
Diane Linne in the Simulated Lunar Operations, SLOPE Lab - Percussive Excavation Bucket reduces reaction forces for extraterrestrial digging of loose and compacted or icy soils.
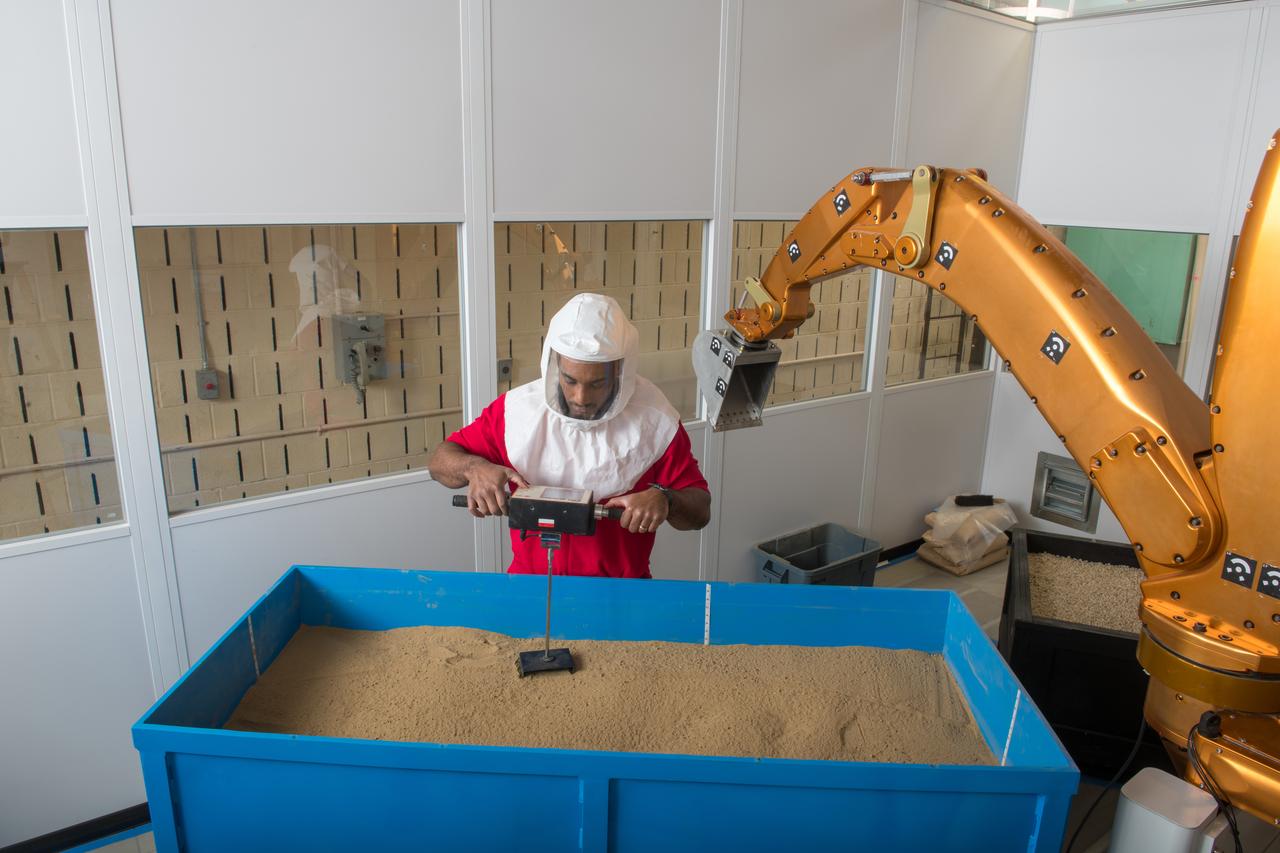

SLOPE Excavation Laboratory

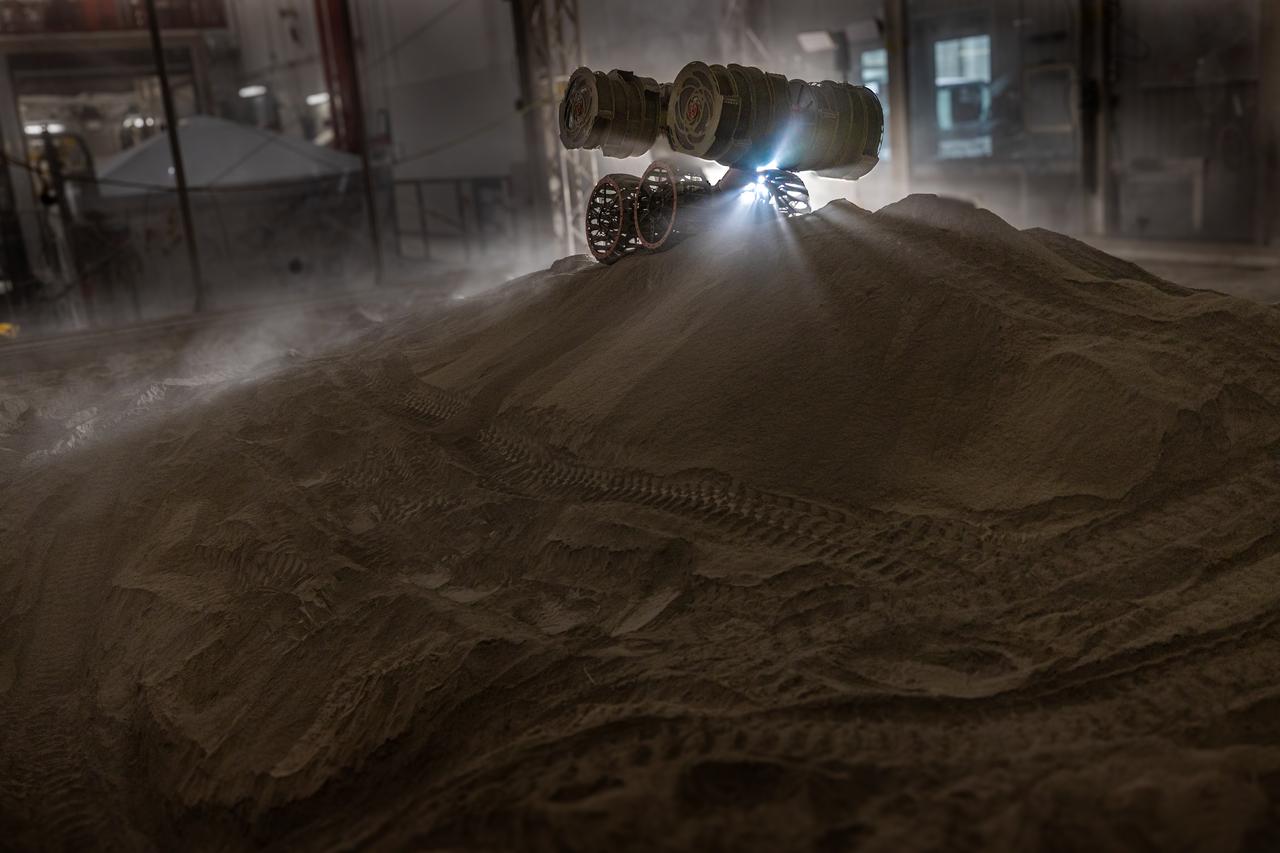
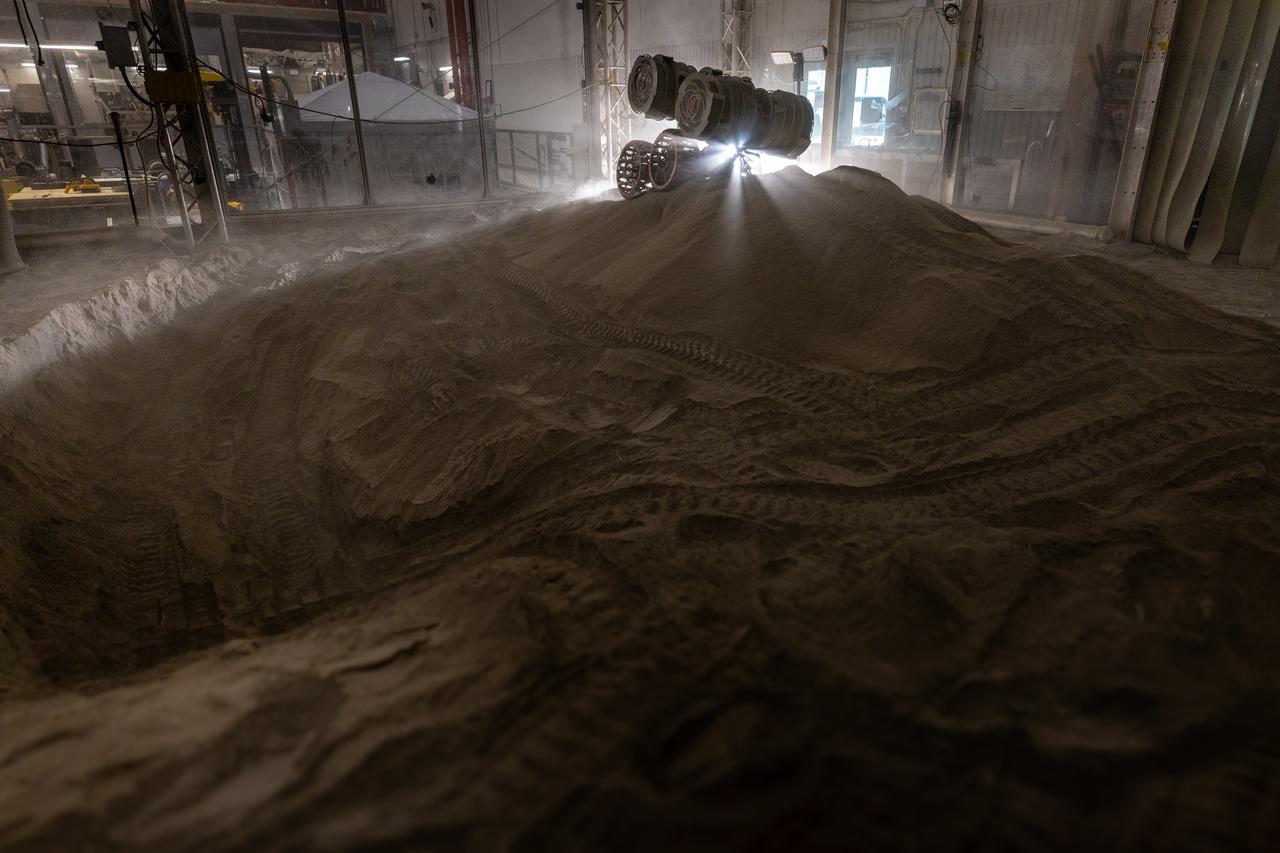
With the lights out, the ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

With the lights out, the ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

The ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in the regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
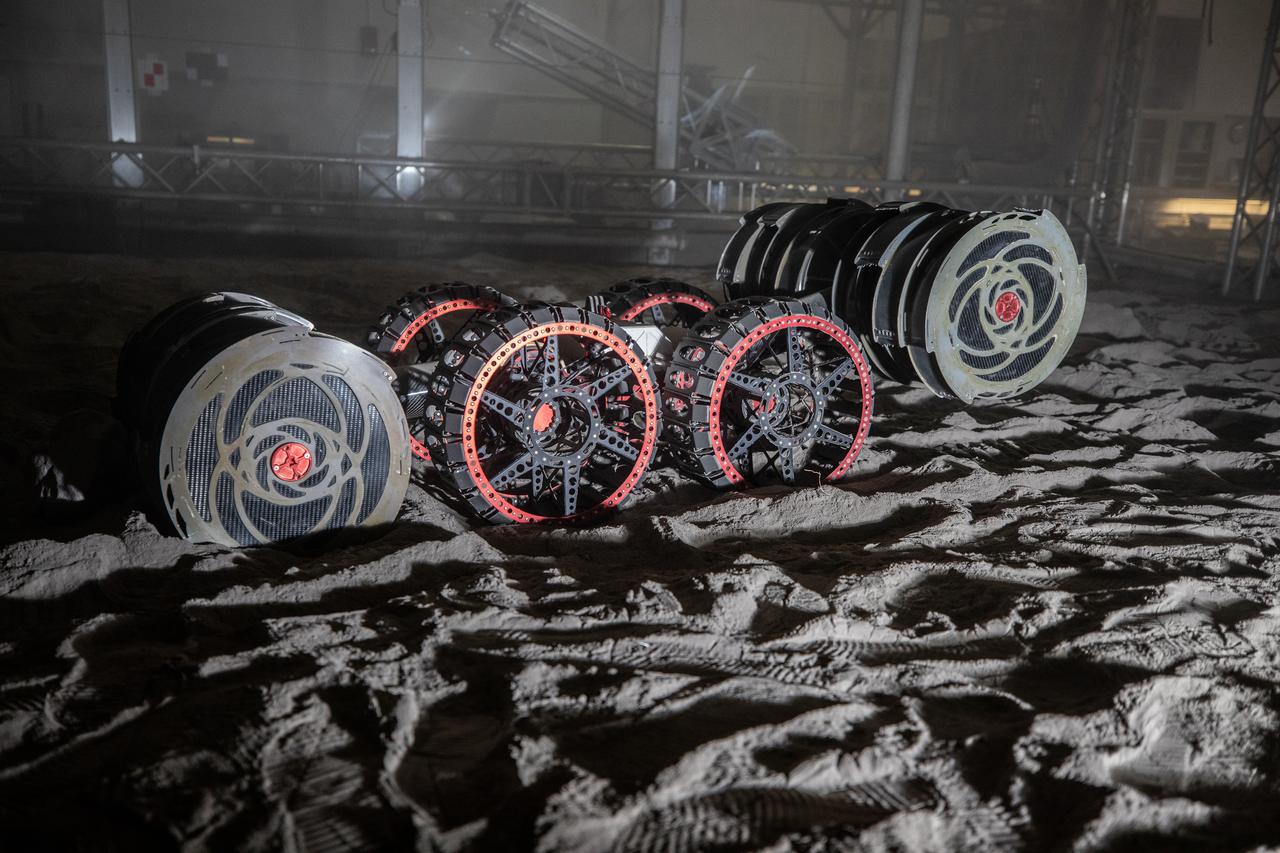

With the lights out, the ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in the regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
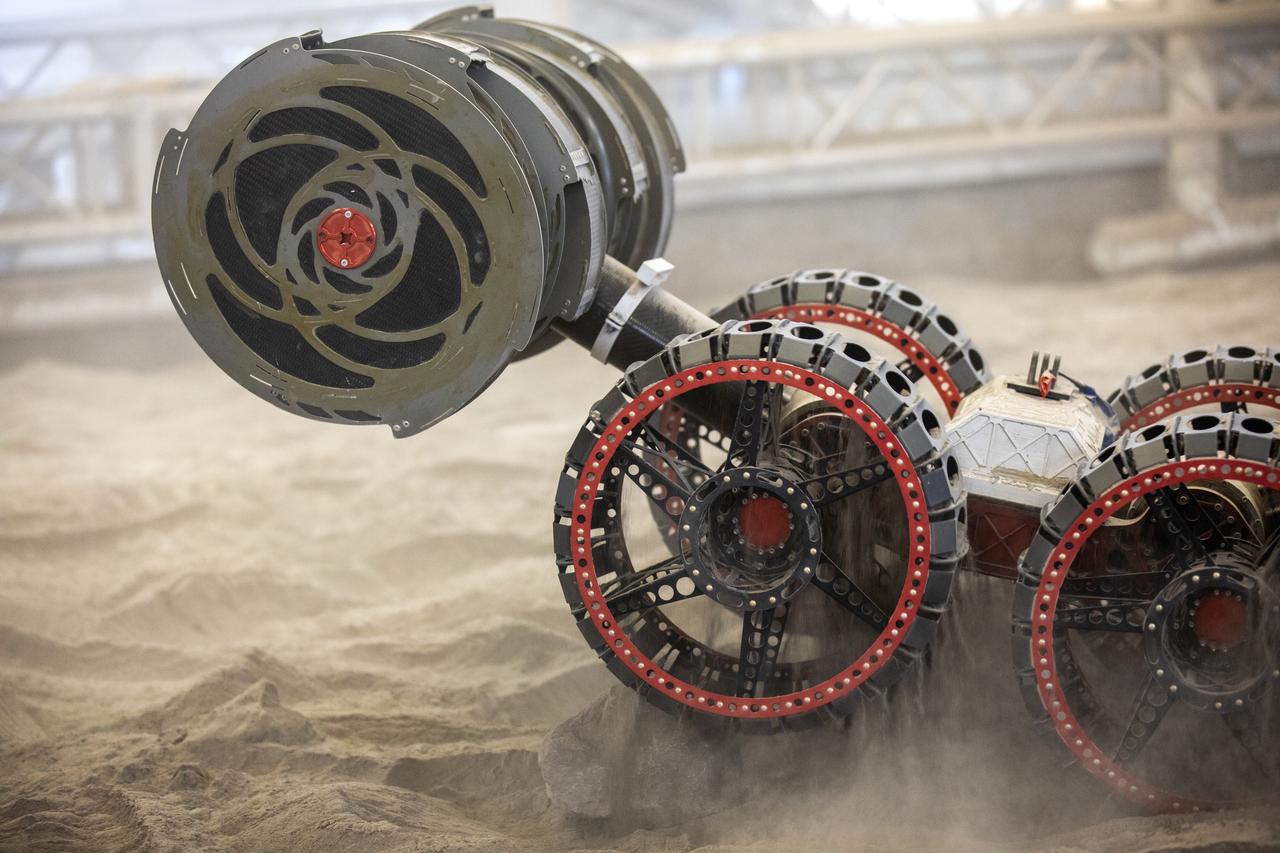

The ISRU Pilot Excavator digs its way through the regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
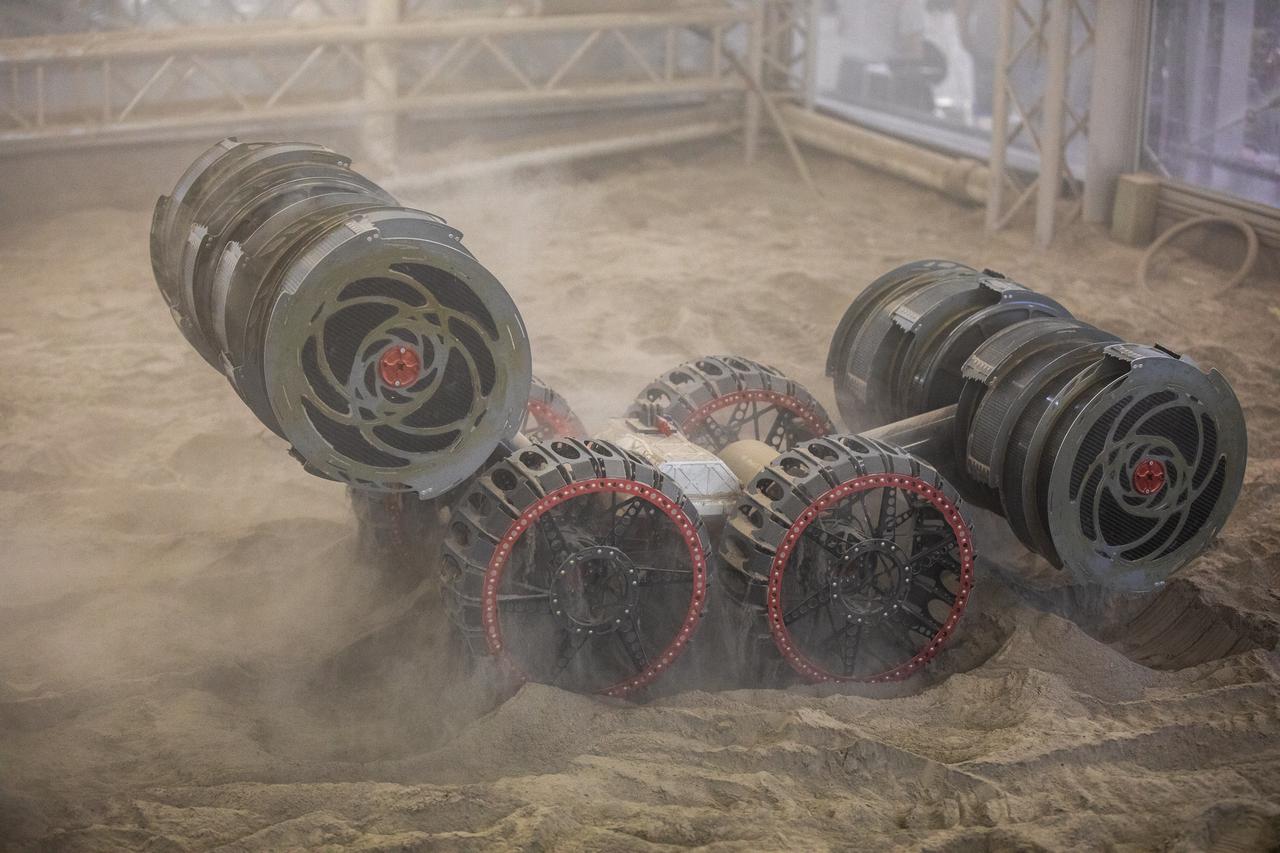

The ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in the regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
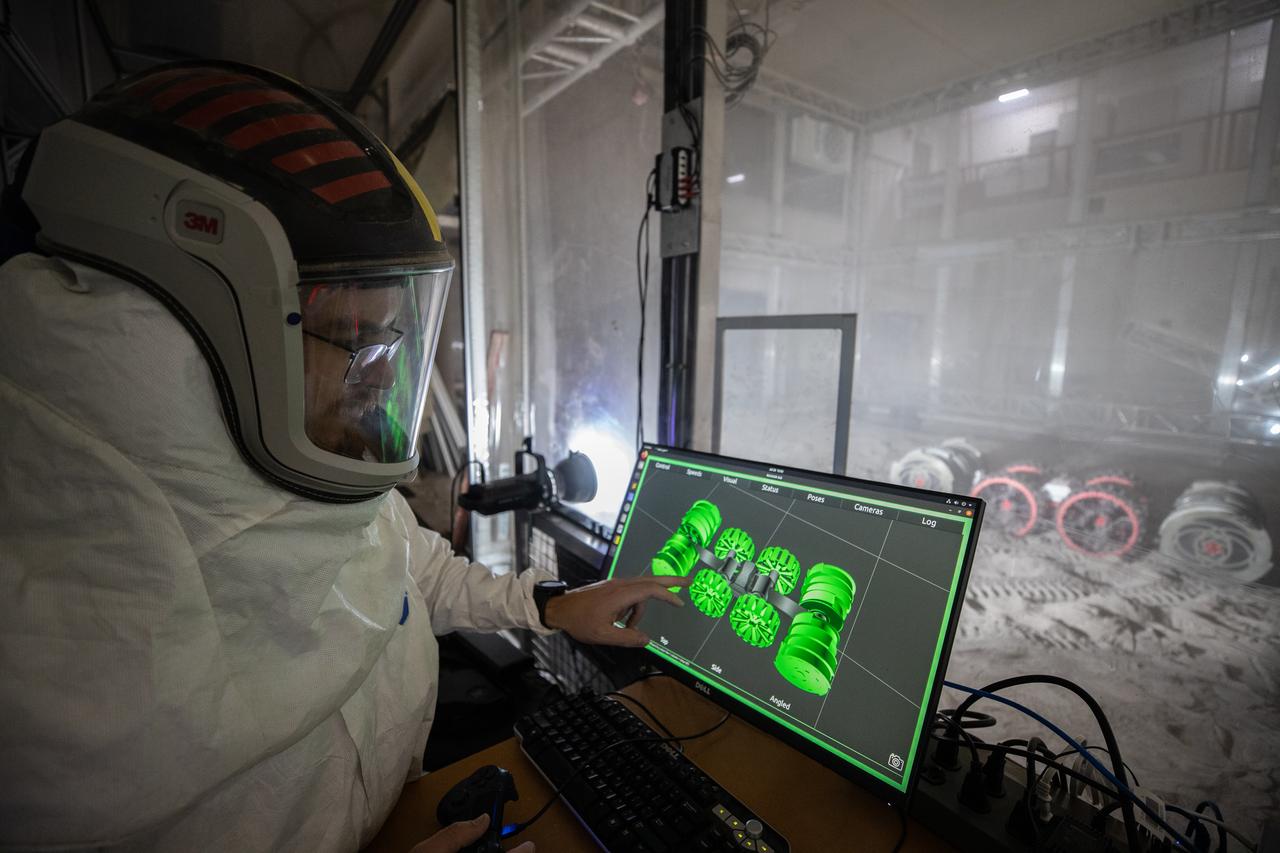

A team from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab operates a test of the ISRU Pilot Excavator in regolith bin inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
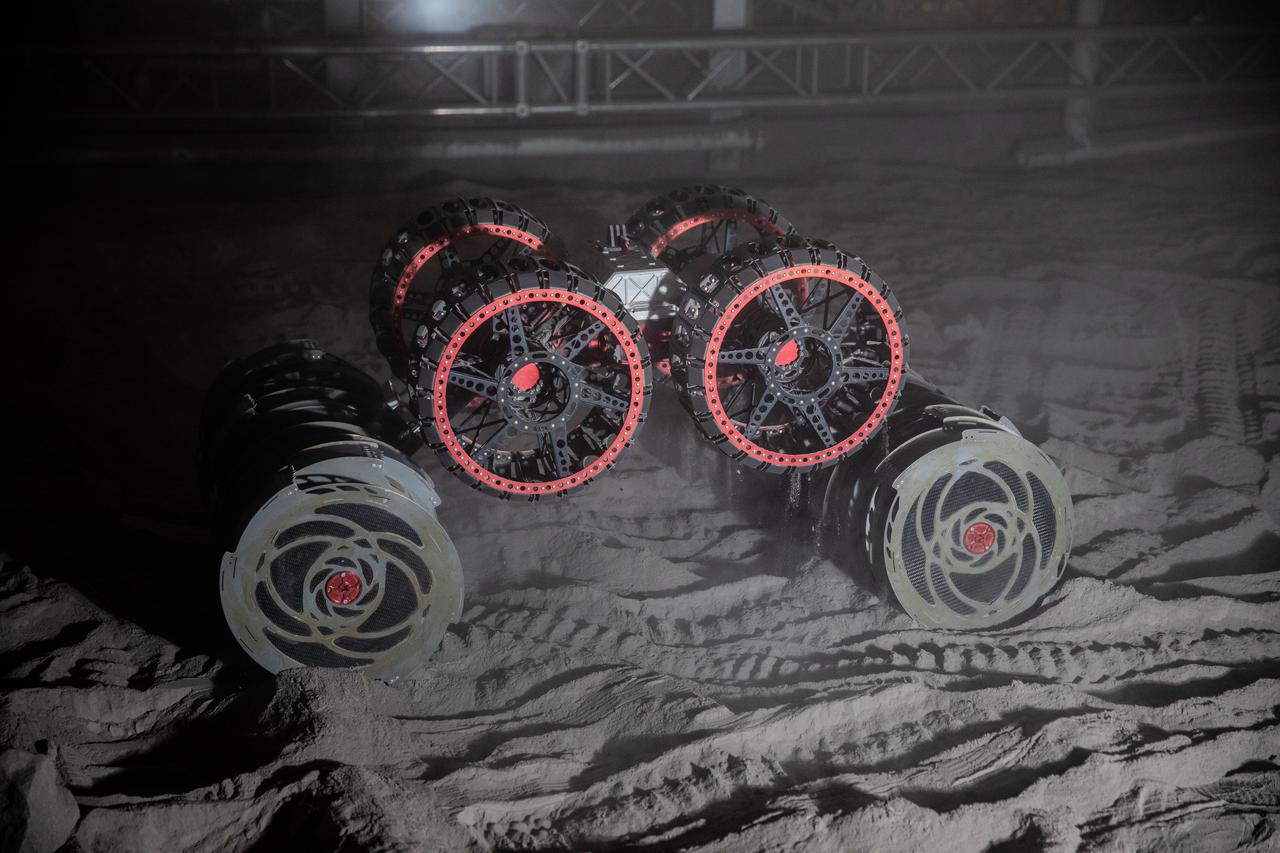

With the lights out, the ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
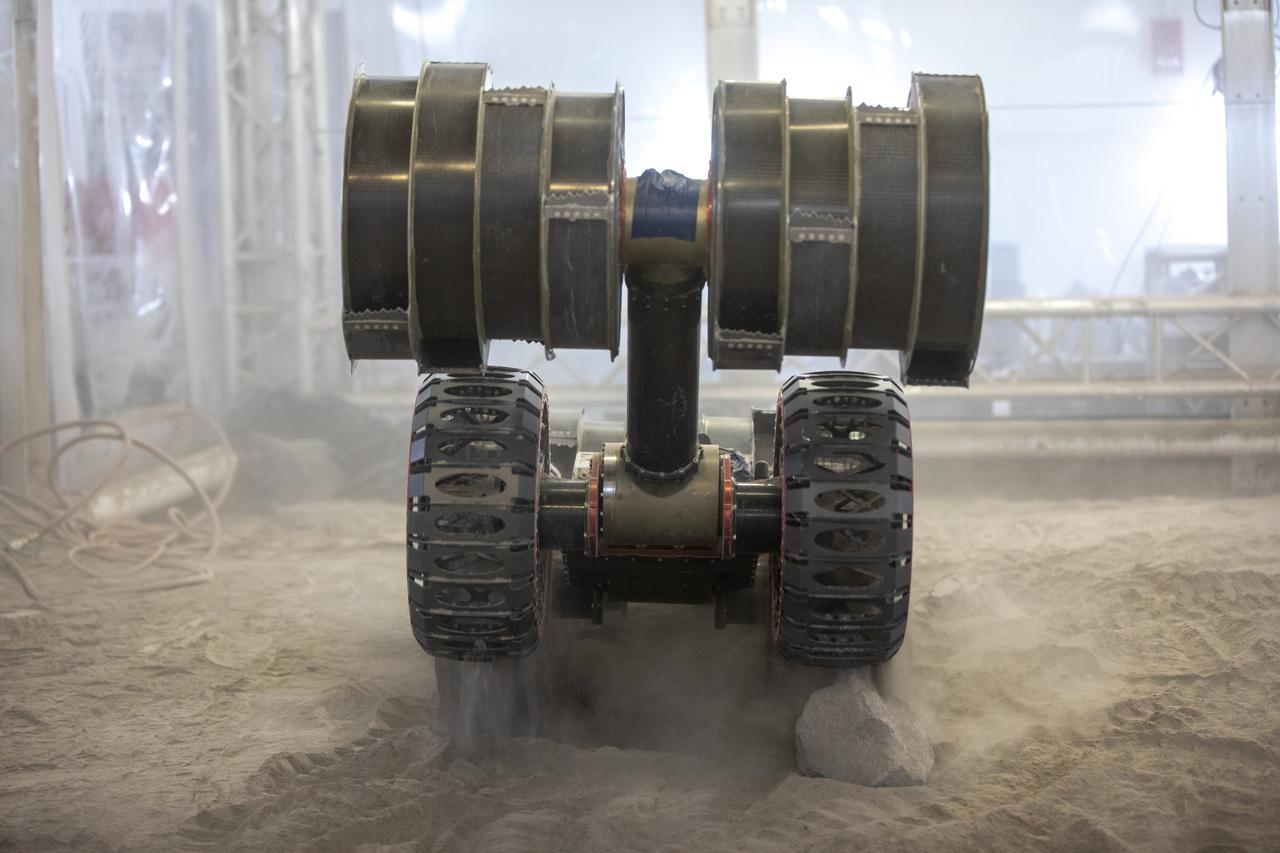

The ISRU Pilot Excavator is tested in the regolith bin inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
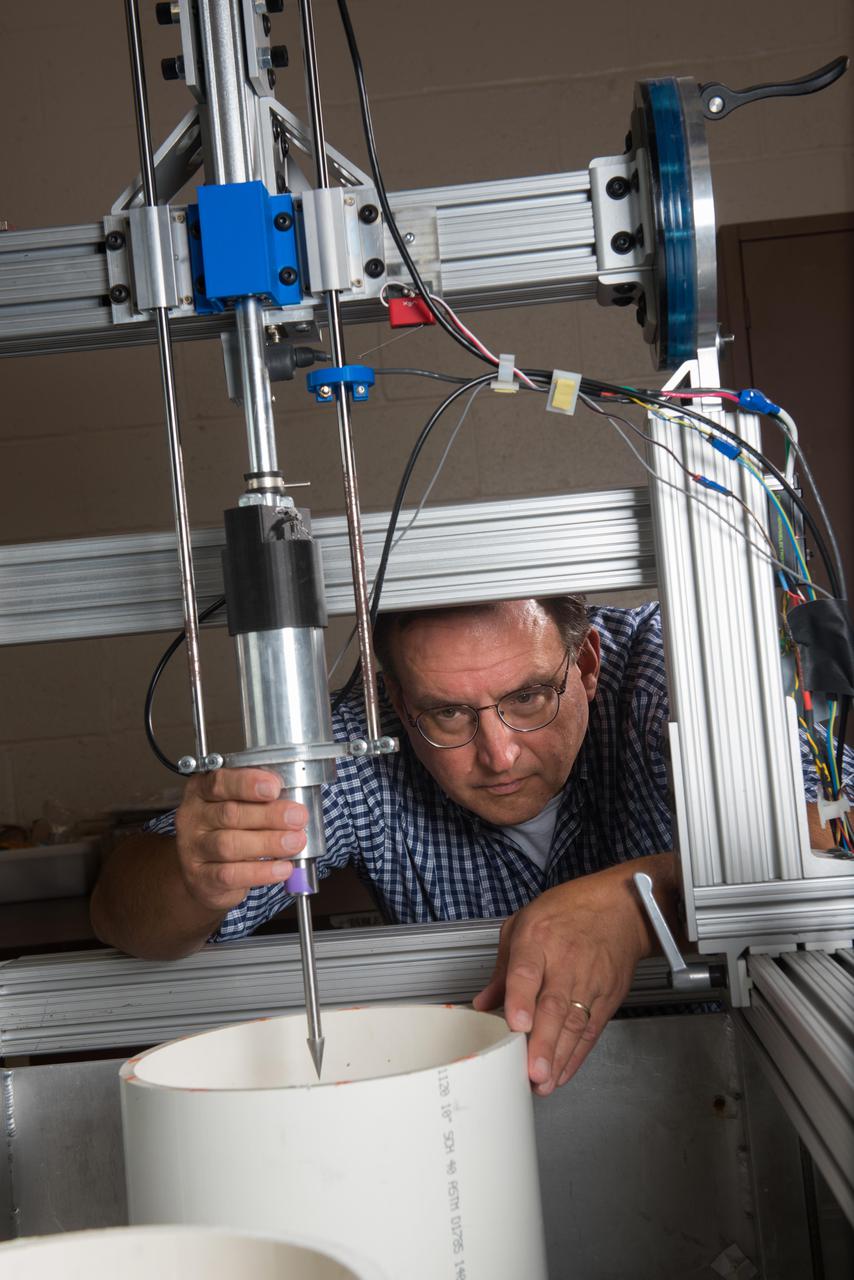
Ultrasonic Teeth for Lunar Bucket Excavation
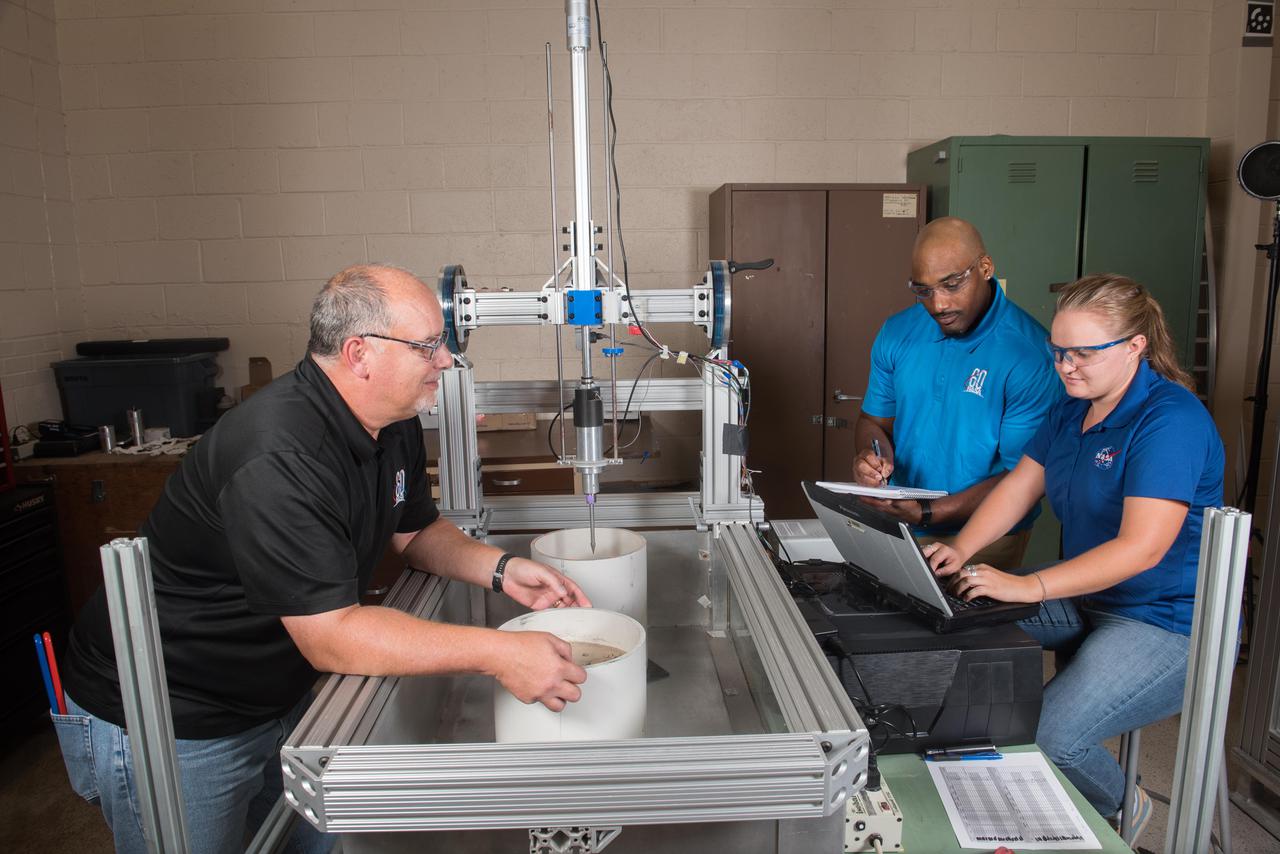

