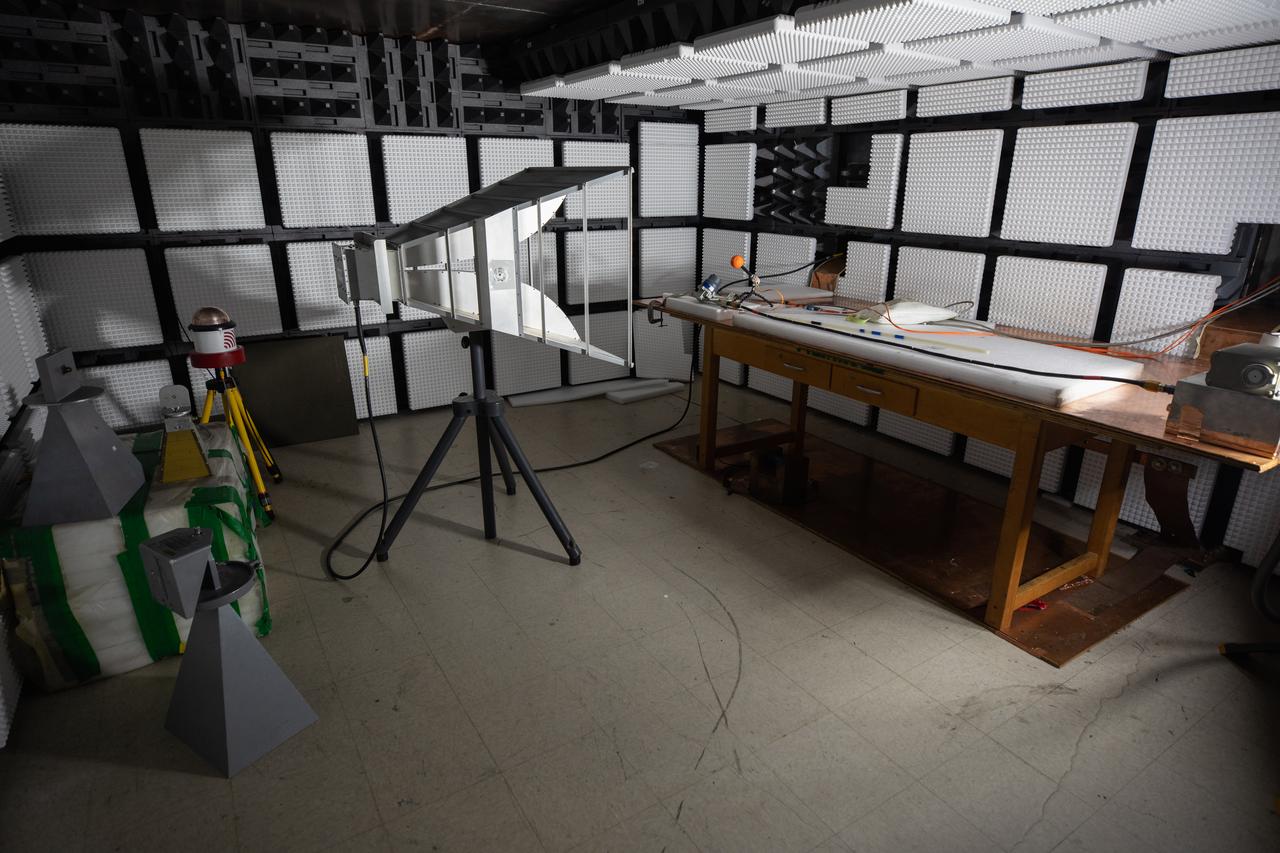

A view inside the Electromagnet Effects Laboratory (EML) on Oct. 13, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The EML is the center’s multi-discipline test facility used for electromagnetic design certification for electrical systems, electromagnetic environment development, and electromagnetic operational validation.

A view inside the Electromagnet Effects Laboratory (EML) on Oct. 13, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The EML is the center’s multi-discipline test facility used for electromagnetic design certification for electrical systems, electromagnetic environment development, and electromagnetic operational validation.
