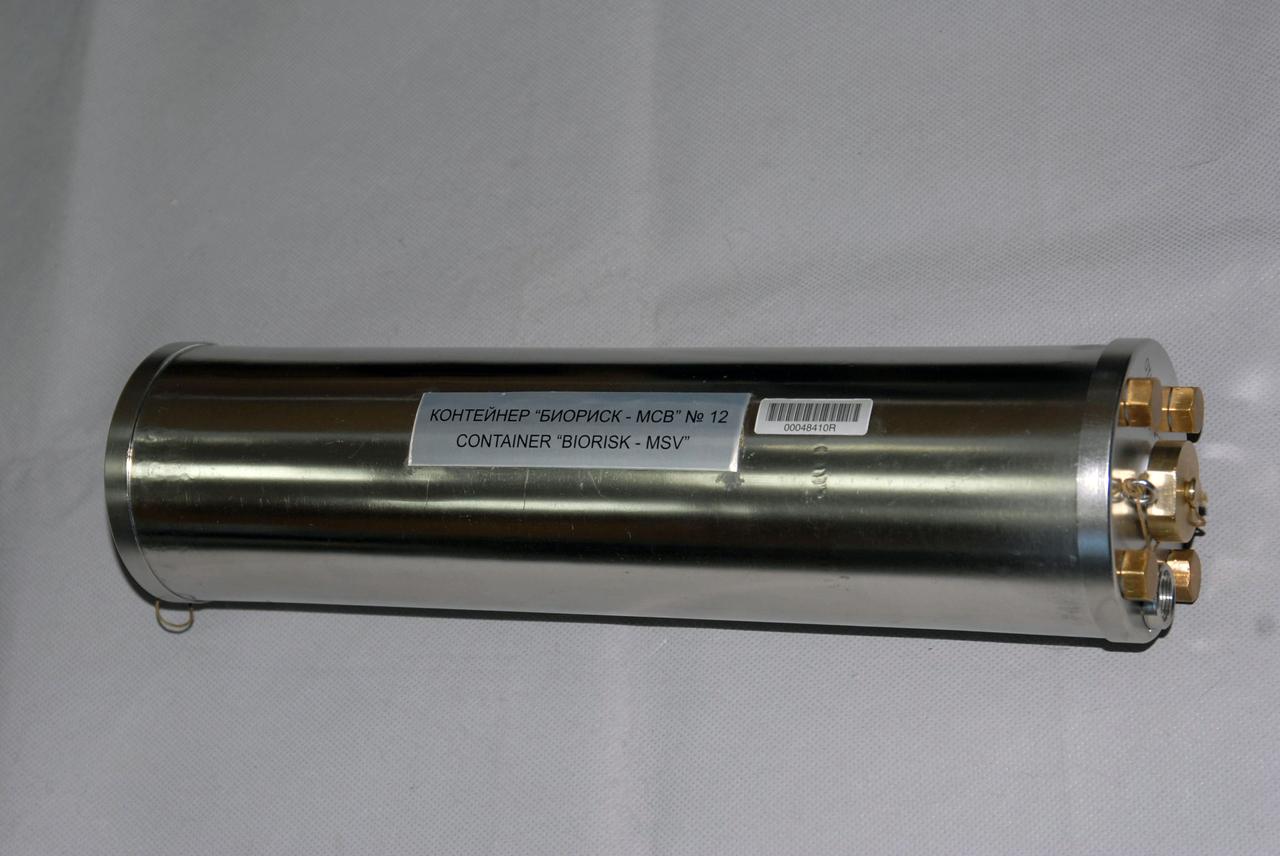

jsc2008e152661 (12/8/2008) --- A preflight view of a Biorisk-MSV container, part of the Biorisk experiment equipment to be delivered to the ISS during the 31P flight. The Influence of Factors of the Space Environment on the Condition of the System of Microorganisms-Hosts Relating to the Problem of Environmental Safety of Flight Techniques and Planetary Quarantine (Biorisk) investigation aims to obtain new data on physical and genetic changes in bacteria and fungi typically found on spacecraft equipment, and also in various biological test objects (higher plant seeds, dormant forms of lower crustaceans) under exposure in the interior ISS compartments and on the exterior ISS surfaces.
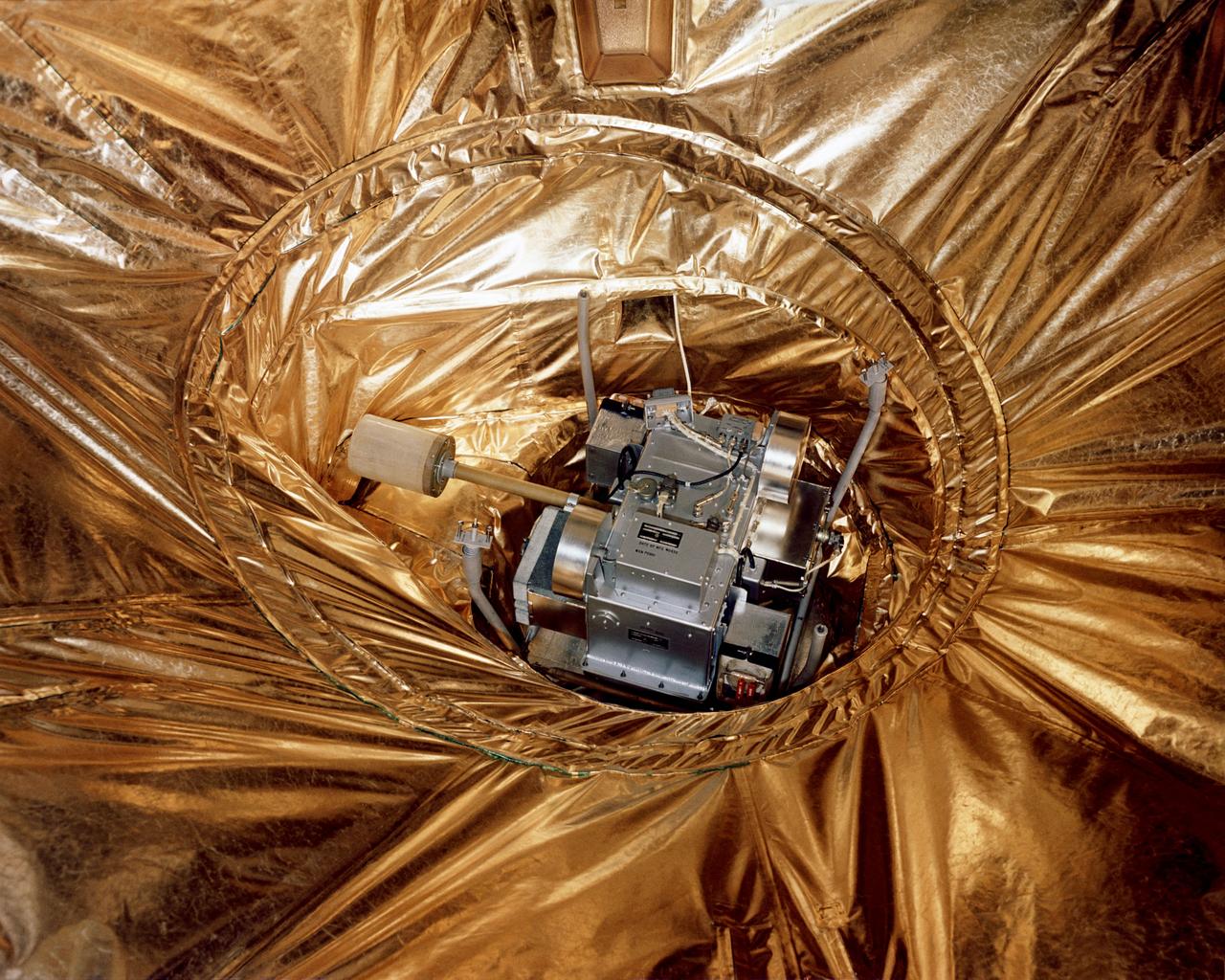

S65-42044 (28 July 1965) --- Close-up view of the Rendezvous Evaluation Pod installed in the equipment section of the Gemini-5 spacecraft at Pad 19.
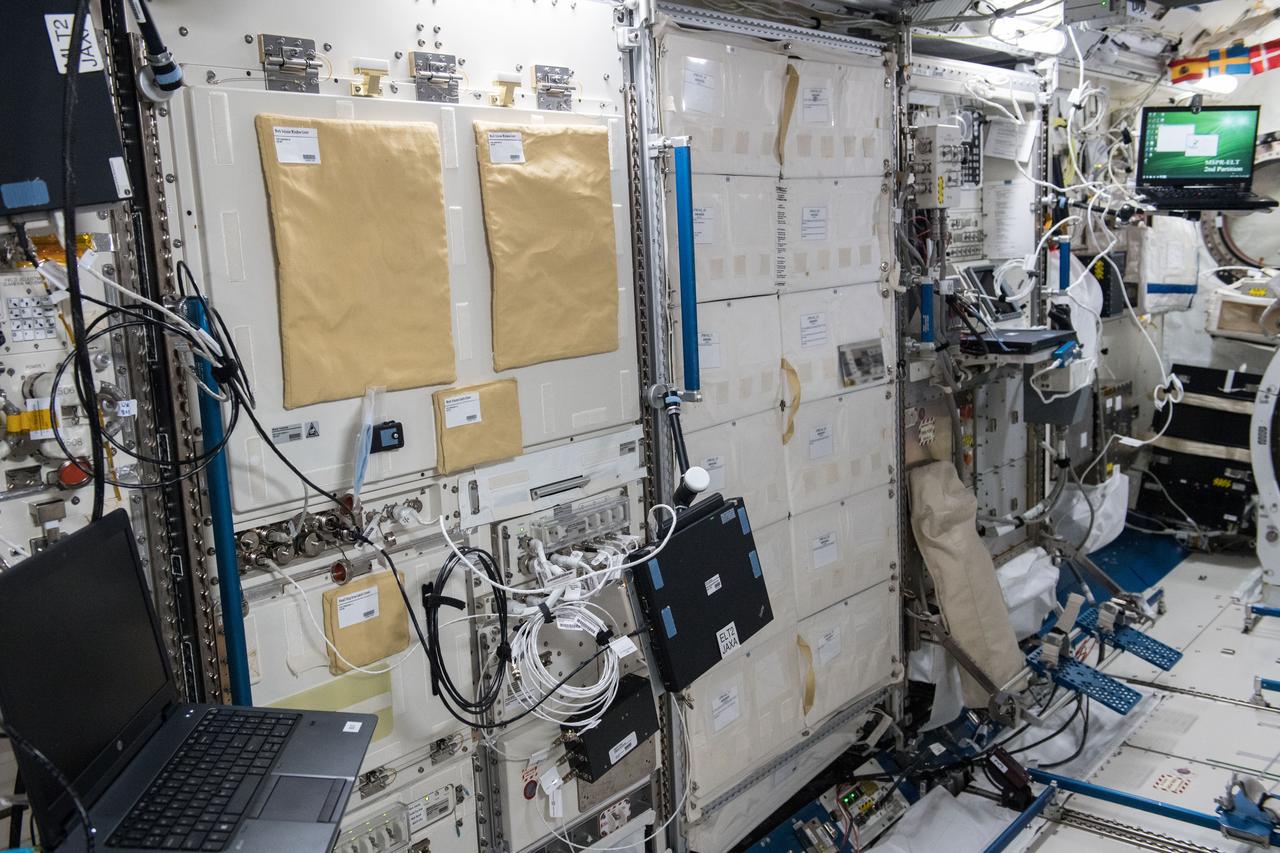