Ultrasonic Teeth for Lunar Bucket Excavation
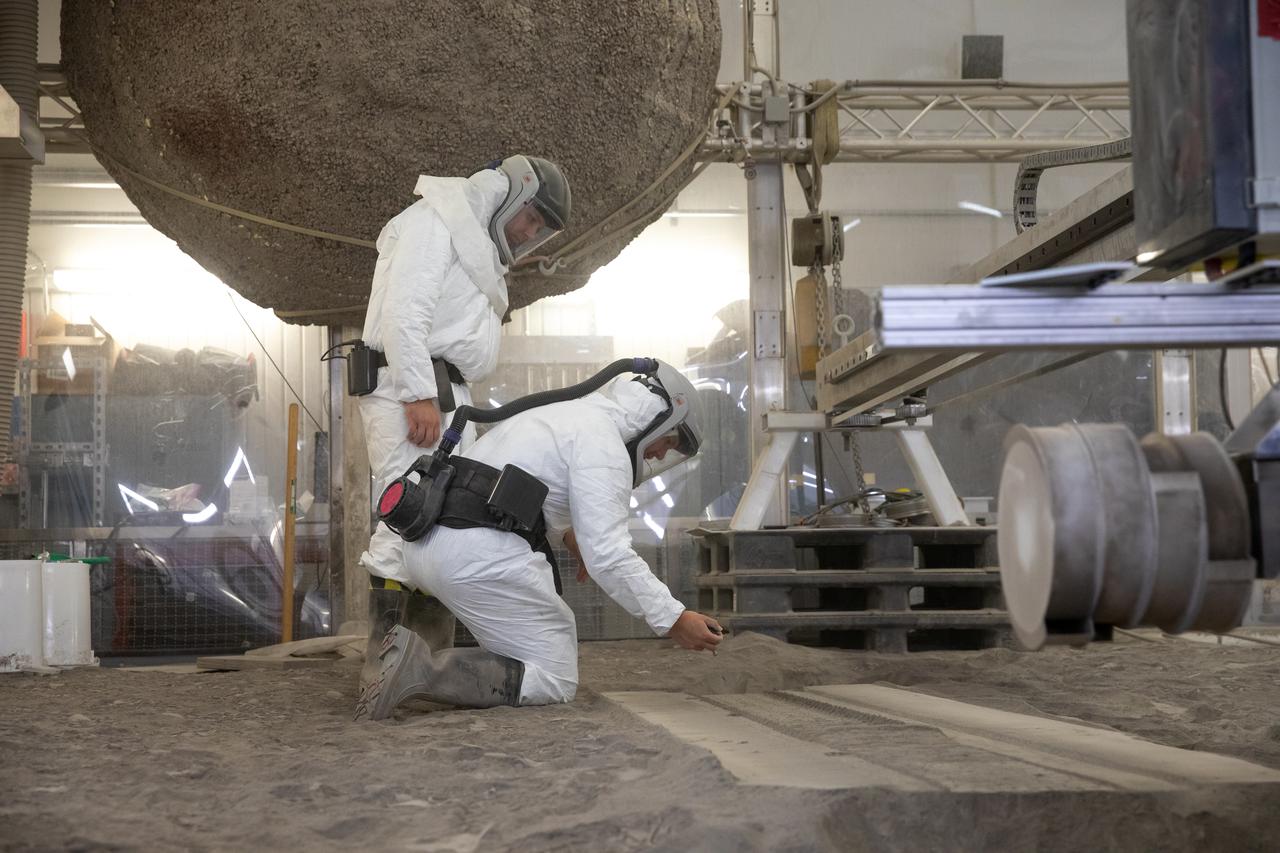

A team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida tests small- and medium-sized bucket drums July 16, 2021, in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab’s “big bin” during prototype development for the pilot excavator, a robotic mission designed for lunar operations. The bucket drum excavated lunar regolith simulant. The Swamp Works team leveled and compacted the simulant before excavation as well as measured penetration during the excavator testing. Robotics engineers Jason Schuler and Austin Langton worked inside the bin, teaming up with software engineer Kurt Leucht, who worked just outside of it.

A team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida tests small- and medium-sized bucket drums July 16, 2021, in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab’s “big bin” during prototype development for the pilot excavator, a robotic mission designed for lunar operations. The bucket drum excavated lunar regolith simulant. The Swamp Works team leveled and compacted the simulant before excavation as well as measured penetration during the excavator testing. Robotics engineers Jason Schuler and Austin Langton worked inside the bin, teaming up with software engineer Kurt Leucht, who worked just outside of it.
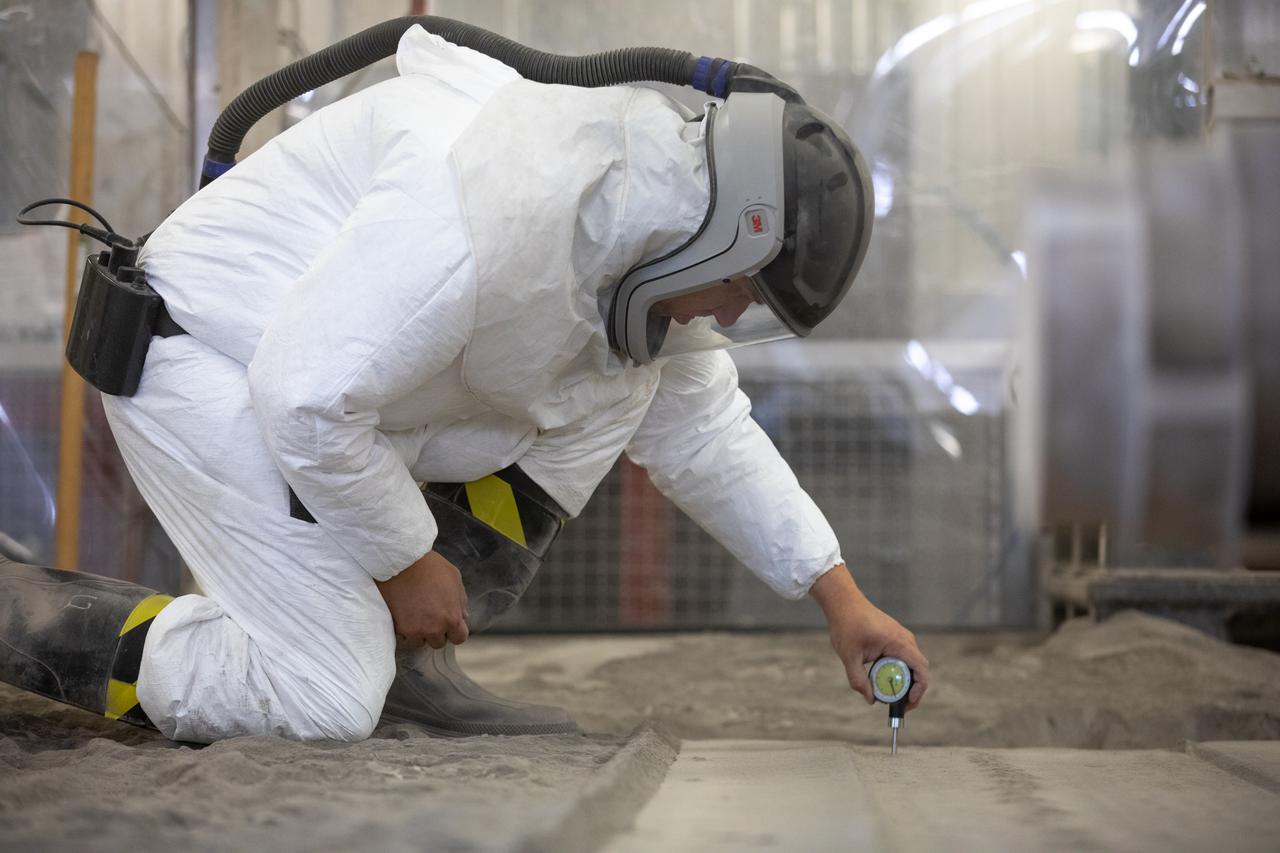

A team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida tests small- and medium-sized bucket drums July 16, 2021, in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab’s “big bin” during prototype development for the pilot excavator, a robotic mission designed for lunar operations. The bucket drum excavated lunar regolith simulant. The Swamp Works team leveled and compacted the simulant before excavation as well as measured penetration during the excavator testing. Robotics engineers Jason Schuler and Austin Langton worked inside the bin, teaming up with software engineer Kurt Leucht, who worked just outside of it.
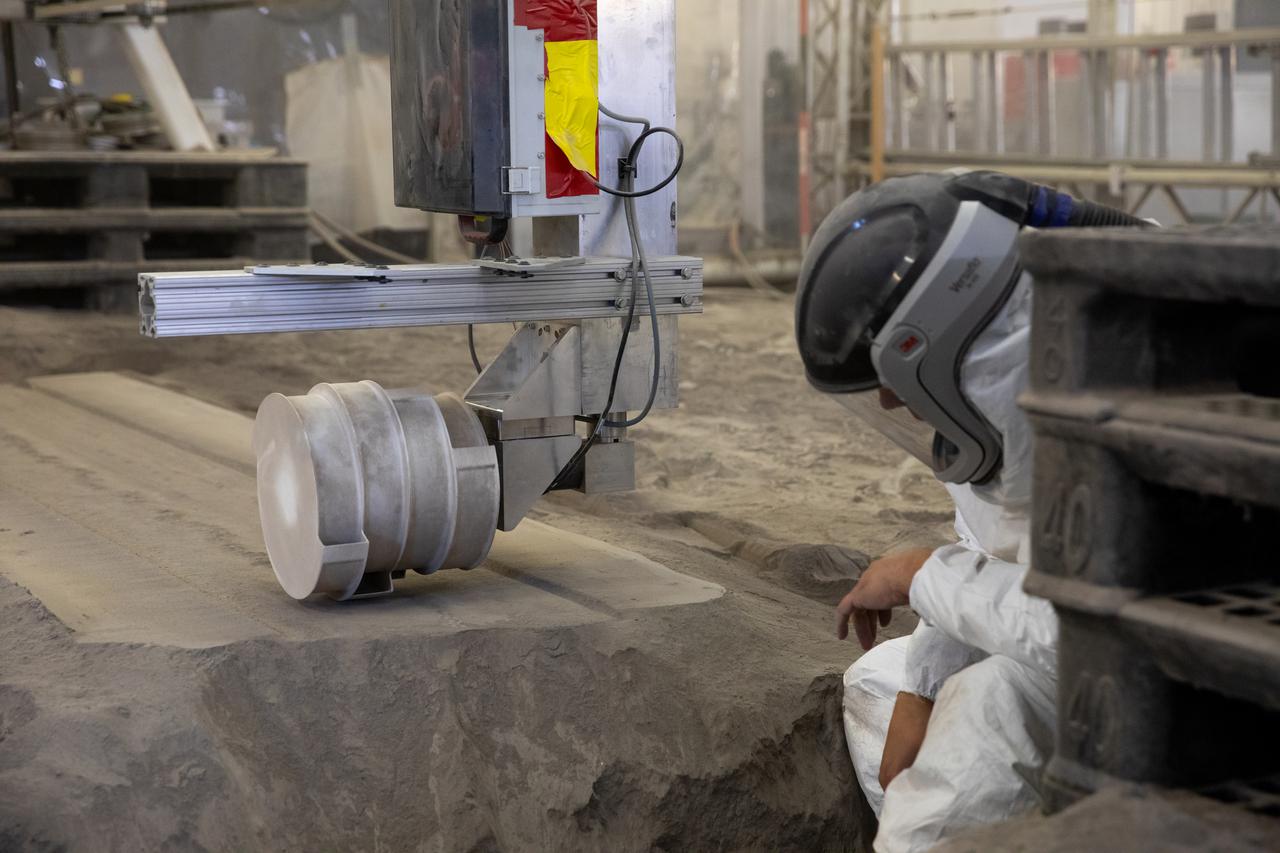

A team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida tests small- and medium-sized bucket drums July 16, 2021, in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab’s “big bin” during prototype development for the pilot excavator, a robotic mission designed for lunar operations. The bucket drum excavated lunar regolith simulant. The Swamp Works team leveled and compacted the simulant before excavation as well as measured penetration during the excavator testing. Robotics engineers Jason Schuler and Austin Langton worked inside the bin, teaming up with software engineer Kurt Leucht, who worked just outside of it.
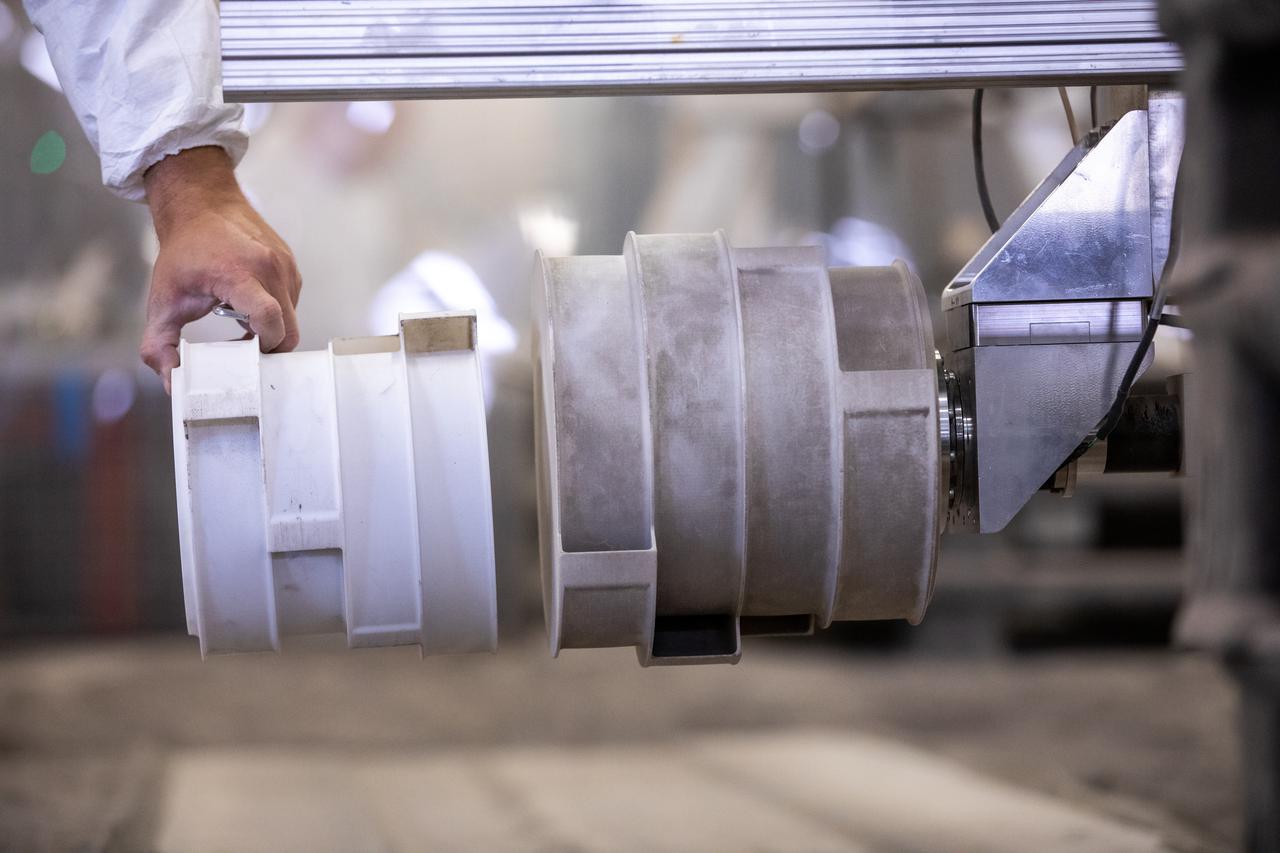

A team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida tests small- and medium-sized bucket drums July 16, 2021, in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab’s “big bin” during prototype development for the pilot excavator, a robotic mission designed for lunar operations. The bucket drum excavated lunar regolith simulant. The Swamp Works team leveled and compacted the simulant before excavation as well as measured penetration during the excavator testing. Robotics engineers Jason Schuler and Austin Langton worked inside the bin, teaming up with software engineer Kurt Leucht, who worked just outside of it.
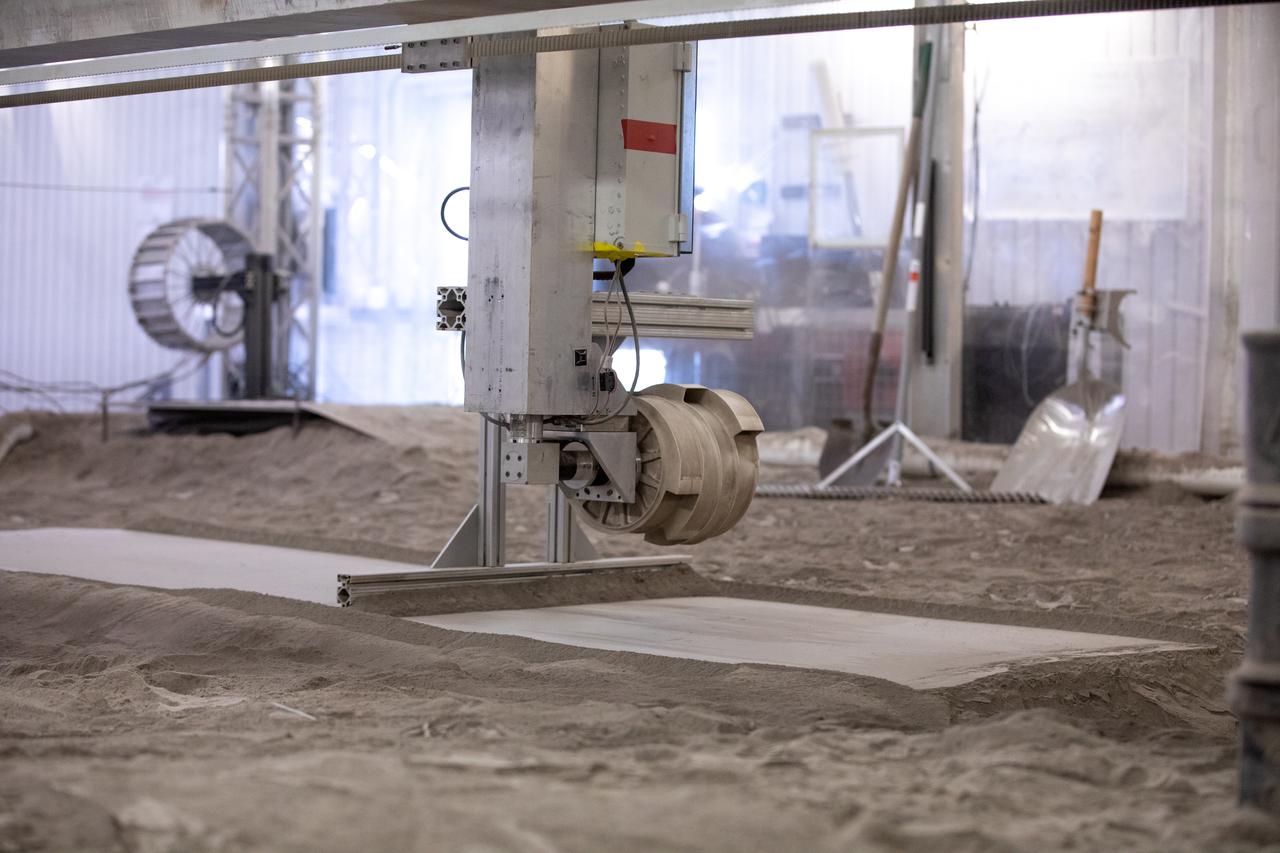

A team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida tests small- and medium-sized bucket drums July 16, 2021, in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab’s “big bin” during prototype development for the pilot excavator, a robotic mission designed for lunar operations. The bucket drum excavated lunar regolith simulant. The Swamp Works team leveled and compacted the simulant before excavation as well as measured penetration during the excavator testing. Robotics engineers Jason Schuler and Austin Langton worked inside the bin, teaming up with software engineer Kurt Leucht, who worked just outside of it.
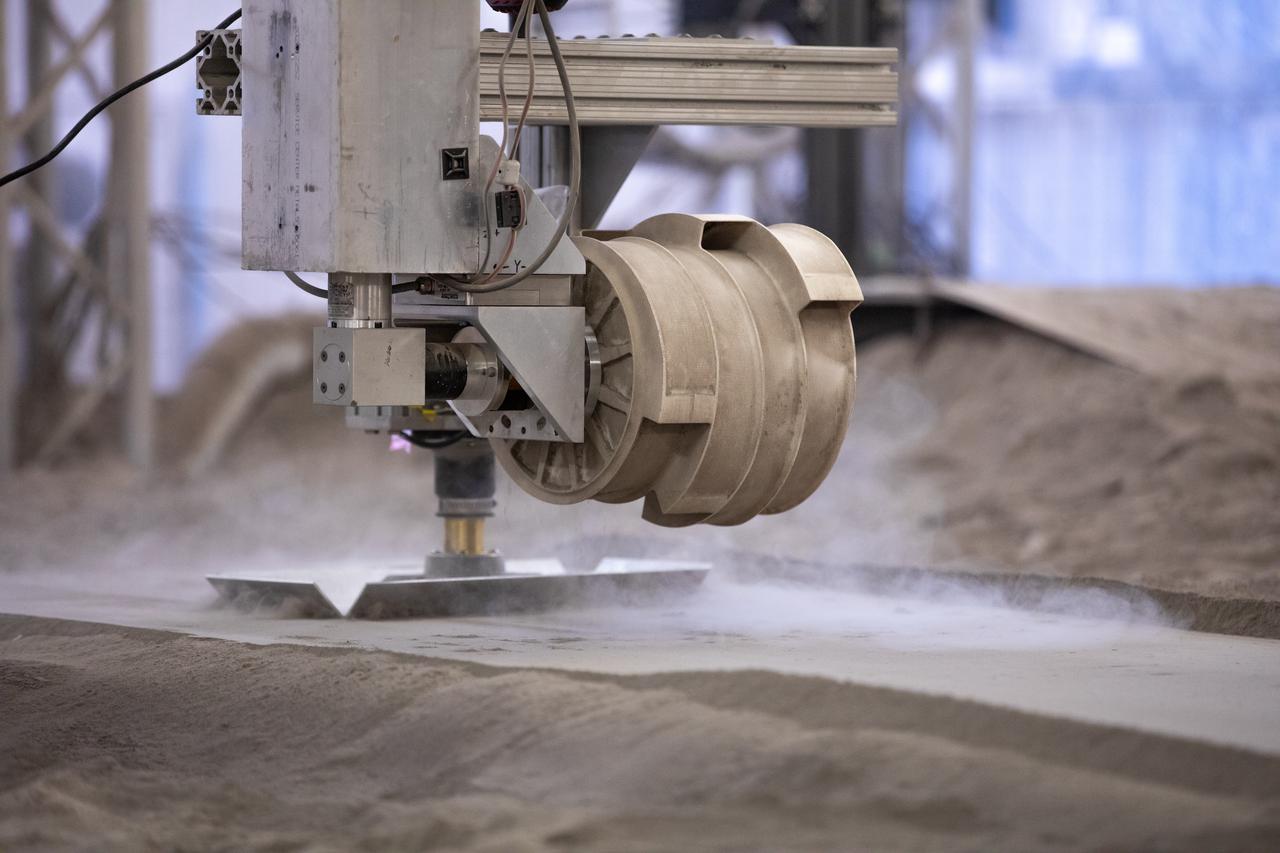

A team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida tests small- and medium-sized bucket drums July 16, 2021, in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab’s “big bin” during prototype development for the pilot excavator, a robotic mission designed for lunar operations. The bucket drum excavated lunar regolith simulant. The Swamp Works team leveled and compacted the simulant before excavation as well as measured penetration during the excavator testing. Robotics engineers Jason Schuler and Austin Langton worked inside the bin, teaming up with software engineer Kurt Leucht, who worked just outside of it.
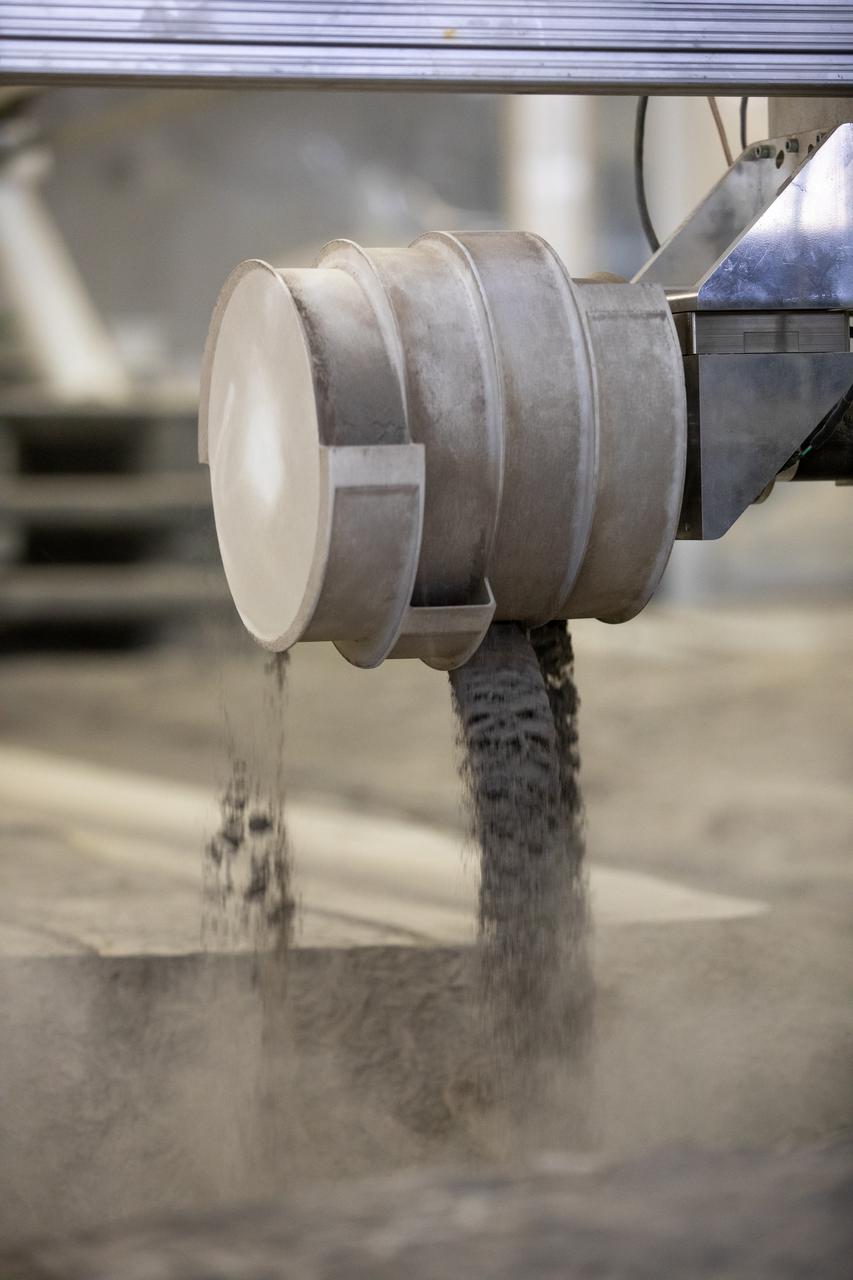

A team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida tests small- and medium-sized bucket drums July 16, 2021, in the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab’s “big bin” during prototype development for the pilot excavator, a robotic mission designed for lunar operations. The bucket drum excavated lunar regolith simulant. The Swamp Works team leveled and compacted the simulant before excavation as well as measured penetration during the excavator testing. Robotics engineers Jason Schuler and Austin Langton worked inside the bin, teaming up with software engineer Kurt Leucht, who worked just outside of it.
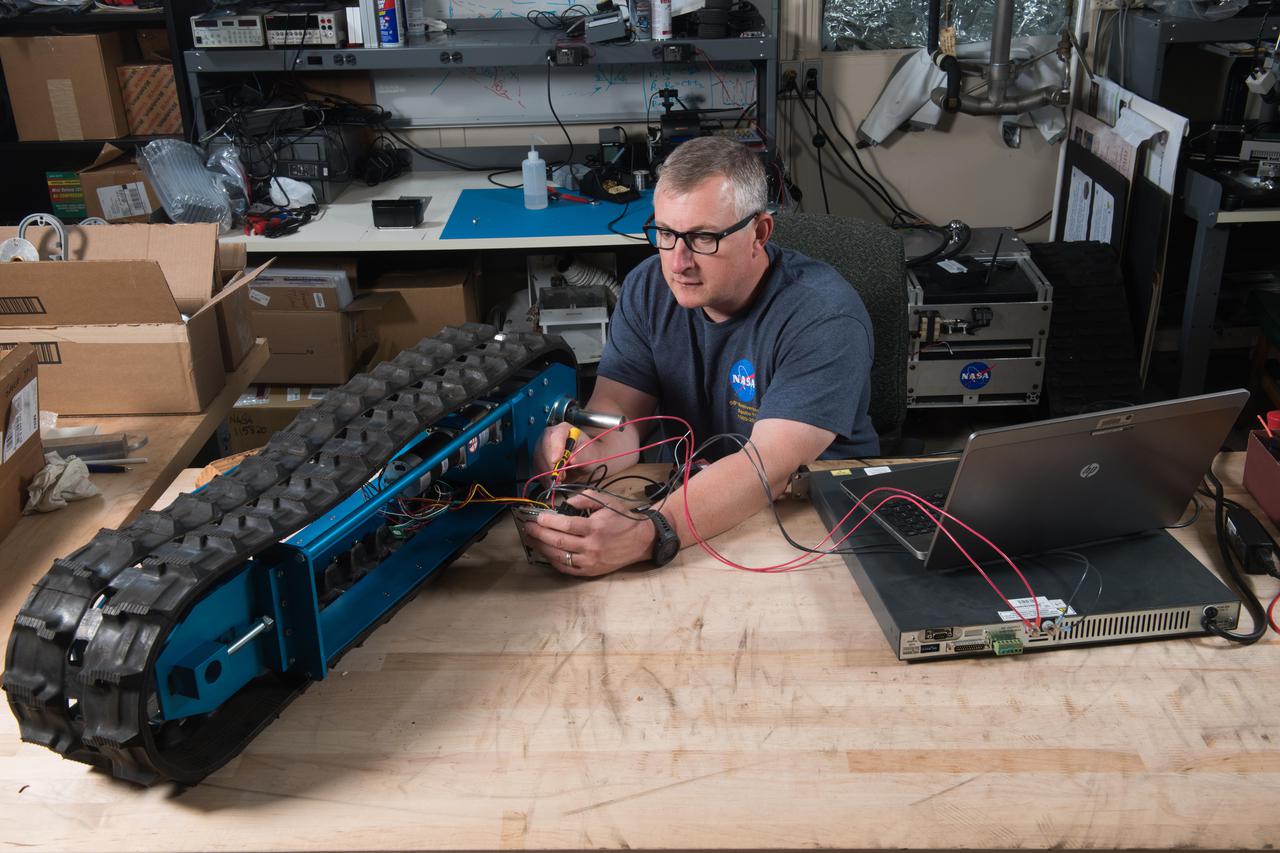
Cratos II: Modular ISRU Excavation Tools
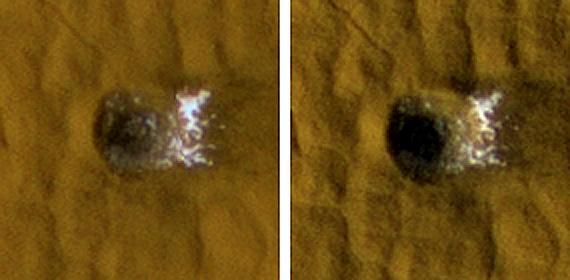
The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment camera on NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter excavates ice in a twelve-meter-wide crater.
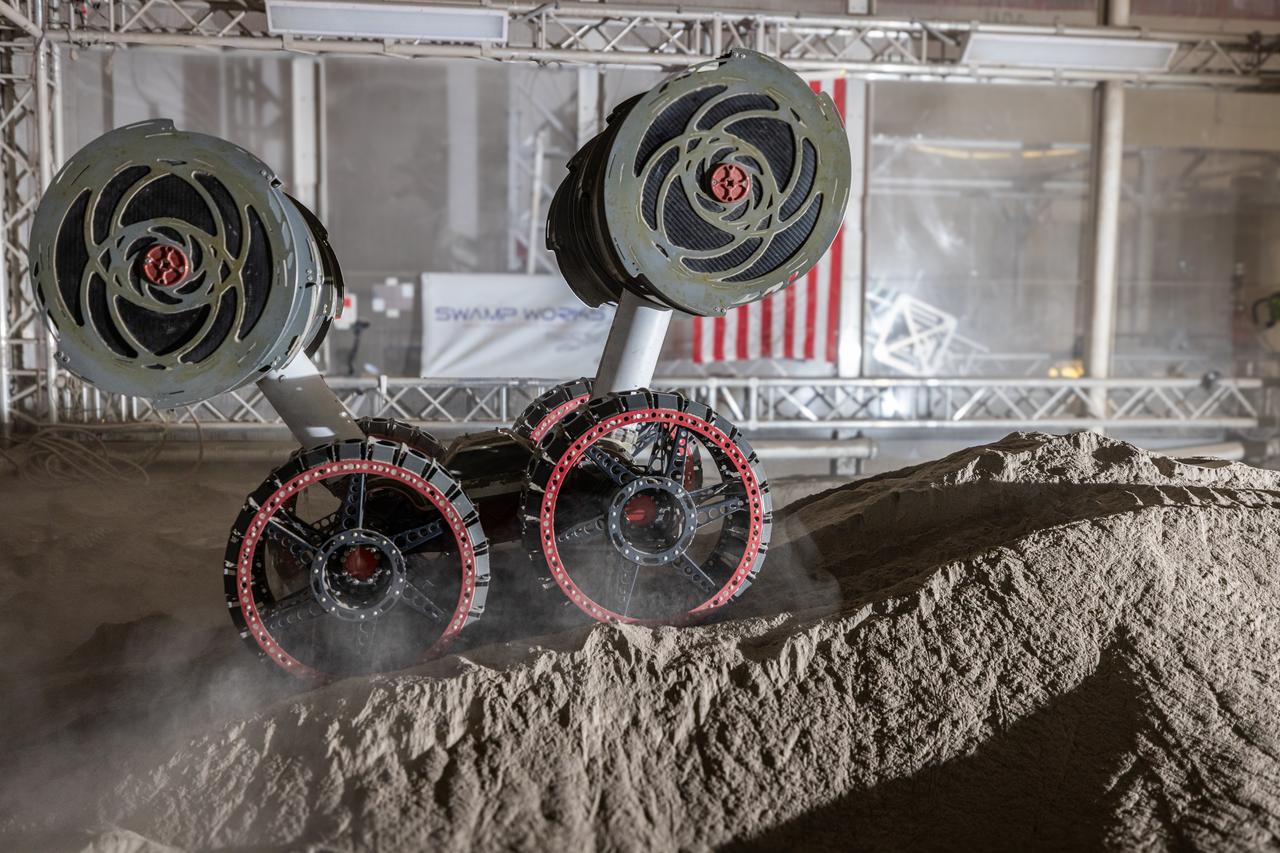

