
This is an artist's impression of how the very early universe (less than one billion years old) might have looked when it went through a voracious onset of star formation, converting primordial hydrogen into myriad stars at an unprecedented rate. The deepest views of the cosmos from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) yield clues that the very first stars may have burst into the universe as brilliantly and spectacularly as a firework finale. Except in this case, the finale came first, long before Earth, the Sun ,and the Milky Way Galaxy formed. Studies of HST's deepest views of the heavens lead to the preliminary conclusion that the universe made a significant portion of its stars in a torrential firestorm of star birth, which abruptly lit up the pitch-dark heavens just a few hundred million years after the "big bang," the tremendous explosion that created the cosmos. Within the starburst galaxies, bright knots of hot blue stars come and go like bursting fireworks shells. Regions of new starbirth glow intensely red under torrent of ultraviolet radiation. The most massive stars self-detonate as supernovas, which explode across the sky like a string of firecrackers. A foreground starburst galaxy at lower right is sculpted with hot bubbles from supernova explosions and torrential stellar winds. Unlike today there is very little dust in these galaxies, because the heavier elements have not yet been cooked up through nucleosynthesis in stars. Recent analysis of HST deep sky images supports the theory that the first stars in the universe appeared in an abrupt eruption of star formation, rather than at a gradual pace. Science Credit: NASA and K. Lanzetta (SUNY). Artwork Credit: Adolf Schaller for STScI.

This artist impression shows how photons from the early universe are deflected by the gravitational lensing effect of massive cosmic structures as they travel across the universe.
This frame from an artist animation depicts the life of a photon, or particle of light, as it travels across space and time, from the very early universe ESA Planck satellite.

Astronomers using NASA Spitzer Space Telescope found evidence that such quasar winds might have forged these dusty particles in the very early universe.
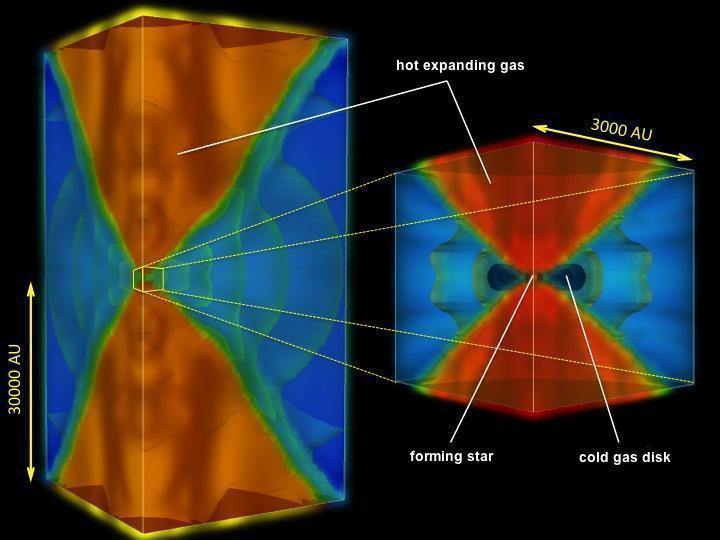
Scientists are simulating how the very first stars in our universe were born. The stars we see today formed out of collapsing clouds of gas and dust. In the very early universe, however, the stars had fewer ingredients available.
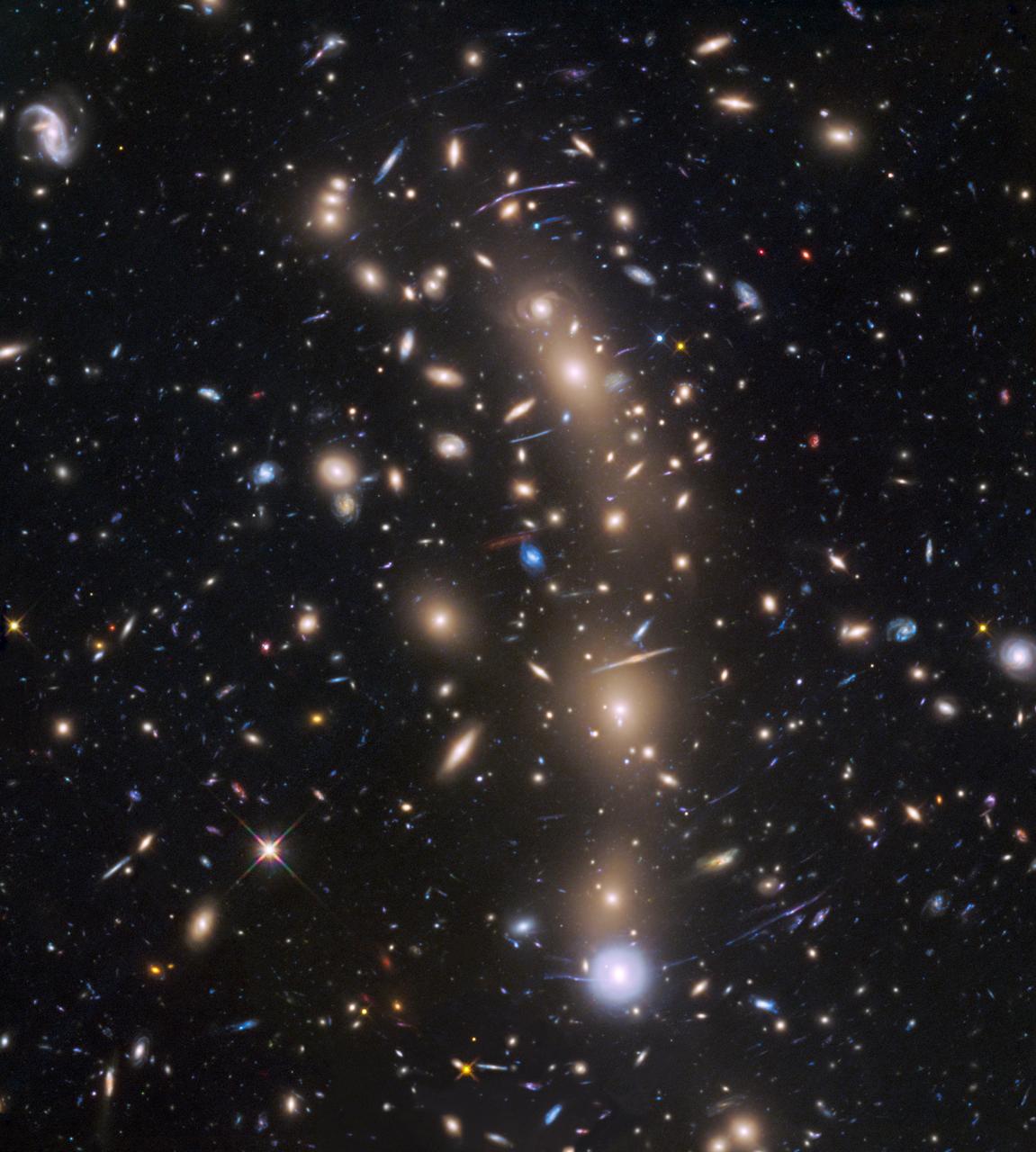

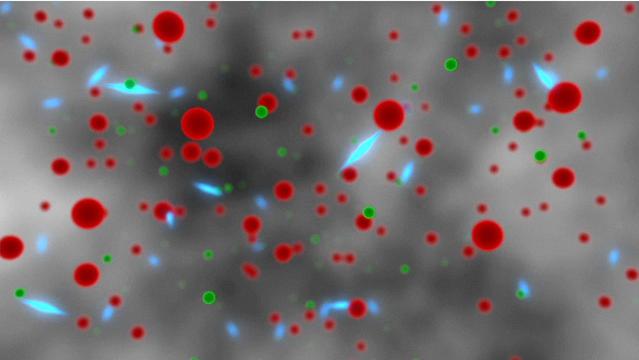
This is a Hubble Space Telescope view of a very massive cluster of galaxies, MACS J0416.1-2403, located roughly 4 billion light-years away and weighing as much as a million billion suns. The cluster's immense gravitational field magnifies the image of galaxies far behind it, in a phenomenon called gravitational lensing. The inset is an image of an extremely faint and distant galaxy that existed only 400 million years after the big bang. It was discovered by Hubble and NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. The gravitational lens makes the galaxy appear 20 times brighter than normal. The galaxy is comparable in size to the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a diminutive satellite galaxy of our Milky Way. It is rapidly making stars at a rate ten times faster than the LMC. This might be the growing core of what was to eventually evolve into a full-sized galaxy. The research team has nicknamed the object Tayna, which means "first-born" in Aymara, a language spoken in the Andes and Altiplano regions of South America. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20054

Dr. Christopher House, Professor of Geosciences, Pennsylvania State University, speaks on a panel at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Six scientists discussed how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
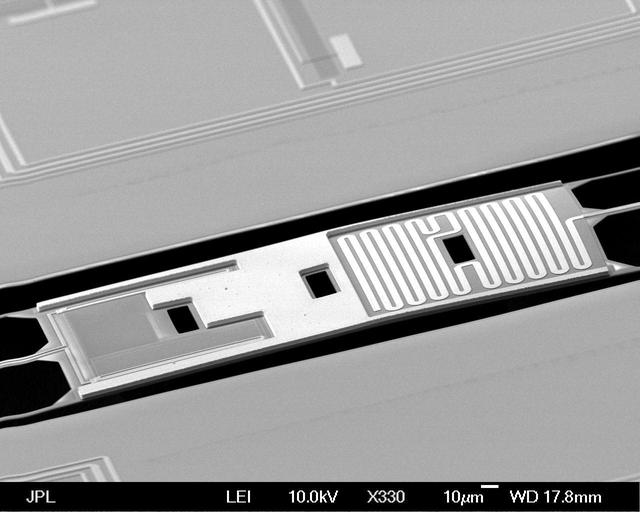
This image shows one of the NASA detectors from the BICEP2 project, developed in collaboration with the NSF. The sensors were used to make the first detection of gravitational waves in the ancient background light from the early universe.
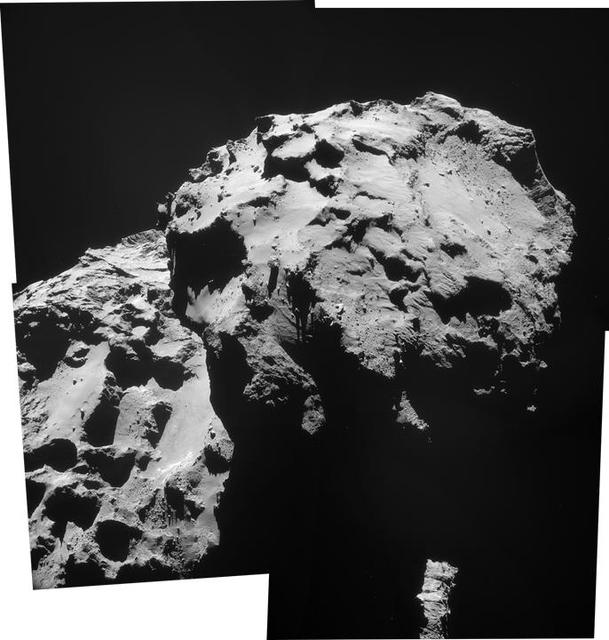

This mosaic of images from the navigation camera on the ESA Rosetta spacecraft shows the nucleus of comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko as it appeared at in the early morning, Universal Coordinated Time, of Dec. 17, 2014 evening of Dec. 16, PST.

Tones represents sound waves that traveled through the early universe, and were later heard by ESA Planck space telescope. The primordial sound waves have been translated into frequencies we can hear.
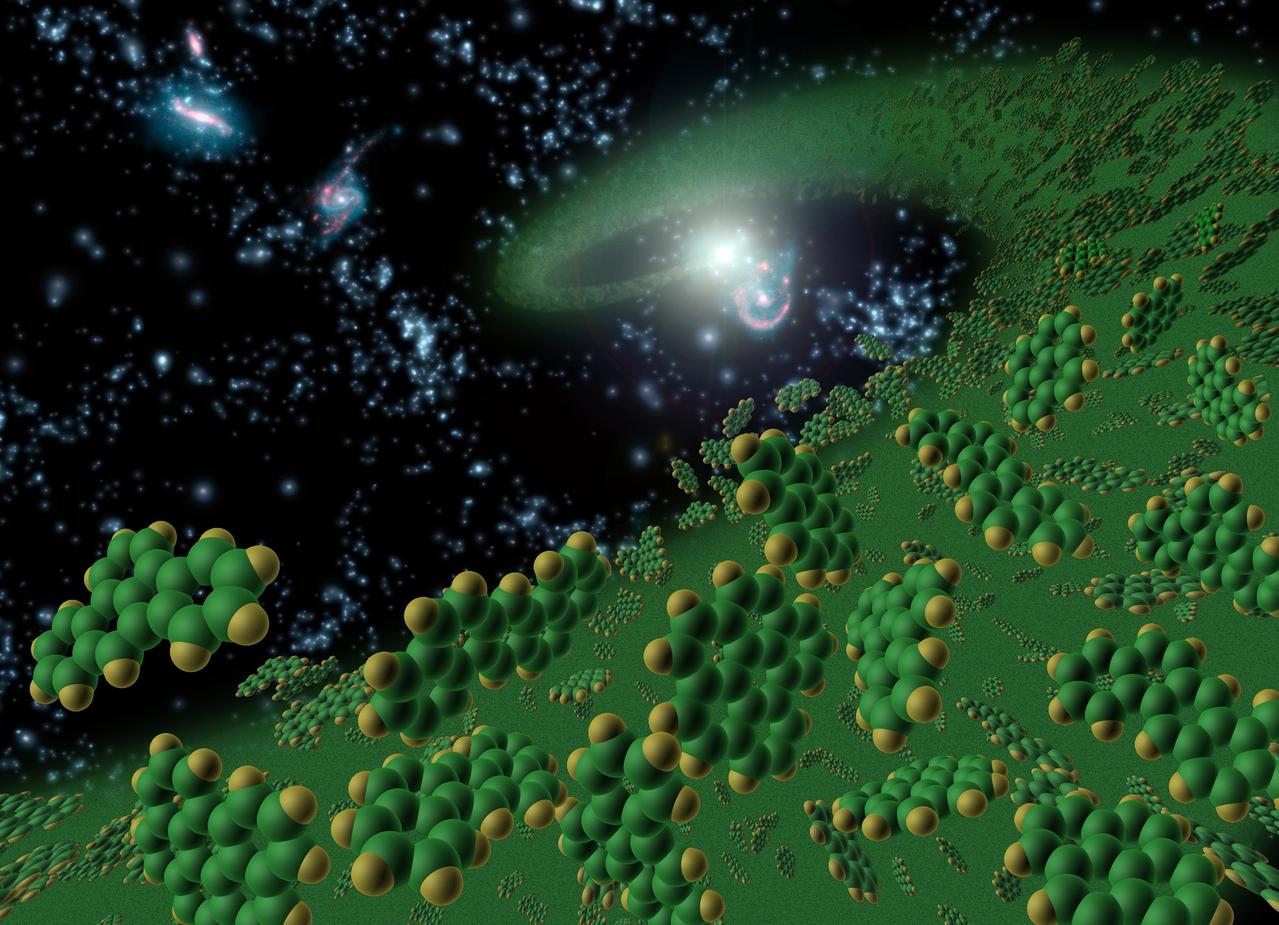

This artist conception symbolically represents complex organic molecules, known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, seen in the early universe. These large molecules, comprised of carbon and hydrogen, are considered among the building blocks of life.
The unique ultraviolet vision of NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer revealed, for the first time, dwarf galaxies forming out of nothing more than pristine gas likely leftover from the early universe.

This image shows an array of the 512 superconducting detectors used on the BICEP2 telescope at the South Pole. The technology was key to detecting the effects of gravitational waves associated with the early epoch of our universe known as inflation.

Resembling curling flames from a campfire, a magnificent nebula in a nearby galaxy observed by NASA Hubble Space Telescope provides new insight into the fierce birth of stars as it may have occurred in the early universe.

This artist animation illustrates the universe early years, from its explosive formation to its dark ages to its first stars and mini-galaxies. Scientists using NASA Spitzer Space Telescope found patches of infrared light splattered across the sky.
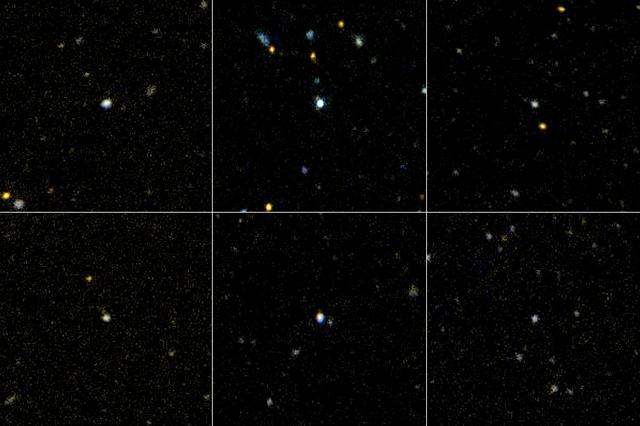

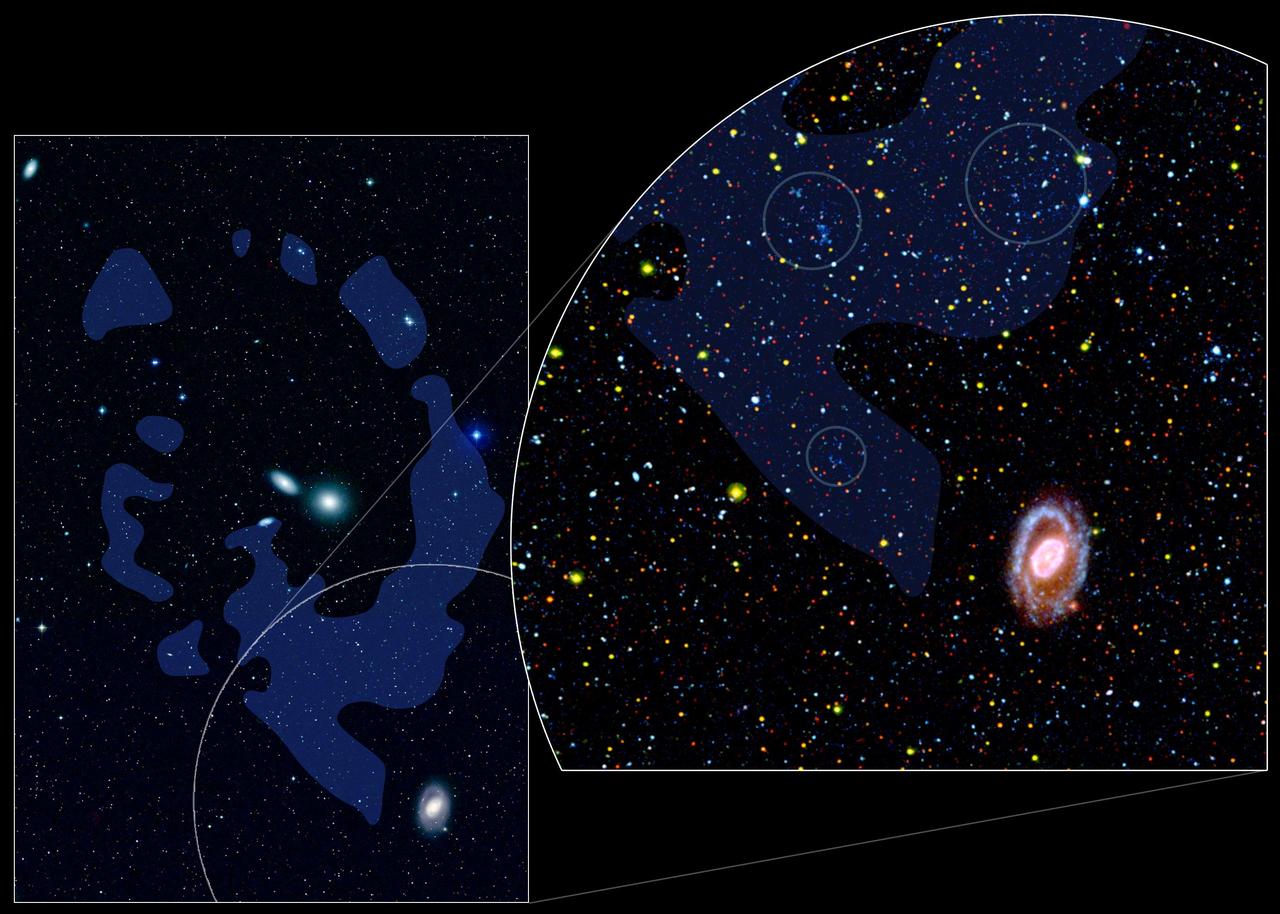
This image shows six of the three-dozen "ultraviolet luminous galaxies" spotted in our corner of the universe by NASA's Galaxy Evolution Explorer. These massive galaxies greatly resemble newborn galaxies that were common in the early universe. The discovery came as a surprise, because astronomers had thought that the universe's "birth-rate" had declined, and that massive galaxies were no longer forming. The galaxies, located in the center of each panel, were discovered after the Galaxy Evolution Explorer scanned a large portion of the sky with its highly sensitive ultraviolet-light detectors. Because young stars pack most of their light into ultraviolet wavelengths, young galaxies appear to the Galaxy Evolution Explorer like diamonds in a field of stones. Astronomers mined for these rare "gems" before, but missed them because they weren't able to examine a large enough slice of the sky. The Galaxy Evolution Explorer surveyed thousands of nearby galaxies before finding three-dozen newborns. While still relatively close in astronomical terms, these galaxies are far enough away to appear small to the Galaxy Evolution Explorer. Clockwise beginning from the upper left, they are called: GALEX_J232539.24+004507.1, GALEX_J231812.98-004126.1, GALEX_J015028.39+130858.5, GALEX_J021348.52+125951.3, GALEX_J143417.15+020742.5, GALEX_J020354.02-092452.5. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07143
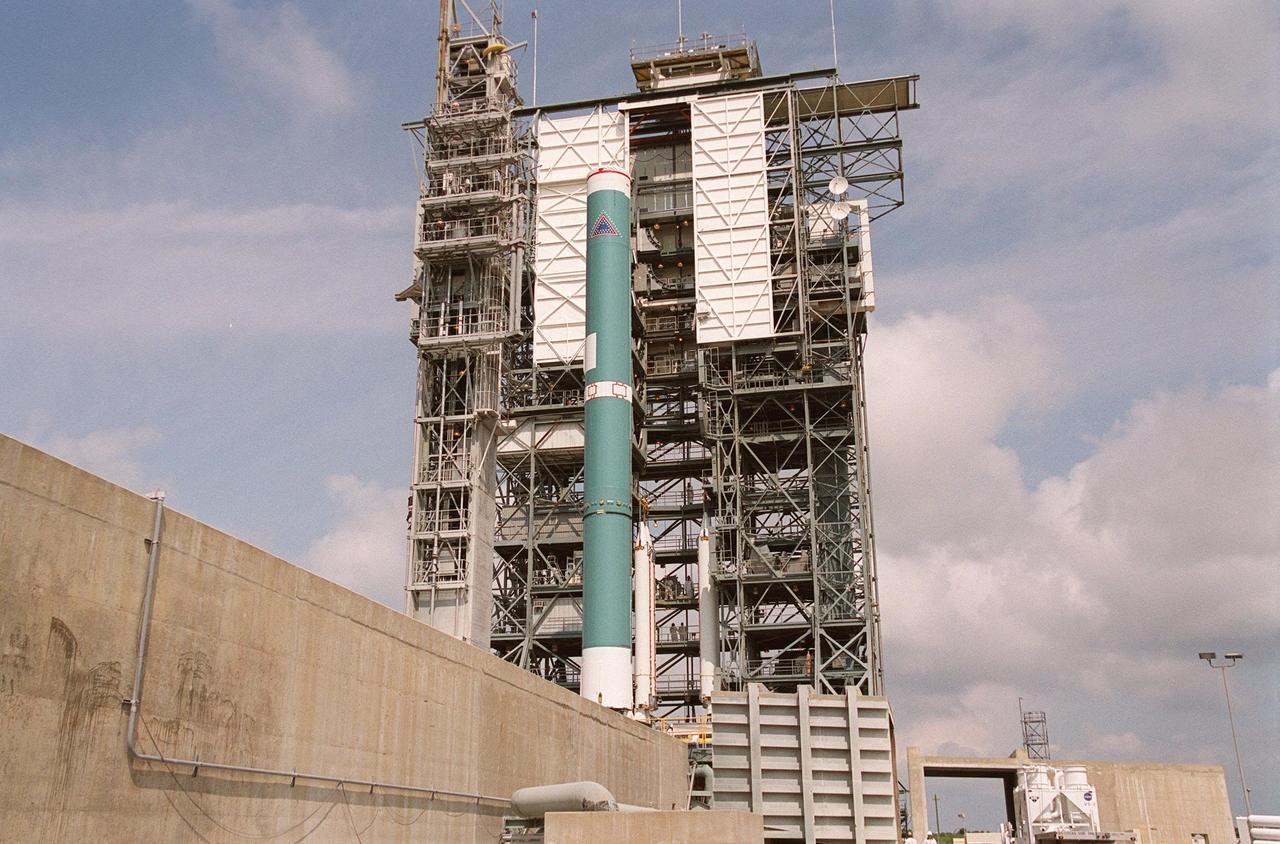
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II rocket waits to be mated to four solid rocket boosters (behind the Delta). The rocket will launch the MAP instrument into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The MAP mission will examine conditions in the early universe by measuring temperature differences in cosmic microwave background radiation, which is the radiant heat left over from the Big Bang. The properties of this radiation directly reflect conditions in the early universe. MAP is scheduled to launch June 30 at 3:46:46 p.m. EDT
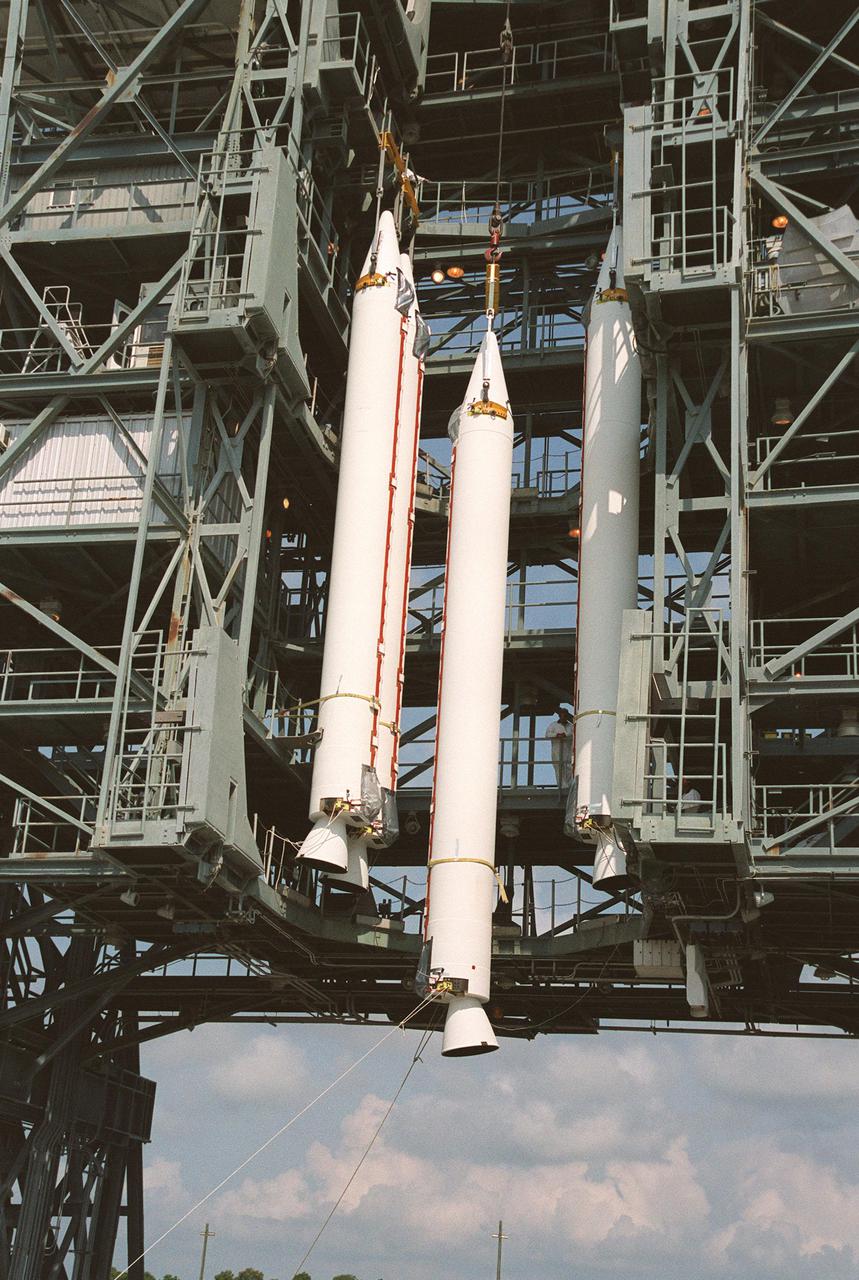

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Four solid rocket boosters are lifted up the gantry at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The SRBs will be mated to the Delta II rocket that will launch the MAP instrument into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The MAP mission will examine conditions in the early universe by measuring temperature differences in cosmic microwave background radiation, which is the radiant heat left over from the Big Bang. The properties of this radiation directly reflect conditions in the early universe. MAP is scheduled to launch June 30 at 3:46:46 p.m. EDT
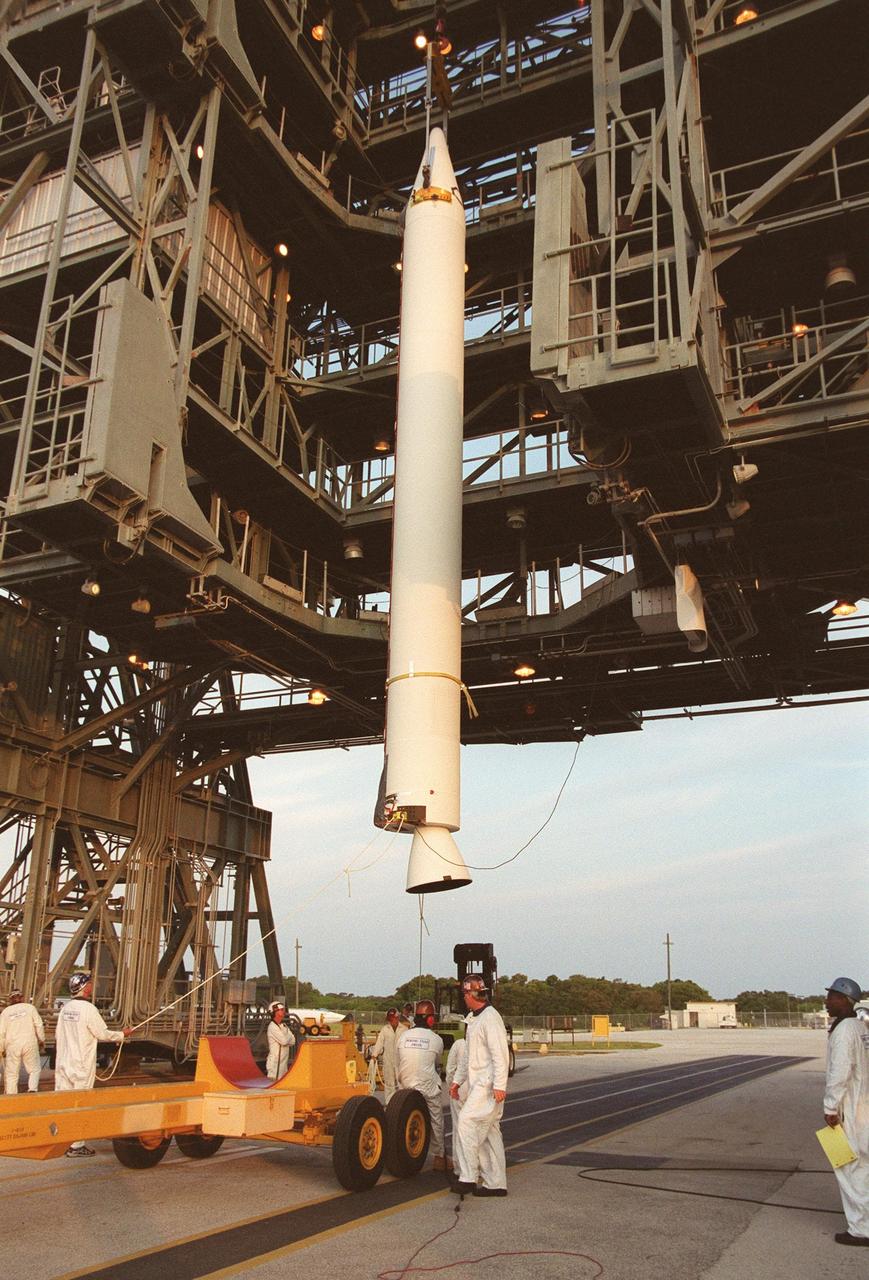

