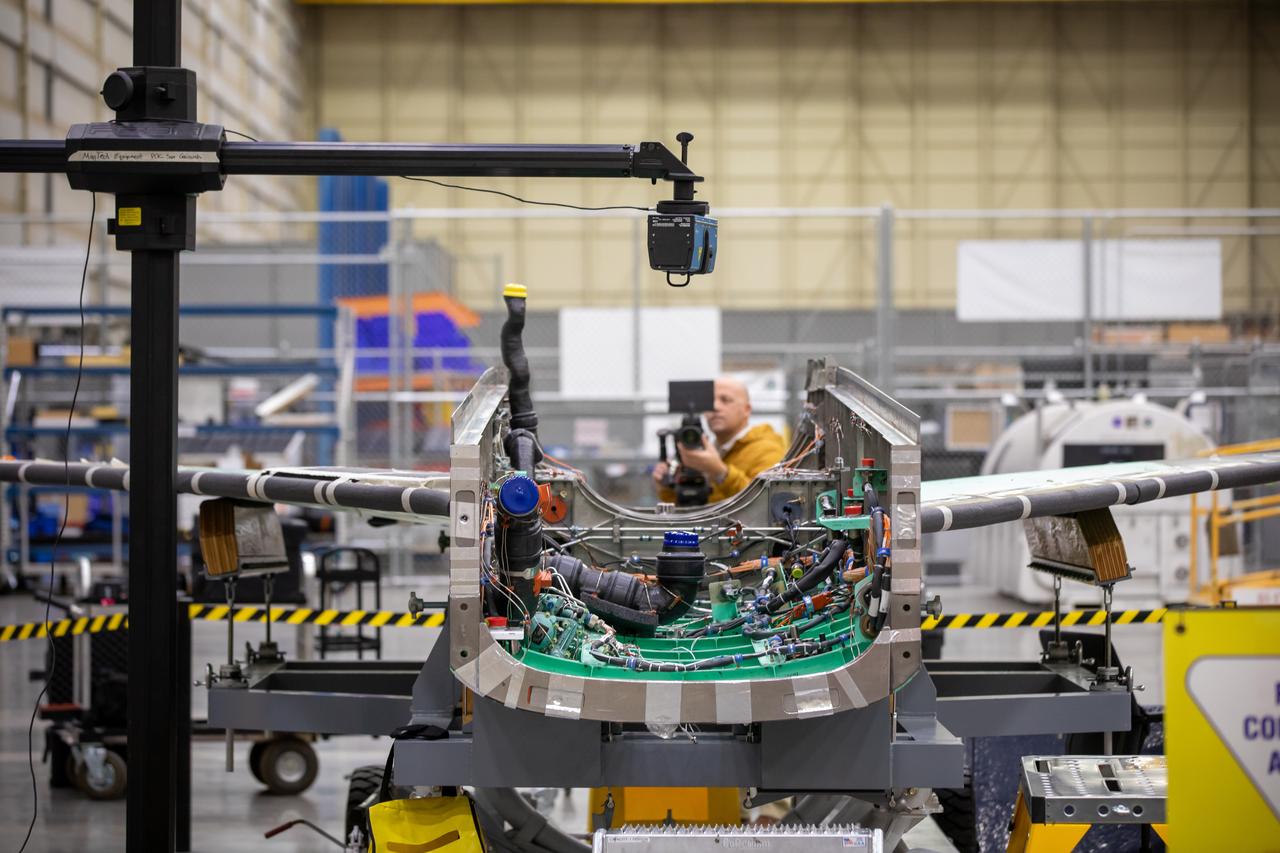

A laser scans the inside of the X-59 aircraft’s lower engine bay at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. These scans can help identify potential hardware or wiring interferences prior to the final installation of the engine and lower tail.

The view members of NASA’s Engineering Management Board had in looking up the Vehicle Assembly Building’s High Bay 3 at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms in High Bay 3, including the one on which the board members are standing, were designed to surround and provide access to NASA’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. The Engineering Management Board toured integral areas of Kennedy to help the agencywide group reach its goal of unifying engineering work across NASA.
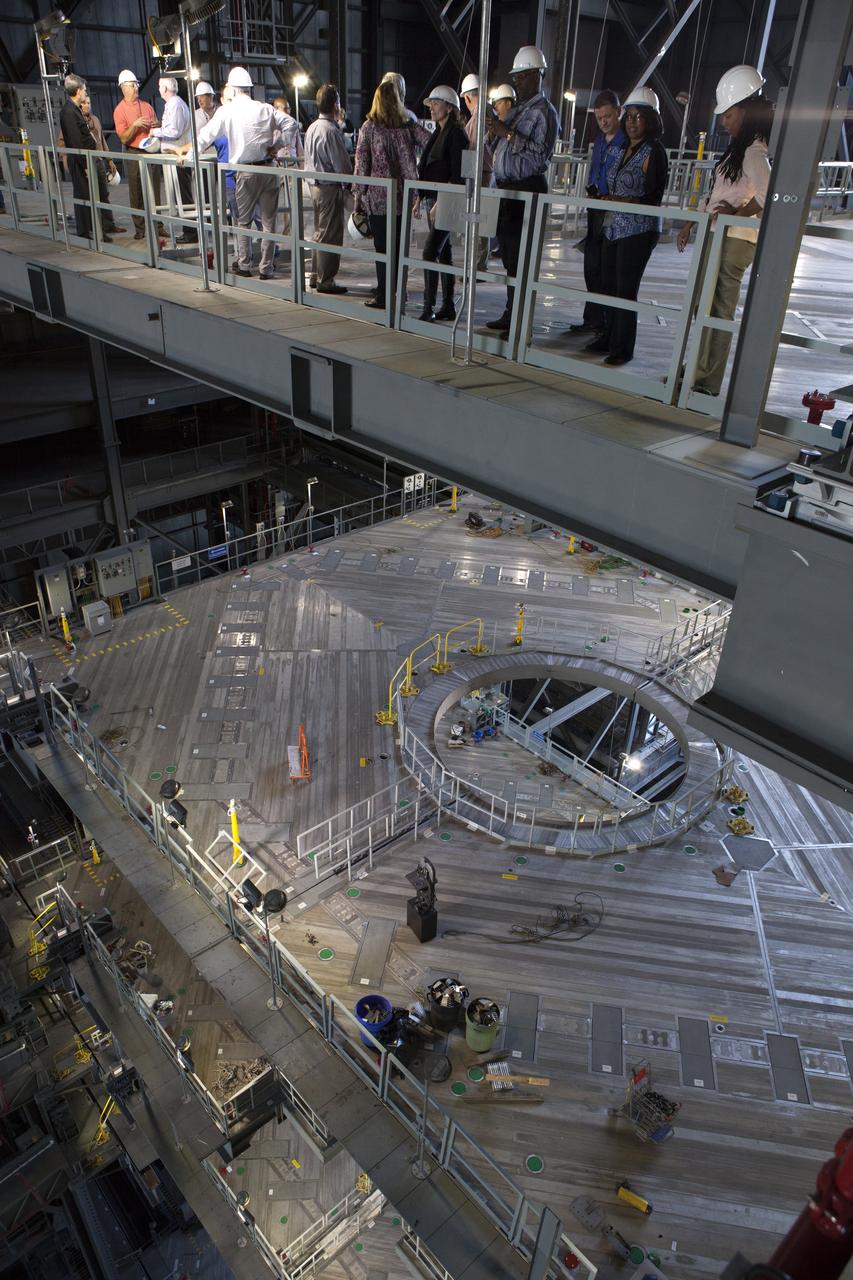

Members of NASA’s Engineering Management Board visit the Vehicle Assembly Building’s High Bay 3 at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms in High Bay 3, including the one on which the board members are standing, were designed to surround and provide access to NASA’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. The Engineering Management Board toured integral areas of Kennedy to help the agencywide group reach its goal of unifying engineering work across NASA.
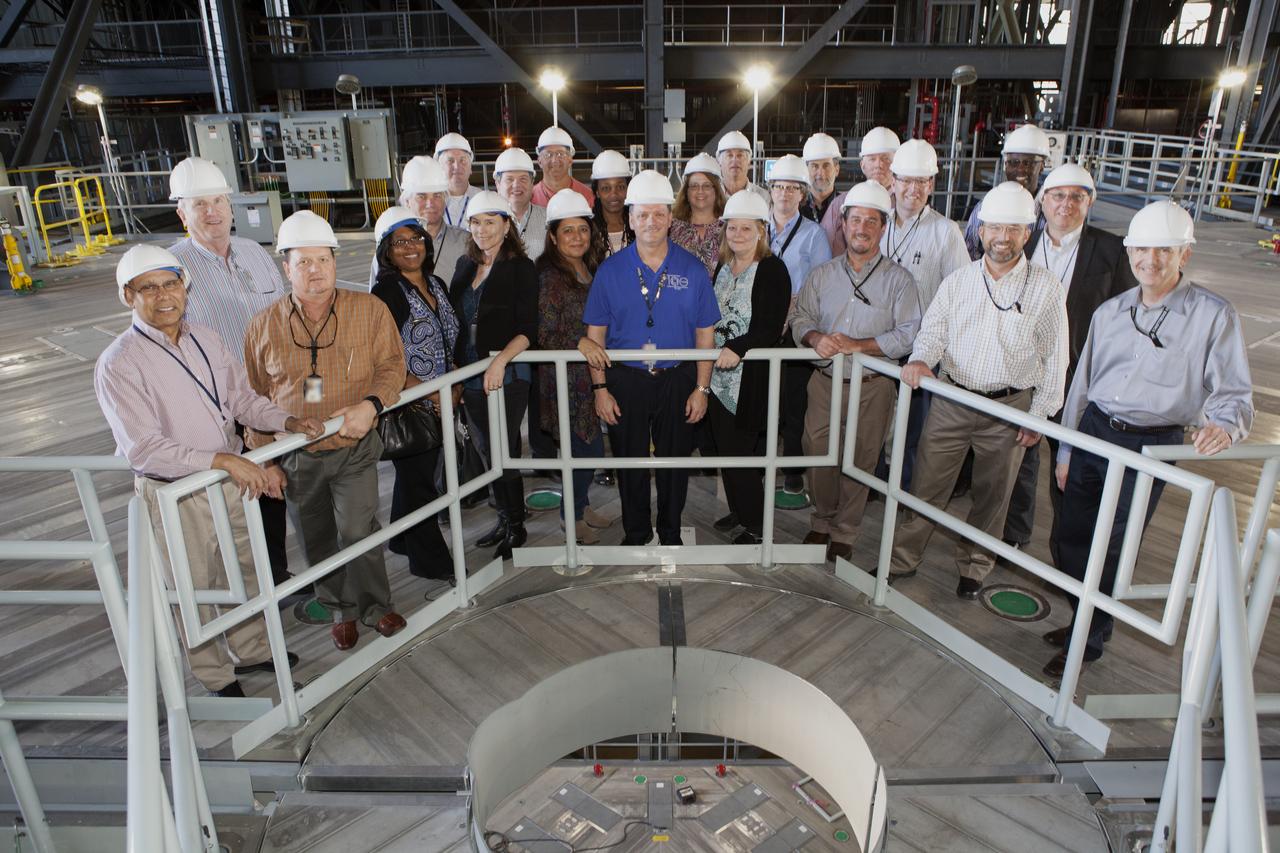

Members of NASA’s Engineering Management Board pause for a group photo during a tour of the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms in High Bay 3, including the one on which the board members are standing, were designed to surround and provide access to NASA’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. The Engineering Management Board toured integral areas of Kennedy to help the agencywide group reach its goal of unifying engineering work across NASA.
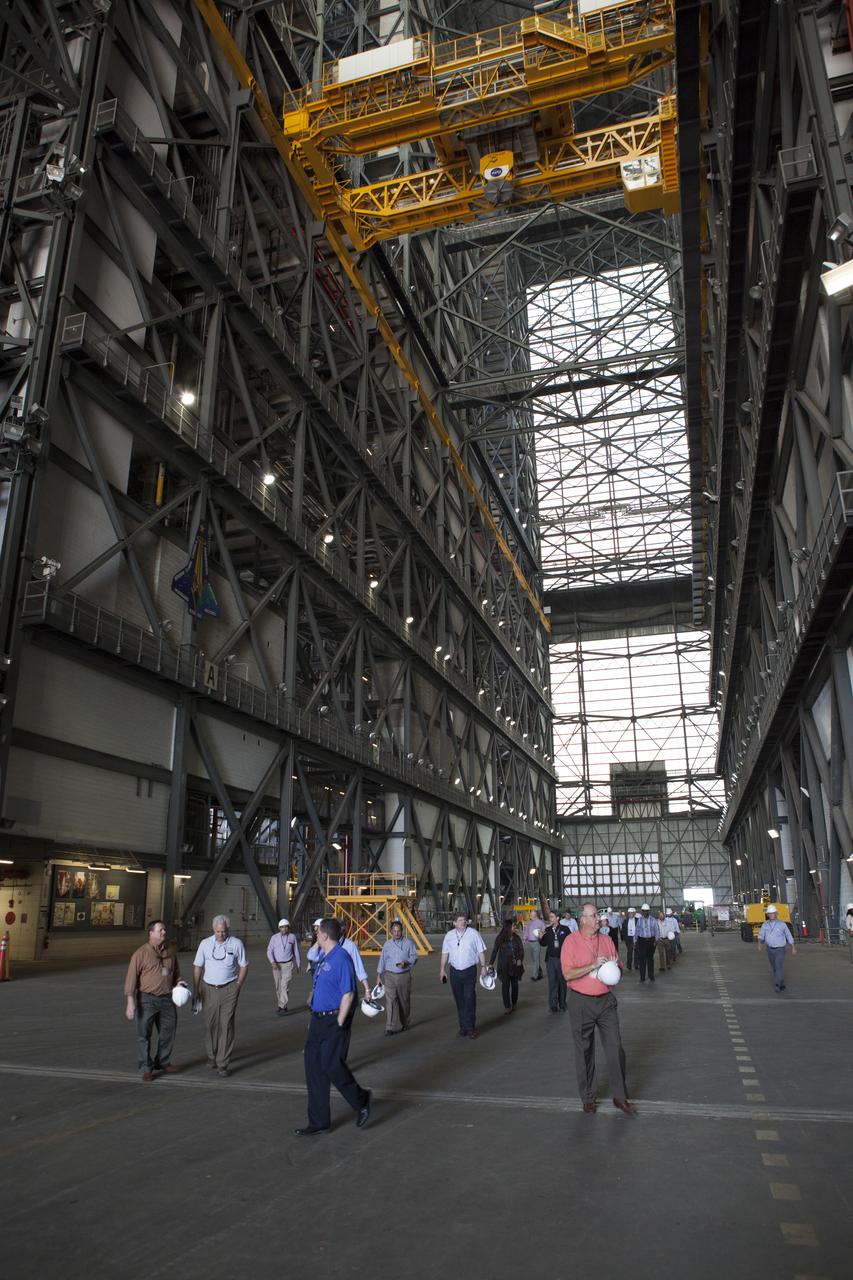

Members of NASA’s Engineering Management Board tour of the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms in High Bay 3, including the one on which the board members are standing, were designed to surround and provide access to NASA’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. The Engineering Management Board toured integral areas of Kennedy to help the agencywide group reach its goal of unifying engineering work across NASA.
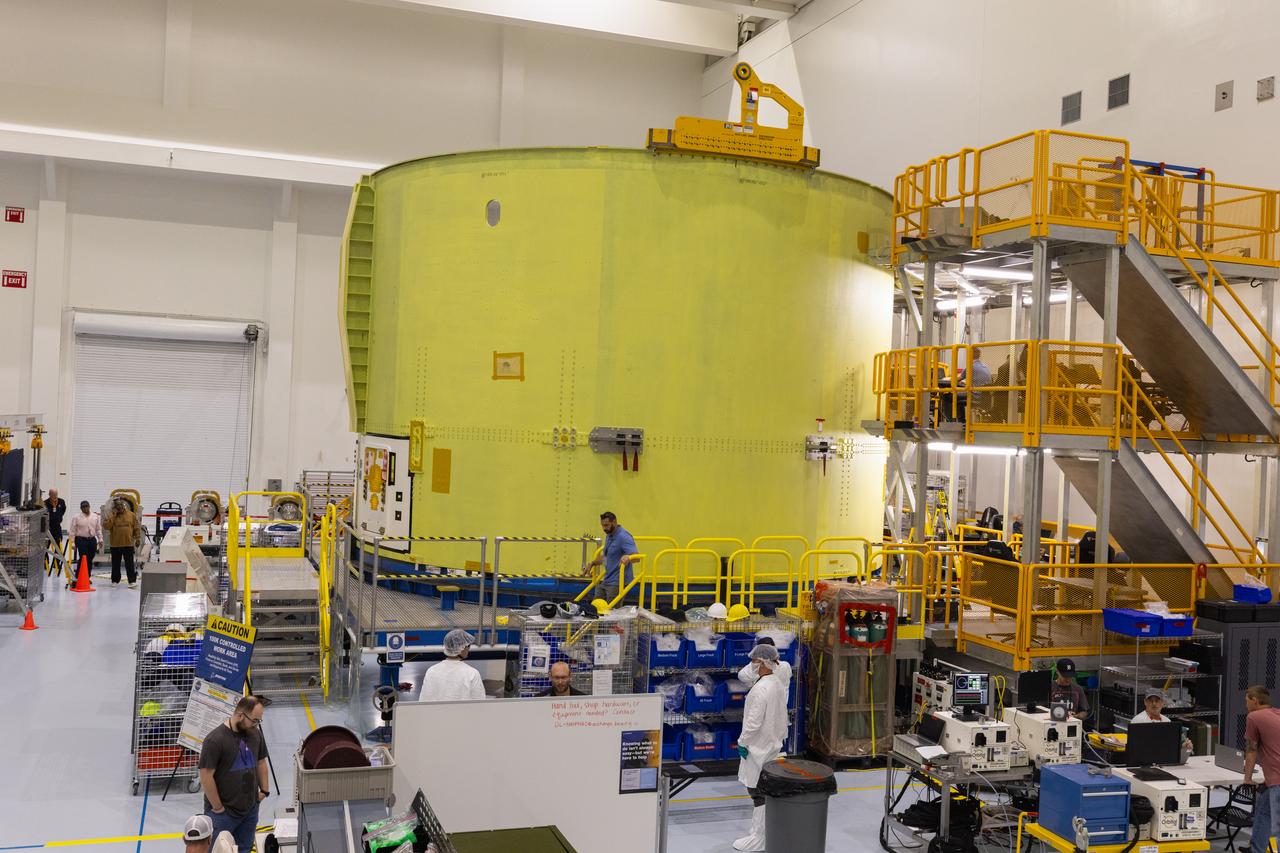

Technicians with NASA and Boeing complete attaching the engine section to the boat-tail for the agency’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) rocket inside the high bay of the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 30, 2024. The engine section is one of five major elements that makes up the SLS rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, which house the rocket’s four RS-25 engines and vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the stage’s two massive liquid propellant tanks to the engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines.

Technicians with NASA and Boeing complete attaching the engine section to the boat-tail for the agency’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) rocket inside the high bay of the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 30, 2024. The engine section is one of five major elements that makes up the SLS rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, which house the rocket’s four RS-25 engines and vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the stage’s two massive liquid propellant tanks to the engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines.

Technicians with NASA and Boeing complete attaching the engine section to the boat-tail for the agency’s Artemis III SLS (Space Launch System) rocket inside the high bay of the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 30, 2024. The engine section is one of five major elements that makes up the SLS rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, which house the rocket’s four RS-25 engines and vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the stage’s two massive liquid propellant tanks to the engines. The boat-tail is designed to protect the bottom end of the core stage and the RS-25 engines.
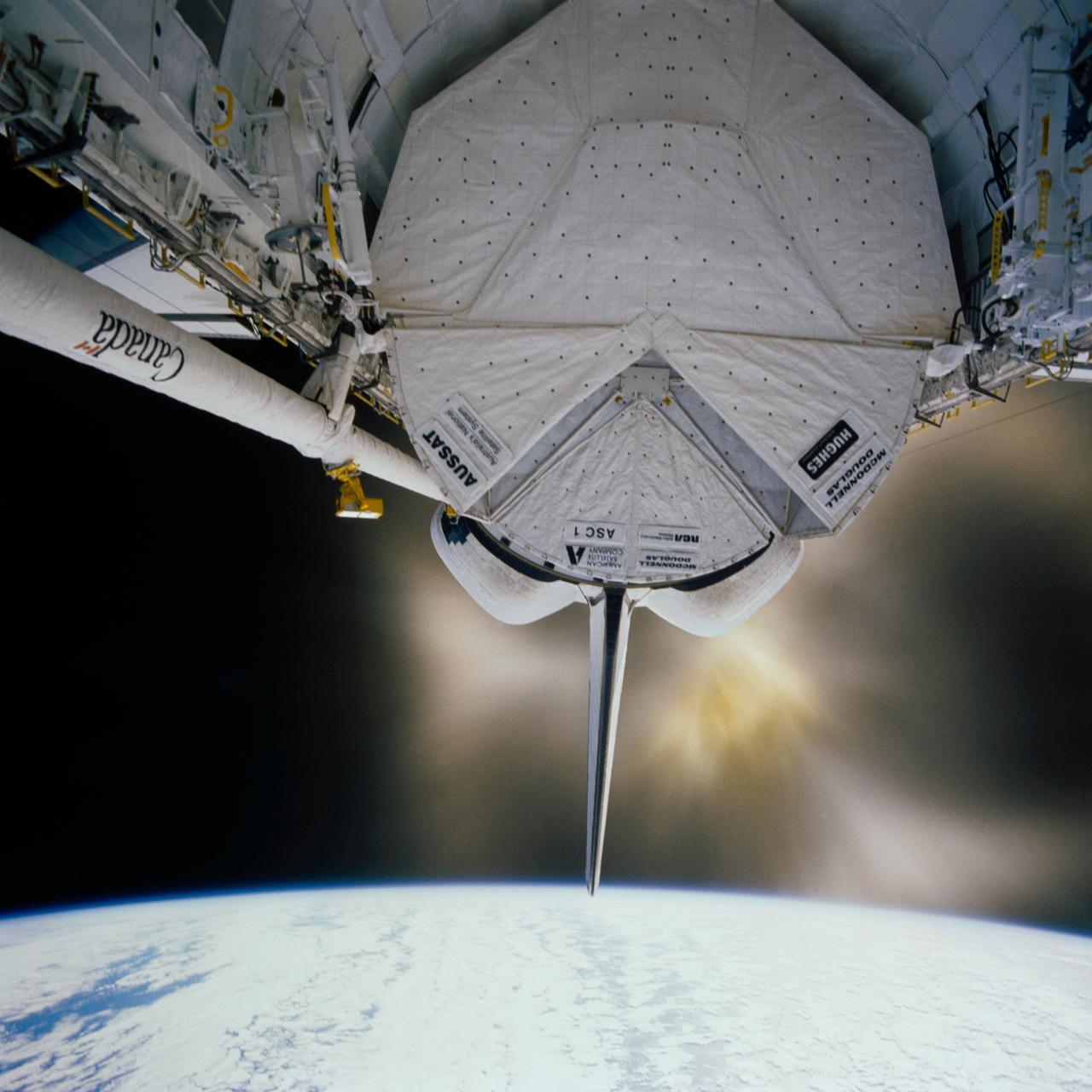

View of a single engine orbital maneuvering system (OMS) firing on the Discovery. The payload bay is open and the protective canisters for the AUSSAT communications satellite (open) and the ASC-1 are visible. A cloudy Earth's horizon can be seen above the orbiter.
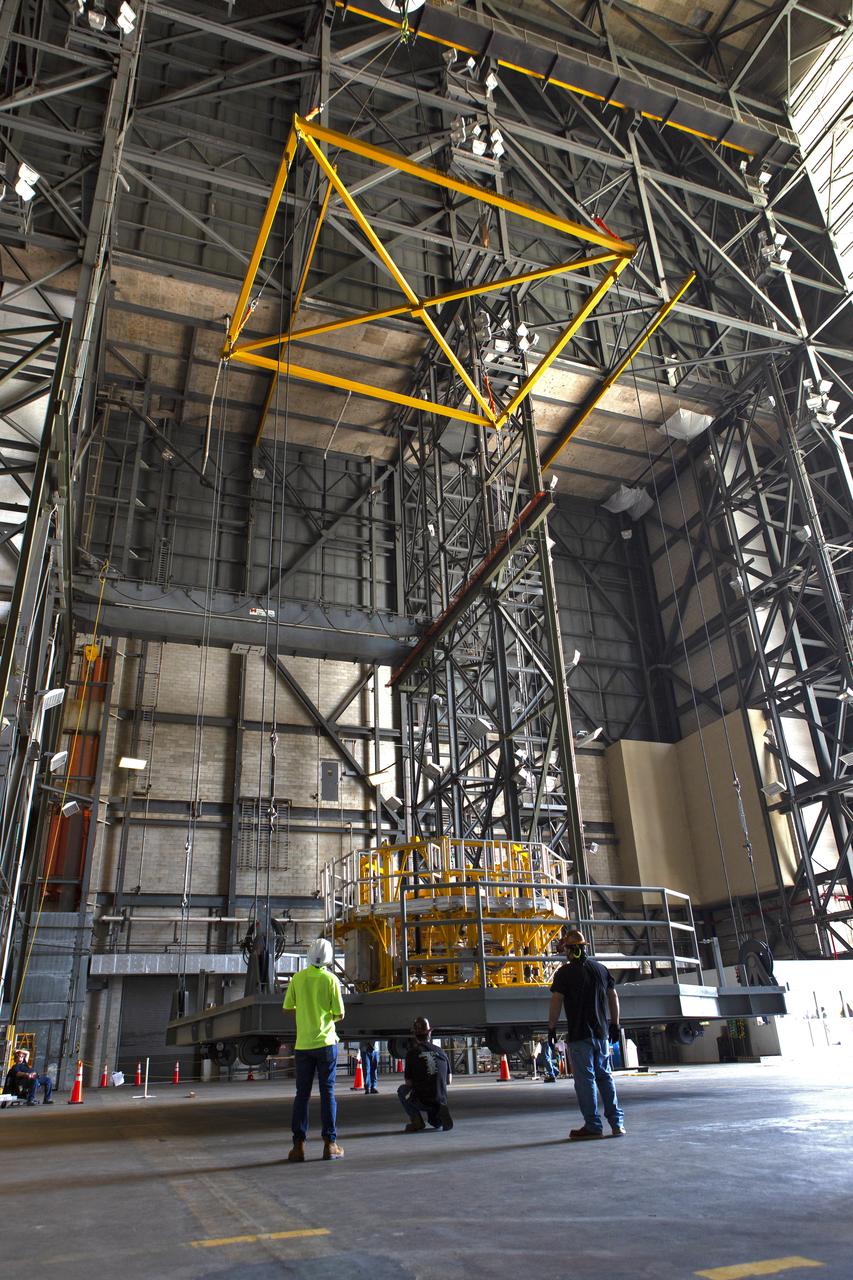

The engine vertical installer for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) is inside the Vehicle Assembly at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 25, 2019. The engine installer is being lifted up by crane for transfer to High Bay 3. The engine installer arrived from the manufacturer, Precision Fabrication and Cleaning in Canaveral Groves, Florida. The new ground support equipment will be ready for preflight processing in the event one of the four RS-25 engines on the core stage of the SLS rocket needs to be replaced. During launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft, the four core stage engines will provide the thrust needed to lift the rocket and Orion spacecraft off Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy for Exploration Mission-1. The uncrewed Orion will travel on a three-week test mission thousands of miles beyond the Moon and back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
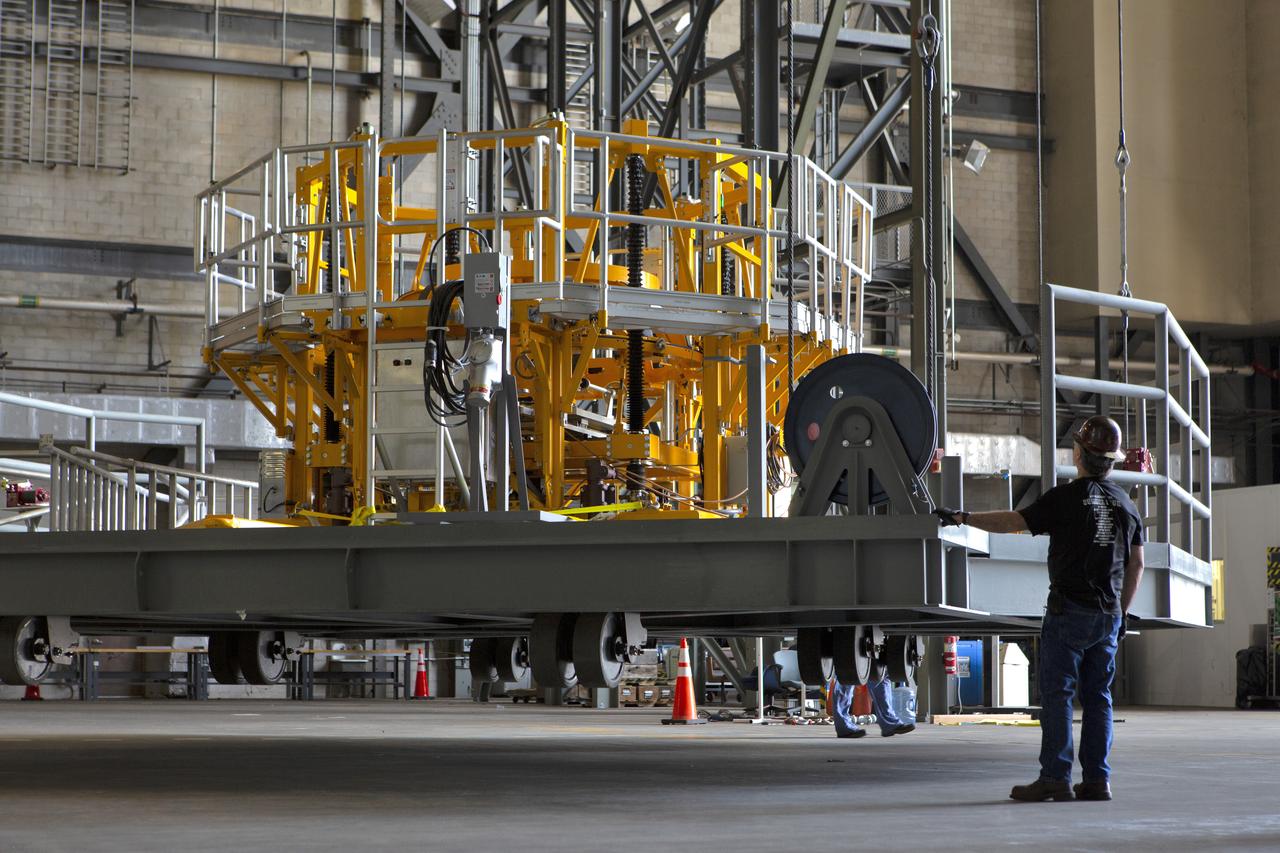

The engine vertical installer for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) is inside the Vehicle Assembly at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 25, 2019. The engine installer is being lifted up by crane for transfer to High Bay 3. The engine installer arrived from the manufacturer, Precision Fabrication and Cleaning in Canaveral Groves, Florida. The new ground support equipment will be ready for preflight processing in the event one of the four RS-25 engines on the core stage of the SLS rocket needs to be replaced. During launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft, the four core stage engines will provide the thrust needed to lift the rocket and Orion spacecraft off Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy for Exploration Mission-1. The uncrewed Orion will travel on a three-week test mission thousands of miles beyond the Moon and back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
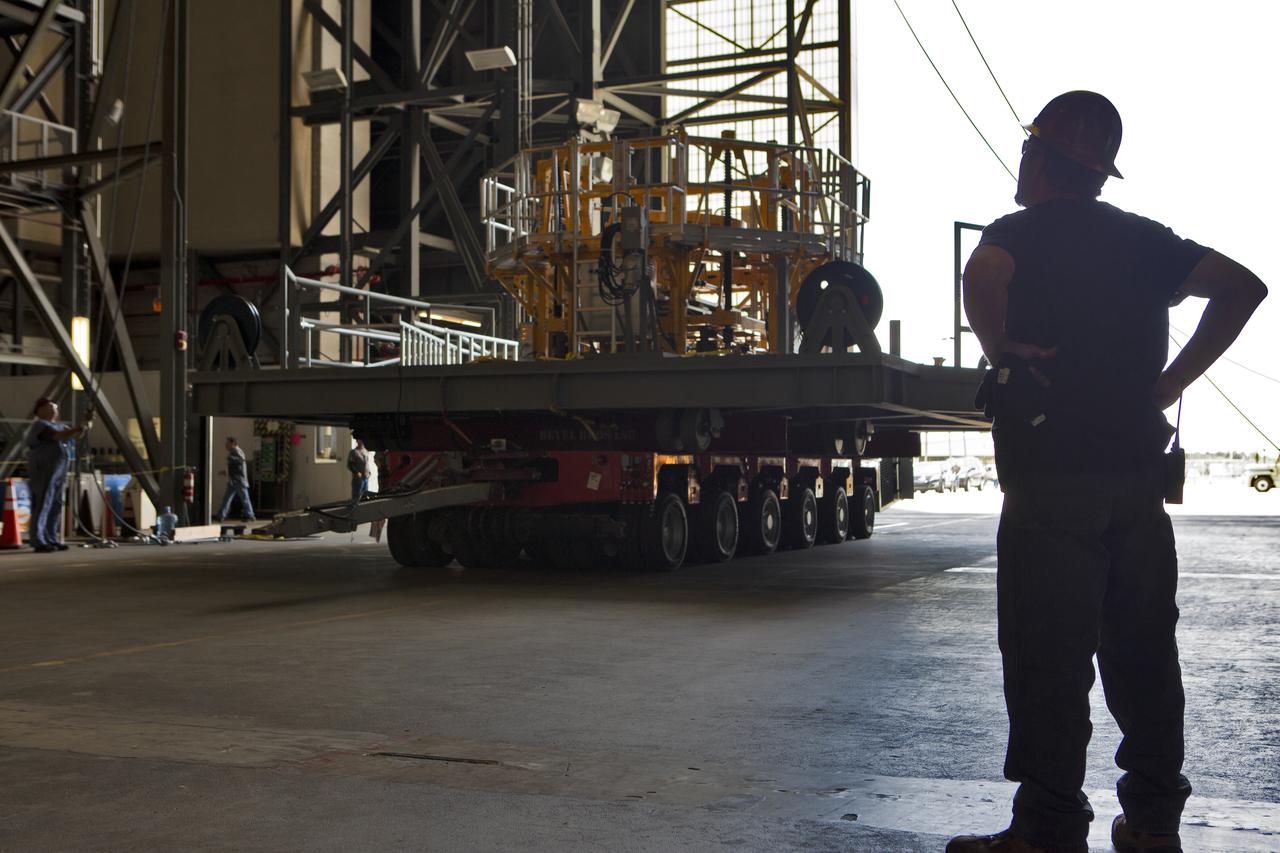