iss055e098109 (3/15/2018) --- Photo taken in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS), showing the Multi-purpose Small Payload Rack (MSPR) Two-Phase Flow (TPF) Experiment Equipment. The Interfacial behaviors and Heat transfer characteristics in Boiling Two-Phase Flow (Two-Phase Flow) investigation helps to provide better fundamental understanding on the behavior of liquid-vapor flow, and the mechanism of heat transfer under microgravity.
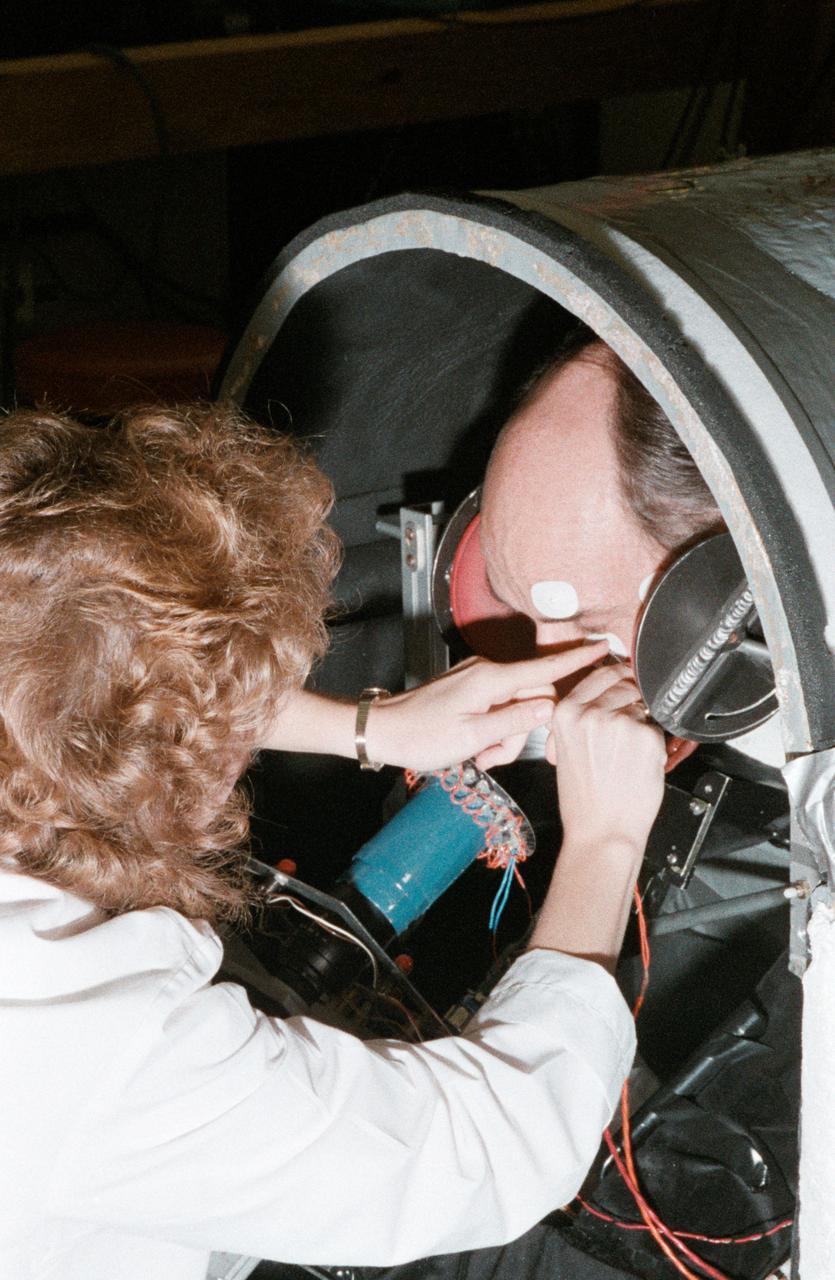

Sen. Jake Garn trains in use of equipment for medical experiments.
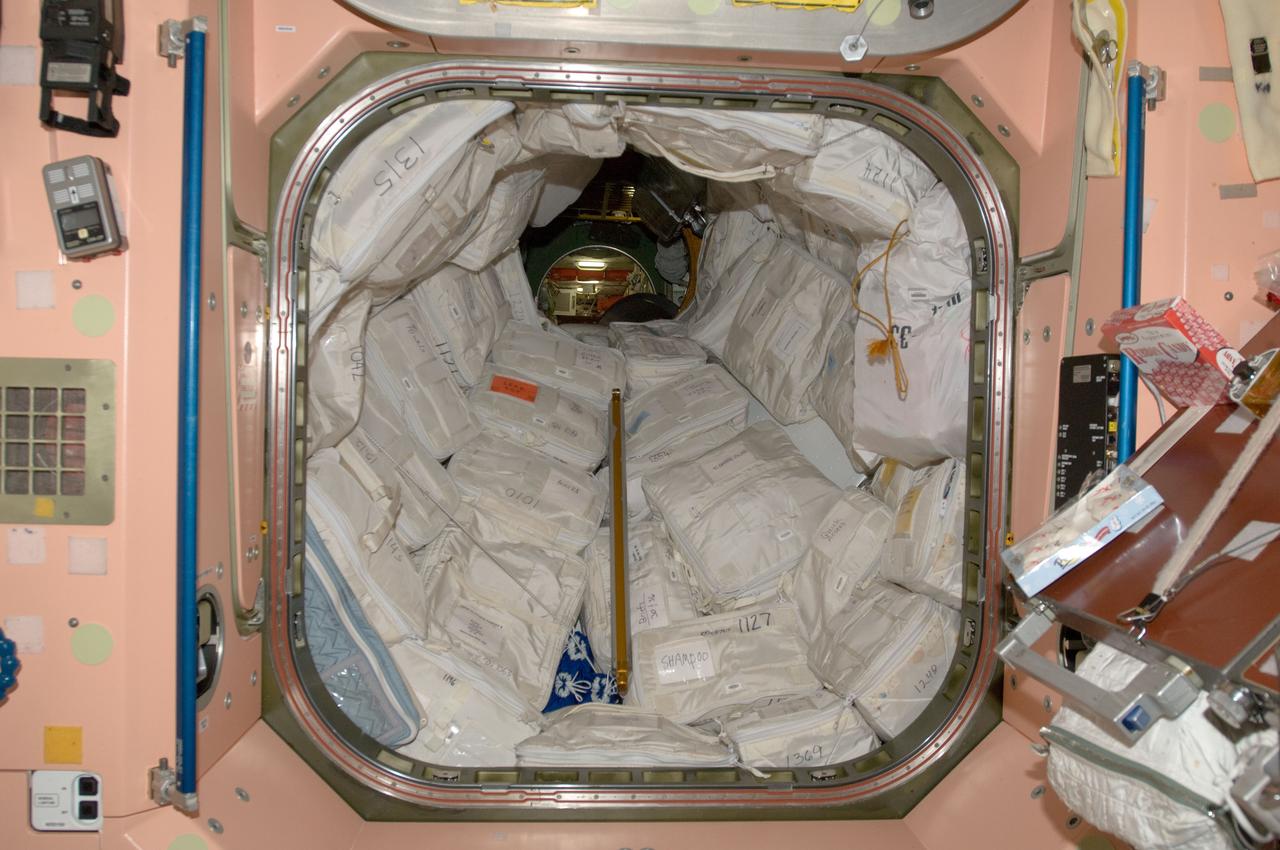

View of stowage in the aft end of the Node 1 and the hatch leading to Pressurized Mating Adapter 1 (PMA1). The PMA1 is also lined with stowed equipment. Photo was taken during Expedition 34.
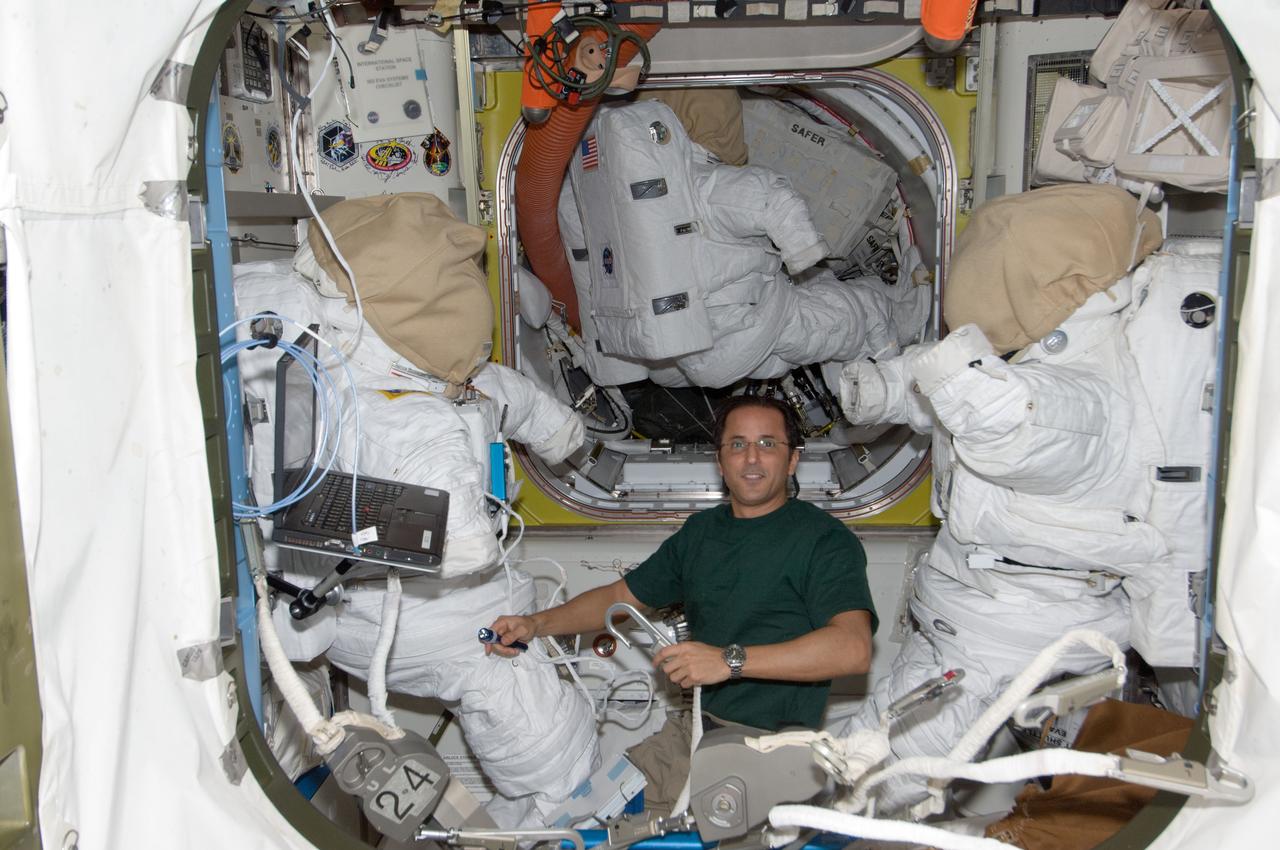

ISS032-E-006433 (9 July 2012) --- NASA astronaut Joe Acaba, Expedition 32 flight engineer, works with extravehicular activity (EVA) equipment between two Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuits in the Quest airlock of the International Space Station.
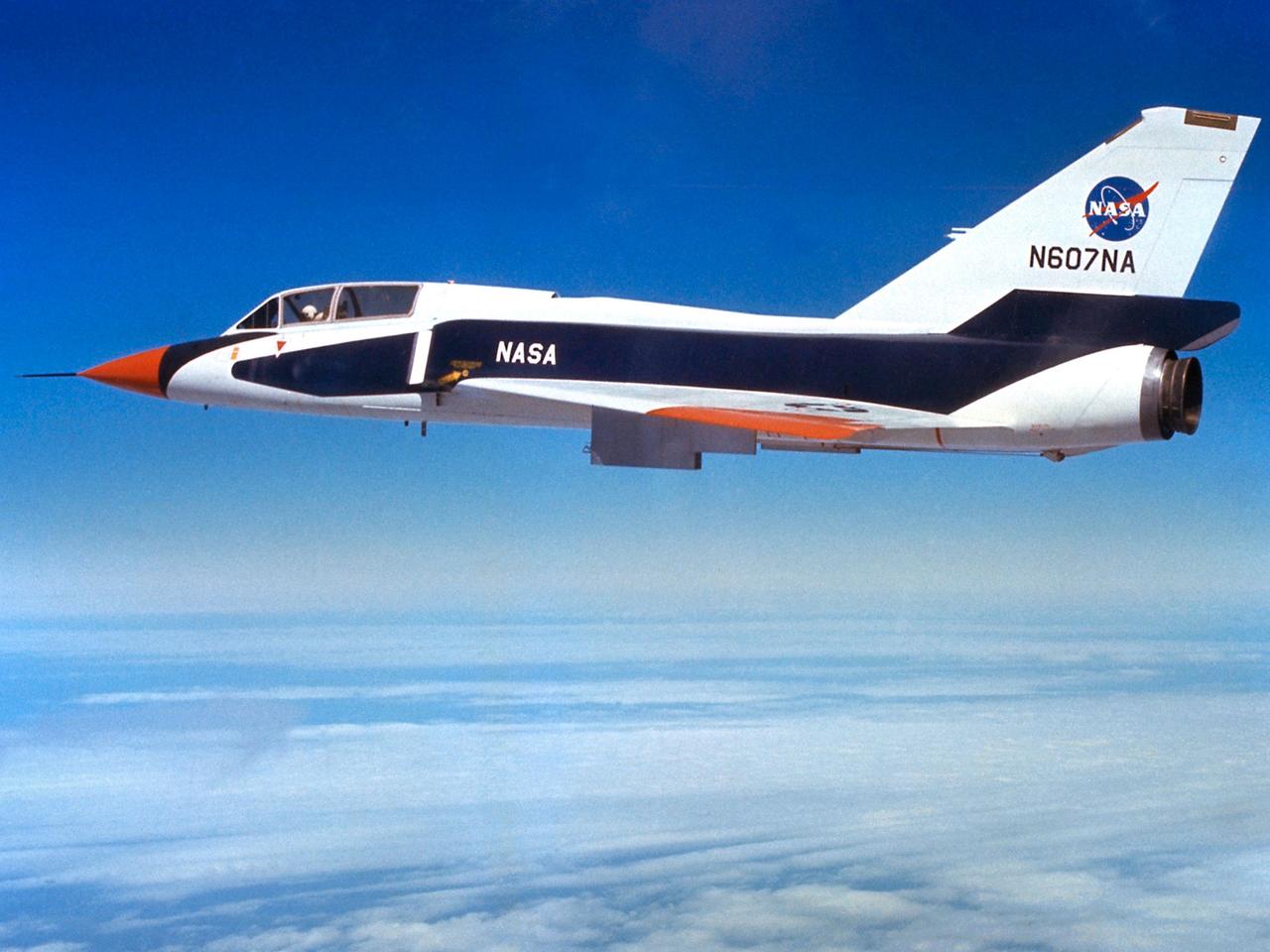