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A solid rocket booster is lifted up the gantry at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The SRB will be mated to the Delta II rocket that will launch the MAP instrument into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The MAP mission will examine conditions in the early universe by measuring temperature differences in cosmic microwave background radiation, which is the radiant heat left over from the Big Bang. The properties of this radiation directly reflect conditions in the early universe. MAP is scheduled to launch June 30 at 3:46:46 p.m. EDT
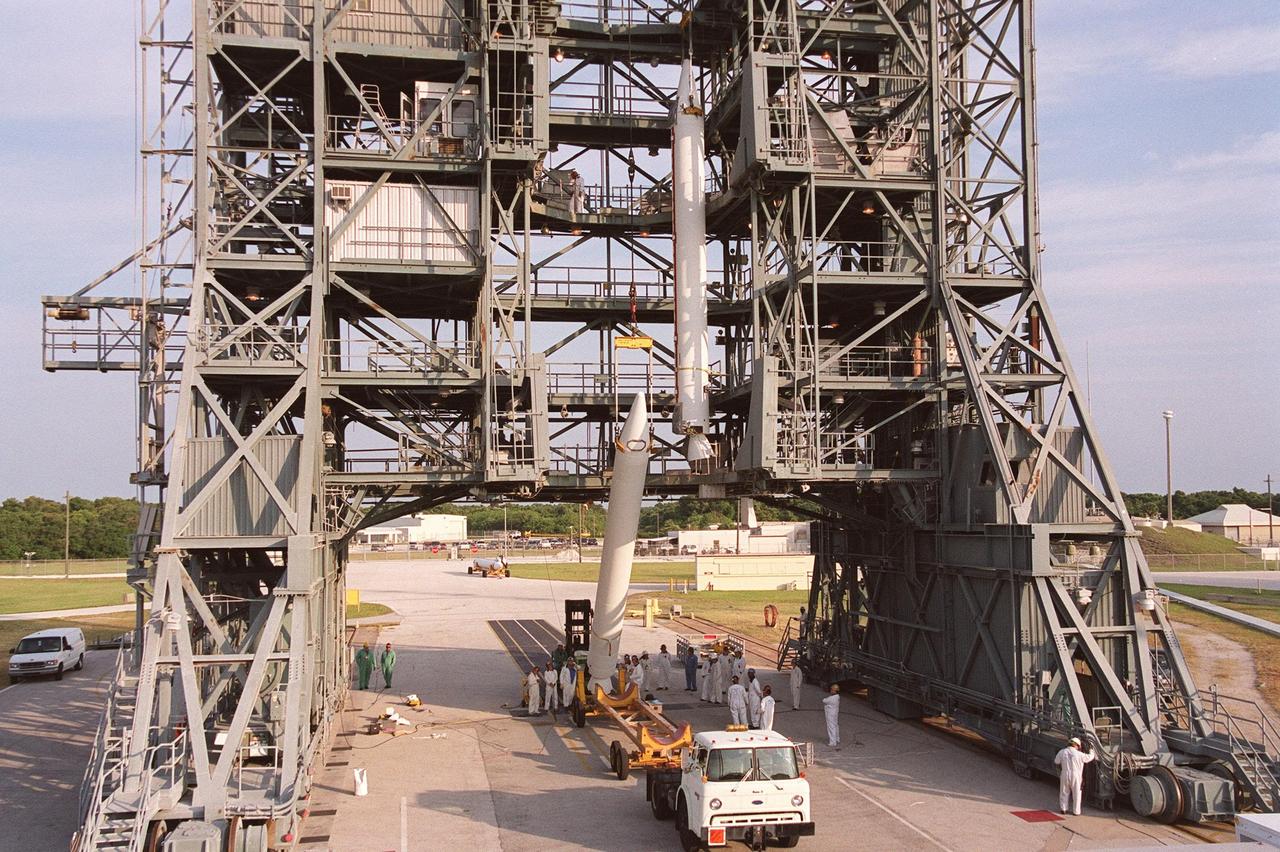

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A second solid rocket booster is lifted up the gantry at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The SRBs will be mated to the Delta II rocket that will launch the MAP instrument into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The MAP mission will examine conditions in the early universe by measuring temperature differences in cosmic microwave background radiation, which is the radiant heat left over from the Big Bang. The properties of this radiation directly reflect conditions in the early universe. MAP is scheduled to launch June 30 at 3:46:46 p.m. EDT
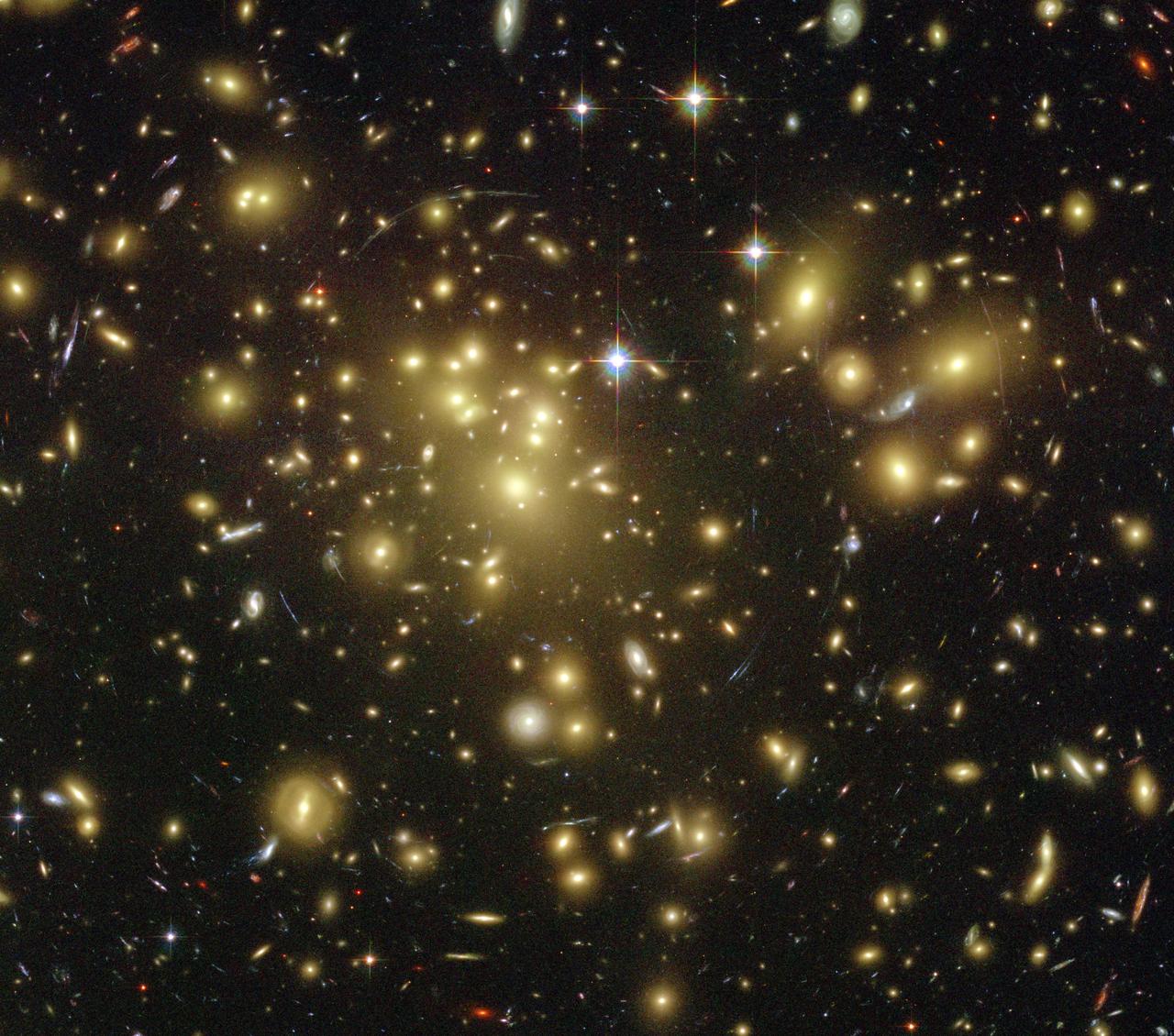

A massive cluster of yellowish galaxies is seemingly caught in a spider web of eerily distorted background galaxies in the left-hand image, taken with the Advanced Camera for Surveys ACS aboard NASA Hubble Space Telescope.
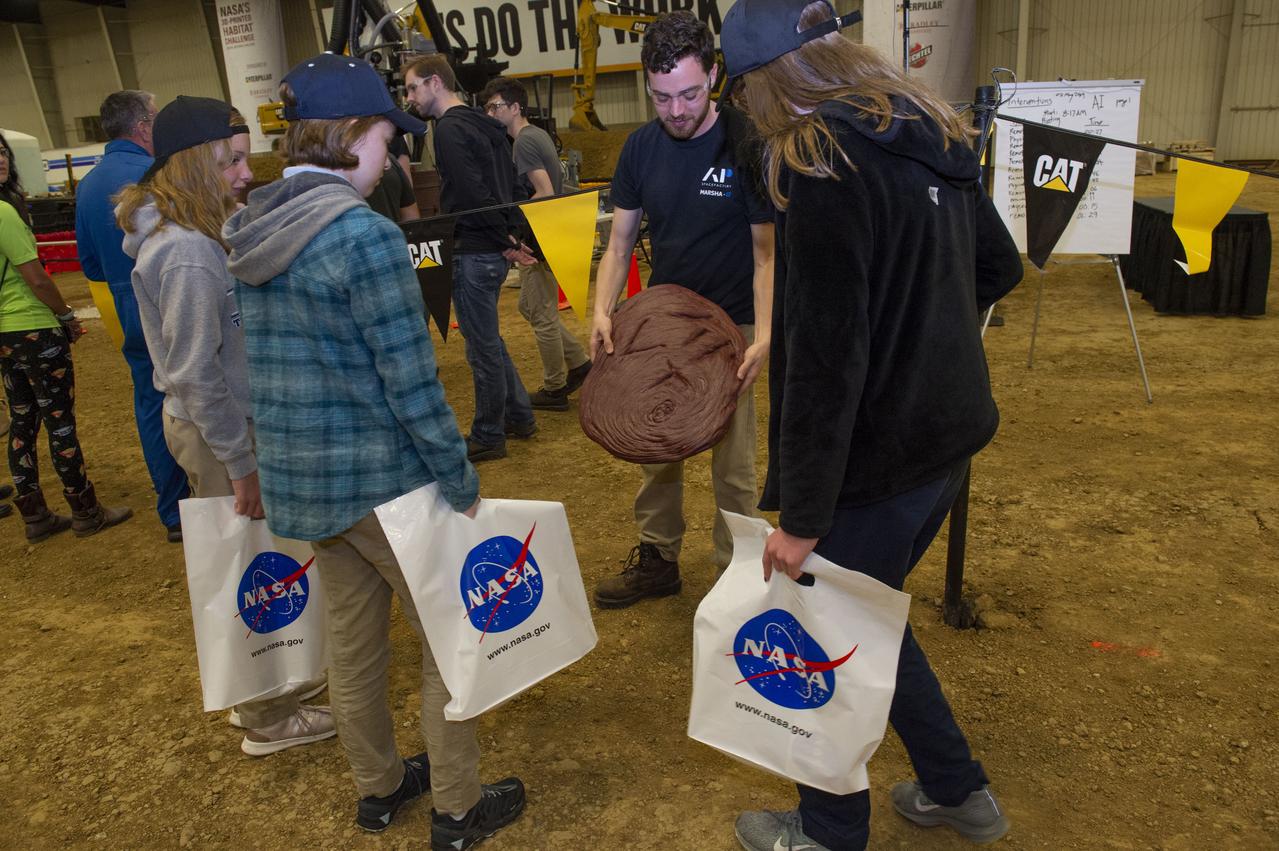

AI. SpaceFactory of New York and Pennsylvania State University of College Park print subscale habitat structures at NASA's 3D-Printed Habitat Challenge, held at the Caterpillar Edwards Demonstration & Learning Center in Edwards, Illinois, May 1-4, 2019. The habitat print is the final level of the multi-phase competition, which began in in 2015. The challenge is managed by NASA's Centennial Challenges program, and partner Bradley University of Peoria, Illinois. AI team member shows early unsuccessful attempt at printing to students viewing the competition.
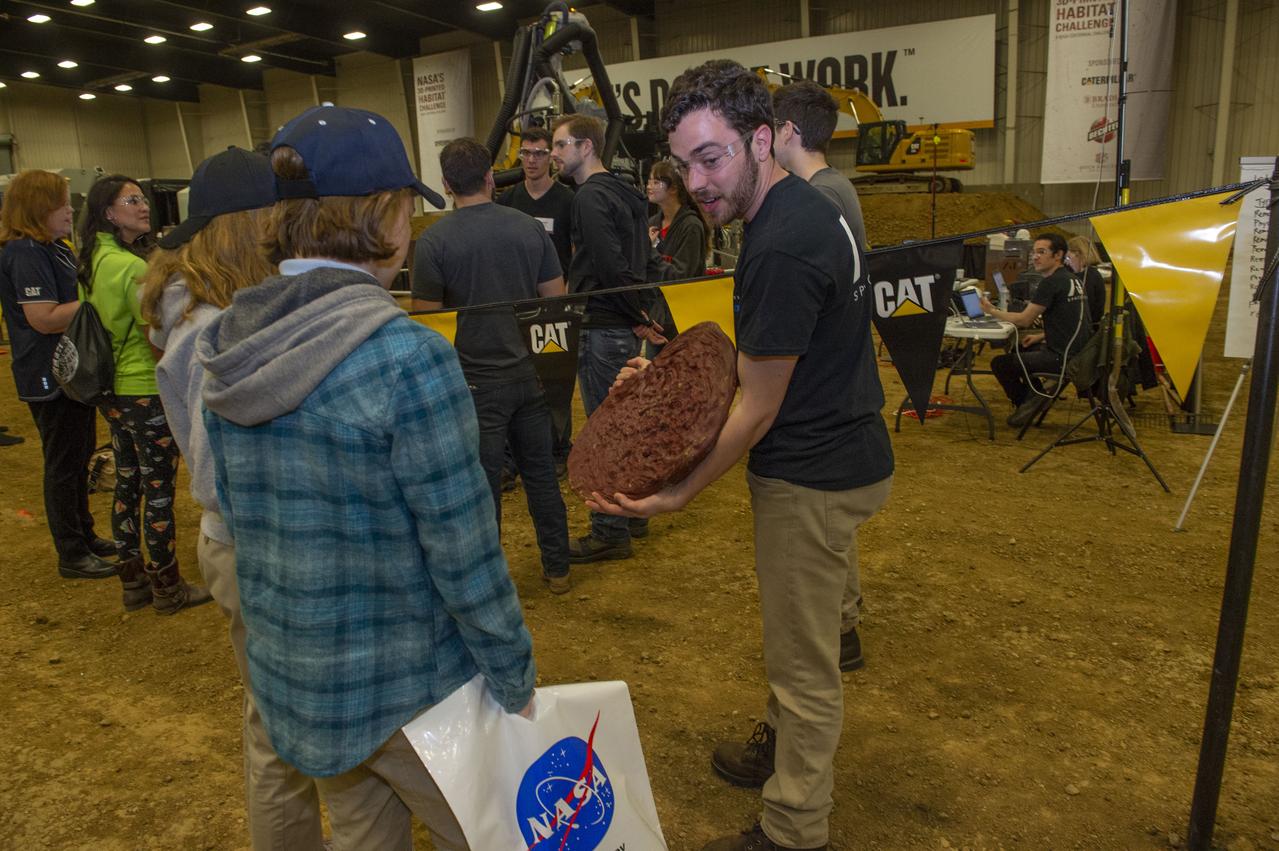

AI. SpaceFactory of New York and Pennsylvania State University of College Park print subscale habitat structures at NASA's 3D-Printed Habitat Challenge, held at the Caterpillar Edwards Demonstration & Learning Center in Edwards, Illinois, May 1-4, 2019. The habitat print is the final level of the multi-phase competition, which began in in 2015. The challenge is managed by NASA's Centennial Challenges program, and partner Bradley University of Peoria, Illinois. AI team member shows early unsuccessful attempt at printing to students viewing the competition.

NASA's SPHEREx mission will study the universe's early expansion, the history of galaxies, and the composition of planetary systems. This animation shows the preliminary design for the spacecraft, including hexagonal sun shields that will help keep the instruments cool. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23869
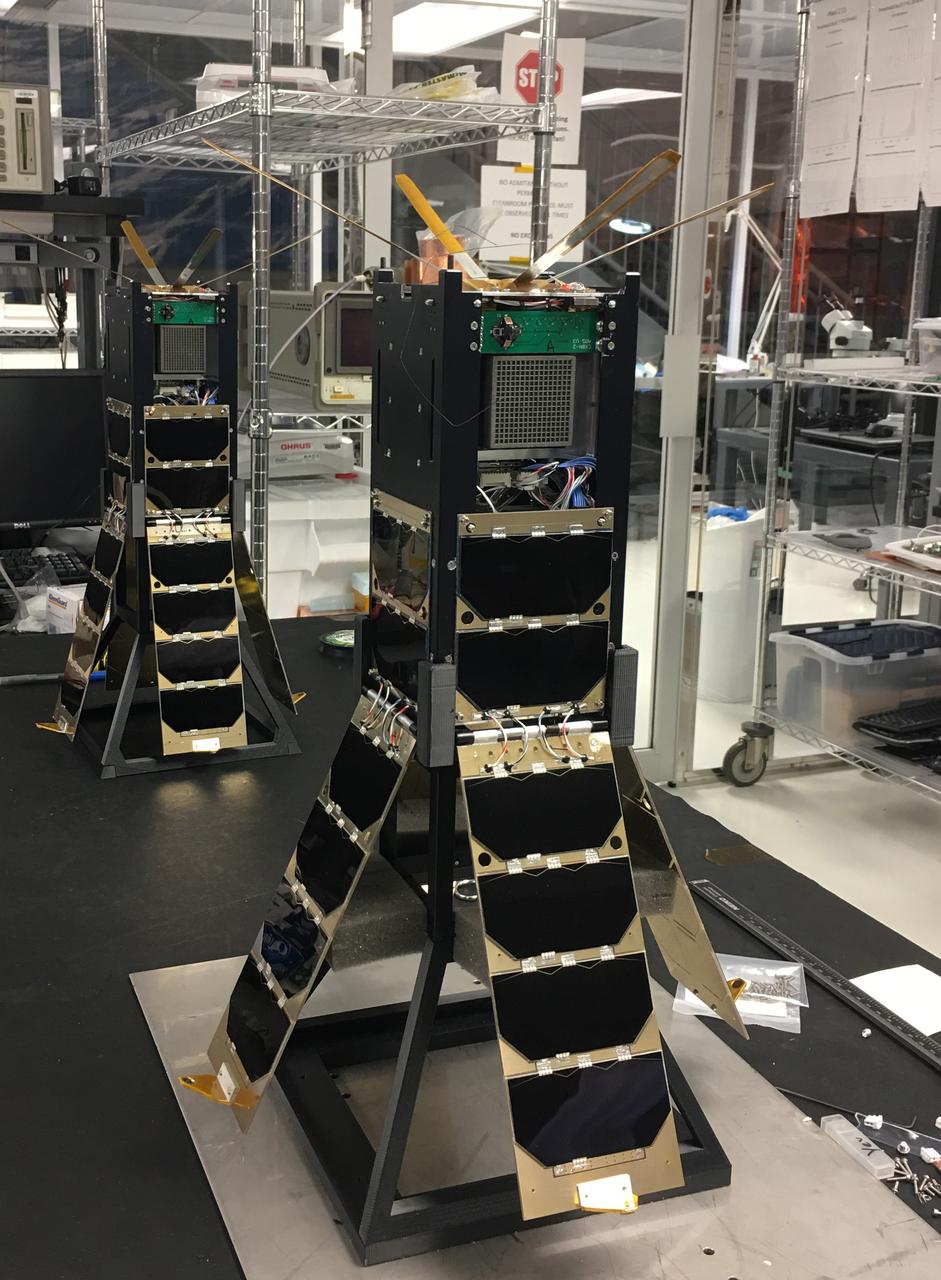

The Cosmic X-Ray Background NanoSat-2 (CXBN-2) CubeSat Mission developed by Morehead State University and its partners the Keldysh Institute (Moscow, Russia), the Maysville Community and Technical College (Morehead, KY) and KYSpace LLC (Lexington, KY) will increase the precision of measurements of the Cosmic X-Ray Background in the 30-50 keV range to a precision of <5%, thereby constraining models that attempt to explain the relative contribution of proposed sources lending insight into the underlying physics of the early universe. The mission addresses a fundamental science question that is central to our understanding of the structure, origin, and evolution of the universe by potentially lending insight into both the high-energy background radiation and into the evolution of primordial galaxies. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative NET April 18, 2017 ELaNa XVII mission on the seventh Orbital-ATK Cygnus Commercial Resupply Services (OA-7) to the International Space Station and deployed on tbd.

Rebecca Spyke-Keiser, NASA's Associate Deputy Administrator for policy integration, gives opening remarks at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

NASA Deputy Administrator, Lori Garver, far right, gives the keynote address at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
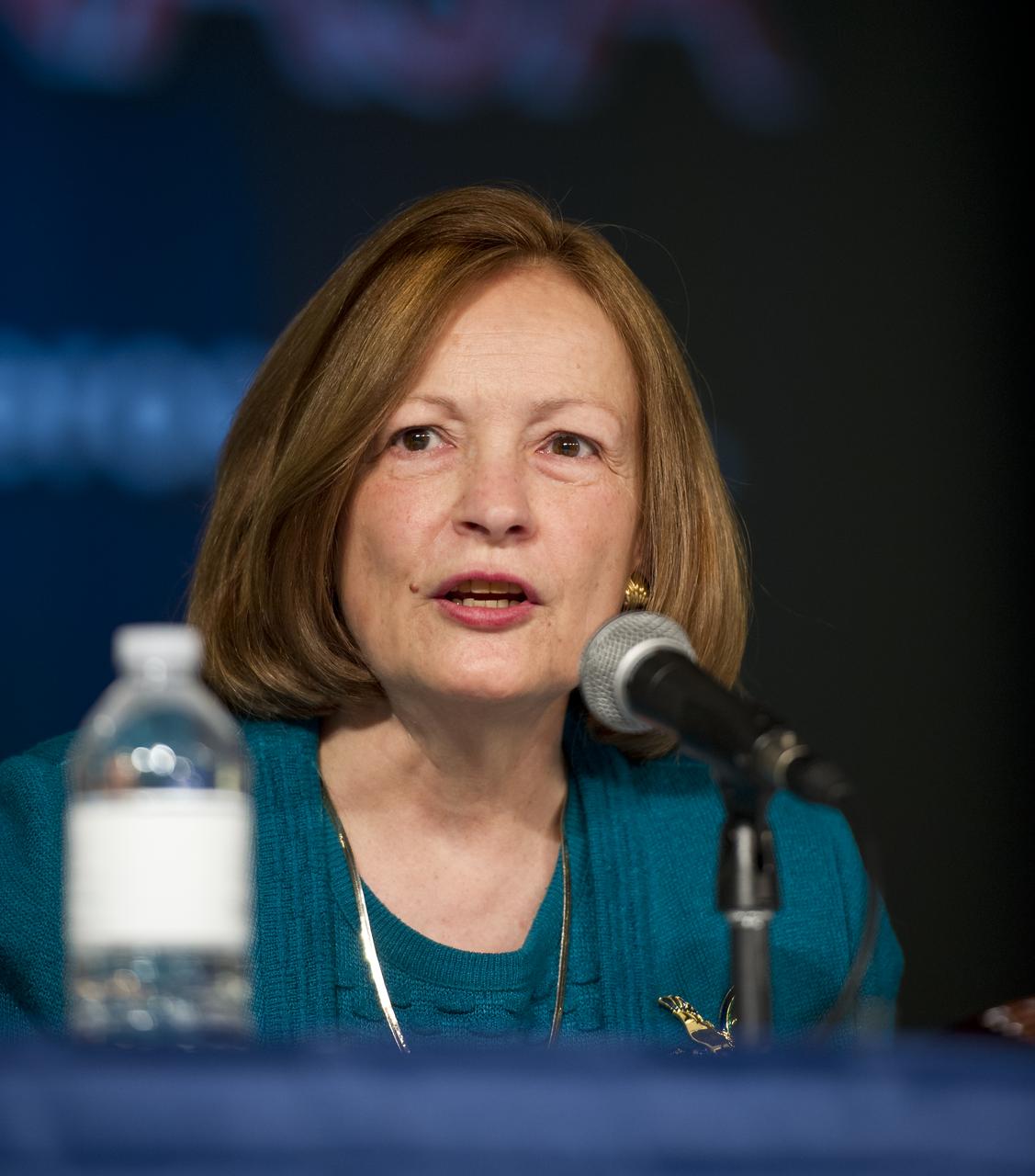

Marcia Smith, President, spacepolicyonline.com, participates in a panel discussion at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
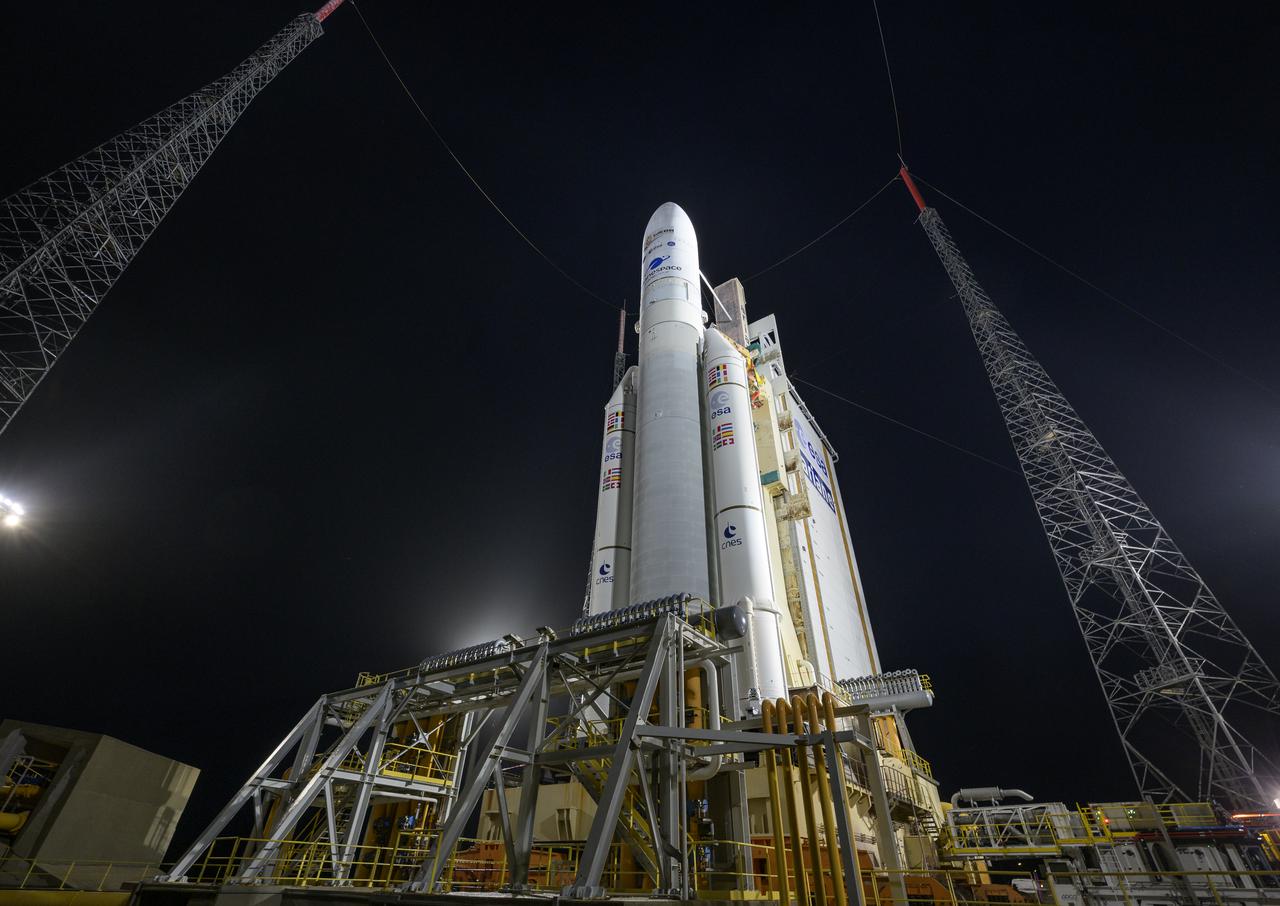

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen at the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Veronica Villalobos, Director, Office of Diversity and Inclusion, Office of Personnel Management, participates in a panel discussion at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
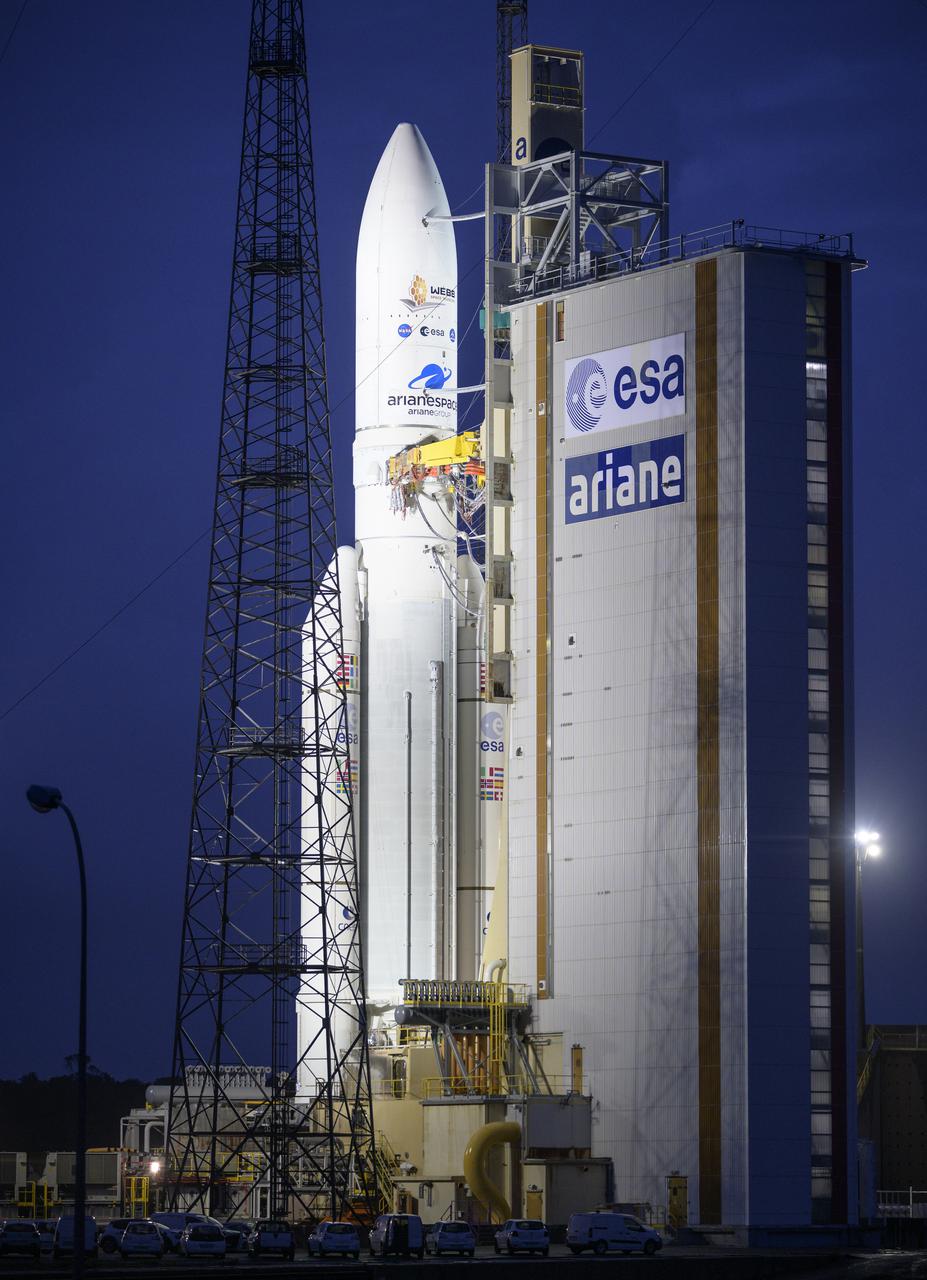

