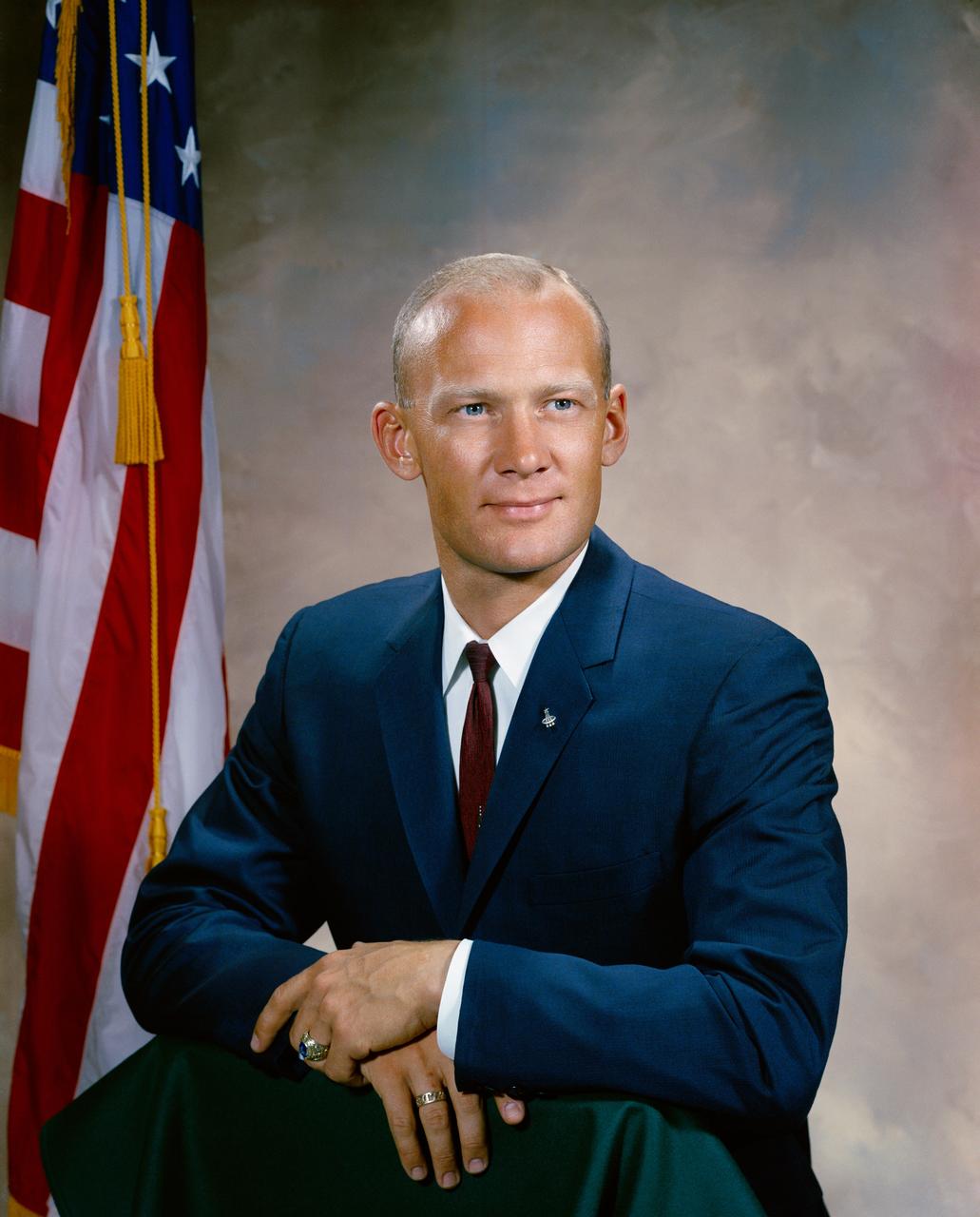

S64-31484 (1964) --- Astronaut Edwin E. "Buzz" Aldrin Jr. Photo credit: NASA
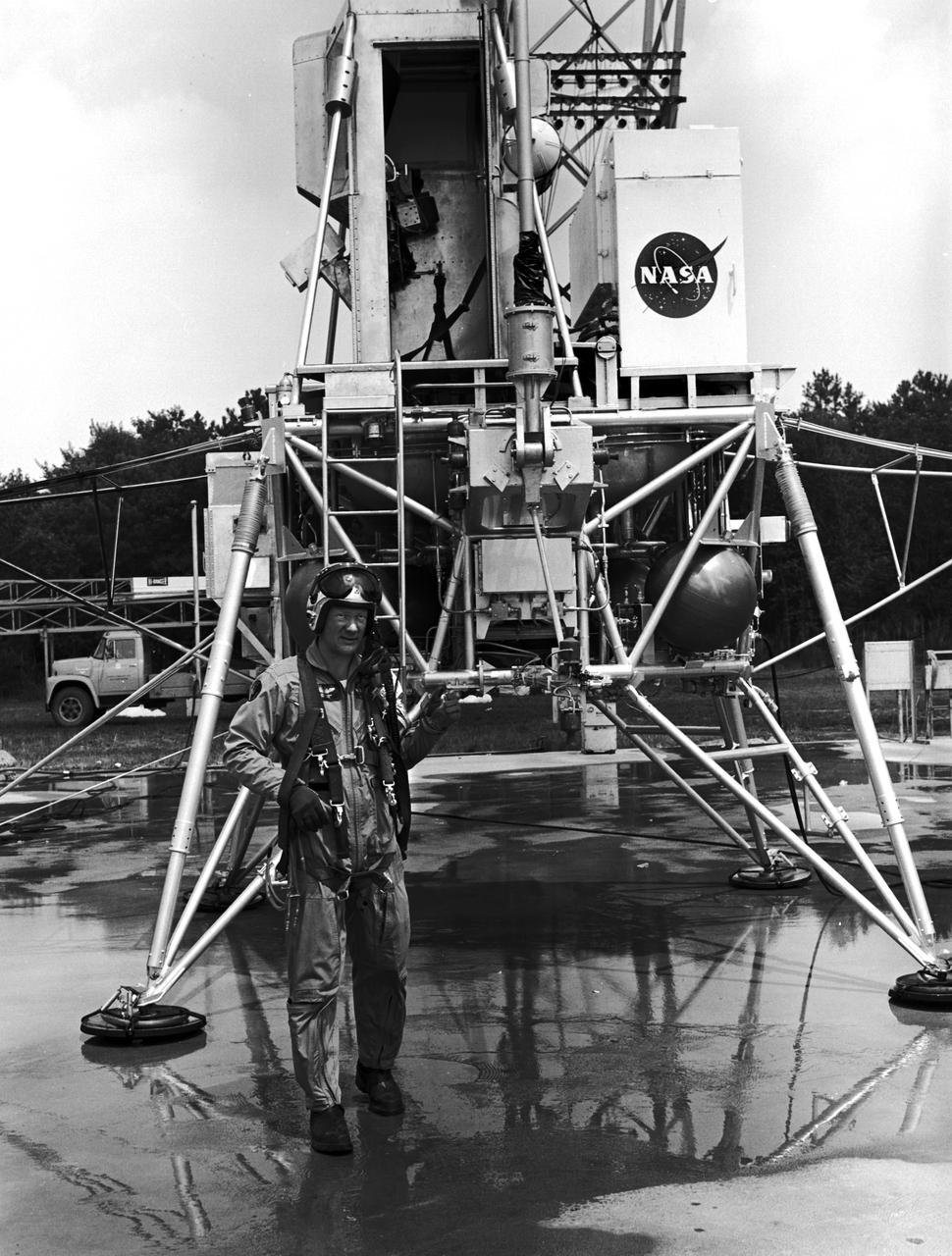

Astronaut Edwin Buzz Aldrin Lunar Module Pilot at the (LLRF) Lunar Landing Research Facility. Aldrin was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. On November 11, 1966, he and command pilot James Lovell were launched into space in the Gemini 12 spacecraft on a 4-day flight, which brought the Gemini program to a successful close. Aldrin established a new record for extravehicular activity (EVA), spending 5-1/2 hours outside the spacecraft. He served as lunar module pilot for Apollo 11, July 16-24, 1969, the first manned lunar landing mission. Aldrin followed Neil Armstrong onto the lunar surface on July 20, 1969, completing a 2-hour and 15 minute lunar EVA. In July 1971, Aldrin resigned from NASA. Aldrin has logged 289 hours and 53 minutes in space, of which, 7 hours and 52 minutes were spent in EVA. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former
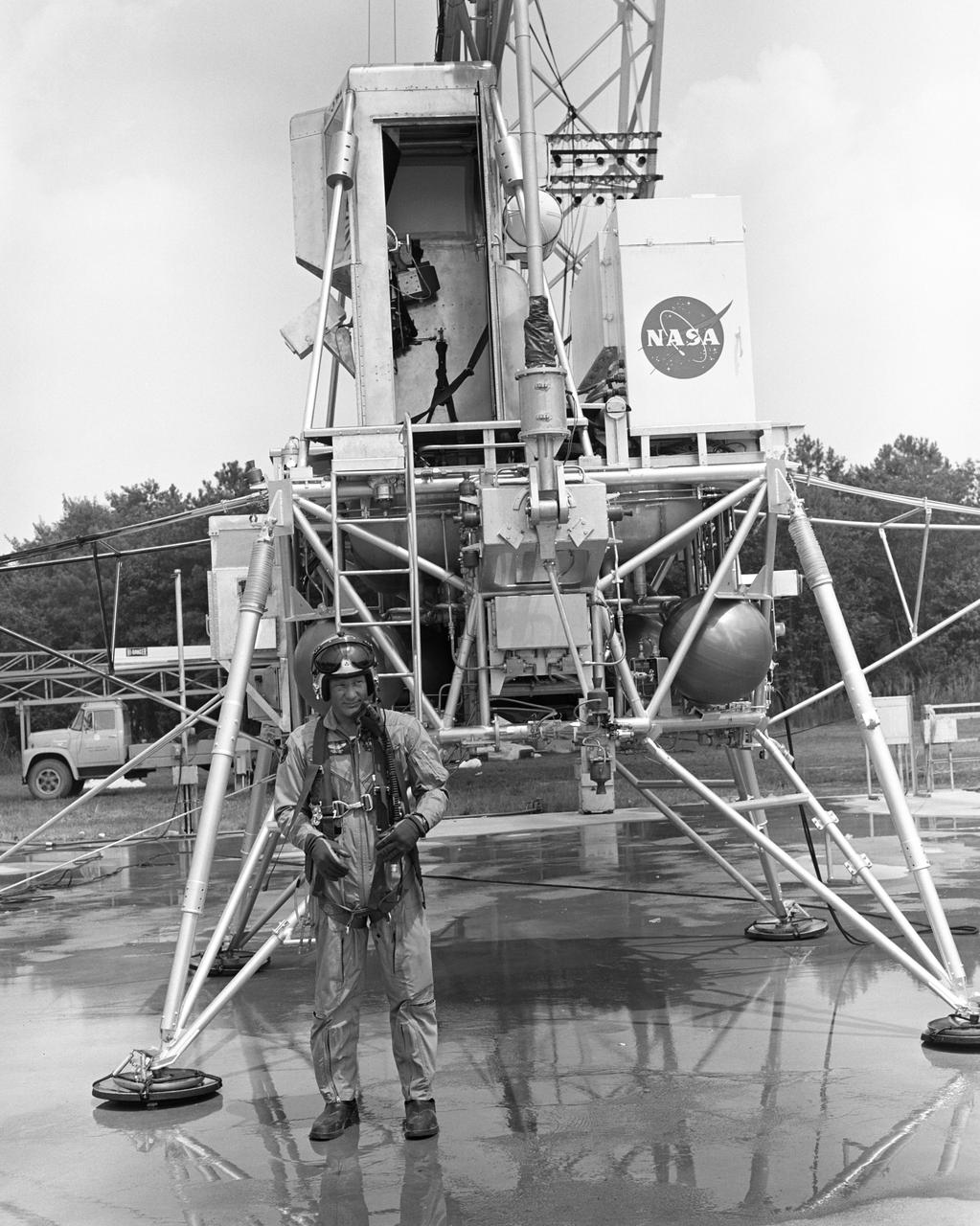

Astronaut Edwin Buzz Aldrin Lunar Module Pilot at the (LLRF) Lunar Landing Research Facility. Aldrin was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. On November 11, 1966, he and command pilot James Lovell were launched into space in the Gemini 12 spacecraft on a 4-day flight, which brought the Gemini program to a successful close. Aldrin established a new record for extravehicular activity (EVA), spending 5-1/2 hours outside the spacecraft. He served as lunar module pilot for Apollo 11, July 16-24, 1969, the first manned lunar landing mission. Aldrin followed Neil Armstrong onto the lunar surface on July 20, 1969, completing a 2-hour and 15 minute lunar EVA. In July 1971, Aldrin resigned from NASA. Aldrin has logged 289 hours and 53 minutes in space, of which, 7 hours and 52 minutes were spent in EVA. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former
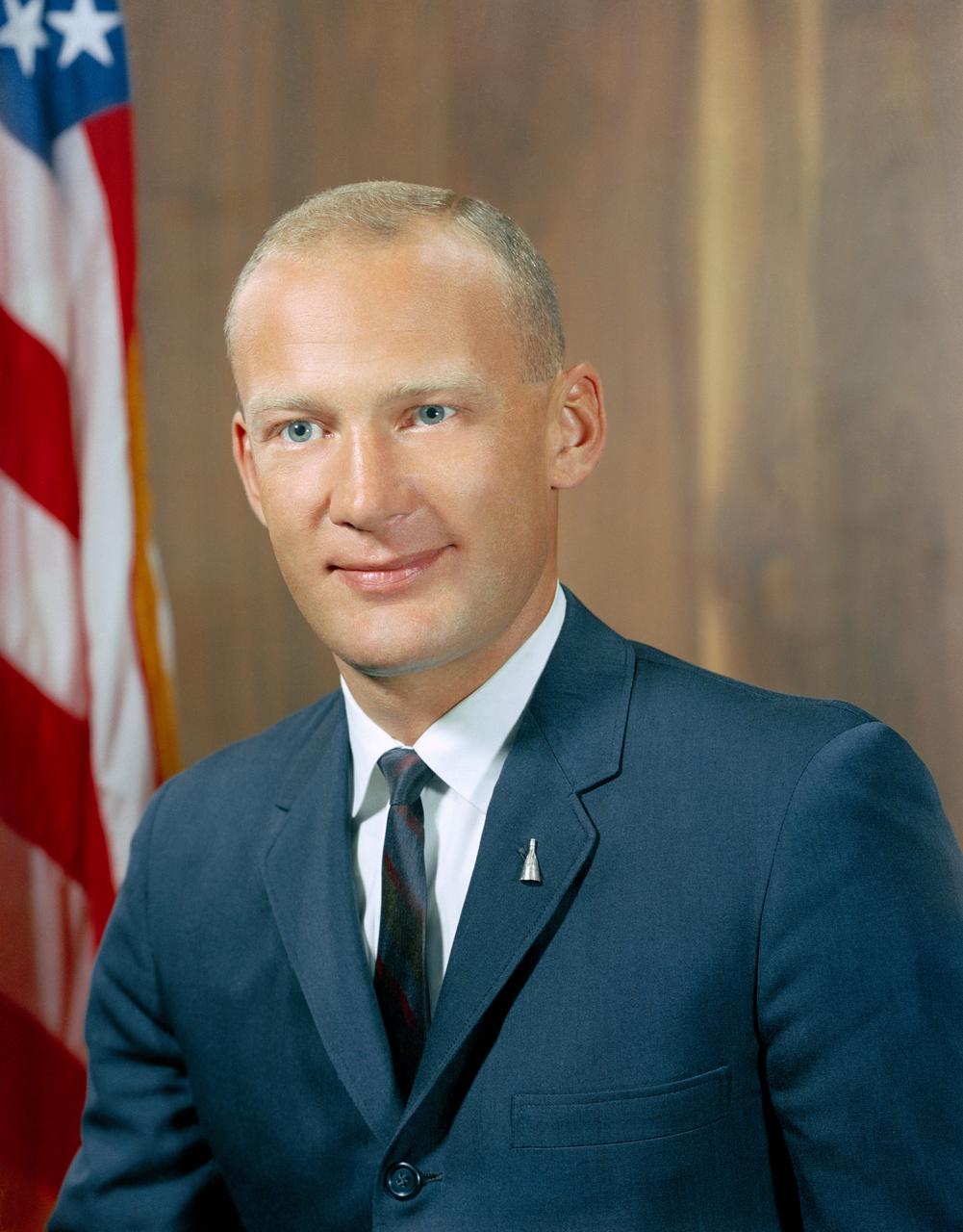

S63-20056 (1963) --- Astronaut Edwin E. "Buzz" Aldrin, Jr. in civilian clothes.
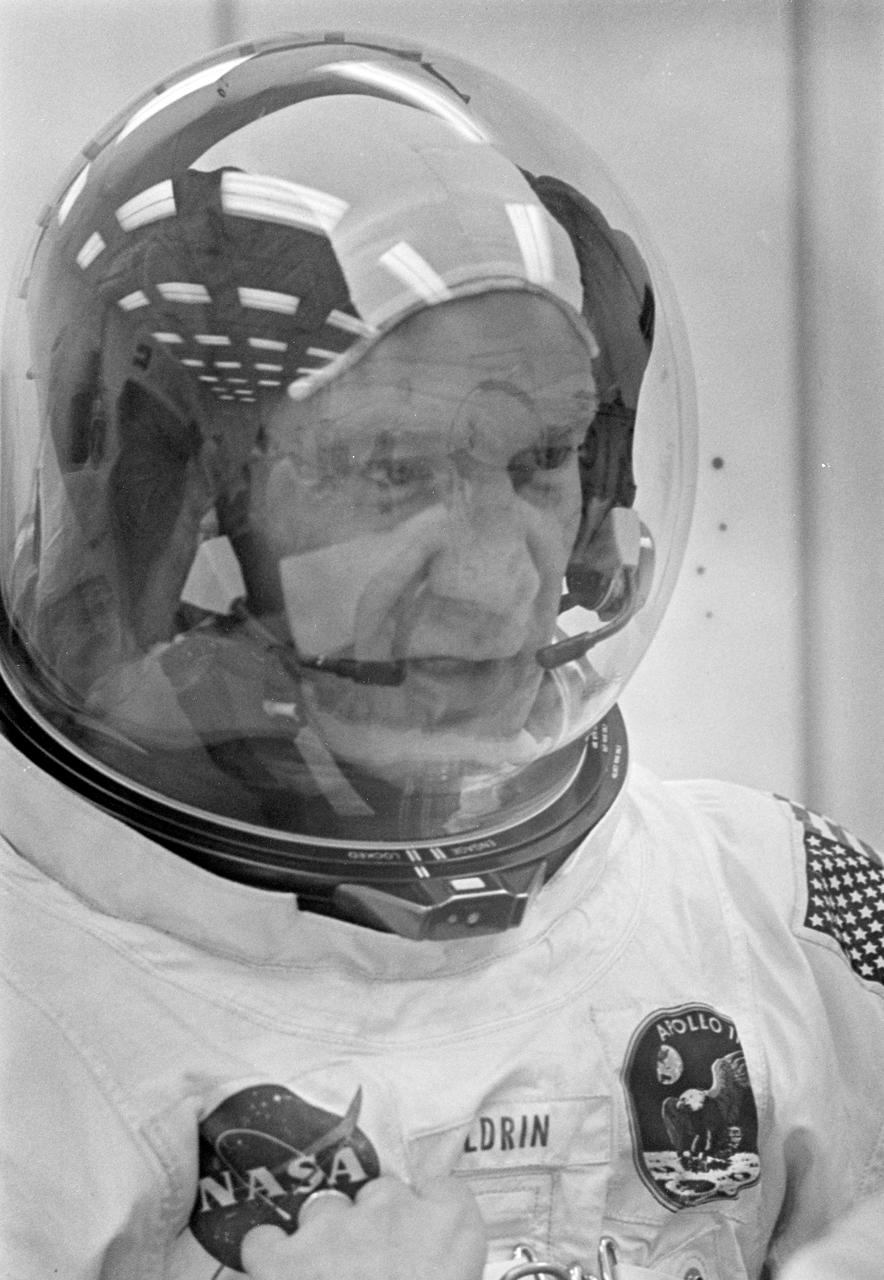

Dunned in his space suit, Lunar Module pilot Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr. does a final check of his communications system before the boarding of the Apollo 11 mission. Launched via a Saturn V launch vehicle, the first manned lunar mission launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. The 3-man crew aboard the flight consisted of astronauts Aldrin; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Neil Armstrong, mission commander. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. Meanwhile, astronaut Collins piloted the CM in a parking orbit around the Moon. During a 2½ hour surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material which was returned to Earth for analysis. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.

Former Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin exiting the bus that brought him to the Apollo 11 Twentieth Aniversary Picnic at the Gilruth Center.
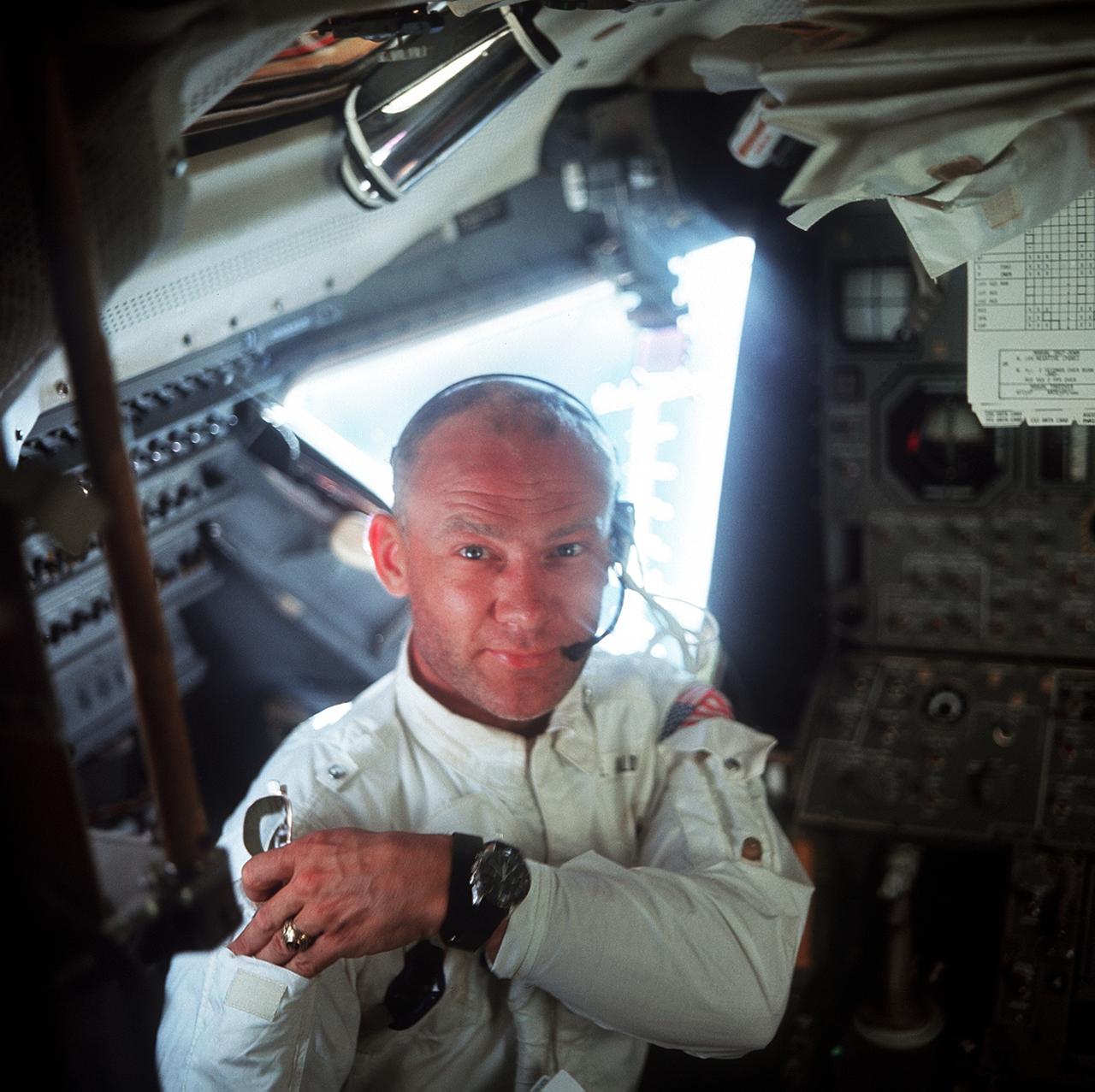

AS11-36-5390 (20 July 1969) --- This interior view of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) shows astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, during the lunar landing mission. This picture was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
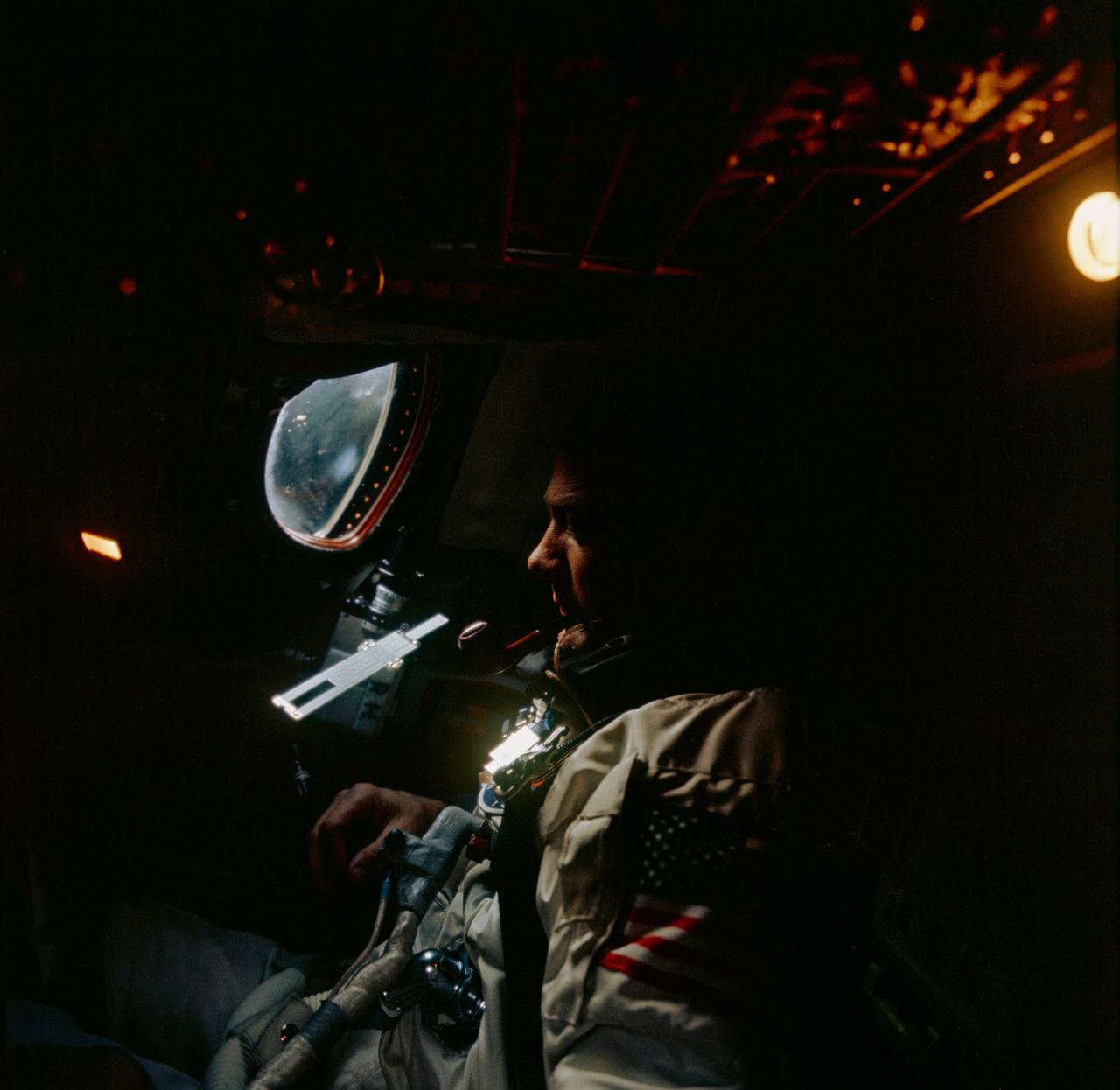
S66-62984 (13 Nov. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin Aldrin Jr. photographed inside the Gemini-12 spacecraft cabin during the spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA
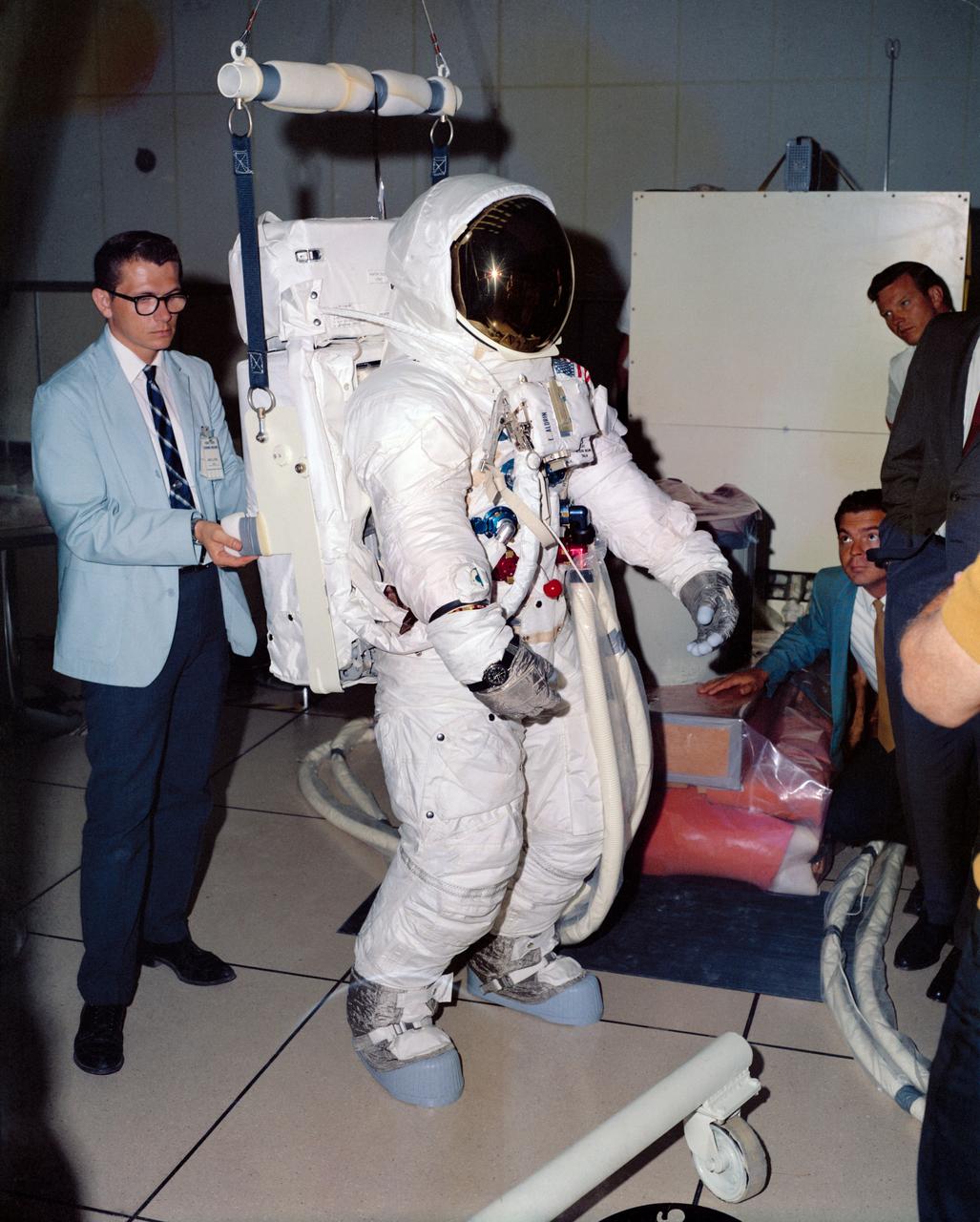

Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), verifies fit of the Portable Life Support System (PLSS) strap length during lunar surface training at the Kennedy Space Center. Aldrin is the prime crew lunar module pilot of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. Aldrin's PLSS backpack is attached to a lunar weight simulator.
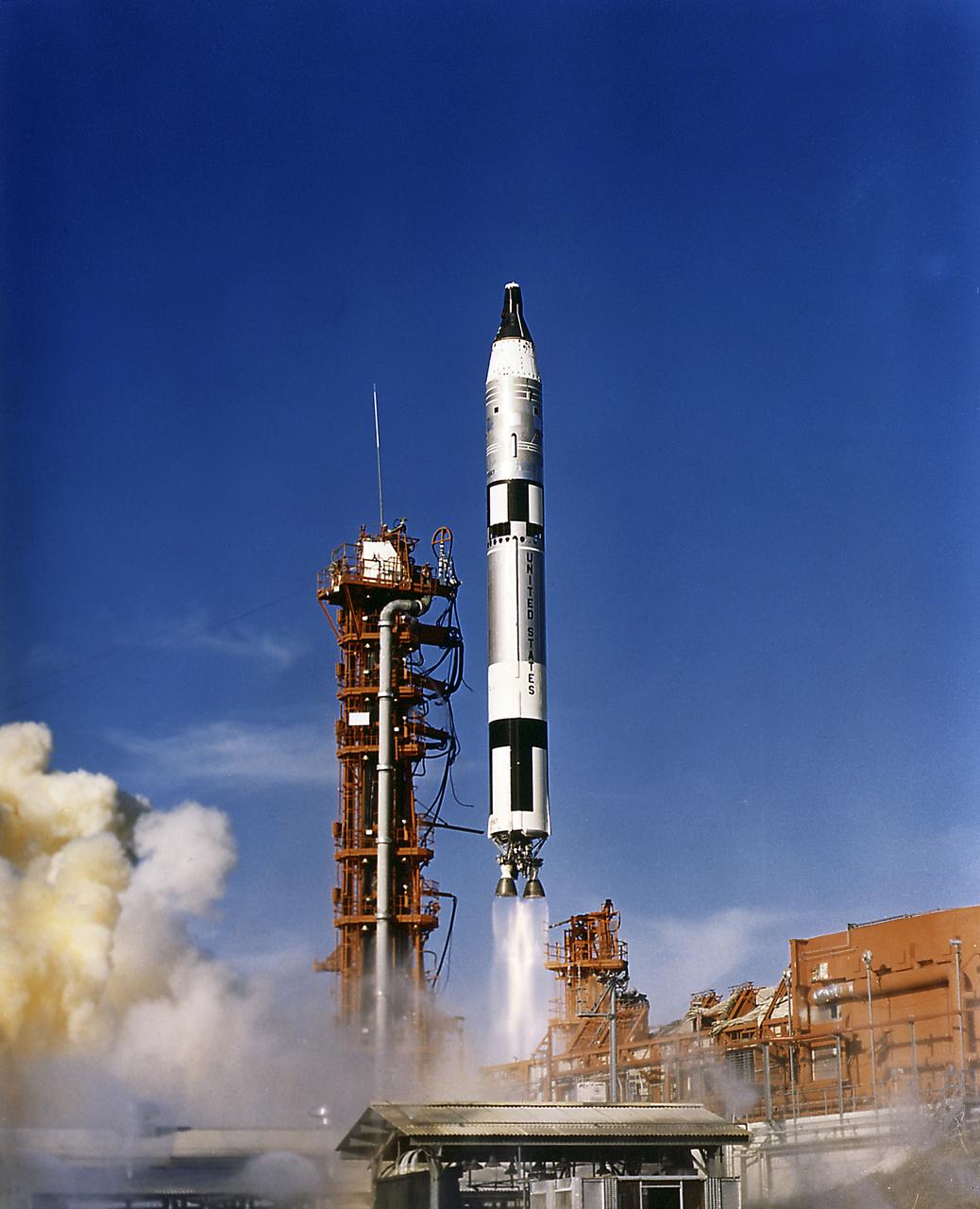

The Gemini 12 astronauts James Lovell and Edwin Aldrin lifted off aboard a Titan launch vehicle from the Kennedy Space Center on November 11, 1966, an hour and a half after their Agena target vehicle was orbited by an Atlas rocket. Launched atop an Atlas booster, the Agena target vehicle (ATV) was a spacecraft used by NASA to develop and practice orbital space rendezvous and docking techniques in preparation for the Apollo program lunar missions. The objective was for Agena and Gemini to rendezvous in space and practice docking procedures. An intermediate step between Project Mercury and the Apollo Program, the Gemini Program's major objectives were to subject two men and supporting equipment to long duration flights, to perfect rendezvous and docking with other orbiting vehicles, methods of reentry, and landing of the spacecraft.
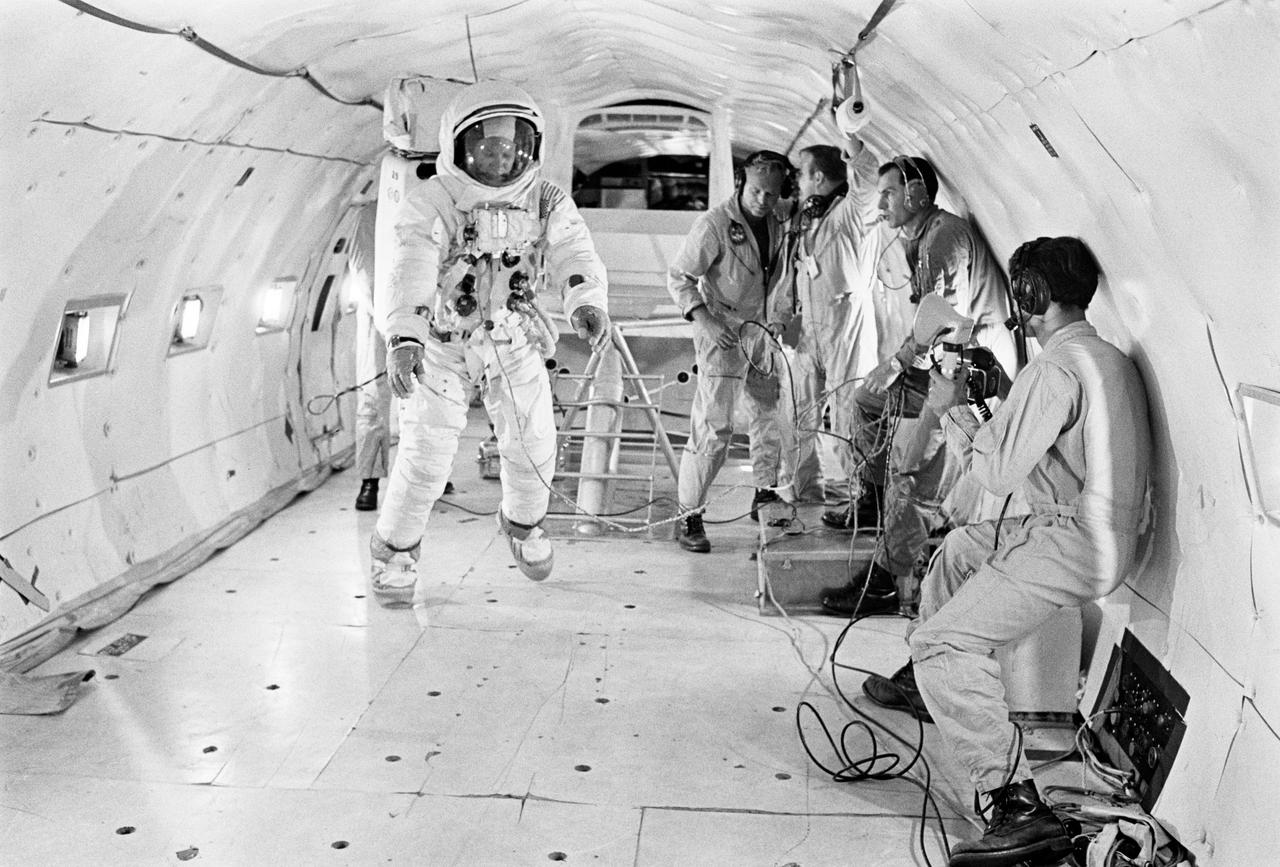