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center’s Convair F-106B Delta Dart equipped with air sampling equipment in the mid-1970s. NASA Lewis created and managed the Global Air Sampling Program (GASP) in 1972 in partnership with several airline companies. NASA researchers used the airliners’ Boeing 747 aircraft to gather air samples to determine the amount of pollution present in the stratosphere. Private companies developed the air sampling equipment for the GASP program, and Lewis created a particle collector. The collector was flight tested on NASA Lewis’ F-106B in the summer of 1973. The sampling equipment was automatically operated once the proper altitude was achieved. The sampling instruments collected dust particles in the air so their chemical composition could be analyzed. The equipment analyzed one second’s worth of data at a time. The researchers also monitored carbon monoxide, monozide, ozone, and water vapor. The 747 flights began in December 1974 and soon included four airlines flying routes all over the globe. The F-106B augmented the airline data with sampling of its own, seen here. It gathered samples throughout this period from locations such as New Mexico, Texas, Michigan, and Ohio. In July 1977 the F-106B flew eight GASP flights in nine days over Alaska to supplement the earlier data gathered by the airlines.
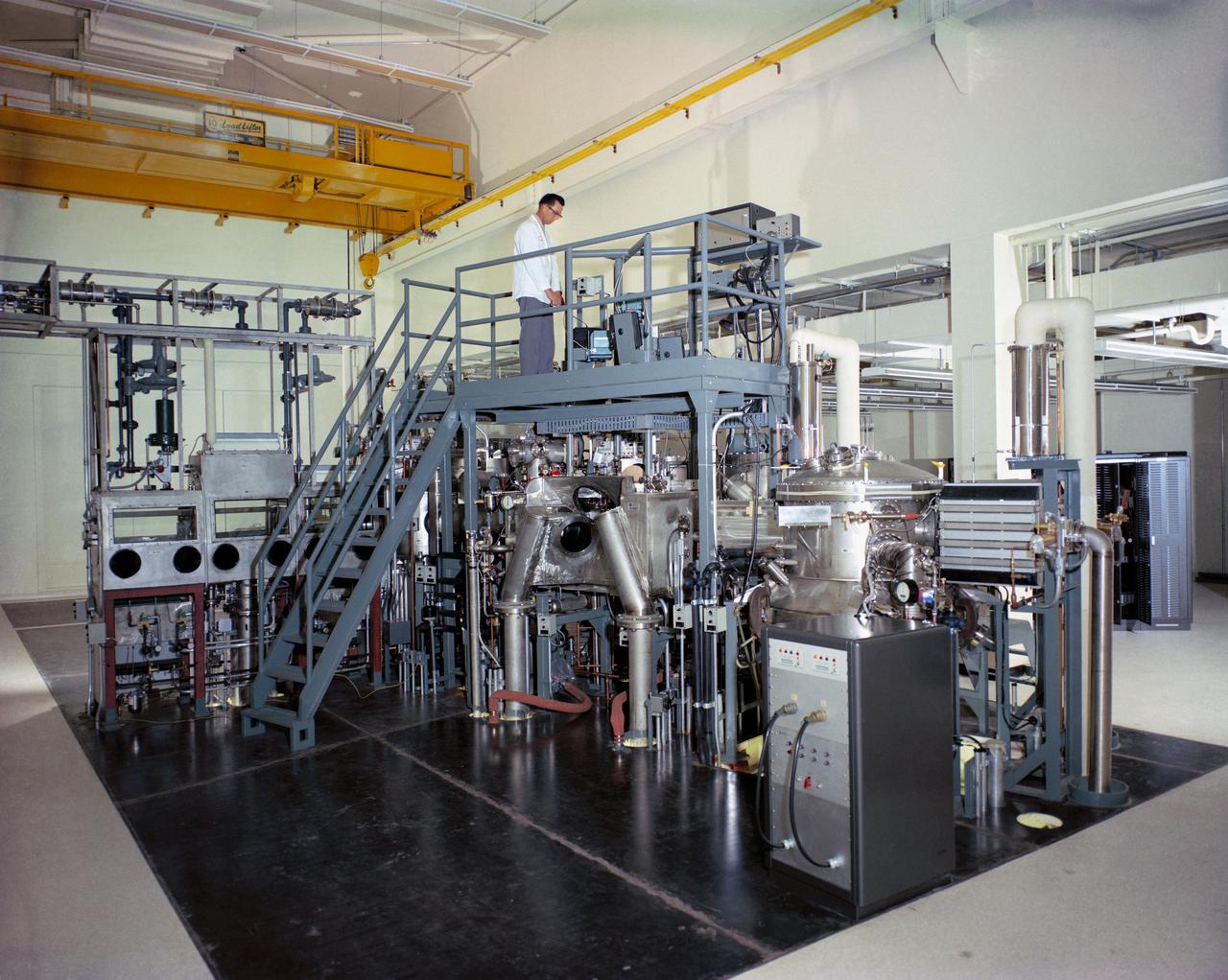

Overall view of the equipment in Room 2-203, Vacuum Laboratory, Sample Operations Area, Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Bldg 37.
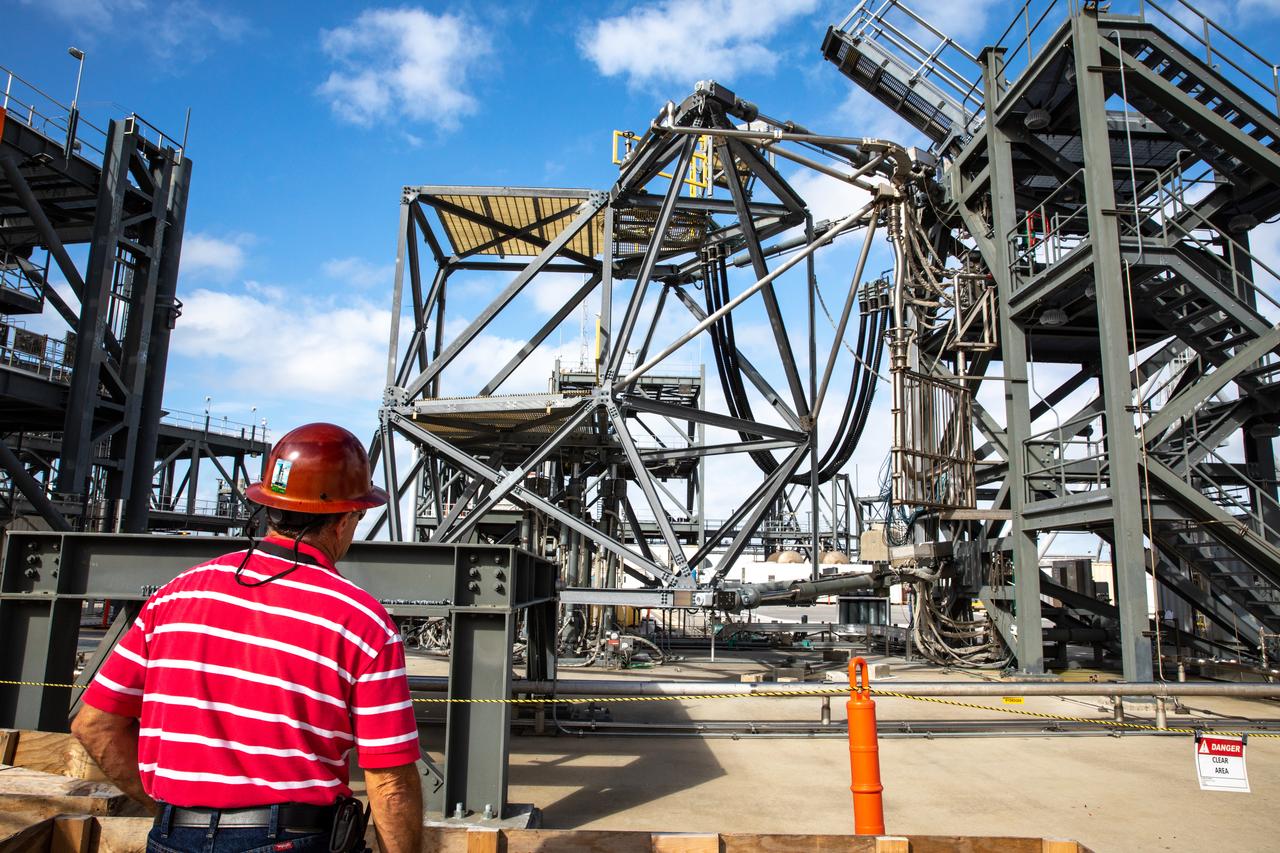

A view of one of the large test structures located at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF) on Oct. 19, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The LETF is a unique set of structures, equipment and tools built to test full-scale umbilicals and release mechanisms for the space shuttle. The facility also was used to test the umbilicals and other mechanisms for the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher will carry the Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft to Launch Pad 39B for Artemis I, a mission that will test the rocket and spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
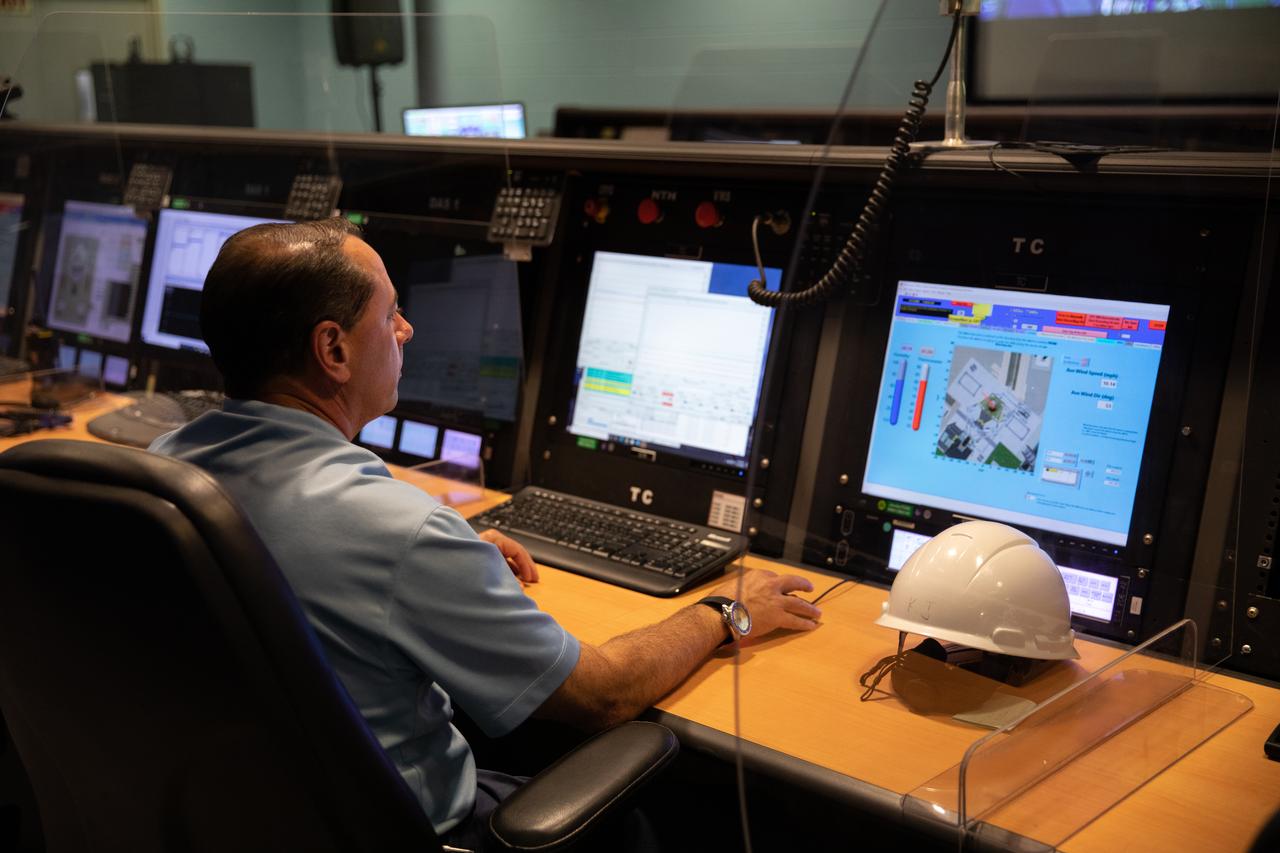