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen at the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
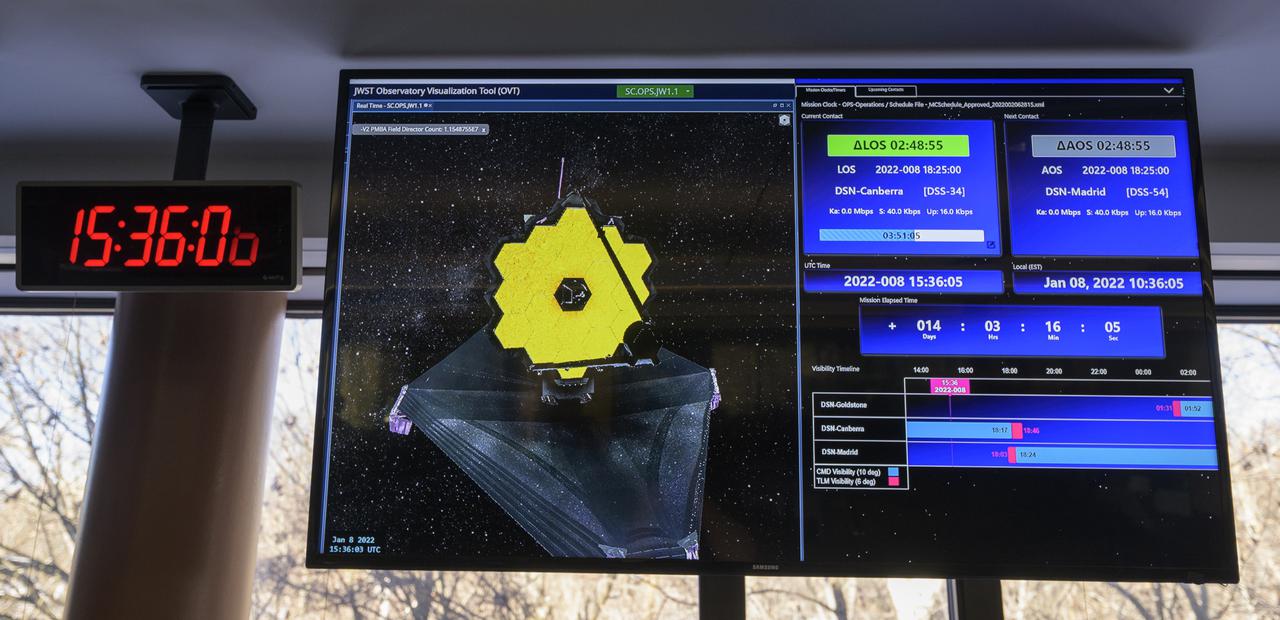
A monitor in the NASA James Webb Space Telescope flight control room of the Space Telescope Science Institute shows the progress of the second primary mirror wing latching on the Webb observatory, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, in Baltimore. When fully latched, the infrared observatory will have completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
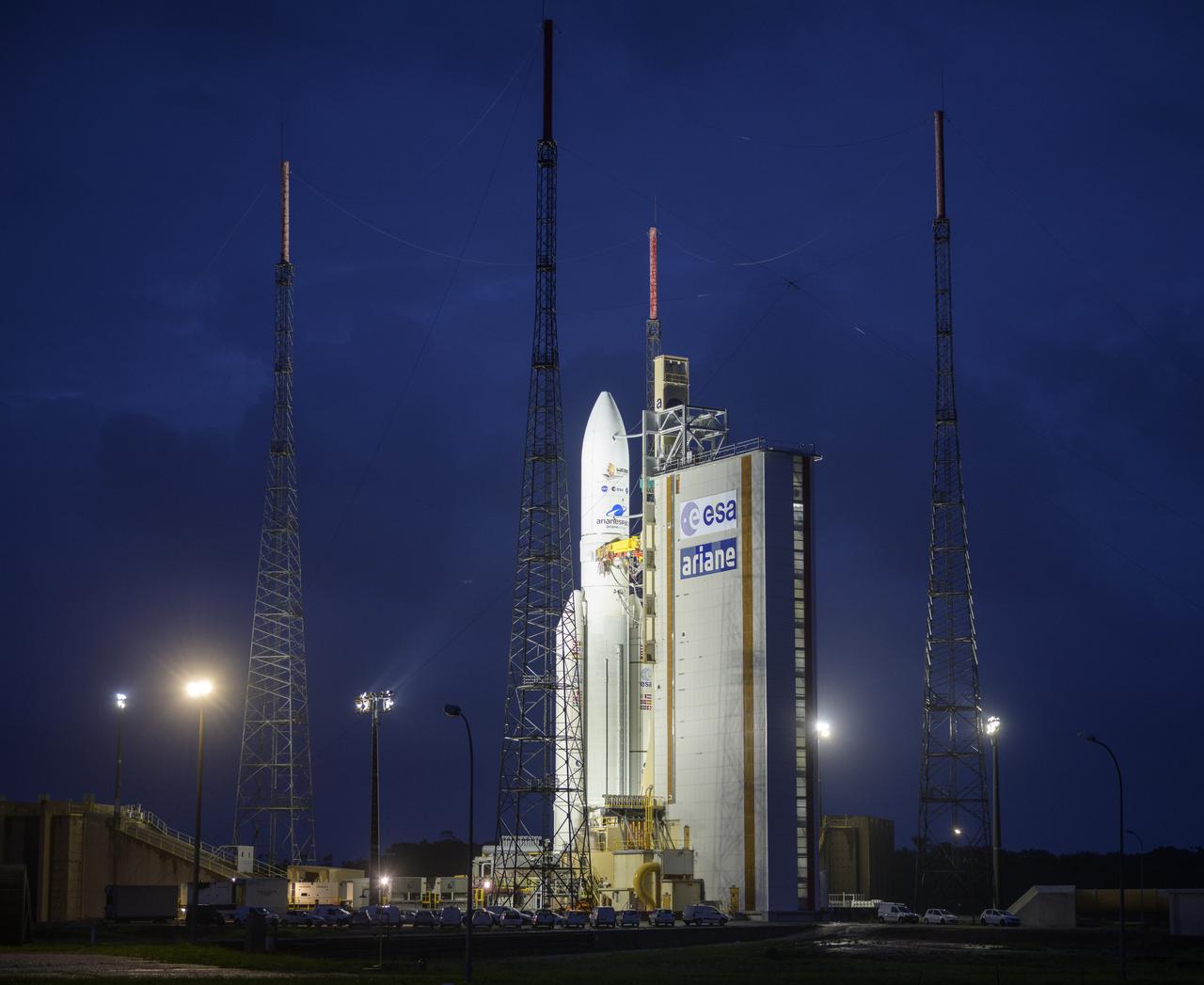

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen at the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
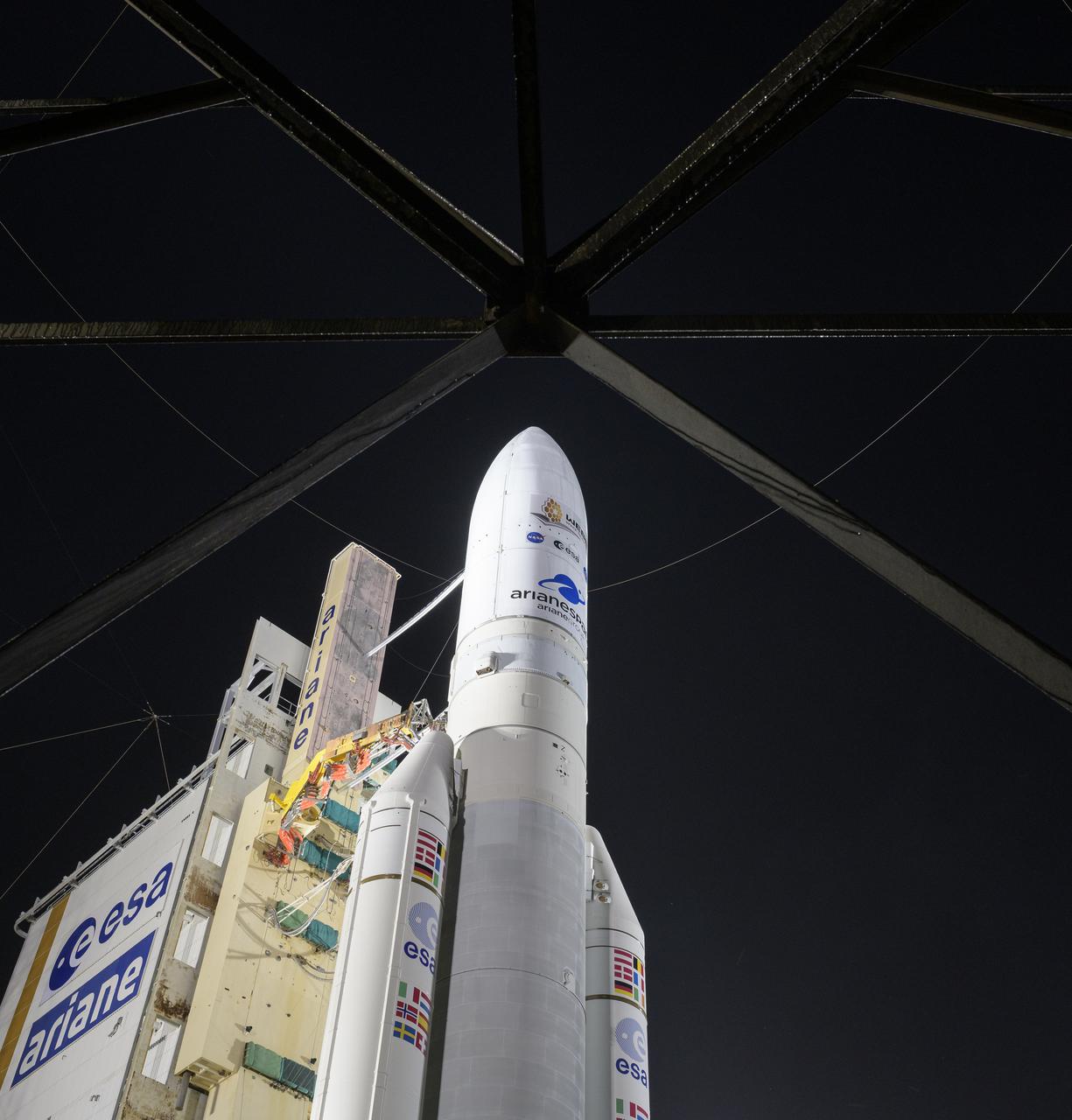

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen at the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
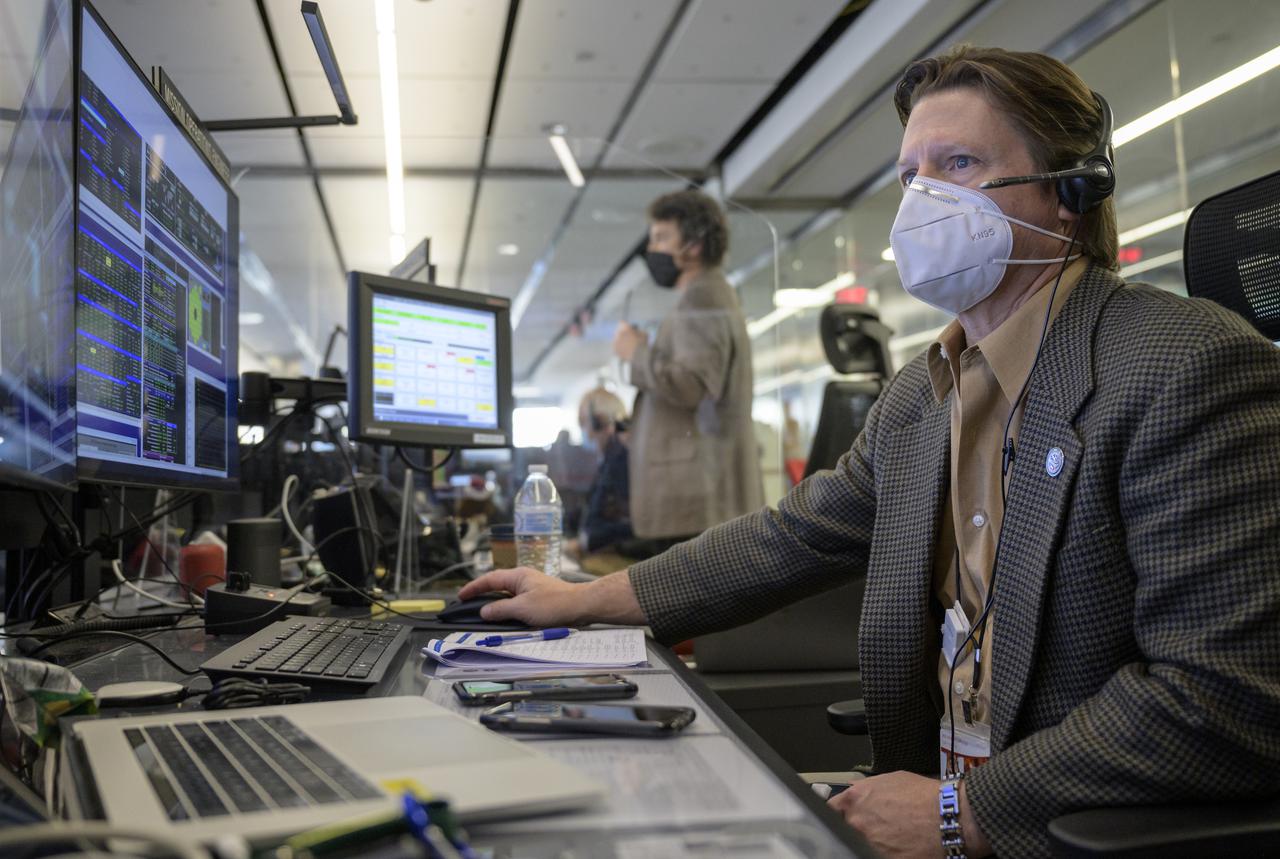

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Engineer Kenny McKenzie monitors the progress of Webb’s second primary mirror wing latching, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, in Baltimore. When fully latched, the infrared observatory will have completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
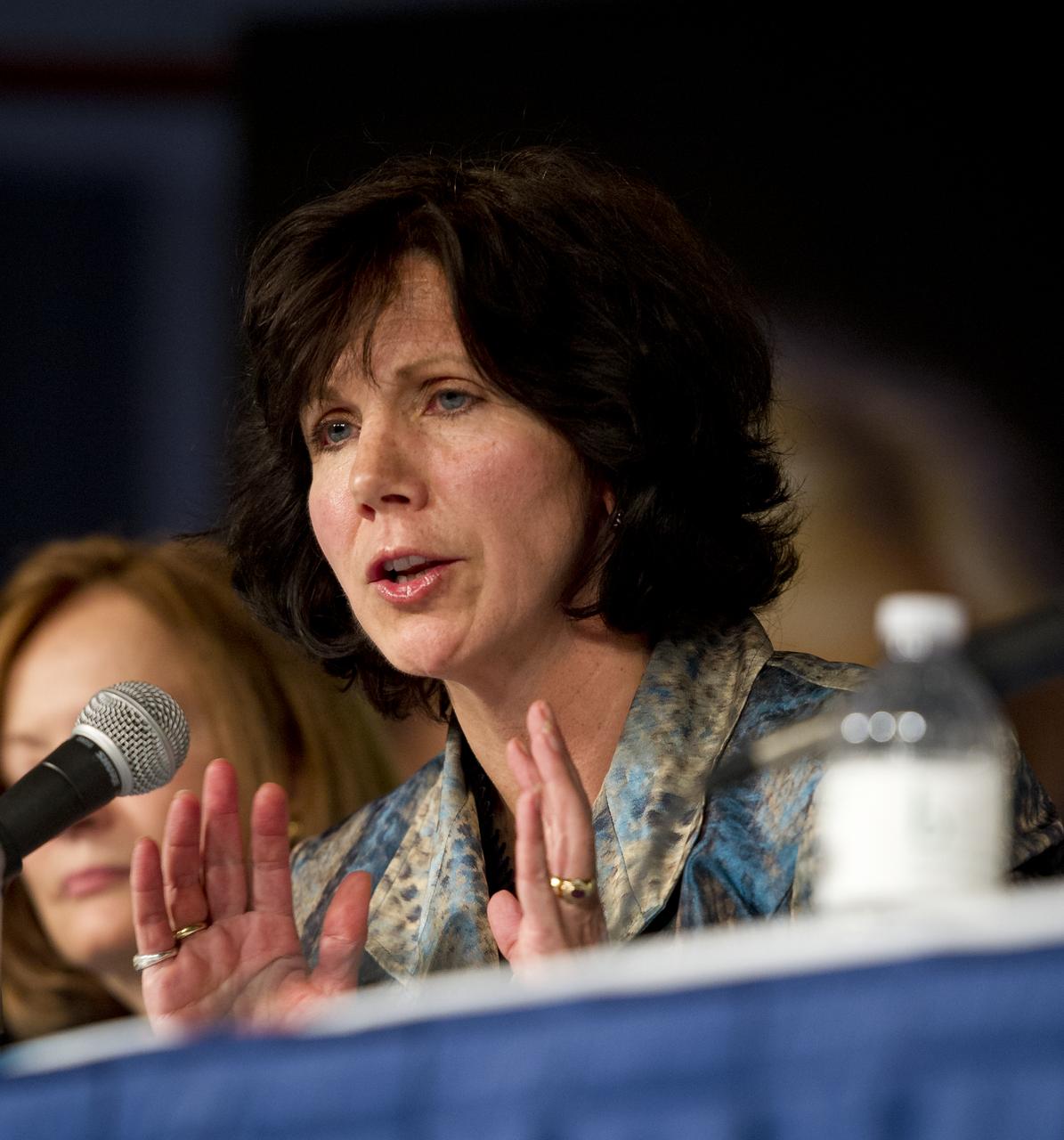

Catherine Didion, Senior Fellow, National Academy of Engineering, participates in a panel discussion at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
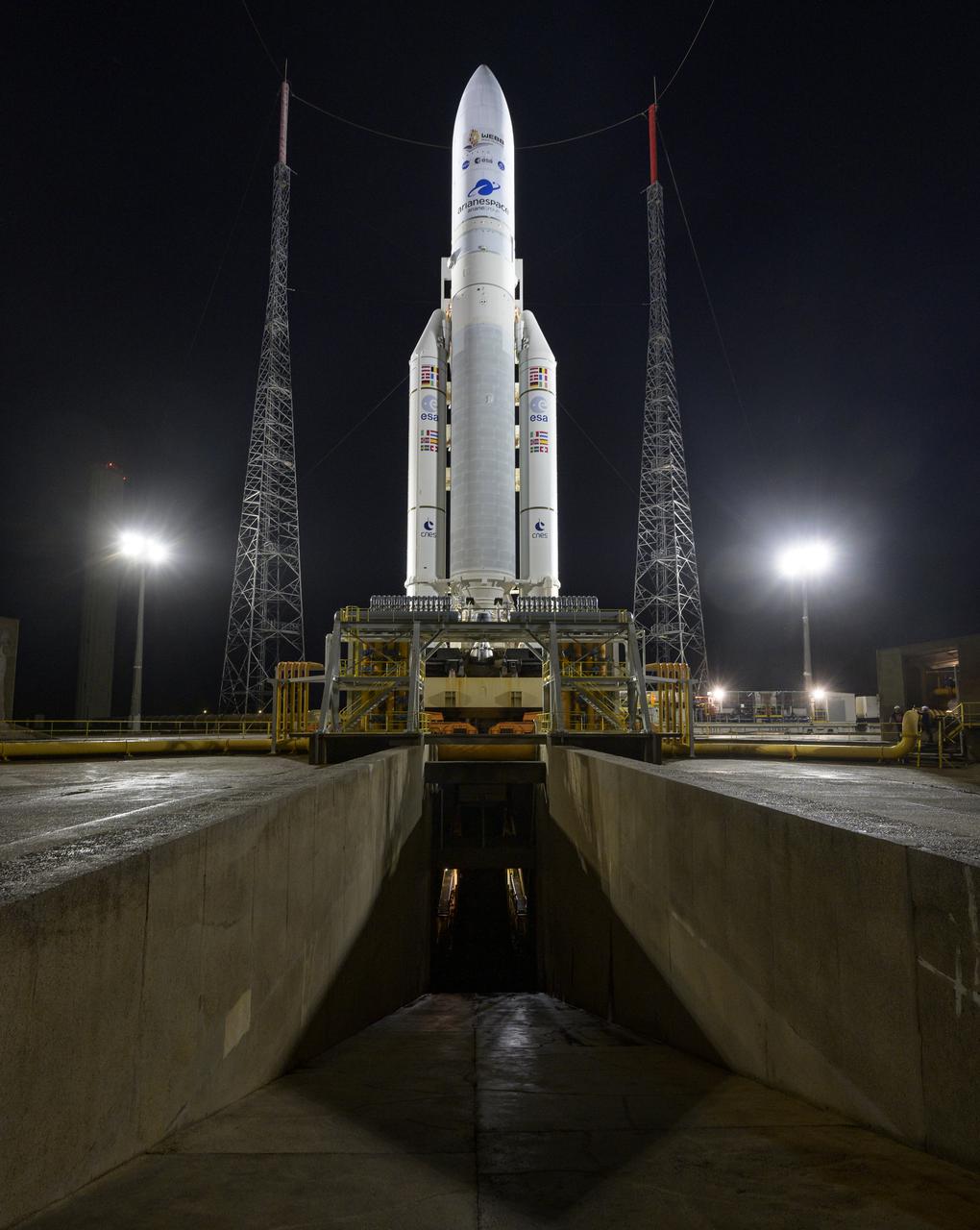

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen at the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
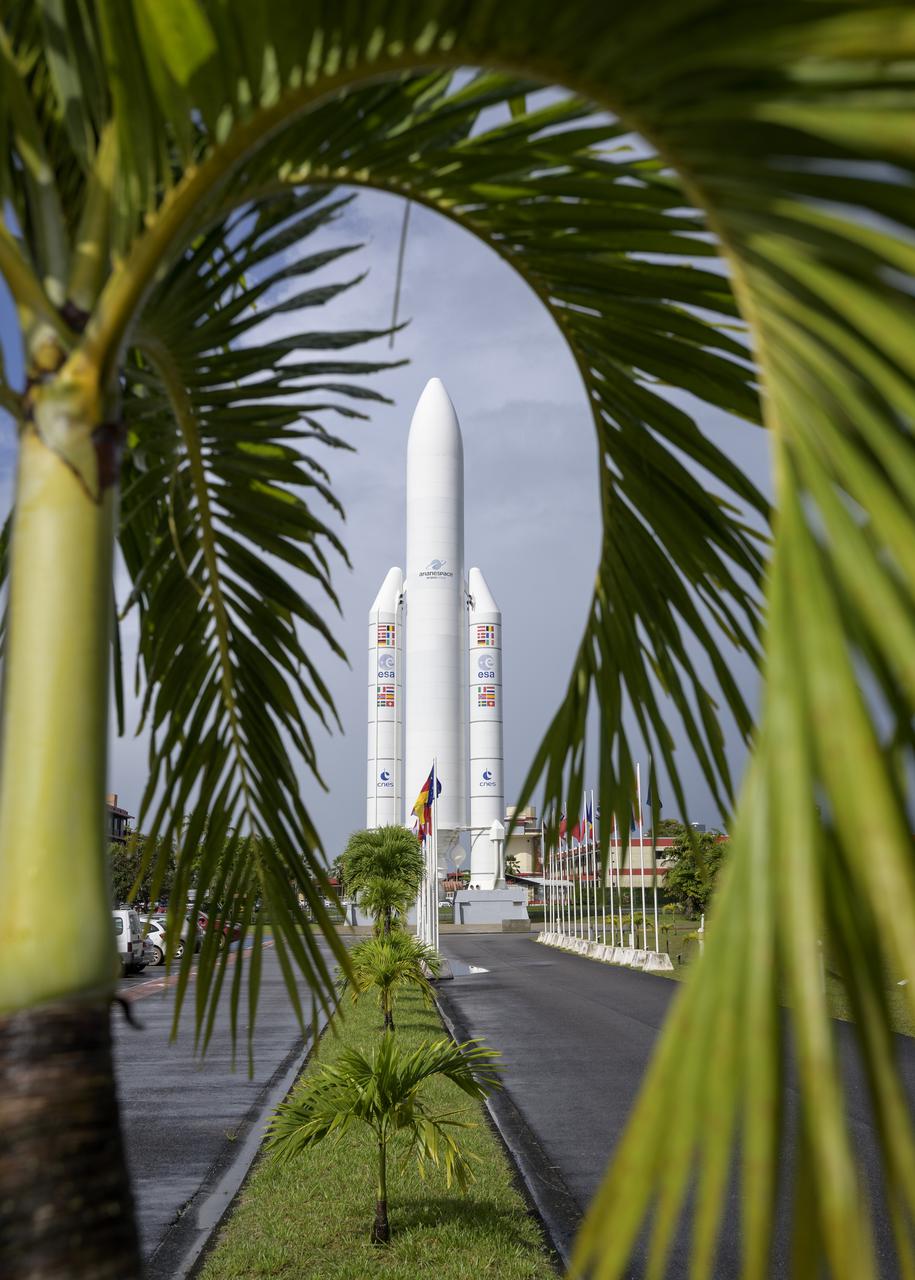

A mockup of Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket is seen at the entrance to the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana, Tuesday, Dec. 21, 2021. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory is scheduled to launch later in the week and will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
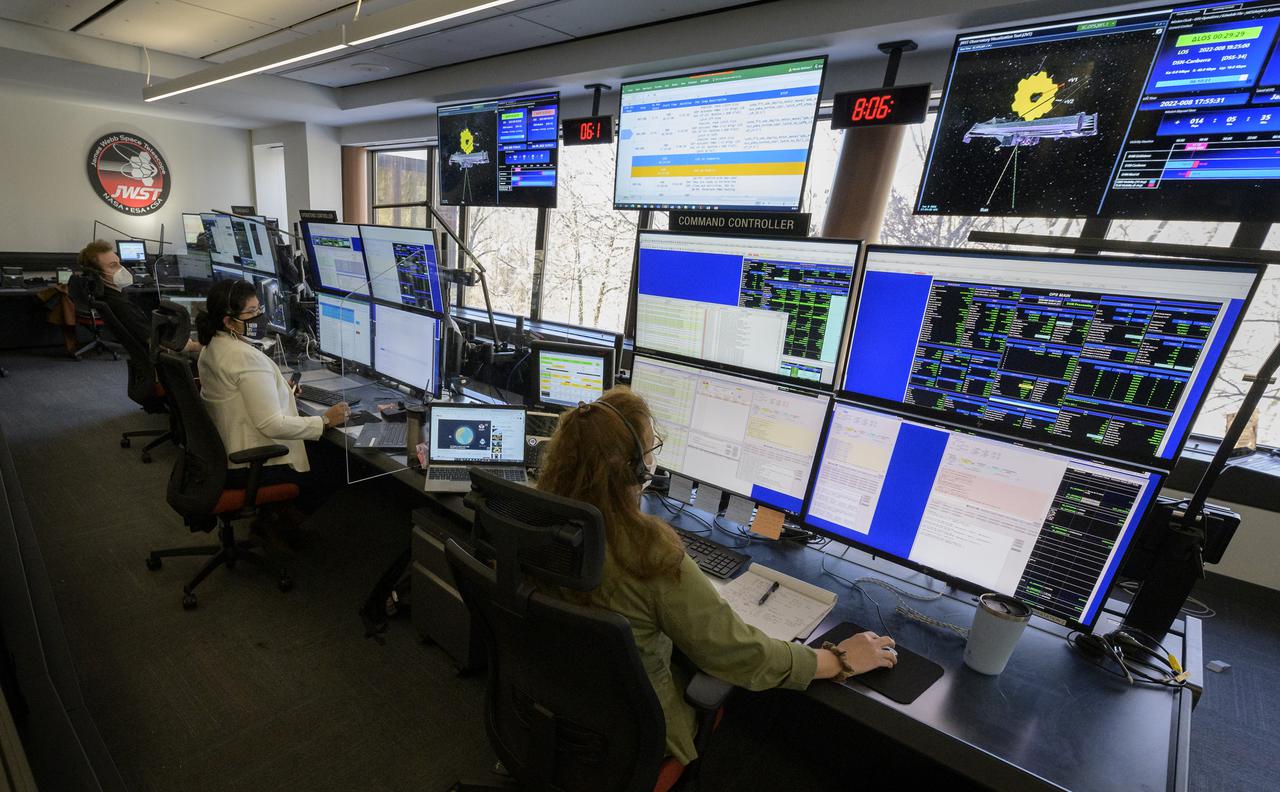

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission team members monitor the progress of Webb’s second primary mirror wing latching, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, in Baltimore. When fully latched, the infrared observatory will have completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
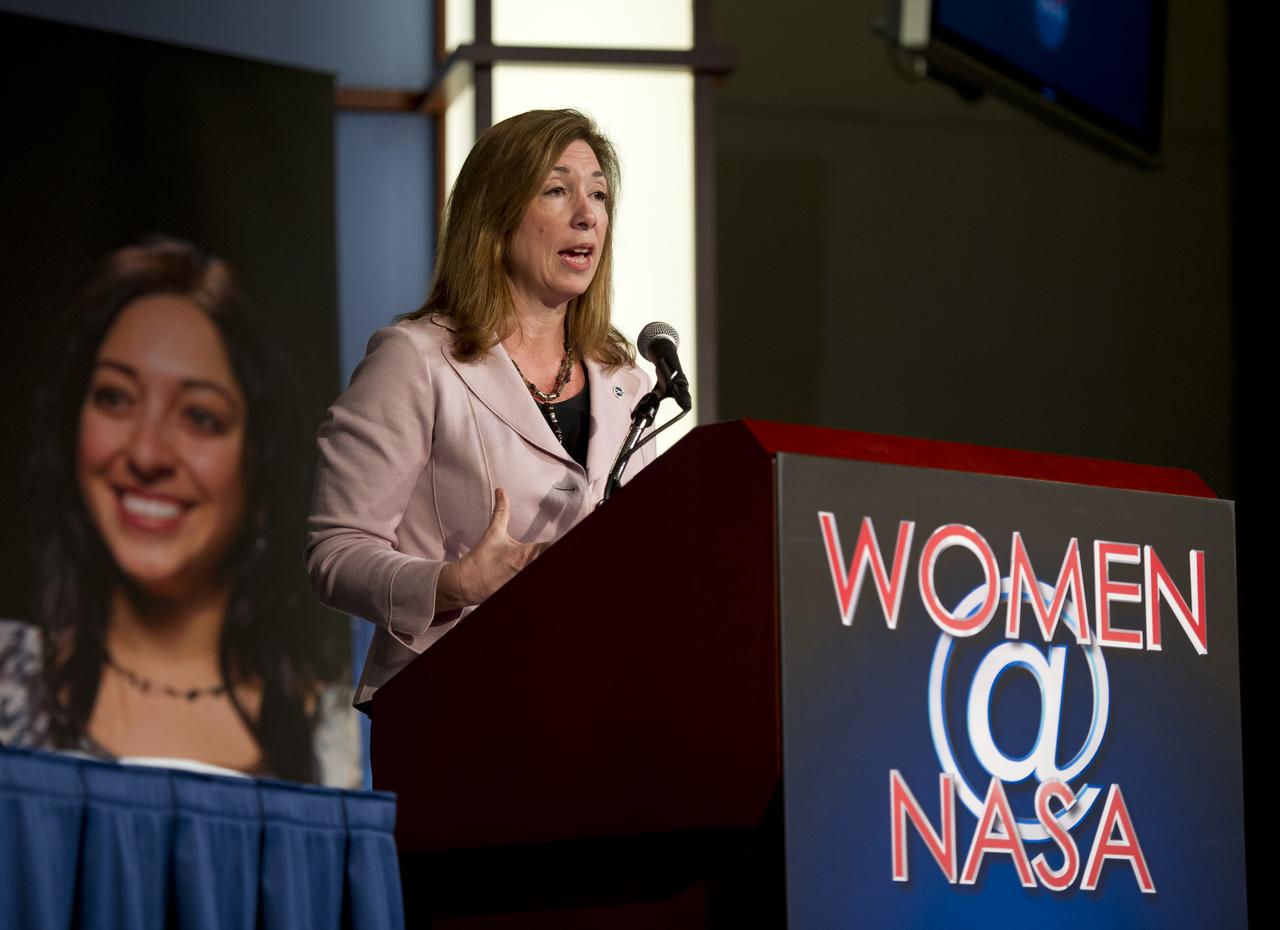