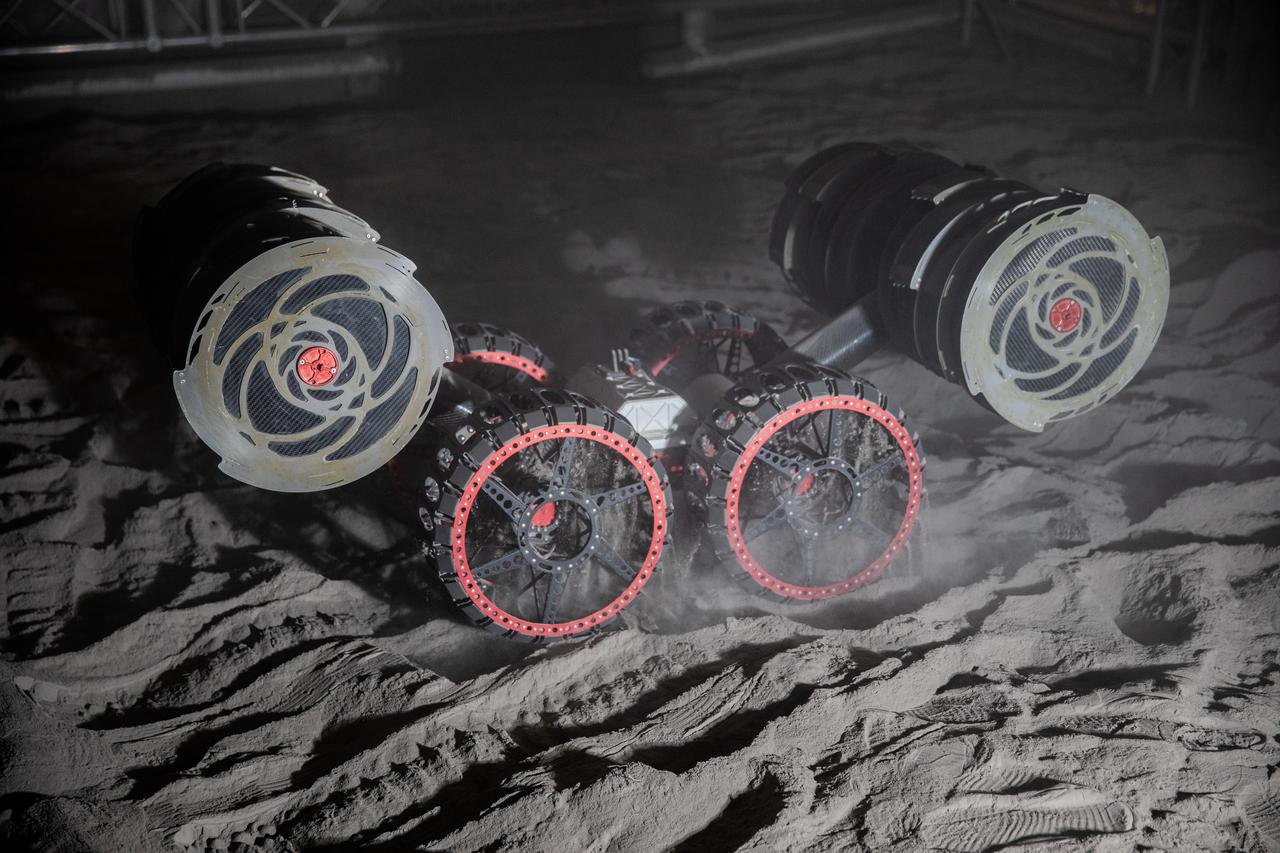
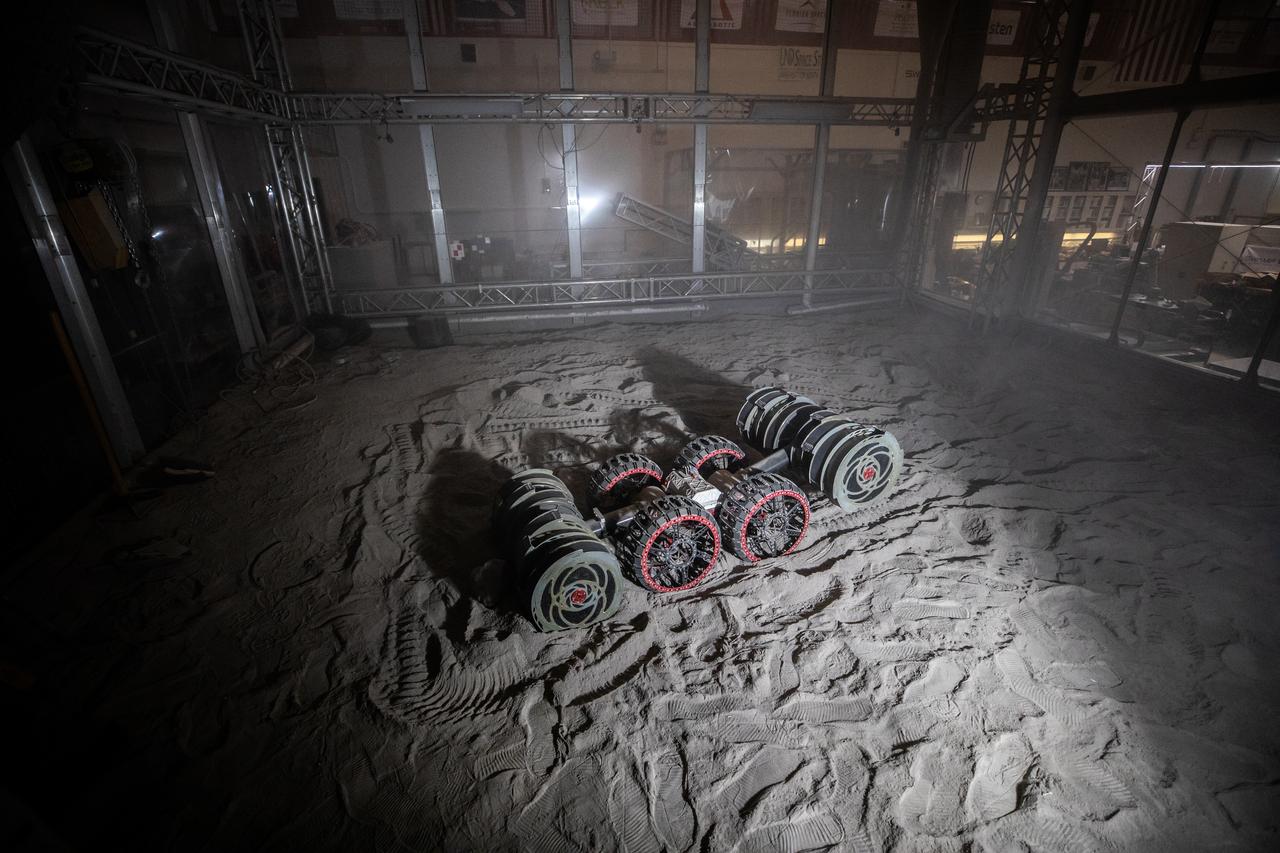
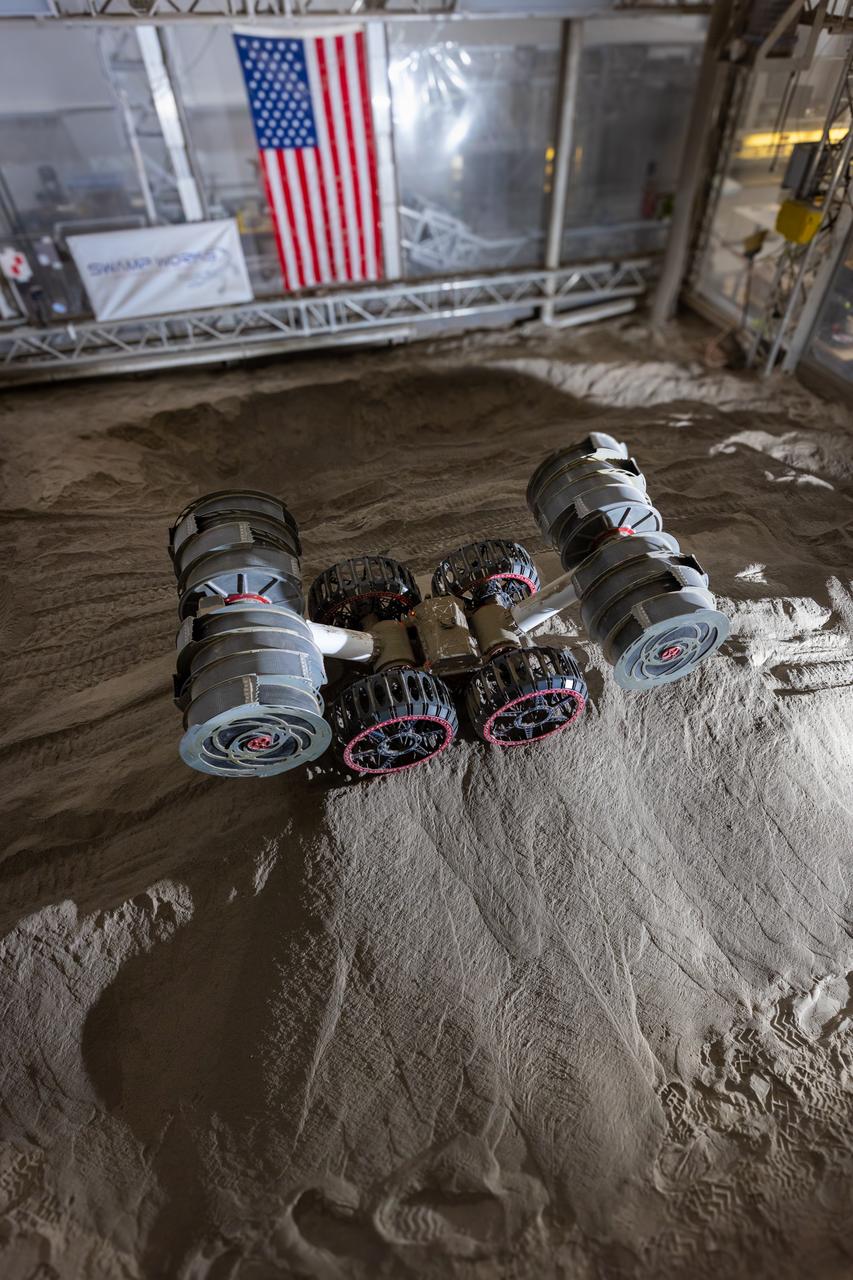
NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) conducts excavation testing of simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 27, 2025. RASSOR is designed to work in low-gravity situations, using counter rotating bucket drums on each arm to collect and dump regolith for the extraction of hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining a habitable presence.
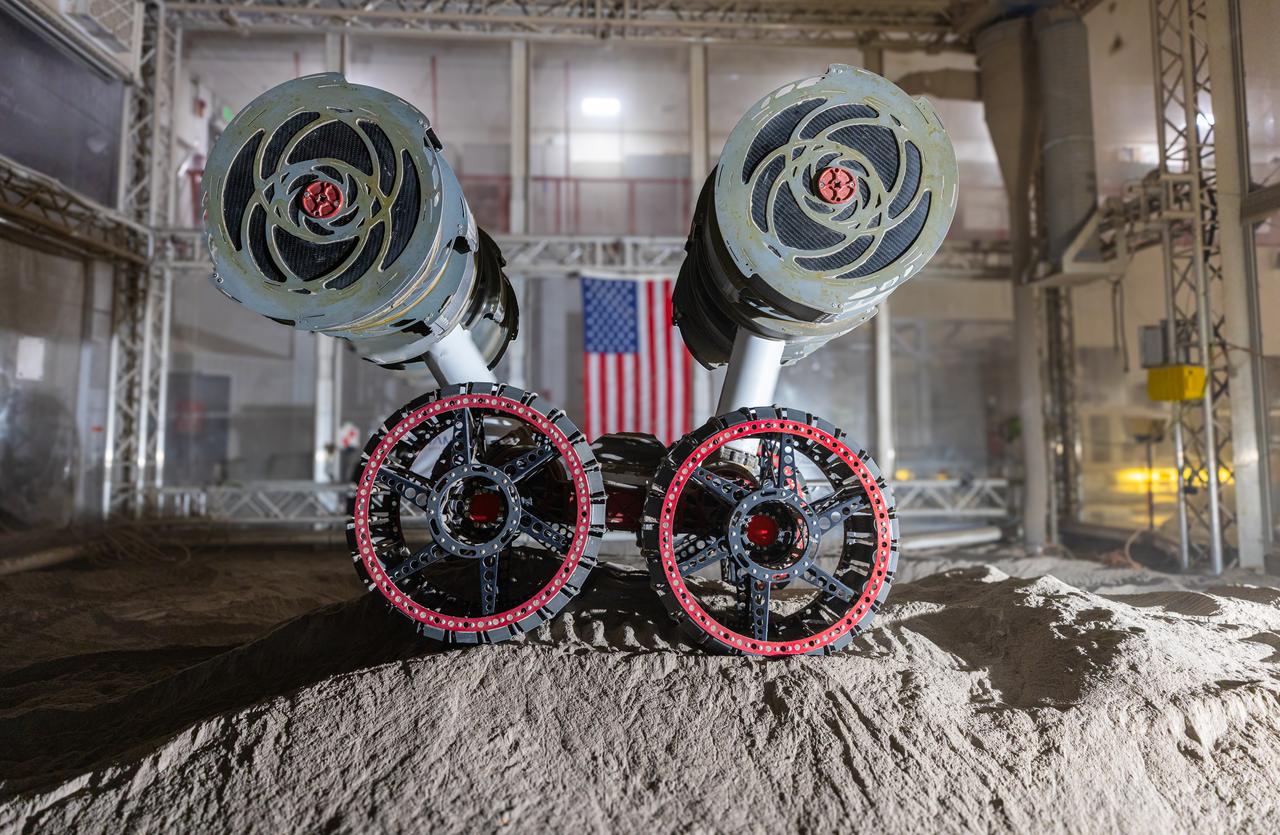

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) conducts excavation testing of simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 27, 2025. RASSOR is designed to work in low-gravity situations, using counter rotating bucket drums on each arm to collect and dump regolith for the extraction of hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining a habitable presence.
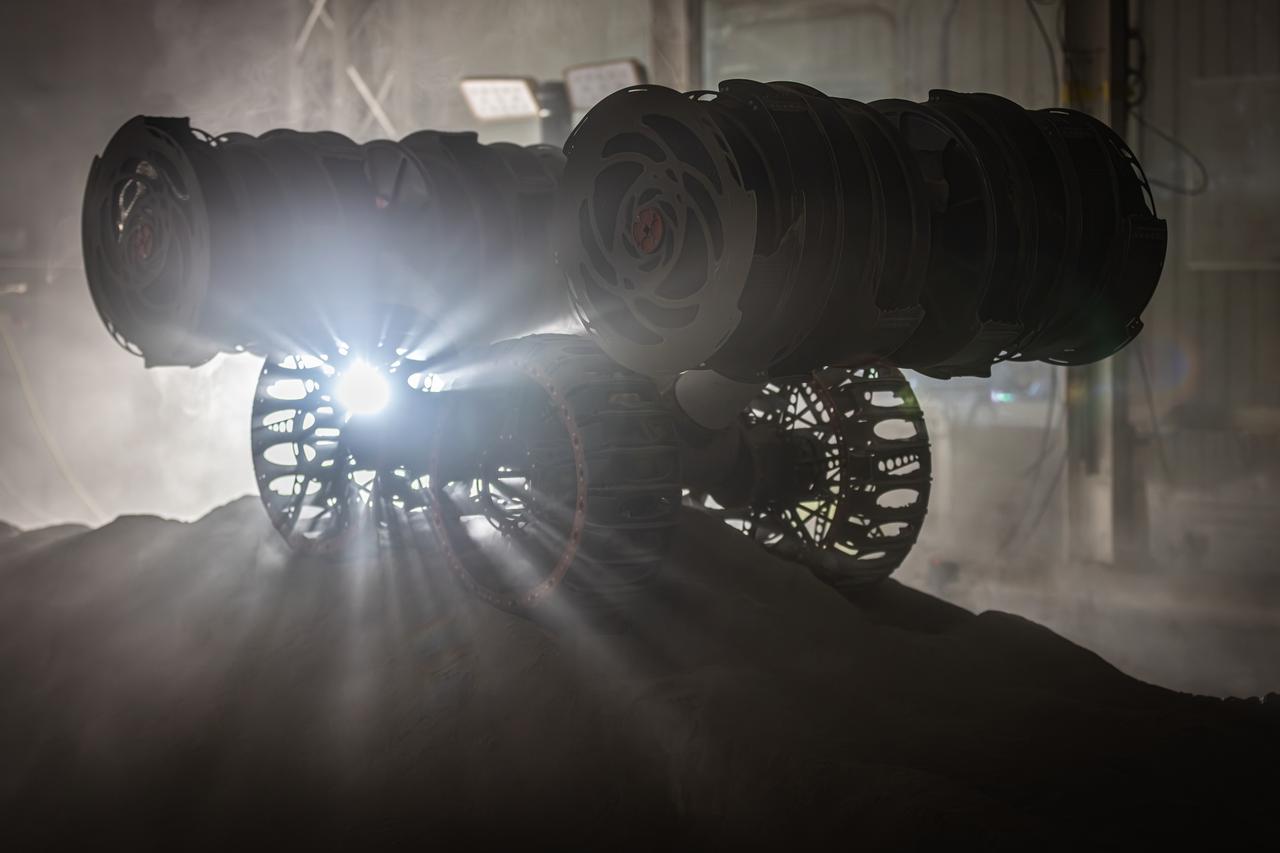

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) conducts excavation testing of simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 27, 2025. RASSOR is designed to work in low-gravity situations, using counter rotating bucket drums on each arm to collect and dump regolith for the extraction of hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining a habitable presence.
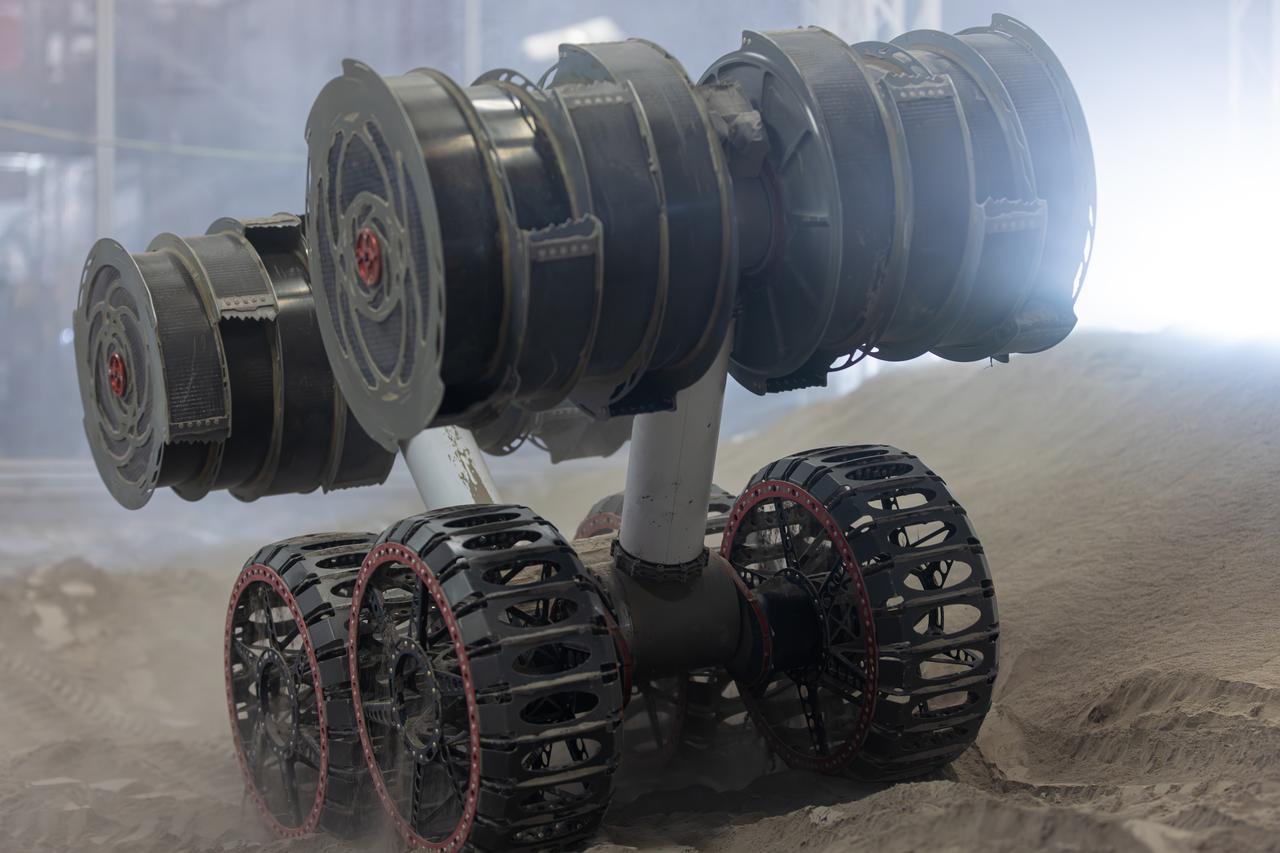

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) conducts excavation testing of simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 27, 2025. RASSOR is designed to work in low-gravity situations, using counter rotating bucket drums on each arm to collect and dump regolith for the extraction of hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining a habitable presence.
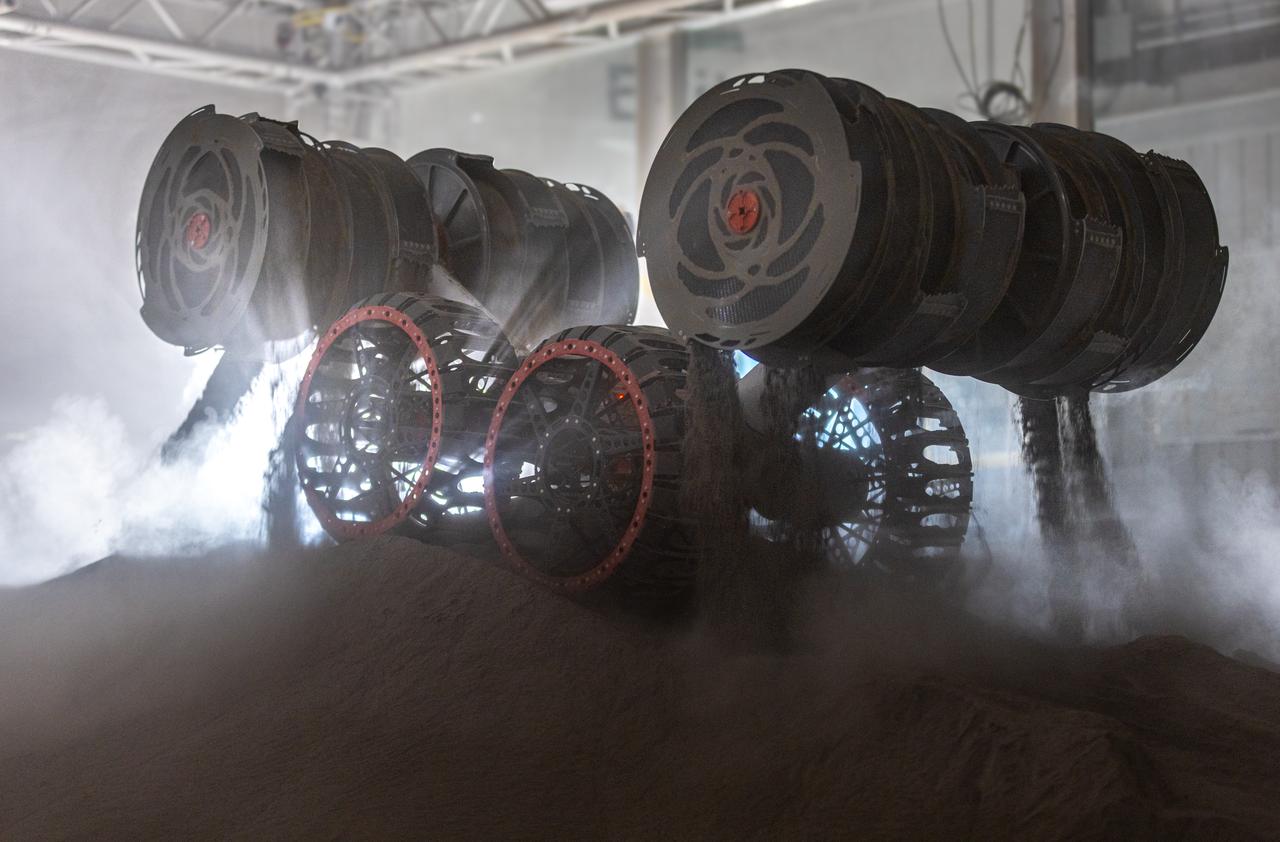

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) conducts excavation testing of simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 27, 2025. RASSOR is designed to work in low-gravity situations, using counter rotating bucket drums on each arm to collect and dump regolith for the extraction of hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining a habitable presence.
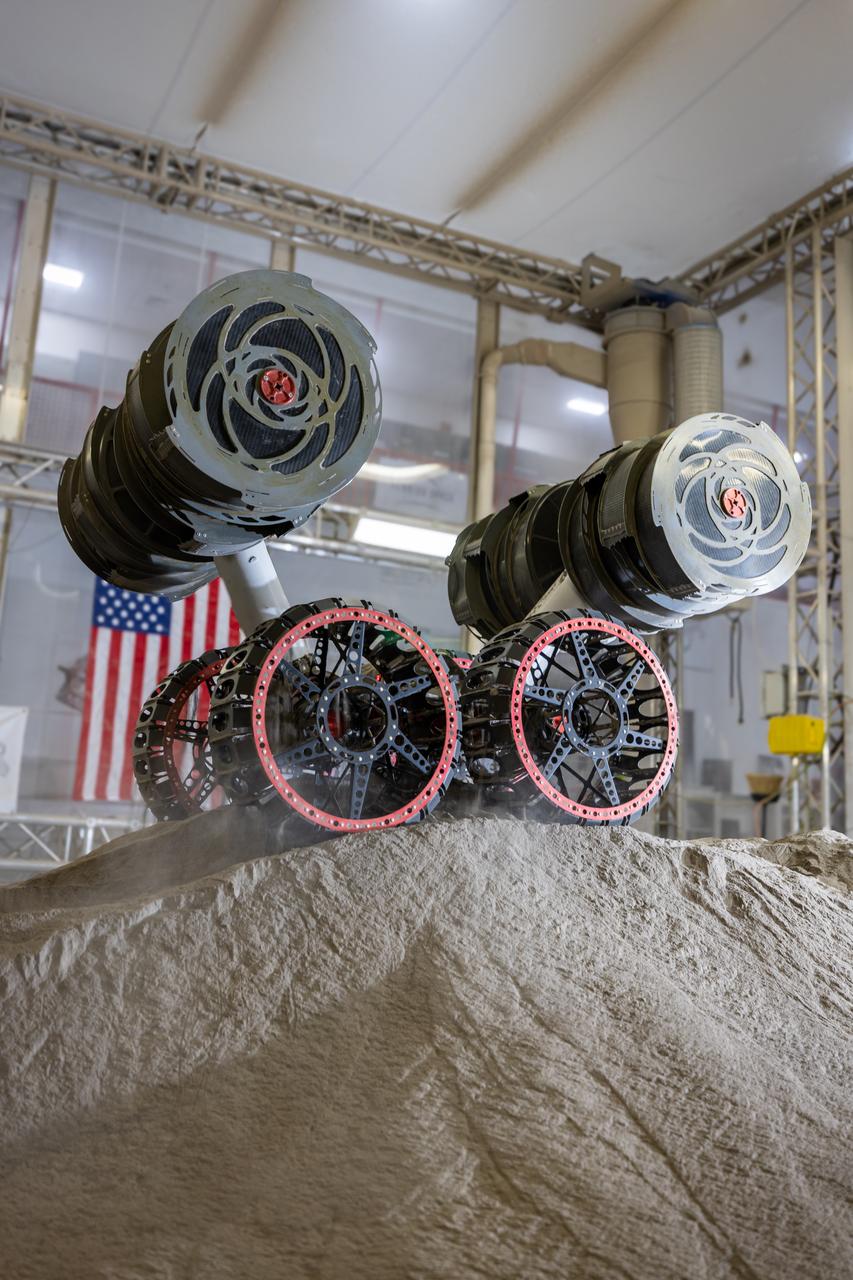

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) conducts excavation testing of simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 27, 2025. RASSOR is designed to work in low-gravity situations, using counter rotating bucket drums on each arm to collect and dump regolith for the extraction of hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining a habitable presence.
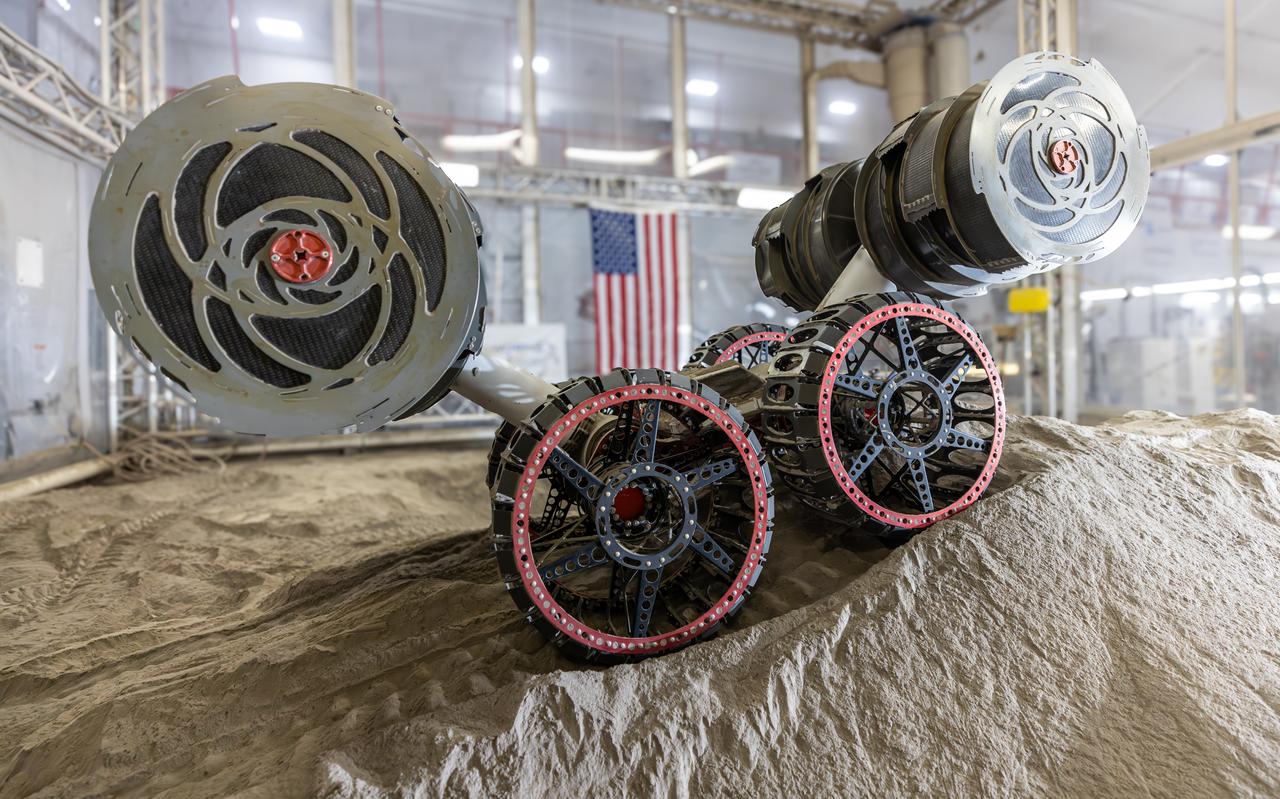

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) conducts excavation testing of simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 27, 2025. RASSOR is designed to work in low-gravity situations, using counter rotating bucket drums on each arm to collect and dump regolith for the extraction of hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining a habitable presence.
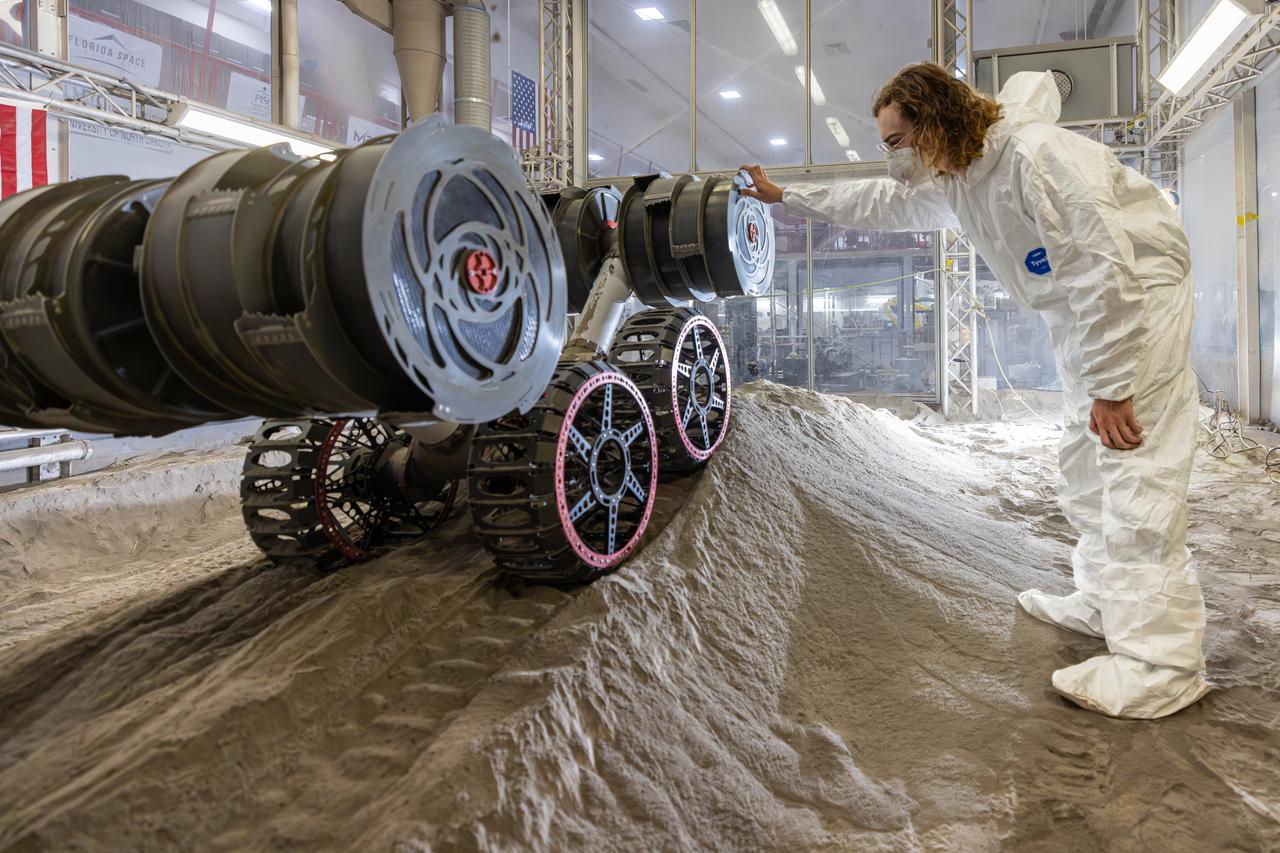

