
Workmen inspect a J-2 engine at Rocketdyne's Canoga Park, California production facility. The J-2, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, was propelled by liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. A single J-2 engine was used in the S-IVB stage (the second stage of the Saturn IB and third stage for the Saturn V) and a cluster of five J-2 engines was used to propel the second stage of the Saturn V, the S-II. Initially rated at 200,000 pounds of thrust, the J-2 engine was later uprated in the Saturn V program to 230,000 pounds.

This figure is a line drawing of the J-2 engine with callouts of the major components and the engine characteristics.
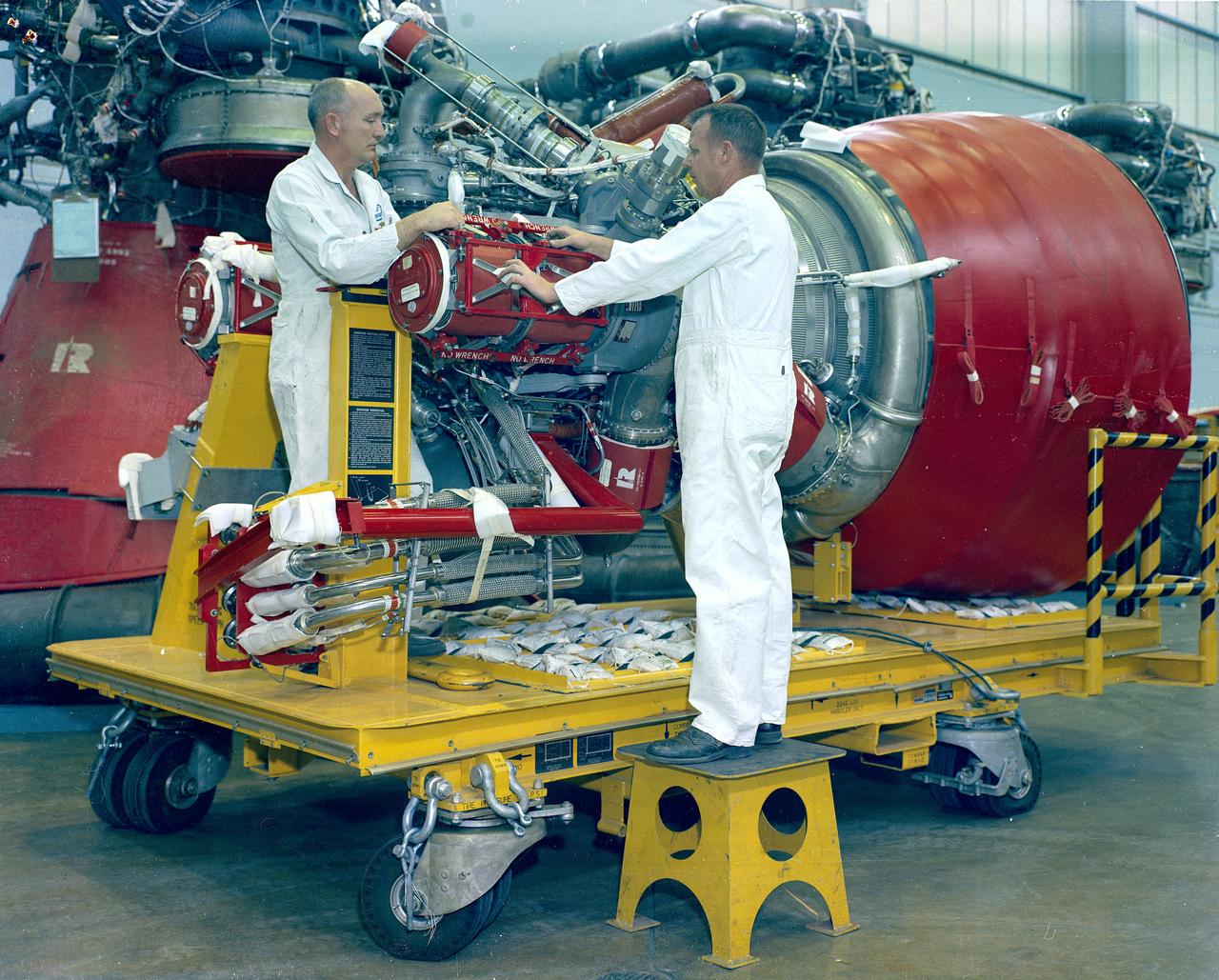

Pictured is a J-2 engine being processed at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). A single J-2 engine was utilized on the S-IVB stage, the second stage of the Saturn IB and the third stage of the Saturn V vehicles, while a cluster of five J-2 engines powered the second (S-II) stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle. The Saturn V was designed, developed, and tested by engineers at MSFC.
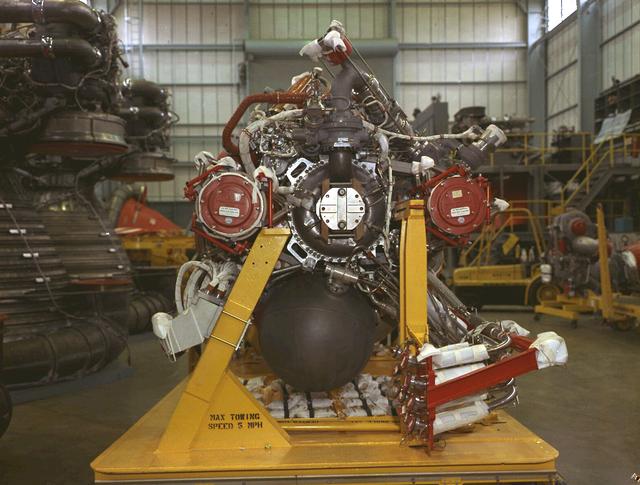

Pictured is a J-2 engine being processed at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). A single J-2 engine was utilized on the S-IVB stage, the second stage of the Saturn IB and the third stage of the Saturn V vehicles, while a cluster of five J-2 engines powered the second (S-II) stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle. The Saturn V was designed, developed, and tested by engineers at MSFC.
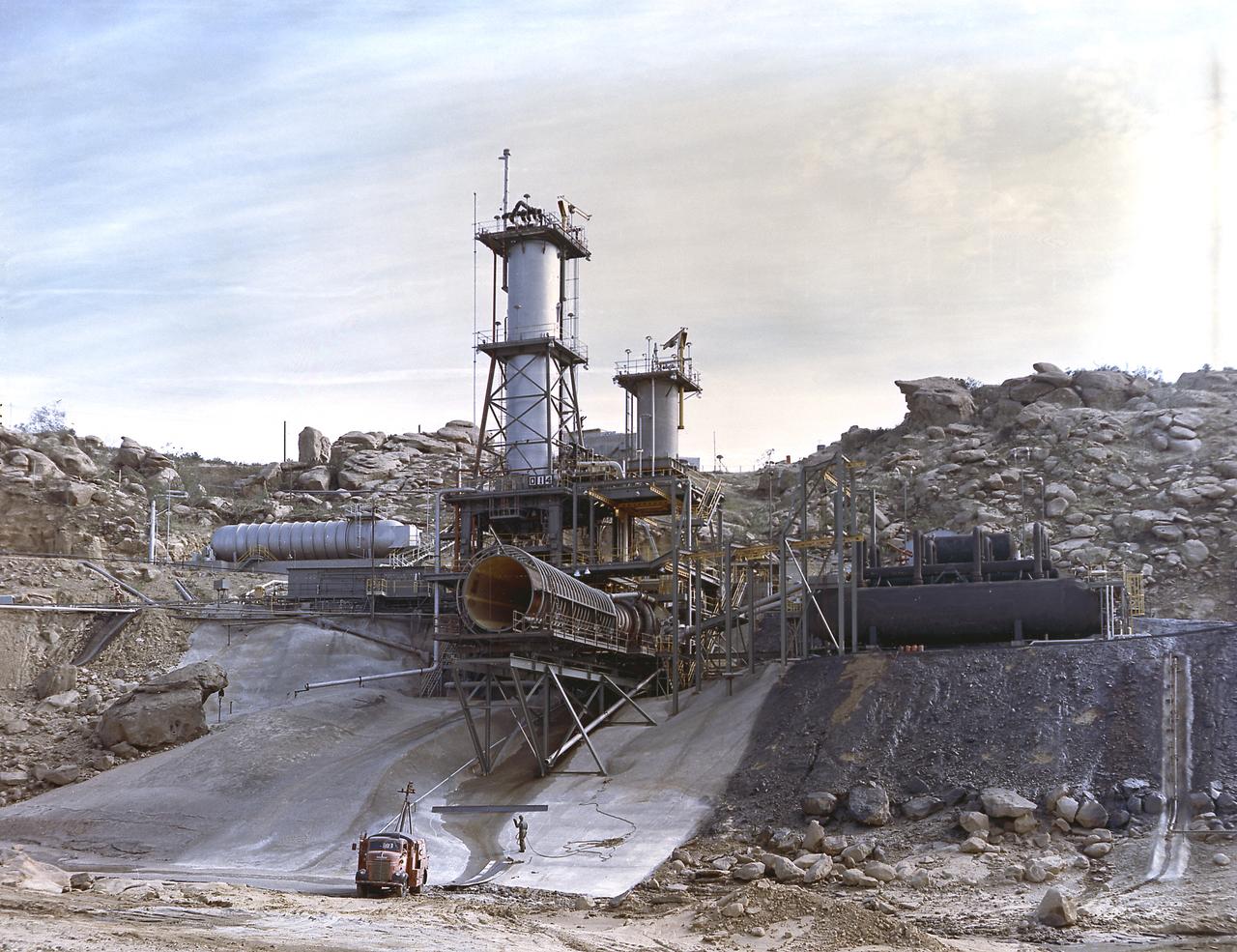

This image depicts an overall view of the vertical test stand for testing the J-2 engine at Rocketdyne's Propulsion Field Laboratory, in the Santa Susana Mountains, near Canoga Park, California. The J-2 engines were assembled and tested at Rocketdyne under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
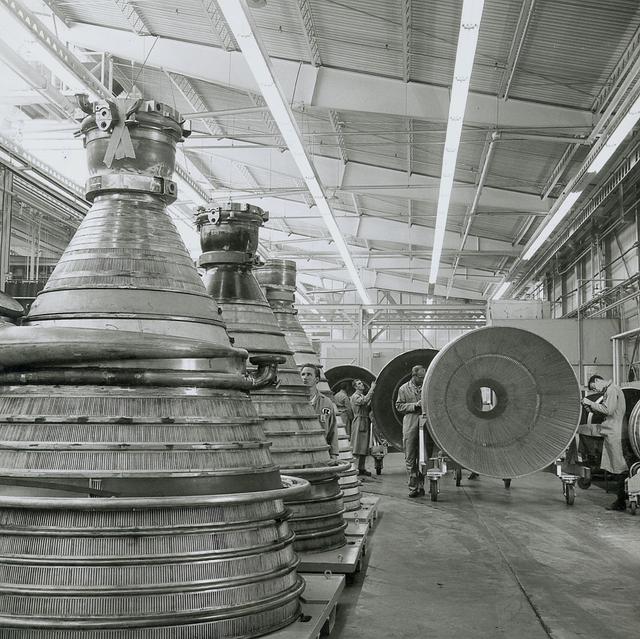

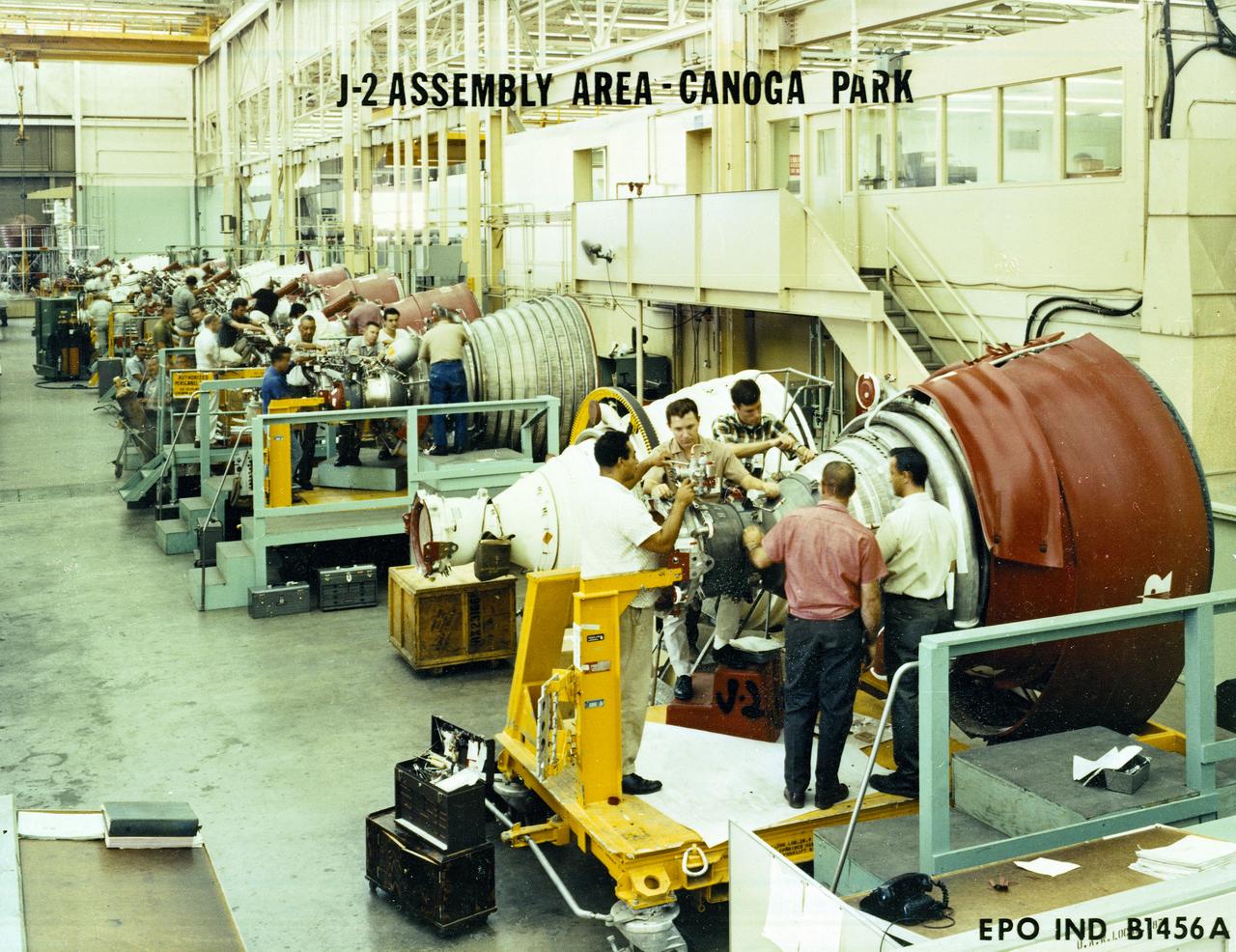
J-2 engines for the Saturn IB/Saturn V launch vehicles are lined up in the assembly area at Rocketdyne's manufacturing plant in Canoga Park, California. Five J-2 engines provided more than 1,000,000 pounds of thrust to accelerate the second stage toward a Moon trajectory.
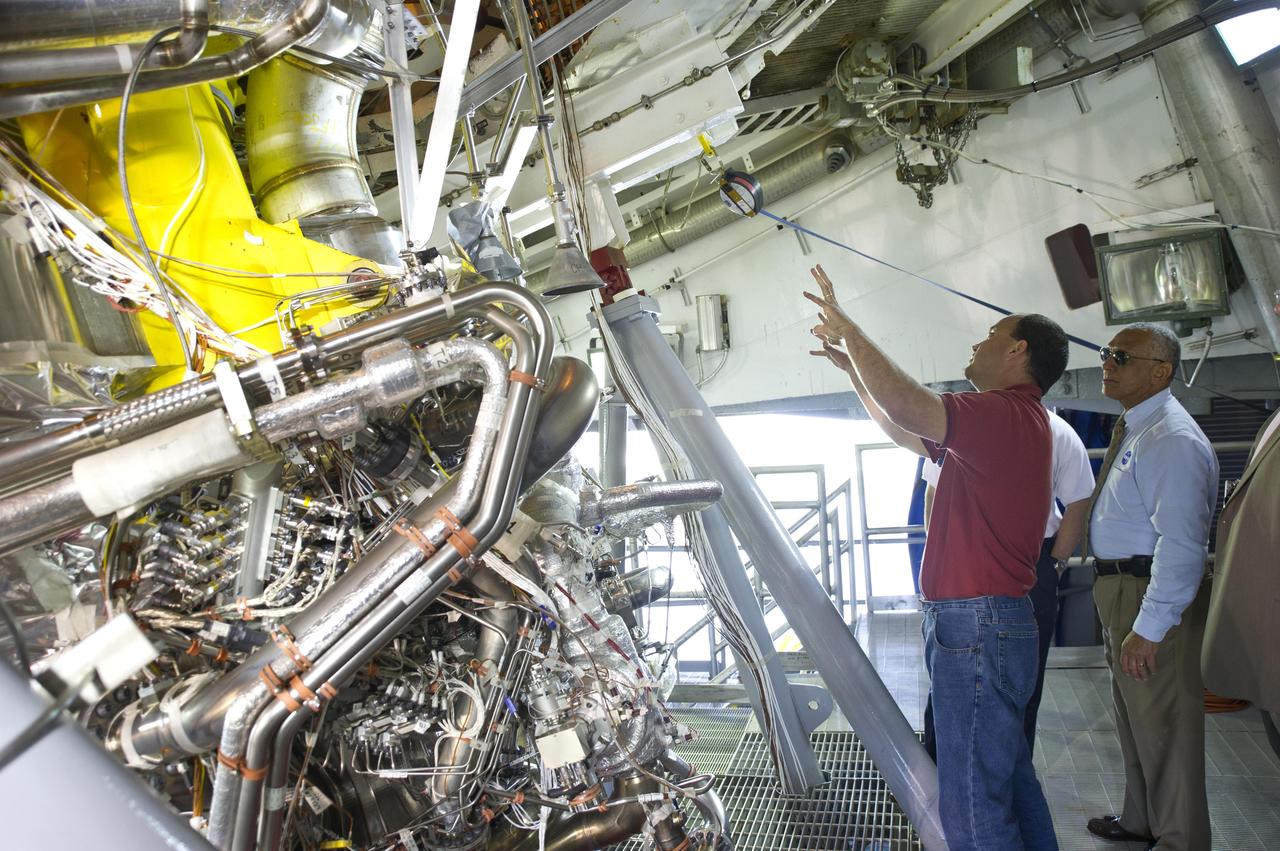
NASA Administrator Charles Bolden (r) takes an up-close look at the first development J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center during an April 20, 2012, visit. Pictured with Bolden is A-2 Test Stand Director Skip Roberts. The J-2X engine is being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne.
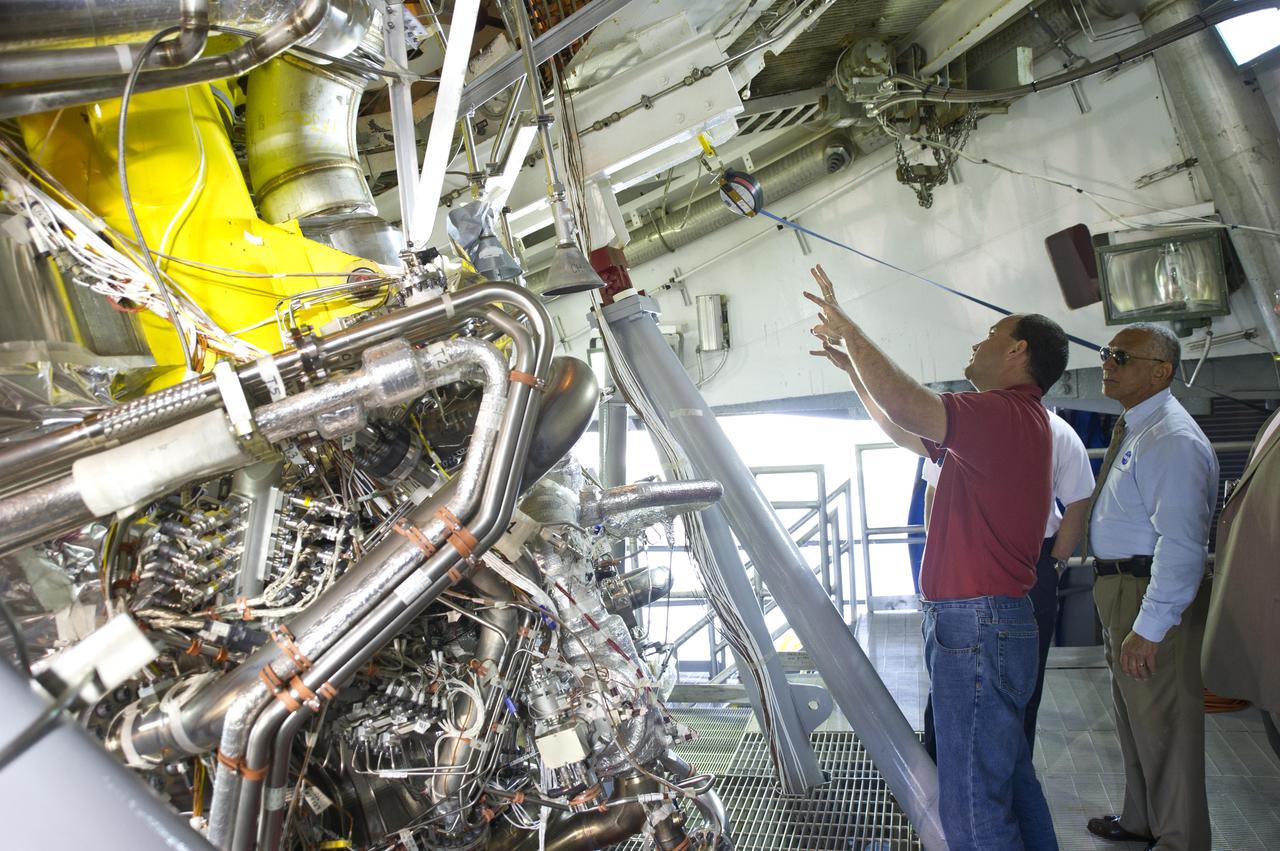
NASA Administrator Charles Bolden (r) takes an up-close look at the first development J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center during an April 20, 2012, visit. Pictured with Bolden is A-2 Test Stand Director Skip Roberts. The J-2X engine i s being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne.

This image depicts the test firing of a J-2 engine in the S-IVB Test Stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The J-2, developed by Rocketdyne under the direction of MSFC, was propelled by liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. A single J-2 was utilized in the S-IVB stage (the second stage for the Saturn IB and third stage for the Saturn V) and in a cluster of five for the second stage (S-II) of the Saturn V. Initially rated at 200,000 pounds of thrust, the engine was later upgraded in the Saturn V program to 230,000 pounds.
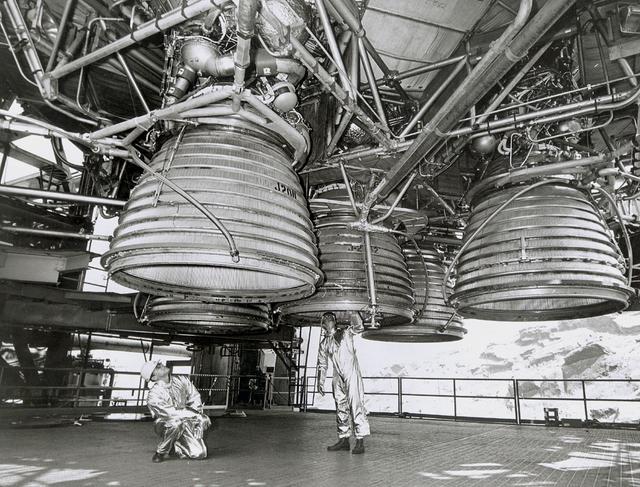

Two workers are dwarfed by the five J-2 engines of the Saturn V second stage (S-II) as they make final inspections prior to a static test firing by North American Space Division. These five hydrogen -fueled engines produced one million pounds of thrust, and placed the Apollo spacecraft into earth orbit before departing for the moon. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.

Smokeless flame juts from the diffuser of a unique vacuum chamber in which the upper stage rocket engine, the hydrogen fueled J-2, was tested at a simulated space altitude in excess of 60,000 feet. The smoke you see is actually steam. In operation, vacuum is established by injecting steam into the chamber and is maintained by the thrust of the engine firing through the diffuser. The engine was tested in this environment for start, stop, coast, restart, and full-duration operations. The chamber was located at Rocketdyne's Propulsion Field Laboratory, in the Santa Susana Mountains, near Canoga Park, California. The J-2 engine was developed by Rocketdyne for the Marshall Space Flight Center.
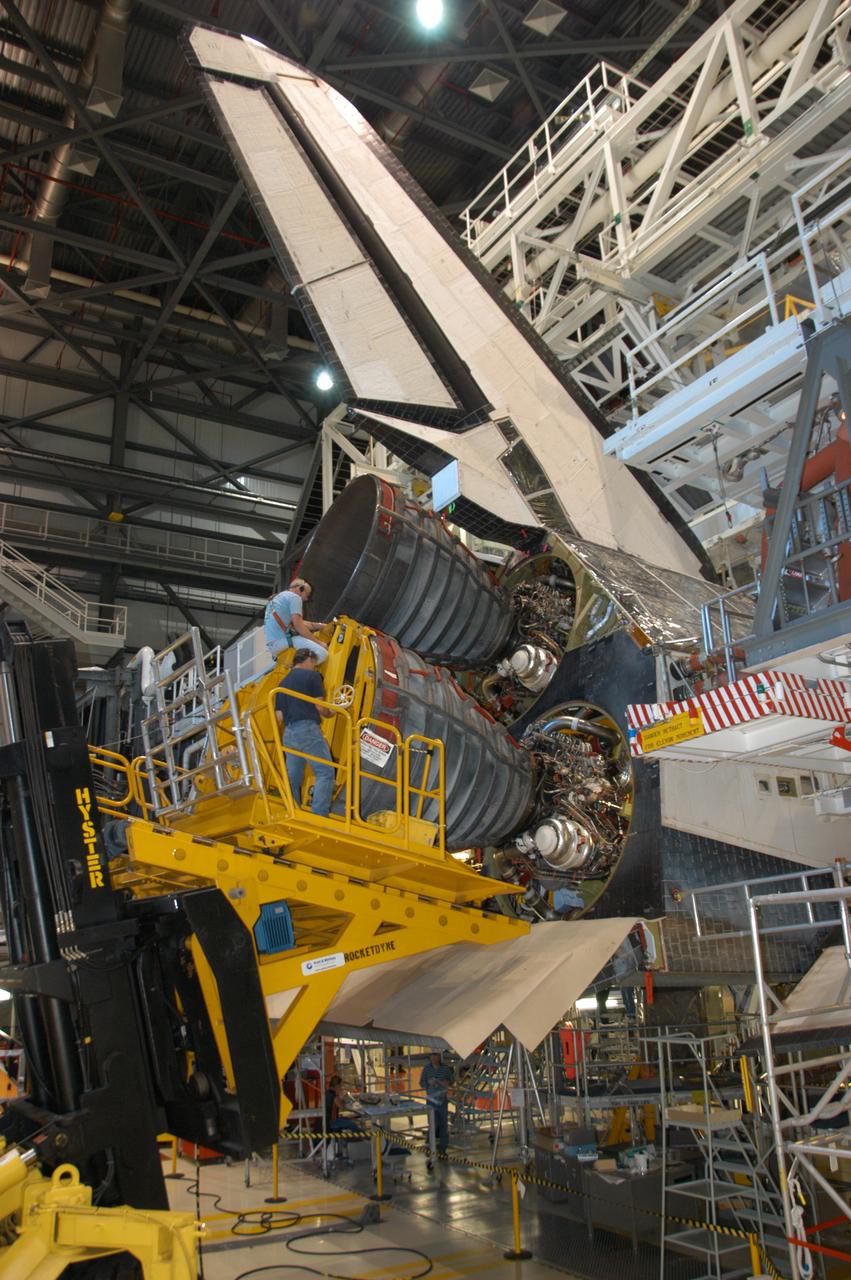

In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, technicians on a Hyster forklift install space shuttle main engine no. 3 into Endeavour. Each space shuttle main engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. The orbiter is scheduled for mission STS-118, targeted for launch on June 28. The mission will be the 22nd flight to the International Space Station, carrying another starboard array, S5, for installation.

In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, technicians on a Hyster forklift maneuver space shuttle main engine no. 3 into place on Endeavour. Each space shuttle main engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. The orbiter is scheduled for mission STS-118, targeted for launch on June 28. The mission will be the 22nd flight to the International Space Station, carrying another starboard array, S5, for installation.
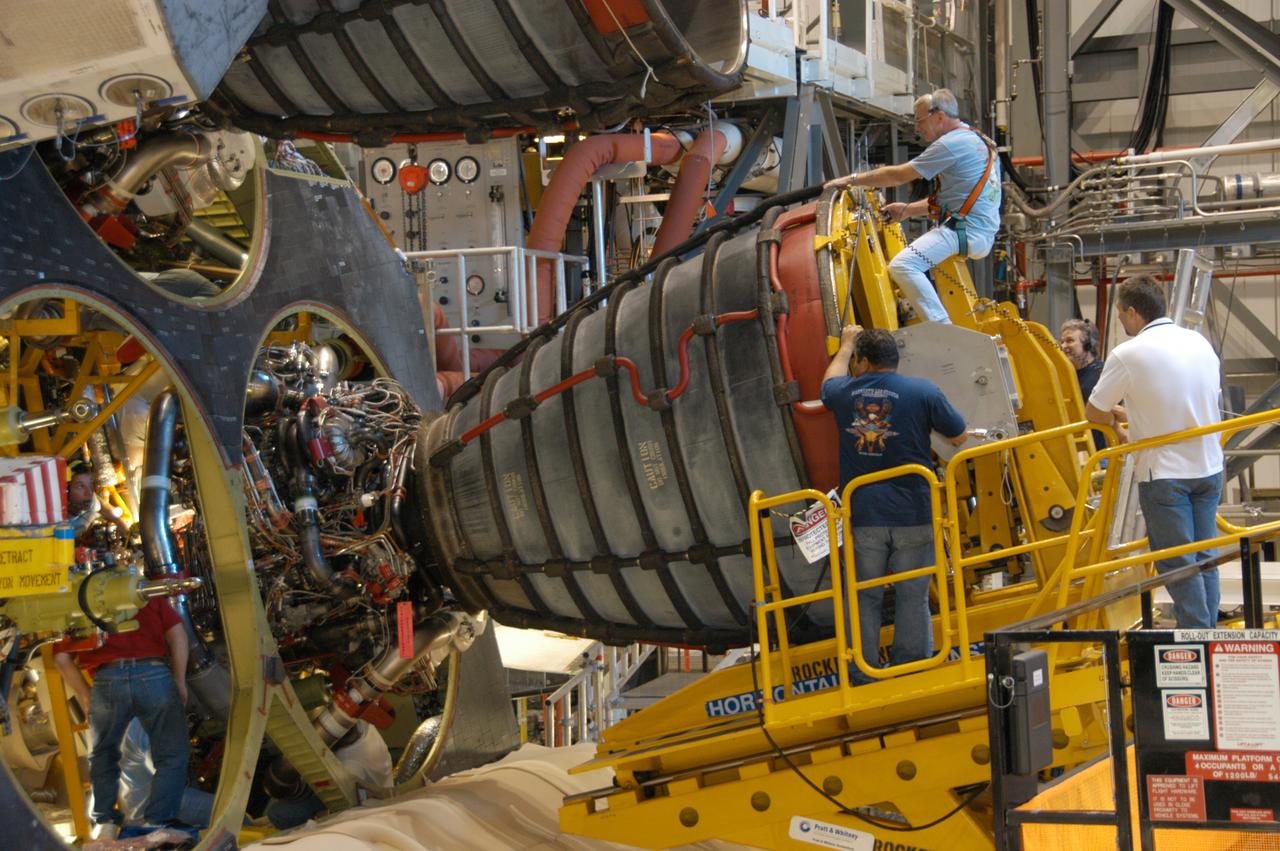

In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, technicians on a Hyster forklift maneuver space shuttle main engine no. 3 into place on Endeavour. Each space shuttle main engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. The orbiter is scheduled for mission STS-118, targeted for launch on June 28. The mission will be the 22nd flight to the International Space Station, carrying another starboard array, S5, for installation.
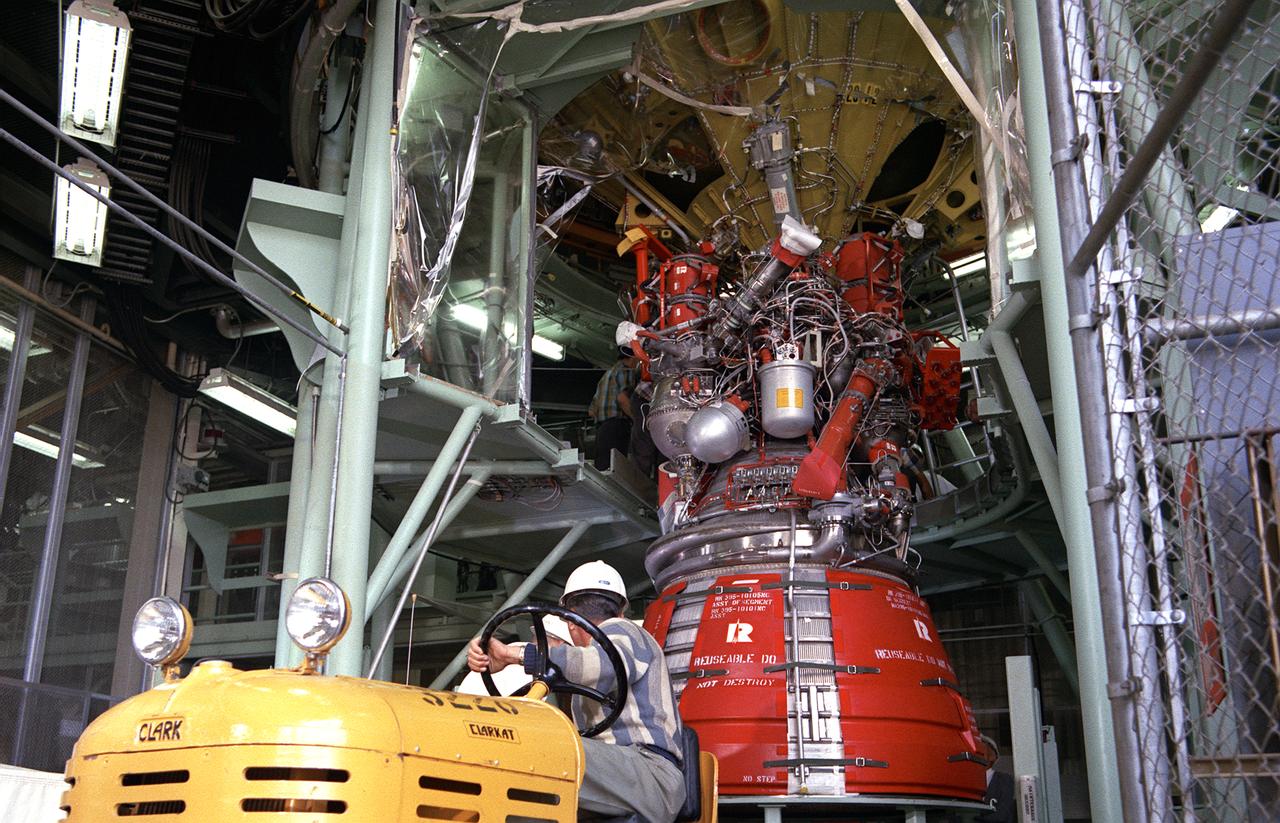

