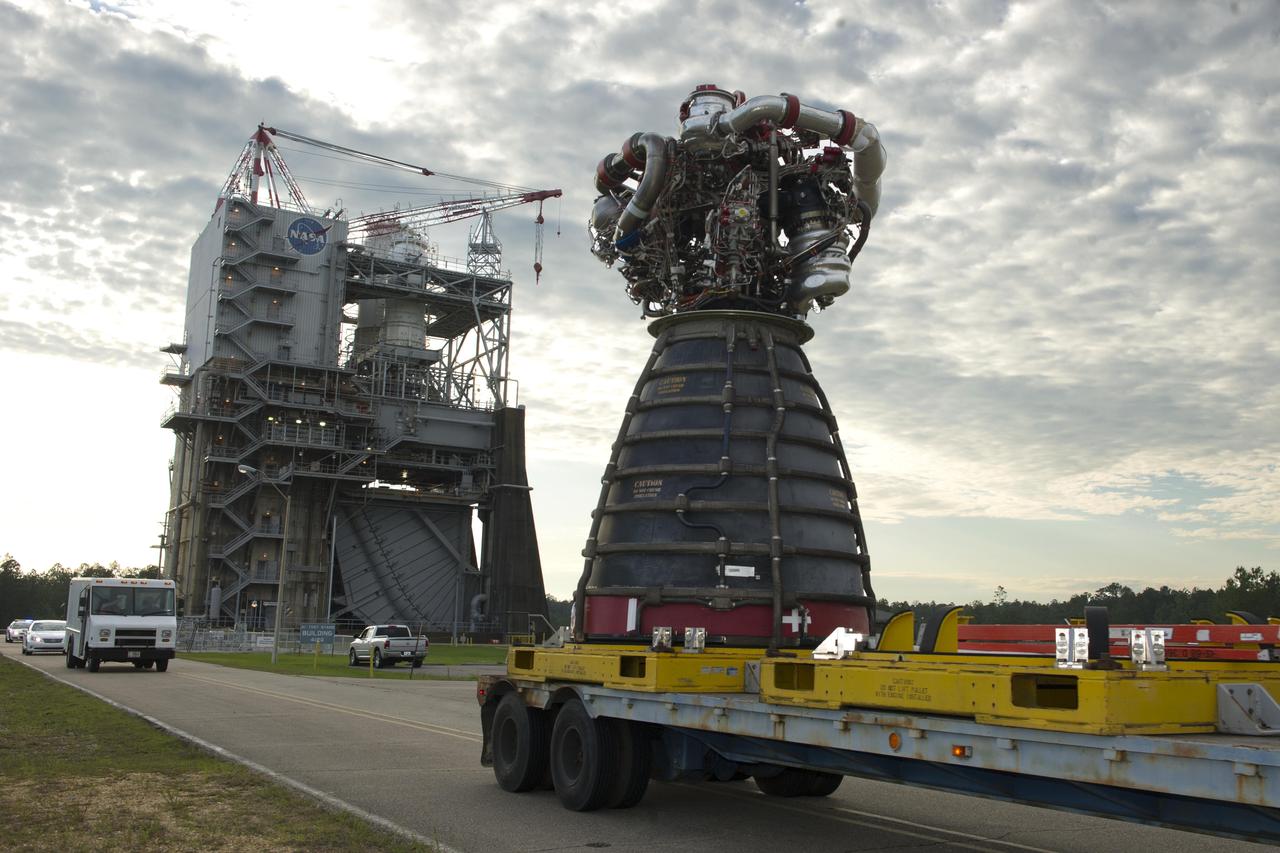
RS-25 rocket engine No. 2059 is removed from the A-1 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on May 19, 2016. The engine was tested March 10 on the stand and is ready for use on NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) vehicle. NASA is developing the SLS to carry humans deeper into space than ever before. The SLS core stage will be powered by four RS-25 engines. Engine No. 2059 is scheduled for use on the first crewed SLS mission, Exploration Mission-2, which will carry American astronauts beyond low-Earth orbit for the first time since 1972. The photo above shows the engine, as well as the yellow thrust frame adapter above it, which holds the engine in place for testing.

The first RS-25 flight engine, engine No. 2059, is lifted onto the A-1 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Nov. 4, 2015. The engine was tested in early 2016 to certify it for use on NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS). The SLS core stage will be powered by four RS-25 engines, all tested at Stennis Space Center. NASA is developing the SLS to carry humans deeper into space than ever before, including on a journey to Mars.