S69-39269 (10 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission, undergoes zero-gravity training aboard a U.S. Air Force KC-135 jet aircraft from nearby Patrick Air Force Base, Florida. Aldrin is wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), the type of equipment which he will wear on the lunar surface.
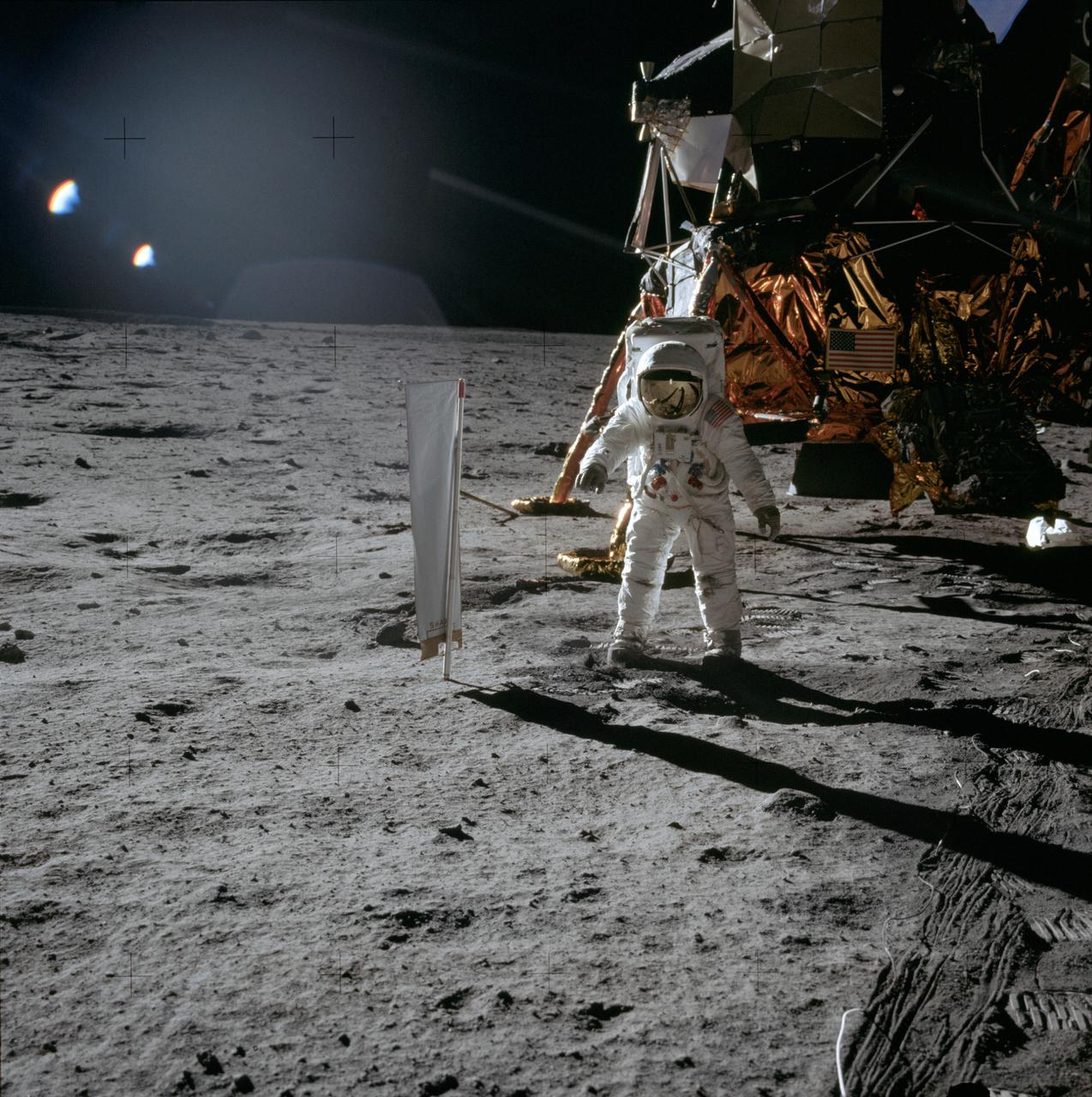

AS11-40-5873 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, is photographed during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. In the right background is the lunar module. On Aldrin's right is the Solar Wind Composition (SWC) experiment, already deployed. This photograph was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, with a 70mm lunar surface camera.
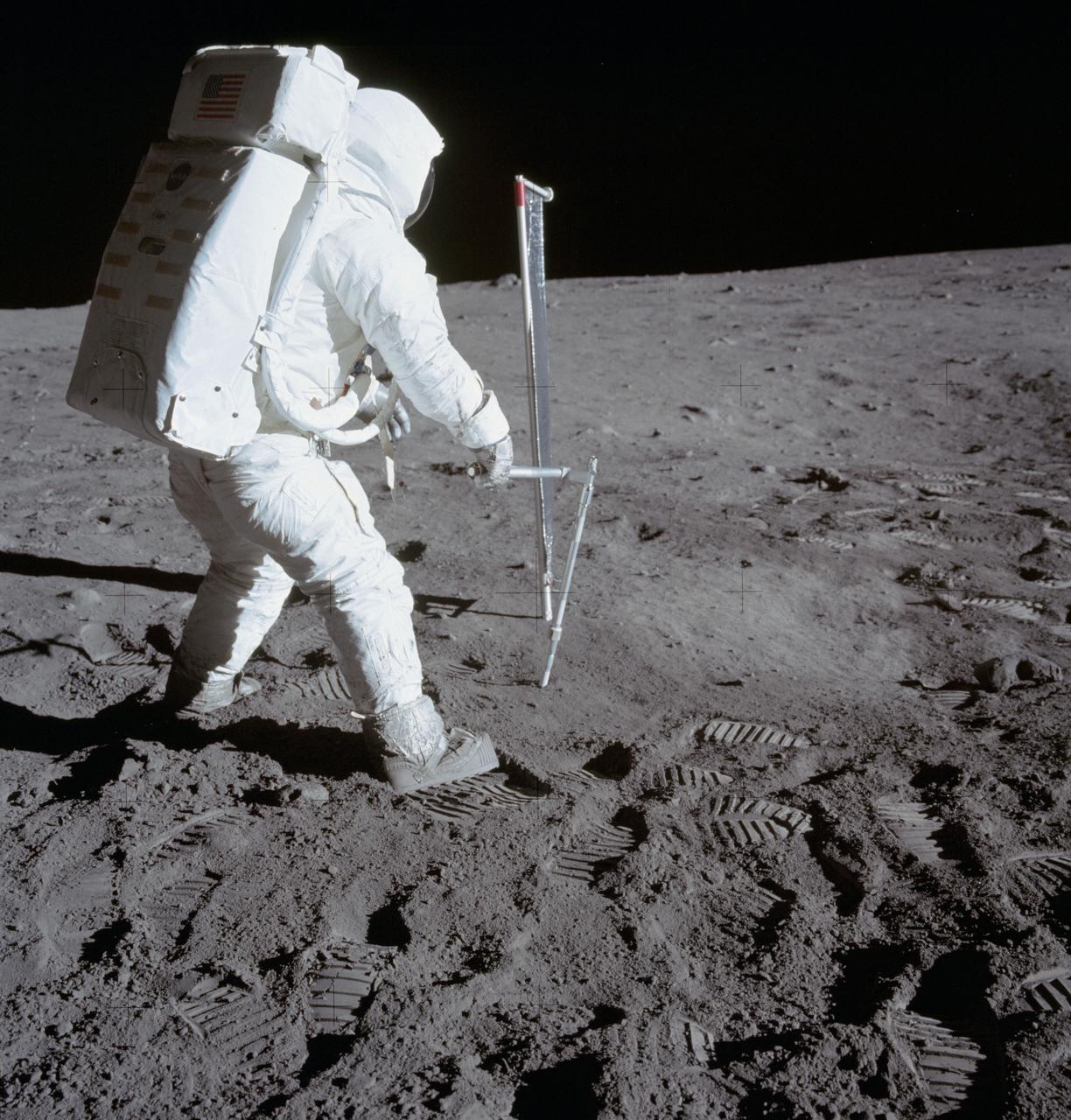

AS11-40-5964 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, is photographed during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. He is driving one of two core tubes into the lunar soil. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm lunar surface camera. Aldrin stands near the Solar Wind Composition (SWC) experiment, a component of the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP, deployed earlier). The SWC is in the center background.
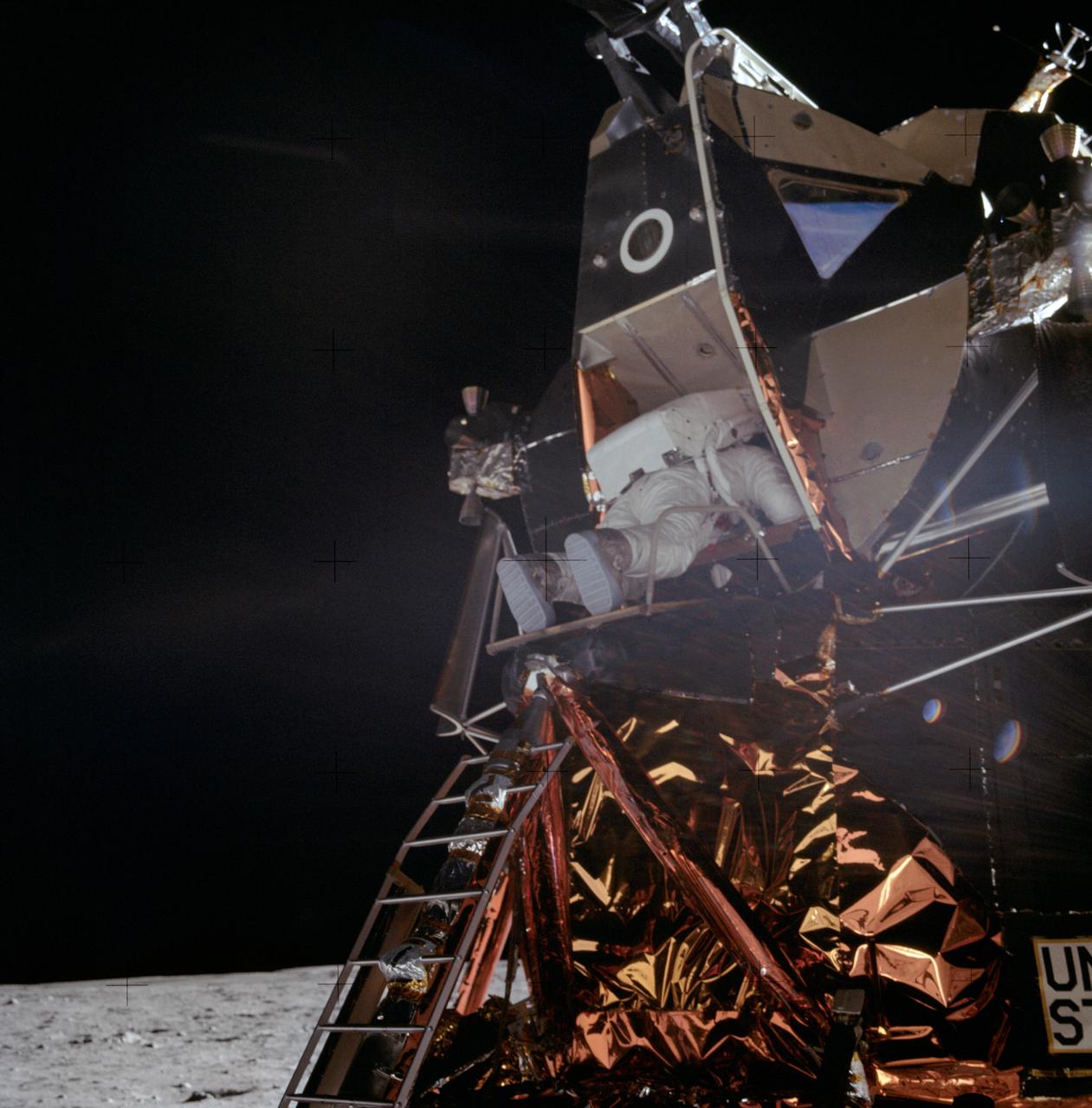

AS11-40-5863 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, is photographed egressing the Lunar Module (LM) during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. This photograph was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, with a 70mm lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
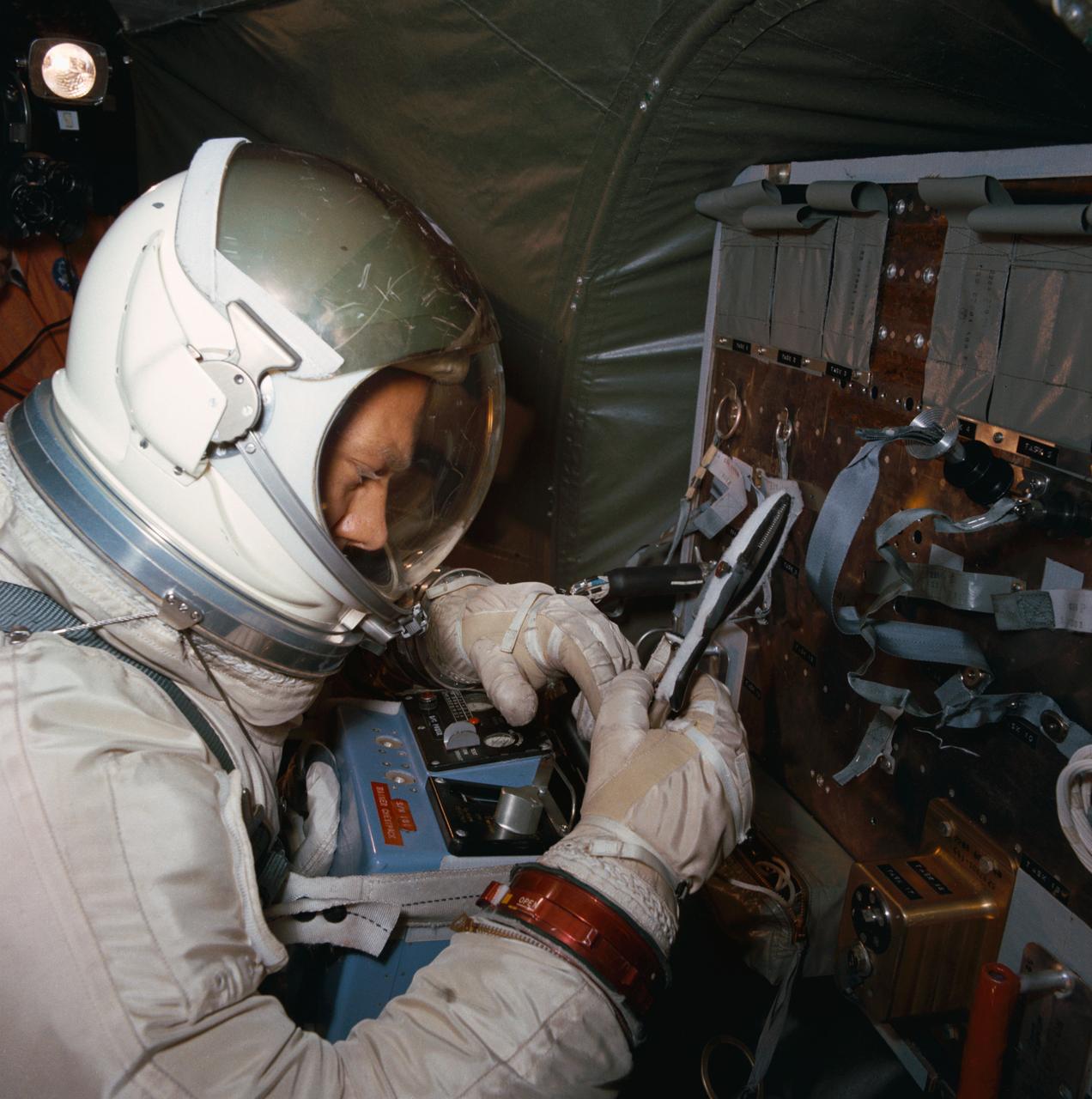

S66-57365 (13 Oct. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot for the Gemini-12 spaceflight, practices work tasks during zero-gravity training. He is standing in a mock-up of the Gemini spacecraft's adapter section onboard an Air Force KC-135 jet aircraft. Photo credit: NASA

AS11-40-5866 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, egresses the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" and begins to descend the steps of the LM ladder as he prepares to walk on the moon. This photograph was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM "Eagle" to explore the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA

AS11-40-5868 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descends the steps of the Lunar Module (LM) ladder as he prepares to walk on the moon. He had just egressed the LM. This photograph was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). While Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM "Eagle" to explore the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

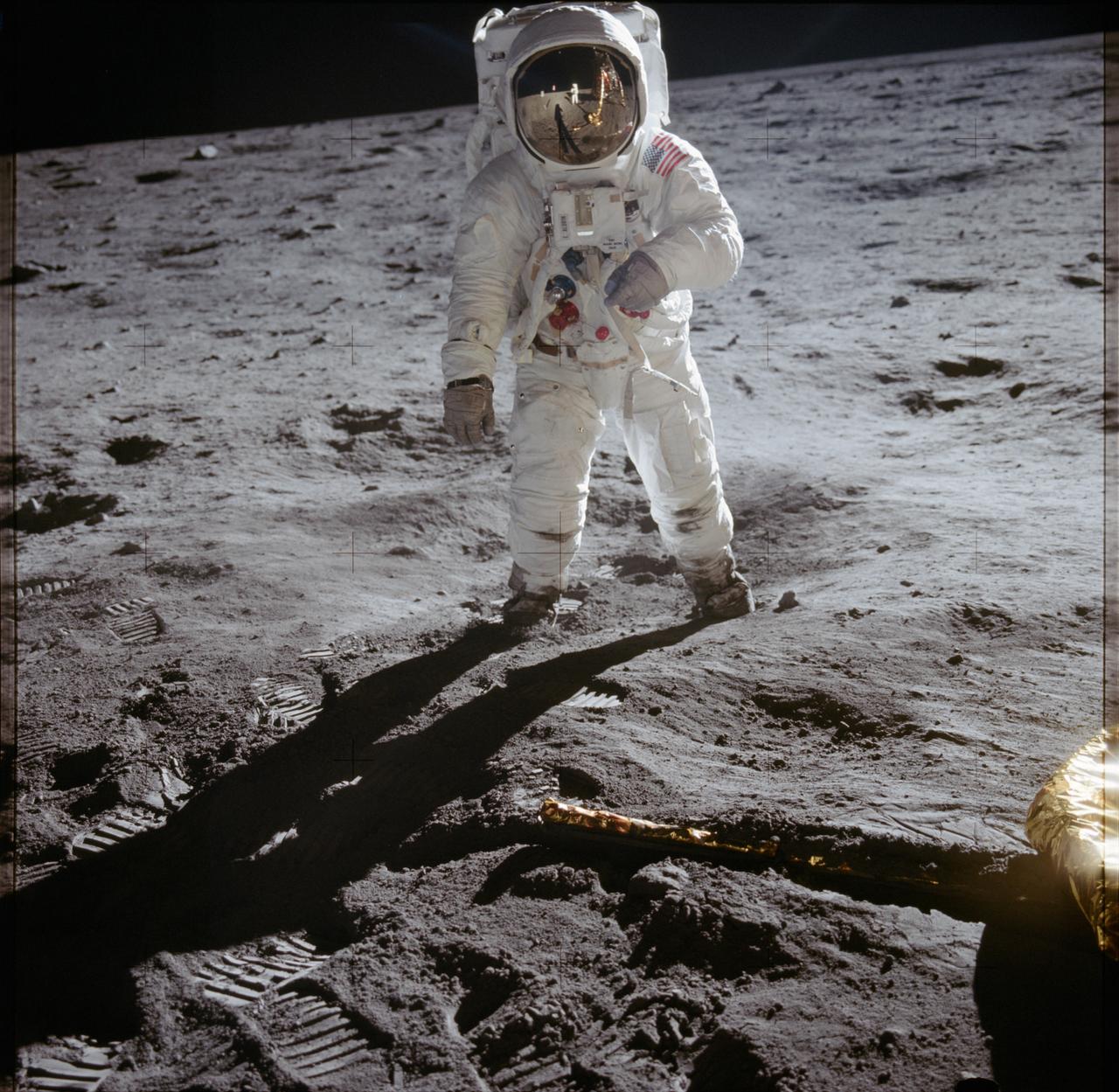
AS11-40-5902 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, walks on the surface of the moon near a leg of the Lunar Module during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, Apollo 11 commander, took this photograph with a 70mm lunar surface camera. The astronauts' bootprints are clearly visible in the foreground. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
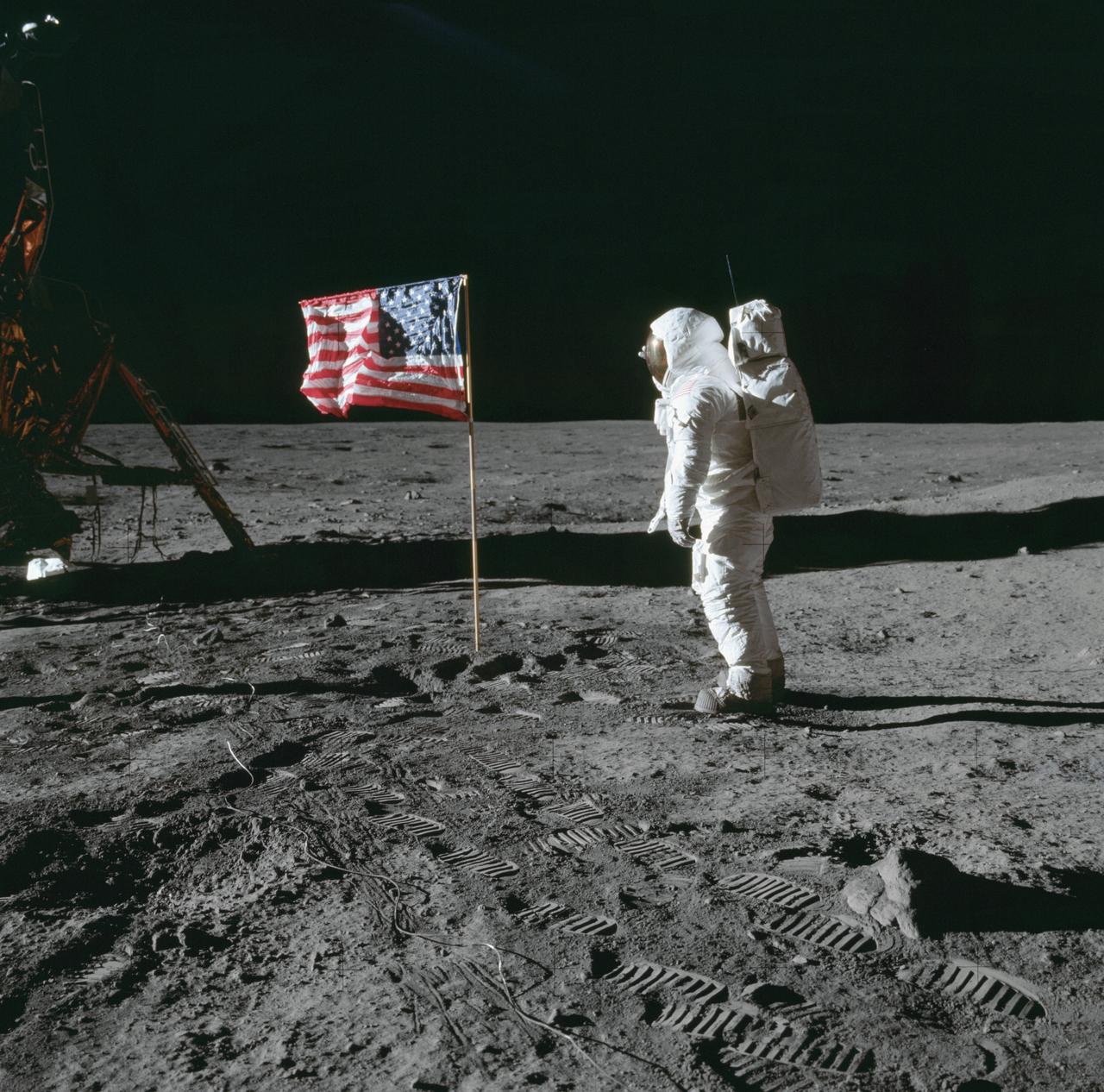

AS11-40-5874 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, poses for a photograph beside the deployed United States flag during Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The Lunar Module (LM) is on the left, and the footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil of the moon. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM the "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

AS11-40-5875 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, poses for a photograph beside the deployed United States flag during an Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The Lunar Module (LM) is on the left, and the footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil of the moon. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM, the "Eagle", to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA
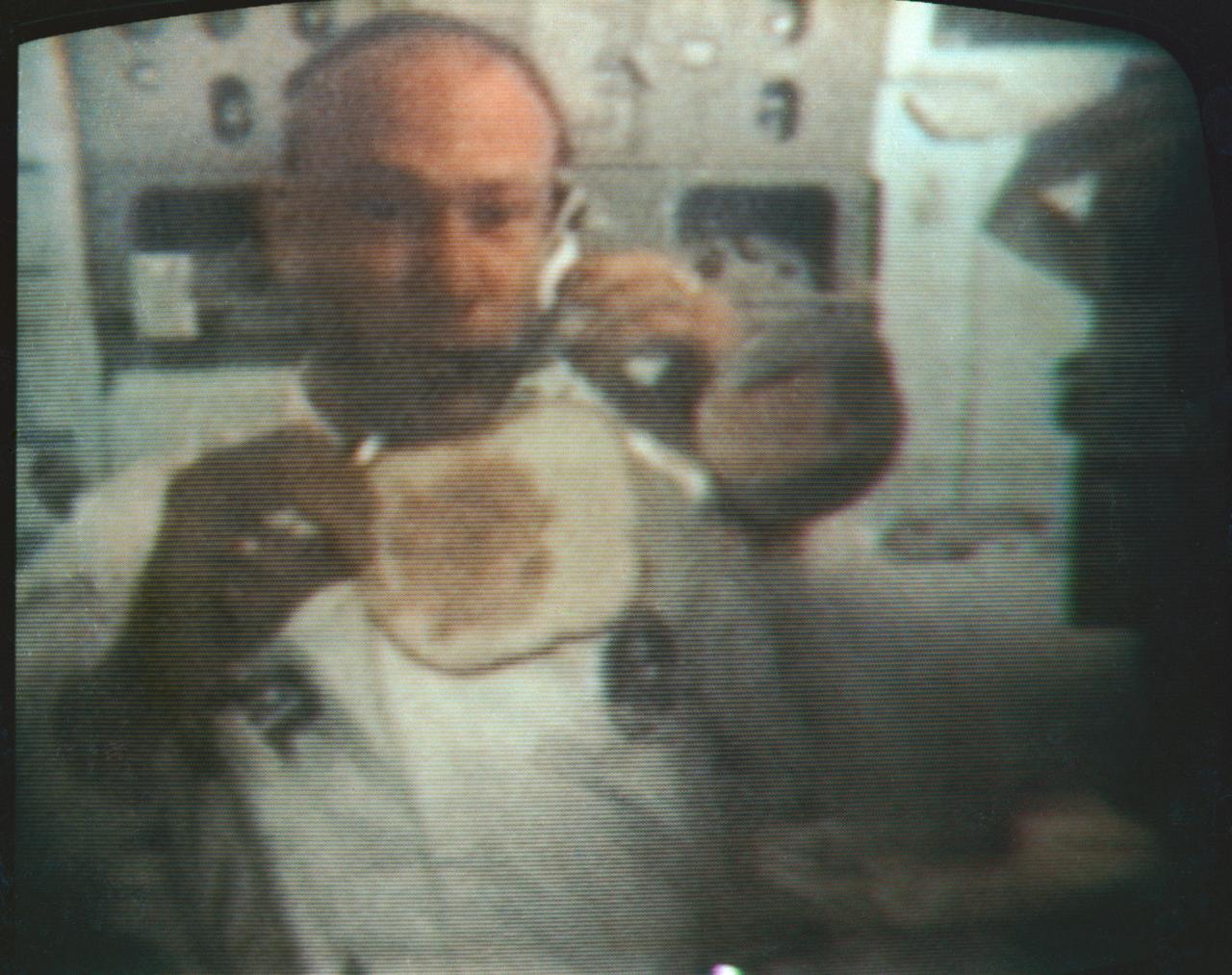

S69-39724 (22 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Apollo 11 lunar module pilot, performs for his Earth-bound television audience, in this color reproduction taken from a TV transmission, from the Apollo 11 spacecraft during its trans-Earth journey home from the moon. Aldrin illustrates how to make a sandwich under zero-gravity conditions. When this picture was made, Apollo 11 was approximately 137,000 nautical miles from Earth, traveling at a speed of about 4,300 feet per second. Also, aboard the spacecraft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; and Michael Collins, command module pilot.

AS11-40-5903 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, walks on the surface of the moon near the leg of the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this photograph with a 70mm lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

AS11-40-5931 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, prepares to deploy the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP) on the surface of the moon during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this photograph with a 70mm lunar surface camera. In the foreground is the Apollo 11 35mm stereo close-up camera.

S66-57387 (13 Oct. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot for the Gemini-12 spaceflight, practices work tasks during zero-gravity training. He is secured to a mock-up of the Agena Target Docking Vehicle by special tethers. The training took place onboard an Air Force KC-135 jet aircraft. Photo credit: NASA
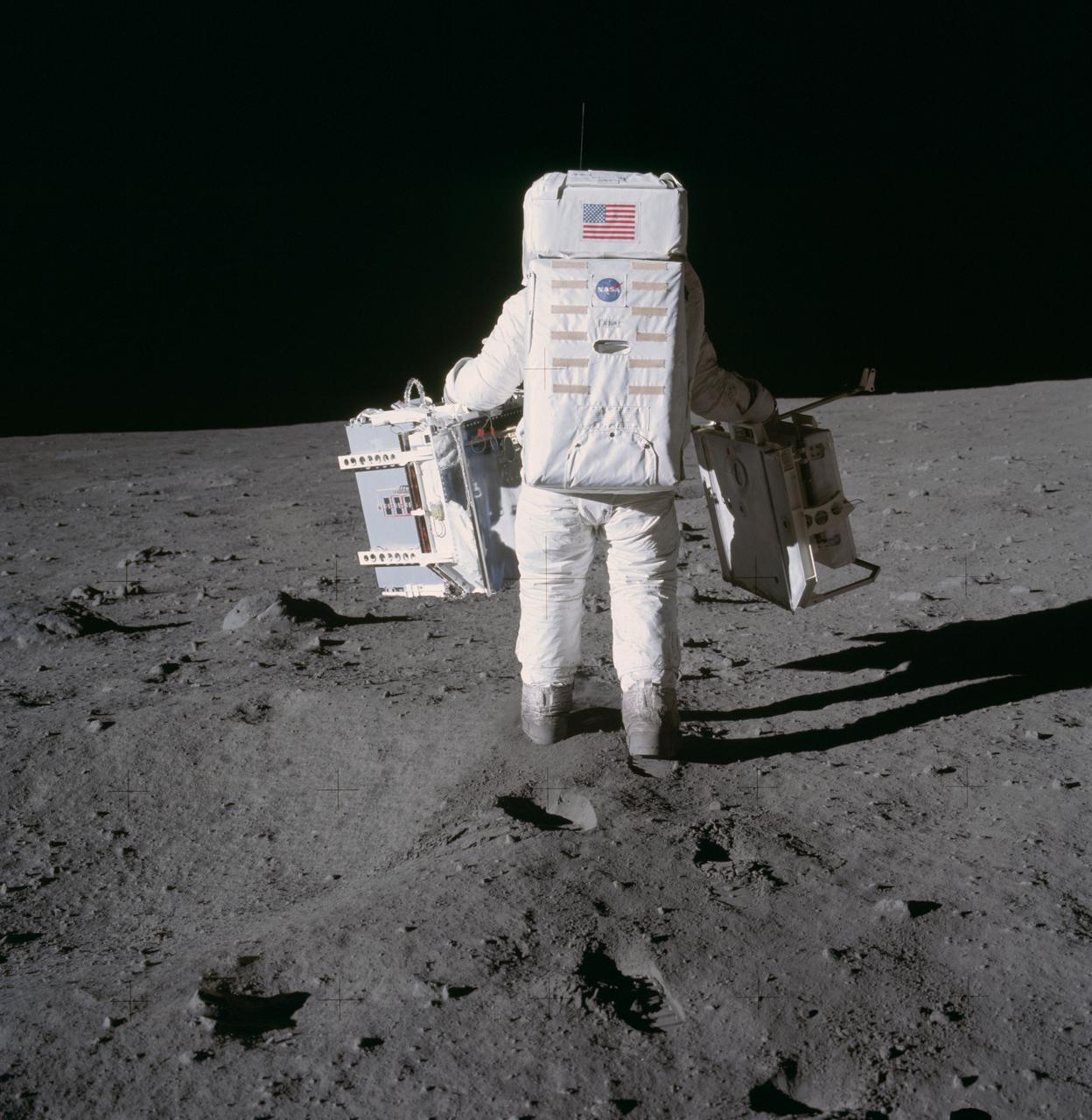

Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, moves toward a position to deploy two components of the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP) on the surface of the Moon during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity. The Passive Seismic Experiments Package (PSEP) is in his left hand; and in his right hand is the Laser Ranging Retro-Reflector (LR3). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this photograph with a 70mm lunar surface camera.
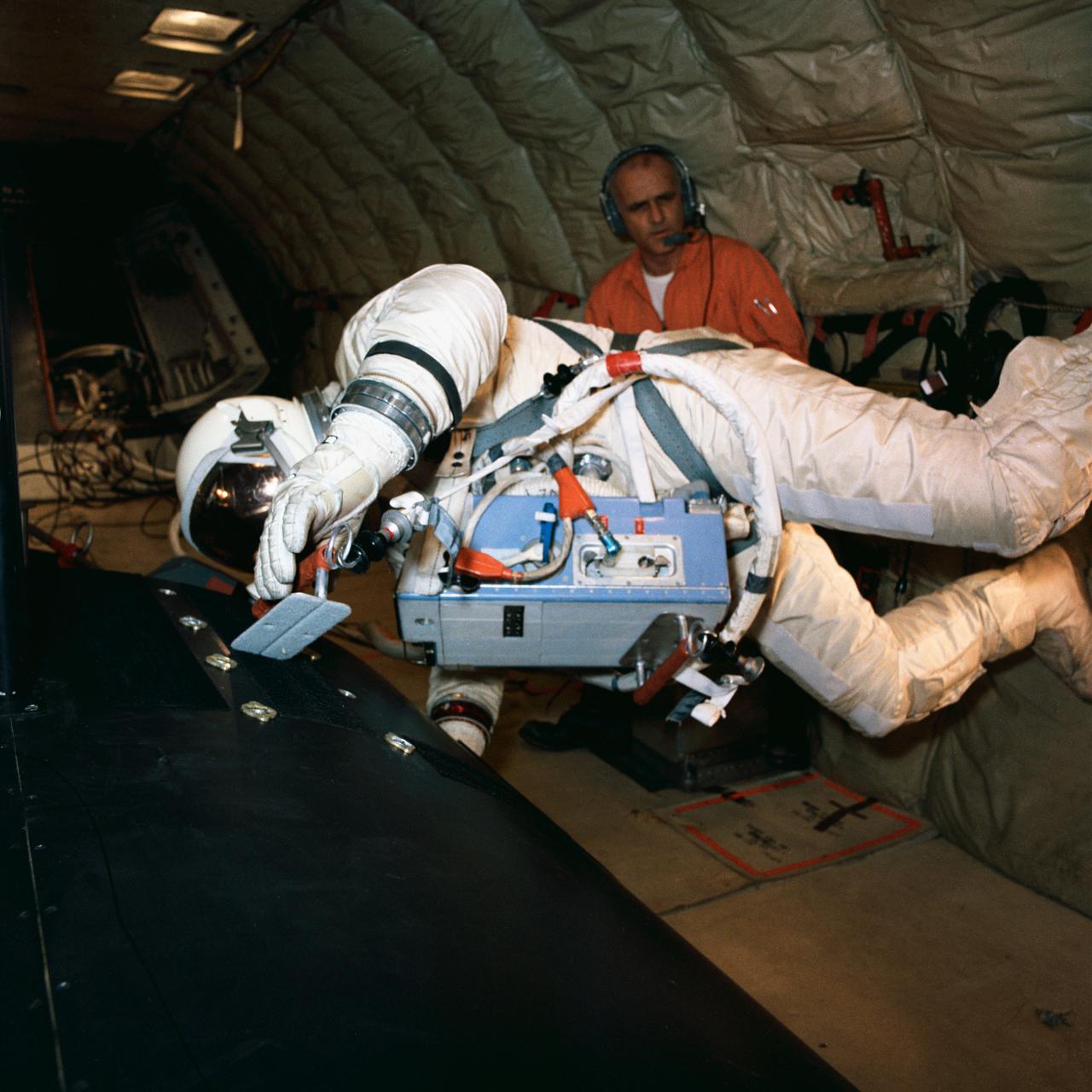

S66-57353 (13 Oct. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot for the Gemini-12 spaceflight, practices work tasks on a mock-up of the adapter section of a spacecraft. Training took place onboard an Air Force KC-135 jet aircraft. He wears a life support chest pack during the exercise. Photo credit: NASA
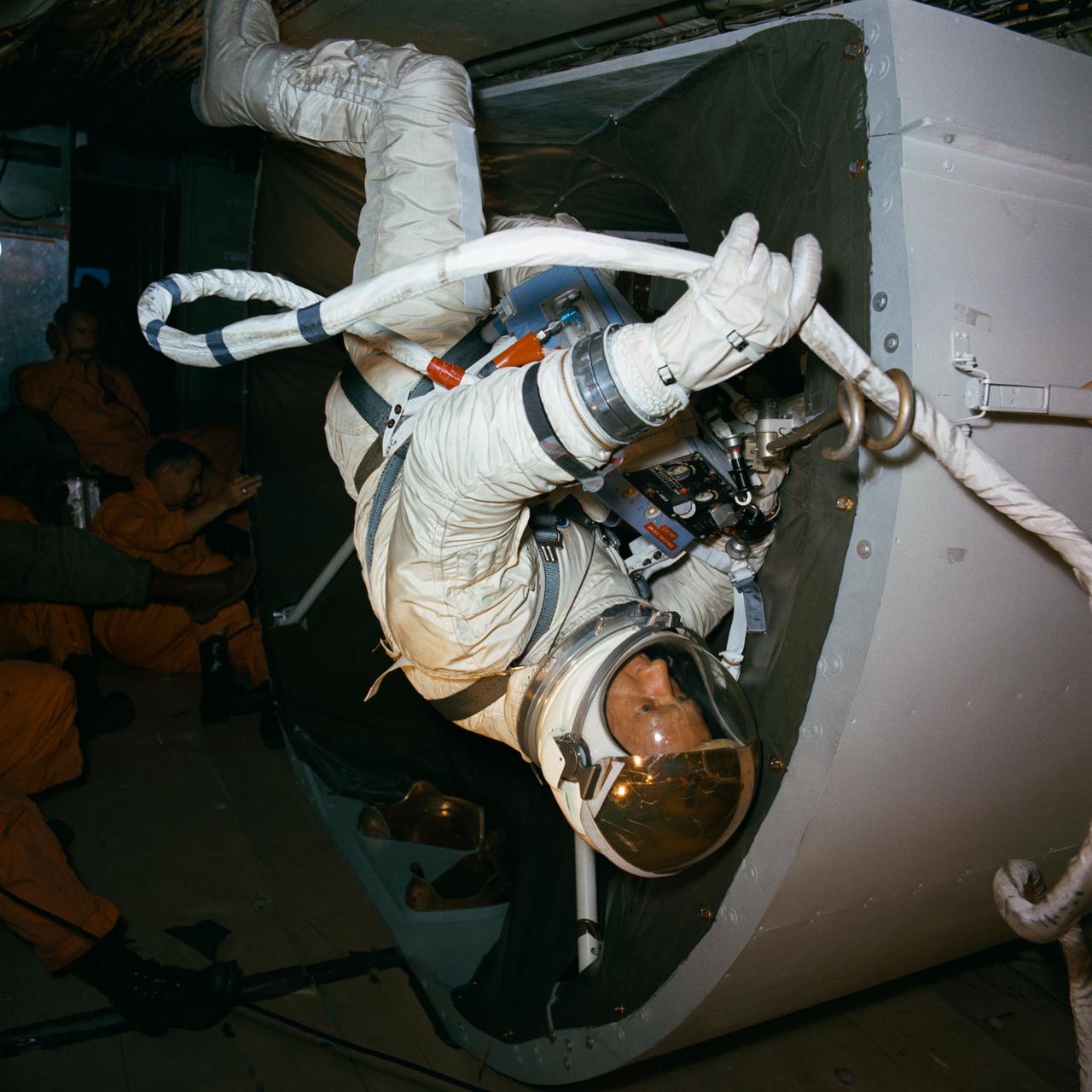

S66-57326 (13 Oct. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot for the Gemini-12 spaceflight, attaches tether to hooks on mock-up of the adapter section of a Gemini spacecraft. He is taking part in zero-gravity training onboard an Air Force KC-135 jet aircraft in preparation for his extravehicular activity (EVA) during the actual mission. Photo credit: NASA

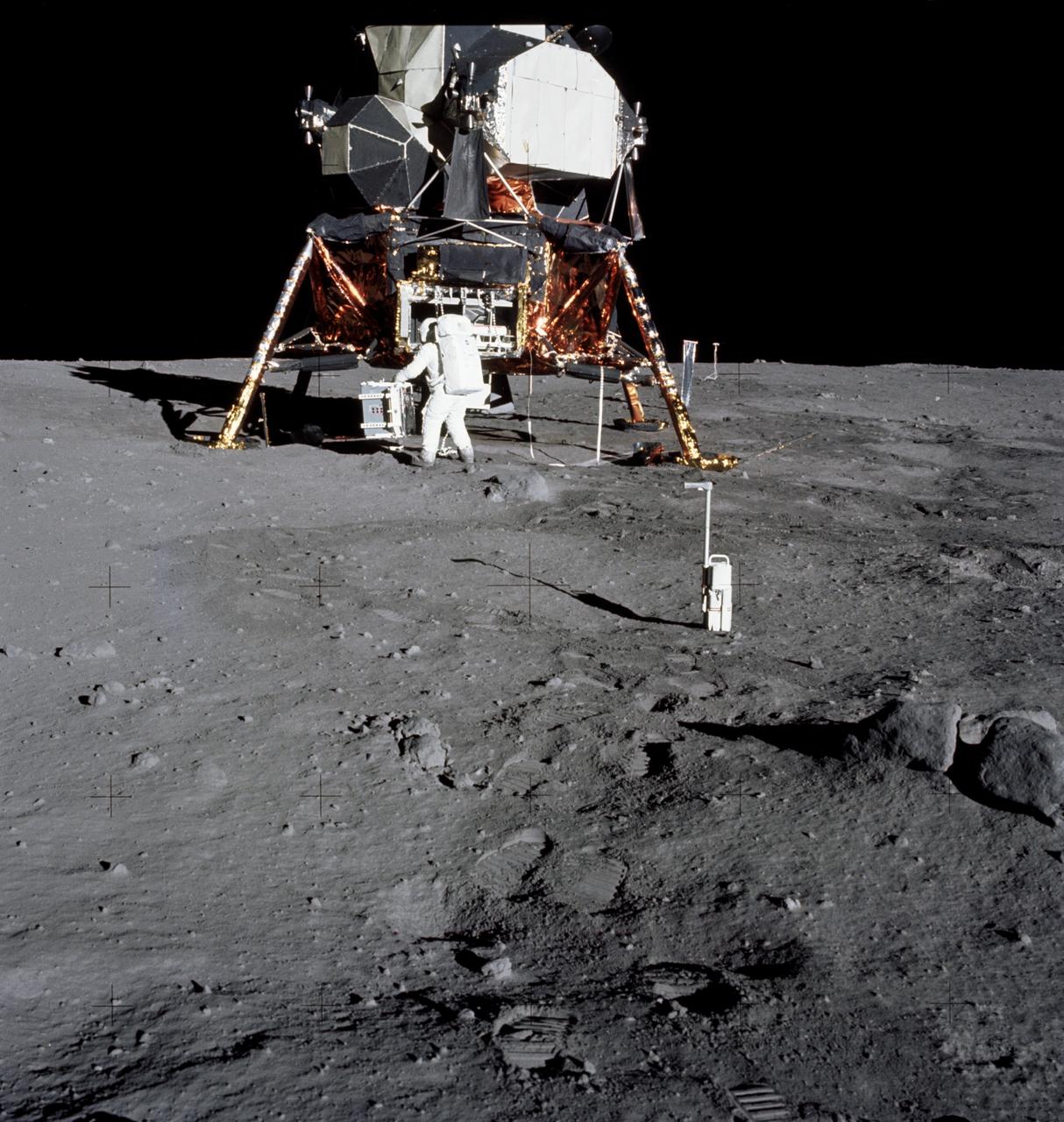
AS11-40-5948 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, is photographed during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. He has just deployed the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP). This is a good view of the deployed equipment. In the foreground is the Passive Seismic Experiment Package (PSEP); beyond it is the Laser Ranging Retro-Reflector (LR-3); in the center background is the United States flag; in the left background is the black and white lunar surface television camera; in the far right background is the Lunar Module (LM). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