Ben Burdess, mechanical engineer, observes NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) excavation testing of simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, May 27, 2025. RASSOR is designed to work in low-gravity situations, using counter rotating bucket drums on each arm to collect and dump regolith for the extraction of hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining a habitable presence.
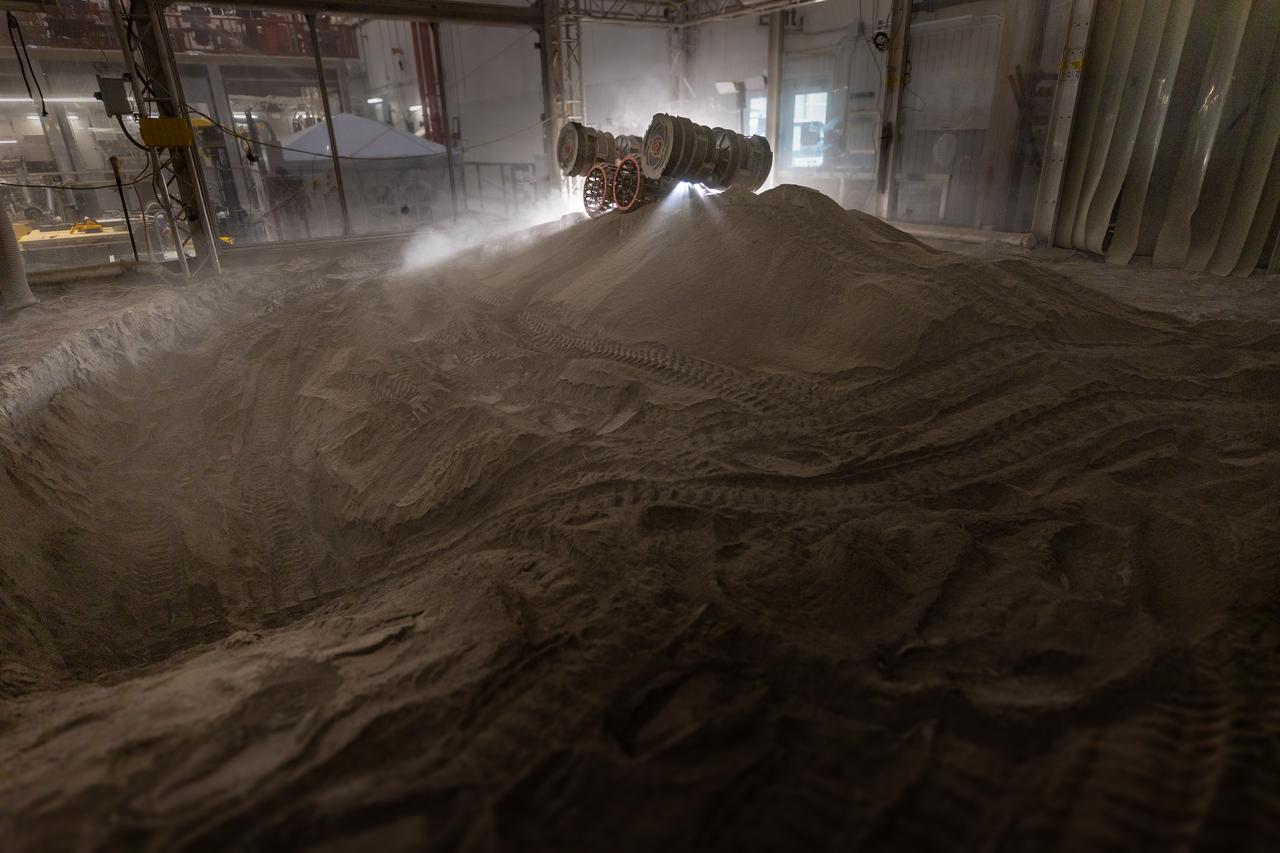

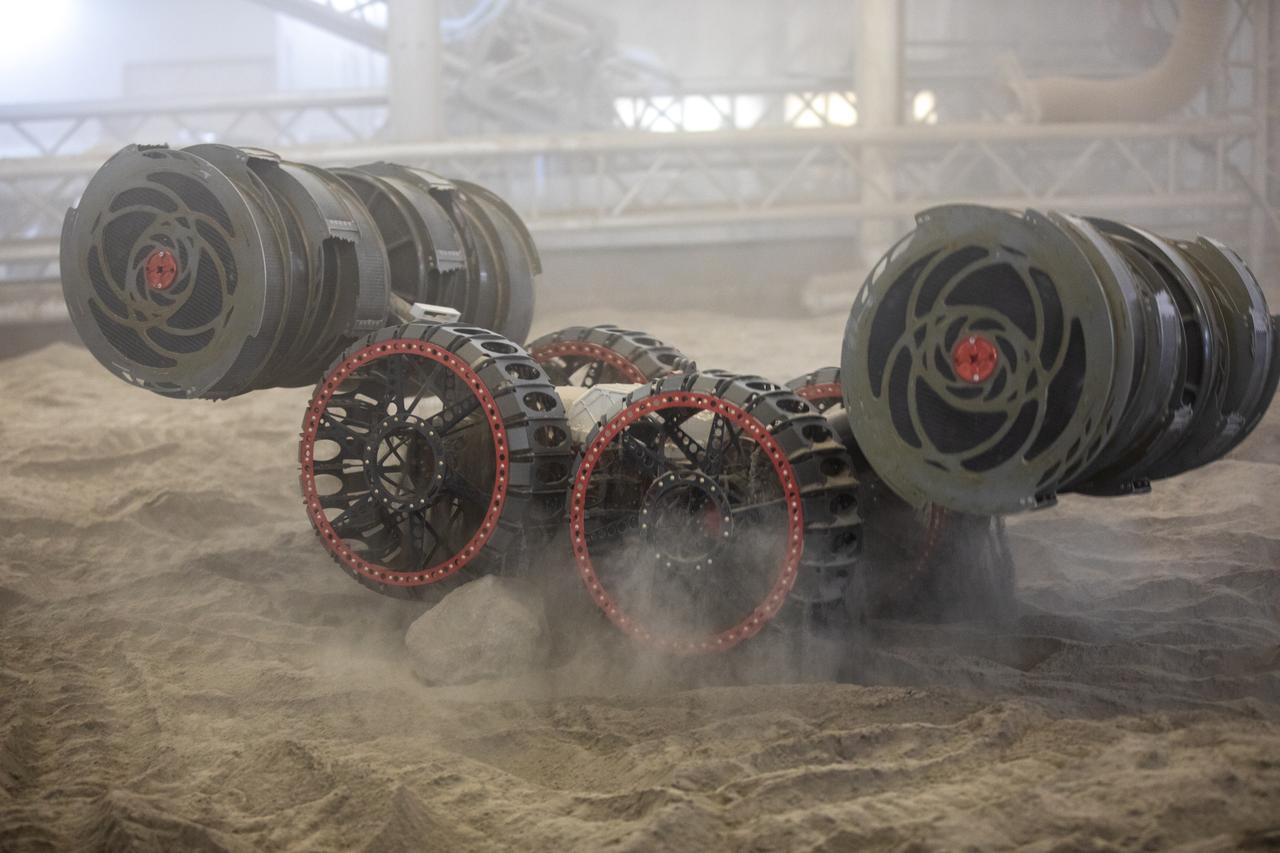
NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) manipulates simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, to create a three-foot berm during a site preparation test inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The opposing motion of the bucket drums helps RASSOR grip the surface in low-gravity environments like the Moon or Mars. With this unique capability, RASSOR can traverse the rough surface to dig, load, haul, and dump regolith that could be used in construction or broken down into hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining human presence. RASSOR represents an earlier generation technology that informed the development of NASA’s IPEx (In-Situ Resource Utilization Pilot Excavator), serving as a precursor and foundational platform for the advanced excavation systems and autonomous capabilities now being demonstrated by this Moon-mining robot.
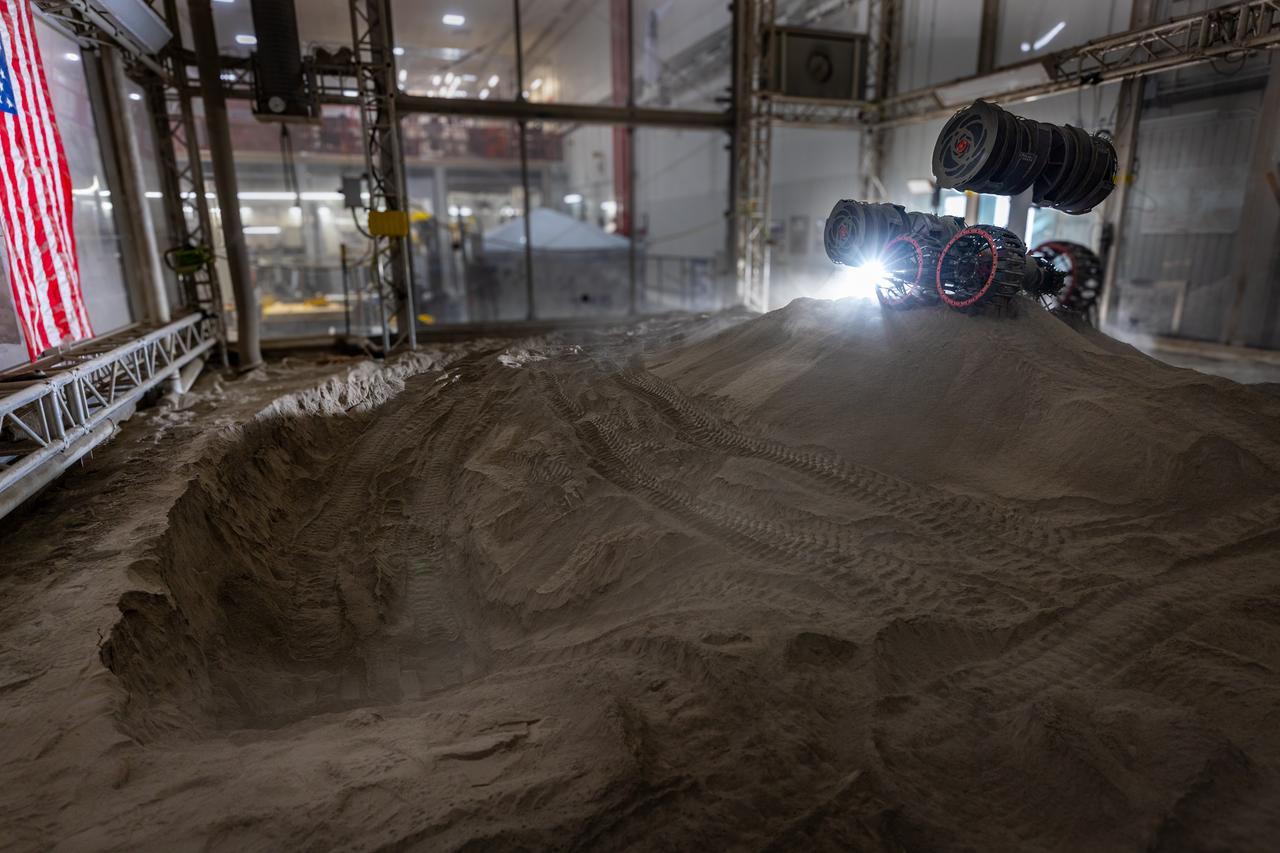

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) manipulates simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, to create a three-foot berm during a site preparation test inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The opposing motion of the bucket drums helps RASSOR grip the surface in low-gravity environments like the Moon or Mars. With this unique capability, RASSOR can traverse the rough surface to dig, load, haul, and dump regolith that could be used in construction or broken down into hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining human presence. RASSOR represents an earlier generation technology that informed the development of NASA’s IPEx (In-Situ Resource Utilization Pilot Excavator), serving as a precursor and foundational platform for the advanced excavation systems and autonomous capabilities now being demonstrated by this Moon-mining robot.
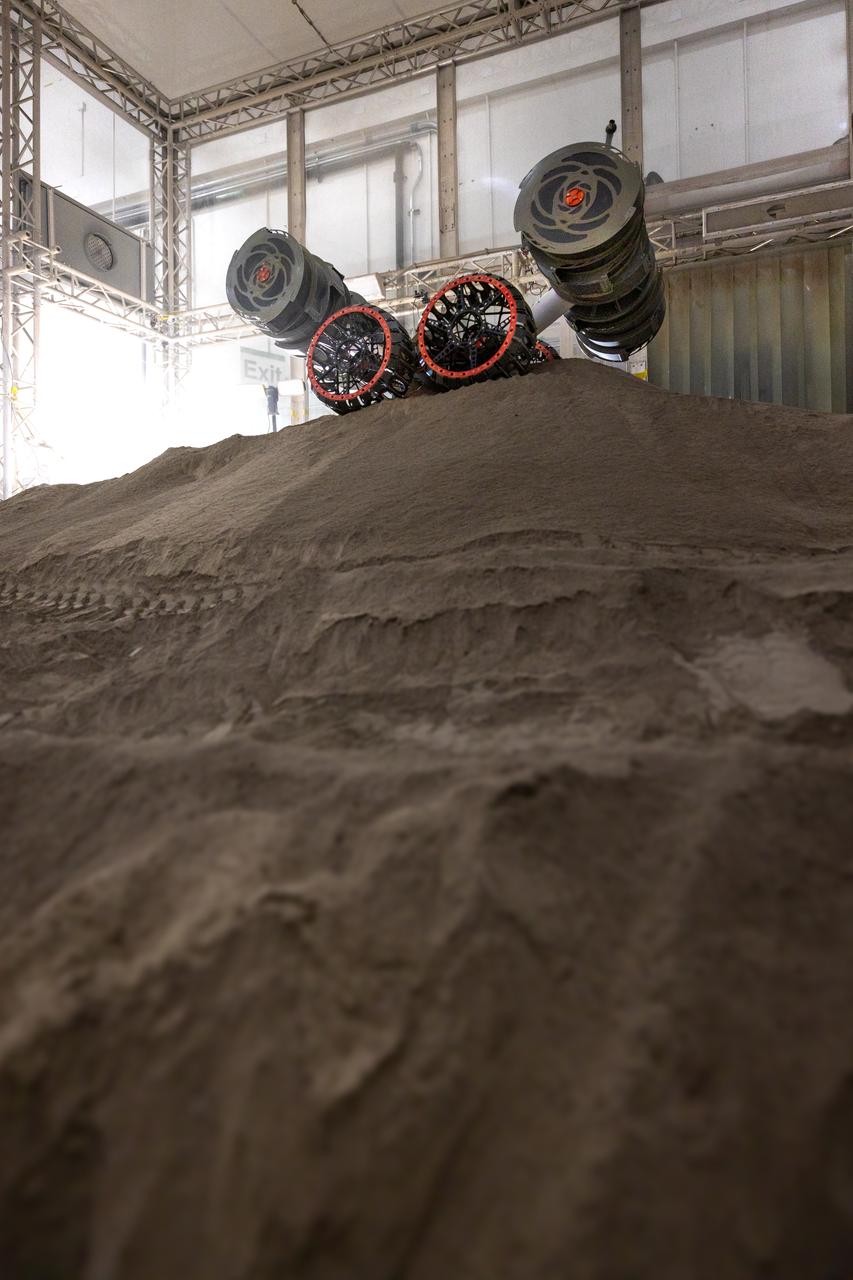

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) manipulates simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, to create a three-foot berm during a site preparation test inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The opposing motion of the bucket drums helps RASSOR grip the surface in low-gravity environments like the Moon or Mars. With this unique capability, RASSOR can traverse the rough surface to dig, load, haul, and dump regolith that could be used in construction or broken down into hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining human presence. RASSOR represents an earlier generation technology that informed the development of NASA’s IPEx (In-Situ Resource Utilization Pilot Excavator), serving as a precursor and foundational platform for the advanced excavation systems and autonomous capabilities now being demonstrated by this Moon-mining robot.

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) manipulates simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, to create a three-foot berm during a site preparation test inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The opposing motion of the bucket drums helps RASSOR grip the surface in low-gravity environments like the Moon or Mars. With this unique capability, RASSOR can traverse the rough surface to dig, load, haul, and dump regolith that could be used in construction or broken down into hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining human presence. RASSOR represents an earlier generation technology that informed the development of NASA’s IPEx (In-Situ Resource Utilization Pilot Excavator), serving as a precursor and foundational platform for the advanced excavation systems and autonomous capabilities now being demonstrated by this Moon-mining robot.

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) manipulates simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, to create a three-foot berm during a site preparation test inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The opposing motion of the bucket drums helps RASSOR grip the surface in low-gravity environments like the Moon or Mars. With this unique capability, RASSOR can traverse the rough surface to dig, load, haul, and dump regolith that could be used in construction or broken down into hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining human presence. RASSOR represents an earlier generation technology that informed the development of NASA’s IPEx (In-Situ Resource Utilization Pilot Excavator), serving as a precursor and foundational platform for the advanced excavation systems and autonomous capabilities now being demonstrated by this Moon-mining robot.

NASA’s RASSOR (Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot) manipulates simulated regolith, or lunar dust found on the Moon’s surface, to create a three-foot berm during a site preparation test inside of the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The opposing motion of the bucket drums helps RASSOR grip the surface in low-gravity environments like the Moon or Mars. With this unique capability, RASSOR can traverse the rough surface to dig, load, haul, and dump regolith that could be used in construction or broken down into hydrogen, oxygen, or water, resources critical for sustaining human presence. RASSOR represents an earlier generation technology that informed the development of NASA’s IPEx (In-Situ Resource Utilization Pilot Excavator), serving as a precursor and foundational platform for the advanced excavation systems and autonomous capabilities now being demonstrated by this Moon-mining robot.
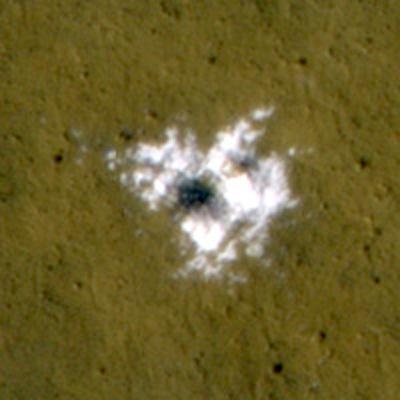

The Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars, an instrument on NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, obtained information confirming material excavated by a fresh impact and Identified as water ice.
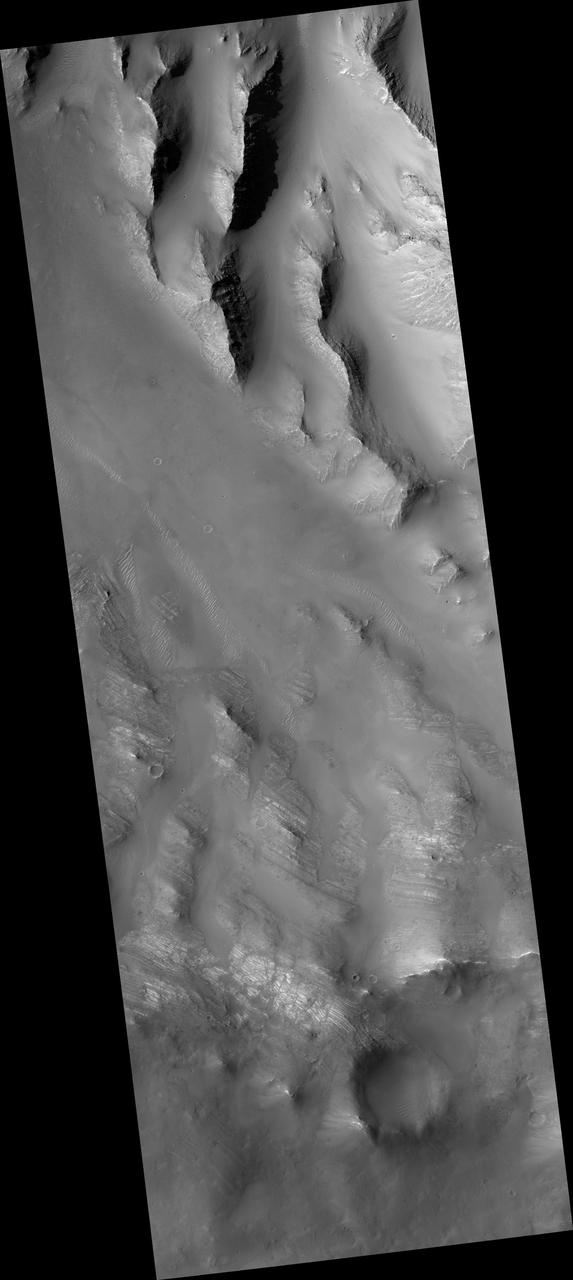

Oudemans Crater Central Uplift: A Sample of Well-Preserved Layering Excavated from Kilometers Below

This image, received today, shows the trench excavated by NASA's Viking 1 surface sampler. The trench was dug by extending the surface sampler collection head in a direction from lower right toward the upper left and then withdrawing the surface sampler collector head. Lumpy piles of material at end of trench at lower right was pulled by plowing from trench by the backhoe which will be used to dig trenches later in the mission. Area around trench has ripple marks produced by Martian wind. The trench which was dug early on Sol 8, is about 3 inches wide, 2 inches deep and 6 inches long. Steep dark crater walls show the grains of the Martian surface material stick together (have adhesion). The doming of the surface at far end of the trench show the granular material is dense. The Martian surface material behaves somewhat like moist sand on Earth. Evidence from the trench indicate a sample was collected and delivered to the experiments after repeated tries. The biology experiment level full indicator indicates a sample was received for analysis. The X-Ray fluorescence experiment has no indication to show it received a sample. The GCMS experiment level full indicator suggests no sample was received but this matter is being investigated. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00389
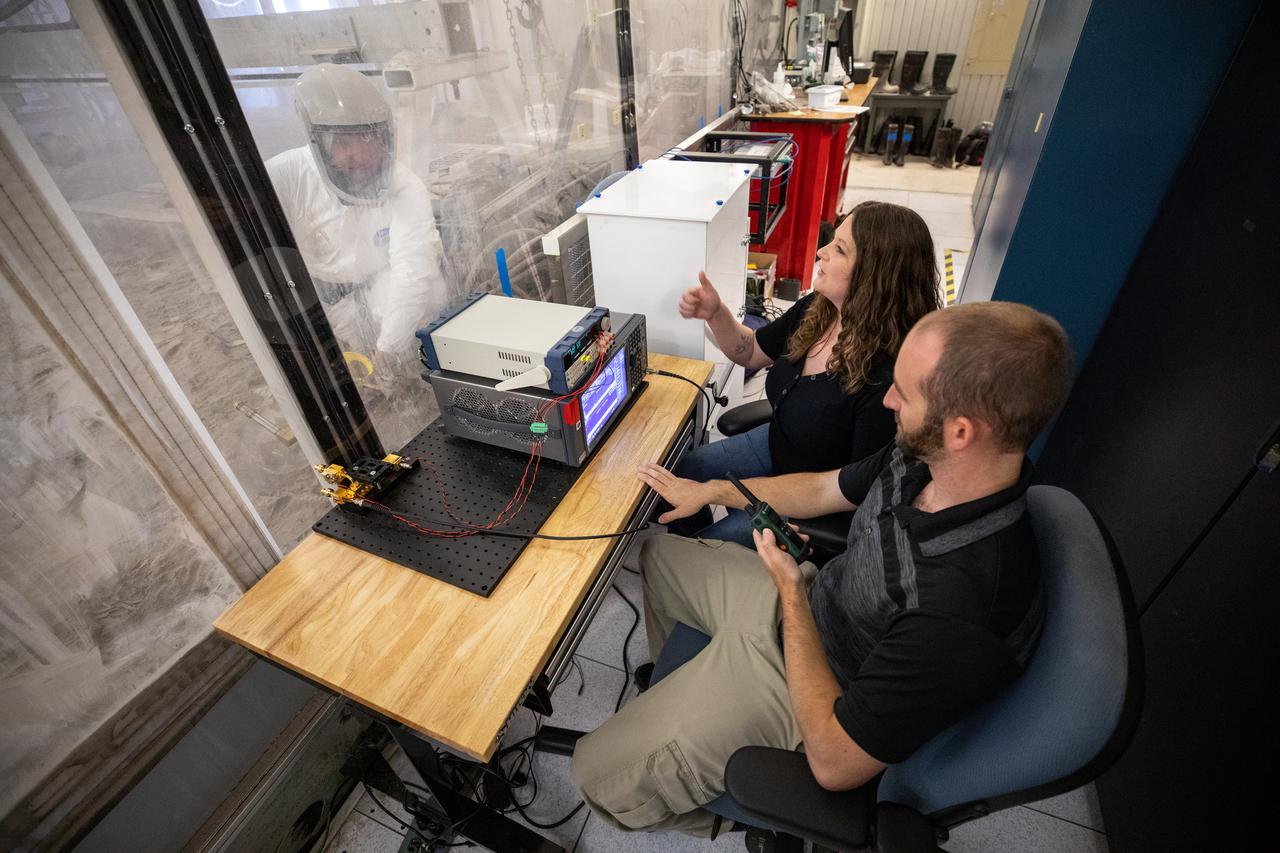

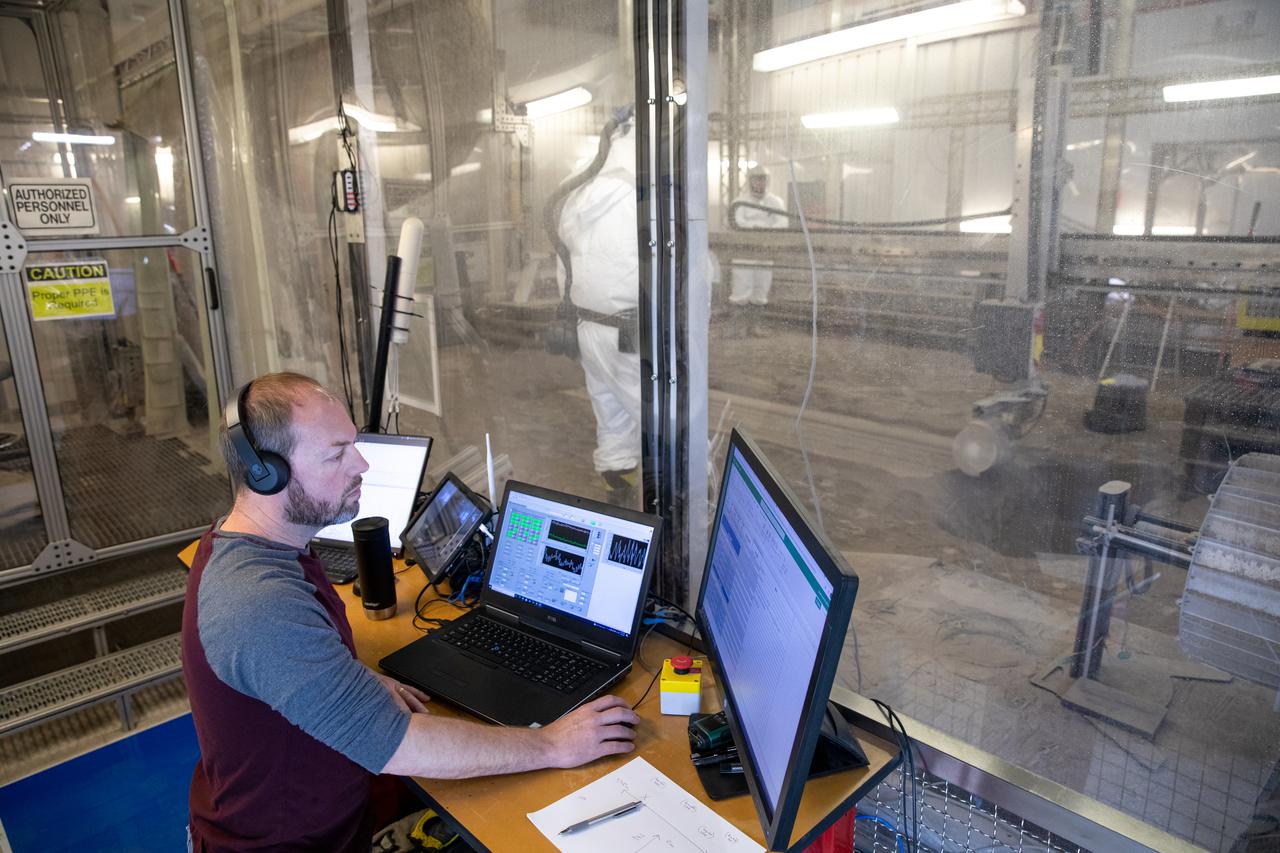
Beverly Kemmerer and Austin Adkins, right, and Austin Langton, perform testing with a Millimeter Wave Doppler Radar at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab on July 16, 2021. The testing at the Florida spaceport is part of a project to identify a suite of instrumentation capable of acquiring a comprehensive set of flight data from a lunar lander. Researchers at NASA will use that data to validate computational models being developed to predict plume surface interaction effects on the Moon.
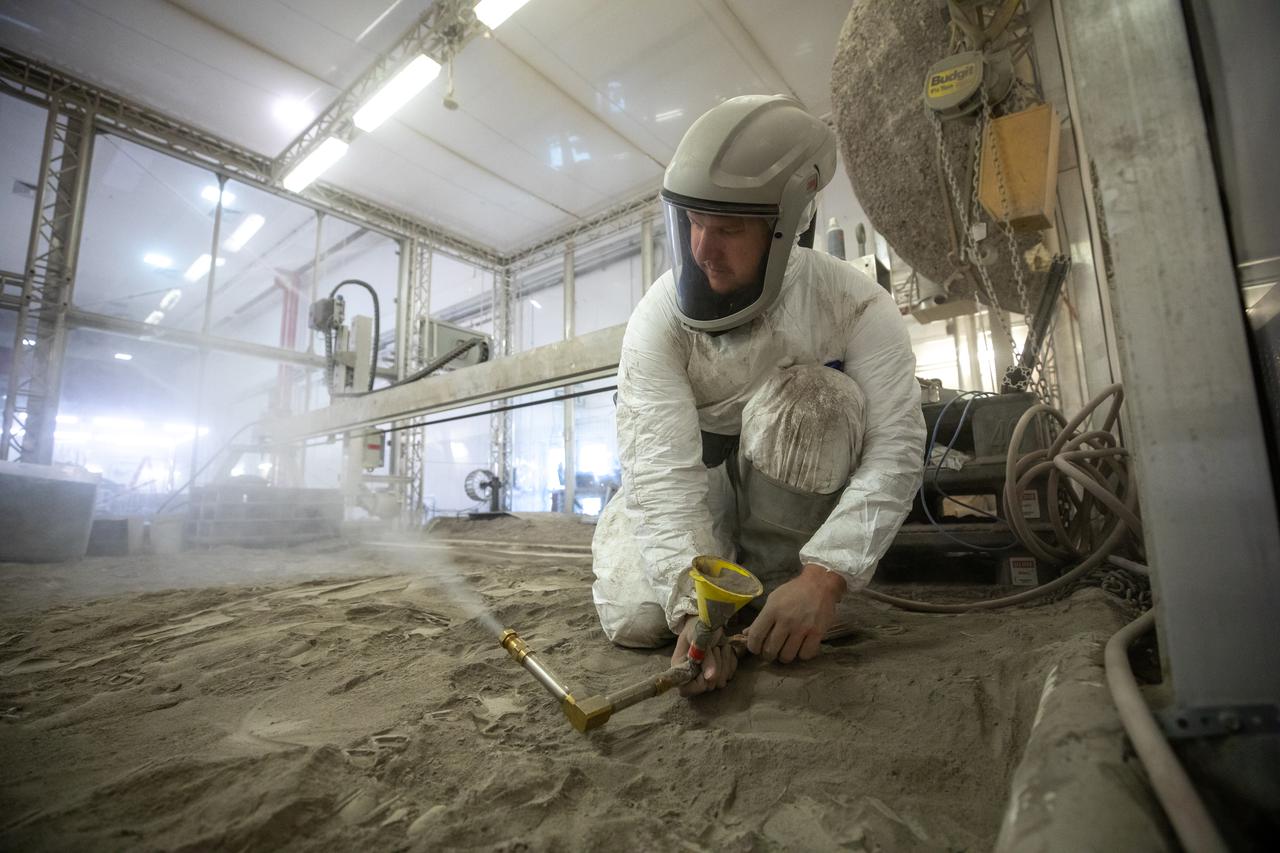

Austin Langton, a researcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, creates a fine spray of the regolith simulant BP-1, to perform testing with a Millimeter Wave Doppler Radar at the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab on July 16, 2021. The testing occurred inside the "Big Bin," an enclosure at Swamp Works that holds 120 tons of regolith simulant. The testing at the Florida spaceport is part of a project to predict plume surface interaction effects on the Moon, with testing happening at Kennedy, and NASA's Marshal Space Flight Center and Glenn Research Center.
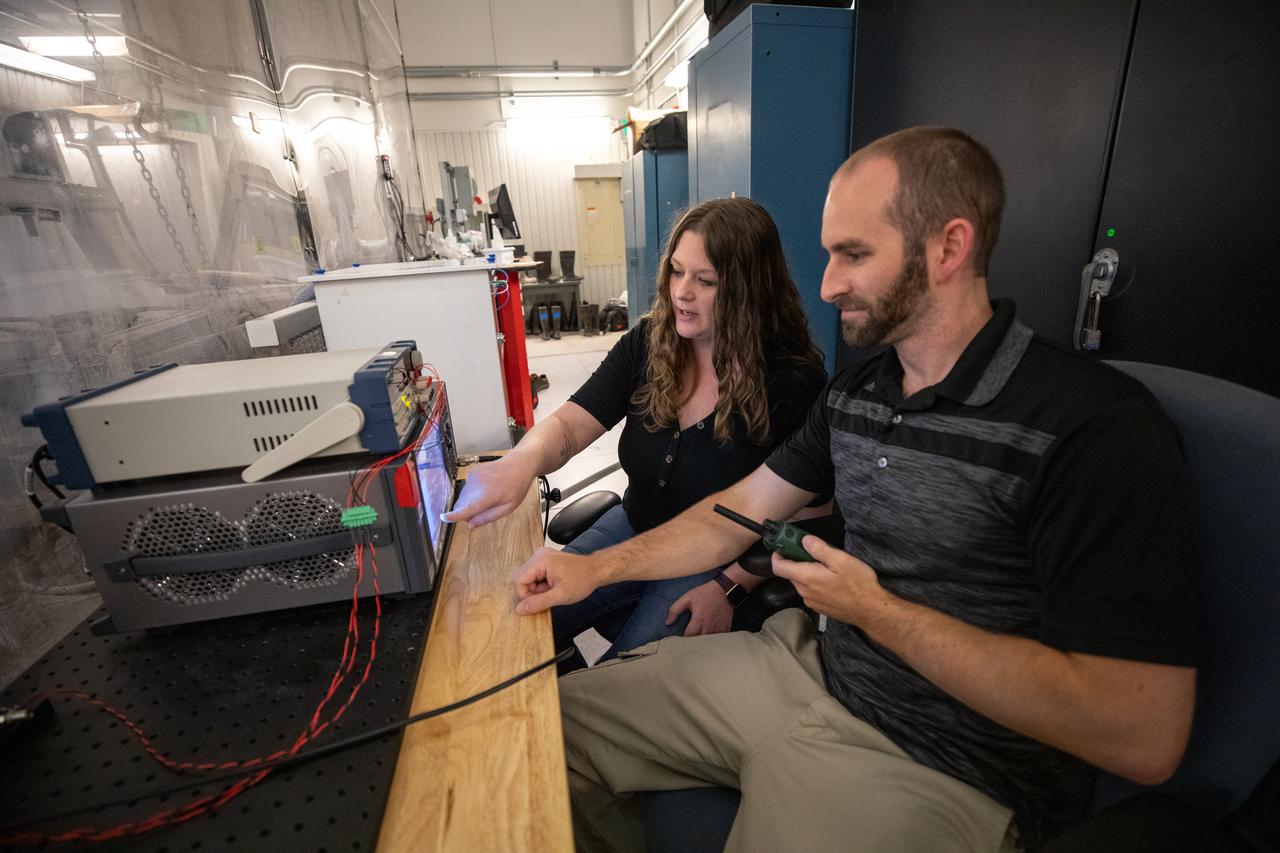