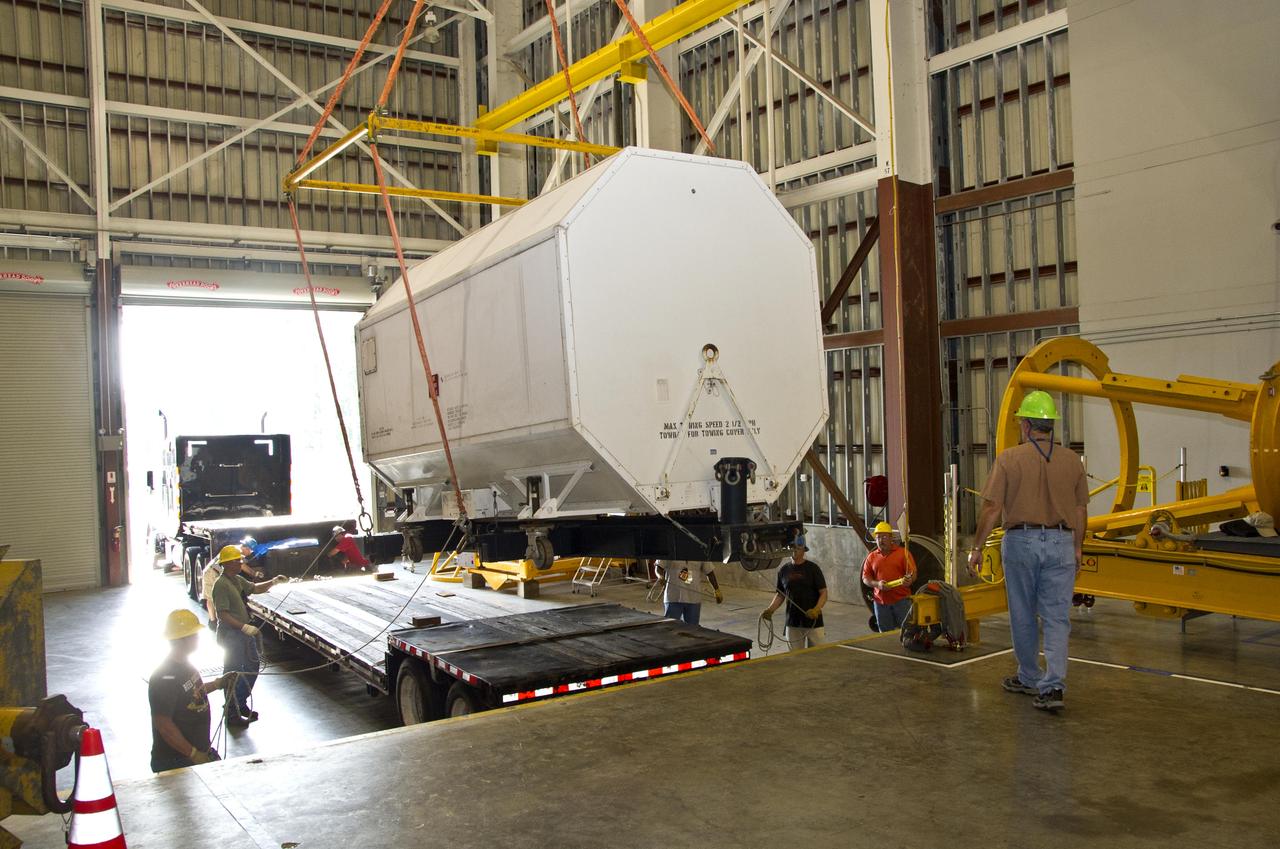

RS-25 series rocket engine No. 2059 is unloaded and positioned at Stennis Space Center on April 10, 2012, for future testing and use on NASA's new Space Launch System. The engine was the last of 15 RS-25 engines to be delivered from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to Stennis, where all will be stored until testing begins.
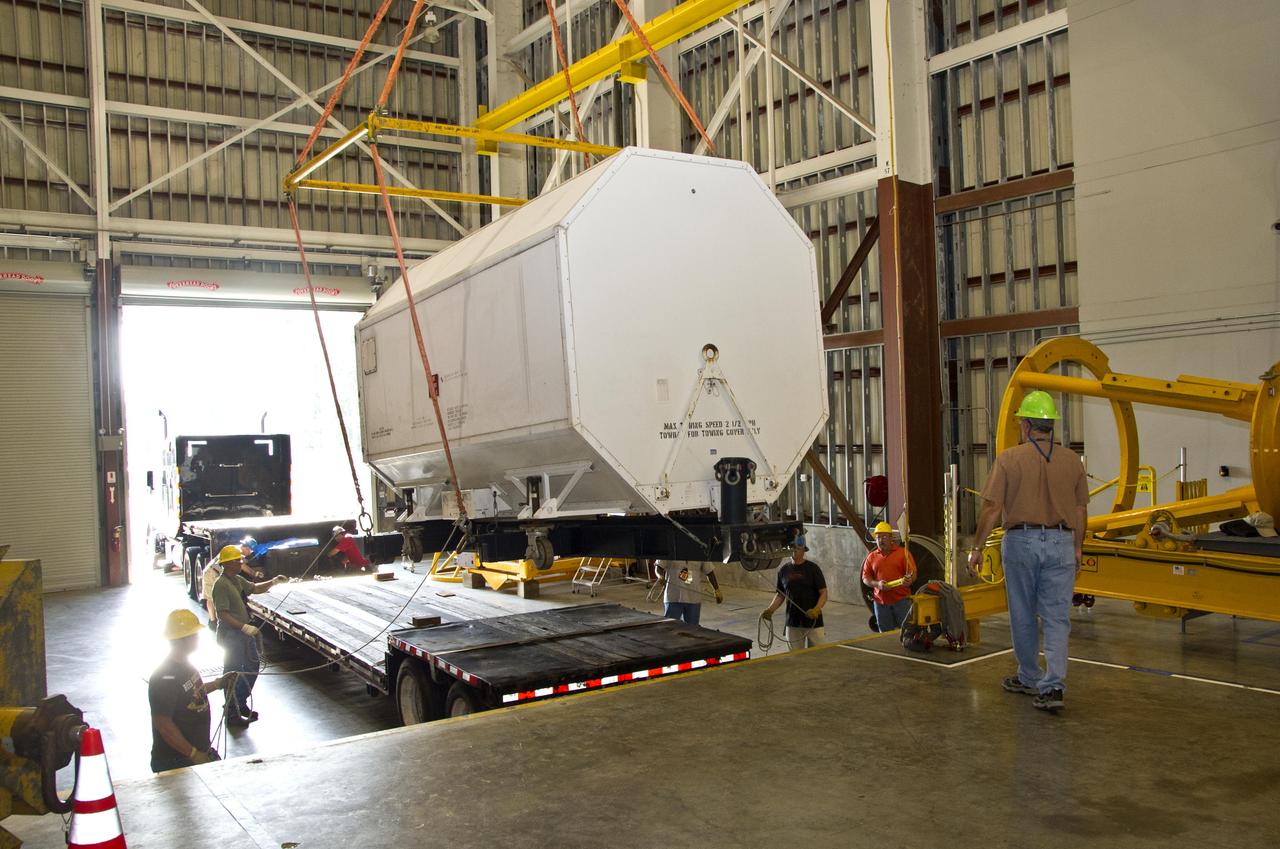

RS-25 series rocket engine No. 2059 is unloaded and positioned at Stennis Space Center on April 