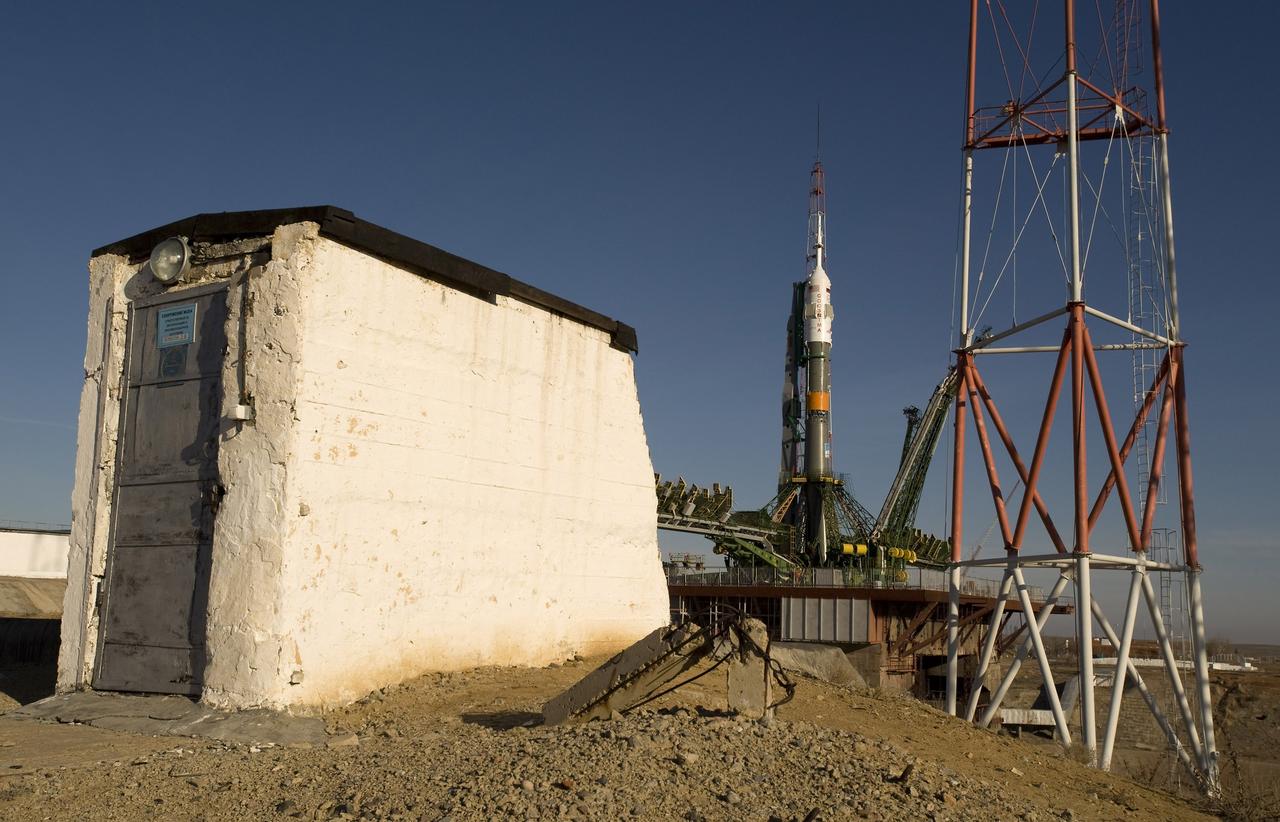

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Soyuz rocket is erected into position at the launch pad March 24, 2009, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The Soyuz is scheduled to launch the crew of Expedition 19 and a spaceflight participant on March 26, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
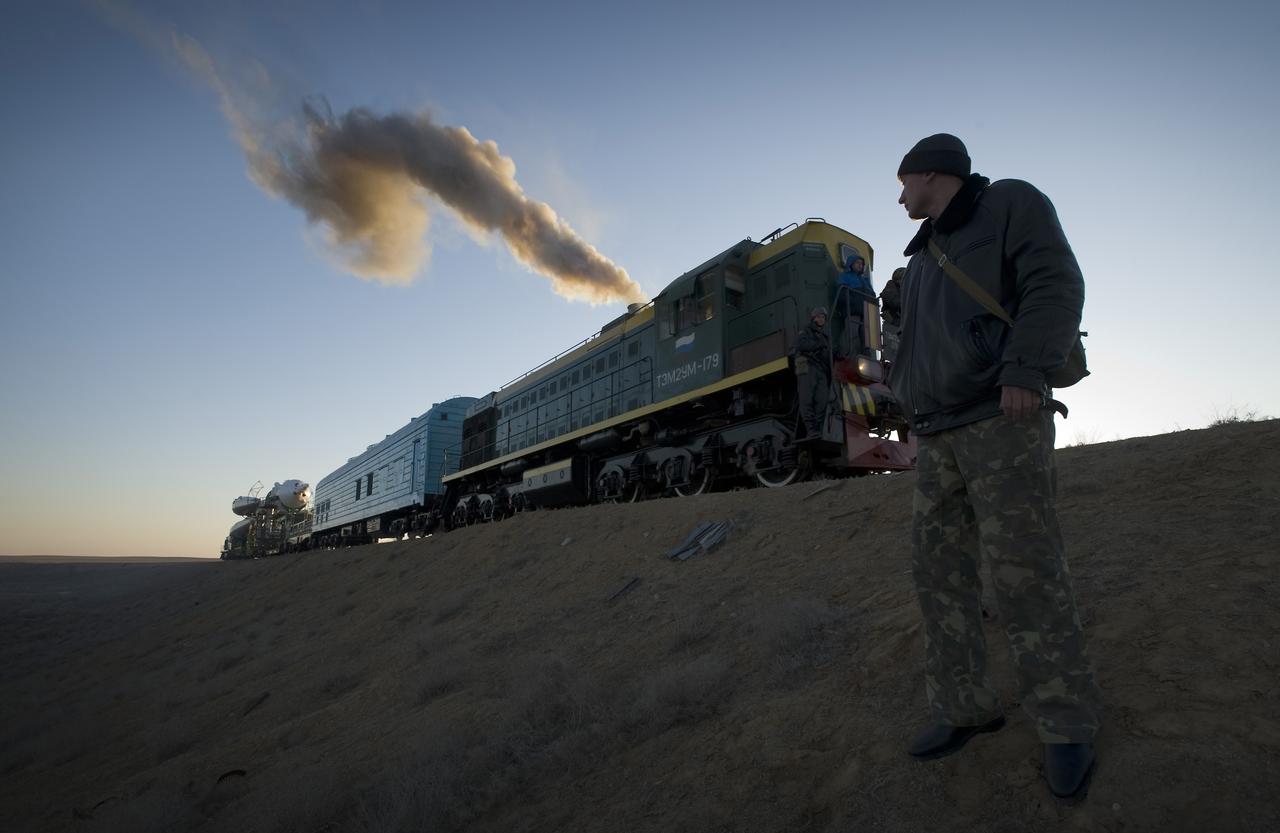

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A Russian security member monitors the railroad tracks as the Soyuz rocket rolls out to the launch pad March 24, 2009, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The Soyuz is scheduled to launch the crew of Expedition 19 and a spaceflight participant on March 26, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
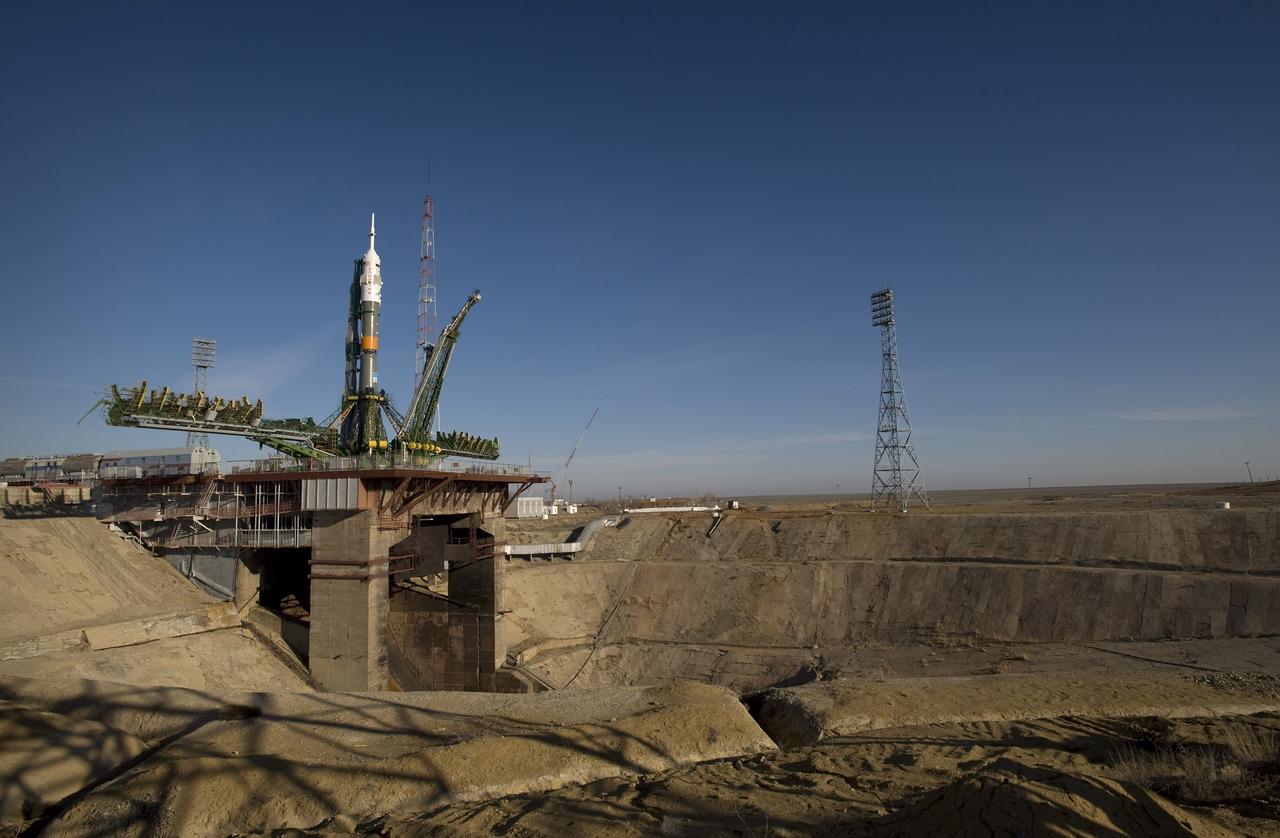

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Soyuz rocket is erected into position at the launch pad March 24, 2009, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The Soyuz is scheduled to launch the crew of Expedition 19 and a spaceflight participant on March 26, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
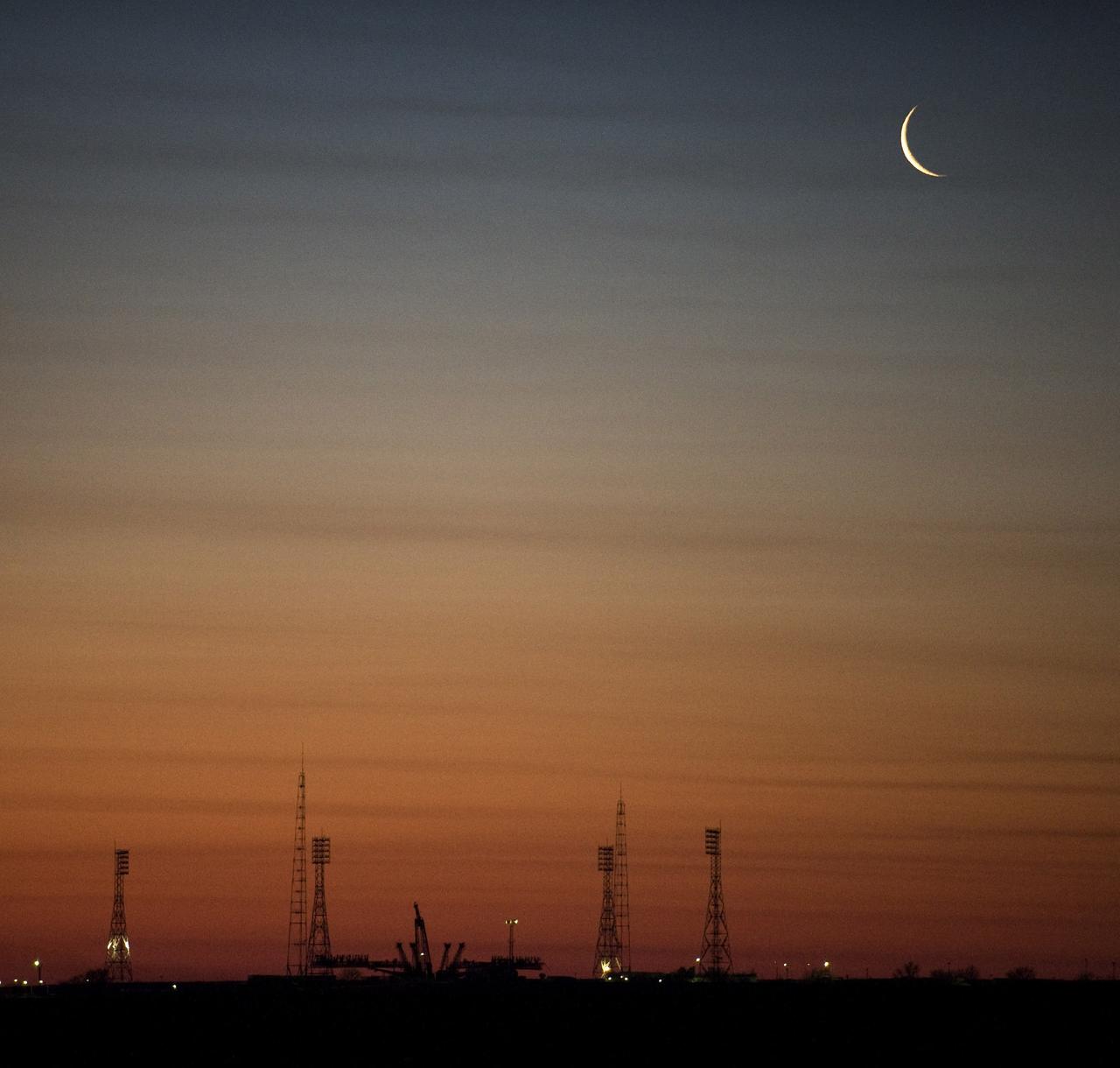

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The moon rises in the early morning hours shortly before the Soyuz rocket is rolled out to the launch pad March 24, 2009, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The Soyuz is scheduled to launch the crew of Expedition 19 and a spaceflight participant on March 26, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
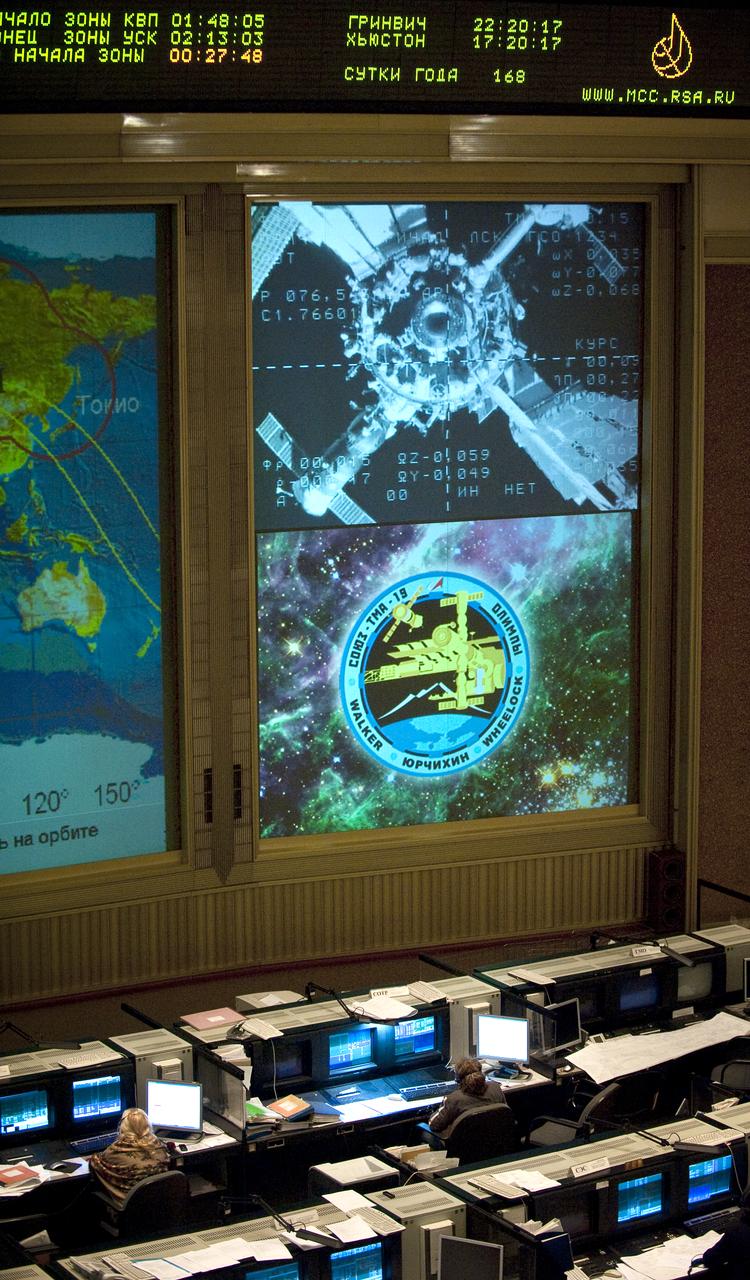

The Soyuz TMA-19 nears its docking with the International Space Station (ISS) as seen in the video monitor at Russian Mission Control Center in Korolev, Russia on Friday, June 18, 2010. The TMA-19 delivered the crew of Expedition 24 Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin, and NASA Flight Engineers Doug Wheelock and Shannon Walker to the ISS. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Expedition 4 crew member Daniel W. Bursch gets help with his launch and entry suit before entering Endeavour. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
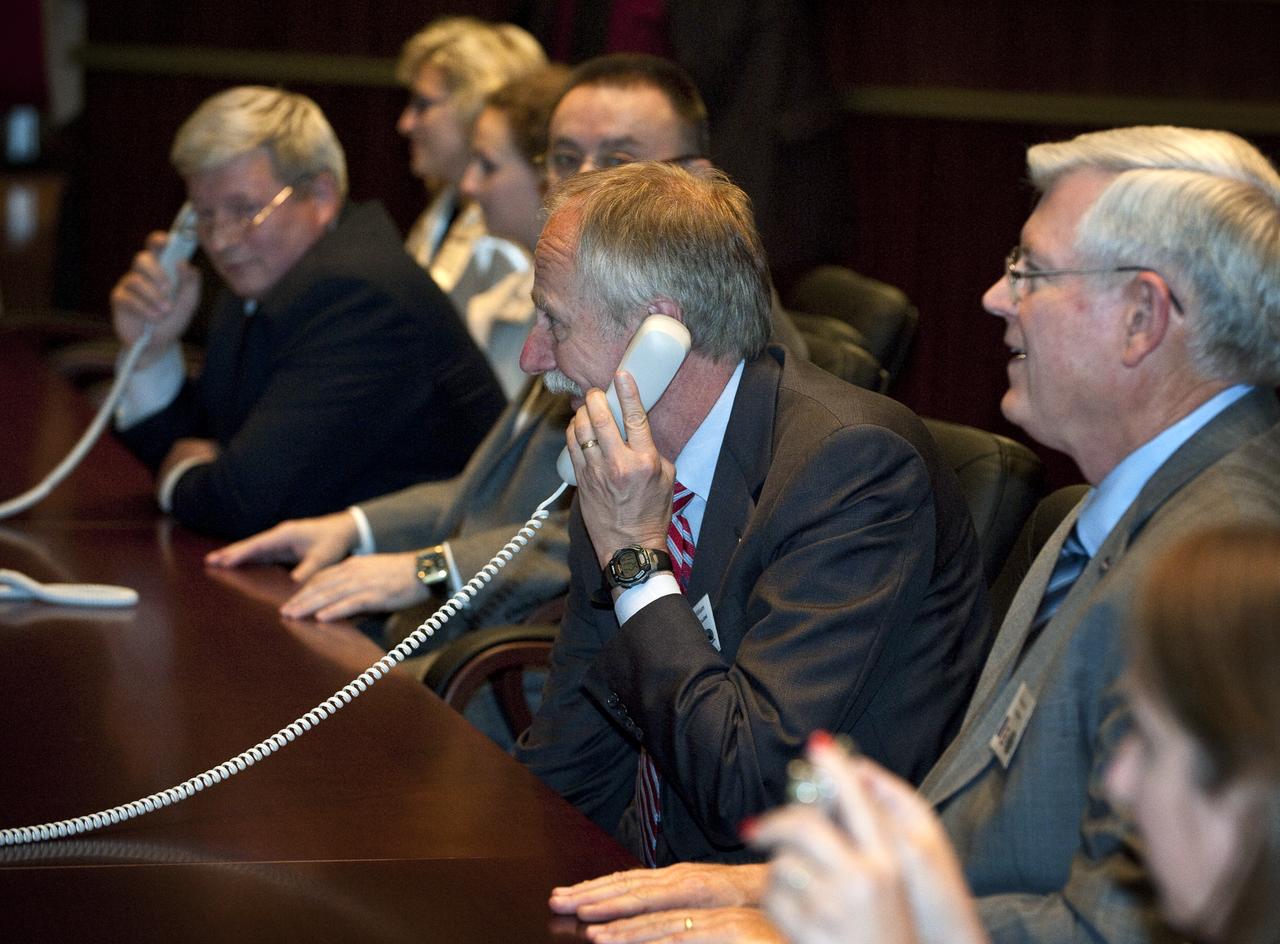

William Gerstenmaier, second from right, NASA Associate Administrator for Space Operations, speaks to the crew of Expedition 24 shortly after their arrival to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard their Soyuz TMA-19 on Friday, June 18, 2010 at Russian Mission Control in Korolev, Russia. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
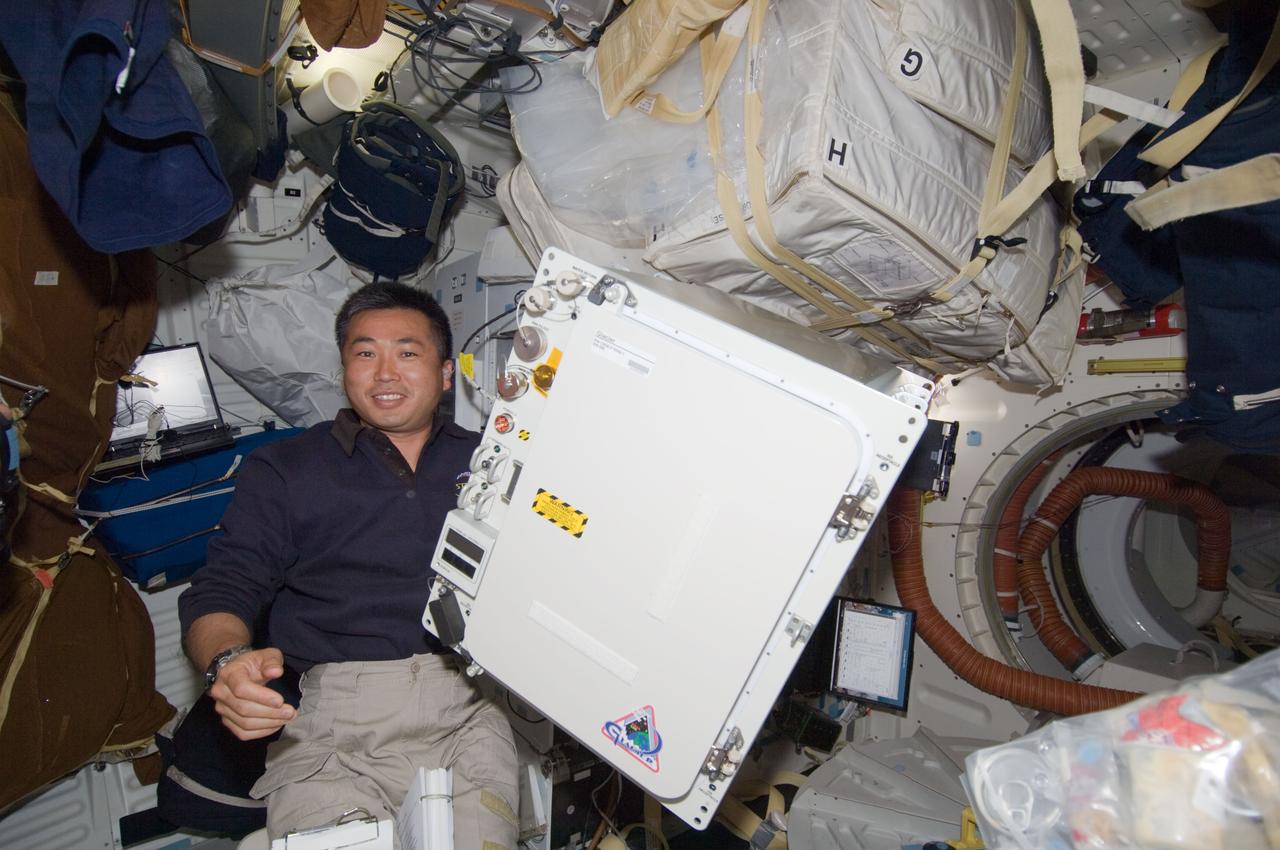

S119-E-006764 (20 March 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Koichi Wakata is pictured on Discovery's middeck with the General Laboratory Active Cryogenic ISS Experiment Refrigerator (GLACIER). The astronauts changed out the International Space Station's glacier with a new one on March 20 to return urine, saliva, and blood samples from the Expedition 18 crew to Earth with Discovery's STS-119 astronauts. Wakata will be serving with both the current (Expedition 18) and the following (Expedition 19) crews aboard the station.
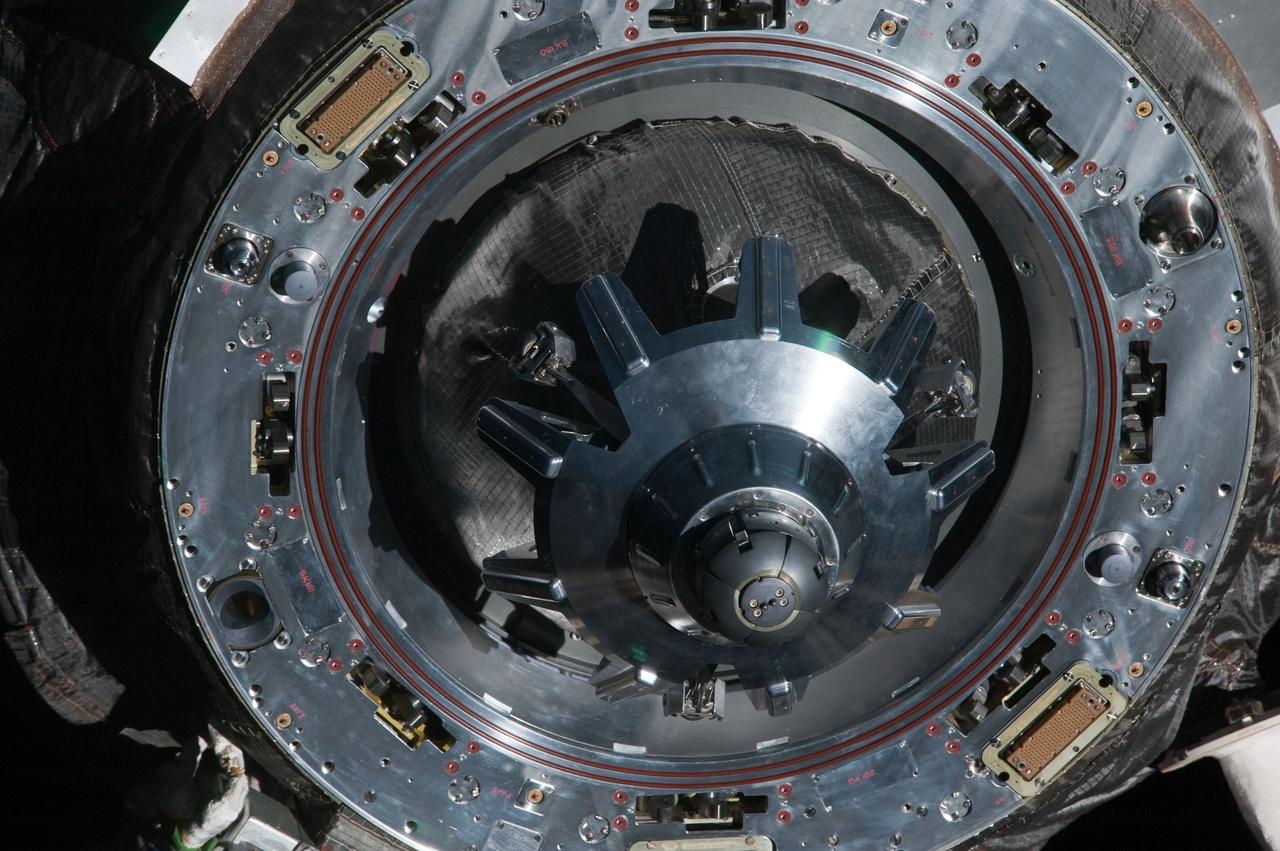
ISS030-E-238803 (19 April 2012) --- A close-up view of the docking mechanism of the unpiloted ISS Russian Progress 46 spacecraft is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 30 crew member as Progress departs from the International Space Station.
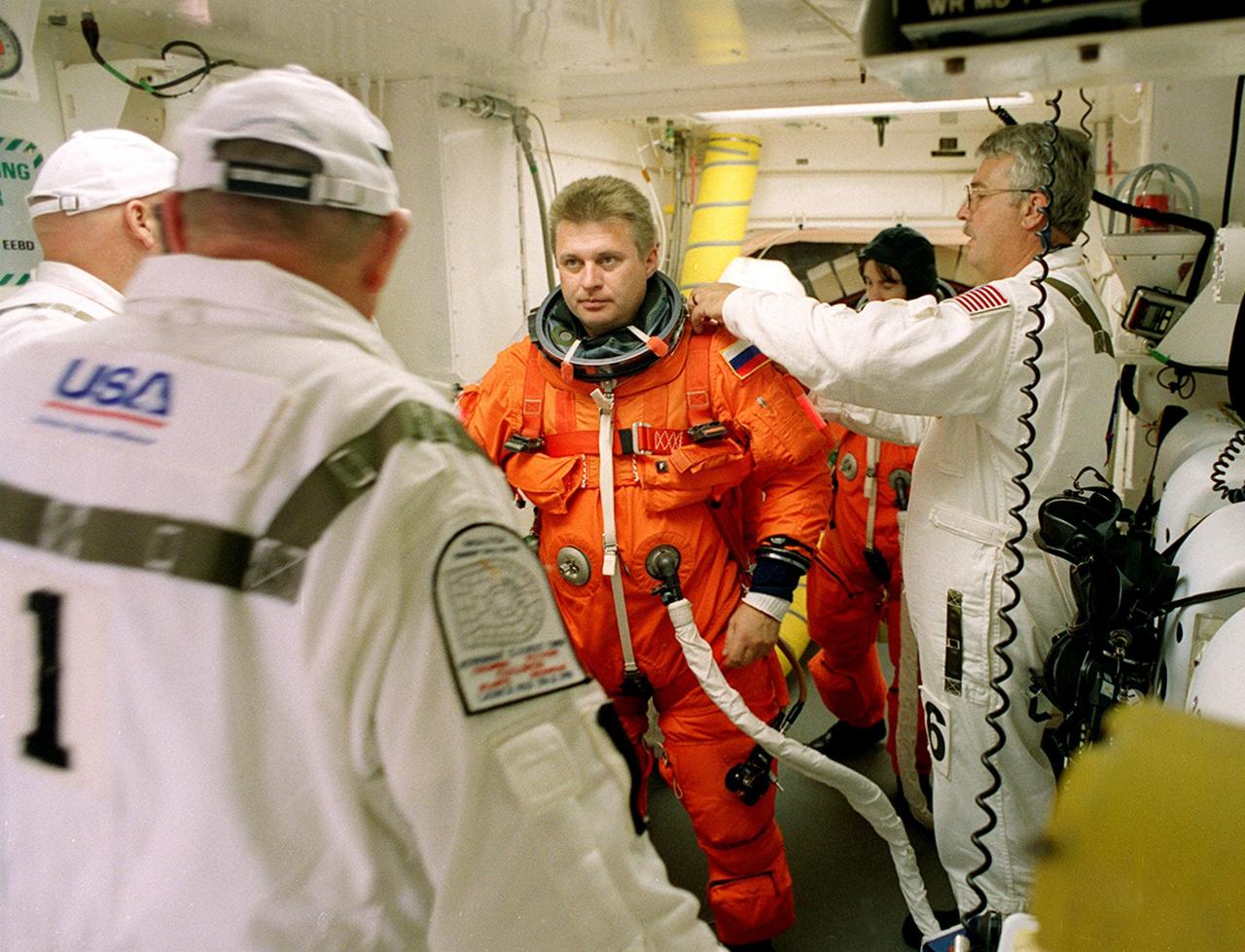

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Expedition 4 Commander Yuri Onufrienko gets help with his launch and entry suit before entering Endeavour. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
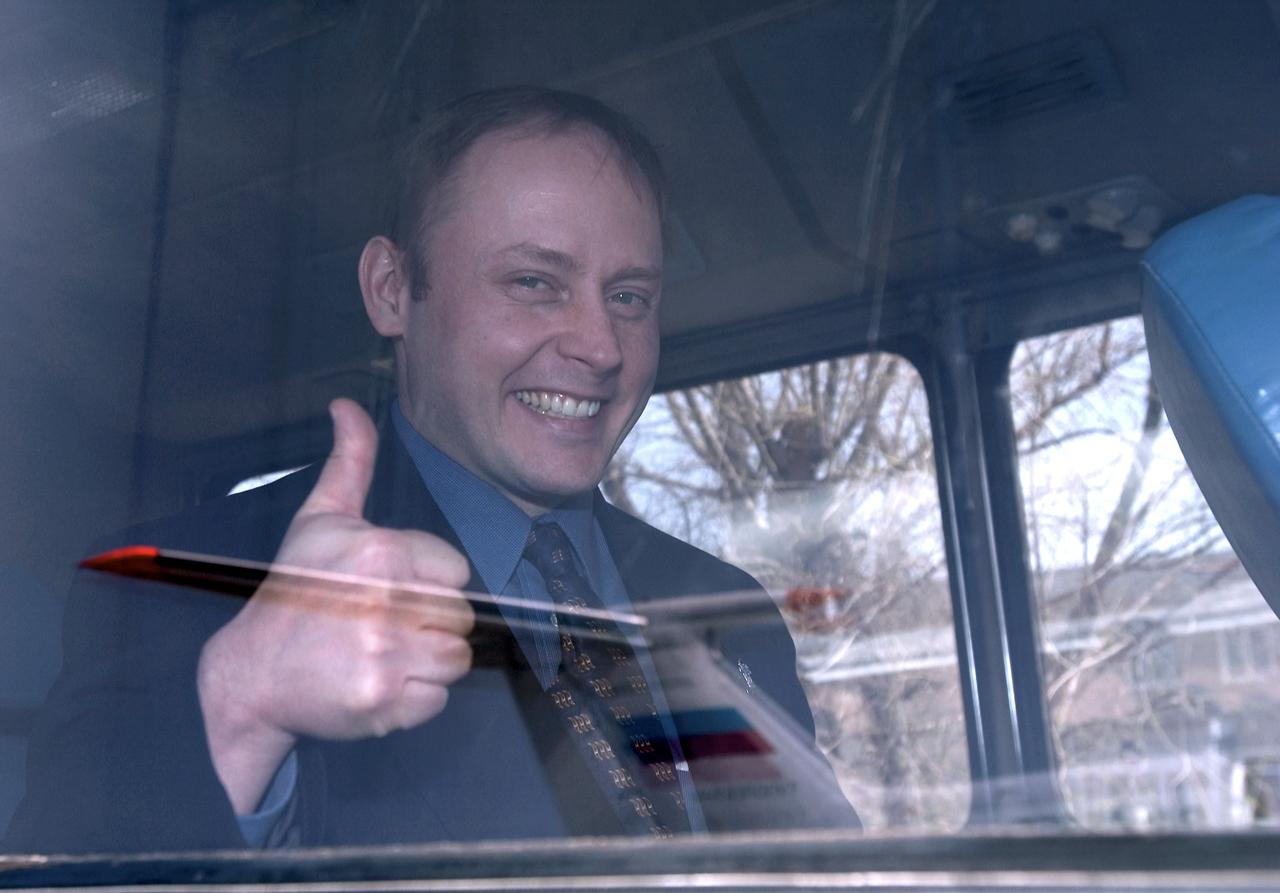

Flight Engineer and NASA International Space Station Science Officer Mike Fincke gives a thumbs up on board the bus after arrival at Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Tuesday, April 13, 2004. Fincke is scheduled to be launched on April 19, 2004 to the International Space Station for an arrival on April 21. He will spend six months on the ISS, replacing the Expedition 8 crew, which has been aboard the ISS since October 20, 2003. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Pictured here is the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, STS-111 mission insignia. The International Space Station (ISS) recieved a new crew, Expedition Five, replacing Expedition Four after a record-setting 196 days in space, when STS-111 visited in June 2002. Three spacewalks enabled the STS-111 crew to accomplish additional mission objectives: the delivery and installation of a new platform for the ISS robotic arm, the Mobile Base System (MBS) which is an important part of the Station's Mobile Servicing System allowing the robotic arm to travel the length of the Station; the replacement of a wrist roll joint on the Station's robotic arm; and unloading supplies and science experiments from the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module, which made its third trip to the orbital outpost. The STS-111 mission, the 14th Shuttle mission to visit the ISS, was launched on June 5, 2002 and landed June 19, 2002.
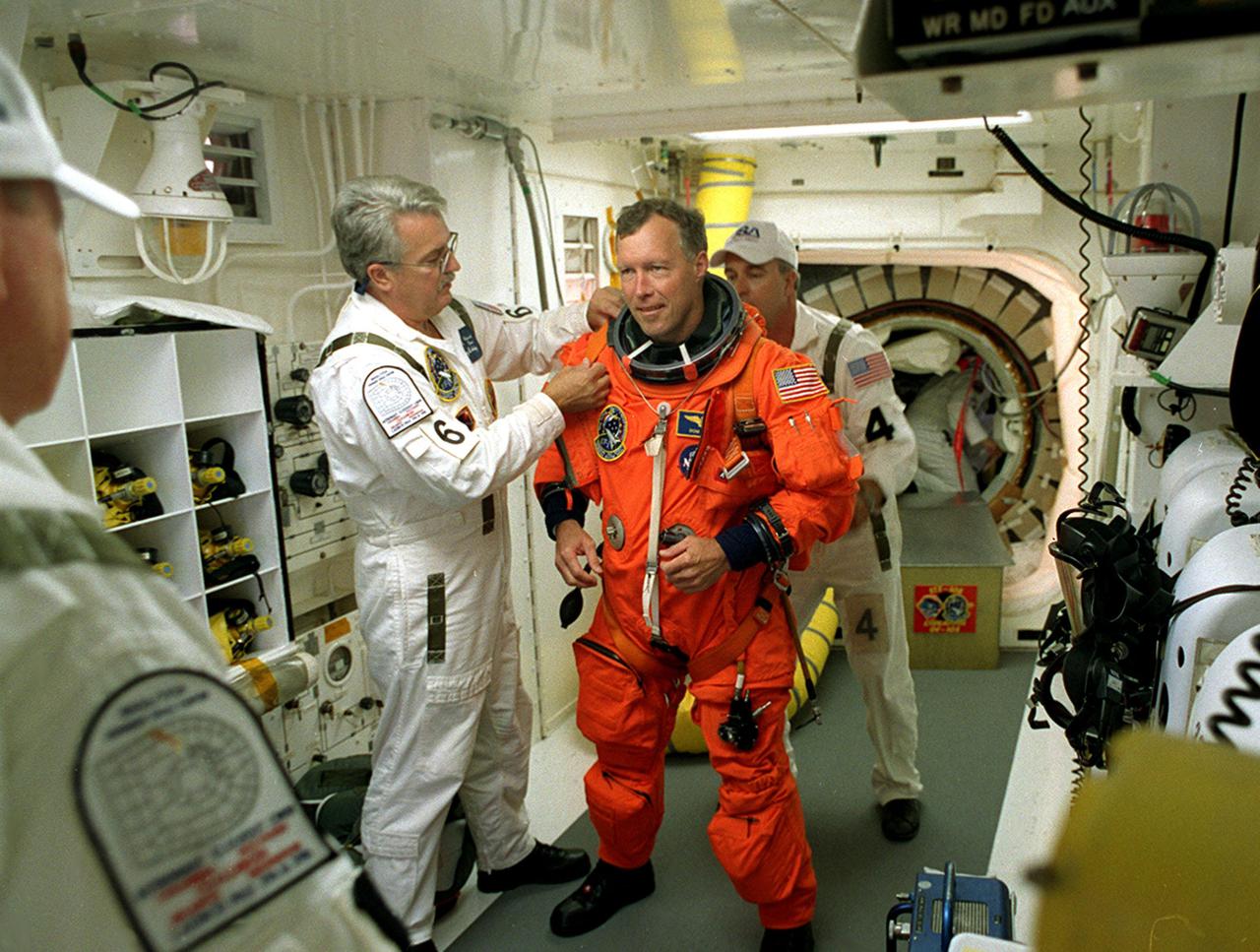

