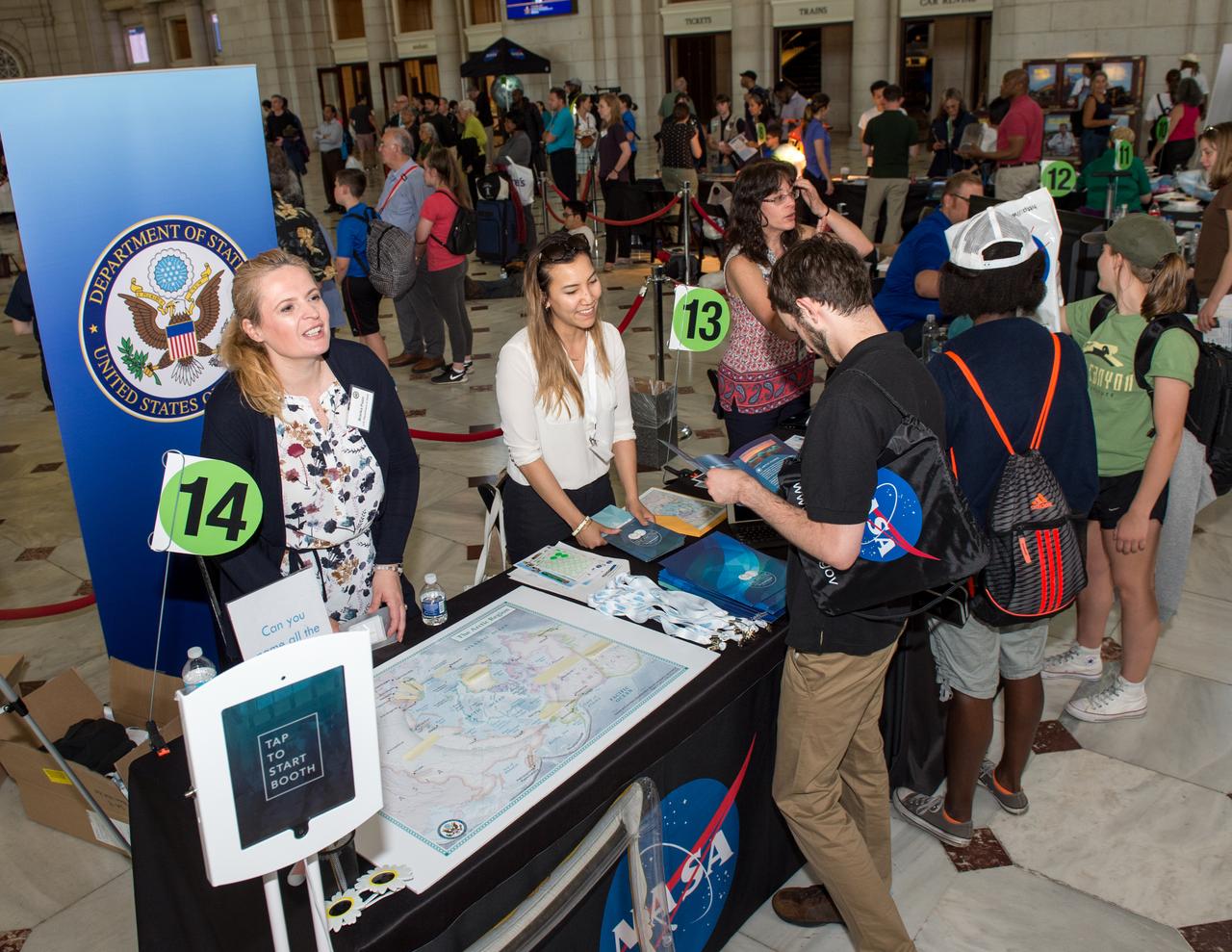

2017 NASA Earth Day at Union Station, Washington DC
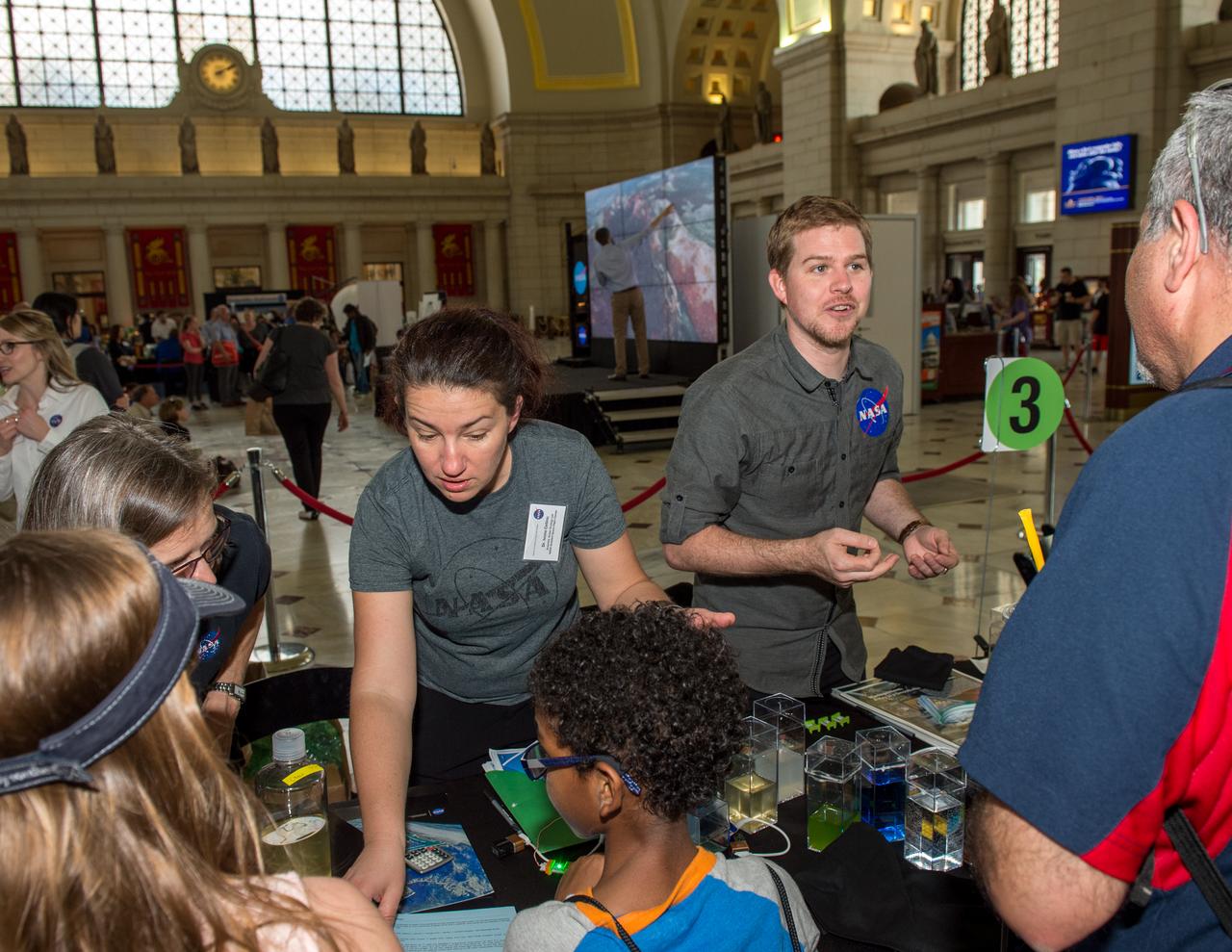

2017 NASA Earth Day at Union Station, Washington DC

Happy Earth Day! Explore the diverse colors, unique shapes and striking patterns of our very favorite planet, Earth - as only NASA can see it. Credit: NASA/Goddard #nasagoddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
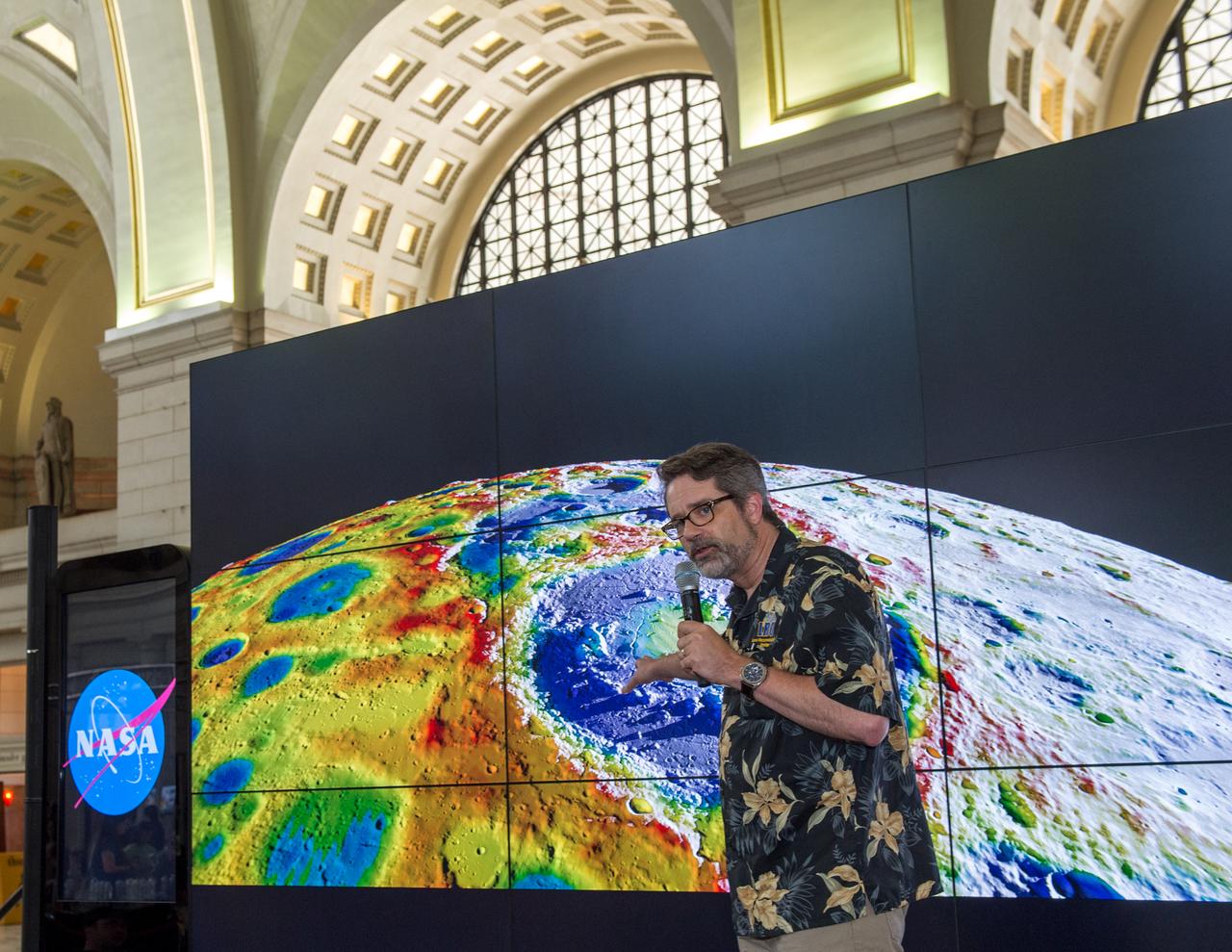

2017 NASA Earth Day at Union Station, Washington DC. Mr. Ernie Wright.
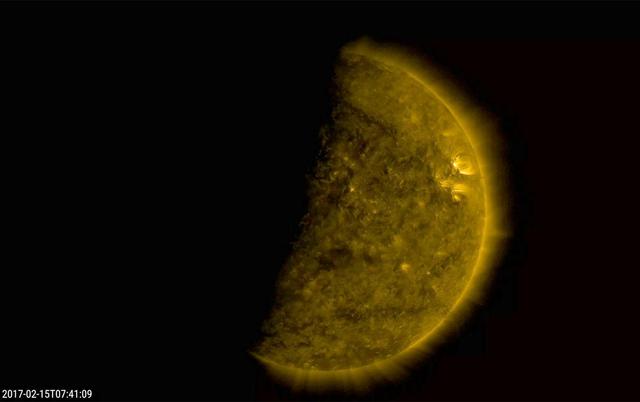
Several times a day for a few days the Earth completely blocked the Sun for about an hour due to NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory's orbital path (Feb. 15, 2017). The edge of the Earth is not crisp, but kind of fuzzy due to Earth's atmosphere. This frame from a video shows the ending of one such eclipse over -- just seven minutes. The sun is shown in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. These eclipses re-occur about every six months. The Moon blocks SDO's view of the sun on occasion as well. Movies are available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21461

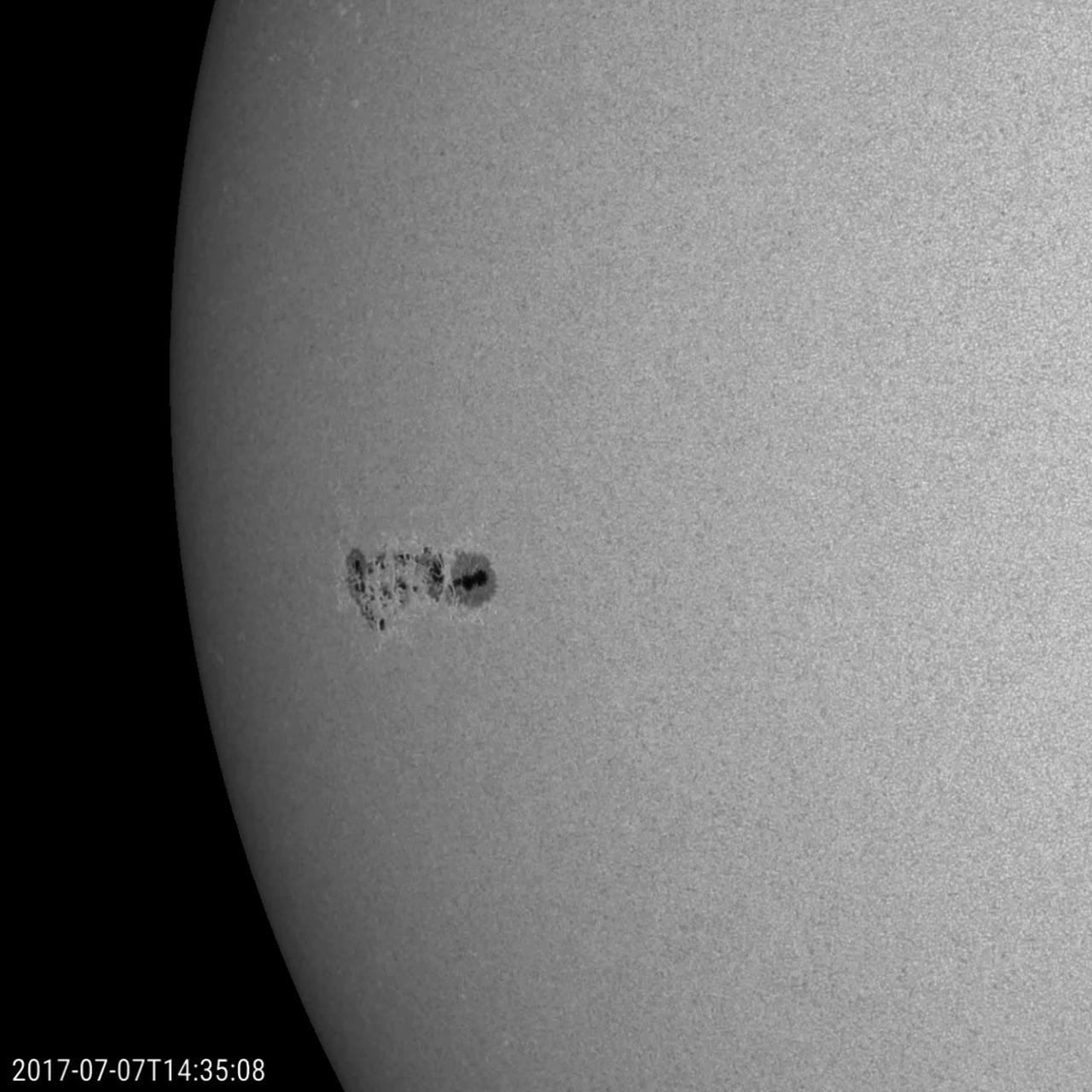
A large coronal hole has been spewing solar wind particles in the general direction of Earth over the past few days (Aug. 31- Sept. 1, 2017). It is the extensive dark area that stretches from the top of the sun and angles down to the right. Coronal holes are areas of open magnetic field, which allow charge particles to escape into space. They appear dark in certain wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light such as shown here. These clouds of particles can cause aurora to appear, particularly in higher latitude regions. Movies are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21942
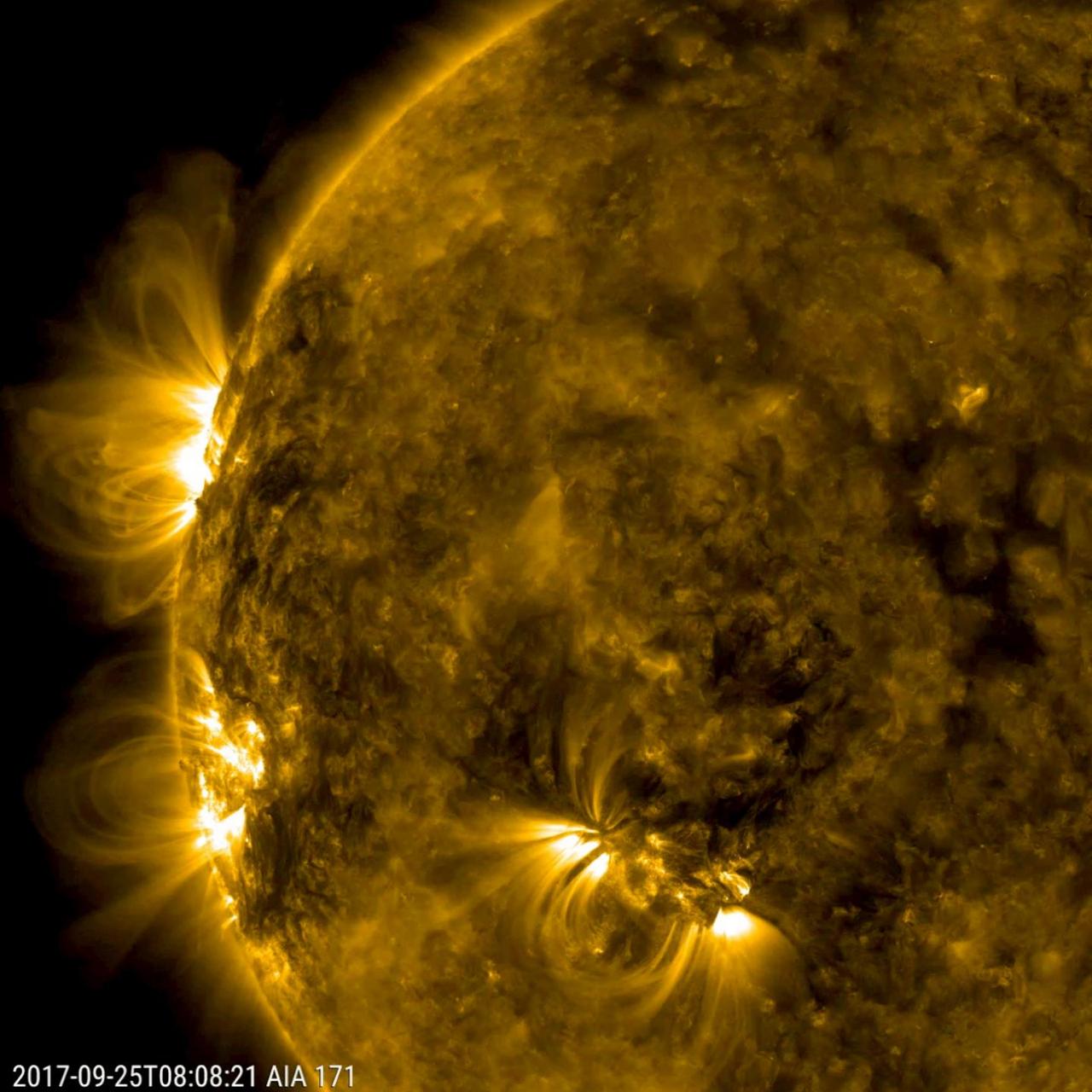
Three distinct active regions with towering arches above them rotated into view over a three-day period (Sept. 24-26, 2017). In extreme ultraviolet light, charged particles that are spinning along the ever-changing magnetic field lines above the active regions make the lines visible. To give some sense of scale, the largest arches rose up many times the size of Earth. Movies are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22038

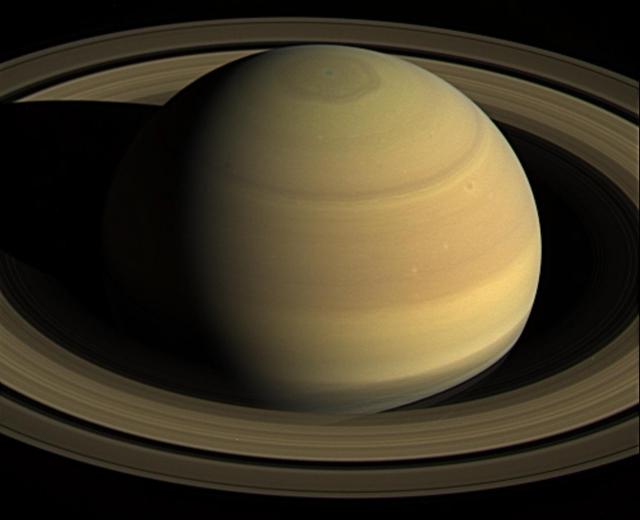
Stunning views like this image of Saturn's night side are only possible thanks to our robotic emissaries like Cassini. Until future missions are sent to Saturn, Cassini's image-rich legacy must suffice. Because Earth is closer to the Sun than Saturn, observers on Earth only see Saturn's day side. With spacecraft, we can capture views (and data) that are simply not possible from Earth, even with the largest telescopes. This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 7 degrees above the ring plane. The image was taken in visible light with the wide-angle camera on NASA's Cassini spacecraft on June 7, 2017. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 751,000 miles (1.21 million kilometers) from Saturn. Image scale is 45 miles (72 kilometers) per pixel. The Cassini spacecraft ended its mission on Sept. 15, 2017. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21350

