
This composite image shows the weather situation over Europe at 12:00 UTC on 13 February 2014. The image is composed of infra-red imagery from the geostationary satellites of EUMETSAT and NOAA, overlaid on NASA's Blue Marble land imagery. Copyright: 2014 EUMETSAT, <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/eumetsat/12500210655">www.flickr.com/photos/eumetsat/12500210655</a>
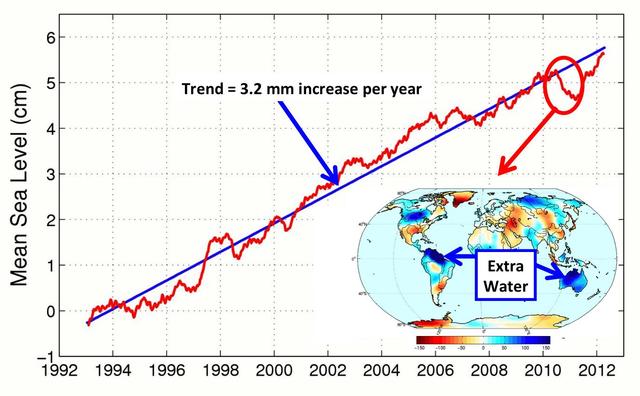
This figure shows changes in global mean sea level as measured by satellite altimetry NASA/CNES Topex/Poseidon and Jason-1; and NASA/CNES/NOAA/EUMETSAT Jason-2 between 1992 to 2012.

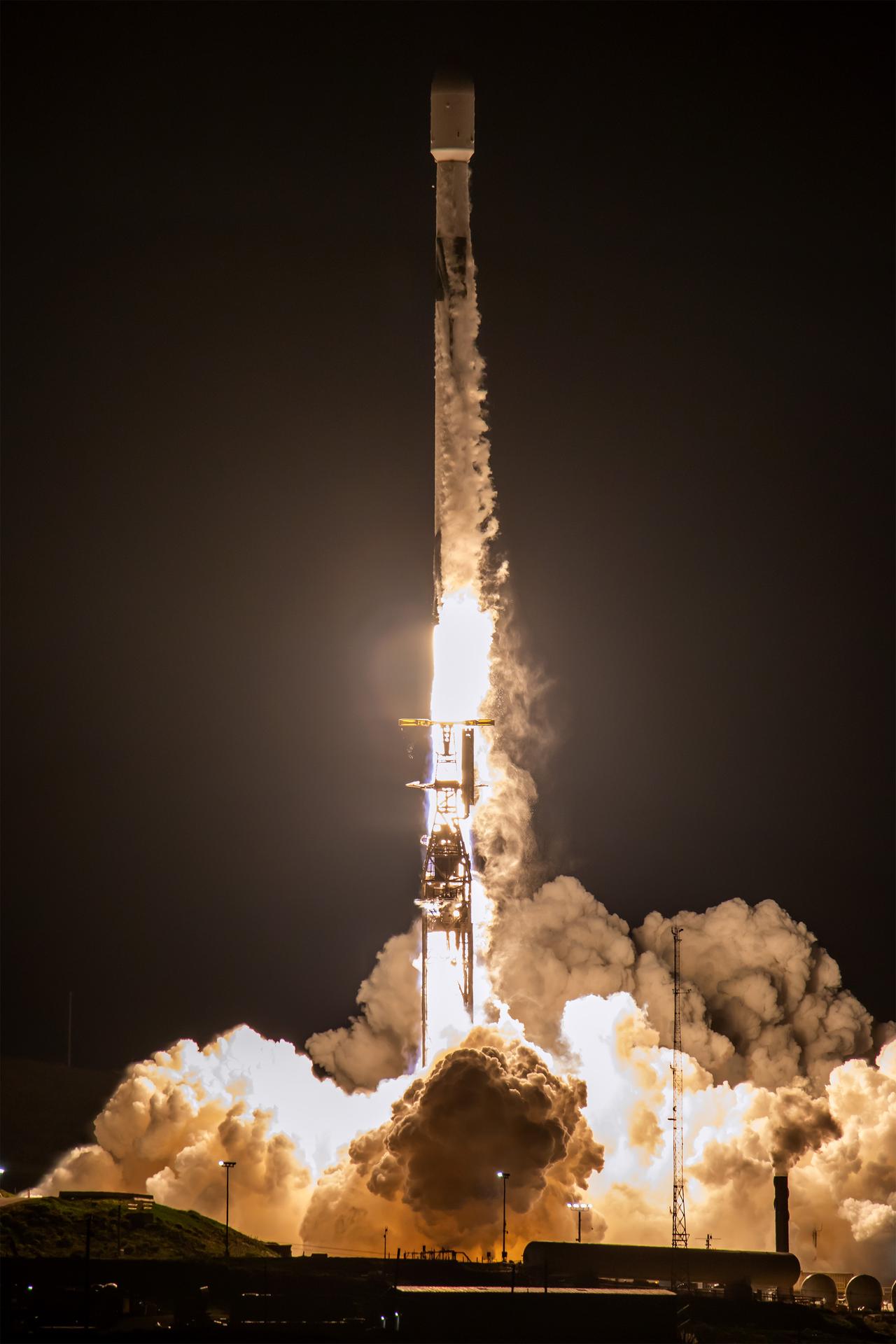
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
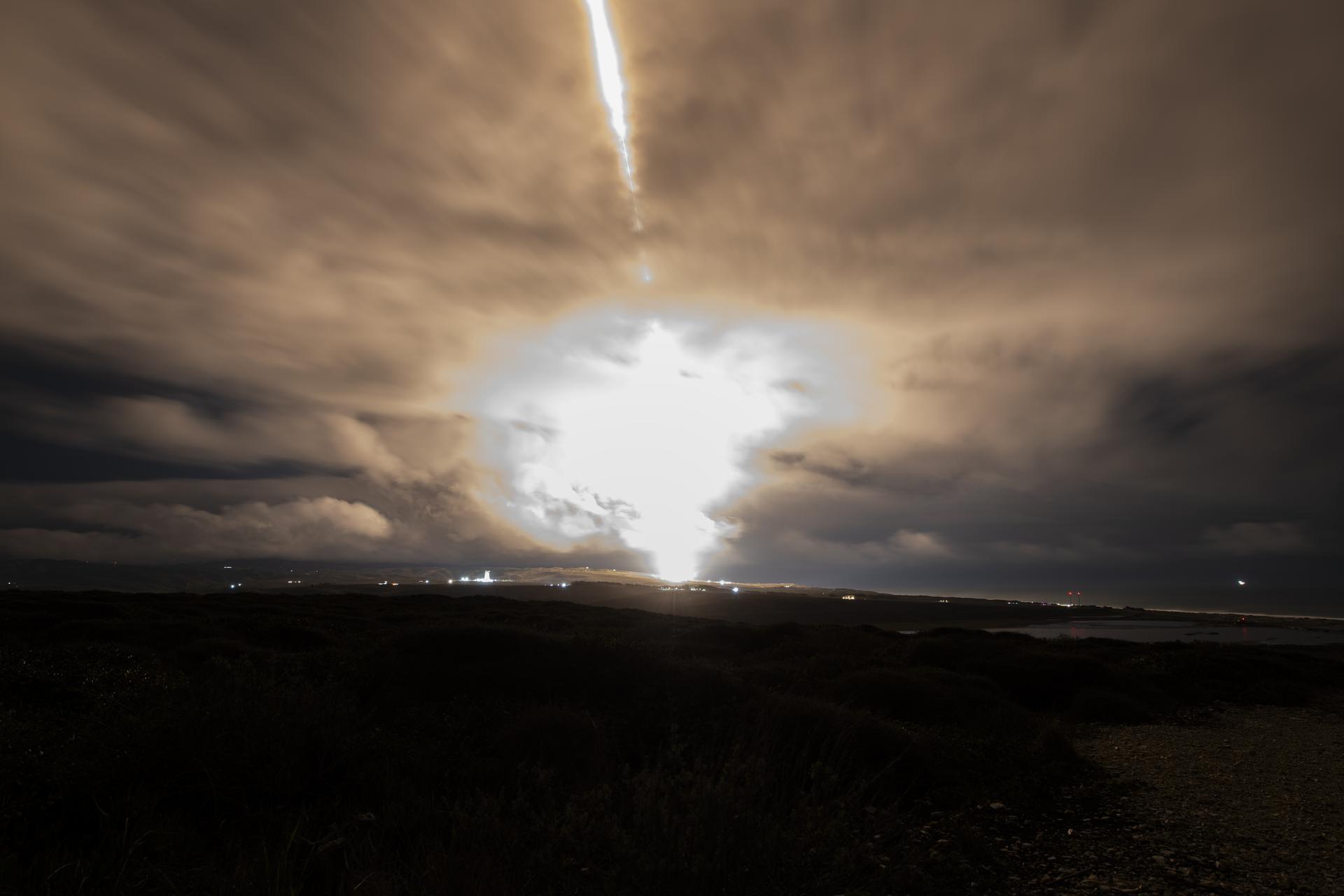

A long exposure photo shows the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the internation Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifting off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
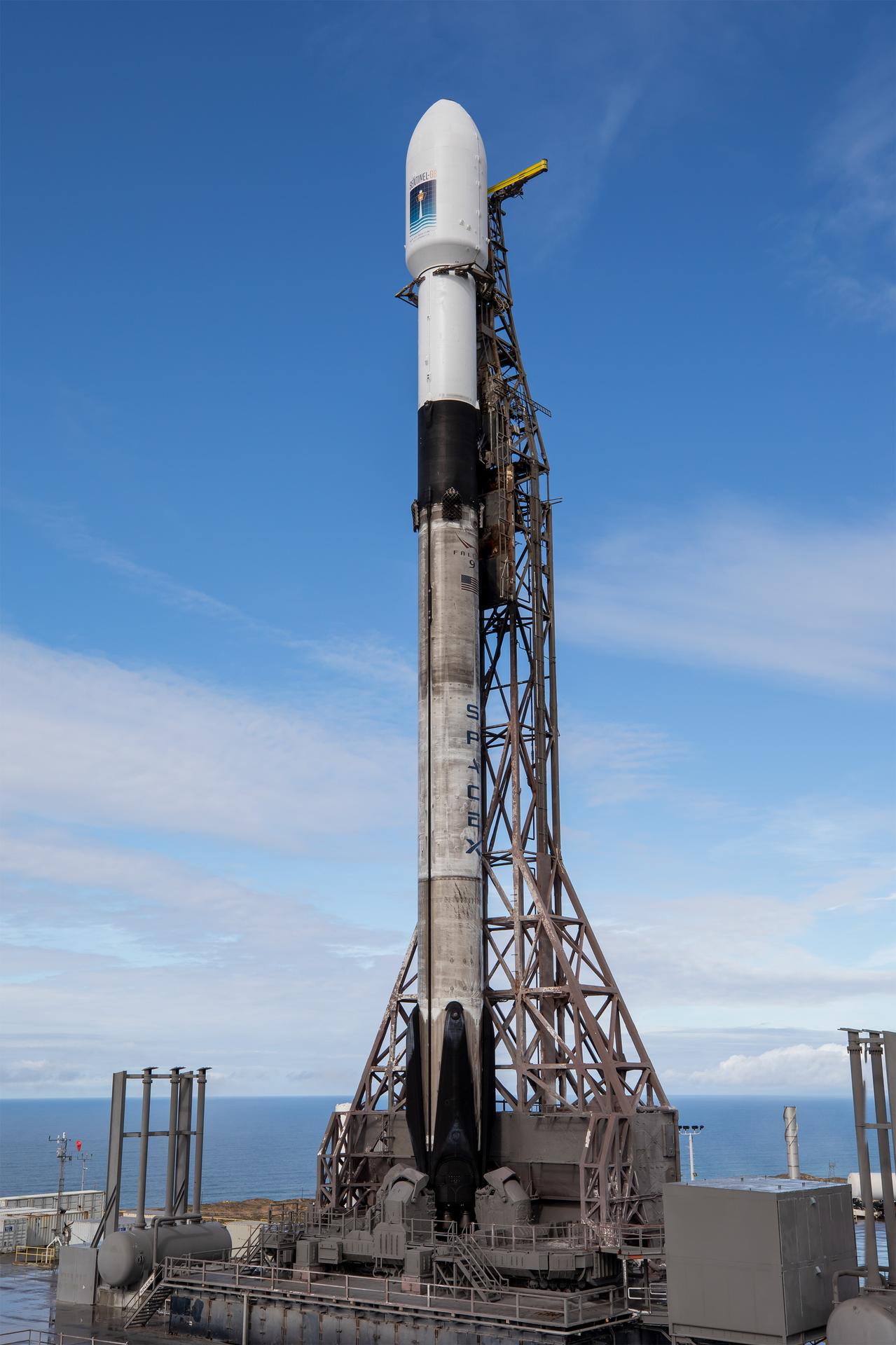

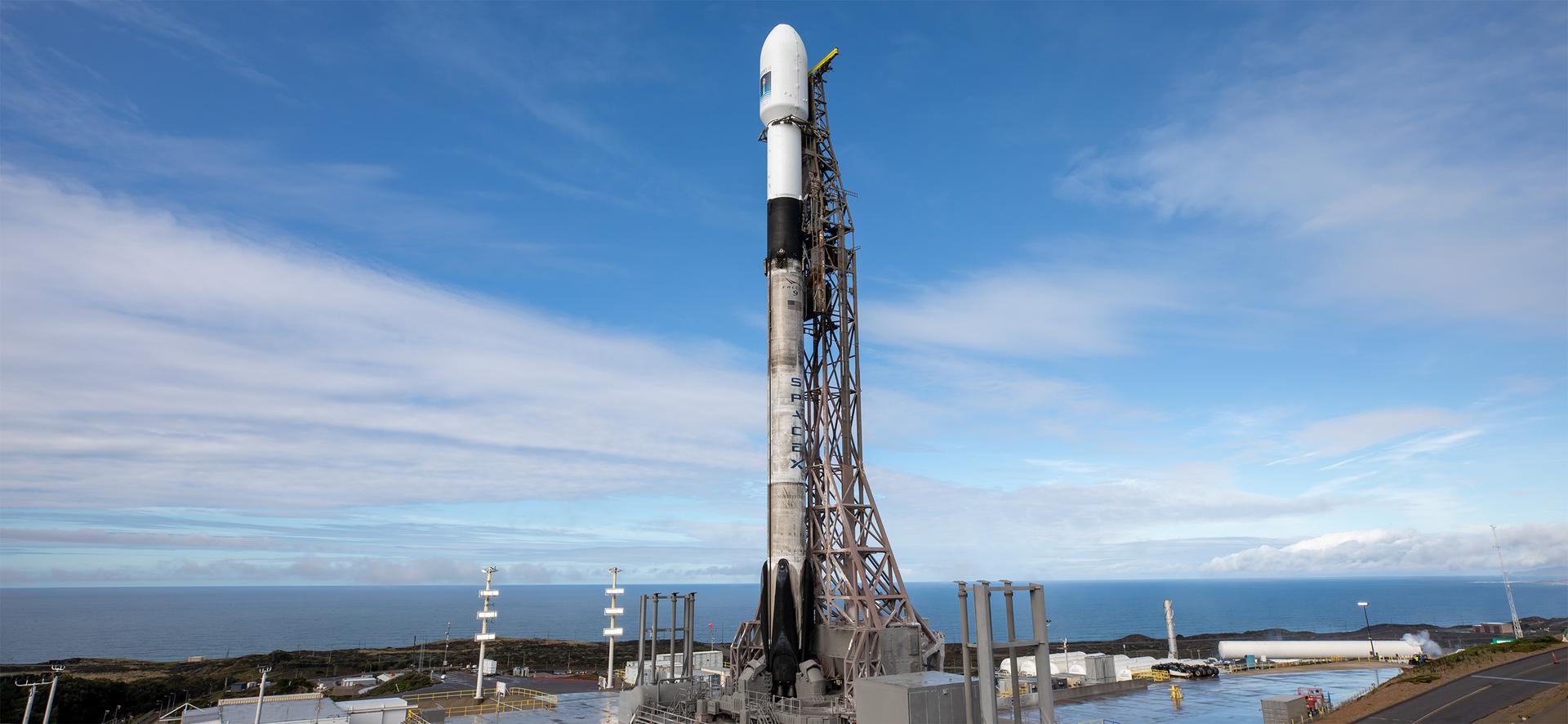
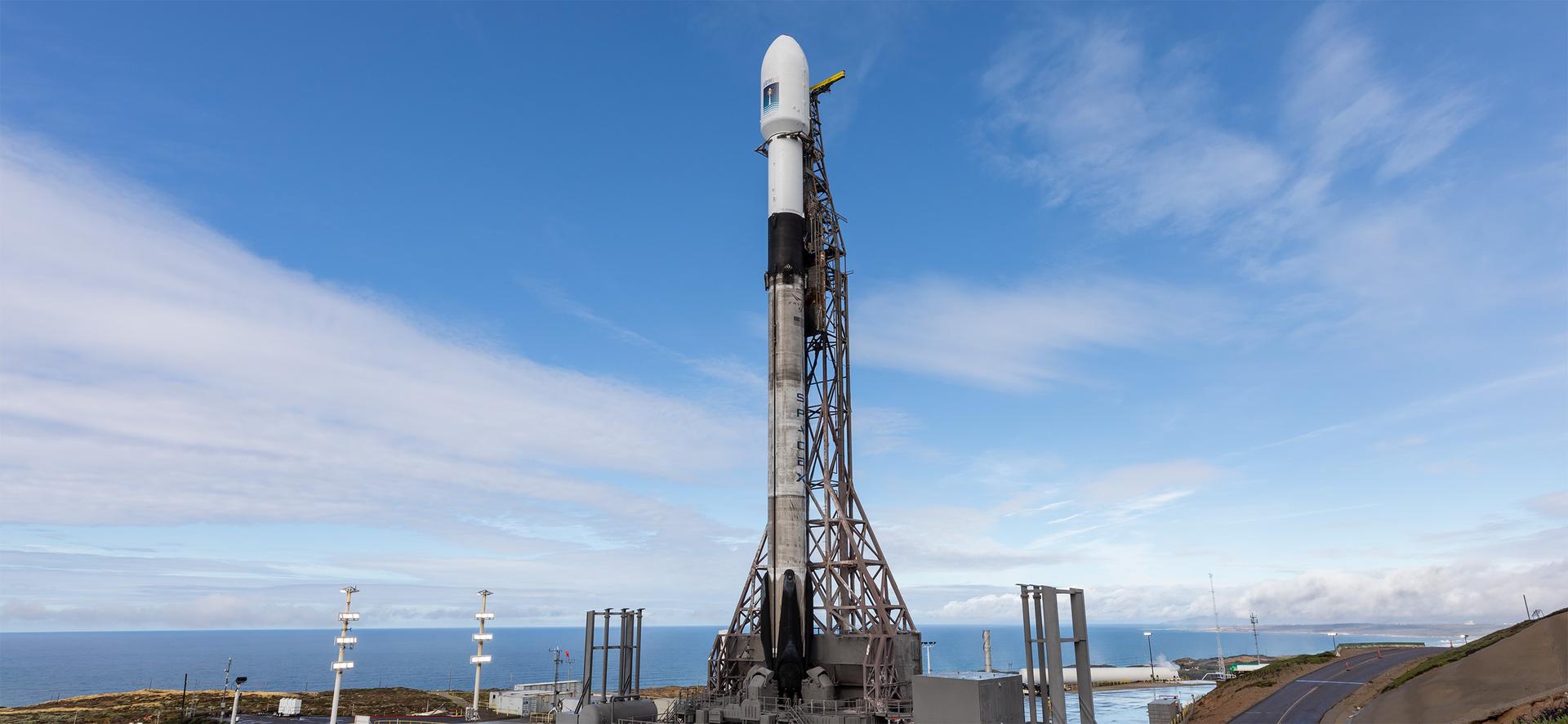
A SpaceX rocket carrying the Sentinel-6B satellite stands vertical on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, ahead of launch targeted for no earlier than 9:21 p.m. PST. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
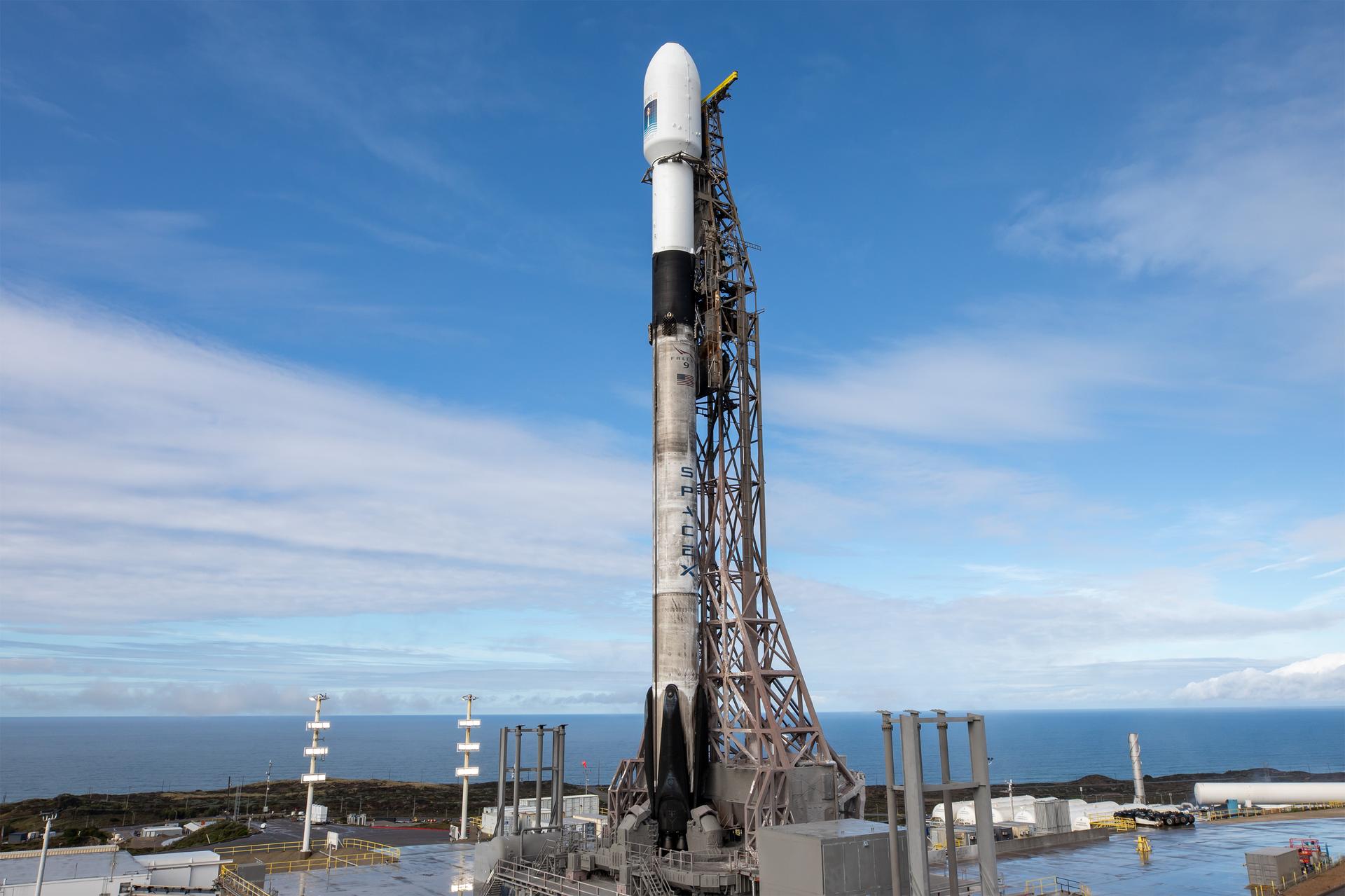

A SpaceX rocket carrying the Sentinel-6B satellite stands vertical on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, ahead of launch targeted for no earlier than 9:21 p.m. PST. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
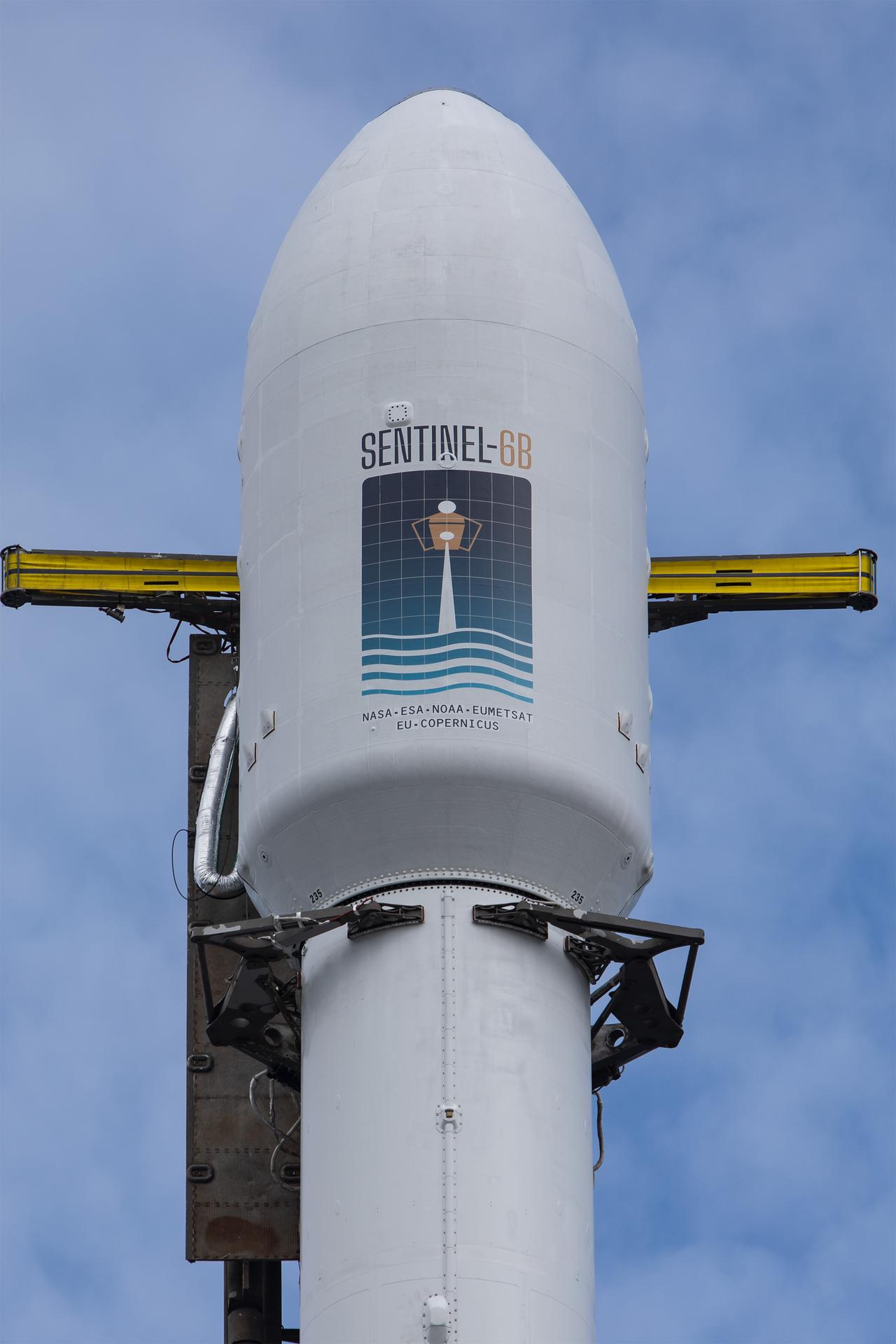

A SpaceX rocket carrying the Sentinel-6B satellite stands vertical on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, ahead of launch targeted for no earlier than 9:21 p.m. PST. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.

A SpaceX rocket carrying the Sentinel-6B satellite stands vertical on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, ahead of launch targeted for no earlier than 9:21 p.m. PST. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.

A SpaceX rocket carrying the Sentinel-6B satellite stands vertical on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, ahead of launch targeted for no earlier than 9:21 p.m. PST. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
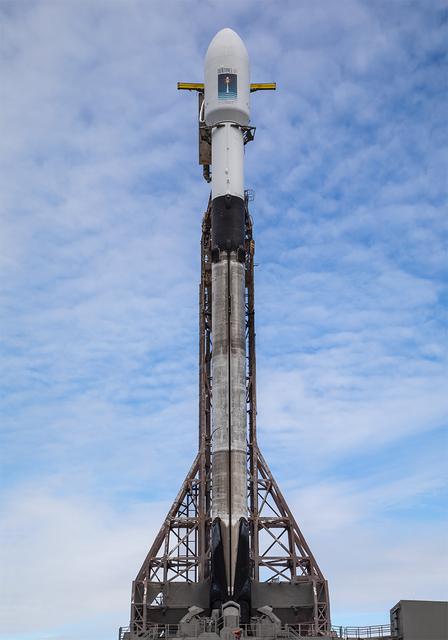

A SpaceX rocket carrying the Sentinel-6B satellite stands vertical on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, ahead of launch targeted for no earlier than 9:21 p.m. PST. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
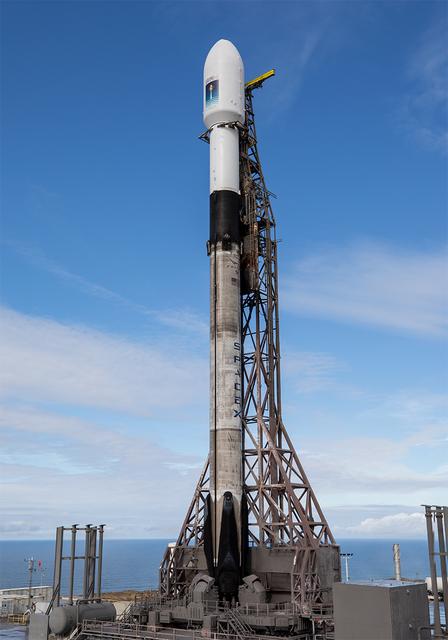

A SpaceX rocket carrying the Sentinel-6B satellite stands vertical on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, ahead of launch targeted for no earlier than 9:21 p.m. PST. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.

A SpaceX rocket carrying the Sentinel-6B satellite stands vertical on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, ahead of launch targeted for no earlier than 9:21 p.m. PST. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
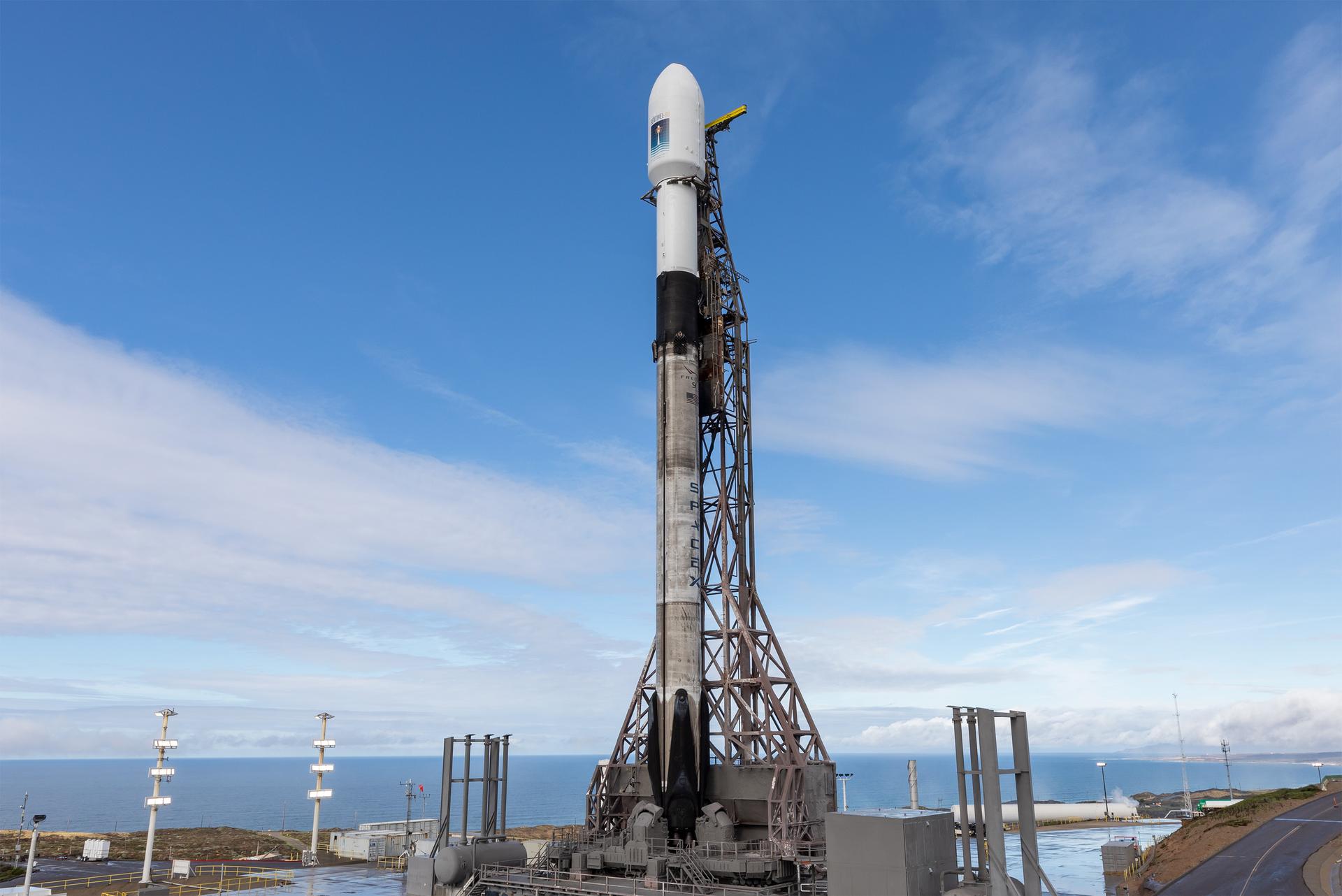

A SpaceX rocket carrying the Sentinel-6B satellite stands vertical on the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, ahead of launch targeted for no earlier than 9:21 p.m. PST. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.