An engineer reviews test data inside a control room at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF) on Oct. 19, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The LETF is a unique set of structures, equipment and tools built to test full-scale umbilicals and release mechanisms for the space shuttle. The facility also was used to test the umbilicals and other mechanisms for the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher will carry the Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft to Launch Pad 39B for Artemis I, a mission that will test the rocket and spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
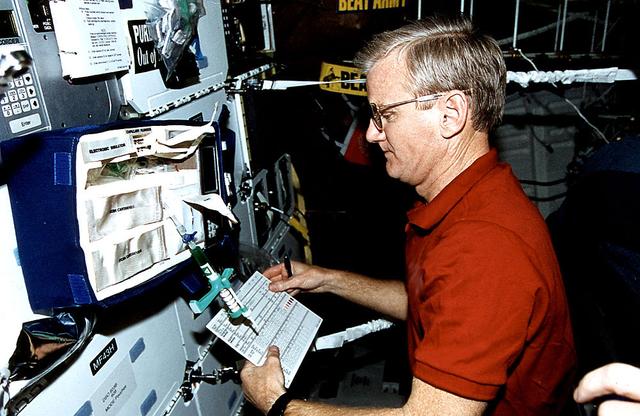

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-62) Mission commander John H. Casper takes stock of paraphenalia used to support medical testing onboard Columbia's mid-deck.
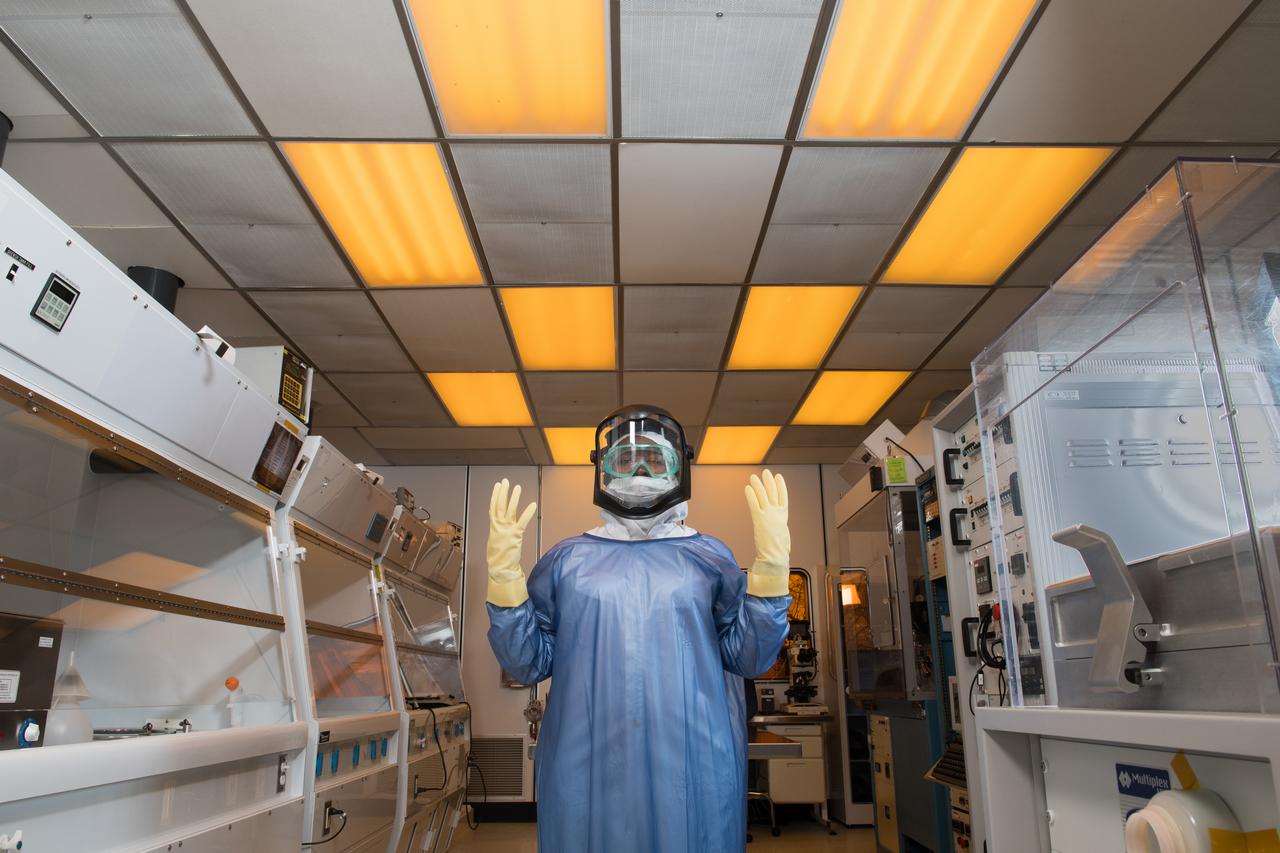

Laboratory Researcher suits up for work in a research clean room. Personal Protective Equipment, PPE, Portait Series

Atmospheric Decontamination System equipment in Room 2-203, Vacuum Laboratory, Sample Operations Area, Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Bldg 37.
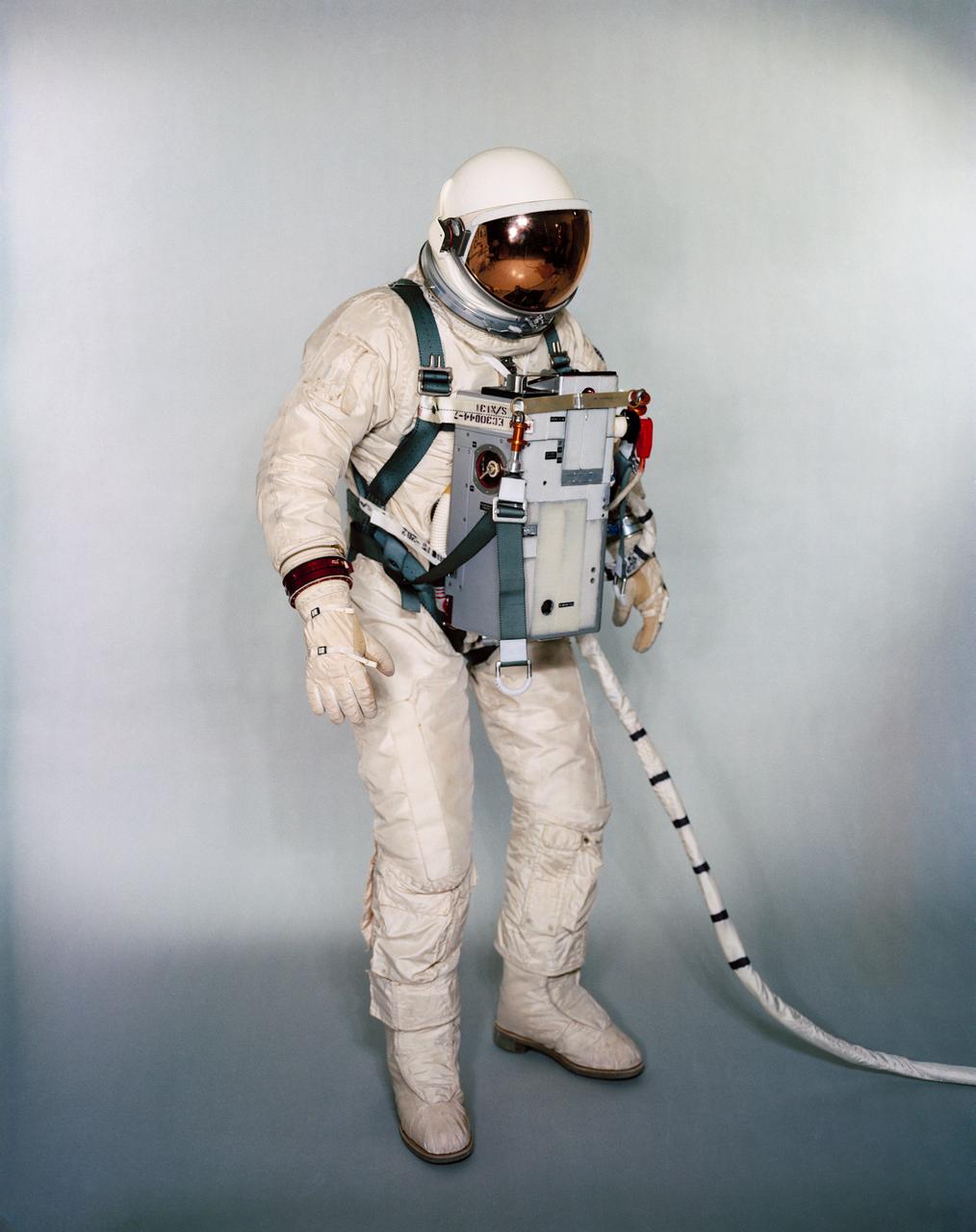

S67-24267 (1966) --- Suited test subject equipped with Gemini-12 Life Support System and waist tethers for extravehicular activity (EVA). Photo credit: NASA
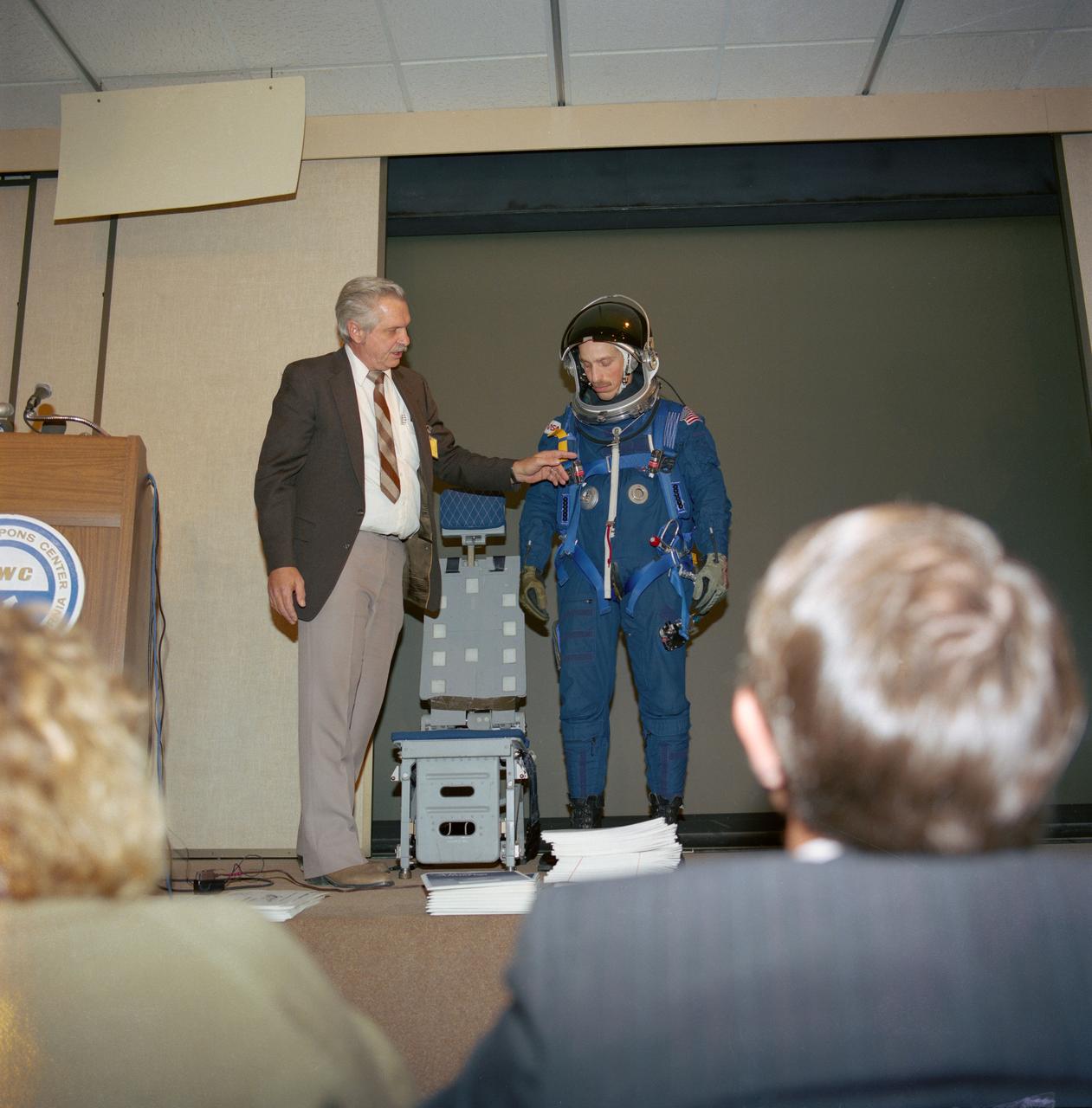

