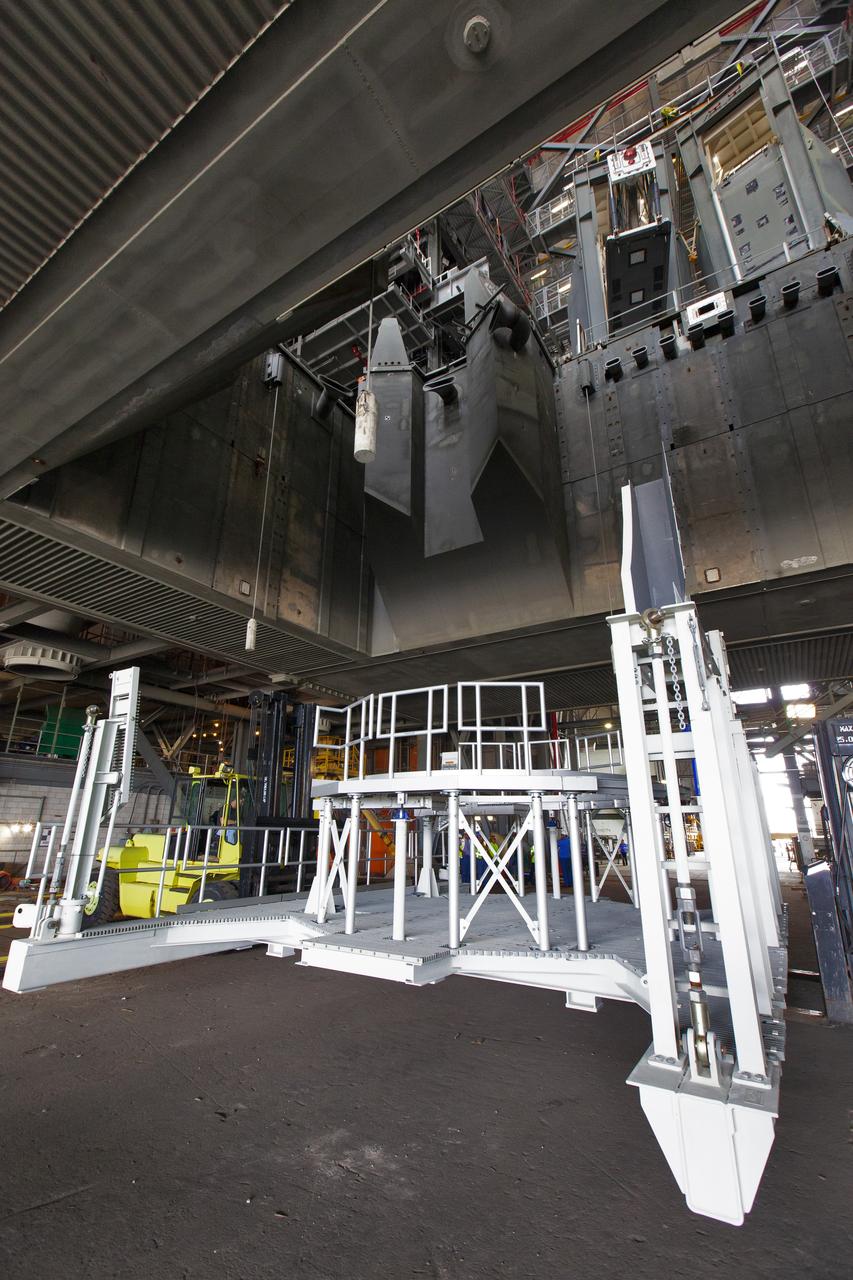

The engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket arrives in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 14, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.

The engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is moved beneath the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 14, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.

The engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is moved beneath the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 14, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.

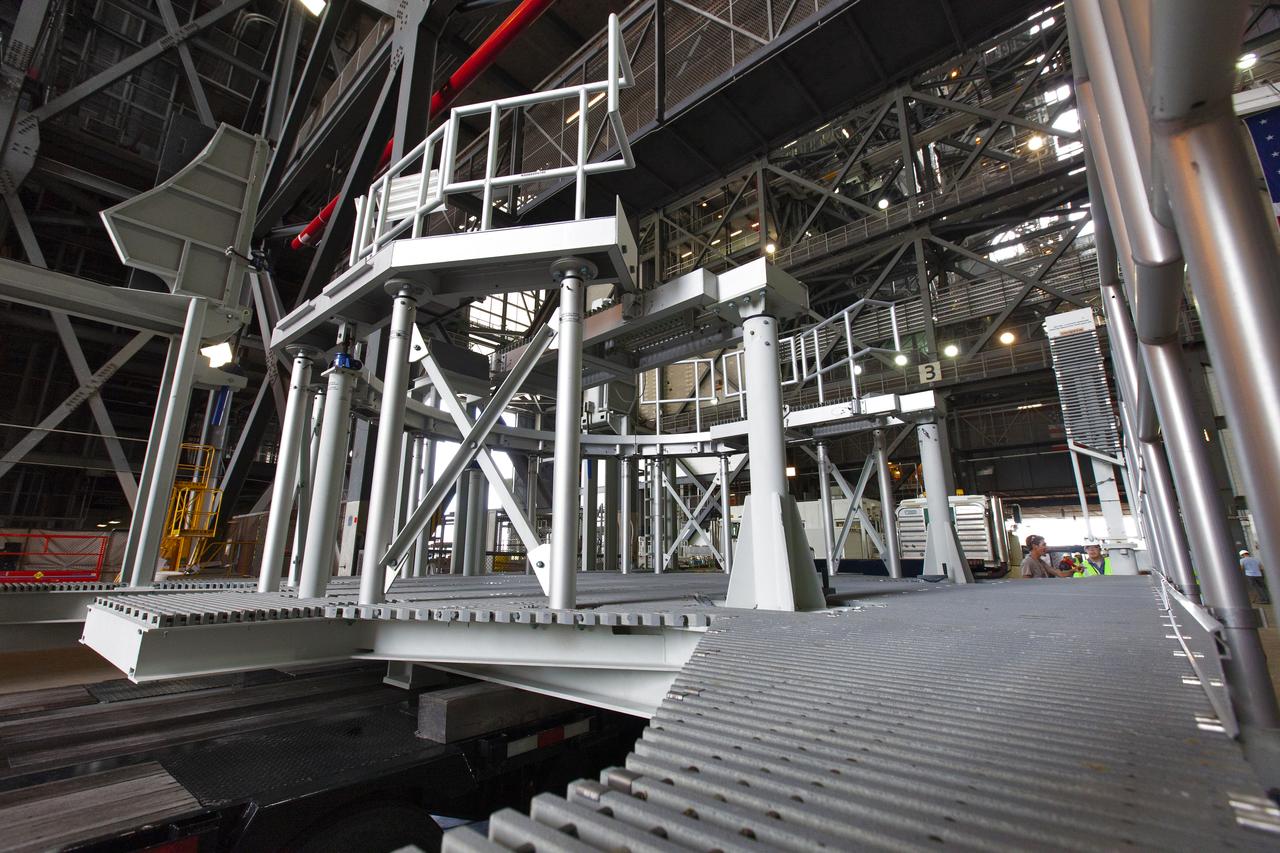
The engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket arrives in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 14, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.

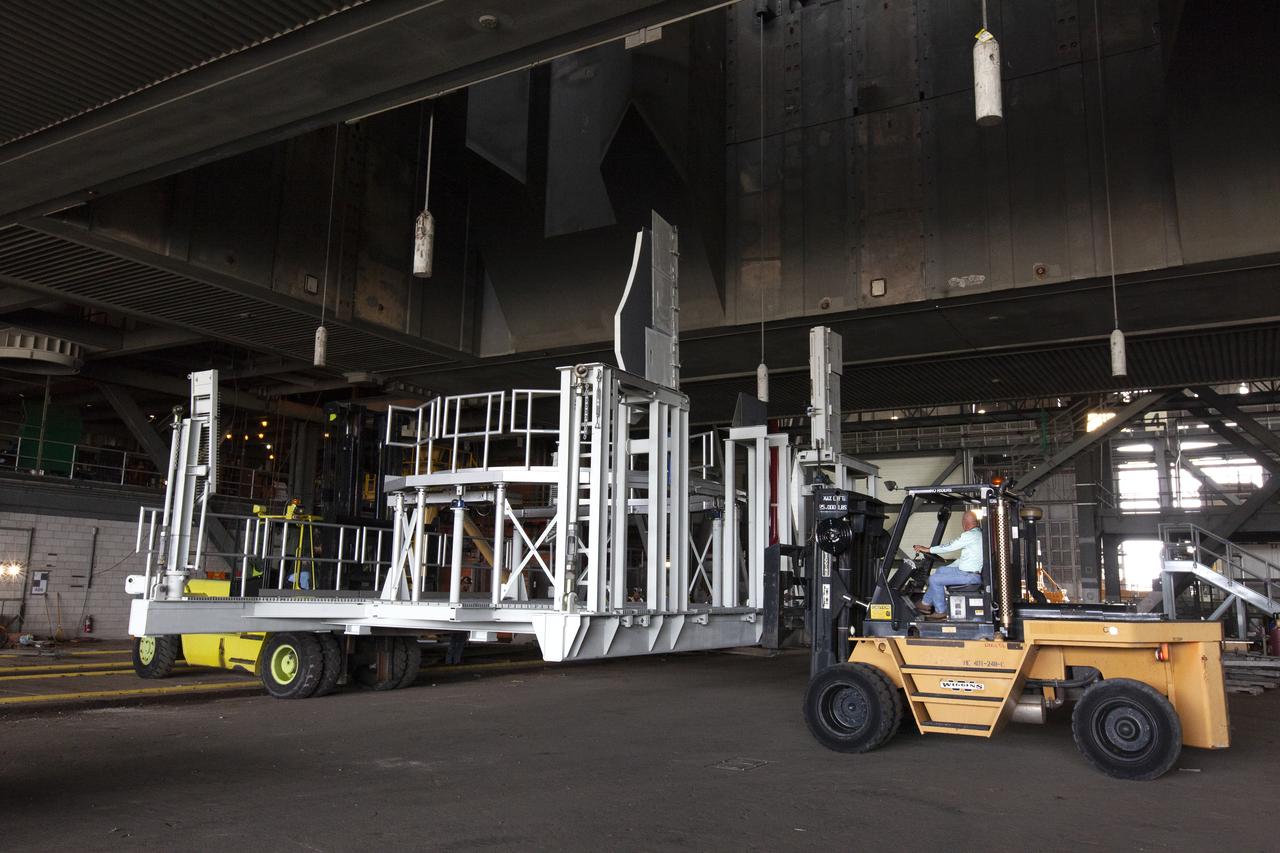
The engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket arrives in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 14, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
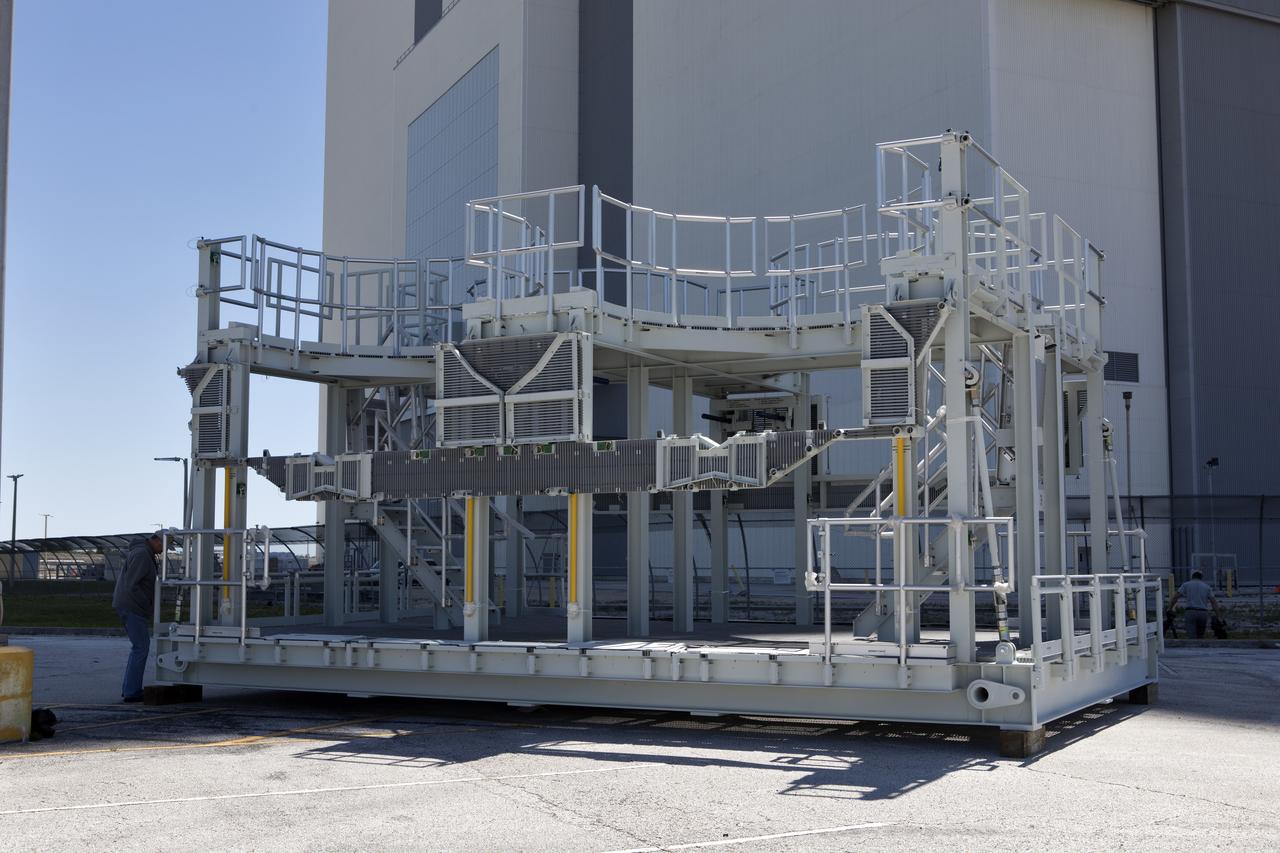

A new service platform for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines is being prepared for the move into the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platform was transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. It will be stored in the VAB, and used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1. EM-1 will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and bring it back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
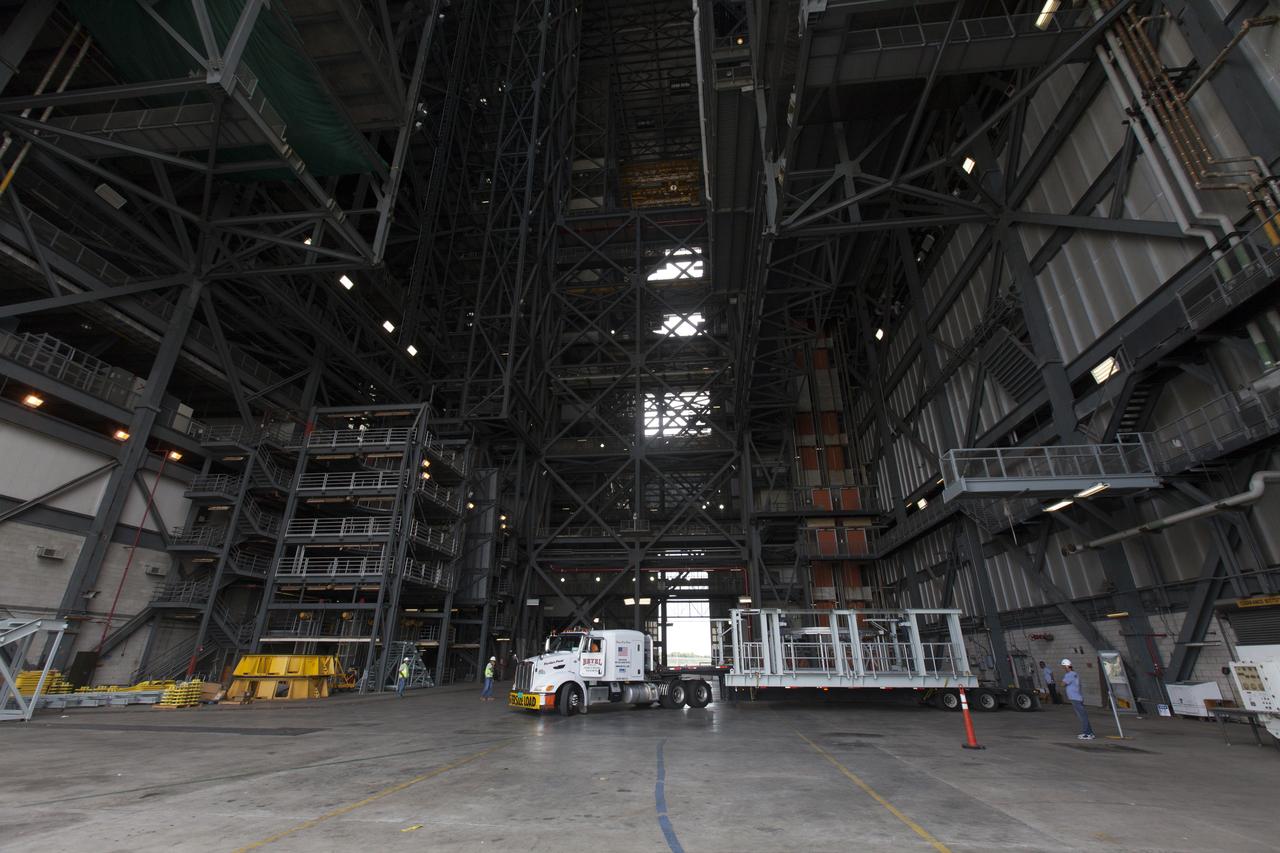

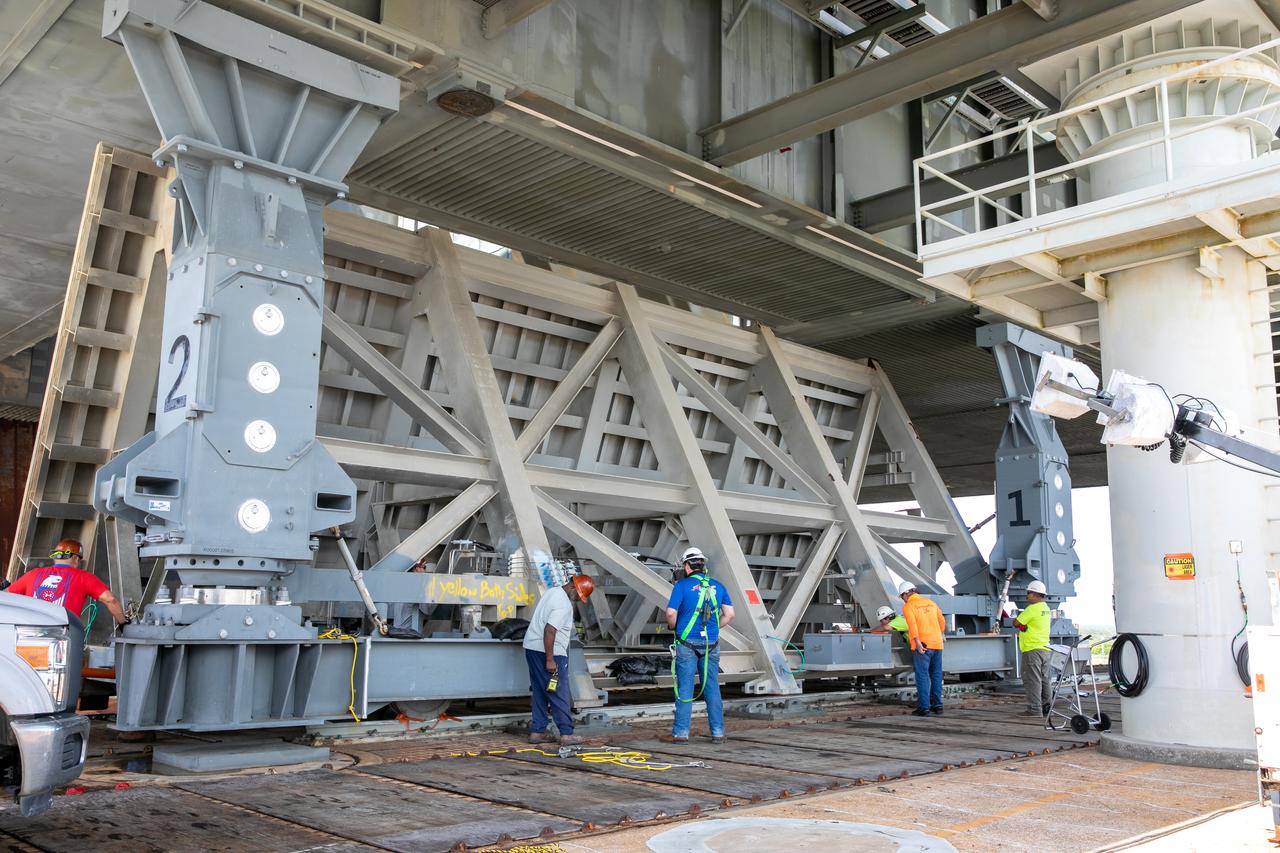
A flatbed truck carrying one of two new service platforms for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines arrives inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms were transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. They will be stored in the VAB, where they will be used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1. EM-1 will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and bring it back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.

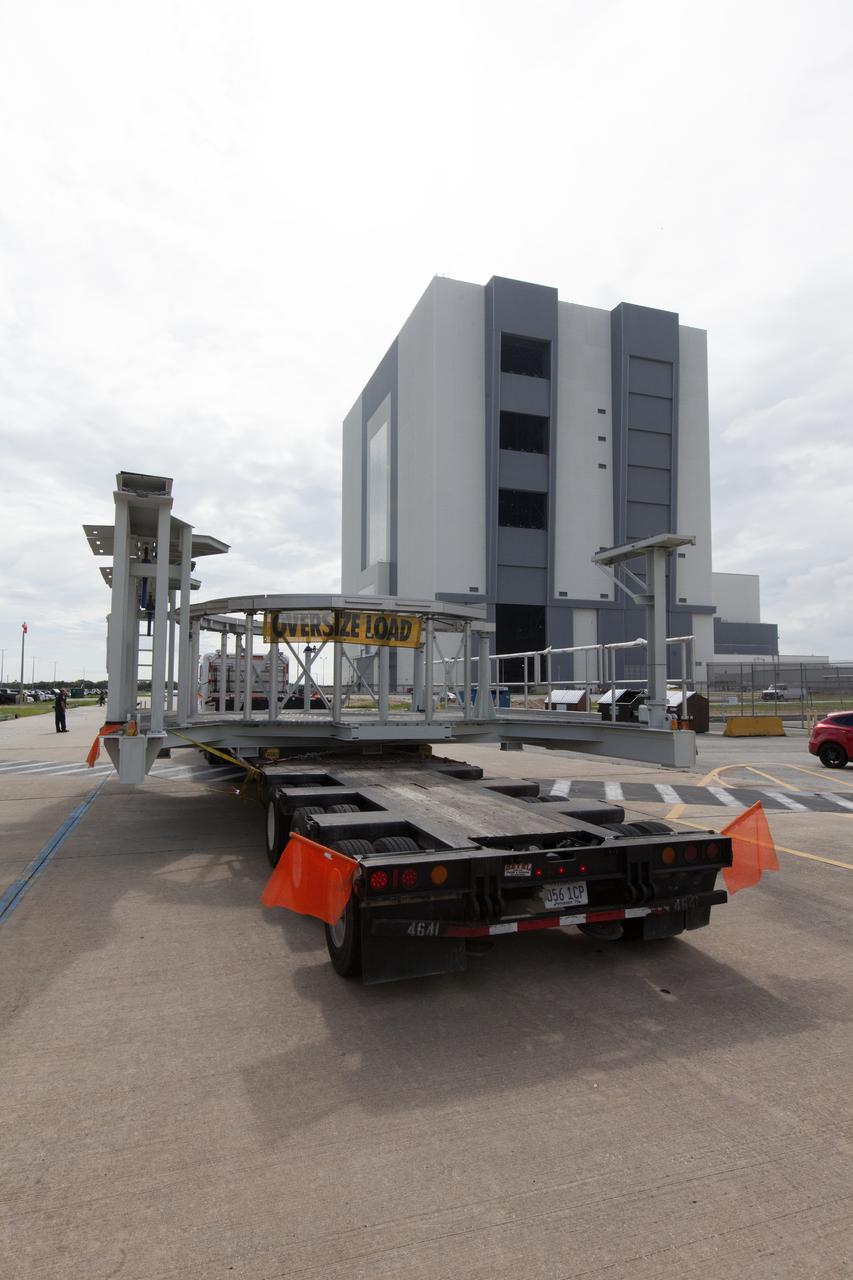
A new service platform for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines, secured on a flatbed truck, is on its way to the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It was transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. The platform will be delivered to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be stored and used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During EM-1, an uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch on the SLS to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and return to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.

A flatbed truck carrying one of two new service platforms for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines arrives at the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms were transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. They will be stored in the VAB, where they will be used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1. EM-1 will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and bring it back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
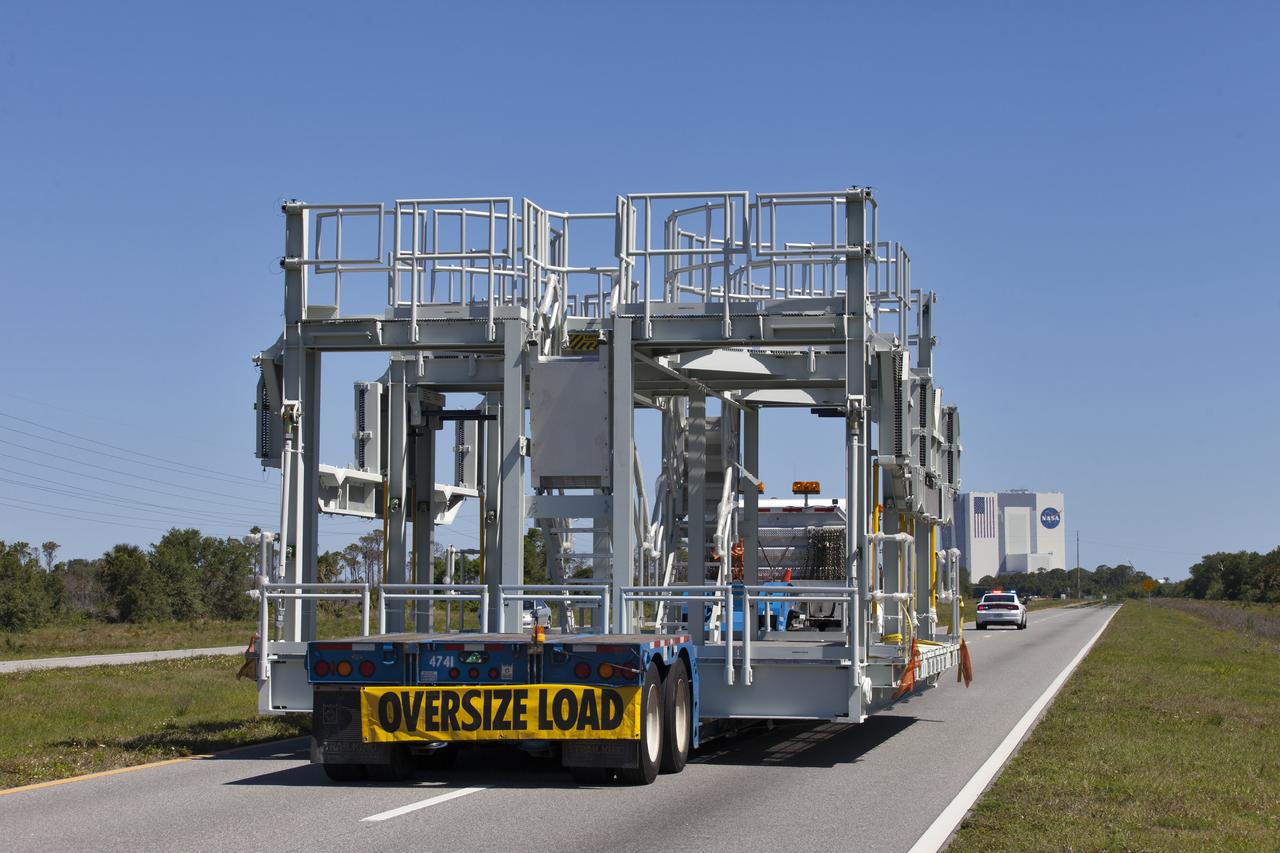

A new service platform for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines, secured on a flatbed truck, is on its way to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), in view in the distance, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It was transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. The platform will be delivered to the VAB, where it will be stored and used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During EM-1, an uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch on the SLS to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and return to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
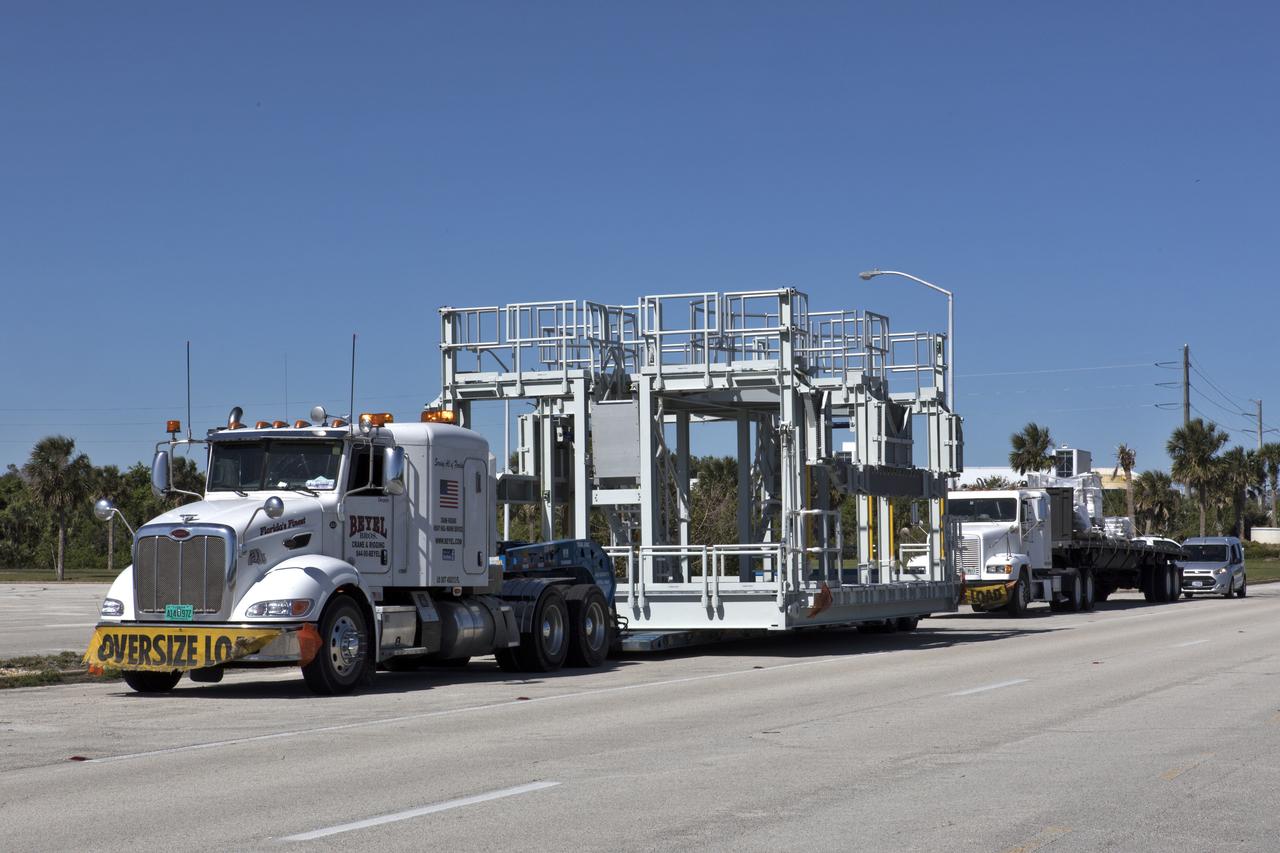

A new service platform for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines, secured on a flatbed truck, is on its way to the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It was transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. The platform will be delivered to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be stored and used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During EM-1, an uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch on the SLS to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and return to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
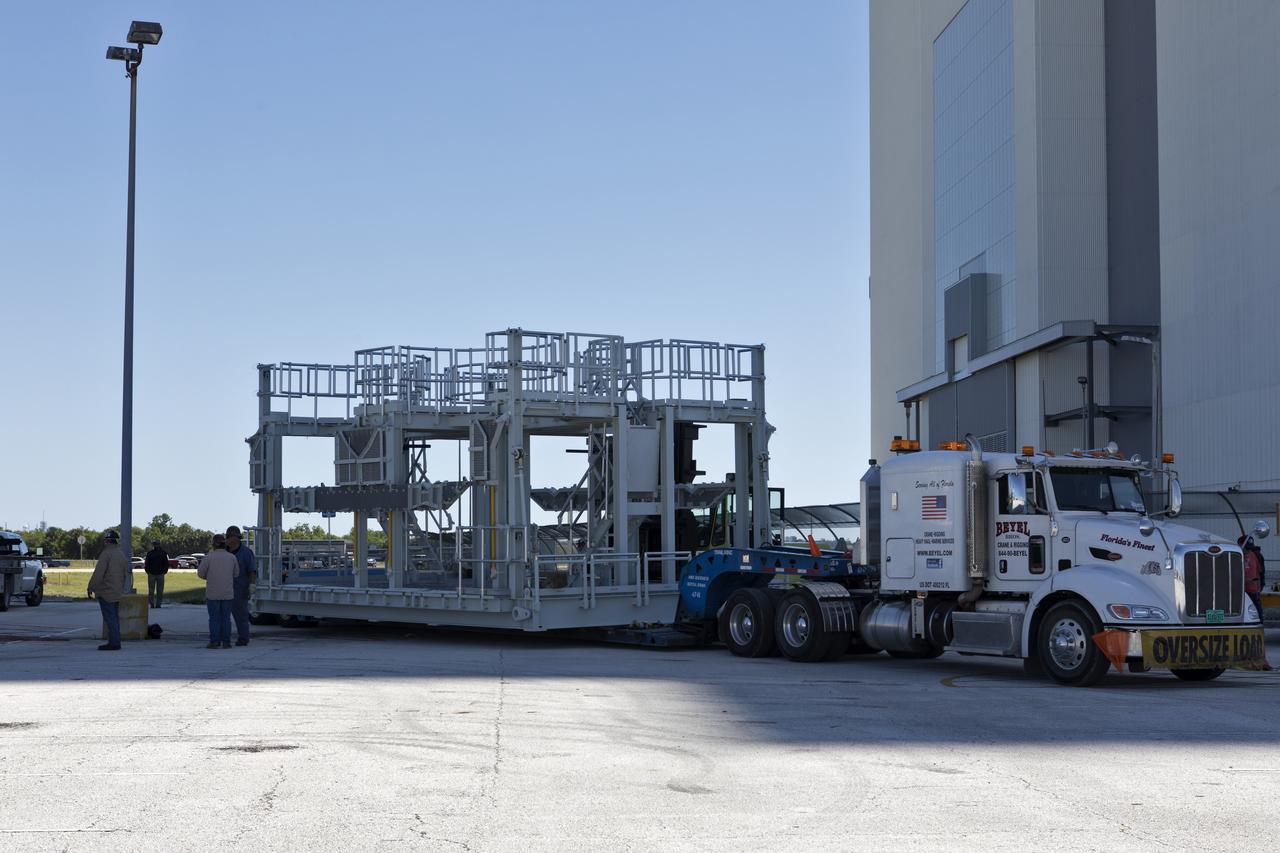

A new service platform for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines, secured on a flatbed truck, has arrived at the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It was transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. The platform will be stored in the VAB and used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During EM-1, an uncrewed Orion spacecraft will launch on the SLS to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and return to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
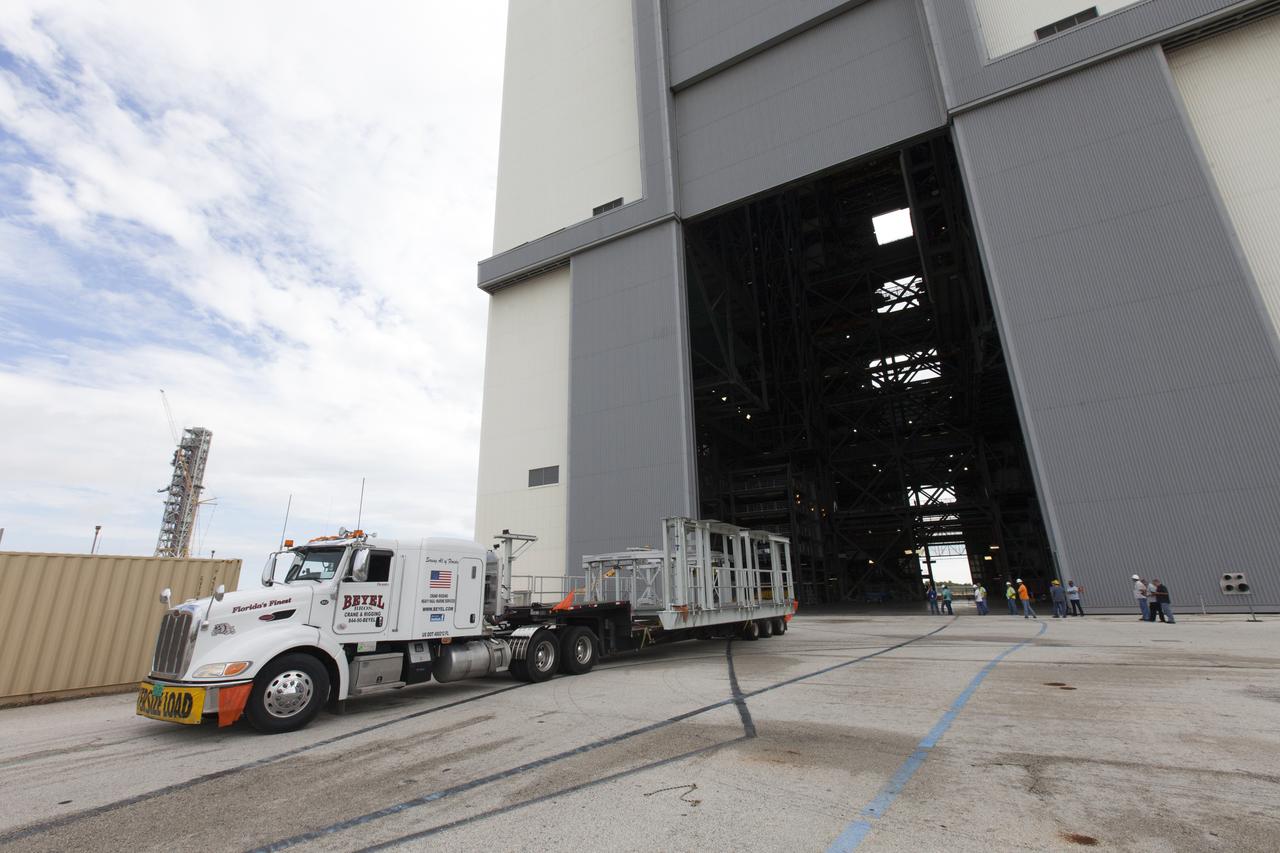

