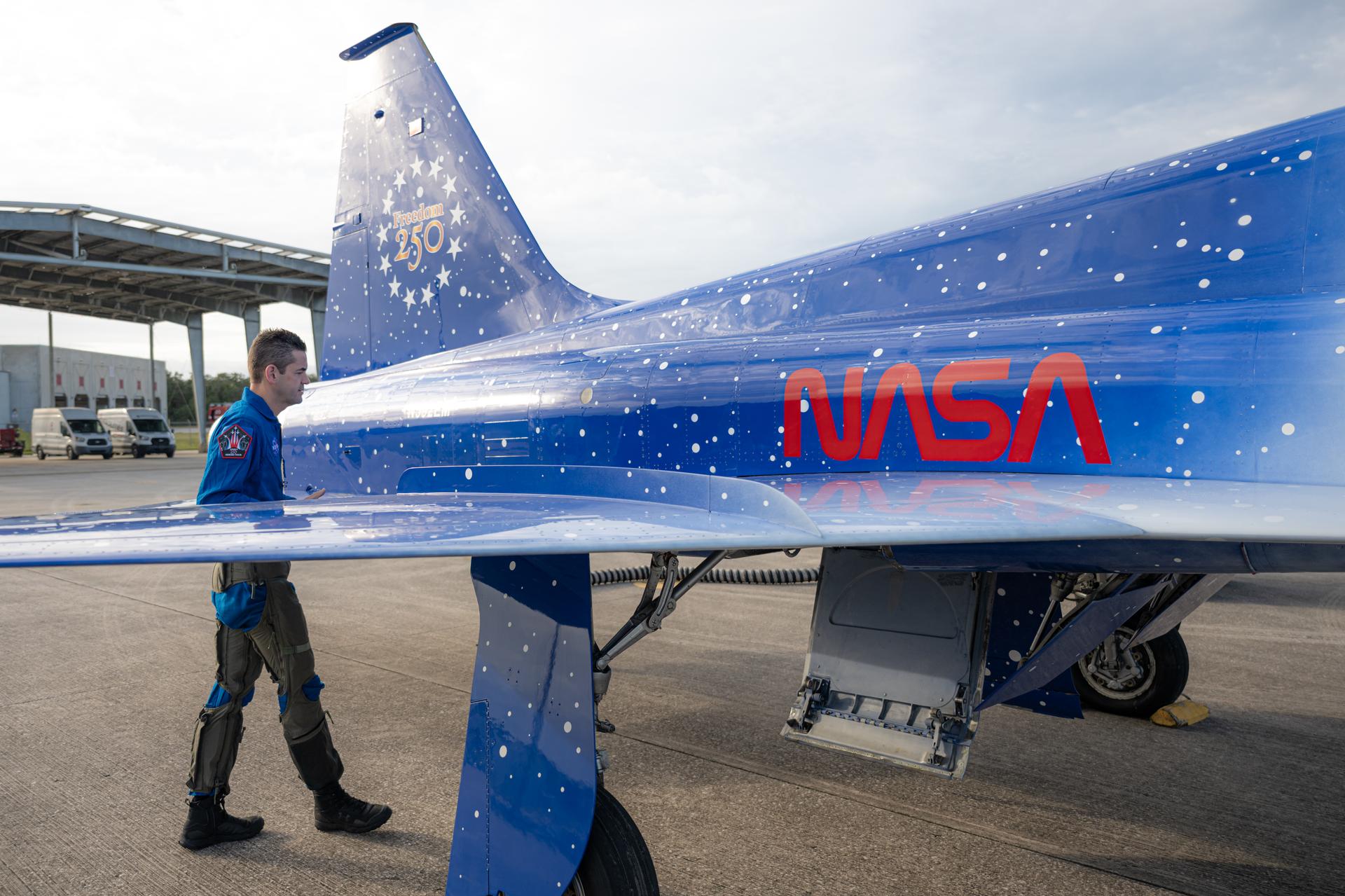

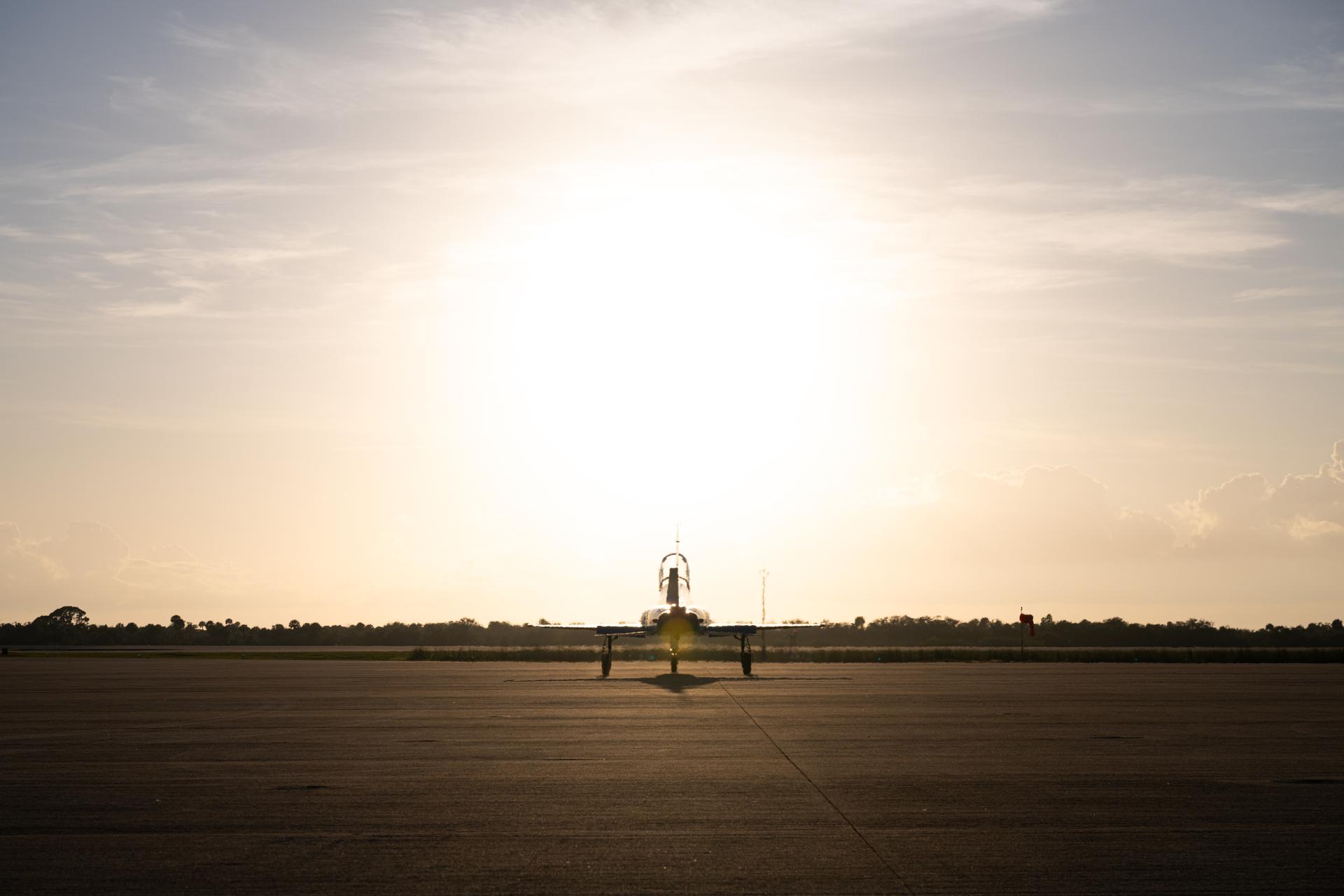
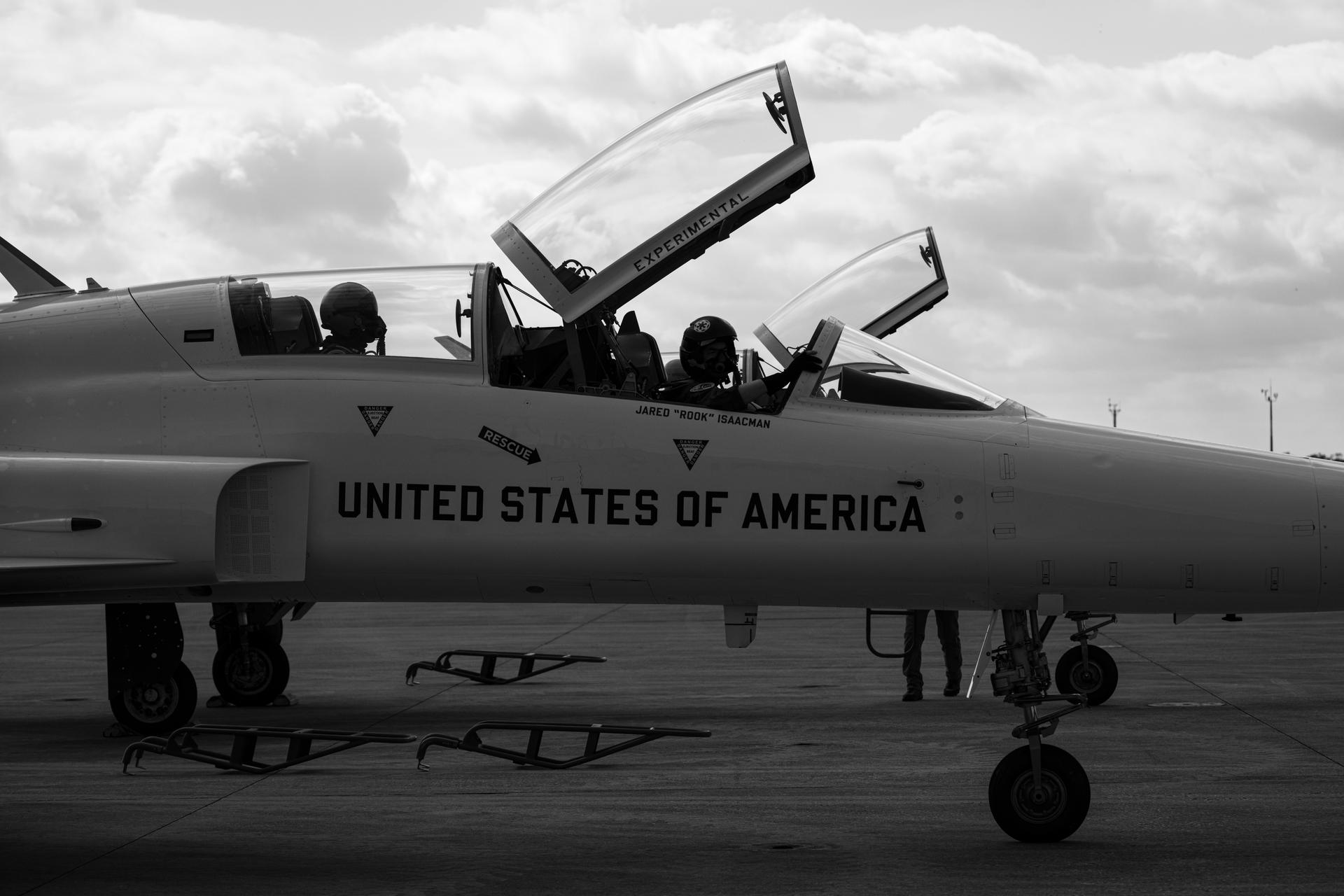
NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman is seen with his personal F-5 aircraft, Thursday, Jan. 22, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
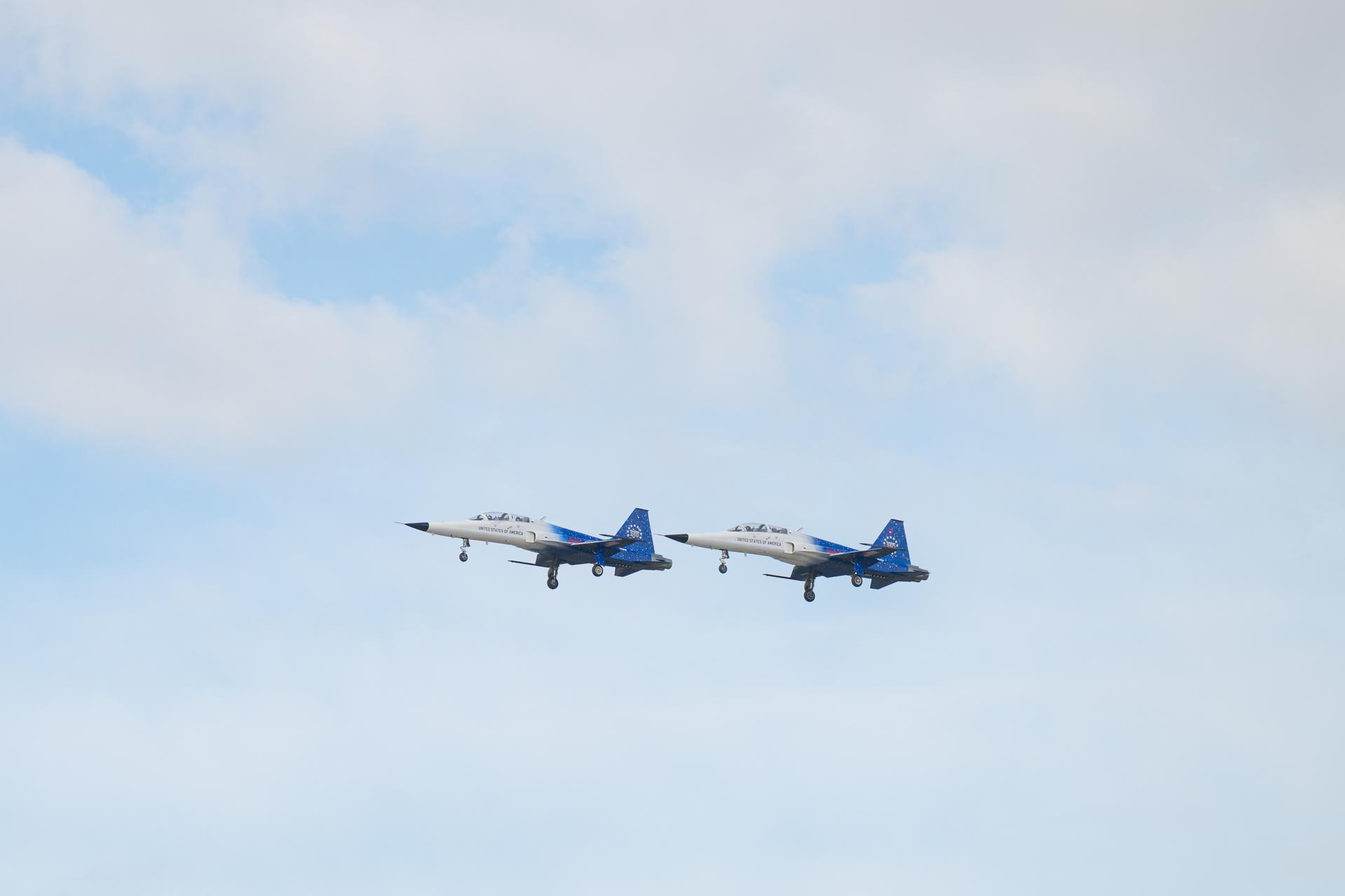

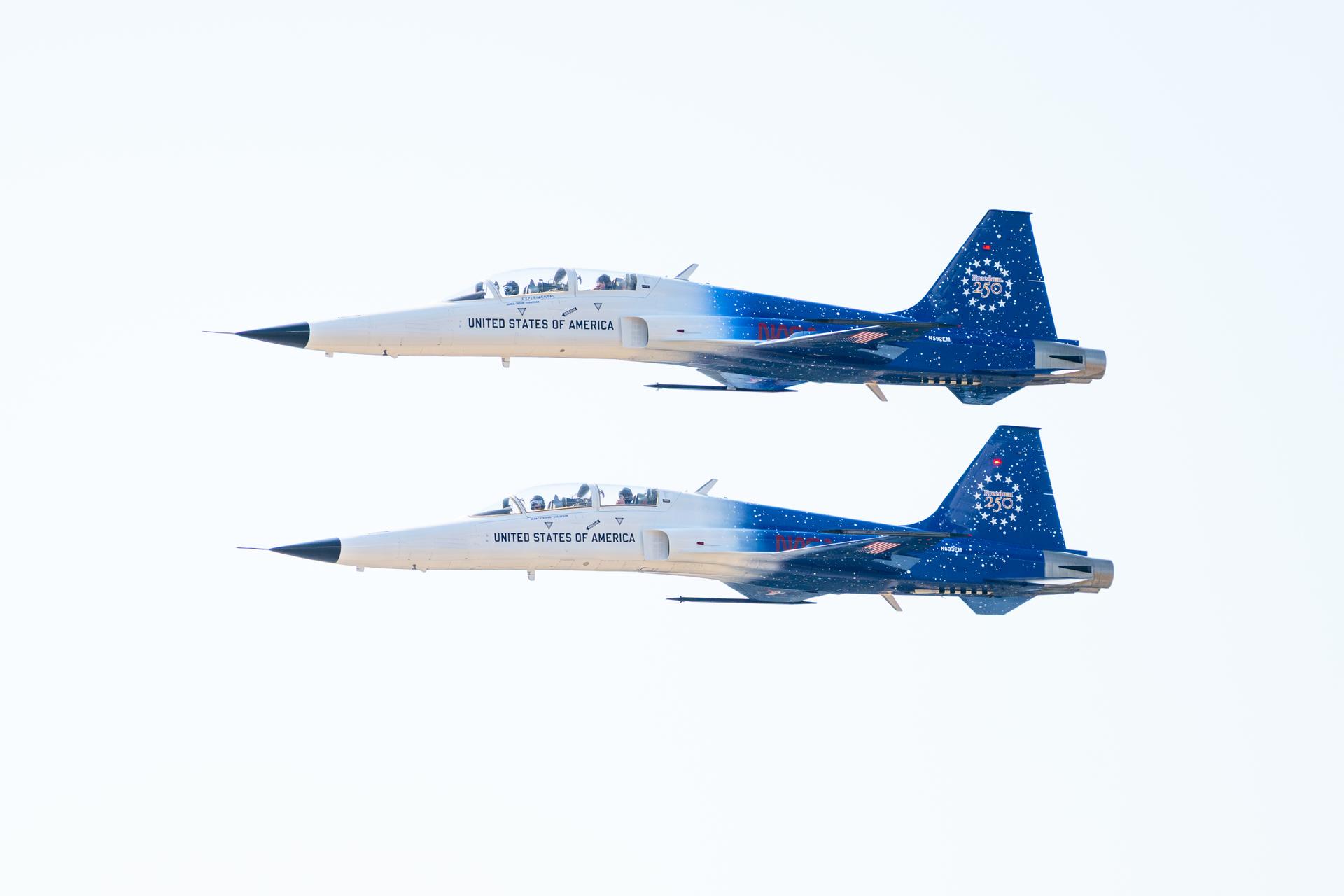
NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman participates in a formation flight with his personal F-5 aircraft, Thursday, Jan. 22, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
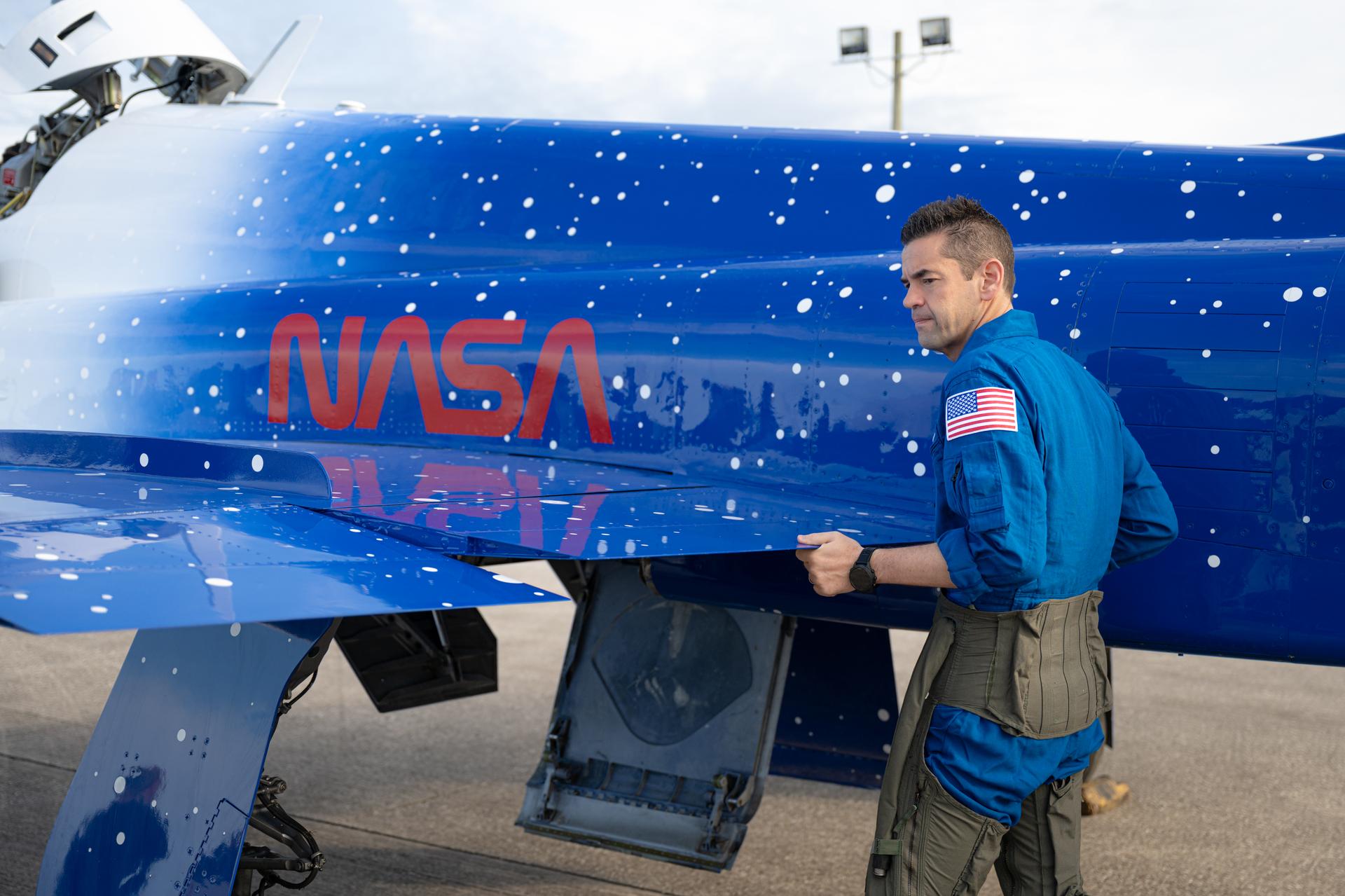

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman is seen with his personal F-5 aircraft, Thursday, Jan. 22, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
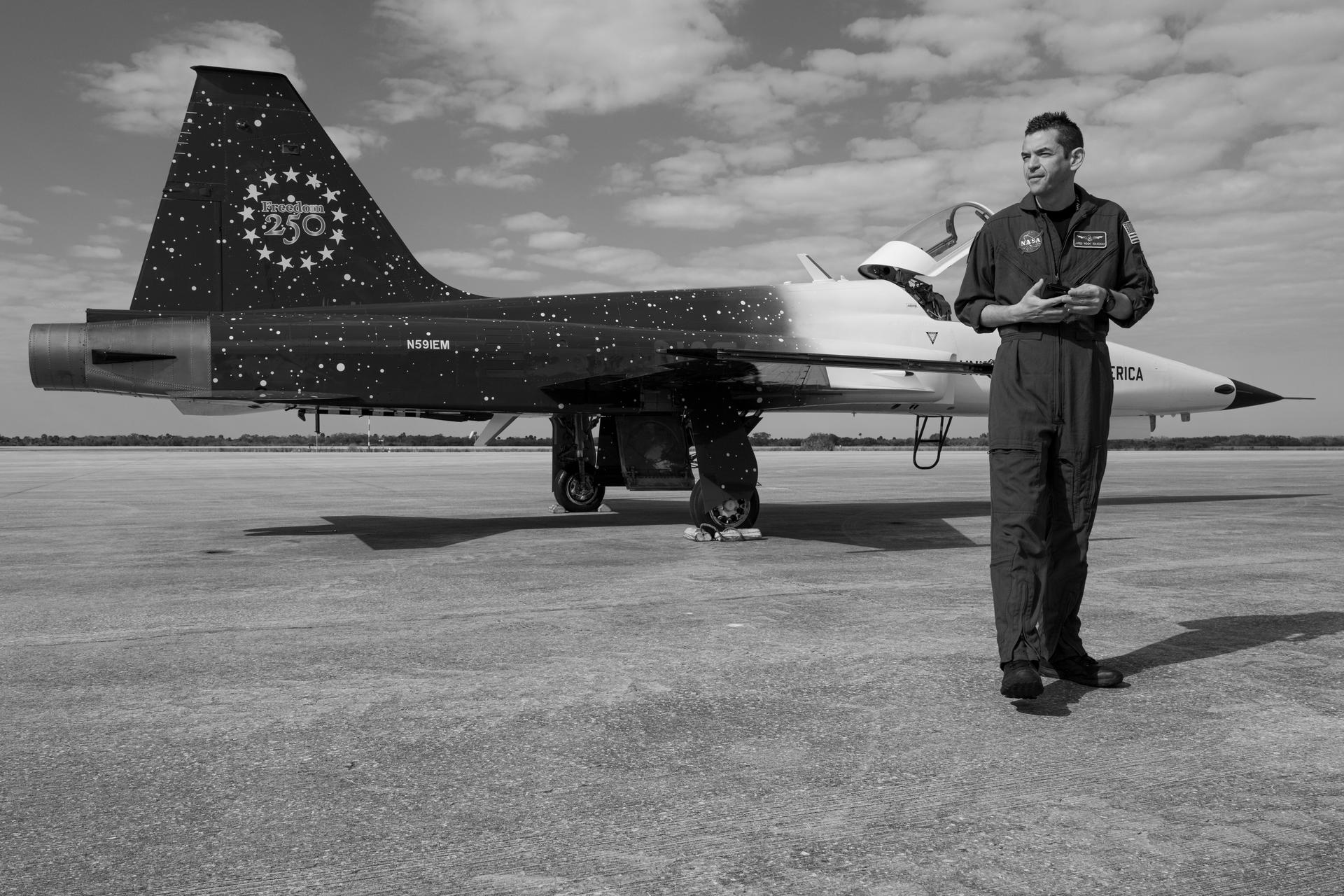

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman is seen with his personal F-5 aircraft, Saturday, Feb. 21, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
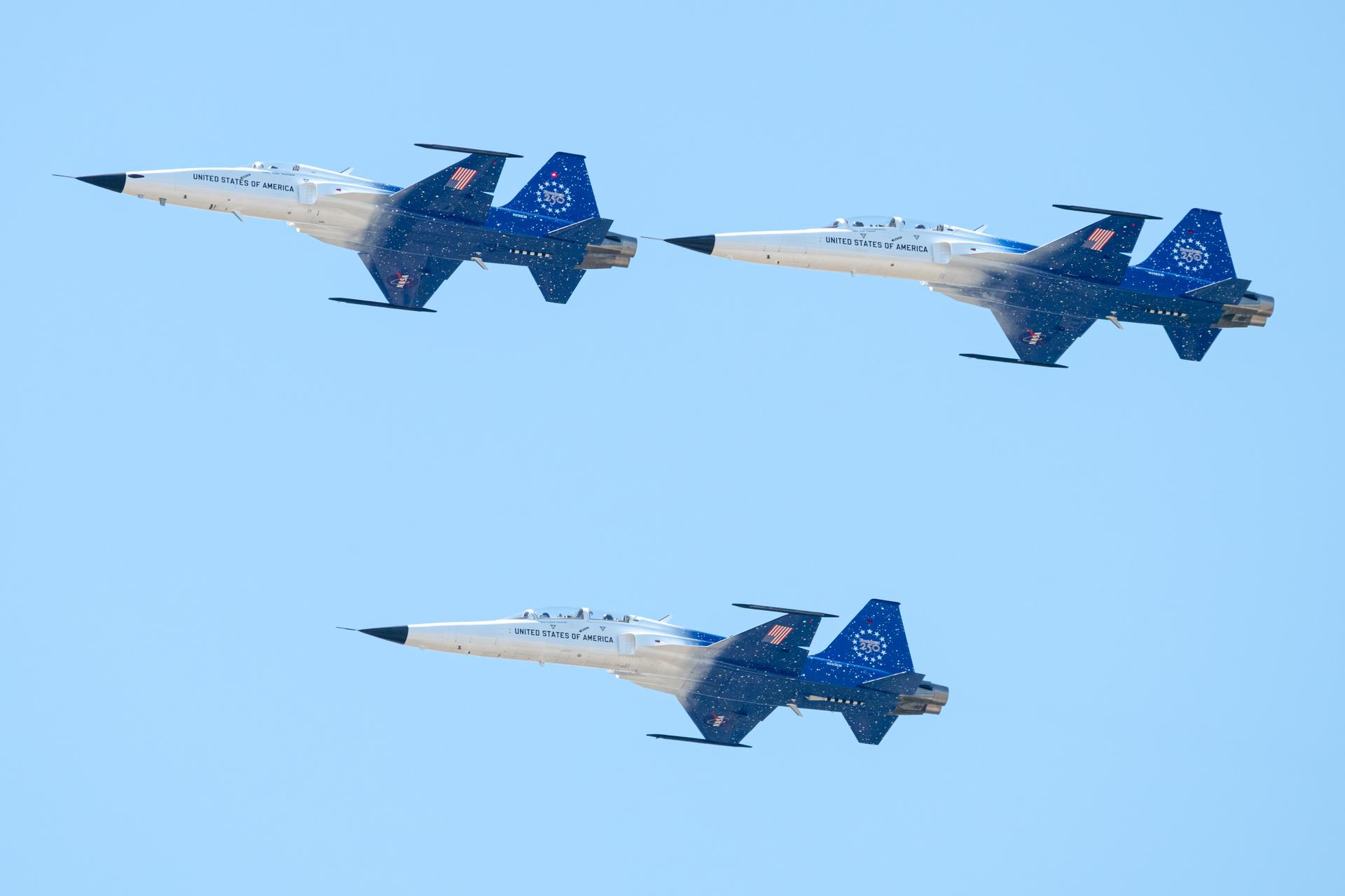

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman participates in a formation flight with his personal F-5 aircraft, Saturday, Feb. 21, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
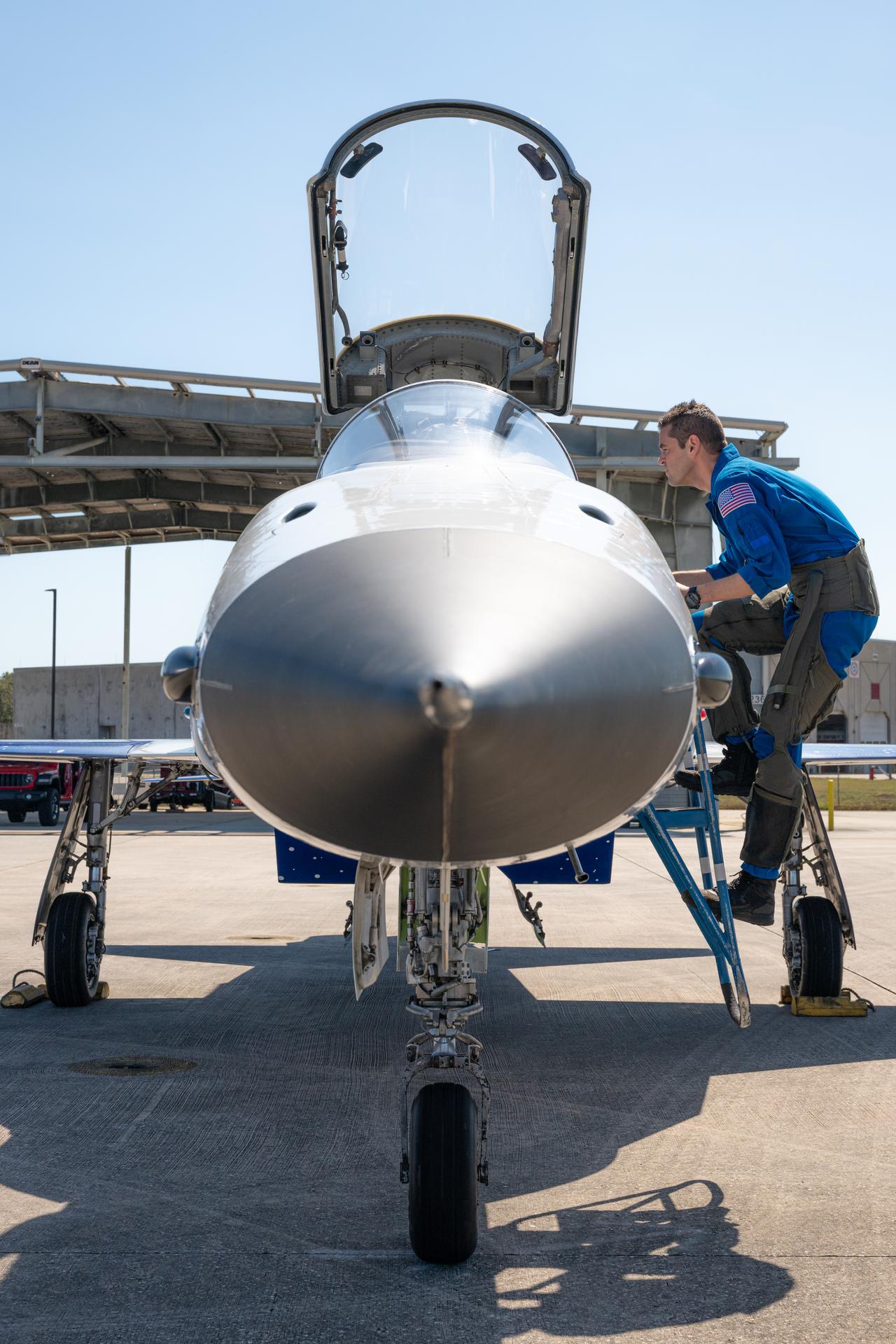

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman is seen ingressing his personal F-5 aircraft, Saturday, Feb. 21, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
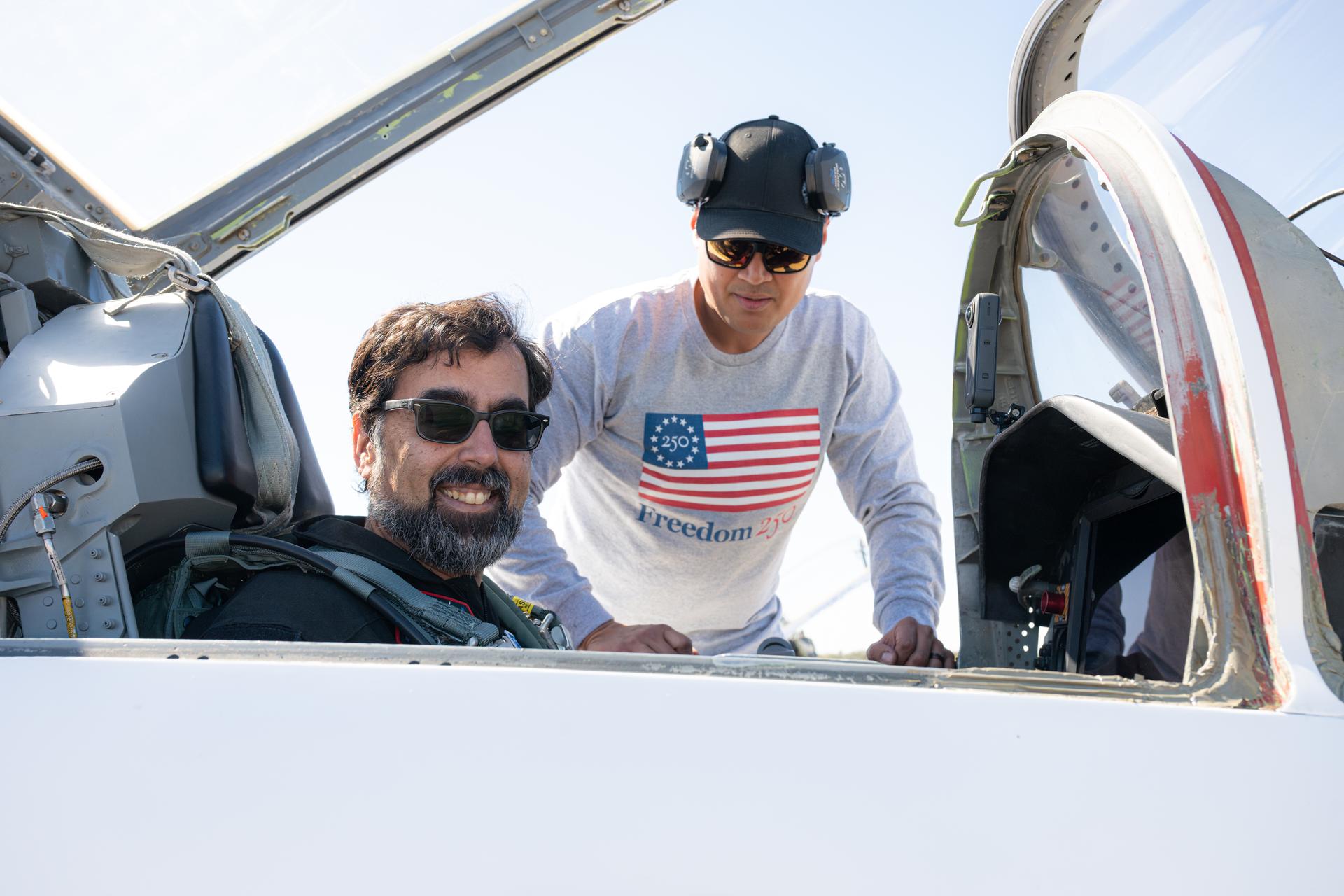