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - STS-108 Commander Dominic L. Gorie gets help with his launch and entry suit before entering Endeavour. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
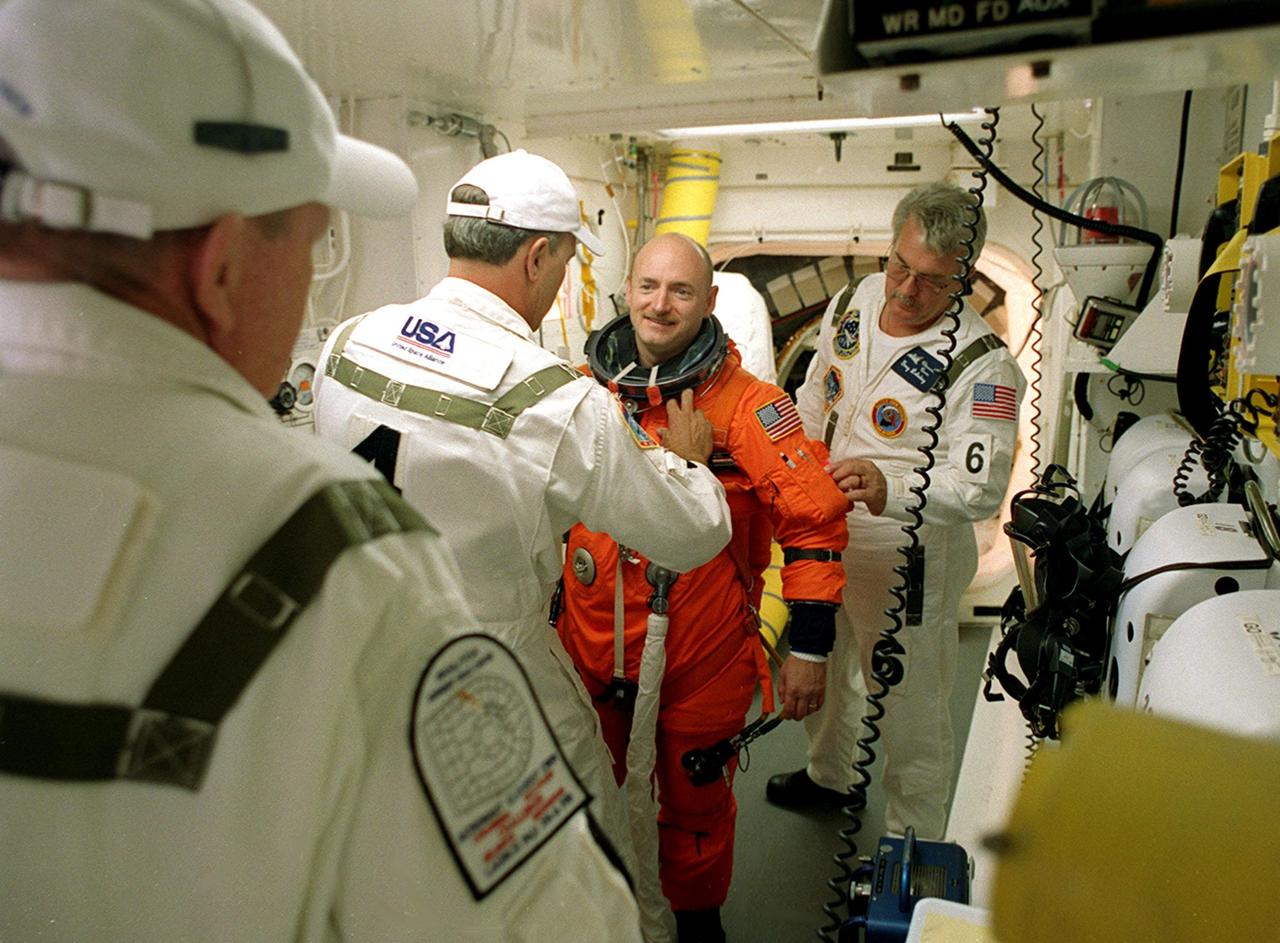

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - STS-108 Pilot Mark E. Kelly is helped with his launch and entry suit before entering Endeavour. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
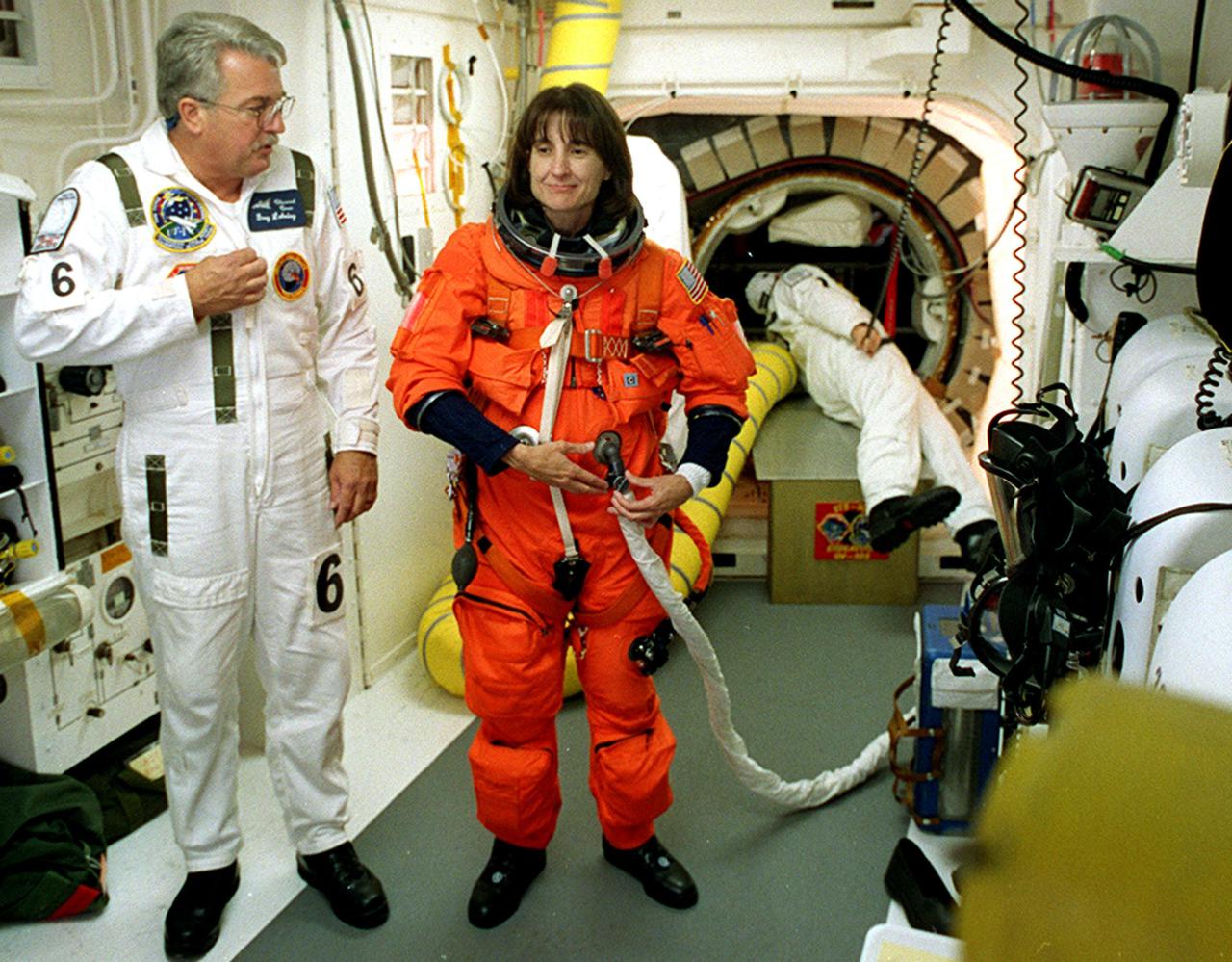

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - STS-108 Mission Specialist Linda A. Godwin gets help with her launch and entry suit before entering Endeavour. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
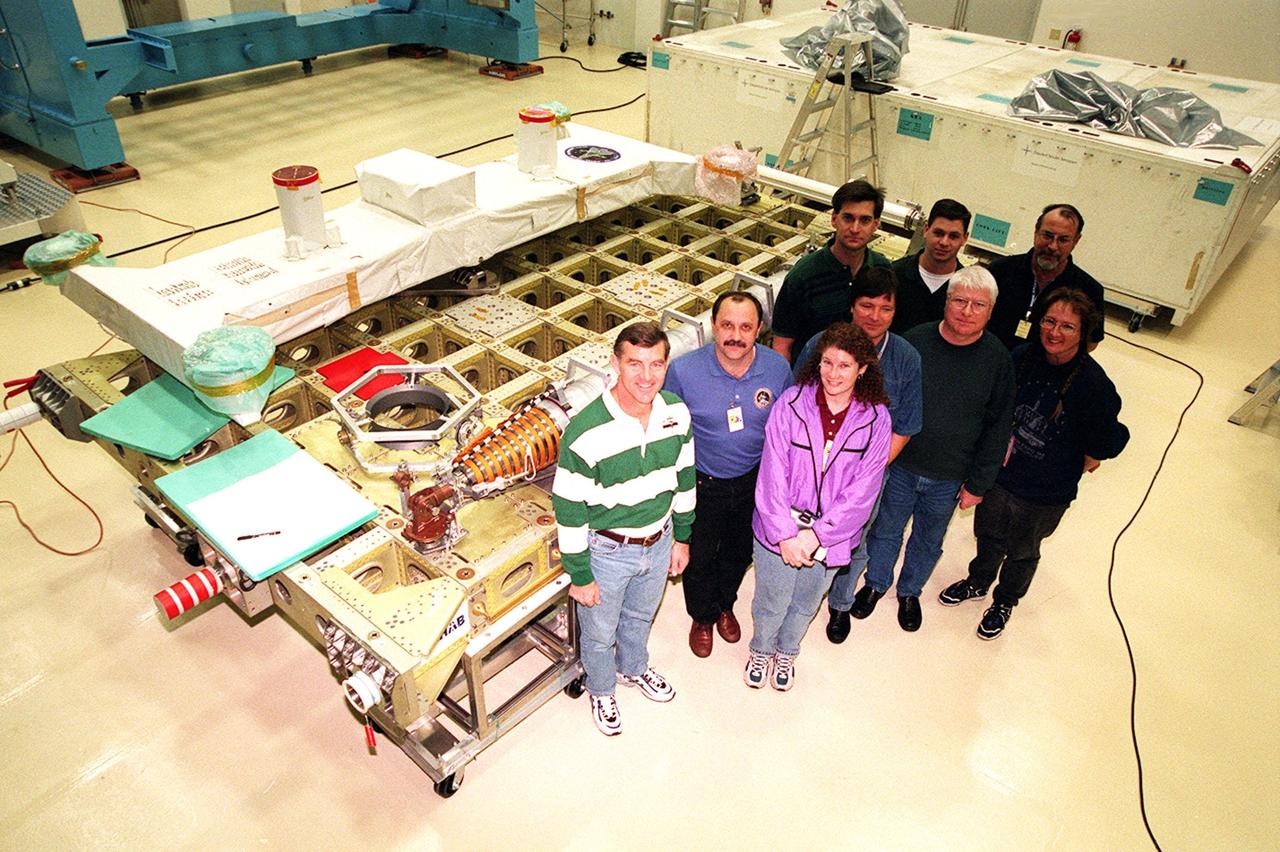

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, in Titusville, Fla., members of the STS-102 crew pose for a photograph with SPACEHAB workers in front of the International Cargo Carrier, which will carry cargo to the International Space Station (ISS). The crew are, left to right, Mission Specialists James Voss, Yuri Usachev, who is with the Russian Space Agency (RSA), and Susan Helms. STS-102 is a resupply mission to the International Space Station, transporting the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) with equipment to assist in outfitting the U.S. Lab, which will already be in place. The mission is also transporting Helms, Voss and Usachev as the second resident crew (designated Expedition crew 2) to the station. In exchange, the mission will return to Earth the first expedition crew on ISS: William Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev (RSA) and Yuri Gidzenko (RSA). STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000
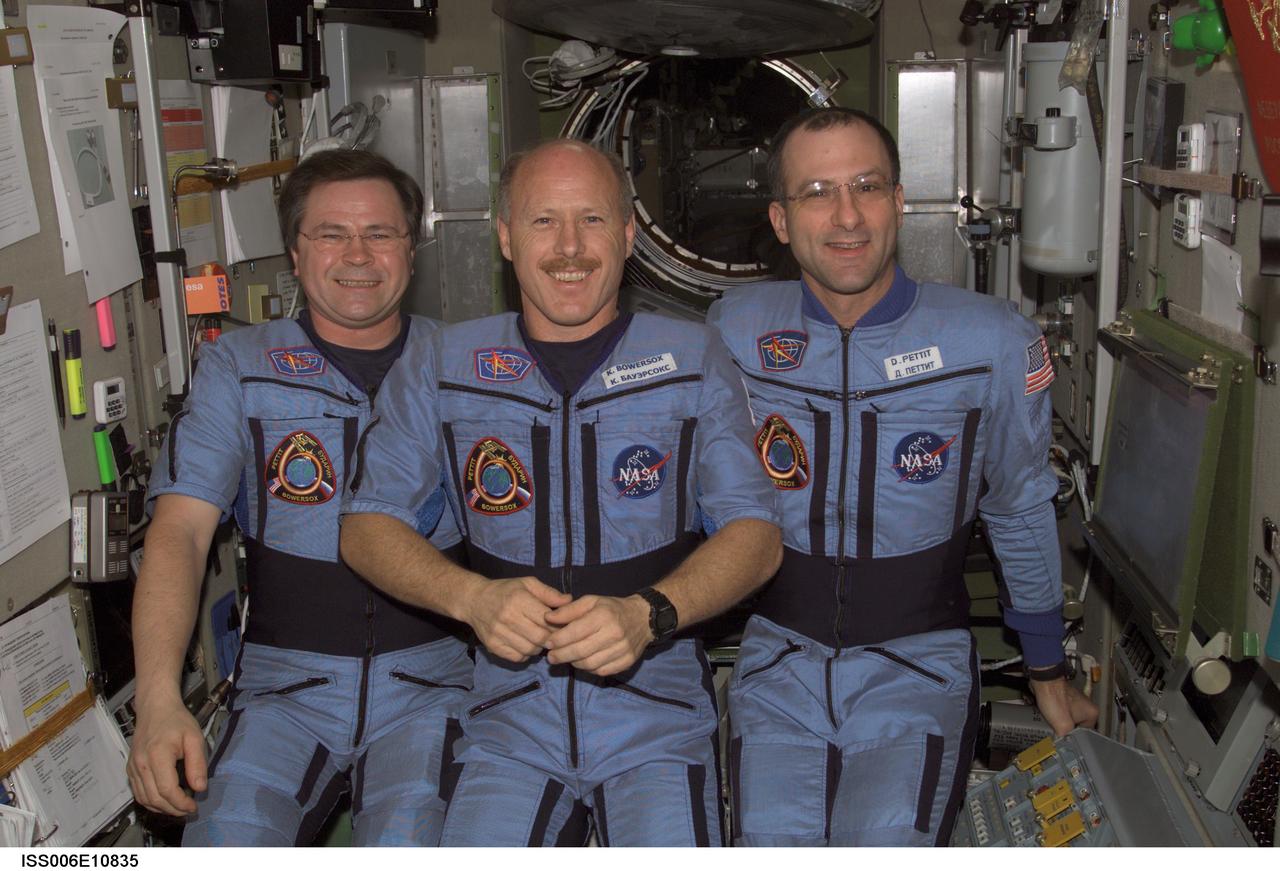

ISS006-E-10835 (19 December 2002) --- The Expedition Six crewmembers pose for a crew photo in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). From the left are cosmonaut Nikolai M. Budarin, flight engineer; astronauts Kenneth D. Bowersox, mission commander; and Donald R. Pettit, NASA ISS science officer. Budarin represents Rosaviakosmos. The photo was taken with a pre-set digital still camera.
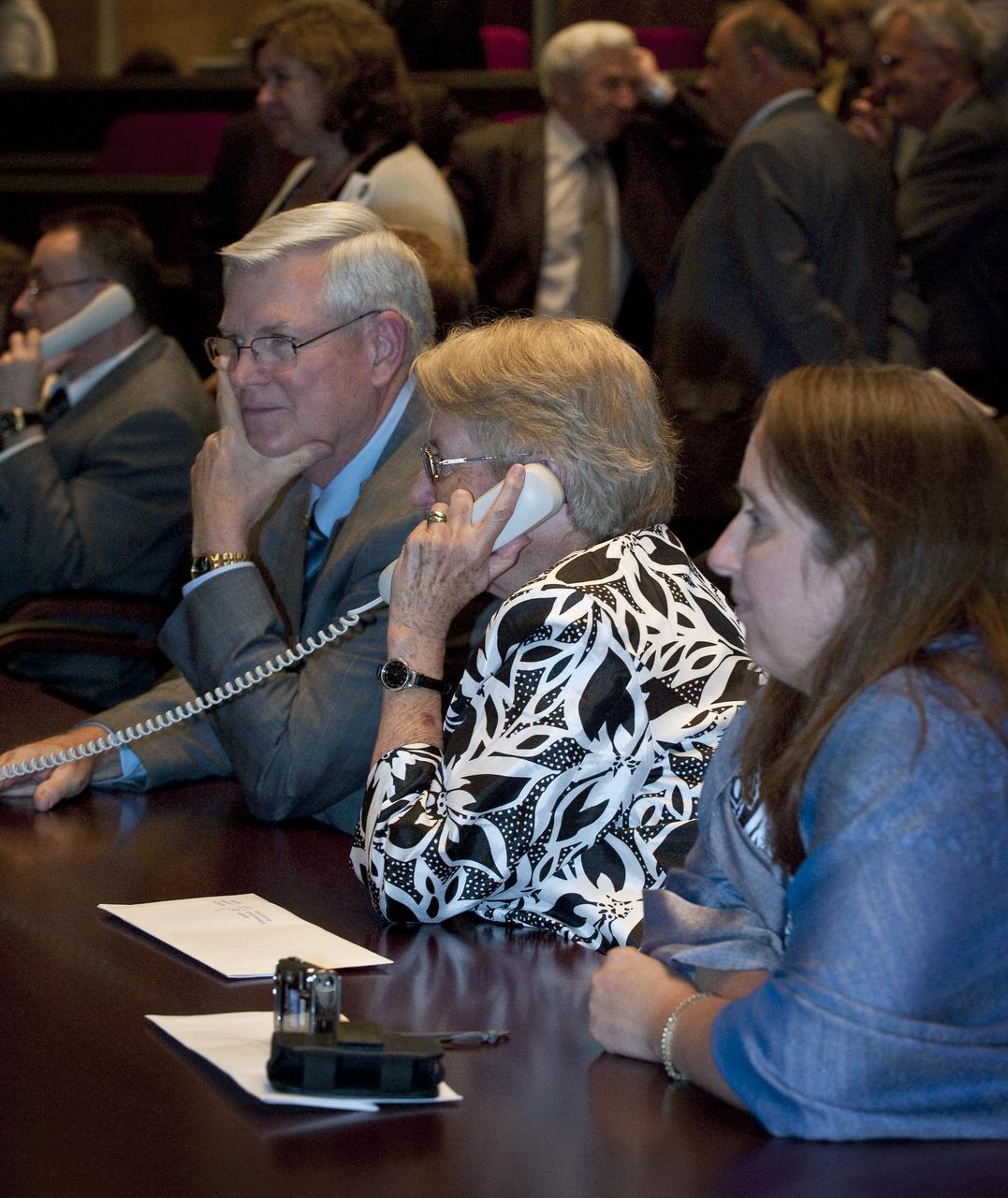

Sherry Walker, second from right, speaks to her daughter NASA Flight Engineer and astronaut Shannon Walker after she and her Expedition 24 crew mates docked to the International Space Station (ISS), Friday, June 18, 2010 in Korolev, Russia. Walker, Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin and Flight Engineer Doug Wheelock launched aboard their Soyuz TMA-19 spacecraft on Wednesday, June 16 to start a six-month tour aboard the ISS.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Expedition 3 crew member Carl E. Walz is wished bon voyage by a closeout crew technician before entering Endeavour for mission STS-108. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST(22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
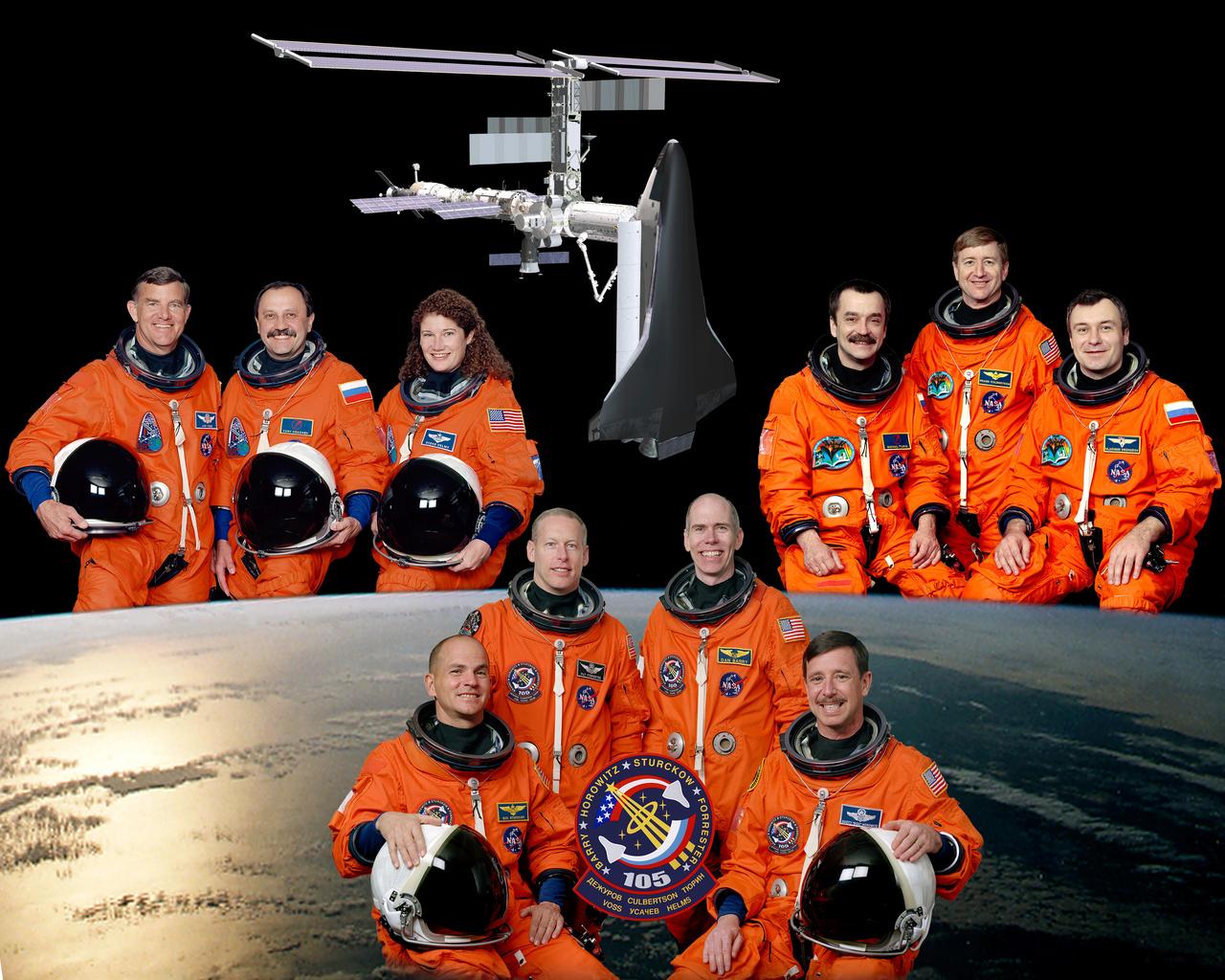

This is the portrait of the astronaut and cosmonaut crewmembers comprising the STS-105 mission. The base crew (bottom center), left to right, are pilot Frederick W. (Rich) Sturckow, Mission Specialists Patrick G. Forester and Daniel T. Barry, and Commander Scott J. Horowitz. The upper right group are the International Space Station (ISS) Expedition Three crew, (left to right) Cosmonaut Mikhail Tyurin, flight engineer; Astronaut Frank L. Culbertson, Jr., commander; and Cosmonaut Vladimir N. Dezhurov, flight engineer. The upper left group are the ISS Expedition Two crew, (left to right) Astronaut James S. Voss, commander; Cosmonaut Yury V. Usachev, flight engineer; and Astronaut Susan J. Helms, flight engineer. The STS-105 was the 11th ISS assembly flight and launched on August 19, 2001 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery.
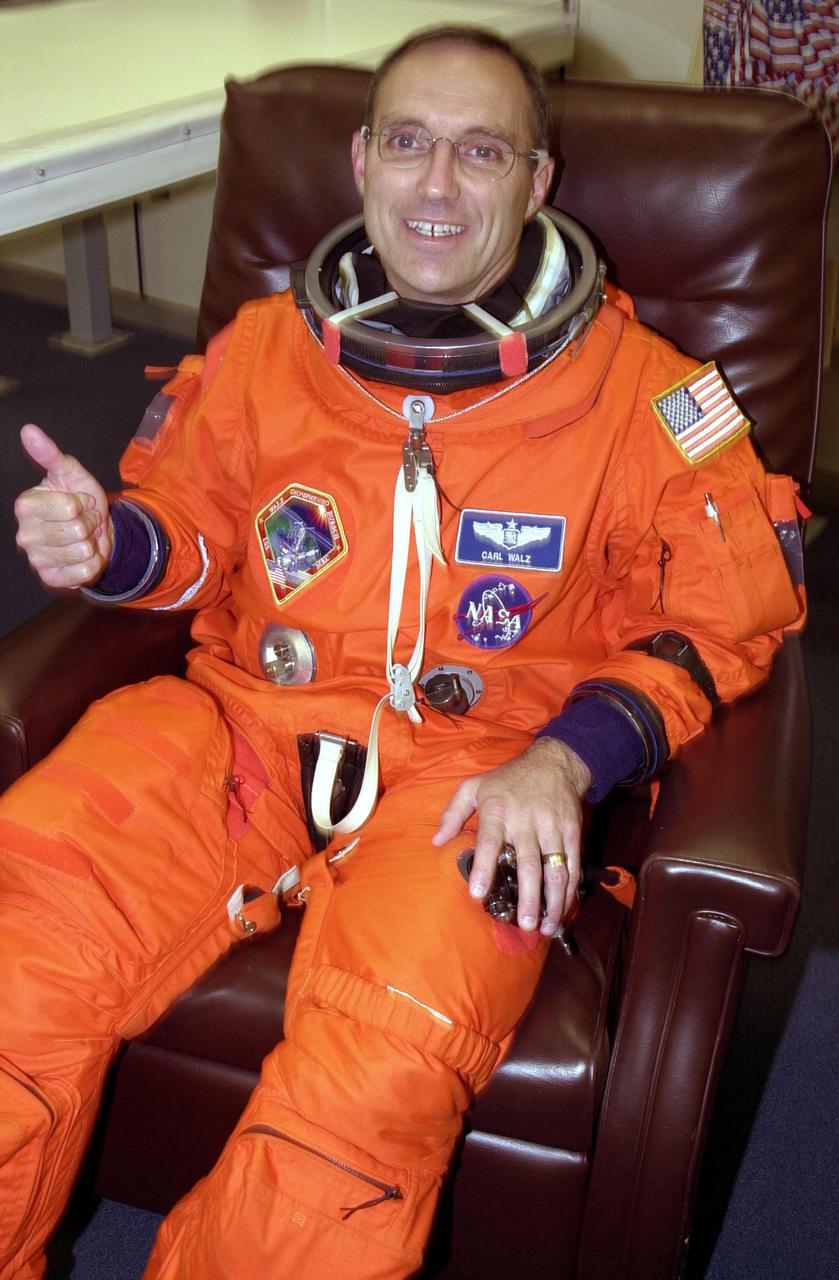

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Expedition 4 crew member Carl E. Walz gives thumbs up for a successful second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
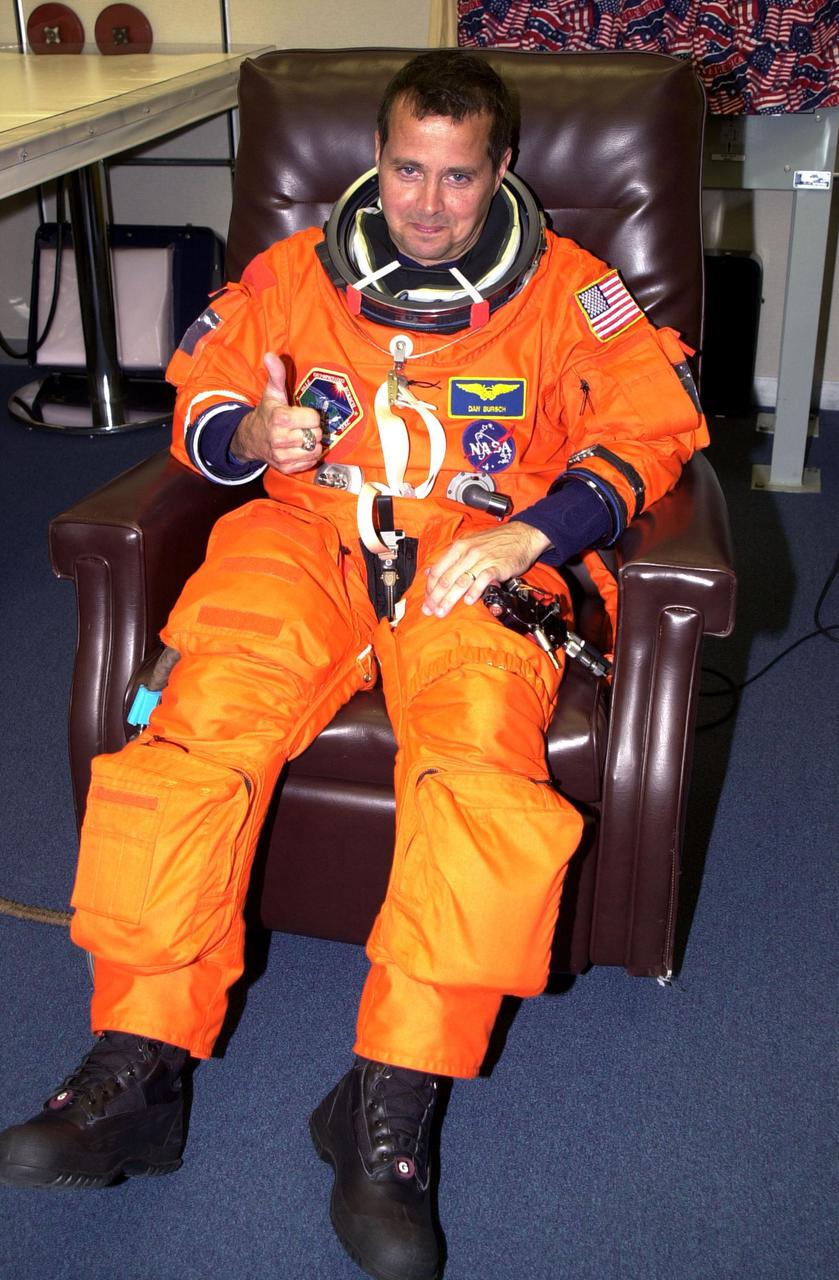

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Expedition 4 crew member Daniel W. Bursch gives a thumbs up for a successful second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
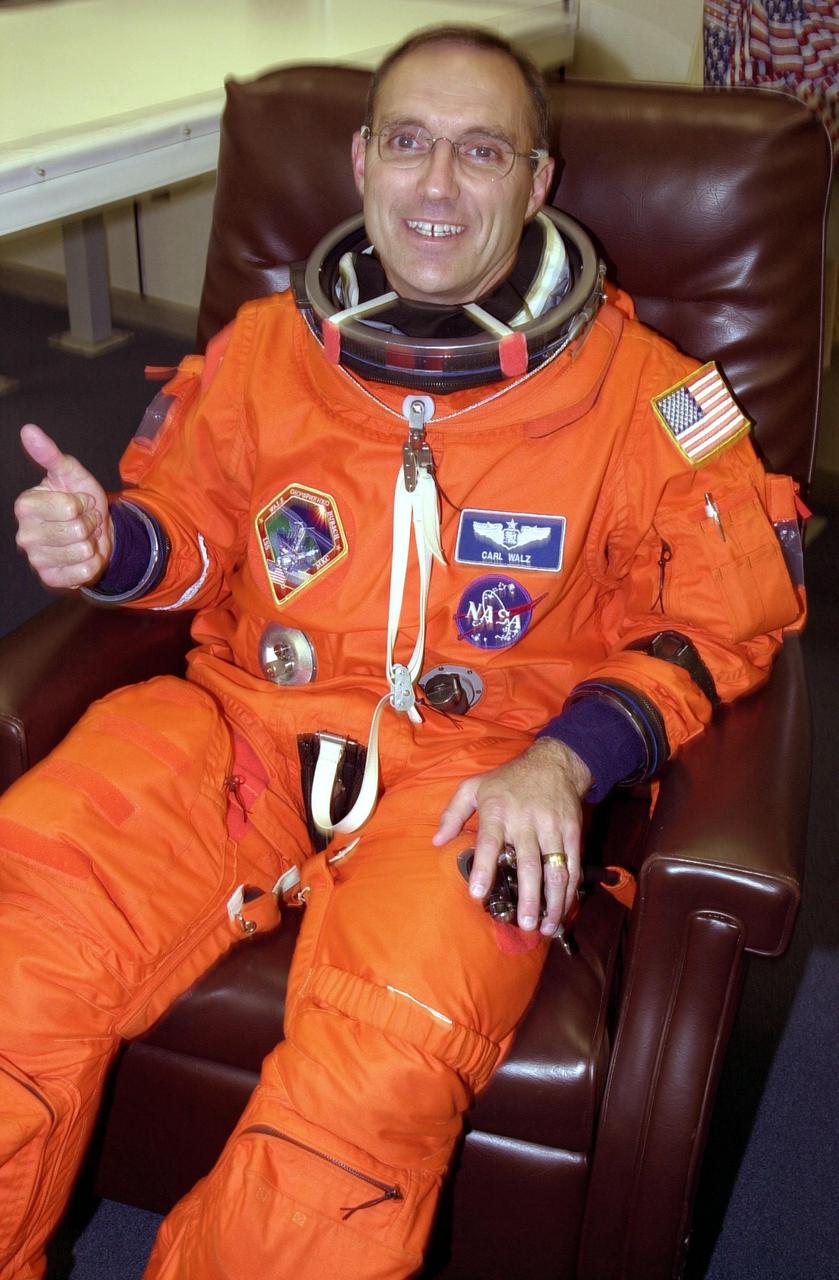

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Expedition 4 crew member Carl E. Walz gives thumbs up for a successful second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
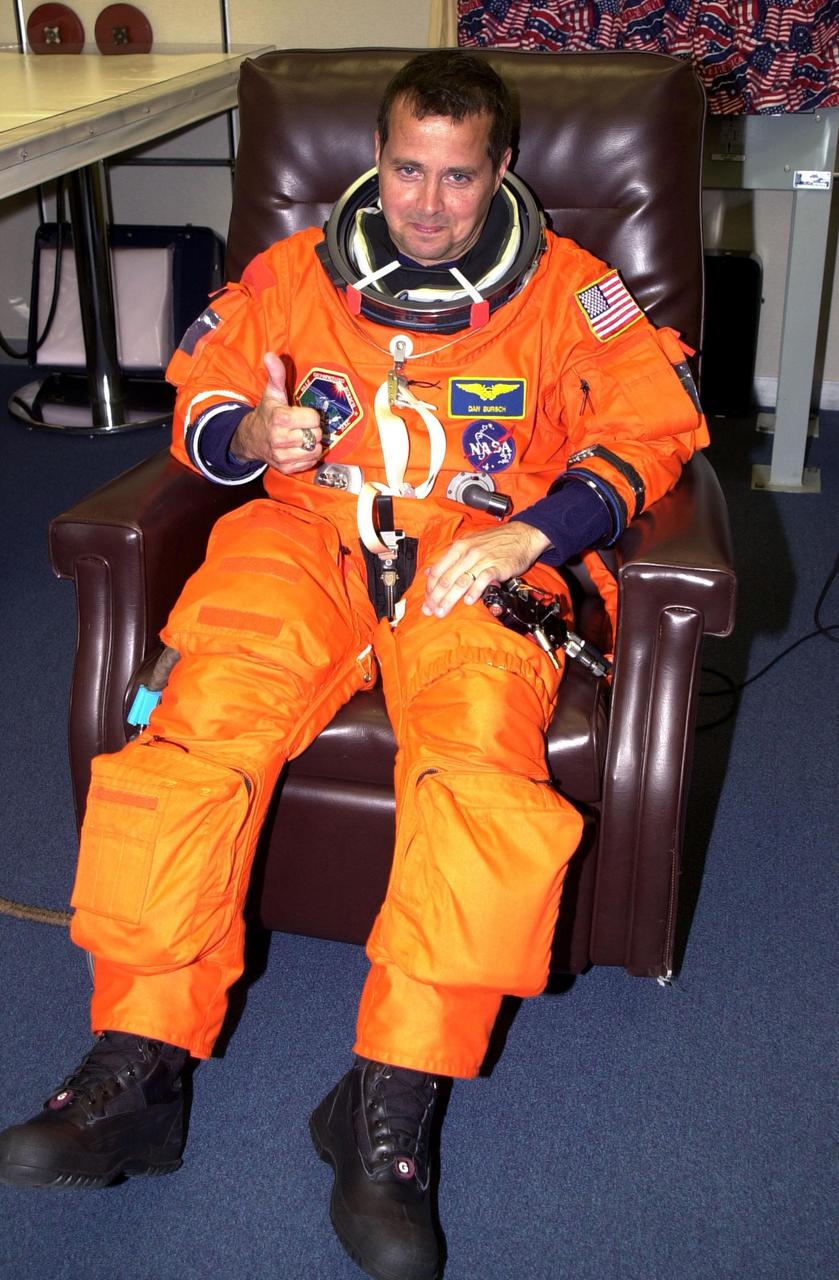