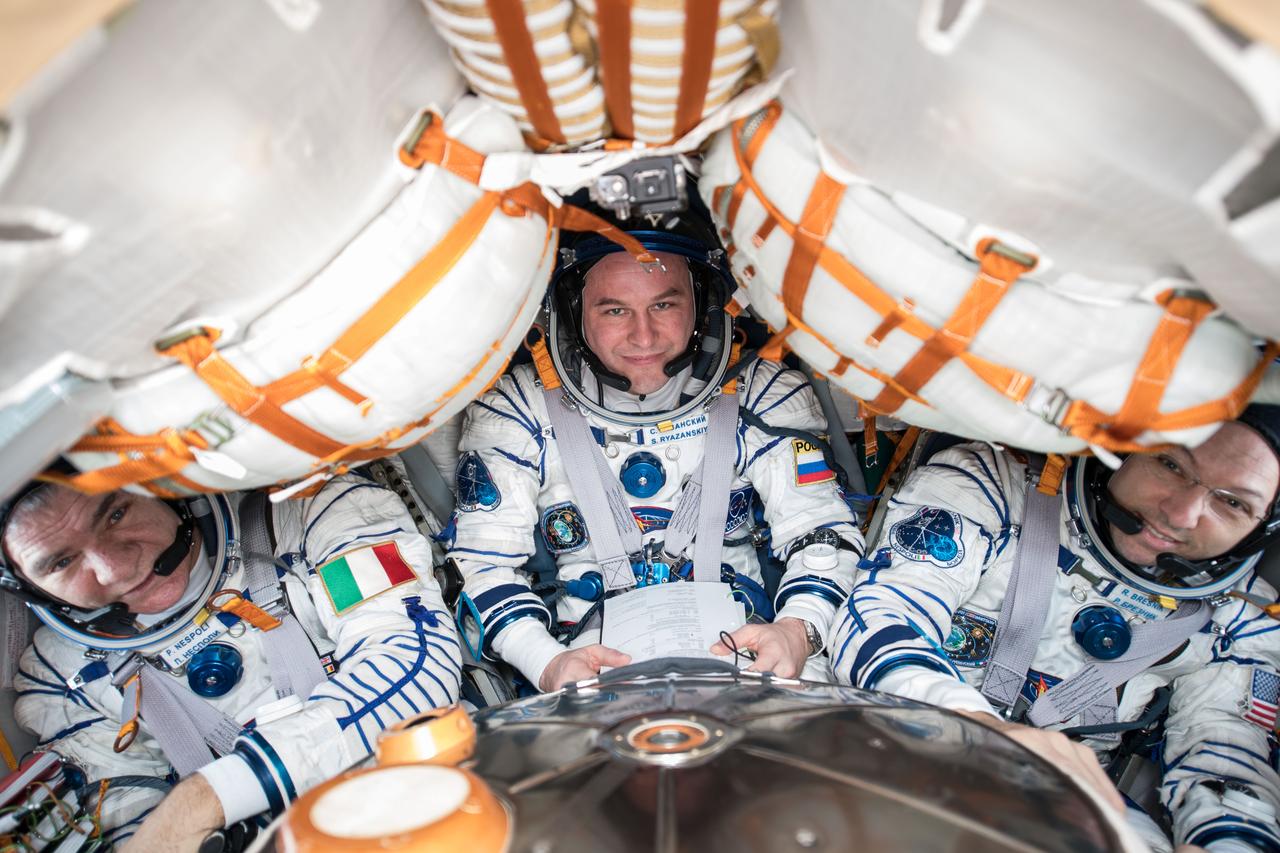
iss053e303563 (Dec. 4, 2017) --- Expedition 52-53 crew members (from left) Paolo Nespoli, Sergey Ryazanskiy and Randy Bresnik are pictured in their Sokol launch and entry suits as they prepare for their return to Earth after 139 days in space. The veteran space travelers were practicing the procedures they will use when they undock from the Rassvet module and parachute to a landing in Kazakhstan inside the Soyuz MS-05 spacecraft Dec.14.
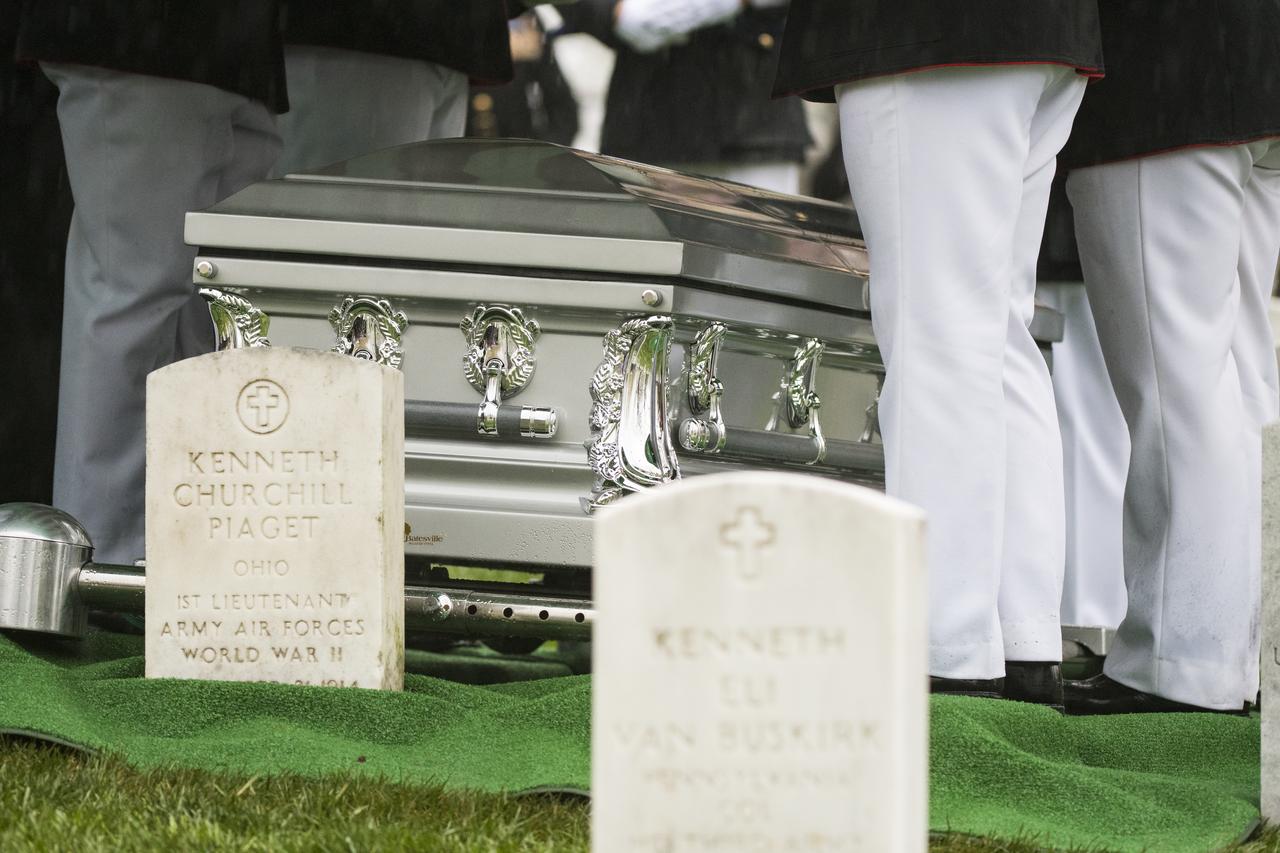

Former astronaut and U.S. Senator John Glenn's casket is seen as he is laid to rest at Arlington National Cemetery in Virginia on Thursday, April 6, 2017, the day on which he and his wife Annie were married in 1943. Glenn was the first American to orbit Earth on Feb. 20, 1962, in a five-hour flight aboard the Friendship 7 spacecraft. In 1998, he broke another record by returning to space at the age of 77 on the Space Shuttle Discovery. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

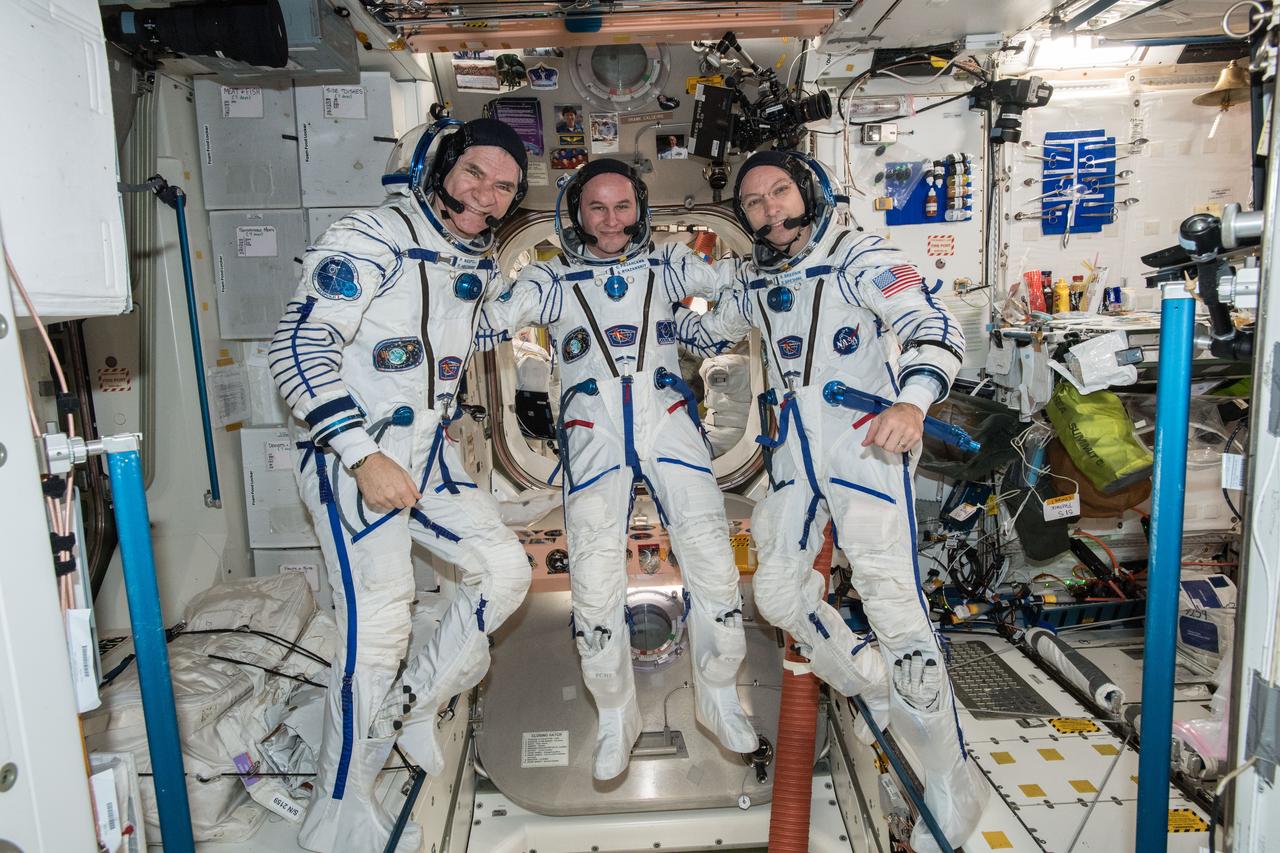
iss053e304918 (Dec. 4, 2017) --- Expedition 52-53 crew members (from left) Paolo Nespoli, Sergey Ryazanskiy and Randy Bresnik are pictured inside the Soyuz MS-05 spacecraft wearing their Sokol launch and entry suits. The veteran space travelers were preparing for their return to Earth after 139 days in space and practicing the procedures they will use when they undock from the Rassvet module in their Soyuz vehicle and parachute to a landing in Kazakhstan Dec.14.
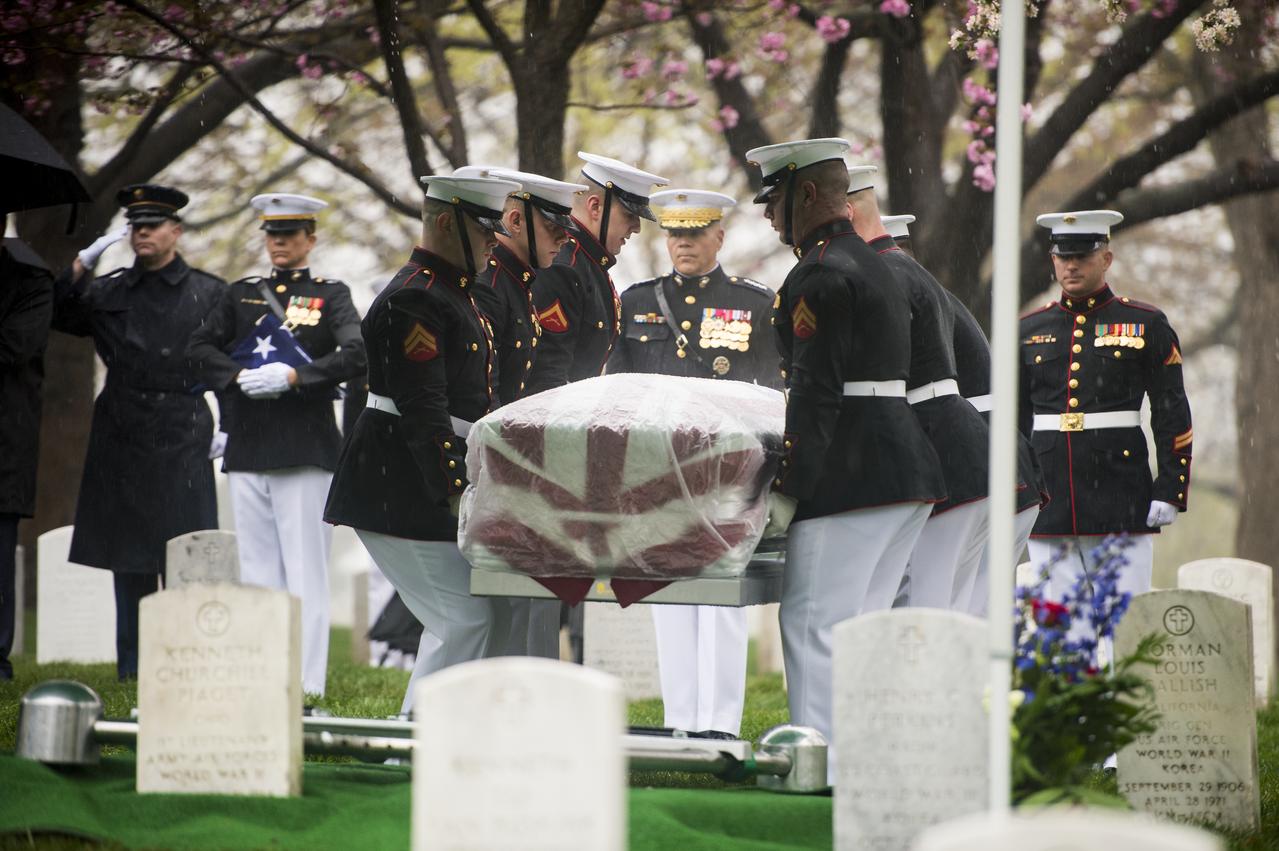

Marine Corps pallbearers lower the casket of former astronaut and U.S. Senator John Glenn at his interment at Arlington National Cemetery in Virginia on Thursday, April 6, 2017, the day on which he and his wife Annie were married in 1943. Glenn was the first American to orbit Earth on Feb. 20, 1962, in a five-hour flight aboard the Friendship 7 spacecraft. In 1998, he broke another record by returning to space at the age of 77 on the Space Shuttle Discovery. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
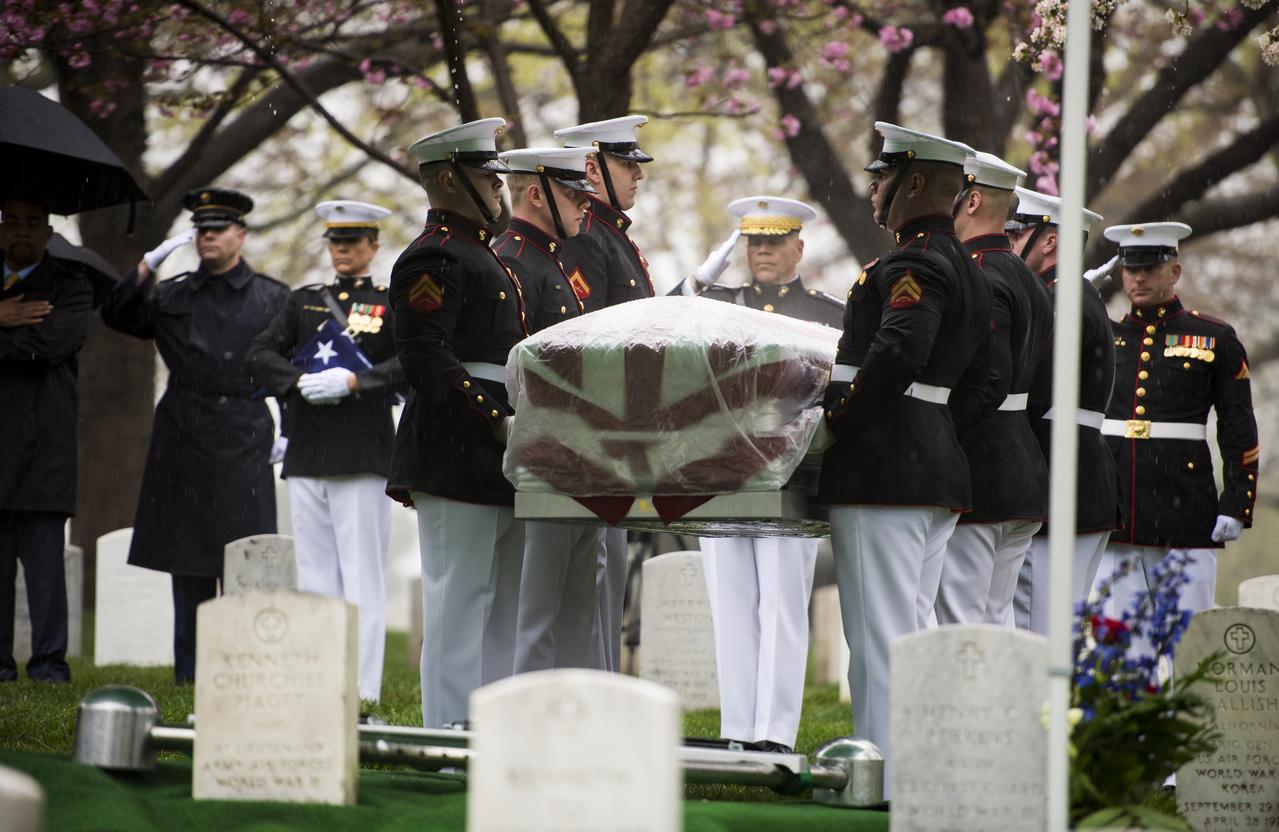

Marine Corp pallbearers carry former astronaut and U.S. Senator John Glenn to be laid to rest at Arlington National Cemetery in Virginia on Thursday, April 6, 2017, the day on which he and his wife Annie were married in 1943. Glenn was the first American to orbit Earth on Feb. 20, 1962, in a five-hour flight aboard the Friendship 7 spacecraft. In 1998, he broke another record by returning to space at the age of 77 on the Space Shuttle Discovery. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

This dark mound, called "Ireson Hill," rises about 16 feet (5 meters) above redder layered outcrop material of the Murray formation on lower Mount Sharp, Mars, near a location where NASA's Curiosity rover examined a linear sand dune in February 2017. Researchers used the rover's Mast Camera (Mastcam) on Feb. 2, 2017, during the 1,598th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars, to take the 41 images combined into this scene. The mosaic has been white-balanced so that the colors of the rock and sand materials resemble how they would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. The view extends from west-southwest on the left to north-northwest on the right. The faint horizon in the distance beyond Ireson Hill is part of the rim of Gale Crater. An annotated figure is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21718
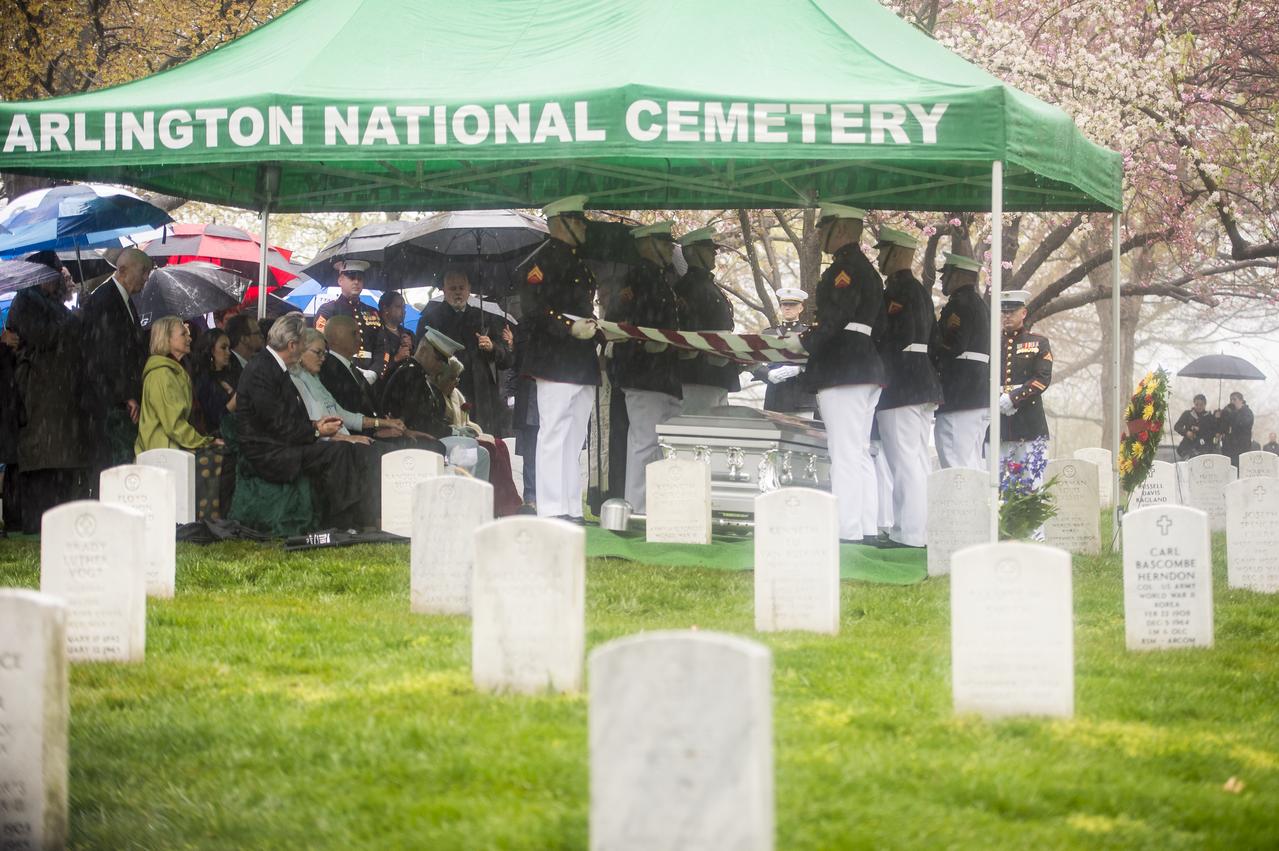

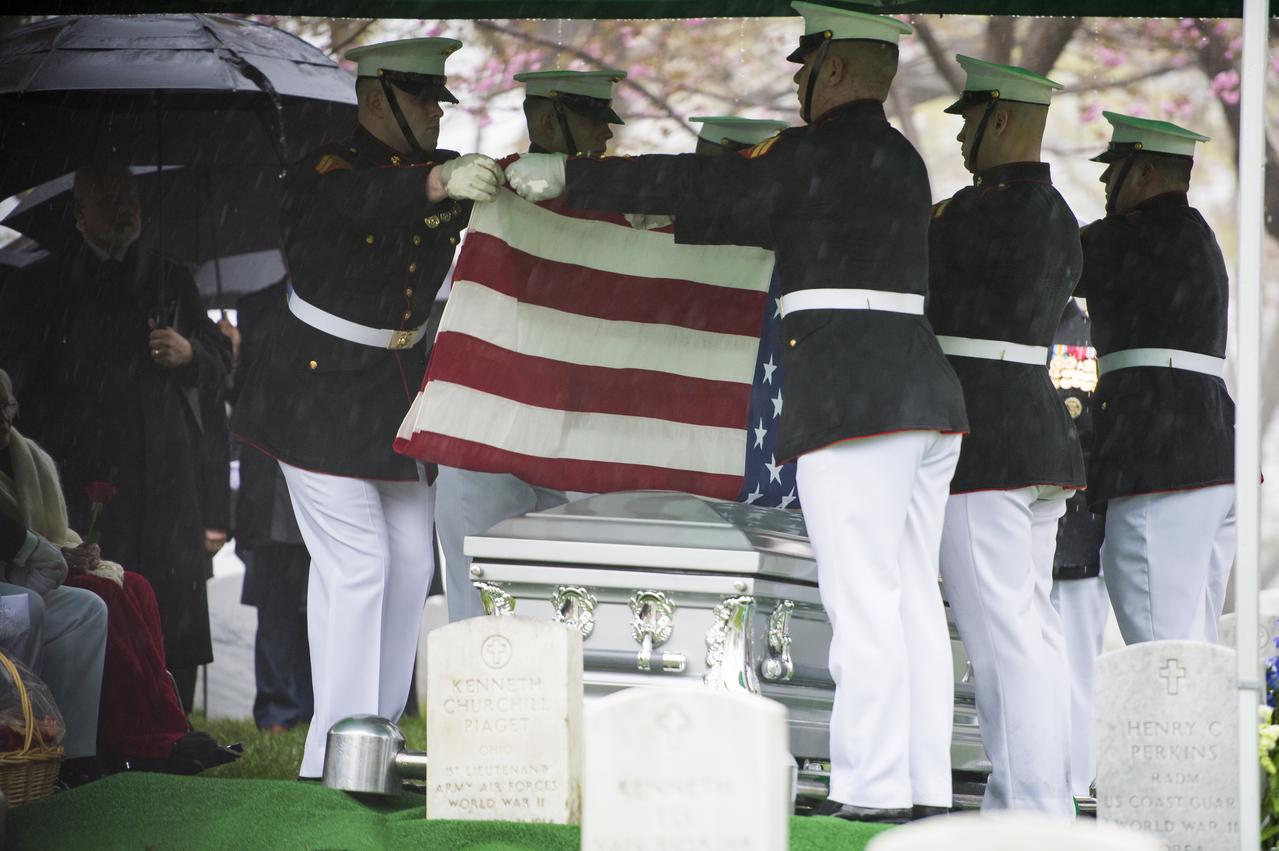
A Marine Corps honor guard holds the American flag over the casket of former astronaut and U.S. Senator John Glenn, who was buried with full military honors, at Arlington National Cemetery in Virginia on Thursday, April 6, 2017, the day on which he and his wife Annie were married in 1943. Glenn was the first American to orbit Earth on Feb. 20, 1962, in a five-hour flight aboard the Friendship 7 spacecraft. In 1998, he broke another record by returning to space at the age of 77 on the Space Shuttle Discovery. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
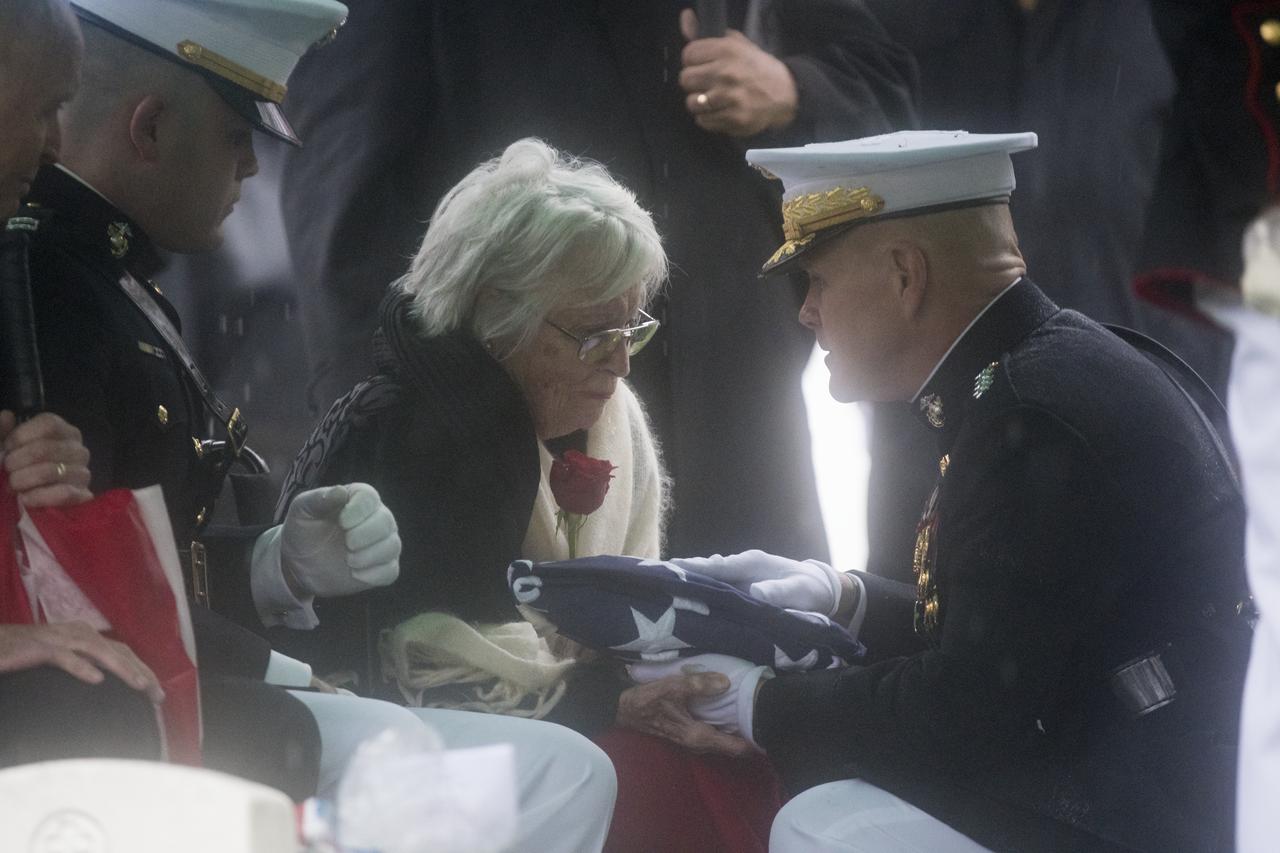