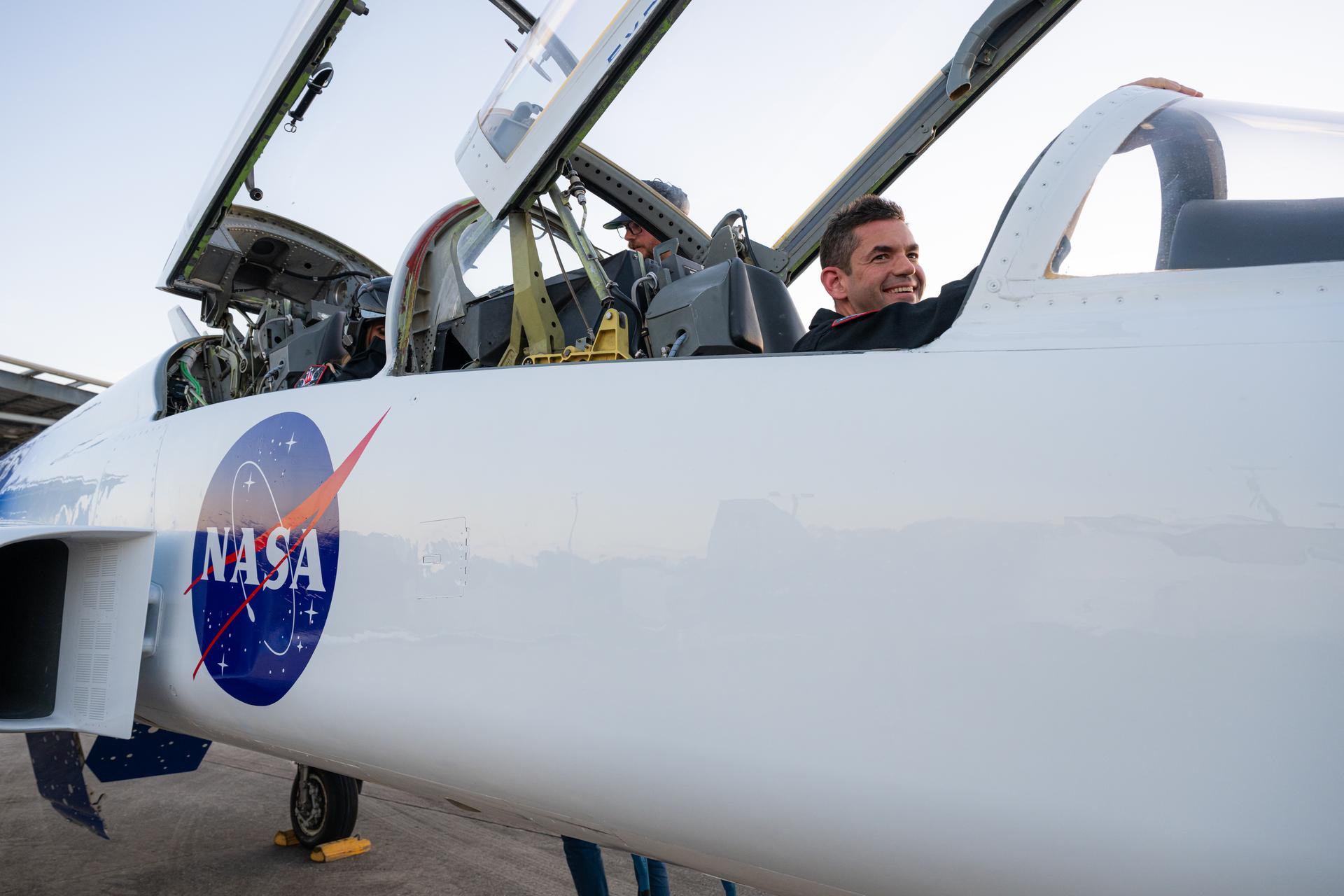
Amit Kshatriya, NASA associate administrator, poses for a photograph in NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman’s personal F-5 aircraft, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, ahead of a formation flight at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
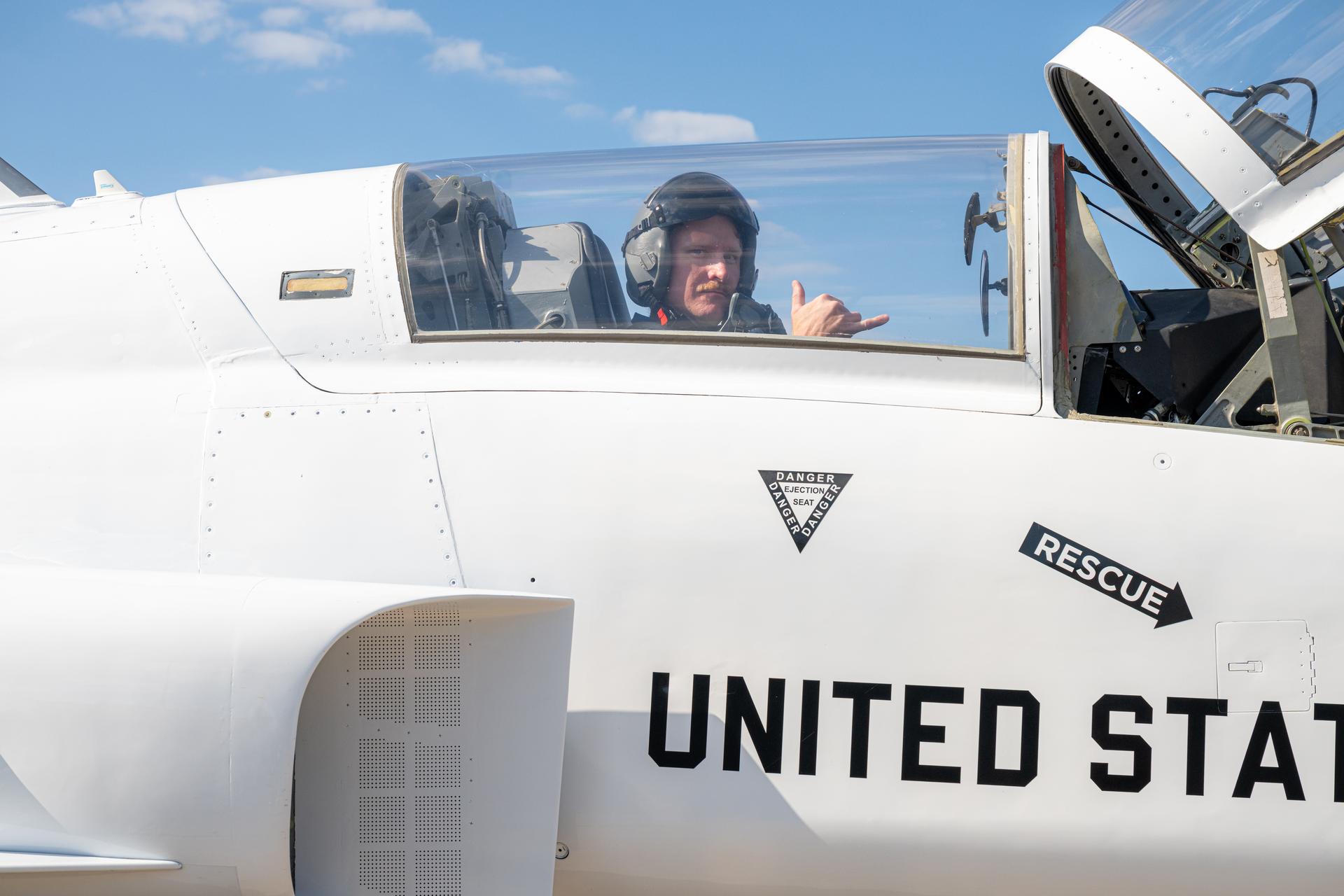

NASA employee Briou Bourgeois, E-3 test director at NASA’s Stennis Space Center, participates in an employee incentive flying event with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Saturday, Feb. 21, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
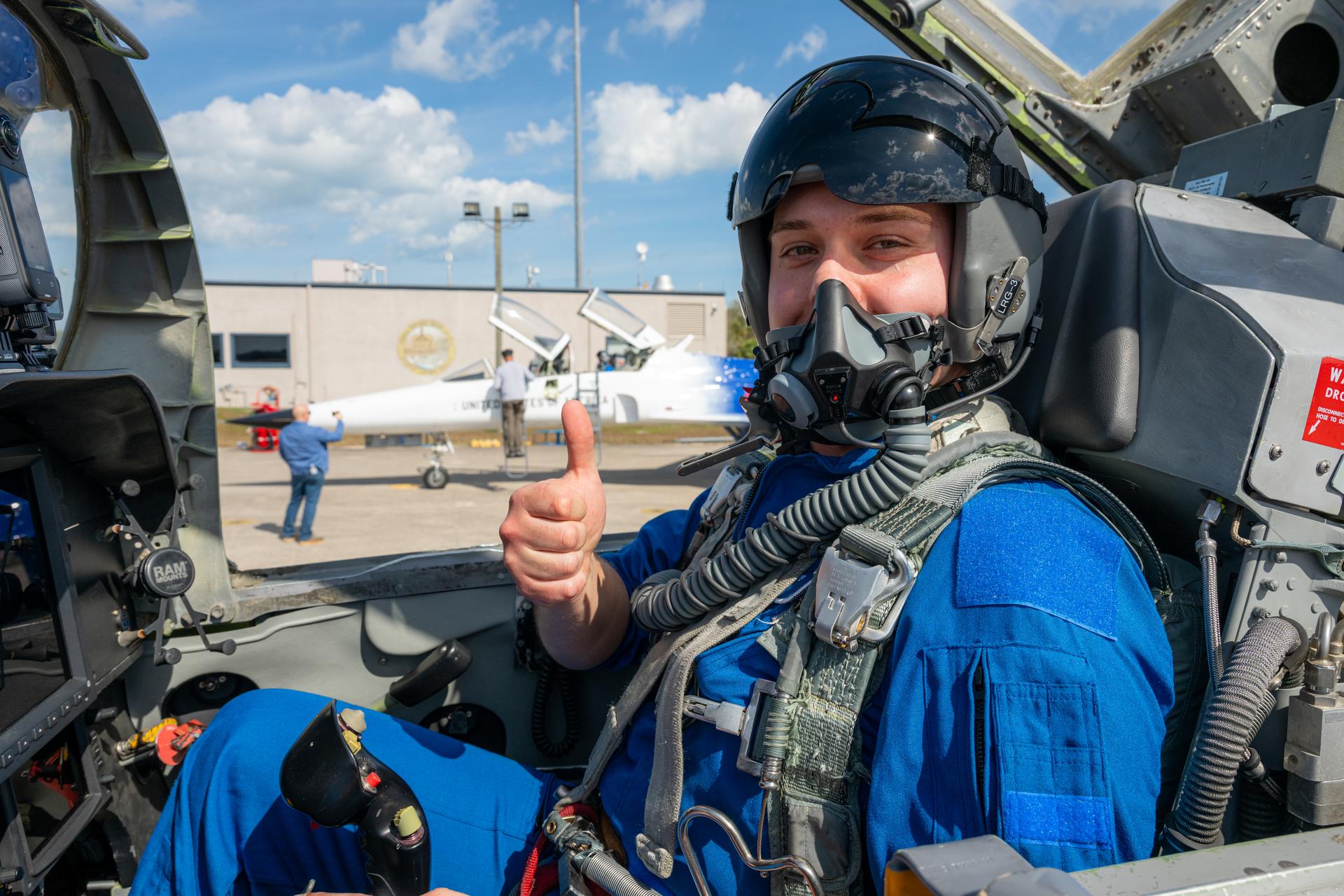

NASA employee Kristian Miasek, ET-10 test engineer at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, participates in an employee incentive flying event with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Friday, Feb. 20, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
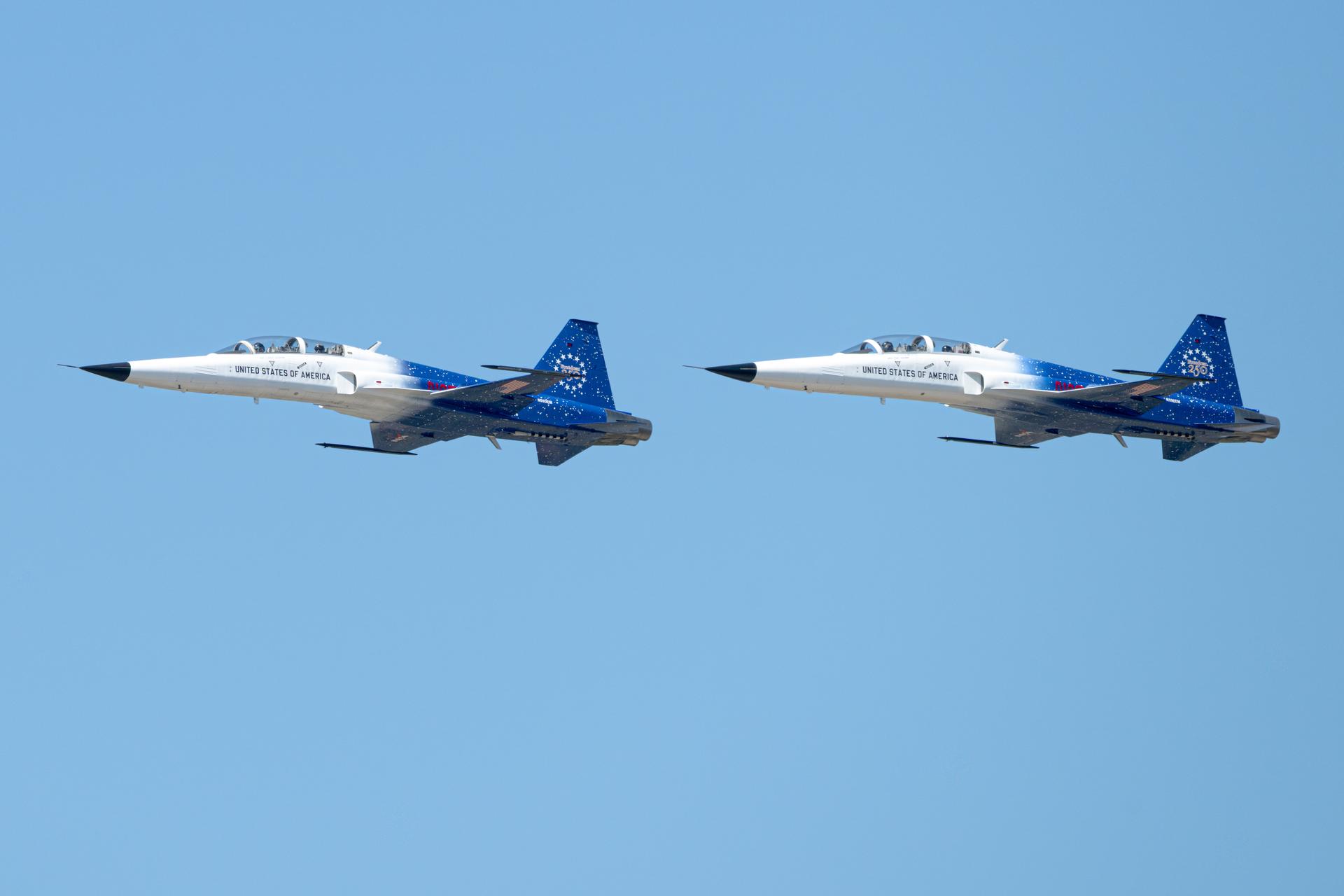

NASA employees participate in an employee incentive flying event using NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Saturday, Feb. 21, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
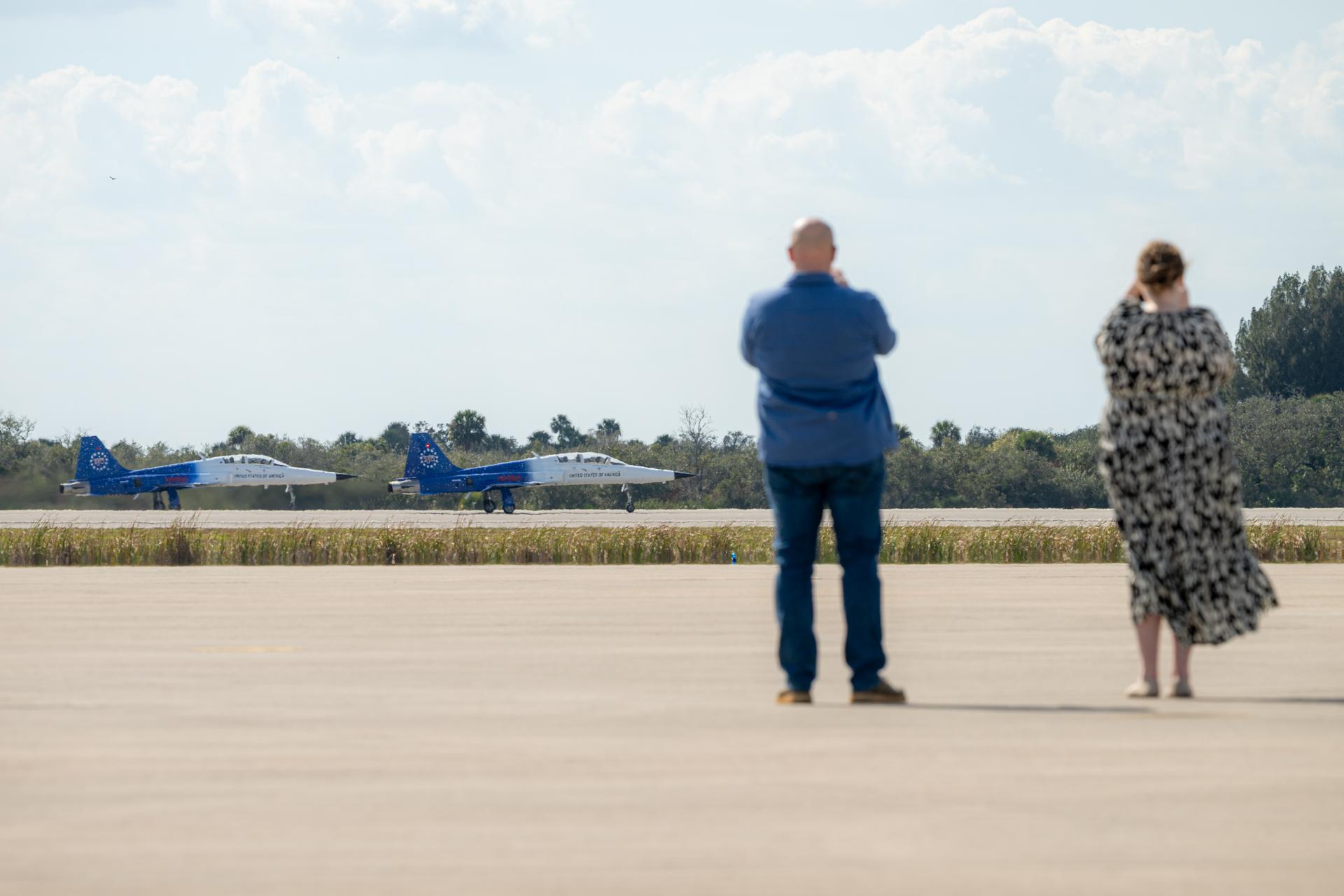

Family members of NASA employees watch as members of the NASA workforce participate in an employee incentive flying event with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Friday, Feb. 20, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
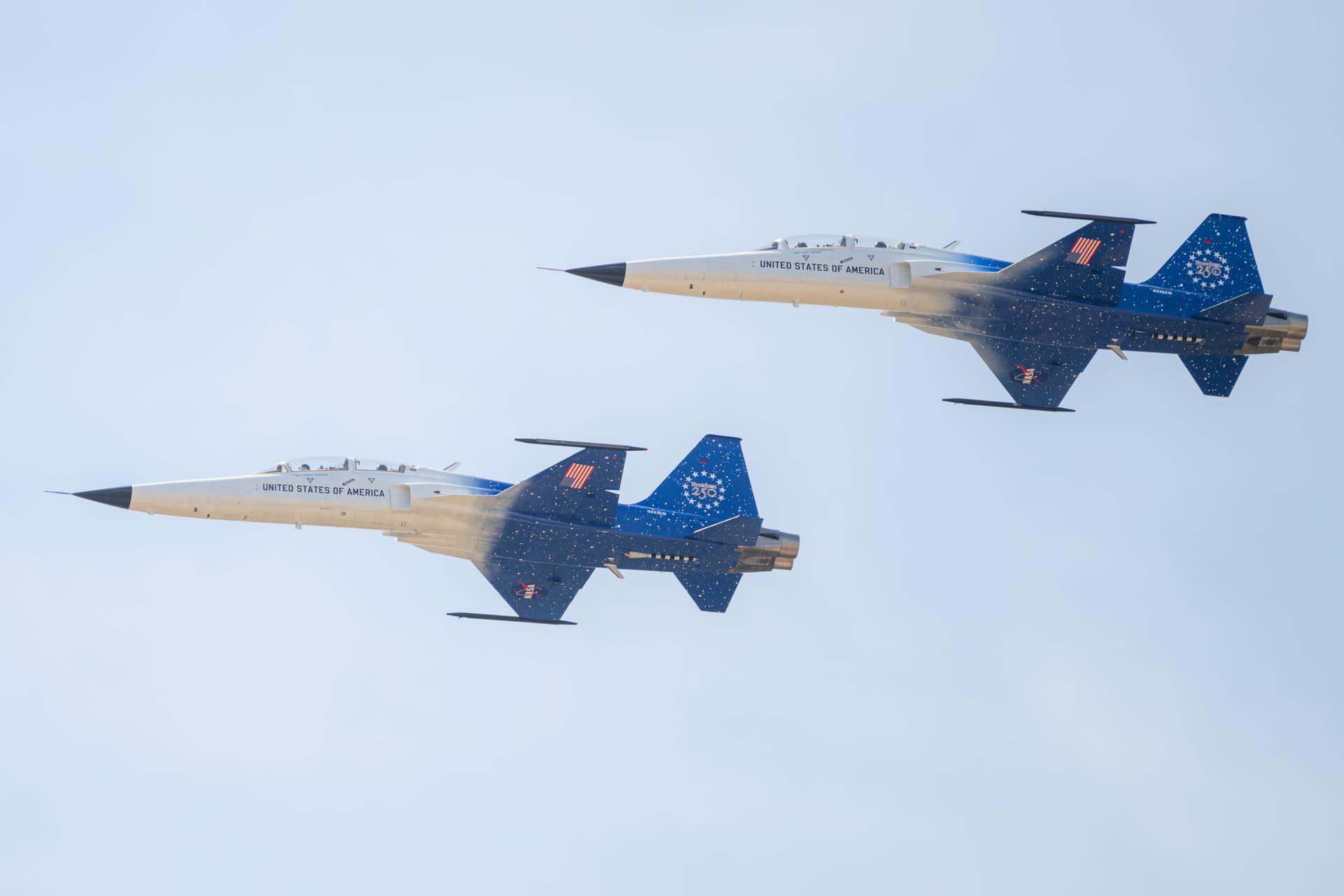

NASA employees participate in an employee incentive flying event using NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Friday, Feb. 20, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
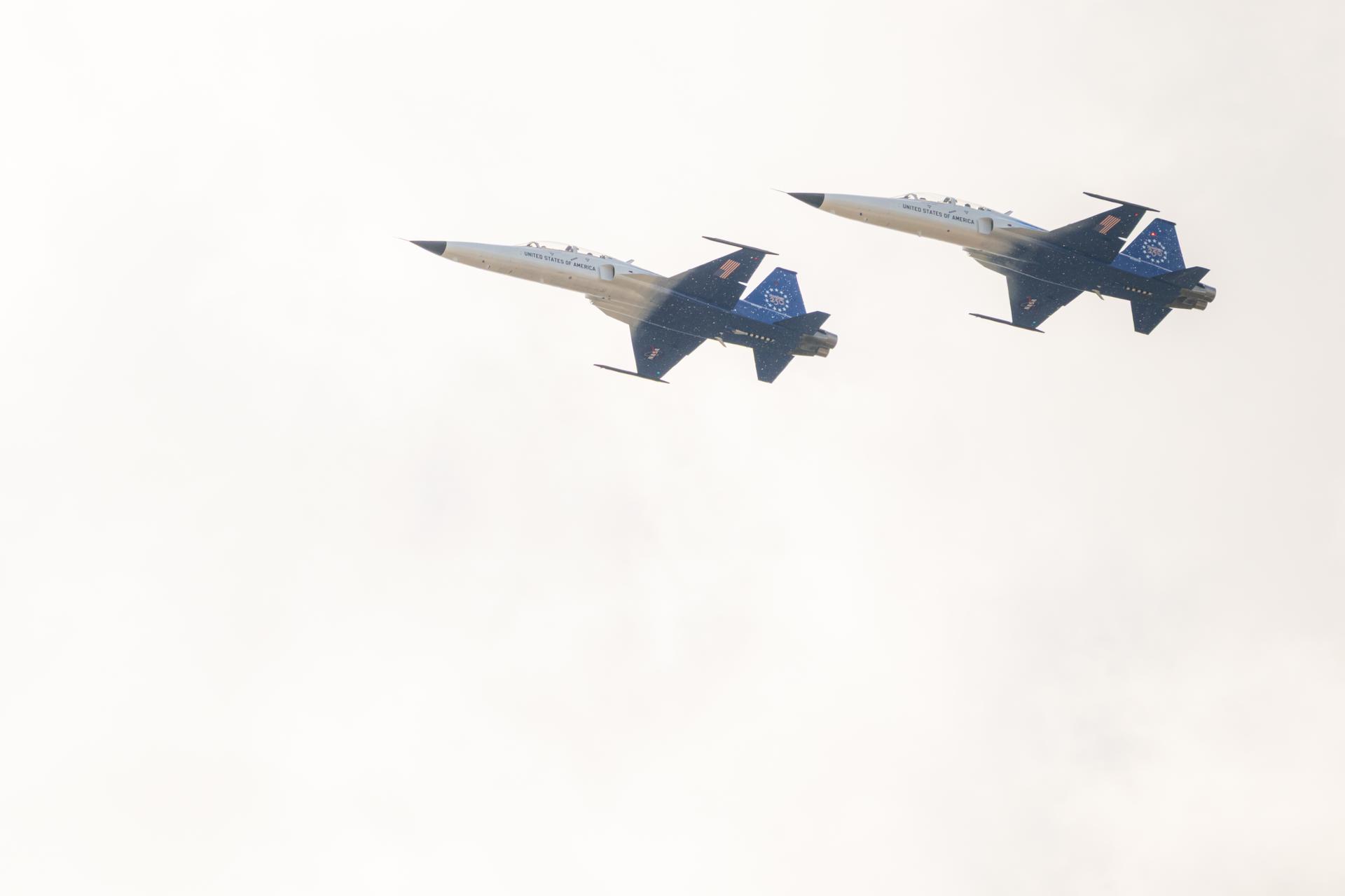

NASA employees participate in an employee incentive flying event using NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Friday, Feb. 20, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
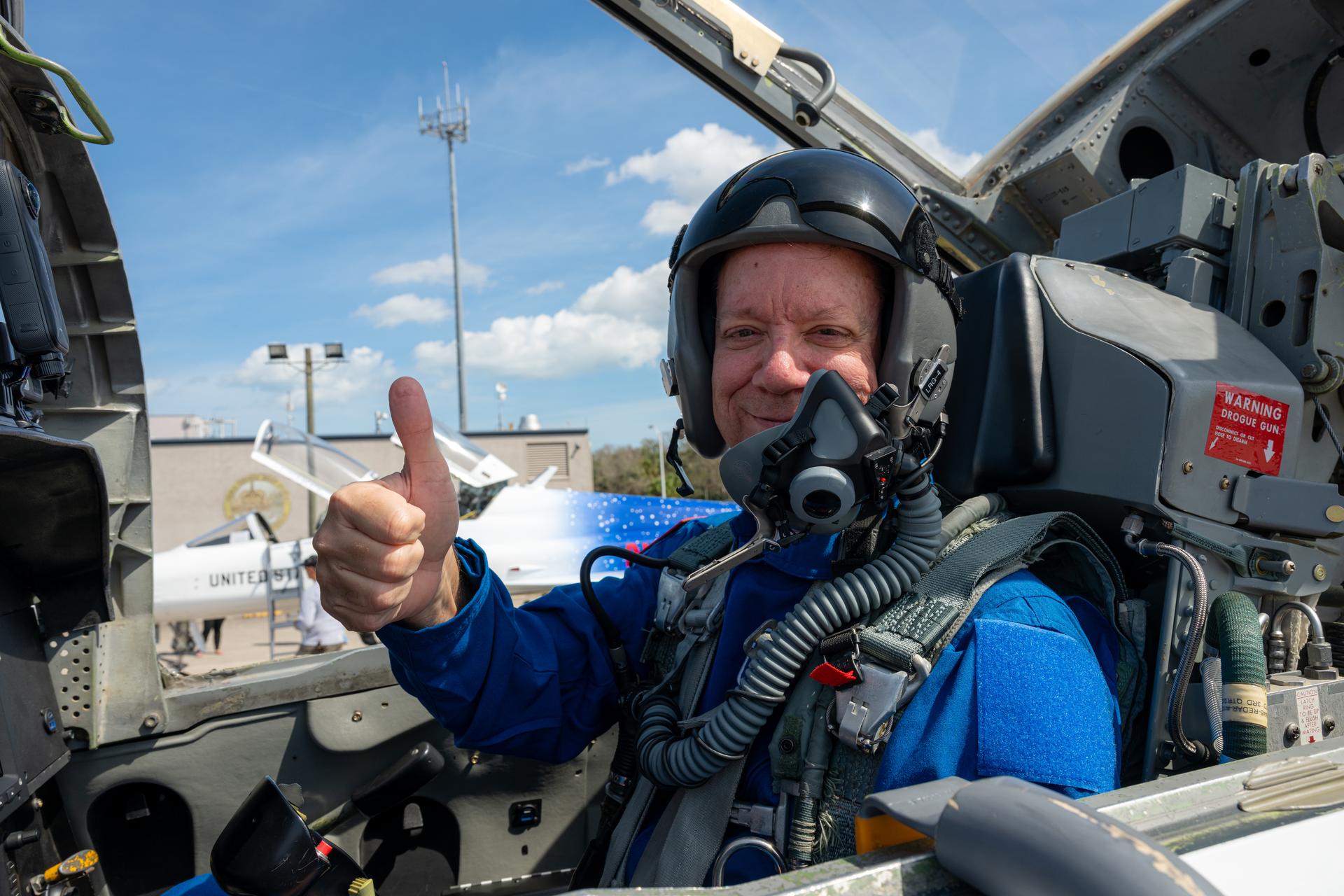

NASA employee Greg Gaddis, spaceport senior operations manager at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, participates in an employee incentive flying event with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Friday, Feb. 20, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
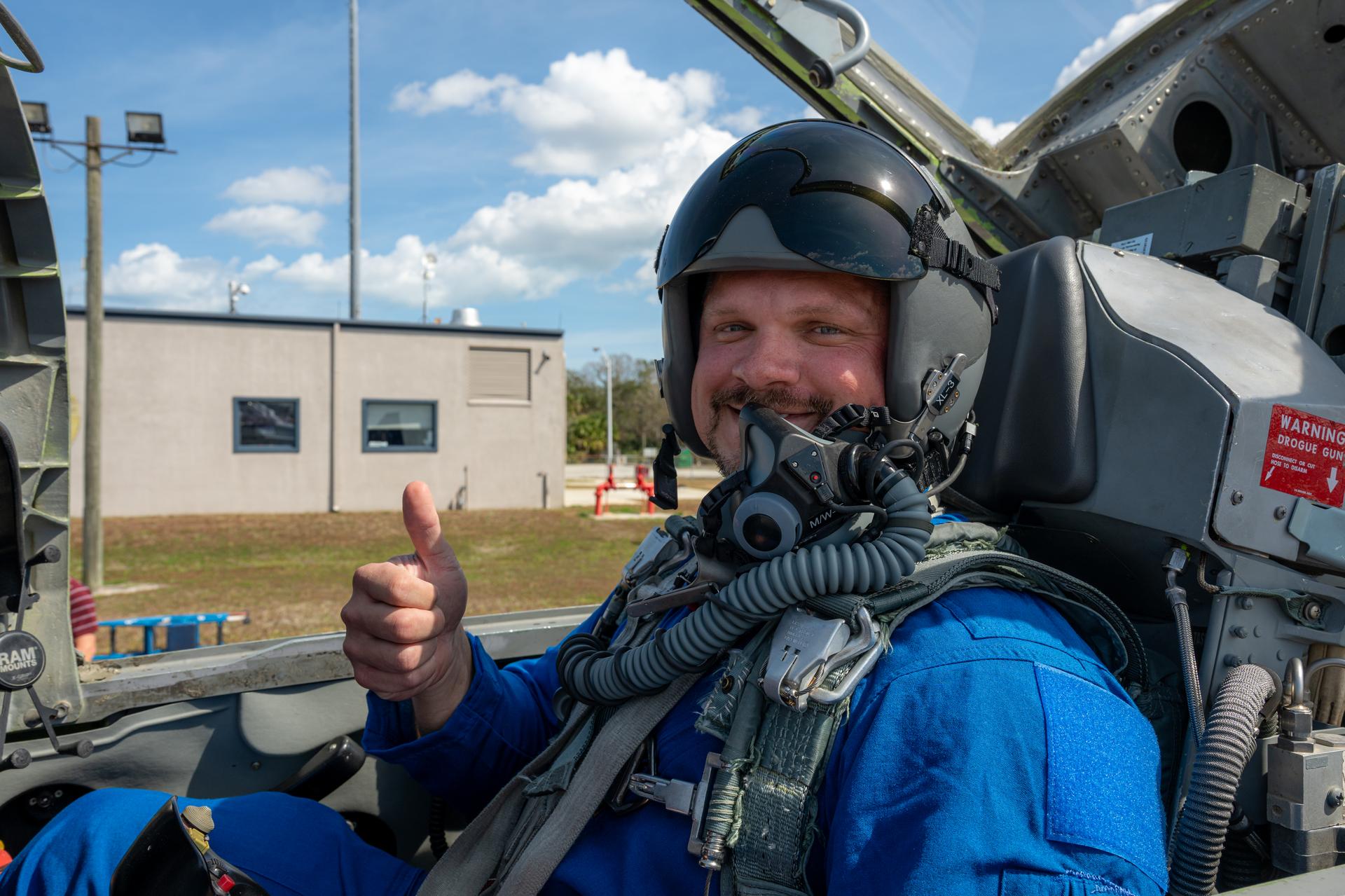

NASA employee James Hamilton, propellant and pressurant manager at NASA’s Stennis Space Center, participates in an employee incentive flying event with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Friday, Feb. 20, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
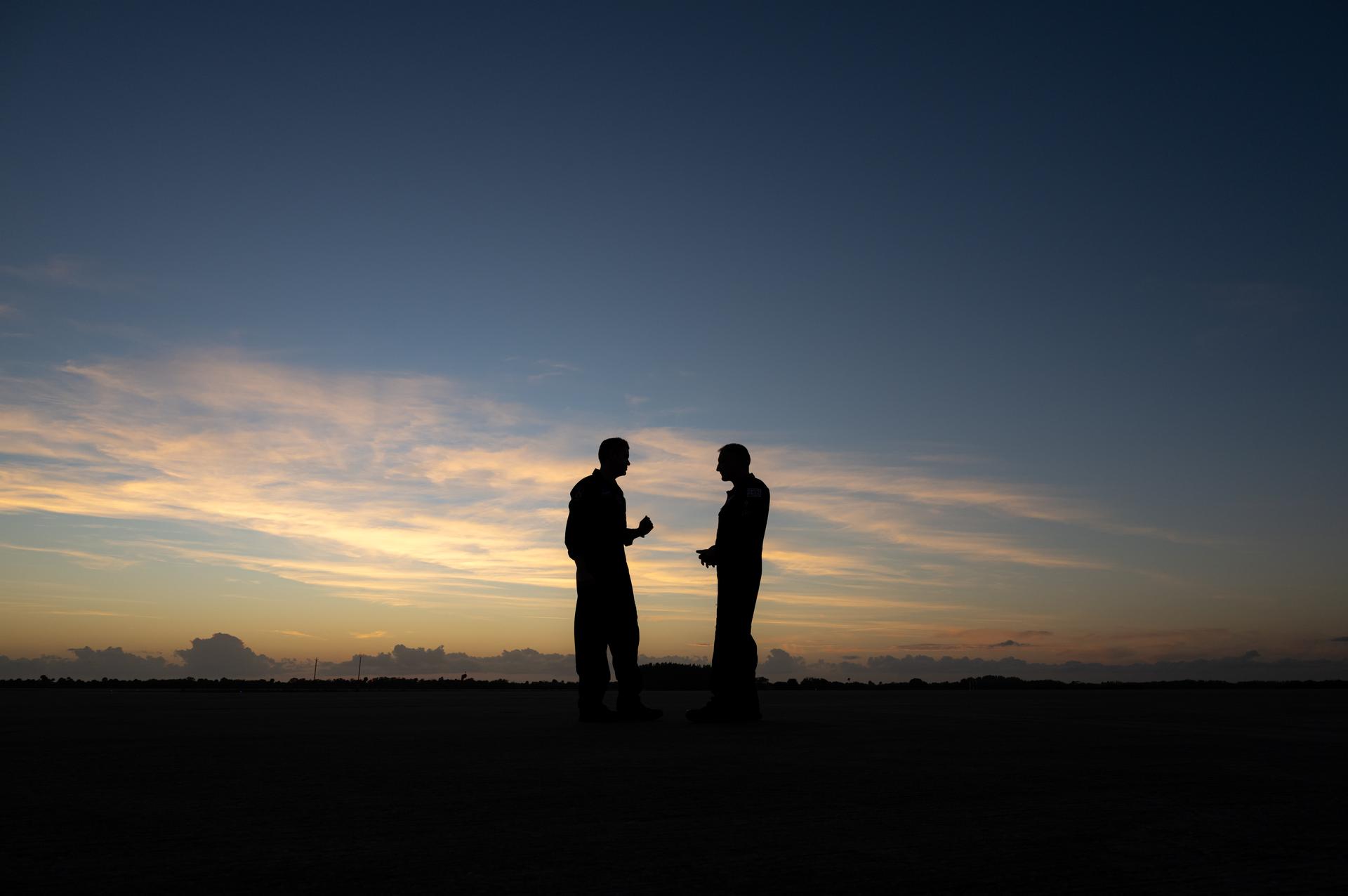