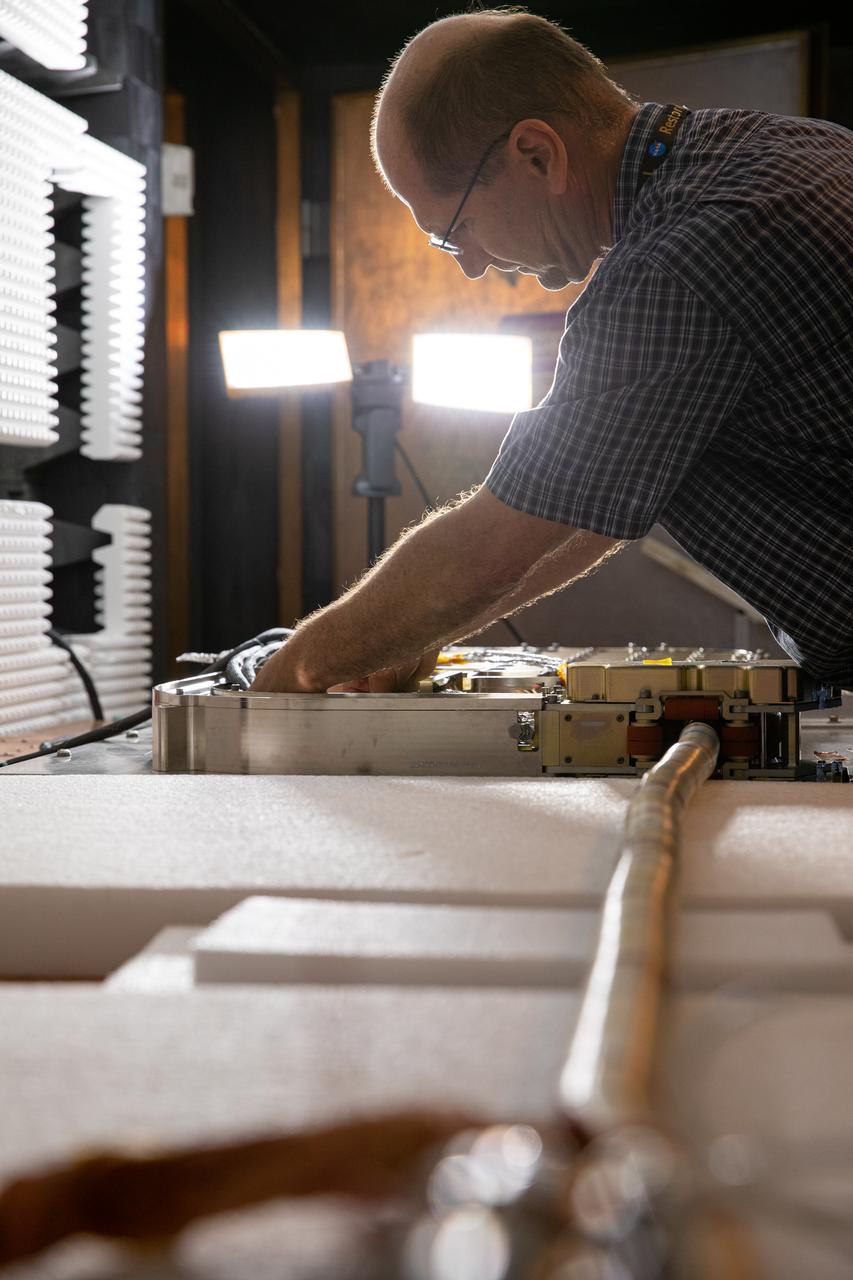

Inside the Electromagnetic Lab at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Gabor Tamasy, Hose Management Assembly (HMA) system lead for Restore-L, prepares the HMA test unit for electromagnetic interference testing on Feb. 19, 2020. The HMA is able to extend and retract the hose, somewhat similar to the function of a tape measure. Managed by the agency's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Restore-L is an inflight robotic satellite servicer spacecraft.
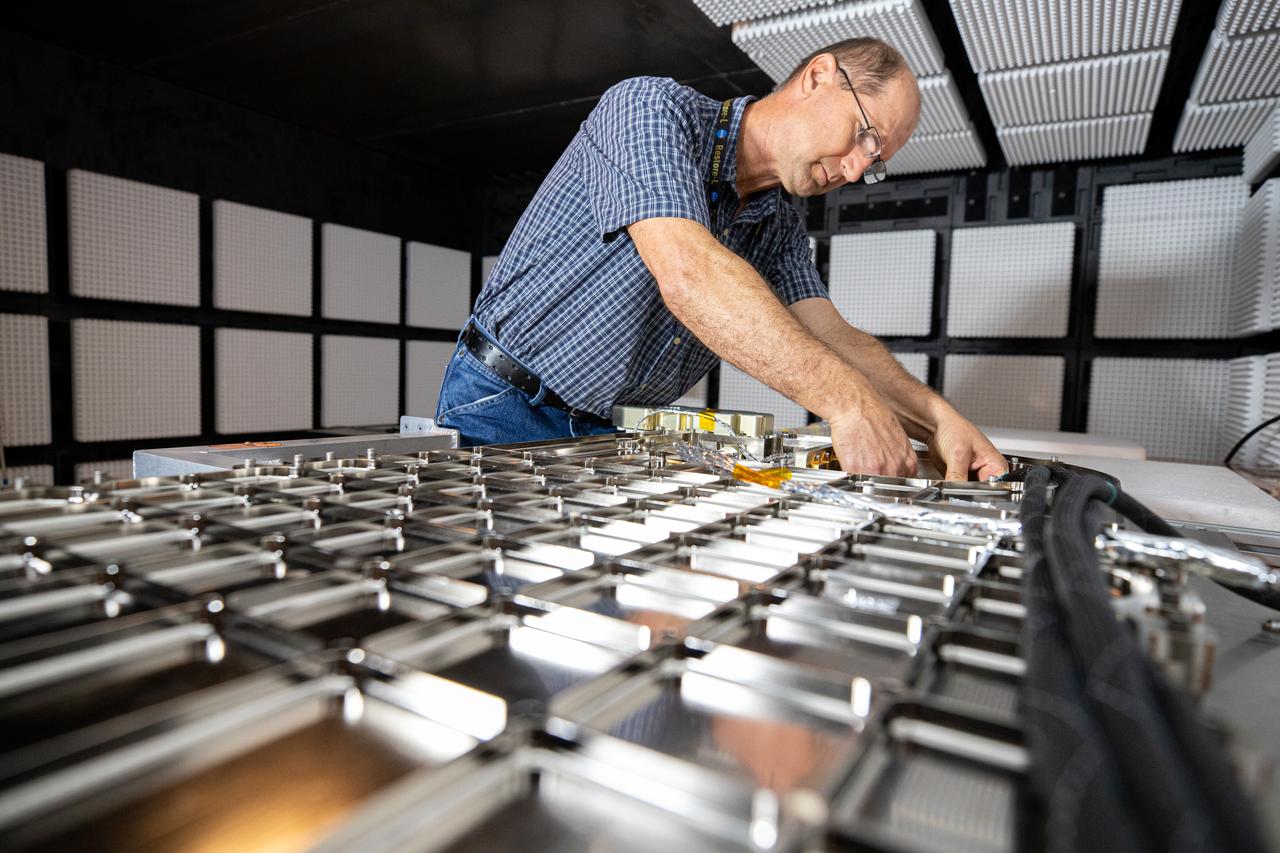

Inside the Electromagnetic Lab at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Gabor Tamasy, Hose Management