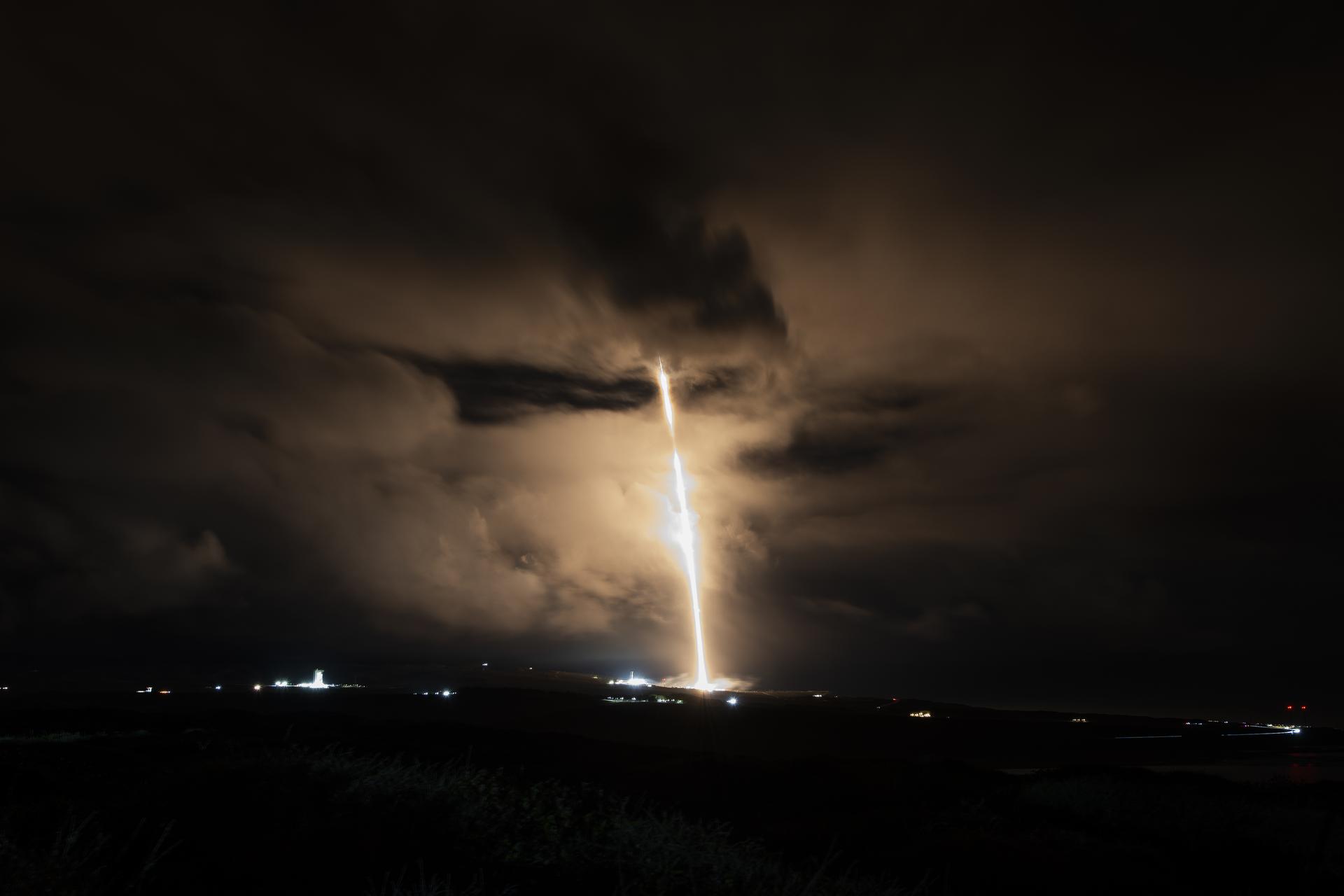
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
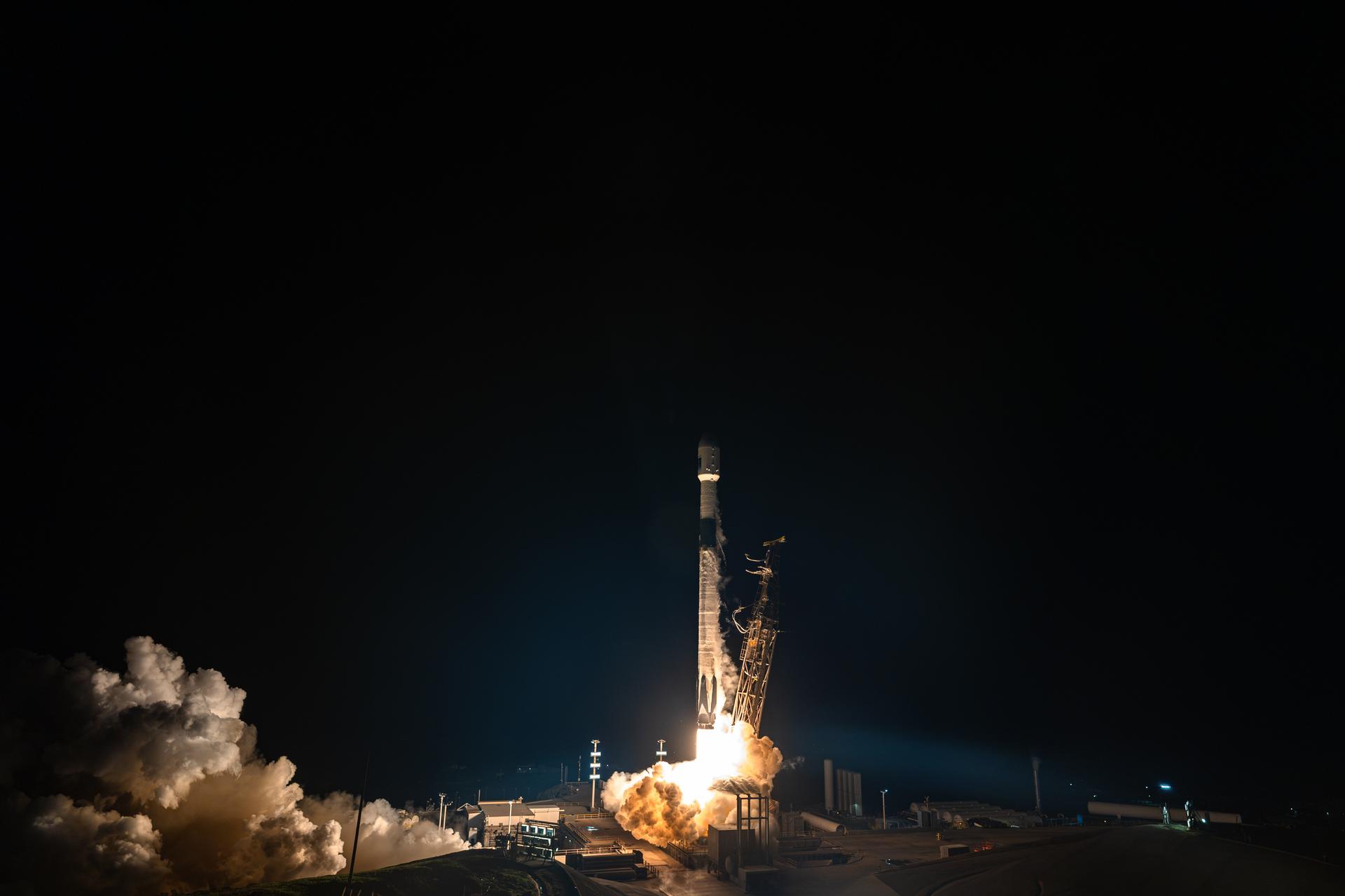

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
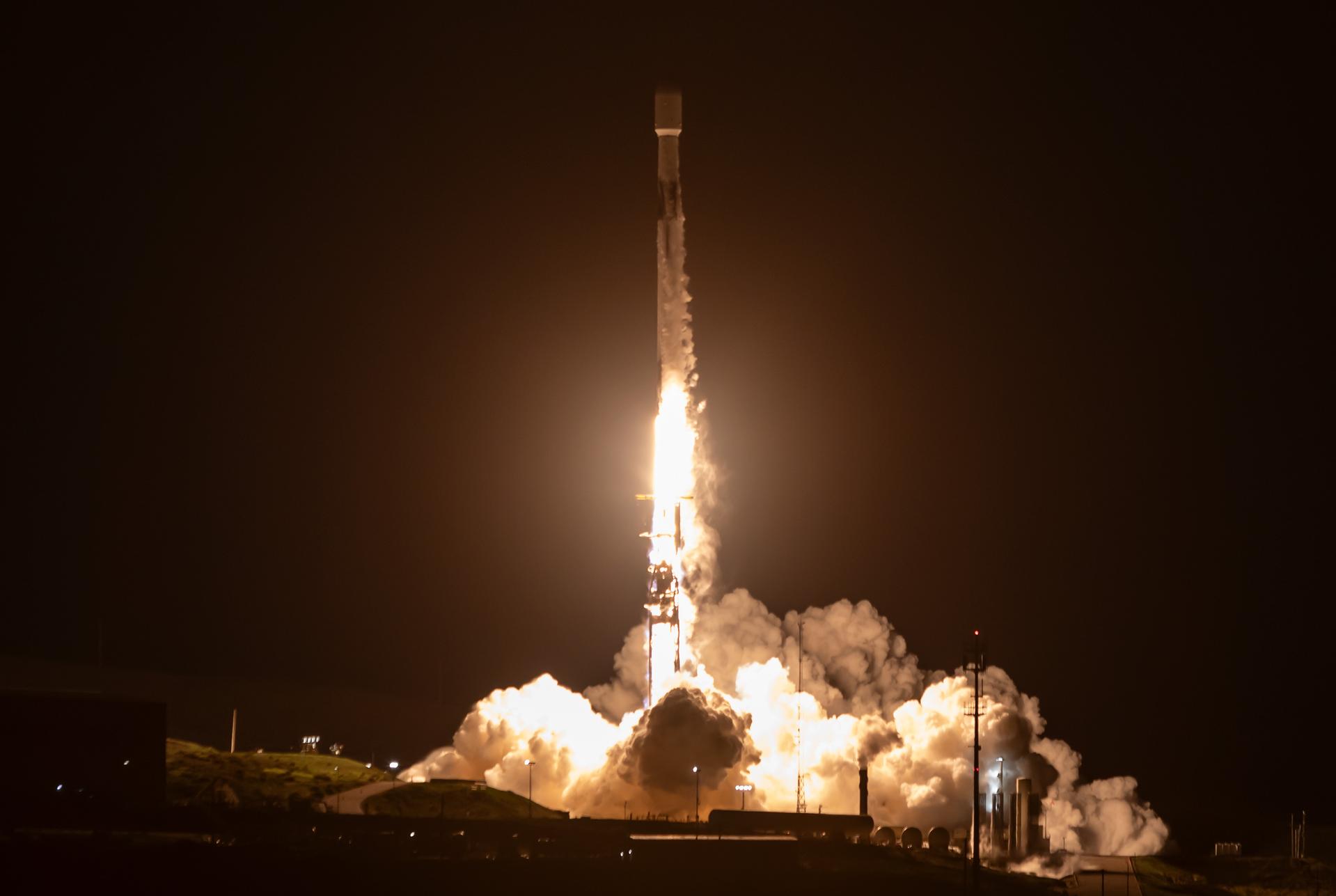

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
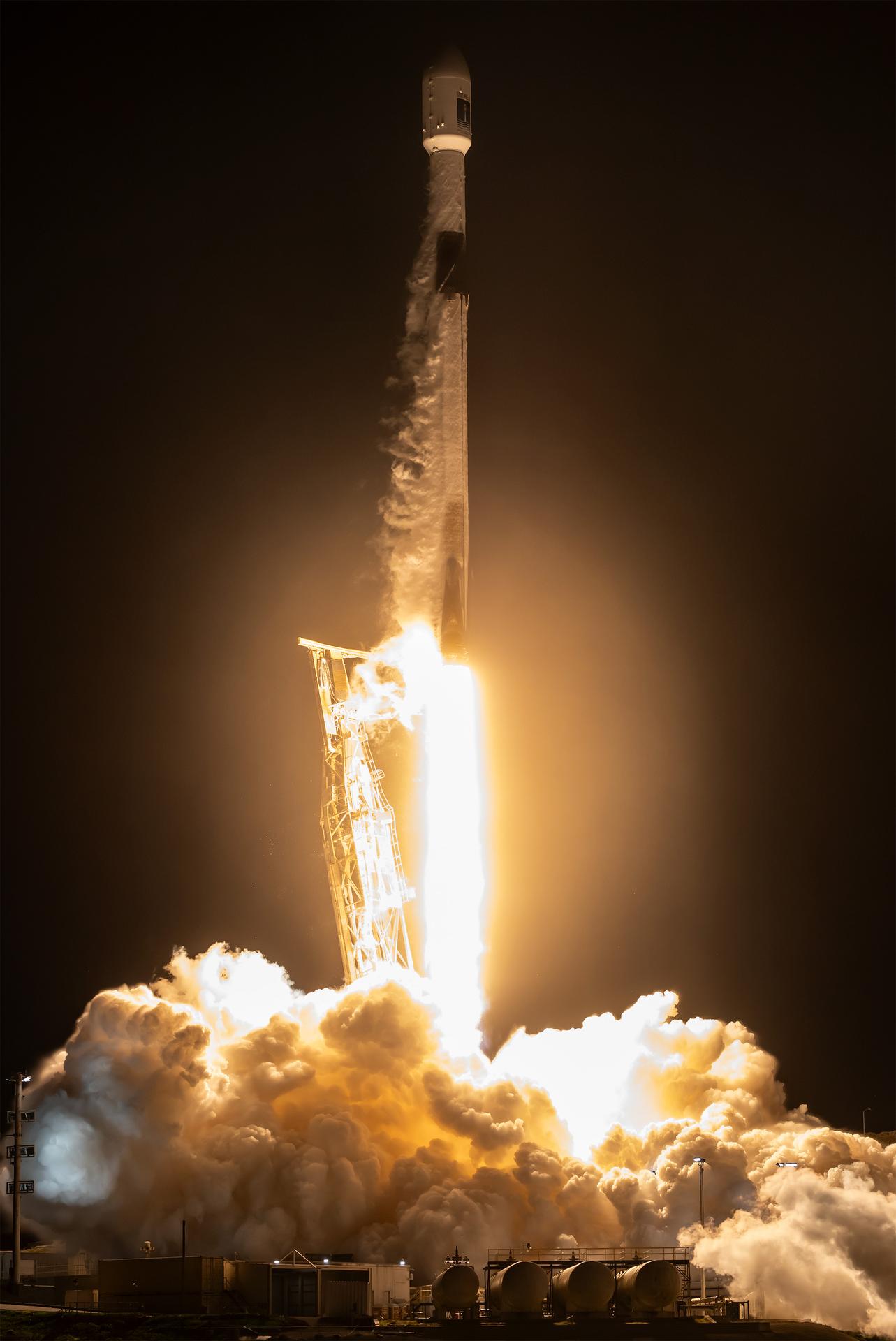

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
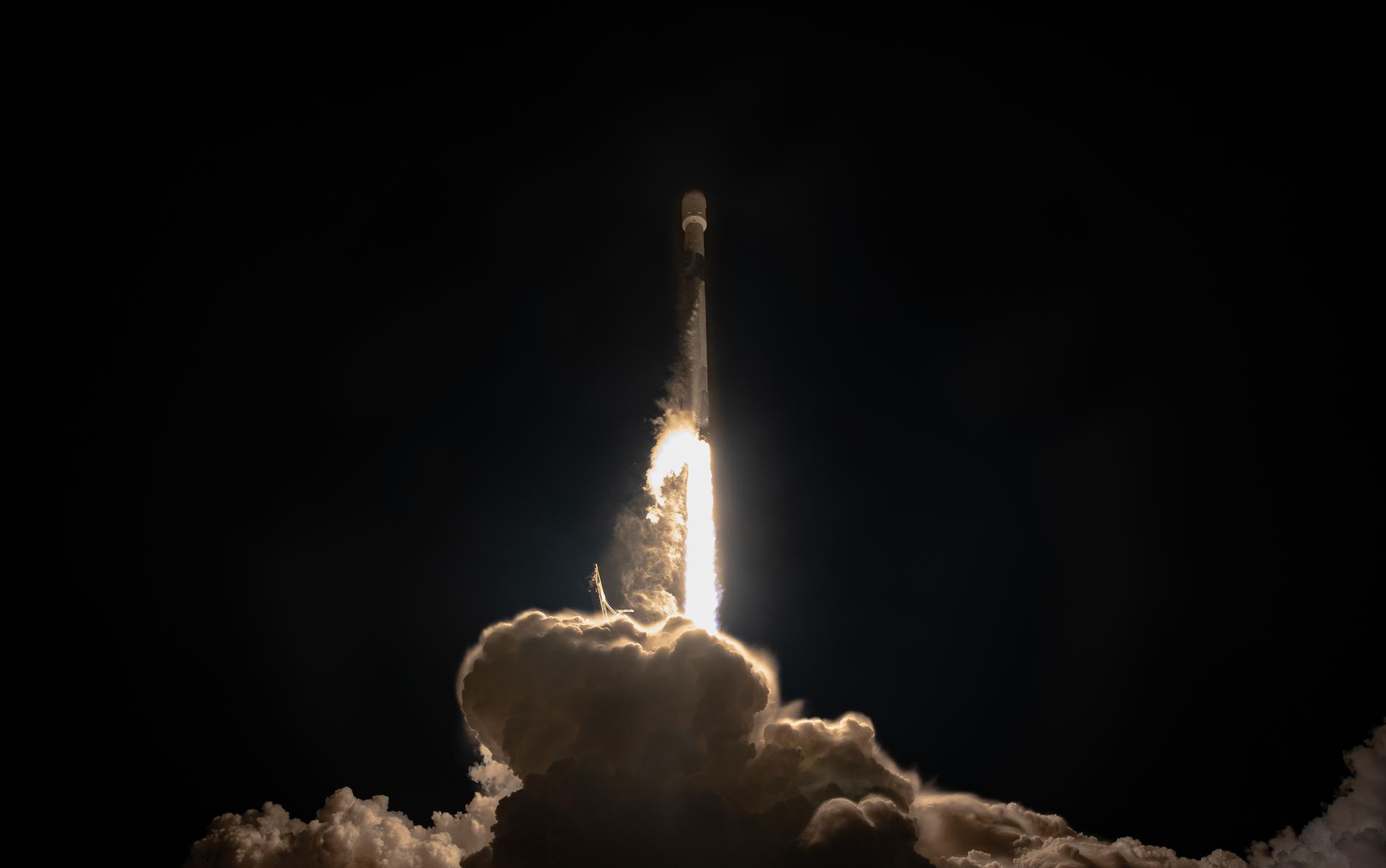

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
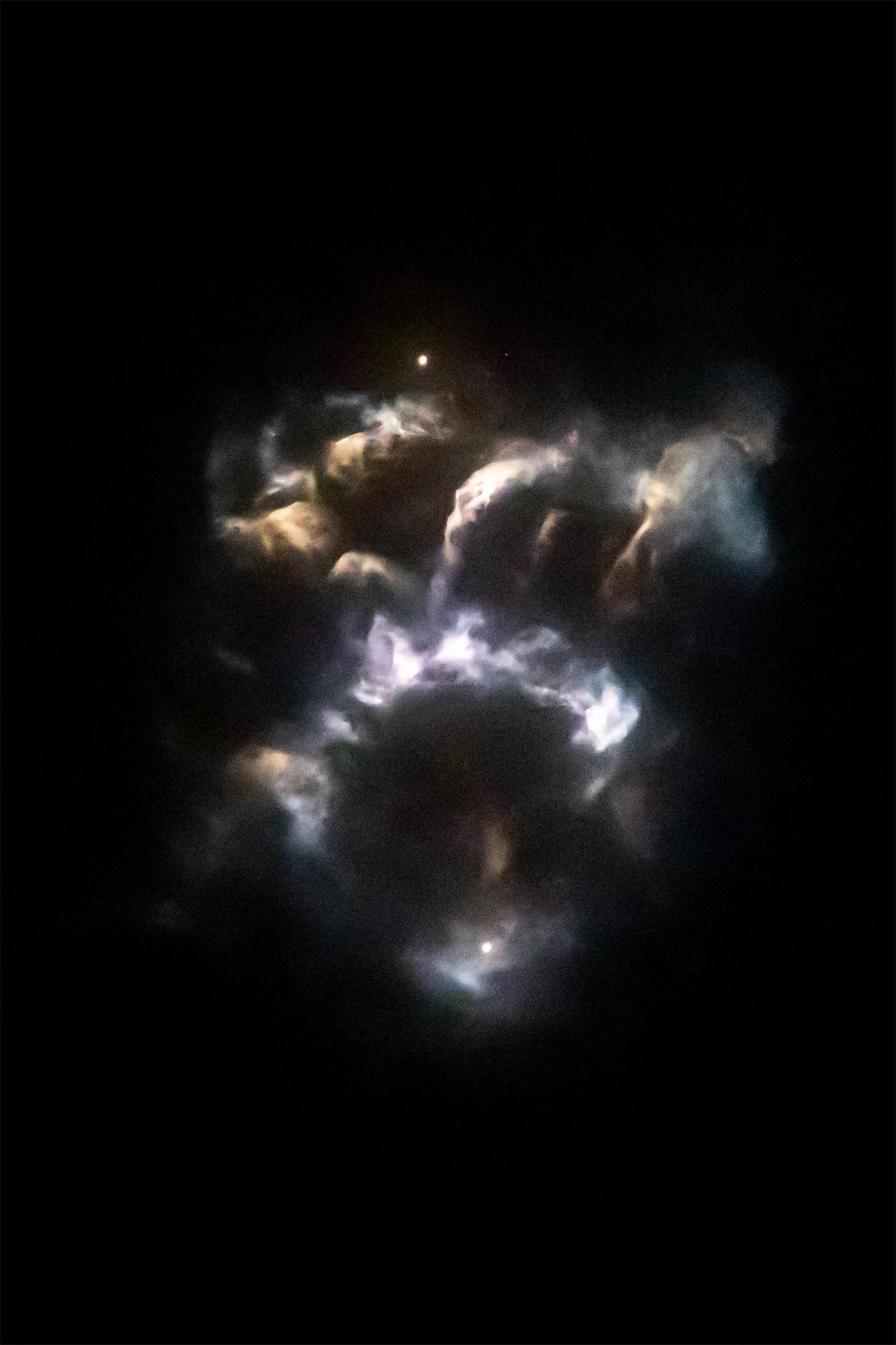
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
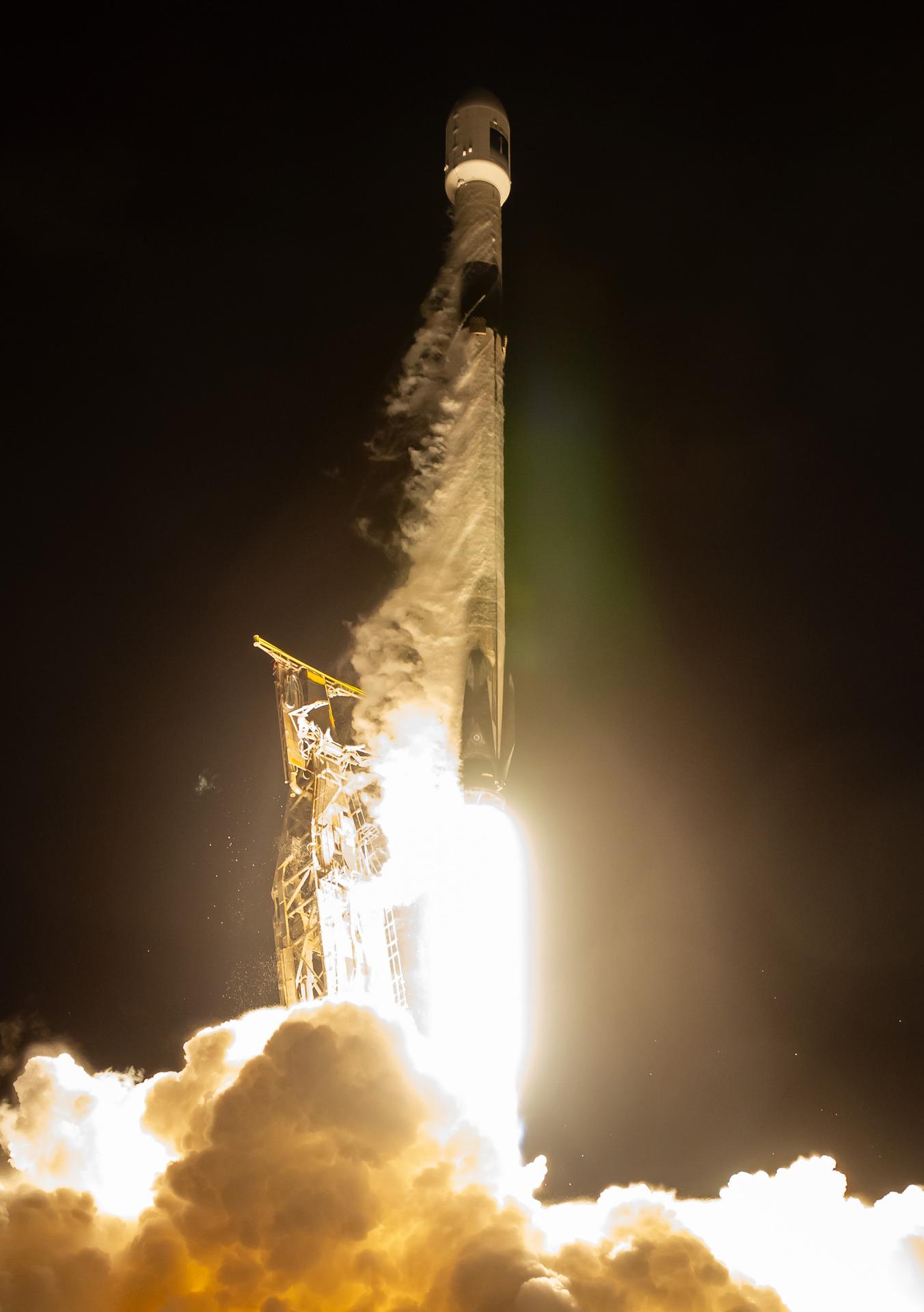

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
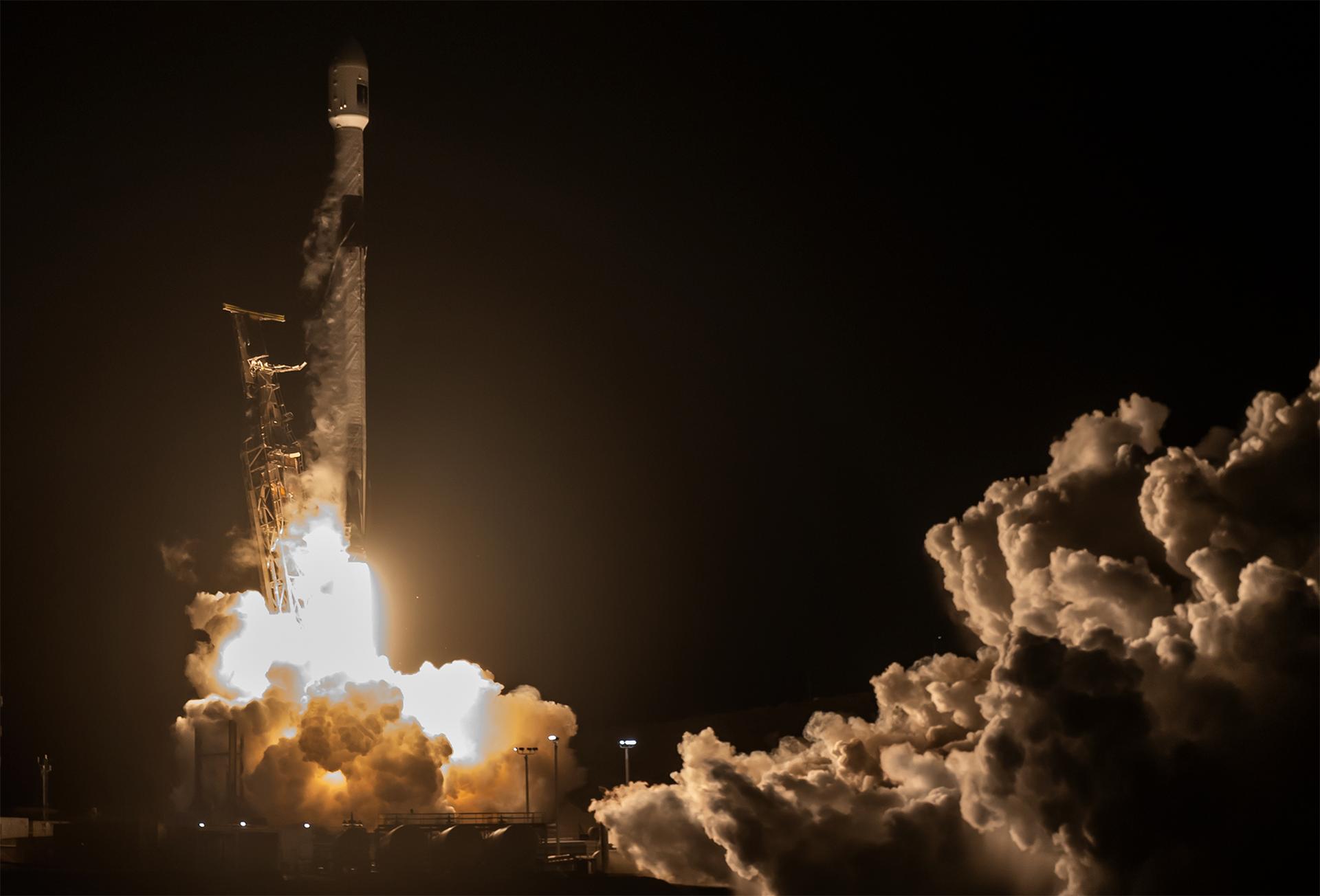

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
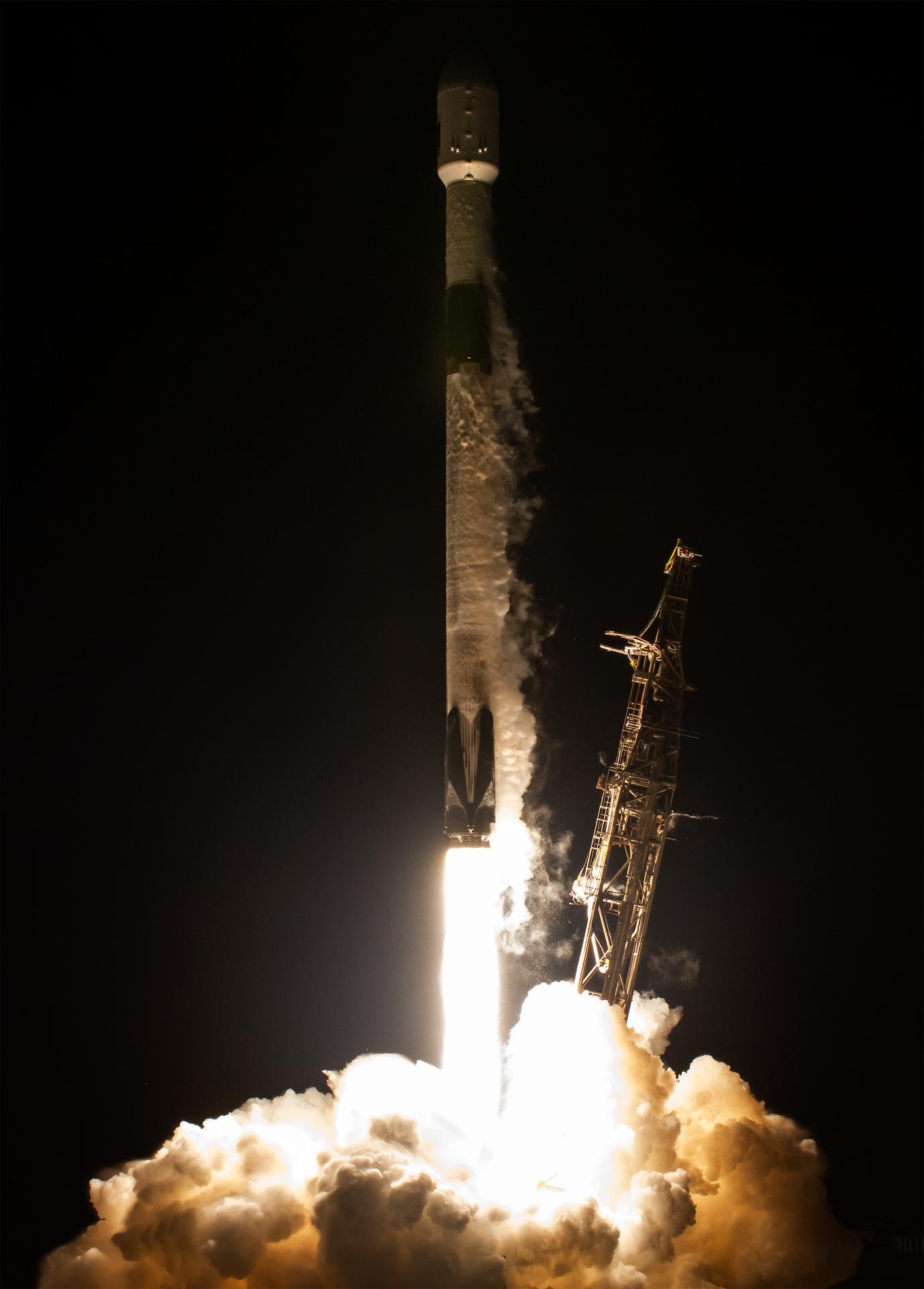

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
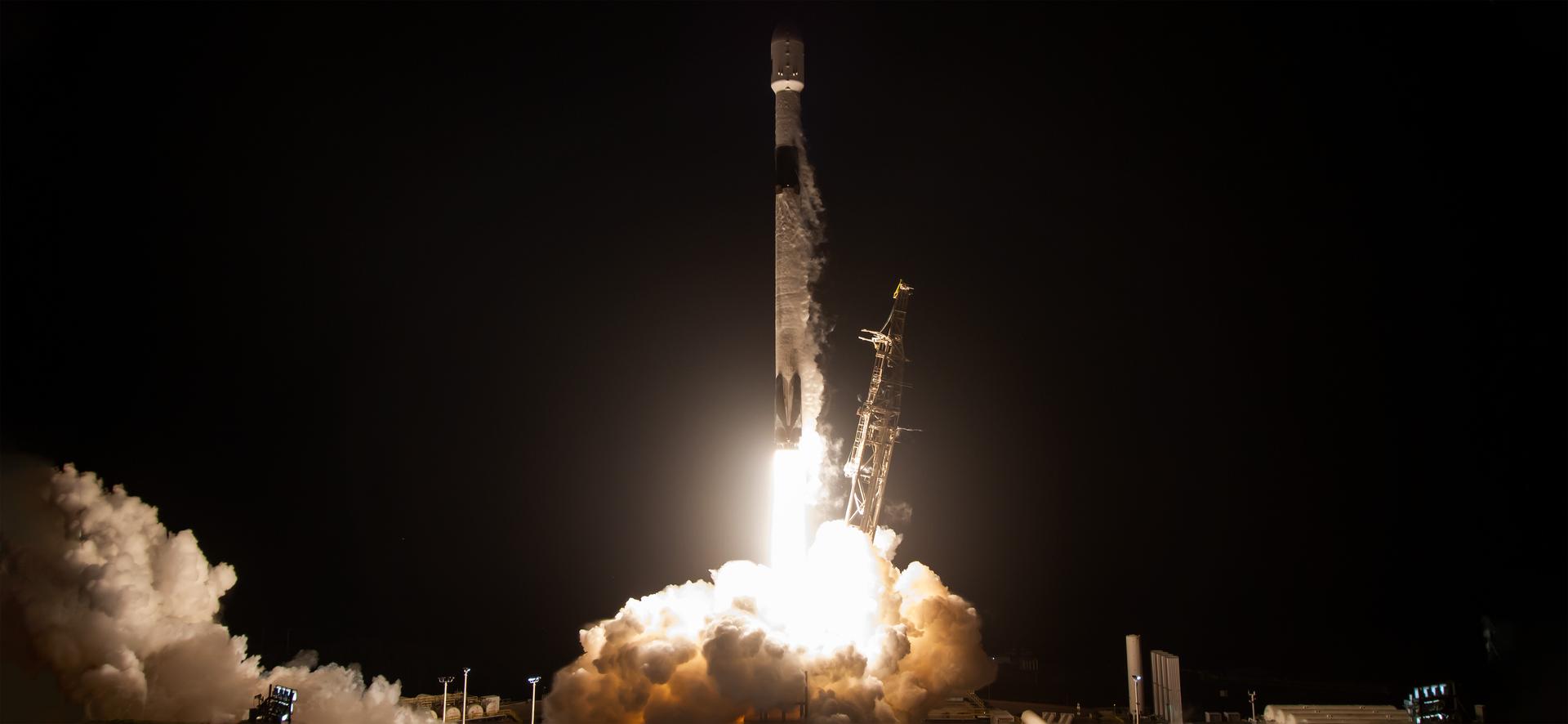

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
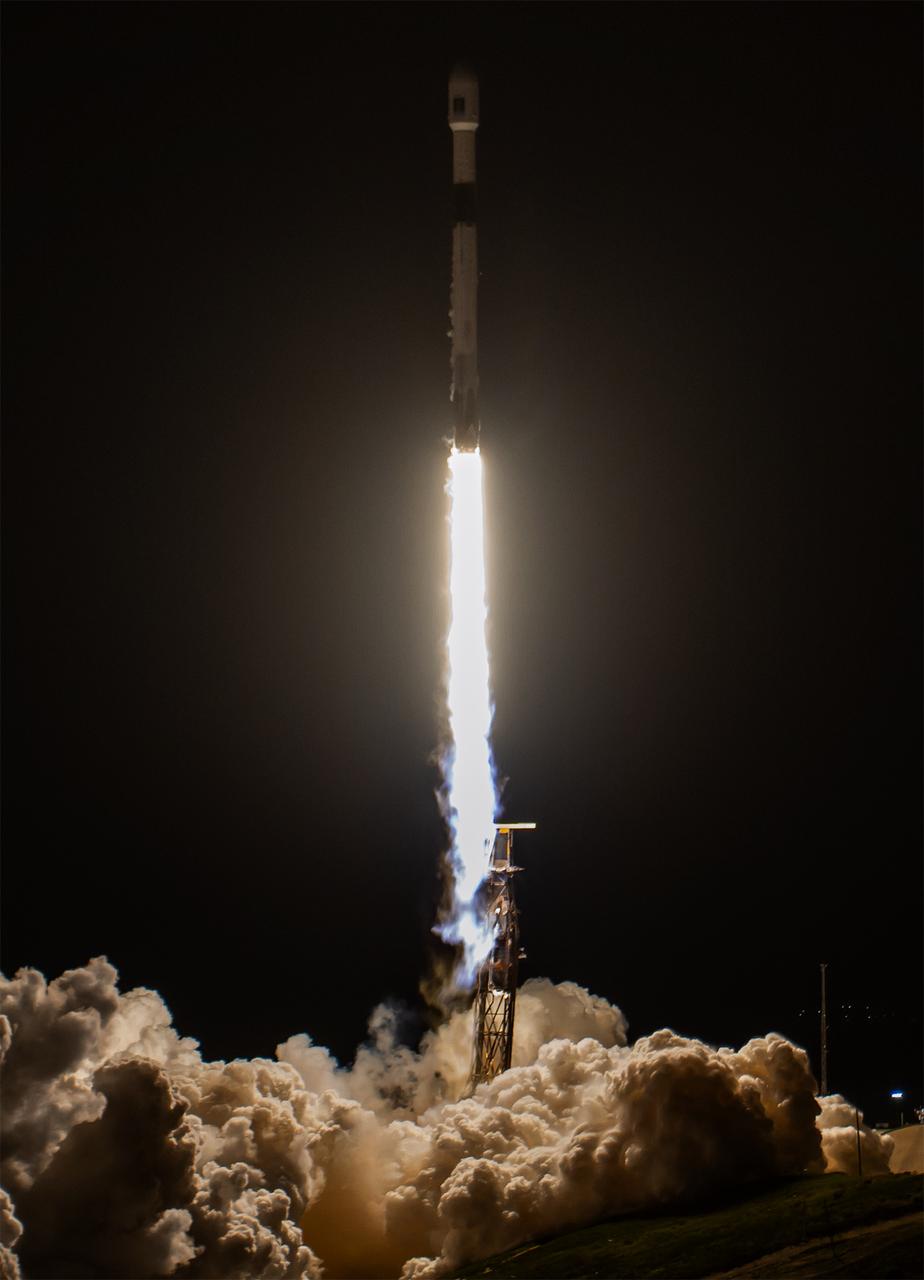