A flatbed truck carrying one of two new service platforms for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines backs in to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms were transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. They will be stored in the VAB, where they will be used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1. EM-1 will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and bring it back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
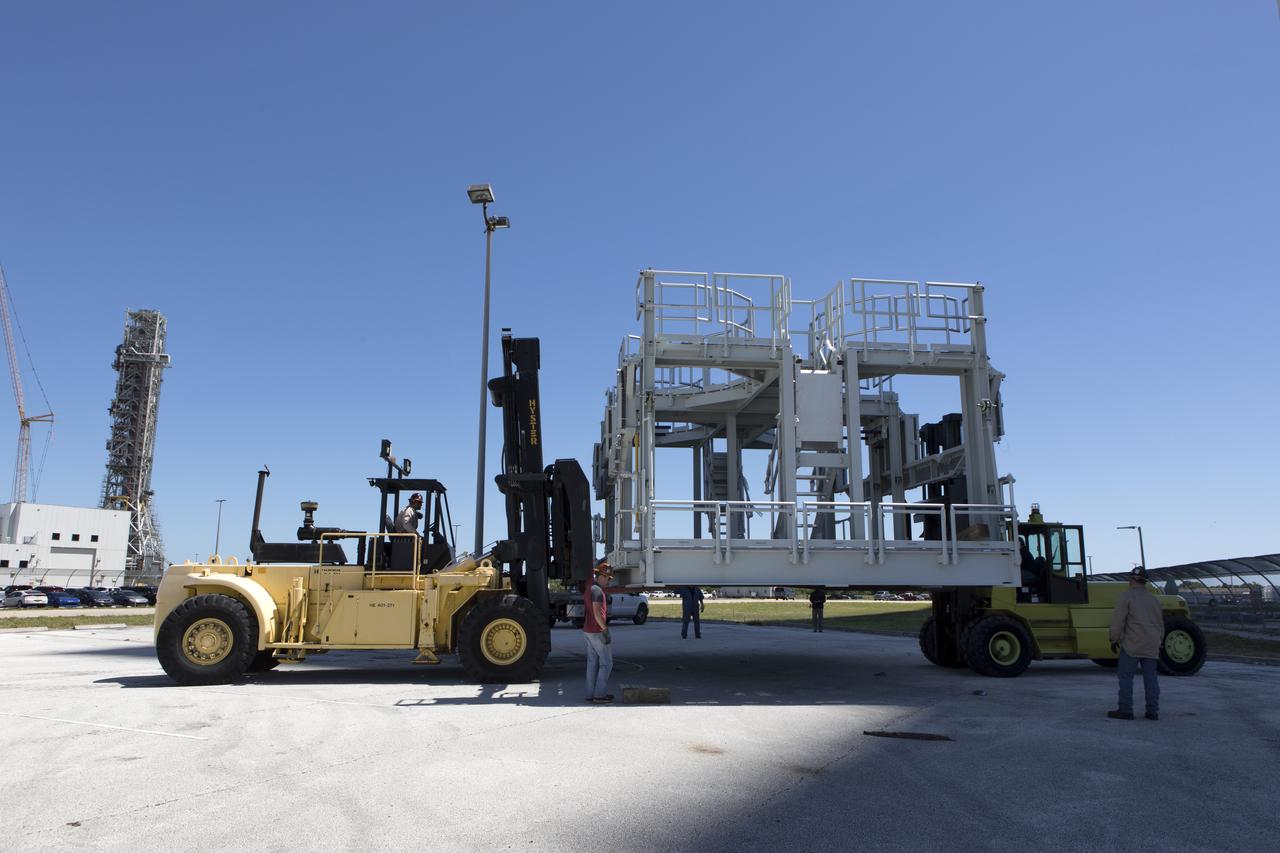

A new service platform for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines has been offloaded from a flatbed truck and is being prepared for the move into the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platform was transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. It will be stored in the VAB, and used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1. EM-1 will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and bring it back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
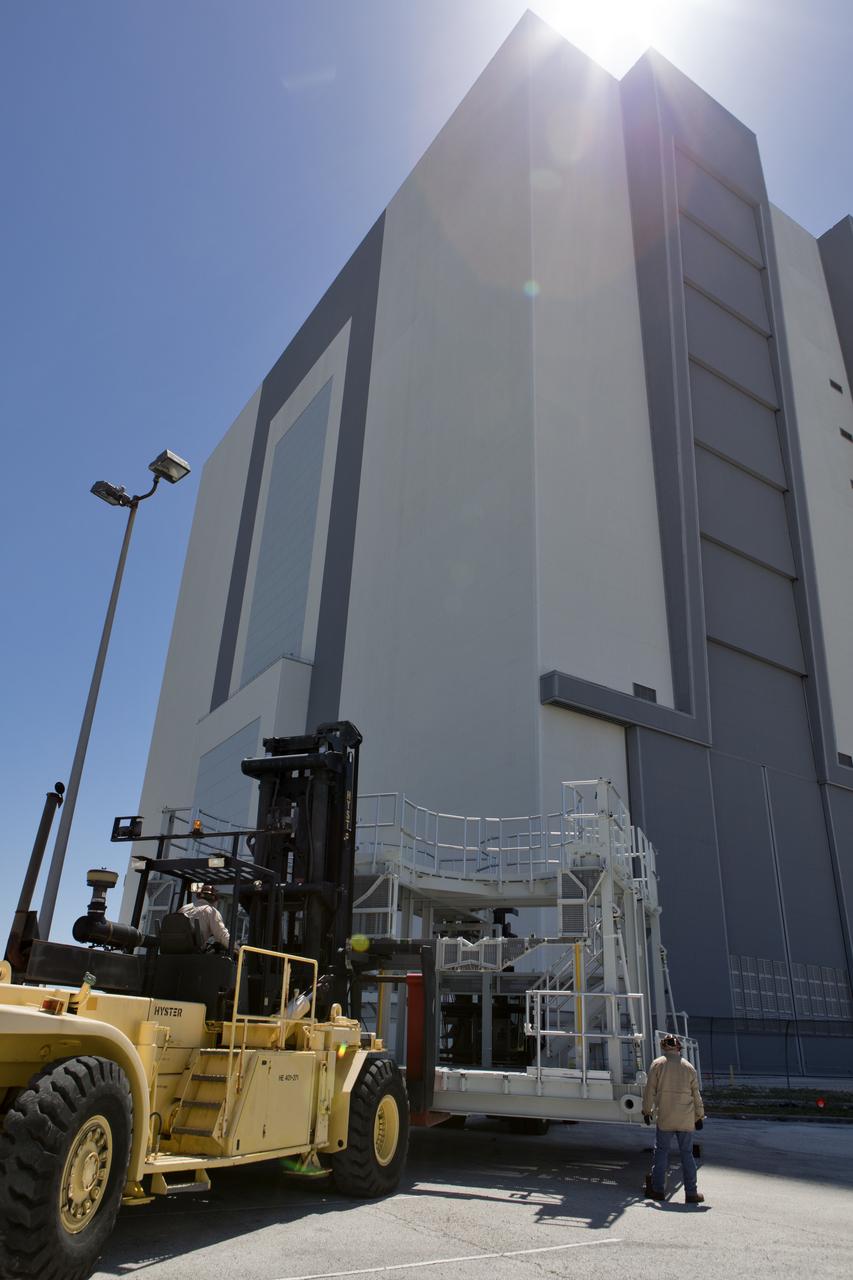

A new service platform for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines has been offloaded from a flatbed truck and is being prepared for the move into the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platform was transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. It will be stored in the VAB, and used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1. EM-1 will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and bring it back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
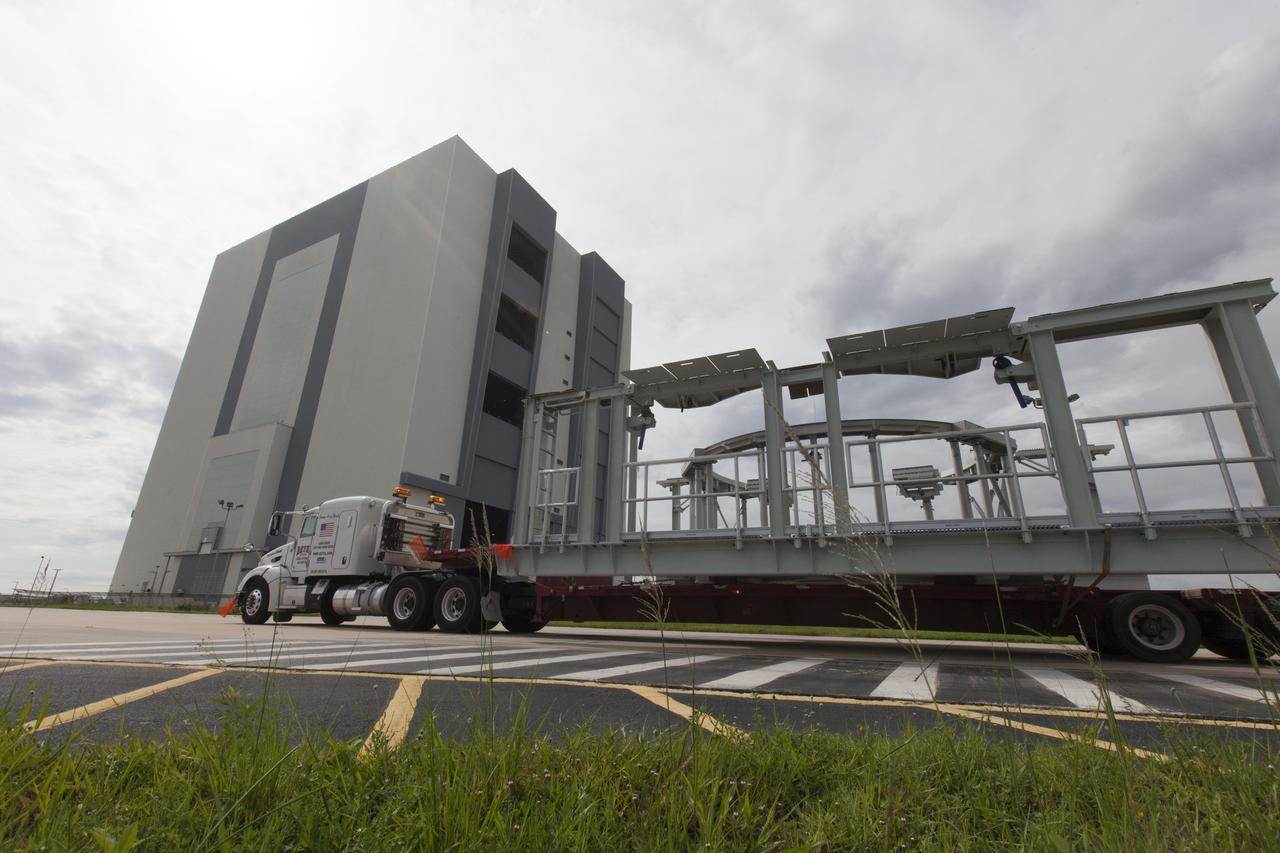

A flatbed truck carrying one of two new service platforms for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines arrives at the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms were transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. They will be stored in the VAB, where they will be used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1. EM-1 will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and bring it back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
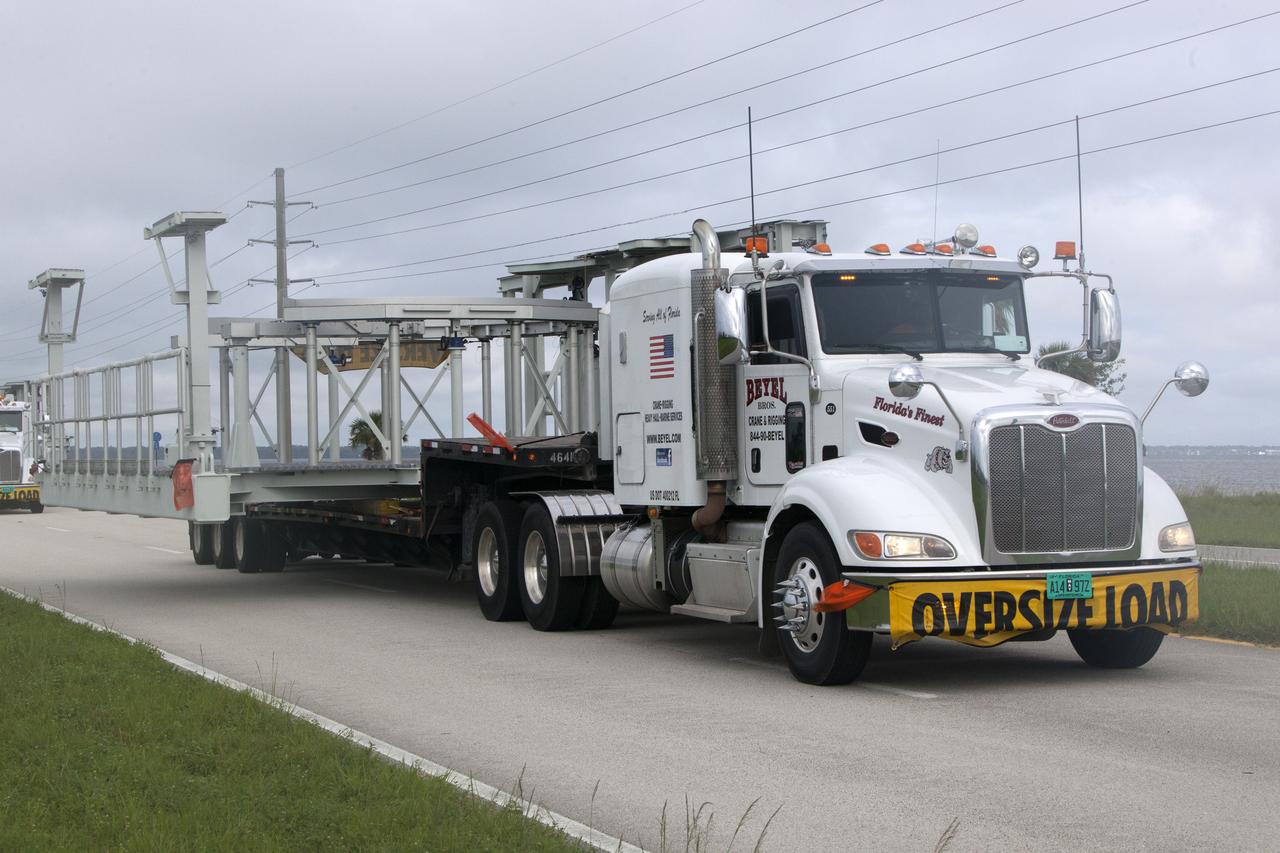

A flatbed truck carrying one of two new service platforms for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines makes its way along the NASA Causeway to the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms were transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. They will be delivered to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where they will be stored and used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1. EM-1 will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and bring it back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
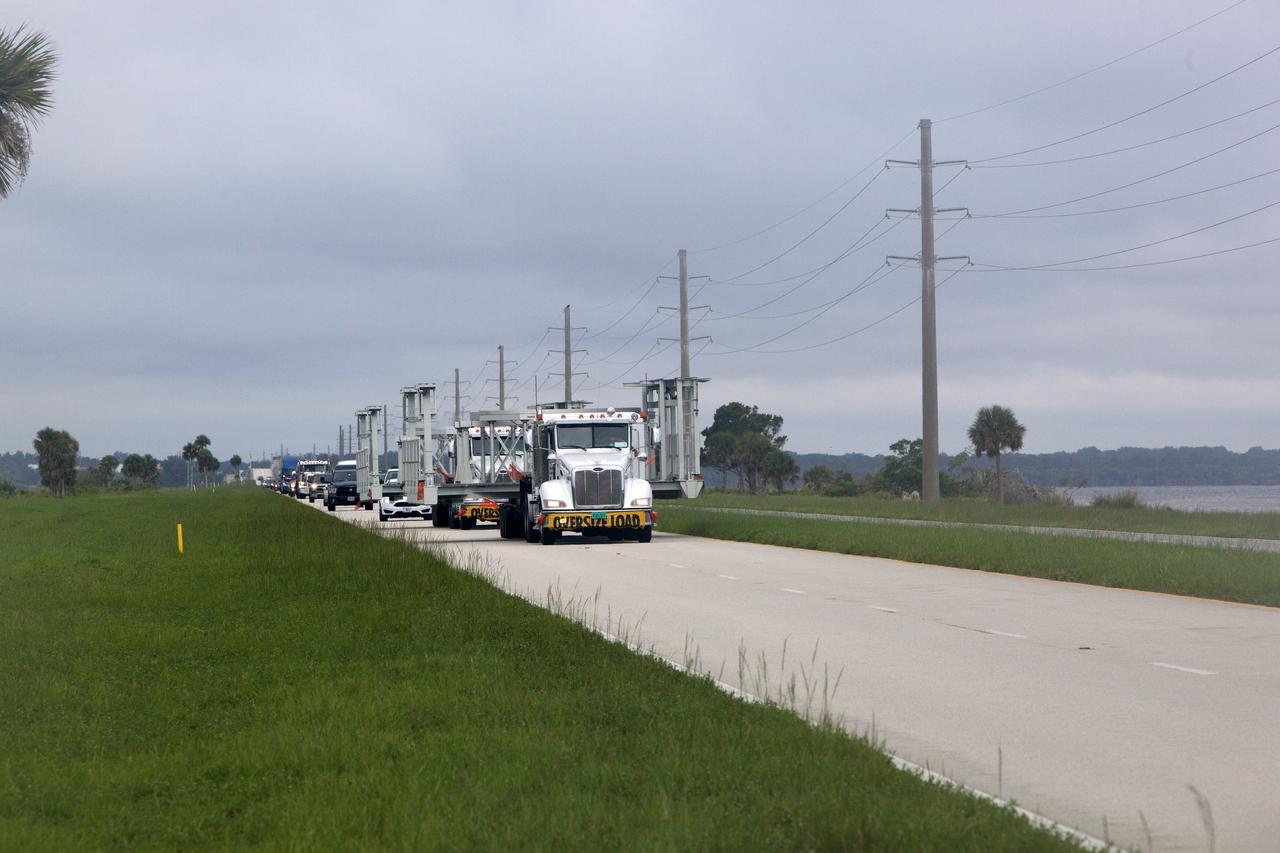

New service platforms for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines, secured on two flatbed trucks, are on their way to the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. They are being transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. The platforms will be delivered to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where they will be stored and used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1. EM-1 will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and bring it back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.

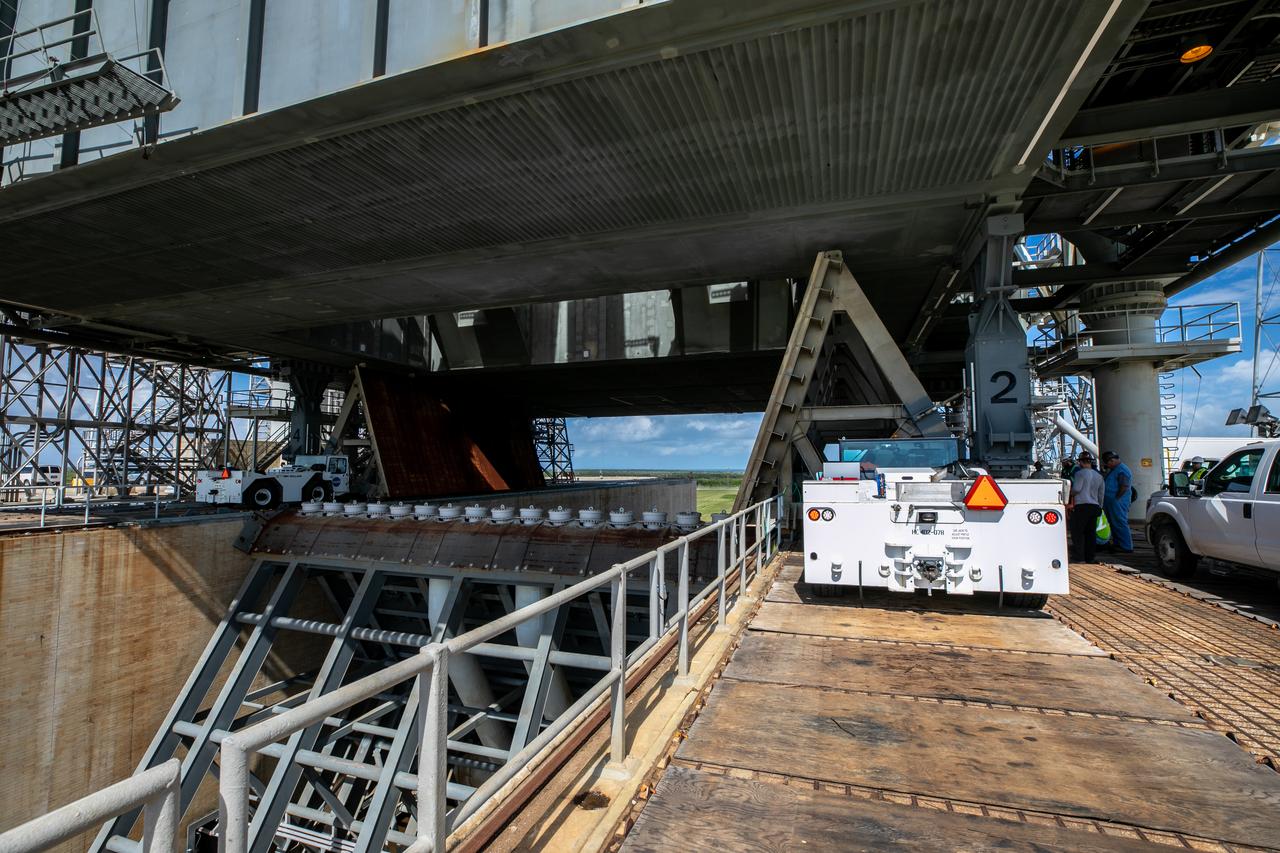
A flatbed truck carrying one of two new service platforms for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines backs up inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms were transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. They will be stored in the VAB, where they will be used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1. EM-1 will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and bring it back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
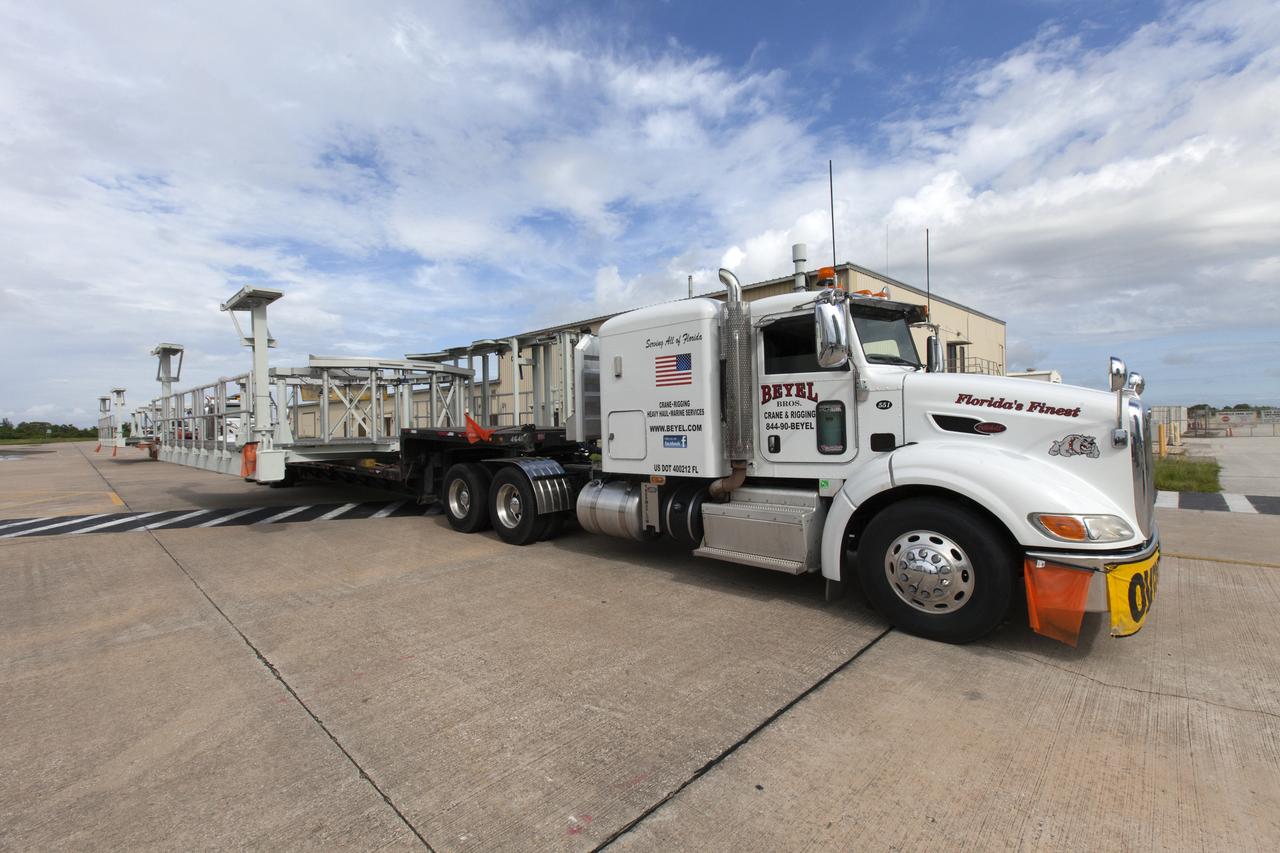

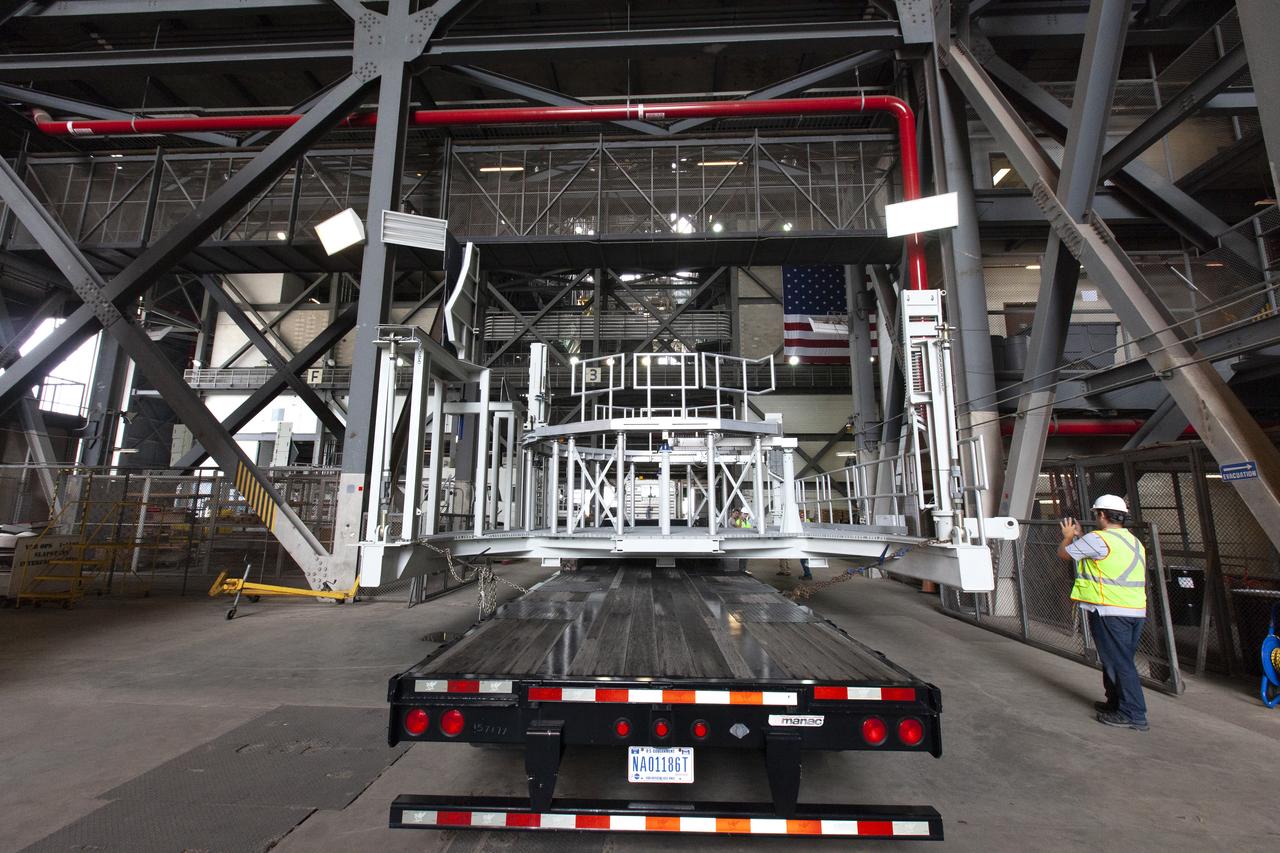
A flatbed truck carrying one of two new service platforms for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines nears the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms were transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. They will be delivered to the VAB, where they will be stored and used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1. EM-1 will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and bring it back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
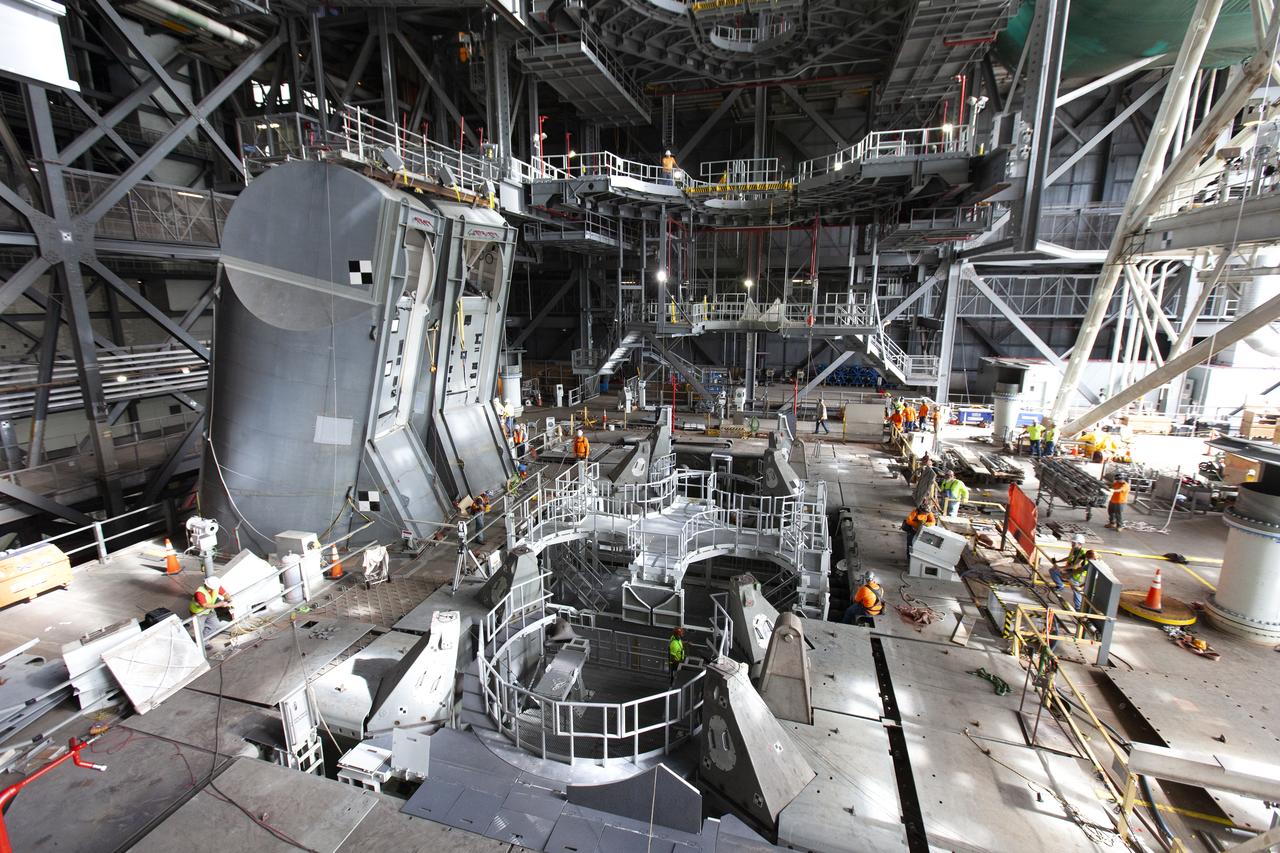
Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is lifted up in the center of the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. In view at left are the two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals. They will provide liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen fluid lines and electrical cable connections to the SLS core stage engine section. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
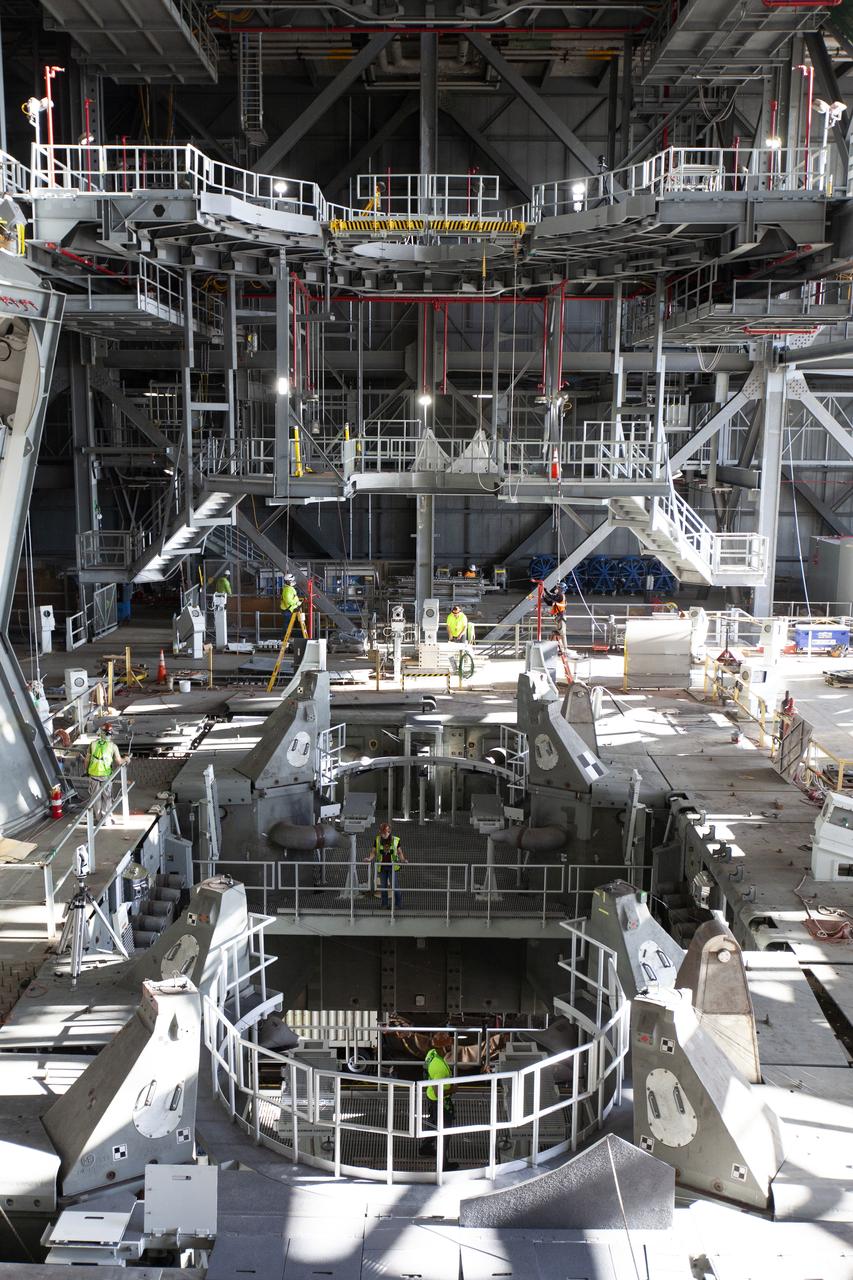

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is lifted up in the center of the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
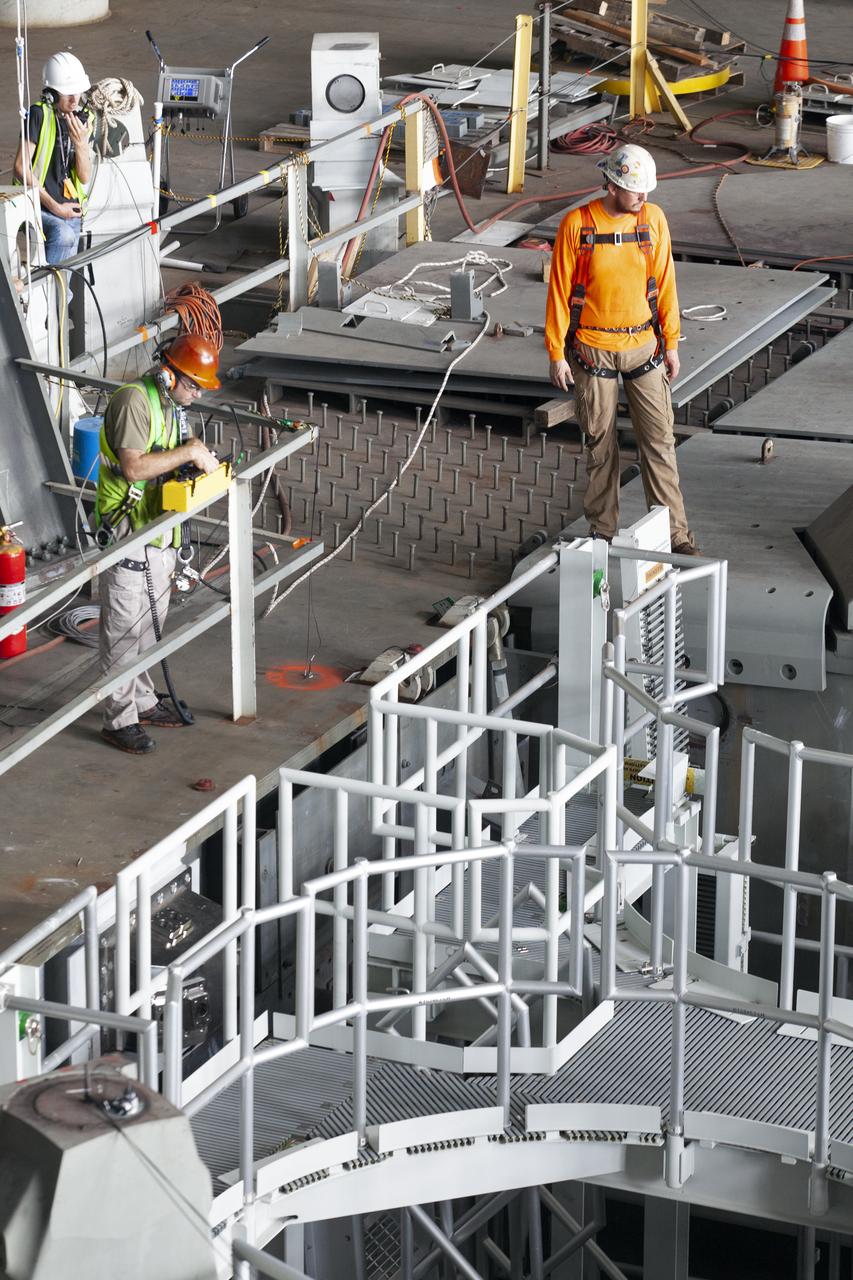

Workers with Bragg Crane and Rigging prepare for the lift of the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the mobile (ML) in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
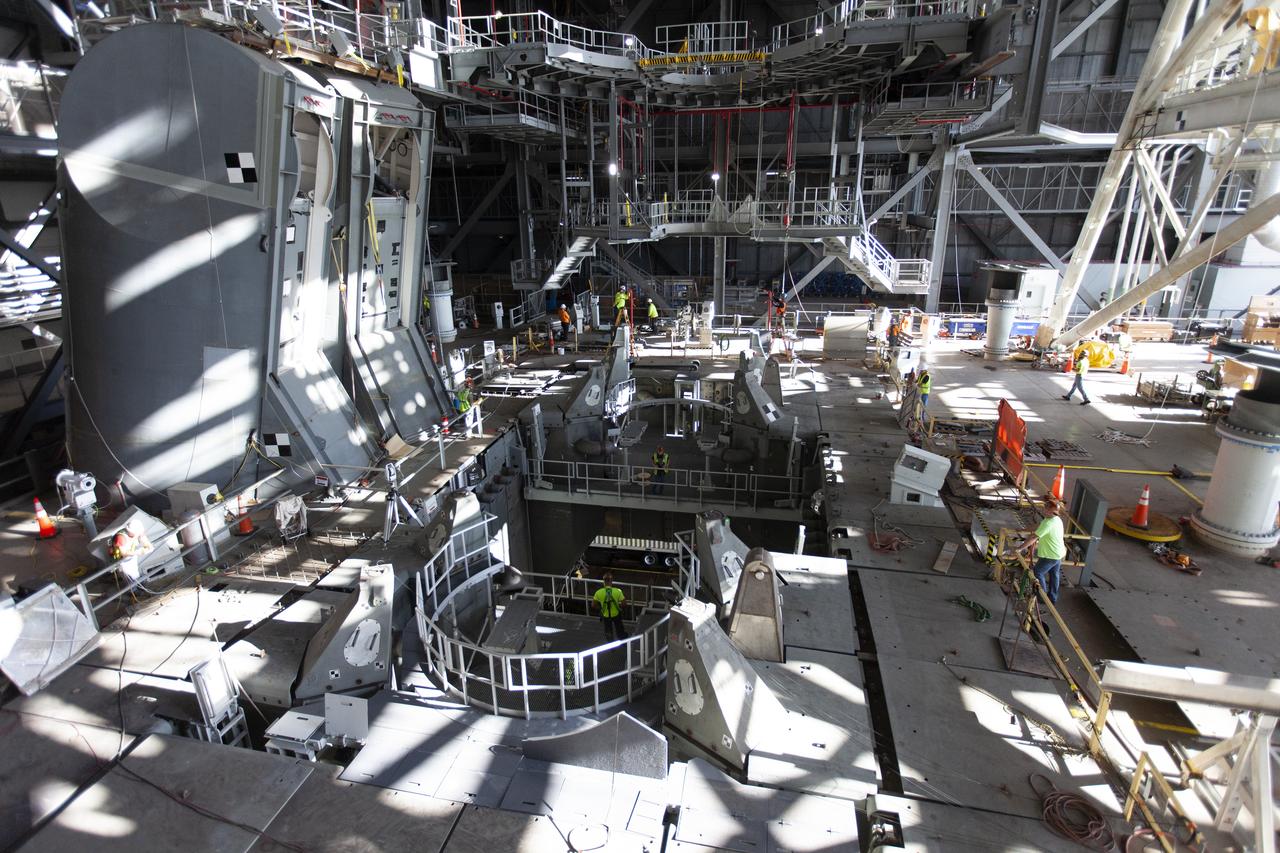