S88-25408 (8 Dec 1987) --- James O. Schlosser (left), JSC crew systems branch employee responsible for crew equipment development, gives a briefing on the crew equipment baselined for STs-26 as astronaut James P. Bagian models the new gear. Included in the package are a partial pressure suit, harness, parachute, life raft and survival gear. The deomonstration took place at the Naval Weapons Center in China Lake, CA.
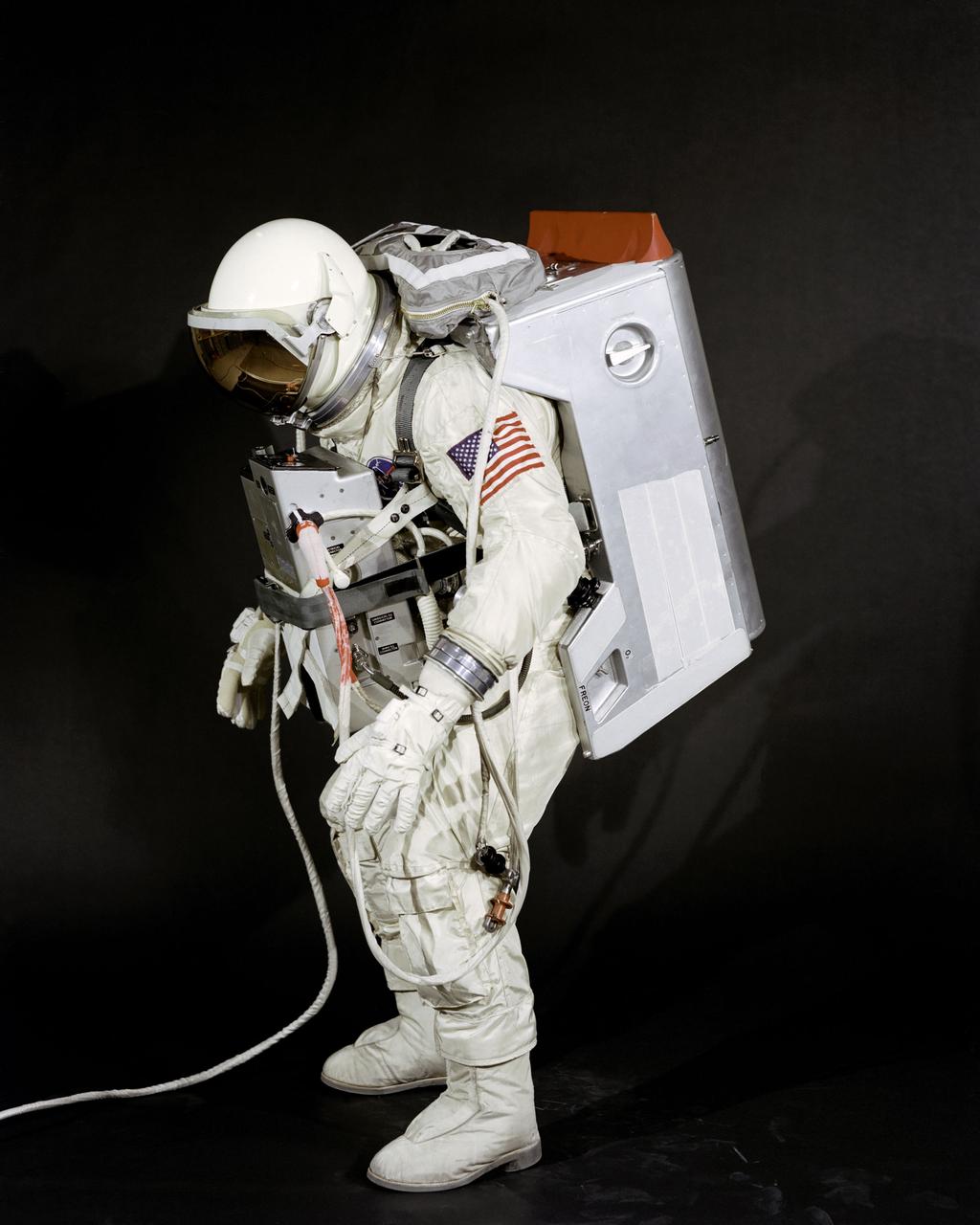

S66-17475 (18 Jan. 1966) --- Test subject Fred Spress, Crew Systems Division, wears the spacesuit and extravehicular equipment planned for use by astronaut David R. Scott. The helmet is equipped with a gold-plated visor to shield the astronaut's face from unfiltered sun rays. The system is composed of a life support pack worn on the chest and a support pack worn on the back. Photo credit: NASA
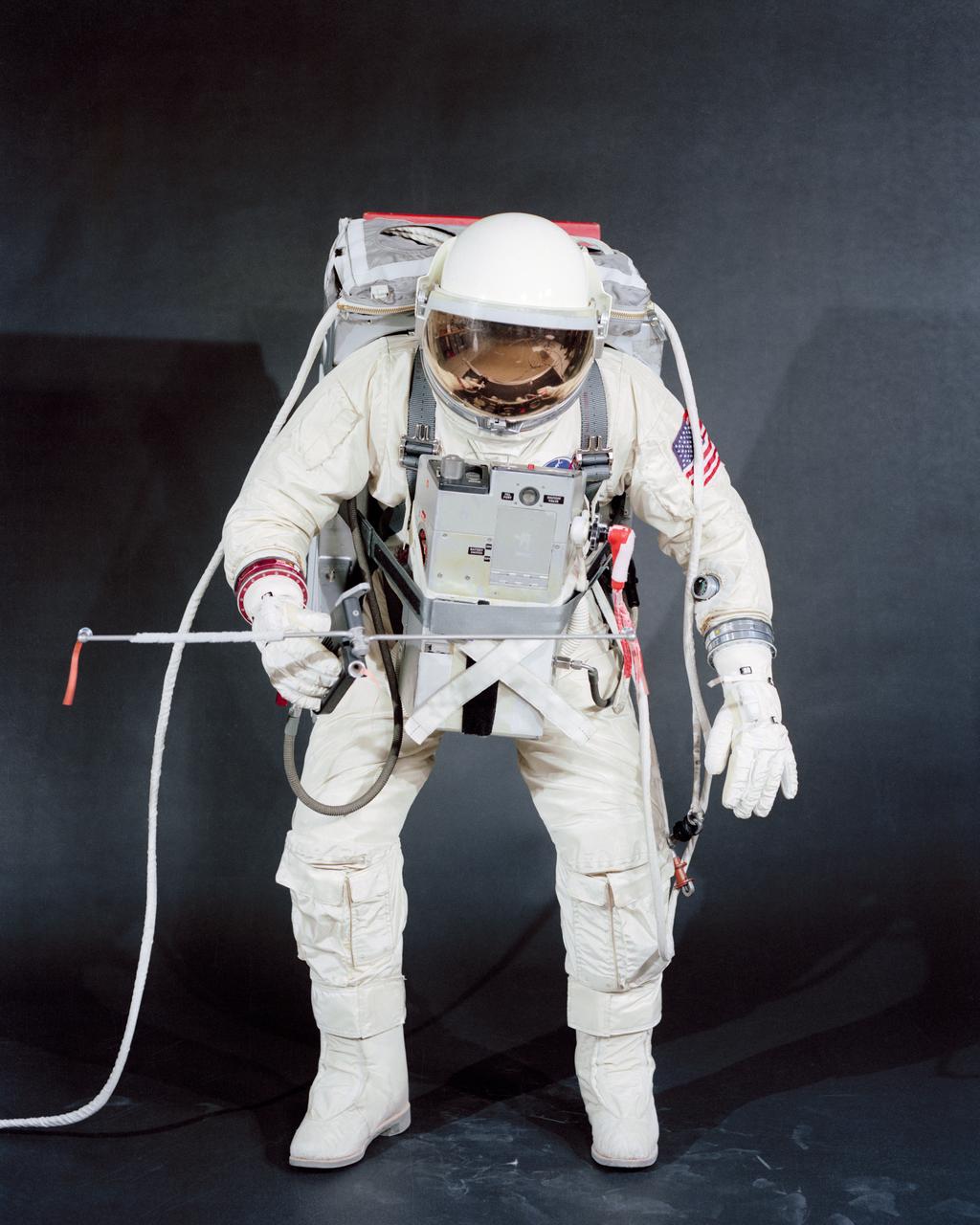

S66-17480 (18 Jan. 1966) --- Test subject Fred Spress, Crew Systems Division, wears the spacesuit and extravehicular equipment planned for use by astronaut David R. Scott. The helmet is equipped with a gold-plated visor to shield the astronaut's face from unfiltered sun rays. The system is composed of a life support pack worn on the chest and a support pack worn on the back. Photo credit: NASA
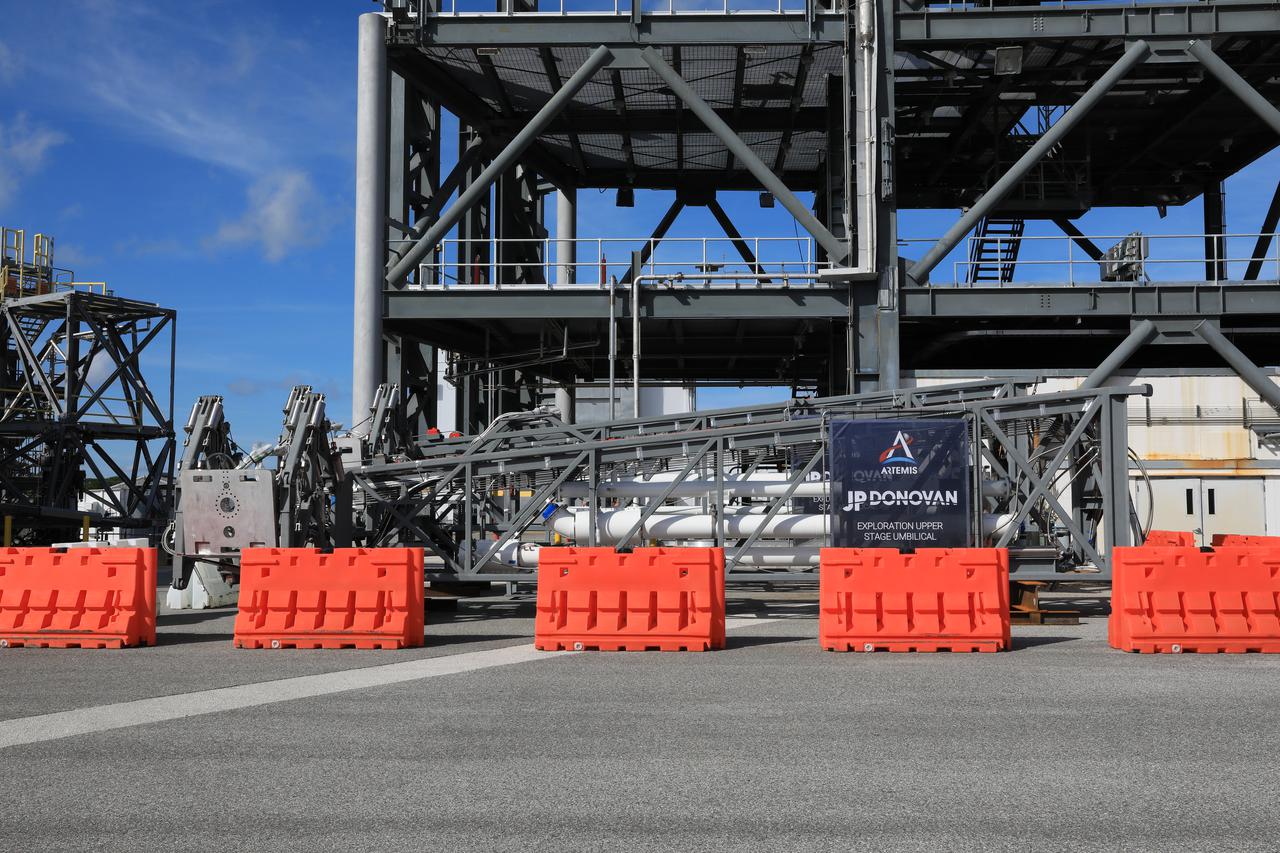