NASA Deputy Administrator, Lori Garver, gives the keynote address at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
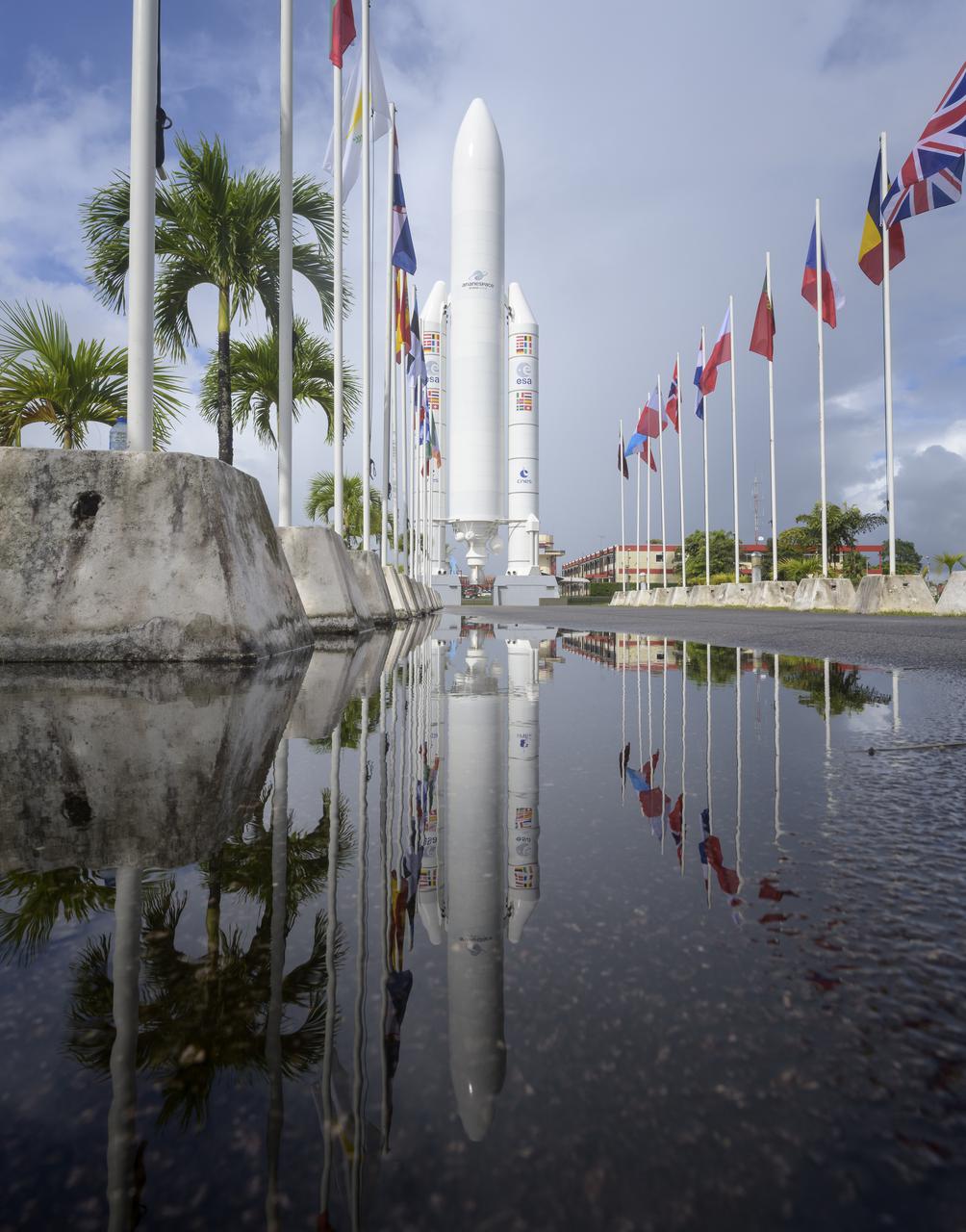

A mockup of Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket is seen at the entrance to the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana, Tuesday, Dec. 21, 2021. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory is scheduled to launch later in the week and will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
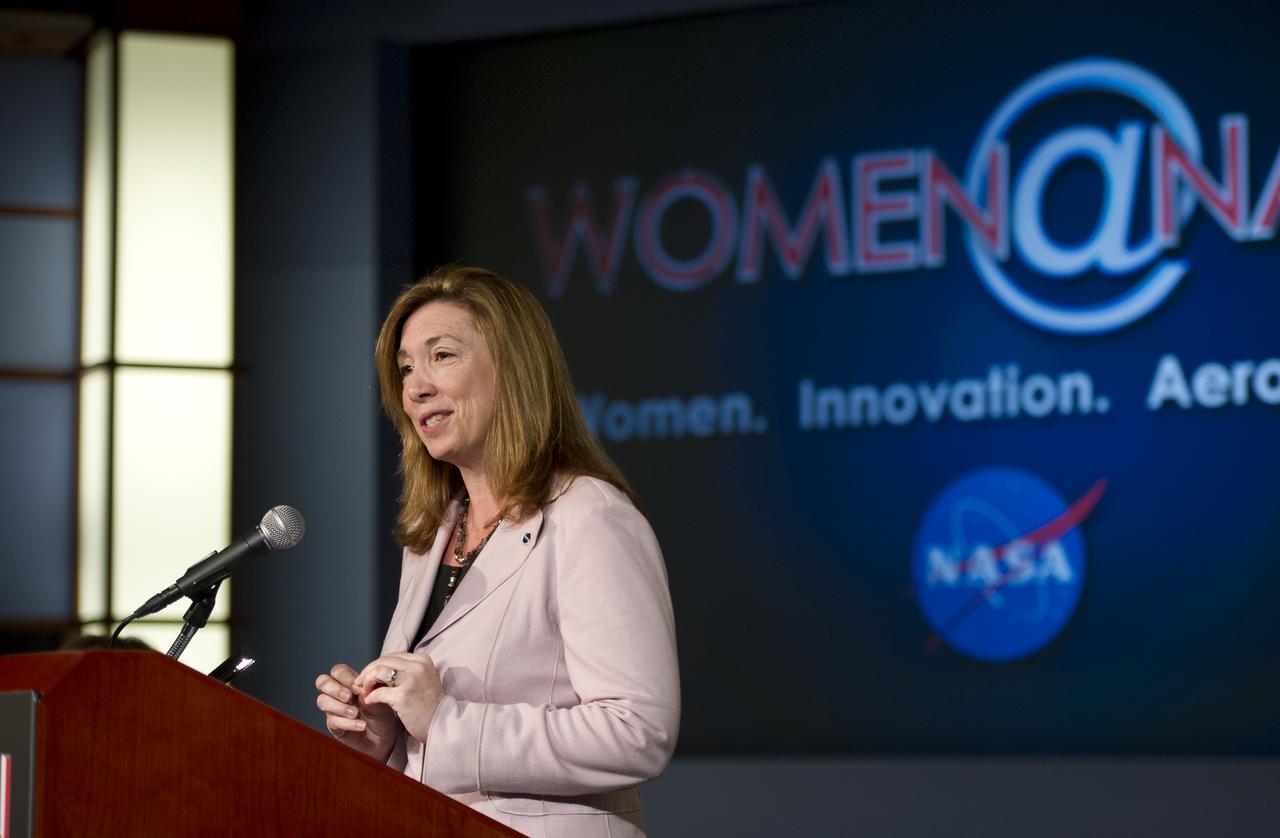

NASA Deputy Administrator, Lori Garver, gives the keynote address at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen at the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A mockup of Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket is seen at the entrance to the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana, Tuesday, Dec. 21, 2021. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory is scheduled to launch later in the week and will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
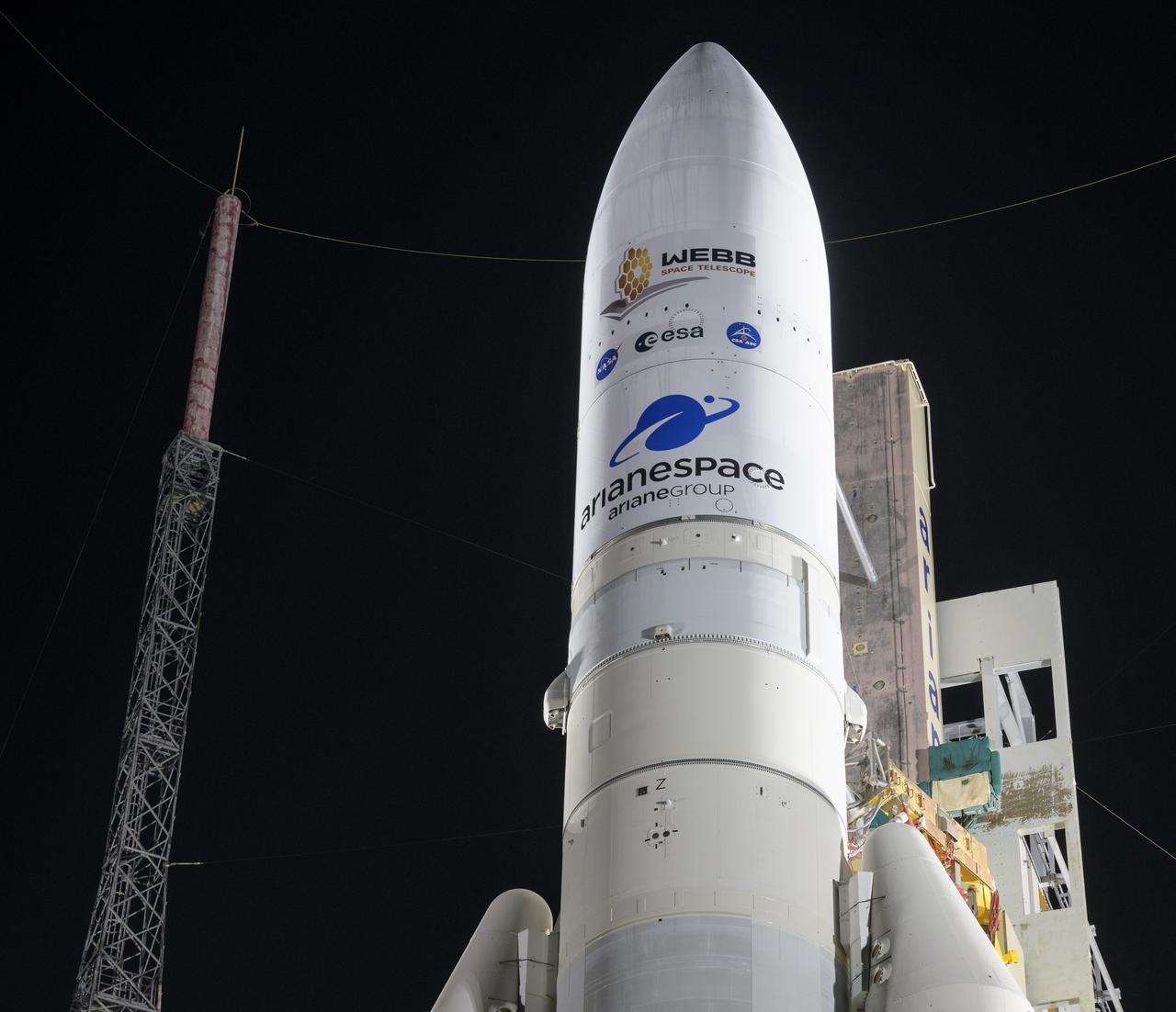

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen at the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Kathy Sullivan, NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Deputy Administrator and former NASA astronaut, participates in a panel discussion at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
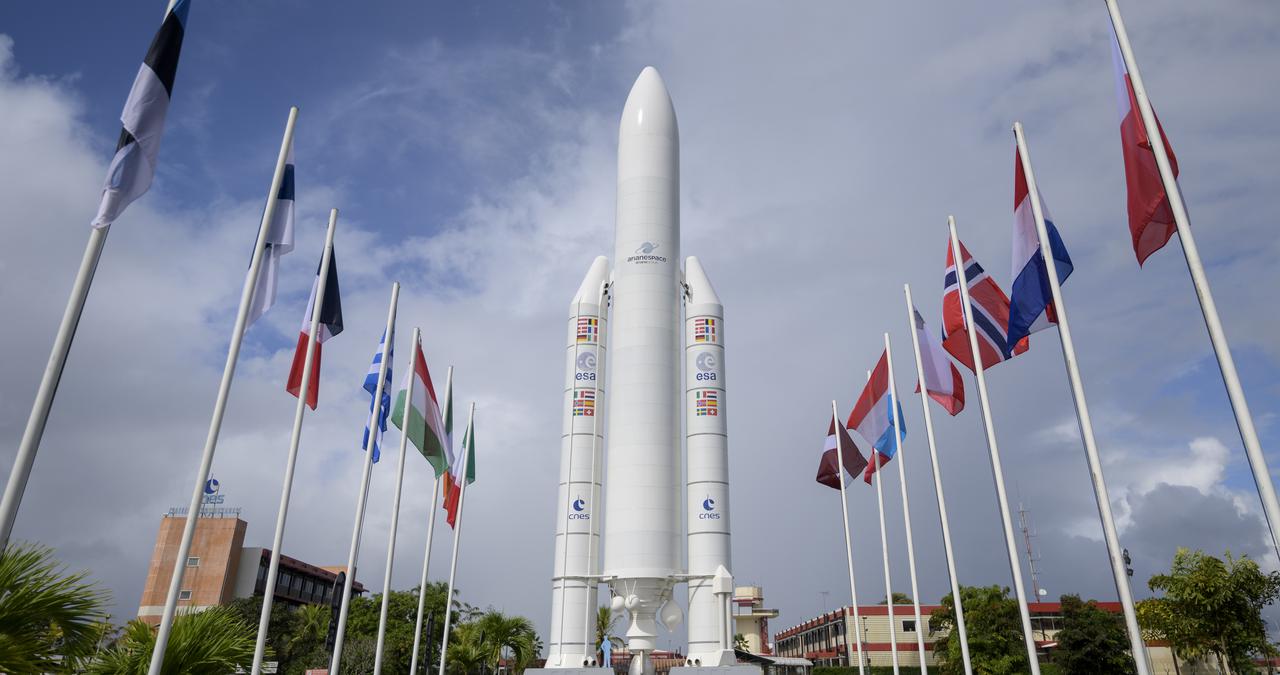

A mockup of Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket is seen at the entrance to the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana, Tuesday, Dec. 21, 2021. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory is scheduled to launch later in the week and will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
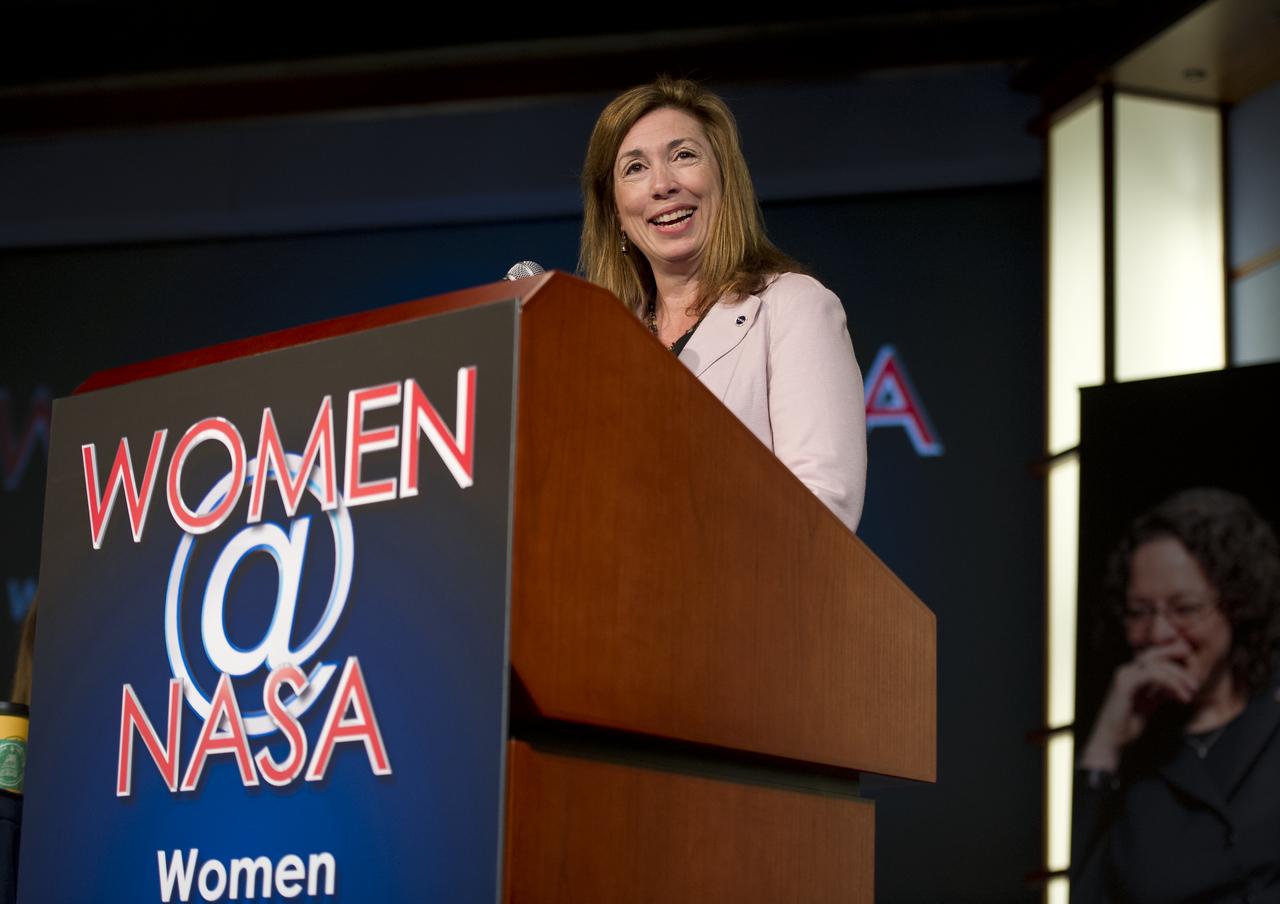

NASA Deputy Administrator, Lori Garver, gives the keynote address at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
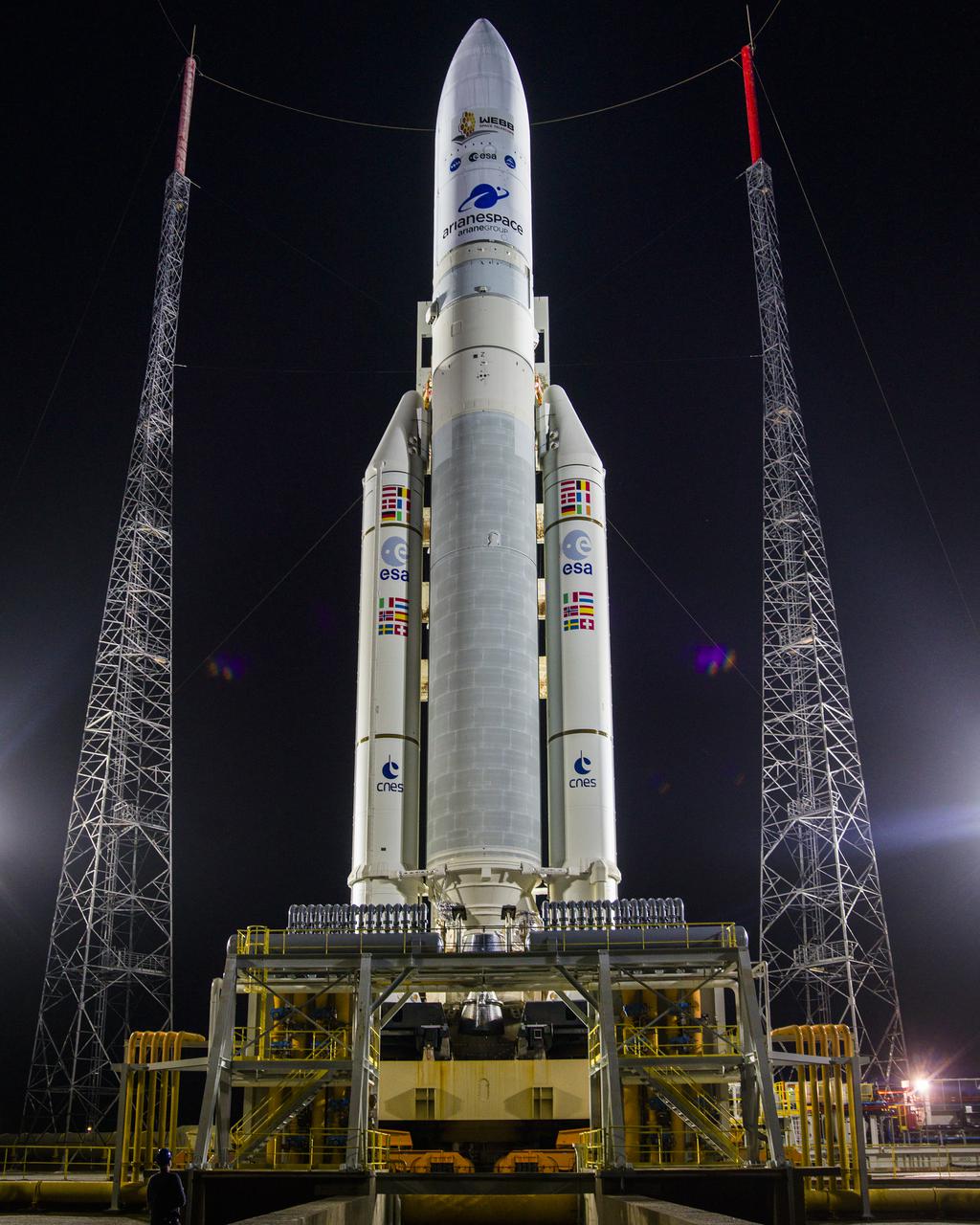

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen at the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Chris Gunn)
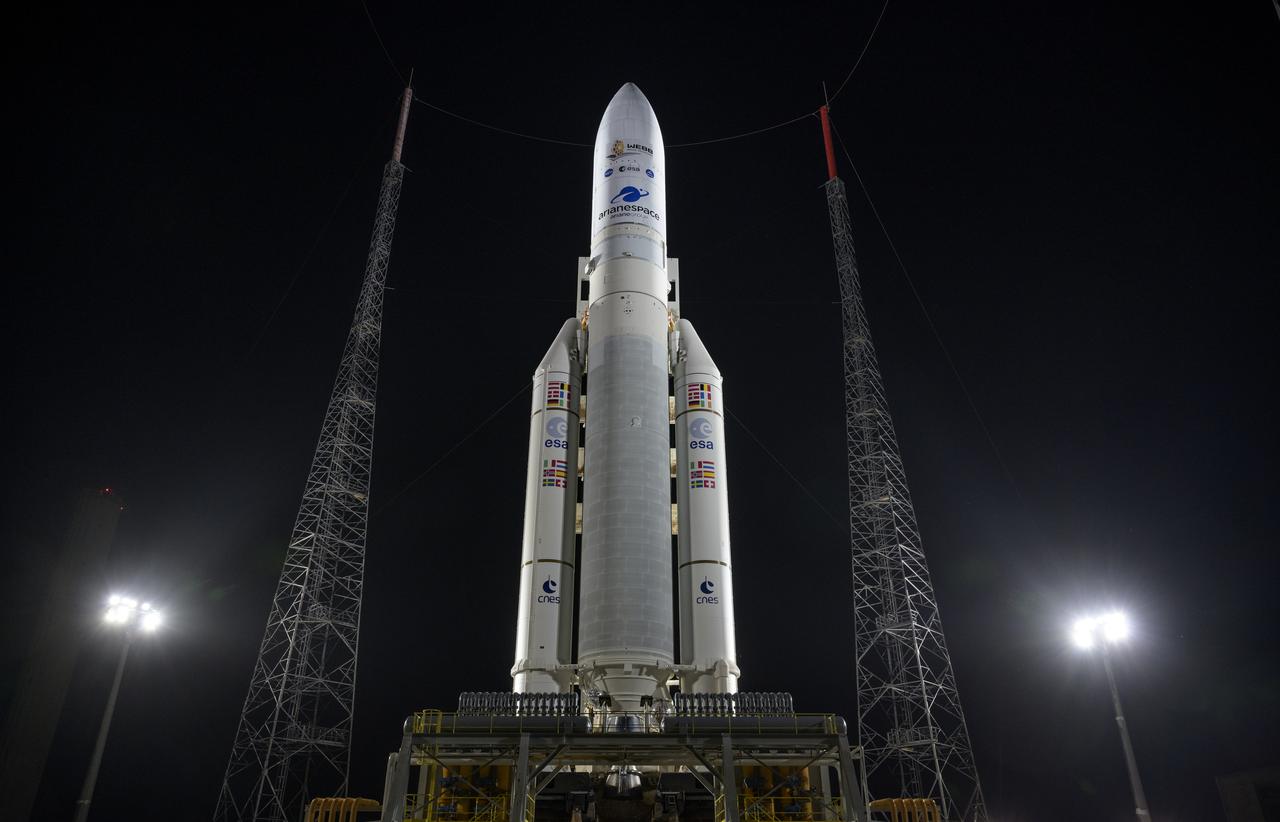

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen at the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
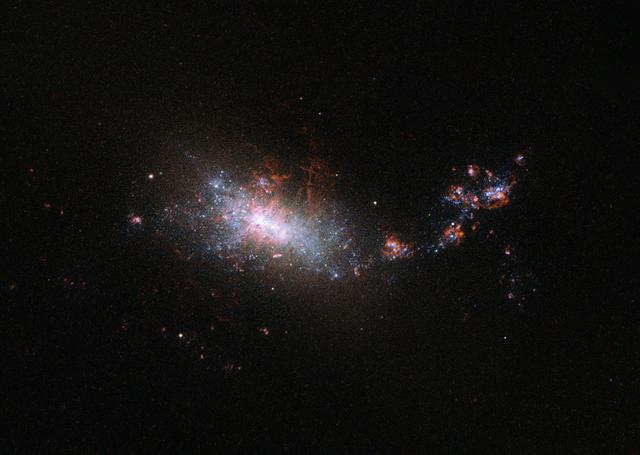

This dramatic image shows the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope’s view of dwarf galaxy known as NGC 1140, which lies 60 million light-years away in the constellation of Eridanus. As can be seen in this image NGC 1140 has an irregular form, much like the Large Magellanic Cloud — a small galaxy that orbits the Milky Way. This small galaxy is undergoing what is known as a starburst. Despite being almost ten times smaller than the Milky Way it is creating stars at about the same rate, with the equivalent of one star the size of the Sun being created per year. This is clearly visible in the image, which shows the galaxy illuminated by bright, blue-white, young stars. Galaxies like NGC 1140 — small, starbursting and containing large amounts of primordial gas with way fewer elements heavier than hydrogen and helium than present in our Sun — are of particular interest to astronomers. Their composition makes them similar to the intensely star-forming galaxies in the early Universe. And these early Universe galaxies were the building blocks of present-day large galaxies like our galaxy, the Milky Way. But, as they are so far away these early Universe galaxies are harder to study so these closer starbursting galaxies are a good substitute for learning more about galaxy evolution . The vigorous star formation will have a very destructive effect on this small dwarf galaxy in its future. When the larger stars in the galaxy die, and explode as supernovae, gas is blown into space and may easily escape the gravitational pull of the galaxy. The ejection of gas from the galaxy means it is throwing out its potential for future stars as this gas is one of the building blocks of star formation. NGC 1140’s starburst cannot last for long.
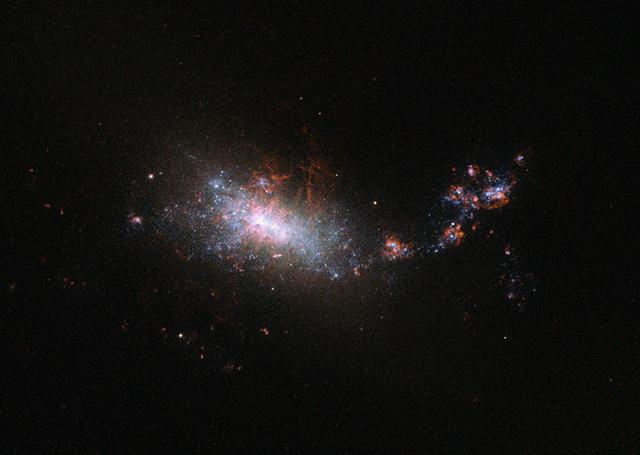

This dramatic image shows the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope’s view of dwarf galaxy known as NGC 1140, which lies 60 million light-years away in the constellation of Eridanus. As can be seen in this image NGC 1140 has an irregular form, much like the Large Magellanic Cloud — a small galaxy that orbits the Milky Way. This small galaxy is undergoing what is known as a starburst. Despite being almost ten times smaller than the Milky Way it is creating stars at about the same rate, with the equivalent of one star the size of our sun being created per year. This is clearly visible in the image, which shows the galaxy illuminated by bright, blue-white, young stars. Galaxies like NGC 1140 — small, starbursting and containing large amounts of primordial gas with far fewer elements heavier than hydrogen and helium than are present in our sun — are of particular interest to astronomers. Their composition makes them similar to the intensely star-forming galaxies in the early Universe. And these early Universe galaxies were the building blocks of present-day large galaxies like our galaxy, the Milky Way. But, as they are so far away these early Universe galaxies are harder to study so these closer starbursting galaxies are a good substitute for learning more about galaxy evolution. The vigorous star formation will have a very destructive effect on this small dwarf galaxy in its future. When the larger stars in the galaxy die, and explode as supernovae, gas is blown into space and may easily escape the gravitational pull of the galaxy. The ejection of gas from the galaxy means it is throwing out its potential for future stars as this gas is one of the building blocks of star formation. NGC 1140’s starburst cannot last for long. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA
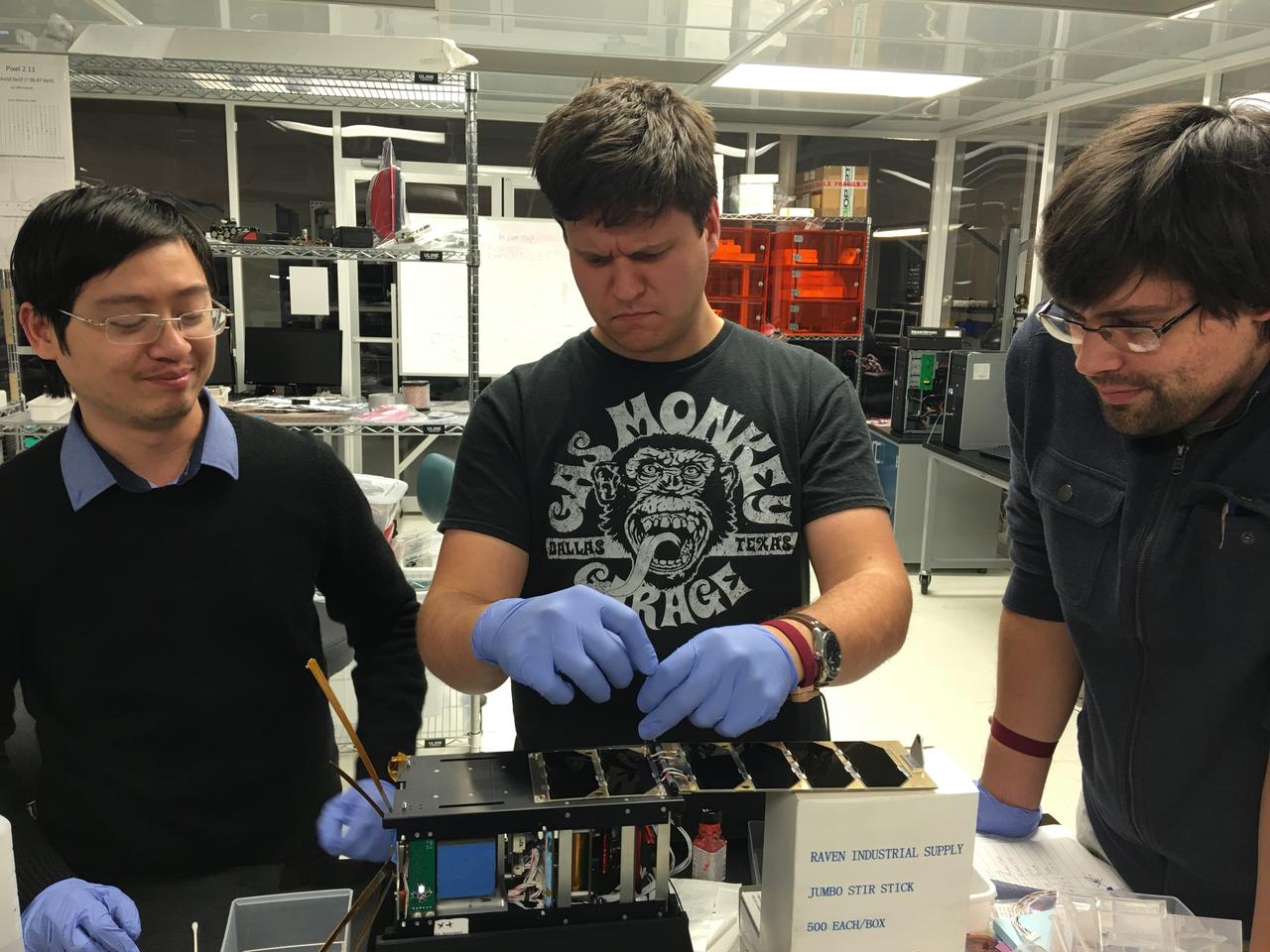
CXBN-2 Integration Team in the Morehead State University Spacecraft Integration and Assembly Facility. Left to right: Kein Dant, Yevgeniy Byleborodov, and Nate Richard. The Cosmic X-Ray Background NanoSat-2 (CXBN-2) CubeSat Mission developed by Morehead State University and its partners the Keldysh Institute (Moscow, Russia), the Maysville Community and Technical College (Morehead, KY) and KYSpace LLC (Lexington, KY) will increase the precision of measurements of the Cosmic X-Ray Background in the 30-50 keV range to a precision of <5%, thereby constraining models that attempt to explain the relative contribution of proposed sources lending insight into the underlying physics of the early universe. The mission addresses a fundamental science question that is central to our understanding of the structure, origin, and evolution of the universe by potentially lending insight into both the high-energy background radiation and into the evolution of primordial galaxies. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative NET April 18, 2017 ELaNa XVII mission on the seventh Orbital-ATK Cygnus Commercial Resupply Services (OA-7) to the International Space Station and deployed on tbd.