Assembly (HMA) system lead for Restore-L, prepares the HMA test unit for electromagnetic interference testing on Feb. 19, 2020. The HMA is able to extend and retract the hose, somewhat similar to the function of a tape measure. Managed by the agency's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Restore-L is an inflight robotic satellite servicer spacecraft.
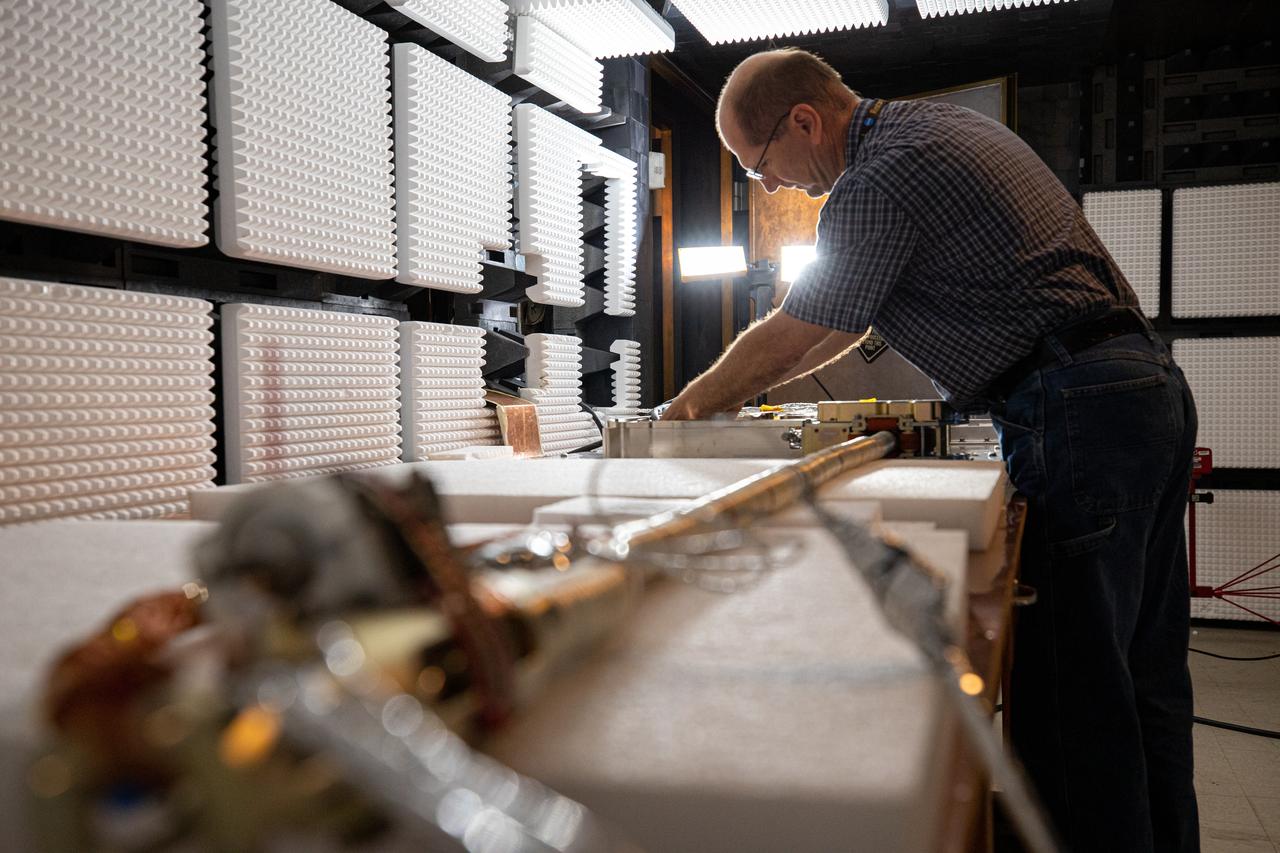

Inside the Electromagnetic Lab at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Gabor Tamasy, Hose Management Assembly (HMA) system lead for Restore-L, prepares the HMA test unit for electromagnetic interference testing on Feb. 19, 2020. The HMA is able to extend and