Annie Glenn, wife of former astronaut and U.S. Senator John Glenn receives the folded American flag from Commandant of the U.S. Marine Corps, General Robert B. Neller, during a graveside interment ceremony at Arlington National Cemetery in Virginia on Thursday, April 6, 2017, the day on which Glenn and Annie were married in 1943. He was the first American to orbit Earth on Feb. 20, 1962, in a five-hour flight aboard the Friendship 7 spacecraft. In 1998, Glenn broke another record by returning to space at the age of 77 on the Space Shuttle Discovery. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
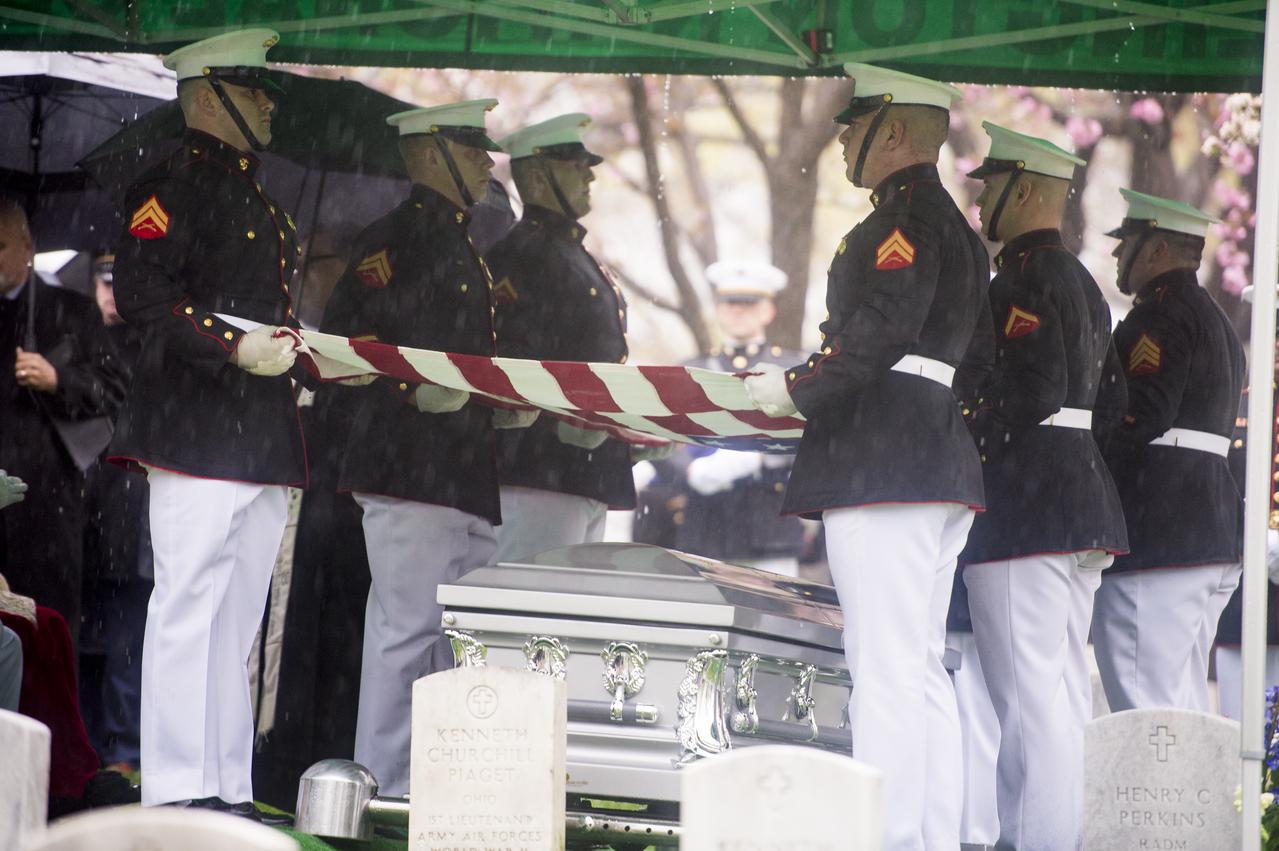

A Marine Corps honor guard holds the American flag over the casket of former astronaut and U.S. Senator John Glenn, who was buried with full military honors, at Arlington National Cemetery in Virginia on Thursday, April 6, 2017, the day on which he and his wife Annie were married in 1943. Glenn was the first American to orbit Earth on Feb. 20, 1962, in a five-hour flight aboard the Friendship 7 spacecraft. In 1998, he broke another record by returning to space at the age of 77 on the Space Shuttle Discovery. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

A prominence at the edge of the sun provided us with a splendid view of solar plasma as it churned and streamed over less than one day (June 25-26, 2017). The charged particles of plasma were being manipulated by strong magnetic forces. When viewed in this wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light, we can trace the movements of the particles. Such occurrences are fairly common but much easier to see when they are near the sun's edge. For a sense of scale, the arch of prominence in the still image has risen up several times the size of Earth. Movies are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21768
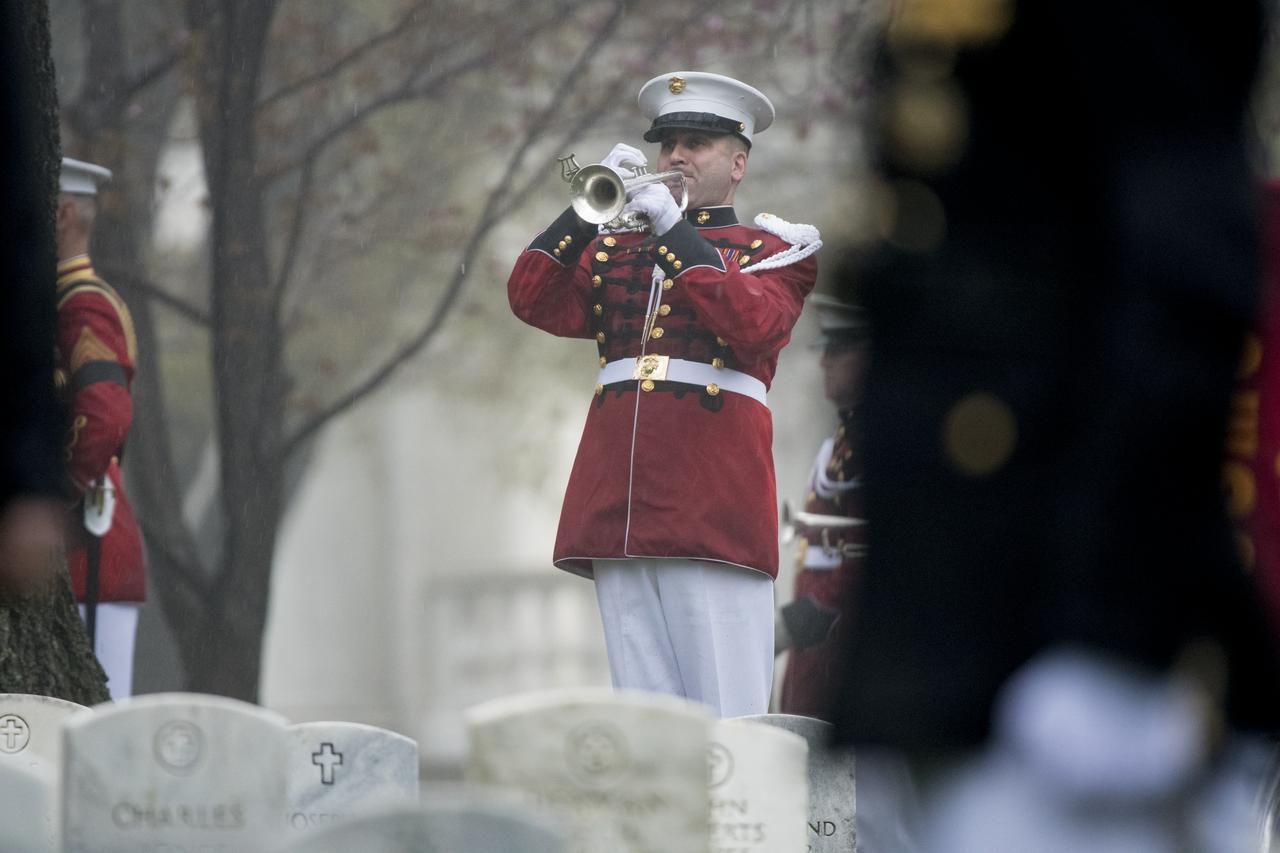

"Taps" is played during the funeral service for former astronaut and U.S. Senator John Glenn, who was buried with full military honors, at Arlington National Cemetery in Virginia on Thursday, April 6, 2017, the day on which he and his wife Annie were married in 1943. Glenn was the first American to orbit Earth on Feb. 20, 1962, in a five-hour flight aboard the Friendship 7 spacecraft. In 1998, he broke another record by returning to space at the age of 77 on the Space Shuttle Discovery. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
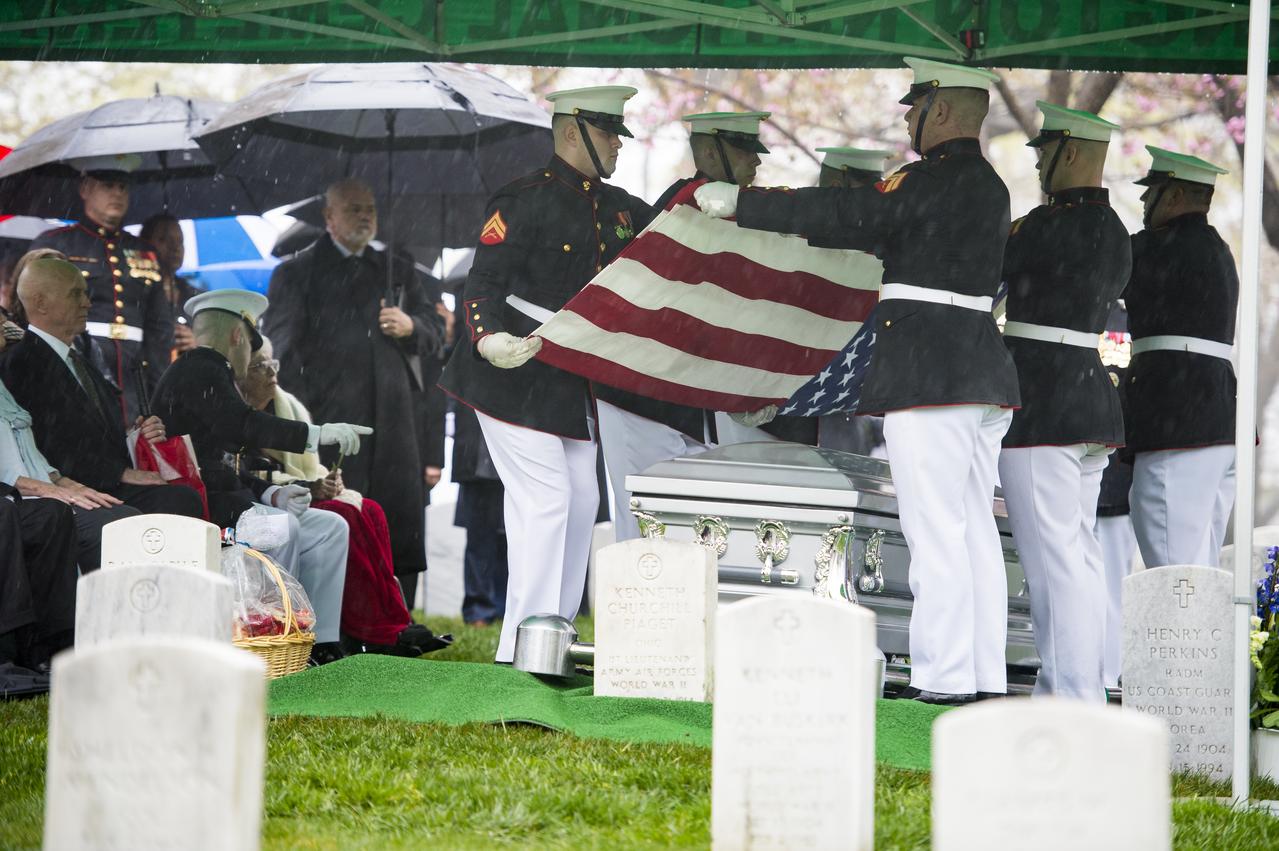

A Marine Corps honor guard folds the colors as family and friends look on during a funeral service for former astronaut and U.S. Senator John Glenn, who was buried with full military honors, at Arlington National Cemetery in Virginia on Thursday, April 6, 2017, the day on which he and his wife Annie were married in 1943. Glenn was the first American to orbit Earth on Feb. 20, 1962, in a five-hour flight aboard the Friendship 7 spacecraft. In 1998, he broke another record by returning to space at the age of 77 on the Space Shuttle Discovery. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

A prominence at the edge of the sun provided us with a splendid view of solar plasma as it churned and streamed over less than one day (June 25-26, 2017). The charged particles of plasma were being manipulated by strong magnetic forces. When viewed in this wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light, we can trace the movements of the particles. Such occurrences are fairly common but much easier to see when they are near the sun's edge. For a sense of scale, the arch of prominence in the still image has risen up several times the size of Earth. Movies are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21783
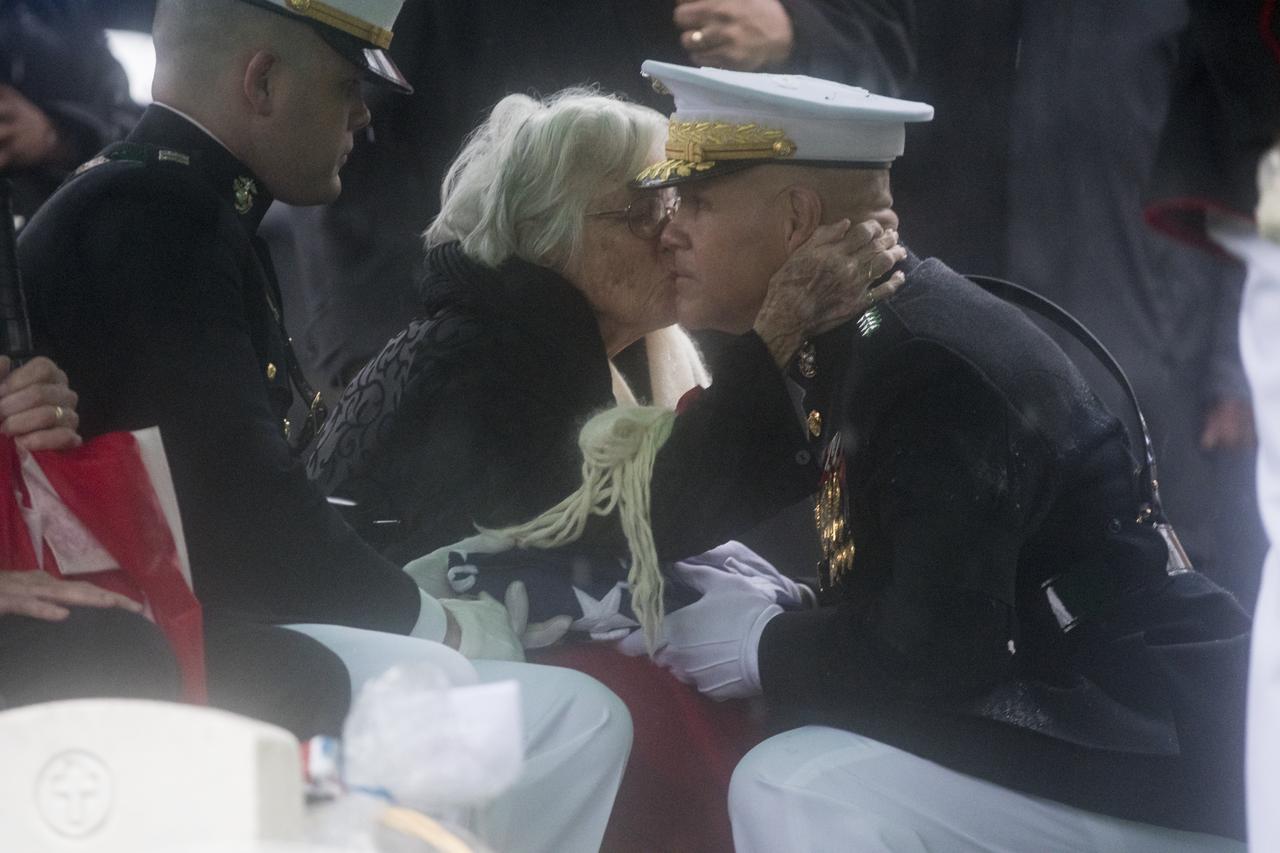

Annie Glenn, wife of former astronaut and U.S. Senator John Glenn gives the Commandant of the U.S. Marine Corps, General Robert B. Neller, a kiss on the cheek after he handed her the folded American flag during a graveside interment ceremony at Arlington National Cemetery in Virginia on Thursday, April 6, 2017, the day on which Glenn and Annie were married in 1943. He was the first American to orbit Earth on Feb. 20, 1962, in a five-hour flight aboard the Friendship 7 spacecraft. In 1998, Glenn broke another record by returning to space at the age of 77 on the Space Shuttle Discovery. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

A Marine Corps honor guard folds the colors during a funeral service for former astronaut and U.S. Senator John Glenn, who was buried with full military honors, at Arlington National Cemetery in Virginia on Thursday, April 6, 2017, the day on which he and his wife Annie were married in 1943. Glenn was the first American to orbit Earth on Feb. 20, 1962, in a five-hour flight aboard the Friendship 7 spacecraft. In 1998, he broke another record by returning to space at the age of 77 on the Space Shuttle Discovery. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
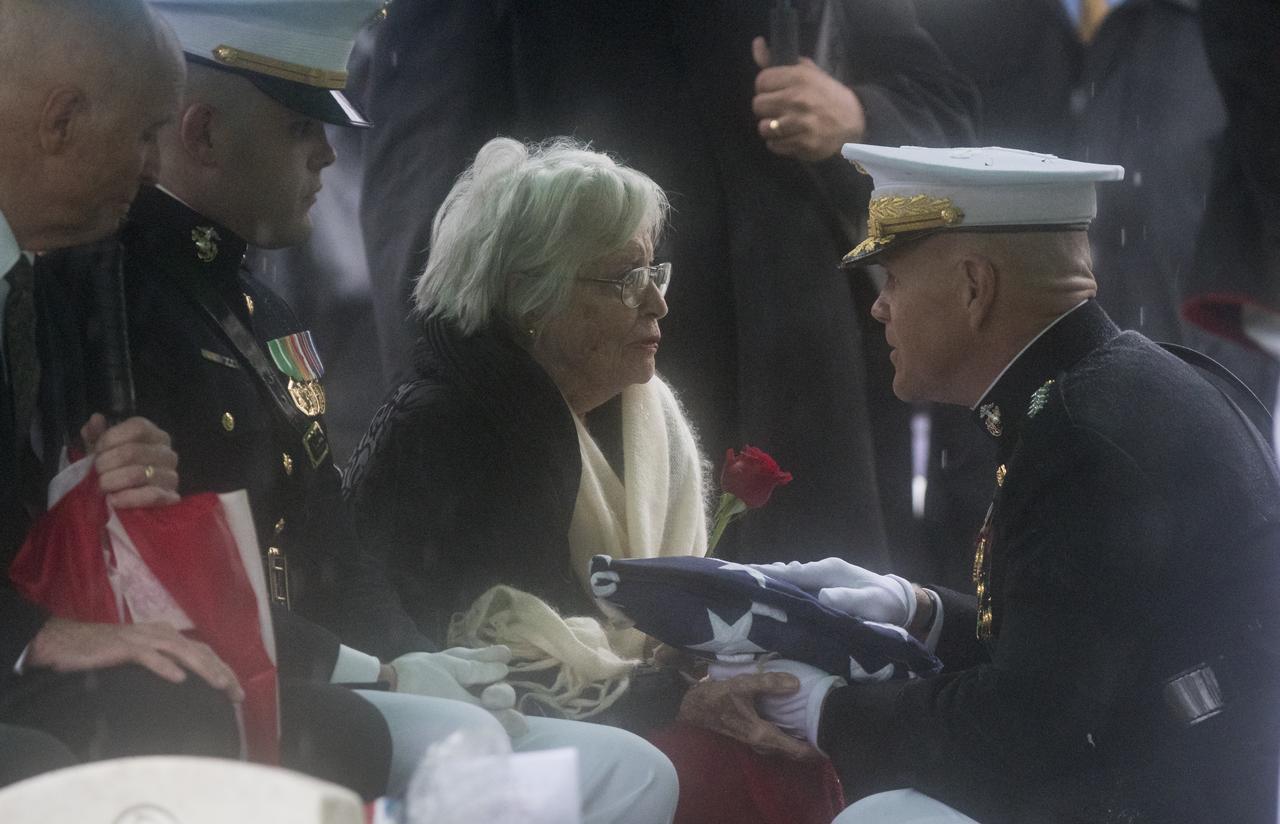

Annie Glenn, wife of former astronaut and U.S. Senator John Glenn receives the folded American flag from Commandant of the U.S. Marine Corps, General Robert B. Neller, during a graveside interment ceremony at Arlington National Cemetery in Virginia on Thursday, April 6, 2017, the day on which Glenn and Annie were married in 1943. He was the first American to orbit Earth on Feb. 20, 1962, in a five-hour flight aboard the Friendship 7 spacecraft. In 1998, Glenn broke another record by returning to space at the age of 77 on the Space Shuttle Discovery. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
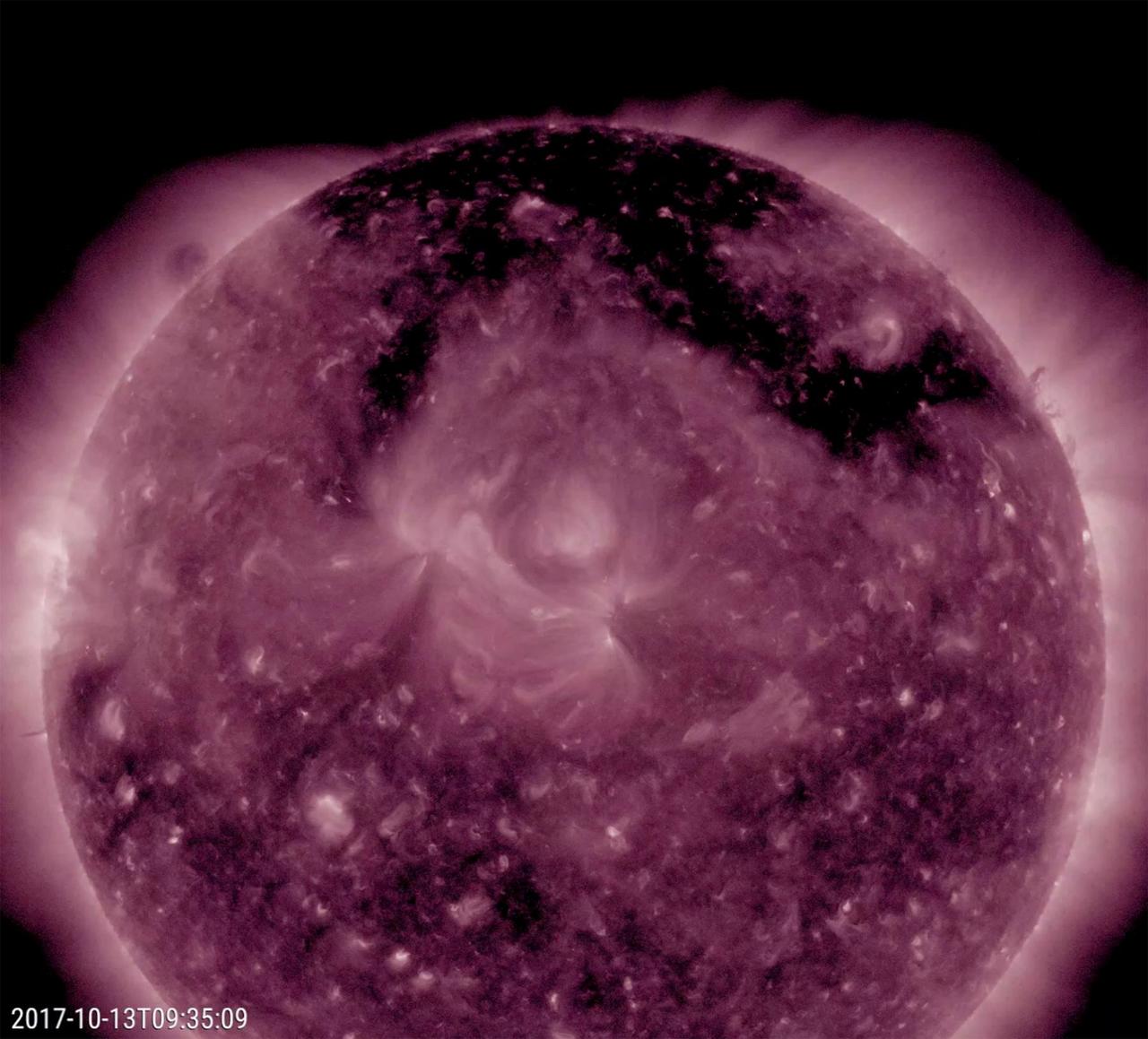
A large coronal hole stands out as the most obvious feature on the sun this week (Oct. 12-13, 2017). The dark structure, shaped kind of like the Pi symbol, spreads across much of the top of the sun. Though one cannot tell from this image and video clip in false-color extreme ultraviolet light, it is spewing high-speed solar wind particles into space and has been doing this all week. It is likely that these charged particles have been interacting with Earth's atmosphere and generating many aurora displays in regions near the poles the past several days. Animations are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22047