Workmen secure a J-2 engine onto the S-IVB (second) stage thrust structure. As part of Marshall Space Center's "building block" approach to the Saturn development, the S-IVB was utilized in the Saturn IBC launch vehicle as a second stage and the Saturn V launch vehicle as a third stage. The booster, built for NASA by McDornell Douglas Corporation, was powered by a single J-2 engine, initially capable of 200,000 pounds of thrust.
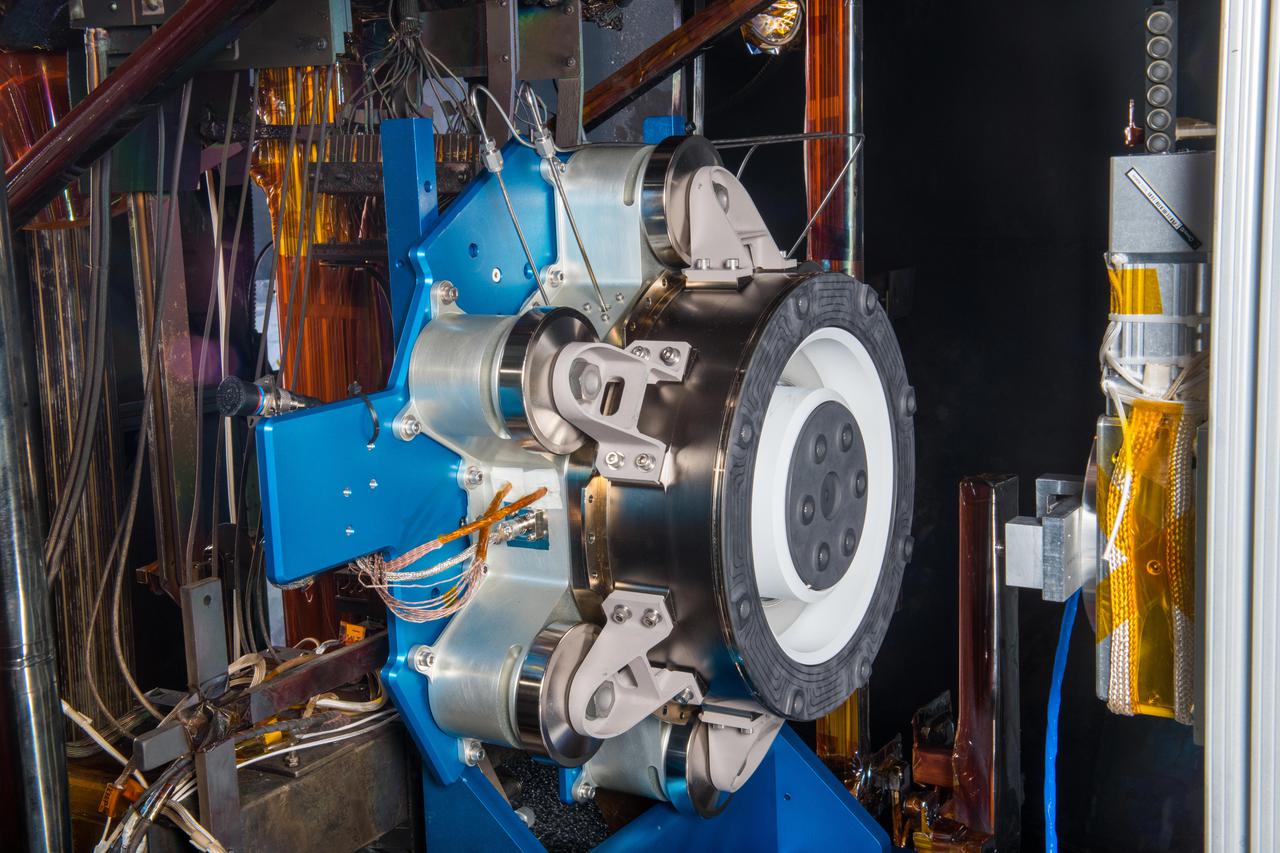
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
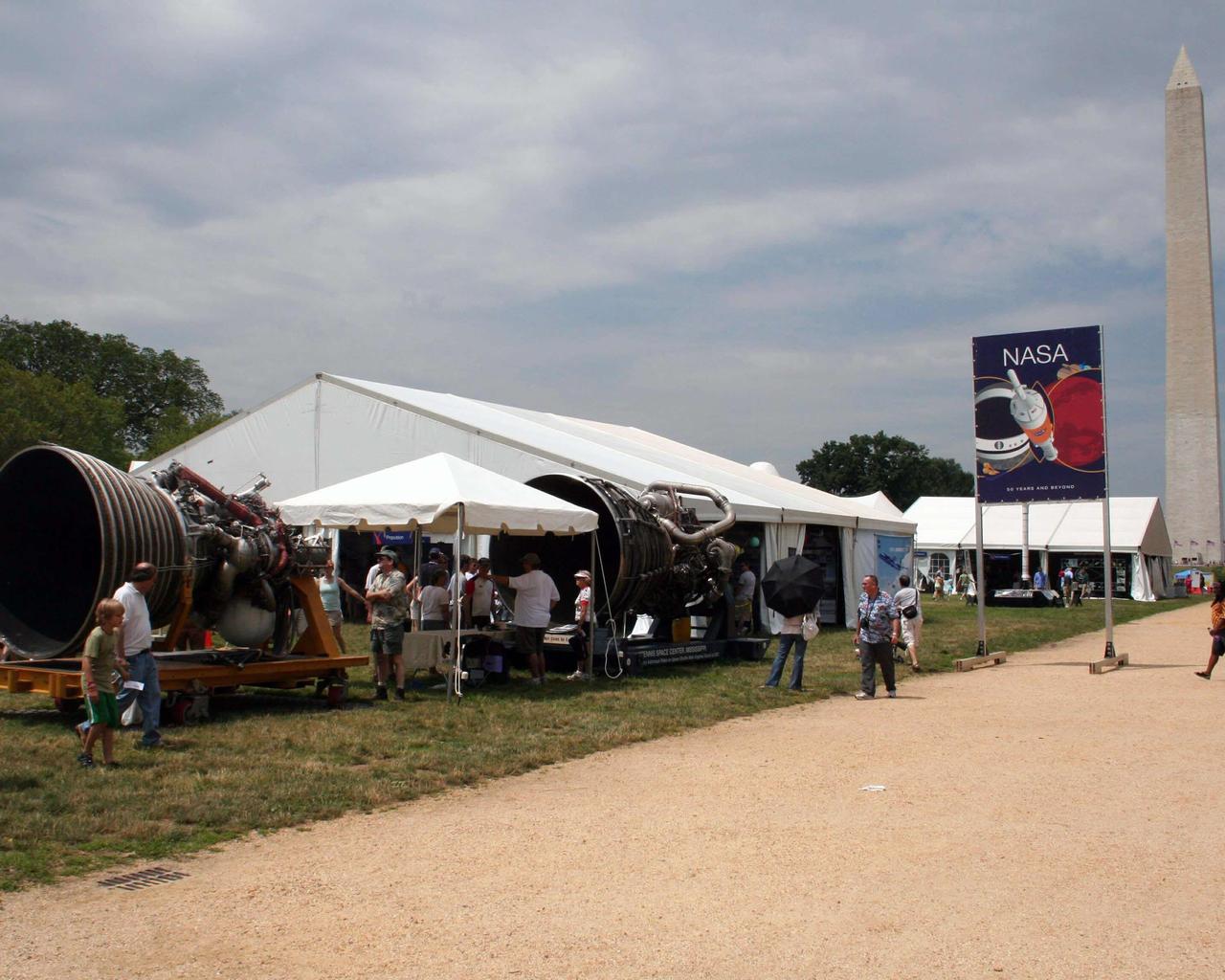

With the Washington Monument as a stirring background, a space shuttle main engine and J-2 engine from Stennis Space Center offer Washington Mall visitors a close-up look at the power of spaceflight
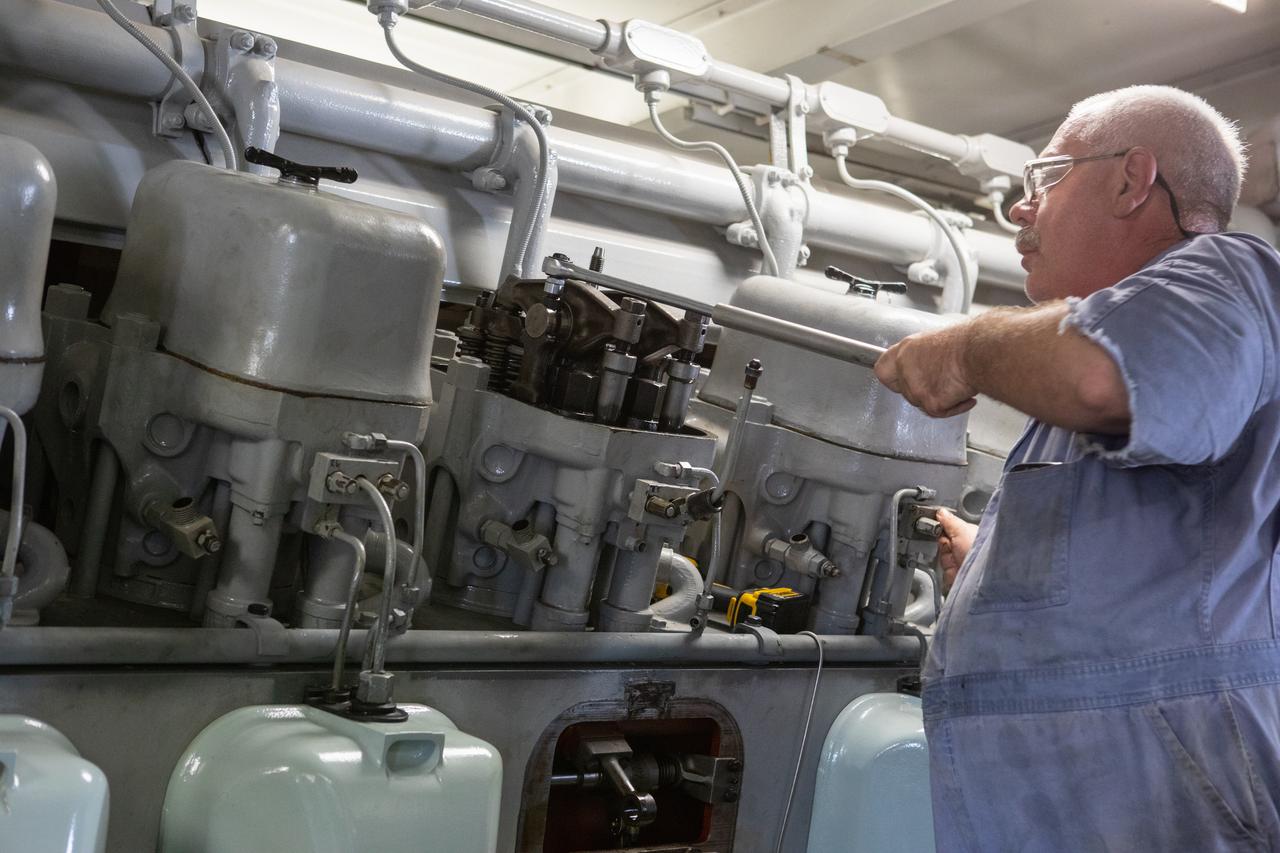

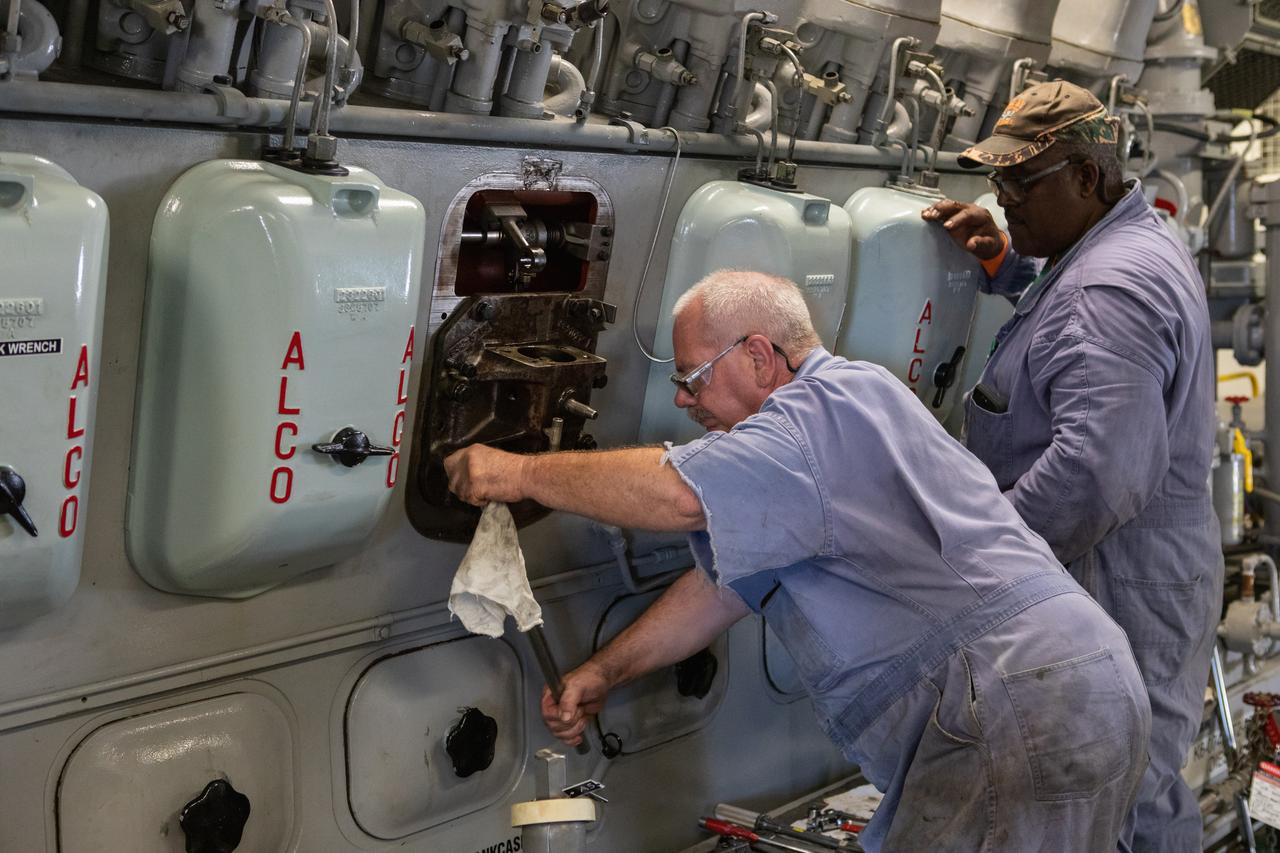
William Vardaman, mechanical technician with the Jacobs contracting team, performs engine maintenance on NASA's crawler-transporter 2 on March 26, 2019, in the crawler yard located in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 area. Recent engine work included rebuilding the vehicles’ fuel pump assemblies and installing new oil pumps that will help minimize future wear. This is one of two crawler-transporters that carried rockets and spacecraft, including the Apollo/Saturn V and space shuttle, from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw modifications and upgrades to crawler-transporter 2 so it can carry the mobile launcher and NASA's Space Launch System rocket, topped by the Orion spacecraft, to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission-1.
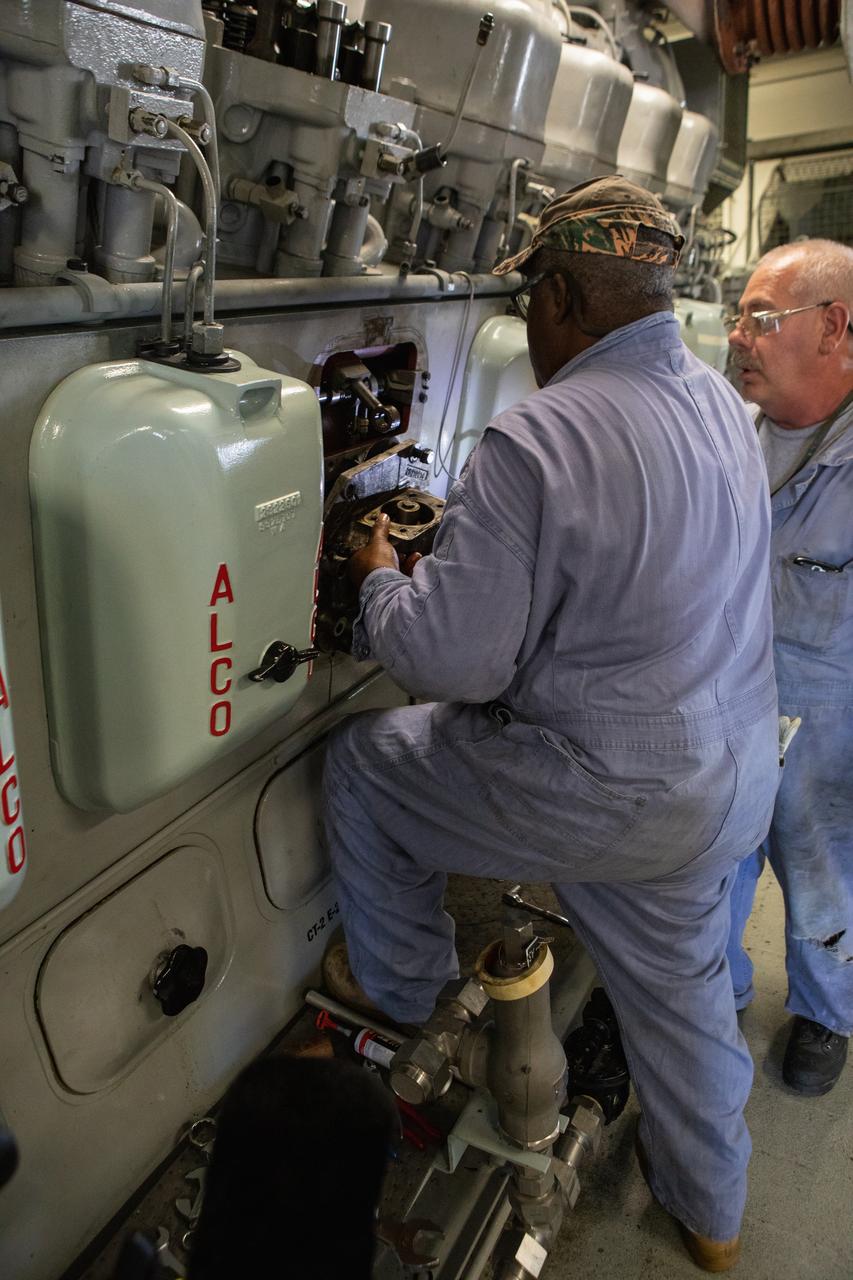

Pat Brown, left, and William Vardaman, mechanical technicians with the Jacobs contracting team, perform engine maintenance on NASA's crawler-transporter 2 on March 26, 2019, in the crawler yard located in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 area. Recent engine work included rebuilding the vehicles’ fuel pump assemblies and installing new oil pumps that will help minimize future wear. This is one of two crawler-transporters that carried rockets and spacecraft, including the Apollo/Saturn V and space shuttle, from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw modifications and upgrades to crawler-transporter 2 so it can carry the mobile launcher and NASA's Space Launch System rocket, topped by the Orion spacecraft, to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission-1.
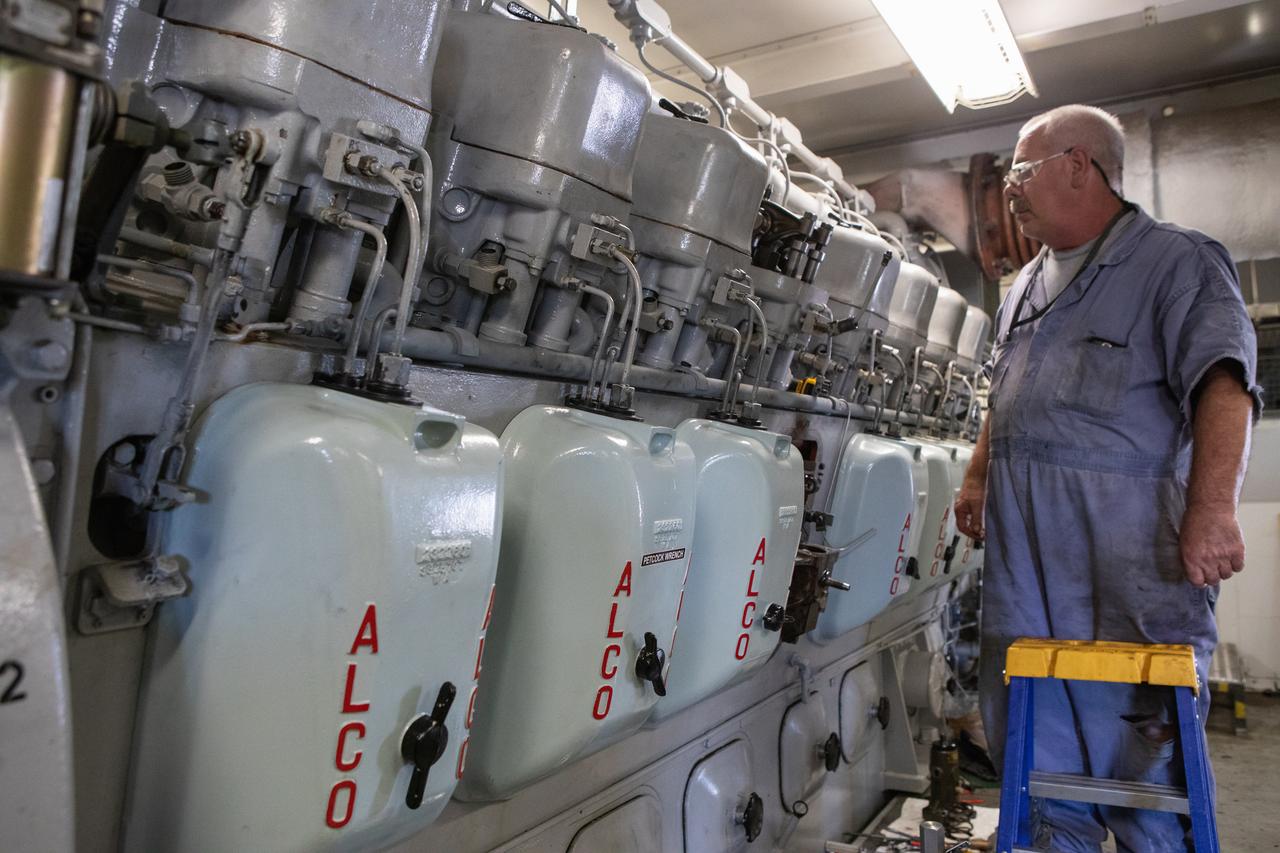

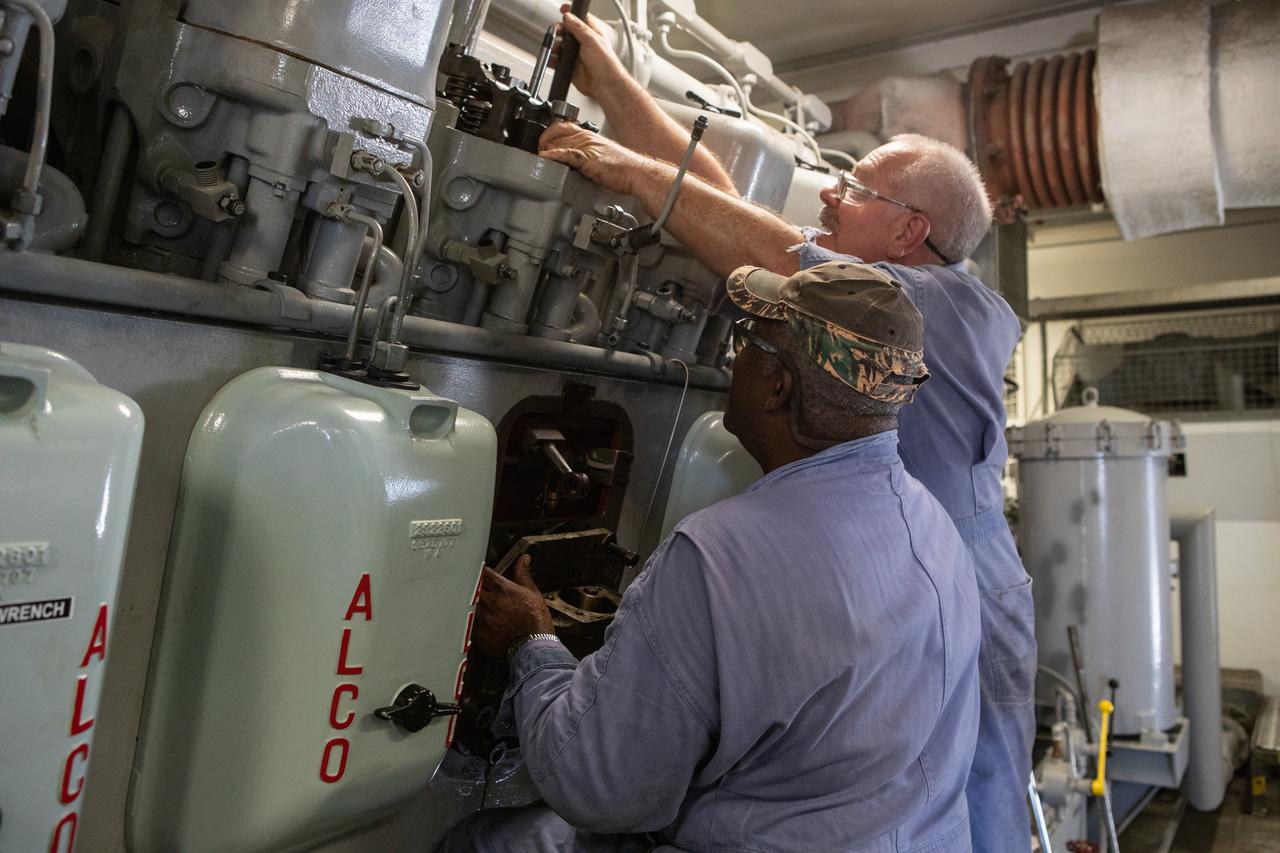
William Vardaman, a mechanical technician with the Jacobs contracting team, performs engine maintenance on NASA's crawler-transporter 2 on March 26, 2019, in the crawler yard located in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 area. Recent engine work included rebuilding the vehicles’ fuel pump assemblies and installing new oil pumps that will help minimize future wear. This is one of two crawler-transporters that carried rockets and spacecraft, including the Apollo/Saturn V and space shuttle, from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw modifications and upgrades to crawler-transporter 2 so it can carry the mobile launcher and NASA's Space Launch System rocket, topped by the Orion spacecraft, to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission-1.
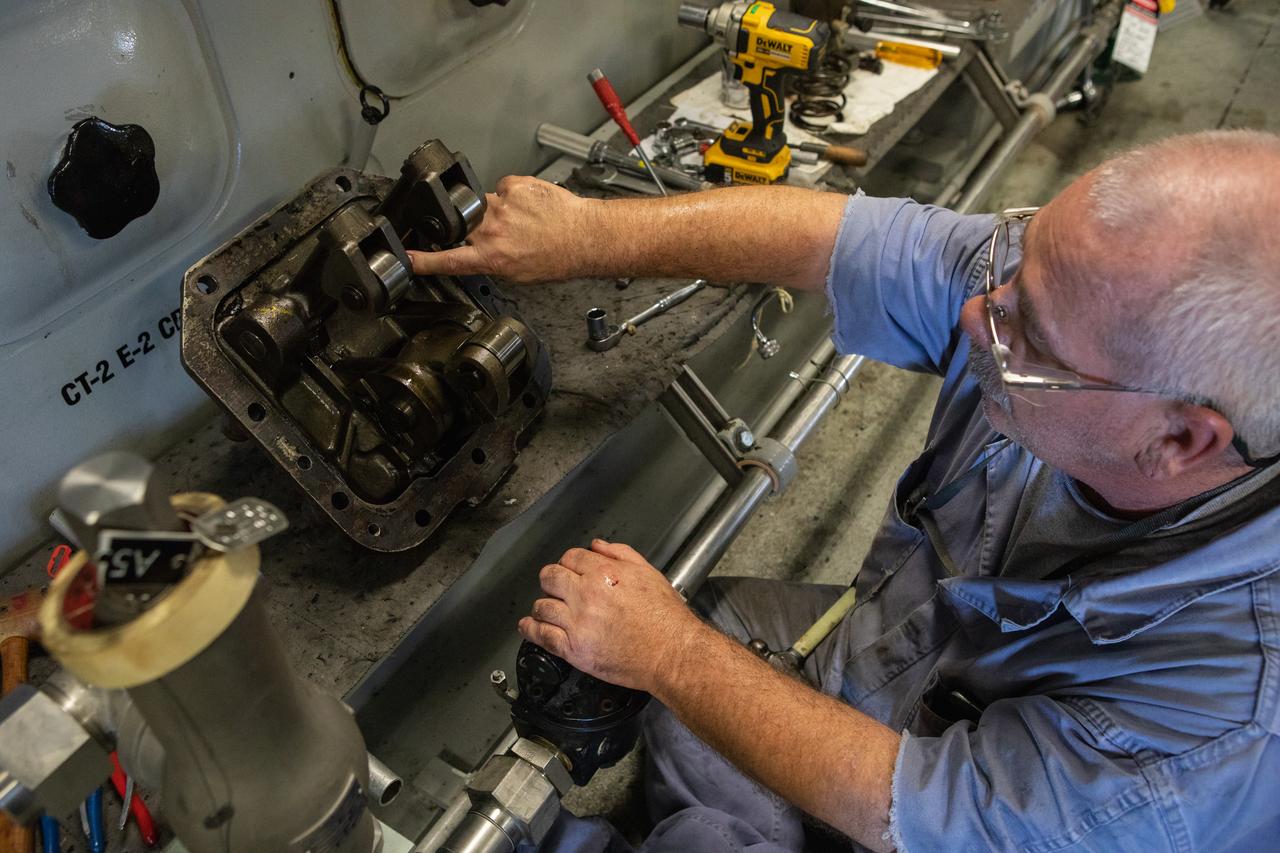

William Vardaman, a mechanical technician with the Jacobs contracting team, performs engine maintenance on NASA's crawler-transporter 2 on March 26, 2019, in the crawler yard located in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 area. Recent engine work included rebuilding the vehicles’ fuel pump assemblies and installing new oil pumps that will help minimize future wear. This is one of two crawler-transporters that carried rockets and spacecraft, including the Apollo/Saturn V and space shuttle, from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw modifications and upgrades to crawler-transporter 2 so it can carry the mobile launcher and NASA's Space Launch System rocket, topped by the Orion spacecraft, to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission-1.
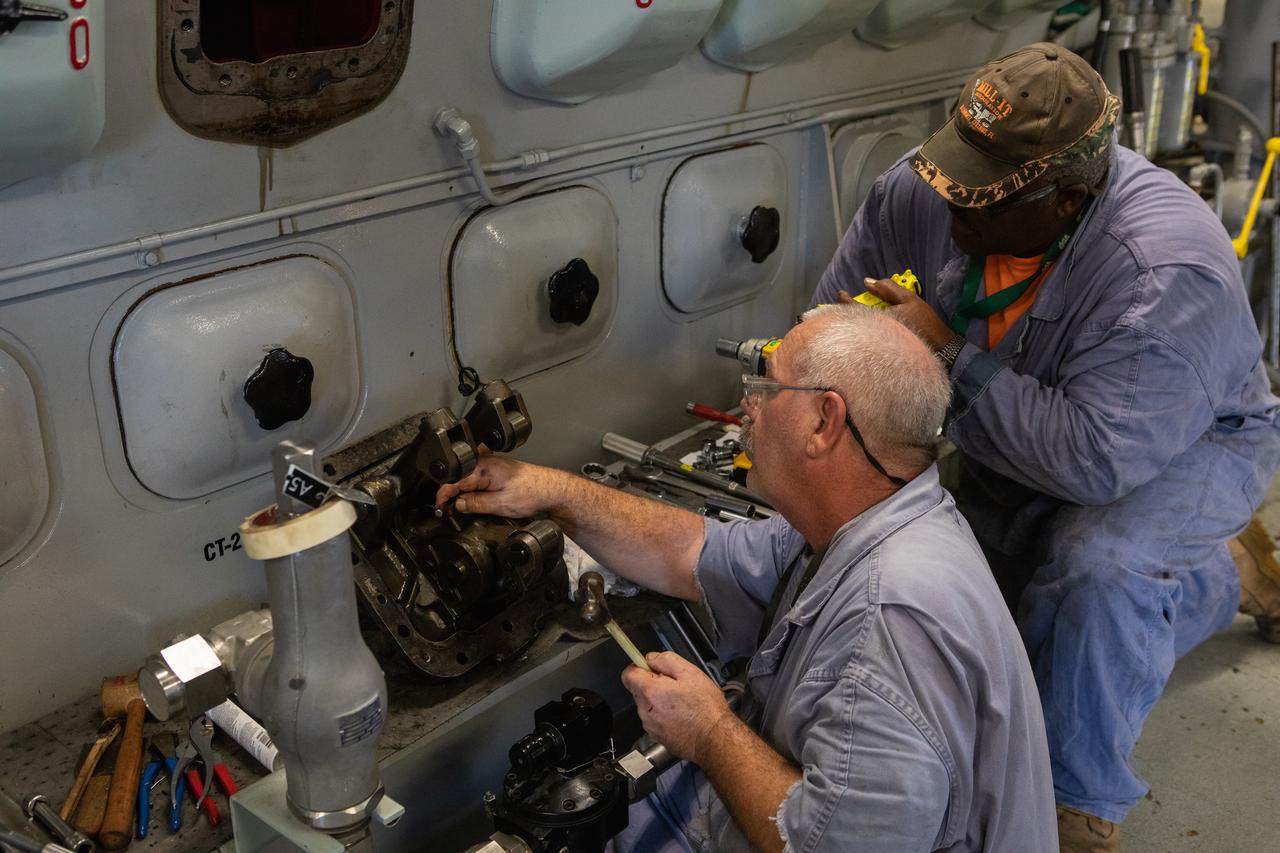

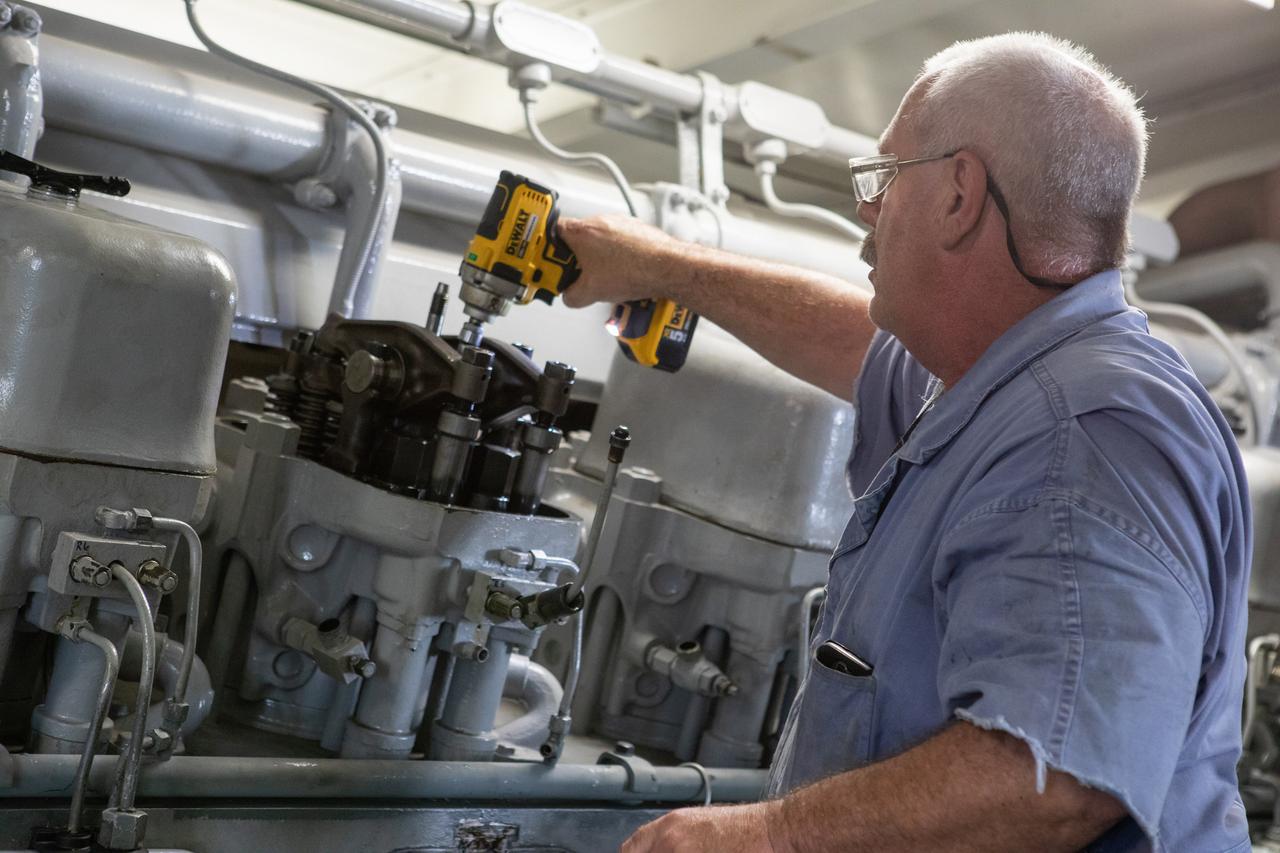
William Vardaman, left, and Pat Brown, mechanical technicians with the Jacobs contracting team, perform engine maintenance on NASA's crawler-transporter 2 on March 26, 2019, in the crawler yard located in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 area. Recent engine work included rebuilding the vehicles’ fuel pump assemblies and installing new oil pumps that will help minimize future wear. This is one of two crawler-transporters that carried rockets and spacecraft, including the Apollo/Saturn V and space shuttle, from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw modifications and upgrades to crawler-transporter 2 so it can carry the mobile launcher and NASA's Space Launch System rocket, topped by the Orion spacecraft, to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission-1.
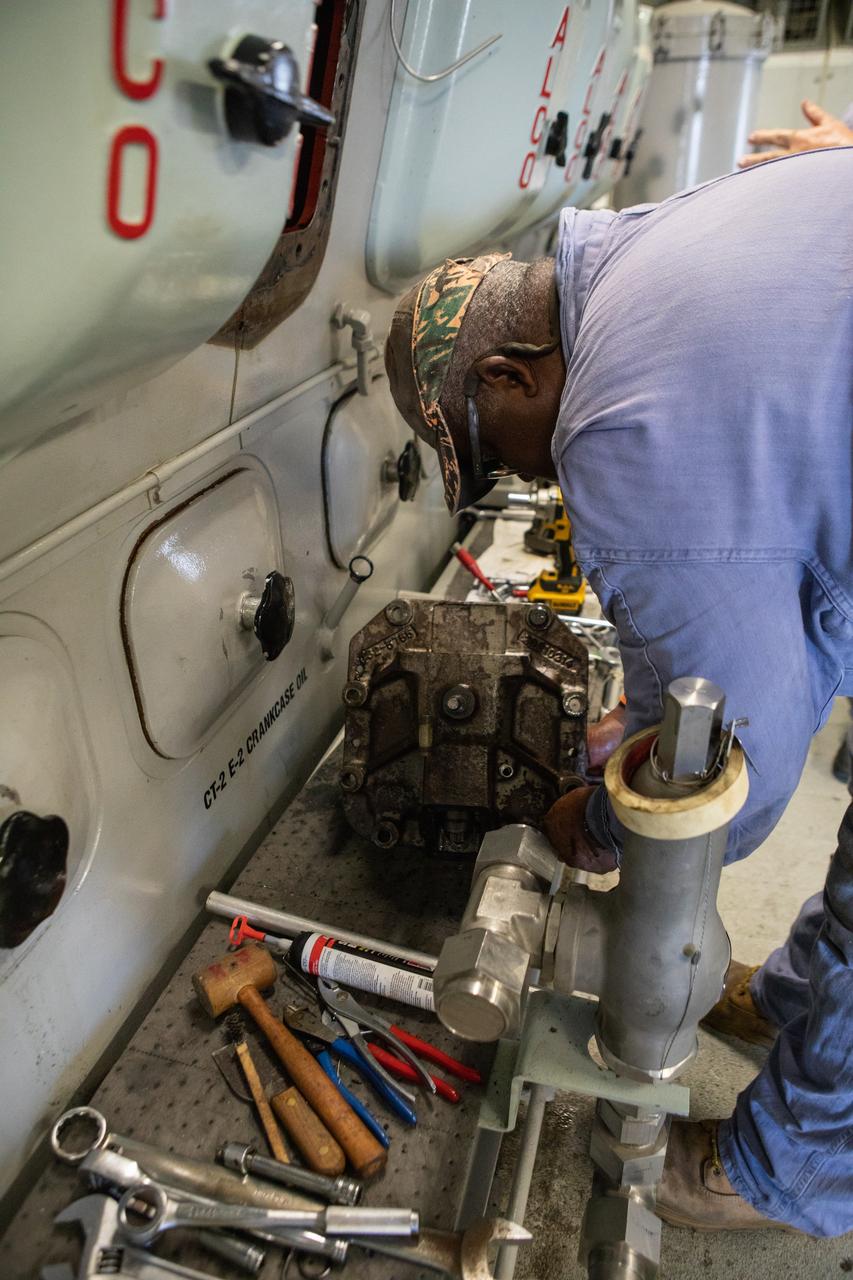

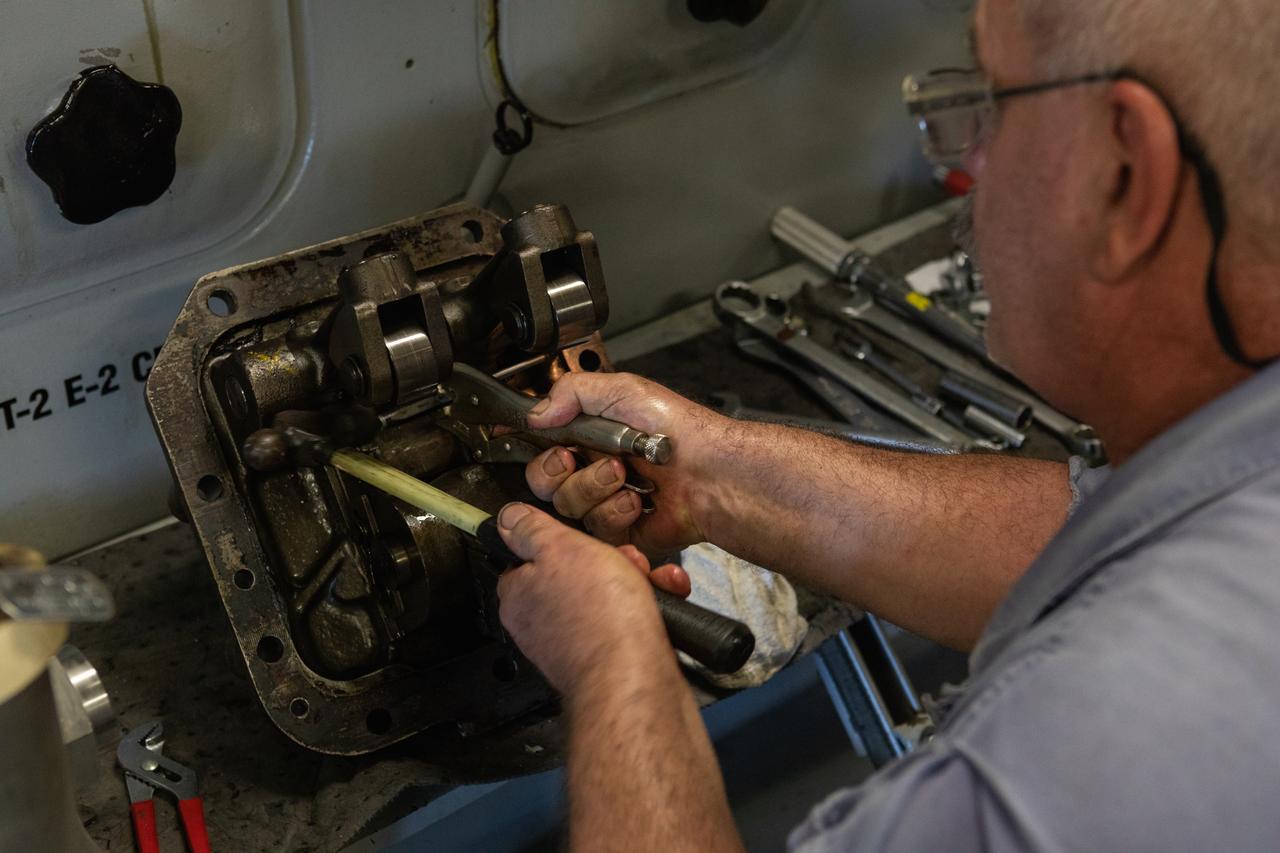
Pat Brown, a mechanical technician with Jacobs, has wrenches, pliers and other tools at the ready as he performs engine maintenance on NASA's crawler-transporter 2 on March 26, 2019, in the crawler yard located in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 area. Recent engine work included rebuilding the vehicles’ fuel pump assemblies and installing new oil pumps that will help minimize future wear. This is one of two crawler-transporters that carried rockets and spacecraft, including the Apollo/Saturn V and space shuttle, from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw modifications and upgrades to crawler-transporter 2 so it can carry the mobile launcher and NASA's Space Launch System rocket, topped by the Orion spacecraft, to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission-1.