retract the hose, somewhat similar to the function of a tape measure. Managed by the agency's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Restore-L is an inflight robotic satellite servicer spacecraft.
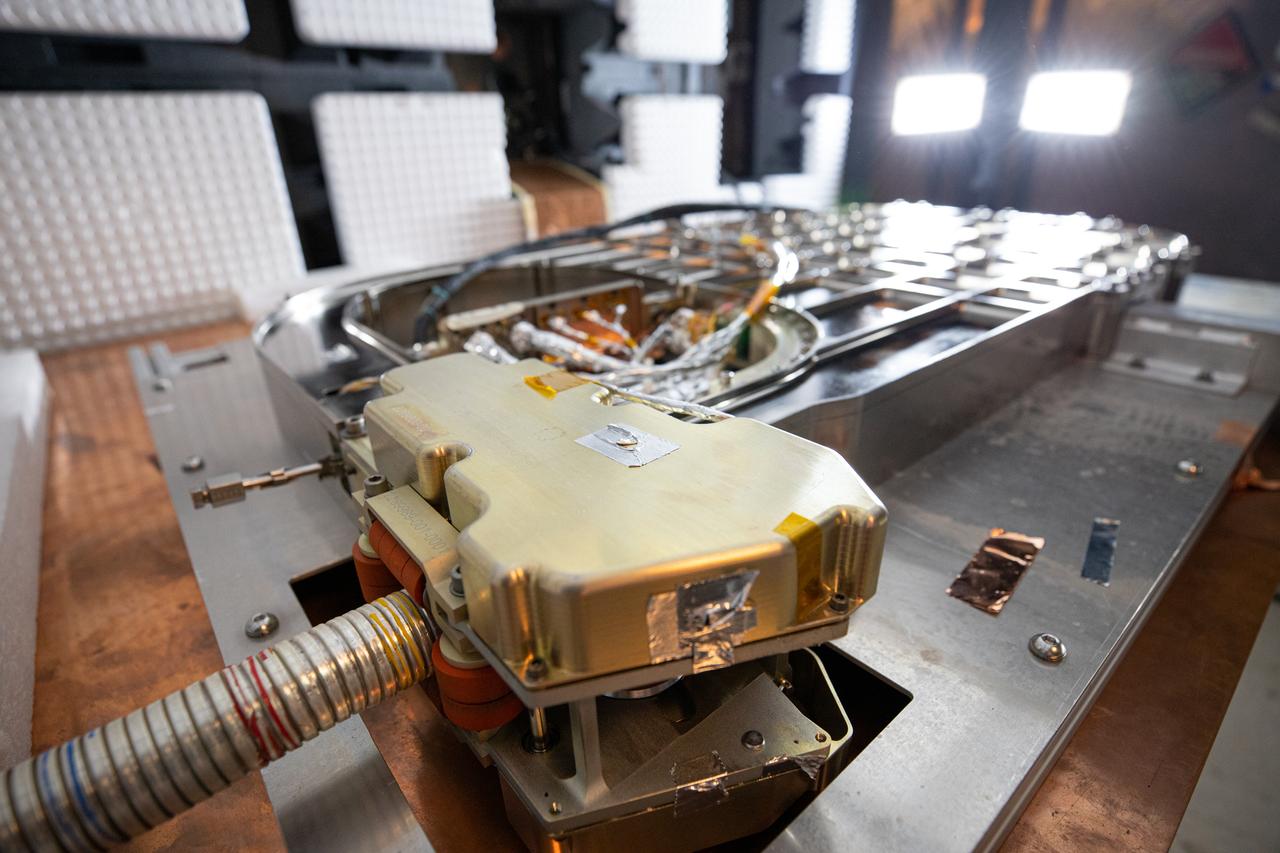
The Restore-L hose management assembly (HMA) test unit undergoes electromagnetic interference testing in the Electromagnetic Lab at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 19, 2020. The HMA is able to extend and retract the hose, somewhat similar to the function of a tape measure. Managed by the agency's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Restore-L is an inflight robotic satellite servicer spacecraft.