A rippled linear dune of dark Martian sand, "Nathan Bridges Dune," dominates this full-circle panorama from the Mast Camera (Mastcam) of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover. This dune was one research stop of the rover mission's campaign to investigate active Martian dunes. The feature was informally named in 2017 in memory of Nathan Bridges (1966-2017), a planetary scientist who was a leader of the Curiosity team's dune campaign. The scene combines 112 images taken with Mastcam's left-eye camera on Feb. 5, 2017, during the 1,601st Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars. The panorama has been white-balanced so that colors of the rock and sand materials resemble how they would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. The center is toward east-southeast and both ends are toward west-northwest. The dark butte on the horizon in the left half is "Ireson Hill." Upper Mount Sharp is on the horizon in the center. An annotated figure and full resolution TIFF file is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21719

This chart shows, on the top row, artist concepts of the seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 with their orbital periods, distances from their star, radii and masses as compared to those of Earth. On the bottom row, the same numbers are displayed for the bodies of our inner solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The TRAPPIST-1 planets orbit their star extremely closely, with periods ranging from 1.5 to only about 20 days. This is much shorter than the period of Mercury, which orbits our sun in about 88 days. The artist concepts show what the TRAPPIST-1 planetary system may look like, based on available data about their diameters, masses and distances from the host star. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial, according to research published in 2017 in the journal Nature. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21425

This panorama from the Mast Camera (Mastcam) of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover shows details of "Vera Rubin Ridge," which stretches about 4 miles (6.5 kilometers), end-to-end, on the northwestern flank of lower Mount Sharp. The view combines 112 images taken with the Mastcam's right-eye camera, which has a telephoto lens, on April 4, 2017, during the 1,657th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars. It has been white-balanced so that colors of the rock and sand materials resemble how they would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. It spans from east-southeast on the left to south-southwest on the right, from a rover location about half a mile (0.8 kilometer) from the closest part of the ridge. Hematite, an iron-oxide mineral, has been detected in this ridge by the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The ridge has been an identified destination for Curiosity since before the rover's August 2012 landing near the base of Mount Sharp, inside Gale Crater. The ridge was informally named in early 2017 in memory of Vera Cooper Rubin (1928-2016), whose astronomical observations provided evidence for the existence of the universe's dark matter. An annotated version and full resolution TIFF files are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21717
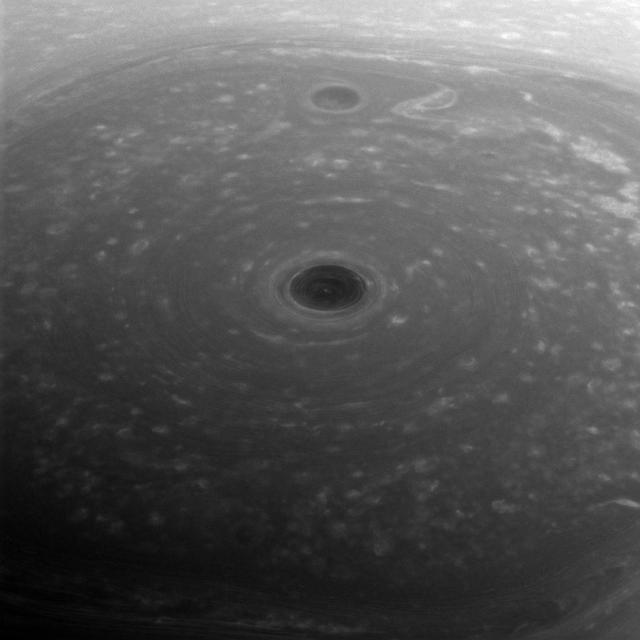

These turbulent clouds are on top of the world at Saturn. NASA's Cassini spacecraft captured this view of Saturn's north pole on April 26, 2017 - the day it began its Grand Finale -- as it approached the planet for its first daring dive through the gap between the planet and its rings. Although the pole is still bathed in sunlight at present, northern summer solstice on Saturn occurred on May 24, 2017, bringing the maximum solar illumination to the north polar region. Now the Sun begins its slow descent in the northern sky, which eventually will plunge the north pole into Earth-years of darkness. Cassini's long mission at Saturn enabled the spacecraft to see the Sun rise over the north, revealing that region in great detail for the first time. This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 44 degrees above the ring plane. The image was taken with the Cassini spacecraft wide-angle camera using a spectral filter which preferentially admits wavelengths of near-infrared light centered at 752 nanometers. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 166,000 miles (267,000 kilometers) from Saturn. Image scale is about 10 miles (16 kilometers) per pixel. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21343
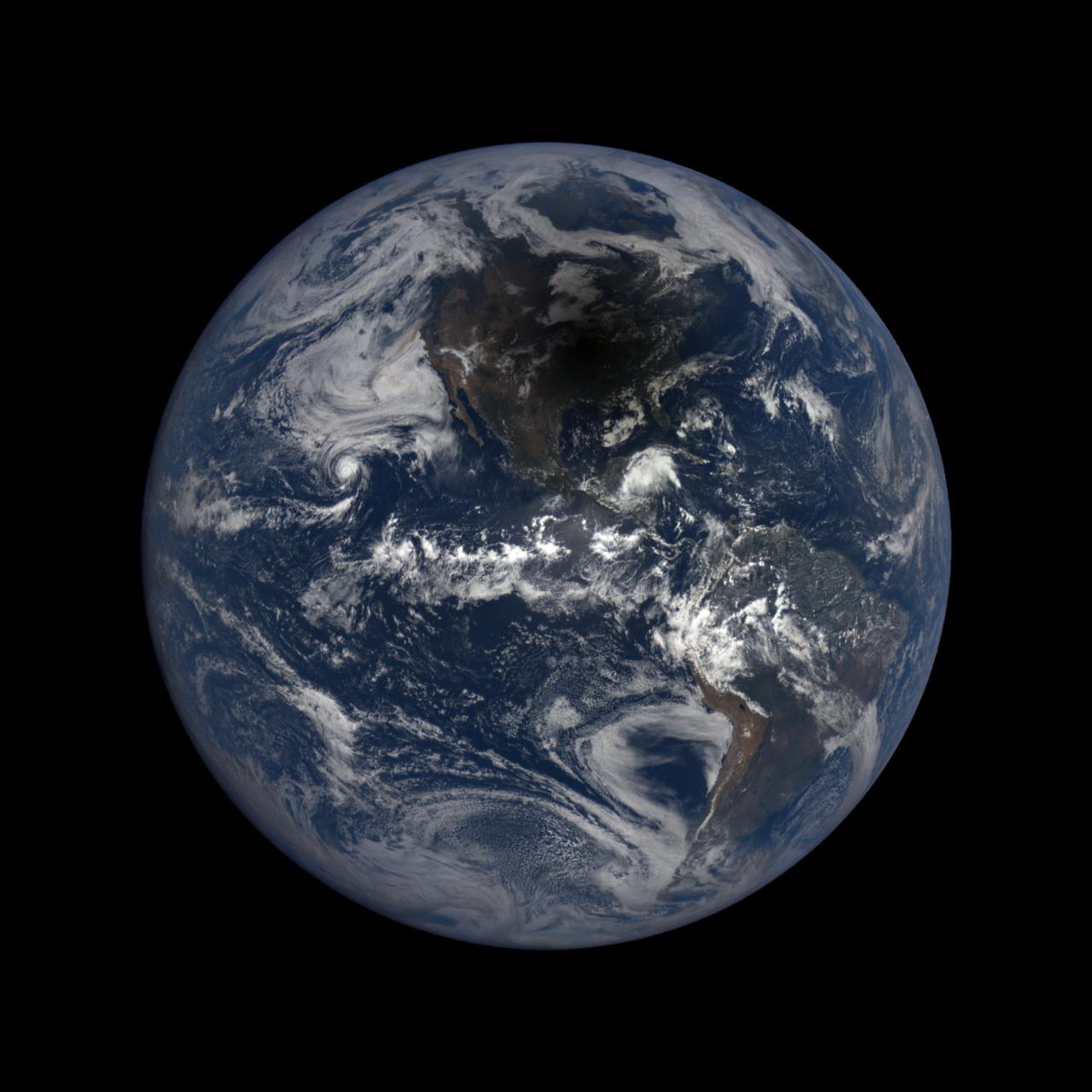

From a million miles out in space, NASA’s Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC) captured natural color images of the moon’s shadow crossing over North America on Aug. 21, 2017. EPIC is aboard NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR), where it photographs the full sunlit side of Earth every day, giving it a unique view of total solar eclipses. EPIC normally takes about 20 to 22 images of Earth per day, so this animation appears to speed up the progression of the eclipse. To see the images of Earth every day, go to: <a href="https://epic.gsfc.nasa.gov" rel="nofollow">epic.gsfc.nasa.gov</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
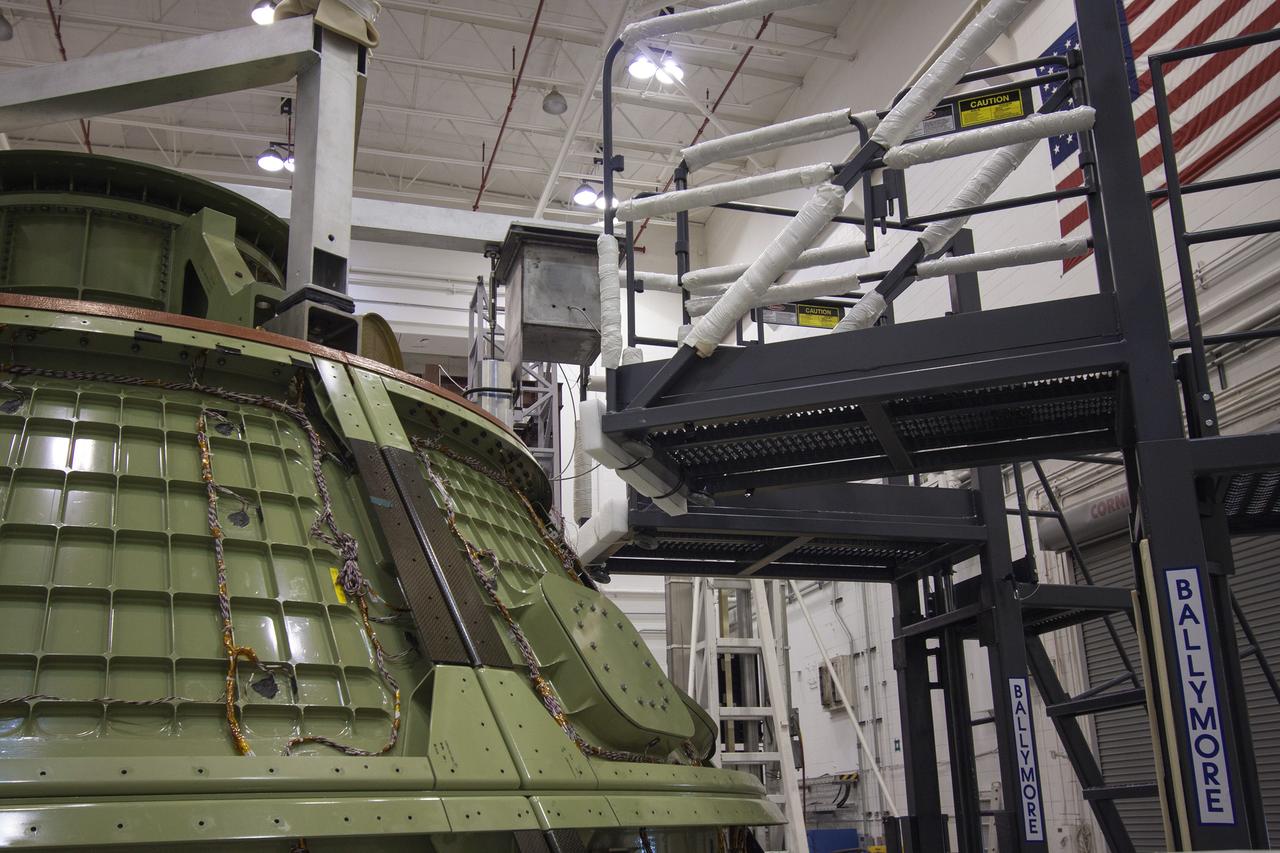

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space in Florida, a second firing of the escape hold down post has occurred during a pyrotechnic bolt test on the Orion ground test vehicle. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
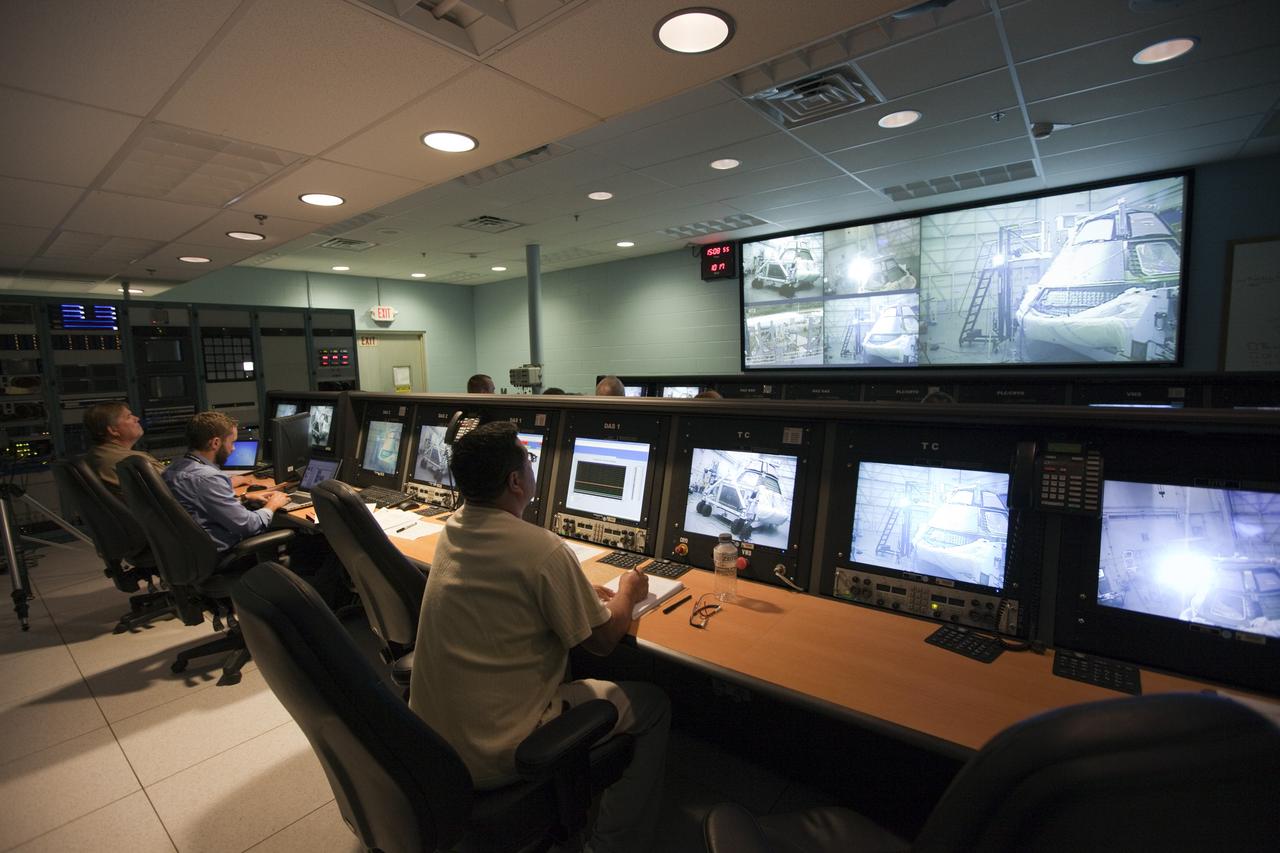

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- Inside the control room at the Launch Equipment Test Facility, or LETF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin engineers monitor the pyrotechnic bolt test on the Orion ground test vehicle at the LETF. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
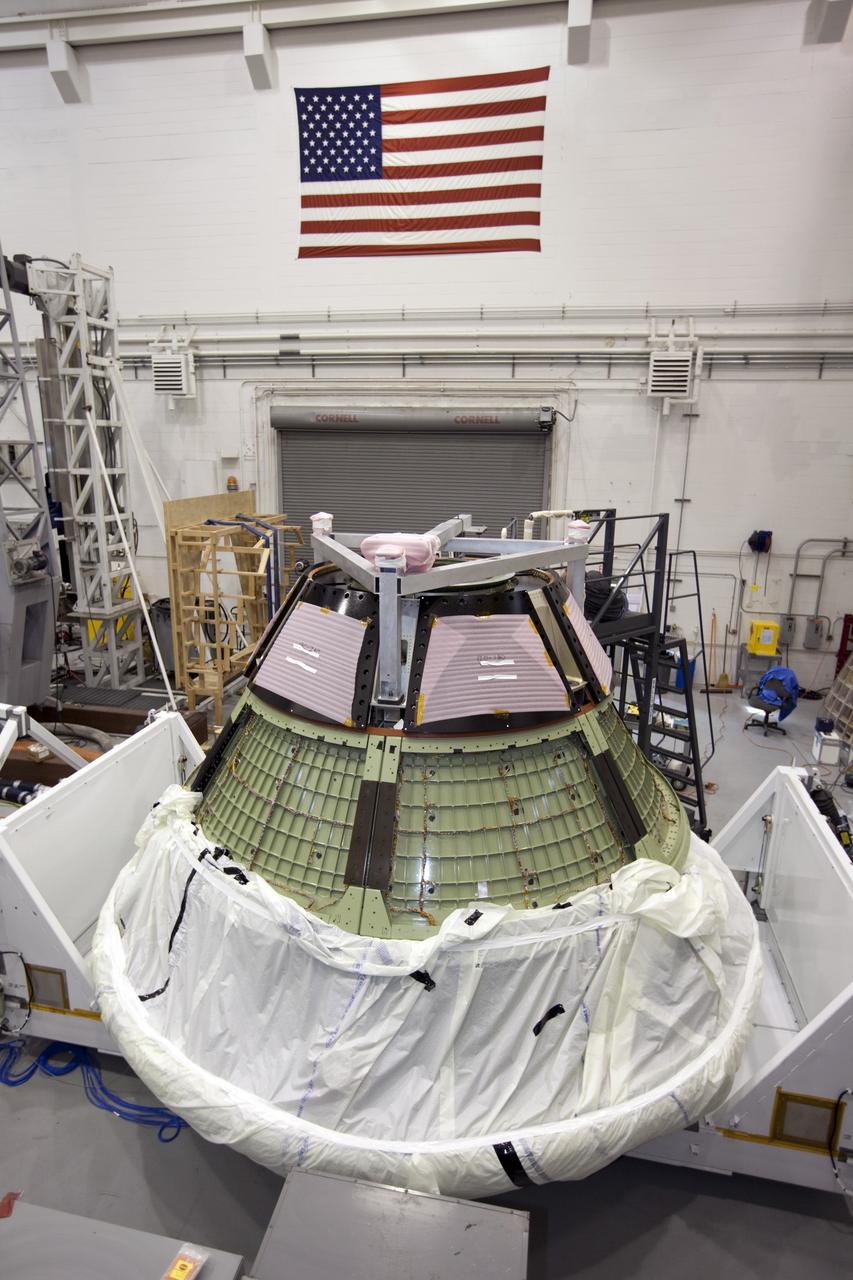

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space in Florida, the Orion ground test vehicle has been transferred to a test stand and prepared for a pyrotechnic bolt test. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
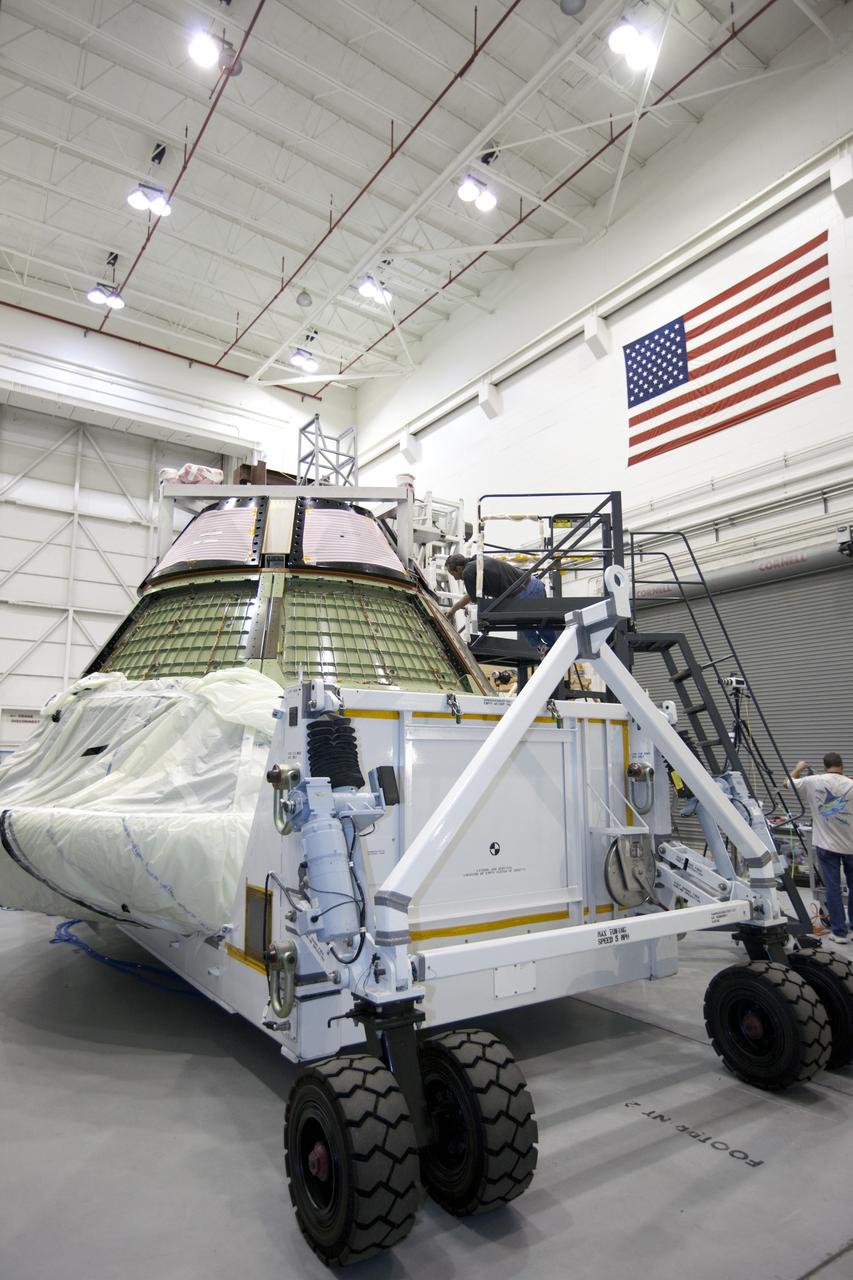

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- The Orion ground test vehicle sits on a test stand in the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida while engineers and technicians prepare it for a pyrotechnic bolt test. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
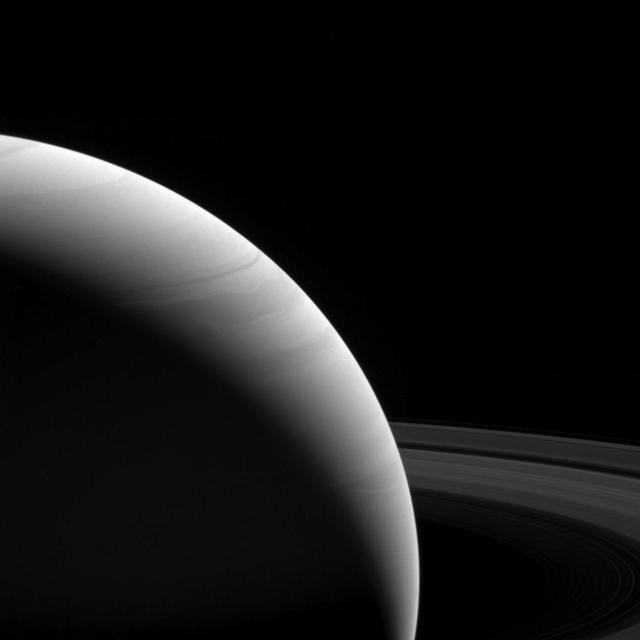