Beverly Kemmerer and Austin Adkins perform testing with a Millimeter Wave Doppler Radar at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab on July 16, 2021. The testing at the Florida spaceport is part of a project to identify a suite of instrumentation capable of acquiring a comprehensive set of flight data from a lunar lander. Researchers at NASA will use that data to validate computational models being developed to predict plume surface interaction effects on the Moon.
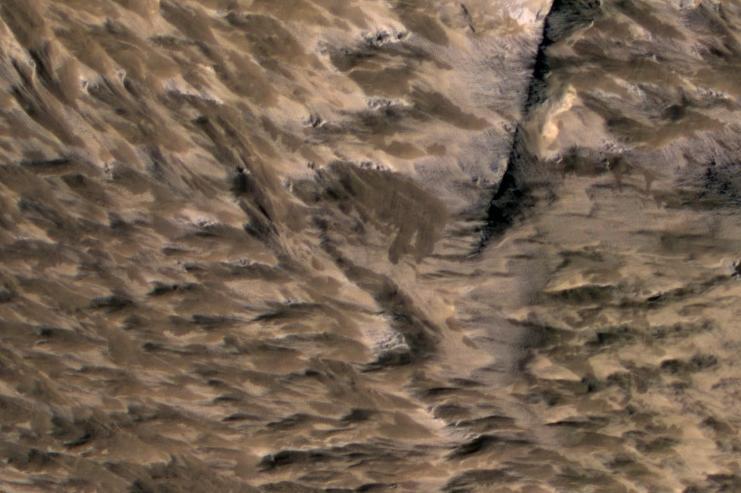

This April 6, 2014, image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows numerous landslides in the vicinity of where an impact crater was excavated in March 2012.
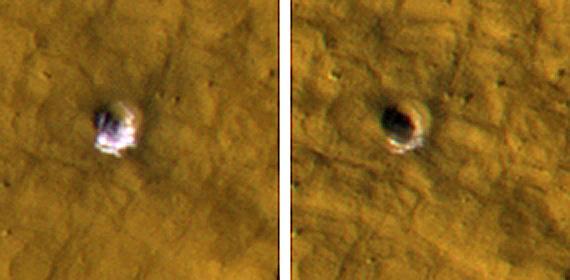
NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter reveals underground ice exposed by impact cratering. The impact that dug the crater excavated water ice from beneath the surface.
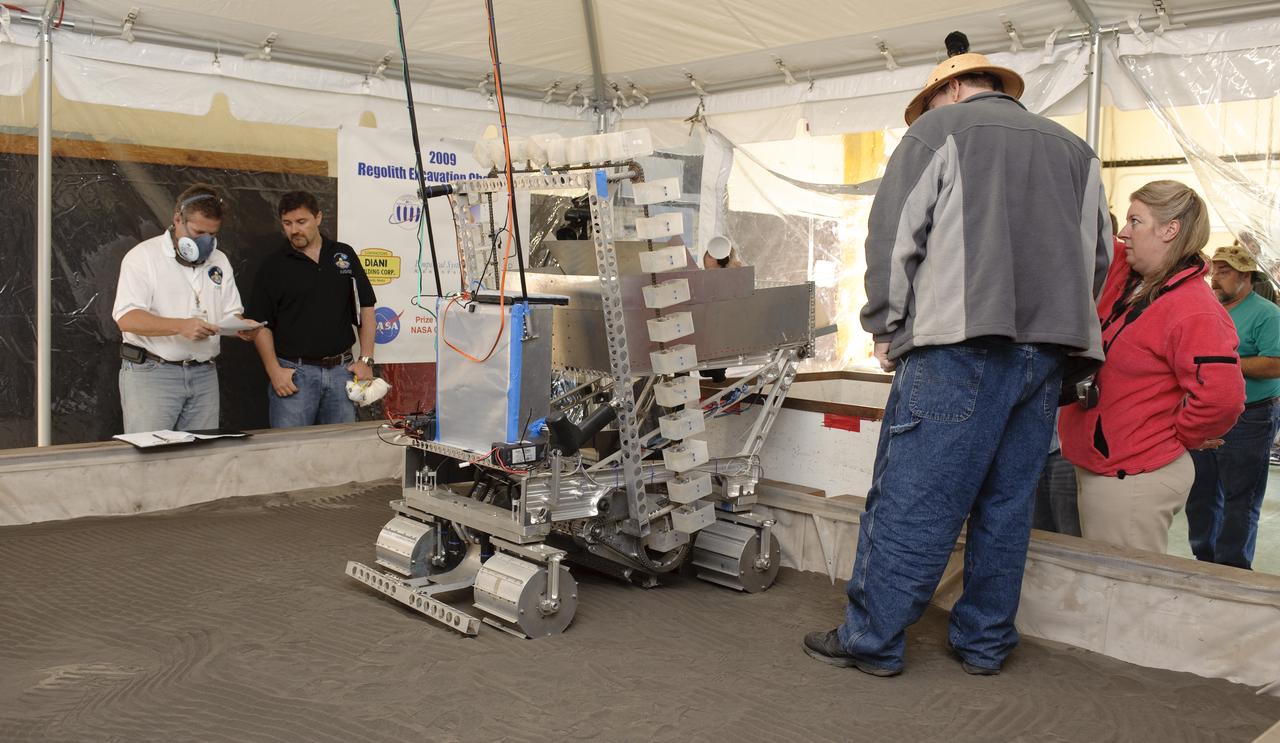

NASA Hosts National Lunar Robotics Excavation Competition '2009 Regolith Excavation Challenge At NASA's Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA
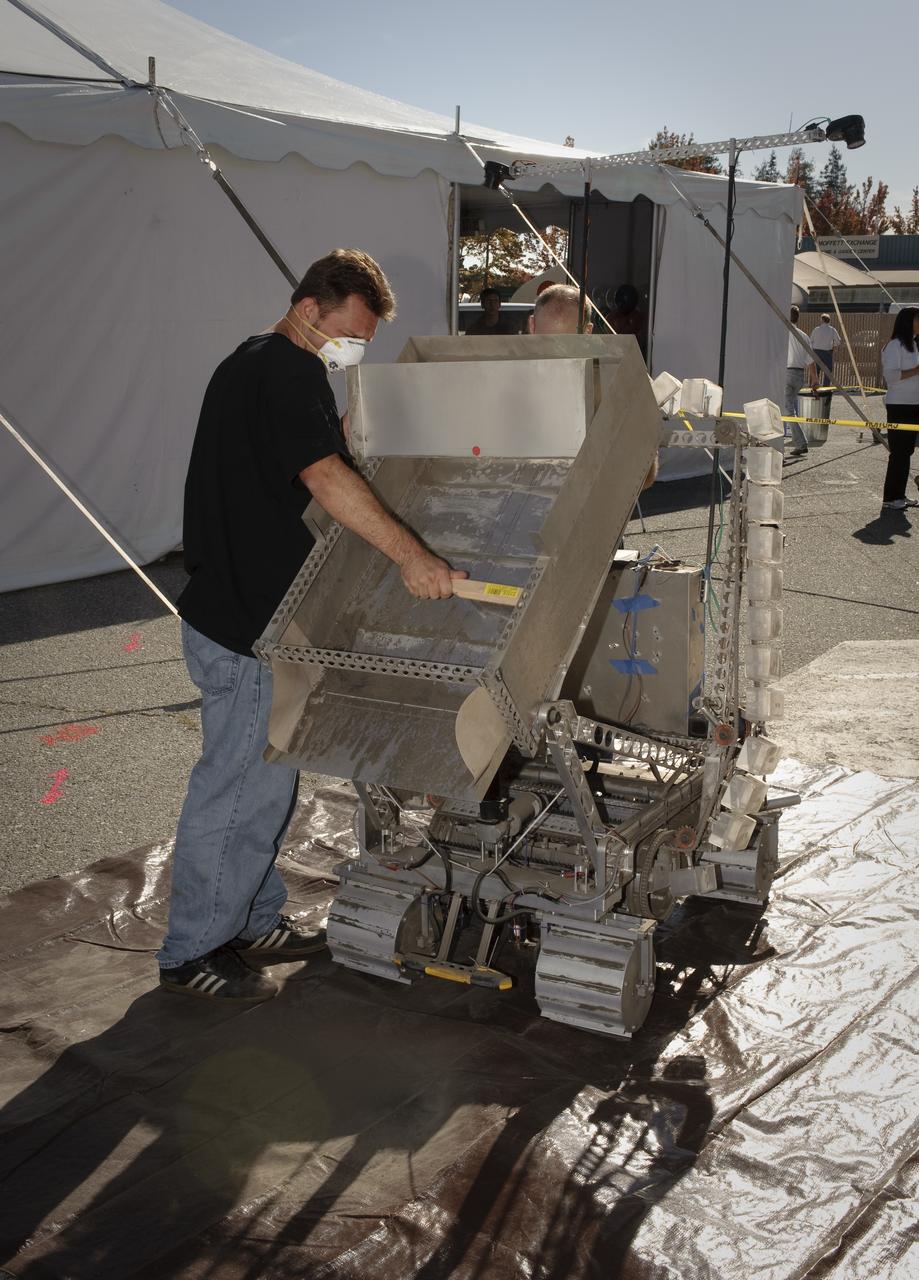

NASA Hosts National Lunar Robotics Excavation Competition '2009 Regolith Excavation Challenge At NASA's Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA

NASA Hosts National Lunar Robotics Excavation Competition '2009 Regolith Excavation Challenge At NASA's Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA
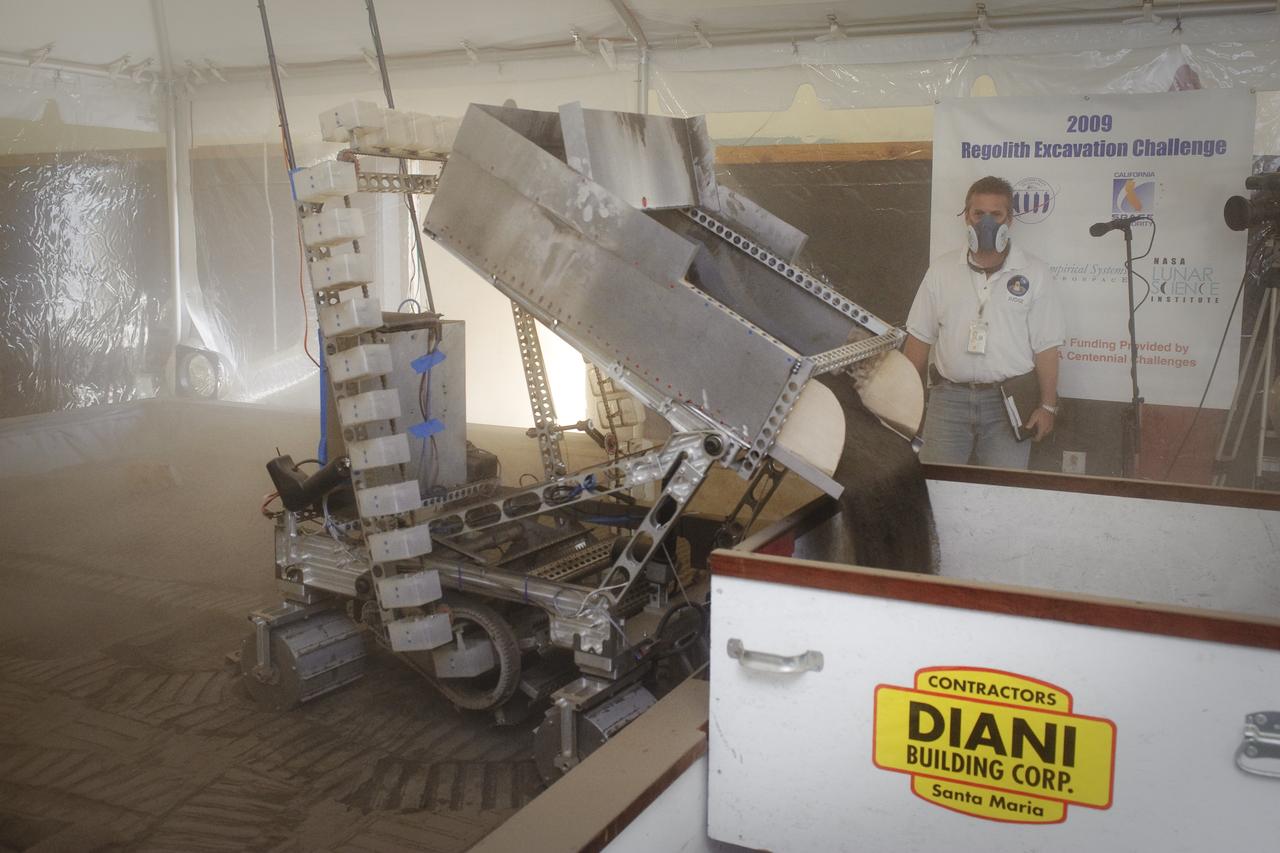

NASA Hosts National Lunar Robotics Excavation Competition '2009 Regolith Excavation Challenge At NASA's Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA
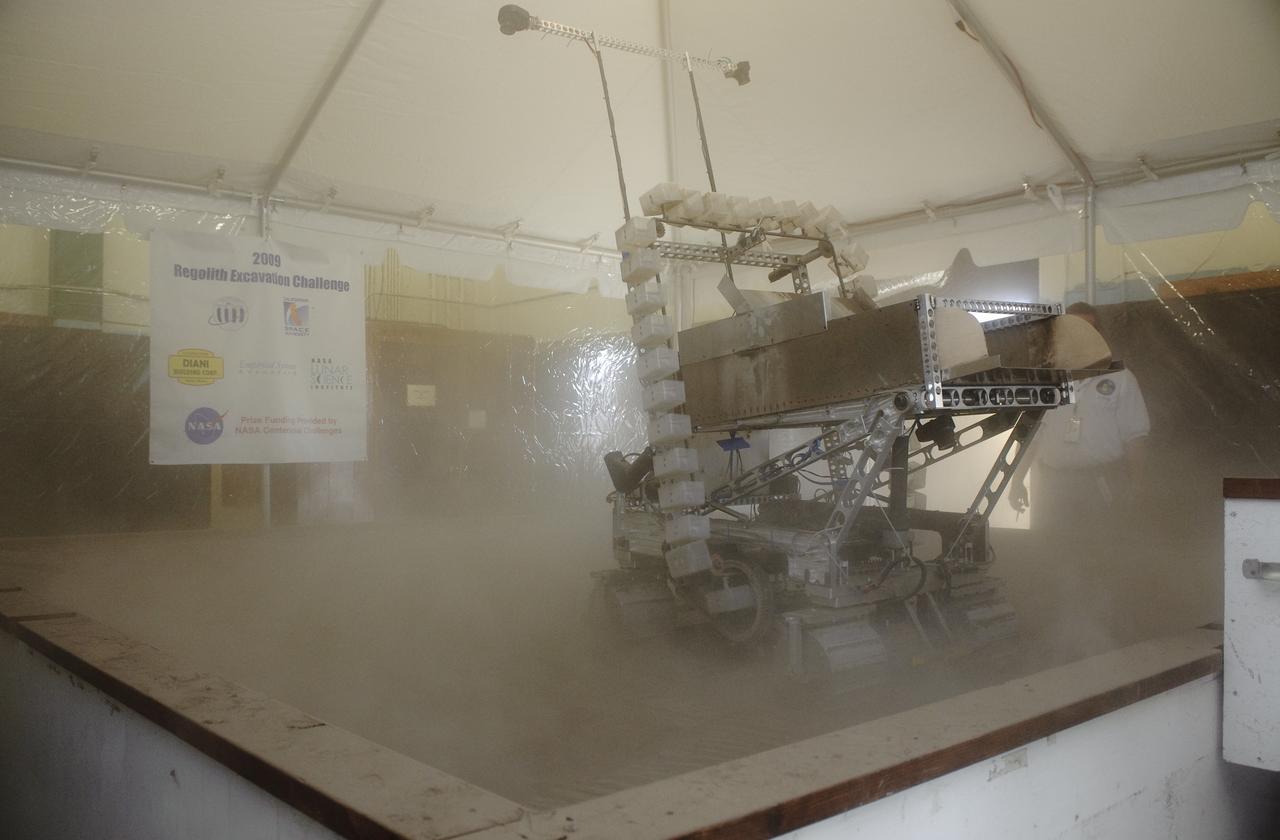

NASA Hosts National Lunar Robotics Excavation Competition '2009 Regolith Excavation Challenge At NASA's Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA

NASA Hosts National Lunar Robotics Excavation Competition '2009 Regolith Excavation Challenge At NASA's Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA
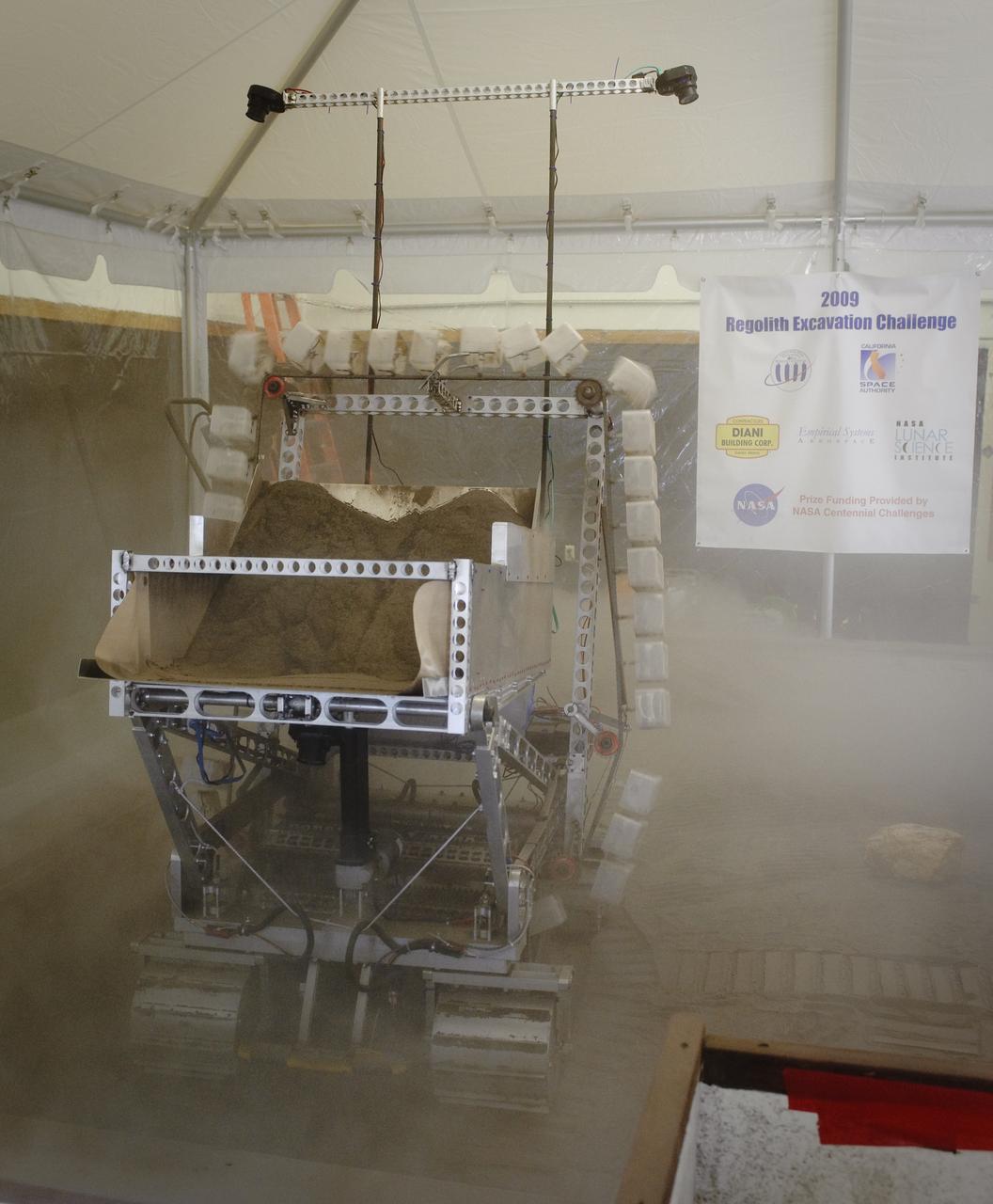

NASA Hosts National Lunar Robotics Excavation Competition '2009 Regolith Excavation Challenge At NASA's Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA
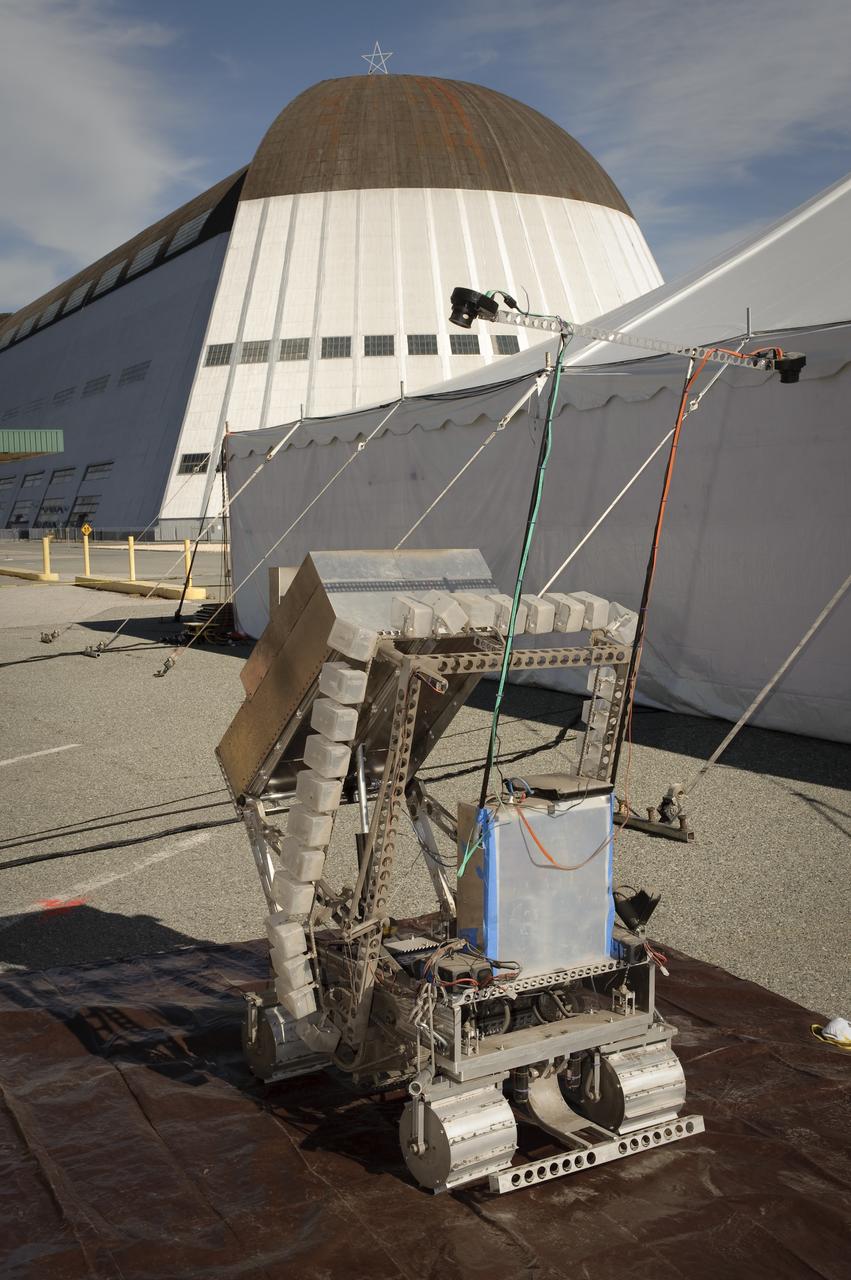

NASA Hosts National Lunar Robotics Excavation Competition '2009 Regolith Excavation Challenge At NASA's Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA

NASA Hosts National Lunar Robotics Excavation Competition '2009 Regolith Excavation Challenge At NASA's Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA
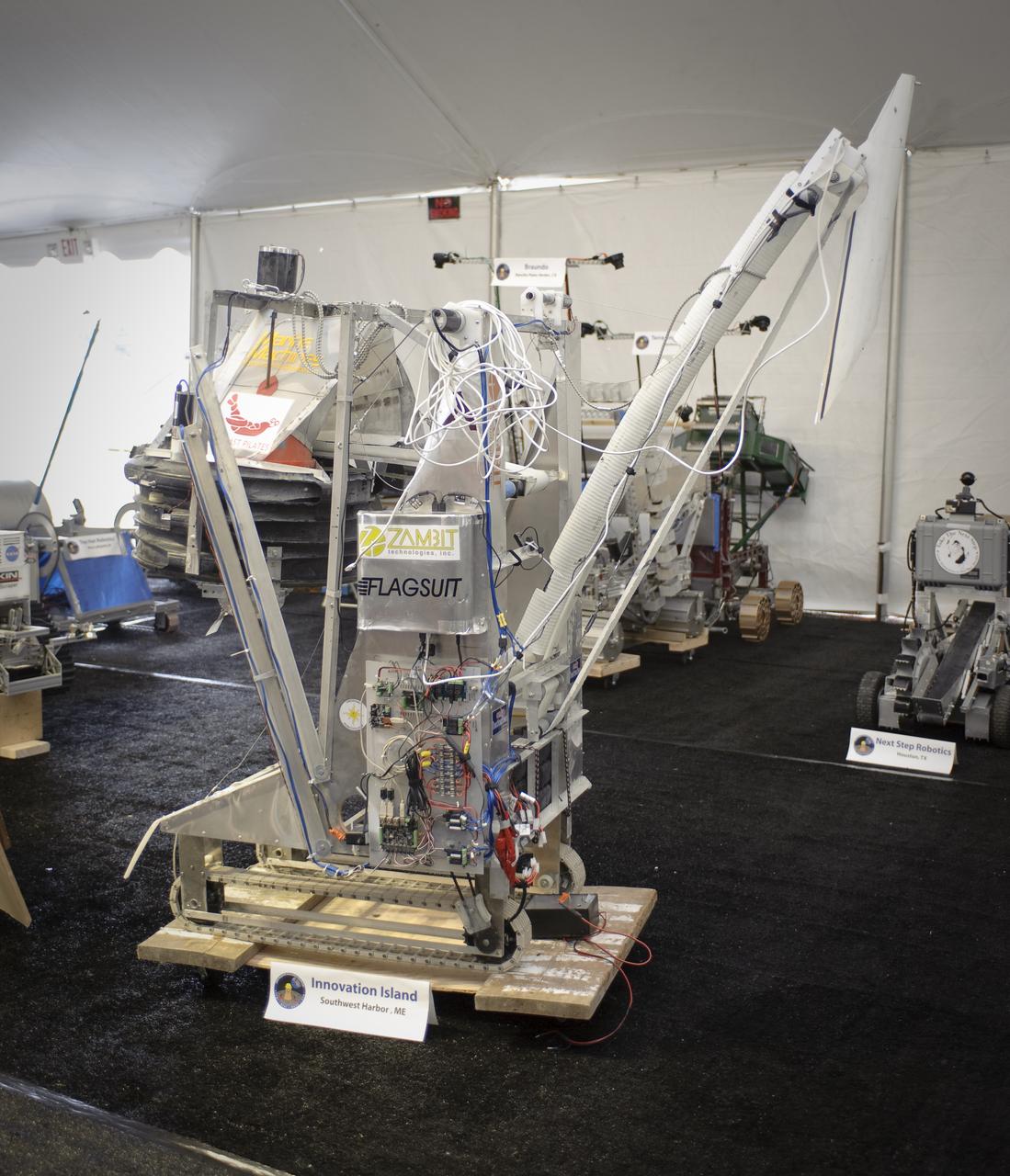

NASA Hosts National Lunar Robotics Excavation Competition '2009 Regolith Excavation Challenge At NASA's Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA
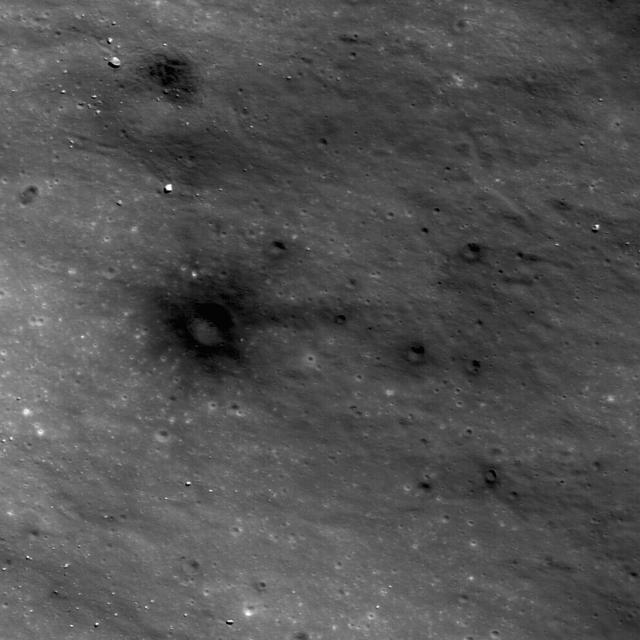

This image from NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter shows dark materials excavated by later small impacts show up clearly on the bright ejecta of a small lunar crater to the west.
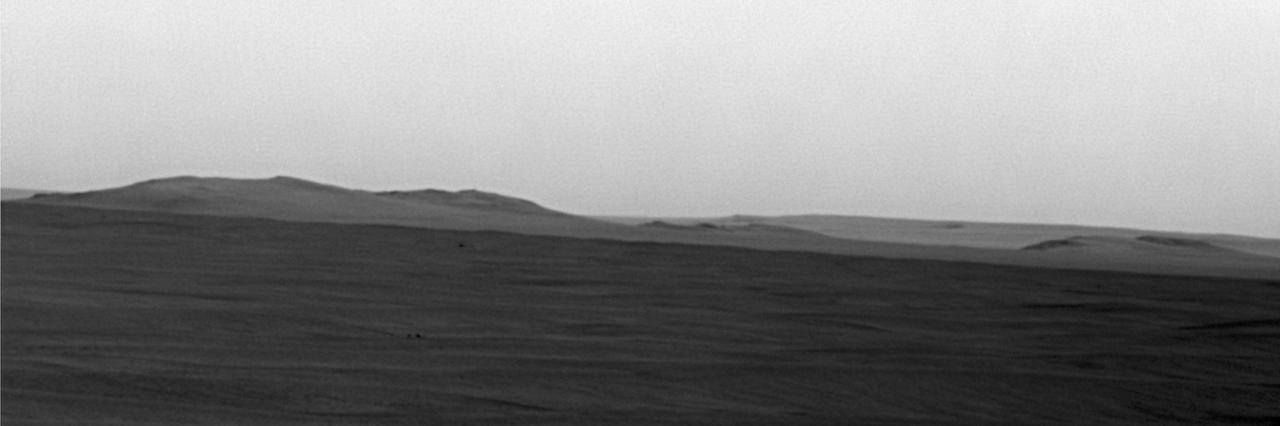

This image from NASA rover Opportunity shows mostly a portion of Endeavour western rim left; a paler-looking terrain on the horizon beyond Endeavour right is part of a thick deposit of material ejected by the impact that excavated Iazu Crater.
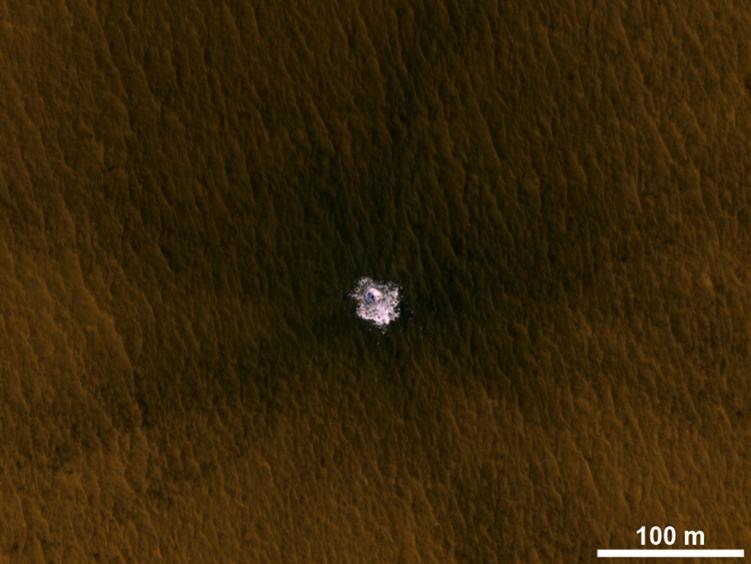

The image is an excerpt from an observation from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter showing a meteorite impact that excavated this crater on Mars exposed bright ice that had been hidden just beneath the surface at this location.