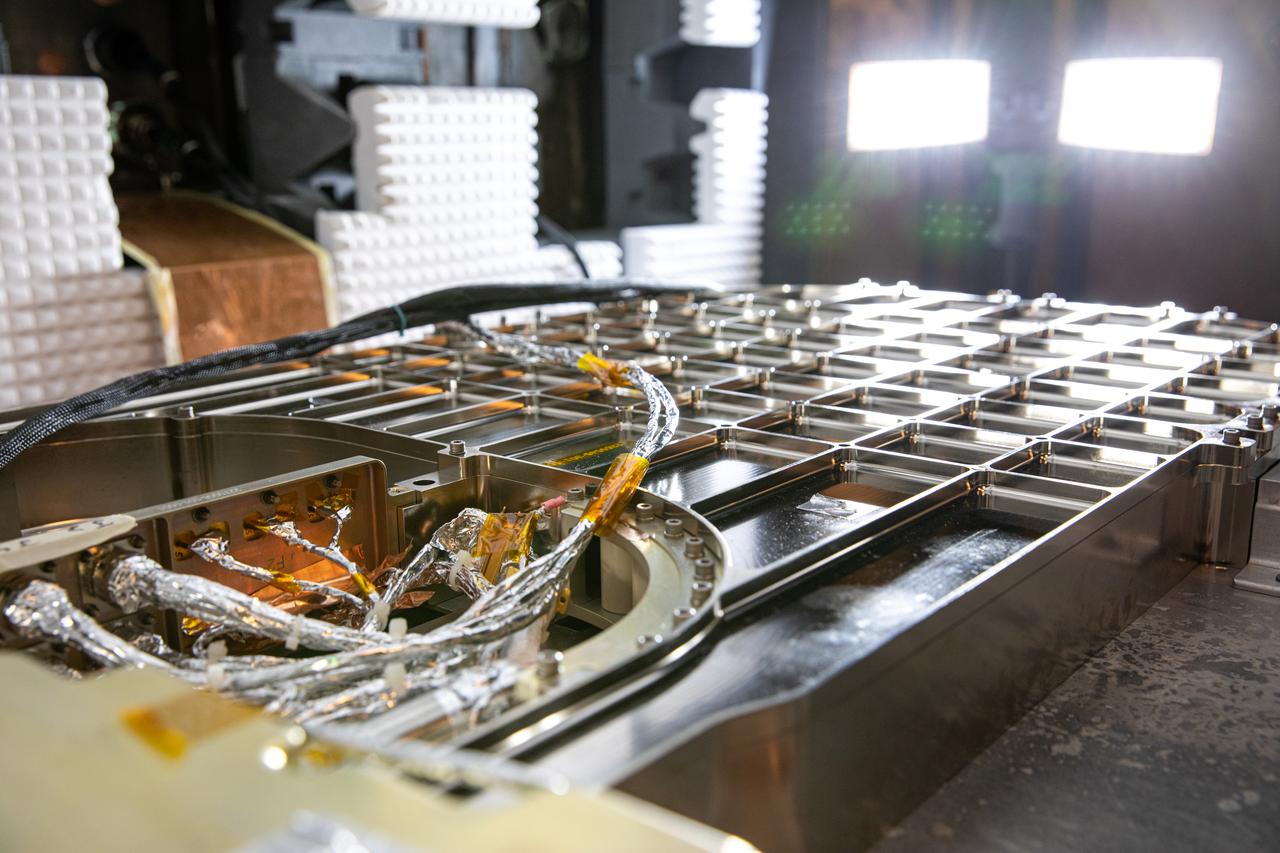

The Restore-L hose management assembly (HMA) test unit undergoes electromagnetic interference testing in the Electromagnetic Lab at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 19, 2020. The HMA is able to extend and retract the hose, somewhat similar to the function of a tape measure. Managed by the agency's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Restore-L is an inflight robotic satellite servicer spacecraft.
