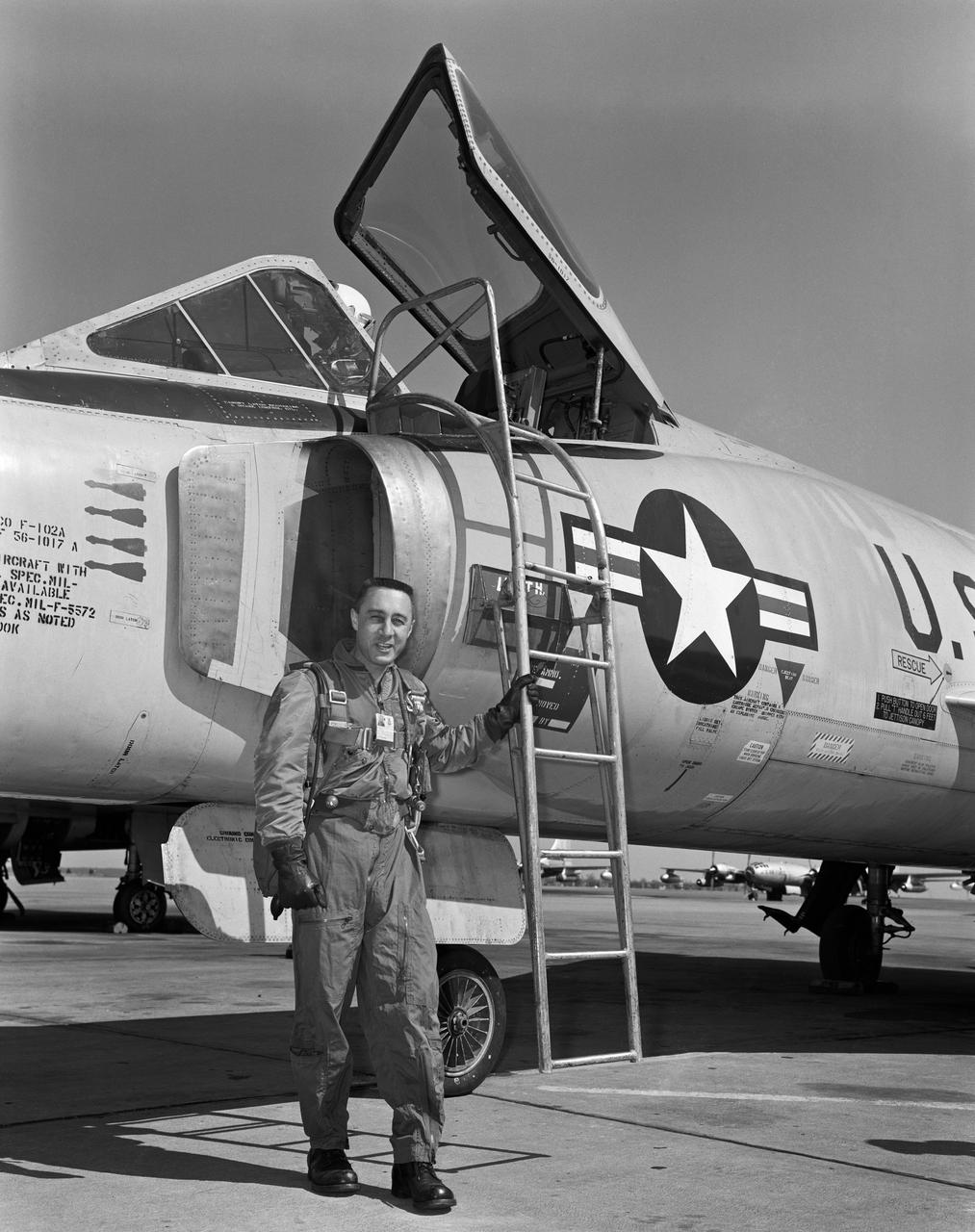

B60-00708 (1960) --- Astronaut Virgil I (Gus) Grissom pictured standing beside a F-102 on the flight line. Photo credit: NASA
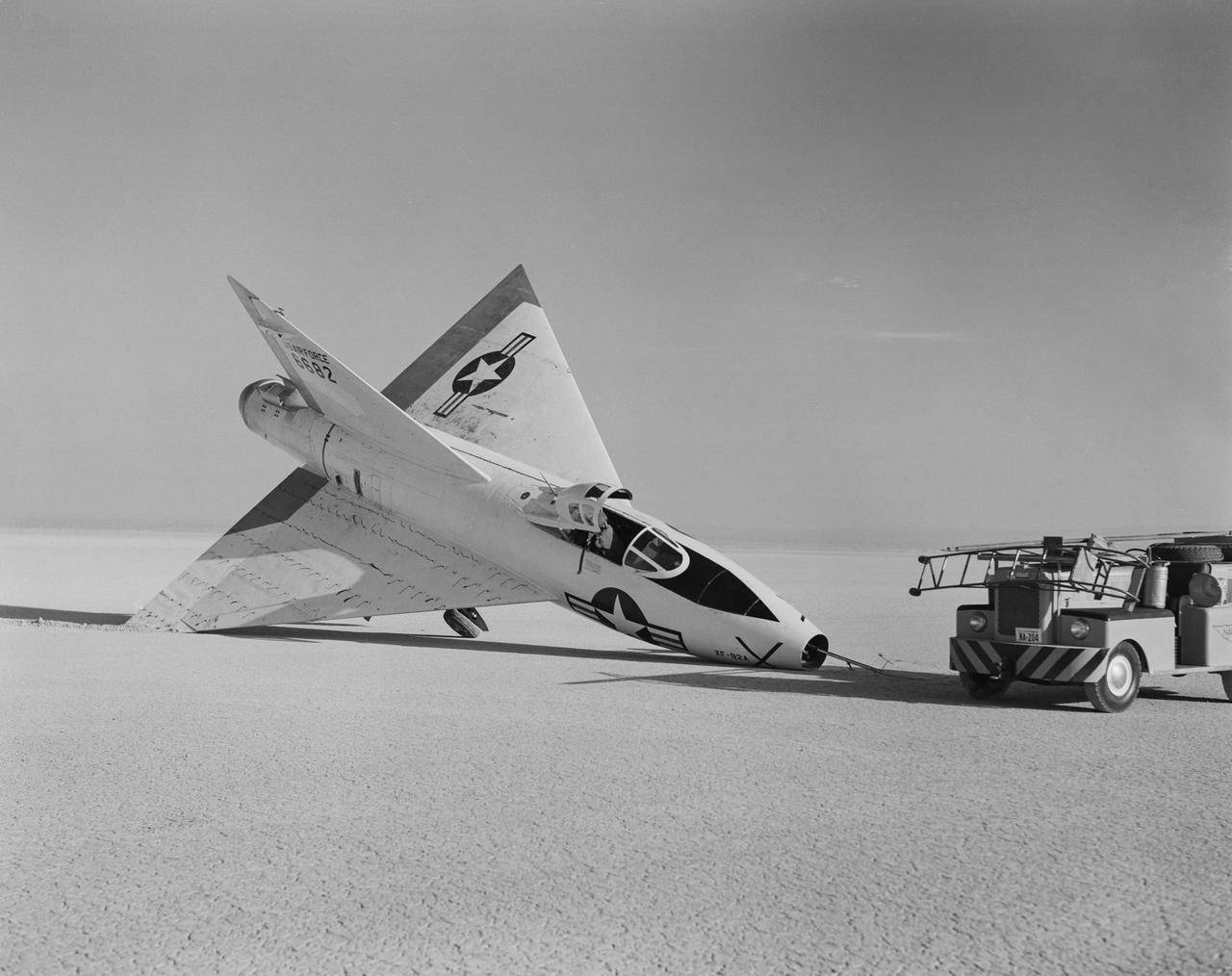

The XF-92A, which had a minor landing mishap in 1953, was the concept for the first delta wing fighter in the U.S. inventory, the F-102.
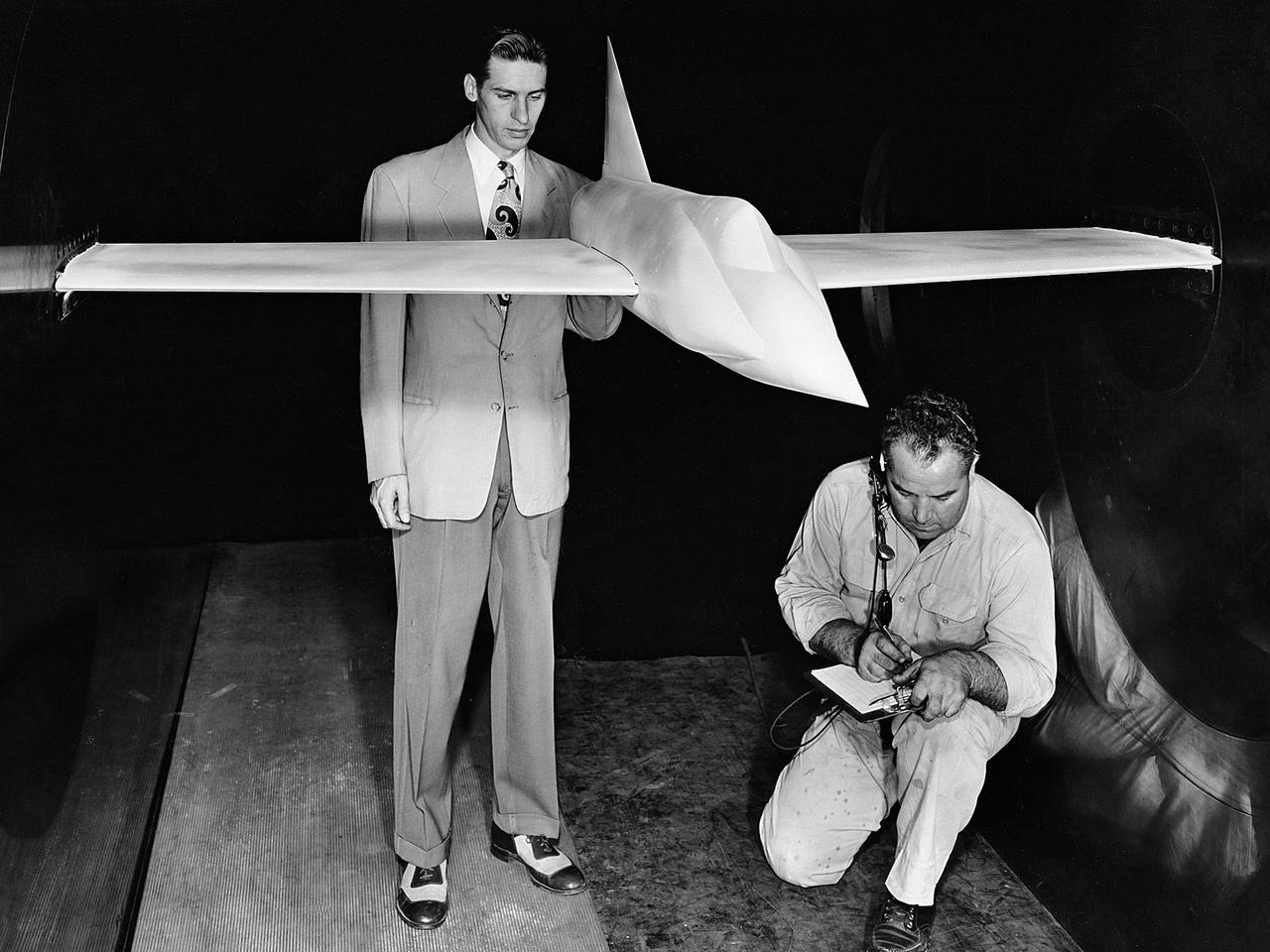