William Vardaman, left, and Pat Brown, mechanical technicians with the Jacobs contracting team, perform engine maintenance on NASA's crawler-transporter 2 on March 26, 2019, in the crawler yard located in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 area. Recent engine work included rebuilding the vehicles’ fuel pump assemblies and installing new oil pumps that will help minimize future wear. This is one of two crawler-transporters that carried rockets and spacecraft, including the Apollo/Saturn V and space shuttle, from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw modifications and upgrades to crawler-transporter 2 so it can carry the mobile launcher and NASA's Space Launch System rocket, topped by the Orion spacecraft, to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission-1.

William Vardaman, a mechanical technician with the Jacobs contracting team, performs engine maintenance on NASA's crawler-transporter 2 on March 26, 2019, in the crawler yard located in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 area. Recent engine work included rebuilding the vehicles’ fuel pump assemblies and installing new oil pumps that will help minimize future wear. This is one of two crawler-transporters that carried rockets and spacecraft, including the Apollo/Saturn V and space shuttle, from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw modifications and upgrades to crawler-transporter 2 so it can carry the mobile launcher and NASA's Space Launch System rocket, topped by the Orion spacecraft, to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission-1.

Pat Brown, left, and William Vardaman, mechanical technicians with the Jacobs contracting team, perform engine maintenance on NASA's crawler-transporter 2 on March 26, 2019, in the crawler yard located in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 area. Recent engine work included rebuilding the vehicles’ fuel pump assemblies and installing new oil pumps that will help minimize future wear. This is one of two crawler-transporters that carried rockets and spacecraft, including the Apollo/Saturn V and space shuttle, from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw modifications and upgrades to crawler-transporter 2 so it can carry the mobile launcher and NASA's Space Launch System rocket, topped by the Orion spacecraft, to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission-1.

William Vardaman, a mechanical technician with the Jacobs contracting team, performs engine maintenance on NASA's crawler-transporter 2 on March 26, 2019, in the crawler yard located in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 area. Recent engine work included rebuilding the vehicles’ fuel pump assemblies and installing new oil pumps that will help minimize future wear. This is one of two crawler-transporters that carried rockets and spacecraft, including the Apollo/Saturn V and space shuttle, from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw modifications and upgrades to crawler-transporter 2 so it can carry the mobile launcher and NASA's Space Launch System rocket, topped by the Orion spacecraft, to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission-1.
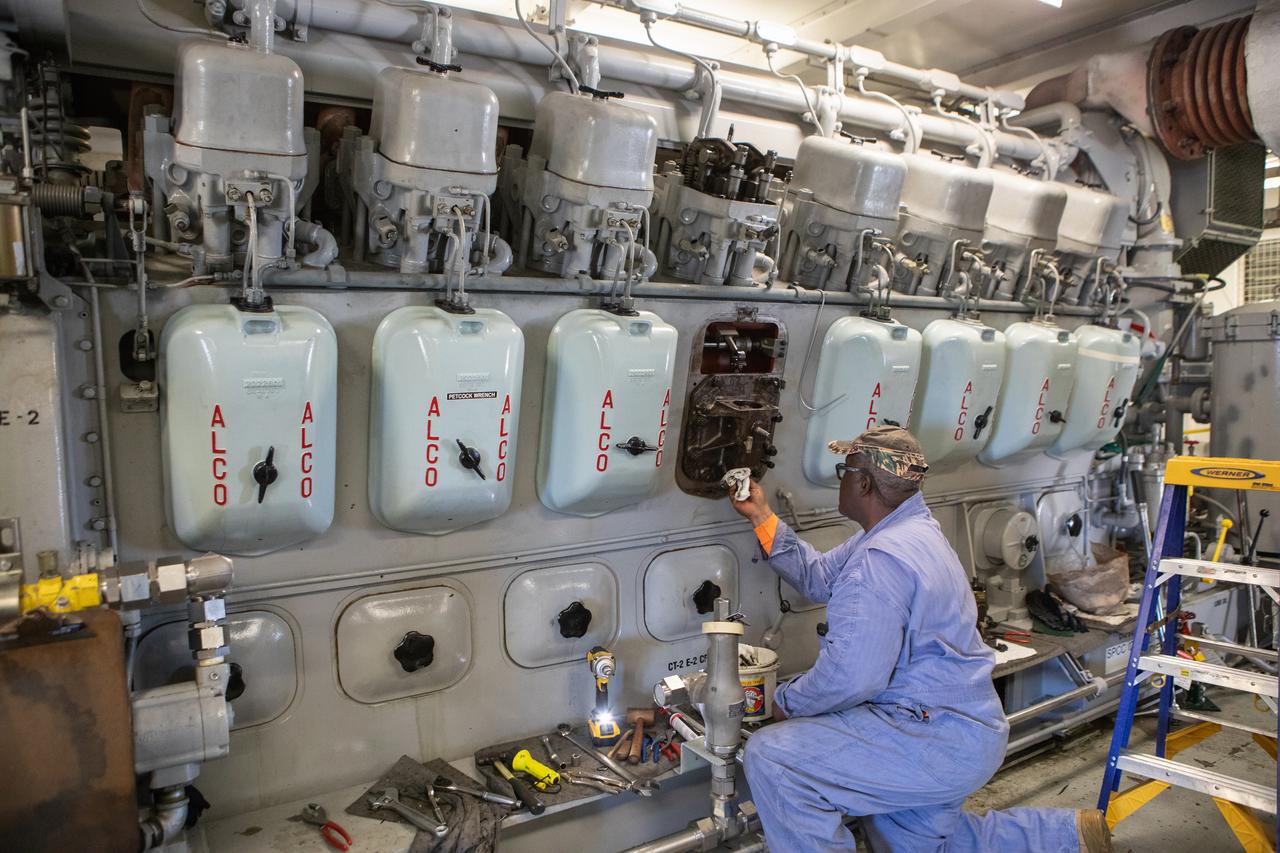

Pat Brown, a mechanical technician with Jacobs, performs engine maintenance on NASA's crawler-transporter 2 on March 26, 2019, in the crawler yard located in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 area. Recent engine work included rebuilding the vehicles’ fuel pump assemblies and installing new oil pumps that will help minimize future wear. This is one of two crawler-transporters that carried rockets and spacecraft, including the Apollo/Saturn V and space shuttle, from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw modifications and upgrades to crawler-transporter 2 so it can carry the mobile launcher and NASA's Space Launch System rocket, topped by the Orion spacecraft, to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission-1.
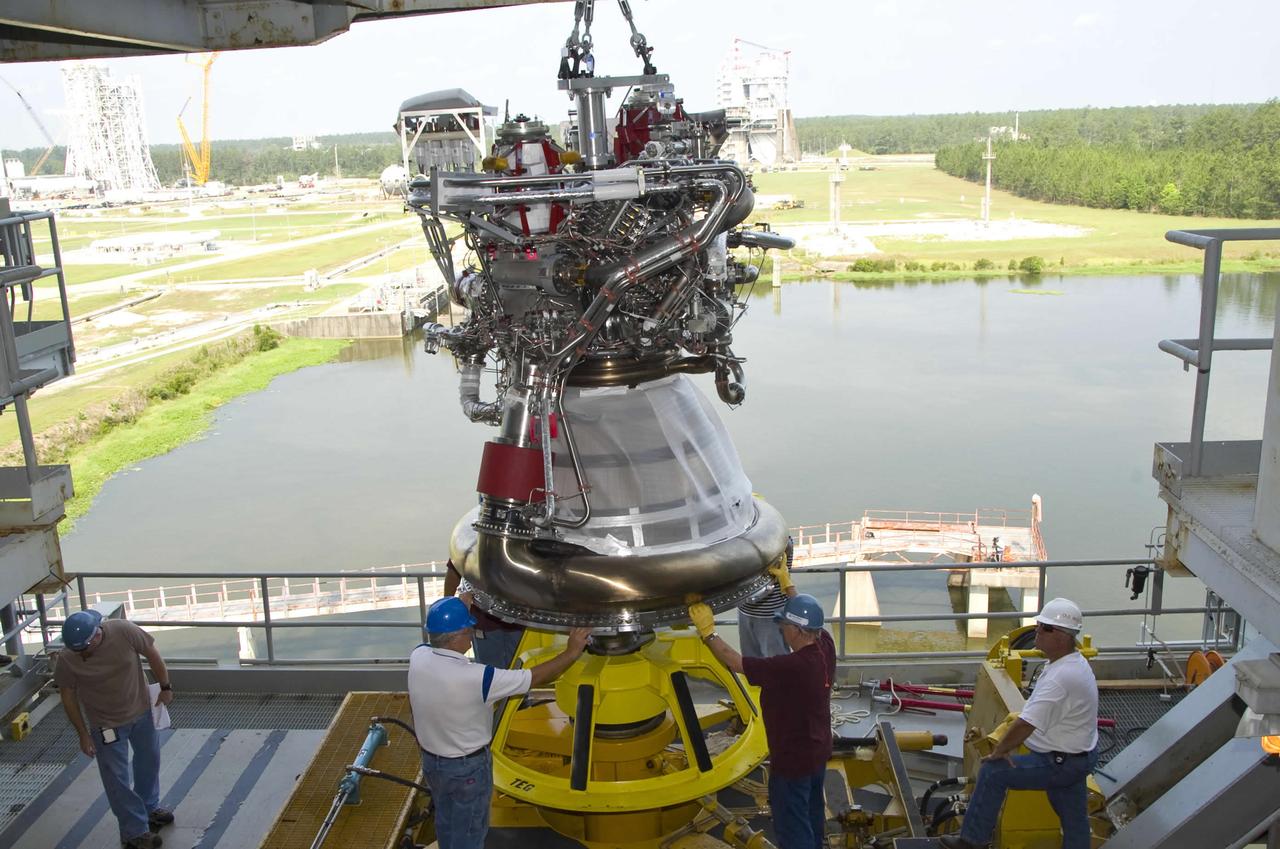

A J-2X next-generation rocket engine is lifted onto the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center. Testing of the engine began the following month. The engine is being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne and could help carry humans beyond low-Earth orbit into deep space once more.
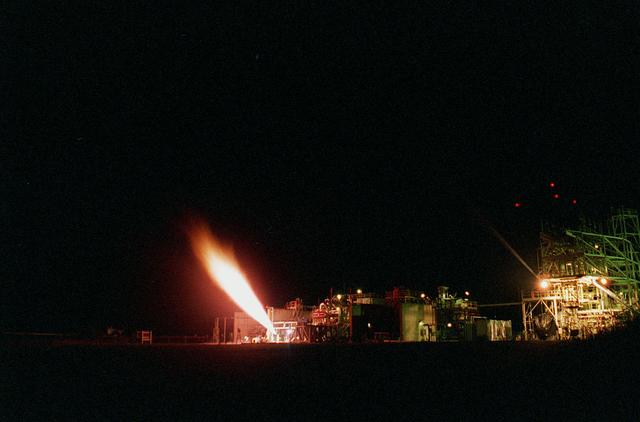

A J-2 Gas Generator (GG) engine's duration test at Marshall's Test Stand-116.
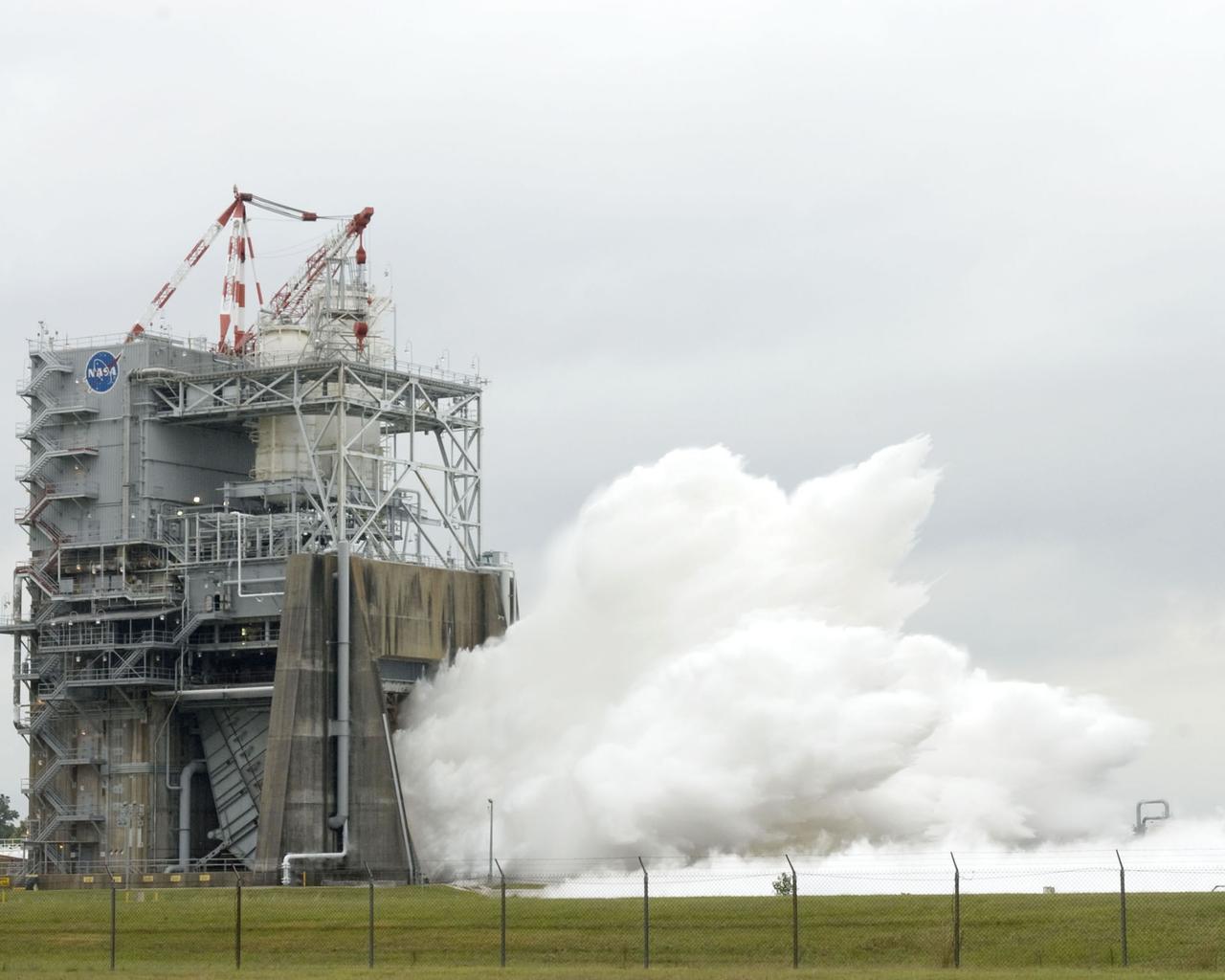

Steam blasts out of the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Oct. 22 as engineers begin a certification test on engine 2061, the last space shuttle main flight engine scheduled to be built. Since 1975, Stennis has tested every space shuttle main engine used in the program - about 50 engines in all. Those engines have powered more than 120 shuttle missions - and no mission has failed as a result of engine malfunction. For the remainder of 2008 and throughout 2009, Stennis will continue testing of various space shuttle main engine components.
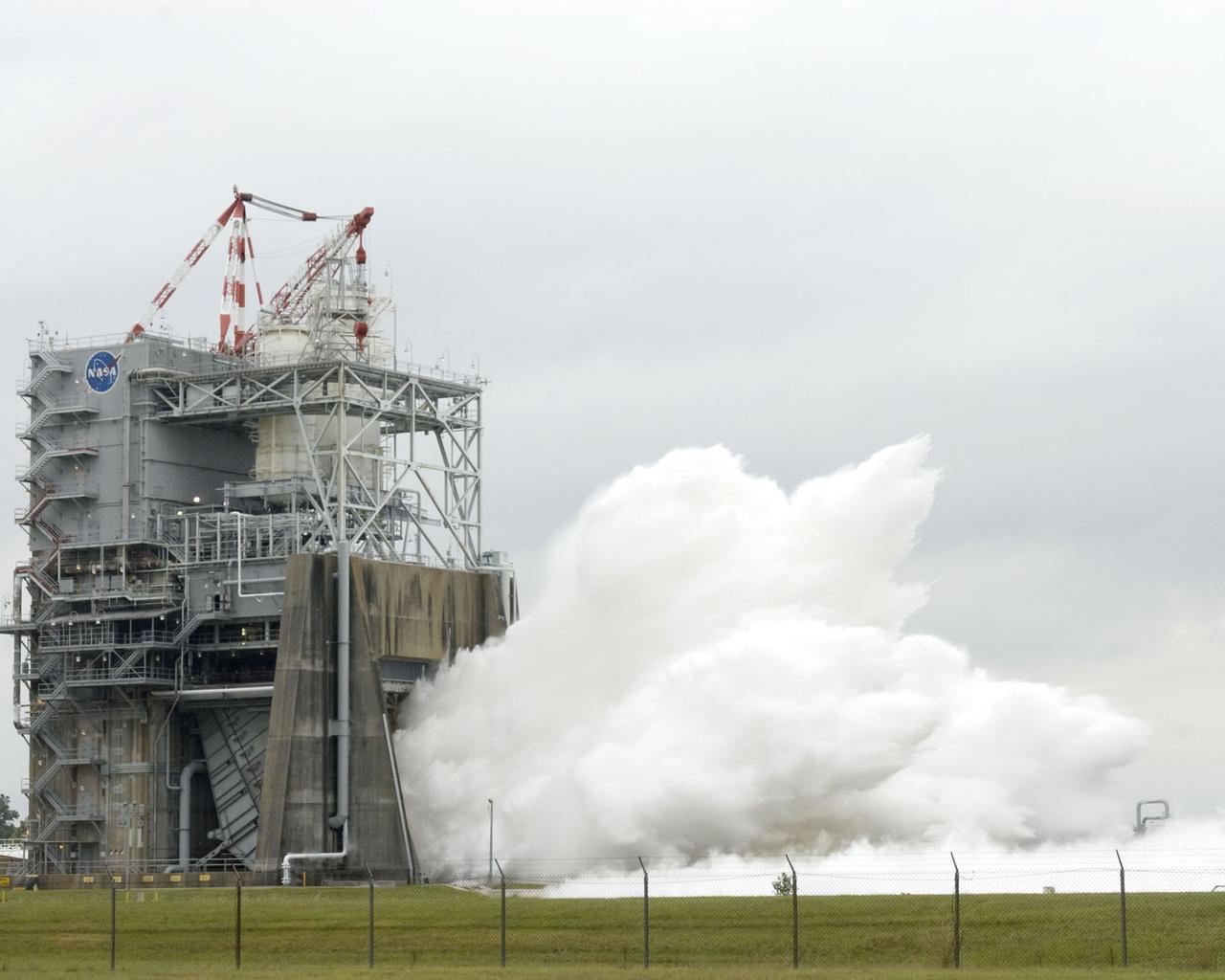

Steam blasts out of the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Oct. 22 as engineers begin a certification test on engine 2061, the last space shuttle main flight engine scheduled to be built. Since 1975, Stennis has tested every space shuttle main engine used in the program - about 50 engines in all. Those engines have powered more than 120 shuttle missions - and no mission has failed as a result of engine malfunction. For the remainder of 2008 and throughout 2009, Stennis will continue testing of various space shuttle main engine components.

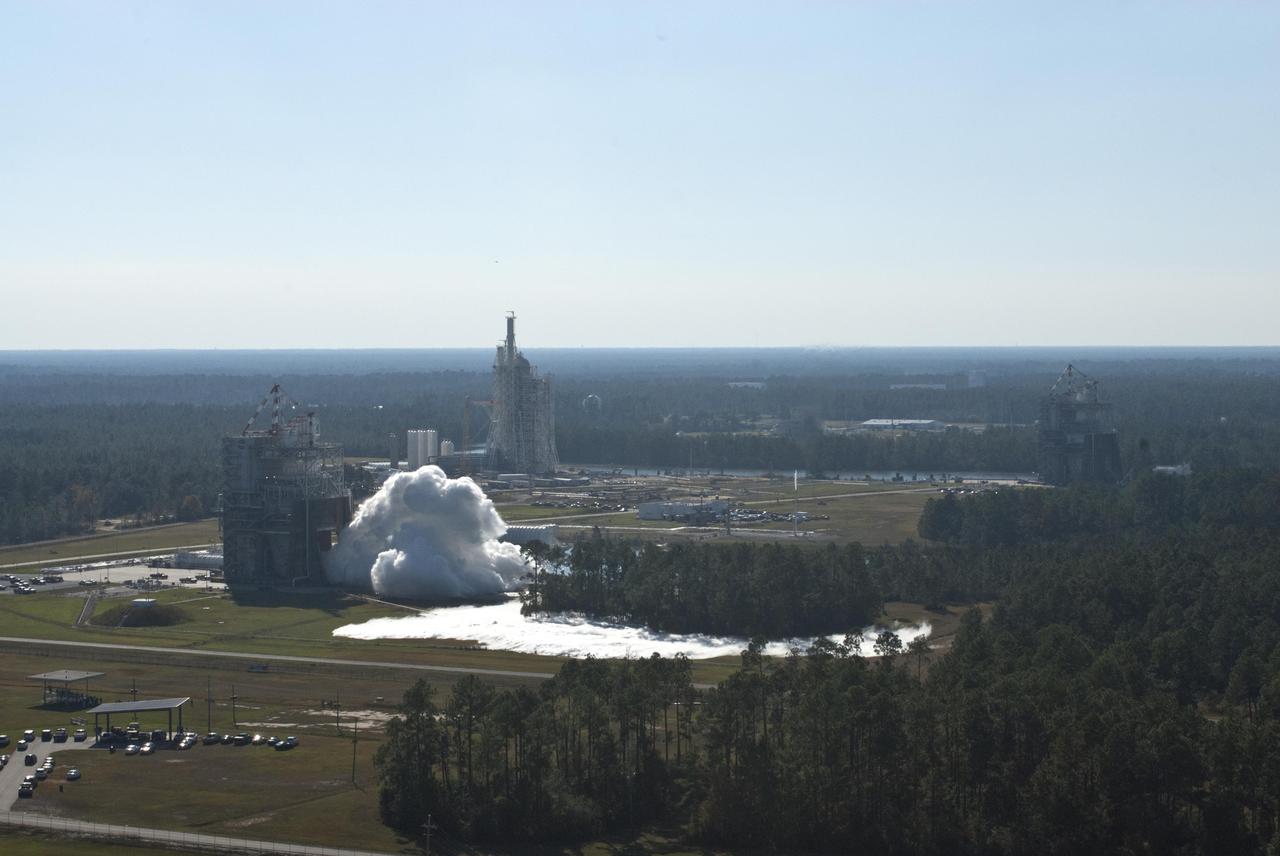
Space shuttle main engine No. 0525 is lifted from the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center against the backdrop of the new A-3 Test Stand under construction, offering a glimpse of the past and future in the nation's space exploration program. With the shuttle program set to end in 2010, Stennis conducted the last planned space shuttle main engine test on July 29 and now is deactivating the A-2 Test Stand to a safe 'standby' status.

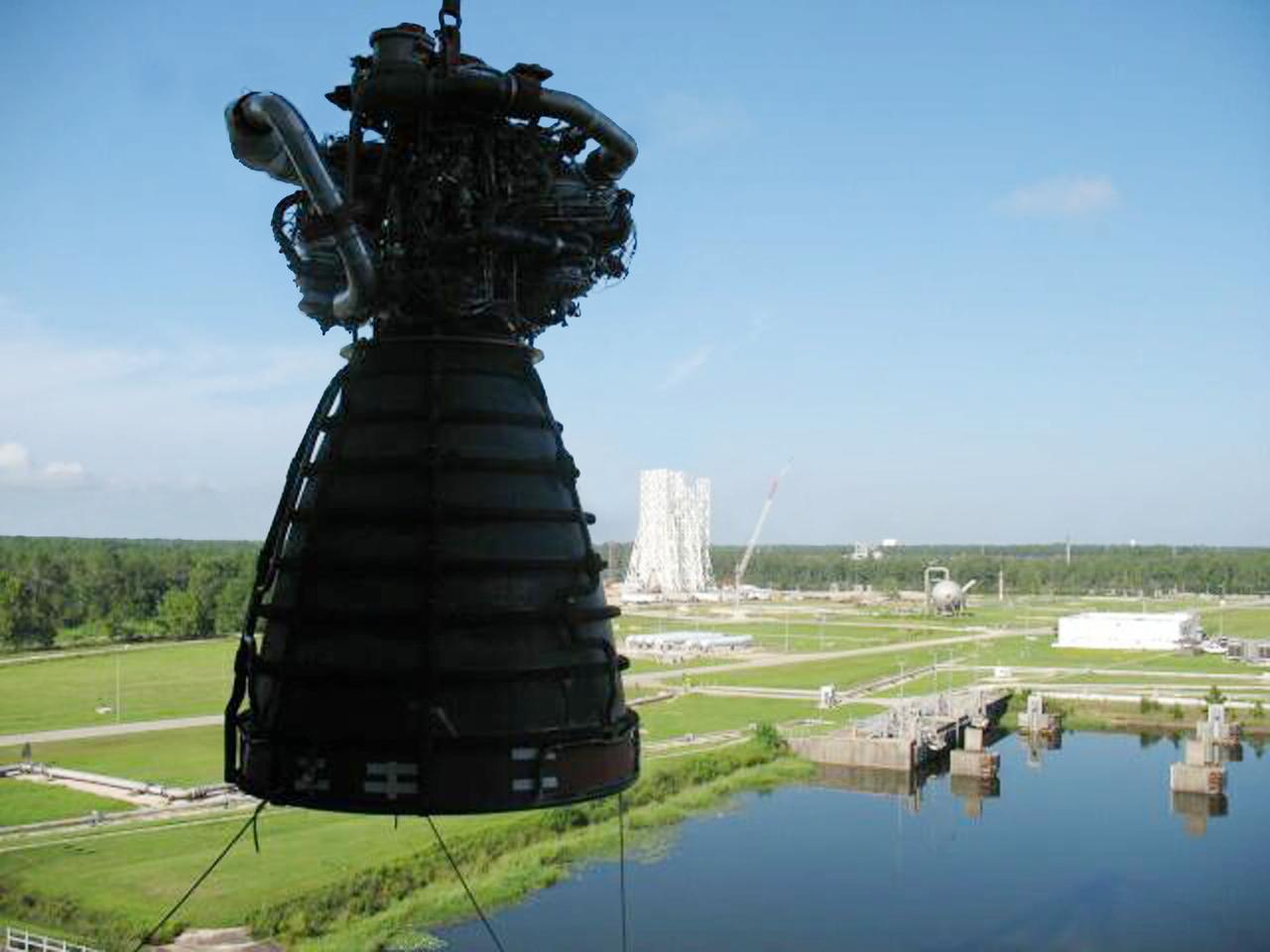
A photograph of a J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand from atop the B Test Stand at Stennis Space Center offers a panoramic view of the A Test Complex. The J-2X engine is being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne to carry humans deeper into space than ever before.

This drawing clearly shows the comparative sizes of the rocket engines used to launch the Saturn vehicles. The RL-10 and the H-1 engines were used to launch the Saturn I rockets. The J-2 engine was used on the second stage of Saturn IB and the second and third stages of Saturn V. The F-1 engine was used on the first stage of the Saturn V.

Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
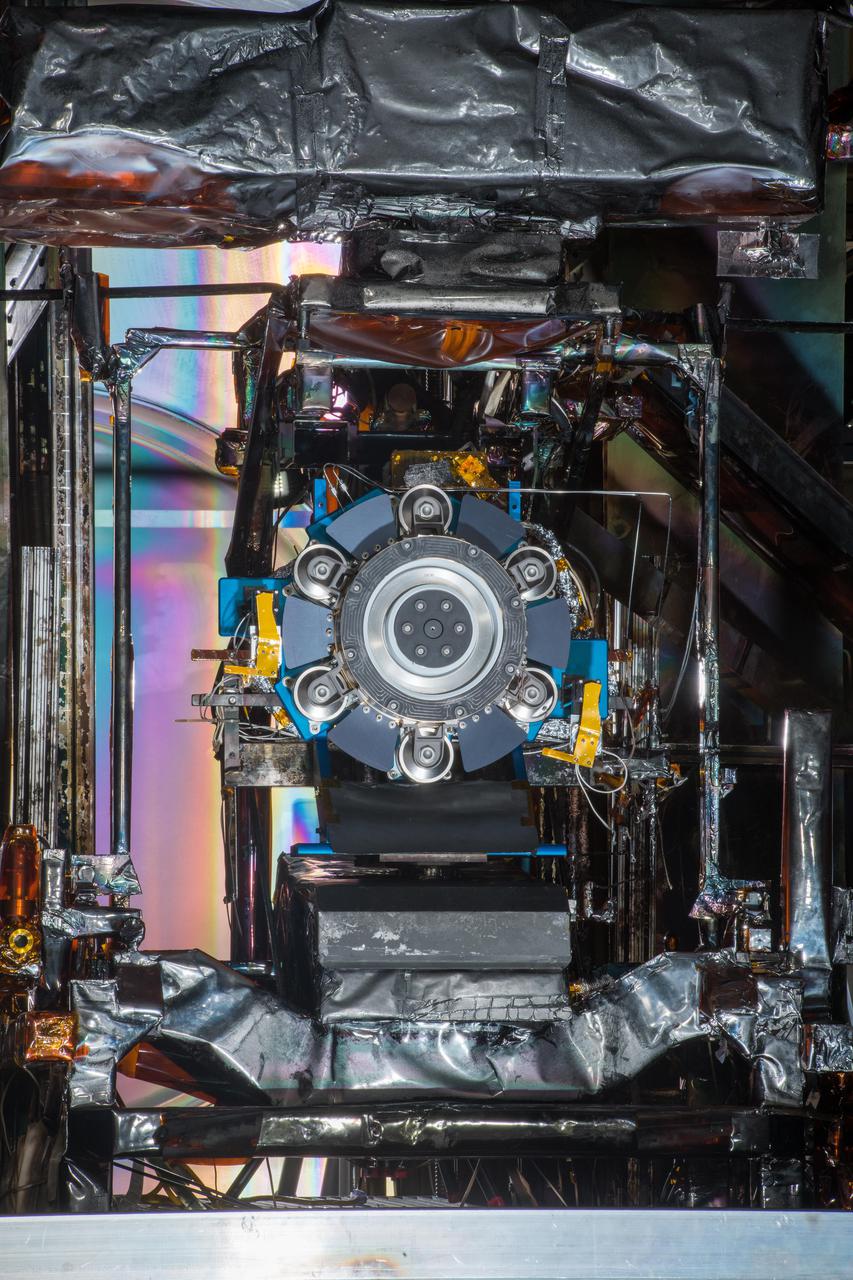
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
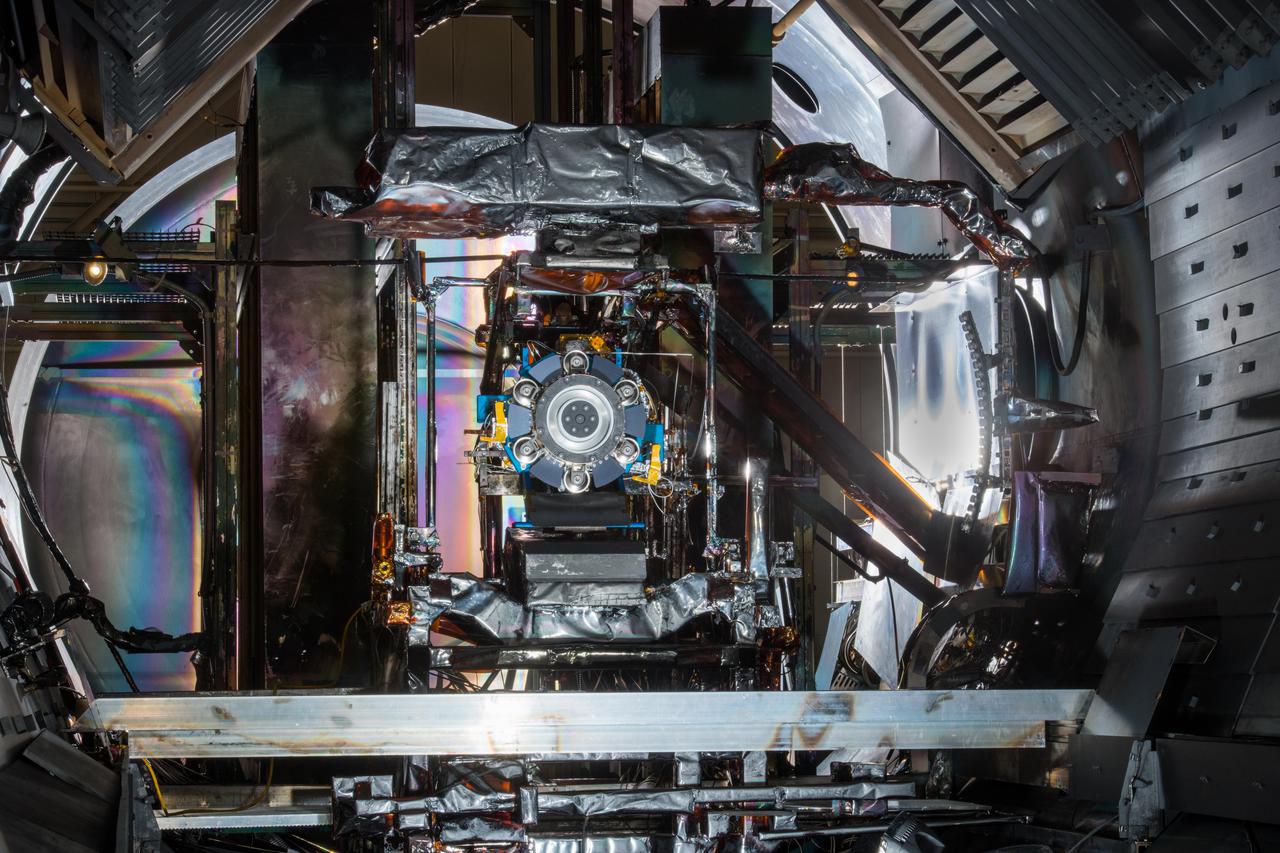
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware

Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
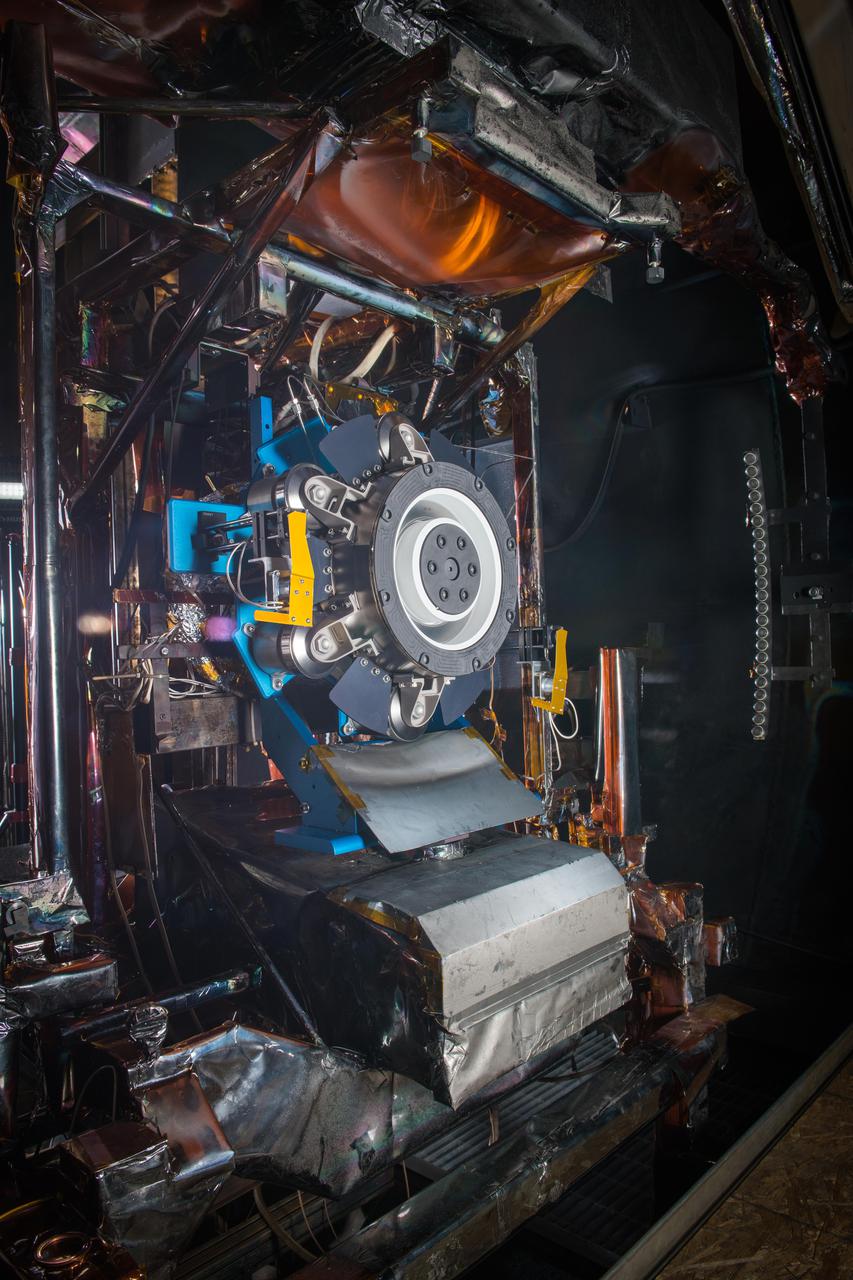
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware

Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
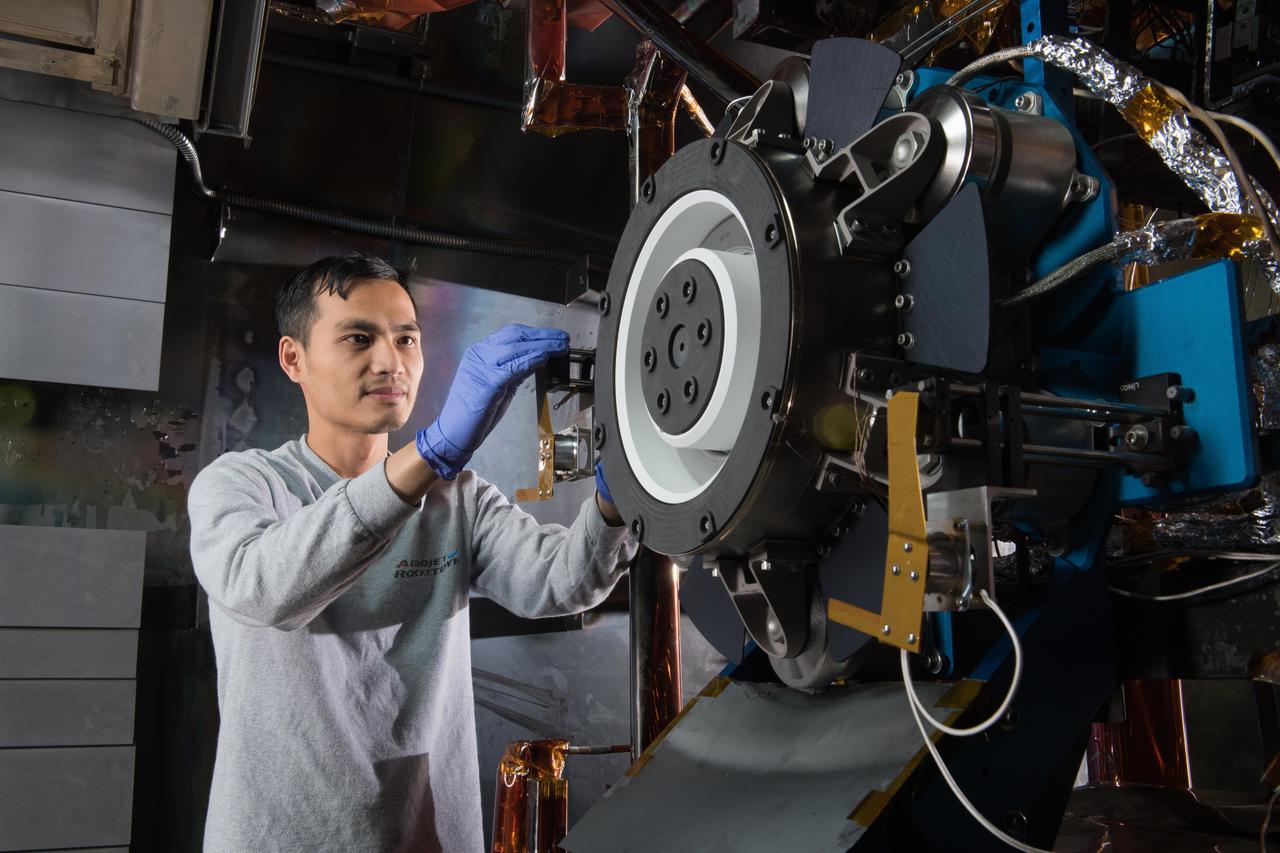
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
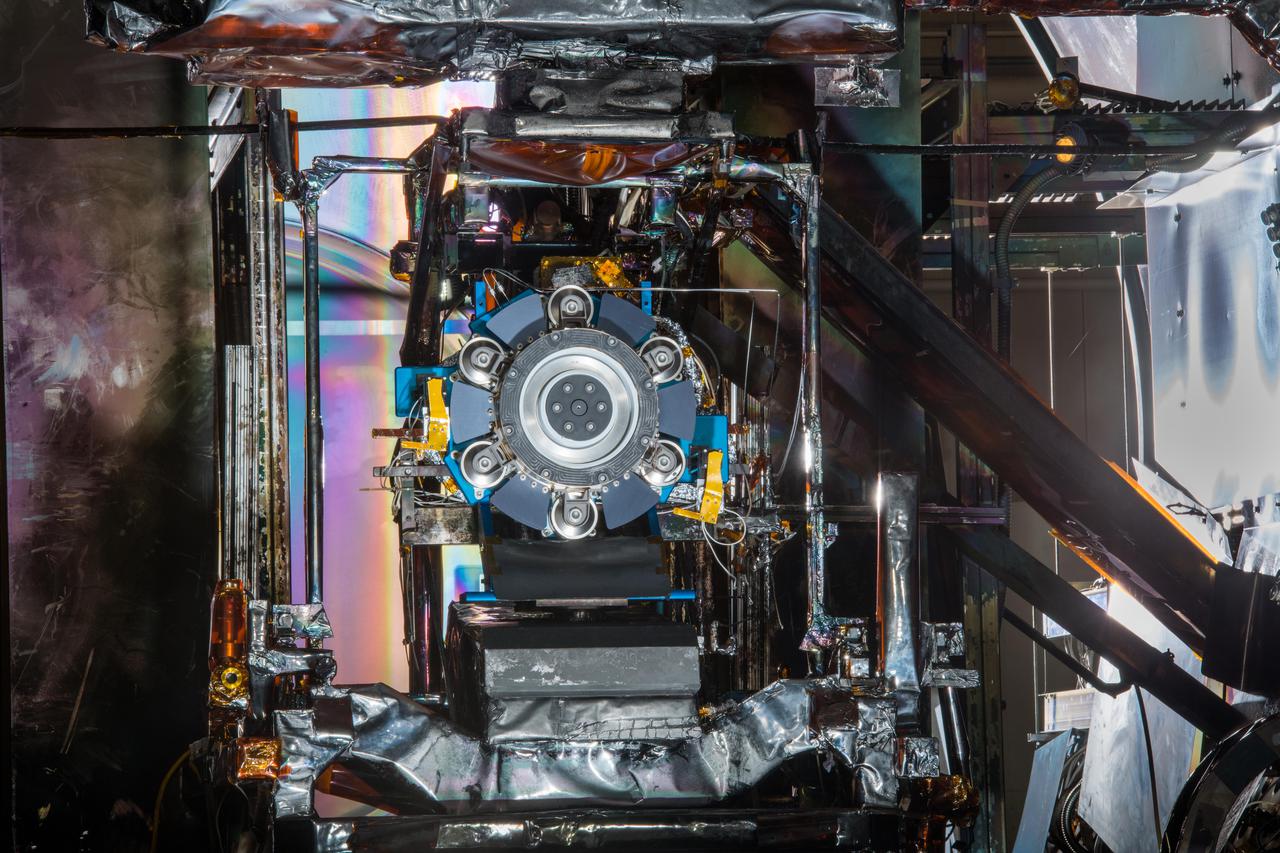
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
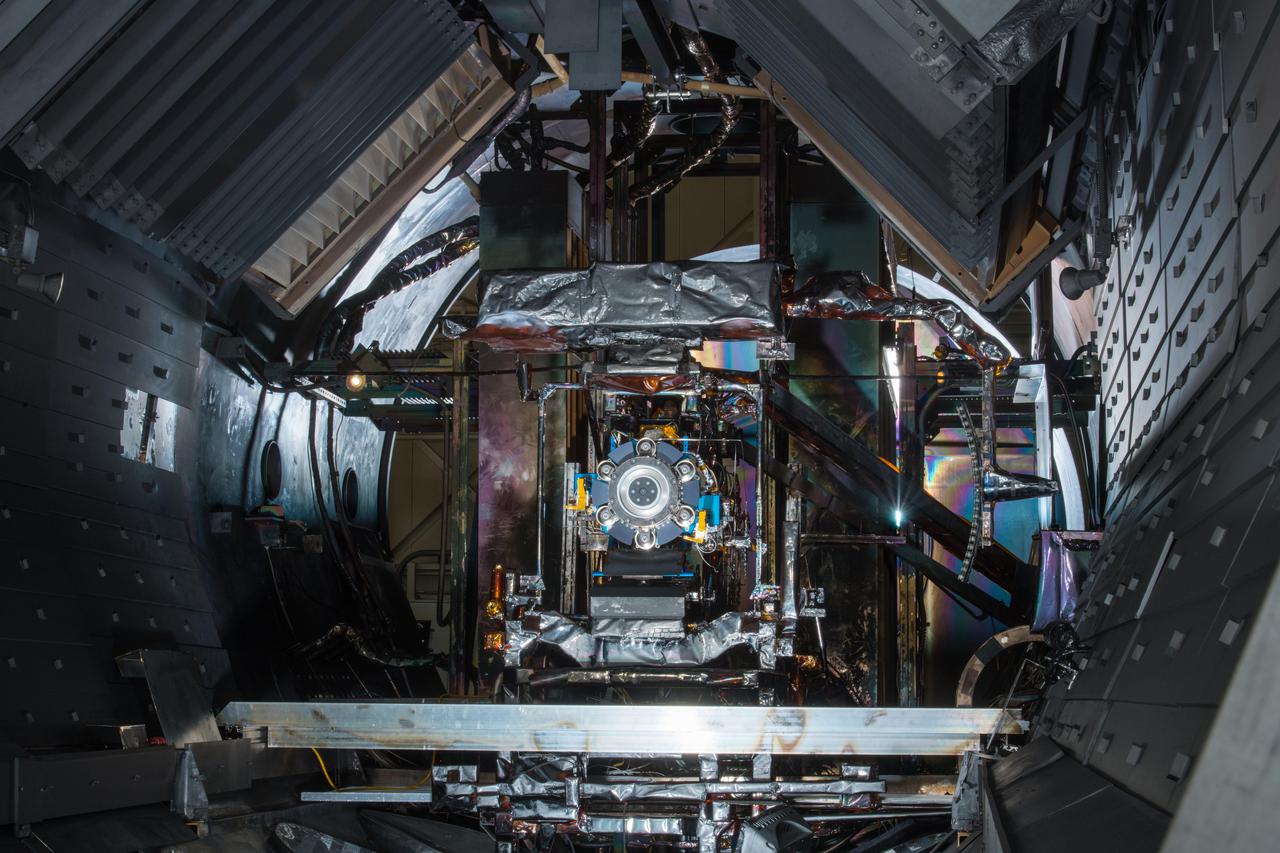
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
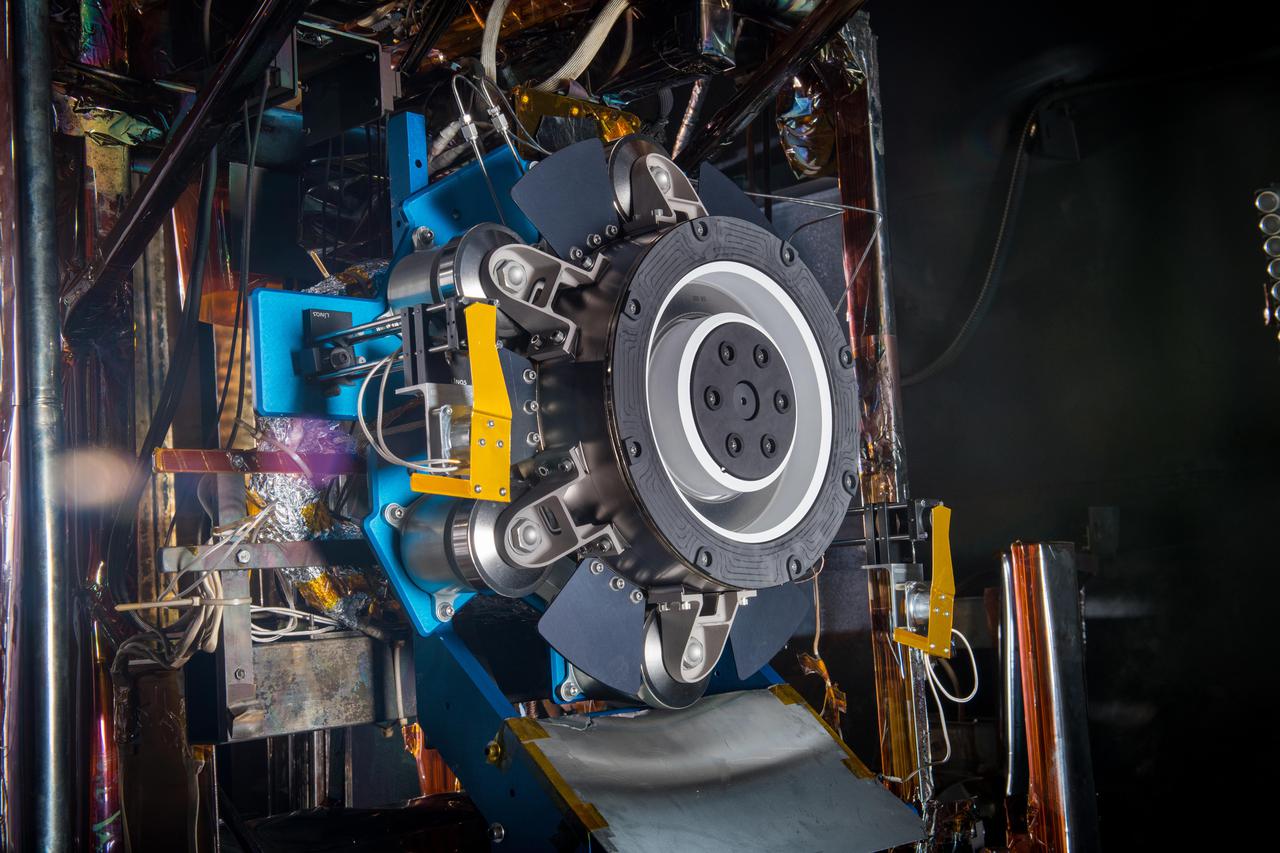
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
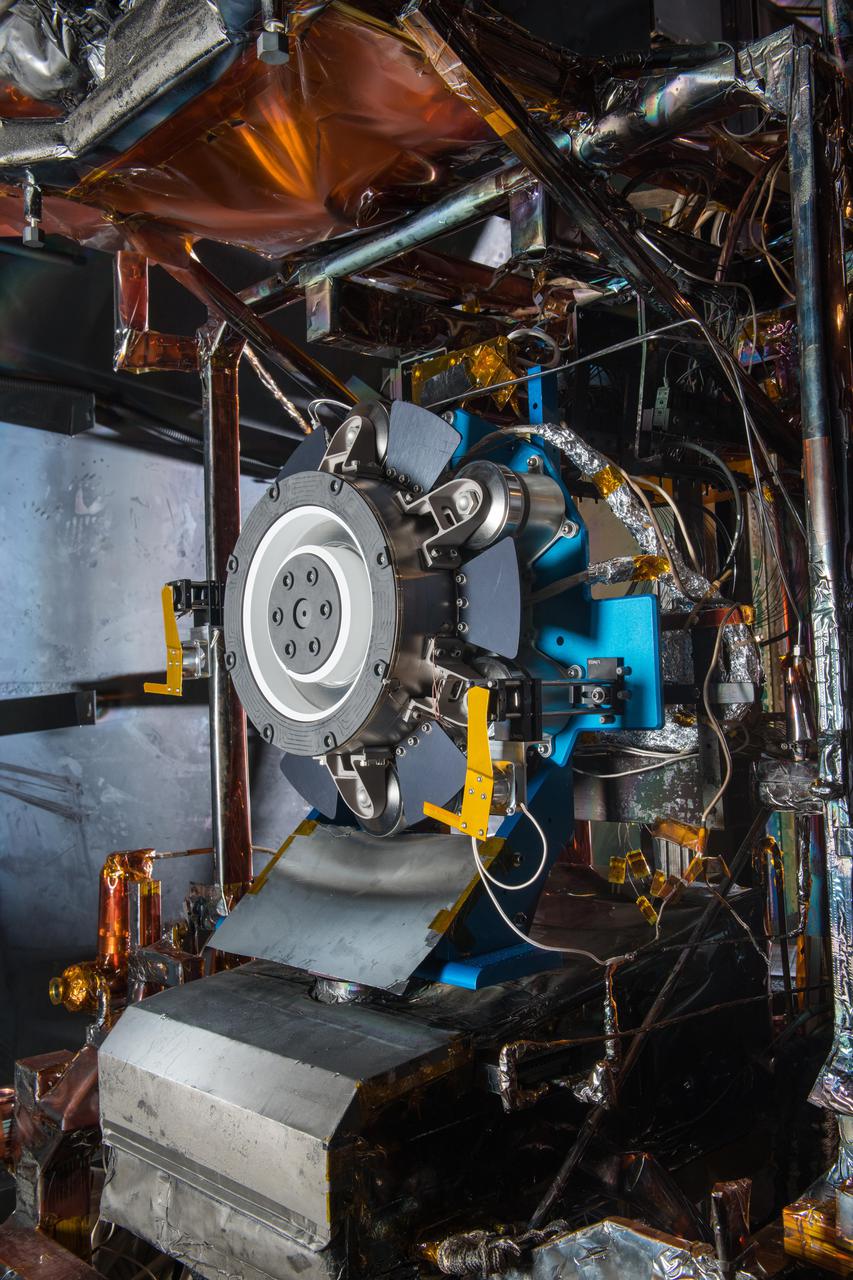
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware
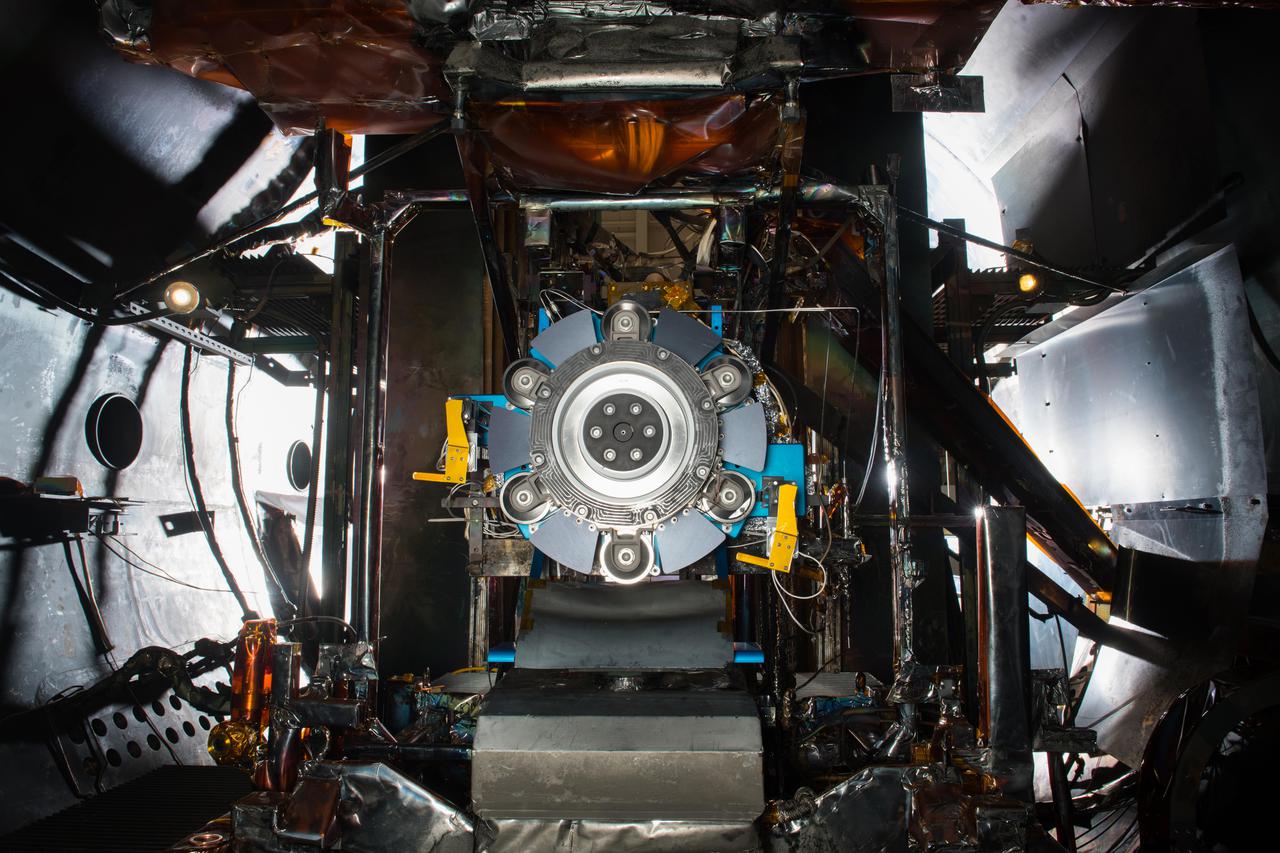
Advanced Electric Propulsion System, AEPS, Engineering Test Unit 2, ETU-2, Thruster Hardware

Water vapor surges from the flame deflector of the A-2 Test Stand at NASA's Stennis Space Center on Jan. 9 during the first space shuttle main engine test of the year. The test was an engine acceptance test of flight engine 2058. It's the first space shuttle main engine to be completely assembled at Kennedy Space Center. Objectives also included first-time (green run) tests of a high-pressure oxidizer turbo pump and an Advanced Health System Monitor engine controller. The test ran for the planned duration of 520 seconds.
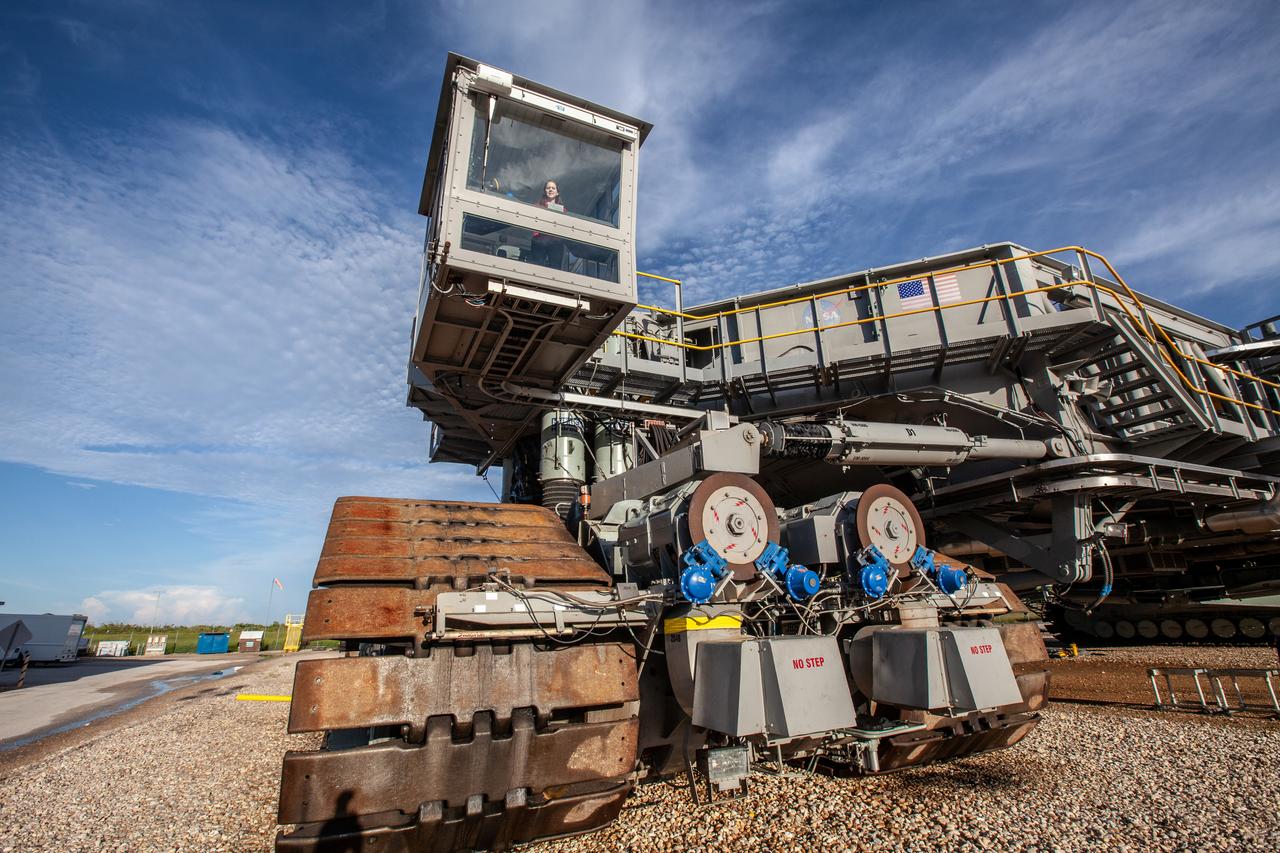

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, is photographed inside the cab of NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
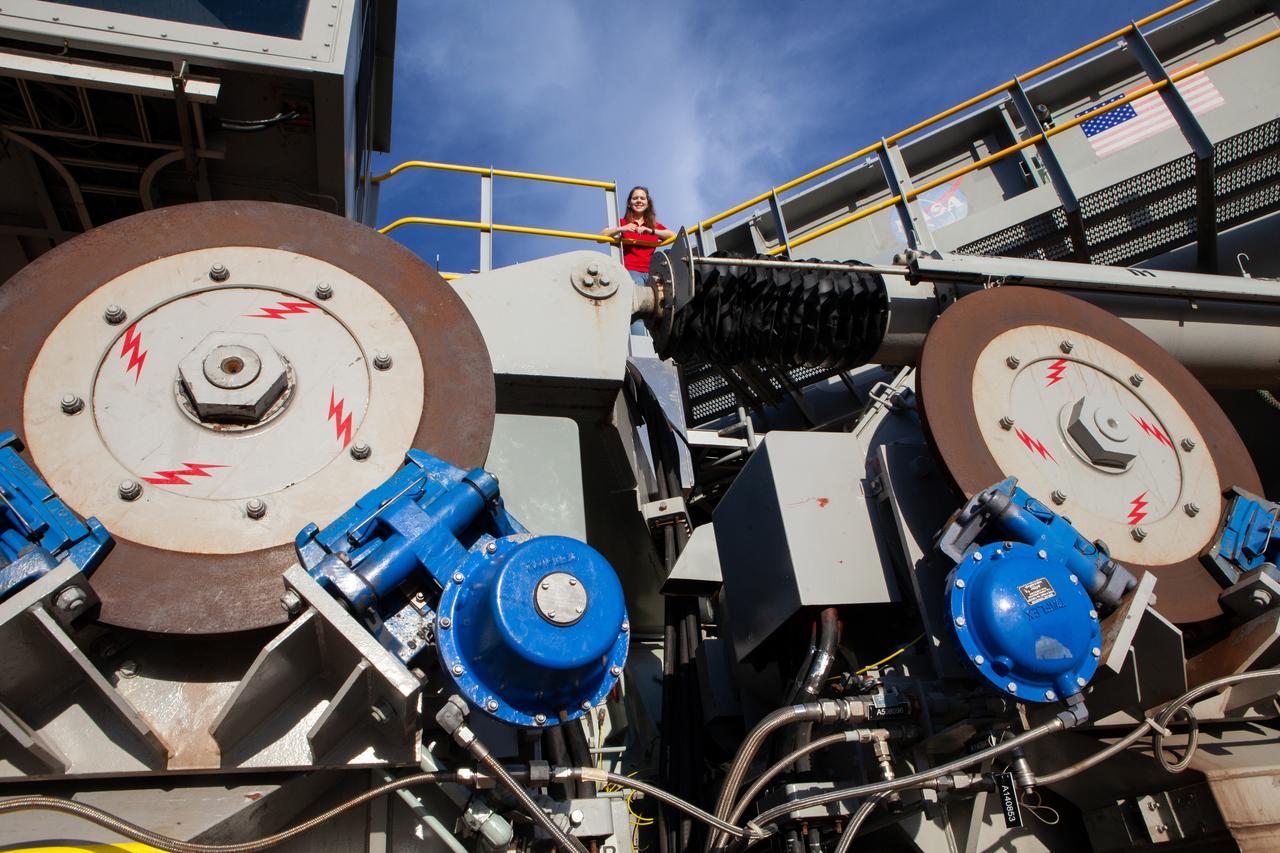

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, is photographed atop NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
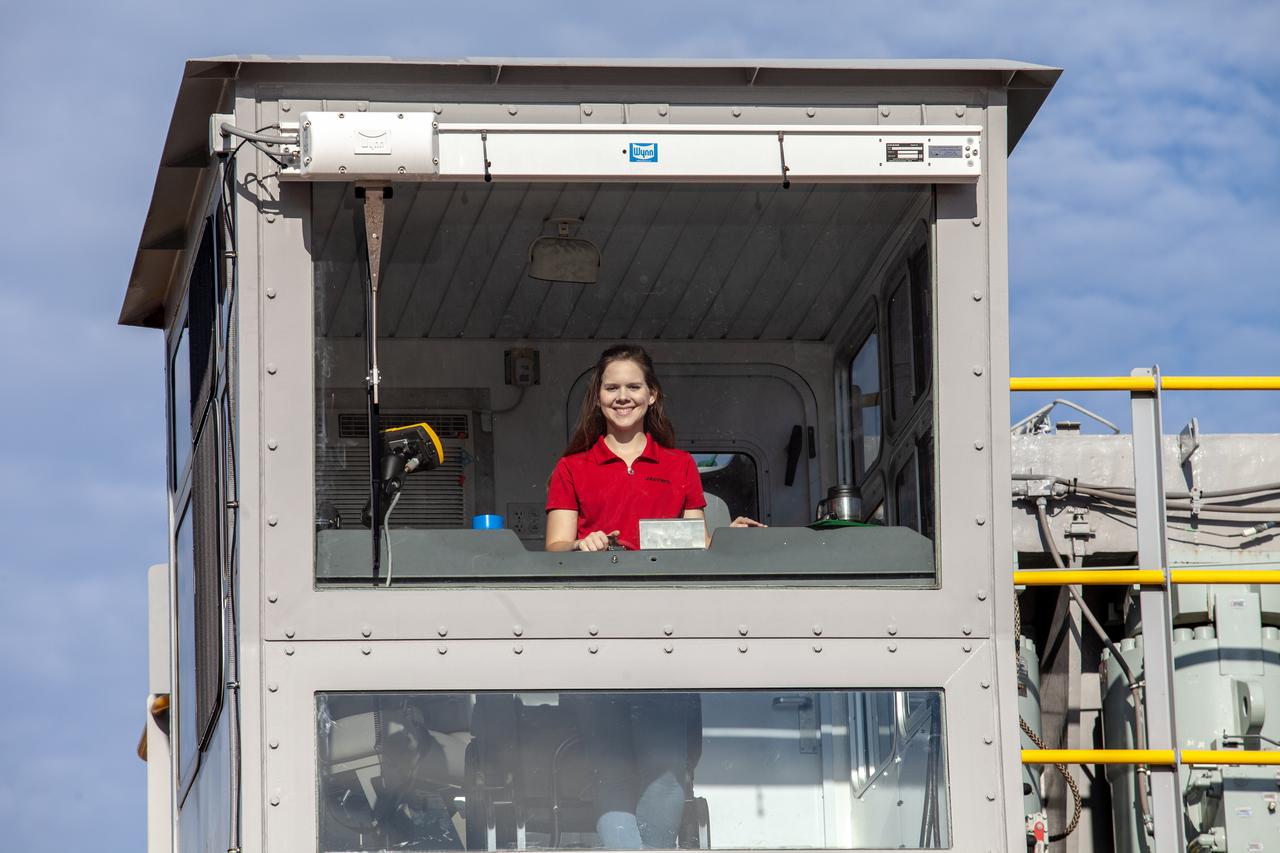

Mechanical Engineer I Breanne Stichler is photographed inside the cab of NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
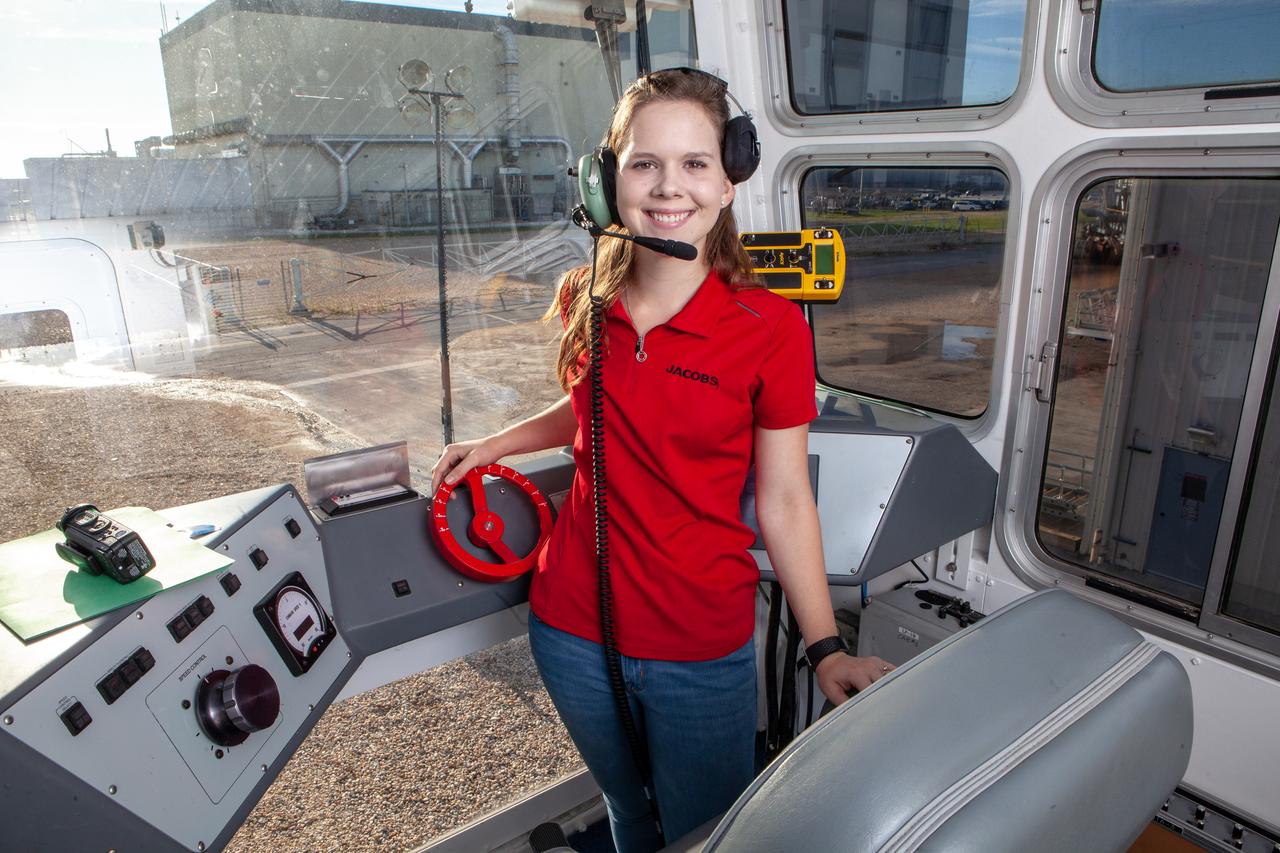

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, is photographed inside the cab of NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
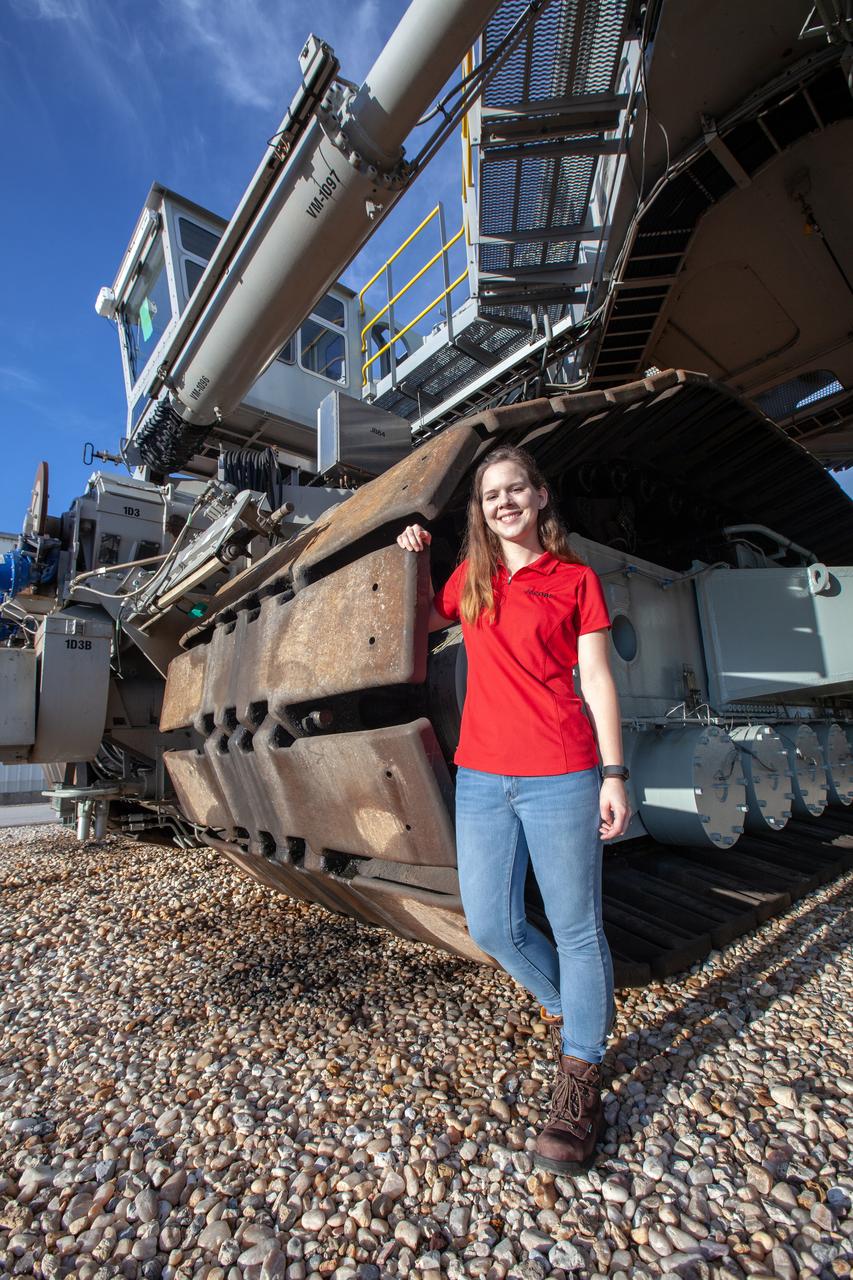