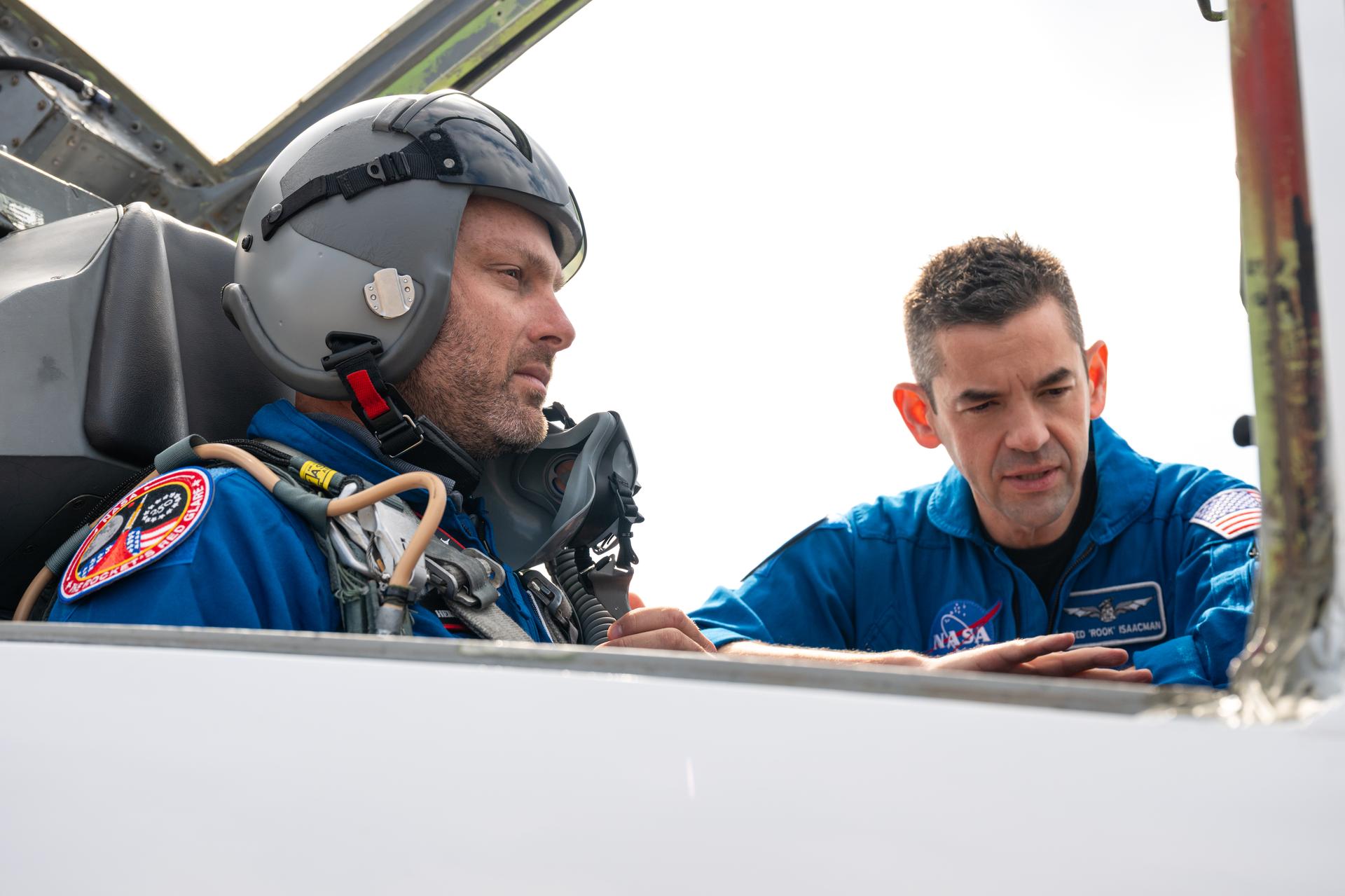
NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman, left, and Sean Gustafson, senior advisor to the administrator, right, are seen at sunset following a formation flight in Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Monday, Jan. 5, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman participates in a formation flight with his personal F-5 aircraft, Monday, Jan. 5, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Isaacman was joined by Lara Trump of Fox News flying in the back seat. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman is seen following a formation flight with his personal F-5 aircraft, Monday, Jan. 5, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Isaacman was joined by Lara Trump of Fox News flying in the back seat. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
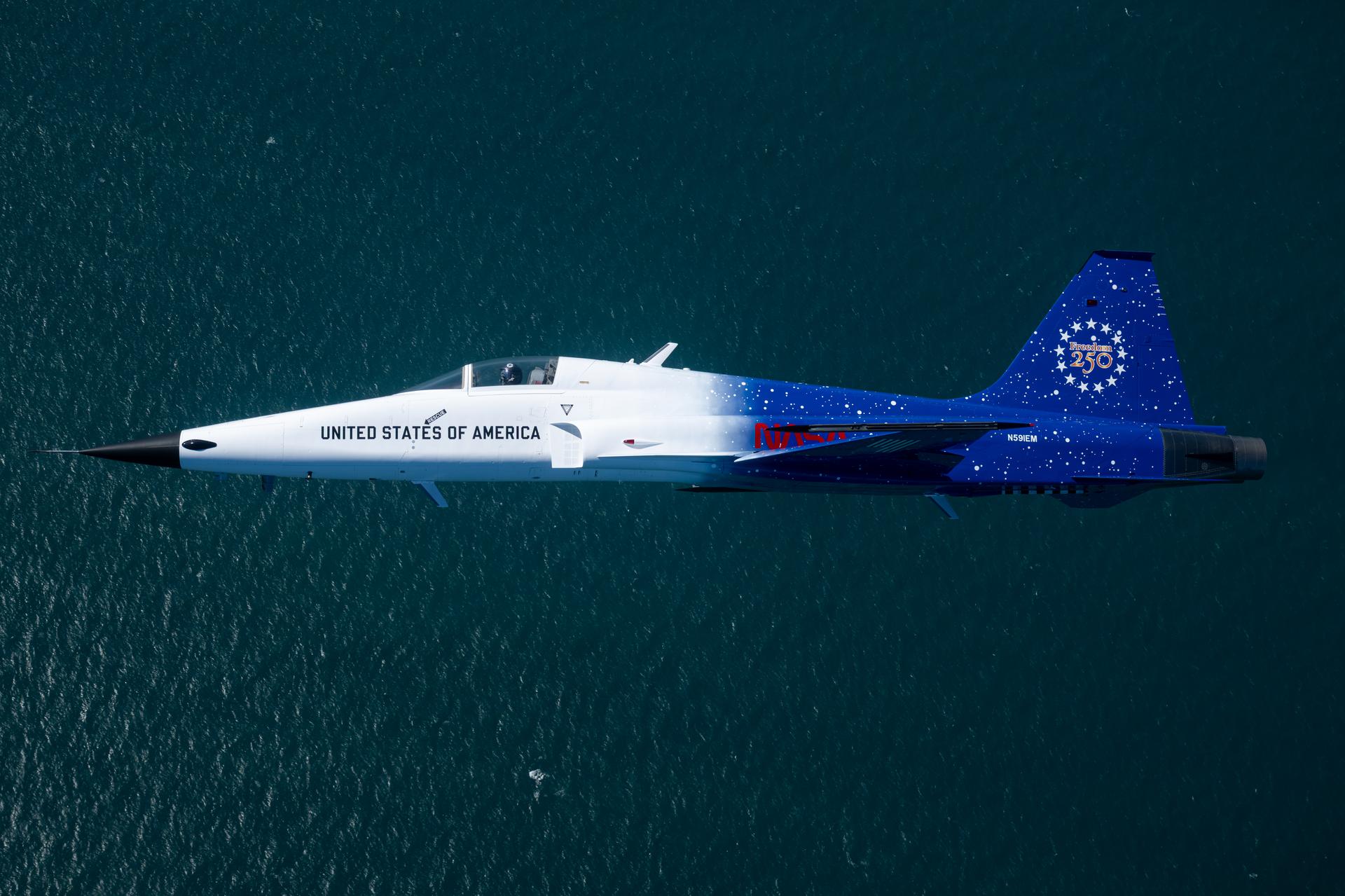

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman is seen flying his personal F-5 aircraft, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
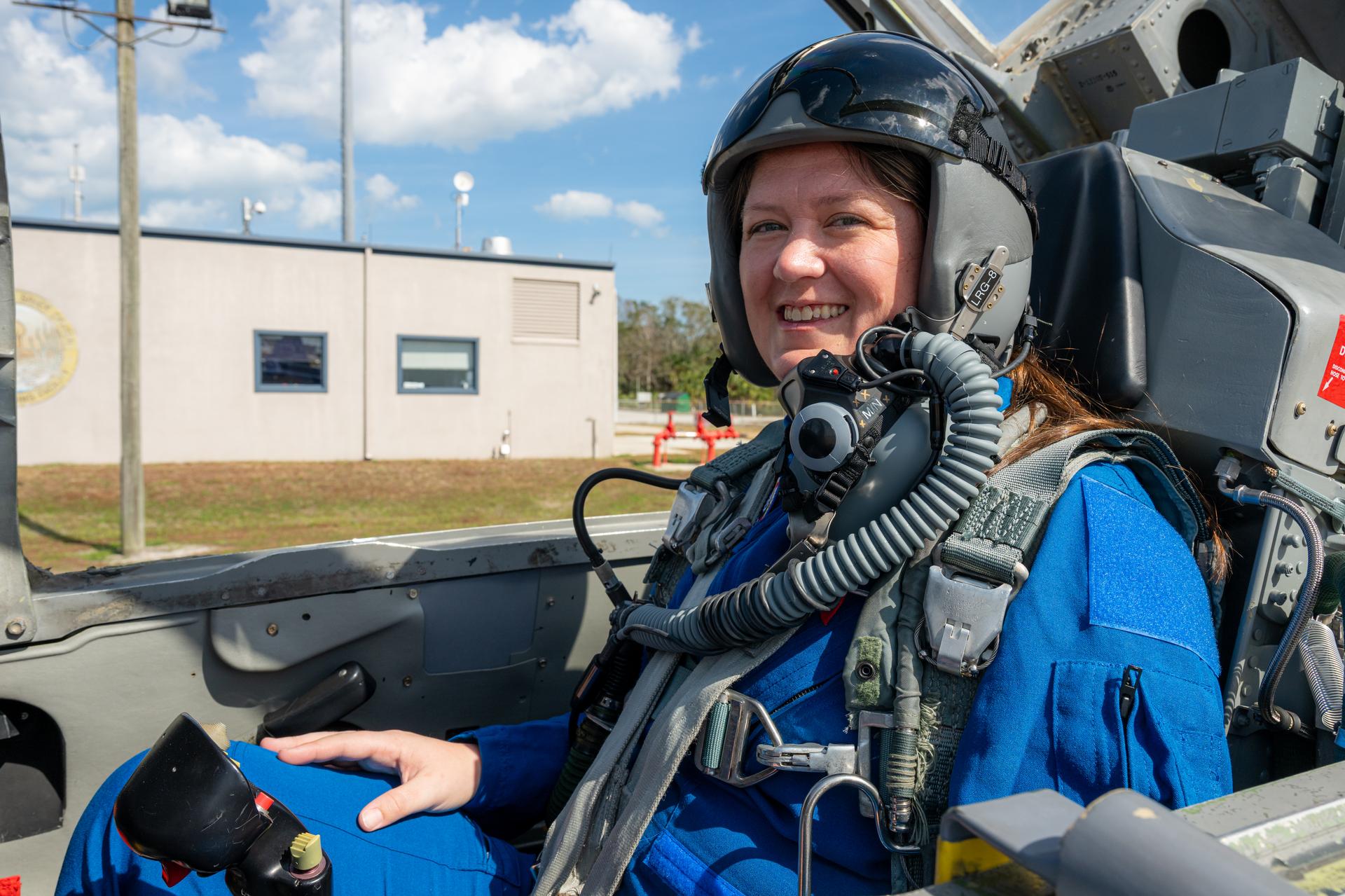

NASA employee Megan Vansant, chief architect and demolition program manager at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, participates in an employee incentive flying event with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Friday, Feb. 20, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
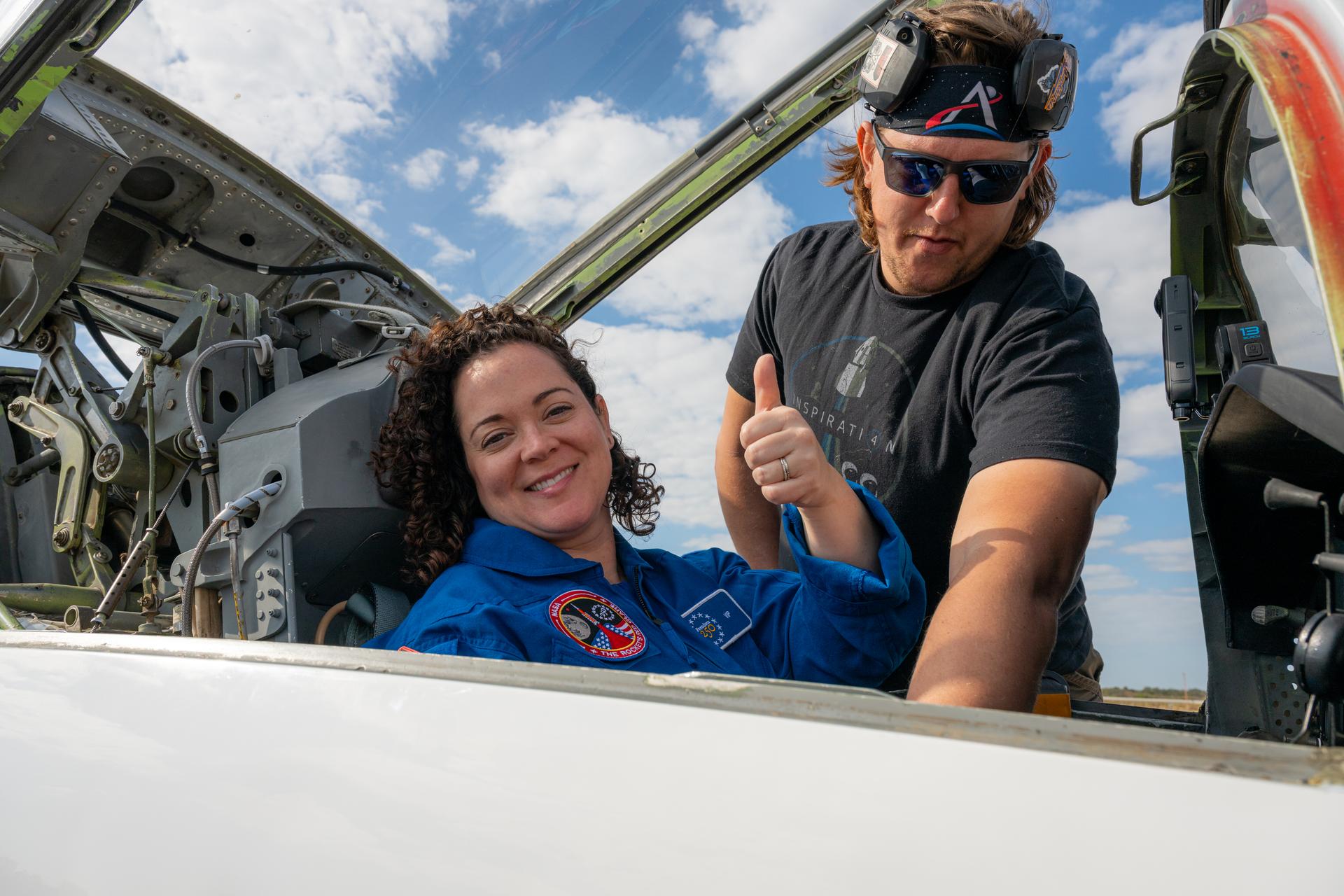

NASA employee Brittany Bouché, acting deputy chief of facility engineering services at NASA’s Stennis Space Center, participates in an employee incentive flying event with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Saturday, Feb. 21, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
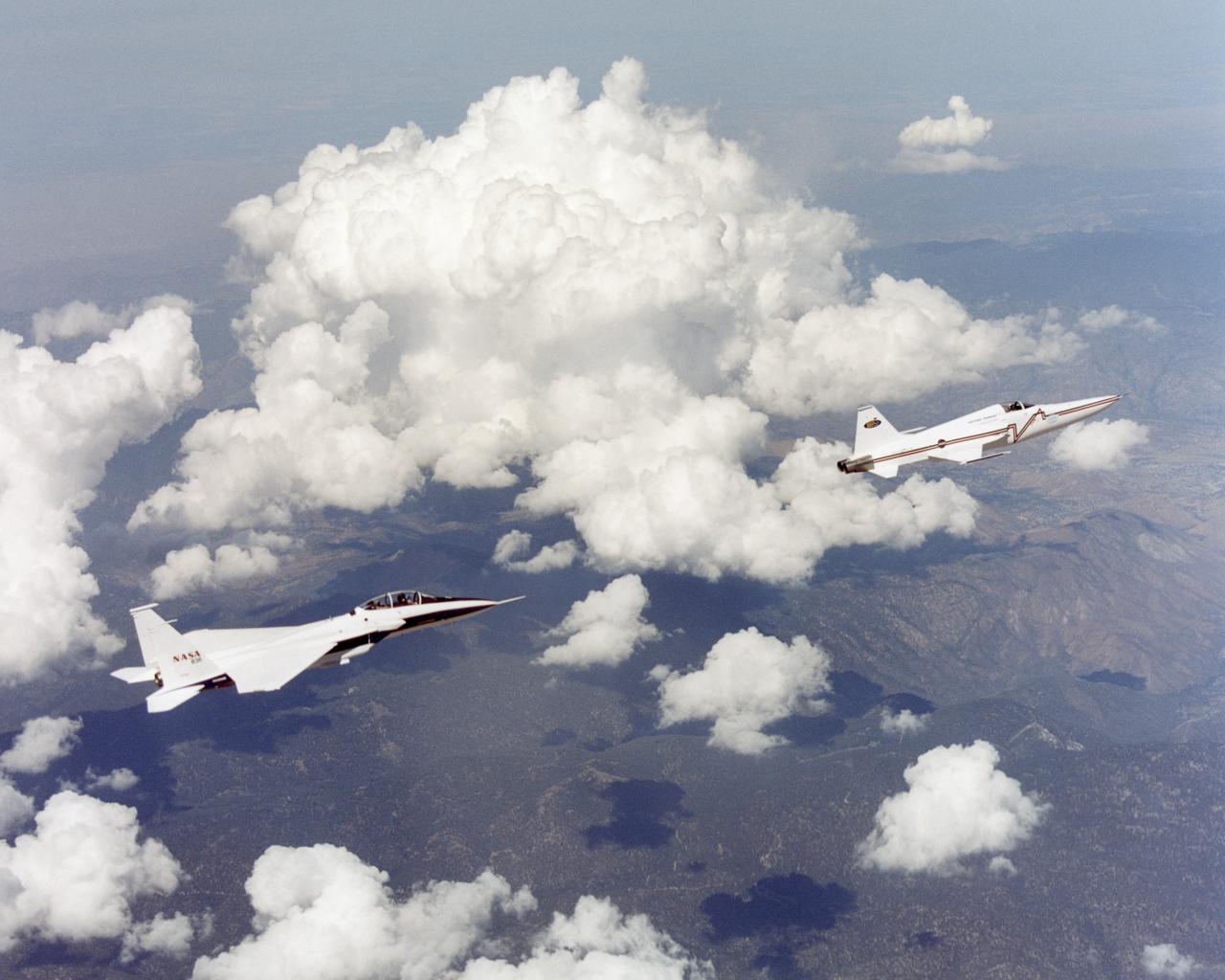

NASA's F-15B research testbed jet from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center flew in the supersonic shockwave of a Northrop Grumman Corp. modified U.S. Navy F-5E jet in support of the Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, which is part of the DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. On Aug. 27, 2003, the F-5 SSBD aircraft demonstrated a method to reduce the intensity of sonic booms.
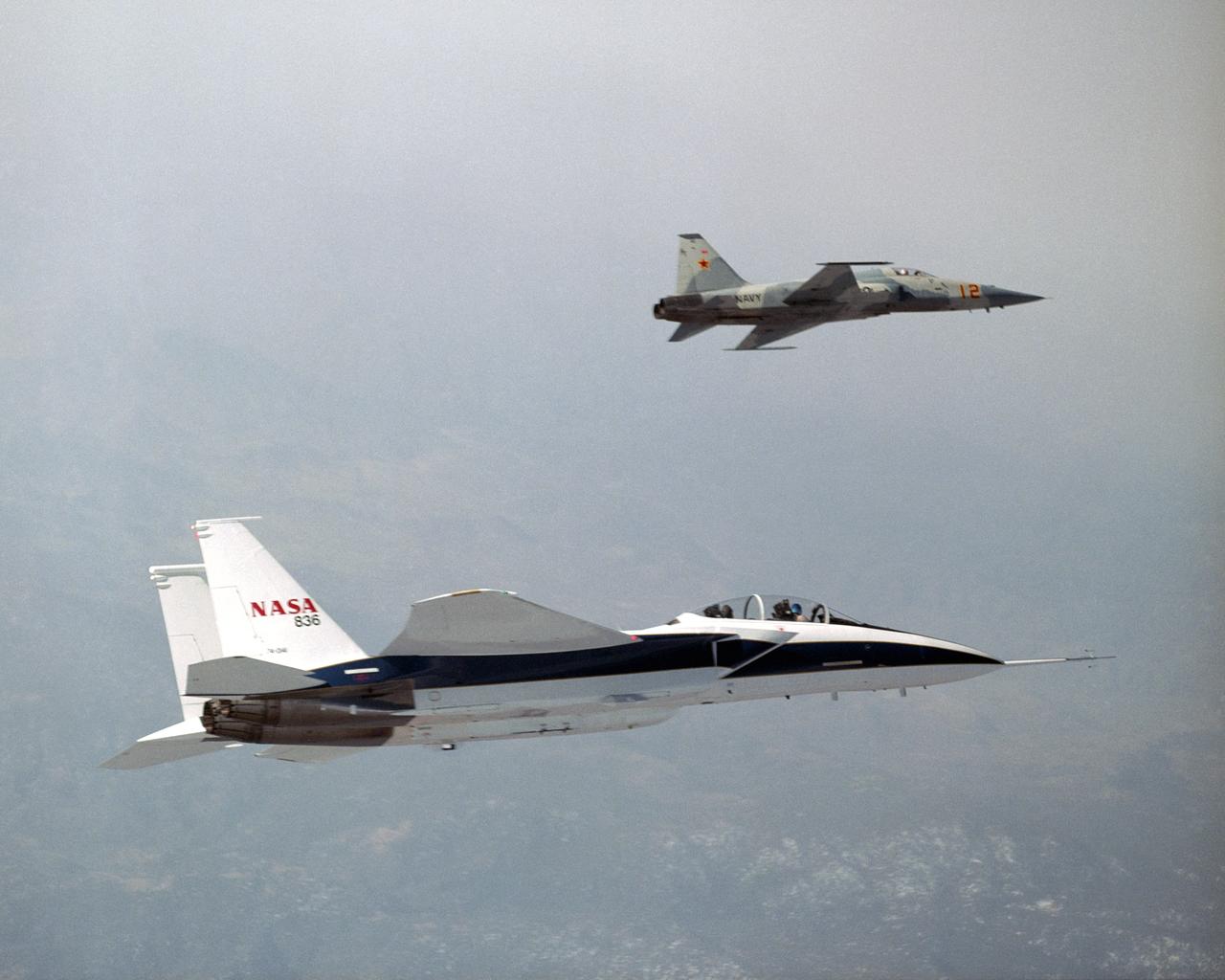

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft recently flew in the supersonic shock wave of a U.S. Navy F-5E in support of the F-5 Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The flights originated from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. Four flights were flown in order to measure the F-5E's near-field (close-up) sonic boom signature at Mach 1.4, during which more than 50 shockwave patterns were measured at distances as close as 100 feet below the F-5E.
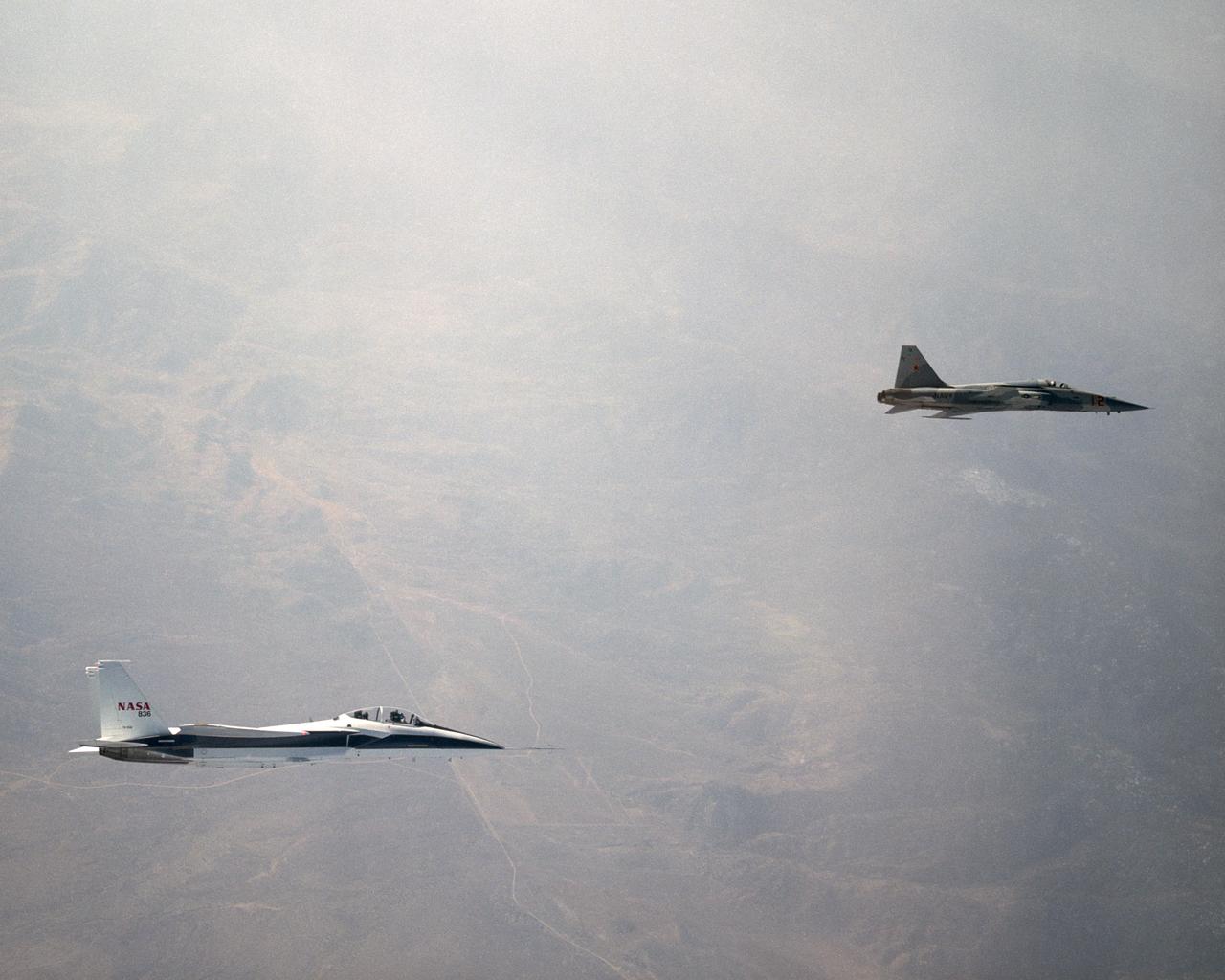

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft recently flew in the supersonic shock wave of a U.S. Navy F-5E in support of the F-5 Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The flights originated from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. Four flights were flown in order to measure the F-5E's near-field (close-up) sonic boom signature at Mach 1.4, during which more than 50 shockwave patterns were measured at distances as close as 100 feet below the F-5E.
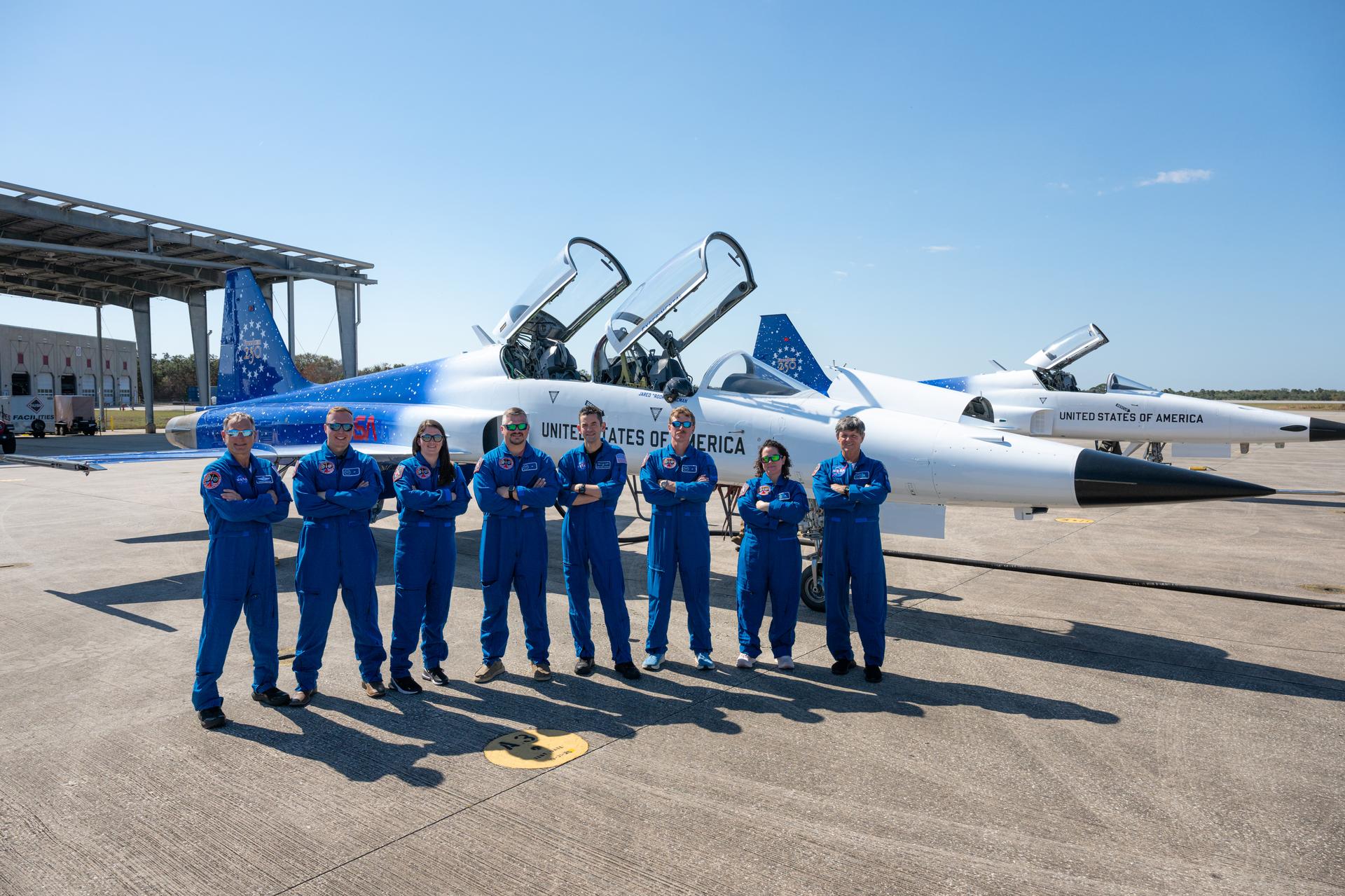

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman, fifth from left, poses for a photograph with NASA employees and F-5 pilots following an employee incentive flying event using Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Saturday, Feb. 21, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left to right: Sean Gustafson, pilot and senior advisor to the administrator; Kristian Miasek, ET-10 test engineer at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Megan Vansant, chief architect and demolition program manager at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; James Hamilton, propellant and pressurant manager at NASA’s Stennis Space Center; NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman; Briou Bourgeois, E-3 test director at NASA’s Stennis Space Center; Brittany Bouché, acting deputy chief of facility engineering services at NASA’s Stennis Space Center; and Jerry Kerby, pilot. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
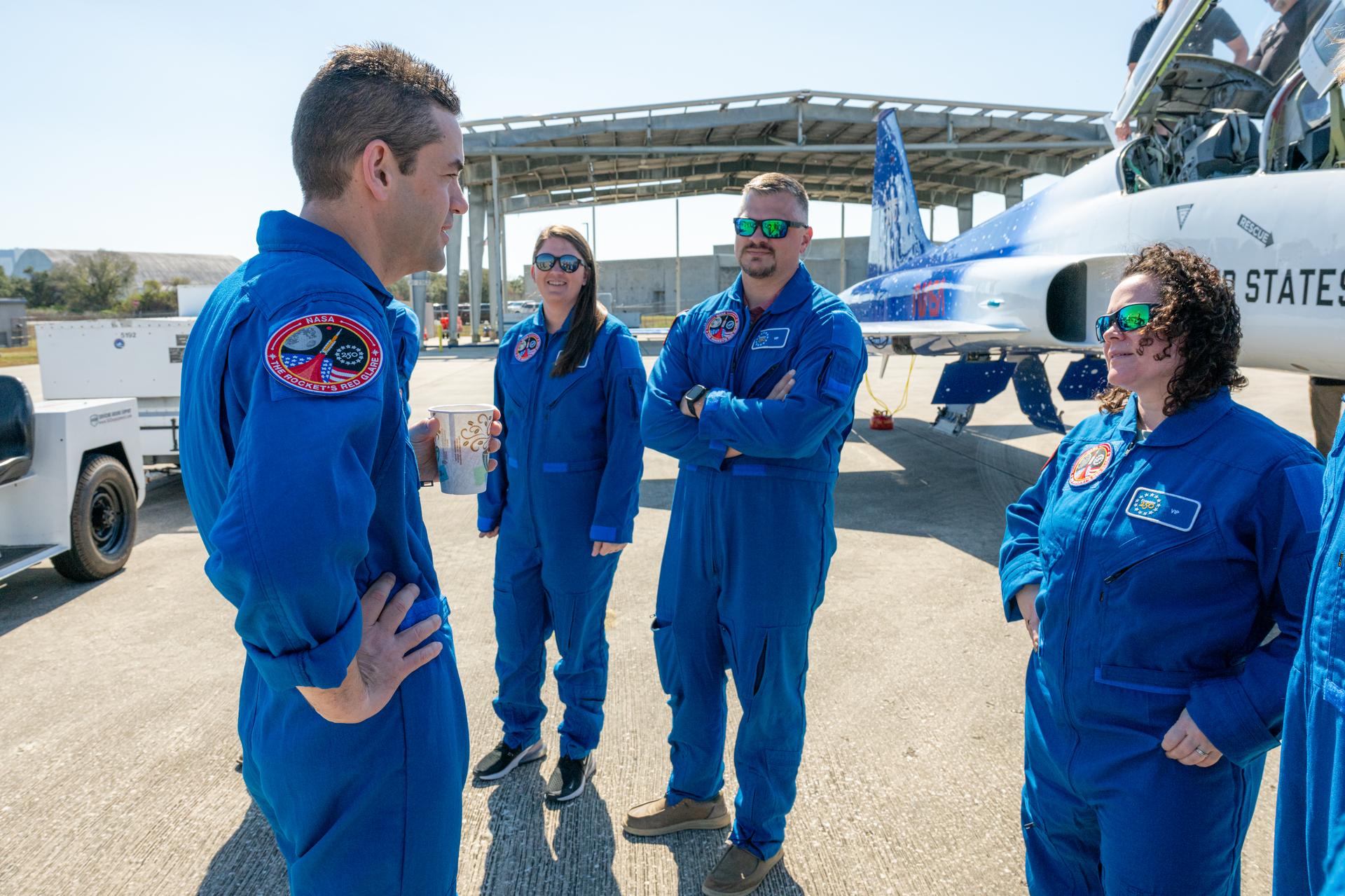

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman, left, speaks with NASA employees Megan Vansant, chief architect and demolition program manager at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, second from left; James Hamilton, propellant and pressurant manager at NASA’s Stennis Space Center, third from left; and Brittany Bouché, acting deputy chief of facility engineering services at NASA’s Stennis Space Center, right, following an employee incentive flying event using Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Saturday, Feb. 21, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
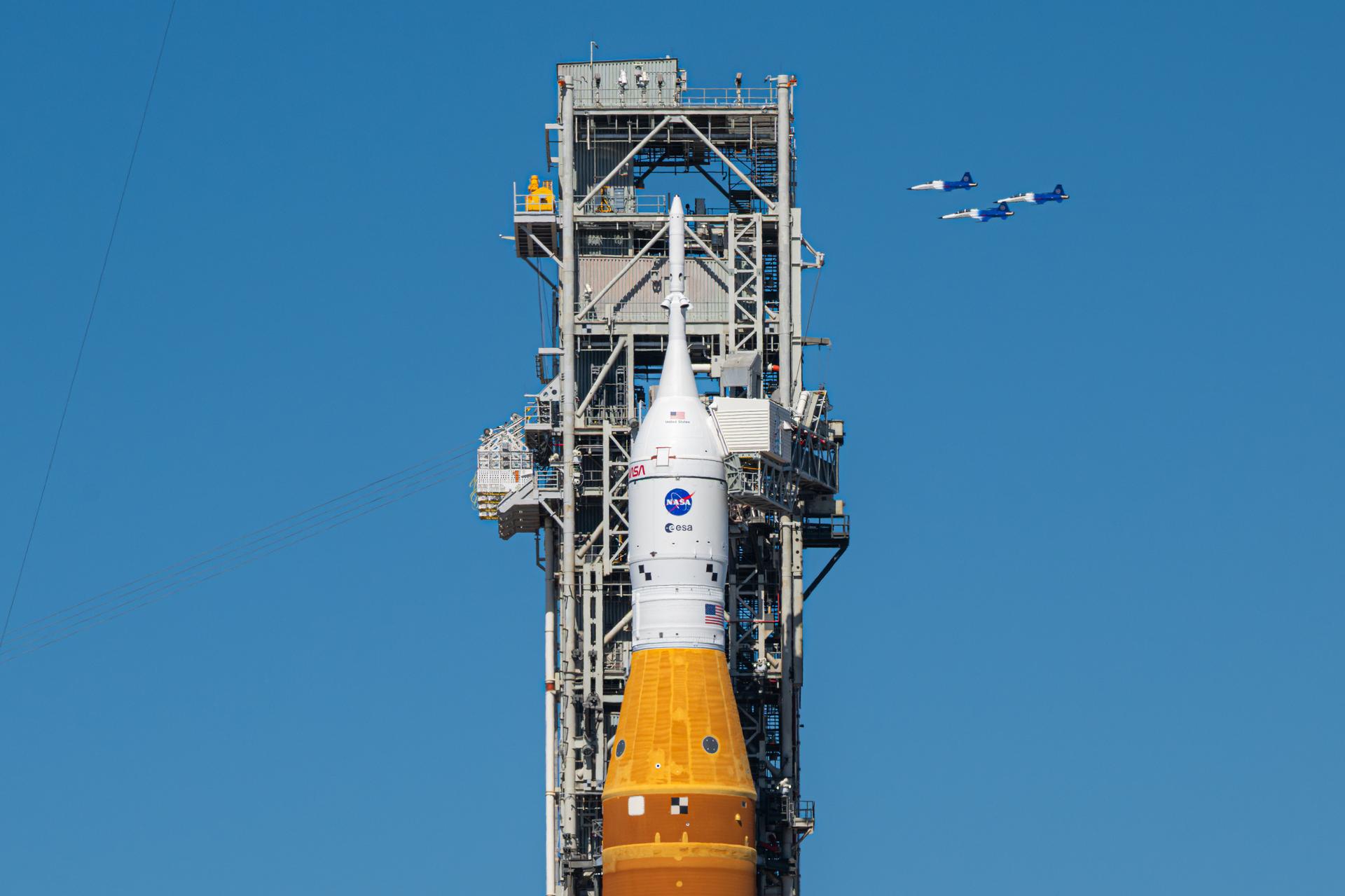