The light of a new day on Saturn illuminates the planet's wavy cloud patterns and the smooth arcs of the vast rings. The light has traveled around 80 minutes since it left the sun's surface by the time it reaches Saturn. The illumination it provides is feeble; Earth gets 100 times the intensity since it's roughly ten times closer to the sun. Yet compared to the deep blackness of space, everything at Saturn still shines bright in the sunlight, be it direct or reflected. This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 10 degrees above the ring plane. The image was taken with the Cassini spacecraft wide-angle camera on Feb. 25, 2017 using a spectral filter which preferentially admits wavelengths of near-infrared light centered at 939 nanometers. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 762,000 miles (1.23 million kilometers) from Saturn. Image scale is 45 miles (73 kilometers) per pixel. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21336
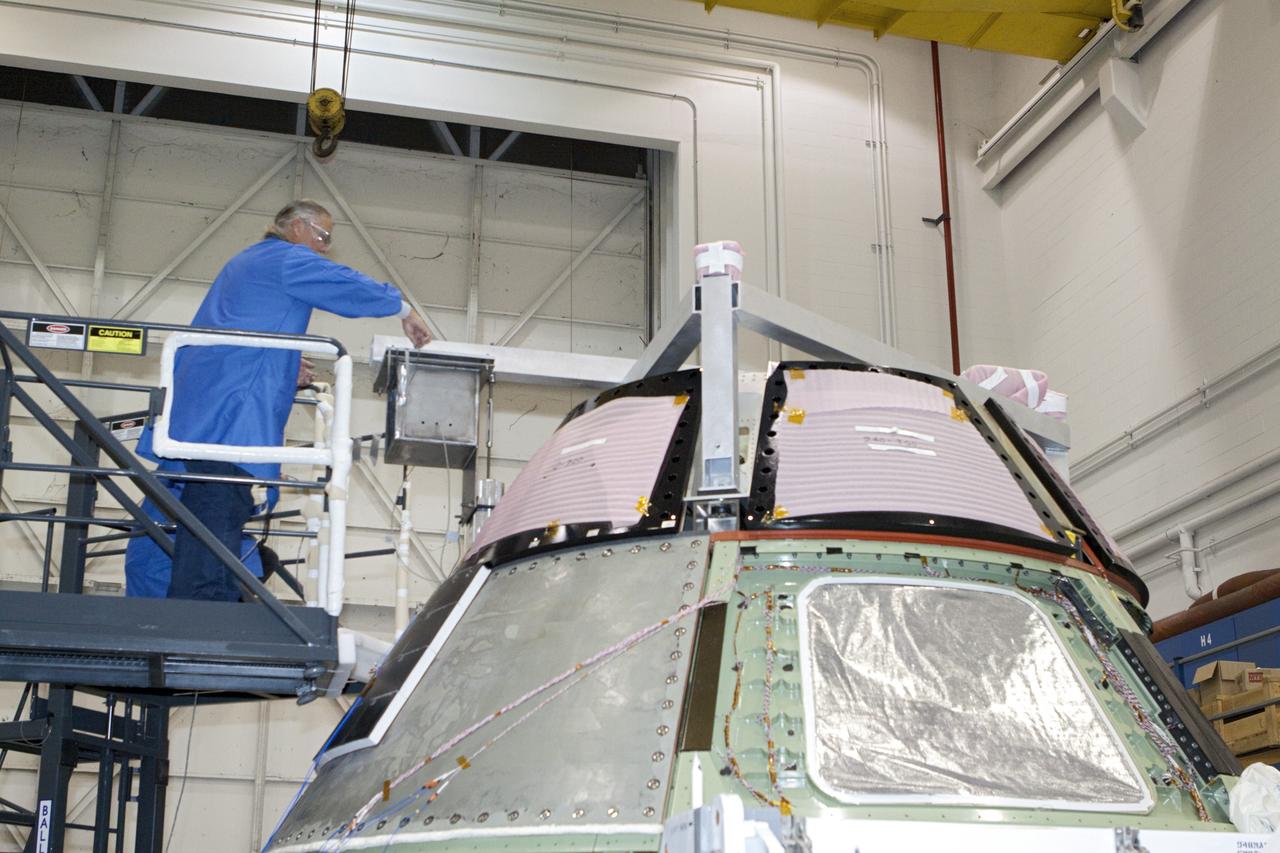

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space in Florida, a Lockheed Martin technician prepares the Orion ground test vehicle for a pyrotechnic bolt test. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
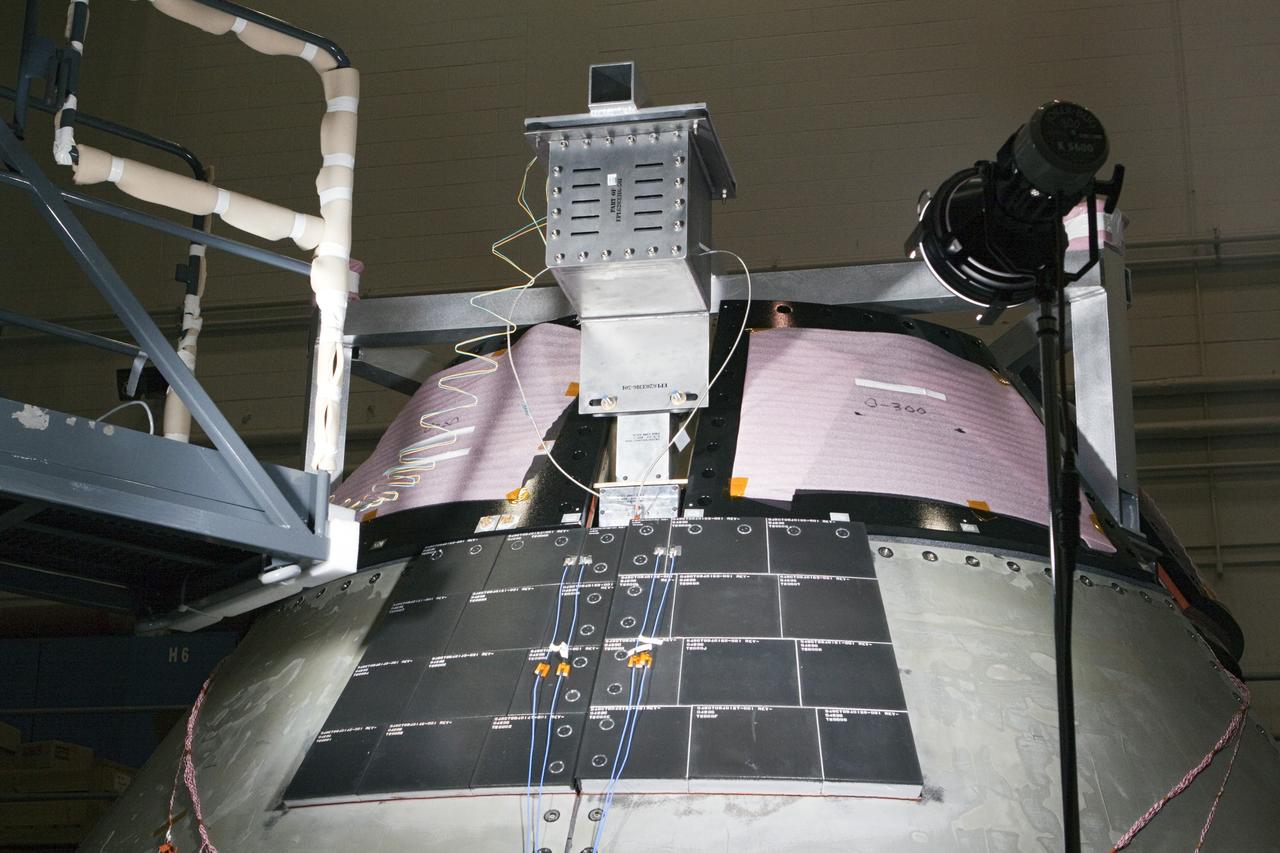

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space in Florida, sensors have been placed on the Orion ground test vehicle and cameras placed nearby in order to monitor pyrotechnic bolt tests. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
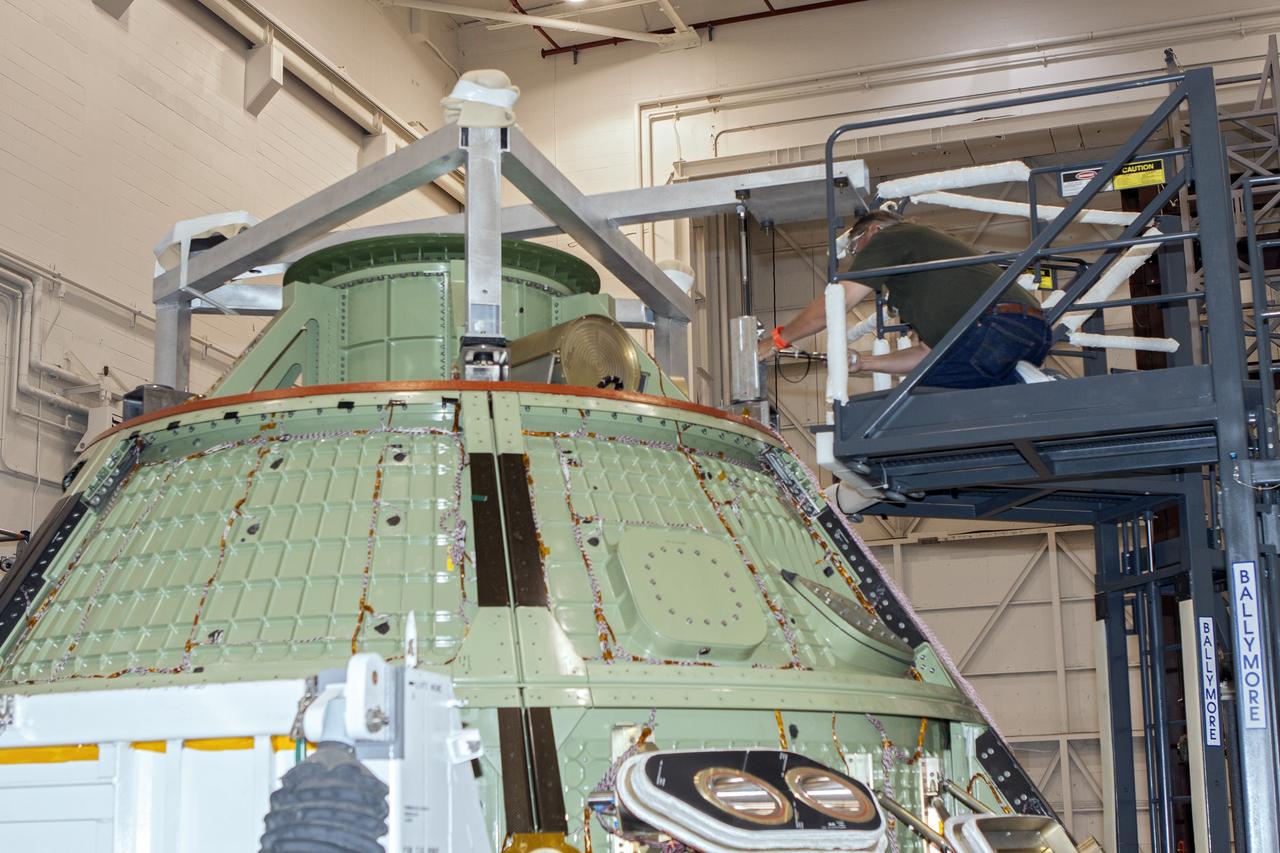

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Orion ground test vehicle sits on a test stand in the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida while engineers and technicians prepare it for a pyrotechnic bolt test. Lockheed Martin performed tests over a series of days on the explosive bolts that separate Orion from the launch abort system. Data was collected on the effect of shock waves on Orion during the explosive bolt separation. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

This 360-degree mosaic from the Mast Camera (Mastcam) on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover looks out over a portion of the Bagnold Dunes, which stretch for several miles. From early February to early April 2017, the rover examined four sites near linear dunes for comparison with what it found in late 2015 and early 2016 during its investigation of crescent-shaped dunes. The dark, rippled surface of a linear dune is visible at the center of the view and receding into the distance to the left. The bedrock of the Murray formation, made from sediments deposited in lakes billions of years ago, is in the foreground, along with some components of the rover. The location, called "Ogunquit Beach," is on the northwestern flank of lower Mount Sharp. Northwest is at both ends of this full-circle panorama; southeast is at the center, where a higher portion of Mount Sharp dominates the horizon. Among the questions this Martian dune campaign is addressing is how winds shape the dunes into different patterns. Others include whether Martian winds sort grains of sand in ways that affect the distribution of mineral compositions, which also would have implications for studies of Martian sandstones. The 115 individual images that were combined into this mosaic were acquired by the Mastcam's left-eye camera on March 24 and March 25, 2017, (PST) during the 1,647th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars. This mosaic is white-balanced so that the colors of the colors of the rock and sand materials resemble how they would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. The rover's position on Sol 1647 is shown at https://mars.nasa.gov/multimedia/images/2017/curiositys-traverse-map-through-sol-1646 as the location reached by a drive on Sol 1646. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11241

Two of the raised treads, called grousers, on the left middle wheel of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover broke during the first quarter of 2017, including the one seen partially detached at the top of the wheel in this image from the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera on the rover's arm. This image was taken on March 19, 2017, as part of a set used by rover team members to inspect the condition of the rover's six wheels during the 1,641st Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars. Holes and tears in the wheels worsened significantly during 2013 as Curiosity was crossing terrain studded with sharp rocks on the route from near its 2012 landing site to the base of Mount Sharp. Team members have used MAHLI systematically since then to watch for when any of the zig-zag shaped grousers begin to break. The last prior set of wheel-inspection images from before Sol 1641 was taken on Jan. 27, 2017, (Sol 1591) and revealed no broken grousers. Longevity testing with identical aluminum wheels on Earth indicates that when three grousers on a given wheel have broken, that wheel has reached about 60 percent of its useful life. Curiosity has driven well over 60 percent of the amount needed for reaching all the geological layers planned as the mission's science destinations, so the start of seeing broken grousers is not expected to affect the mission's operations. Curiosity's six aluminum wheels are about 20 inches (50 centimeters) in diameter and 16 inches (40 centimeters) wide. Each of the six wheels has its own drive motor, and the four corner wheels also have steering motors. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21486
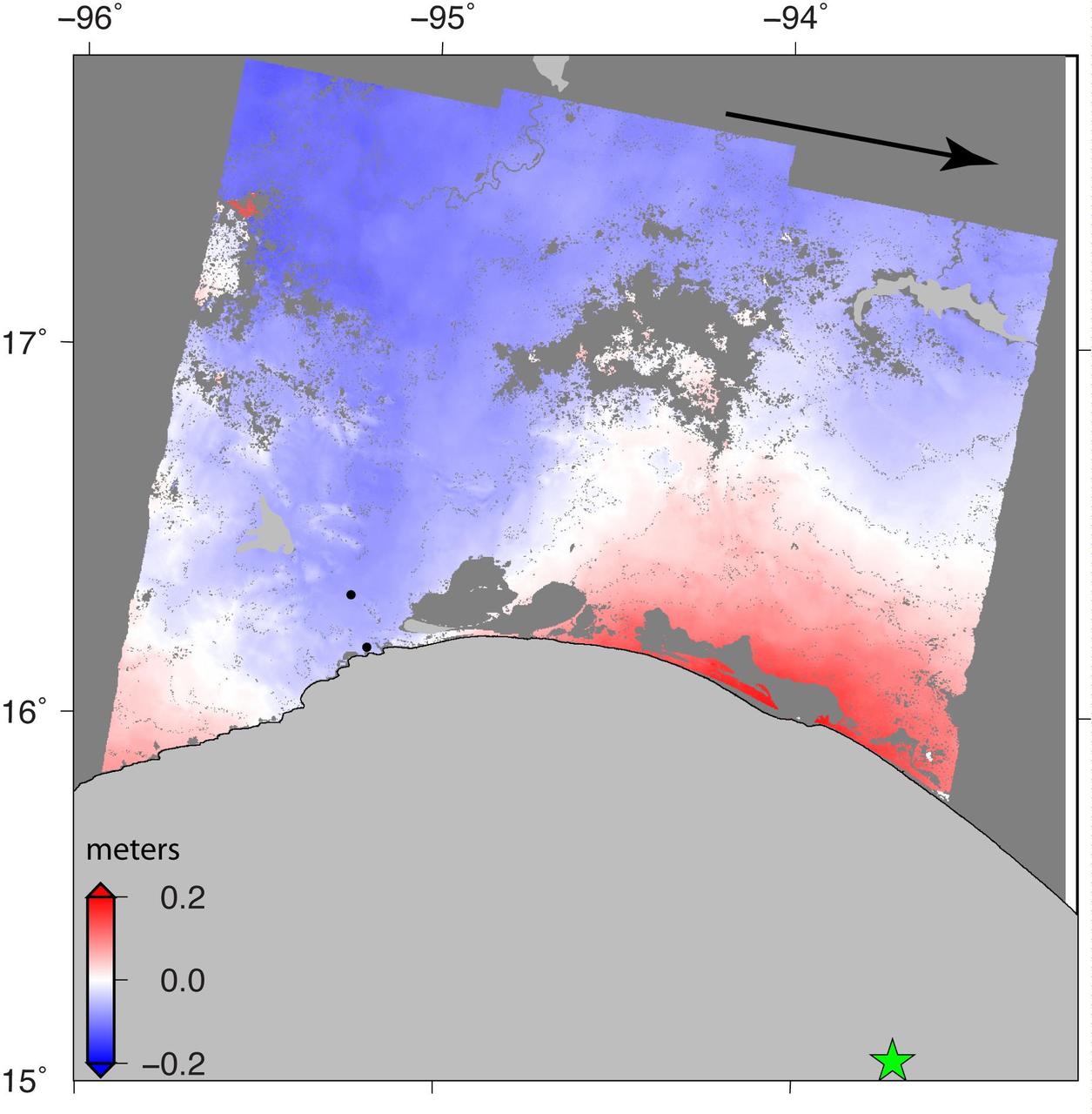
NASA and its partners are contributing important observations and expertise to the ongoing response to the Sept. 7, 2017 (local time), magnitude 8.1 Oaxaca-Chiapas earthquake in Mexico. This earthquake was the strongest in more than a century in Mexico. It has caused a significant humanitarian crisis, with widespread building damage and triggered landslides throughout the region. Scientists with the Advanced Rapid Imaging and Analysis project (ARIA), a collaboration between NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California; and Caltech, also in Pasadena, analyzed interferometric synthetic aperture radar images from the radar instrument on the Copernicus Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-1B satellites operated by the European Space Agency (ESA) to calculate a map of the deformation of Earth's surface caused by the quake. This false-color map shows the amount of permanent surface movement caused almost entirely by the earthquake, as viewed by the satellite, during a six-day interval between radar images acquired by the two Sentinel-1 satellites on Sept. 7 and Sept. 13, 2017. In this map, the colors of the surface displacements are proportional to the surface motion. The red tones show the areas along the coast of Chiapas and Oaxaca have moved toward the satellite by as much as 9 inches (22 centimeters) in a combination of up and eastward motion. The area in between and farther north with various shades of blue moved away from the satellite, mostly downward or westward, by as much as 6 inches (15 centimeters). Areas without color are open water or heavy vegetation, which prevent the radar from measuring change between the satellite images. Scientists use these maps to build detailed models of the fault slip at depth and associated land movements to better understand the impact on future earthquake activity. The green star shows the location of the earthquake epicenter estimated by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) National Earthquake Information Center. Map contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data 2017, processed by ESA and analyzed by the NASA-JPL/Caltech ARIA team. This research was carried out at JPL under a contract with NASA. Sentinel-1 data were accessed through the Copernicus Open Access Hub. An annotated figures is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21962

This view from the Mast Camera (Mastcam) on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover shows two scales of ripples, plus other textures, in an area where the mission examined a linear-shaped dune in the Bagnold dune field on lower Mount Sharp. The scene is an excerpt from a 360-degree panorama acquired on March 24 and March 25, 2017, (PST) during the 1,647th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars, at a location called "Ogunquit Beach." Crests of the longer ripples visible in the dark sand of the dune are several feet (a few meters) apart. This medium-scale feature in active sand dunes on Mars was one of Curiosity's findings at the crescent-shaped dunes that the rover examined in late 2015 and early 2016. Ripples that scale are not seen on Earth's sand dunes. Overlaid on those ripples are much smaller ripples, with crests about ten times closer together. Textures of the local bedrock in the foreground -- part of the Murray formation that originated as lakebed sediments -- and of gravel-covered ground (at right) are also visible. The image has been white-balanced so that the colors of the colors of the rock and sand materials resemble how they would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11242
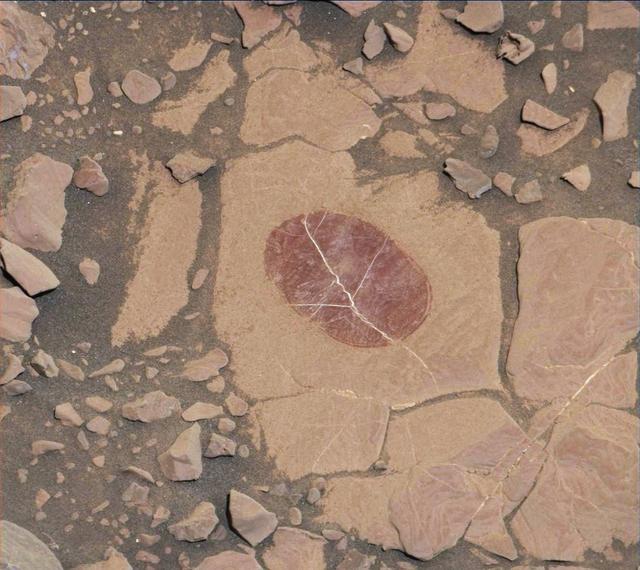

On a part of "Vera Rubin Ridge" where rover-team researchers sought to determine whether dust coatings are hiding rocks' hematite content, the Mast Camera (Mastcam) on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover took this image of a rock surface that had been brushed with the rover's Dust Removal Tool. The image is shown in the usual full color of featured Mastcam images: with a color adjustment similar to white balancing for approximating how the rocks and sand would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. Sunlight on Mars is tinged by the dusty atmosphere and this adjustment helps geologists recognize color patterns they are familiar with on Earth. In this case, the purplish tint of the brushed area suggested fine-grained hematite. Bright lines within the rocks are fractures filled with calcium sulfate minerals. The brushed area is about 2.5 inches (6 centimeters) across. The image was taken on Sept. 17, 2017, during the 1,819th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars. Mastcam also imaged this same scene using three special filters that help to identify hematite, an iron-oxide mineral that can provide information about ancient environmental conditions. A science-filters image identifies hematite in this brushed target even more clearly. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22067

This illustration shows what the TRAPPIST-1 system might look like from a vantage point near planet TRAPPIST-1f (at right). The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial, according to research published in 2017 in the journal Nature. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. They are likely all tidally locked, meaning the same face of the planet is always pointed at the star, as the same side of our moon is always pointed at Earth. This creates a perpetual night side and perpetual day side on each planet. TRAPPIST-1b and c receive the most light from the star and would be the warmest. TRAPPIST-1e, f and g all orbit in the habitable zone, the area where liquid water is most likely to be detected. But any of the planets could potentially harbor liquid water, depending on their compositions. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21751

NASA's Juno spacecraft soared directly over Jupiter's south pole when JunoCam acquired this image on February 2, 2017 at 6:06 a.m. PT (9:06 a.m. ET), from an altitude of about 62,800 miles (101,000 kilometers) above the cloud tops. From this unique vantage point we see the terminator (where day meets night) cutting across the Jovian south polar region's restless, marbled atmosphere with the south pole itself approximately in the center of that border. The terminator is offset a bit because it's summer in Jupiter's southern hemisphere. However, the tilt of Jupiter's spin axis is only 3 degrees, much less than Earth's 23.5-degree tilt. This image was processed by citizen scientist John Landino. This enhanced color version highlights the bright high clouds and numerous meandering oval storms. Away from the polar region, the seeming chaos of Jupiter's polar region gives way to the more familiar color banding that Jupiter is known for. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21382
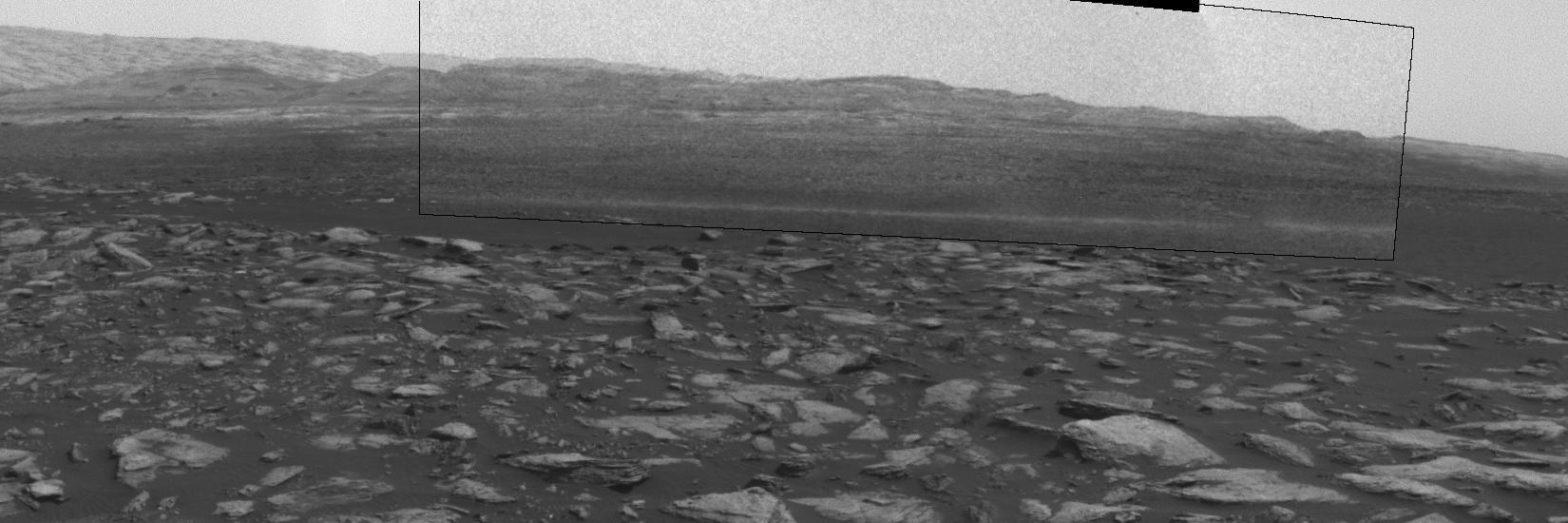