STS125-S-001 (December 2007) --- This STS-125 crew patch shows HST along with a representation of its many scientific discoveries. The overall structure and composition of the Universe is shown in blue and filled with planets, stars, and galaxies. The black background is indicative of the mysteries of dark-energy and dark-matter. The new instruments to be installed on HST during this mission, Wide Field Camera-3 and the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, will make observations to help understand these unseen components which seem to dominate the structure of the Universe. The red border of the patch represents the red-shifted glow of the early Universe, and the limit of the Hubble's view into the cosmos. Upon completion of STS-125, the fifth mission to service HST, the Hubble will provide even deeper and more detailed views of the Universe. Soaring by the telescope is the space shuttle which initially deployed Hubble and has enabled astronauts to continually upgrade the telescope, significantly contributing to the expansion of human knowledge. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, Houston, Texas --- STS125-S-001 (December 2007) -- This STS-125 crew patch shows HST along with a representation of its many scientific discoveries. The overall structure and composition of the Universe is shown in blue and filled with planets, stars, and galaxies. The black background is indicative of the mysteries of dark-energy and dark-matter. The new instruments to be installed on HST during this mission, Wide Field Camera-3 and the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, will make observations to help understand these unseen components which seem to dominate the structure of the Universe. The red border of the patch represents the red-shifted glow of the early Universe, and the limit of the Hubble's view into the cosmos. Upon completion of STS-125, the fifth mission to service HST, the Hubble will provide even deeper and more detailed views of the Universe. Soaring by the telescope is the space shuttle which initially deployed Hubble and has enabled astronauts to continually upgrade the telescope, significantly contributing to the expansion of human knowledge. The NASA insignia design for shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, it will be publicly announced.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Vertical Integration Facility on Launch Complex 41, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Hal Weaver, New Horizons project scientist with the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, signs the fairing enclosing the New Horizons spacecraft. The fairing protects the spacecraft during launch and flight through the atmosphere. Once out of the atmosphere, the fairing is jettisoned. The compact 1,060-pound New Horizons probe carries seven scientific instruments that will characterize the global geology and geomorphology of Pluto and its moon Charon, map their surface compositions and temperatures, and examine Pluto's complex atmosphere. New Horizons is the first mission in NASA's New Frontiers program of medium-class planetary missions. The spacecraft, designed for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md., will fly by Pluto and Charon as early as summer 2015.
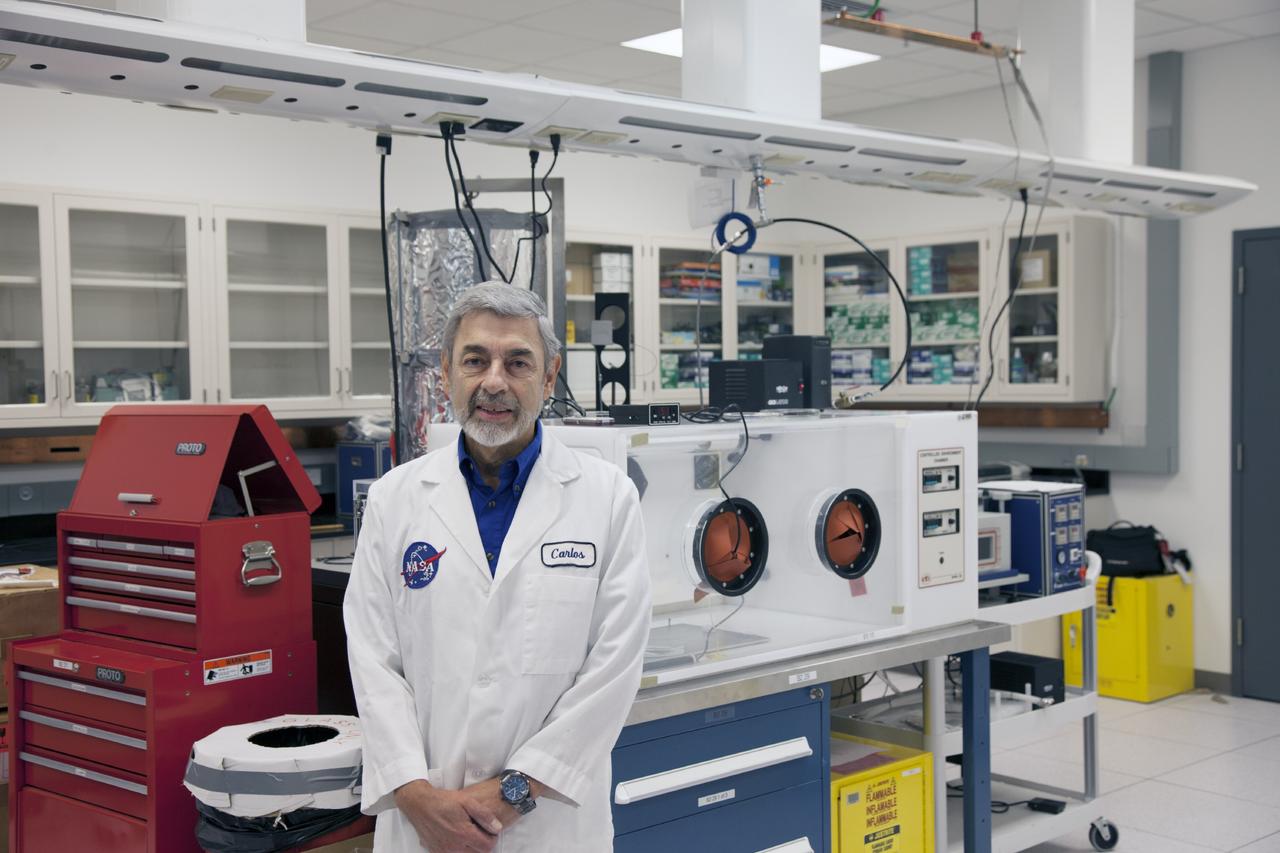

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dr. Carlos Calle, senior research scientist on the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project, manages the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Electrodynamic dust shield, or EDS, technology is based on concepts originally developed by NASA as early as 1967 and later by the University of Tokyo. In 2003, NASA, in collaboration with the University of Arkansas at Little Rock, started development of the EDS for dust particle removal from solar panels to be used on future missions to the moon, an asteroid or Mars. A flight experiment to expose the dust shields to the space environment currently is under development. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/content/scientists-developing-ways-to-mitigate-dust-problem-for-explorers/ Photo credit: NASA/Dan Casper
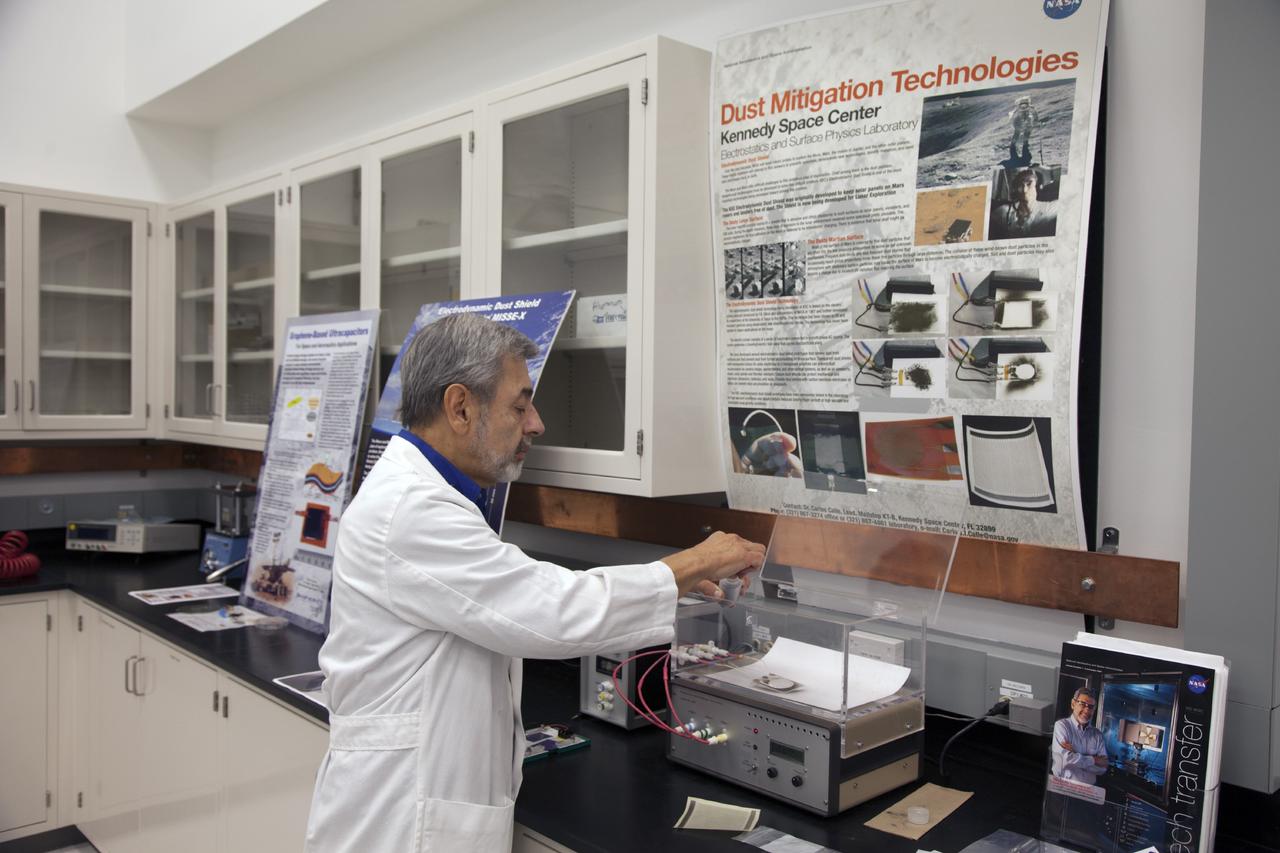

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dr. Carlos Calle, senior research scientist on the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project, demonstrates equipment used in his experiments in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Electrodynamic dust shield, or EDS, technology is based on concepts originally developed by NASA as early as 1967 and later by the University of Tokyo. In 2003, NASA, in collaboration with the University of Arkansas at Little Rock, started development of the EDS for dust particle removal from solar panels to be used on future missions to the moon, an asteroid or Mars. A flight experiment to expose the dust shields to the space environment currently is under development. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/content/scientists-developing-ways-to-mitigate-dust-problem-for-explorers/ Photo credit: NASA/Dan Casper
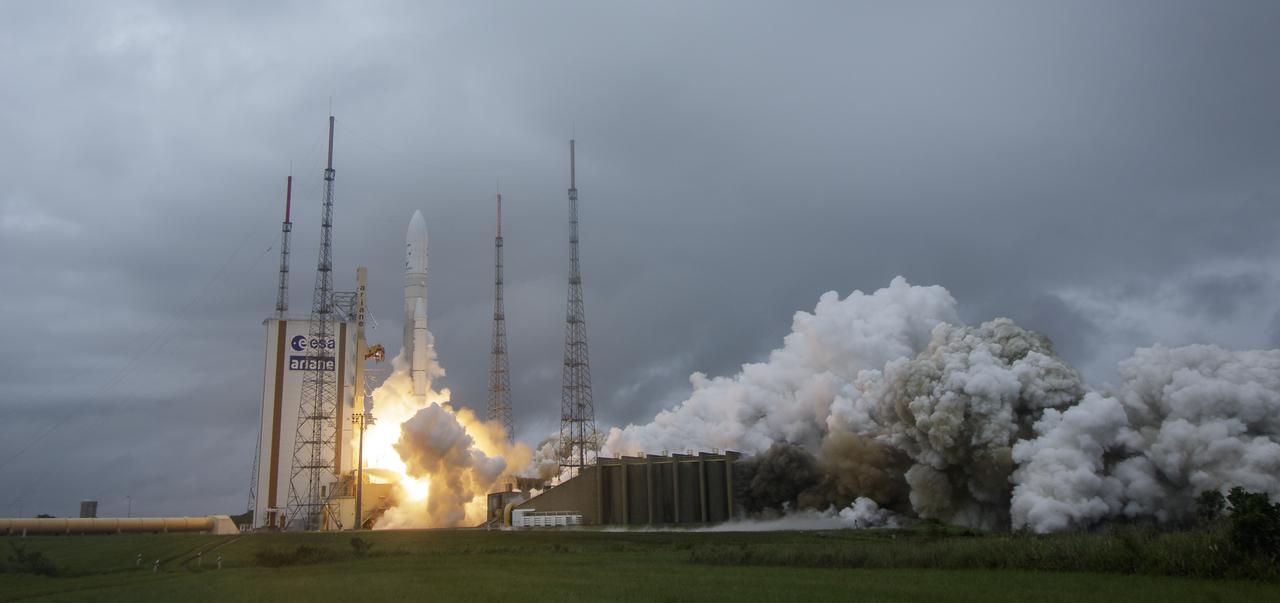

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
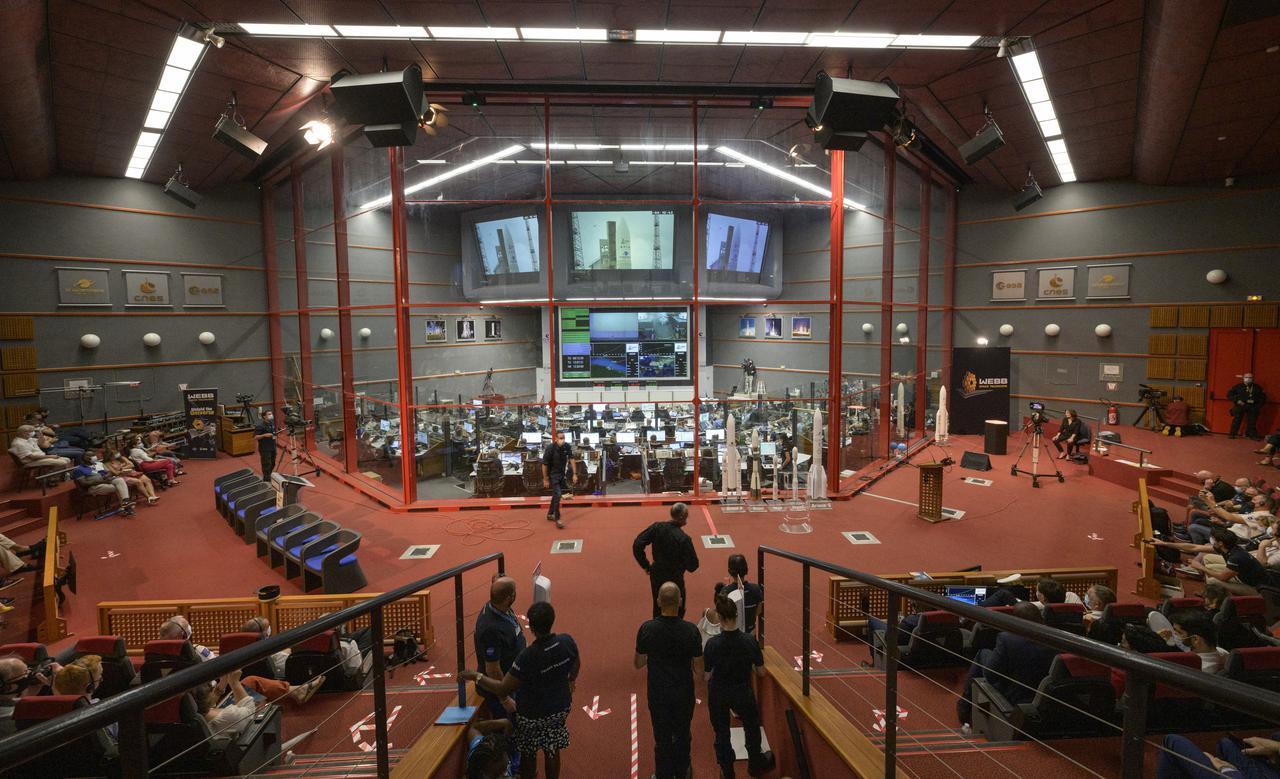

Launch teams monitor the countdown of the launch of Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket carrying NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, in the Jupiter Center at the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
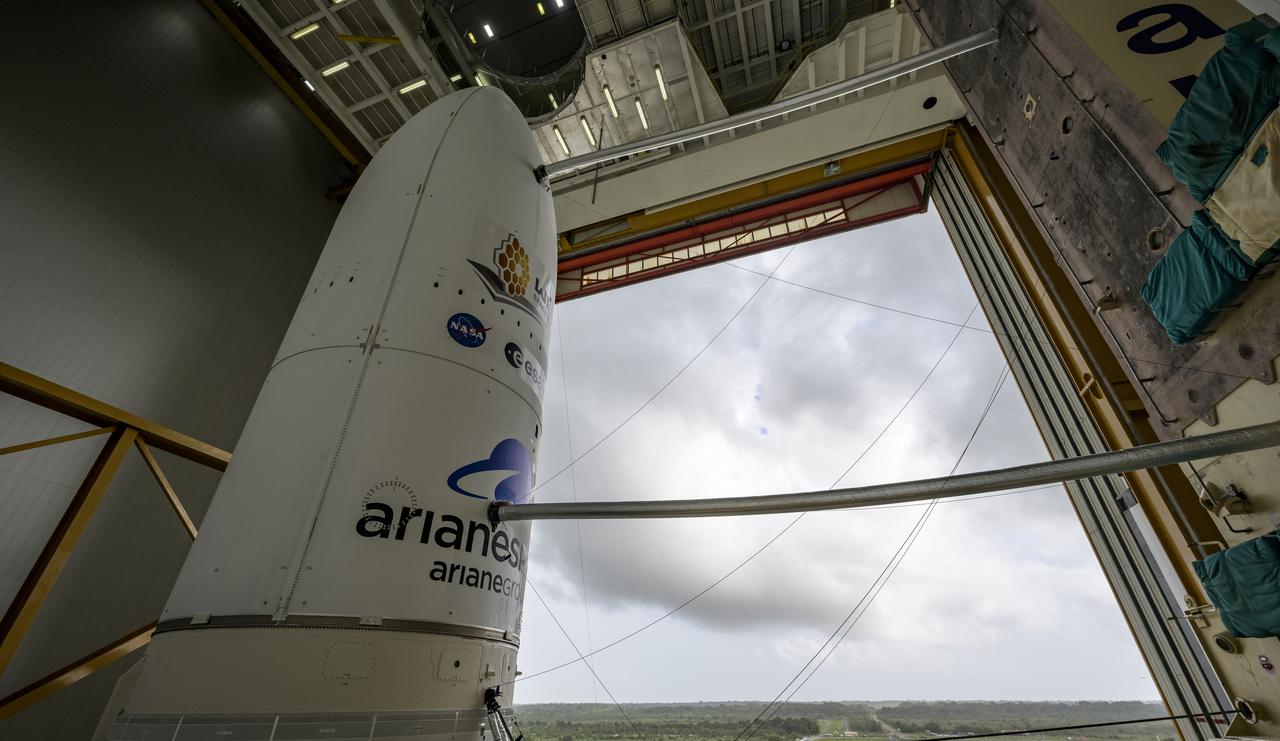

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen ahead of rollout to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
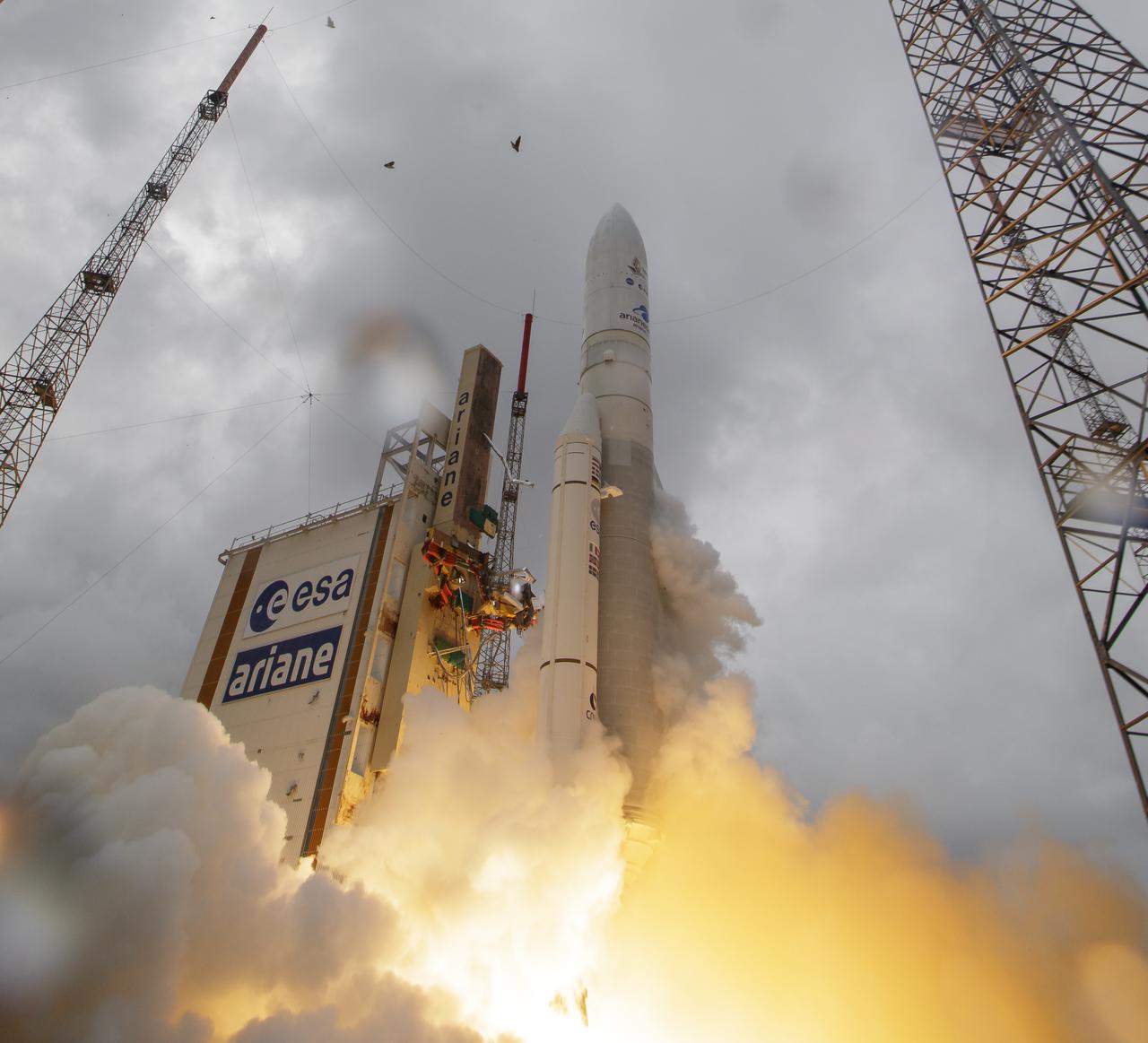

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
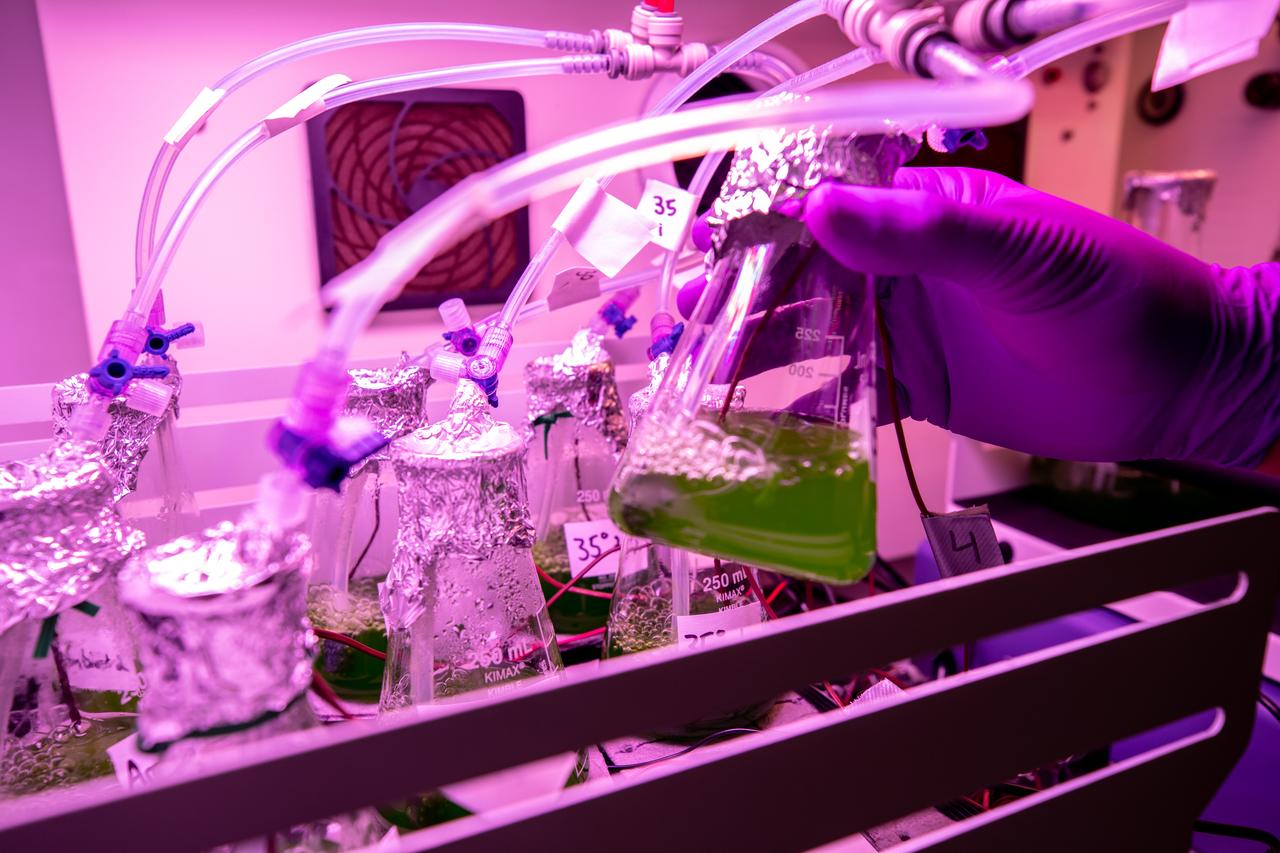

A prototype of Organic Processor Assembly (OPA) – technology capable of treating mixed organic wastes – arrives at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 19, 2020. At the heart of the OPA is an anaerobic membrane bioreactor – a hybrid technology that couples anaerobic digestion with membrane filtration. Developed through a collaboration between Kennedy’s Dr. Luke Roberson and the University of South Florida’s Dr. Daniel Yeh, the OPA was designed for an early planetary base scenario to help close the resource recovery loop, decreasing the agency’s dependence on resupply missions.
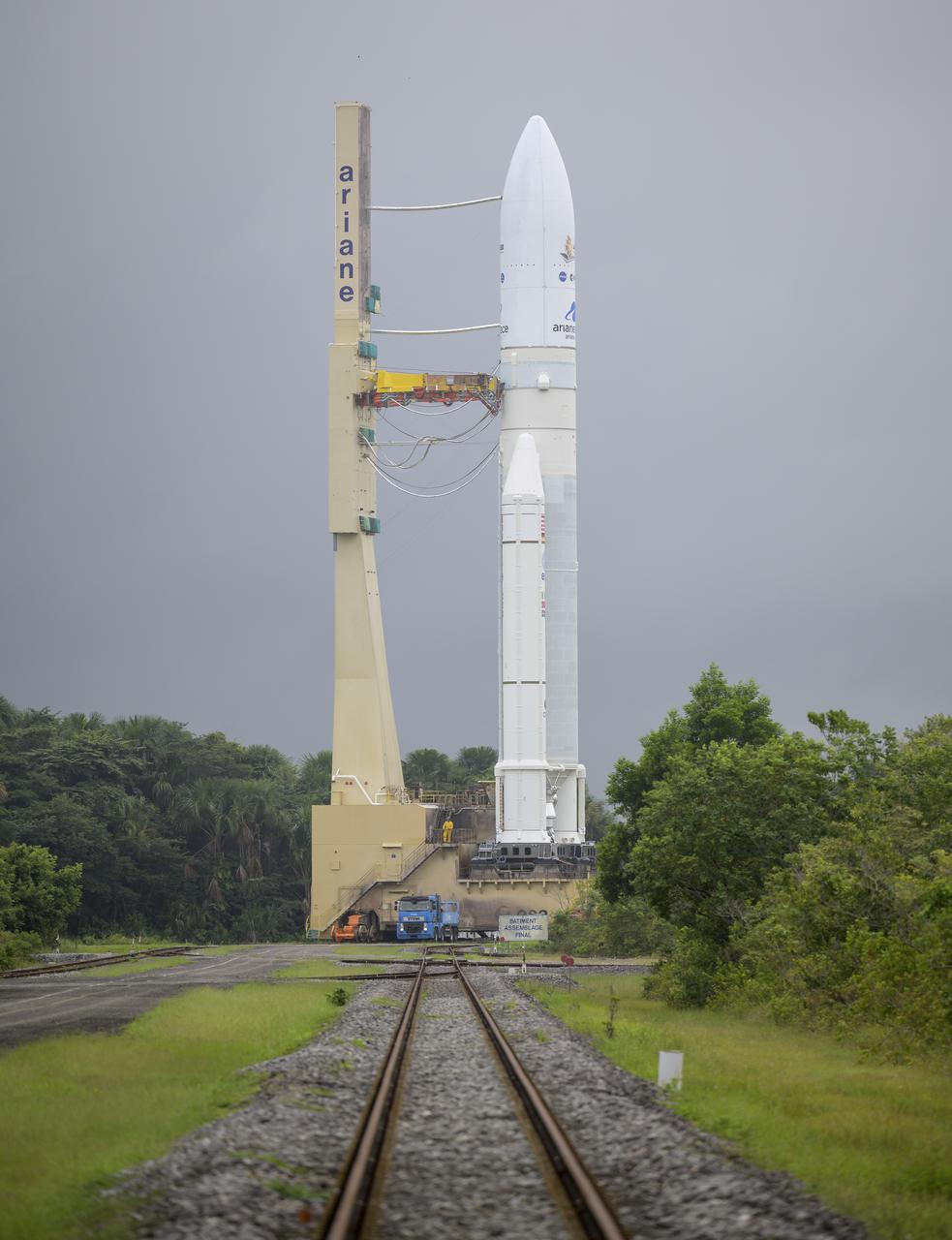

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is rolled out to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
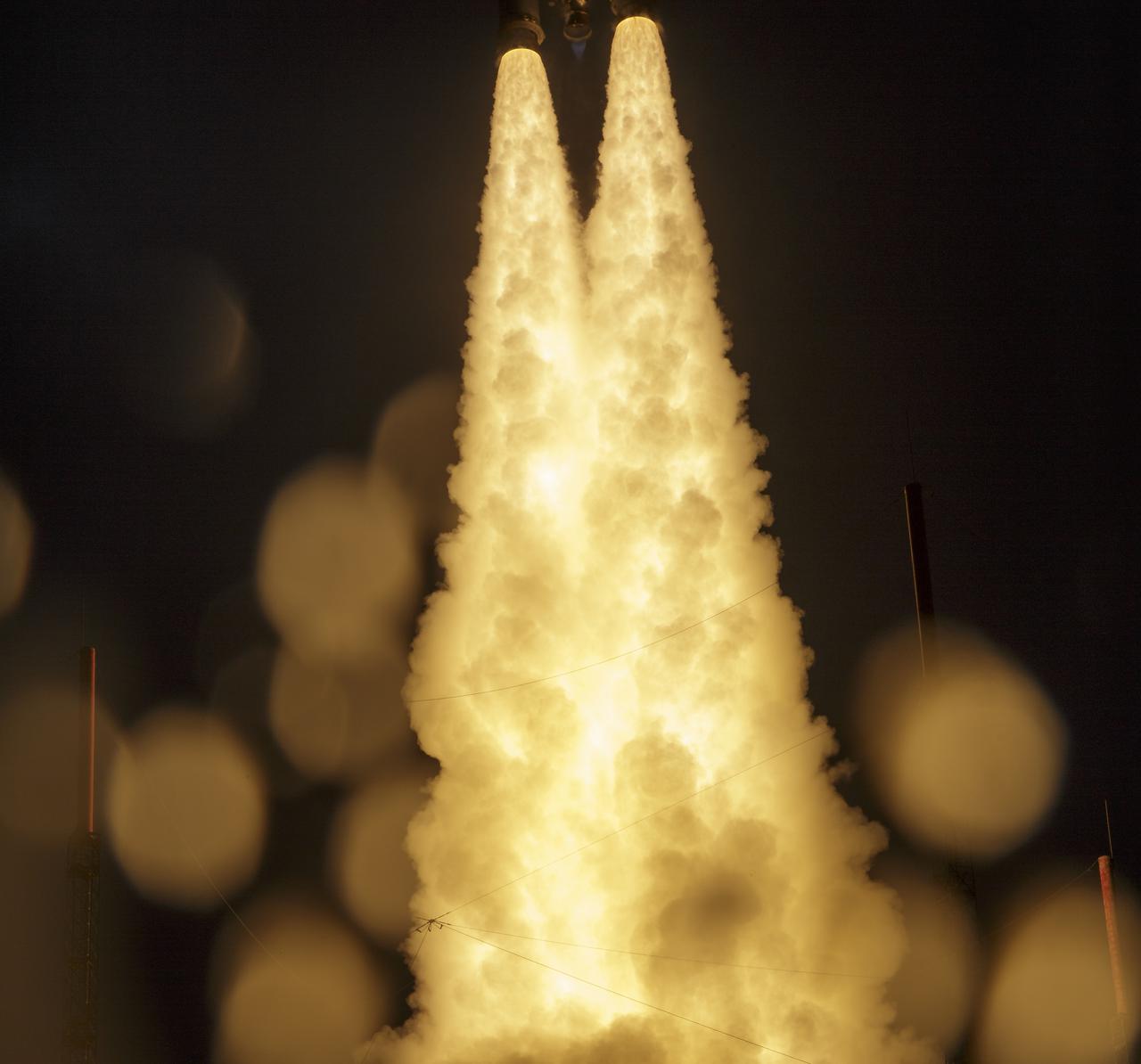