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is lifted up in the center of the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
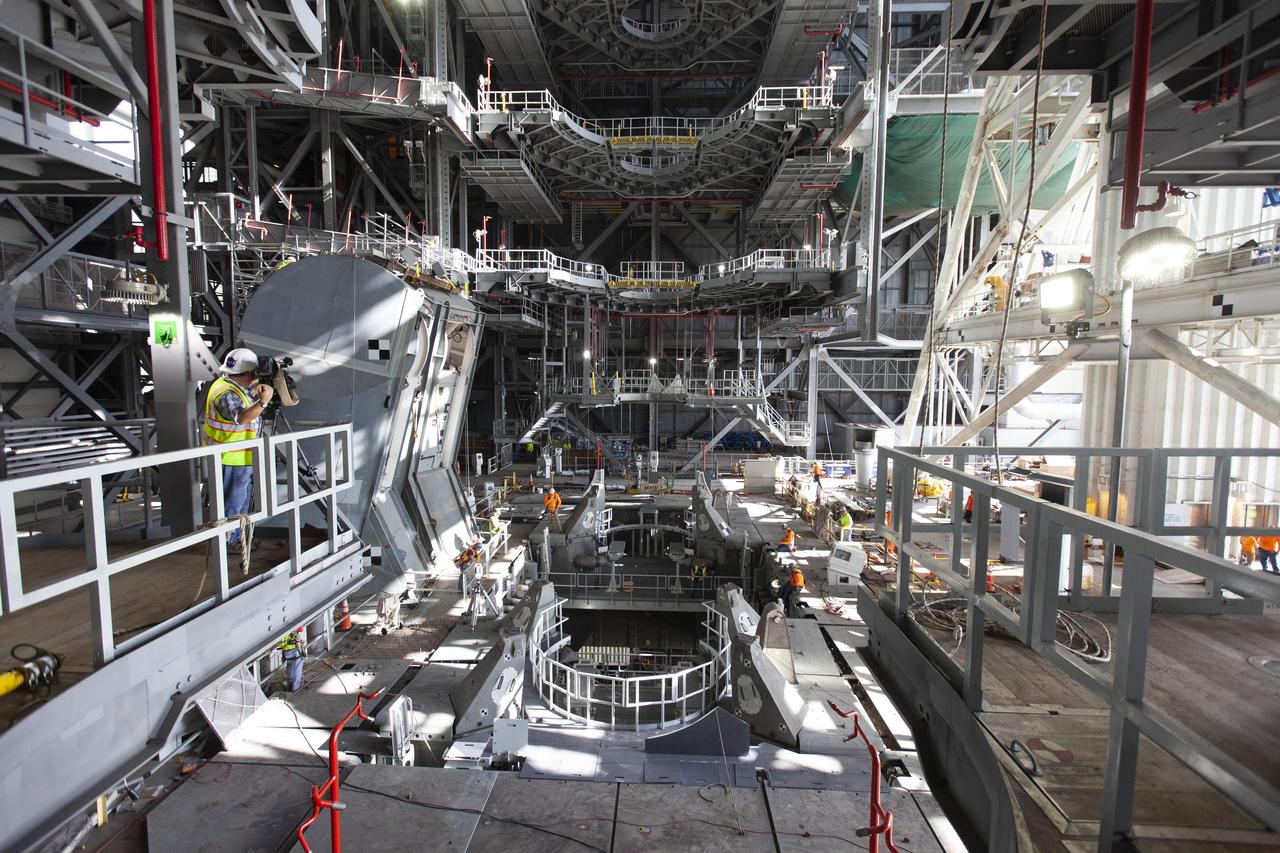
Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is lifted up in the center of the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
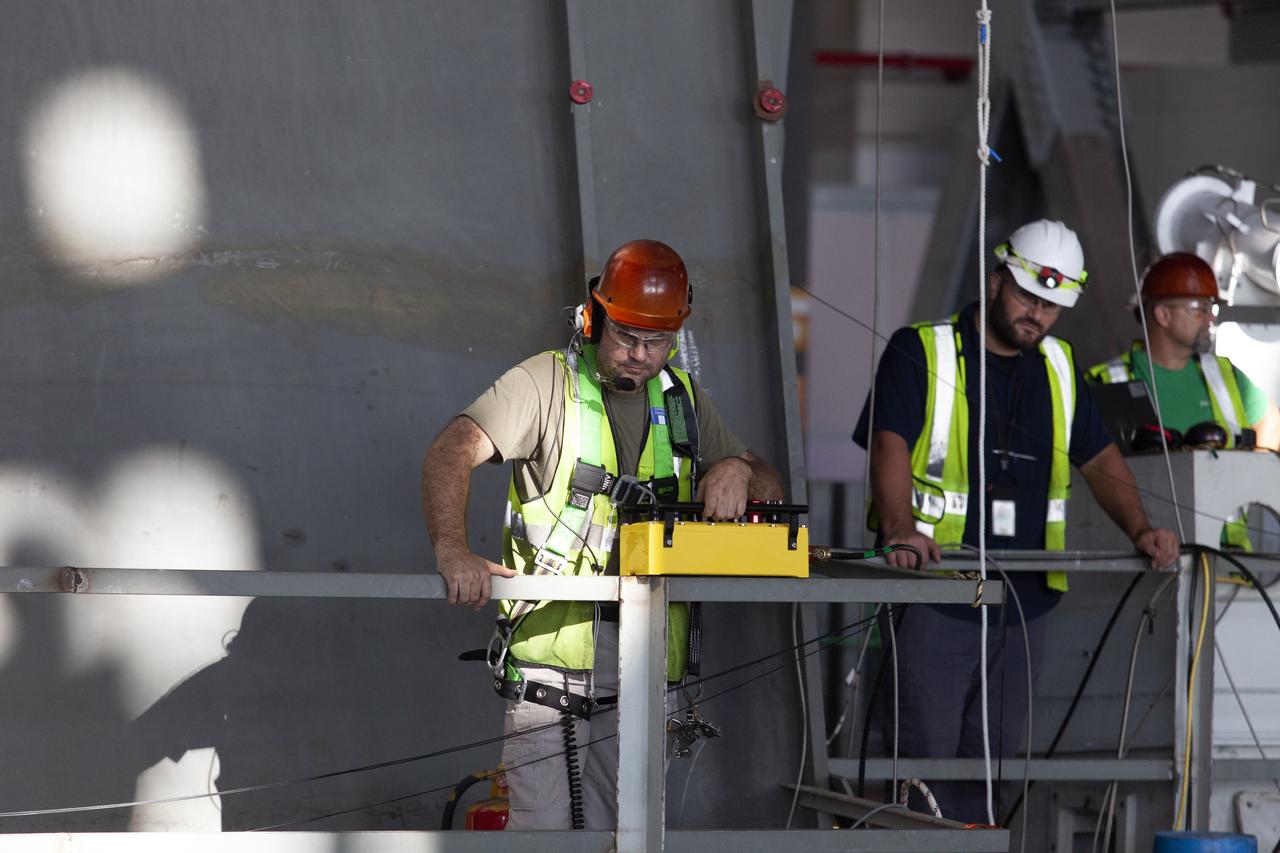

Jacobs TOSC workers prepare for the lift of the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
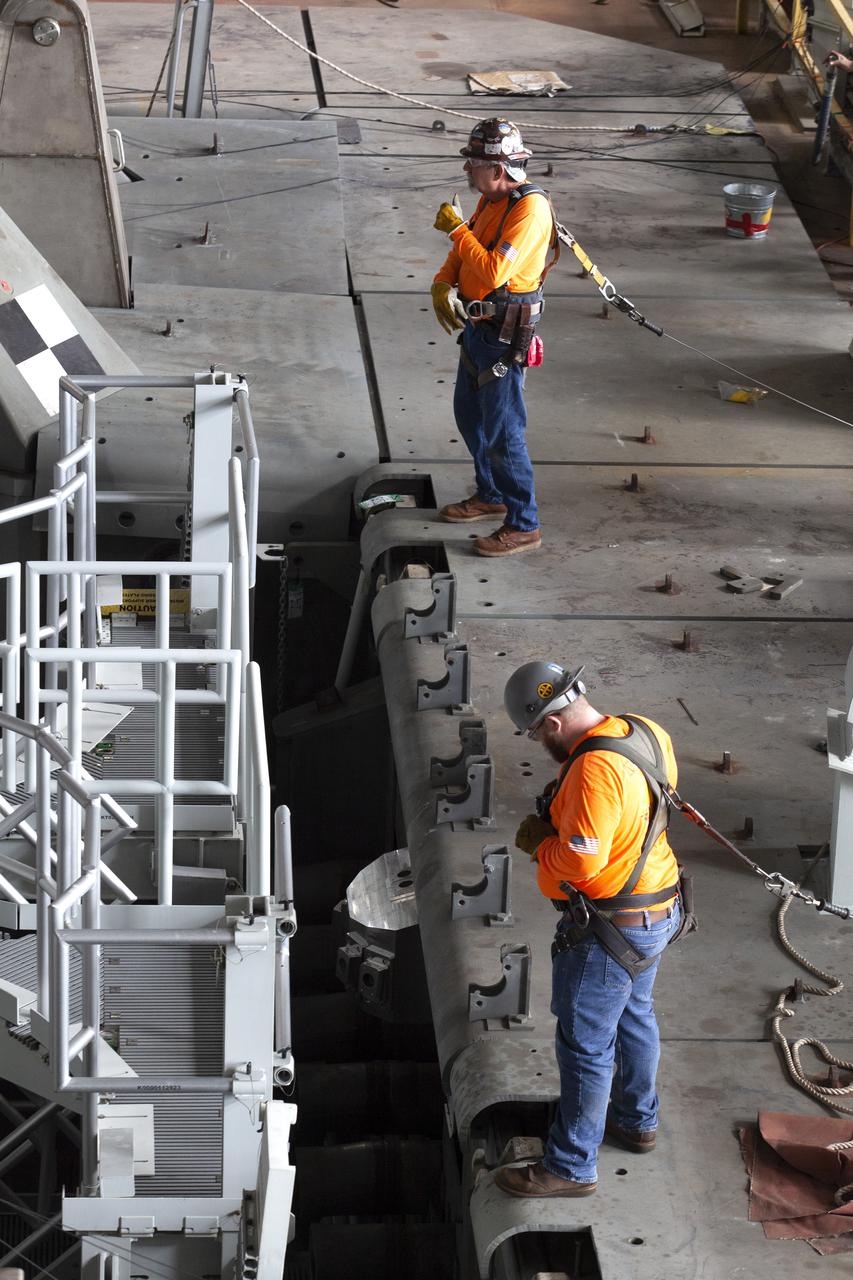

Workers with Bragg Crane and Rigging prepare to assist with the lift of the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the mobile (ML) in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
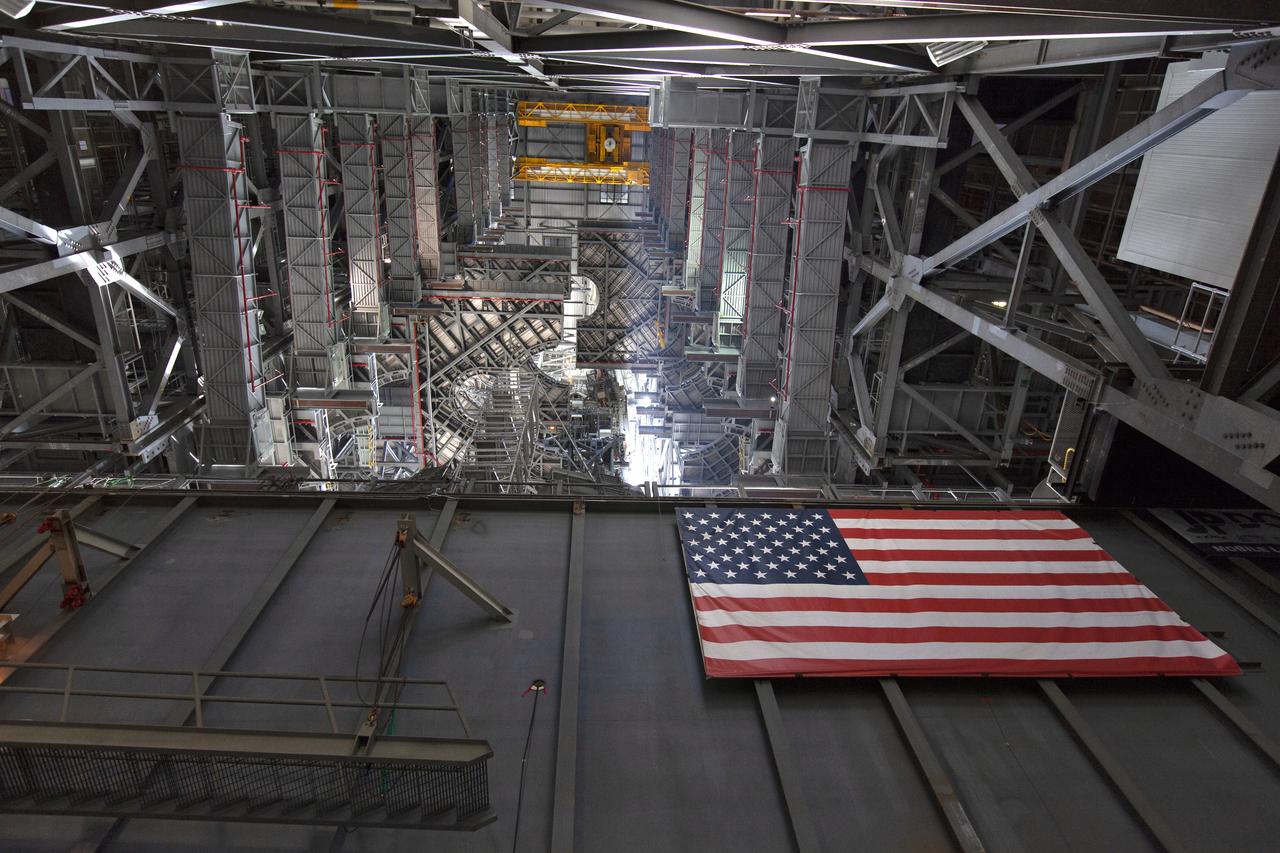

A view looking up at the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 18, 2019. Work is underway to lift the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in the center of the ML. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
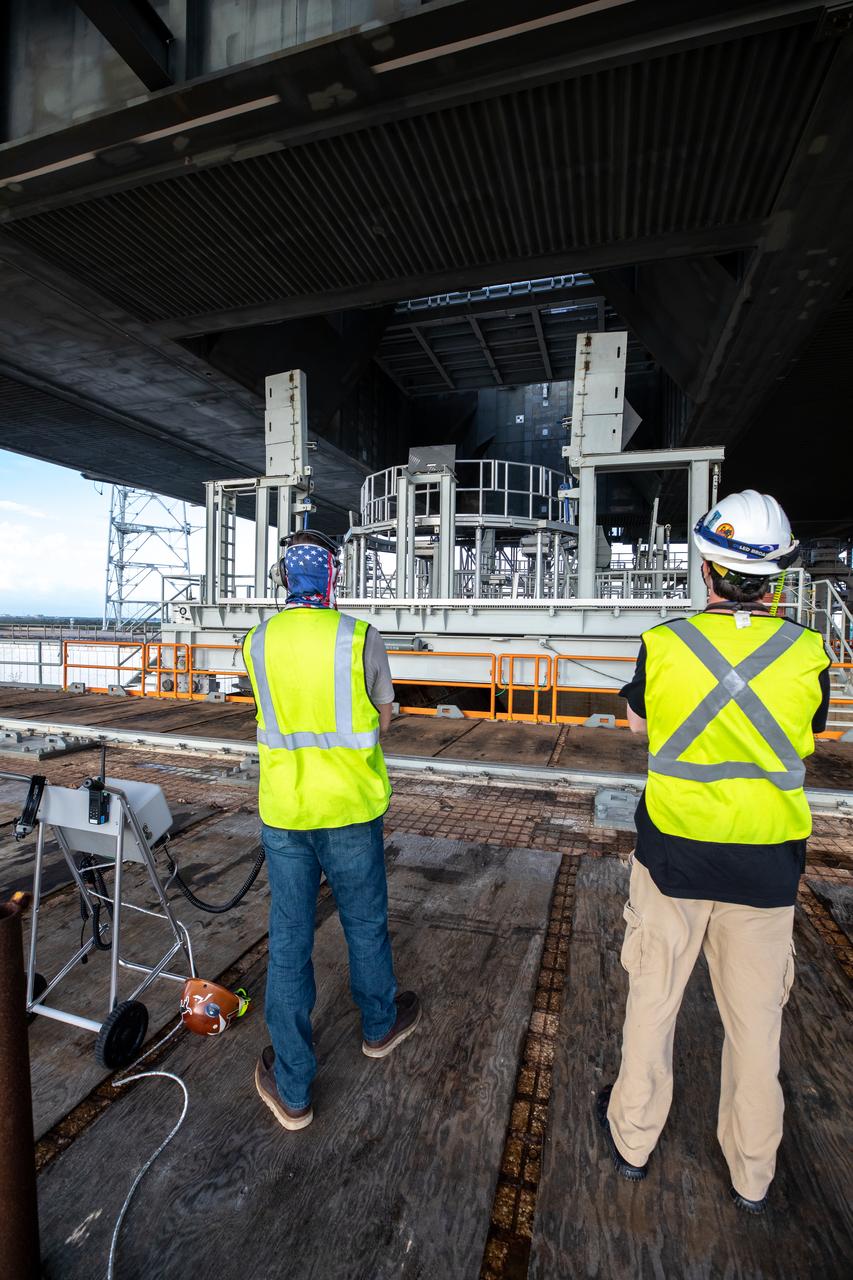

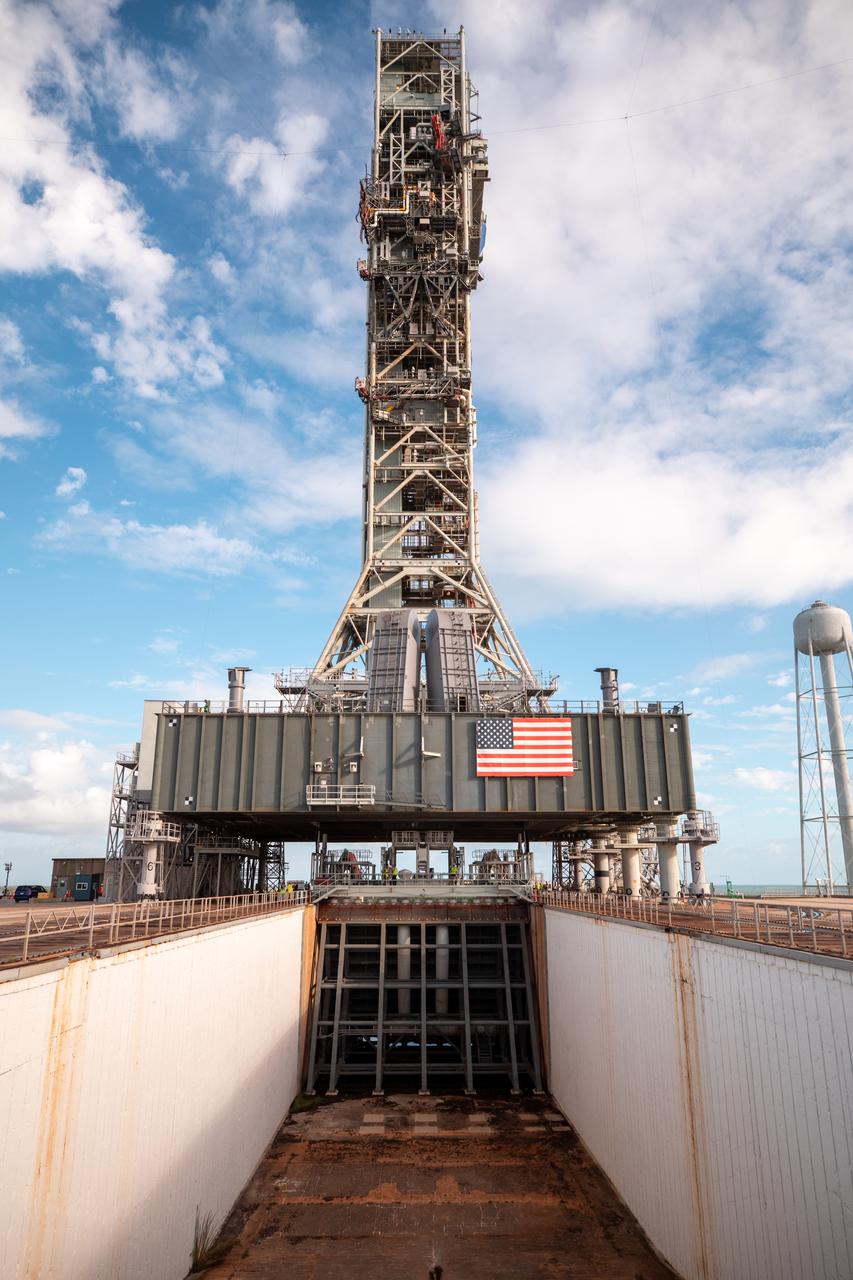
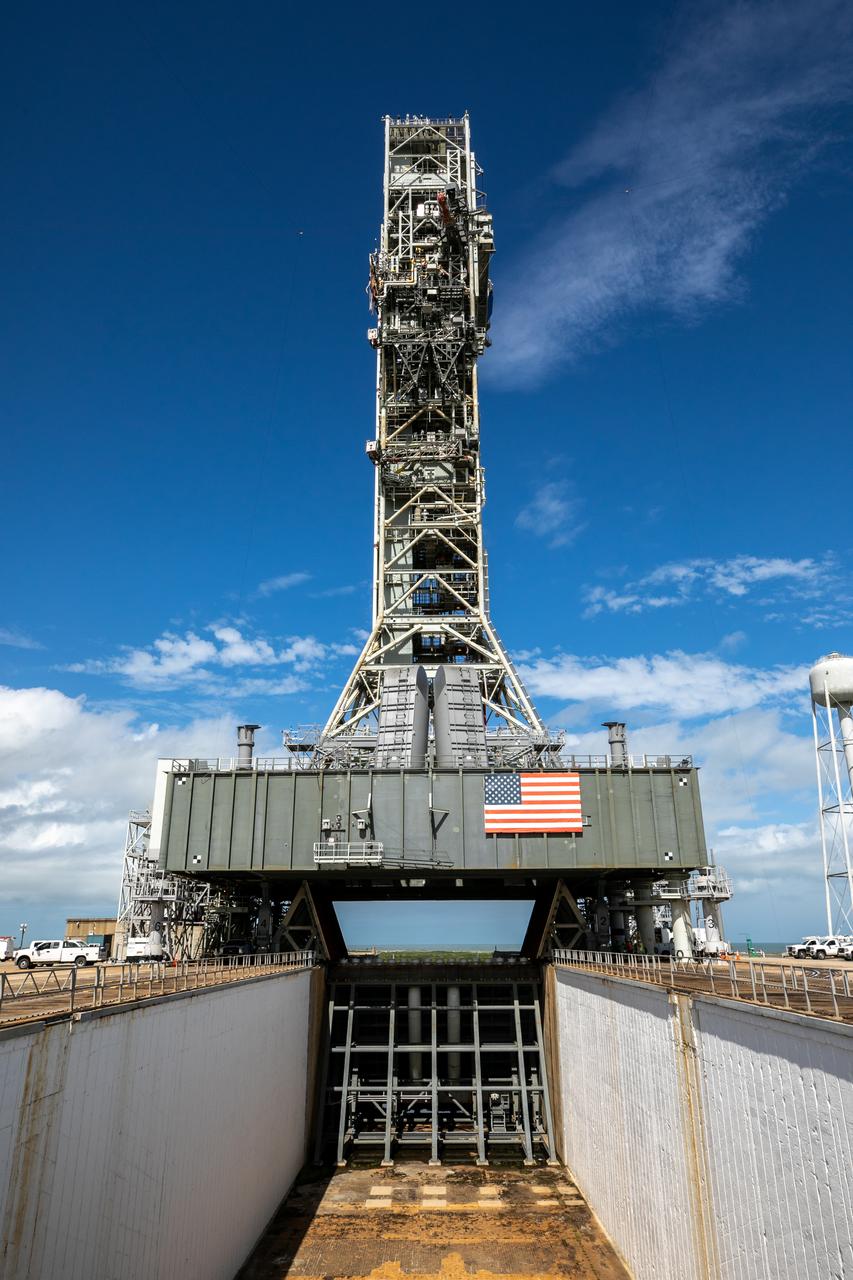
The engine service platform is moved into position beneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B on Oct. 23, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The service platform allows access to the RS-25 engines on the Space Launch System core stage for routine work or inspections. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher will remain at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs will complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
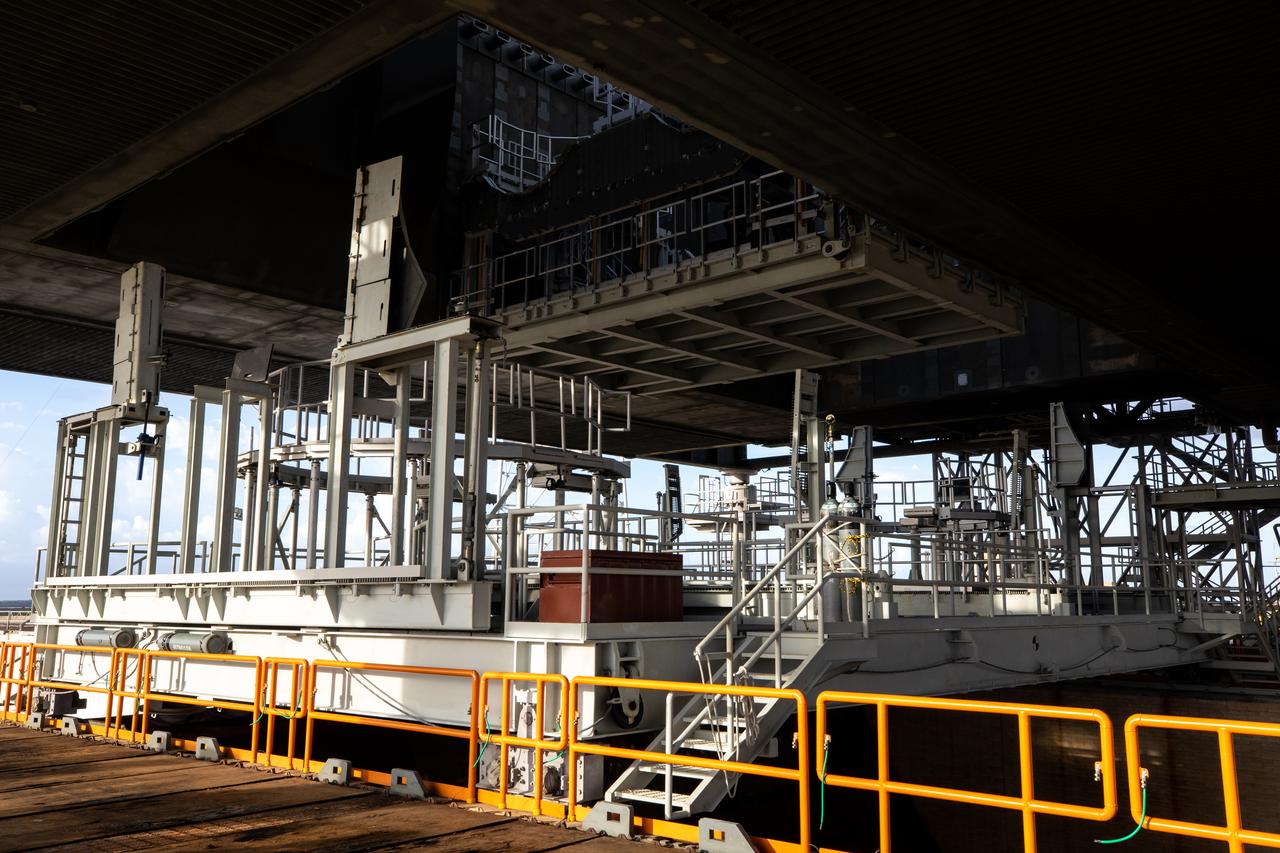

The engine service platform is moved into position beneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B on Oct. 23, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The service platform allows access to the RS-25 engines on the Space Launch System core stage for routine work or inspections. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher will remain at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
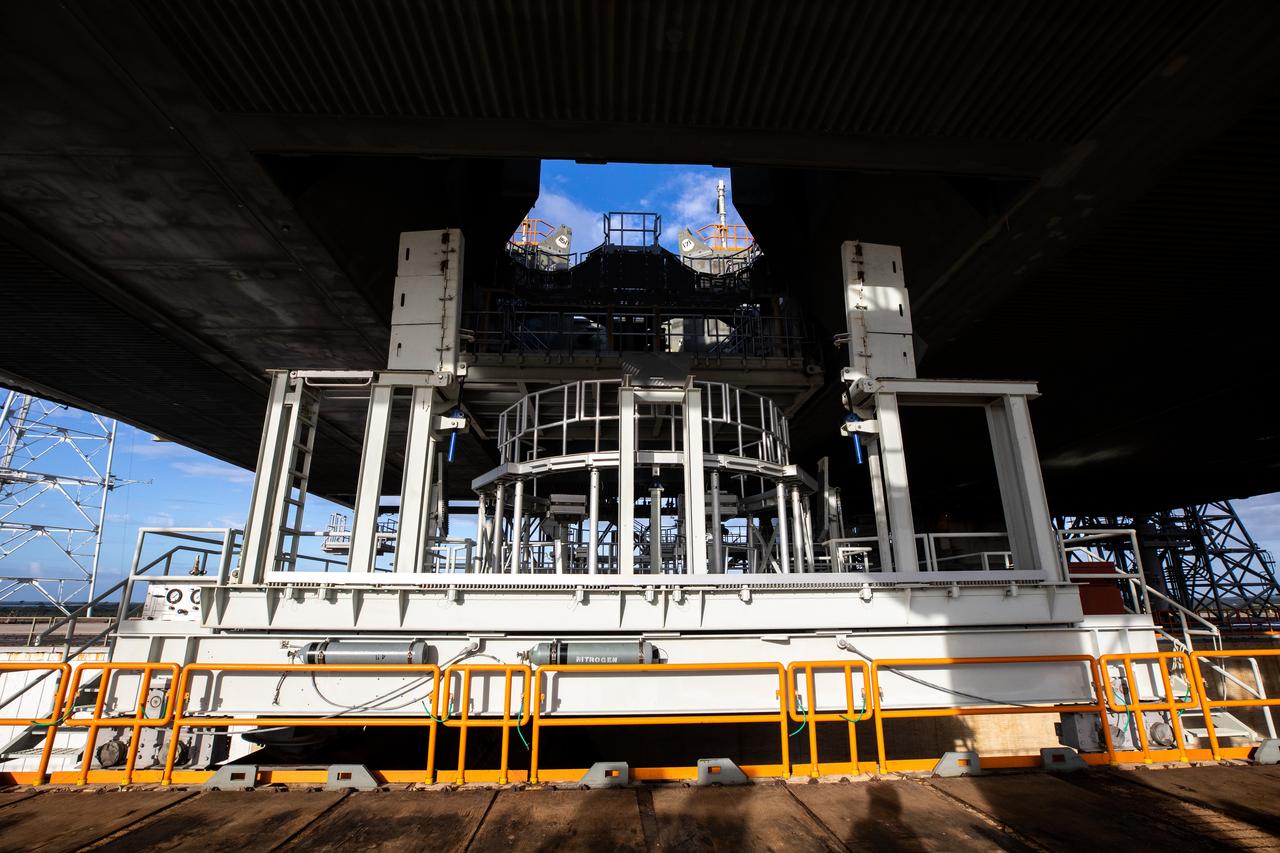

The engine service platform is moved into position beneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B on Oct. 23, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The service platform allows access to the RS-25 engines on the Space Launch System core stage for routine work or inspections. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher will remain at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs will complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
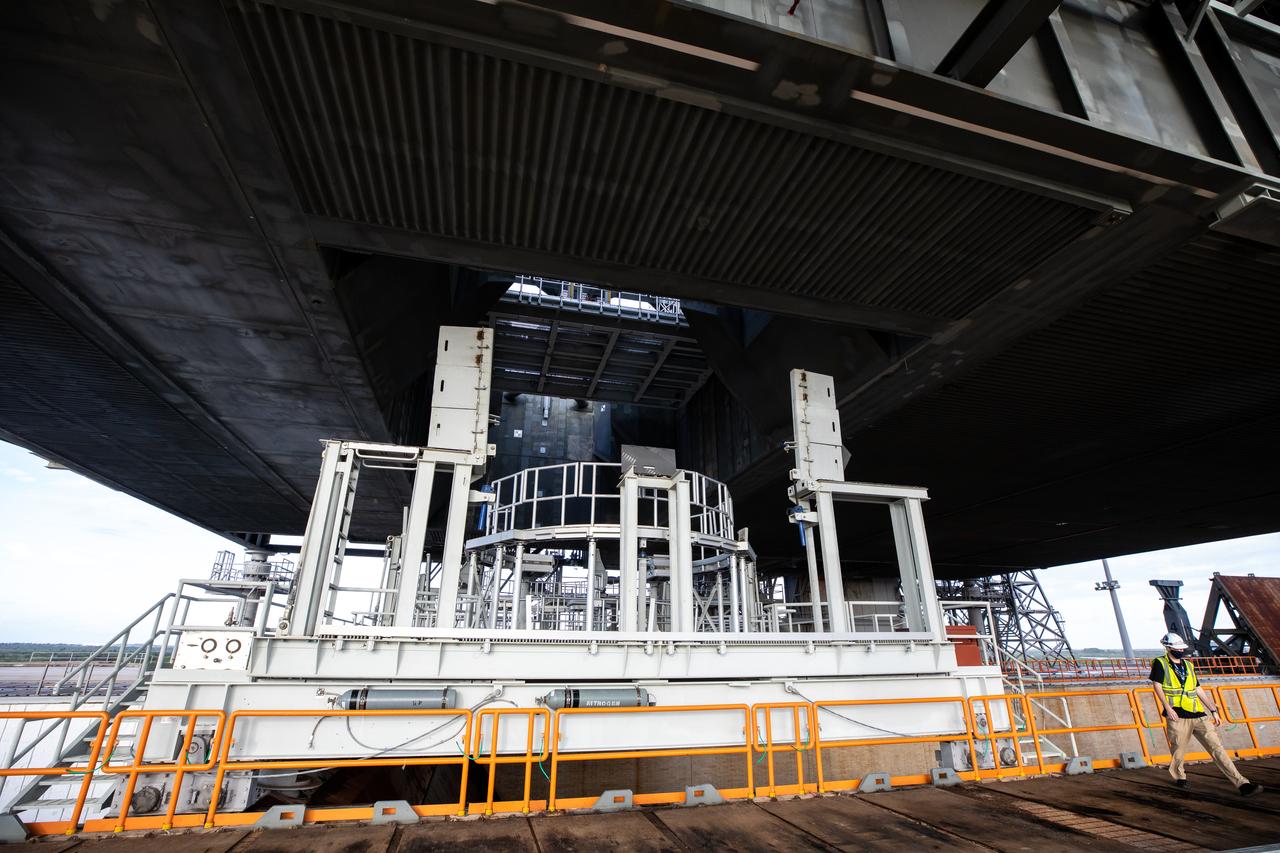

The engine service platform is moved into position beneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B on Oct. 23, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The service platform allows access to the RS-25 engines on the Space Launch System core stage for routine work or inspections. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher will remain at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

The engine service platform has been lowered and removed from the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The platform is in view on a flatbed truck. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
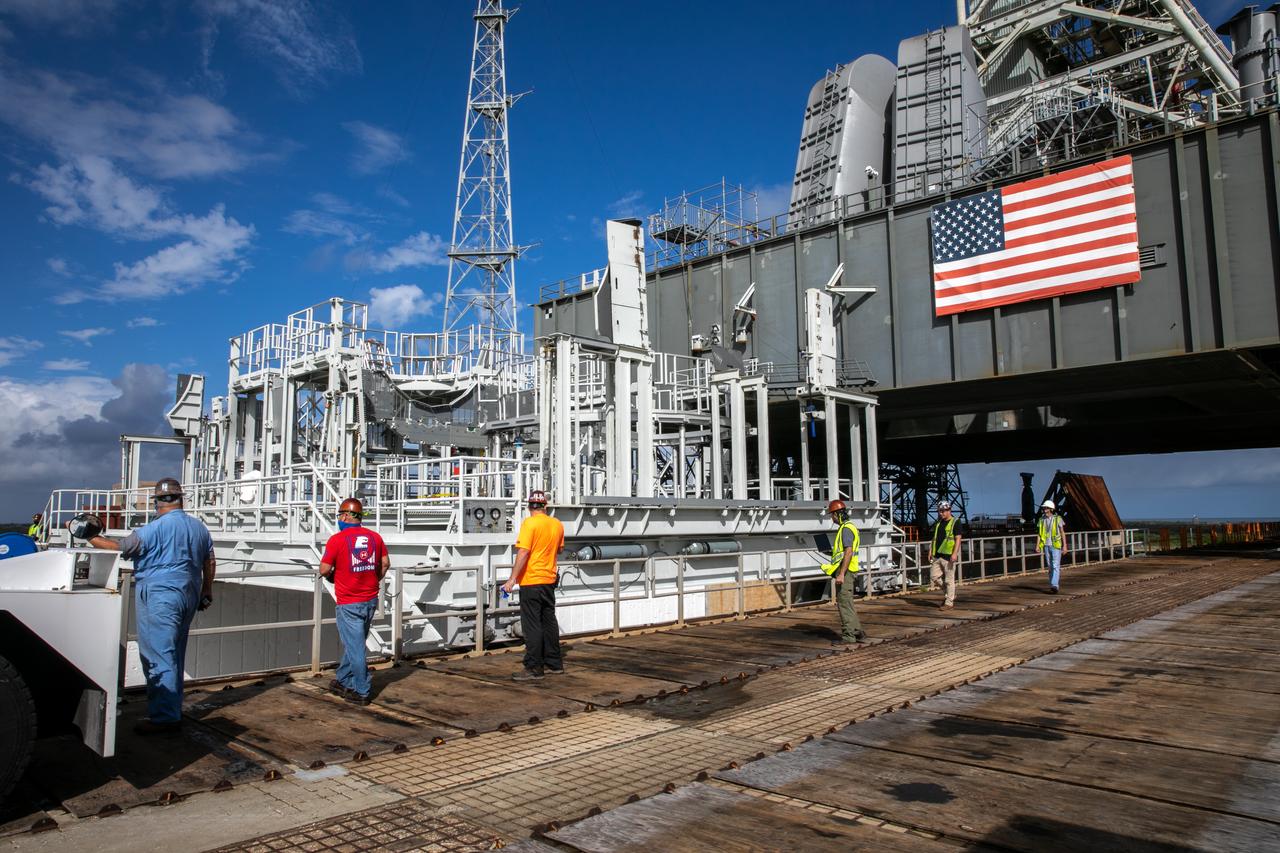