A .10-scale model of Convair’s XF-102 in the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory for jet exit studies. The XF-102 was a prototype of the F-102 Delta Dagger. The F-102 served as an interceptor against long range bombers from the Soviet Union. The aircraft was powered by a Pratt and Whitney J57 turbojet. The first prototype crashed two weeks after is first flight on October 24, 1953, just months after this photograph. Engineers then incorporated the fixed-wing design to reduce drag at supersonic speeds. The production model F-102 became the first delta-wing supersonic aircraft in operation. The 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel is used to study propulsion systems, including inlets and exit nozzles, combustion fuel injectors, flame holders, exit nozzles, and controls on ramjet and turbojet engines. Flexible sidewalls alter the tunnel’s nozzle shape to vary the Mach number during operation. A seven-stage axial compressor, driven by three electric motors that yield a total of 87,000 horsepower, generates air speeds from Mach 0.36 to 2.0.
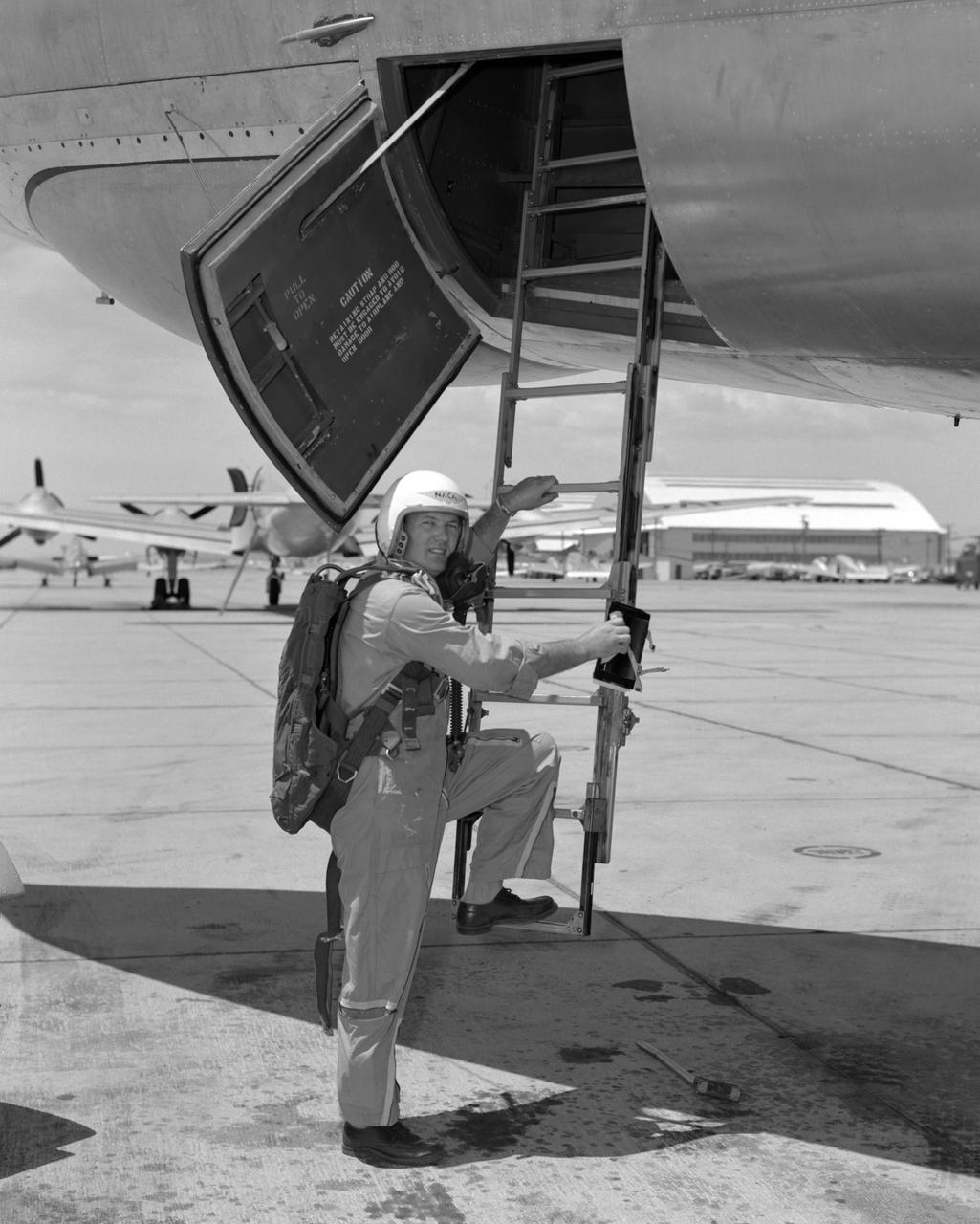

From December 10, 1966, until his retirement on February 27, 1976, Stanley P. Butchart served as Chief (later, Director) of Flight Operations at NASA's Flight Research Center (renamed on March 26, 1976, the Hugh L. Dryden Flight Research Center). Initially, his responsibilities in this position included the Research Pilots Branch, a Maintenance and Manufacturing Branch, and an Operations Engineering Branch, the last of which not only included propulsion and electrical/electronic sections but project engineers for the X-15 and lifting bodies. During his tenure, however, the responsibilities of his directorate came to include not only Flight Test Engineering Support but Flight Systems and Loads laboratories. Before becoming Chief of Flight Operations, Butchart had served since June of 1966 as head of the Research Pilots Branch (Chief Pilot) and then as acting chief of Flight Operations. He had joined the Center (then known as the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics' High-Speed Flight Research Station) as a research pilot on May 10, 1951. During his career as a research pilot, he flew a great variety of research and air-launch aircraft including the D-558-I, D-558-II, B-29 (plus its Navy version, the P2B), X-4, X-5, KC-135, CV-880, CV-990, B-47, B-52, B-747, F-100A, F-101, F-102, F-104, PA-30 Twin Comanche, JetStar, F-111, R4D, B-720, and B-47. Although previously a single-engine pilot, he became the Center's principal multi-engine pilot during a period of air-launches in which the pilot of the air-launch aircraft (B-29 or P2B) basically directed the operations. It was he who called for the chase planes before each drop, directed the positioning of fire rescue vehicles, and released the experimental aircraft after ensuring that all was ready for the drop. As pilot of the B-29 and P2B, Butchart launched the X-1A once, the X-1B 13 times, the X-1E 22 times, and the D-558-II 102 times. In addition, he towed the M2-F1 lightweight lifting body 14 times behind an R4
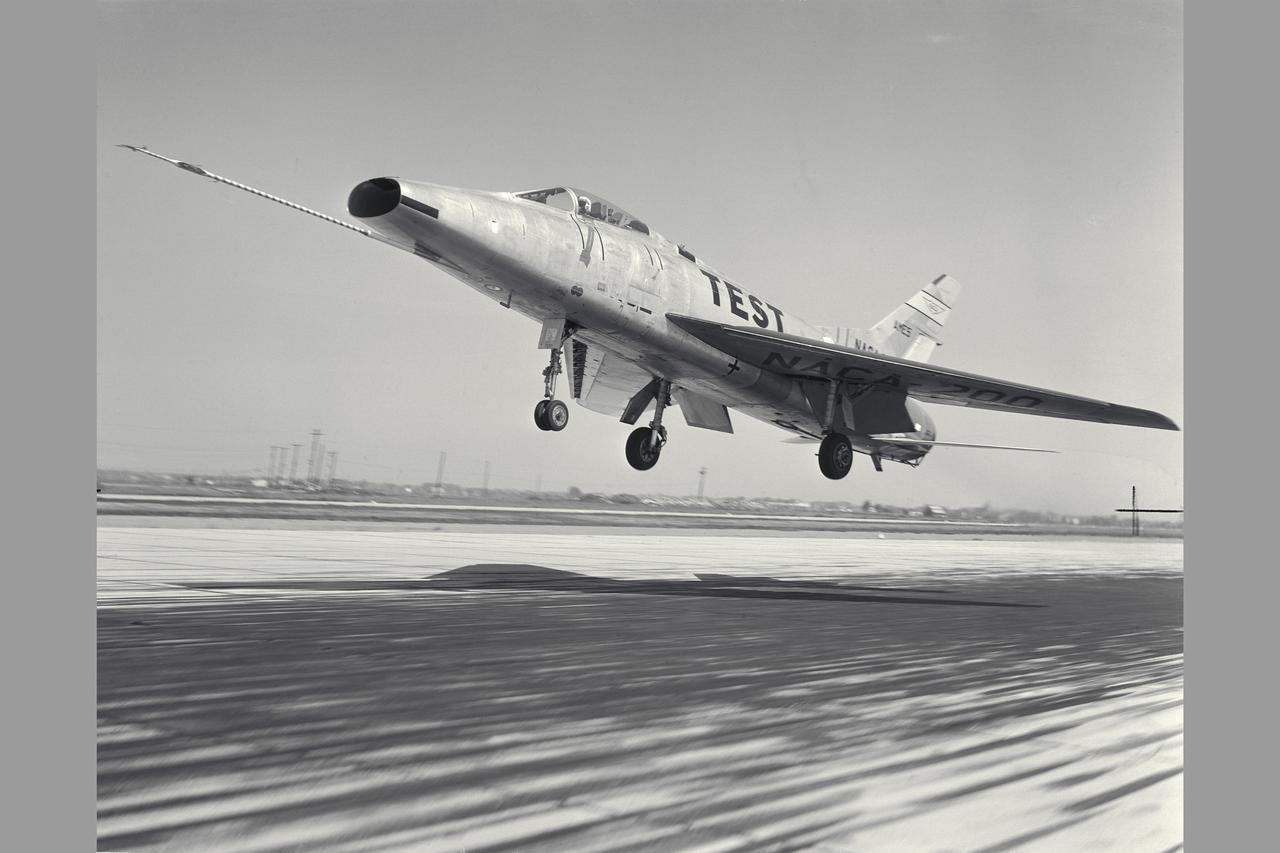