This frame from a sequence of images shows a dust-carrying whirlwind, called a dust devil, scooting across the ground inside Gale Crater, as observed on the local summer afternoon of NASA's Curiosity Mars Rover's 1,597th Martian day, or sol (Feb. 1, 2017). Set within a broader southward view from the rover's Navigation Camera, the rectangular area outlined in black was imaged multiple times over a span of several minutes to check for dust devils. Images from the period with most activity are shown in the inset area. The images are in pairs that were taken about 12 seconds apart, with an interval of about 90 seconds between pairs. Timing is accelerated and not fully proportional in this animation. A dust devil is most evident in the 10th, 11th and 12th frames. In the first and fifth frames, dust blowing across the ground appears as pale horizontal streak. Contrast has been modified to make frame-to-frame changes easier to see. A black frame is added between repeats of the sequence. On Mars as on Earth, dust devils are whirlwinds that result from sunshine warming the ground, prompting convective rising of air that has gained heat from the ground. Observations of Martian dust devils provide information about wind directions and interaction between the surface and the atmosphere. An animation is available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21270
NASA's Cassini spacecraft stared at Saturn for nearly 44 hours on April 25 to 27, 2016, to obtain this movie showing just over four Saturn days. With Cassini's orbit being moved closer to the planet in preparation for the mission's 2017 finale, scientists took this final opportunity to capture a long movie in which the planet's full disk fit into a single wide-angle camera frame. Visible at top is the giant hexagon-shaped jet stream that surrounds the planet's north pole. Each side of this huge shape is slightly wider than Earth. The resolution of the 250 natural color wide-angle camera frames comprising this movie is 512x512 pixels, rather than the camera's full resolution of 1024x1024 pixels. Cassini's imaging cameras have the ability to take reduced-size images like these in order to decrease the amount of data storage space required for an observation. The spacecraft began acquiring this sequence of images just after it obtained the images to make a three-panel color mosaic. When it began taking images for this movie sequence, Cassini was 1,847,000 miles (2,973,000 kilometers) from Saturn, with an image scale of 355 kilometers per pixel. When it finished gathering the images, the spacecraft had moved 171,000 miles (275,000 kilometers) closer to the planet, with an image scale of 200 miles (322 kilometers) per pixel. A movie is available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21047
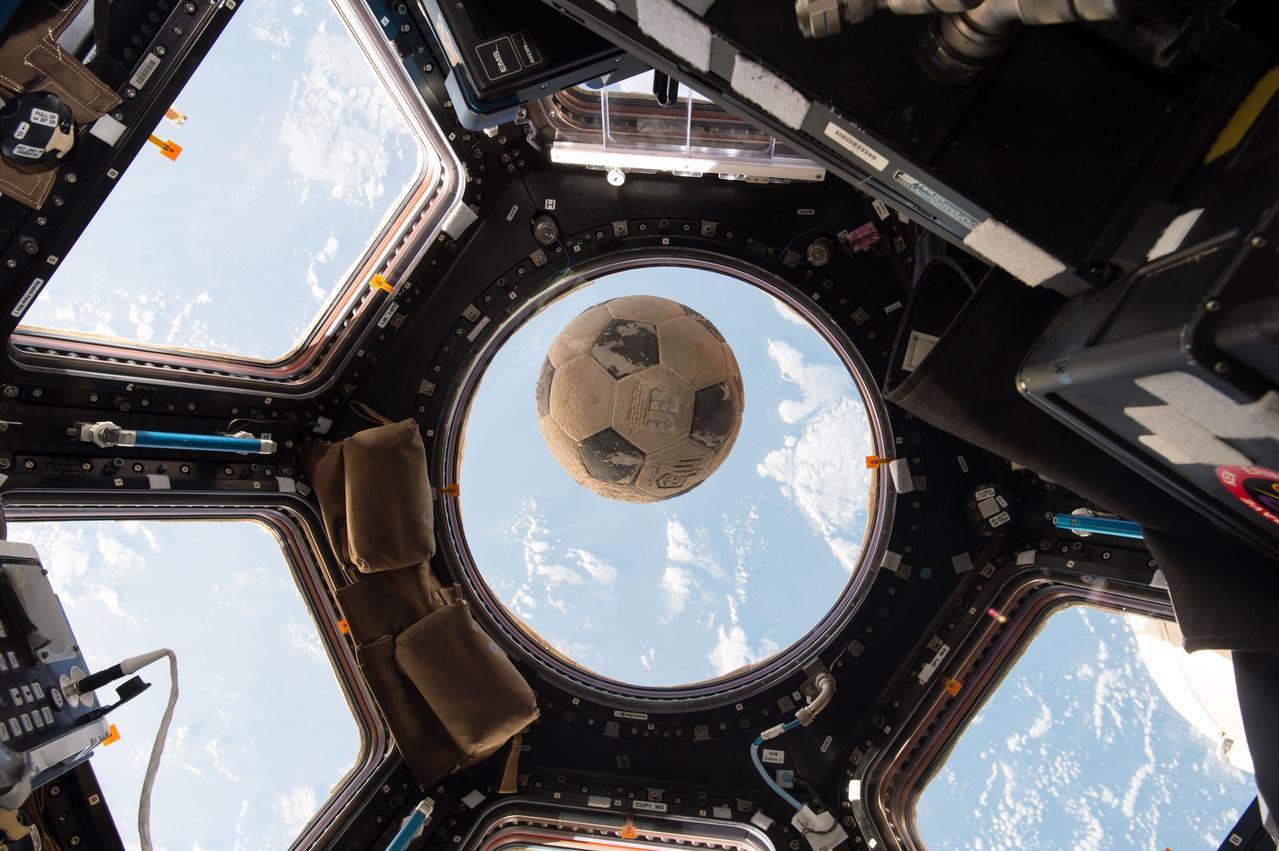

iss050e033912 (01/21/2017) --- A soccer ball originally packed onto space shuttle Challenger in 1986 is now orbiting the Earth on board the International Space Station, 31 years later. The soccer ball was signed and presented to NASA astronaut Ellison Onizuka by soccer players – including his daughter – from Clear Lake High School, near NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Onizuka was one of seven astronauts on board Challenger on Jan. 28, 1986, when it exploded shortly after liftoff. Following the accident, the ball was recovered and returned to the high school, where it has been on display for the past three decades. Its history had begun to fade into obscurity when Principal Karen Engle learned of its origin. Soon after, astronaut Shane Kimbrough, whose son attends Clear Lake High School, offered to carry up a memento on the school’s behalf, and she had the idea to send the soccer ball into space. Kimbrough snapped this photo of the ball floating in front of the station’s Cupola window in advance of Challenger anniversary and NASA’s Day of Remembrance.

Bands of lake effect snow drift eastward from the western Great Lakes in this true-color image captured by the NOAA/NASA Suomi NPP satellite's Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument on January 5, 2017. National Weather Service forecasters expect light to moderate lake effect snow showers to continue throughout the day today and into Saturday (1/7). Lake-effect snow forms when cold air passes over the warmer waters of a lake. This causes some lake water to evaporate into the air and warm it. This warmer, wetter air rises and cools as it moves away from the lake. When it cools, it releases that moisture and, if it’s cold enough, that moisture turns into snow. Although true-color images like this may appear to be photographs of Earth, they aren't. They are created by combining data from the three color channels on the VIIRS instrument sensitive to the red, green and blue (or RGB) wavelengths of light into one composite image. In addition, data from several other channels are often also included to cancel out or correct atmospheric interference that may blur parts of the image. Credit: NOAA/NASA/Suomi NPP via NOAA's Environmental Visualization Laboratory

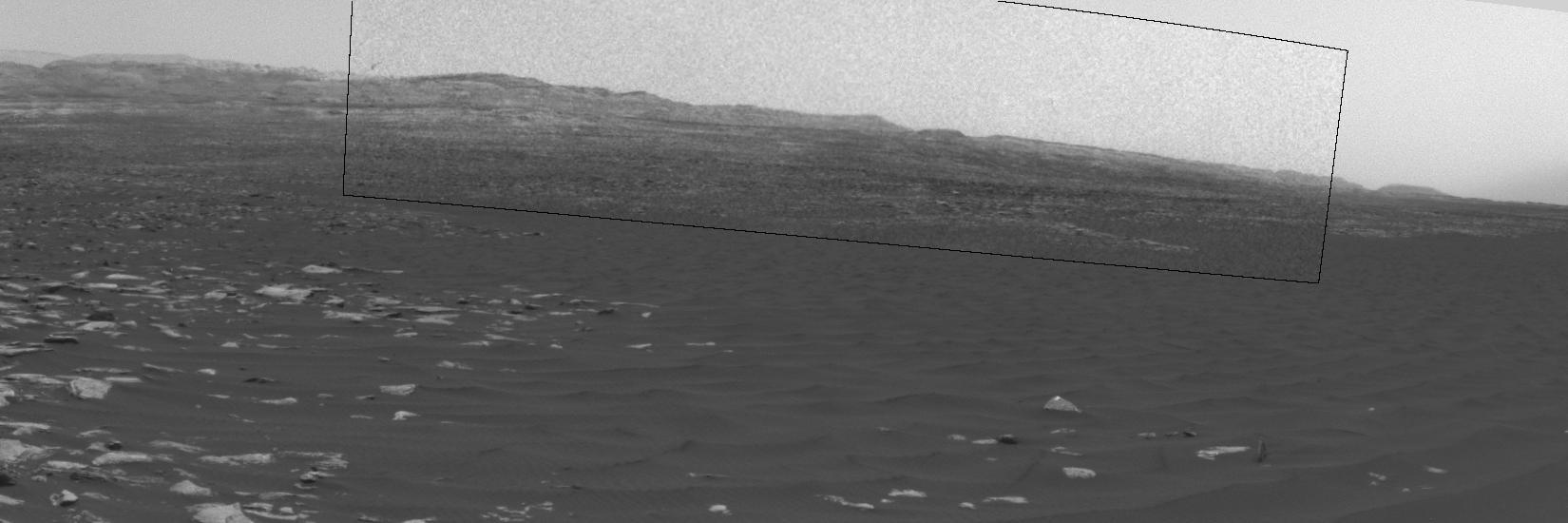
Late-afternoon shadows include one cast by the rover itself in this look toward the floor of Endeavour Crater by NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity. The rover recorded this scene on Nov. 11, 2017, during the 4,911th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's work on Mars. That was about a week before Opportunity's eighth Martian winter solstice. Opportunity's location is partway down a narrow valley that descends from the crest of the western rim of Endeavour Crater to the crater's floor. This fluid-carved set of troughs, called "Perseverance Valley," is the length of about two football fields, at a slope of about 15 to 17 degrees. The Navigation Camera (Navcam) on Opportunity's mast took the three component images stitched together into this scene. The images were taken about three minutes apart, long enough to see how the shadow was changing on the slope, at the seams between the images. Wheel tracks in the lower right of the scene were made before the rover climbed back uphill for a closer look at some rocks it had passed. The portions of the rover in the shadow at upper right include the mast with the Navcam and Panoramic Camera (Pancam) on top and the UHF radio antenna, which Opportunity uses to transmit images and other data to overflying orbiters for relay to Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22071
This frame from a sequence of images shows a dust-carrying whirlwind, called a dust devil, on lower Mount Sharp inside Gale Crater, as viewed by NASA's Curiosity Mars Rover during the summer afternoon of the rover's 1,613rd Martian day, or sol (Feb. 18, 2017). Set within a broader southward view from the rover's Navigation Camera, the rectangular area outlined in black was imaged multiple times over a span of several minutes to check for dust devils. Images from the period with most activity are shown in the inset area. The images are in pairs that were taken about 12 seconds apart, with an interval of about 90 seconds between pairs. Timing is accelerated and not fully proportional in this animation. Contrast has been modified to make frame-to-frame changes easier to see. A black frame provides a marker between repeats of the sequence. On Mars as on Earth, dust devils result from sunshine warming the ground, prompting convective rising of air that has gained heat from the ground. Observations of dust devils provide information about wind directions and interaction between the surface and the atmosphere. An animation is available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21483

Twice a year, NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, has an eclipse season — a weeks-long period in which Earth blocks SDO’s view of the sun for part of each day. This footage captured by SDO on Feb. 15, 2017, shows one such eclipse. Earth’s edge appears fuzzy, rather than crisp, because the sun’s light is able to shine through Earth’s atmosphere in some places. These images were captured in wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light, which is typically invisible to our eyes, but is colorized here in gold. Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This artist's concept shows what the TRAPPIST-1 planetary system may look like, based on available data about the planets' diameters, masses and distances from the host star. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial, according to research published in 2017 in the journal Nature. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. They are likely all tidally locked, meaning the same face of the planet is always pointed at the star, as the same side of our moon is always pointed at Earth. This creates a perpetual night side and perpetual day side on each planet. TRAPPIST-1b and c receive the most light from the star and would be the warmest. TRAPPIST-1e, f and g all orbit in the habitable zone, the area where liquid water is most likely to be detected. But any of the planets could potentially harbor liquid water, depending on their compositions. In the imagined planets shown here, TRAPPIST-1b is shown as a larger analogue to Jupiter's moon Io. TRAPPIST-1d is depicted with a narrow band of water near the terminator, the divide between a hot, dry day and an ice-covered night side. TRAPPIST-1e and TRAPPIST-1f are both shown covered in water, but with progressively larger ice caps on the night side. TRAPPIST-1g is portrayed with an atmosphere like Neptune's, although it is still a rocky world. TRAPPIST-1h, the farthest from the star, would be the coldest. It is portrayed here as an icy world, similar to Jupiter's moon Europa, but the least is known about it. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21422
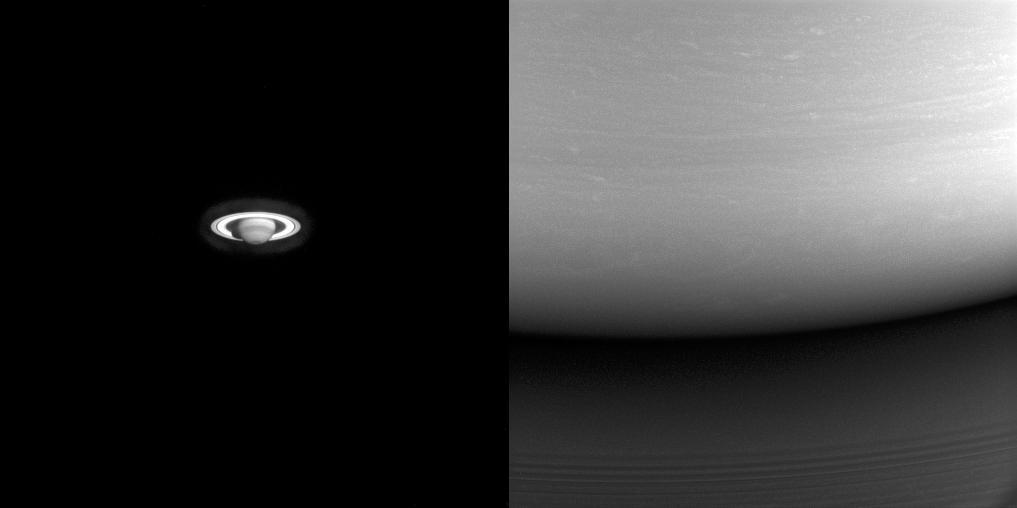

These two images illustrate just how far Cassini traveled to get to Saturn. On the left is one of the earliest images Cassini took of the ringed planet, captured during the long voyage from the inner solar system. On the right is one of Cassini's final images of Saturn, showing the site where the spacecraft would enter the atmosphere on the following day. In the left image, taken in 2001, about six months after the spacecraft passed Jupiter for a gravity assist flyby, the best view of Saturn using the spacecraft's high-resolution (narrow-angle) camera was on the order of what could be seen using the Earth-orbiting Hubble Space Telescope. At the end of the mission (at right), from close to Saturn, even the lower resolution (wide-angle) camera could capture just a tiny part of the planet. The left image looks toward Saturn from 20 degrees below the ring plane and was taken on July 13, 2001 in wavelengths of infrared light centered at 727 nanometers using the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera. The view at right is centered on a point 6 degrees north of the equator and was taken in visible light using the wide-angle camera on Sept. 14, 2017. The view on the left was acquired at a distance of approximately 317 million miles (510 million kilometers) from Saturn. Image scale is about 1,900 miles (3,100 kilometers) per pixel. The view at right was acquired at a distance of approximately 360,000 miles (579,000 kilometers) from Saturn. Image scale is 22 miles (35 kilometers) per pixel. The Cassini spacecraft ended its mission on Sept. 15, 2017. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21353

Researchers used the Mast Camera (Mastcam) on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover to gain this detailed view of layers in "Vera Rubin Ridge" from just below the ridge. The scene combines 70 images taken with the Mastcam's right-eye, telephoto-lens camera, on Aug. 13, 2017, during the 1,785th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars. This and other Mastcam panoramas show details of the sedimentary rocks that make up the "Vera Rubin Ridge." This distinct topographic feature located on the lower slopes of Mount Sharp (Aeolis Mons) is characterized by the presence of hematite, an iron-oxide mineral, which has been detected from orbit. The Mastcam images show that the rocks making up the lower part of the ridge are characterized by distinct horizontal stratification with individual rock layers of the order of several inches (tens of centimeters) thick. Scientists on the mission are using such images to determine the ancient environment these rocks were deposited in. The repeated beds indicate progressive accumulation of sediments that now make up the lower part of Mount Sharp, although from this distance it is not possible to know if they were formed by aqueous or wind-blown processes. Close-up images collected as the rover climbs the ridge will help answer this question. The stratified rocks are cross cut by veins filled with a white mineral, likely calcium sulfate, that provide evidence of later episodes of fluid flow through the rocks. The panorama has been white-balanced so that the colors of the rock materials resemble how they would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. It spans from southeast on the left to west on the right. The Sol 1785 location just north of the ridge is shown in a Sol 1782 traverse map. The ridge was informally named in early 2017 in memory of Vera Cooper Rubin (1928-2016), whose astronomical observations provided evidence for the existence of the universe's dark matter. An annotated figure is shown at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21850
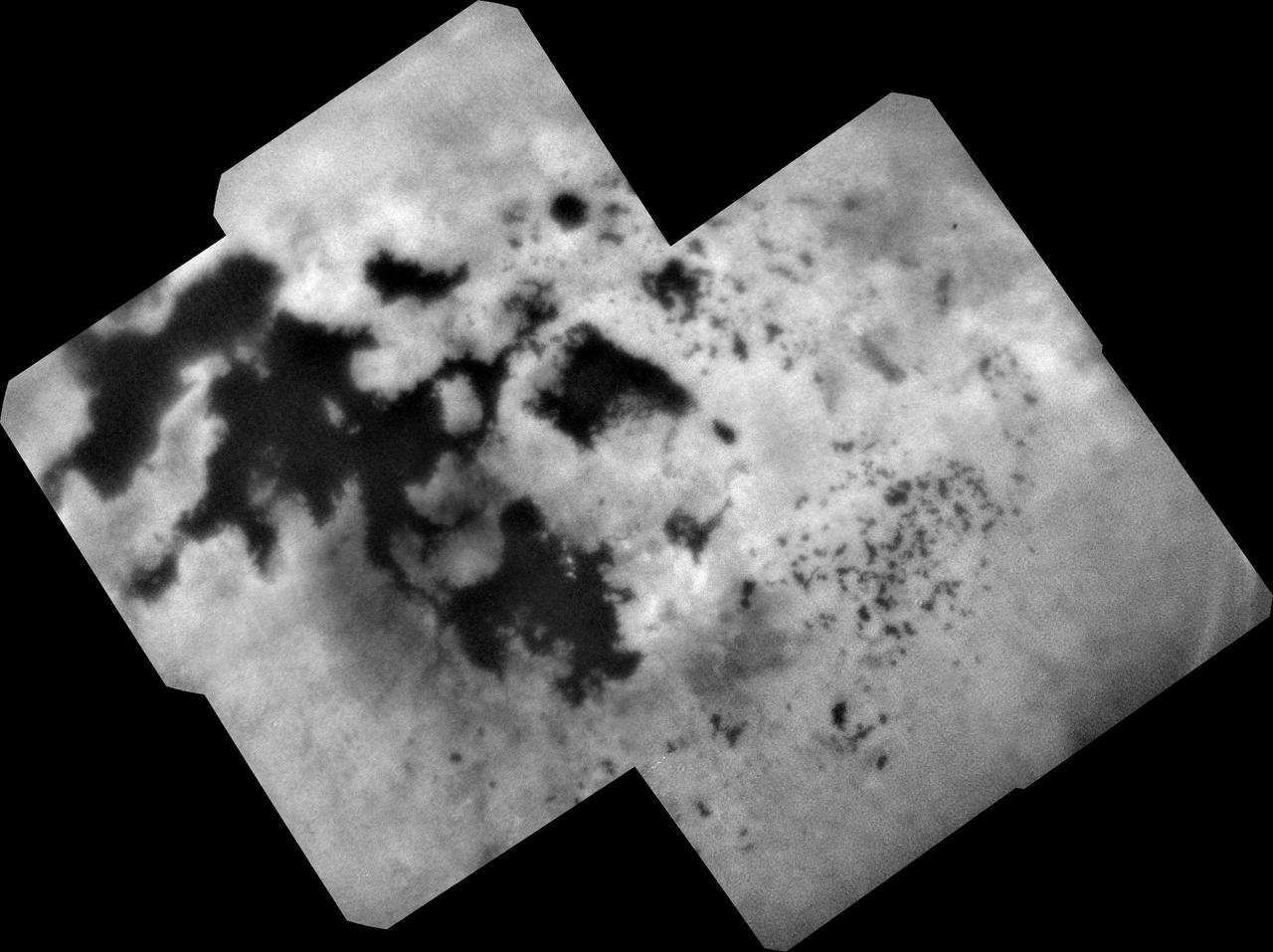
During NASA's Cassini mission's final distant encounter with Saturn's giant moon Titan, the spacecraft captured this view of the enigmatic moon's north polar landscape of lakes and seas, which are filled with liquid methane and ethane. Punga Mare (240 miles, or 390 kilometers, across) is seen just above the center of the mosaic, with Ligeia Mare (300 miles, or 500 kilometers, wide) below center and vast Kraken Mare stretching off 730 miles (1,200 kilometers) to the left of the mosaic. Titan's numerous smaller lakes can be seen around the seas and scattered around the right side of the mosaic. Among the ongoing mysteries about Titan is how these lakes are formed. Another mystery at Titan has been the weather. With its dense atmosphere, Titan has a methane cycle much like Earth's water cycle of evaporation, cloud formation, rainfall, surface runoff into rivers, and collection in lakes and seas. During Titan's southern summer, Cassini observed cloud activity over the south pole (see PIA06112 and PIA06109). However, typical of observations taken during northern spring and summer, the view here reveals only a few small clouds. They appear as bright features just below the center of the mosaic, including a few above Ligeia Mare. The images in this mosaic were taken with the ISS narrow-angle camera, using a spectral filter sensitive to wavelengths of near-infrared light centered at 938 nanometers. They were captured on Sept. 11, 2017, during Cassini's last encounter with Titan. Four days later, Cassini was deliberately plunged into the atmosphere of Saturn. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 87,000 miles (140,000 kilometers) from Titan. Image scale is about 0.5 miles (800 meters) per pixel. The image is an orthographic projection centered on 67.19 degrees north latitude, 212.67 degrees west longitude. An orthographic view is most like the view seen by a distant observer looking through a telescope. The Cassini spacecraft ended its mission on Sept. 15, 2017. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22481

This look ahead from NASA's Curiosity Mars rover includes four geological layers to be examined by the mission, and higher reaches of Mount Sharp beyond the planned study area. The redder rocks of the foreground are part of the Murray formation. Pale gray rocks in the middle distance of the right half of the image are in the Clay Unit. A band between those terrains is "Vera Rubin Ridge." Rounded brown knobs beyond the Clay Unit are in the Sulfate Unit, beyond which lie higher portions of the mountain. The view combines six images taken with the rover's Mast Camera (Mastcam) on Jan. 24, 2017, during the 1,589th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars, when the rover was still more than half a mile (about a kilometer) north of Vera Rubin Ridge. The panorama has been white-balanced so that the colors of the rock and sand materials resemble how they would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. It spans from east-southeast on the left to south on the right. The Sol 1589 location was just north of the waypoint labeled "Ogunquit Beach" on a map of the area that also shows locations of the Murray formation, Vera Rubin Ridge, Clay Unit and Sulfate Unit. The ridge was informally named in early 2017 in memory of Vera Cooper Rubin (1928-2016), whose astronomical observations provided evidence for the existence of the universe's dark matter. Annotated and full resolution TIFF files are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21716