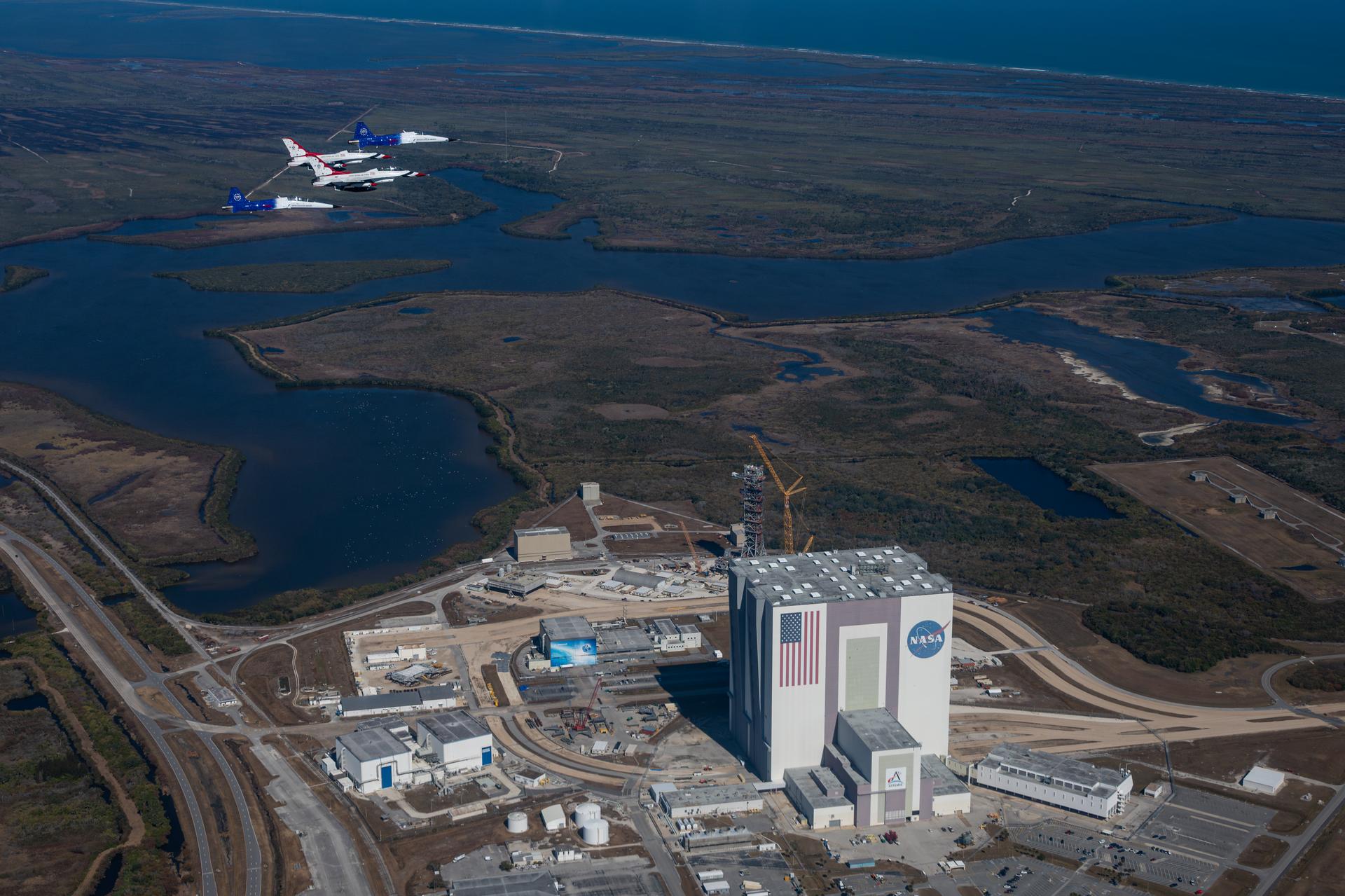
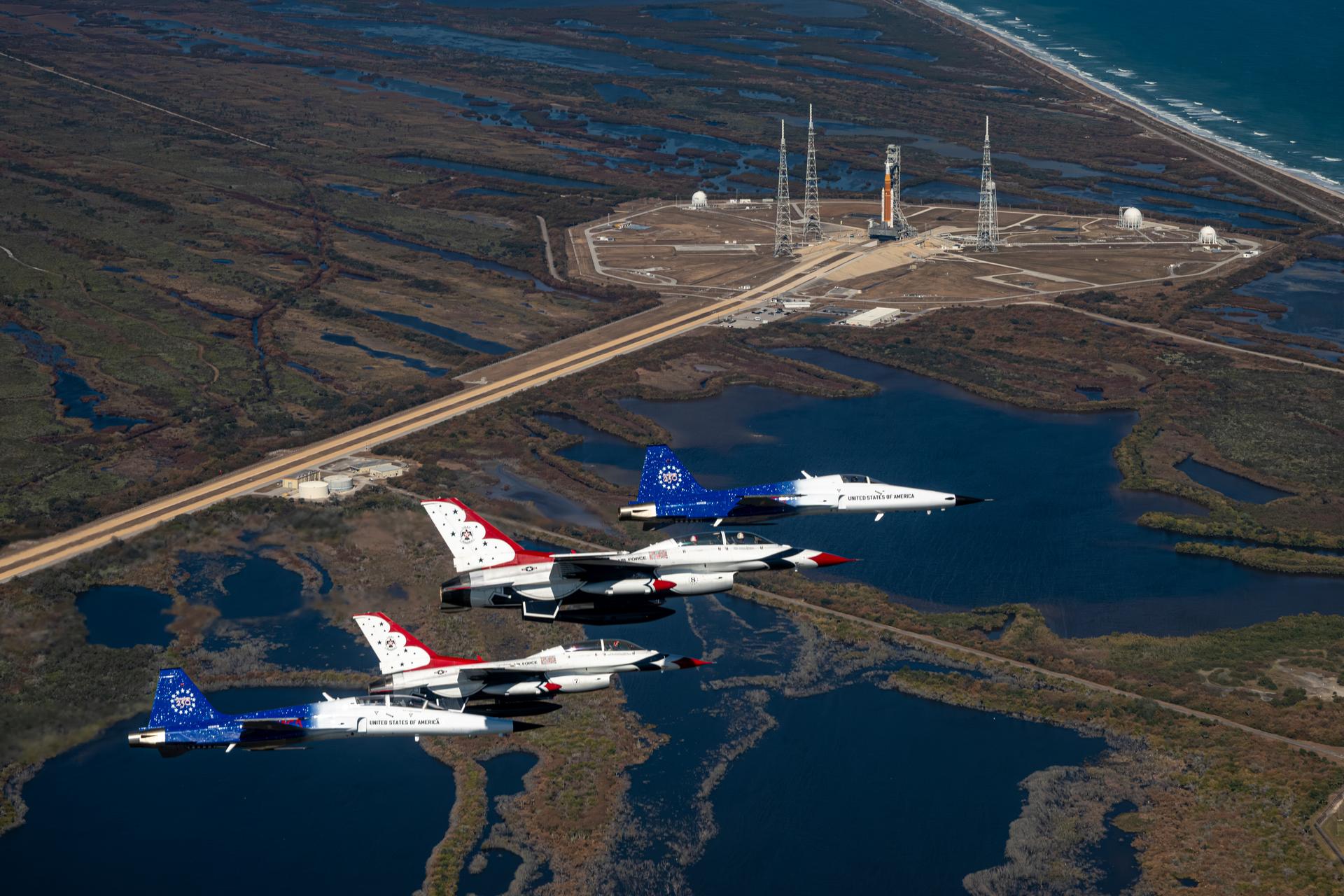
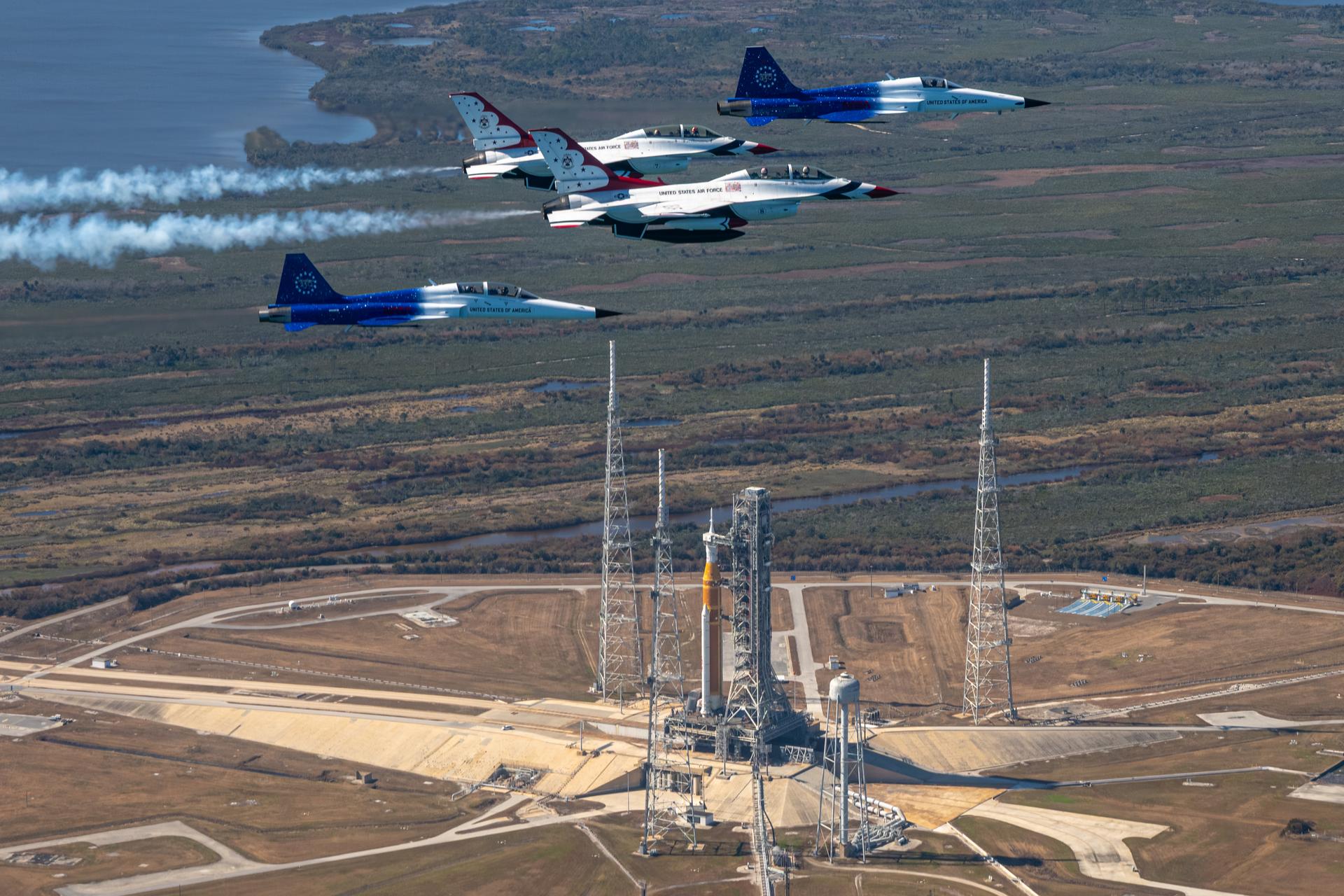
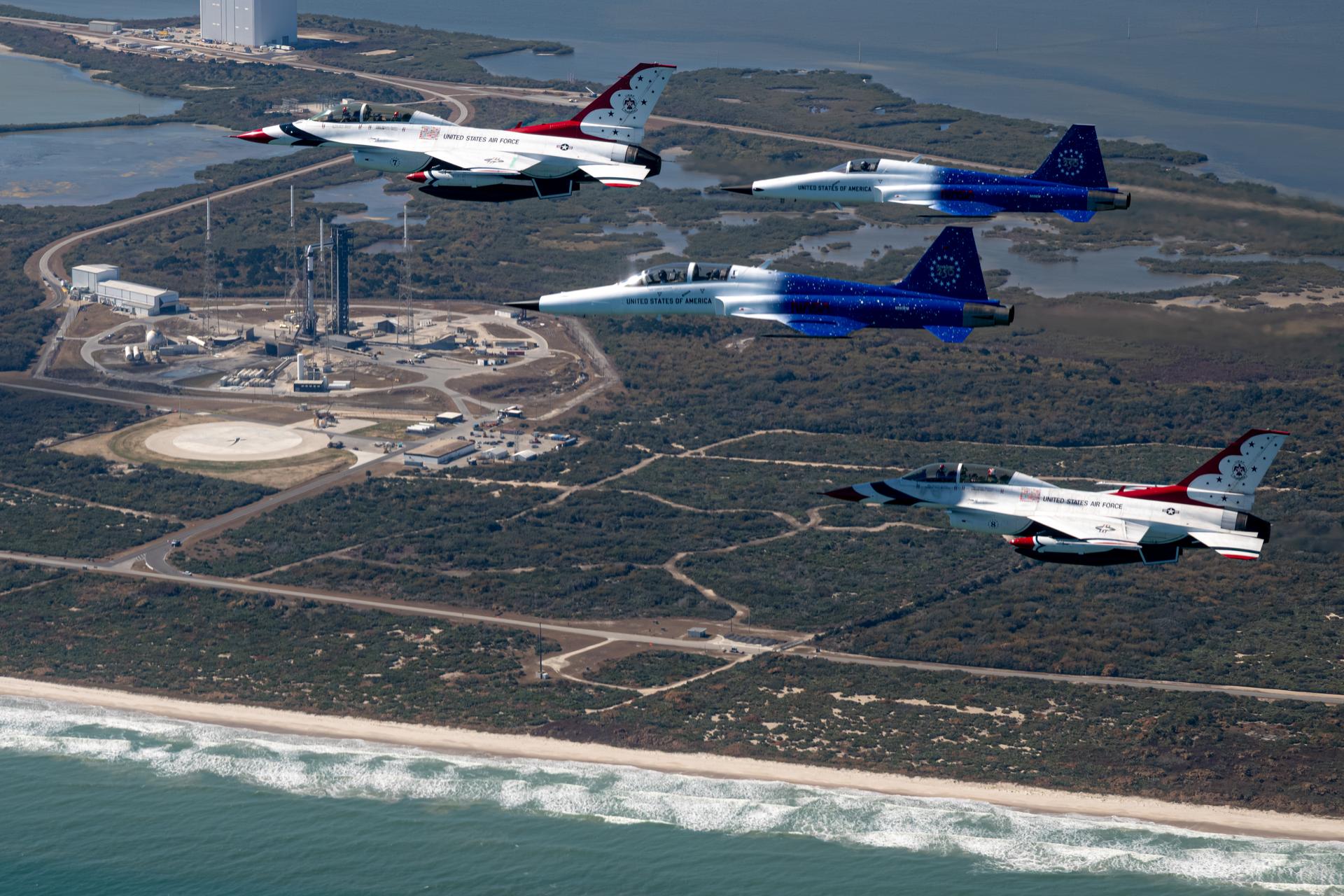
NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman conducts a formation flight with three of his personal F-5 aircraft, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The formation flew near the Artemis II SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft at Launch Complex 39B and the surrounding area at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
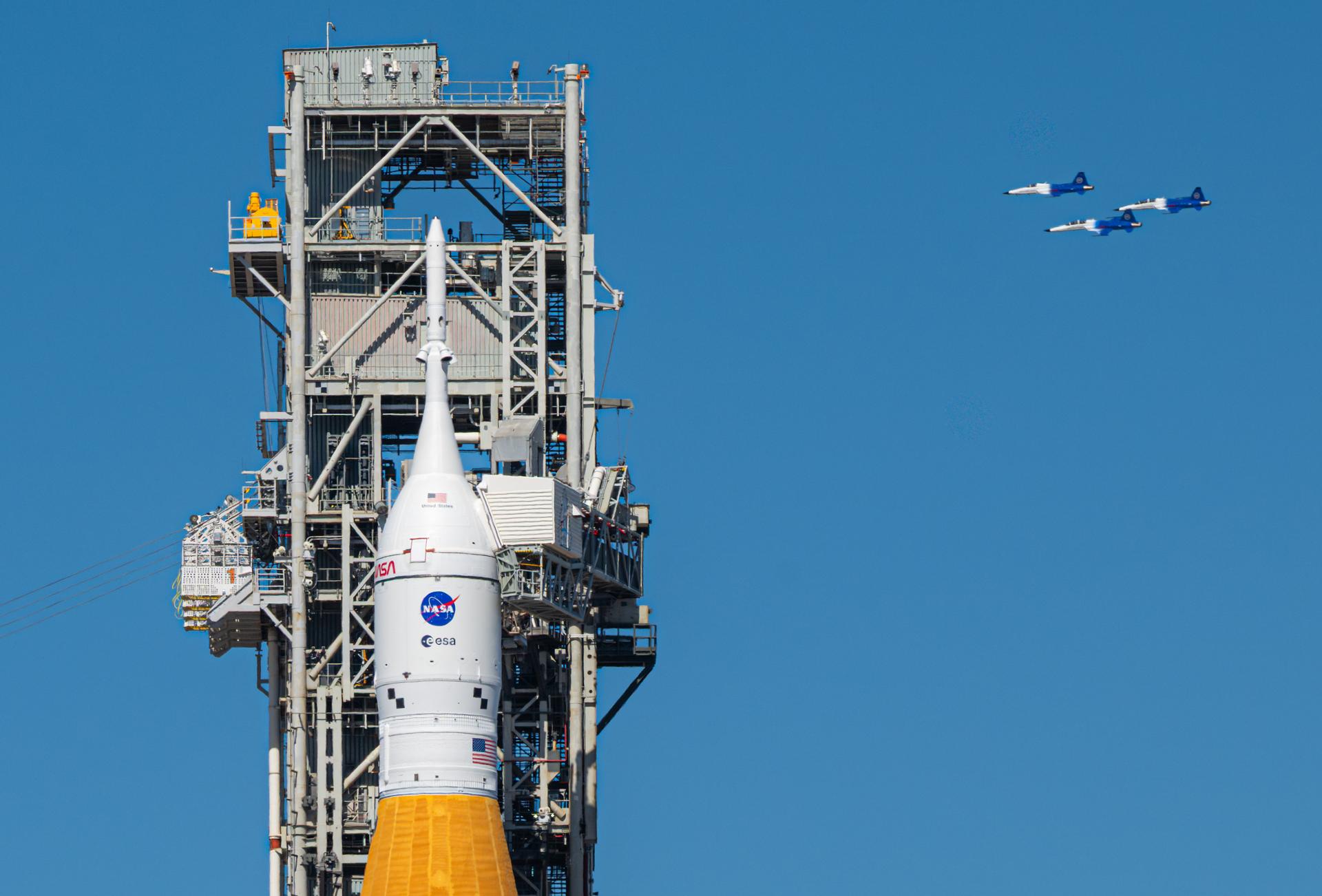

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman conducts a formation flight with three of his personal F-5 aircraft, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The formation flew near the Artemis II SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft at Launch Complex 39B and the surrounding area at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
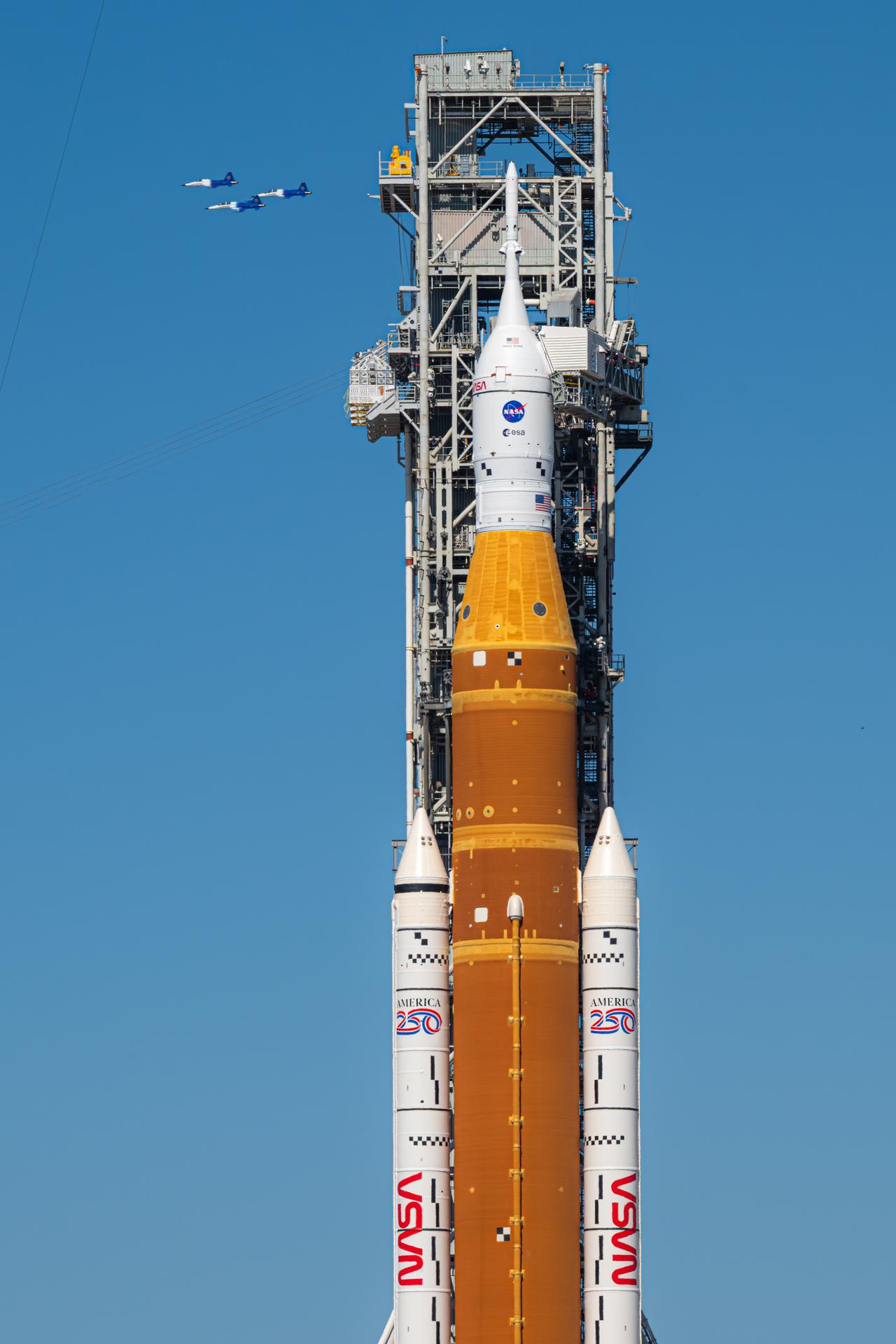

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman conducts a formation flight with three of his personal F-5 aircraft, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The formation flew near the Artemis II SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft at Launch Complex 39B and the surrounding area at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

One of NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman’s personal F-5 aircraft is seen through the jet wash of another F-5 aircraft during an employee incentive flying event, Thursday, Feb. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman is seen before an employee incentive flying event using his personal F-5 aircraft, Thursday, Feb. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman is seen before an employee incentive flying event using his personal F-5 aircraft, Thursday, Feb. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman is seen before an employee incentive flying event using his personal F-5 aircraft, Thursday, Feb. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
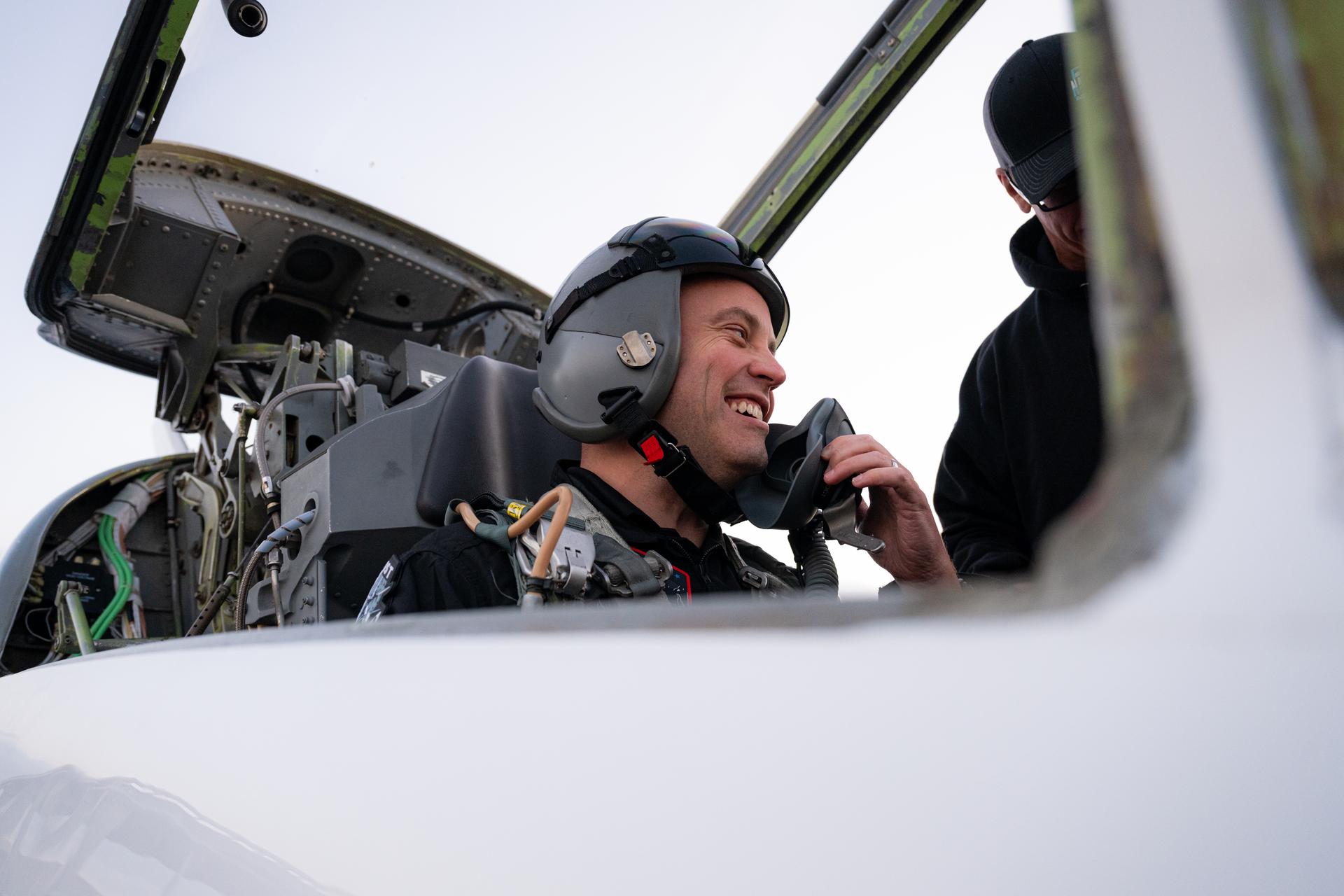

NASA employee Daniel Forrestel participates in an employee incentive flying event with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman and his personal F-5 aircraft, Tuesday, Jan. 13, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
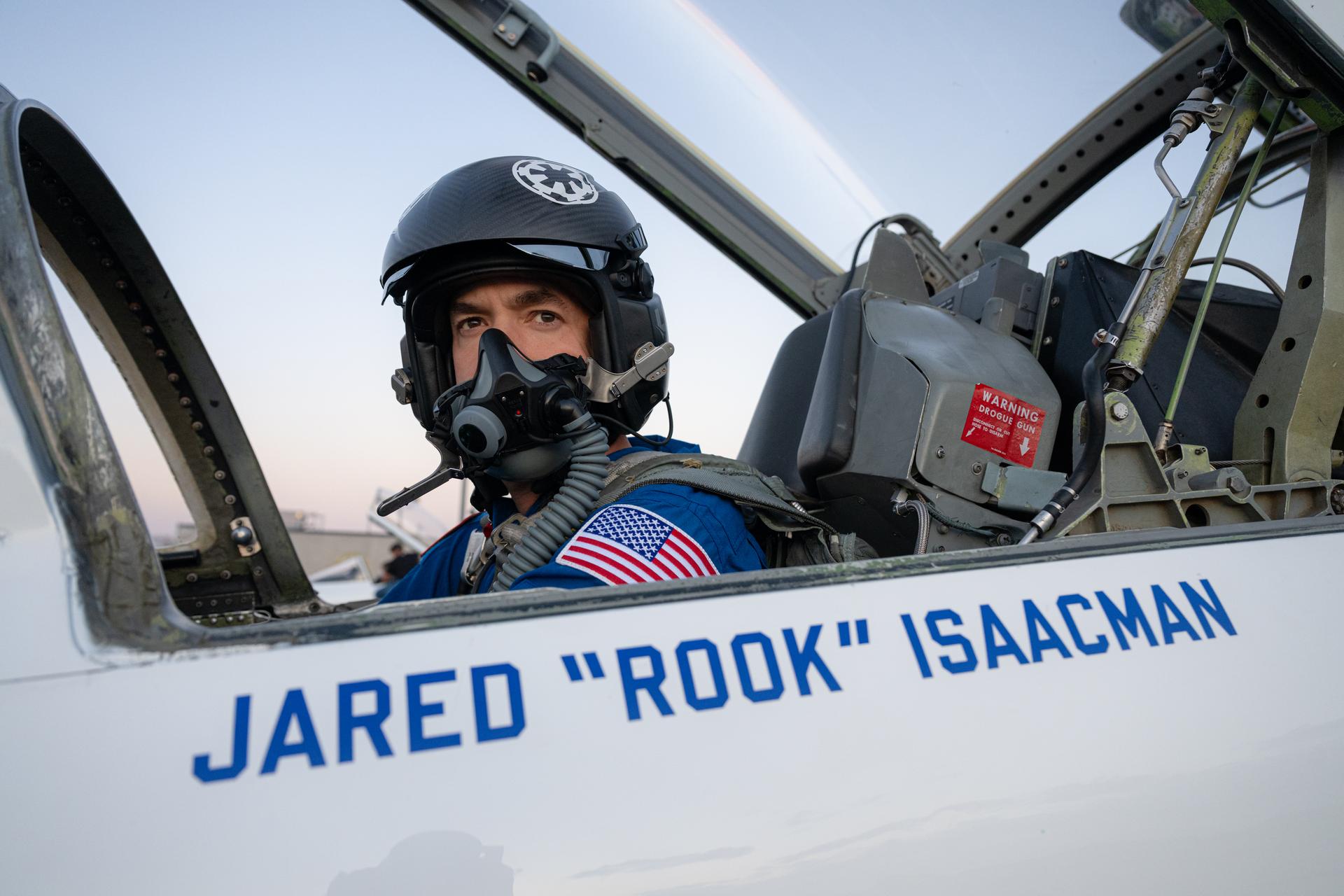

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman participates in an employee incentive flying event using his personal F-5 aircraft, Tuesday, Jan. 13, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
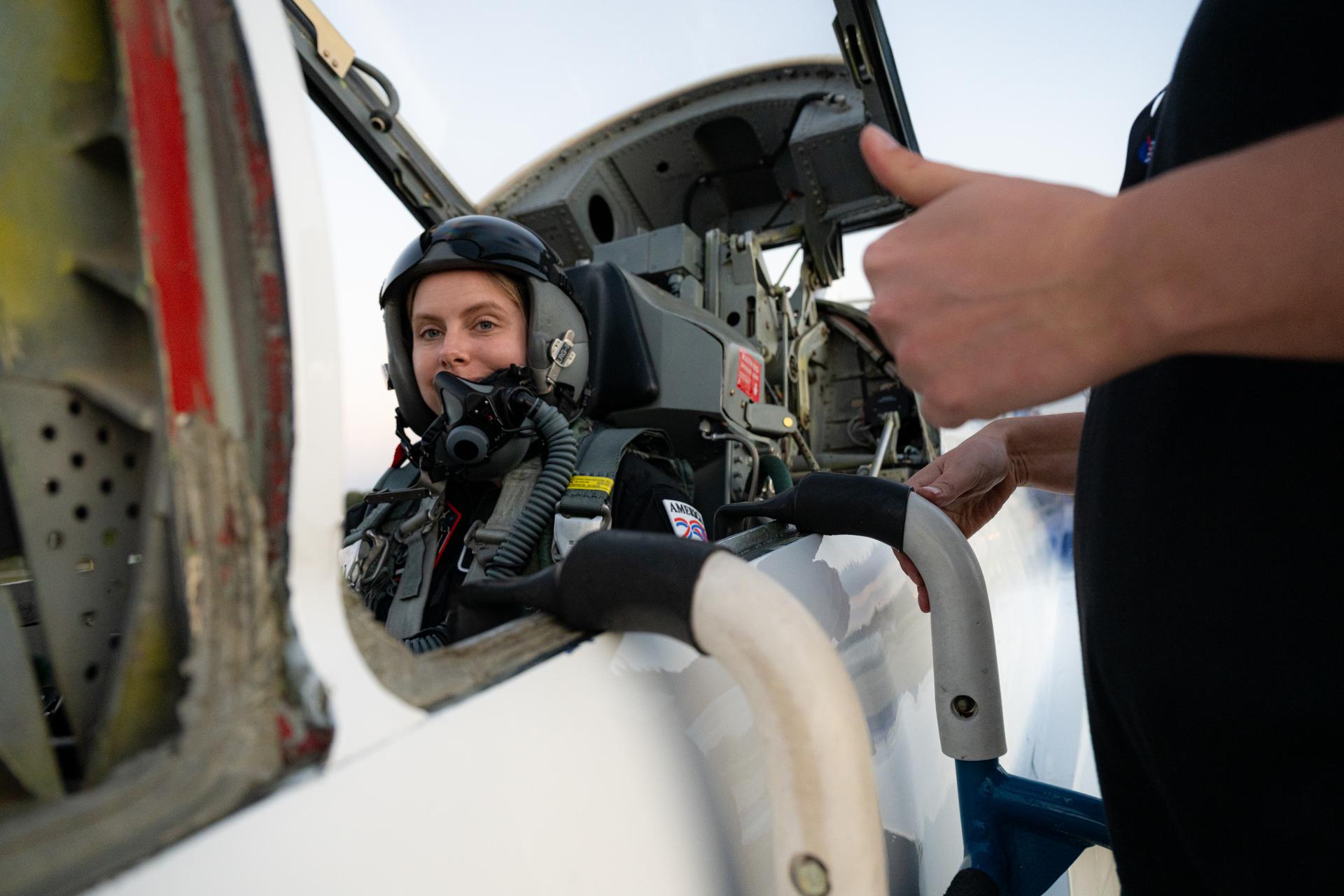