NACA Photographer North American F-100A (NACA-200) Super Sabre Airplane take-off. The blowing-tupe boundary-layer control on the leading- and trailing-edge provided large reductions in takeoff and landing approach speeds. Approach speeds were reduced by about 10 knots (Mar 1960). Note: Used in publication in Flight Research at Ames; 57 Years of Development and Validation of Aeronautical Technology NASA SP-1998-3300 fig. 102 and and Memoirs of a Flight Test Engneer NASA SP-2002-4525
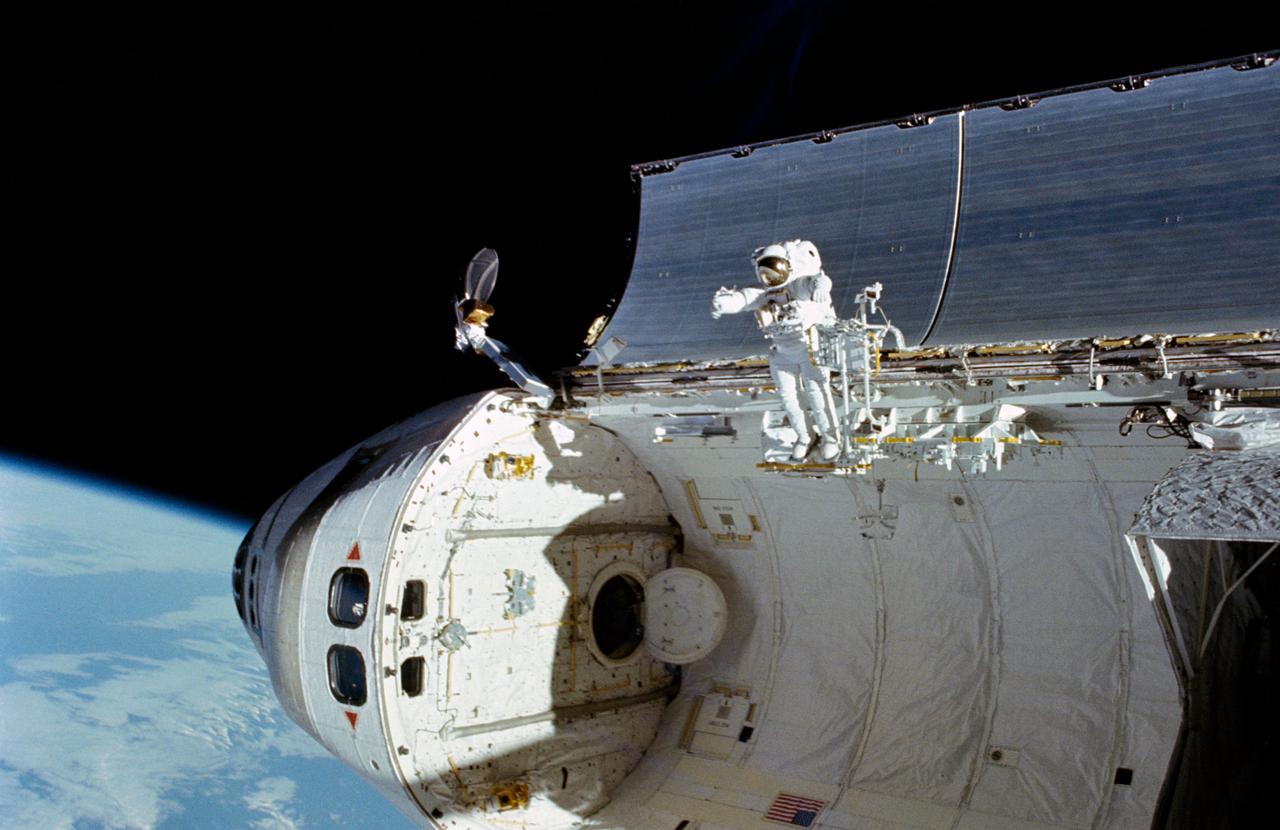

51I-102-048 (4-5 Sept 1985) --- A 35mm frame showing astronaut William F. Fisher standing on the edge of Discovery's cargo bay (in foot restraint) during the second day of a two-day effort to capture, repair and re-release the Syncom IV-3 communications satellite. Astronaut James D. van Hoften, standing on the Discovery's RMS arm, exposed the frame.
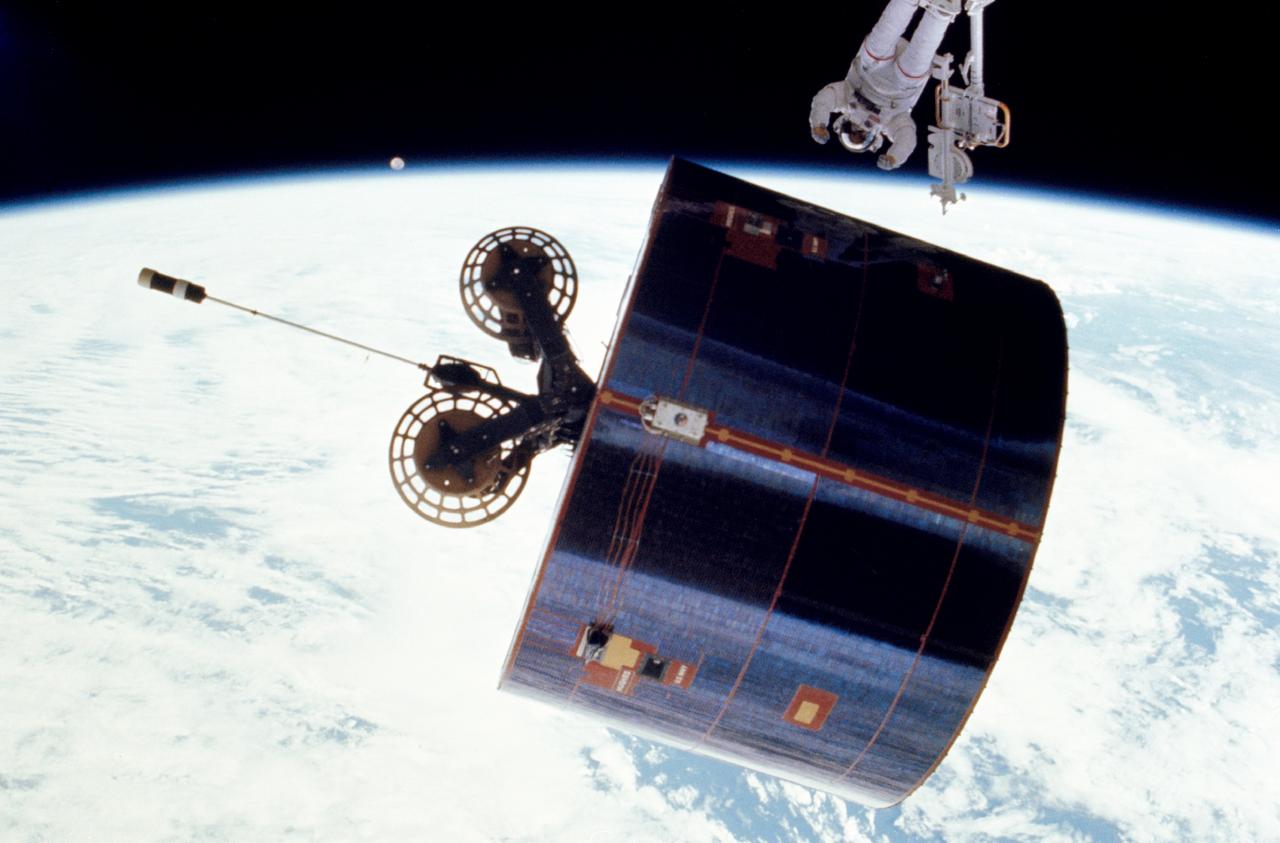

51I-102-033 (31 August - 1 September 1985) --- This is one of a series of six photographs released by NASA covering the extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts James D. van Hoften and William F. Fisher, who helped to capture, repair and release the previously errant Syncom IV-3 communications satellite. Here, Dr. van Hoften has just given a shove to the the Syncom. (For orientation, moon should be in lower right quadrant).
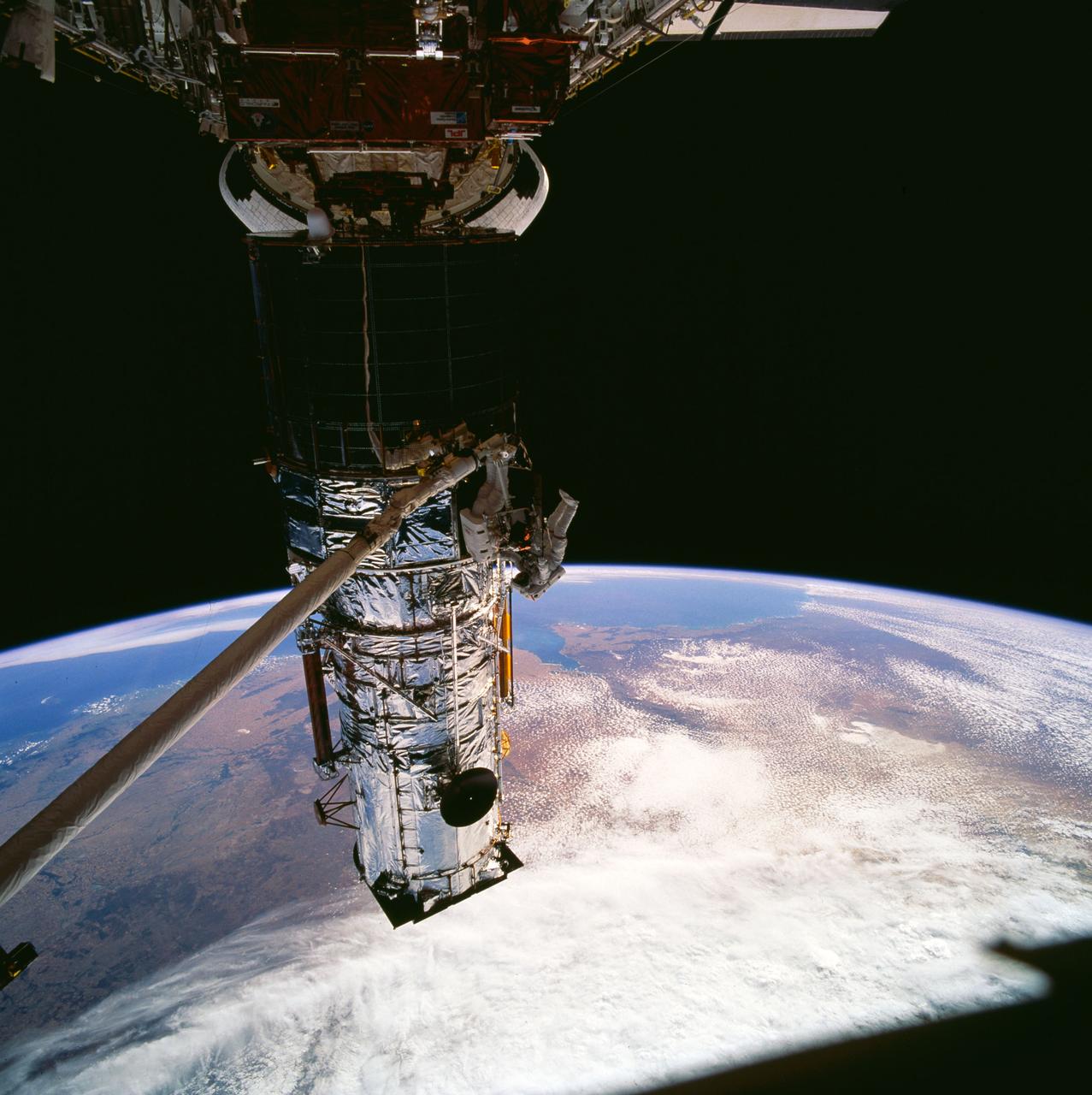