The engine service platform has been lowered and removed from the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The platform is in view on a flatbed truck. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
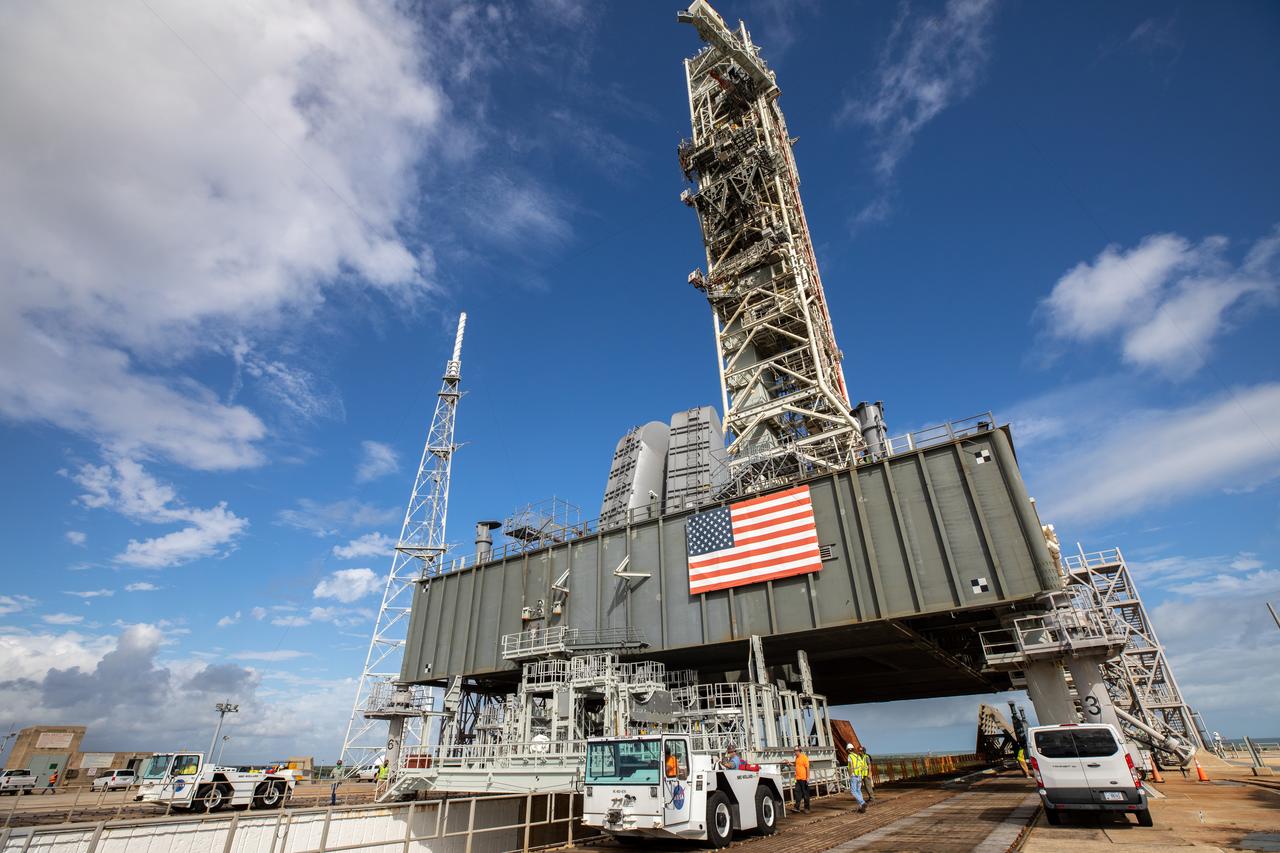

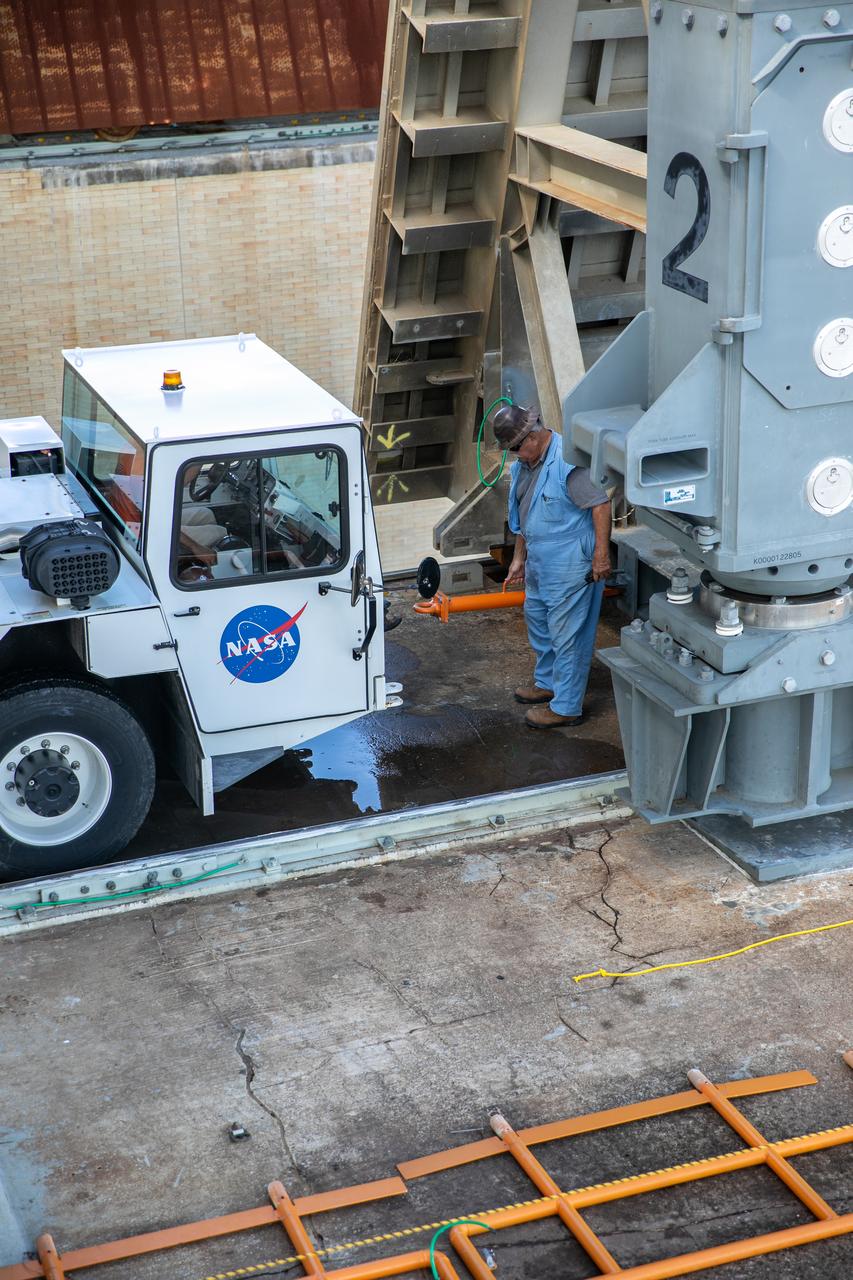
Engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs assist with lowering the engine service platform beneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
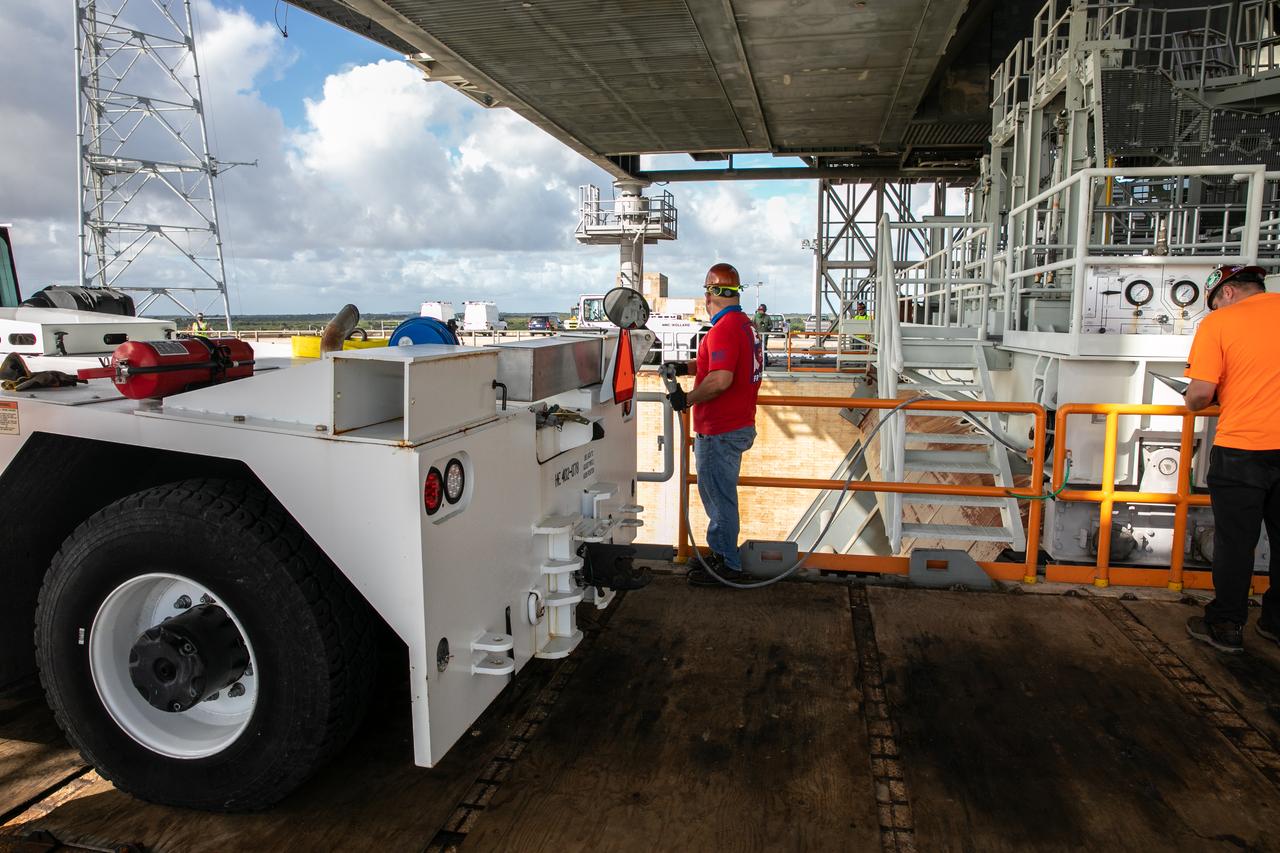

Engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs assist with raising the engine service platform beneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
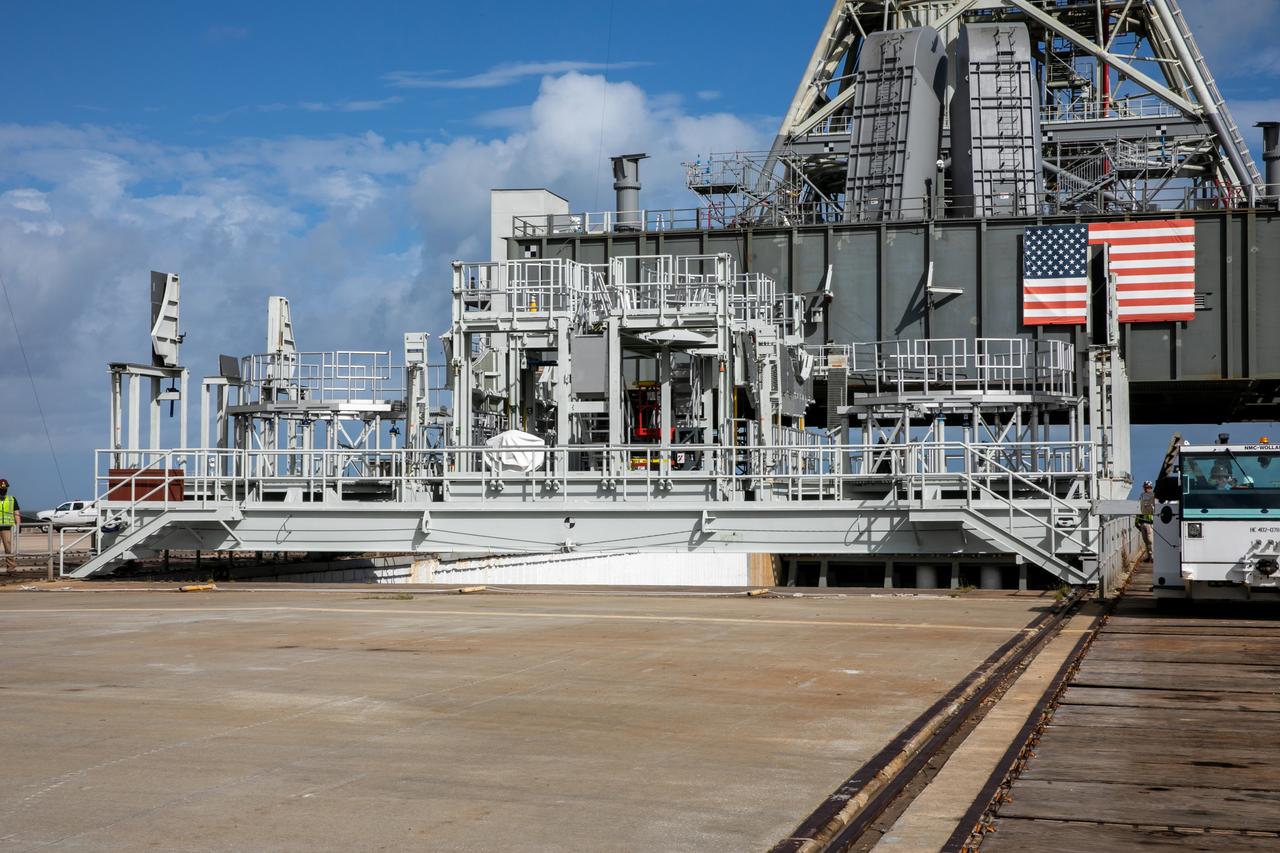
The engine service platform has been lowered and removed from underneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
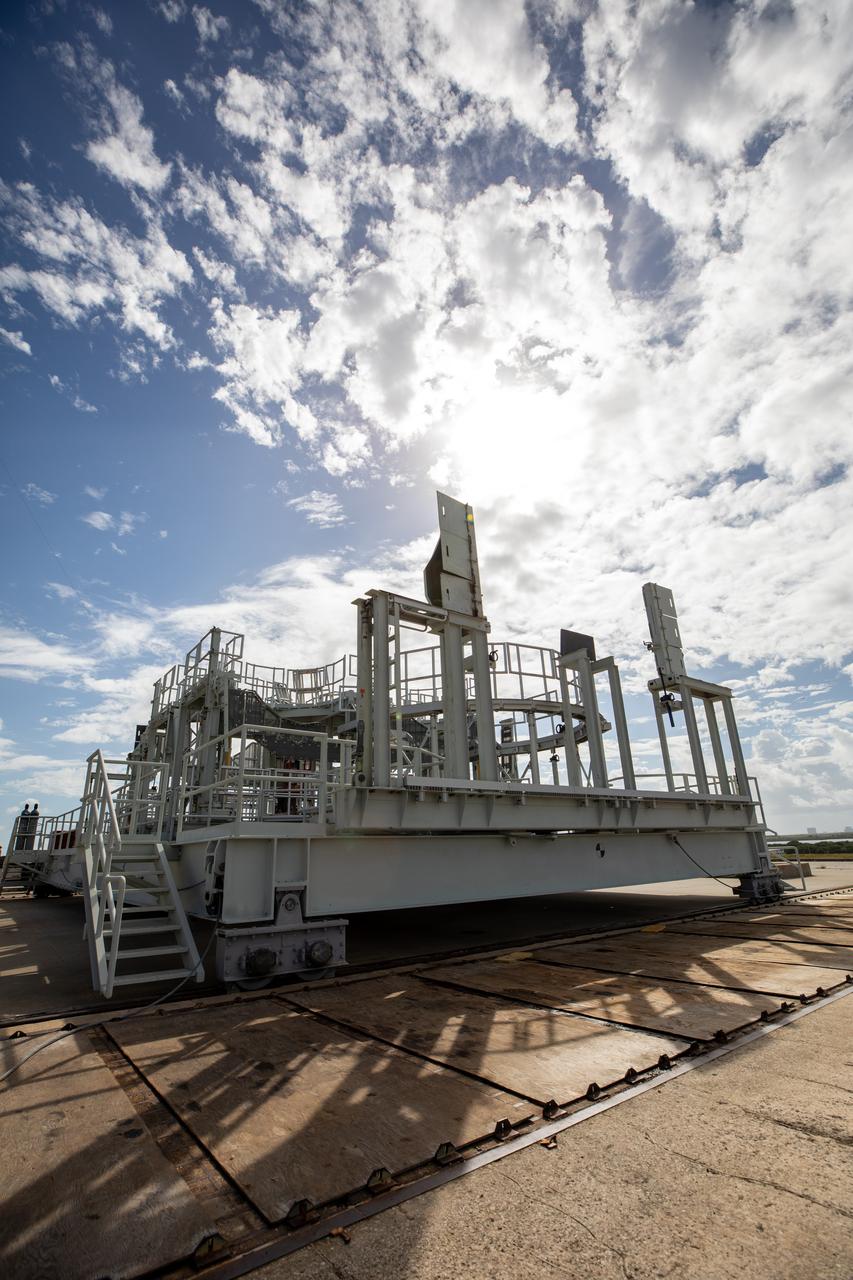

The engine service platform has been lowered and removed from the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. It is staged on the top of the pad. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
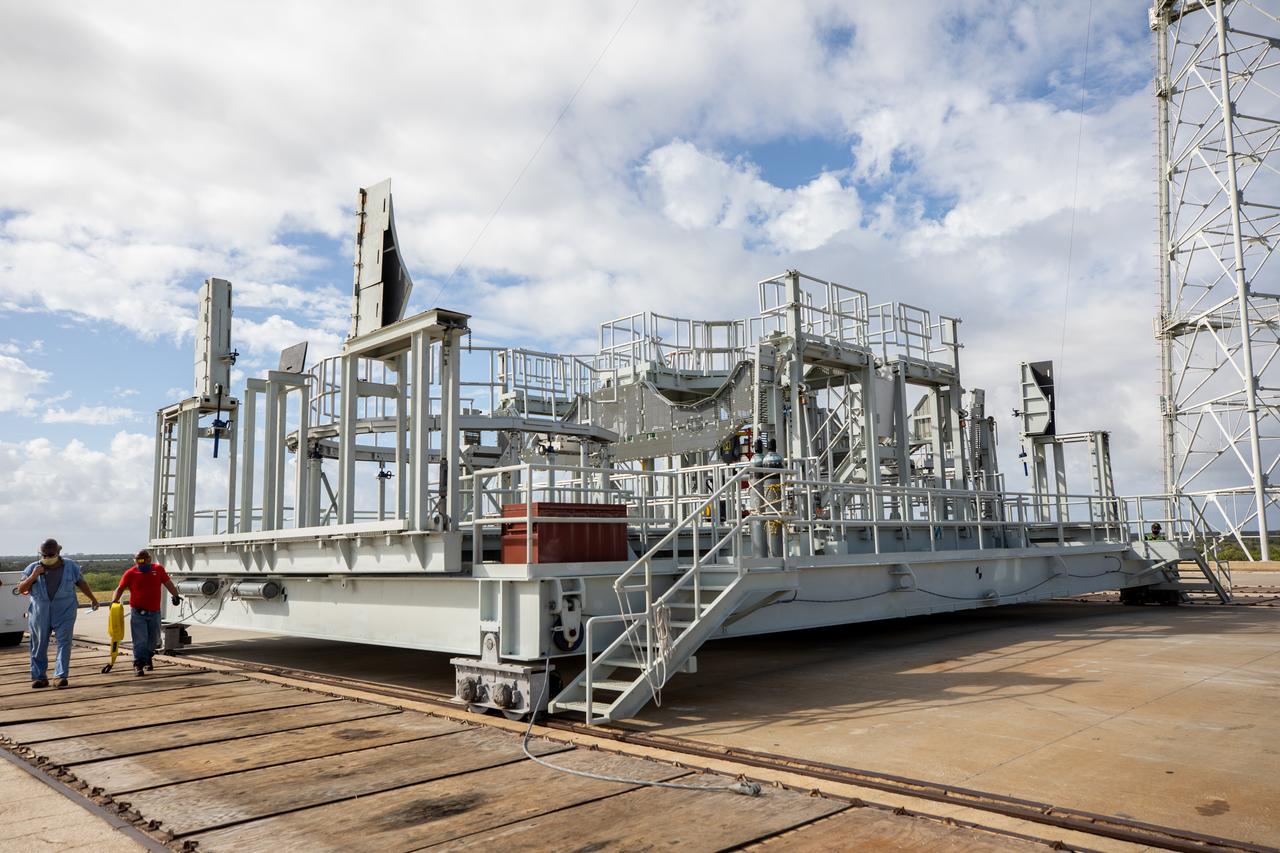

The engine service platform has been lowered and removed from the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. It is staged on the top of the pad. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
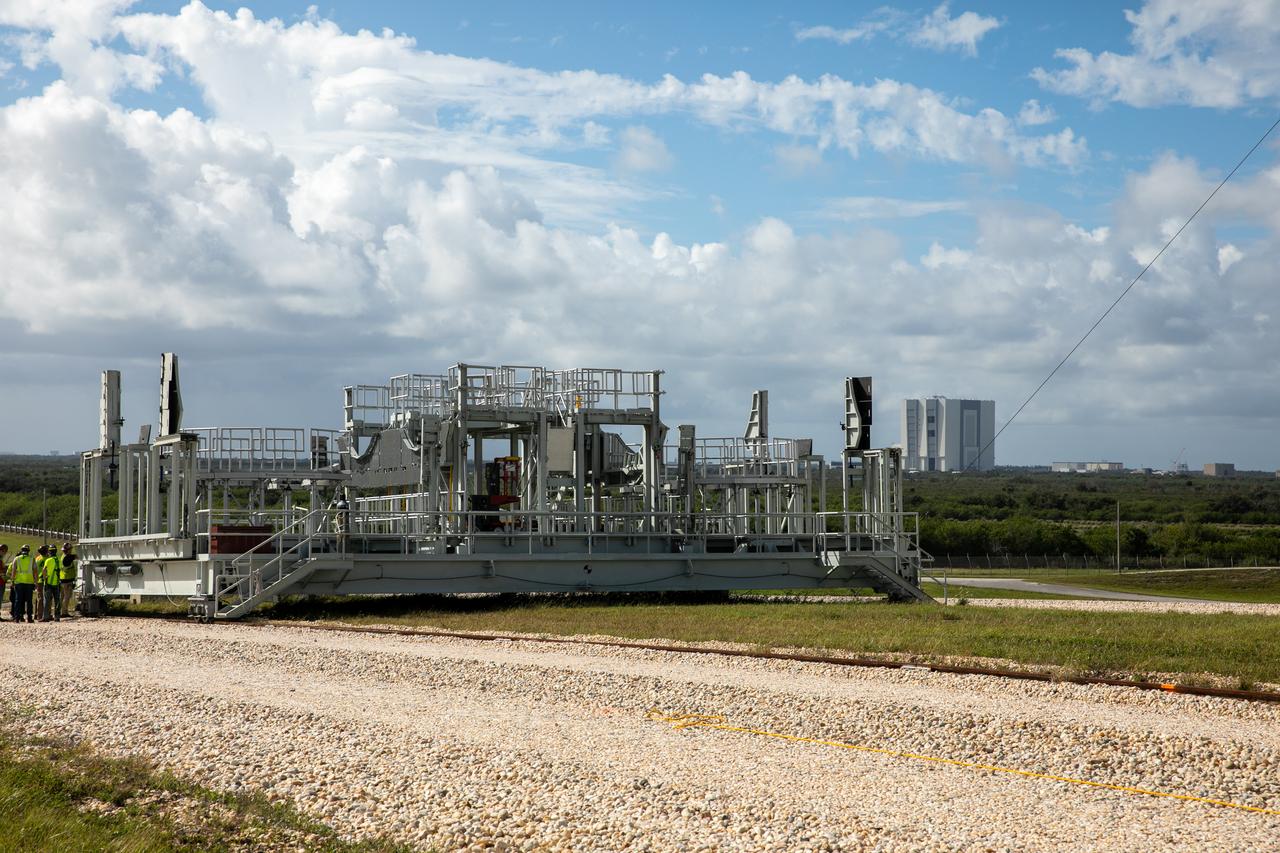

The engine service platform has been lowered and removed from the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. It is being moved from the pad. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
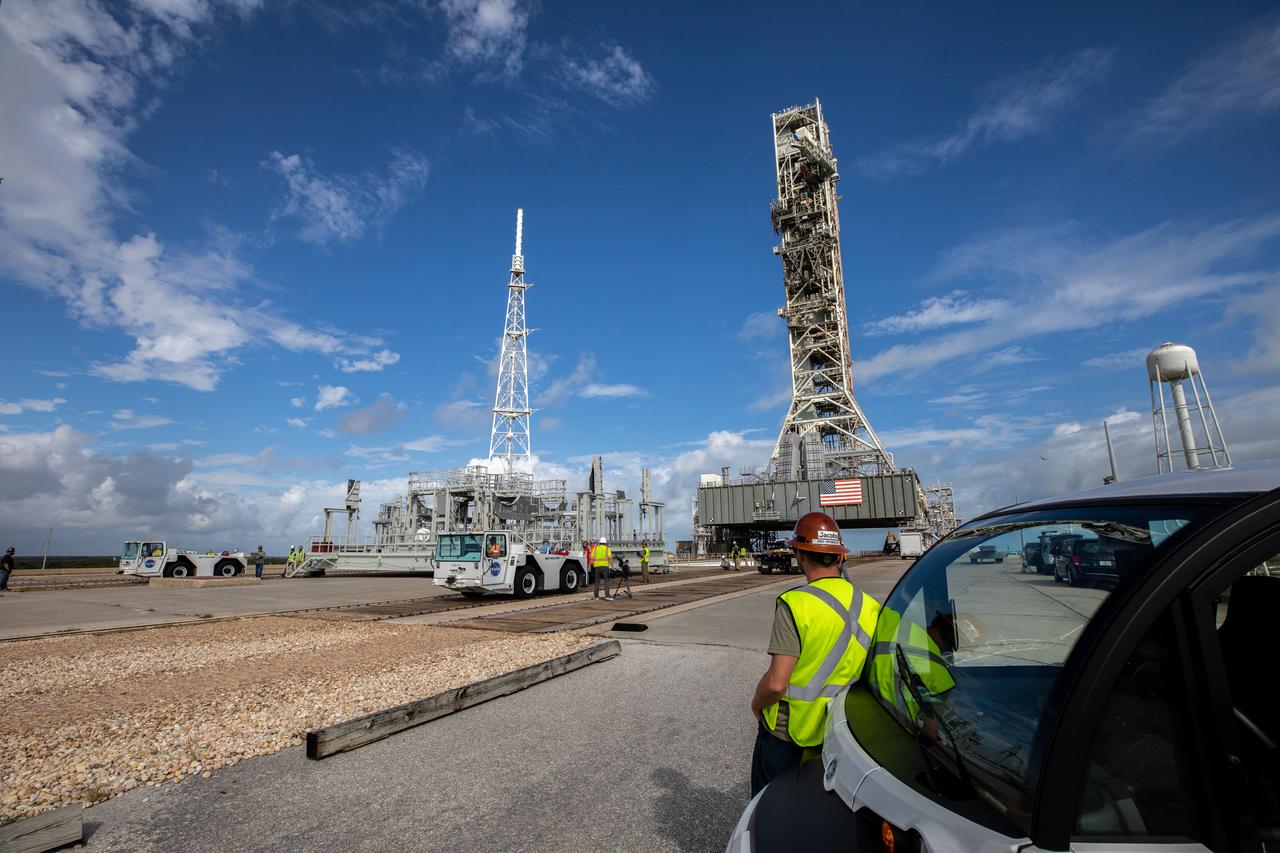

A view of the mobile launcher for Artemis I on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The engine service platform has been lowered and removed from the mobile launcher and is in view on a flatbed carrier. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

The cab of a flatbed carrier is in view on the surface of Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. It will carry the engine service platform that was lowered and removed from the mobile launcher for Artemis I. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
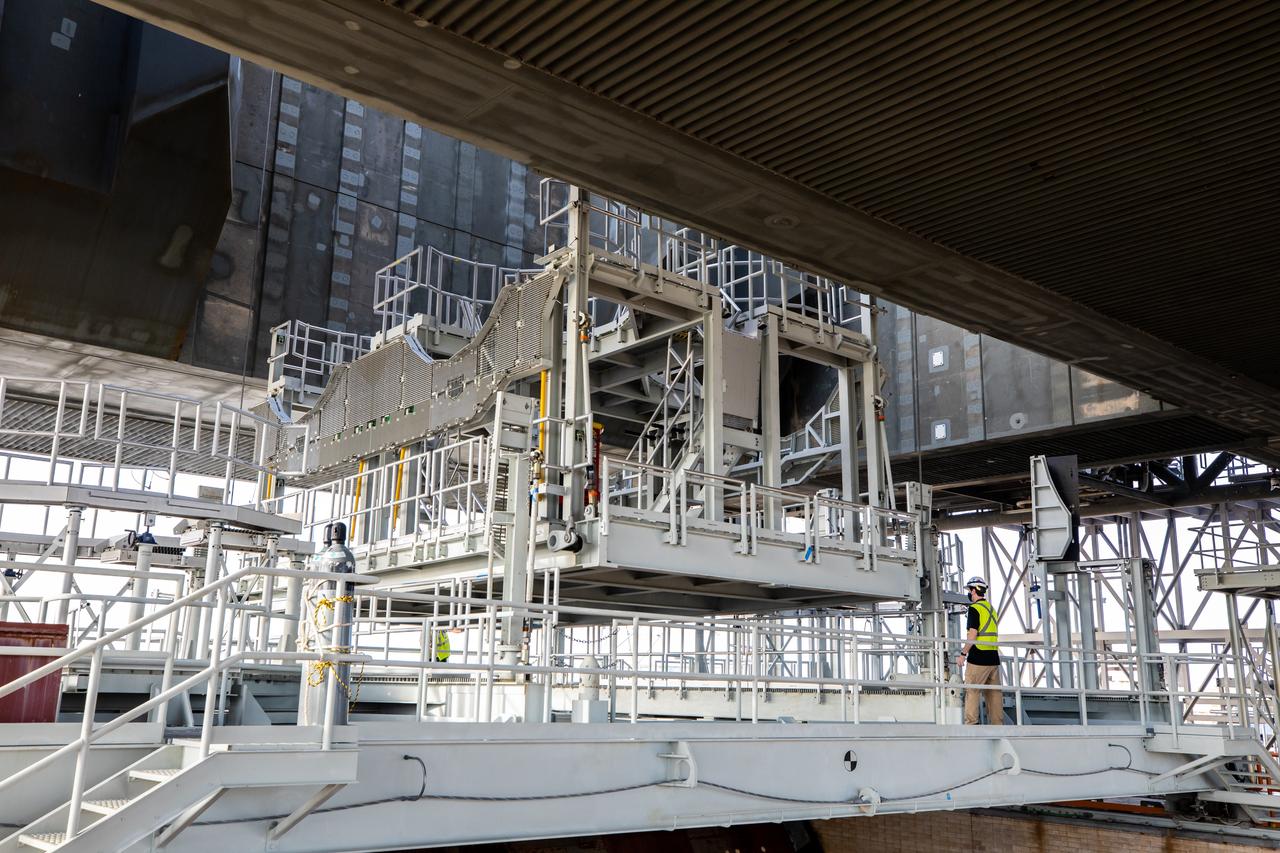

The engine service platform is being raised beneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
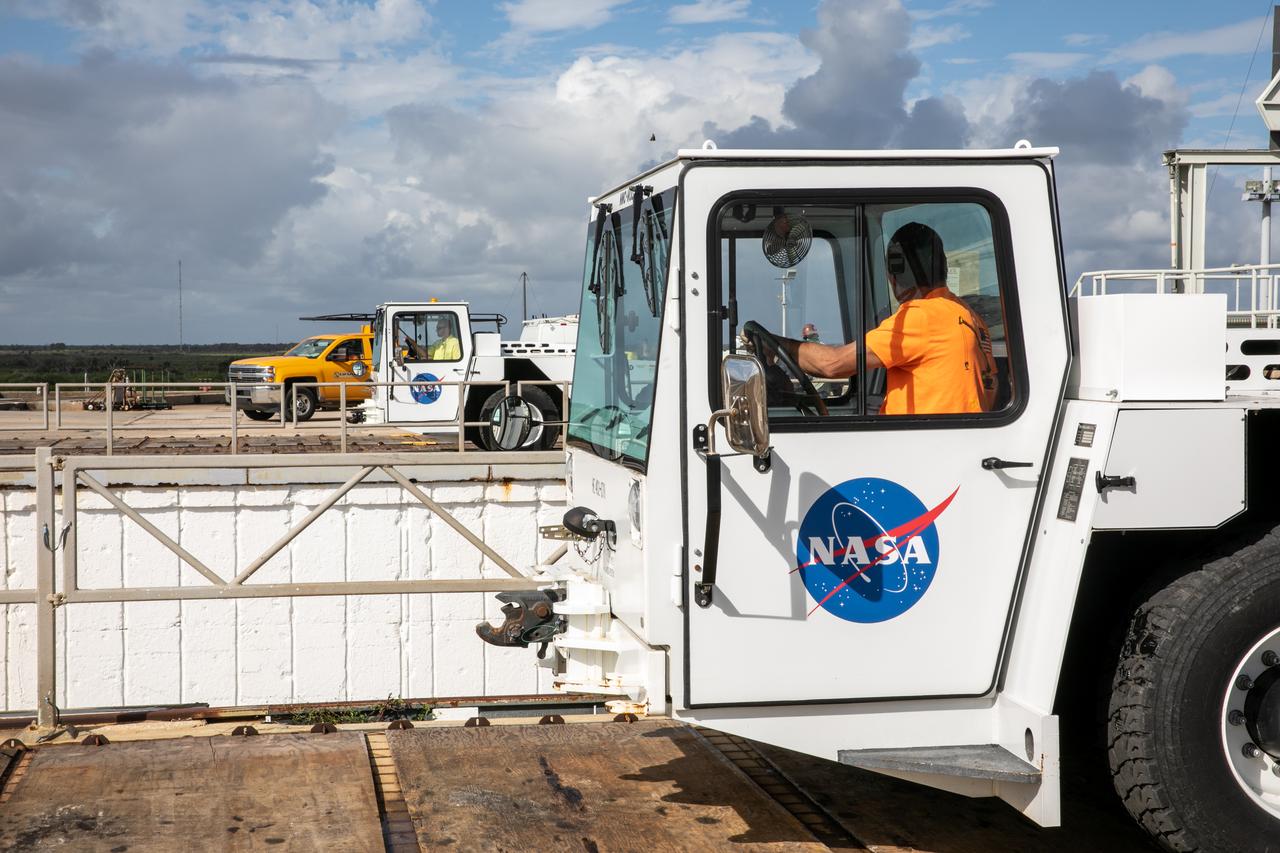

A flatbed carrier is in view on the surface of Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. It is carrying the engine service platform that was lowered and removed from the mobile launcher for Artemis I. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
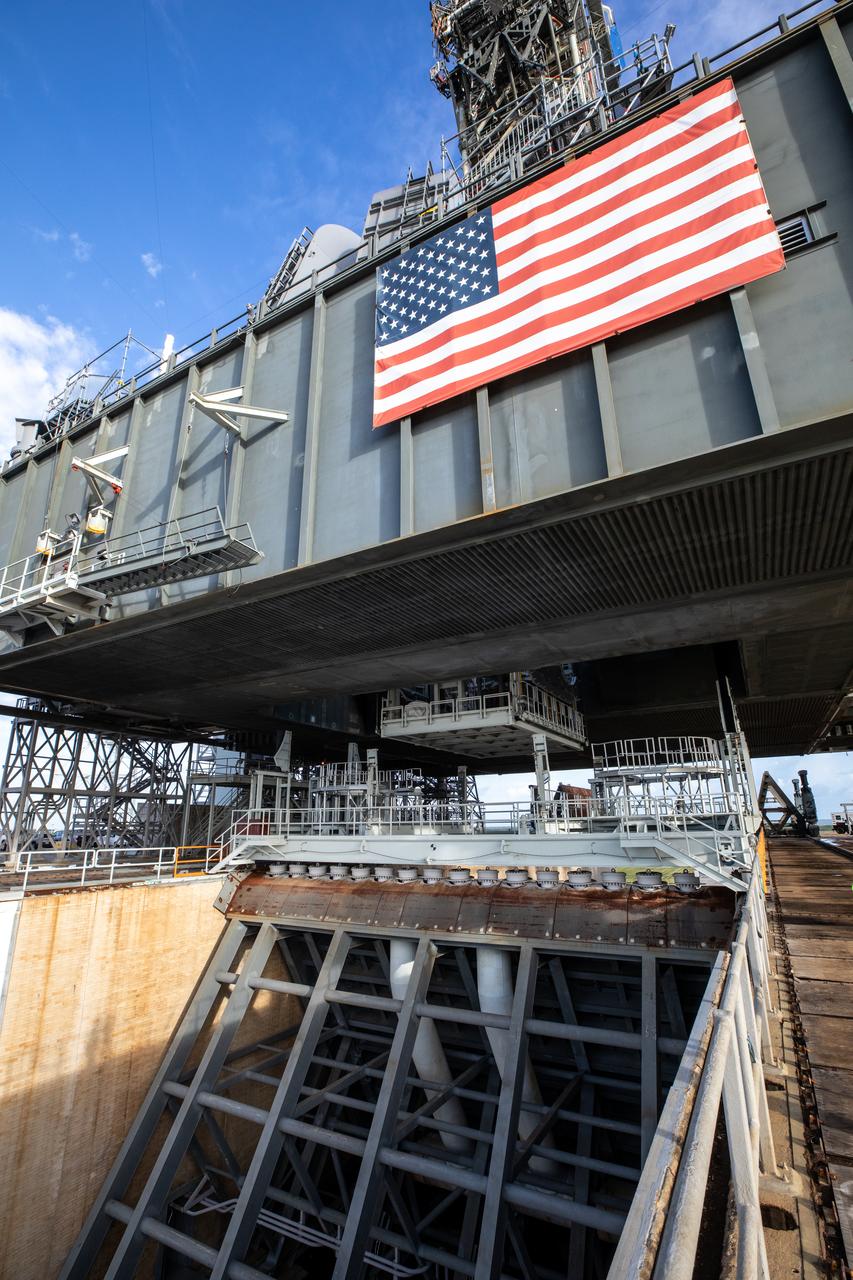
A view of the base of the mobile launcher for Artemis I and the flame trench below as the engine service platform is being raised into position below the mobile launcher at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
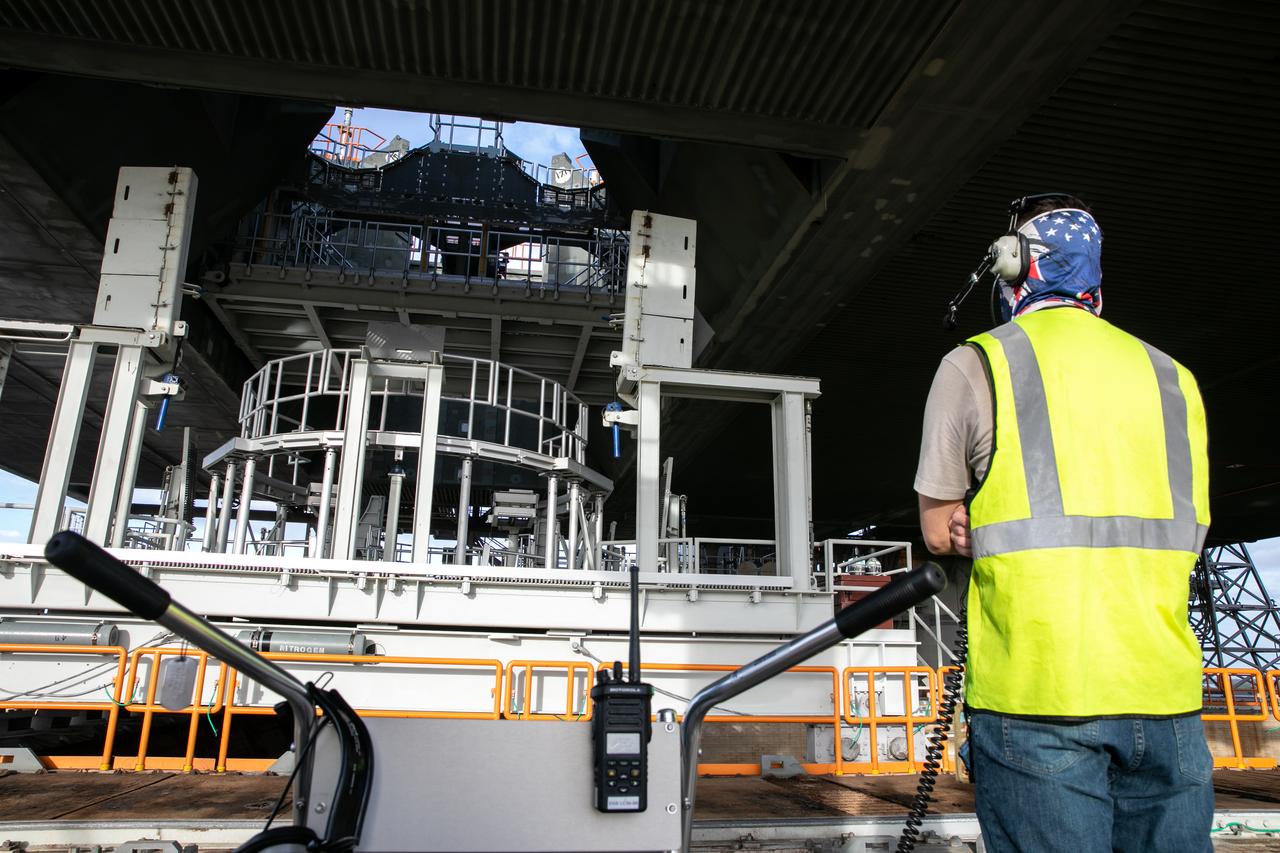