10, 2012, for future testing and use on NASA's new Space Launch System. The engine was the last of 15 RS-25 engines to be delivered from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to Stennis, where all will be stored until testing begins.
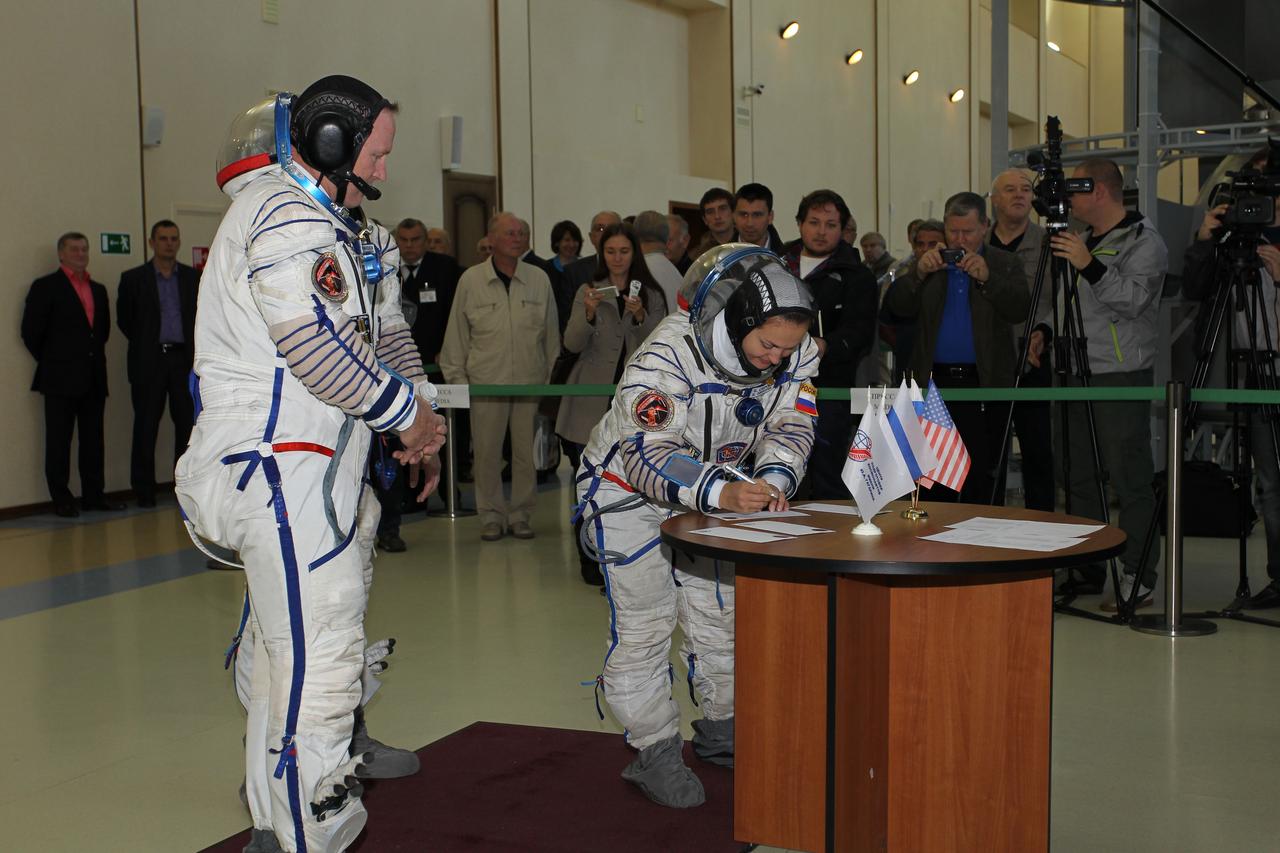

2059: At the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center in Star City, Russia, Expedition 41/42 Flight Engineer Elena Serova of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) signs in September 4 at the start