STS061-102-010 (9 Dec 1993) --- Astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman (left) and F. Story Musgrave team to replace one of two Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) units on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Musgrave is standing on a foot restraint mounted on the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. The black object, in upper left corner, is part of the window frame, through which this 70mm frame was exposed, inside Endeavour's cabin.
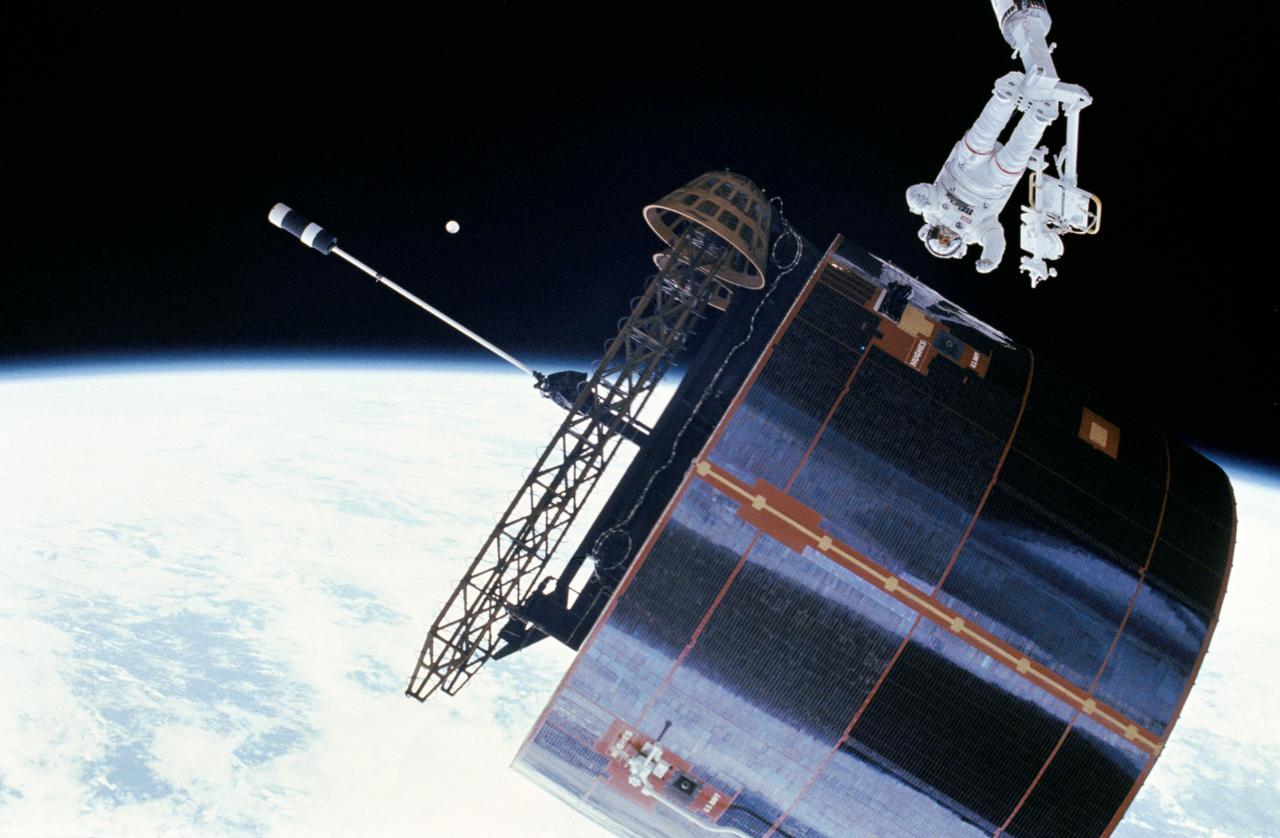

51I-102-029 (31 August - 1 September 1985) --- This is one of a series of six photographs released by NASA covering the extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts James D. van Hoften and William F. Fisher, who helped to capture, repair and release the previously errant Syncom IV-3 communications satellite. Here, Dr. van Hoften has just given a shove to the the Syncom. (For orientation, moon should be in lower right quadrant).
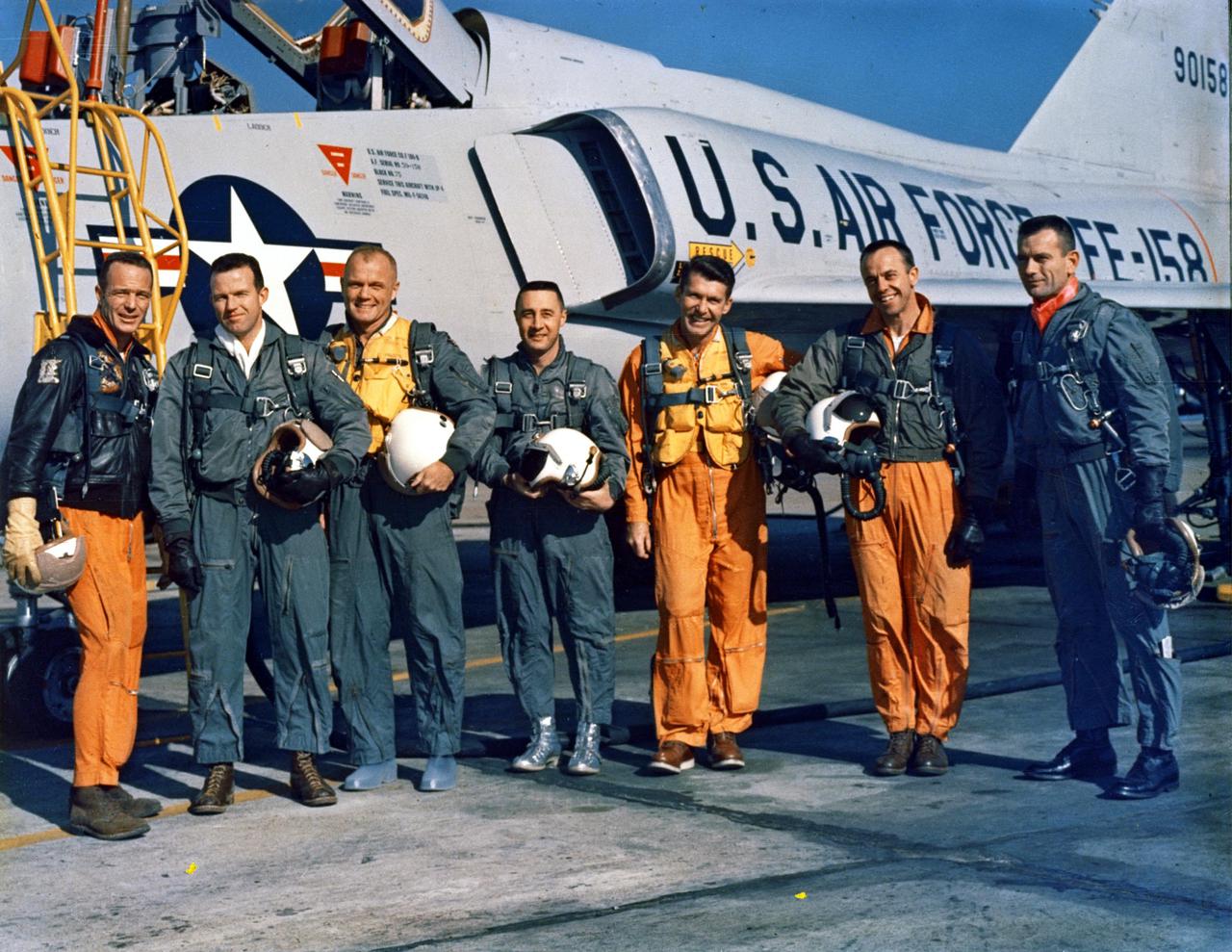