Workers assists with raising the engine service platform beneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
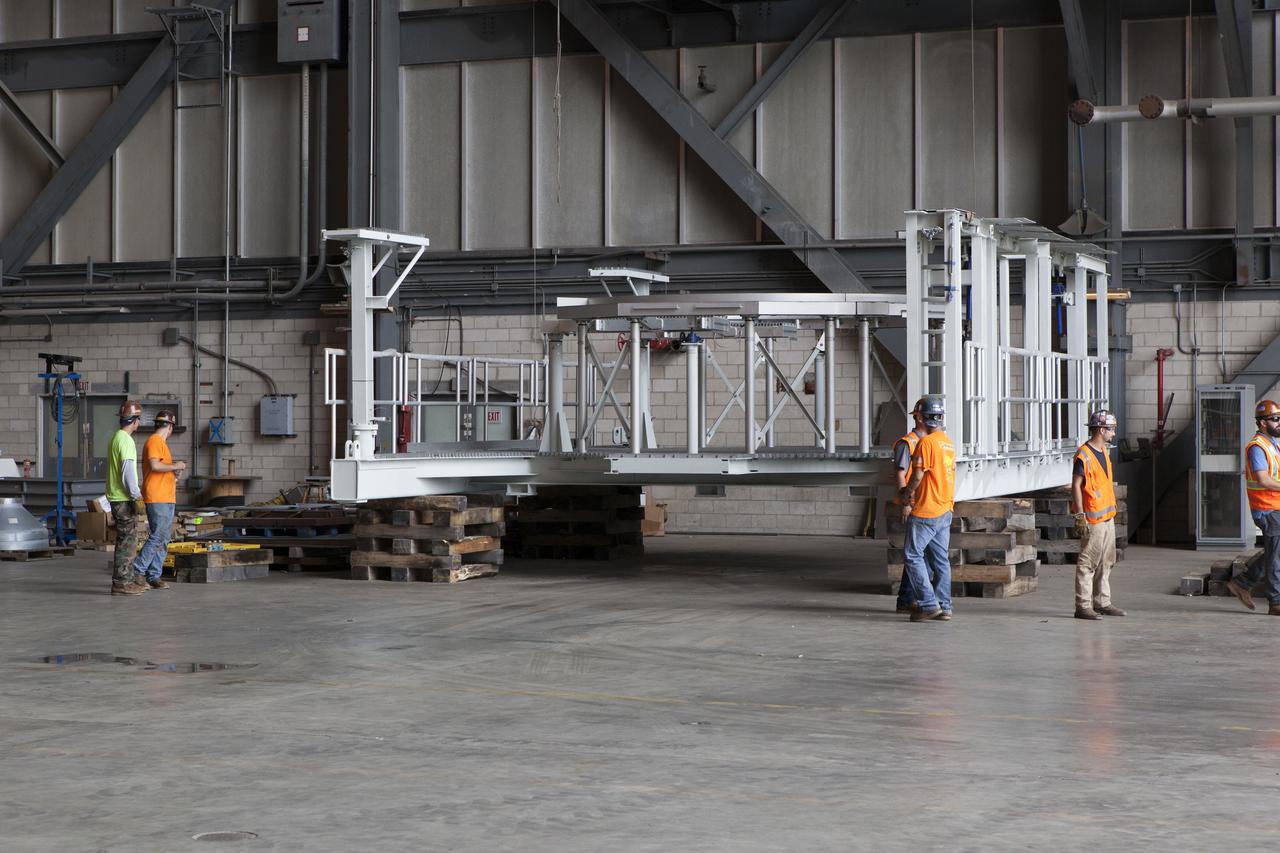

One of two new work platforms for NASA's Space Launch System booster engines is secured on dunnage inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platforms were transported from fabricator Met-Con Inc. in Cocoa, Florida. They will be stored in the VAB, where they will be used for processing and checkout of the engines for the rocket's twin five-segment solid rocket boosters for Exploration Mission-1. EM-1 will launch an uncrewed Orion spacecraft to a stable orbit beyond the Moon and bring it back to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
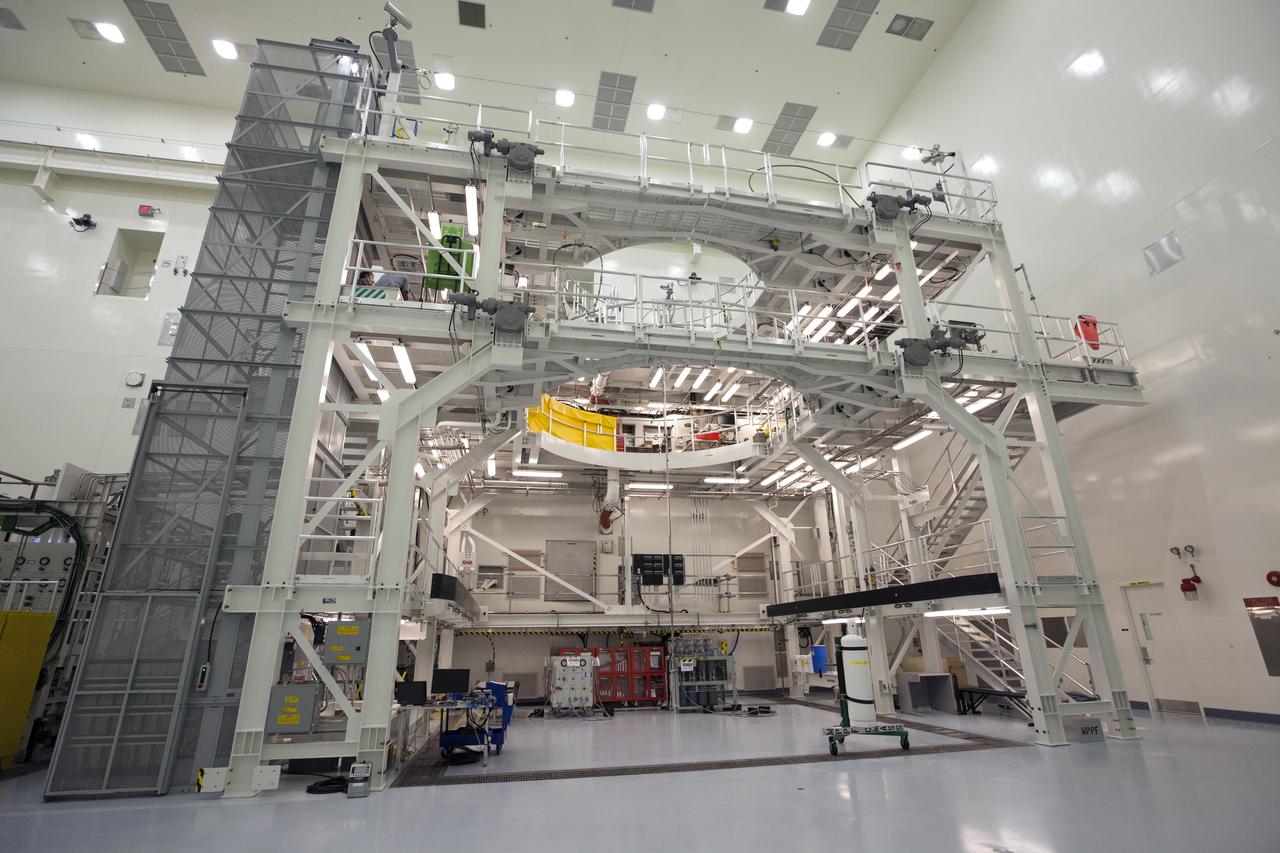

Engineers and technicians completed verification and validation testing of several pneumatic systems inside and outside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view is the service platform for Orion spacecraft processing. The MPPF will be used for offline processing and fueling of the Orion spacecraft and service module stack before launch. Orion also will be de-serviced in the MPPF after a mission. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program (GSDO) is overseeing upgrades to the facility. The Engineering Directorate led the recent pneumatic tests.
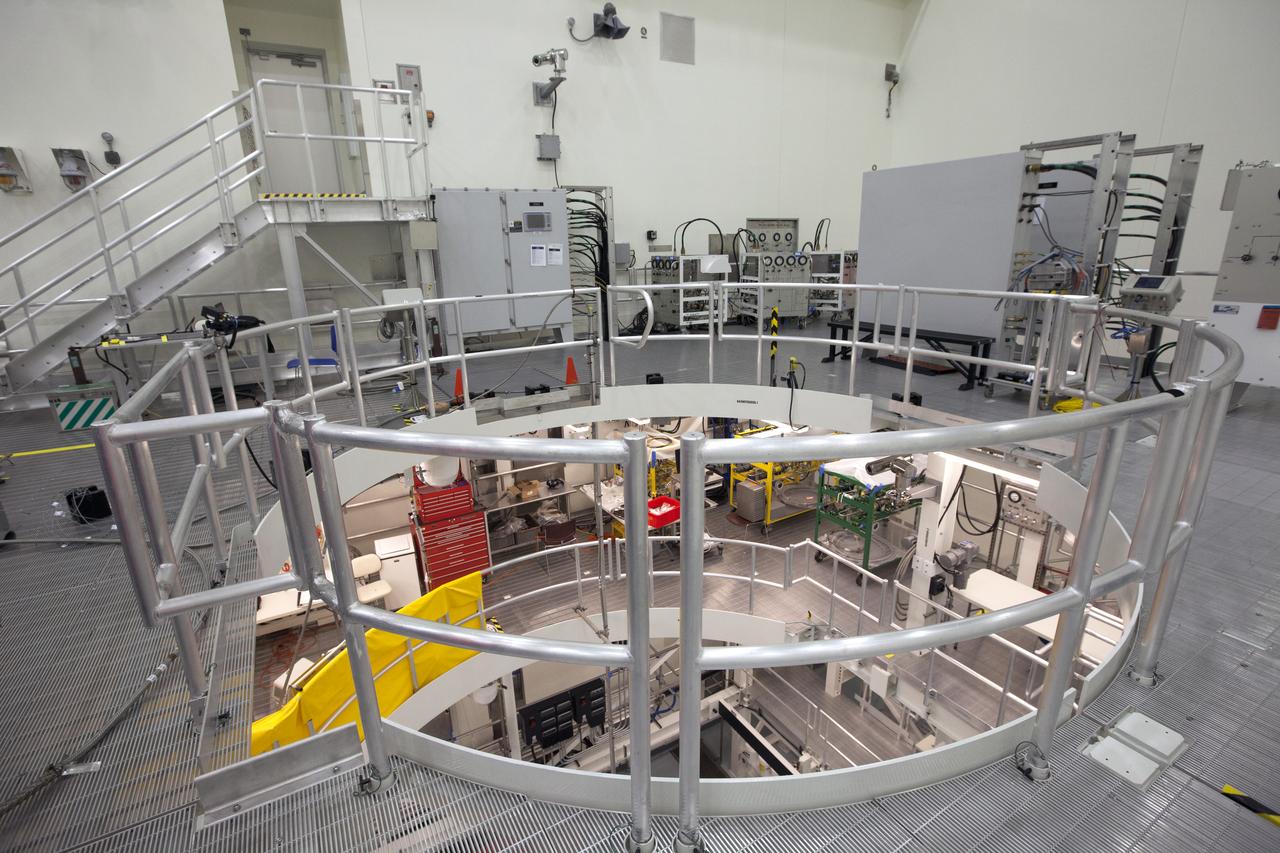

Engineers and technicians completed verification and validation testing of several pneumatic systems inside and outside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view is the top level of the service platform for Orion spacecraft processing. The MPPF will be used for offline processing and fueling of the Orion spacecraft and service module stack before launch. Orion also will be de-serviced in the MPPF after a mission. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program (GSDO) is overseeing upgrades to the facility. The Engineering Directorate led the recent pneumatic tests.
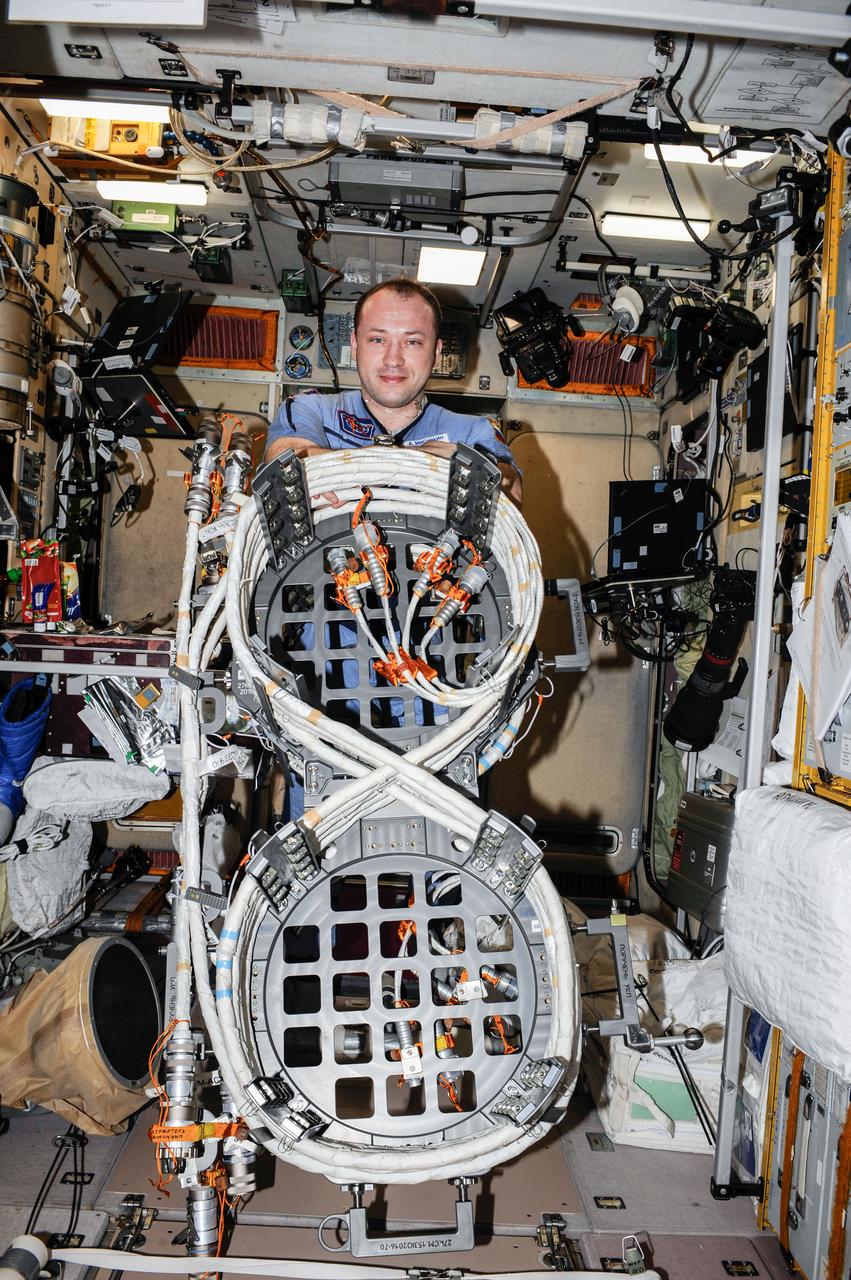

ISS036-E-029455 (6 Aug. 2013) --- In the International Space Station’s Zvezda Service Module, Russian cosmonaut Alexander Misurkin, Expedition 36 flight engineer, holds an EVA multi-purpose cable platform which will be used in an upcoming spacewalk.
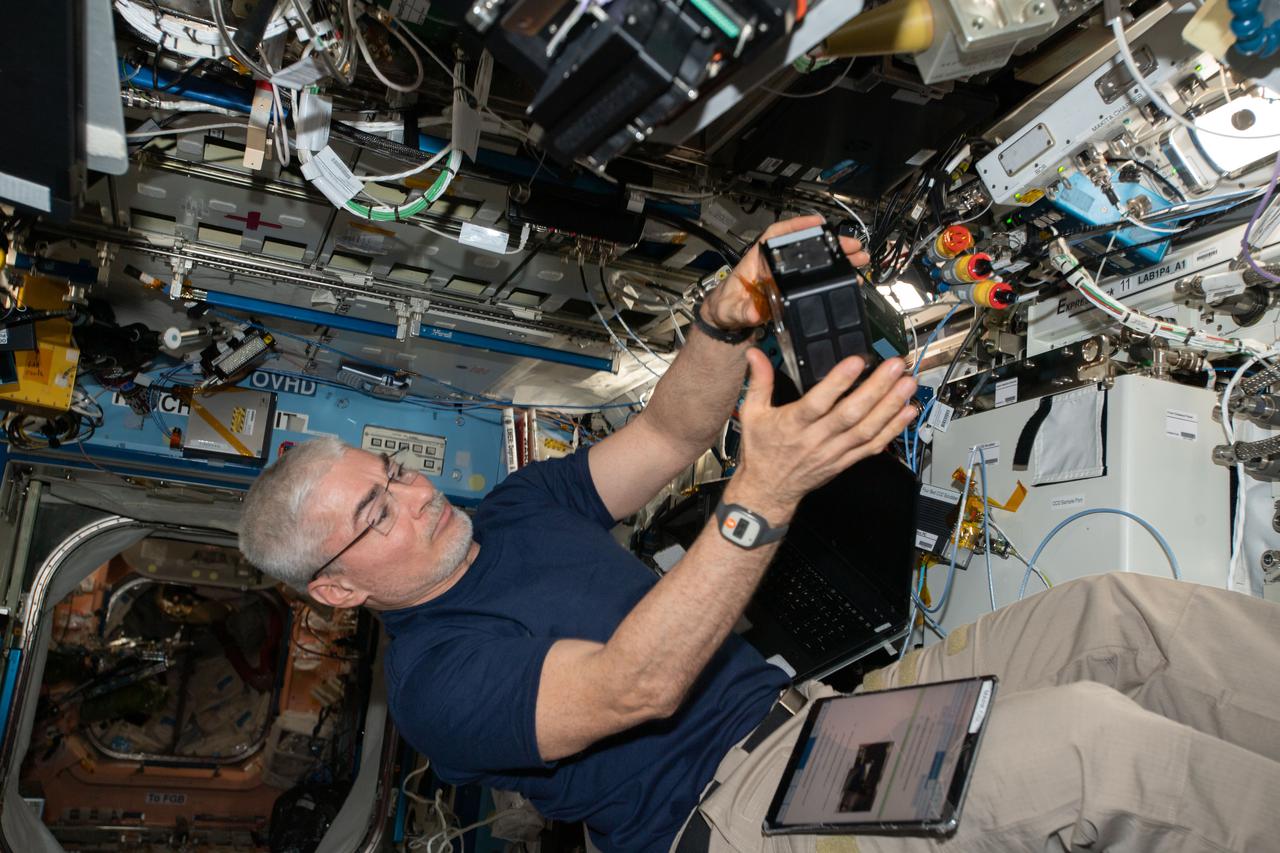

iss066e137913 (Feb. 9, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei services components inside the Multi-use Variable-G Platform, a biology research device that can generate up to 2G of artfifical gravity.
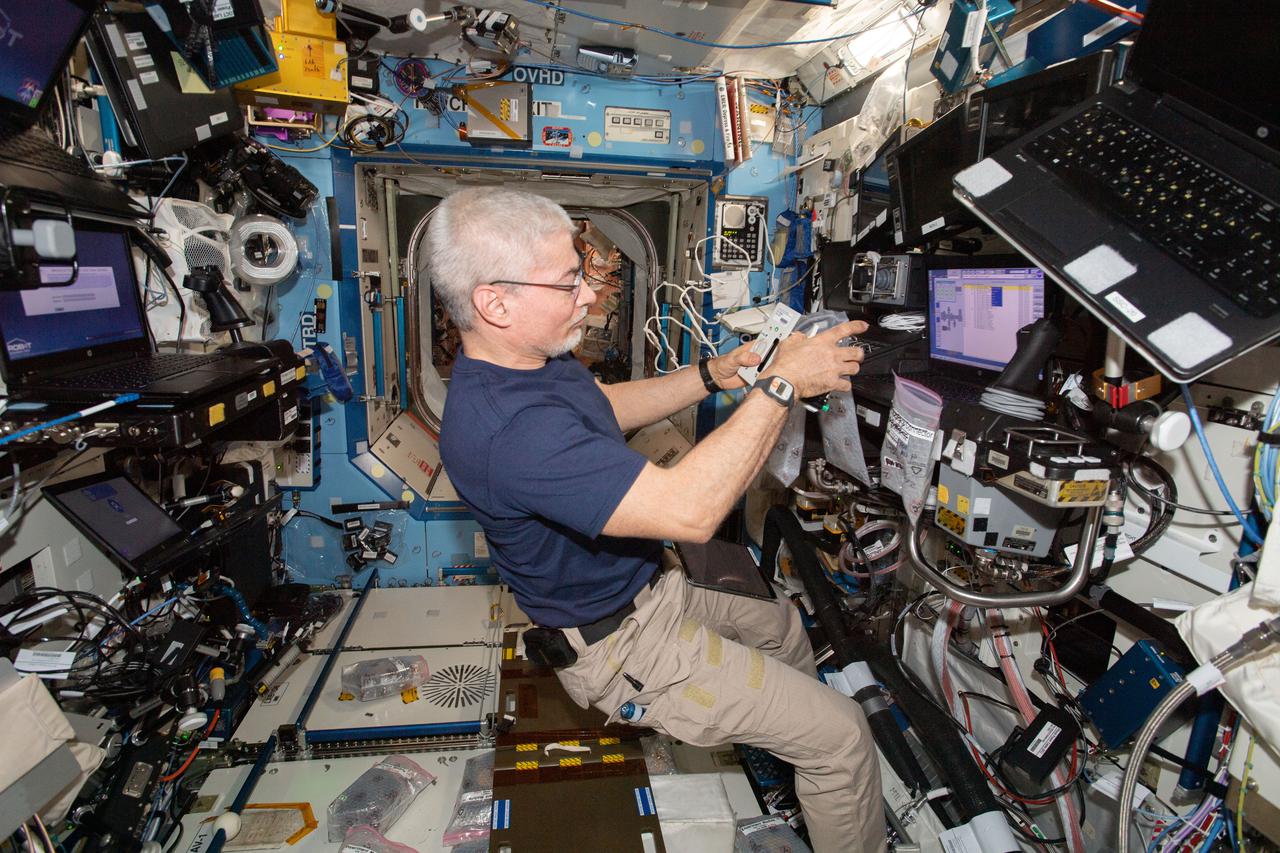

iss066e137924 (Feb. 9, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei services components inside the Multi-use Variable-G Platform, a biology research device that can generate up to 2G of artfifical gravity.
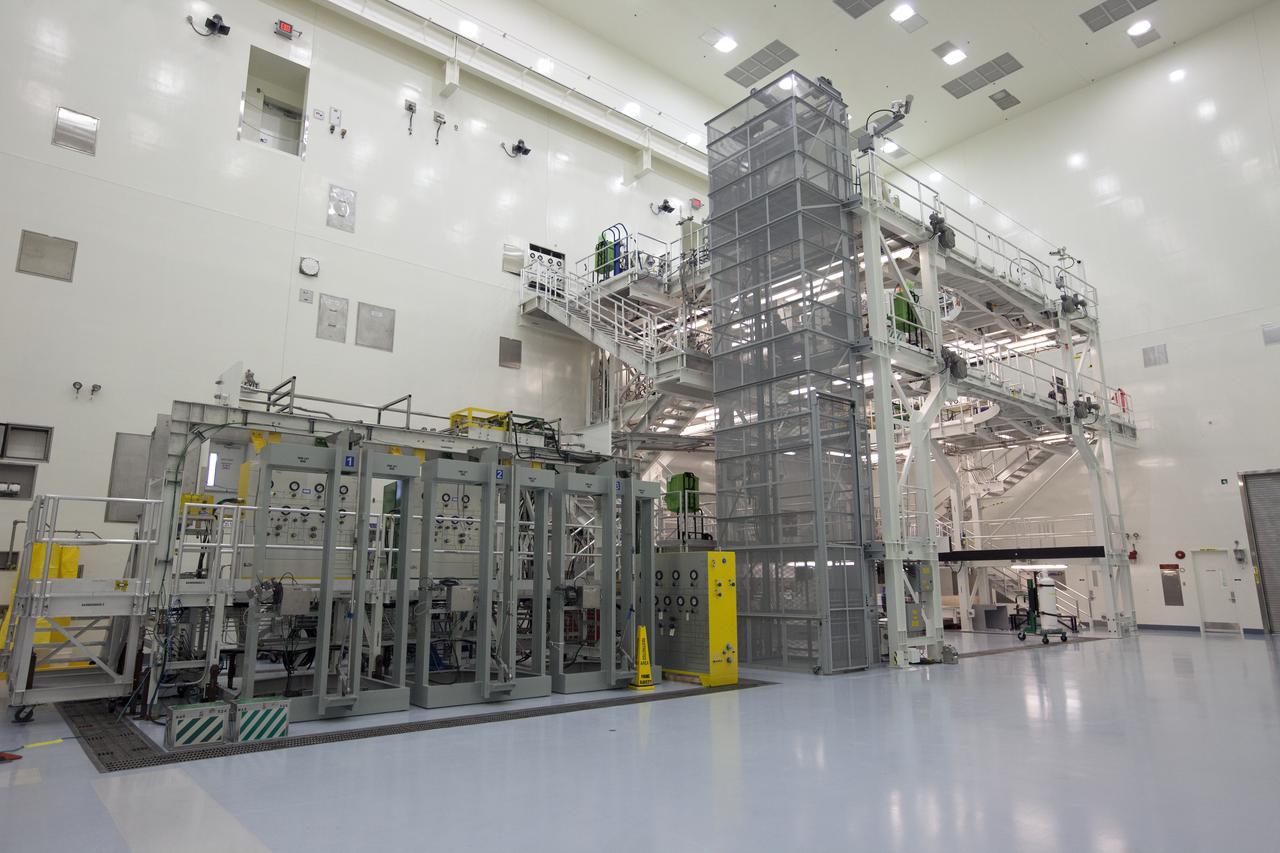

Engineers and technicians completed verification and validation testing of several pneumatic systems inside and outside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view is the service platform for Orion spacecraft processing. To the left are several pneumatic panels. The MPPF will be used for offline processing and fueling of the Orion spacecraft and service module stack before launch. Orion also will be de-serviced in the MPPF after a mission. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program (GSDO) is overseeing upgrades to the facility. The Engineering Directorate led the recent pneumatic tests.

On Oct. 23, 2020, an engineer with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) is at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as a brilliant sunrise illuminates the sky. The mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission is at the pad to allow engineers with EGS and Jacobs to complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
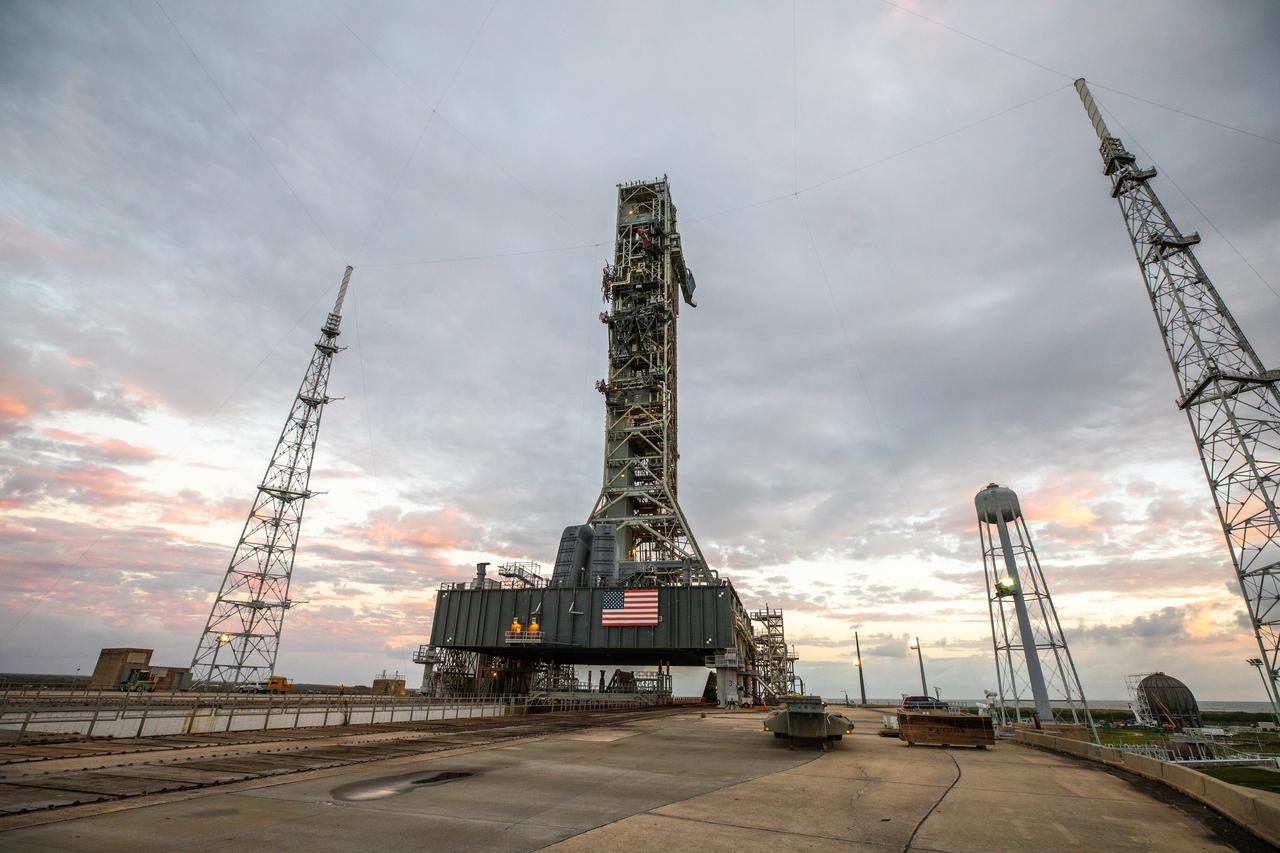

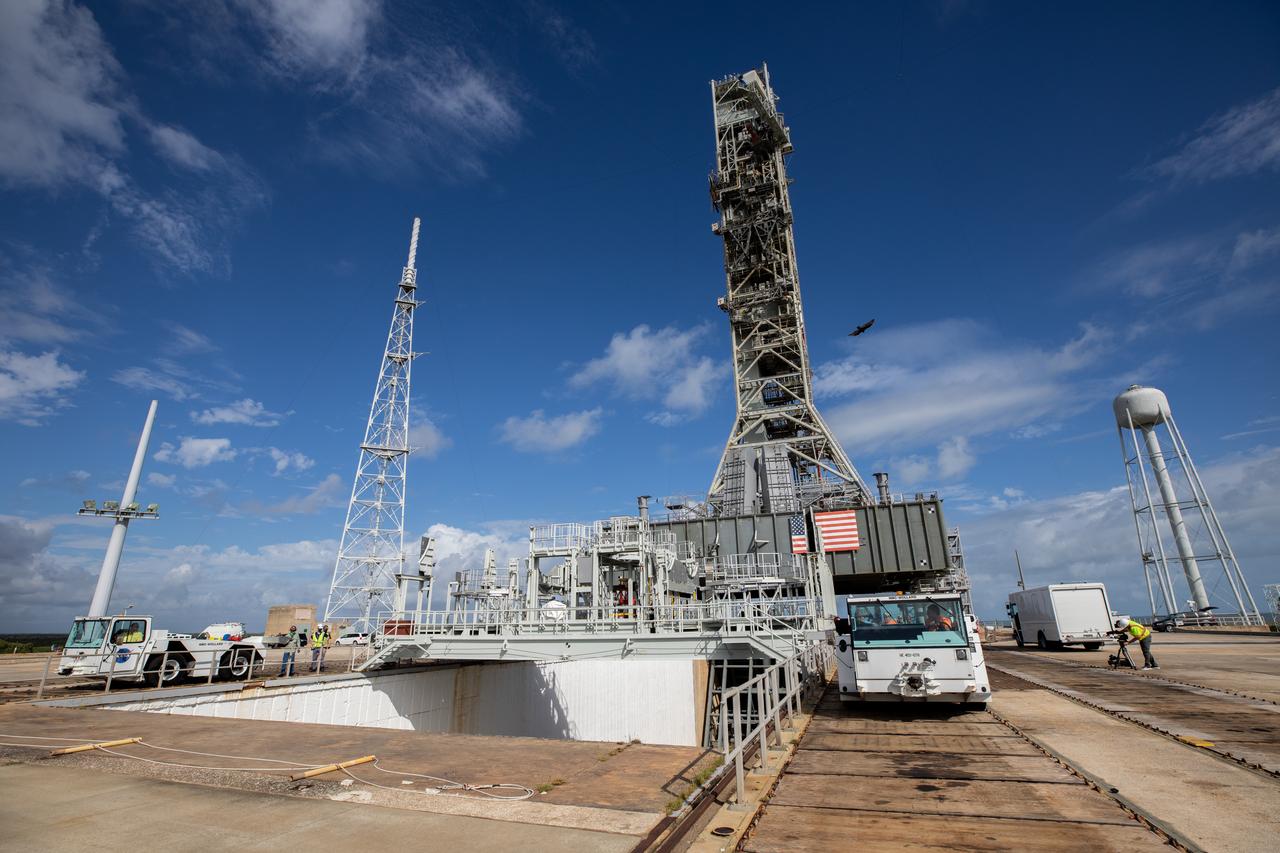
The mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission is in view on the top of Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad to allow engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs to complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
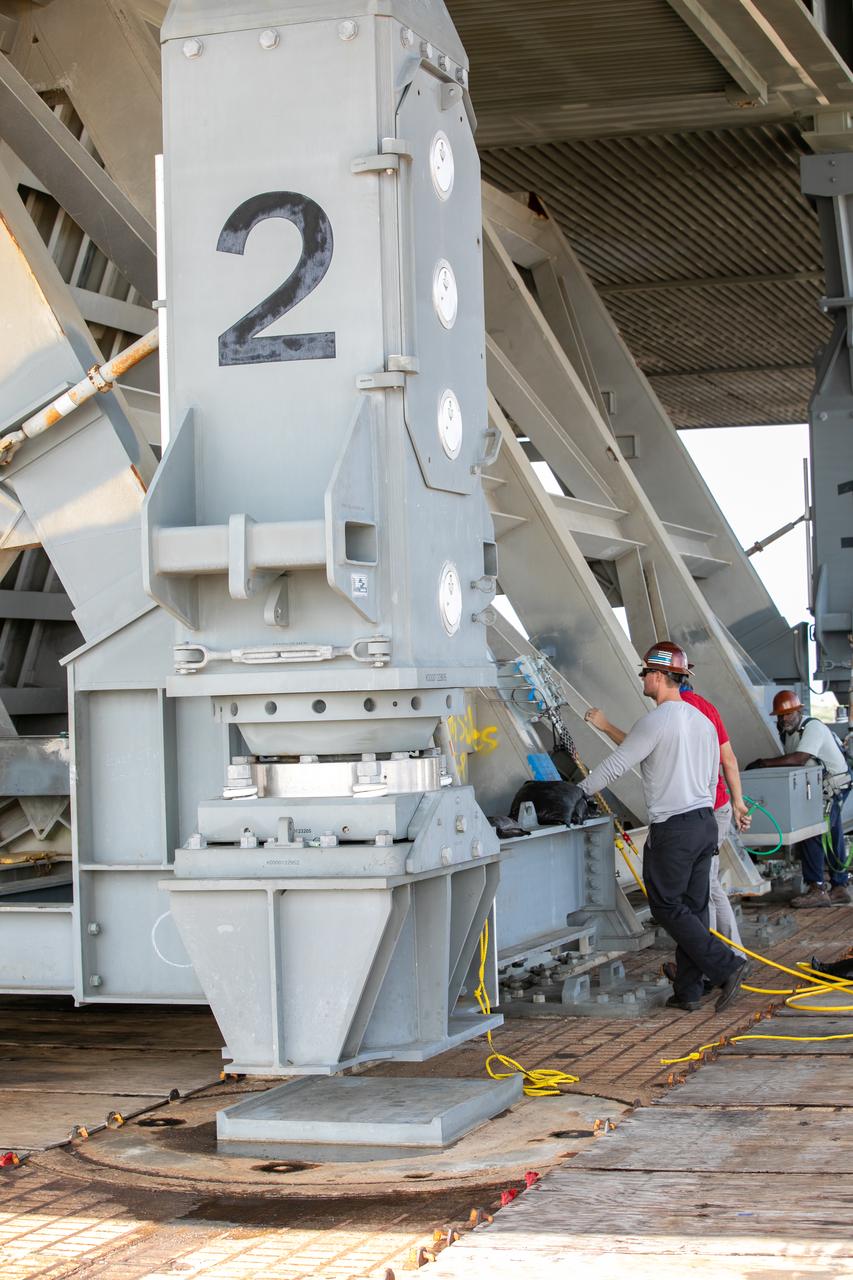

Special ground support equipment is used to position one of two side flame deflectors underneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I during a countdown demonstration test at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

A view of the mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The flame trench and flame deflector are in view below the mobile launcher. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher will remain at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