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen ahead of rollout to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen is interviewed by Katy Haswell on NASA television as he and the launch team monitor the countdown of the launch of Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket carrying NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, in the Jupiter Center at the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
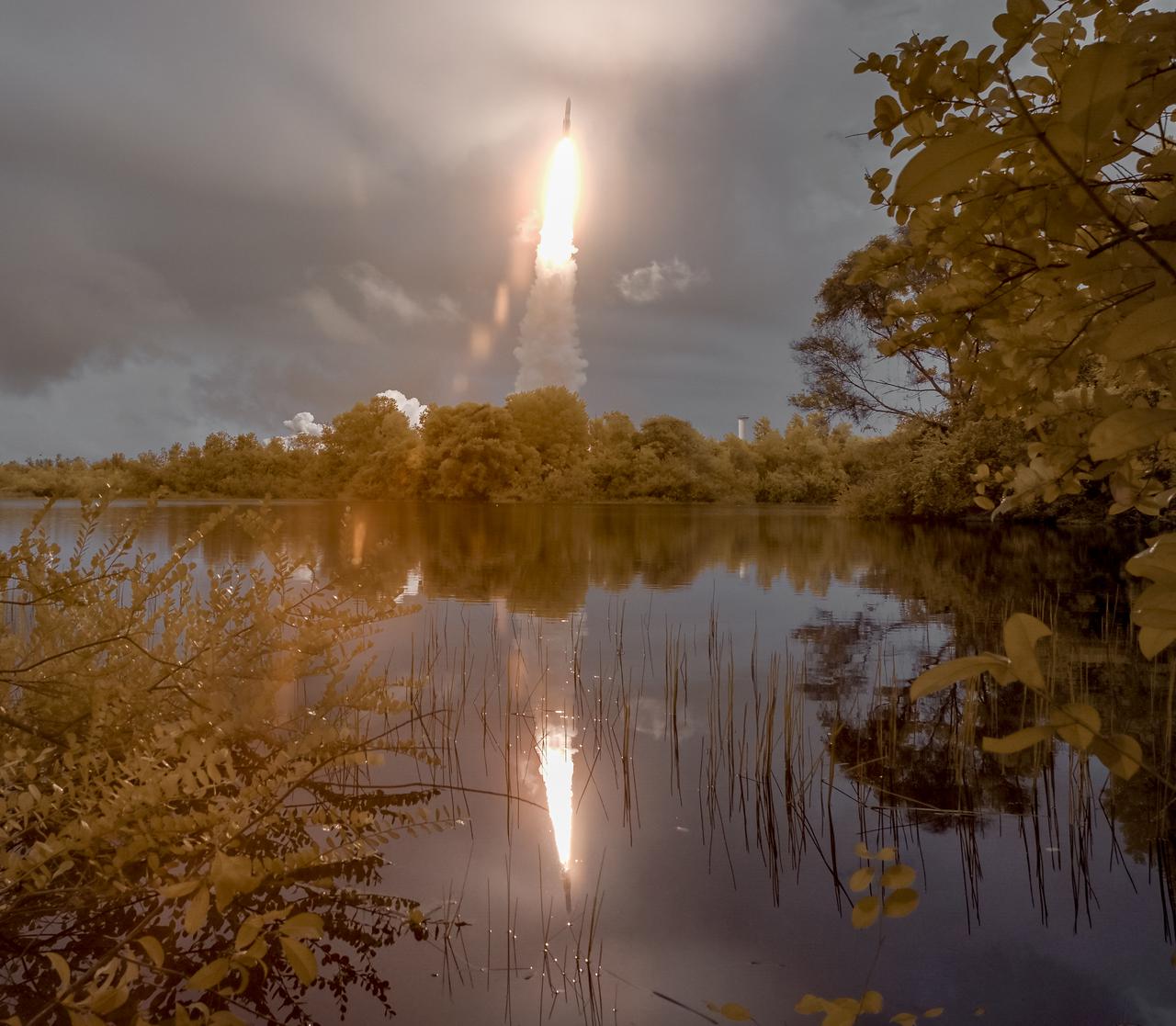

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket is seen in this false color infrared exposure as it launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
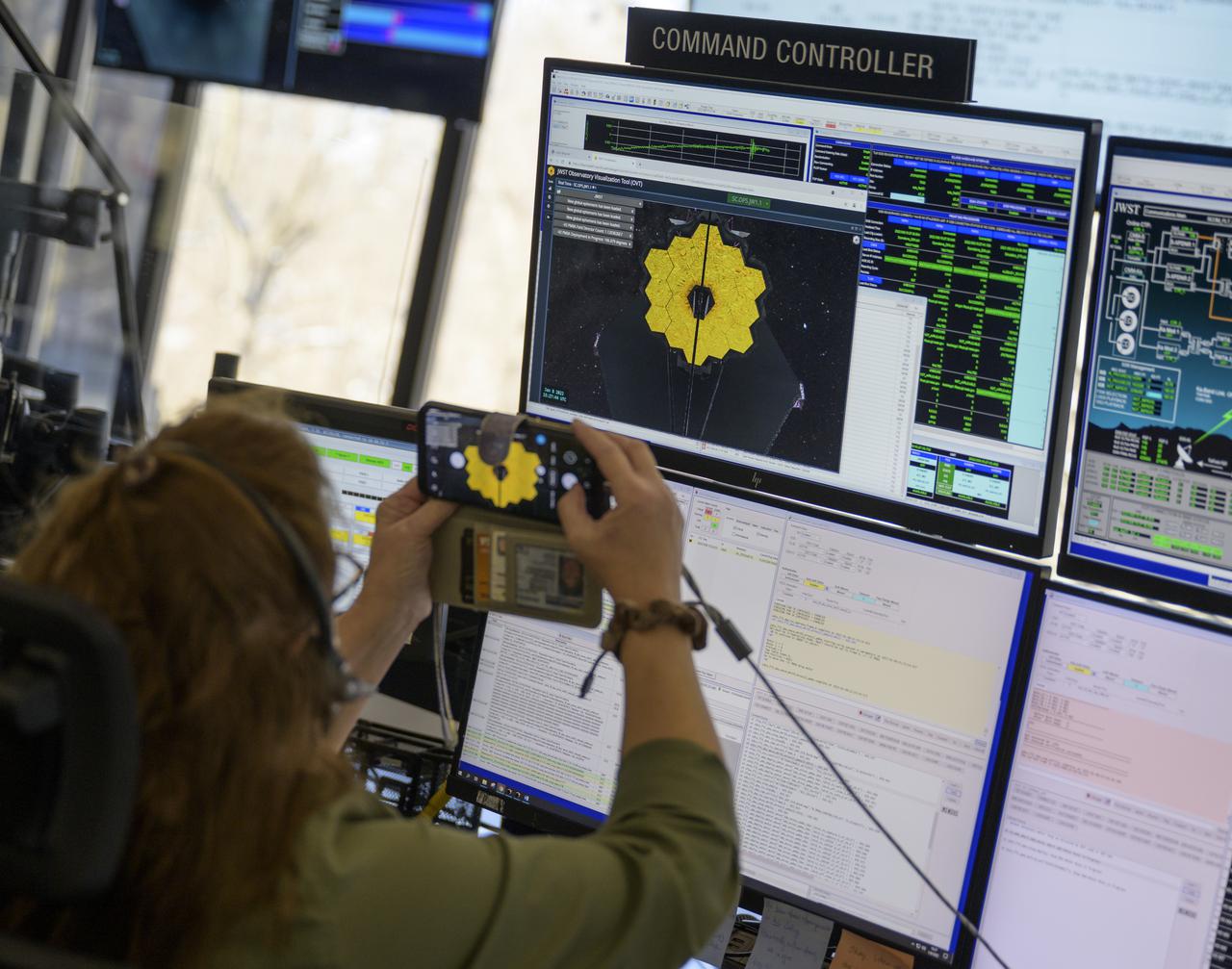

Engineering teams at NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore monitor progress as the observatory’s second primary mirror wing rotates into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
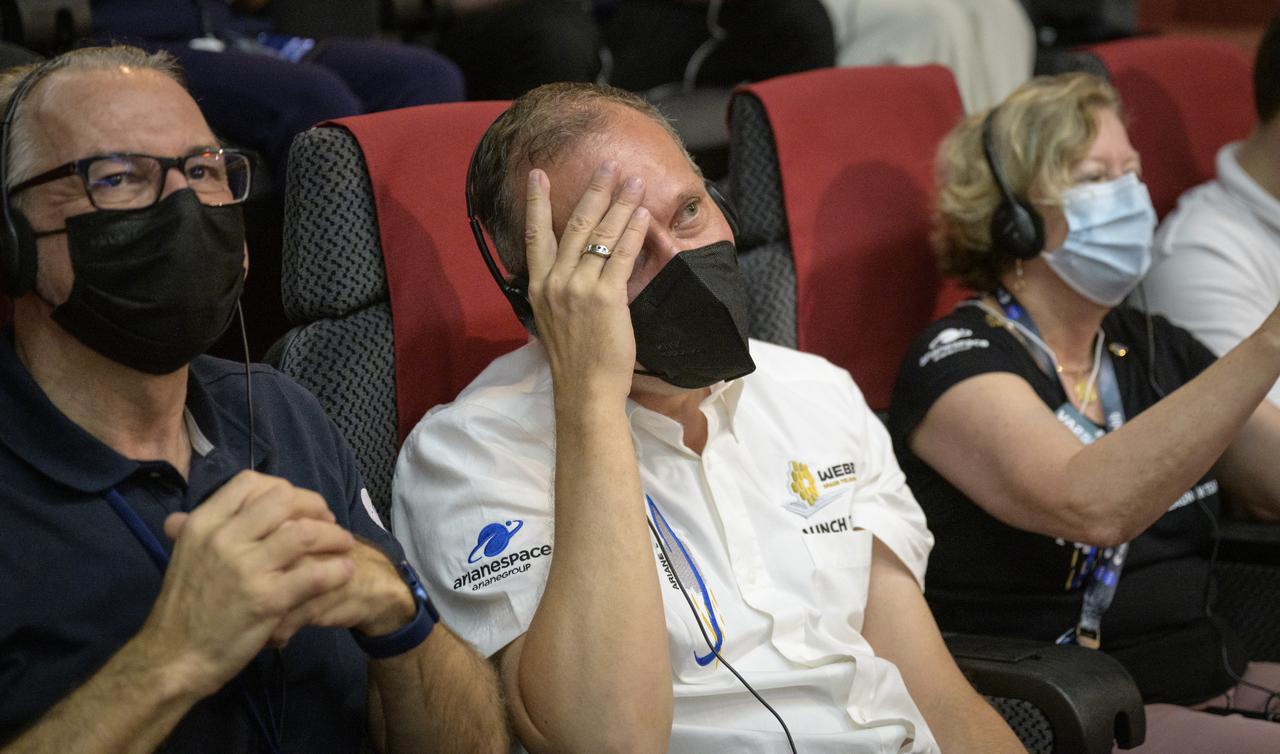

NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen, center, reacts after hearing confirmation that the James Webb Space Telescope successfully separated from the Ariane 5 rocket, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, in the Jupiter Hall of the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
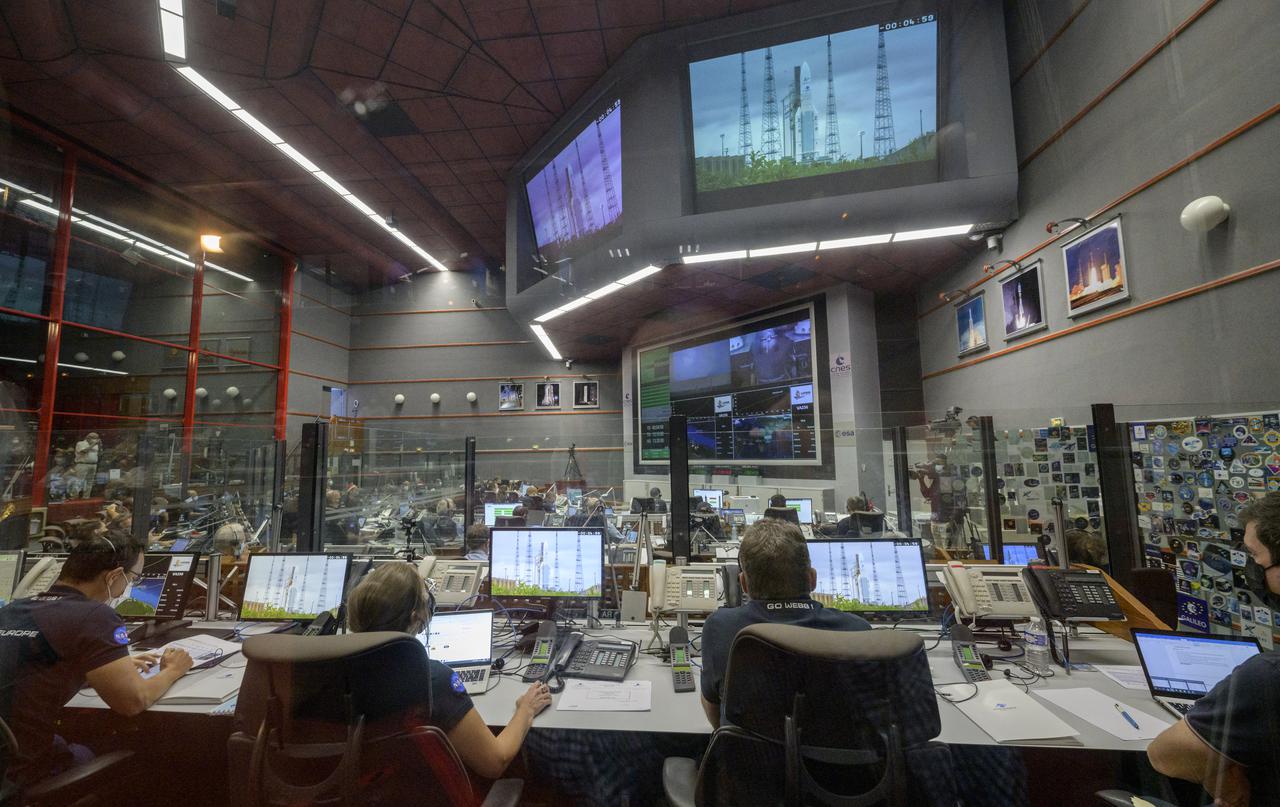

Launch teams monitor the countdown of the launch of Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket carrying NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, in the Jupiter Center at the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
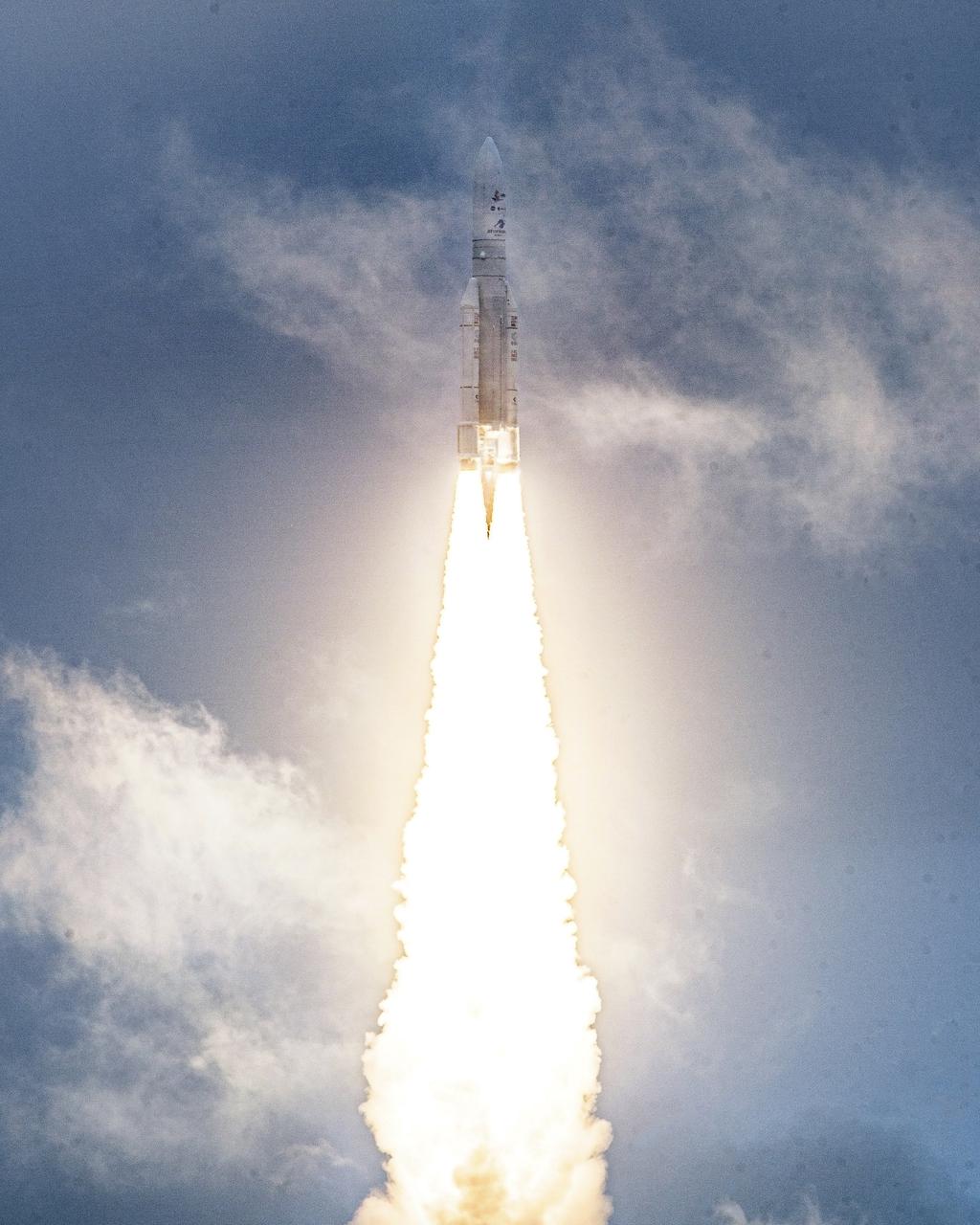

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Chris Gunn)
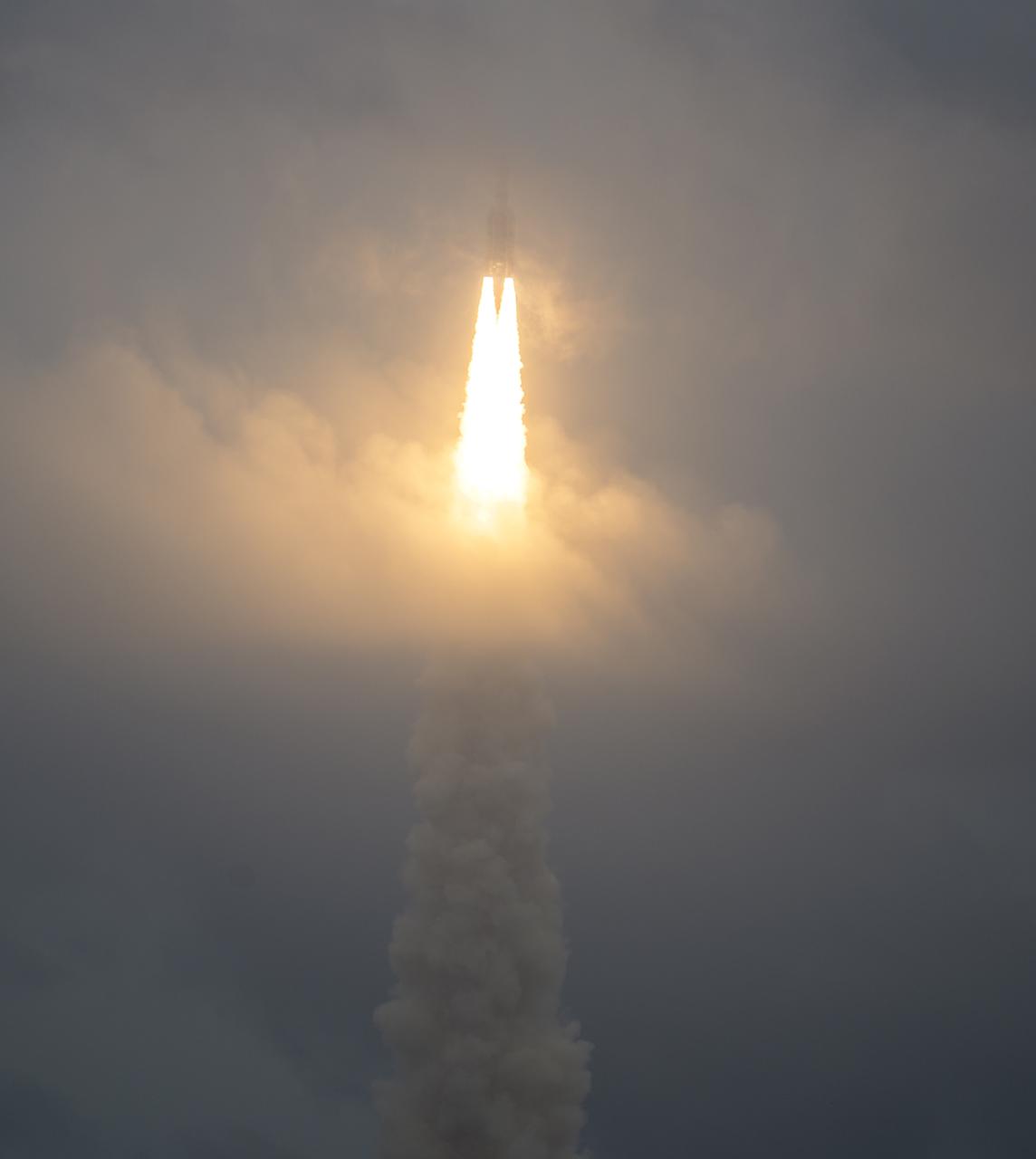

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
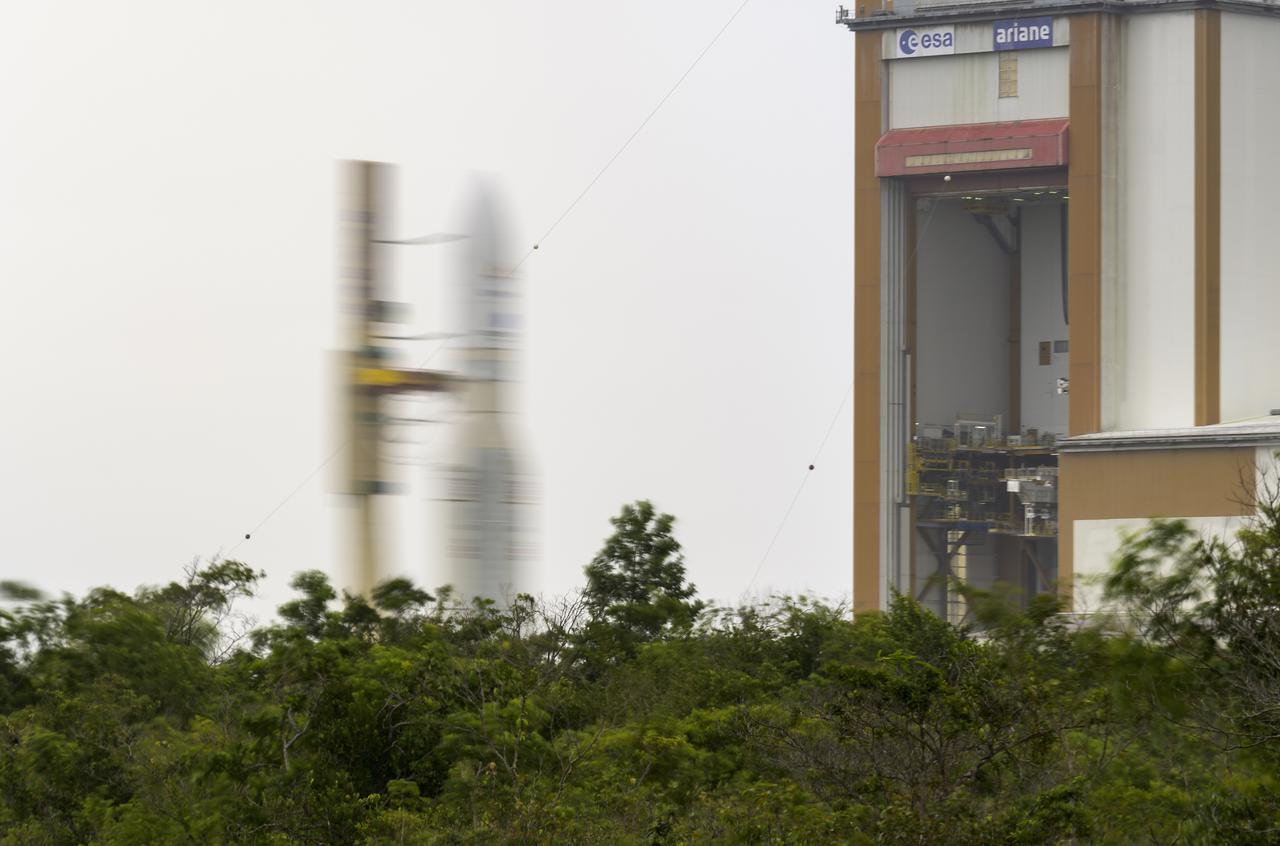

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen in this 30 second exposure, as it is rolled out to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Senior Systems Engineer, Webb, Northrop Grumman, Nanci Shawger answers questions from the media during a briefing following the successful deployment of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope primary mirror, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from the Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. With Webb’s 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror fully deployed, the infrared observatory has completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
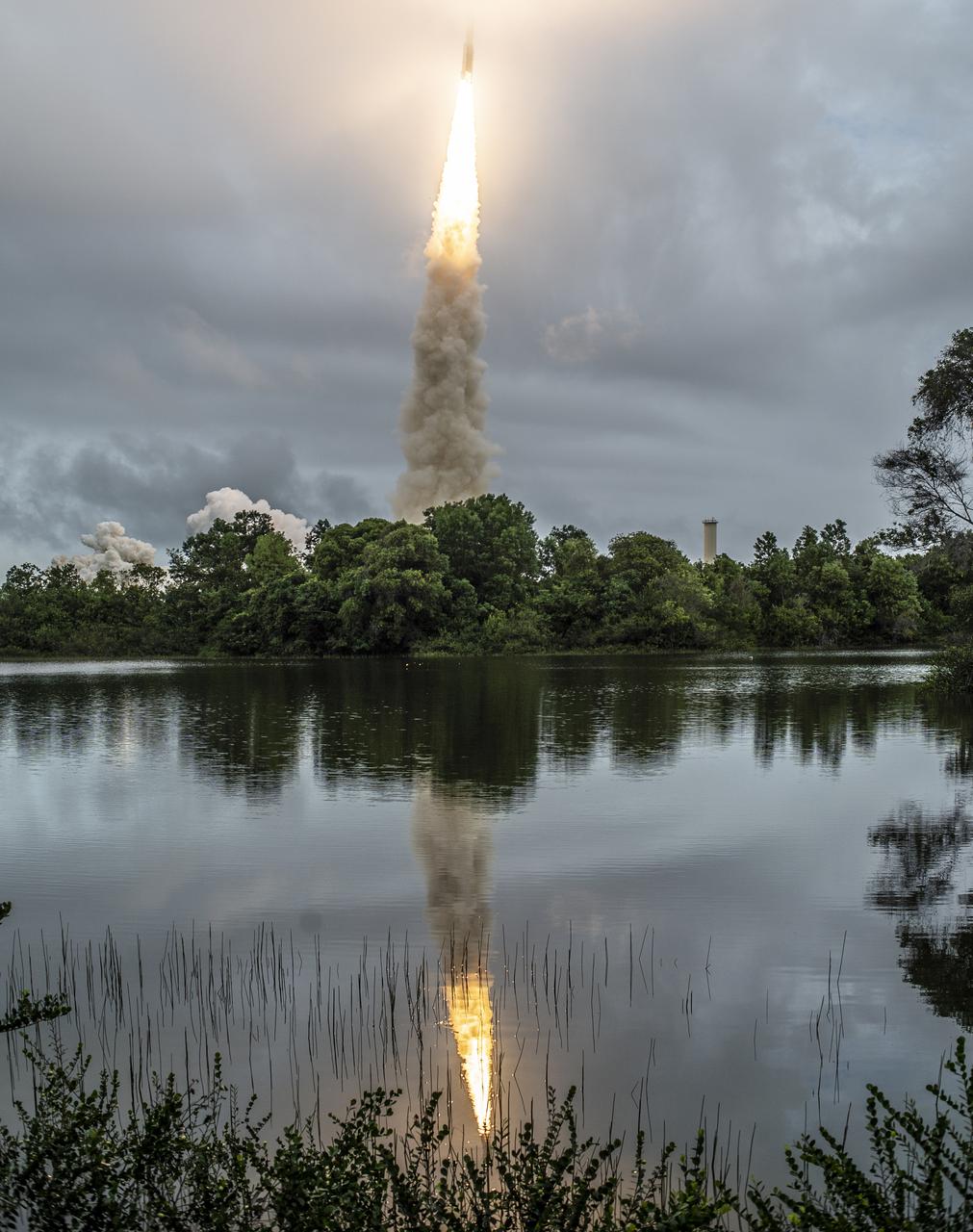

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Chris Gunn)