The first umbilical – one of many swing arms that will provide power, communications, and propellants to a larger configuration of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket – for the agency’s mobile launcher 2 (ML2) arrives at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2021. The umbilical will go through rounds of testing at the LETF to verify it functions properly before getting installed on the ML2 tower. This particular umbilical will provide propellants, environmental control systems, and a variety of purge gasses to the rocket’s Exploration Upper Stage. ML2 will be used to launch SLS Block 1B and Block 2 configurations to the Moon, starting with the Artemis IV mission, allowing NASA to send astronauts and heavy cargo to the lunar surface.
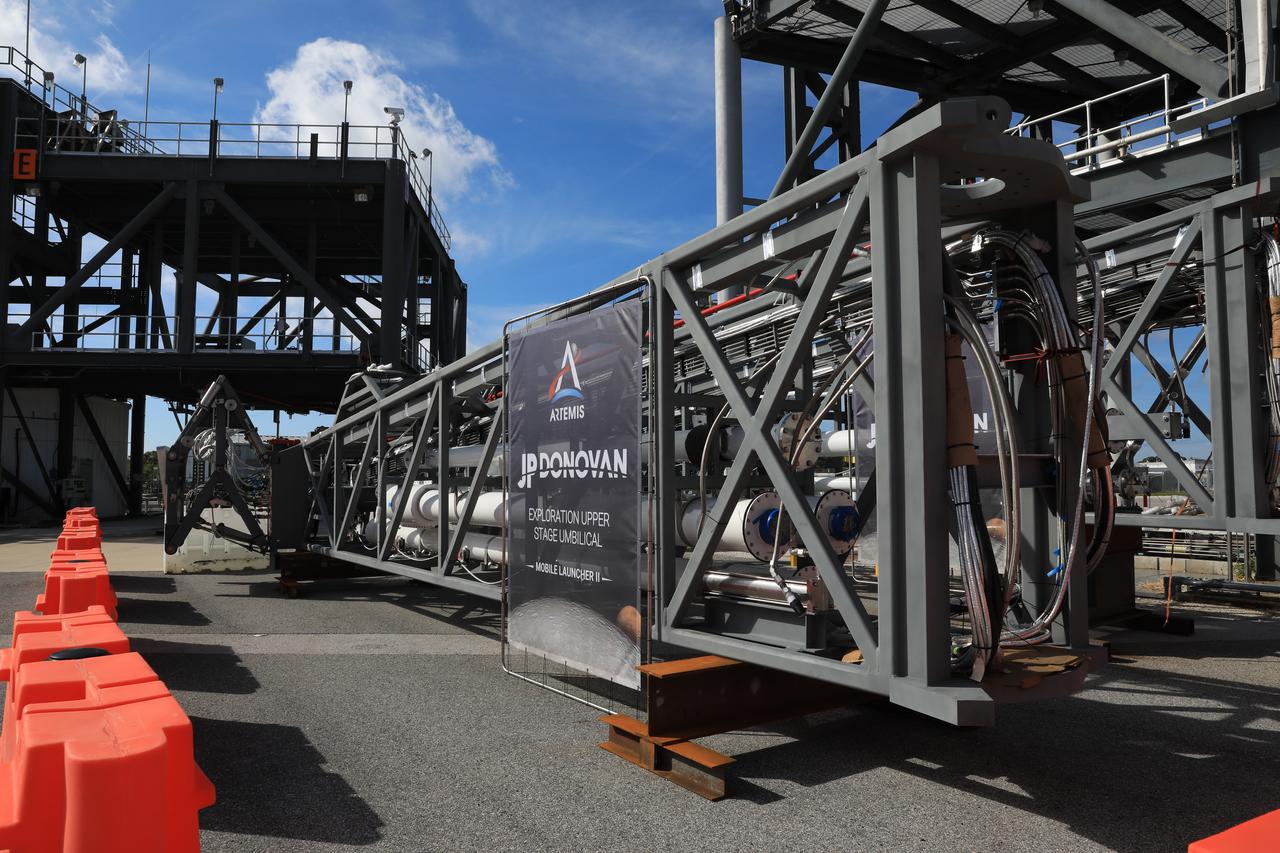

The first umbilical – one of many swing arms that will provide power, communications, and propellants to a larger configuration of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket – for the agency’s mobile launcher 2 (ML2) arrives at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2021. The umbilical will go through rounds of testing at the LETF to verify it functions properly before getting installed on the ML2 tower. This particular umbilical will provide propellants, environmental control systems, and a variety of purge gasses to the rocket’s Exploration Upper Stage. ML2 will be used to launch SLS Block 1B and Block 2 configurations to the Moon, starting with the Artemis IV mission, allowing NASA to send astronauts and heavy cargo to the lunar surface.
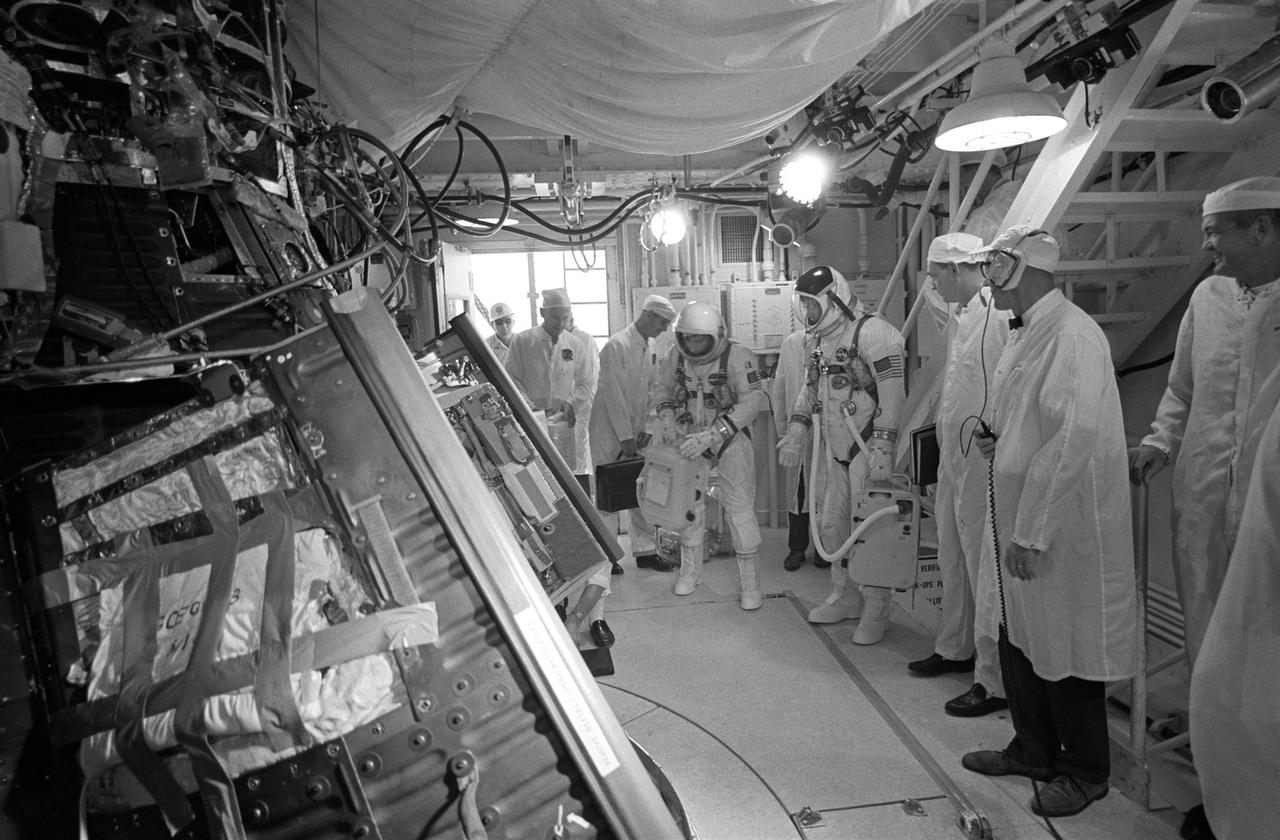

S66-42702 (12 July 1966) --- Gemini-10 prime crew, astronauts John W. Young (left), command pilot, and Michael Collins (right), pilot, check equipment in the White Room atop Pad 19 where they participated in a Simultaneous Launch Demonstration. Photo credit: NASA

NASA's Pegasus barge arrived at Stennis Space Center on Nov. 16, delivering space shuttle main engine ground support equipment to the south Mississippi facility. Stennis tested every main engine used on all 135 space shuttle flights.
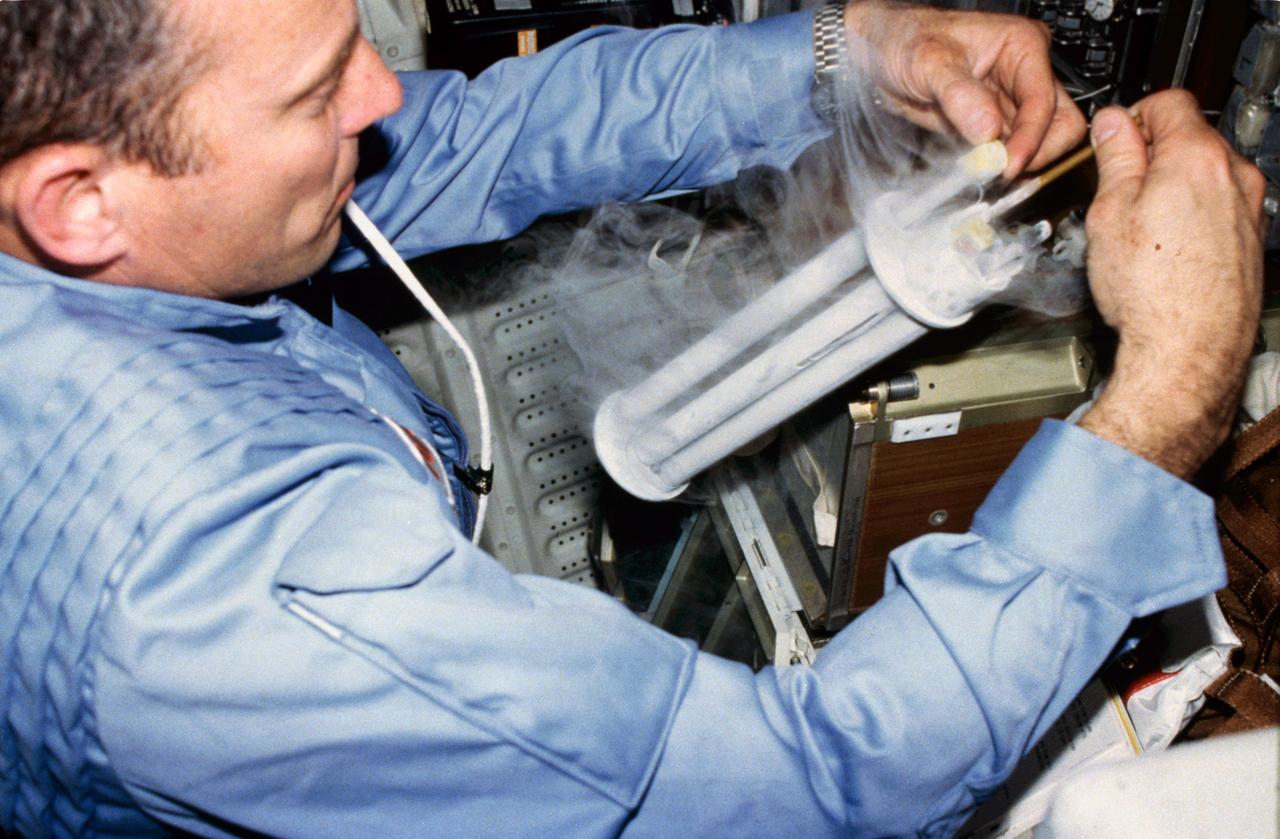