"Vera Rubin Ridge," a favored destination for NASA's Curiosity Mars rover even before the rover landed in 2012, rises near the rover nearly five years later in this panorama from Curiosity's Mast Camera (Mastcam). The scene combines 23 images taken with the Mastcam's right-eye, telephoto-lens camera, on June 22, 2017, during the 1,734th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars. The rover began ascending the ridge in September 2017. This and other Mastcam panoramas show details of the sedimentary rocks that make up the "Vera Rubin Ridge." This distinct topographic feature located on the lower slopes of Mount Sharp (Aeolis Mons) is characterized by the presence of hematite, an iron-oxide mineral, which has been detected from orbit. The Mastcam images show that the rocks making up the lower part of the ridge are characterized by distinct horizontal stratification with individual rock layers of the order of several inches (tens of centimeters) thick. Scientists on the mission are using such images to determine the ancient environment these rocks were deposited in. The repeated beds indicate progressive accumulation of sediments that now make up the lower part of Mount Sharp, although from this distance it is not possible to know if they were formed by aqueous or wind-blown processes. Close-up images collected as the rover climbs the ridge will help answer this question. The stratified rocks are cross cut by veins filled with a white mineral, likely calcium sulfate, that provide evidence of later episodes of fluid flow through the rocks. The panorama has been white-balanced so that the colors of the rock materials resemble how they would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. It spans about 65 compass degrees, centered toward the south-southeast. Higher portions of Mount Sharp are visible at upper left. The Sol 1734 location just north of the ridge is shown in a Sol 1732 traverse map. An annotated figure is shown at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21849

The Mast Camera (Mastcam) on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover captured this view of "Vera Rubin Ridge" about two weeks before the rover started ascending this steep ridge on lower Mount Sharp. The view combines 13 images taken with the Mastcam's right-eye, telephoto-lens camera, on Aug. 19, 2017, during the 1,790th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars. This and other Mastcam panoramas show details of the sedimentary rocks that make up the "Vera Rubin Ridge." This distinct topographic feature located on the lower slopes of Mount Sharp (Aeolis Mons) is characterized by the presence of hematite, an iron-oxide mineral, which has been detected from orbit. The Mastcam images show that the rocks making up the lower part of the ridge are characterized by distinct horizontal stratification with individual rock layers of the order of several inches (tens of centimeters) thick. Scientists on the mission are using such images to determine the ancient environment these rocks were deposited in. The repeated beds indicate progressive accumulation of sediments that now make up the lower part of Mount Sharp, although from this distance it is not possible to know if they were formed by aqueous or wind-blown processes. Close-up images collected as the rover climbs the ridge will help answer this question. The stratified rocks are cross cut by veins filled with a white mineral, likely calcium sulfate, that provide evidence of later episodes of fluid flow through the rocks. The panorama has been white-balanced so that the colors of the rock materials resemble how they would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. It spans about 55 compass degrees centered to the south-southeast. The Sol 1790 location just north of the ridge is shown in a Sol 1789 traverse map. The ridge was informally named in early 2017 in memory of Vera Cooper Rubin (1928-2016), whose astronomical observations provided evidence for the existence of the universe's dark matter. An annotated figure is shown at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21851
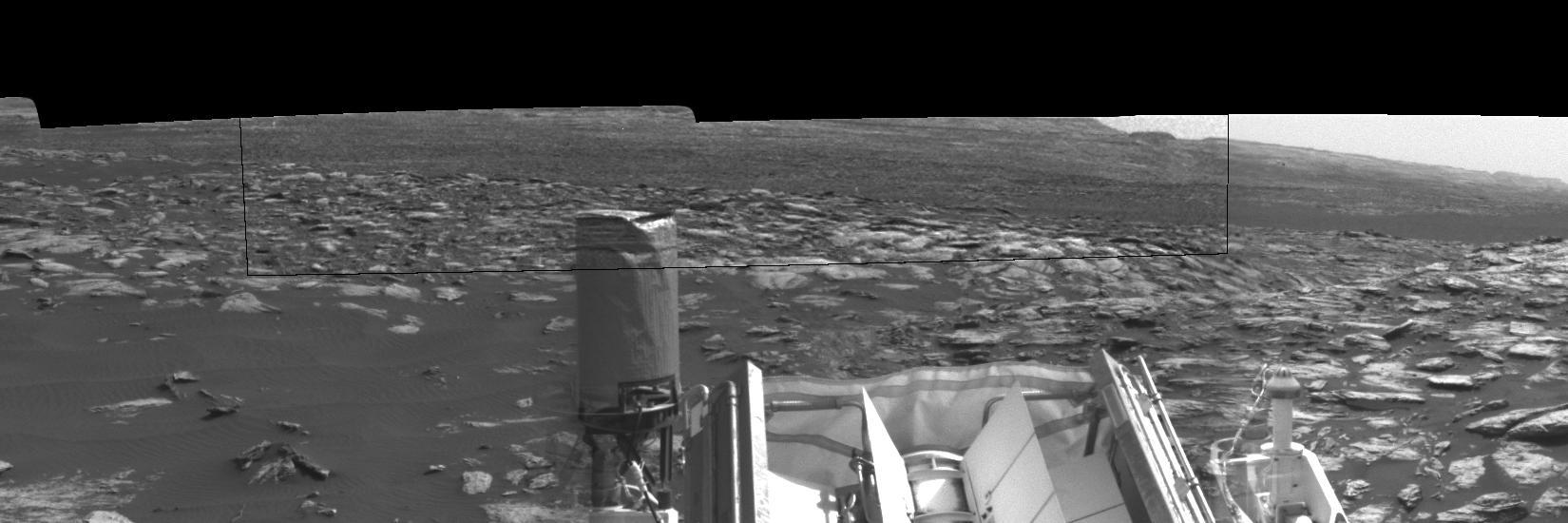

Dust devils dance in the distance in this frame from a sequence of images taken by the Navigation Camera on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover on Feb. 12, 2017, during the summer afternoon of the rover's 1,607th Martian day, or sol. Within a broader context view, the rectangular area outlined in black was imaged multiple times over a span of several minutes to check for dust devils. Images from the period with most activity are shown in the inset area. The images are in pairs that were taken about 12 seconds apart, with an interval of about 90 seconds between pairs. Timing is accelerated and not fully proportional in this animation. One dust devil appears at the right edge of the inset -- toward the south from the rover -- in the first few frames. Another appears on the left -- toward south-southeast -- later in the sequence. Contrast has been modified to make frame-to-frame changes easier to see. A black frame is added between repeats of the sequence. Portions of Curiosity are visible in the foreground. The cylindrical UHF (ultra-high frequency) antenna on the left is used for sending data to Mars orbiters, which relay the data to Earth. The angled planes to the right of this antenna are fins of the rover's radioisotope thermoelectric generator, which provides the vehicle's power. The post with a knob on top at right is a low-gain, non-directional antenna that can be used for receiving transmissions from Earth, as backup to the main high-gain antenna (not shown here) used for that purpose. On Mars as on Earth, dust devils are whirlwinds that result from sunshine warming the ground, prompting convective rising of air that has gained heat from the ground. Observations of Martian dust devils provide information about wind directions and interaction between the surface and the atmosphere. An animation is available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21482
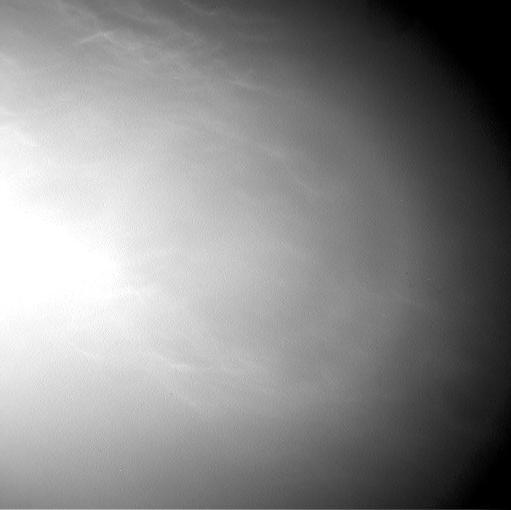

Wispy clouds float across the Martian sky in this accelerated sequence of images from NASA's Curiosity Mars rover. The rover's Navigation Camera (Navcam) took these eight images over a span of four minutes early in the morning of the mission's 1,758th Martian day, or sol (July 17, 2017), aiming nearly straight overhead. This sequence uses raw images, which include a bright ring around the center of the frame that is an artifact of sunlight striking the camera lens even though the Sun is not in the shot. A processed version removing that artifact and emphasizing changes between images is also available. The clouds resemble Earth's cirrus clouds, which are ice crystals at high altitudes. These Martian clouds are likely composed of crystals of water ice that condense onto dust grains in the cold Martian atmosphere. Cirrus wisps appear as ice crystals fall and evaporate in patterns known as "fall streaks" or "mare's tails." Such patterns have been seen before at high latitudes on Mars, for instance by the Phoenix Mars Lander in 2008, and seasonally nearer the equator, for instance by the Opportunity rover. However, Curiosity has not previously observed such clouds so clearly visible from the rover's study area about five degrees south of the equator. The Hubble Space Telescope and spacecraft orbiting Mars have observed a band of clouds to appear near the Martian equator around the time of the Martian year when the planet is farthest from the Sun. With a more elliptical orbit than Earth's, Mars experiences more annual variation than Earth in its distance from the Sun. The most distant point in an orbit around the Sun is called the aphelion. The near-equatorial Martian cloud pattern observed at that time of year is called the "aphelion cloud belt." These new images from Curiosity were taken about two months before aphelion, but the morning clouds observed may be an early stage of the aphelion cloud belt. An animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21842
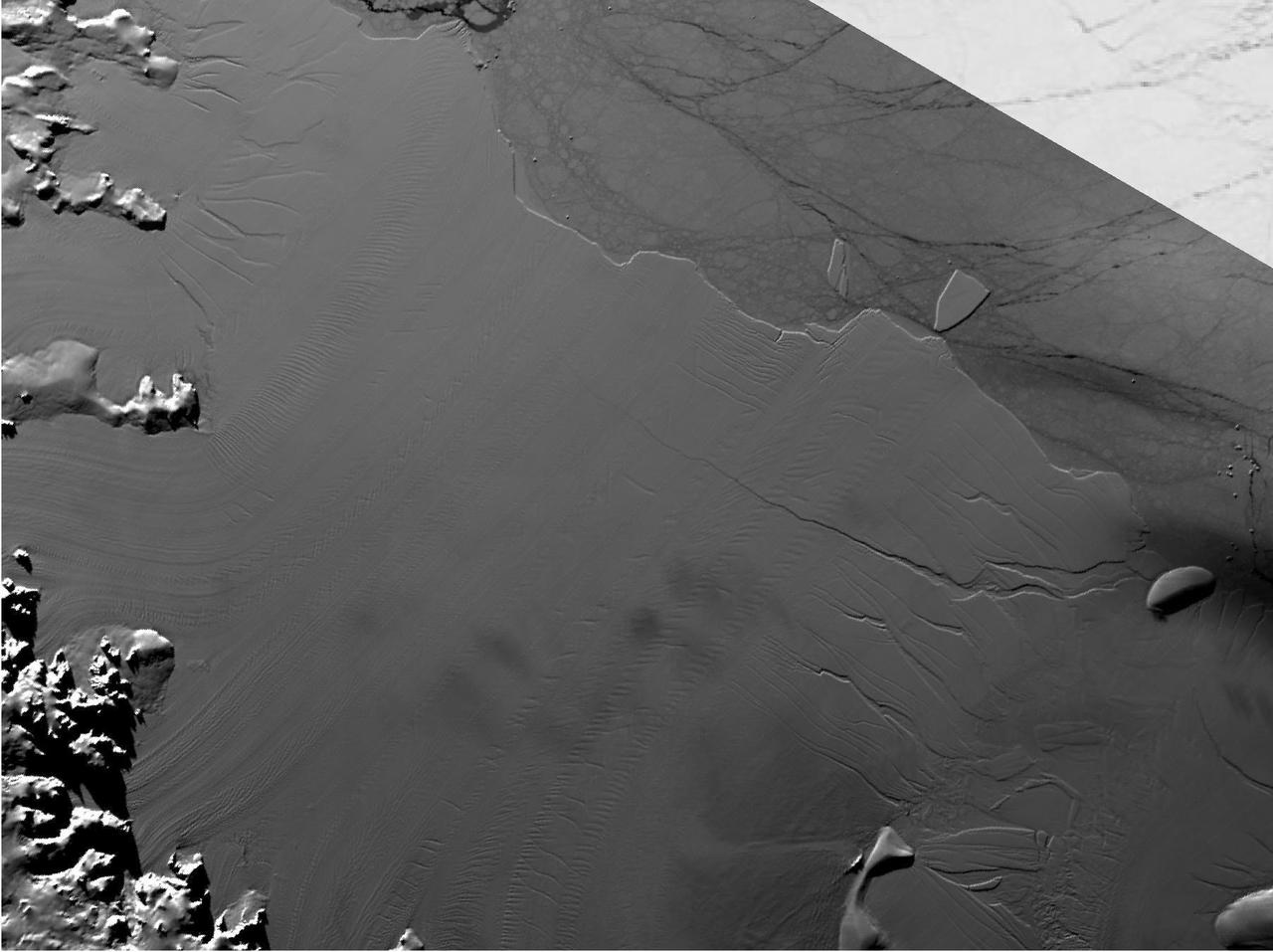

Between July 10 and 12, 2017, the Larsen C Ice Shelf in West Antarctica calved one of the largest icebergs in history (named "A-68"), weighing approximately one trillion tons. The rift in the ice shelf that spawned the iceberg has been present on the shelf since at least the beginning of the Landsat era (approximately the 1970s), but remained relatively dormant until around 2012, when it was observed actively moving through a suture zone in the ice shelf (Jansen et al., 2015). Suture zones are wide bands of ice that extend from glacier grounding lines (the boundary between a floating ice shelf and ice resting on bedrock) to the sea comprised of a frozen mixture of glacial ice and sea water, traditionally considered to be stabilizing features in ice shelves. When the Antarctic entered its annual dark period in late April, scientists knew the rift only had a few more miles to go before it completely calved the large iceberg. However, due to the lack of sunlight during the Antarctic winter, visible imagery is generally not available each year between May and August. This frame is from an animation that shows the ice shelf as imaged by the NASA/NOAA satellite Suomi NPP, which features the VIIRS (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite) instrument. VIIRS has a day/night panchromatic band capable of collecting nighttime imagery of Earth with a spatial resolution of 2,460 feet (750 meters). An image from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument on NASA's Terra satellite shows the last cloud-free, daytime image of the ice shelf on April 6; the MODIS thermal imagery band is shown on April 29. The images from May 9 to July 14 show available cloud-free imagery from Suomi NPP. Luckily, despite several cloudy days leading up to the break, the weather mostly cleared on July 11, allowing scientists to see the newly formed iceberg on July 12. The animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21785
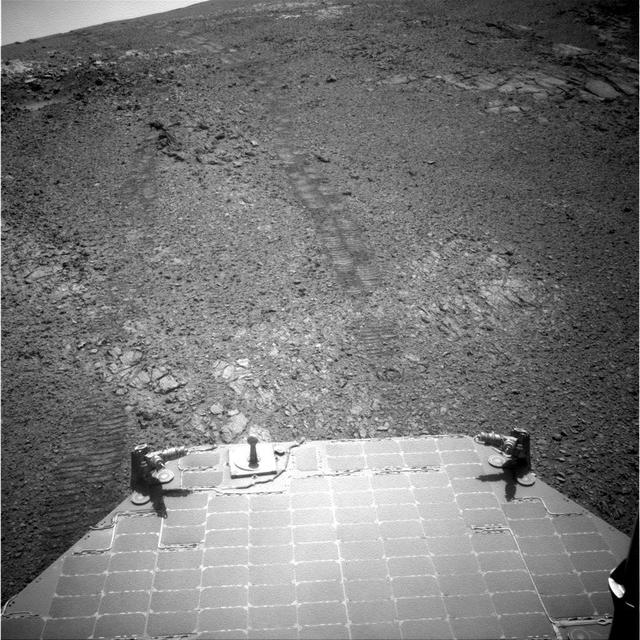

This image from the navigation camera (Navcam) on the mast of NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity provides a look back to the crest of Endeavour Crater's rim after the rover began descending "Perseverance Valley" on the rim's inner slope. The Navcam took this image on July 18, 2017, during the 4,793rd Martian day, or sol, of Opportunity's work on Mars. Wheel tracks from the top of the rim to the rover are visible above the rear solar panel of the vehicle. For scale, the distance between tracks from right-side wheels and tracks from left-side wheels is about 3.3 feet (1 meter). The knob-topped cylinder mounted at the edge of the solar panel is the calibration target for Opportunity's panoramic camera (Pancam). Opportunity's location on Sol 4793 was a site within the upper end of Perseverance Valley that the rover reached with a drive of about 45 feet (13.8 meters) on July 7 (Sol 4782). The rover team chose this location for Opportunity to spend about three weeks during a driving moratorium for the Mars solar conjunction period. Mars solar conjunction occurs once about every 26 months when Mars passes nearly behind the sun, from Earth's perspective. The relative positions of the three bodies makes radio transmission of commands from Earth to Mars unreliable. One advantage of this chosen location for Opportunity is a slight northward tilt for the solar panels, which adds to their power output during these weeks of southern-hemisphere autumn when daily sunshine is diminishing. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21725
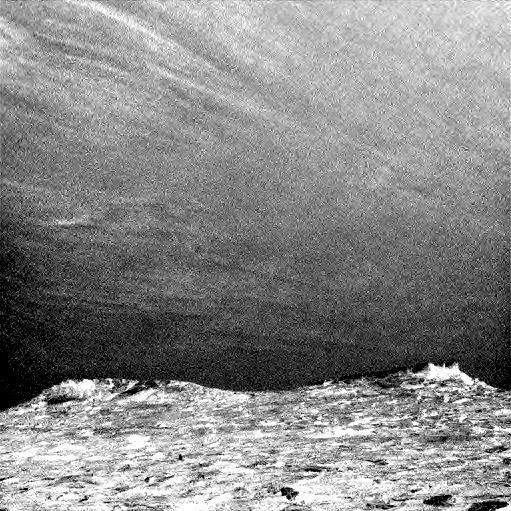

Clouds drift across the sky above a Martian horizon in this accelerated sequence of enhanced images from NASA's Curiosity Mars rover. The rover's Navigation Camera (Navcam) took these eight images over a span of four minutes early in the morning of the mission's 1,758th Martian day, or sol (July 17, 2017), aiming toward the south horizon. They have been processed by first making a "flat field' adjustment for known differences in sensitivity among pixels and correcting for camera artifacts due to light reflecting within the camera, and then generating an "average" of all the frames and subtracting that average from each frame. This subtraction emphasizes changes whether due to movement -- such as the clouds' motion -- or due to lighting -- such as changing shadows on the ground as the morning sunlight angle changed. On the same Martian morning, Curiosity also observed clouds nearly straight overhead. The clouds resemble Earth's cirrus clouds, which are ice crystals at high altitudes. These Martian clouds are likely composed of crystals of water ice that condense onto dust grains in the cold Martian atmosphere. Cirrus wisps appear as ice crystals fall and evaporate in patterns known as "fall streaks" or "mare's tails." Such patterns have been seen before at high latitudes on Mars, for instance by the Phoenix Mars Lander in 2008, and seasonally nearer the equator, for instance by the Opportunity rover. However, Curiosity has not previously observed such clouds so clearly visible from the rover's study area about five degrees south of the equator. The Hubble Space Telescope and spacecraft orbiting Mars have observed a band of clouds to appear near the Martian equator around the time of the Martian year when the planet is farthest from the Sun. With a more elliptical orbit than Earth's, Mars experiences more annual variation than Earth in its distance from the Sun. The most distant point in an orbit around the Sun is called the aphelion. The near-equatorial Martian cloud pattern observed at that time of year is called the "aphelion cloud belt." These new images from Curiosity were taken about two months before aphelion, but the morning clouds observed may be an early stage of the aphelion cloud belt. An animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21840
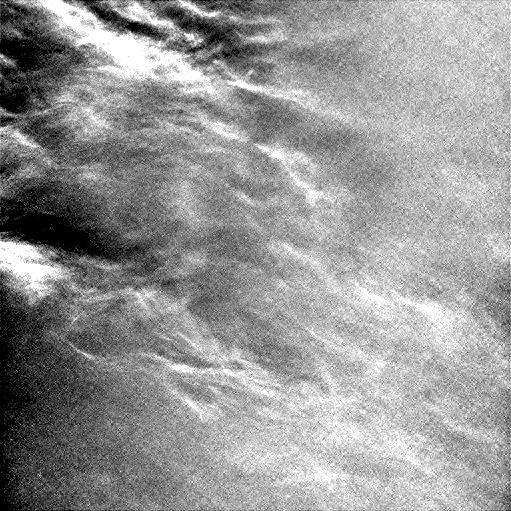
Wispy clouds float across the Martian sky in this accelerated sequence of enhanced images from NASA's Curiosity Mars rover. The rover's Navigation Camera (Navcam) took these eight images over a span of four minutes early in the morning of the mission's 1,758th Martian day, or sol (July 17, 2017), aiming nearly straight overhead. They have been processed by first making a "flat field' adjustment for known differences in sensitivity among pixels and correcting for camera artifacts due to light reflecting within the camera, and then generating an "average" of all the frames and subtracting that average from each frame. This subtraction results in emphasizing any changes due to movement or lighting. The clouds are also visible, though fainter, in a raw image sequence from these same observations. On the same Martian morning, Curiosity also observed clouds near the southern horizon. The clouds resemble Earth's cirrus clouds, which are ice crystals at high altitudes. These Martian clouds are likely composed of crystals of water ice that condense onto dust grains in the cold Martian atmosphere. Cirrus wisps appear as ice crystals fall and evaporate in patterns known as "fall streaks" or "mare's tails." Such patterns have been seen before at high latitudes on Mars, for instance by the Phoenix Mars Lander in 2008, and seasonally nearer the equator, for instance by the Opportunity rover. However, Curiosity has not previously observed such clouds so clearly visible from the rover's study area about five degrees south of the equator. The Hubble Space Telescope and spacecraft orbiting Mars have observed a band of clouds to appear near the Martian equator around the time of the Martian year when the planet is farthest from the Sun. With a more elliptical orbit than Earth's, Mars experiences more annual variation than Earth in its distance from the Sun. The most distant point in an orbit around the Sun is called the aphelion. The near-equatorial Martian cloud pattern observed at that time of year is called the "aphelion cloud belt." These new images from Curiosity were taken about two months before aphelion, but the morning clouds observed may be an early stage of the aphelion cloud belt. An animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21841