This is a close-up view of the zones where the soil at Curiosity landing site was blown away by the thrusters on the rover descent stage. The excavation of the soil reveals probable bedrock outcrop.
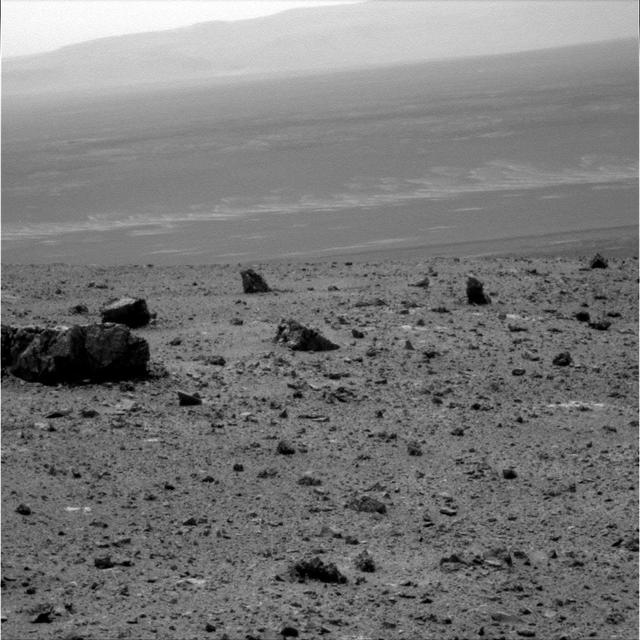

The large rock on the left in the foreground, informally named Tisdale 1. It is part of a group of rocks that appear to have been ejected by the excavation of Odyssey crater on the rim of Endeavour crater by NASA Mars rover Odyssey.
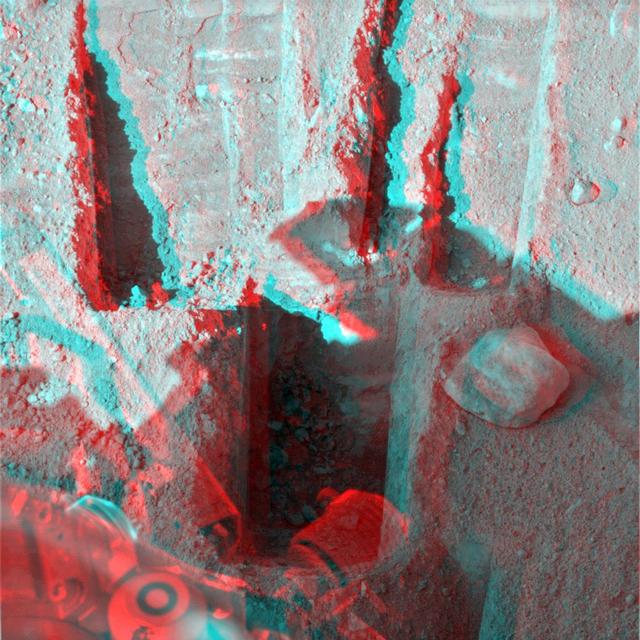
Digging by NASA Phoenix Mars Lander on Aug. 23, 2008, reached a depth about three times greater than in any trench Phoenix has excavated. 3D glasses are necessary.
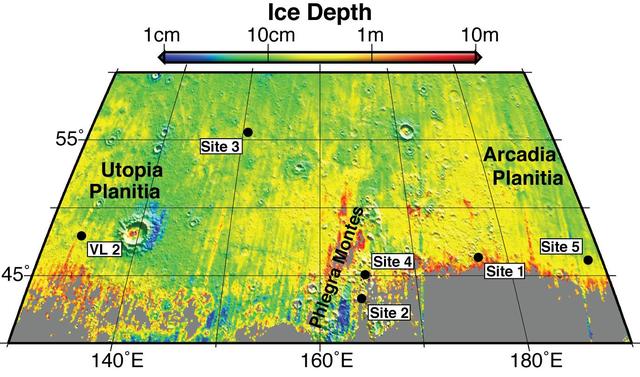
Using observations from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, this map shows five locations where fresh impact cratering has excavated water ice from just beneath the surface of Mars.

As NASA Phoenix Mars Lander excavates trenches, it also builds piles with most of the material scooped from the holes. The piles, like this one called Caterpillar, provide researchers some information about the soil. 3D glasses are necessary.
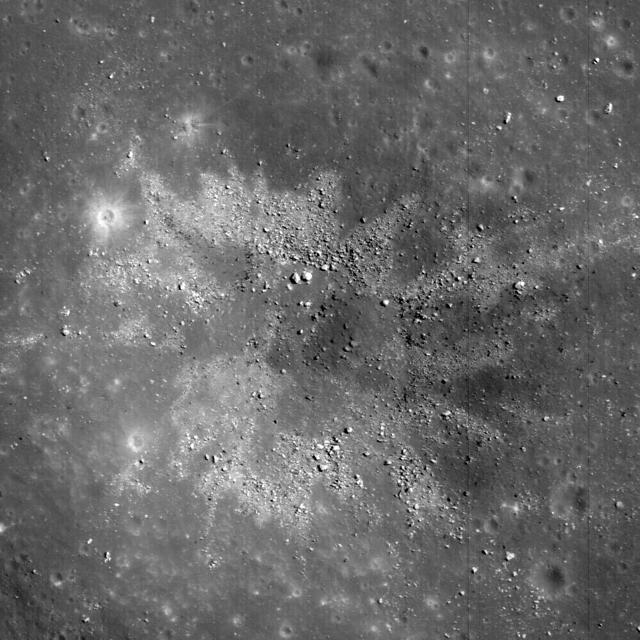

Materials excavated during formation of this ~450 m diameter impact crater have an unusual two-toned character, likely a reflection of heterogeneity in the target materials. This crater occurs in Balmer Basin. This image was taken by NASA Lunar Reconnai
The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment camera on NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter reveals subsurface ice in a crater formed in 2008. The impact that dug the crater excavated water ice from beneath the surface.
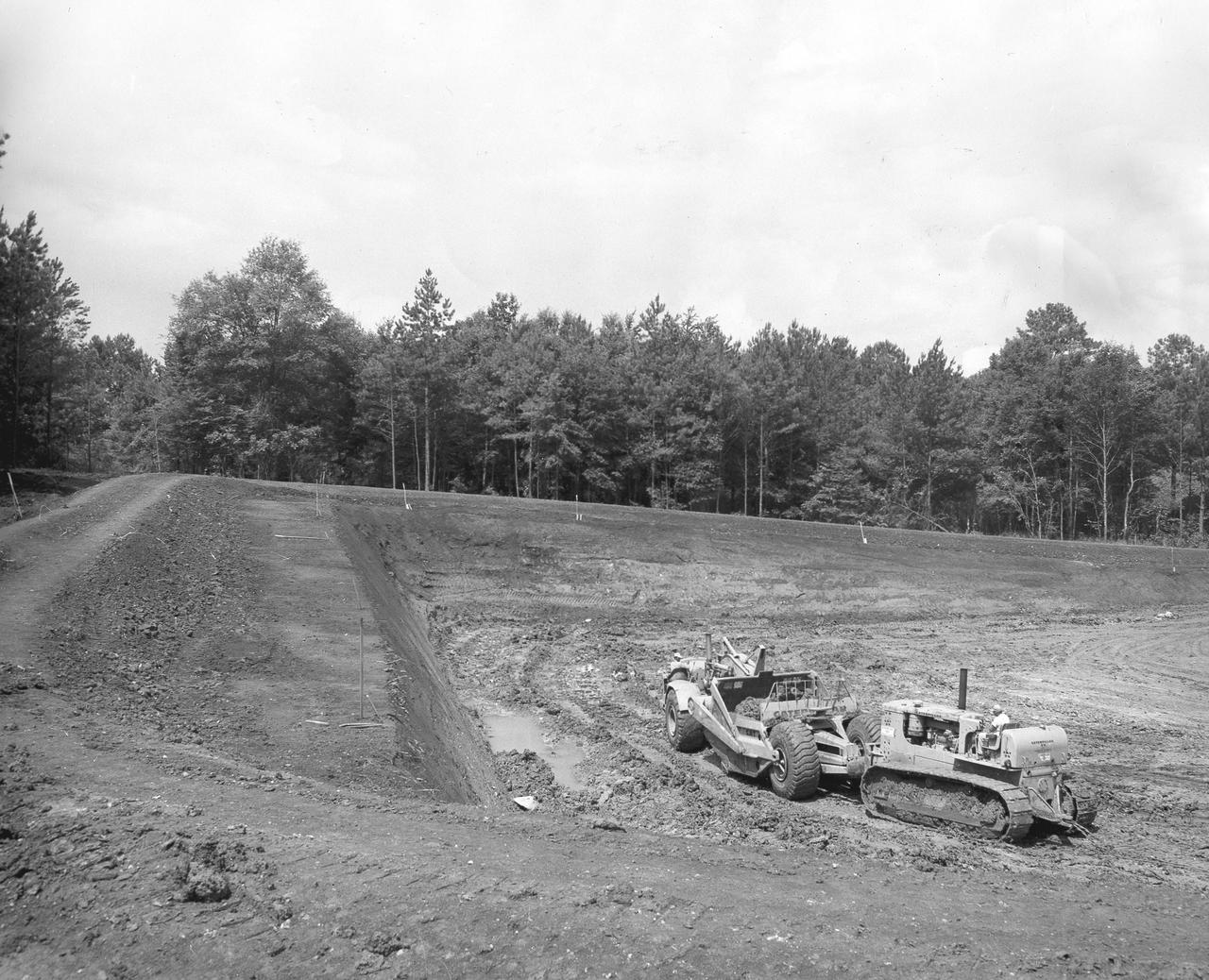

At its founding, the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) inherited the Army’s Jupiter and Redstone test stands, but much larger facilities were needed for the giant stages of the Saturn V. From 1960 to 1964, the existing stands were remodeled and a sizable new test area was developed. The new comprehensive test complex for propulsion and structural dynamics was unique within the nation and the free world, and they remain so today because they were constructed with foresight to meet the future as well as on going needs. Construction of the S-IC Static test stand complex began in 1961 in the west test area of MSFC, and was completed in 1964. The S-IC static test stand was designed to develop and test the 138-ft long and 33-ft diameter Saturn V S-IC first stage, or booster stage, weighing in at 280,000 pounds. Required to hold down the brute force of a 7,500,000-pound thrust produced by 5 F-1 engines, the S-IC static test stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and 12,000,000 pounds of cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level. The foundation walls, constructed with concrete and steel, are 4 feet thick. The base structure consists of four towers with 40-foot-thick walls extending upward 144 feet above ground level. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the upright position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. In this photo, taken July 13, 1961, progress is made with the excavation and preparation of the S-IC test stand site.
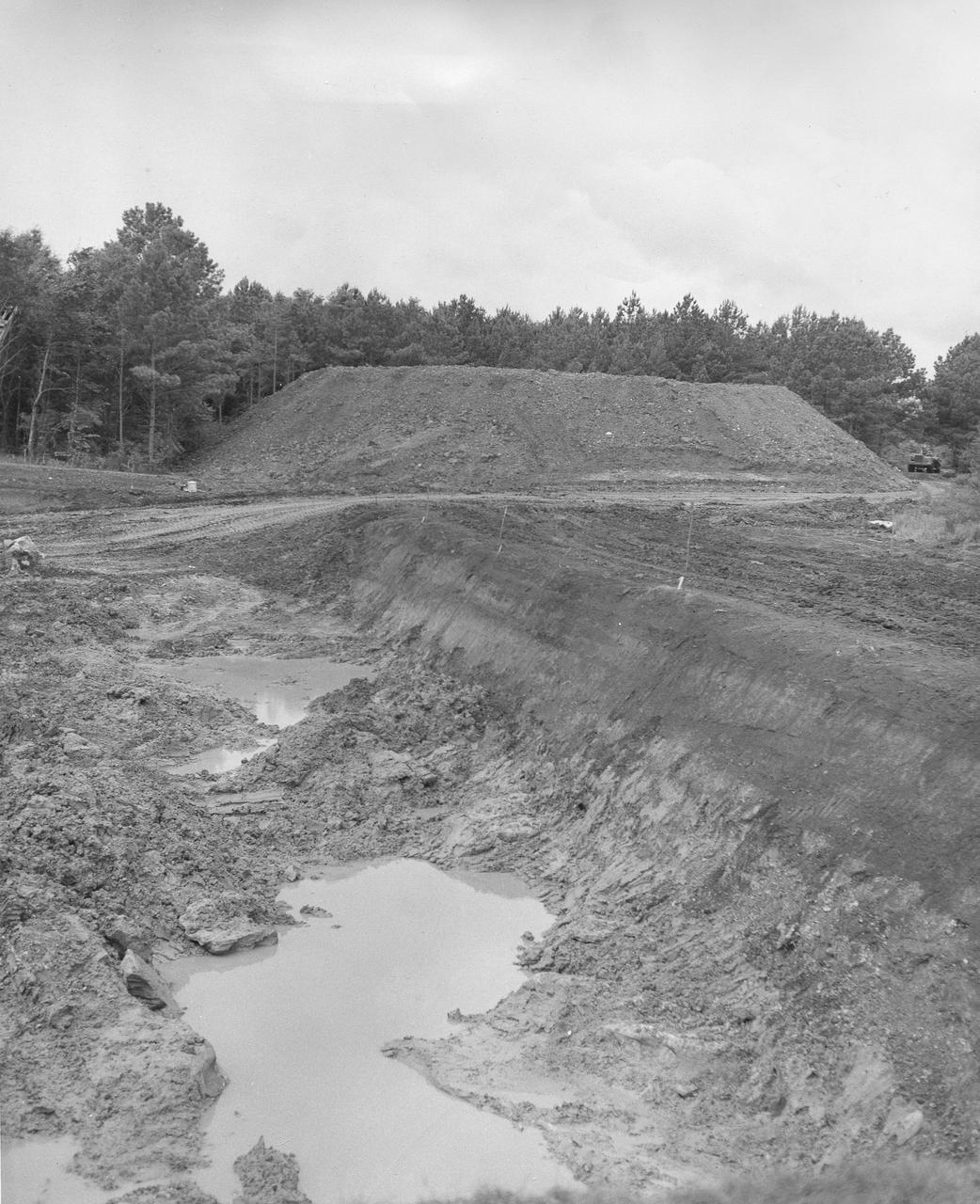

At its founding, the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) inherited the Army’s Jupiter and Redstone test stands, but much larger facilities were needed for the giant stages of the Saturn V. From 1960 to 1964, the existing stands were remodeled and a sizable new test area was developed. The new comprehensive test complex for propulsion and structural dynamics was unique within the nation and the free world, and they remain so today because they were constructed with foresight to meet the future as well as on going needs. Construction of the S-IC Static test stand complex began in 1961 in the west test area of MSFC, and was completed in 1964. The S-IC static test stand was designed to develop and test the 138-ft long and 33-ft diameter Saturn V S-IC first stage, or booster stage, weighing in at 280,000 pounds. Required to hold down the brute force of a 7,500,000-pound thrust produced by 5 F-1 engines, the S-IC static test stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and 12,000,000 pounds of cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level. The foundation walls, constructed with concrete and steel, are 4 feet thick. The base structure consists of four towers with 40-foot-thick walls extending upward 144 feet above ground level. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the upright position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. In this photo, taken July 13, 1961, progress is being made with the excavation of the S-IC test stand site. During the digging, a natural spring was disturbed which caused a constant flooding problem. Pumps were used to remove the water all through the construction process and the site is still pumped today.

While NASA's InSight spacecraft landed on Mars, thrusters on the bottom of the spacecraft churned up the soil beneath it. This image shows pits that the thrusters excavated. This image was taken Dec. 14, 2018, the 18th Martian day, or sol, of the mission, using the Instrument Deployment Camera on InSight's robotic arm. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23250
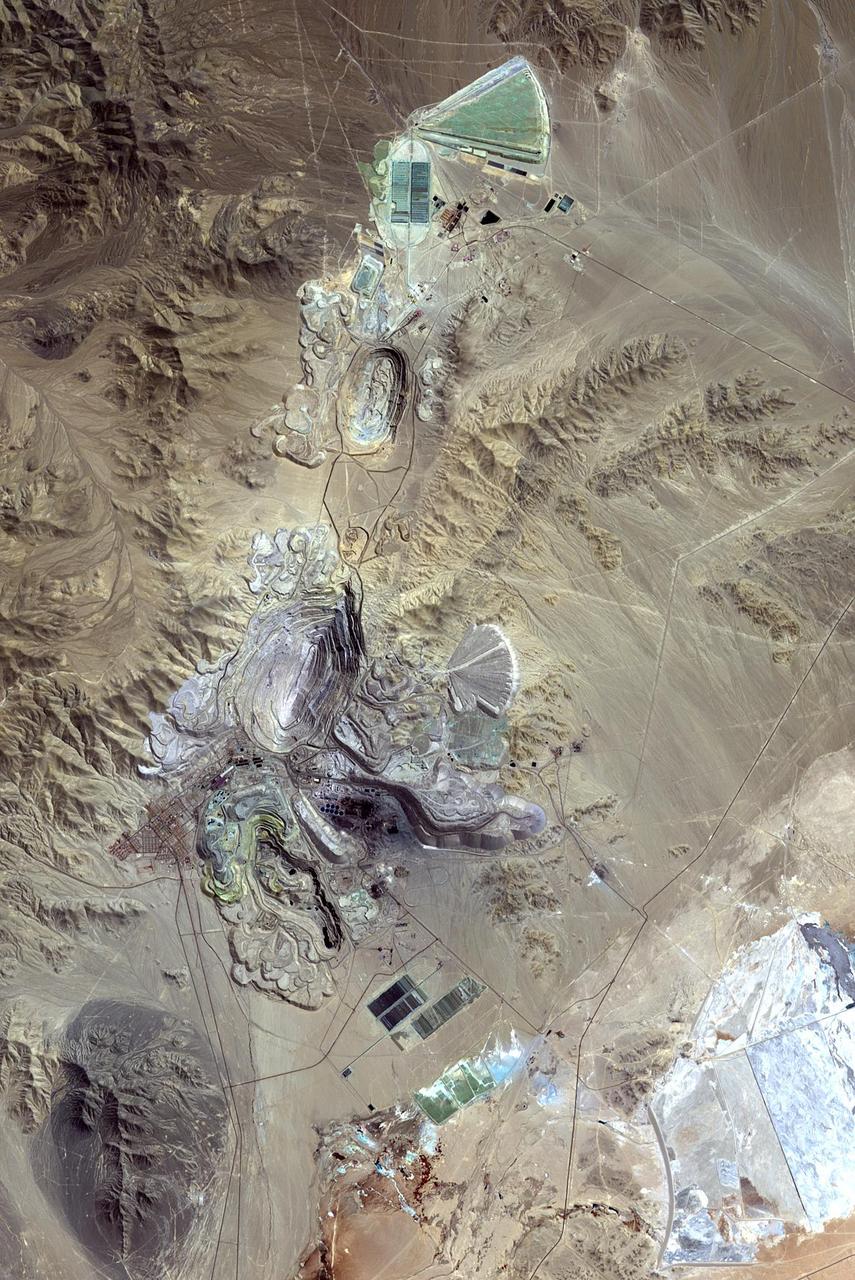

Chuquicamata, in Chile's Atacama Desert, is the largest open pit copper mine in the world, by excavated volume. The copper deposits were first exploited in pre-Hispanic times. Open pit mining began in the early 20th century when a method was developed to work low grade oxidized copper ores. The image was acquired September 2, 2007, covers an area of 19.5 by 29.3 km, and is located at 22.1 degrees south, 68.9 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20973
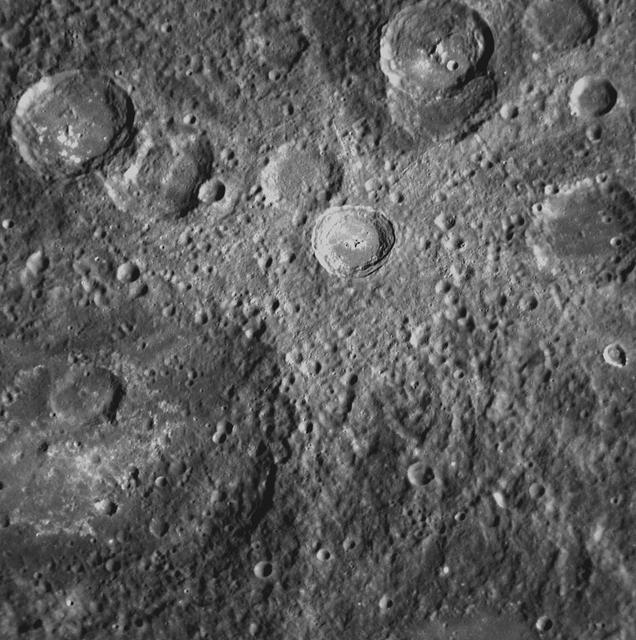

This NAC image from MESSENGER’s second Mercury flyby shows a crater with a set of light-colored rays radiating outward from it. Such rays are formed when an impact excavates material from below the surface and throws it outward from the crater.
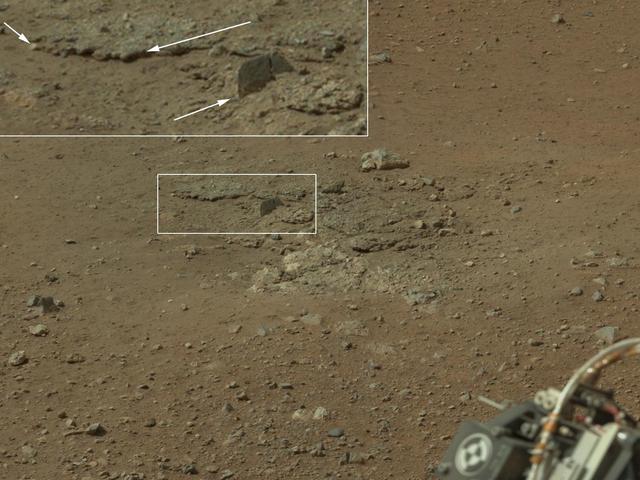

This color image from NASA Curiosity rover shows an area excavated by the blast of the Mars Science Laboratory descent stage rocket engines. This is part of a larger, high-resolution color mosaic made from images obtained by Curiosity Mast Camera.
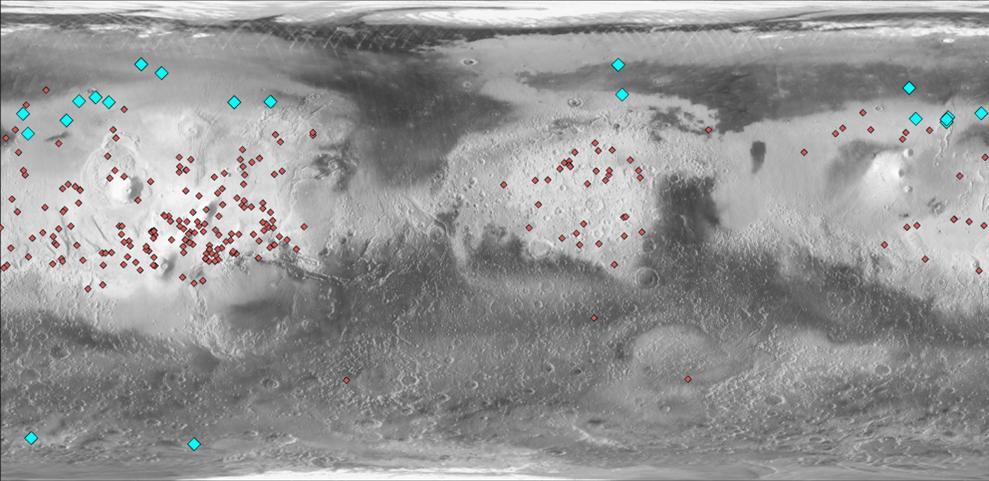
This map of Mars indicates locations of new craters that have excavated ice blue and those that have not red. Albedo information comes from NASA Mars Odyssey orbiter, and the map comes from NASA Mars Global Surveyor orbiter.
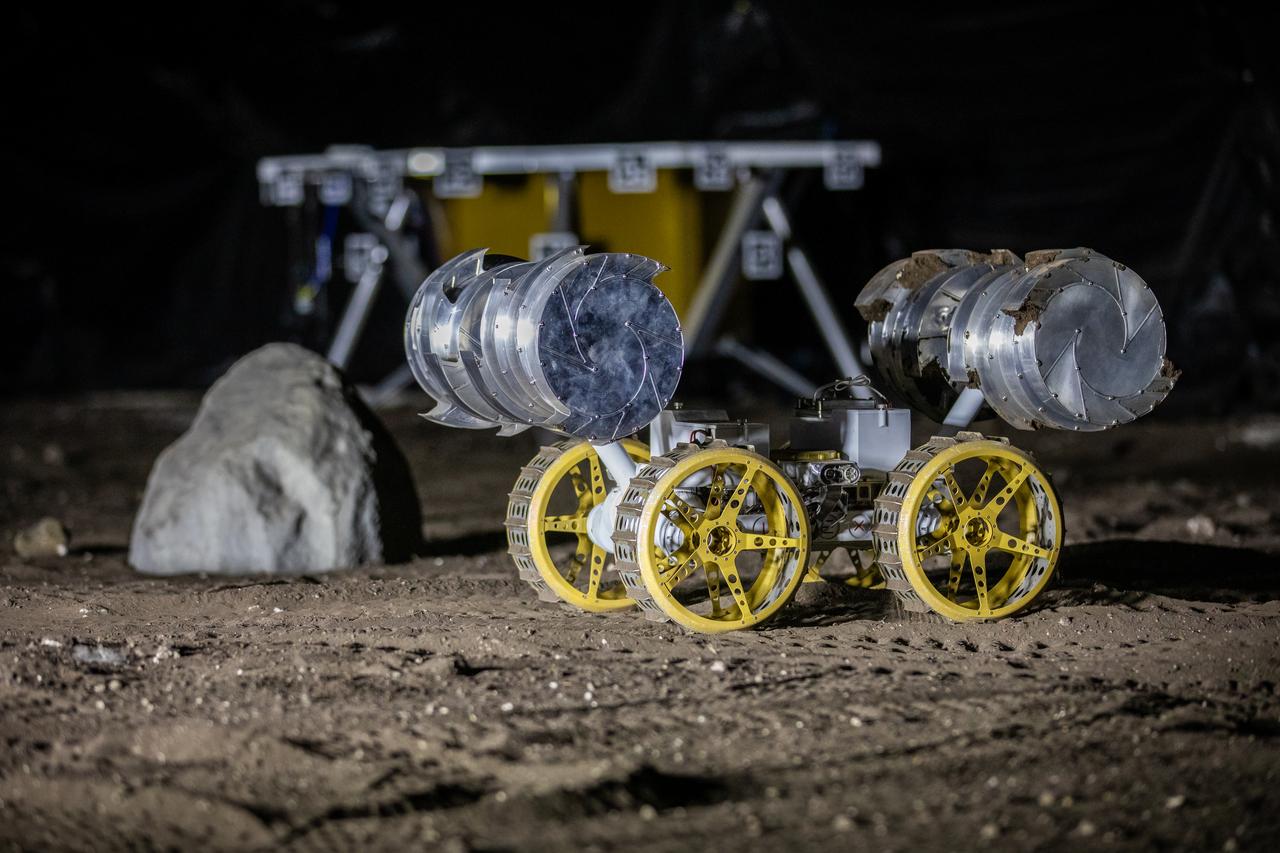

NASA’s ISRU Pilot Excavator (IPEx) performs a simulated lunar mission in a testbed at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center on Friday, Aug. 30, 2024. IPEx functions as both an excavator and a dump truck to mine and transport lunar regolith, the loose rocky material on the Moon’s surface, which is crucial for future lunar missions and In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) processes. This dual capability makes IPEx an indispensable tool for sustainable lunar exploration.
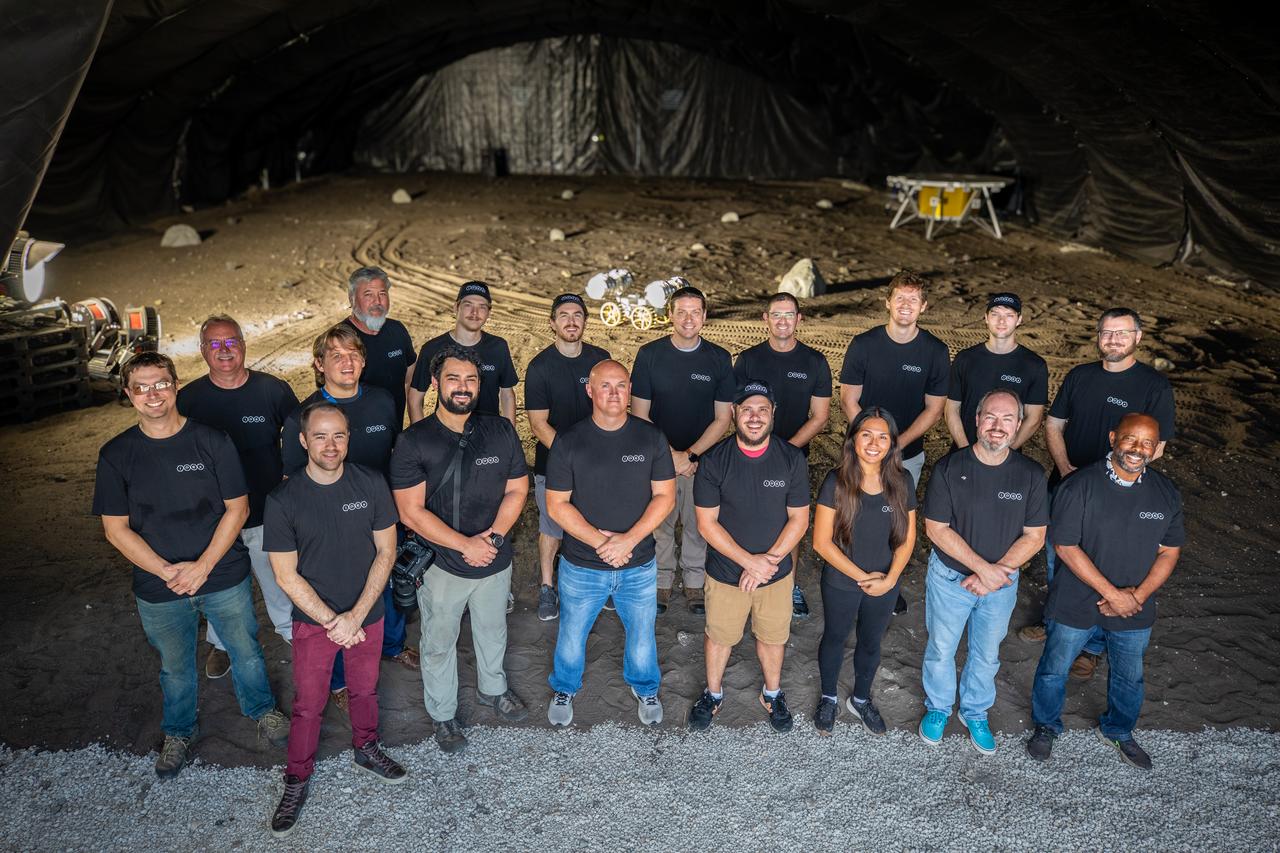

A team from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations lab who developed and tested NASA’s ISRU Pilot Excavator (IPEx) pose for a photo on Friday, Aug. 30, 2024, in a testbed located at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IPEx functions as both an excavator and a dump truck to mine and transport lunar regolith, the loose rocky material on the Moon’s surface, which is crucial for future lunar missions and In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) processes. This dual capability makes IPEx an indispensable tool for sustainable lunar exploration.
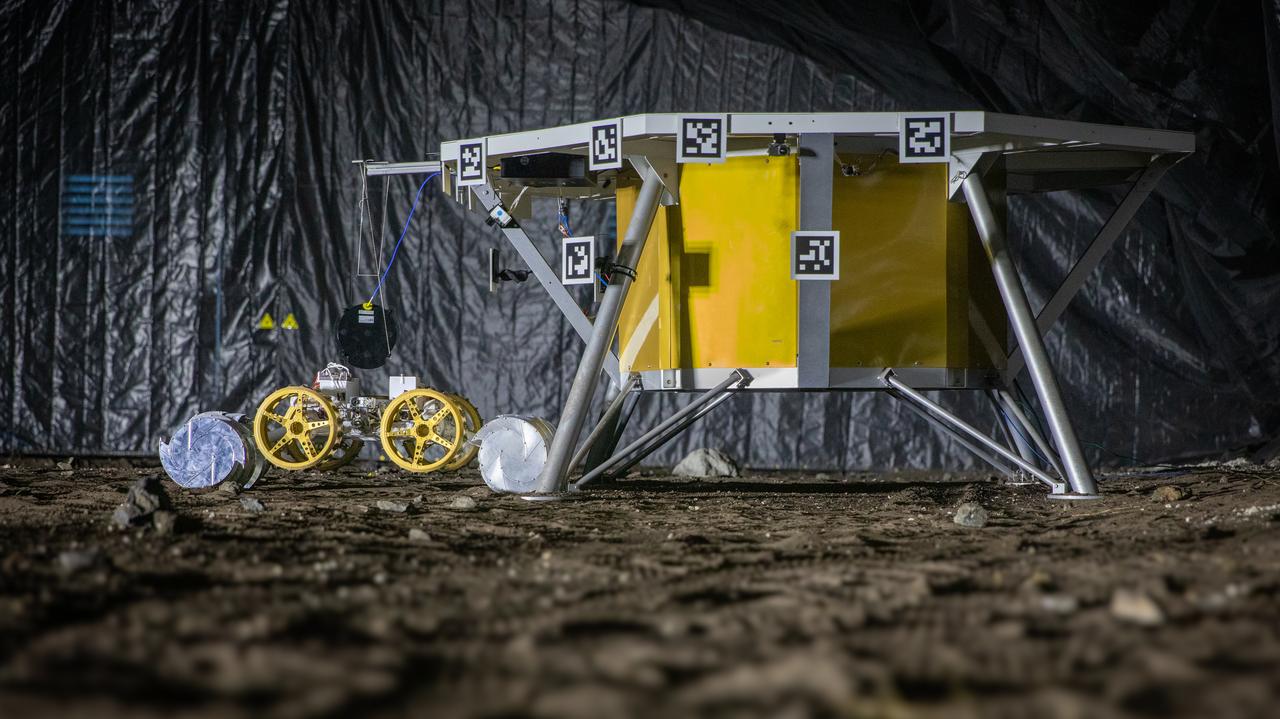

NASA’s ISRU Pilot Excavator (IPEx) performs a simulated lunar mission in a testbed at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center on Friday, Aug. 30, 2024. IPEx functions as both an excavator and a dump truck to mine and transport lunar regolith, the loose rocky material on the Moon’s surface, which is crucial for future lunar missions and In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) processes. This dual capability makes IPEx an indispensable tool for sustainable lunar exploration.