NASA employee Ashley Scharfenberg participates in an employee incentive flying event with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman and his personal F-5 aircraft, Tuesday, Jan. 13, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
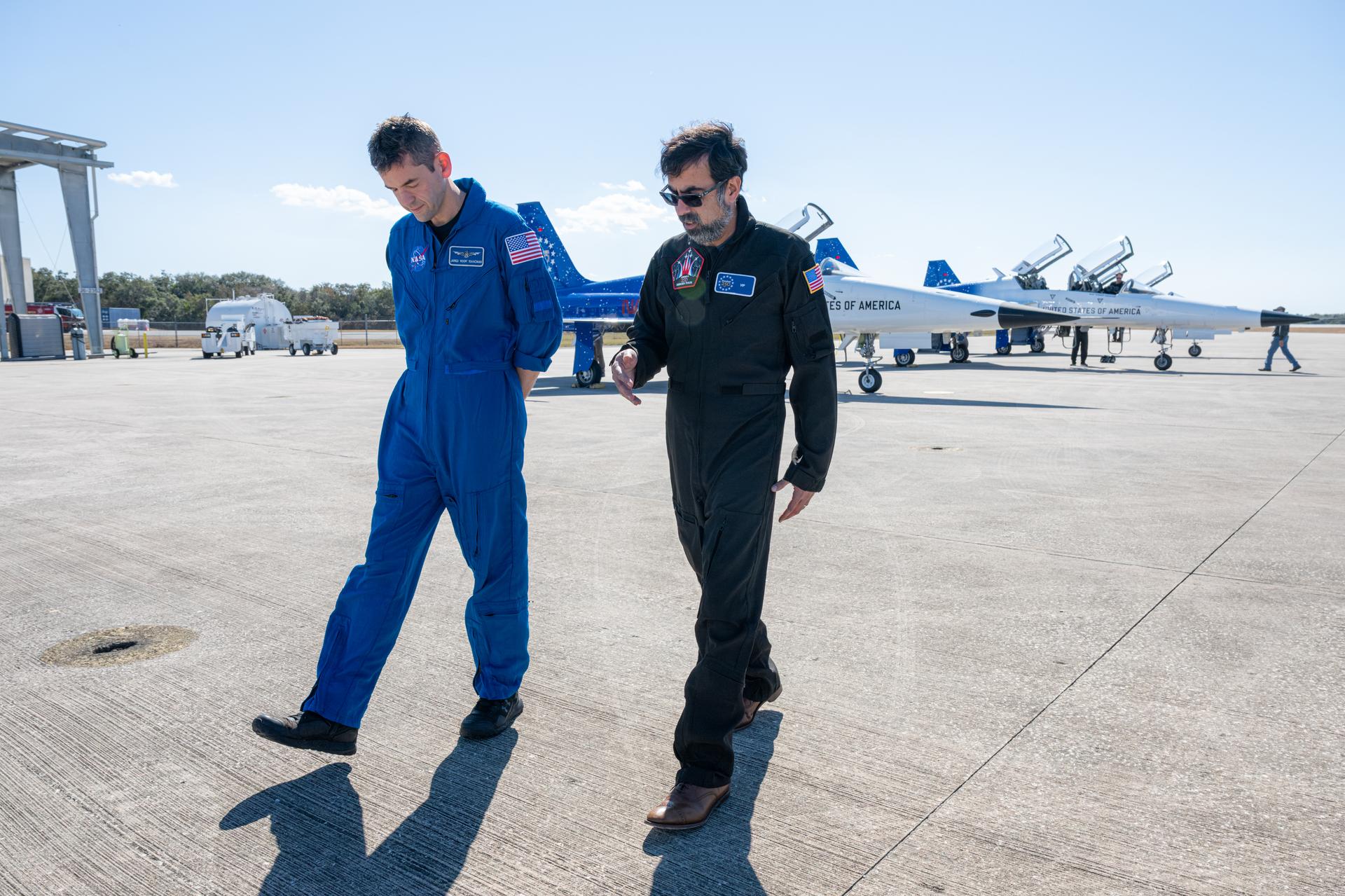

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman and Amit Kshatriya, NASA associate administrator, are seen following a formation flight in Isaacman’s personal F-5 aircraft, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
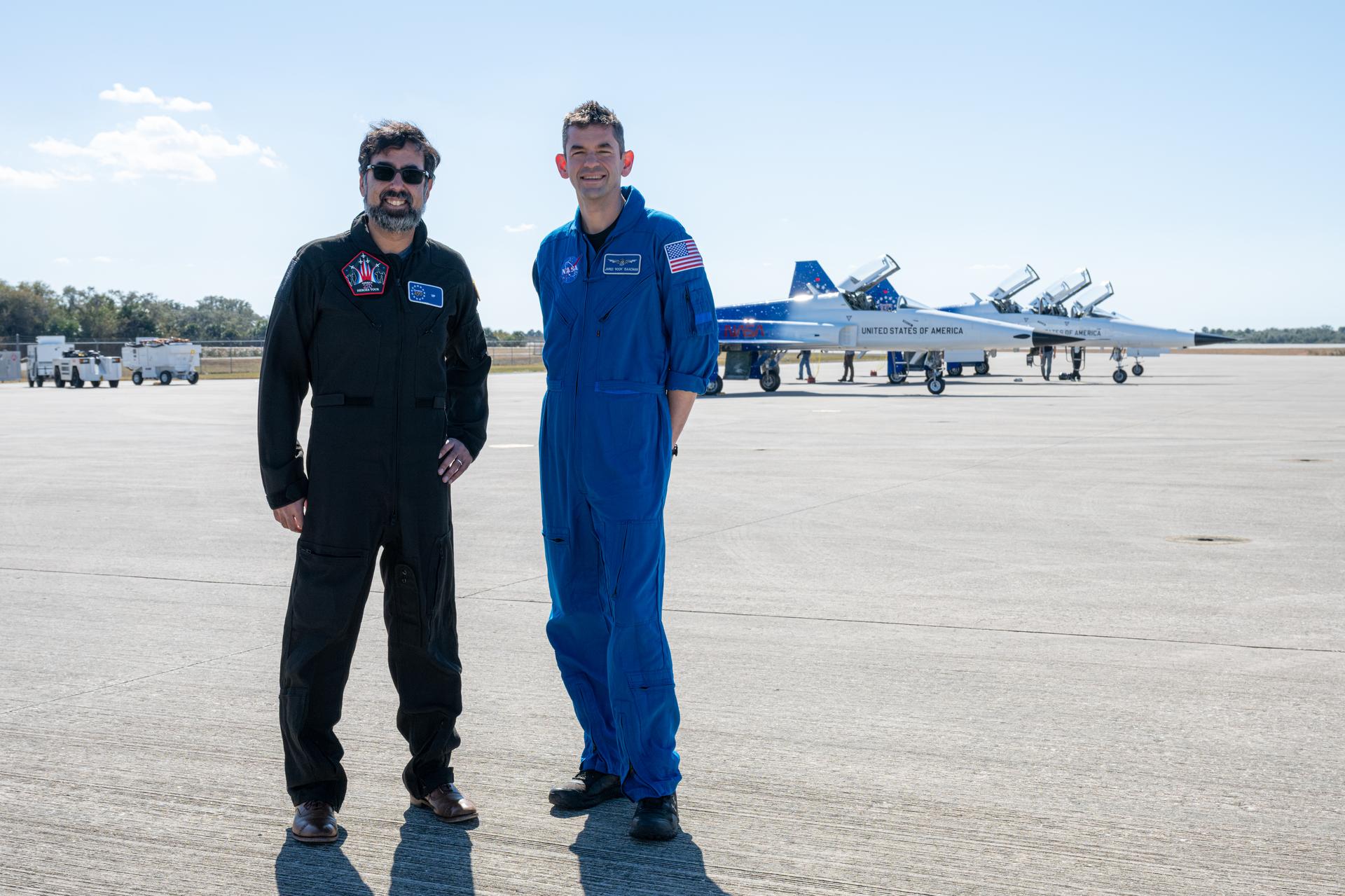

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman and Amit Kshatriya, NASA associate administrator, pose for a photograph following a formation flight in Isaacman’s personal F-5 aircraft, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman participates in an employee incentive flying event using his personal F-5 aircraft with NASA employees Daniel Forrestel and Ashley Scharfenberg, Tuesday, Jan. 13, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA employee Jonathan Baker, chief of the spaceport development division at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is seen before an employee incentive flying event with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman and his personal F-5 aircraft, Thursday, Feb. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman conducts a formation flight with two of his personal F-5 aircraft, piloted by Isaacman and Sean Gustafson, senior advisor to the administrator, and two U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds F-16s, piloted by Thunderbird 7 Lt. Col. Tyler Keener and Thunderbird 8 Maj. Samuel Larson, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The formation flew near the Vehicle Assembly Building and the surrounding area at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman participates in an employee incentive flying event using his personal F-5 aircraft, Thursday, Feb. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA employee Jonathan Baker, chief of the spaceport development division at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, left, is seen before an employee incentive flying event with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman, right, and his personal F-5 aircraft, Thursday, Feb. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA employee Jonathan Baker, chief of the spaceport development division at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, left, participates in an employee incentive flying event with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman, center, and his personal F-5 aircraft, Thursday, Feb. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
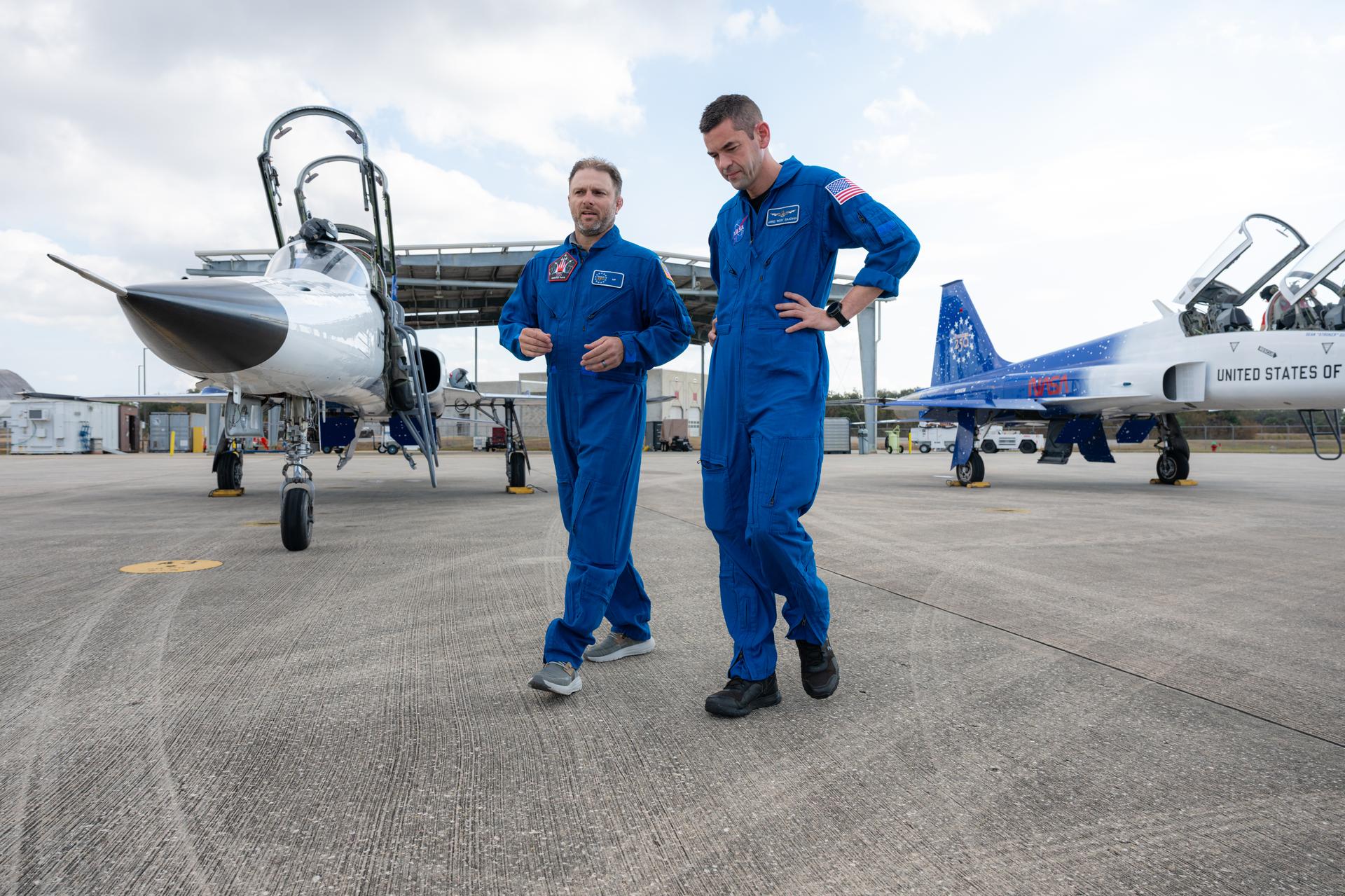

NASA employee Jonathan Baker, chief of the spaceport development division at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, left, speaks with NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman, right, following an employee incentive flying event using Isaacman's personal F-5 aircraft, Thursday, Feb. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
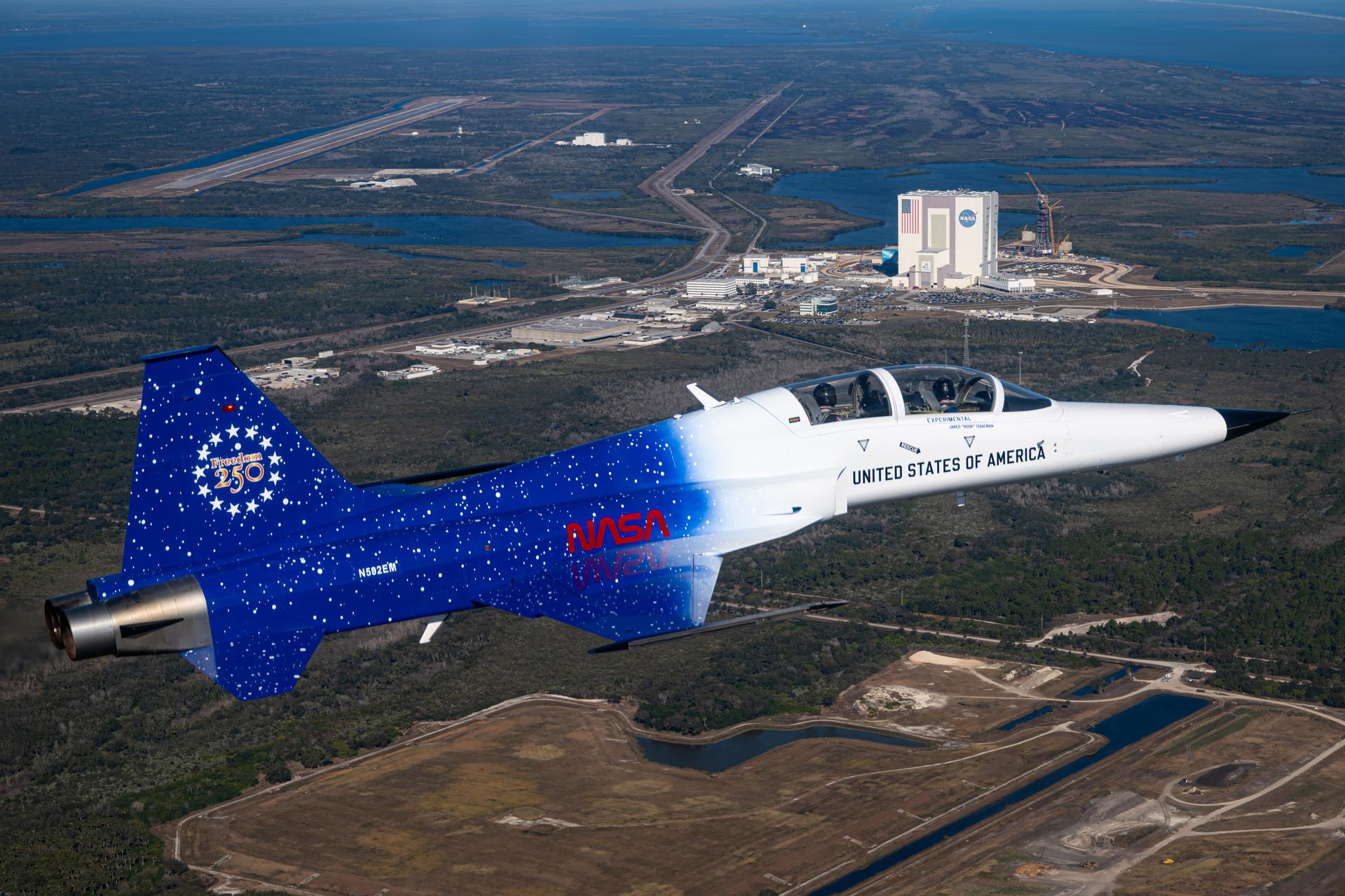

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman flies in his personal F-5 aircraft, Monday, Feb. 2, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Isaacman was joined by Secretary of War Pete Hegseth in the back seat for a flight around Launch Complex 39B, the Vehicle Assembly Building, and surrounding areas at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
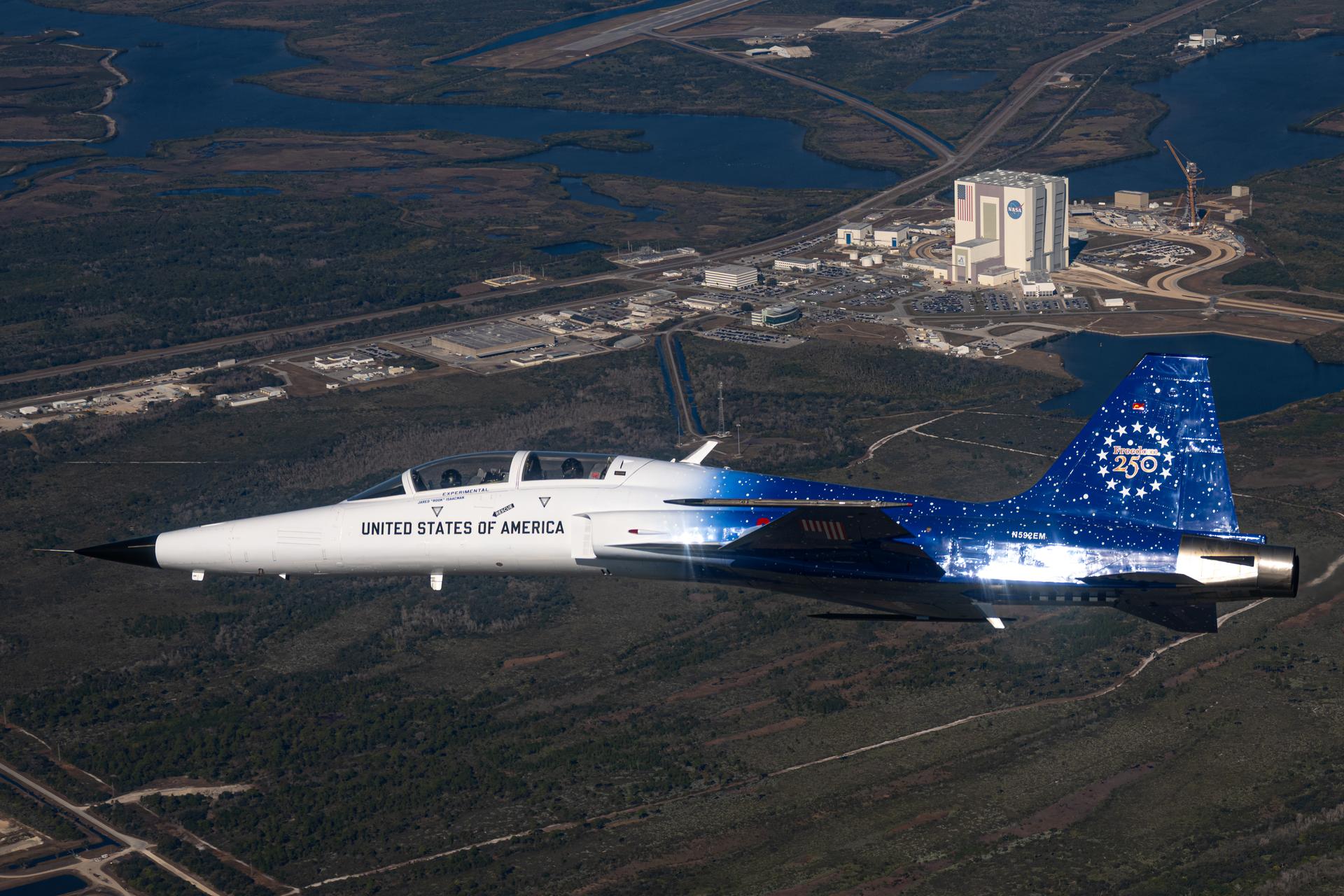

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman flies in his personal F-5 aircraft, Monday, Feb. 2, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Isaacman was joined by Secretary of War Pete Hegseth in the back seat for a flight around Launch Complex 39B, the Vehicle Assembly Building, and surrounding areas at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
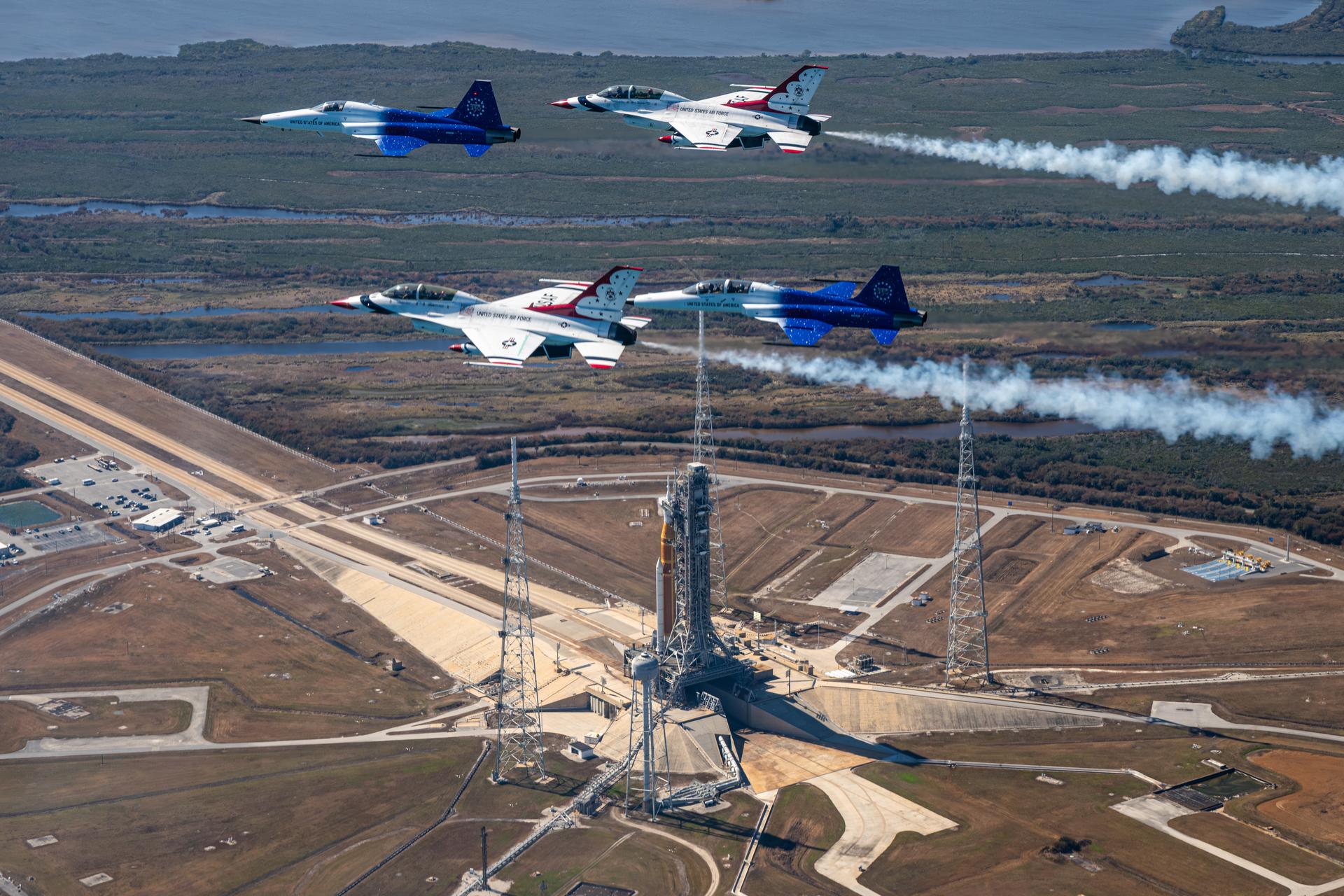

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman conducts a formation flight with two of his personal F-5 aircraft, piloted by Isaacman and Sean Gustafson, senior advisor to the administrator, and two U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds F-16s, piloted by Thunderbird 7 Lt. Col. Tyler Keener and Thunderbird 8 Maj. Samuel Larson, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The formation flew near the Artemis II SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft at Launch Complex 39B and the surrounding area at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
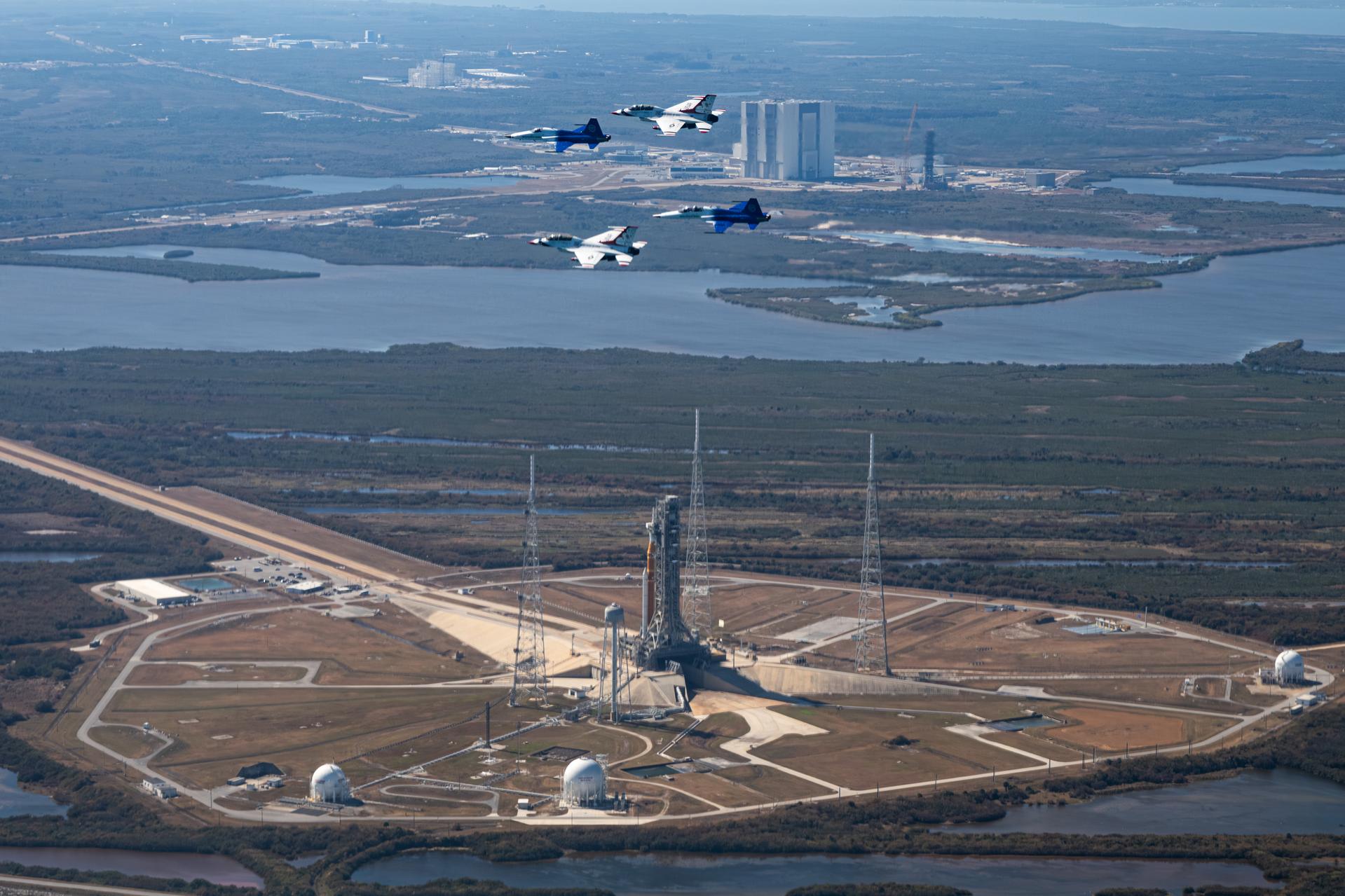

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman conducts a formation flight with two of his personal F-5 aircraft, piloted by Isaacman and Sean Gustafson, senior advisor to the administrator, and two U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds F-16s, piloted by Thunderbird 7 Lt. Col. Tyler Keener and Thunderbird 8 Maj. Samuel Larson, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The formation flew near the Artemis II SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft at Launch Complex 39B and the surrounding area at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman conducts a formation flight with two of his personal F-5 aircraft, piloted by Isaacman and Sean Gustafson, senior advisor to the administrator, and two U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds F-16s, piloted by Thunderbird 7 Lt. Col. Tyler Keener and Thunderbird 8 Maj. Samuel Larson, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The formation flew near the Artemis II SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft at Launch Complex 39B and the surrounding area at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman conducts a formation flight with two of his personal F-5 aircraft, piloted by Isaacman and Sean Gustafson, senior advisor to the administrator, and two U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds F-16s, piloted by Thunderbird 7 Lt. Col. Tyler Keener and Thunderbird 8 Maj. Samuel Larson, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The formation flew near the Artemis II SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft at Launch Complex 39B and the surrounding area at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman conducts a formation flight with two of his personal F-5 aircraft, piloted by Isaacman and Sean Gustafson, senior advisor to the administrator, and two U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds F-16s, piloted by Thunderbird 7 Lt. Col. Tyler Keener and Thunderbird 8 Maj. Samuel Larson, Sunday, Feb. 8, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The formation flew near Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and the surrounding area at Kennedy ahead of Crew-12’s mission to the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
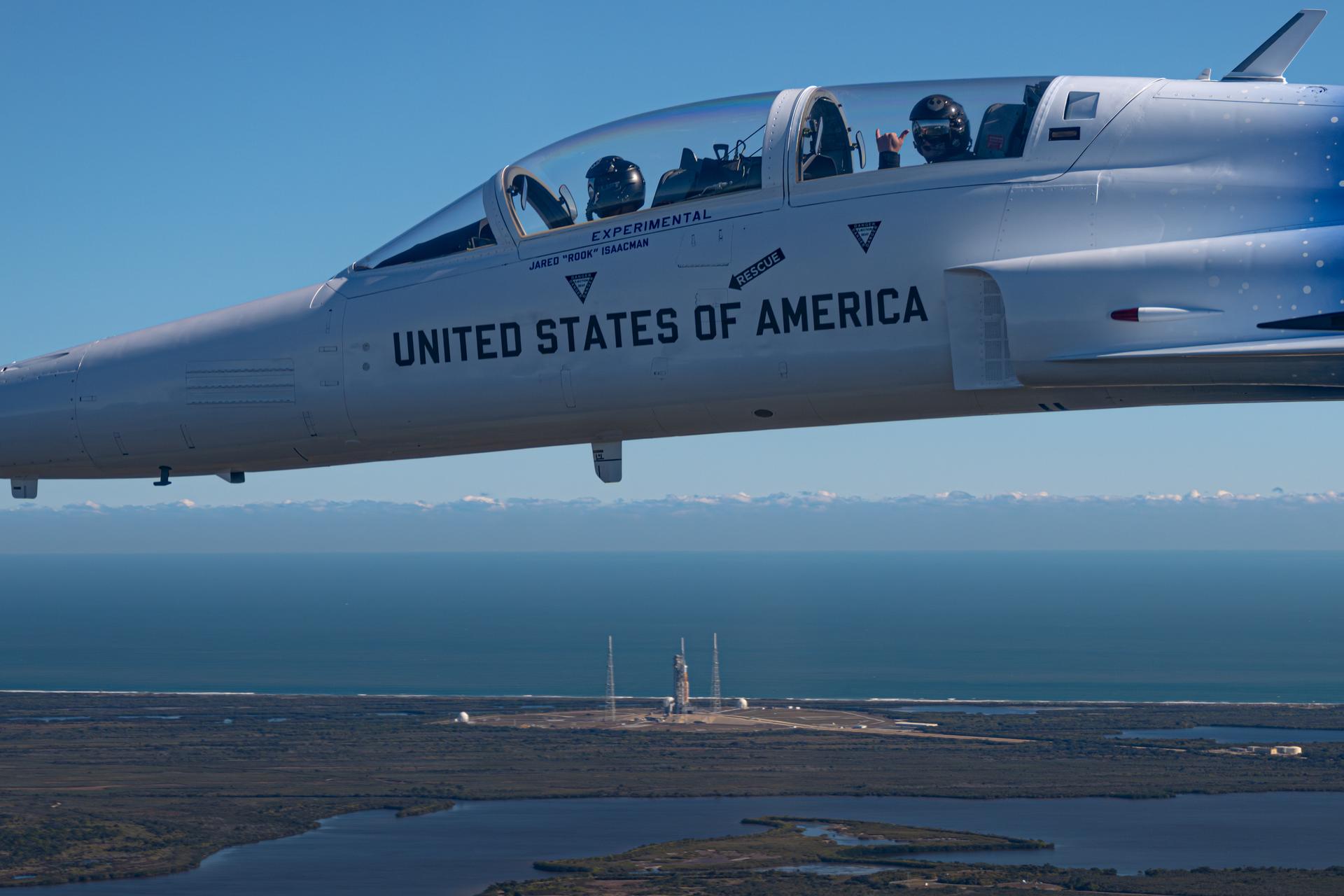

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman flies in his personal F-5 aircraft, Monday, Feb. 2, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Isaacman was joined by Secretary of War Pete Hegseth in the back seat for a flight around Launch Complex 39B, the Vehicle Assembly Building, and surrounding areas at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
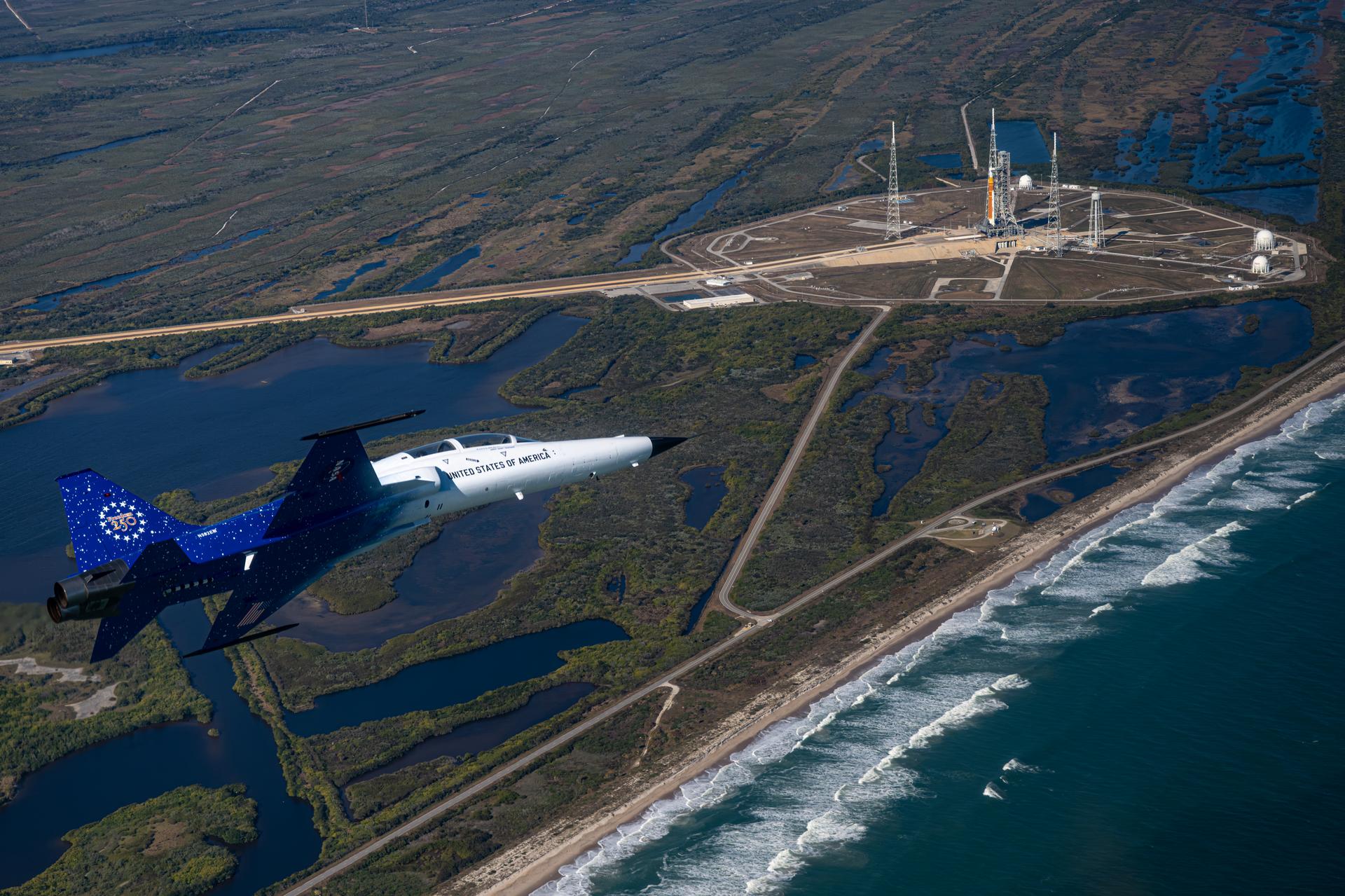