The engine vertical installer for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) is inside the Vehicle Assembly at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 25, 2019. The engine installer will be lifted up by crane for transfer to High Bay 3. The engine installer arrived from the manufacturer, Precision Fabrication and Cleaning in Canaveral Groves, Florida. The new ground support equipment will be ready for preflight processing in the event one of the four RS-25 engines on the core stage of the SLS rocket needs to be replaced. During launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft, the four core stage engines will provide the thrust needed to lift the rocket and Orion spacecraft off Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy for Exploration Mission-1. The uncrewed Orion will travel on a three-week test mission thousands of miles beyond the Moon and back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
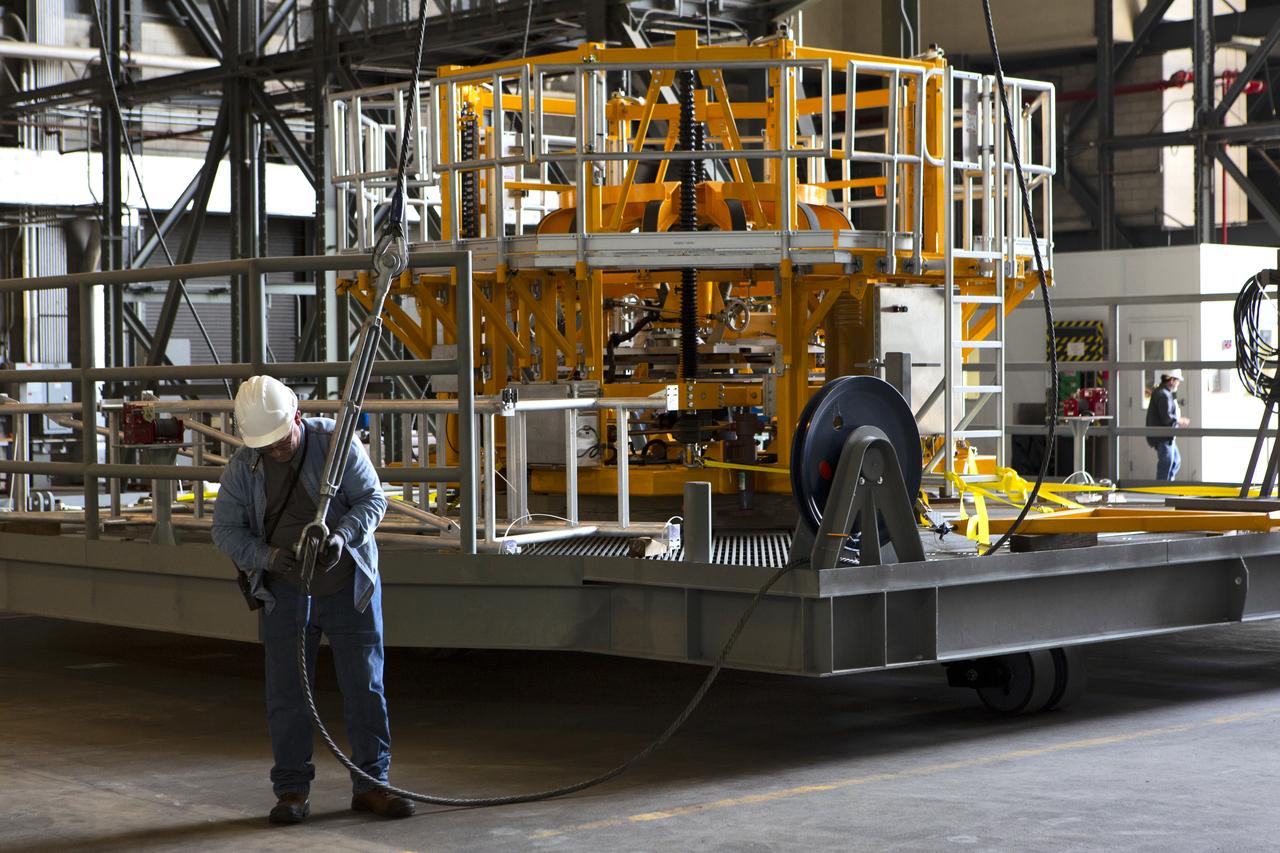

The engine vertical installer for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) is inside the Vehicle Assembly at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 25, 2019. Preparations are underway to lift the engine installer up and into High Bay 3. The engine installer arrived from the manufacturer, Precision Fabrication and Cleaning in Canaveral Groves, Florida. The new ground support equipment will be ready for preflight processing in the event one of the four RS-25 engines on the core stage of the SLS rocket needs to be replaced. During launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft, the four core stage engines will provide the thrust needed to lift the rocket and Orion spacecraft off Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy for Exploration Mission-1. The uncrewed Orion will travel on a three-week test mission thousands of miles beyond the Moon and back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
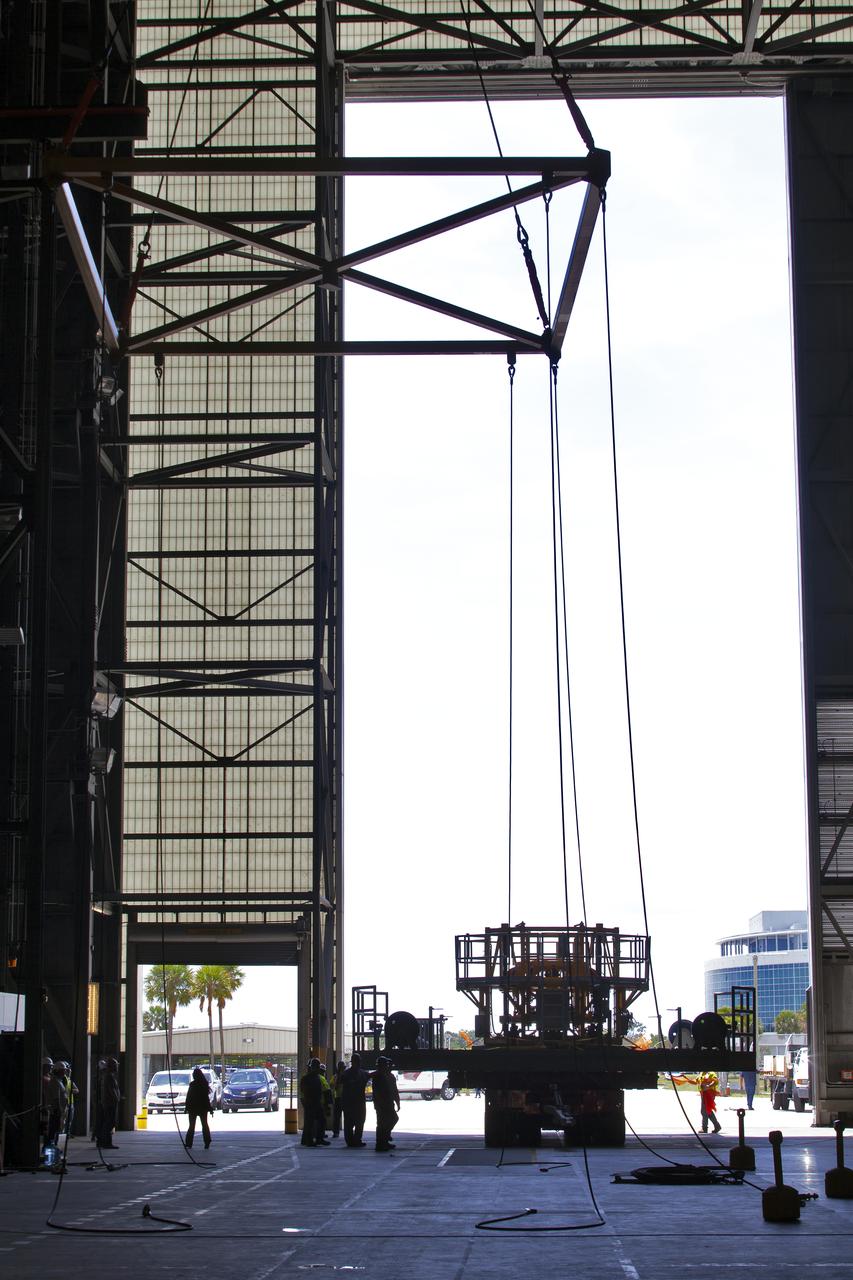

The engine vertical installer for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) is being lifted by crane in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 25, 2019. The engine installer arrived from the manufacturer, Precision Fabrication and Cleaning in Canaveral Groves, Florida. The new ground support equipment will be transferred into High Bay 3 where it will be ready for preflight processing in the event one of the four RS-25 engines on the core stage of the SLS rocket needs to be replaced. During launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft, the four core stage engines will provide the thrust needed to lift the rocket and Orion spacecraft off Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy for Exploration Mission-1. The uncrewed Orion will travel on a three-week test mission thousands of miles beyond the Moon and back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
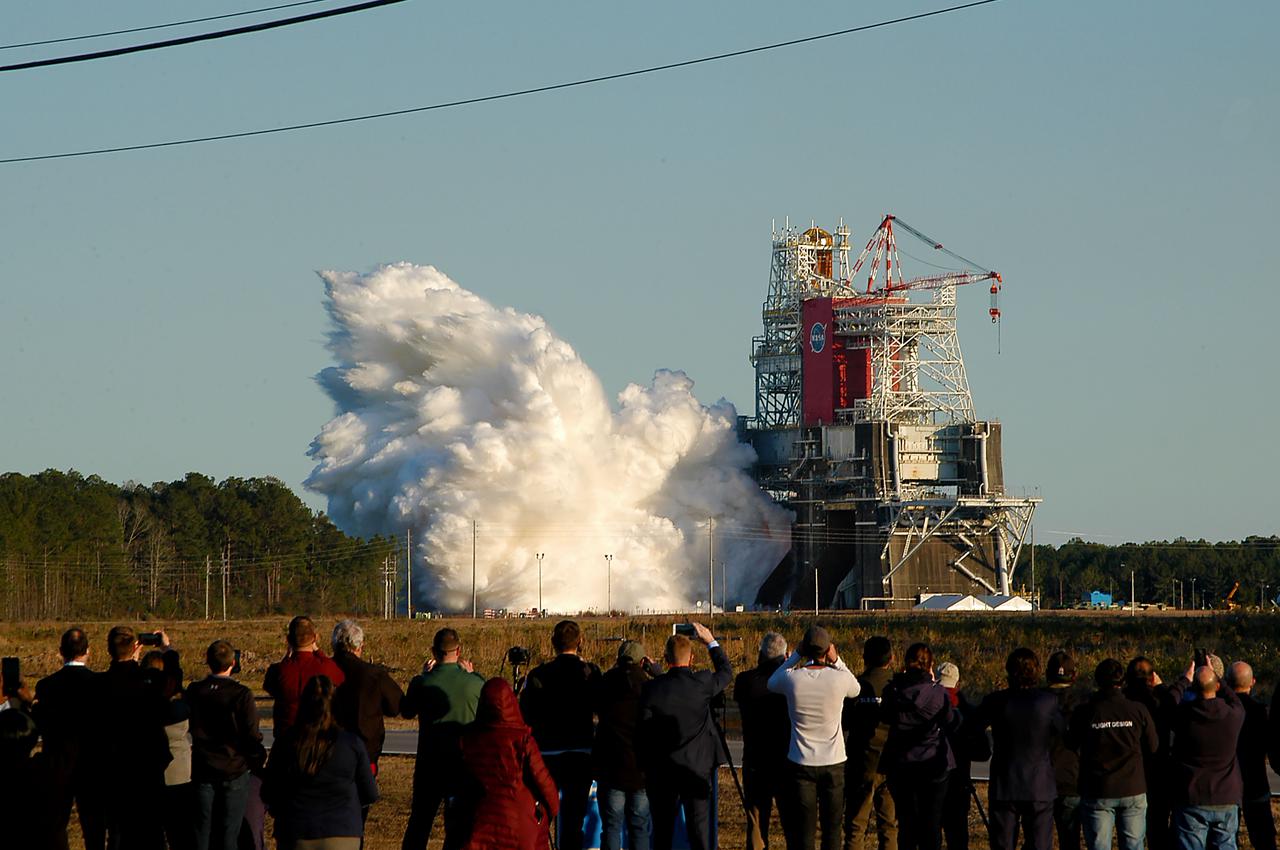

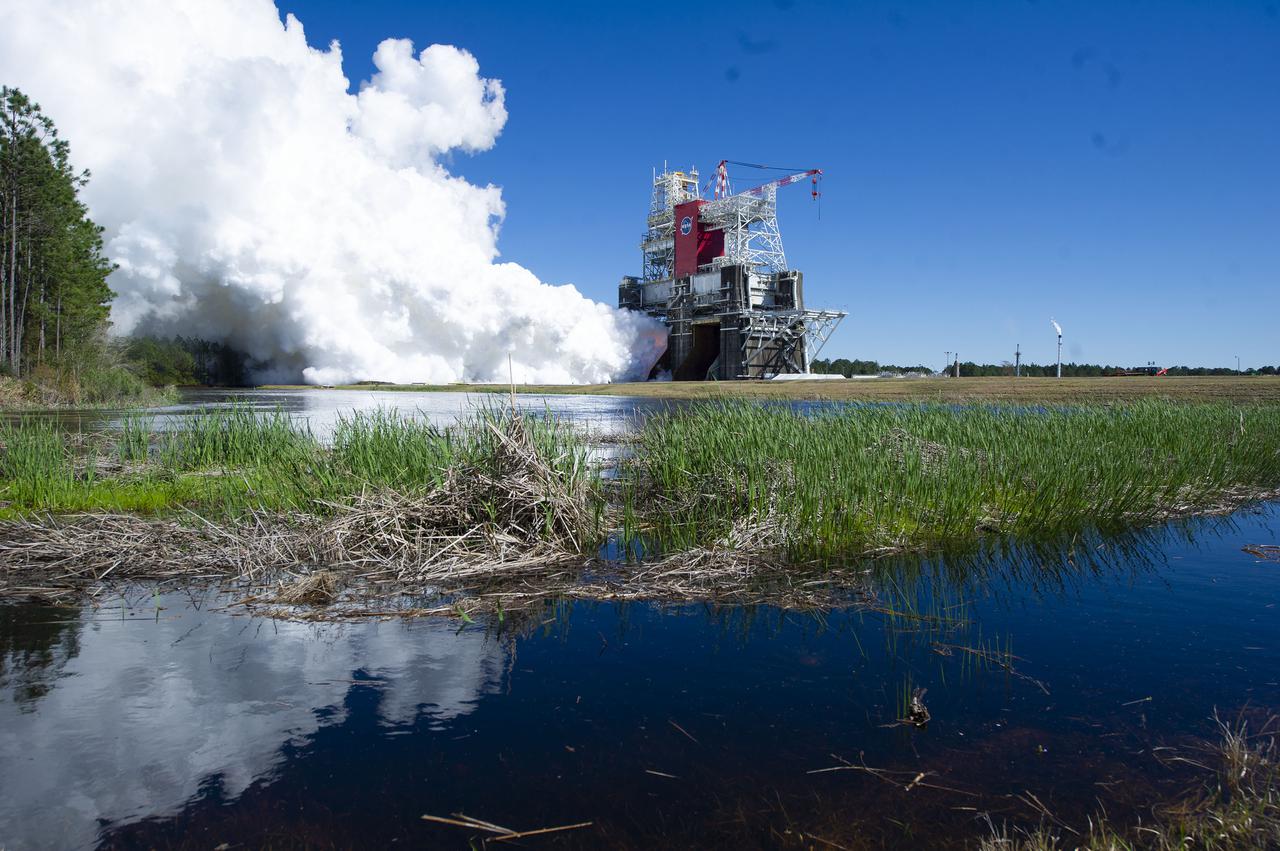
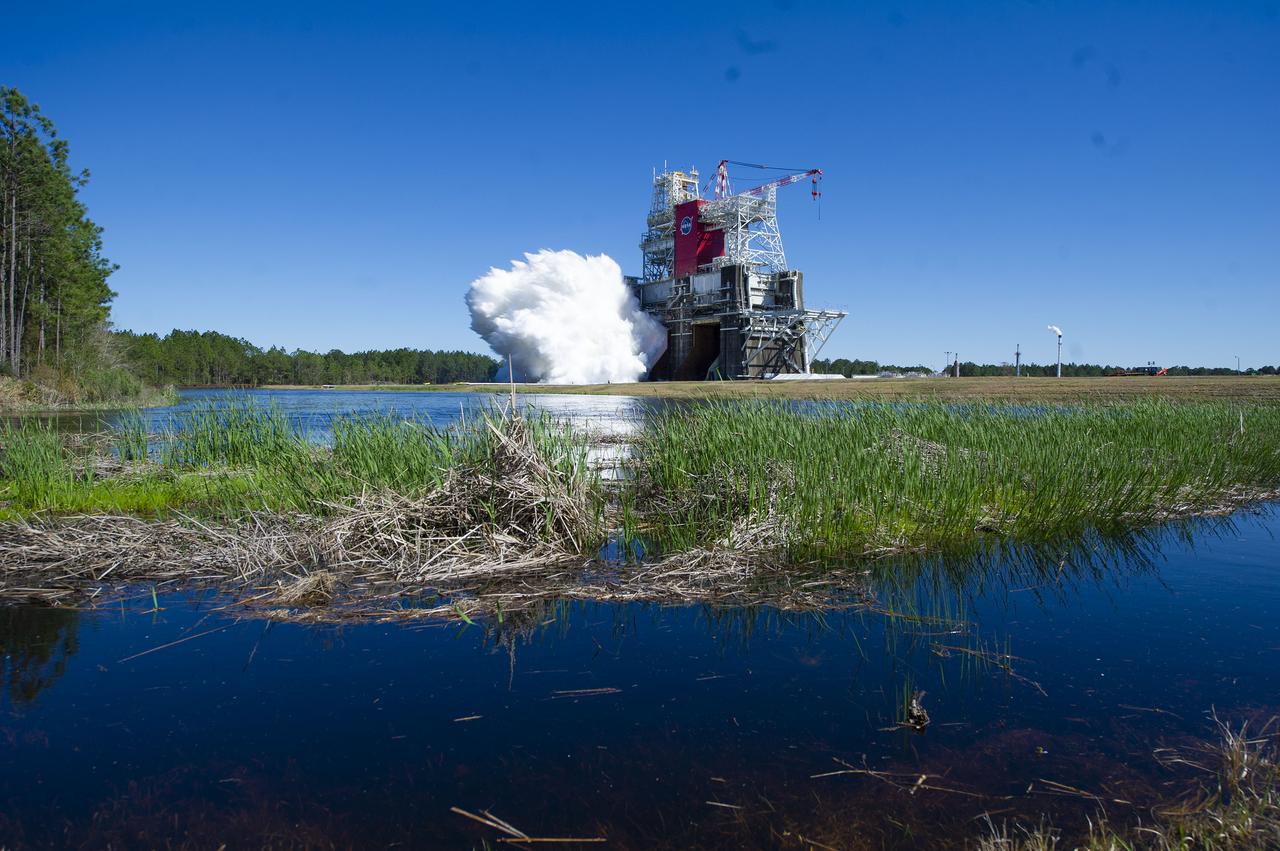
NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
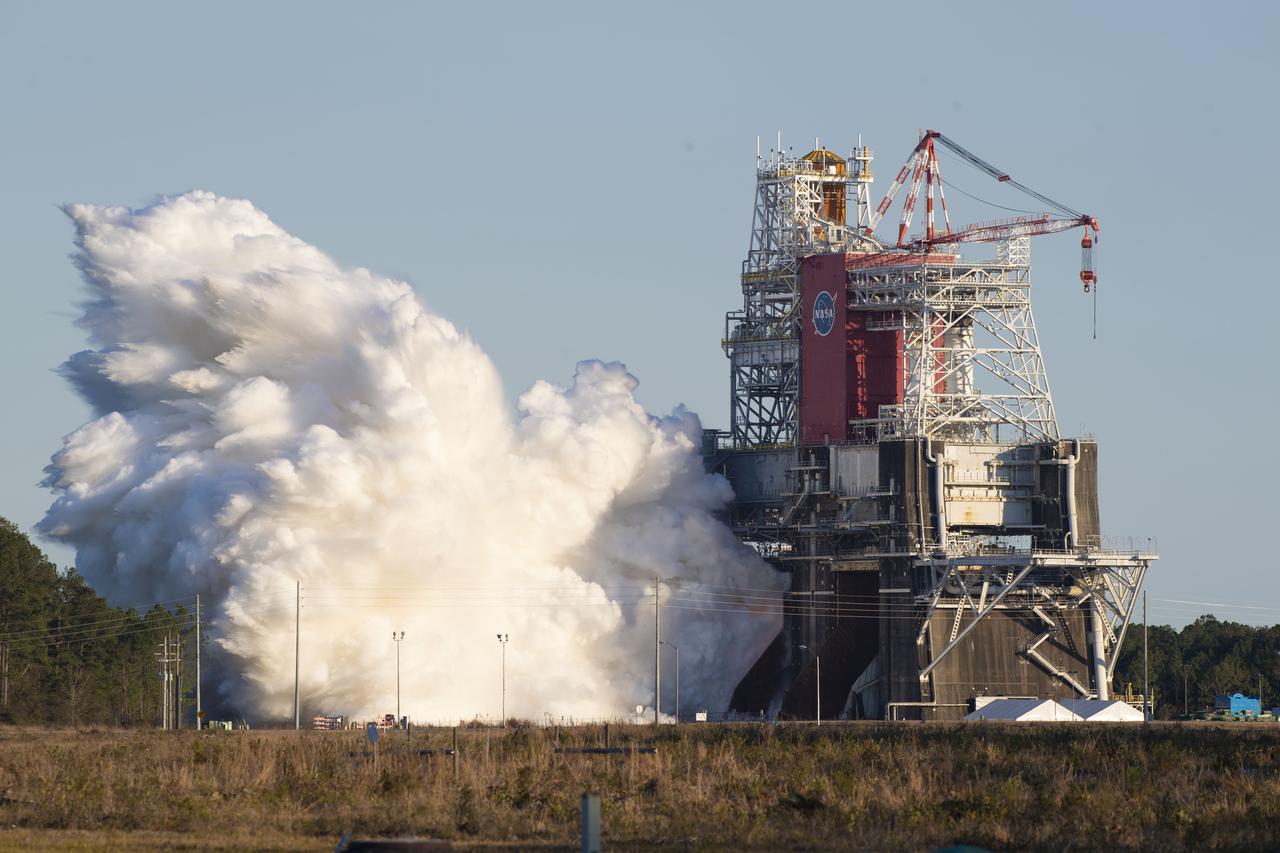

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
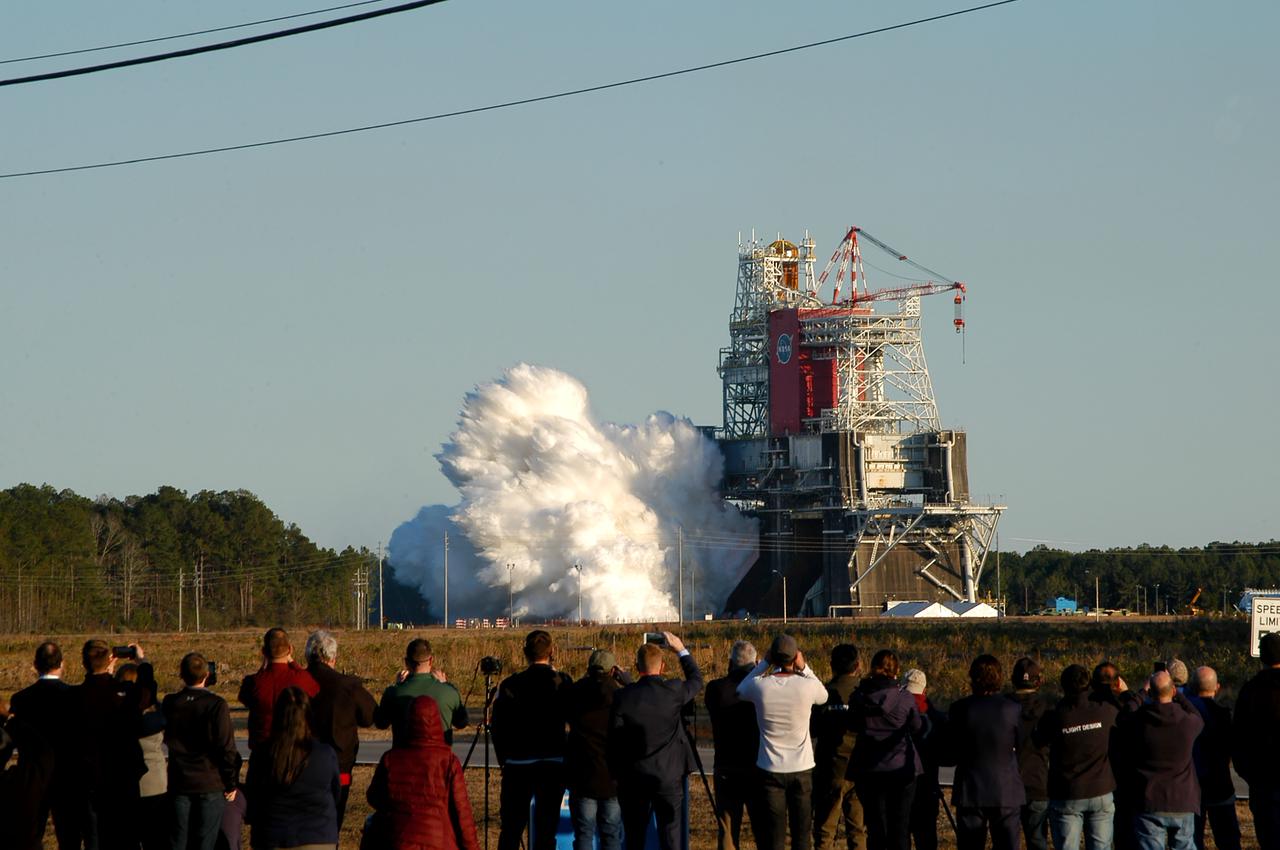

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

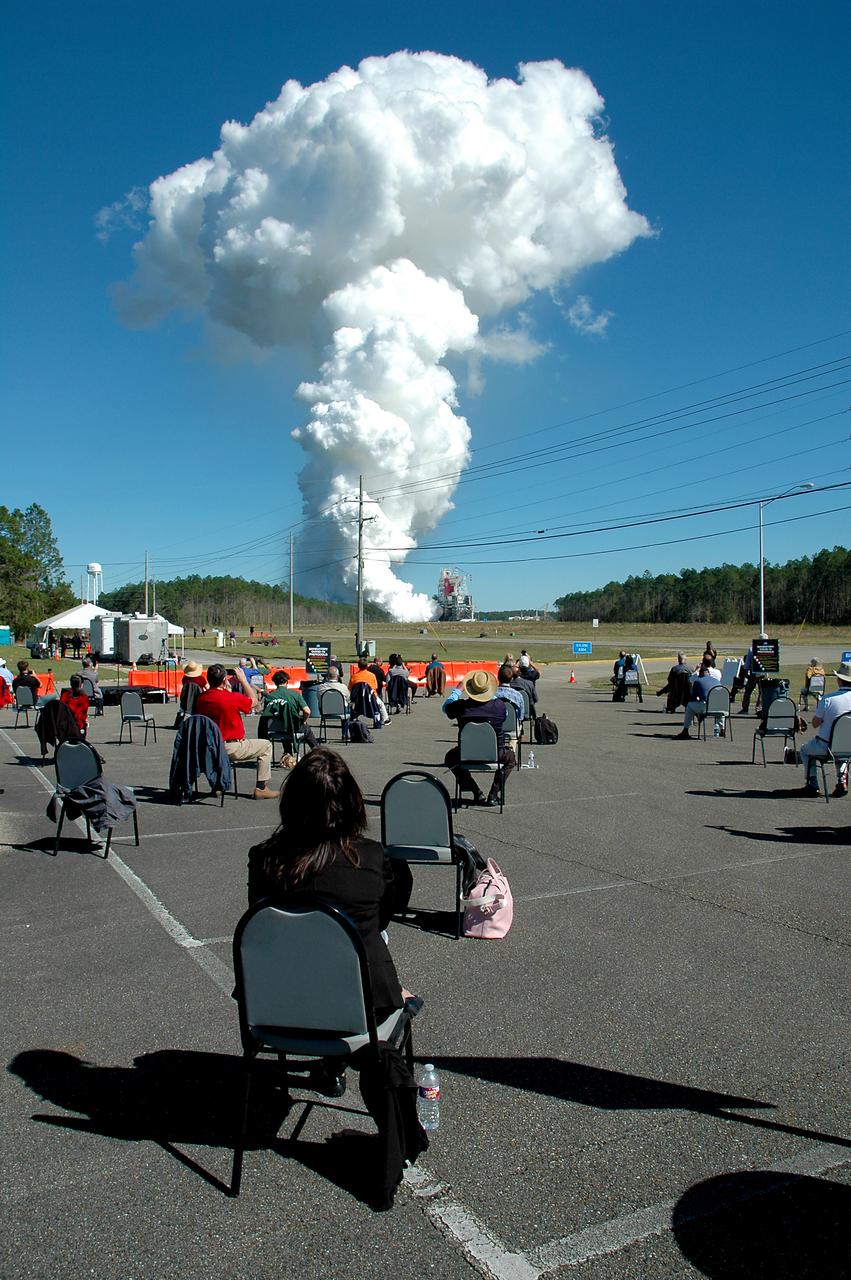
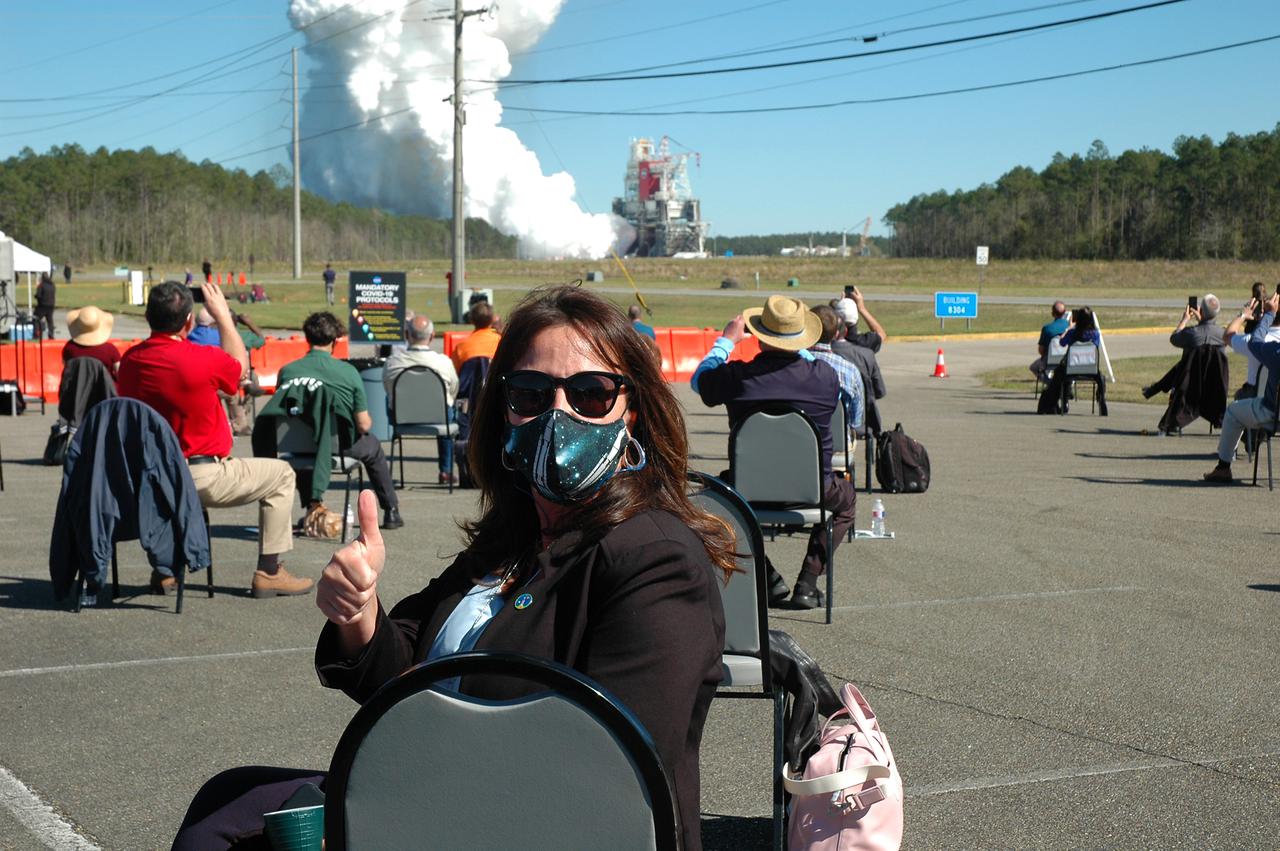
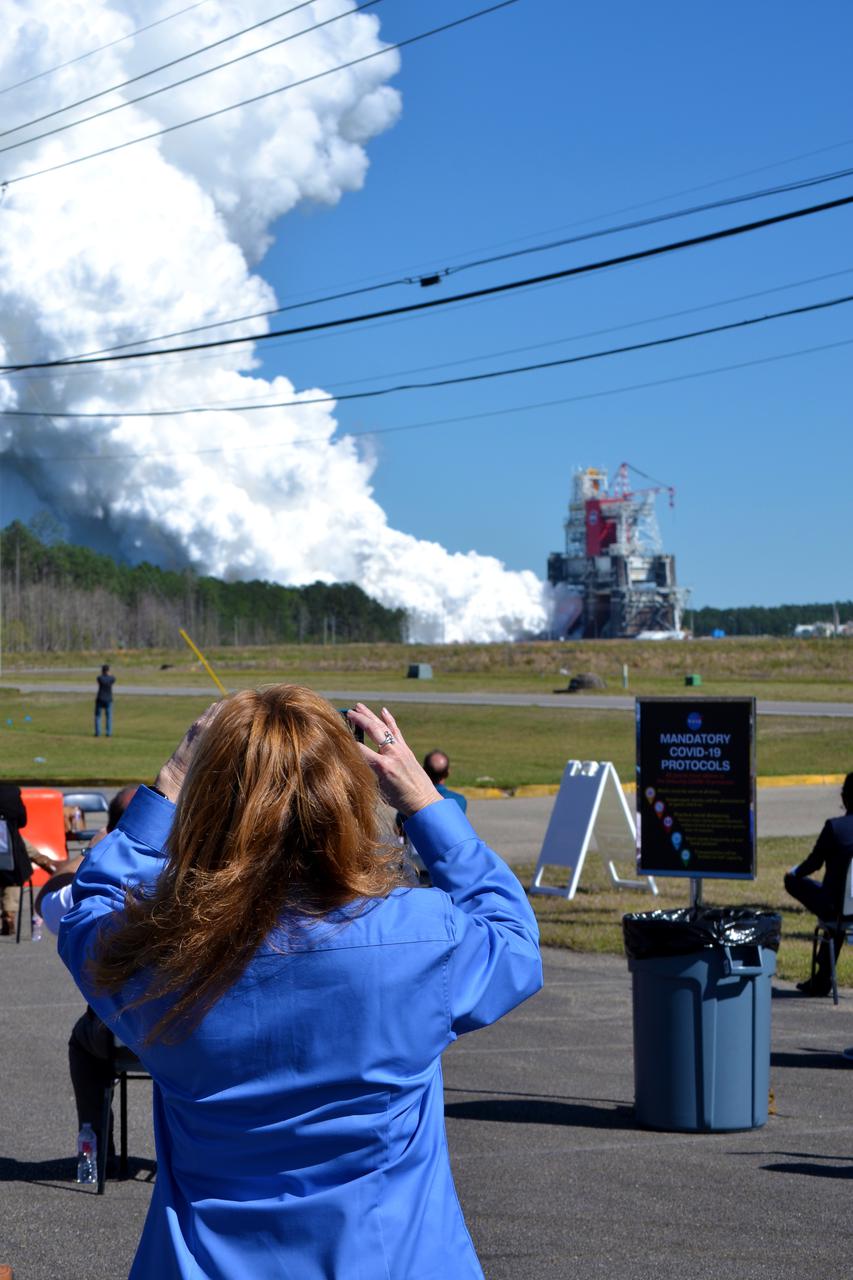
A staff member administers a COVID-19 temperature check to media and guests arriving to view the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
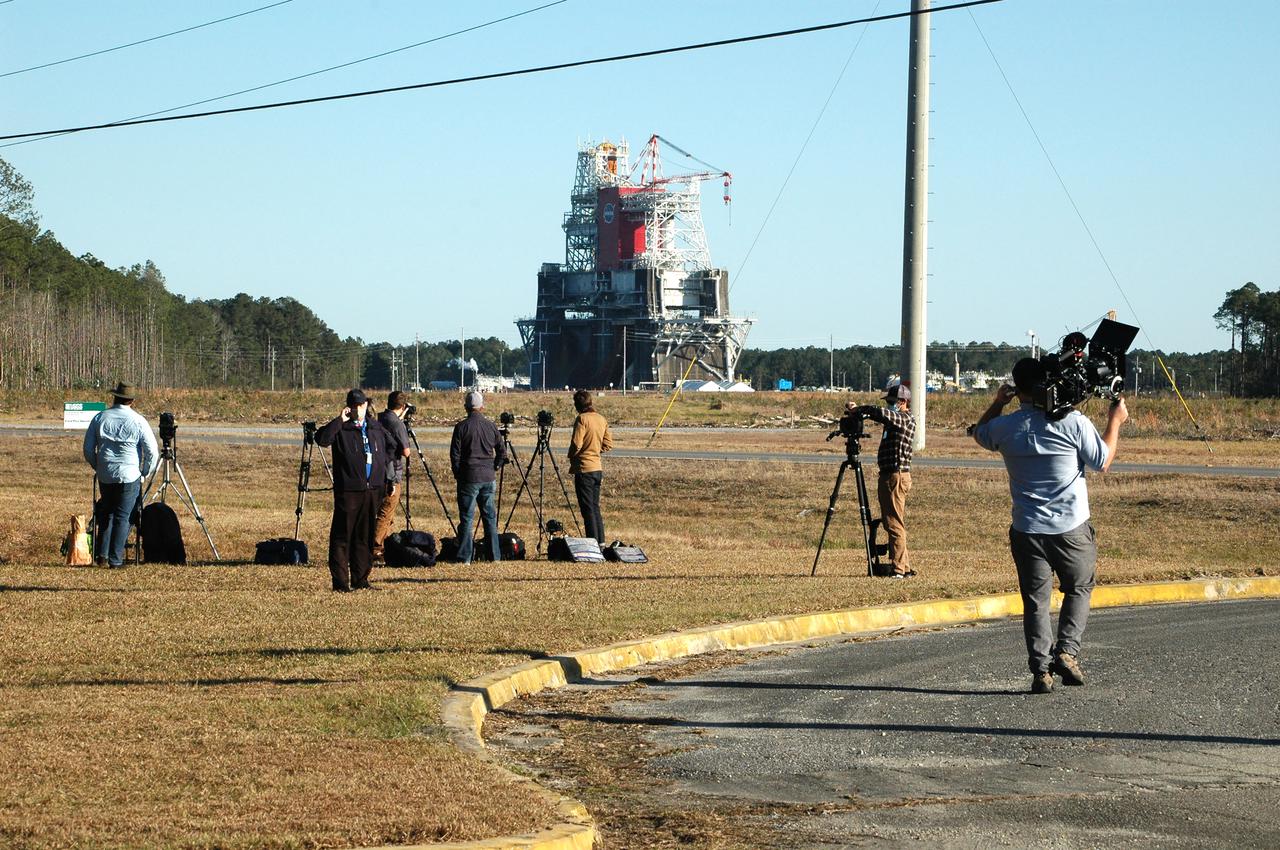