University students prepare their team's remote controlled or autonomous excavator, called a lunabot, to maneuver in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
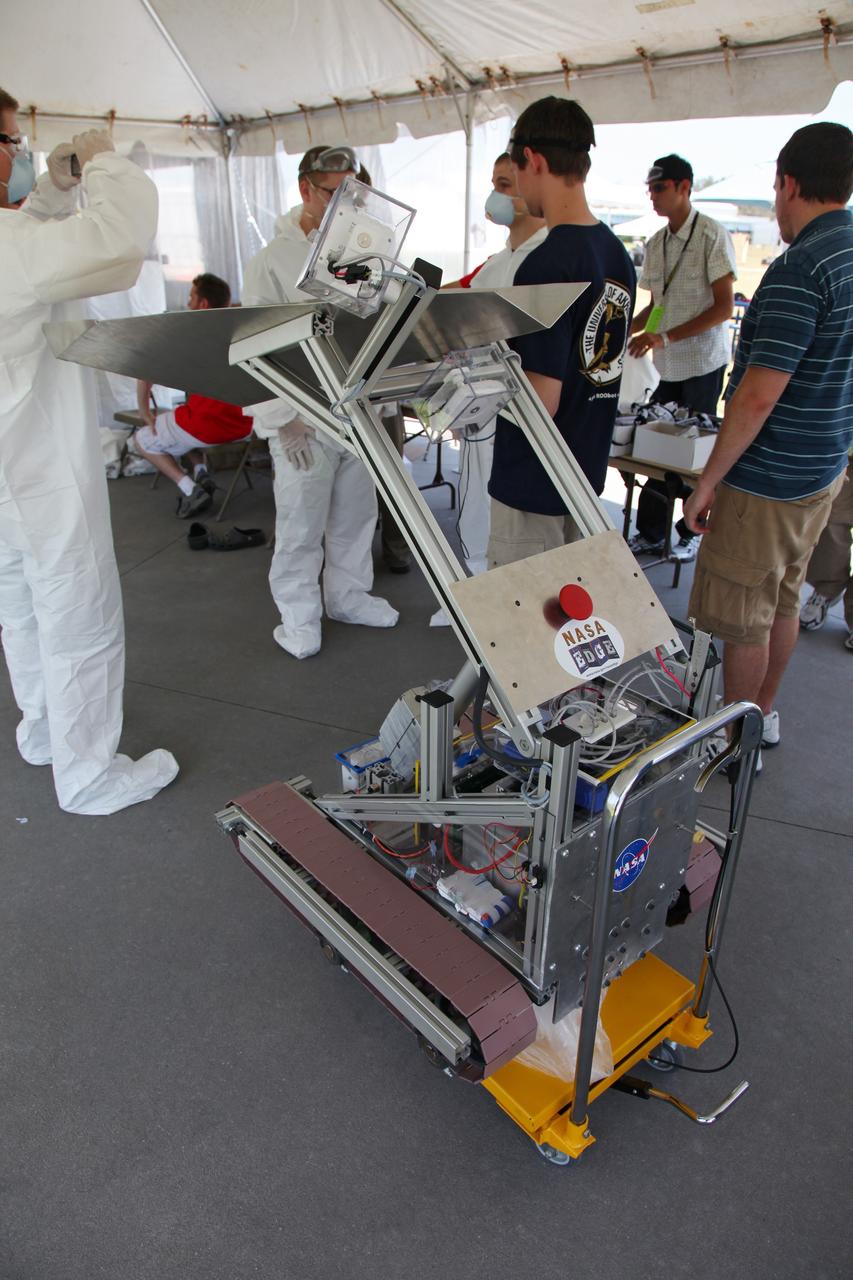

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- University students prepare their remote controlled or autonomous excavator, called a lunabot, in a tent next to the "Lunarena" at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
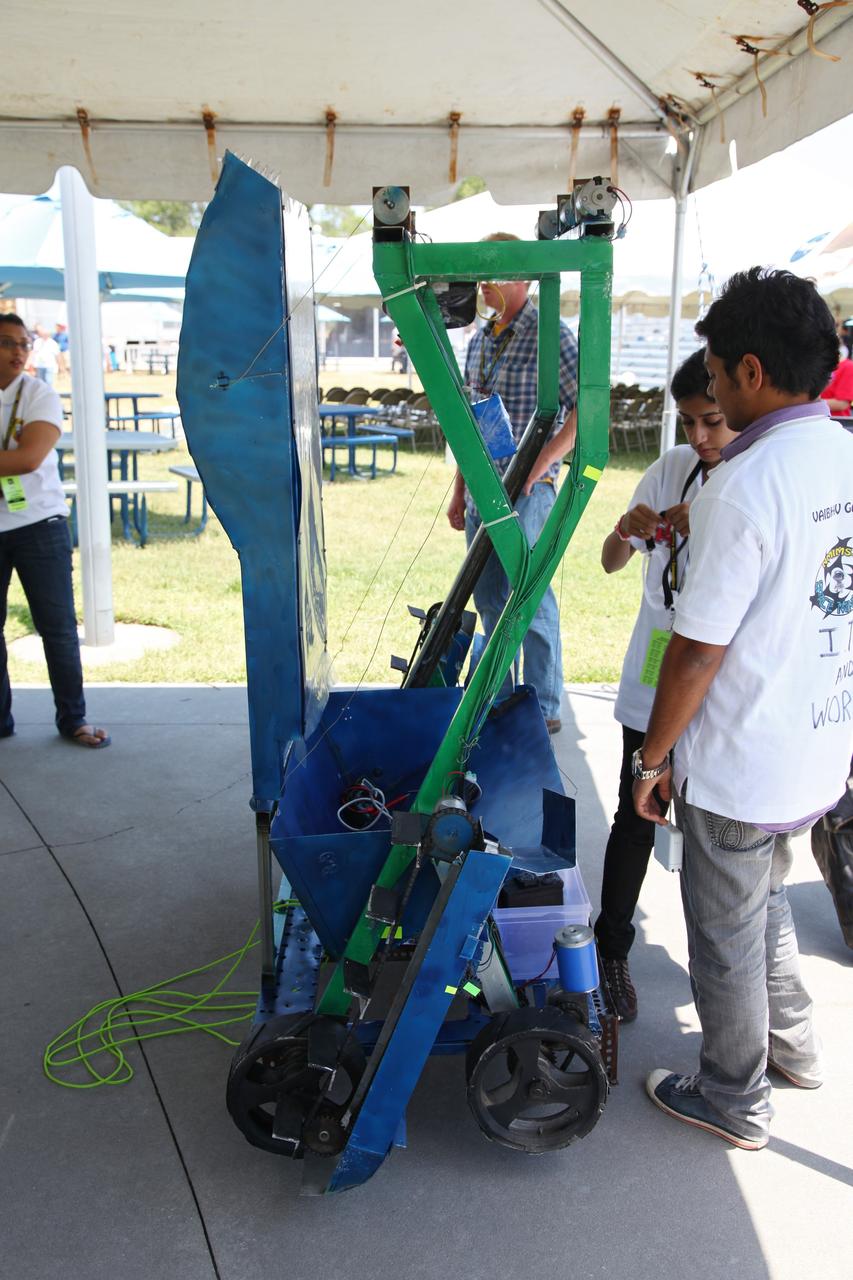

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- University students prepare their remote controlled or autonomous excavator, called a lunabot, in a tent next to the "Lunarena" at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the "Lunarena" at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is a remote controlled or autonomous excavator, called a lunabot. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
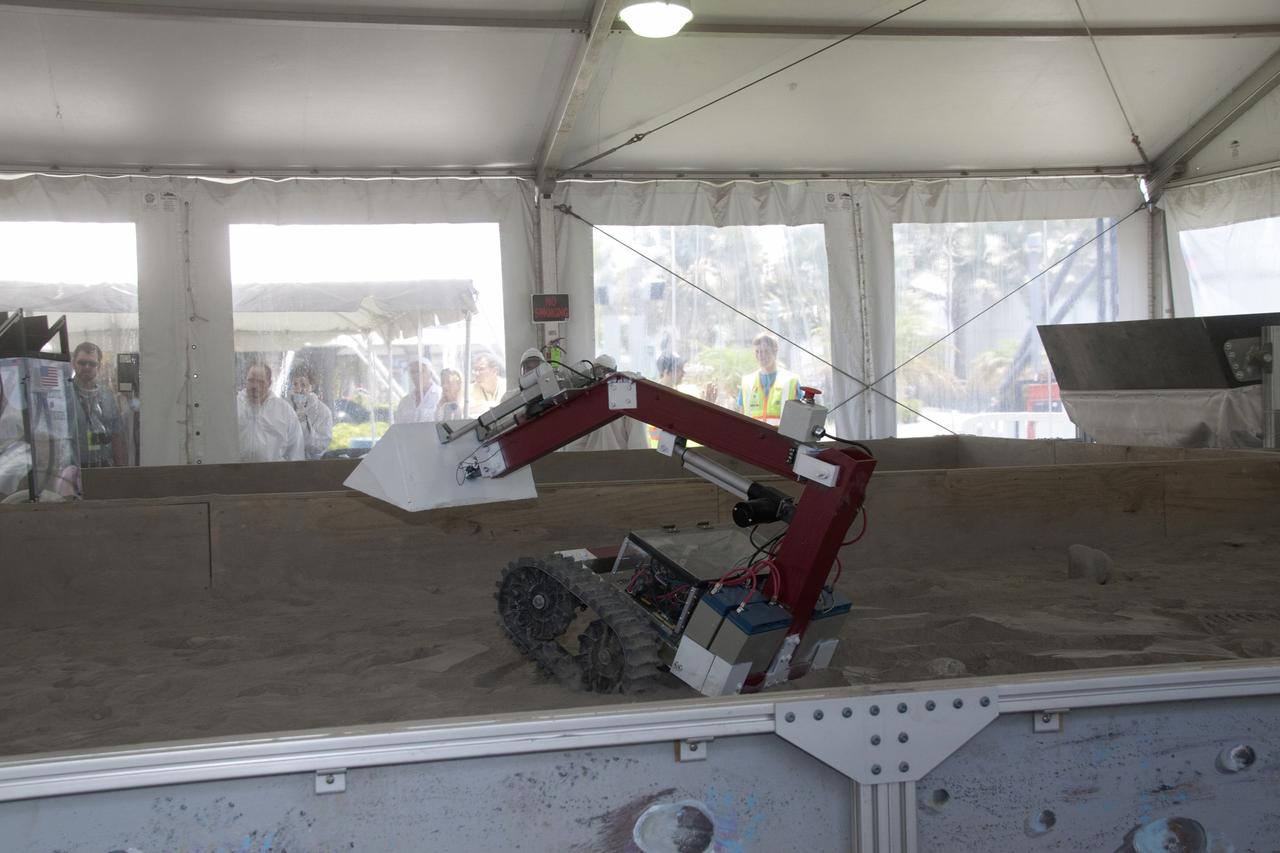

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the "Lunarena" at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex is a remote controlled or autonomous excavator, called a lunabot. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
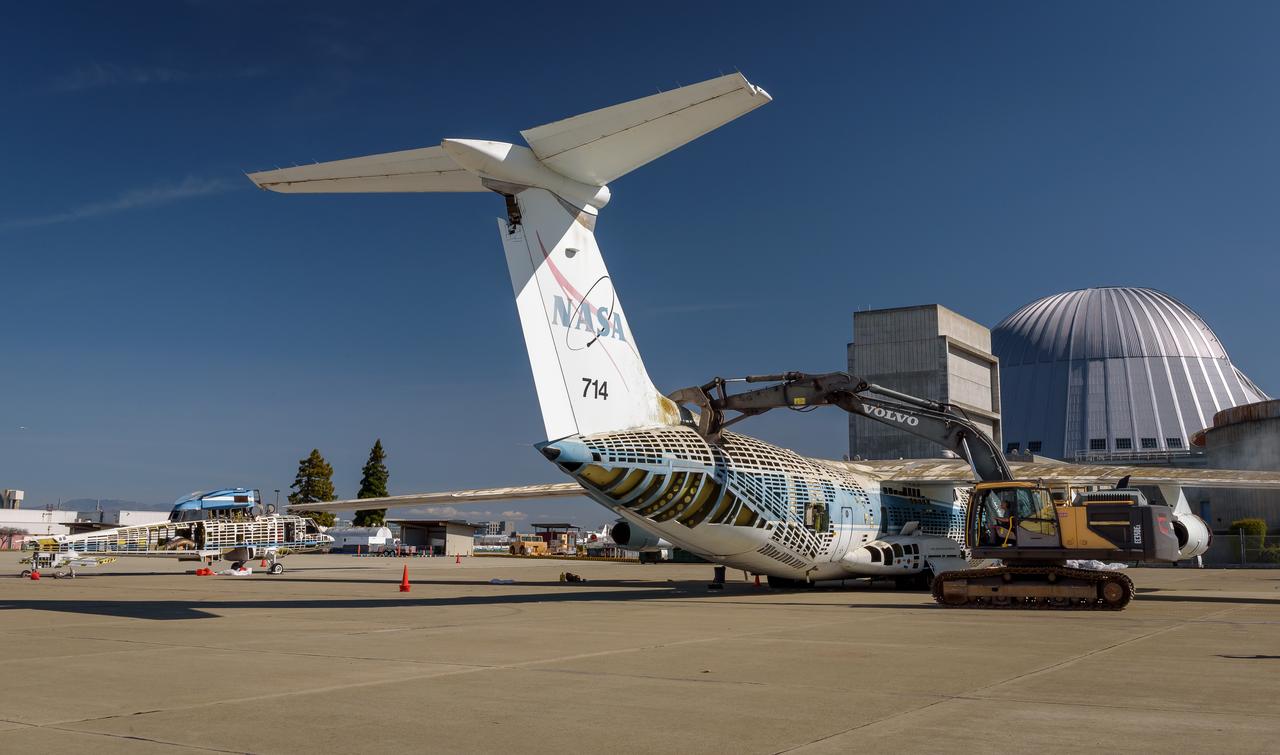

A Volvo Crawler Excavator severs the airframe, separating the tail section from the fuselage, of the modified C-141 Kuiper Airborne Observatory, (KAO) (NASA-714), on the N211 apron of Moffett Field, California.
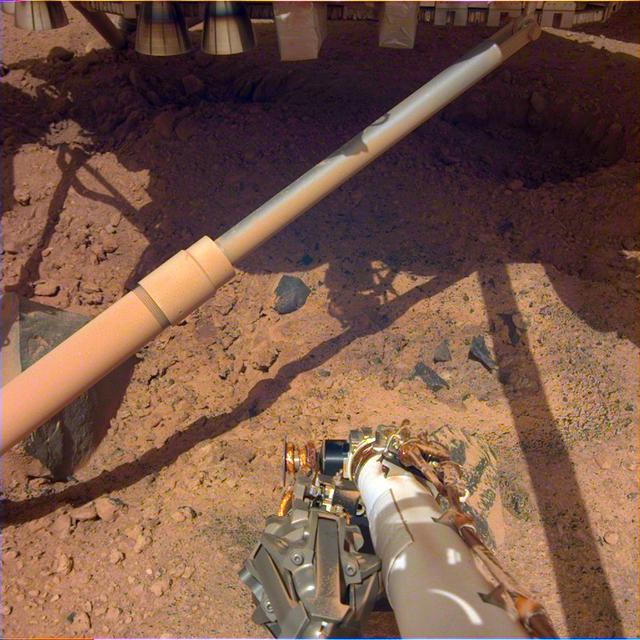

Thrusters under NASA's InSight lander churned up soil during landing on Mars. This image shows two pits excavated by the thrusters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23301
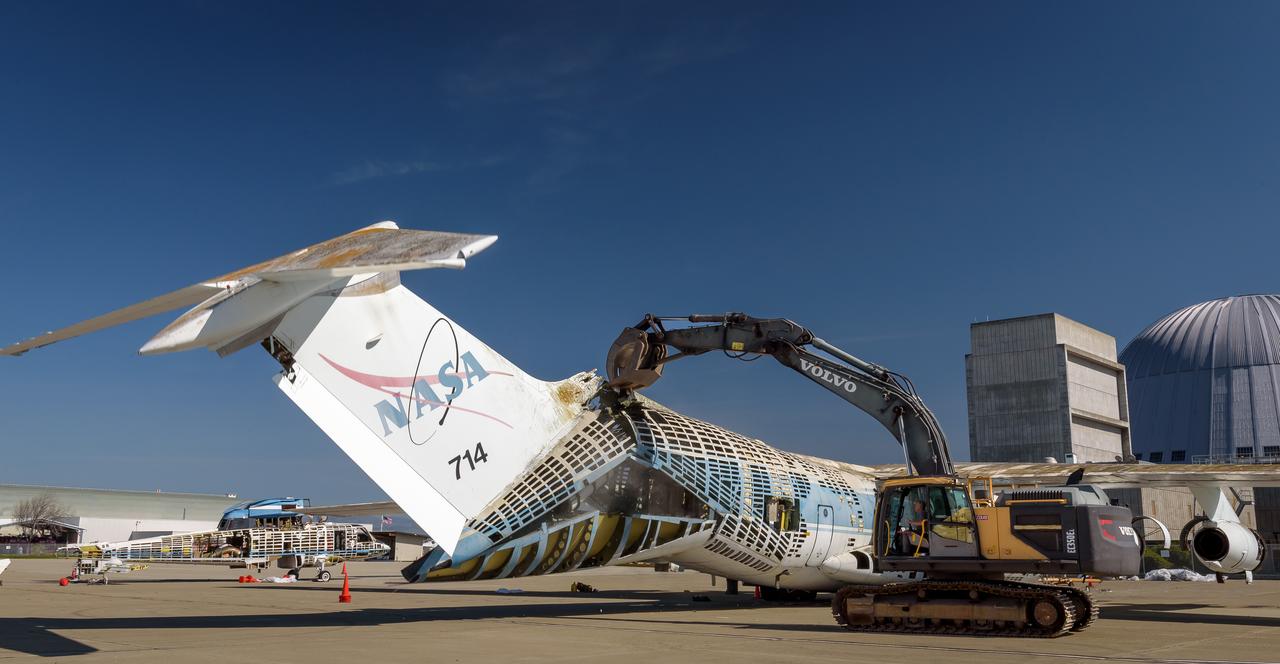

A Volvo Crawler Excavator severs the airframe, separating the tail section from the fuselage, of the modified C-141 Kuiper Airborne Observatory, (KAO) (NASA-714), on the N211 apron of Moffett Field, California.
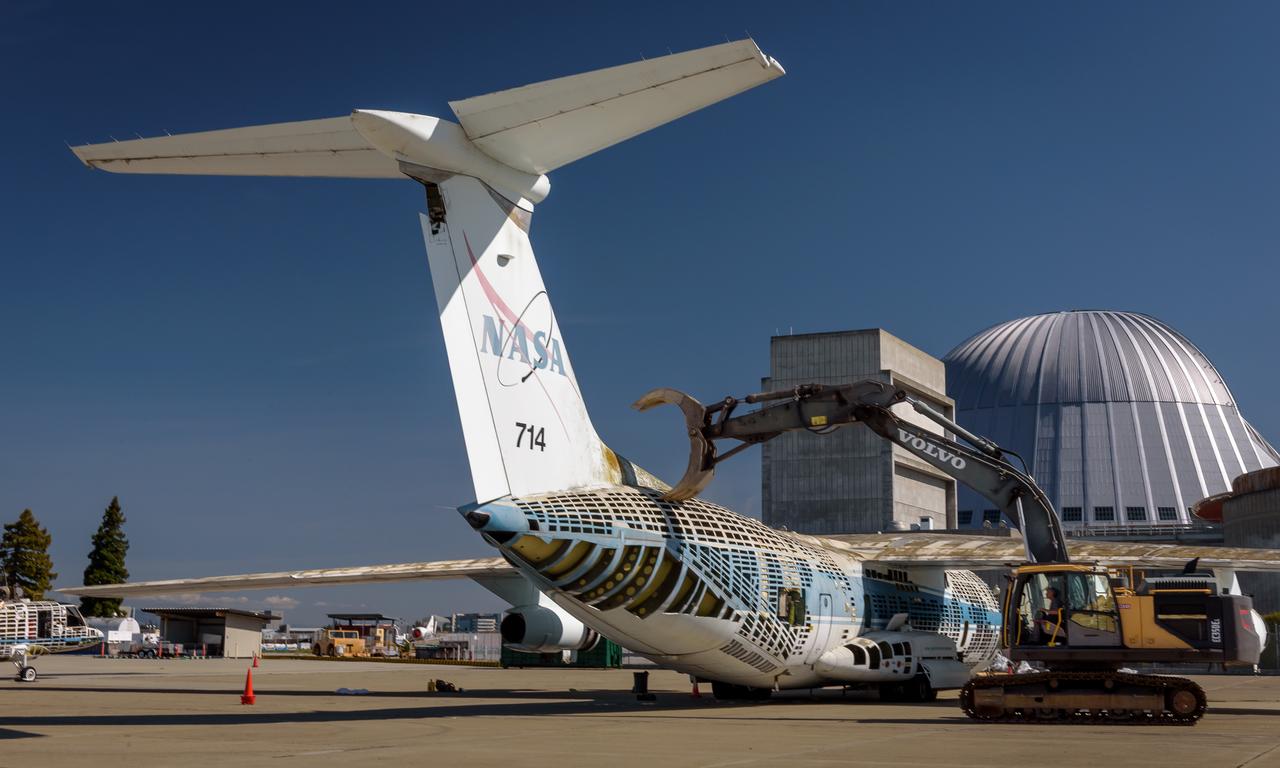

A Volvo Crawler Excavator severs the airframe, separating the tail section from the fuselage, of the modified C-141 Kuiper Airborne Observatory, (KAO) (NASA-714), on the N211 apron of Moffett Field, California.
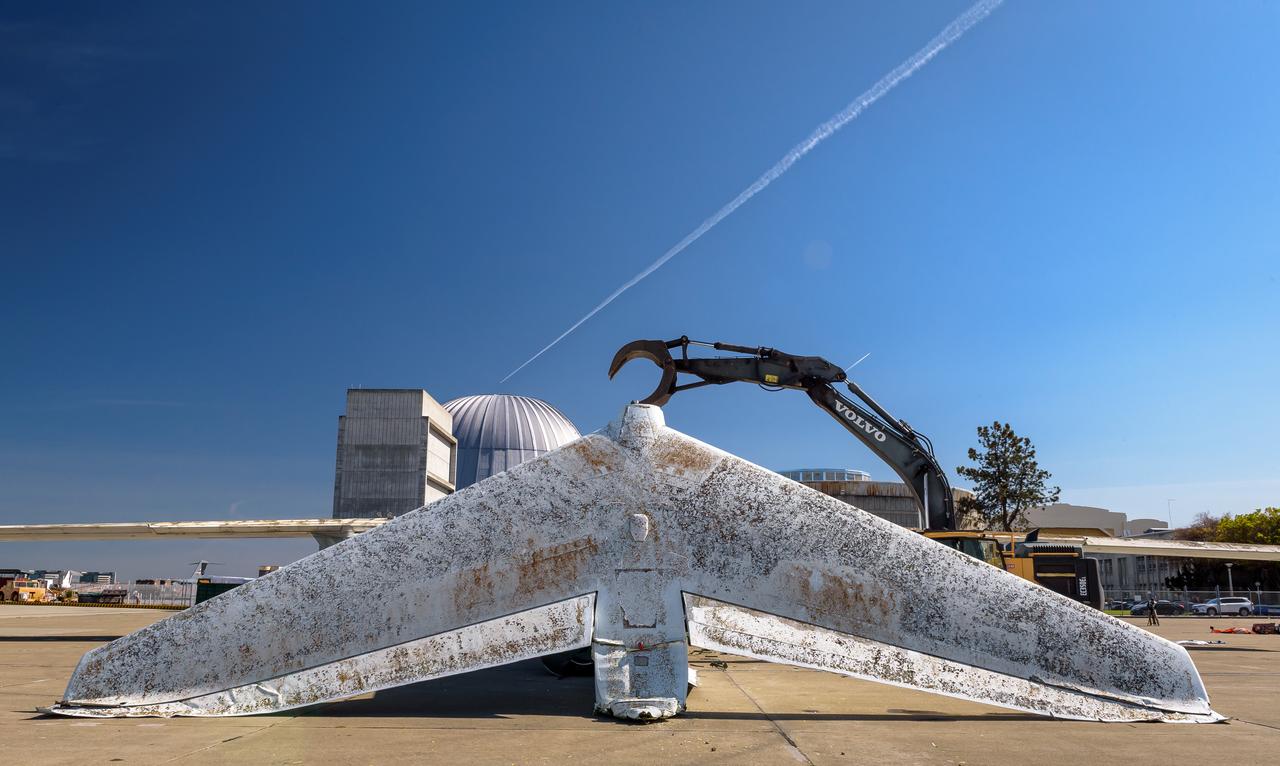

A Volvo Crawler Excavator severs the airframe, separating the tail section from the fuselage, of the modified C-141 Kuiper Airborne Observatory, (KAO) (NASA-714), on the N211 apron of Moffett Field, California.
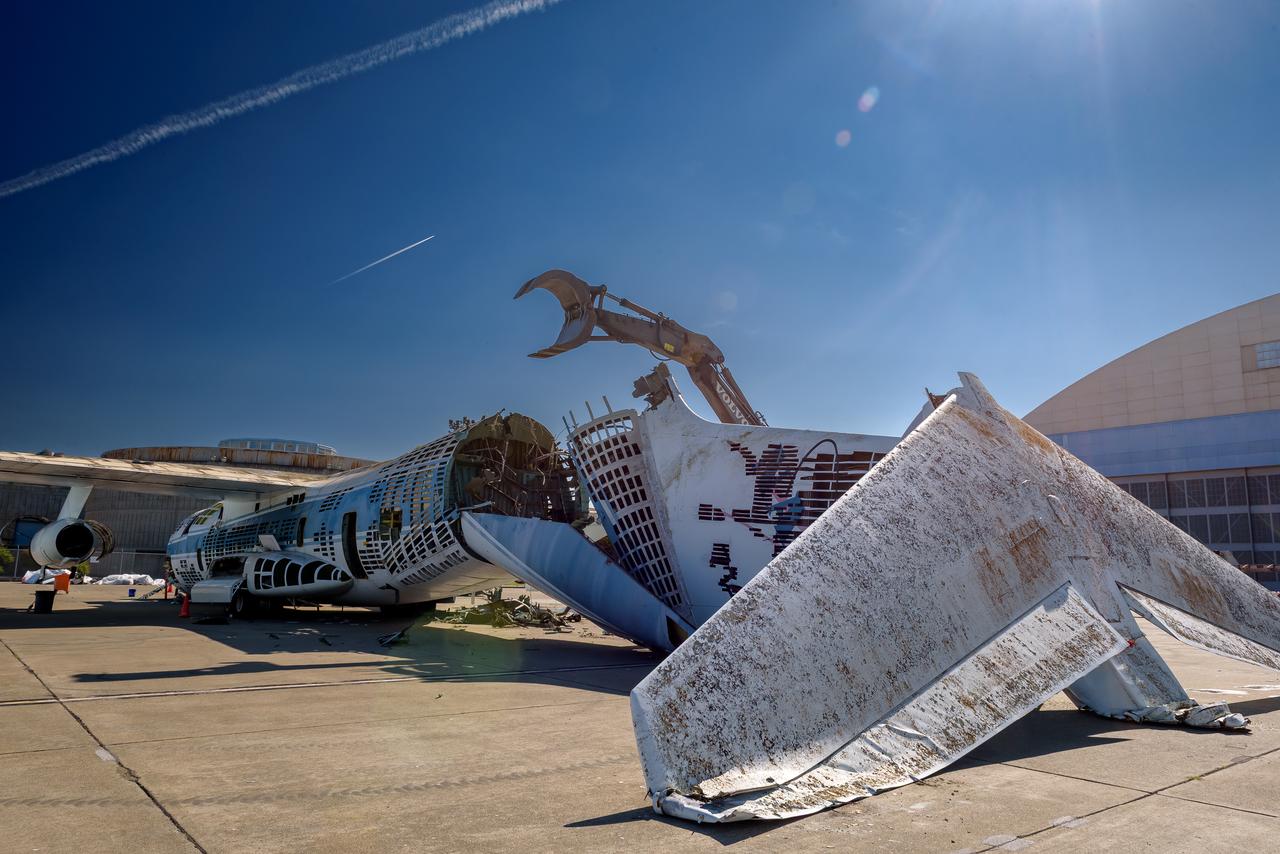

A Volvo Crawler Excavator severs the airframe, separating the tail section from the fuselage, of the modified C-141 Kuiper Airborne Observatory, (KAO) (NASA-714), on the N211 apron of Moffett Field, California.
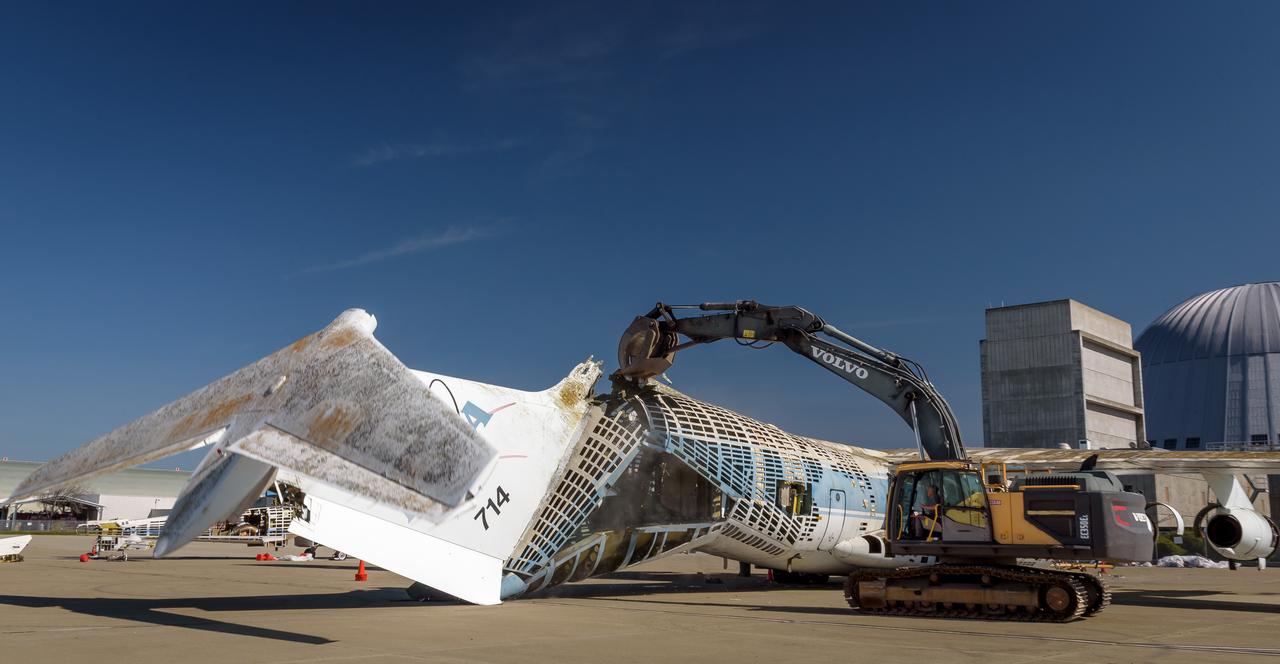

A Volvo Crawler Excavator severs the airframe, separating the tail section from the fuselage, of the modified C-141 Kuiper Airborne Observatory, (KAO) (NASA-714), on the N211 apron of Moffett Field, California.
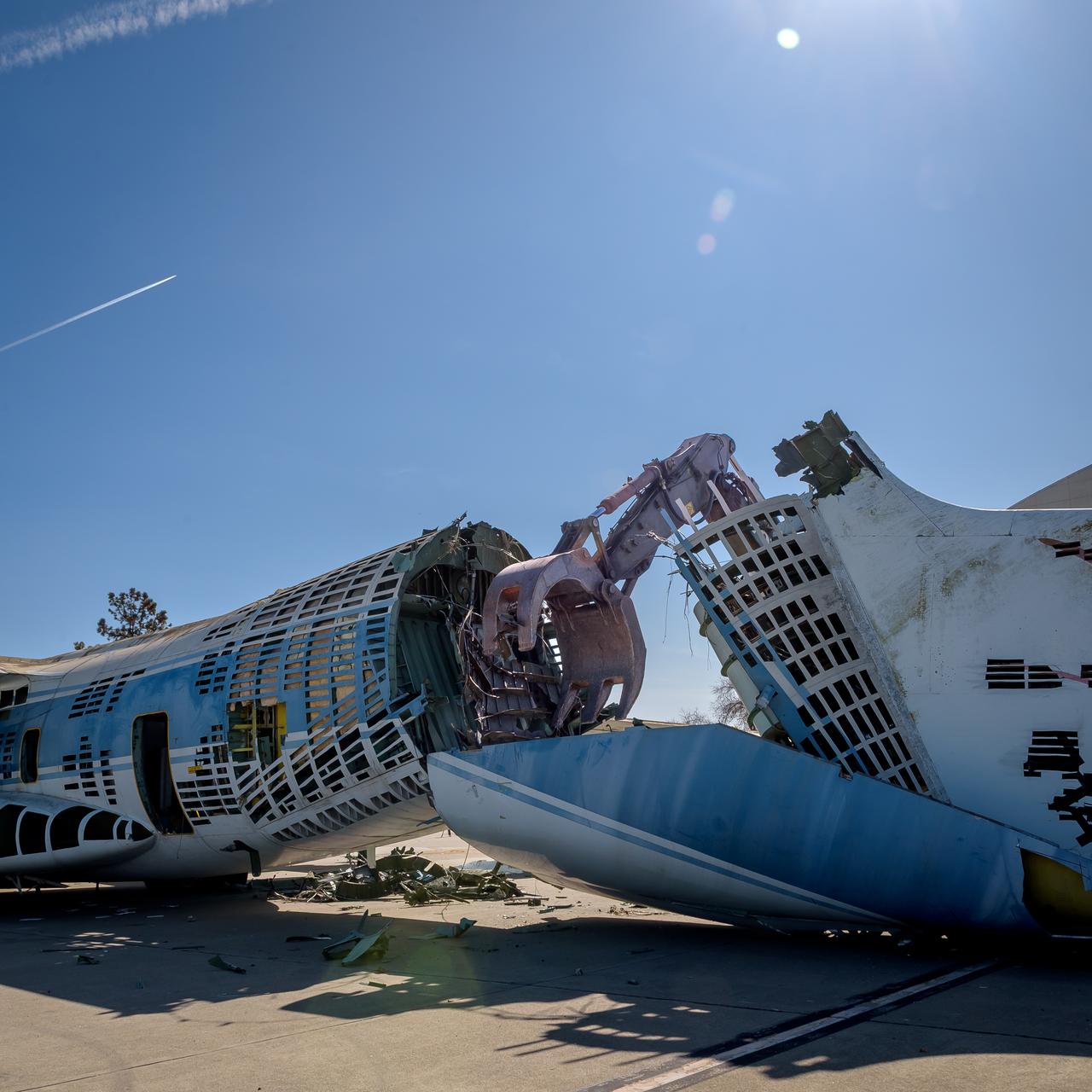

A Volvo Crawler Excavator severs the airframe, separating the tail section from the fuselage, of the modified C-141 Kuiper Airborne Observatory, (KAO) (NASA-714), on the N211 apron of Moffett Field, California.
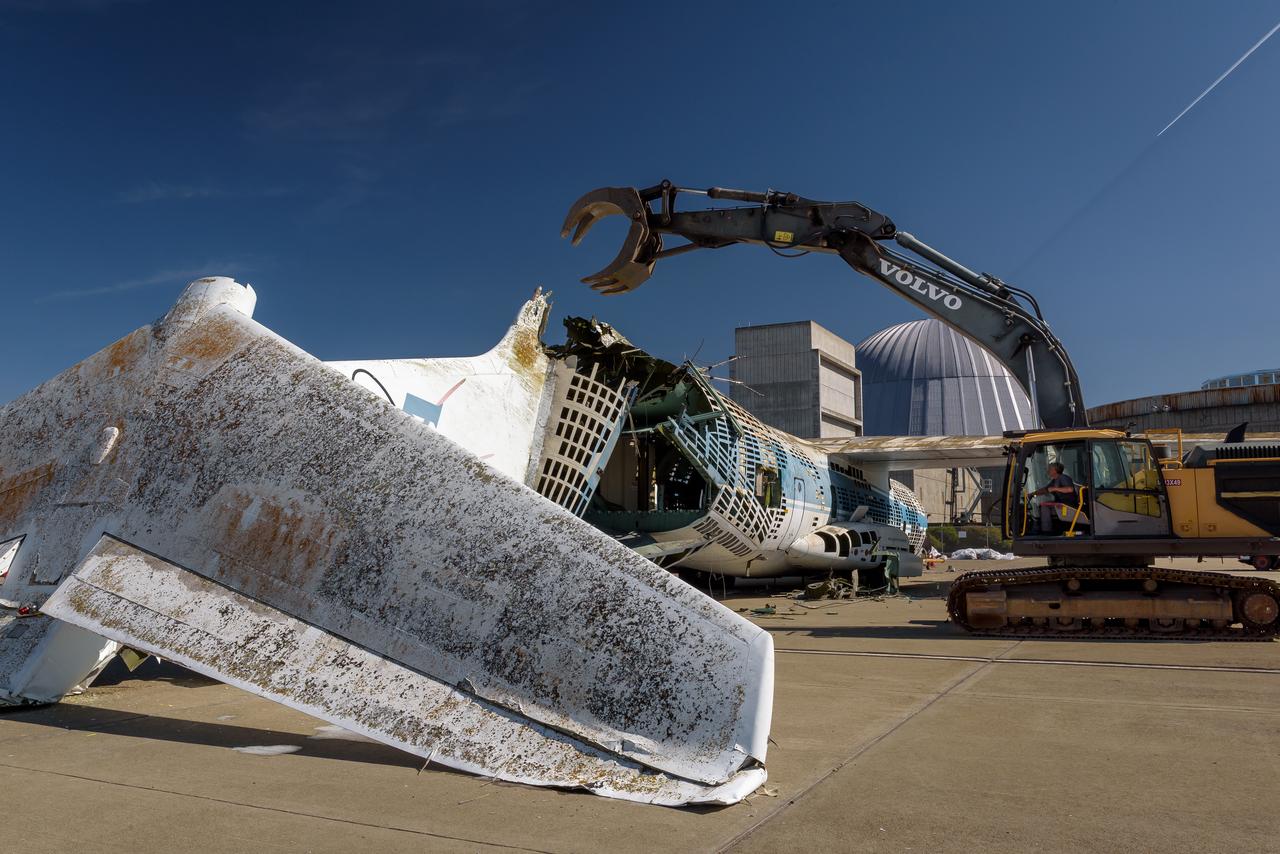