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Expedition 4 crew member Daniel W. Bursch gives a thumbs up for a successful second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
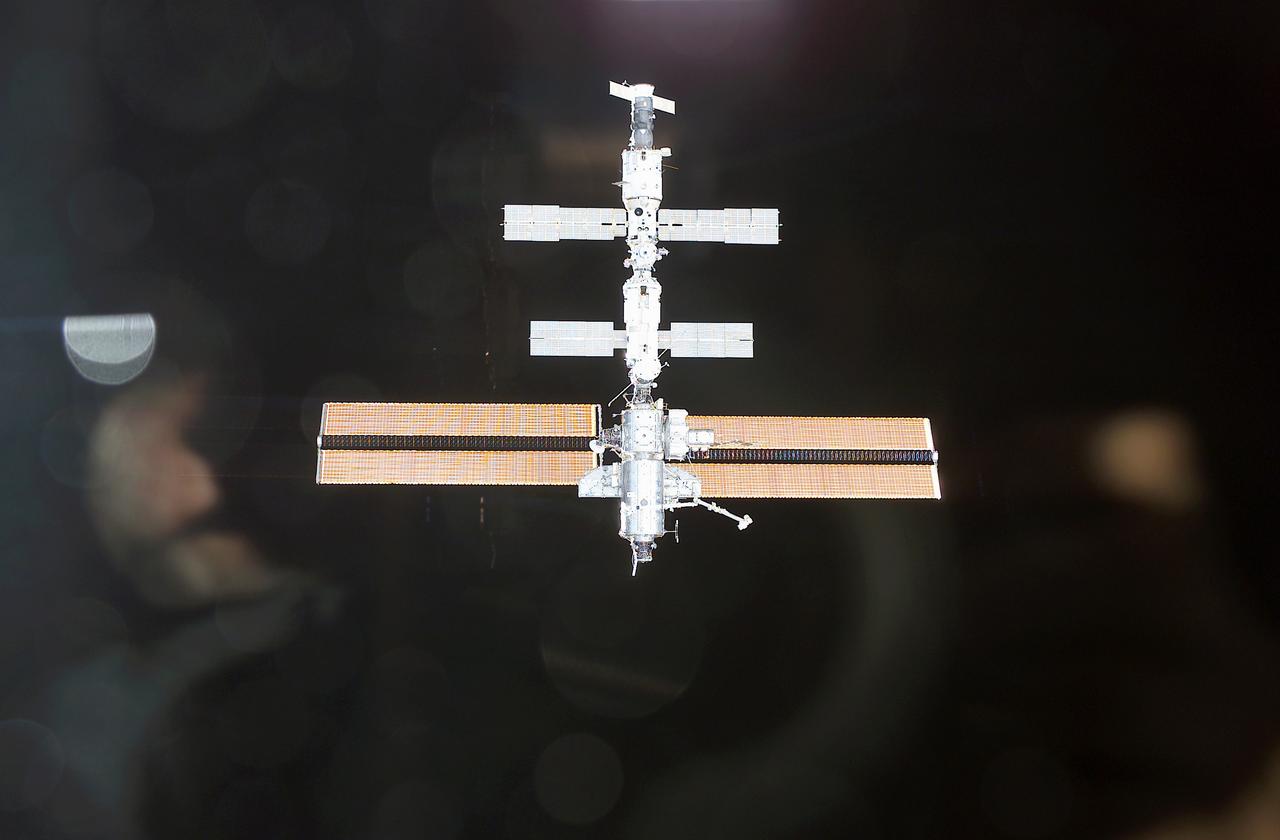
Backdropped against the blackness of space is the International Space Station (ISS), as viewed from the approching Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, STS-111 mission, in June 2002. Expedition Five replaced Expedition Four crew after remaining a record-setting 196 days in space. Three spacewalks enabled the STS-111 crew to accomplish the delivery and installation of the Mobile Remote Servicer Base System (MBS), an important part of the Station's Mobile Servicing System that allows the robotic arm to travel the length of the Station, which is necessary for future construction tasks; the replacement of a wrist roll joint on the Station's robotic arm, and the task of unloading supplies and science experiments from the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module, which made its third trip to the orbital outpost. The STS-111 mission, the 14th Shuttle mission to visit the ISS, was launched on June 5, 2002 and landed June 19, 2002.
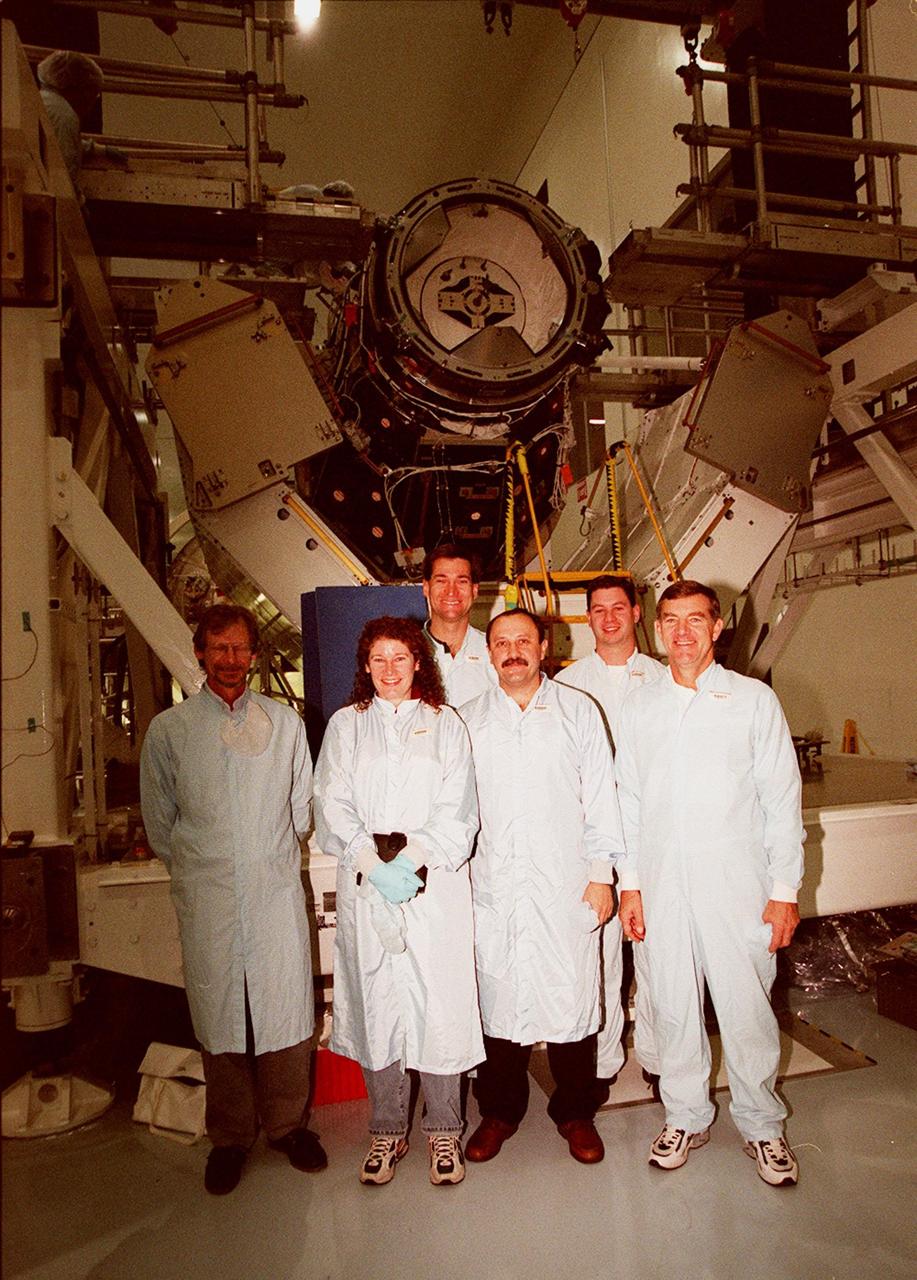

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-102 crew pose with workers from Johnson Space Center in front of the Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), a component of the International Space Station (ISS). From left are Dave Moore (JSC), Susan J. Helms, Arne Aamodt (JSC), Yuriy Vladimirovich Usachev, Matt Myers (JSC) and James S. Voss. Voss, Helms and Usachev, known as the Expedition II crew, will be staying on the ISS, replacing the Expedition I crew, Bill Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev and Yuri Gidzenko. Along with the crew, Mission STS-102 also will be carrying the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) to the ISS. The Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module, which will have been carried to the ISS on a preceding Shuttle flight. In order to function as an attached station module as well as a cargo transport, logistics modules (there are three) also include components that provide some life support, fire detection and suppression, electrical distribution and computer functions. Eventually, the modules also will carry refrigerator freezers for transporting experiment samples and food to and from the station. STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000, from Launch Pad 39A, Kennedy Space Center
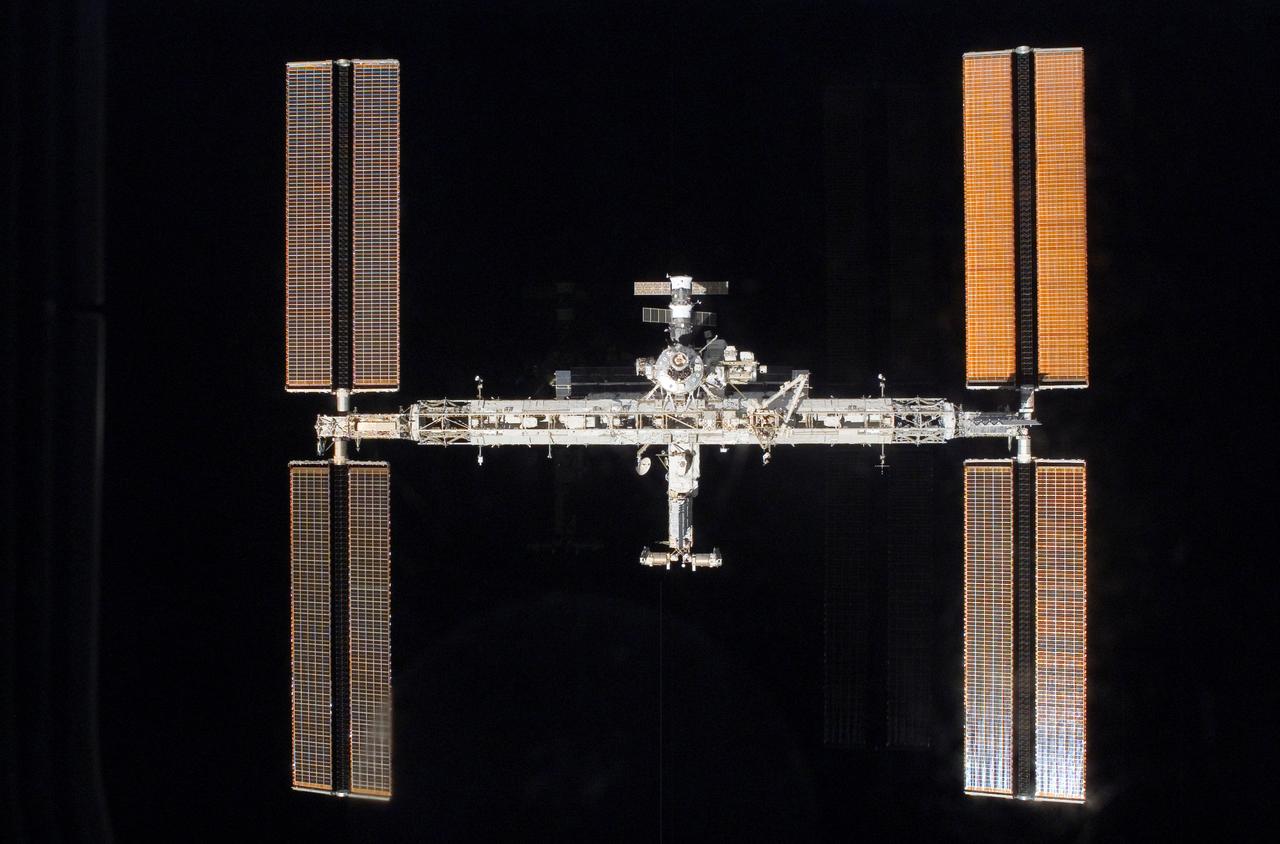
Eight days of construction resumed on the International Space Station (ISS), as STS-117 astronauts and mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the second and third starboard truss segments (S3 and S4). Back dropped by the blackness of space, its newly expanded configuration is revealed as pilot Lee Archambault conducts a fly around upon departure from the station on June 19, 2007.
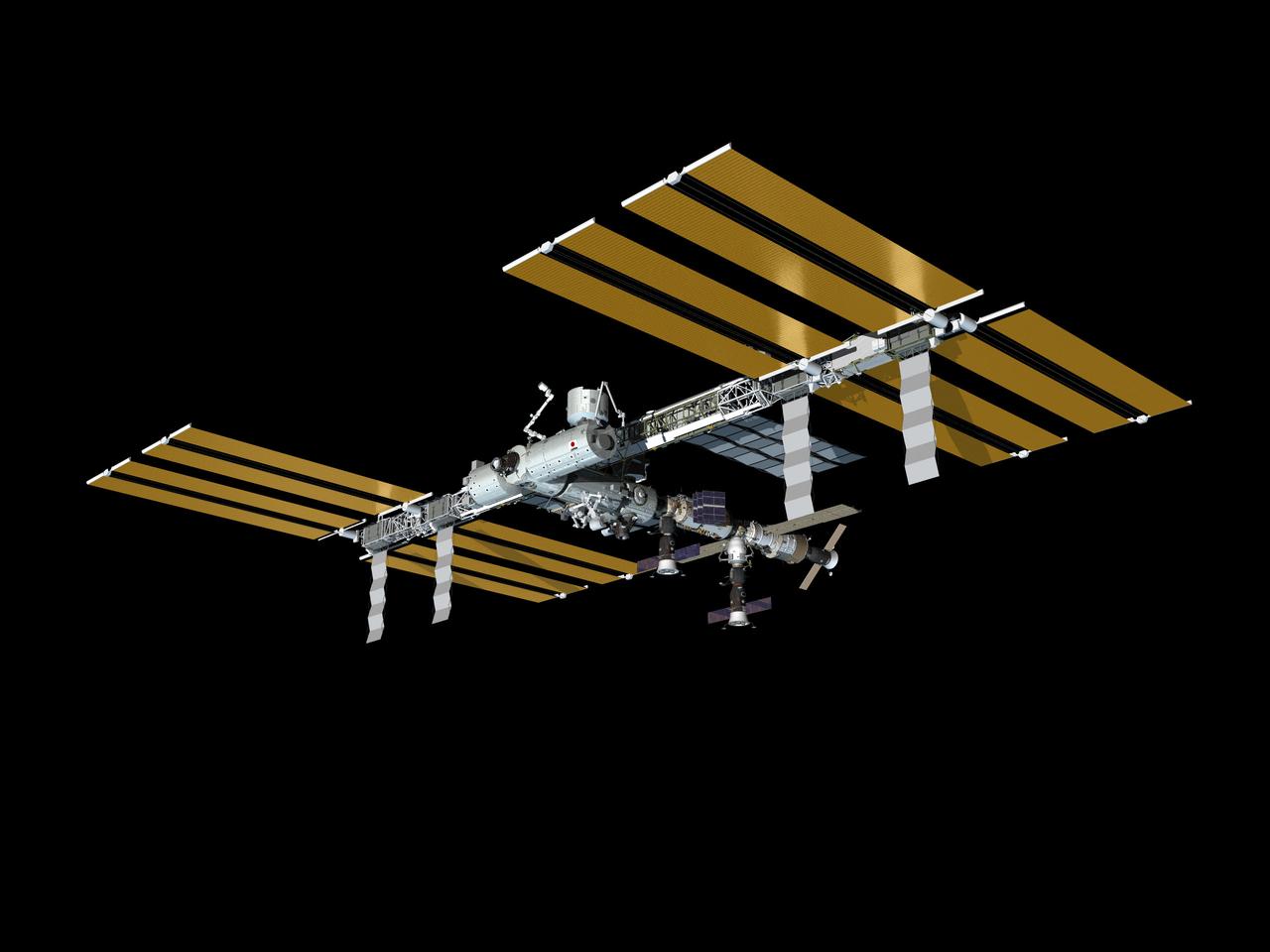

JSC2009-E-088614 (May 2009) --- Computer-generated artist?s rendering of the International Space Station as of May 29, 2009. Soyuz 19 (TMA-15) docks to the Zarya nadir port, bringing the Expedition 20 crew and marking the start of the six-person crew aboard the ISS. Progress 33 supply vehicle remains linked to the Pirs Docking Compartment. Soyuz 18 (TMA-14) remains docked to the Zvezda Service Module?s aft port.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-102 crew, known as the Expedition II crew, and workers from Johnson Space Center get a close look at the Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3) in the Space Station Processing Facility. The PMA-3 is a component of the International Space Station (ISS). Making up the Expedition II crew are James S. Voss, Susan J. Helms and Yuriy Vladimirovich Usachev, of Russia. Along with the crew, Mission STS-102 also will be carrying the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) to the ISS. The Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module, which will have been carried to the ISS on a preceding Shuttle flight. In order to function as an attached station module as well as a cargo transport, logistics modules (there are three) also include components that provide some life support, fire detection and suppression, electrical distribution and computer functions. Eventually, the modules also will carry refrigerator freezers for transporting experiment samples and food to and from the station. On the return of STS-102 to Earth, it will bring back the first crew on the station: Bill Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev and Yuri Gidzenko. STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000, from Launch Pad 39A, Kennedy Space Center

STS100-342-035 (19 April-1 May 2001) --- Astronaut John L. Phillips, mission specialist, works with the IMAX camera on the International Space Station (ISS). Phillips and his STS-100 crew mates transferred supplies to the station and recorded video, motion picture and still photography of their activities, including interaction with the Expedition Two crewmembers.
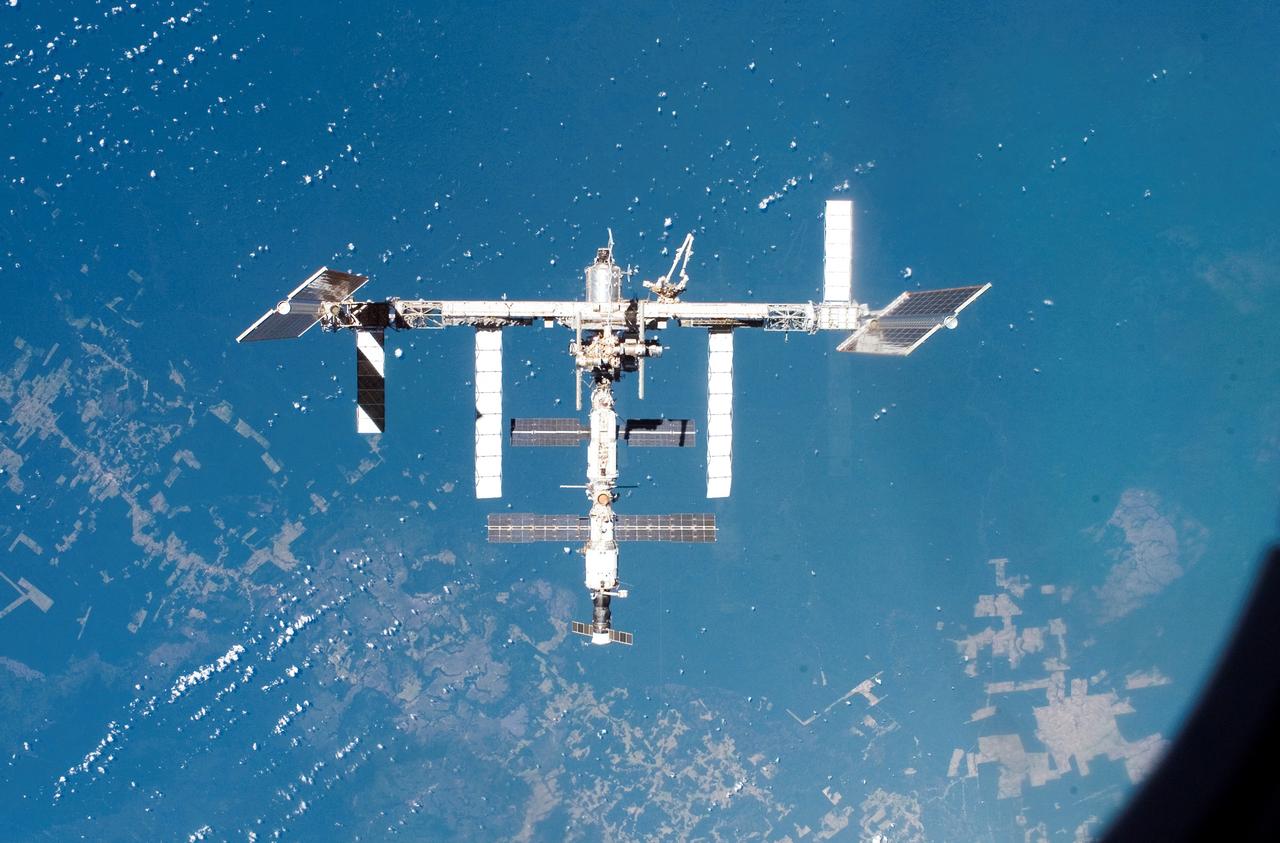

Eight days of construction resumed on the International Space Station (ISS), as STS-117 astronauts and mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the second and third starboard truss segments (S3 and S4). Back dropped by our colorful Earth, its newly expanded configuration is revealed as pilot Lee Archambault conducts a fly around upon departure from the station on June 19, 2007.
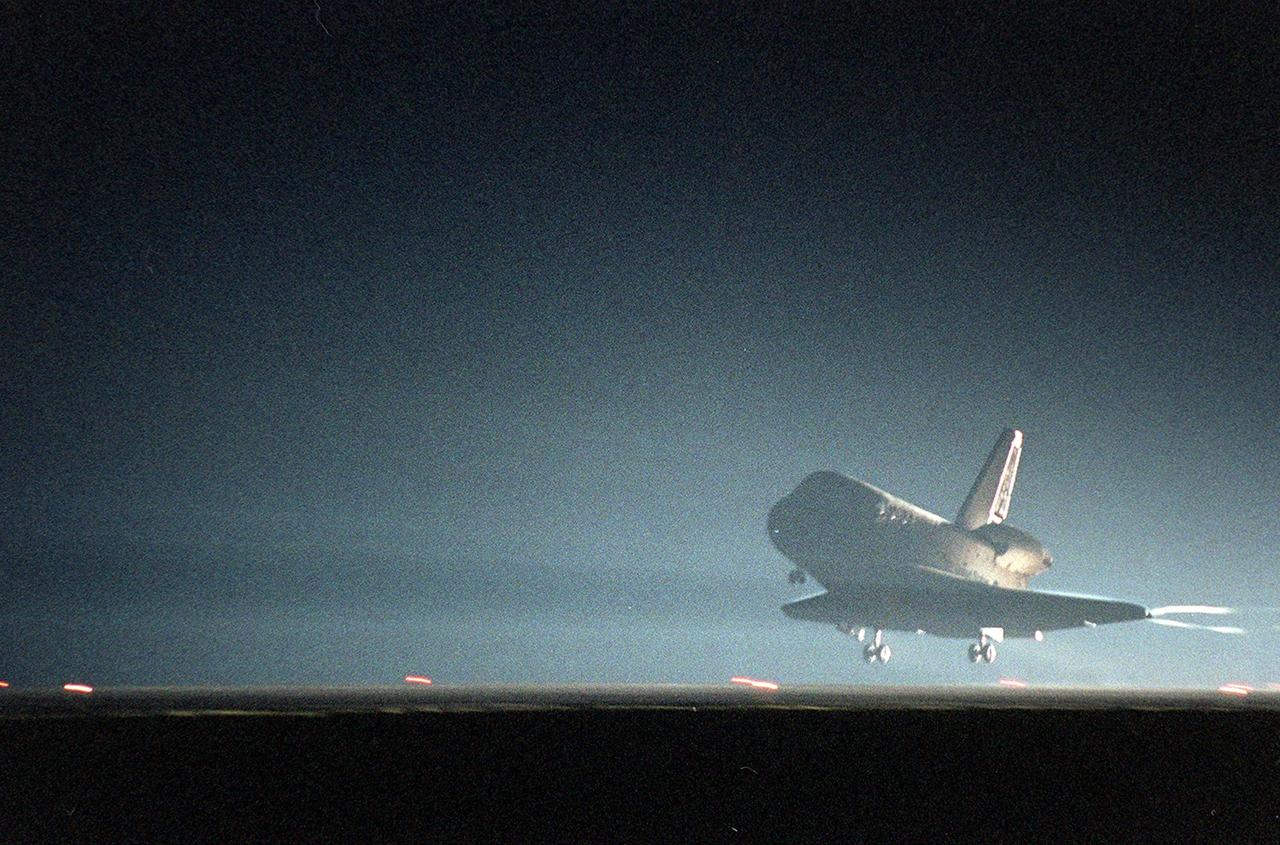

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery prepares to land at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility on runway 15. Main gear touchdown occurred about 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing, on orbit 201, concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
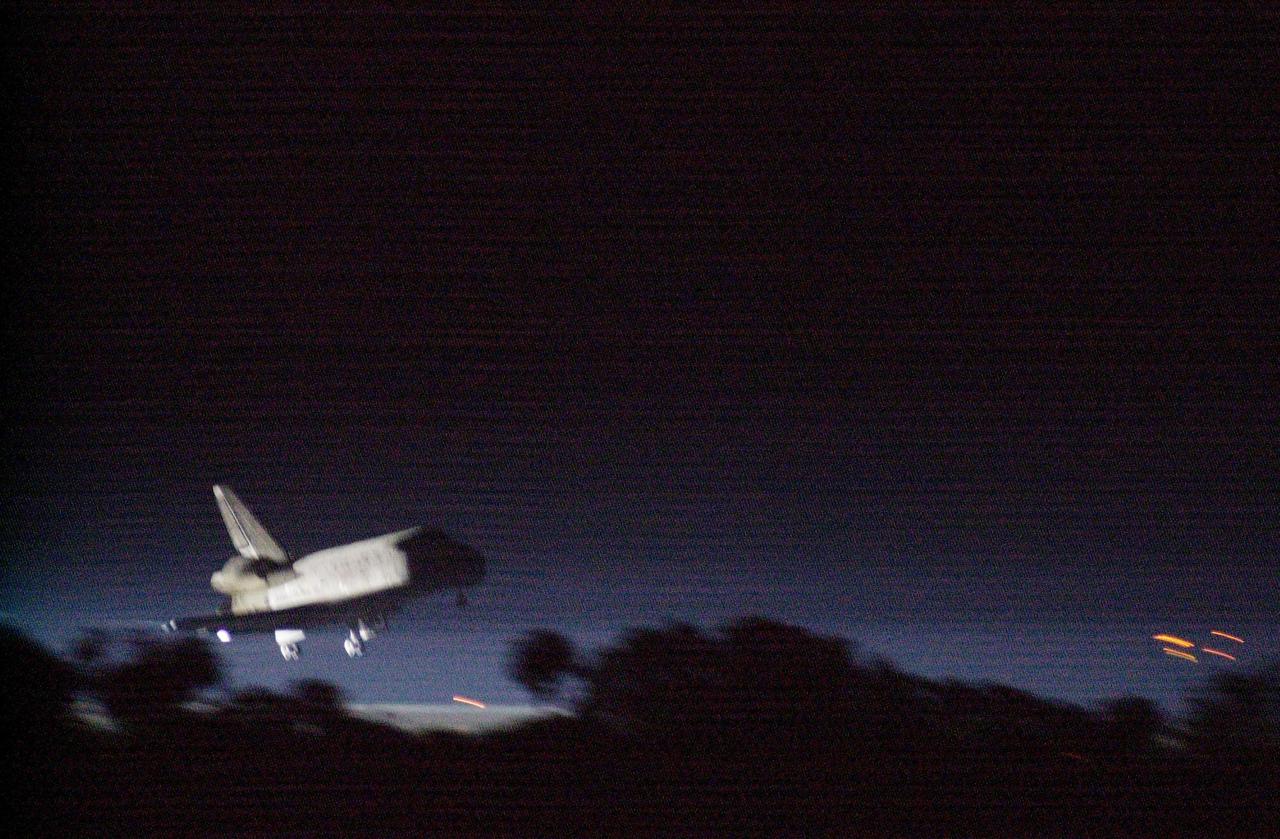

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Getting a break in the weather, Space Shuttle Discovery prepares to land at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility March 21, on runway 15. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
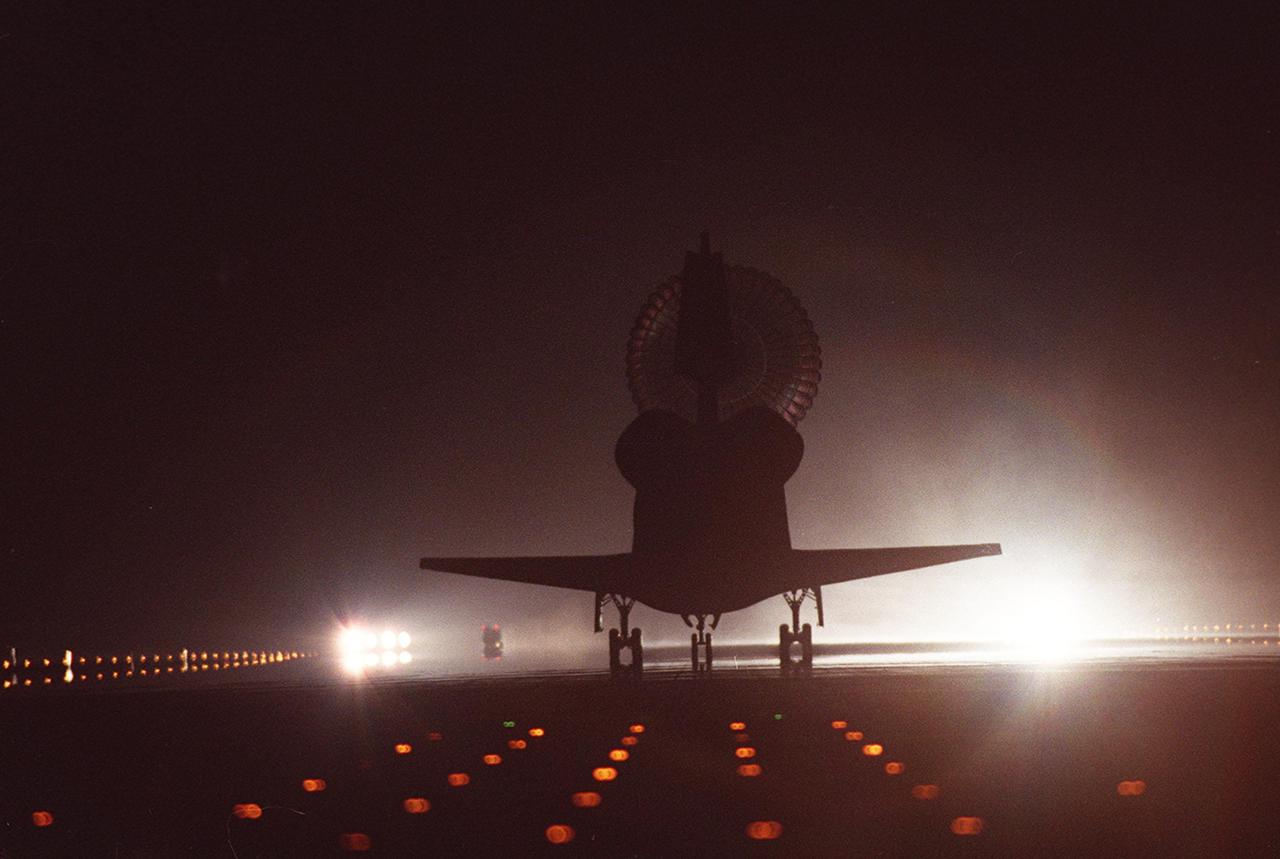

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery is silhouetted by the brilliant runway lights of runway 15 as it lands at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST. Nose wheel touchdown occurred at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module, Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
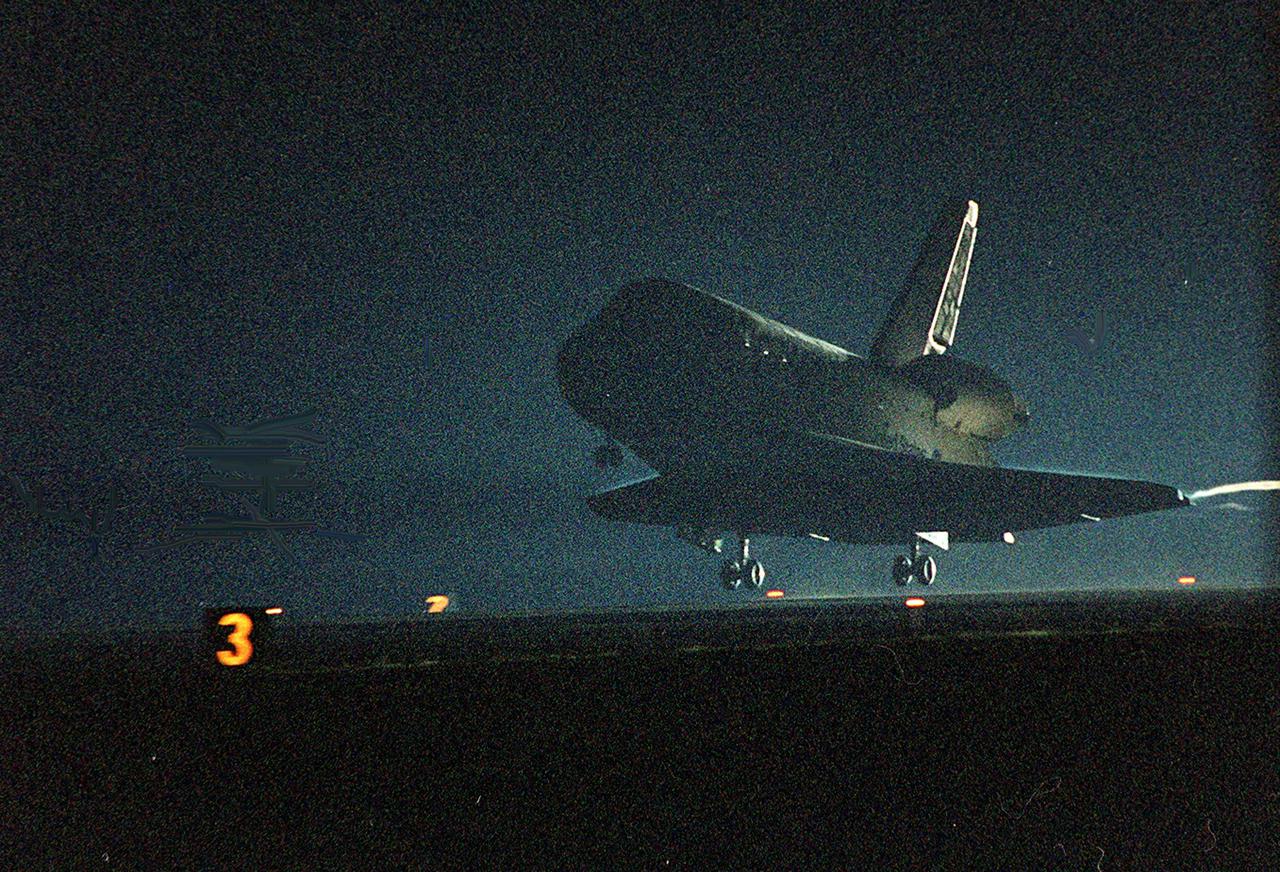

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery approaches touchdown on runway 15 at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred about 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing, on orbit 201, concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
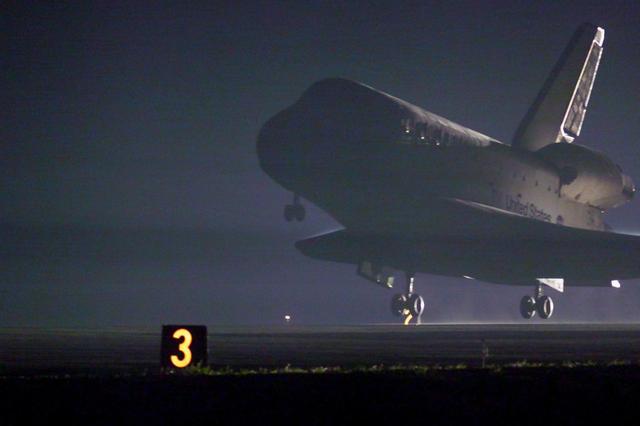

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery approaches touchdown on runway 15 at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC . Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
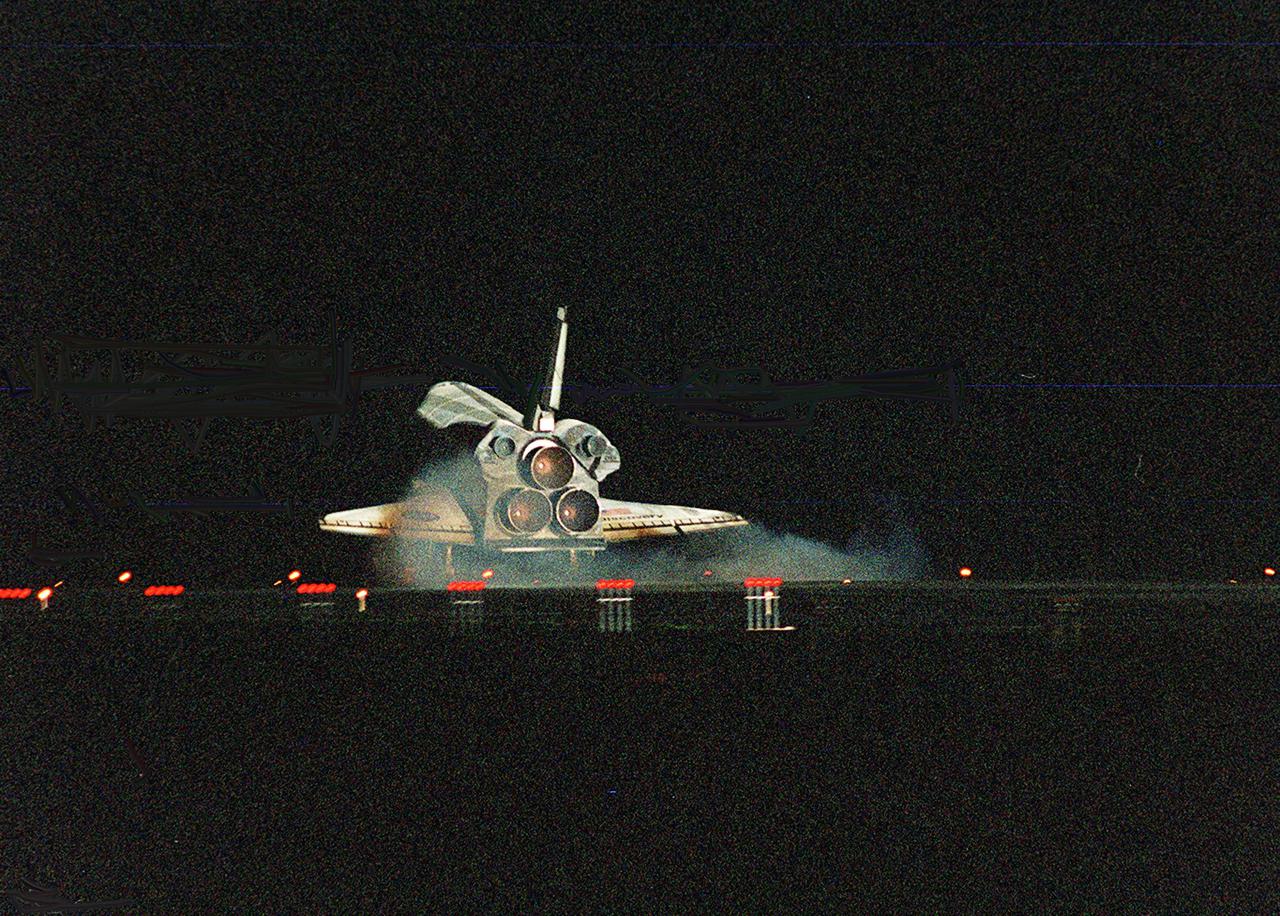