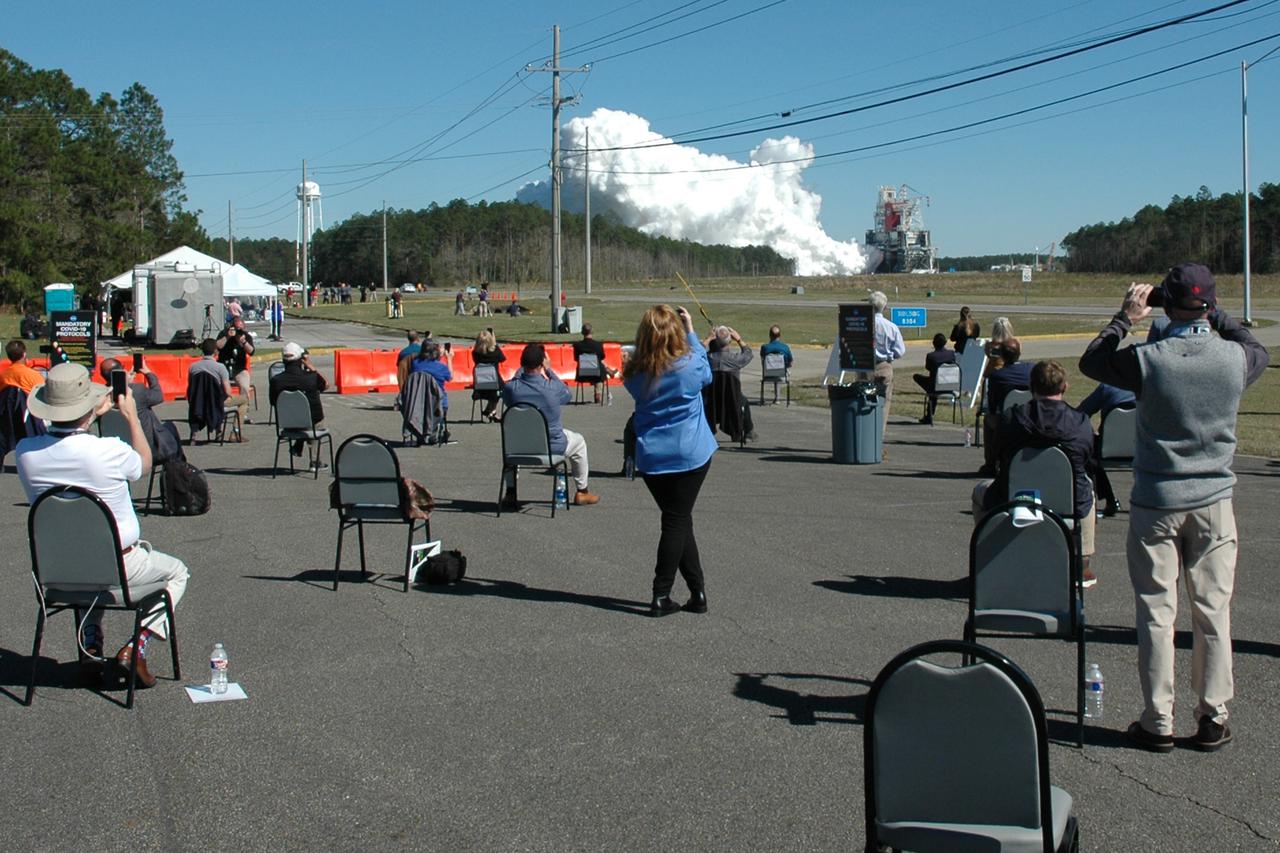
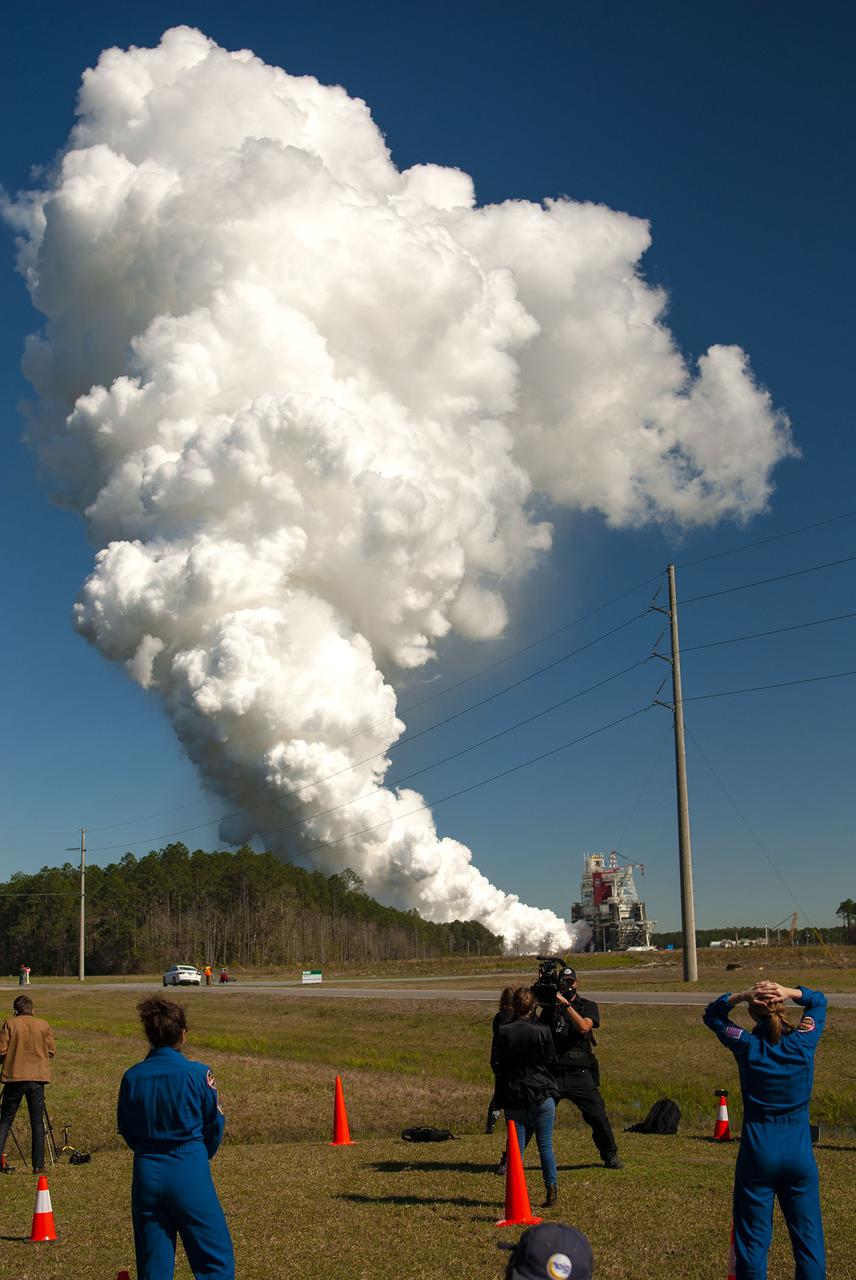
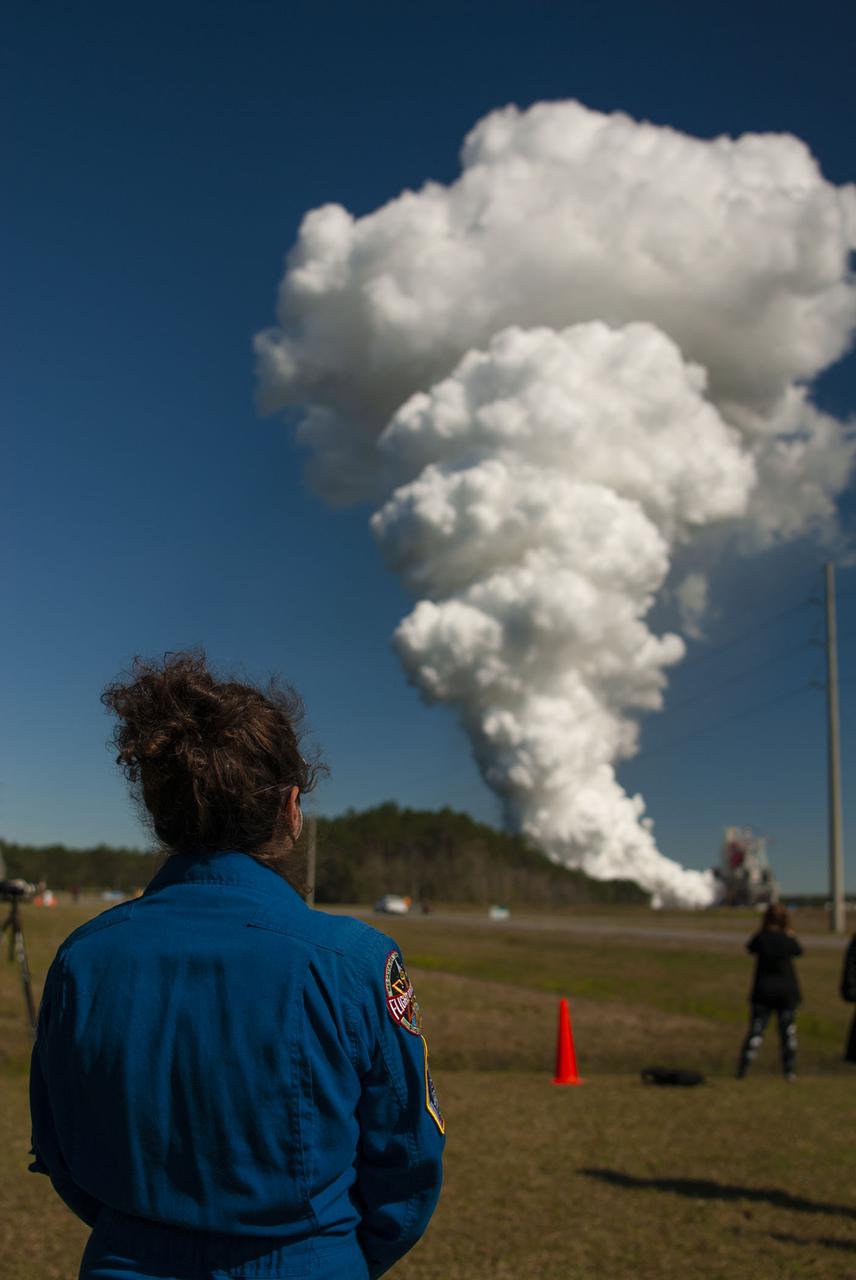
Members of the media stake out viewing spots prior to the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Jan. 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

A posted sign outlines COVID-19 protocol for media and guests arriving to view the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
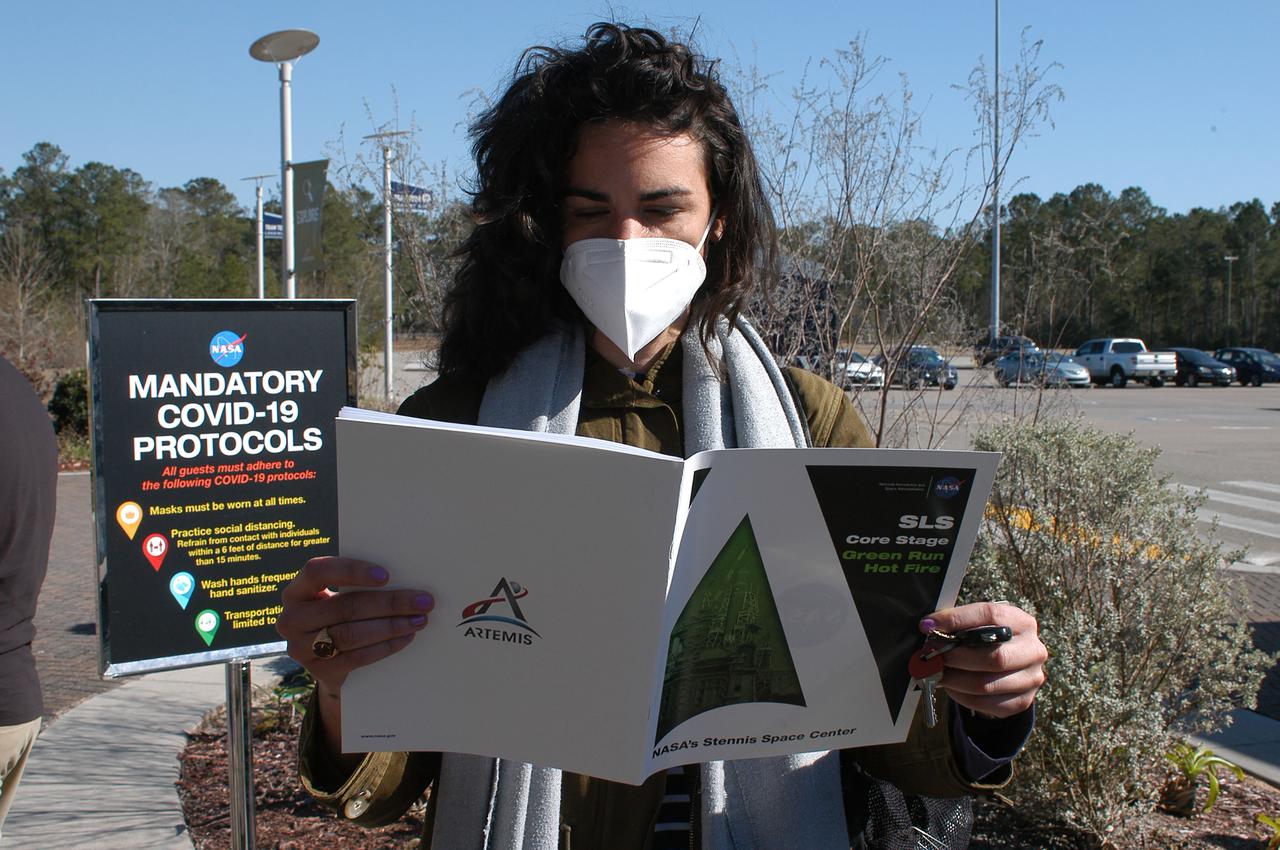

A guest reviews a commemorative Green Run booklet after arriving to view the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
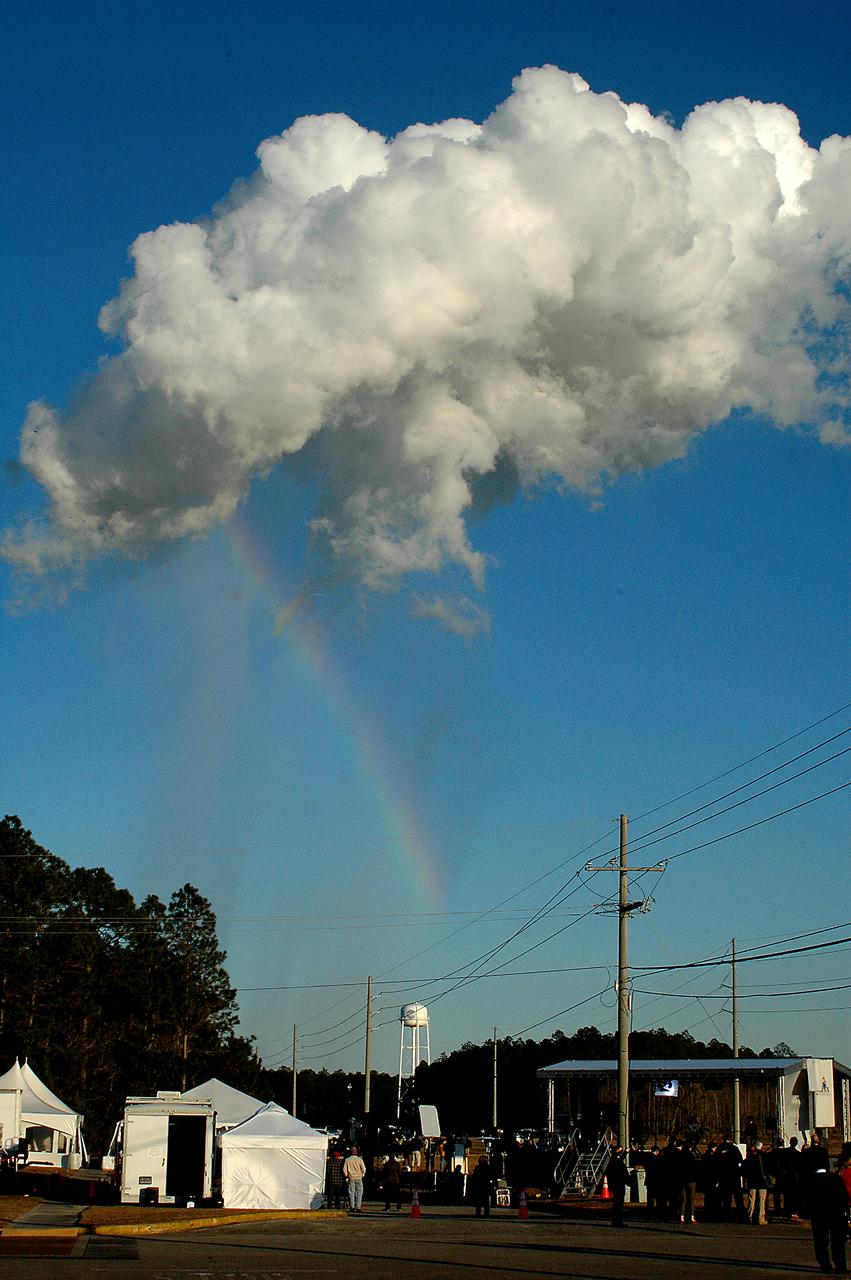

A rainbow appears as the steam cloud dissipates following the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
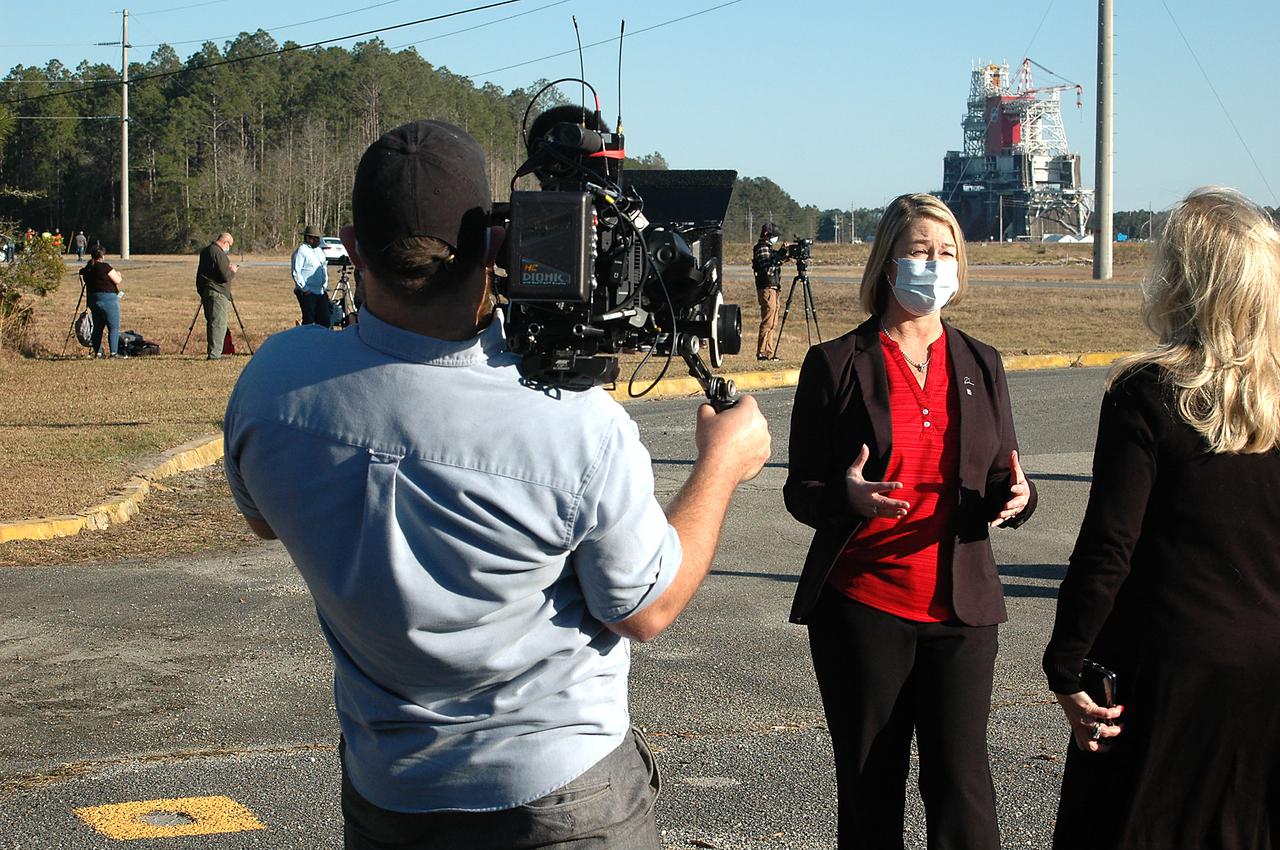

Jennifer Boland-Masterson, director of Boeing Operations at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, talks with media prior to the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Jan. 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
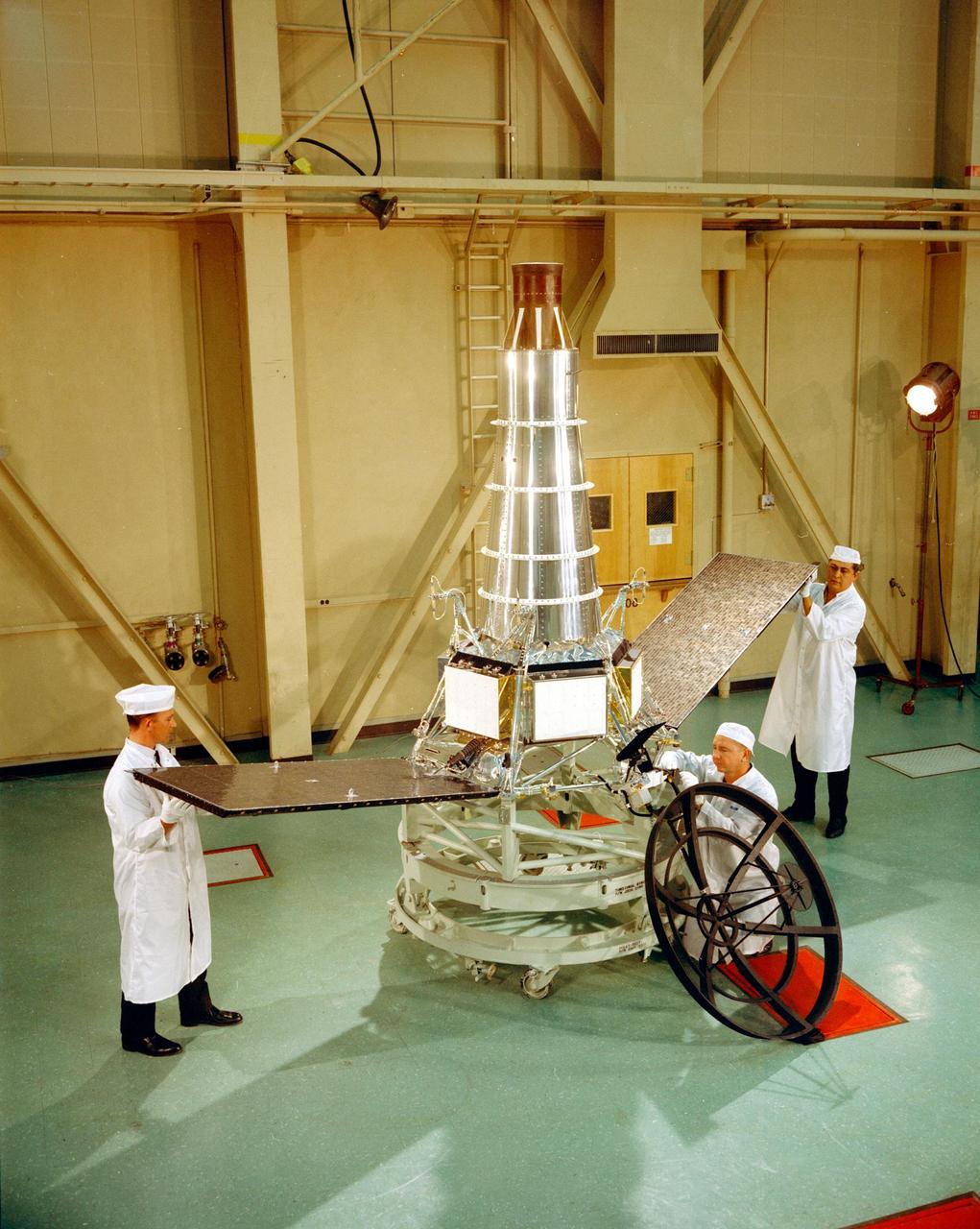

Engineers stand with Ranger 7 on Dec. 10, 1963, in High Bay 1, located at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Ranger 7 was the first U.S. mission to transmit images from the surface of the Moon. The Ranger program included a series of robotic spacecraft launched at the Moon. JPL developed the art of spacecraft assembly and testing with each iteration of the Ranger spacecraft. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23520