CAPE CANAVERAL, FLA. -- The Original Seven Mercury Astronauts pose beside an Air Force F-102 jet. Standing, left to right, are M. Scott Carpenter, L. Gordon Cooper, John H. Glenn Jr., Virgil I. 'Gus' Grissom, Walter M. Schirra Jr., Alan B. Shepherd Jr., and Donald K. 'Deke' Slayton.
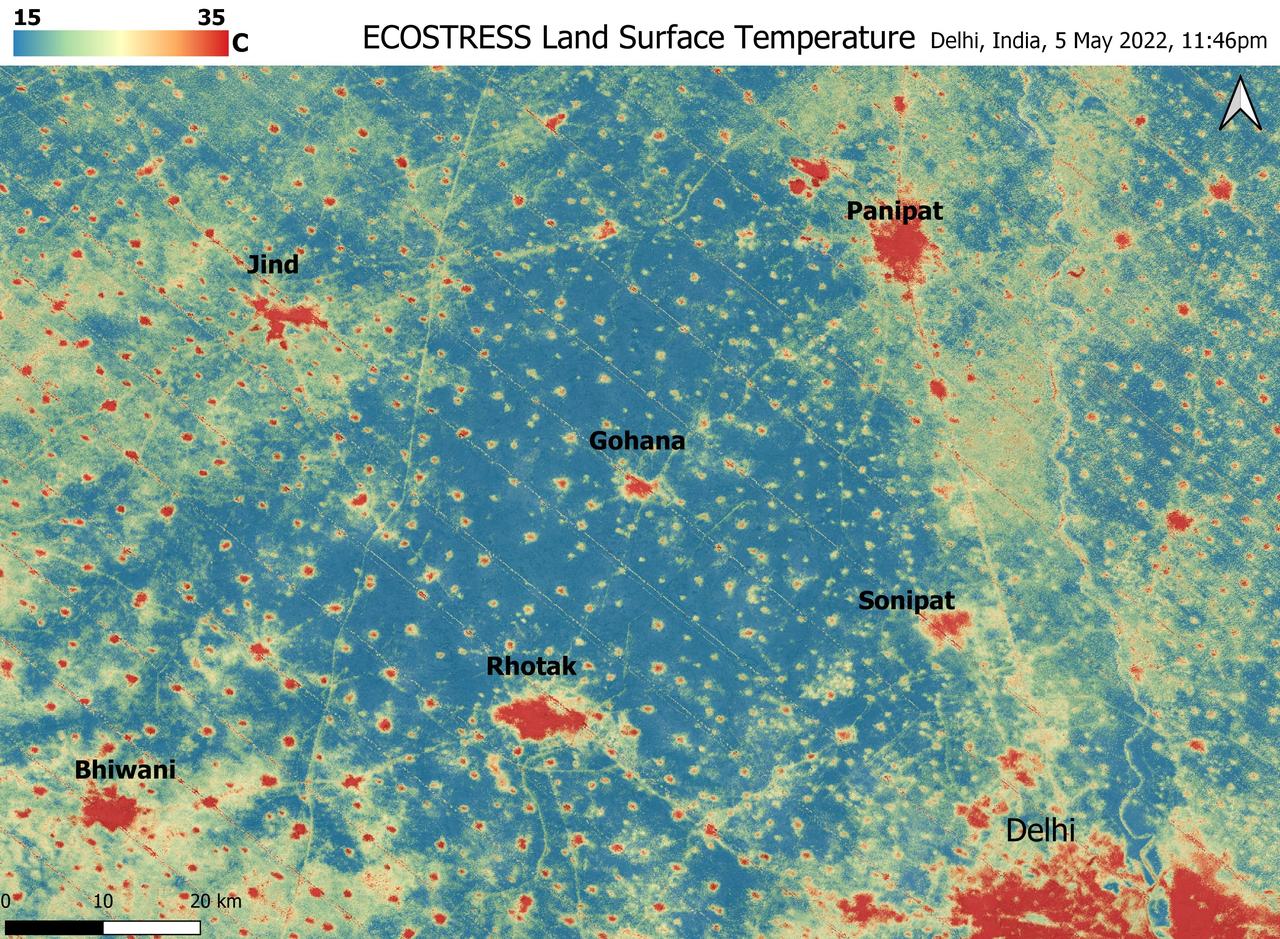
A relentless heat wave has blanketed India and Pakistan since mid-March 2022, causing dozens of deaths, fires, increased air pollution, and reduced crop yields. NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station instrument (ECOSTRESS) has been measuring these temperatures from space, at the highest spatial resolution of any satellite instrument. This image, taken shortly before local midnight on May 5, shows urban areas and agricultural lands northwest of Delhi that are home to about 28 million people. The image covers about 4,800 square miles (12,350 square kilometers). Cities are usually markedly warmer than the surrounding countryside due to human activities and the materials used in the built environment. The image clearly delineates these urban "heat islands." Nighttime temperatures in Delhi and several smaller villages were above 95 degrees Fahrenheit (35 degrees Celsius), peaking at about 102 degrees F (39 degrees C), while the rural fields nearby had cooled to around 60 degrees F (15 degrees C). This data suggests that city dwellers are experiencing considerably higher temperatures than the average temperatures reported for their regions. ECOSTRESS measures the temperature of the ground itself, which is very similar to air temperature at night (though the ground may be warmer than the air in daylight hours). The instrument launched to the space station in 2018. Its primary mission is to identify plants' thresholds for water use and water stress, giving insight into their ability to adapt to a warming climate. However, ECOSTRESS also records other heat-related phenomena like this heat wave. Its high-resolution images, with a pixel size of about 225 feet (70 meters) by 125 feet (38 meters), are a powerful tool for understanding aspects of the weather event that might be overlooked by traditional observation networks. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24987

From just outside the faint edge of Saturn's F ring, the moon Pandora keeps watch over her fine-grained flock. The outer flanks of the F ring region are populated by ice particles approaching the size of the particles comprising smoke. As a shepherd moon, Pandora helps her cohort Prometheus confine and shape the main F ring. Pandora is 84 kilometers (52 miles) across. Prometheus is 102 kilometers (63 miles) wide and orbits interior to the F ring. The small knot seen attached to the core is one of several that Cassini scientists are eyeing as they attempt to distinguish embedded moons from transient clumps of material (see PIA07716). The image was taken with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on Aug. 2, 2005, using a filter sensitive to wavelengths of infrared light centered at 930 nanometers at a distance of approximately 610,000 kilometers (379,000 miles) from Pandora and at a Sun-Pandora-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 146 degrees. Image scale is 4 kilometers (2 miles) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07579
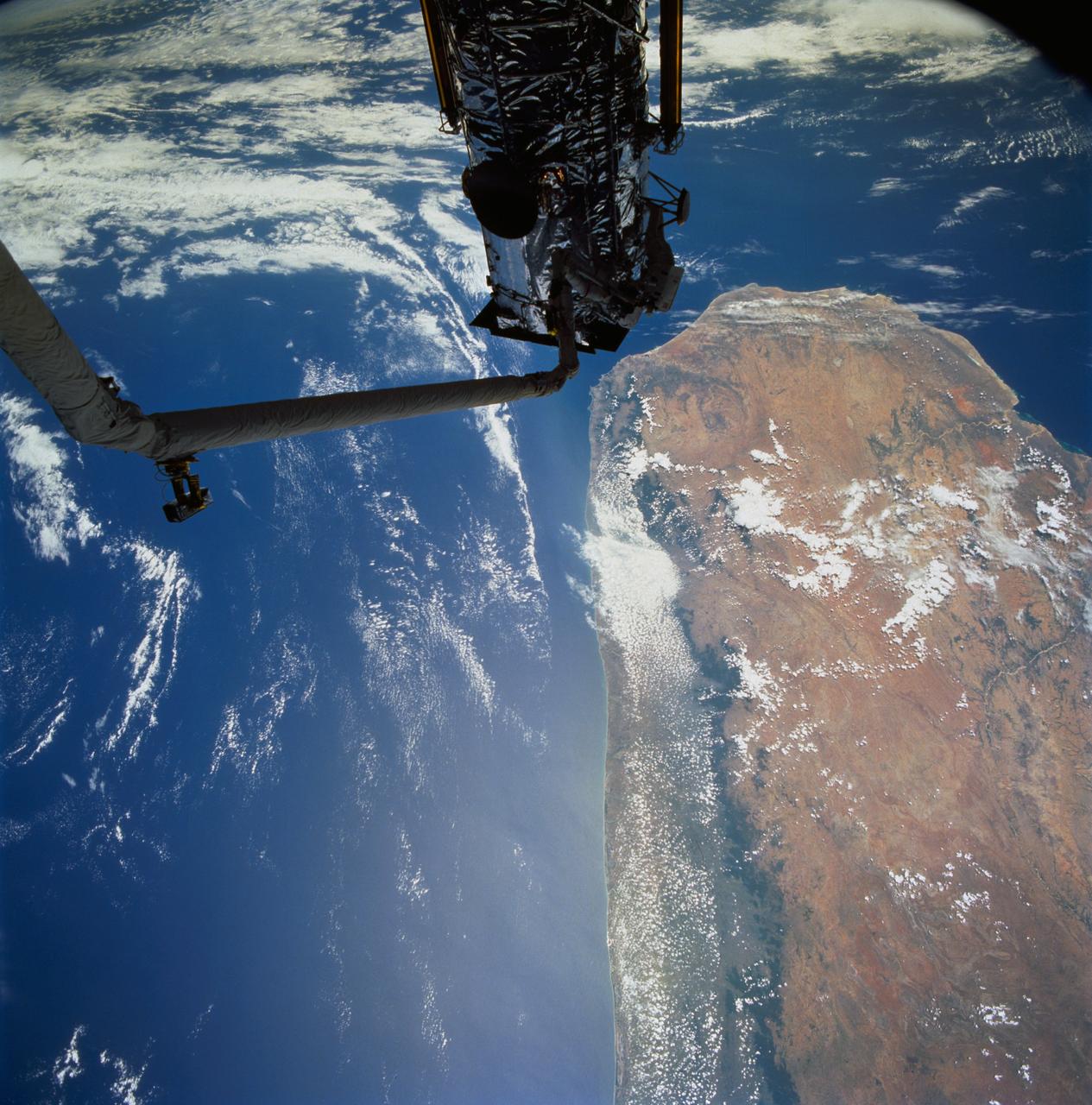