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery kicks up a swirl of dust as it touches down on runway 15 at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred about 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing, on orbit 201, concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
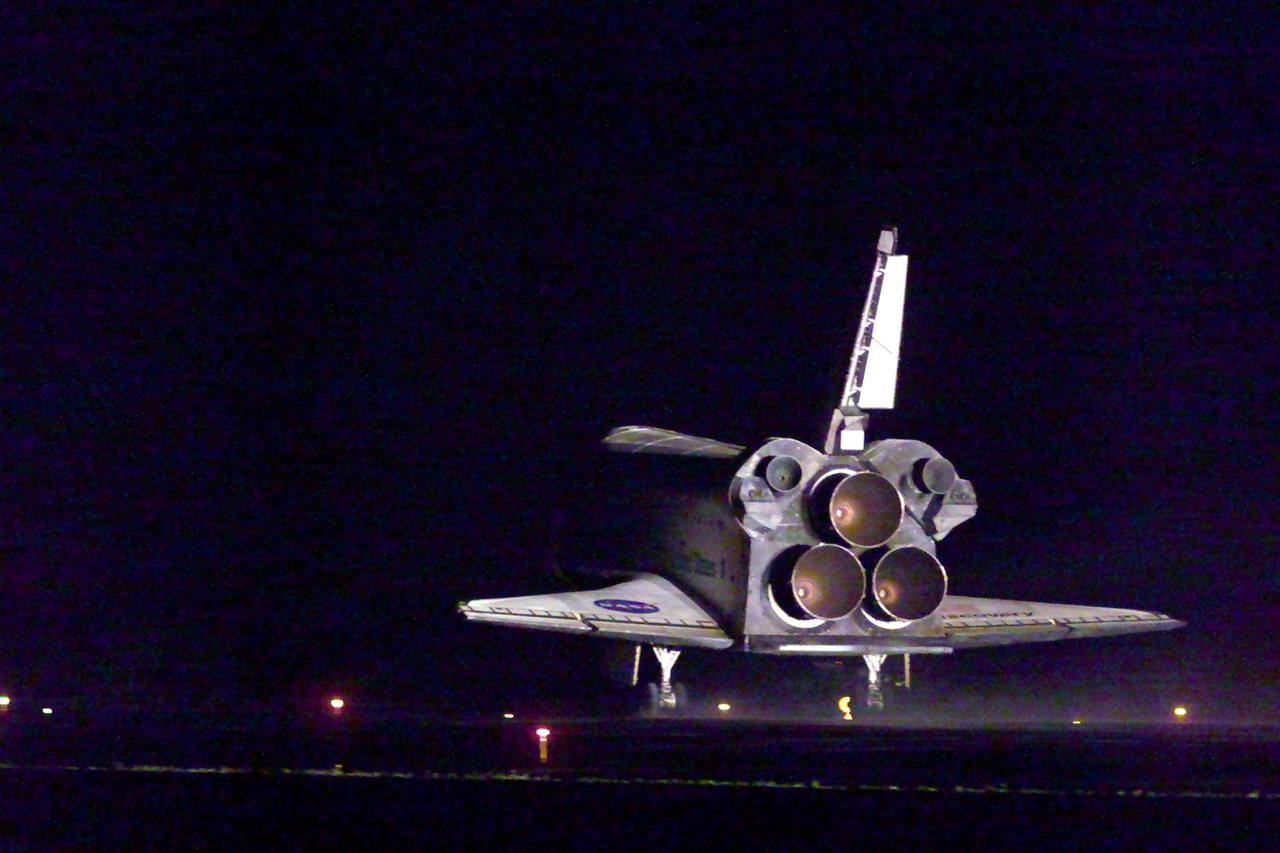

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Viewed from behind, Space Shuttle Discovery is seen landing on runway 15 of the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST. Nose wheel touchdown occurred at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
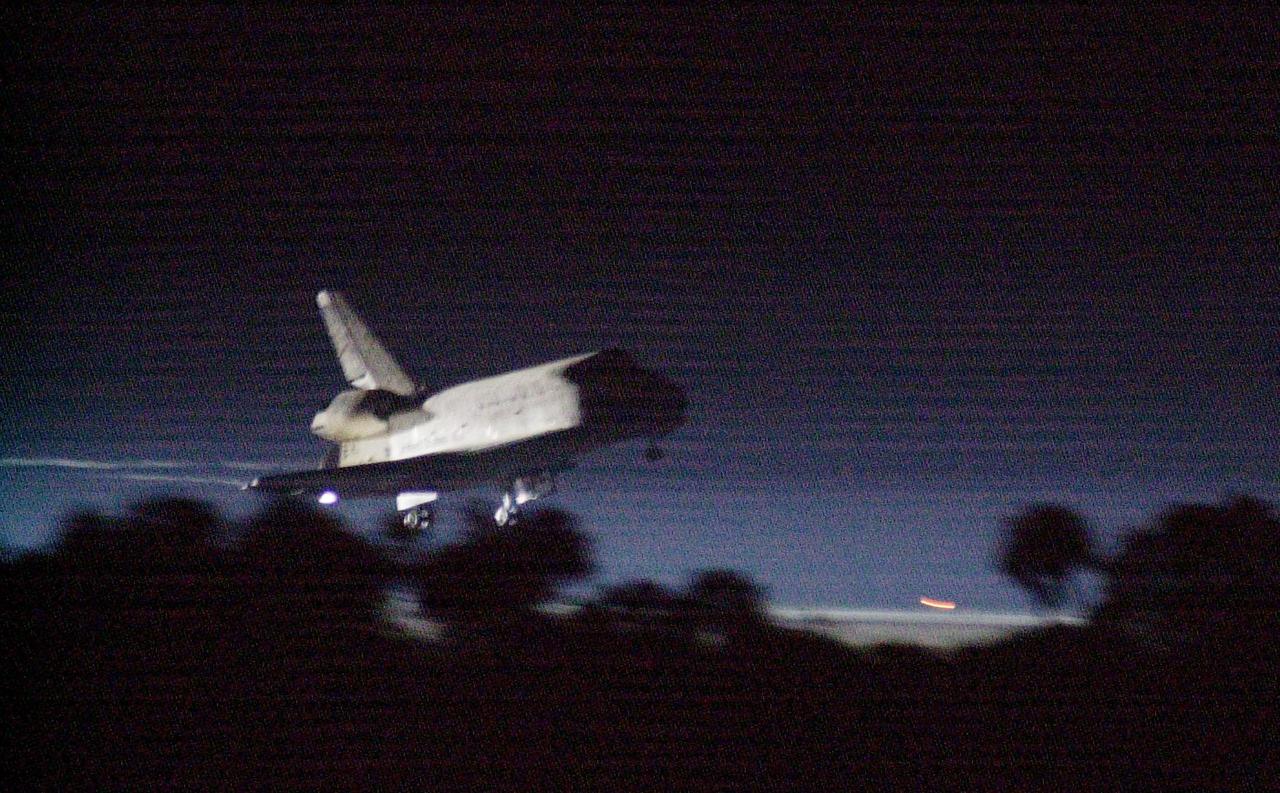

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Getting a break in the weather, Space Shuttle Discovery prepares to land at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility March 21, on runway 15. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo; and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
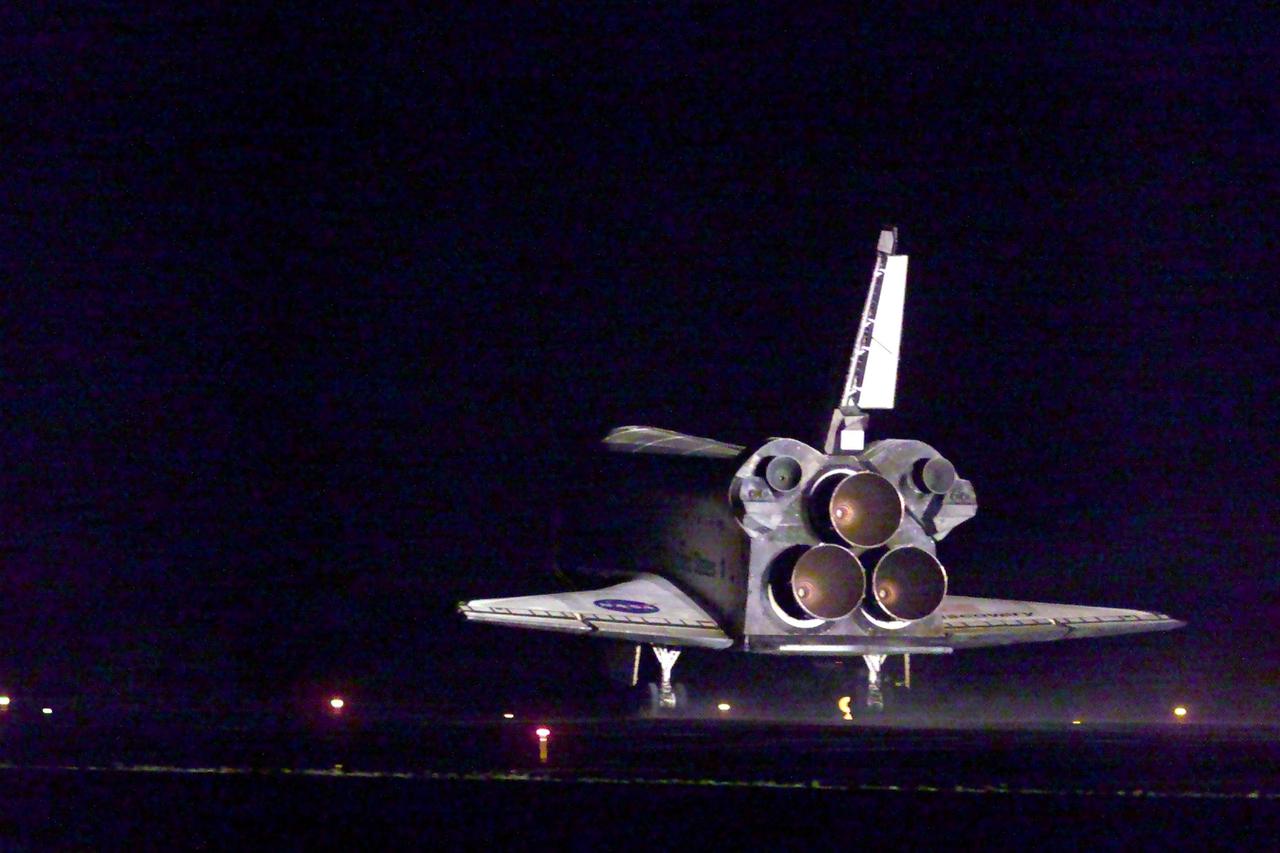

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Viewed from behind, Space Shuttle Discovery is seen landing on runway 15 of the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST. Nose wheel touchdown occurred at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
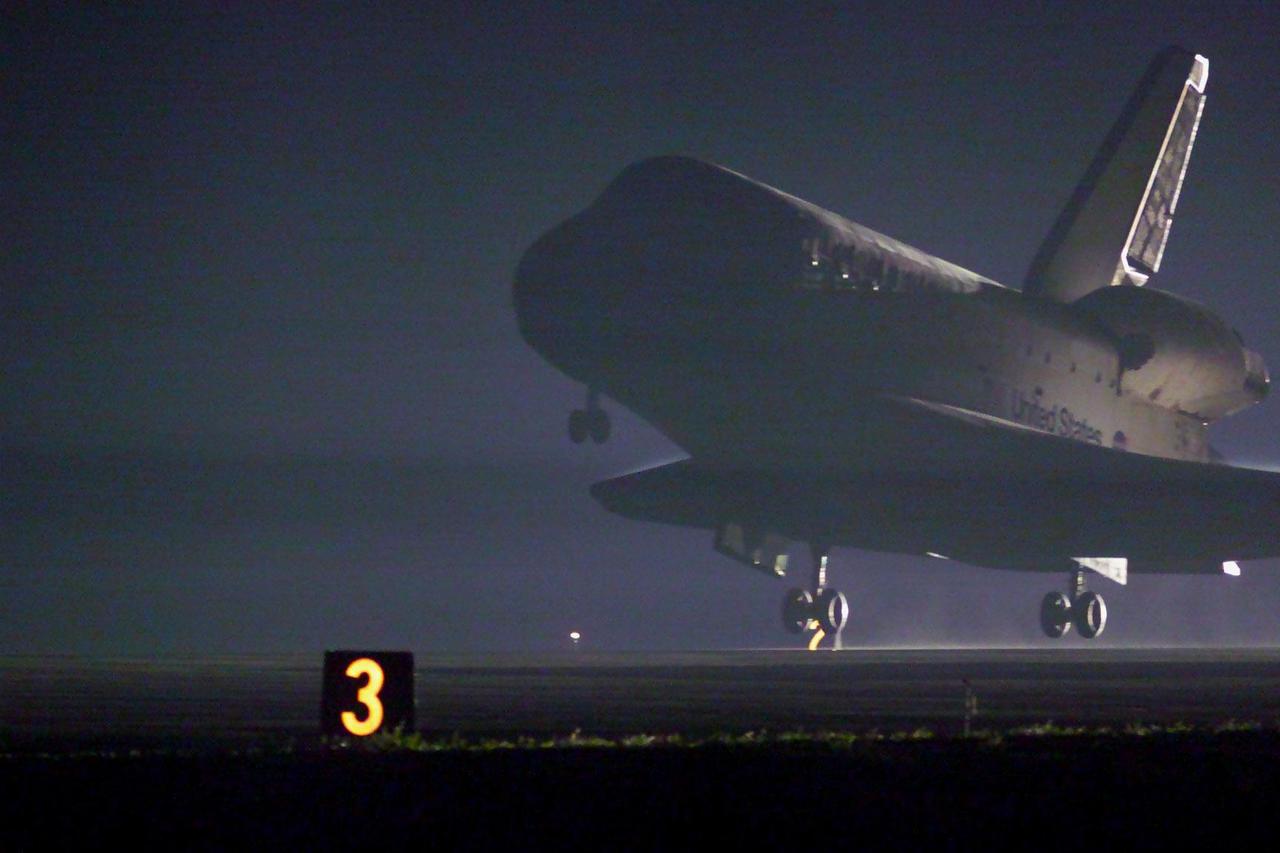

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery approaches touchdown on runway 15 at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC . Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
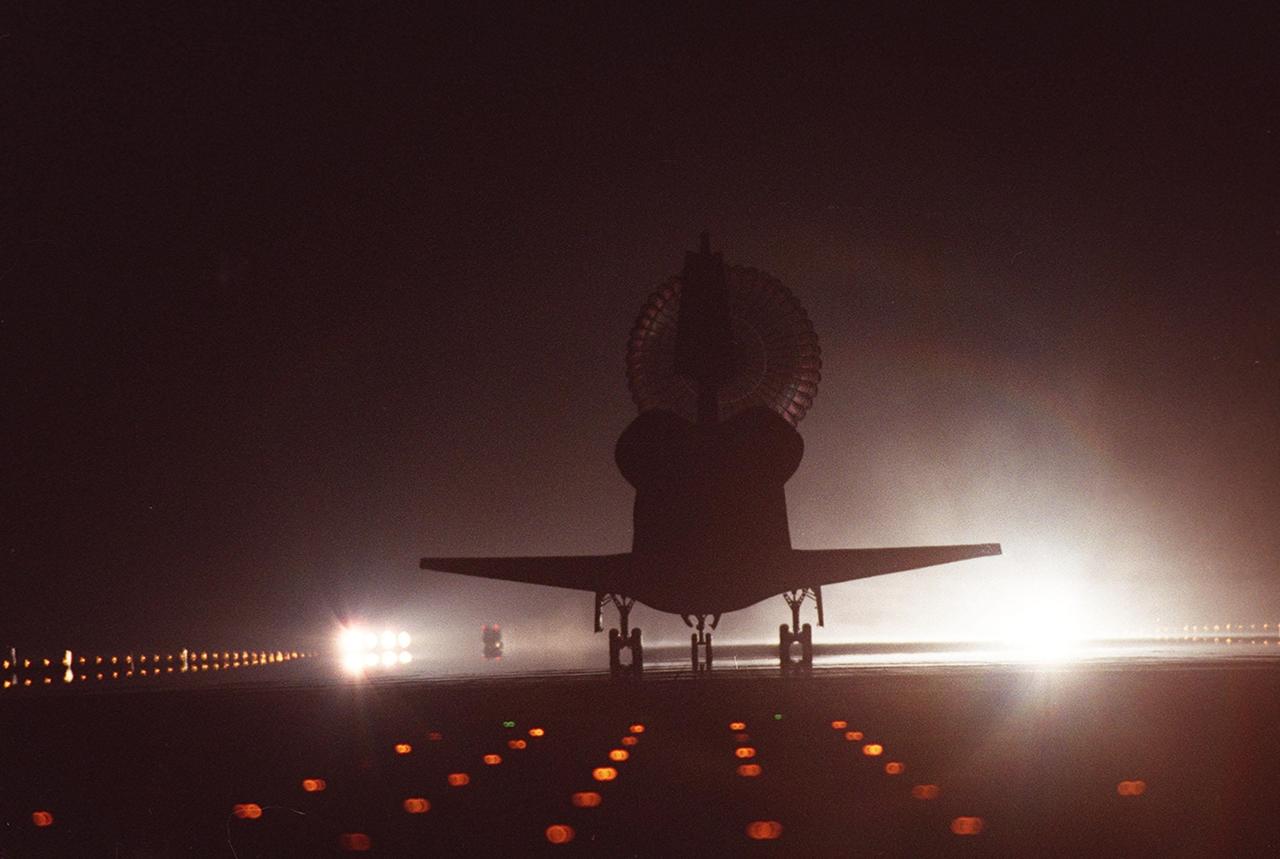

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery is silhouetted by the brilliant runway lights of runway 15 as it lands at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST. Nose wheel touchdown occurred at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module, Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
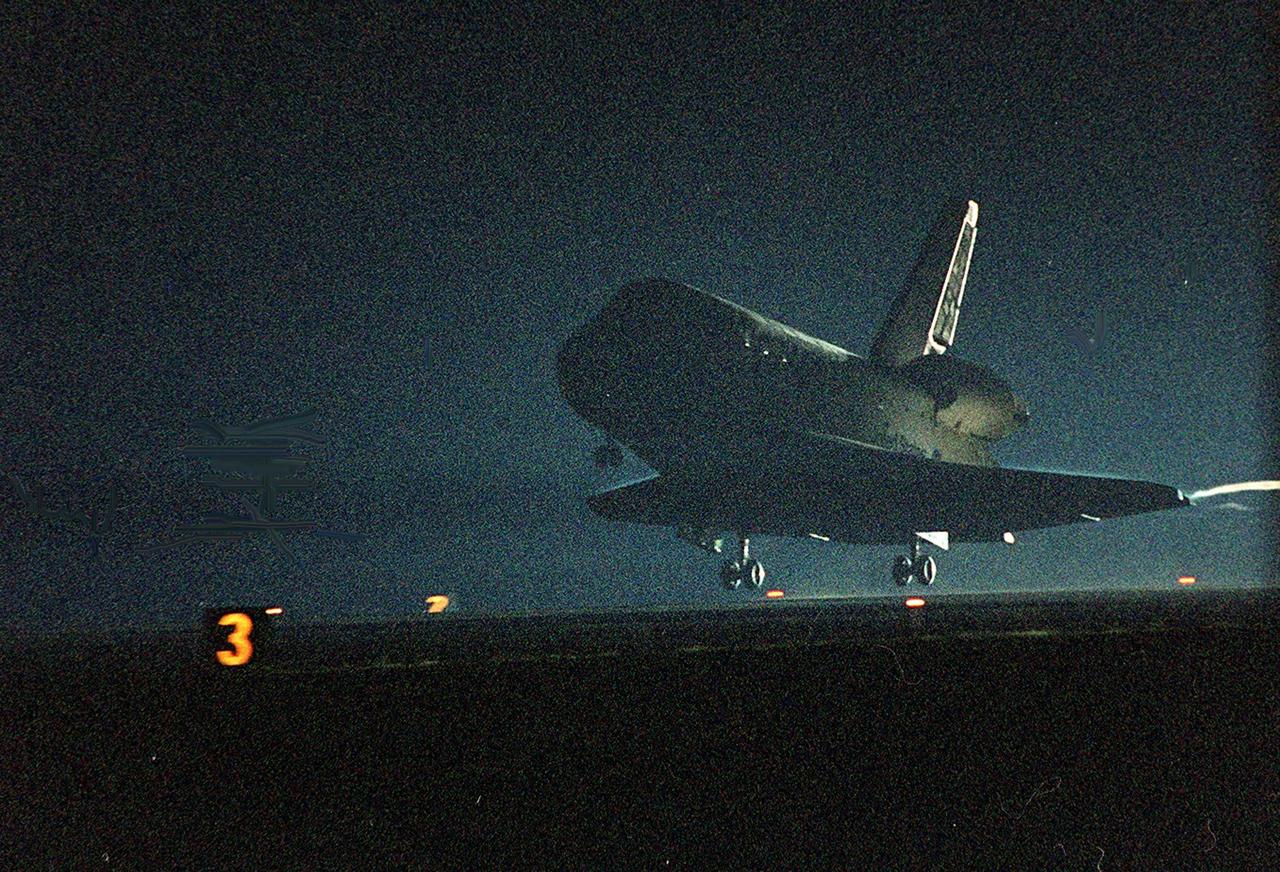

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery approaches touchdown on runway 15 at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred about 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing, on orbit 201, concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
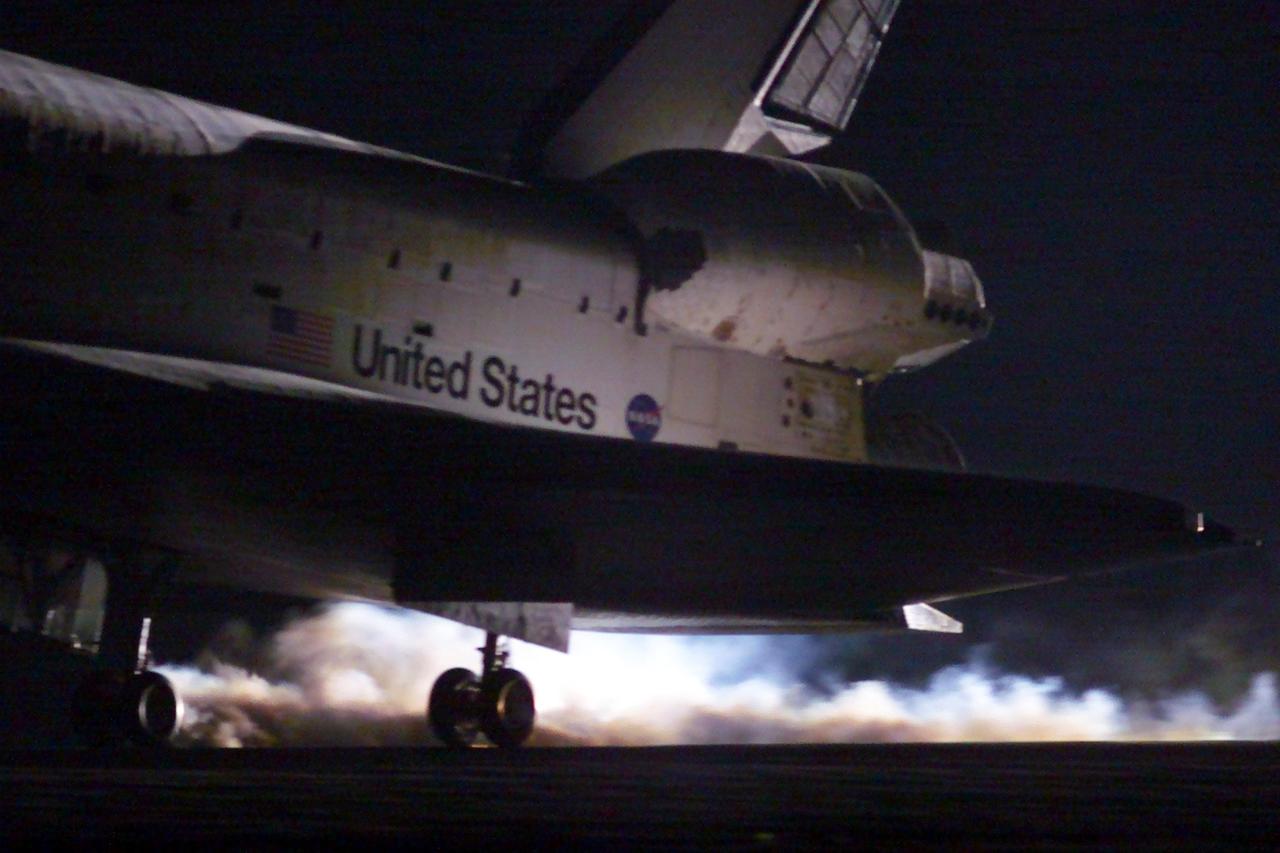

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In this view, the rear wheels on Space Shuttle Discovery are seen touching down on runway 15 of the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST. Nose wheel touchdown occurred at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC

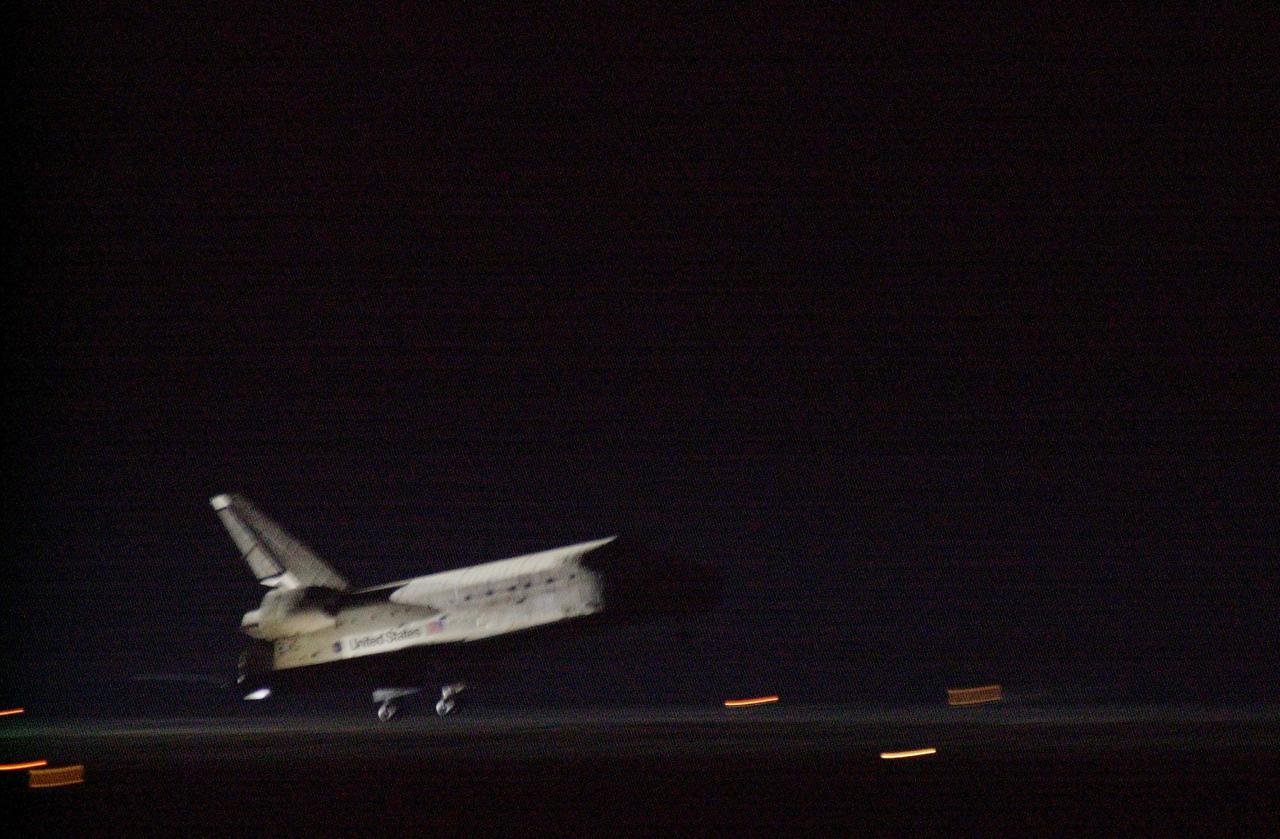
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Getting a break in the weather, Space Shuttle Discovery prepares to land at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility March 21, on runway 15. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC

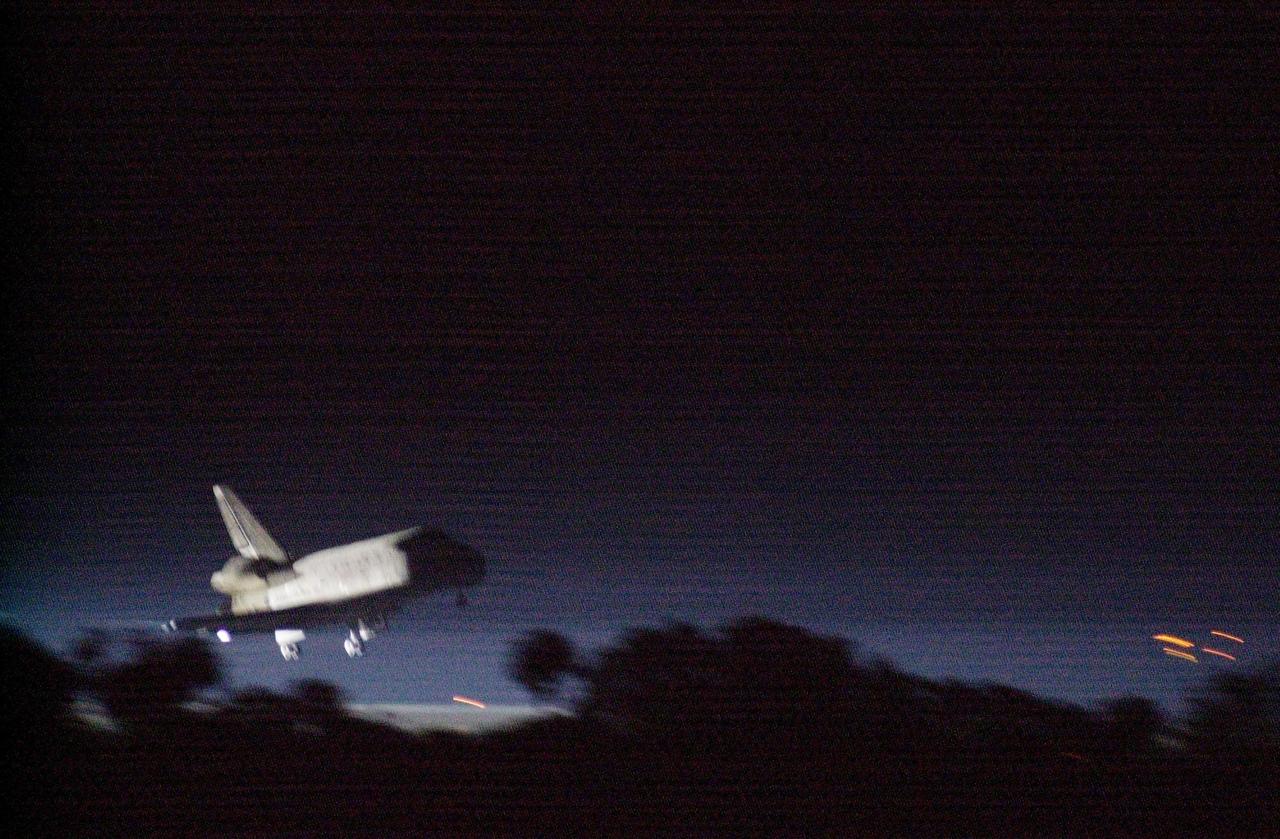
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery approaches runway 15 at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility March 21. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC . Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
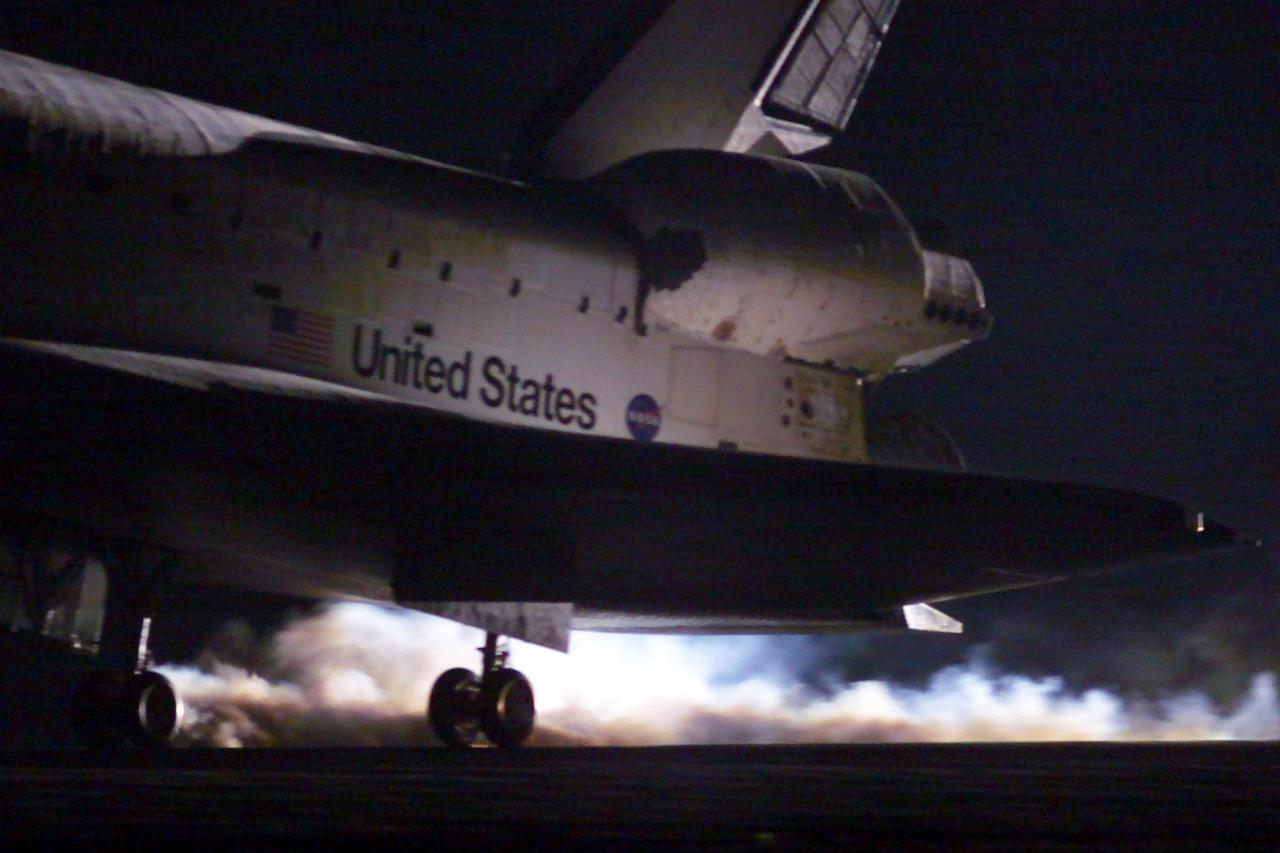

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In this view, the rear wheels on Space Shuttle Discovery are seen touching down on runway 15 of the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST. Nose wheel touchdown occurred at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
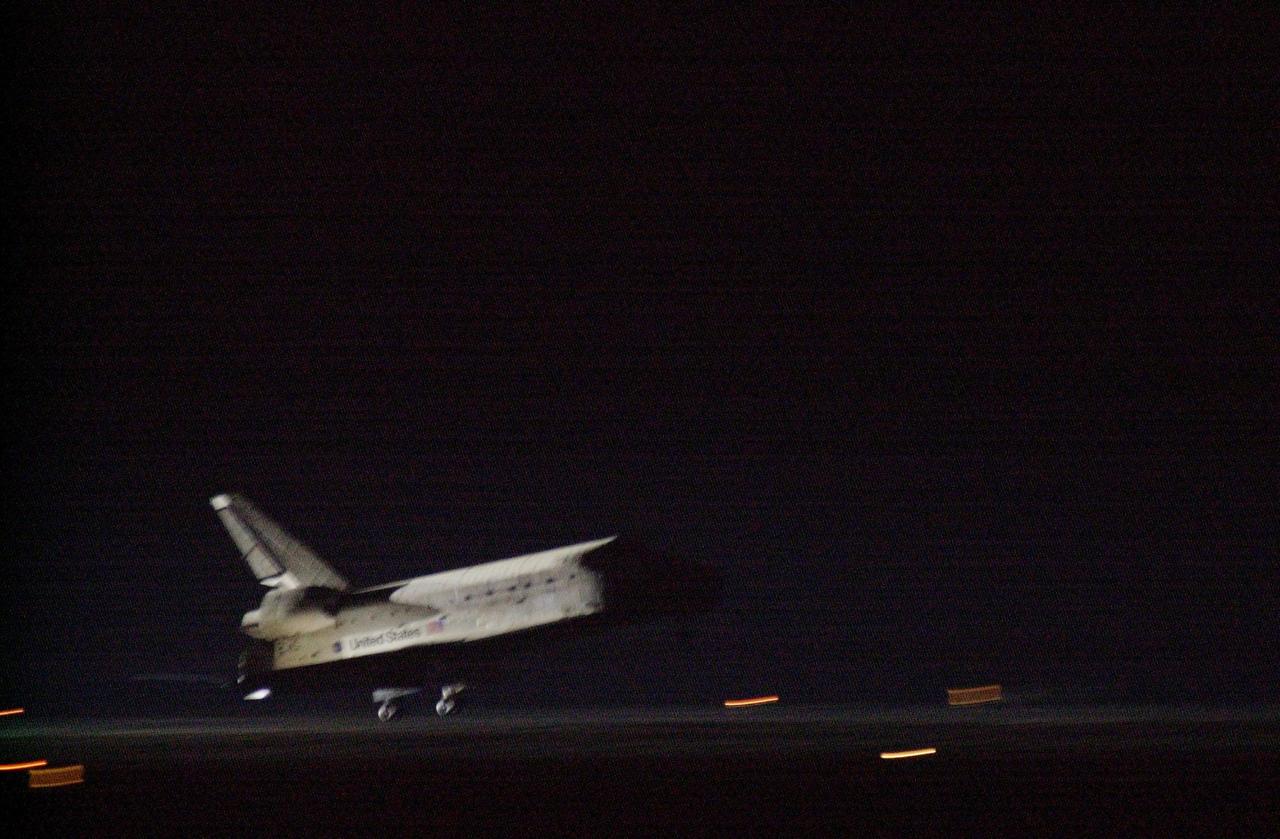

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery approaches runway 15 at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility March 21. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC . Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
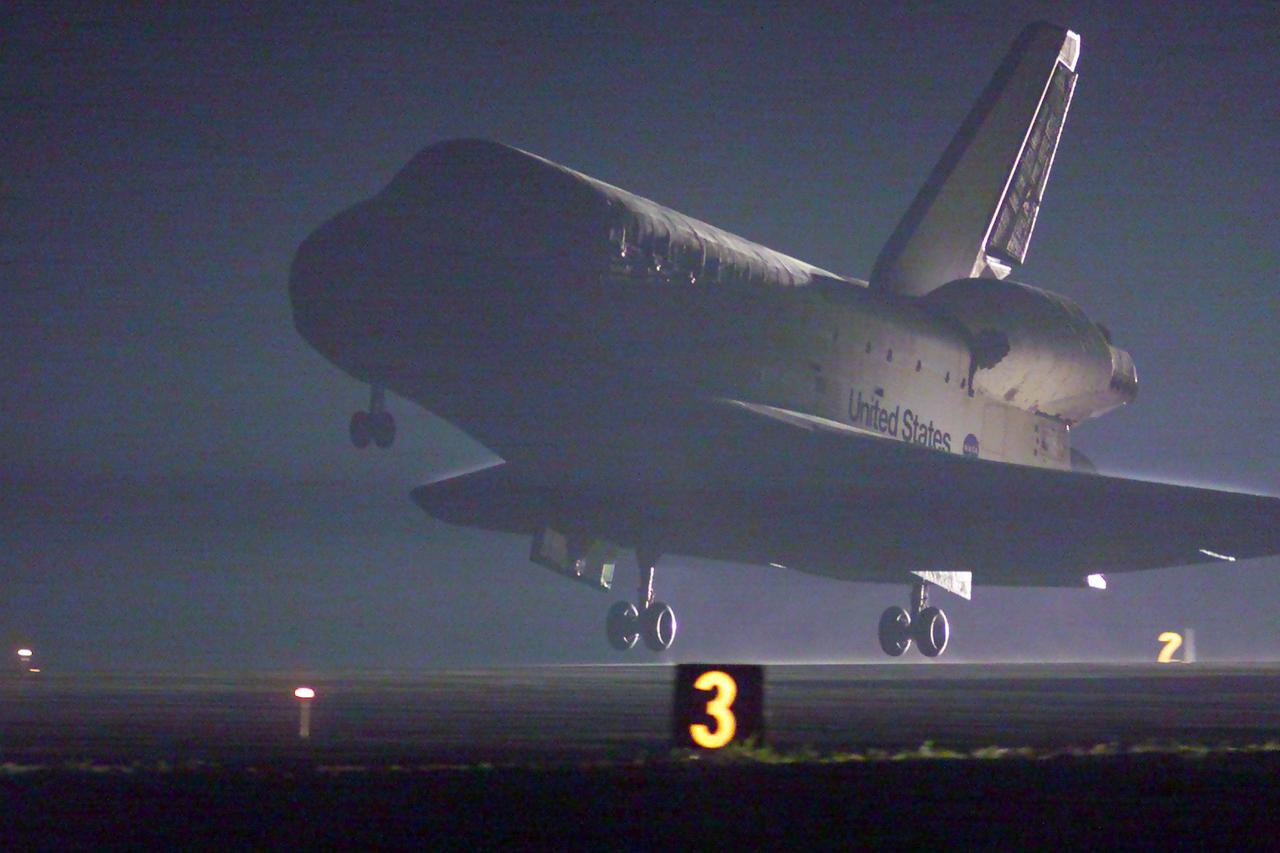

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery prepares to land at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility on runway 15. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
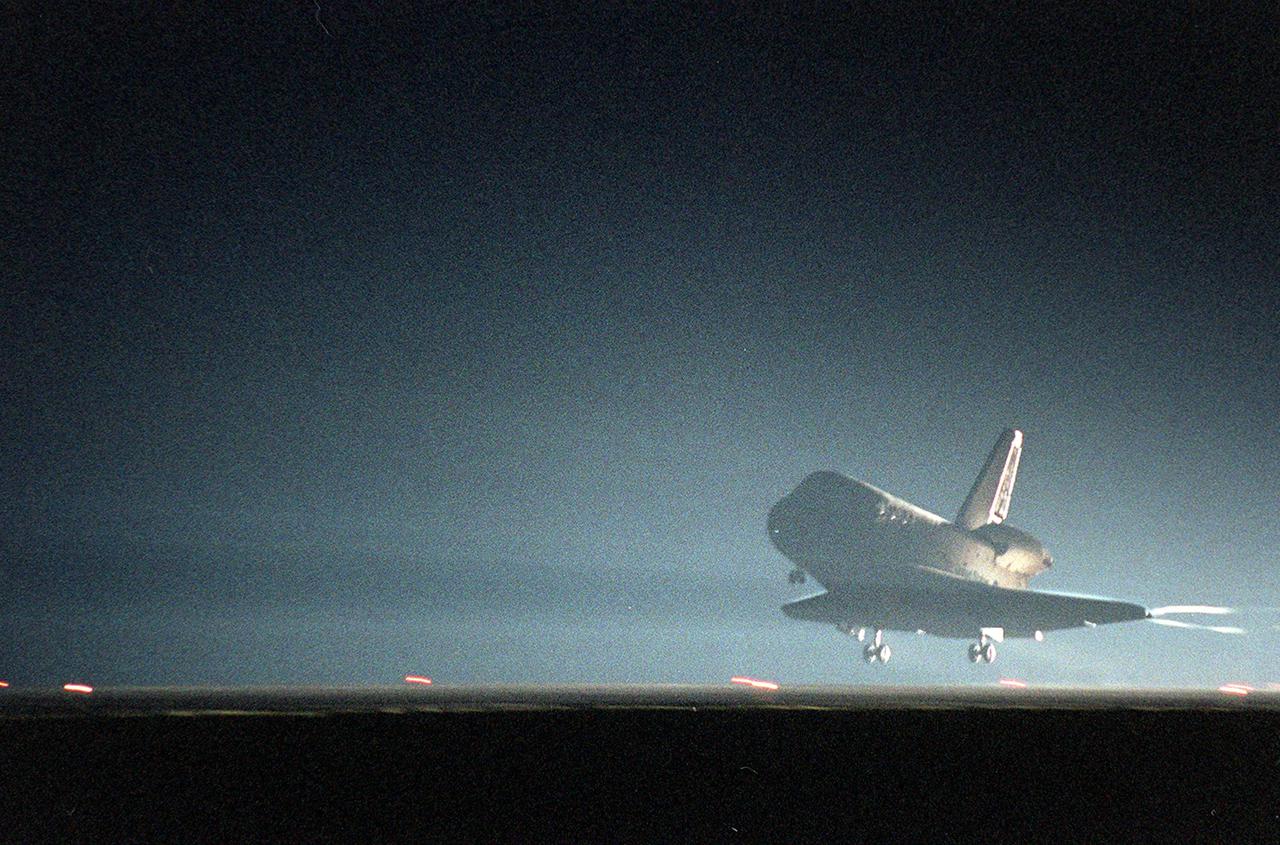

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery prepares to land at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility on runway 15. Main gear touchdown occurred about 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing, on orbit 201, concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
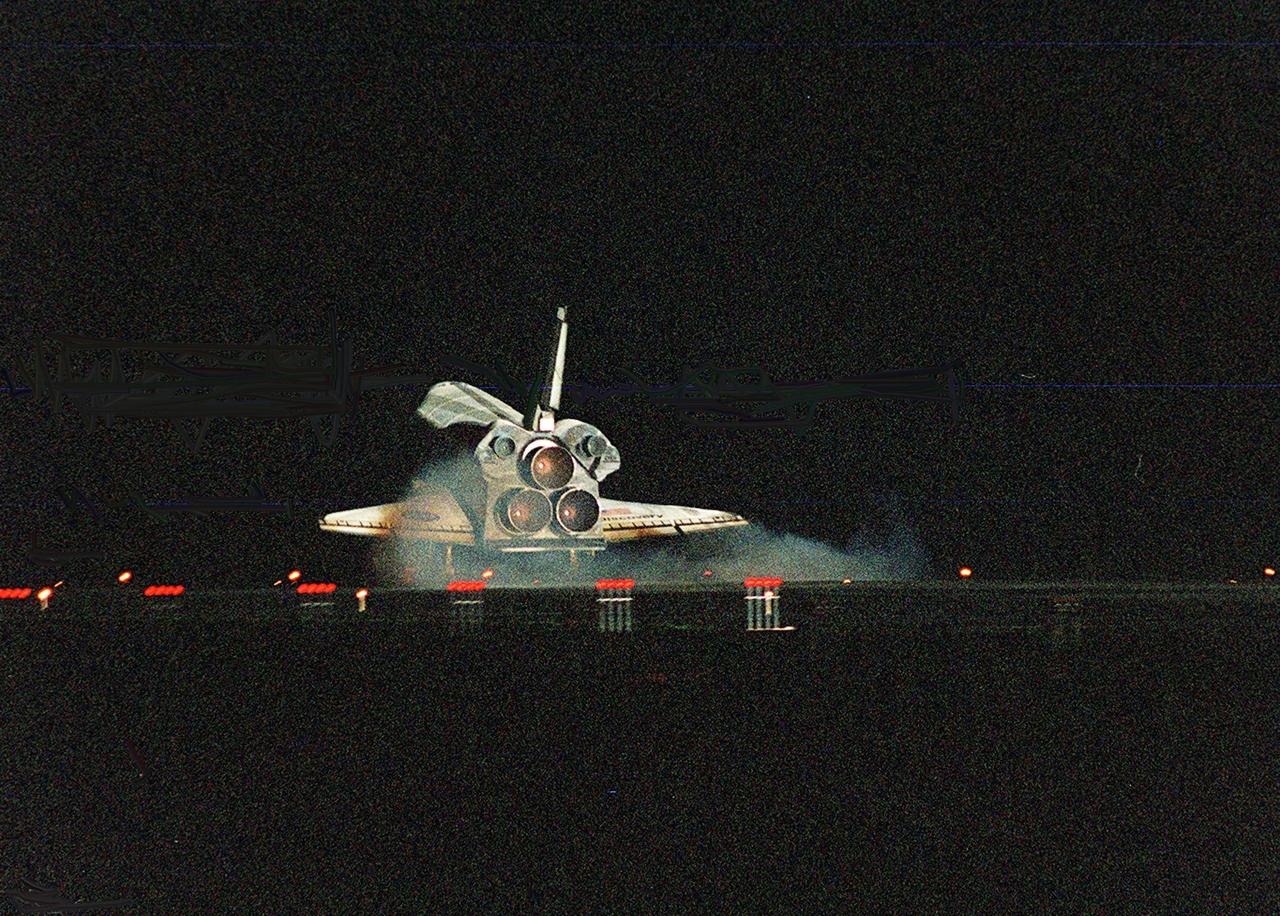

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery kicks up a swirl of dust as it touches down on runway 15 at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred about 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing, on orbit 201, concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
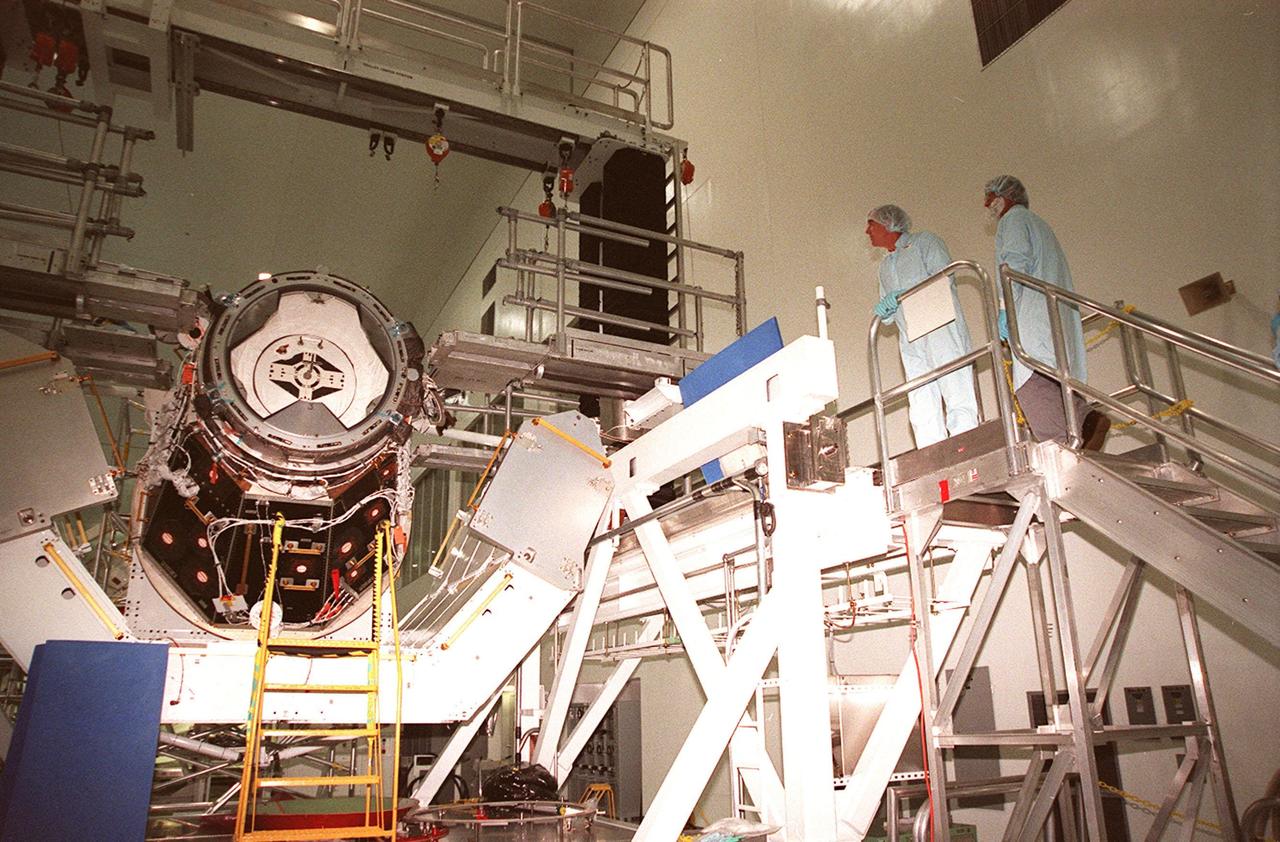

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- From a work stand in the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-102 crew members James S. Voss (left) and Yuriy Vladimirovich Usachev (right), of Russia, look over the Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3). The PMA-3 is a component of the International Space Station (ISS). Voss and Usachev are two crew members who will be staying on the ISS as the Expedition II crew. The third is Susan J. Helms. Along with the crew, Mission STS-102 also will be carrying the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) to the ISS. The Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module, which will have been carried to the ISS on a preceding Shuttle flight. In order to function as an attached station module as well as a cargo transport, logistics modules (there are three) also include components that provide some life support, fire detection and suppression, electrical distribution and computer functions. Eventually, the modules also will carry refrigerator freezers for transporting experiment samples and food to and from the station. On the return of STS-102 to Earth, it will bring back the first crew on the station: Bill Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev and Yuri Gidzenko. STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000, from Launch Pad 39A, Kennedy Space Center
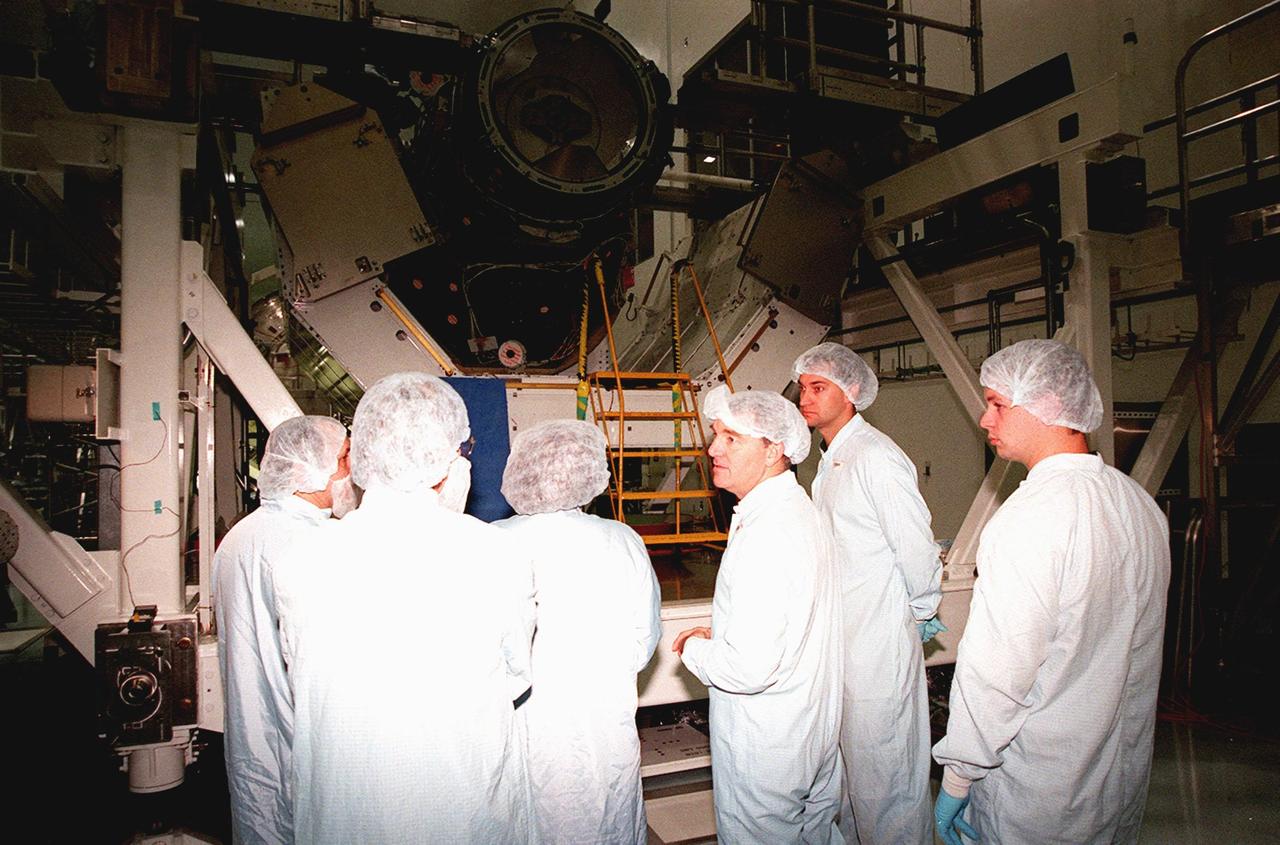

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-102's Expedition II discuss the Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3) (top of photo) with workers from Johnson Space Center. From left are Yuriy Vladimirovich Usachev, Dave Moore (JSC), Susan J. Helms, James S. Voss, Arne Aamodt and Matt Myers (both of JSC). The PMA-3 is a component of the International Space Station (ISS). Voss, Helms and Usachev will be staying on the ISS, replacing the Expedition I crew, Bill Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev and Yuri Gidzenko. Along with the crew, Mission STS-102 also will be carrying the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) to the ISS. The Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module, which will have been carried to the ISS on a preceding Shuttle flight. In order to function as an attached station module as well as a cargo transport, logistics modules (there are three) also include components that provide some life support, fire detection and suppression, electrical distribution and computer functions. Eventually, the modules also will carry refrigerator freezers for transporting experiment samples and food to and from the station. STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000, from Launch Pad 39A, Kennedy Space Center
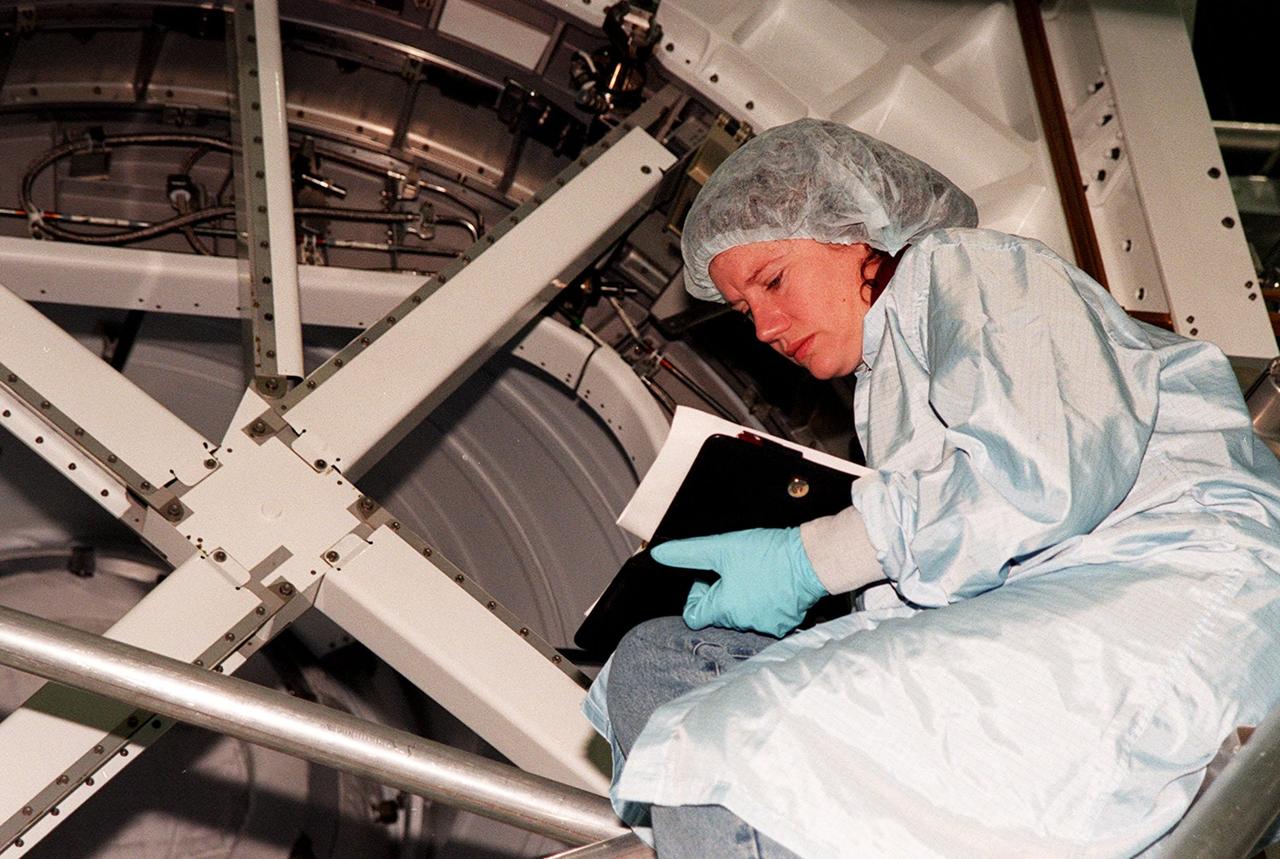

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-102 crew member Susan J. Helms looks over a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3) in the Space Station Processing Facility. The PMA-3 is a component of the International Space Station (ISS). Helms is one of three who will be staying on the ISS as the Expedition II crew. The others are Yuriy Vladimirovich Usachev and James S. Voss. Along with the crew, Mission STS-102 also will be carrying the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) to the ISS. The Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module, which will have been carried to the ISS on a preceding Shuttle flight. In order to function as an attached station module as well as a cargo transport, logistics modules (there are three) also include components that provide some life support, fire detection and suppression, electrical distribution and computer functions. Eventually, the modules also will carry refrigerator freezers for transporting experiment samples and food to and from the station. On the return of STS-102 to Earth, it will bring back the first crew on the station: Bill Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev and Yuri Gidzenko. STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000, from Launch Pad 39A, Kennedy Space Center
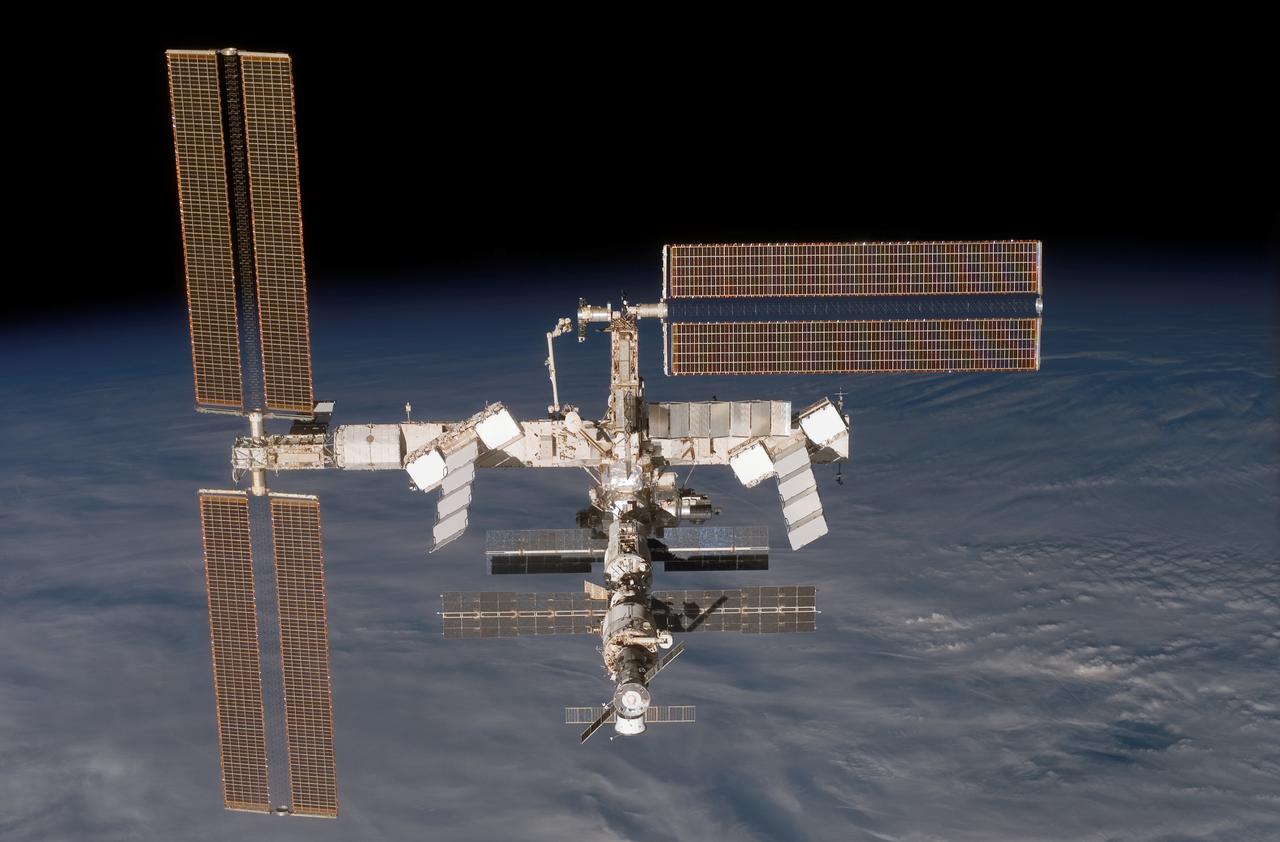

Photographed from the Space Shuttle Discovery upon its separation from the orbital outpost, the International Space Station (ISS) is shown sporting its new additions. A fly-around gave the crew a look at their handiwork, a new P5 spacer truss segment and a fully retracted P6 solar array wing. Earlier, the STS-116 and Expedition 14 crews concluded eight days of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station where they accomplished the installation of the newest piece of the station and completely rewired the power grid over the course of four space walks. The station is currently the size of a typical three-bedroom house, with a surface area large enough to cover four basketball courts. The image reflects the latest configuration of the ISS as of December 19, 2006.
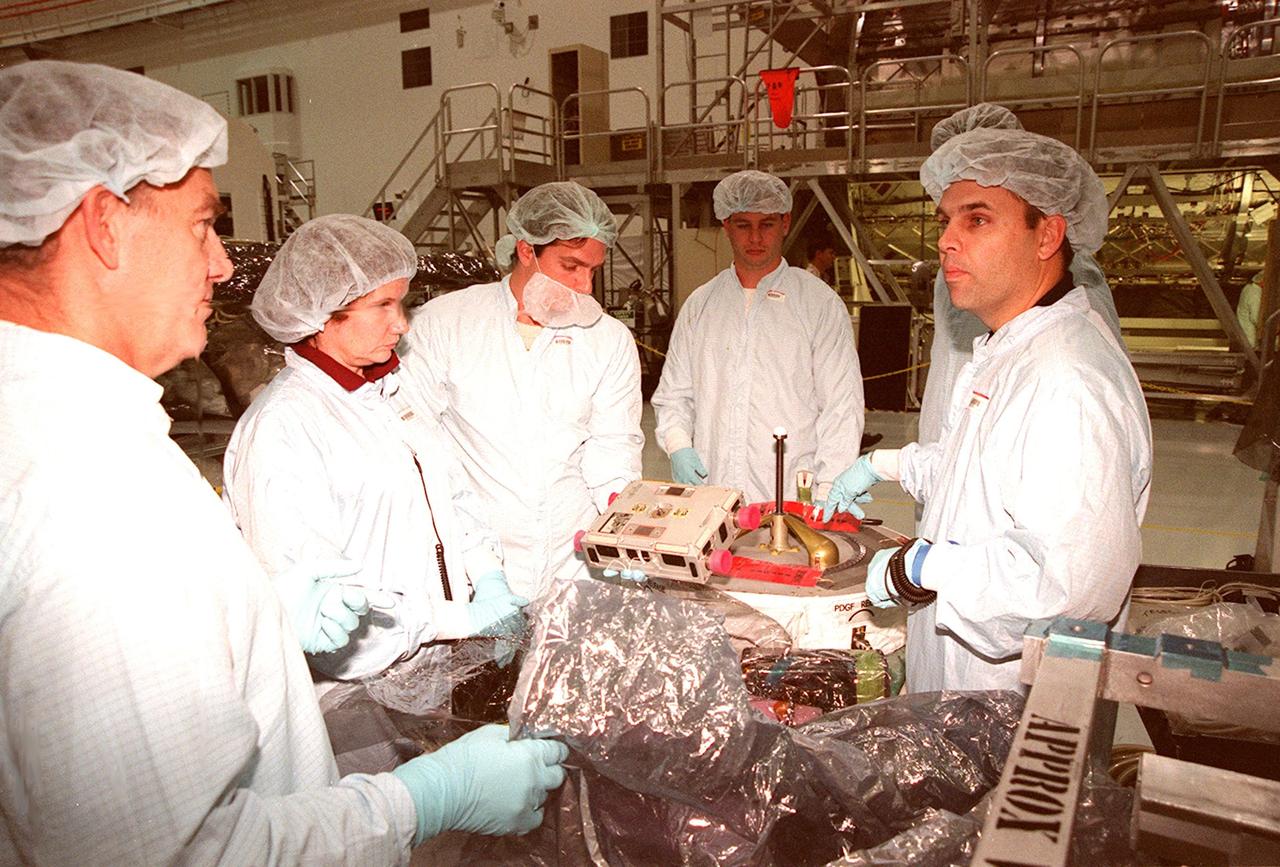

STS-102 crew members at left are briefed by workers (right) in the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) on equipment for their mission. From left are Mission Specialists James Voss, Susan Helms and Yuri Usachev, with the Russian Space Agency (RSA). STS-102 is a resupply mission to the International Space Station, transporting the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) with equipment to assist in outfitting the U.S. Lab, which will already be in place. The mission is also transporting Helms, Voss and Usachev as the second resident crew (designated Expedition crew 2) to the station. In exchange, the mission will return to Earth the first expedition crew on ISS: William Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev (RSA) and Yuri Gidzenko (RSA). STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000
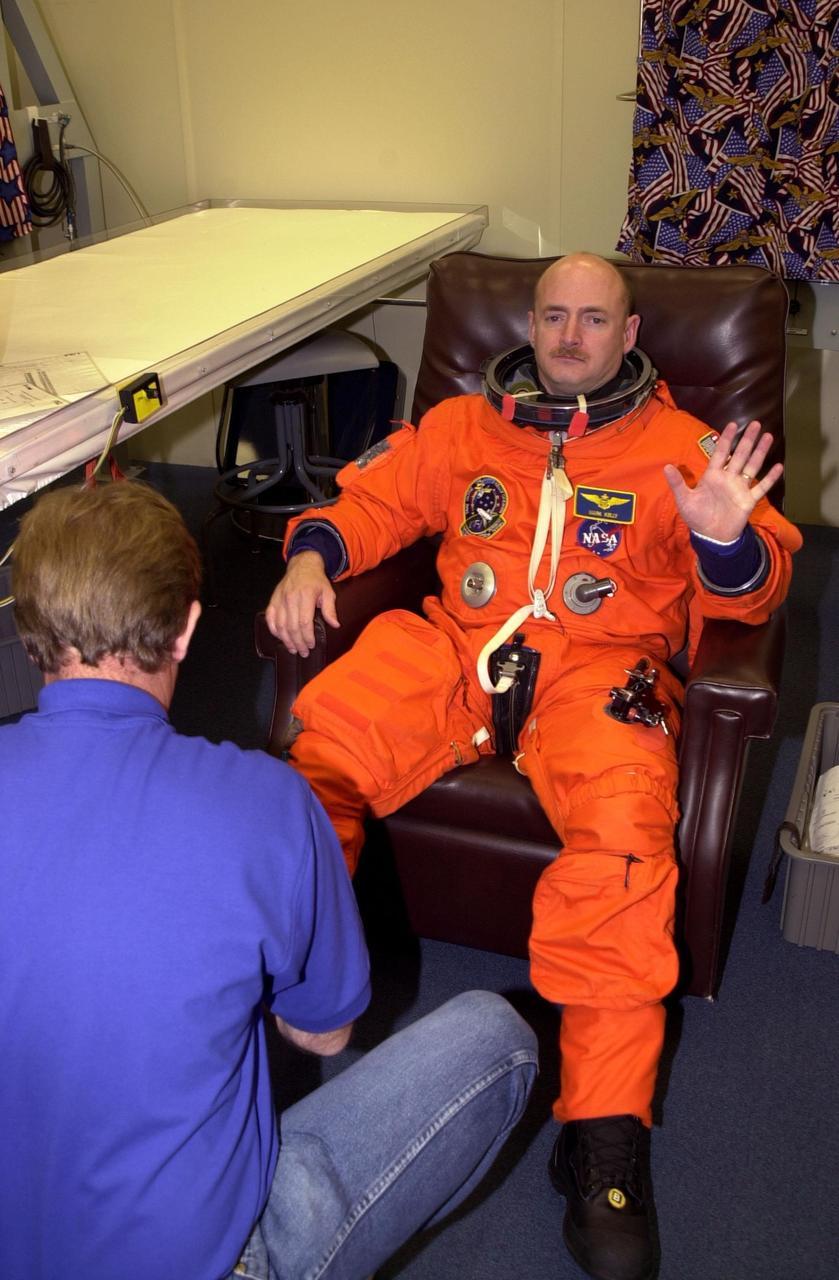

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STs-108 Pilot Mark E. Kelly is helped with his launch and entry suit in preparation for the second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
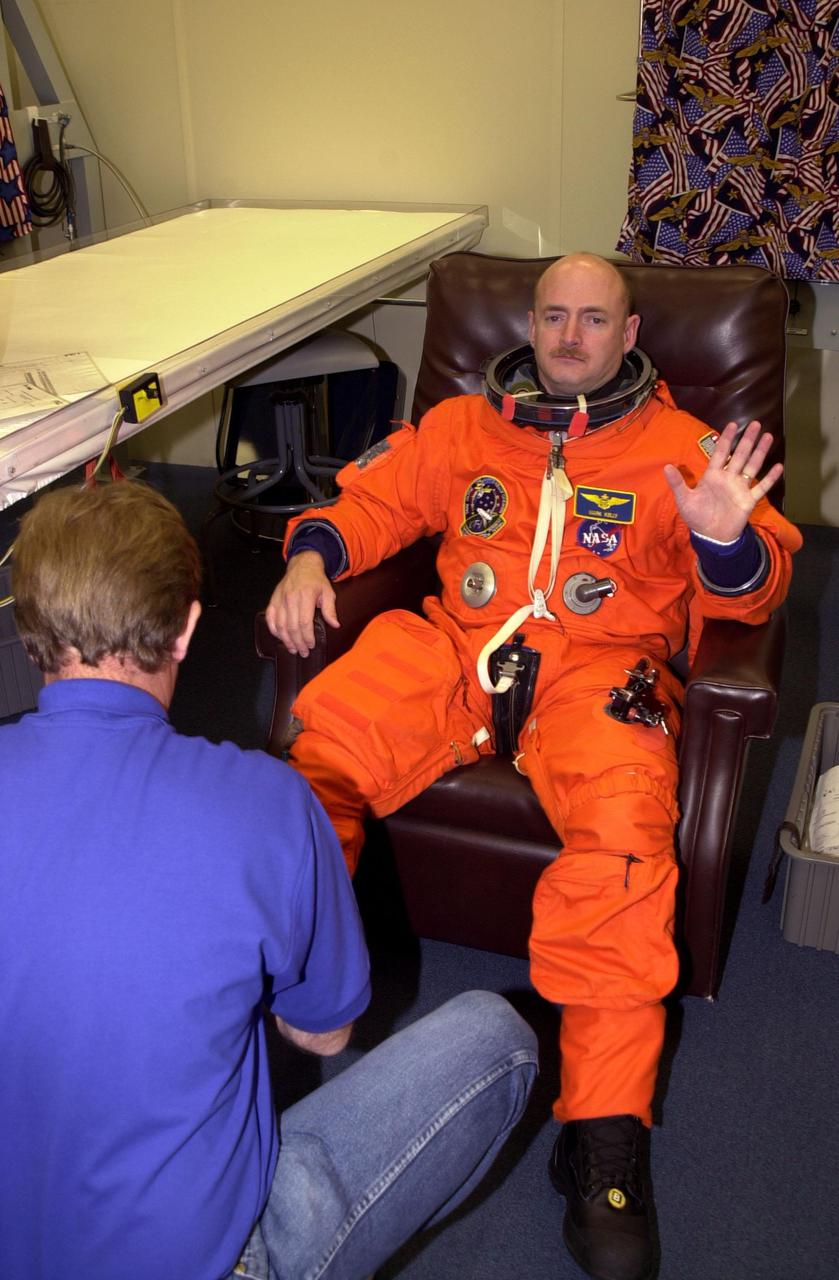

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STs-108 Pilot Mark E. Kelly is helped with his launch and entry suit in preparation for the second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-108 Commander Dominic L. Gorie is ready in his launch and entry suit for the second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
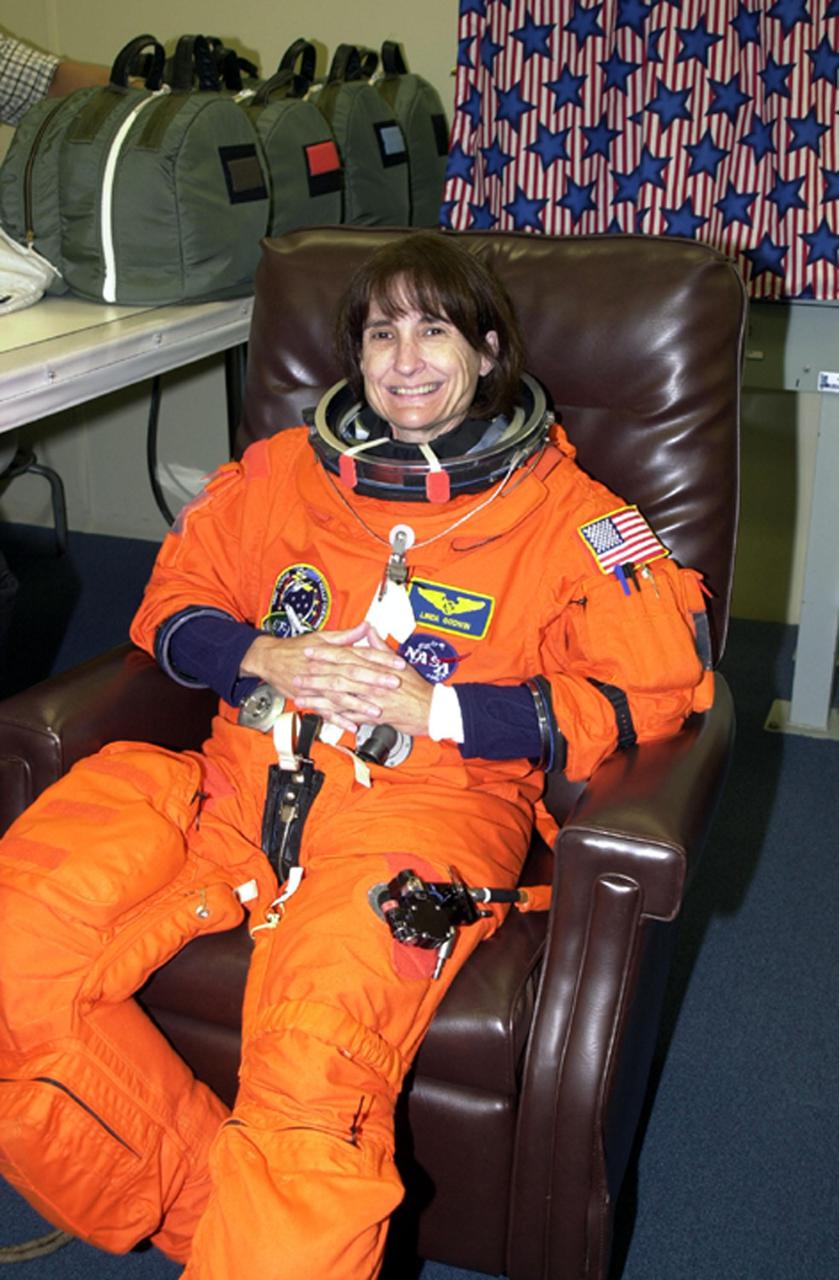

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-108 Mission Specialist Linda A. Godwin is relaxed and happy to be preparing for the second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
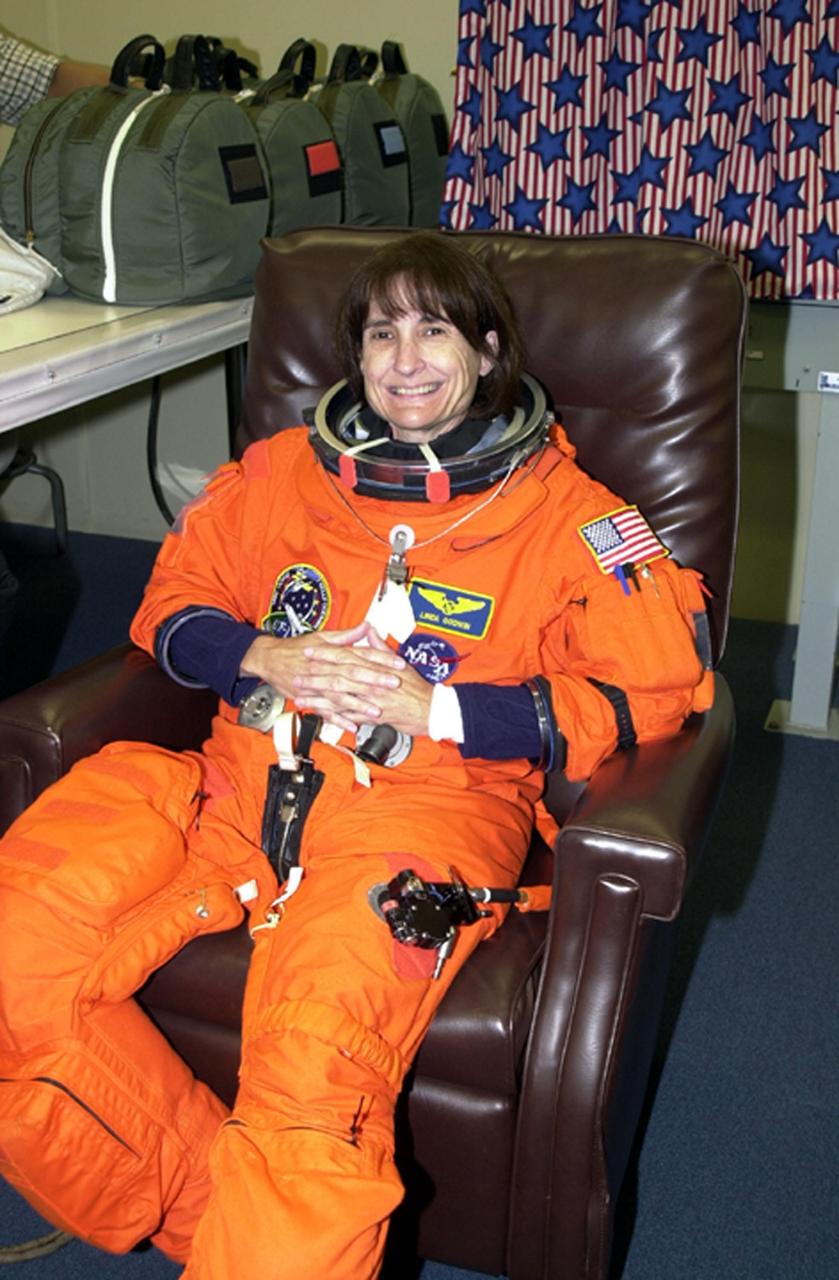

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-108 Mission Specialist Linda A. Godwin is relaxed and happy to be preparing for the second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
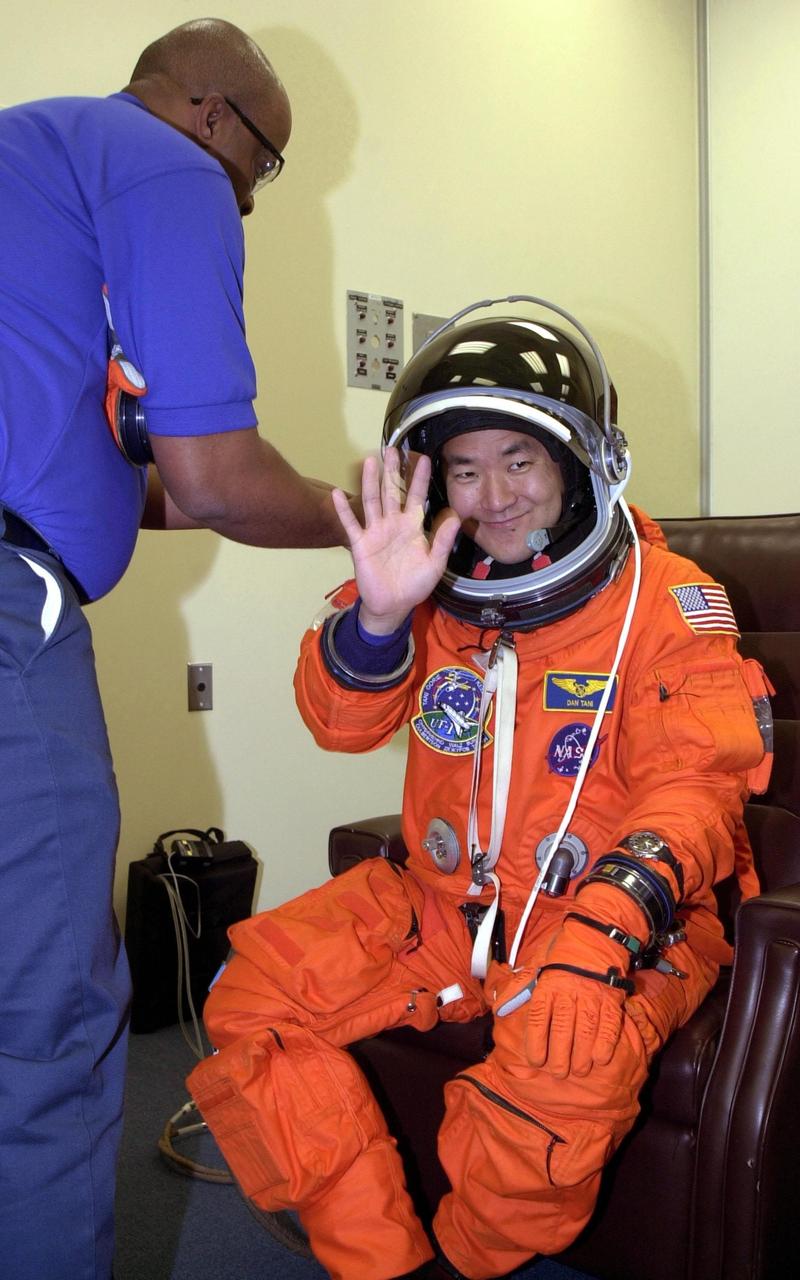

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-108 Mission Specialist Daniel M. Tani is happy to be suiting up for the second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
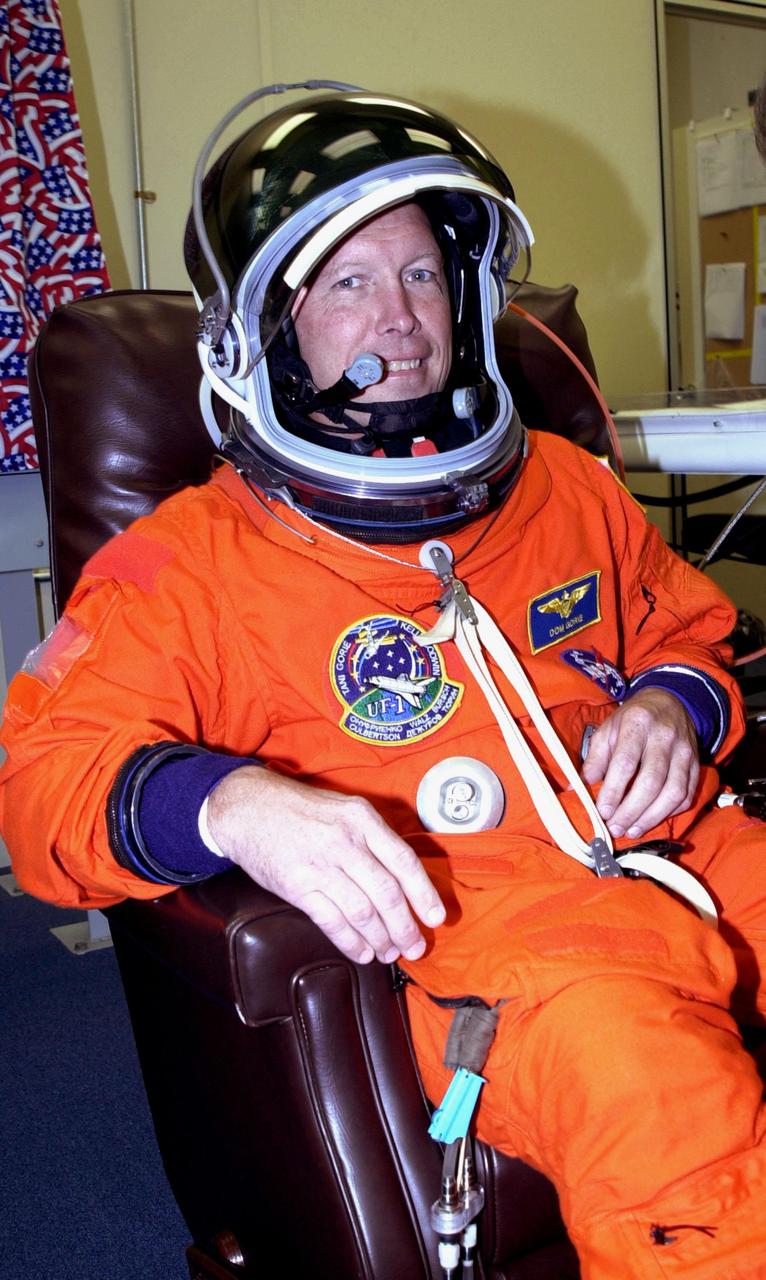

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-108 Commander Dominic L. Gorie is ready in his launch and entry suit for the second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
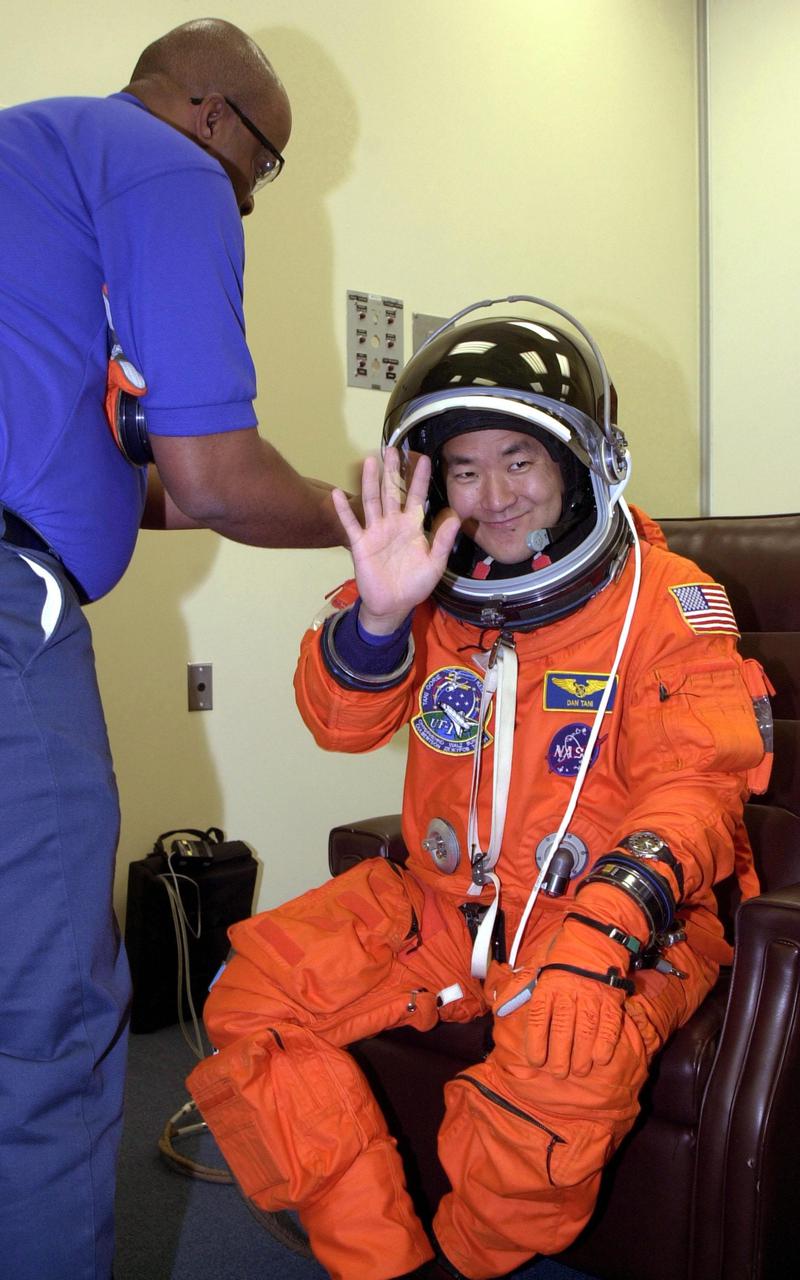

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-108 Mission Specialist Daniel M. Tani is happy to be suiting up for the second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Expedition 4 Commander Yuri Onufrienko gets ready in his launch and entry suit for the second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-108. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
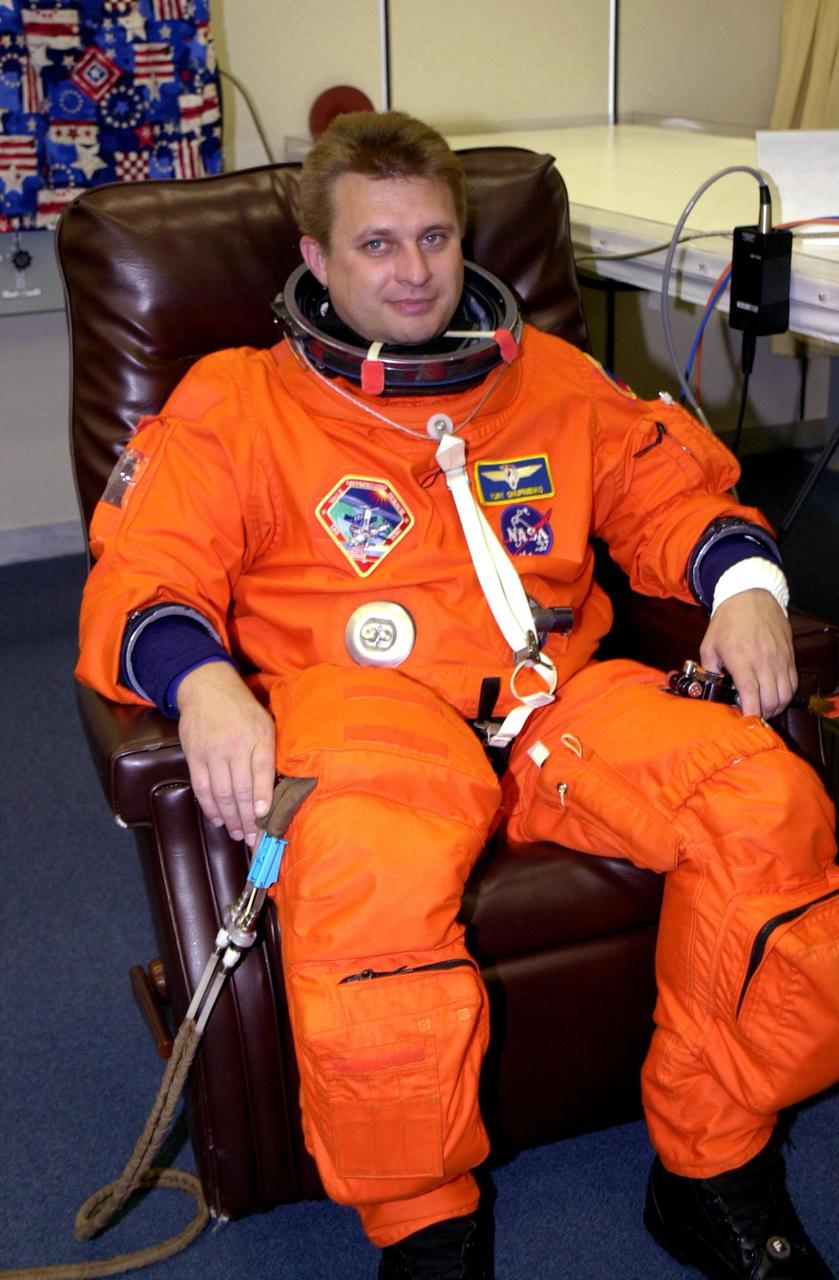

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Expedition 4 Commander Yuri Onufrienko gets ready in his launch and entry suit for the second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-108. The first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-108 Mission Specialist Daniel M. Tani waits in the White Room for final preparations of his launch and entry suit before entering Endeavour. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
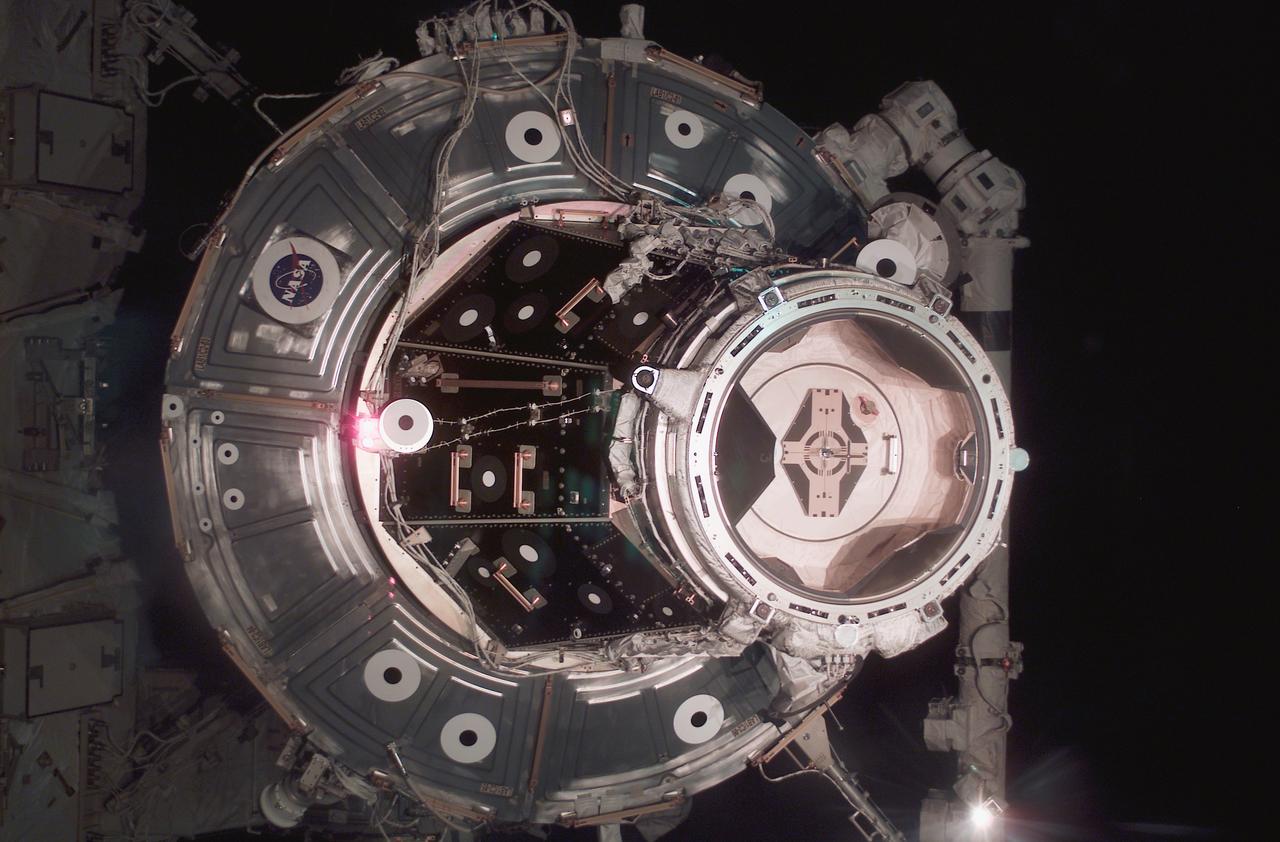
Pictured here is the forward docking port on the International Space Station's (ISS) Destiny Laboratory as seen by one of the STS-111 crewmembers from the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour just prior to docking. In June 2002, STS-111 provided the Space Station with a new crew, Expedition Five, replacing Expedition Four after remaining a record-setting 196 days in space. Three spacewalks enabled the STS-111 crew to accomplish additional mission objectives: the delivery and installation of a new platform for the ISS robotic arm, the Mobile Base System (MBS) which is an important part of the Station's Mobile Servicing System allowing the robotic arm to travel the length of the Station; the replacement of a wrist roll joint on the Station's robotic arm; and unloading supplies and science experiments form the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module, which made its third trip to the orbital outpost. The STS-111 mission, the 14th Shuttle mission to visit the ISS, was launched on June 5, 2002 and landed June 19, 2002.
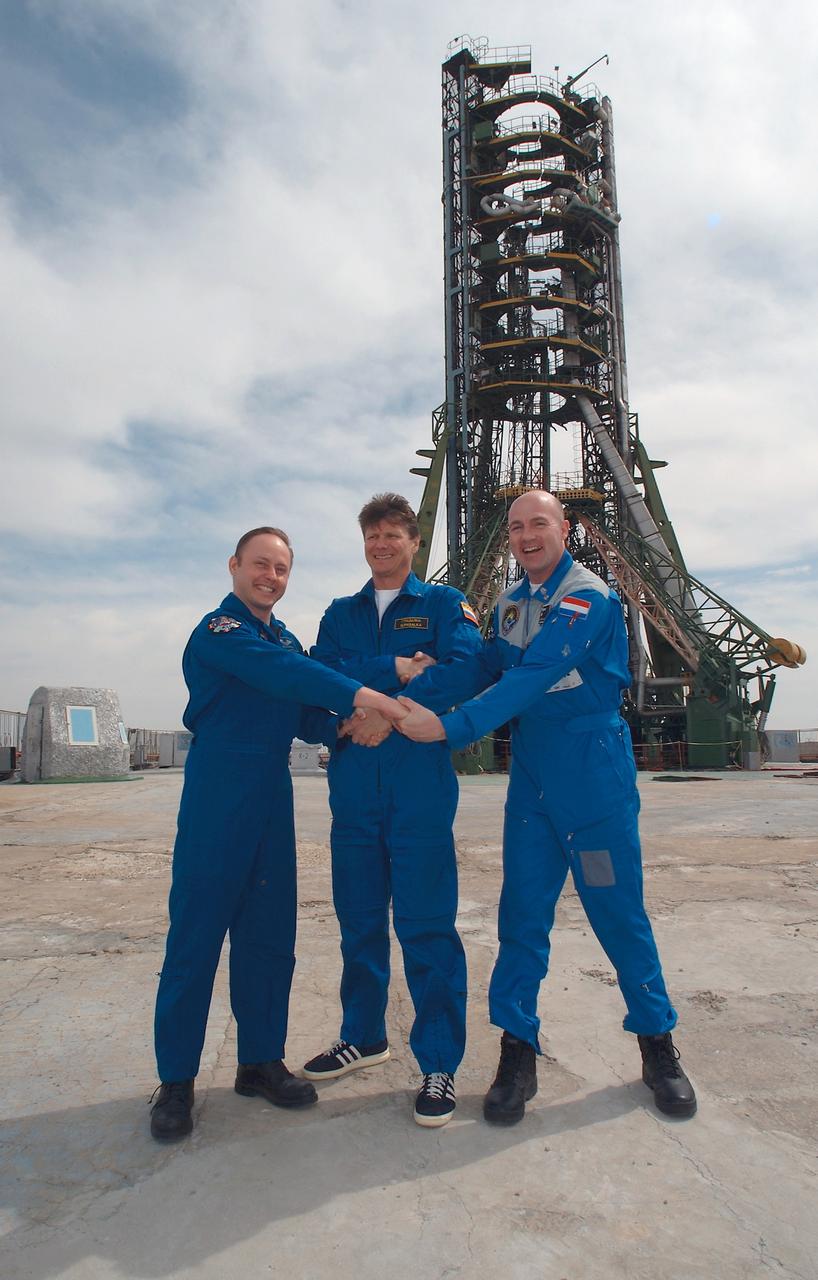

JSC2004-E-19694 (14 April 2004) --- Astronaut Edward M. (Mike) Fincke (left), NASA International Space Station (ISS) science officer and flight engineer; cosmonaut Gennady I. Padalka (center), Russia’s Federal Space Agency Expedition 9 mission commander; and European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Andre Kuipers of the Netherlands pose for a photo during a tour of the Soyuz launch pad, Baikonur, Kazakhstan. The trio is scheduled to launch on April 19, 2004, to the ISS for arrival on April 21. Padalka and Fincke will spend six months on the ISS, replacing the Expedition 8 crew, which has been aboard the Station since October 20, 2003. European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Andre Kuipers of the Netherlands, who is flying under a commercial contract between ESA and Russia’s Federal Space Agency, will return to Earth with the Expedition 8 crew on April 30, 2004. Photo Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls

Expedition 43 backup crew members: Jeff Williams of NASA, left, Sergei Volkov, Alexey Ovchinin, of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), and prime crew members: NASA Astronaut Scott Kelly, Russian Cosmonauts Gennady Padalka, and Mikhail Kornienko of Roscosmos attend the ISS Russian Segment Safety briefing, Thursday, March 19, 2015 at Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Kelly, Padalka, and Kornienko are preparing for launch to the International Space Station in their Soyuz TMA-16M spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan March 28, Kazakh time. As the one-year crew, Kelly and Kornienko will return to Earth on Soyuz TMA-18M in March 2016. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
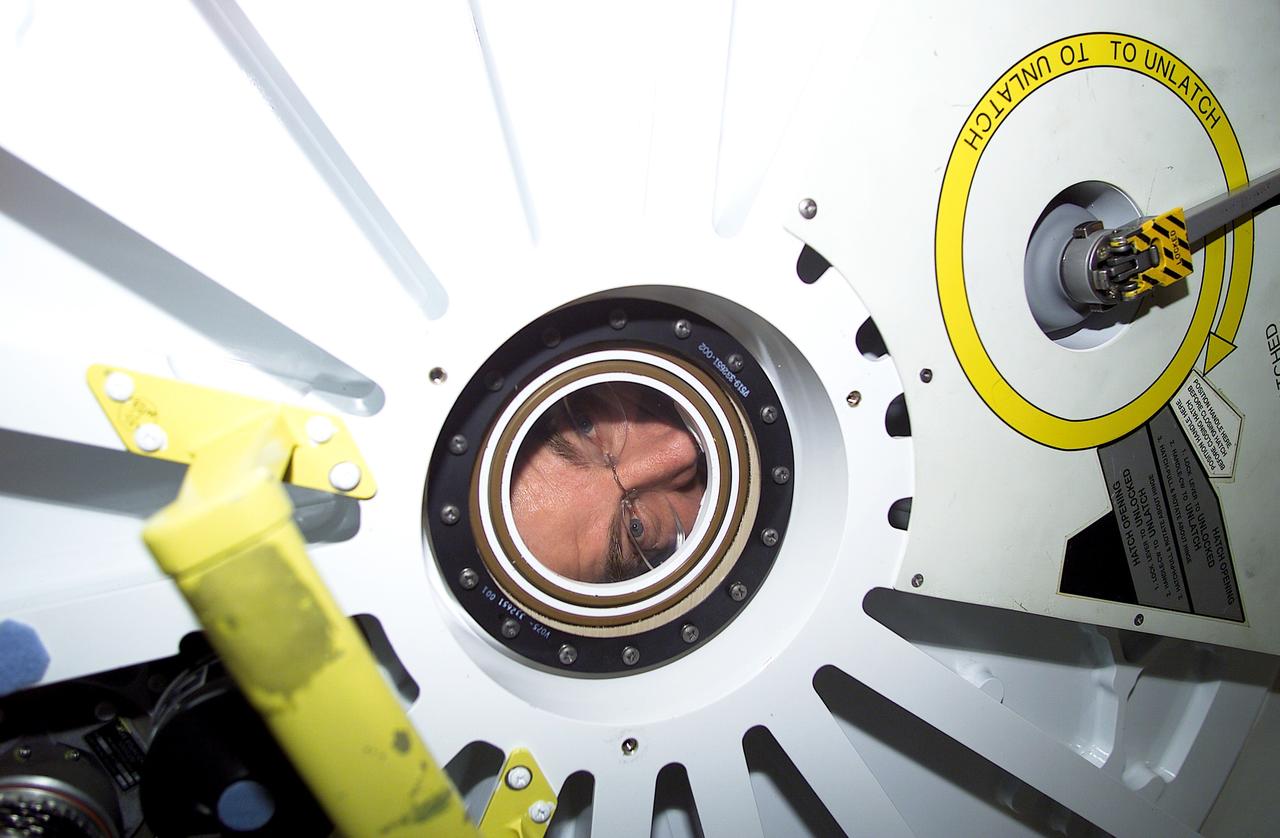
The STS-100 mission launched for the International Space Station (ISS) on April 19, 2001 as the sixth station assembly flight. Main objectives included the delivery and installation of the Canadian-built Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS), or Canadarm2, the installation of a UHF anterna for space-to-space communications for U.S. based space walks, and the delivery of supplies via the Italian Multipurpose Logistics Module (MPLM) "Raffaello". This is an STS-110 onboard photo of Astronaut James S. Voss, Expedition Two flight engineer, peering into the pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-2) prior hatch opening. The picture was taken by one of the STS-100 crew members inside the PMA.
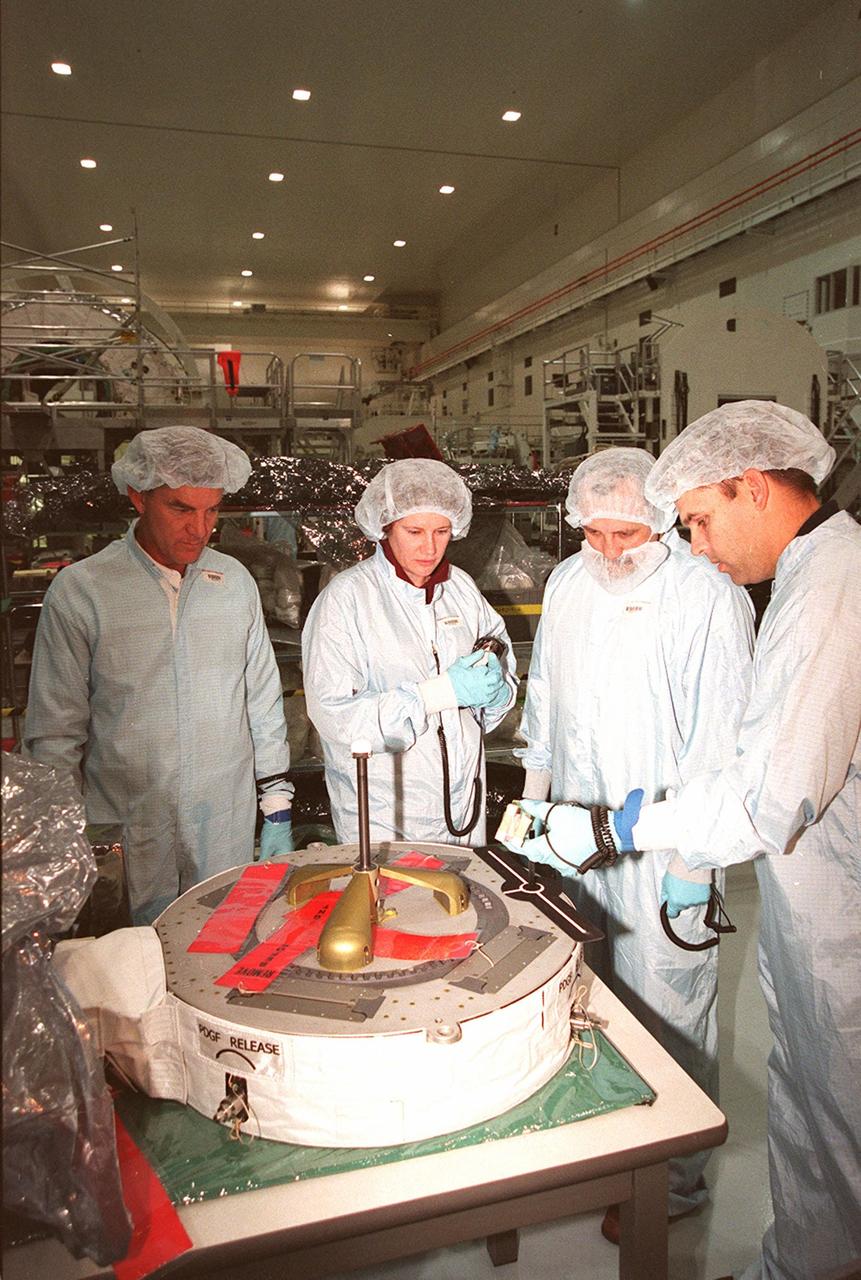

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF), a technician (right) explains use of the equipment in front of (left) STS-102 Mission Specialists James Voss, Susan Helms and Yuri Usachev, with the Russian Space Agency (RSA). STS-102 is a resupply mission to the International Space Station, transporting the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) with equipment to assist in outfitting the U.S. Lab, which will already be in place. The mission is also transporting Helms, Voss and Usachev as the second resident crew (designated Expedition crew 2) to the station. In exchange, the mission will return to Earth the first expedition crew on ISS: William Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev (RSA) and Yuri Gidzenko (RSA). STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000

STS-102 Mission Specialists James Voss, Susan Helms and Yuri Usachev, with the Russian Space Agency (RSA), pose in front of the U.S. Lab module, named Destiny, in the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). STS-102 is a resupply mission to the International Space Station, transporting the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) with equipment to assist in outfitting the U.S. Lab, which will already be in place. The mission is also transporting Helms, Voss and Usachev as the second resident crew (designated Expedition crew 2) to the station. In exchange, the mission will return to Earth the first expedition crew on ISS: William Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev (RSA) and Yuri Gidzenko (RSA). STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000
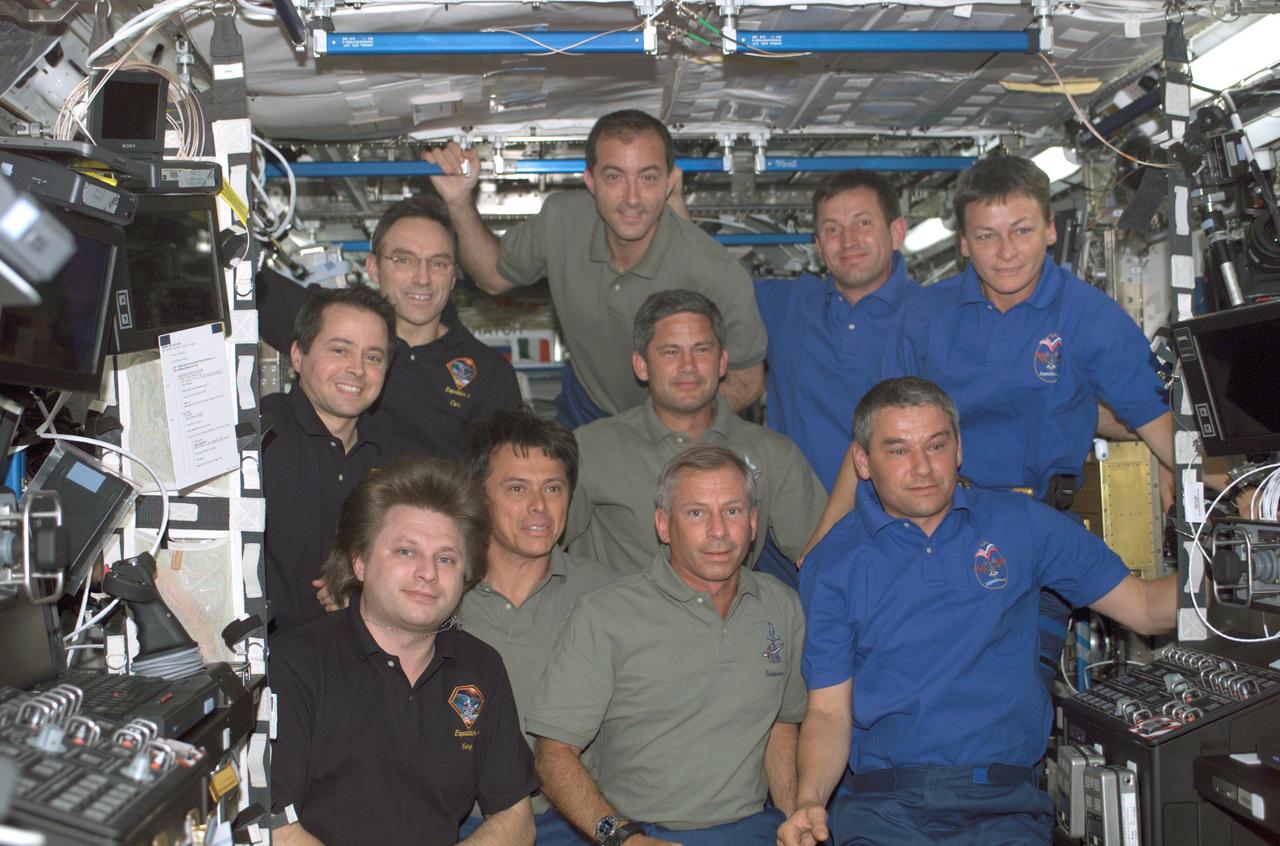

Huddled together in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station (ISS) are the Expedition Four crew (dark blue shirts), Expedition Five crew (medium blue shirts) and the STS-111 crew (green shirts). The Expedition Four crewmembers are, from front to back, Cosmonaut Ury I. Onufrienko, mission commander; and Astronauts Daniel W. Bursch and Carl E. Waltz, flight engineers. The ISS crewmembers are, from front to back, Astronauts Kerneth D. Cockrell, mission commander; Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, mission specialist; Paul S. Lockhart, pilot; and Philippe Perrin, mission specialist. Expedition Five crewmembers are, from front to back, Cosmonaut Valery G. Korzun, mission commander; Astronaut Peggy A. Whitson and Cosmonaut Sergei Y. Treschev, flight engineers. The ISS recieved a new crew, Expedition Five, replacing Expedition Four after a record-setting 196 days in space, when the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour STS-111 mission visited in June 2002. Three spacewalks enabled the STS-111 crew to accomplish additional mission objectives: the delivery and installation of the Mobile Base System (MBS), which is an important part of the station's Mobile Servicing System allowing the robotic arm to travel the length of the station; the replacement of a wrist roll joint on the Station's robotic arm; and unloading supplies and science experiments from the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module, which made its third trip to the orbital outpost. The STS-111 mission, the 14th Shuttle mission to visit the ISS, was launched on June 5, 2002 and landed June 19, 2002.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers at SPACEHAB, in Titusville, Fla., help members of the STS-102 crew become familiar with the Integrated Cargo Carrier and elements of its cargo for their mission. Starting second from left are Mission Specialists James Voss and Susan Helms and, fourth from left, cosmonaut Yuri Usachev, who is with the Russian Space Agency (RSA). STS-102 is a resupply mission to the International Space Station, transporting the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) with equipment to assist in outfitting the U.S. Lab, which will already be in place. It is also transporting Voss, Helms and Usachev as the second resident crew (designated Expedition crew 2) to the station. The mission will also return to Earth the first expedition crew on ISS: William Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev (RSA) and Yuri Gidzenko (RSA). STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000
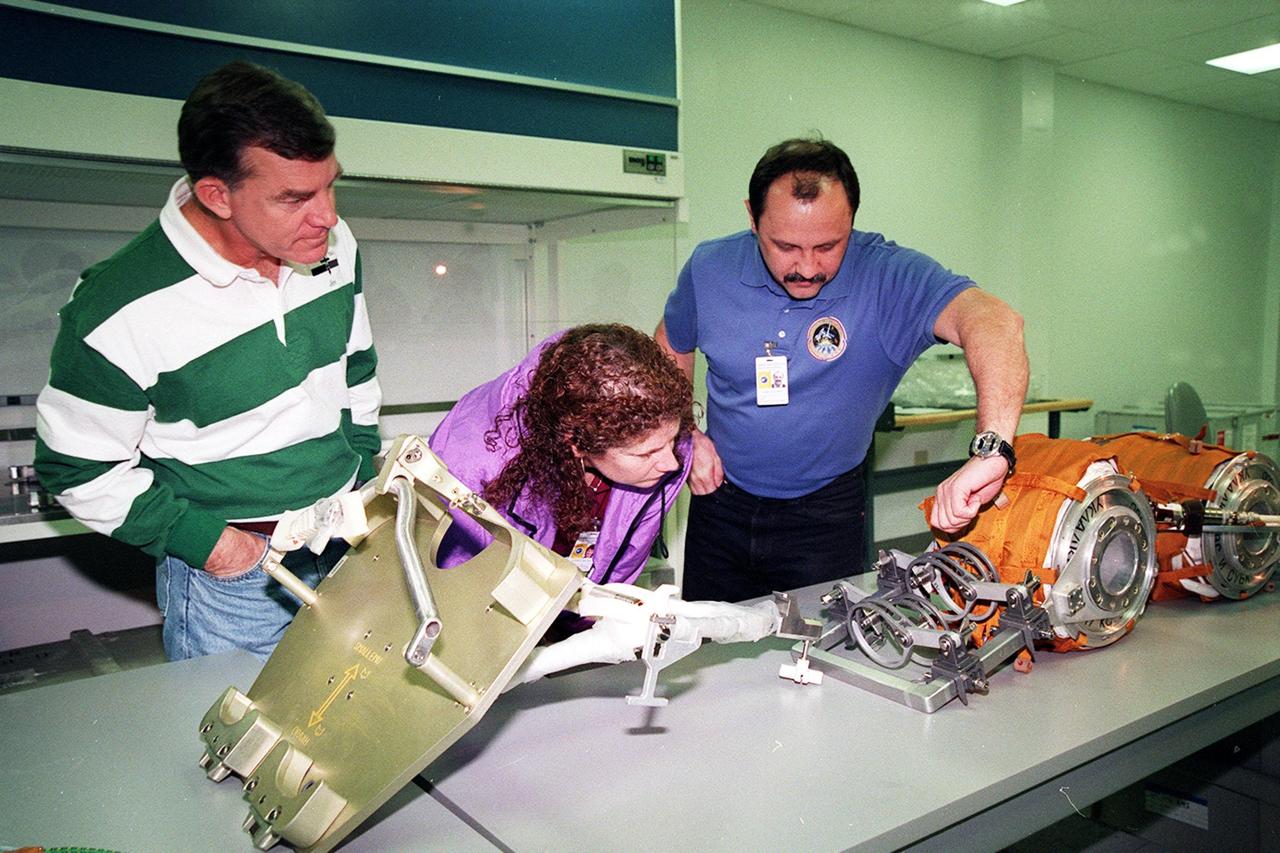