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
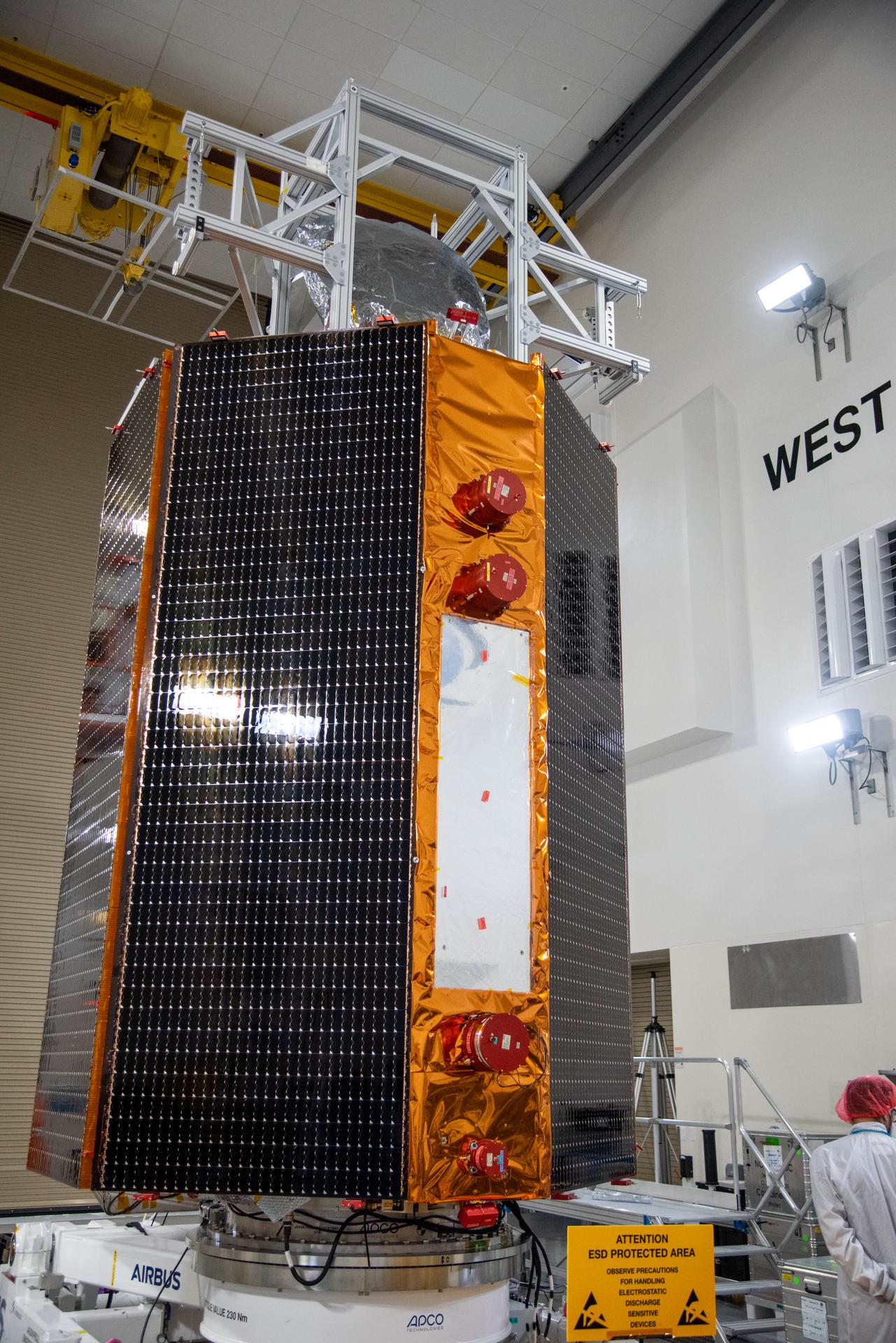

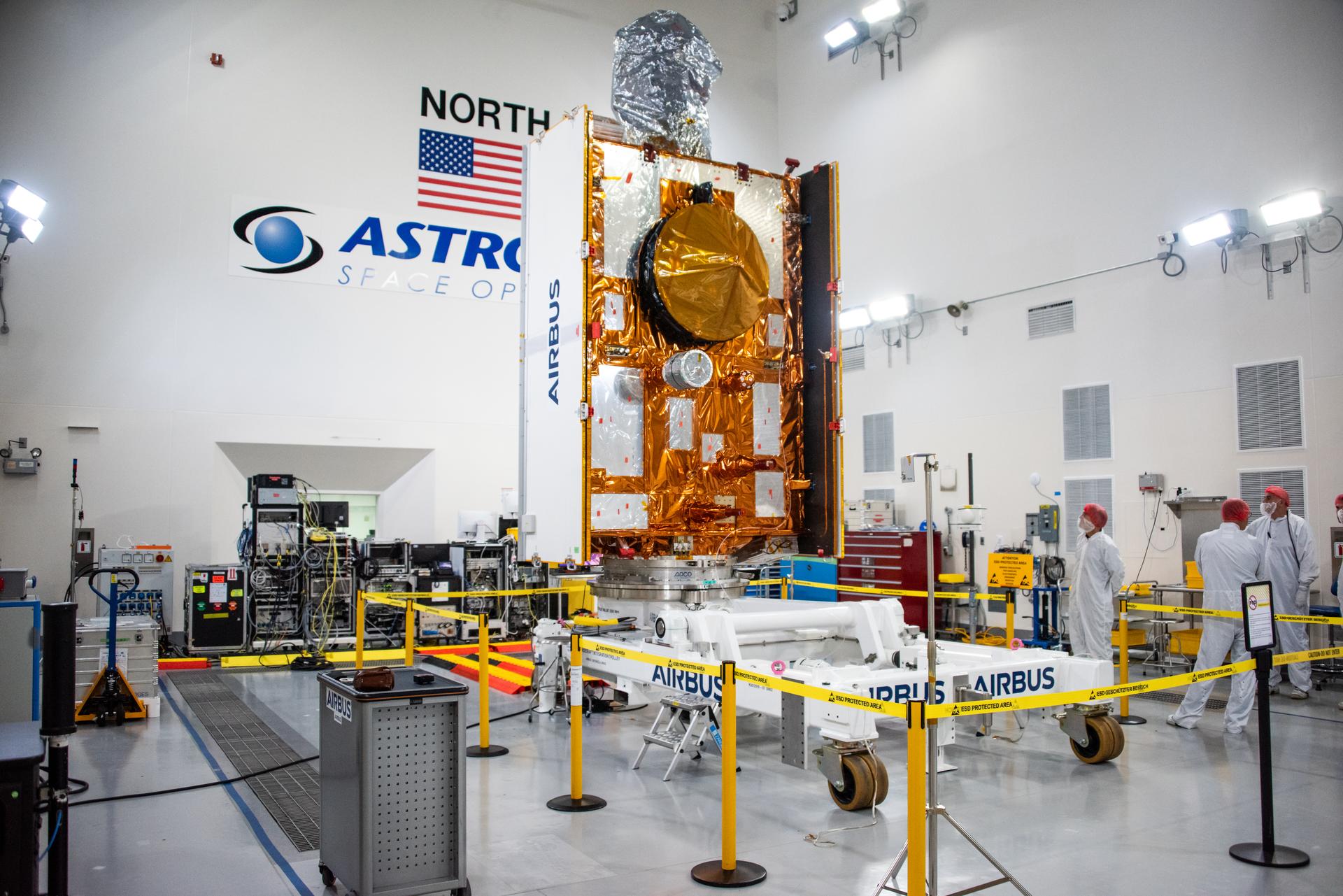
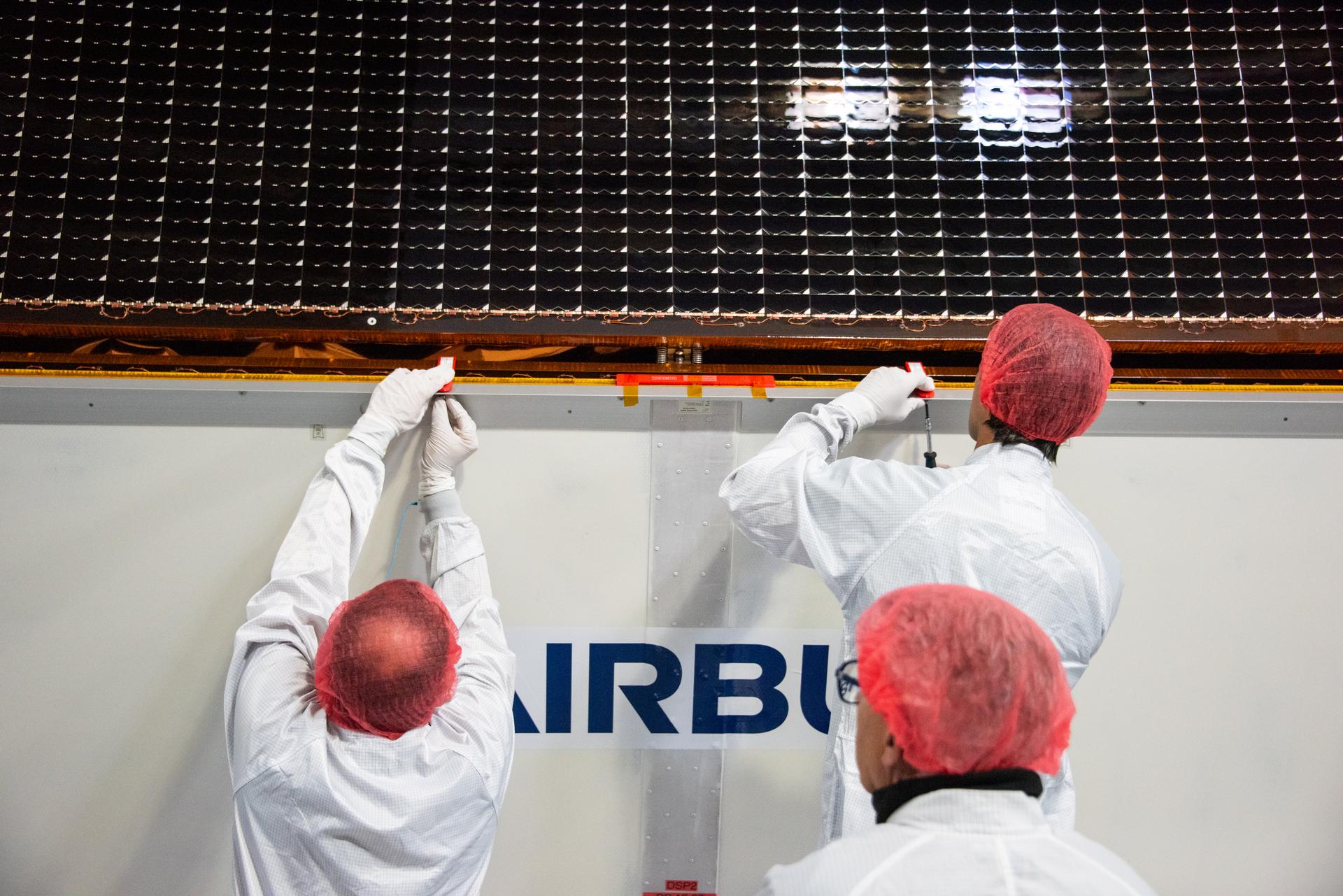
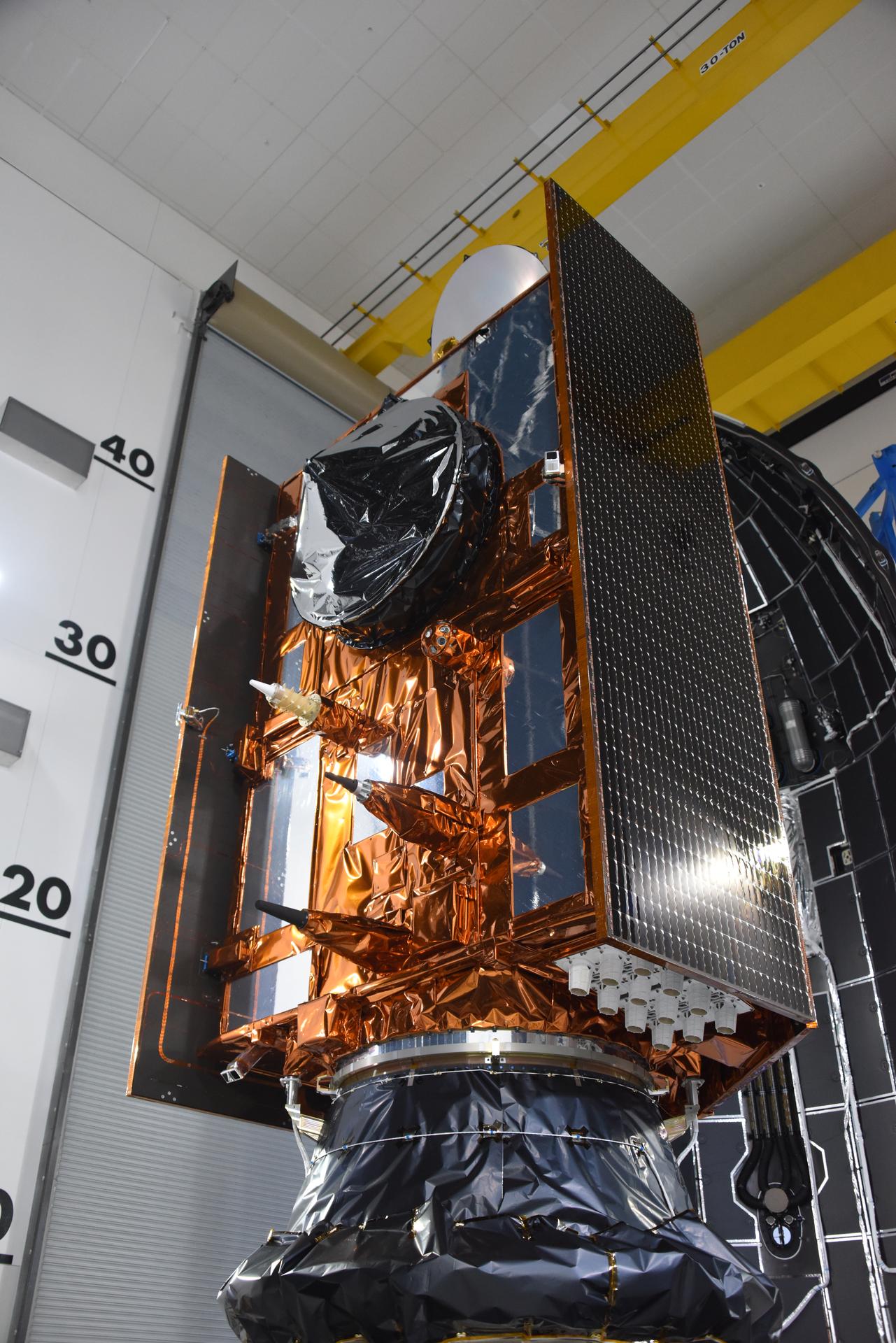
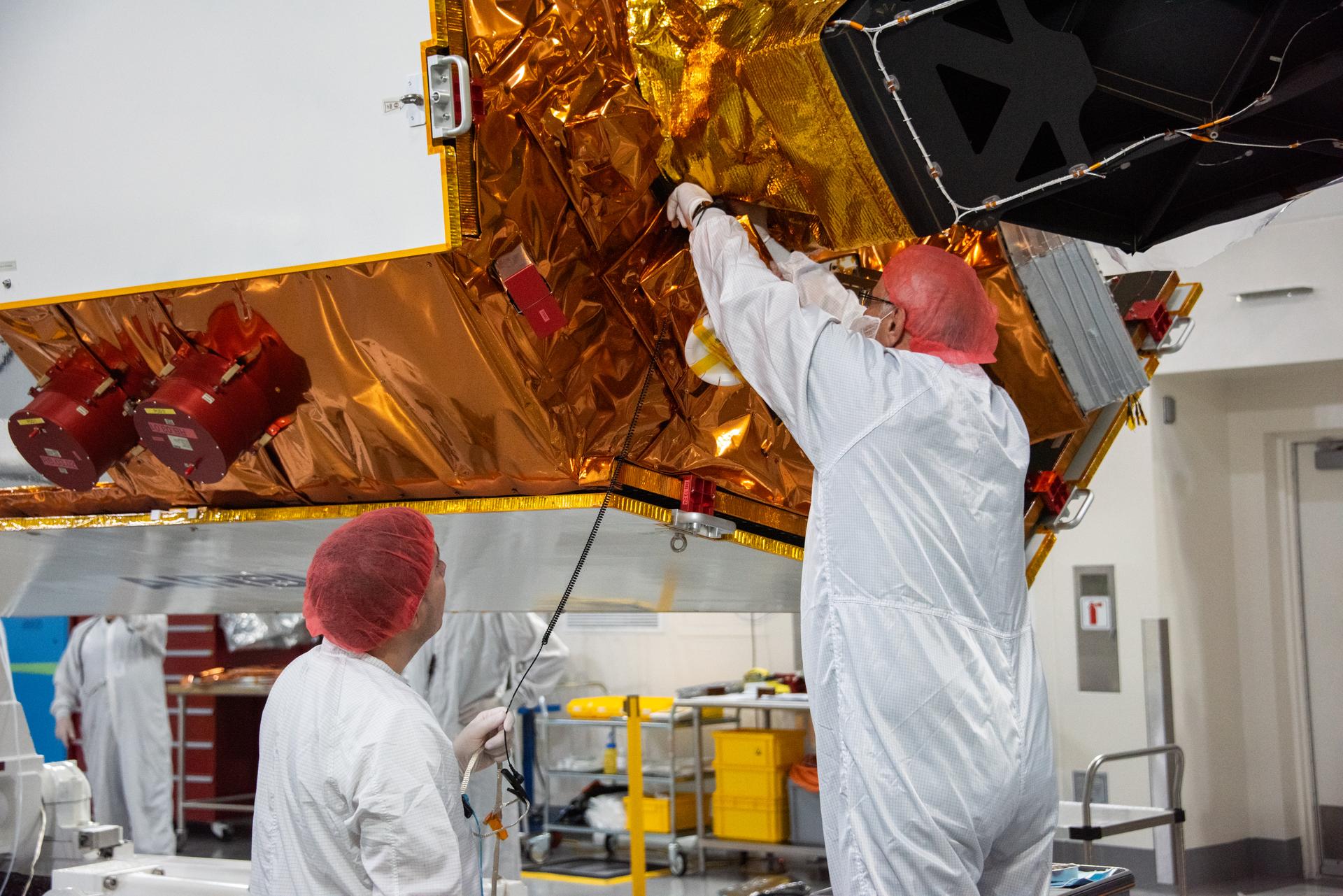
Technicians test the solar arrays during processing of the Sentinel-6B spacecraft during prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 16, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
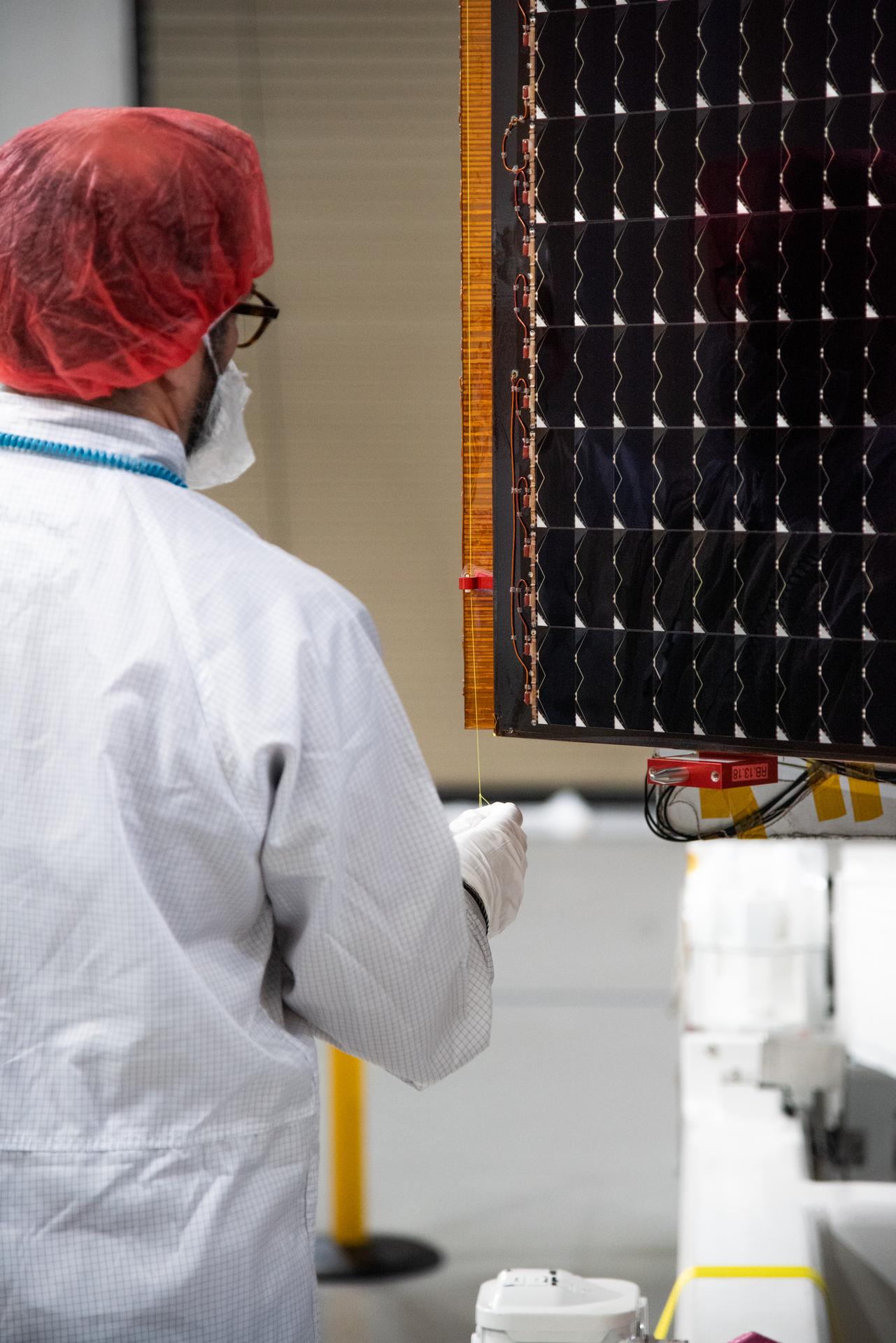

Technicians test the solar arrays during processing of the Sentinel-6B spacecraft during prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 16, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
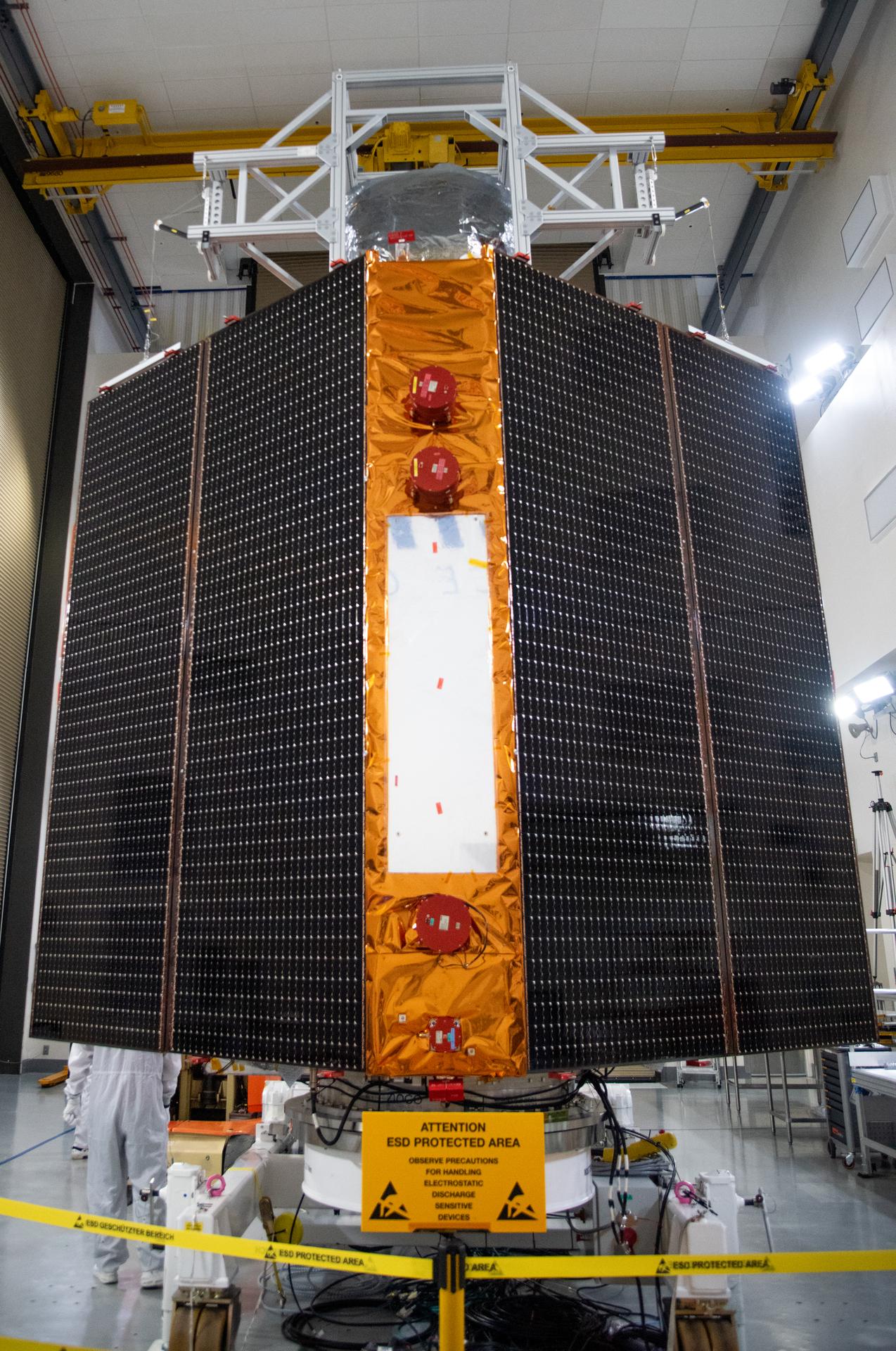

Technicians test the solar arrays during processing of the Sentinel-6B spacecraft during prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 16, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
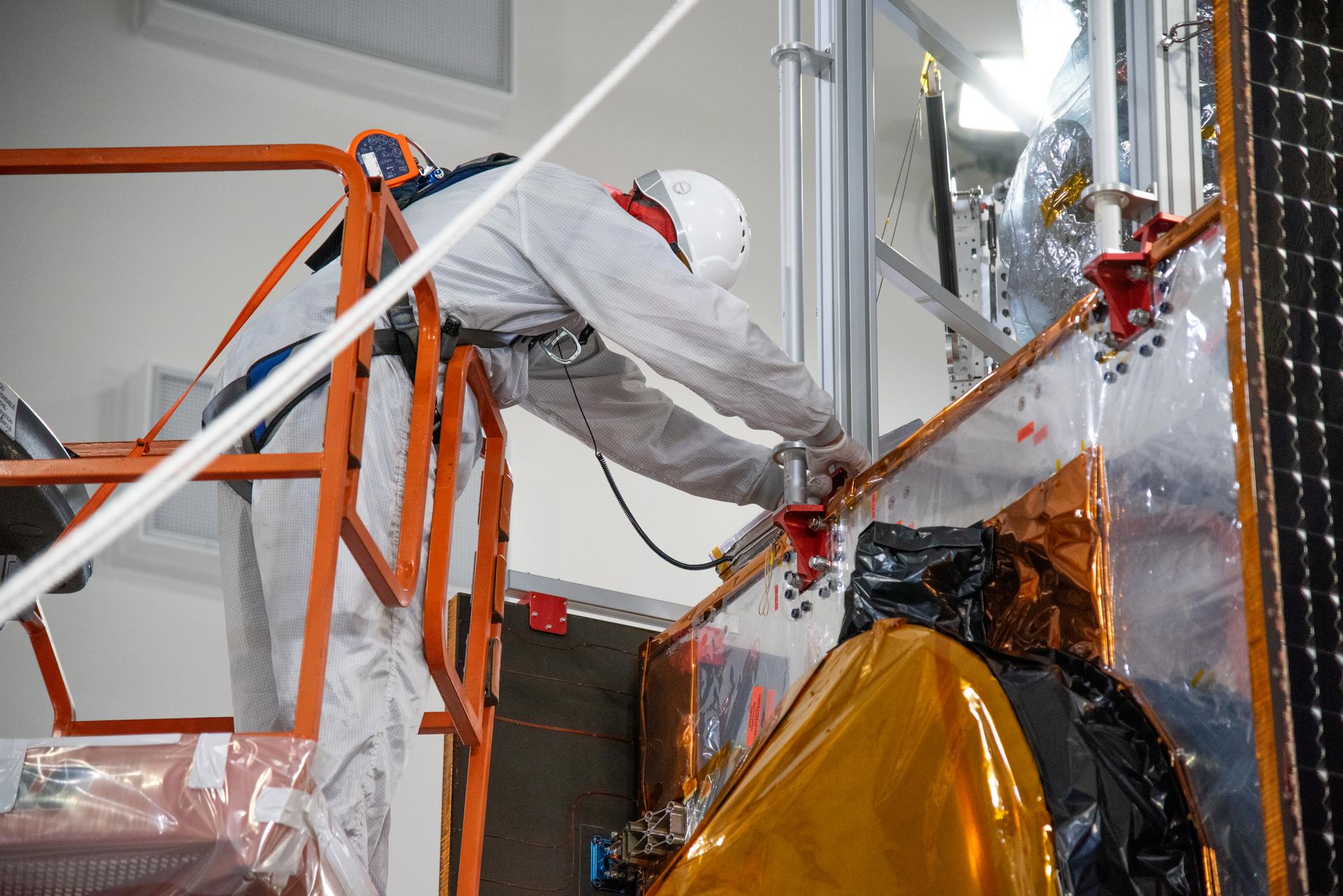