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, is photographed with NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
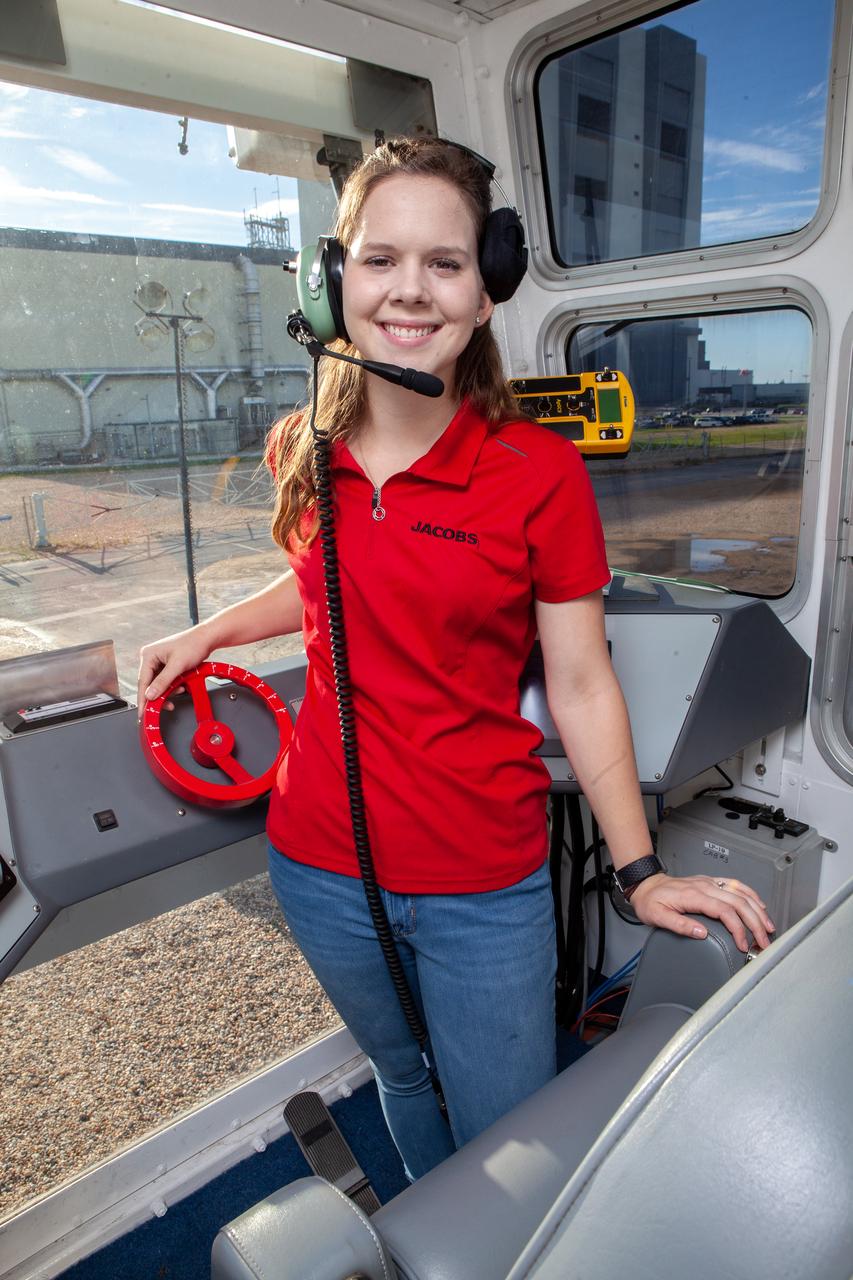

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, is photographed inside the cab of NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
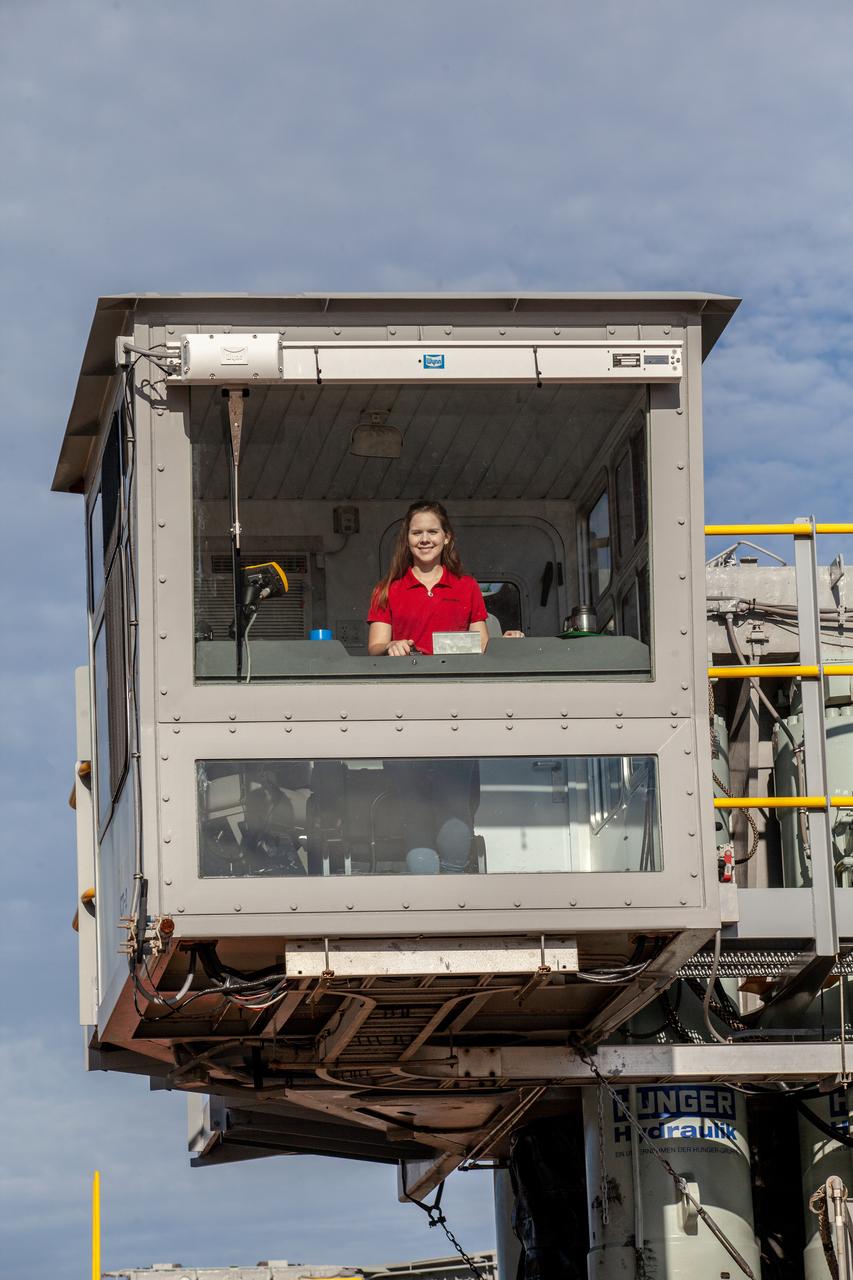

Mechanical Engineer I Breanne Stichler is photographed inside the cab of NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
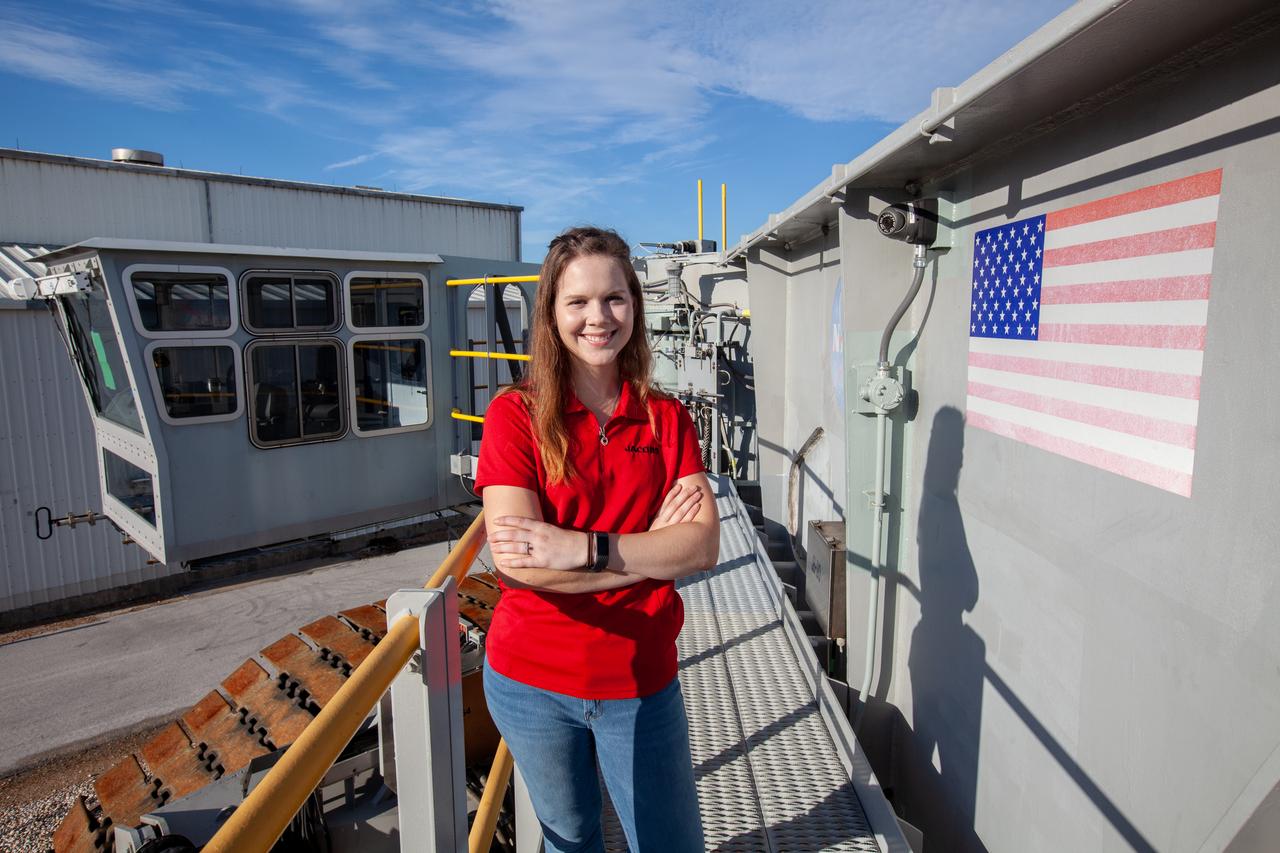

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, stands atop NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
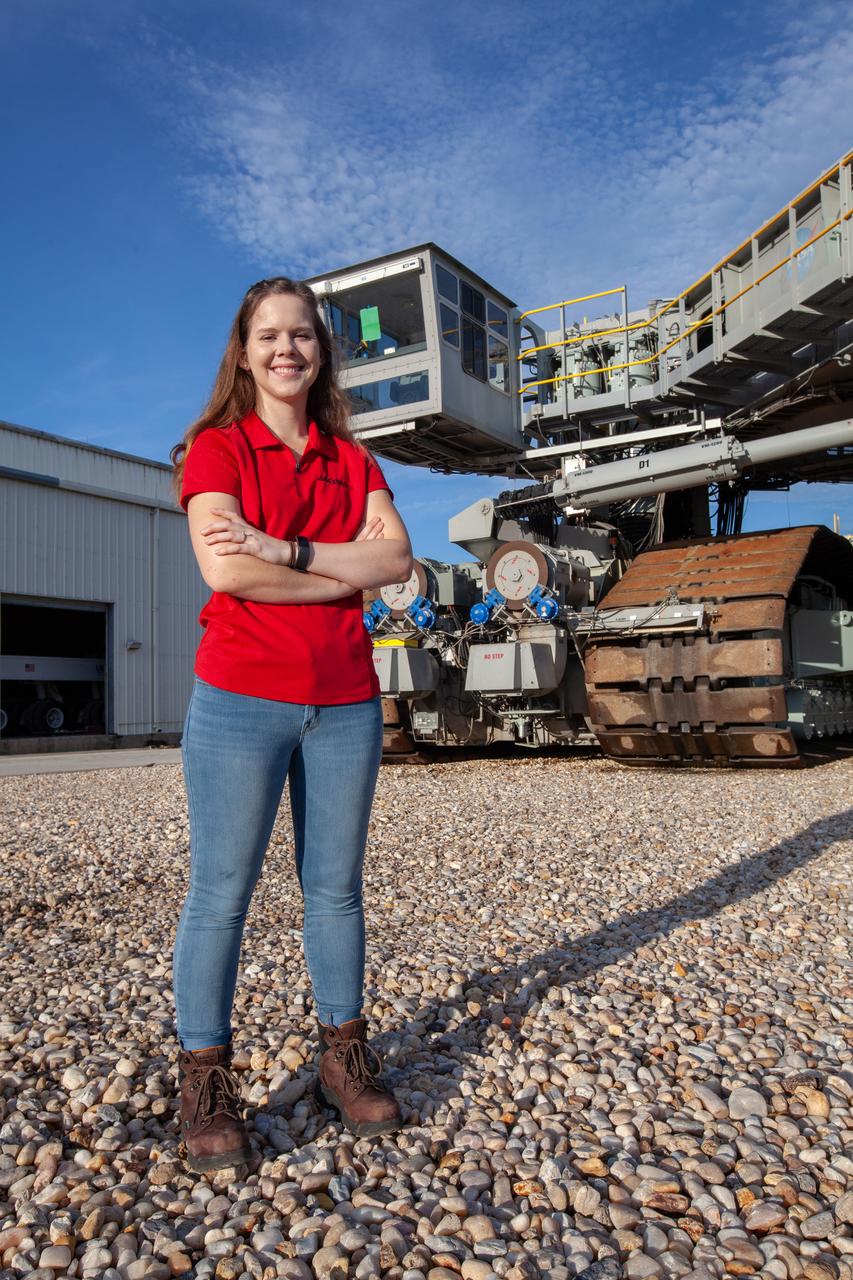

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, is photographed in front of NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
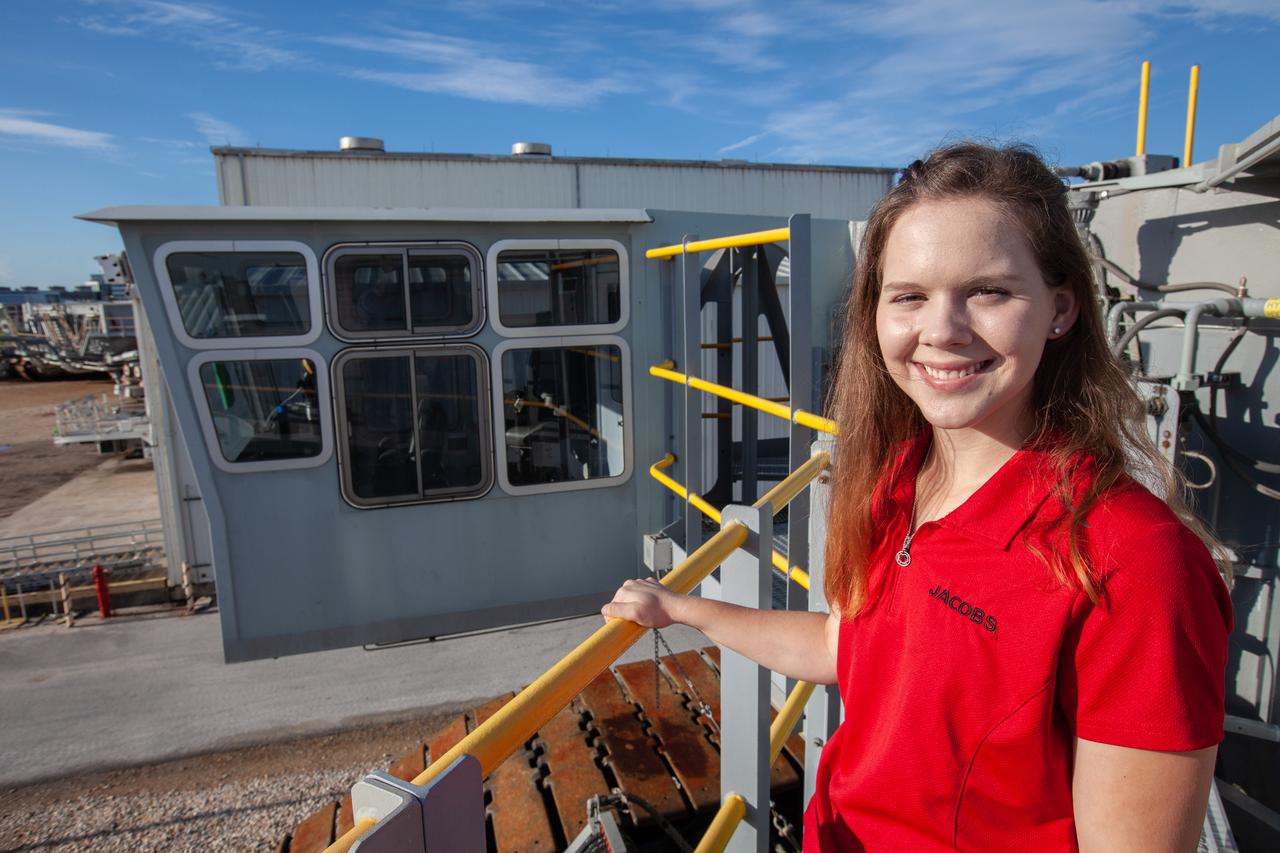

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, stands atop NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
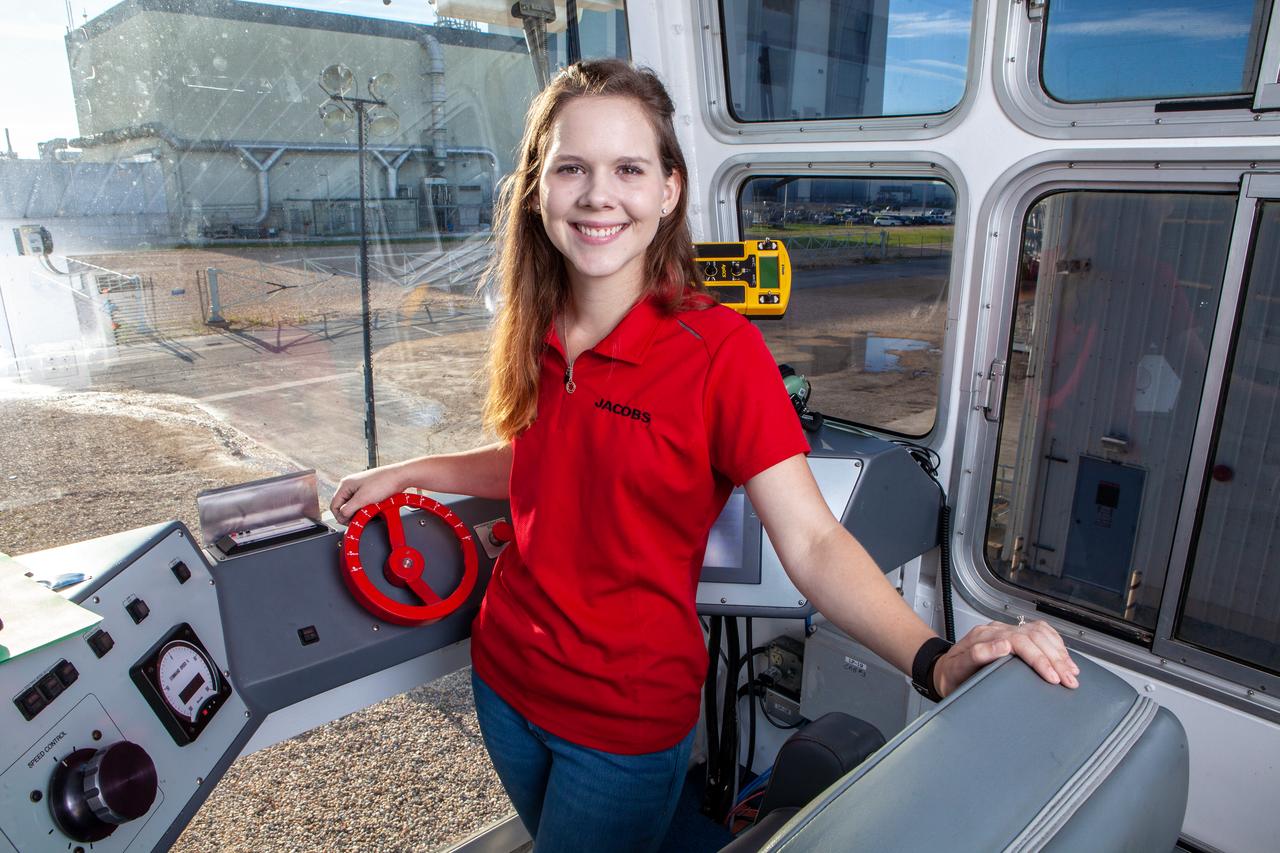

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, is photographed inside the cab of NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
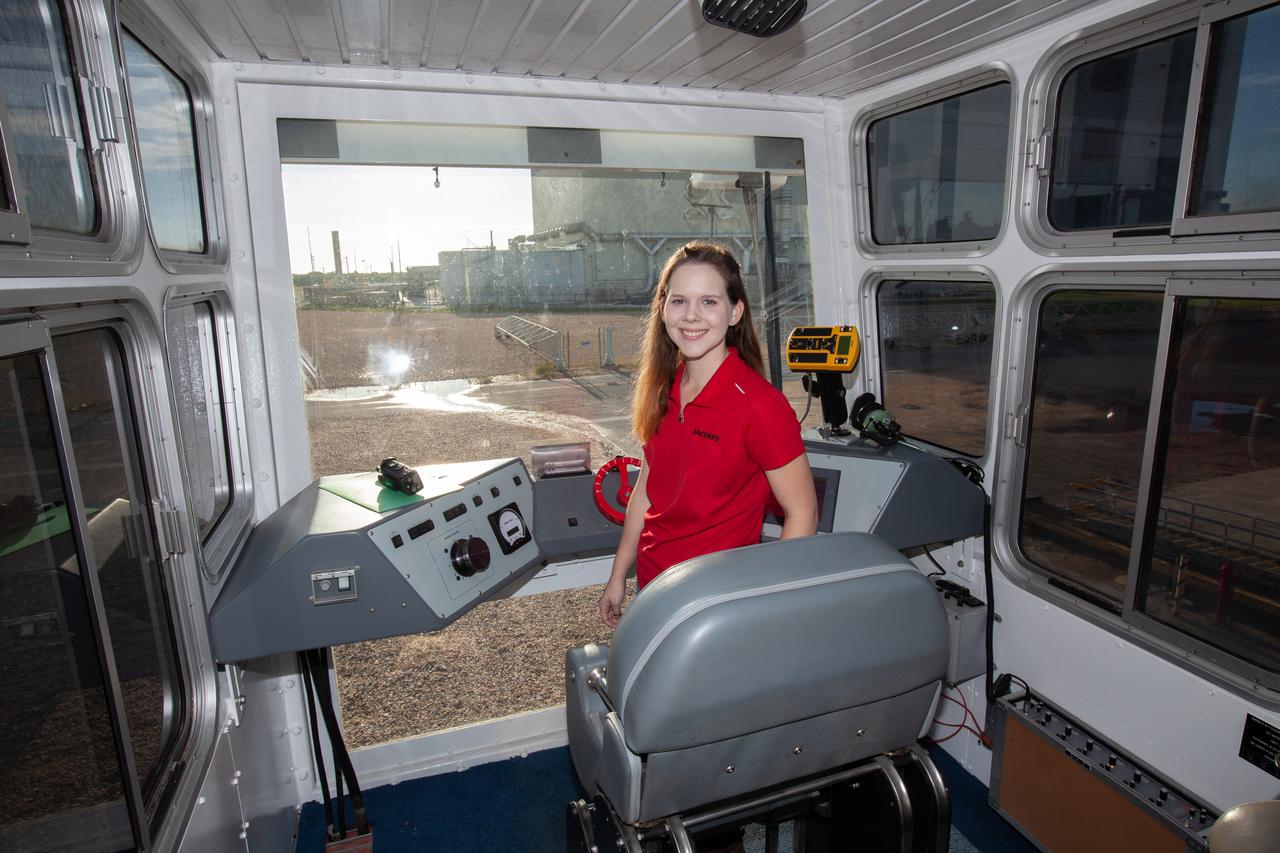

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, is photographed inside the cab of NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
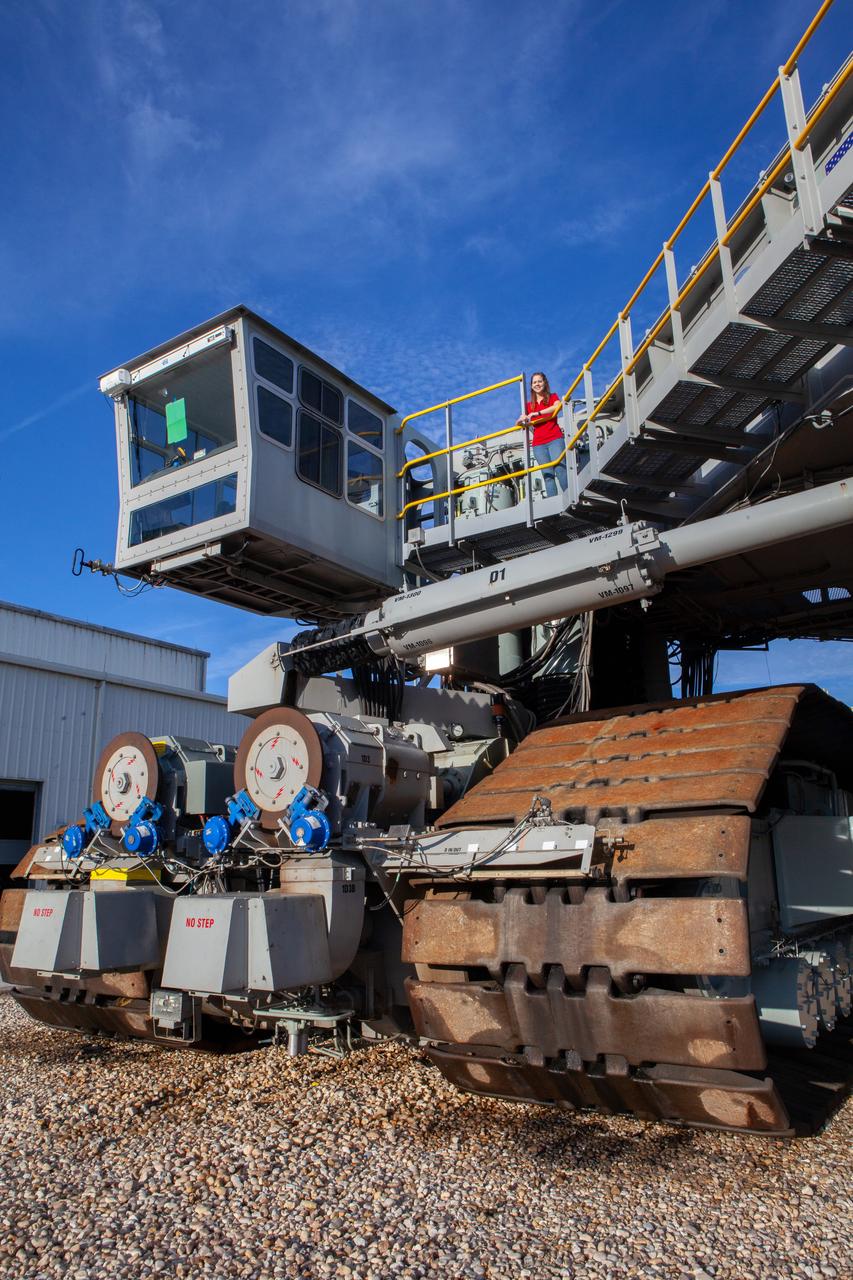

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, stands atop NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
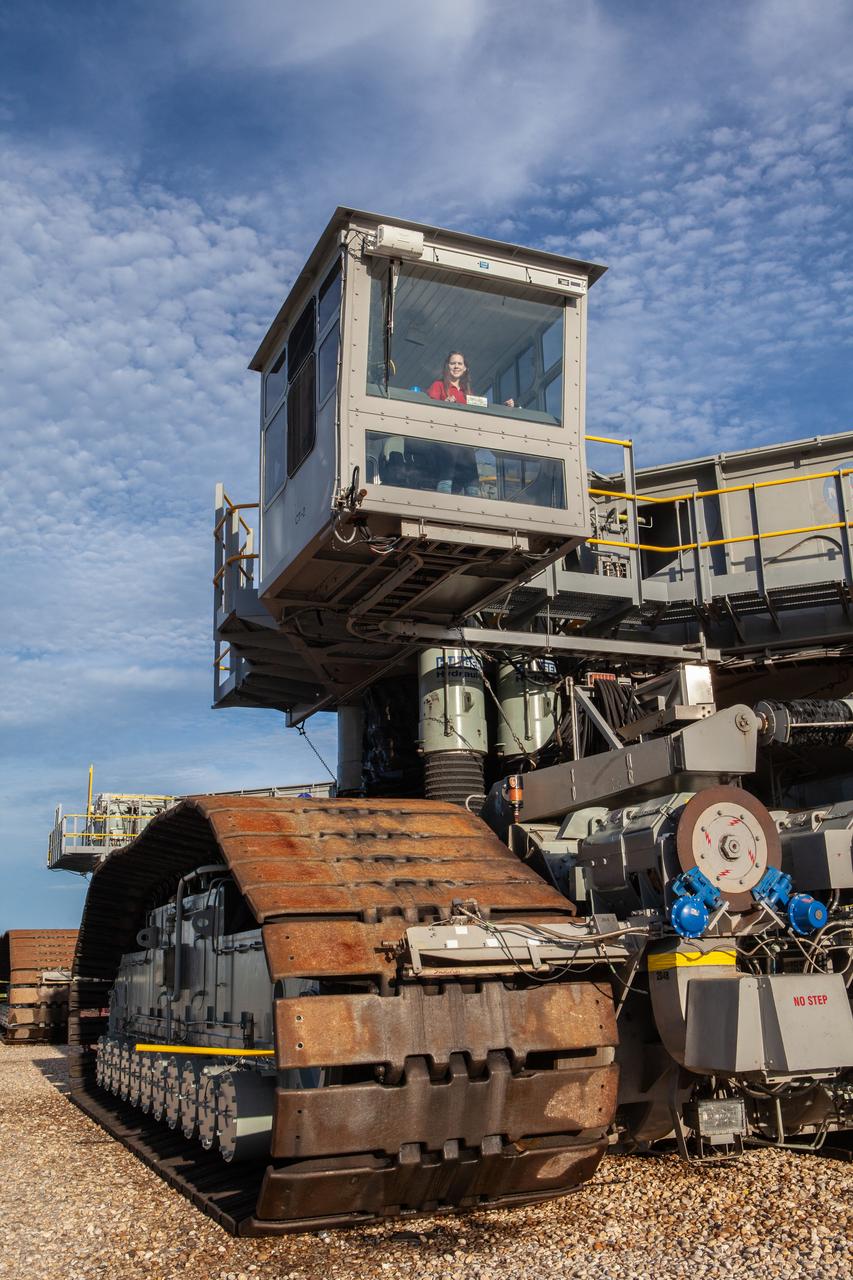

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, is photographed inside the cab of NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
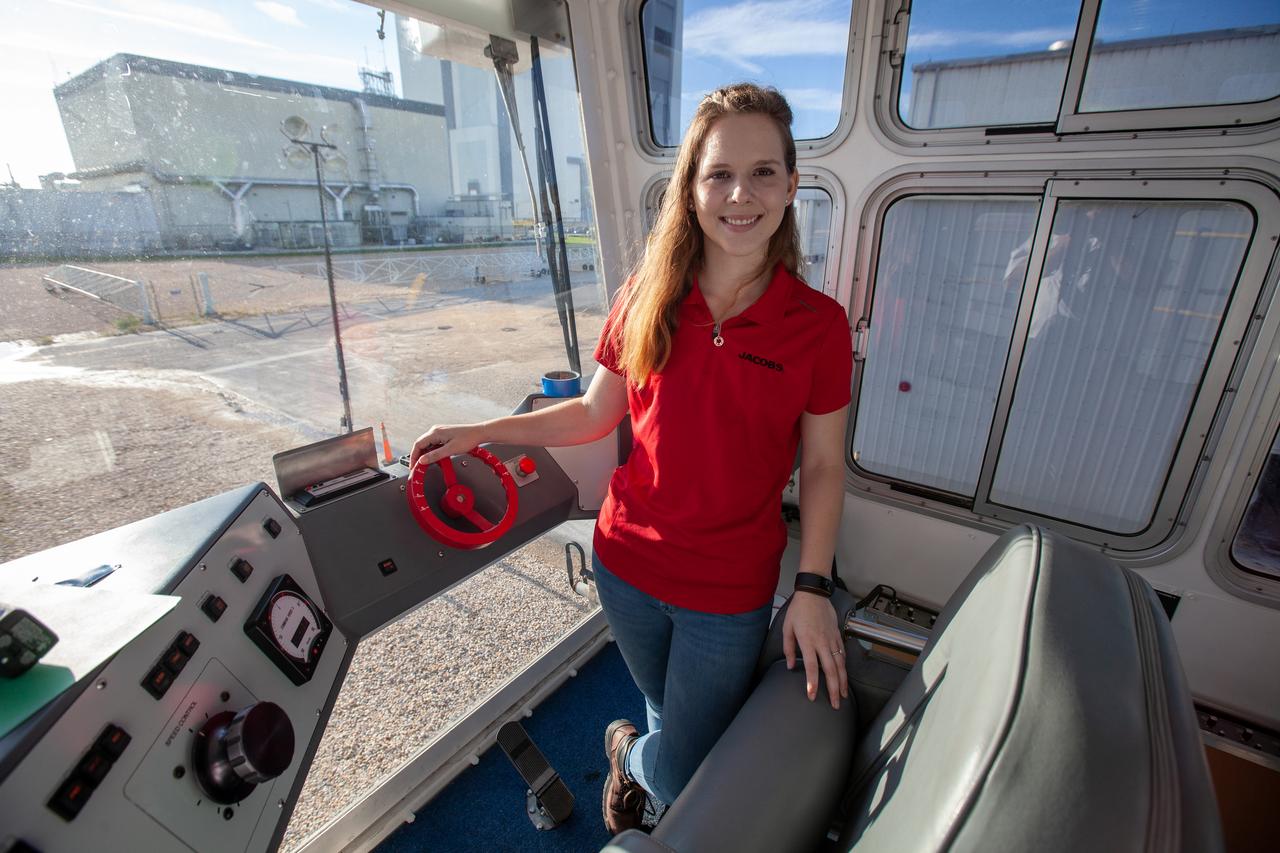

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, is photographed inside the cab of NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
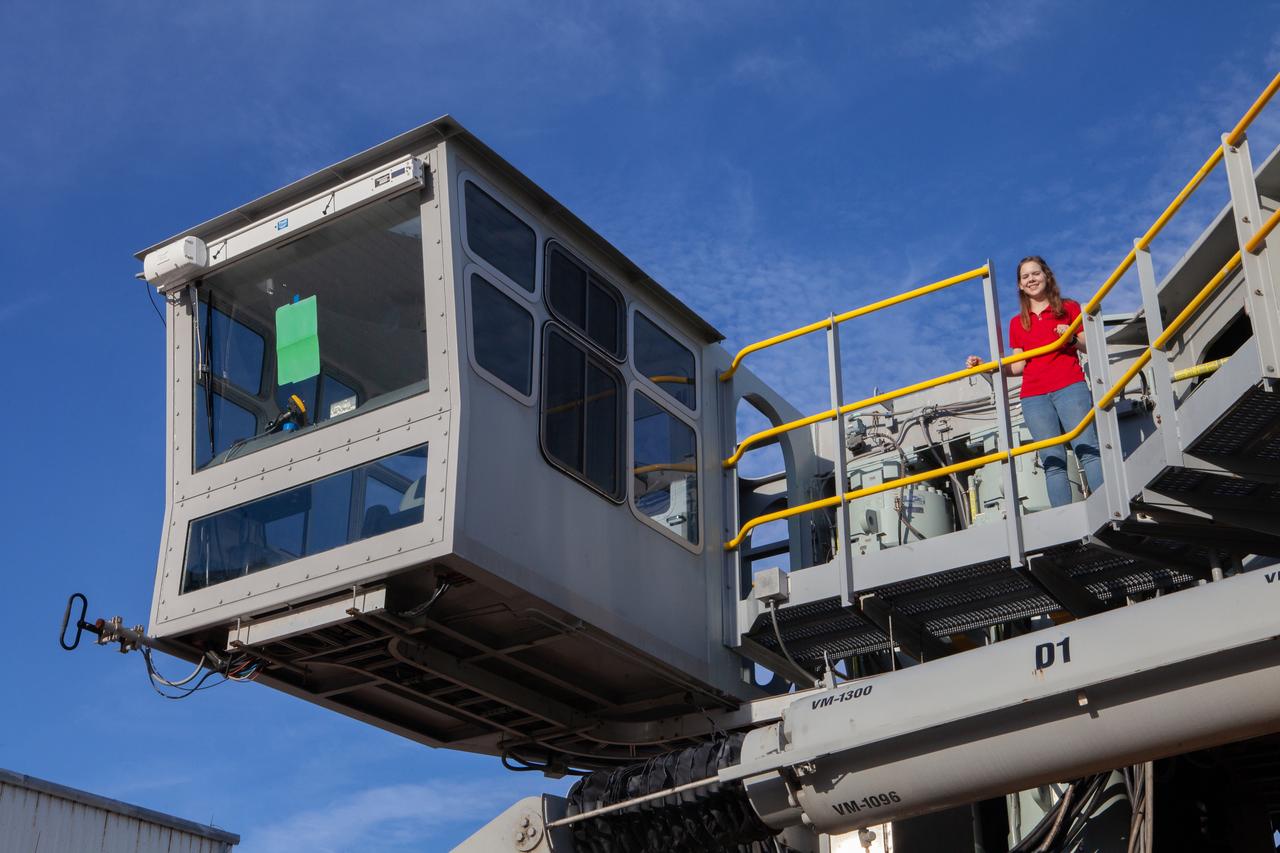