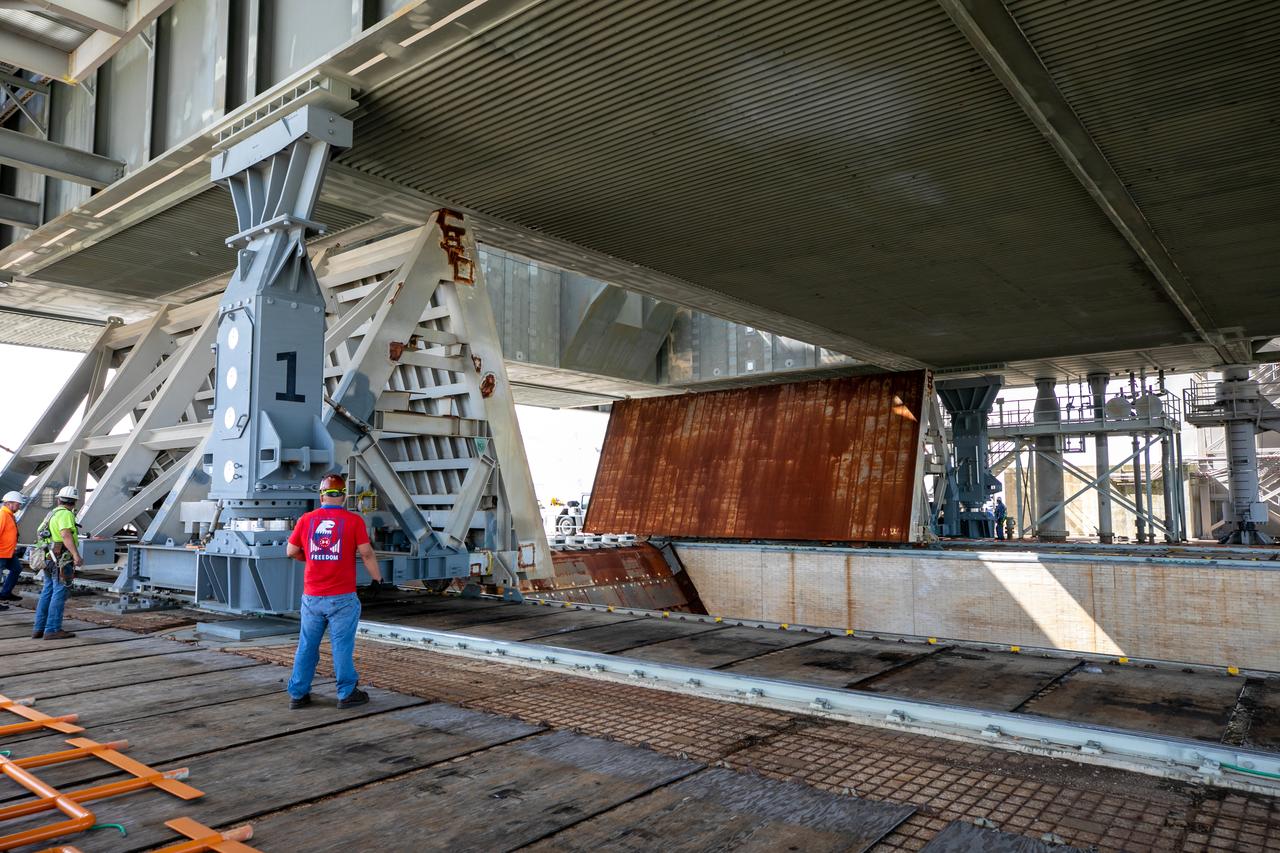
Special ground support equipment is used to move the side flame deflectors into place during a countdown demonstration test using the mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
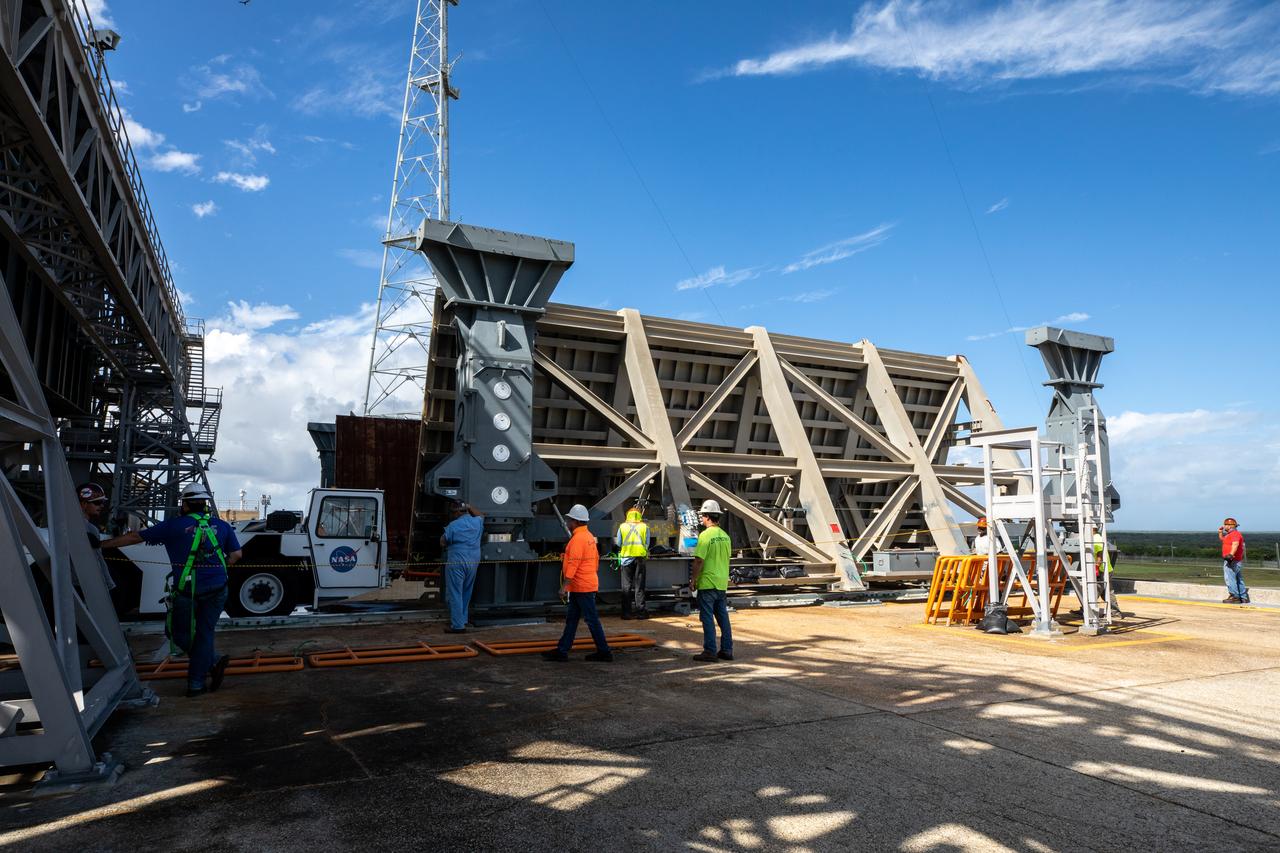

Special ground support equipment is used to move the side flame deflectors into place during a countdown demonstration test using the mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

A view of the mobile launcher for Artemis I with the two side flame deflectors positioned underneath during a countdown demonstration test at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. Also in view is the main flame deflector in the flame trench. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
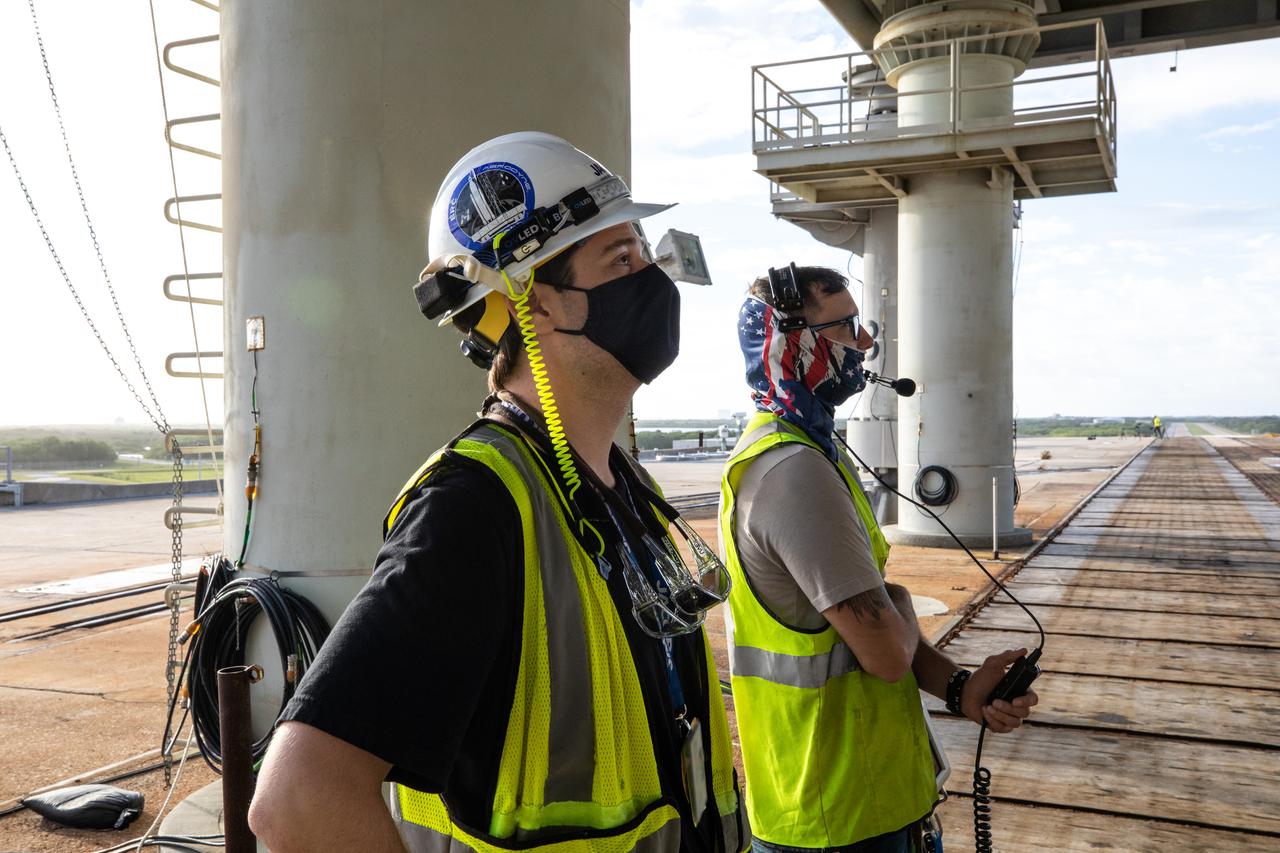

Workers stand on the surface of Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. They are monitoring launch countdown timeline demonstration activities occurring on the mobile launcher for Artemis I. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
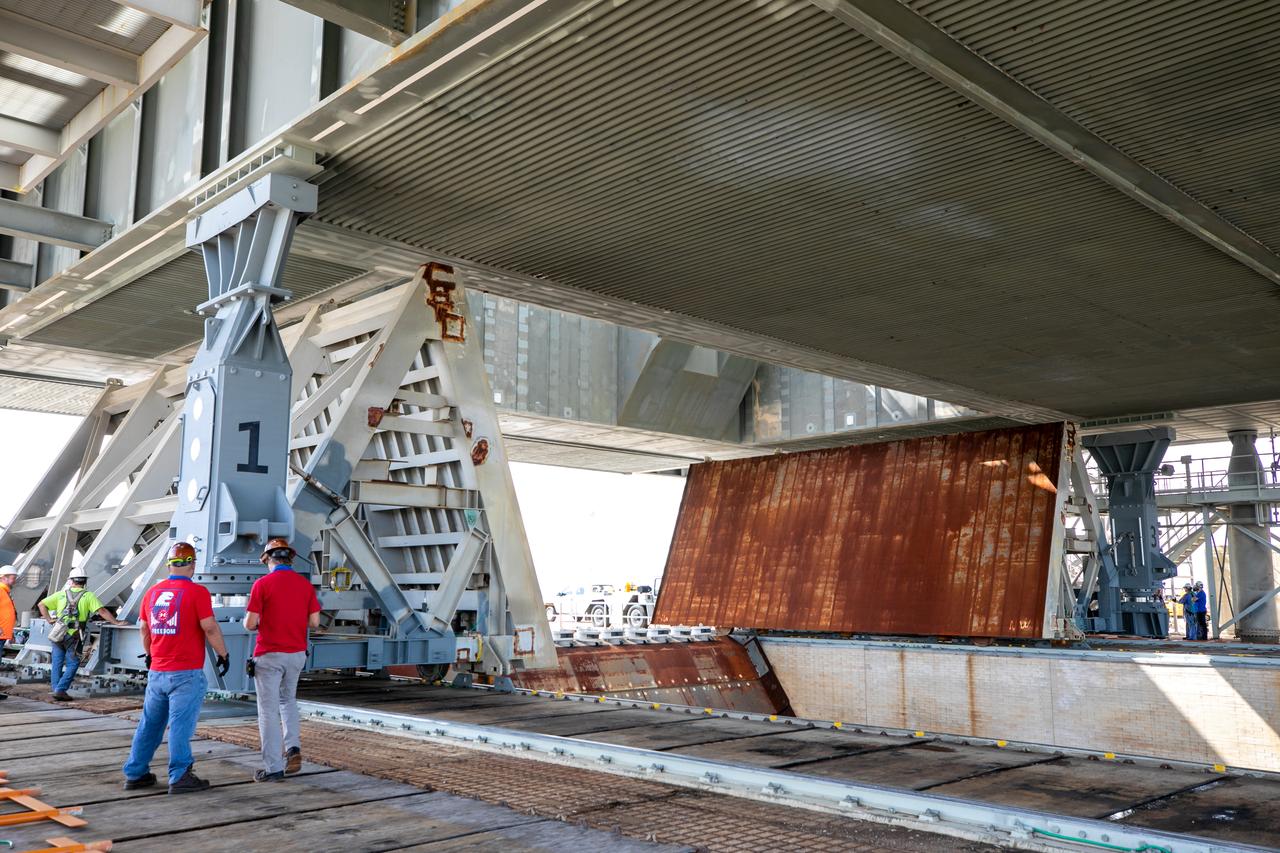

Special ground support equipment is used to position the two side flame deflectors underneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I during a countdown demonstration test at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
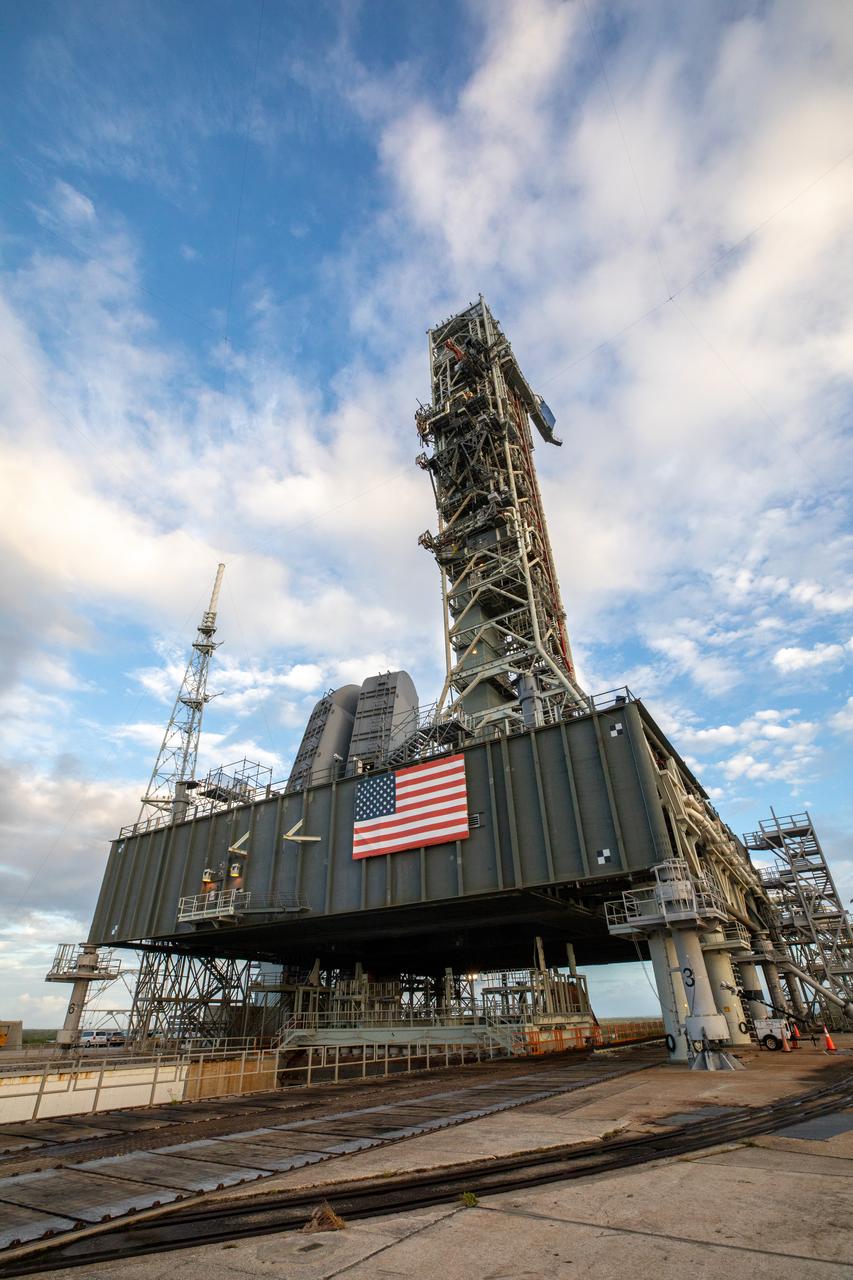

The mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission is in view on the top of Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad to allow engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs to complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Special ground support equipment is used to position the two side flame deflectors underneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I during a countdown demonstration test at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
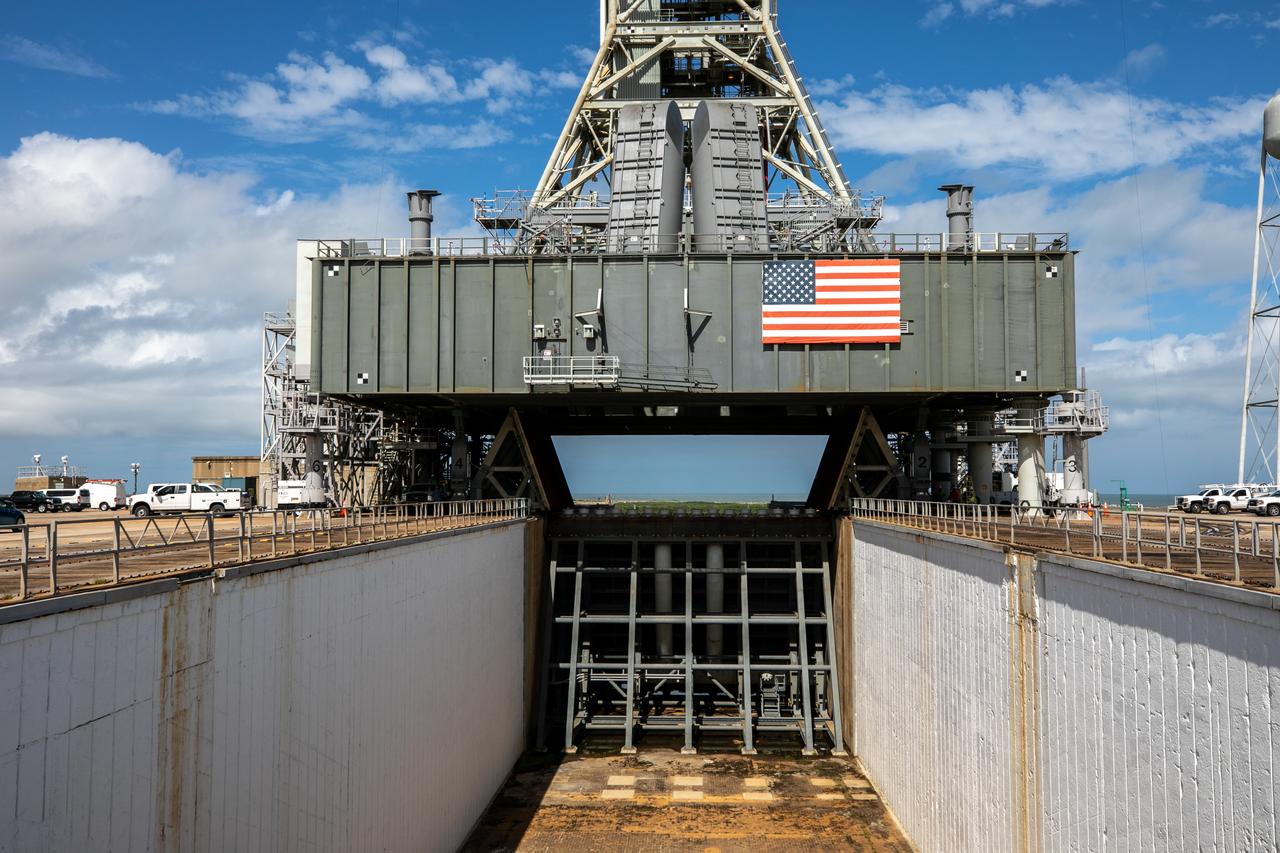

A close-up view of the mobile launcher for Artemis I with the two side flame deflectors positioned underneath during a countdown demonstration test at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. Also in view is the main flame deflector in the flame trench. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
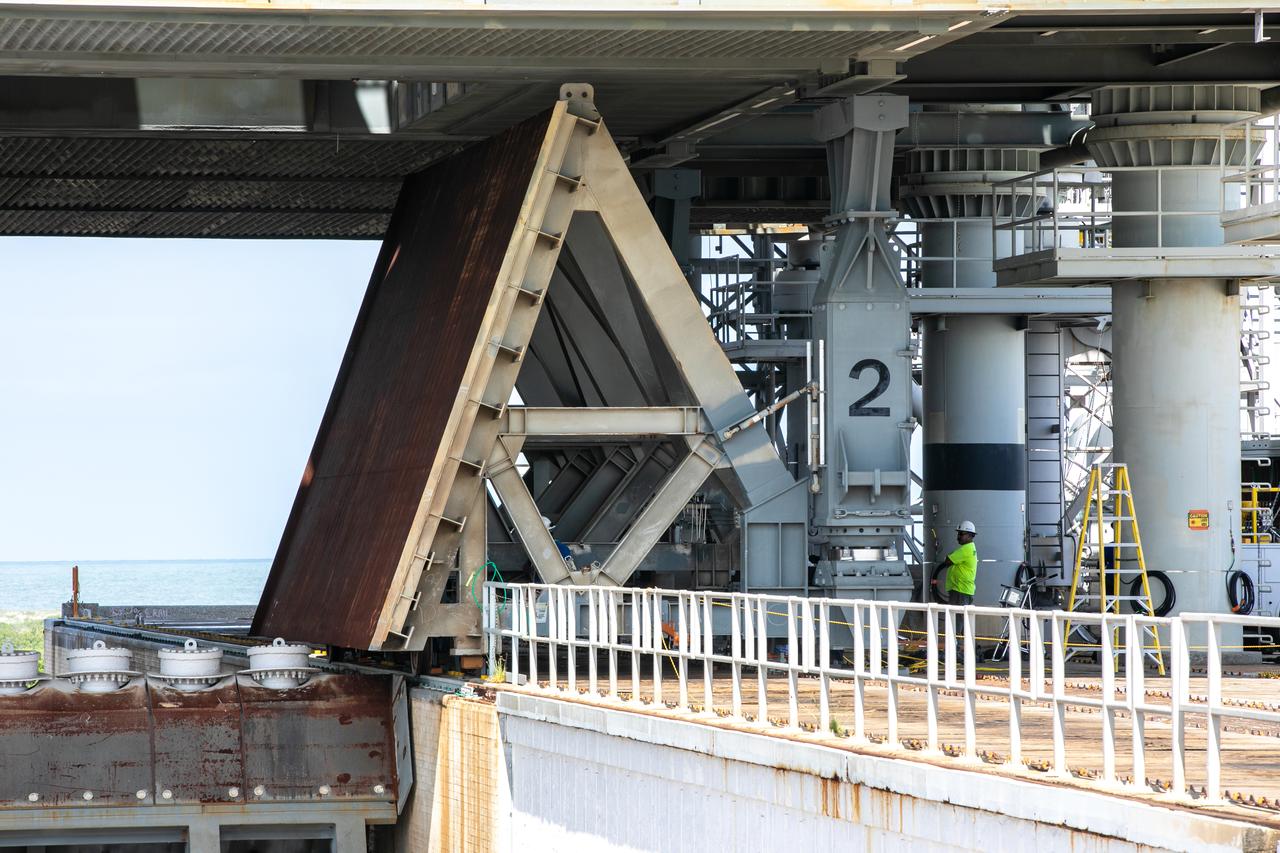

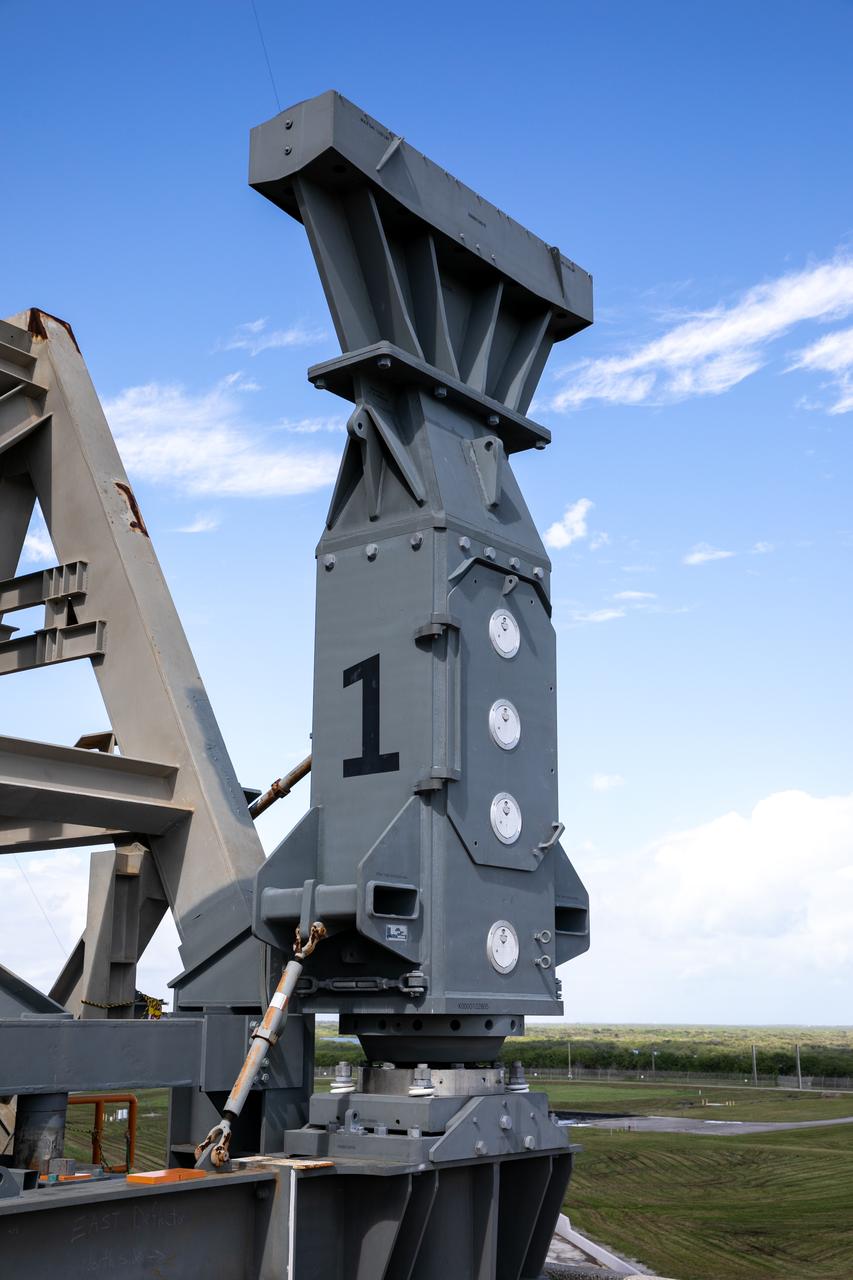
A close-up view of the base of one of the side flame deflectors positioned underneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I during a countdown demonstration test at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

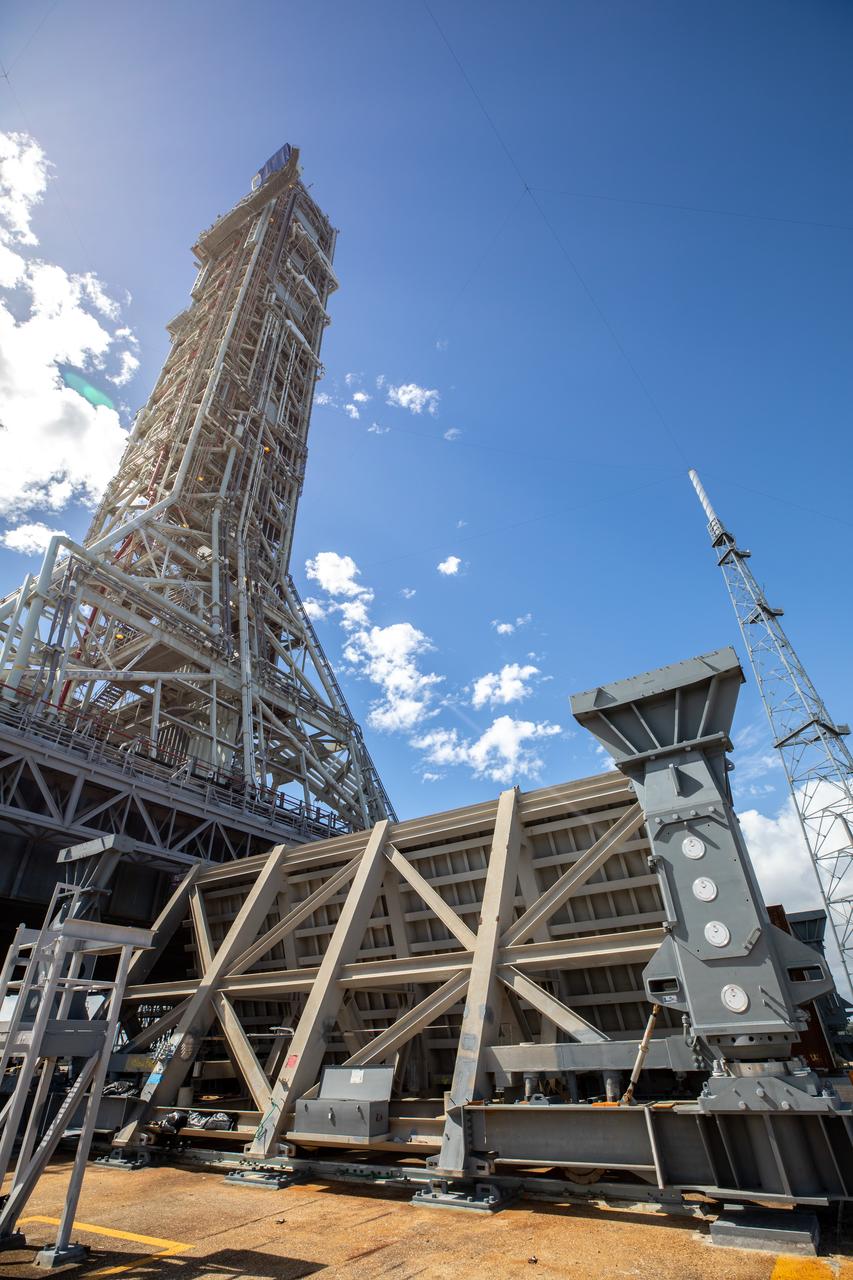
A view of the mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

The base of the mobile launcher for Artemis I is in view on Launch Pad 3B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. Workers on scaffolding are preparing for a launch countdown demonstration. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher will remain at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
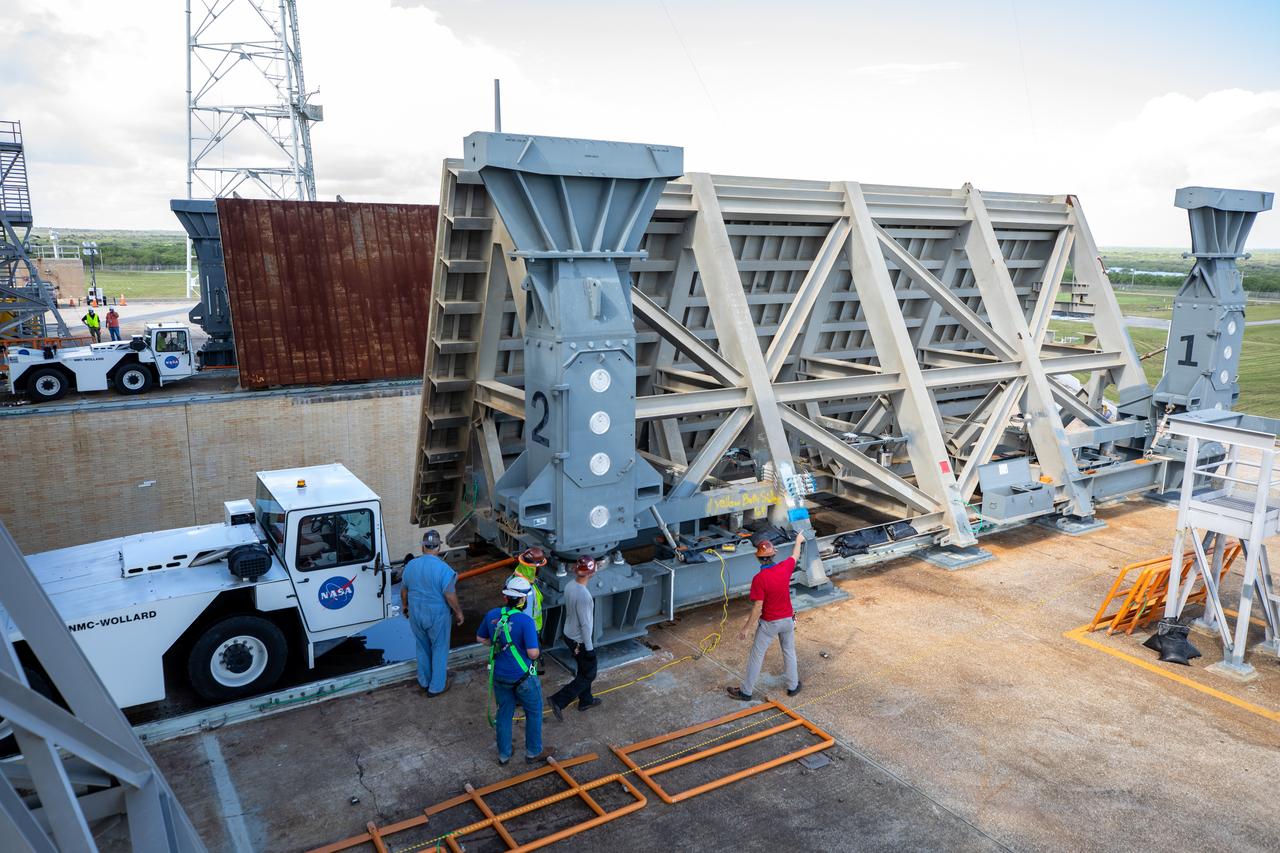

Technicians help move the side flame deflectors into place during a countdown demonstration test using the mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Special ground support equipment is used to move the side flame deflectors into place during a countdown demonstration test using the mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
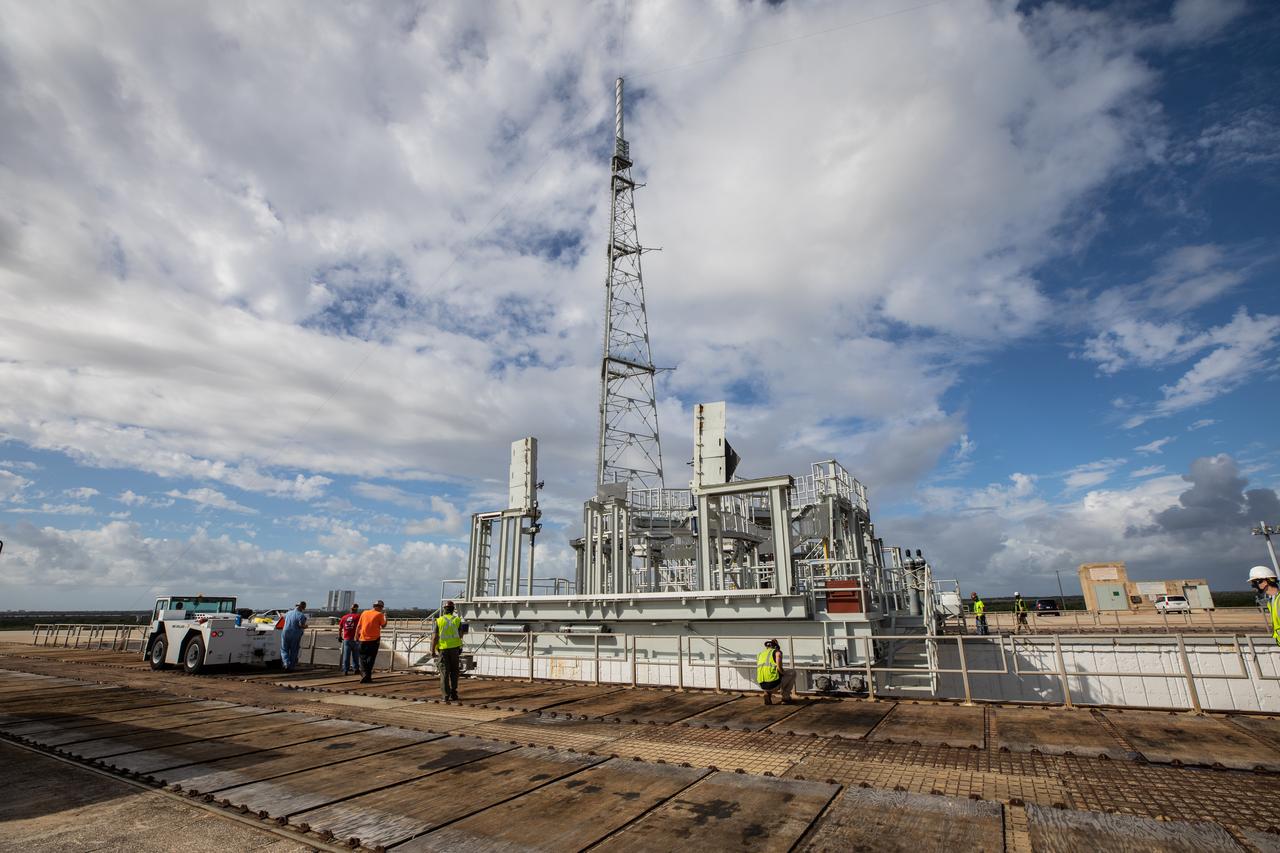

A view of Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The mobile launcher for Artemis I is at the pad. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
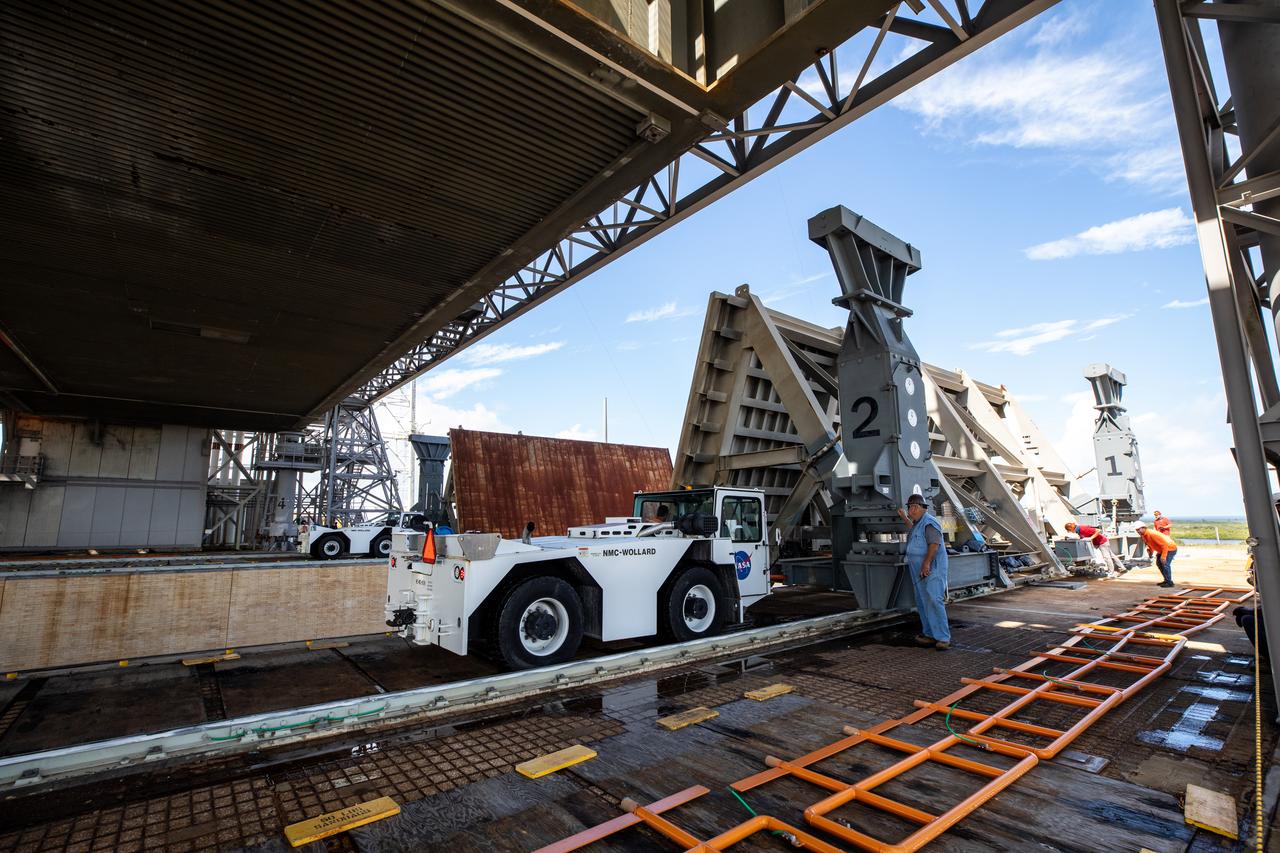