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman flies in his personal F-5 aircraft, Monday, Feb. 2, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Isaacman was joined by Secretary of War Pete Hegseth in the back seat for a flight around Launch Complex 39B, the Vehicle Assembly Building, and surrounding areas at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
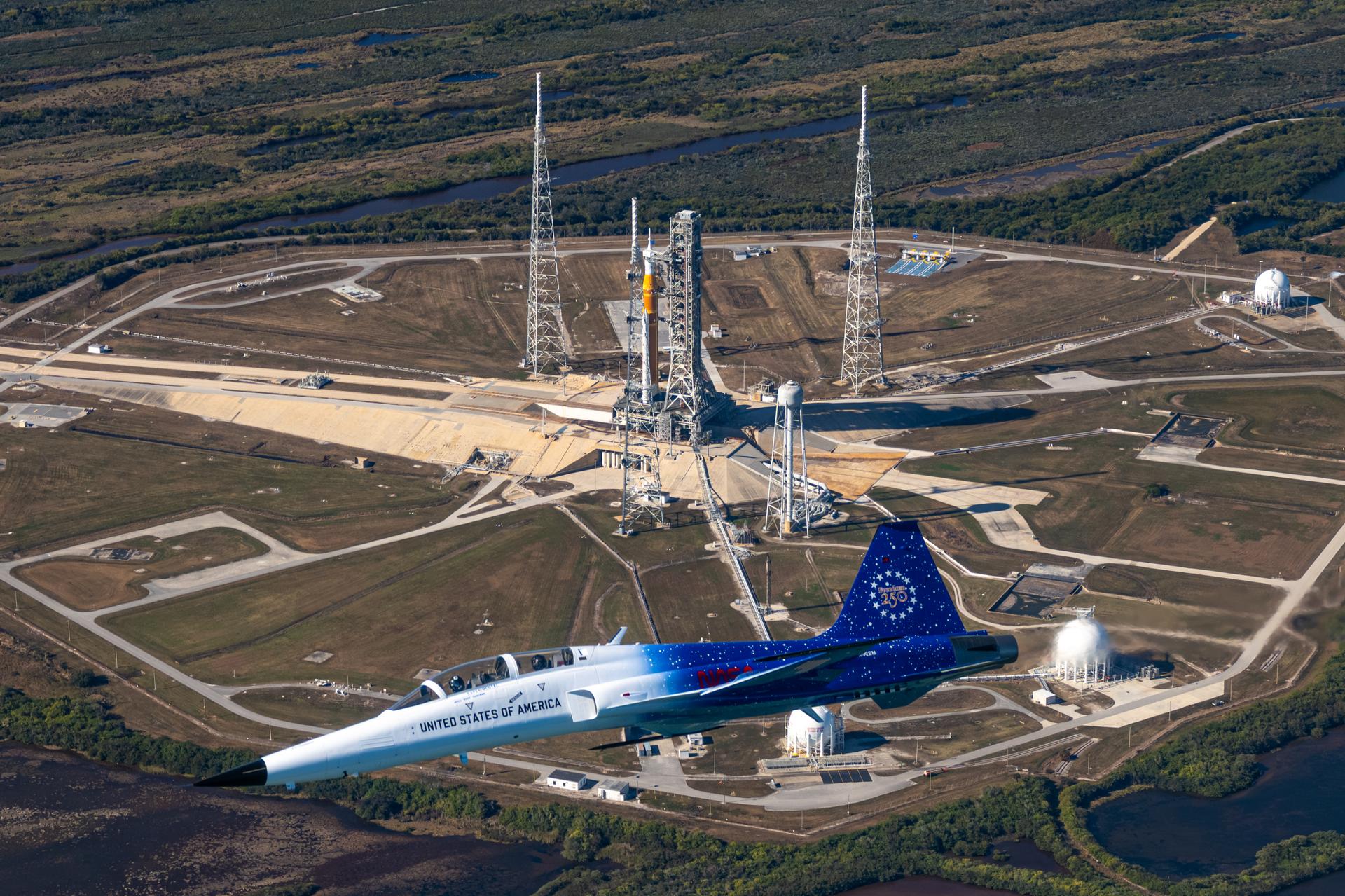

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman flies in his personal F-5 aircraft, Monday, Feb. 2, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Isaacman was joined by Secretary of War Pete Hegseth in the back seat for a flight around Launch Complex 39B, the Vehicle Assembly Building, and surrounding areas at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
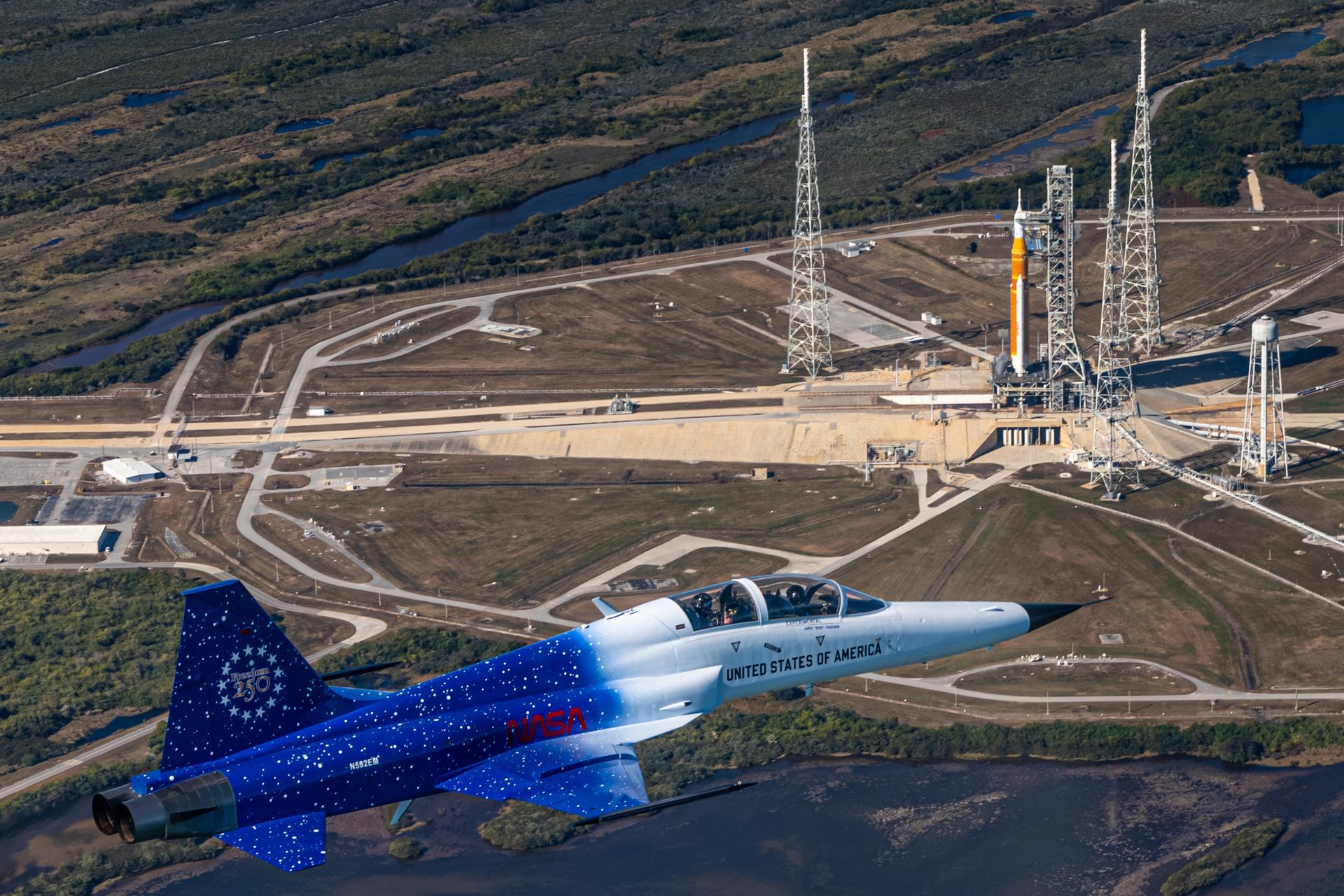

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman flies in his personal F-5 aircraft, Monday, Feb. 2, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Isaacman was joined by Secretary of War Pete Hegseth in the back seat for a flight around Launch Complex 39B, the Vehicle Assembly Building, and surrounding areas at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
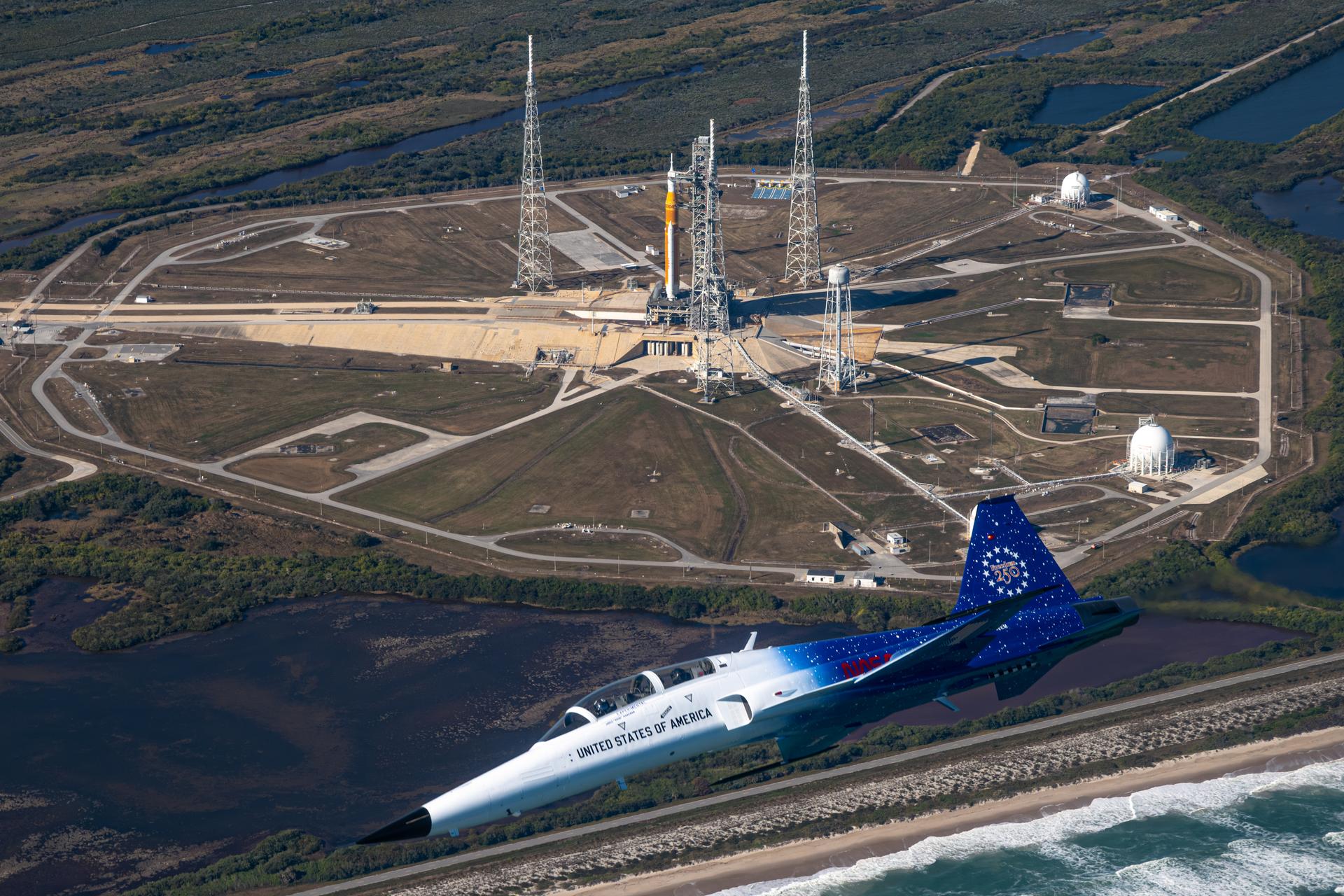

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman flies in his personal F-5 aircraft, Monday, Feb. 2, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Isaacman was joined by Secretary of War Pete Hegseth in the back seat for a flight around Launch Complex 39B, the Vehicle Assembly Building, and surrounding areas at Kennedy. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
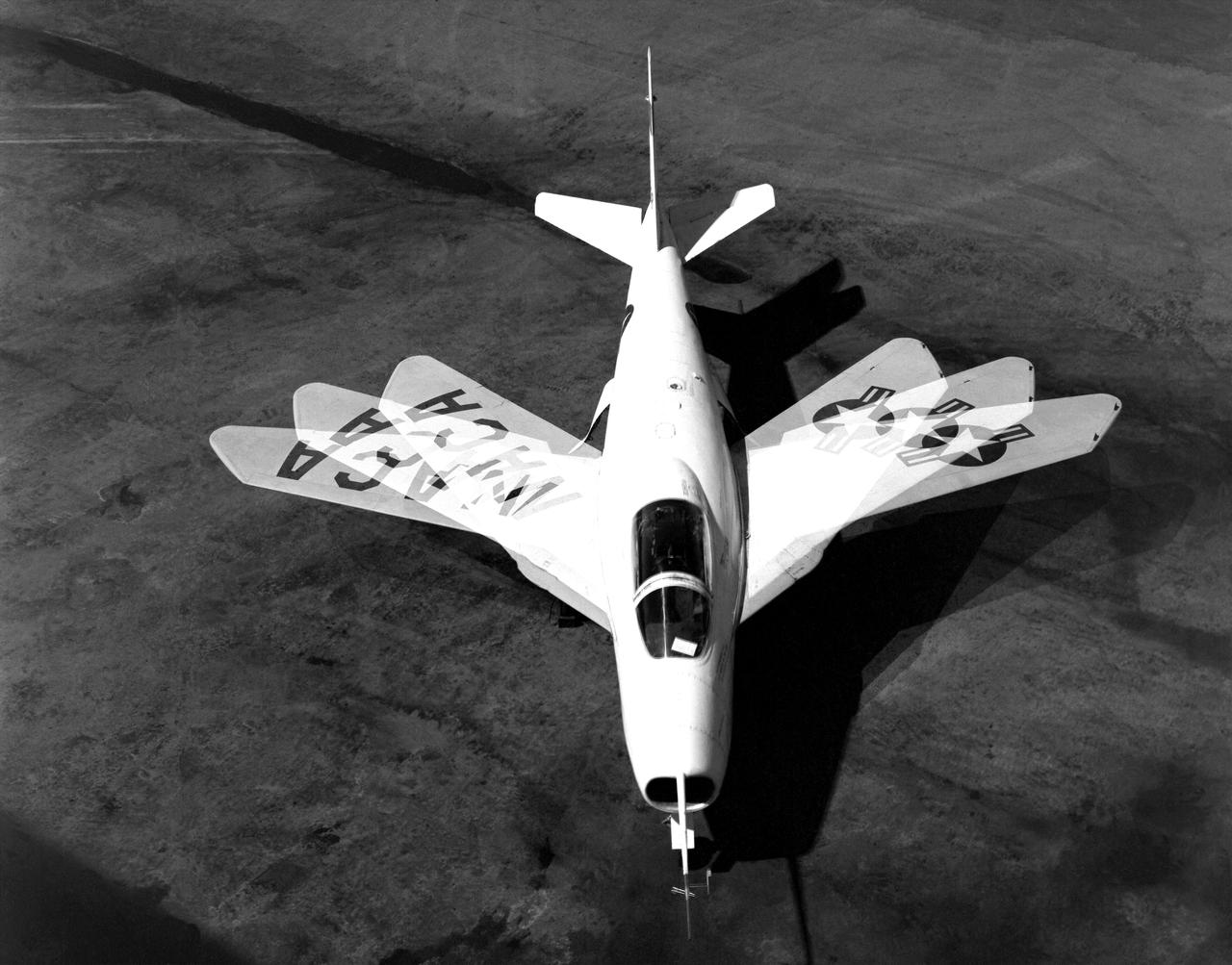

The Bell X-5 swings its wings in this multiple exposure photograph. Variable-sweep wing technology later appeared on the F-111, F-14 and B-1.
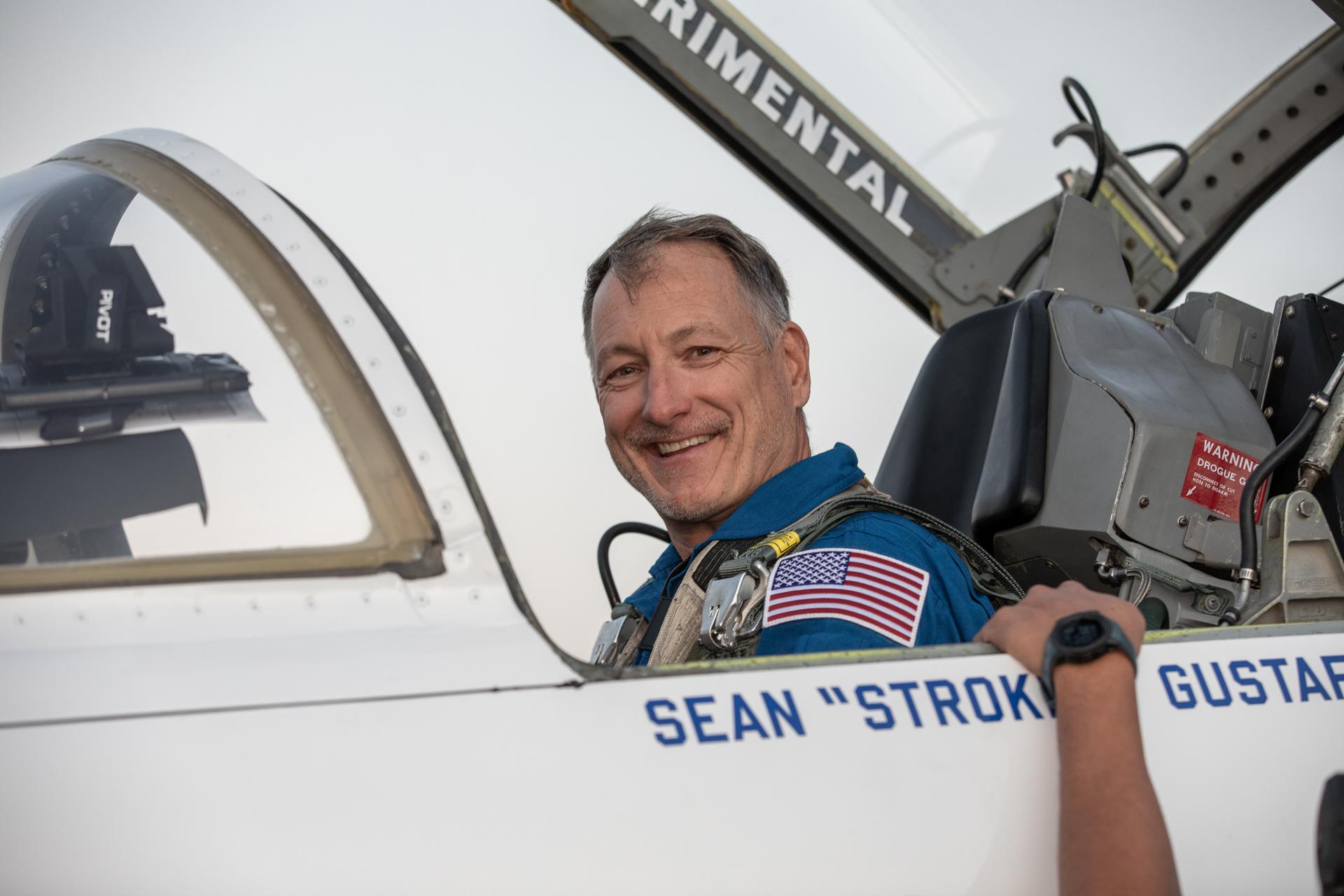

Sean “Stroker” Gustafson, pilot, sits in the cockpit of an Northrop F-5 Tiger II aircraft at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 13, 2026. As the newly 15th administrator of the agency, Jared Isaacman created a ride-along program to recognize and reward members of the workforce for their dedication to accomplishing agency priorities with opportunities to fly in Isaacman’s Northrop F-5 Tiger II aircraft.
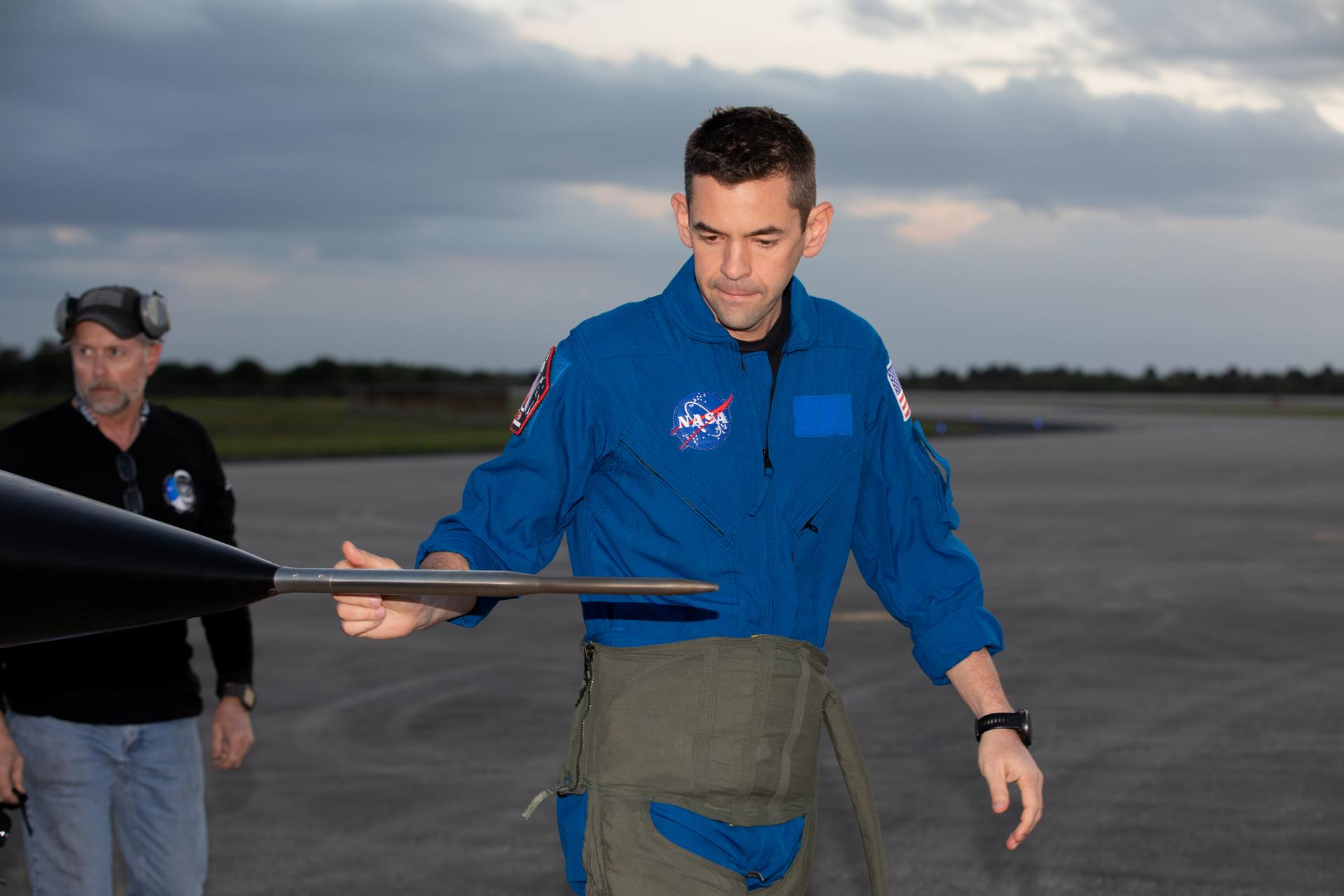

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman inspects the nose his Northrop F-5 Tiger II aircraft before his flight at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 13, 2026. As the newly appointed 15th administrator of the agency, Isaacman created a ride-along program to recognize and reward members of the workforce to fly in Isaacman’s F-5 Tiger II aircraft around NASA Kennedy for their dedication to accomplishing agency priorities.
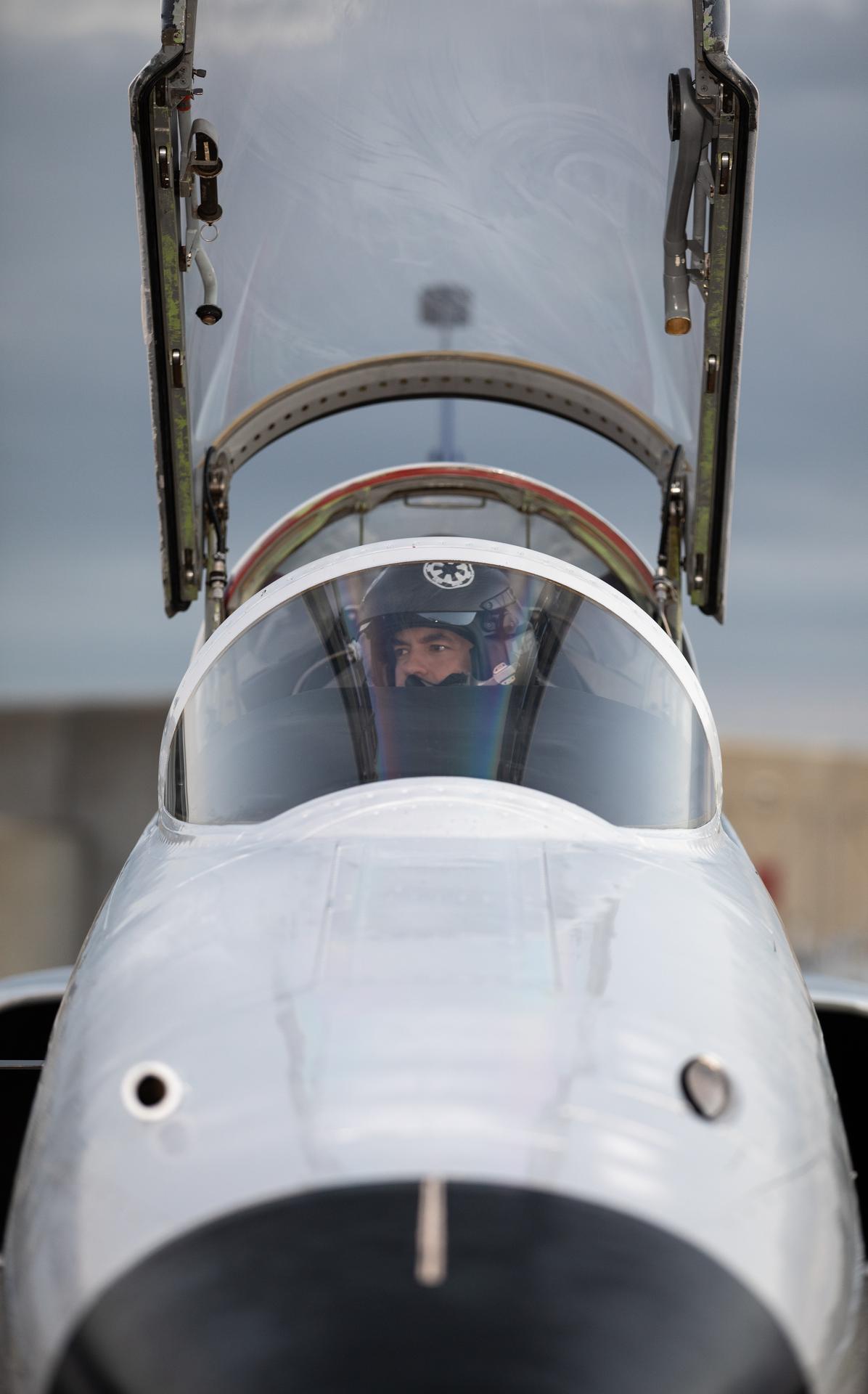

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman sits in the cockpit of a Northrop F-5 aircraft at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 13, 2026. As the newly 15th administrator of the agency, Isaacman created a ride-along program to recognize and reward members of the workforce to fly in Isaacman’s personal F-5 Tiger II aircraft. NASA’s first “A” stands for aeronautics, and the agency is continuing efforts to the efforts to safely and sustainably transform aviation for the 21st century.
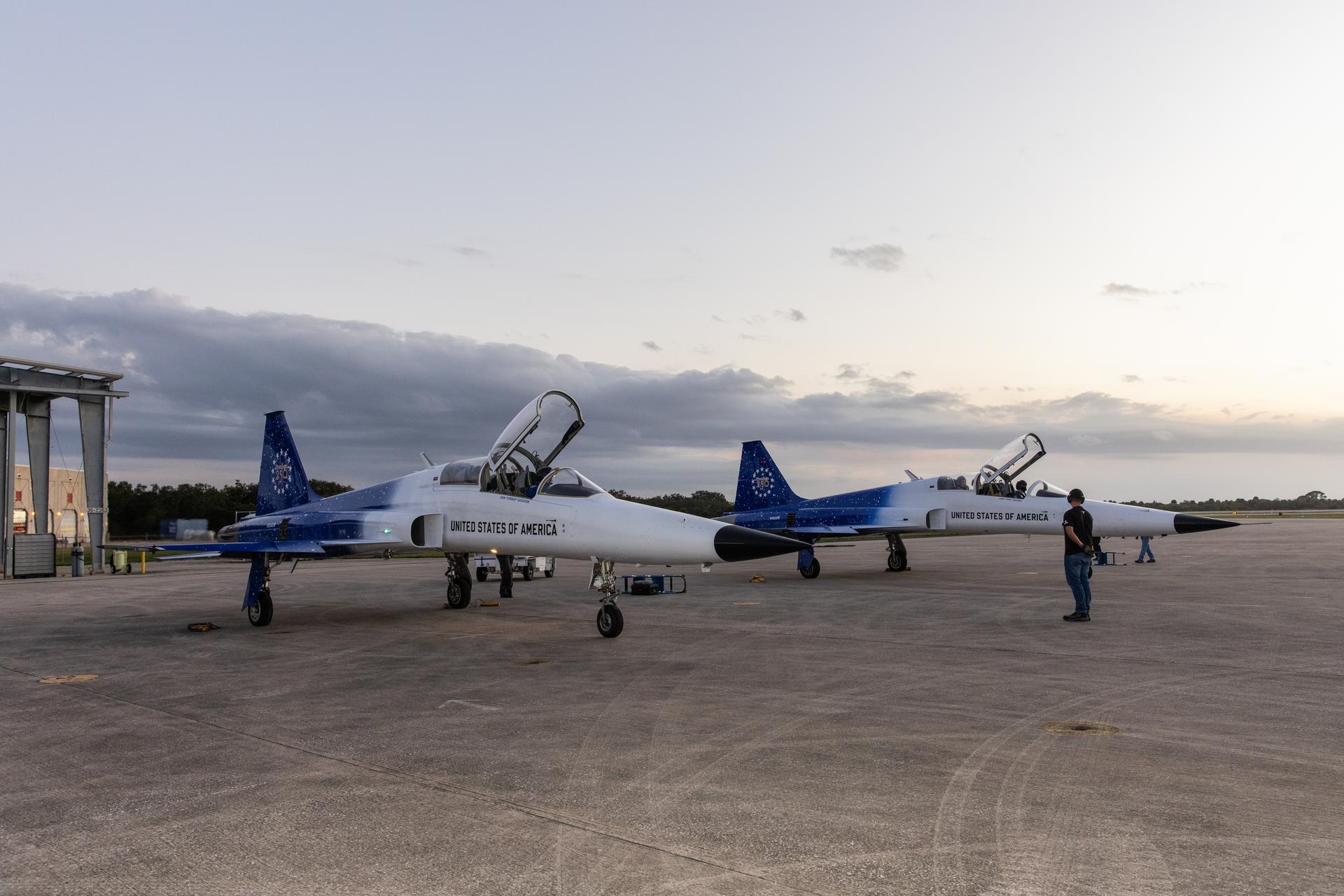

Two Northrop F-5 Tiger II aircraft prepare for flight at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 13, 2026. As the newly 15th administrator of the agency, Jared Isaacman created a ride-along program to recognize and reward members of the workforce for their dedication to accomplishing agency priorities to fly in Isaacman’s personal F-5 aircraft.
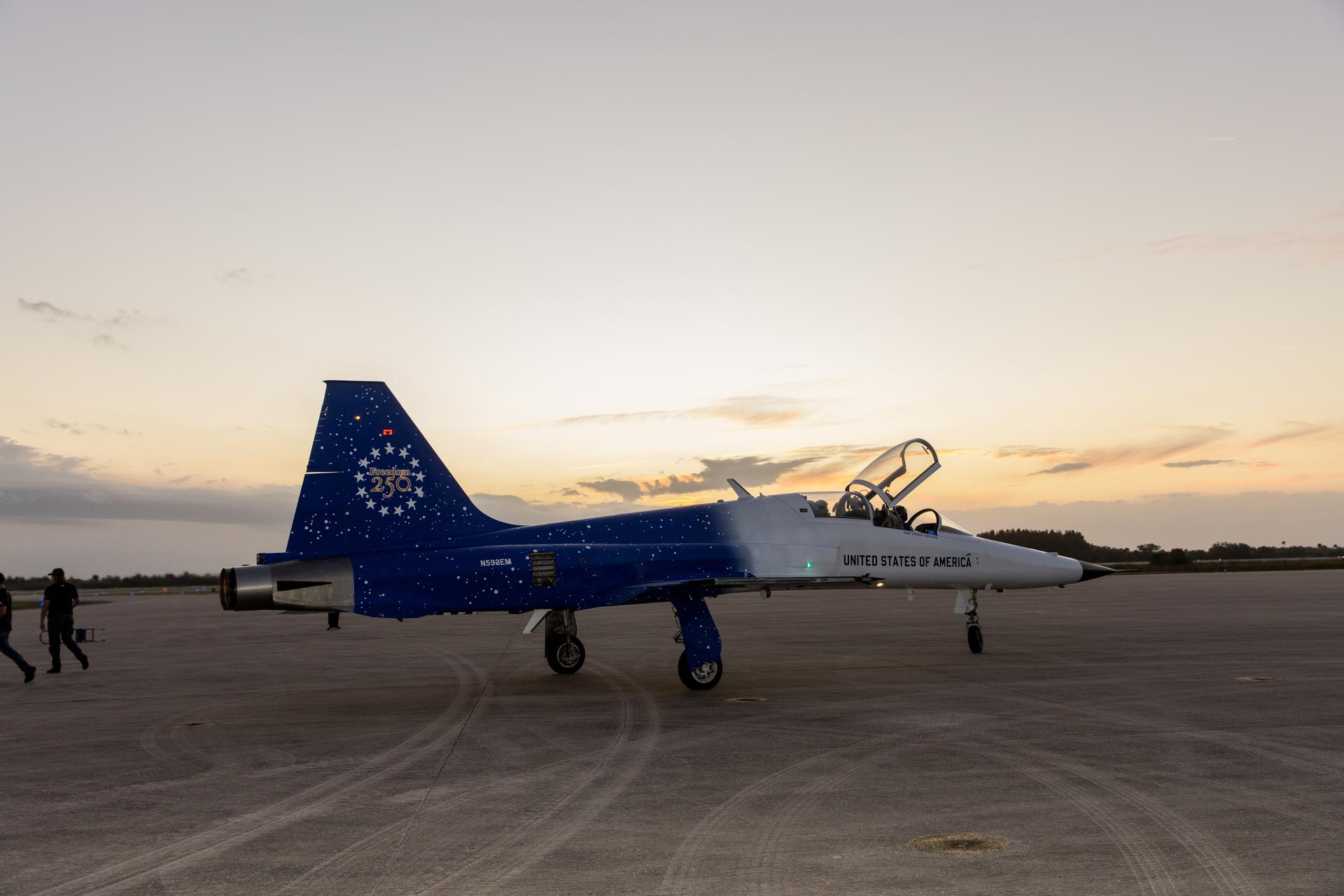

A Northrop F-5 Tiger II aircraft prepares for flight at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 13, 2026. As the newly 15th administrator of the agency, Jared Isaacman created a ride-along program to recognize and reward members of the workforce for their dedication to accomplishing agency priorities to fly in Isaacman’s personal F-5 aircraft.
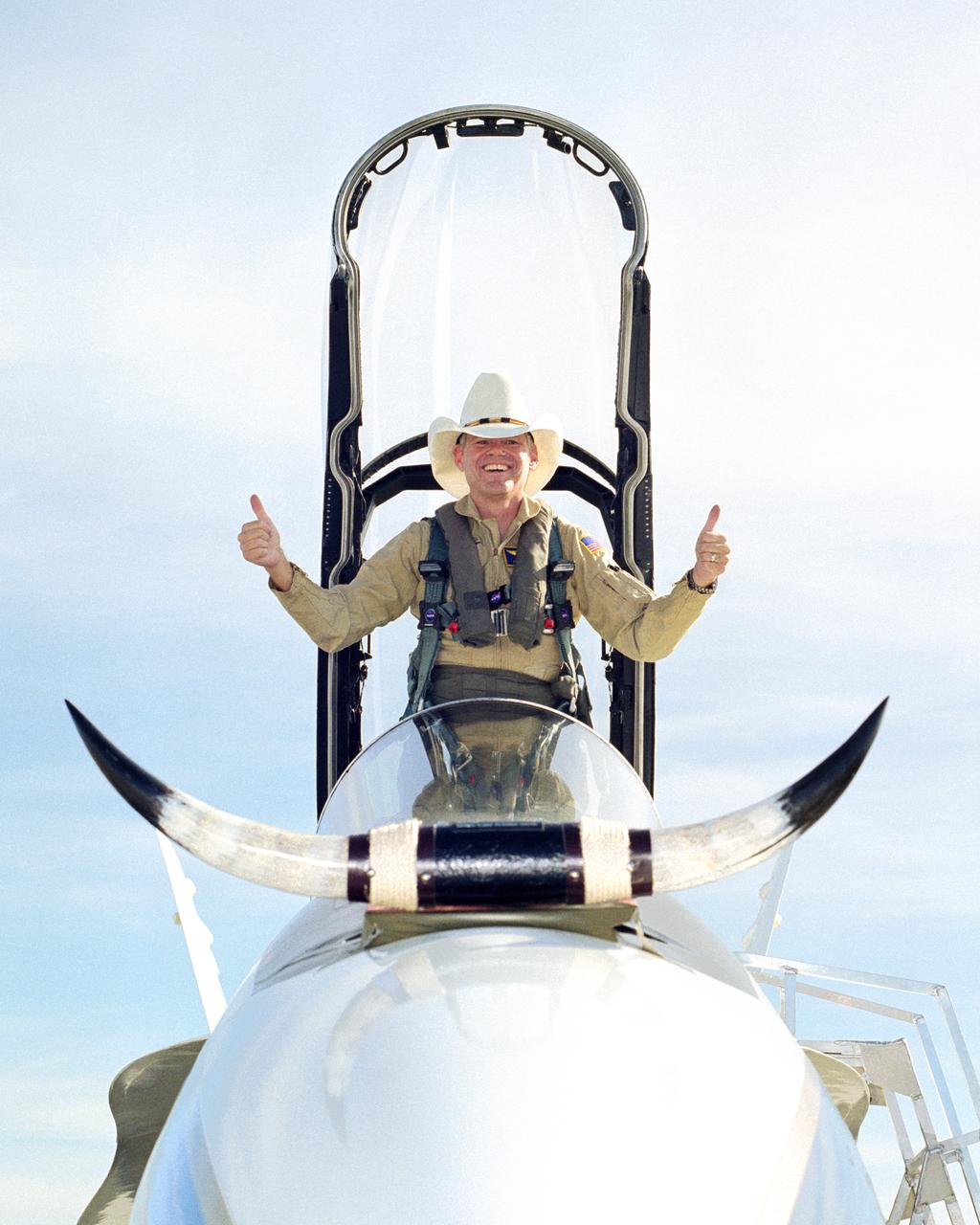