Commander Jack Lousma works with Electrophoresis Equipment Verification Test (EEVT) electrophoresis unit, cryogenic freezer and tube, and stowage locker equipment located on crew compartment middeck aft bulkhead.
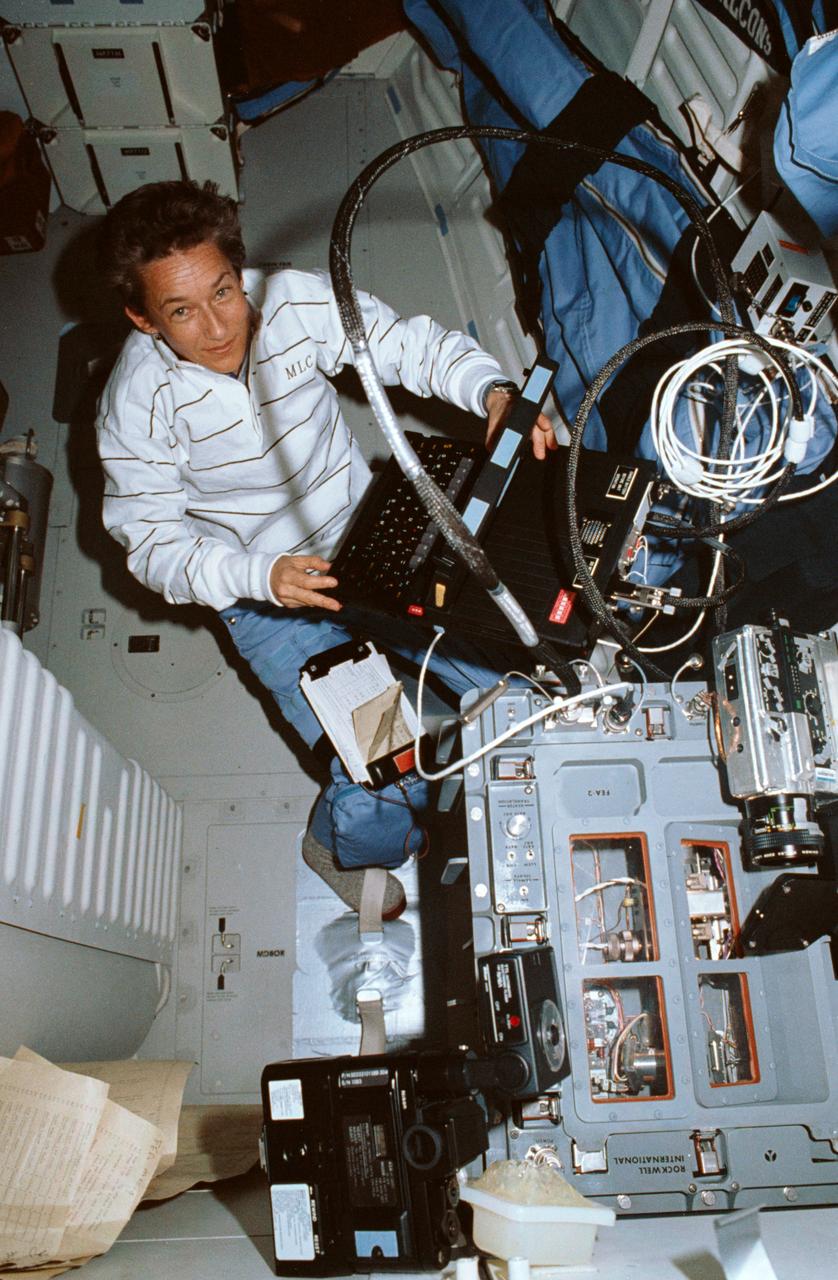

STS030-02-018 (4-8 May 1989) --- A 35mm overall scene of the operations devoted to the fluids experiment apparatus (FEA) aboard Atlantis for NASA’s STS-30 mission. Astronaut Mary L. Cleave, mission specialist, is seen with the computer which is instrumental in the carrying out of a variety of materials science experiments. Rockwell International is engaged in a joint endeavor agreement with NASA’s Office of Commercial Programs in the field of floating zone crystal growth and purification research. The March 1987 agreement provides for microgravity experiments to be performed in the company’s Microgravity Laboratory, the FEA. An 8 mm camcorder which documented details inside the apparatus is visible at bottom of the frame.
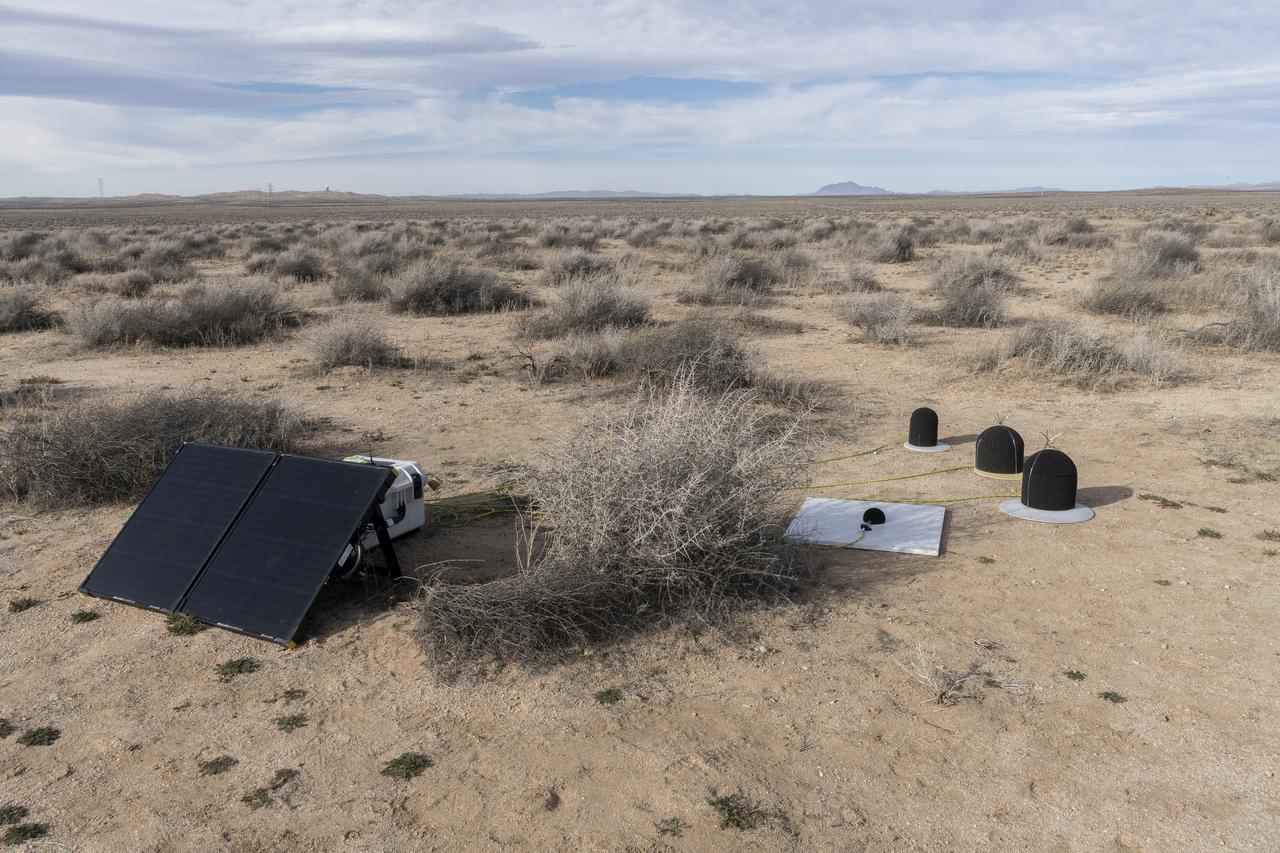

The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. Shown is one of 10 ground recording stations set up along a 30-mile stretch of desert to record sonic booms during the third phase of the of CarpetDIEM, Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights. An F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center created sonic booms, both loud and soft, to verify the operations of ground recording systems.
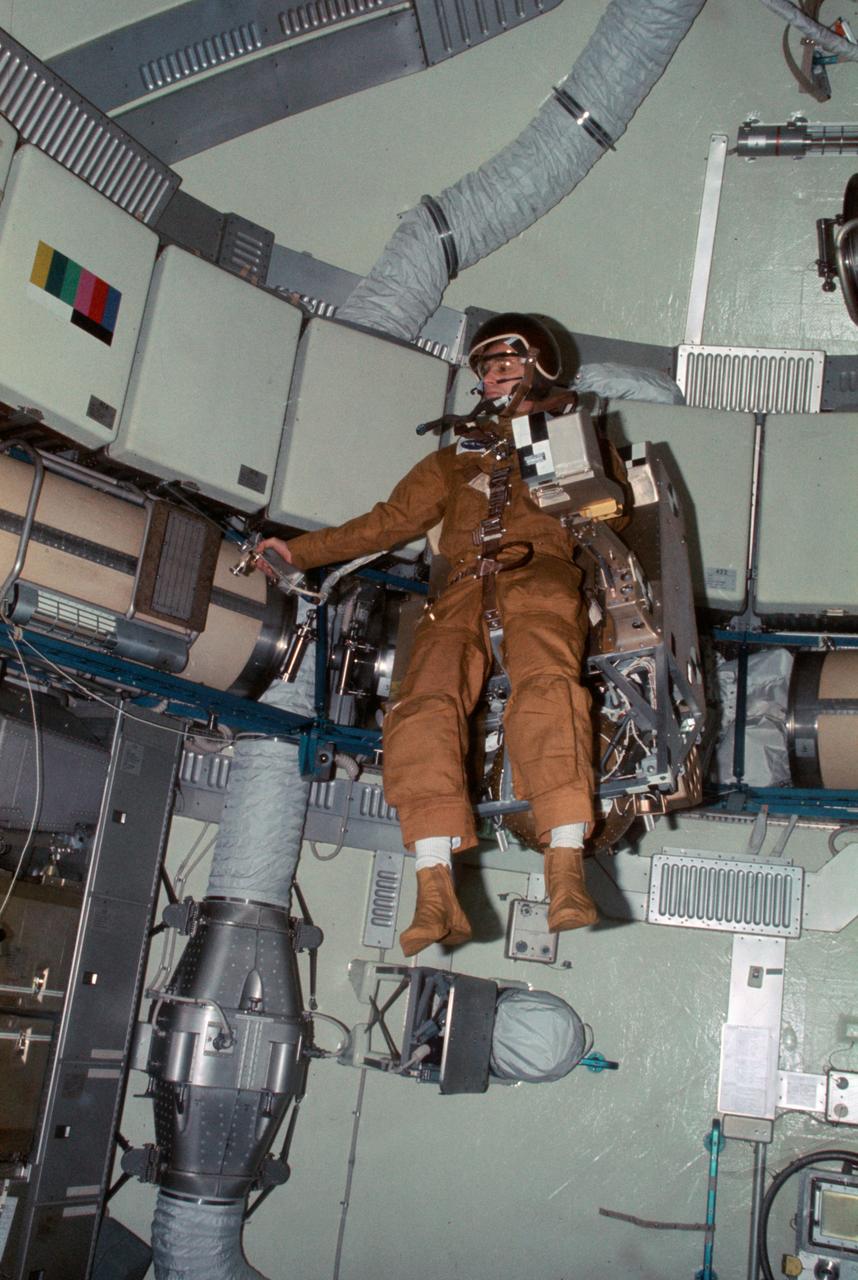