Special ground support equipment is used to move one of two side flame deflectors underneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I during a countdown demonstration test at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
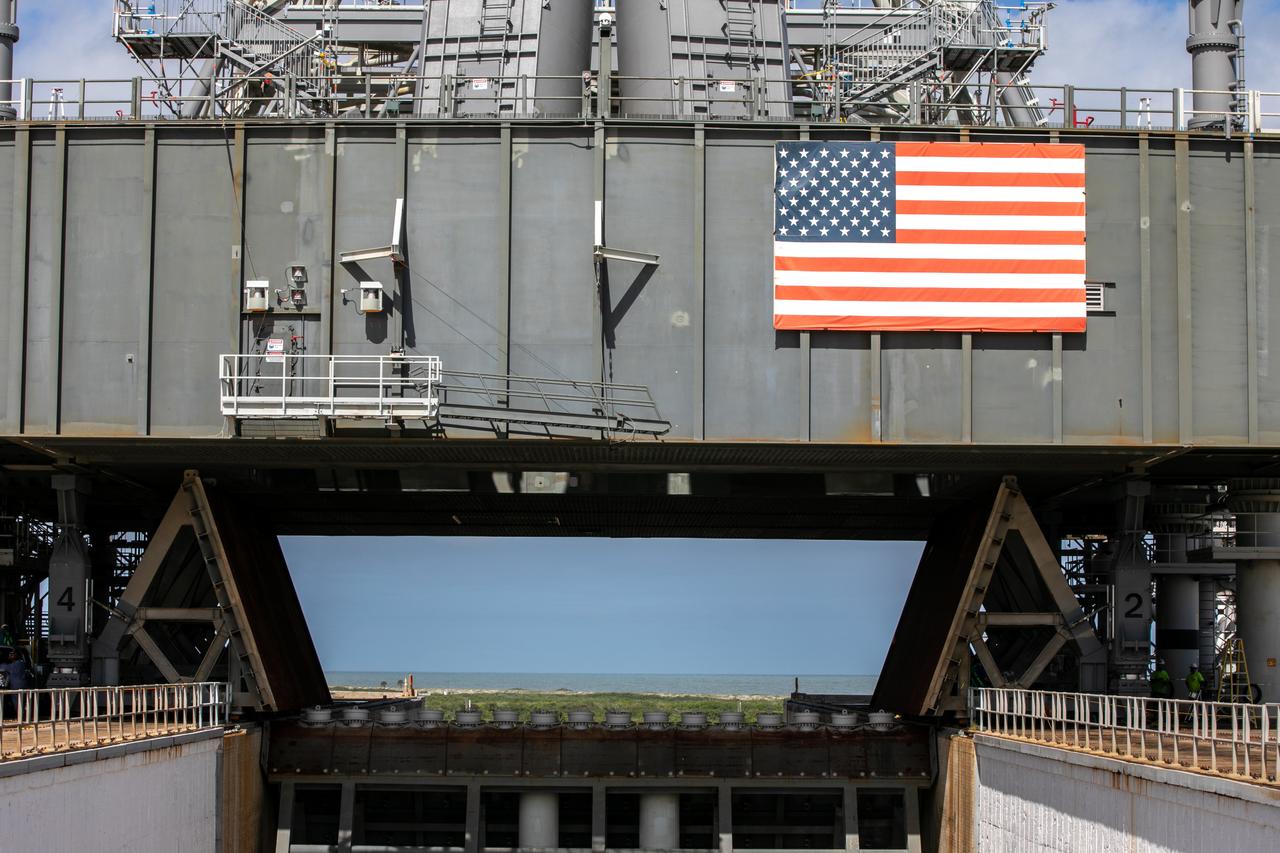
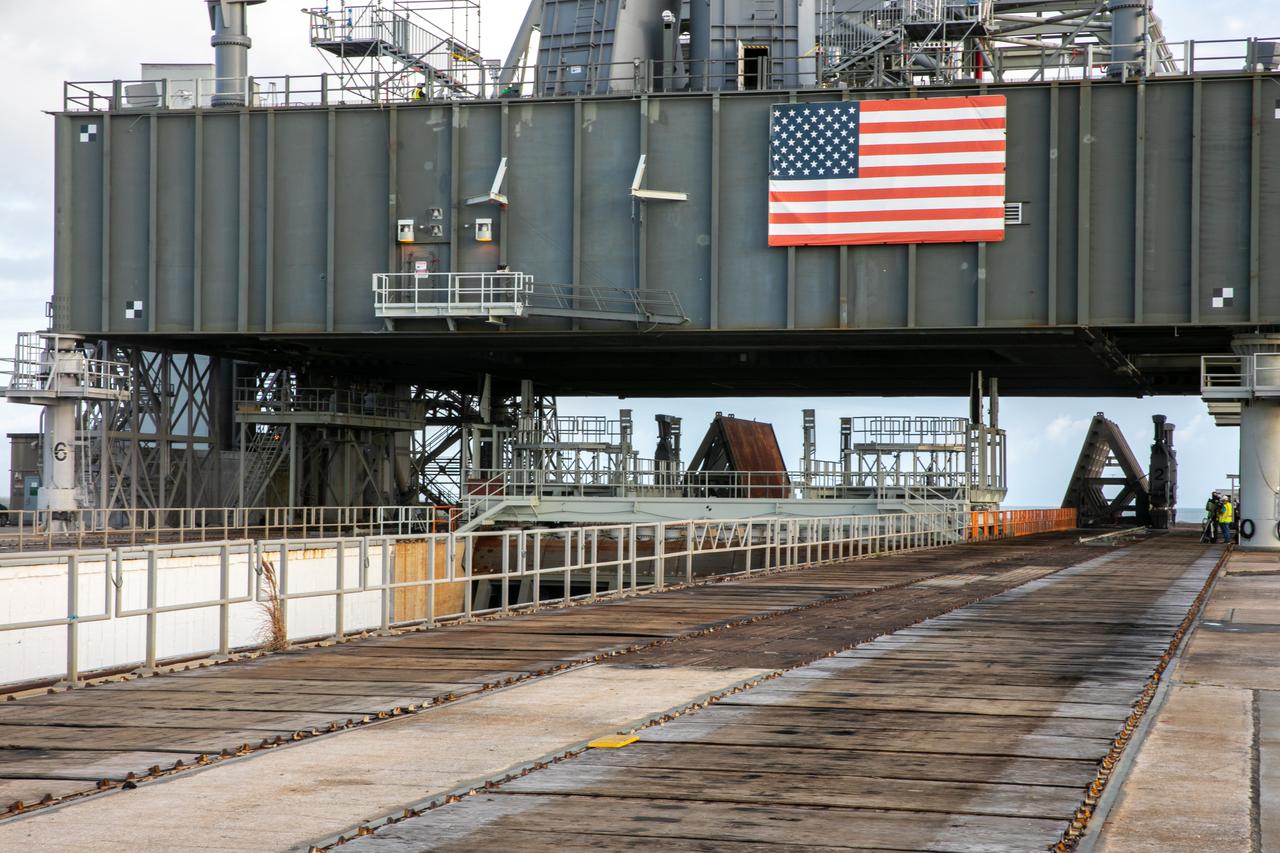
A close-up view of the base of the mobile launcher for Artemis I with the two side flame deflectors positioned underneath during a countdown demonstration test at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Special ground support equipment is used to move the side flame deflectors into place during a countdown demonstration test using the mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
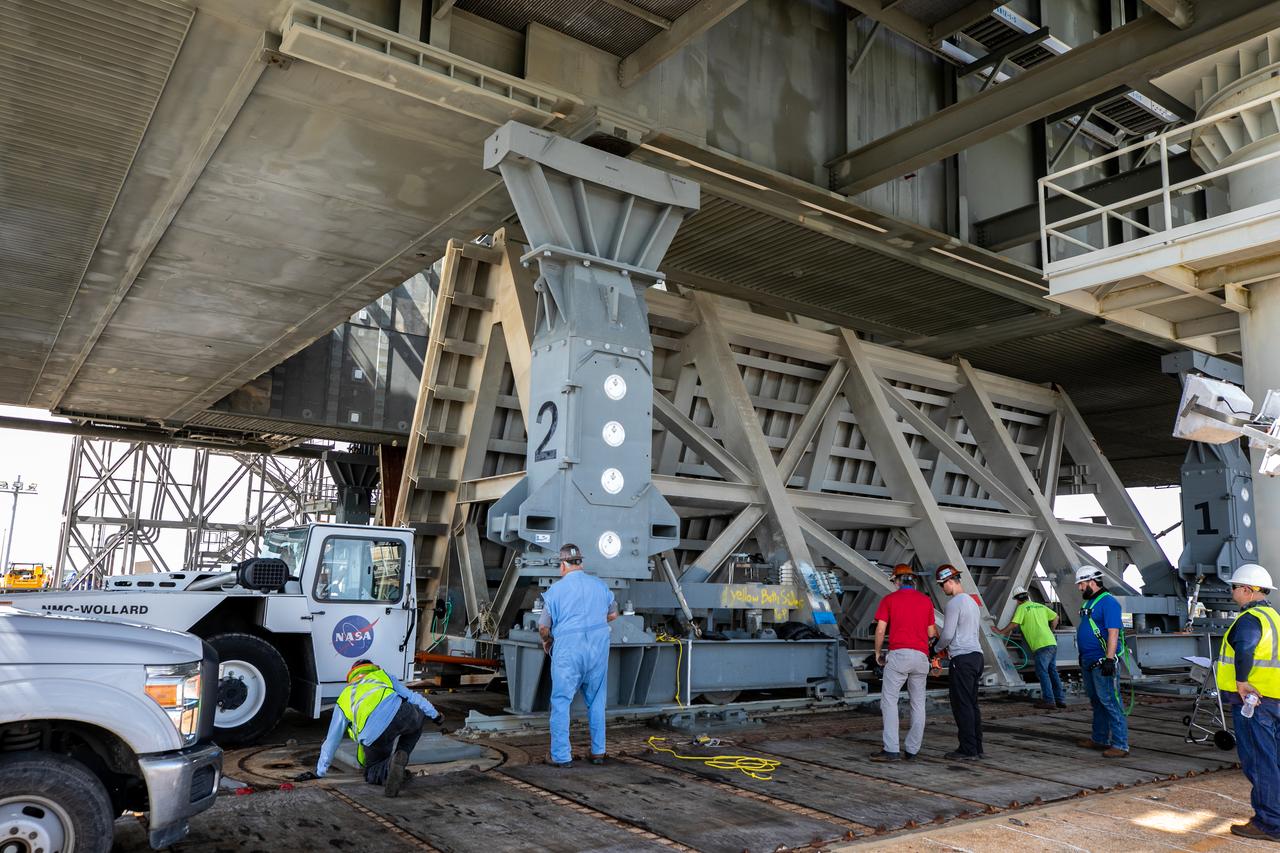

Special ground support equipment is used to move one of two side flame deflectors underneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I during a countdown demonstration test at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Special ground support equipment is used to move the side flame deflectors into place during a countdown demonstration test using the mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

A view of the mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Special ground support equipment is used to position one of two side flame deflectors underneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I during a countdown demonstration test at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Special ground support equipment is used to move one of two side flame deflectors underneath the mobile launcher for Artemis I during a countdown demonstration test at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
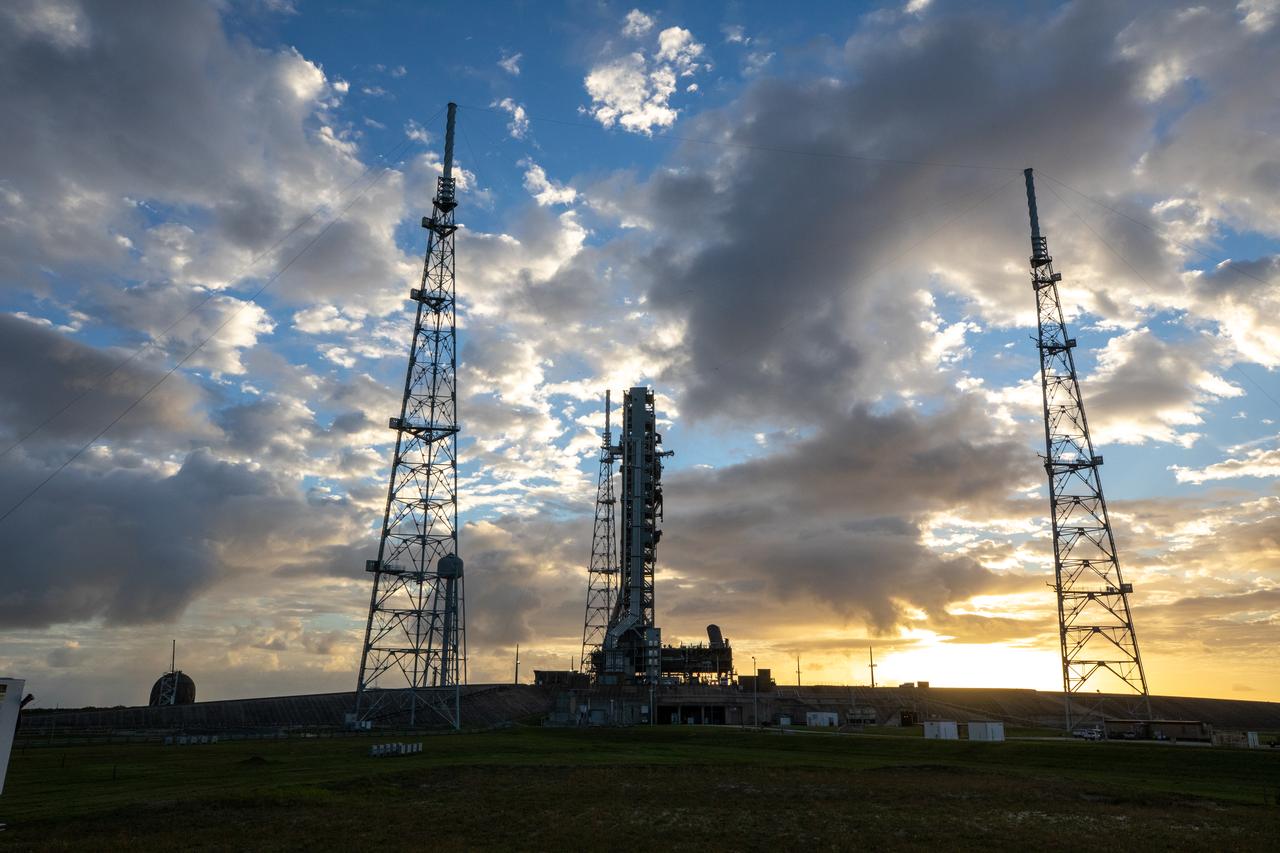

The mobile launcher for the Artemis I mission is in view on the top of Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 23, 2020. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad to allow engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs to complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

An engineer with Exploration Ground Systems monitors countdown demonstration activities occurring on the mobile launcher for Artemis I on Oct. 23, 2020, at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nearly 400-foot-tall mobile launcher is at the pad while engineers with Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs complete several tasks, including a timing test to validate the launch team’s countdown timeline, and a thorough, top-to-bottom wash down of the mobile launcher to remove any debris remaining from construction and installation of the umbilical arms. Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
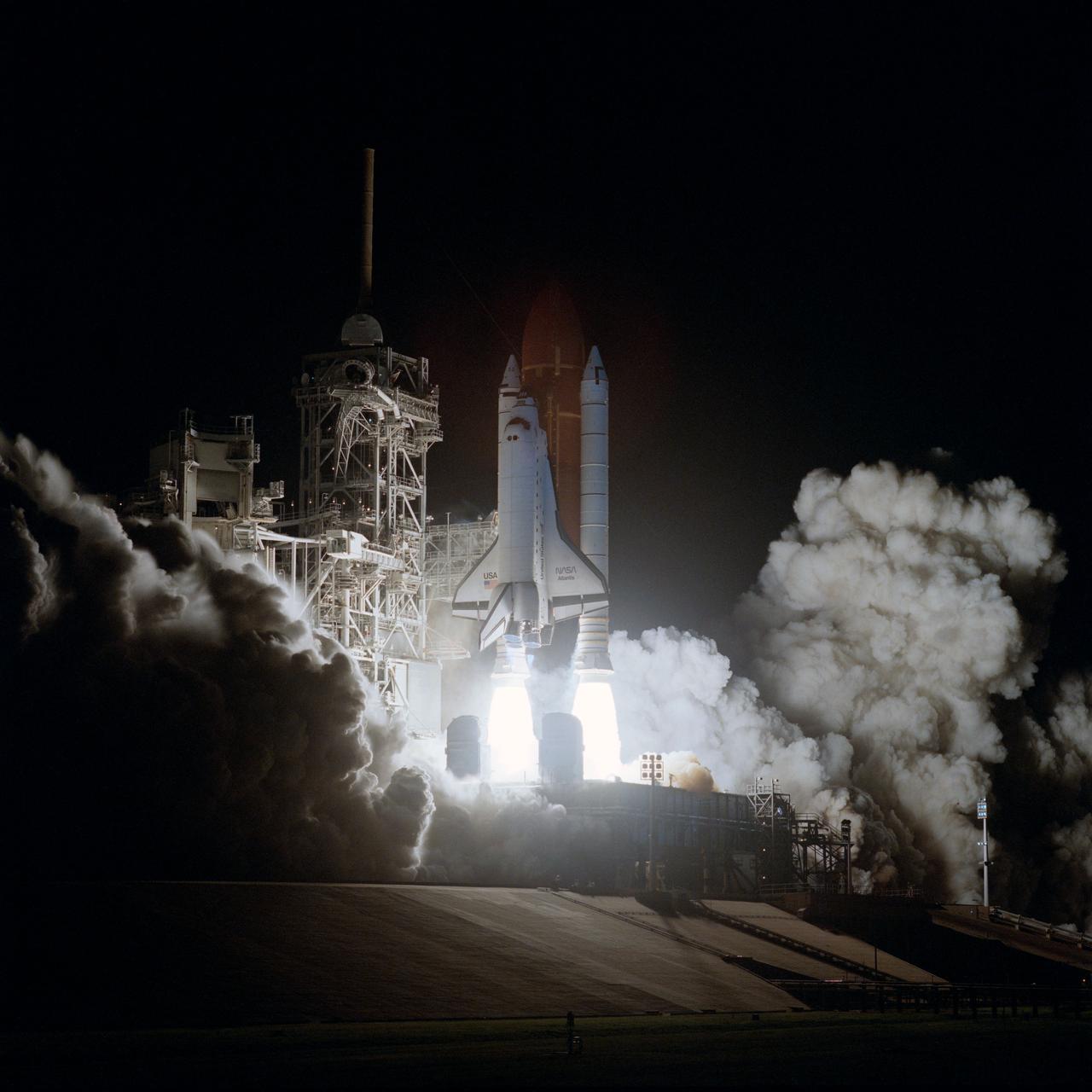

STS-38 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, lifts off from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex Pad at 6:46:15:0639 pm (Eastern Standard Time (EST)). As OV-104, atop the external tank (ET) and flanked by two solid rocket boosters (SRBs), rises above the mobile launcher platform, exhaust smoke fills the area surrounding the launch pad. SRB and space shuttle main engine (SSME) firings glow against the night darkness and light up the fixed service structure (FSS) and retracted rotating service structure (RSS). STS-38 is a Department of Defense (DOD) devoted mission.
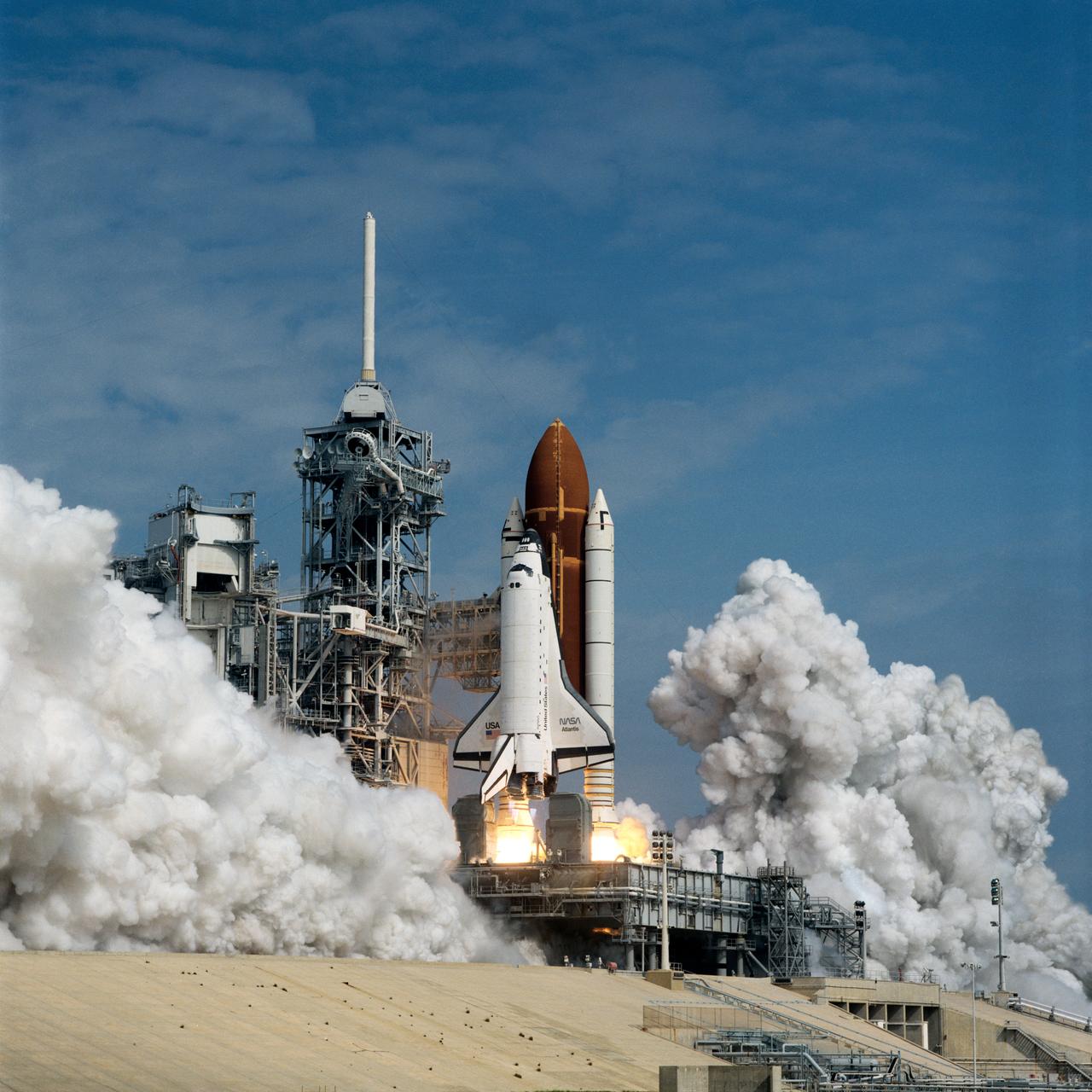

STS-37 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, lifts off from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad at 9:22:45:0439 (Eastern Standard Time (EST)). OV-104, atop its external tank (ET) and flanked by its two solid rocket boosters (SRBs), is captured just after space shuttle main engine (SSME) firing and as it rises above the mobile launcher platform. The fixed service structure (FSS) and retracted rotating service structure (RSS) appear along side OV-104. Clouds of exhaust smoke begin to fill the launch pad area.
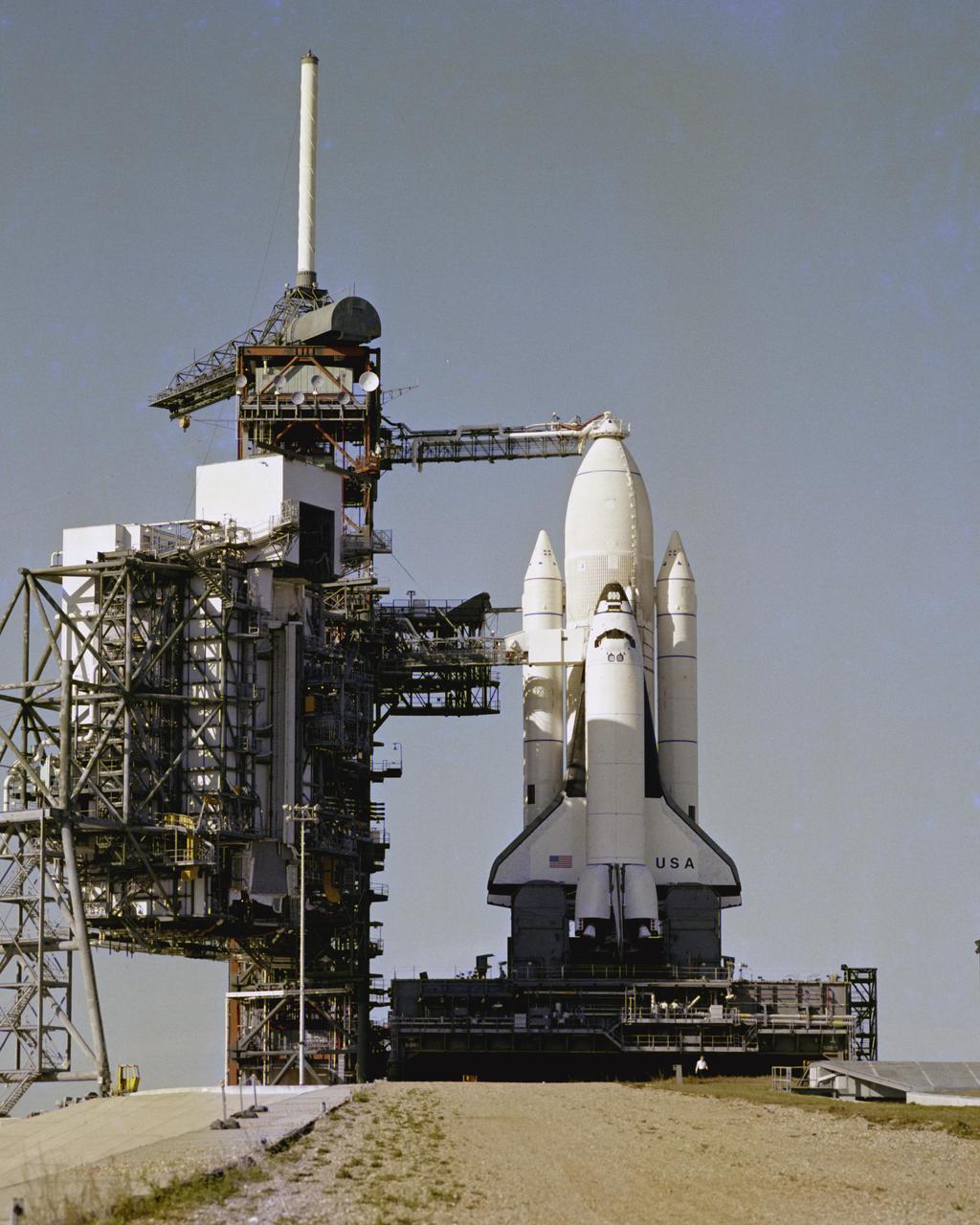

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - America's Space Shuttle stands poised on Launch Pad 39A, ready for Flight Readiness Firing of the main engines of the orbiter Columbia. The Rotating Service Structure has been retracted in this view, moving the 'White Room' access to the Cargo Bay and other support facilities away from the exhaust damage zone. This view was taken from the base of the approach ramp used by the Crawler when the Shuttle and its Mobile Launch Platform are moved from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the Pad.
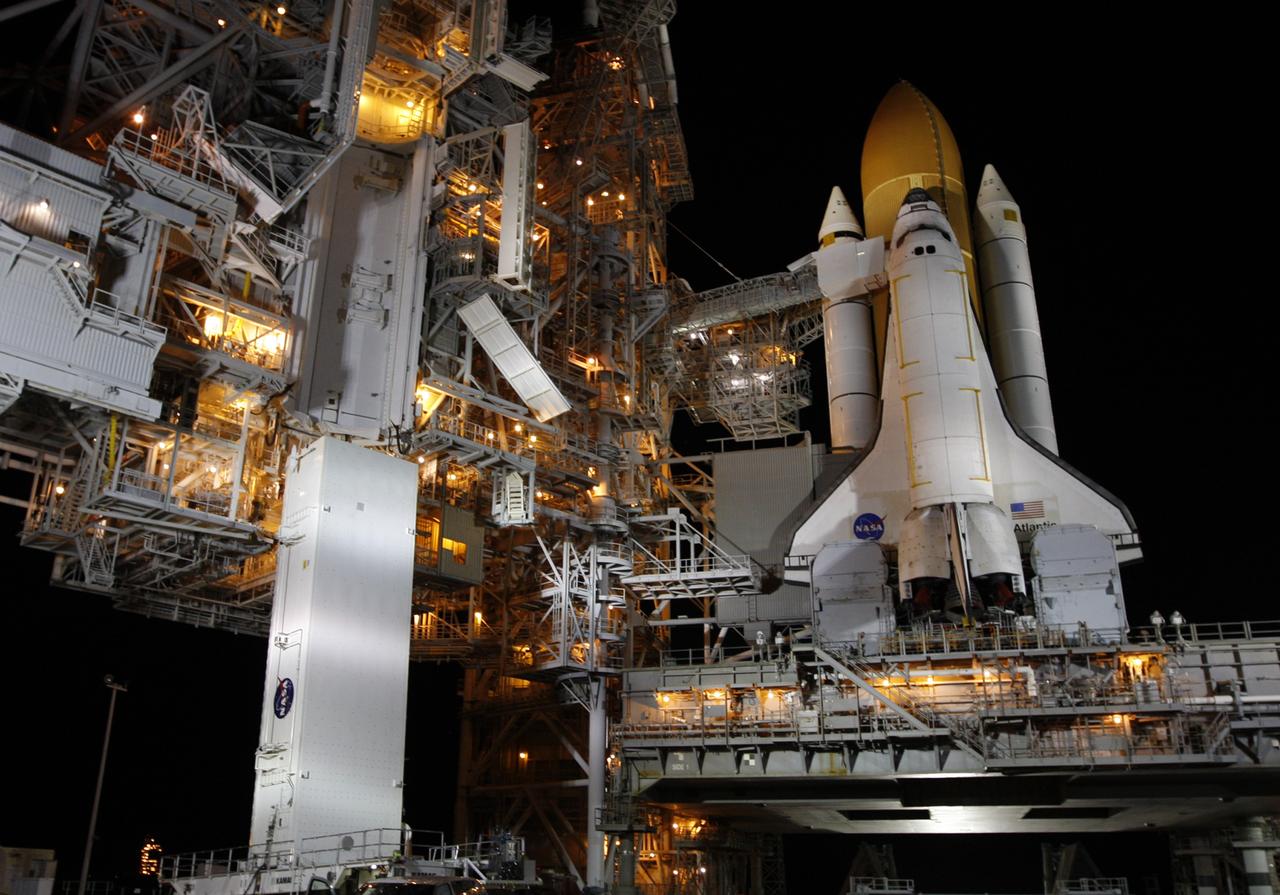

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the payload canister arrives beneath the payload changeout room in the rotating service structure (left). Space shuttle Atlantis is at right. The two tail service masts on the mobile launcher platform flank the engines in front of the wings. The canister carries a cargo of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the payload canister, at left, is lifted from its transporter toward the payload changeout room in the rotating service structure. The canister carries a cargo of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. Atlantis is seen at right, atop the mobile launcher platform. The two tail service masts flank the engines in front of the wings. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
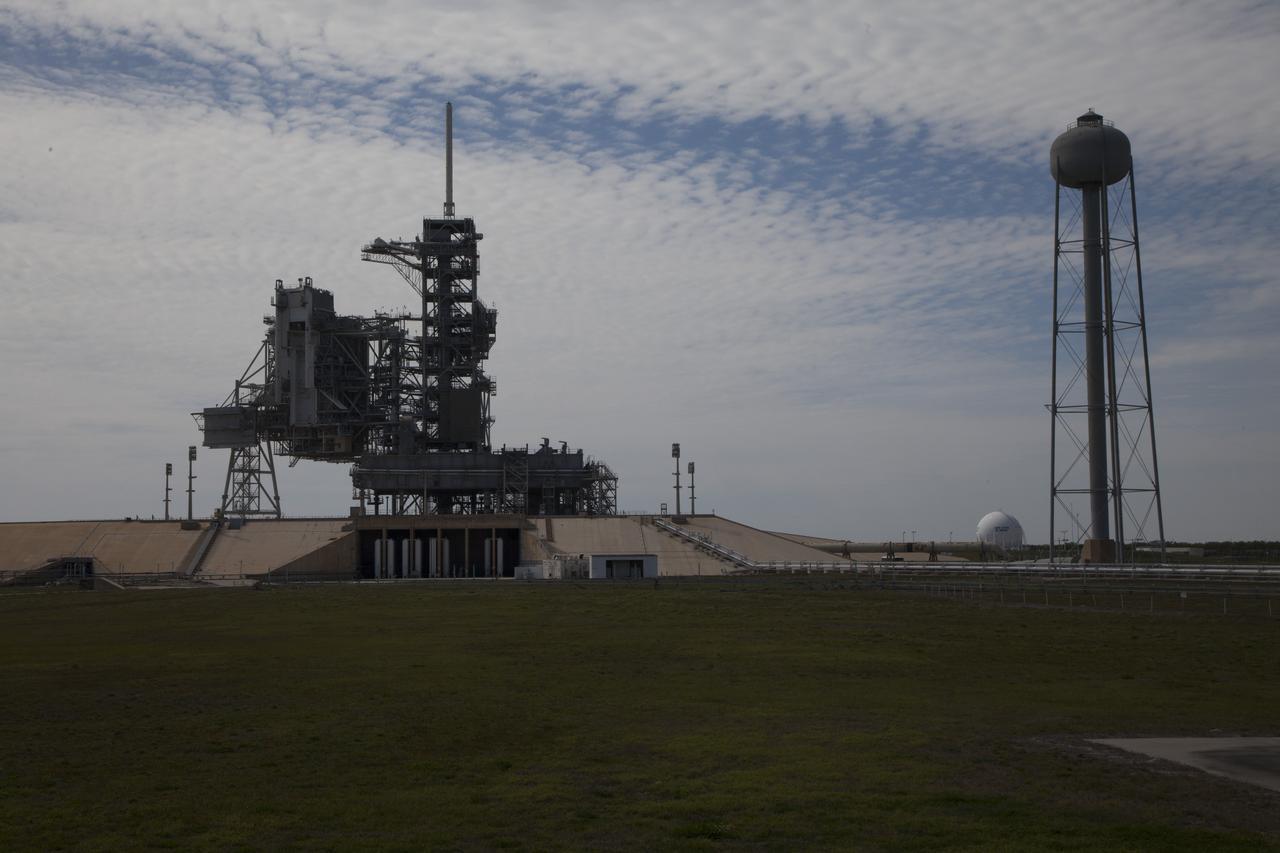

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch pad 39A looks much like it did after the liftoff of STS-135, the final space shuttle mission, on July 8, 2011. The mobile launcher platform remains in place next to the fixed service structure and rotating service structure. During the shuttle program, water was stored in the 290-foot-high, 300,000 gallon tank on the right. Water was released just prior to the main engine ignition and flows by gravity to special outlets on the platform to protect the orbiter and its payloads from being damaged by acoustical energy reflected from the platform during liftoff. Both launch pad 39A and 39B pad 39A was originally built for the Apollo/Saturn V rockets that launched American astronauts on their historic journeys to the moon and later modified to support the 30-year shuttle program. To learn more about Launch Pad 39A visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/launch/launch-complex39-toc.html Photo credit: NASA/Dan Casper
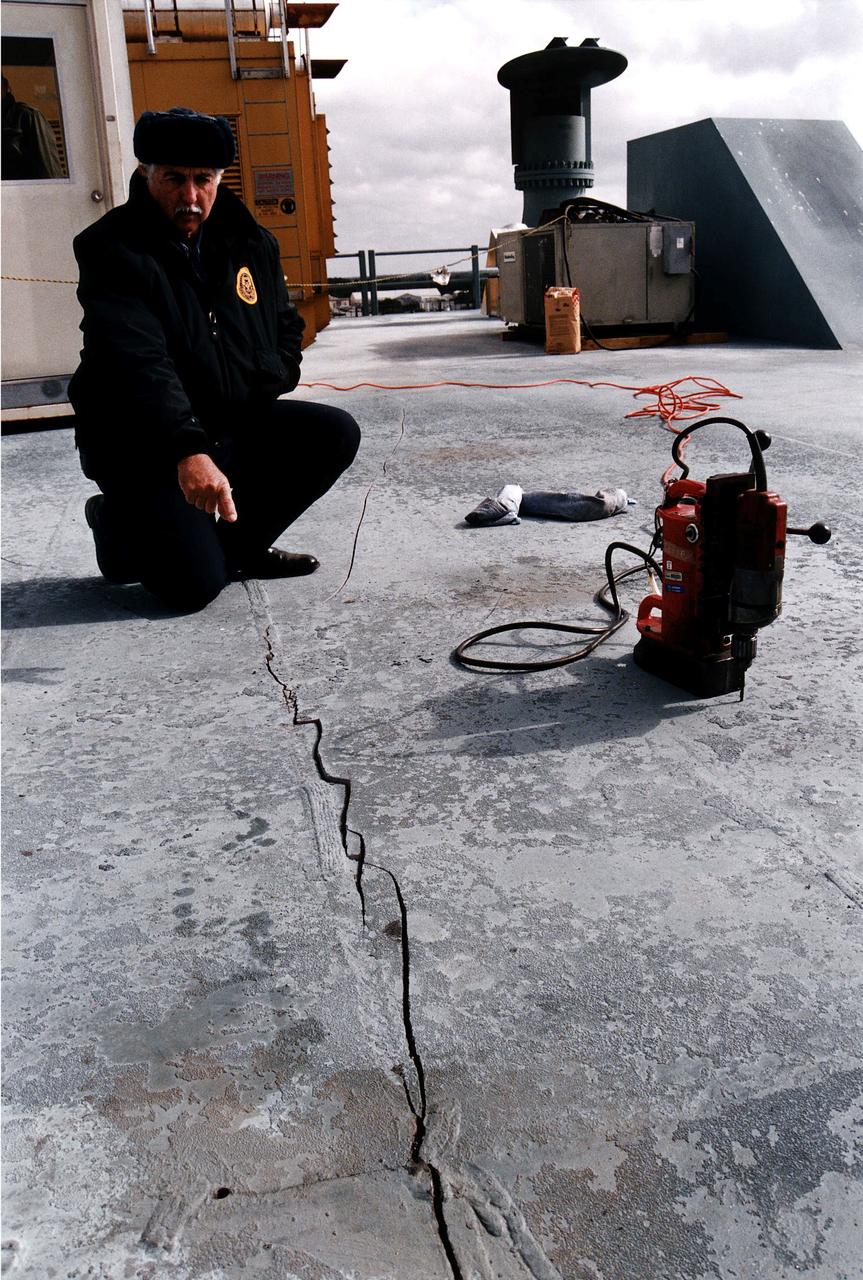

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Robert T. Nelson of KSC Security points to an approximately 24-foot-long crack on the Mobile Launcher Platform (MLP), which is holding the Space Shuttle Discovery en route to Launch Pad 39A for the STS-82 mission. Nelson was riding on the MLP when he heard a loud noise and noticed the crack. Rollout had begun shortly after 7 a.m. EST and was stopped at about 8:25 a.m. This Y-shaped crack is on the MLP surface and runs from near the left-hand solid rocket booster flame hole toward the near corner of the MLP. Rollout of Discovery resumed just past noon after structural engineers determined that the integrity of the MLP had not been compromised. Discovery is scheduled to lift off on the second Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission on Feb. 11.
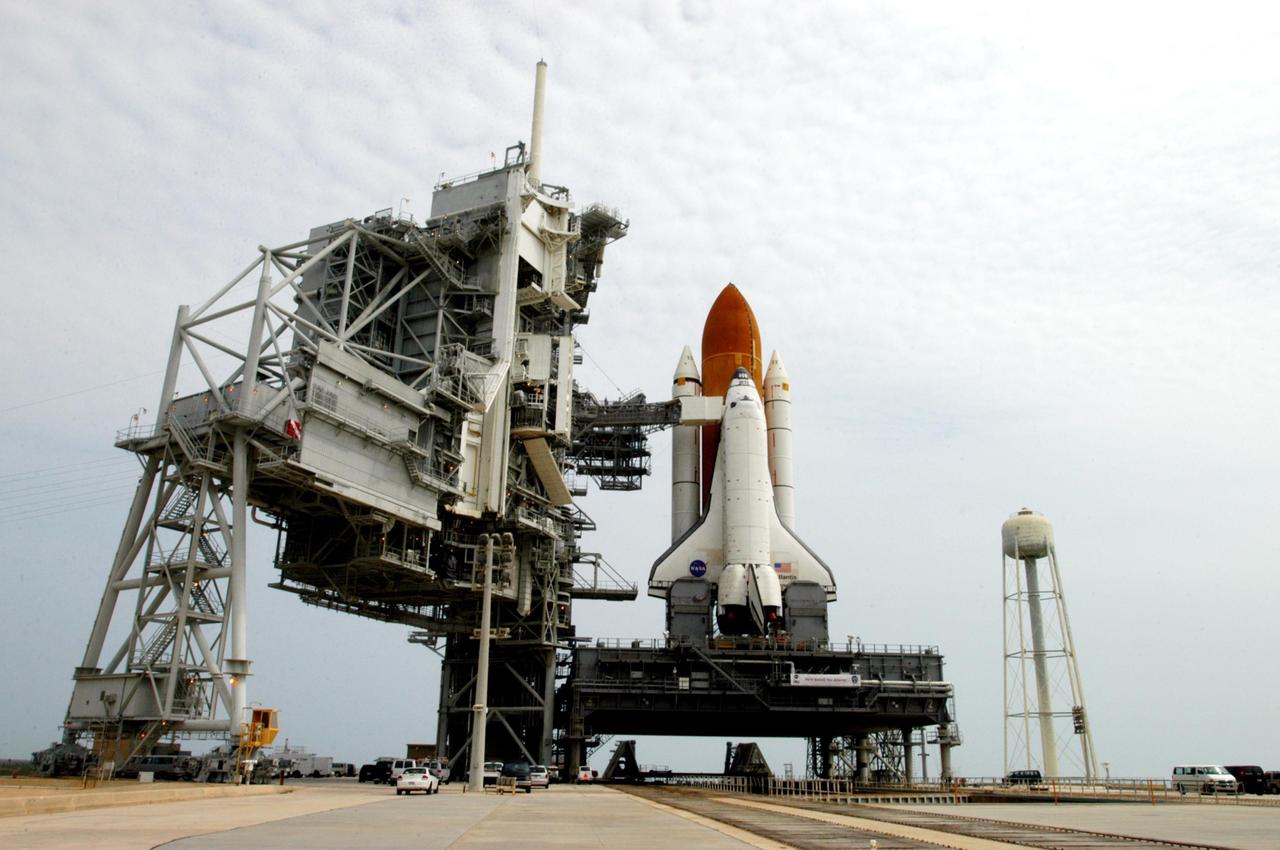