STS061-77-102 (7 Dec 1993) --- Astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman (left) and F. Story Musgrave are partially silhouetted against the Indian Ocean as they work to install the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Musgrave is anchored to the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. The HST is positioned along the southern end of Madagascar, 325 nautical miles away. Visible on the western coast are the sediment laden Onilahy and Fiherenana Rivers which empty into Saint Augustin Bay. North of Fiherenana River is the Mangoky River. The circular feature on the southern end of Madagascar and to the right of HST is the L'ivakoany Mountains. The eastern coast is relatively straight compared to the western coast.
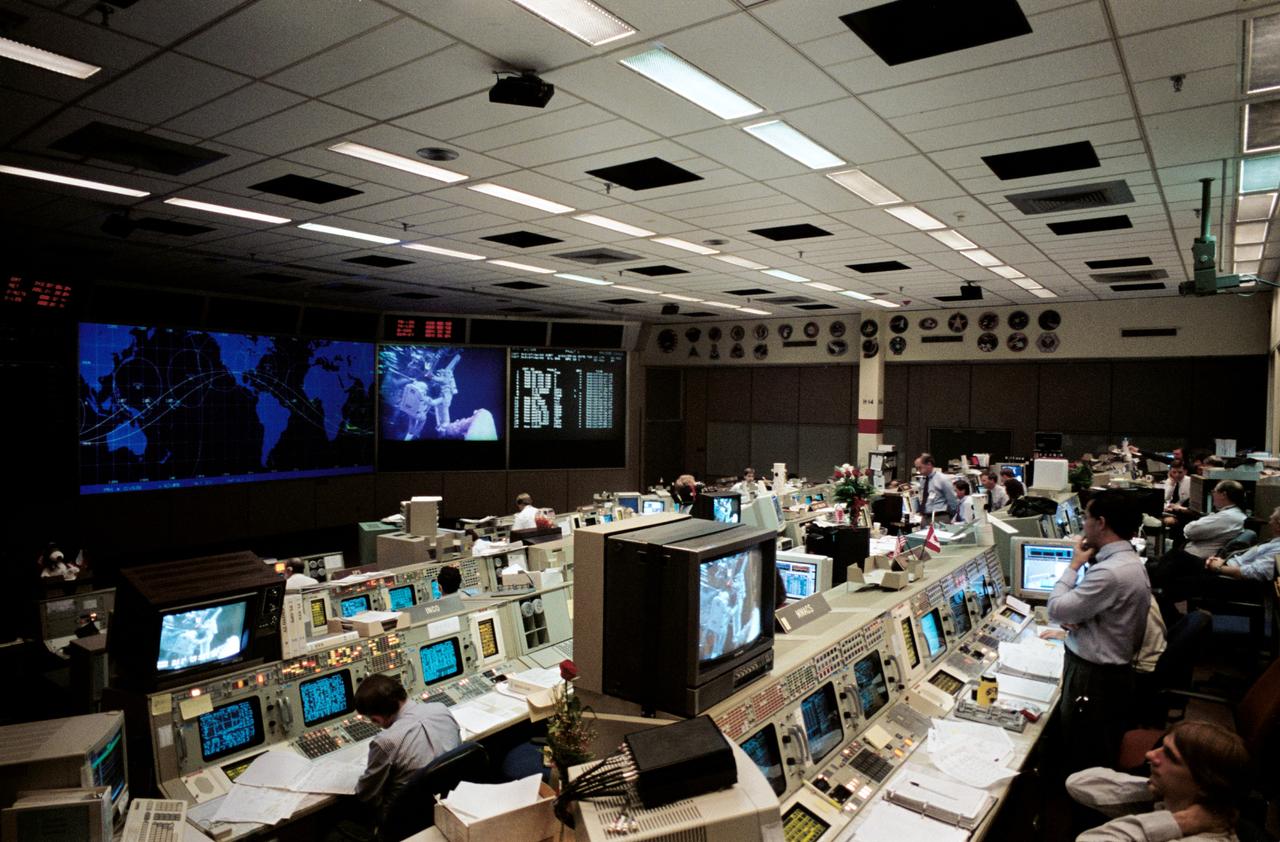

STS061-S-102 (5 Dec. 1993) --- Flight controllers Harry Black (left foreground) and Kevin McCluney (right foreground) monitor the televised activity of two space walkers during the first STS-61 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronauts F. Story Musgrave and Jeffrey A. Hoffman were performing a variety of equipment replacements. At the Integrated Communications Officer Console (INCO) Black plays a roill in controlling the TV while McLuney's duties deal with maintenance, mechanical, arm and crew systems, meaning that they and their colleagues will be busy for the next five days. Four astronauts in alternating pairs will perform a variety of tasks on the giant telescope during that period.
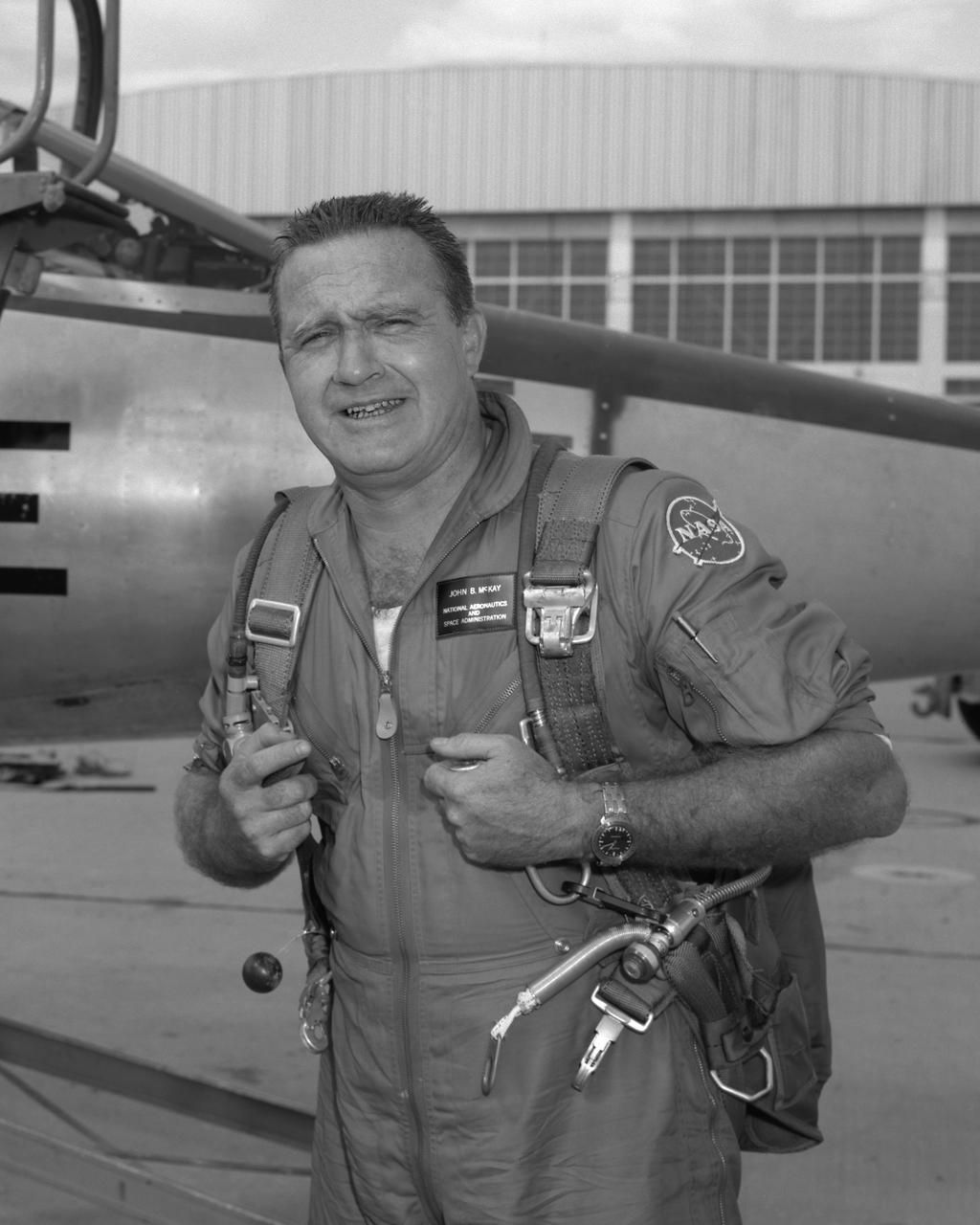

John McKay after flight in F-104B
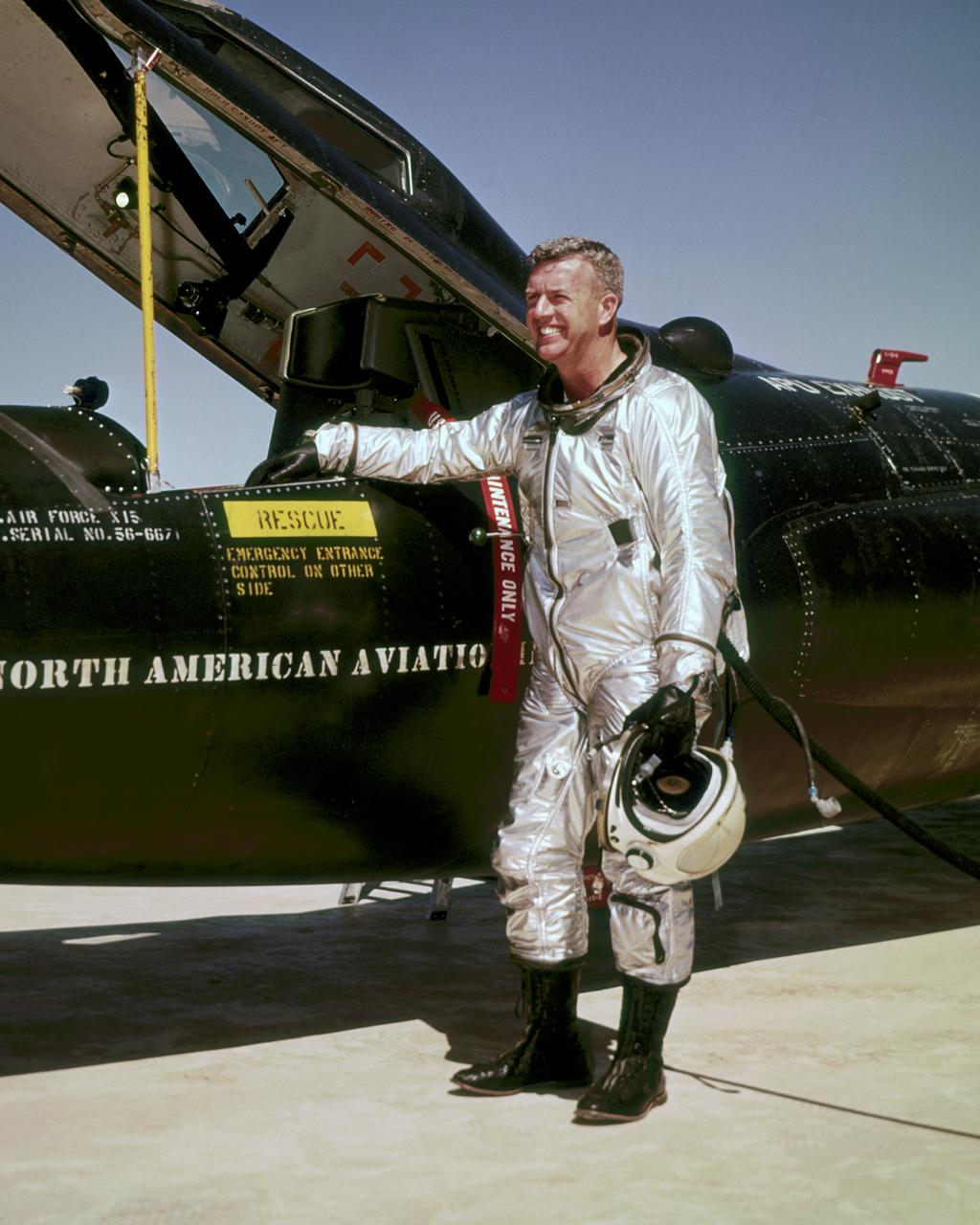

Joseph A. Walker was a Chief Research Pilot at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center during the mid-1960s. He joined the NACA in March 1945, and served as project pilot at the Edwards flight research facility on such pioneering research projects as the D-558-1, D-558-2, X-1, X-3, X-4, X-5, and the X-15. He also flew programs involving the F-100, F-101, F-102, F-104, and the B-47. Walker made the first NASA X-15 flight on March 25, 1960. He flew the research aircraft 24 times and achieved its fastest speed and highest altitude. He attained a speed of 4,104 mph (Mach 5.92) during a flight on June 27, 1962, and reached an altitude of 354,300 feet on August 22, 1963 (his last X-15 flight). He was the first man to pilot the Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) that was used to develop piloting and operational techniques for lunar landings. Walker was born February 20, 1921, in Washington, Pa. He lived there until graduating from Washington and Jefferson College in 1942, with a B.A. degree in Physics. During World War II he flew P-38 fighters for the Air Force, earning the Distinguished Flying Cross and the Air Medal with Seven Oak Clusters. Walker was the recipient of many awards during his 21 years as a research pilot. These include the 1961 Robert J. Collier Trophy, 1961 Harmon International Trophy for Aviators, the 1961 Kincheloe Award and 1961 Octave Chanute Award. He received an honorary Doctor of Aeronautical Sciences degree from his alma mater in June of 1962. Walker was named Pilot of the Year in 1963 by the National Pilots Association. He was a charter member of the Society of Experimental Test Pilots, and one of the first to be designated a Fellow. He was fatally injured on June 8, 1966, in a mid-air collision between an F-104 he was piloting and the XB-70.
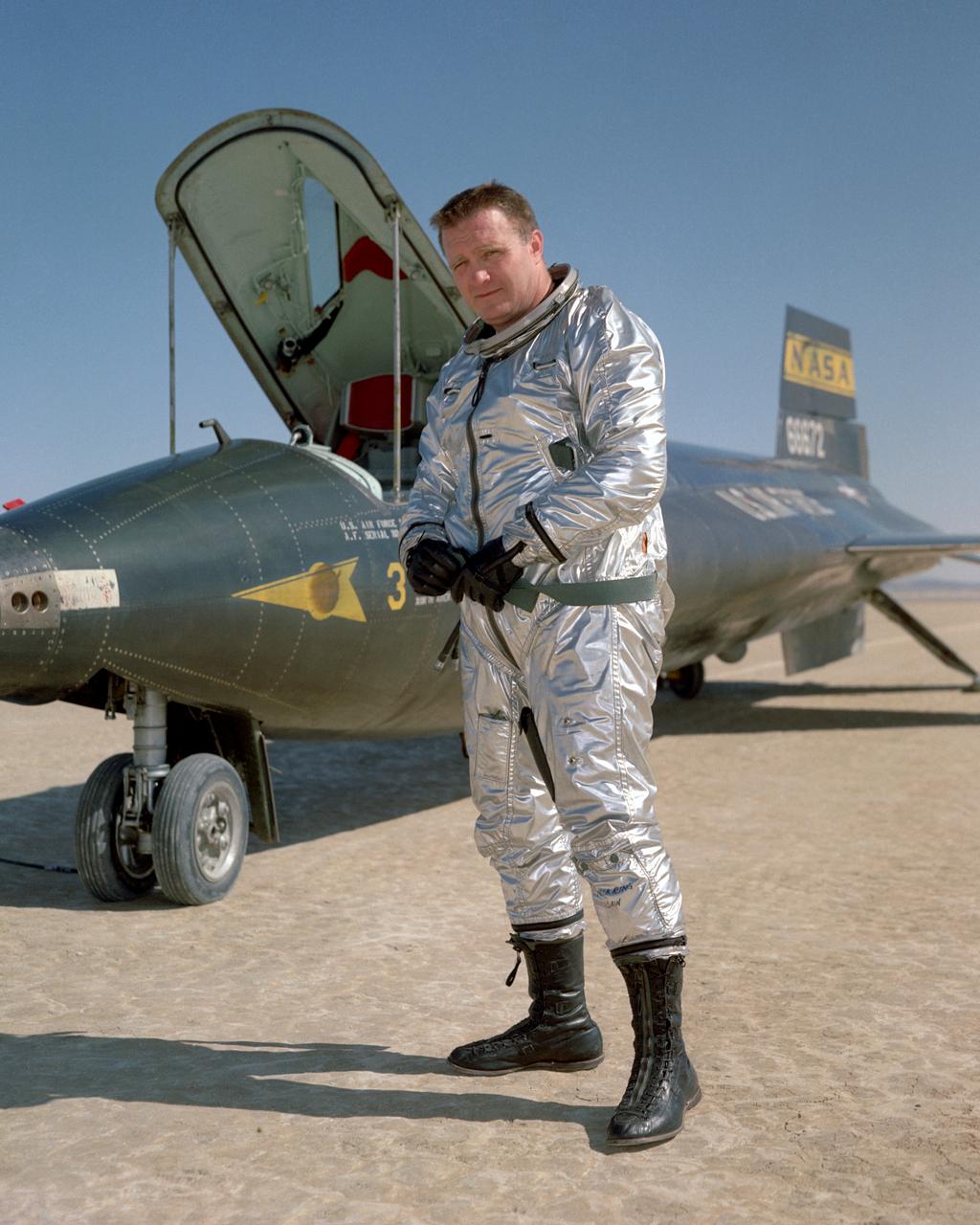

John B. McKay was one of the first pilots assigned to the X-15 flight research program at NASA's Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif. As a civilian research pilot and aeronautical engineer, he made 30 flights in X-15s from October 28, 1960, until September 8, 1966. His peak altitude was 295,600 feet, and his highest speed was 3863 mph (Mach 5.64). McKay was with the NACA and NASA from February 8,1951 until October 5, 1971 and specialized in high-speed flight research programs. He began as an NACA intern, but assumed pilot status on July 11, 1952. In addition to the X-l5, he flew such experimental aircraft as the D-558-1, D-558-2, X-lB, and the X-lE. He has also served as a research pilot on flight programs involving the F-100, F-102, F-104, and the F-107. Born on December 8, 1922, in Portsmouth, Va., McKay graduated from Virginia Polytechnic Institute in 195O with a Bachelor of Science degree in Aeronautical Engineering. During World War II he served as a Navy pilot in the Pacific Theater, earning the Air Medal and Two Clusters, and a Presidential Unit Citation. McKay wrote several technical papers, and was a member of the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, as well as the Society of Experimental Test Pilots. He passed away on April 27, 1975.