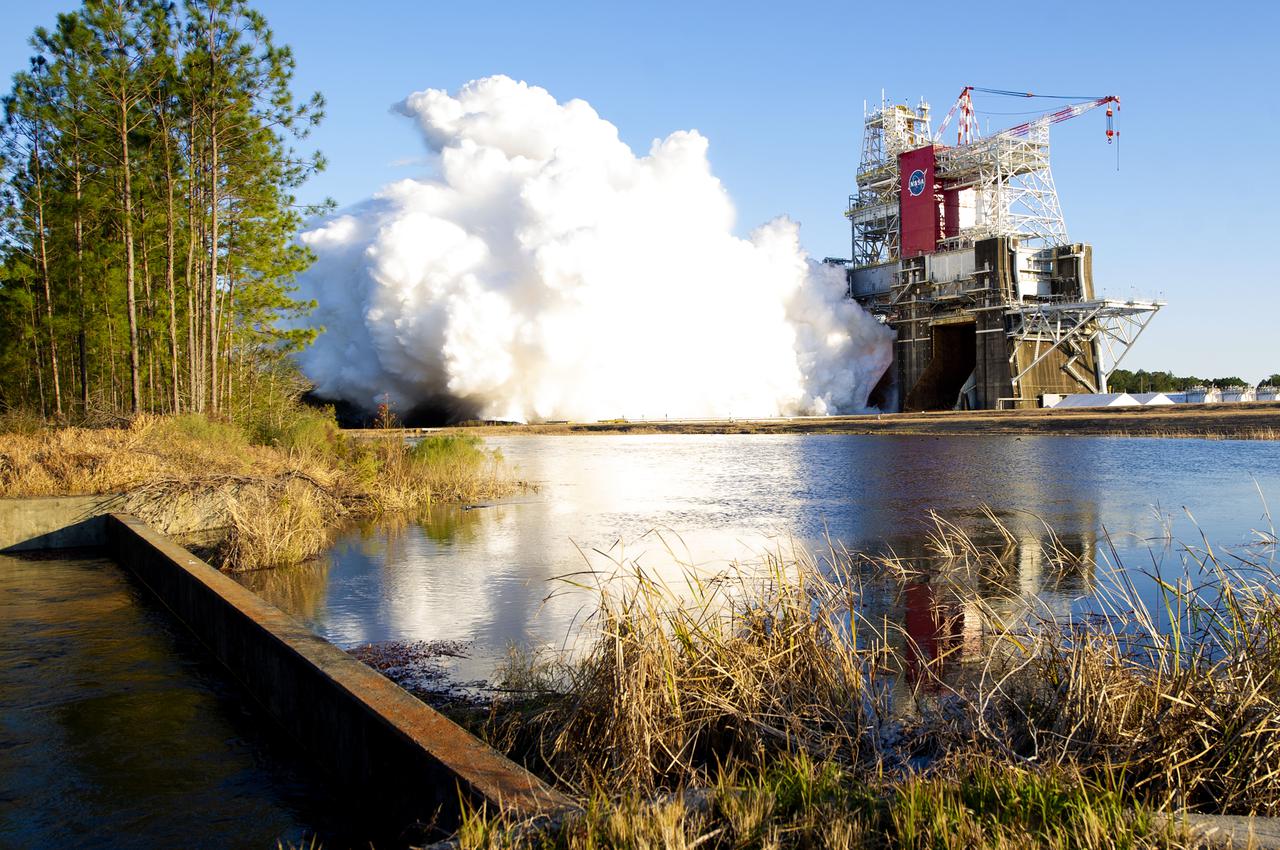
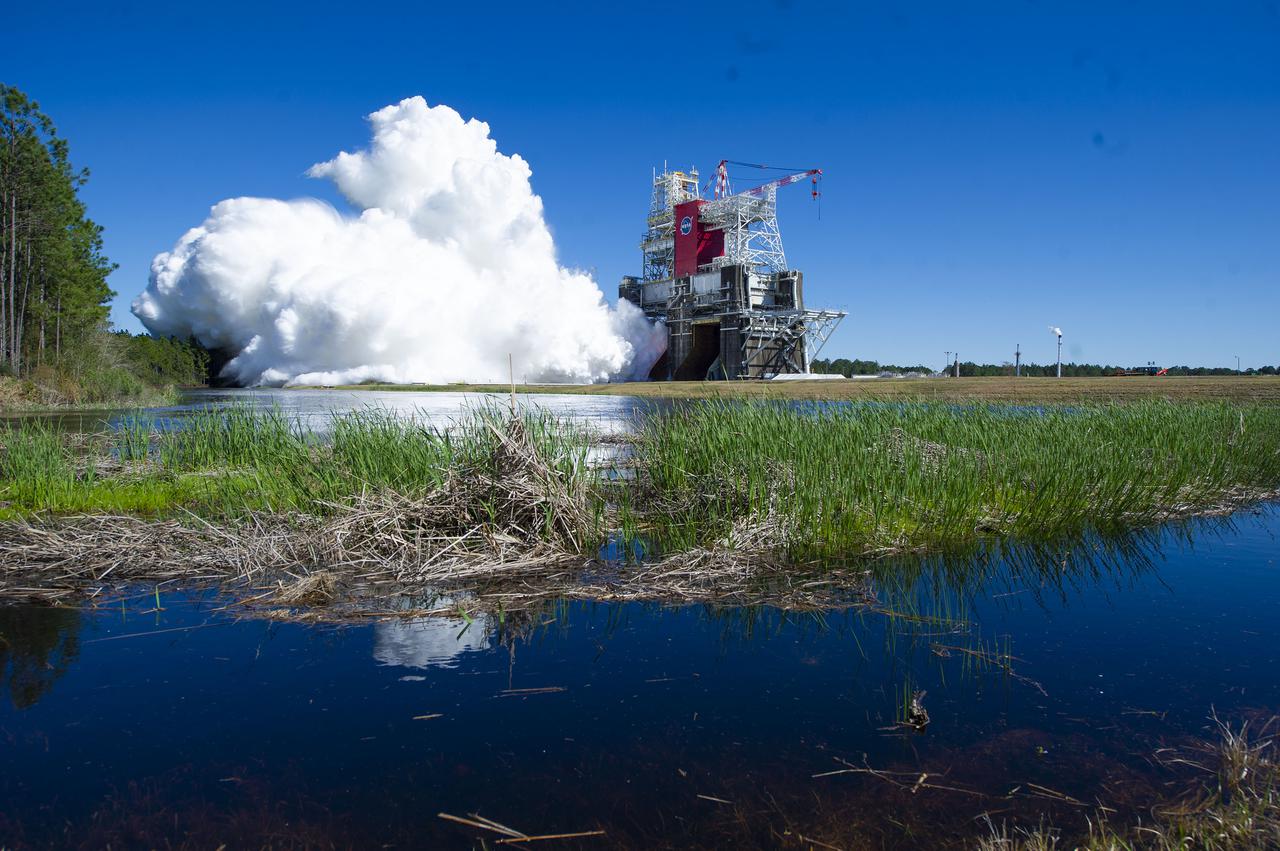
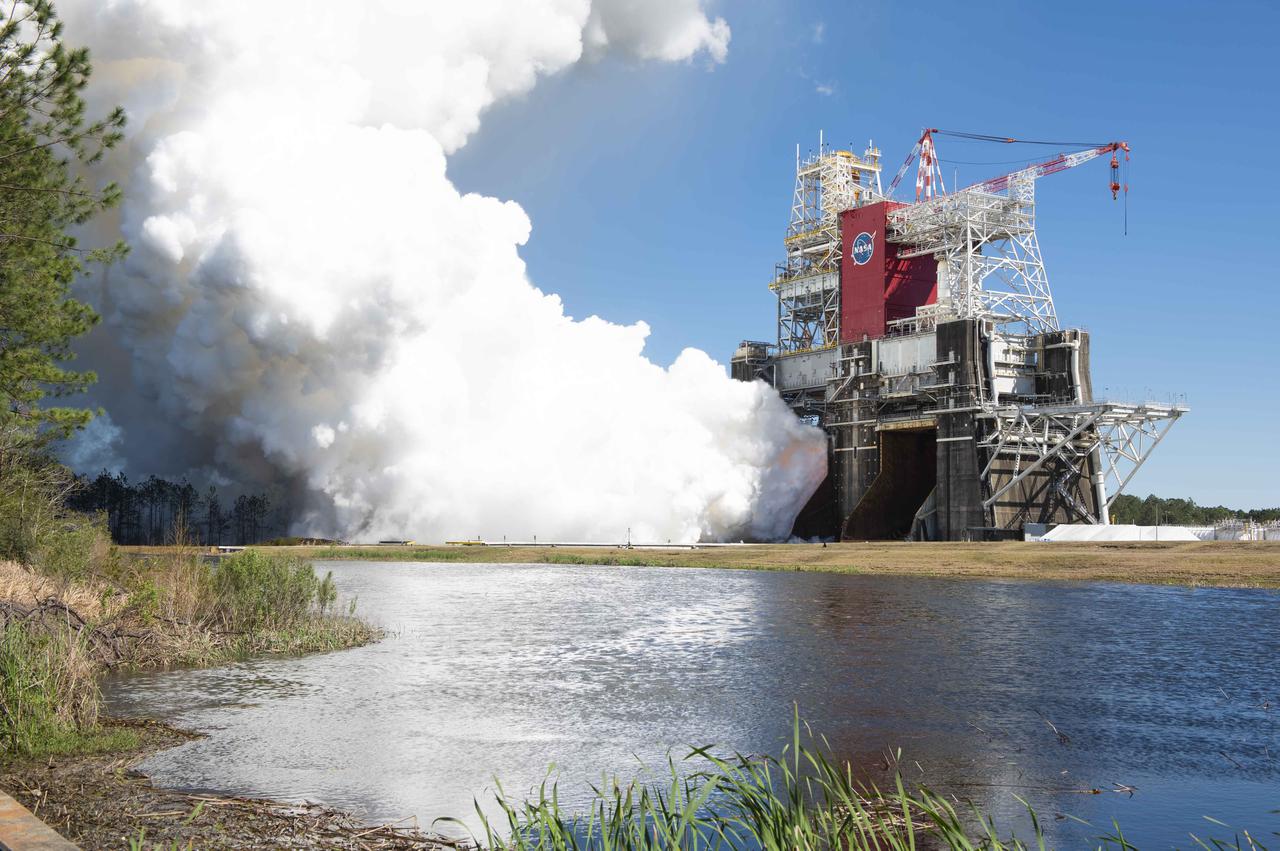
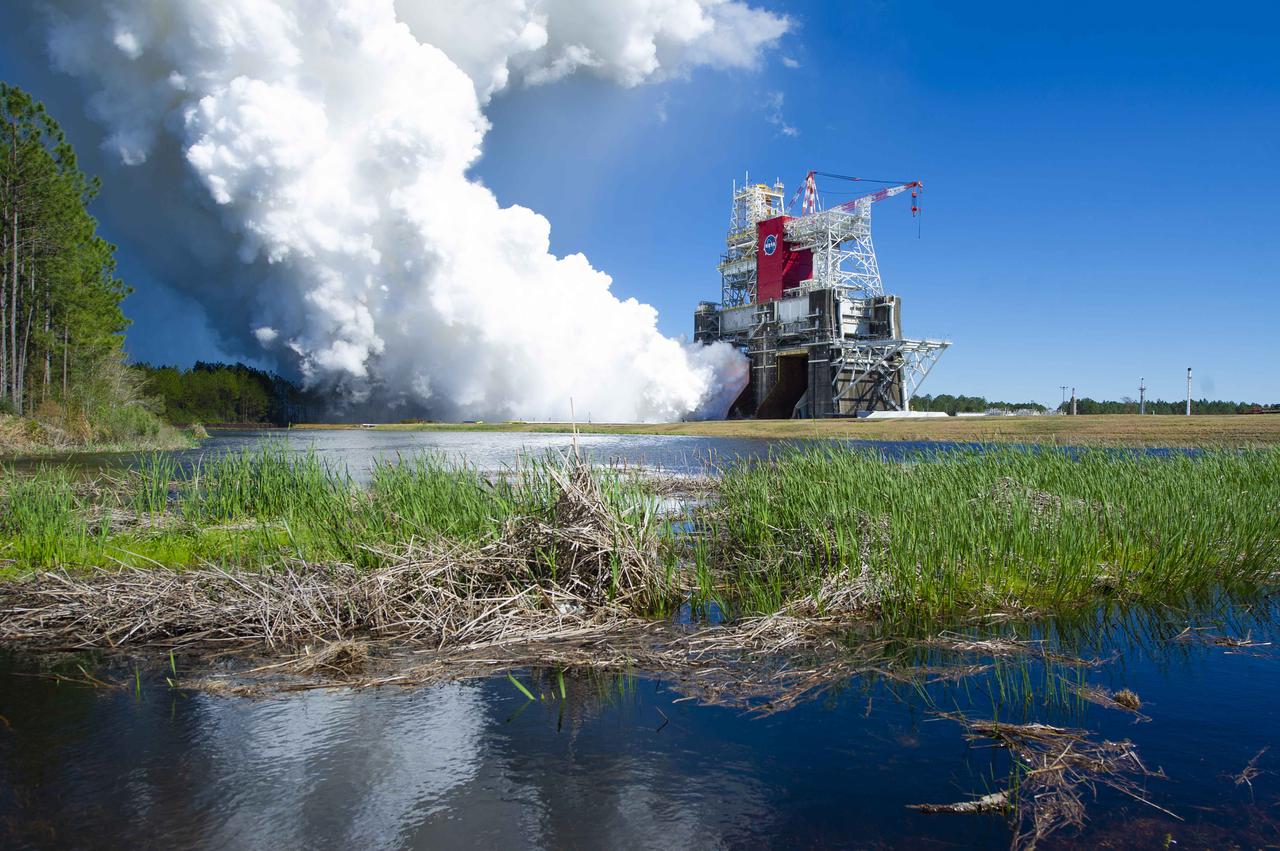
NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
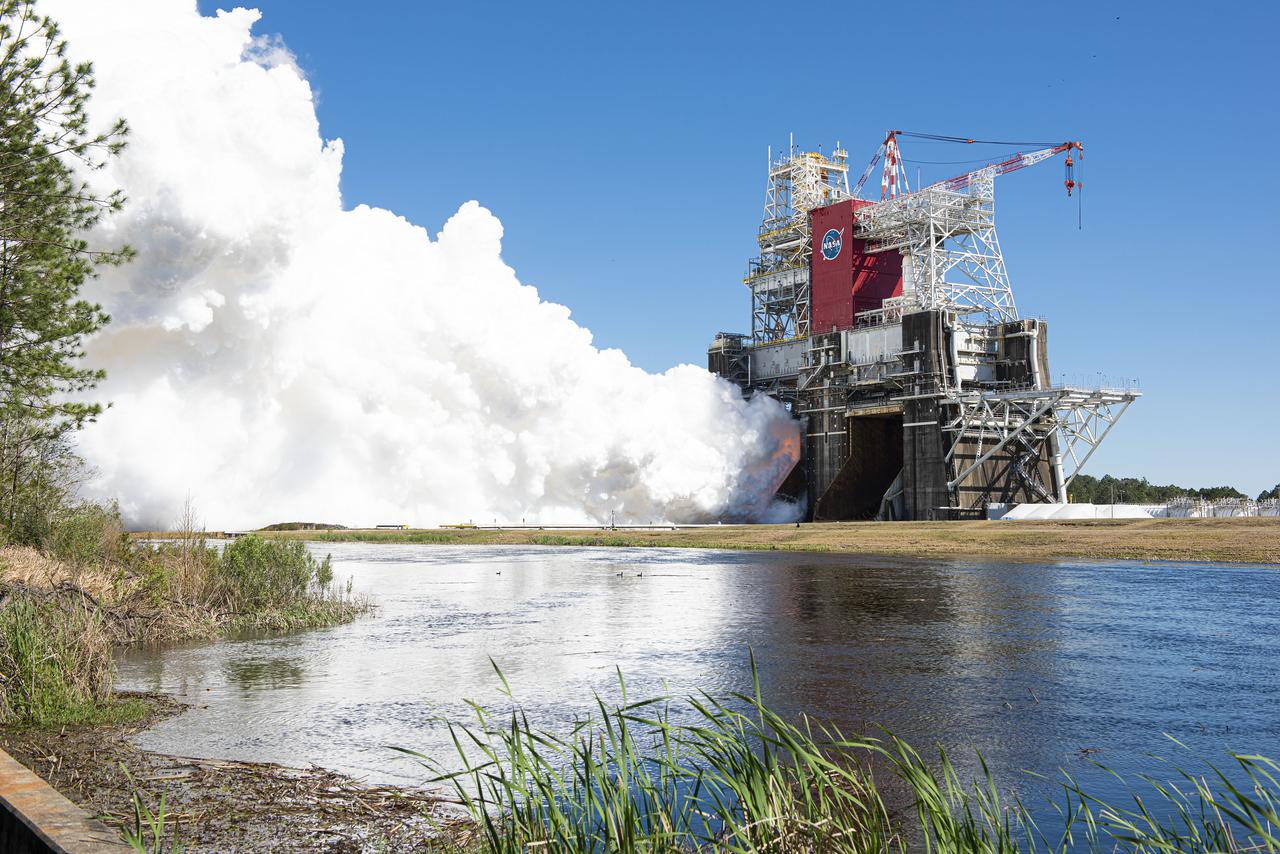

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

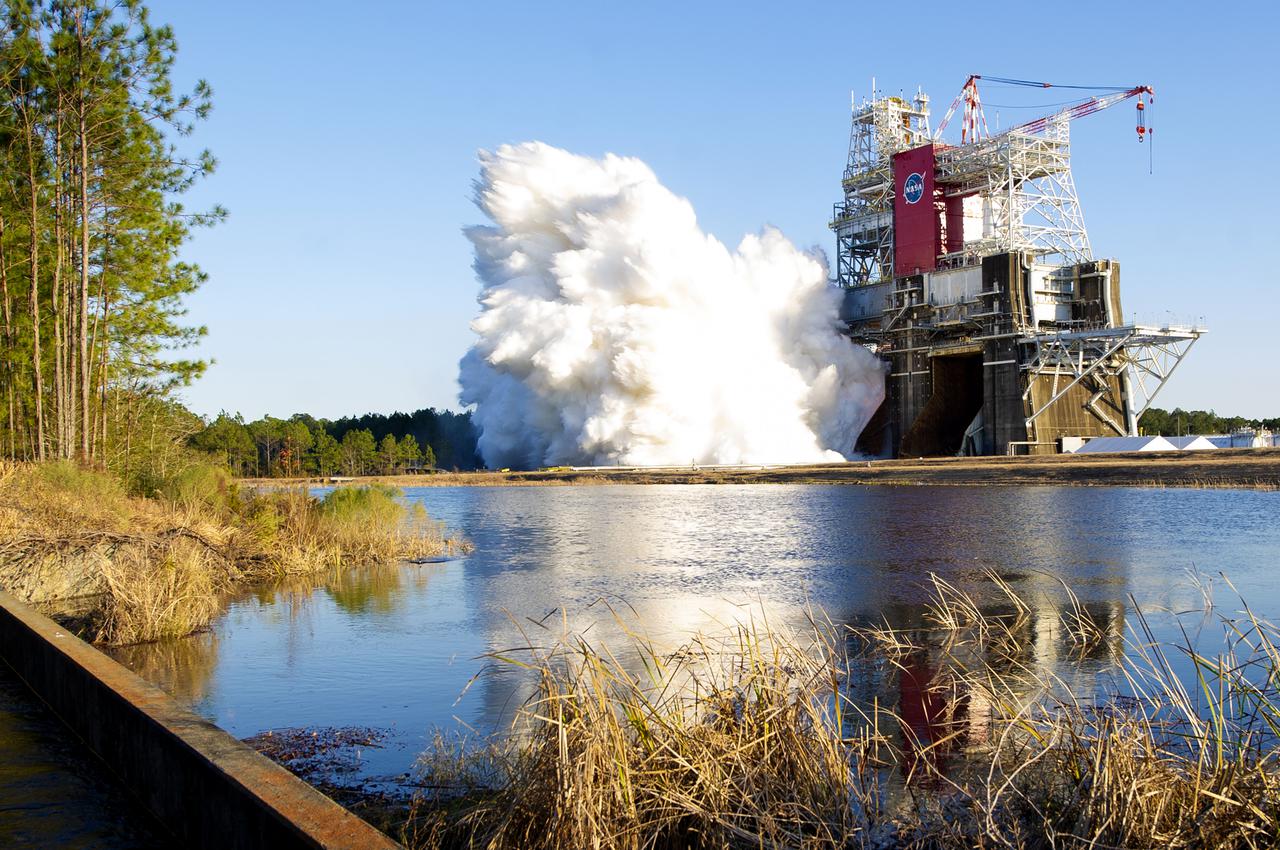
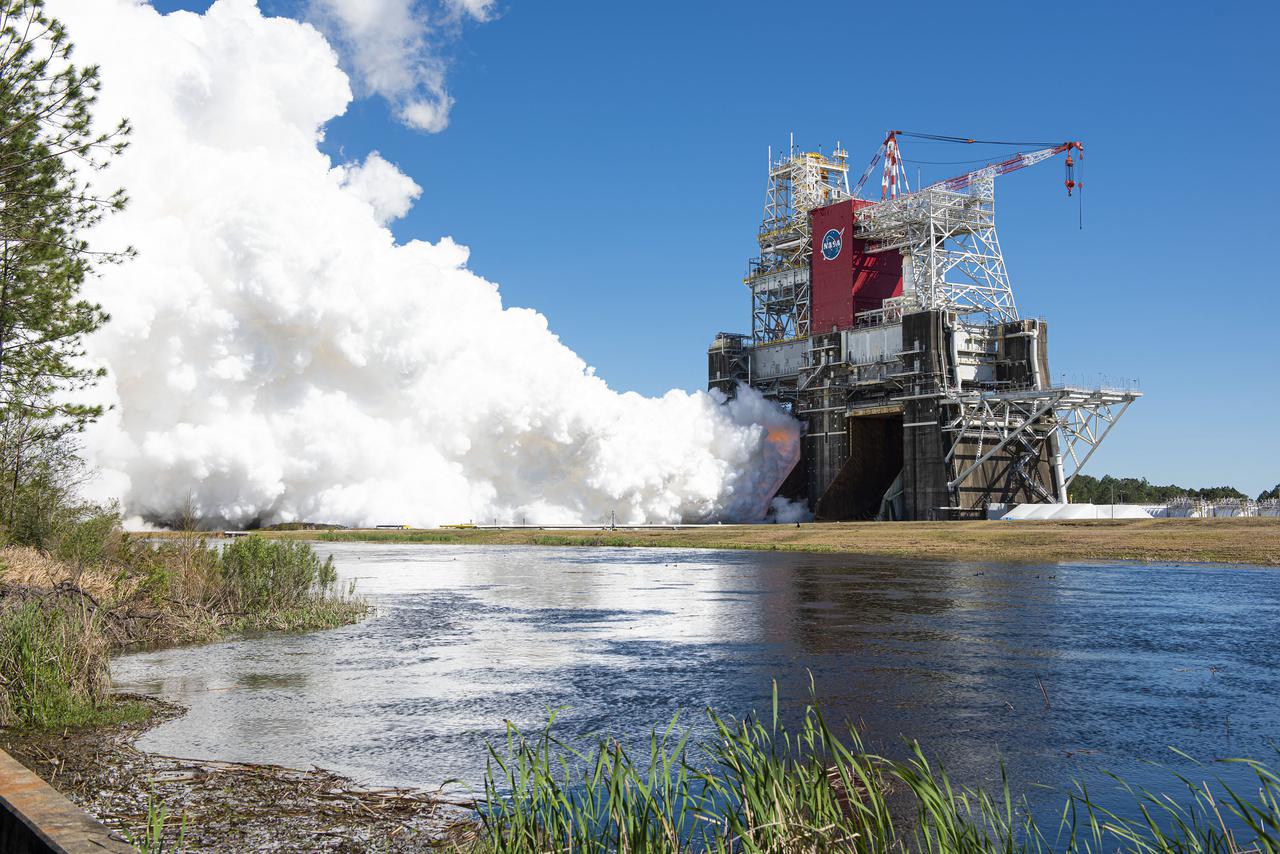
NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
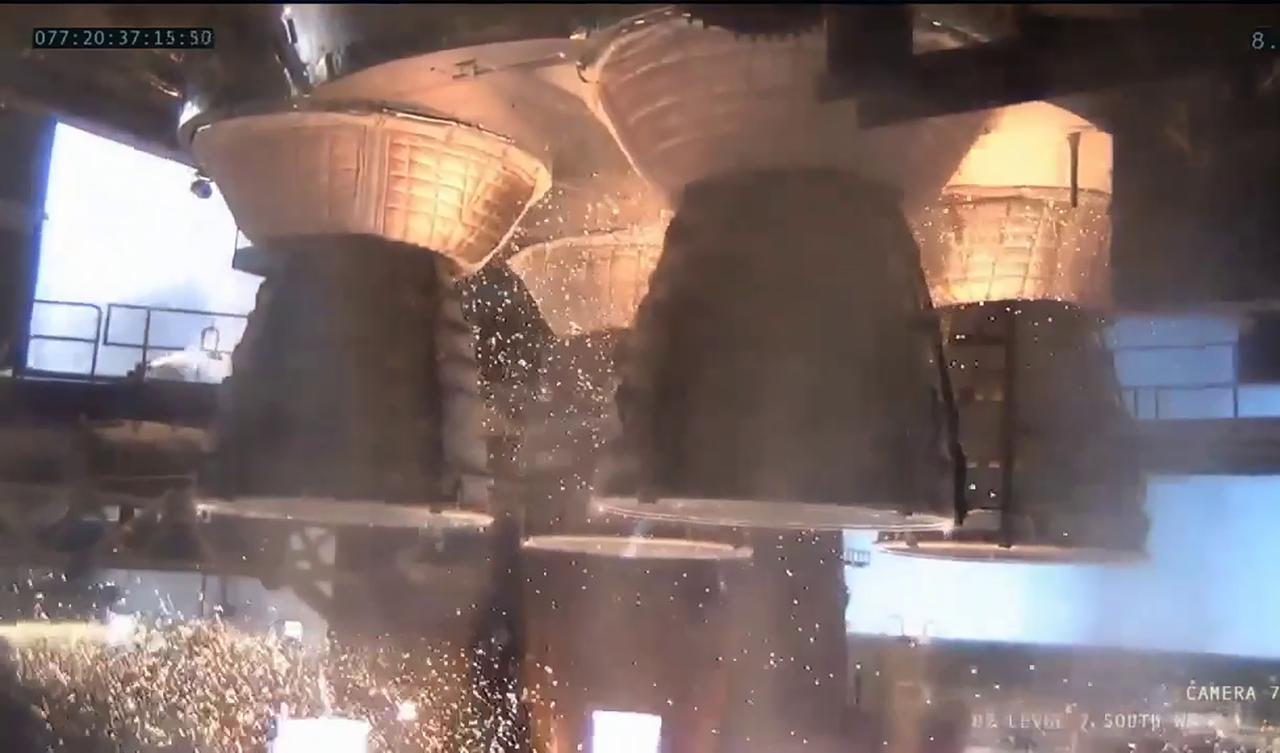

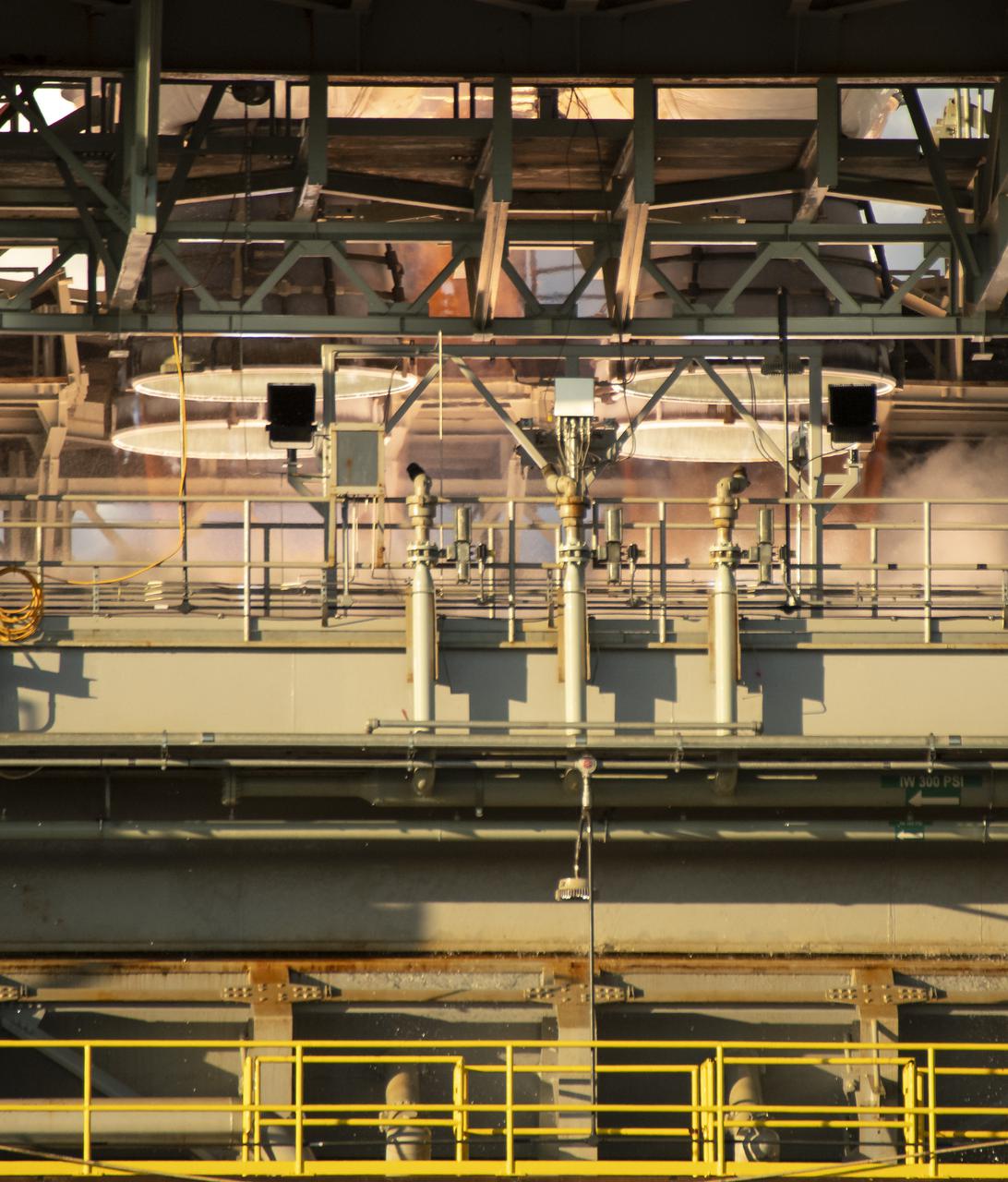
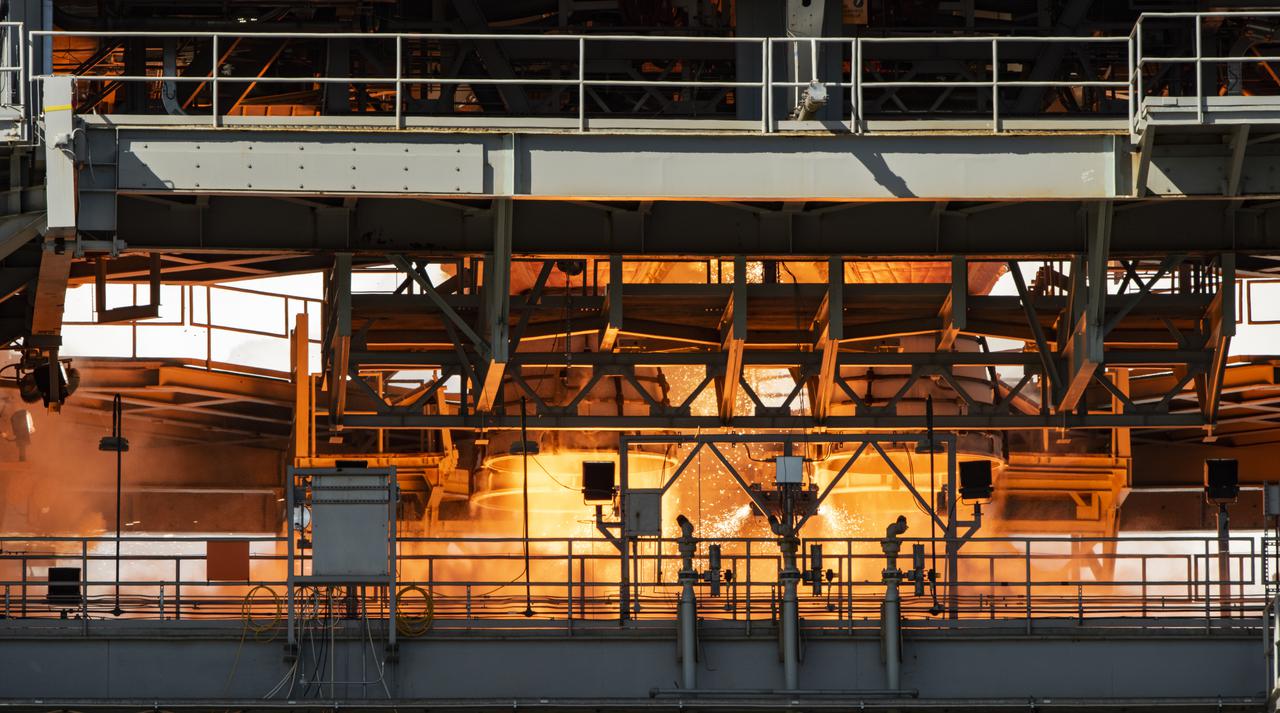
A on-stand camera offers a close-up view as NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines shown in the photo generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
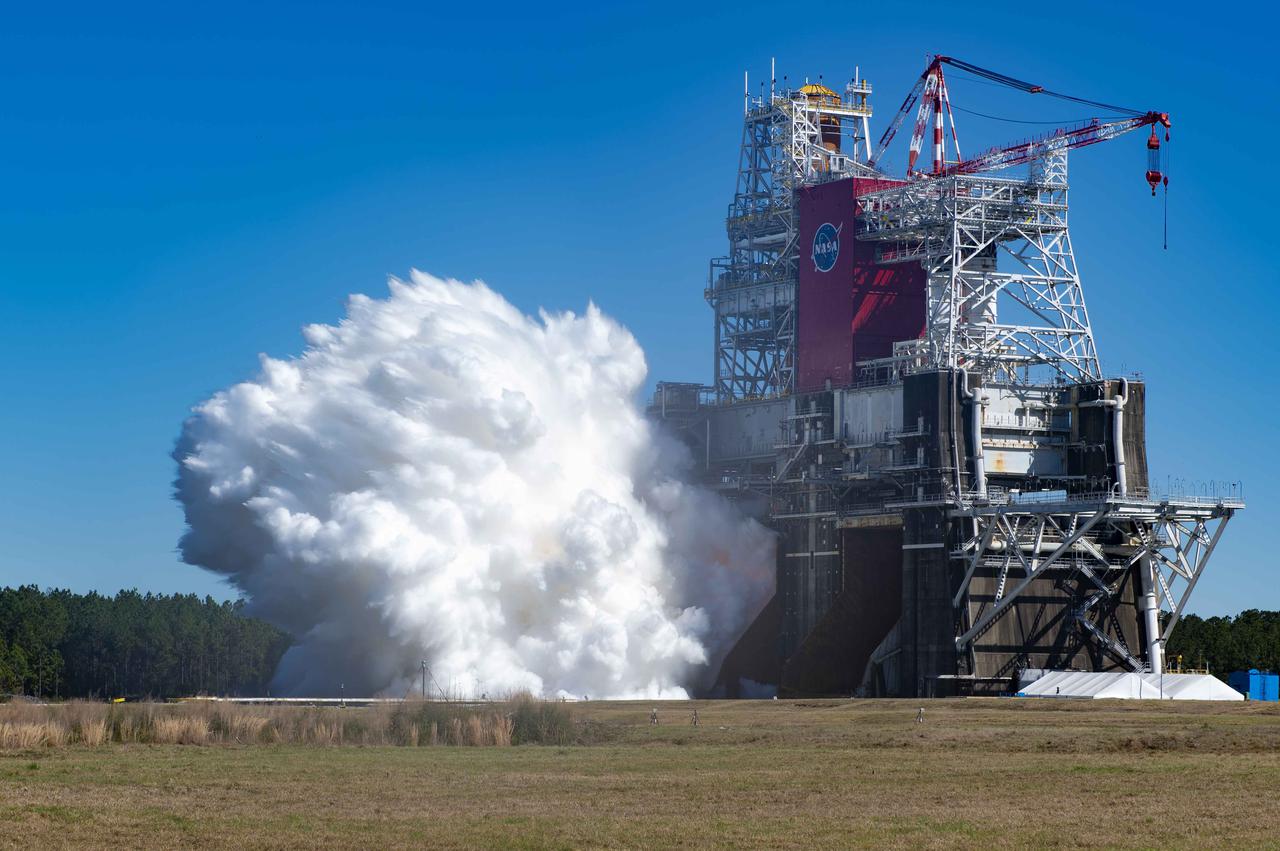

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
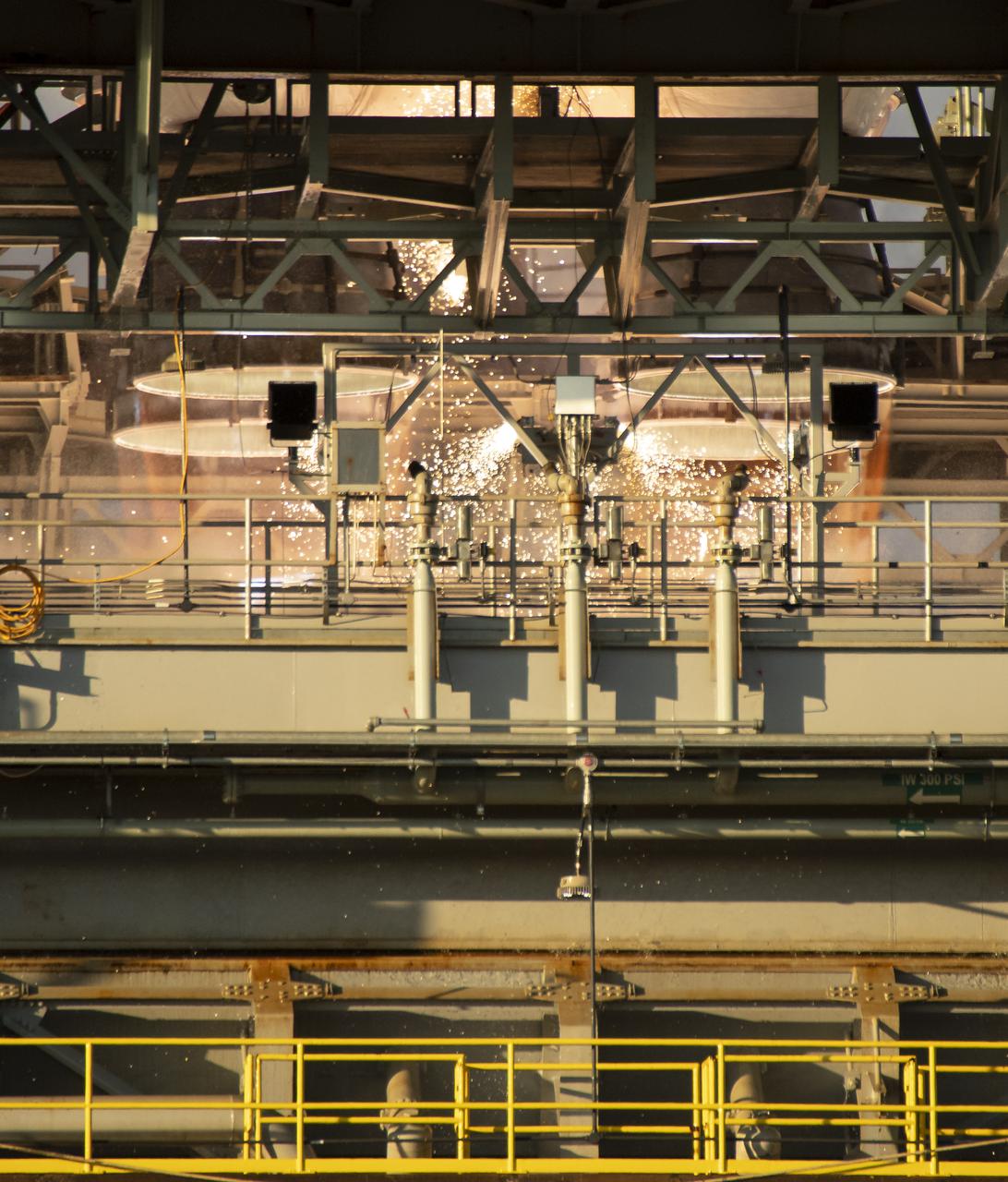