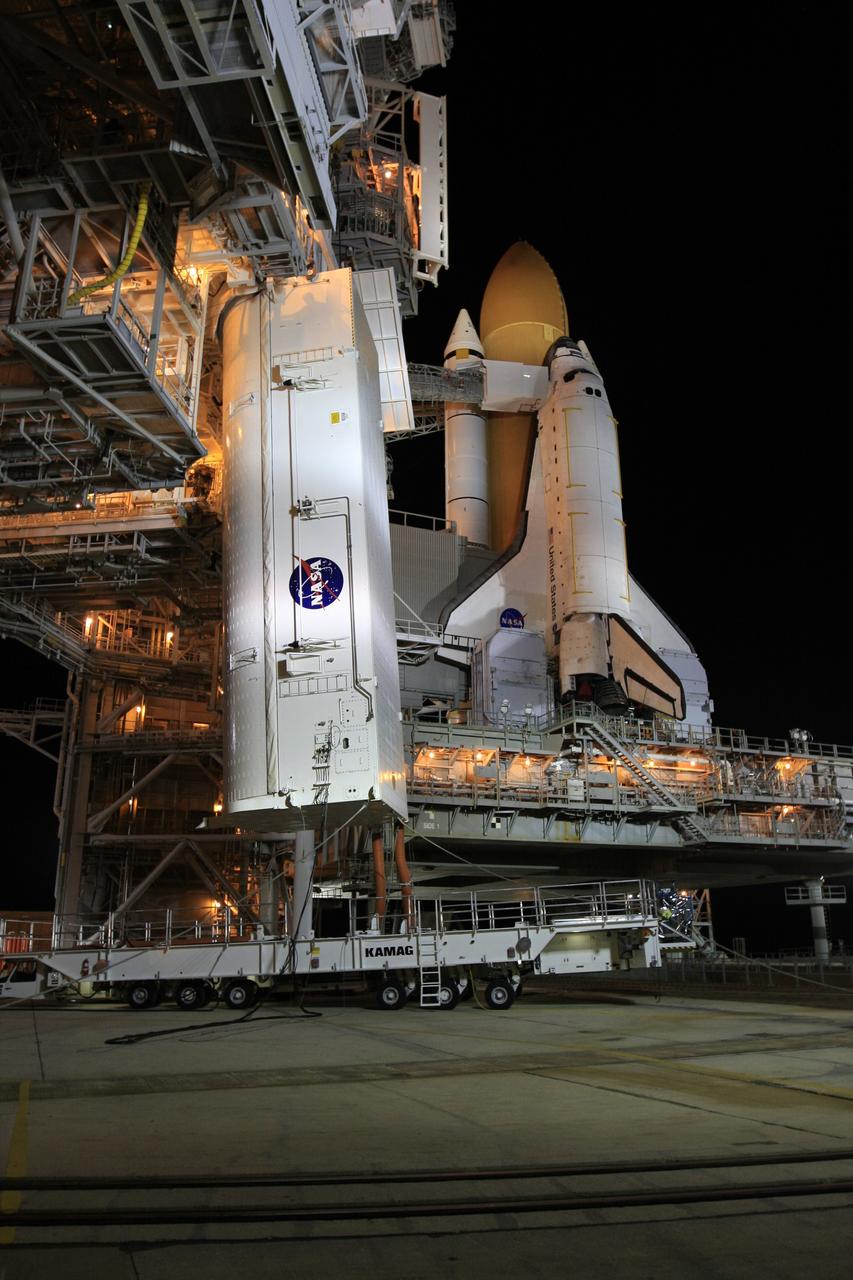
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Atlantis, atop the mobile launcher platform, sits on Launch Pad 39B after a nearly 8-hour crawl from the Vehicle Assembly Building. At left is the open rotating service structure and fixed service structure with the 80-foot lightning mast on top. Extended from the fixed structure is the orbiter access arm, with the White Room adjacent to Atlantis. At right is the 290-foot high, 300,000- gallon water tank that aids in sound suppression during launch. The water releases just prior to the ignition of the shuttle engines and flows through 7-foot-diameter pipes for about 20 seconds, pouring into 16 nozzles atop the flame deflectors and from outlets in the main engines exhaust hole in the mobile launcher platform. Atlantis' launch window begins Aug. 27 for an 11-day mission to the International Space Station. The STS-115 crew of six astronauts will continue construction of the station and install their cargo, the Port 3/4 truss segment with its two large solar arrays. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder & George Shelton
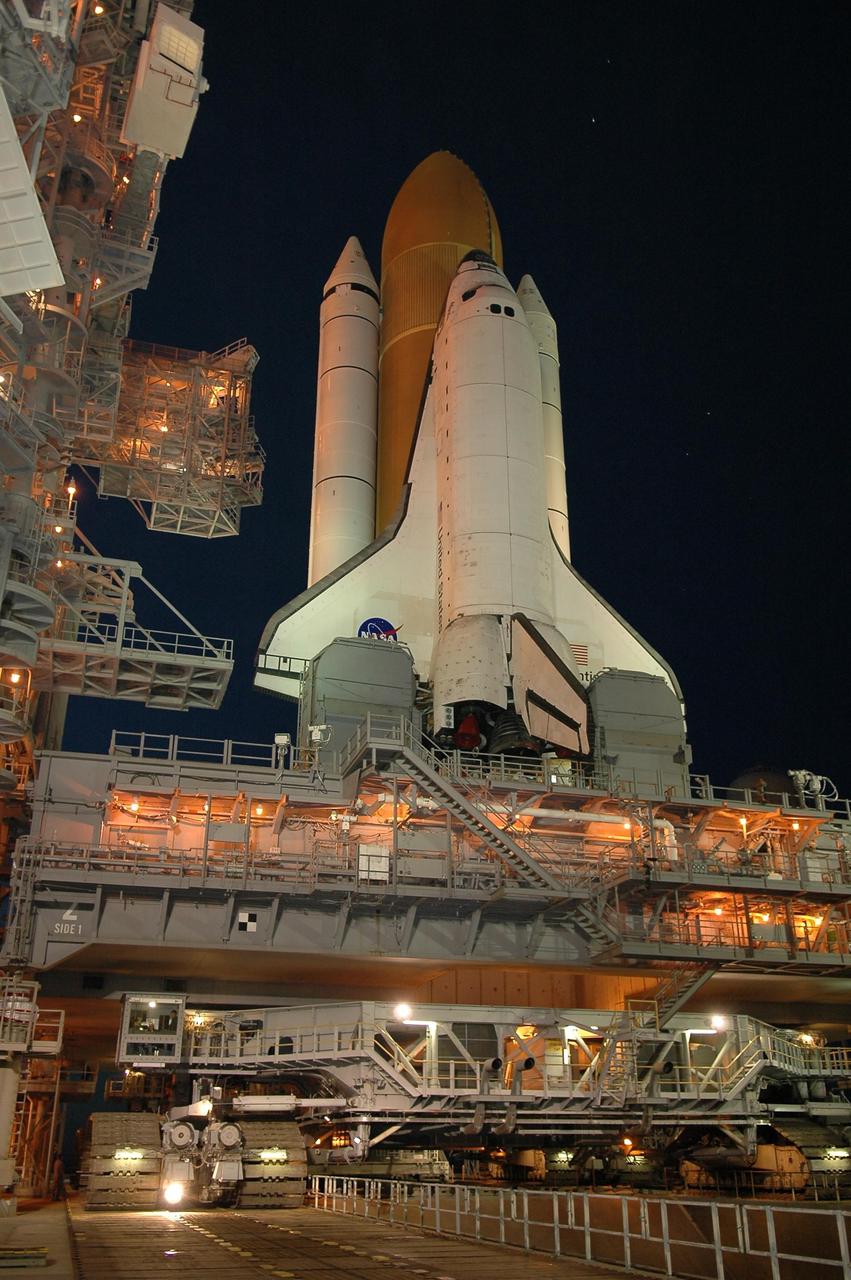

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After sunset, Space Shuttle Atlantis is bathed in light from the fixed service structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen on either side of Atlantis' engine nozzles are the tail masts, which provide several umbilical connections to the orbiter, including a liquid-oxygen line through one and a liquid-hydrogen line through another. Below the mobile launcher platform, on which Atlantis rests, is the crawler-transporter beginning to move away from the platform. The shuttle had been moved off the launch pad due to concerns about the impact of Tropical Storm Ernesto, expected within 24 hours. The forecast of lesser winds expected from Ernesto and its projected direction convinced Launch Integration Manager LeRoy Cain and Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach to return the shuttle to the launch pad. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
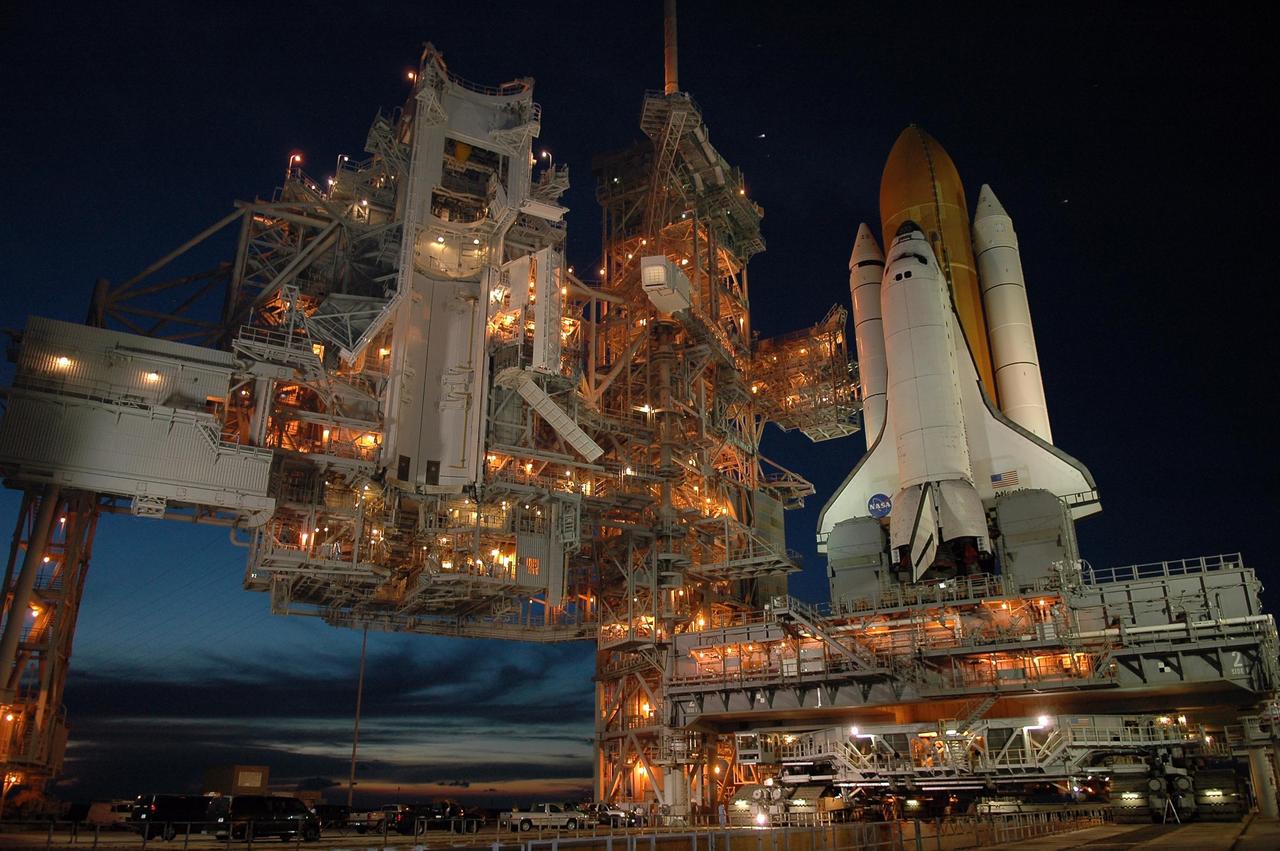

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After sunset, Space Shuttle Atlantis is bathed in light from the fixed service structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen on either side of Atlantis' engine nozzles are the tail masts, which provide several umbilical connections to the orbiter, including a liquid-oxygen line through one and a liquid-hydrogen line through another. Below the mobile launcher platform, on which Atlantis rests, is the crawler-transporter beginning to move away from the platform. The shuttle had been moved off the launch pad due to concerns about the impact of Tropical Storm Ernesto, expected within 24 hours. The forecast of lesser winds expected from Ernesto and its projected direction convinced Launch Integration Manager LeRoy Cain and Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach to return the shuttle to the launch pad. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
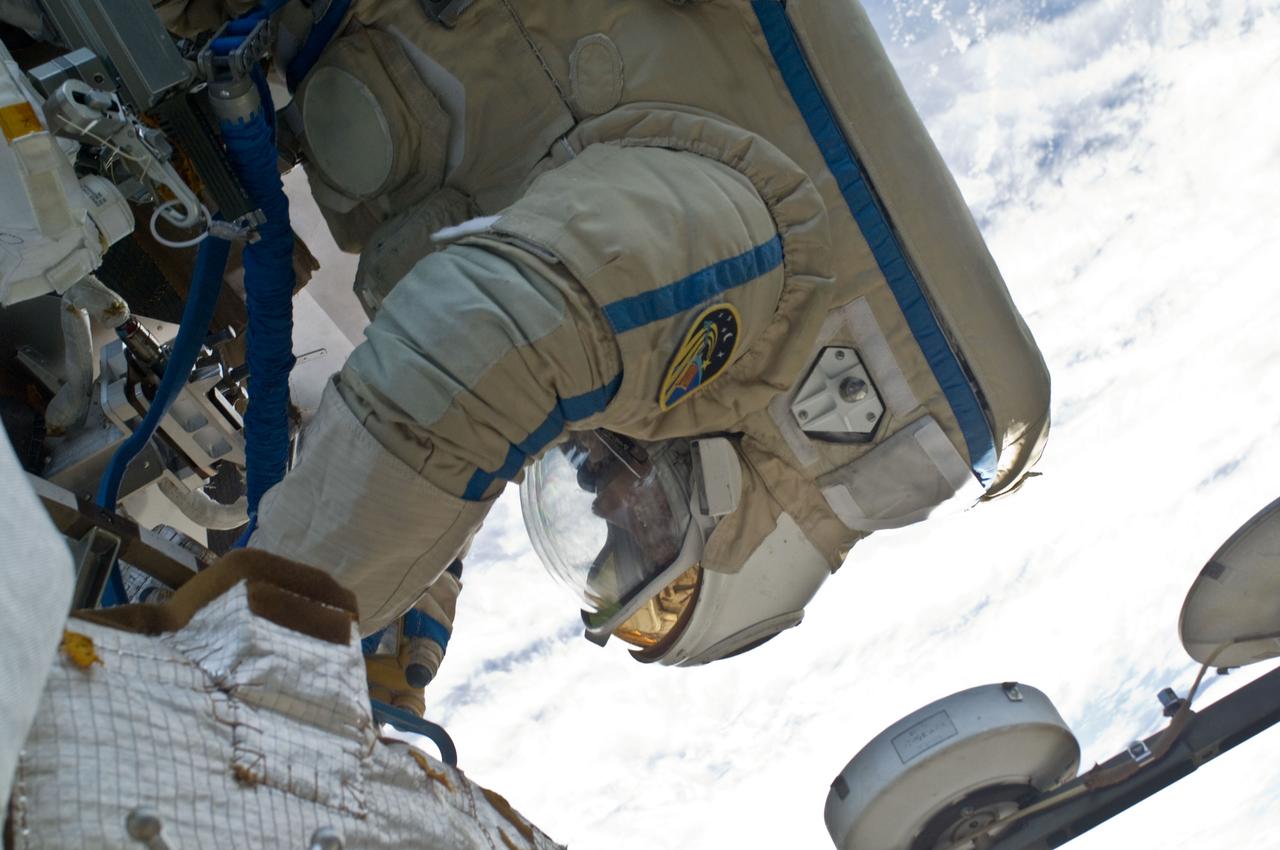

ISS018-E-039156 (10 March 2009) --- Cosmonaut Yury Lonchakov, Expedition 18 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to perform maintenance on the International Space Station. During the 4-hour, 49-minute spacewalk, Lonchakov and astronaut Michael Fincke (out of frame), commander, reinstalled the Exposing Specimens of Organic and Biological Materials to Open Space (Expose-R) experiment on the universal science platform mounted to the exterior of the Zvezda Service Module. The spacewalkers also removed straps, or tape, from the area of the docking target on the Pirs airlock and docking compartment. The tape was removed to ensure it does not get in the way during the arrival of visiting Soyuz or Progress spacecraft.
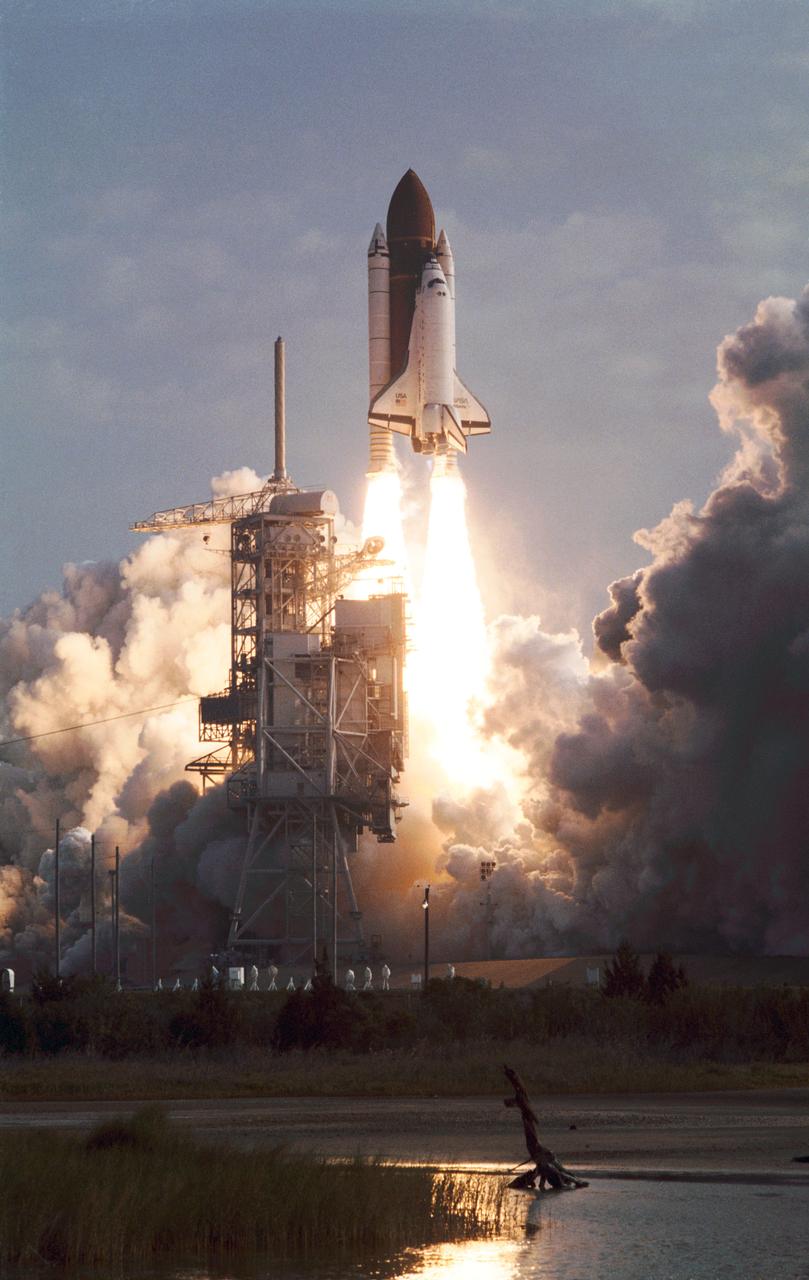

STS-45 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, lifts off from a Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad at 8:13:40:048 am (Eastern Standard Time (EST)). Exhaust billows out the solid rocket boosters (SRBs) as OV-104 atop its external tank (ET) soars above the mobile launcher platform and is nearly clear of the fixed service structure (FSS) tower. The diamond shock effect produced by the space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) is visible. The glow of the SRB/SSME firings is reflected in a nearby waterway. An exhaust cloud covers the launch pad area.
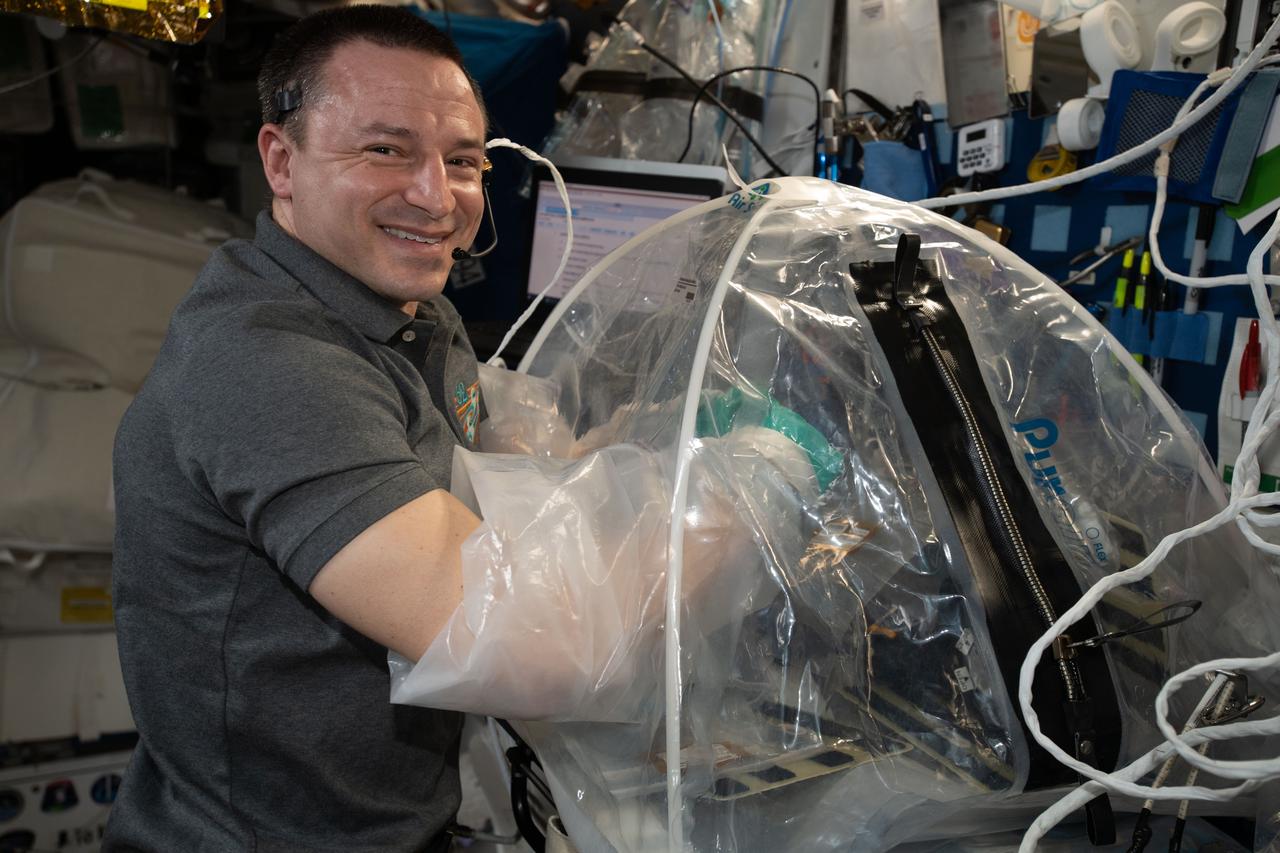

iss062e098371 (March 17, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 62 Flight Engineer Andrew Morgan conducts cardiac research activities inside the portable glovebag. Morgan was servicing heart cell samples for the Multi-use Variable-g Platform-02 Cell-03 experiment. The investigation induces stem cells to generate heart precursor cells and cultures those cells on the space station to analyze and compare with cultures grown on Earth. Results may help treat spaceflight-induced cardiac abnormalities and accelerate development and reduce costs of drug therapies on Earth.
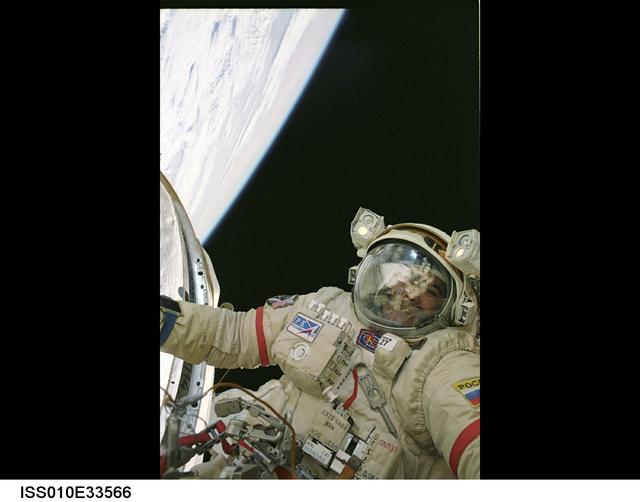

ISS010-E-33566 (26 January 2005) --- Cosmonaut Salizhan S. Sharipov, Expedition 10 flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, participates in the first of two sessions of extravehicular activities (EVA) performed by the Expedition 10 crew during their six-month mission. Sharipov and astronaut Leroy Chiao (out of frame), mission commander and NASA ISS science officer, spent 5 ½ hours outside the International Space Station (ISS) installing a work platform, cables and robotic and scientific experiments on the exterior of the Zvezda Service Module. Earth’s horizon and the blackness of space provided the backdrop for the image.
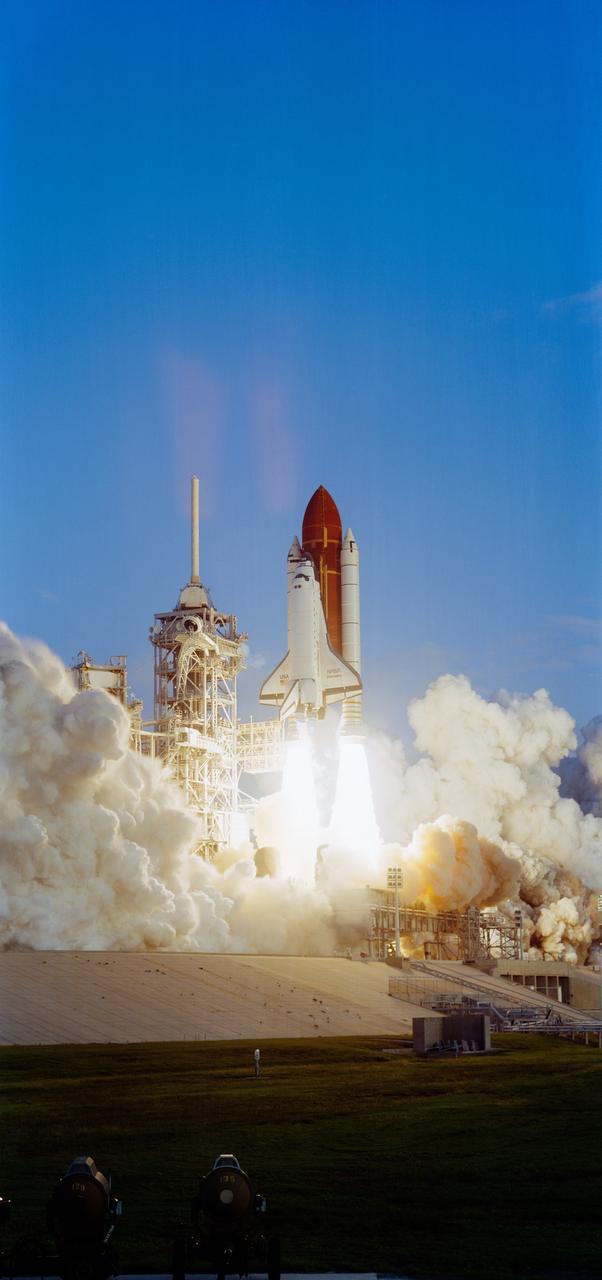

STS-41 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, lifts off from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39 mobile launcher platform at 7:47 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). OV-103 riding atop the external tank (ET) and flanked by two solid rocket boosters (SRBs), is captured just moments after liftoff. Not yet clear of the fixed service structure (FSS) tower, OV-103 is highlighted against the cloudless morning sky. Exhaust smoke billows from the SRBs and the space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) creating a cloud over the launch pad area.
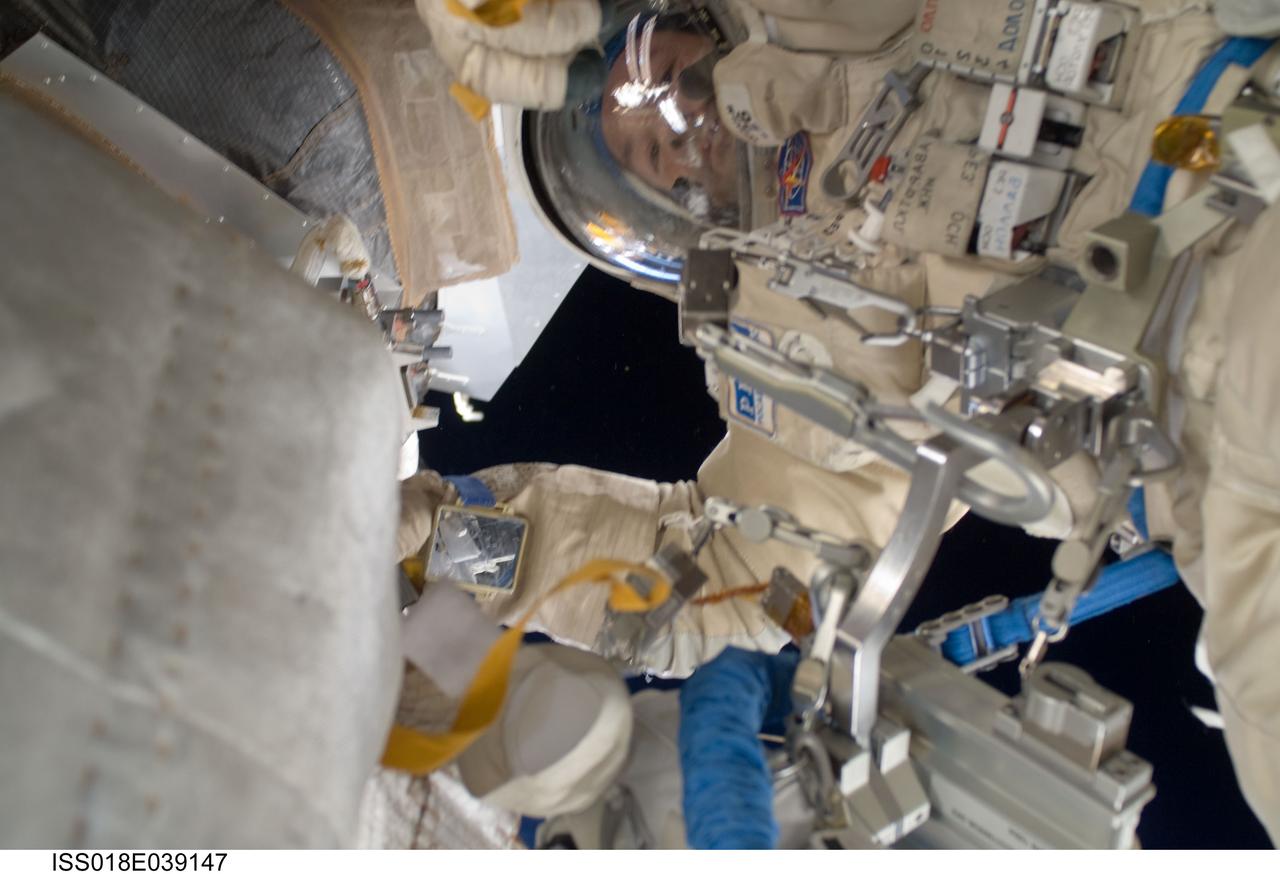

ISS018-E-039147 (10 March 2009) --- Cosmonaut Yury Lonchakov, Expedition 18 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to perform maintenance on the International Space Station. During the 4-hour, 49-minute spacewalk, Lonchakov and astronaut Michael Fincke (out of frame), commander, reinstalled the Exposing Specimens of Organic and Biological Materials to Open Space (Expose-R) experiment on the universal science platform mounted to the exterior of the Zvezda Service Module. The spacewalkers also removed straps, or tape, from the area of the docking target on the Pirs airlock and docking compartment. The tape was removed to ensure it does not get in the way during the arrival of visiting Soyuz or Progress spacecraft.
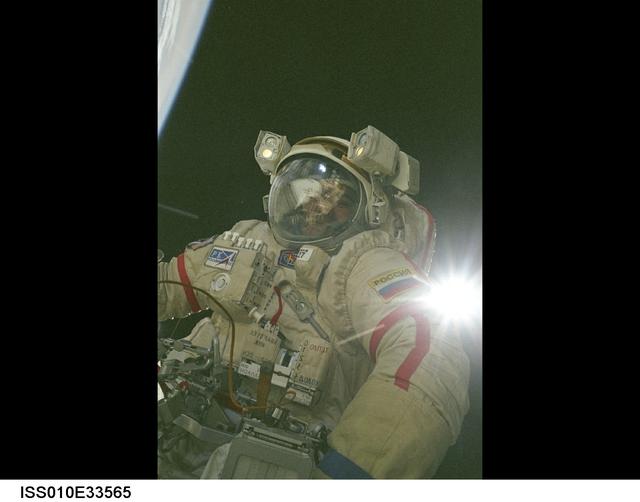

ISS010-E-33565 (26 January 2005) --- Cosmonaut Salizhan S. Sharipov, Expedition 10 flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, participates in the first of two sessions of extravehicular activities (EVA) performed by the Expedition 10 crew during their six-month mission. Sharipov and astronaut Leroy Chiao (out of frame), mission commander and NASA ISS science officer, spent 5 ½ hours outside the International Space Station (ISS) installing a work platform, cables and robotic and scientific experiments on the exterior of the Zvezda Service Module.
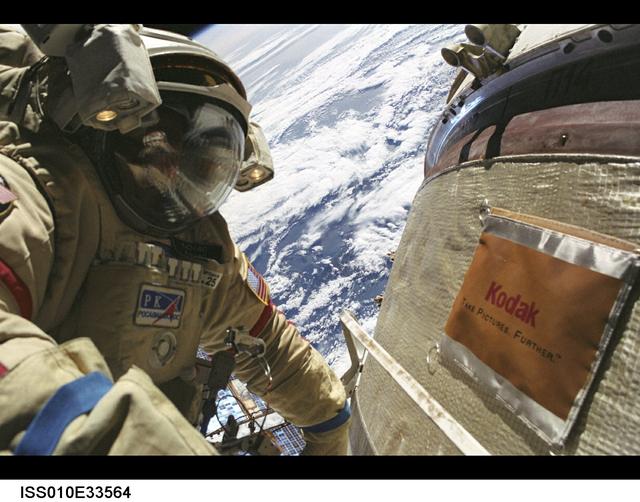

ISS010-E-33564 (26 January 2005) --- Astronaut Leroy Chiao, Expedition 10 commander and NASA ISS science officer, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, participates in the first of two sessions of extravehicular activities (EVA) performed by the Expedition 10 crew during their six-month mission. Chiao and cosmonaut Salizhan S. Sharipov (out of frame), flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, spent 5 ½ hours outside the International Space Station (ISS) installing a work platform, cables and robotic and scientific experiments on the exterior of the Zvezda Service Module. A cloudy Earth provided the backdrop for the image.
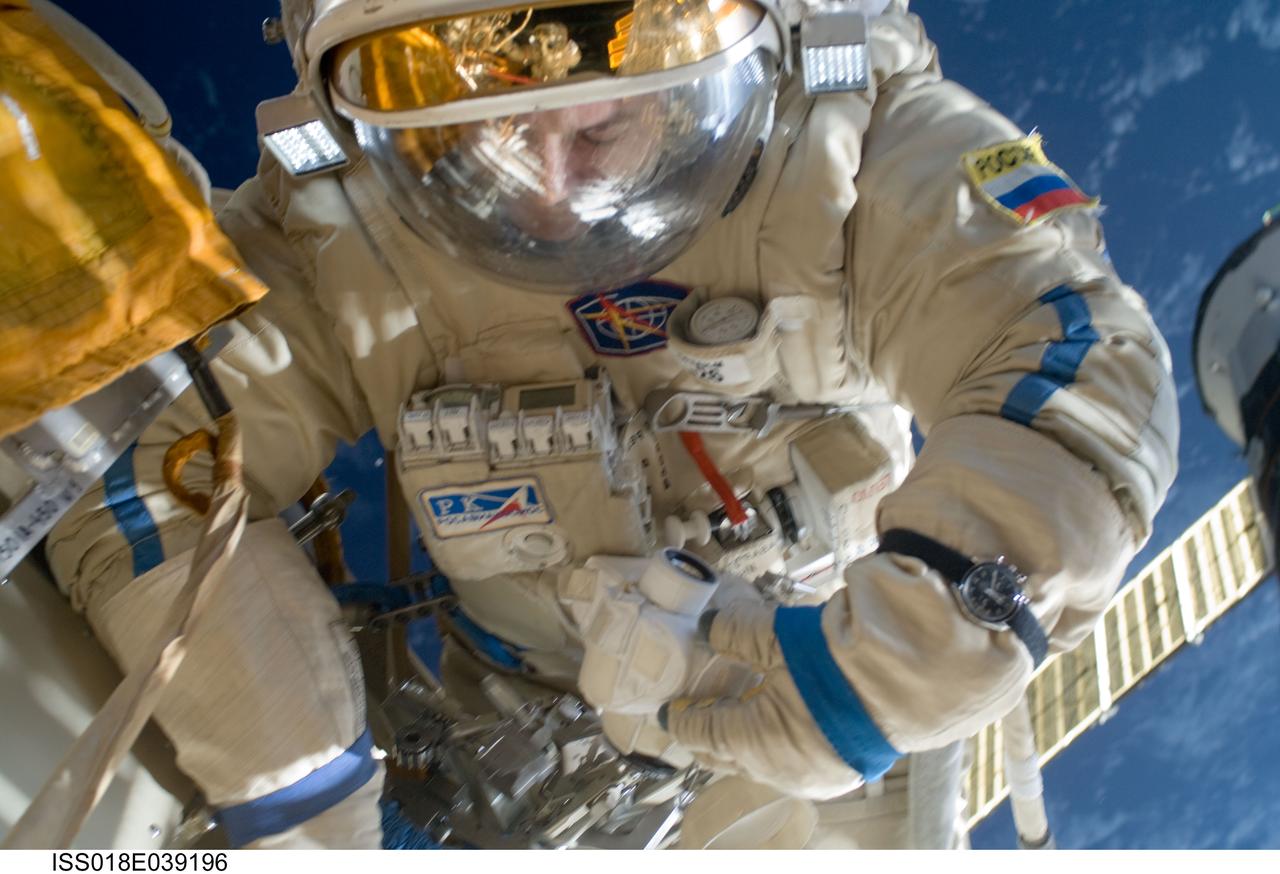

ISS018-E-039196 (10 March 2009) --- Cosmonaut Yury Lonchakov, Expedition 18 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to perform maintenance on the International Space Station. During the 4-hour, 49-minute spacewalk, Lonchakov and astronaut Michael Fincke (out of frame), commander, reinstalled the Exposing Specimens of Organic and Biological Materials to Open Space (Expose-R) experiment on the universal science platform mounted to the exterior of the Zvezda Service Module. The spacewalkers also removed straps, or tape, from the area of the docking target on the Pirs airlock and docking compartment. The tape was removed to ensure it does not get in the way during the arrival of visiting Soyuz or Progress spacecraft.