of the second day of final qualification exams. Looking on is crewmate Barry Wilmore of NASA (left). Soyuz Commander Alexander Samokutyaev of Roscosmos is hidden from view. The trio will launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, Sept. 26, Kazakh time, in their Soyuz TMA-14M spacecraft for a 5 ½ month mission on the International Space Station. Serova will become the fourth Russian woman to fly in space and the first Russian woman to conduct a long duration mission on the station. NASA/Stephanie Stoll
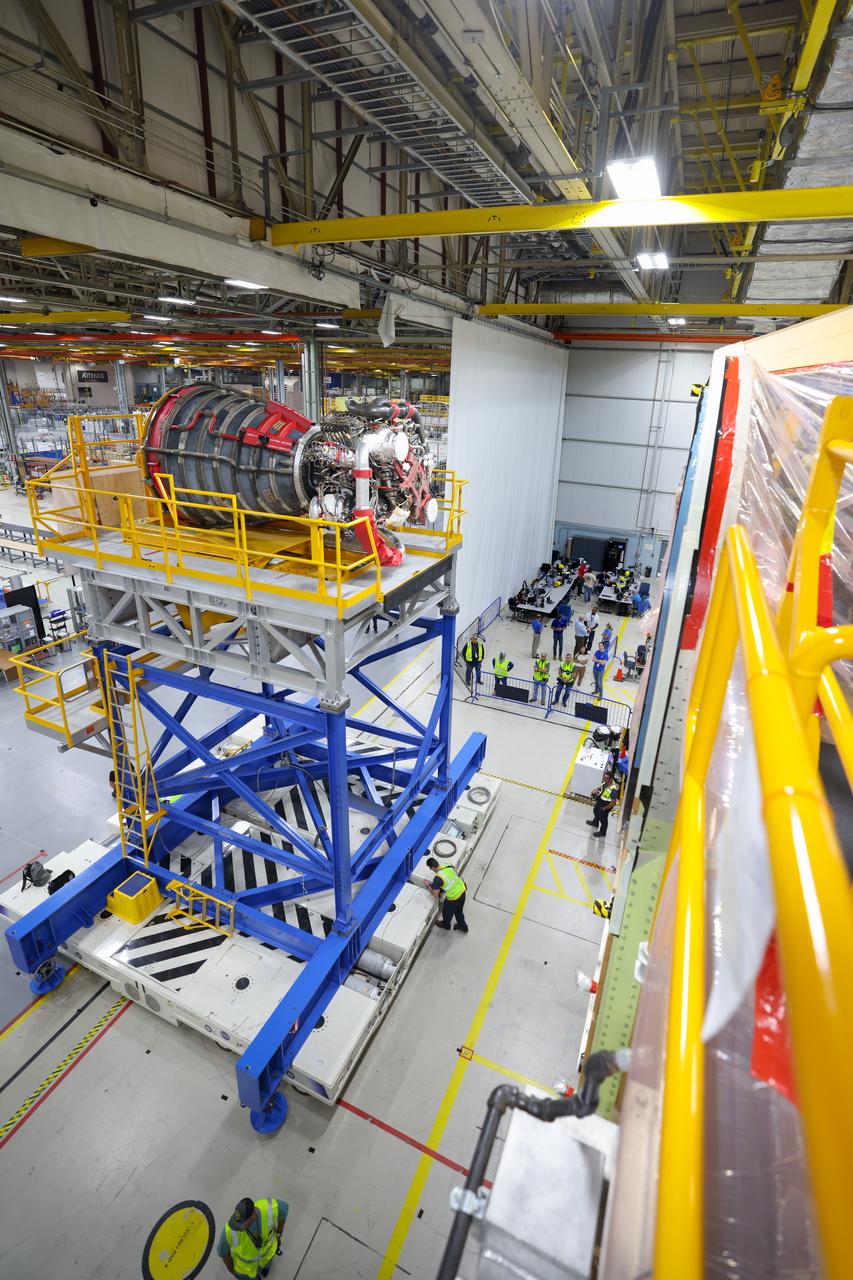

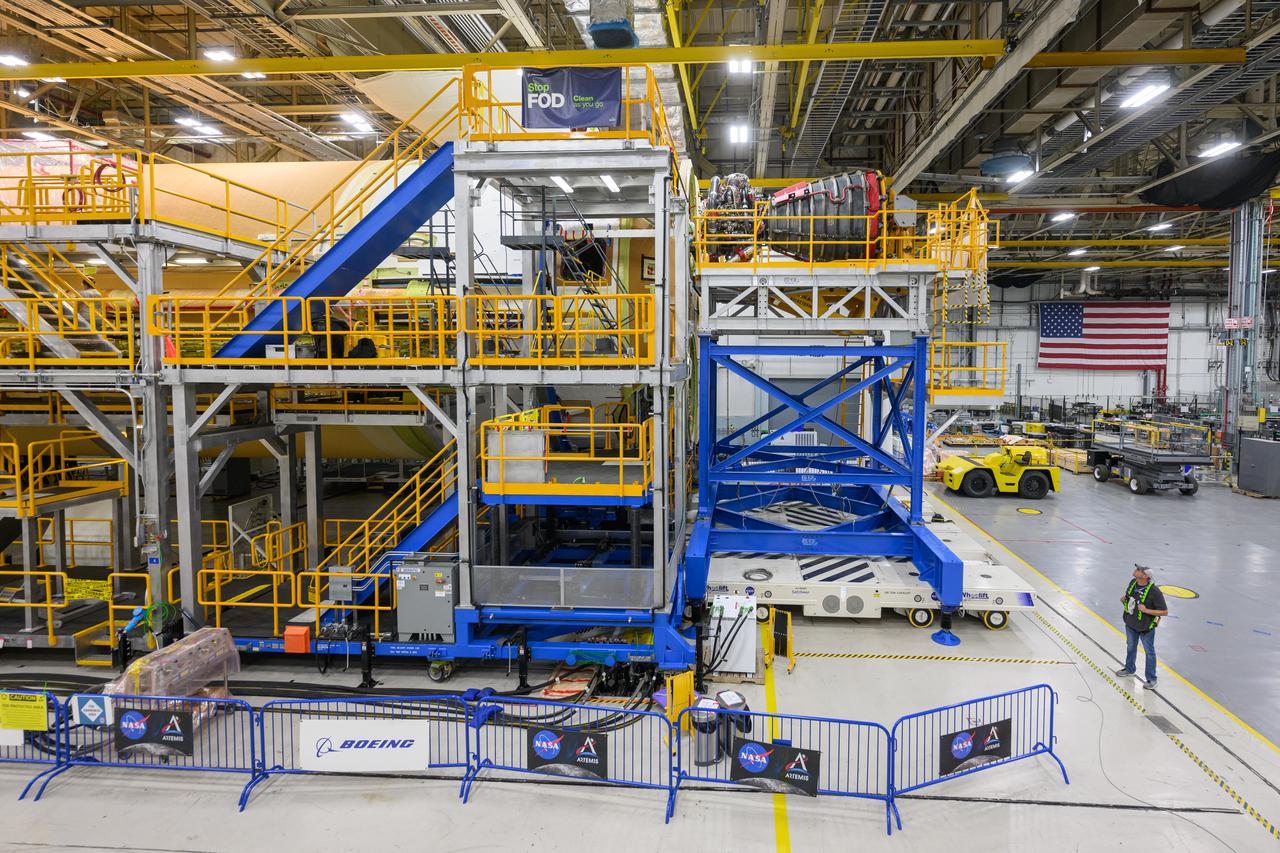
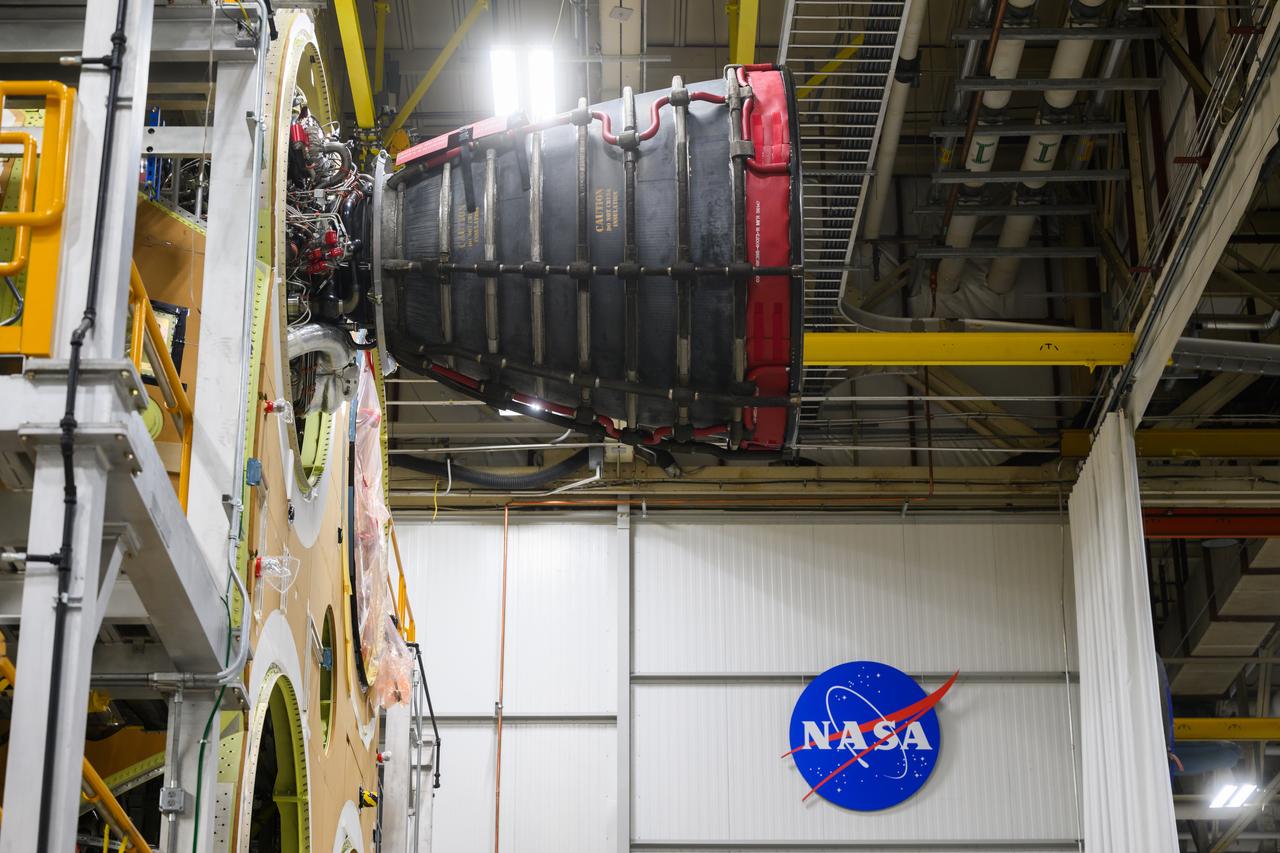
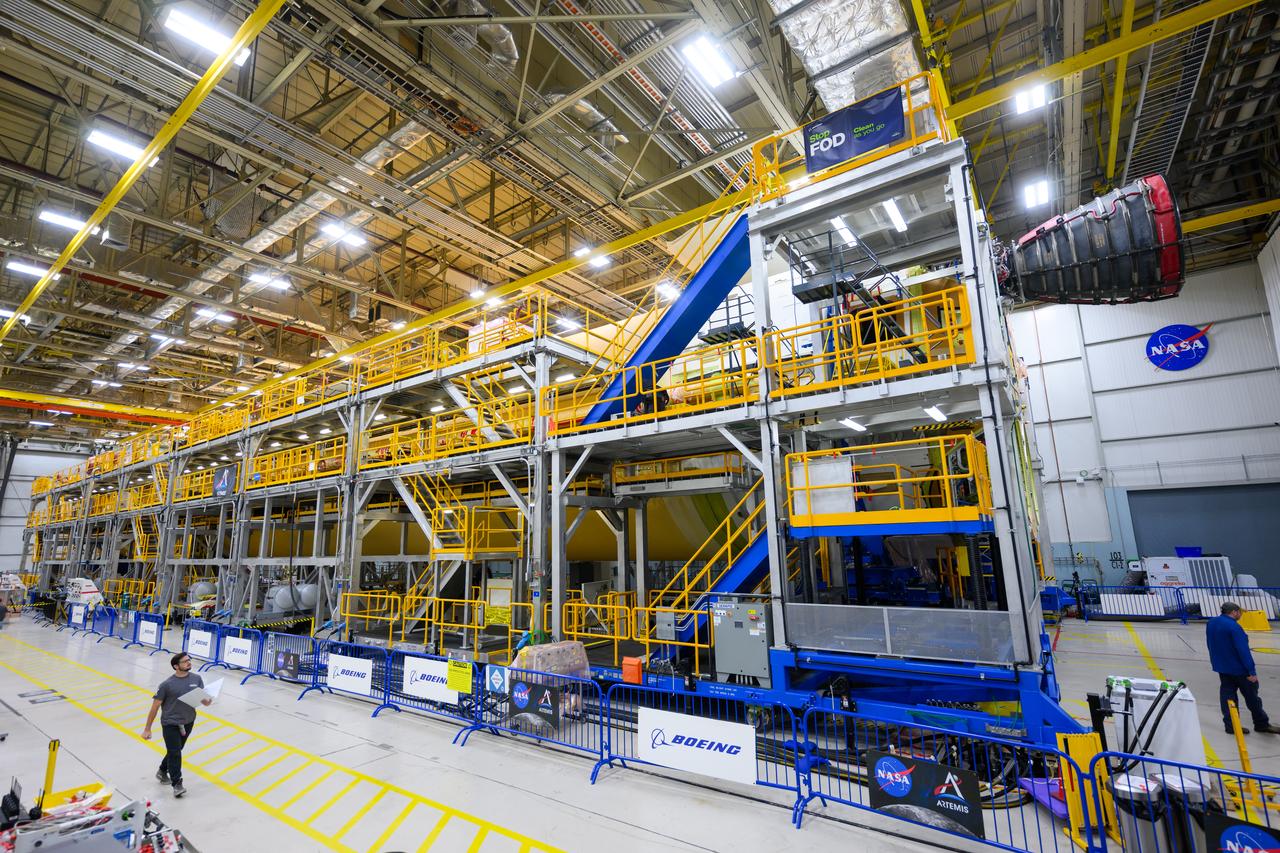
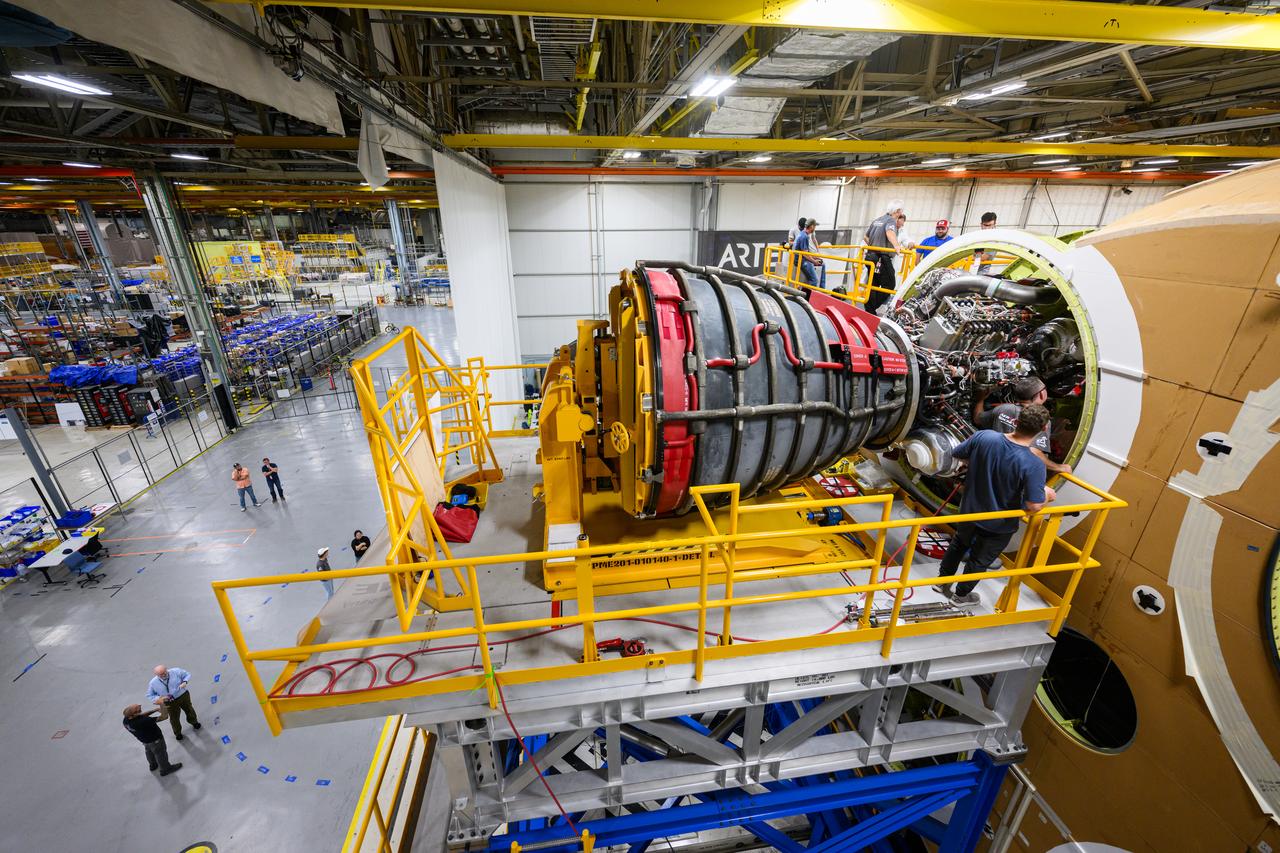
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans have installed the first of four RS-25 engines on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. The Sept. 11 engine installation follows the joining of all five major structures that make up the SLS core stage earlier this spring. NASA, lead RS-25 engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3 Harris Technologies company, and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will continue integrating the remaining three engines into the stage and installing the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
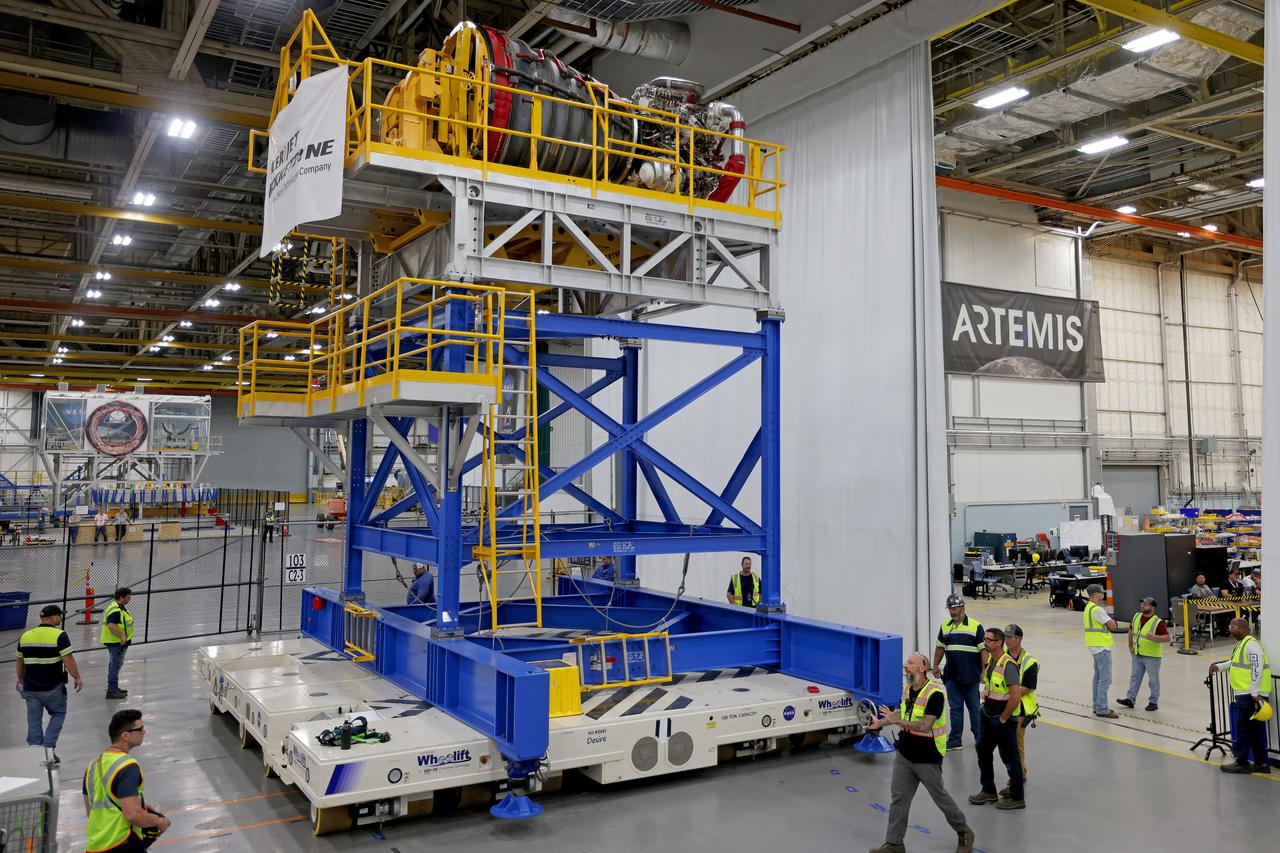

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans have installed the first of four RS-25 engines on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. The Sept. 11 engine installation