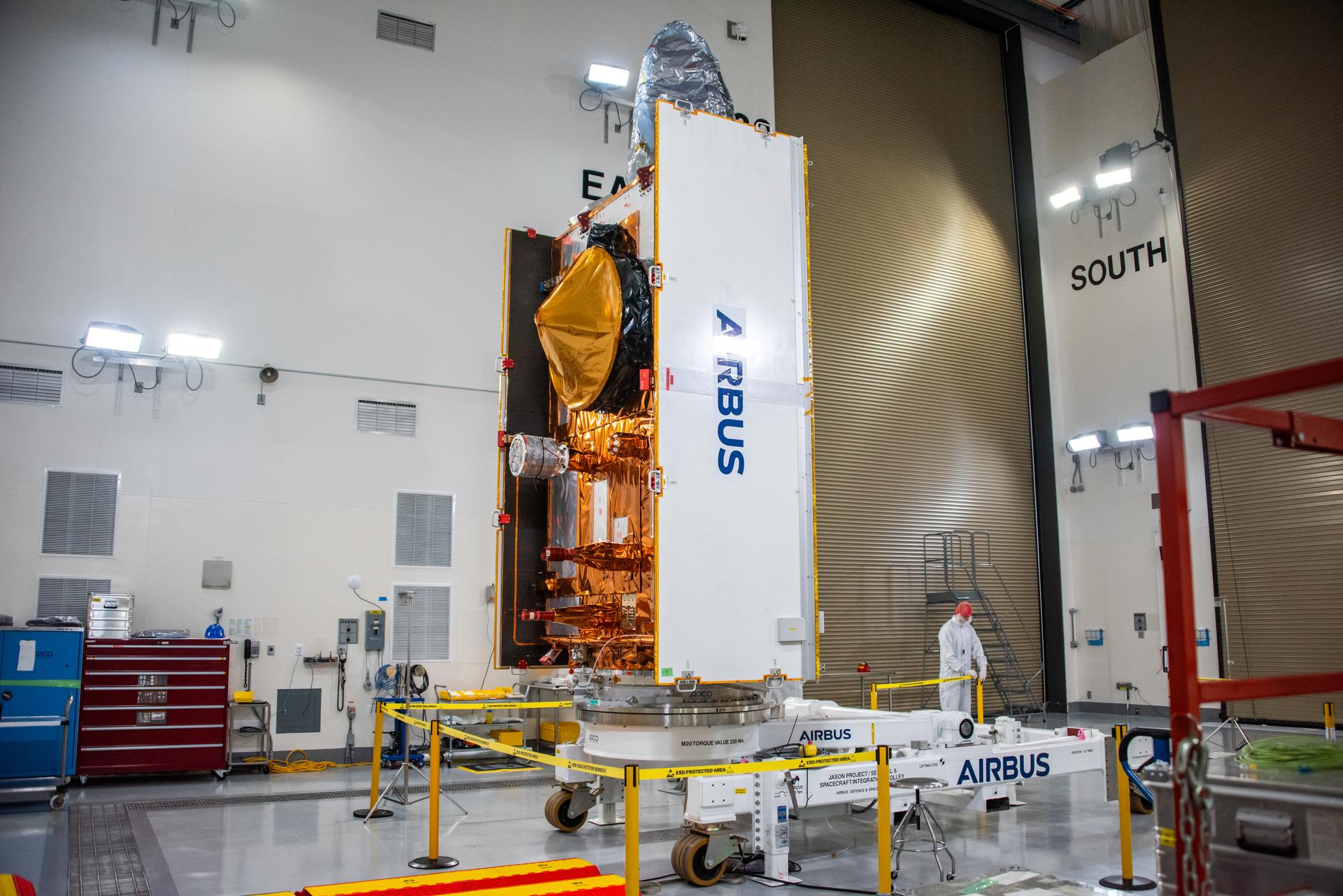
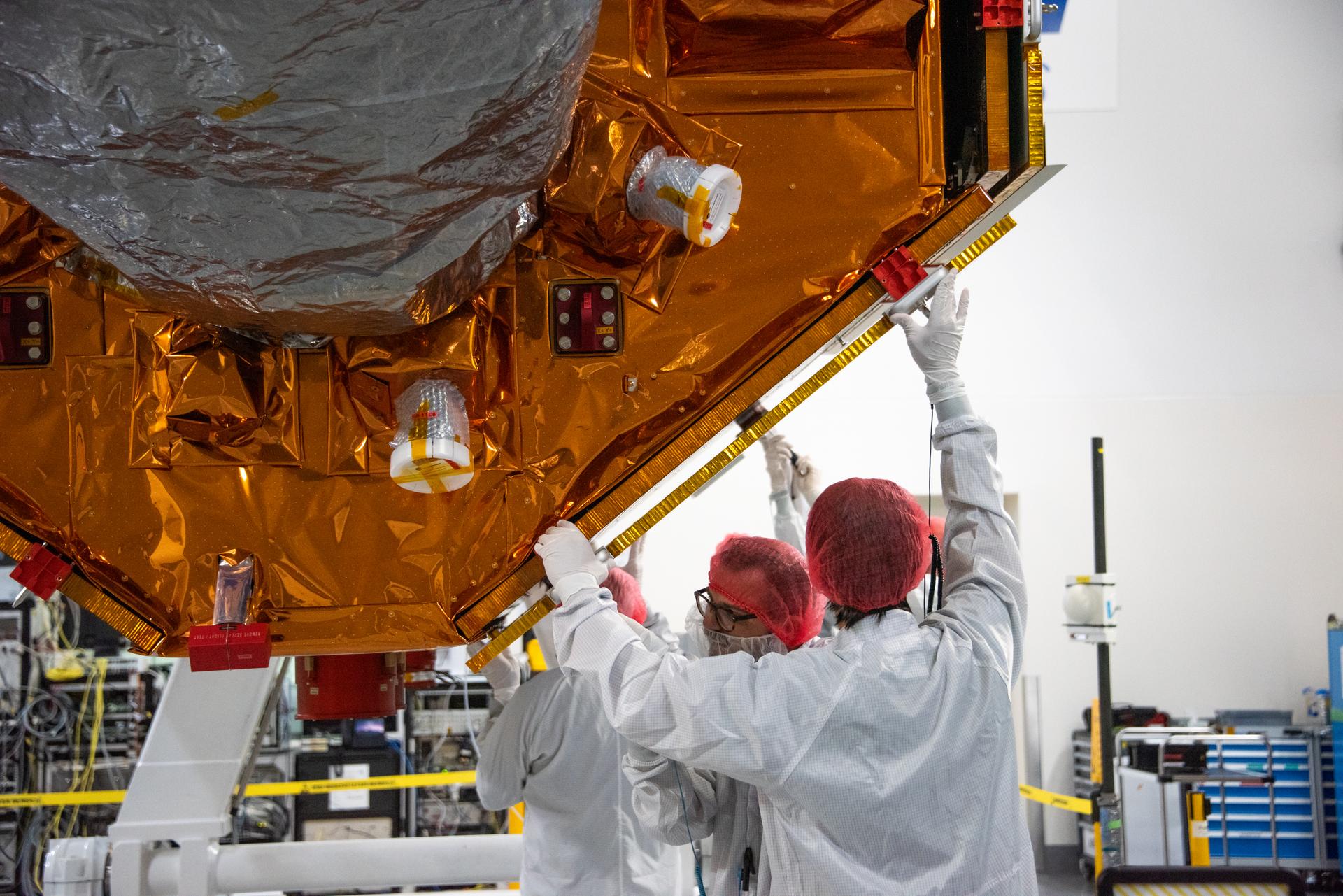
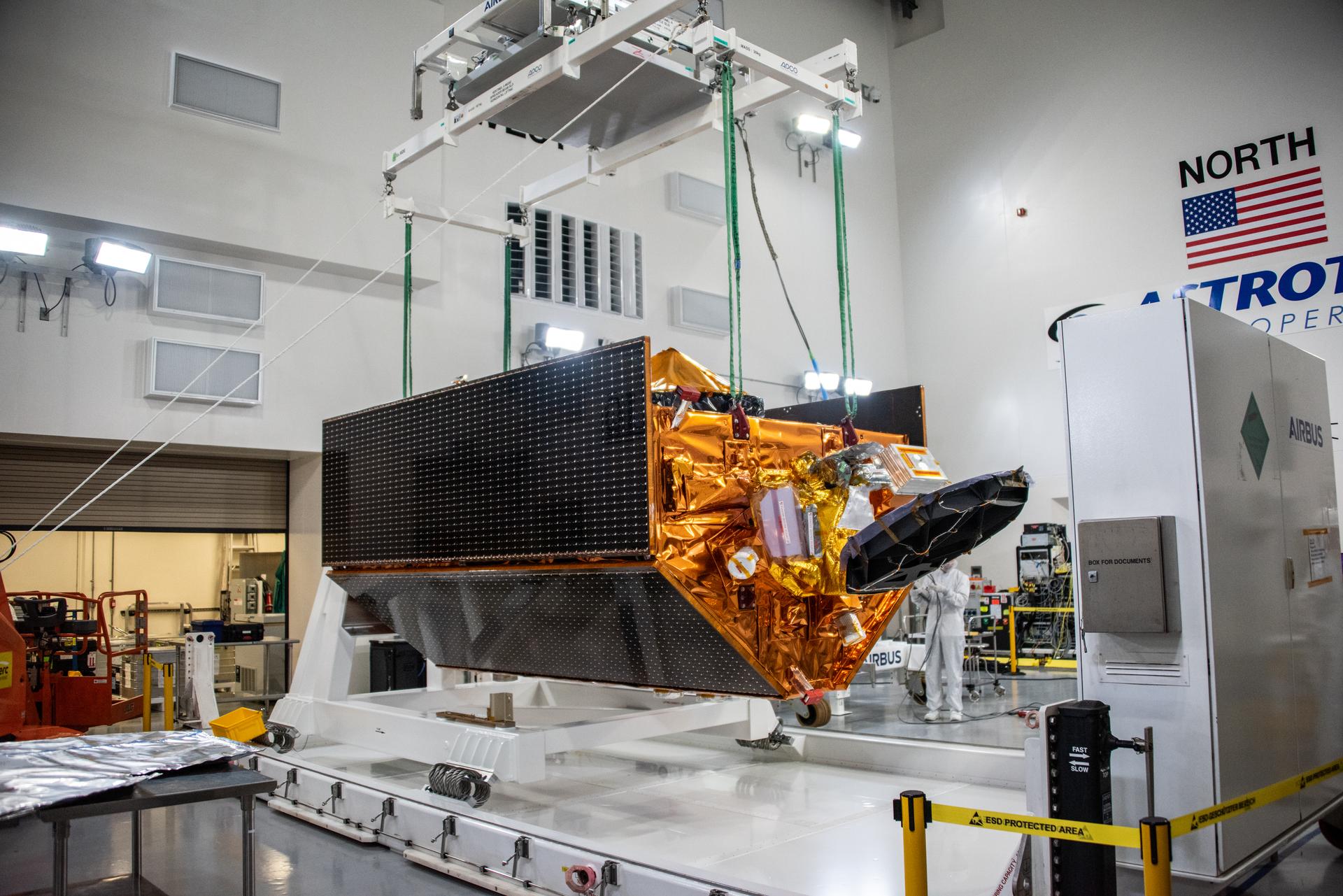
Technicians use a crane during processing of the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on its work stand during prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 16, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
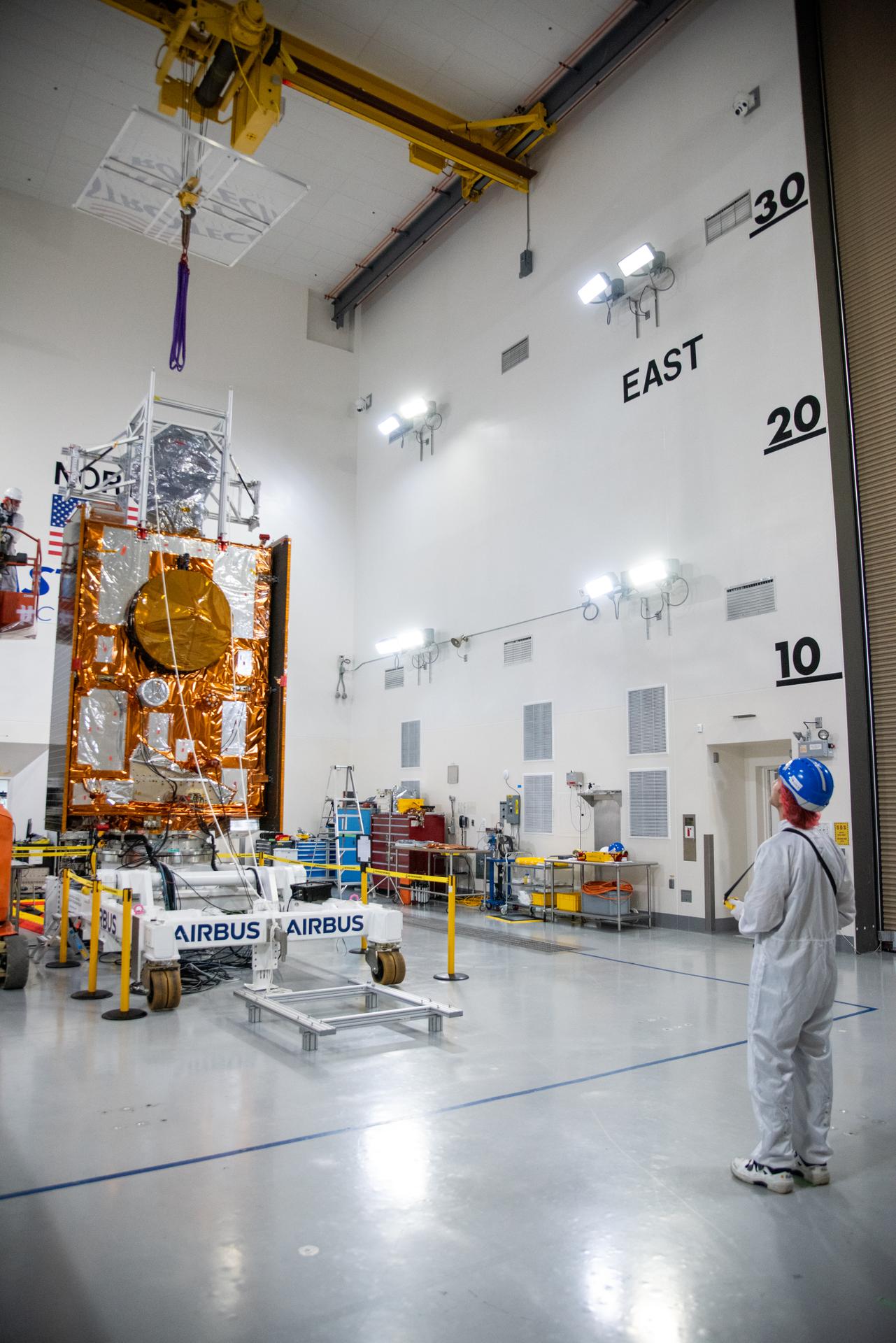

Technicians use a crane during processing of the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on its work stand during prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 16, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
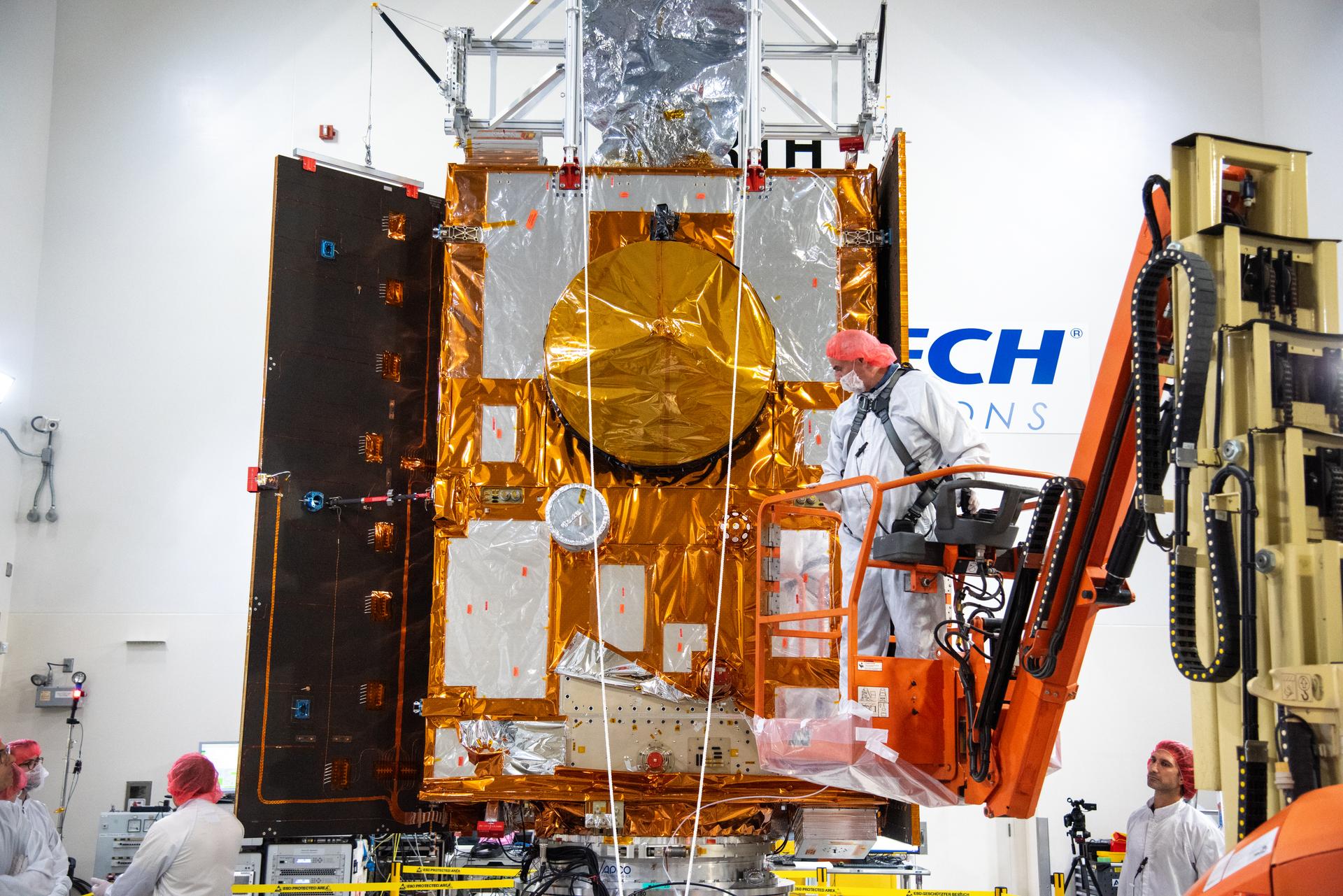

Technicians test the solar arrays during processing of the Sentinel-6B spacecraft during prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 16, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
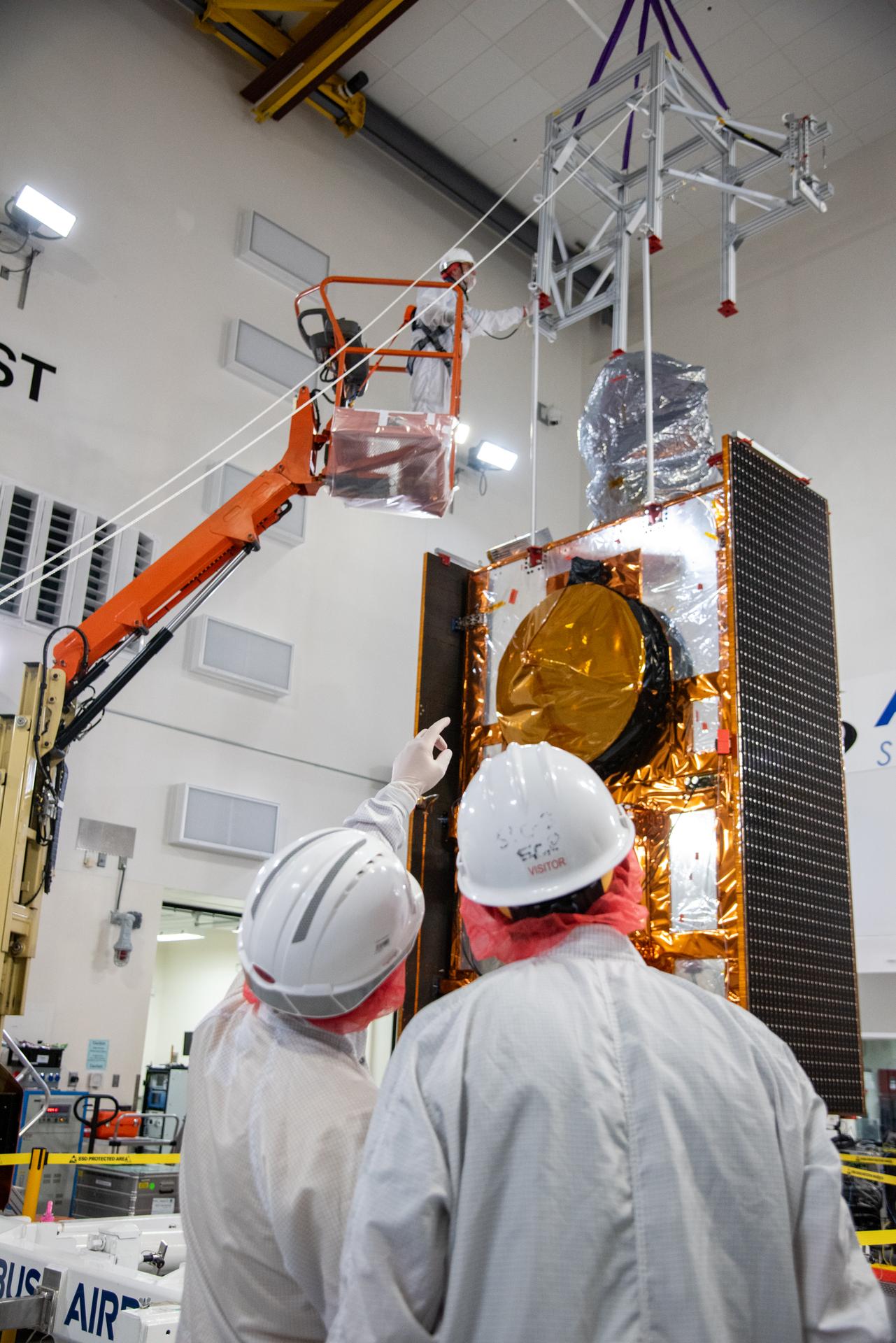

Technicians use a crane during processing of the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on its work stand during prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 16, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.

Technicians test the solar arrays during processing of the Sentinel-6B spacecraft during prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 16, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.

Technicians test the solar arrays during processing of the Sentinel-6B spacecraft during prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 16, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.

Technicians use a crane during processing of the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on its work stand during prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 16, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians install protective solar array covers for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Friday, Sept. 26, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.
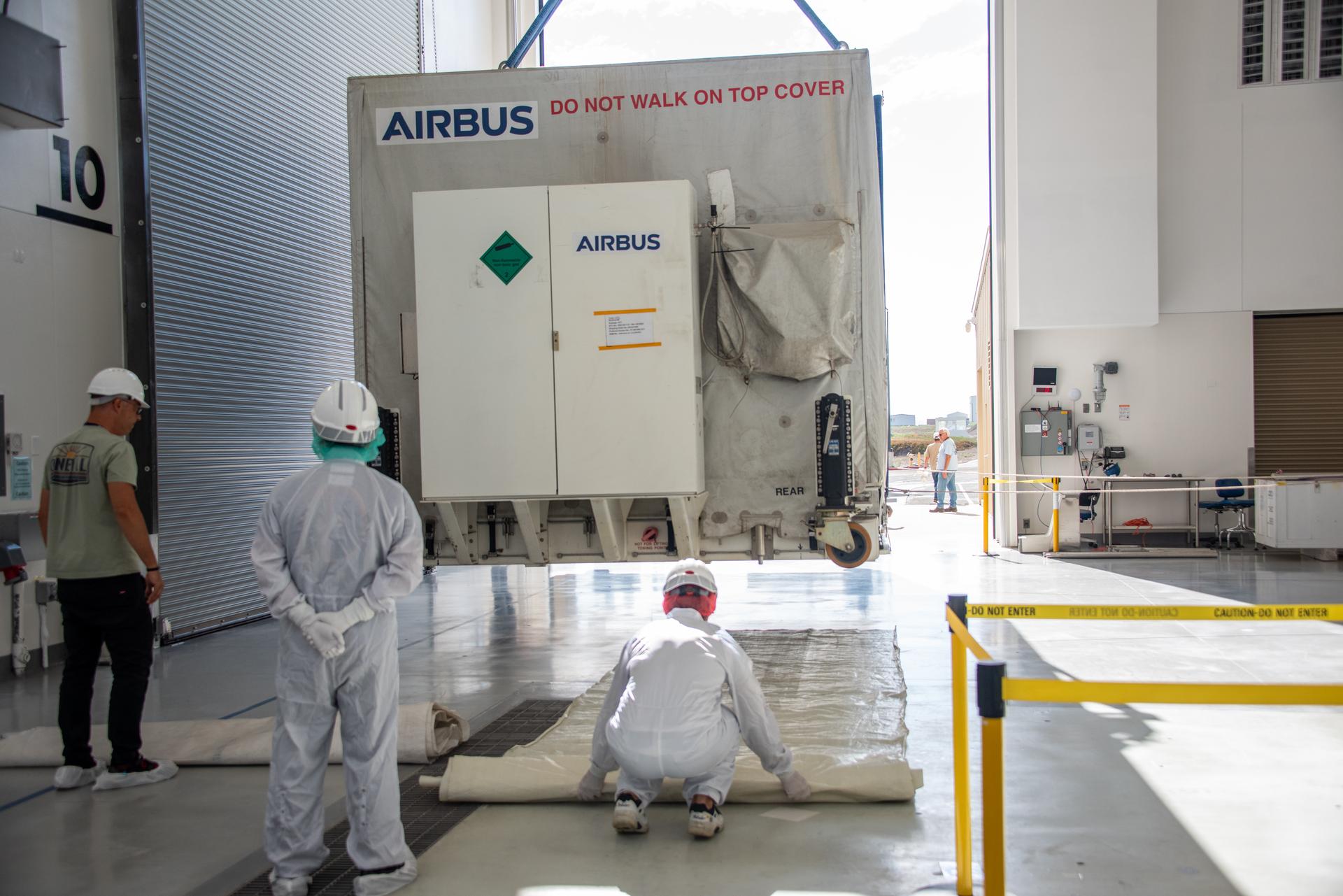

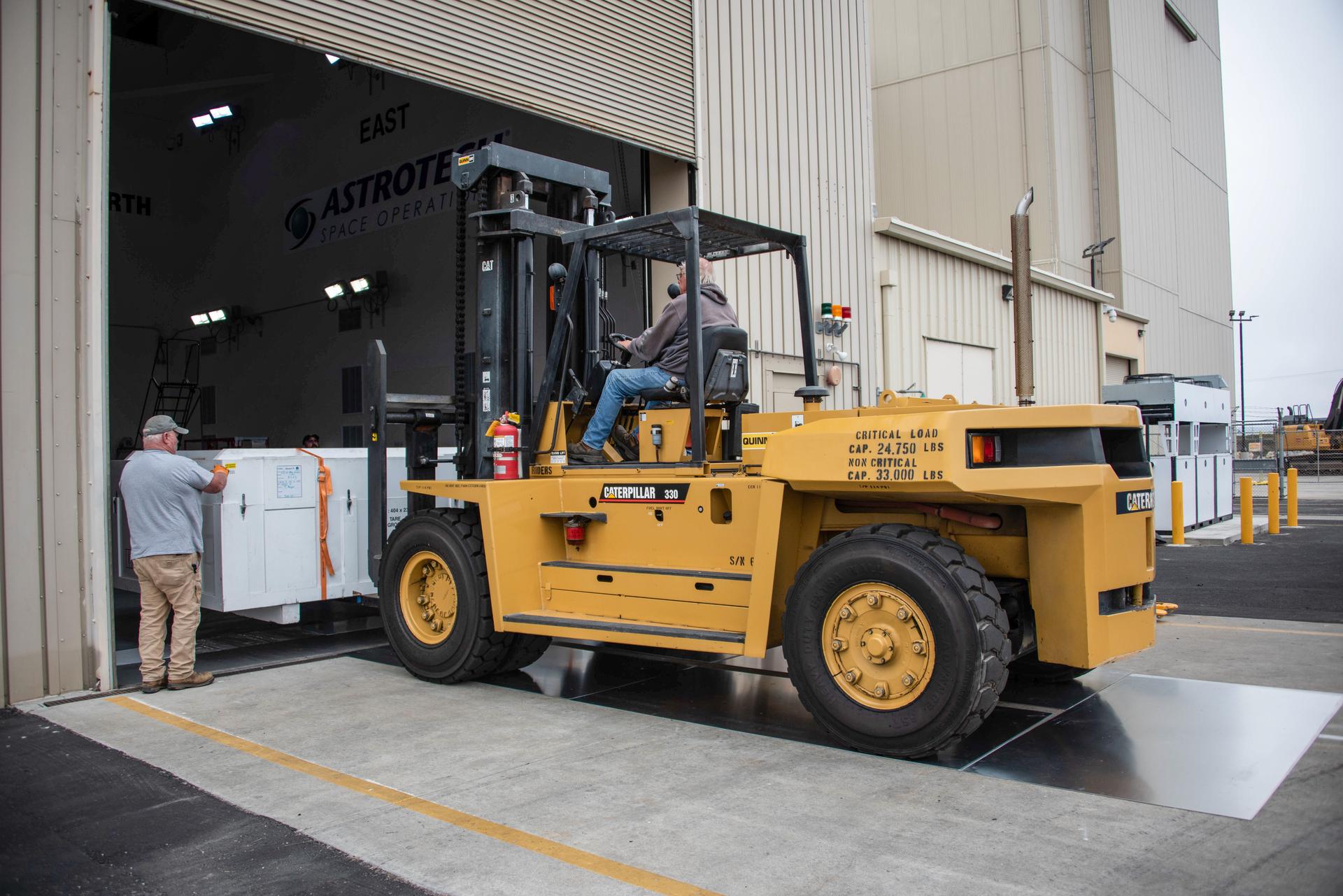
Technicians transfer the Sentinel-6B spacecraft from the NASA hangar to the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians transfer the Sentinel-6B spacecraft from the NASA hangar to the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians transfer the Sentinel-6B spacecraft from the NASA hangar to the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

The first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lands at Vandenberg Space Force Base’s Landing Zone 4 in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, following the launch of the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifting off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 East. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
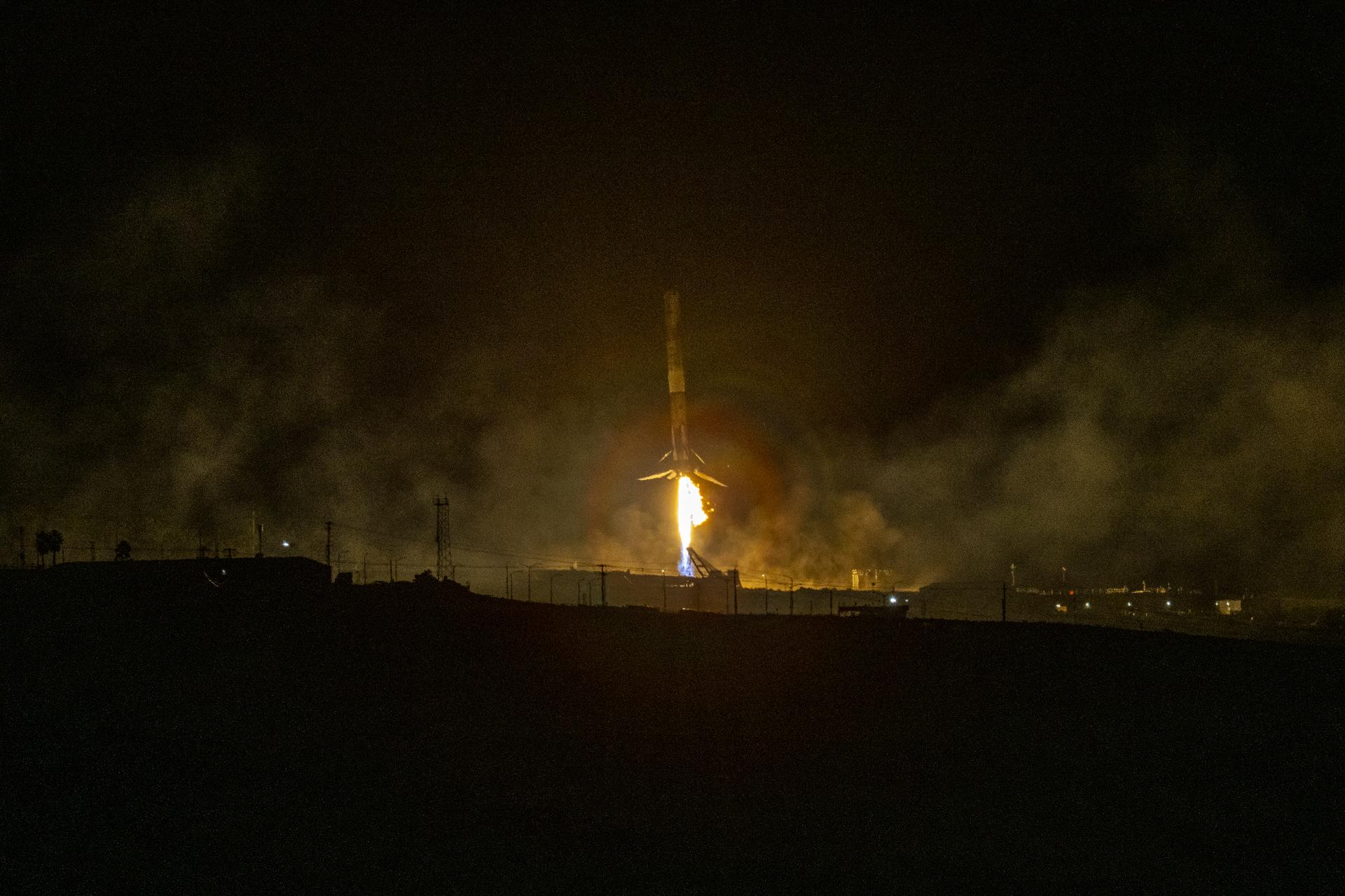

The first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lands at Vandenberg Space Force Base’s Landing Zone 4 in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, following the launch of the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifting off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 East. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
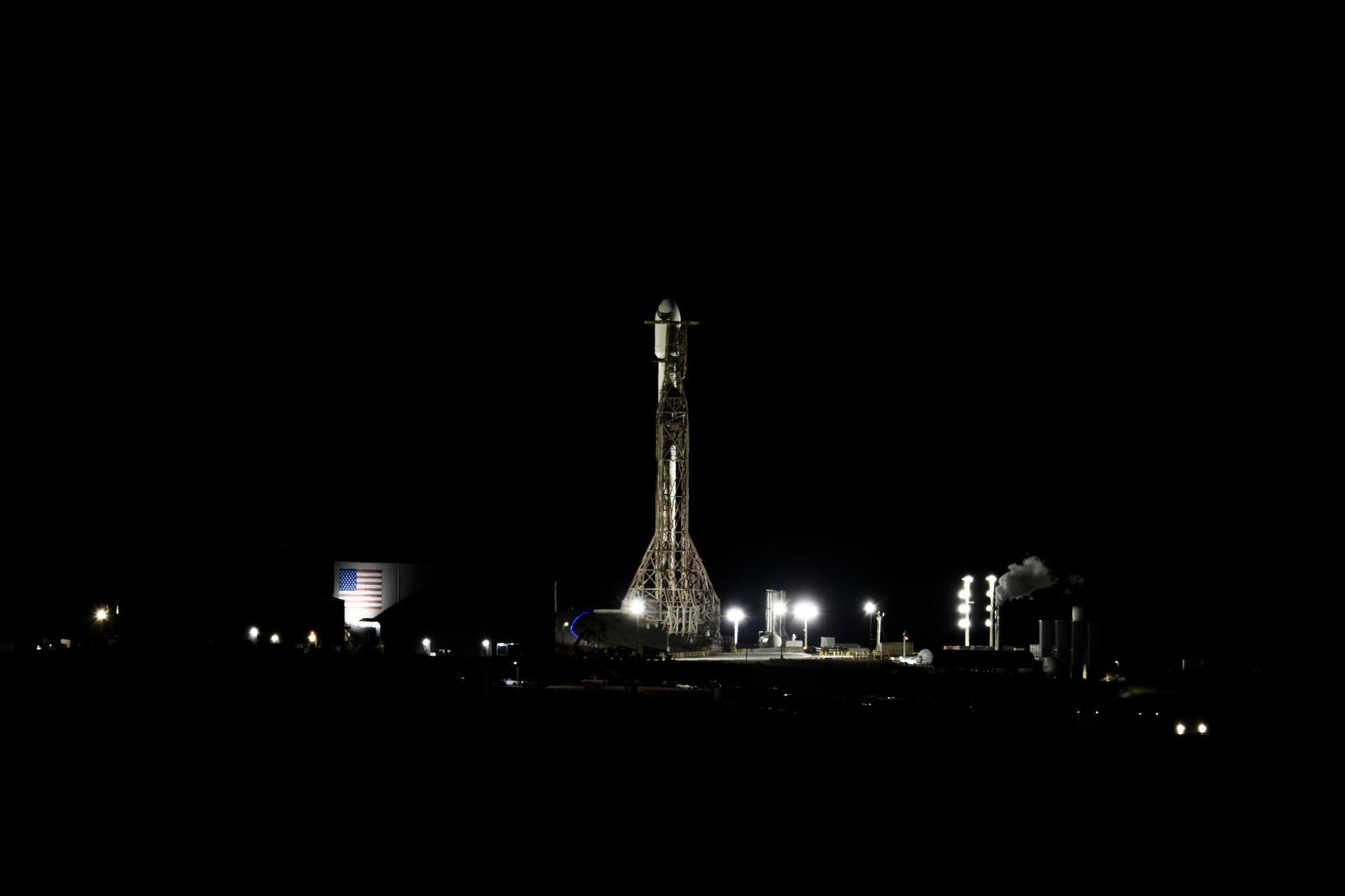

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft atop stands vertical ahead of launch from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than 9:21 p.m. PST.
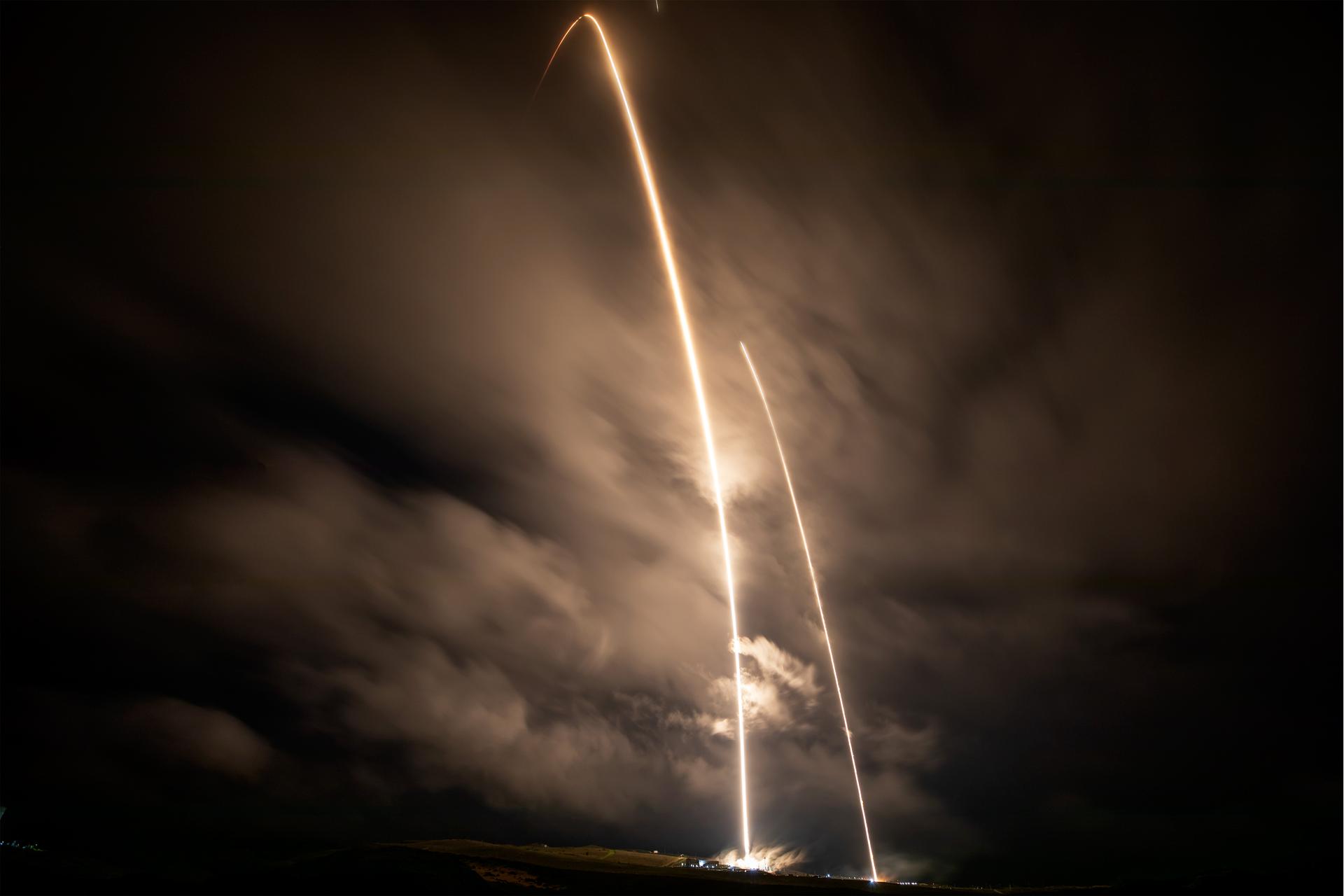

A long exposure photo shows two streaks – the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifting off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, and the rocket’s first stage returning minutes later to land at Vandenberg’s Landing Zone 4 East. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
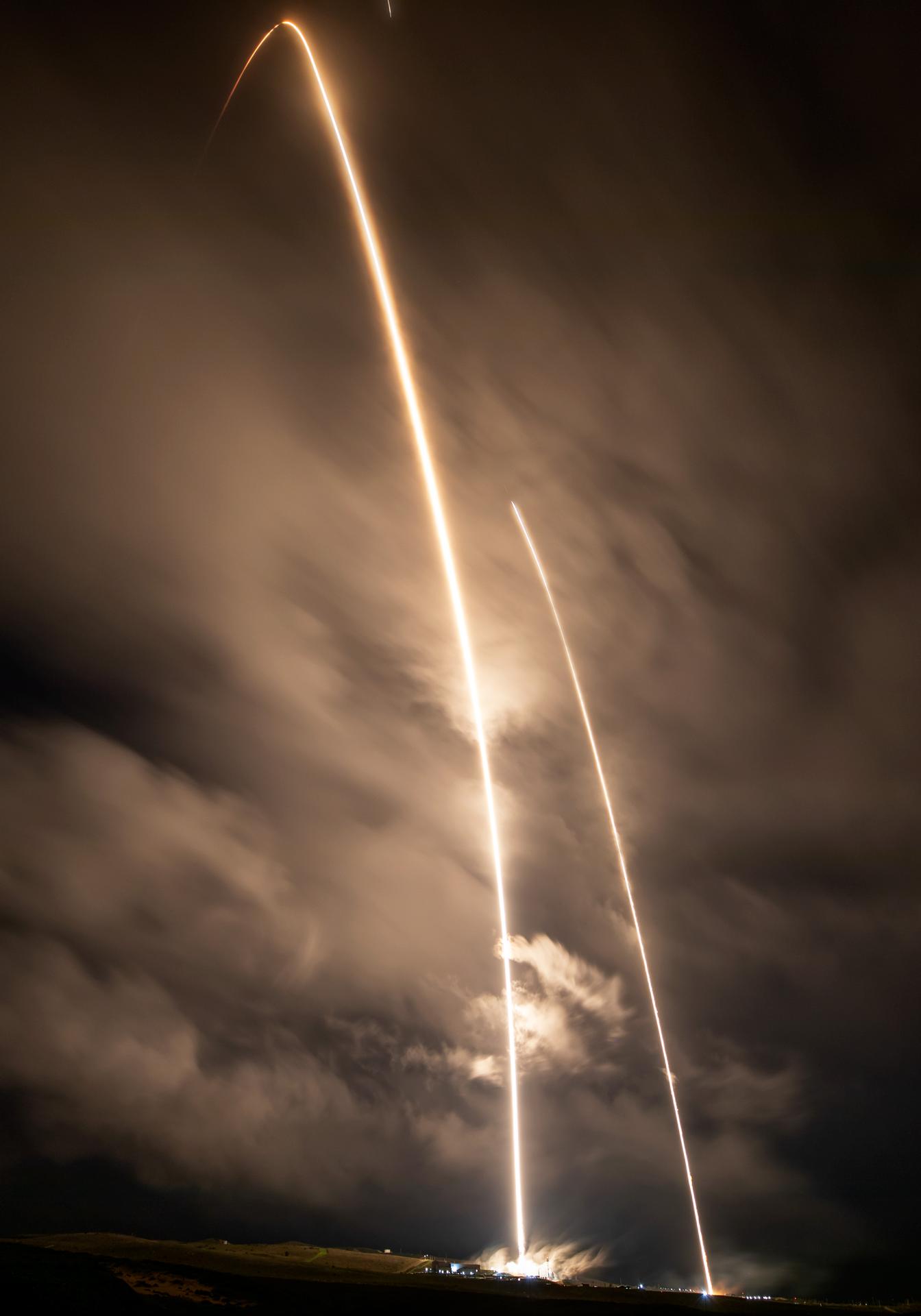

A long exposure photo shows two streaks – the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifting off from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:21 p.m. PST Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, and the rocket’s first stage returning minutes later to land at Vandenberg’s Landing Zone 4 East. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
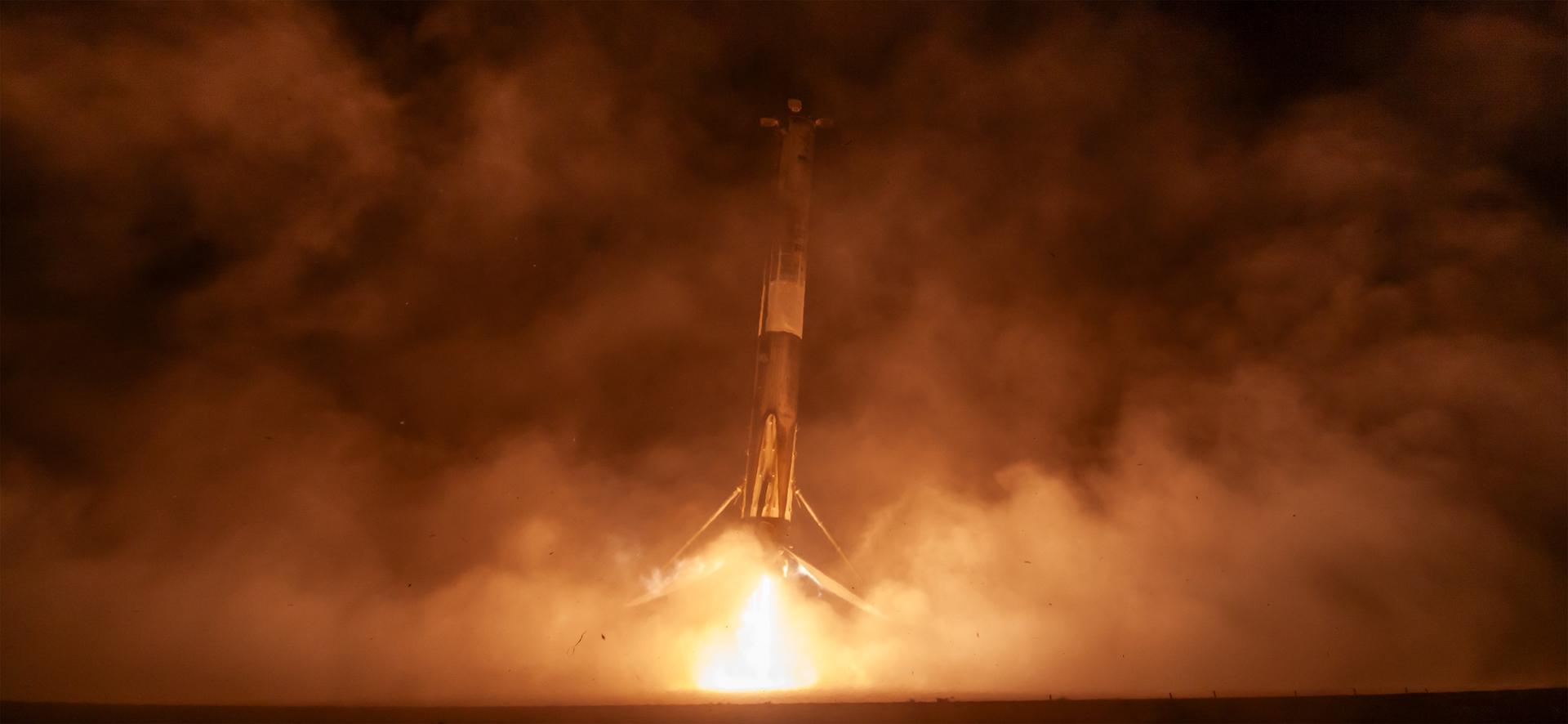

The first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lands at Vandenberg Space Force Base’s Landing Zone 4 in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, following the launch of the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifting off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 East. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
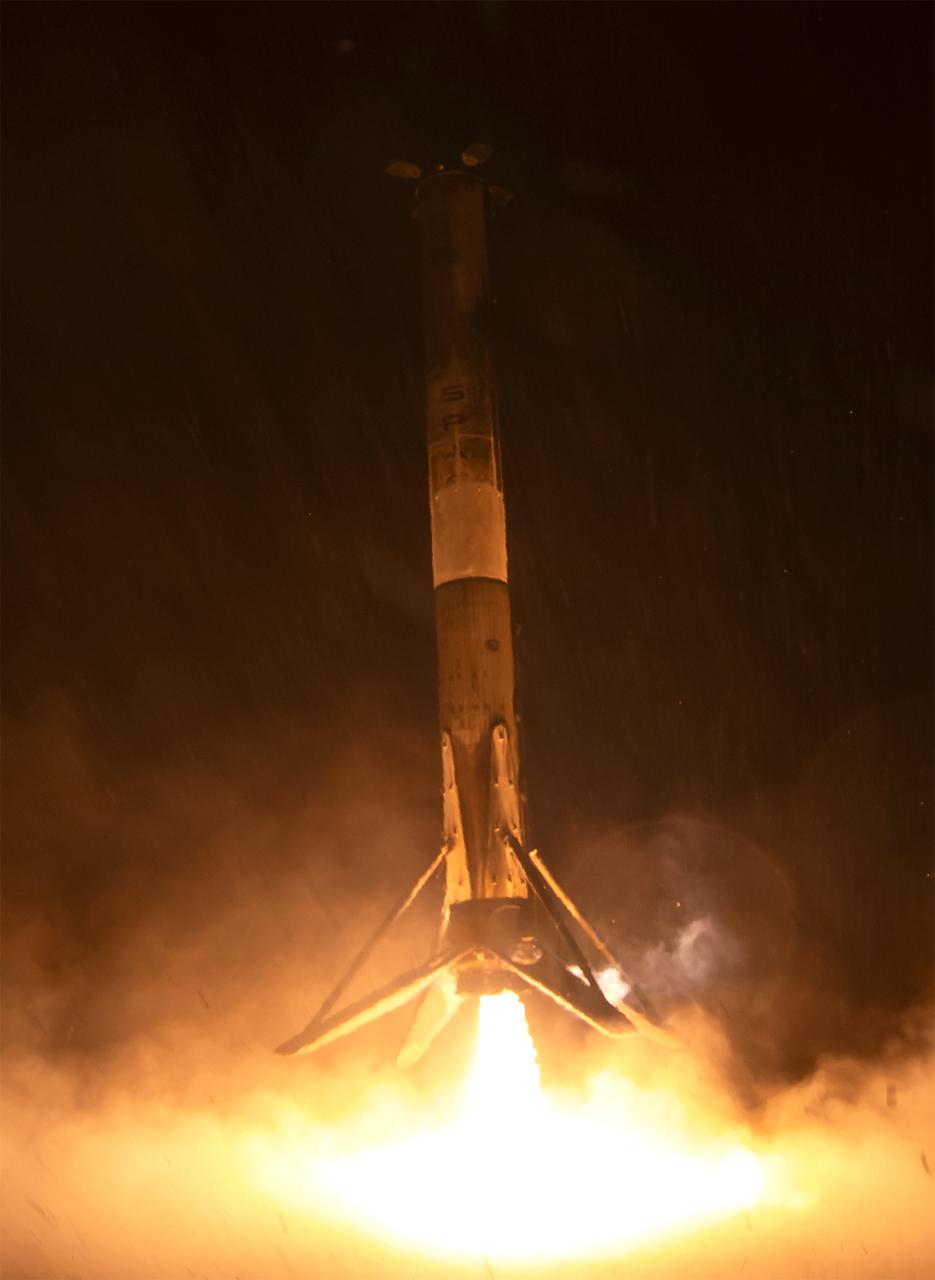

The first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lands at Vandenberg Space Force Base’s Landing Zone 4 in California on Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, following the launch of the international Sentinel-6B spacecraft lifting off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 East. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans.
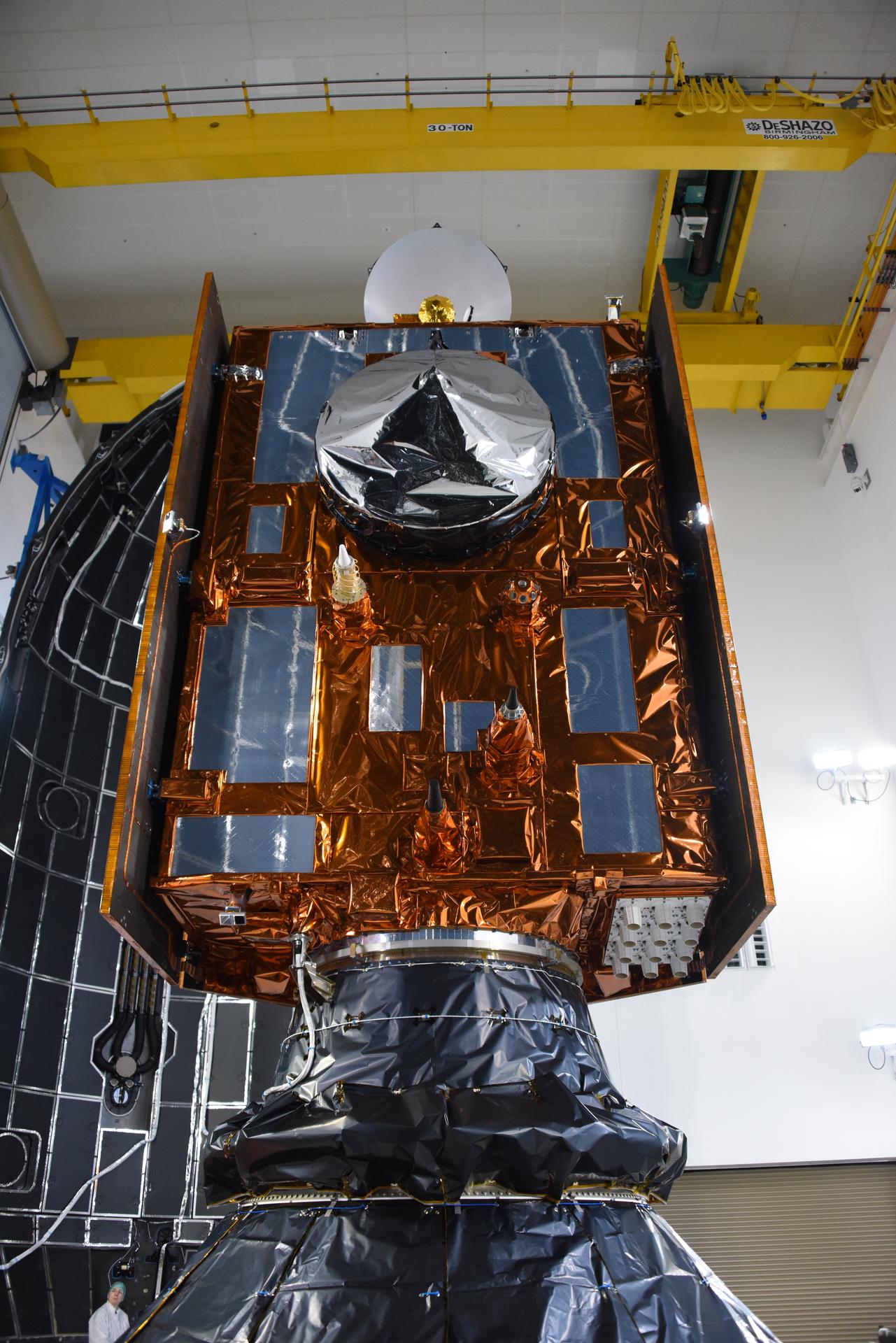

Technicians and engineers encapsulate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft within a protective payload fairing inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on Monday, Nov. 10, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
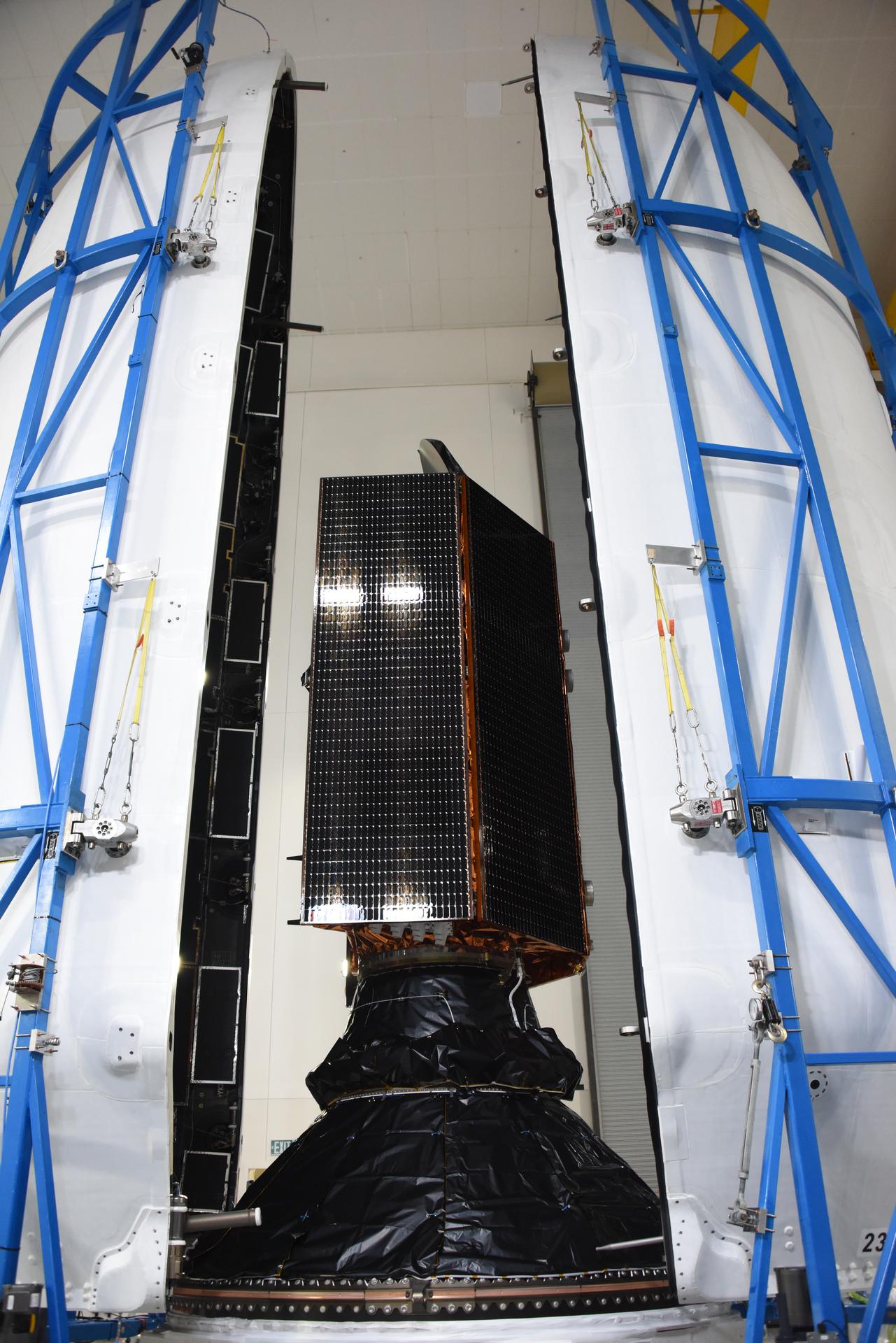

Technicians and engineers encapsulate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft within a protective payload fairing inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on Monday, Nov. 10, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians and engineers encapsulate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft within a protective payload fairing inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on Monday, Nov. 10, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
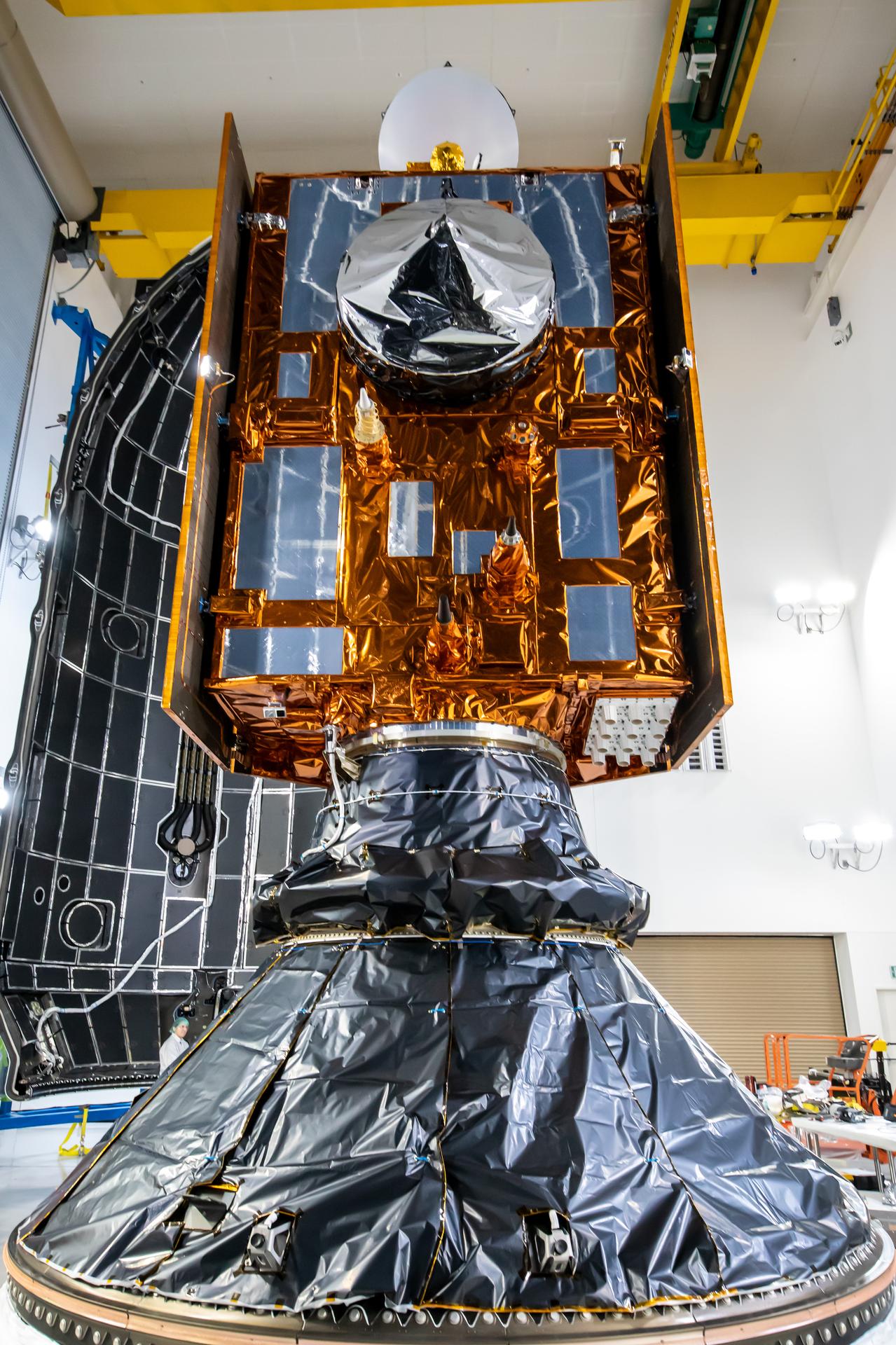

Technicians and engineers encapsulate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft within a protective payload fairing inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on Monday, Nov. 10, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians and engineers encapsulate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft within a protective payload fairing inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on Monday, Nov. 10, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians and engineers encapsulate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft within a protective payload fairing inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on Monday, Nov. 10, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians and engineers encapsulate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft within a protective payload fairing inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on Monday, Nov. 10, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
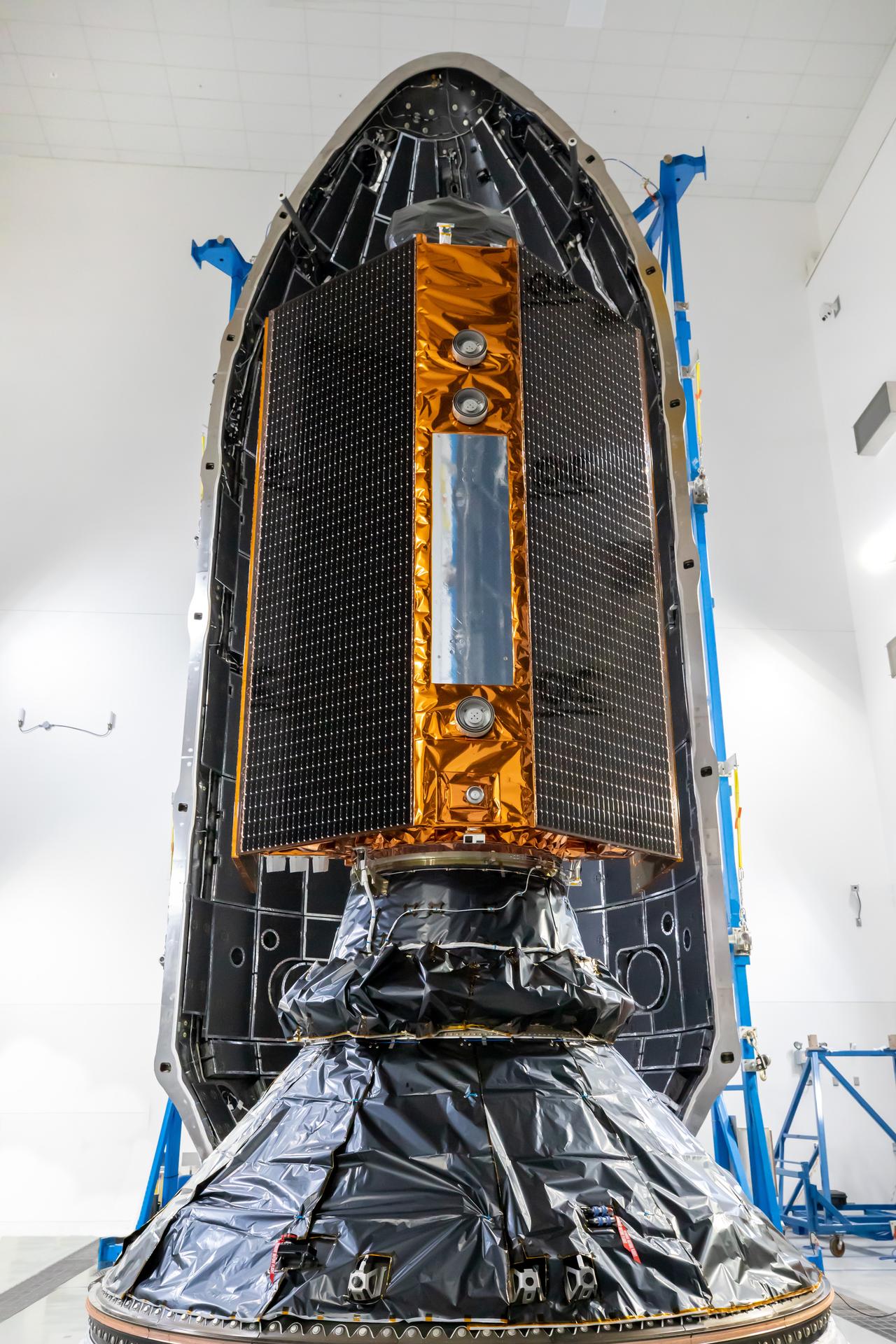

Technicians and engineers encapsulate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft within a protective payload fairing inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on Monday, Nov. 10, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians and engineers encapsulate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft within a protective payload fairing inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on Monday, Nov. 10, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
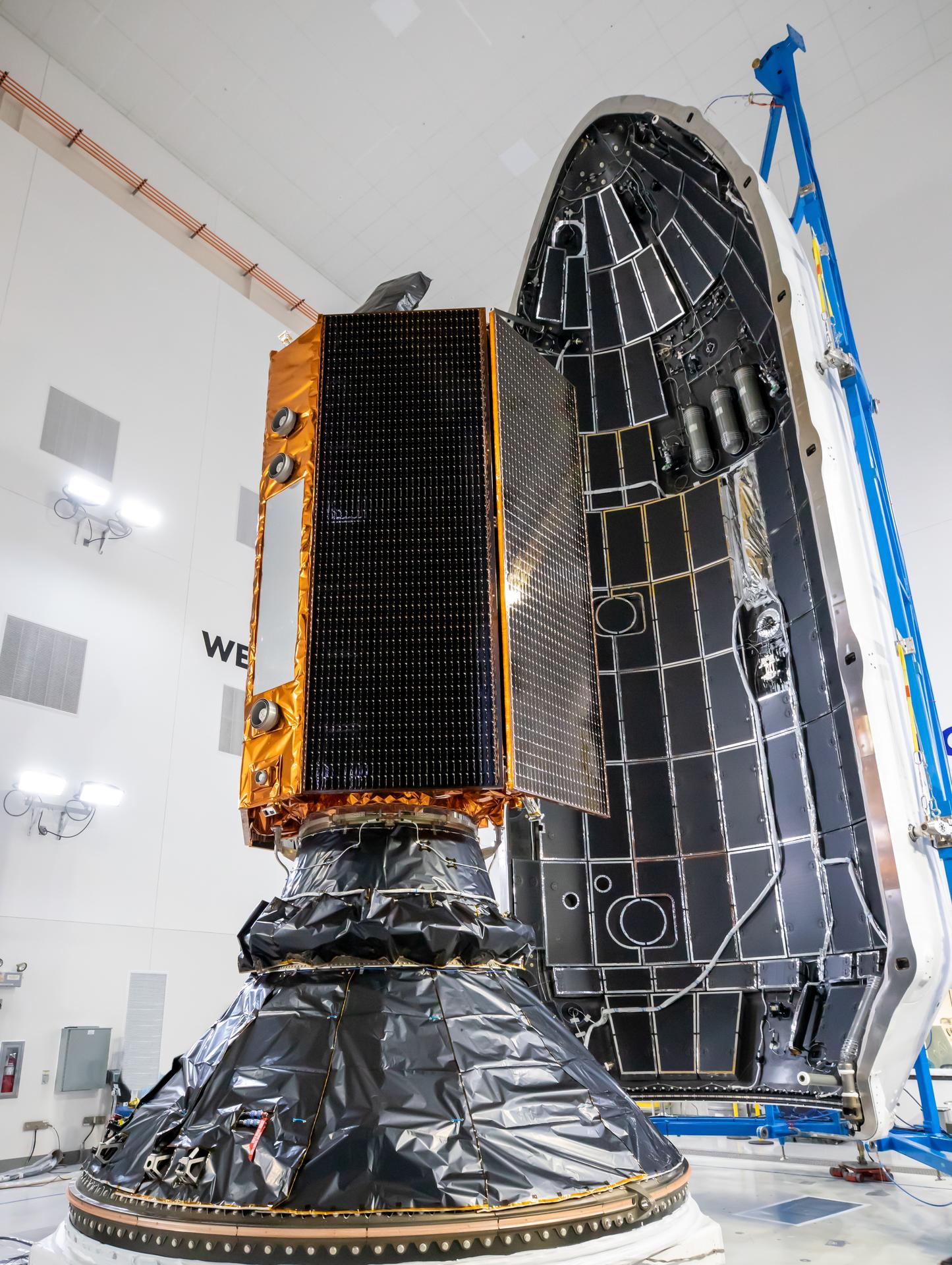

Technicians and engineers encapsulate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft within a protective payload fairing inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on Monday, Nov. 10, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
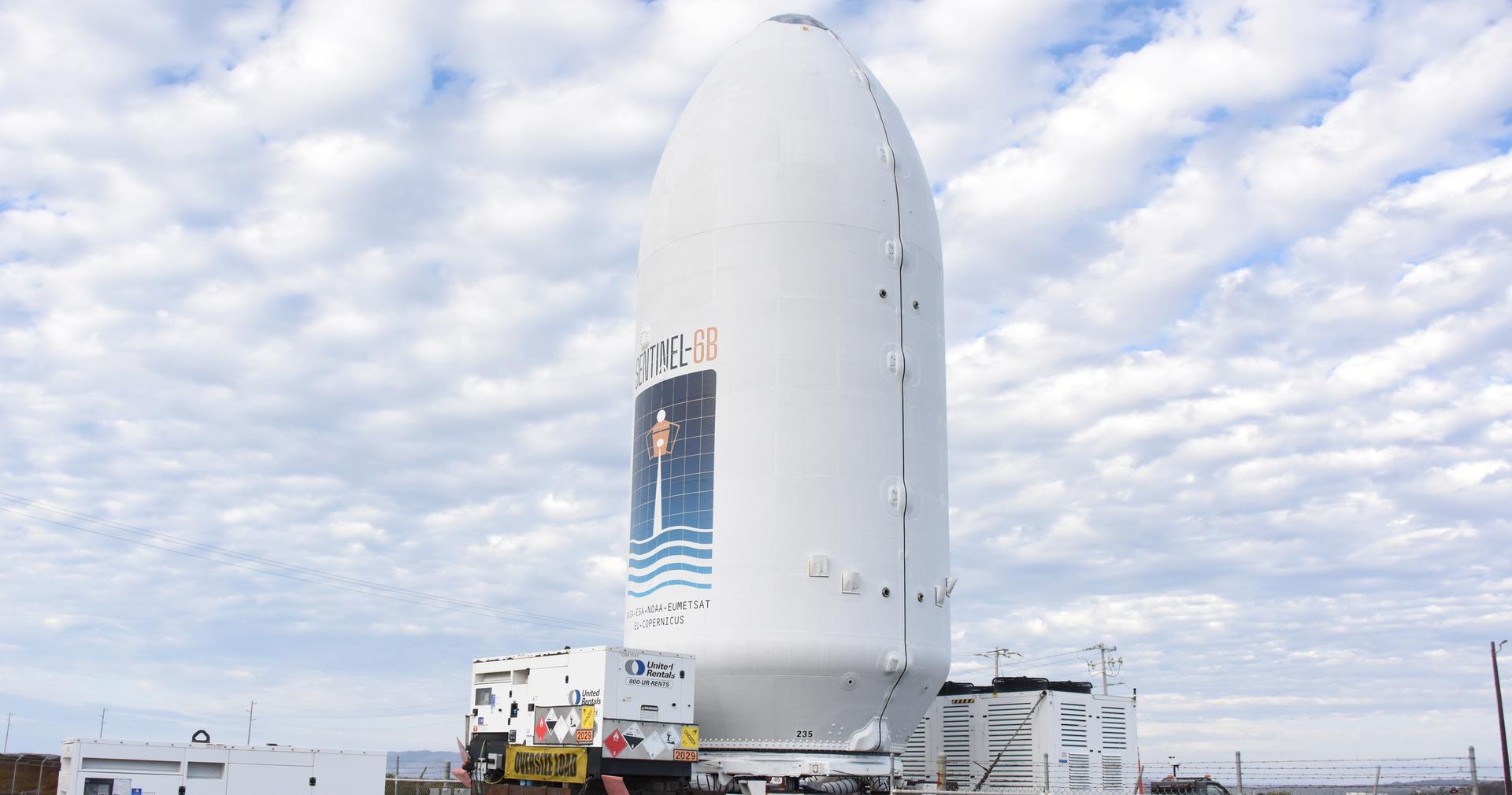

Workers transport the international Sentinel-6B satellite, encapsulated in the SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing, from the Astrotech Space Operations Facility to Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Nov. 12, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, for launch.