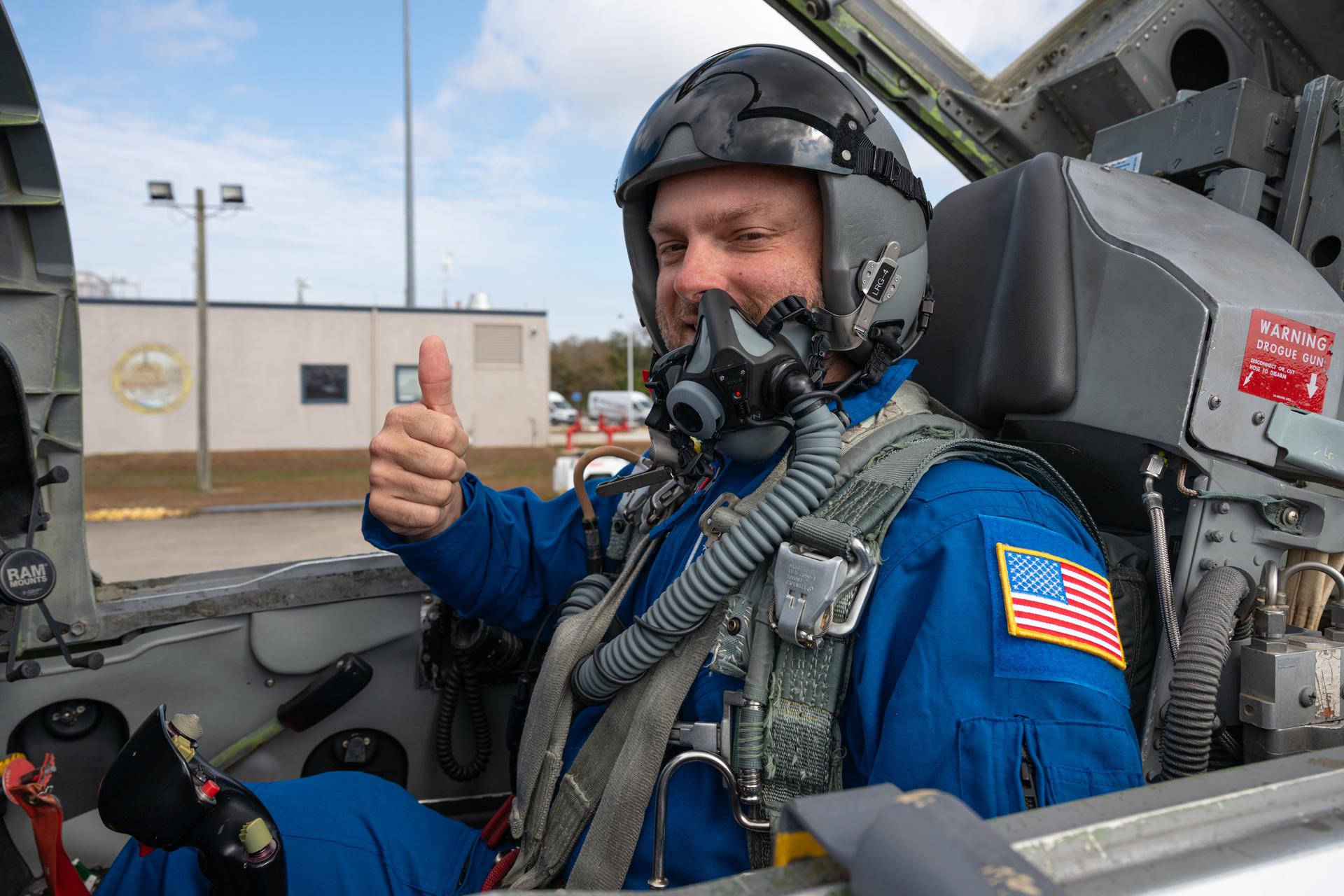
In a lighter mood, Ed Schneider gives a "thumbs-up" after his last flight at the Dryden Flight Research Center on September 19, 2000. Schneider arrived at the NASA Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility on July 5, 1982, as a Navy Liaison Officer, becoming a NASA research pilot one year later. He has been project pilot for the F-18 High Angle-of-Attack program (HARV), the F-15 aeronautical research aircraft, the NASA B-52 launch aircraft, and the SR-71 "Blackbird" aircraft. He also participated in such programs as the F-8 Digital Fly-By-Wire, the FAA/NASA 720 Controlled Impact Demonstration, the F-14 Automatic Rudder Interconnect and Laminar Flow, and the F-104 Aeronautical Research and Microgravity projects.
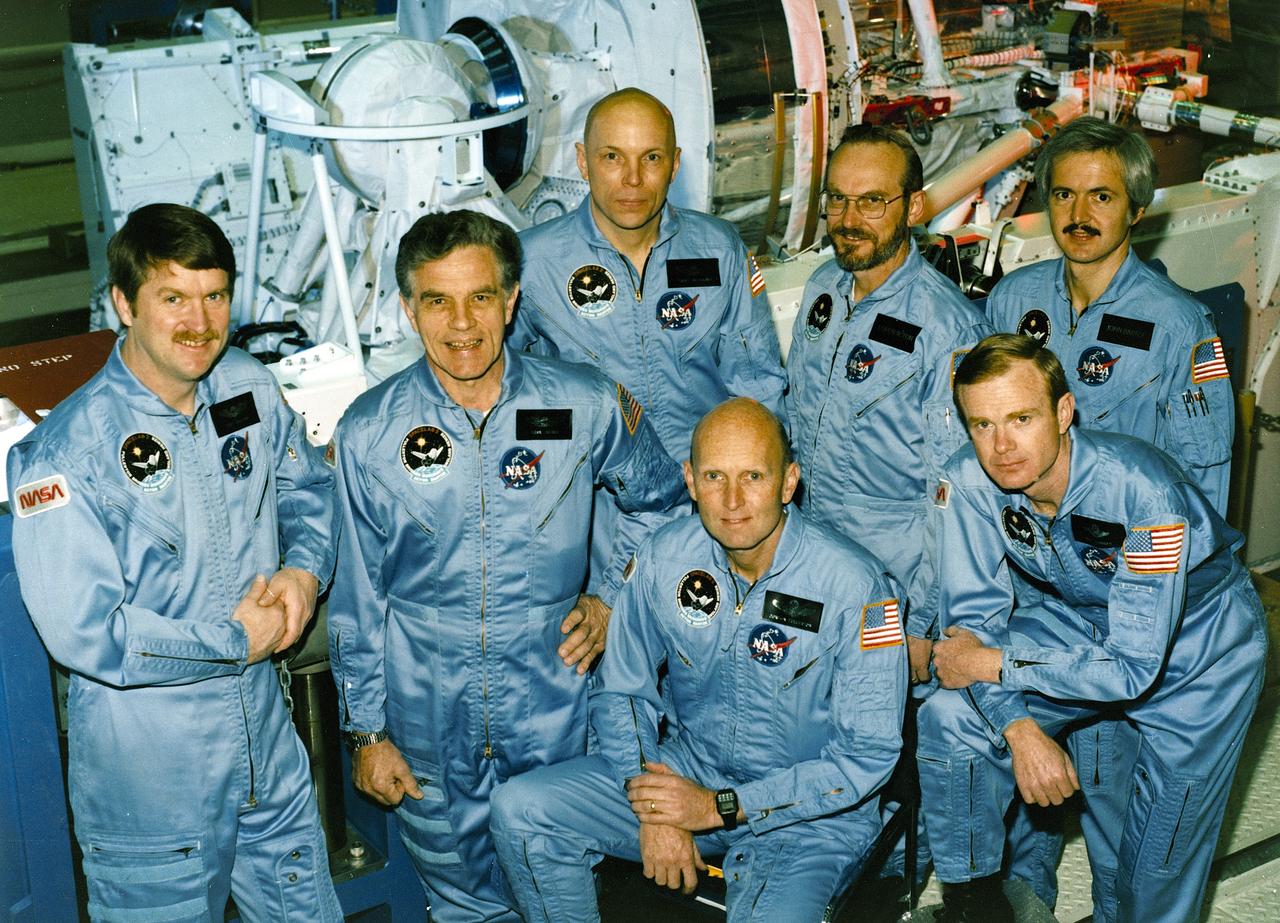

The crew assigned to the STS-51F mission included (kneeling left to right) Gordon Fullerton, commander; and Roy D. Bridges, pilot. Standing, left to right, are mission specialists Anthony W. England, Karl J. Henize, and F. Story Musgrave; and payload specialists Loren W. Acton, and John-David F. Bartoe. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Challenger on July 29, 1985 at 5:00:00 pm (EDT), the STS-51F mission’s primary payload was the Spacelab-2.
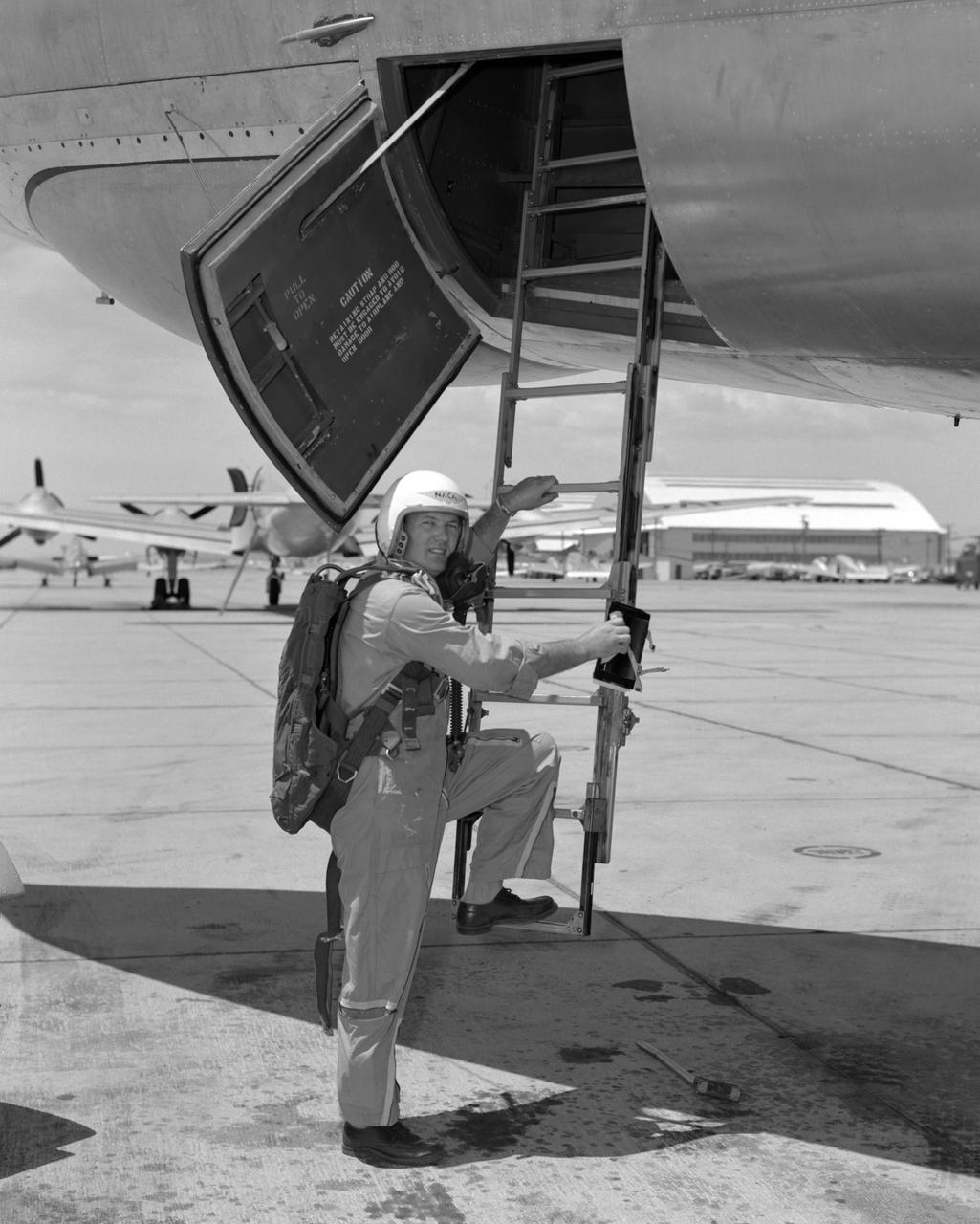

From December 10, 1966, until his retirement on February 27, 1976, Stanley P. Butchart served as Chief (later, Director) of Flight Operations at NASA's Flight Research Center (renamed on March 26, 1976, the Hugh L. Dryden Flight Research Center). Initially, his responsibilities in this position included the Research Pilots Branch, a Maintenance and Manufacturing Branch, and an Operations Engineering Branch, the last of which not only included propulsion and electrical/electronic sections but project engineers for the X-15 and lifting bodies. During his tenure, however, the responsibilities of his directorate came to include not only Flight Test Engineering Support but Flight Systems and Loads laboratories. Before becoming Chief of Flight Operations, Butchart had served since June of 1966 as head of the Research Pilots Branch (Chief Pilot) and then as acting chief of Flight Operations. He had joined the Center (then known as the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics' High-Speed Flight Research Station) as a research pilot on May 10, 1951. During his career as a research pilot, he flew a great variety of research and air-launch aircraft including the D-558-I, D-558-II, B-29 (plus its Navy version, the P2B), X-4, X-5, KC-135, CV-880, CV-990, B-47, B-52, B-747, F-100A, F-101, F-102, F-104, PA-30 Twin Comanche, JetStar, F-111, R4D, B-720, and B-47. Although previously a single-engine pilot, he became the Center's principal multi-engine pilot during a period of air-launches in which the pilot of the air-launch aircraft (B-29 or P2B) basically directed the operations. It was he who called for the chase planes before each drop, directed the positioning of fire rescue vehicles, and released the experimental aircraft after ensuring that all was ready for the drop. As pilot of the B-29 and P2B, Butchart launched the X-1A once, the X-1B 13 times, the X-1E 22 times, and the D-558-II 102 times. In addition, he towed the M2-F1 lightweight lifting body 14 times behind an R4

S68-42343 (5 Aug. 1968) --- The prime crew of the first manned Apollo space mission, Apollo 7, stands on the deck of the NASA Motor Vessel Retriever after suiting up for water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. Left to right, are astronauts Walter Cunningham, Donn F. Eisele, and Walter M. Schirra Jr.
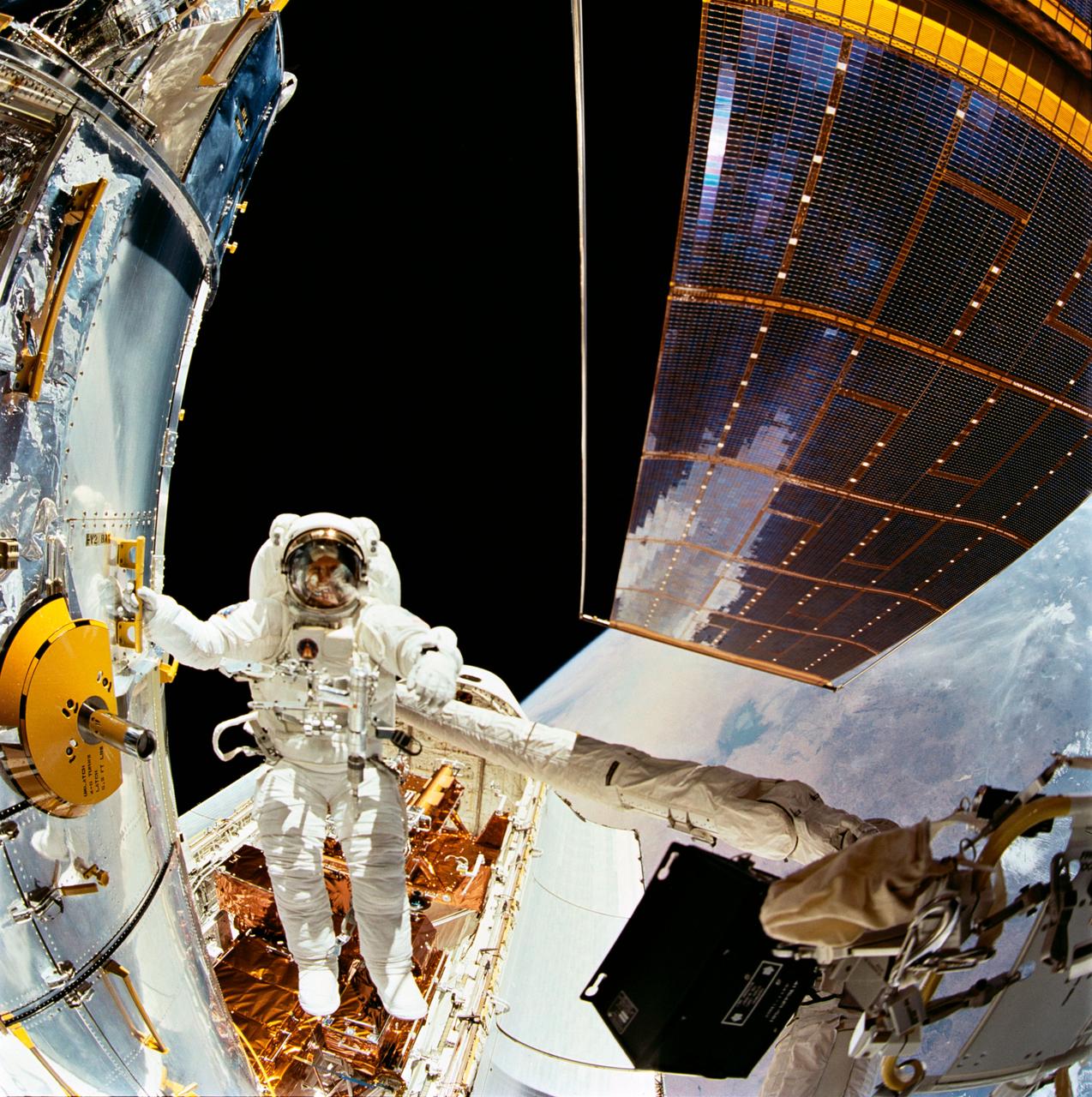

STS061-104-007 (5 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut F. Story Musgrave, holding to one of many strategically placed handrails on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), is photographed during the first of five extravehicular activity?s (EVA) on the HST-servicing mission, aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour.

S66-44497 (23 July 1966) --- Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. (left) and Richard F. Gordon Jr. (right), prime crew for the Gemini-11 spaceflight, practice water egress procedures in the Gulf of Mexico. Static Article 5 was used in the training exercise. A MSC swimmer is in the water assisting in the training. Photo credit: NASA
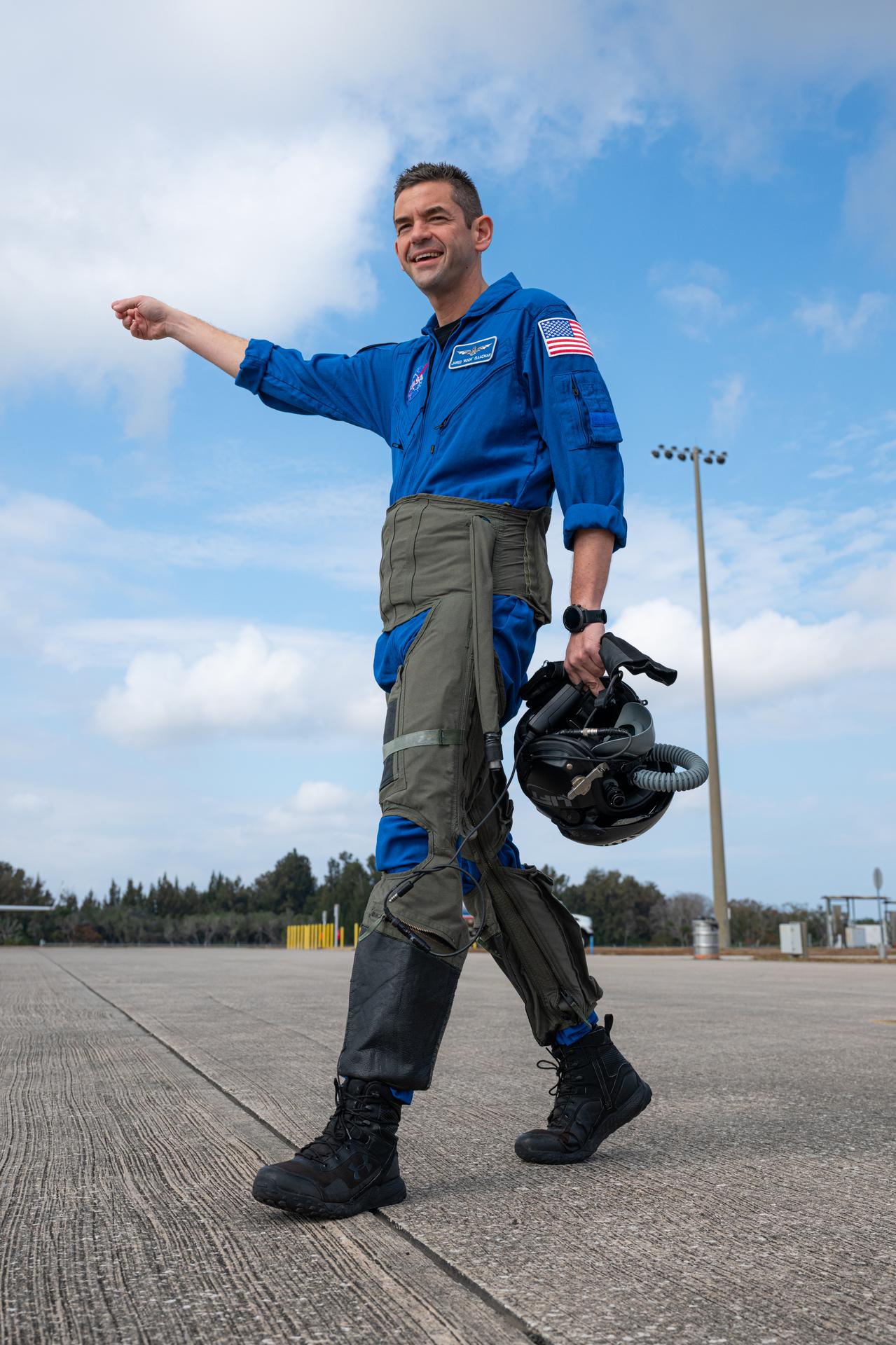

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman is seen before an employee incentive flying event using his personal F-5 aircraft, Thursday, Feb. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)

NASA 916, a T-38 jet aircraft, carrying astronauts Vance D. Brand (front station) and Robert F. Overmyer, heads for Kennedy Space Center in Florida. 1. STS-5 - PREFLIGHT KSC, FL Also available in 4x5 CN
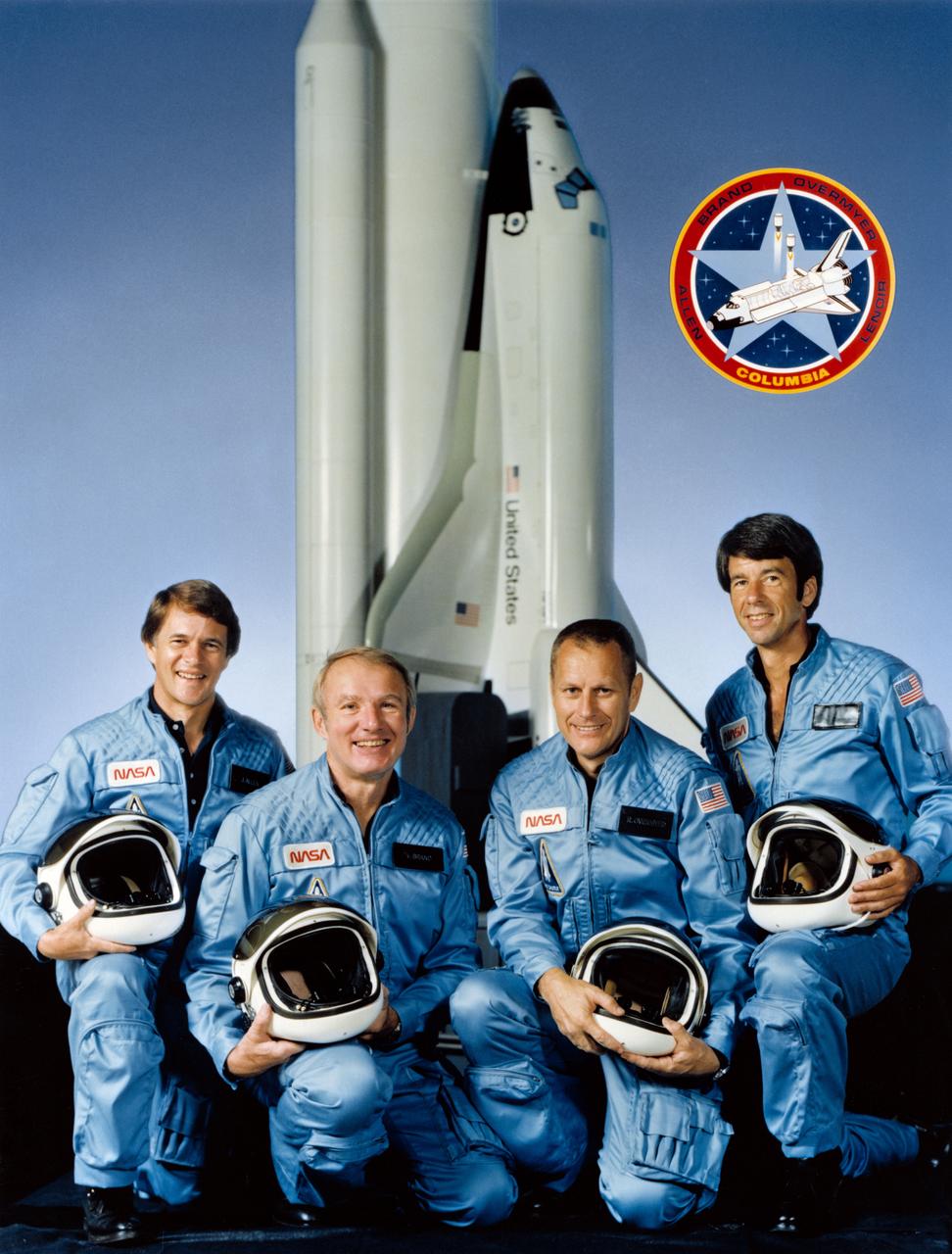

S82-36286 (15 Aug. 1982) --- These four men will be aboard the space shuttle Columbia for NASA's first operational Space Transportation System (STS) mission. They are astronauts Vance D. Brand (second left), STS-5 commander; Robert F. Overmyer (second right), pilot; and Joseph P. Allen (left) and William B. Lenoir, both mission specialists. They pose with a space shuttle model and the official insignia for STS-5. Their flight is scheduled for November of this year. Photo credit: NASA
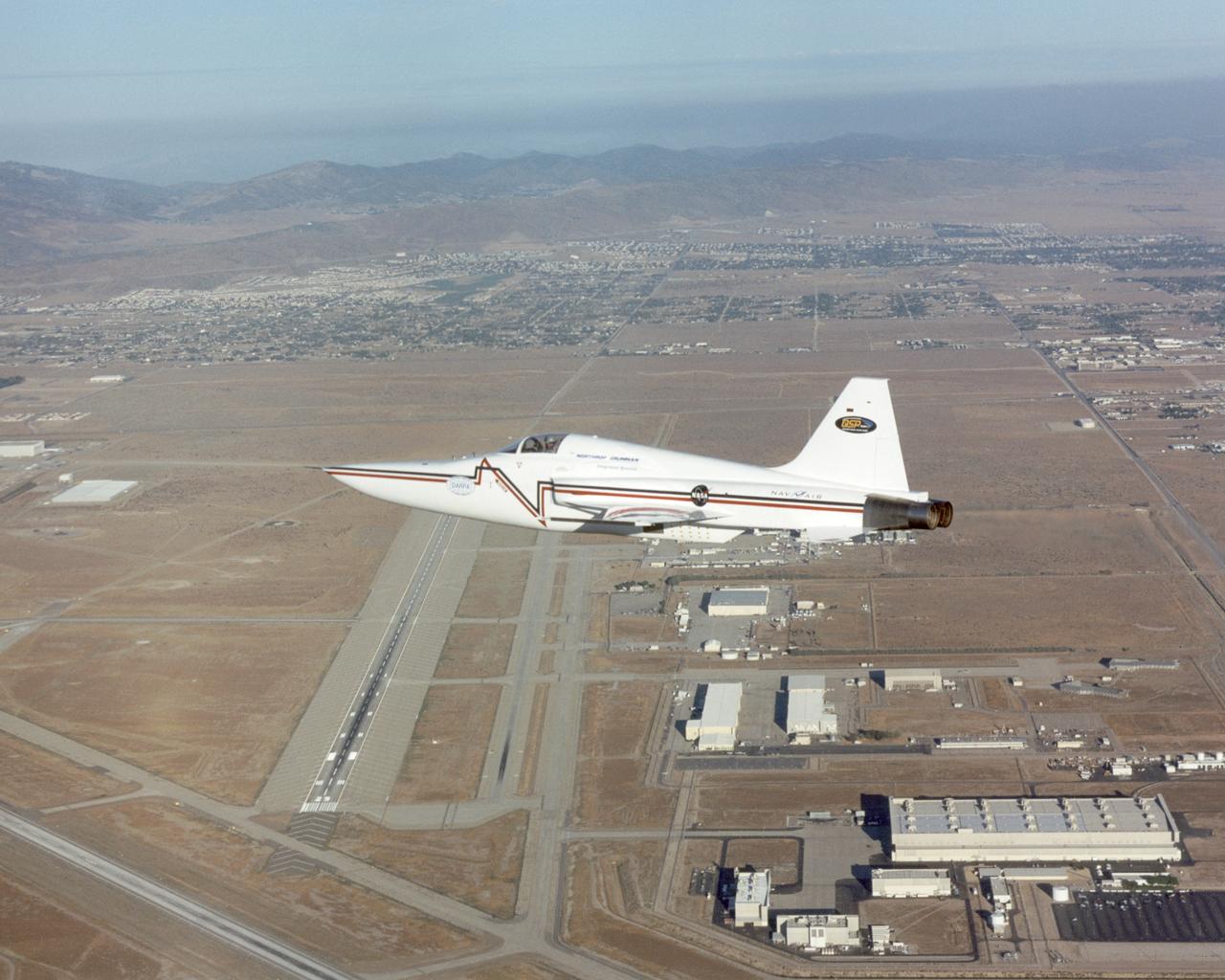

Northrop Grumman Corporation's modified U.S. Navy F-5E Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) aircraft flies over the company's Palmdale, California facilities on Aug. 2, 2003. NASA Dryden provided range, air and ground data-gathering support for the SSBD project, which is part of DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program.
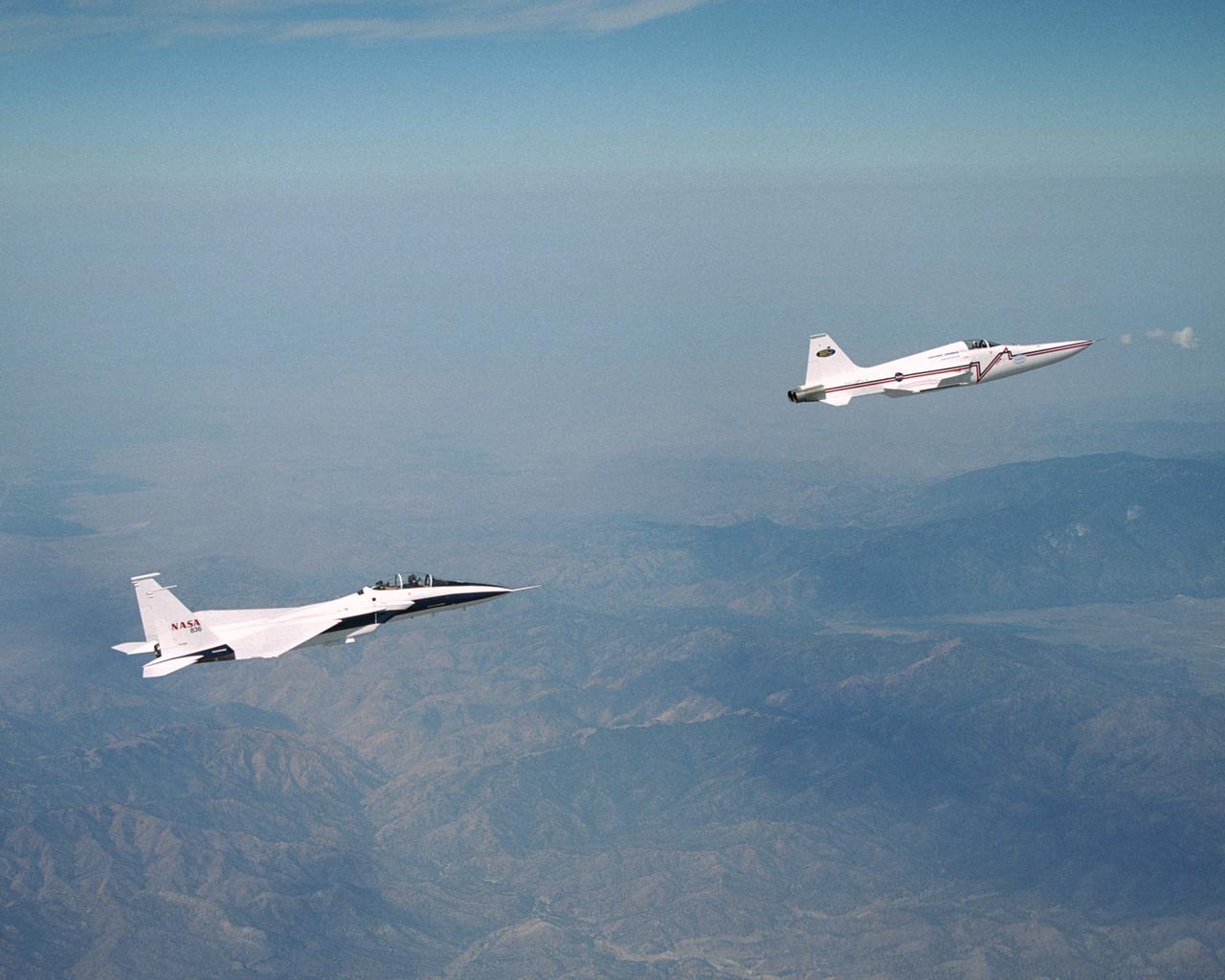

NASA's F-15B research testbed jet from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center flew in the supersonic shockwave of a Northrop Grumman Corp. modified F-5E in support of the Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, which is part of the DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program.
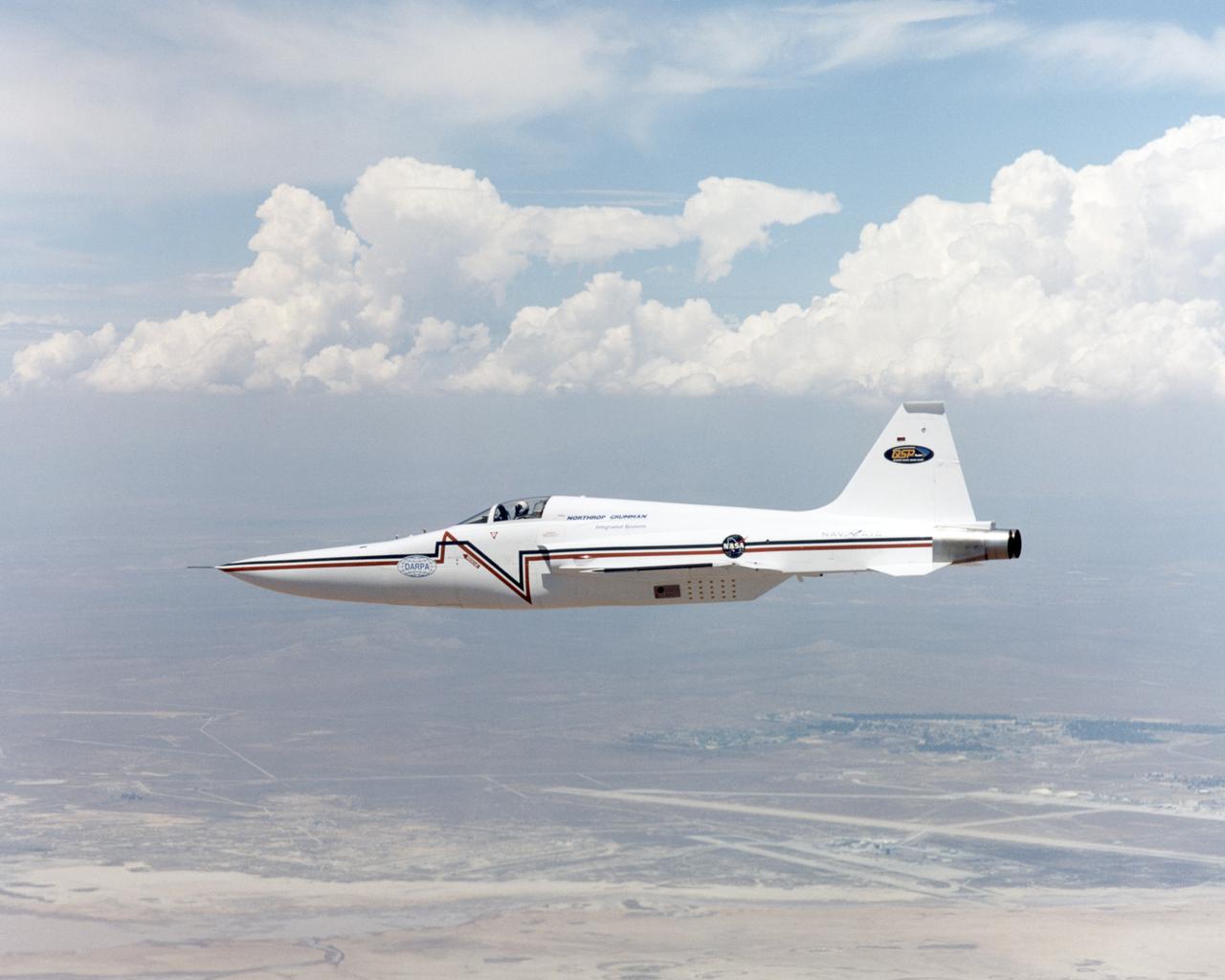