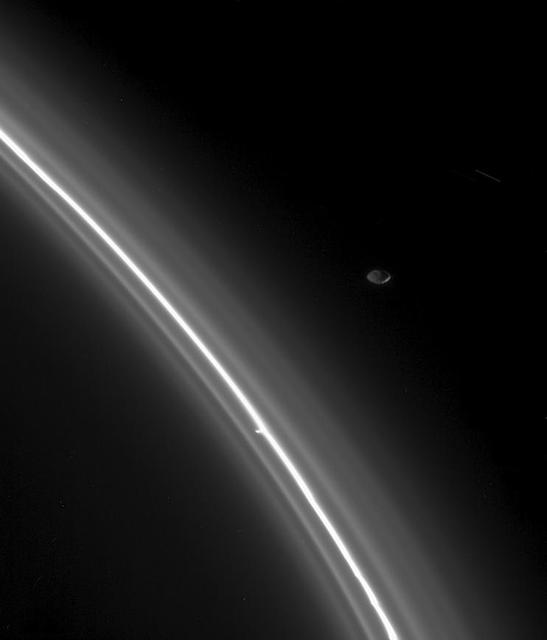
Cassini has sighted Prometheus and Pandora, the two F-ring-shepherding moons whose unpredictable orbits both fascinate scientists and wreak havoc on the F ring. Prometheus (102 kilometers, or 63 miles across) is visible left of center in the image, inside the F ring. Pandora (84 kilometers, or 52 miles across) appears above center, outside the ring. The dark shadow cast by the planet stretches more than halfway across the A ring, the outermost main ring. The mottled pattern appearing in the dark regions of the image is 'noise' in the signal recorded by the camera system, which has subsequently been magnified by the image processing. The F ring is a narrow, ribbon-like structure, with a width seen in this geometry equivalent to a few kilometers. The two small, irregularly shaped moons exert a gravitational influence on particles that make up the F ring, confining it and possibly leading to the formation of clumps, strands and other structures observed there. Pandora prevents the F ring from spreading outward and Prometheus prevents it from spreading inward. However, their interaction with the ring is complex and not fully understood. The shepherds are also known to be responsible for many of the observed structures in Saturn's A ring. The moons, which were discovered in images returned by the Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1980, are in chaotic orbits--their orbits can change unpredictably when the moons get very close to each other. This strange behavior was first noticed in ground-based and Hubble Space Telescope observations in 1995, when the rings were seen nearly edge-on from Earth and the usual glare of the rings was reduced, making the satellites more readily visible than usual. The positions of both satellites at that time were different than expected based on Voyager data. One of the goals for the Cassini-Huygens mission is to derive more precise orbits for Prometheus and Pandora. Seeing how their orbits change over the duration of the mission will help to determine their masses, which in turn will help constrain models of their interiors and provide a more complete understanding of their effect on the rings. This narrow angle camera image was snapped through the broadband green spectral filter, centered at 568 nanometers, on March 10, 2004, when the spacecraft was 55.5 million kilometers (34.5 million miles) from the planet. Image scale is approximately 333 kilometers (207 miles) per pixel. Contrast has been greatly enhanced, and the image has been magnified to aid visibility of the moons as well as structure in the rings. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05387
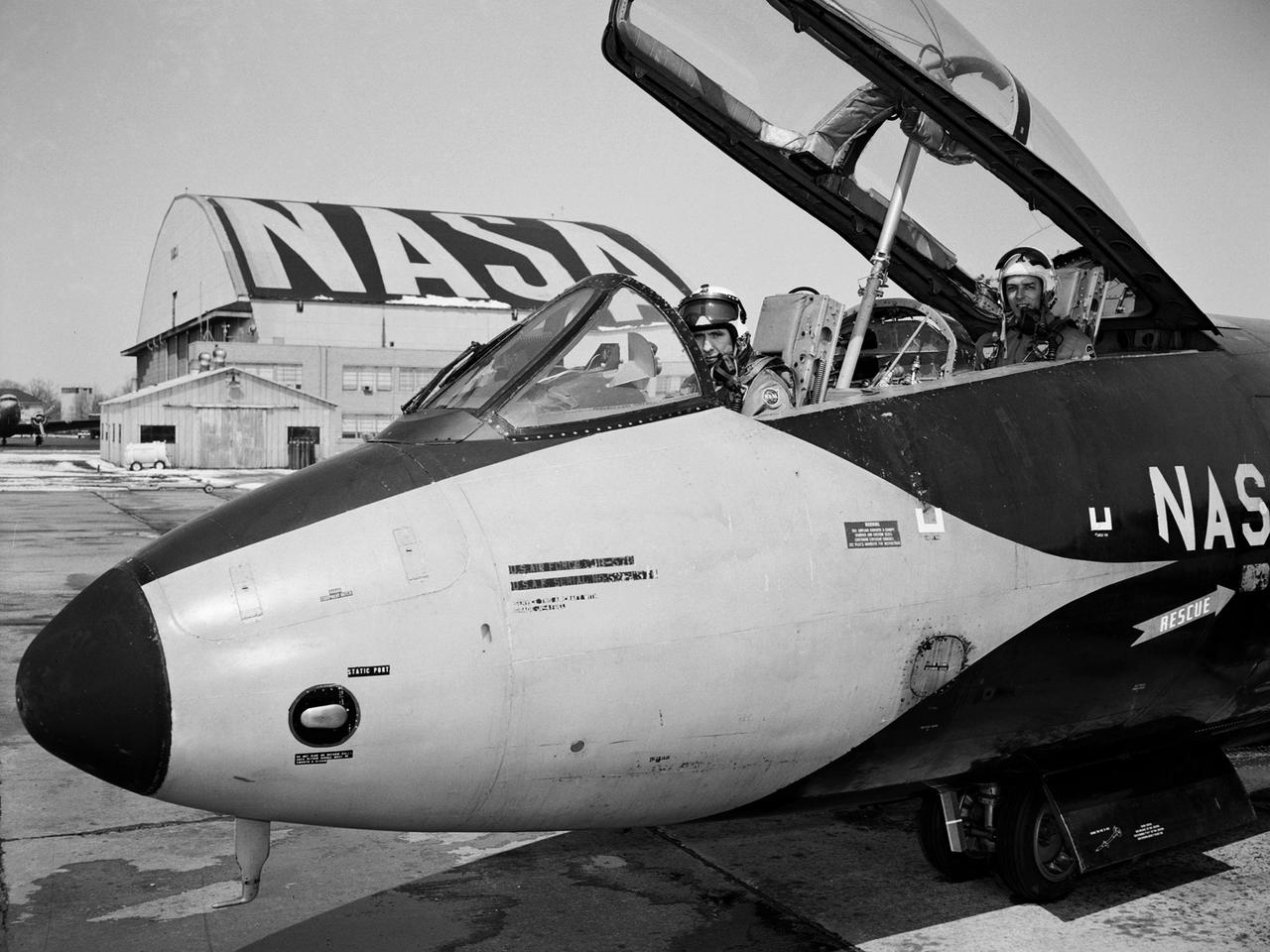

Pilot Earle Boyer and researcher Henry Brandhorst prepare for a solar cell calibration flight in a Martin B-57B Canberra at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Lewis was in the early stages of decades-long energy conversion and space power research effort. Brandhorst, a member of the Chemistry and Energy Conversion Division, led a team of Lewis researchers in a quest to develop new power sources to sustain spacecraft in orbit. Solar cells proved to be an important source of energy, but researchers discovered that their behavior varied at different atmospheric levels. Their standardization and calibration were critical. Brandhorst initiated a standardized way to calibrate solar cells in the early 1960s using the B-57B aircraft. The pilots would take the aircraft up into the troposphere and open the solar cell to the sunlight. The aircraft would steadily descend while instruments recorded how much energy was being captured by the solar cell. From this data, Brandhorst could determine the estimated power for a particular solar cell at any altitude. Pilot Earle Boyer joined NASA Lewis in October 1962. He had flown Convair F-102 Delta Dagger fighters in the Air Force and served briefly in the National Guard before joining the Langley Research Center. Boyer was only at Langley a few months before he transferred to Cleveland. He flew the B-57B, a Convair F-106 Delta Dart, Gulfstream G-1 with an experimental turboprop, Learjet and many other aircraft over the next 32 years at Lewis.

NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard the Aqua satellite captured imagery of Typhoon Hinnamnor in the West Pacific Ocean just before 2 p.m. local time on Sept. 5, 2022. Typhoon Hinnamnor was one of the strongest in South Korea's recorded history, dropping some 40 inches (102 centimeters) of rain and unleashing record winds. In this infrared AIRS image, the typhoon is moving northward over the Korean Peninsula (center), with the coast of China to the west and the southernmost Japanese islands to the east. The large purple area indicates very cold clouds at about minus 90 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 67 degrees Celsius), carried high into the atmosphere by deep thunderstorms. These storm clouds are associated with very heavy rainfall. The extensive areas of red away from the storm indicate temperatures of around 80 F (26 C), typical of Earth's daytime surface during late summer. These red areas are mostly cloud-free, with the clear air caused by air motion outward from the cold clouds in the storm center then downward in the surrounding areas. U.S. Hurricane Hunter planes don't monitor the vast expanse of the Pacific Ocean, so AIRS and other satellite instruments are essential for tracking typhoons as they grow. AIRS, launched in 2002, was the first instrument to reveal the 3D distribution of rain within tropical storms like Hinnamnor. These 3D images have made a major contribution to our knowledge of how hurricanes and typhoons develop, improving forecasts and saving lives. AIRS senses infrared and microwave radiation emitted from Earth to provide a 3D look at the planet's weather and climate, making observations down to Earth's surface. With more than 2,000 channels sensing different regions of the atmosphere, the system creates a global, 3D map of atmospheric temperature and humidity, cloud amounts and heights, greenhouse gas concentrations and many other atmospheric phenomena. Launched in 2002, AIRS is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. JPL is a division of Caltech. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25521
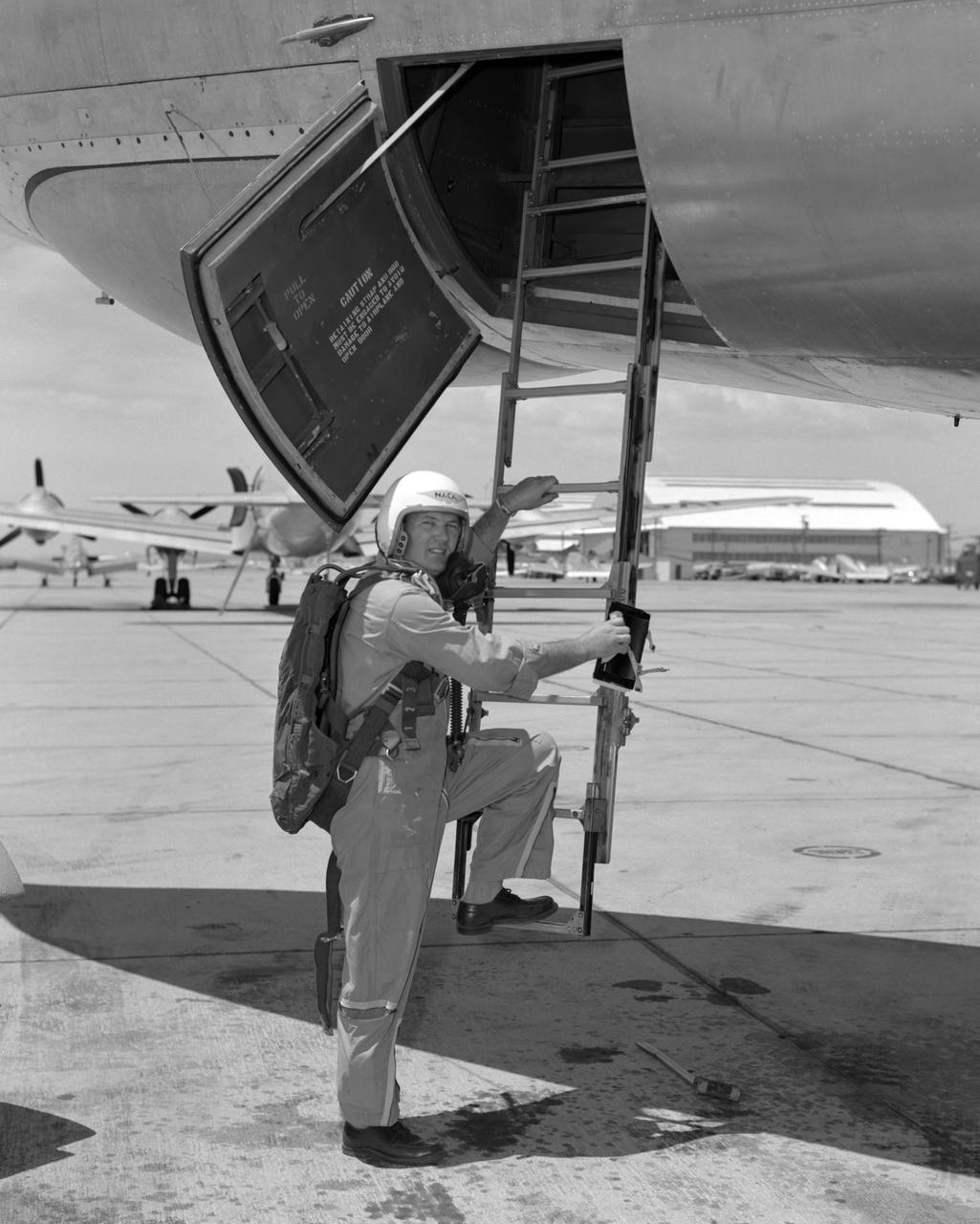

Stan Butchart climbing into B-47.