Engineering teams at NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore monitor progress as the observatory’s second primary mirror wing rotates into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
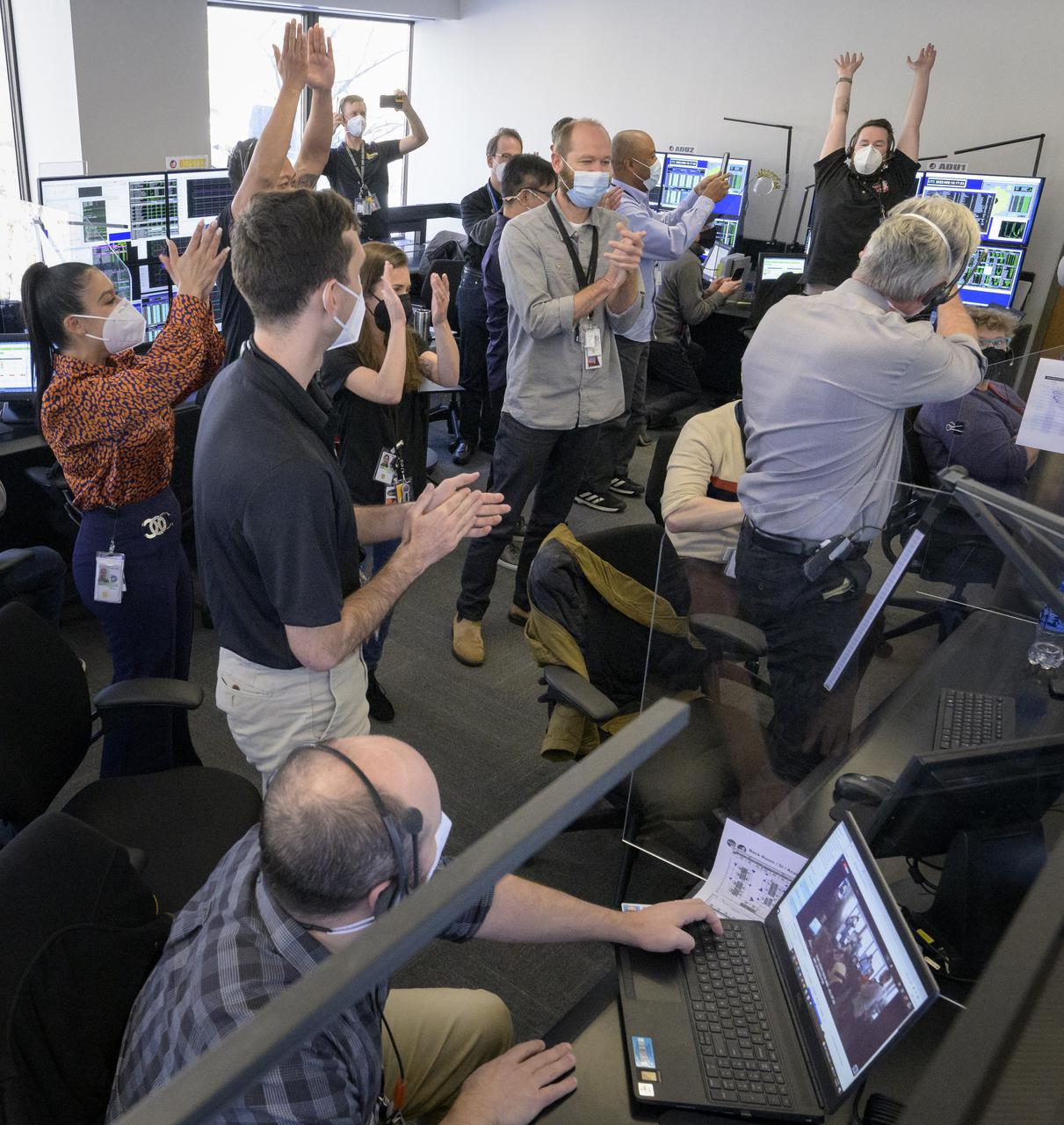

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope mission operations team celebrates, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, after confirming that the observatory’s final primary mirror wing successfully extended and locked into place. With Webb’s 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror fully deployed, the infrared observatory has completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
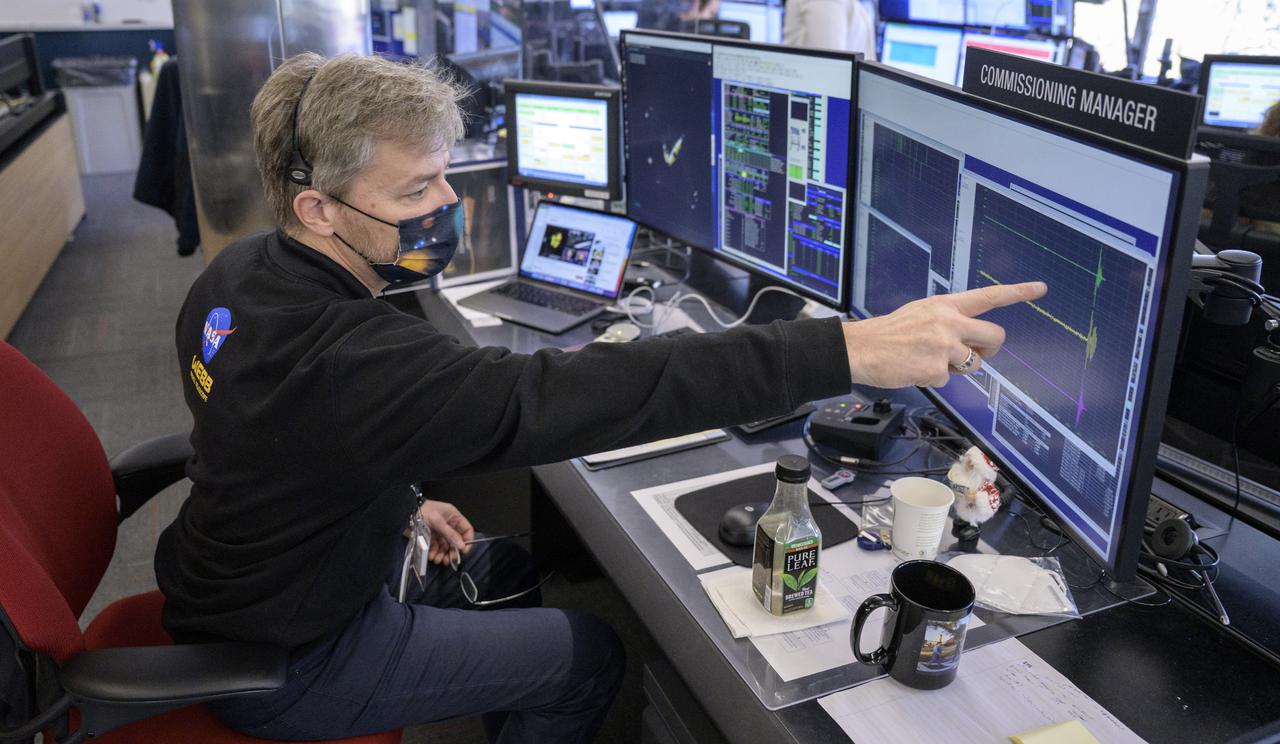

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Commissioning Manager John Durning monitors the progress of the Webb observatory as it’s second primary mirror wing is prepared to rotate into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
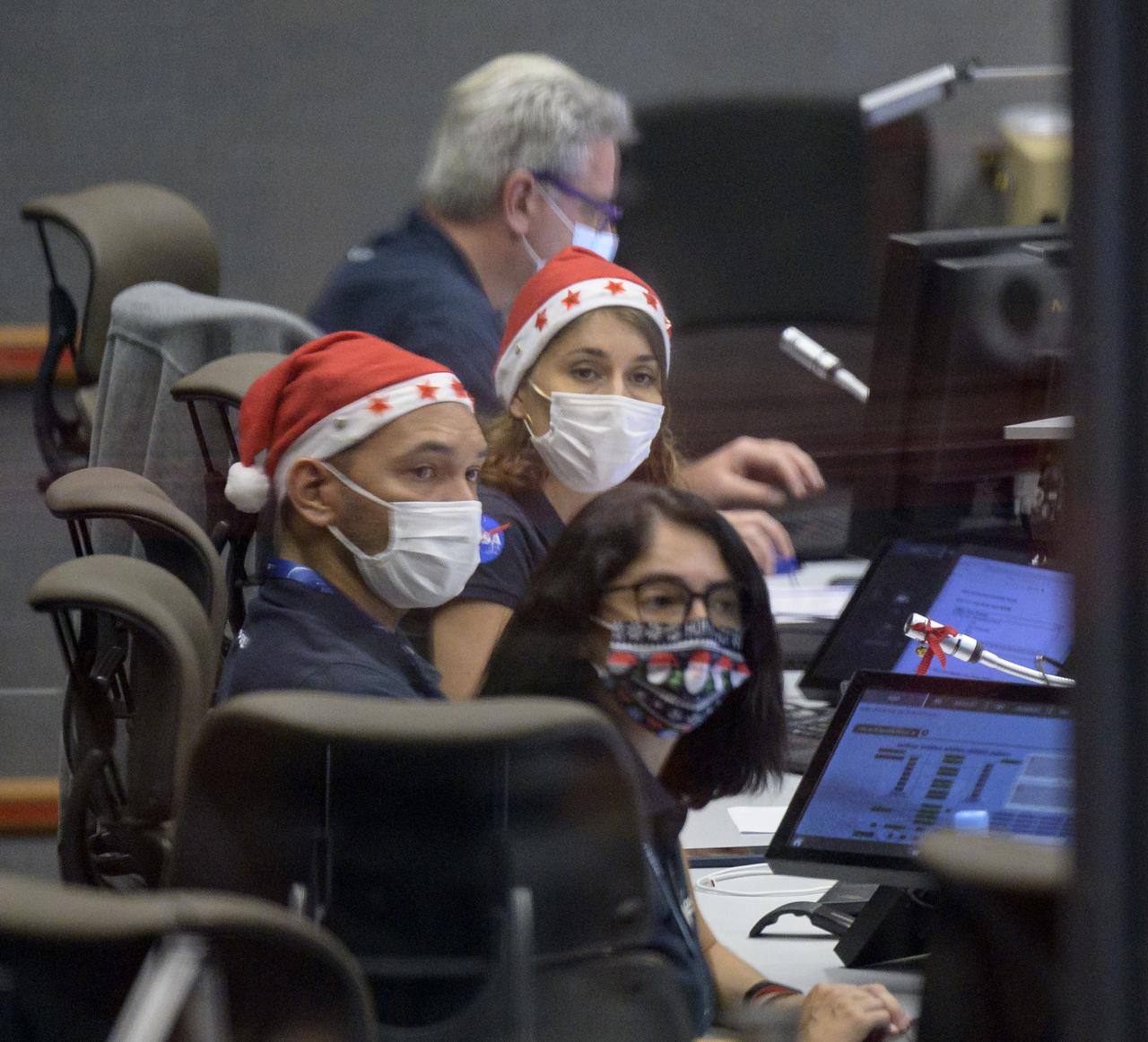

Launch teams monitor the countdown to the launch of Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket carrying NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, in the Jupiter Center at the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is rolled out to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
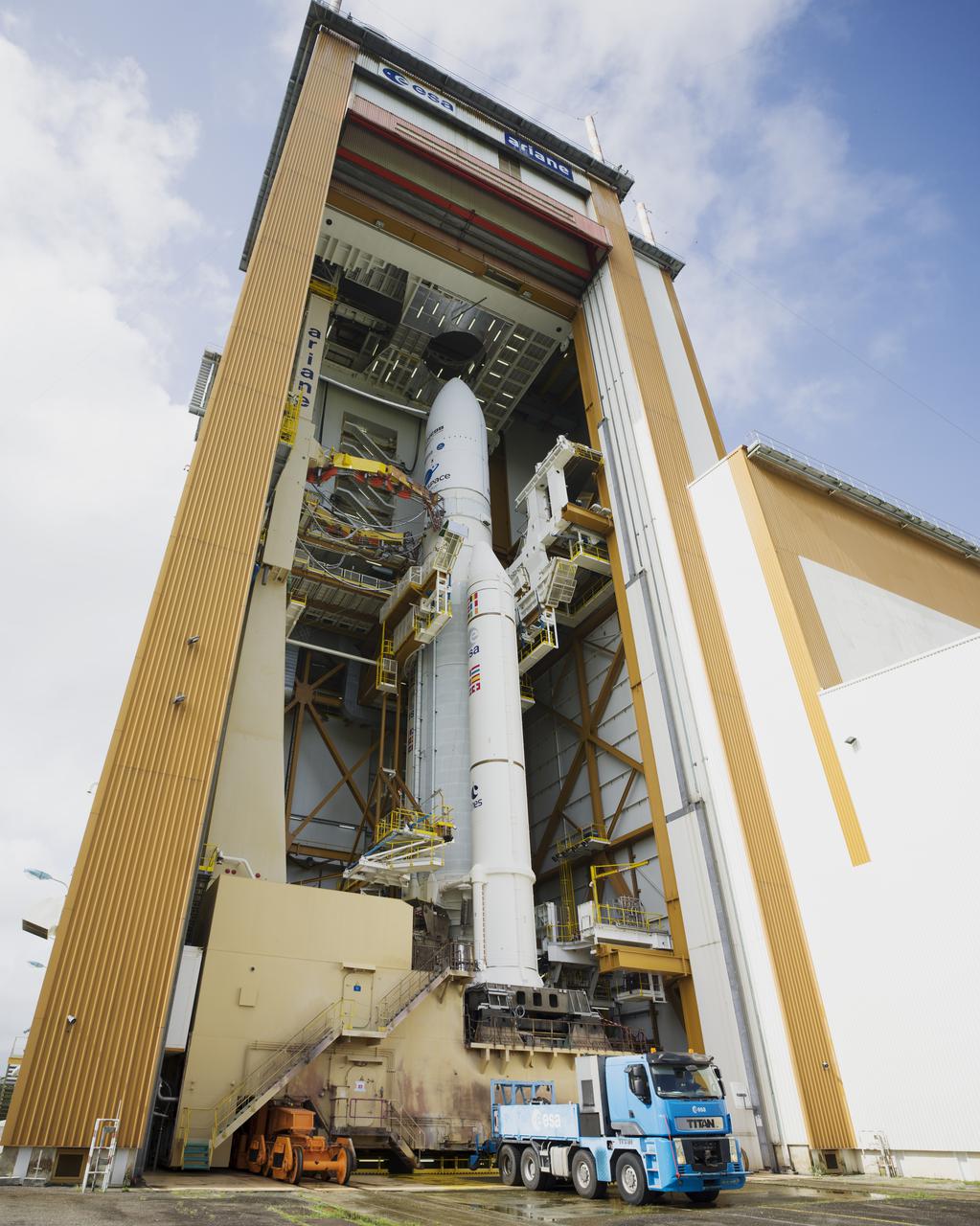

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen in the final assembly building ahead of the planned roll to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Chris Gunn)
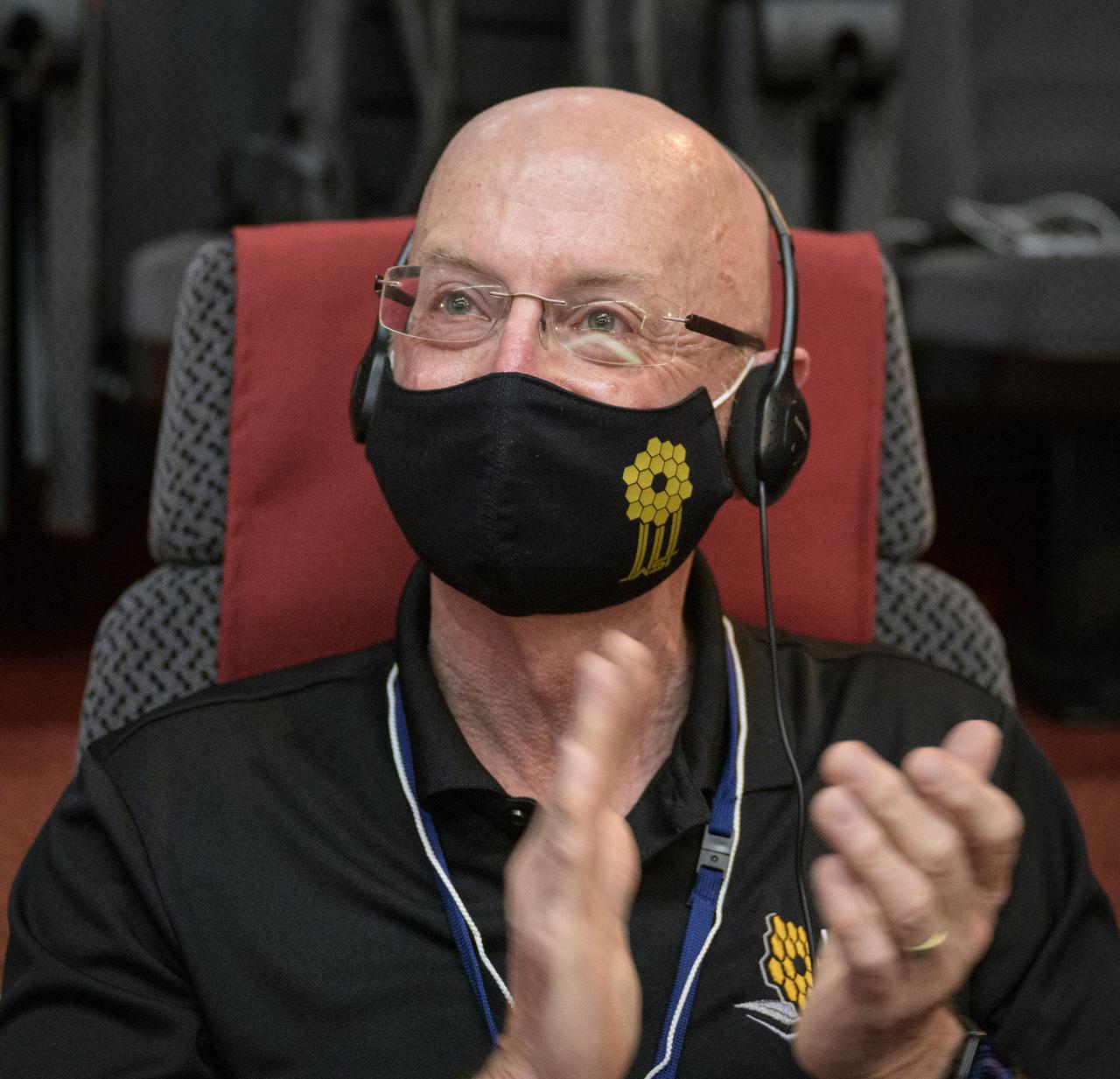

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Program Scientist Eric Smith reacts after hearing confirmation that the James Webb Space Telescope successfully separated from the Ariane 5 rocket, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, in the Jupiter Hall of the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
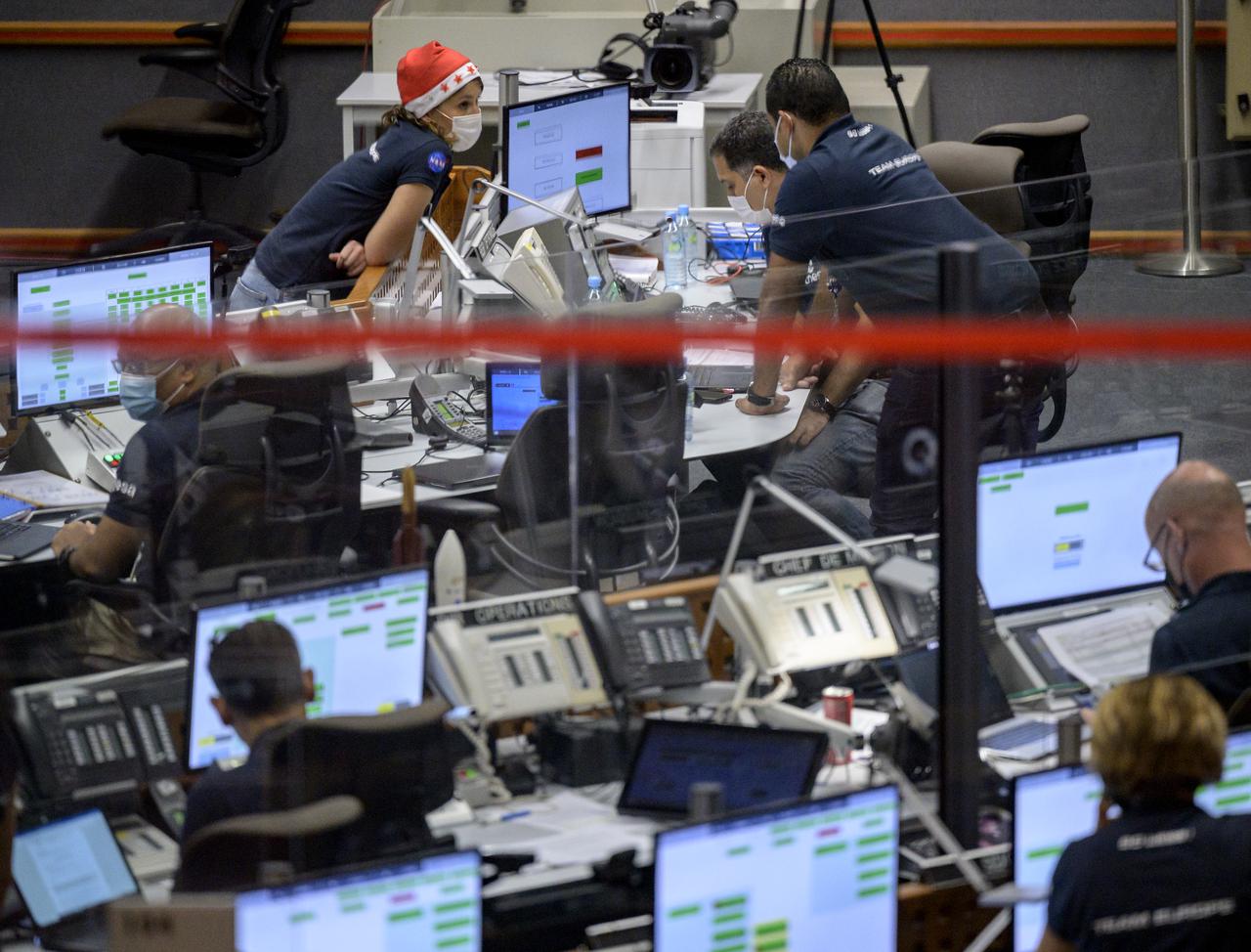

Launch teams monitor the countdown to the launch of Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket carrying NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, in the Jupiter Center at the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
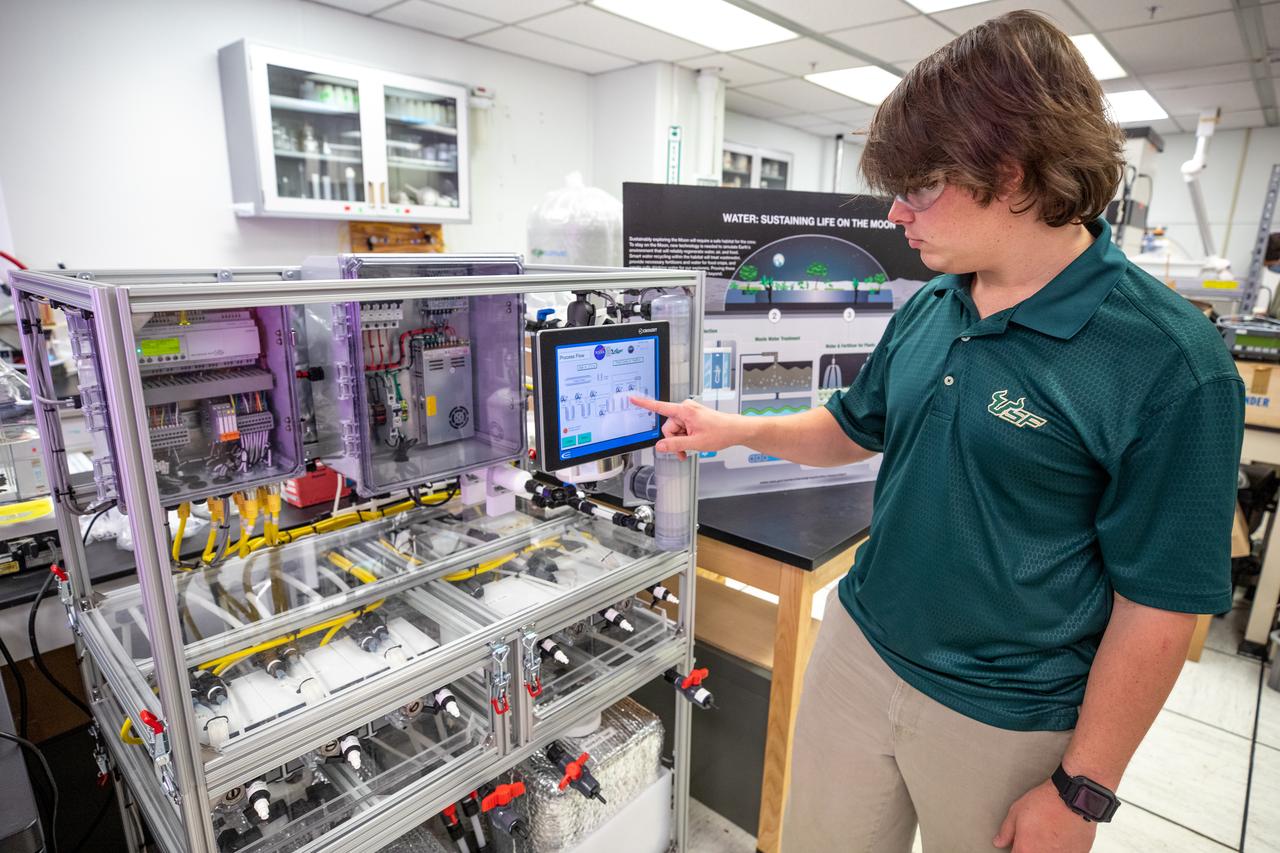

A prototype of Organic Processor Assembly (OPA) – technology capable of treating mixed organic wastes – arrives at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 19, 2020. Developed through a collaboration between Kennedy’s Dr. Luke Roberson and the University of South Florida’s Dr. Daniel Yeh, the OPA was designed for an early planetary base scenario to help close the resource recovery loop, decreasing the agency’s dependence on resupply missions. At the heart of the OPA is an anaerobic membrane bioreactor – a hybrid technology that couples anaerobic digestion with membrane filtration.
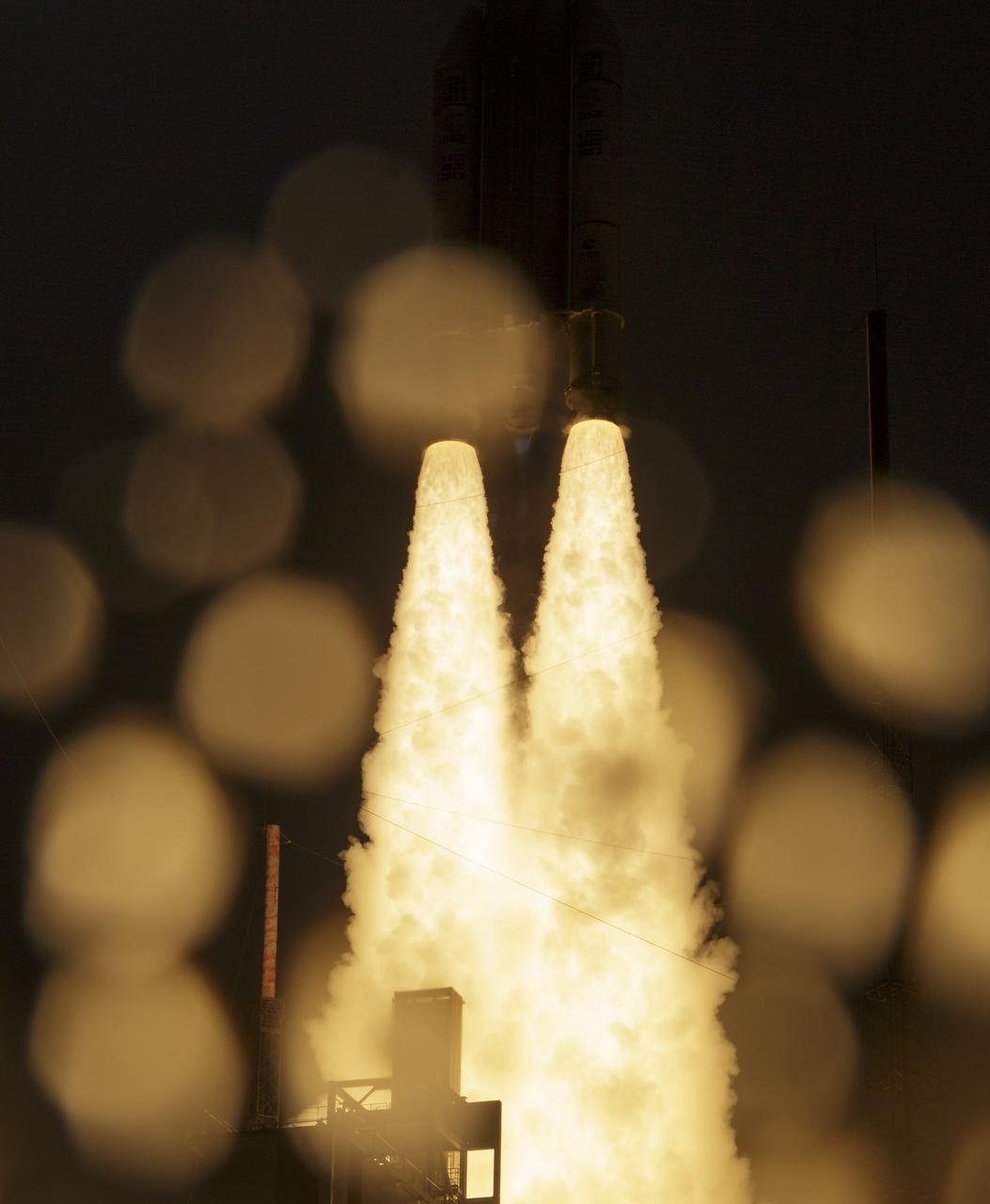

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
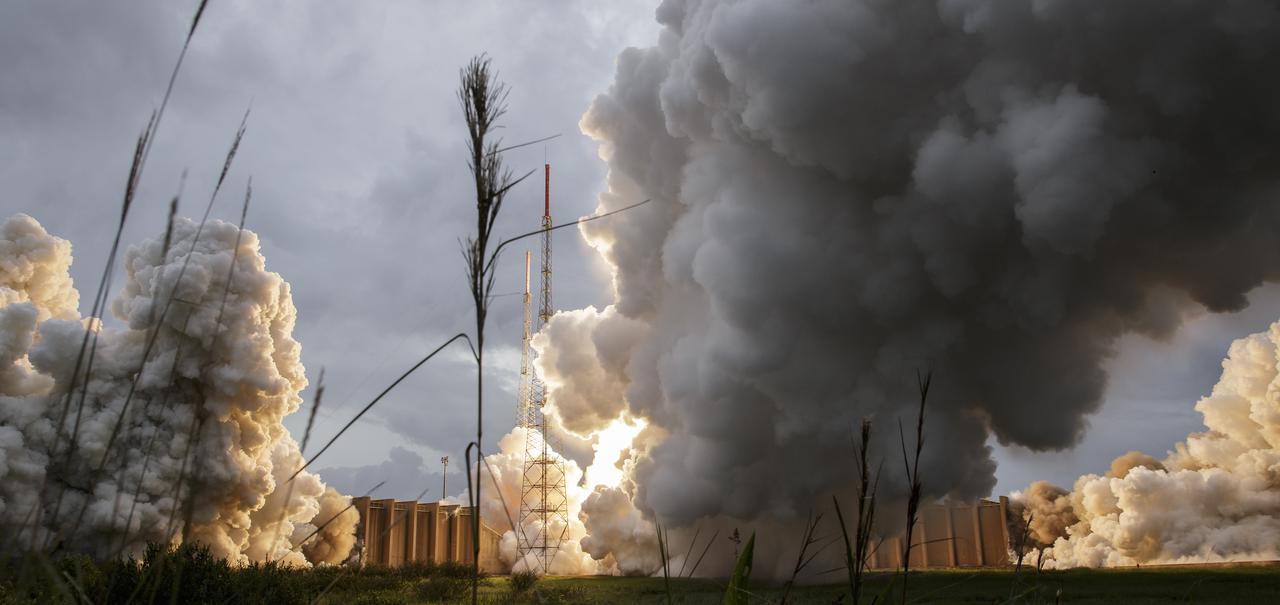

Steam and smoke from Arianespace's Ariane 5 Vulcain engine, center, and two solid rocket boosters, is seen as it launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
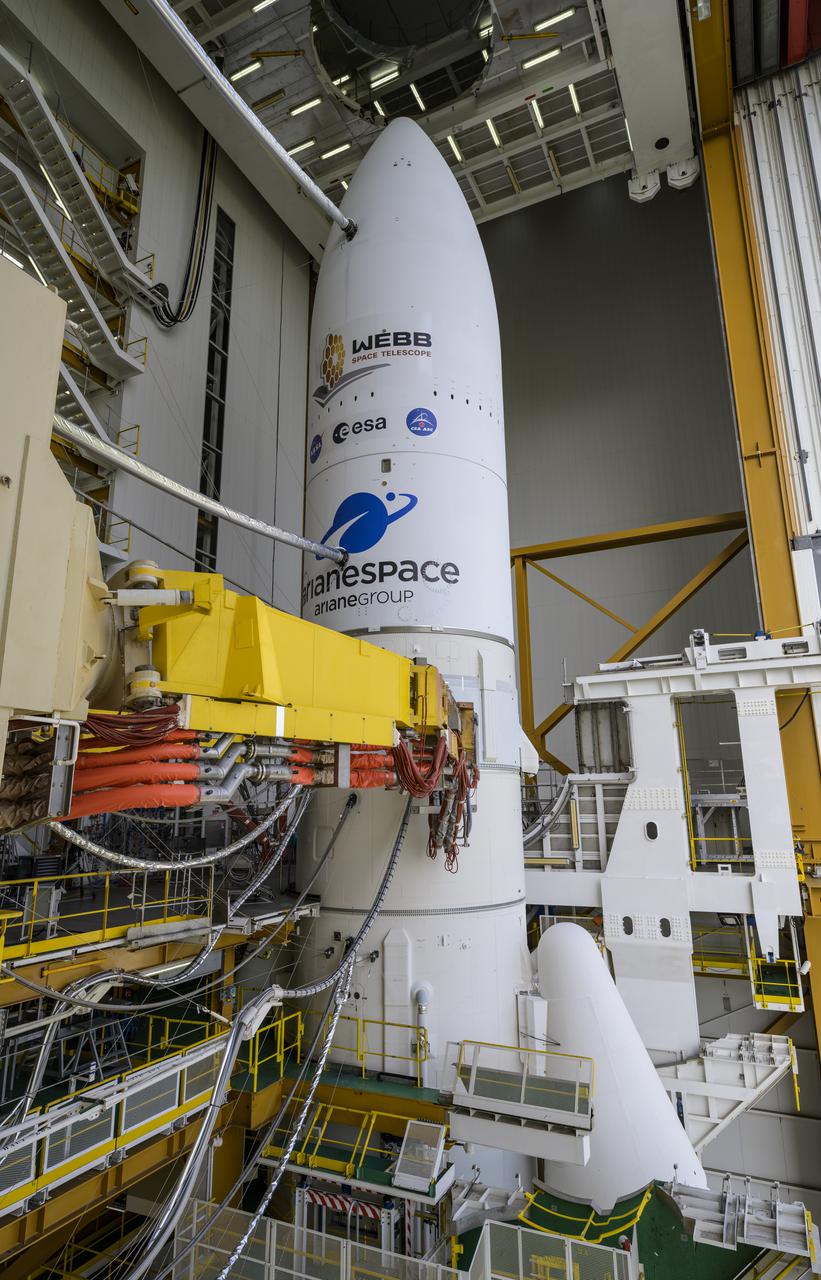