SL3-107-1215 (27 Aug. 1973) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, Skylab 3 commander, flies the M509 Astronaut Maneuvering Equipment in the forward dome area of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) on the space station cluster in Earth orbit. One of his fellow crewmen took this photograph with a 35mm Nikon camera. Bean is strapped into the back mounted, hand-controlled Automatically Stabilized Maneuvering Unit (ASMU). The dome area is about 22 feet in diameter and 19 feet from top to bottom. Photo credit: NASA
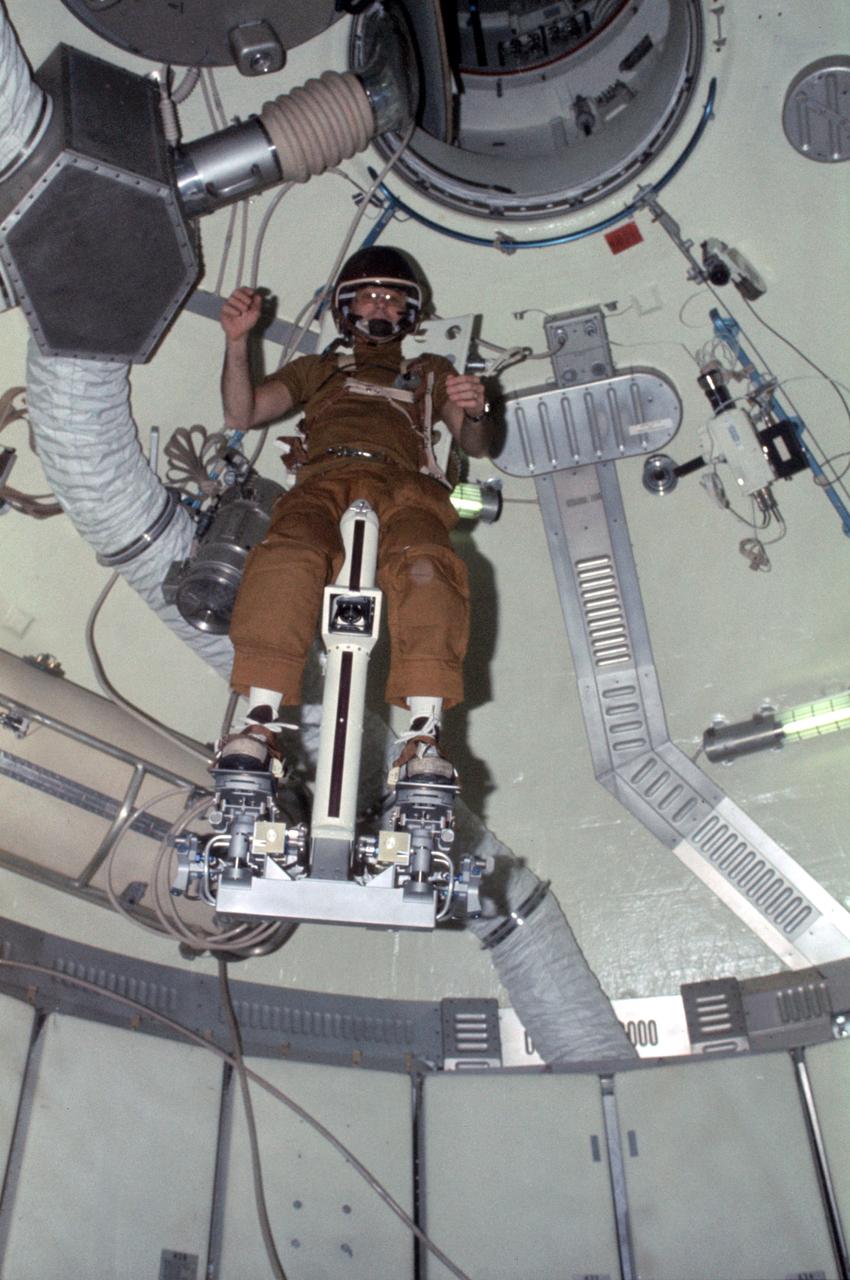

SL3-108-1304 (July-September 1973) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, Skylab 3 commander, flies the M509 Astronaut Maneuvering Equipment in the forward dome area of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) on the space station cluster in Earth orbit. Bean is strapped in to the back-mounted, hand-controlled Automatically Stabilized Maneuvering Unit (ASMU). This ASMU experiment is being done in shirt sleeves. The dome area where the experiment is conducted is about 22 feet in diameter and 19 feet from top to bottom. Photo credit: NASA
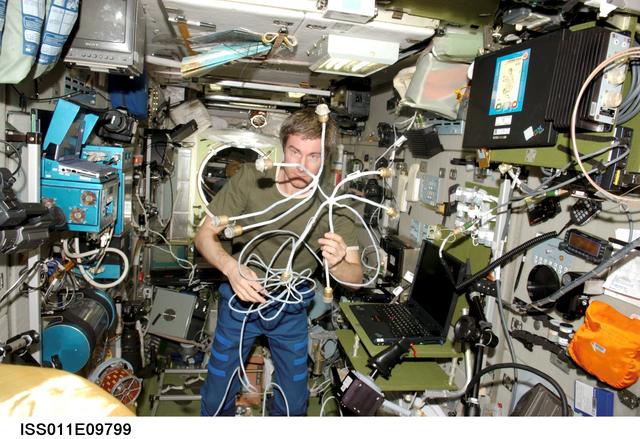

ISS011-E-09799 (27 June 2005) --- Cosmonaut Sergei K. Krikalev, Expedition 11 commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, works with the new Proximity Communications Equipment (PCE) hardware of the ASN-M satellite navigation system for the European Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) “Jules Verne” in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station. The ATV is scheduled to arrive at the Station next year.
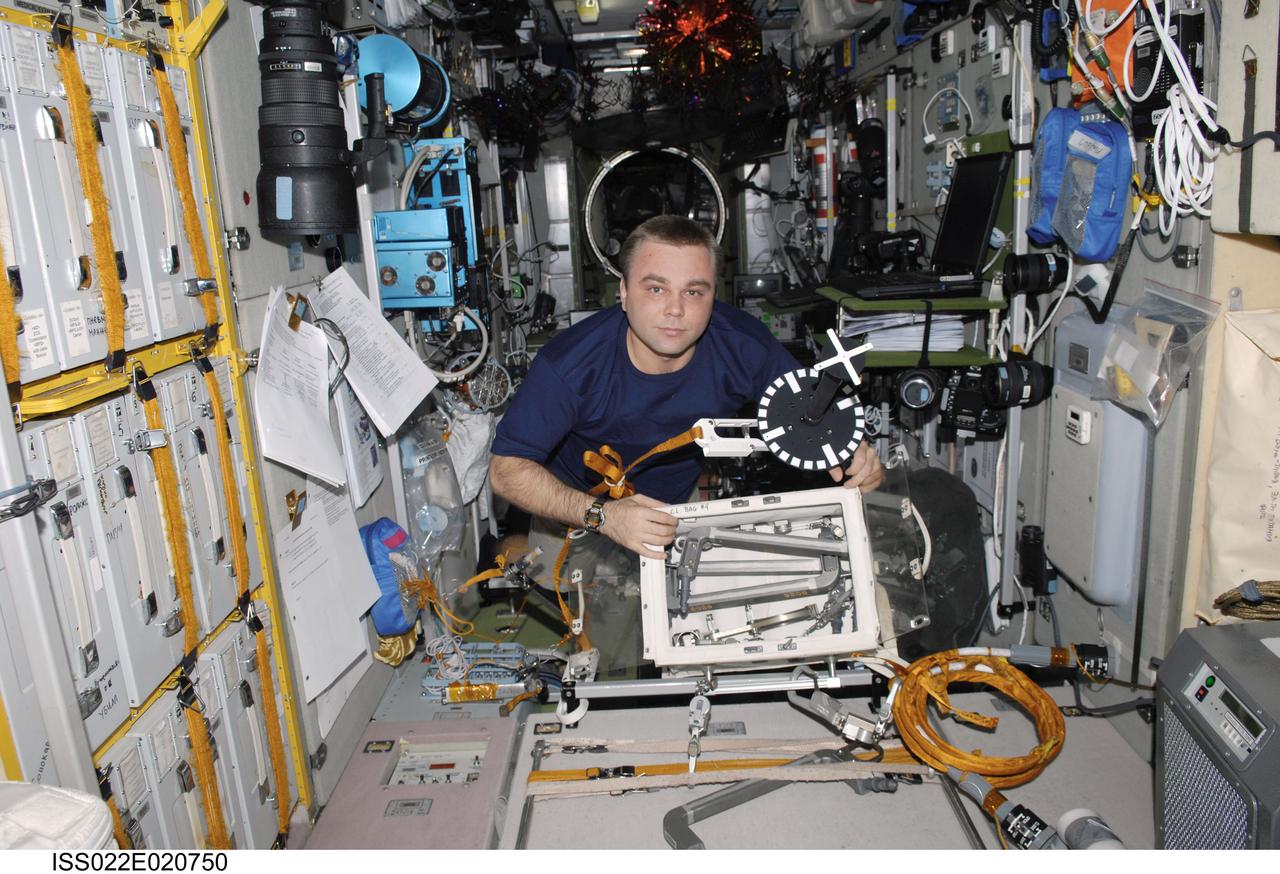

ISS022-E-020750 (6 Jan. 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Maxim Suraev, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with extravehicular activity (EVA) equipment in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
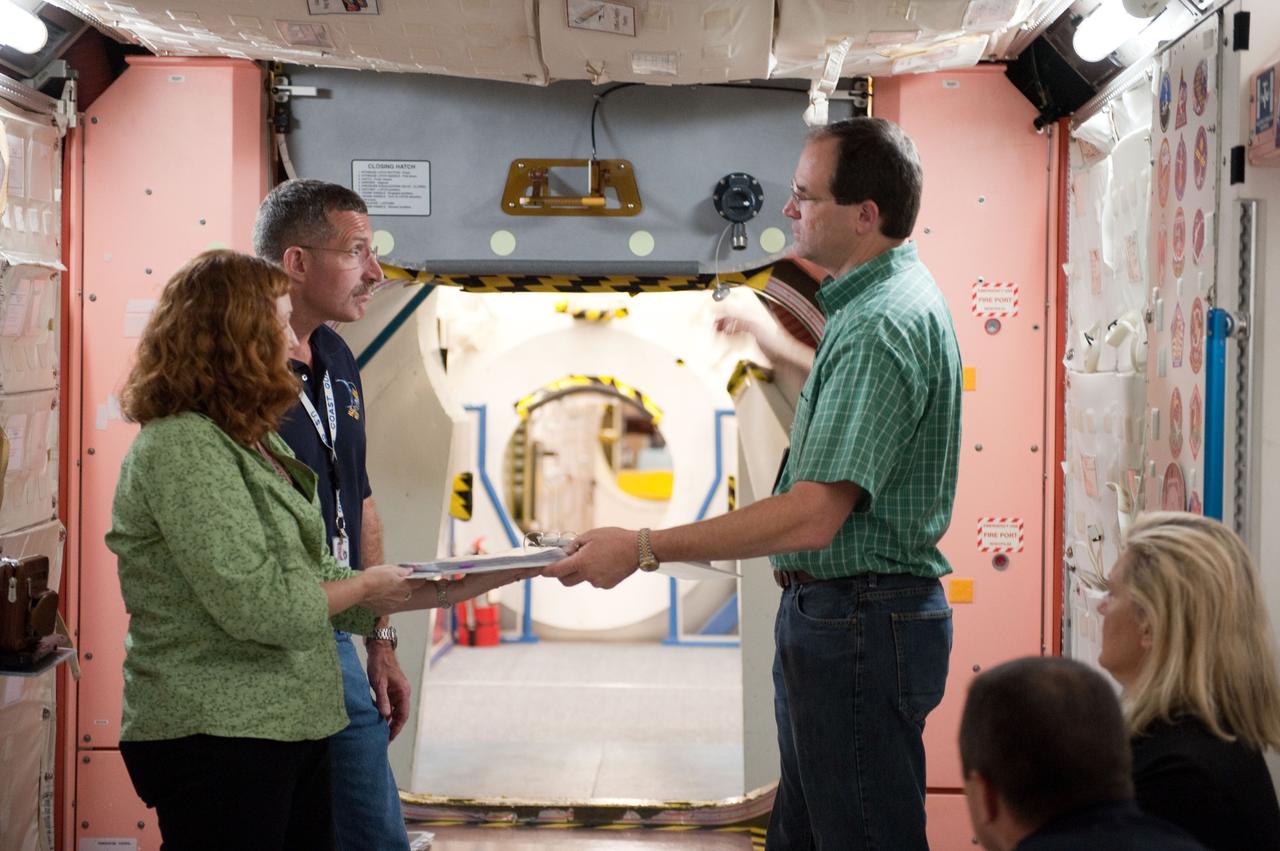

Expedition 29/30 ISS Habitability Equipment and Procedures training in ISS mockups. Photo Date: May 17, 2011. Location: Bldg. 9NW - ISS Mockups. Photographer: Robert Markowitz.