Workers transport the international Sentinel-6B satellite, encapsulated in the SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing, from the Astrotech Space Operations Facility to Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Nov. 12, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, for launch.
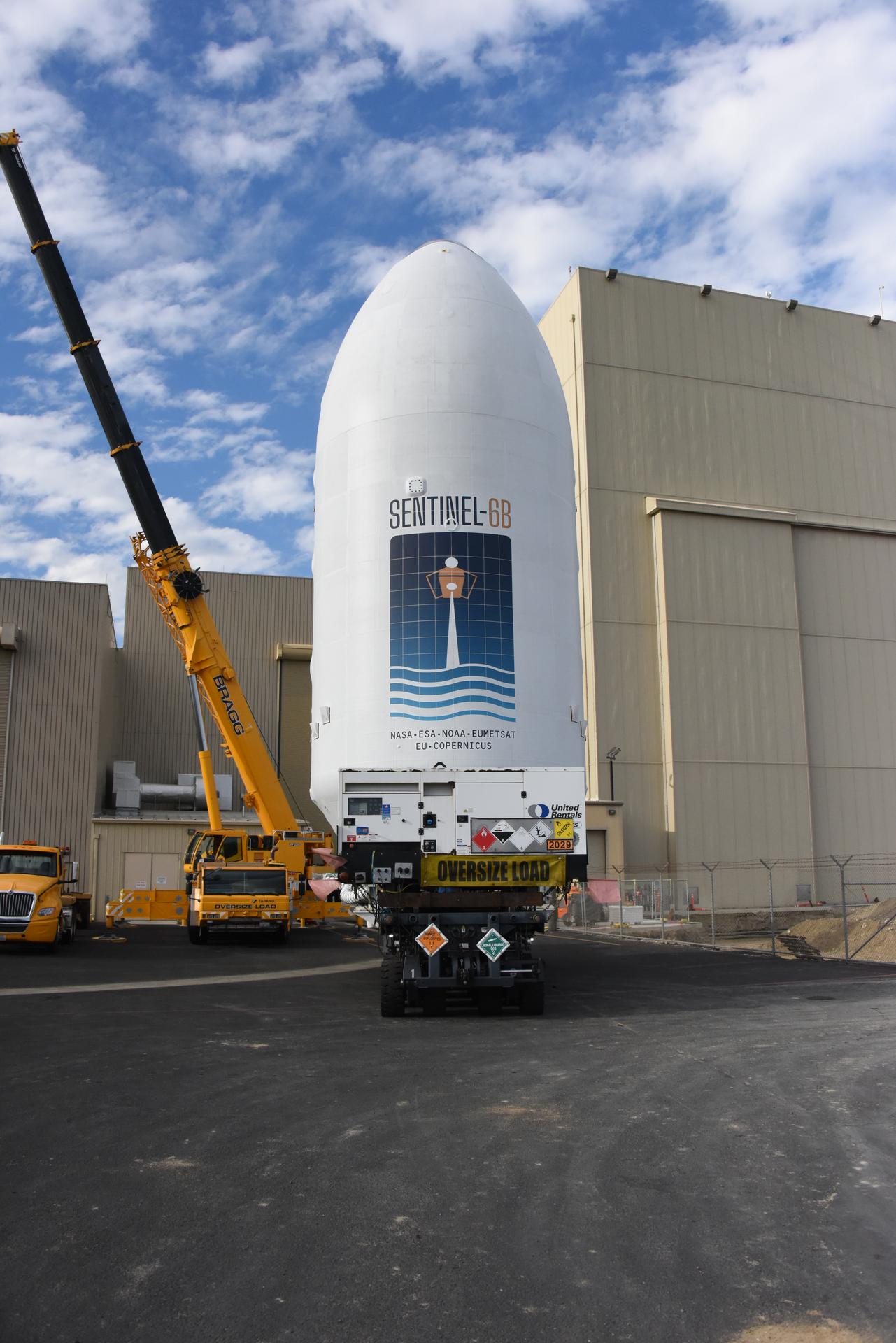

Workers transport the international Sentinel-6B satellite, encapsulated in the SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing, from the Astrotech Space Operations Facility to Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Nov. 12, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, for launch.
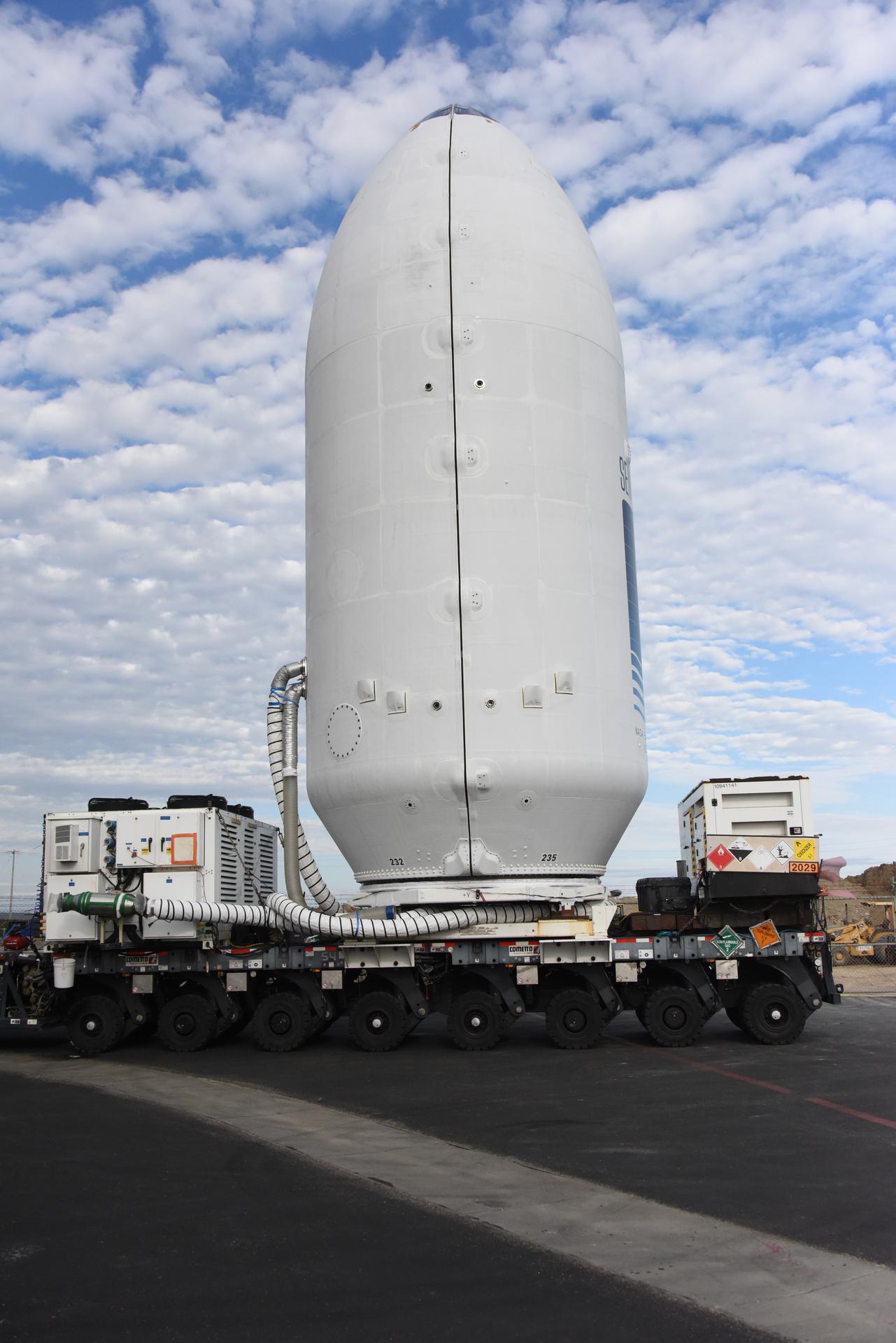

Workers transport the international Sentinel-6B satellite, encapsulated in the SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing, from the Astrotech Space Operations Facility to Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Nov. 12, 2025. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, for launch.

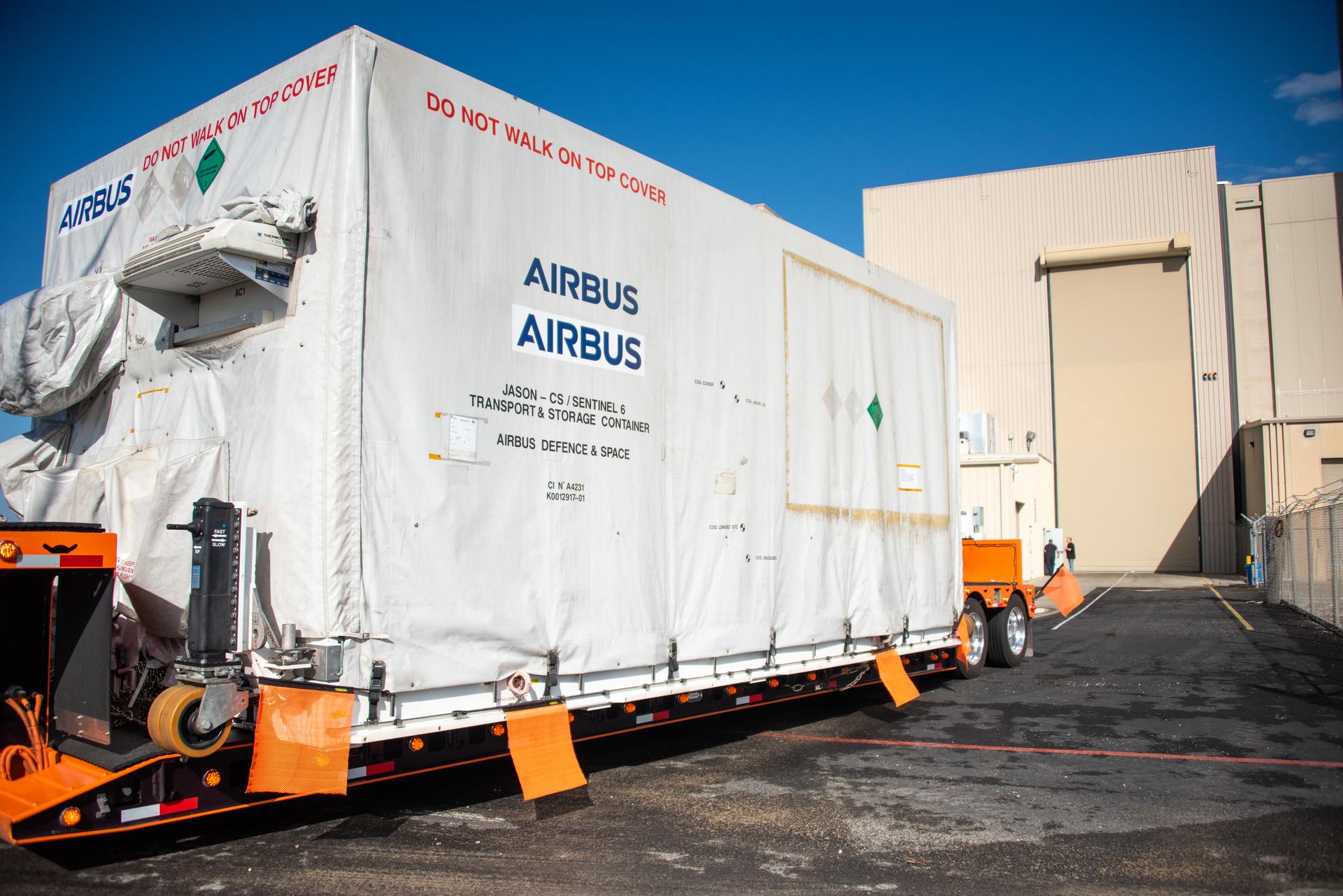
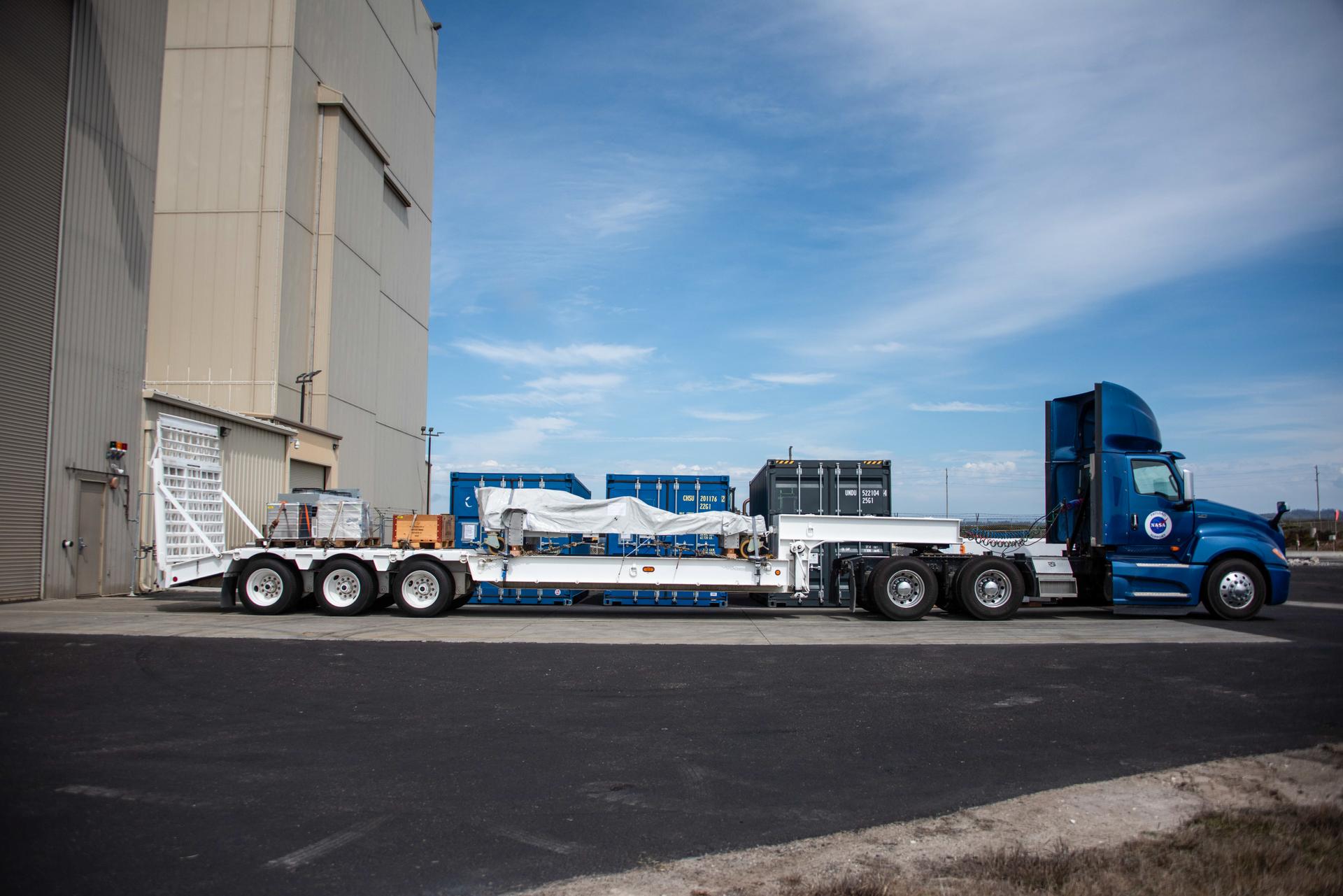
Packed in its shipping container, the Sentinel-6B spacecraft, a collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), arrives by truck at the entrance NASA’s Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Monday, Aug. 18, 2025. The second of two spacecraft that constitutes the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, Sentinel-6B will measure sea surface height and provide crucial information to help improve coastal planning, enabling local and state governments to make informed decisions about protecting coastal infrastructure, real estate, and energy sites. Launch is targeted for no earlier than November on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Vandenberg.
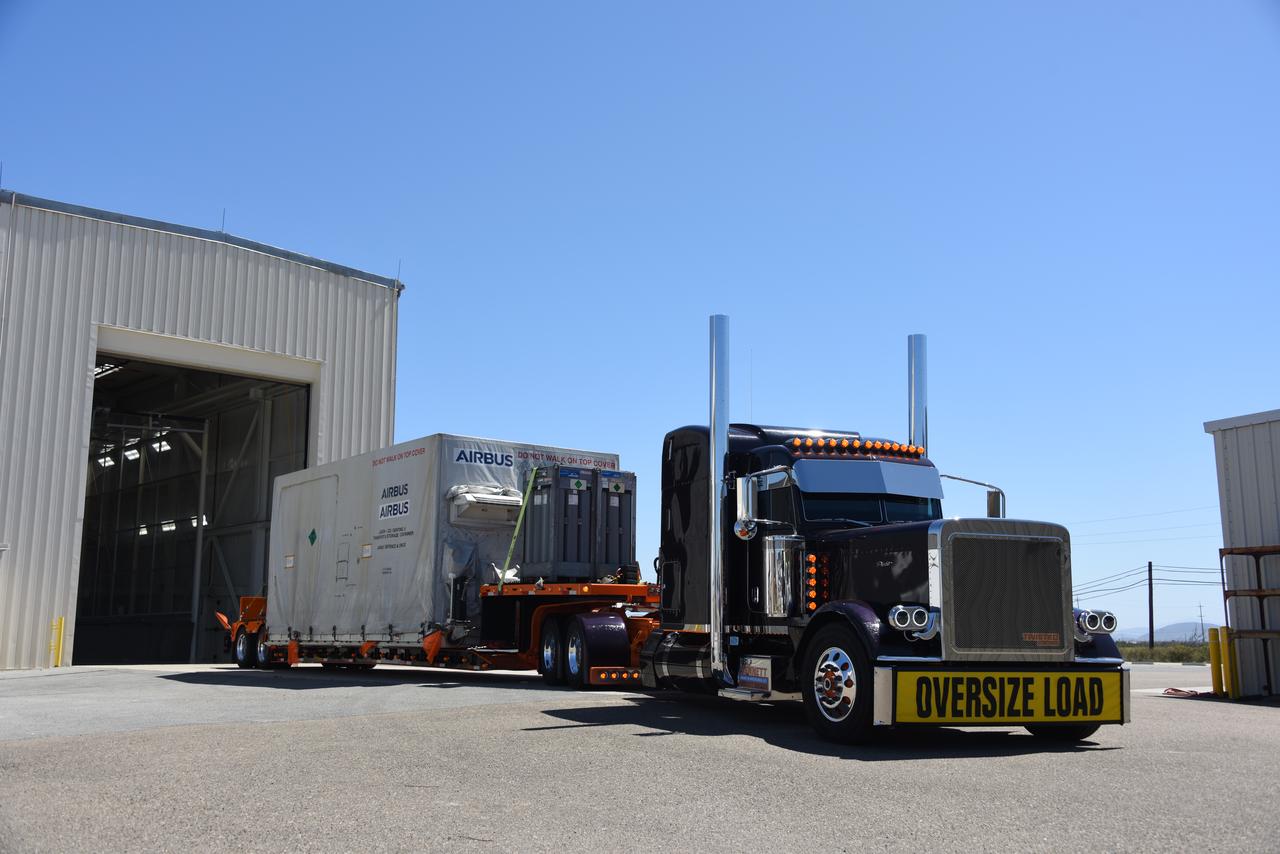

Packed in its shipping container, the Sentinel-6B spacecraft, a collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), arrives by truck at the entrance NASA’s Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Monday, Aug. 18, 2025. The second of two spacecraft that constitutes the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, Sentinel-6B will measure sea surface height and provide crucial information to help improve coastal planning, enabling local and state governments to make informed decisions about protecting coastal infrastructure, real estate, and energy sites. Launch is targeted for no earlier than November on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Vandenberg.
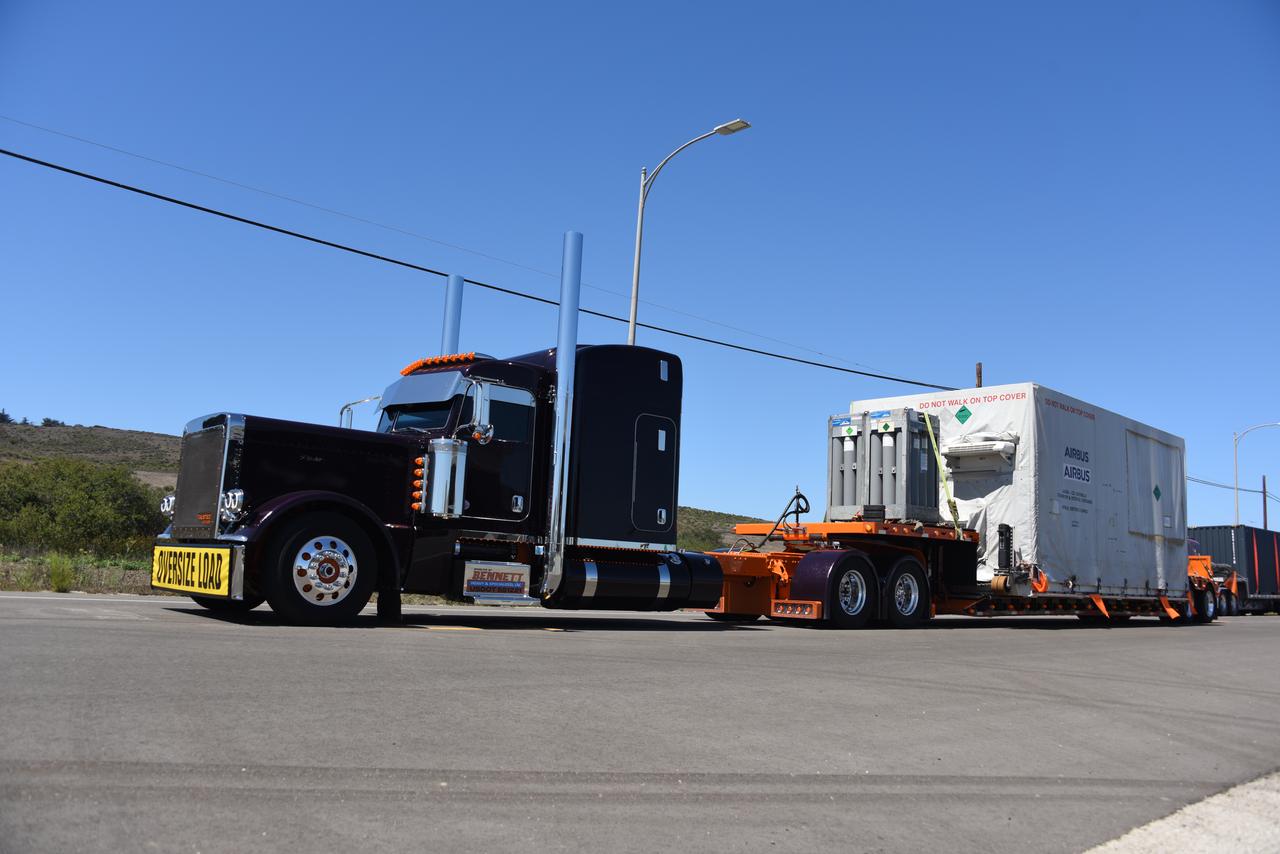

Packed in its shipping container, the Sentinel-6B spacecraft, a collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), arrives by truck at the entrance NASA’s Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Monday, Aug. 18, 2025. The second of two spacecraft that constitutes the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, Sentinel-6B will measure sea surface height and provide crucial information to help improve coastal planning, enabling local and state governments to make informed decisions about protecting coastal infrastructure, real estate, and energy sites. Launch is targeted for no earlier than November on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Vandenberg.
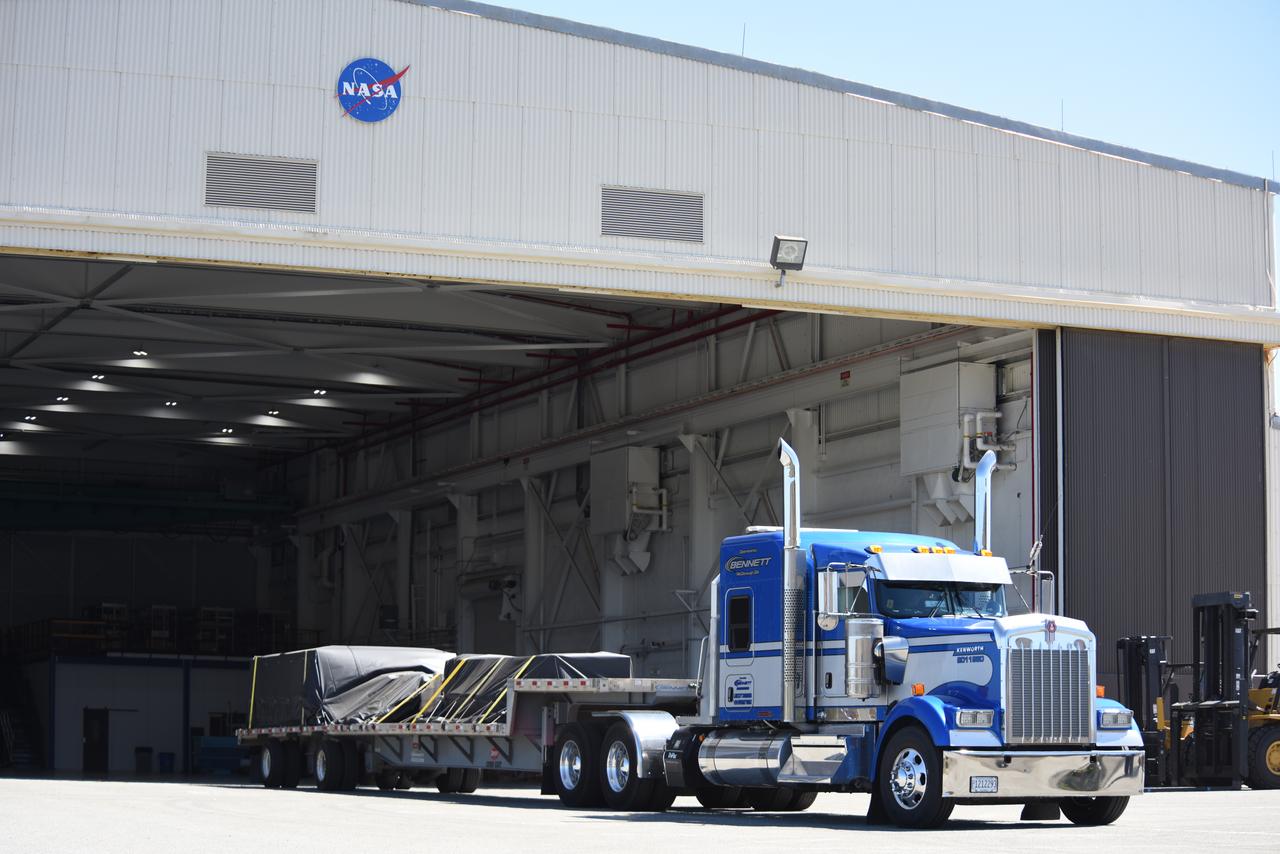

Wrapped in protective coverings, ground support equipment for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft, a collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), arrives by truck to NASA’s Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Monday, Aug. 18, 2025. The second of two spacecraft that constitutes the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, Sentinel-6B will measure sea surface height and provide crucial information to help improve coastal planning, enabling local and state governments to make informed decisions about protecting coastal infrastructure, real estate, and energy sites. Launch is targeted for no earlier than November on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Vandenberg.
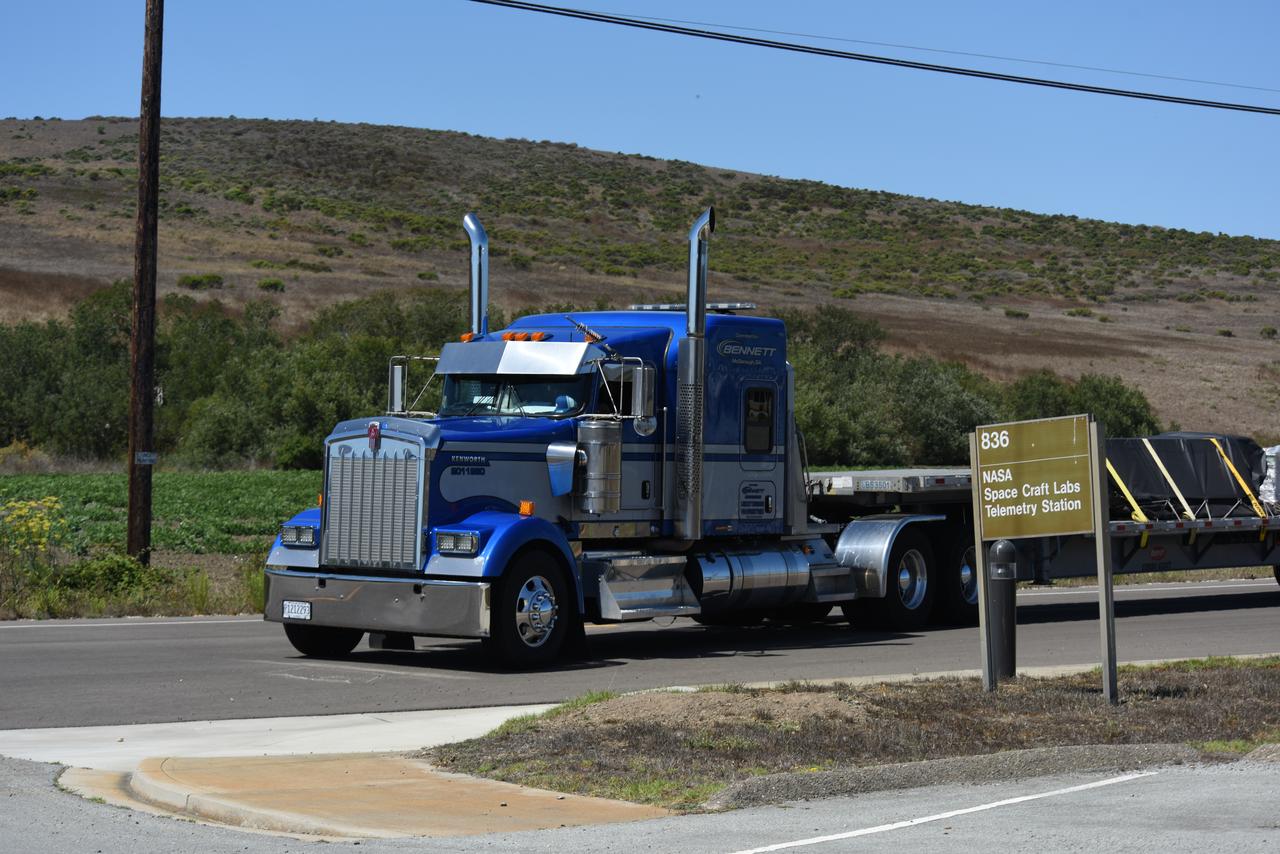

Wrapped in protective coverings, ground support equipment for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft, a collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), arrives by truck to NASA’s Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Monday, Aug. 18, 2025. The second of two spacecraft that constitutes the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, Sentinel-6B will measure sea surface height and provide crucial information to help improve coastal planning, enabling local and state governments to make informed decisions about protecting coastal infrastructure, real estate, and energy sites. Launch is targeted for no earlier than November on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Vandenberg.
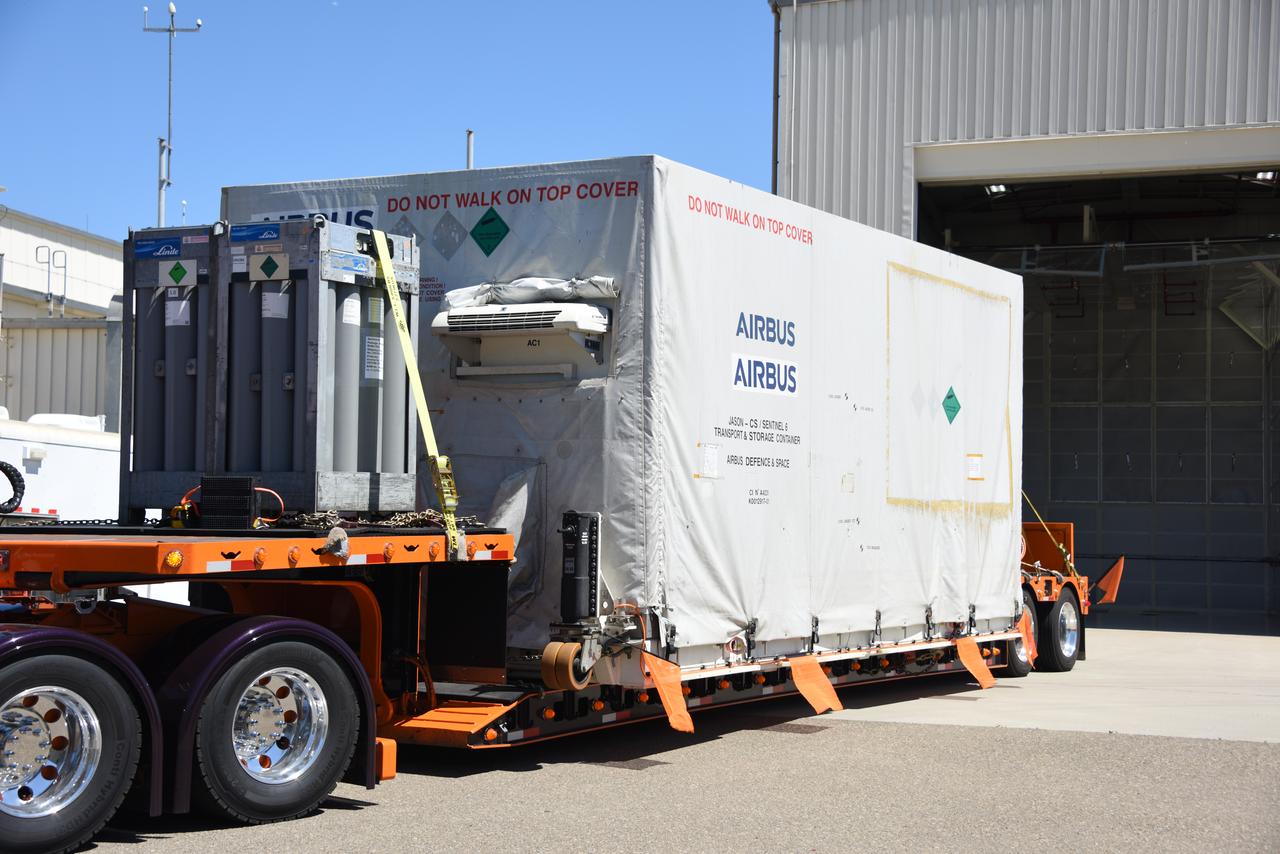

Packed in its shipping container, the Sentinel-6B spacecraft, a collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), arrives by truck at the entrance NASA’s Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Monday, Aug. 18, 2025. The second of two spacecraft that constitutes the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, Sentinel-6B will measure sea surface height and provide crucial information to help improve coastal planning, enabling local and state governments to make informed decisions about protecting coastal infrastructure, real estate, and energy sites. Launch is targeted for no earlier than November on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Vandenberg.
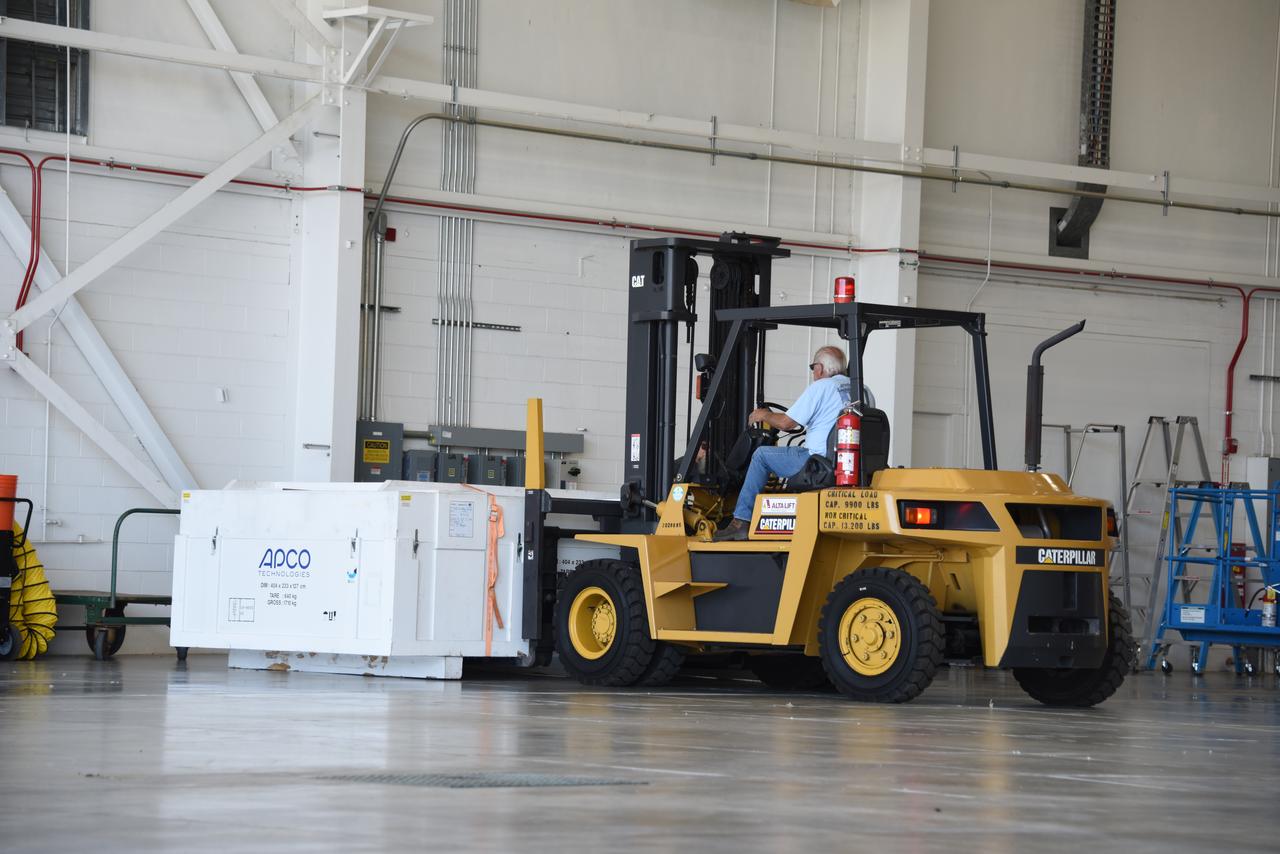

Ground support equipment for the Sentinel-6B spacecraft, a collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), is offloaded inside NASA’s Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Monday, Aug. 18, 2025. The second of two spacecraft that constitutes the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, Sentinel-6B will measure sea surface height and provide crucial information to help improve coastal planning, enabling local and state governments to make informed decisions about protecting coastal infrastructure, real estate, and energy sites. Launch is targeted for no earlier than November on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Vandenberg.
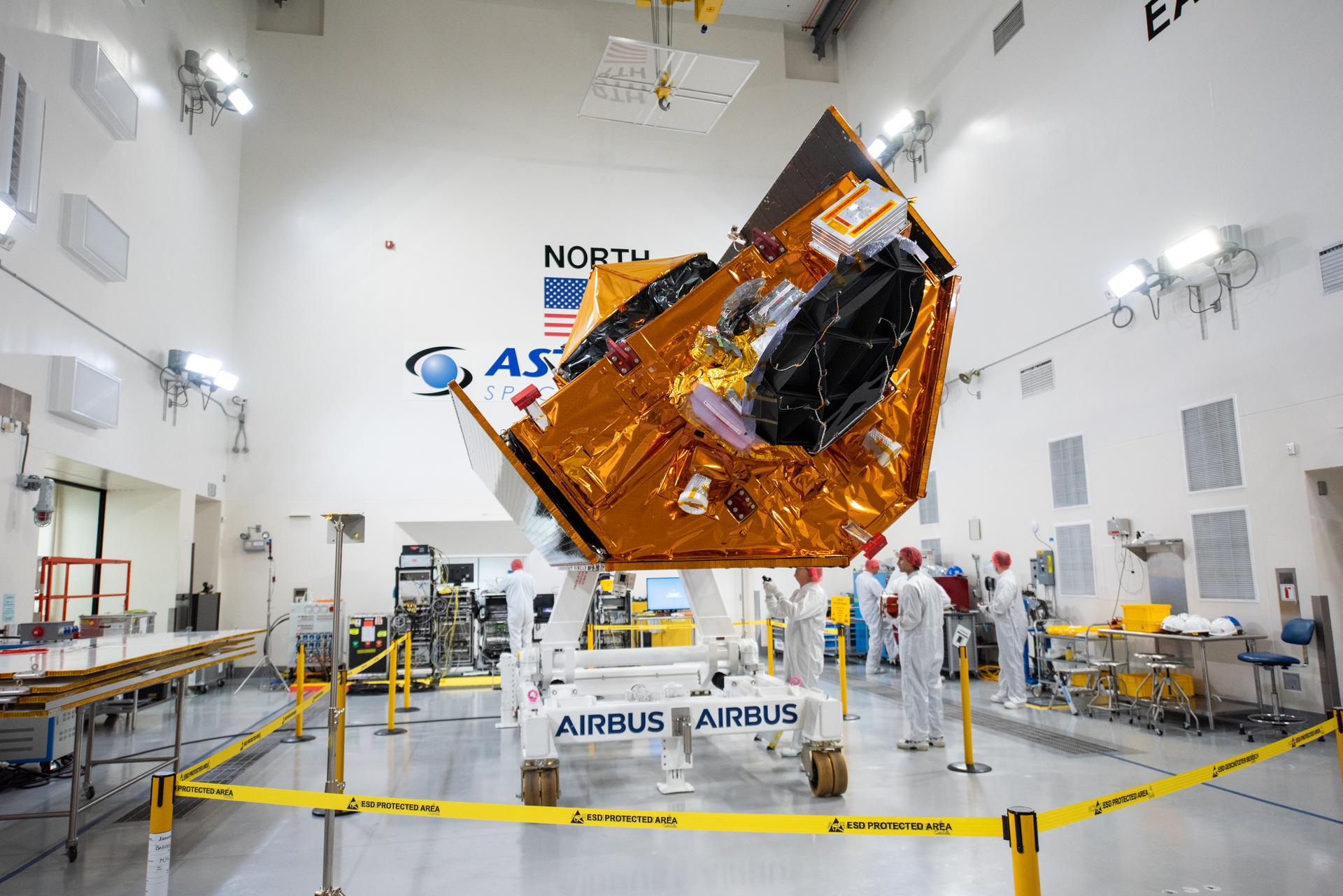

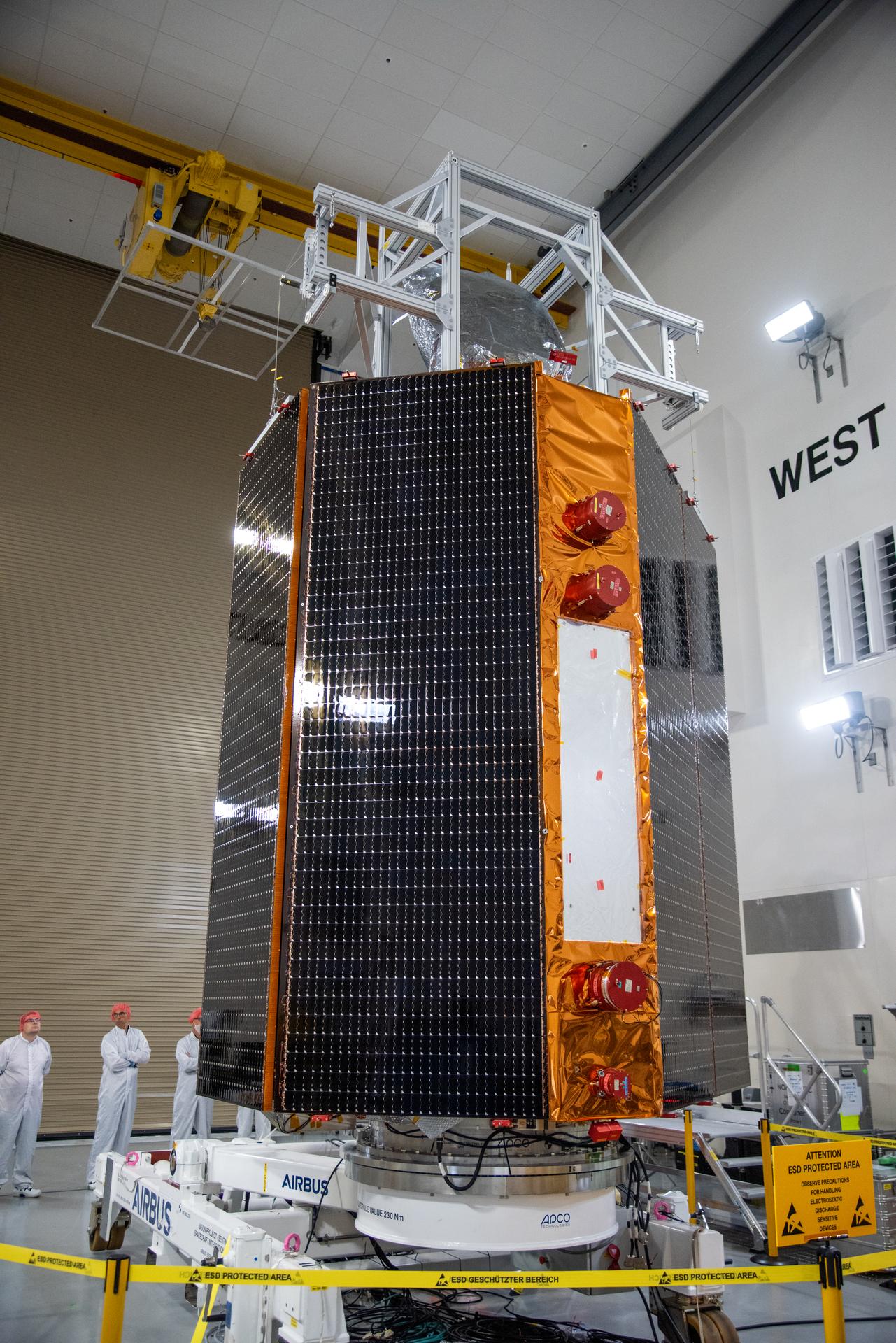
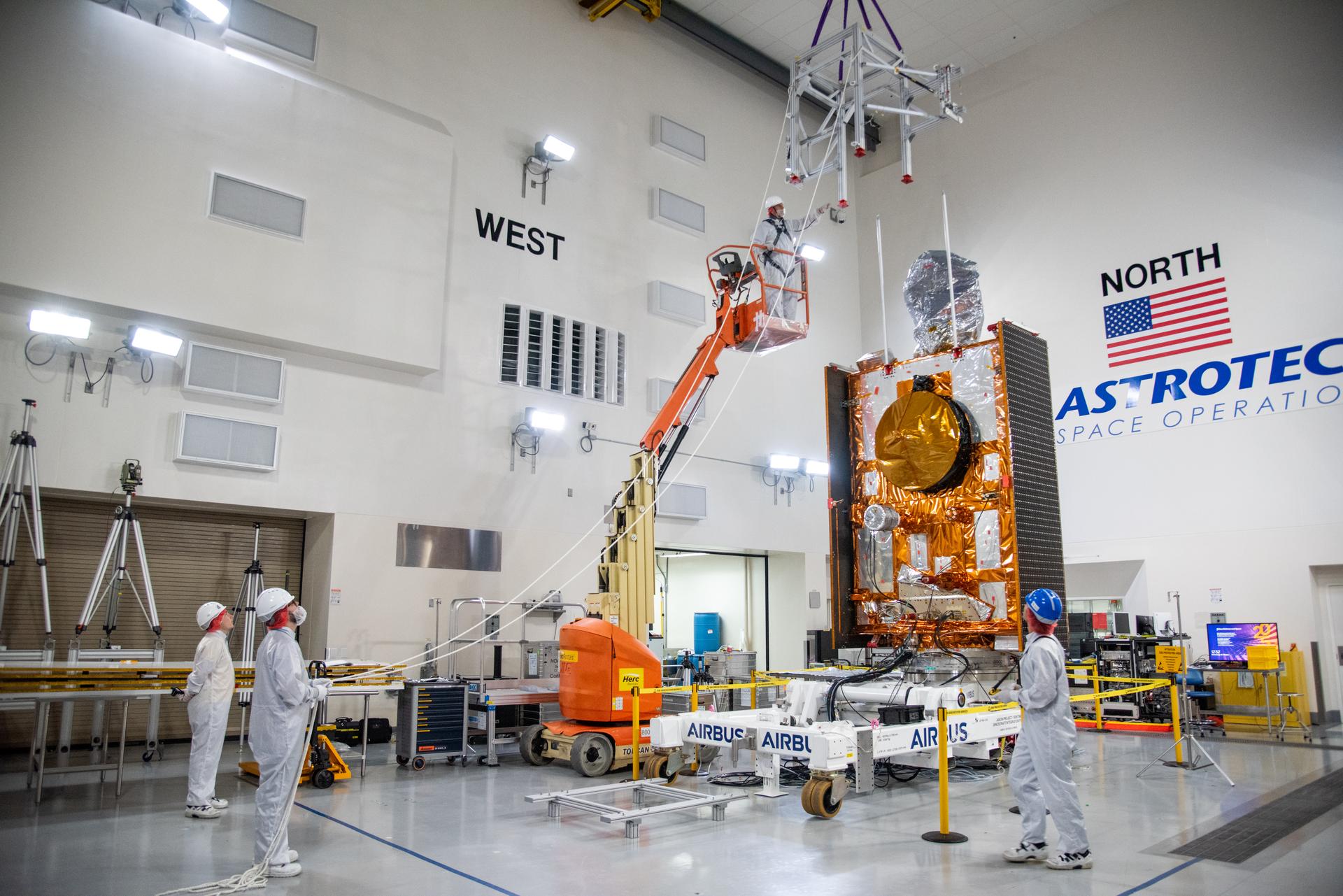
Technicians use a crane to place the Sentinel-6B spacecraft onto a work stand ahead of prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.
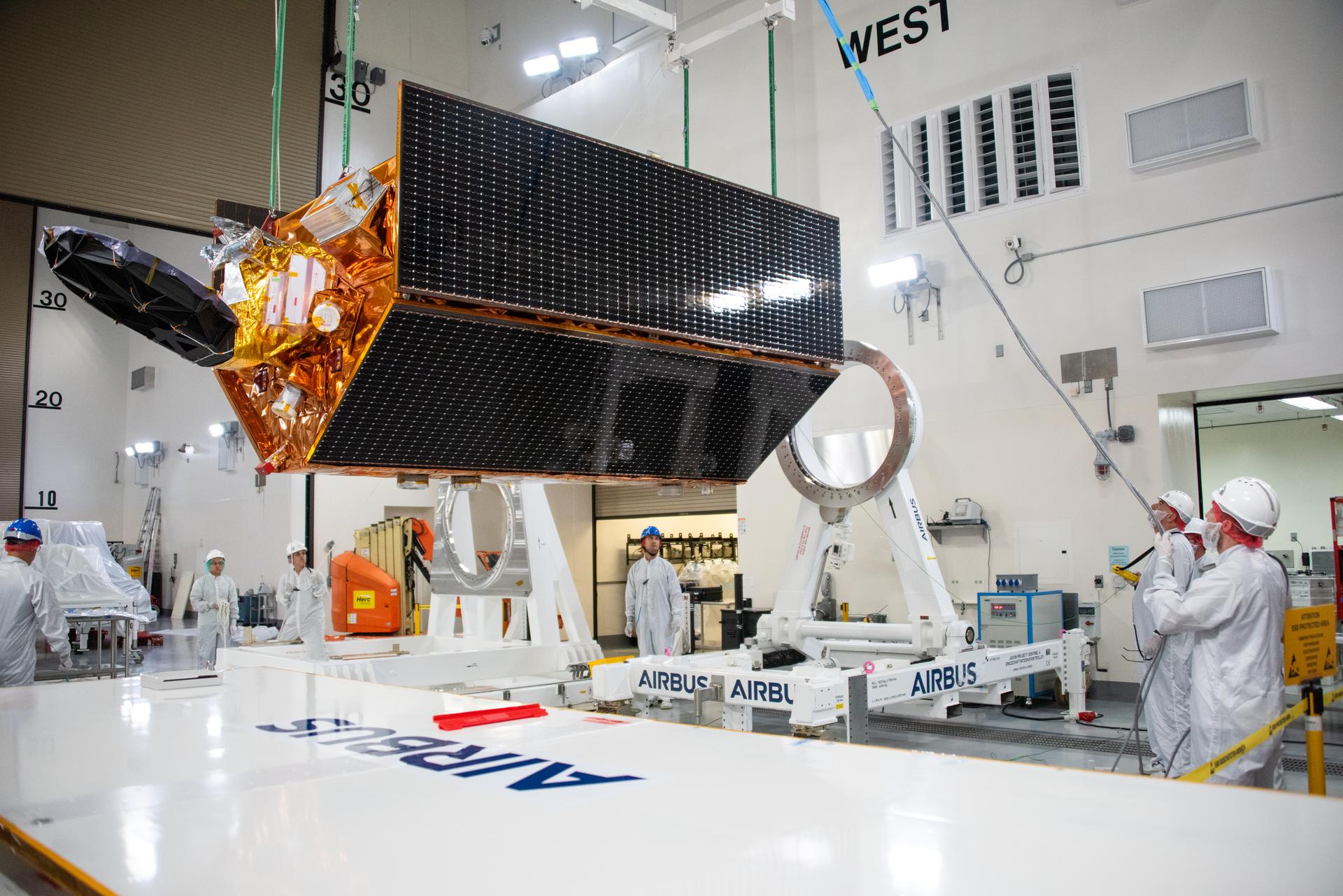

Technicians use a crane to place the Sentinel-6B spacecraft onto a work stand ahead of prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.
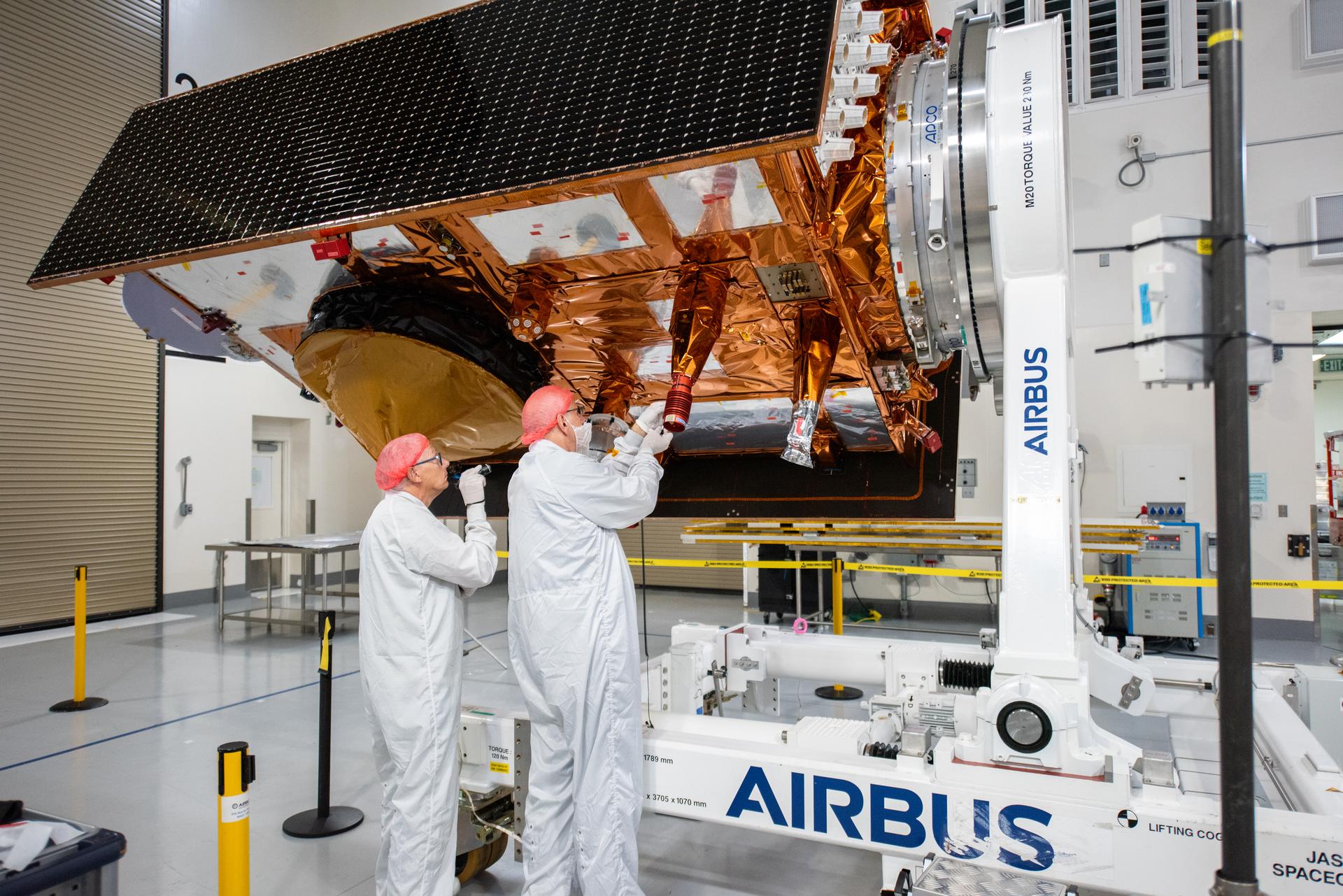

Technicians use a crane to place the Sentinel-6B spacecraft onto a work stand ahead of prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians use a crane to place the Sentinel-6B spacecraft onto a work stand ahead of prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians use a crane to place the Sentinel-6B spacecraft onto a work stand ahead of prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians use a crane to place the Sentinel-6B spacecraft onto a work stand ahead of prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.
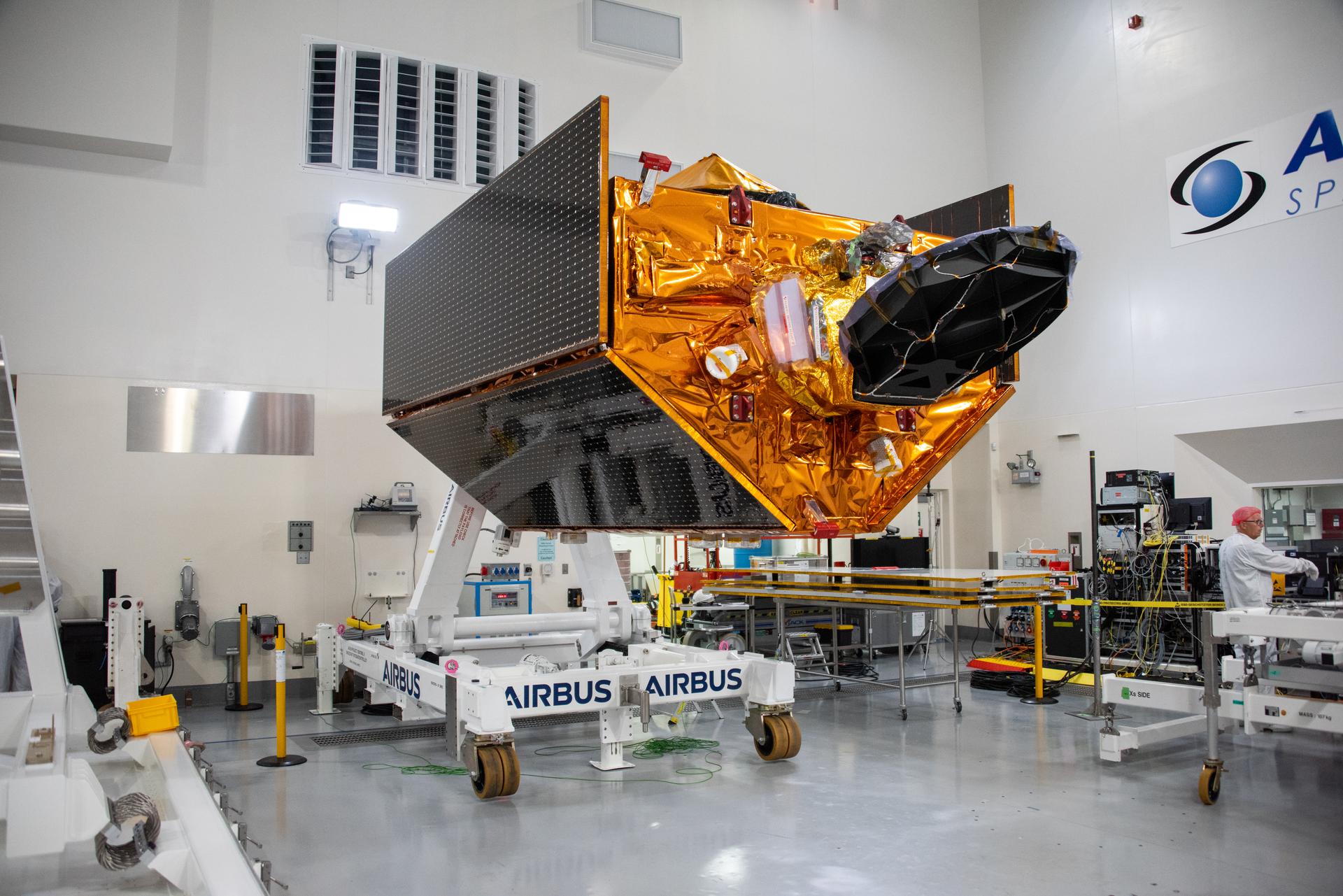

Technicians use a crane to place the Sentinel-6B spacecraft onto a work stand ahead of prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians use a crane to place the Sentinel-6B spacecraft onto a work stand ahead of prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Technicians use a crane to place the Sentinel-6B spacecraft onto a work stand ahead of prelaunch operations at the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2025. Sentinel-6B will undergo detailed inspections, tests, and fueling in a cleanroom as it prepares for a November launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans and will extend out to a decade the record of atmospheric temperatures begun by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich.

Packed in its shipping container, the Sentinel-6B spacecraft, a collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), arrives by truck to the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2025. The second of two spacecraft that constitutes the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, Sentinel-6B will measure sea surface height and provide crucial information to help improve coastal planning, enabling local and state governments to make informed decisions about protecting coastal infrastructure, real estate, and energy sites. Launch is targeted for no earlier than November on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Vandenberg.
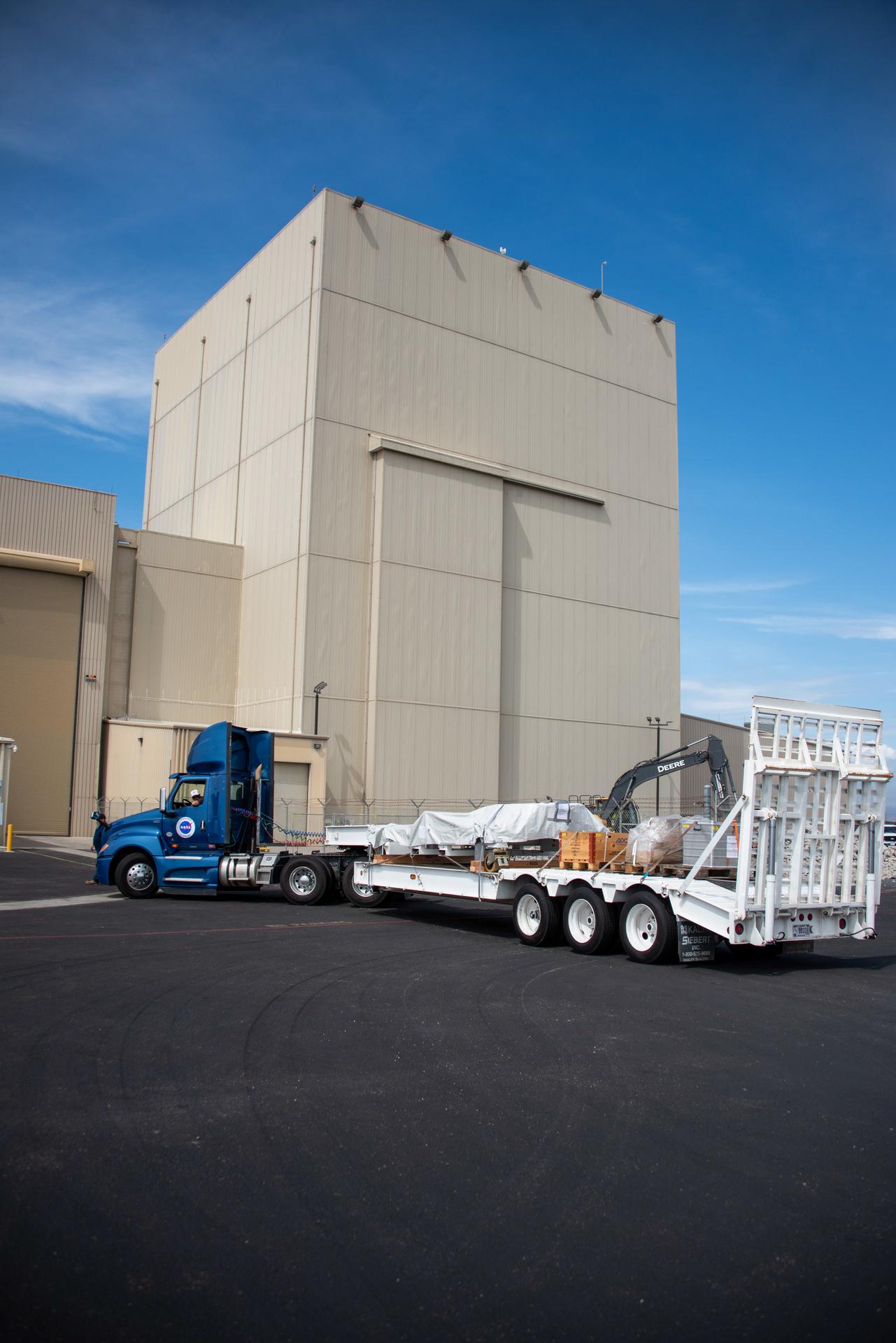

Packed in its shipping container, the Sentinel-6B spacecraft, a collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), arrives by truck to the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2025. The second of two spacecraft that constitutes the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, Sentinel-6B will measure sea surface height and provide crucial information to help improve coastal planning, enabling local and state governments to make informed decisions about protecting coastal infrastructure, real estate, and energy sites. Launch is targeted for no earlier than November on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Vandenberg.

Packed in its shipping container, the Sentinel-6B spacecraft, a collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), arrives by truck to the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2025. The second of two spacecraft that constitutes the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, Sentinel-6B will measure sea surface height and provide crucial information to help improve coastal planning, enabling local and state governments to make informed decisions about protecting coastal infrastructure, real estate, and energy sites. Launch is targeted for no earlier than November on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Vandenberg.
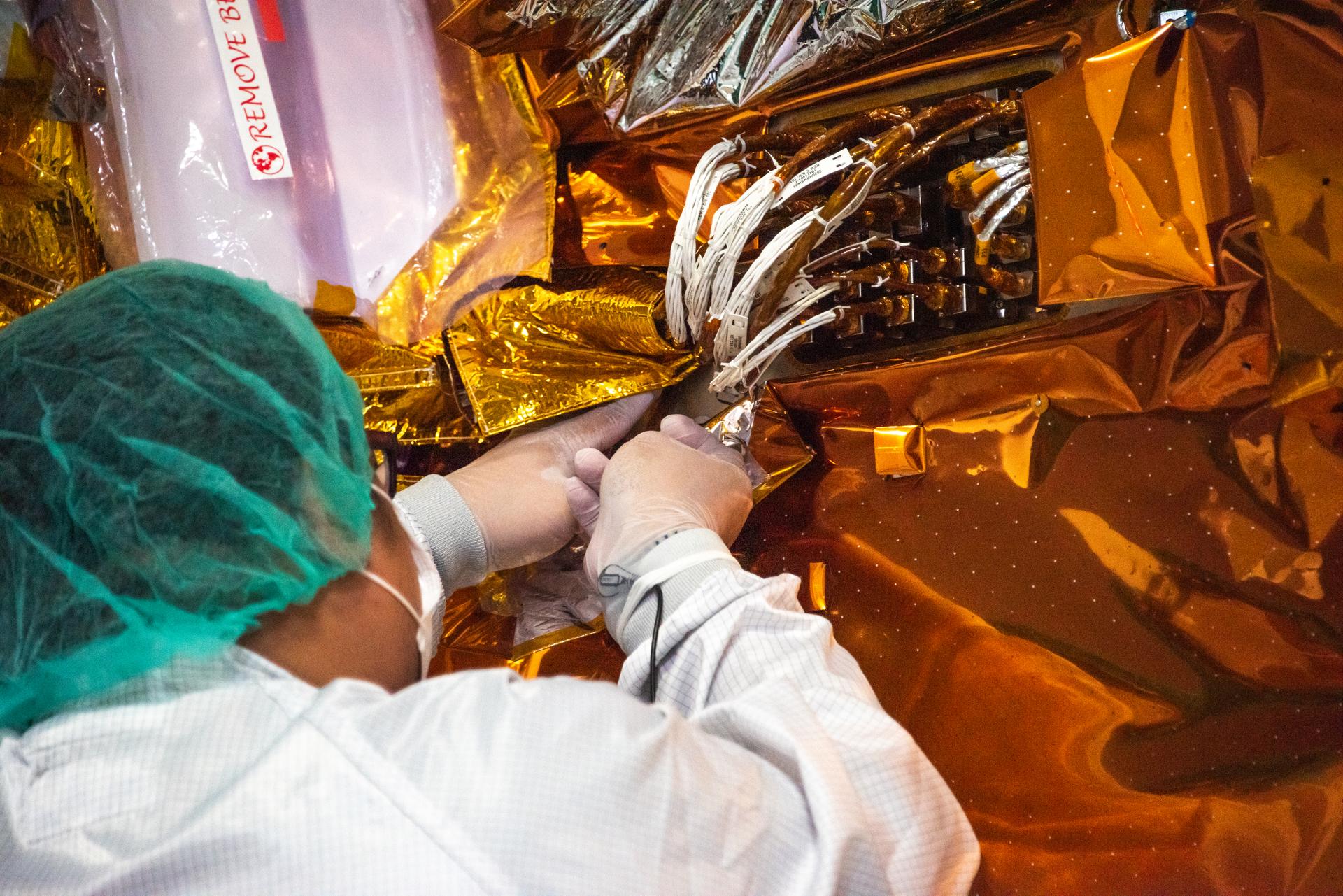

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
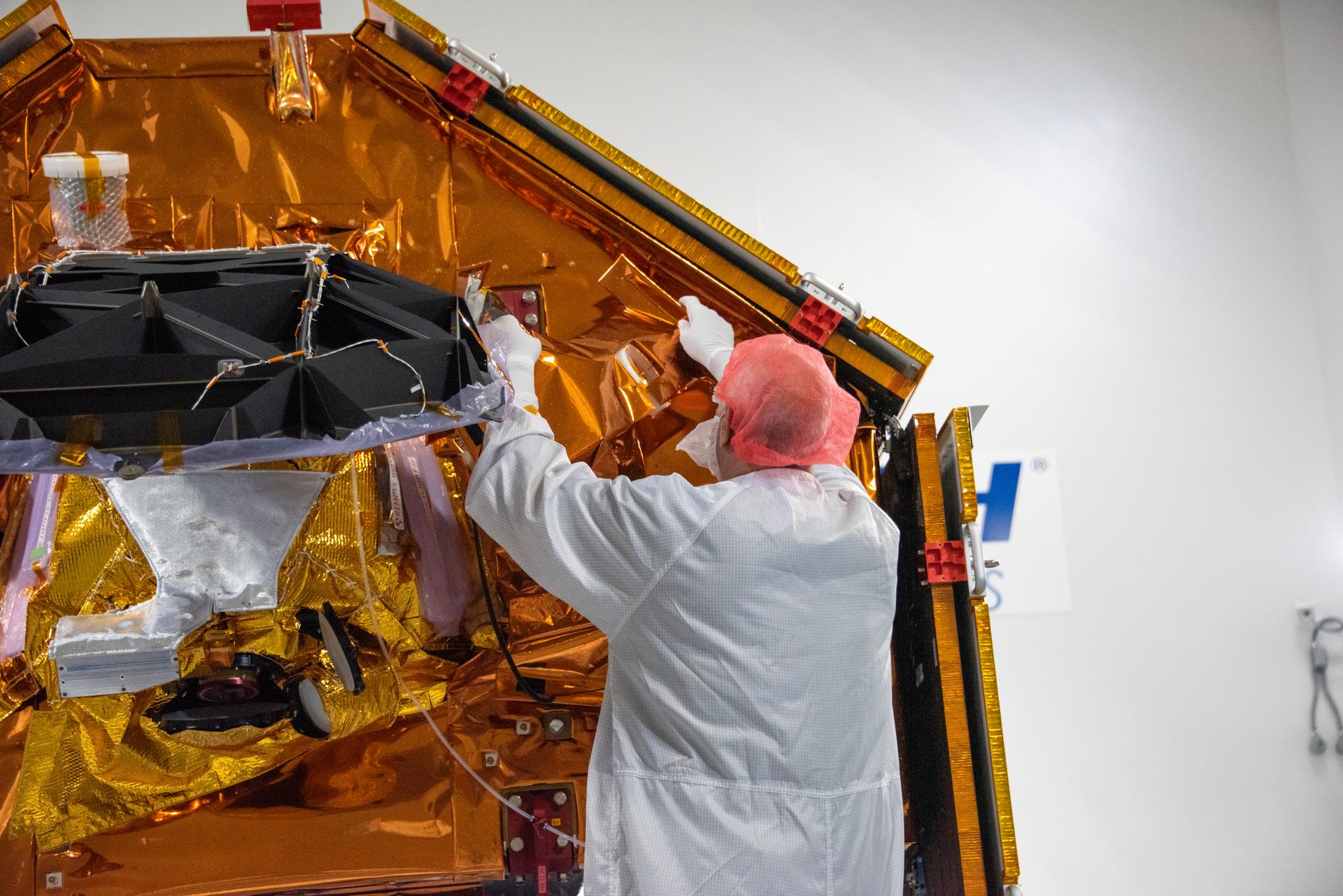

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
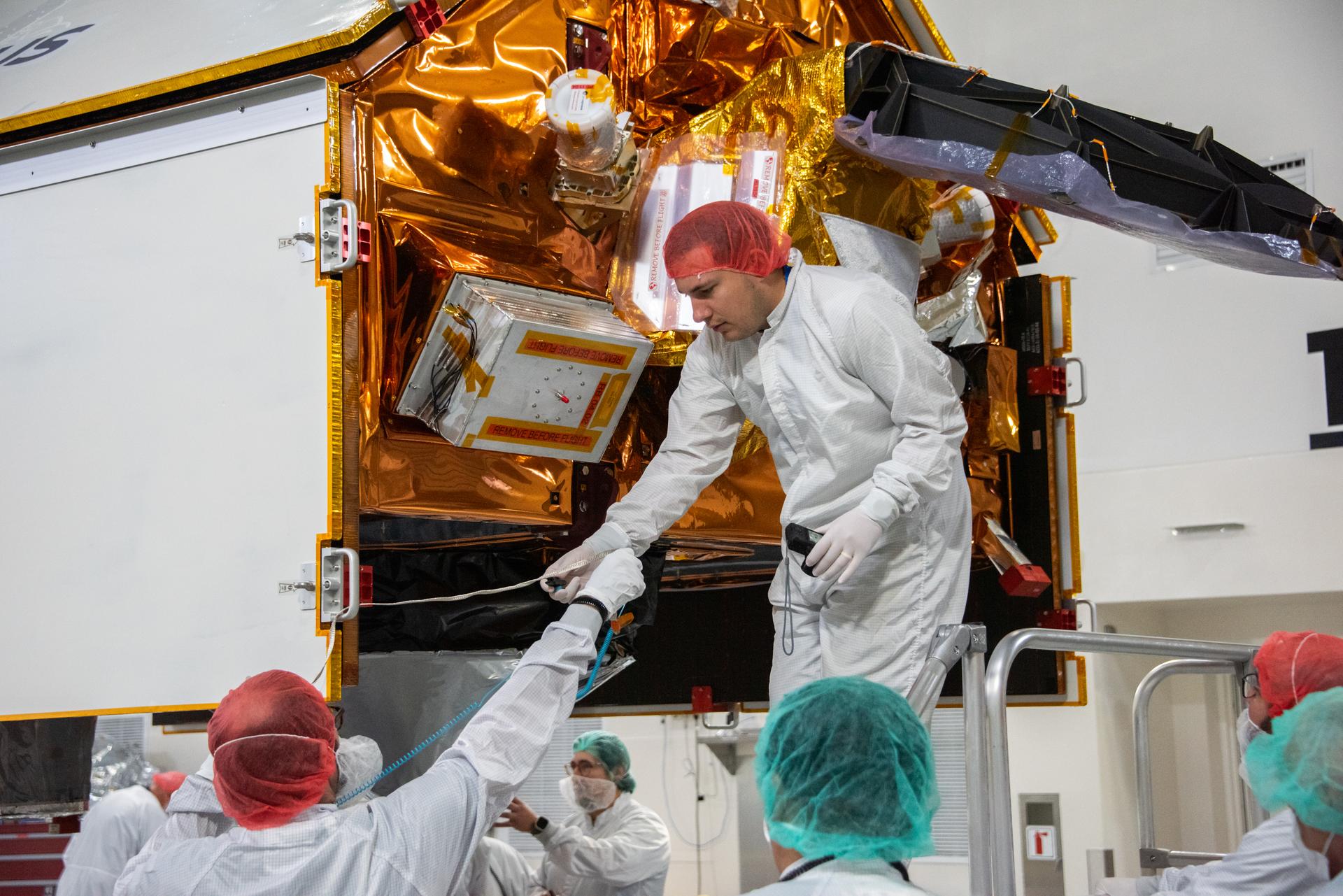

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
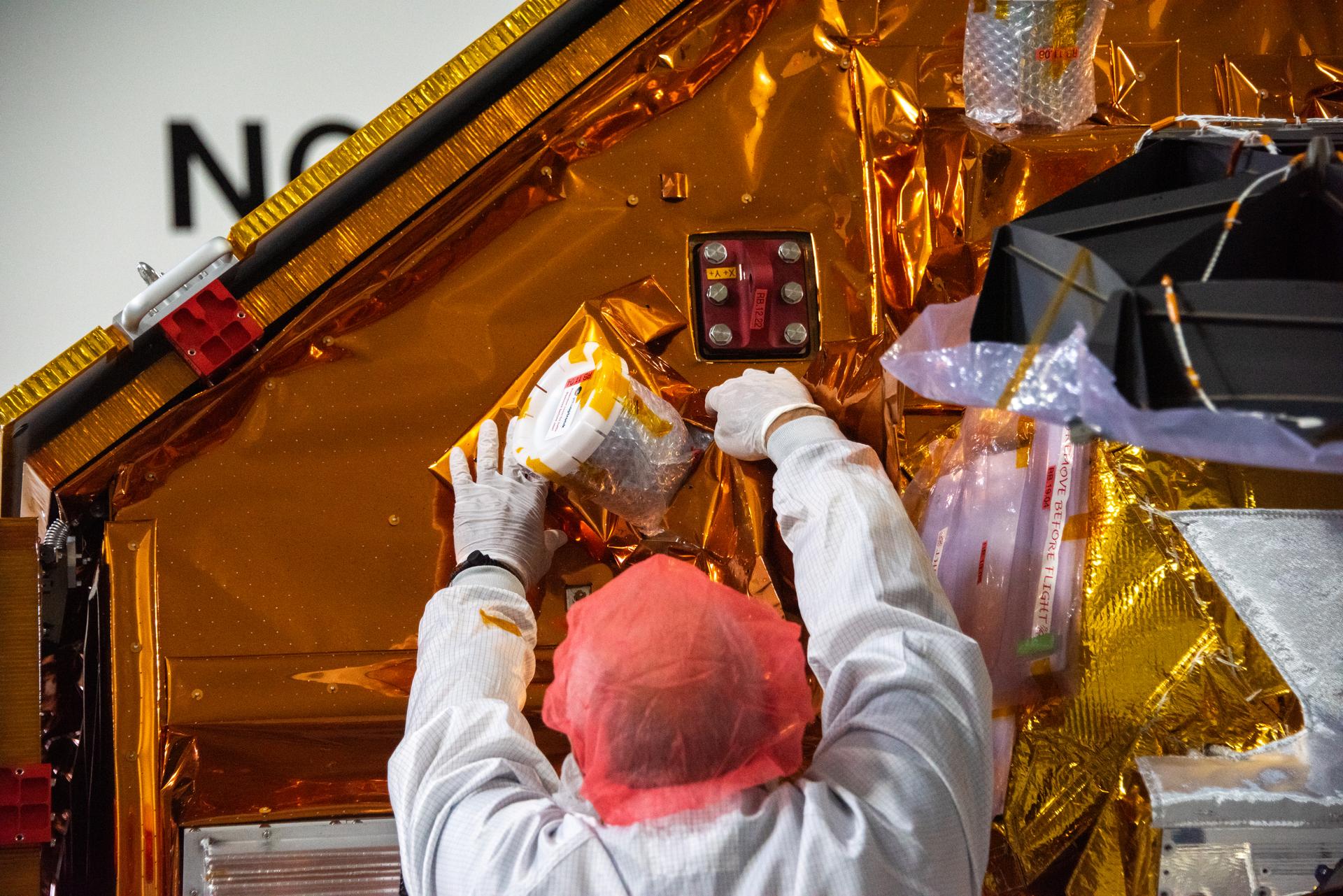

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
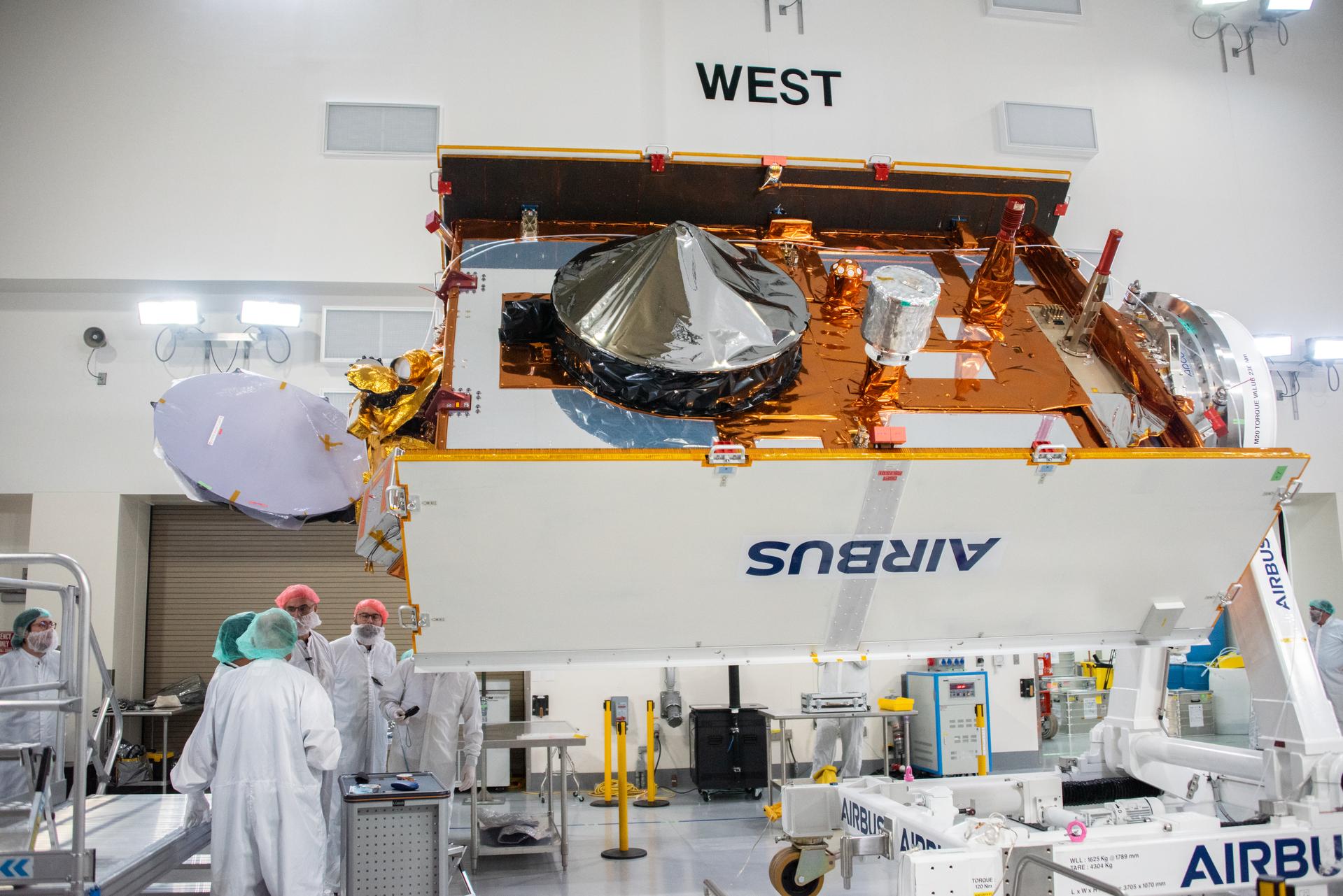

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
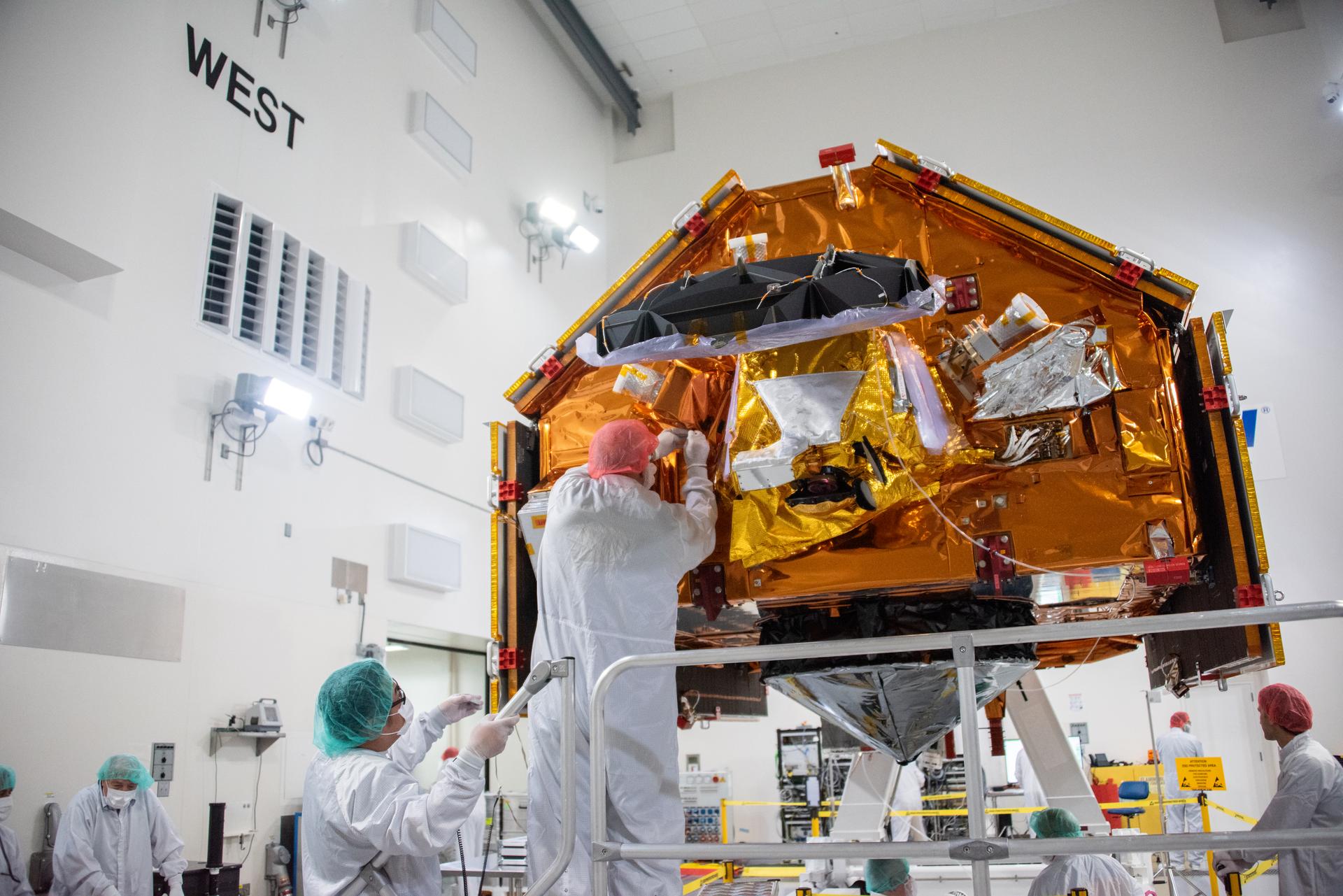

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians install multi-layer insulation on the Sentinel-6B spacecraft on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Thursday, Oct. 23, 2025. Critical for protecting spacecraft from extreme temperatures and environmental conditions in space, the thin, reflective multi-layer insulation will create a barrier to help reduce heat transfer through radiation while Sentinel-6B is in orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, 2025, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
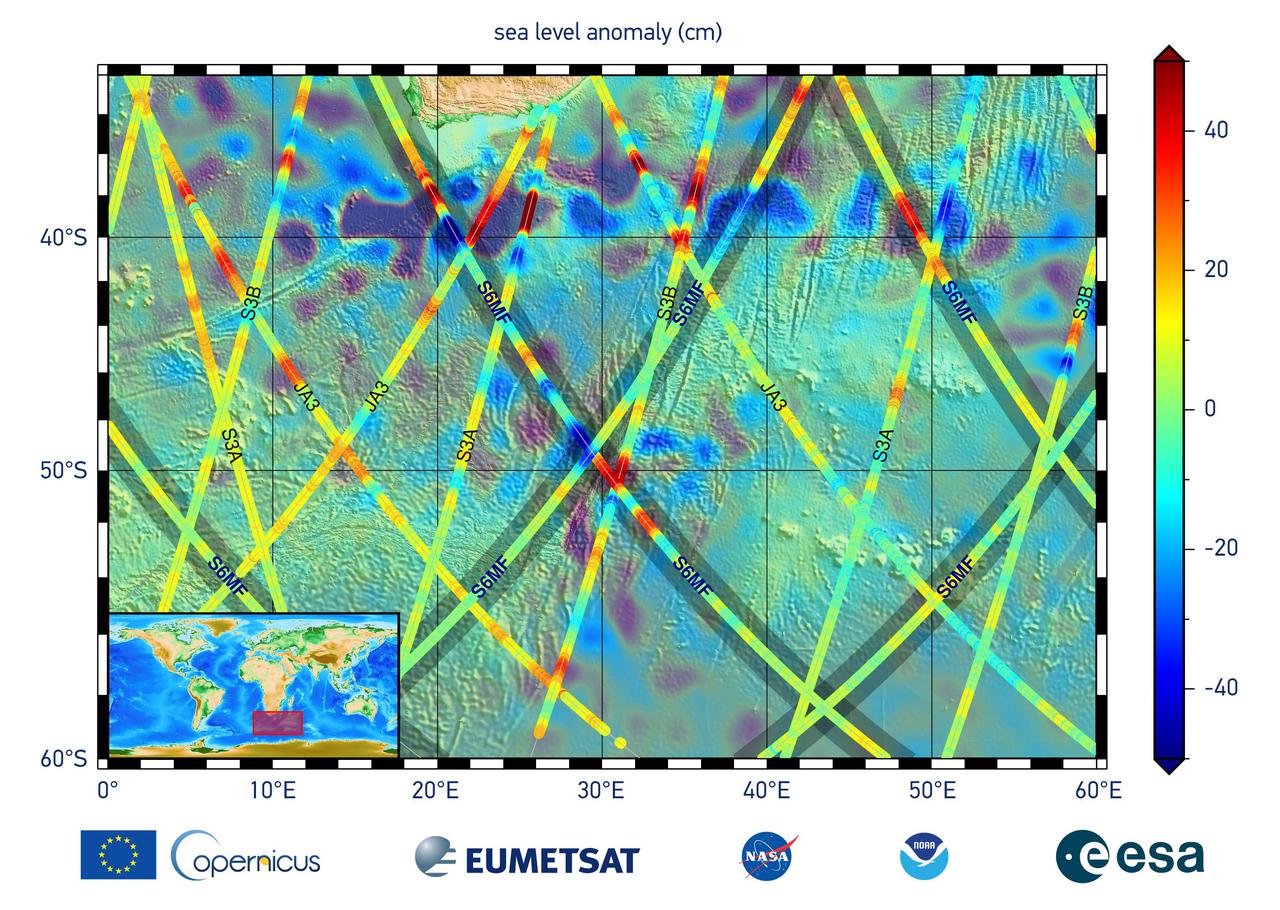
This graphic, released on Dec. 10, 2020, shows the first sea level measurements taken by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich (S6MF), which launched Nov. 21, 2020. It focuses on the ocean off the southern tip of Africa, where red colors indicate higher sea level relative to blue areas, which are lower. Also included are sea surface height measurements from three other satellites for comparison: Jason-3 (JA3), Sentinel-3A (S3A), and Sentinel-3B (S3B). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24135
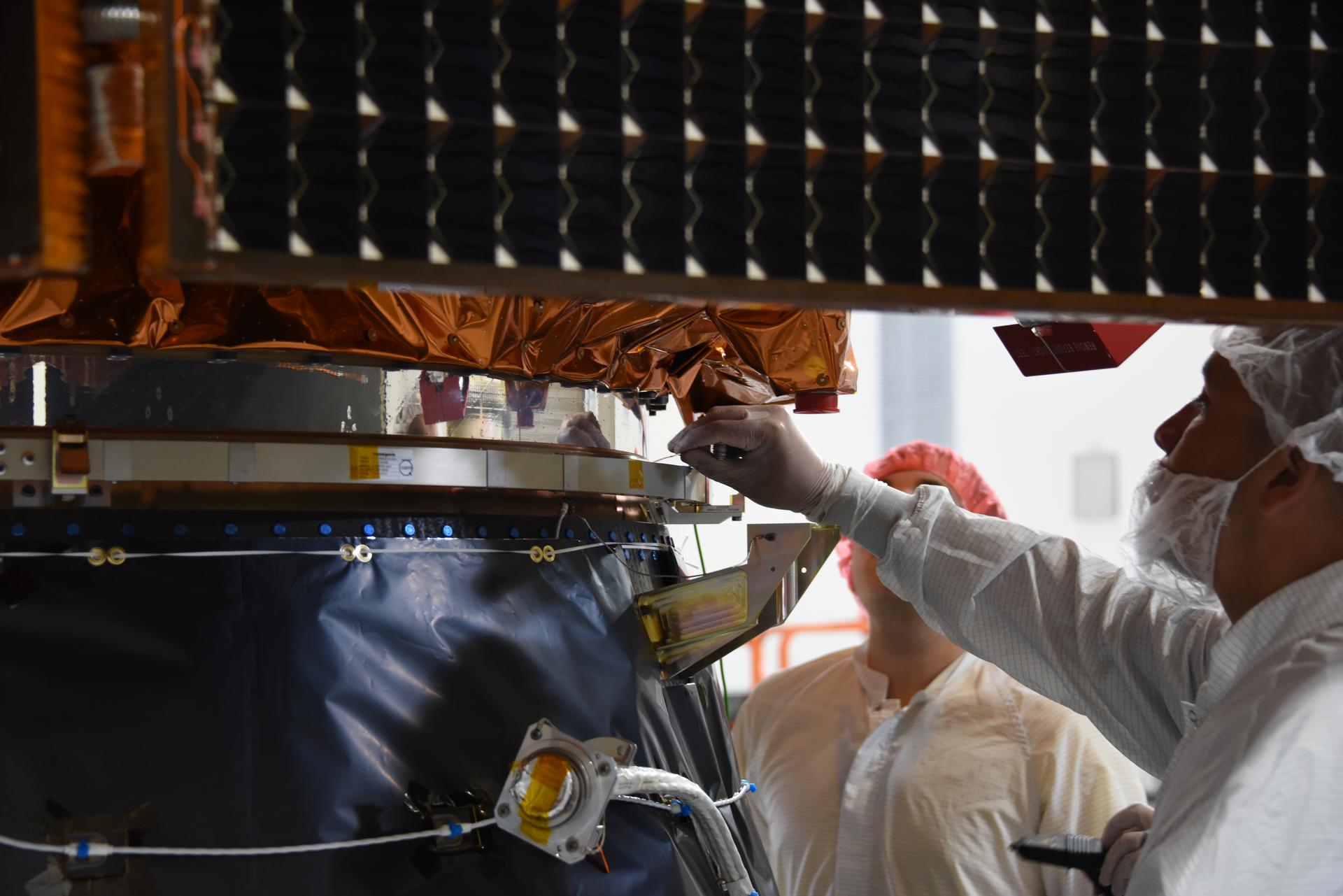

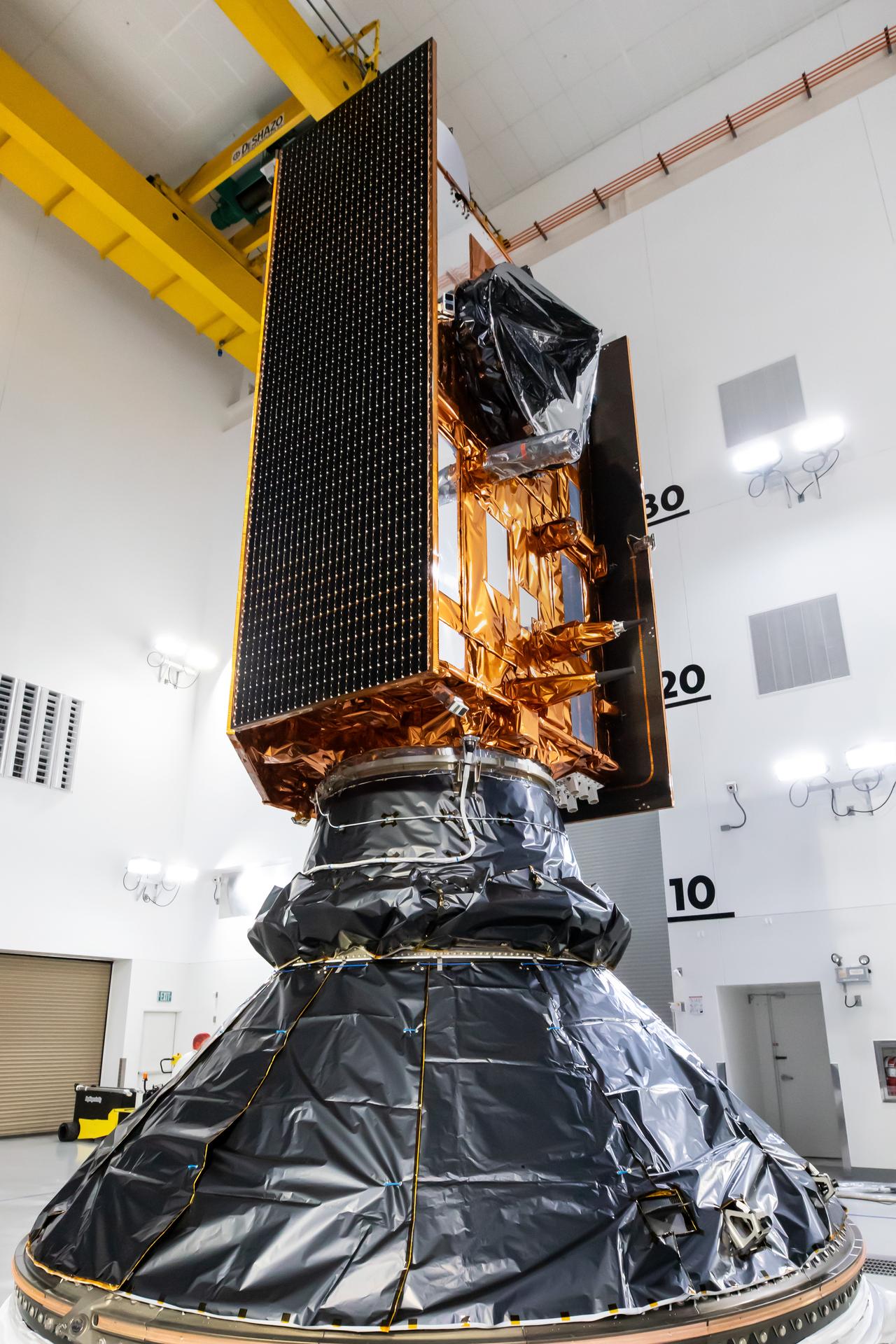
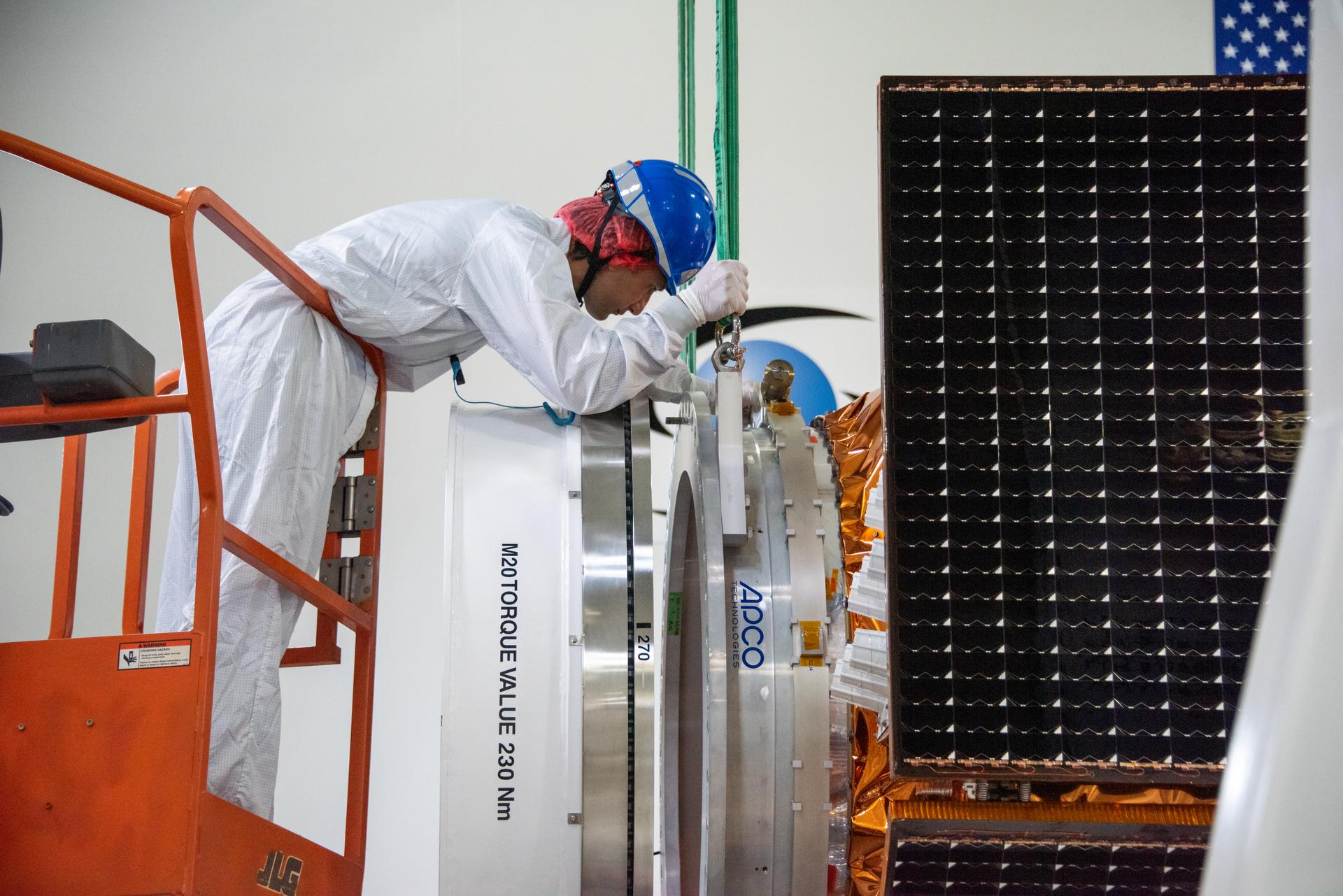
Technicians integrate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft to the payload adapter inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Nov. 4, 2025. The payload adapter is part of the system that connects Sentinel-6B to the second stage of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket that will carry it to orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
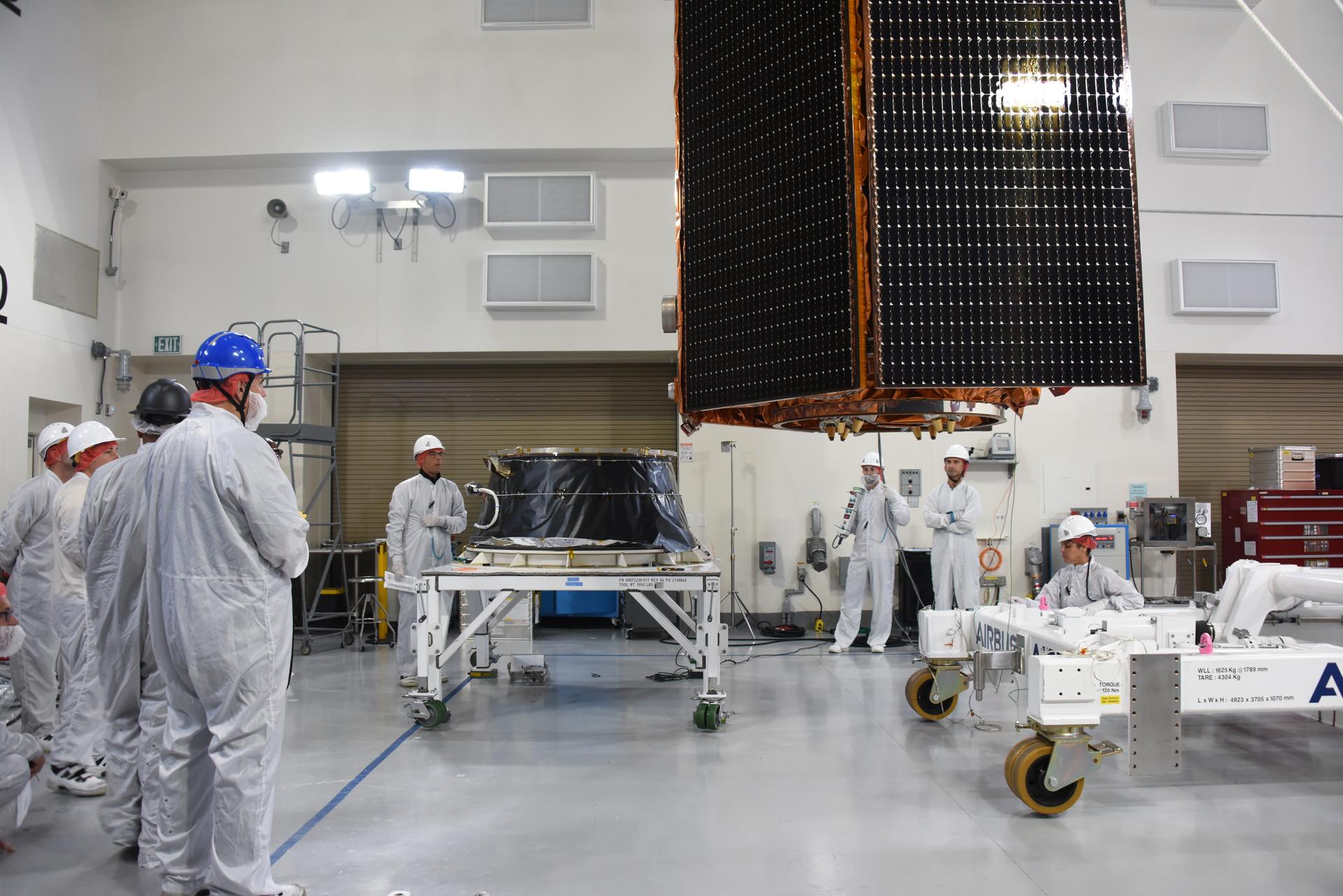

Technicians integrate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft to the payload adapter inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Nov. 4, 2025. The payload adapter is part of the system that connects Sentinel-6B to the second stage of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket that will carry it to orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians integrate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft to the payload adapter inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Nov. 4, 2025. The payload adapter is part of the system that connects Sentinel-6B to the second stage of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket that will carry it to orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
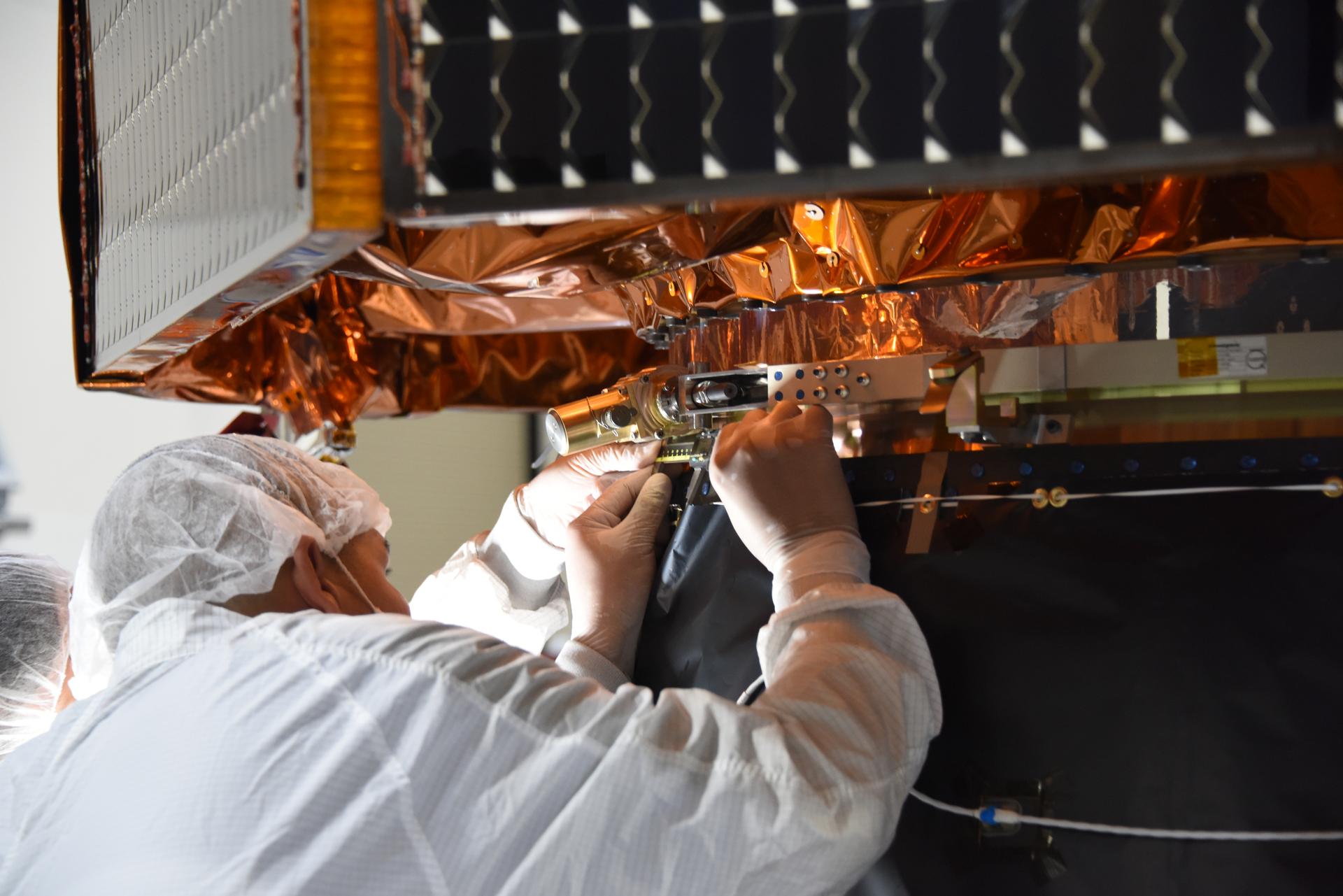

Technicians integrate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft to the payload adapter inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Nov. 4, 2025. The payload adapter is part of the system that connects Sentinel-6B to the second stage of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket that will carry it to orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.