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen ahead of rollout to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
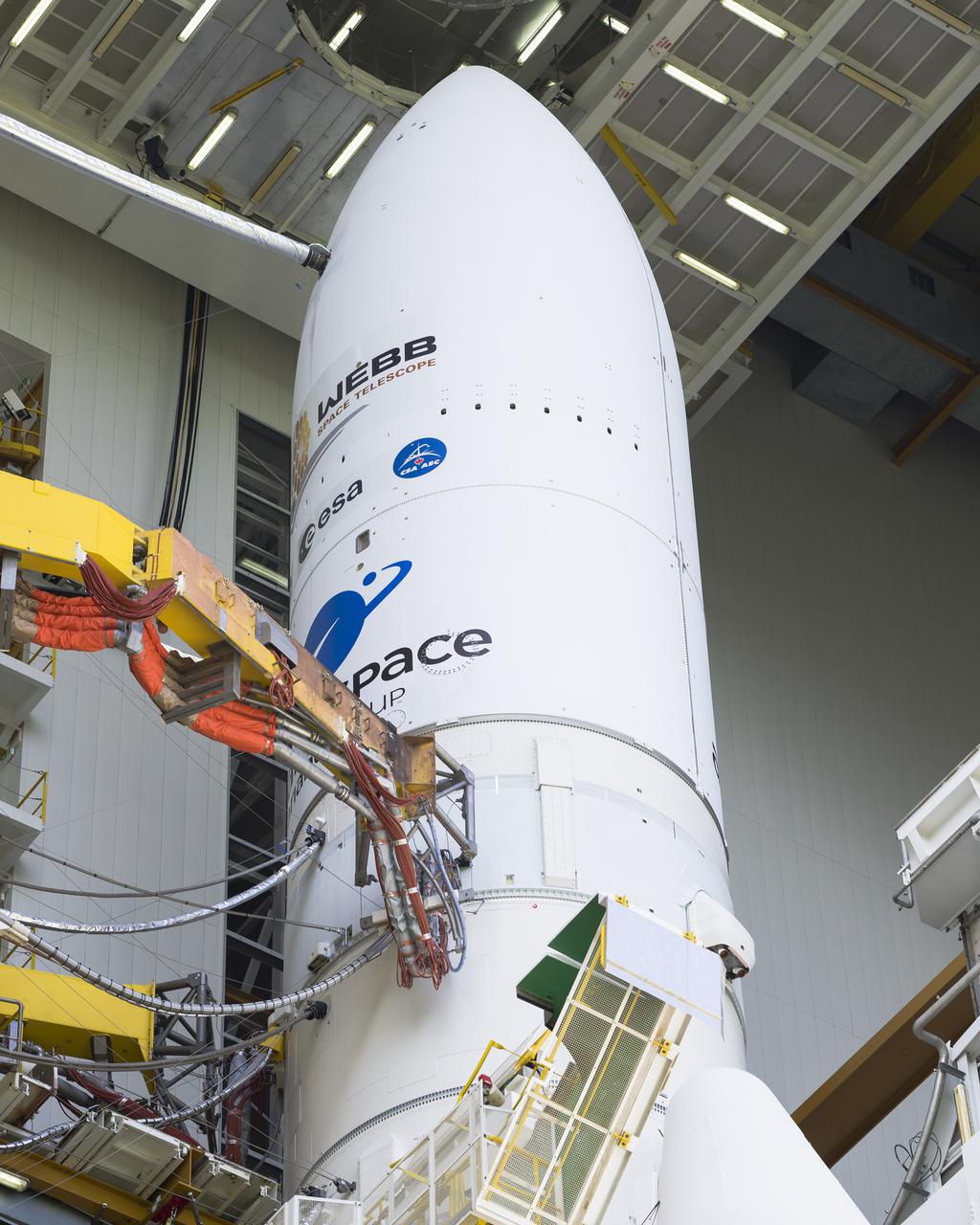

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen in the final assembly building ahead of the planned roll to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Chris Gunn)

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen in the final assembly building ahead of the planned roll to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
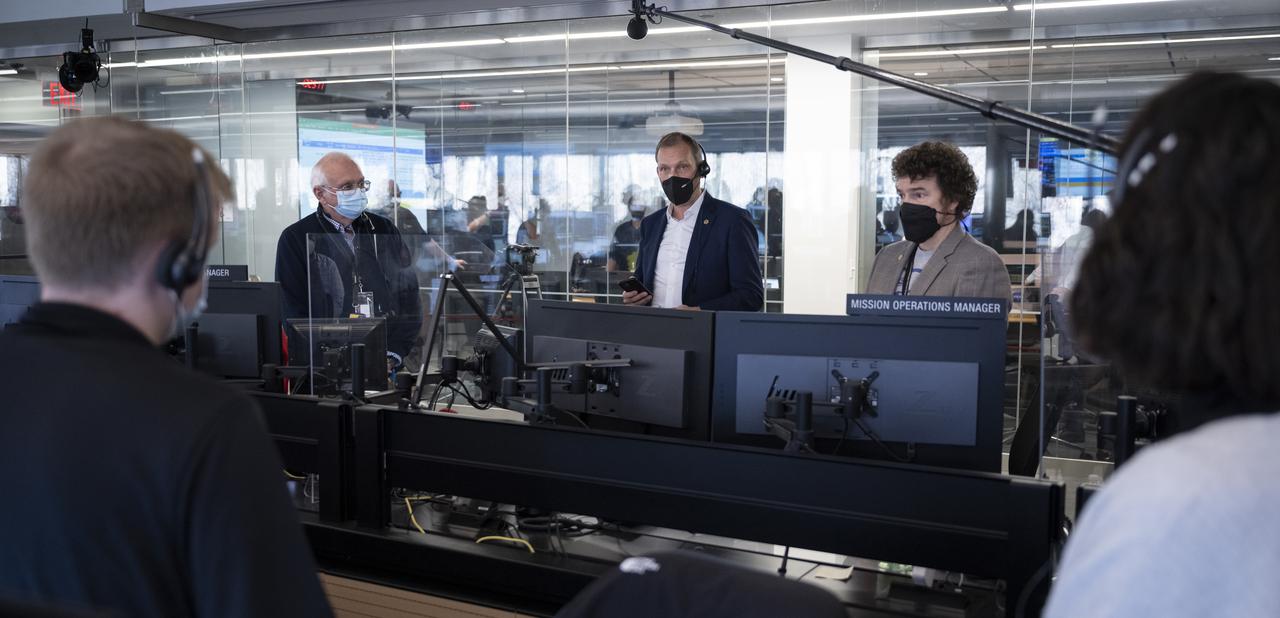

NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen congratulates the NASA James Webb Space Telescope mission operations team after confirming that the observatory’s final primary mirror wing successfully extended and locked into place, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. With Webb’s 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror fully deployed, the infrared observatory has completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
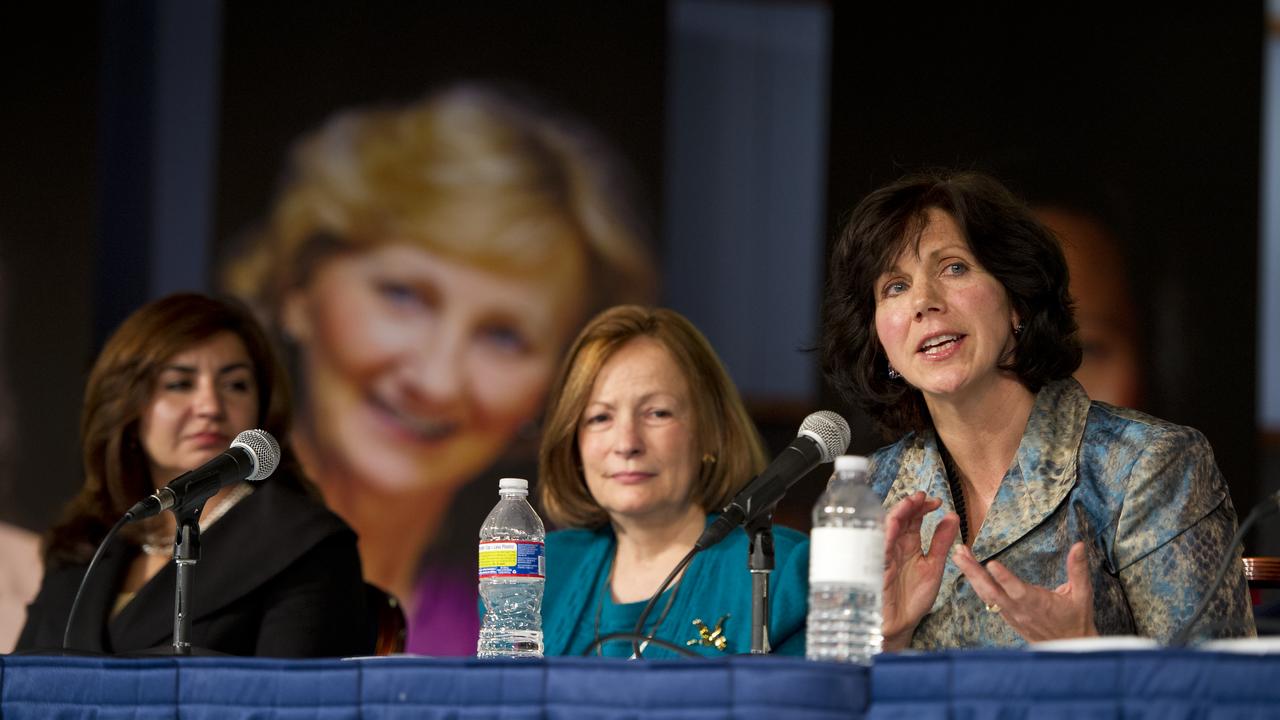

Catherine Didion, far right, Senior Fellow, National Academy of Engineering, participates in a panel discussion at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. Didion is joined by Marcia Smith, President, Space Policy Online.com, and Veronica Villalobos, Director, Office of Diversity and Inclusion, Office of Personnel Management, far left. The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
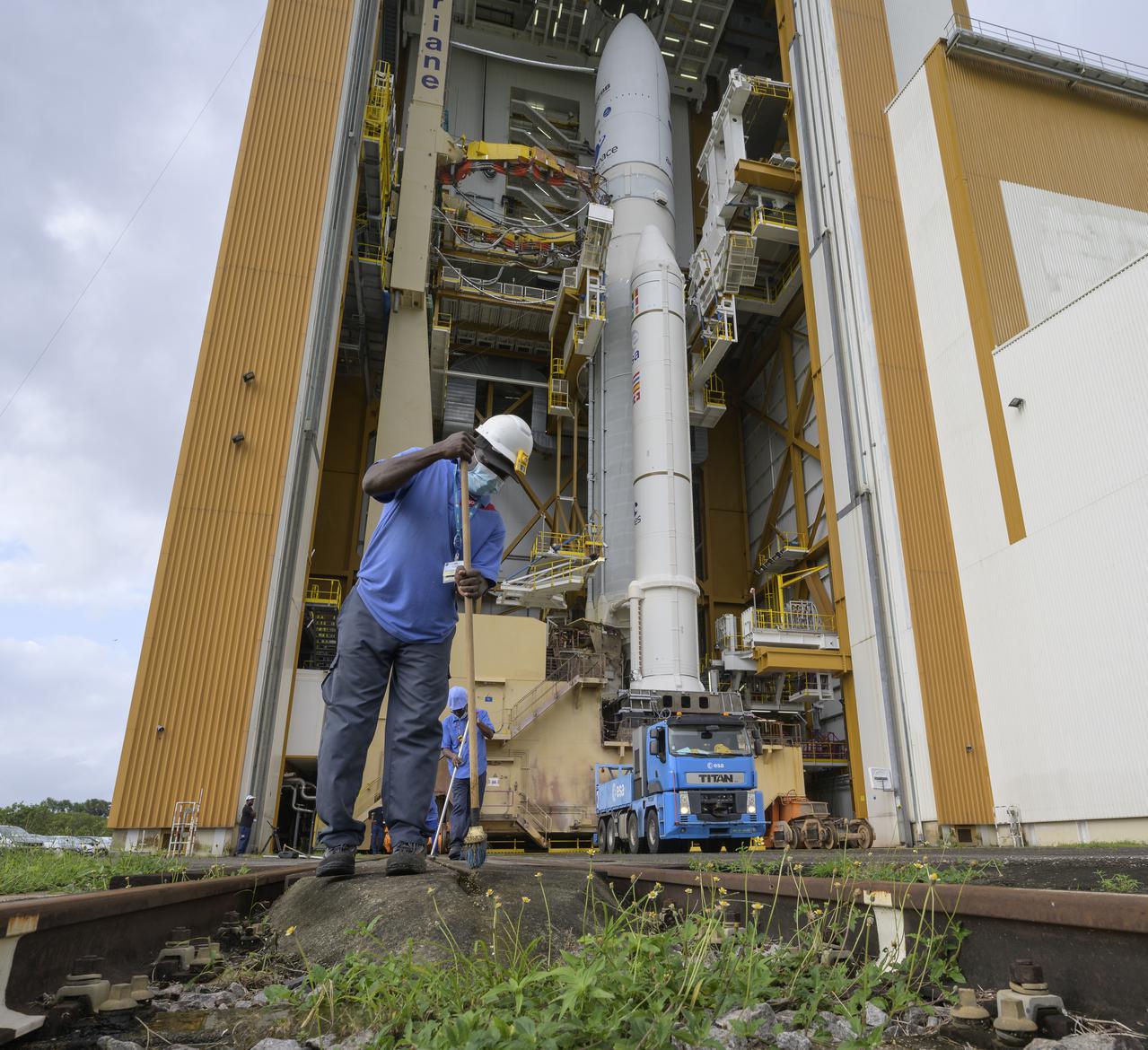

Workers sweep the tracks in advance of the rollout to the launch pad of Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
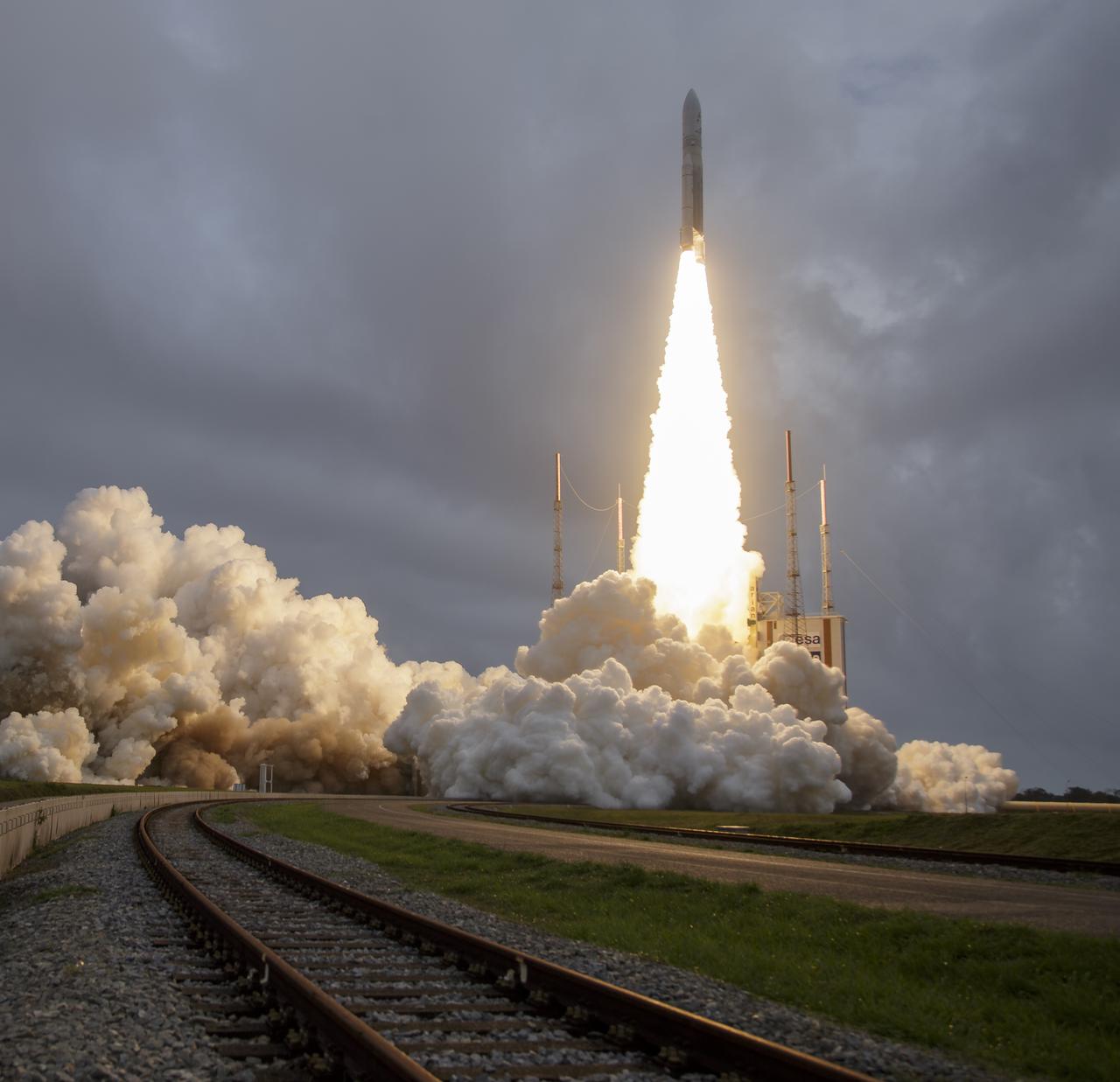

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
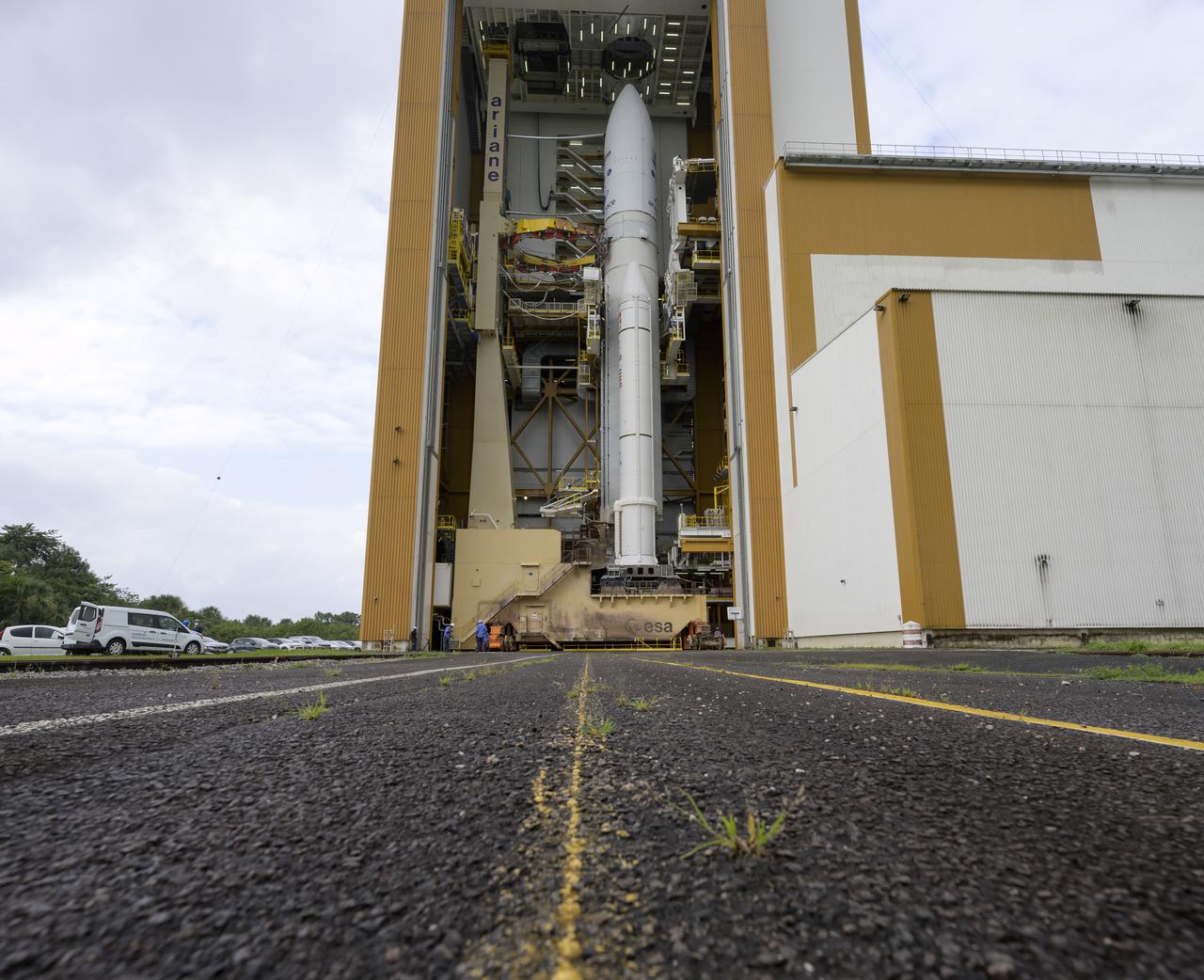

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen in the final assembly building ahead of the planned roll to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Engineering teams celebrate at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore as the second primary mirror wing of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope unfolds, before beginning the process of latching the mirror wing into place, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022. When fully latched, the infrared observatory will have completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
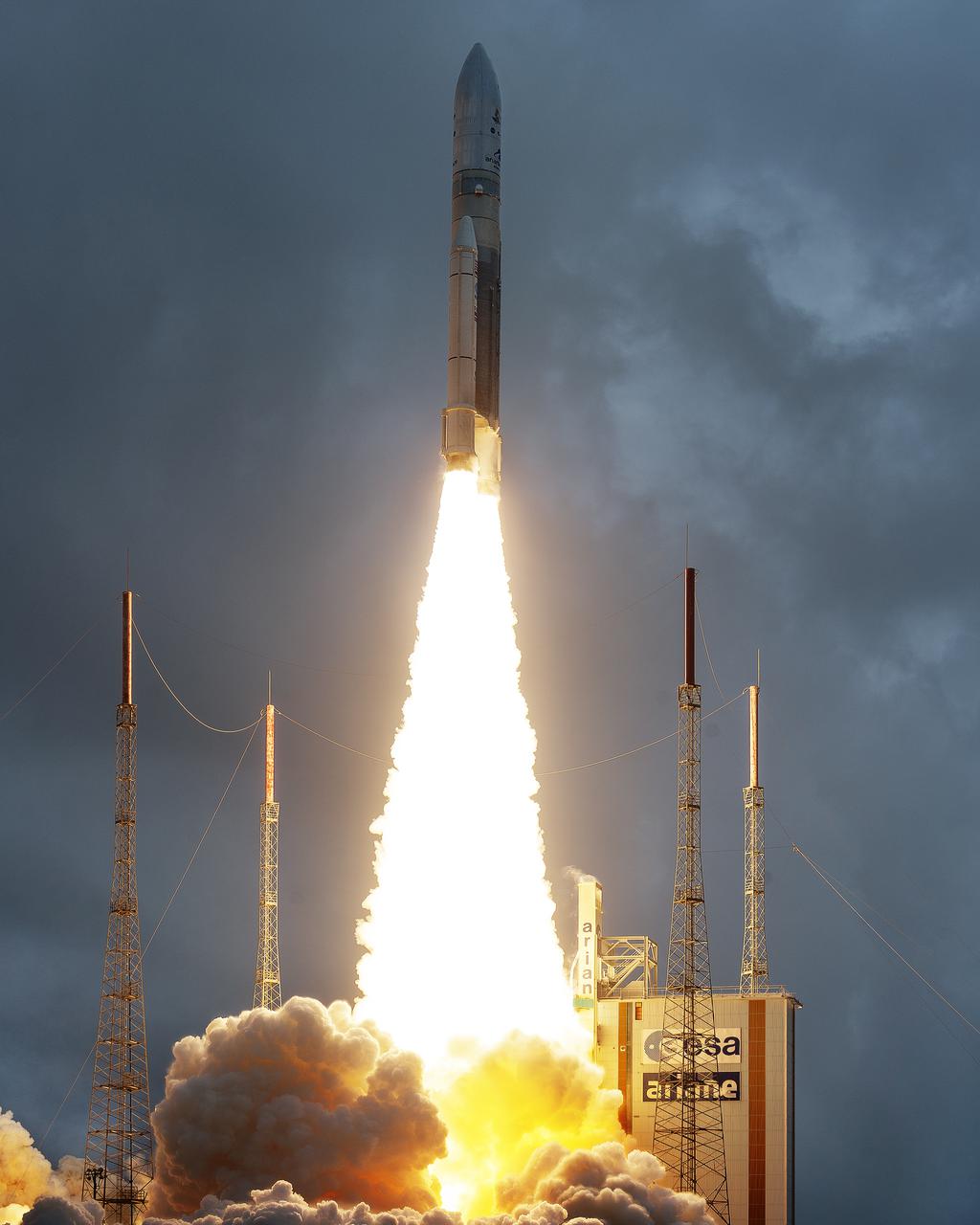

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Chris Gunn)
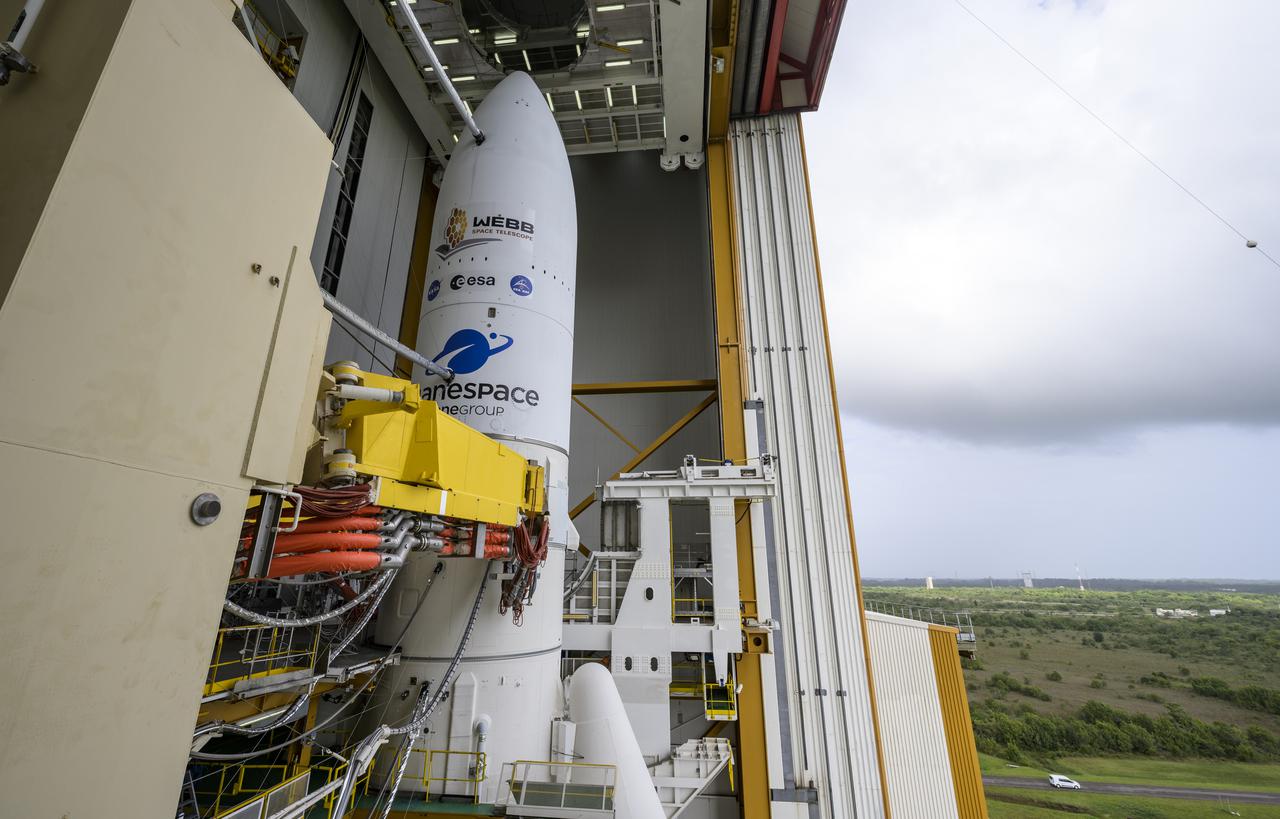

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is seen ahead of rollout to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, is ready to be rolled out to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
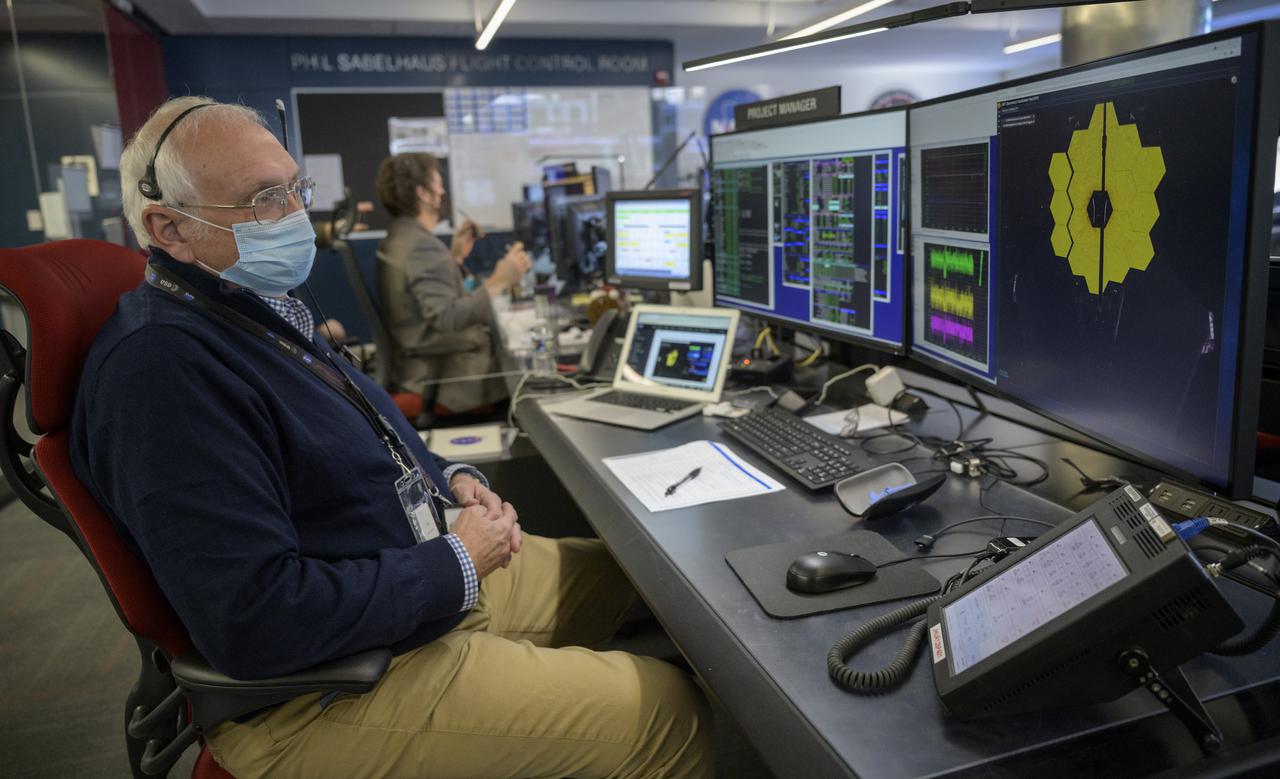

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Project Manager Bill Ochs monitors the progress of the observatory’s second primary mirror wing as it rotates into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)