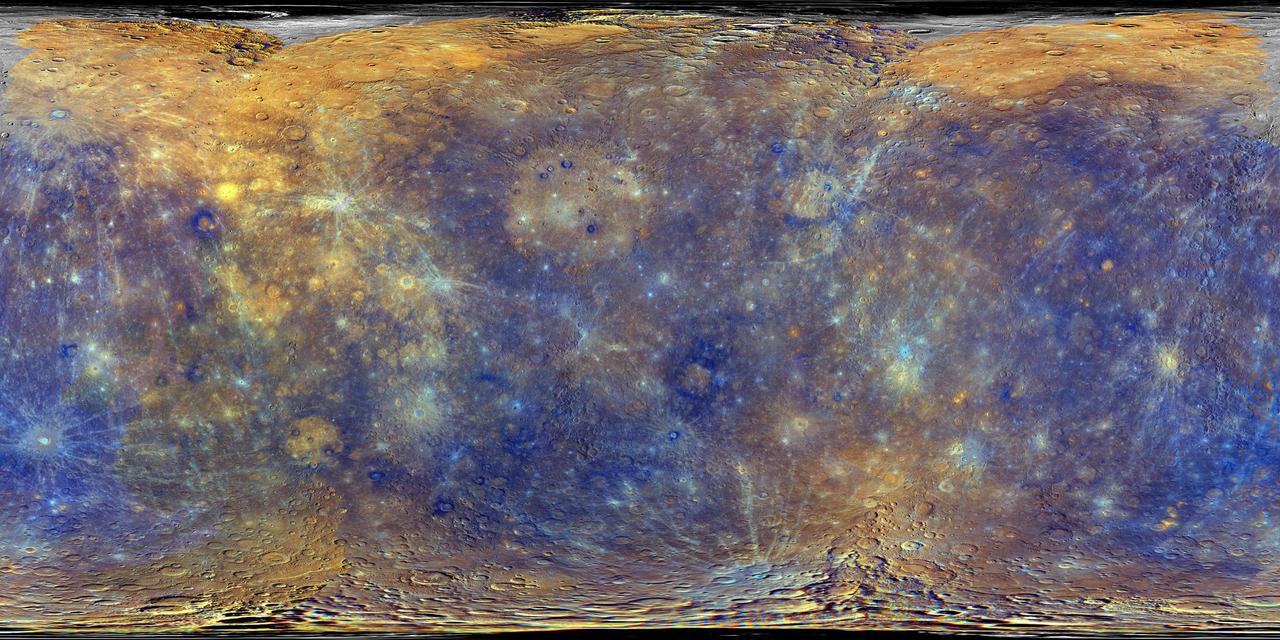
Enhanced Color Mercury Map
This colorful view of Mercury was produced by using images from the color base map imaging campaign during MESSENGER's primary mission. These colors are not what Mercury would look like to the human eye, but rather the colors enhance the chemical, mineralogical, and physical differences between the rocks that make up Mercury's surface. This specific color combination places the second principle component in the red channel, the first principle component in the green channel, and the ratio of the 430 nm/1000 nm filters in the blue channel. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. During the first two years of orbital operations, MESSENGER acquired over 150,000 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is capable of continuing orbital operations until early 2015. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
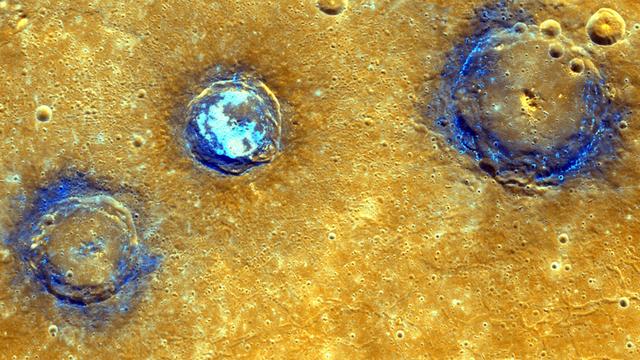
Measurements from NASA MESSENGER MLA instrument during the spacecraft greater than four-year orbital mission have mapped the topography of Mercury northern hemisphere in great detail. This enhanced color mosaic shows (from left to right) Munch (61 km/38 mi.), Sander (52 km/32 mi.), and Poe (81 km/50 mi.) craters, which lie in the northwest portion of the Caloris basin. The smooth volcanic plains that fill the Caloris basin appear orange in this image. All three craters are superposed on these volcanic plains and have excavated low-reflectance material, which appears blue in this image, from the subsurface. Hollows, typically associated with low-reflectance material, dot the rims of Munch and Poe and cover the floor of Sander. These images were acquired as high-resolution targeted color observations. Targeted color observations are images of a small area on Mercury's surface at resolutions higher than the 1-kilometer/pixel 8-color base map. During MESSENGER's one-year primary mission, hundreds of targeted color observations were obtained. During MESSENGER's extended