A Volvo Crawler Excavator severs the airframe, separating the tail section from the fuselage, of the modified C-141 Kuiper Airborne Observatory, (KAO) (NASA-714), on the N211 apron of Moffett Field, California.
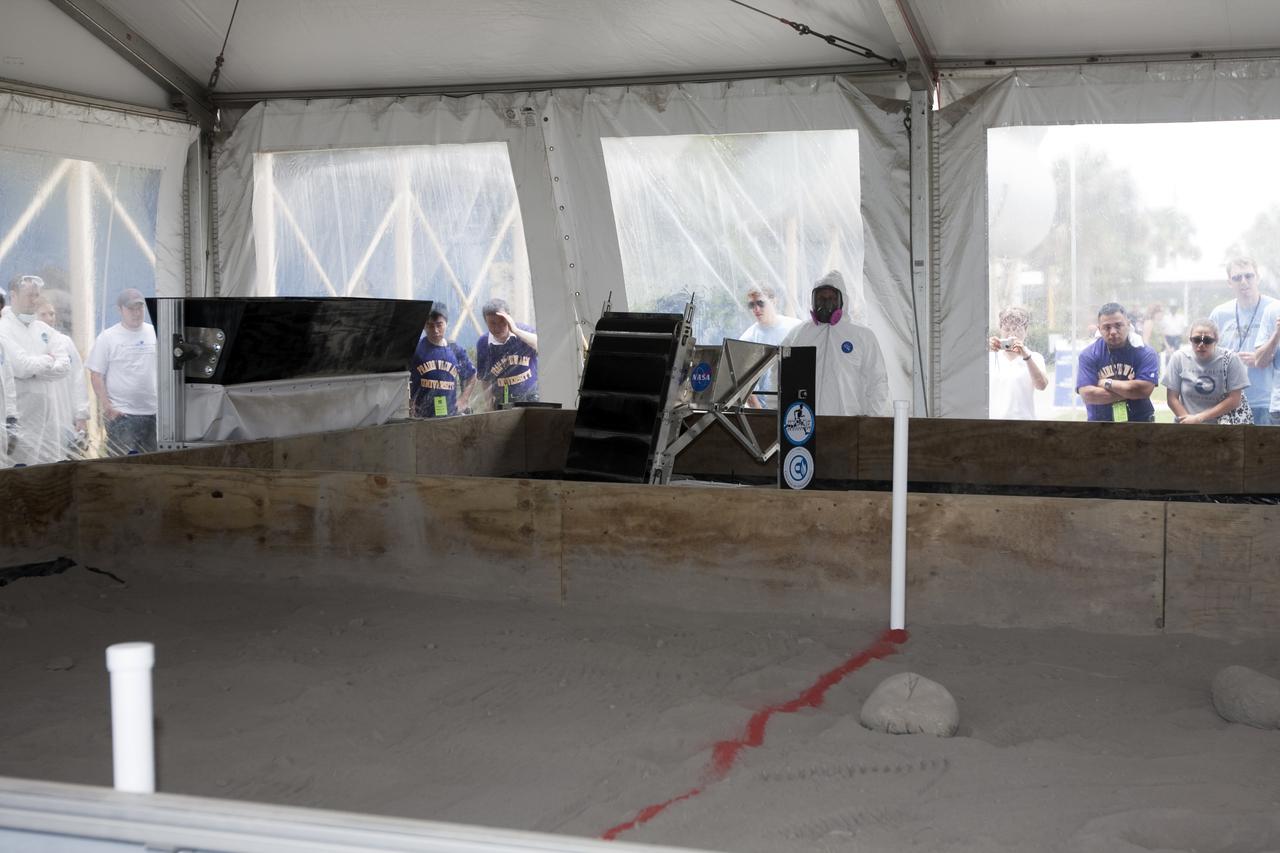

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the 'Lunarena' at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex's Astronaut Hall of Fame, university students are ready to maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. Twenty-two teams from around the country are competing in NASA's first Lunabotics Mining Competition. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The purpose is to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, fields. It also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - University students gather for the opening ceremony of NASA's first Lunabotics Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex's Astronaut Hall of Fame. Twenty-two teams from around the country will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The purpose is to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, fields. It also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis
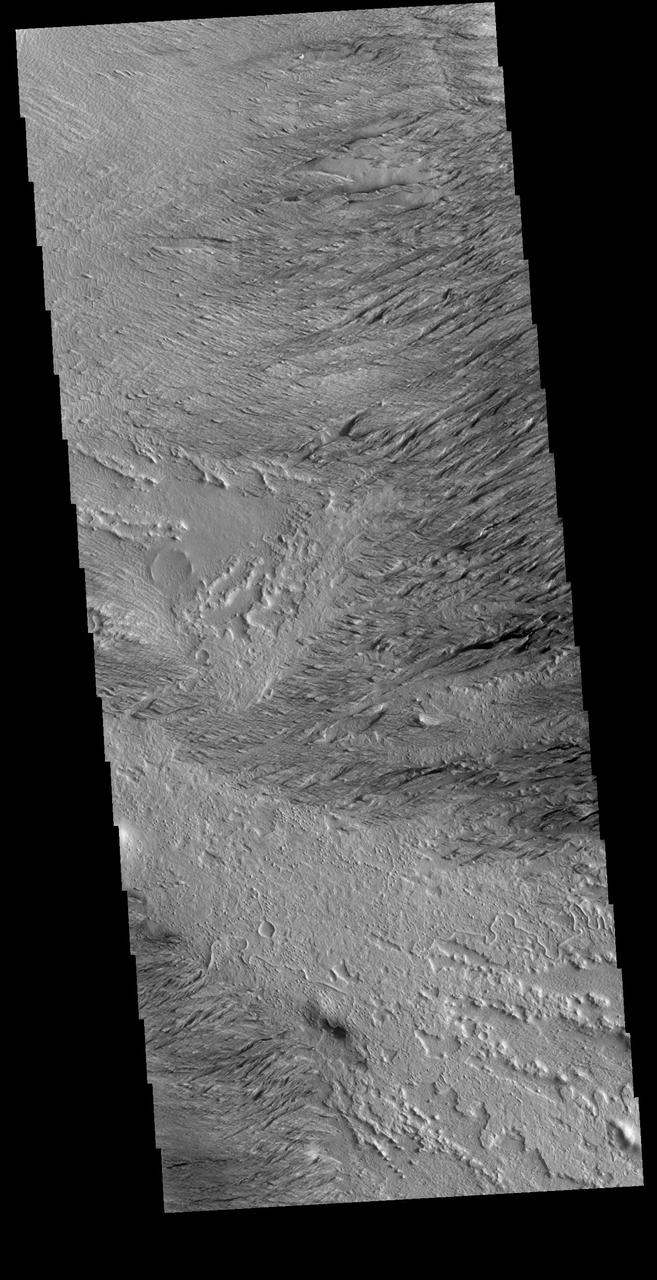

This VIS image is located near Zephyria Planum. Winds of two different directions have excavated a poorly cemented surface into linear ridge features called yardangs. Examining the structure of the ridges, it appears that winds first blew from the upper left of the image. Then perhaps after a change in climate, winds blew toward the upper right, carving a new pattern on top of the older one. The ridges are not perpendicular, but intersect at a wider angle. Orbit Number: 72496 Latitude: -4.75332 Longitude: 154.461 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2018-04-18 12:20 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22612
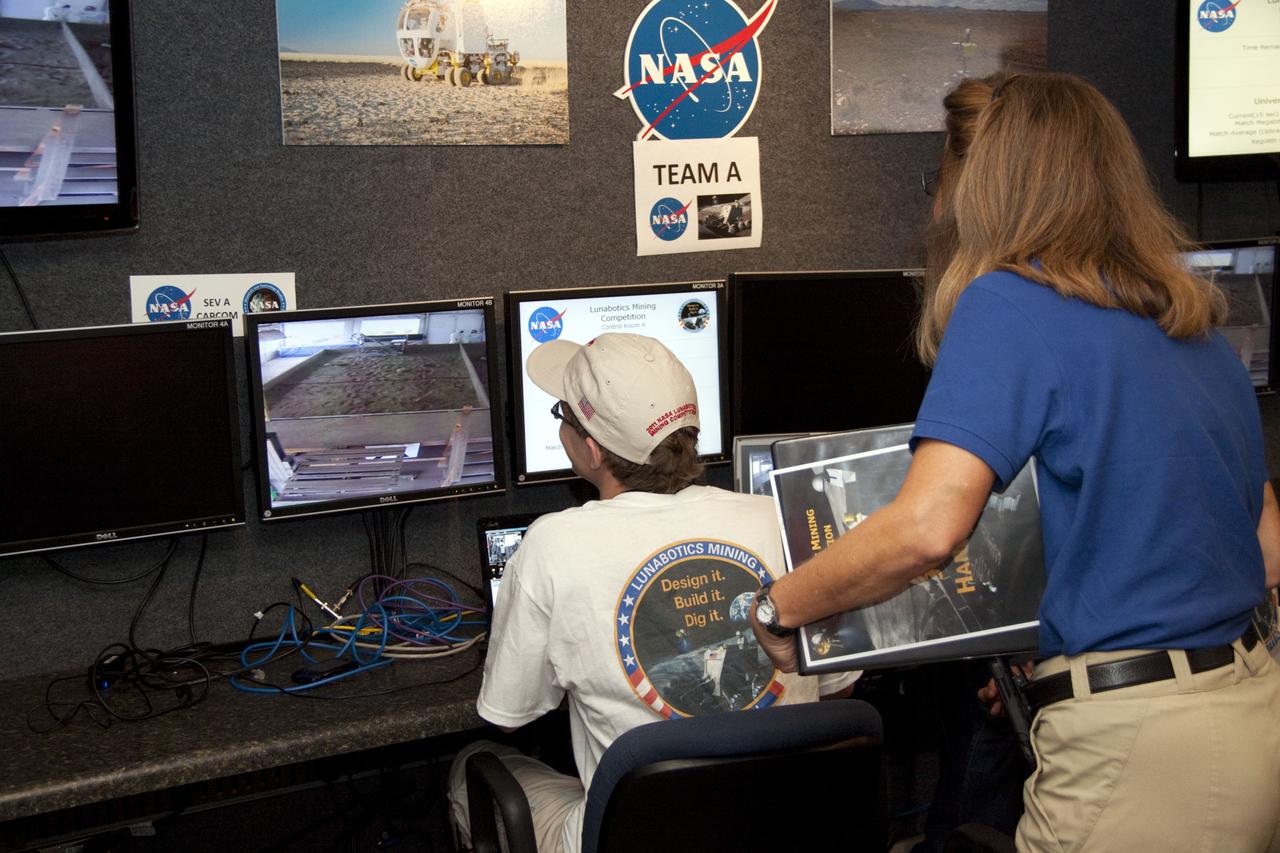

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- University students monitor their team's remote controlled or autonomous excavator, called a lunabot, as it is maneuvered in a "sand box" of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil during NASA's second annual Lunabotics Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
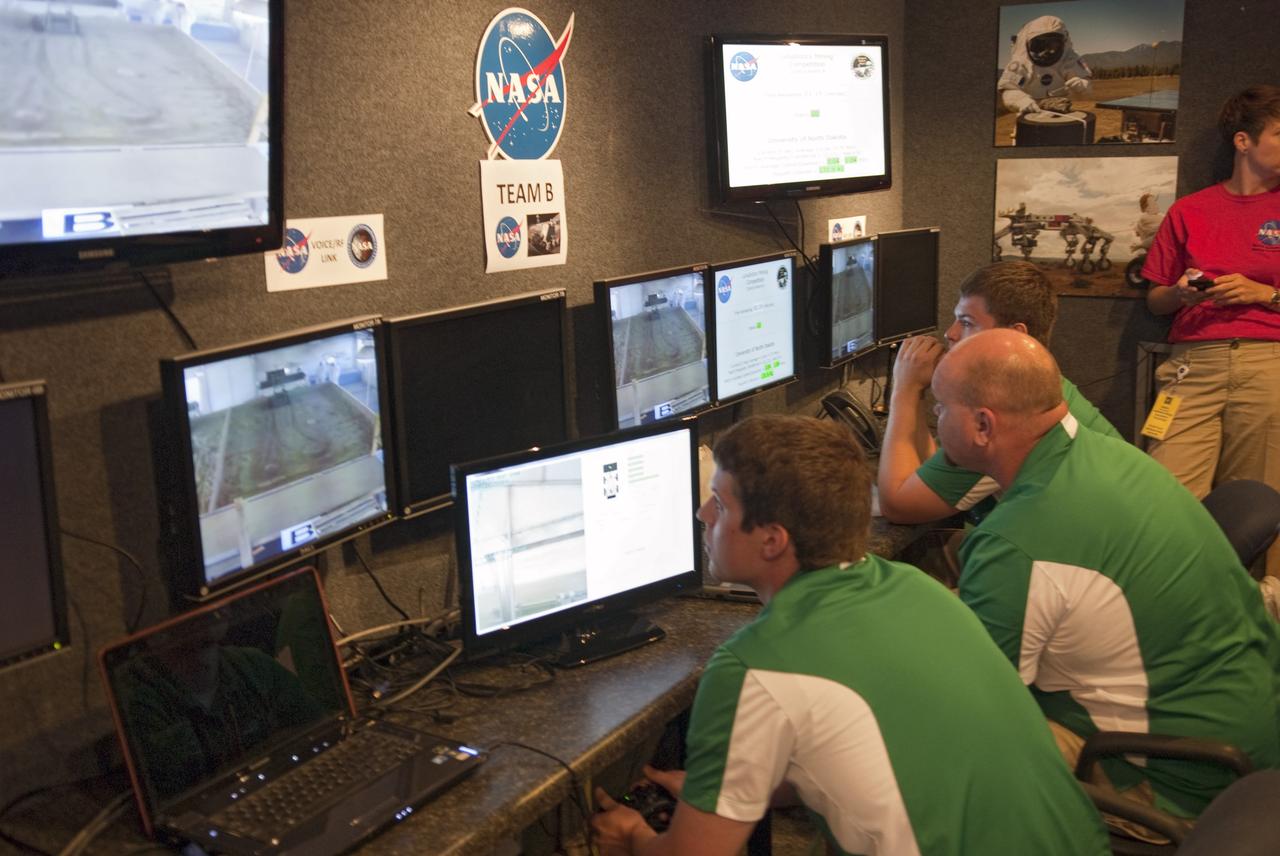

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- University students monitor their team's remote controlled or autonomous excavator, called a lunabot, as it is maneuvered in a "sand box" of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil during NASA's second annual Lunabotics Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
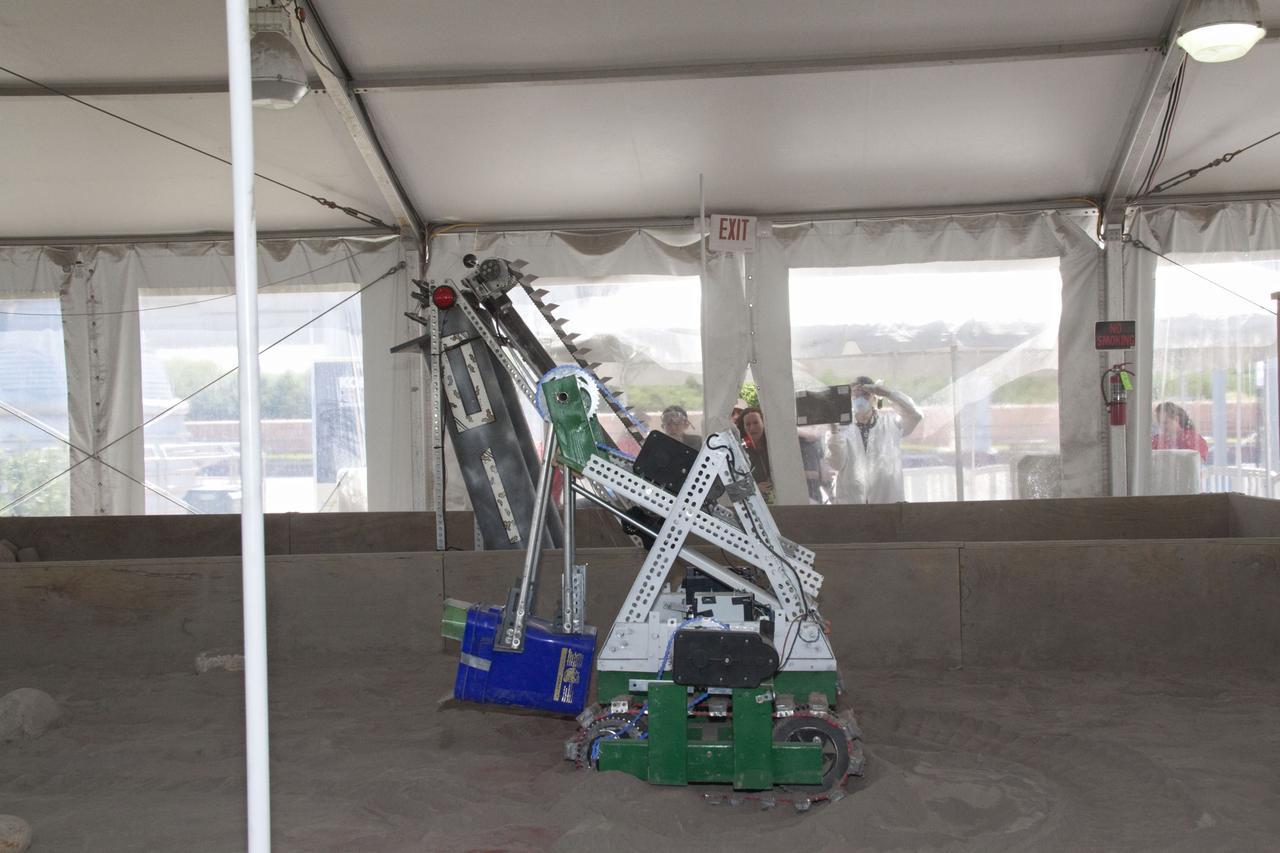

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the "Lunarena" at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida, university students maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in a "sand box" of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil during NASA's second annual Lunabotics Mining Competition. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
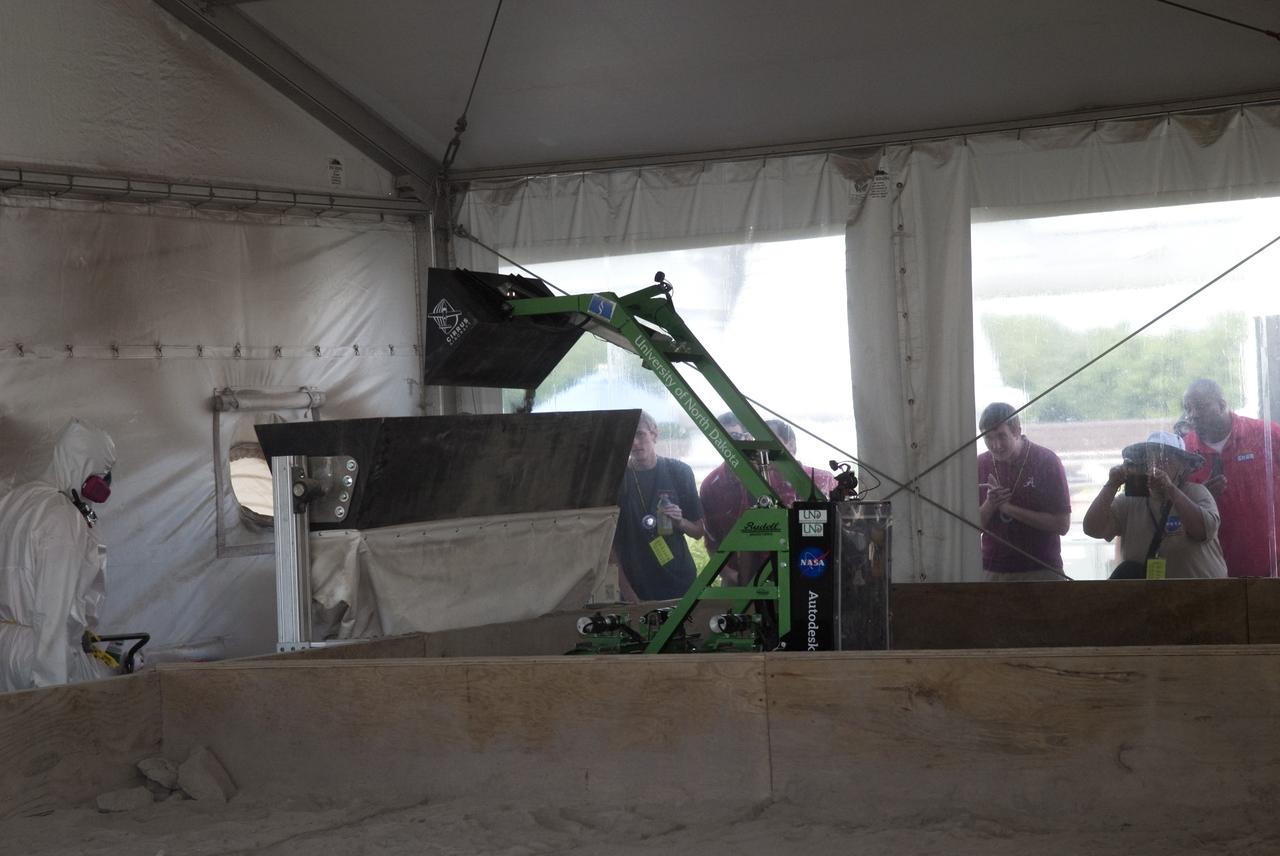

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the "Lunarena" at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor in Florida, university students maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in a "sand box" of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil during NASA's second annual Lunabotics Mining Competition. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
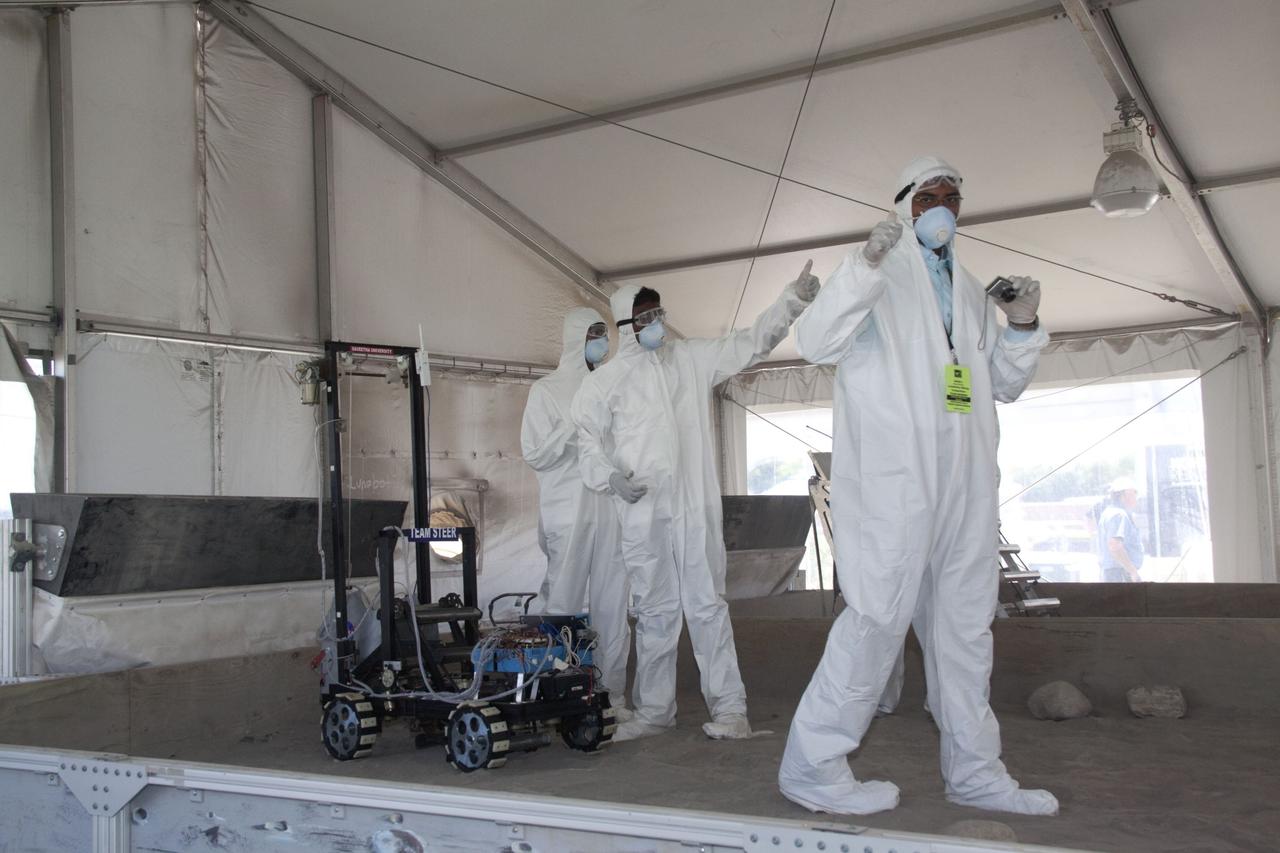

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the "Lunarena" at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida, university students give their "thumbs up" after maneuvering their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in a "sand box" of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil during NASA's second annual Lunabotics Mining Competition. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
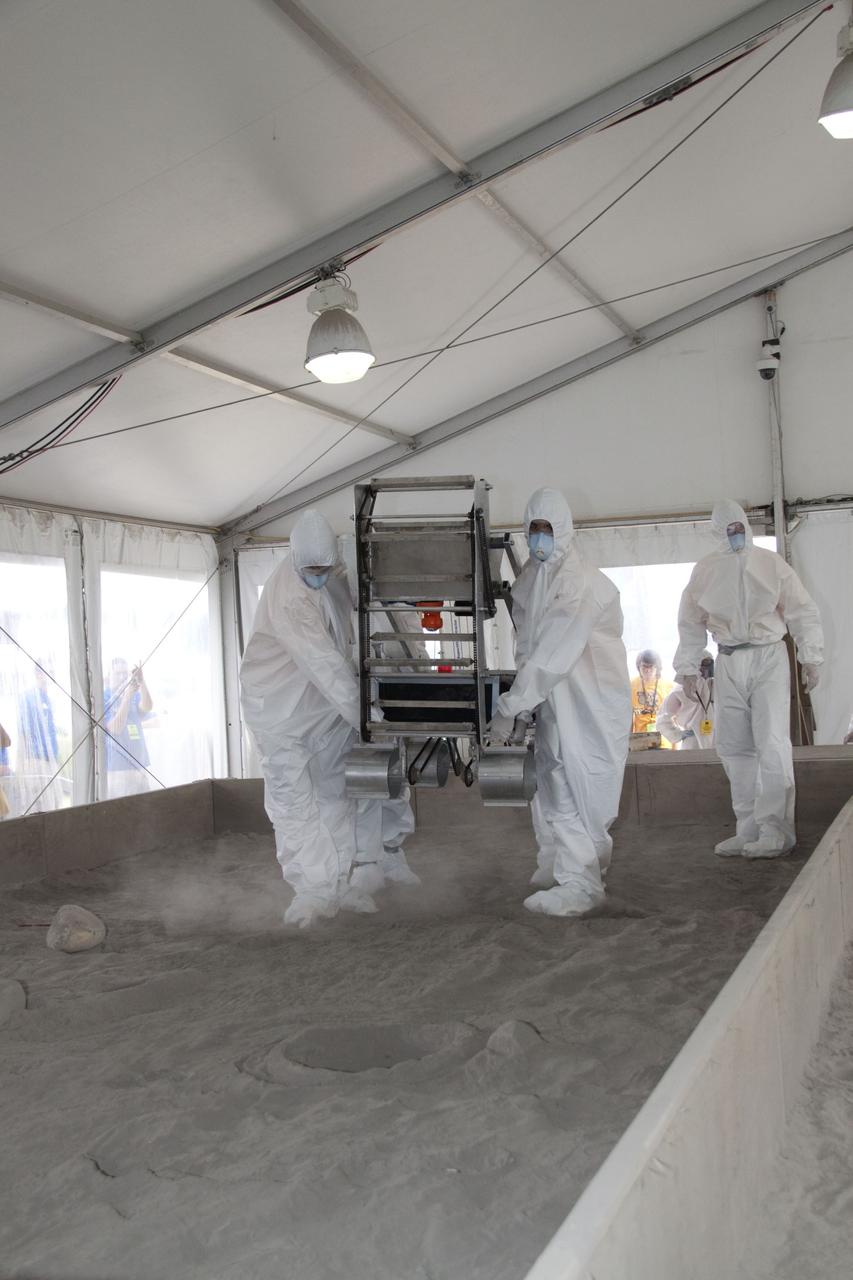

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the "Lunarena" at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida, university students maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in a "sand box" of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil during NASA's second annual Lunabotics Mining Competition. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
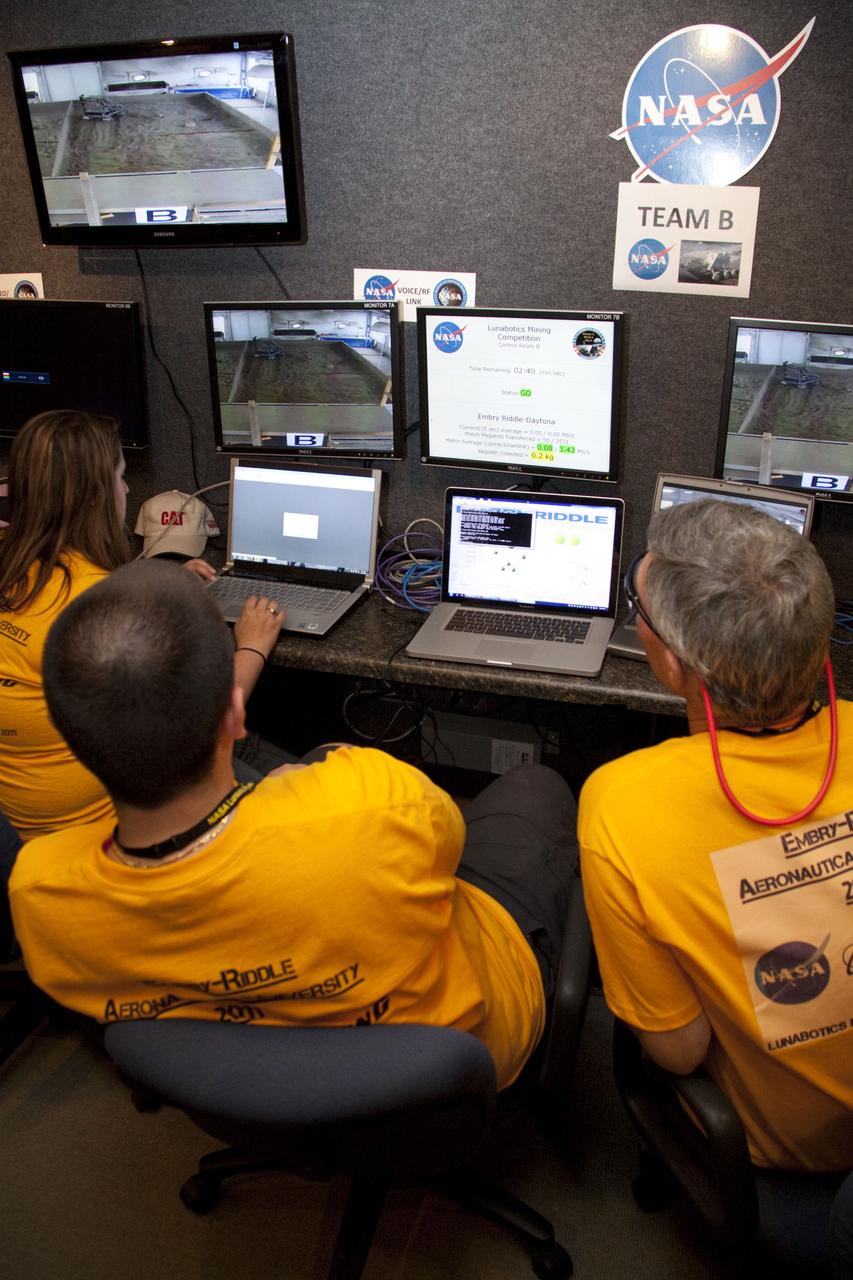

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- University students monitor their team's remote controlled or autonomous excavator, called a lunabot, as it is maneuvered in a "sand box" of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil during NASA's second annual Lunabotics Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
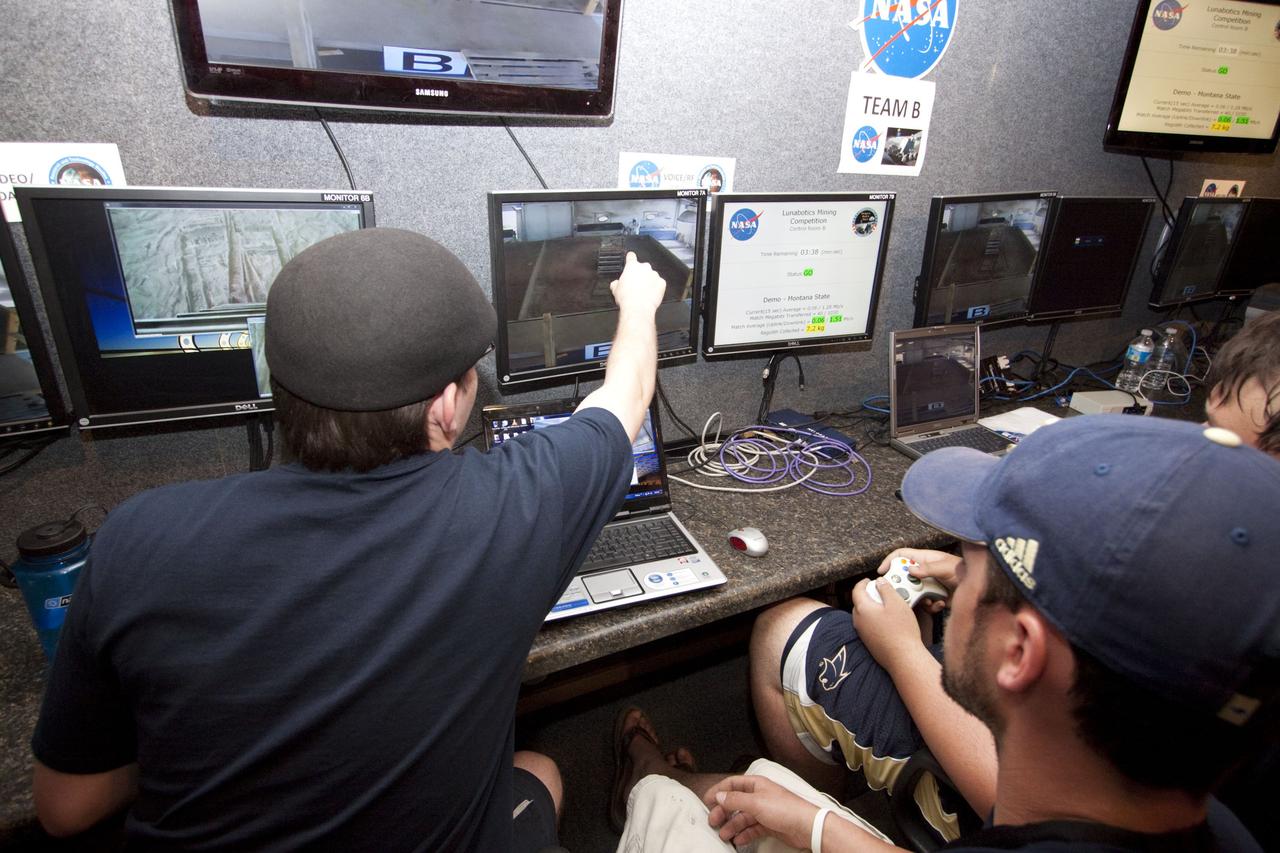

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- University students monitor their team's remote controlled or autonomous excavator, called a lunabot, as it is maneuvered in a "sand box" of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil during NASA's second annual Lunabotics Mining Competition at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Thirty-six teams of undergraduate and graduate students from the United States, Bangladesh, Canada, Colombia and India will participate in NASA's Lunabotics Mining Competition May 26 - 28 at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The competition is designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Teams will maneuver their remote controlled or autonomous excavators, called lunabots, in about 60 tons of ultra-fine simulated lunar soil, called BP-1. The competition is an Exploration Systems Mission Directorate project managed by Kennedy's Education Division. The event also provides a competitive environment that could result in innovative ideas and solutions for NASA's future excavation of the moon. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller