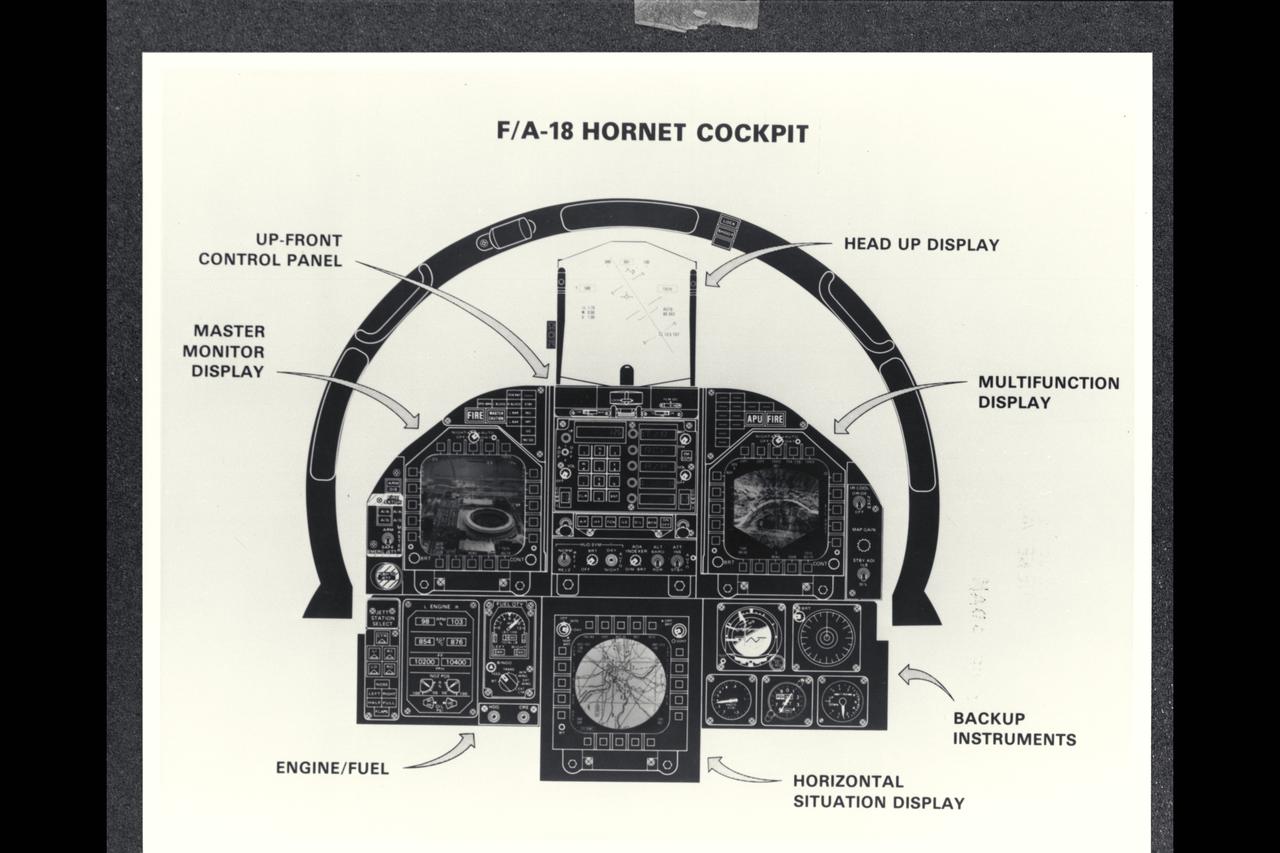
McDonnell Douglas F/A-18A Hornet cockpit drawing
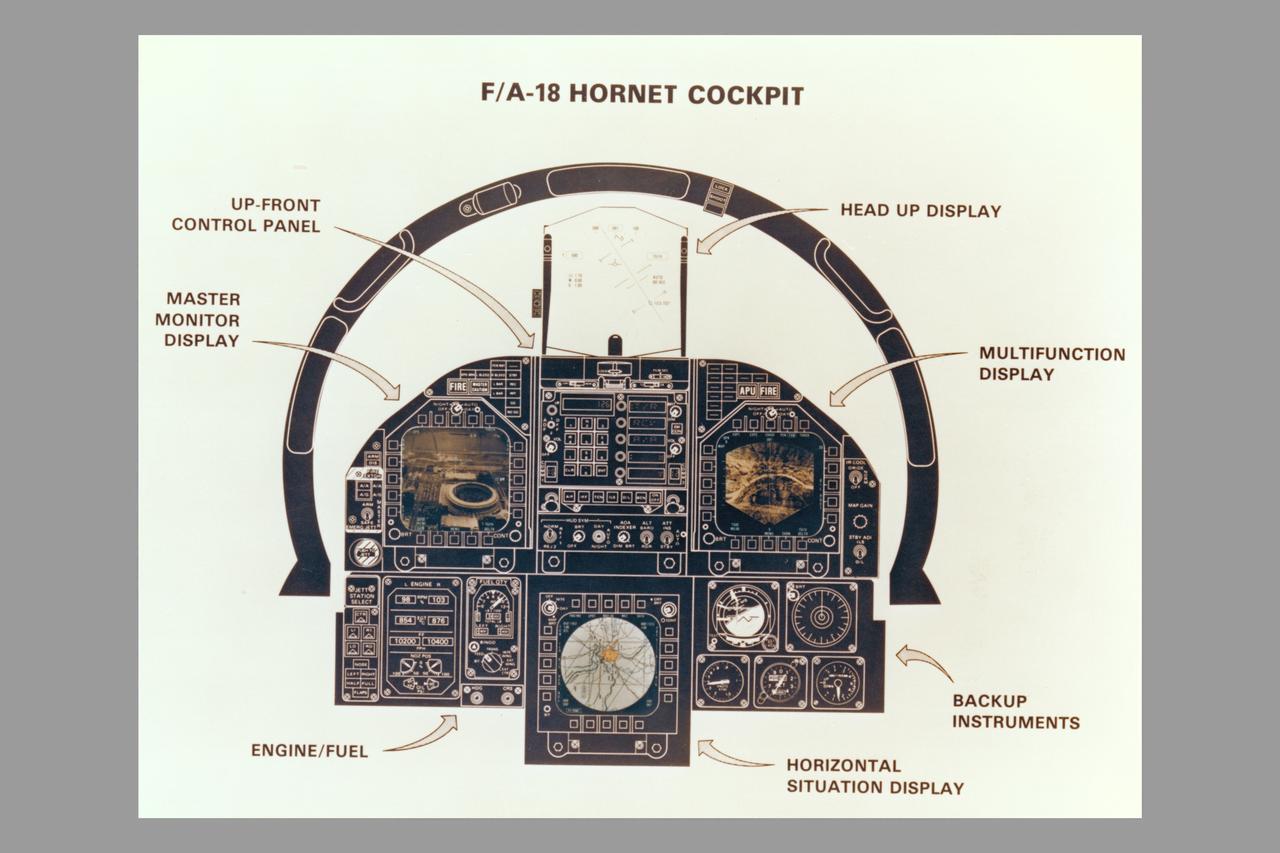
McDonnell Douglas F/A-18A Hornet cockpit drawing

McDonnell Douglas F/A-18A Hornet in flight

McDonnell Douglas F/A-18A Hornet in flight
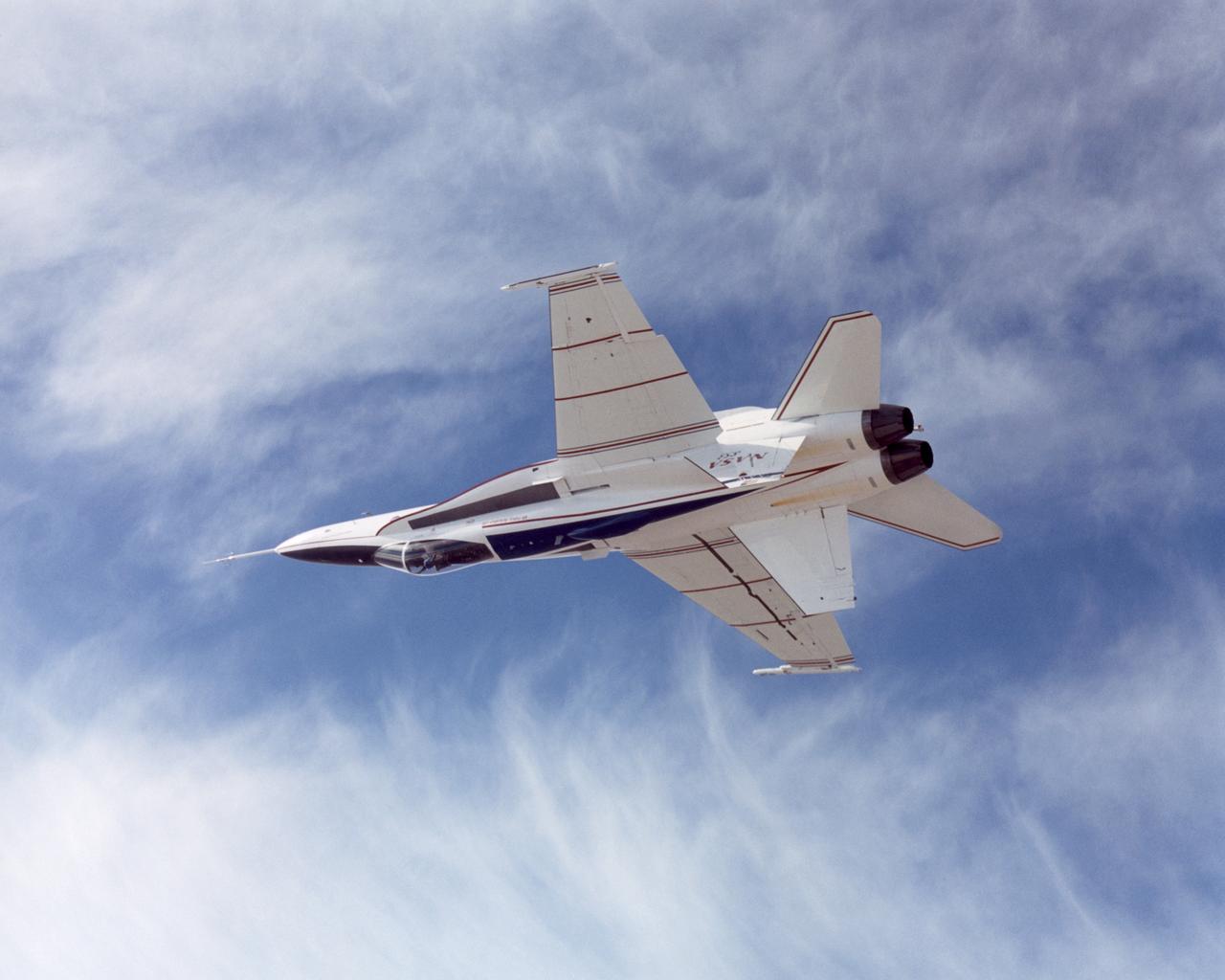

NASA's Active Aeroelastic Wing F/A-18A research aircraft rolls upside down during a 360-degree aileron roll on a test mission.
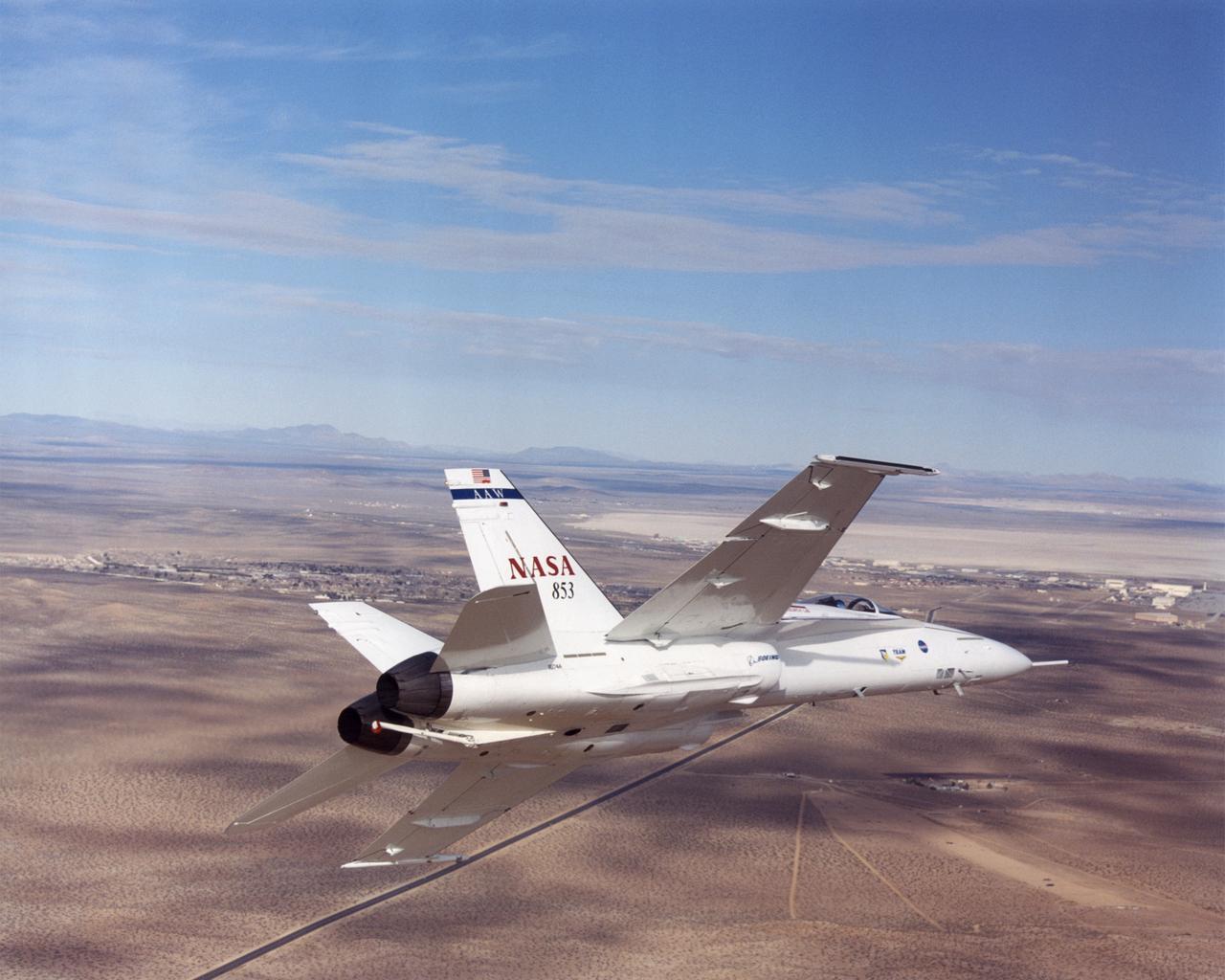

NASA 853, a modified former Navy F/A-18A fighter plane, is now performing research duties in the Active Aeroelastic Wing project at NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards AFB, California.
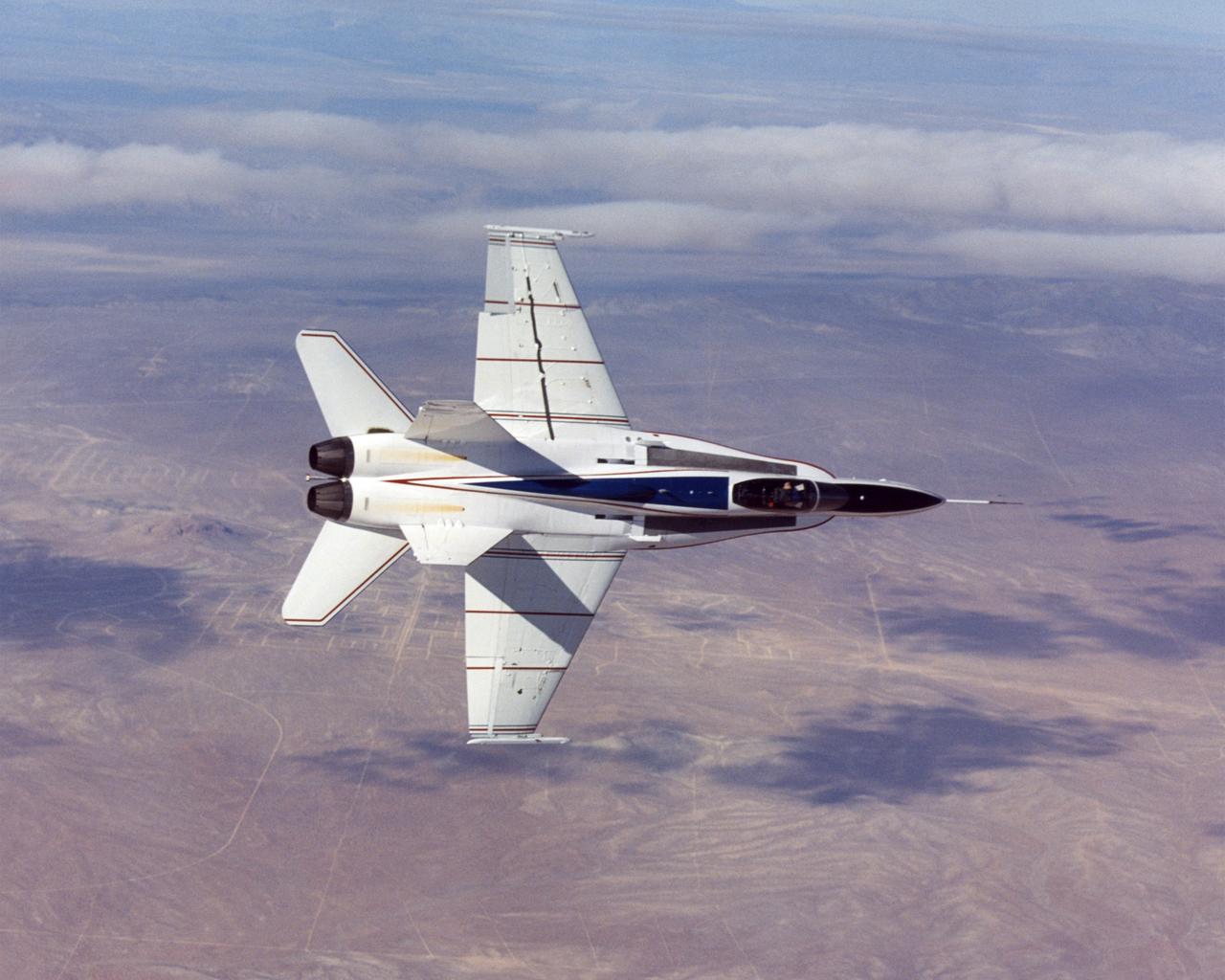

NASA Dryden's highly-modified Active Aeroelastic Wing F/A-18A shows off its form during a 360-degree aileron roll during a research flight.
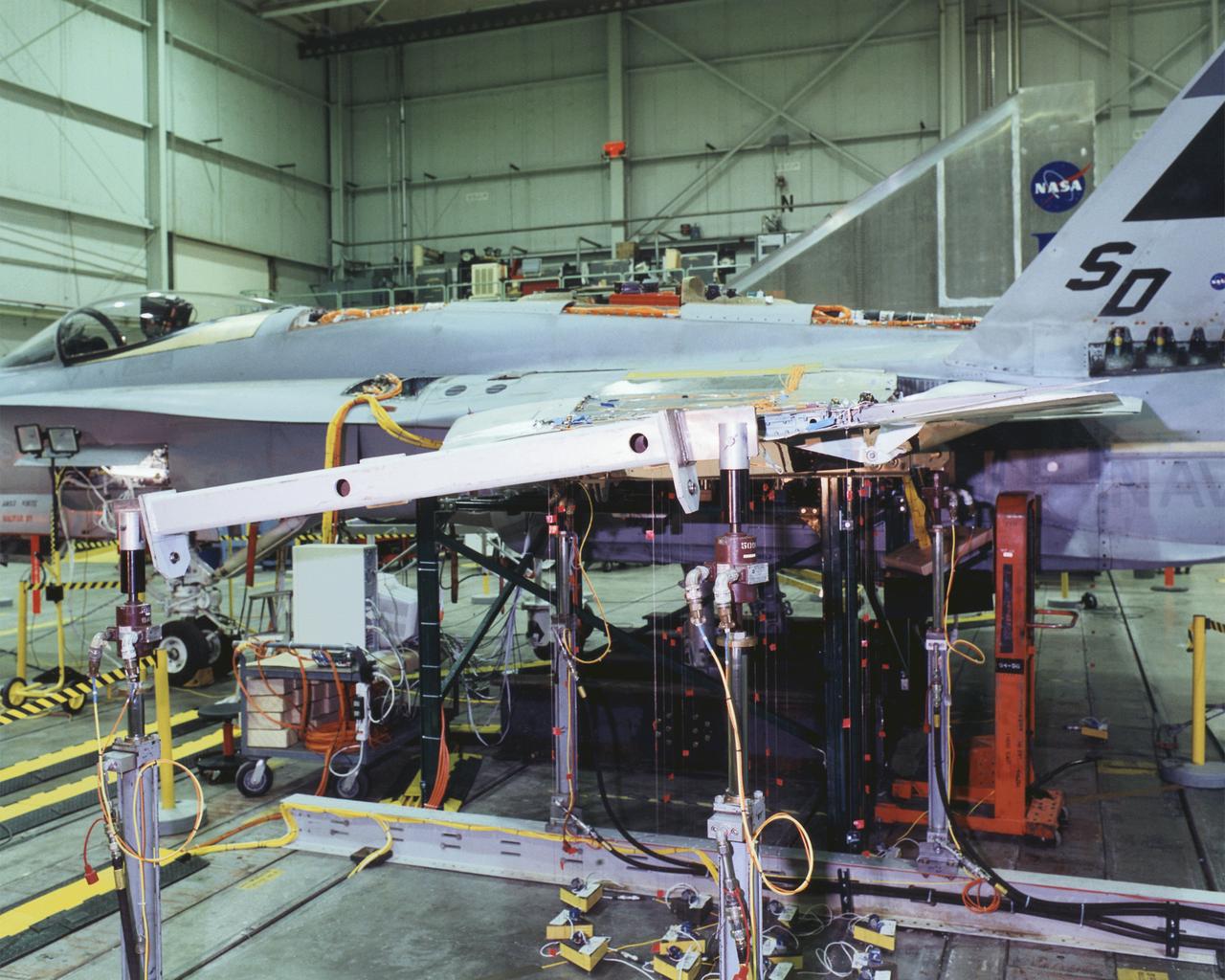

A modified F/A-18A undergoes wing torsion testing in the Flight Dynamics Laboratory at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California
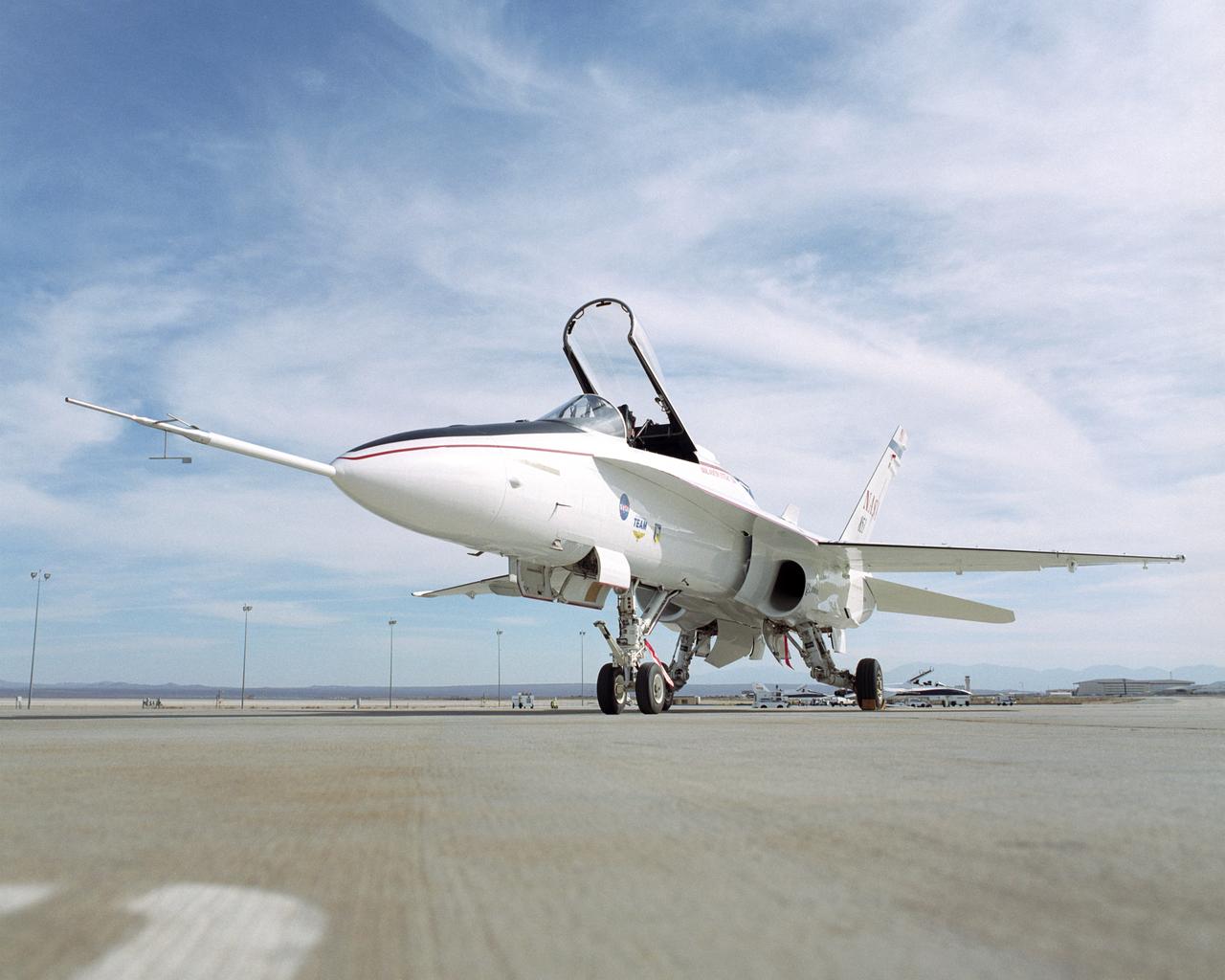

This modified F/A-18A is the test aircraft for the Active Aeroelastic Wing (AAW) project at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.
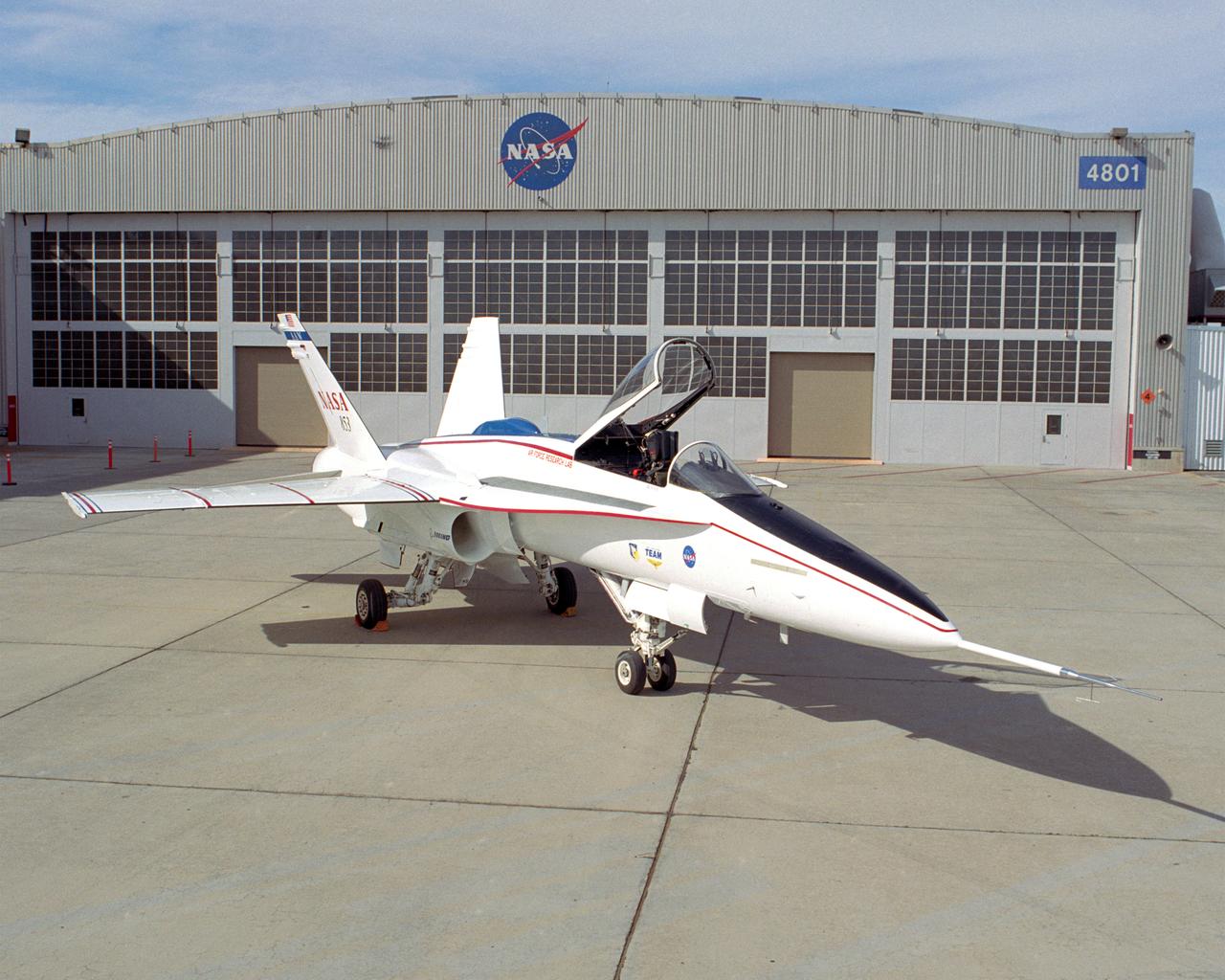

This modified F/A-18A is the test aircraft for the Active Aeroelastic Wing (AAW) project at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.
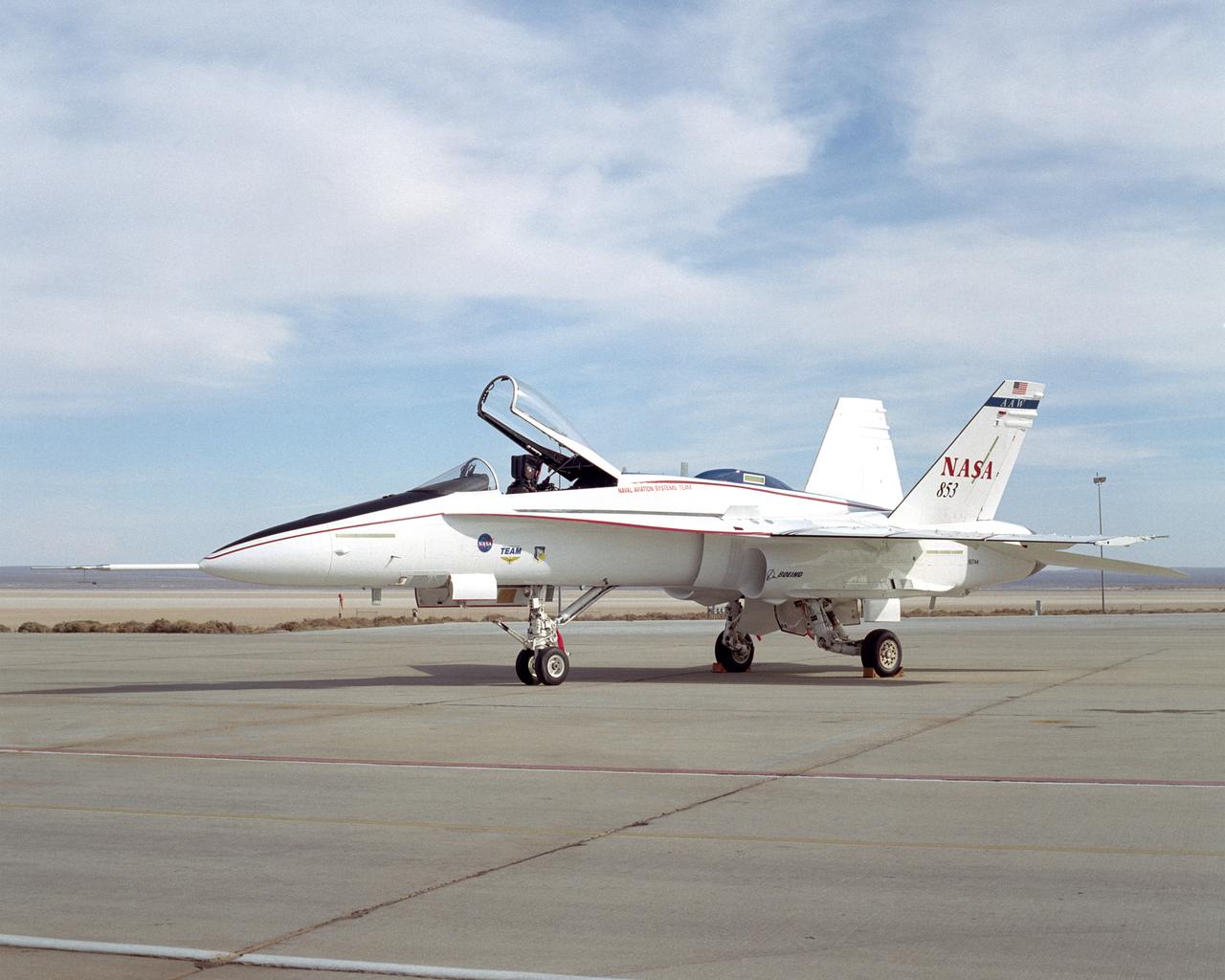

This modified F/A-18A is the test aircraft for the Active Aeroelastic Wing (AAW) project at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.
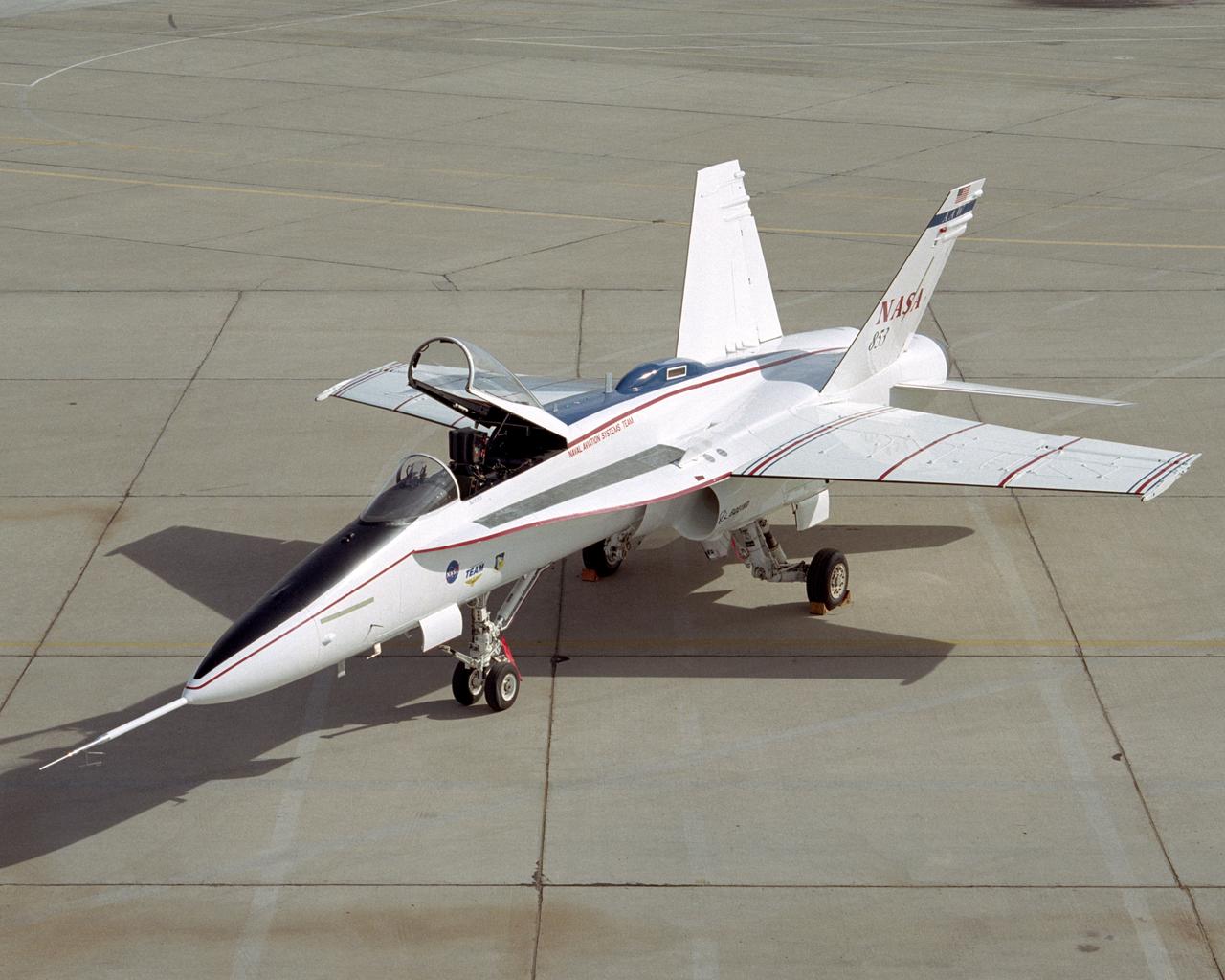

This modified F/A-18A is the test aircraft for the Active Aeroelastic Wing (AAW) project at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.
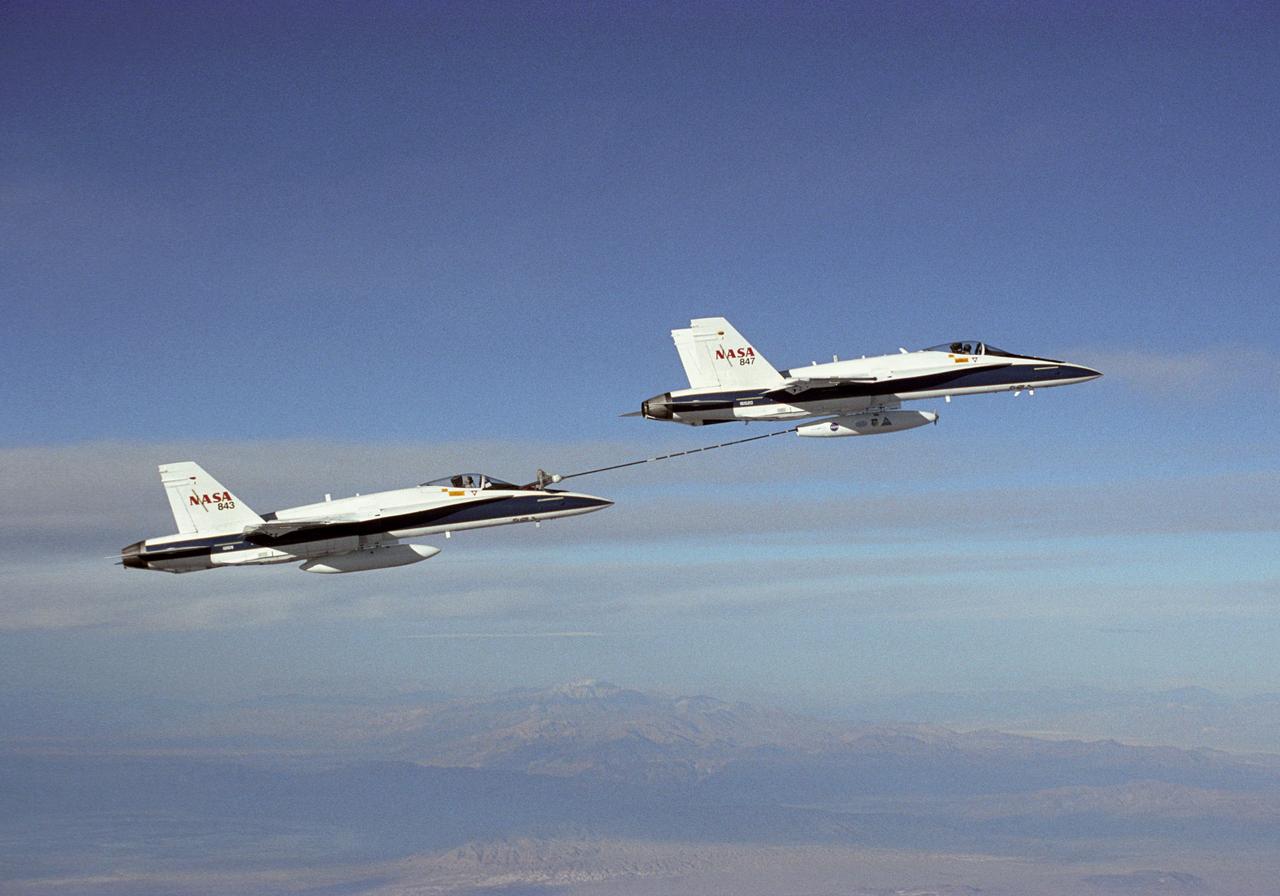

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft (No. 843) flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
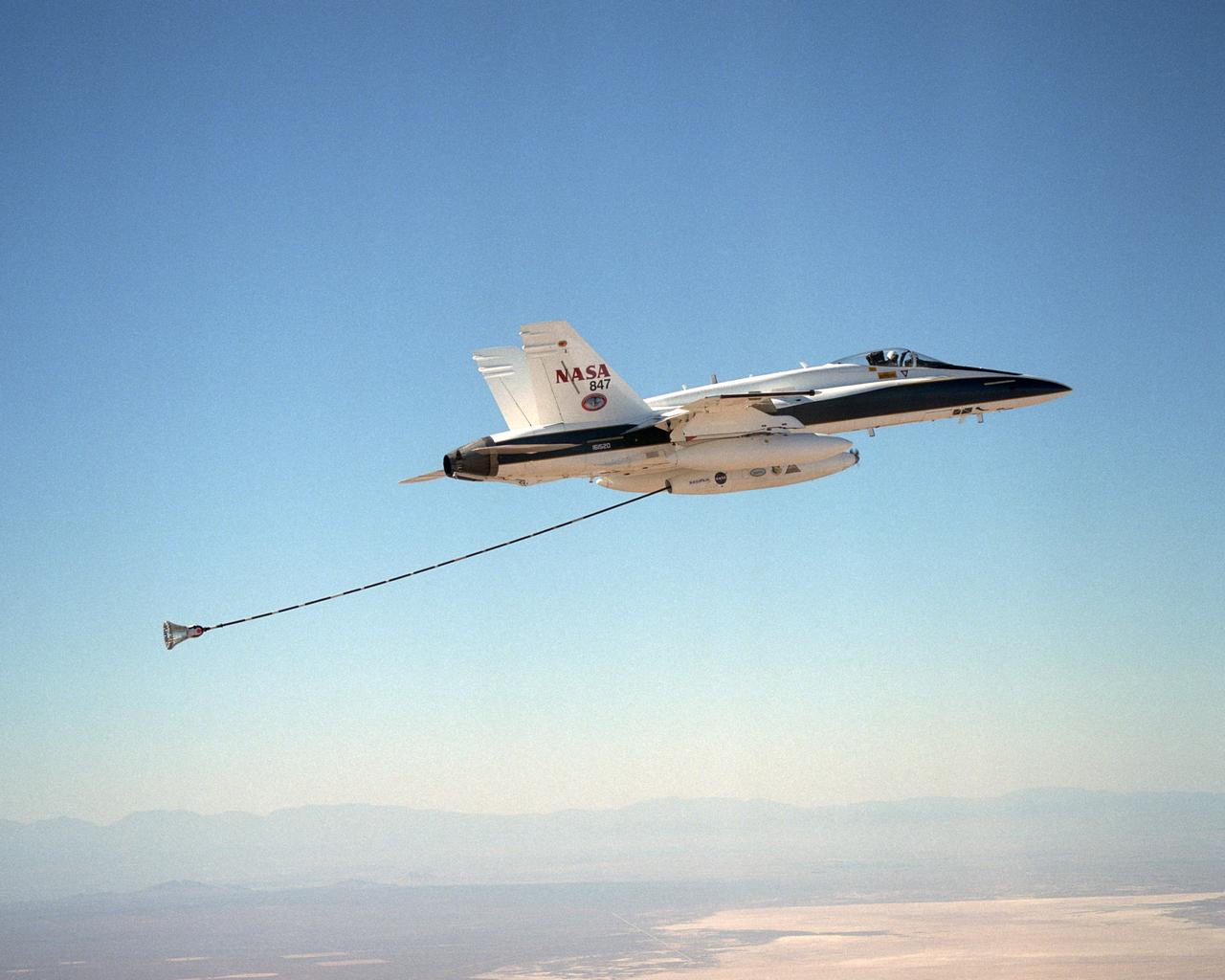

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
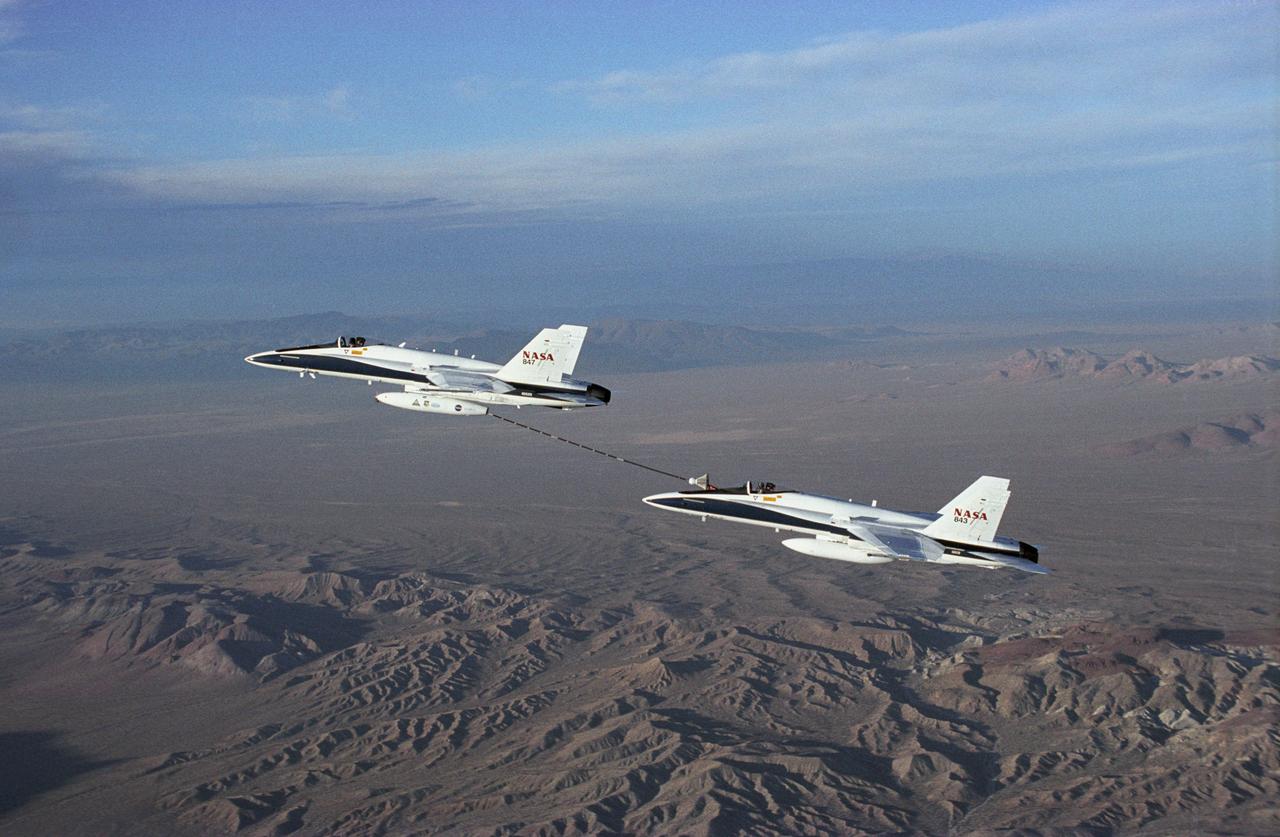

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft (No. 843) flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
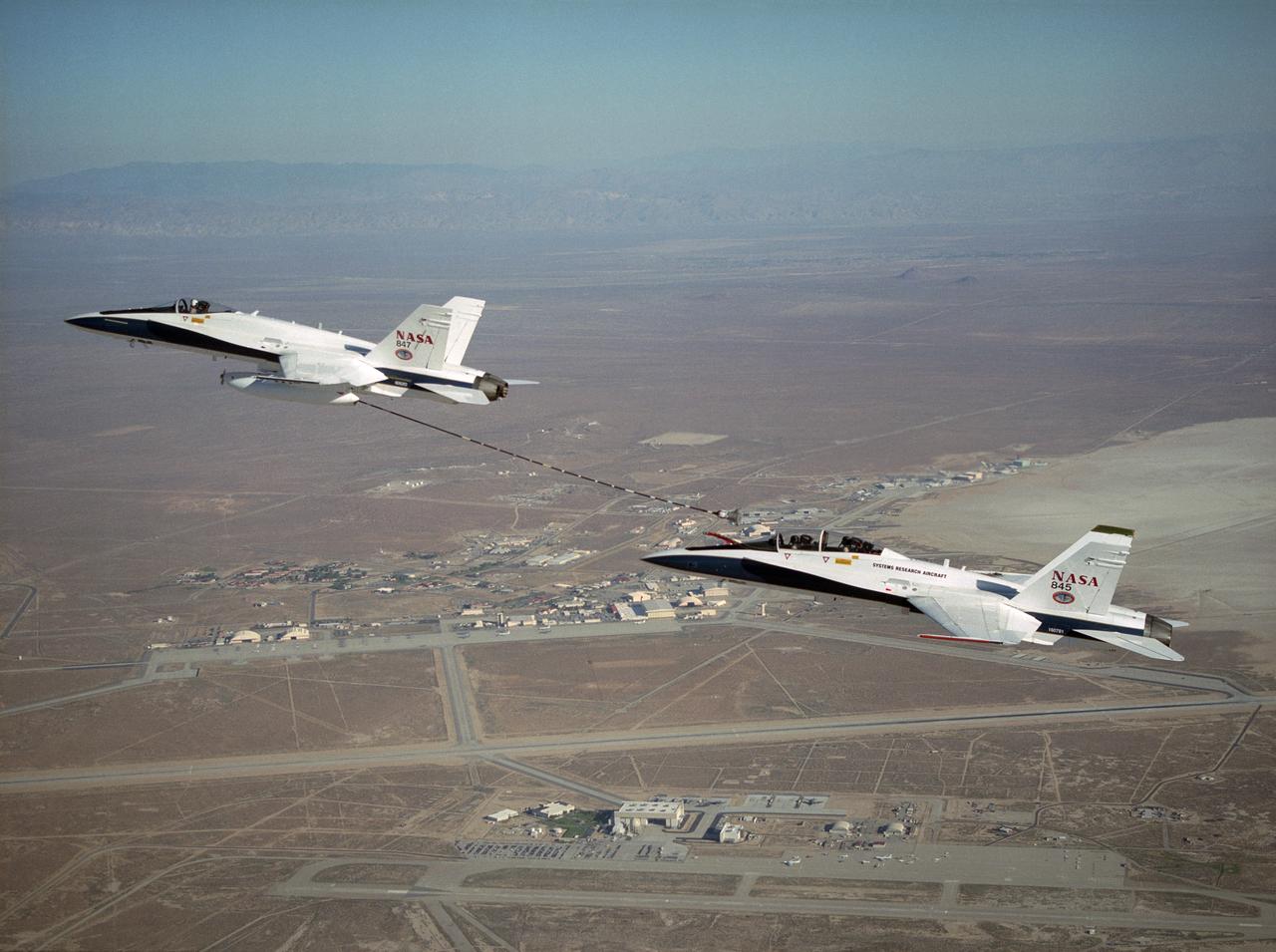

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
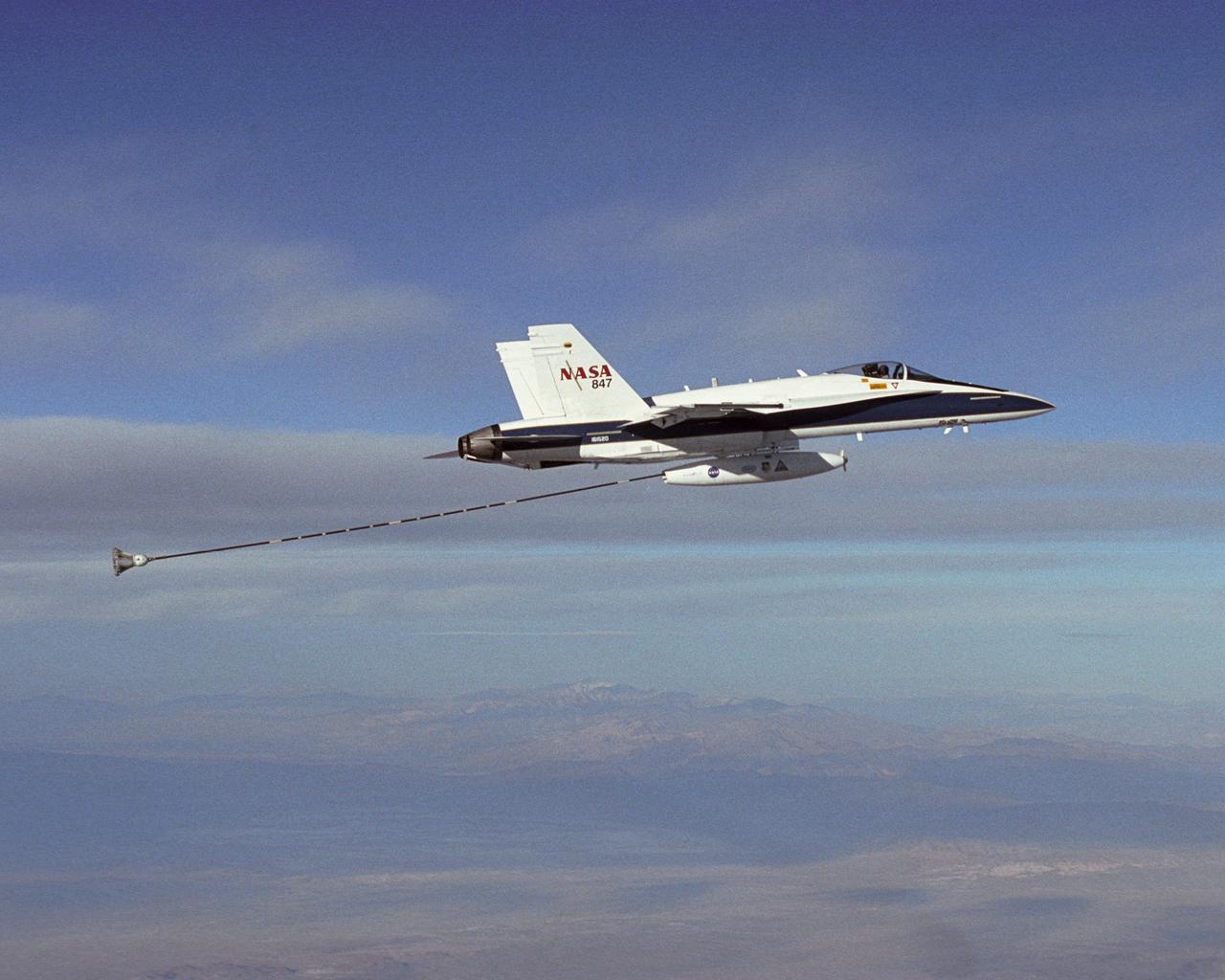

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft (No. 843) flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
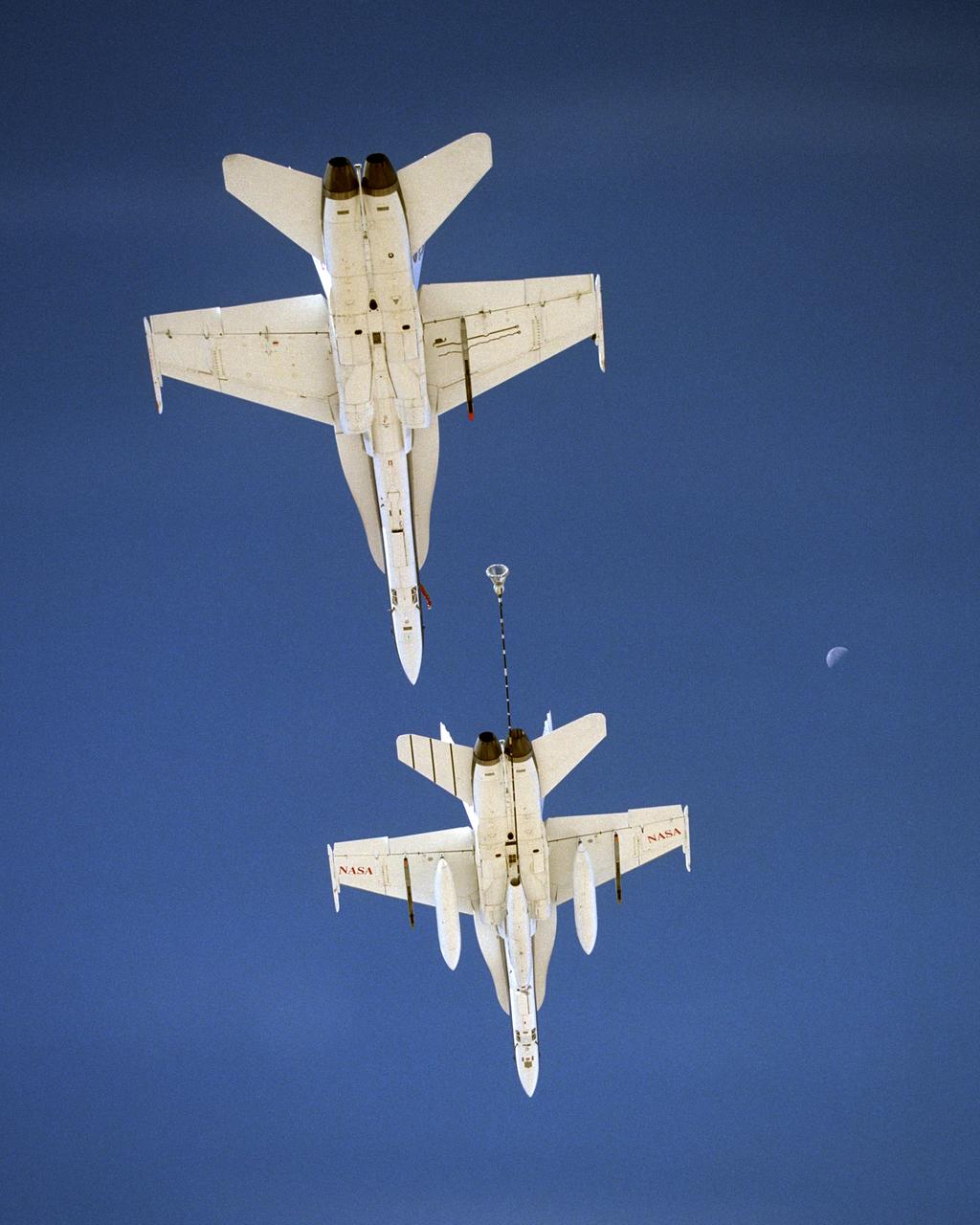

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.

How differential deflection of the inboard and outboard leading-edge flaps affected the handling qualities of this modified F/A-18A was evaluated during the first check flight in the Active Aeroelastic Wing program at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center.
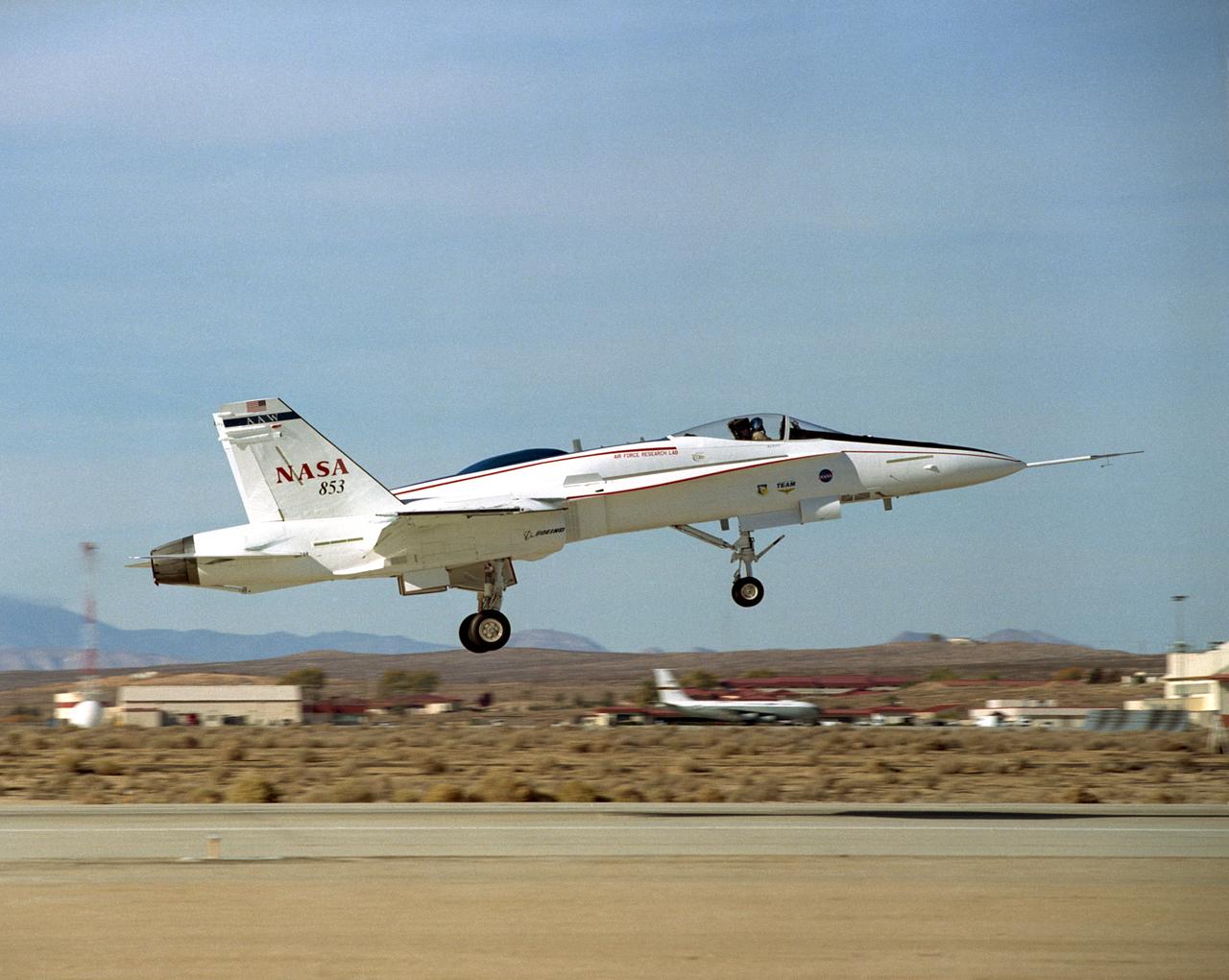

The Active Aeroelastic Wing F-18A lifts off on its first checkout flight November 15, 2002, from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. The checkout flight initiated a two-phase NASA--Air Force flight research program that will investigate the potential of aerodynamically twisting flexible wings to improve maneuverability of high-performance aircraft at transonic and supersonic speeds.
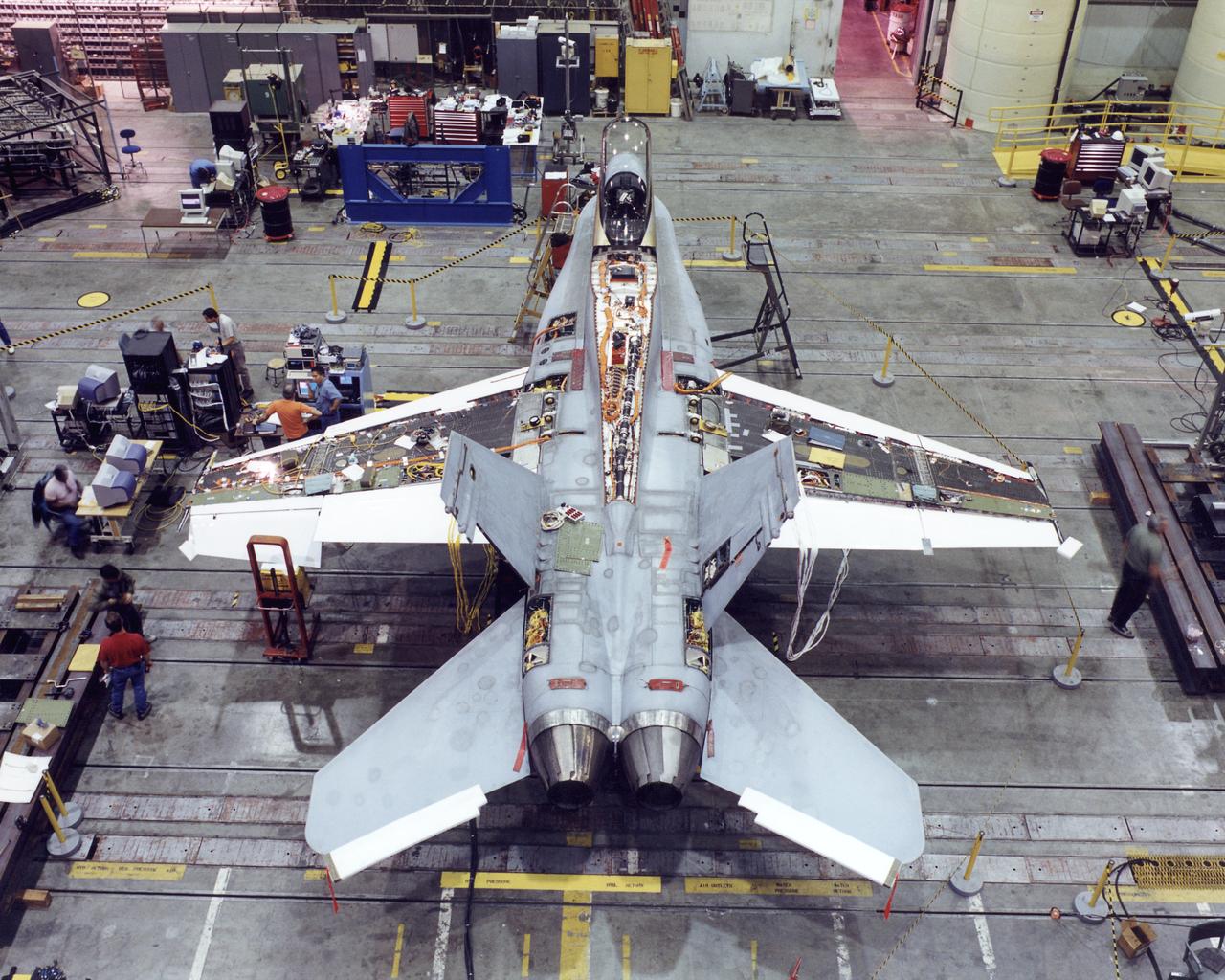

Structural loads testing on the Active Aeroelastic Wing F-18 in the Flight Loads Laboratory at NASA's Dryden flight Research Center, Edwards, California
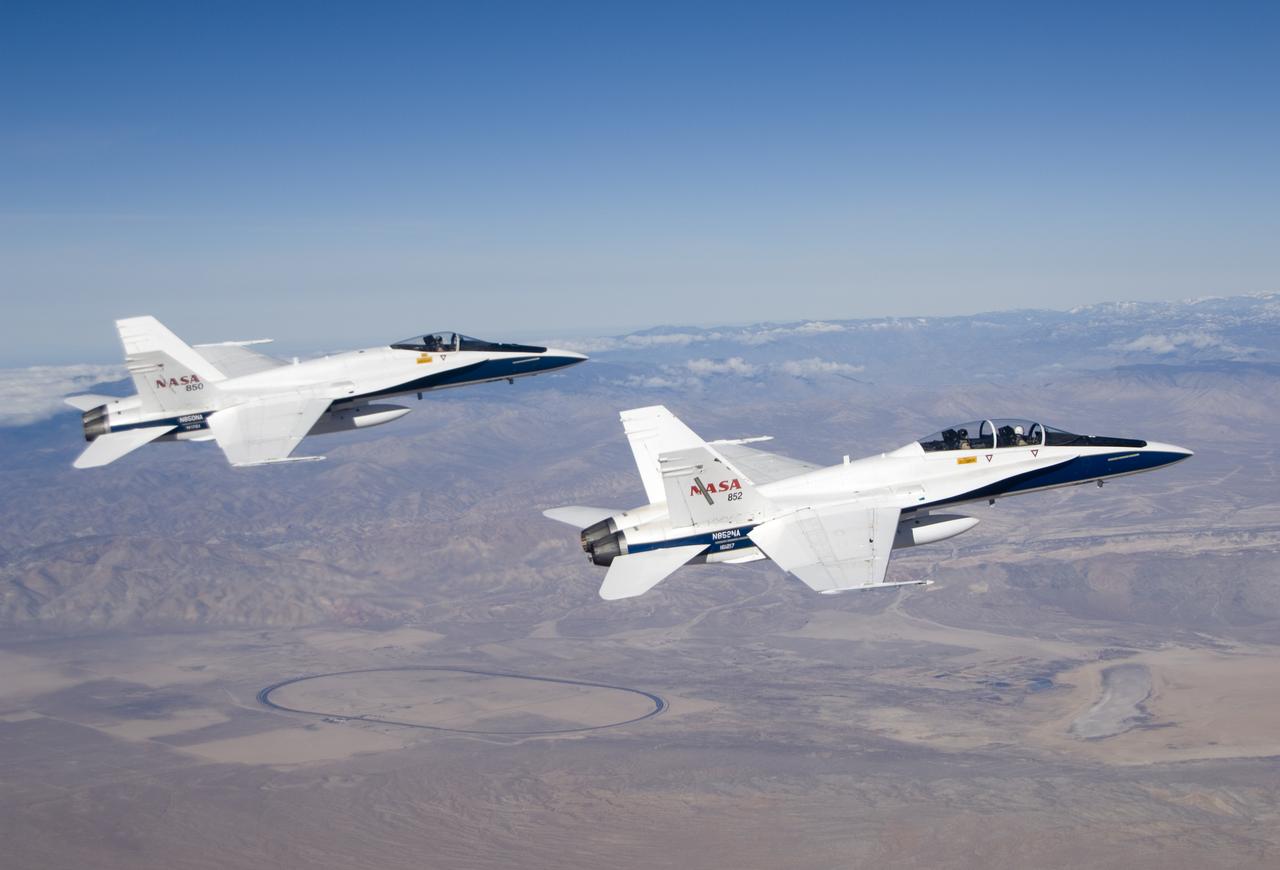

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of sp