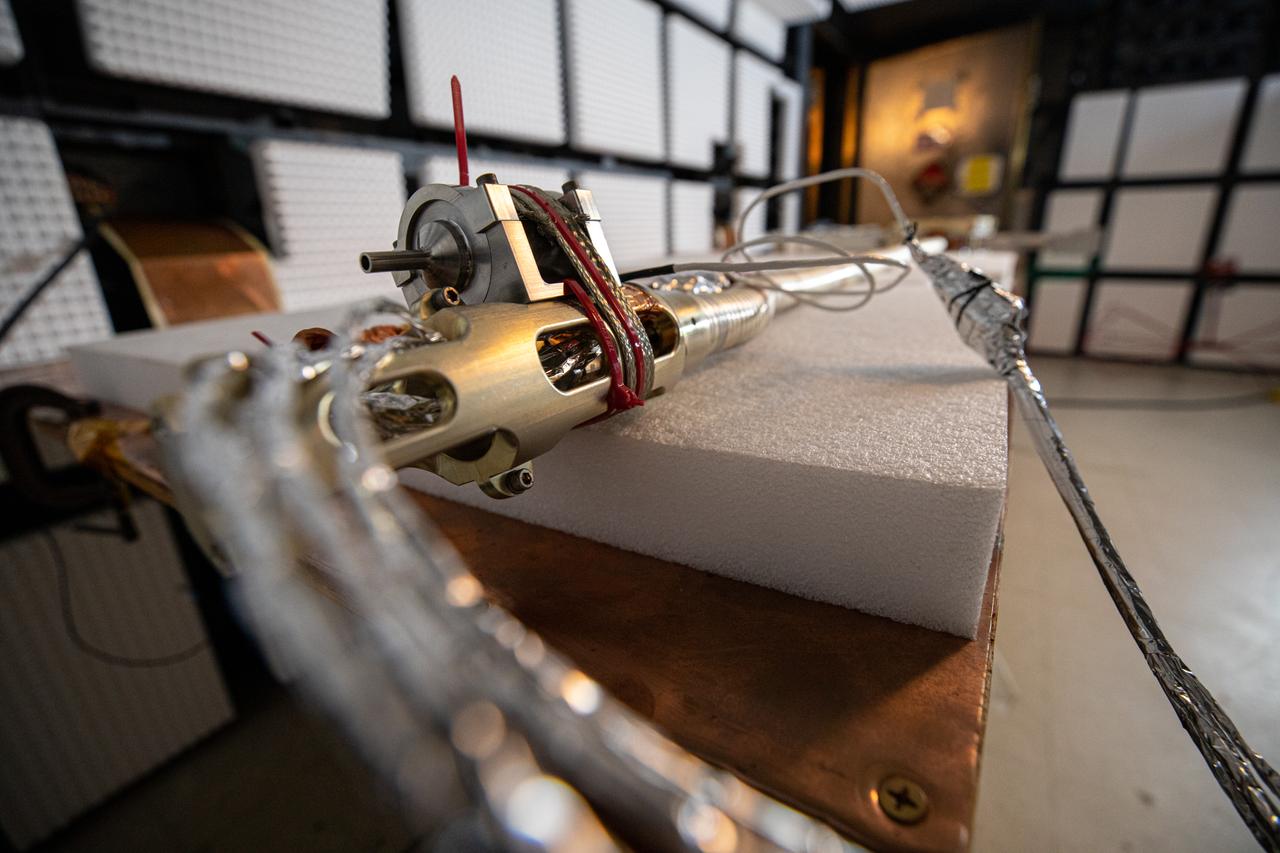
The Restore-L hose management assembly (HMA) test unit undergoes electromagnetic interference testing in the Electromagnetic Lab at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 19, 2020. The HMA is able to extend and retract the hose, somewhat similar to the function of a tape measure. Managed by the agency's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Restore-L is an inflight robotic satellite servicer spacecraft.

The Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI) & Electrical Ground Support Equipment (EGSE) Team pose in the control room. From this room, they are able to analyze the data from the test remotely and send commands through electrical cables that run through the walls into the EMI lab. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
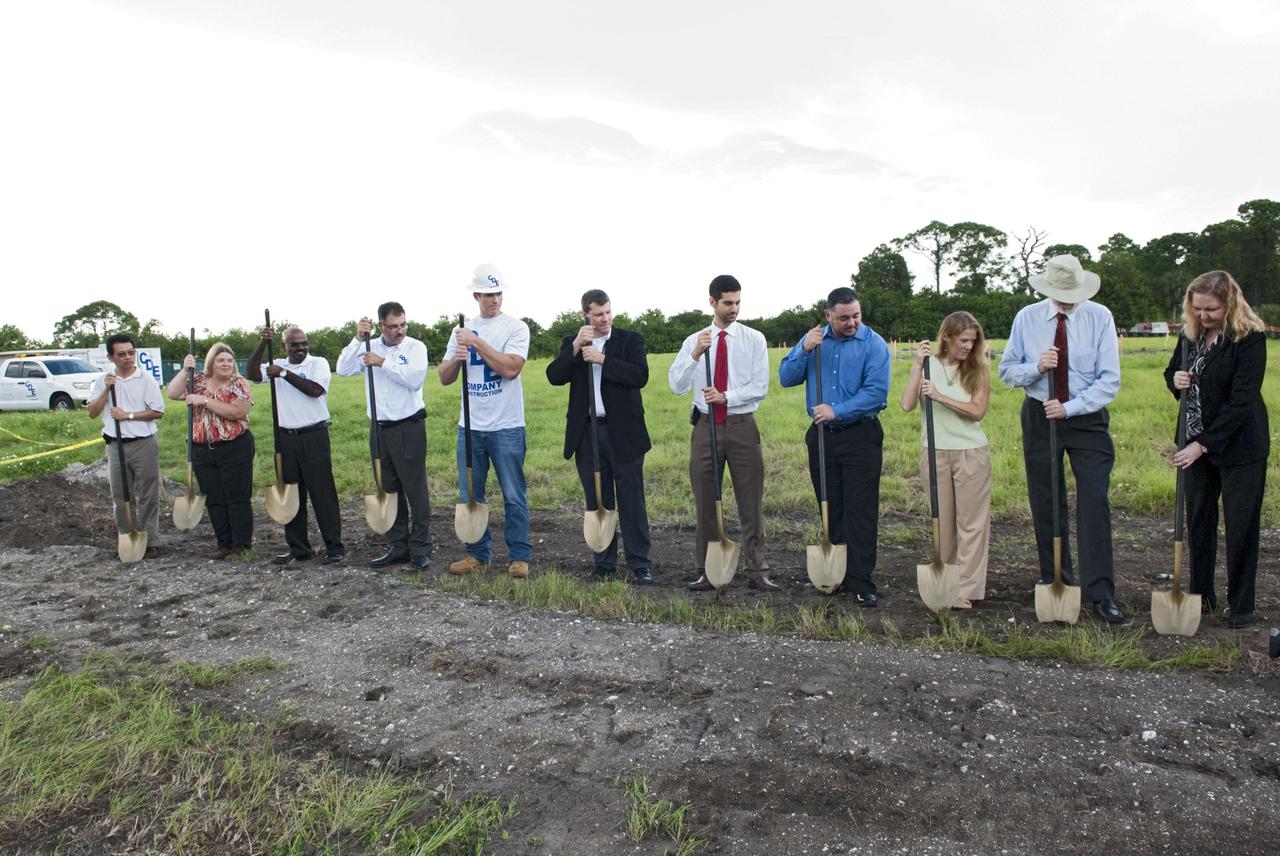

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a groundbreaking was held to mark the start of construction on the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. Holding ceremonial shovels, from left are Michael Le, lead design engineer and construction manager Sue Vingris, Cape Design Engineer Co. project manager Kannan Rengarajan, chief executive officer of Cape Design Engineer Co. Lutfi Mized, president of Cape Design Engineer Co. David Roelandt, construction site superintendent with Cape Design Engineer Co. Marc Seibert, NASA project manager Michael Miller, NASA project manager Peter Aragona, KSC’s Electromagnetic Lab manager Stacy Hopper, KSCs master planning supervisor Dr. Bary Geldzabler, NASA chief scientist and KSC’s Chief Technologist Karen Thompson. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Workers will begin construction on the pile foundations for the 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays and their associated utilities, and prepare the site for the operations command center facility. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
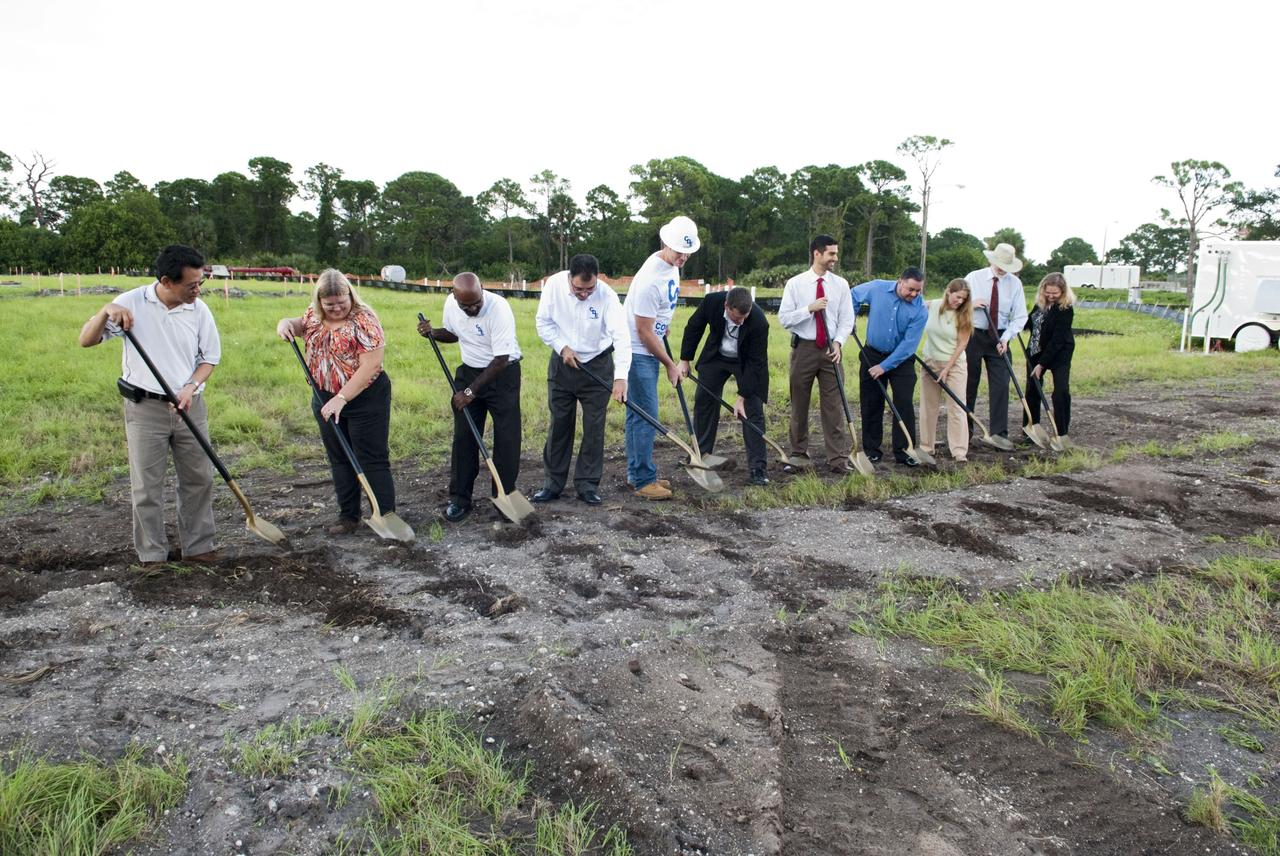

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a groundbreaking was held to mark the start of construction on the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. Using ceremonial shovels to mark the site, from left are Michael Le, lead design engineer and construction manager Sue Vingris, Cape Design Engineer Co. project manager Kannan Rengarajan, chief executive officer of Cape Design Engineer Co. Lutfi Mized, president of Cape Design Engineer Co. David Roelandt, construction site superintendent with Cape Design Engineer Co. Marc Seibert, NASA project manager Michael Miller, NASA project manager Peter Aragona, KSC’s Electromagnetic Lab manager Stacy Hopper, KSCs master planning supervisor Dr. Bary Geldzabler, NASA chief scientist and KSC’s Chief Technologist Karen Thompson. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Workers will begin construction on the pile foundations for the 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays and their associated utilities, and prepare the site for the operations command center facility. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

Engineers in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in April 2023 examine the imaging spectrometer that will ride aboard the first of two satellites to be launched by the Carbon Mapper Coalition. The instrument will help researchers detect emissions of carbon dioxide and methane from sources on Earth's surface from space. The gold-colored component is the spectrometer, which was developed at JPL. It's designed to receive sunlight reflected from Earth and divide that light into hundreds of distinct colors in the near-infrared and visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. By analyzing the light's spectroscopic signature – the wavelengths that show up in the signal as well as those that do not – researchers can determine whether the instrument is observing greenhouse gas emissions and, if so, estimate their concentrations. The black portion at the base of the instrument is a telescope that captures light from Earth's surface and reflects it into the spectrometer. When released into the atmosphere, carbon dioxide and methane are the greenhouse gases most responsible for human-caused global warming. Both have unique spectral signatures that make them detectable from space via spectroscopy. The imaging spectrometer is JPL's contribution to the Carbon Mapper Coalition, a joint effort led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper that also includes Planet Labs PBC, the California Air Resources Board, Arizona State University, and the University of Arizona. Once the instrument is in orbit, researchers will use its measurements to identify the sources of carbon dioxide and methane plumes it detects. Identification of the origins of emissions is considered the first step towards mitigation. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25869