mission, high-resolution targeted color observations are more rare, as the 3-color base map is covering Mercury's northern hemisphere with the highest-resolution color images that are possible. Date acquired: July 03, 2011, July 04, 2011 Image Mission Elapsed Time (MET): 218204186, 218204190, 218204194, 218246487, 218246491, 218246495 Image ID: 458397, 458398, 458399, 460433, 460434, 460435 Instrument: Wide Angle Camera (WAC) of the Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS) Center Latitude: 42° N Center Longitude: 154° E Projection: Equirectangular Resolution: 239 meters/pixel Scale: Munch crater is approximately 61 km (38 mi.) in diameter Incidence Angle: 43°, 42° Emission Angle: 35°, 13° Phase Angle: 79°, 55° http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19421
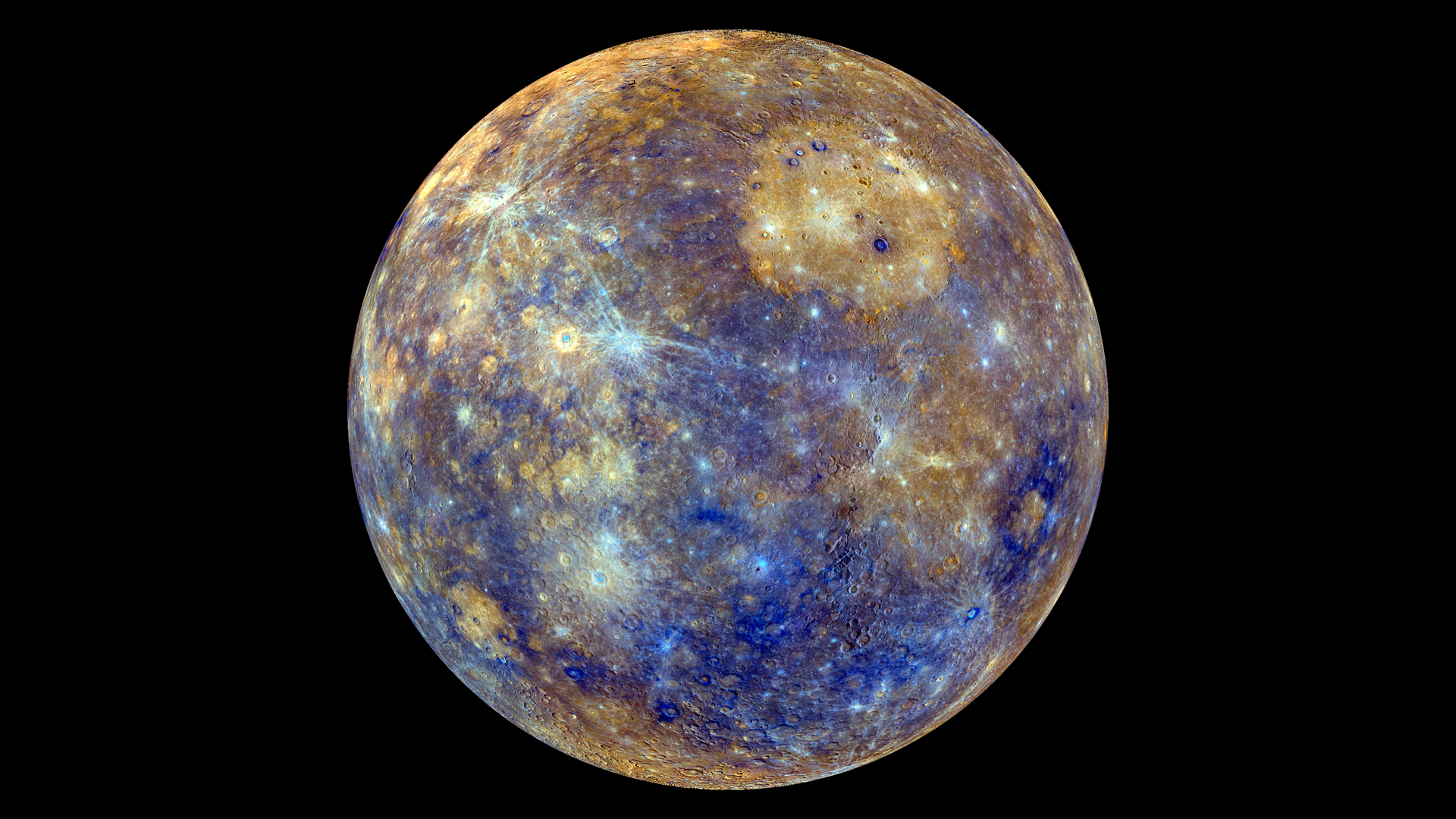
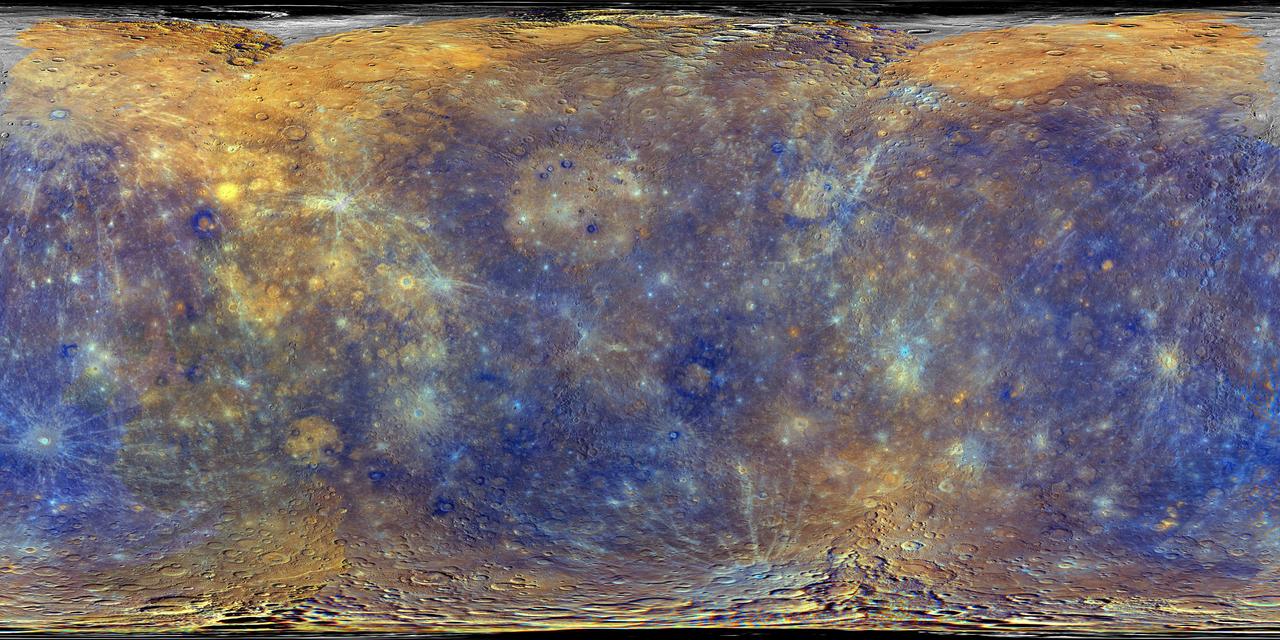
This colorful view of Mercury was produced by using images from the color base map imaging campaign during MESSENGER's primary mission. These colors are not what Mercury would look like to the human eye, but rather the colors enhance the chemical, mineralogical, and physical differences between the rocks that make up Mercury's surface. <b>To watch a movie of this colorful view of Mercury as a spinning globe go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8497927473">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8497927473</a></b> Young crater rays, extending radially from fresh impact craters, appear light blue or white. Medium- and dark-blue areas are a geologic unit of Mercury's crust known as the "low-reflectance material", thought to be rich in a dark, opaque mineral. Tan areas are plains formed by eruption of highly fluid lavas. The giant Caloris basin is the large circular tan feature located just to the upper right of center of the image. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the key science questions that the MESSENGER mission is addressing. During the one-year primary mission, MESSENGER acquired 88,746 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is now in a yearlong extended mission, during which plans call for the acquisition of more than 80,000 additional images to support MESSENGER's science goals. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This colorful view of Mercury was produced by using images from the color base map imaging campaign during MESSENGER's primary mission. These colors are not what Mercury would look like to the human eye, but rather the colors enhance the chemical, mineralogical, and physical differences between the rocks that make up Mercury's surface. Young crater rays, extending radially from fresh impact craters, appear light blue or white. Medium- and dark-blue areas are a geologic unit of Mercury's crust known as the "low-reflectance material", thought to be rich in a dark, opaque mineral. Tan areas are plains formed by eruption of highly fluid lavas. The crater in the upper right whose rays stretch across the planet is Hokusai. <b>To watch a movie of this colorful view of Mercury as a spinning globe go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8497927473">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8497927473</a></b> Young crater rays, extending radially from fresh impact craters, appear light blue or white. Medium- and dark-blue areas are a geologic unit of Mercury's crust known as the "low-reflectance material", thought to be rich in a dark, opaque mineral. Tan areas are plains formed by eruption of highly fluid lavas. The giant Caloris basin is the large circular tan feature located just to the upper right of center of the image. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the key science questions that the MESSENGER mission is addressing. During the one-year primary mission, MESSENGER acquired 88,746 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is now in a yearlong extended mission, during which plans call for the acquisition of more than 80,000 additional images to support MESSENGER's science goals. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>