S66-56738 (4 Oct. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., prime crew pilot of the Gemini-12 spaceflight, undergoes zero-gravity ingress and egress training aboard an Air Force KC-135 aircraft. He practices using camera equipment. Photo credit: NASA
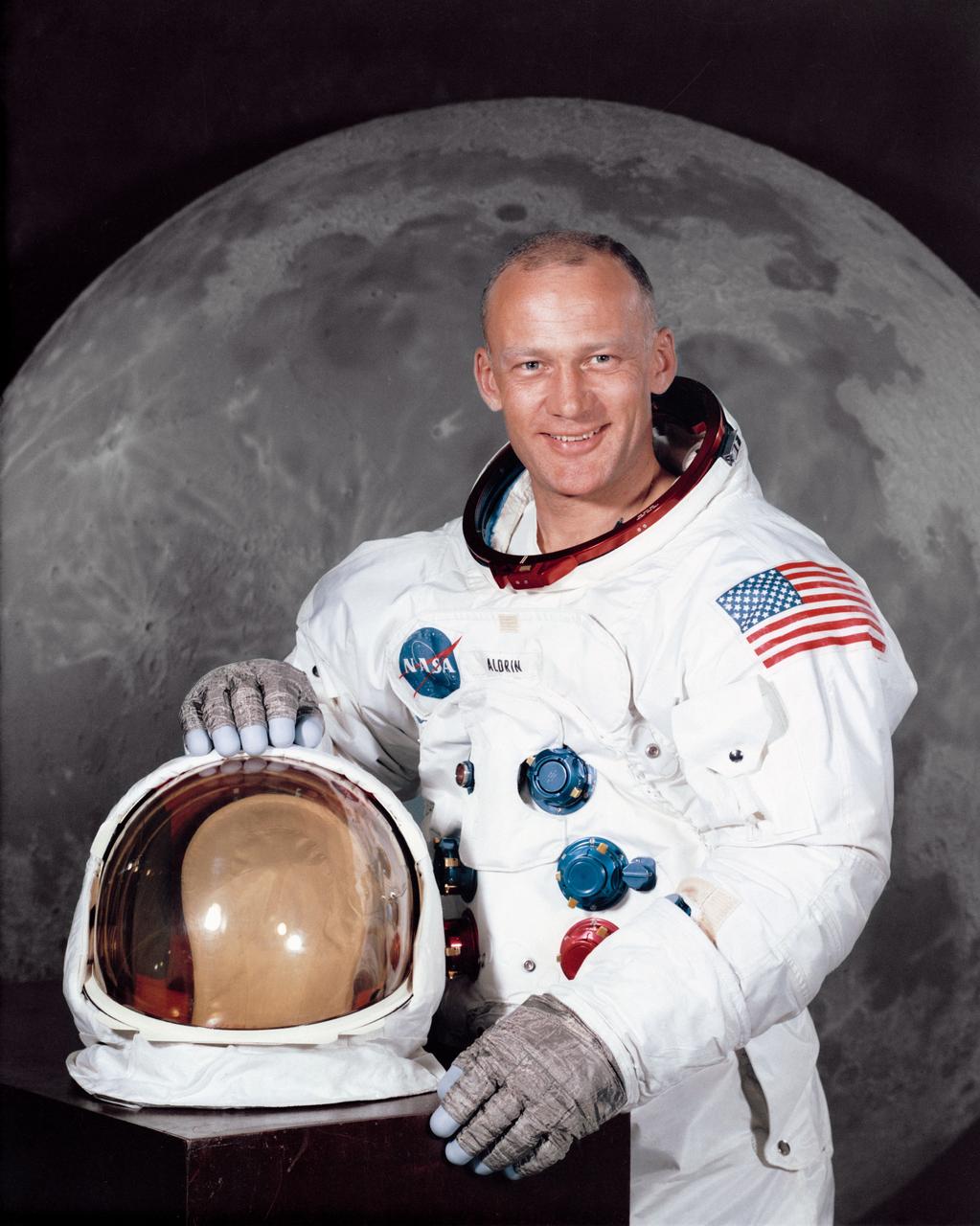

S69-31743 (July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. EDITOR'S NOTE: Aldrin was lunar module pilot of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission.
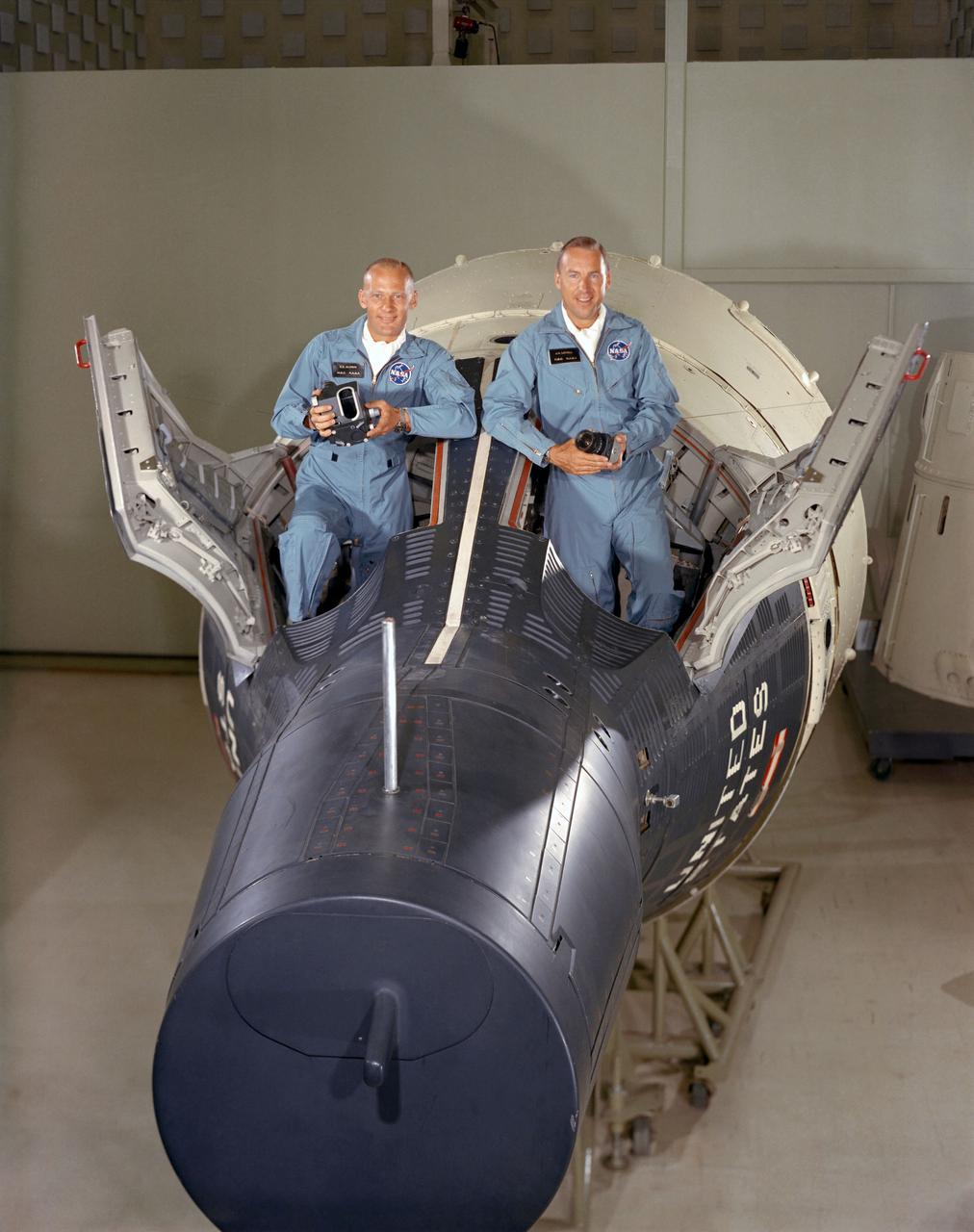

S66-46952 (September 1966) --- Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr. (right), command pilot, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot. Photo credit: NASA
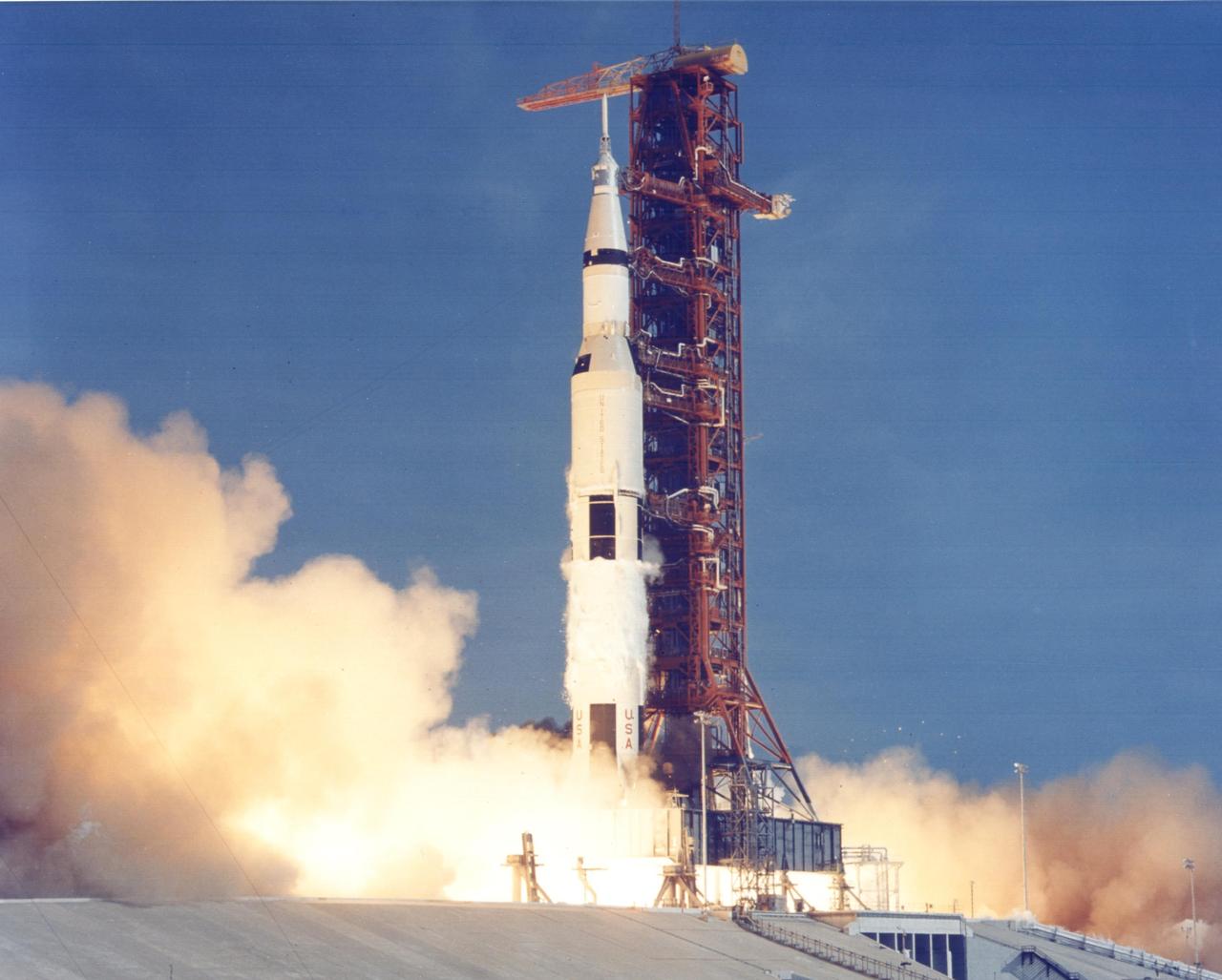
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Liftoff of Apollo 11 from Launch Pad 39A with astronauts Neil Armstrong, Edwin Aldrin Jr. and Miichael Collins onboard.
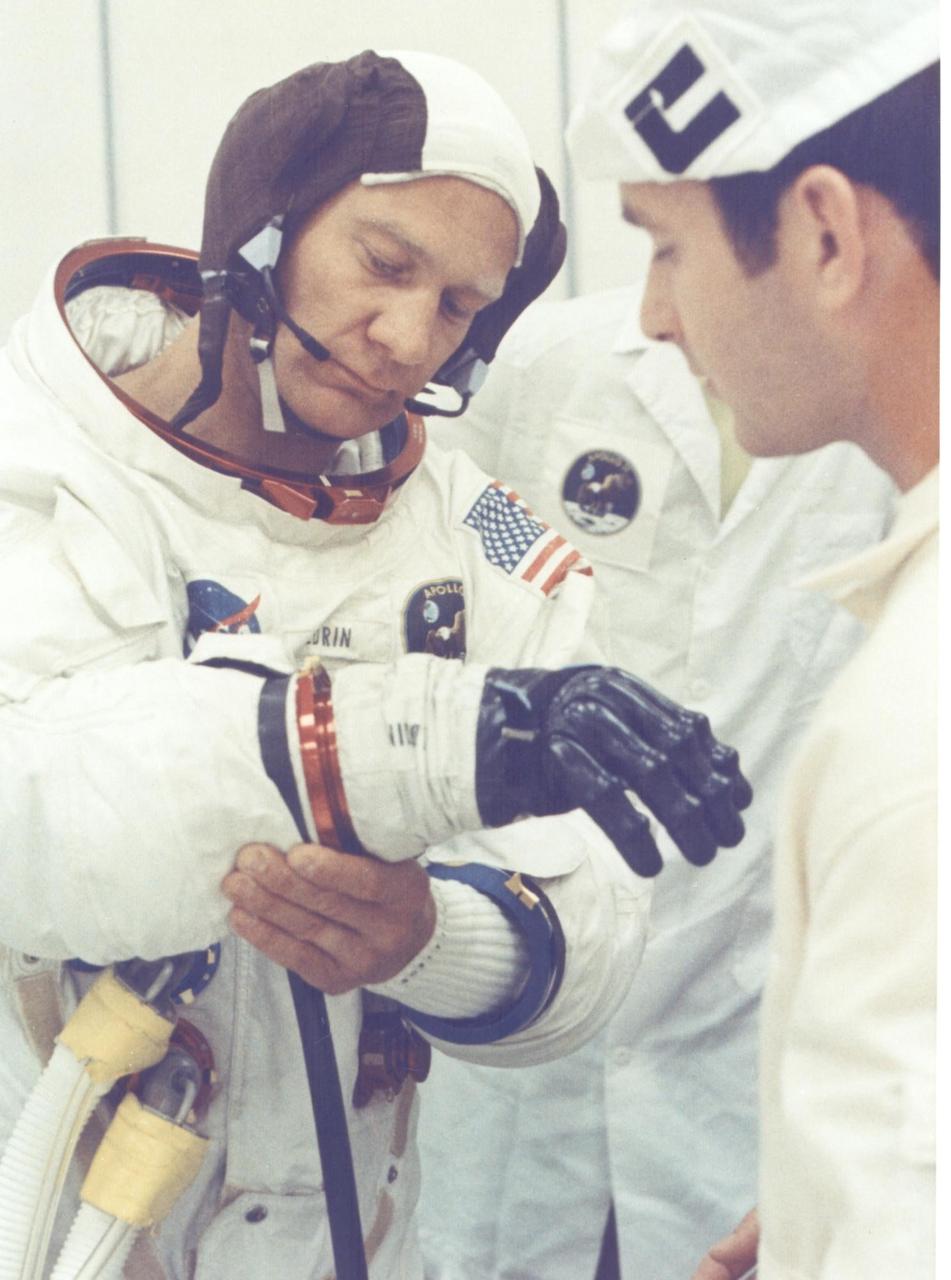

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Apollo 11 astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. is being assisted by a spacesuit technician during suiting operations in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building prior to the astronauts' departure to Launch Pad 39A. The three astronauts, Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Neil A Armstrong and Michael Collins, will then board the Saturn V launch vehicle, scheduled for a 9:32 a.m. EDT liftoff for the first manned lunar landing mission.
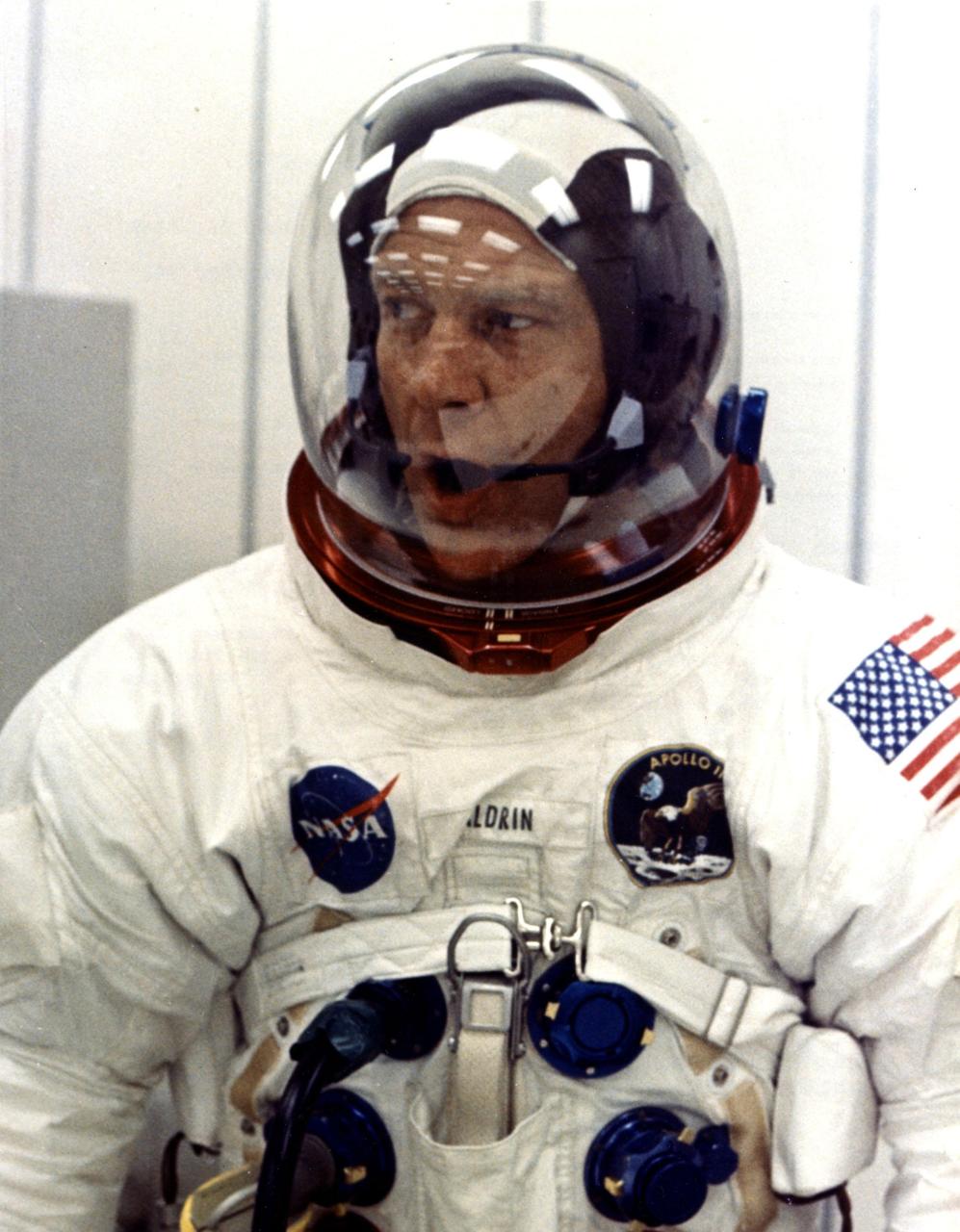

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Apollo 11 astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. appears to be relaxed during suiting operations in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building (MSOB) prior to the astronauts' departure to Launch Pad 39A. The three astronauts, Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Neil A. Armstrong and Michael Collins, will then board the Saturn V launch vehicle, scheduled for a 9:32 a.m. EDT liftoff, for the first manned lunar landing mission
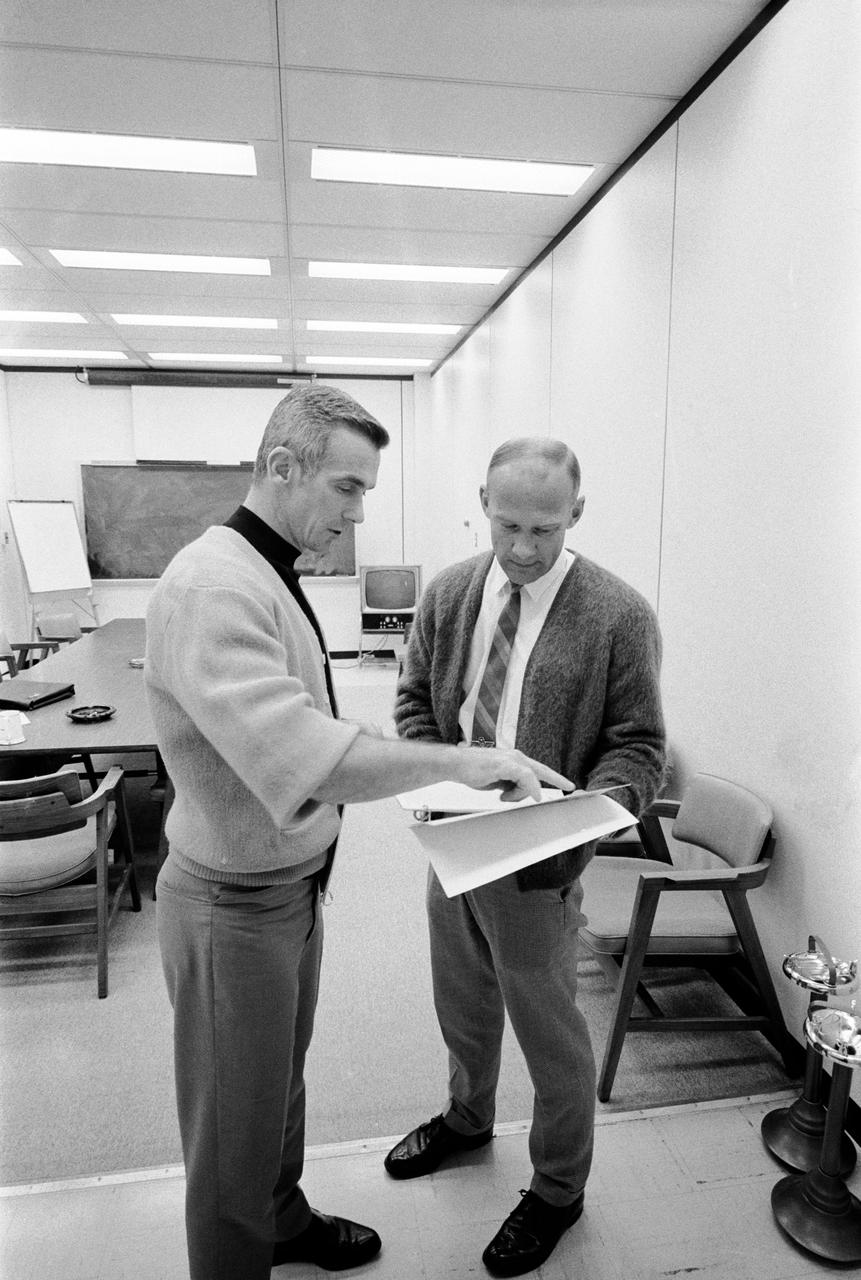

S69-35502 (June 1969) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (left), lunar module pilot of the Apollo 10 lunar orbit mission, confers with astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during an Apollo 10 postflight de-briefing session. Aldrin is the lunar module pilot of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission.
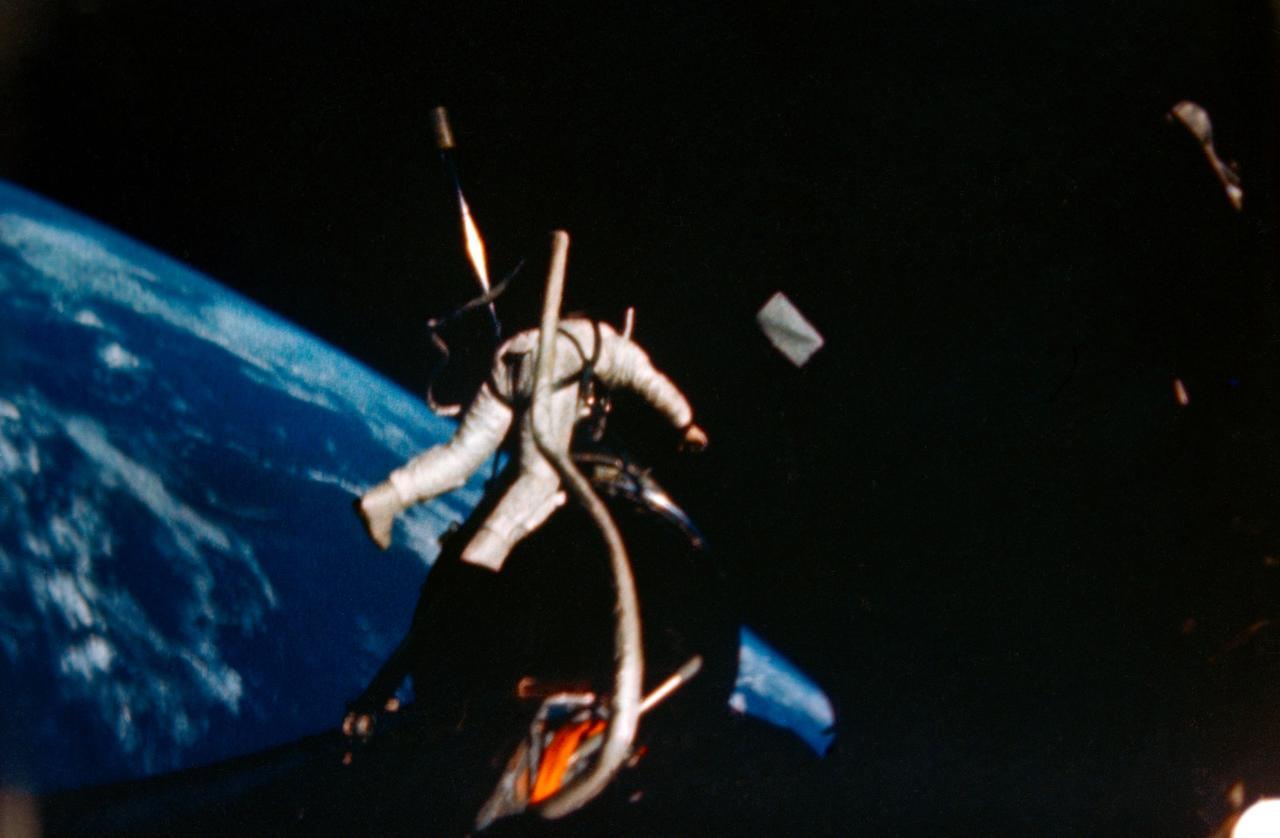

S66-62939 (12 Nov. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot of the Gemini-12 spaceflight, performs extravehicular activity (EVA) during the second day of the four-day mission in space. Aldrin is at the Agena work station. Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr. was the command pilot. Photo credit: NASA

The crowning achievement for the Saturn V rocket came when it launched Apollo 11 astronauts, Neil Armstrong, Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin, and Michael Collins, to the Moon in July 1969. In this photograph, astronaut Aldrin takes his first step onto the surface of the Moon.
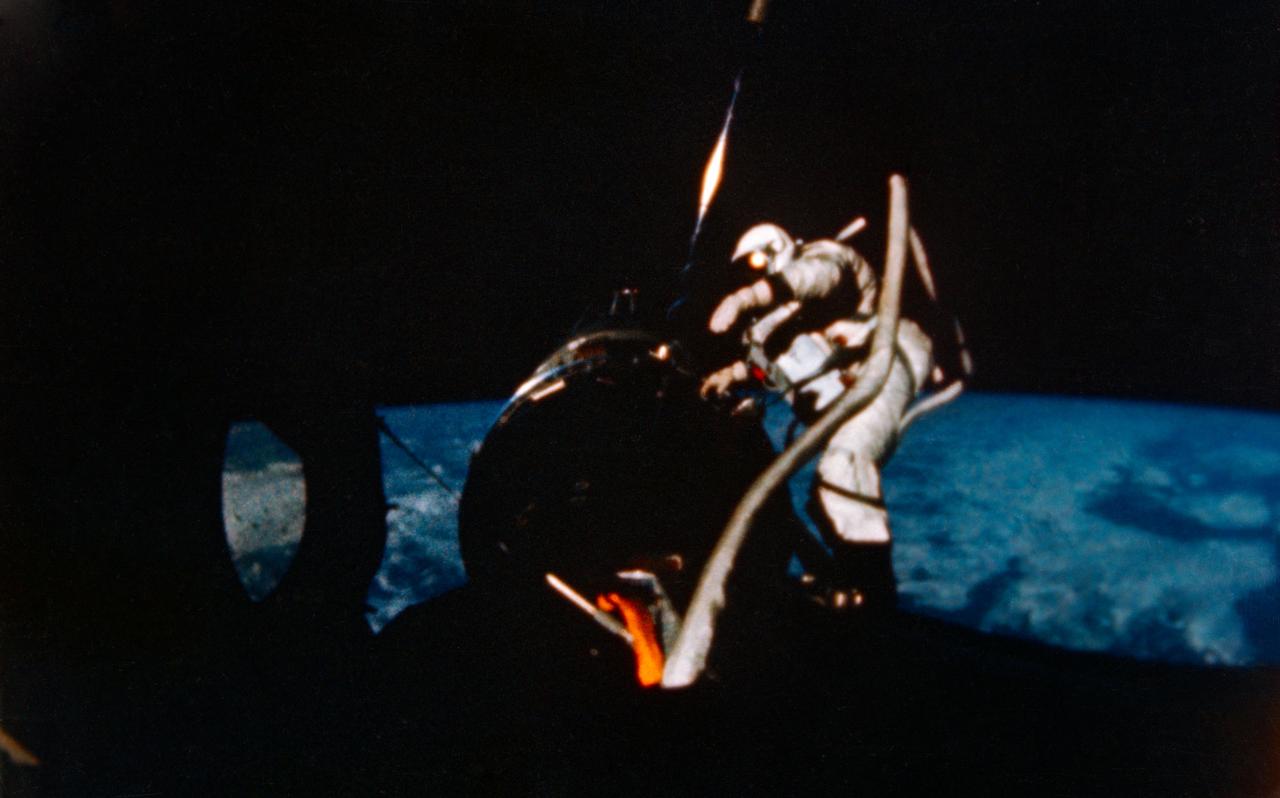
S66-62937 (12 Nov. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot of the Gemini-12 spaceflight, performs extravehicular activity (EVA) during the second day of the four-day mission in space. Aldrin is at the Agena work station. Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr. was the command pilot. Photo credit: NASA
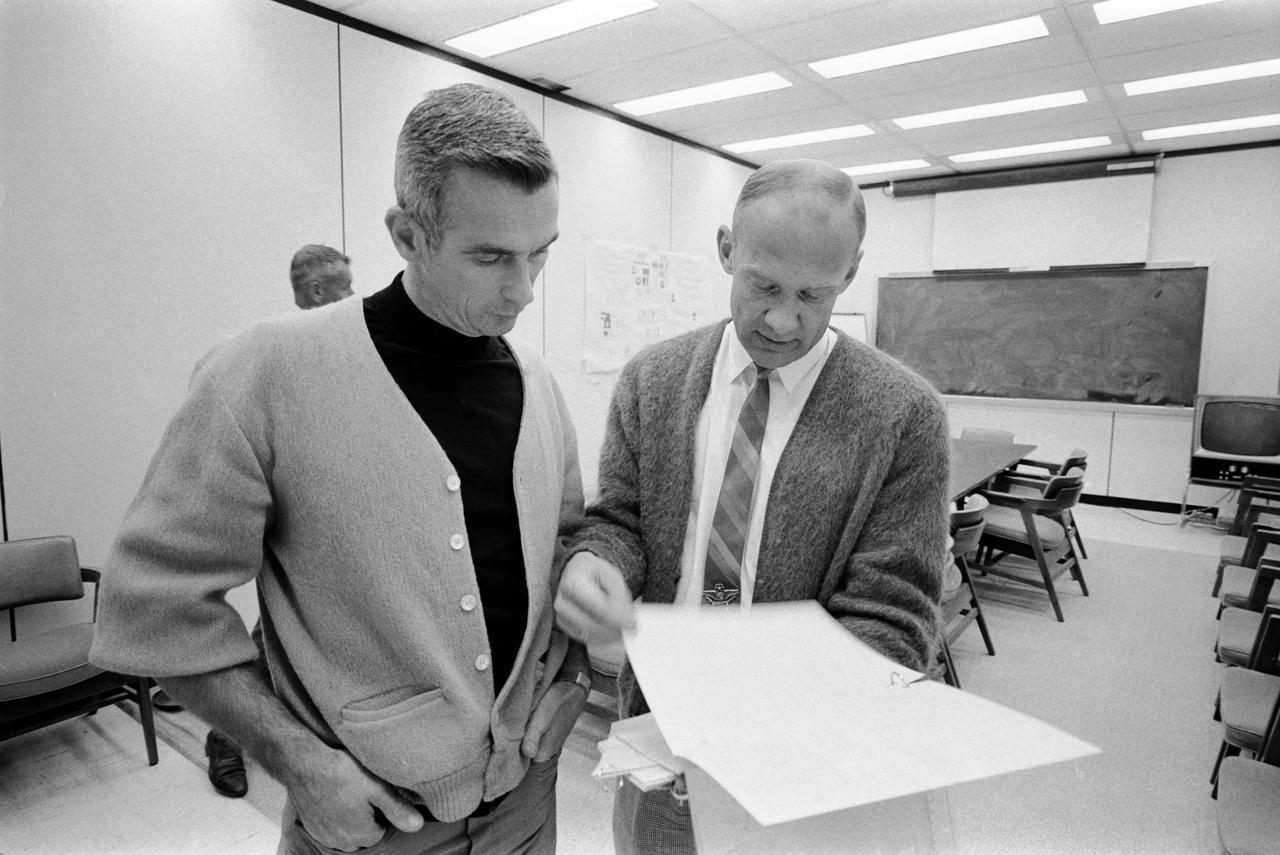

S69-35503 (June 1969) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (left), lunar module pilot of the Apollo 10 lunar orbit mission, confers with astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during an Apollo 10 postflight de-briefing session. Aldrin is the lunar module pilot of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission.
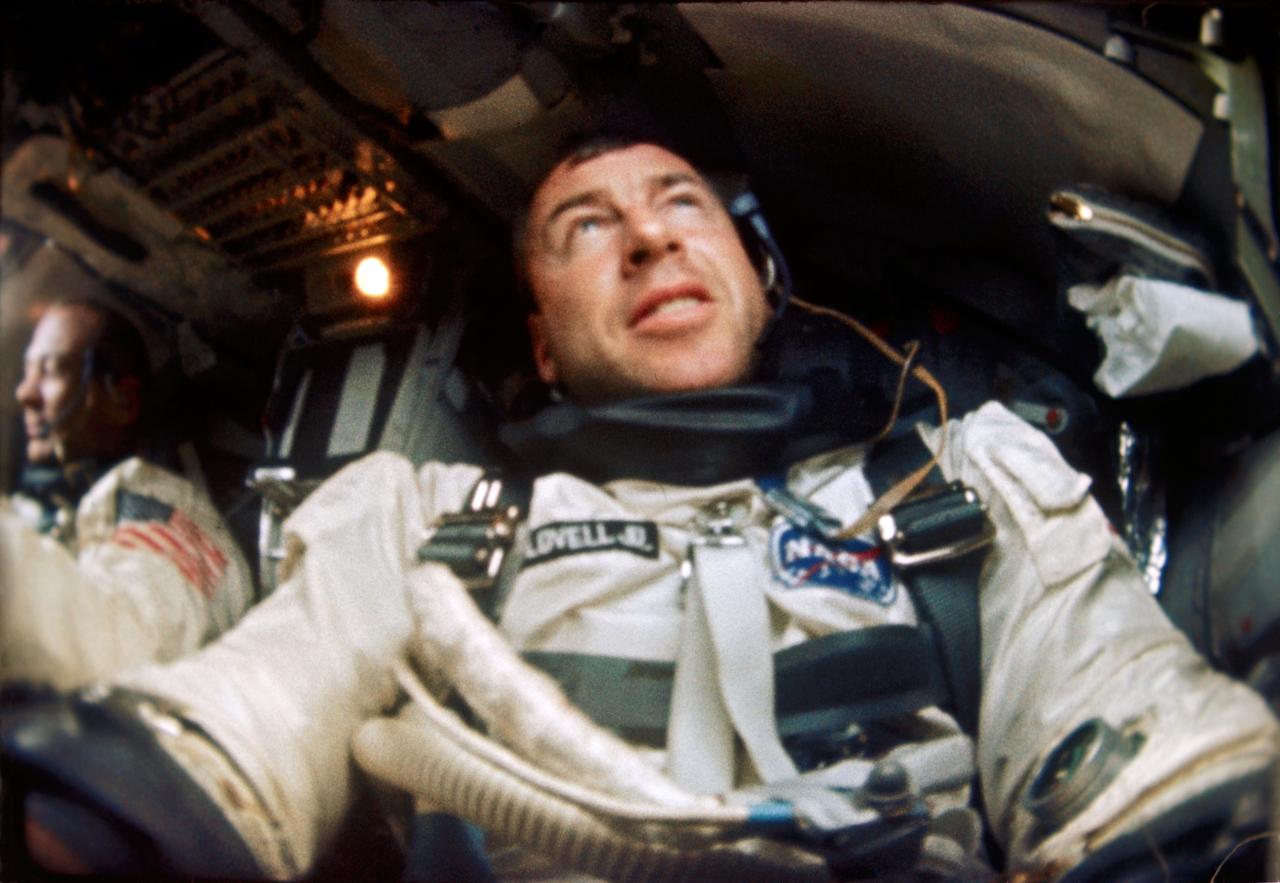

S66-63540 (12 Nov. 1966) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell is photographed inside his Gemini spacecraft during the Gemini-12 mission. Astronaut Edwin Aldrin is seen in the background and to the left. Photo credit: NASA
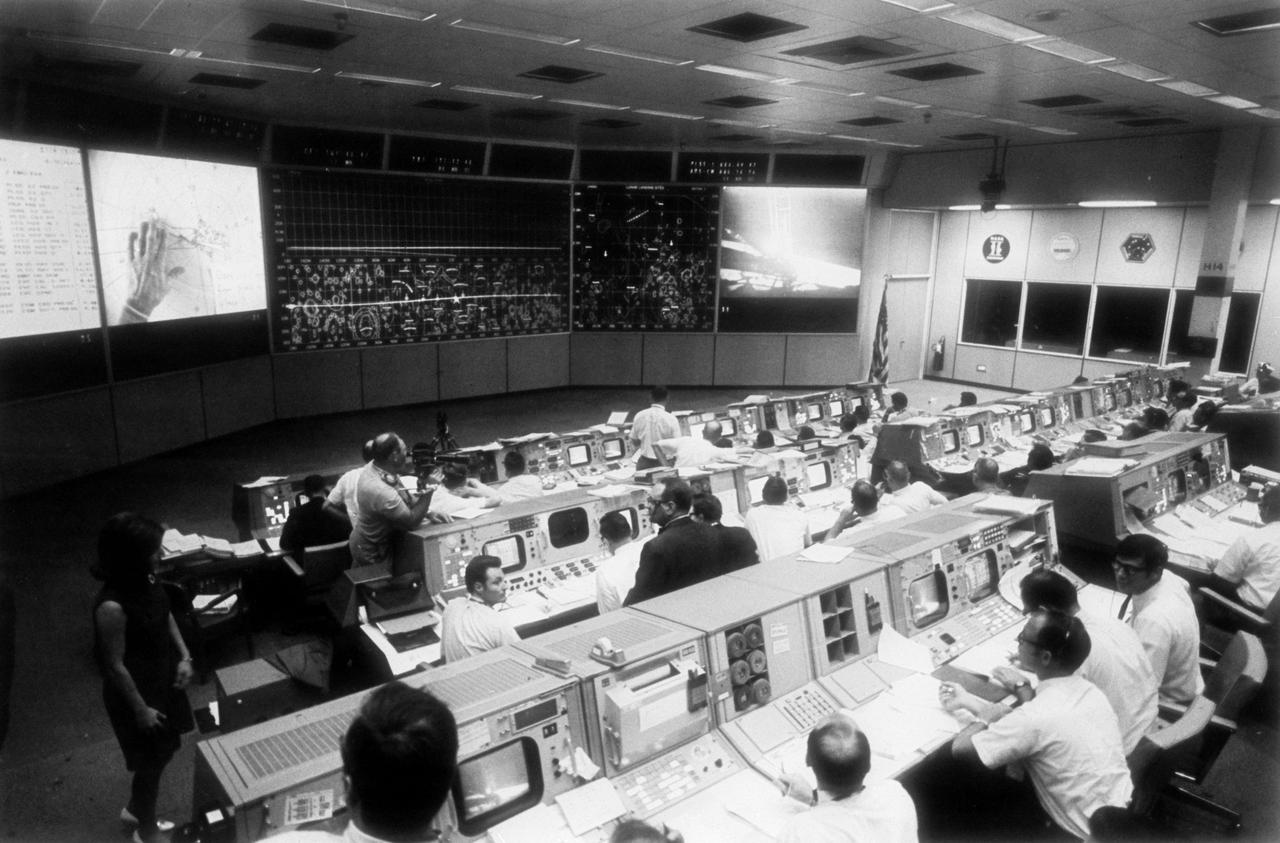

Overall view of the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center, bldg 30, during the lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) of Apollo 11 Astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr.
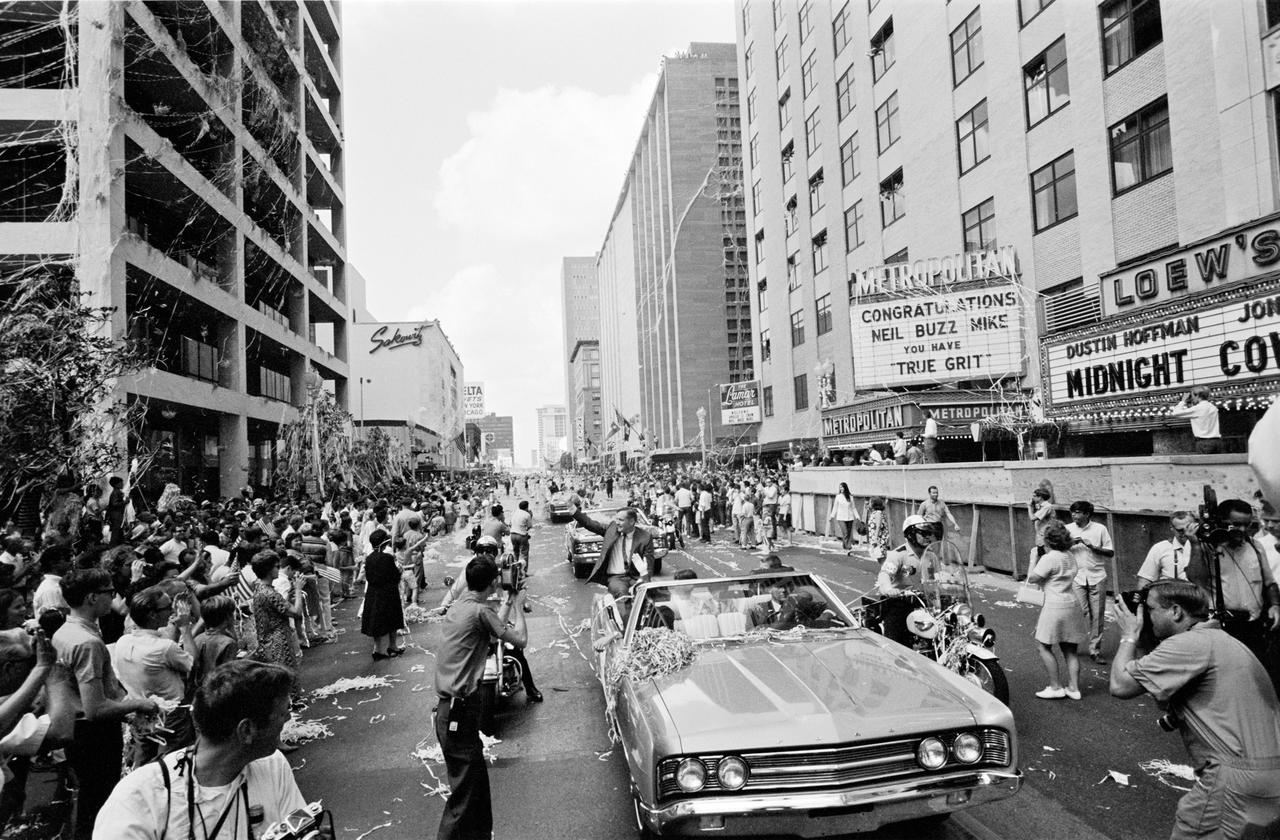

Apollo 11 parade downtown Houston, TX, 08/16/1969. Astronauts Edwin Aldrin, Michael Collins and Neil Armstrong are in the cars with general public welcoming them home.
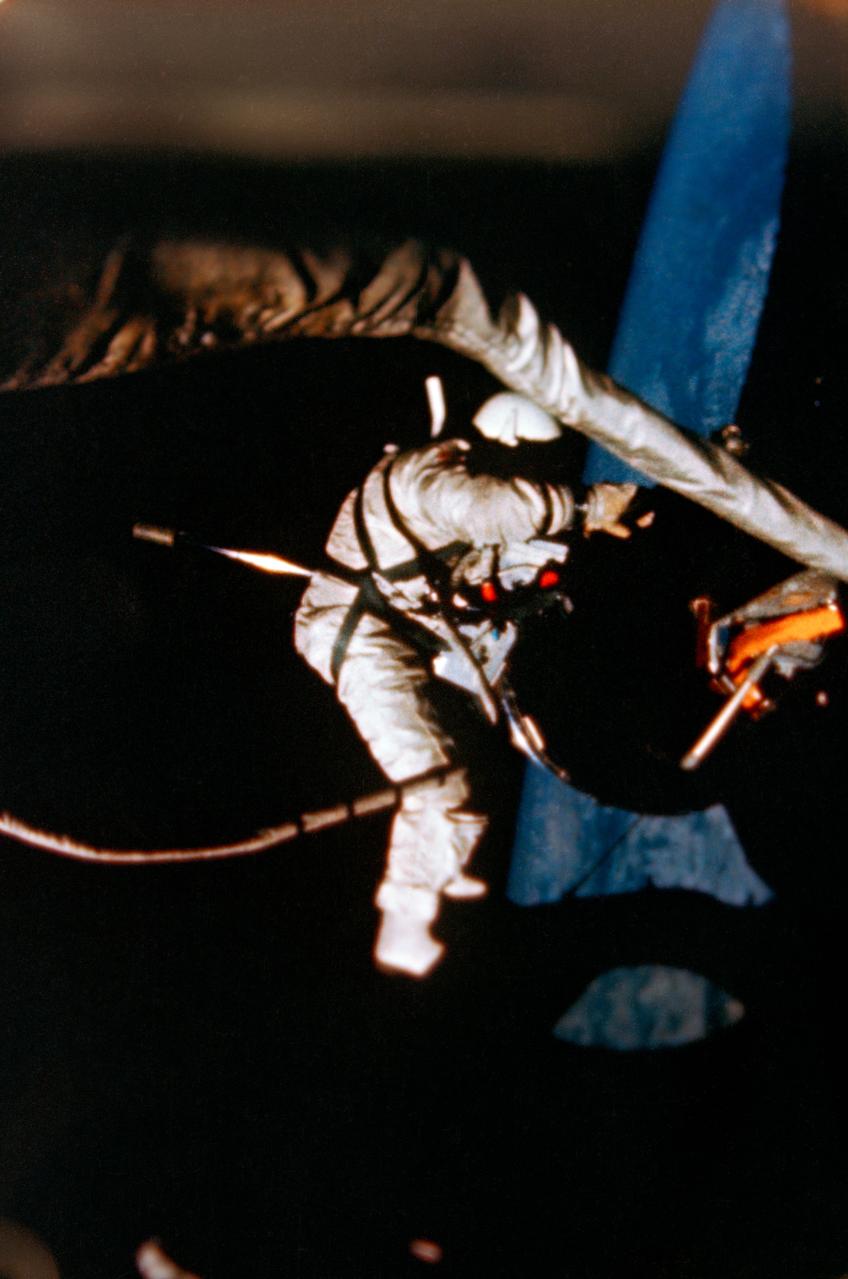
S66-62938 (12 Nov. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot of the Gemini-12 spaceflight, performs extravehicular activity (EVA) during the second day of the four-day mission in space. Photo credit: NASA
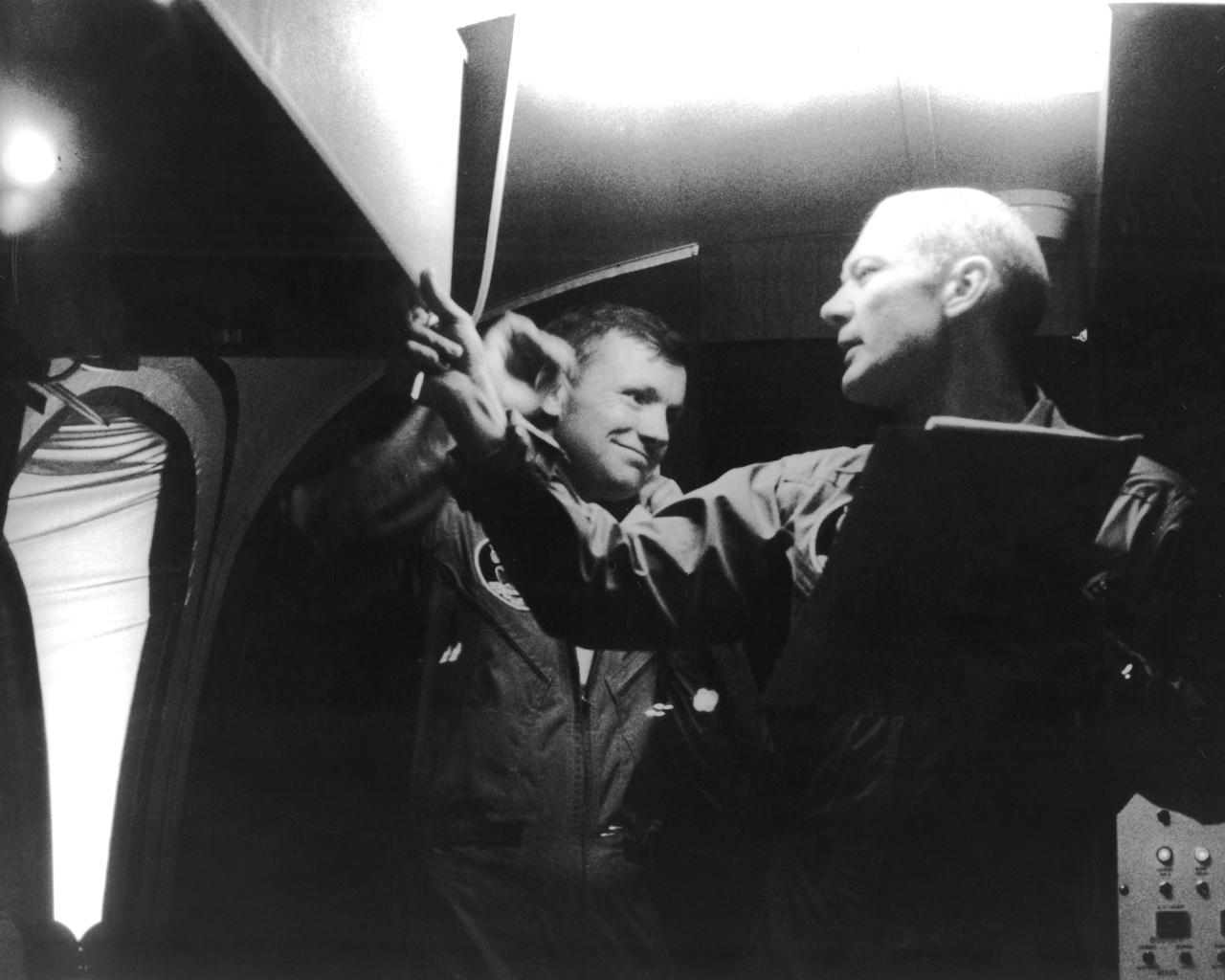

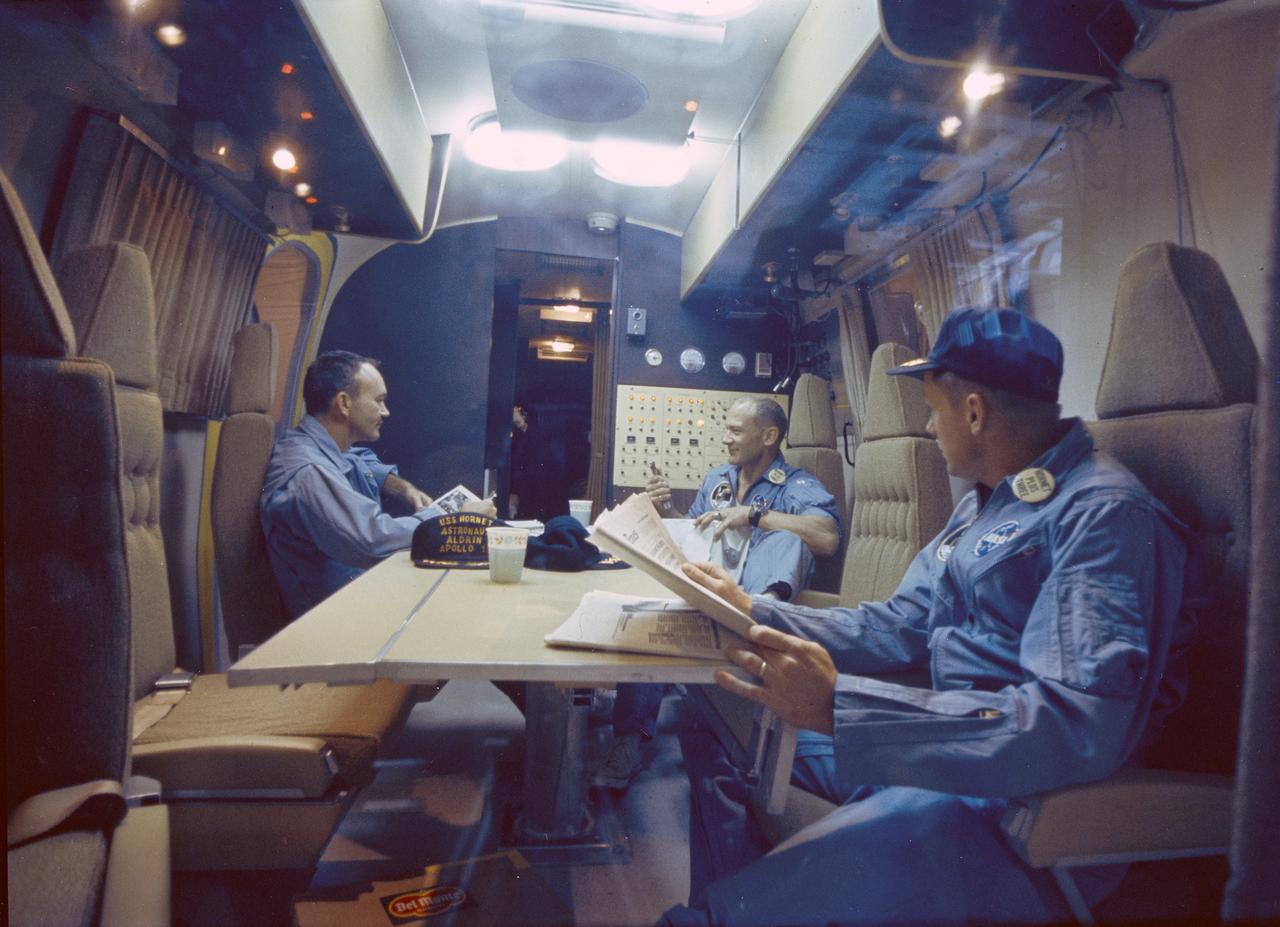
The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched aboard the Saturn V launch vehicle from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. The surface exploration was concluded in 2½ hours. Once the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth, the LM redocked with the CM for the crew’s return to Earth. Following splash down in the Pacific Ocean, Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF). Astronaut Collins took this snapshot of astronauts Armstrong (center) and Aldrin inside of the MQF.
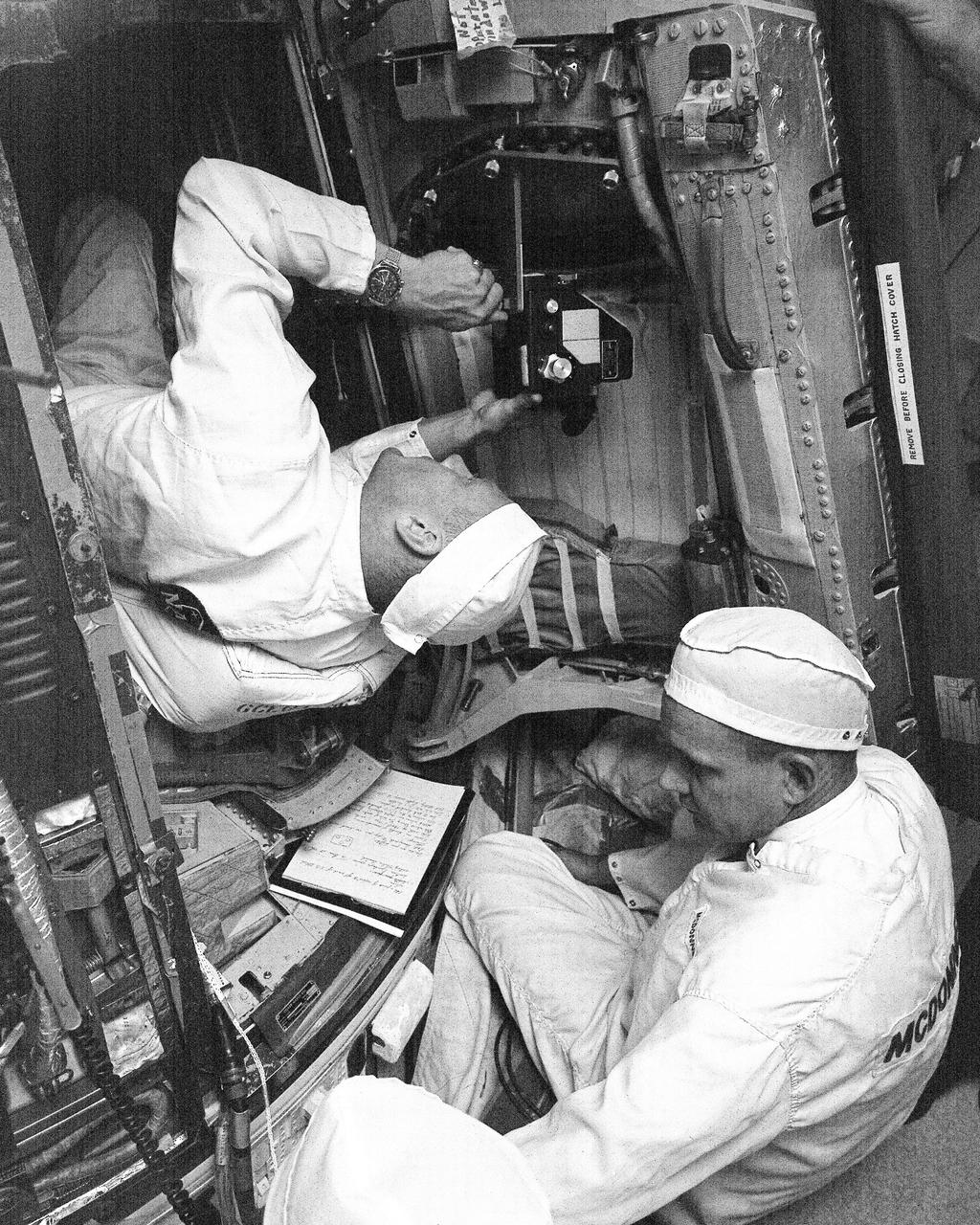

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- At Cape Kennedy Air Force Station in Florida, Gemini 12 pilot Edwin E. Buzz Aldrin Jr., seated in the spacecraft, practice stowing cameras and other equipment he and command pilot James A. Lovell will take along on their upcoming four-day Earth orbital mission. Lovell and Aldrin examined the equipment in the "White Room" atop Launch Complex 19. During Gemini 12, Lovell and Aldrin plan to rendezvous and dock with an Agena target satellite and Aldrin will perform two spacewalks. Photo Credit: NASA
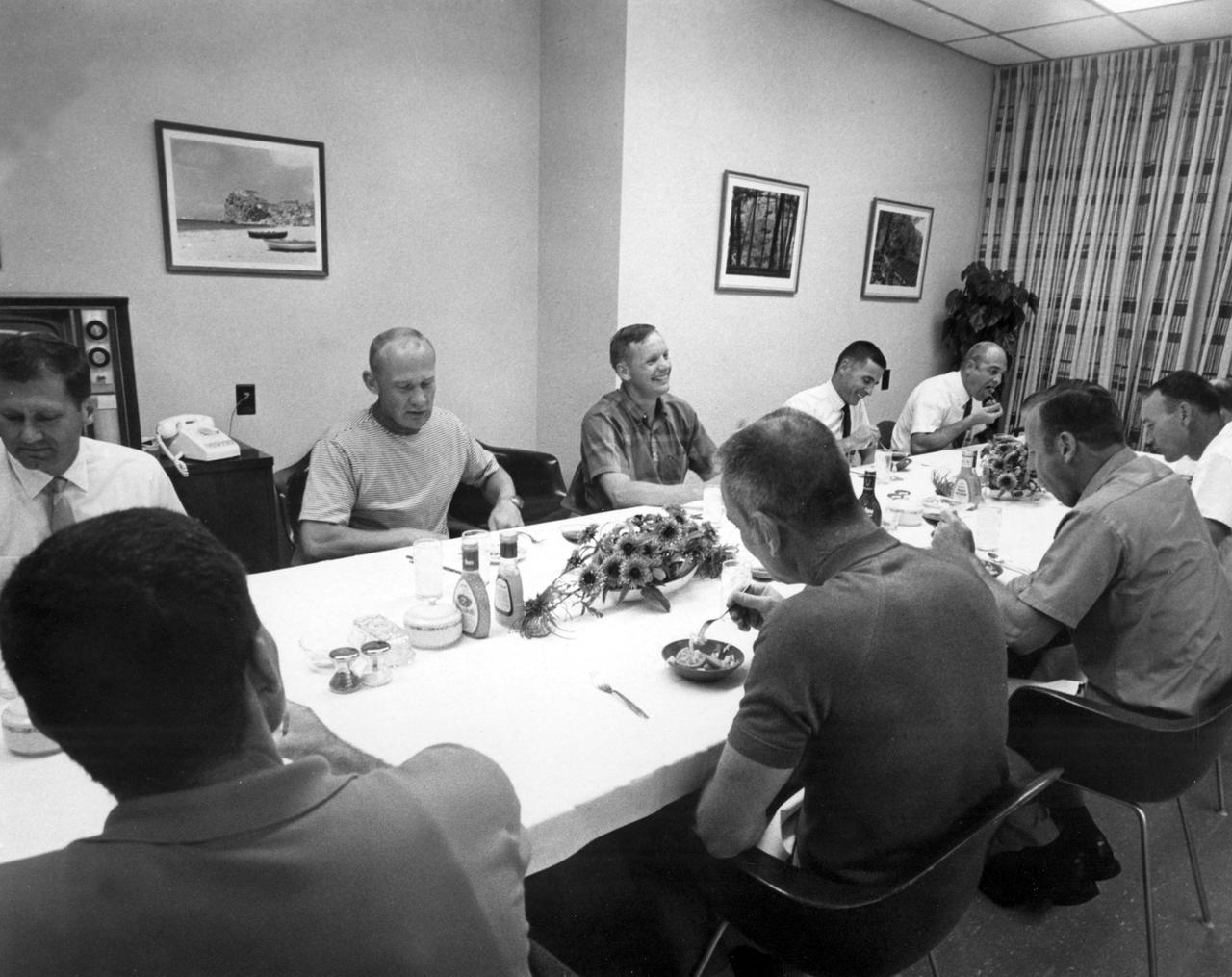

Apollo 11 astronauts Edwin E. Aldrin (striped shirt), Neil A. Armstrong, (left of Aldrin), and Michael Collins (extreme right on opposite side of table) had dinner with other astronauts the night before launching for the first lunar landing mission. The Apollo 11 mission launched from the NASA Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
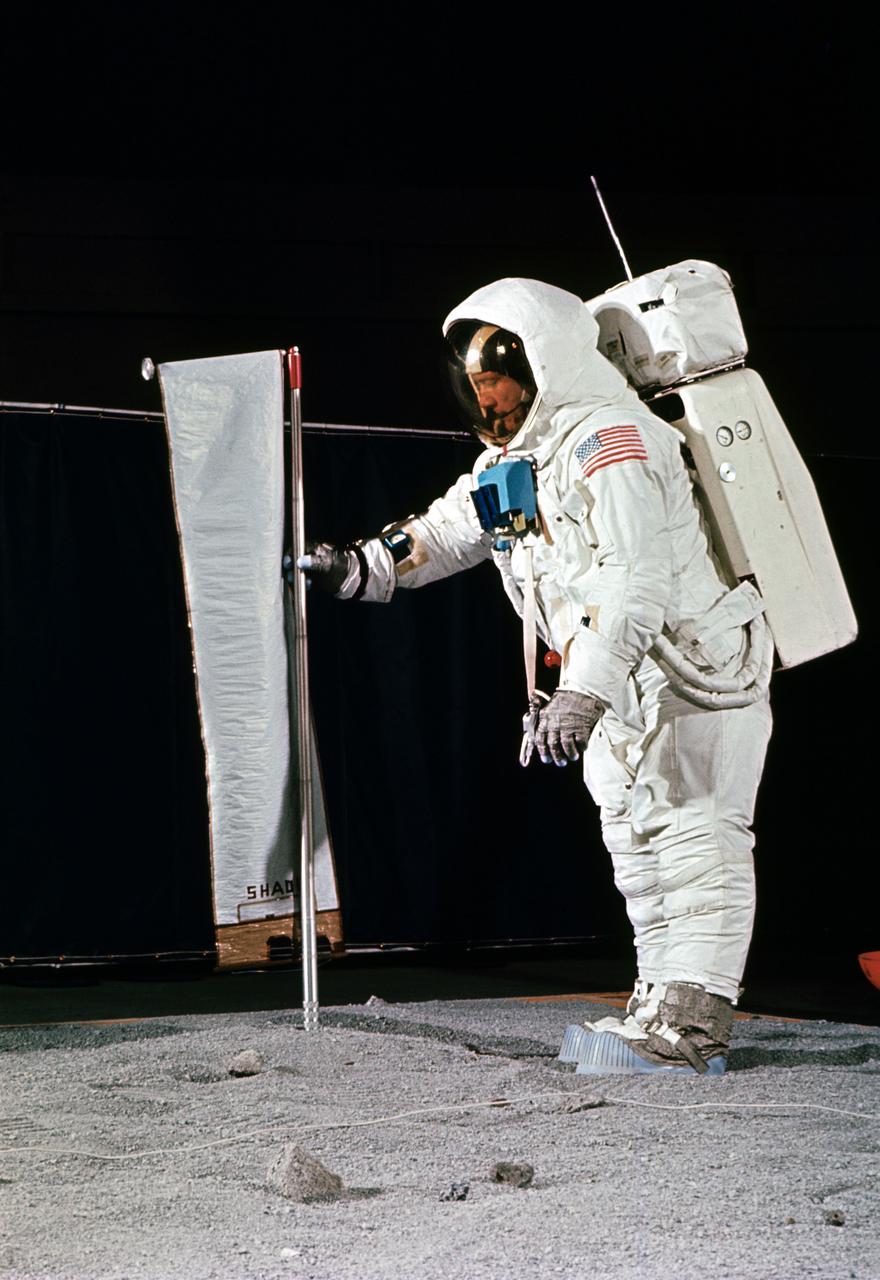

S69-32247 (22 April 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), simulates deploying the Solar Wind Composition (SWC) experiment, on the surface of the moon, during a training exercise in Building 9 on April 22, 1969. The SWC is a component of the Early Apollo Scientific Experiment Package (EASEP). Aldrin is the lunar module pilot of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission.
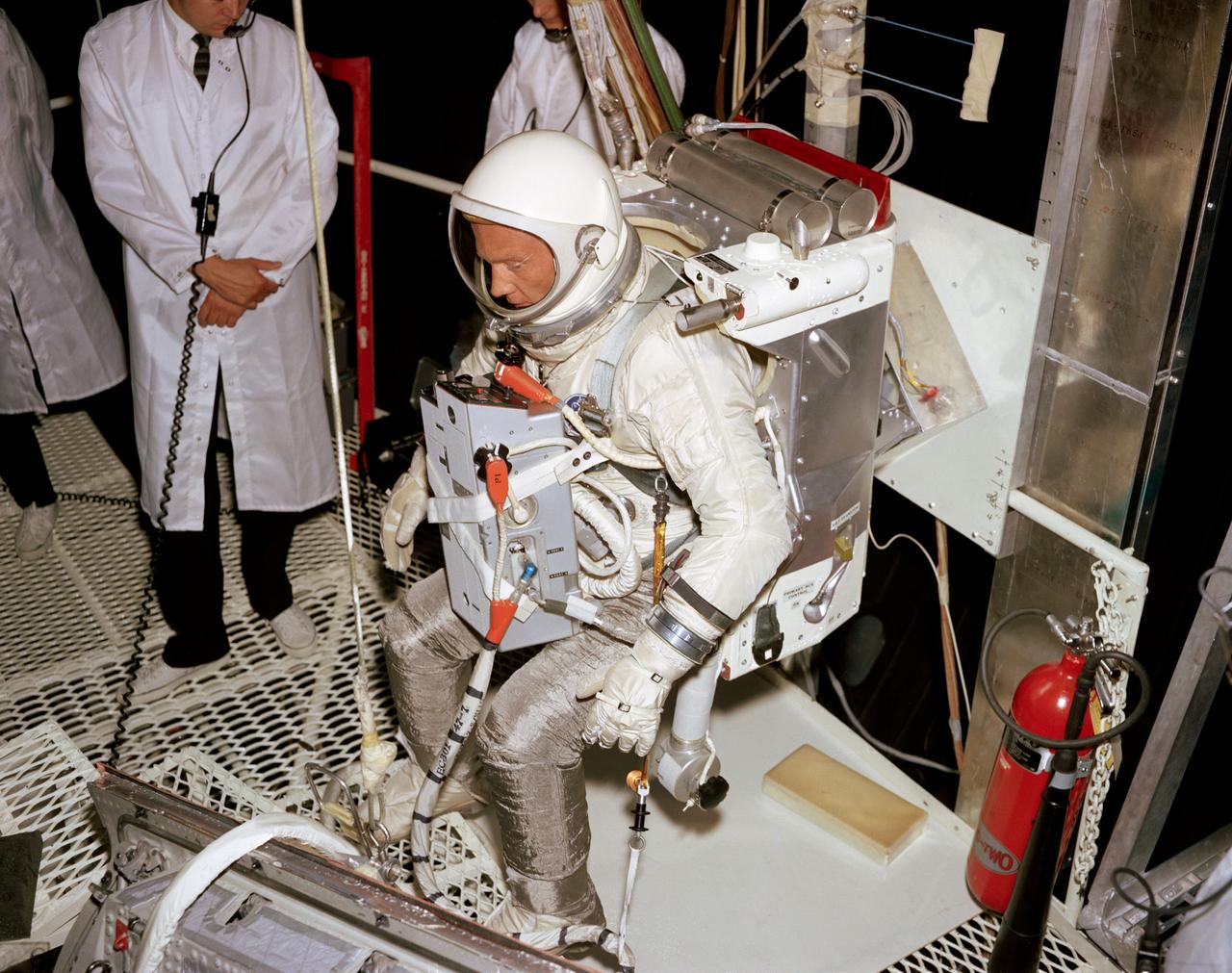

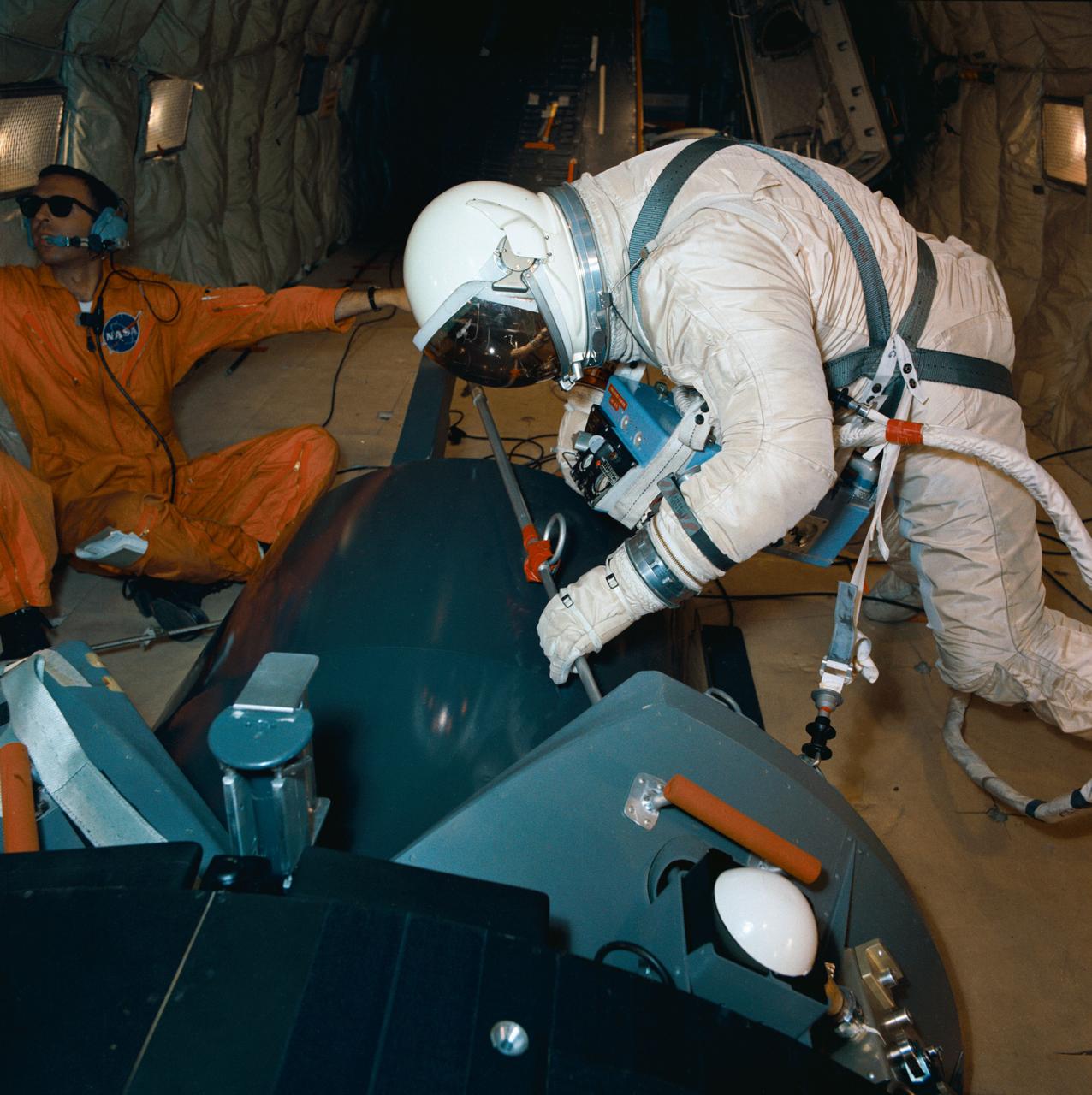
S66-51073 (15 Aug. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., prime crew pilot of the Gemini-12 spaceflight, undergoes evaluation procedures with the Astronaut Maneuvering Unit in the 30-foot altitude chamber at McDonnell. The suited Aldrin is wearing an AMU backpack and an Extravehicular Life Support System (ELSS) chest pack. Photo credit: NASA
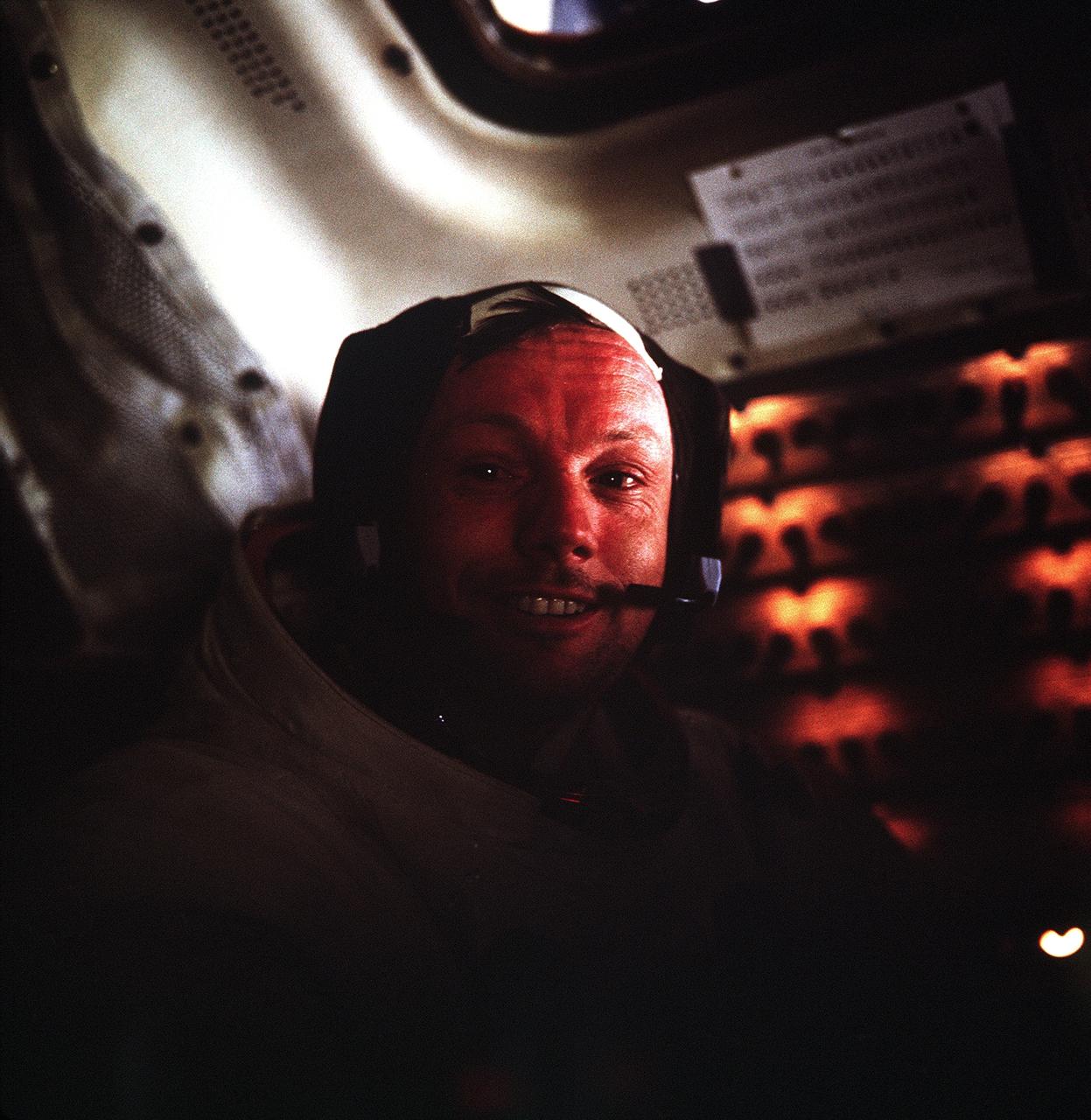

AS11-37-5528 (20 July 1969) --- This photograph of astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, Apollo 11 commander, was taken inside the Lunar Module (LM) while the LM rested on the lunar surface. Astronauts Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, had already completed their historic extravehicular activity (EVA) when this picture was made. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while Armstrong and Aldrin explored the moon's surface.
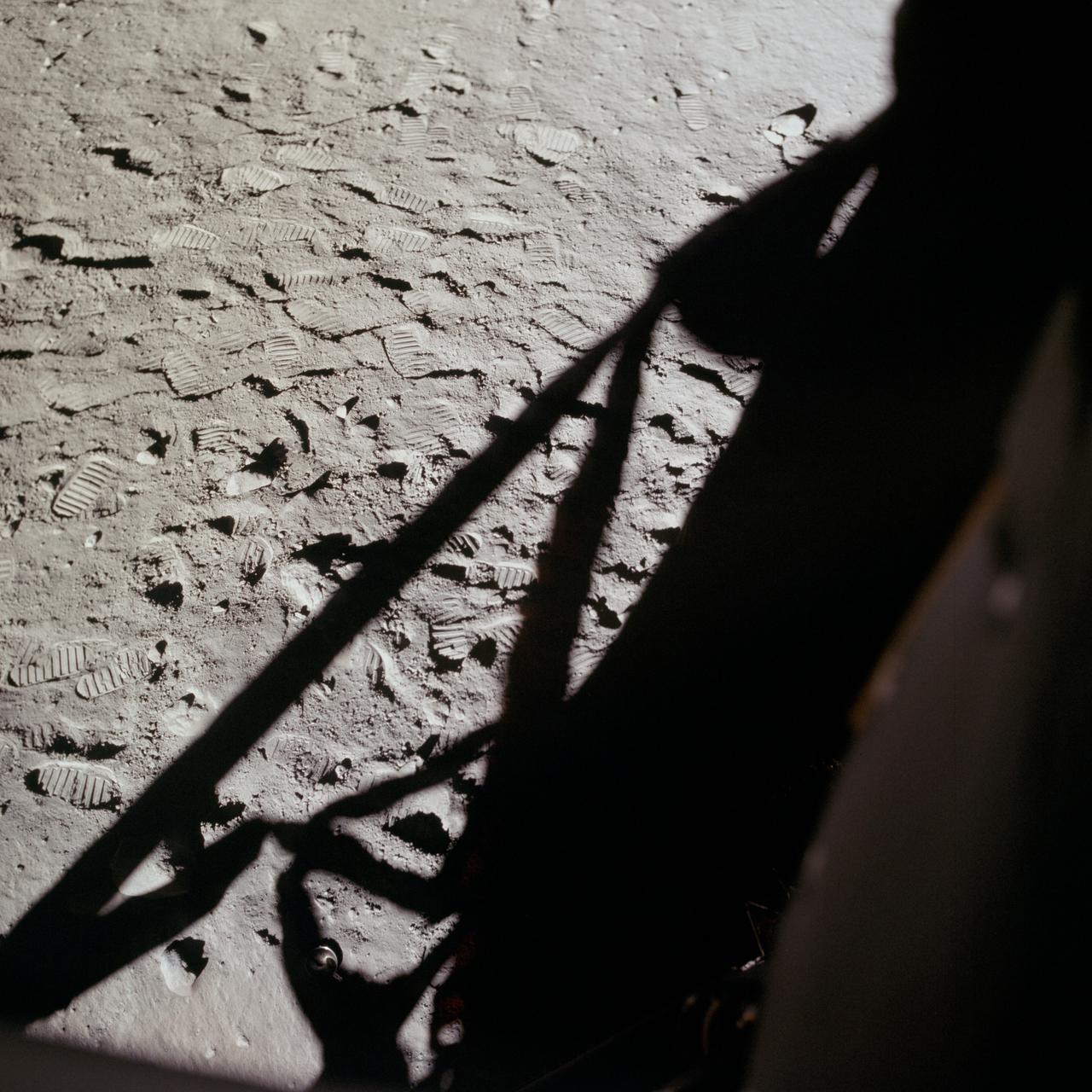

AS11-37-5505 (20 July 1969) --- This photograph shows in fine detail the impressions in the lunar soil made by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Armstrong, commander, and Aldrin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
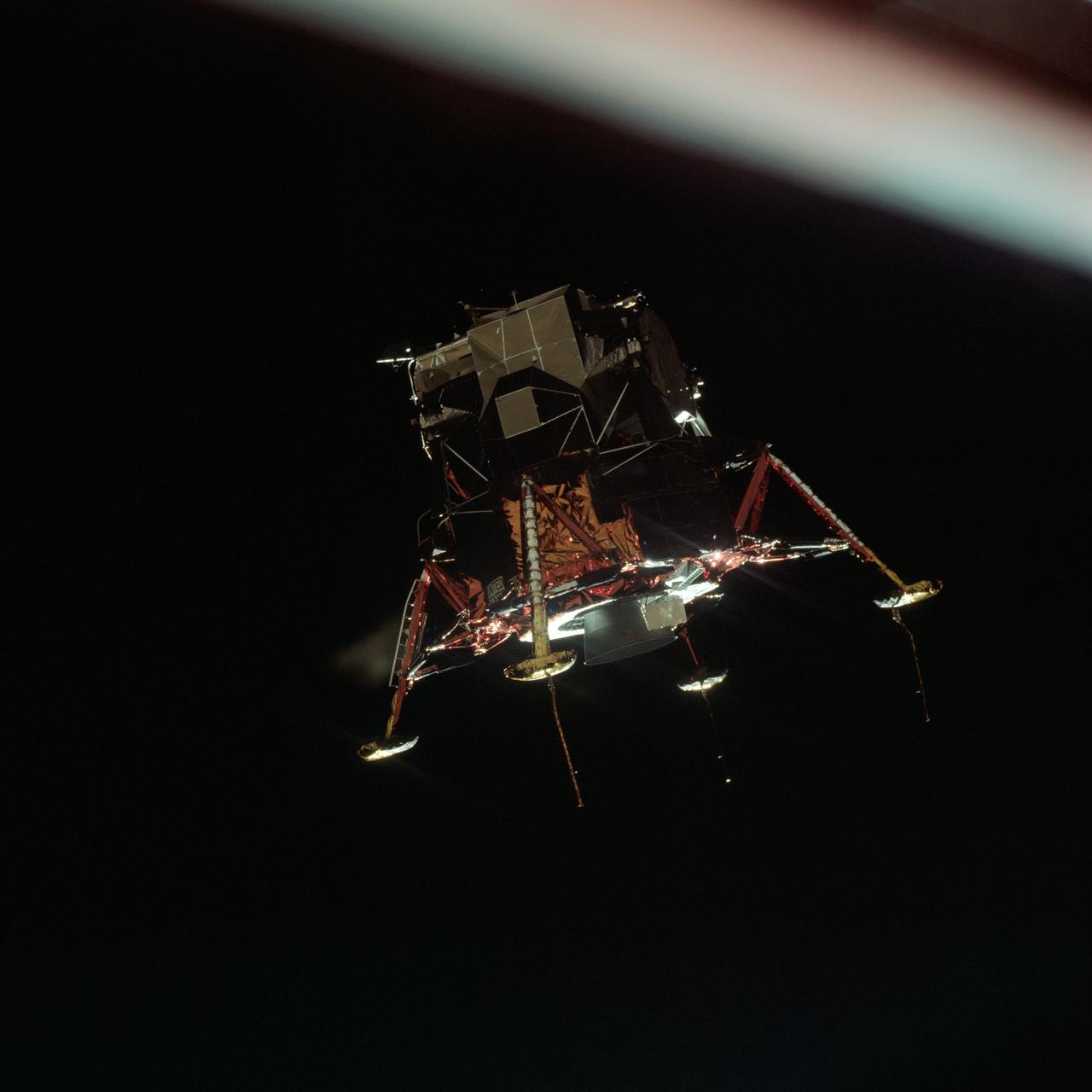

AS11-44-6581 (20 July 1969) --- The Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM), in a lunar landing configuration, is photographed in lunar orbit from the Command and Service Modules (CSM). Inside the LM were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM to explore the lunar surface. The protrusions connected to the landing pods are sensors to aid in the touchdown or landing process.
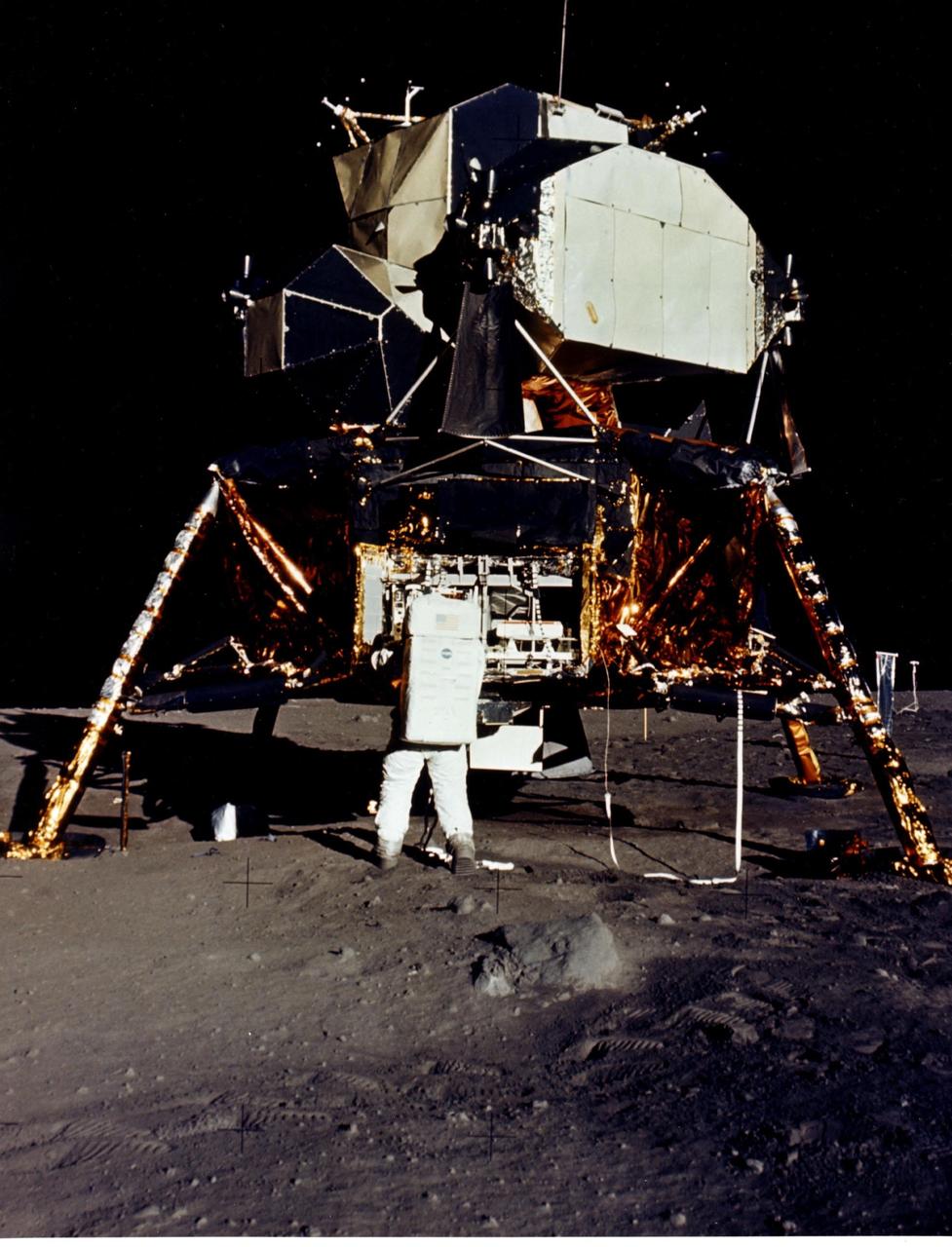

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - Man's first landing on the Moon was accomplished at 4:17 p.m. today as Lunar Module "Eagle" touched down gently on the Sea of Tranquility on the east side of the Moon. Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module Pilot, removes scientific experiment packages from a stowage area in the Lunar Module's descent stage. Left behind on the lunar surface by Aldrin and Neil A. Armstrong, Apollo 11 commander, were a Passive Seismic Experiments Package and a Laser-Ranging Retro-Reflector.
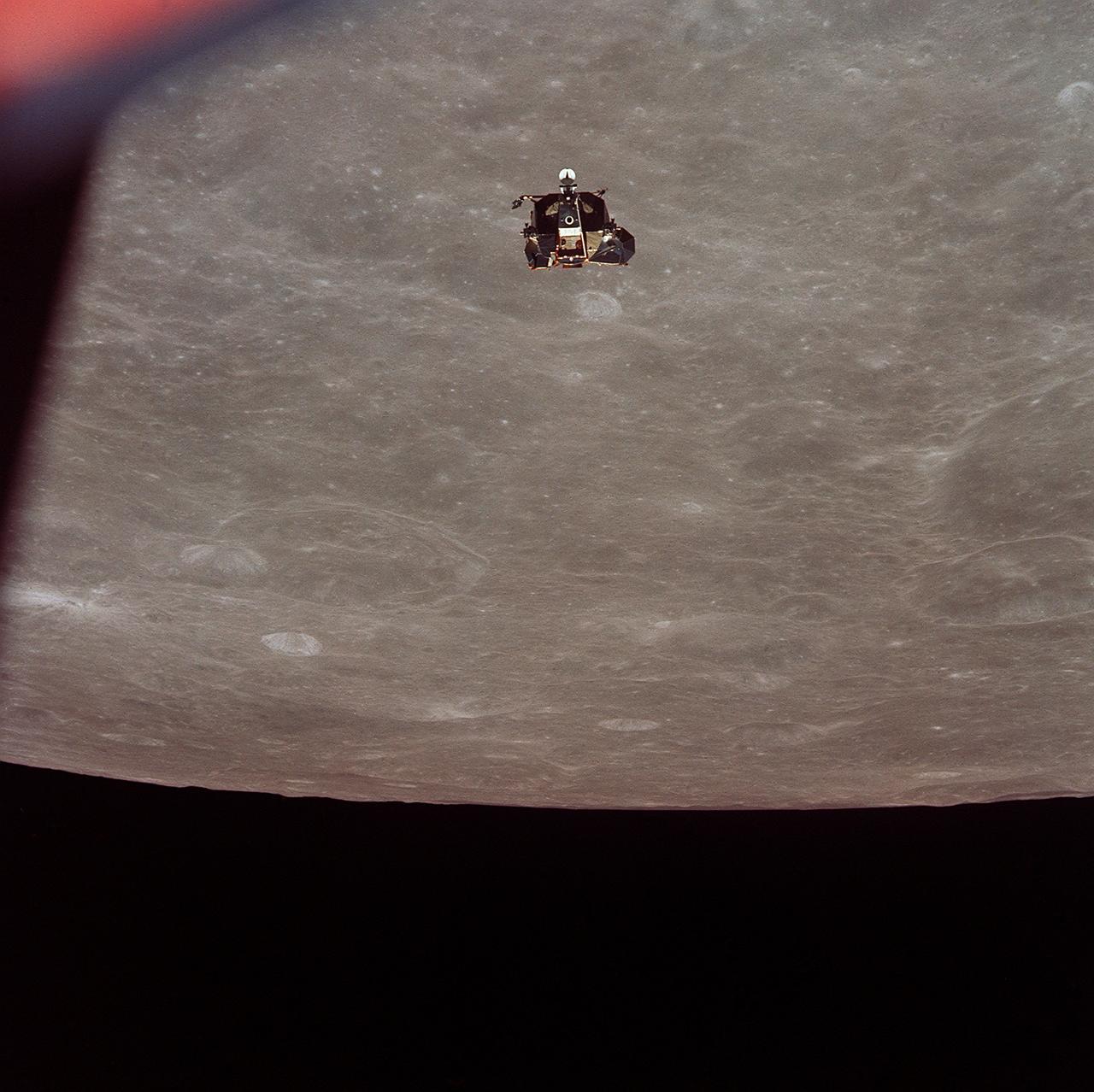

AS11-44-6626 (21 July 1969) --- The Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) ascent stage, with astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. aboard, is photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Armstrong and Aldrin explored the moon. The LM is approaching from below. The coordinates of the center of the lunar terrain seen below is located at 102 degrees east longitude and 1 degree north latitude.
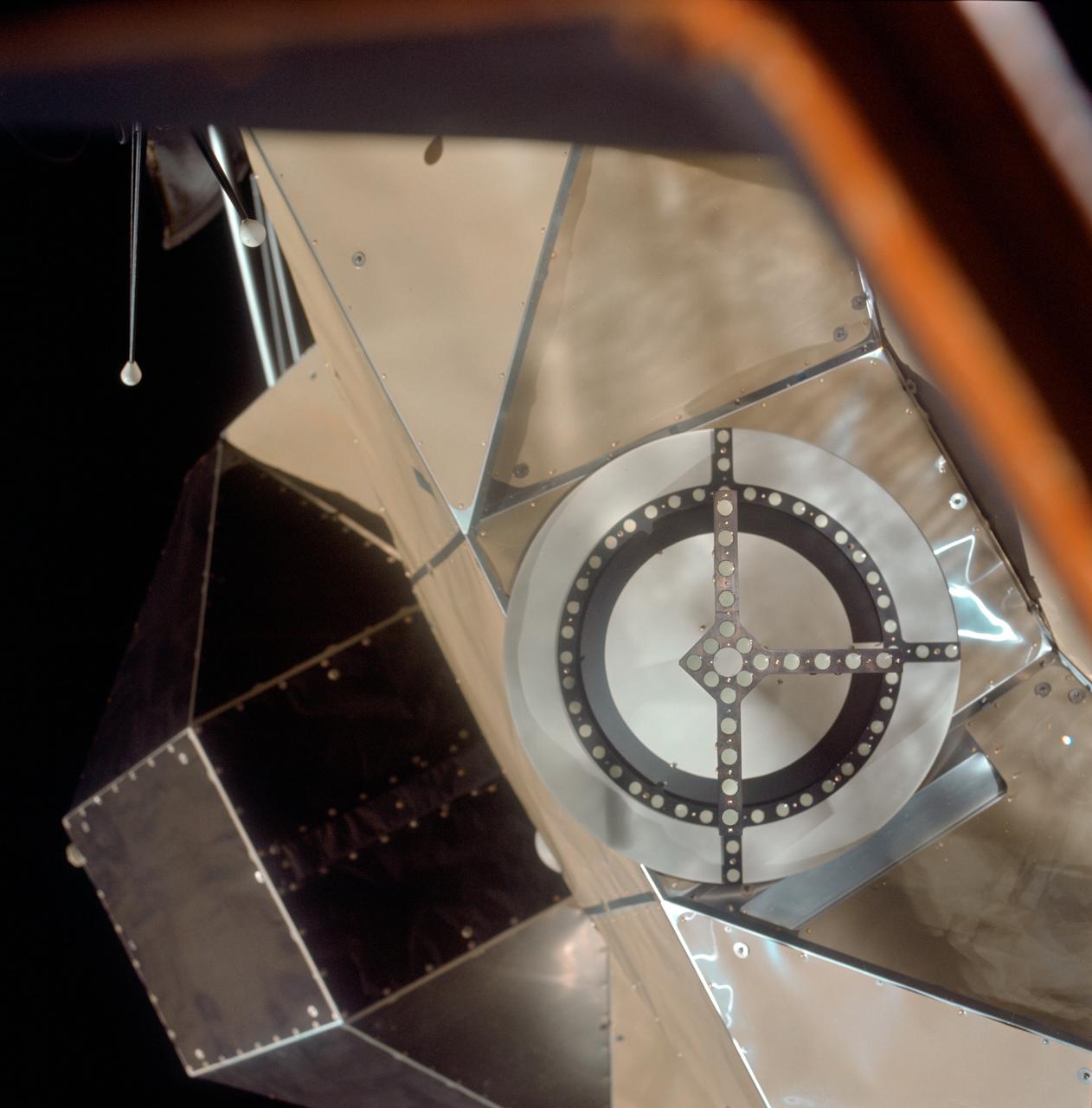

AS11-36-5365 (21 July 1969) --- A close-up view of the docking target on the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) photographed from the Command Module during the LM/CSM docking in lunar orbit. Astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, in the LM, were returning from the lunar surface. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while Armstrong and Aldrin explored the moon.
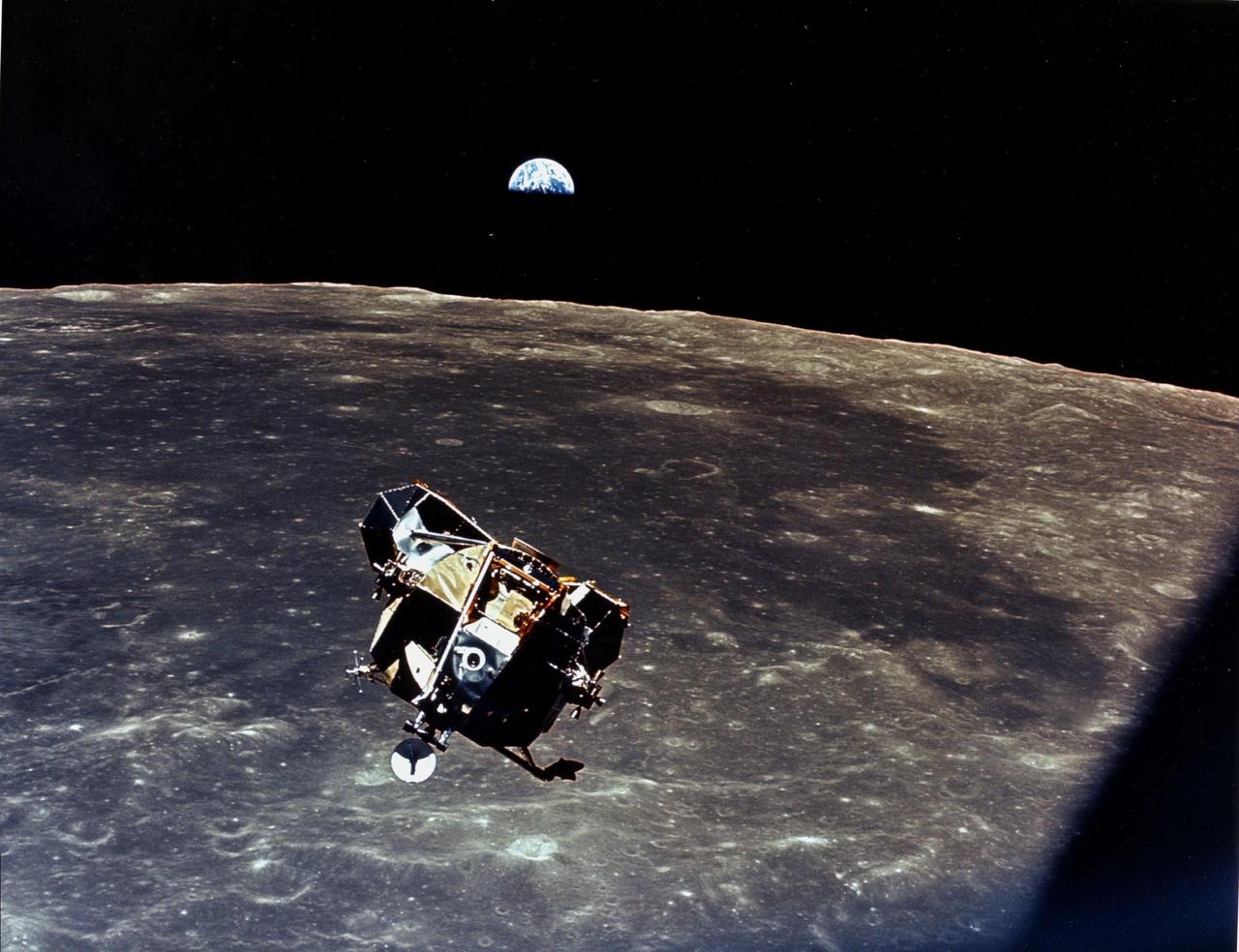

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - With a half-Earth in the background, the Lunar Module ascent stage with Moon-walking astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin Jr. approaches for a rendezvous with the Apollo Command Module manned by Michael Collins. The Apollo 11 liftoff from the Moon came early, ending a 22-hour stay on the Moon by Armstrong and Aldrin.
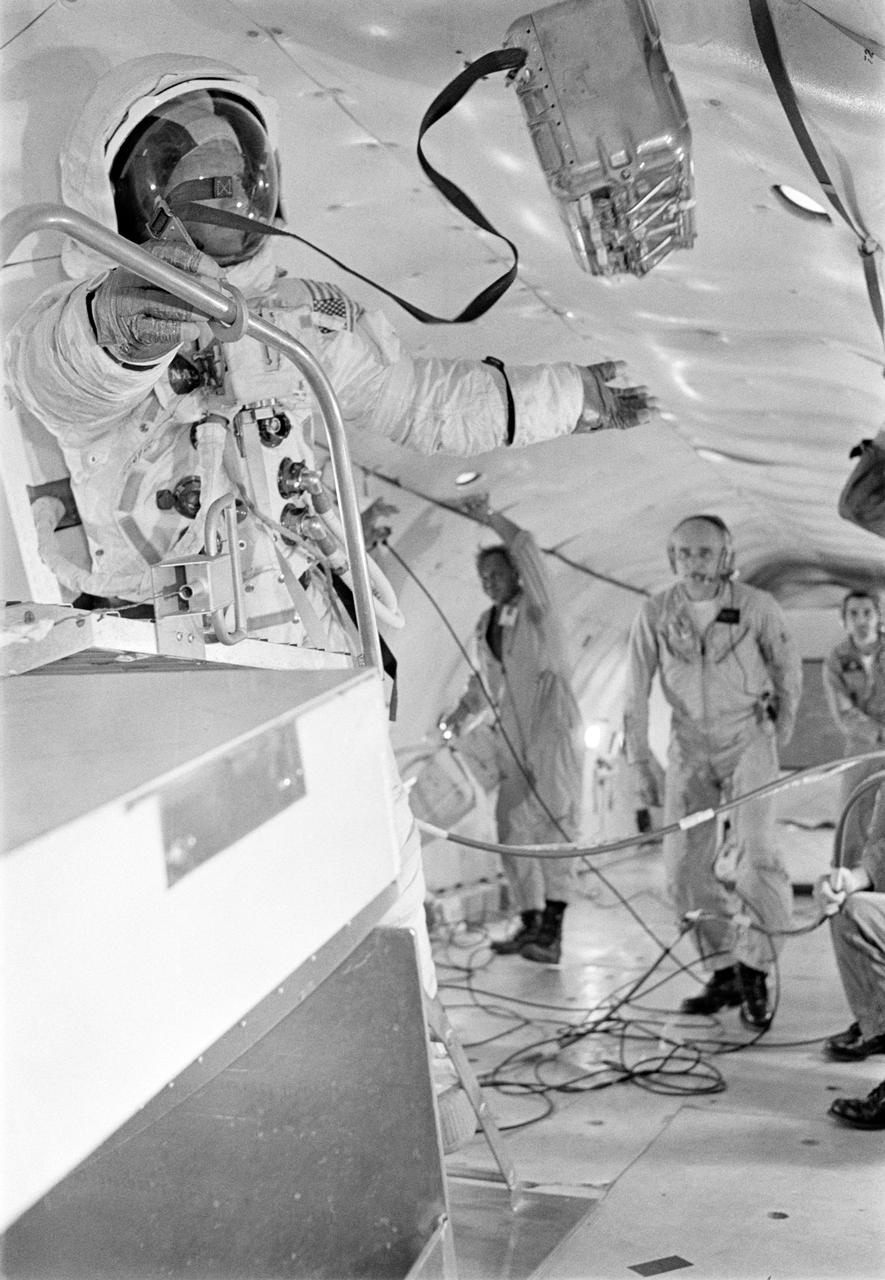

S69-39270 (10 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission, participates in lunar extravehicular activity training under weightlessness conditions aboard a U.S. Air Force KC-135 jet aircraft from nearby Patrick Air Force Base. Aldrin is wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit, the type of equipment which he will wear on the lunar surface.

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) which served as their home until they reached the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas. The three are seen here at the MSC, still inside the MQF, undergoing their first debriefing on Sunday, August 3, 1969. Behind the glass are (L-R): Edwin Aldrin, Michael Collins, and Neil Armstrong.

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via a Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module pilot. The Command Module (CM), piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the Lunar Module (LM), named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. The surface exploration was concluded in 2½ hours, in which the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. Upon splash down in the Pacific Ocean, Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was taken to safety aboard the USS Hornet, where they were quartered in a mobile quarantine facility. Shown here is the Apollo 11 crew inside the quarantine facility. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished. This photograph of Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin was taken upon his arrival at the Flight Crew Training building at the NASA Kennedy Space Center (KSC) a few days prior to launch.
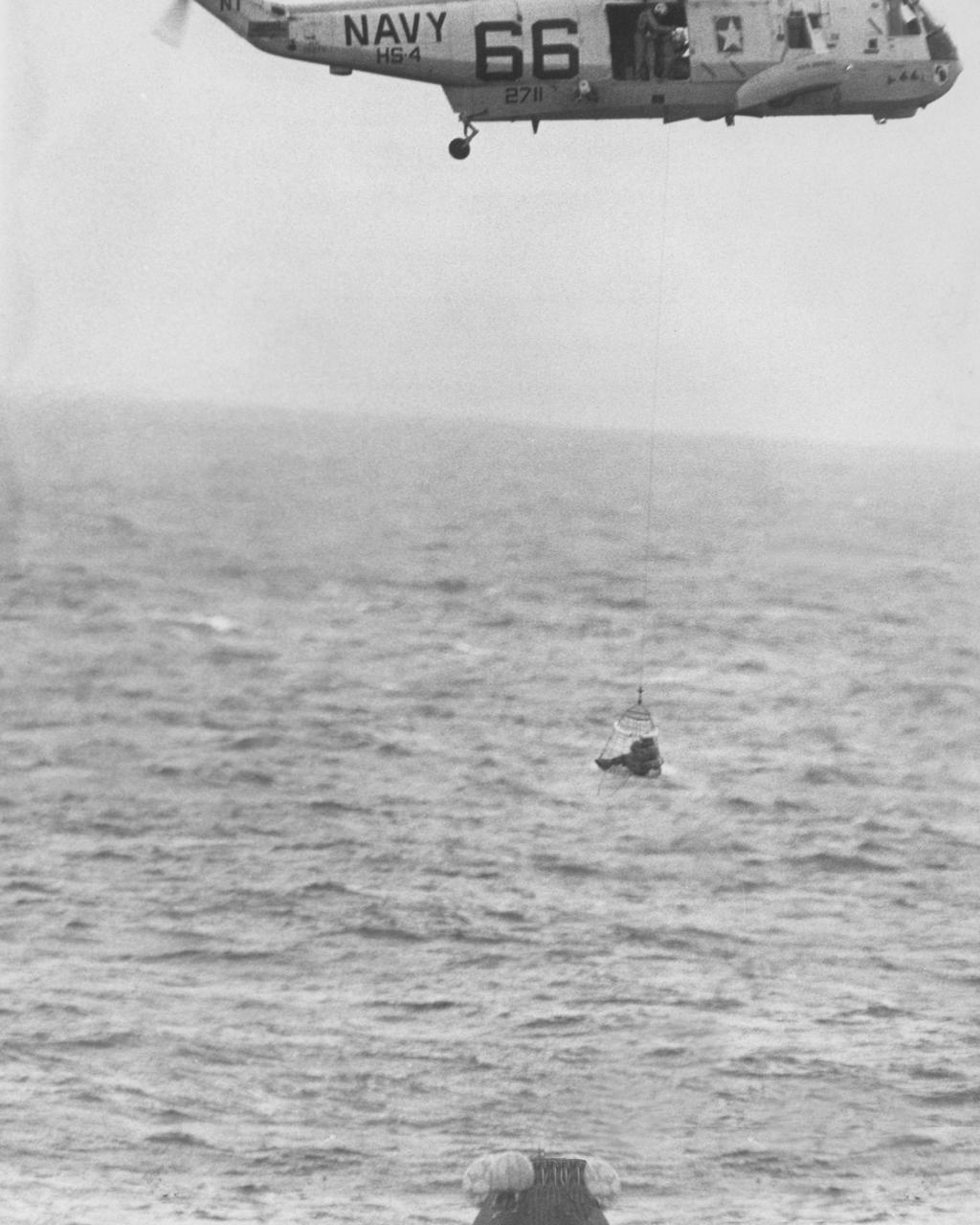

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. Shown here is the recovery operation of the capsule in the Pacific Ocean after splashdown. One of the three astronauts is airlifted from the life raft into a helicopter. The helicopter airlifted the crew to safety aboard the prime recovery ship, the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF). With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
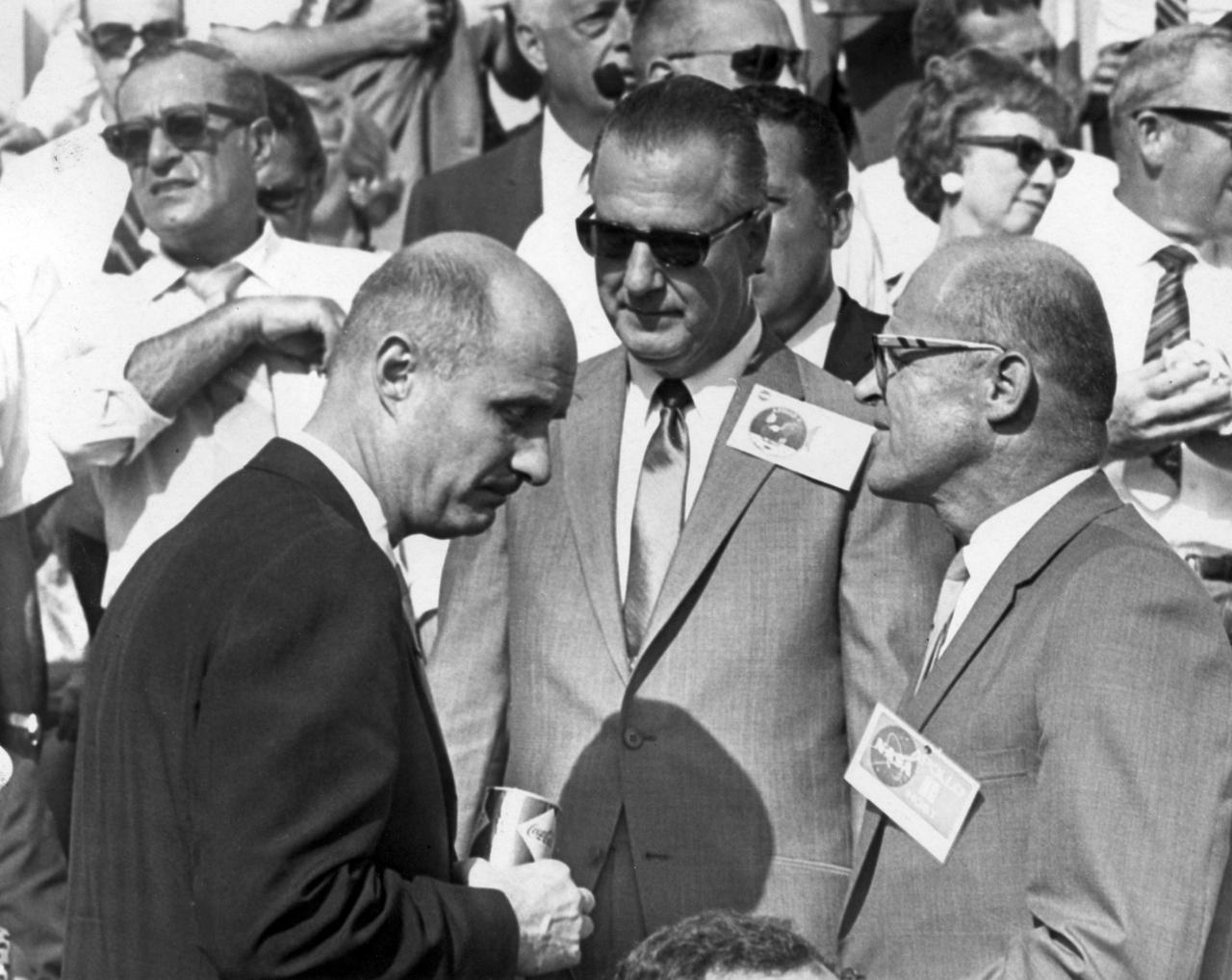

Apollo 10 commander, Thomas P. Stafford (left) and Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Deputy Director Albert Siepert (right) talk with U.S. Vice President Spiro T. Agnew a few minutes before the launch of Apollo 11. The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from KSC, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
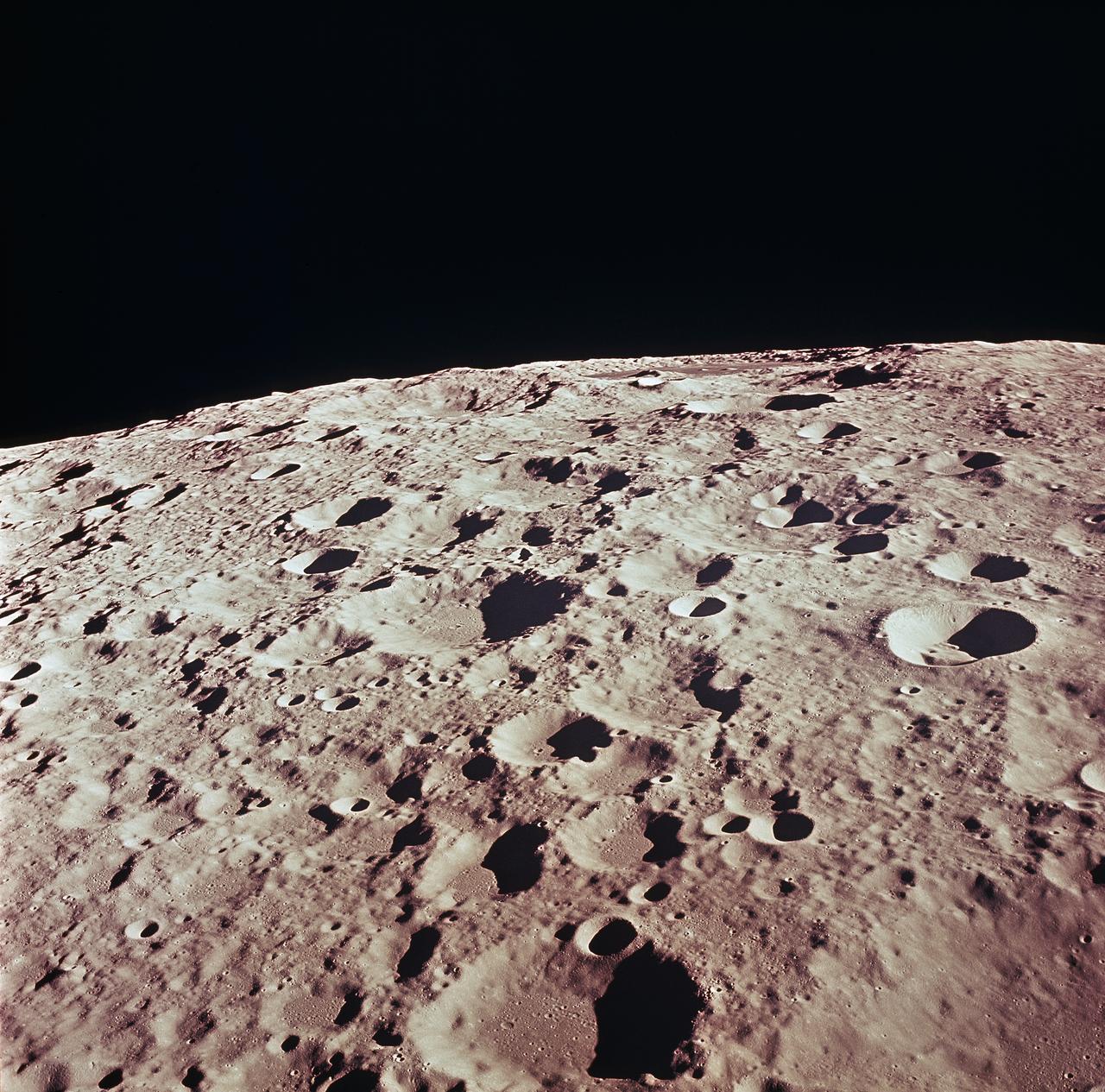

This is a detailed view of the back side of Moon in the vicinity of Crater No. 308 taken during the Apollo 11 mission. Apollo 11, the first manned lunar mission, launched from The Kennedy Space Center, Florida via a Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. The 3-man crew aboard the flight consisted of Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module pilot. The Lunar Module (LM), named “Eagle, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, was the first crewed vehicle to land on the Moon. Meanwhile, astronaut Collins piloted the Command Module in a parking orbit around the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. The crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material which was returned to Earth for analysis. The surface exploration was concluded in 2½ hours. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
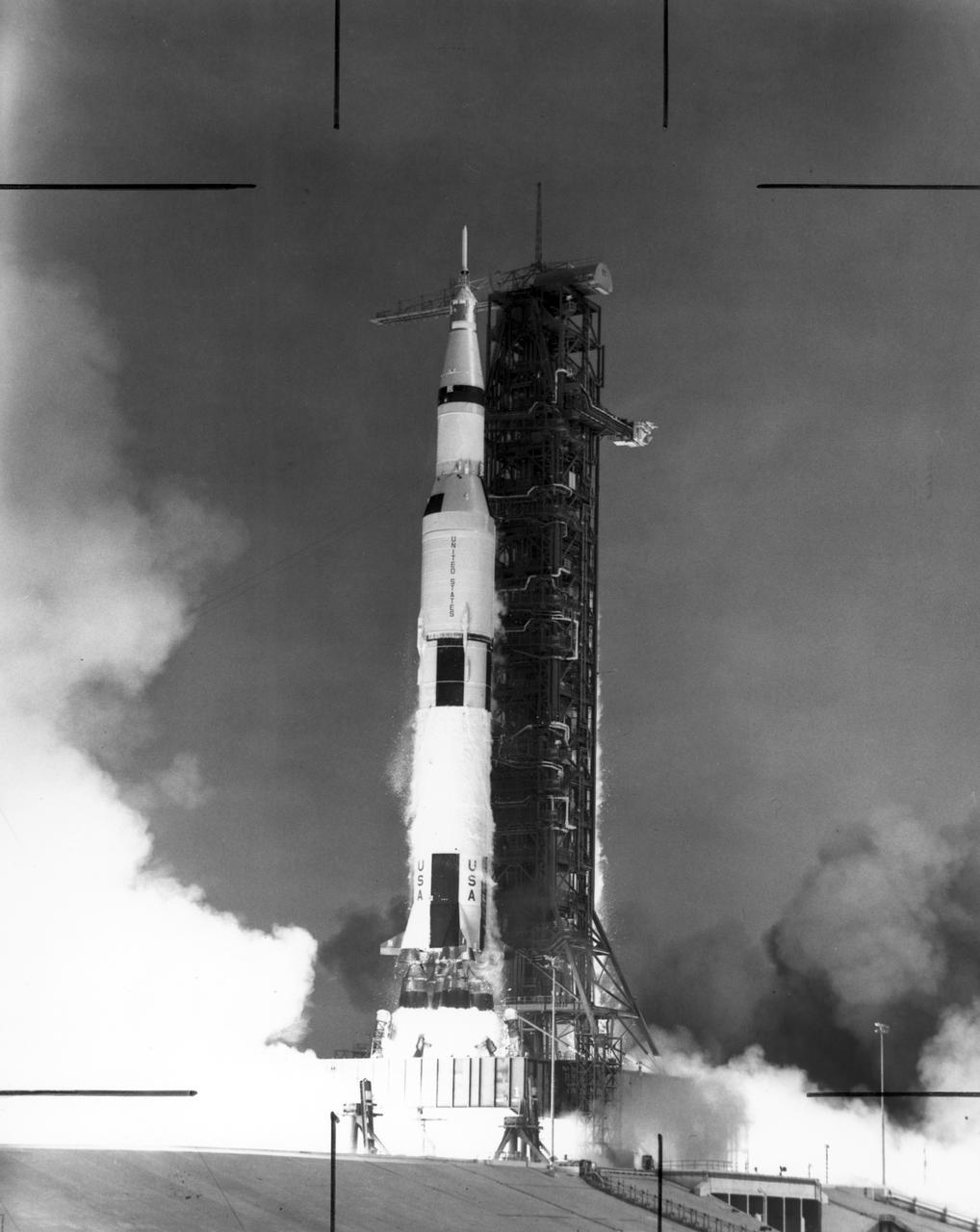

The Saturn V launch vehicle, developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun, lifts off from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida carrying the Apollo 11 spacecraft and crew. The massive rocket hurled the spacecraft into Earth orbit and then onto the trajectory to the Moon. Apollo 11, the first manned lunar mission, launched from KSC on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
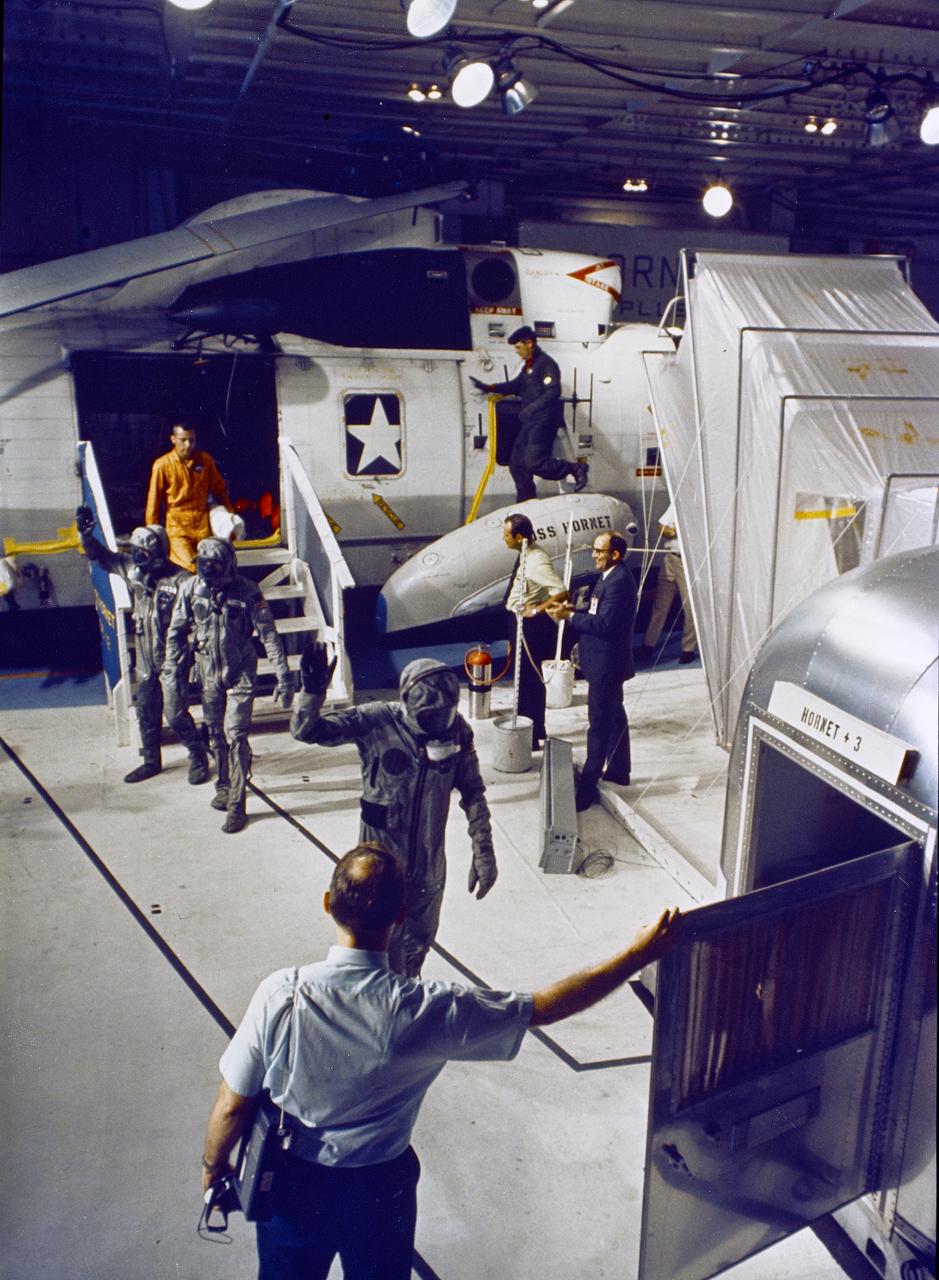

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via a Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place after splash down in the Pacific Ocean. Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was taken to safety aboard the USS Hornet, where they were quartered in a mobile quarantine facility. Here the astronauts are shown waving as they enter the quarantine facility. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
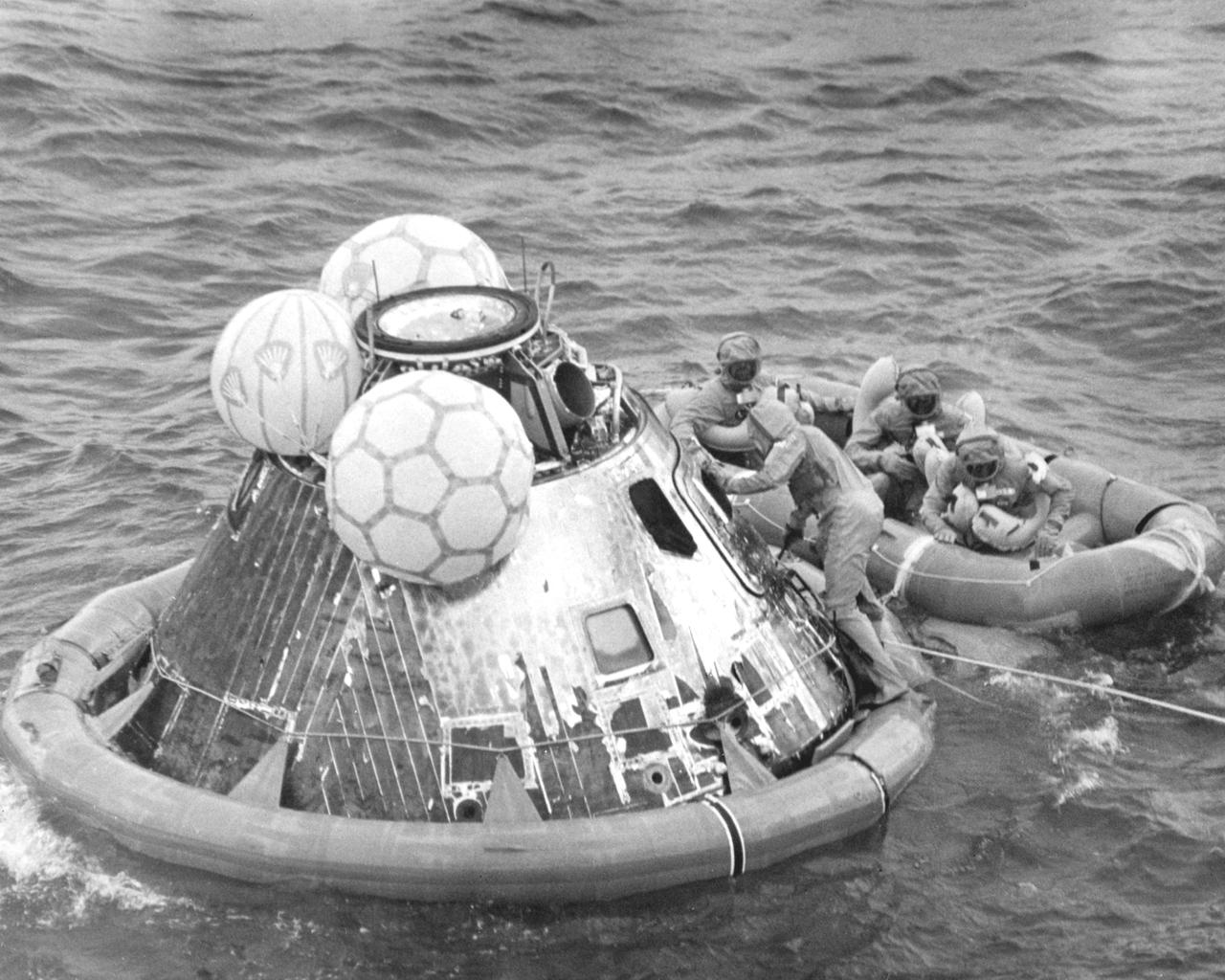

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. Shown here is the recovery operation of the capsule in the Pacific Ocean after splashdown. The three astronauts wait in the life raft as a pararescue man closes and secures the capsule hatch. The crew was then air lifted to the prime recovery ship, the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were housed in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF).
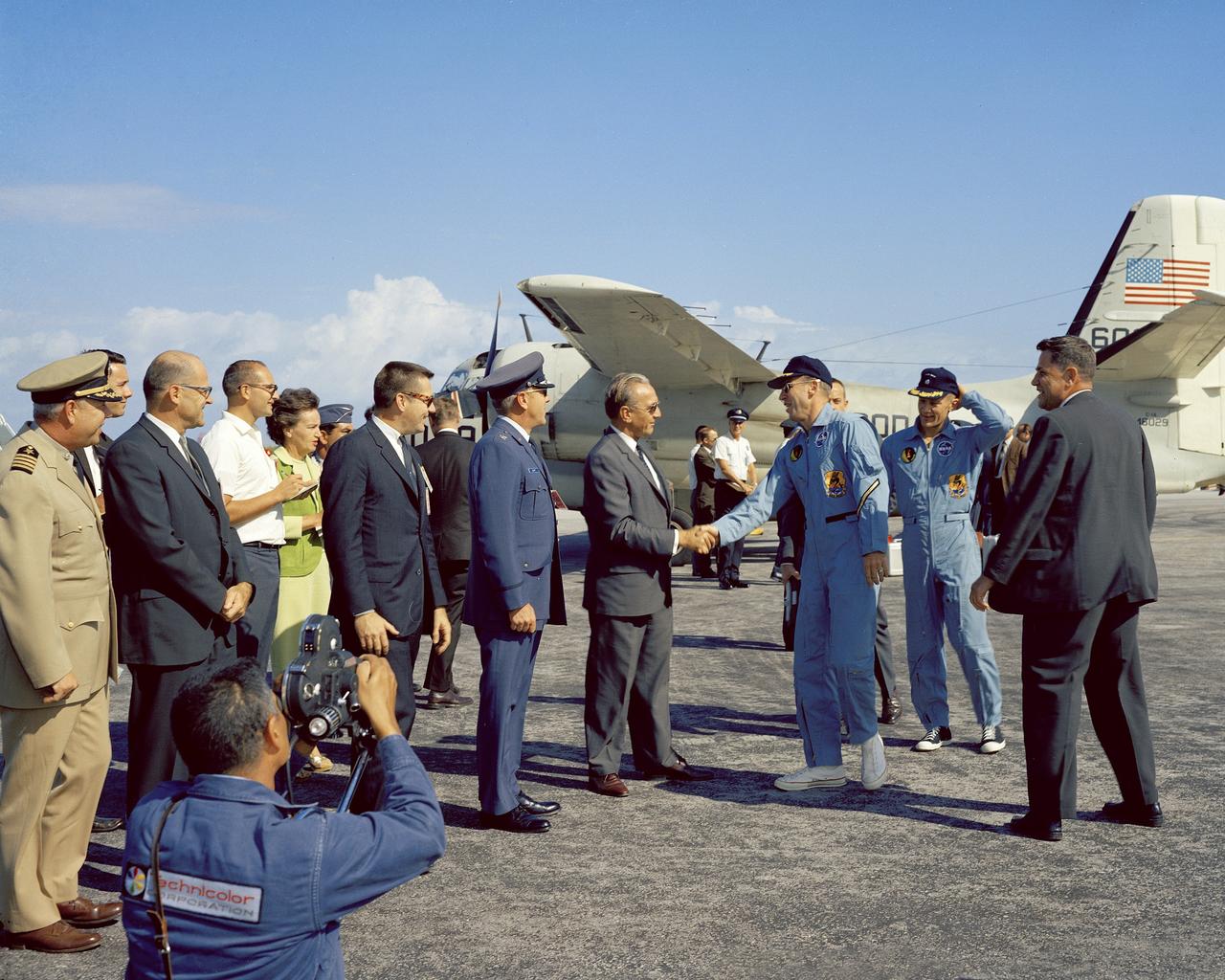

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- At the Cape Kennedy Air Force Station skid strip, Dr. Kurt H. Debus, director of the Kennedy Space Center, greets returning Gemini 12 astronauts James A. Lovell and Edwin E. Buzz Aldrin Jr. following their four-day Earth orbital mission. Photo Credit: NASA
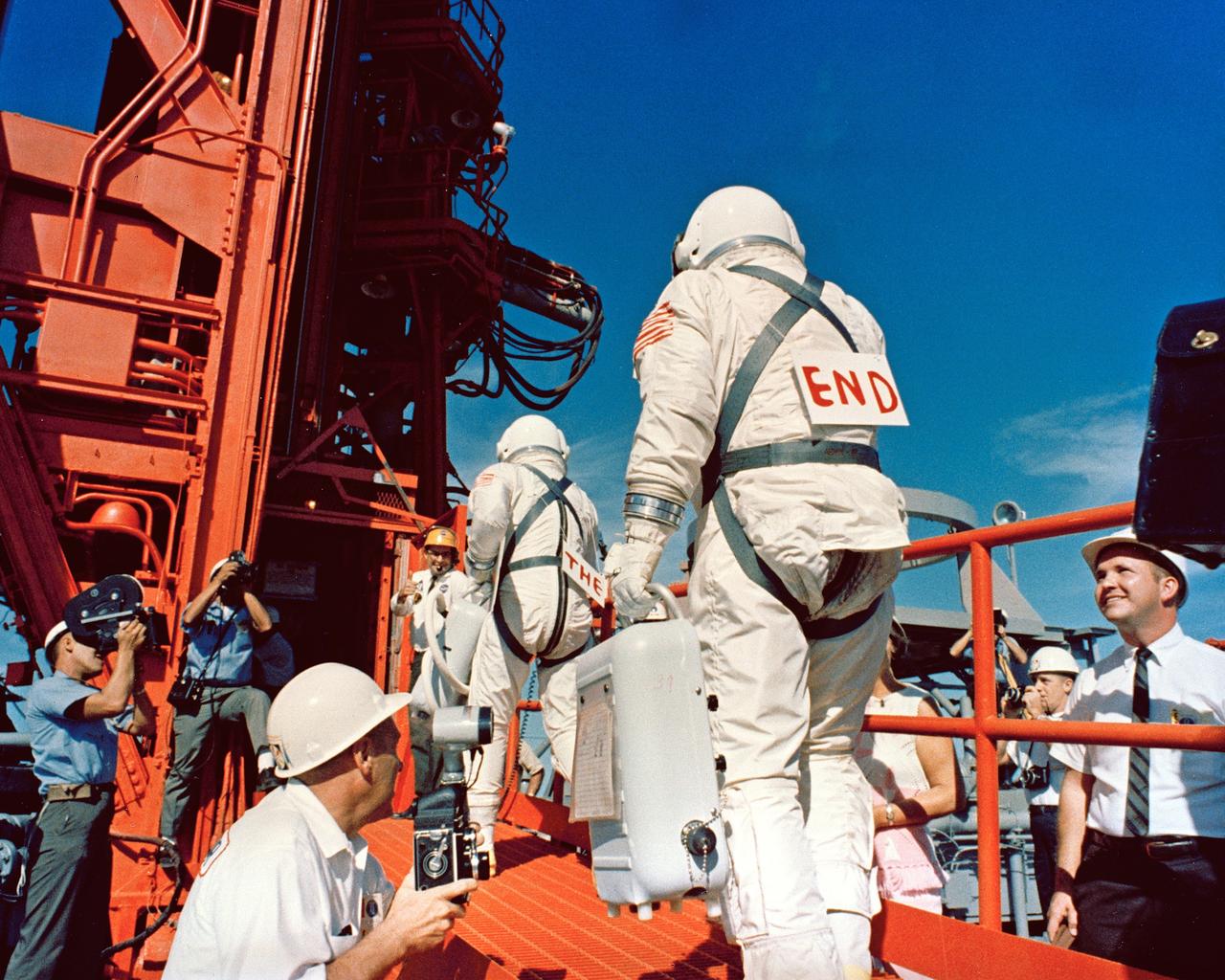

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- At Cape Kennedy Air Force Station in Florida, the crew for Gemini 12 arrives at Launch Complex 19. Command pilot James A. Lovell is followed by pilot Edwin E. Buzz Aldrin Jr. The signs on their backs note that this mission is the final flight of the Gemini Program. Photo Credit: NASA
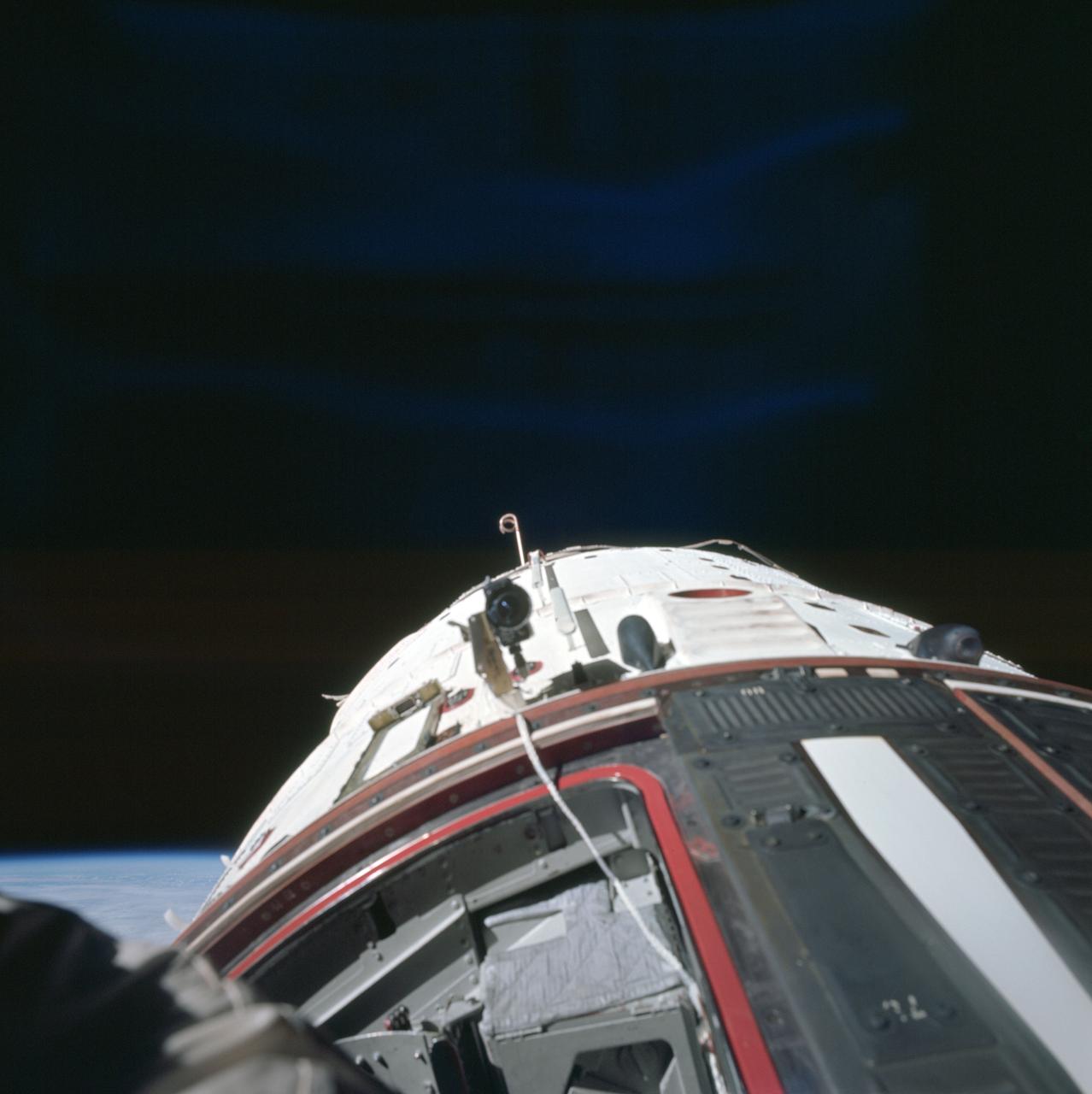

S66-62920 (13 Nov. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot of the Gemini-12 spaceflight, took this picture of the Gemini-12 spacecraft during standup extravehicular activity (EVA) with the hatch open. This is a view to the rear showing the adapter section. Photo credit: NASA
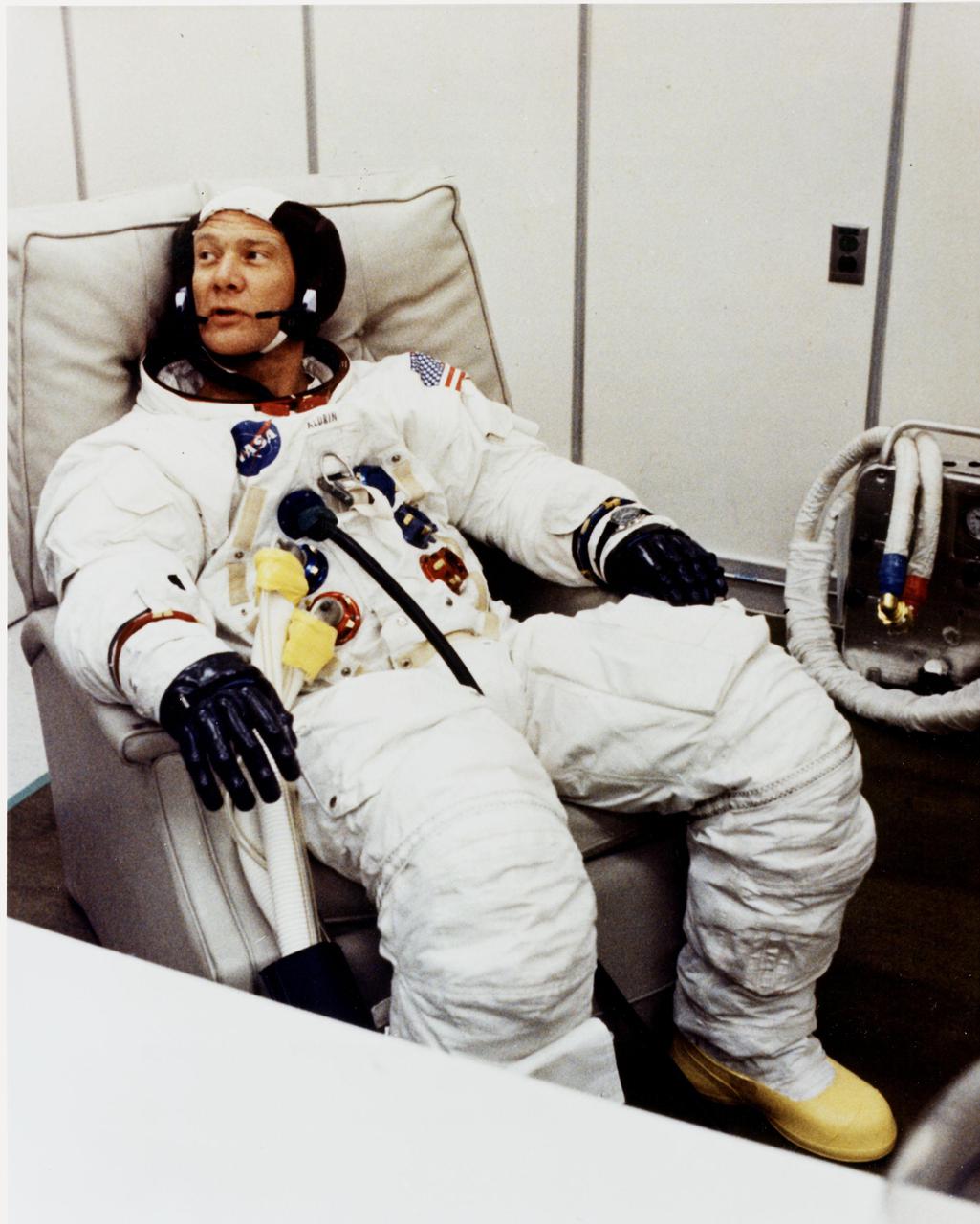

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Apollo 11 Lunar Module Pilot Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. relaxes after suiting up to participate in a space vehicle Countdown Demonstration Test with astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Michael Collins. They will be launched on a lunar landing mission.
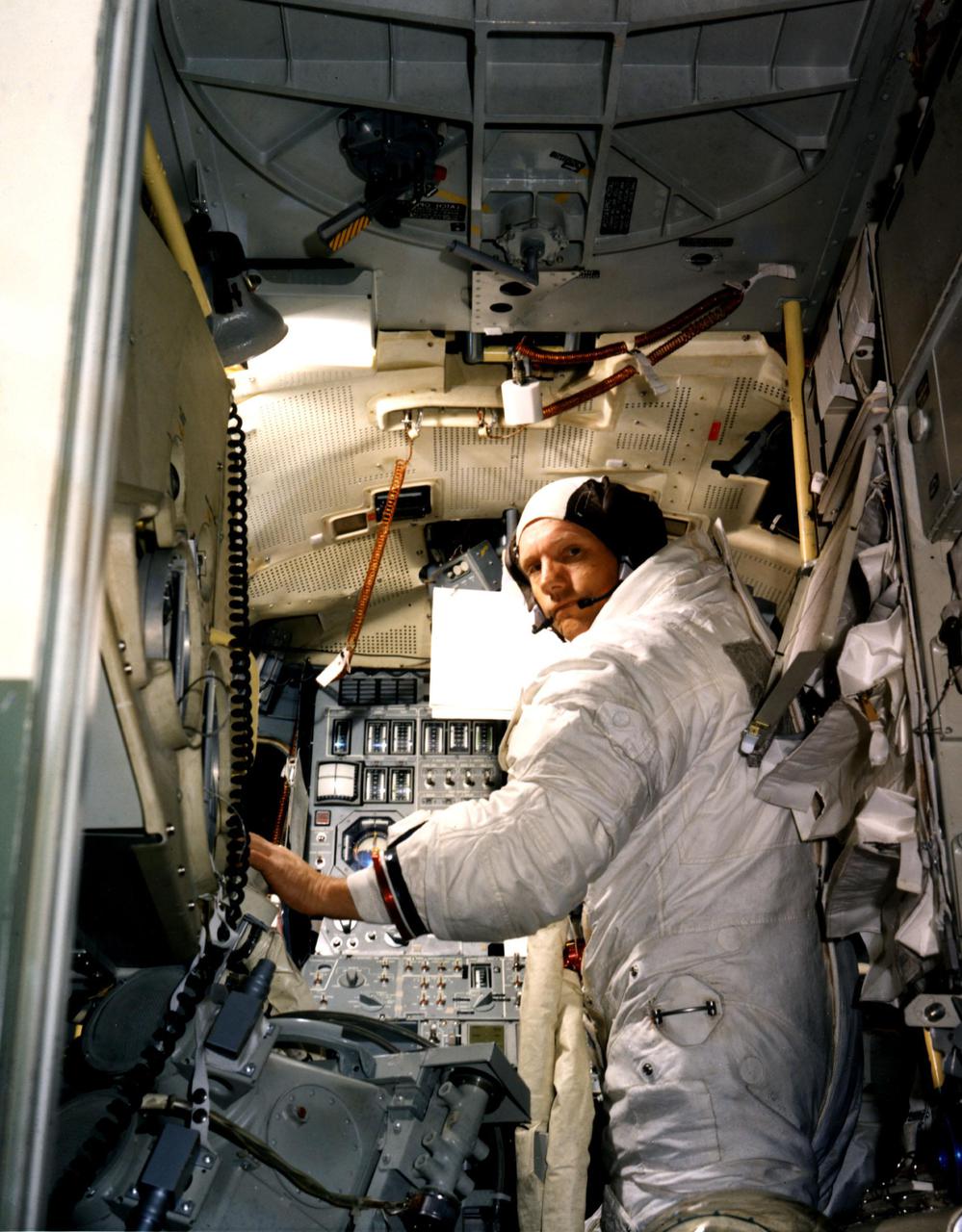

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Neil A. Armstrong, commander for the Apollo 11 Moon-landing mission, practices for the historic event in a Lunar Module simulator in the Flight Crew Training Building at KSC. Accompanying Armstrong on the Moon flight will be Command Module Pilot Michael Collins and Lunar Module Pilot Edwin E. Aldrin Jr.
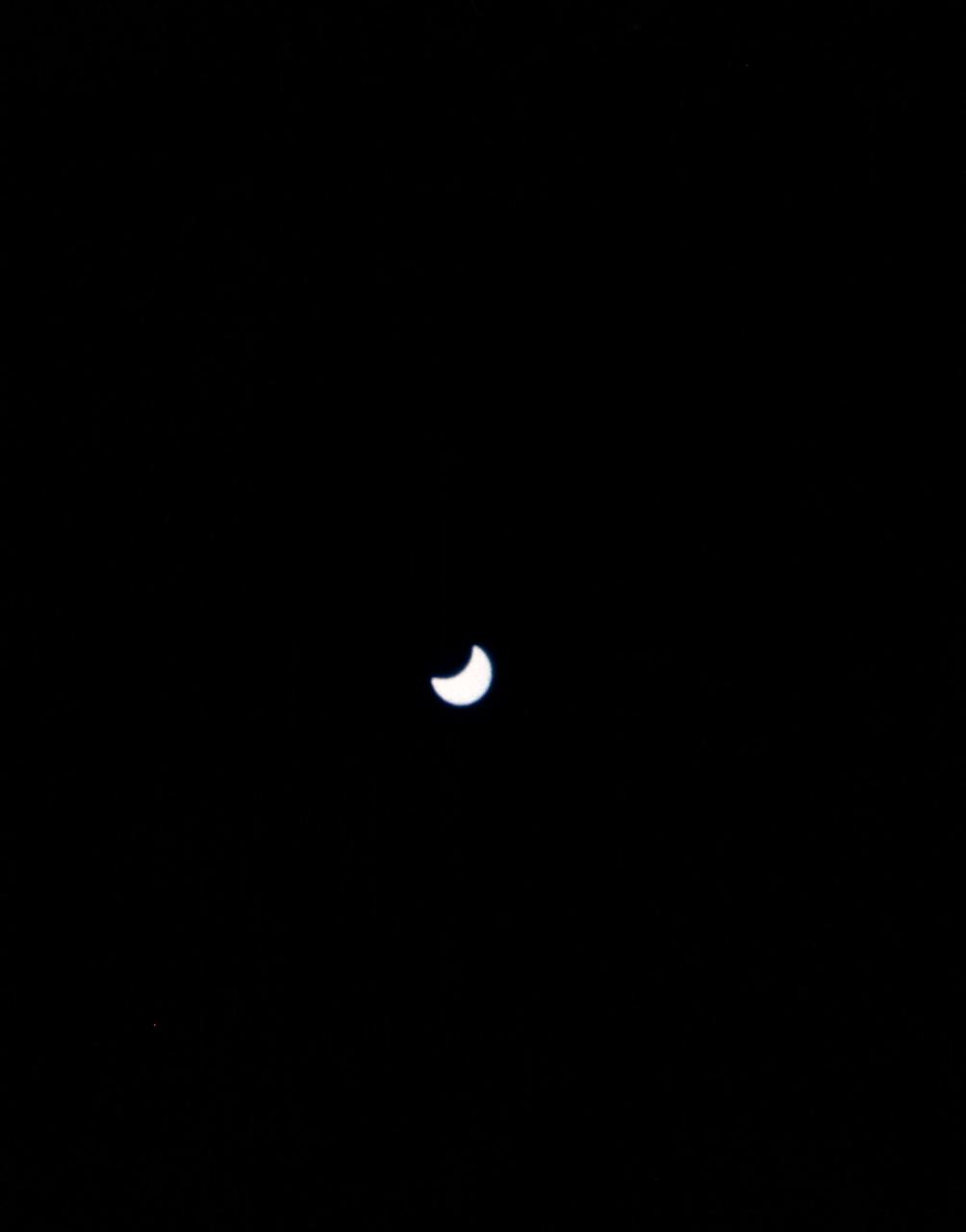

S66-63414 (12 Nov. 1966) --- Partial solar eclipse as seen from the Gemini-12 spacecraft during it 12th revolution of Earth. Crew members for the flight were astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., command pilot, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot. Photo credit: NASA
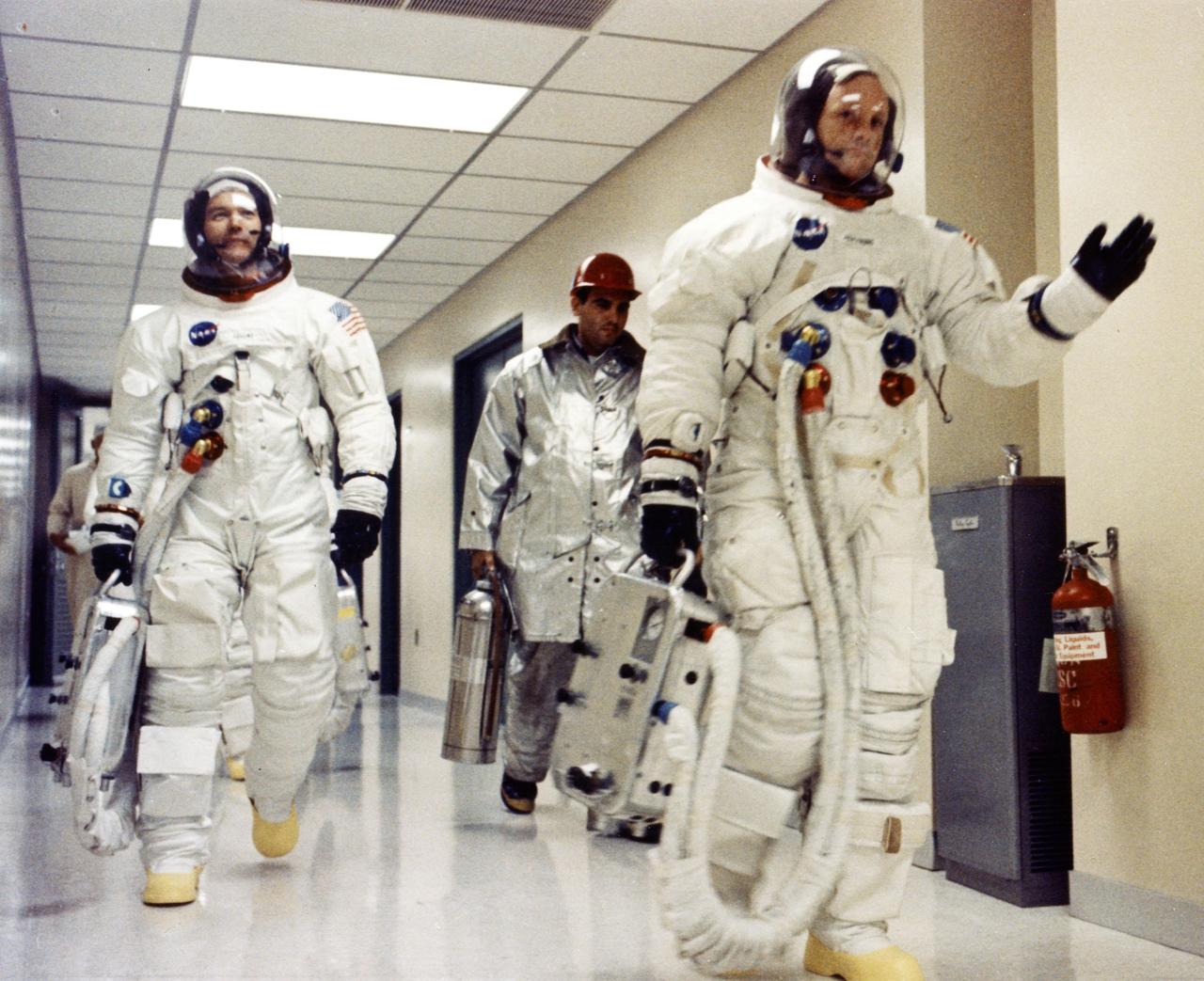

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Apollo 11 Commander Neil A. Armstrong waves to well-wishers in the hallway of the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building as he and Michael Collins and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. prepare to be transported to Launch Complex 39A for the first manned lunar landing mission
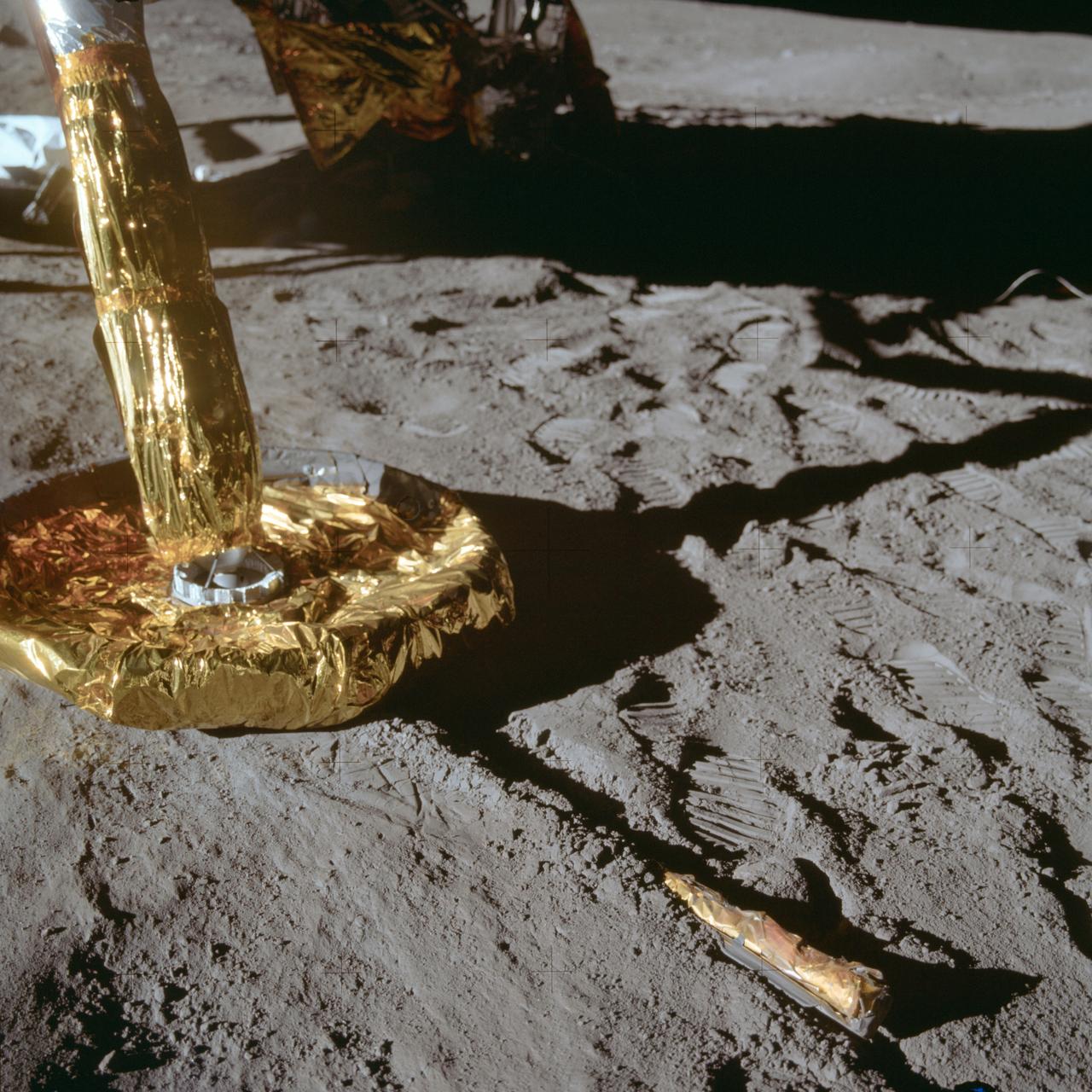

A close-up view of a footpad of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module as it rested on the surface of the Moon. The stick-like protruding object is a lunar surface sensing probe. This photograph was take with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the extravehicular activity of Astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin on July 20, 1969.

S66-59988 (16 Nov. 1966) --- Gemini-12 astronauts James A. Lovell Jr. (left), command pilot, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot, shake hands in front of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's Gemini progress report sign at the Cape Kennedy skid strip. Photo credit: NASA
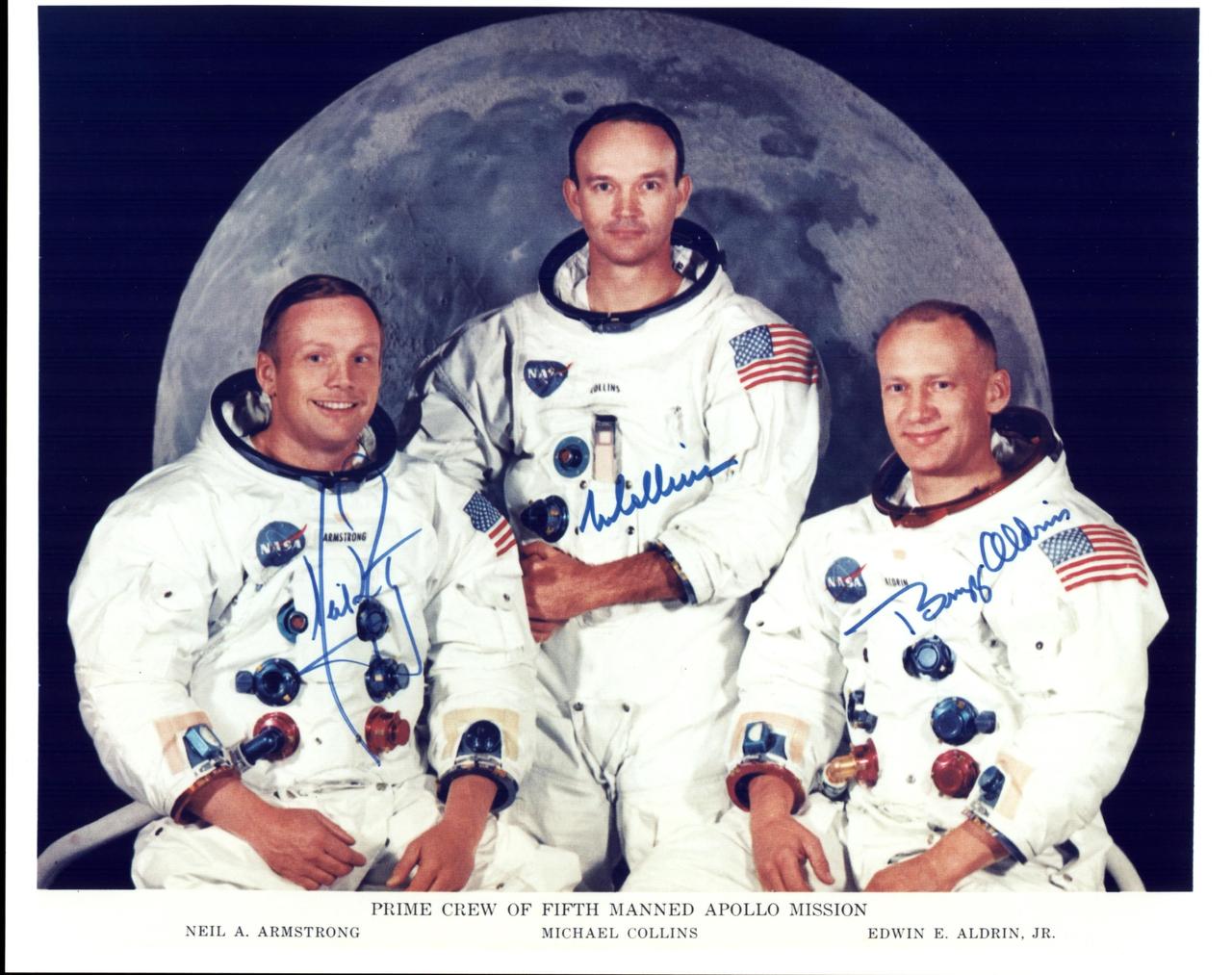

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Official Crew photo of the Apollow 11 Prime Crew. From left to right are astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, Commander; Michael Collins, Command Module Pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module Pilot.

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. walks on the surface of the Moon near a leg of the Lunar Module during the Apollo 11 EVA. Armstrong also took this picture with the 70-mm lunar surface camera. Note footprints in the foreground.
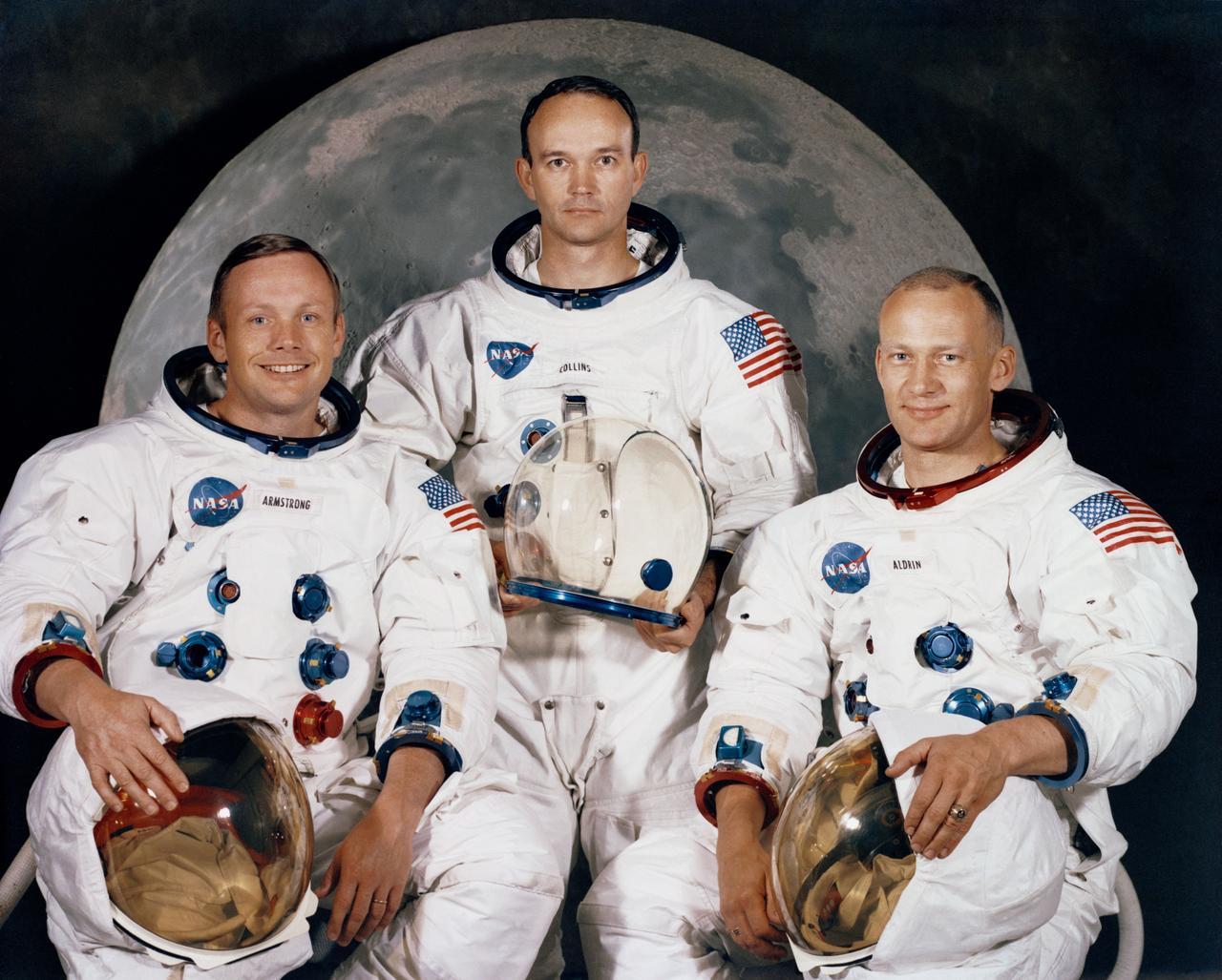

S69-31740 (May 1969) --- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has named these three astronauts as the prime crew of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. Left to right, are Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, command module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot.
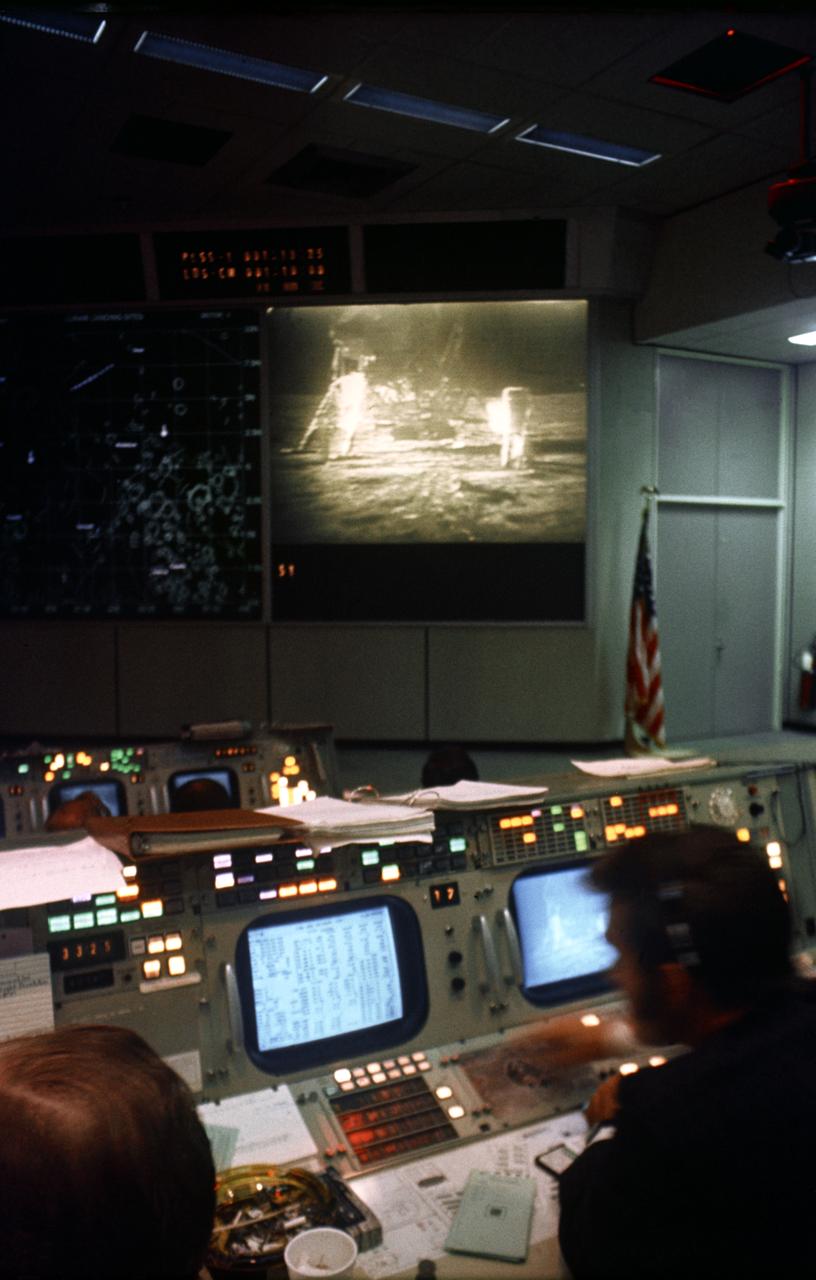

S69-39815 (20 July 1969) --- Interior view of the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center (MCC) during the Apollo 11 lunar extravehicular activity (EVA). The television monitor shows astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. on the surface of the moon.
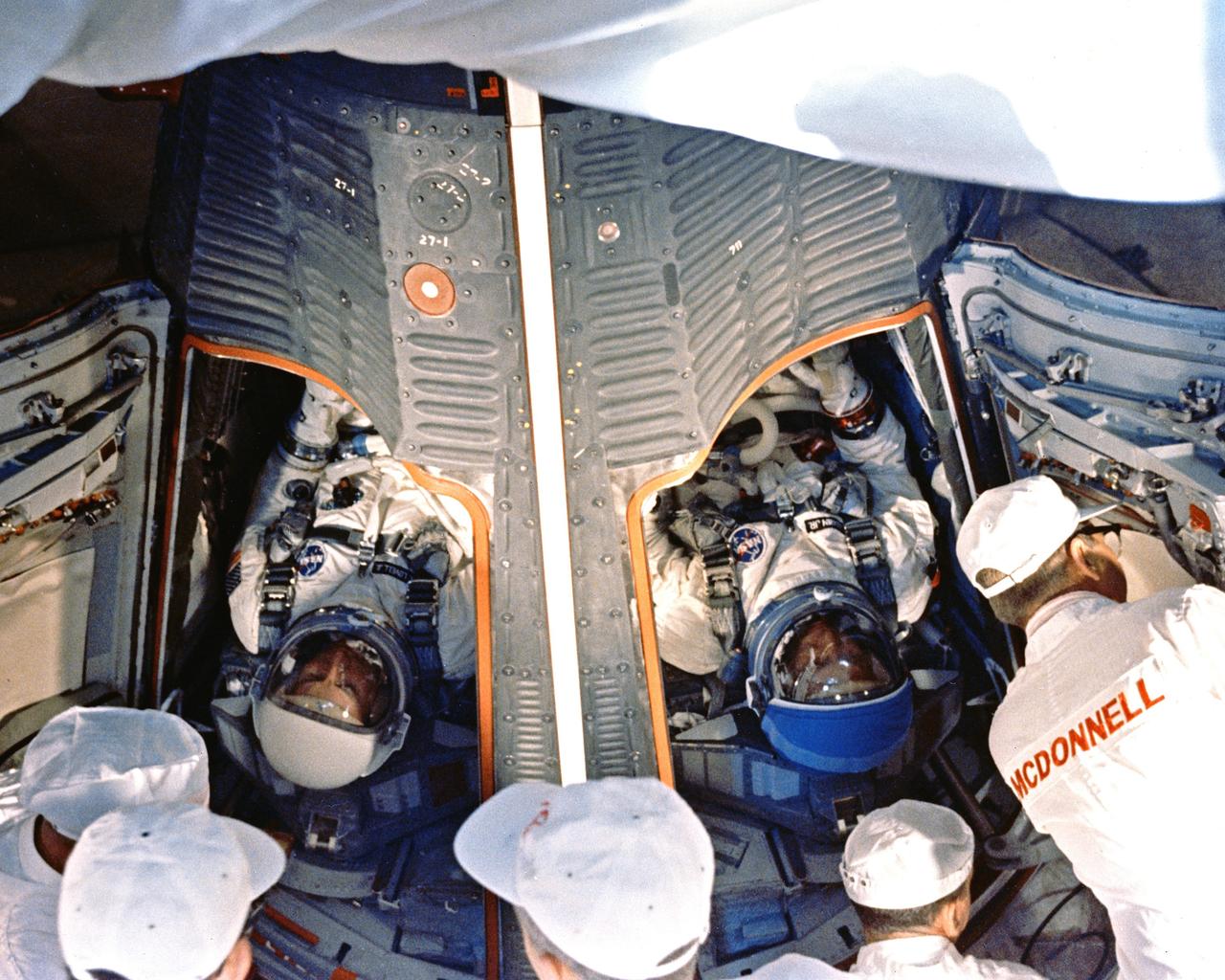

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- At Cape Kennedy Air Force Station in Florida, Gemini 12 command pilot James A. Lovell, left, and Edwin E. Buzz Aldrin Jr. wait for launch as technicians complete preparations of the spacecraft. Photo Credit: NASA
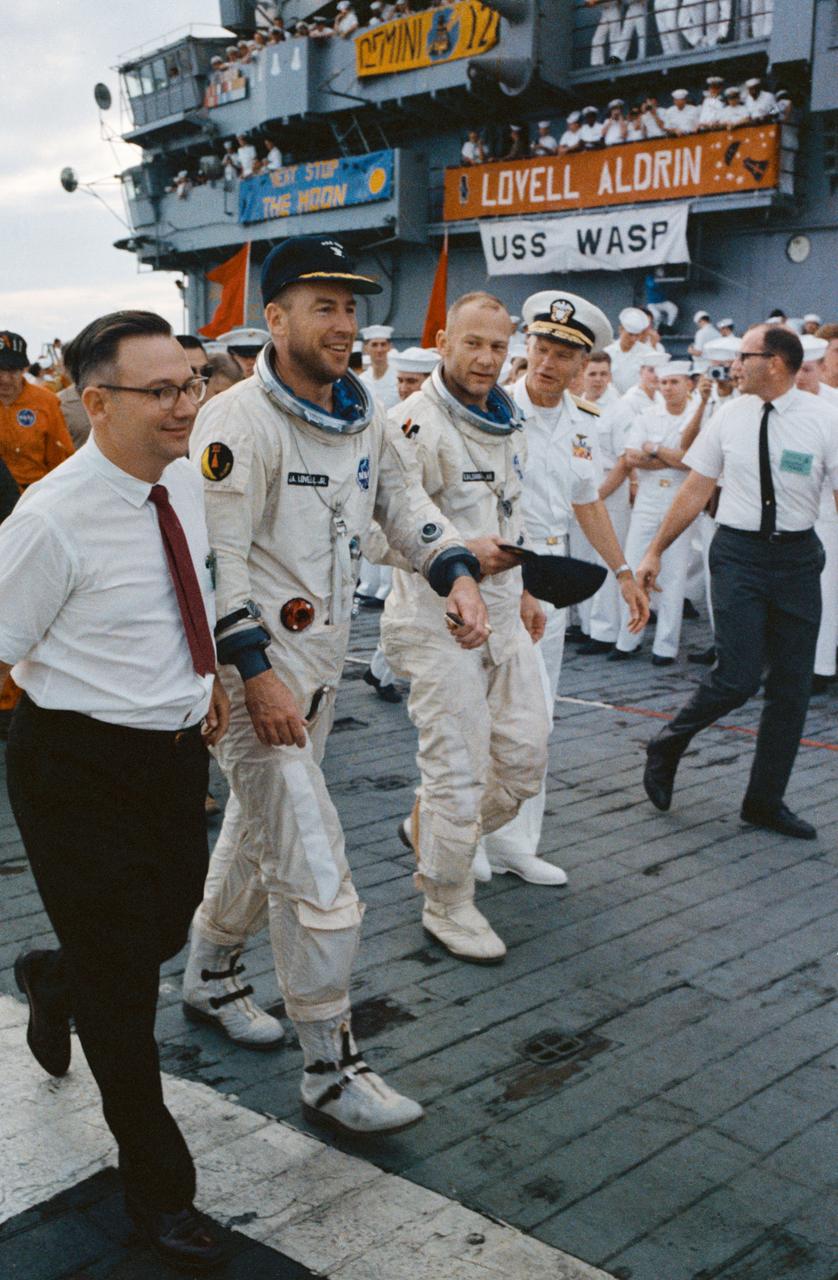

S66-59997 (15 Nov. 1966) --- A happy Gemini-12 prime crew arrives aboard the aircraft carrier, USS Wasp. Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr. (left), command pilot, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot, had just been picked up from the splashdown area by helicopter. Photo credit: NASA
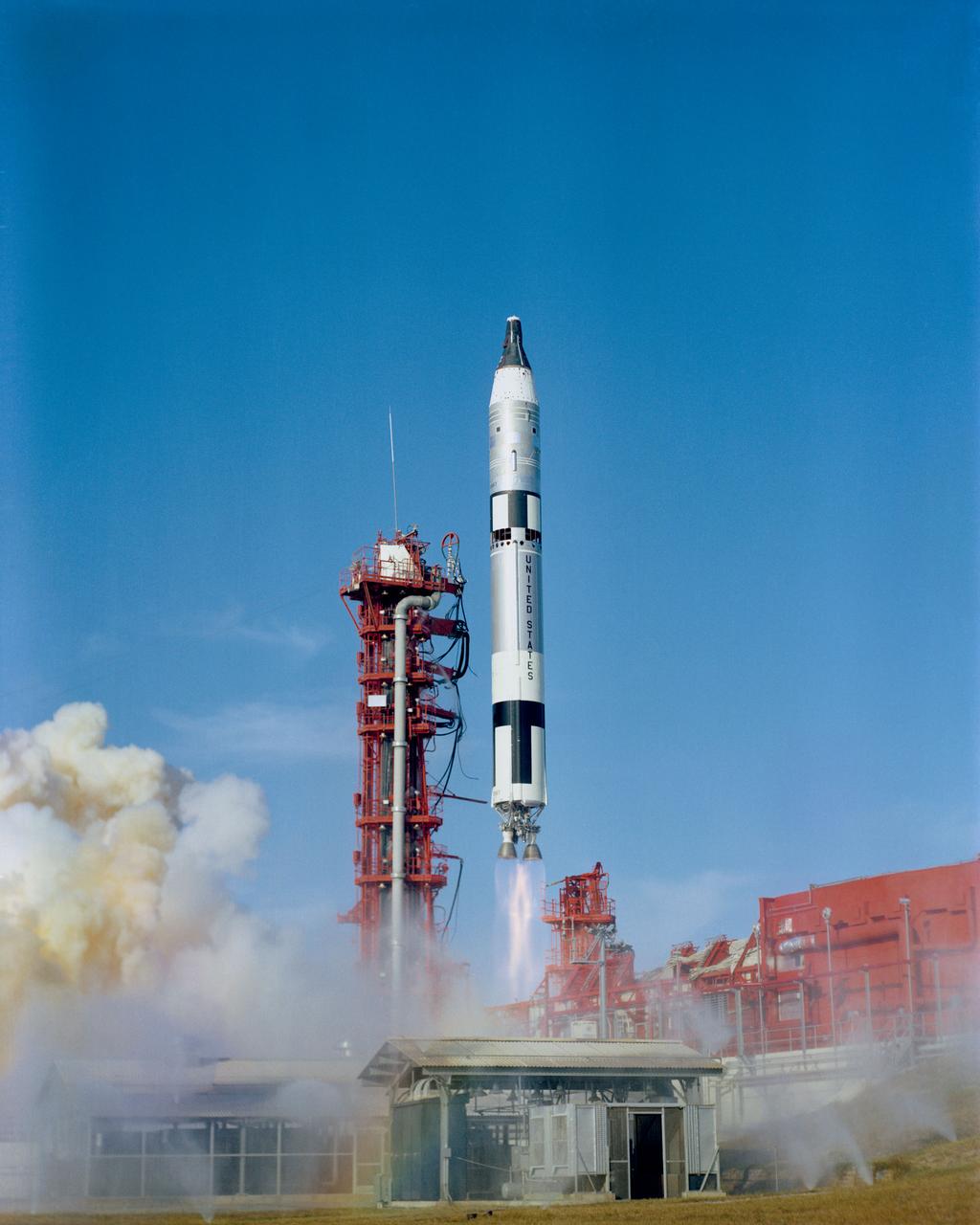

S66-59975 (11 Nov. 1966) --- Gemini-12 spacecraft, carrying astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., command pilot, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot, was launched from the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 19 at 3:46 p.m. (EST), Nov. 11, 1966. Photo credit: NASA

S69-31739 (May 1969) --- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has named these three astronauts as the prime crew of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. Left to right, are Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, command module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot.
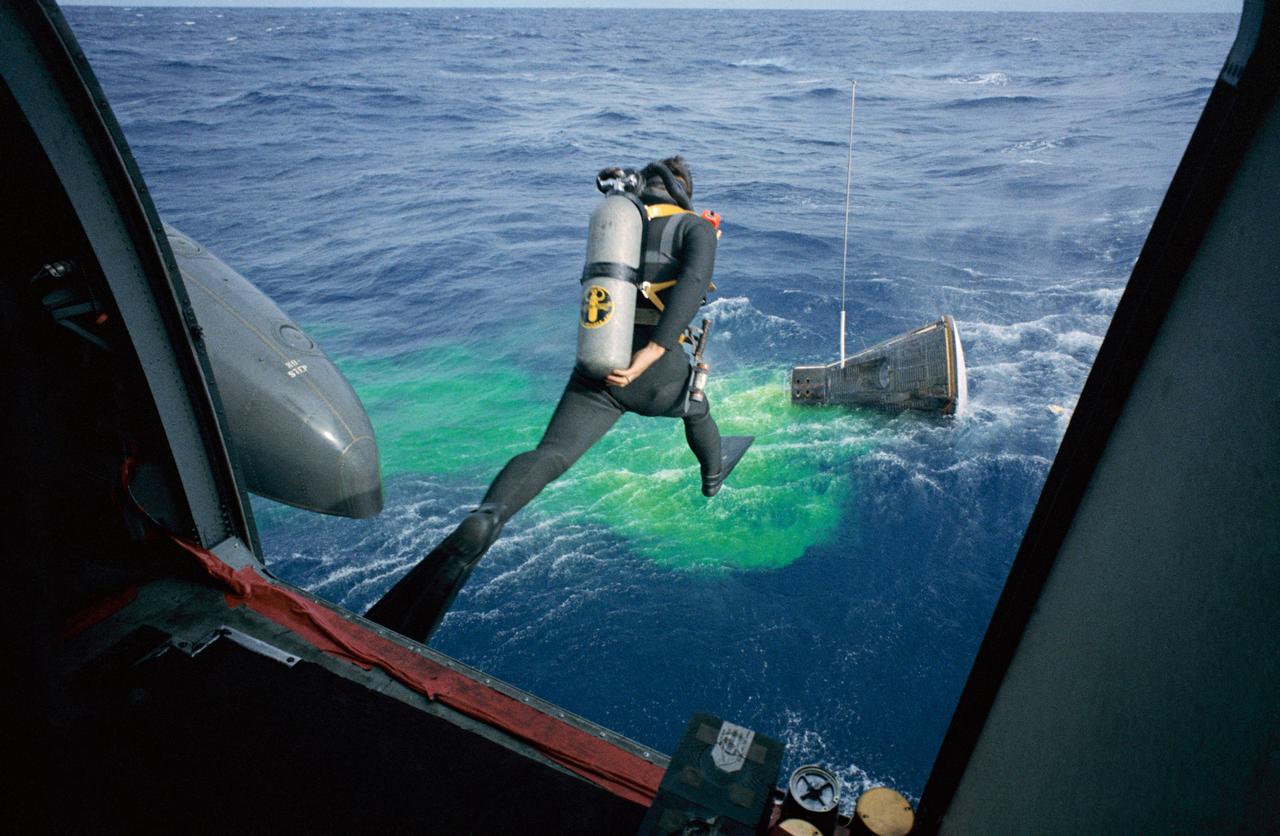

S66-59987 (15 Nov. 1966) --- A Navy frogman leaps from a recovery helicopter into the water to assist in the Gemini-12 recovery operations. Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., command pilot, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot, had just completed their four-day space mission. Photo credit: NASA
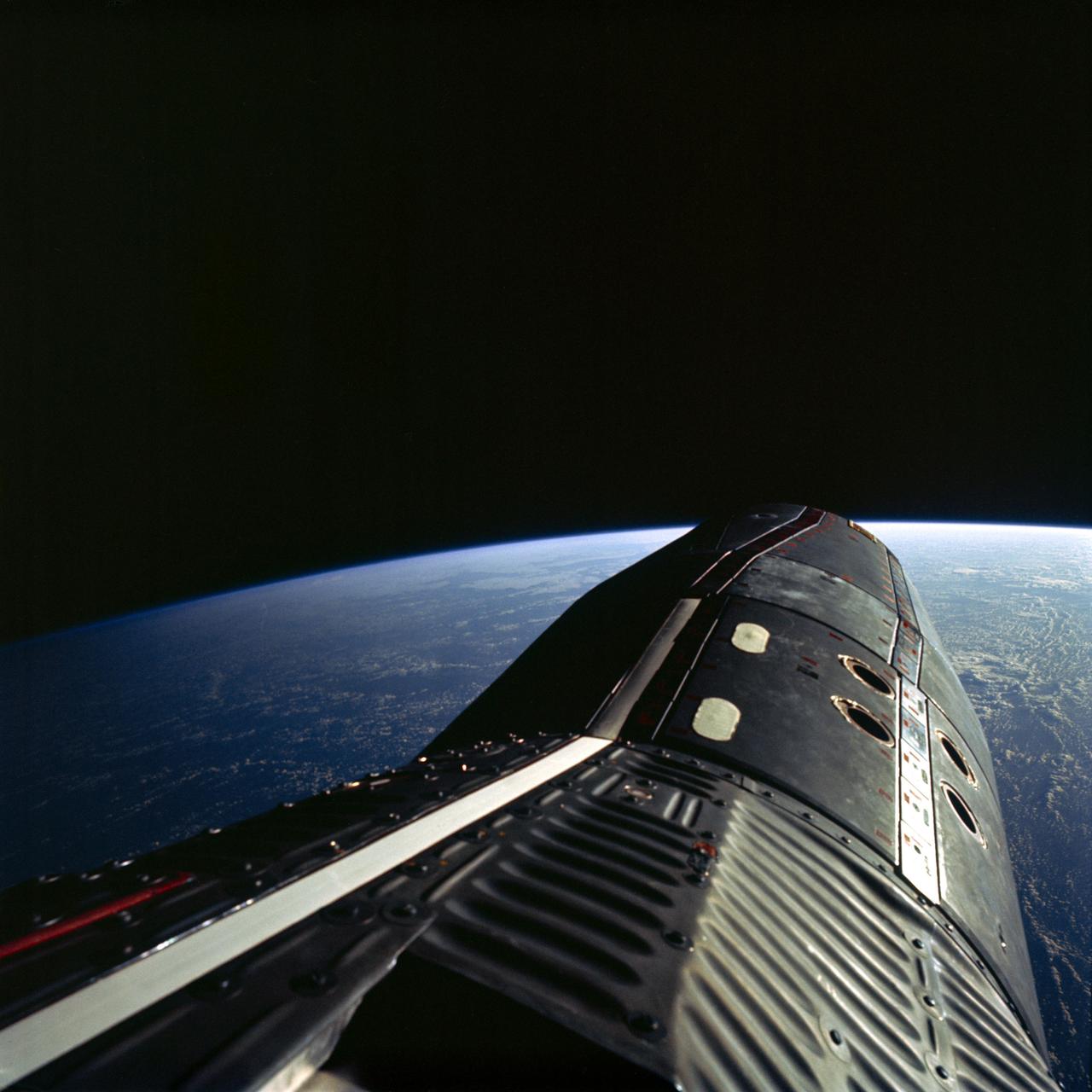

S66-63011 (13 Nov. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot of the Gemini-12 spaceflight, took this picture of the Gemini-12 spacecraft during standup extravehicular activity (EVA) with the hatch open. Photo credit: NASA
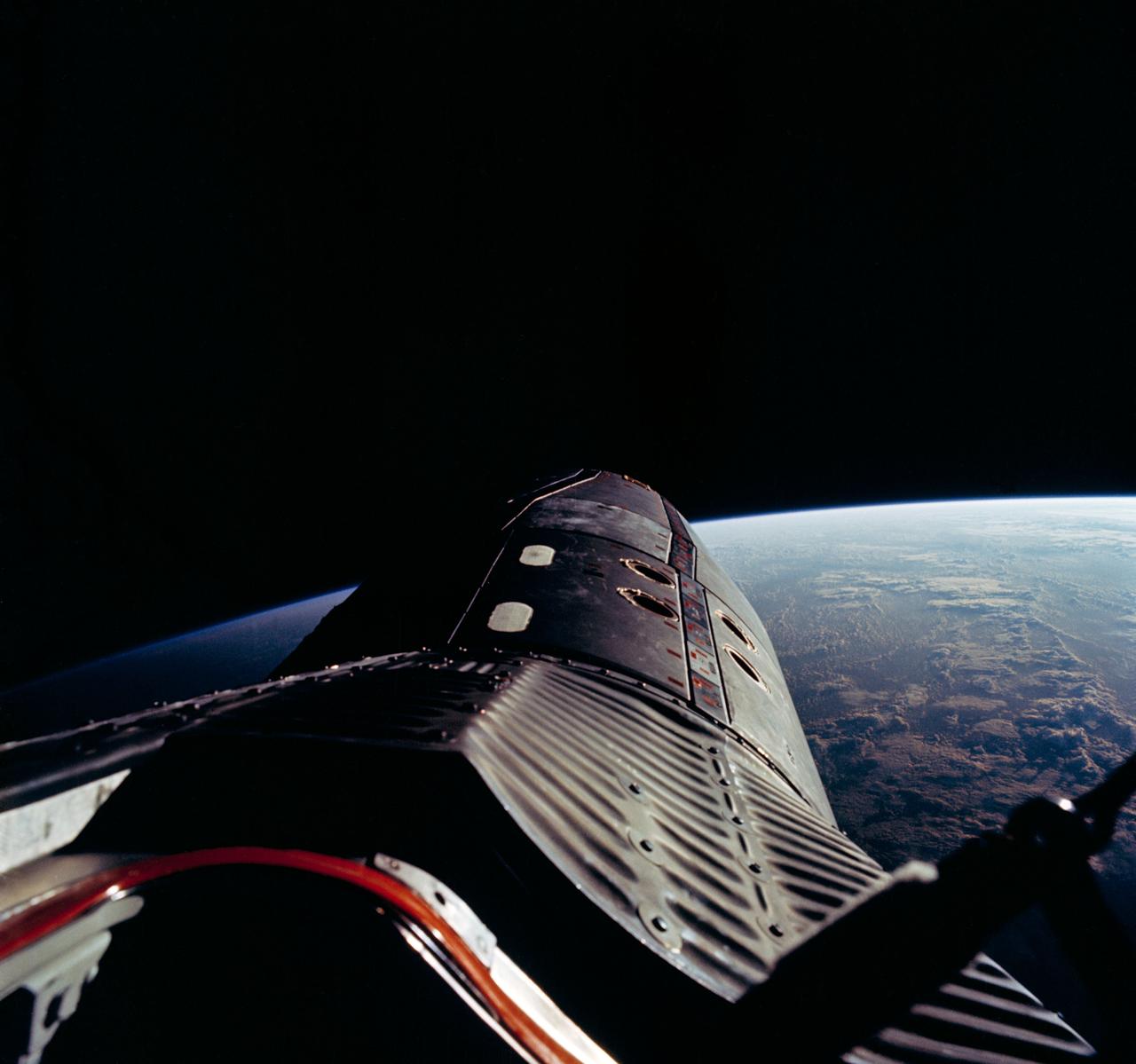

S66-63007 (12 Nov. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot of the Gemini-12 spaceflight, took this picture of the Gemini-12 spacecraft during standup extravehicular activity (EVA) with the hatch open. This is a view looking forward showing the adapter section. Photo credit: NASA
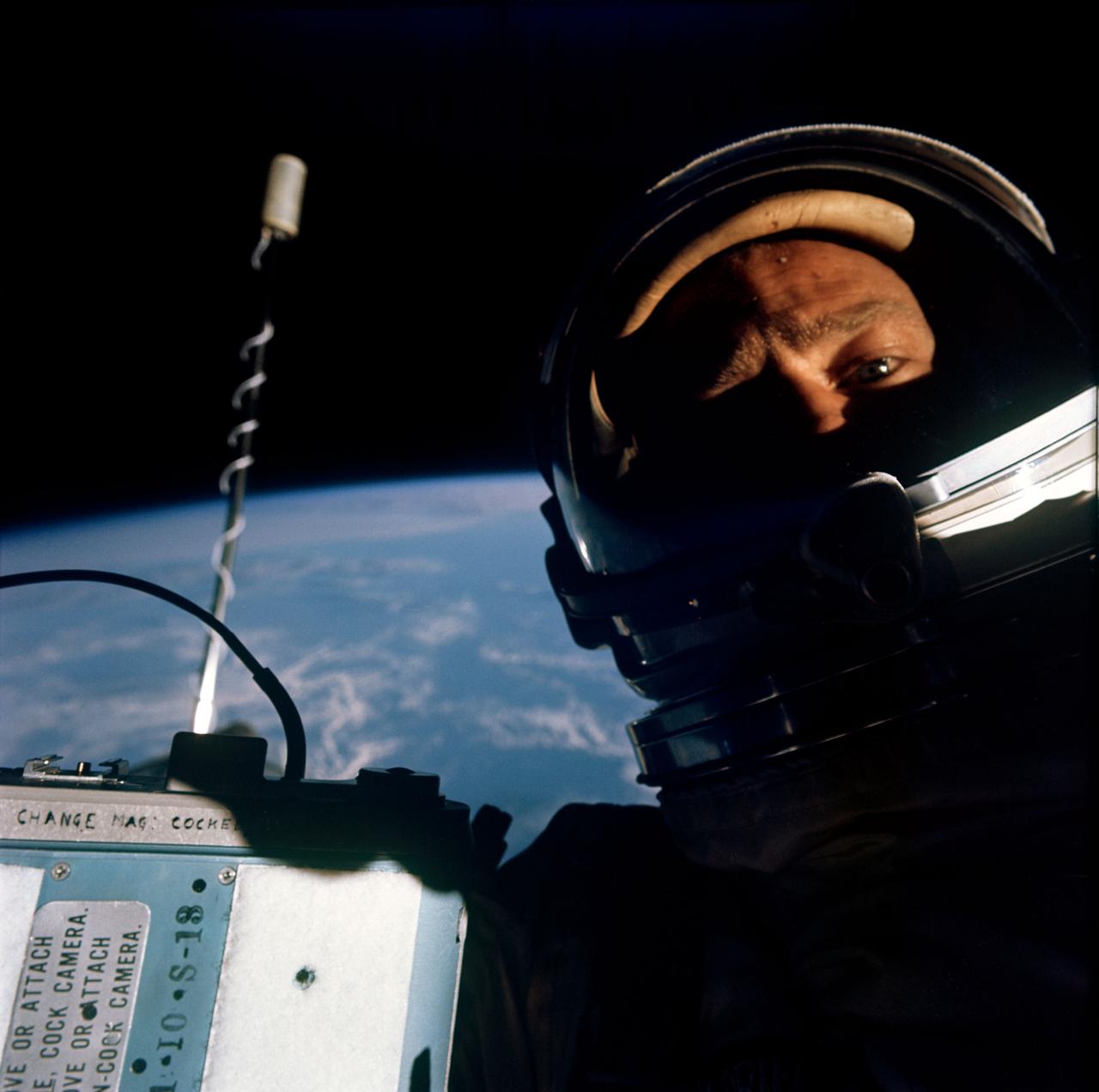

S66-62926 (12 Nov. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot of the Gemini-12 spaceflight, is photographed with pilot's hatch of the spacecraft open. Note: J.A. Maurer camera which was used to photograph some of his extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr. was the command pilot. Photo credit: NASA
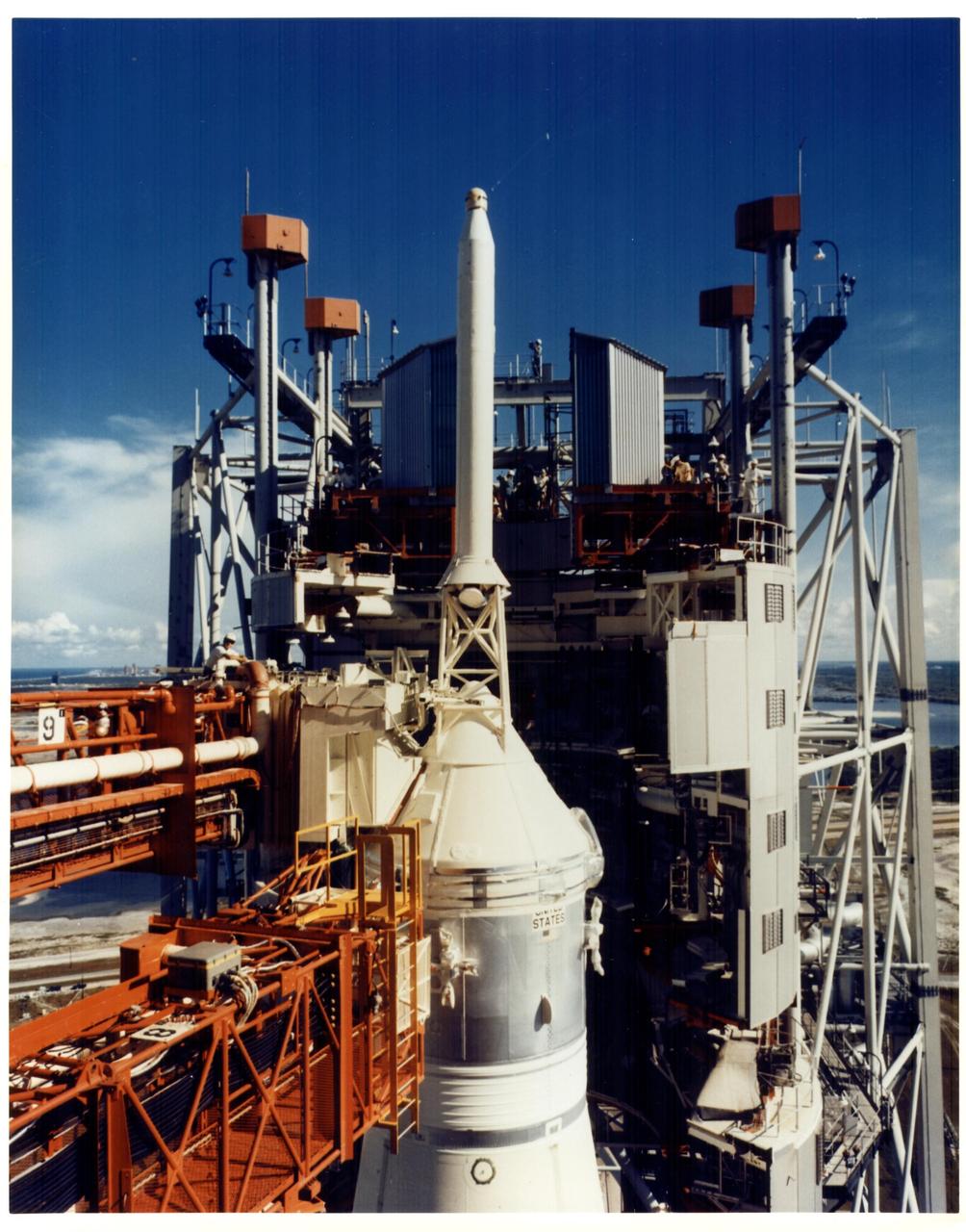

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The 402-foot-tall mobile service structure is moved away from the Apollo 11 spacecraft at Launch Pad 39A. The move was made during a recent Countdown Demonstration Test, participated in by Apollo 11 astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, Michael Collins and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr.
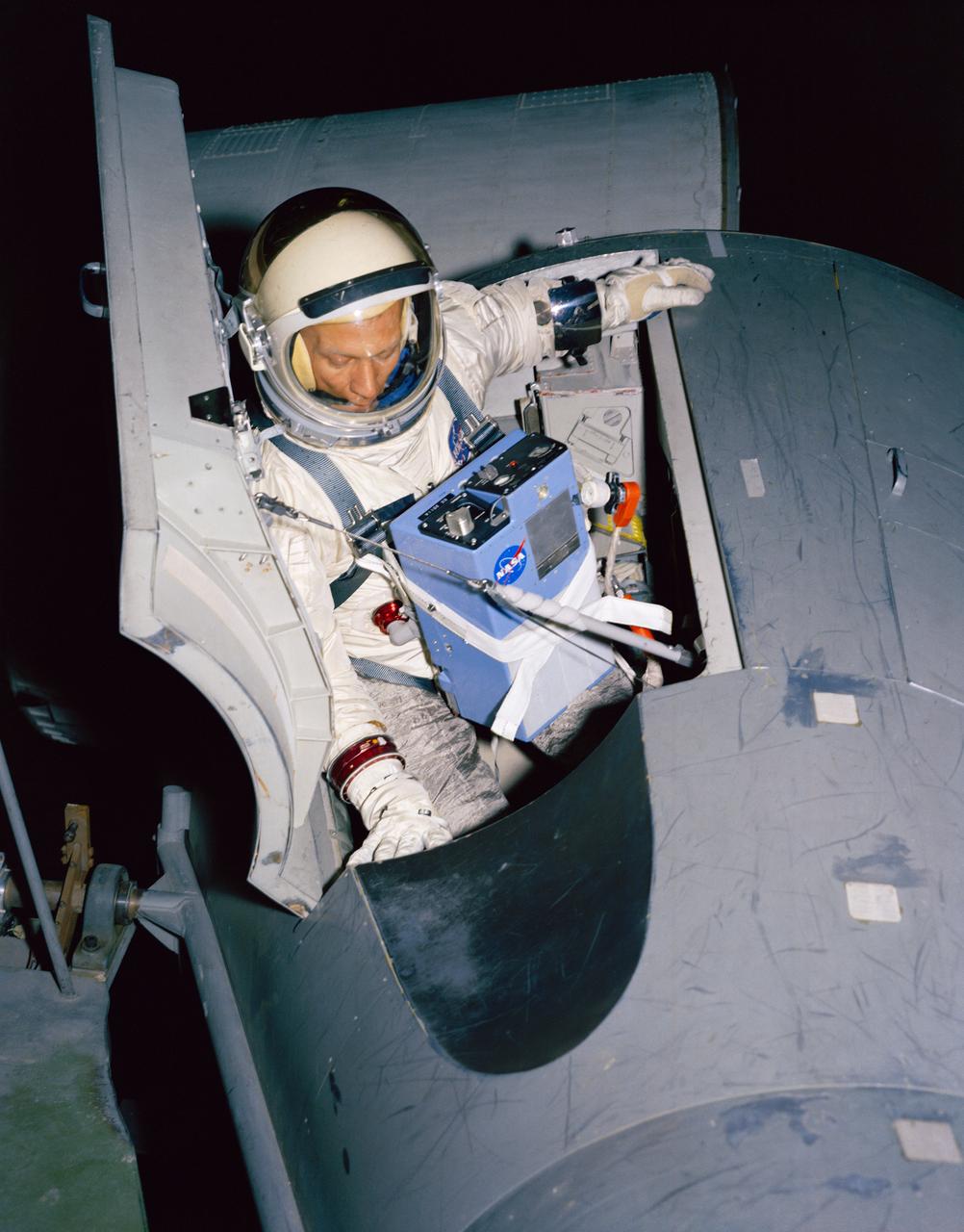

S66-28114 (1 April 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot of the Gemini-12 spaceflight, undergoes zero-gravity egress training. A KC-135 Air Force plane, flying a parabolic curve, creates a weightless environment as a training exercise in preparation for spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - A view of the Earth appears over the lunar horizon as the Apollo 11 Command Module comes into view of the Moon before astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin Jr. leave in the Lunar Module, Eagle, to become the first men to walk on the Moon's surface.

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - Surrounded by Man's footprints on the lunar surface, Apollo 11 Lunar Module Pilot Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. erects a solar wind experiment near the Tranquility Base established by the Lunar Module, Eagle.
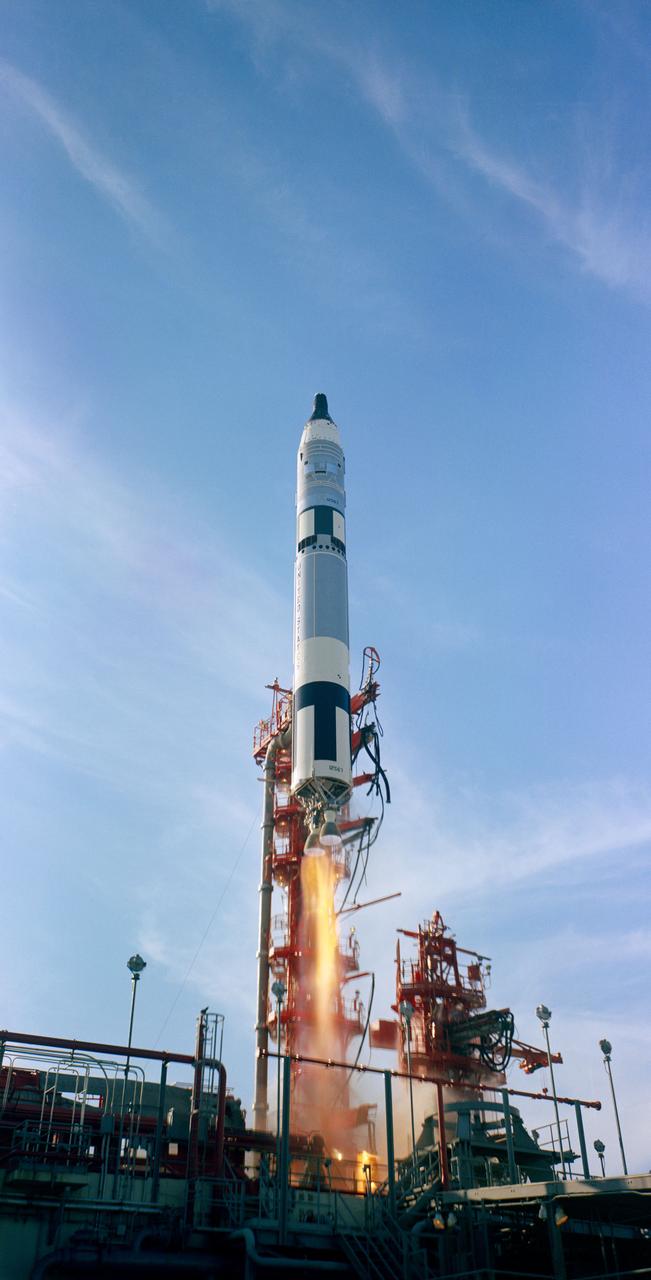

S66-59970 (11 Nov. 1966) --- Gemini-12 spacecraft, carrying astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., command pilot, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot, was launched from the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 19 at 3:46 p.m. (EST), Nov. 11, 1966. Photo credit: NASA
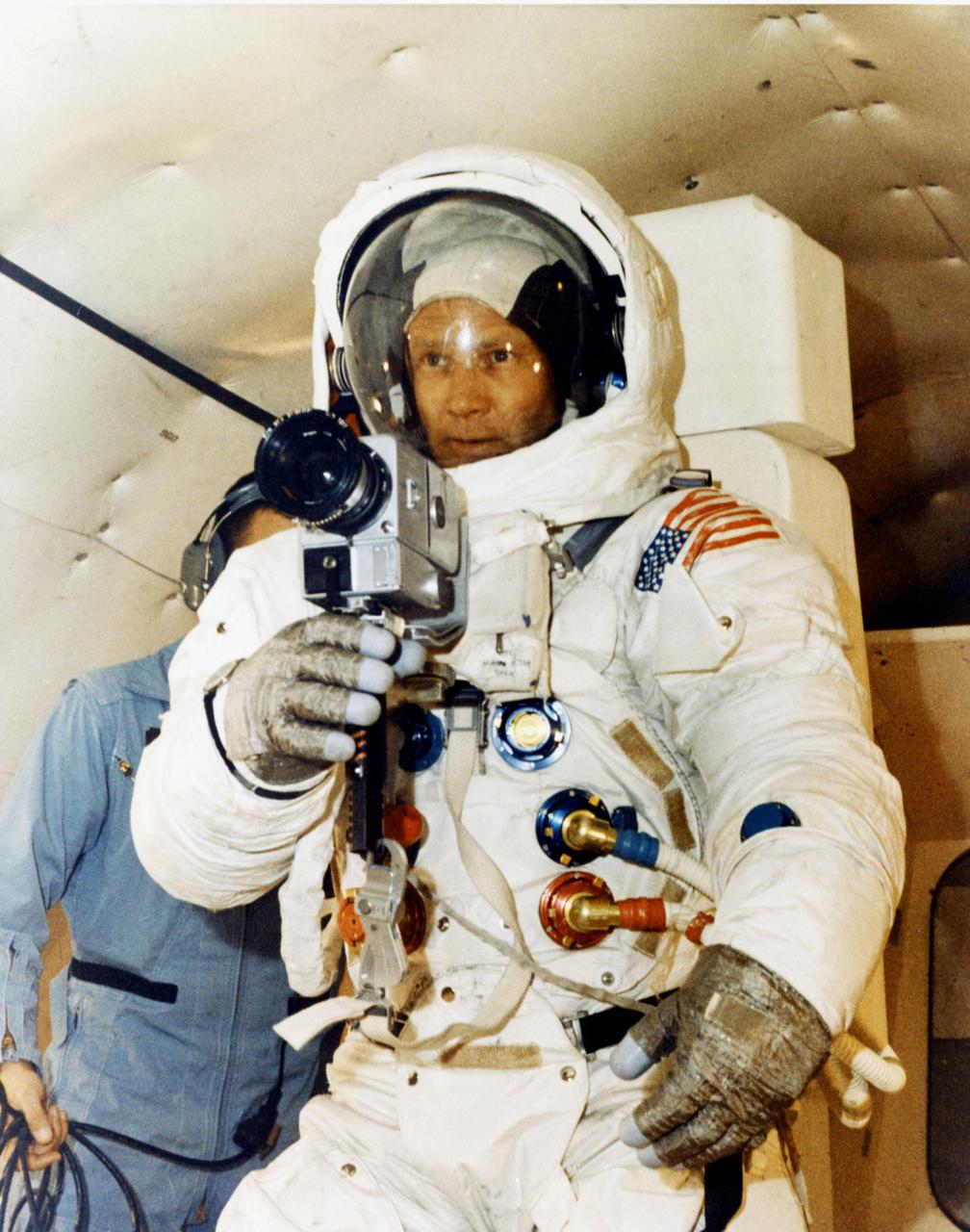

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - Flying in a KC-135 aircraft, Apollo 11 Lunar Module Pilot Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. takes pictures during training for the upcoming first manned lunar landing with astronauts Neil A. Armstrong Jr. and Michael Collins.
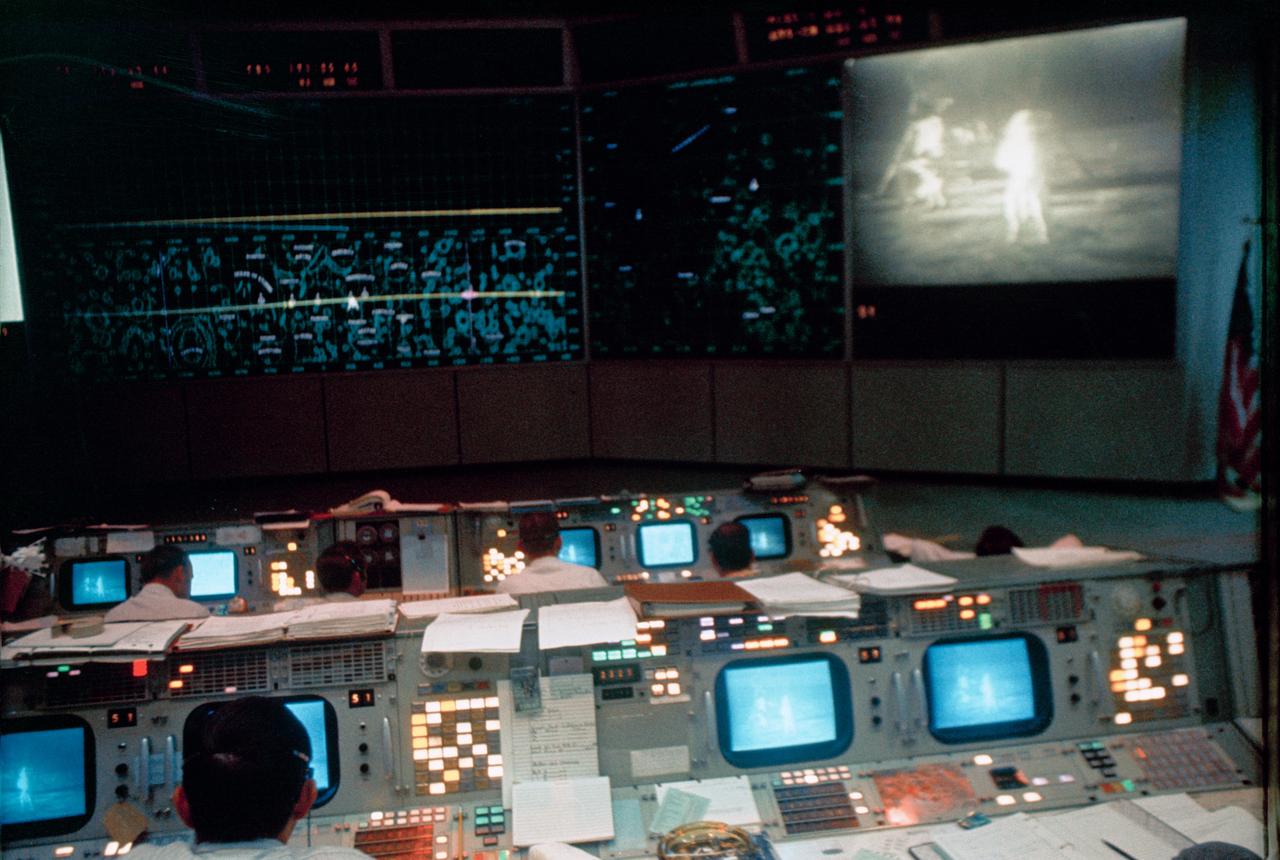

S69-39817 (20 July 1969) --- Interior view of the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center (MCC), Building 30, during the Apollo 11 lunar extravehicular activity (EVA). The television monitor shows astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. on the surface of the moon.
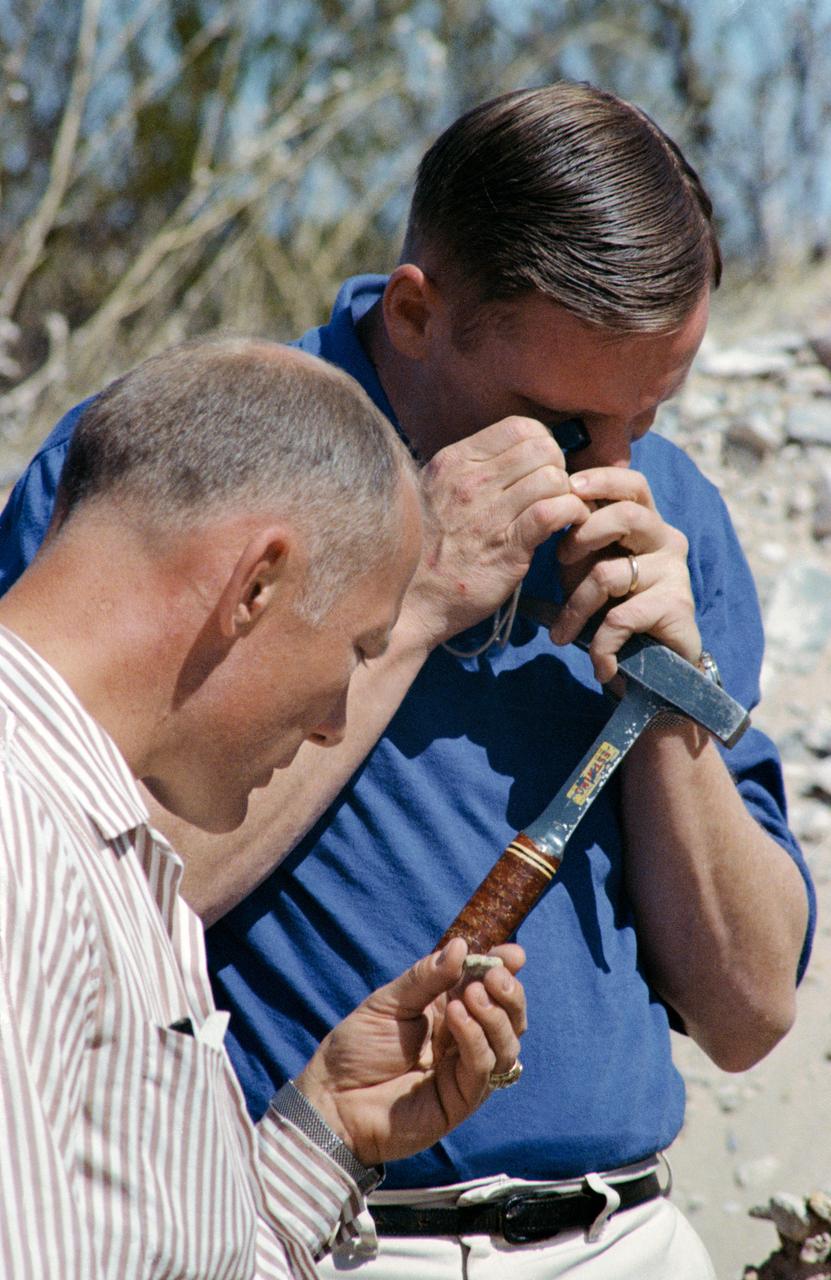

S69-25944 (25 Feb. 1969) --- These two Apollo 11 crew astronauts study rock samples during a geological field trip to the Quitman Mountains area near the Fort Quitman ruins in far west Texas. Neil A. Armstrong (in background) is the Apollo 11 commander; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. is the lunar module pilot.
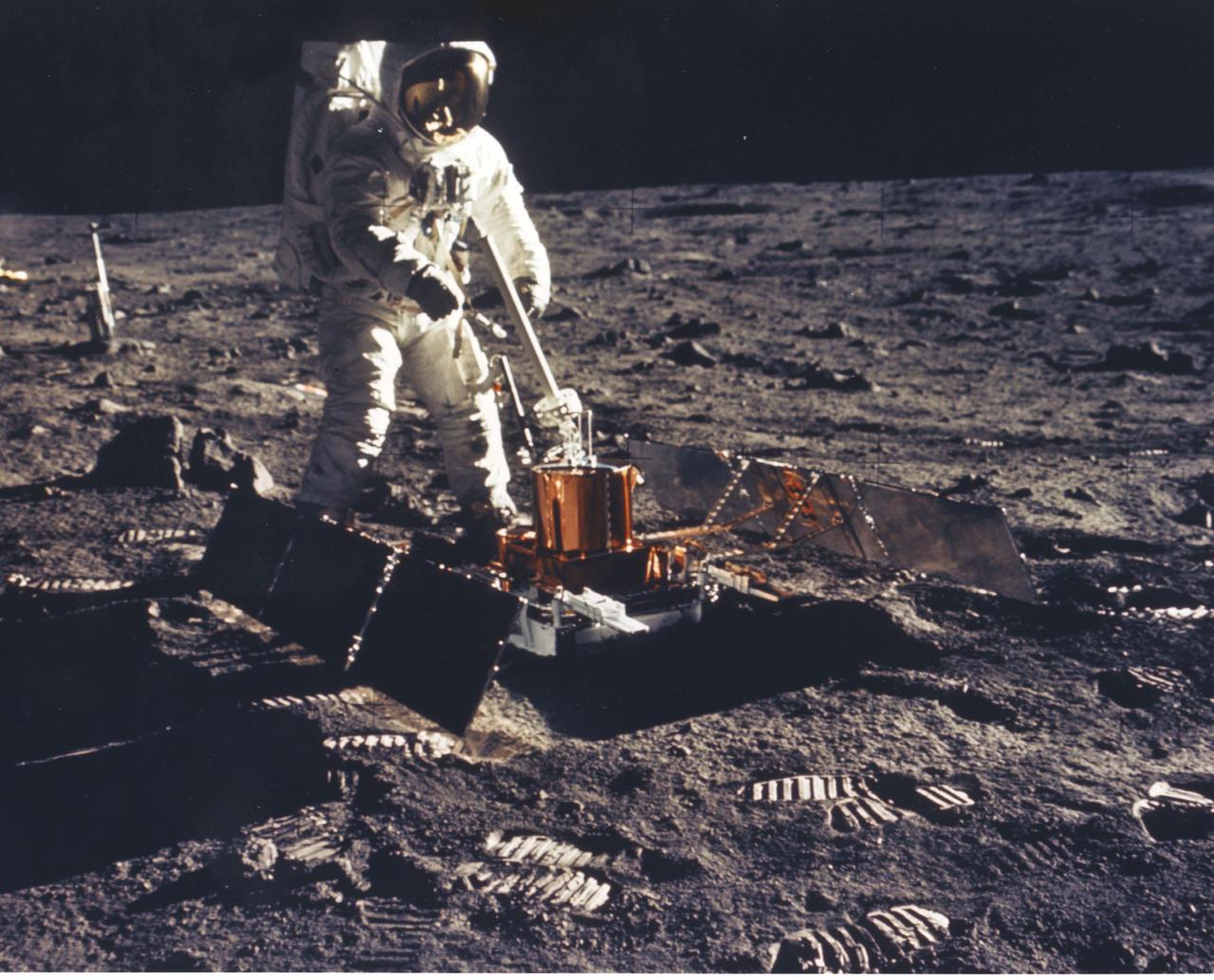
JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - Apollo 11 Lunar Module Pilot Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. deployes the Passive Seismic Experiment Package (PSE) on the Moon's surface near Tranquility Base. The sensitive instrument remained behind on the lunar surface to radio back information concerning moonquakes, landslides and meteorite impacts.
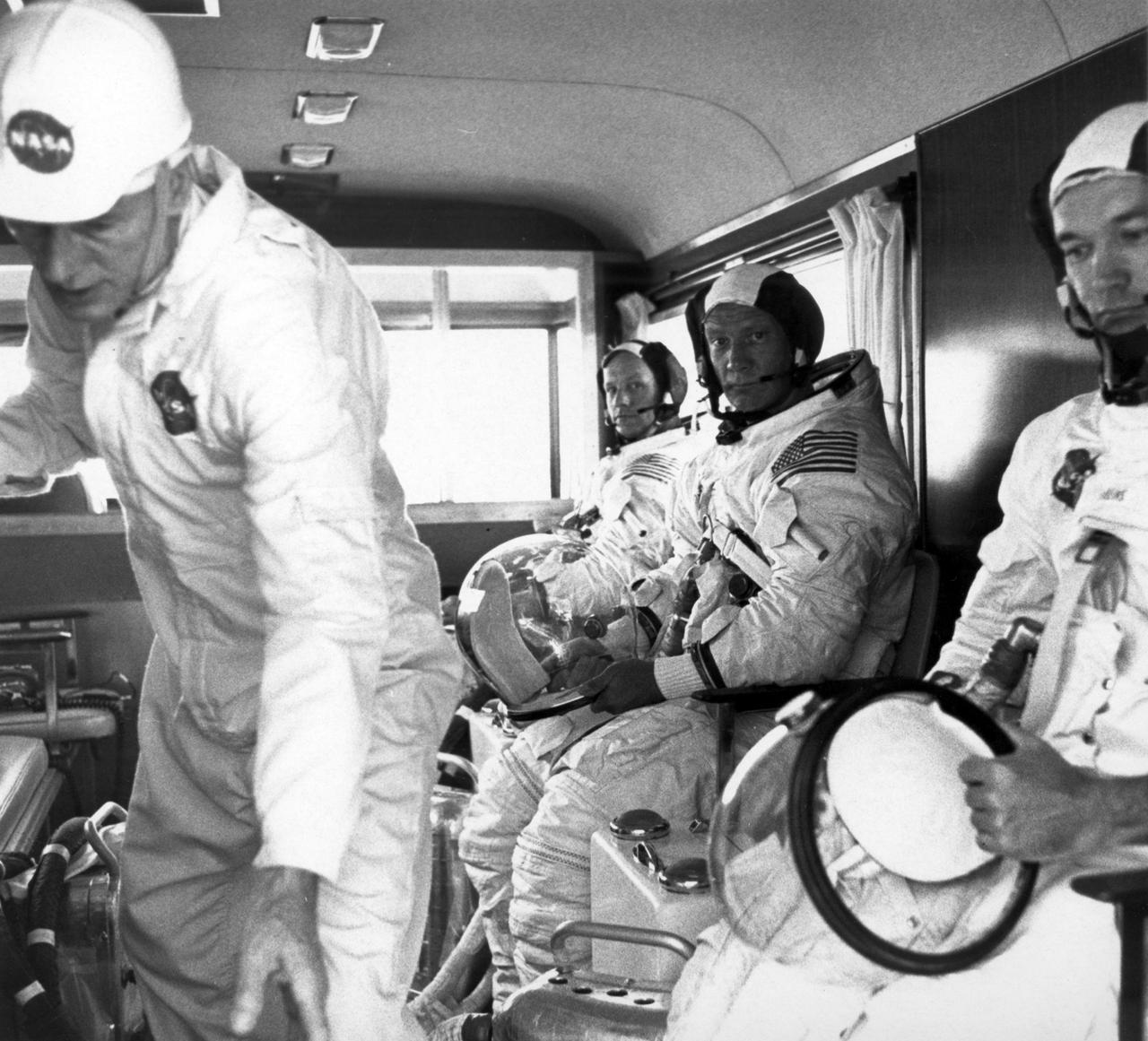

Apollo 11 crew members (rear to front) Neil Armstrong, Edwin Aldrin, and Michael Collins, wearing space suits, ride the van to the launch pad to participate in the countdown demonstration test for the upcoming Apollo 11 mission. The Apollo 11 mission, the first lunar landing mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
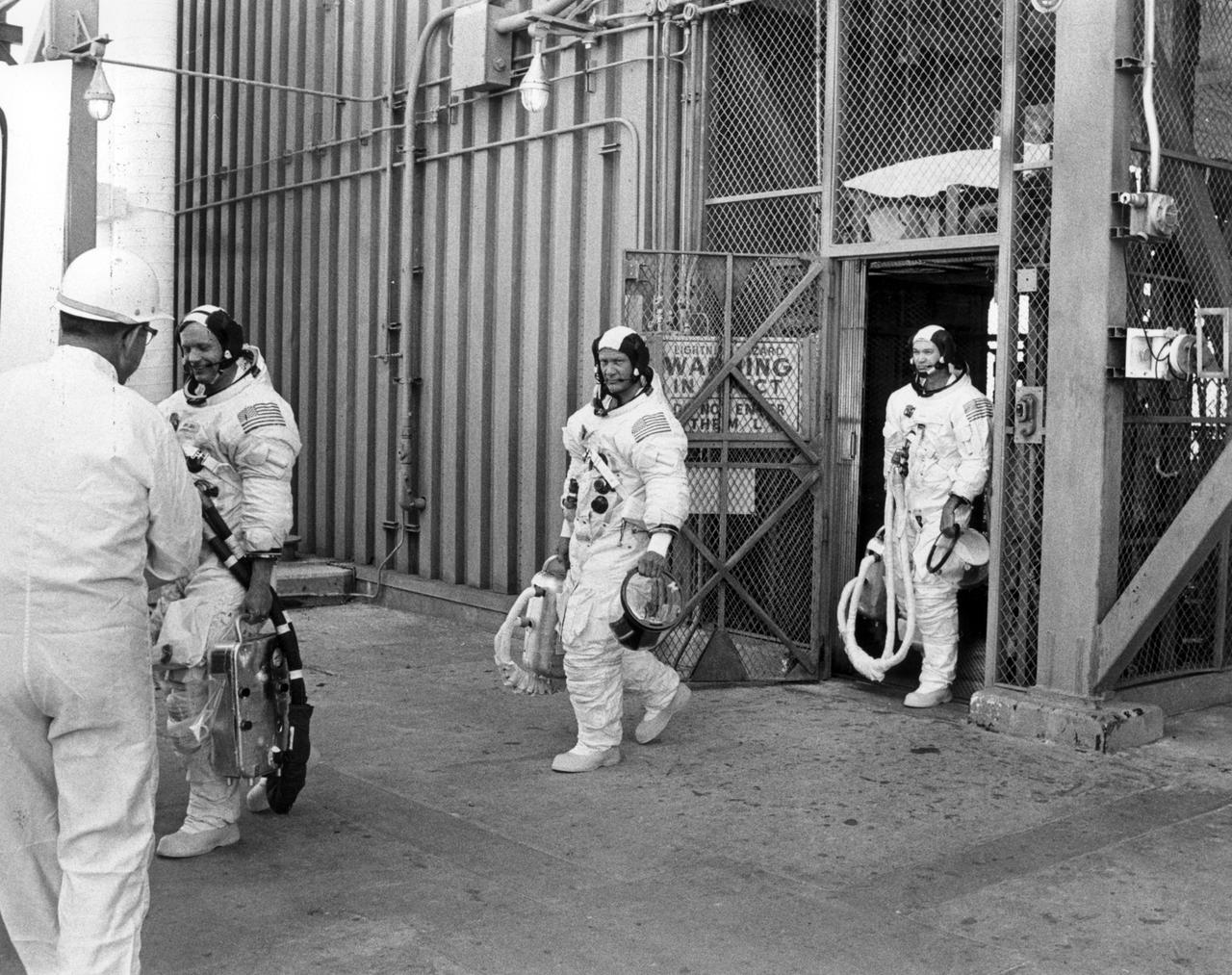

Apollo 11 crew members (left to right) Neil Armstrong, Edwin Aldrin, and Michael Collins, wearing space suits, leave the elevator after descending from the top of the launch tower. The three had just completed participation in the countdown demonstration test for the upcoming Apollo 11 mission. The Apollo 11 mission, the first lunar landing mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
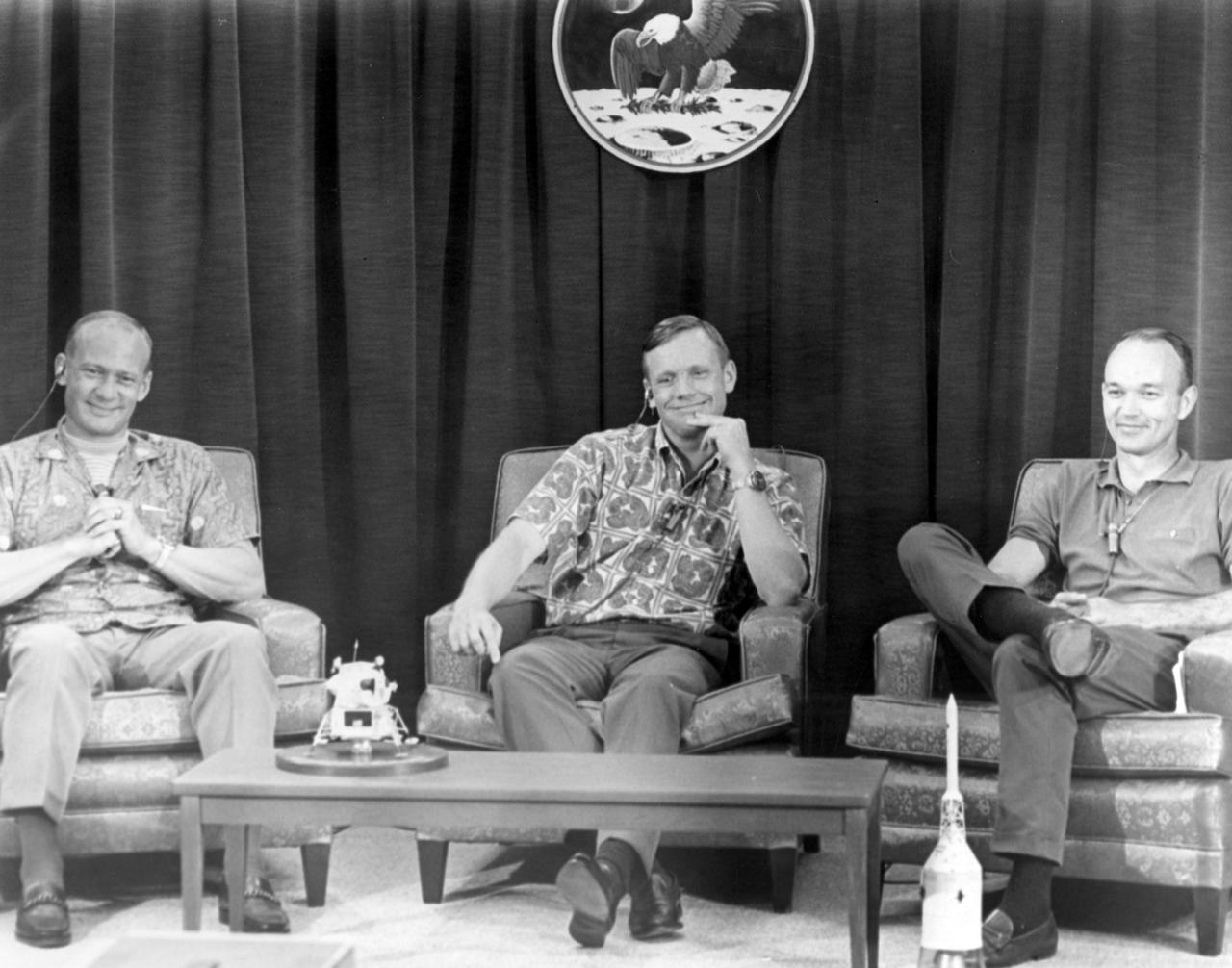

Apollo 11 crew members (L-R) Edwin Aldrin, Neil Armstrong, and Michael Collins were amused by a question posed during a closed circuit press conference the night before they began their historic first lunar landing mission. The press conference with questions via intercom, was held under semi-isolation conditions to avoid exposing the astronauts to possible illness at the last minute. The Apollo 11 mission launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
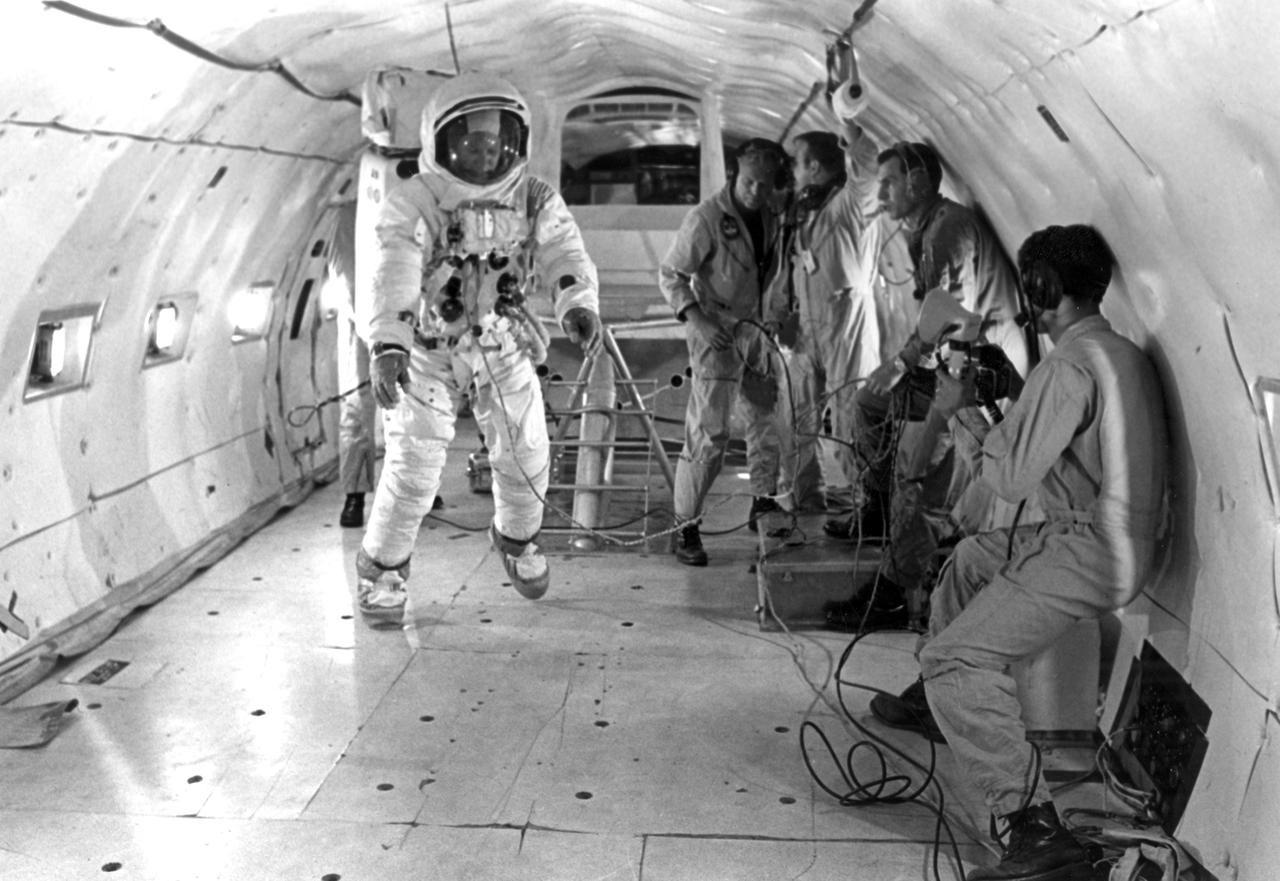

In preparation of the nation’s first lunar landing mission, Apollo 11 crew members underwent training to practice activities they would be performing during the mission. In this photograph, astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin, donned in his space suit, gets in more time under weightless conditions aboard a KC-135 aircraft from the Wright-Patterson Air Force Base. The Apollo 11 mission launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
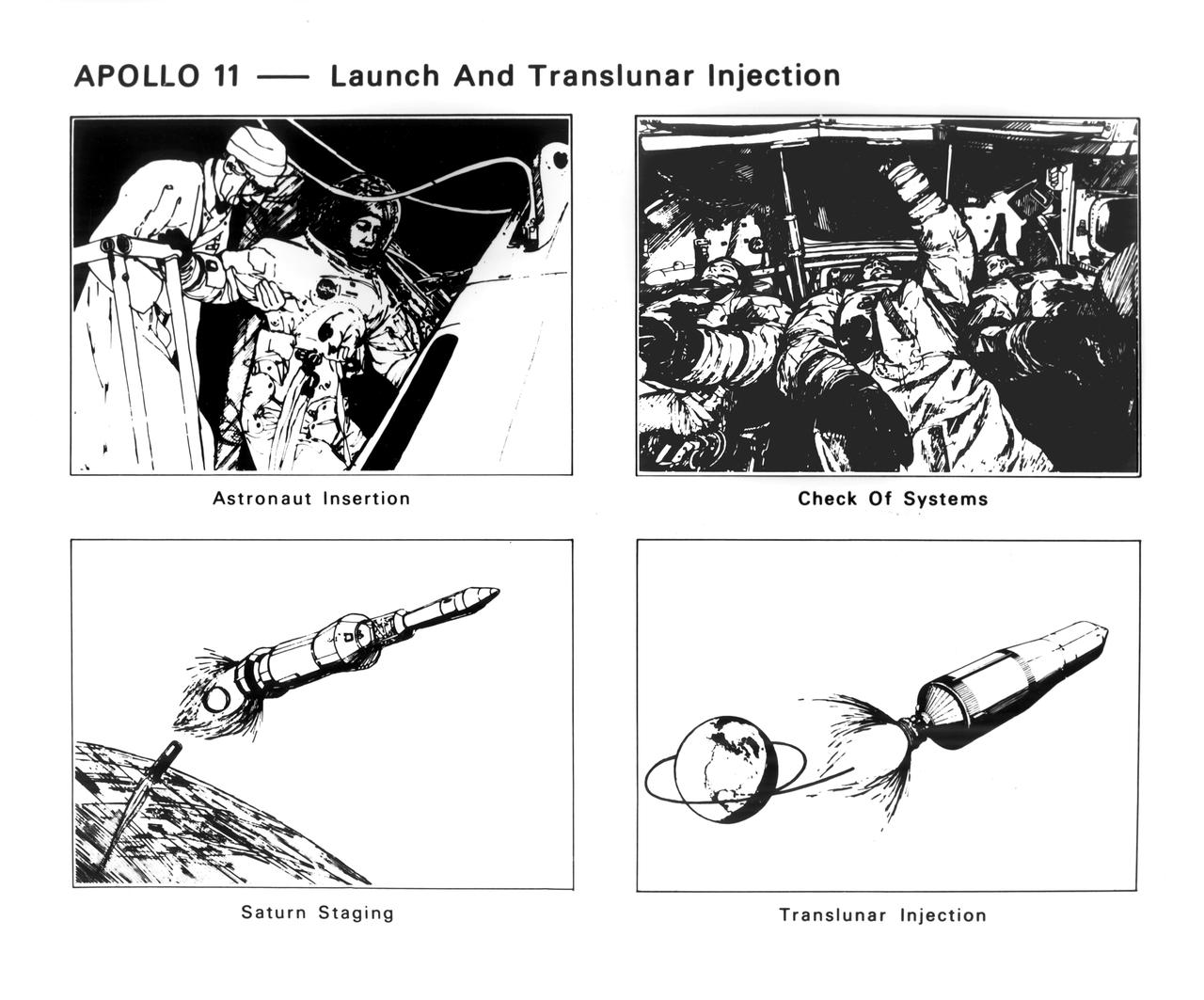
The Apollo 11 mission launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished. These sketches illustrate four of the early steps in the first manned lunar landing mission. The series begins with insertion of astronauts Neil Armstrong, Edwin Aldrin, and Michael Collins in the Apollo Command Module (CM). They checked out spacecraft systems and prepared for the launch. After two revolutions in Earth orbit, the Saturn V third stage reignited to place them into the translunar trajectory.