follows the joining of all five major structures that make up the SLS core stage earlier this spring. NASA, lead RS-25 engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3 Harris Technologies company, and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will continue integrating the remaining three engines into the stage and installing the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
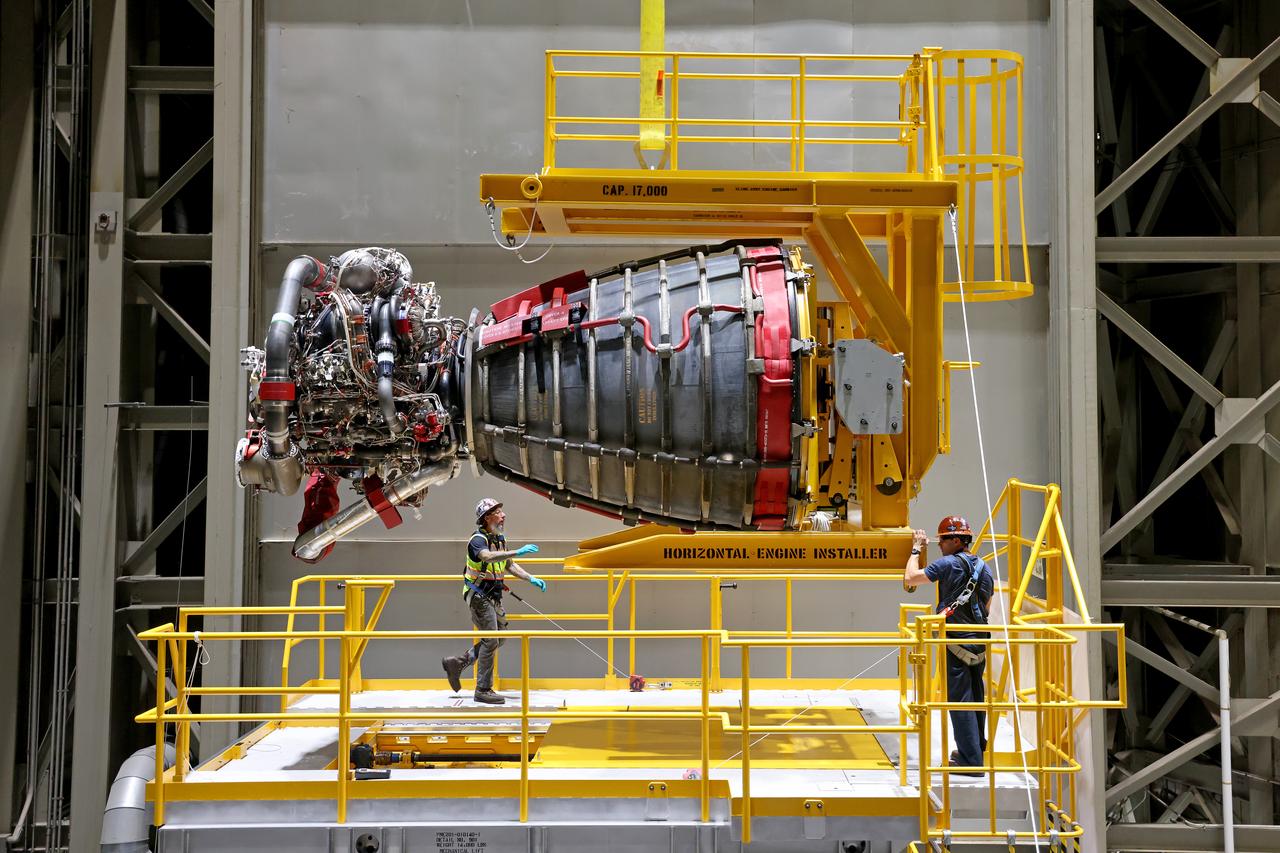
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans have installed the first of four RS-25 engines on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. The Sept. 11 engine installation follows the joining of all five major structures that make up the SLS core stage earlier this spring. NASA, lead RS-25 engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3 Harris Technologies company, and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will continue integrating the remaining three engines into the stage and installing the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.