Aviators, skydivers and other altitude-seeking enthusiasts flying out of Wanaka Airport, New Zealand, are double taking at a new topographical feature reminiscent of an alien crop circle. Rest assured, the nearly 2,000-foot (600-meter) diameter circle with a pie-shaped wedge on one side and spokes on the other is no extraterrestrial footprint and it’s definitely no hoax. It’s NASA’s newest launch pad for launching the agency’s most advanced high-altitude, heavy-lift scientific balloon: the super pressure balloon. The four spokes emanating from the center and toward the west, each nearly 1,000 feet (300 meters) long, align with magnetic compass directions at 240, 260, 290 and 320 degrees. On launch day, balloon flight experts from NASA’s Columbia Scientific Balloon Facility will assess meteorological data and determine if the conditions are suitable to support a launch opportunity. The new pad is the first major project in developing a long-term super pressure balloon launch site in Wanaka. Earlier in 2017, NASA signed a 10-year lease with the Queenstown Airport Corporation to conduct balloon operations from a newly acquired piece of land adjacent to the Wanaka Airport. Credit: NASA/Dave Webb <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
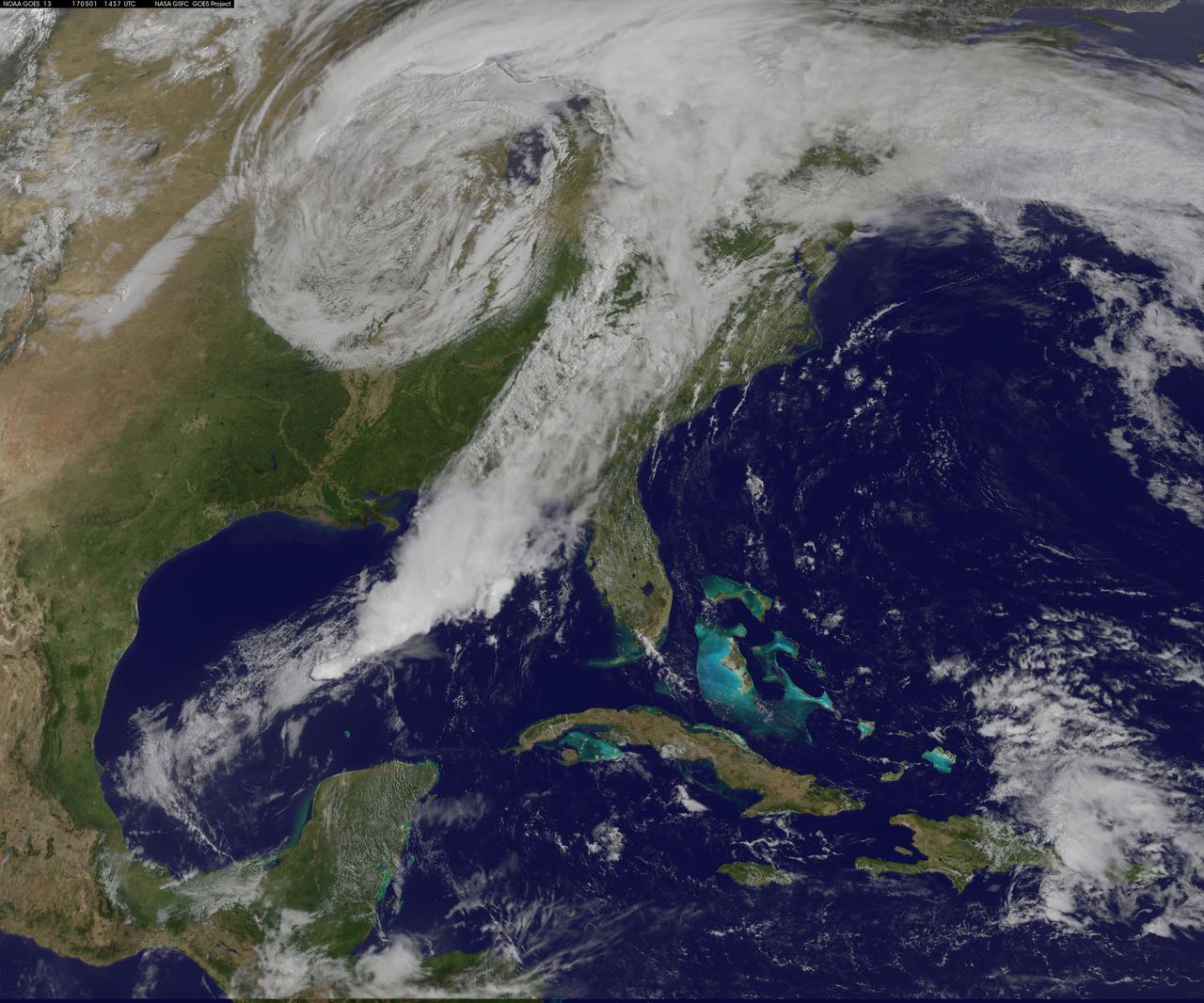
NASA Sees Severe Weather from Central to Eastern US A vigorous weather system has generated severe weather over the mid-section of the U.S. and satellites are providing a look at it as it is moving toward the East Coast. NASA and NOAA satellites have been tracking a storm system that has generated flooding and tornadic thunderstorms in the central U.S. and is expected bring severe weather to the U.S. Mid-Atlantic region. At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite were used to create images and an animation of the movement of the powerful storm. On April 30, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of the storms moving over eastern Texas and Louisiana. Tornadoes in eastern Texas killed four people. The system generated heavy rainfall and caused additional fatalities and damages in Arkansas, Missouri, Mississippi, Alabama and Tennessee. On Monday, May 1, NOAA's National Weather Service noted, "Major to record flooding continues over portions of the central U.S. Severe thunderstorms are possible from the Mid-Atlantic to the northeastern U.S. "Major to record flooding will continue over portions of eastern Oklahoma, northern Arkansas, Missouri, Illinois and Indiana. Rivers will gradually recede over the next several days. Additional strong to severe thunderstorms will be possible Monday afternoon and evening over portions of the Mid-Atlantic and Northeast U.S. Damaging winds, large hail, and isolated tornadoes will be possible." Image caption: On May 1, 2017, at 10:37 a.m. EDT (1437 UTC) NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured this visible image of the storm system centered over Iowa with an associated cold front that stretches into the Gulf of Mexico. Credits: NASA/NOAA GOES Project <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
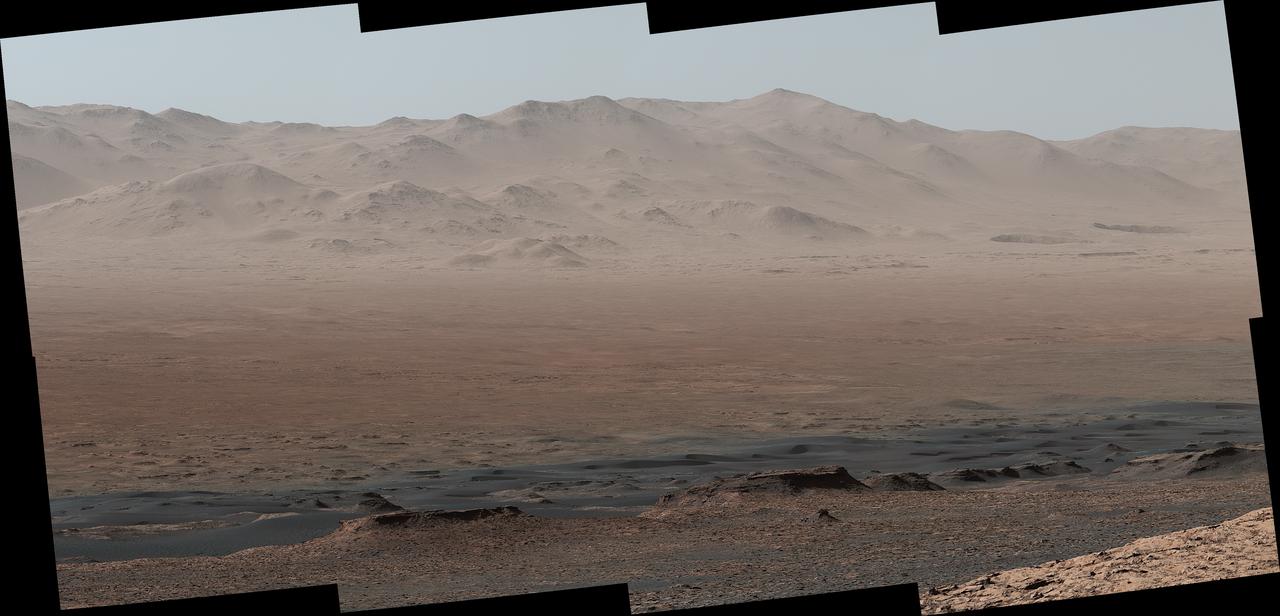

A vantage point on "Vera Rubin Ridge" provided NASA's Curiosity Mars rover this detailed look back over the area where it began its mission inside Gale Crater, plus more-distant features of the crater. This view toward the north-northeast combines eight images taken by the right-eye, telephoto-lens camera of Curiosity's Mast Camera (Mastcam). It shows more detail of a fraction of the area pictured in a more sweeping panorama (see PIA22210) acquired from the same rover location using Mastcam's left-eye, wider-angle-lens camera. The scene has been white-balanced so the colors of the rock materials resemble how they would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. The component images were taken on Oct. 25, 2017, during the 1,856th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's work on Mars. At that point, Curiosity had gained 1,073 feet (327 meters) in elevation and driven 10.95 miles (17.63 kilometers) from its landing site. Mount Sharp stands about 3 miles (5 kilometers) high in the middle of Gale Crater, which spans 96 miles (154 kilometers) in diameter. Vera Rubin Ridge is on the northwestern flank of lower Mount Sharp. The right foreground of this panorama shows a portion of Vera Rubin Ridge. In the distance is the northern wall of Gale Crater, with the rim crest forming the horizon roughly 25 miles (40 kilometers) from the rover's location. An annotated version, Figure 1, indicates where the rover landed (at "Bradbury Landing") in 2012 and the initial portion of its drive, including investigation sites "Yellowknife Bay," "Darwin" and "Cooperstown." The rover's exact landing site is hidden behind a slight rise. The heat shield, back shell, and parachute used during the spacecraft's descent are within the pictured area but not recognizable due to the distance and to camouflaging by dust. At Yellowknife Bay in 2013, the mission found evidence of an ancient freshwater-lake environment that offered all of the basic chemical ingredients for microbial life. Figure 2 includes three scale bars: of 40 meters (131 feet) at a distance of about 1,530 meters (1,673 yards) near the base of Mount Sharp; of 1,500 meters (1,640 yards) at a distance of about 30.75 kilometers (19.1 miles) near the base of the crater wall; and of 2,000 meters (1.2 miles) at a distance of about 41.2 kilometers (25.6 miles) at the crest of the rim. Annotated images are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22209

Climbing "Vera Rubin Ridge" provided NASA's Curiosity Mars rover this sweeping vista of the interior and rim of Gale Crater, including much of the rover's route during its first five-and-a-half years on Mars and features up to about 50 miles (85 kilometers) away. The scene spans from southwest on the left to northeast on the right, combining 16 side-by-side images taken by the left-eye, wider-angle-lens camera of Curiosity's Mast Camera (Mastcam). It has been white-balanced so the colors of the rock materials resemble how they would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. The component images were taken on Oct. 25, 2017, during the 1,856th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's work on Mars. At that point, Curiosity had gained 1,073 feet (327 meters) in elevation and driven 10.95 miles (17.63 kilometers) from its landing site. Mount Sharp stands about 3 miles (5 kilometers) high in the middle of Gale Crater, which spans 96 miles (154 kilometers) in diameter. Vera Rubin Ridge is on the northwestern flank of lower Mount Sharp. The foreground of this panorama shows portions of lower Mount Sharp. The middle distance shows the floor of Gale Crater. Most of the horizon is formed by the crater's rim. The top of the rim is about 1.2 miles (2 kilometers) higher than the rover's position. On the horizon near the center of the image is a glimpse outside of Gale Crater, to a peak about 50 miles (85 kilometers) from the rover. An annotated version, Figure 1, indicates the rover's approximate path since its 2012 landing, identifies some of the sites it has investigated along the way, such as "Yellowknife Bay," "The Kimberley," "Namib Dune" and "Murray Buttes"; and points out other geological features visible in the scene, such as the channel of Peace Vallis, an ancient streambed descending from the crater rim. The relative positions of the labeled features are also mapped on an accompanying orbital view in PIA22208, with two areas color-coded for ease of matching them in the annotated panorama and the orbital view. Figure 2 is a version with a white-line box indicating the smaller area covered in a more-detailed vista (see PIA22209) taken from this same rover location by Mastcam's right-eye, telephoto-lens camera. It also includes three scale bars: of 50 meters (164 feet) at a distance of 1,170 meters (1,280 yards) near the base of Mount Sharp; of 1,000 meters (1,094 yards) at a distance of about 23.4 kilometers (14.5 miles) near the base of the crater wall; and of 2 kilometers (1.2 miles) at a distance of about 31.5 kilometers (19.6 miles) at the crest of the rim. Annotated images are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22210
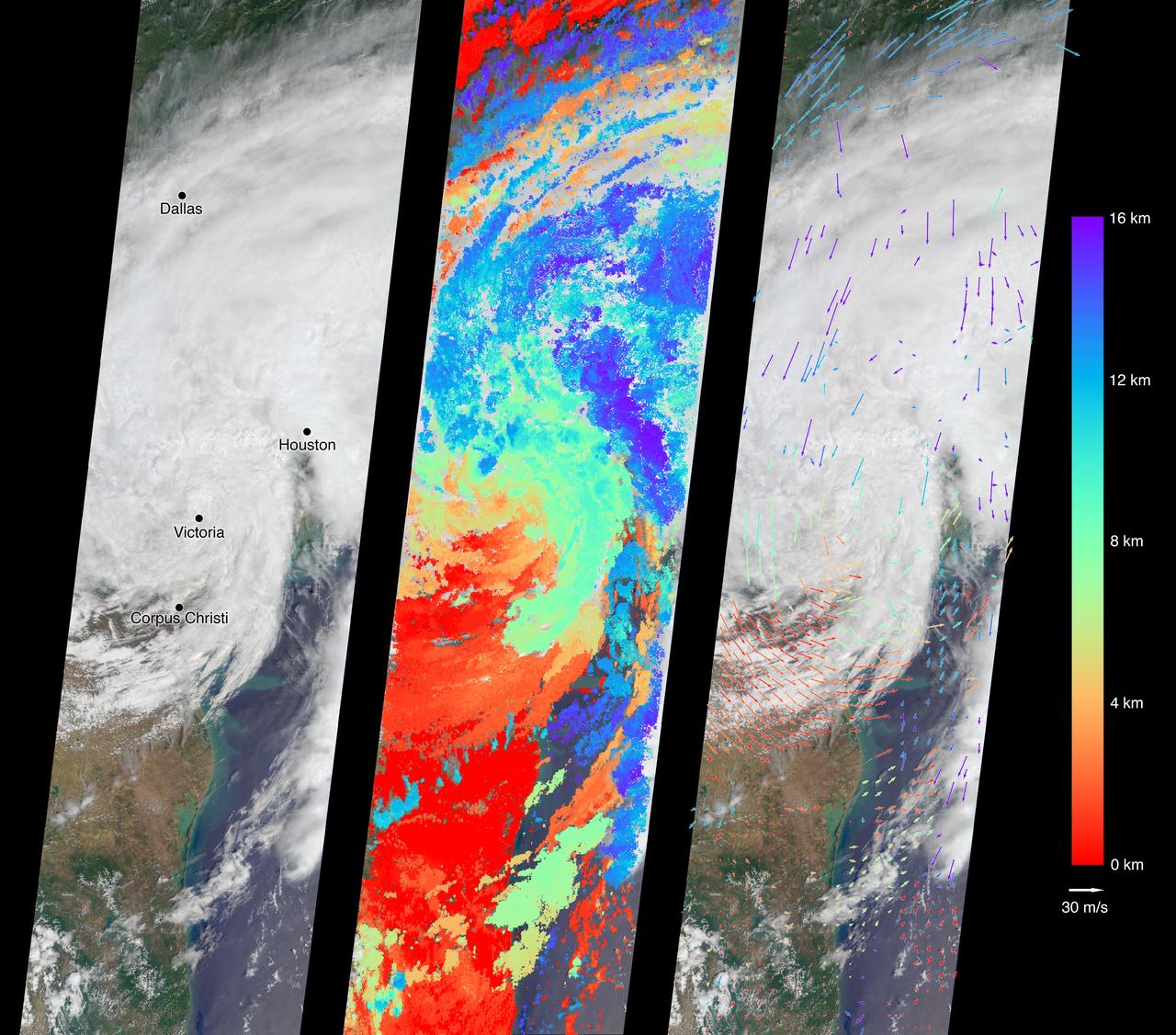
On Aug. 27, 2017, the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument on NASA's Terra satellite passed over then-Tropical Storm Harvey about noon local time, the day after the storm first made landfall in Texas as a Category 4 hurricane. The MISR instrument is equipped with nine cameras that observe Earth at different angles over a time period of seven minutes. Geometric information from the multiple camera views is used to compute the cloud top heights, and motion of the clouds during the image sequence is used to calculate wind speed. This composite image shows the storm as viewed by the central, downward-looking camera (left), as well as the cloud top heights in kilometers (center) and the wind speeds (right) superimposed on the image. The length of the arrows is proportional to the wind speed, while their color shows the altitude at which the winds were calculated. Also included is an animation made by combining all nine images from the MISR cameras, showing the motion of the storm during the seven-minute period. At this time, the center of the tropical storm was located just northwest of the city of Victoria and maximum wind speeds on the ground were around 40 miles per hour (65 kilometers per hour) according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), which matches well with the near-surface winds calculated by MISR to the west of Corpus Christi. In the 36 hours or so since it had made landfall, Harvey had weakened considerably -- these images show that the eye had disappeared and much of the circular motion of storm had dissipated, as shown by the calculated wind directions. However, the area of very high clouds and strong winds near Houston shows that the storm was continuing to produce powerful rain bands. At this point, hydrographs managed by NOAA in downtown Houston were already recording flood stage at both the Buffalo Bayou (28 feet or 8.5 meters as of 12:15 p.m. CDT August 27) and the White Oak Bayou (40 feet or 12 meters at last record that morning). The MISR data show the storm clouds reaching an altitude of about 10 miles (16 kilometers). These data were captured during Terra orbit 94108. An animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21927
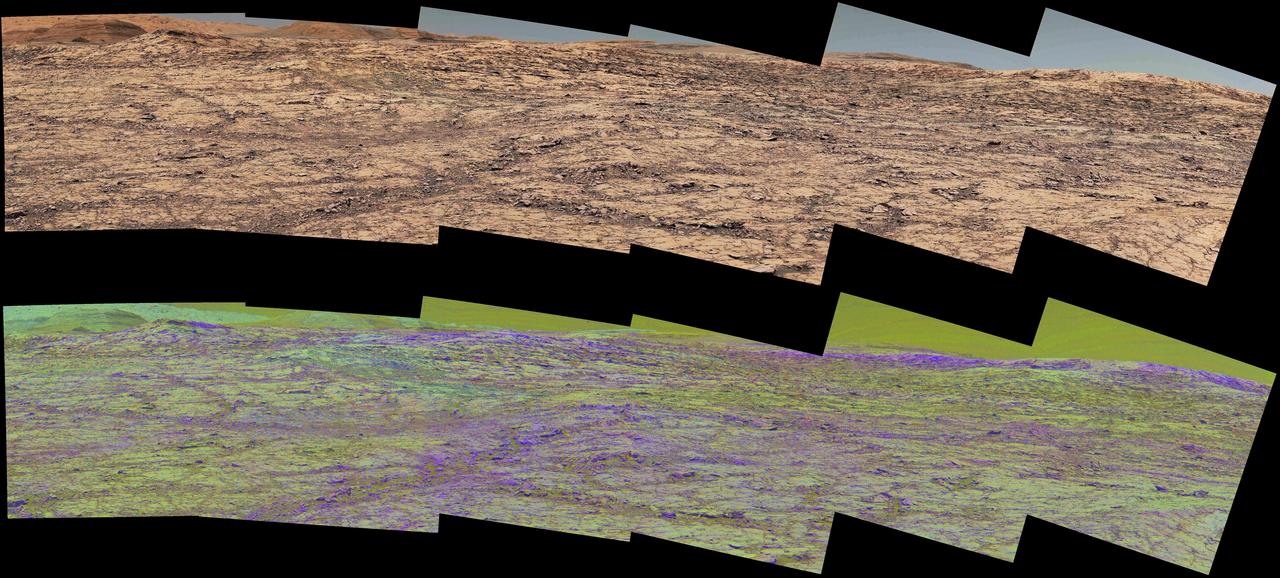
This pair of images from the Mast Camera (Mastcam) on NASA's Curiosity rover illustrates how special filters are used to scout terrain ahead for variations in the local bedrock. The upper panorama is in the Mastcam's usual full color, for comparison. The lower panorama of the same scene, in false color, combines three exposures taken through different "science filters," each selecting for a narrow band of wavelengths. Filters and image processing steps were selected to make stronger signatures of hematite, an iron-oxide mineral, evident as purple. Hematite is of interest in this area of Mars -- partway up "Vera Rubin Ridge" on lower Mount Sharp -- as holding clues about ancient environmental conditions under which that mineral originated. In this pair of panoramas, the strongest indications of hematite appear related to areas where the bedrock is broken up. With information from this Mastcam reconnaissance, the rover team selected destinations in the scene for close-up investigations to gain understanding about the apparent patchiness in hematite spectral features. The Mastcam's left-eye camera took the component images of both panoramas on Sept. 12, 2017, during the 1,814th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars. The view spans from south-southeast on the left to south-southwest on the right. The foreground across the bottom of the scene is about 50 feet (about 15 meters) wide. Figure 1 includes scale bars of 1 meter (3.3 feet) in the middle distance and 5 meters (16 feet) at upper right. Curiosity's Mastcam combines two cameras: the right eye with a telephoto lens and the left eye with a wider-angle lens. Each camera has a filter wheel that can be rotated in front of the lens for a choice of eight different filters. One filter for each camera is clear to all visible light, for regular full-color photos, and another is specifically for viewing the Sun. Some of the other filters were selected to admit wavelengths of light that are useful for identifying iron minerals. Each of the filters used for the lower panorama shown here admits light from a narrow band of wavelengths, extending to only about 5 to 10 nanometers longer or shorter than the filter's central wavelength. The three observations combined into this product used filters centered at three near-infrared wavelengths: 751 nanometers, 867 nanometers and 1,012 nanometers. Hematite distinctively absorbs some frequencies of infrared light more than others. Usual color photographs from digital cameras -- such as the upper panorama here from Mastcam -- combine information from red, green and blue filtering. The filters are in a microscopic grid in a "Bayer" filter array situated directly over the detector behind the lens, with wider bands of wavelengths. The colors of the upper panorama, as with most featured images from Mastcam, have been tuned with a color adjustment similar to white balancing for approximating how the rocks and sand would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22065
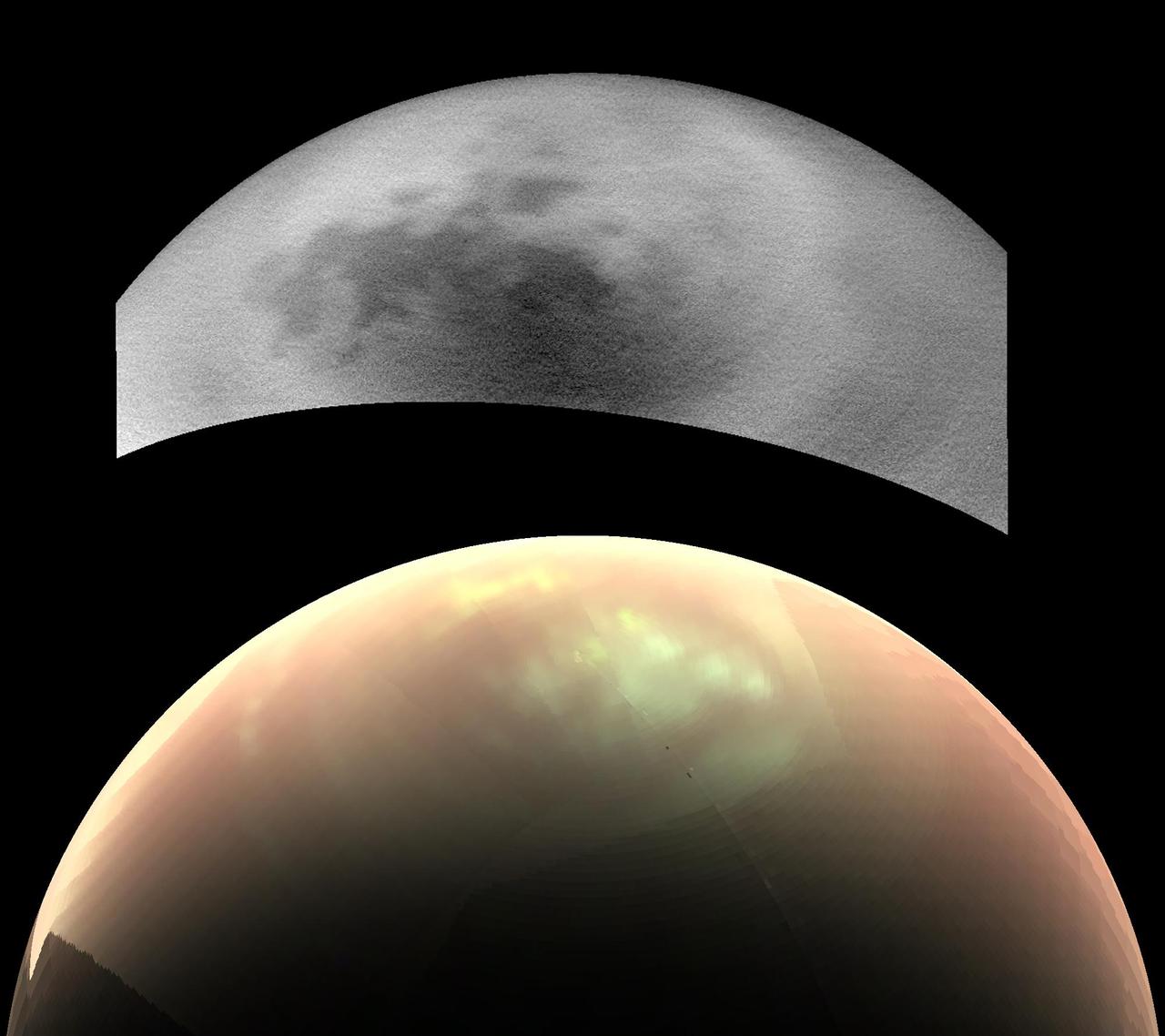
This comparison of two views from NASA's Cassini spacecraft, taken fairly close together in time, illustrates a peculiar mystery: Why would clouds on Saturn's moon Titan be visible in some images, but not in others? In the top view, a near-infrared image from Cassini's imaging cameras, the skies above Saturn's moon Titan look relatively cloud free. But in the bottom view, at longer infrared wavelengths, Cassini sees a large field of bright clouds. Even though these views were taken at different wavelengths, researchers would expect at least a hint of the clouds to show up in the upper image. Thus they have been trying to understand what's behind the difference. As northern summer approaches on Titan, atmospheric models have predicted that clouds will become more common at high northern latitudes, similar to what was observed at high southern latitudes during Titan's late southern summer in 2004. Cassini's Imaging Science Subsystem (ISS) and Visual and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS) teams have been observing Titan to document changes in weather patterns as the seasons change, and there is particular interest in following the onset of clouds in the north polar region where Titan's lakes and seas are concentrated. Cassini's "T120" and "T121" flybys of Titan, on June 7 and July 25, 2016, respectively, provided views of high northern latitudes over extended time periods -- more than 24 hours during both flybys. Intriguingly, the ISS and VIMS observations appear strikingly different from each other. In the ISS observations (monochrome image at top), surface features are easily identifiable and only a few small, isolated clouds were detected. In contrast, the VIMS observations (color image at bottom) suggest widespread cloud cover during both flybys. The observations were made over the same time period, so differences in illumination geometry or changes in the clouds themselves are unlikely to be the cause for the apparent discrepancy: VIMS shows persistent atmospheric features over the entire observation period and ISS consistently detects surface features with just a few localized clouds. The answer to what could be causing the discrepancy appears to lie with Titan's hazy atmosphere, which is much easier to see through at the longer infrared wavelengths that VIMS is sensitive to (up to 5 microns) than at the shorter, near-infrared wavelength used by ISS to image Titan's surface and lower atmosphere (0.94 microns). High, thin cirrus clouds that are optically thicker than the atmospheric haze at longer wavelengths, but optically thinner than the haze at the shorter wavelength of the ISS observations, could be detected by VIMS and simultaneously lost in the haze to ISS -- similar to trying to see a thin cloud layer on a hazy day on Earth. This phenomenon has not been seen again since July 2016, but Cassini has several more opportunities to observe Titan over the last months of the mission in 2017, and scientists will be watching to see if and how the weather changes. These two images were taken as part of the T120 flyby on June 7 (VIMS) and 8 (ISS), 2016. The distance to Titan was about 28,000 miles (45,000 kilometers) for the VIMS image and about 398,000 miles (640,000 kilometers) for the ISS image. The VIMS image has been processed to enhance the visibility of the clouds; in this false-color view, clouds appear nearly white, atmospheric haze is pink, and surface areas would appear green. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21054