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

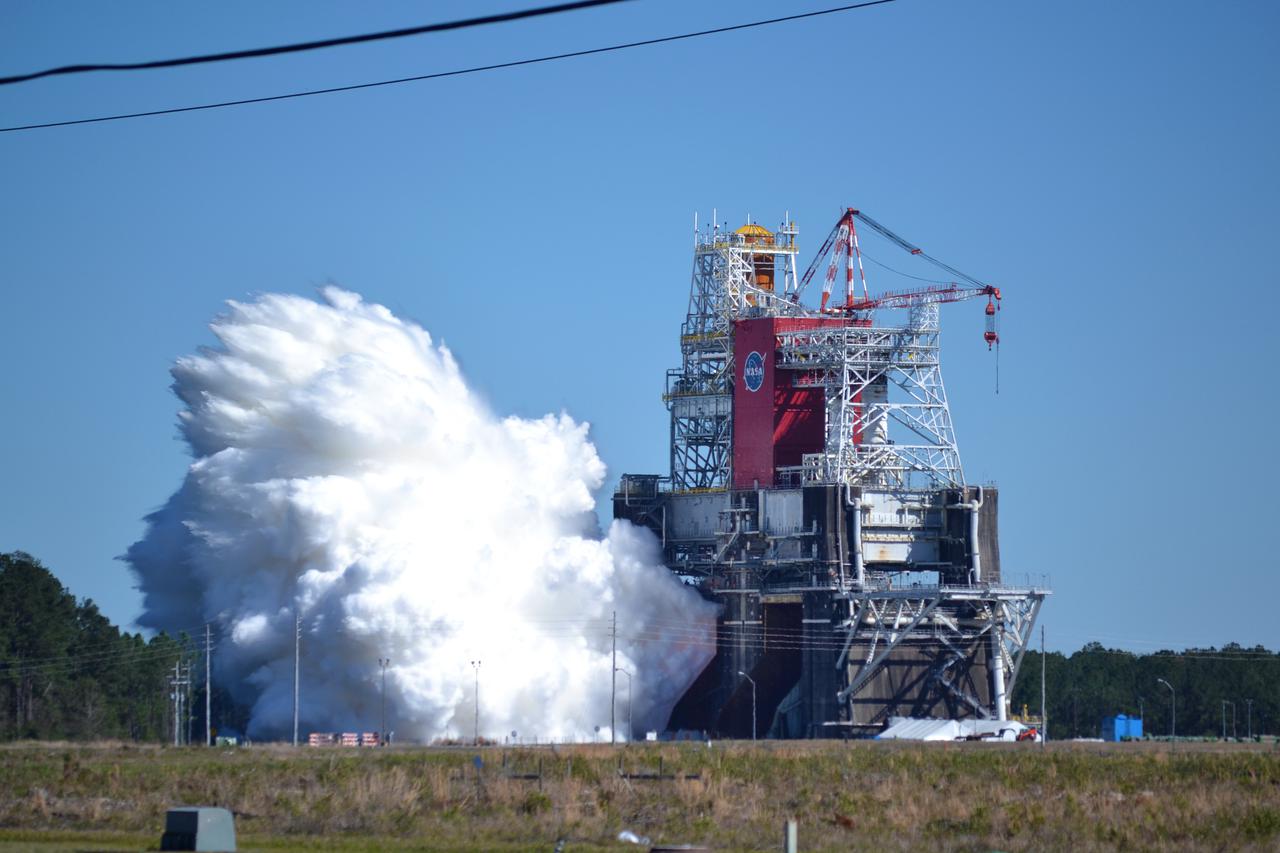
NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
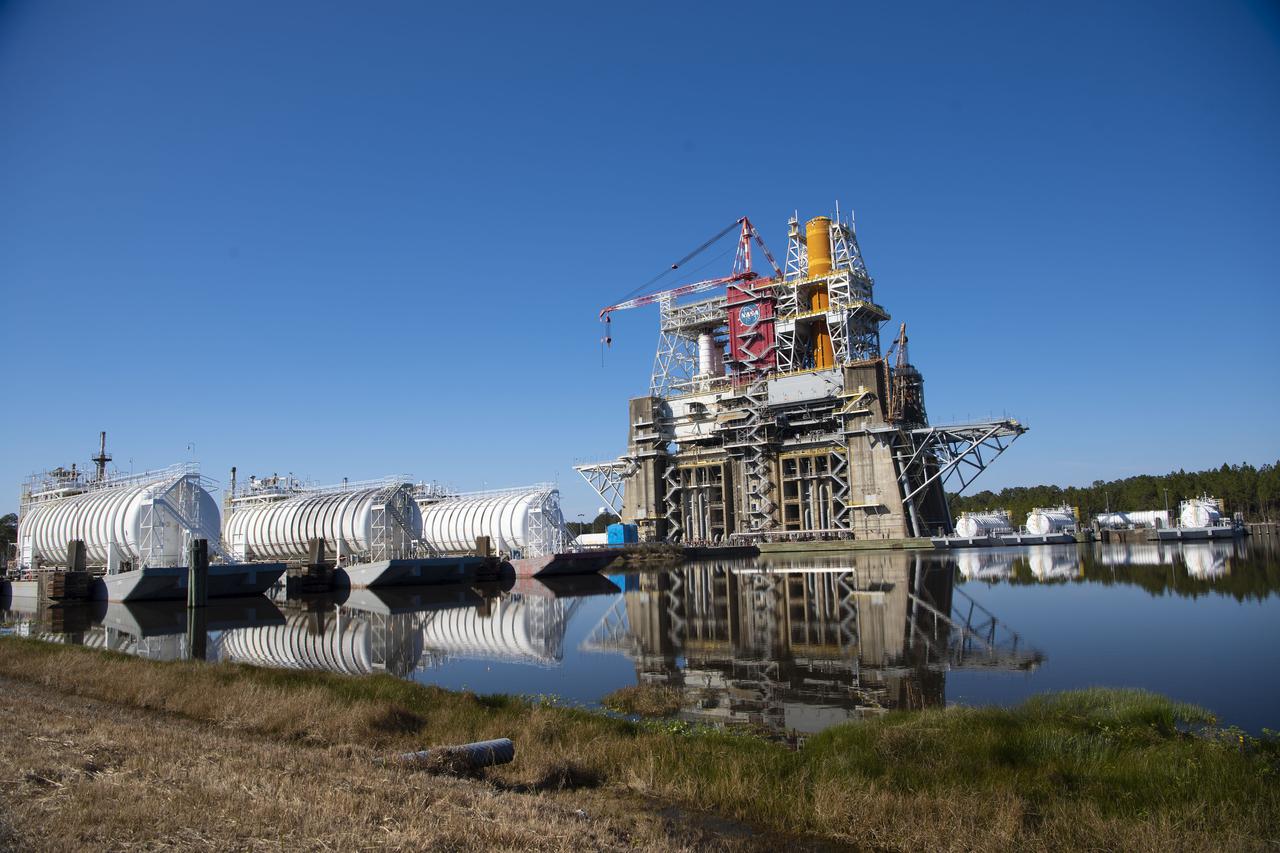

Propellant barges are docked at the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, prior the hot fire test of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket. The hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021 of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
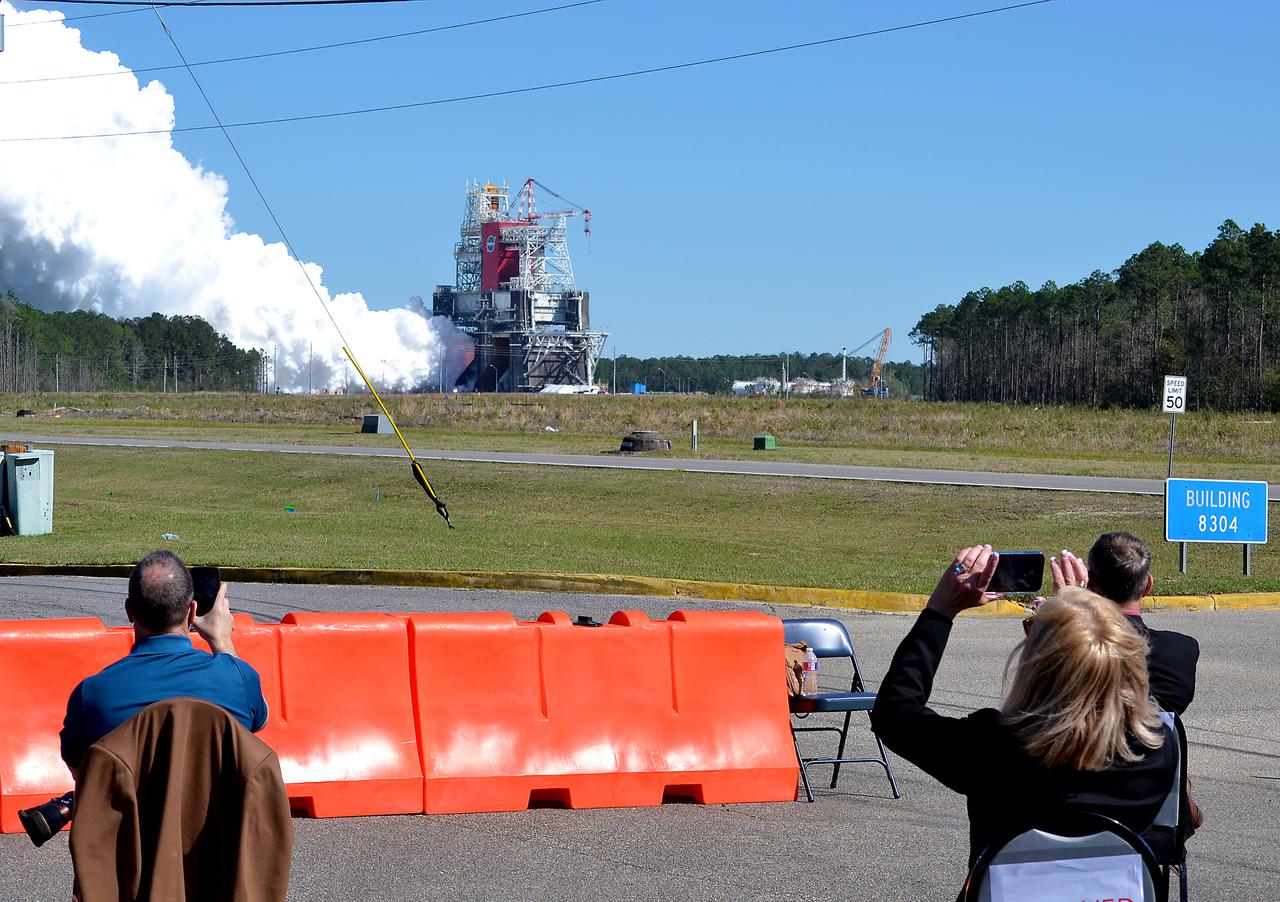

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
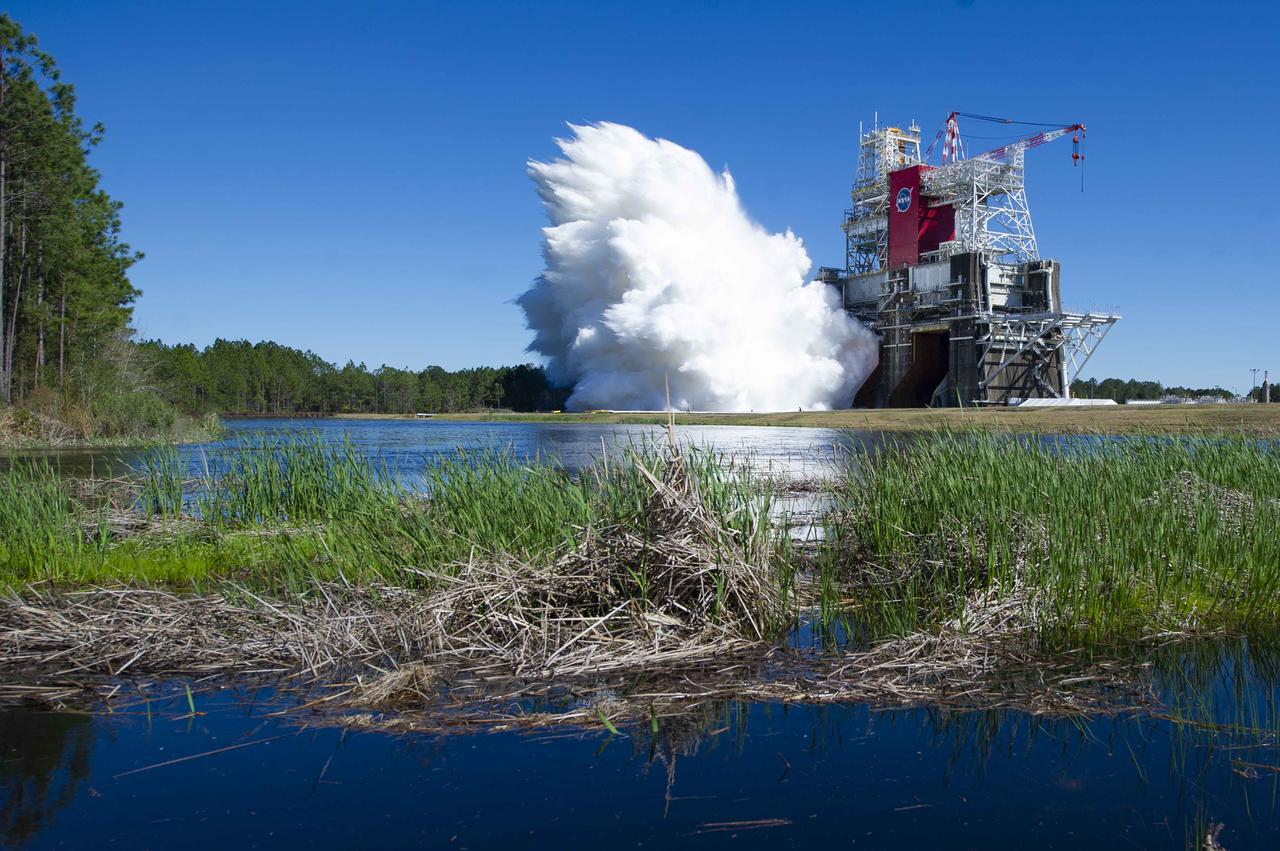

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
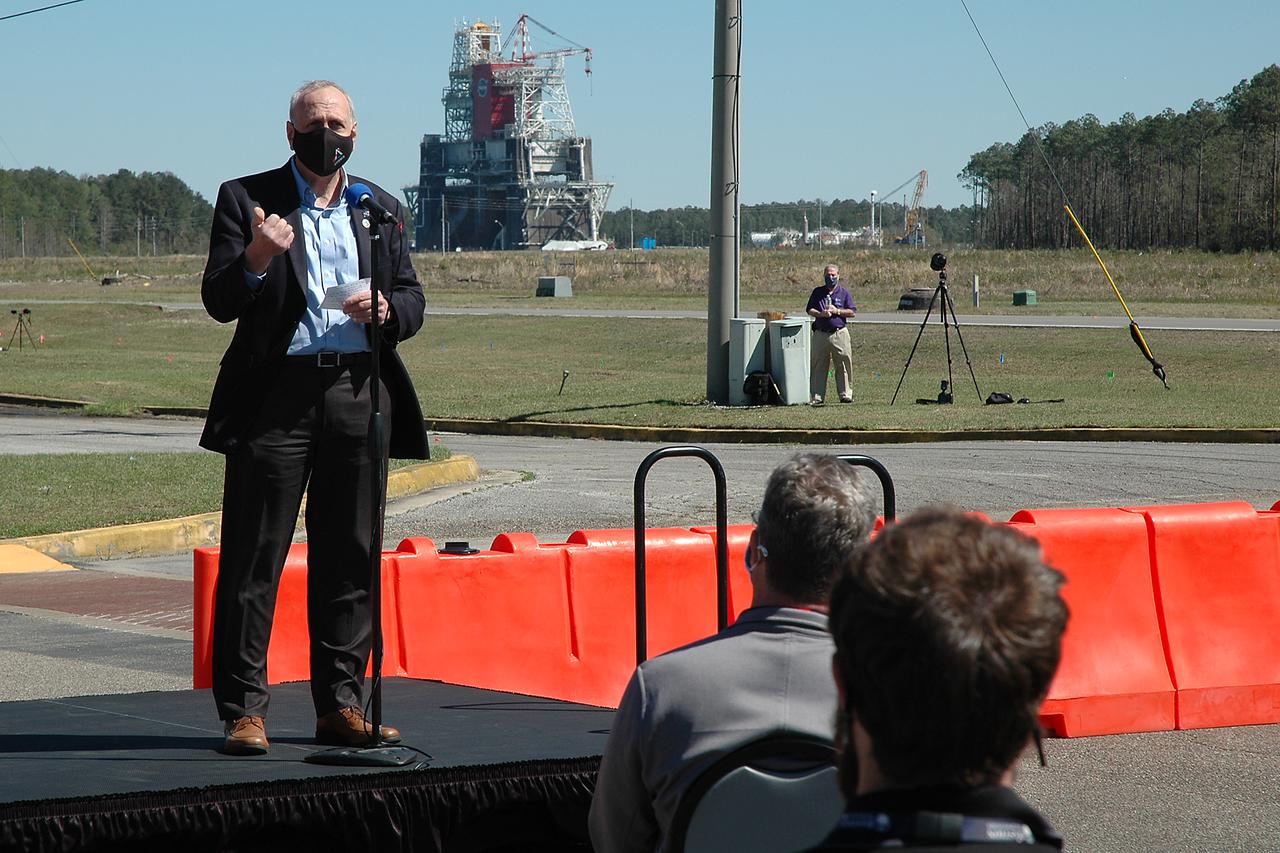

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
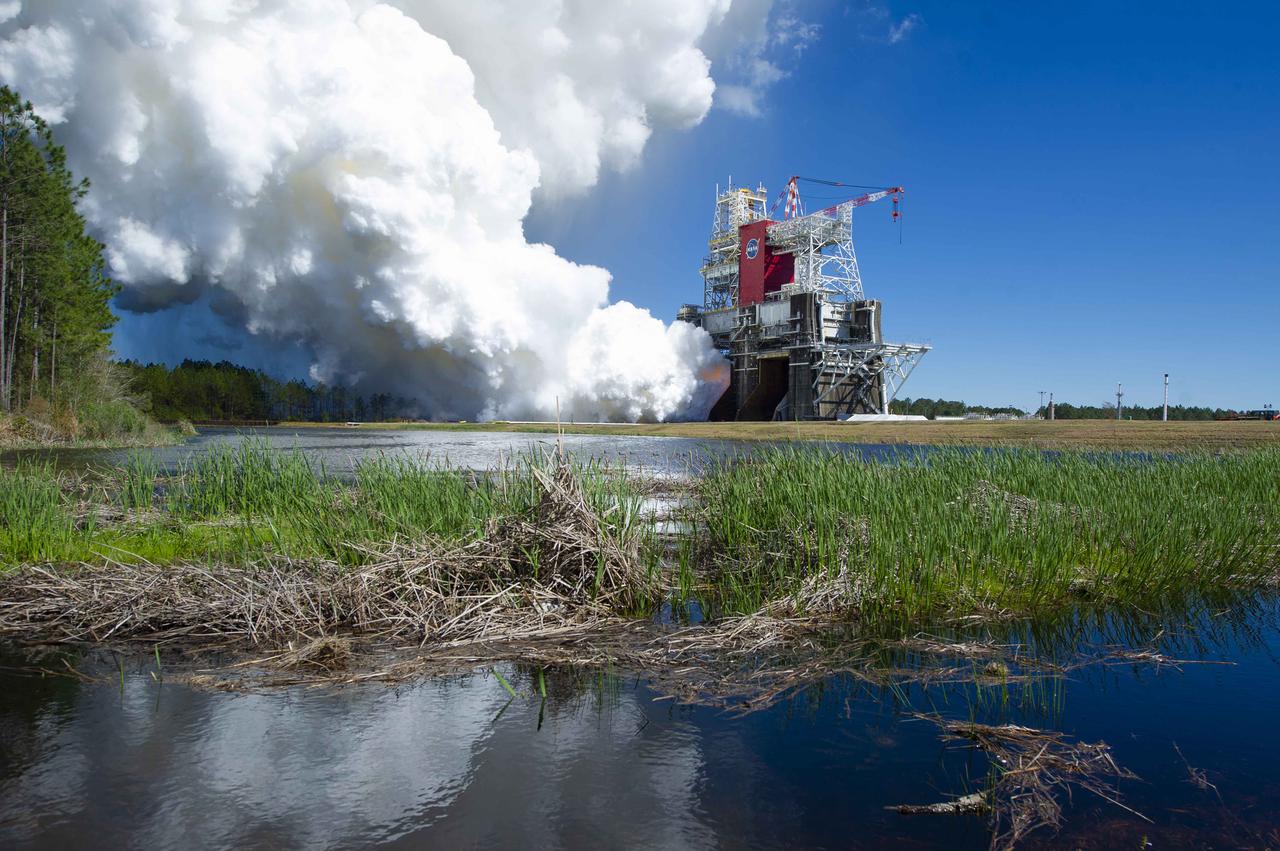

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
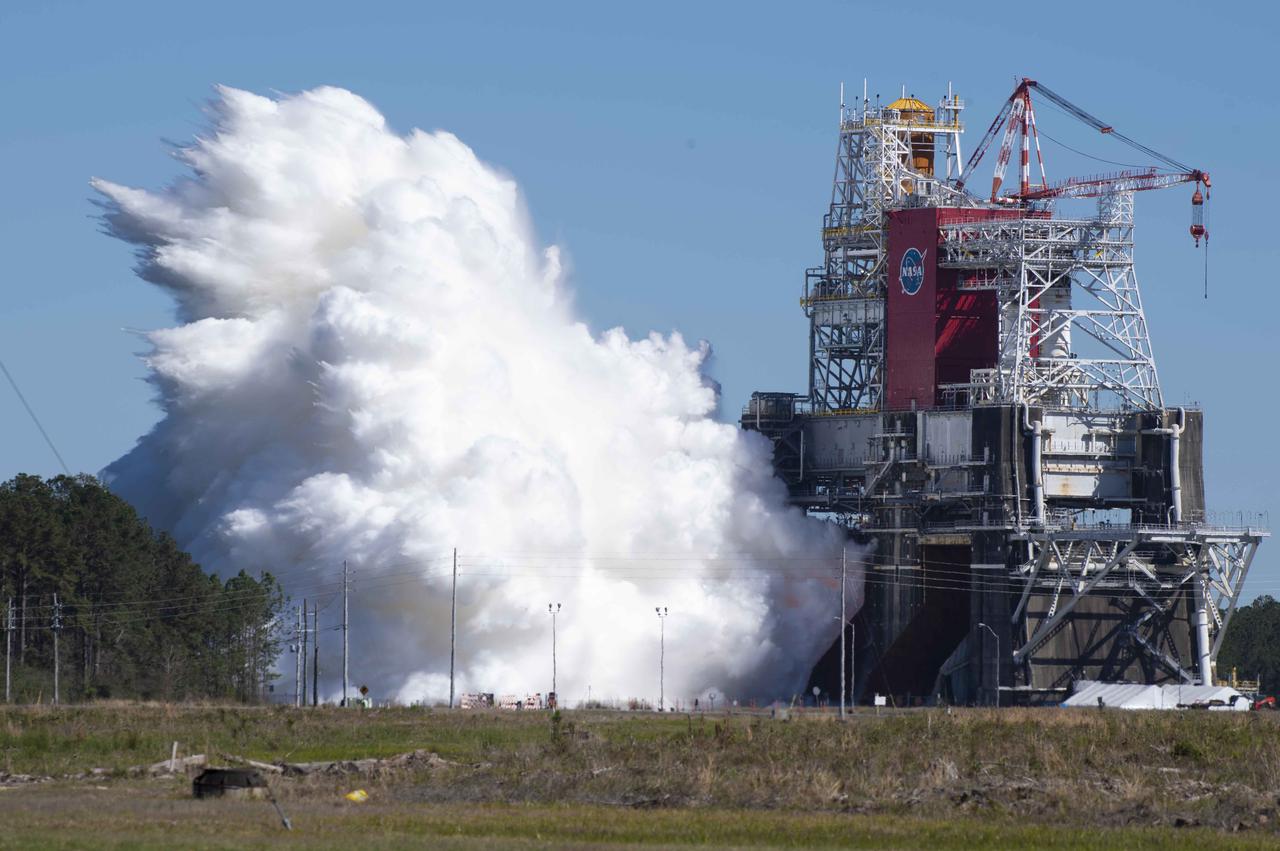

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
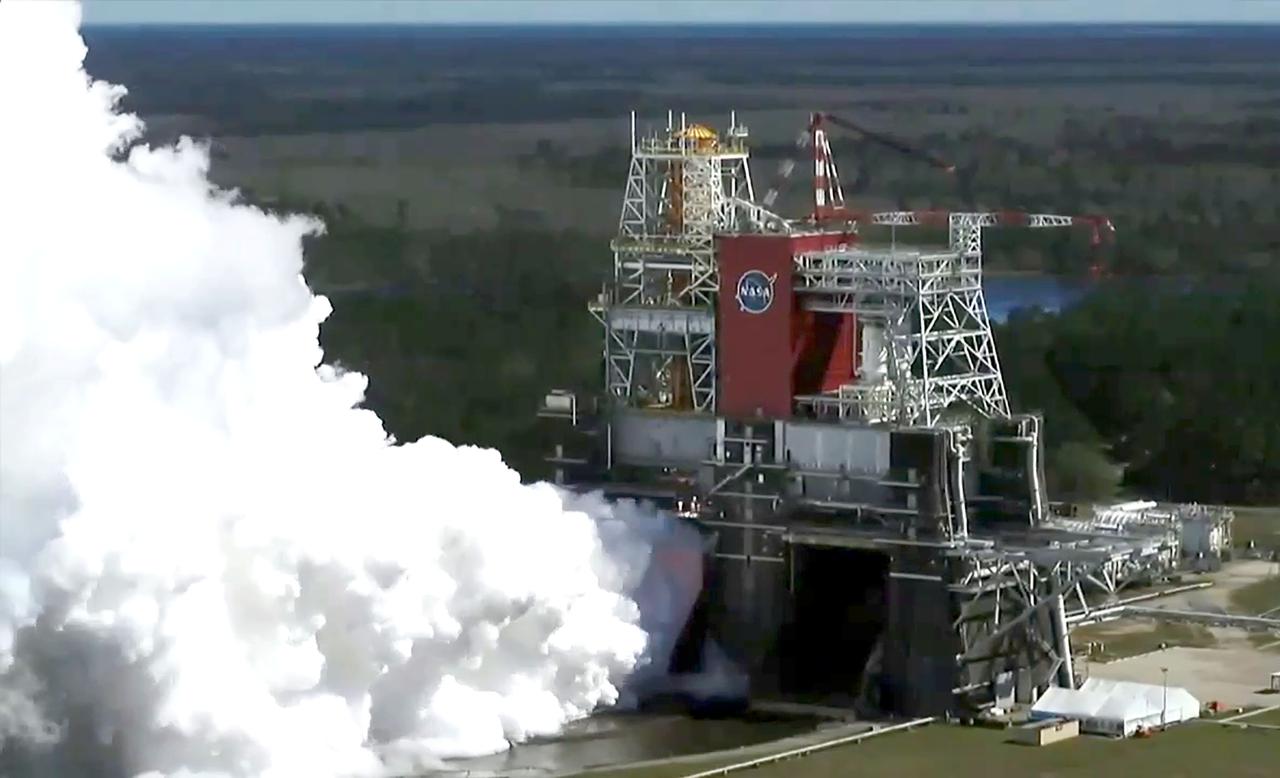

A drone camera offers a bird’s-eye view as NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
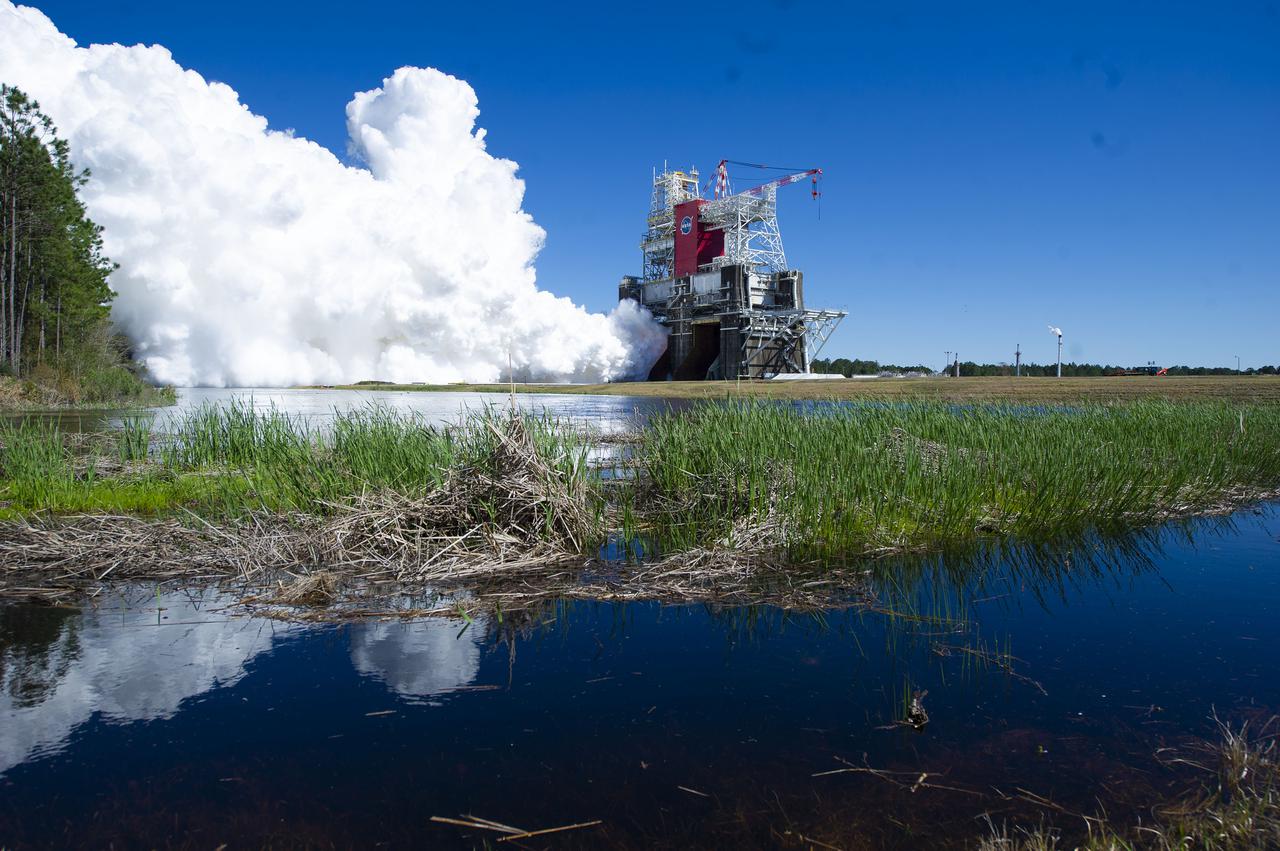

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
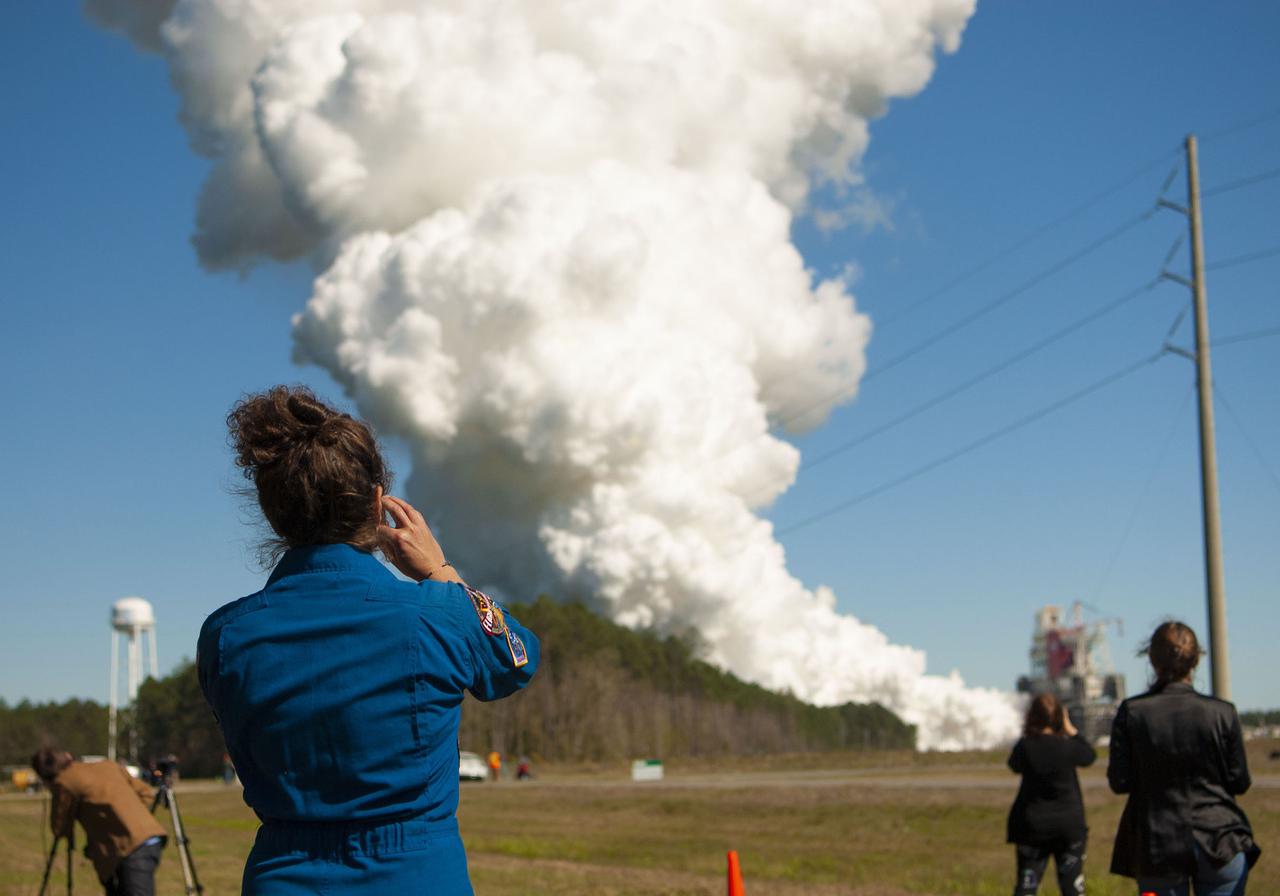

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
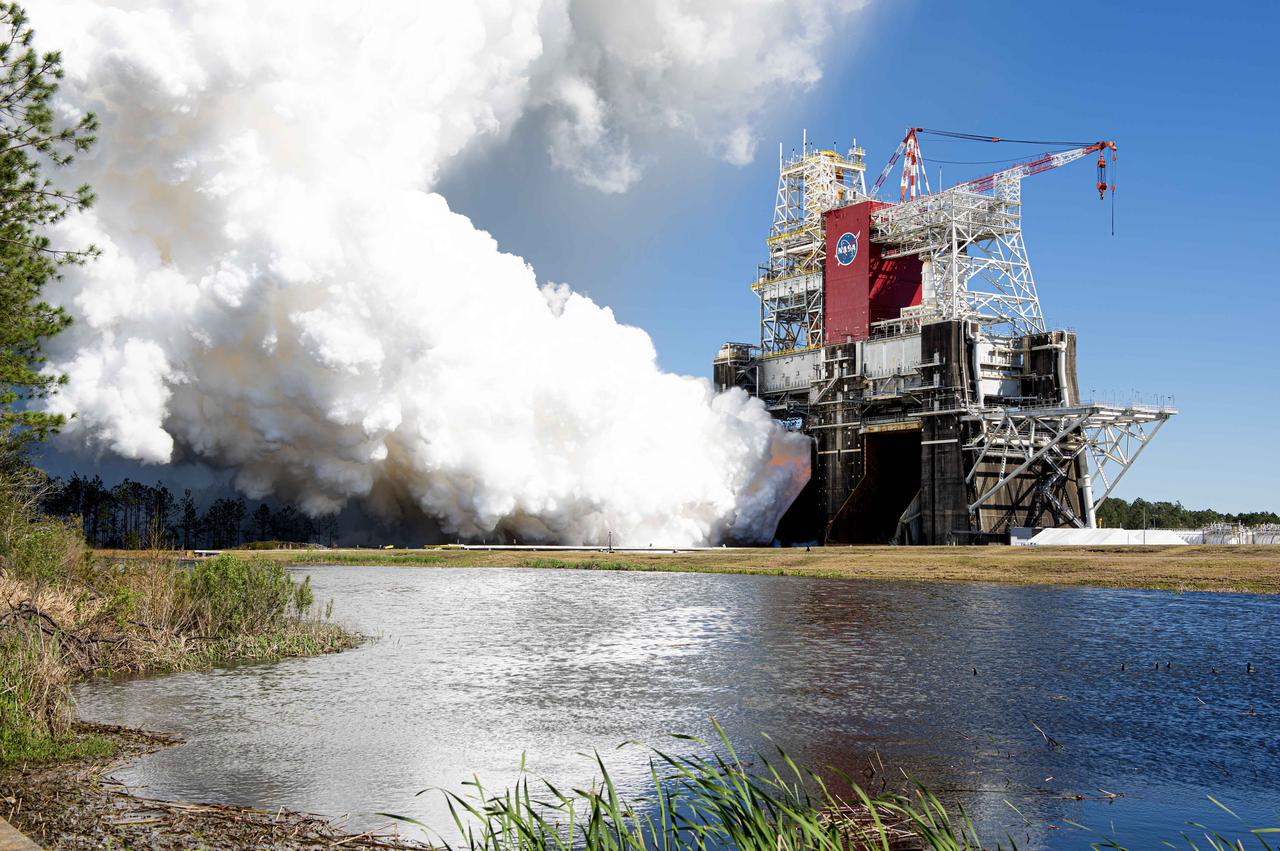

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
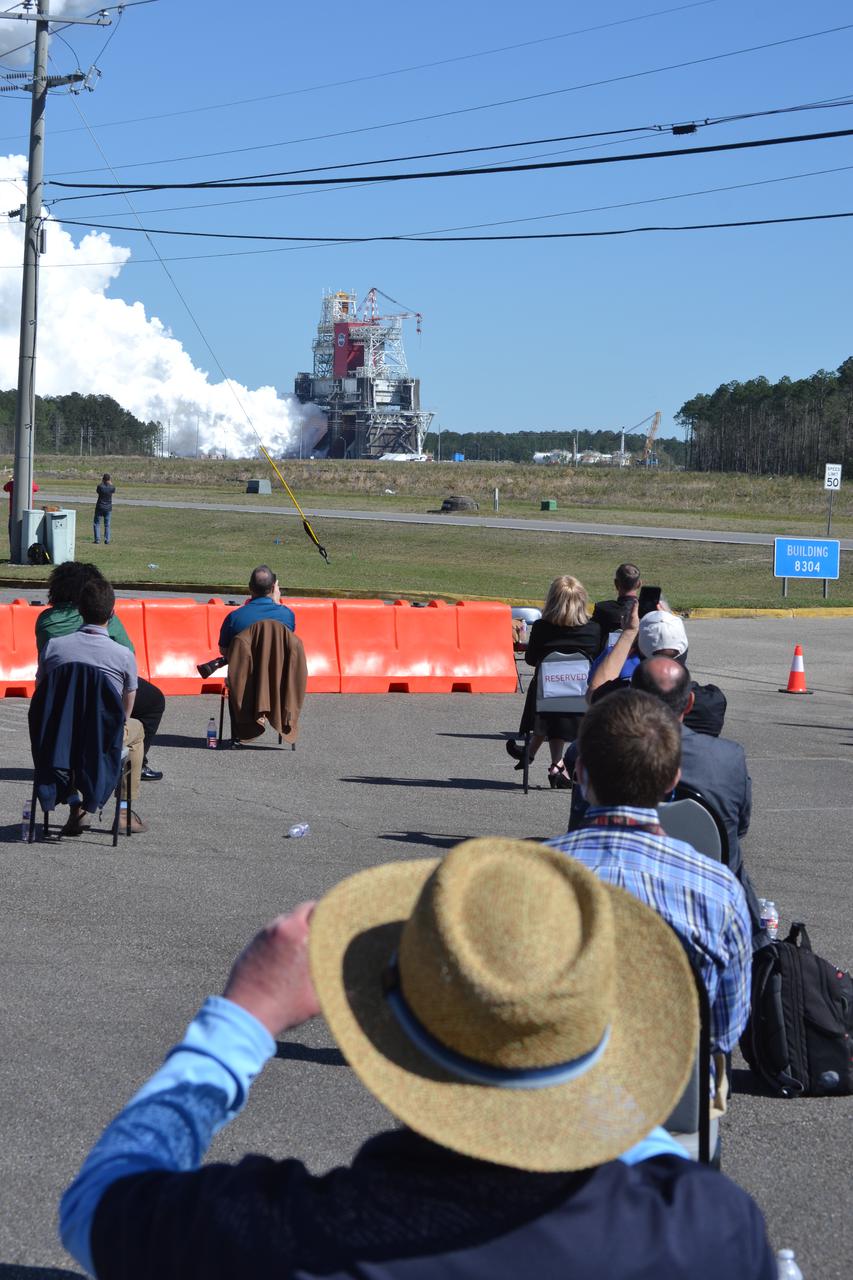
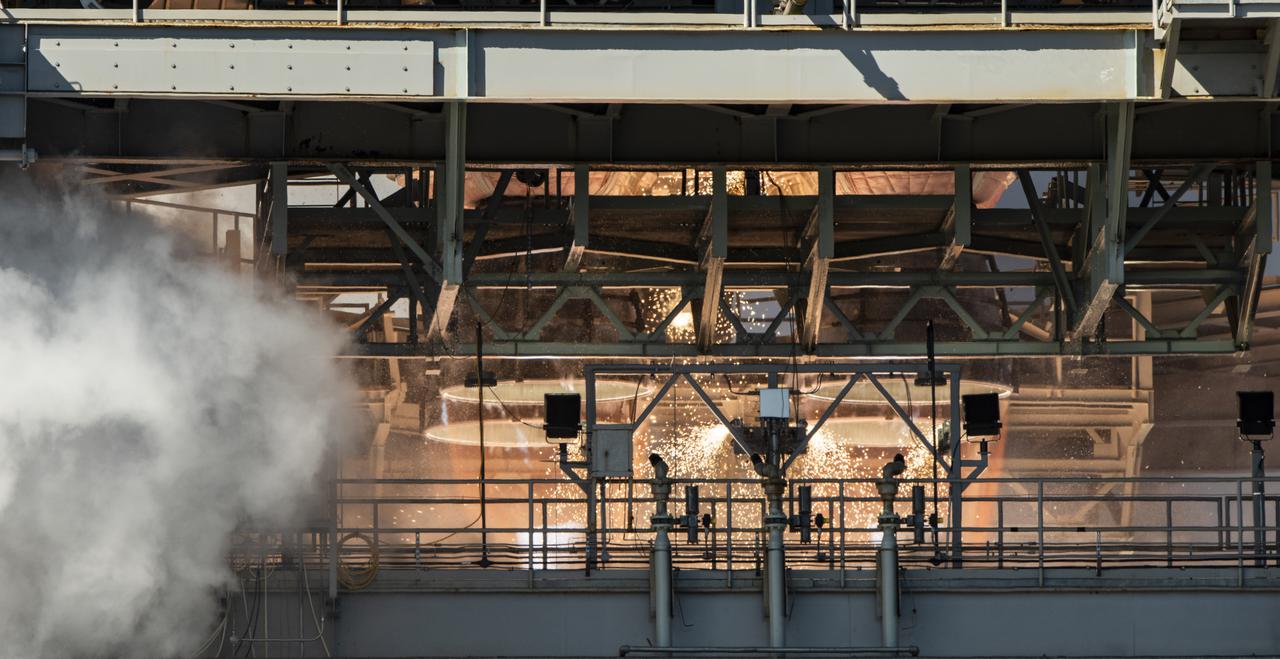
NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
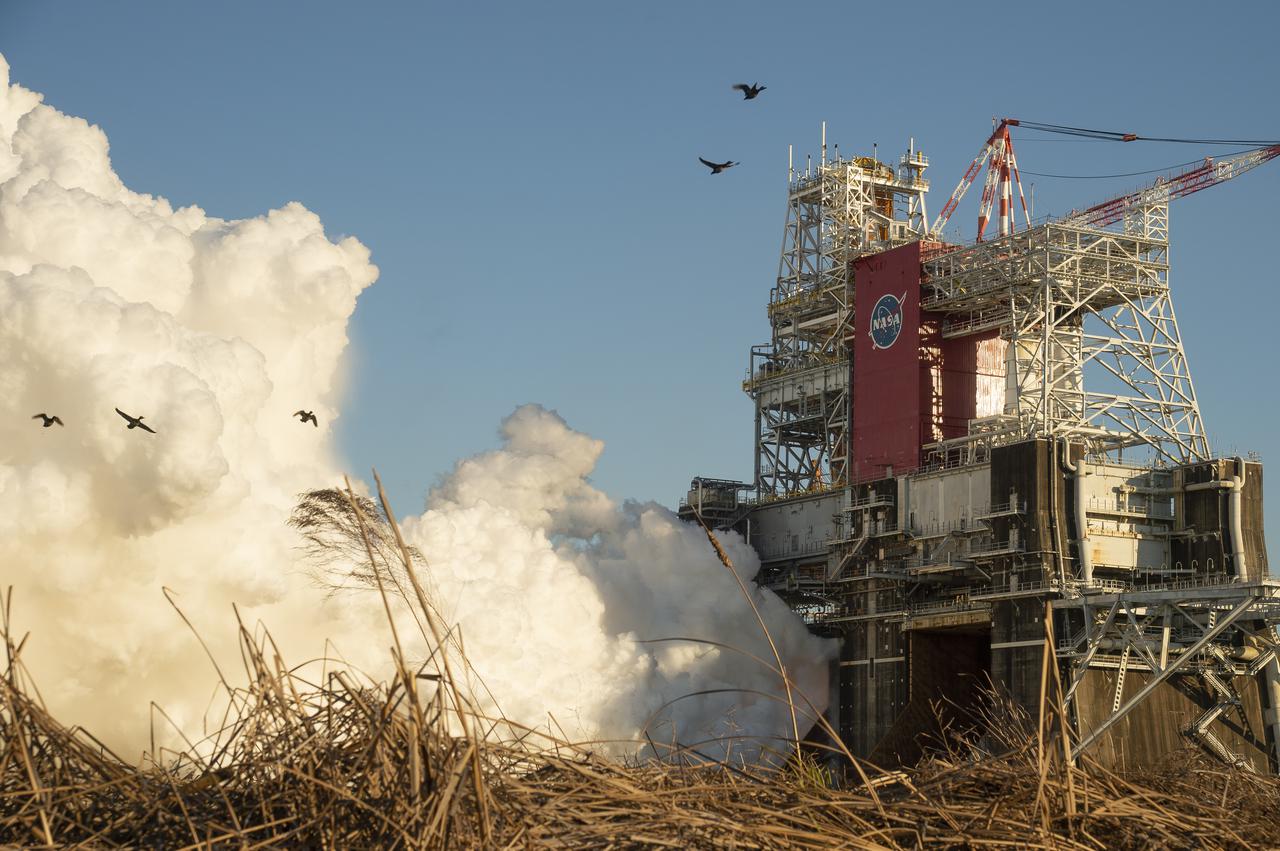

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
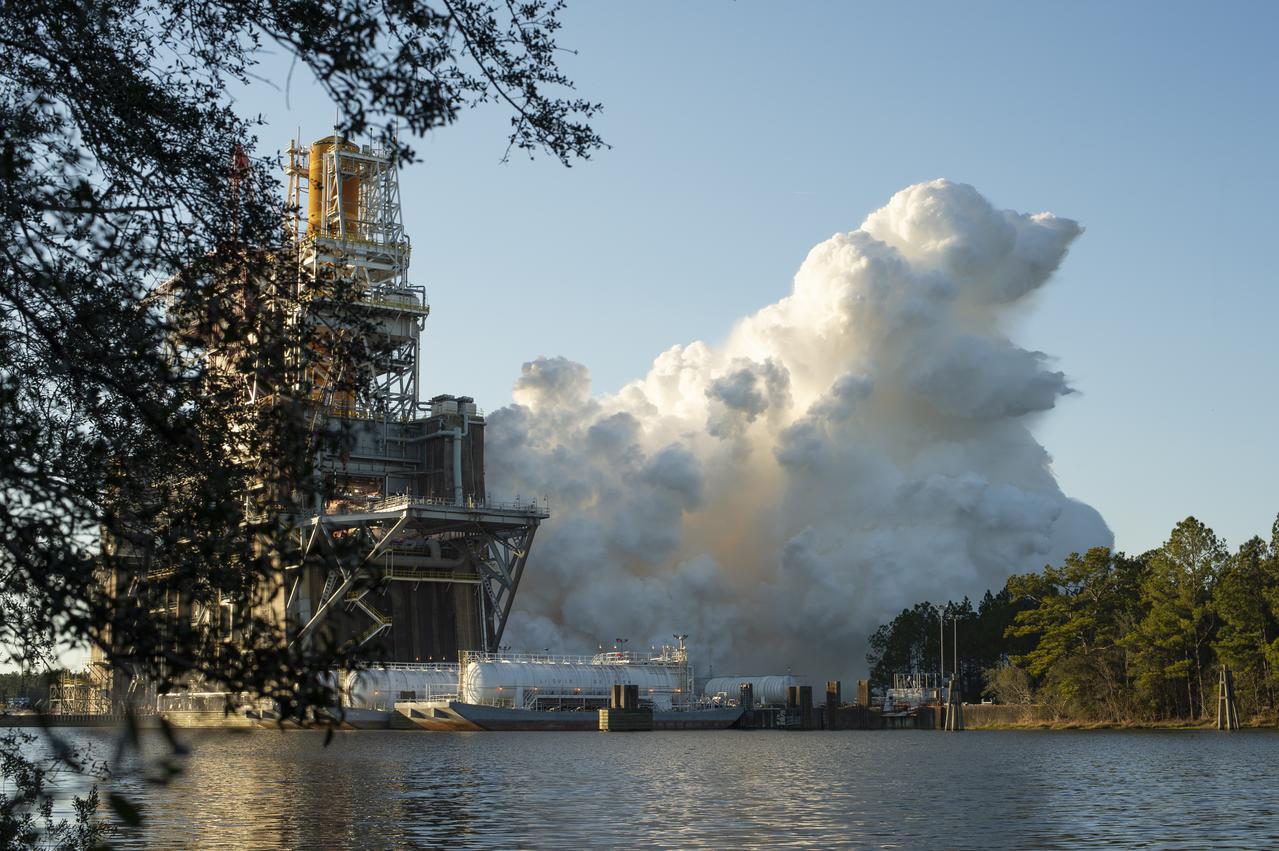

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
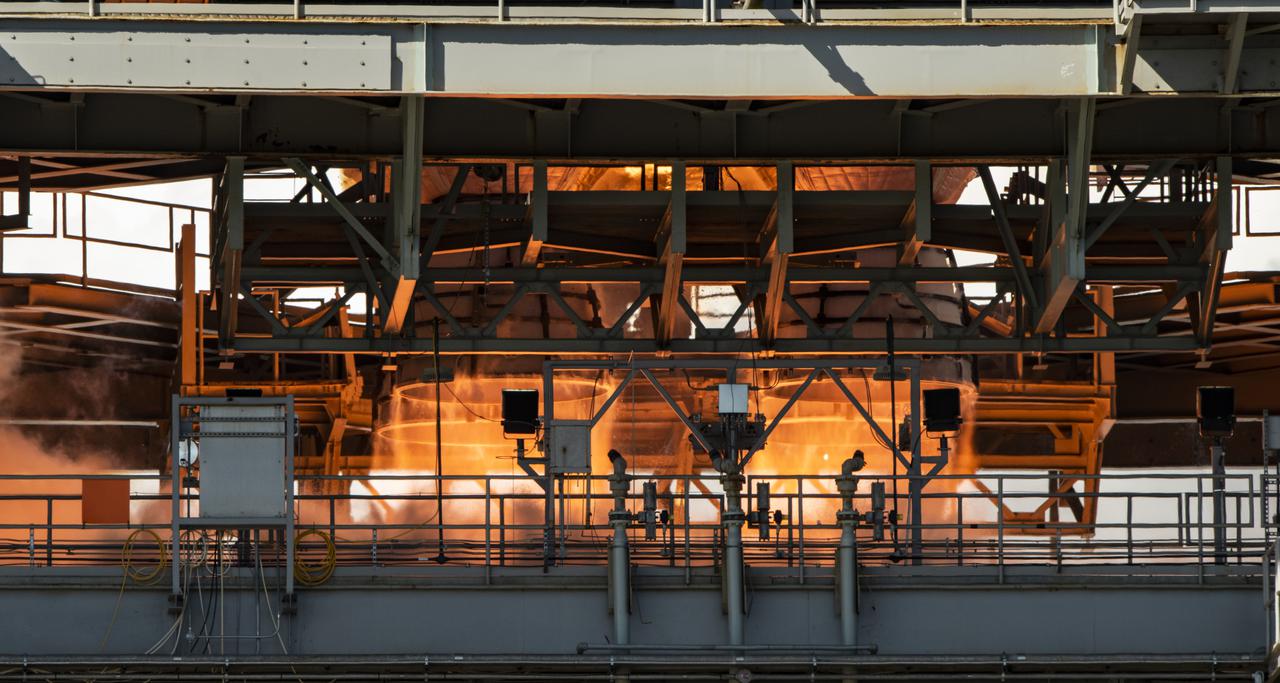

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
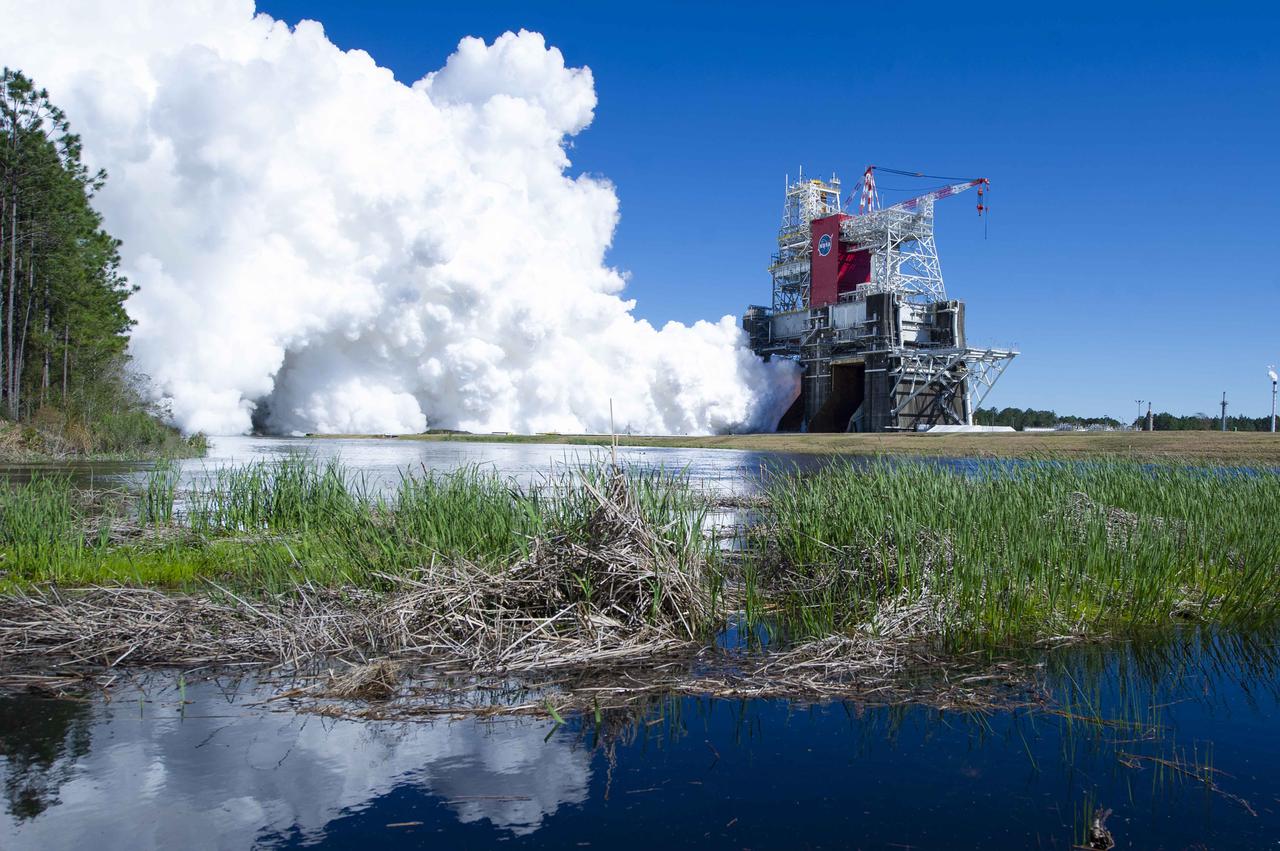

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
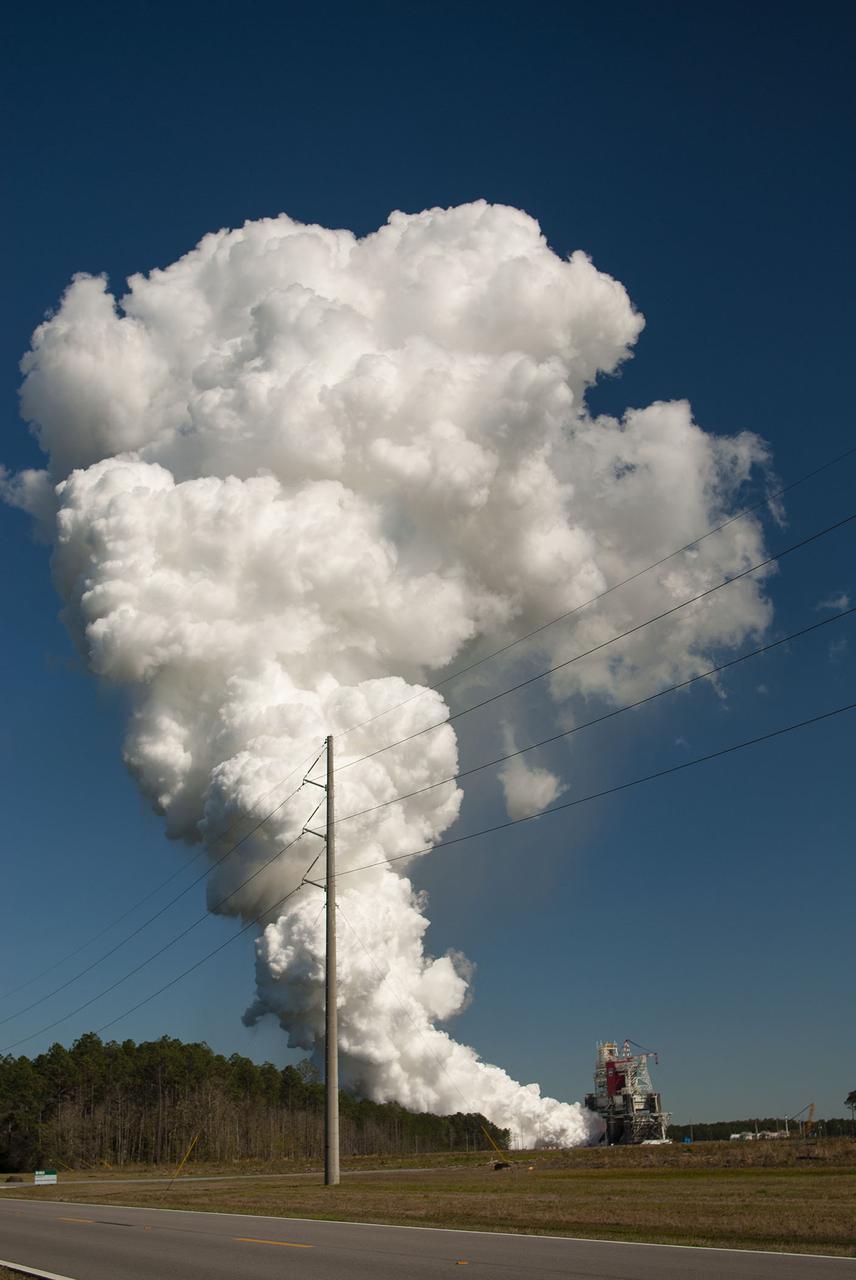

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
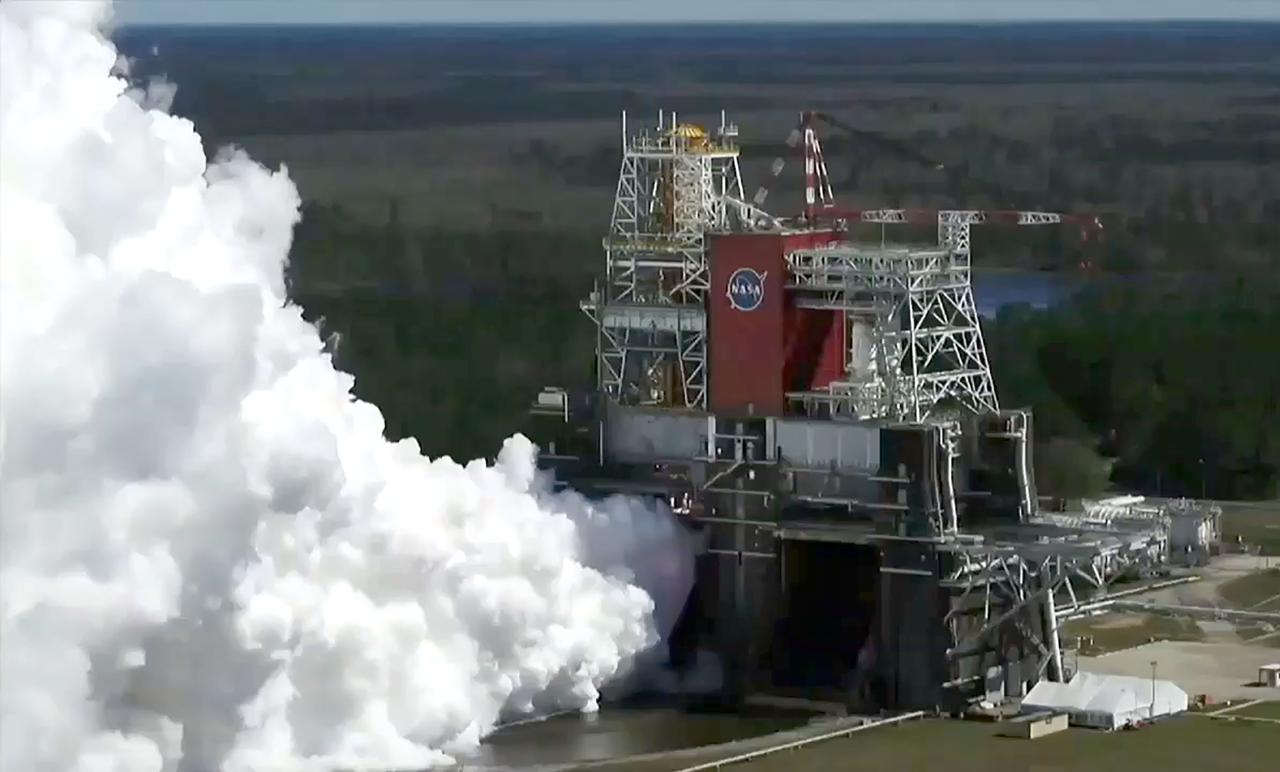

A drone camera offers a bird’s-eye view as NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
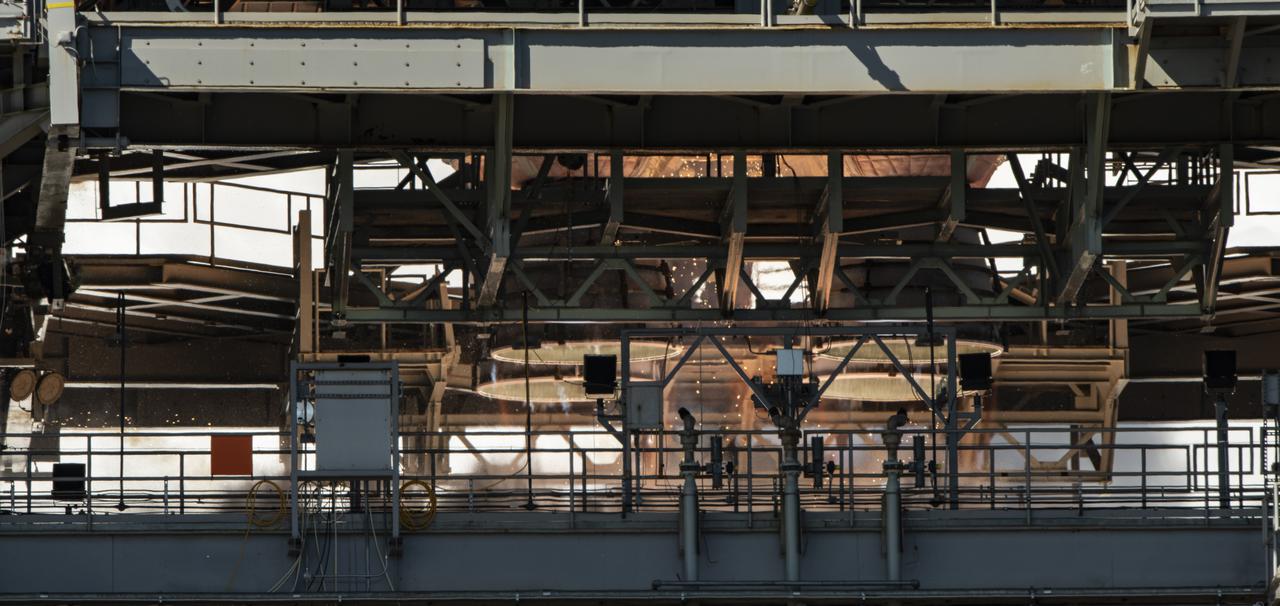

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
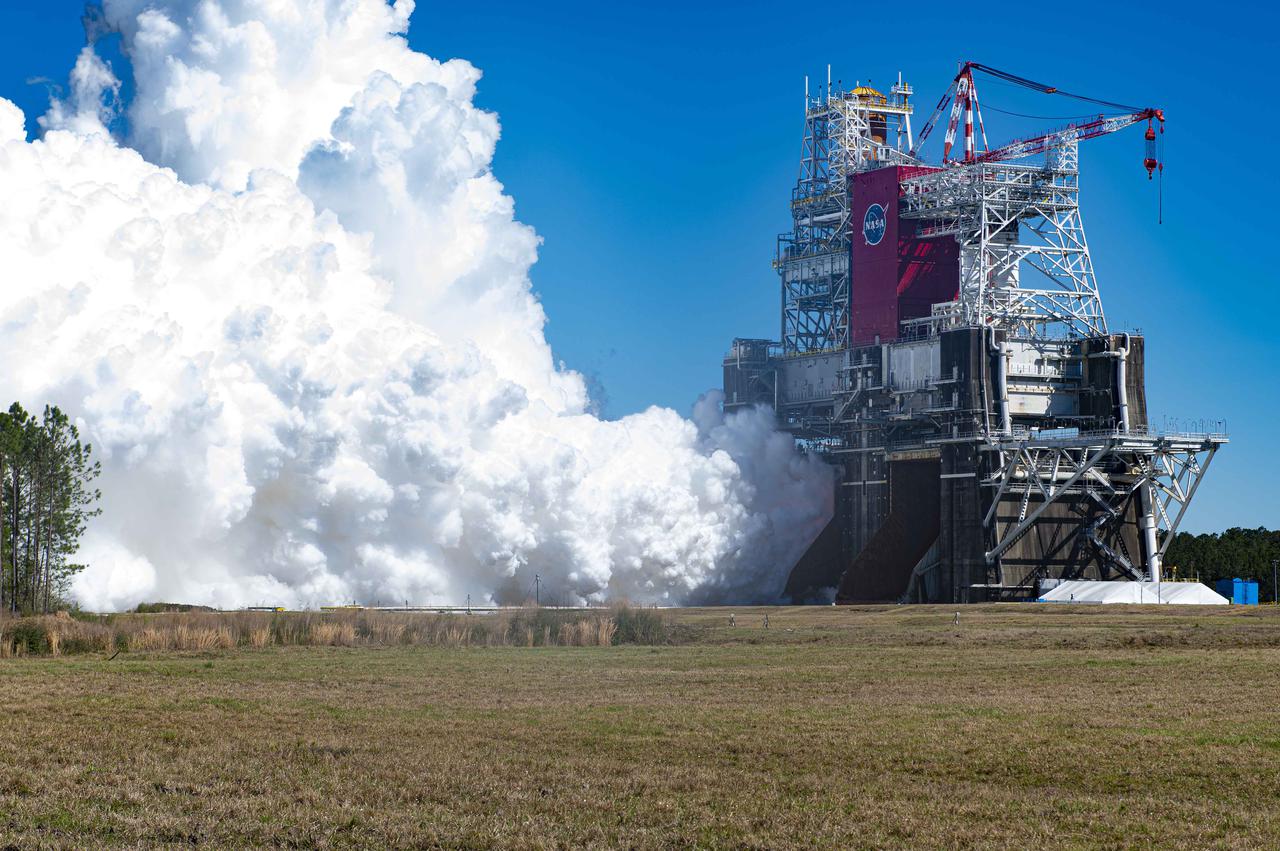

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
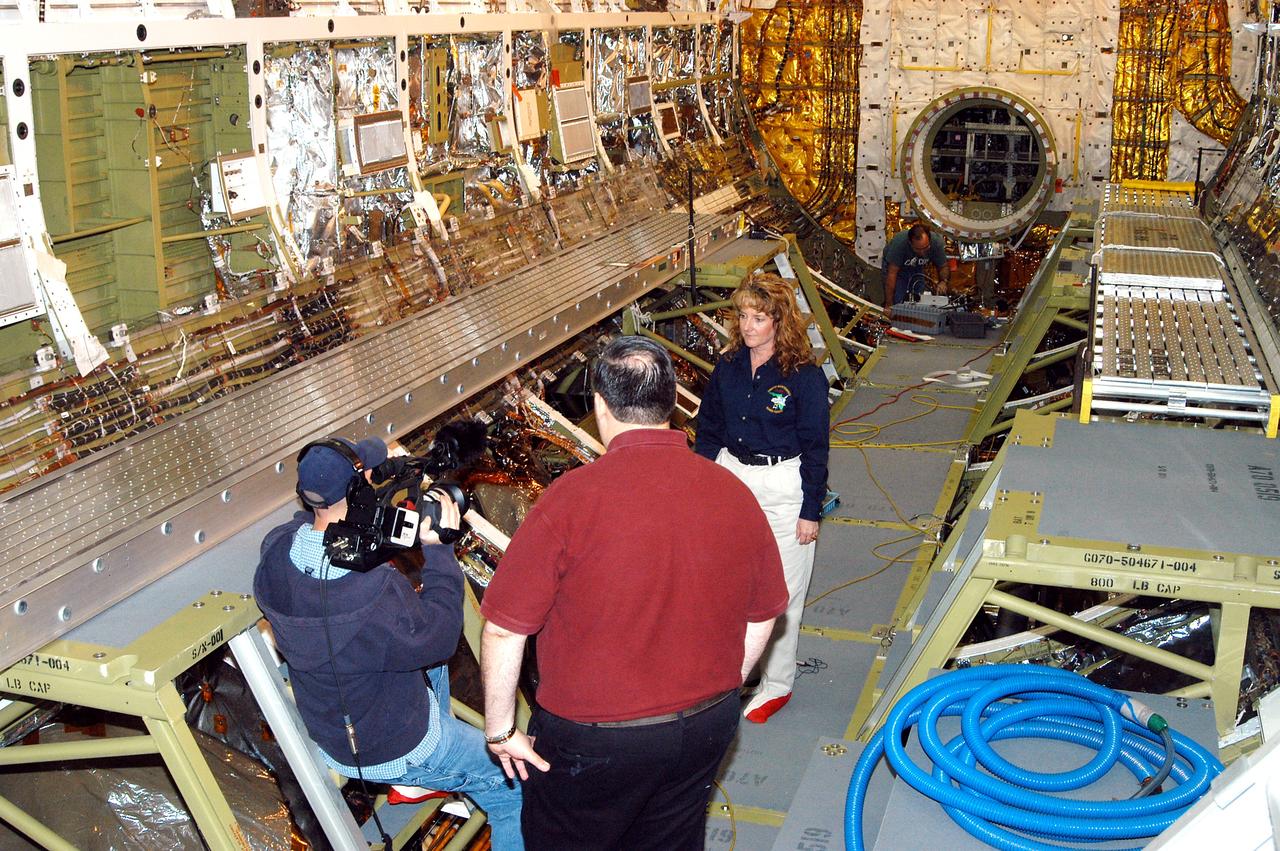

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Standing inside Discovery’s payload bay, Carol Scott (right), lead orbiter engineer, talks about her job as part of a special feature for the KSC Web. With his back to the camera is Bill Kallus, Media manager in the KSC Web Studio. Behind Scott can be seen the open hatch of the airlock, which provides support functions such as airlock depressurization and repressurization, extravehicular activity equipment recharge, liquid-cooled garment water cooling, EVA equipment checkout, donning and communications. The outer hatch isolates the airlock from the unpressurized payload bay when closed and permits the EVA crew members to exit from the airlock to the payload bay when open.
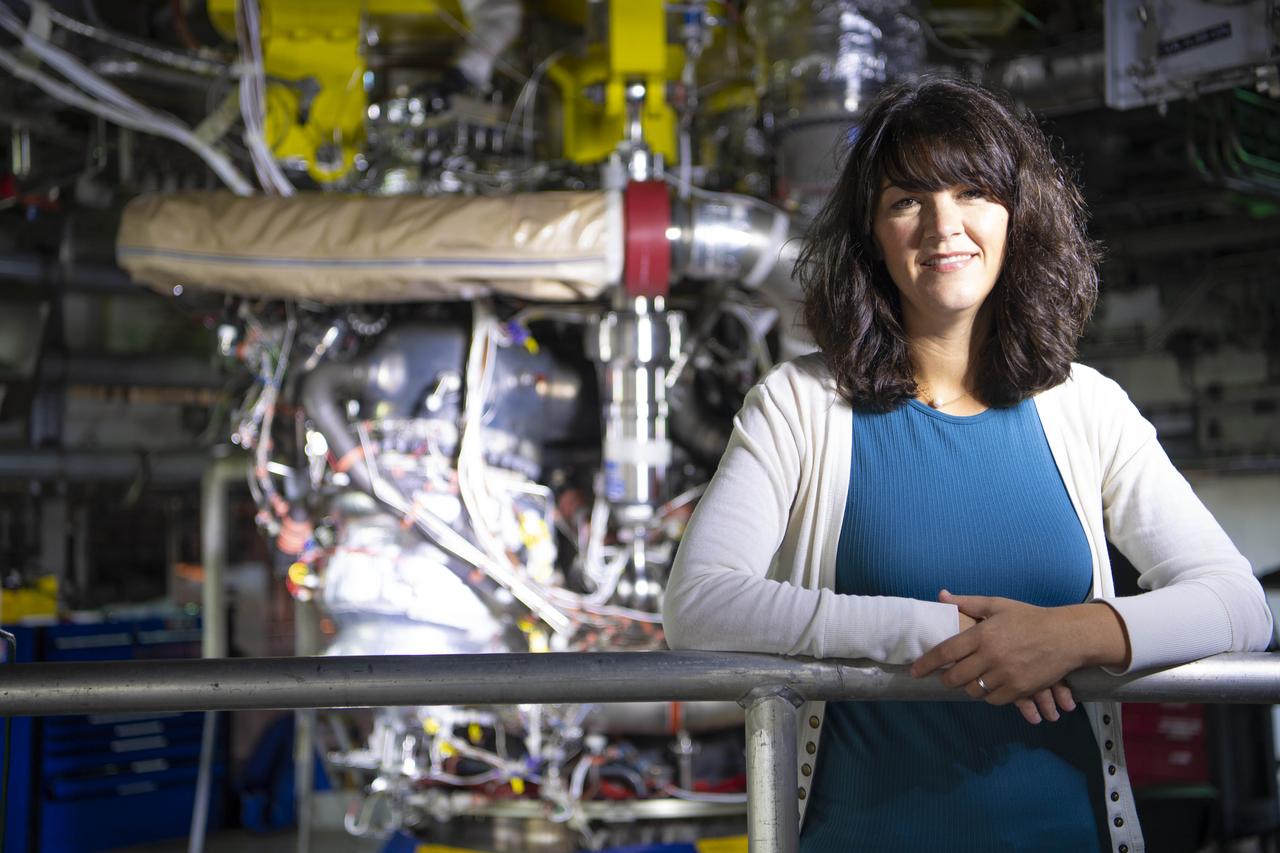
Nyla Trumbach, a NASA lead mechanical engineer, broke barriers as the first female to conduct a J-2X powerpack engine test at Stennis Space Center. She currently works on testing of the RS-25 rocket engine, shown installed on the A-1 Test Stand at SSC.
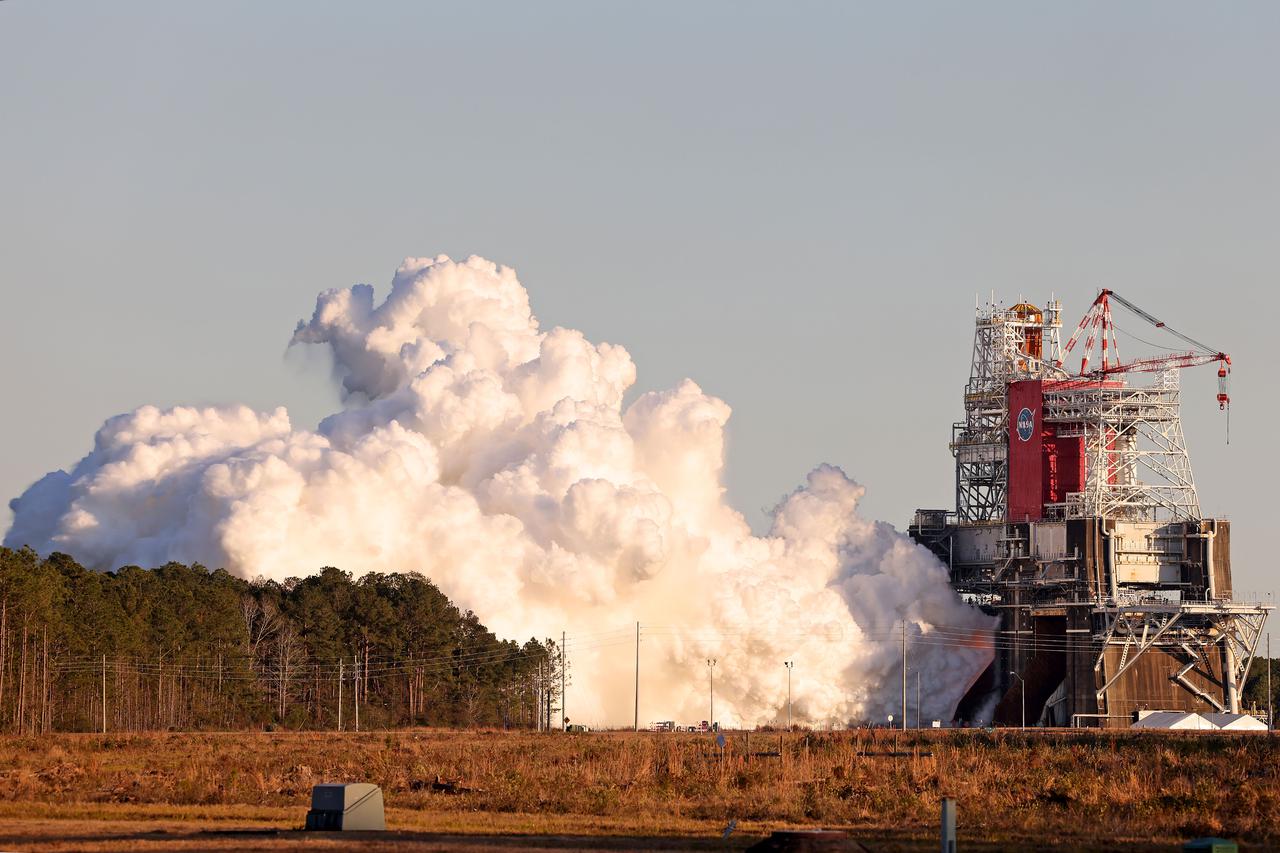

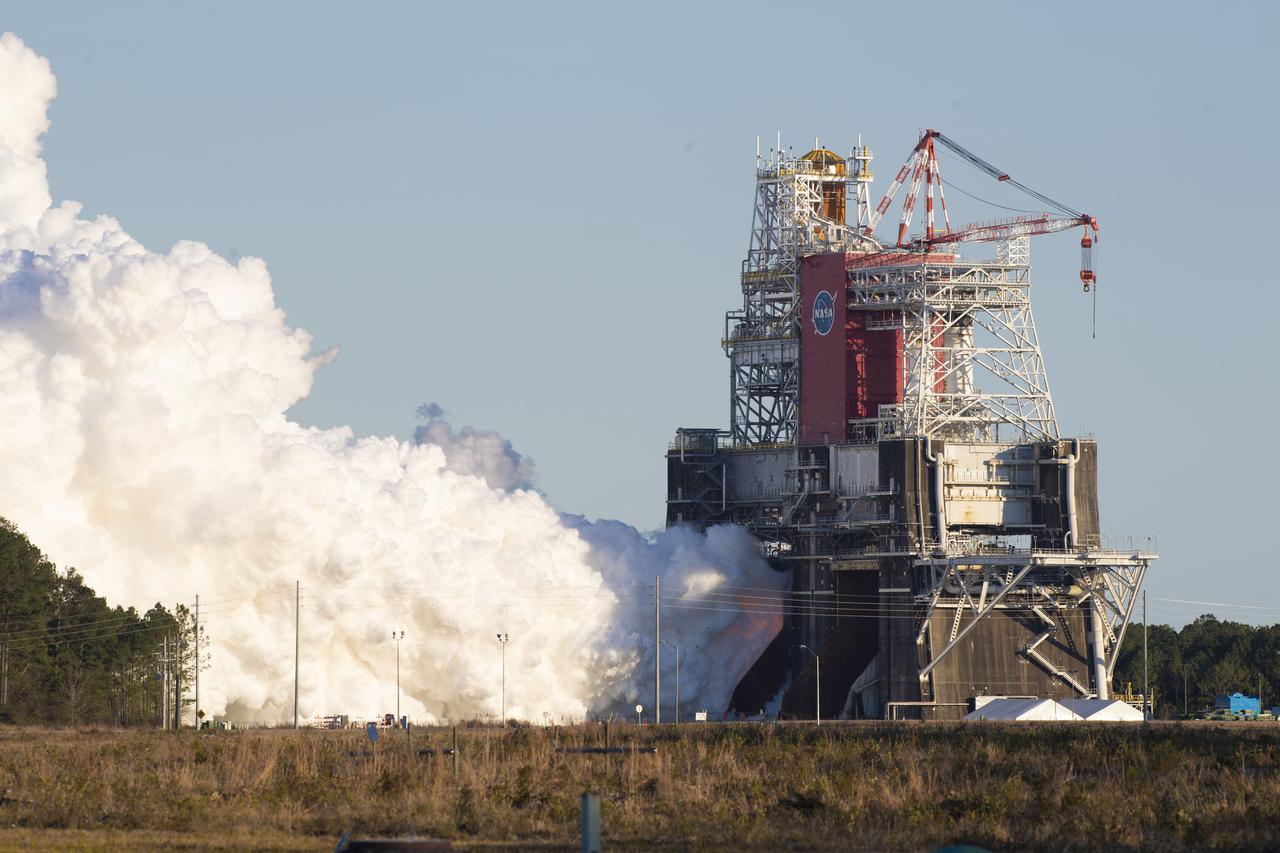
NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
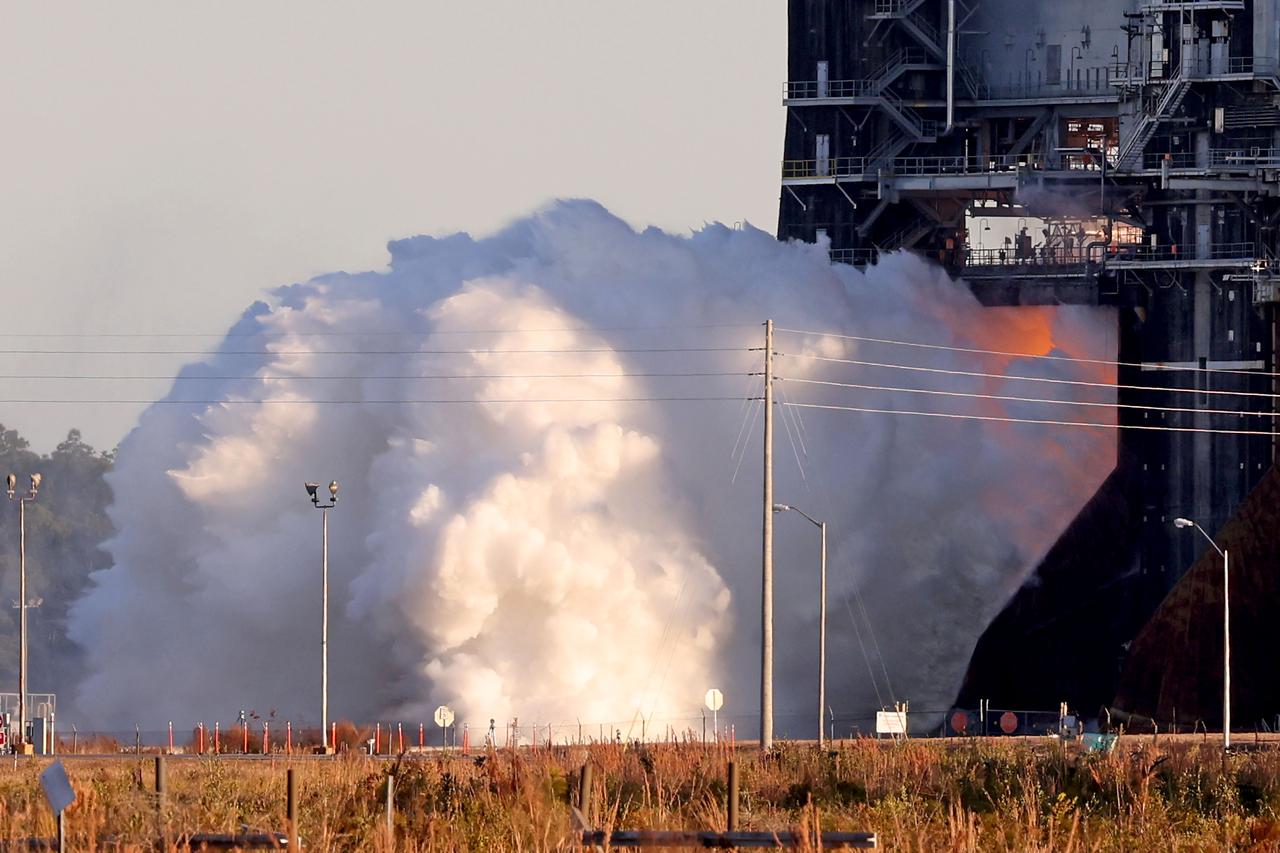

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
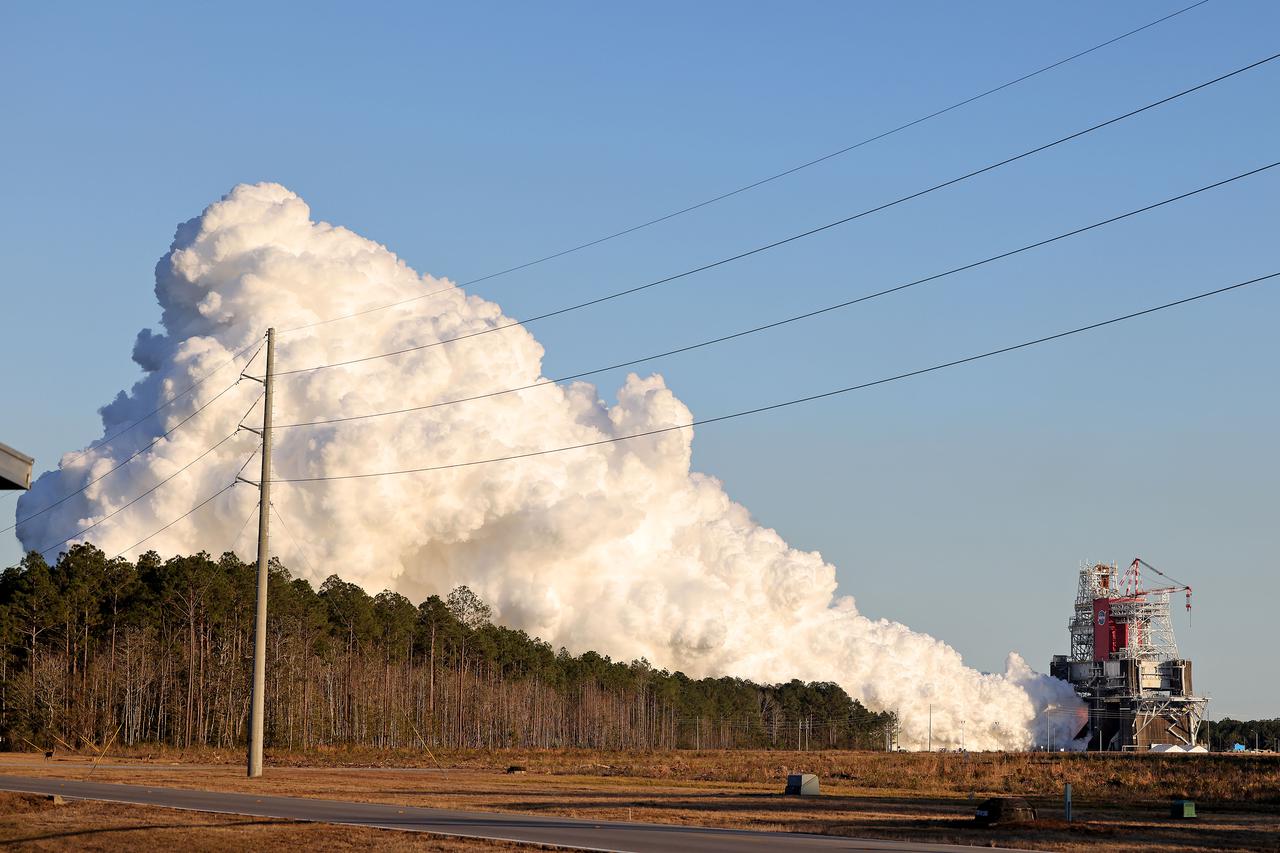

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
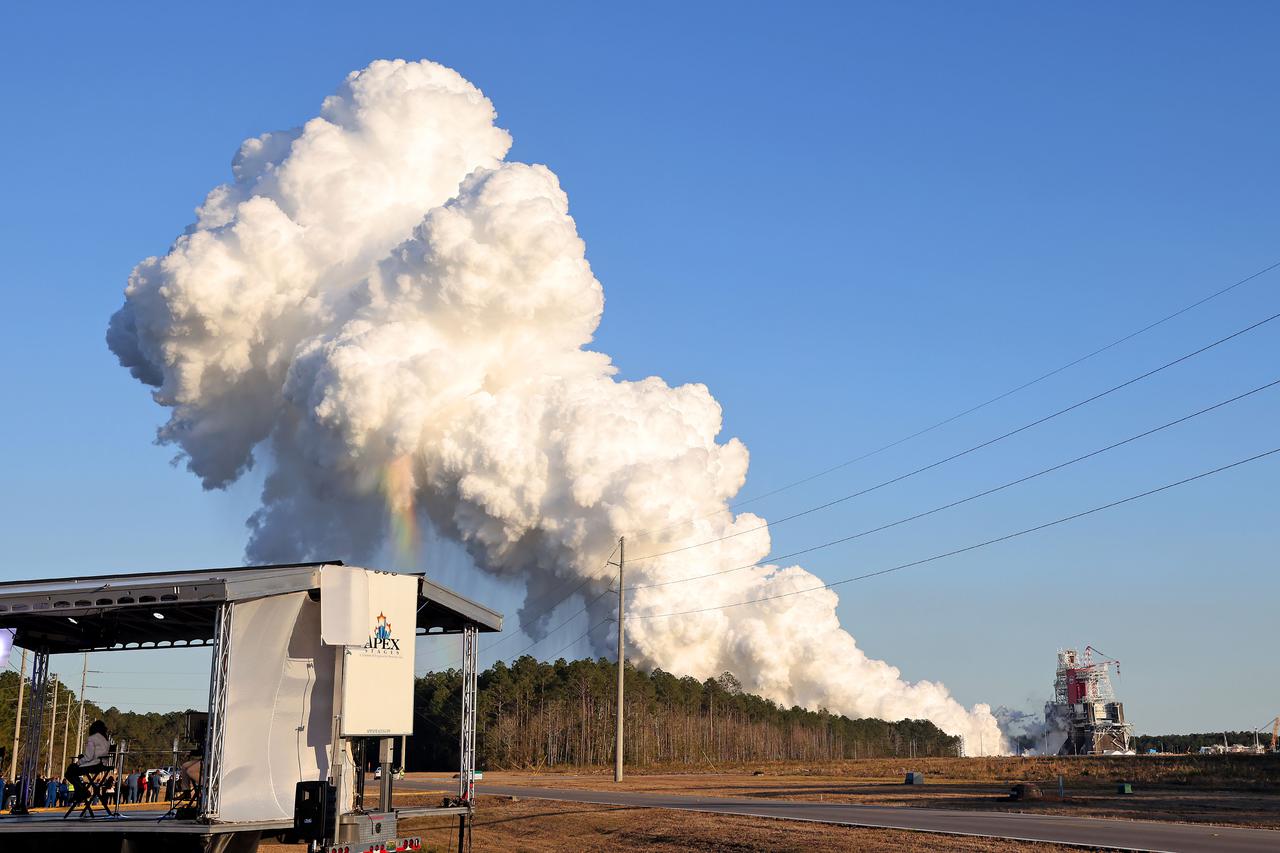

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
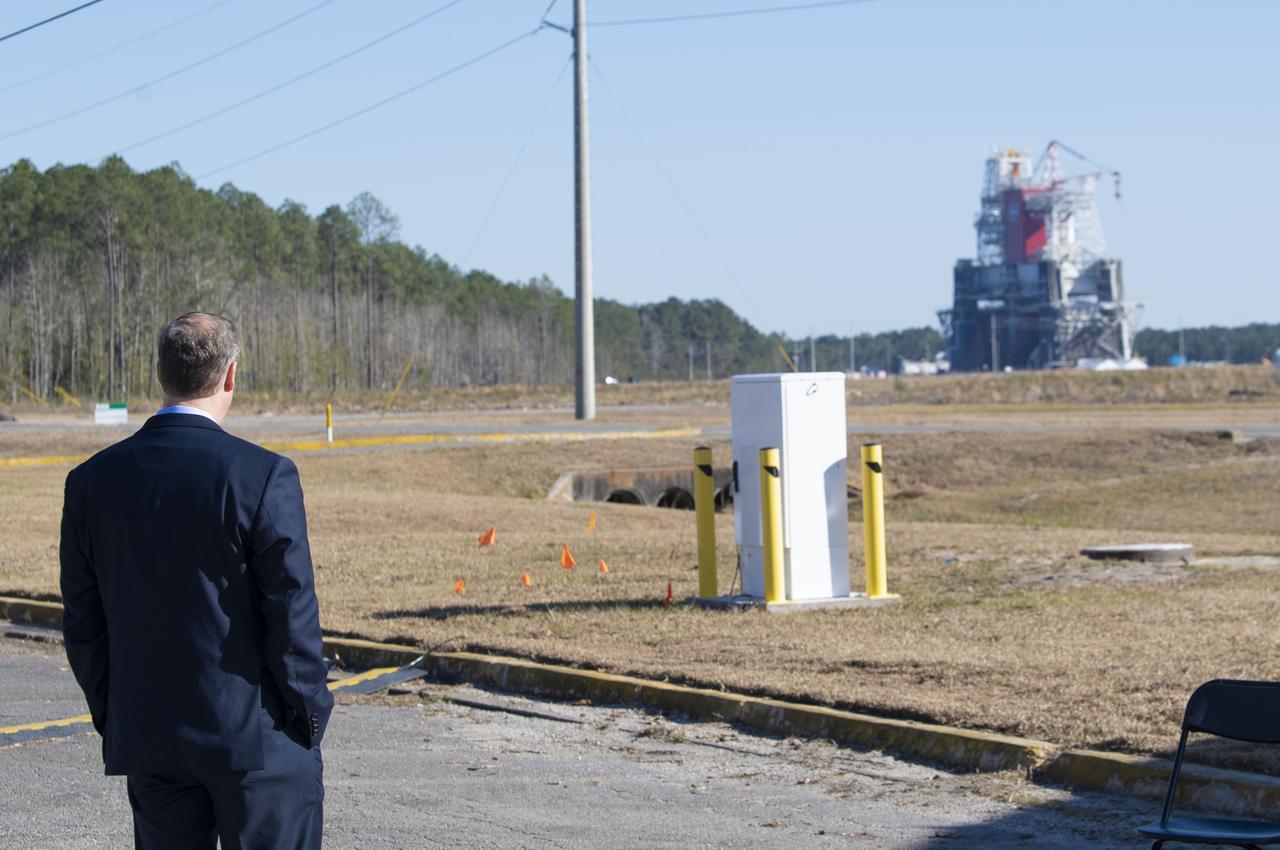

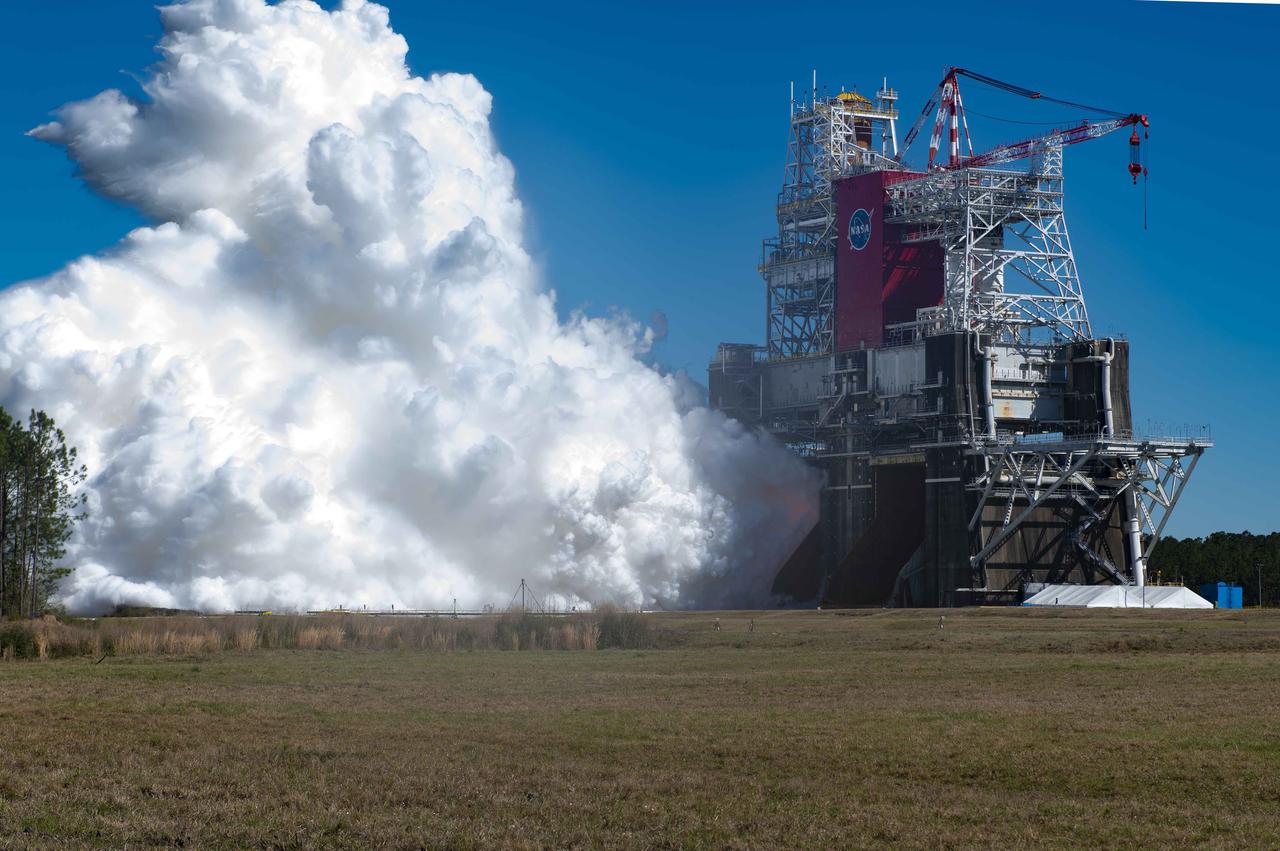
Outgoing NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine peers at the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, prior to a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire at the B-2 Test Stand culminated a series of eight Green Run tests on the core stage and its integrated systems. The core stage now will be prepared and transported to Kennedy Space Center to be joined with the rest of the SLS rocket for launch on the Artemis I test mission.

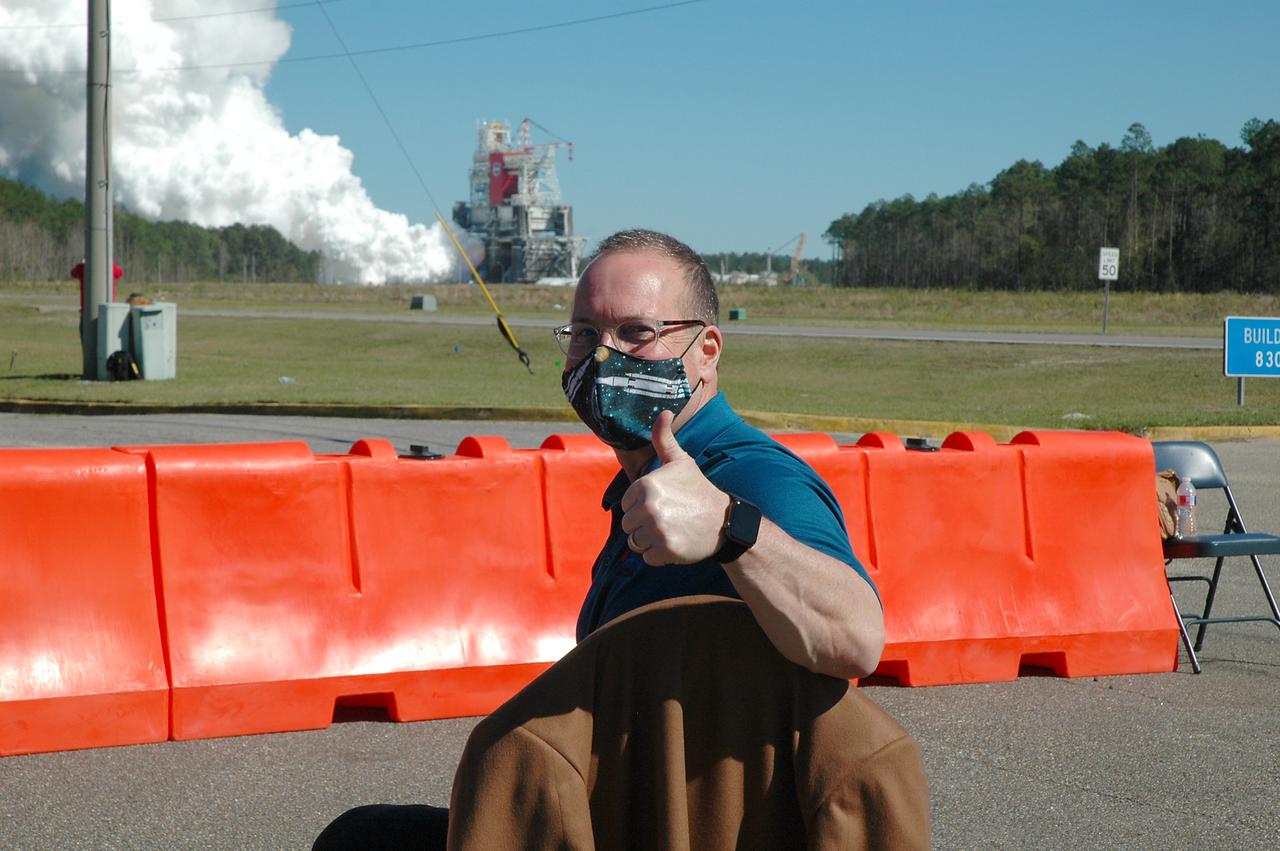
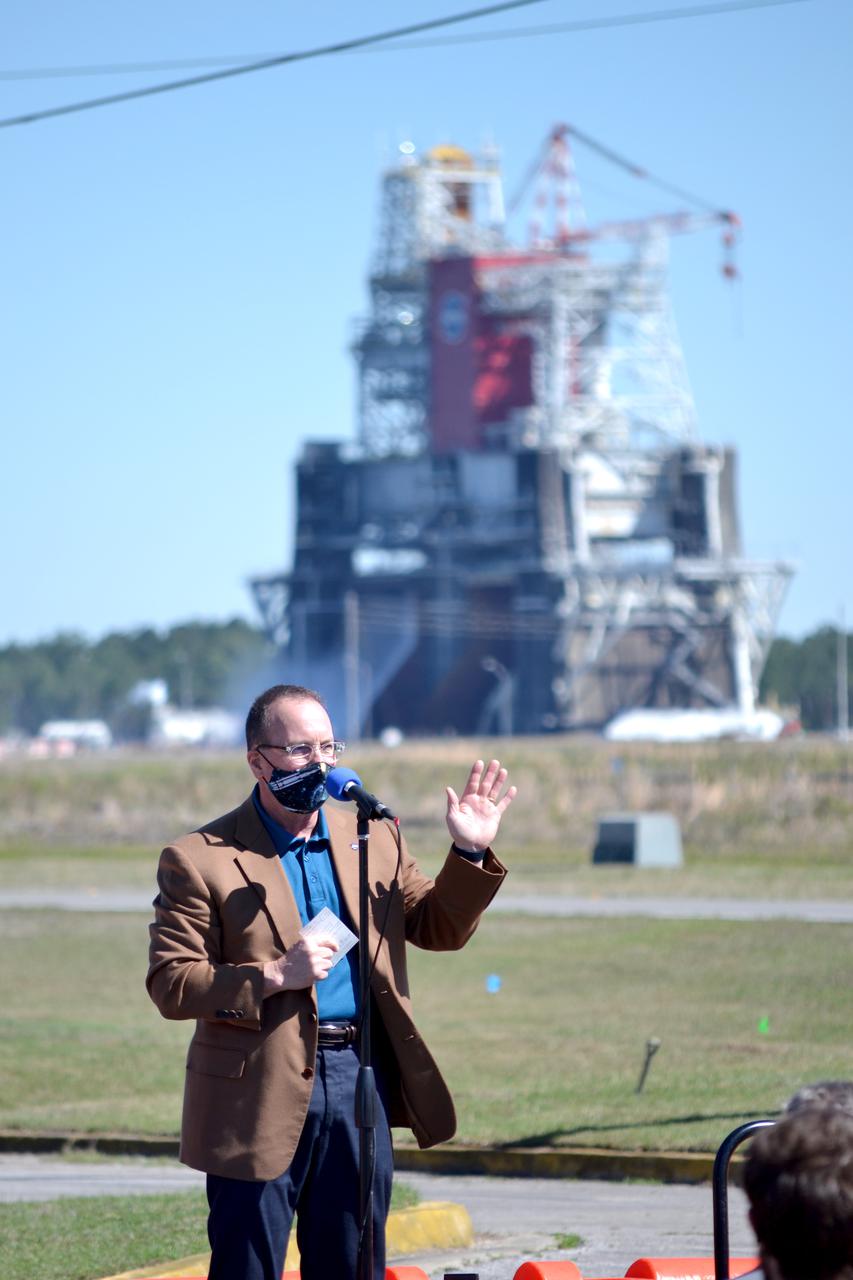
Astronaut Matthew Dominick speaks with media representatives prior to the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

Astronaut Matthew Dominick speaks with media representatives prior to the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

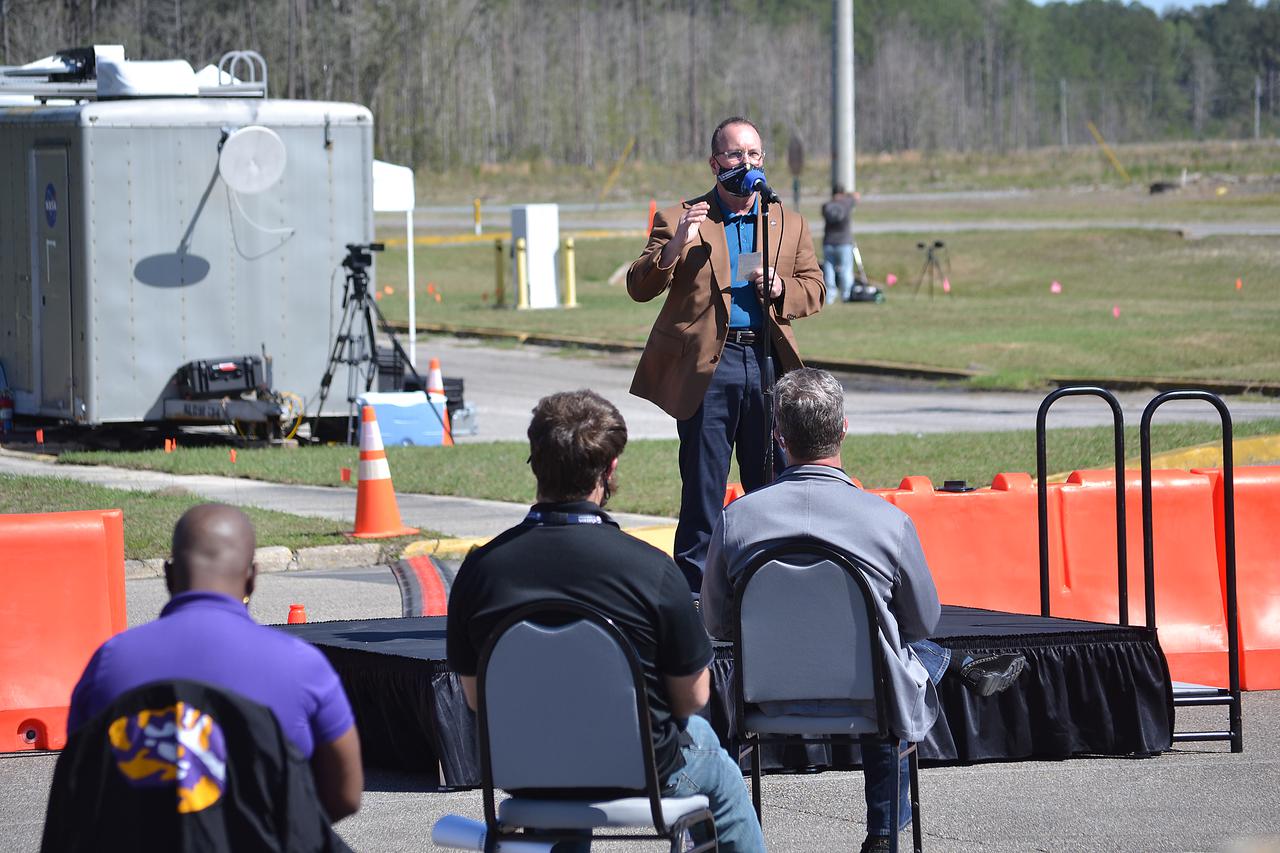
Stennis Space Center Director Rick Gilbrech participates in a press conference following the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
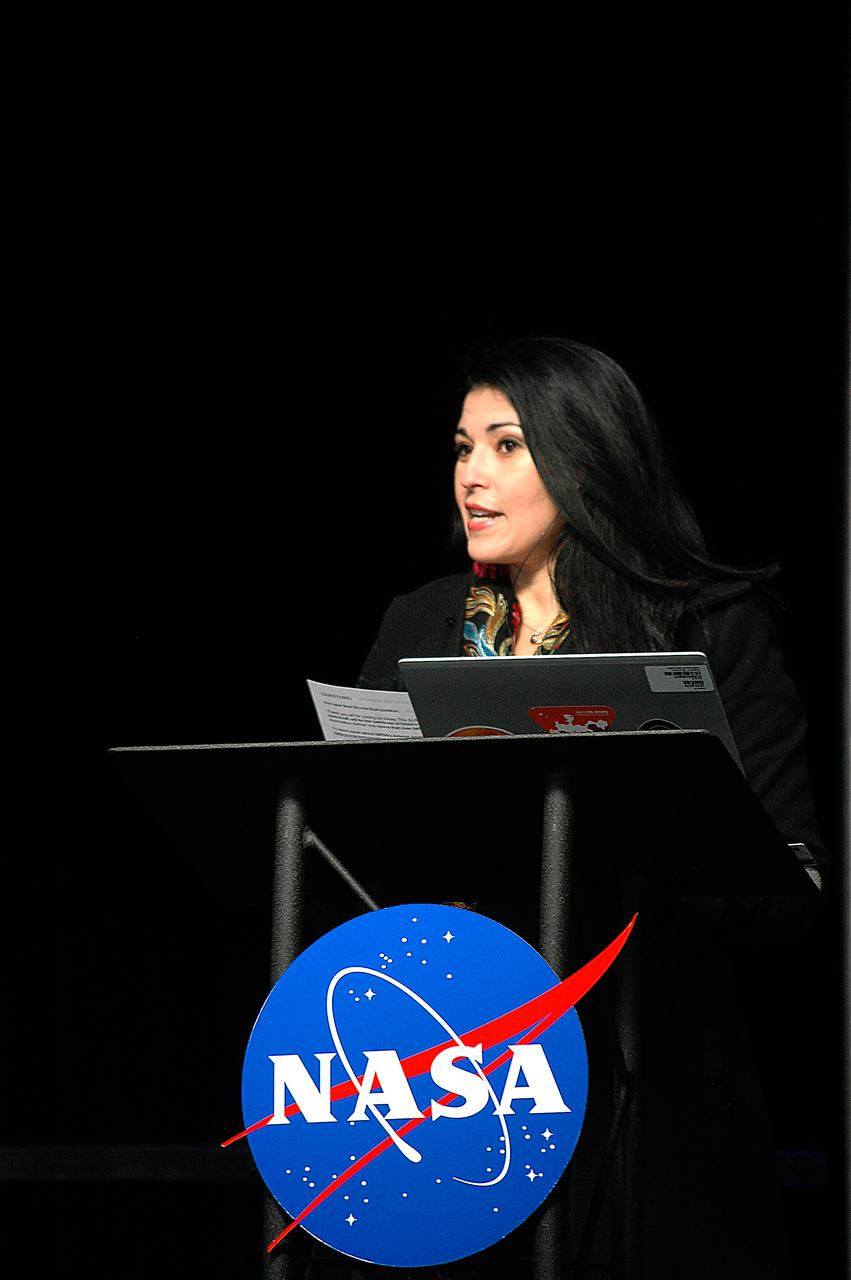

Outgoing NASA Associate Administrator for Communications Bettina Inclan hosts a press conference following the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
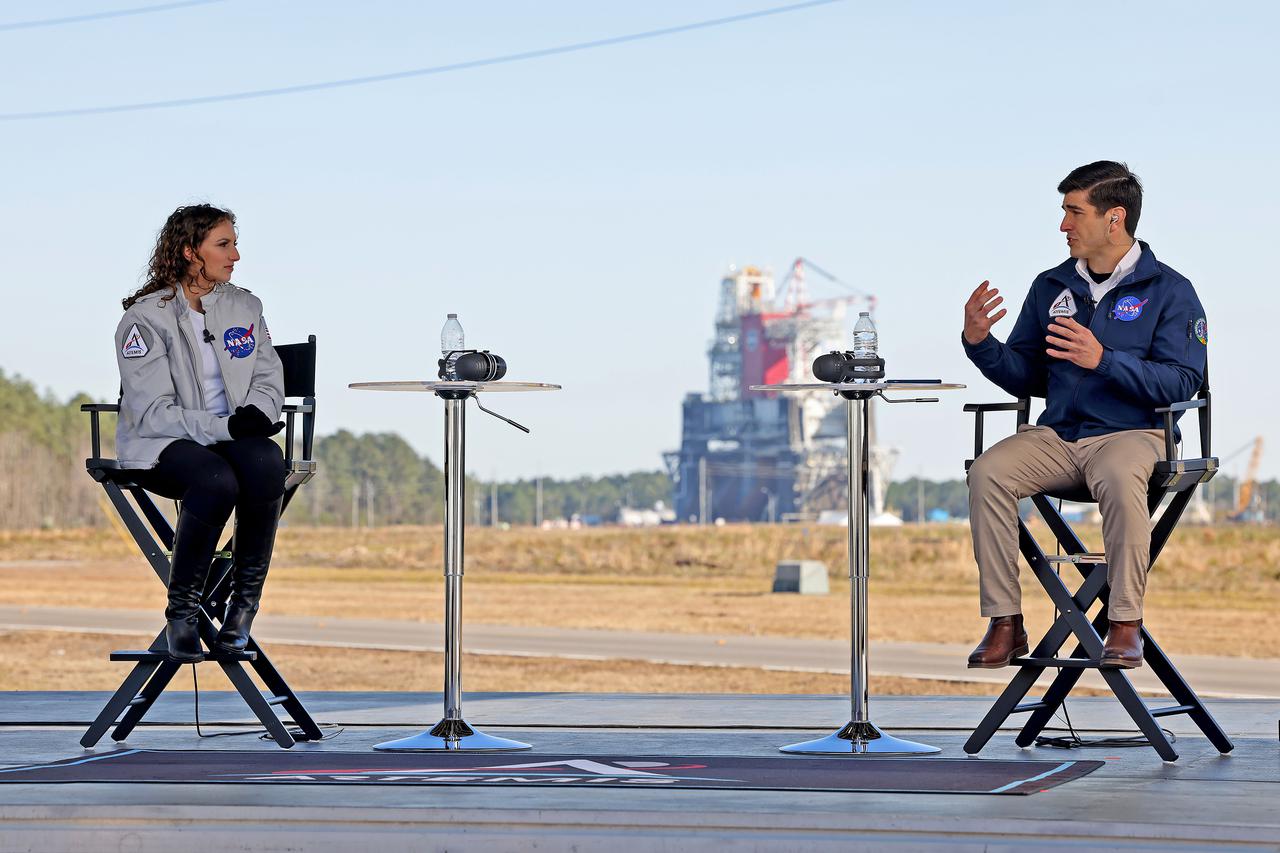

Host Leigh D’Angelo (left) talks with NASA Space Launch System core stage engineer Alex Cagnola from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, during NASA TV live coverage from Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Jan. 16, 2021. D’Angelo, also from Michoud Assembly Facility, hosted the NASA TV coverage prior to the hot fire test of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
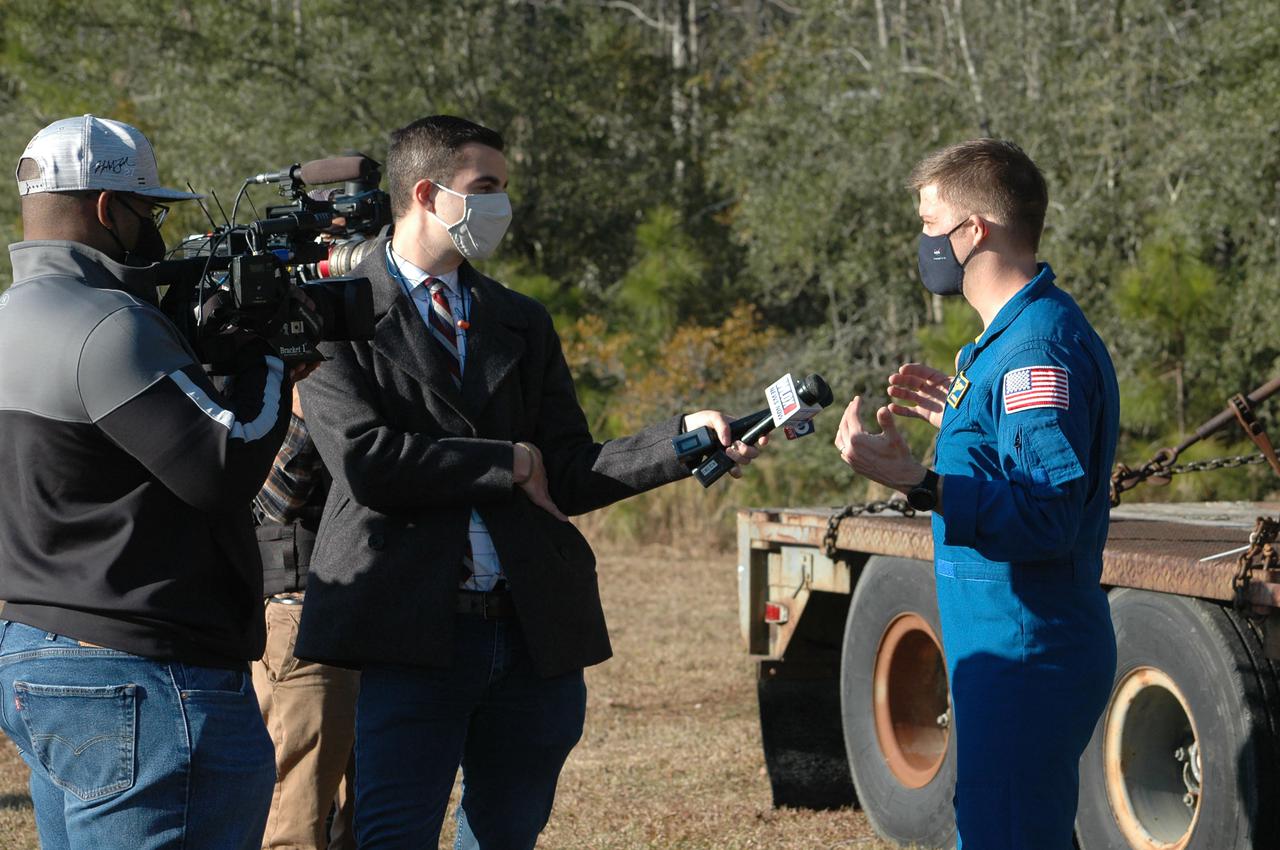

Astronaut Matthew Dominick speaks with media representatives prior to the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

Astronaut Matthew Dominick speaks with media representatives prior to the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
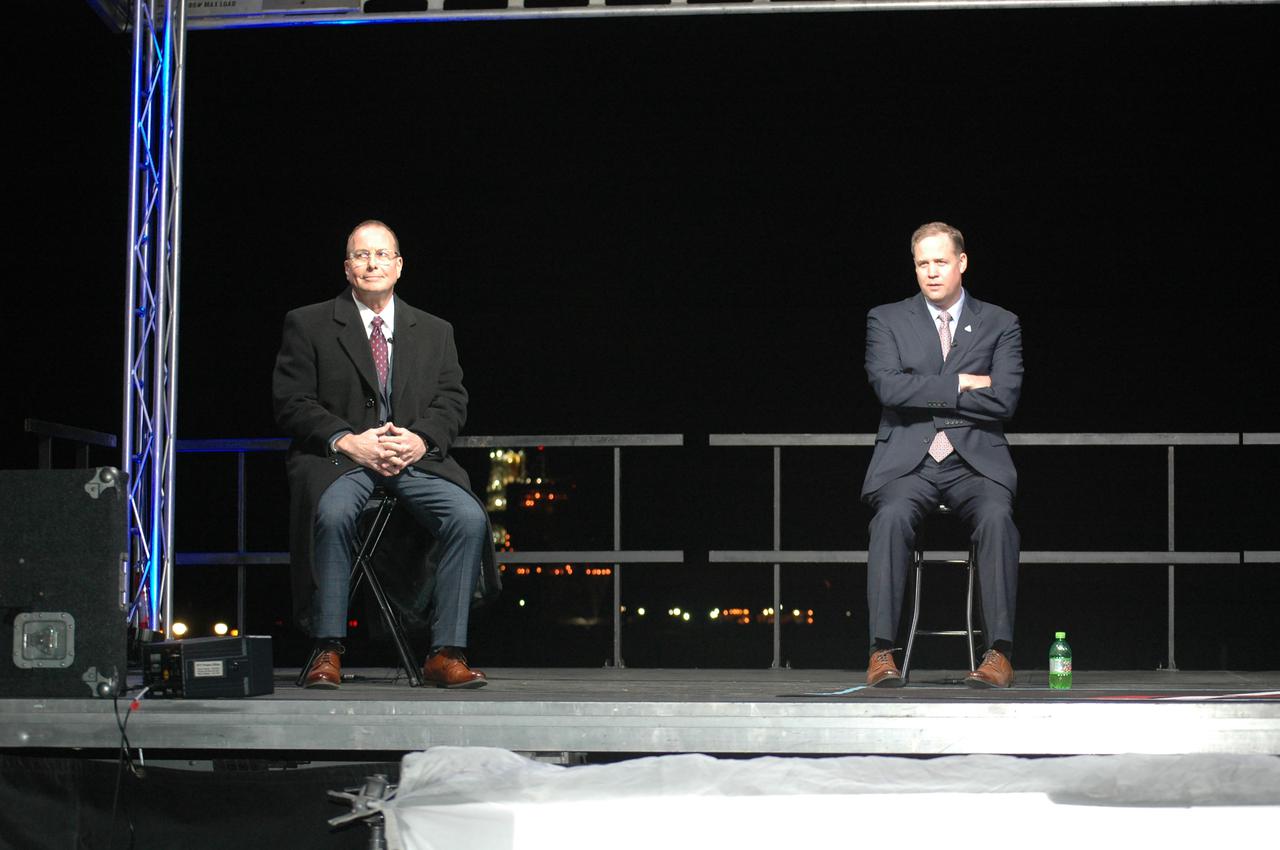

Outgoing NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine (right) and Stennis Space Center Director Rick Gilbrech participate in a press conference following the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
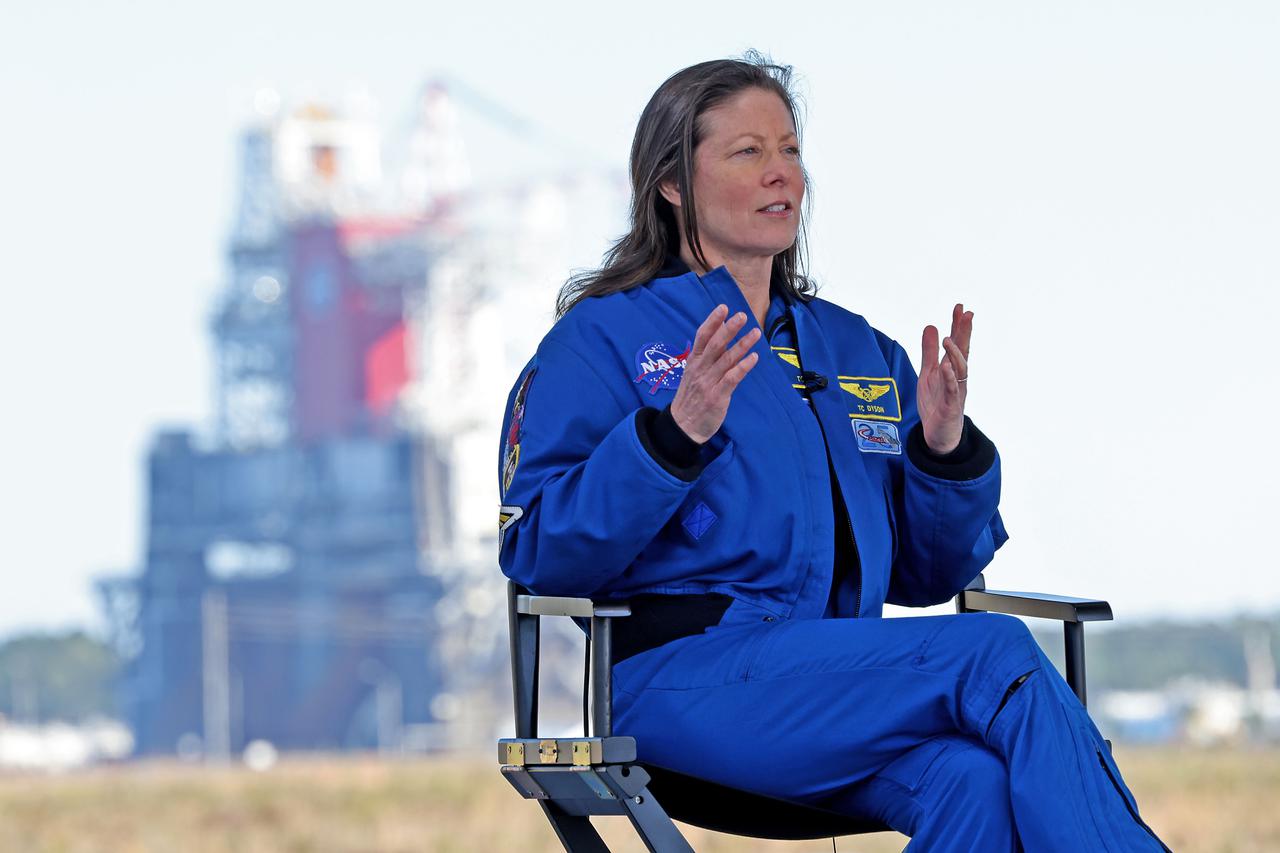

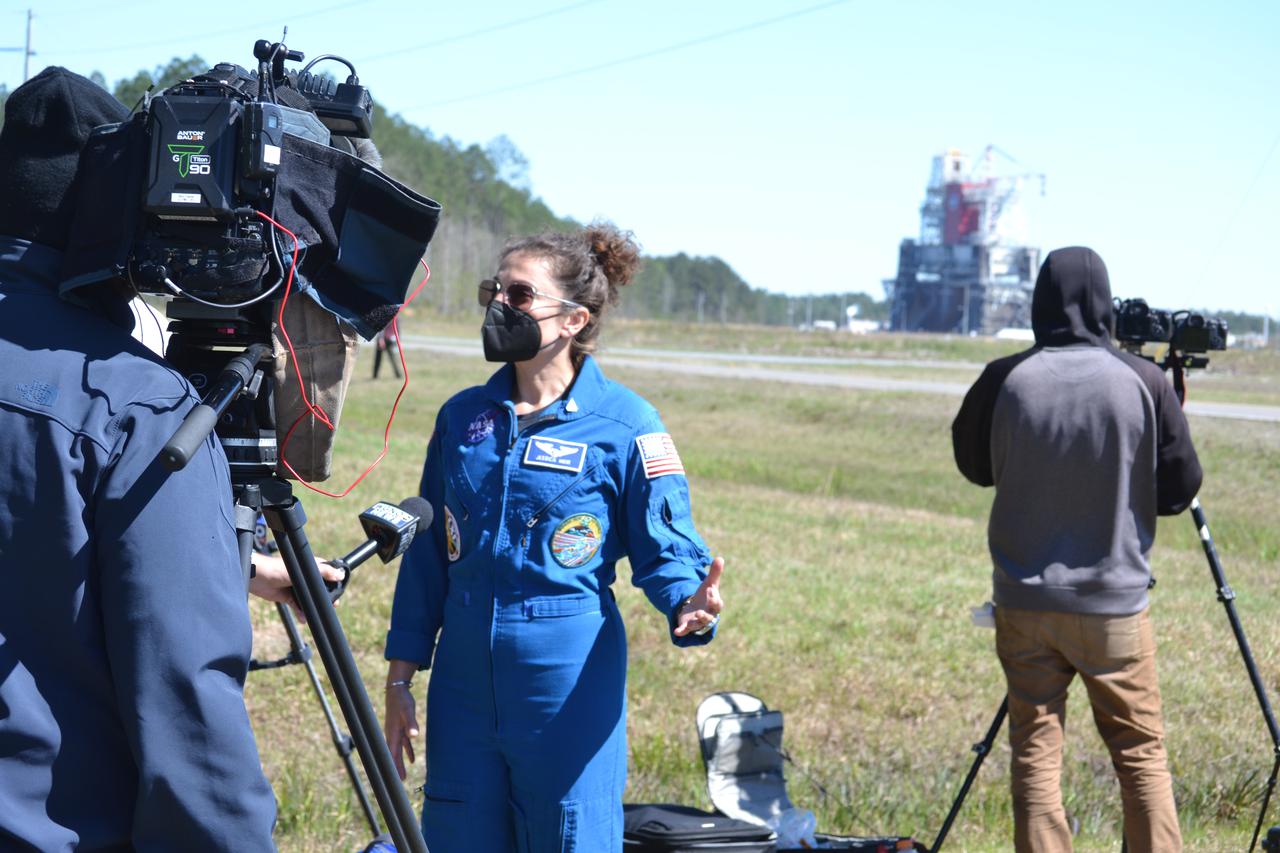
Astronaut Tracy Caldwell Dyson speaks on NASA TV prior to the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
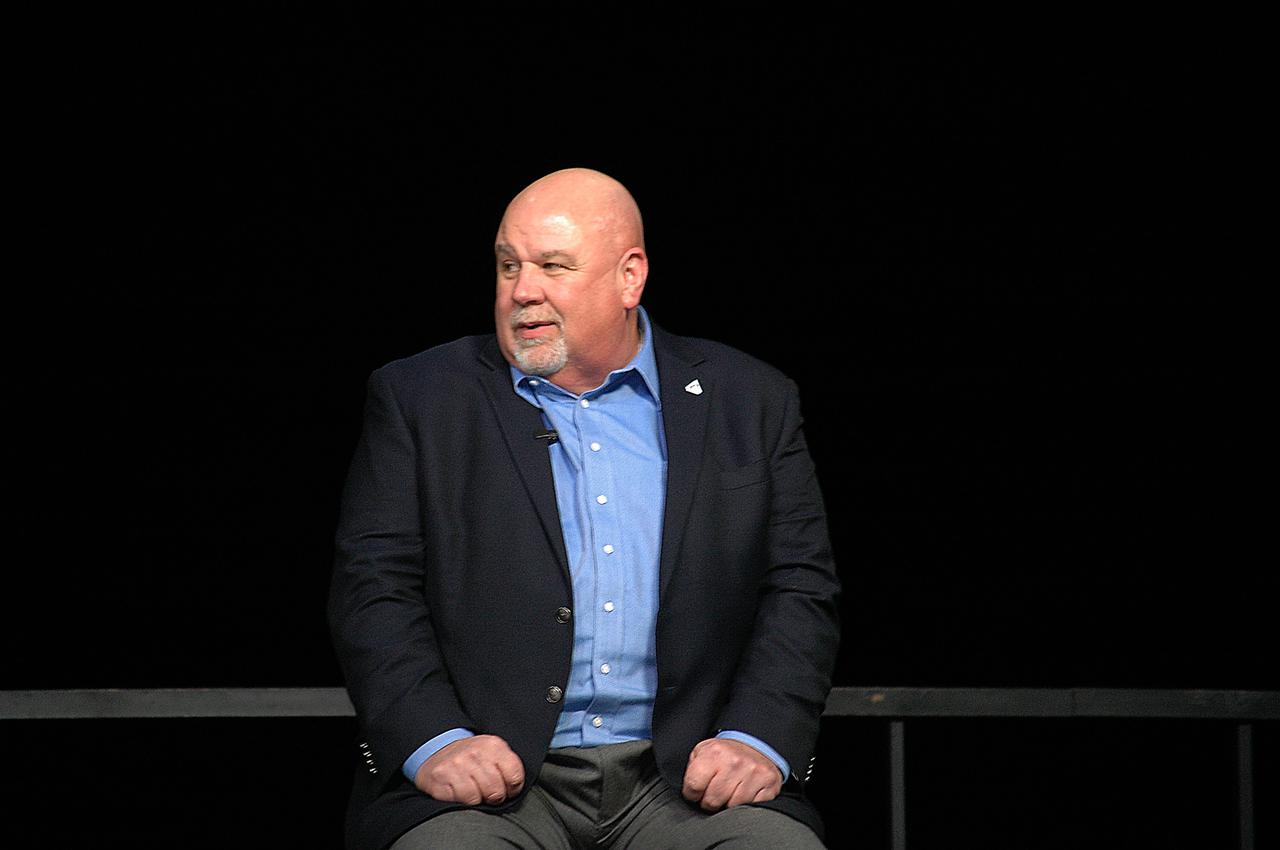

SLS Program Manager John Honeycutt from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center participates in a press conference following the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
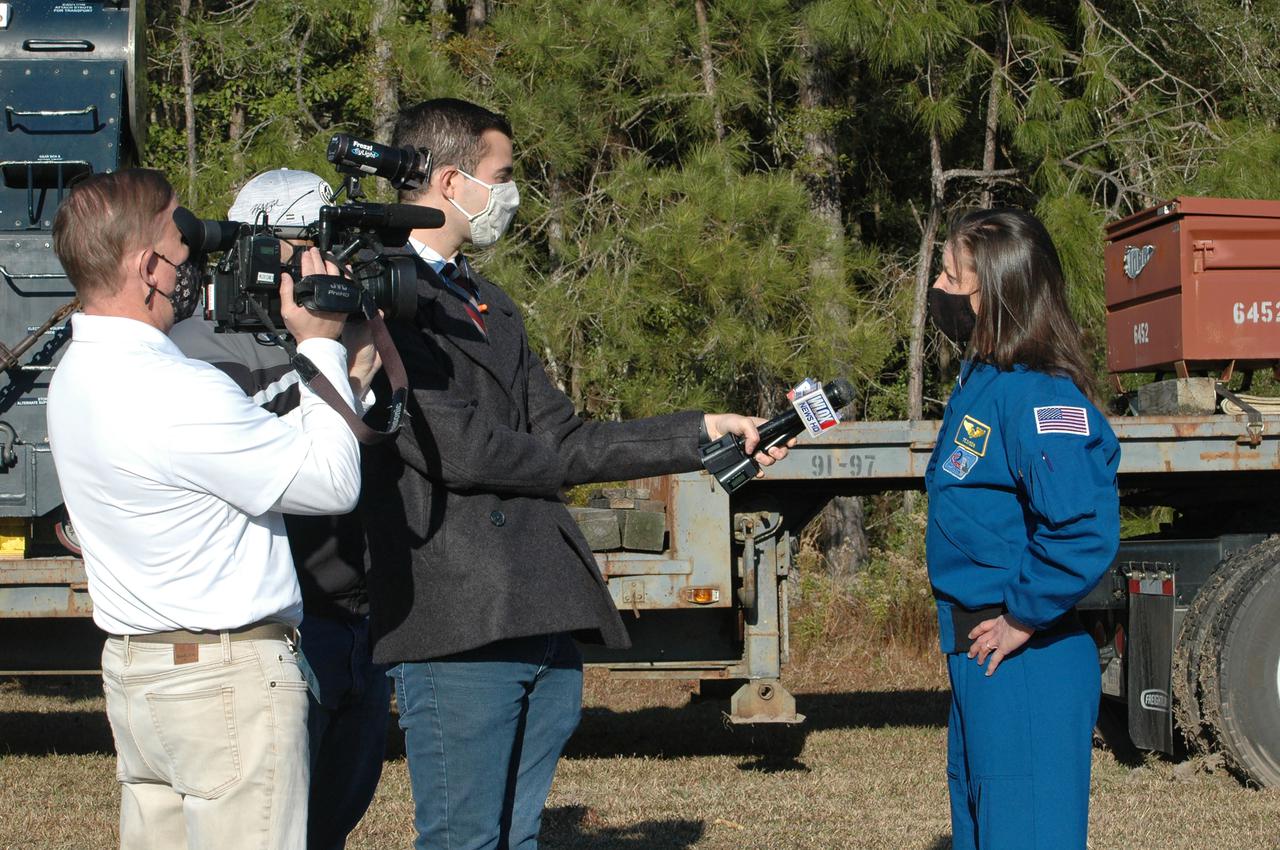

Astronaut Tracy Caldwell Dyson speaks with media representatives prior to the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Saturday, January 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.