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, in Titusville, Fla., members of the STS-102 crew look at part of the cargo for their mission. From left are Mission Specialists James Voss, Susan Helms and Yuri Usachev, with the Russian Space Agency (RSA). STS-102 is a resupply mission to the International Space Station, transporting the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) with equipment to assist in outfitting the U.S. Lab, which will already be in place. The mission is also transporting Helms, Voss and Usachev as the second resident crew (designated Expedition crew 2) to the station. In exchange, the mission will return to Earth the first expedition crew on ISS: William Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev (RSA) and Yuri Gidzenko (RSA). STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000
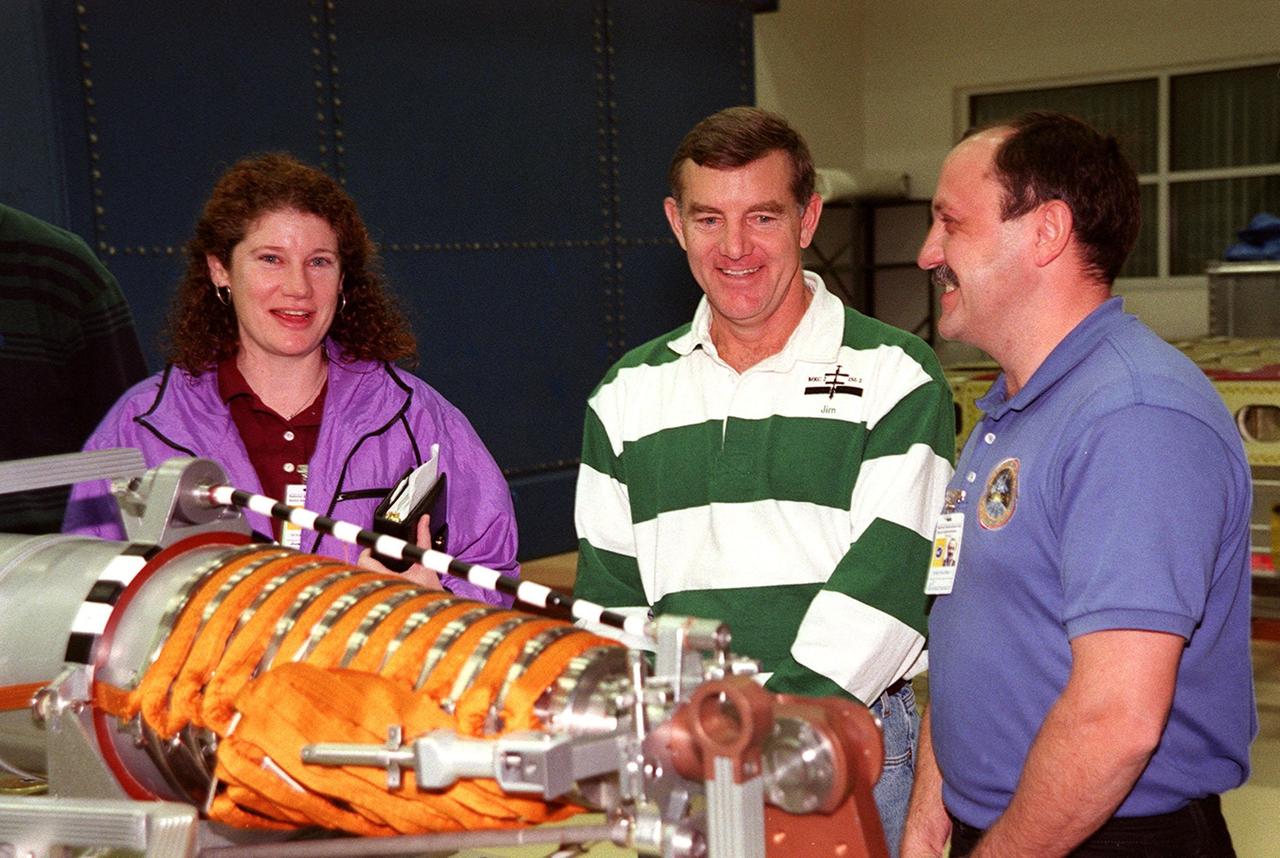

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, in Titusville, Fla., members of the STS-102 crew look at part of the equipment on the Integrated Cargo Carrier that will be on their mission. From left are Mission Specialists Susan Helms, James Voss and Yuri Usachev, who is with the Russian Space Agency (RSA). STS-102 is a resupply mission to the International Space Station, transporting the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) with equipment to assist in outfitting the U.S. Lab, which will already be in place. The mission is also transporting Helms, Voss and Usachev as the second resident crew (designated Expedition crew 2) to the station. In exchange, the mission will return to Earth the first expedition crew on ISS: William Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev (RSA) and Yuri Gidzenko (RSA). STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000.
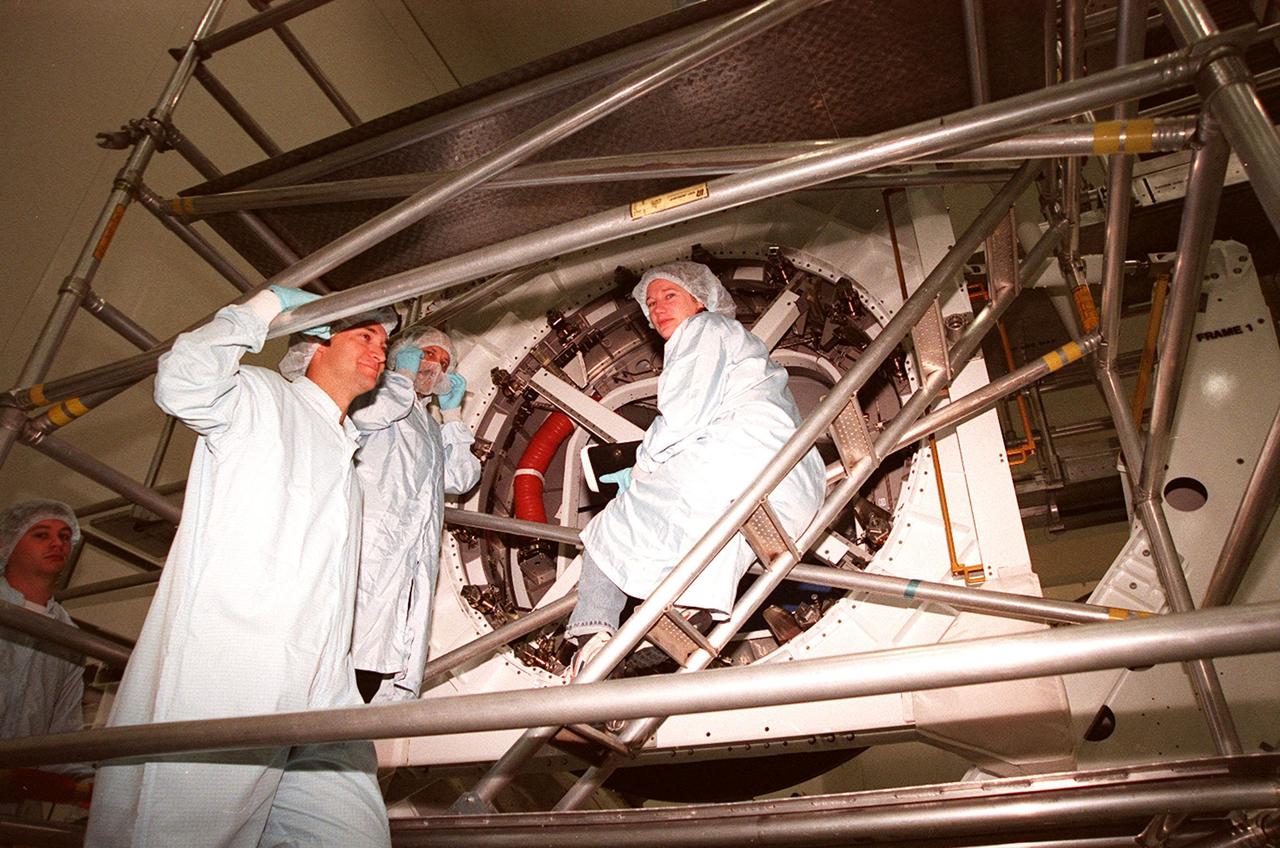

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Looking over a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3) in the Space Station Processing Facility are Arne Aamodt, with Johnson Space Center, Yuriy Vladimirovich Usachev and Susan J. Helms. Usachev and Helms are two members of the STS-102 crew, who will be staying on the International Space Station (ISS). The third crew member is James S. Voss. They have been designated the Expedition II crew. Mission STS-102 also will be carrying the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) to the ISS. The Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module, which will have been carried to the ISS on a preceding Shuttle flight. In order to function as an attached station module as well as a cargo transport, logistics modules (there are three) also include components that provide some life support, fire detection and suppression, electrical distribution and computer functions. Eventually, the modules also will carry refrigerator freezers for transporting experiment samples and food to and from the station. On the return of STS-102 to Earth, it will bring back the first crew on the station: Bill Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev and Yuri Gidzenko. STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000, from Launch Pad 39A, Kennedy Space Center
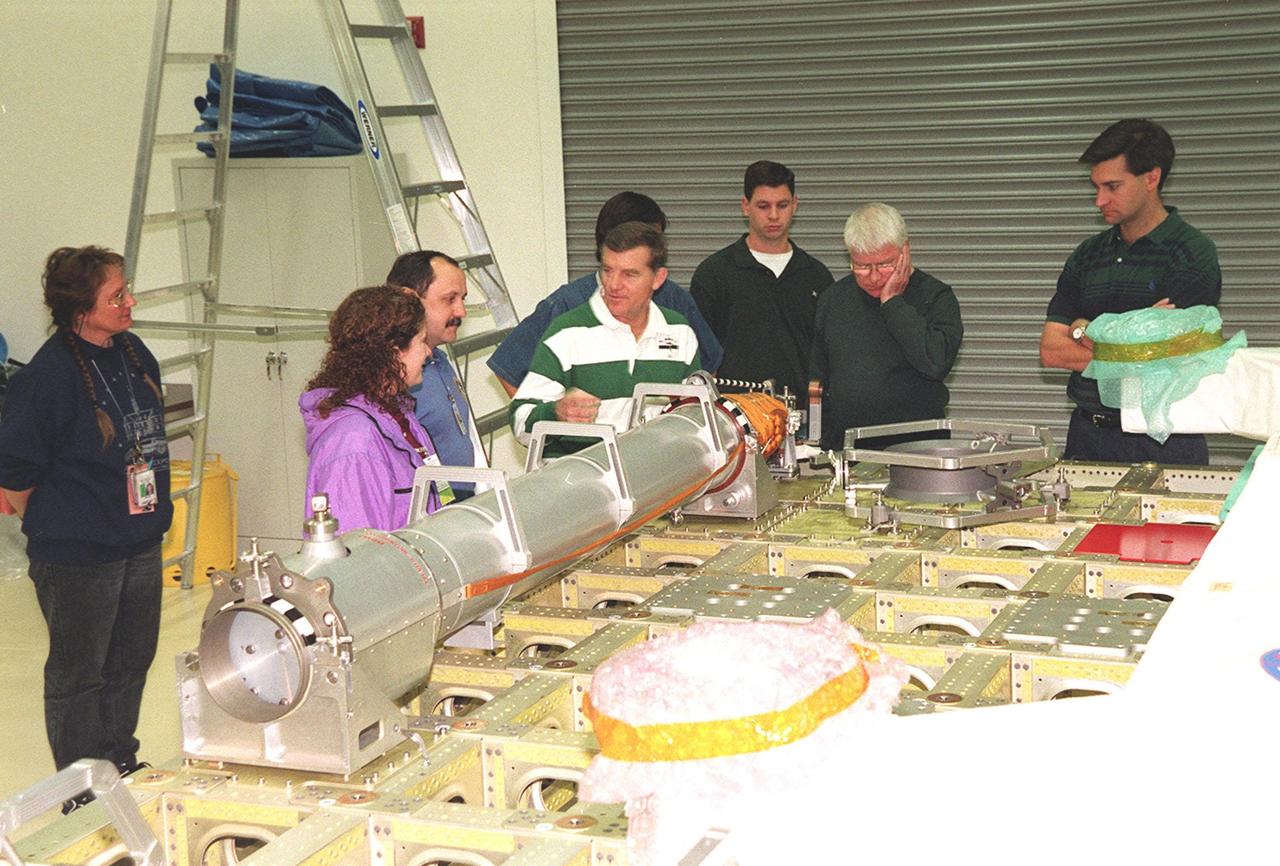

At SPACEHAB, in Titusville, Fla., members of the STS-102 crew look over the Integrated Cargo Carrier and the Russian crane Strela as part of familiarization activities. Starting second to left are Mission Specialists Susan Helms, cosmonaut Yuri Usachev, who is with the Russian Space Agency (RSA), and James Voss. STS-102 is a resupply mission to the International Space Station, transporting the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) with equipment to assist in outfitting the U.S. Lab, which will already be in place. It is also transporting Voss, Helms and Usachev as the second resident crew (designated Expedition crew 2) to the station. The mission will also return to Earth the first expedition crew on ISS: William Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev (RSA) and Yuri Gidzenko (RSA). STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000
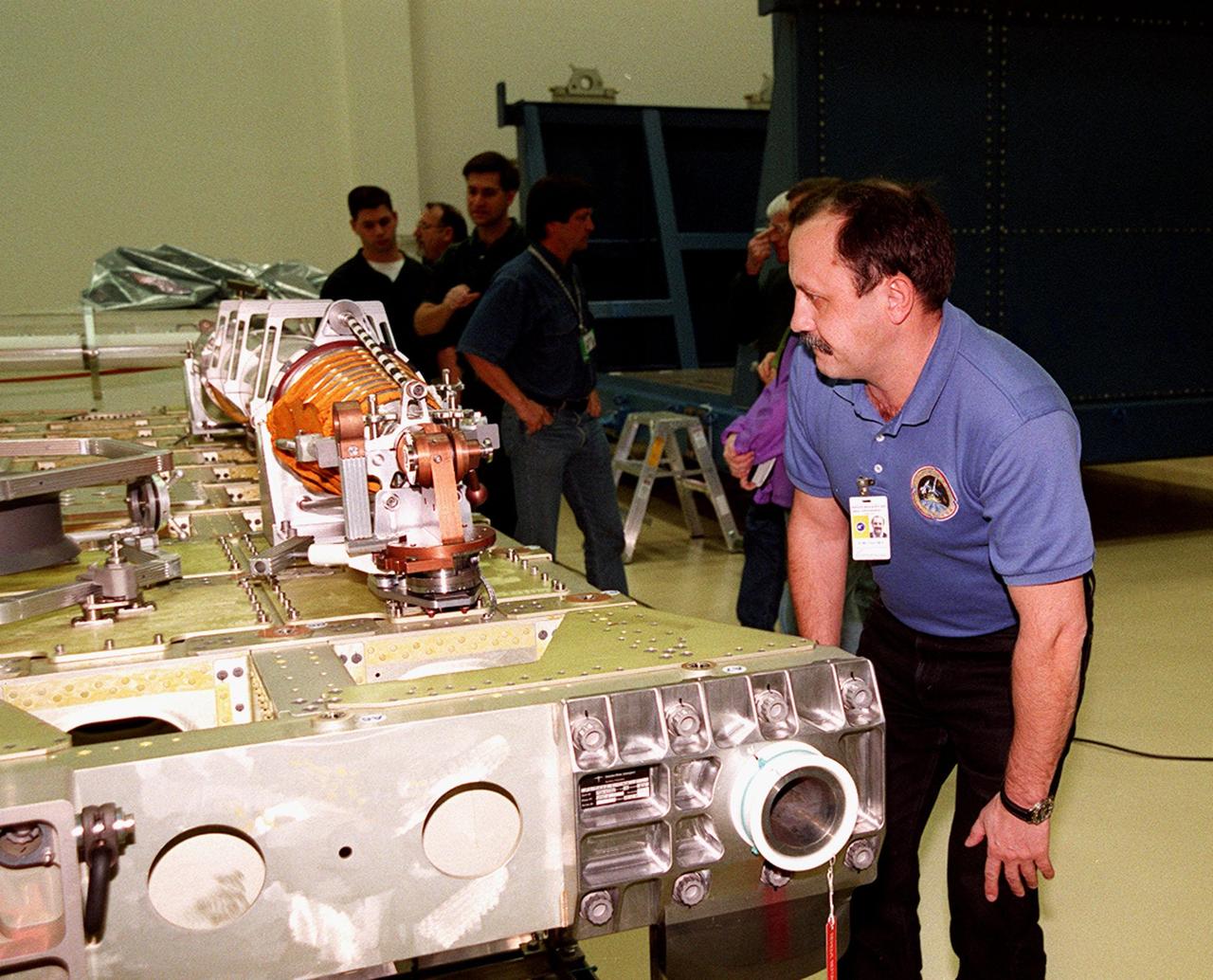

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, in Titusville, Fla., STS-102 Mission Specialist Yuri Usachev, who is with the Russian Space Agency (RSA), looks at part of the cargo on the Integrated Cargo Carrier. STS-102 is a resupply mission to the International Space Station, transporting the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) with equipment to assist in outfitting the U.S. Lab, which will already be in place. It is also transporting Usachev, and Mission Specialists James Voss and Susan Helms as the second resident crew (designated Expedition crew 2) to the station. The mission will also return to Earth the first expedition crew on ISS: William Shepherd, Sergei Krikalev (RSA) and Yuri Gidzenko (RSA). STS-102 is scheduled to launch no earlier than Oct. 19, 2000

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Eagerly stepping out from the Operations and Checkout Building are the STS-108 crew, leading the way, and the Expedition 4 crew as they head for Launch Pad 39B and Space Shuttle Endeavour. From front to back are, left to right, Pilot Mark E. Kelly and Commander Dominic L. Gorie; Mission Specialists Daniel M. Tani and Linda A. Godwin; Expedition 4 members Daniel W. Bursch, Commander Yuri Onufrienko and Carl E. Walz. This is the second launch attempt after the first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
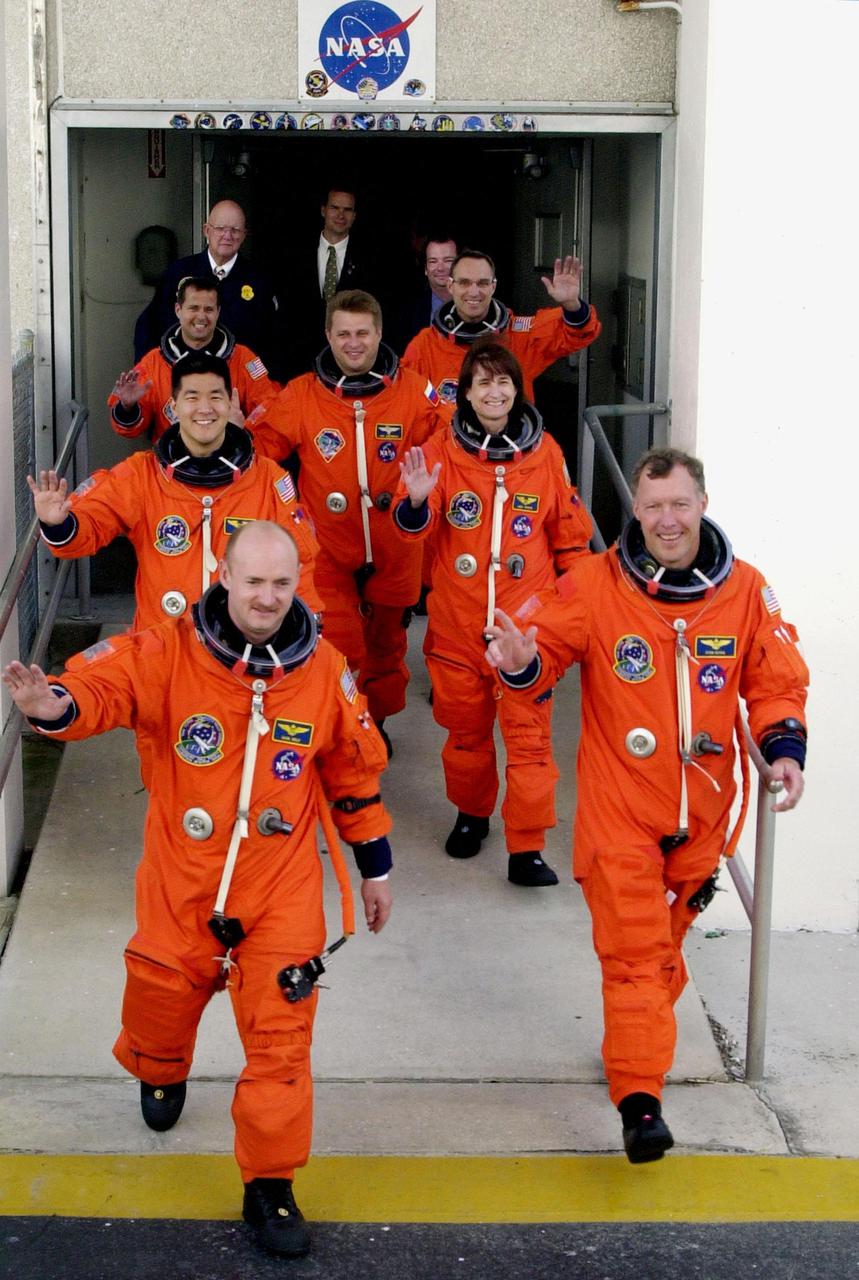

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Eagerly stepping out from the Operations and Checkout Building are the STS-108 crew, leading the way, and the Expedition 4 crew as they head for Launch Pad 39B and Space Shuttle Endeavour. From front to back are, left to right, Pilot Mark E. Kelly and Commander Dominic L. Gorie; Mission Specialists Daniel M. Tani and Linda A. Godwin; Expedition 4 members Daniel W. Bursch, Commander Yuri Onufrienko and Carl E. Walz. This is the second launch attempt after the first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
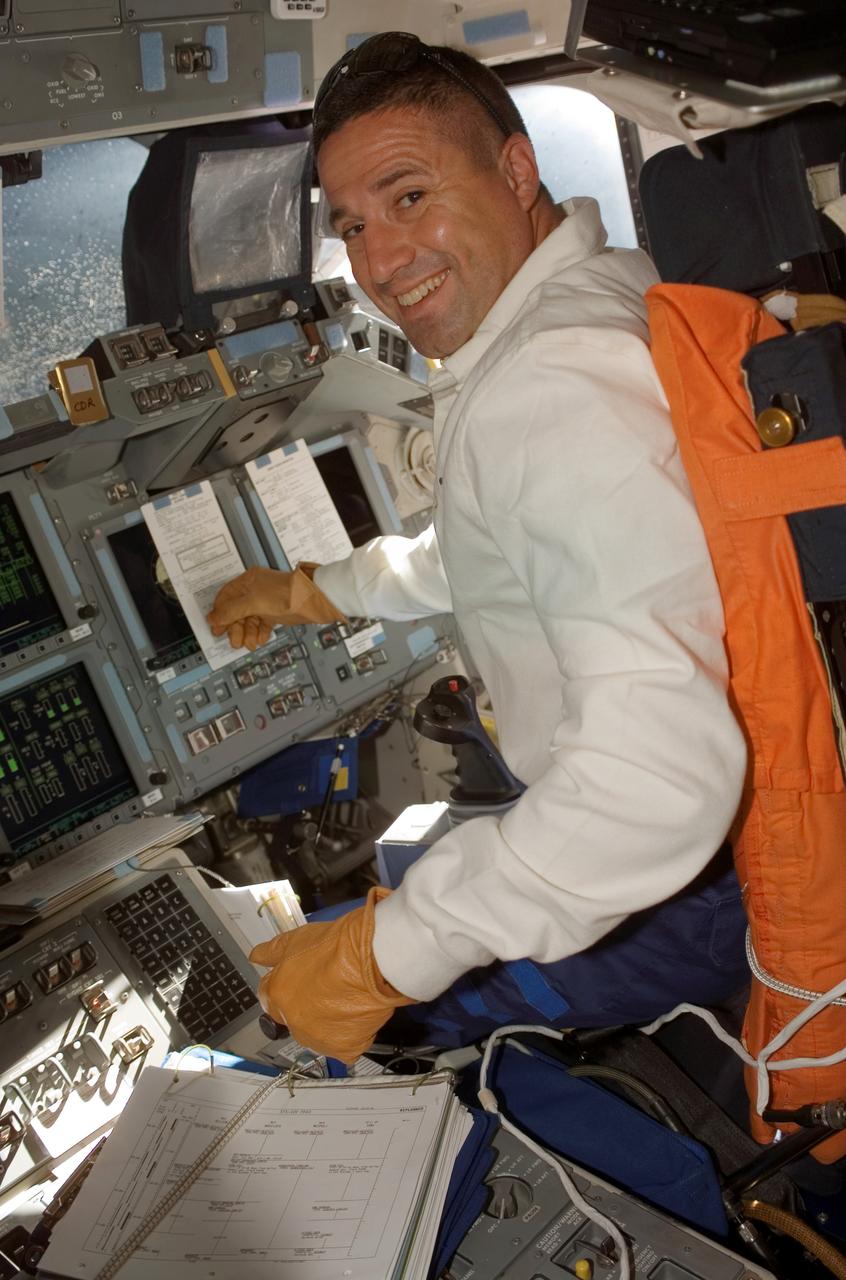

Astronaut George Zamka, STS-120 pilot, is seated at the pilot's station on the forward flight deck of the Space Shuttle Discovery during rendezvous and docking operations with the International Space Station (ISS). The STS-120 mission launched from Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39A at 11:38:19 a.m. (EDT) on October 23, 2007. The crew also included Scott E. Parazynski, Douglas H. Wheelock, Stephanie D. Wilson, all mission specialists; Pamela A. Melroy, commander; Daniel M. Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer; and Paolo A. Nespoli, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA). Major objectives included the installation of the P6 solar array of the port truss and delivery and installment of Harmony, the Italian-built U.S. Node 2 on the ISS.
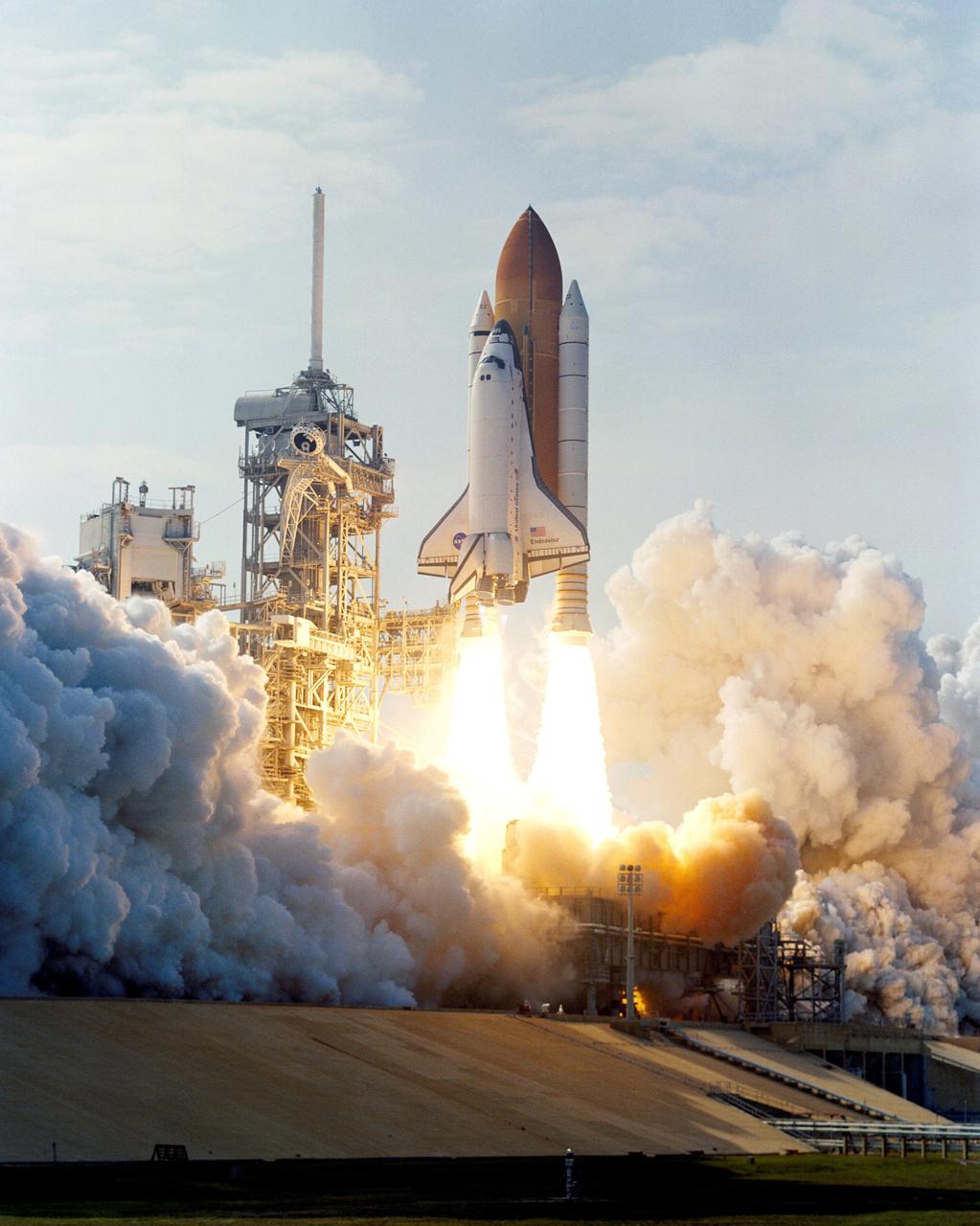

Aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, the STS-111 mission was launched on June 5, 2002 at 5:22 pm EDT from Kennedy's launch pad. On board were the STS-111 and Expedition Five crew members. Astronauts Kenneth D. Cockrell, commander; Paul S. Lockhart, pilot, and mission specialists Franklin R. Chang-Diaz and Philippe Perrin were the STS-111 crew members. Expedition Five crew members included Cosmonaut Valeri G. Korzun, commander, Astronaut Peggy A. Whitson and Cosmonaut Sergei Y. Treschev, flight engineers. Three space walks enabled the STS-111 crew to accomplish mission objectives: the delivery and installation of a new platform for the ISS robotic arm, the Mobile Base System (MBS) which is an important part of the Station's Mobile Servicing System allowing the robotic arm to travel the length of the Station; the replacement of a wrist roll joint on the Station's robotic arm; and unloading supplies and science experiments from the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module, which made its third trip to the orbital outpost. Landing on June 19, 2002, the 14-day STS-111 mission was the 14th Shuttle mission to visit the ISS.
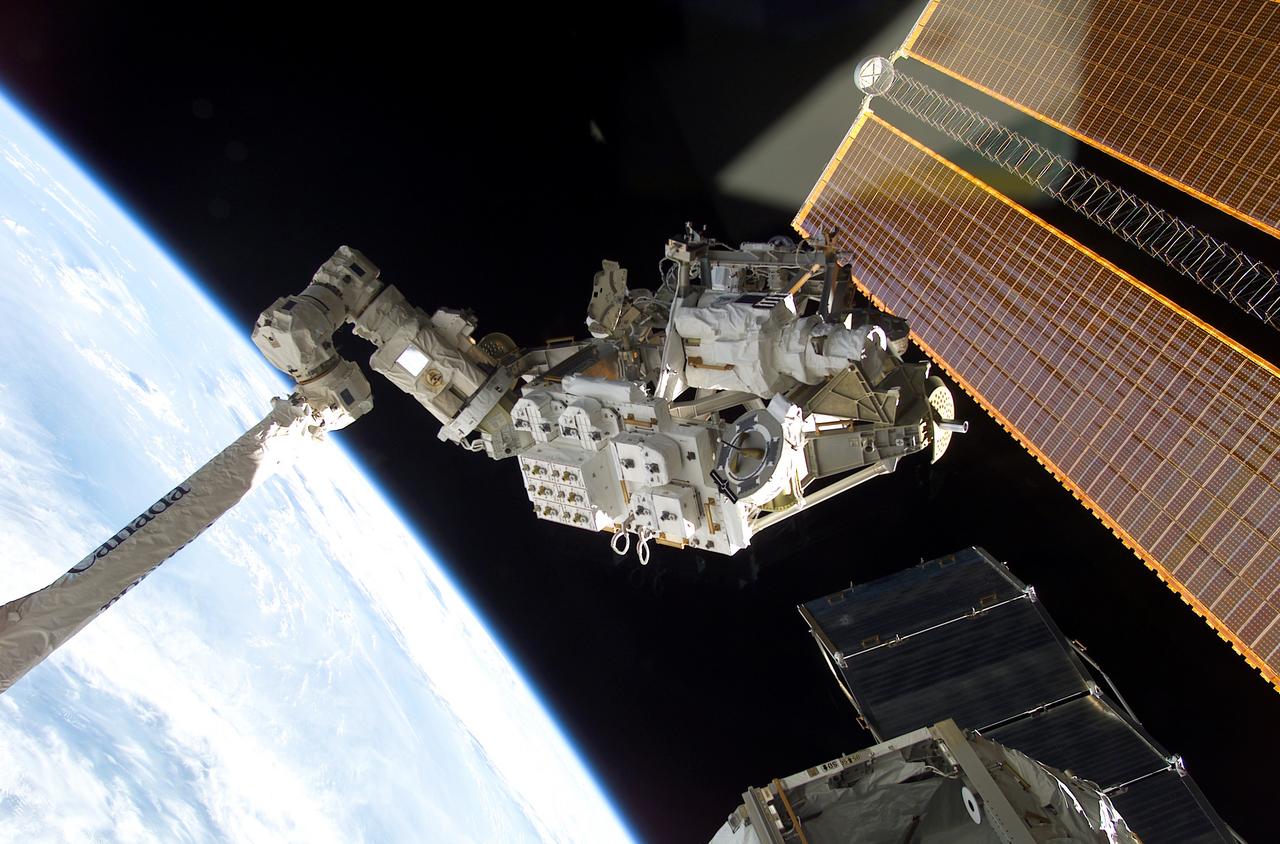

Backdropped against the blackness of space and the Earth's horizon, the Mobile Remote Base System (MBS) is moved by the Canadarm2 for installation on the International Space Station (ISS). Delivered by the STS-111 mission aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in June 2002, the MBS is an important part of the Station's Mobile Servicing System allowing the robotic arm to travel the length of the Station, which is neccessary for future construction tasks. In addition, STS-111 delivered a new crew, Expedition Five, replacing Expedition Four after remaining a record-setting 196 days in space. Three spacewalks enabled the STS-111 crew to accomplish the delivery and installation of the MBS to the Mobile Transporter on the S0 (S-zero) truss, the replacement of a wrist roll joint on the Station's robotic arm, and the task of unloading supplies and science experiments from the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module, which made its third trip to the orbital outpost. The STS-111 mission, the 14th Shuttle mission to visit the ISS, was launched on June 5, 2002 and landed June 19, 2002.
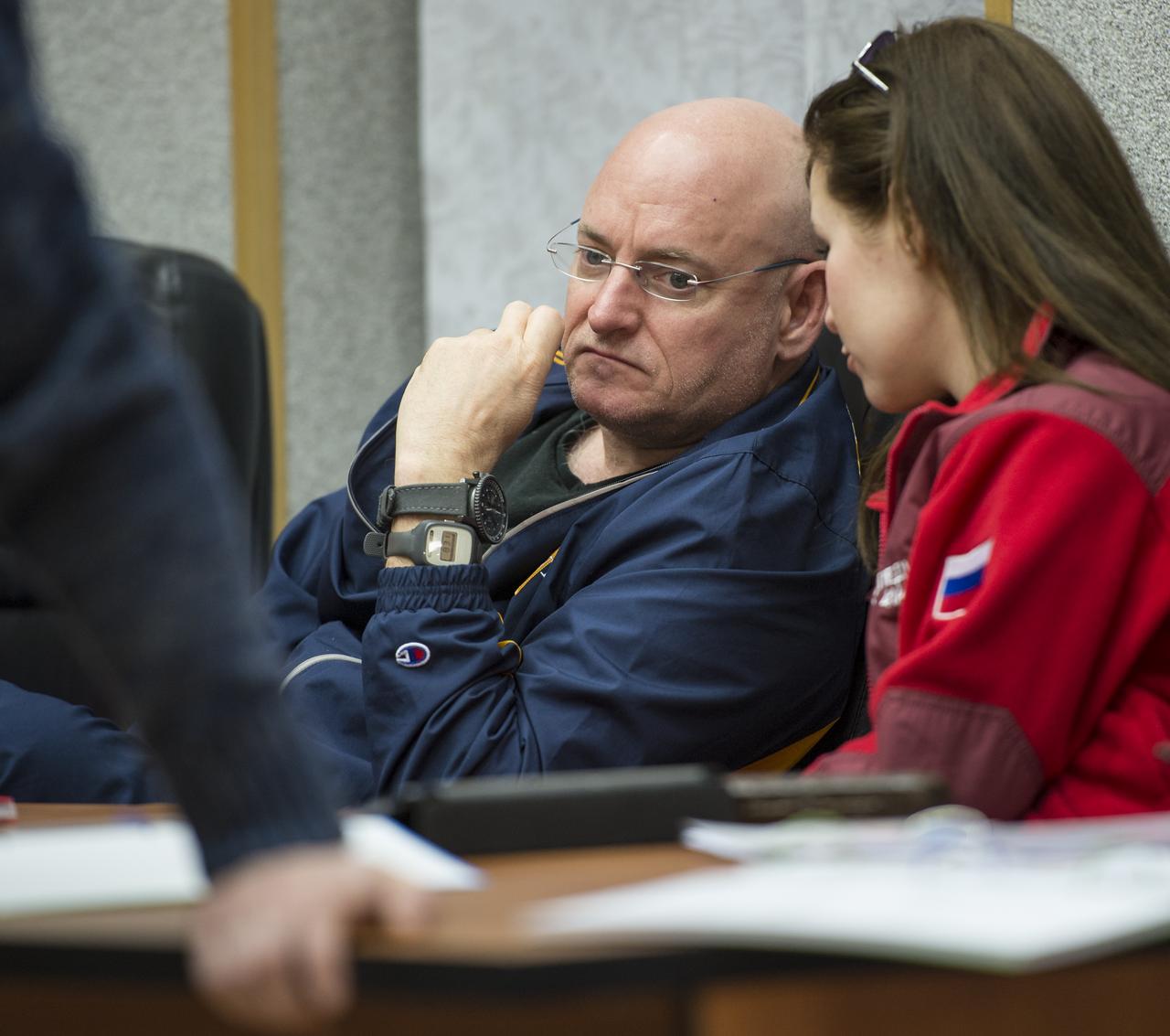

Expedition 43 NASA Astronaut Scott Kelly listens to an interpreter during an ISS Russian Segment Safety briefing, Thursday, March 19, 2015 at Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Kelly, and Russian Cosmonauts Gennady Padalka, and Mikhail Kornienko of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) are preparing for launch to the International Space Station in their Soyuz TMA-16M spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan March 28, Kazakh time. As the one-year crew, Kelly and Kornienko will return to Earth on Soyuz TMA-18M in March 2016. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
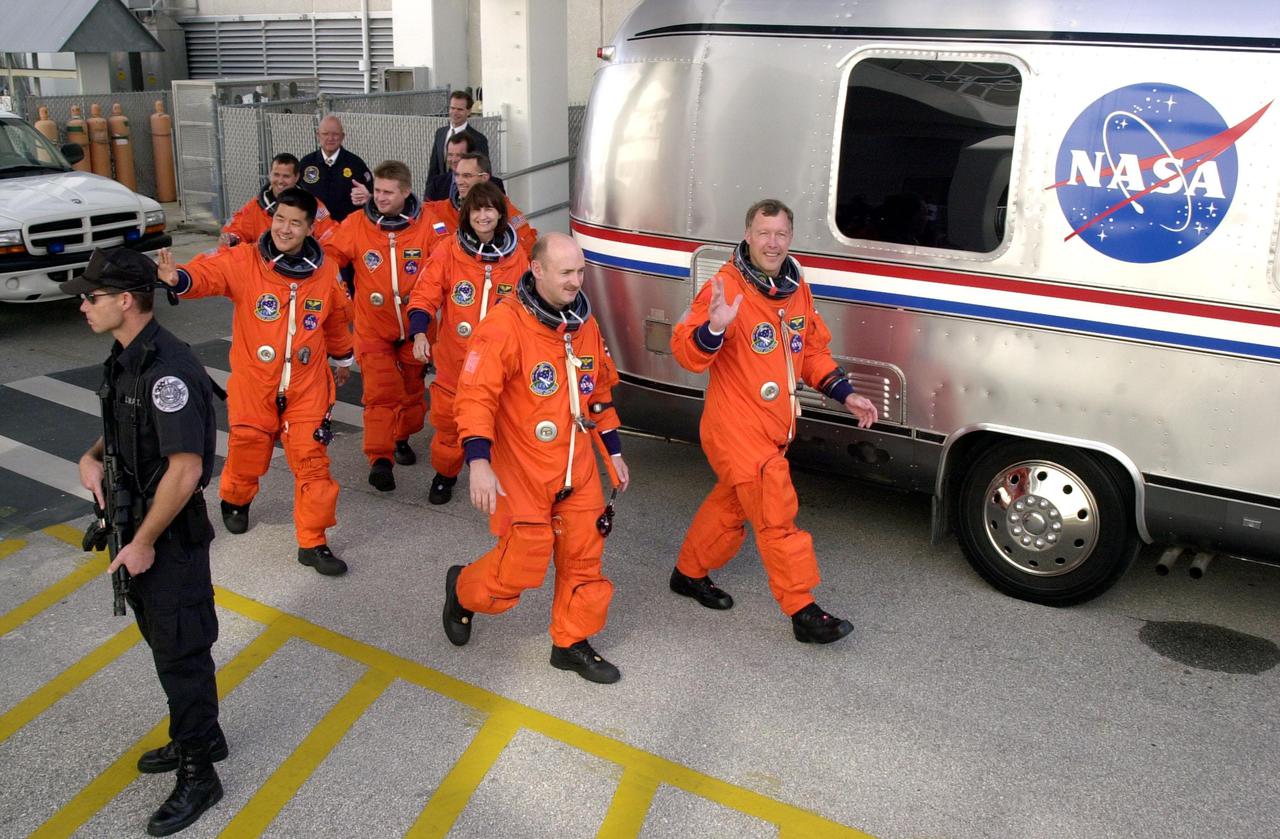

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-108 and Expedition 4 crews head for the Astrovan and a ride to Launch Pad 39B. Leading the way are Pilot Mark E. Kelly (left) and Commander Dominic L. Gorie; behind them are Mission Specialists Daniel M. Tani and Linda A. Godwin; next is Expedition 4 Commander Yuri Onufrienko, followed by astronauts Daniel W. Bursch (left) and Carl E. Walz. This is the second launch attempt after the first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
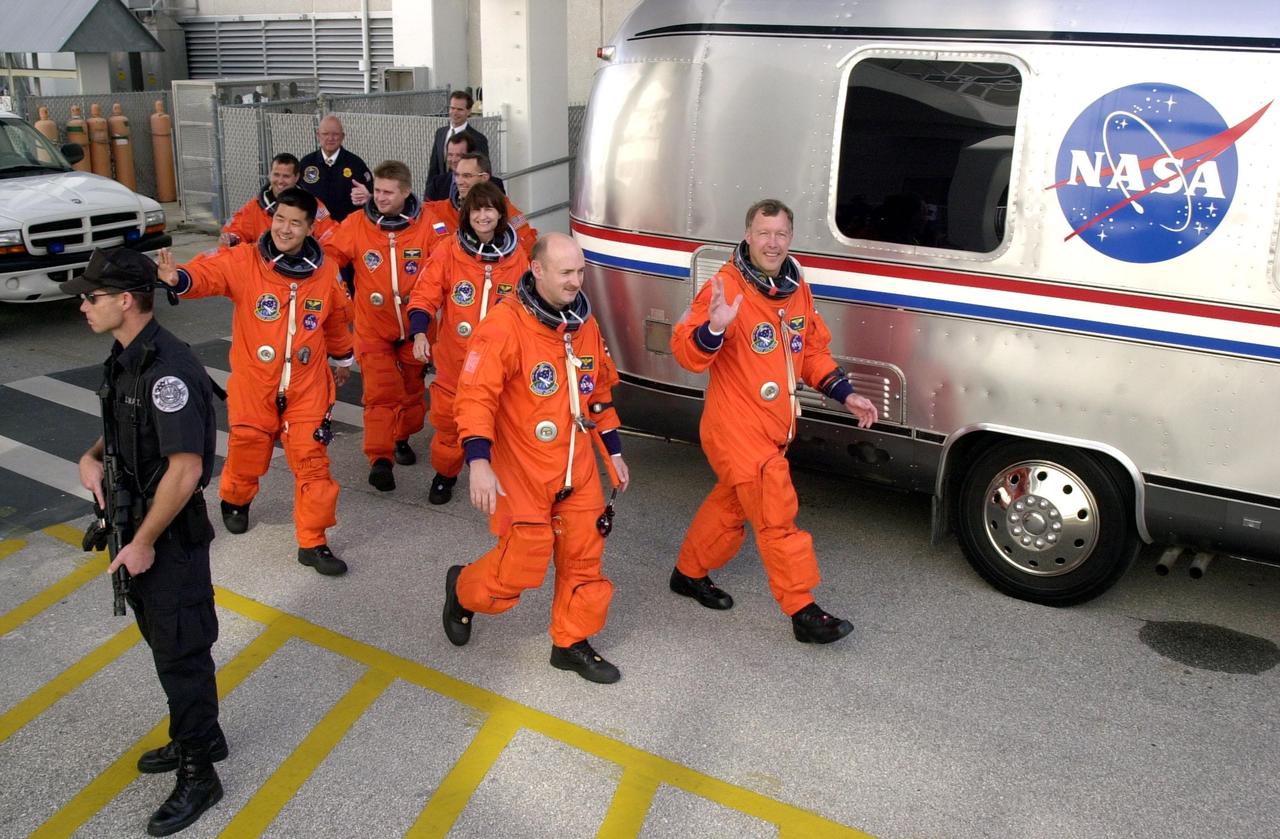

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-108 and Expedition 4 crews head for the Astrovan and a ride to Launch Pad 39B. Leading the way are Pilot Mark E. Kelly (left) and Commander Dominic L. Gorie; behind them are Mission Specialists Daniel M. Tani and Linda A. Godwin; next is Expedition 4 Commander Yuri Onufrienko, followed by astronauts Daniel W. Bursch (left) and Carl E. Walz. This is the second launch attempt after the first attempt Dec. 4 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at KSC. The main goals of the mission are to carry the Expedition 4 crew to the International Space Station as replacement for Expedition 3; carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello filled with water, equipment and supplies; and install thermal blankets over equipment at the base of the ISS solar wings. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001 and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. Launch is scheduled for 5:19 p.m. EST (22:19 GMT) Dec. 5, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B
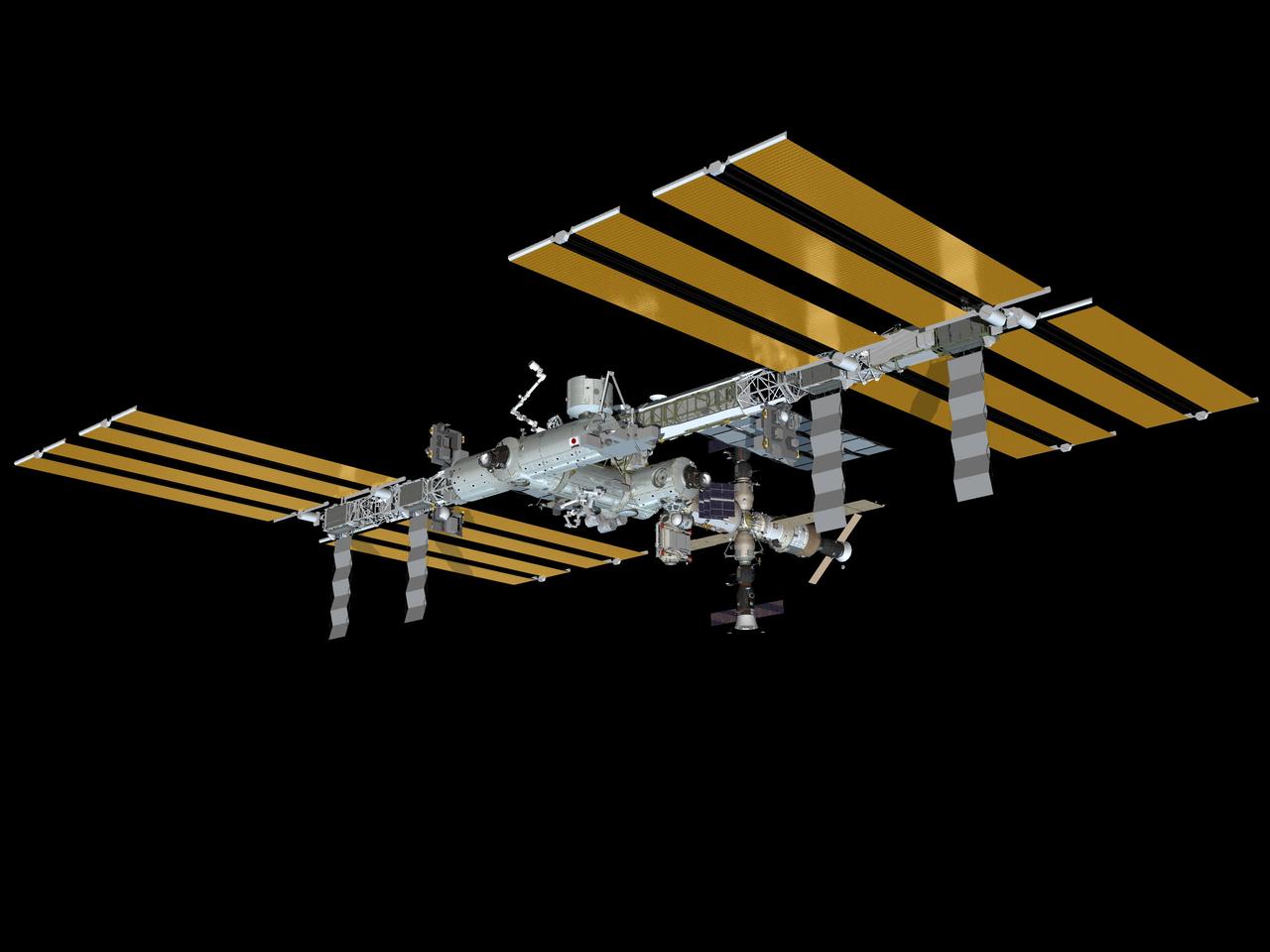

JSC2010-E-086855 (June 2010) --- Computer-generated artist?s rendering of the International Space Station as of June 17, 2010. Soyuz 23 (TMA-19) docks to the Zvezda Service Module?s aft port, bringing Expedition 24/25 crew members (Wheeler, Walker, Yurchikhin) to the ISS. The Rassvet Mini-Research Module 1 (MRM1) is attached to the Zarya nadir port. Progress 37 resupply vehicle is linked to the Pirs Docking Compartment and Soyuz 22 (TMA-18) remains docked to the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2).
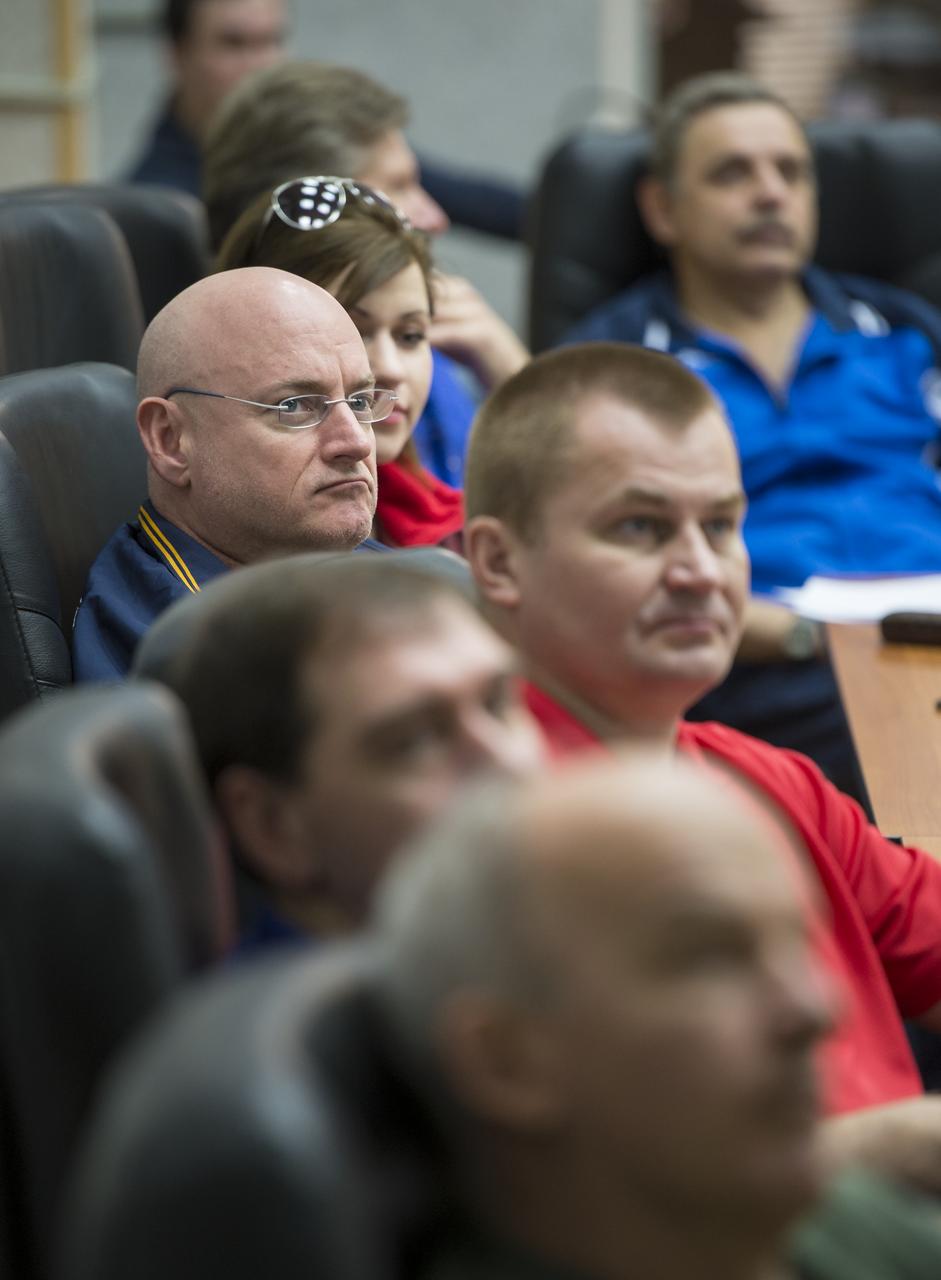

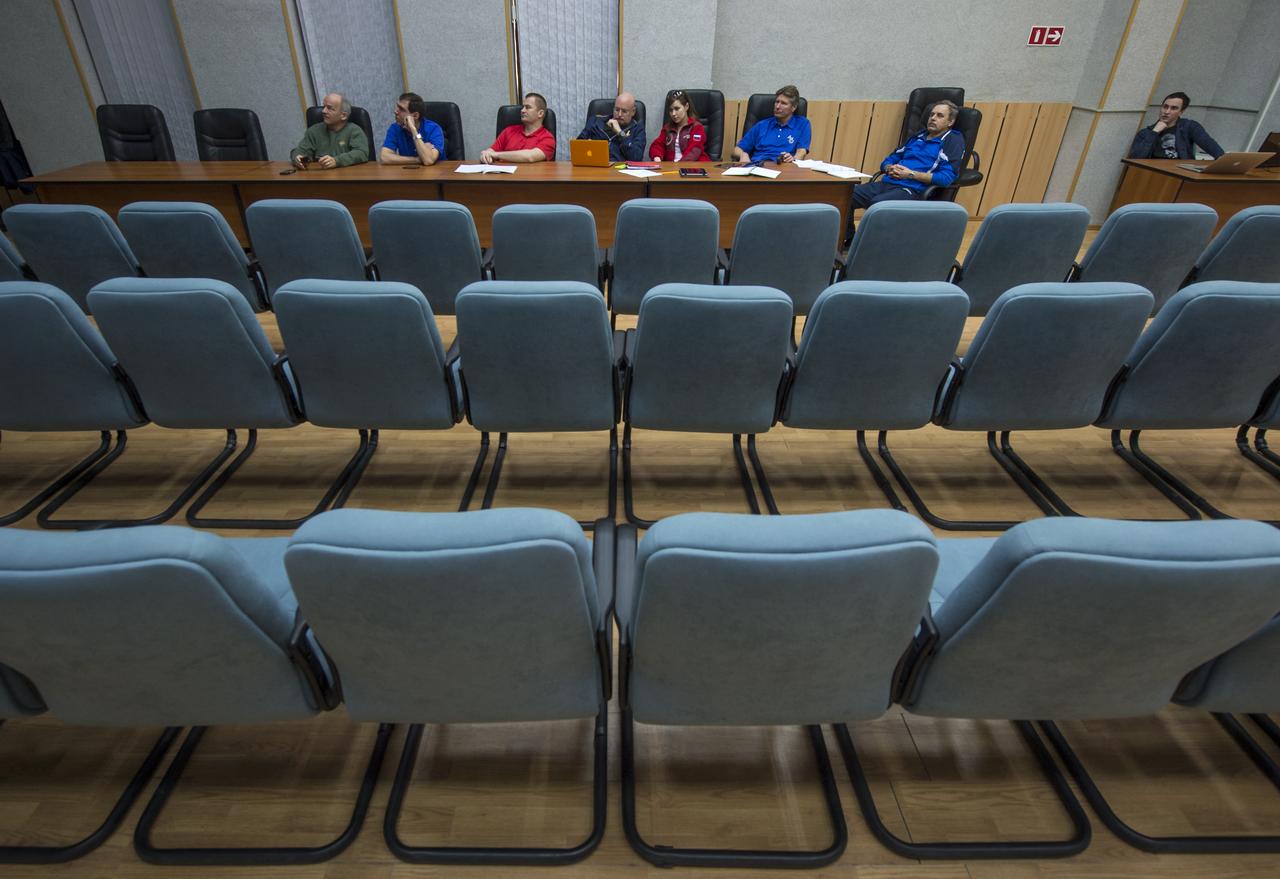
Expedition 43 NASA Astronaut Scott Kelly, left, along with fellow prime crew members: Russian Cosmonauts Gennady Padalka, and Mikhail Kornienko of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) and backup crew members Jeff Williams of NASA, Alexey Ovchinin, and Sergei Volkov of Roscosmos attend the ISS Russian Segment Safety briefing, Thursday, March 19, 2015 at Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Kelly, Padalka, and Kornienko are preparing for launch to the International Space Station in their Soyuz TMA-16M spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan March 28, Kazakh time. As the one-year crew, Kelly and Kornienko will return to Earth on Soyuz TMA-18M in March 2016. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
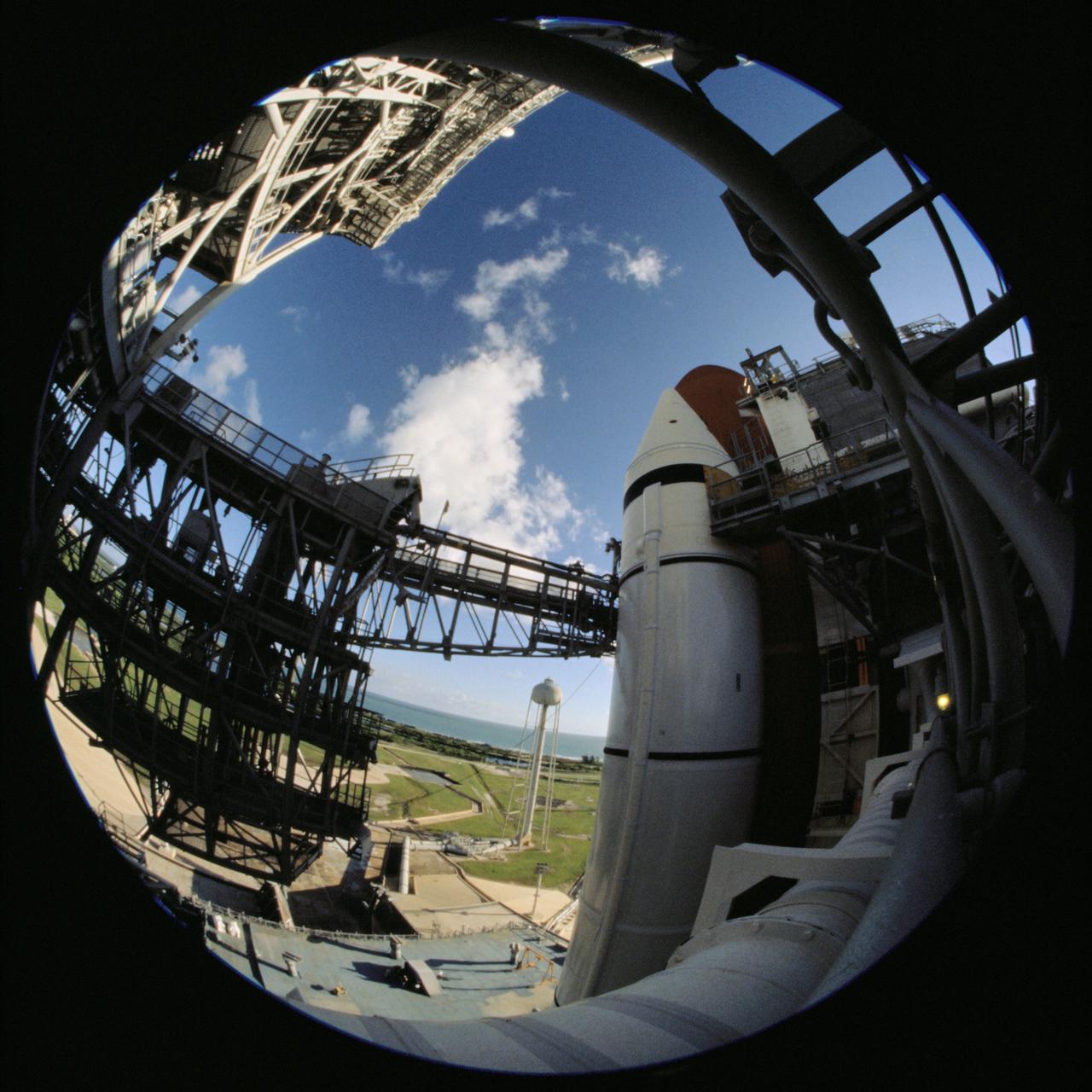

A photographer used a fisheye lens attached to an electronic still camera to record a series of photos of the Space Shuttle Discovery at the launch pad while the STS-120 crew was at Kennedy Space Center for the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test in October 2007. The STS-120 mission launched from Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39A at 11:38:19 a.m. (EDT) on October 23, 2007. The crew included Scott E. Parazynski, Douglas H. Wheelock, Stephanie D. Wilson, all mission specialists; George D. Zamka, pilot; Pamela A. Melroy, commander; Daniel M. Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer; and Paolo A. Nespoli, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA). Major objectives included the installation of the P6 solar array of the port truss and delivery and installment of Harmony, the Italian-built U.S. Node 2 on the International Space Station (ISS).
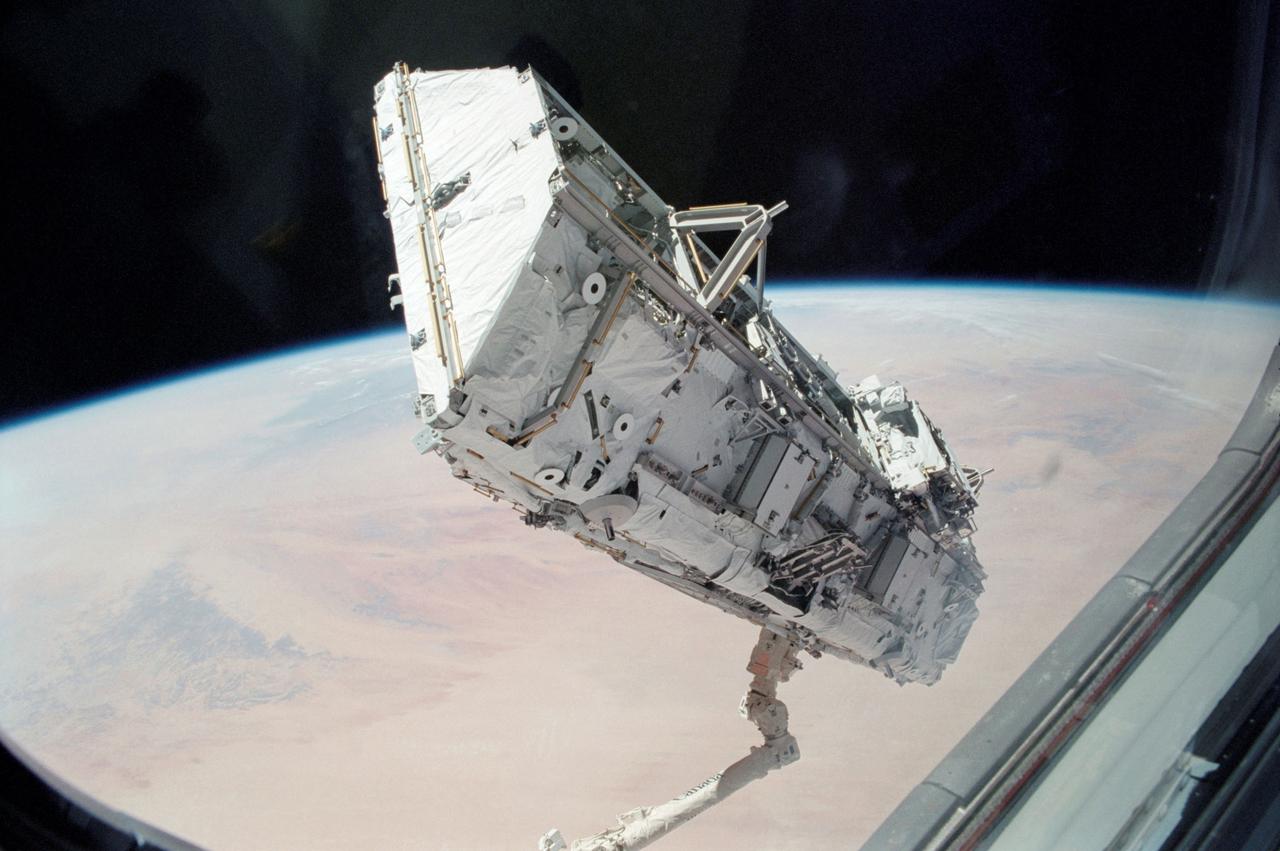

Backdropped against the blackness of space and the Earth's horizon, the S0 (S-zero) truss is removed from Atlantis' cargo bay and onto the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station (ISS) by Astronauts Ellen Ochoa, STS-110 mission specialist, and Daniel W. Bursch, Expedition Four flight engineer, using the ISS' Canadarm2. Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis, STS-110 mission, prepared the International Space Station (ISS) for future spacewalks by installing and outfitting the 43-foot-long S0 truss and preparing the first railroad in space, the Mobile Transporter. The 27,000-pound S0 truss was the first of 9 segments that will make up the Station's external framework that will eventually stretch 356 feet (109 meters), or approximately the length of a football field. This central truss segment also includes a flatcar called the Mobile Transporter and rails that will become the first "space railroad," which will allow the Station's robotic arm to travel up and down the finished truss for future assembly and maintenance. The completed truss structure will hold solar arrays and radiators to provide power and cooling for additional international research laboratories from Japan and Europe that will be attached to the Station. Milestones of the STS-110 mission included the first use of the Station's robotic arm to maneuver spacewalkers around the Station and it was the first time all of a Shuttle crew's spacewalks were based out of the Station's Quest Airlock. It was also the first Shuttle to use three Block II Main Engines. The Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis, STS-110 mission, was launched April 8, 2002 and returned to Earth April 19, 2002.
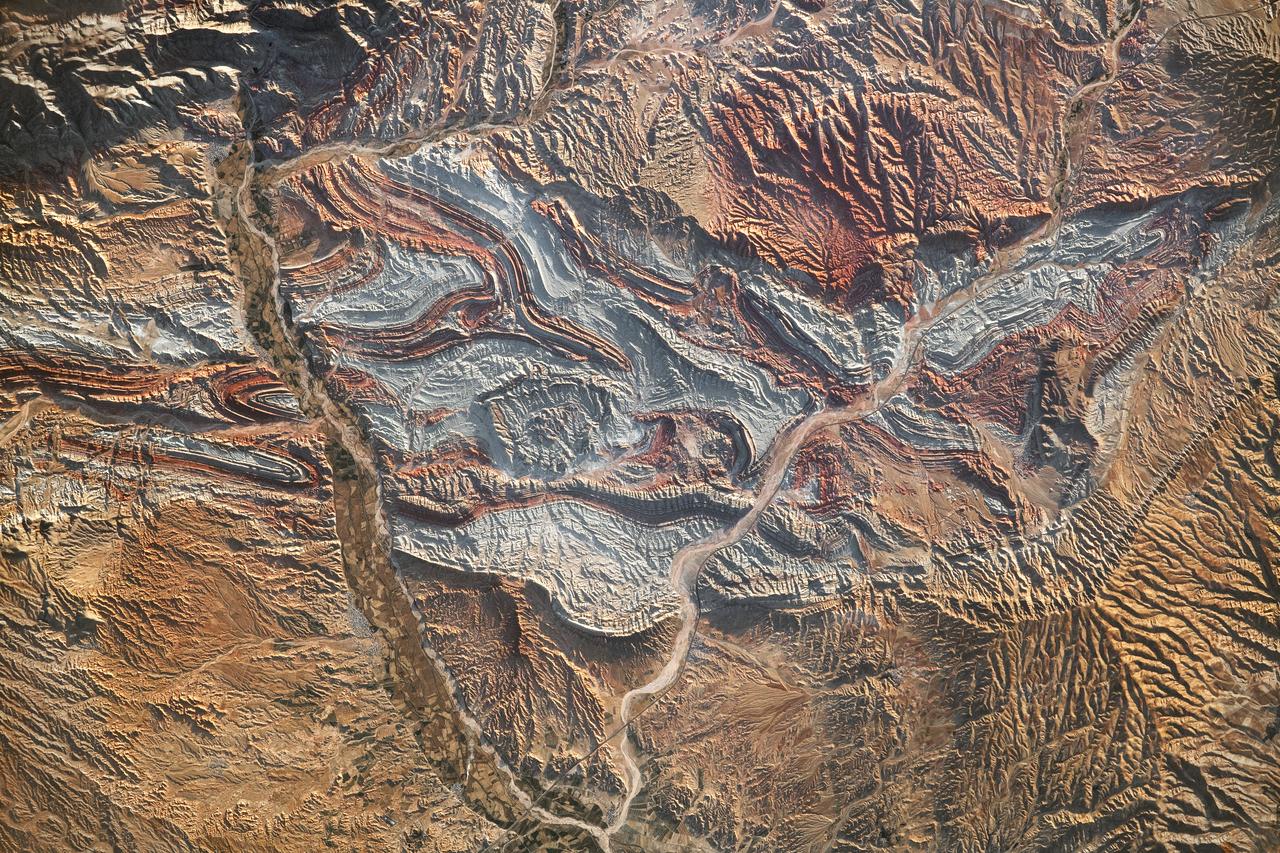

iss069-e-089946_lrg (09/19/2023) --- An astronaut aboard the International Space Station took this photograph of the rugged landscape of the Aladaghlar Mountains in northwestern Iran. Ridges cast shadows in the valleys and other low elevation areas, creating a three-dimensional appearance. Human alterations to the landscape are most evident in riverbeds, where the even topography is easier to build on and navigate. Natural processes over millions of years have folded rock layers of various compositions and colors into the curved patterns seen here. These folds are produced by tectonic forces operating along the convergent plate boundary of the Arabia and Eurasia plates. The convergence of these tectonic plates causes uplift, folding, and deformation of the colorful rock layers, and subsequent erosion exposes them. On the left side of this photo, the Qezel Ozan River, a major river in northern Iran, cuts across the landscape. Agricultural fields are visible along the riverbanks tucked between the mountains. The Qezel Ozan also intersects the Zanjan-Tabriz freeway (Freeway 2), a major thoroughfare built on a dried riverbed connecting the cities of Tehran and Tabriz. Astronaut photograph ISS069-E-89946 was acquired on September 19, 2023, with a Nikon D5 digital camera using a focal length of 400 millimeters. The image was provided by the ISS Crew Earth Observations Facility and the Earth Science and Remote Sensing Unit at Johnson Space Center. The image was taken by a member of the Expedition 69 crew. It has been cropped and enhanced to improve contrast, and lens artifacts have been removed. The International Space Station Program supports the laboratory as part of the ISS National Lab to help astronauts take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth. Caption by Sara Schmidt, GeoControl Systems, JETS II Contract at NASA-JSC and Andrea Wenzel, Jacobs-JETS II Contract at NASA-JSC.
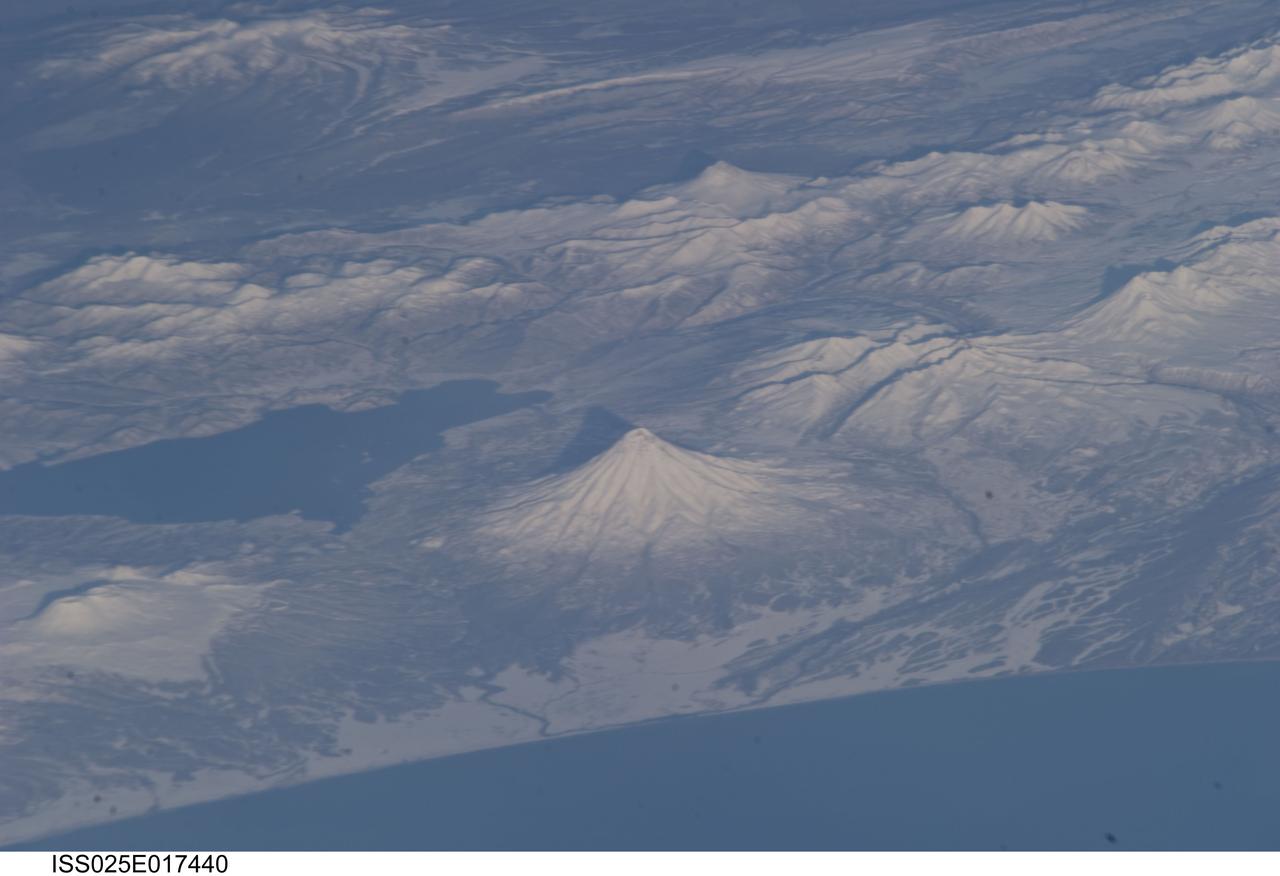

ISS025-E-017440 (19 Nov. 2010) --- Kamchatka volcanoes are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 25 crew member on the International Space Station. This striking photograph features several snow-covered volcanoes located on the Kamchatka Peninsula of the Russian Federation, as seen from the orbital perspective of the International Space Station (ISS). This image also illustrates one of the unique attributes provided by the ISS – the ability to view Earth landscapes at an angle, rather than the “straight down” view typical of many orbital satellite-based sensors. This oblique view, together with shadows cast by the volcanoes and other mountains provides perspective about the setting and a sense of topography of the region, especially highlighting the symmetrical cones of Kronotsky (center) and Kizimen (top right) stratovolcanoes. Kizimen Volcano last erupted in 1928, while Kronotsky Volcano—one of the largest on the peninsula—last erupted in 1923. Schmidt Volcano, located to the north of Kronotsky, has the morphology of a shield volcano and is not known to have erupted during the period of historical record. To the south of Kronotsky is Krasheninnikov Volcano, comprised of two overlapping stratovolcanoes that formed within an earlier caldera. Scientists believe Krasheninnikov may have last erupted in 1550. The two summit craters of the stratovolcanoes are clearly visible in this image (lower left). Lake Kronotsky (left) is Kamchatka’s largest lake; it was formed when lava flows from Kronotsky Volcano dammed the Listvenichnaya River. The Kamchatka Peninsula lies along the so-called “Ring of Fire” in the Pacific Ocean. The Ring of Fire is characterized by the presence of active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes; these are associated with the many active subduction and transform boundary zones that ring the Pacific tectonic plate. According to scientists, there are currently 114 volcanoes identified on the Kamchatka Peninsula that have erupted during the Holocene Epoch (approximately 12,000 years ago to the present).