
Cynthia Hall, support scientist for the Early Career Research Program in NASA’s Earth Science Division, speaks to the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
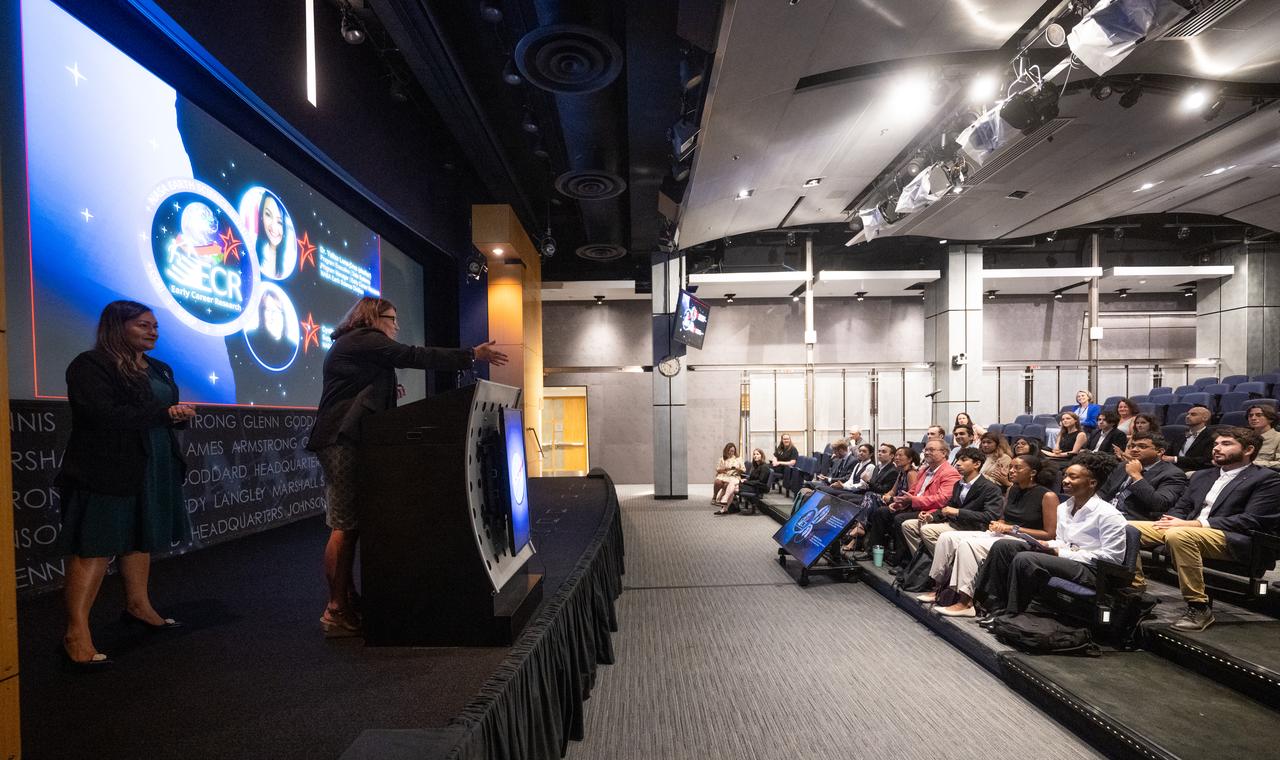

Cynthia Hall, support scientist for the Early Career Research Program in NASA’s Earth Science Division, right, and Yaítza Luna-Cruz, a program executive in the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate and program manager for the Early Career Research Program speak to the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
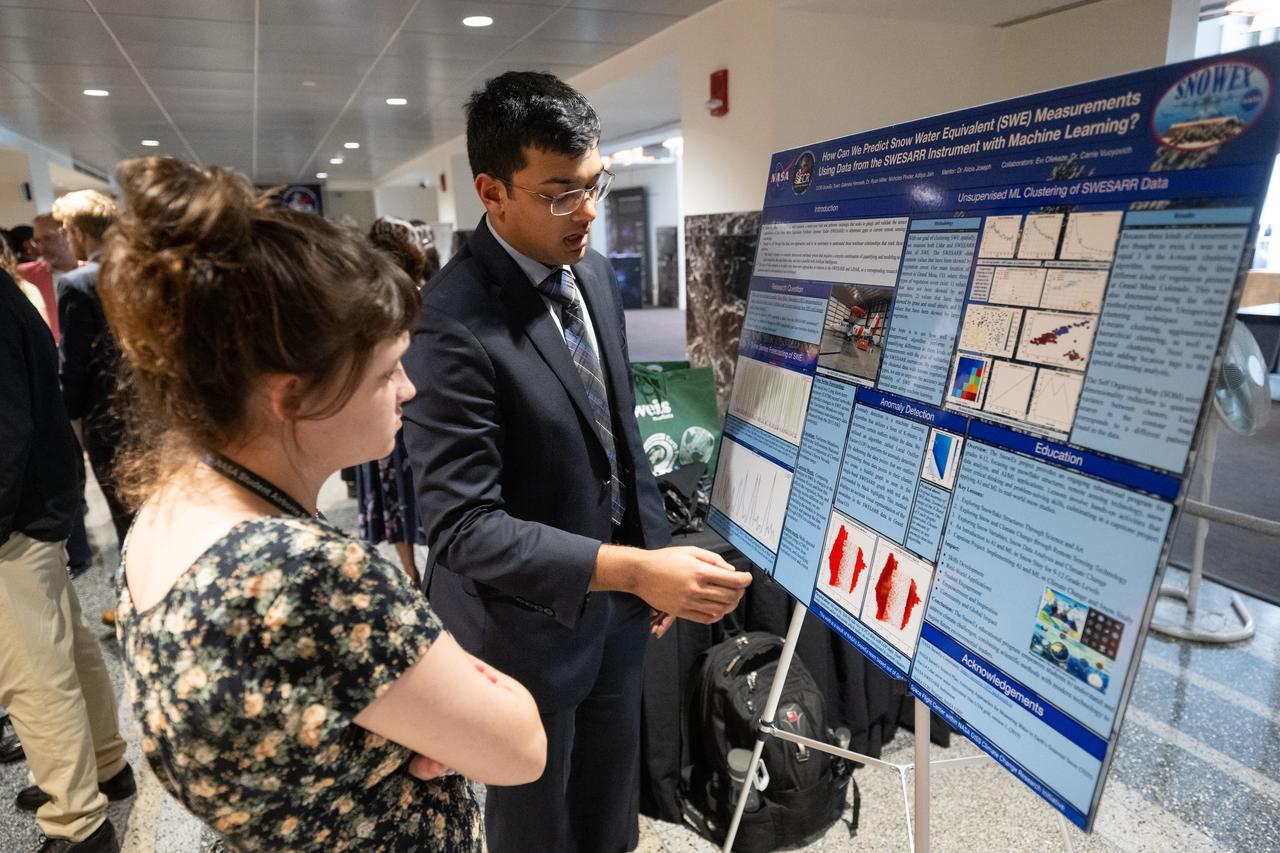

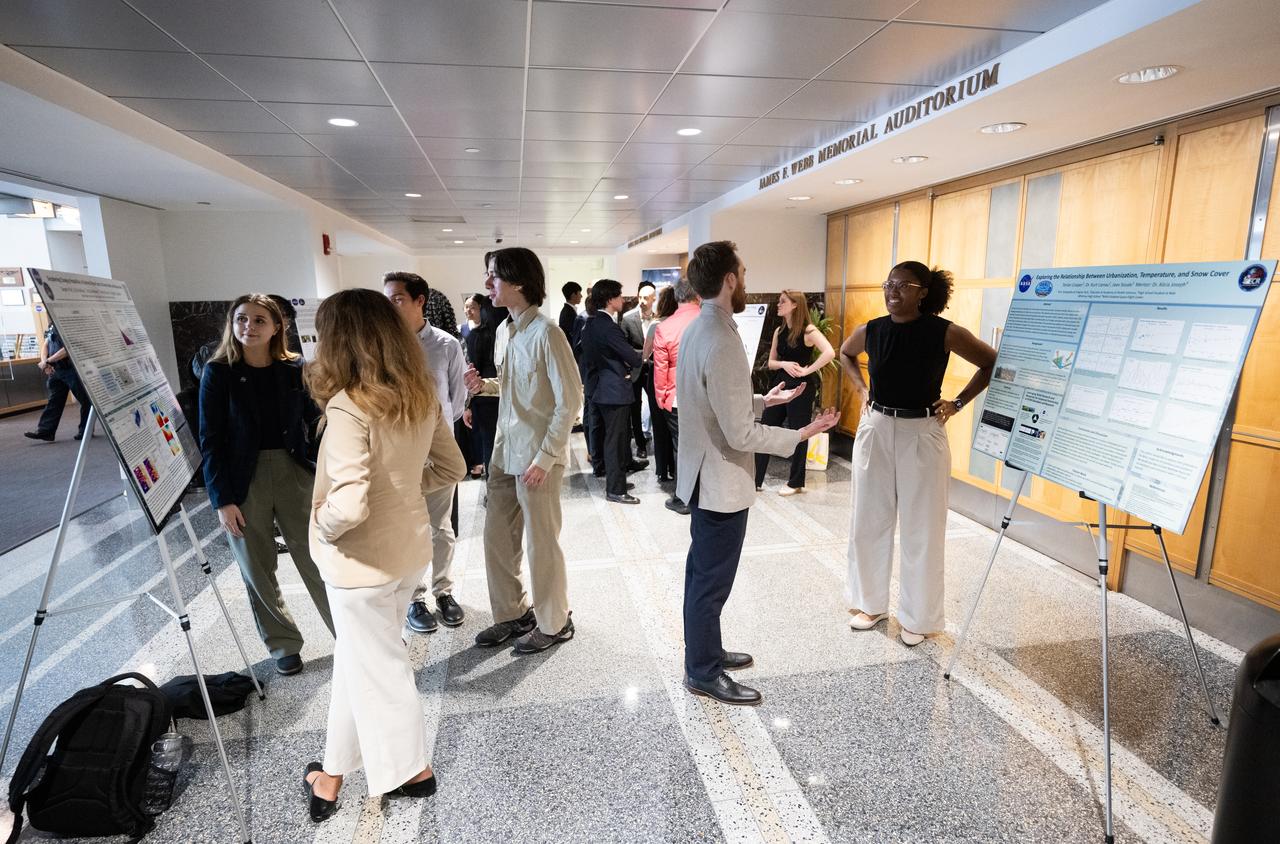
Members of the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort discuss their research during a poster session, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
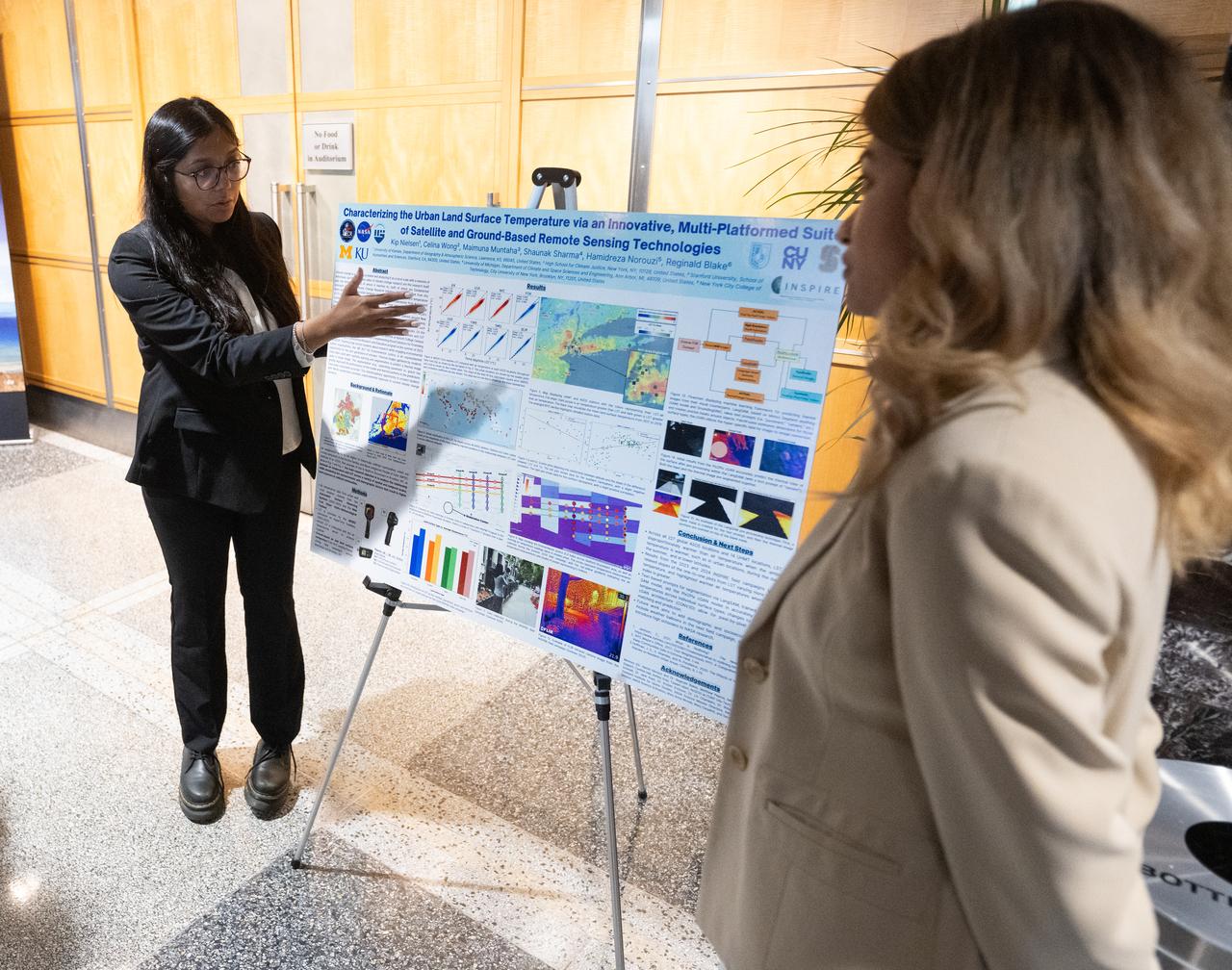

Members of the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort discuss their research during a poster session, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Members of the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort listen as Karen St. Germain, director of the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate speaks, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Members of the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort discuss their research during a poster session, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Members of the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort listen as Karen St. Germain, director of the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate speaks, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
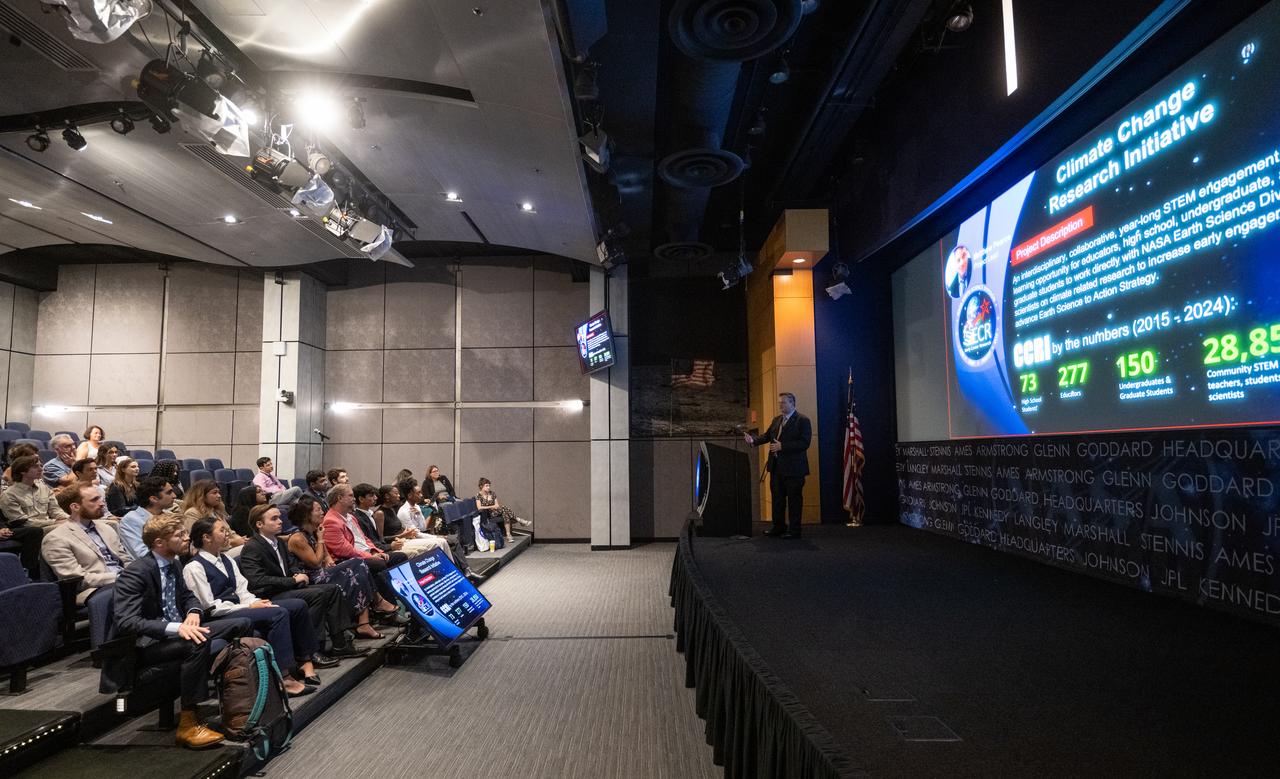

Matthew Pearce, education officer at NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies and project lead for the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI), speaks with the CCRI cohort, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Matthew Pearce, education officer at NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies and project lead for the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI), speaks with the CCRI cohort, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
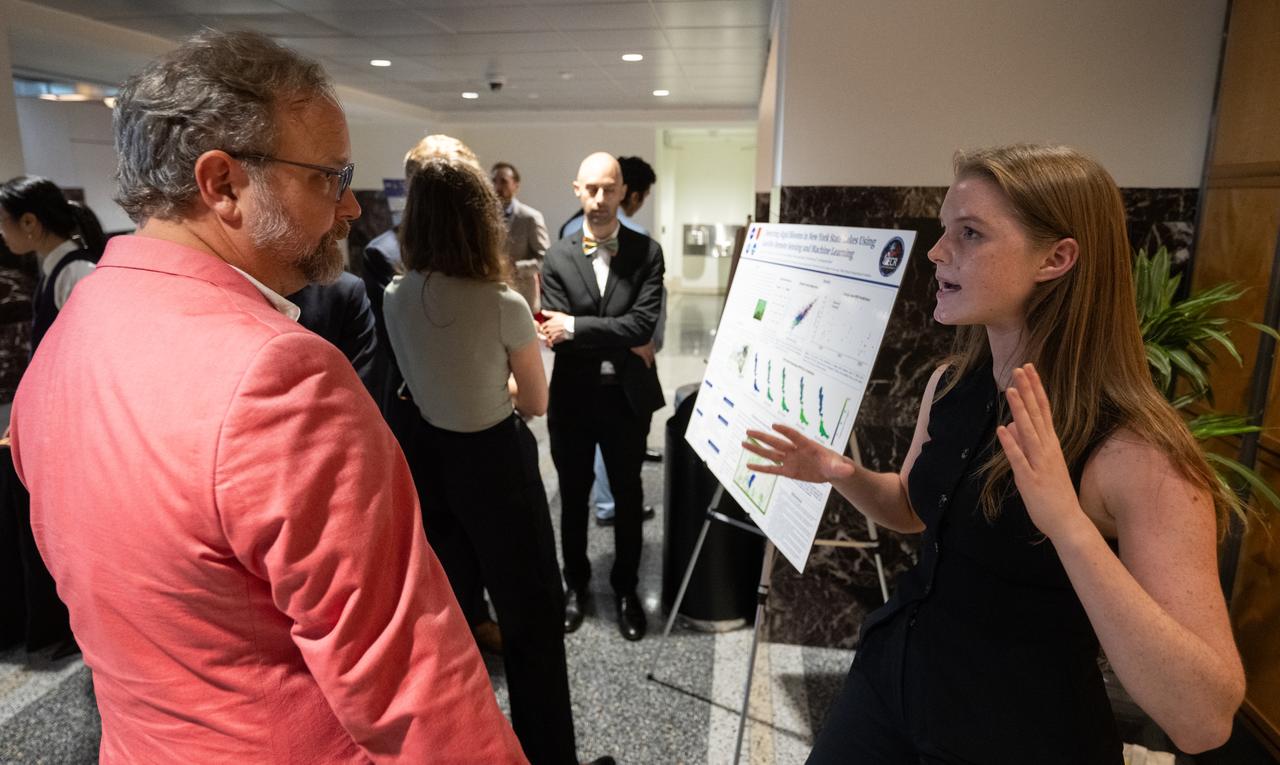

Members of the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort discuss their research during a poster session, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Jack Kaye, associate director for research in the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, speaks with the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
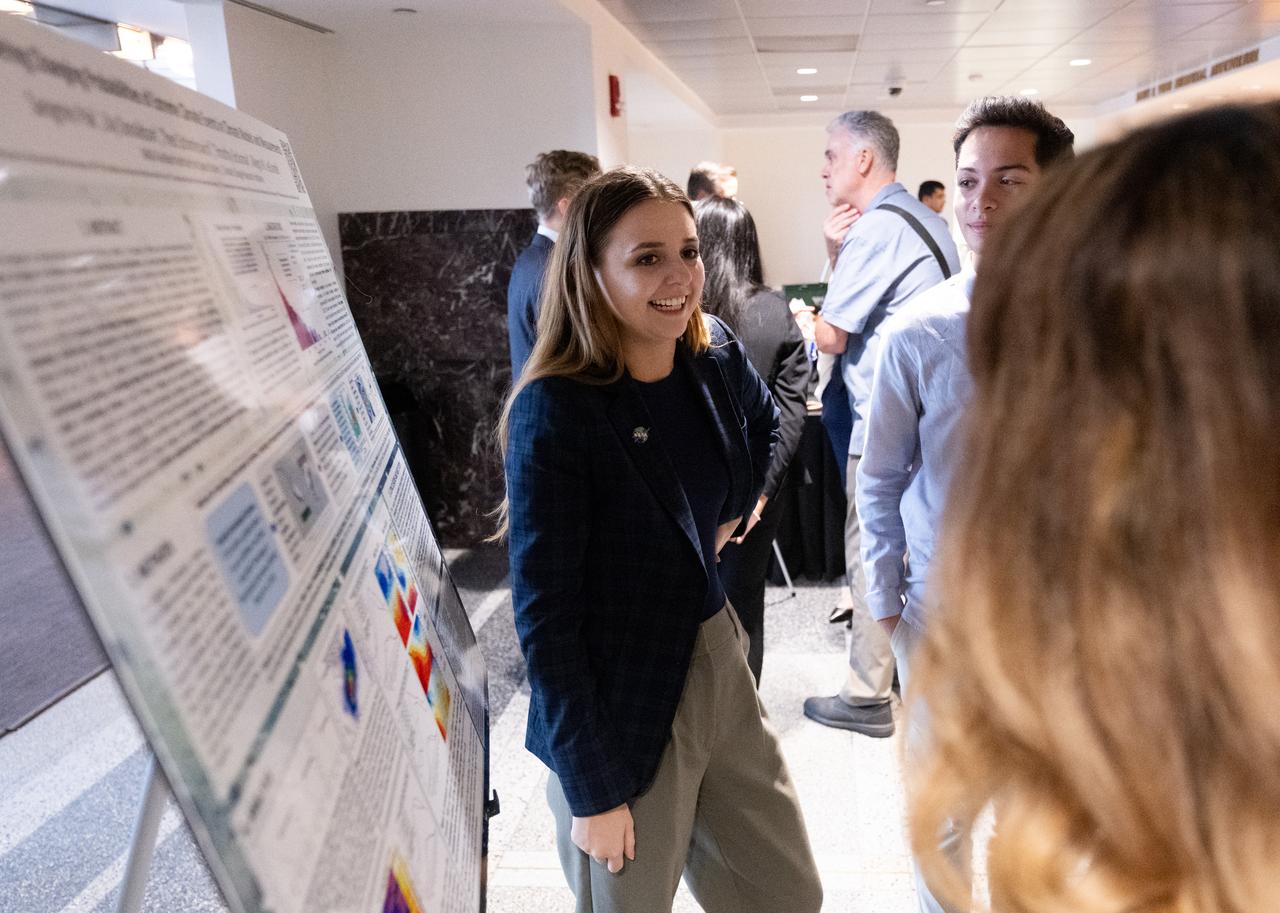

Members of the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort discuss their research during a poster session, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
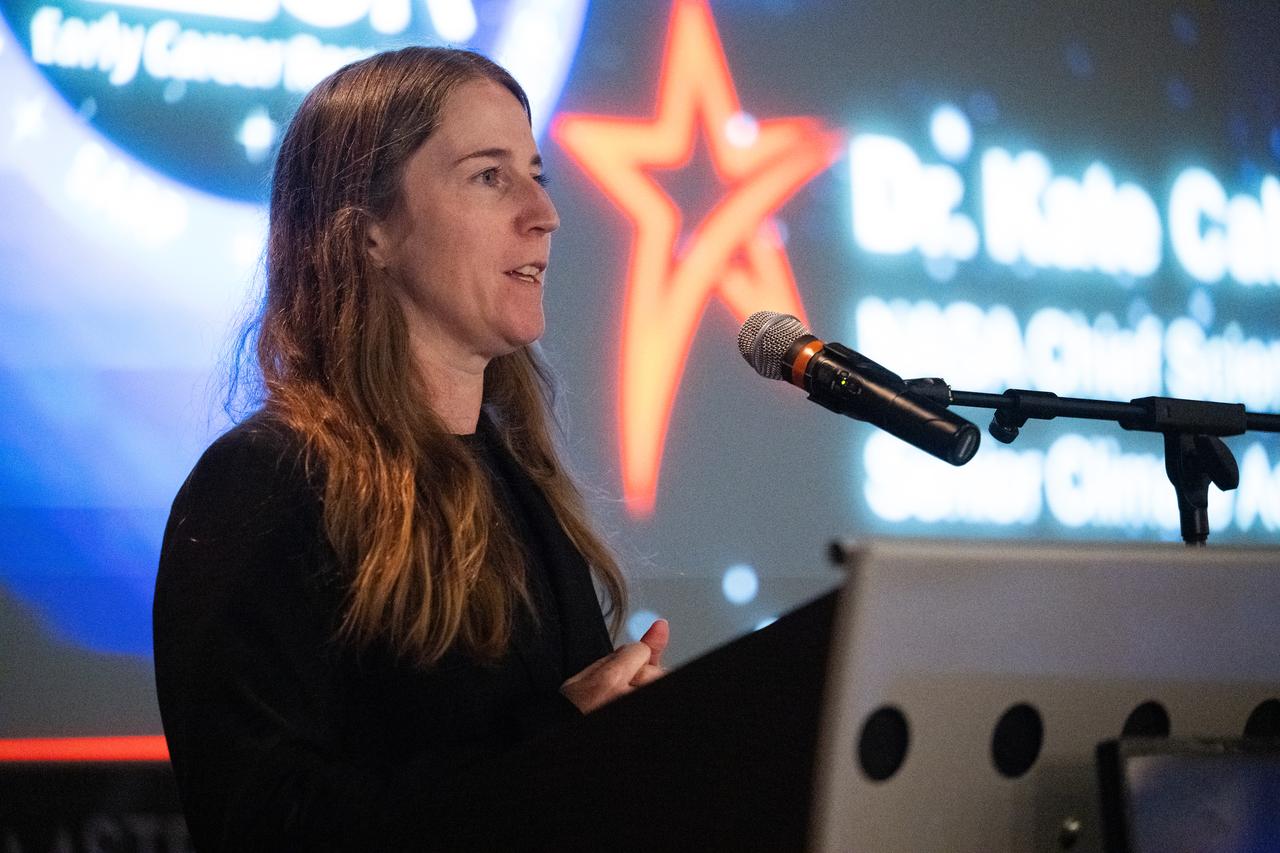

Kate Calvin, NASA’s Chief Scientist, speaks to the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
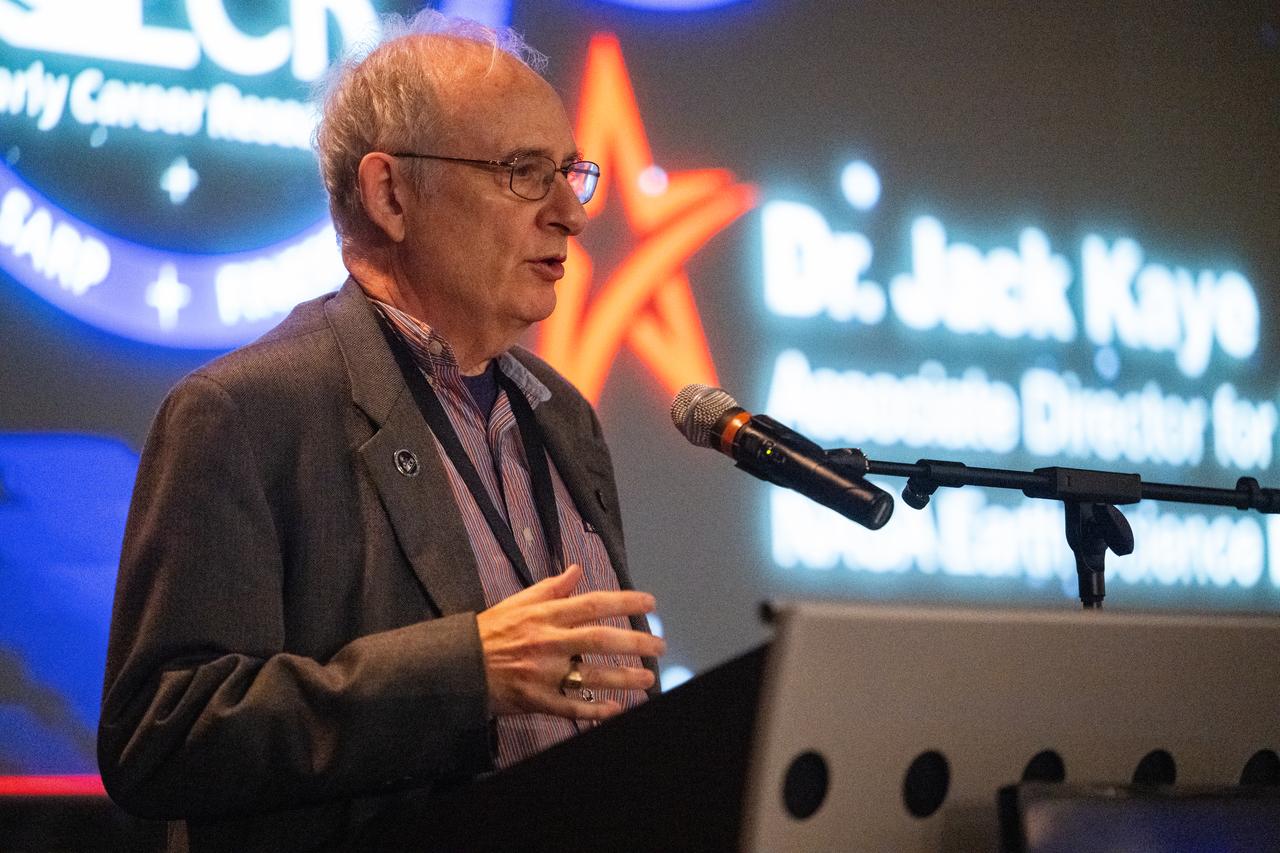

Jack Kaye, associate director for research in the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, speaks with the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
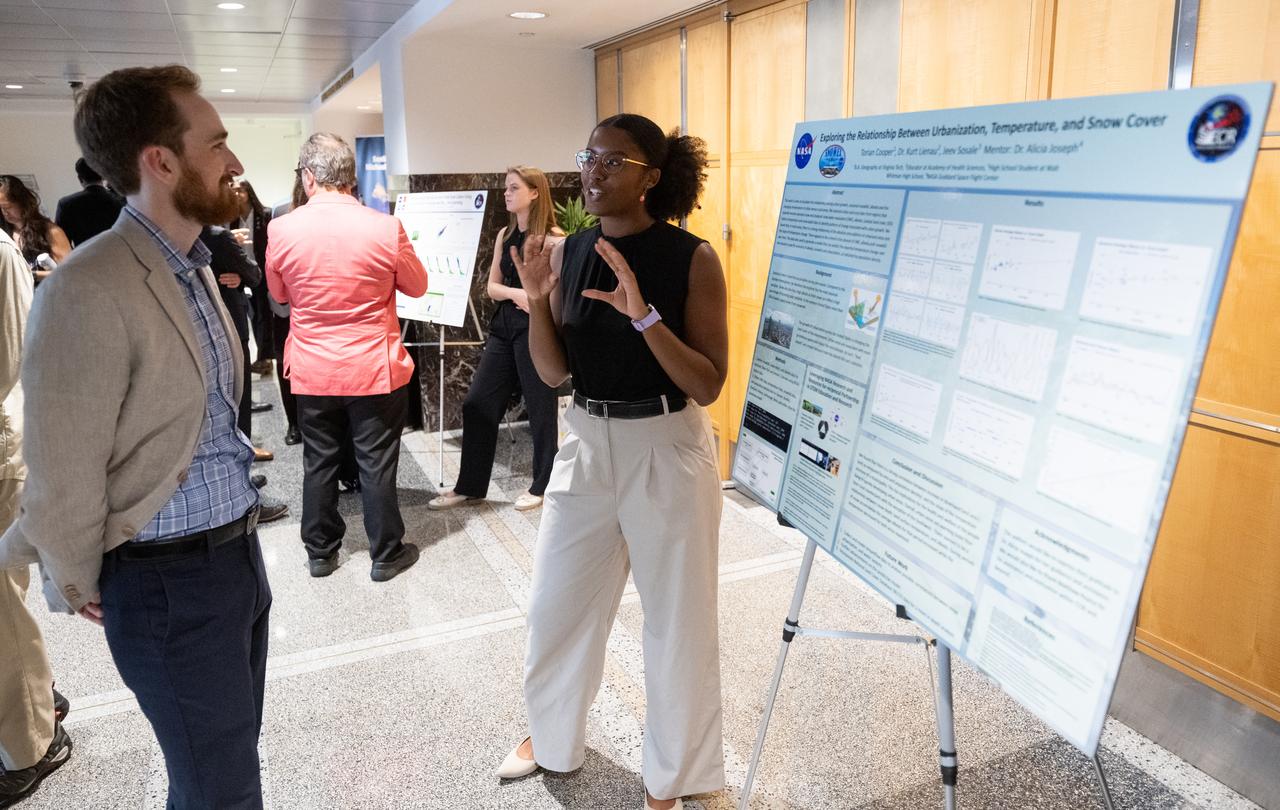

Members of the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort discuss their research during a poster session, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
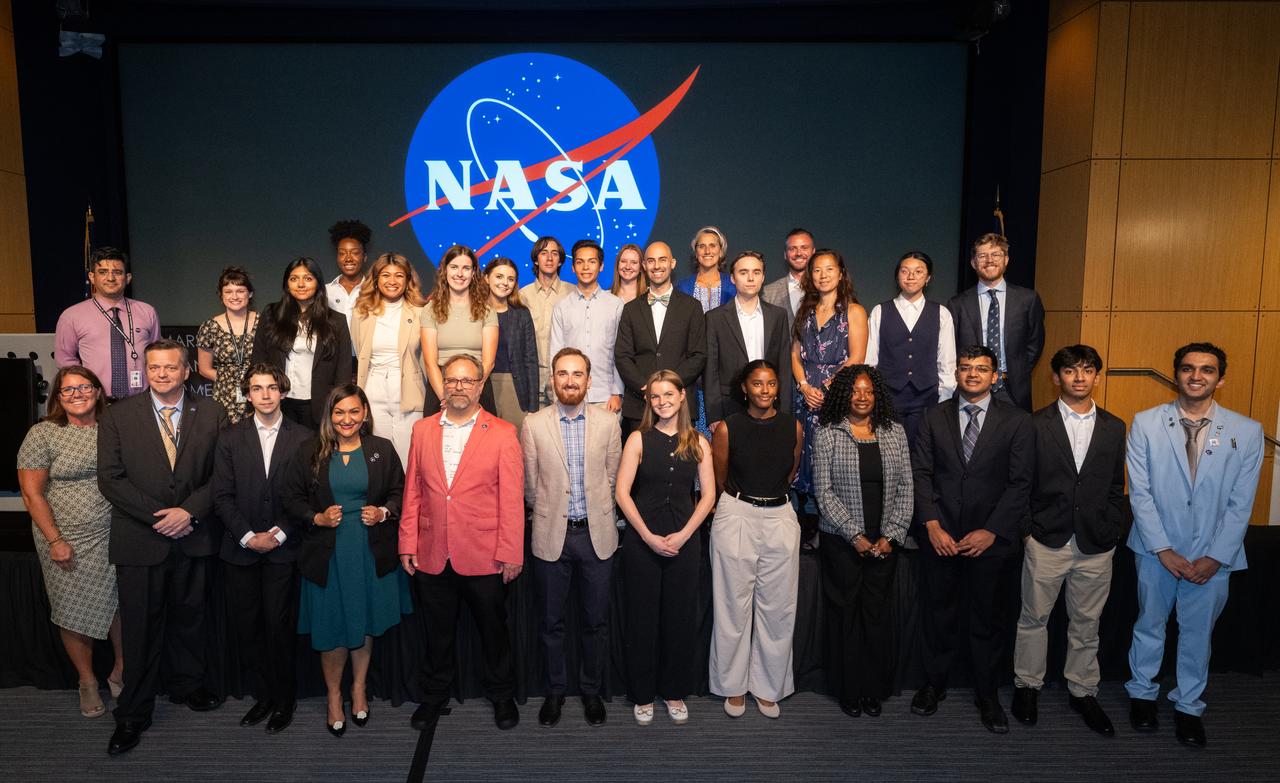

The Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort poses for a group photo, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
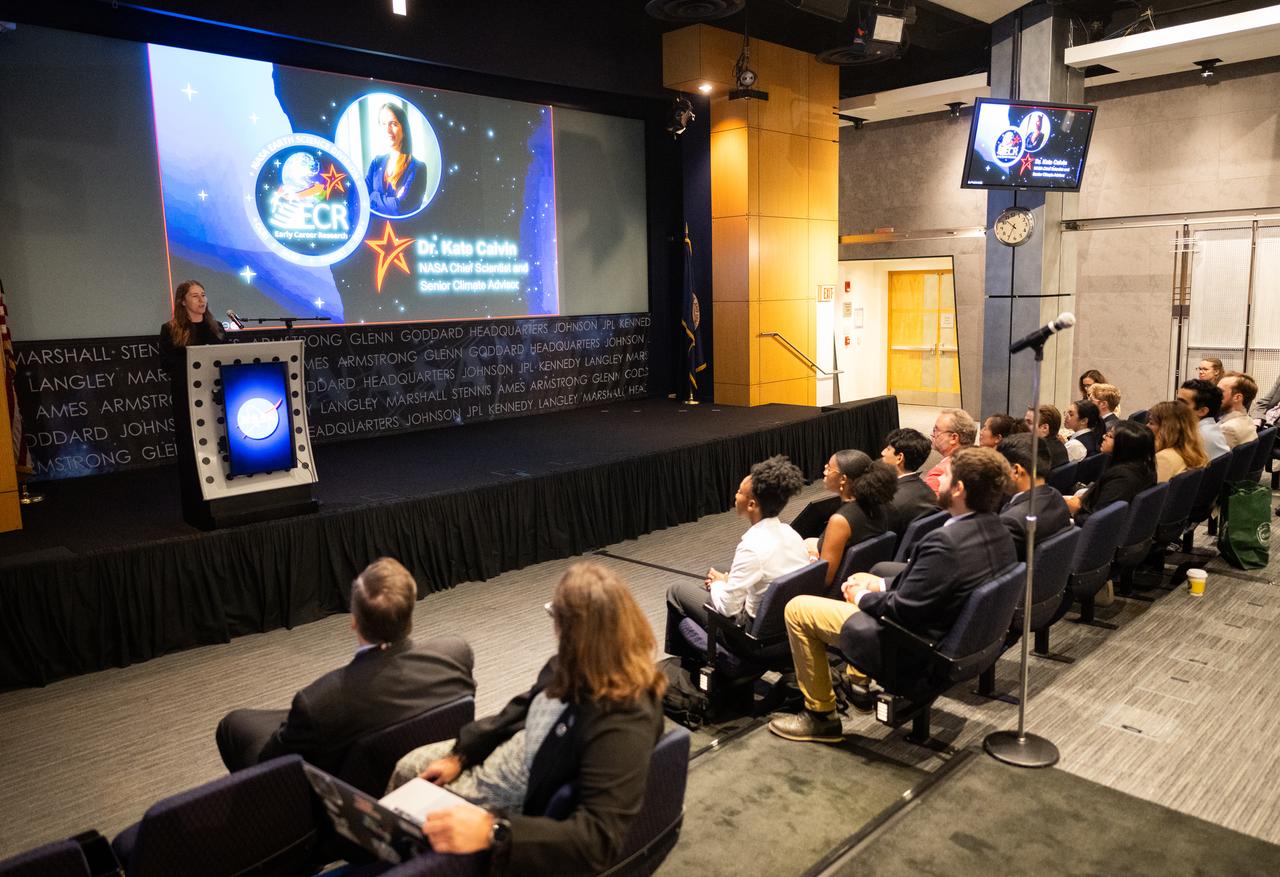

Kate Calvin, NASA’s Chief Scientist, speaks to the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
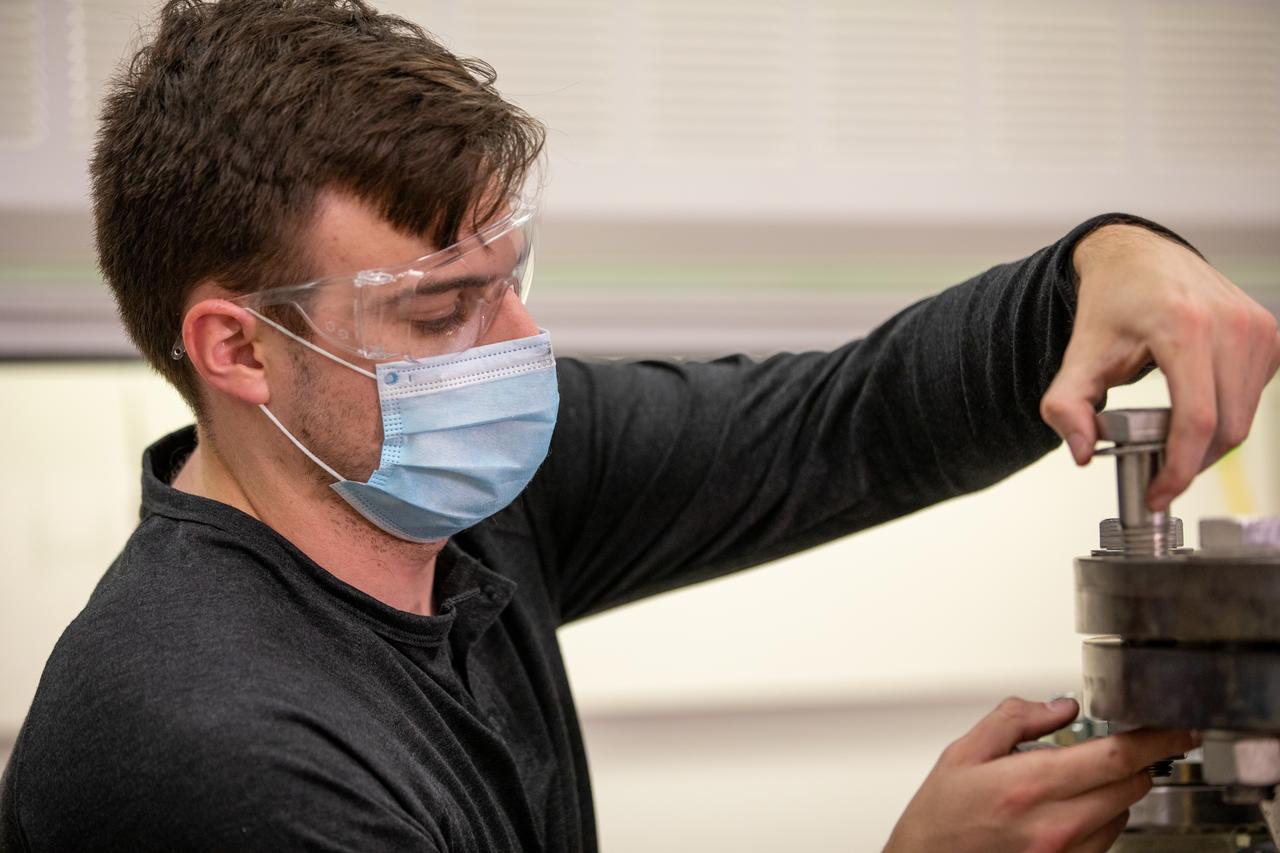
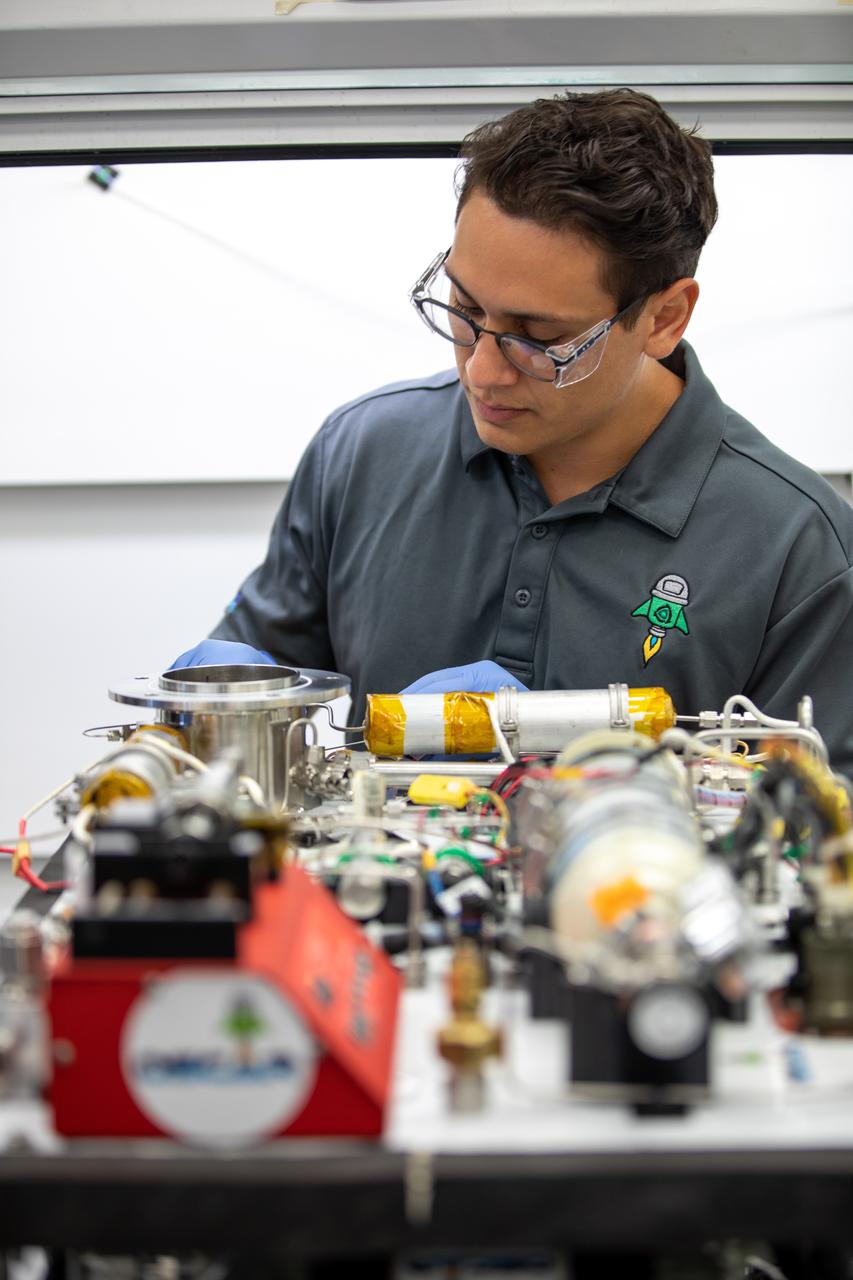
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
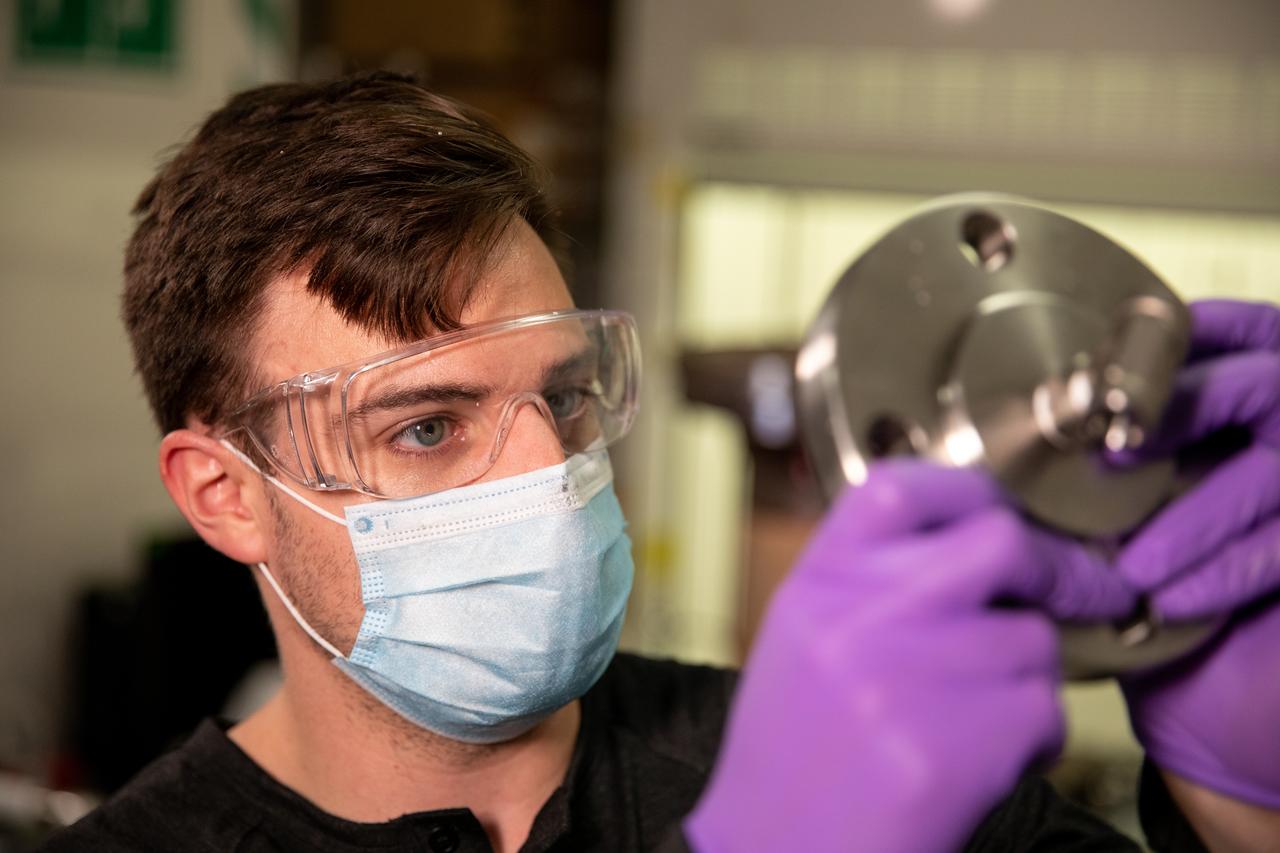

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
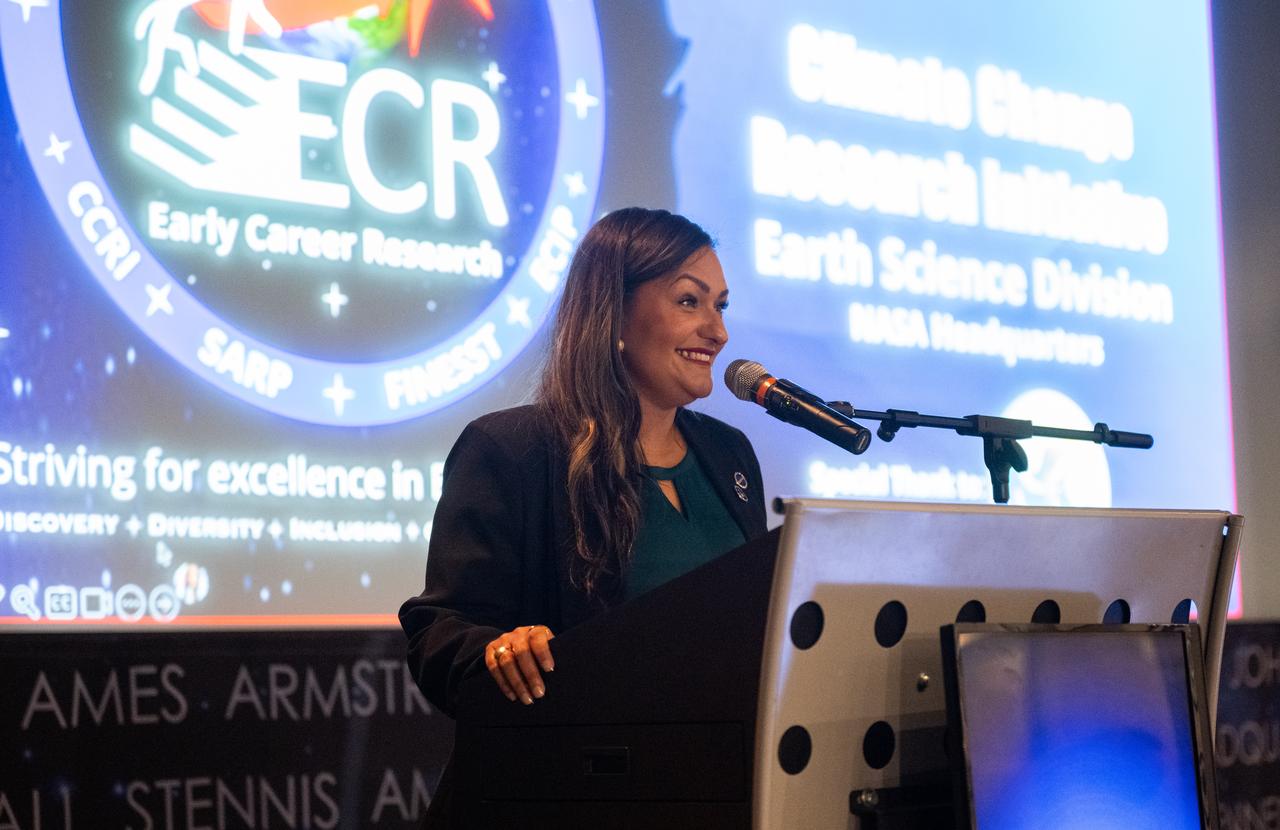

Yaítza Luna-Cruz, a program executive in the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate and program manager for the Early Career Research Program, speaks to the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
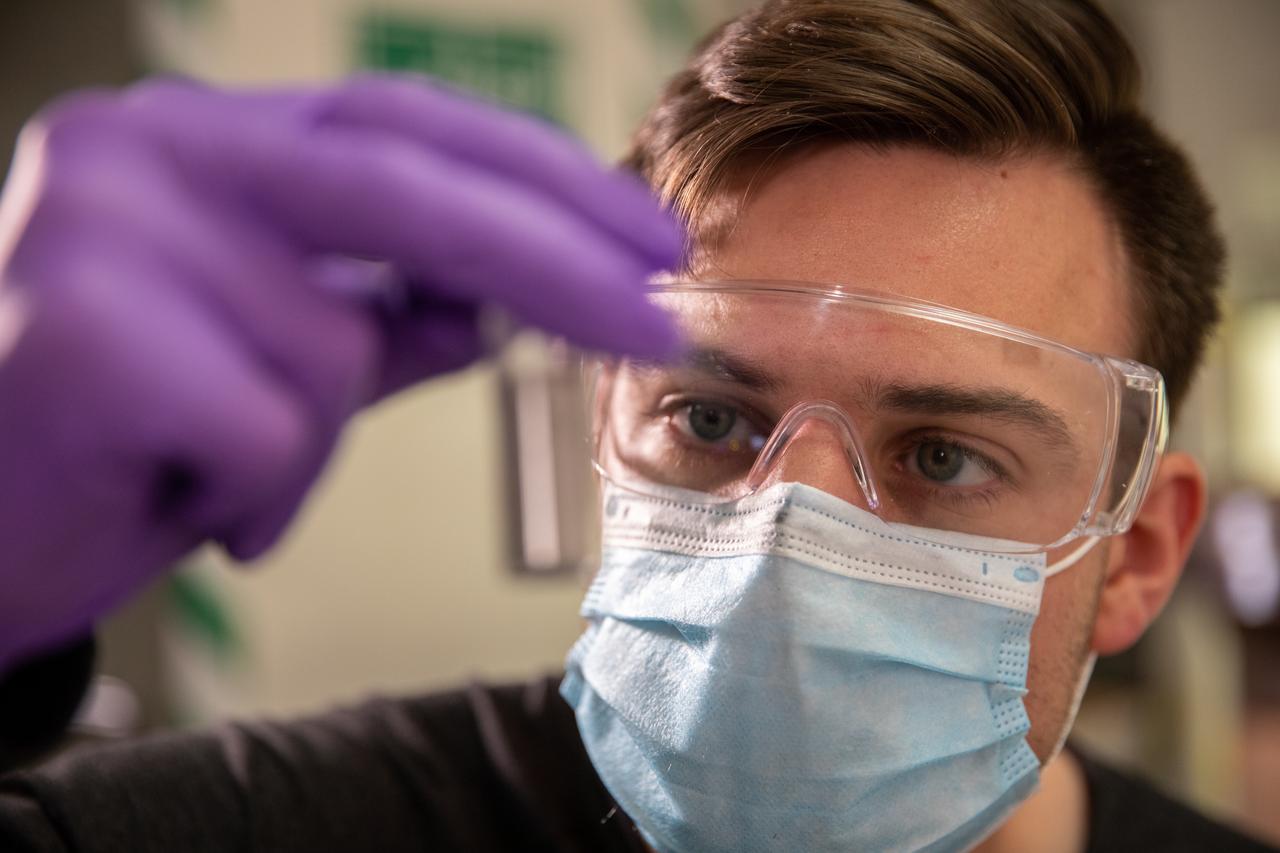
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
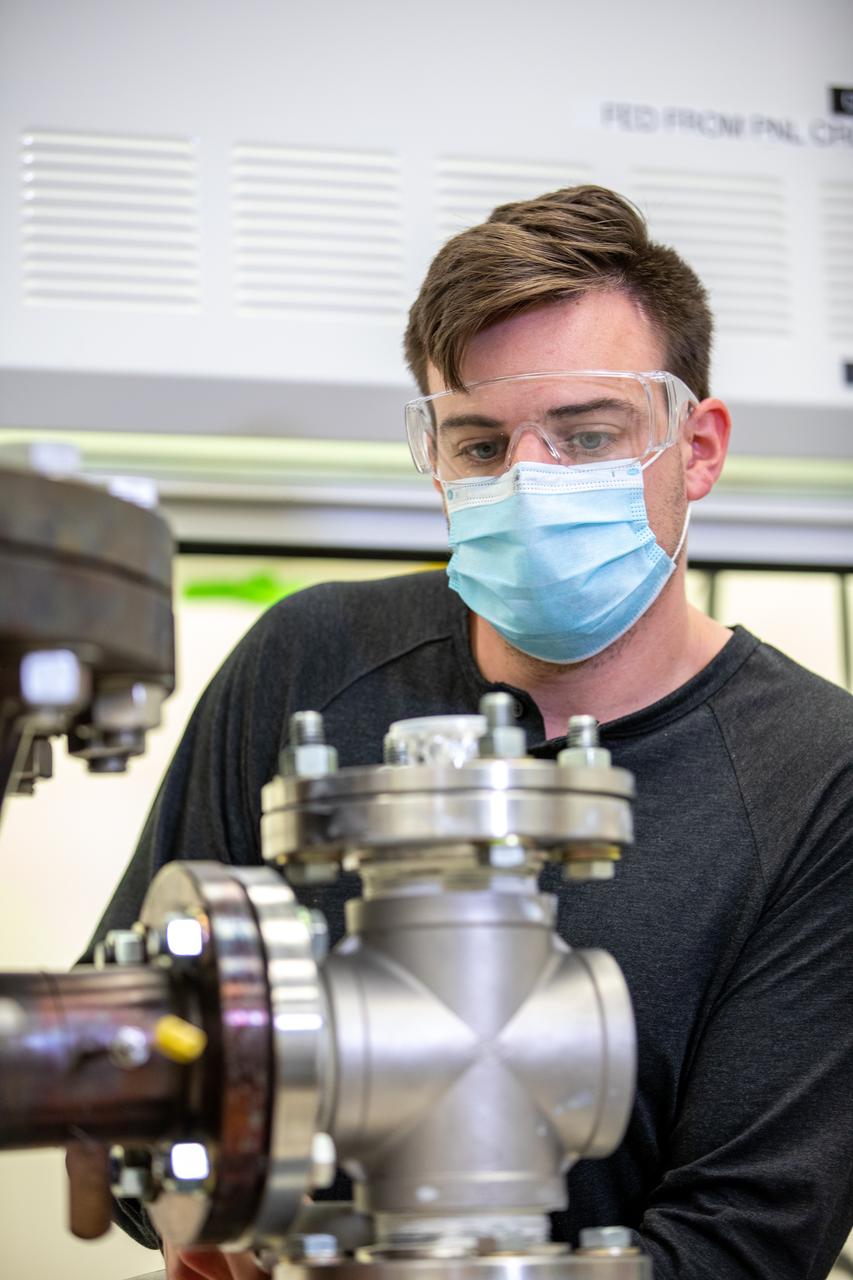

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
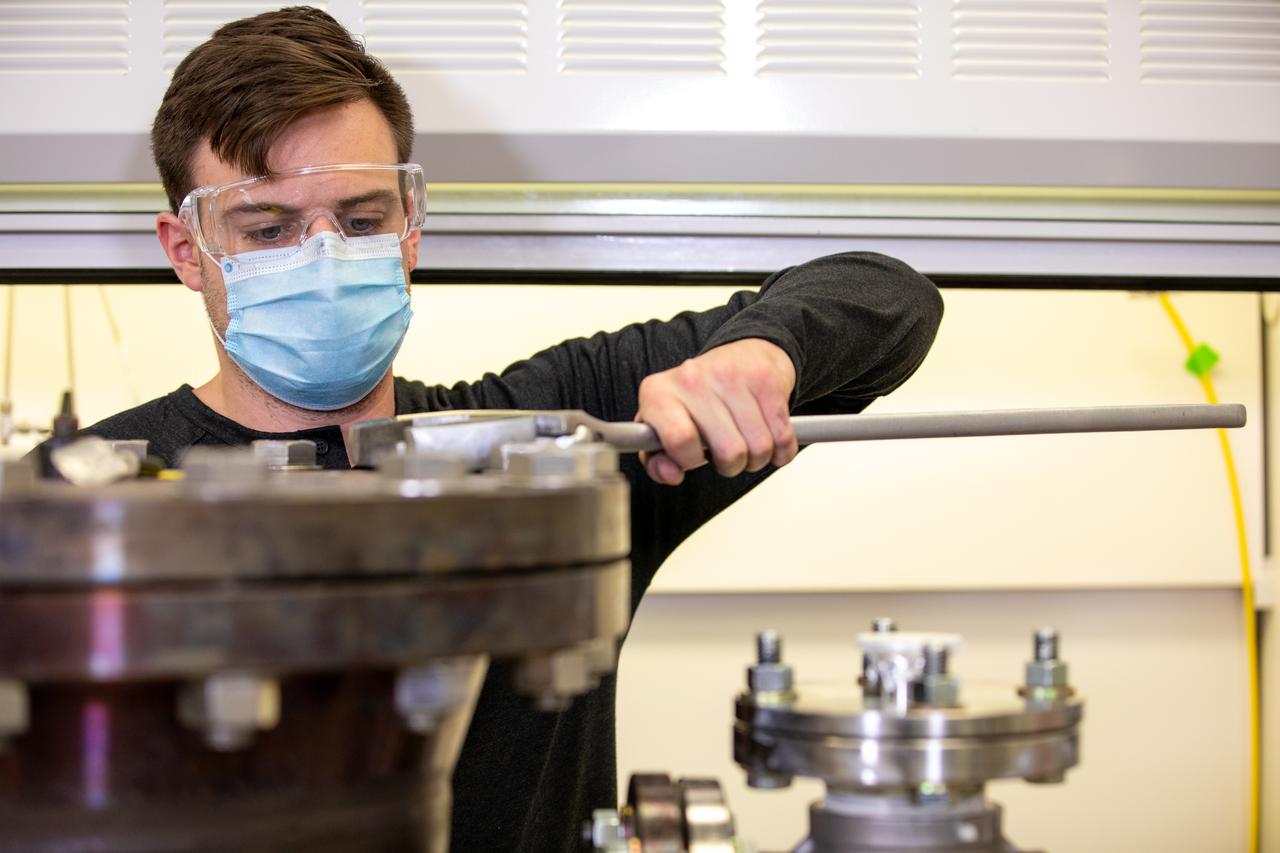

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
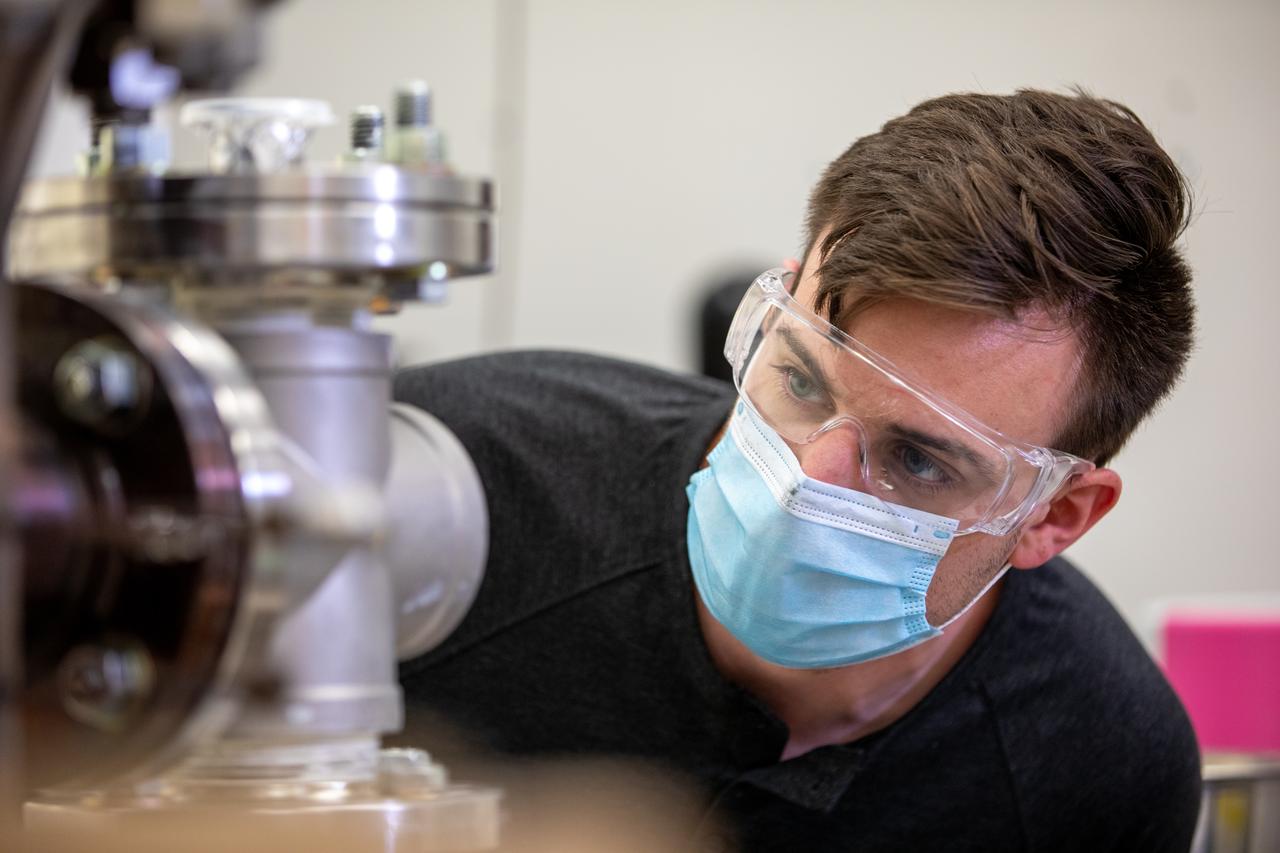

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
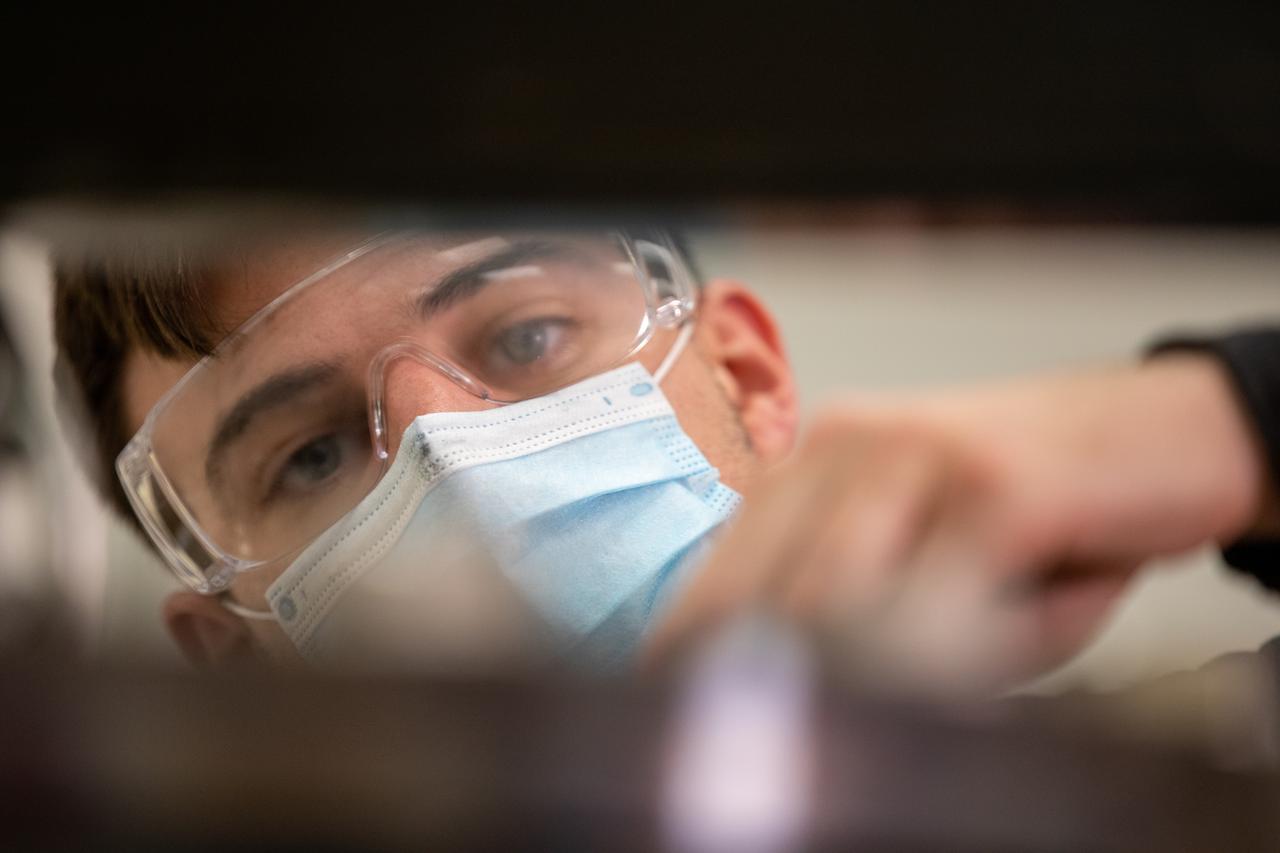

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
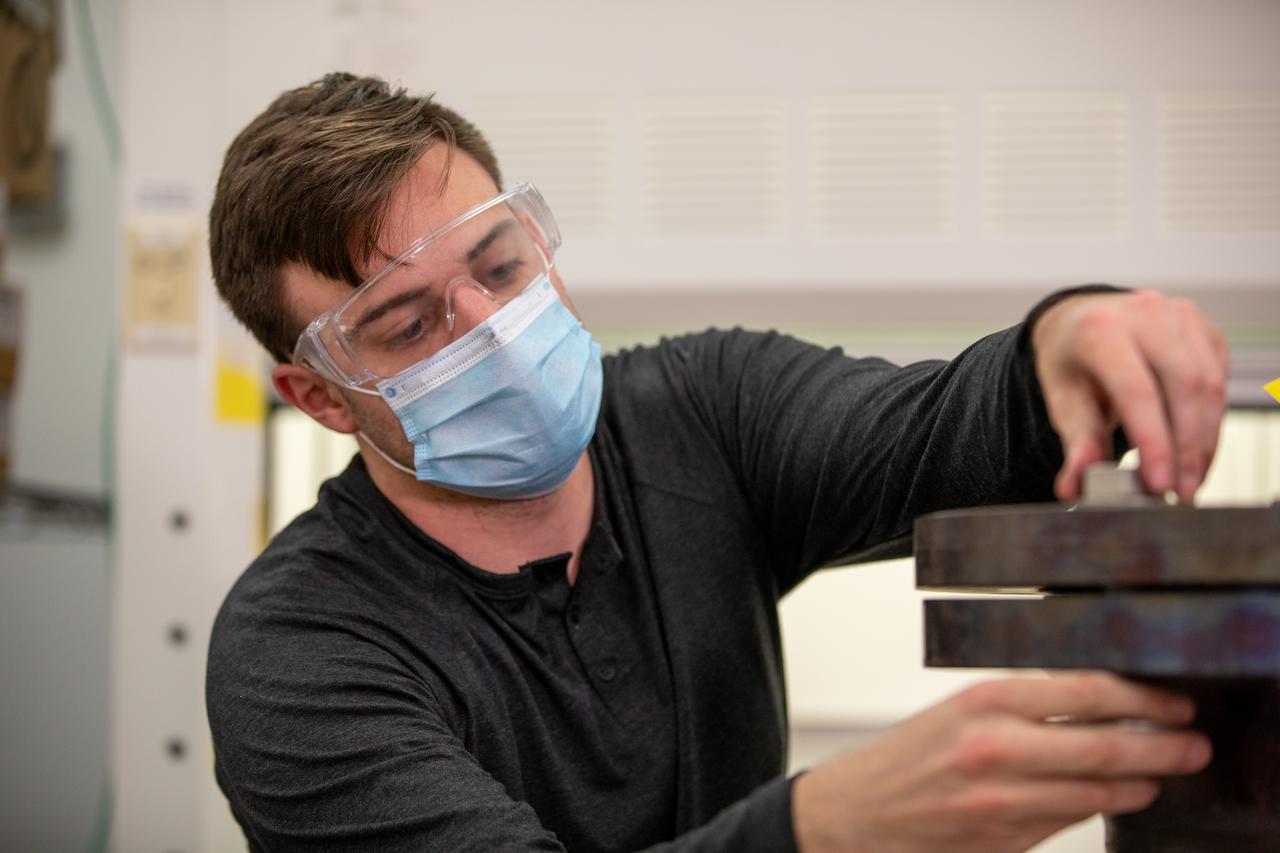

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
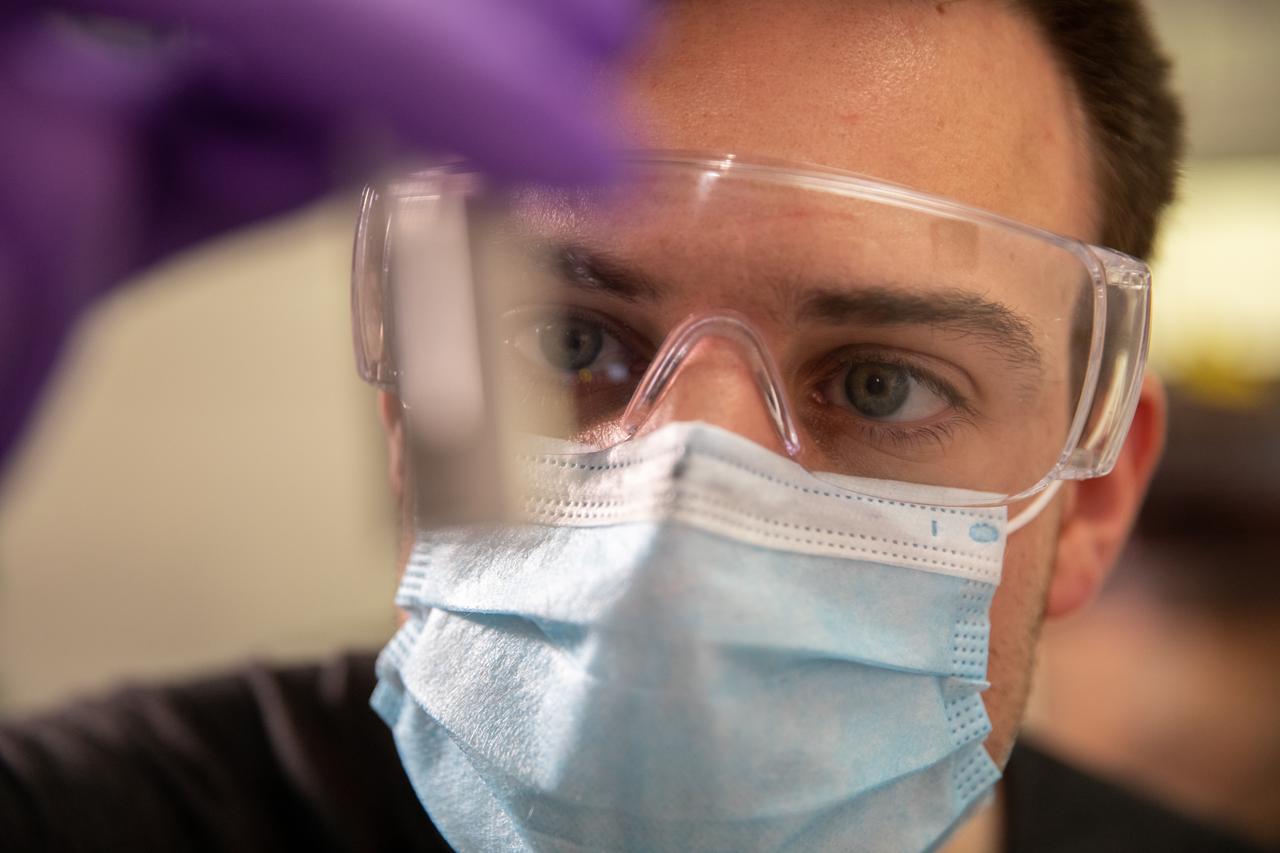
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
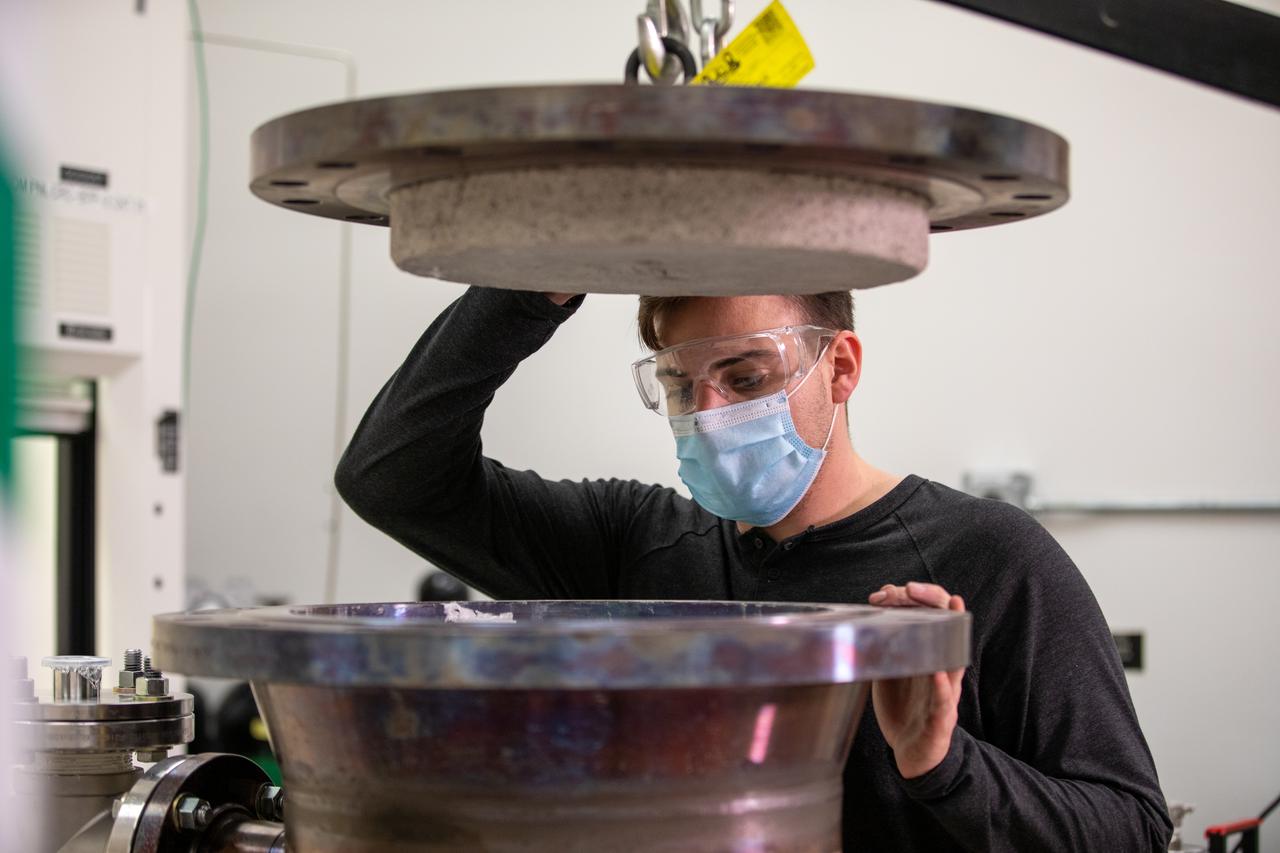

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
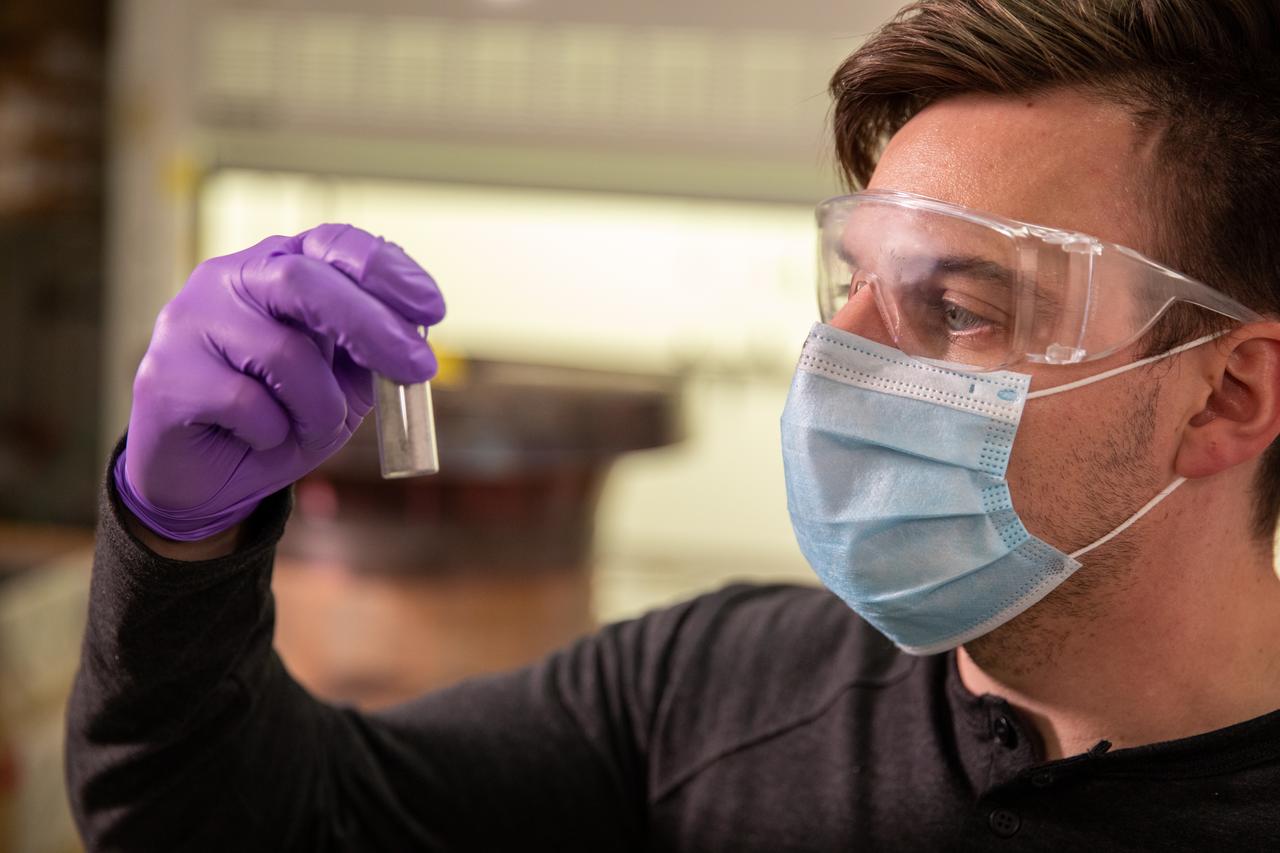

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
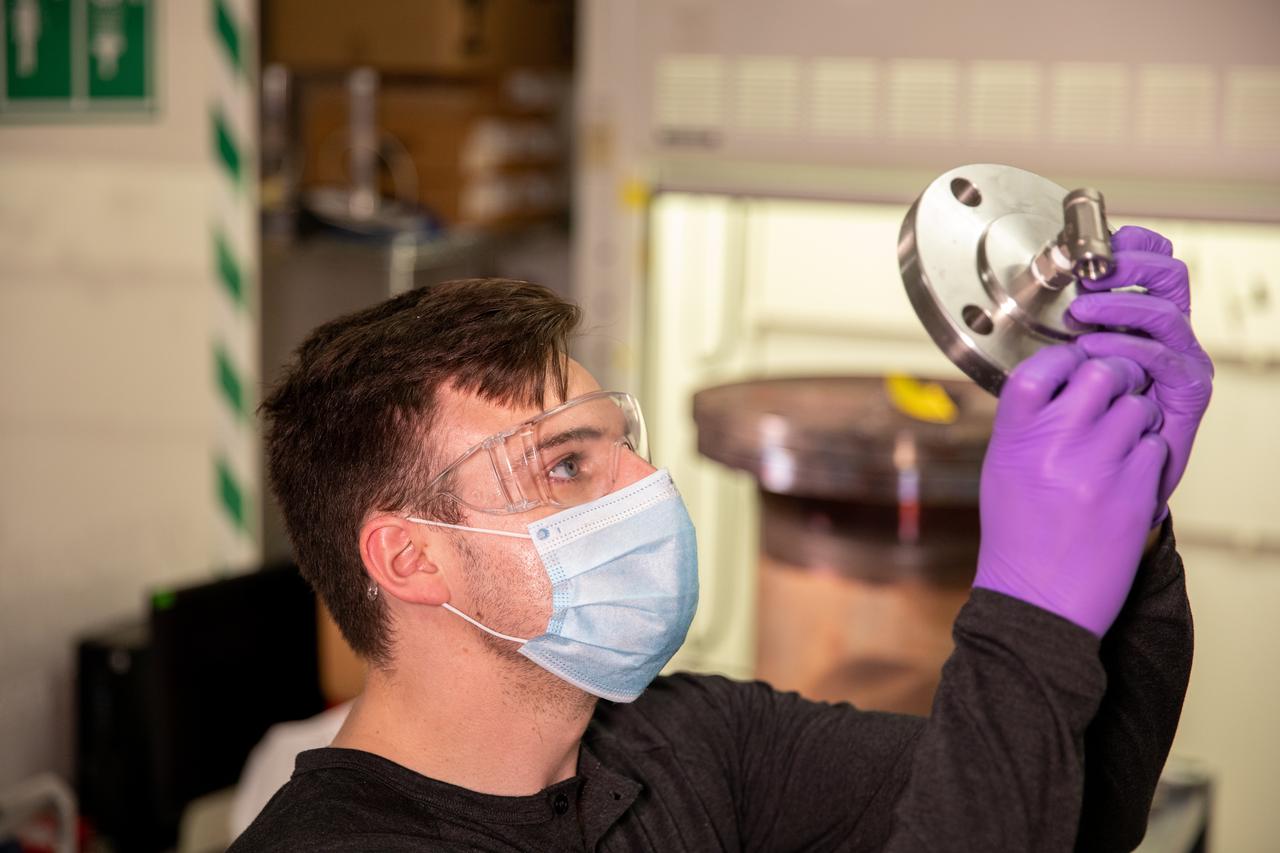

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
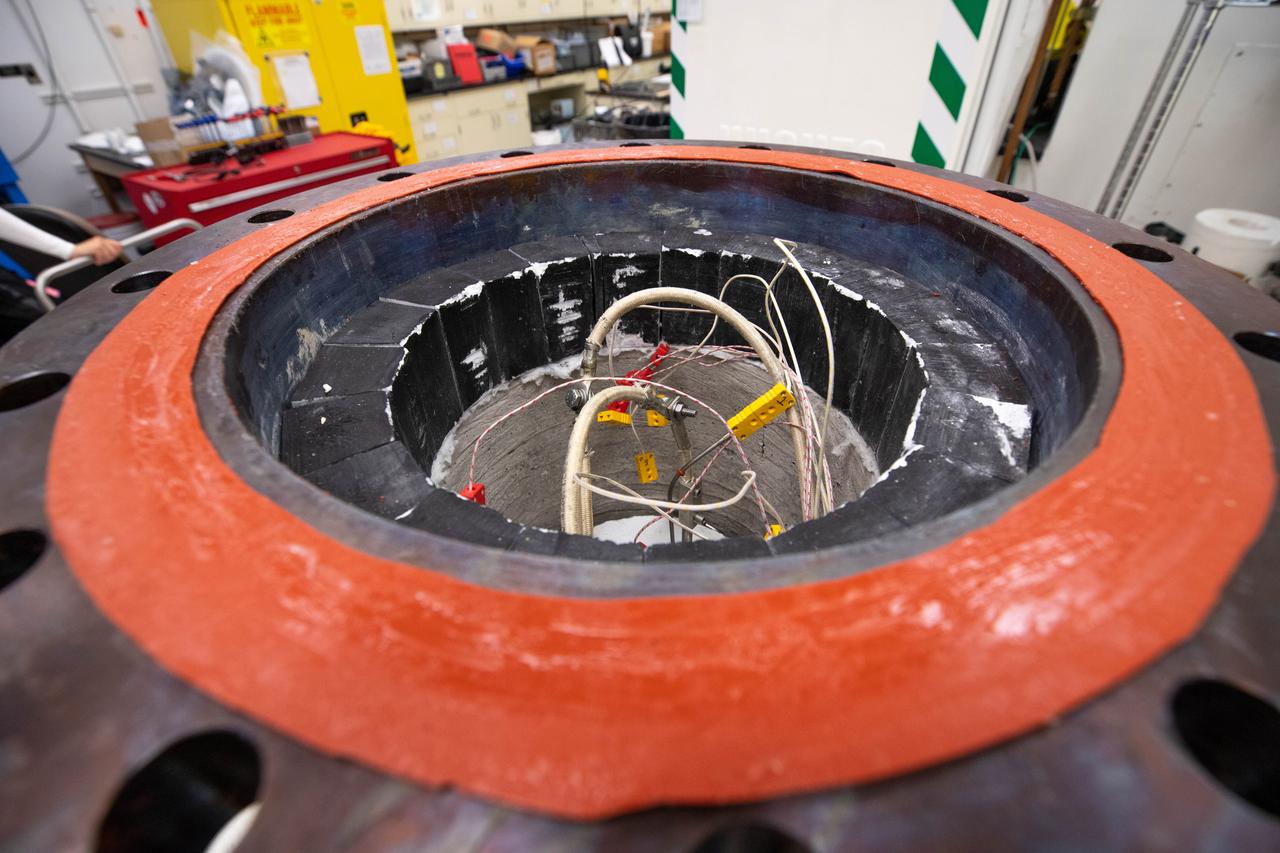

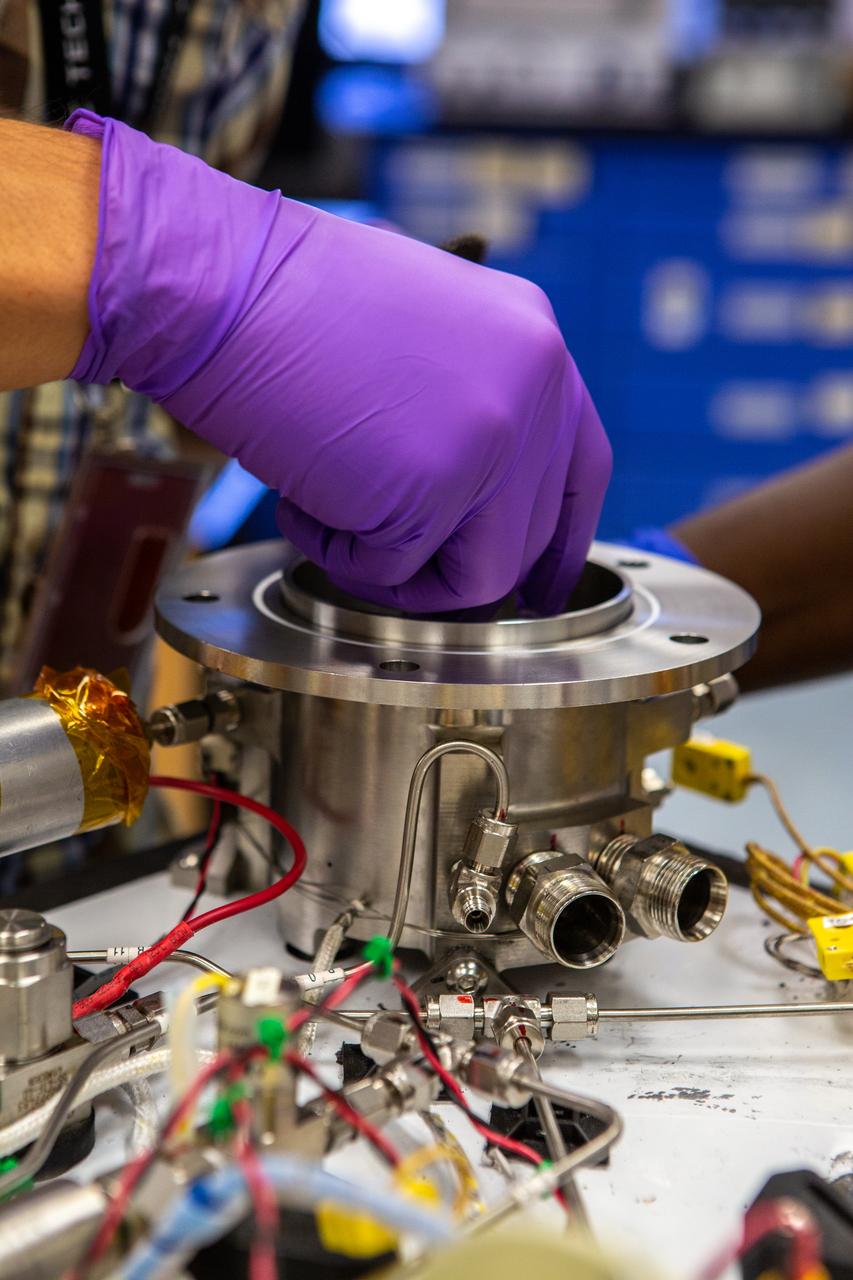
A team investigating molten regolith electrolysis prepares to test a reactor inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 29, 2020. The Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project seeks to develop technology to extract oxygen and metals from the crushed rock, or regolith, that covers the Moon’s surface. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
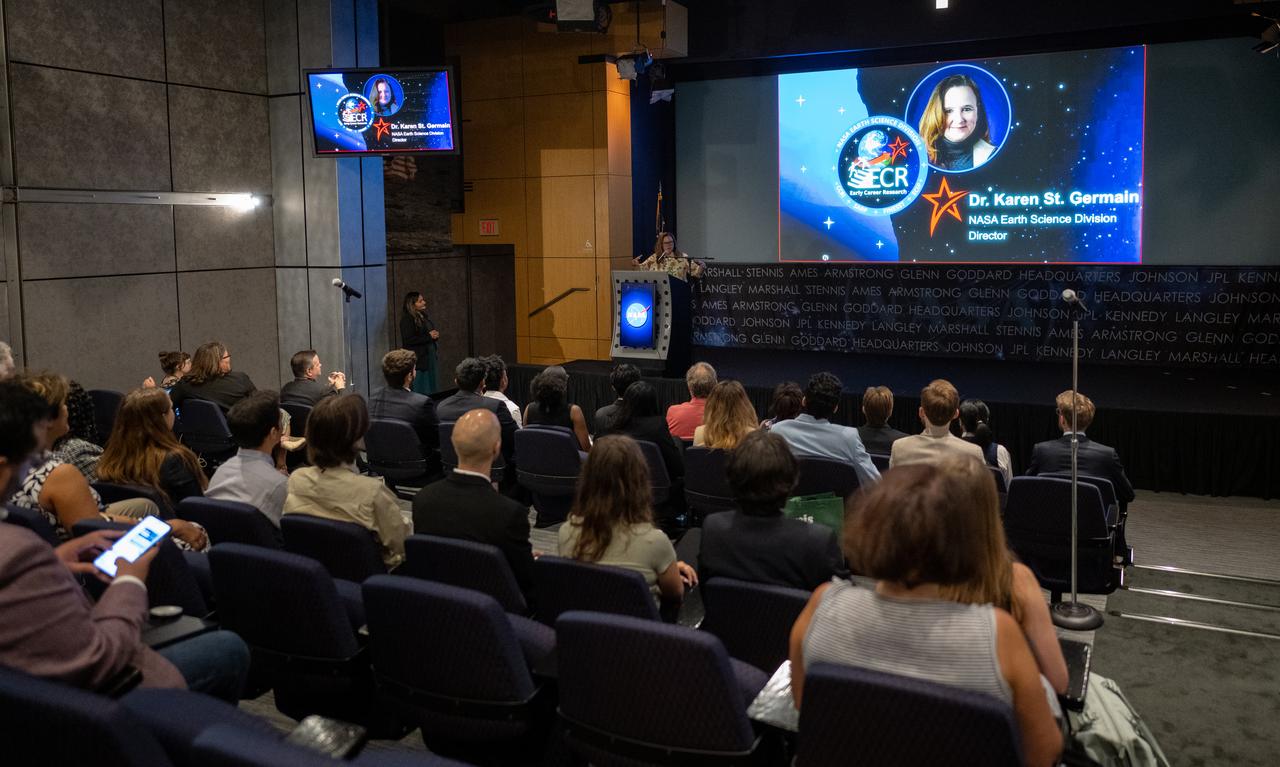

Karen St. Germain, director of the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, speaks with the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
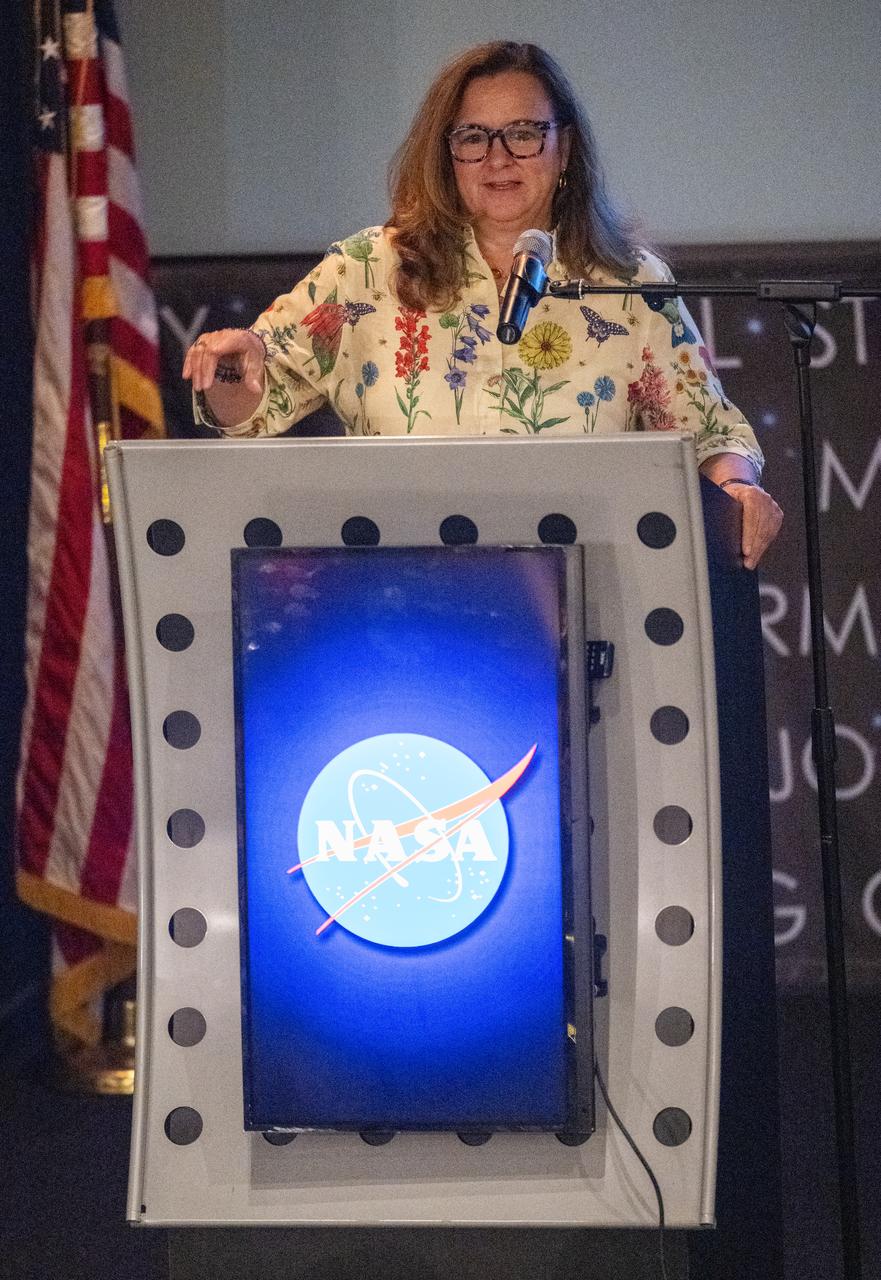

Karen St. Germain, director of the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, speaks with the Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) cohort, Wednesday, Aug. 7, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington, DC. The Earth Science Division’s Early Career Research Program’s Climate Change Research Initiative (CCRI) is a year-long STEM engagement and experiential learning opportunity for educators and students from high school to graduate level. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
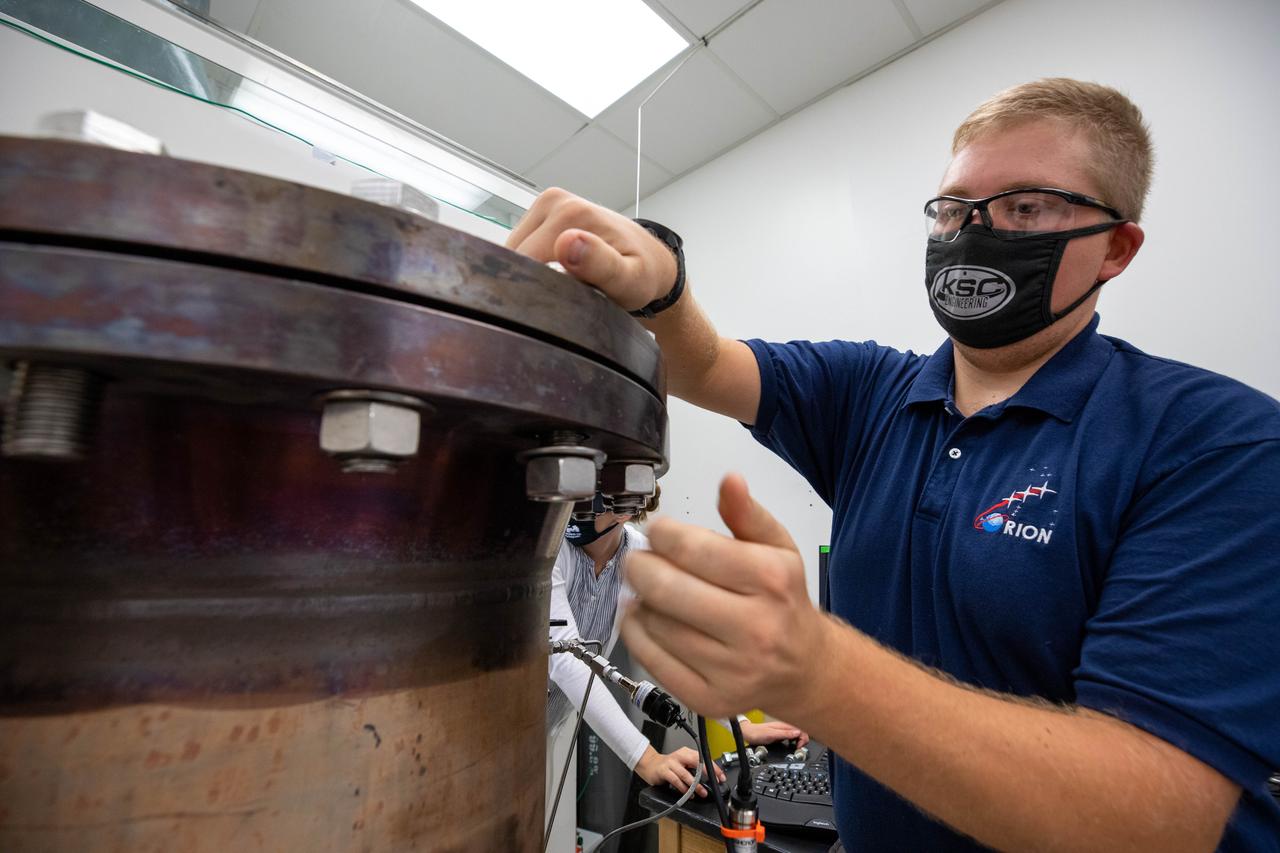

Evan Bell, a mechanical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
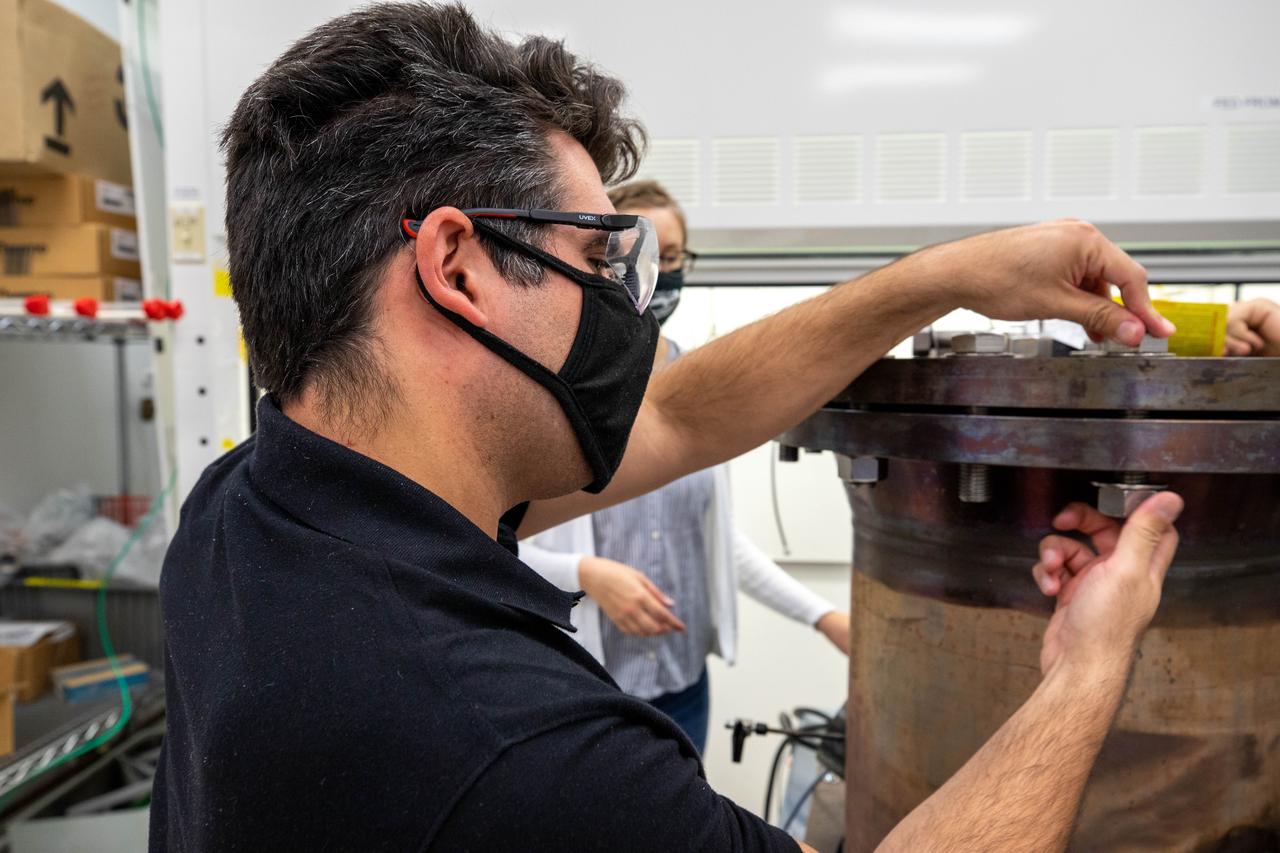

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
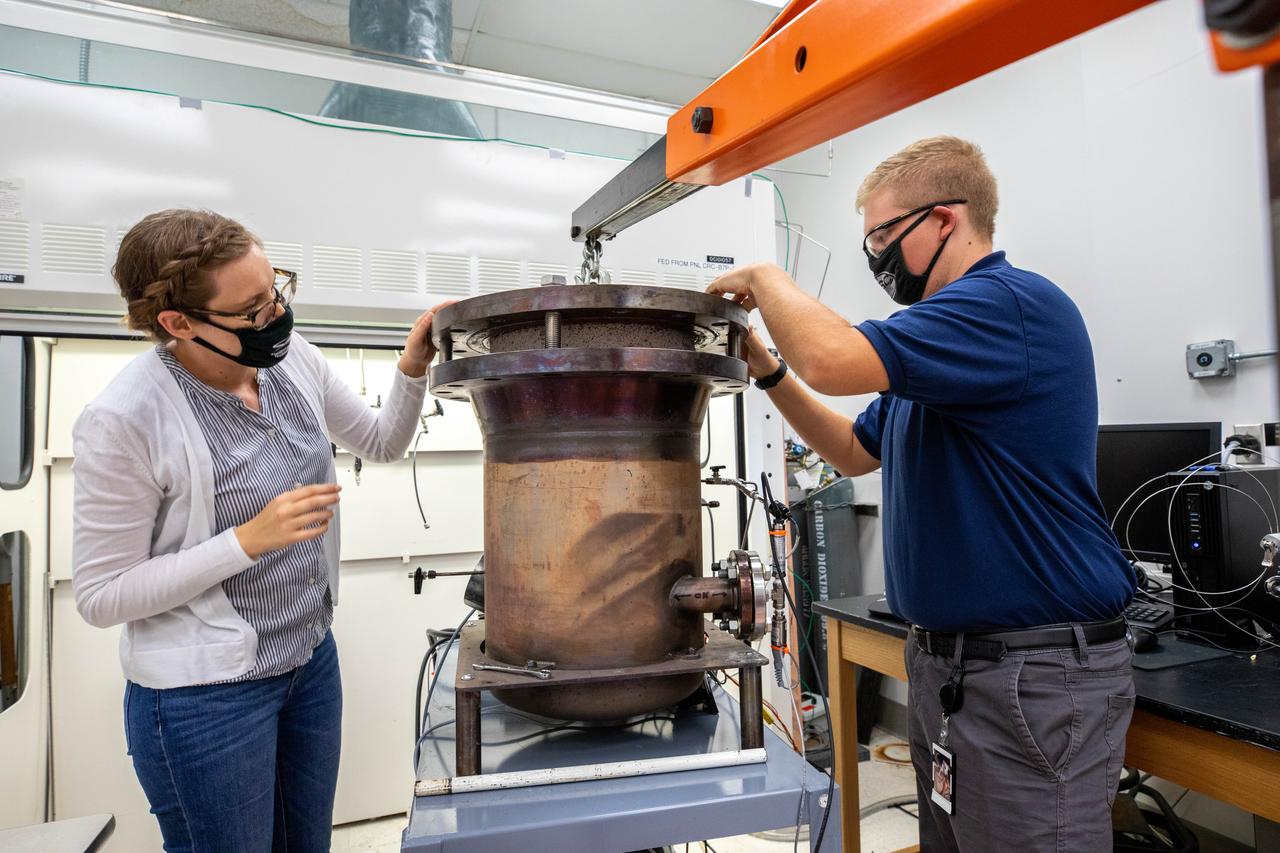

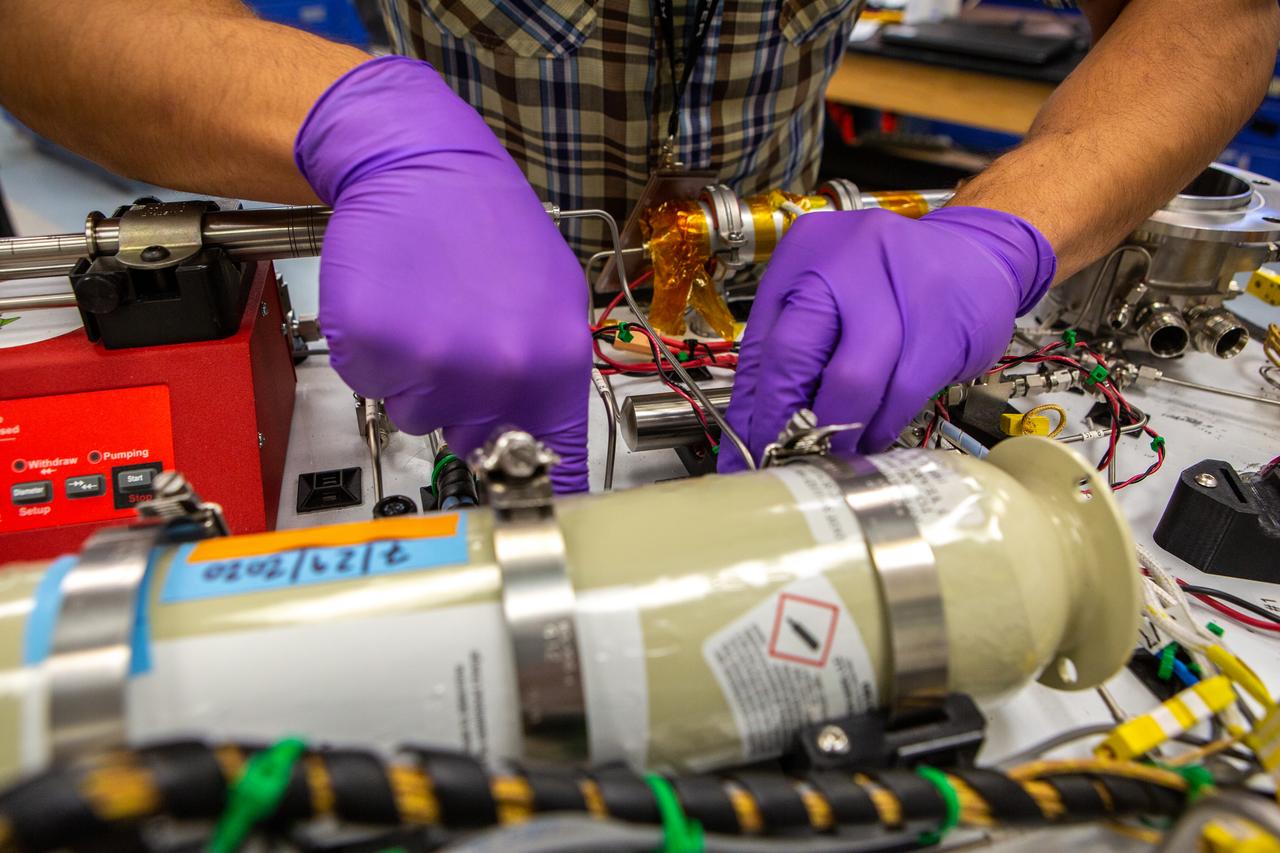
Elspeth Petersen, left, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and Evan Bell, GaLORE mechanical engineer, inspect hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – stimulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
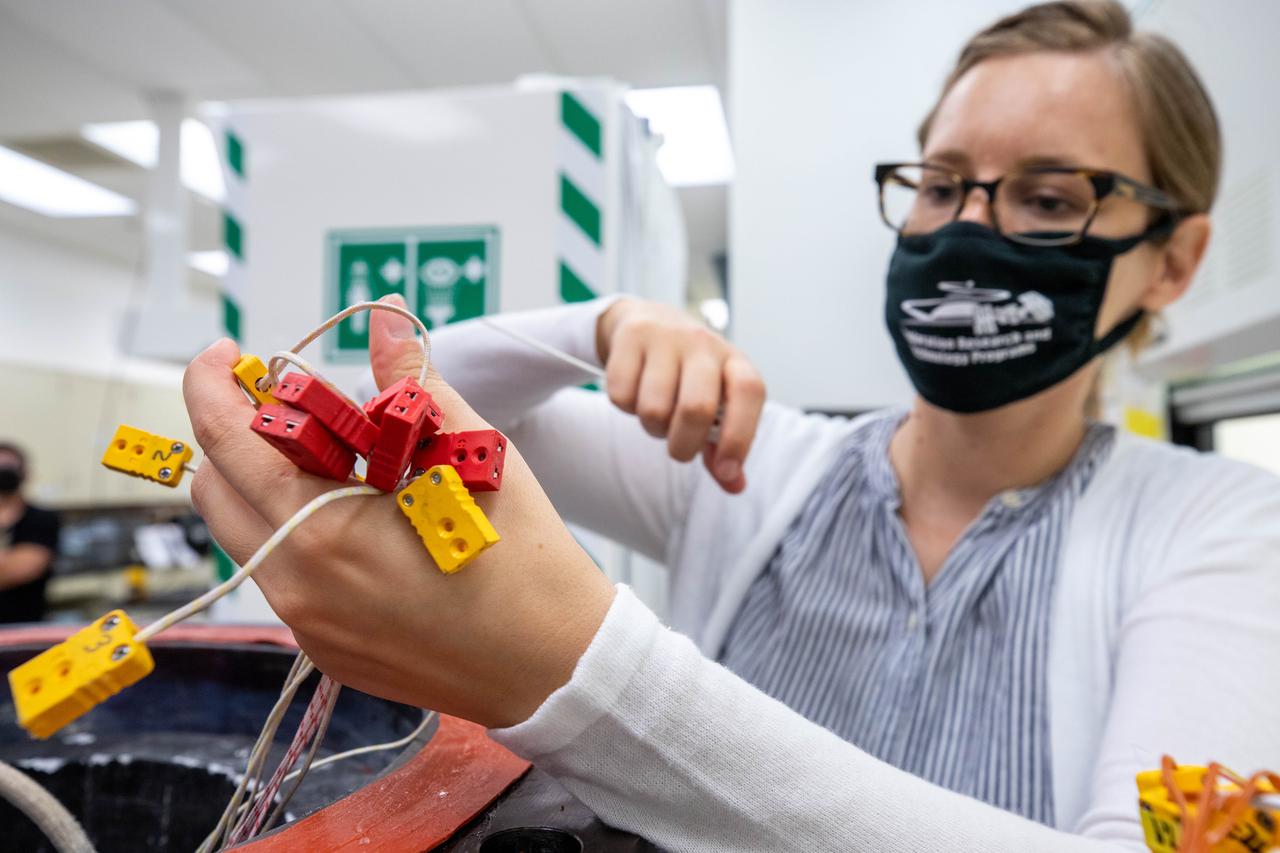

Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects some of the GaLORE hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
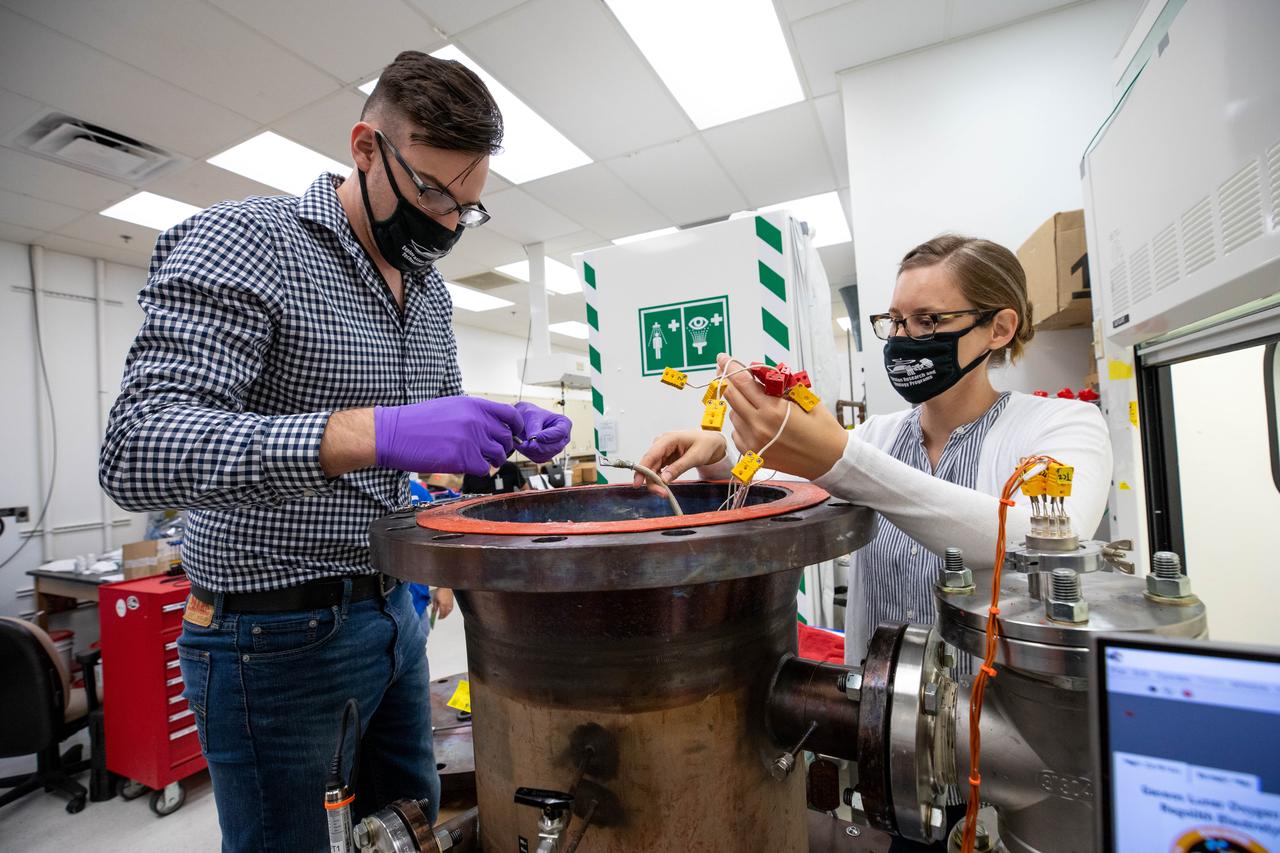

Kevin Grossman, left, principal investigator of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project, and Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the GaLORE team, check some of the project’s hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
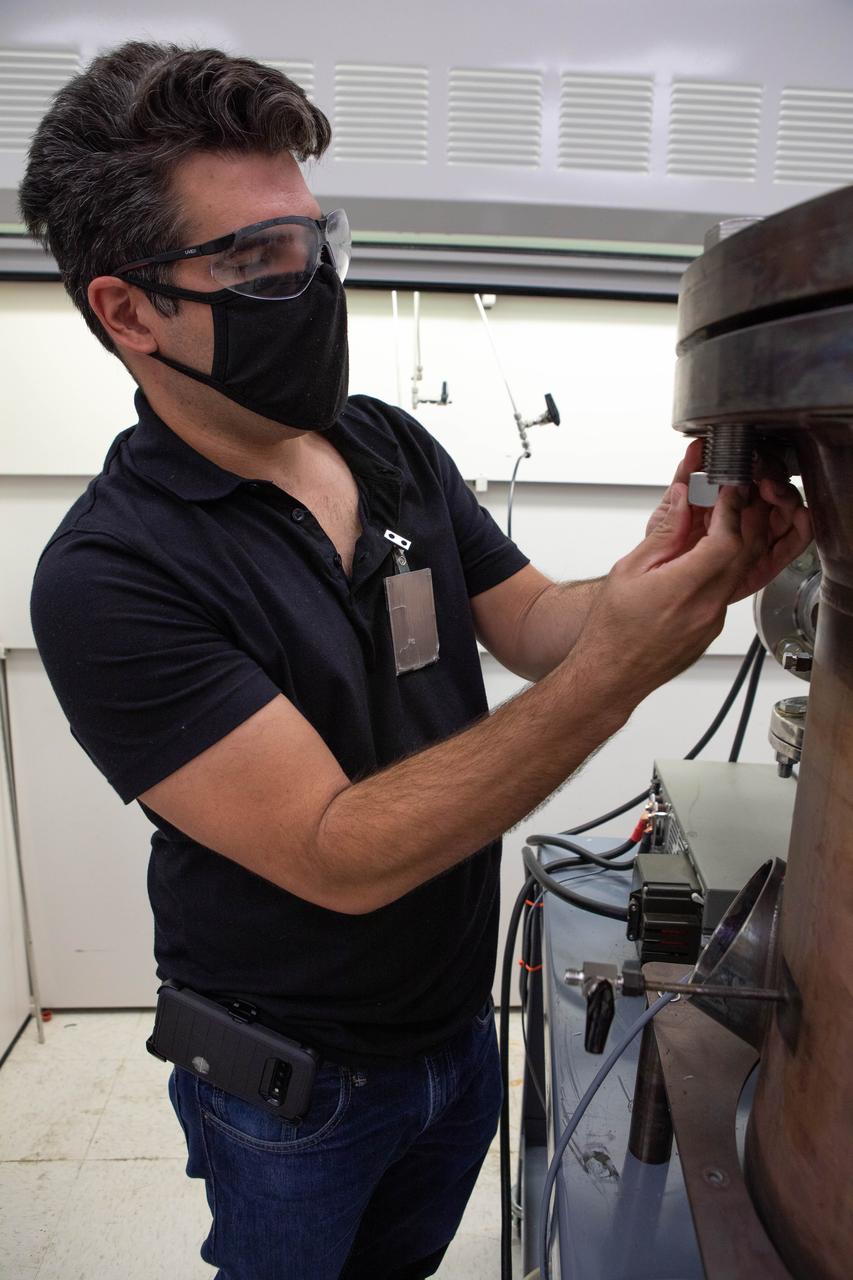

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
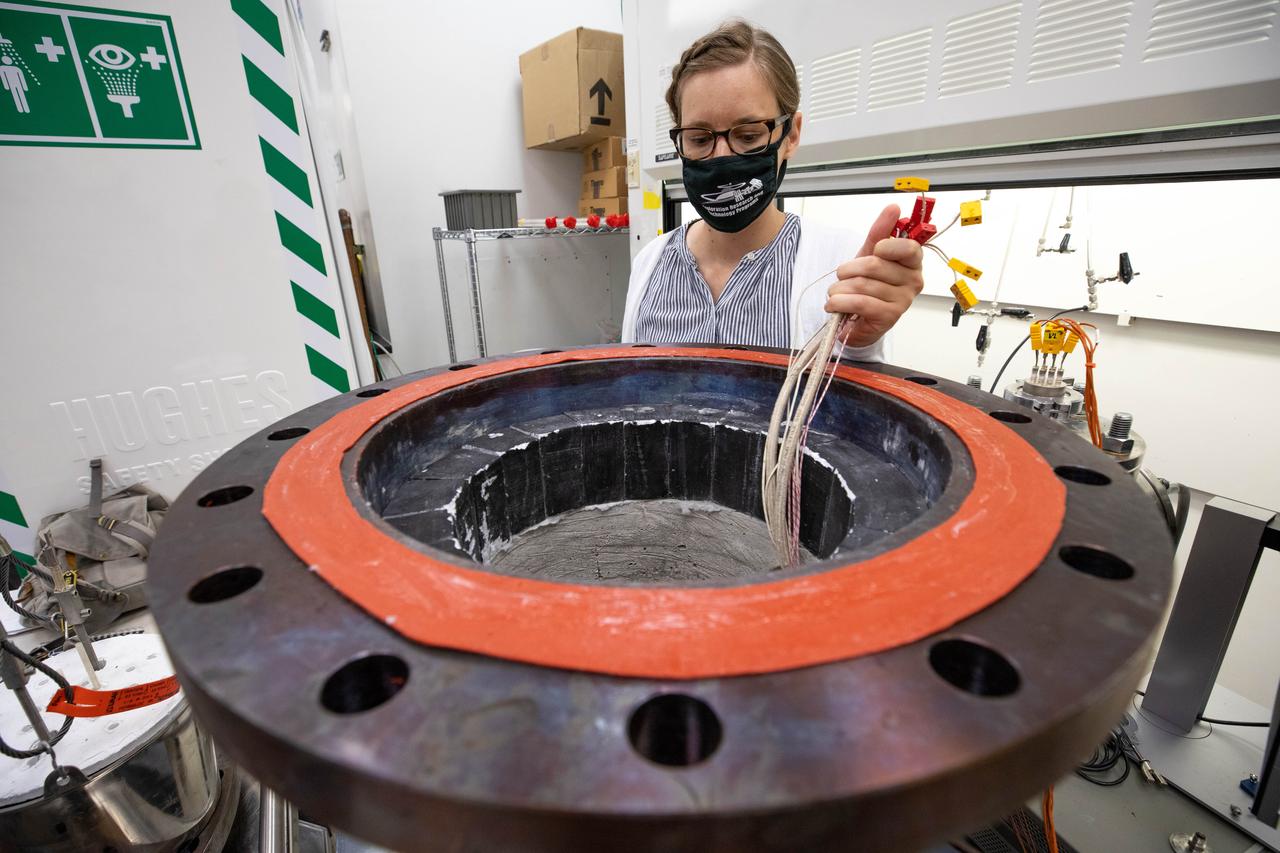

Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects hardware before a test to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
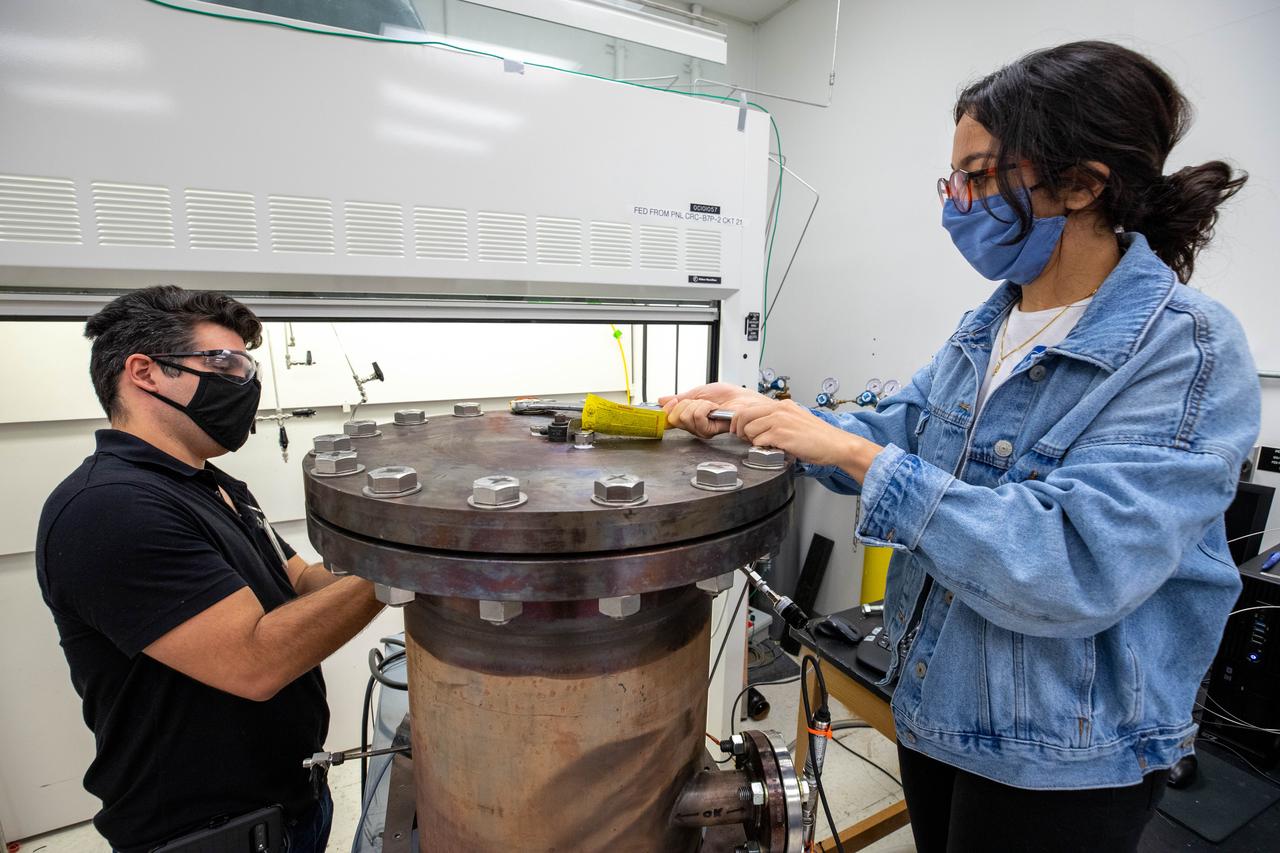

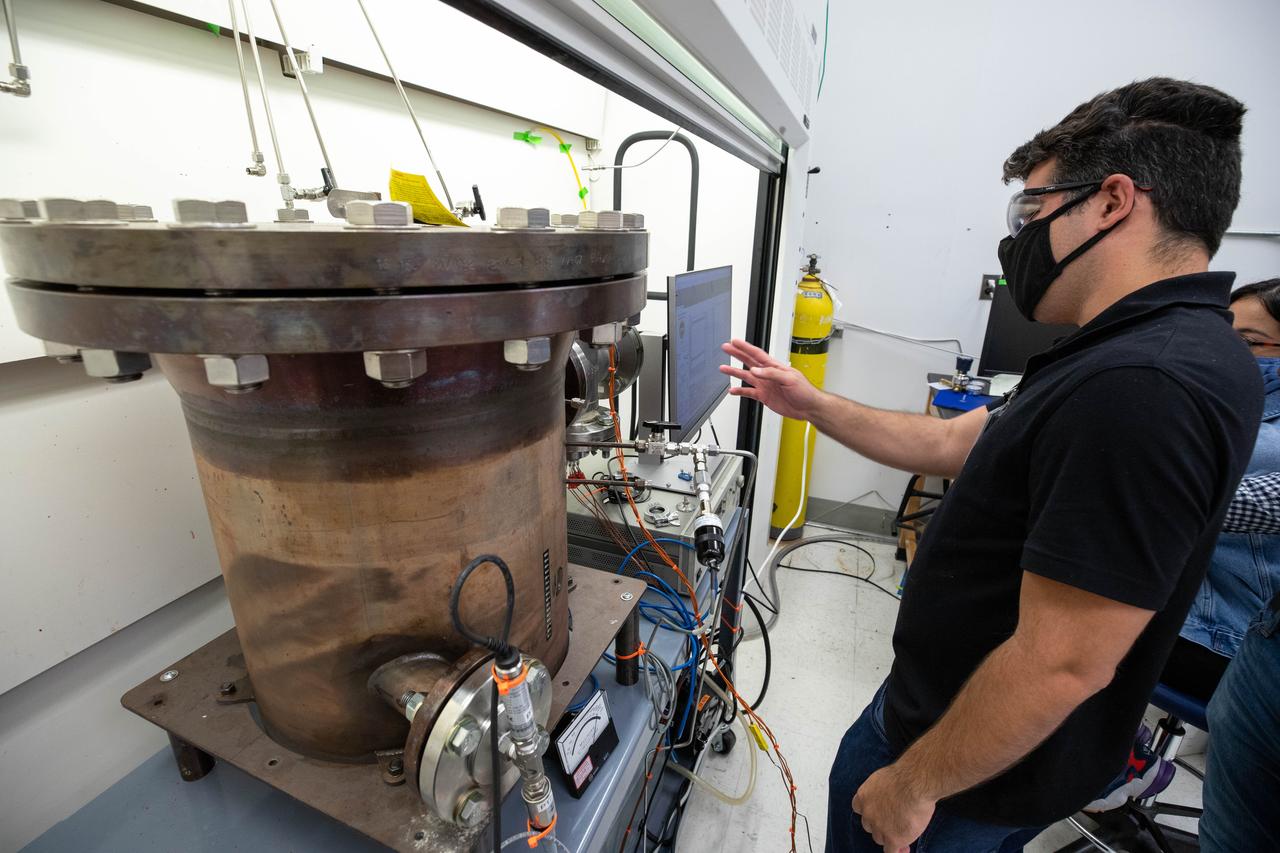
Members of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team inspect hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
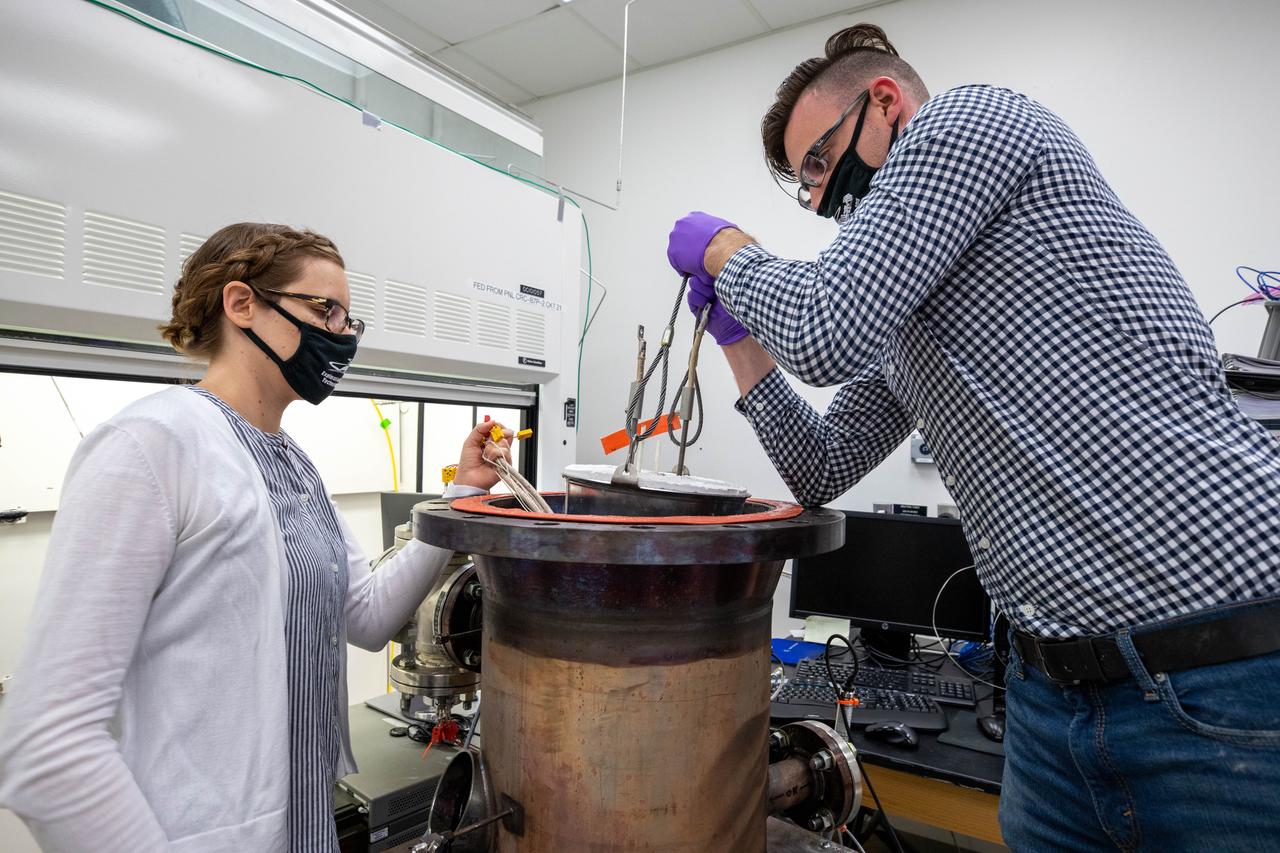

Elspeth Petersen, left, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team, and Kevin Grossman, GaLORE principal investigator, inspect a reactor before a test to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
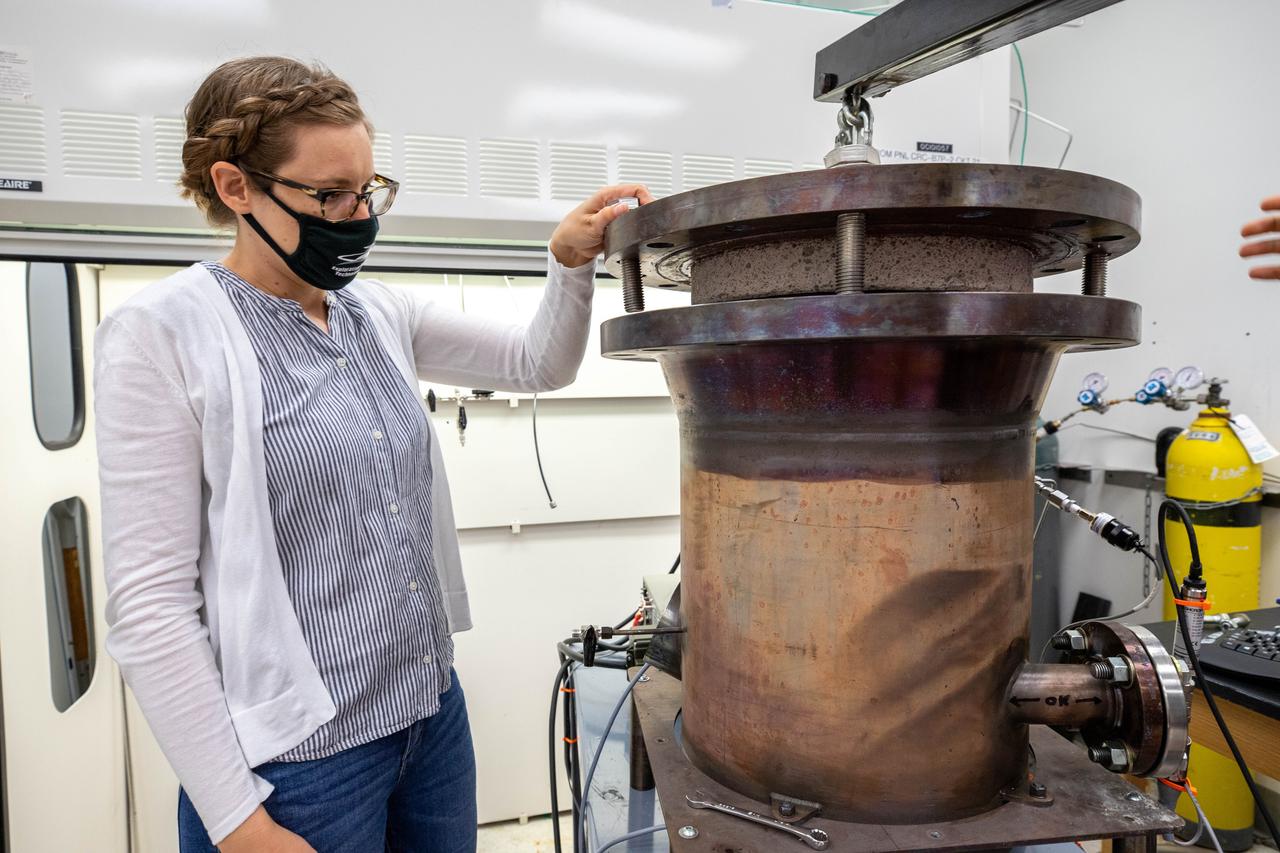

Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects the GaLORE hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
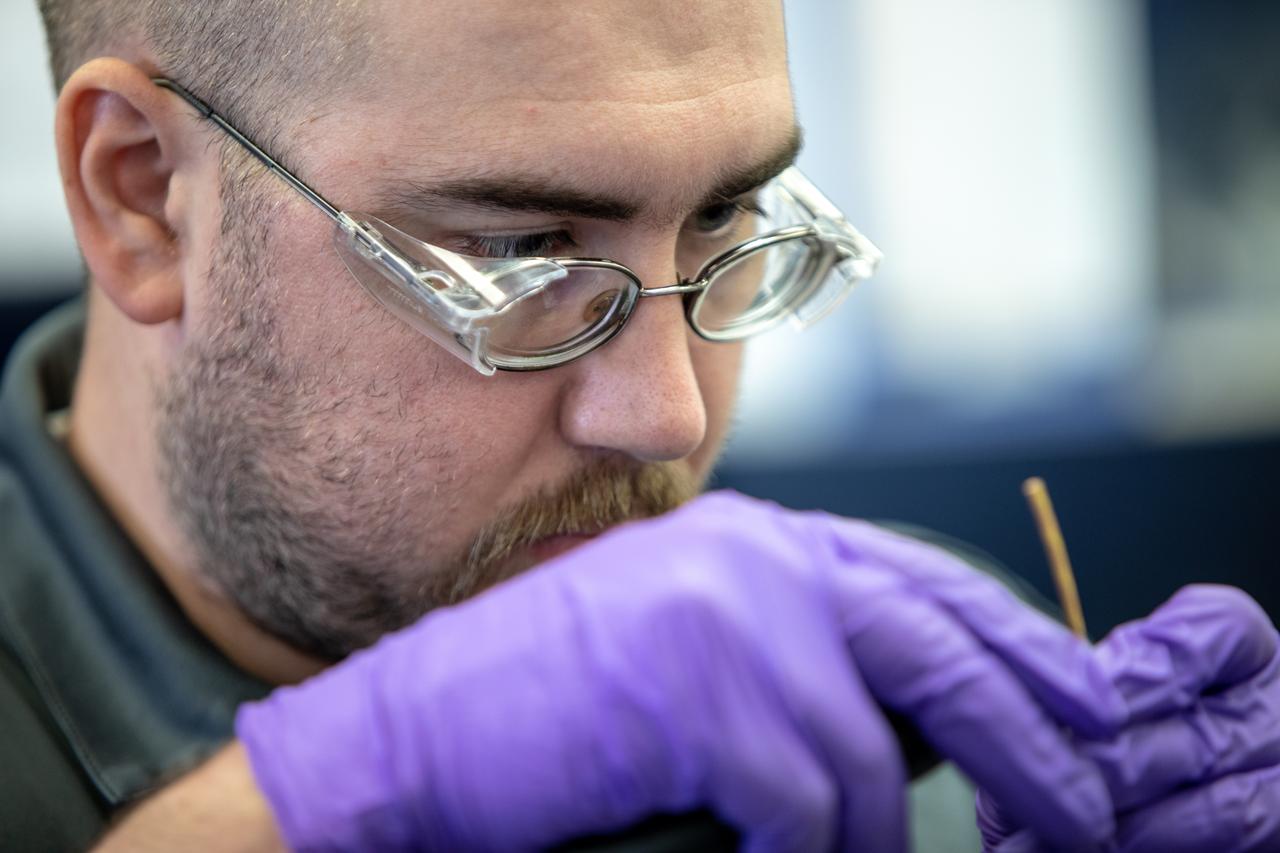

Thomas Cauvel, an intern assisting with software/electrical engineering on NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at Kennedy Space Center assembles the flight hardware. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
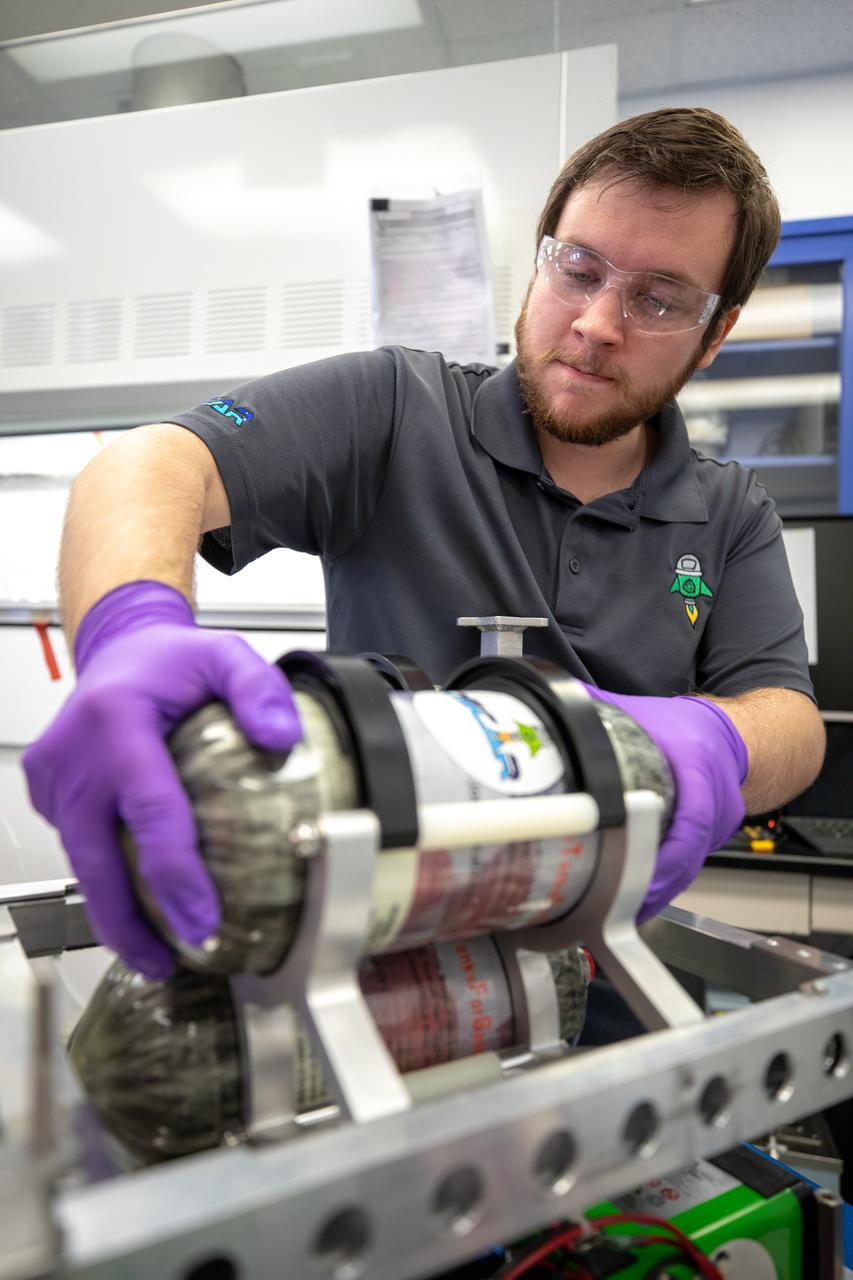

Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy Space Center employee providing support for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, installs OSCAR to the flight hardware that will carry it on its suborbital flight test. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees have worked on constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
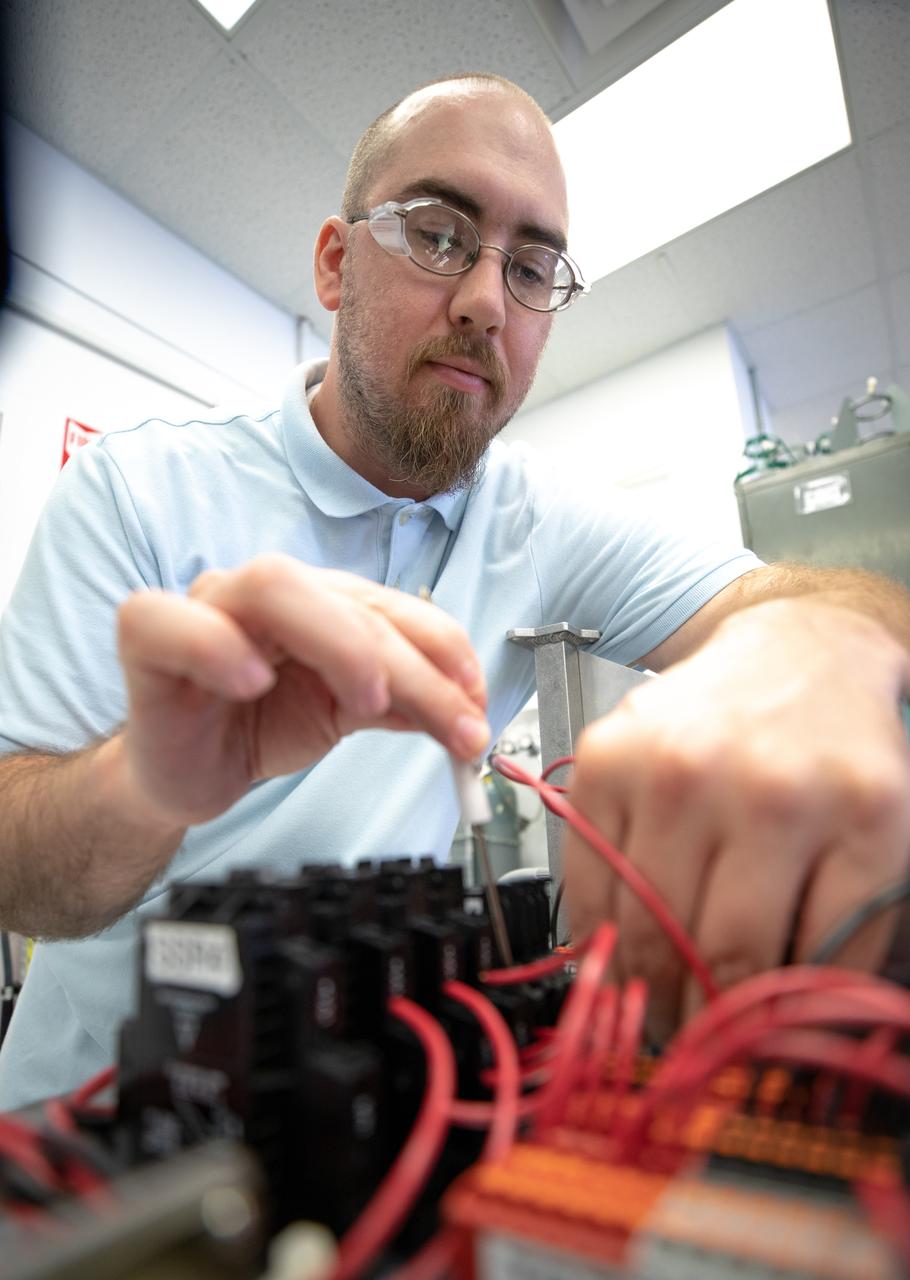
Thomas Cauvel, an intern assisting with software/electrical engineering on NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at Kennedy Space Center assembles the flight hardware. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
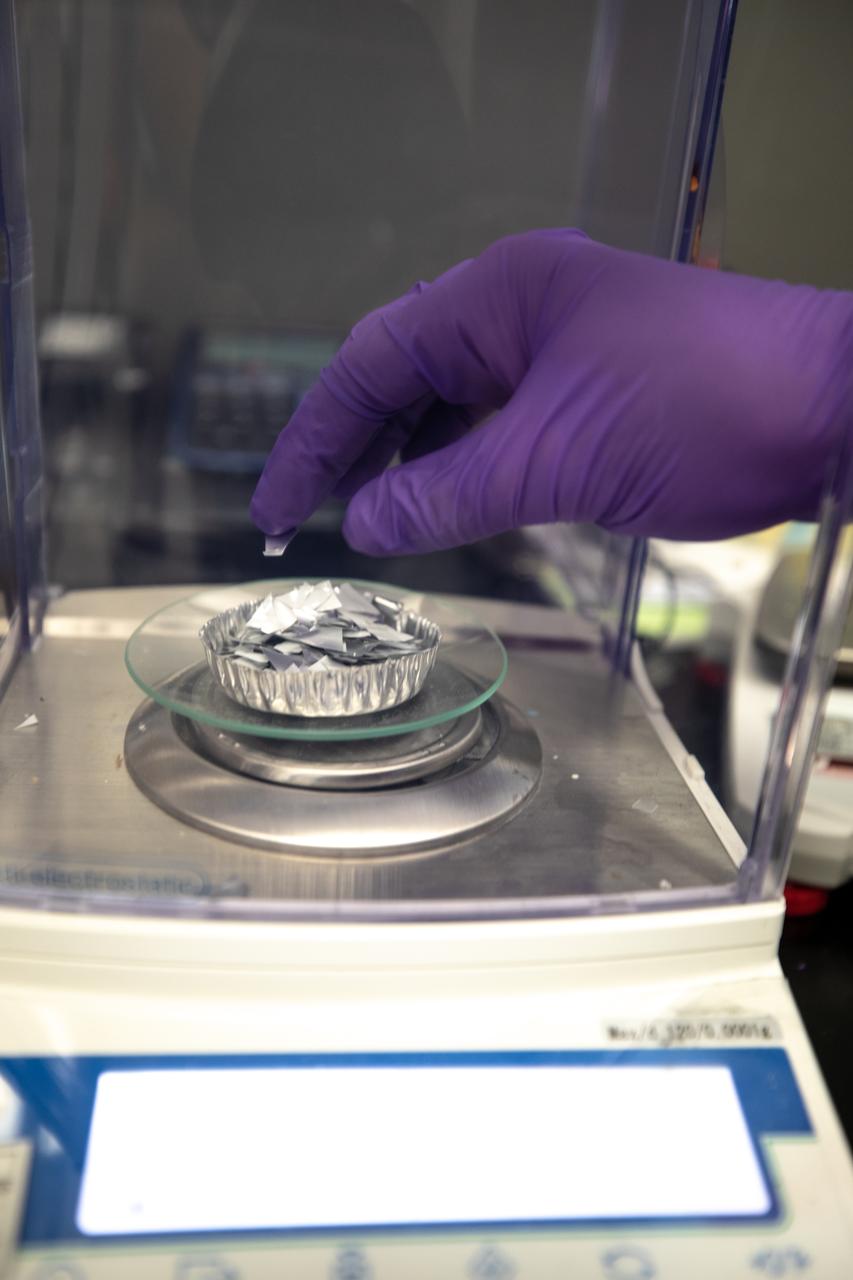
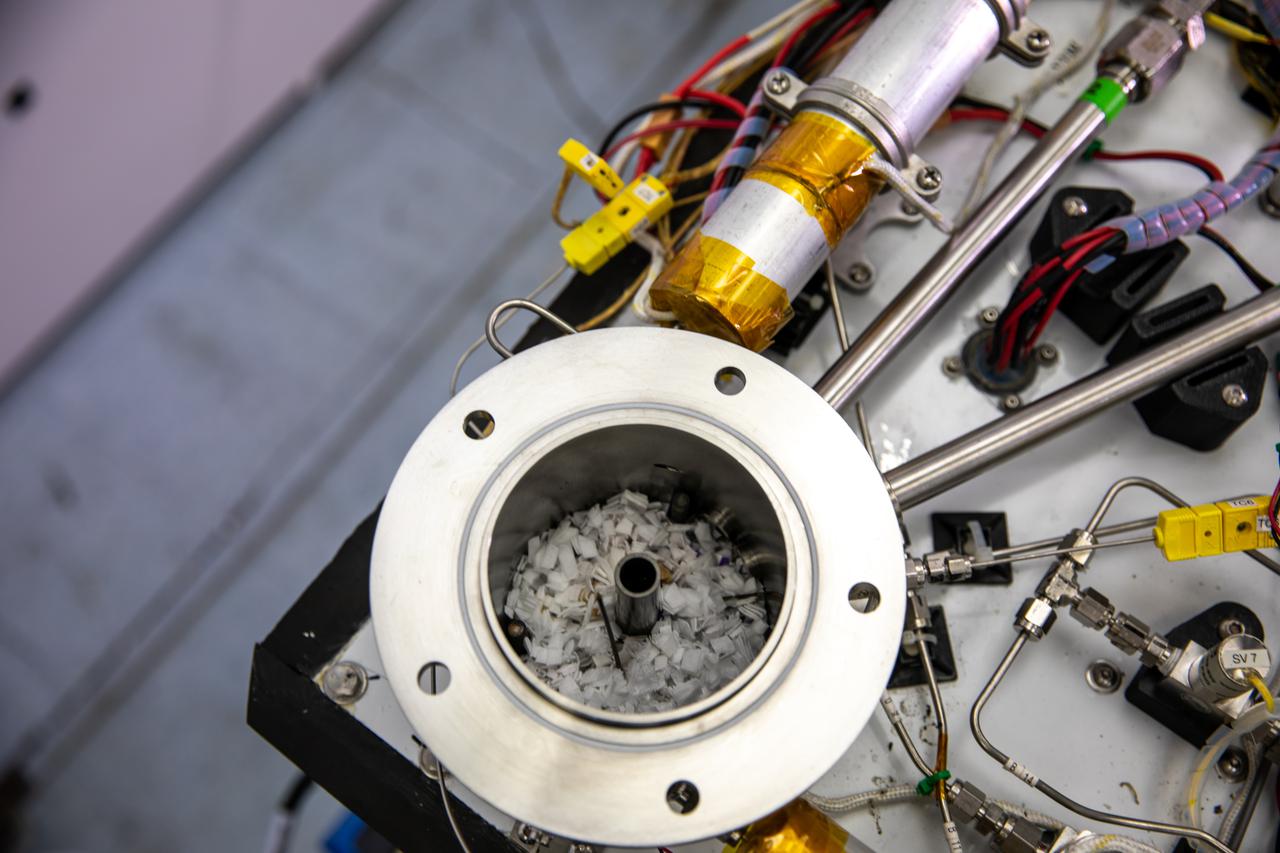
A Kennedy Space Center intern weighs trash simulant – comprised of different types of material that have been cut into tiny pieces – that will be utilized for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
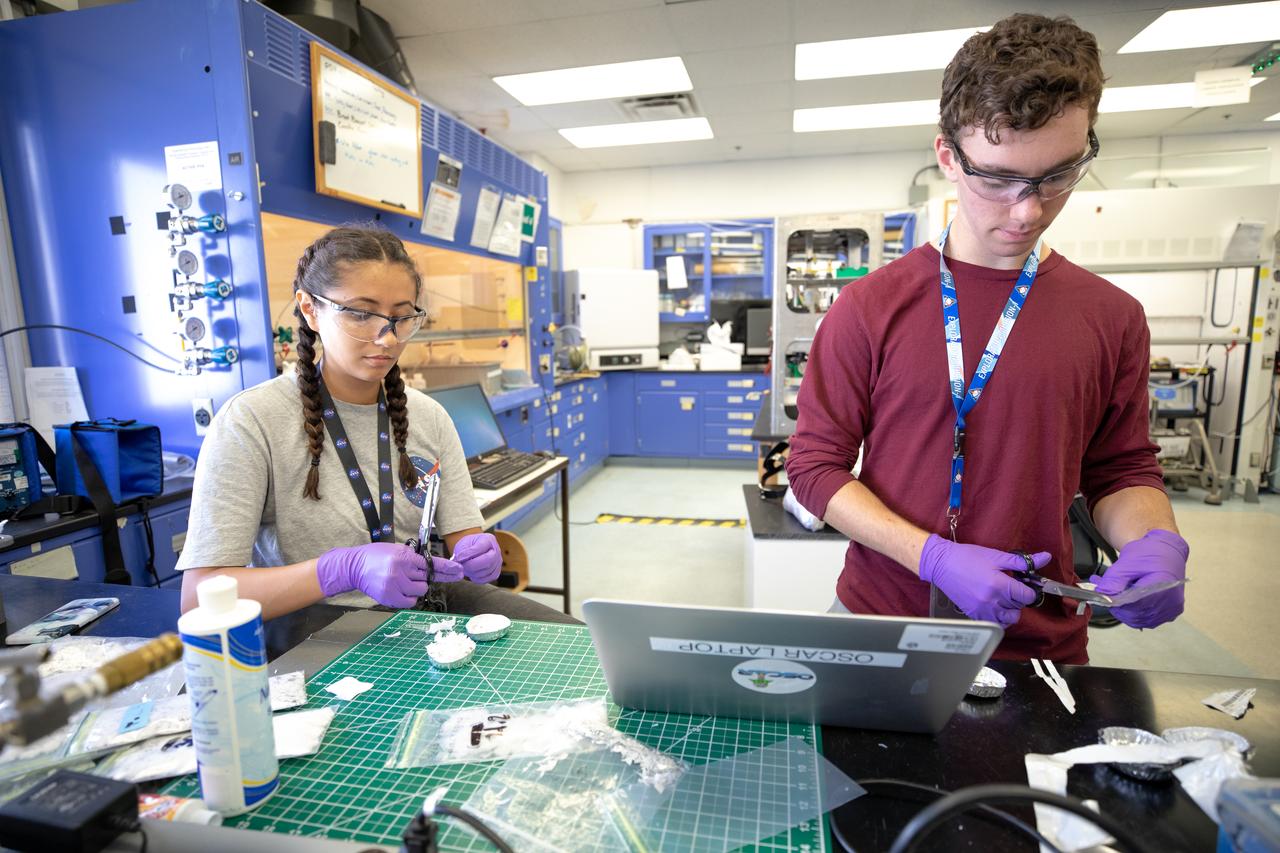

From left, interns Isabella Aviles and Patrick Follis at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida cut up different types of material for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, to use as a trash simulant during microgravity testing. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, recover water from trash and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
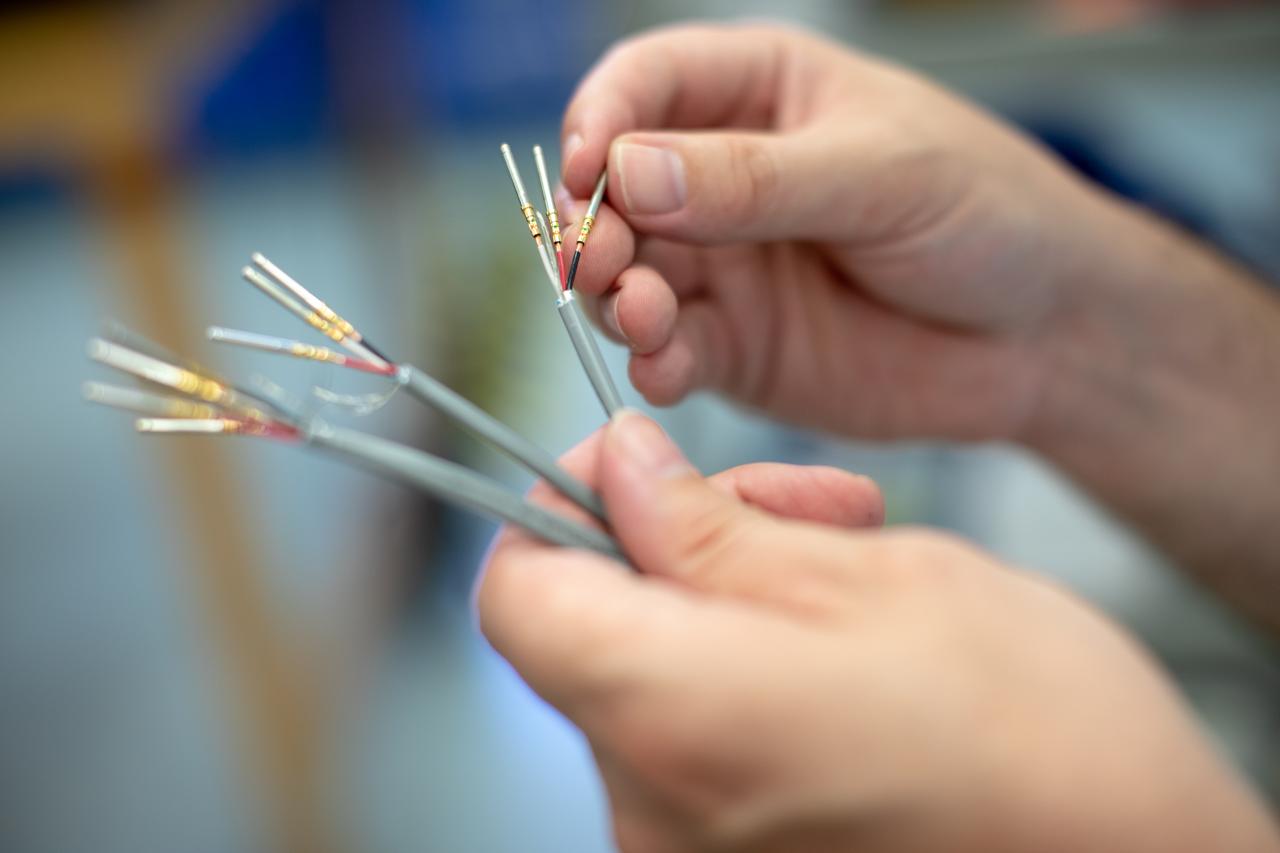
Flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Rector, or OSCAR, is photographed at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
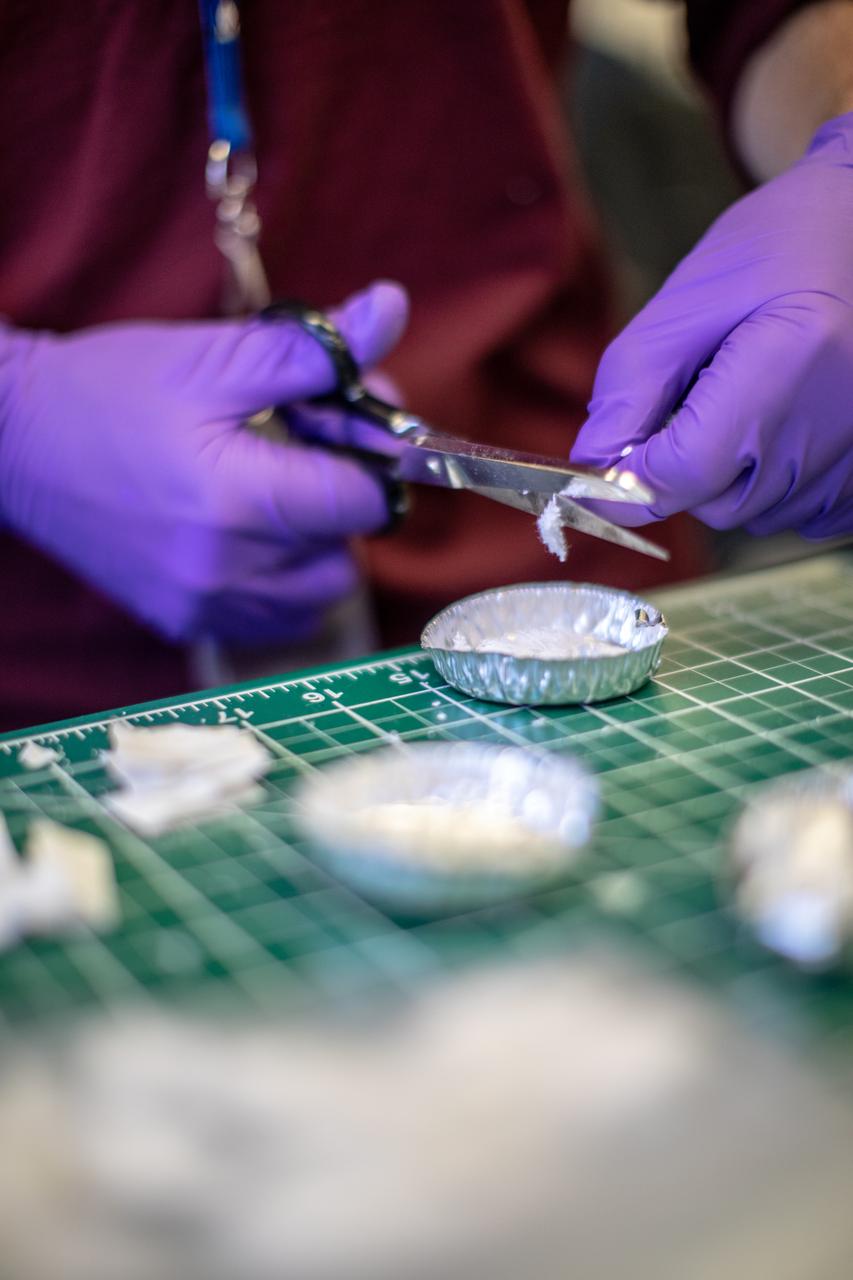

An intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida cuts up different types of material to be utilized as trash simulant for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
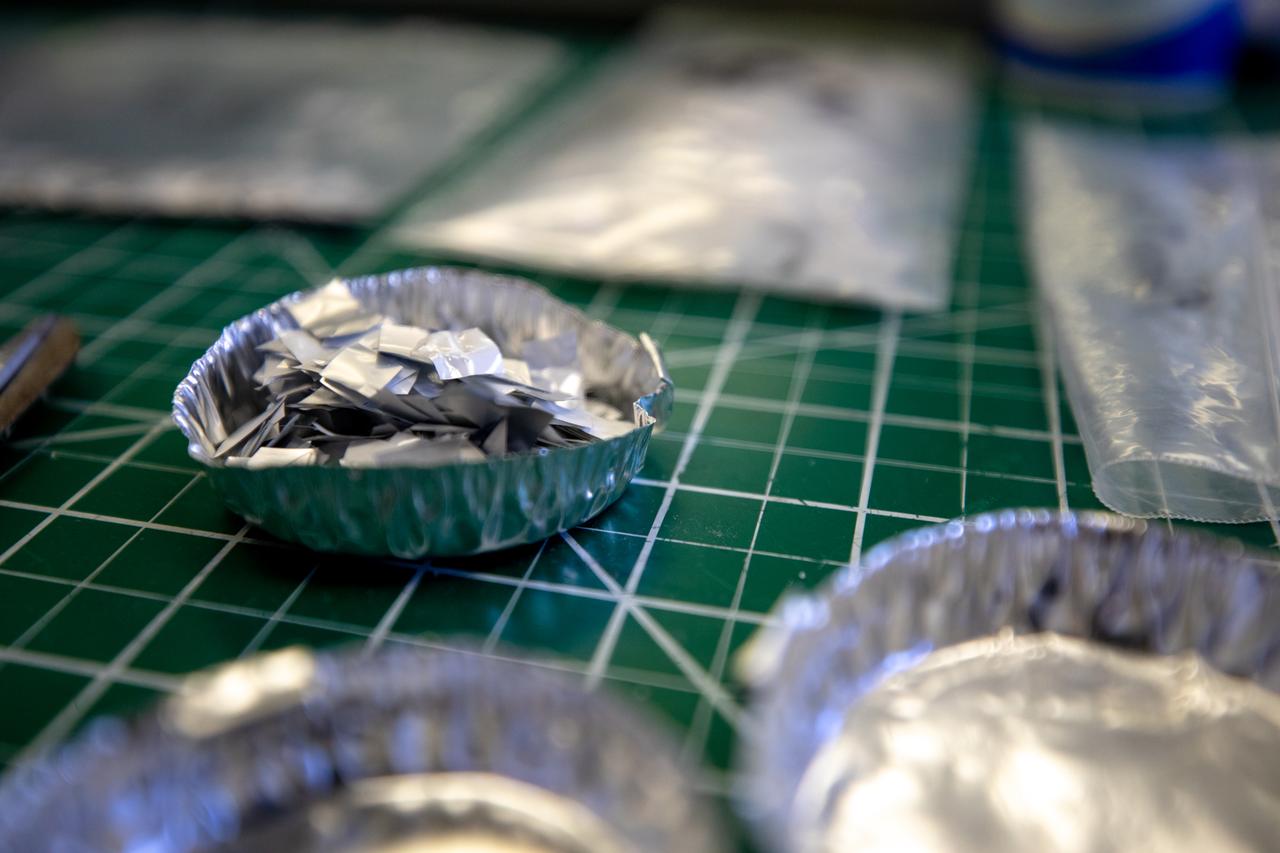

Pictured at Kennedy Space Center is trash simulant – comprised of different types of material that have been cut into tiny pieces – that will be utilized for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
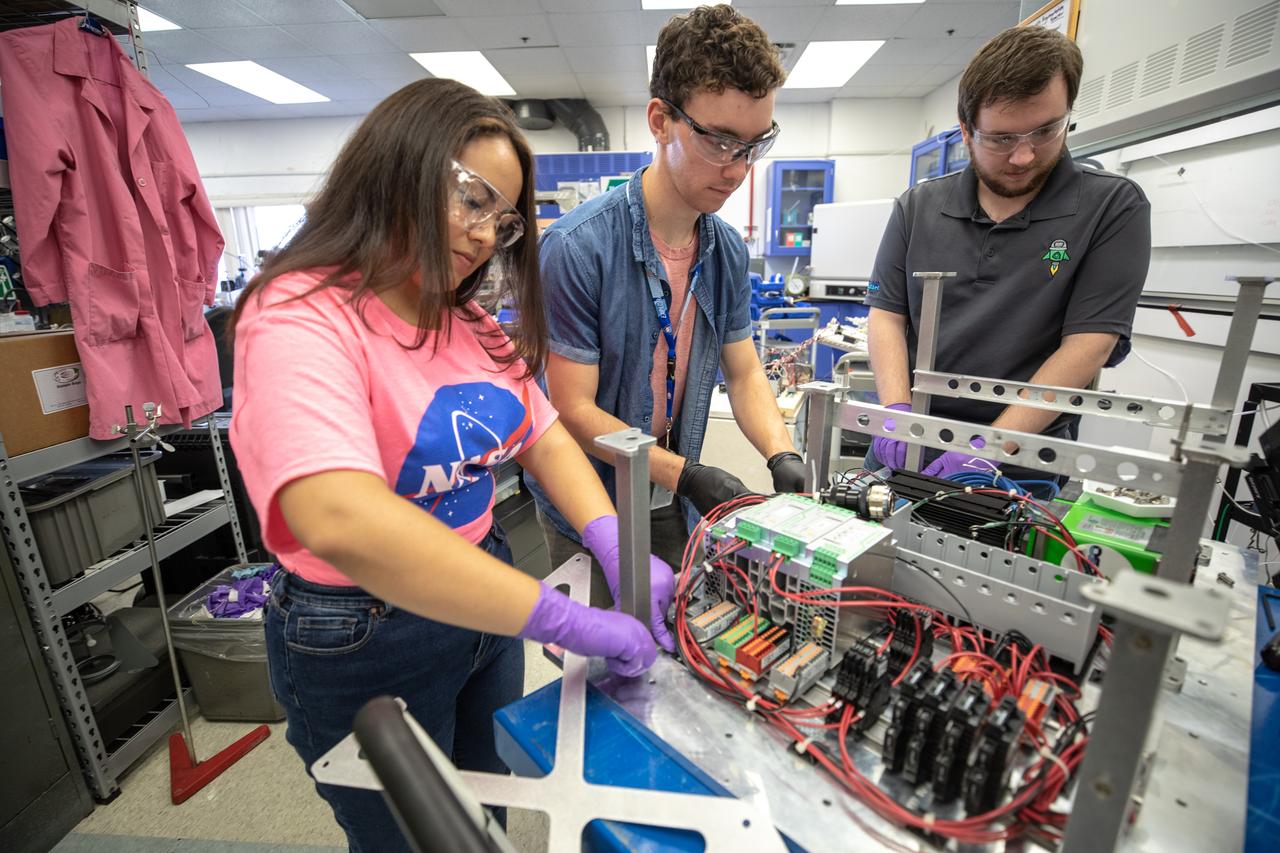

From left, Kennedy Space Center interns Brianna Sandoval and Patrick Follis, and Kennedy employee Jonathan Gleeson assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
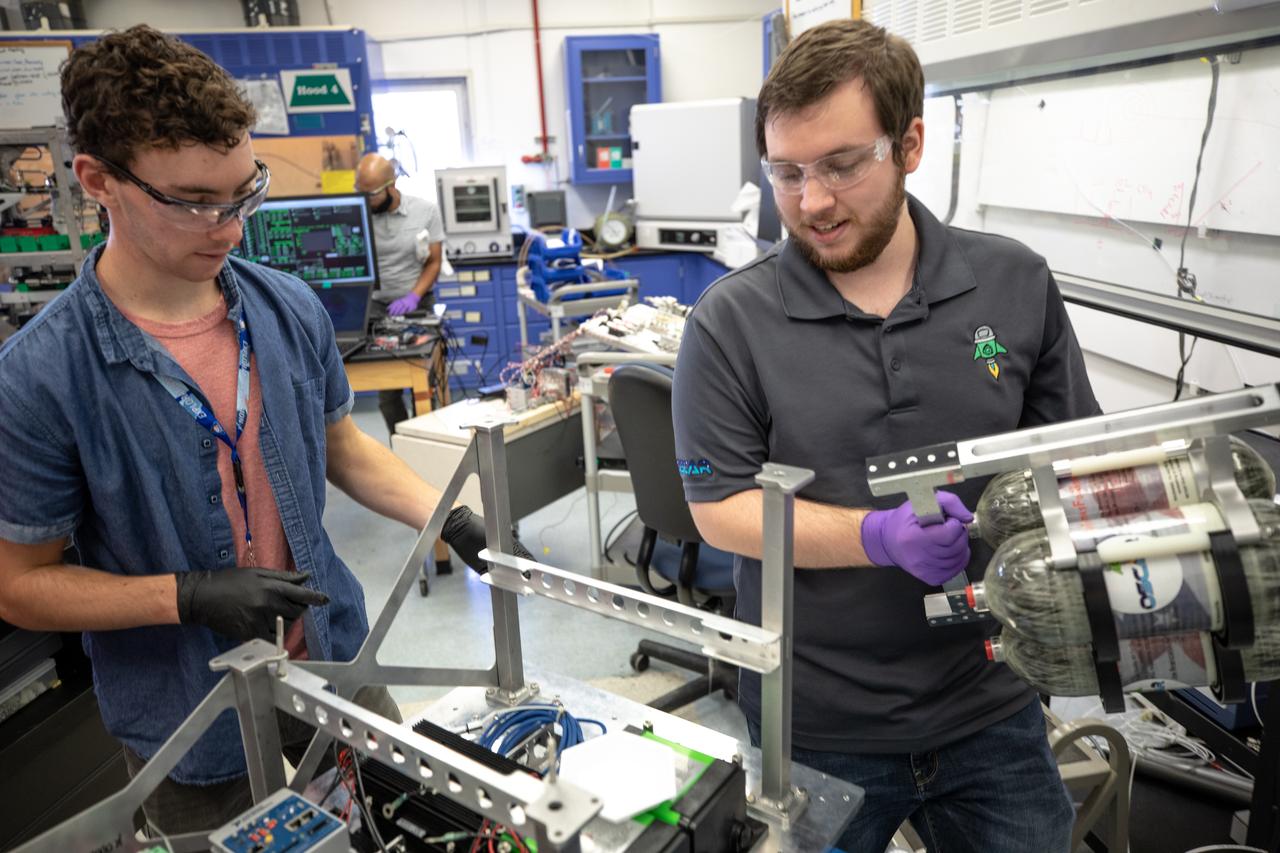
Kennedy Space Center employee Jonathan Gleeson (right) and Kennedy intern Patrick Follis assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
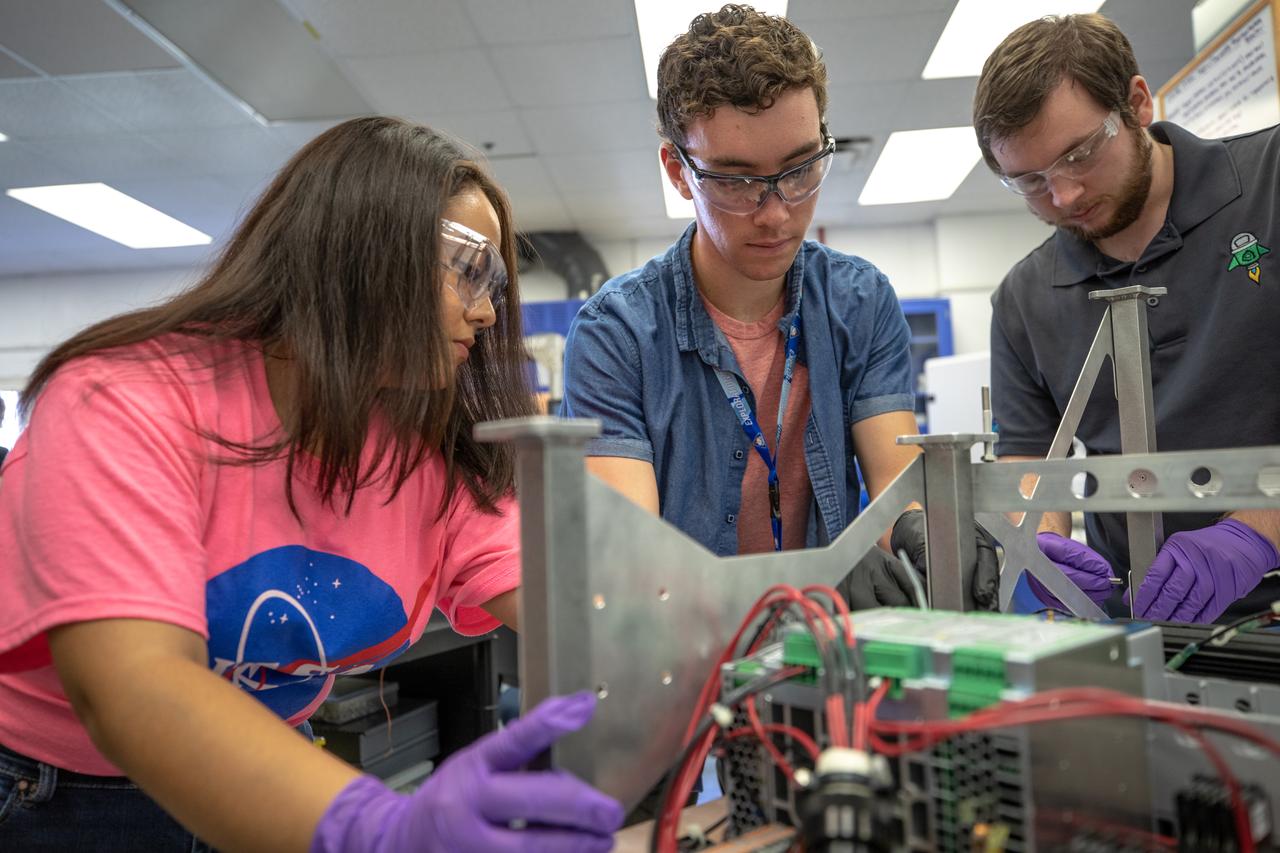

From left, Kennedy Space Center interns Brianna Sandoval and Patrick Follis, and Kennedy employee Jonathan Gleeson assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
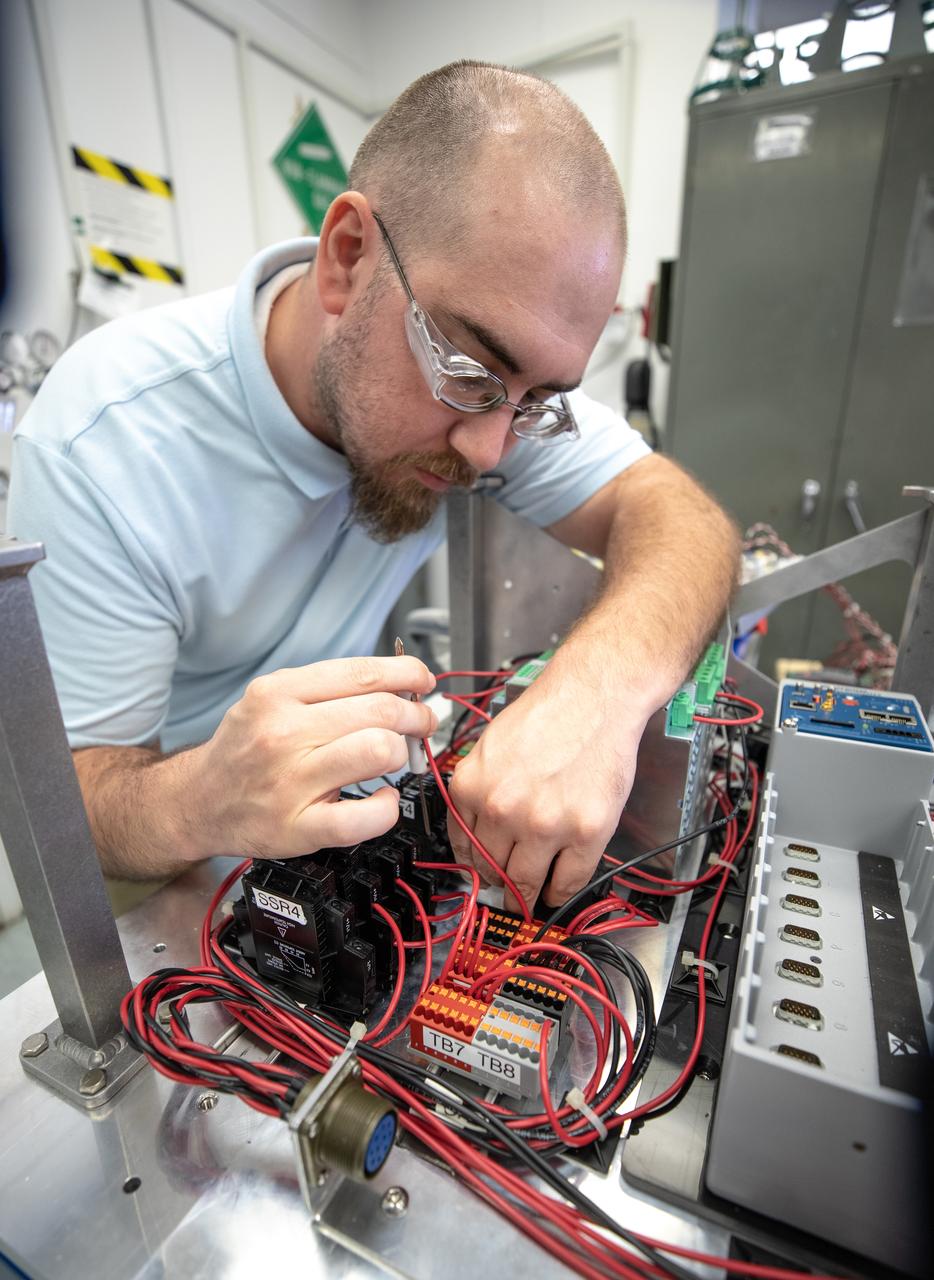

Thomas Cauvel, an intern assisting with software/electrical engineering on NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at Kennedy Space Center assembles the flight hardware. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
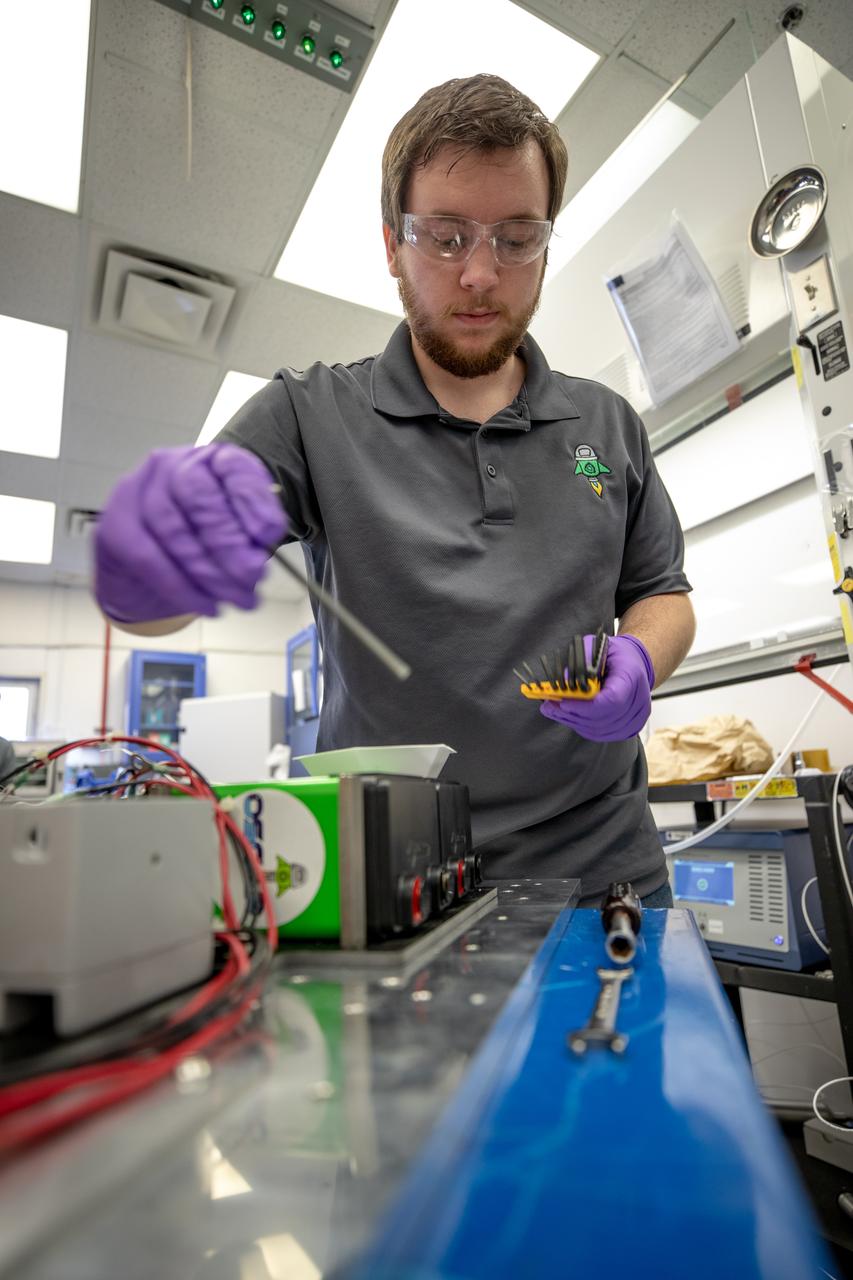

Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy Space Center employee providing support for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, assembles the flight hardware of OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
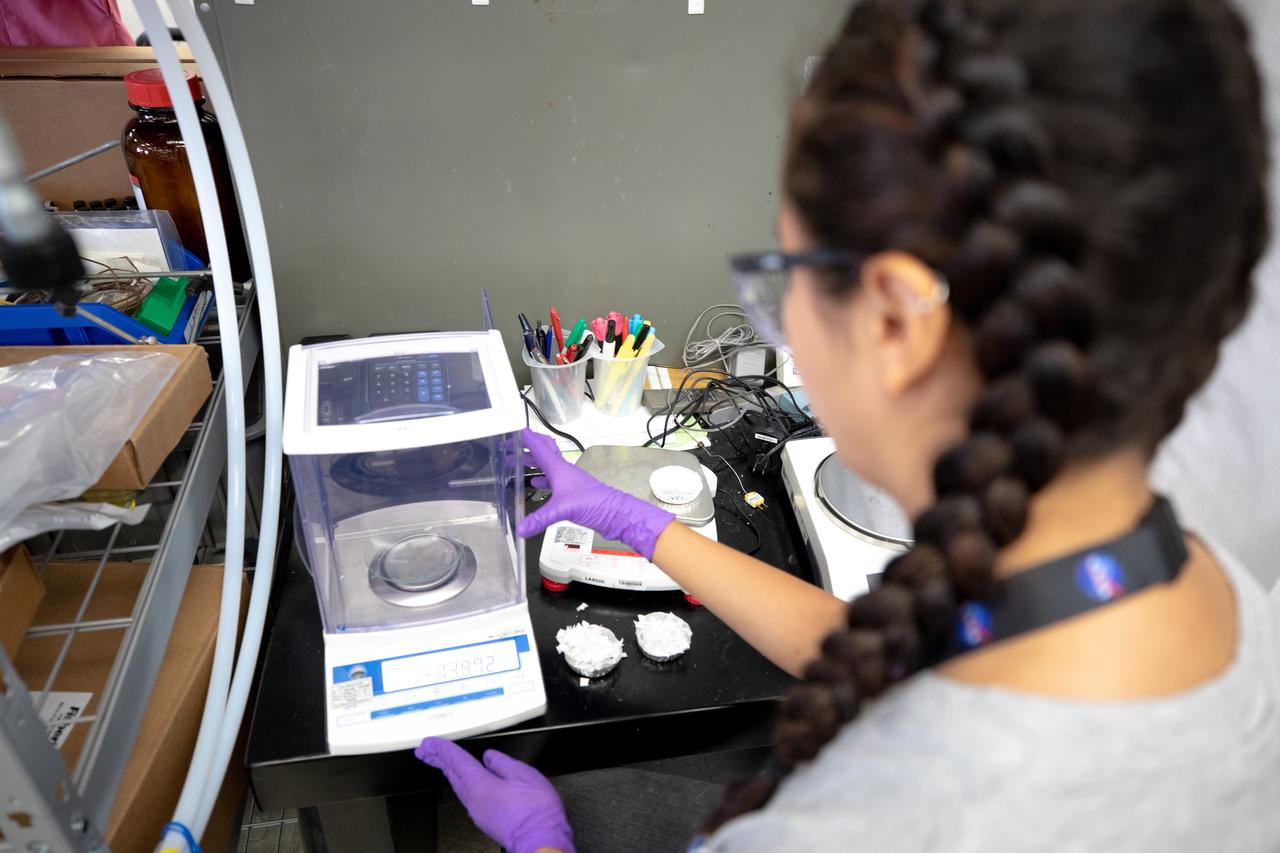
Isabella Aviles, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, weighs trash simulant – comprised of different types of material that have been cut into tiny pieces – that will be utilized for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
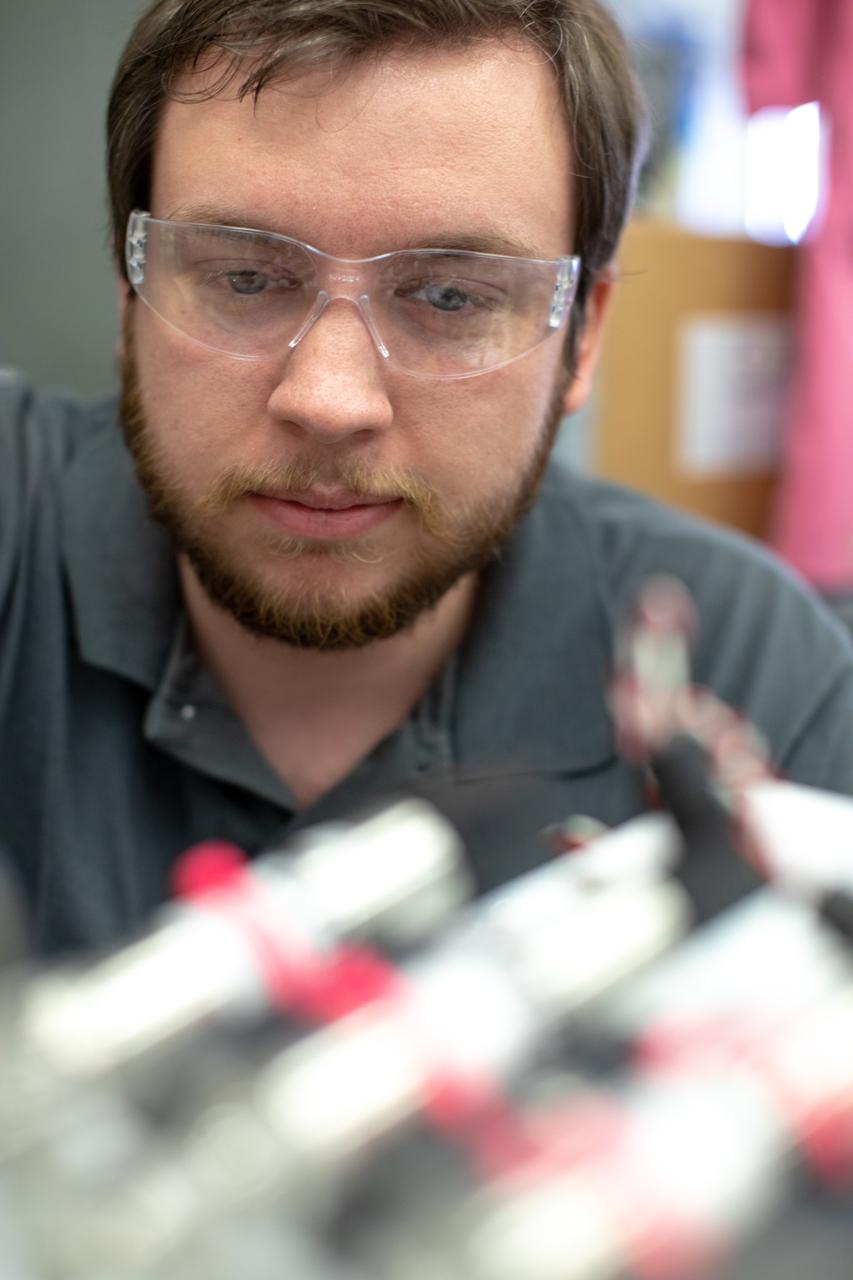

Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy Space Center employee providing support for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, assembles the flight hardware of OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
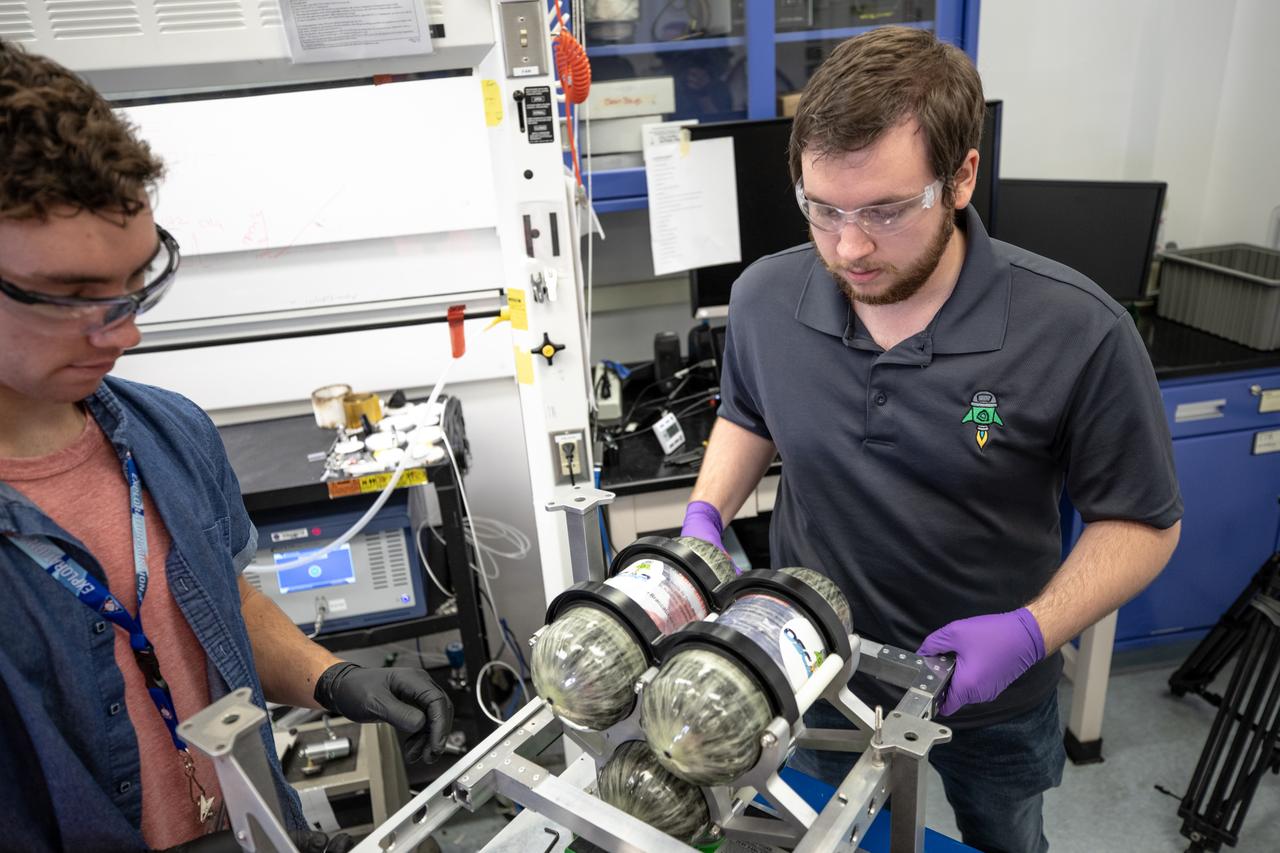

Kennedy Space Center employee Jonathan Gleeson (right) and Kennedy intern Patrick Follis assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.

Patrick Follis, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, assembles the flight hardware for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.

NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, is being prepared for suborbital flight testing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for the suborbital flight test.
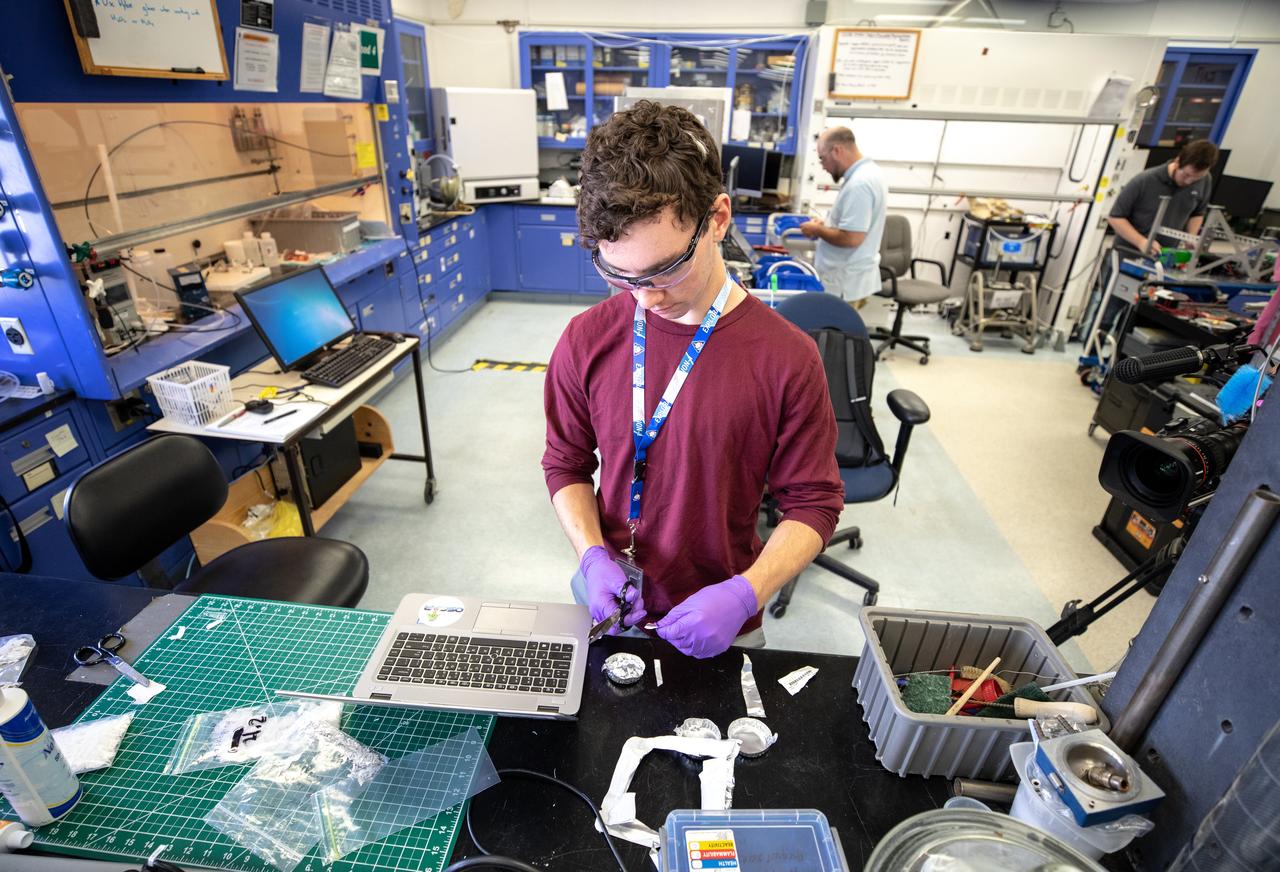

Patrick Follis, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, cuts up different types of material for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, to use as a trash simulant during microgravity testing. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
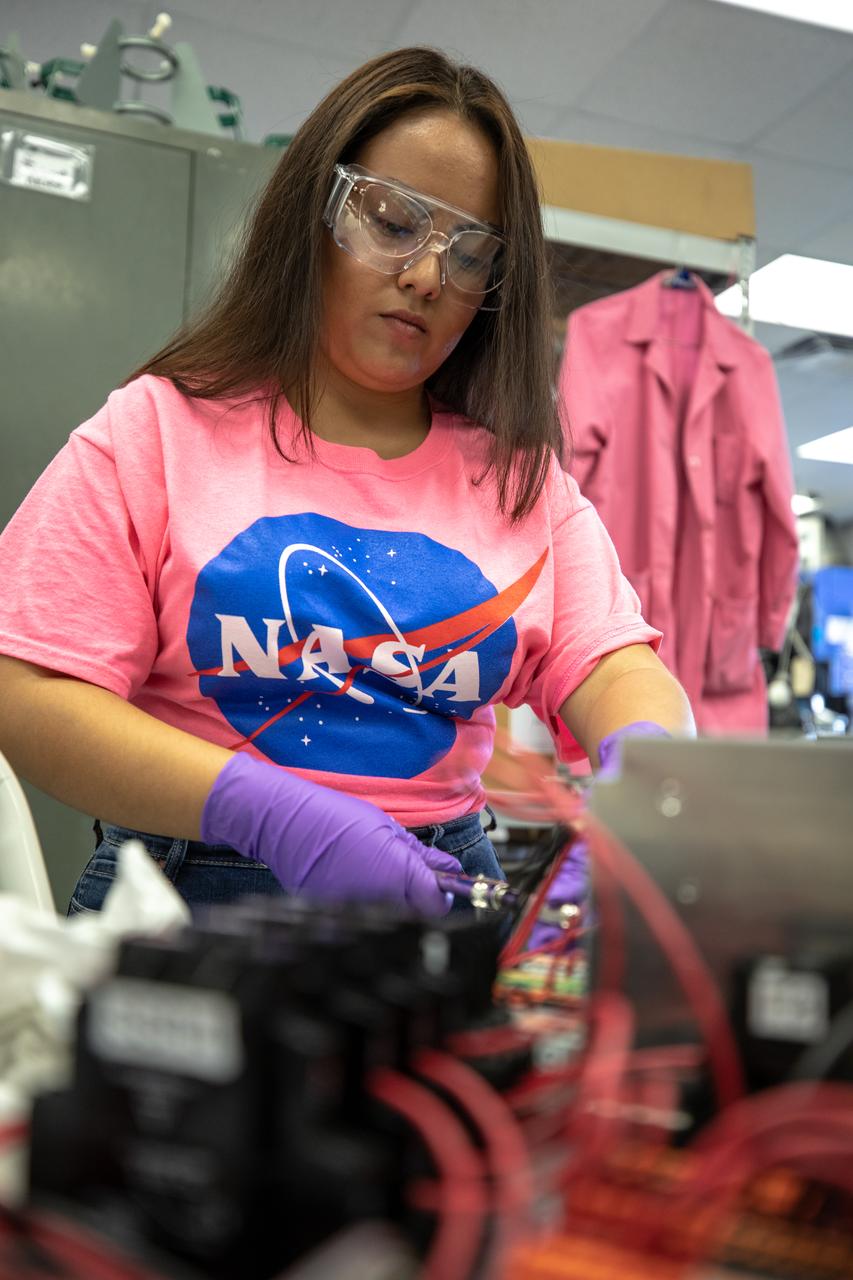

Brianna Sandoval, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, assembles the flight hardware of the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.

Kennedy Space Center intern Patrick Follis (left) and Kennedy employee Jonathan Gleeson assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
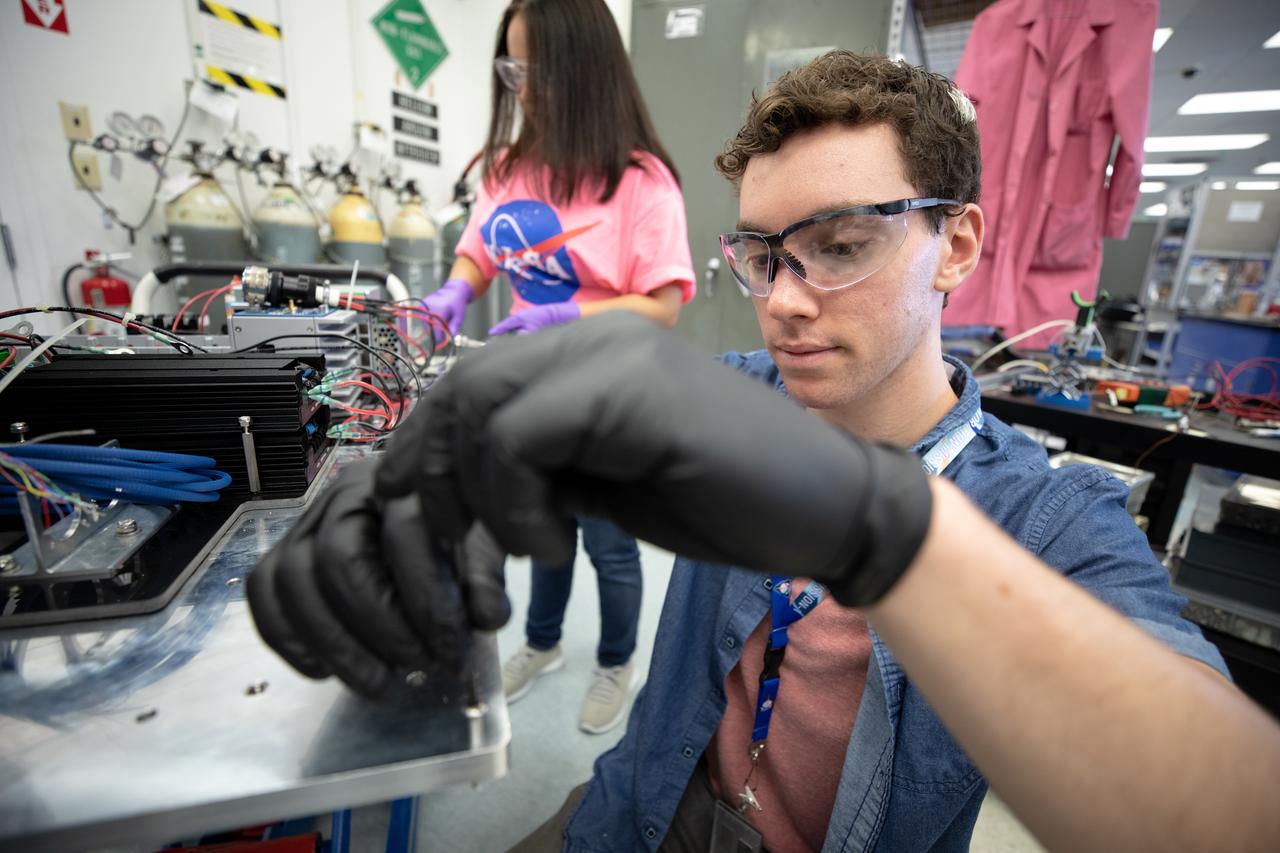

Interns Brianna Sandoval (left) and Patrick Follis at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida assemble the flight hardware for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
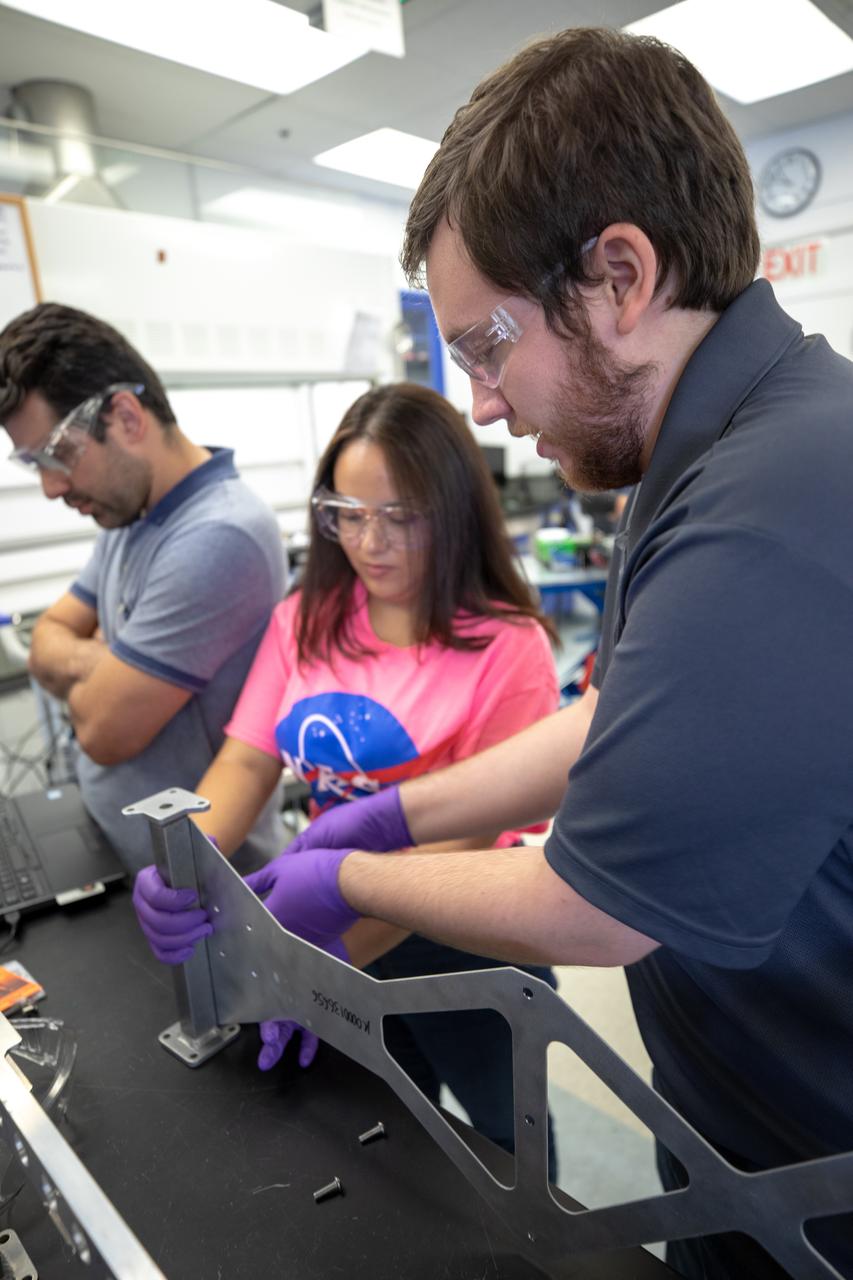

From left, Kennedy Space Center Mechanical Engineer Jaime Toro, NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) data acquisition and testing; Brianna Sandoval, OSCAR intern; and Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy employee providing support for OSCAR under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, assemble the flight hardware of OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
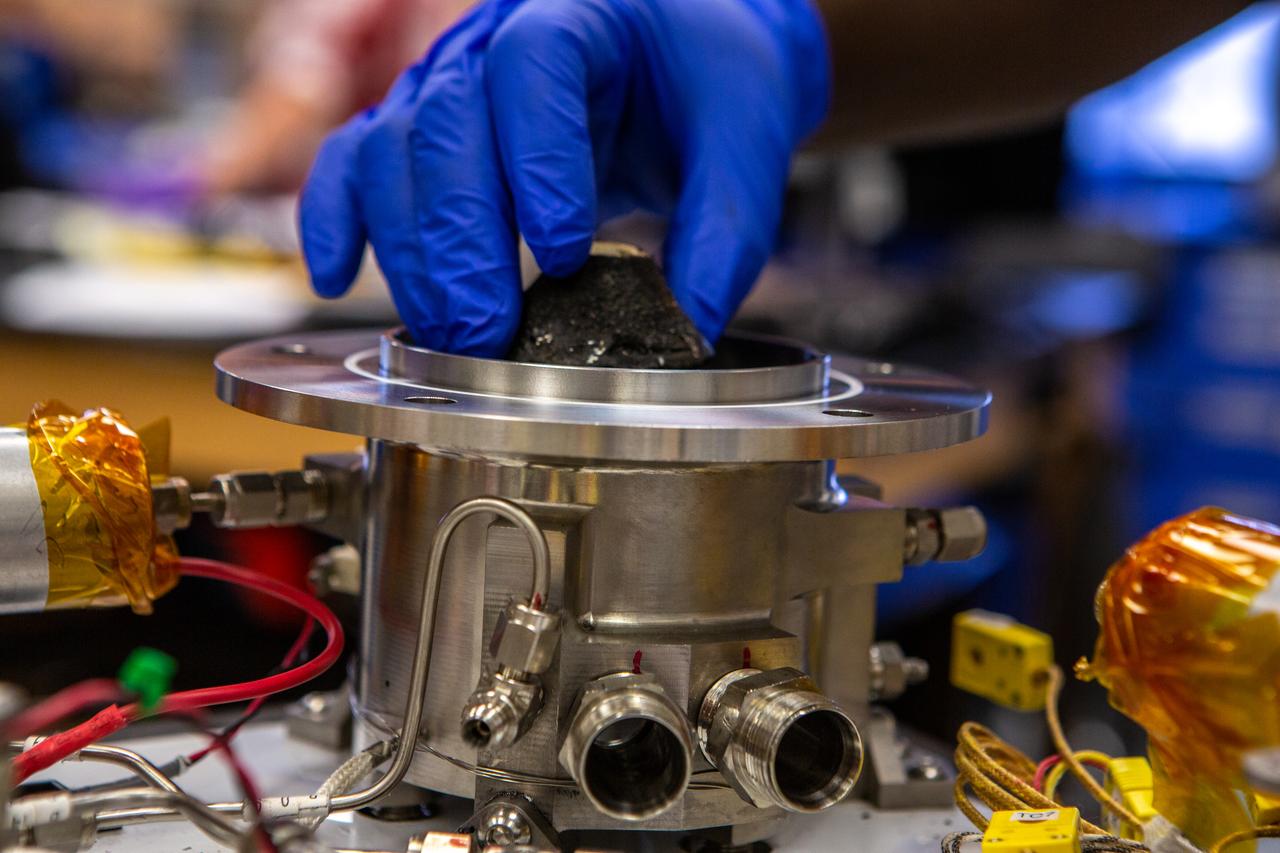
Technicians wearing protective equipment perform work for a future mission on flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 10, 2020. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
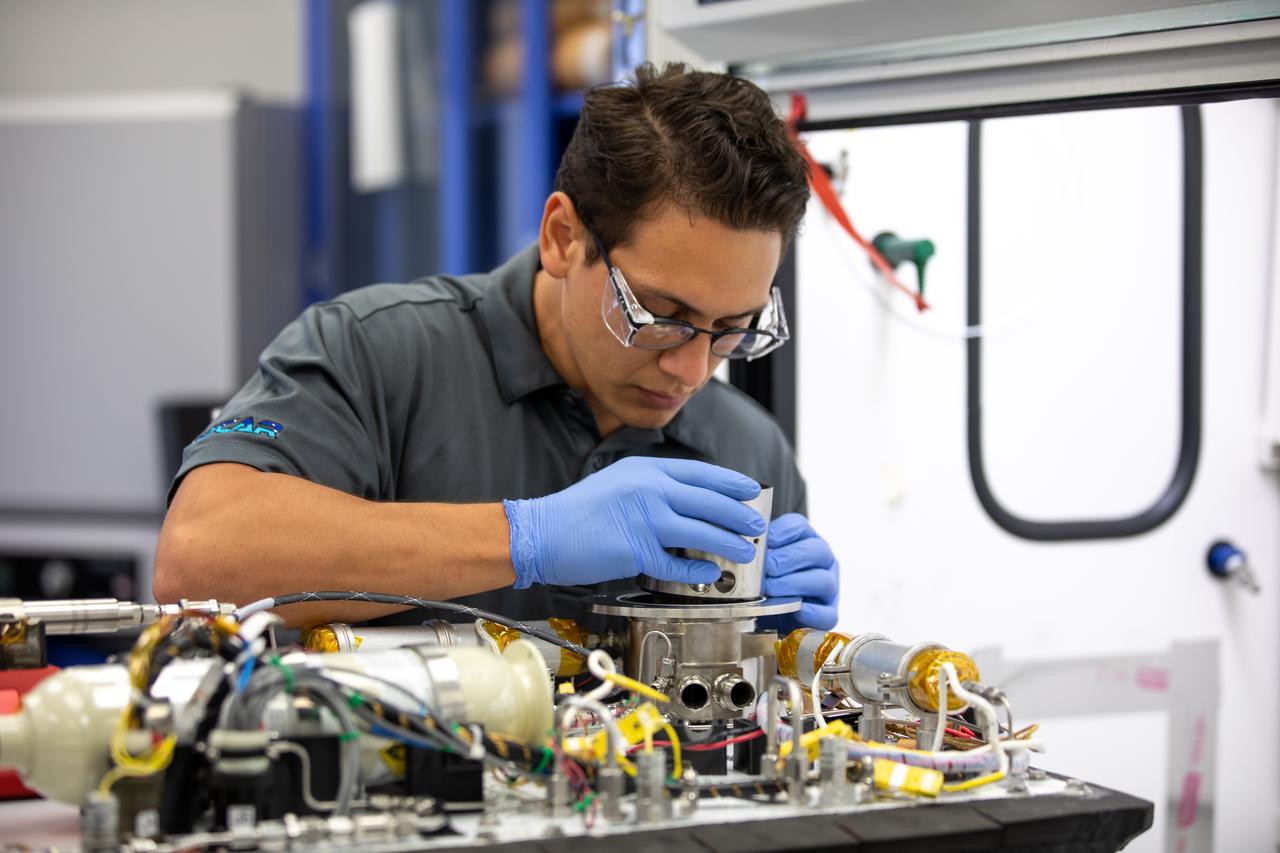

Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR), performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
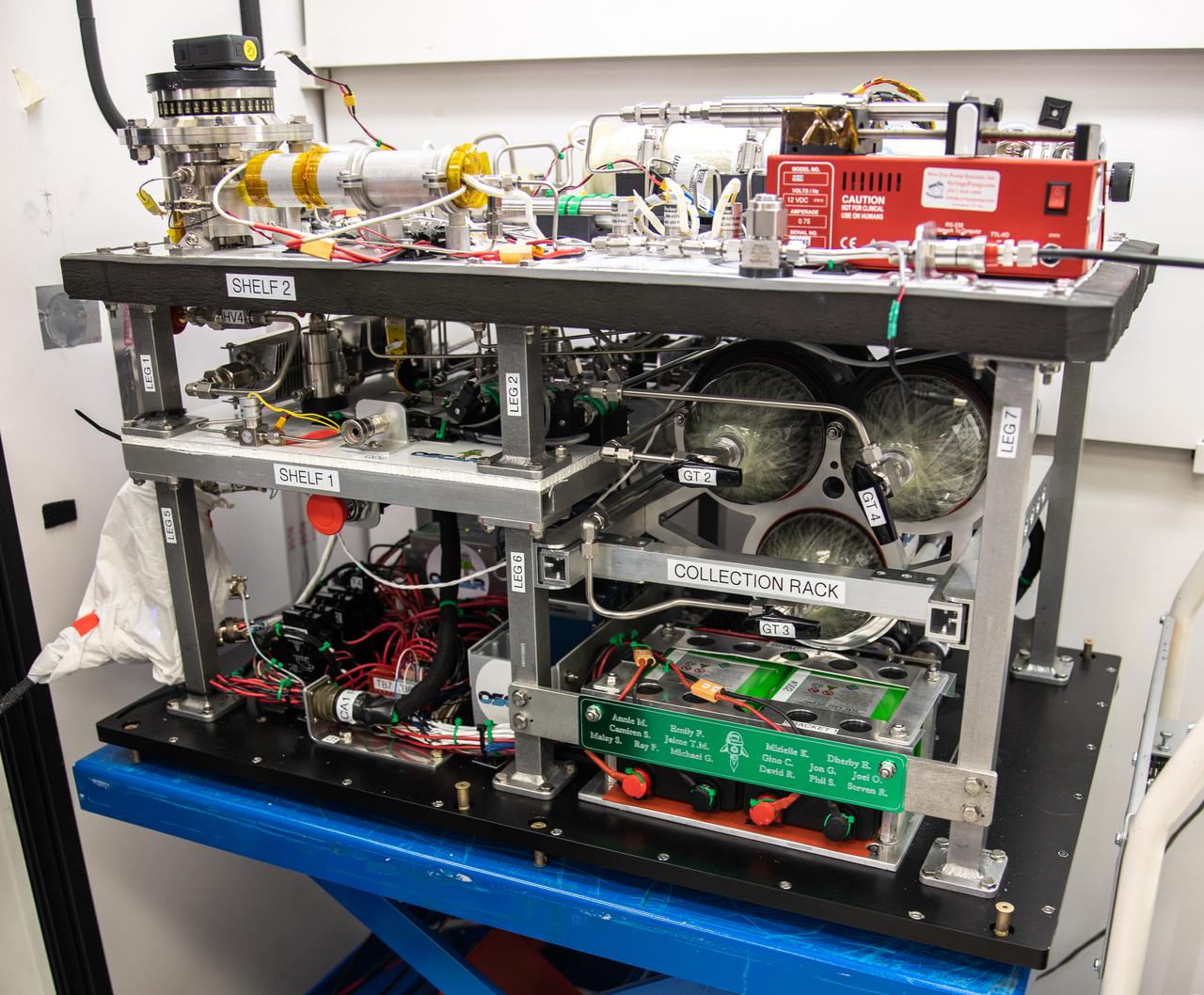
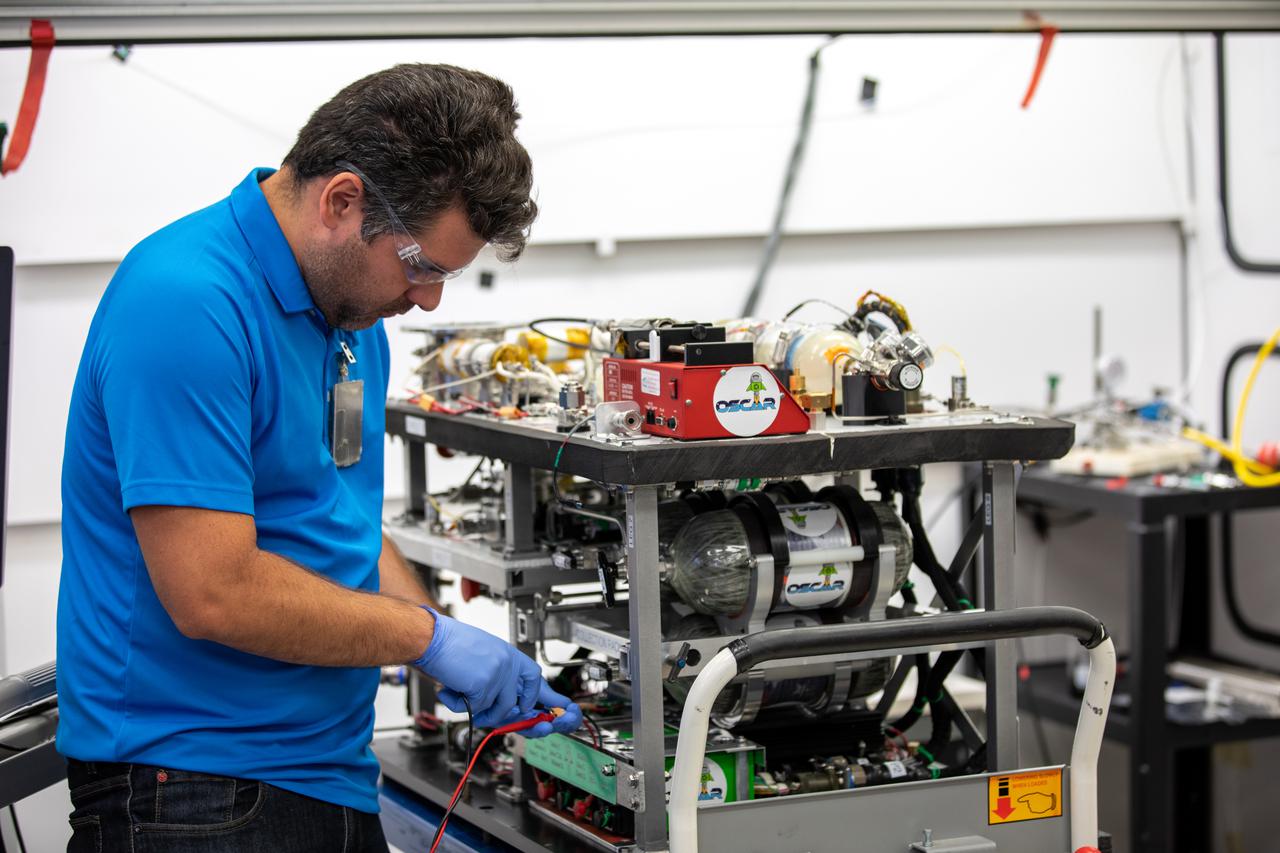
Members of the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) team perform ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
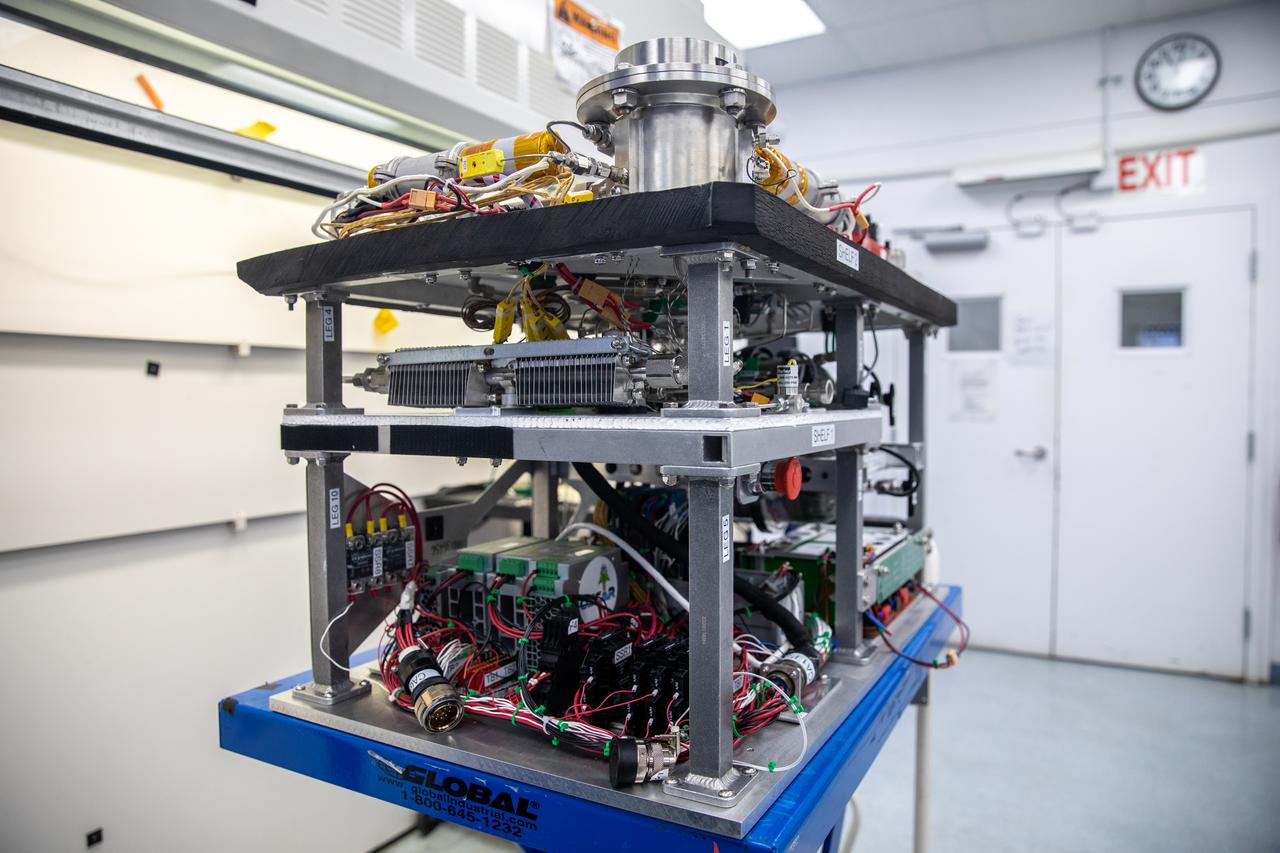
A member of the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) team performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.

Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR), performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
Flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, is inside the Applied Physics Lab inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.

Flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, is in view inside the Applied Physics Lab in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.

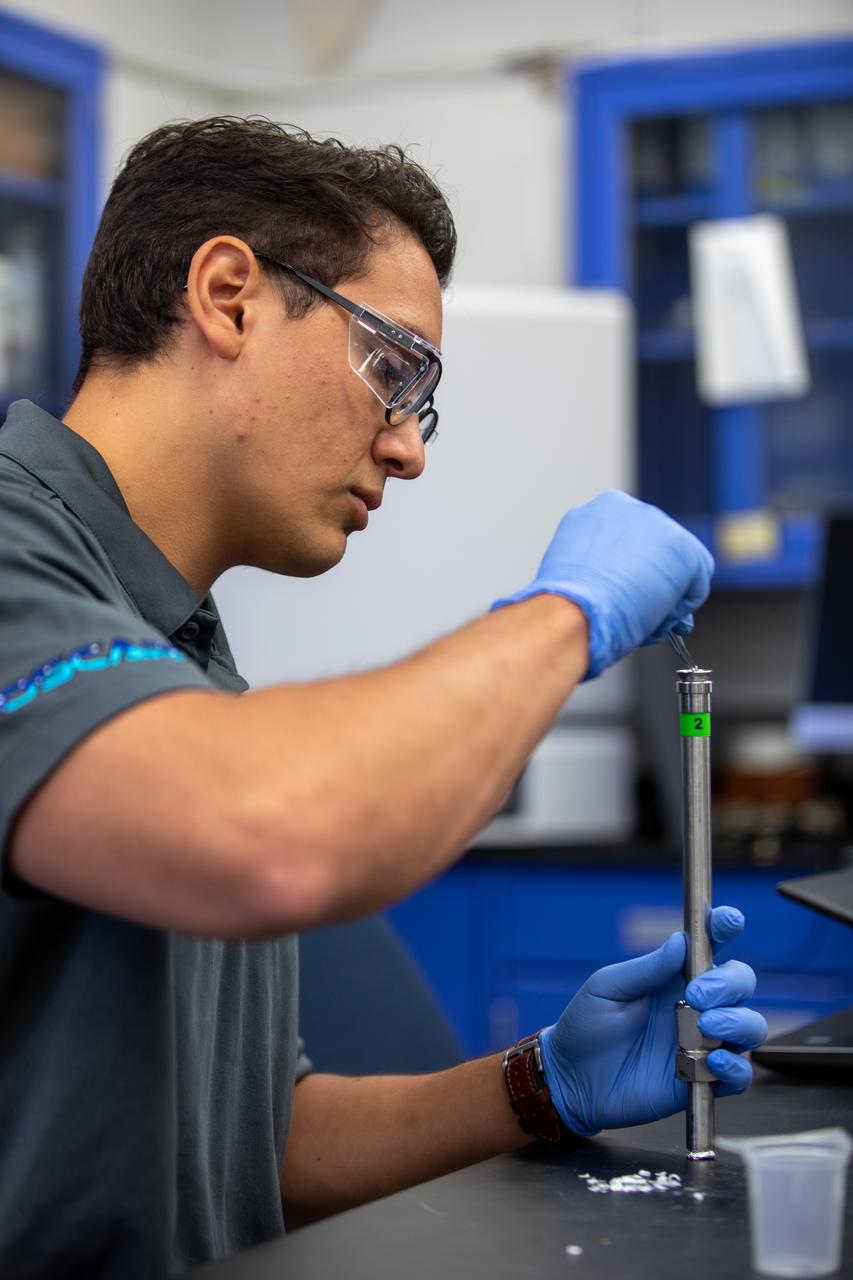
Jaime Toro, an aerospace/mechanical engineer and member of the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) team, performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.

Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR), performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
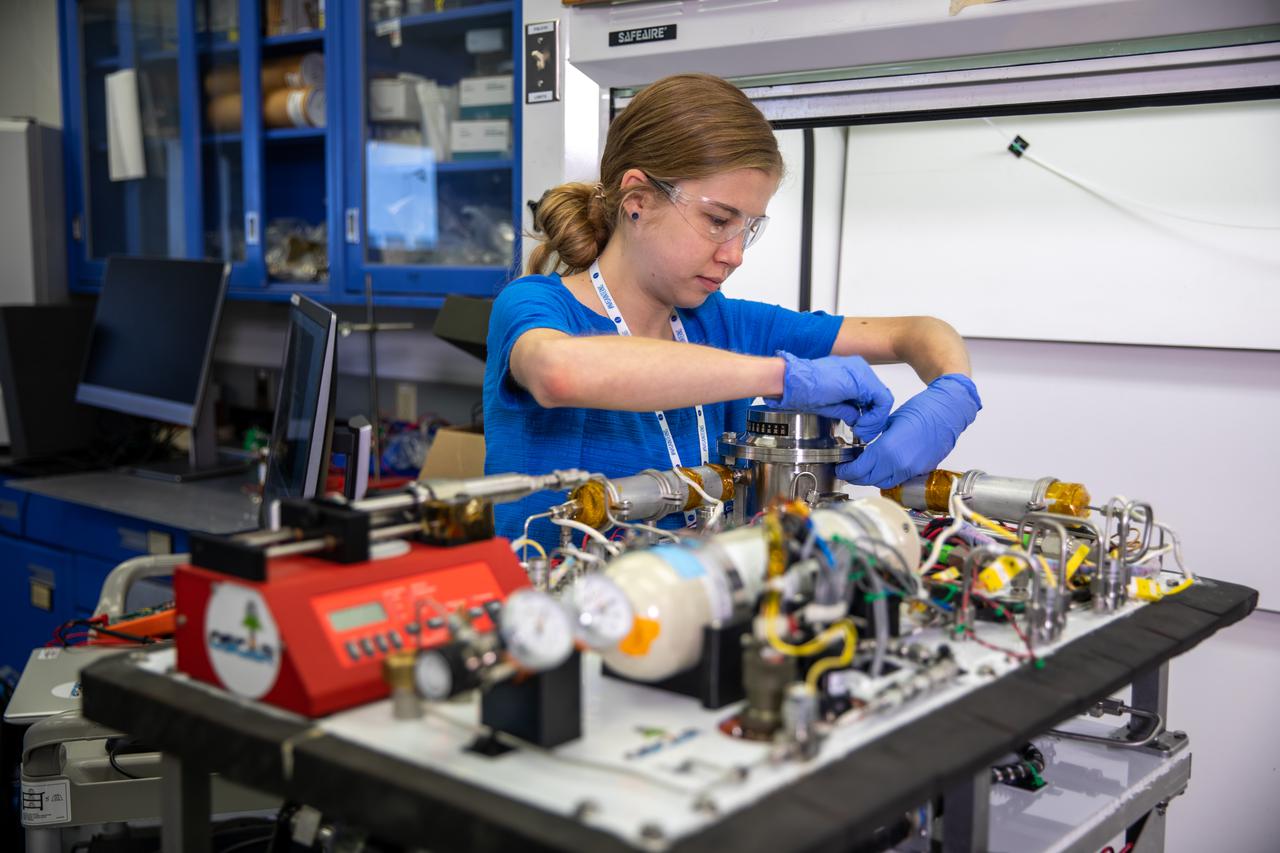
A member of the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) team performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
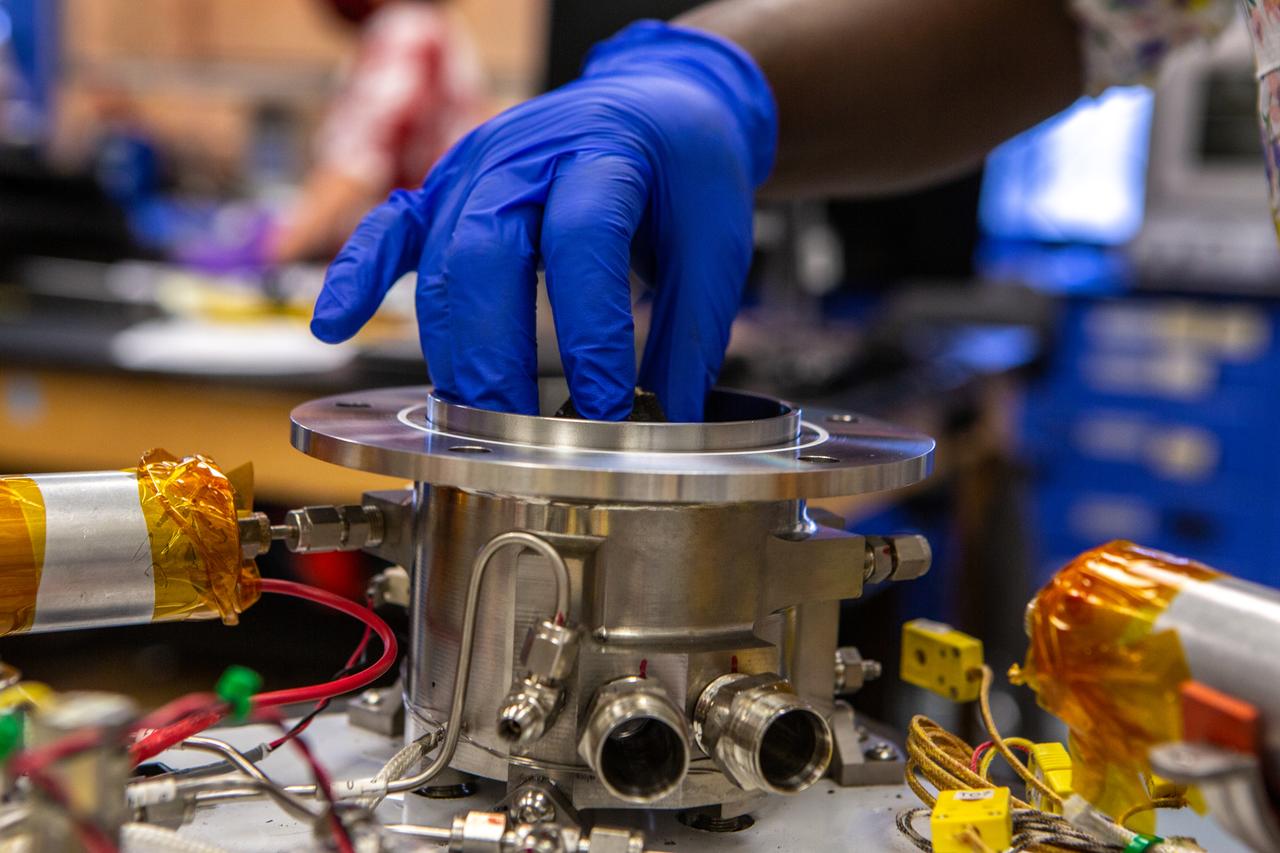
Technicians wearing protective equipment perform work for a future mission on flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 10, 2020. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
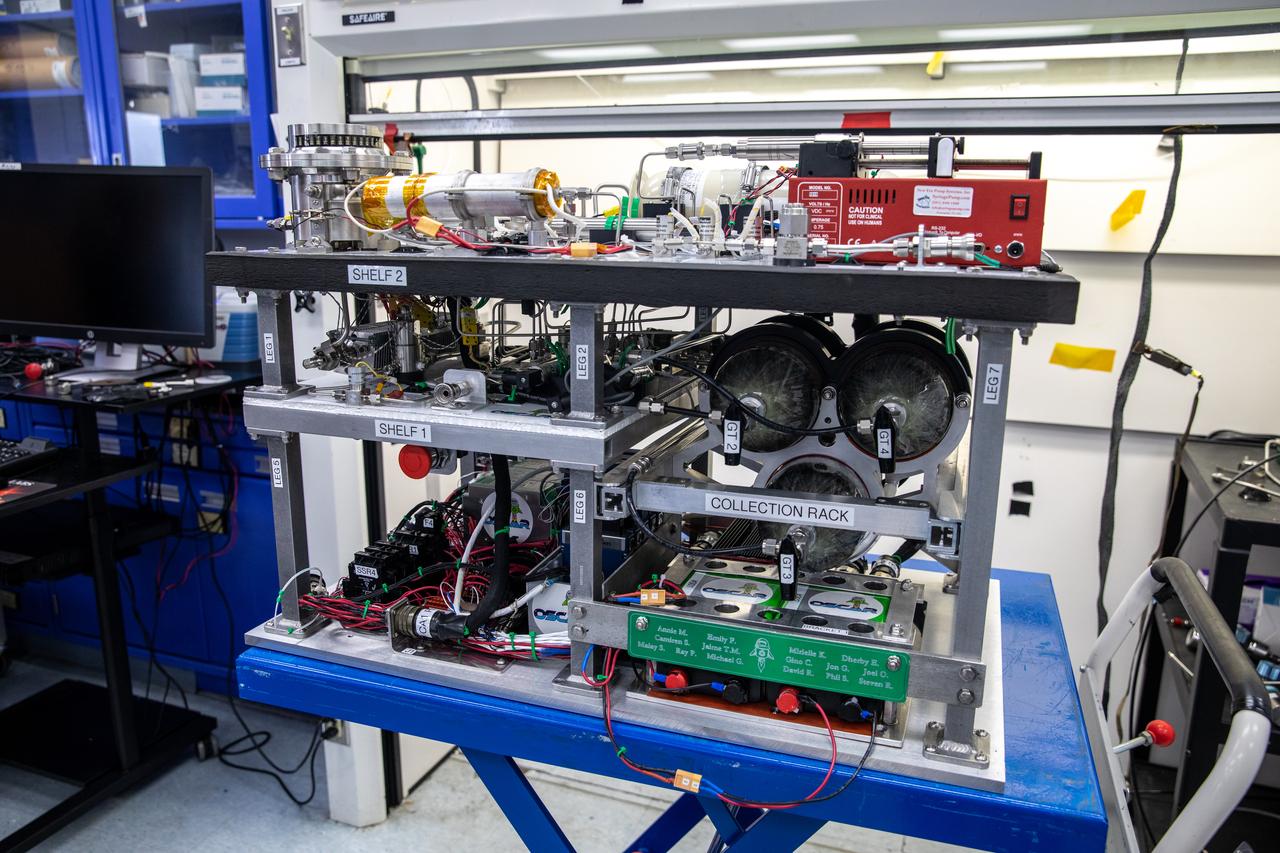
Flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, is inside the Applied Physics Lab inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.

Technicians wearing protective equipment perform work for a future mission on flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 10, 2020. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.

Technicians wearing protective equipment perform work for a future mission on flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 10, 2020. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.

Flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, is inside the Applied Physics Lab inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
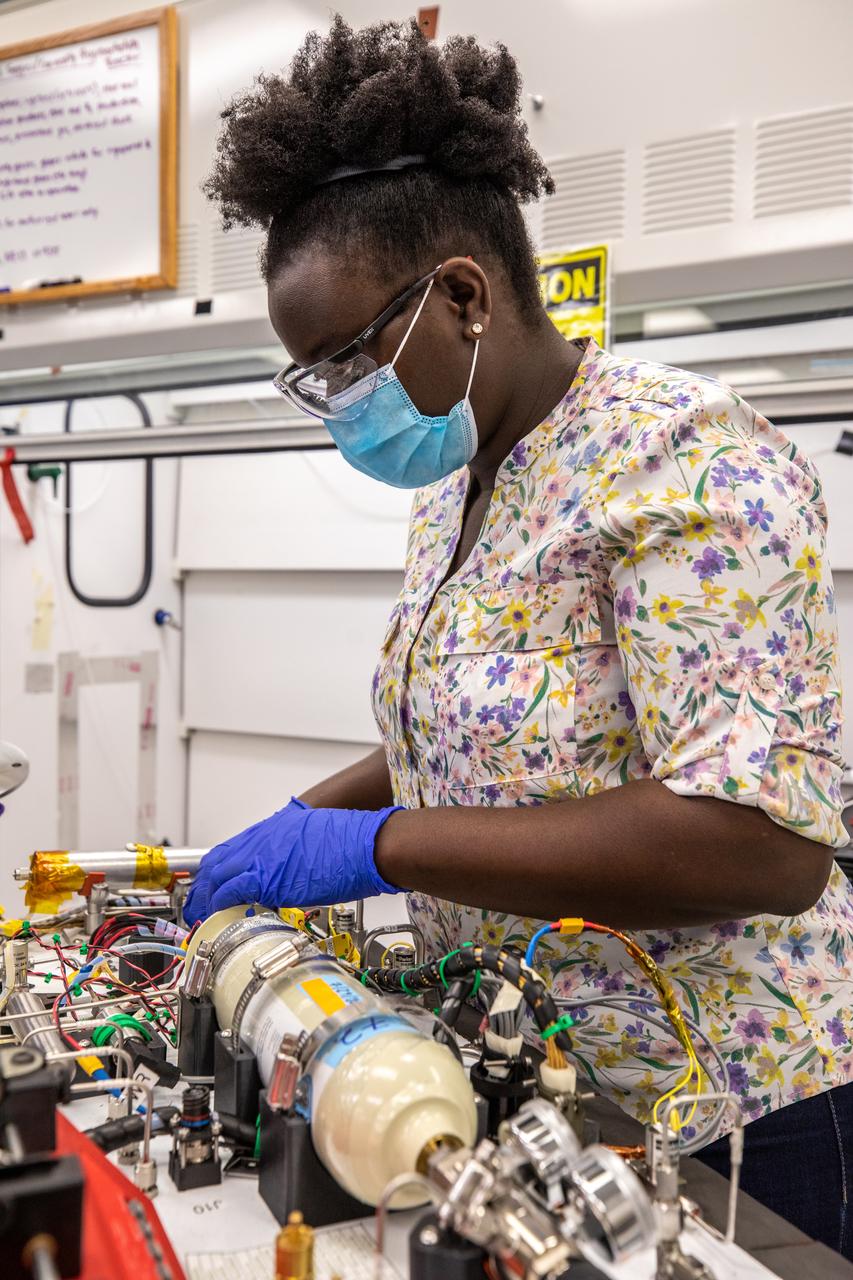

Technicians wearing protective equipment perform work for a future mission on flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 10, 2020. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
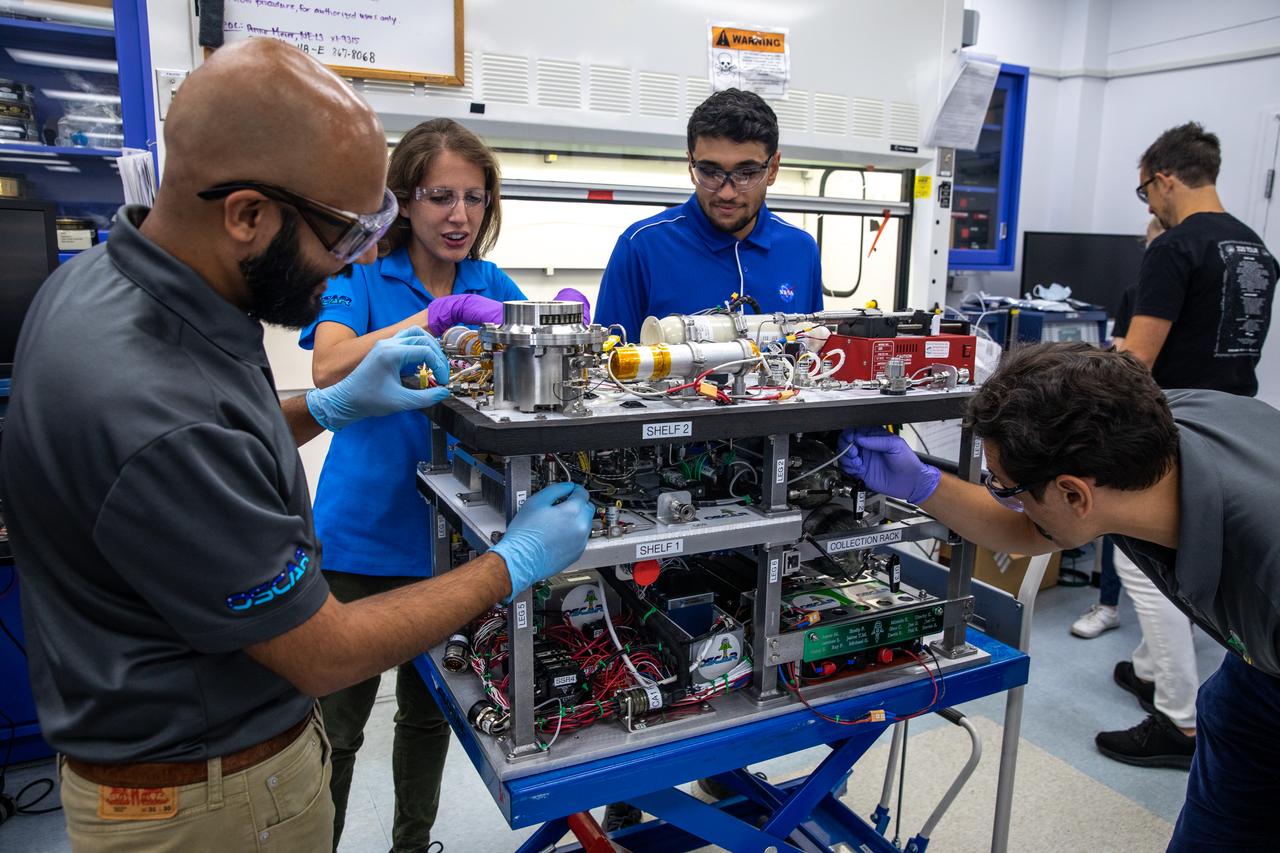
The Trash to Gas team members prepare flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, inside the Applied Physics Lab in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
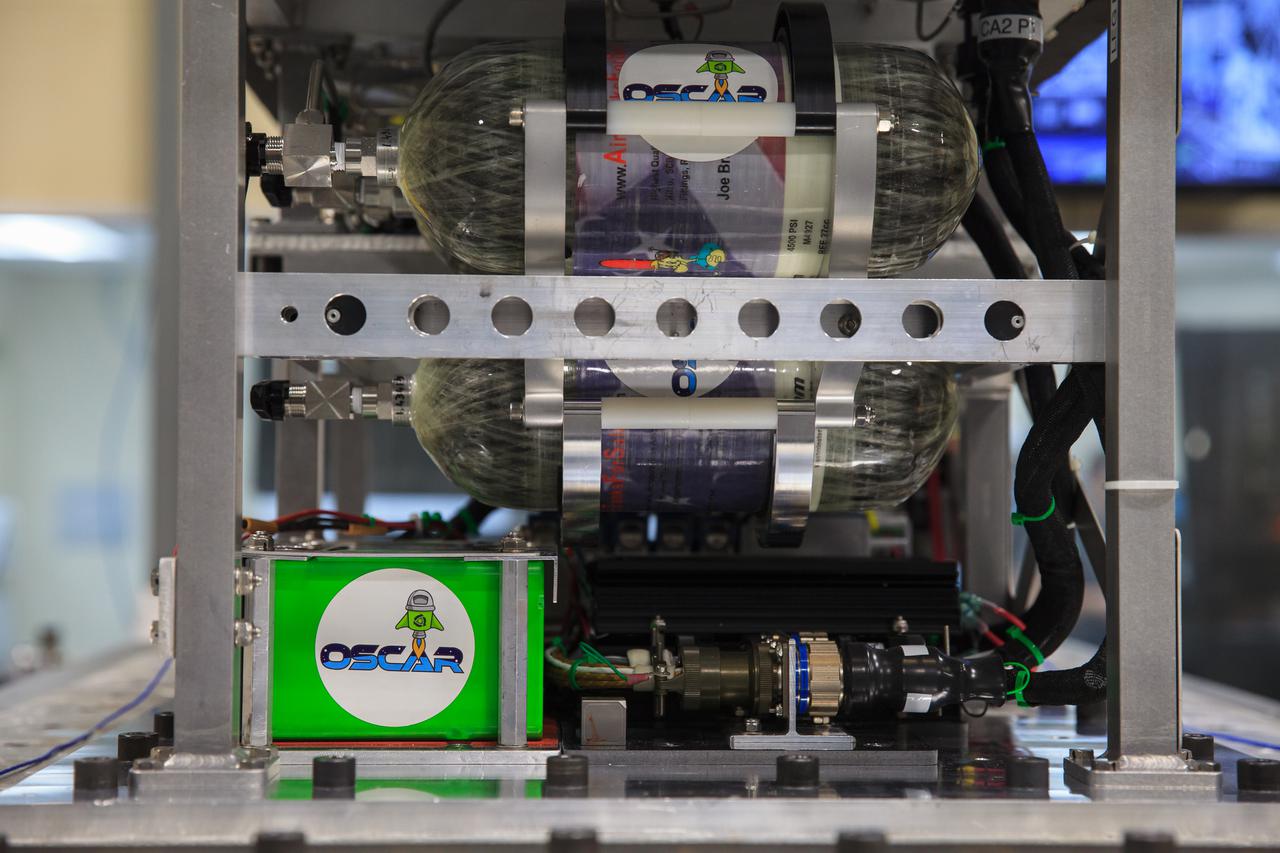
NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, undergoes vibration testing inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
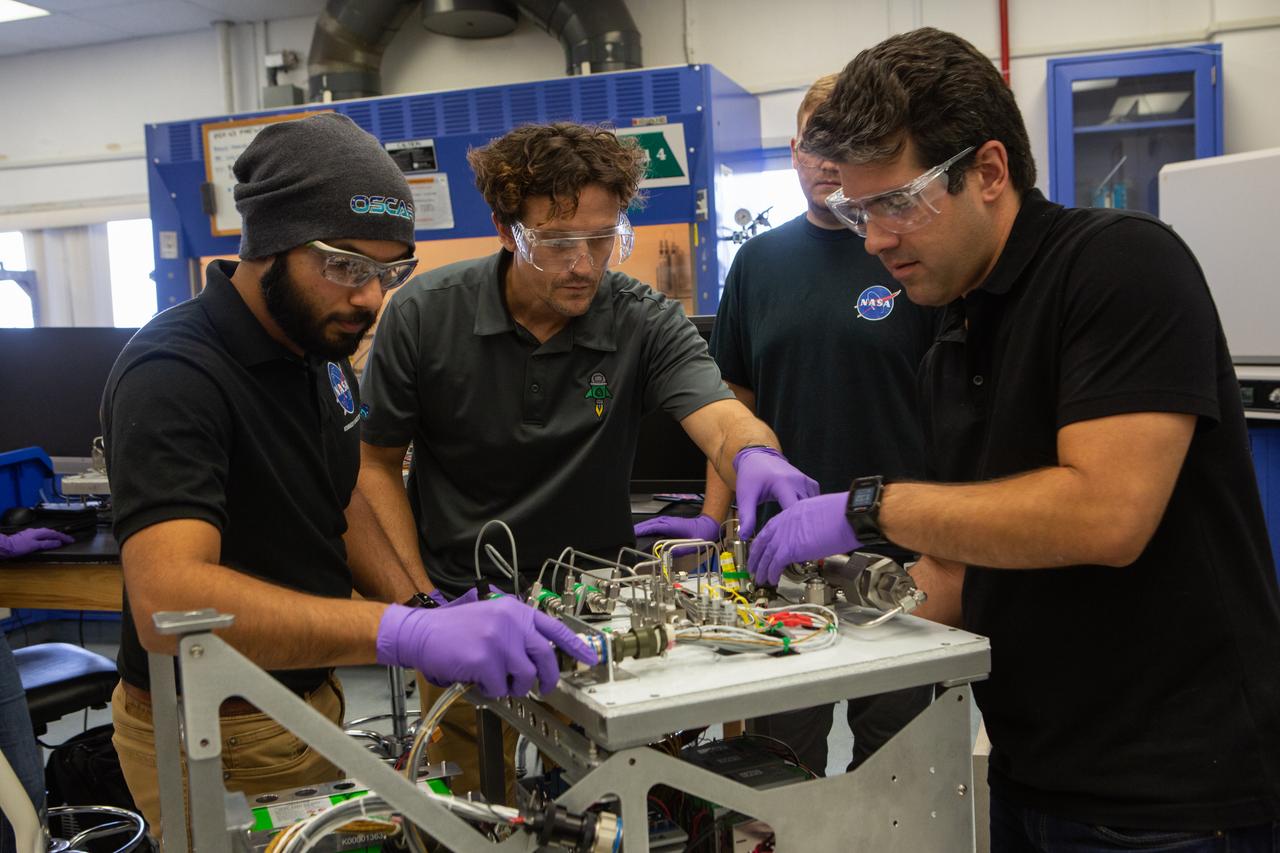

From left, team members Malay Shah, Gino Carro, Evan Bell and Jamie Toro assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
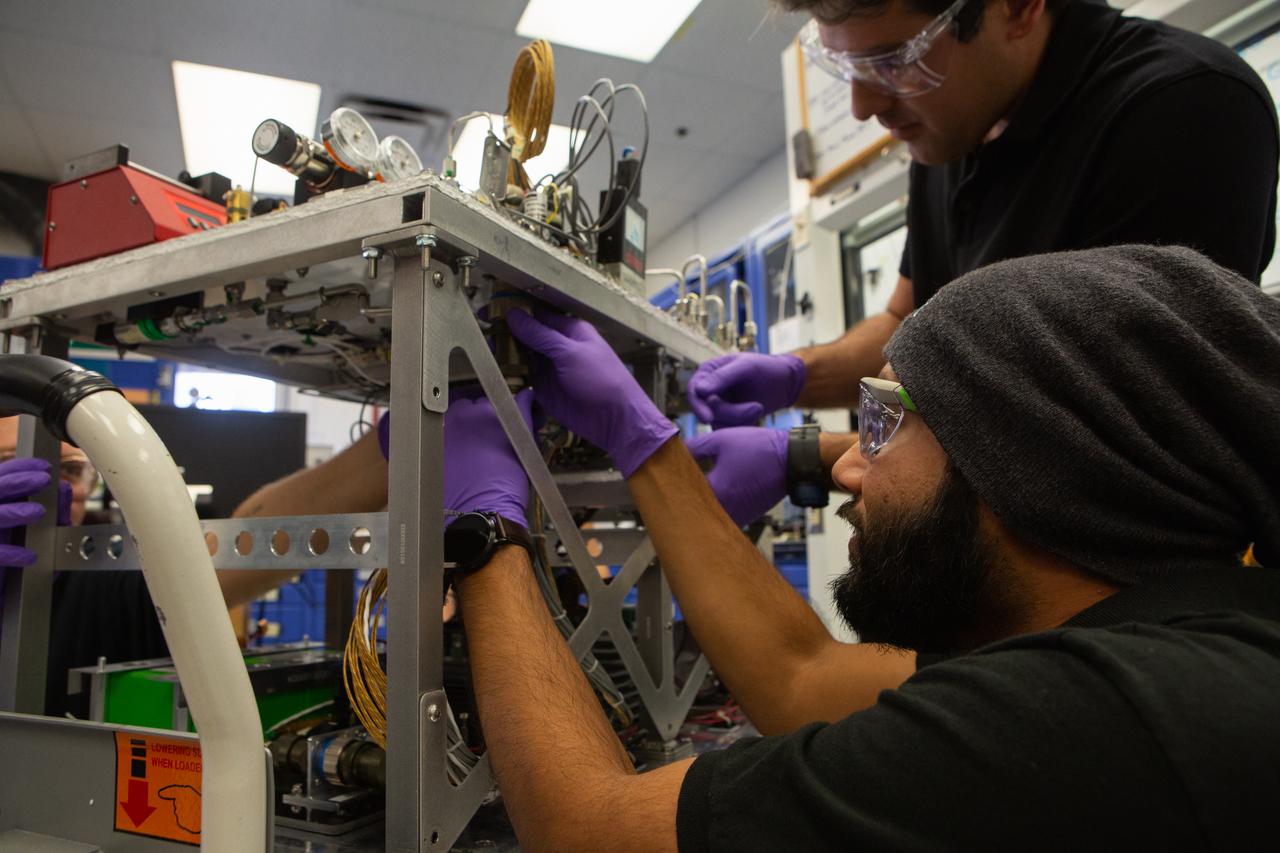
Team members Malay Shah, foreground, and Gino Carro assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
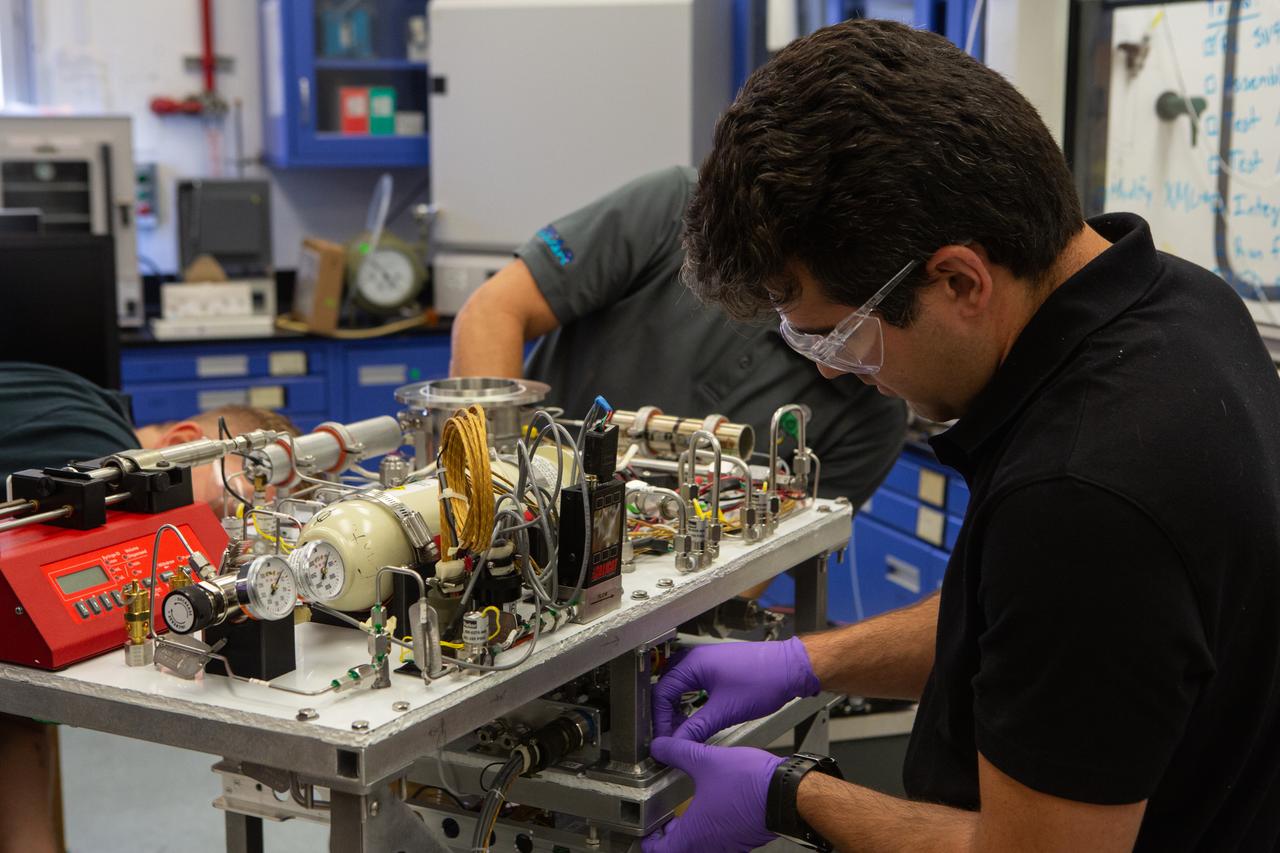
Jaime Toro assembles the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
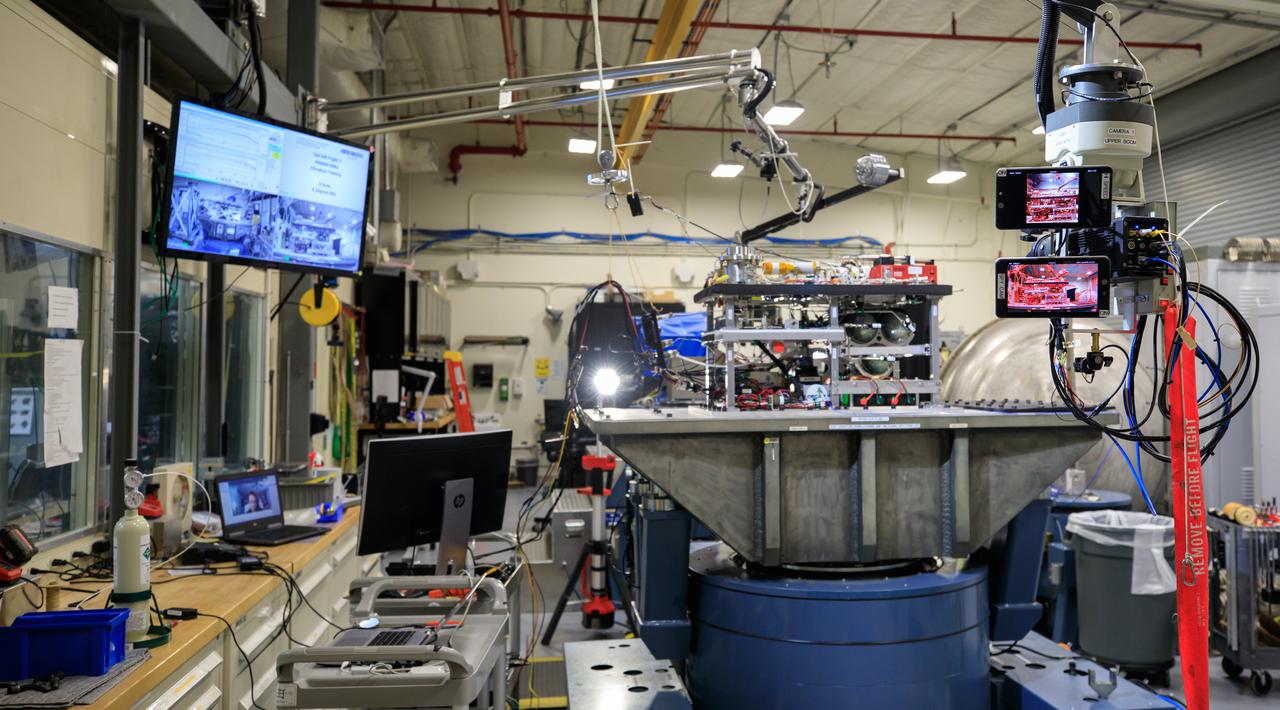

NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, undergoes vibration testing inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The tests are part of ongoing preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
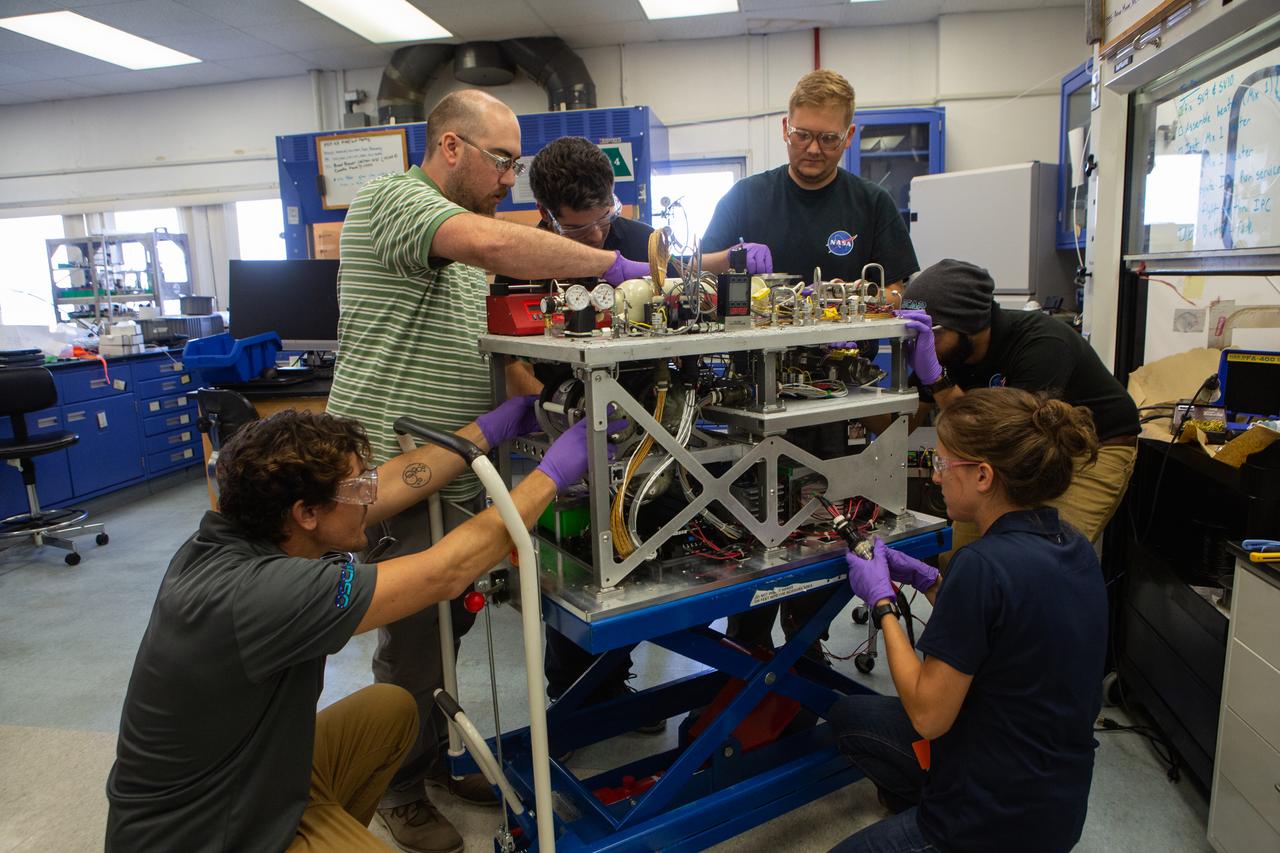

Team members assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Gino Carro, Tom Cauvel, Jaime Toro, Evan Bell, Malay Shah and Annie Meier. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
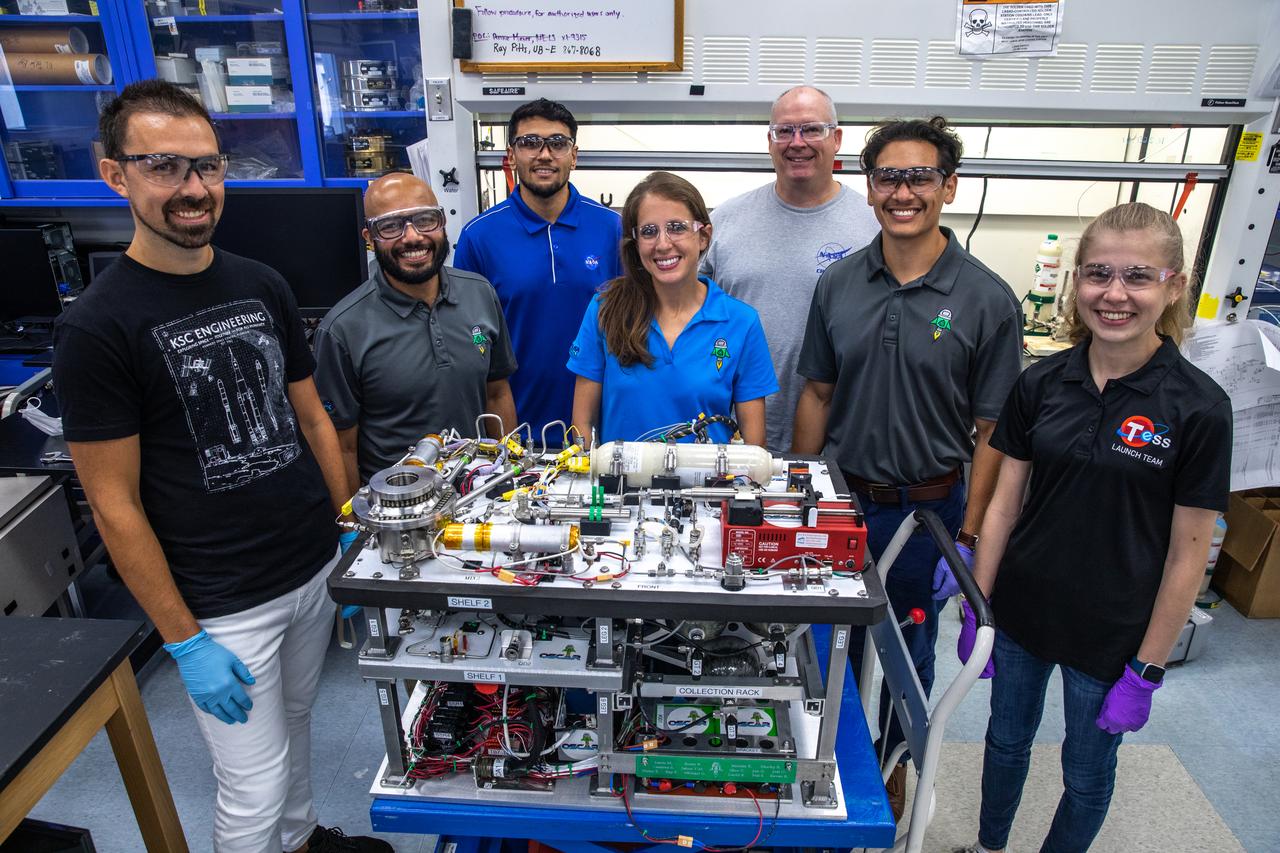
The Trash to Gas team members prepare flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, inside the Applied Physics Lab in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.

Inside the Vibration Test Lab at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) undergoes vibration testing on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.
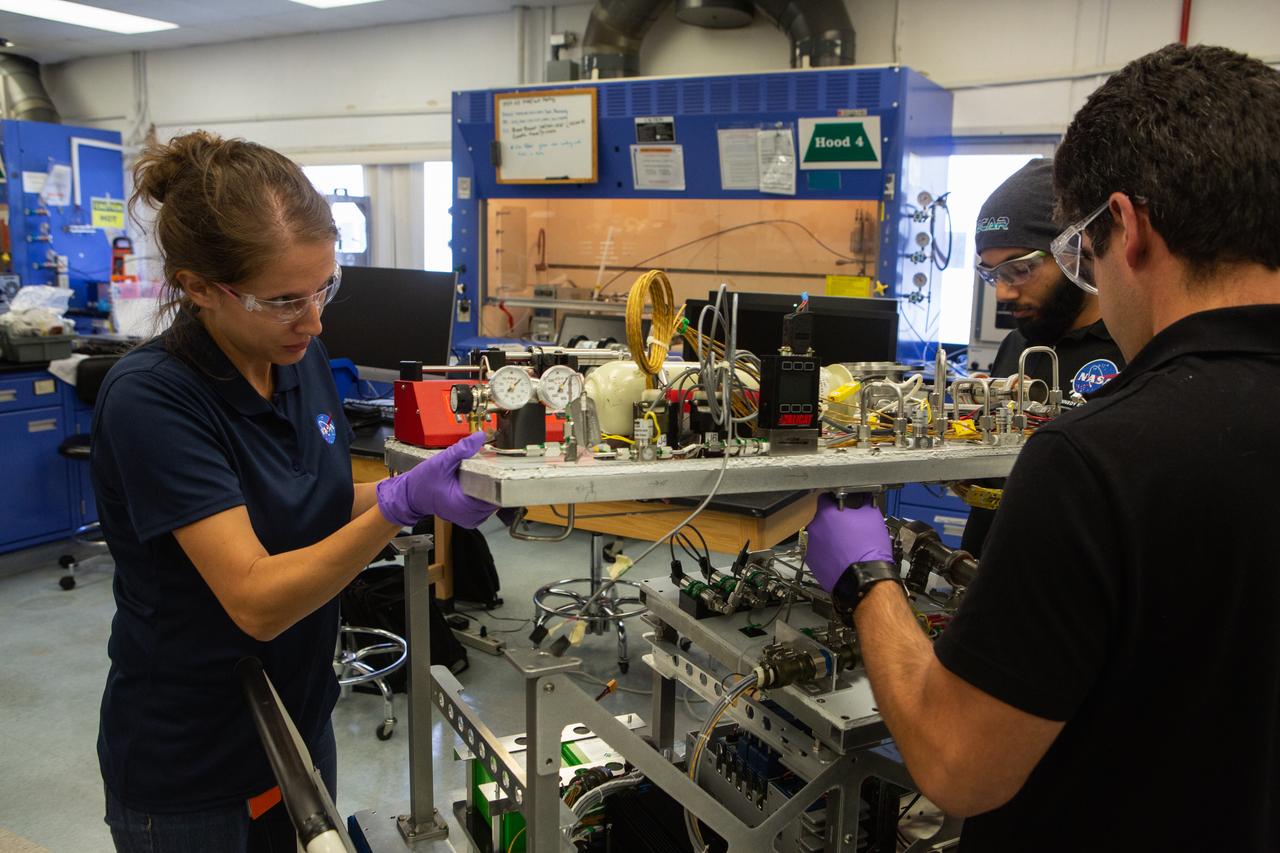

From left, team members Annie Meier, Malay Shah and Jamie Toro assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
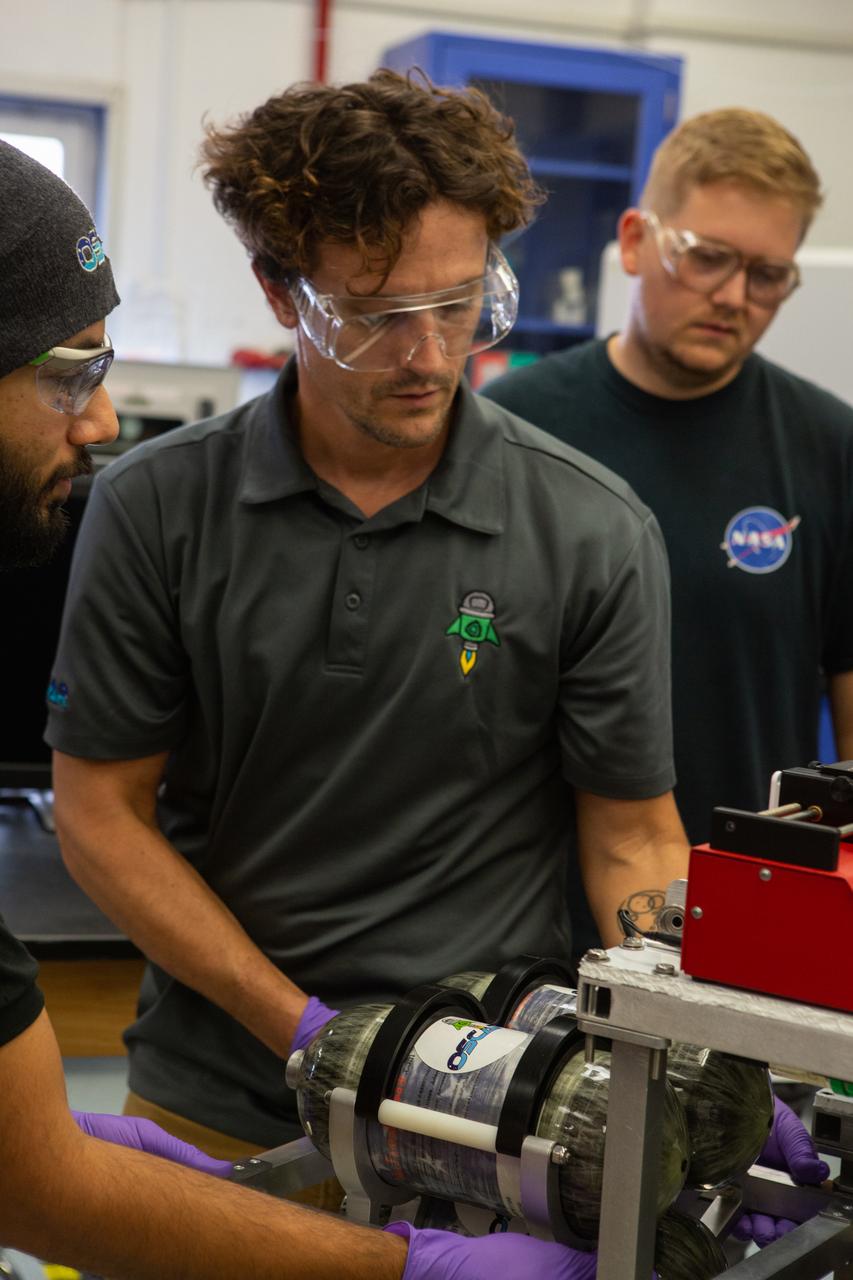

From left, team members Malay Shah, Gino Carro and Evan Bell assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
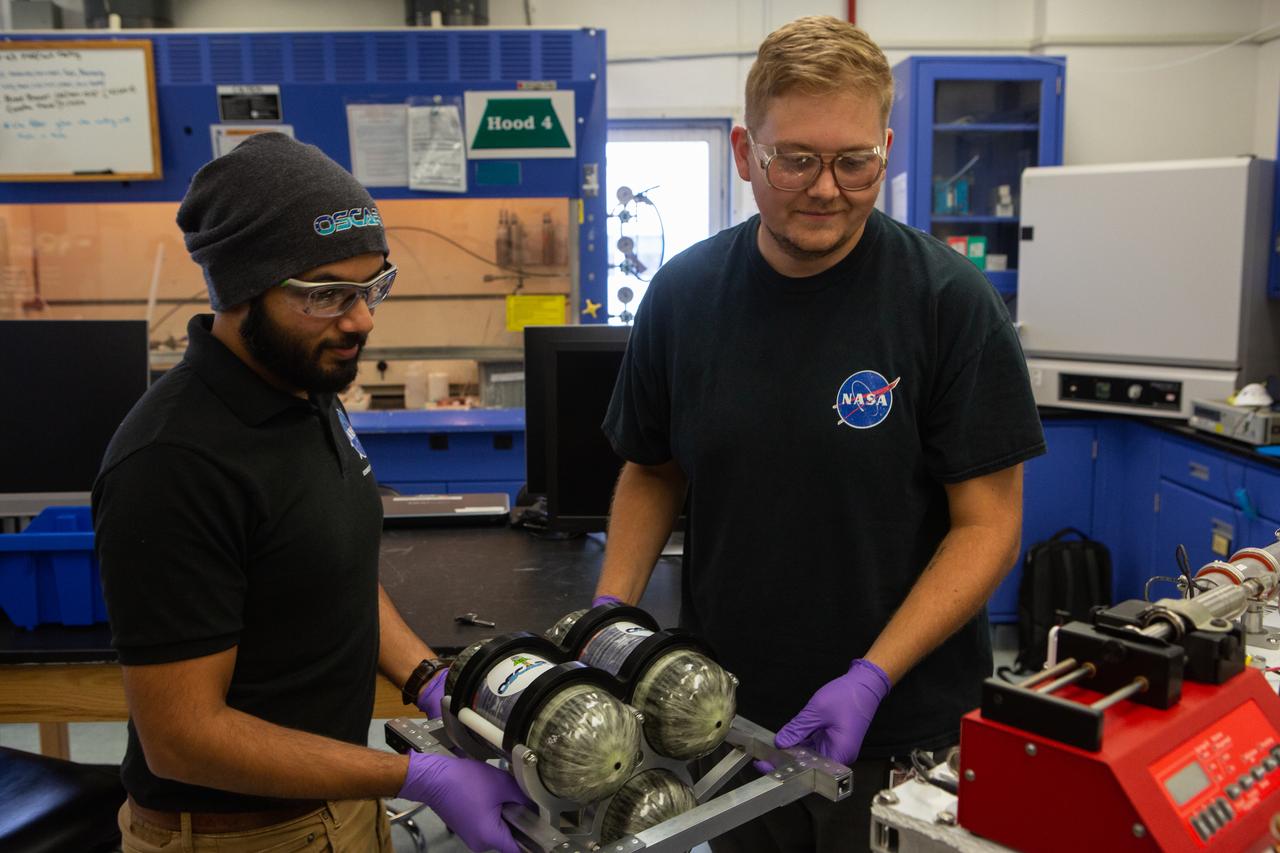

Team members Malay Shah, left, and Evan Bell assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.

The Trash to Gas team members prepare flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, inside Applied Physics lab in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
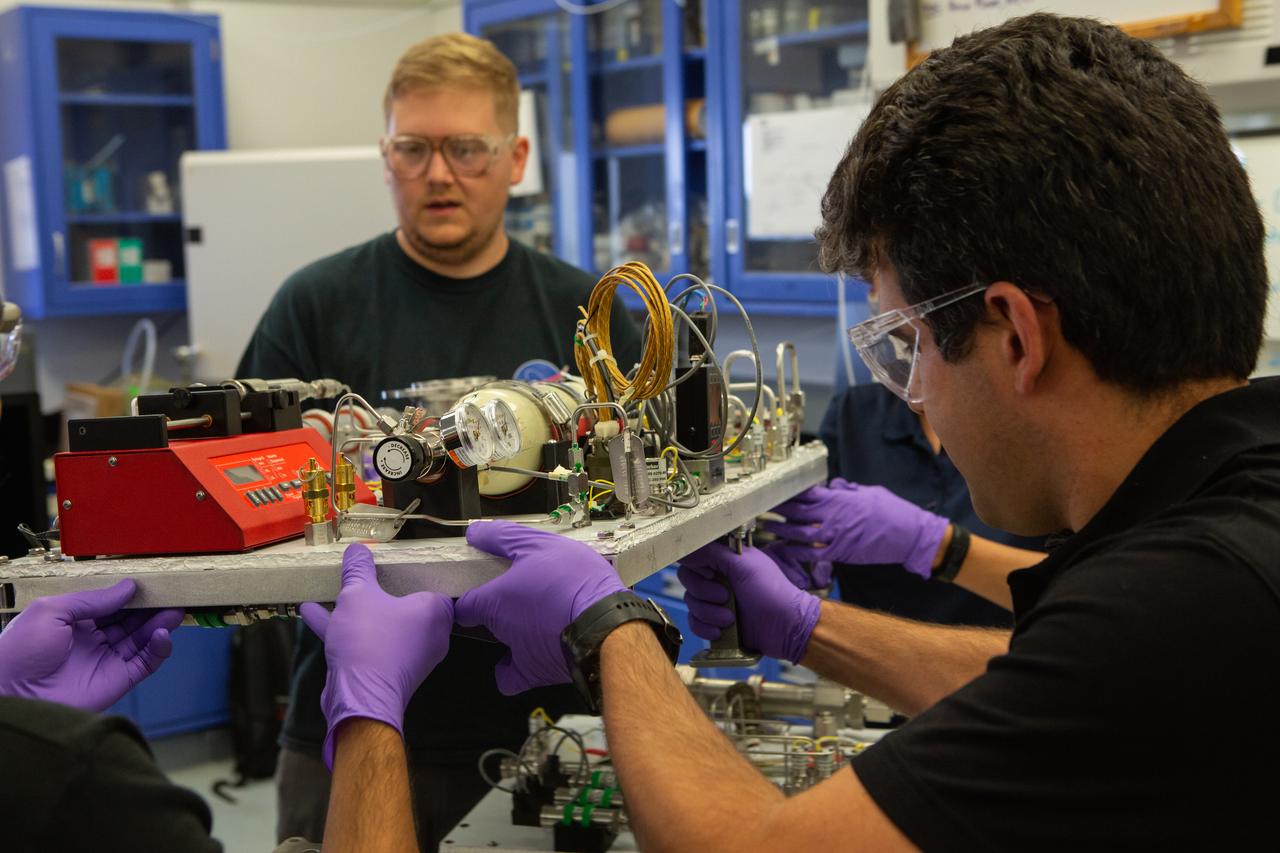
Team members Evan Bell, left, and Jaime Toro assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
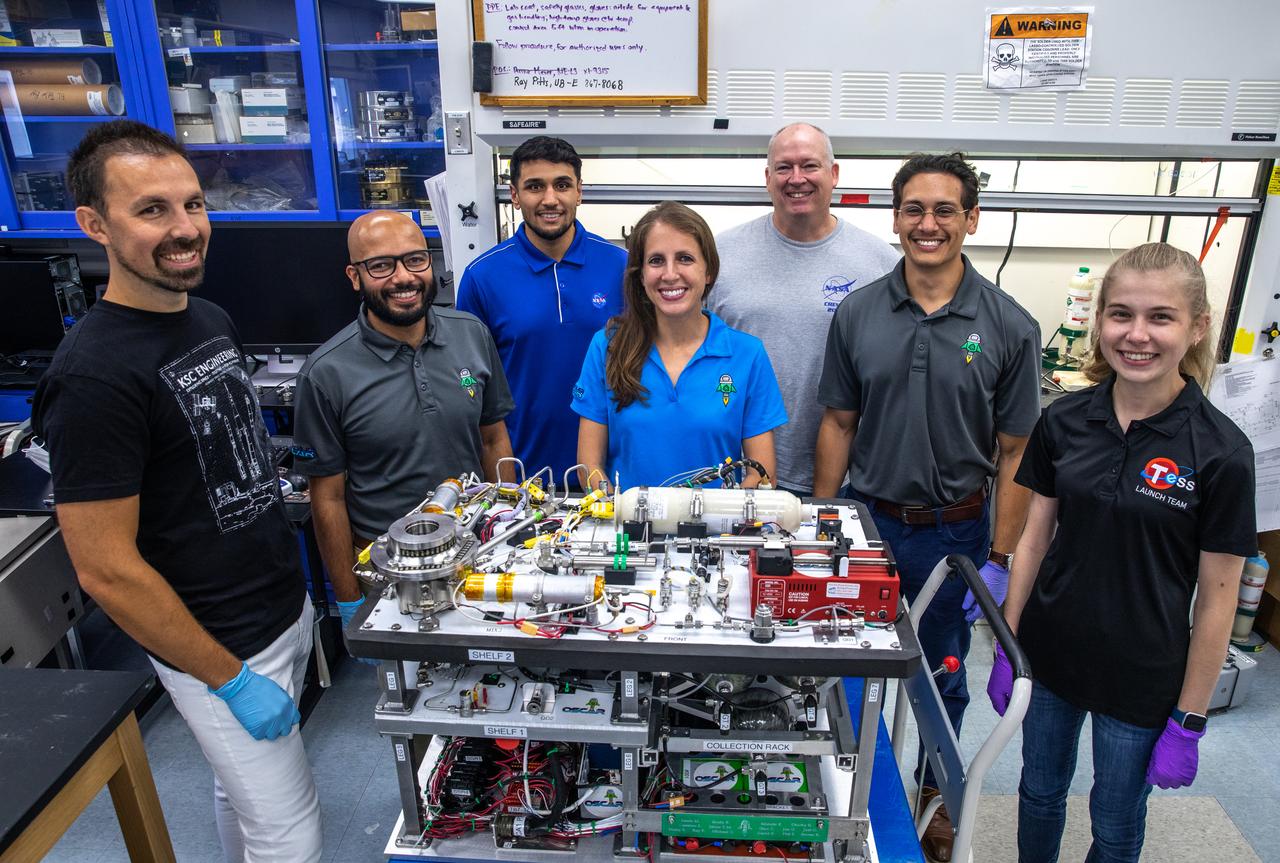
The Trash to Gas team members gather around the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, inside the Applied Physics Lab in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
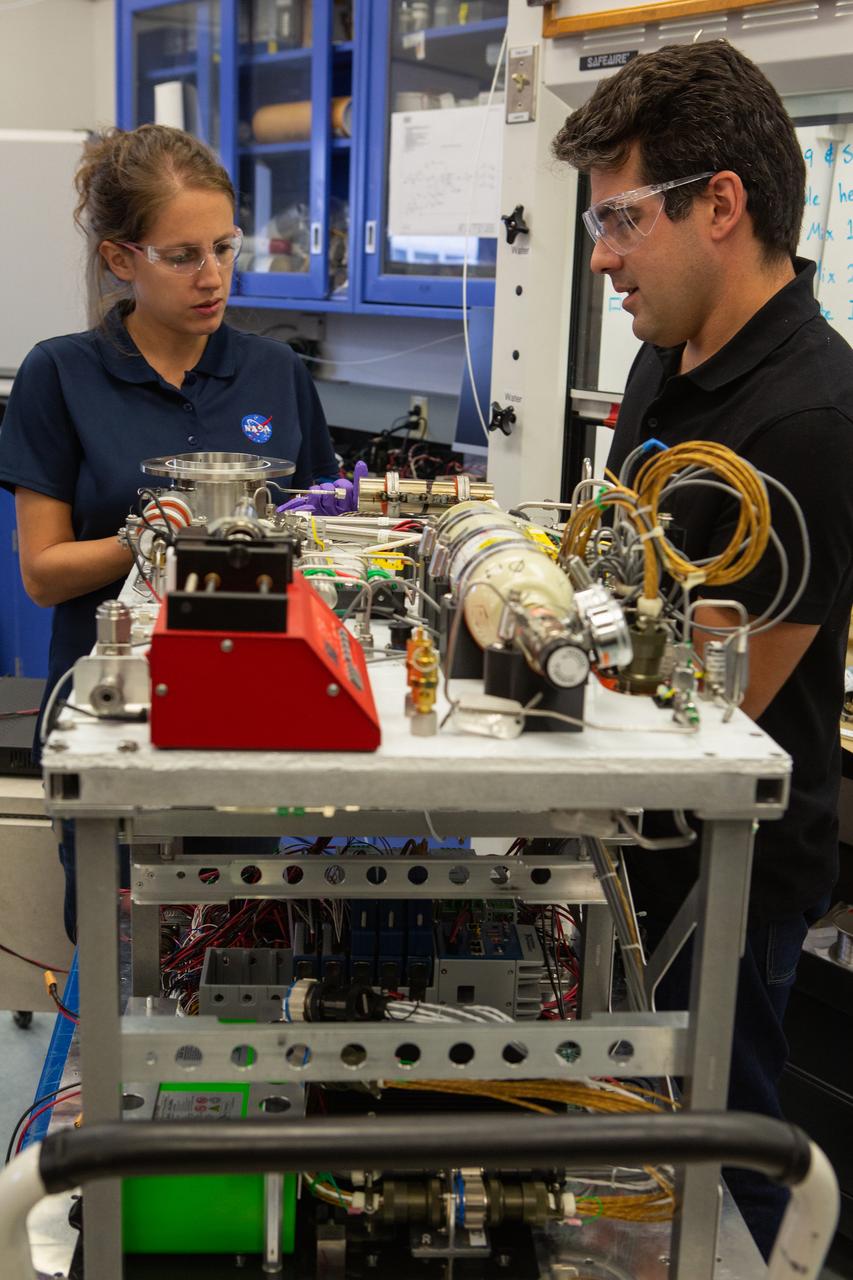

Team members Annie Meier, left, and Jamie Toro assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
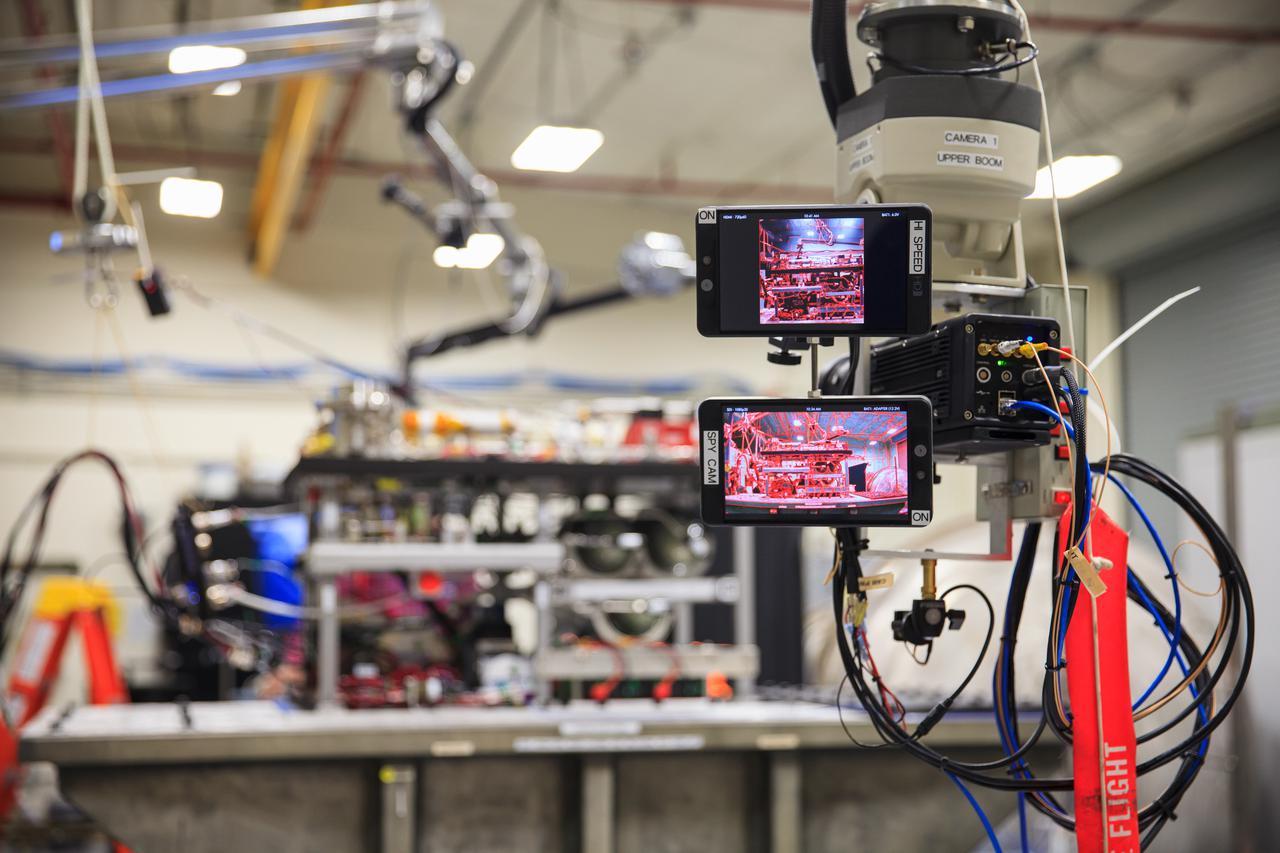

NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, undergoes vibration testing inside the Vibration Test Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight later this year. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active.