Breanne Stichler, mechanical engineer I, is photographed next to the cab of NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
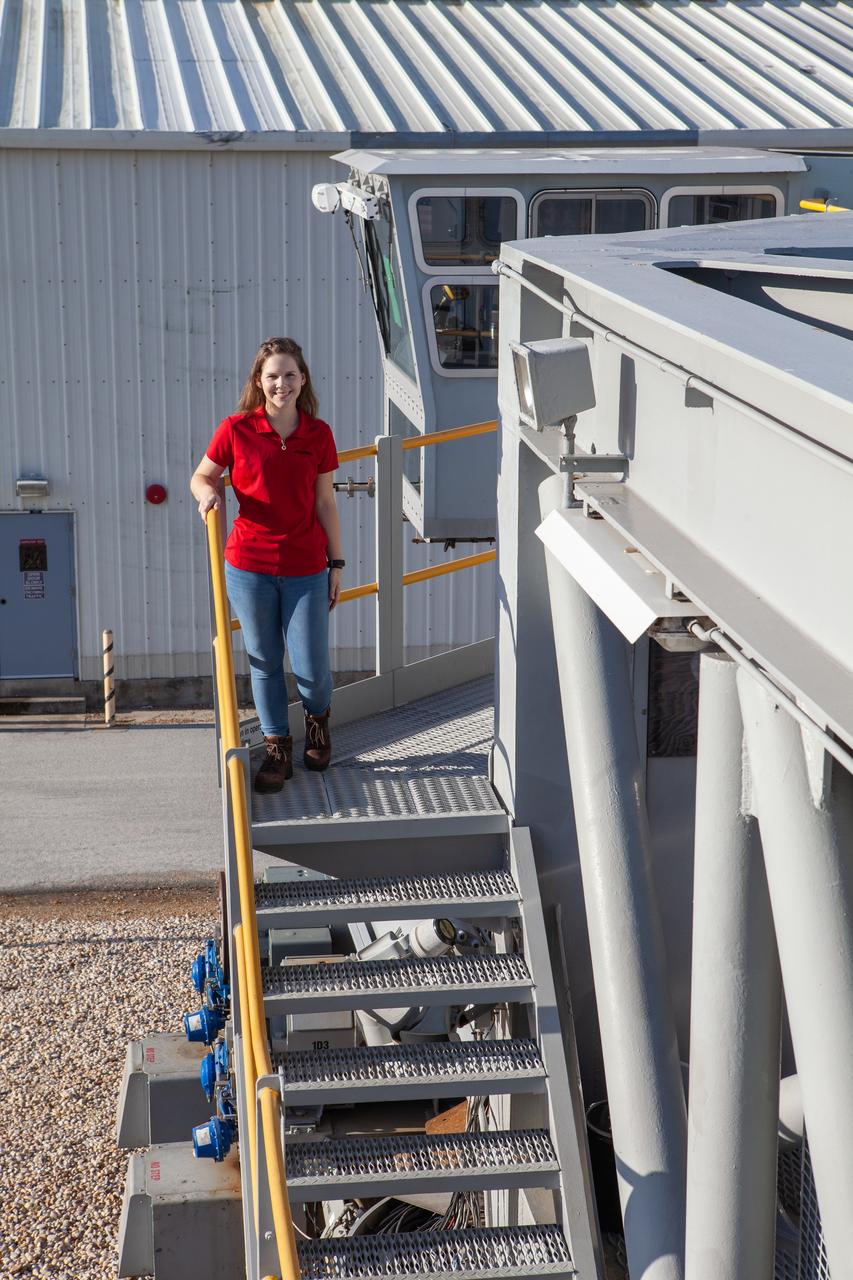

Mechanical Engineer I Breanne Stichler is photographed atop NASA’s Crawler-Transporter 2 (CT-2) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 8, 2019. Stichler started working at Kennedy in June and is among one of the few females to have ever driven the crawler. CT-2 will carry the agency’s mobile launcher with the Space Launch System rocket from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B for the launch of Artemis 1, the first in a series of complex missions that will provide the foundation for human deep space exploration.
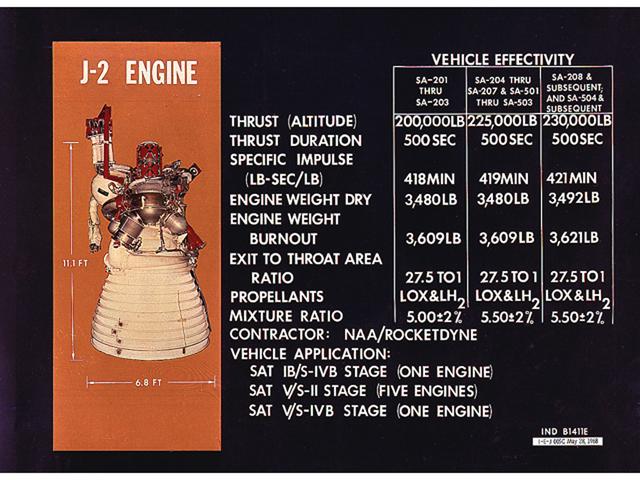
This chart is an illustration of J-2 Engine characteristics. A cluster of five J-2 engines powered the Saturn V S-II (second) stage with each engine providing a thrust of 200,000 pounds. A single J-2 engine powered the S-IVB stage, the Saturn IB second stage, and the Saturn V third stage. The engine was uprated to provide 230,000 pounds of thrust for the fourth Apollo Saturn V flight and subsequent missions. Burning liquid hydrogen as fuel and using liquid oxygen as the oxidizer, the cluster of five J-2 engines for the S-II stage burned over one ton of propellant per second, during about 6 1/2 minutes of operation, to take the vehicle to an altitude of about 108 miles and a speed of near orbital velocity, about 17,400 miles per hour.
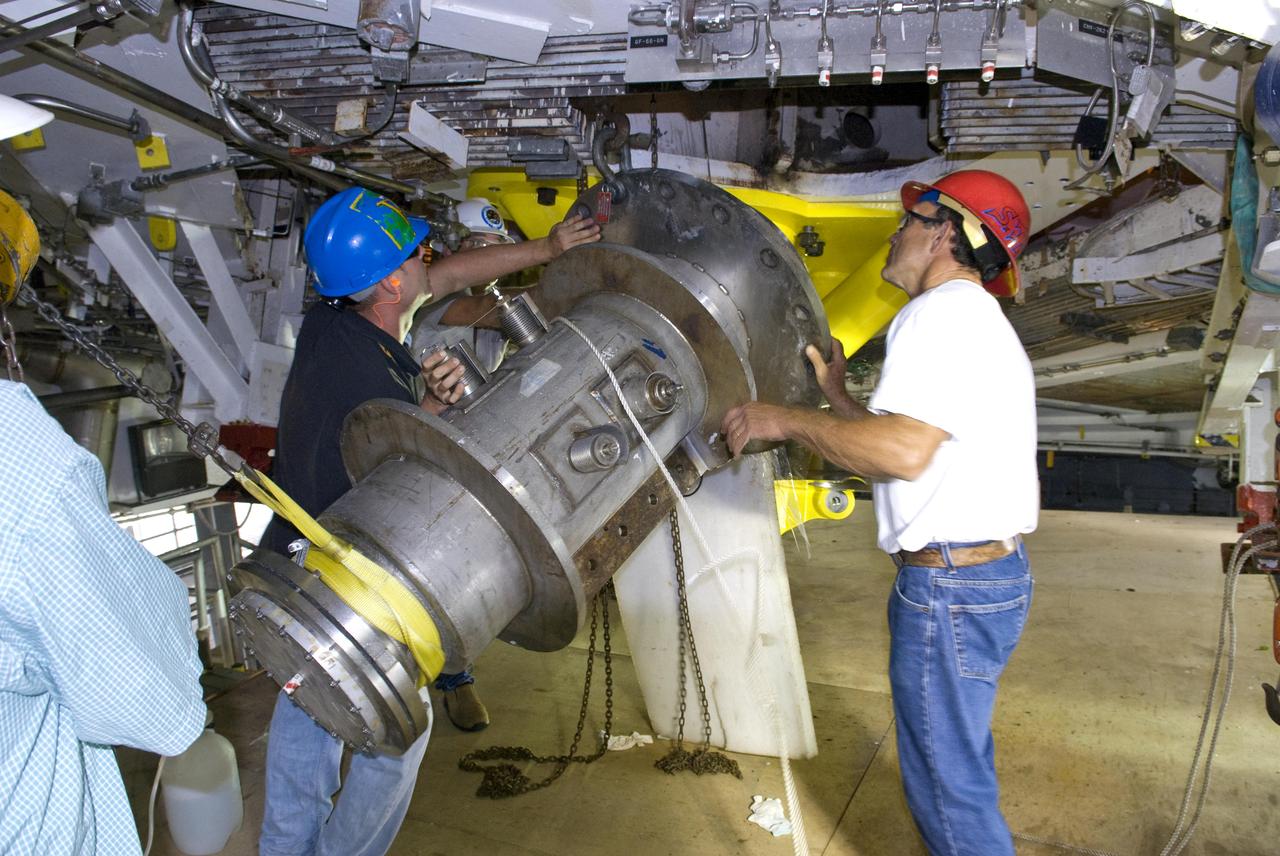

John C. Stennis Space Center employees remove space shuttle main engine run ducts from the A-2 Test Stand engine deck Oct. 25, 2010. Testing of space shuttle main engines concluded in July 2009. Stennis is preparing the A-2 Test Stand for testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine being developed. Testing of the new engine is scheduled to begin in 2011.
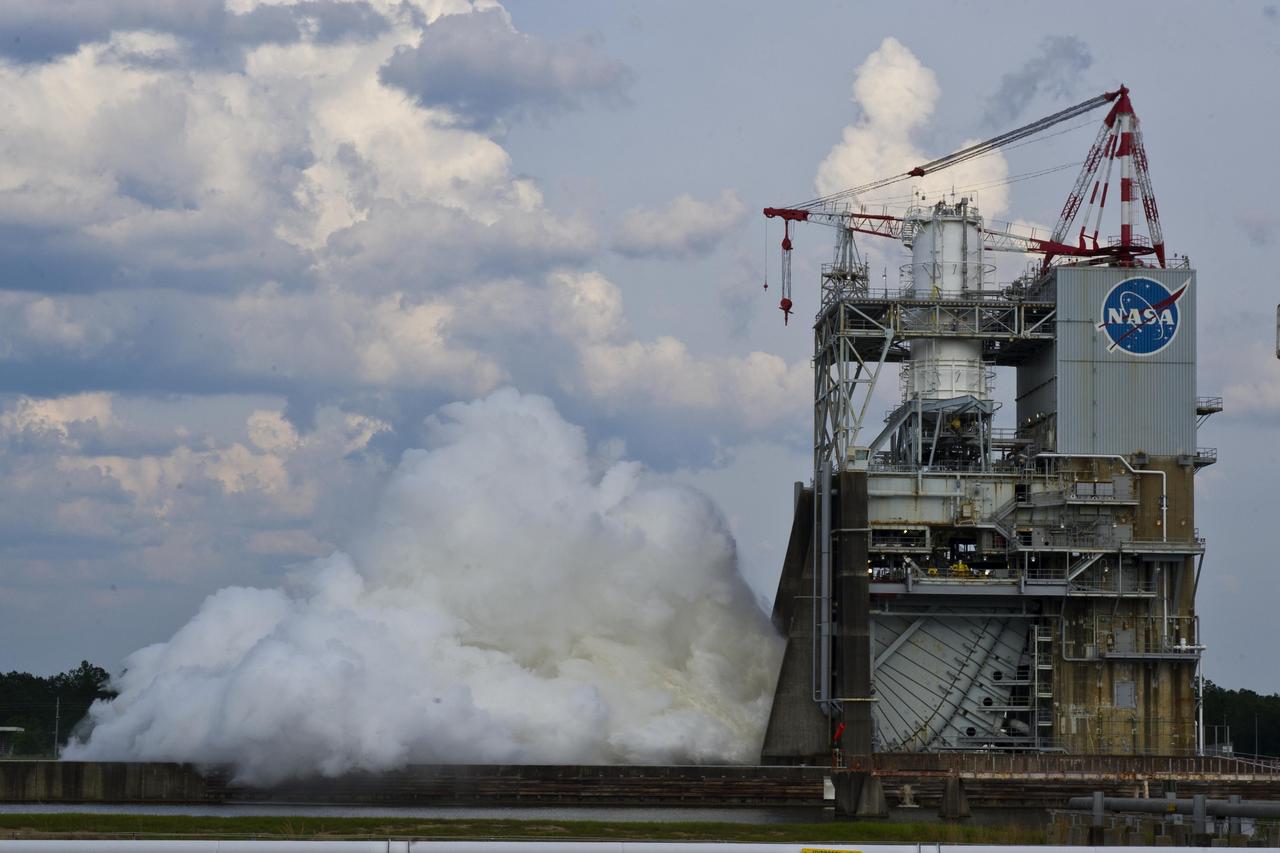

NASA conducted a successful seven-second test of the next-generation J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on May 16, 2012. The J-2X is being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne.

The J-2 engine for Saturn V S-IVB (third) stage blasted from the test stand at Douglas Aircraft Co., Sacramento Test Operation (SACTO) facility in California. This third stage was used on the unmarned Saturn V flight of Apollo 6 in April 1968.
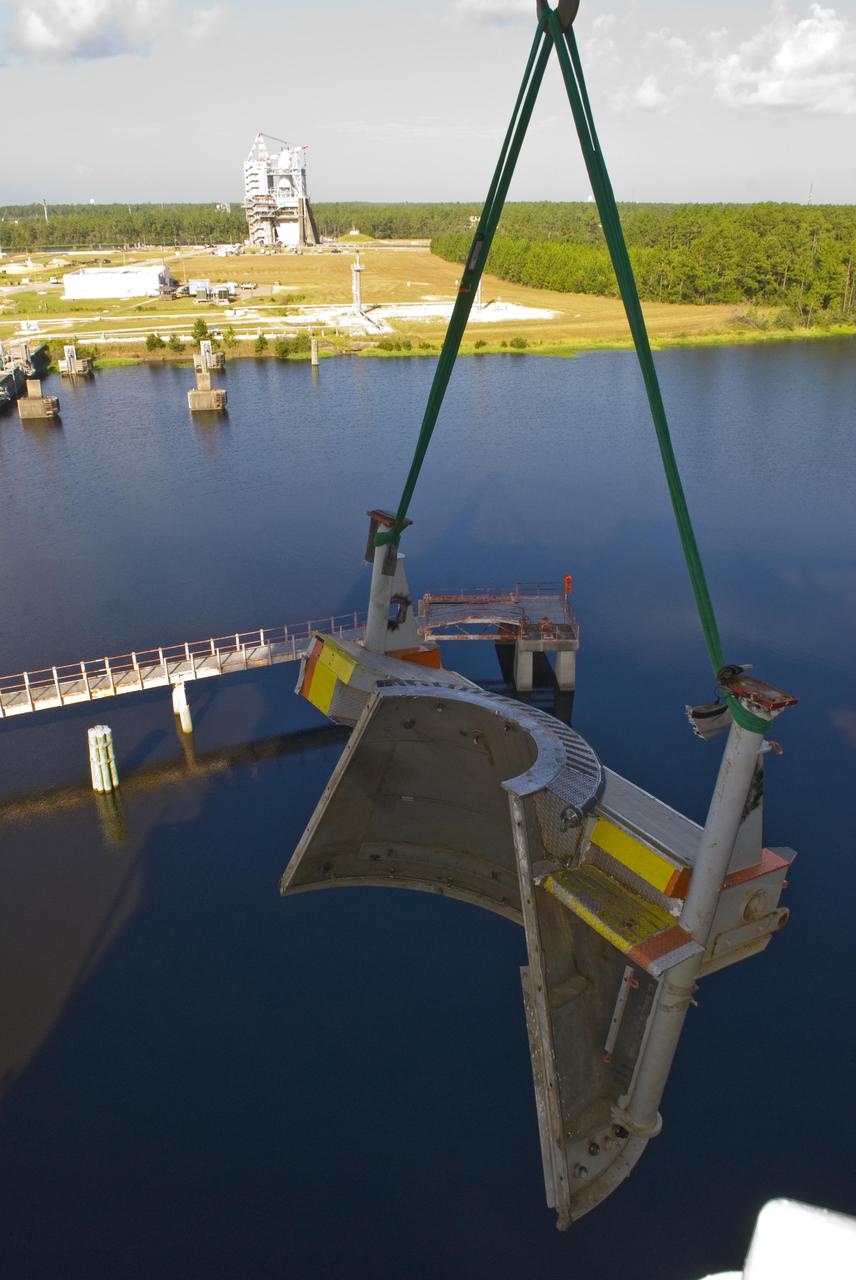

John C. Stennis Space Center employees remove one-half of the A-2 Test Stand clamshell used for testing space shuttle main engines. Space shuttle main engine testing concluded July 2009; the A-2 stand now is being prepared for testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine in development. Testing of the J-2X engine is scheduled to begin in 2011.
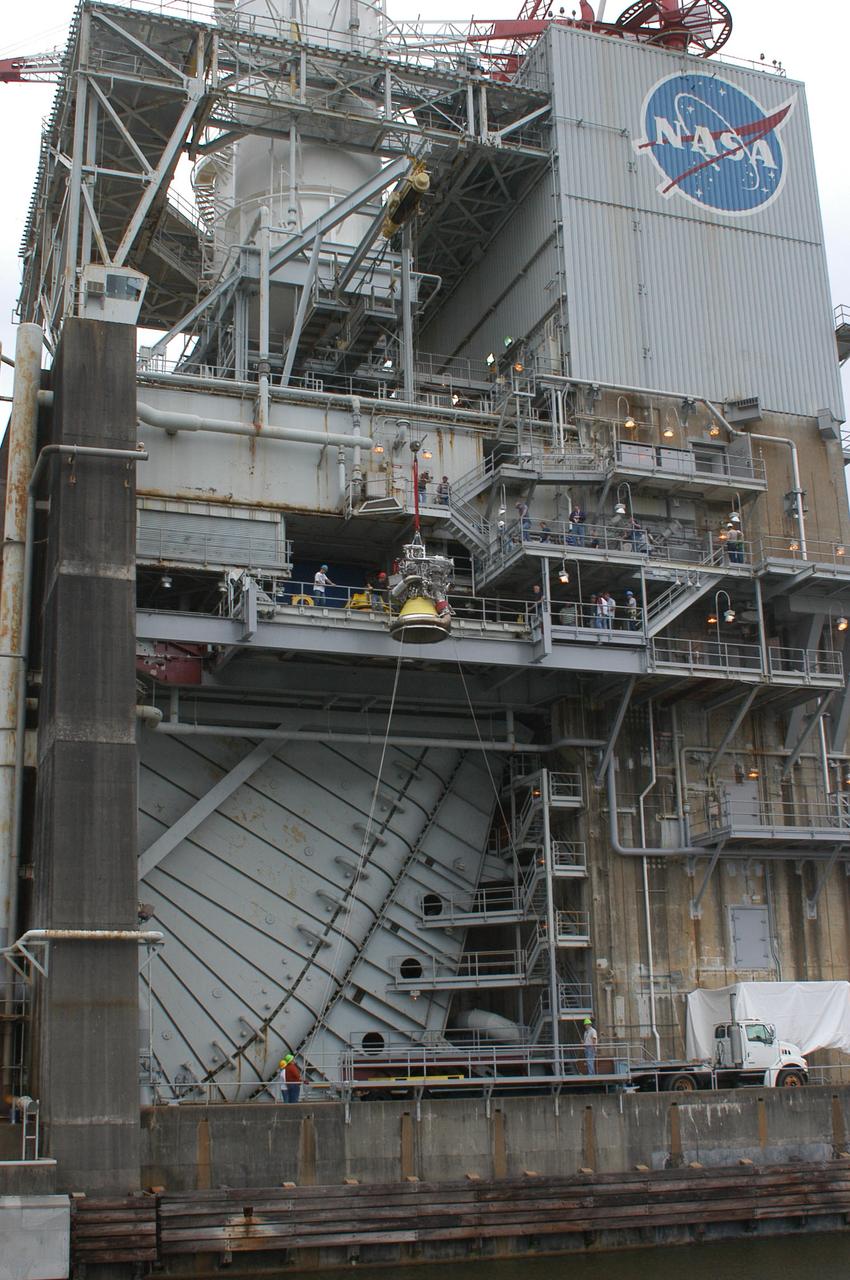

J-2X engine No. 10001 is returned March 8, 2012, to the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center for its second round of tests. The developmental engine underwent an initial series of tests last year. The J-2X engine is being built for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne.
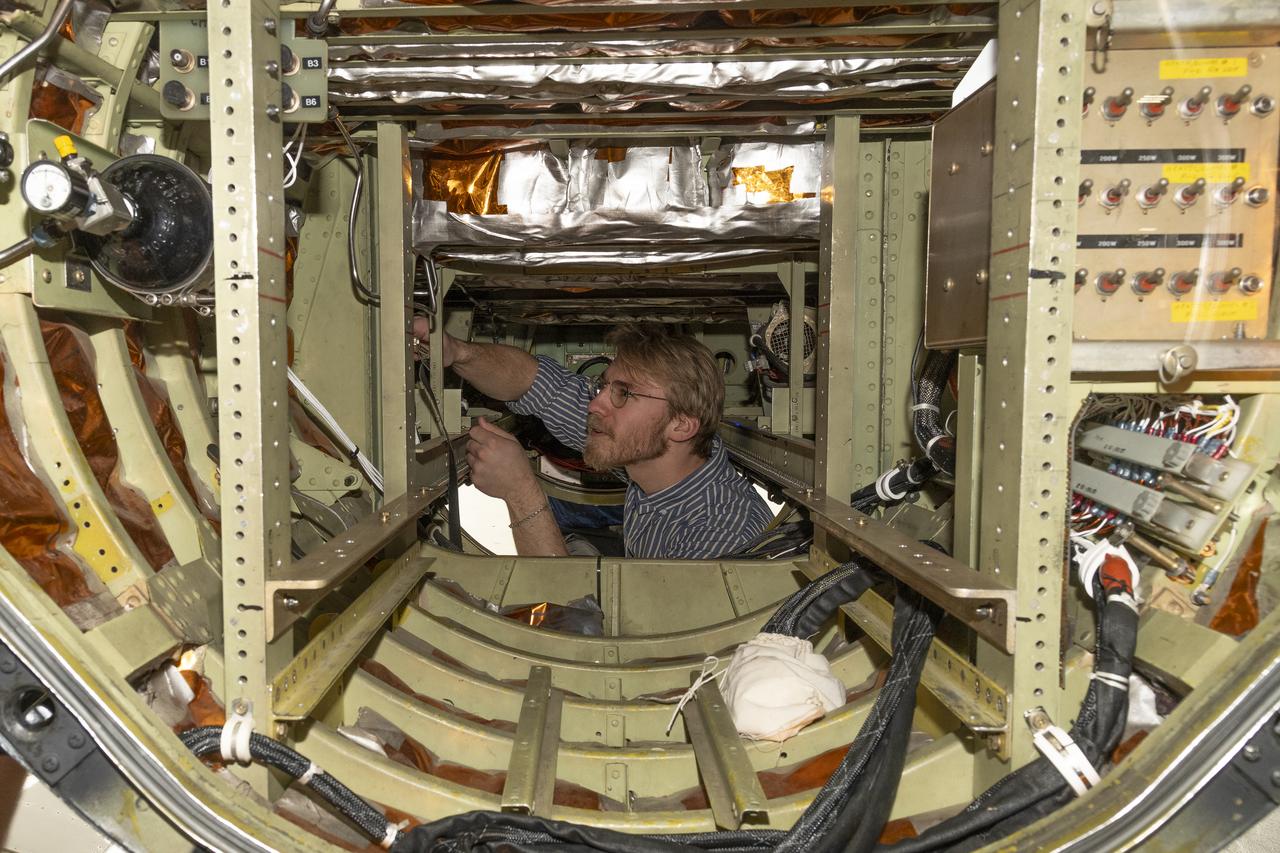

A team of experts prepares the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California for the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Researcher Jackson Begolka from the University of Iowa examines the instrument connectors in the ER-2 onboard the ER-2, which flies at high altitudes to validate satellite-borne data. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
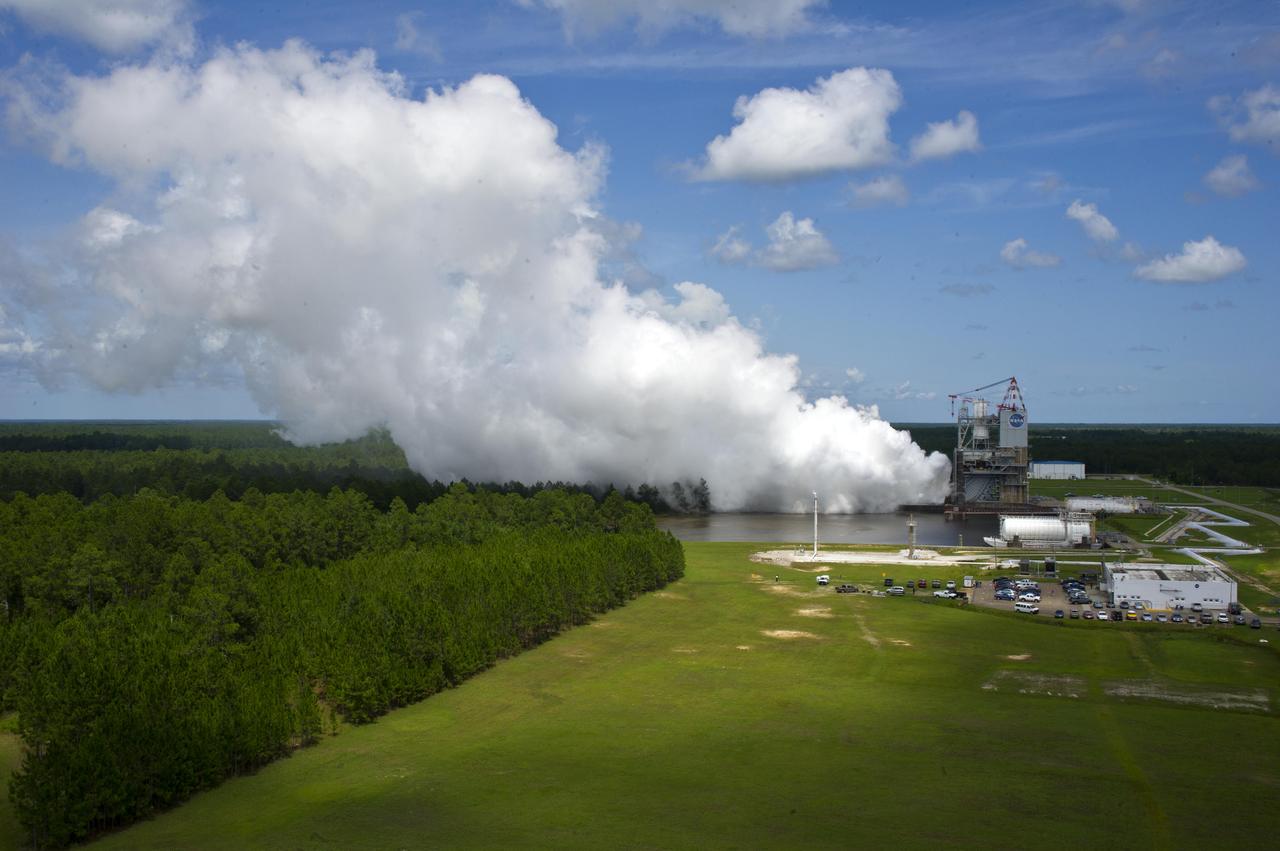

NASA's test of the J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on July 13 was picture perfect in more ways than one. Not only did the test provide a breathtaking view from atop the nearby A-1 Test Stand, and with the center's B-1/B-2 Test Stand in the background, but it achieved its target of 550 seconds. The test continued a series of firings to gather critical data for engine development.
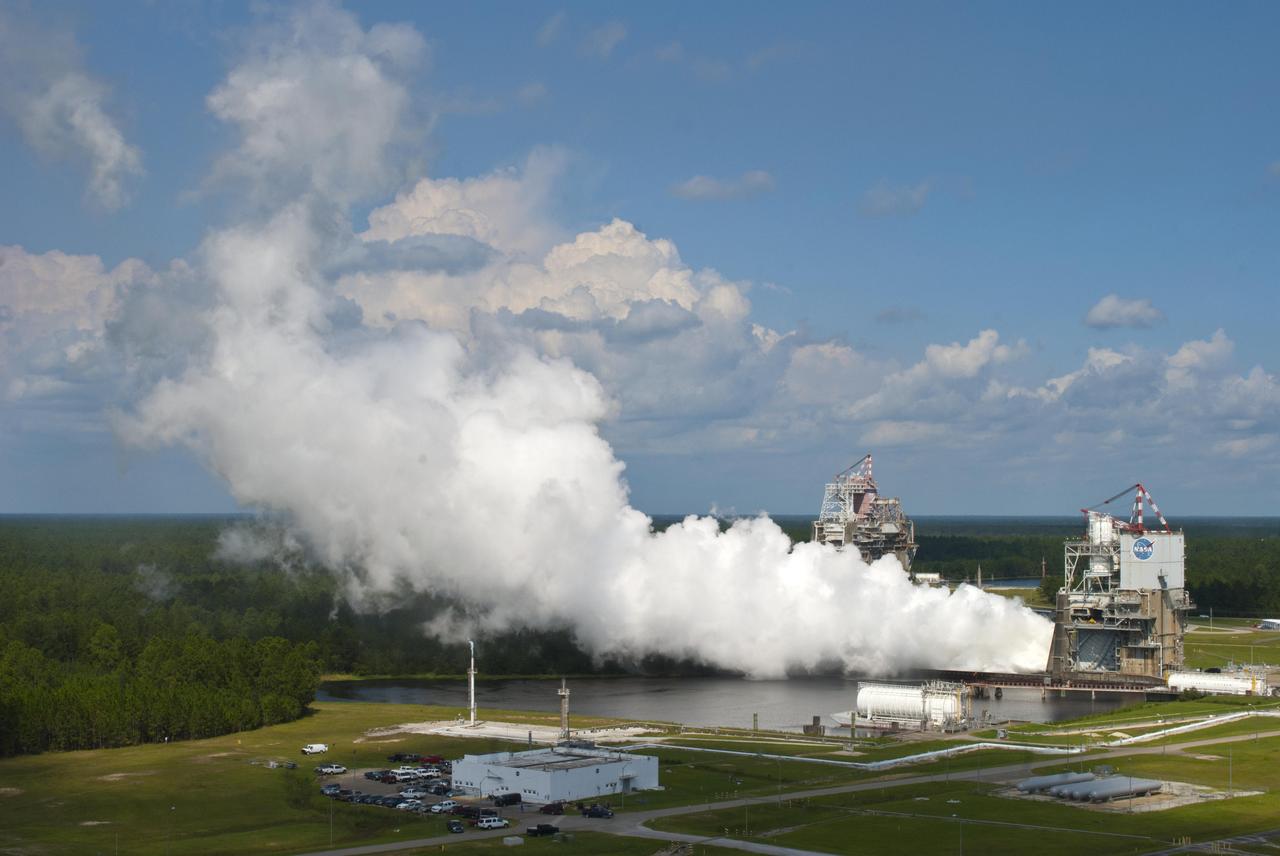

NASA engineers continued testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine at Stennis Space Center with a 250-second test on Sept. 7. The test was the first conducted after the arrival of Hurricane Isaac forced closure of the Stennis facility for three days in late August. The est was conducted on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis. The facility's B-1/B-2 Test Stand can be seen in the left background.
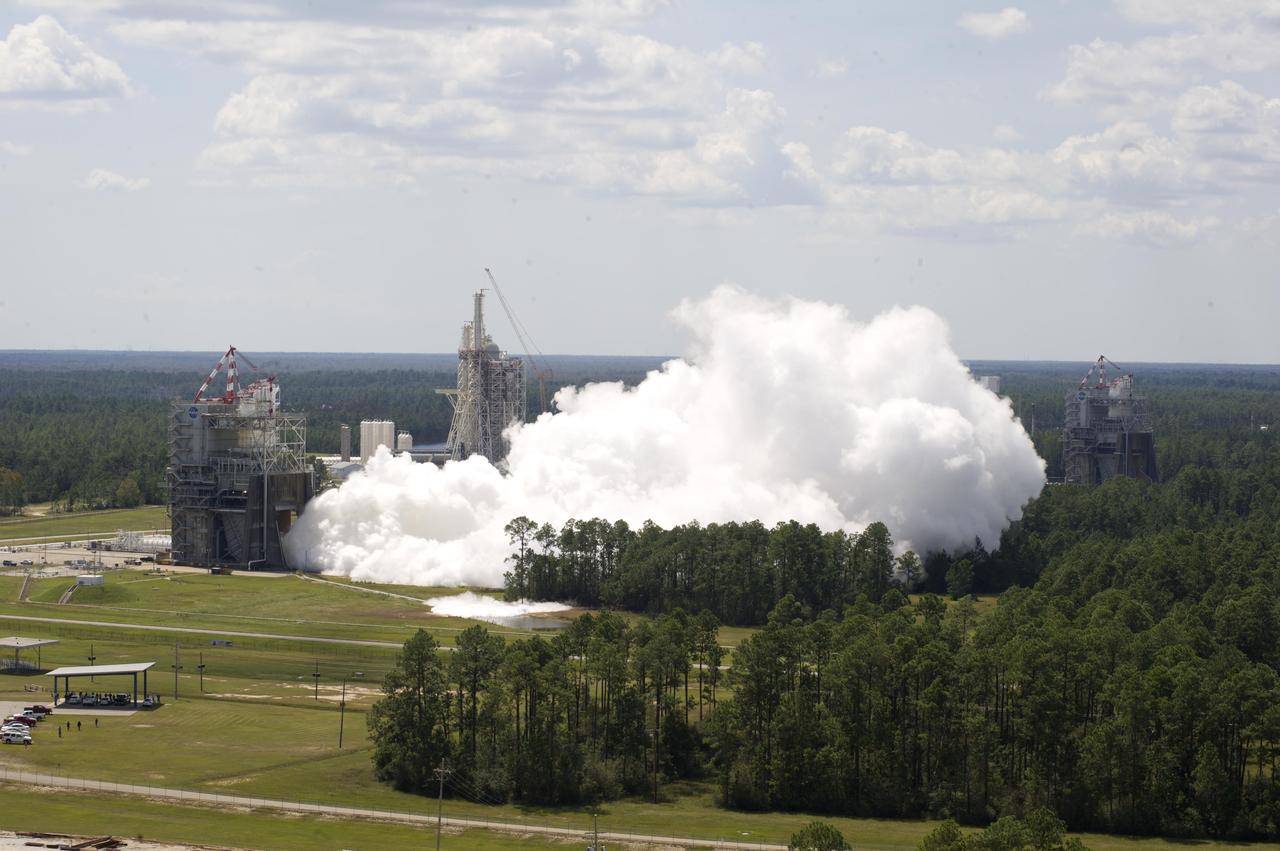

NASA engineers continued to collect test performance data on the new J-2X rocket engine at Stennis Space Center with a 250-second test Sept. 14. The test on the A-2 Test Stand was the 19th in a series of firings to gather critical data for continued development of the engine. The J-2X is being developed by Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne for NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. It is the first liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen rocket engine rated to carry humans into space to be developed in 40 years.
A team of experts prepares the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California for the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Researcher Jennifer Moore checks the cabling on the Roscoe instrument which flew at high altitudes on the ER-2. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
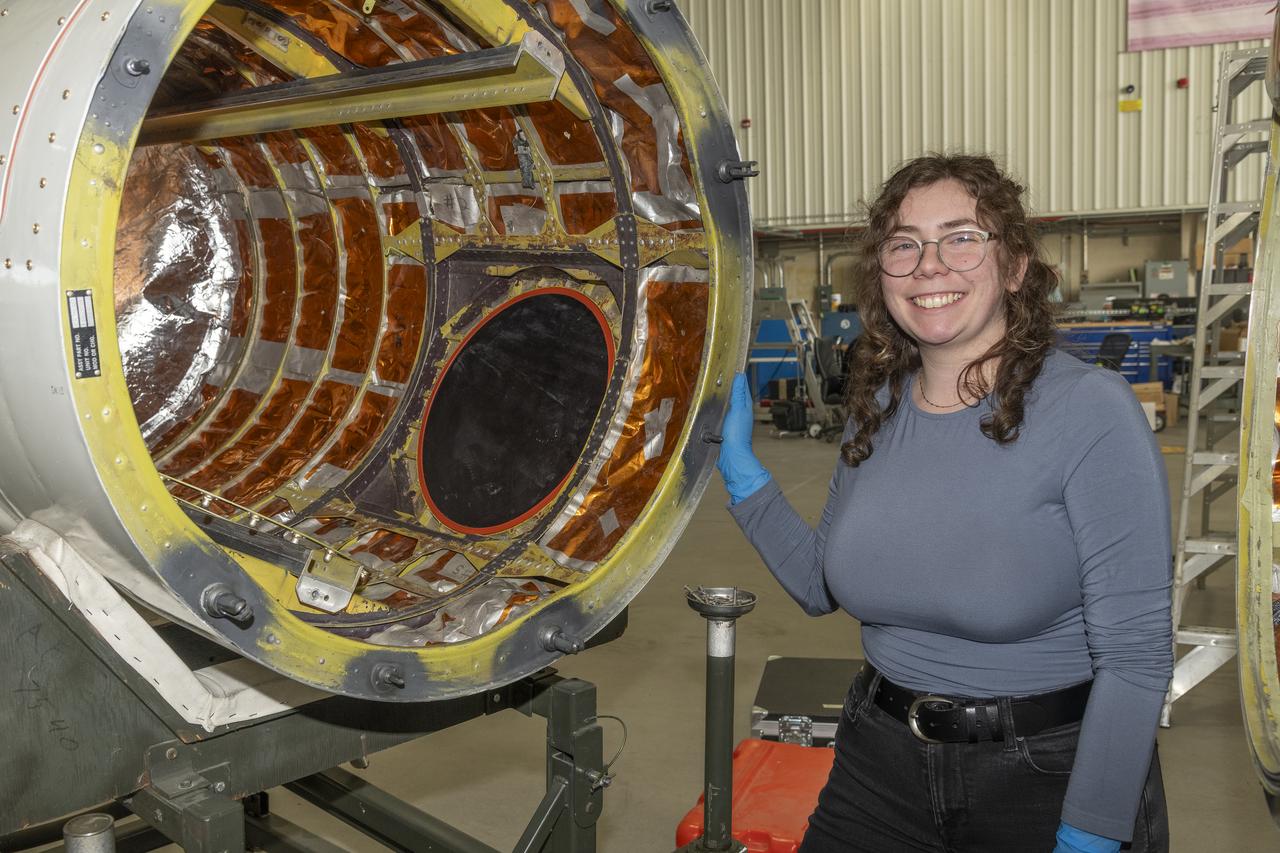

A team of experts prepares the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California for the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Researcher Jennifer Moore from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center smiles beside the ER-2 aircraft’s forebody pod where the Cloud Physics Lidar (CPL) instrument will be installed. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
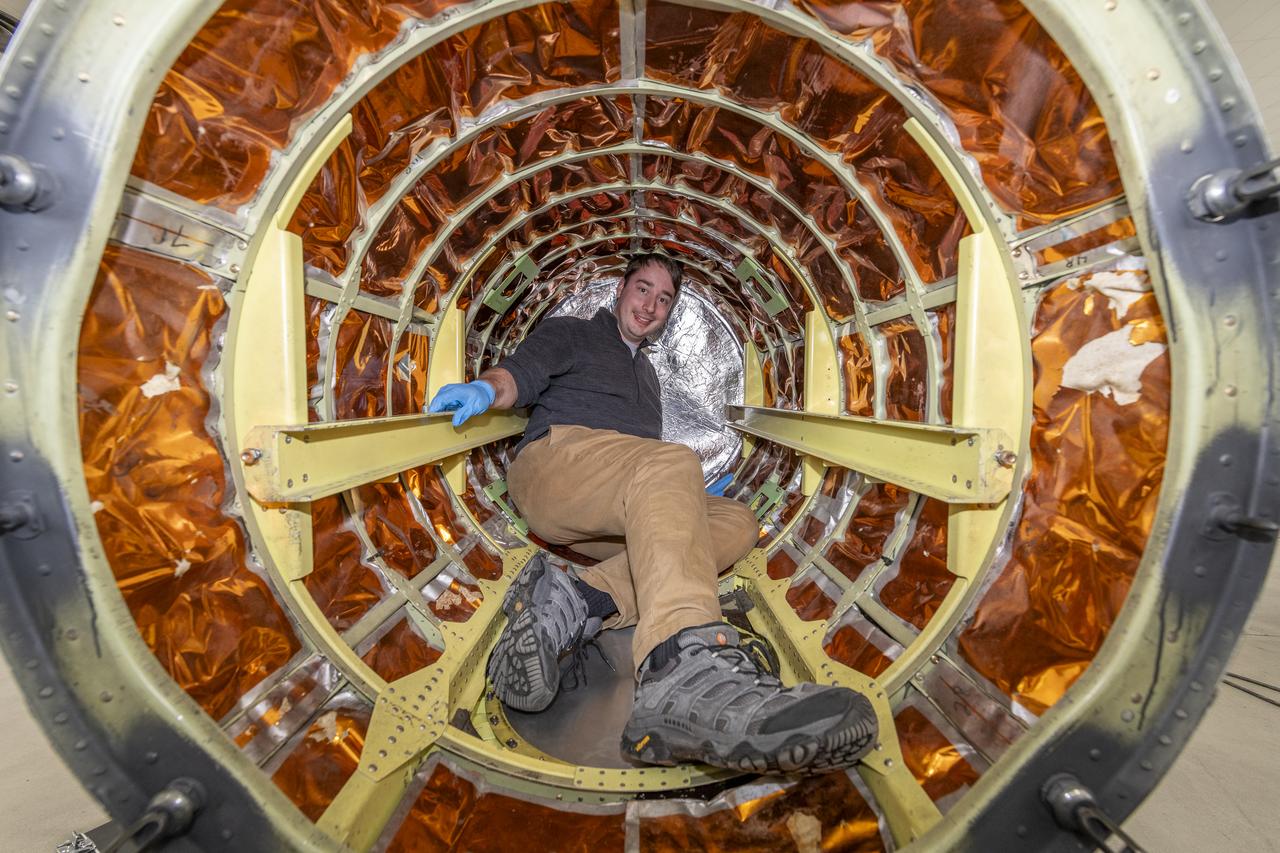

A team of experts prepares the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California for the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Researcher Grant Finneman from the University of Iowa installs the insulations at the front of the ER-2 forebody pod where the Cloud Physics Lidar (CPL) flies. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
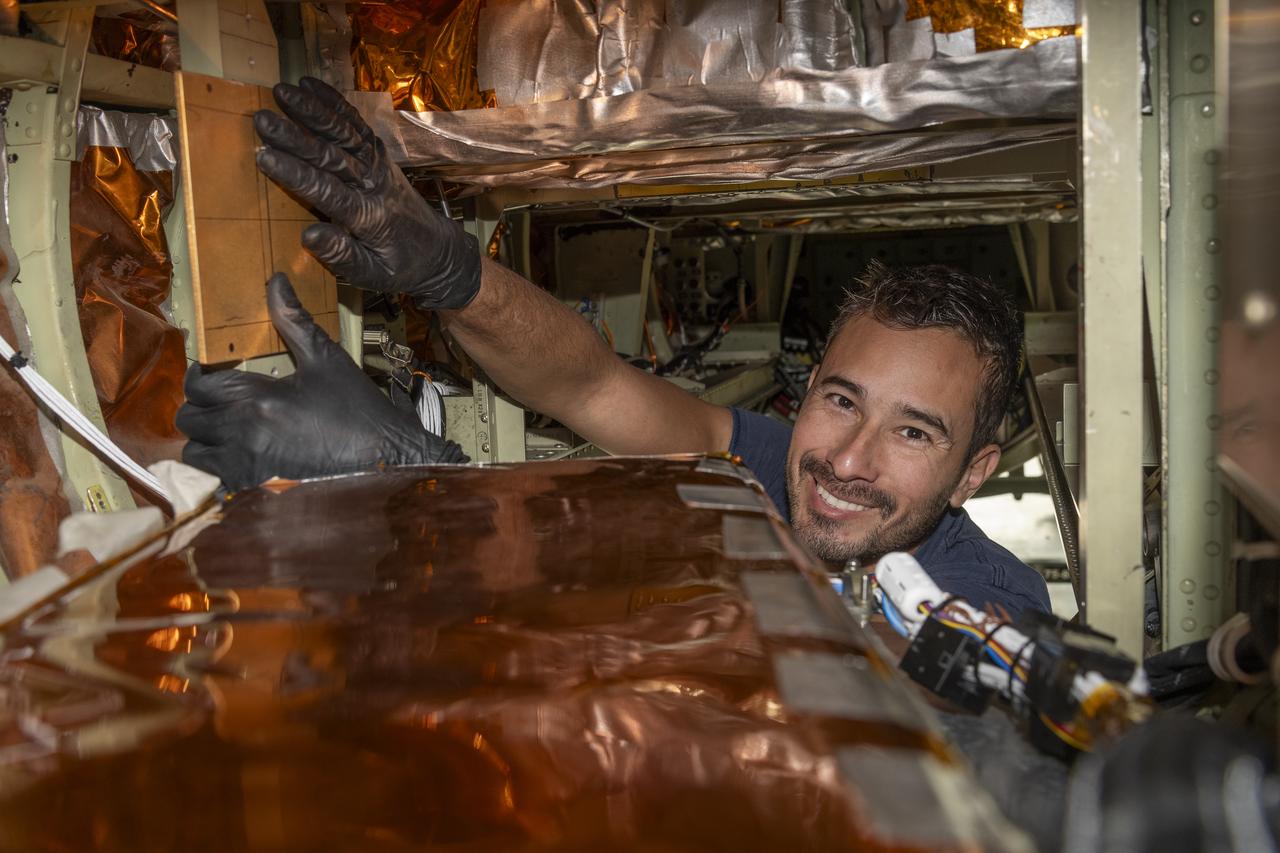

A team of experts prepares the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California for the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Aircraft mechanic Darick Alvarez-Alonzo installs a satellite-simulating instrument which will fly at high altitudes on the ER-2 to validate satellite-borne data. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
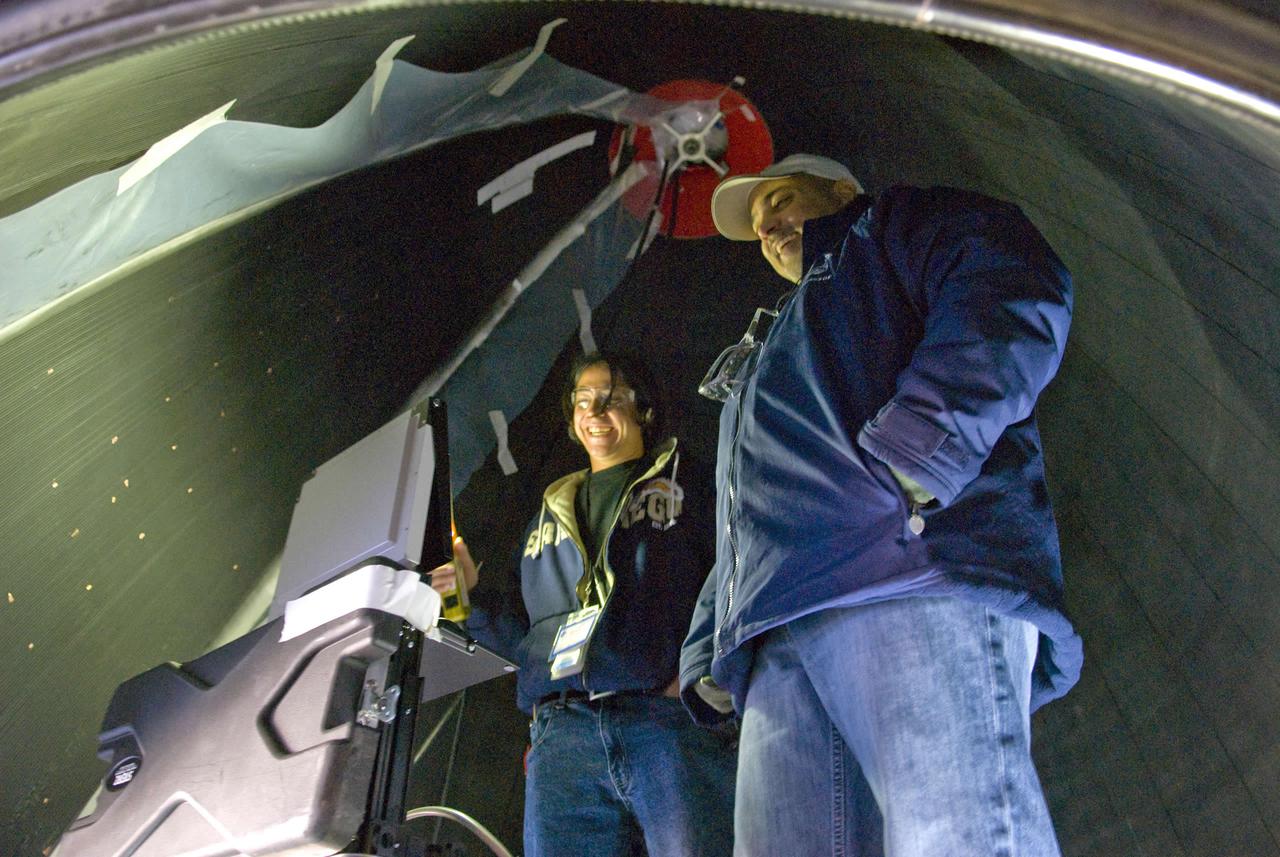

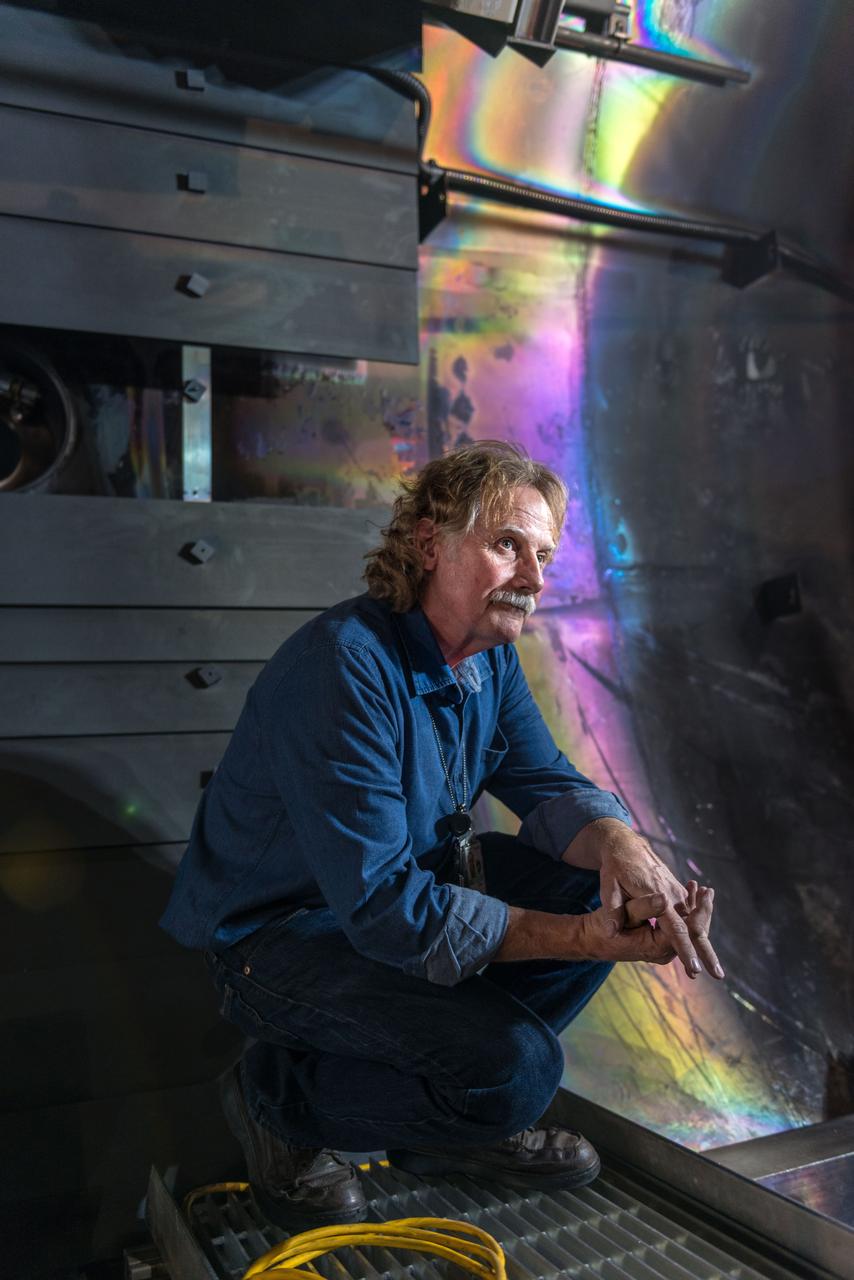
Joel Perez (left) and Jay Labat, both of Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne, are in close quarters as they check for leaks inside the nozzle of a space shuttle main engine mounted on the A-2 Test Stand.
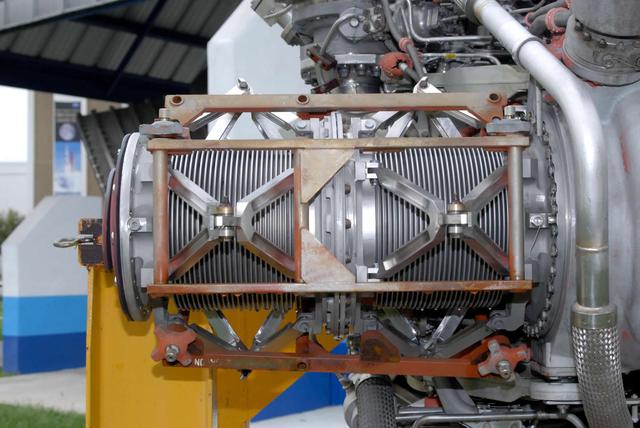

Stennis Space Center engineers are preparing to conduct water tests on an updated version of the scissors duct component of the J-2X engine. Measuring about 2 feet long and about 8 inches in diameter, the duct on the J-2X predecessor, the J-2, connected its fuel turbo pumps to the flight vehicle's upper stage run tanks. According to NASA's J-2X project manager at SSC, Gary Benton, the water tests should establish the limits of the duct's ability to withstand vibration.
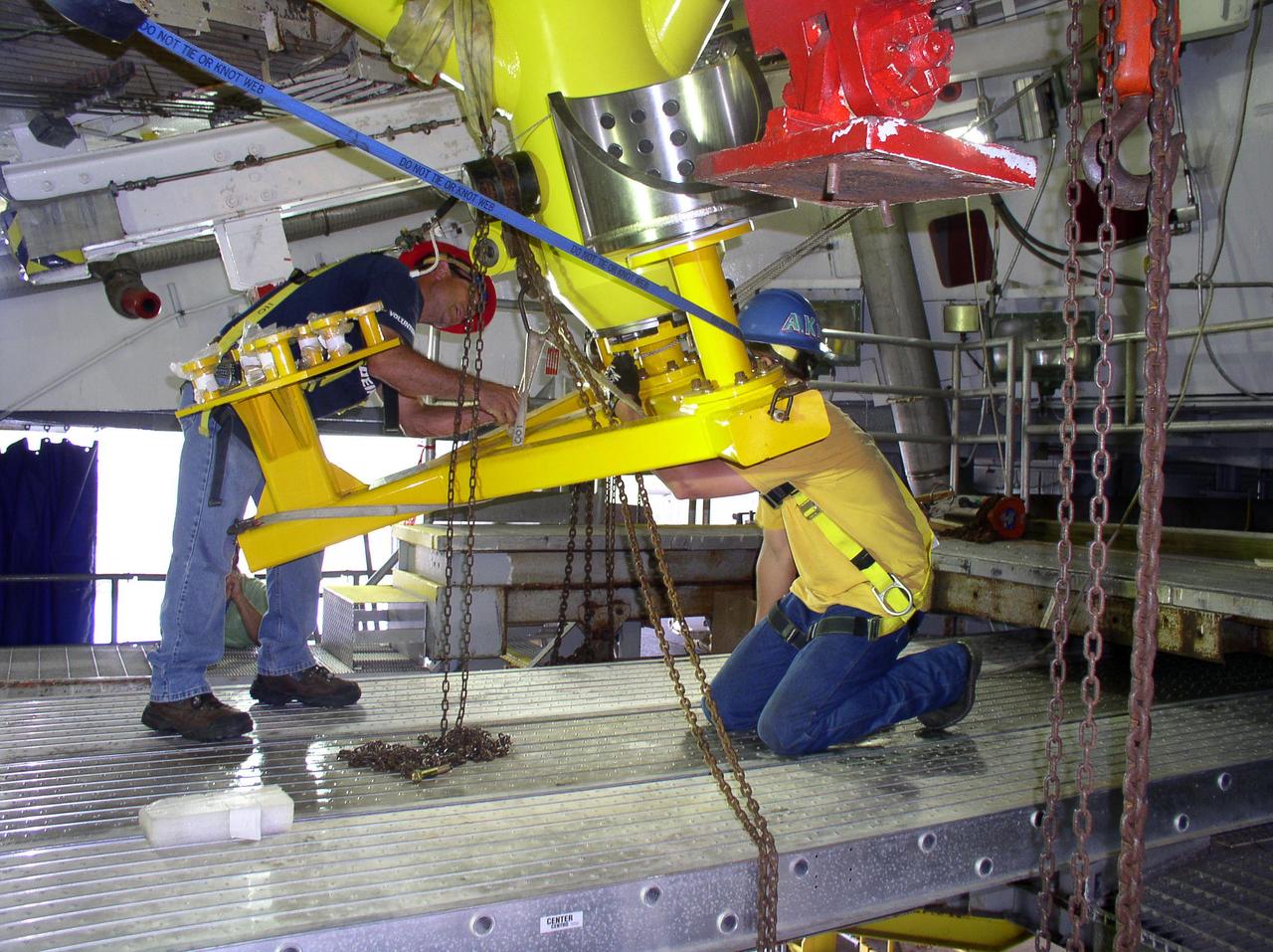

John C. Stennis Space Center employees install a new master interface tool on the A-2 Test Stand on Oct. 27, 2010. Until July 2009, the stand had been used for testing space shuttle main engines. With that test series complete, employees are preparing the stand for testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine being developed. Testing of the new engine is scheduled to begin in 2011.
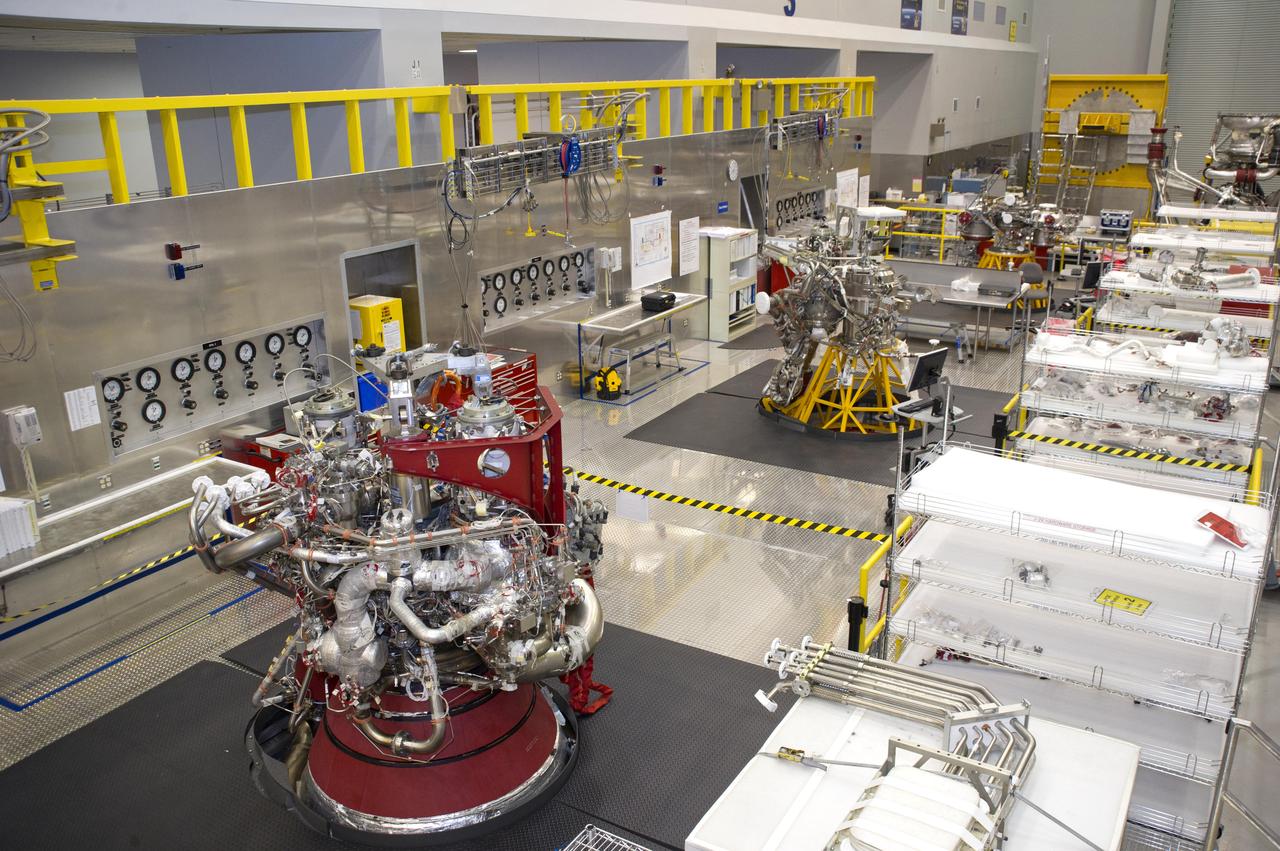
Two J-2X engines and a powerpack, developed for NASA by Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne, sit side-by-side Oct. 11 at Stennis Space Center as work continues on the Space Launch System. Engine 10001 (far left) has been removed from the A-2 Test Stand after being hot-fire tested 21 times, for a total of 2,697 seconds. The engine is now undergoing a series of post-test inspections. A J-2X powerpack (center) has been removed from the A-1 Test Stand to receive additional instrumentation. So far, the powerpack been hot-fire tested 10 times, for a total of 4,162 seconds. Meanwhile, assembly on the second J-2X engine, known as Engine 10002 and located to the far right, has begun in earnest, with engine completion scheduled for this November. Engine 10002 is about 15 percent complete.
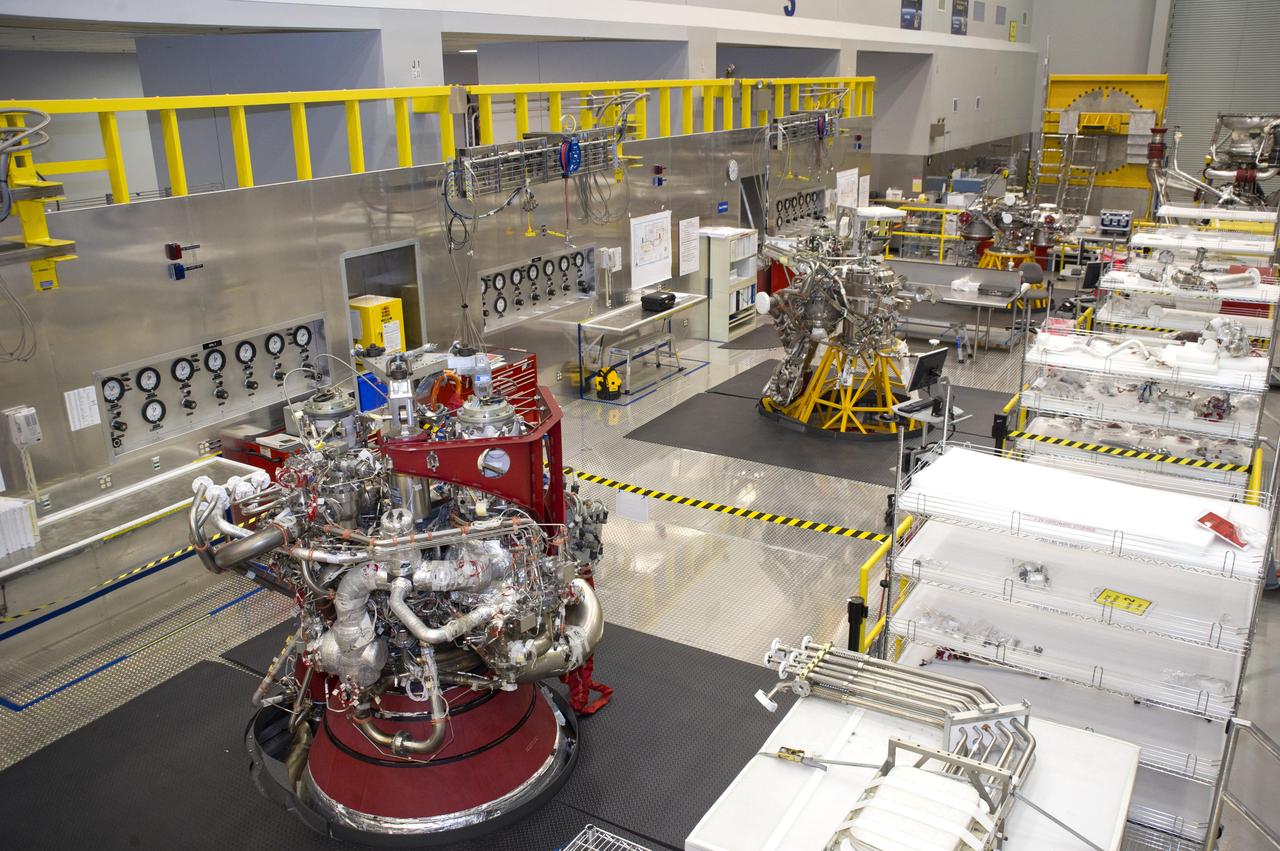
Two J-2X engines and a powerpack, developed for NASA by Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne, sit side-by-side Oct. 11 at Stennis Space Center as work continues on the Space Launch System. Engine 10001 (far left) has been removed from the A-2 Test Stand after being hot-fire tested 21 times, for a total of 2,697 seconds. The engine is now undergoing a series of post-test inspections. A J-2X powerpack (center) has been removed from the A-1 Test Stand to receive additional instrumentation. So far, the powerpack been hot-fire tested 10 times, for a total of 4,162 seconds. Meanwhile, assembly on the second J-2X engine, known as Engine 10002 and located to the far right, has begun in earnest, with engine completion scheduled for this November. Engine 10002 is about 15 percent complete.
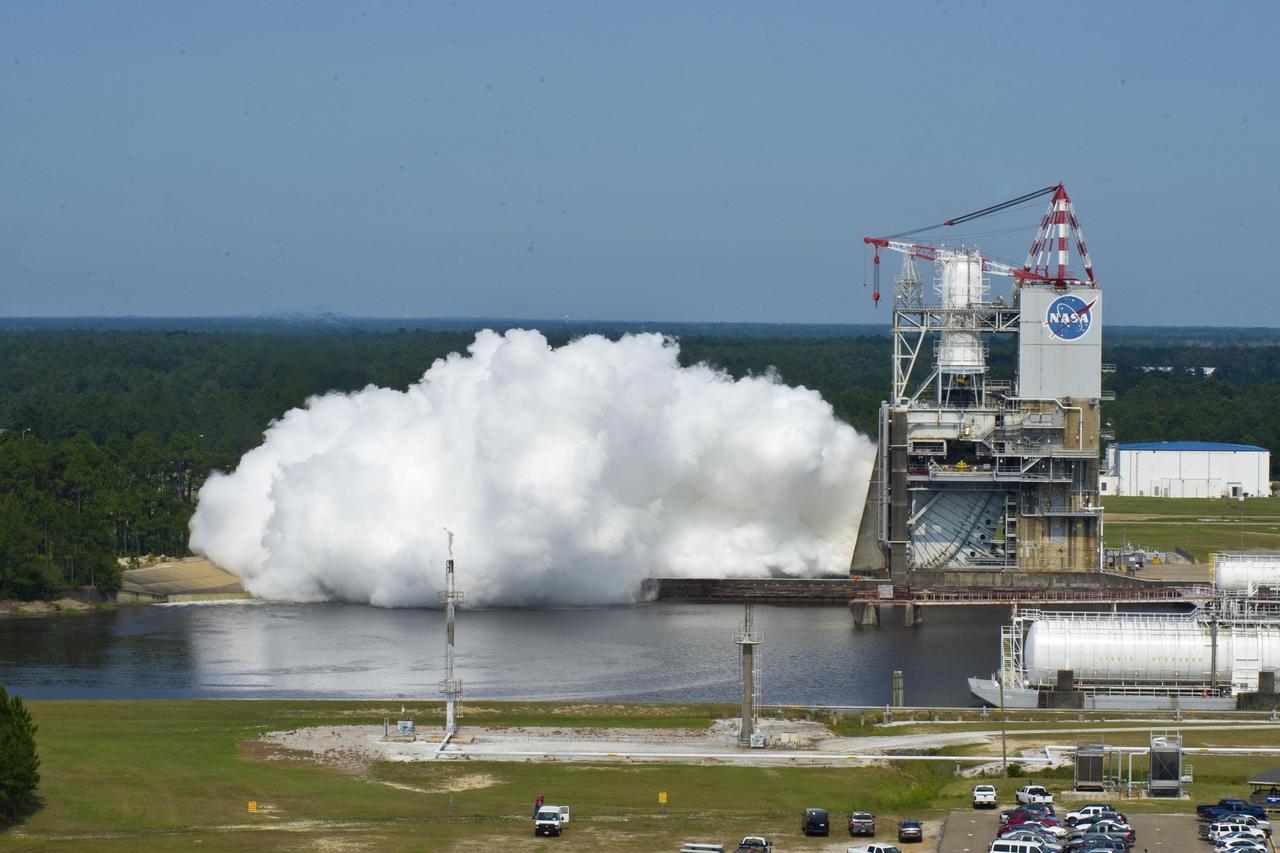

On May 25, 2012, NASA recorded another first during a 40-second test of the next-generation J-2X engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center. Test conductors fired the J-2X in both the secondary and primary modes of operation. Previous tests were run in one mode only; combining the two allowed operators to collect critical data on engine performance.
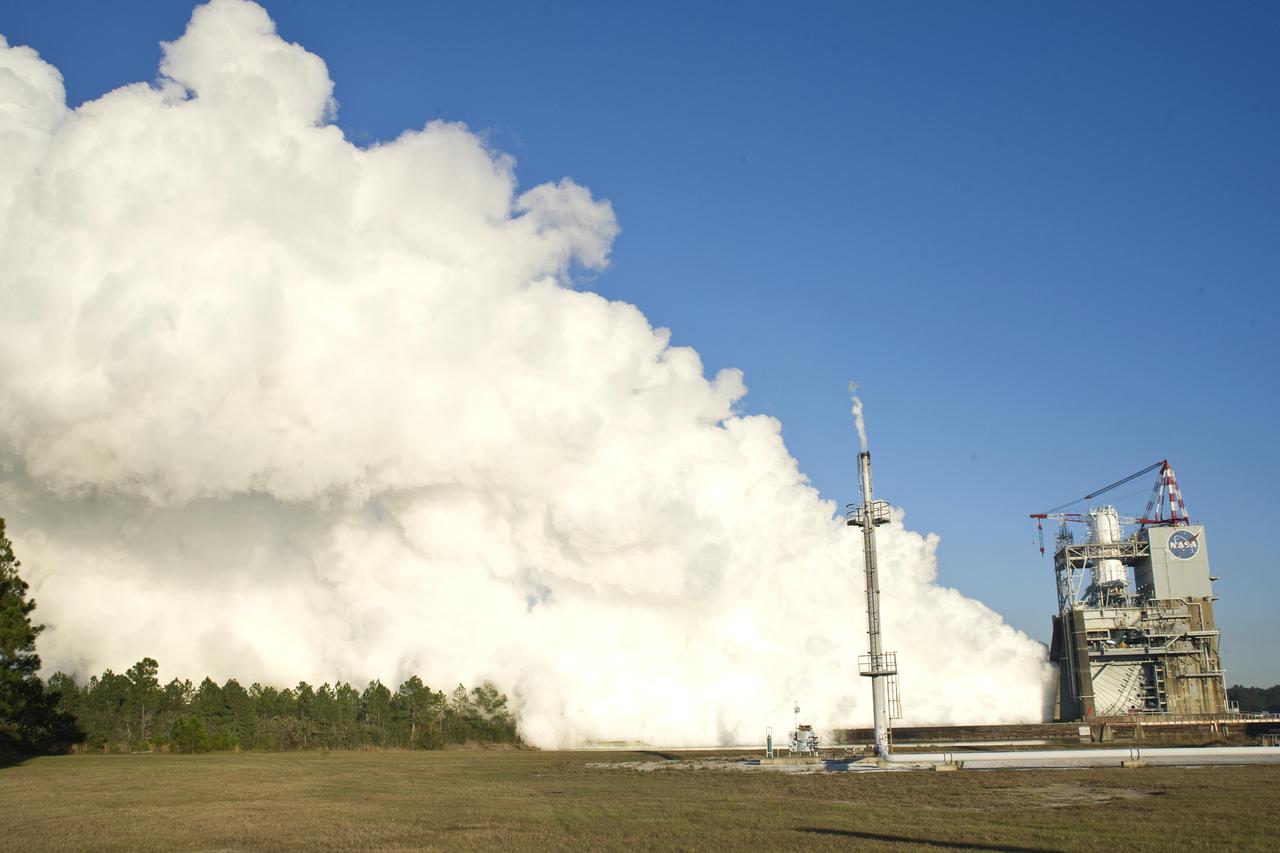

NASA conducted a key stability test firing of the J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Dec. 1, marking another step forward in development of the upper-stage engine that will carry humans deeper into space than ever before. The J-2X will provide upper-stage power for NASA's new Space Launch System.
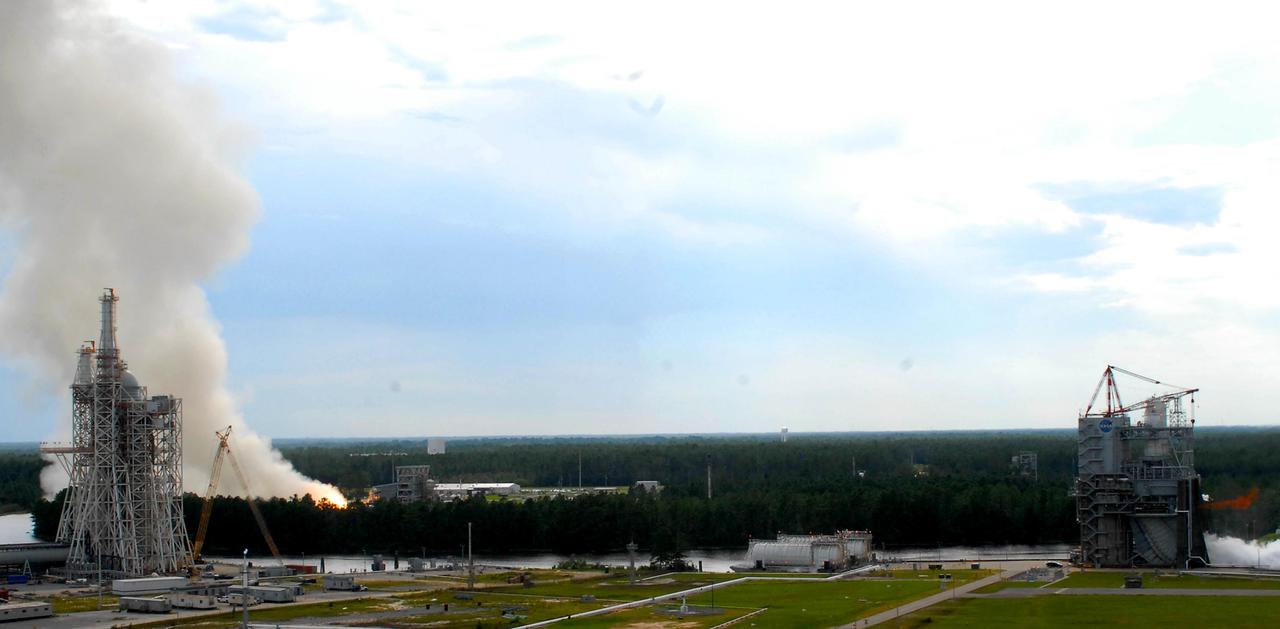

Two large-engine tests were conducted simultaneously for the first time at Stennis Space Center on Aug. 16. A plume on the left indicates a test on the facility's E-1 Test Stand. On the right, a finger of fire indicates a test under way on the A-1 Test Stand. In another first, both tests were conducted by female engineers. The image was taken from atop the facility's A-2 Test Stand, offering a panoramic view that includes the new A-3 Test Stand under construction to the left.
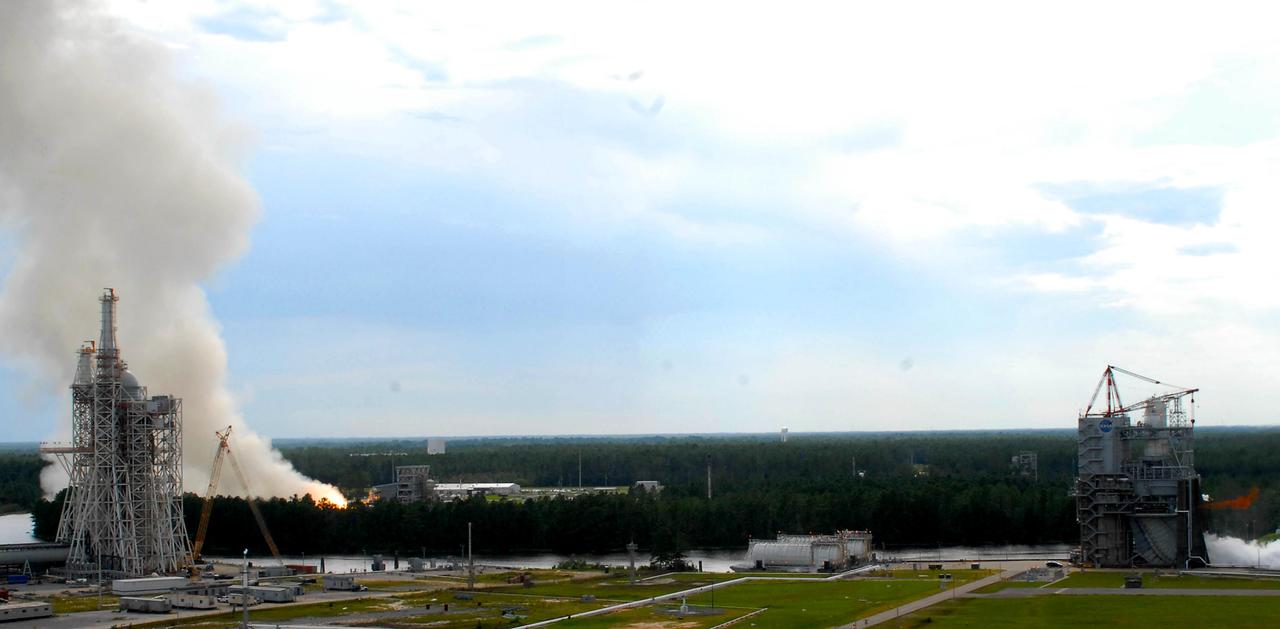

Two large-engine tests were conducted simultaneously for the first time at Stennis Space Center on Aug. 16. A plume on the left indicates a test on the facility's E-1 Test Stand. On the right, a finger of fire indicates a test under way on the A-1 Test Stand. In another first, both tests were conducted by female engineers. The image was taken from atop the facility's A-2 Test Stand, offering a panoramic view that includes the new A-3 Test Stand under construction to the left.
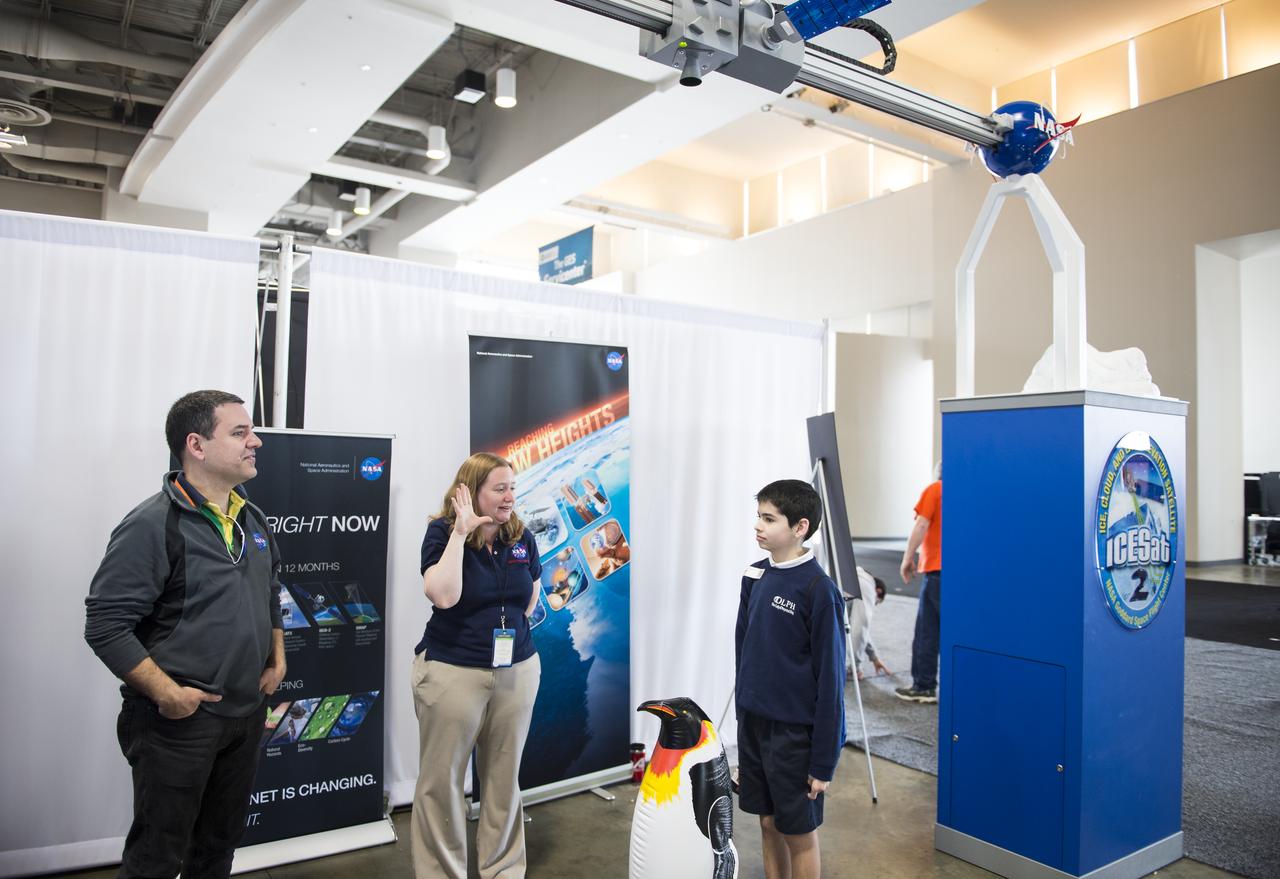

An attendee of the USA Science and Engineering Festival is measured by a laser at the NASA Stage. A NASA Staff member describes the Ice, Cloud, and land Elevation Satellite (ICESat) mission, which operated from 2003-2009, and pioneered the use of laser altimeters in space to study the elevation of the Earth's surface and its changes. ICESat-2 is a follow-on mission to continue the ICESat observations and is scheduled to launch in 2017. The USA Science and Engineering Festival took place at the Washington Convention Center in Washington, DC on April 26 and 27, 2014. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
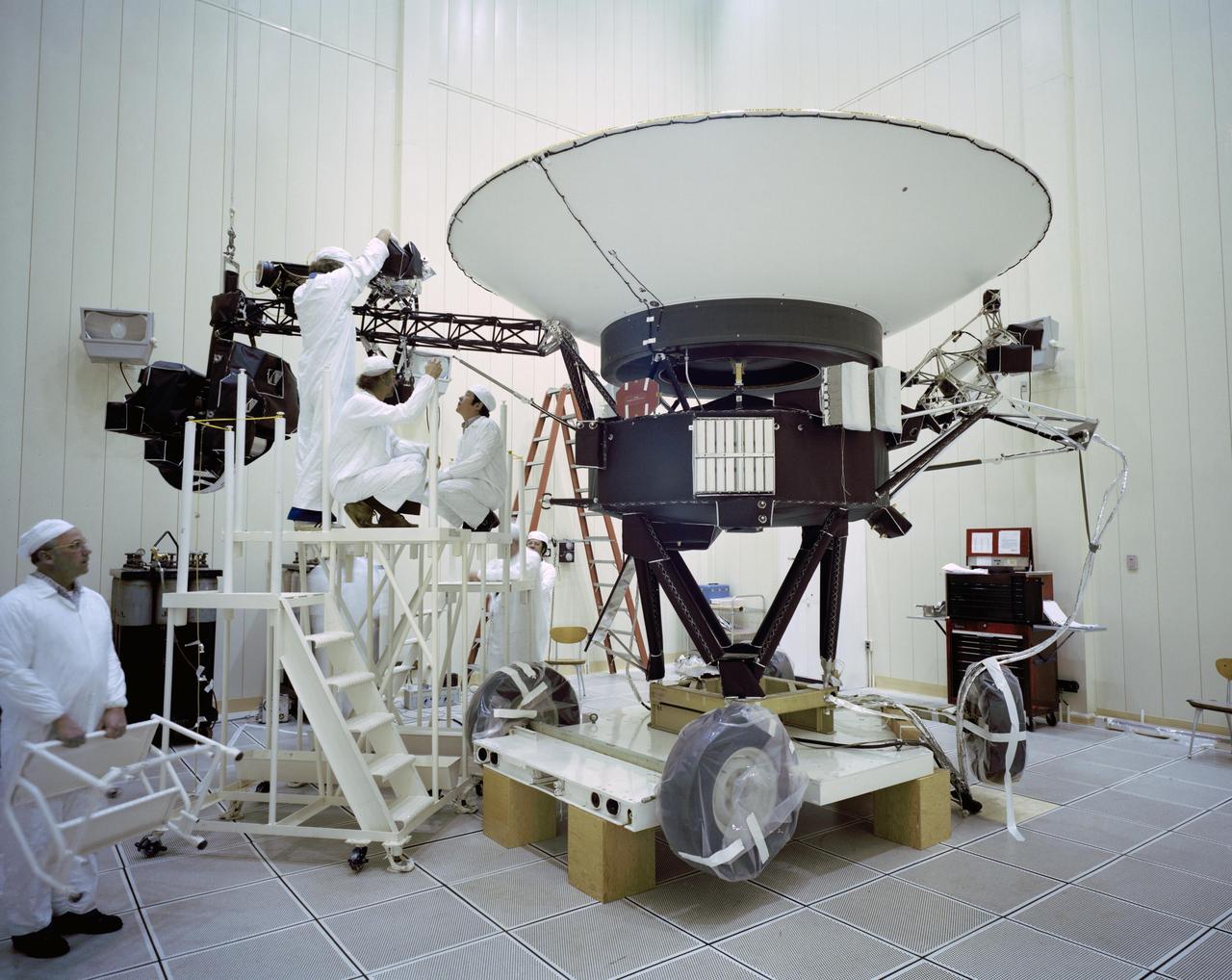
This archival photo shows engineers working on NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft on March 23, 1977. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21736
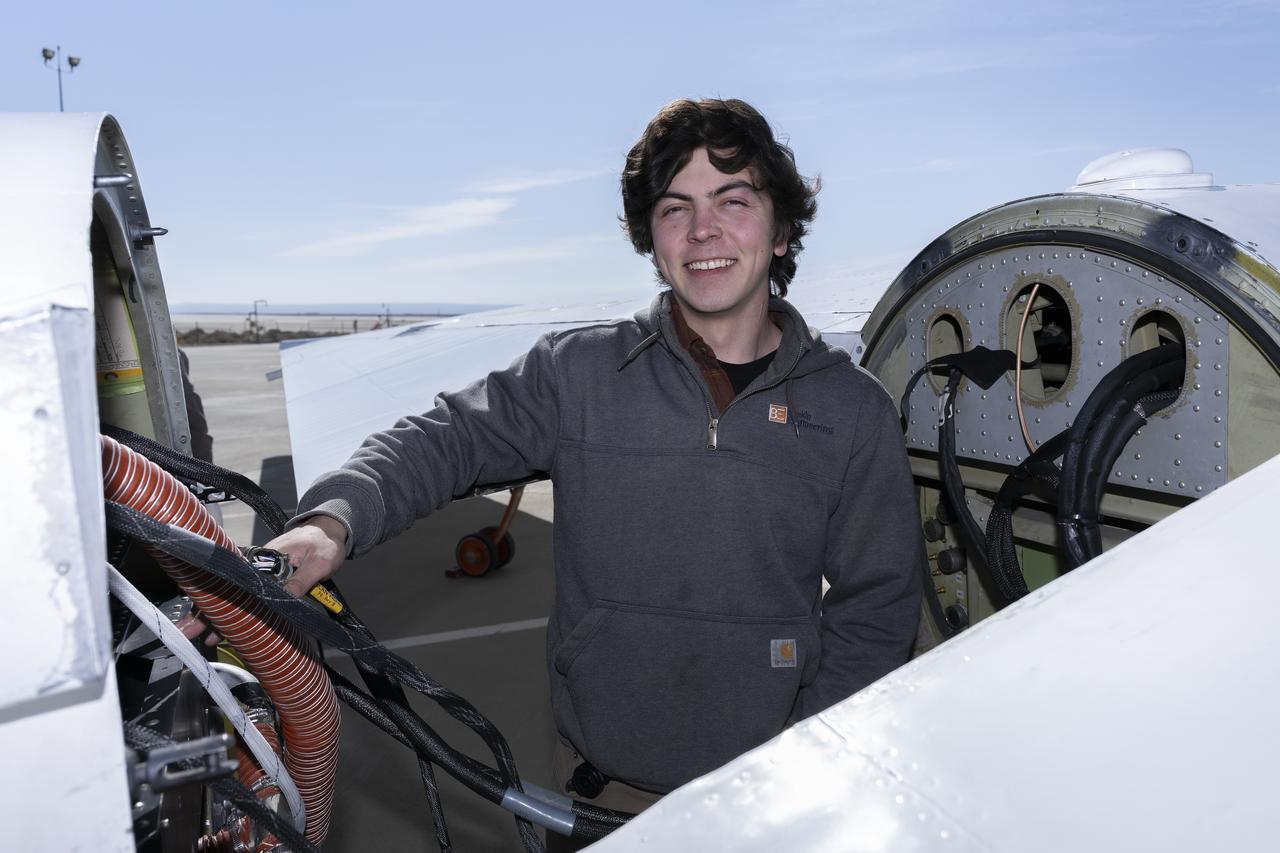

A team of experts wrap up science flights on the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California after the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Nikolas Gibson from NASA Ames Research Center integrates the enhanced MODIS Airbrone Simulator (eMAS) instrument onto the ER-2. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
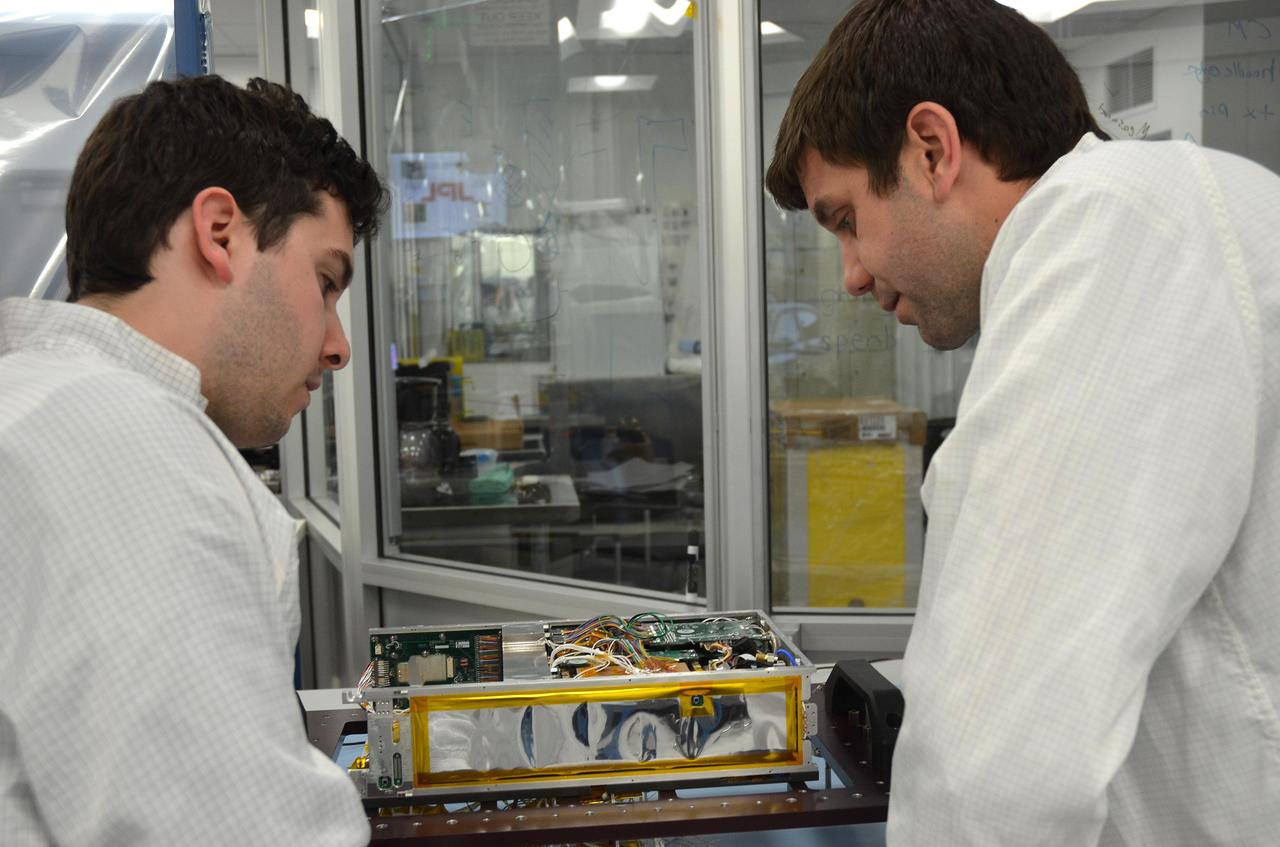

Engineers for NASA's MarCO (Mars Cube One) technology demonstration inspect one of the two MarCO CubeSats. Cody Colley, MarCO integration and test deputy, left, and Andy Klesh, MarCO chief engineer, are on the team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, preparing twin MarCO CubeSats. The briefcase-size MarCO twins were designed to ride along with NASA's next Mars lander, InSight. Its planned March 2016 launch was suspended. InSight -- an acronym for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport -- will study the interior of Mars to improve understanding of the processes that formed and shaped rocky planets, including Earth. Note: After thorough examination, NASA managers have decided to suspend the planned March 2016 launch of the Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) mission. The decision follows unsuccessful attempts to repair a leak in a section of the prime instrument in the science payload. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20342

JPL's Spacecraft Assembly Facility looks more like a hangar in this photo of two engineers standing with Mariner 1 on May 2, 1962. However, the gowning procedures were far less rigorous than they are today. Mariner 1 was destroyed during its attempted launch to Venus. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23310
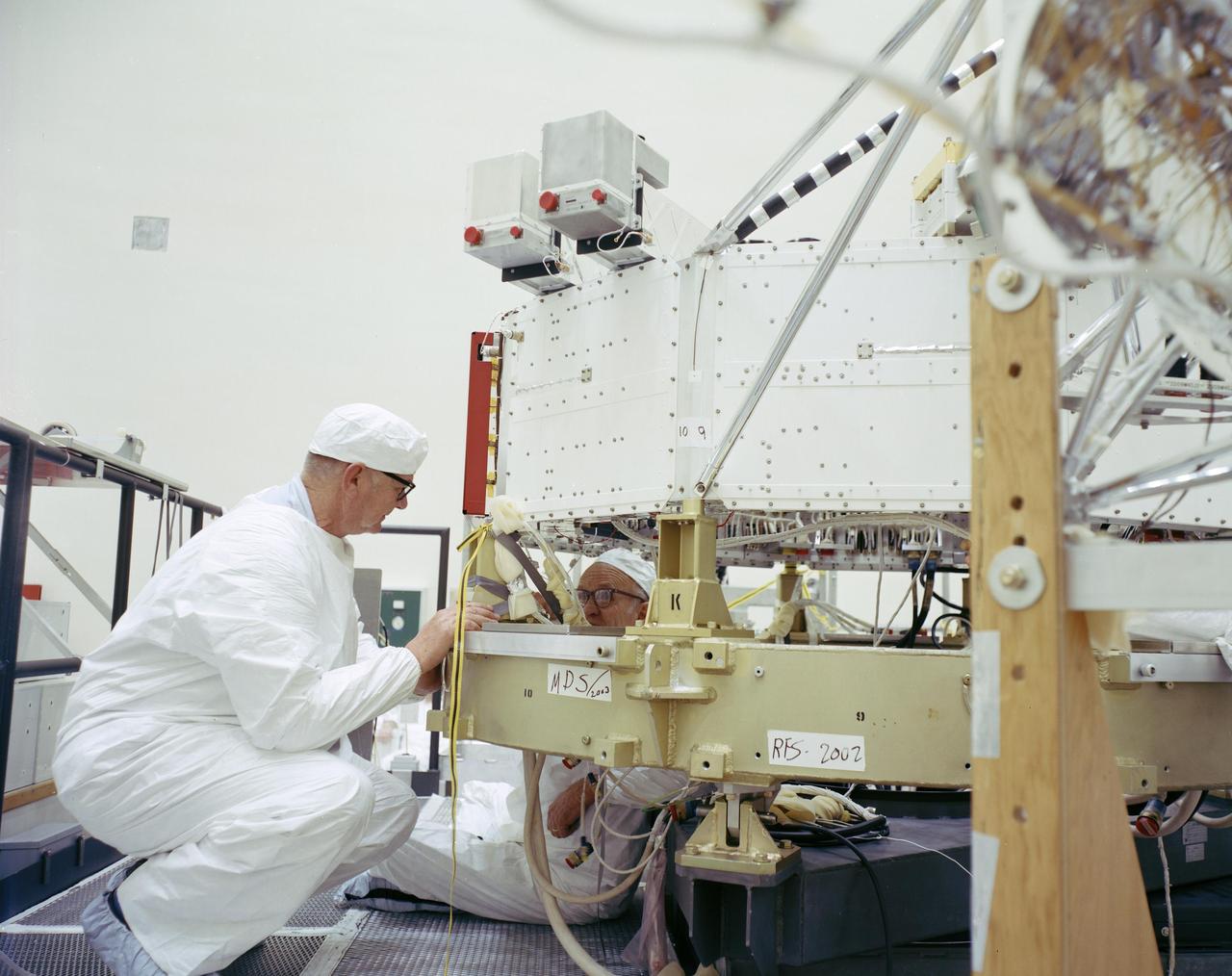

This archival photo shows engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory working on the 10-sided central structure, or "bus," of the Voyager 2 spacecraft on February 24,1977. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21478
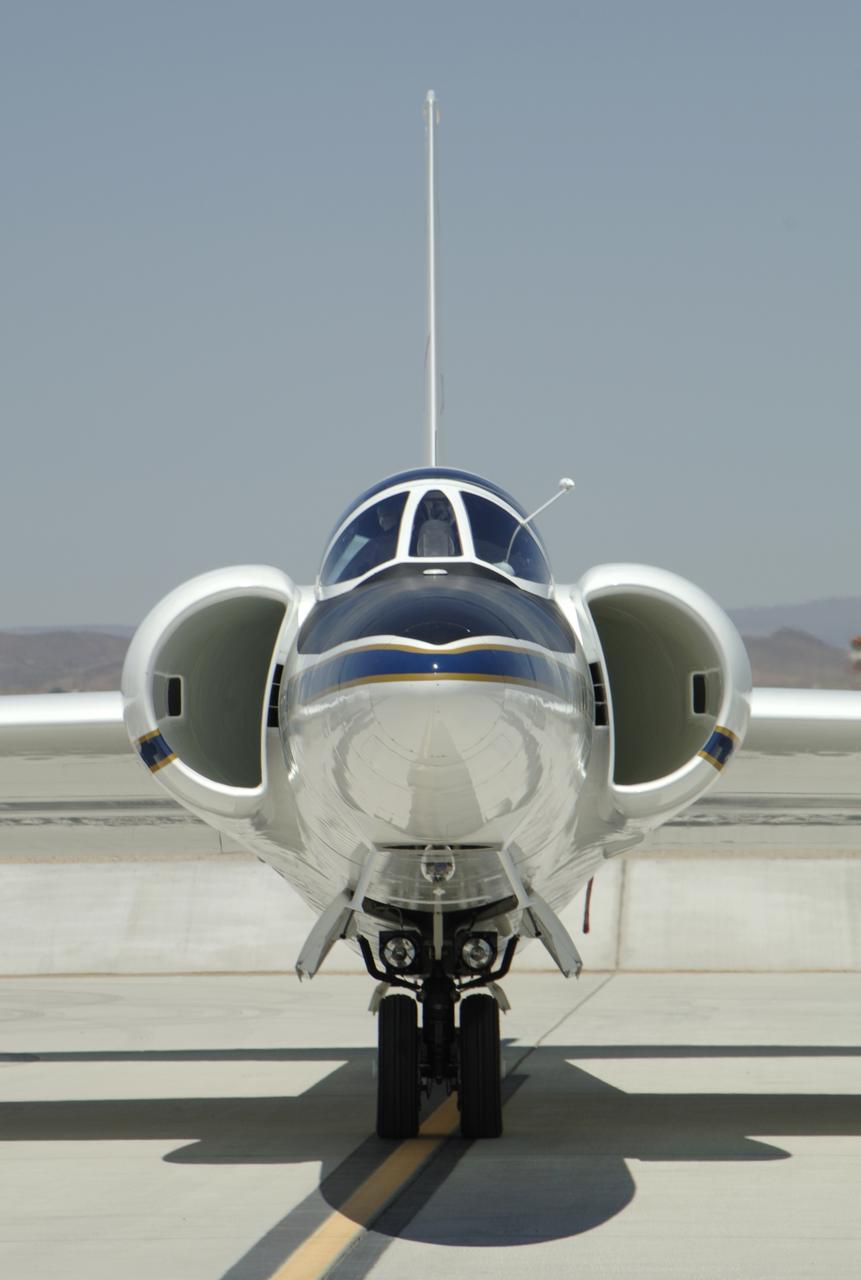

The large air intakes for its powerful engine are obvious as NASA's high-flying ER-2 #806 Earth resources aircraft taxies out for another science mission.
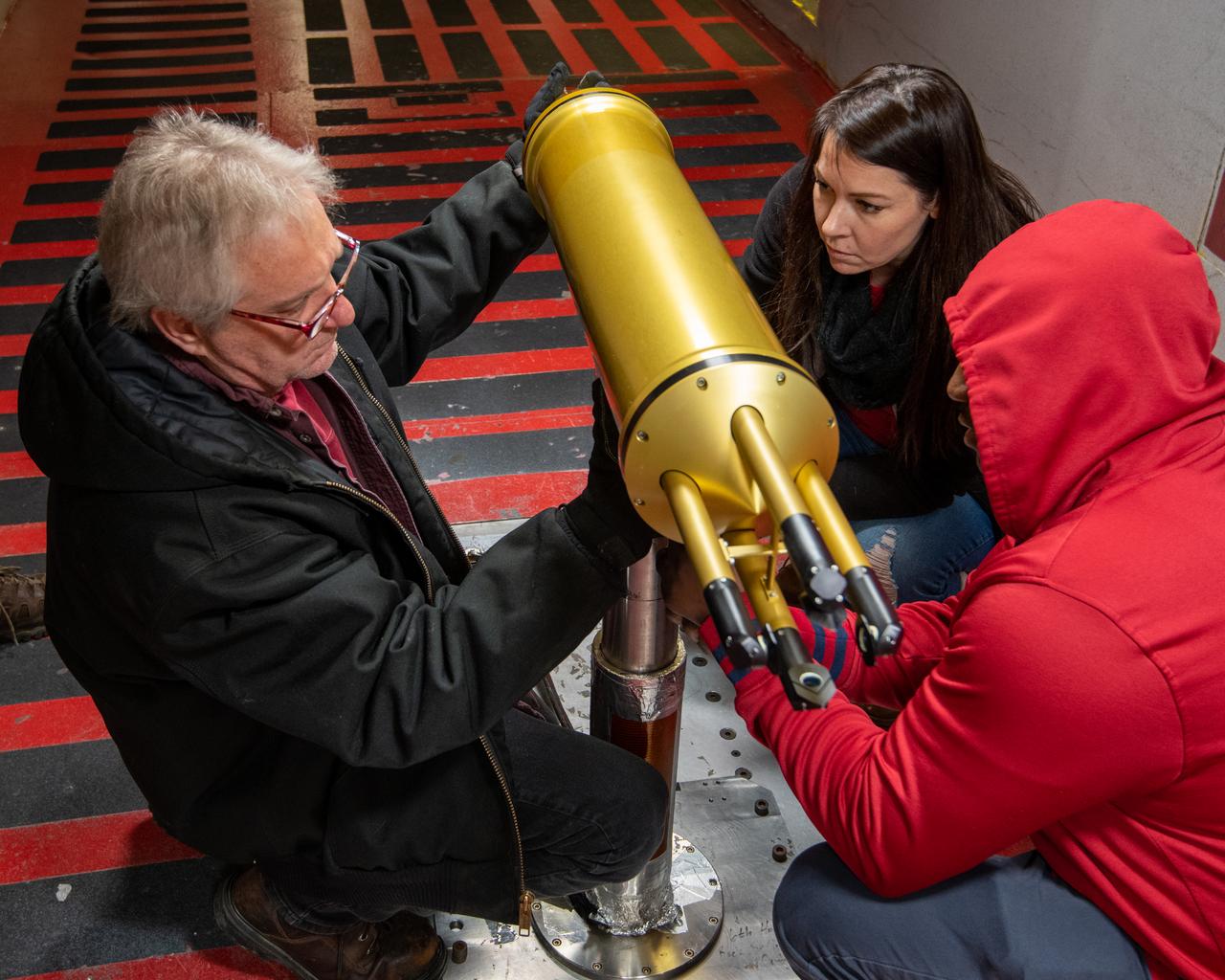

Installation of the 2D-S (2-Dimensional Stereo) optical array probe made by Stratton Park Engineering Company (SPEC)
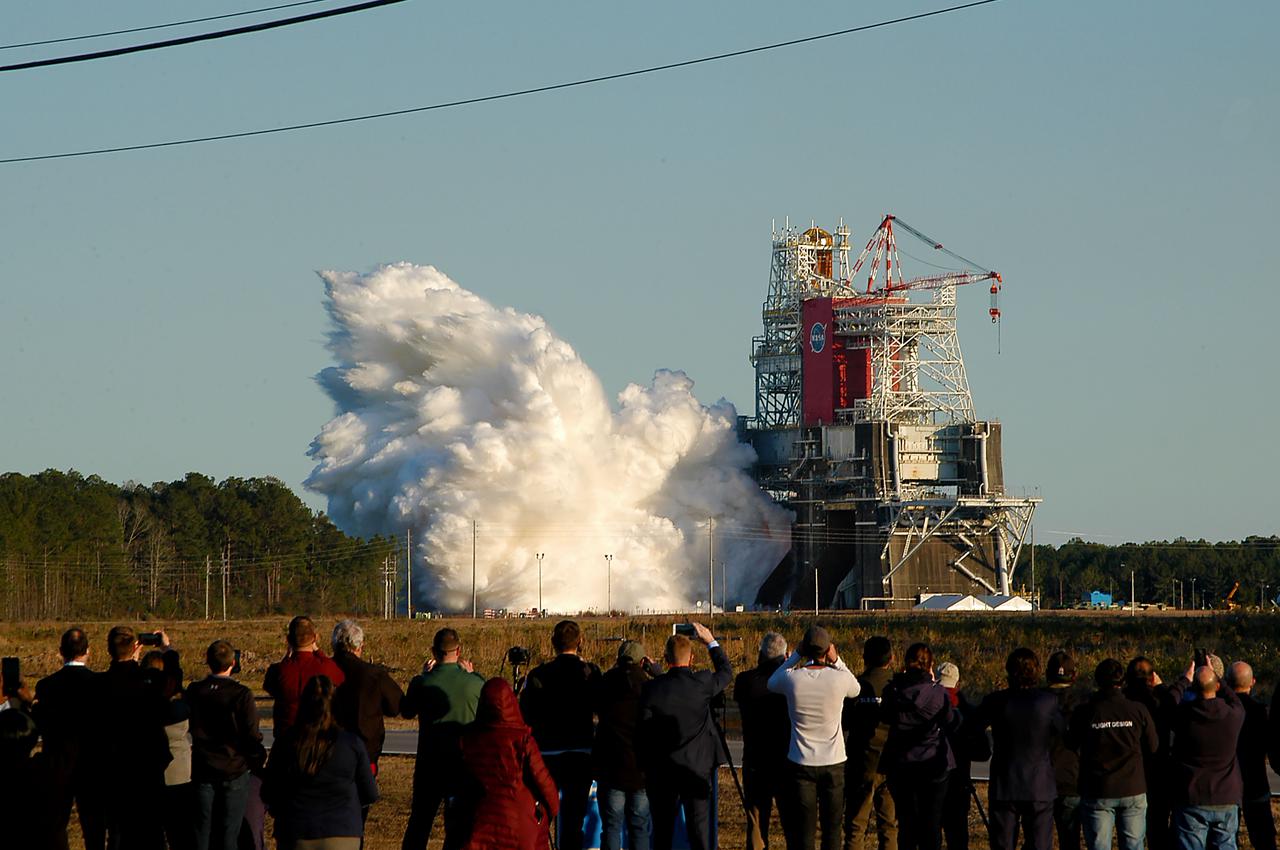

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
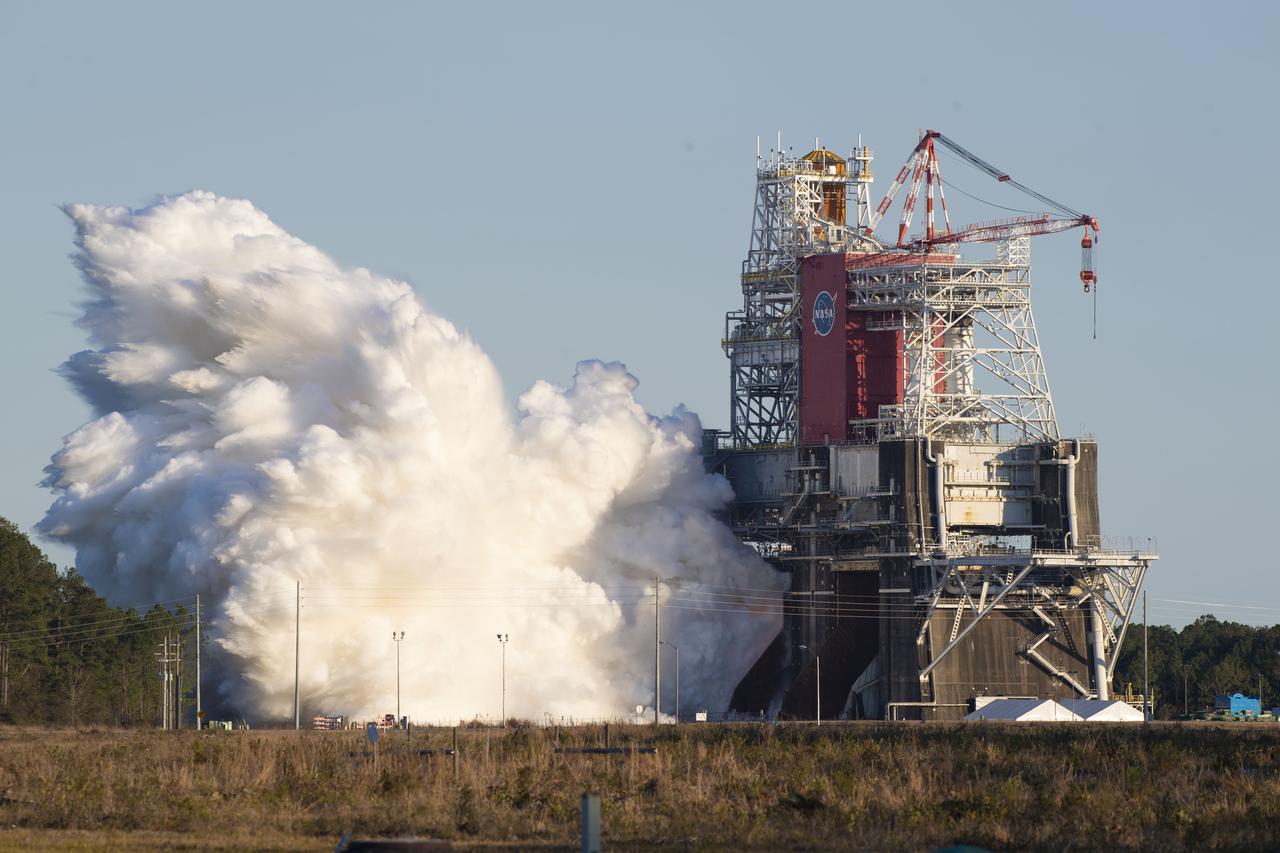

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
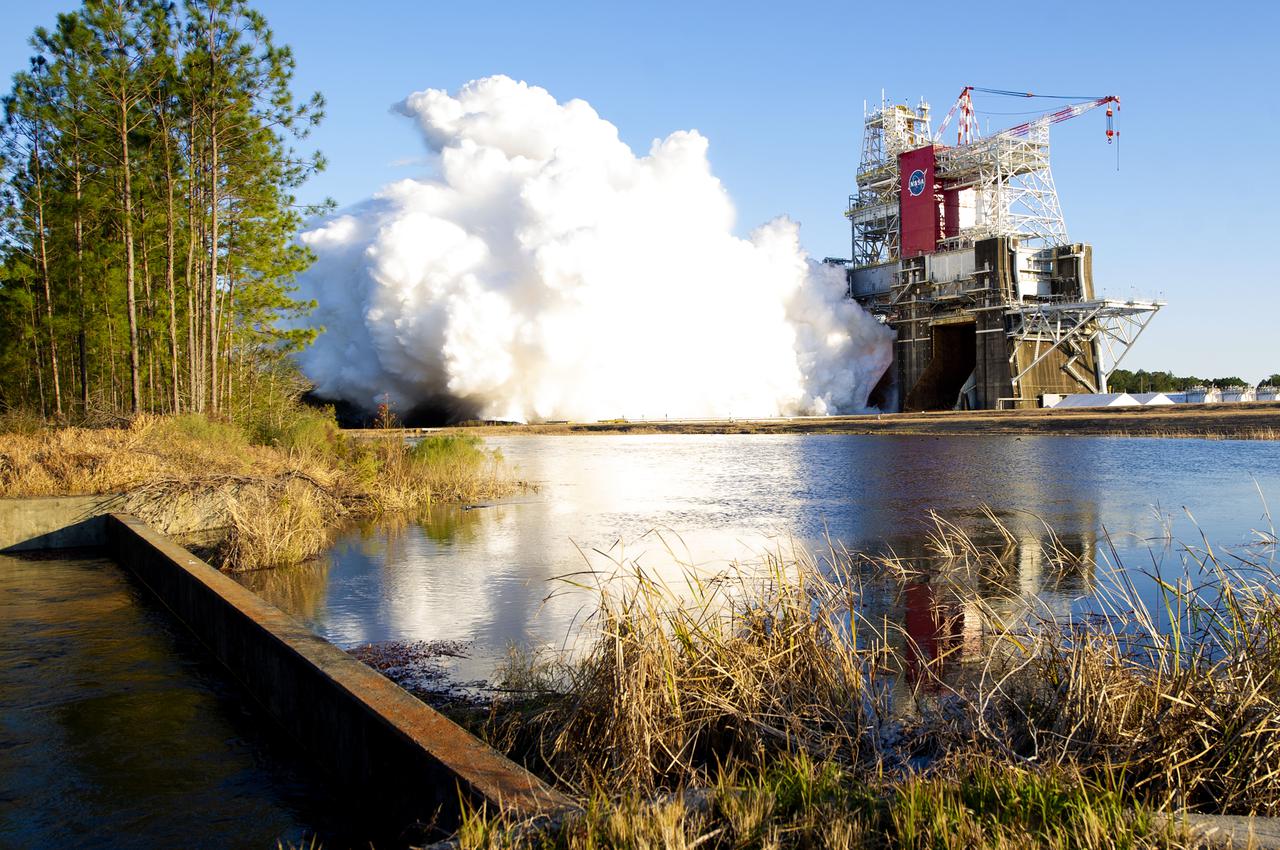

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.