Northrop-Grumman Corporation's modified U.S. Navy F-5E Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) aircraft.
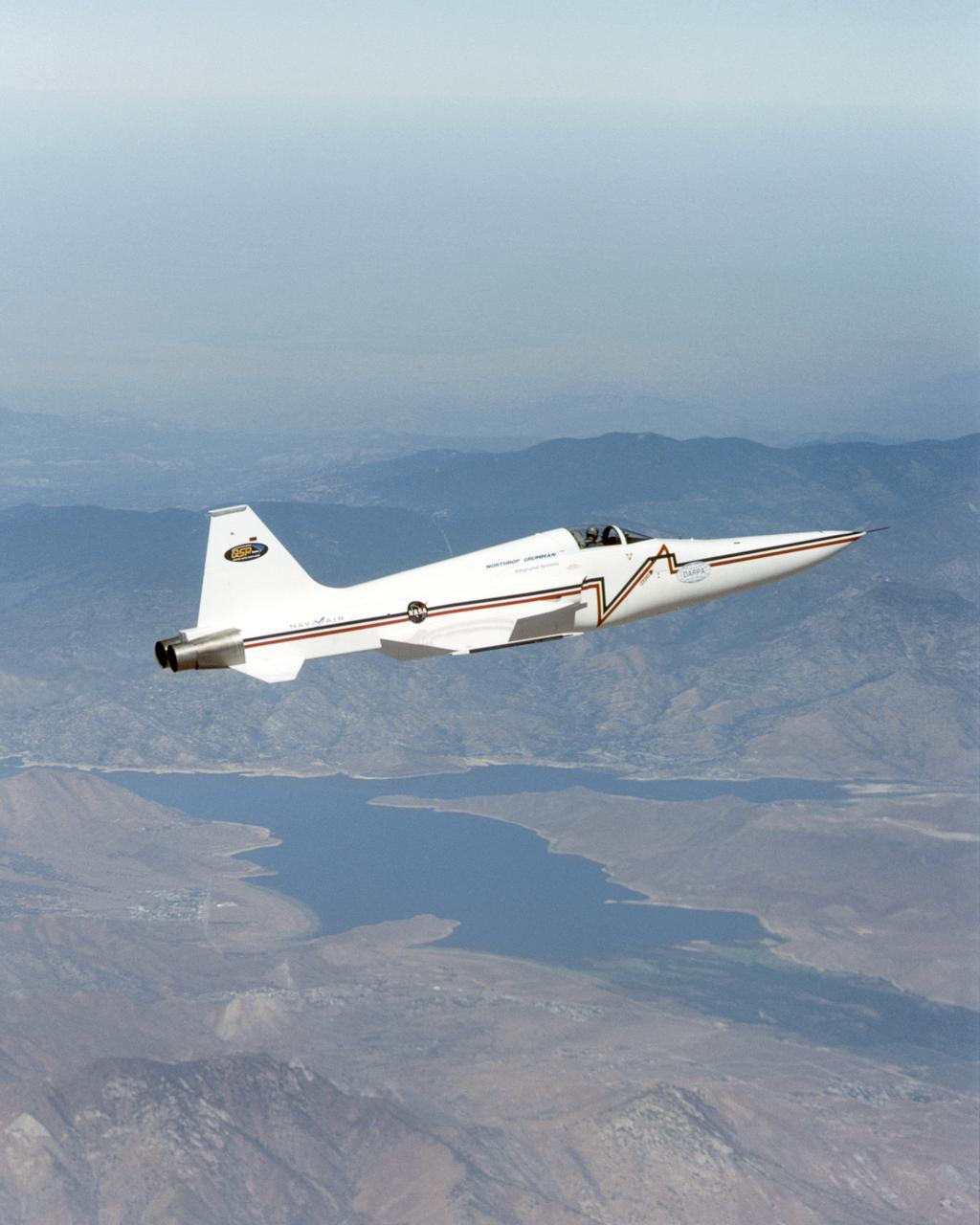

Northrop Grumman Corporation's modified U.S. Navy F-5E Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) aircraft flies over Lake Isabella, California on Aug. 4, 2003. NASA Dryden provided range, air and ground data-gathering support for the SSBD project, which is part of DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program.
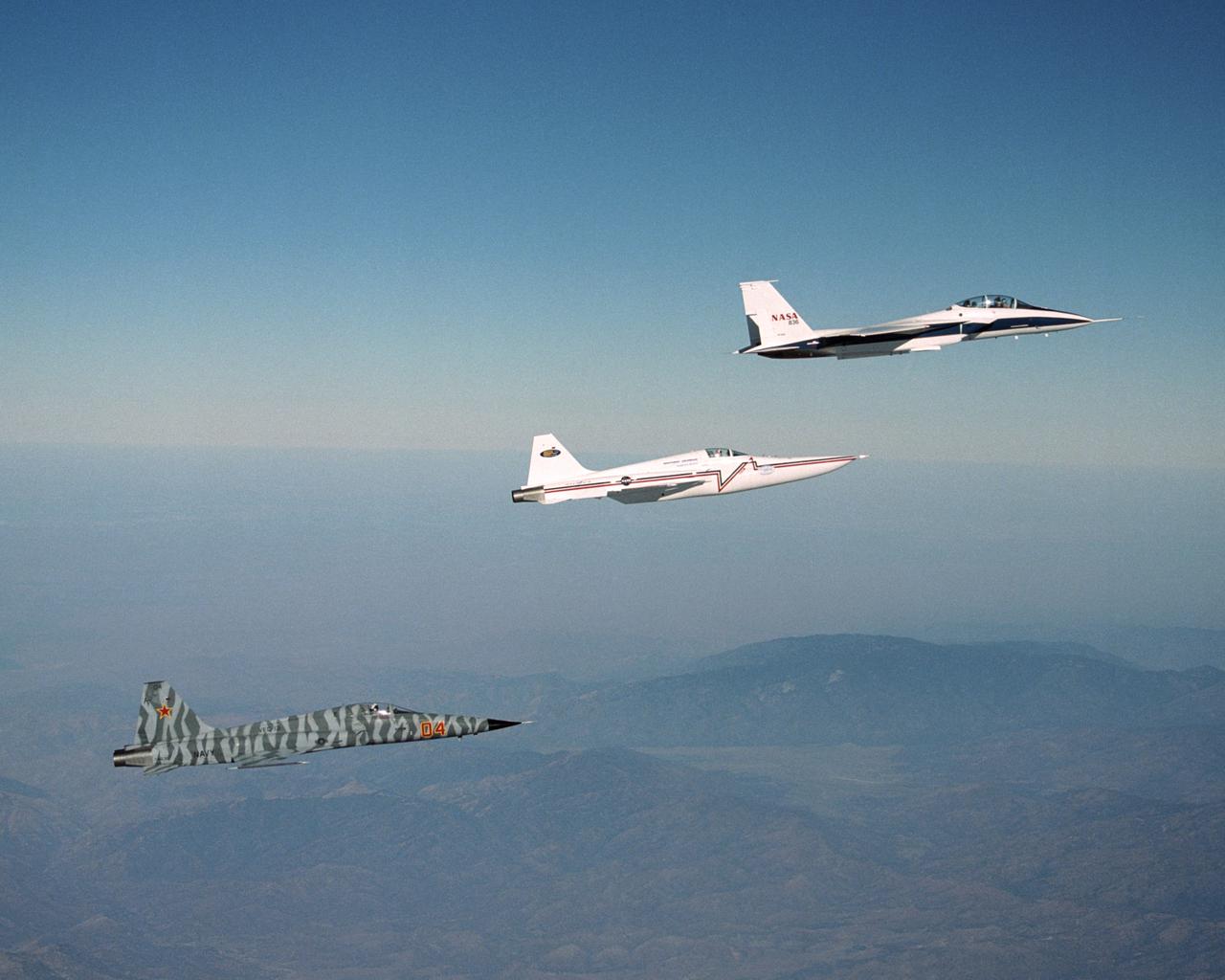

In a role-reversal, Northrop Grumman Corp.'s modified F-5E Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) aircraft flies off the wing of NASA's F-15B Research testbed aircraft. The F-15B, from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, flew in the supersonic shockwave of the F-5E as part of the SSBD project. Following the two aircraft is an unmodified U.S. Navy F-5E used for baseline sonic boom measurements.
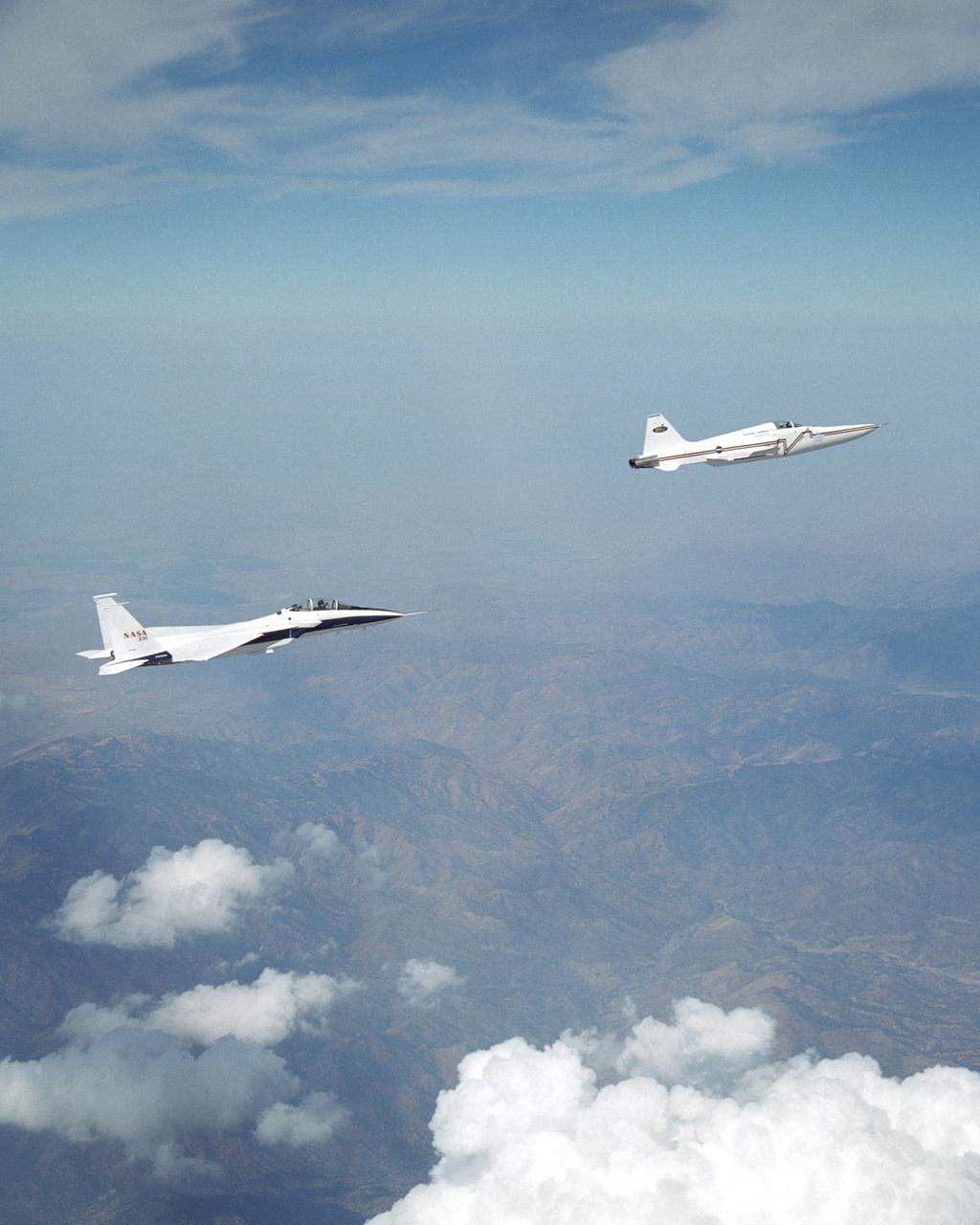

NASA's F-15B research testbed jet from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center flew in the supersonic shockwave of a Northrop Grumman Corp. modified U.S. Navy F-5E jet in support of the Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, which is part of the DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The project is an effort to lessen sonic booms. During the recent demonstration, the F-15B flew behind the modified F-5E sonic boom demonstrator aircraft in order to measure the aircraft's sonic boom characteristics. Flying behind and below the F-5E, and using its specially-instrumented nose boom, the F-15B recorded many shockwave patterns from the F-5E at various distances and orientations from the aircraft.
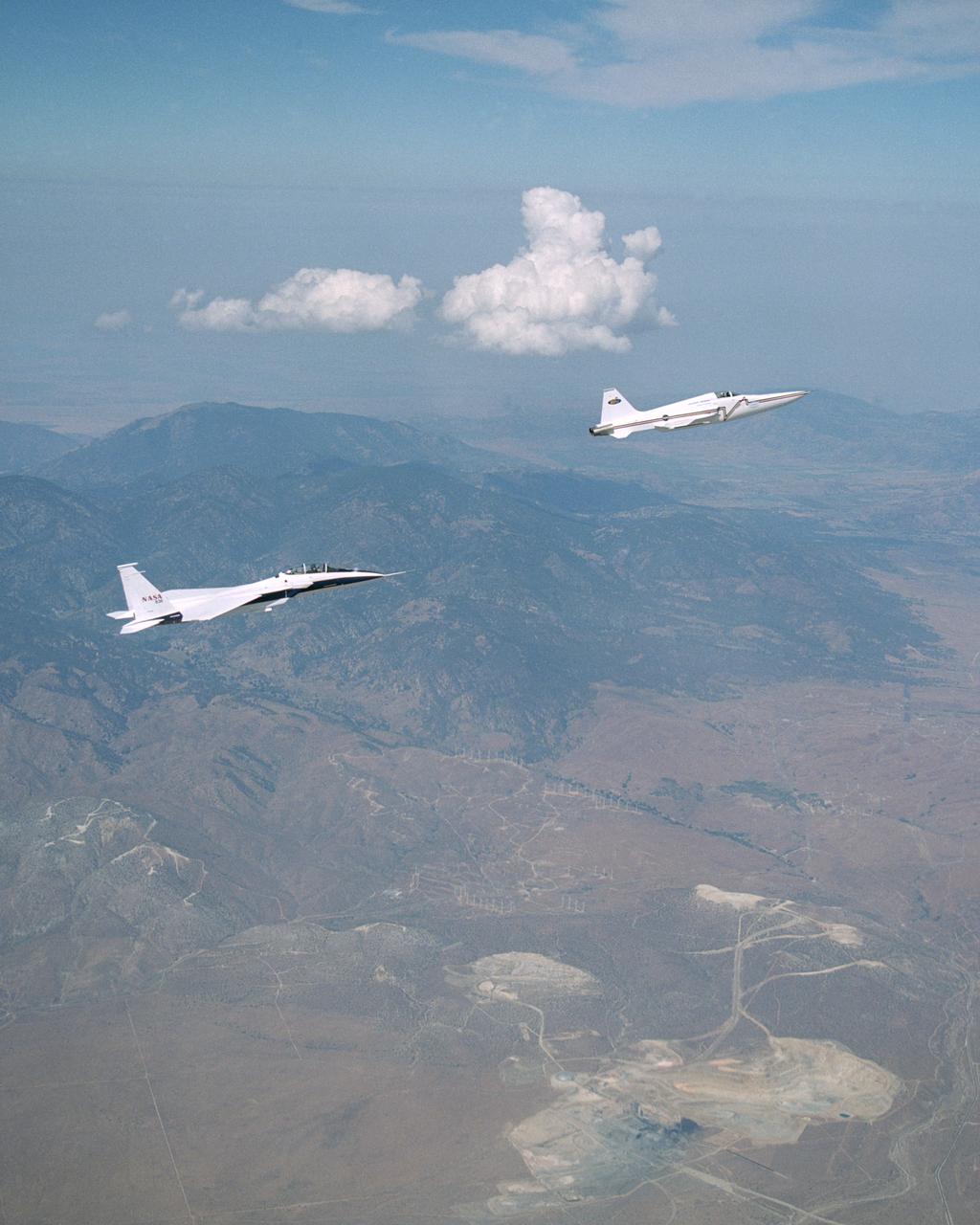

NASA's F-15B research testbed jet from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center flew in the supersonic shockwave of a Northrop Grumman Corp. modified U.S. Navy F-5E jet in support of the Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, which is part of the DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The project is an effort to lessen sonic booms. During the recent demonstration, the F-15B flew behind the modified F-5E sonic boom demonstrator aircraft in order to measure the aircraft's sonic boom characteristics. Flying behind and below the F-5E, and using its specially-instrumented nose boom, the F-15B recorded many shockwave patterns from the F-5E at various distances and orientations from the aircraft.
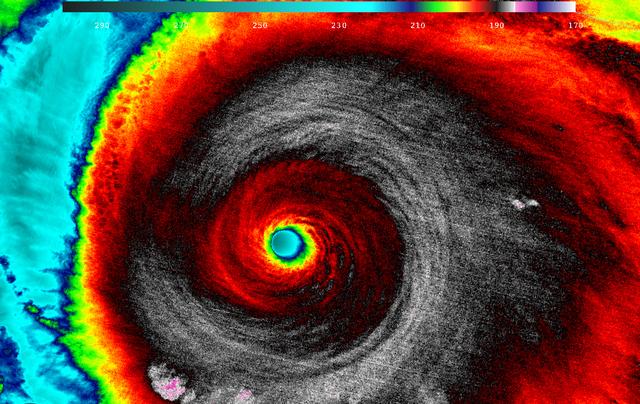
When NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Patricia on October 23 at 5:20 a.m. EDT the VIIRS instrument that flies aboard Suomi NPP looked at the storm in infrared light. Cloud top temperatures of thunderstorms around the eyewall were between 180K (-135.7F/ -93.1C) and 190 Kelvin (-117.7F/ -83.1C). Credit: UW/CIMSS/William Straka III Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/f…/goddard/patricia-eastern-pacific-2015" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/f…/goddard/patricia-eastern-pacific-2015</a>
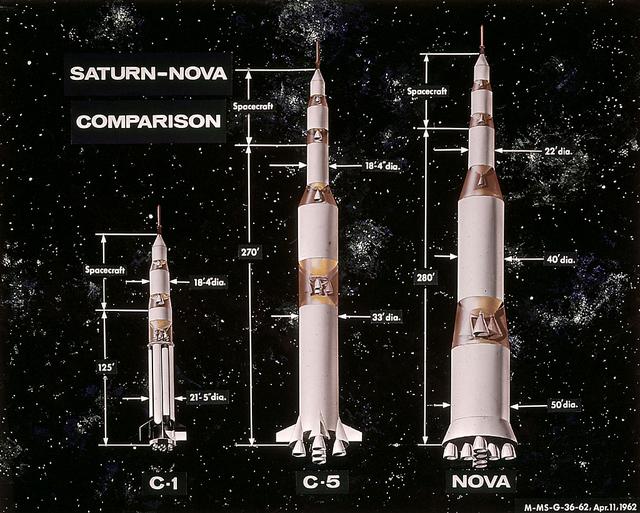

In this 1962 artist's concept , a proposed Nova rocket, shown at right, is compared to a Saturn C-1, left, and a Saturn C-5, center. The Marshall Space Flight Center directed studies of Nova configuration from 1960 to 1962 as a means of achieving a marned lunar landing with a direct flight to the Moon. Various configurations of the vehicle were examined, the largest being a five-stage vehicle using eight F-1 engines in the first stage. Although the program was effectively cancelled in 1962 when NASA planners selected the lunar-orbital rendezvous mode, the proposed F-1 engine was eventually used to propel the first stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle in the Apollo Program.
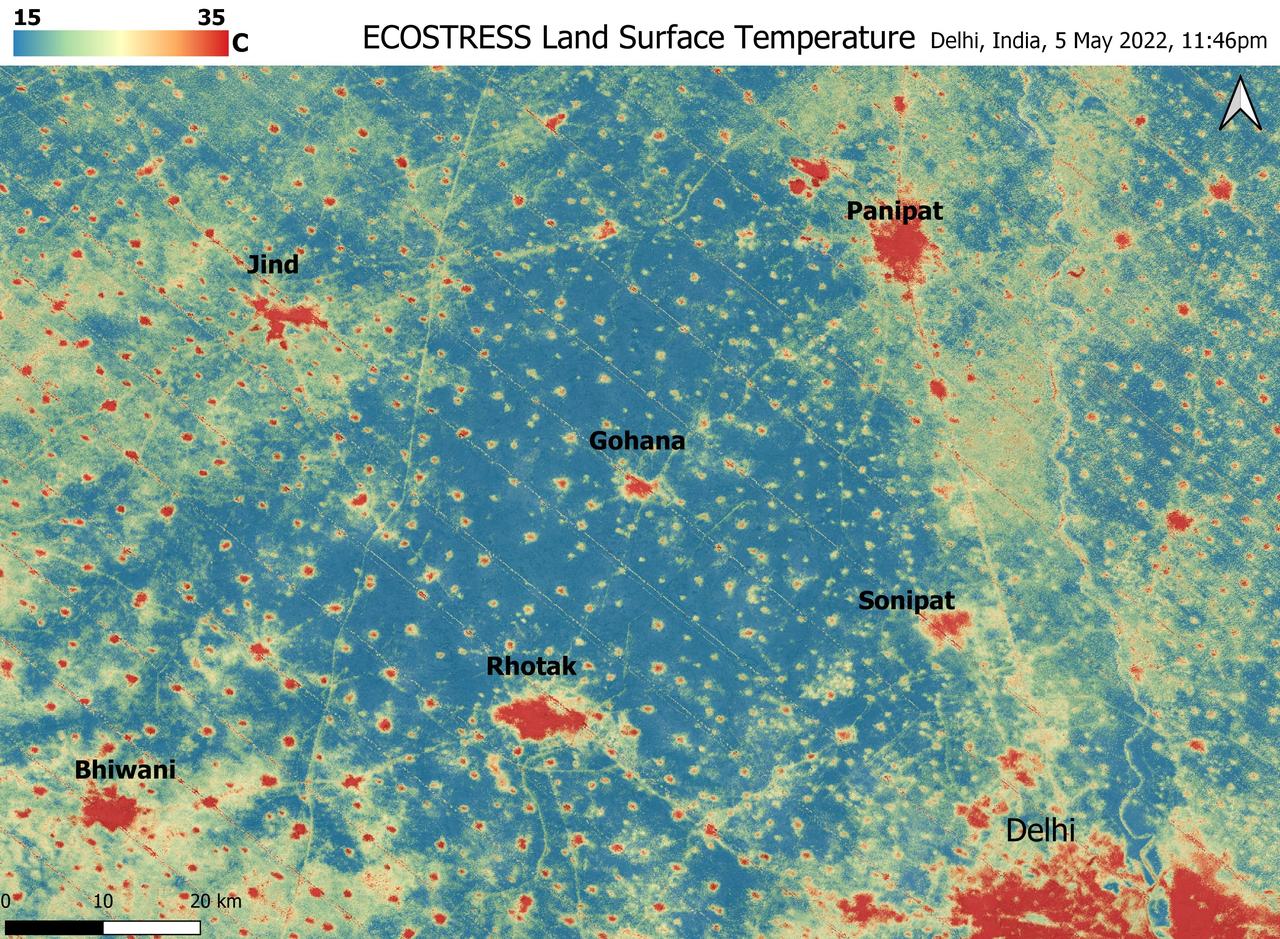
A relentless heat wave has blanketed India and Pakistan since mid-March 2022, causing dozens of deaths, fires, increased air pollution, and reduced crop yields. NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station instrument (ECOSTRESS) has been measuring these temperatures from space, at the highest spatial resolution of any satellite instrument. This image, taken shortly before local midnight on May 5, shows urban areas and agricultural lands northwest of Delhi that are home to about 28 million people. The image covers about 4,800 square miles (12,350 square kilometers). Cities are usually markedly warmer than the surrounding countryside due to human activities and the materials used in the built environment. The image clearly delineates these urban "heat islands." Nighttime temperatures in Delhi and several smaller villages were above 95 degrees Fahrenheit (35 degrees Celsius), peaking at about 102 degrees F (39 degrees C), while the rural fields nearby had cooled to around 60 degrees F (15 degrees C). This data suggests that city dwellers are experiencing considerably higher temperatures than the average temperatures reported for their regions. ECOSTRESS measures the temperature of the ground itself, which is very similar to air temperature at night (though the ground may be warmer than the air in daylight hours). The instrument launched to the space station in 2018. Its primary mission is to identify plants' thresholds for water use and water stress, giving insight into their ability to adapt to a warming climate. However, ECOSTRESS also records other heat-related phenomena like this heat wave. Its high-resolution images, with a pixel size of about 225 feet (70 meters) by 125 feet (38 meters), are a powerful tool for understanding aspects of the weather event that might be overlooked by traditional observation networks. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24987
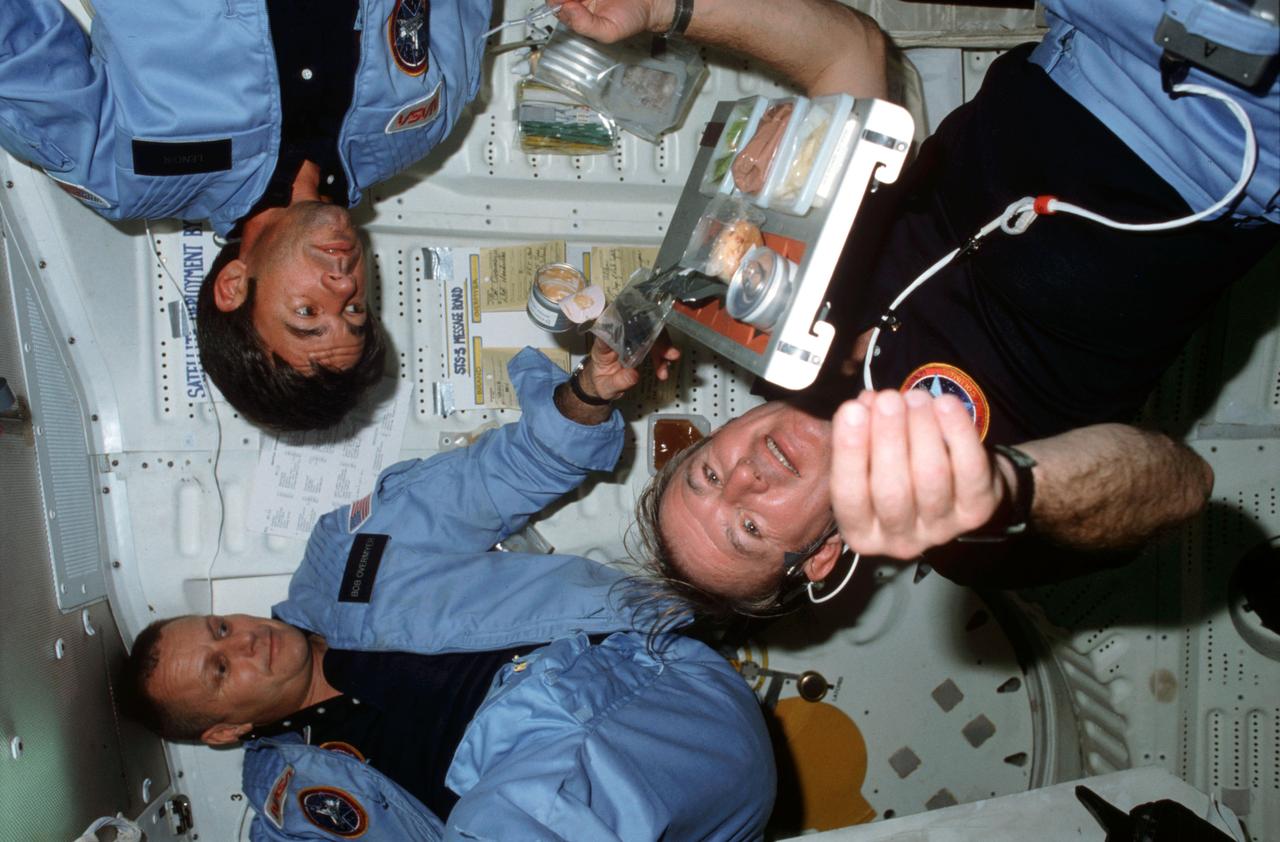

STS005-06-210 (16 Nov. 1982) --- Astronaut Vance D. Brand (in dark blue shirt), STS-5 commander; Robert F. Overmyer (left), pilot; and William B. Lenoir, mission specialist, conduct microgravity experiments with food containers and meal tray assemblies in front of middeck port side wall and side hatch. Brand prepares to eat as meal tray assembly floats above his chest and Overmeyer and Lenoir look on. Sign on port side wall is labeled STS-5 message board. Photo credit: NASA
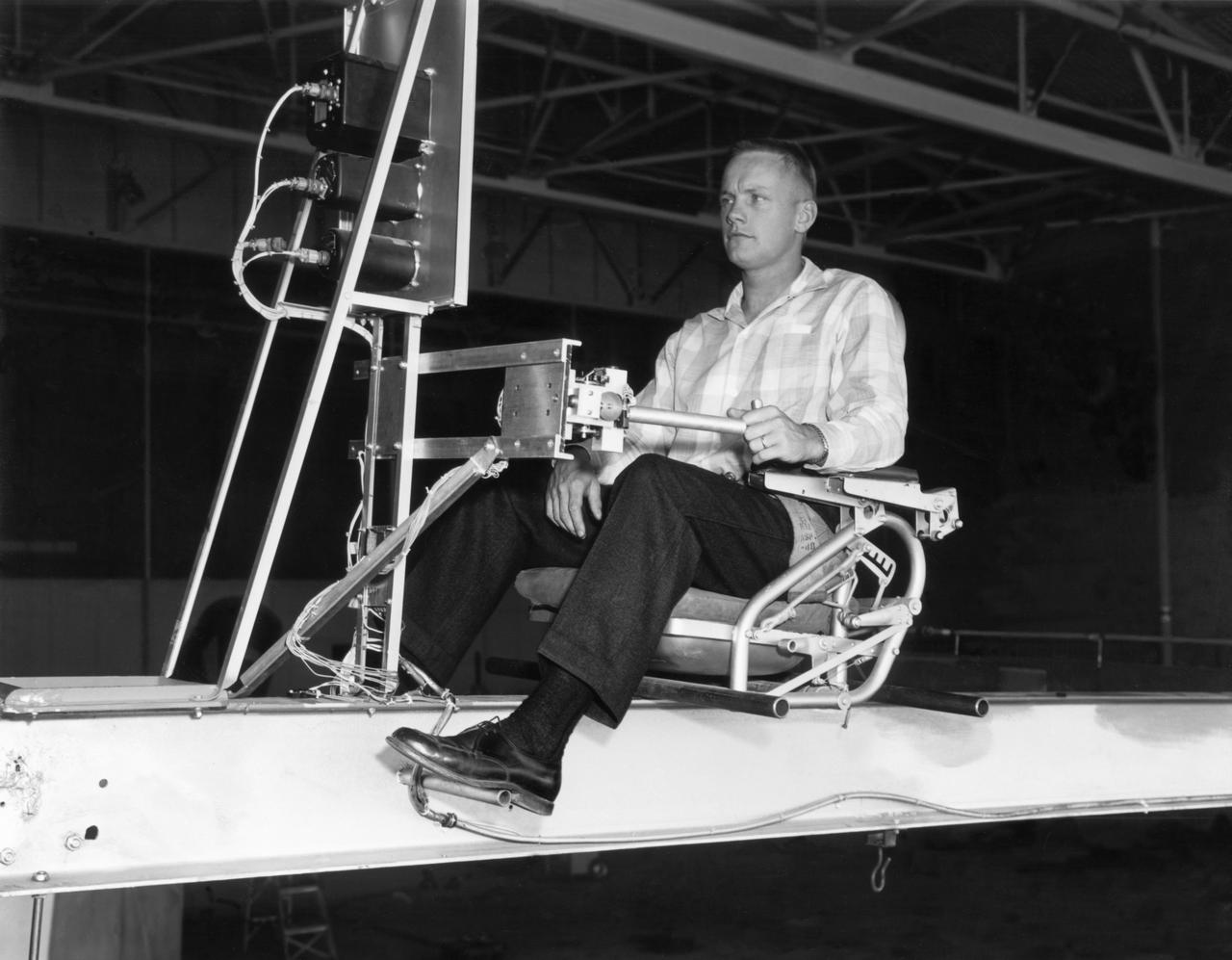

Famed astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, the first man to set foot on the moon during the historic Apollo 11 space mission in July 1969, served for seven years as a research pilot at the NACA-NASA High-Speed Flight Station, now the Dryden Flight Research Center, at Edwards, California, before he entered the space program. Armstrong joined the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) at the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory (later NASA's Lewis Research Center, Cleveland, Ohio, and today the Glenn Research Center) in 1955. Later that year, he transferred to the High-Speed Flight Station at Edwards as an aeronautical research scientist and then as a pilot, a position he held until becoming an astronaut in 1962. He was one of nine NASA astronauts in the second class to be chosen. As a research pilot Armstrong served as project pilot on the F-100A and F-100C aircraft, F-101, and the F-104A. He also flew the X-1B, X-5, F-105, F-106, B-47, KC-135, and Paresev. He left Dryden with a total of over 2450 flying hours. He was a member of the USAF-NASA Dyna-Soar Pilot Consultant Group before the Dyna-Soar project was cancelled, and studied X-20 Dyna-Soar approaches and abort maneuvers through use of the F-102A and F5D jet aircraft. Armstrong was actively engaged in both piloting and engineering aspects of the X-15 program from its inception. He completed the first flight in the aircraft equipped with a new flow-direction sensor (ball nose) and the initial flight in an X-15 equipped with a self-adaptive flight control system. He worked closely with designers and engineers in development of the adaptive system, and made seven flights in the rocket plane from December 1960 until July 1962. During those fights he reached a peak altitude of 207,500 feet in the X-15-3, and a speed of 3,989 mph (Mach 5.74) in the X-15-1. Armstrong has a total of 8 days and 14 hours in space, including 2 hours and 48 minutes walking on the Moon. In March 1966 he was commander of the Gemini 8 or

Deputy Director Colleen Hartman from NASA Goddard Space Flight Center looks on as Kamal Amiral, 5, of Arlington, Va., looks at the moon through a telescope during a stargazing event at Hoffman-Boston Elementary School in Arlington, Va. on Thursday, Nov. 7, 2013. NASA Administrator Charles F. Bolden is also pictured. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jay Westcott)

Acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot listens to remarks by panelists during the National Space Council's first meeting, Thursday, Oct. 5, 2017 at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. The National Space Council, chaired by Vice President Mike Pence heard testimony from representatives from civil space, commercial space, and national security space industry representatives. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
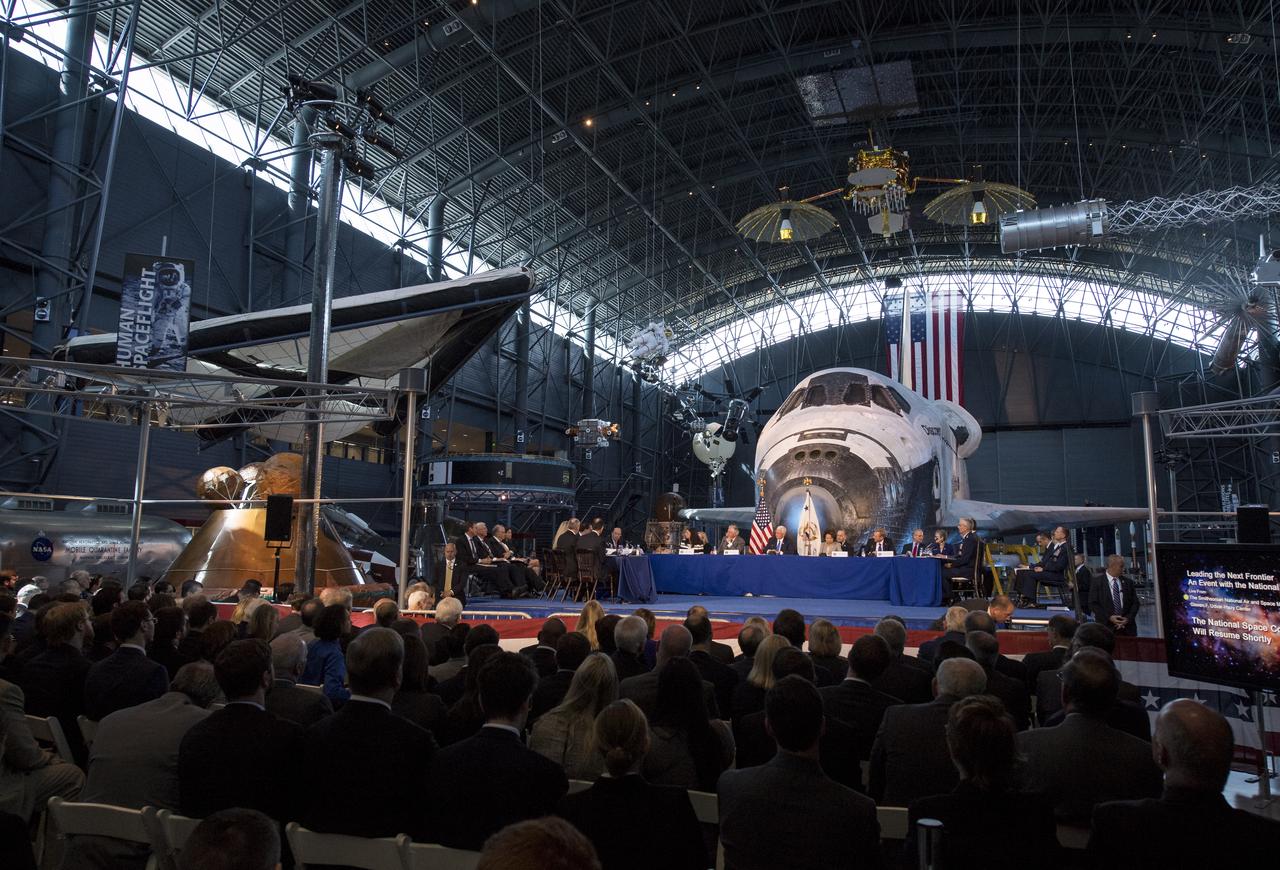

Members of the National Space Council are seen during the council's first meeting, Thursday, Oct. 5, 2017 at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. The National Space Council, chaired by Vice President Mike Pence heard testimony from representatives from civil space, commercial space, and national security space industry representatives. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
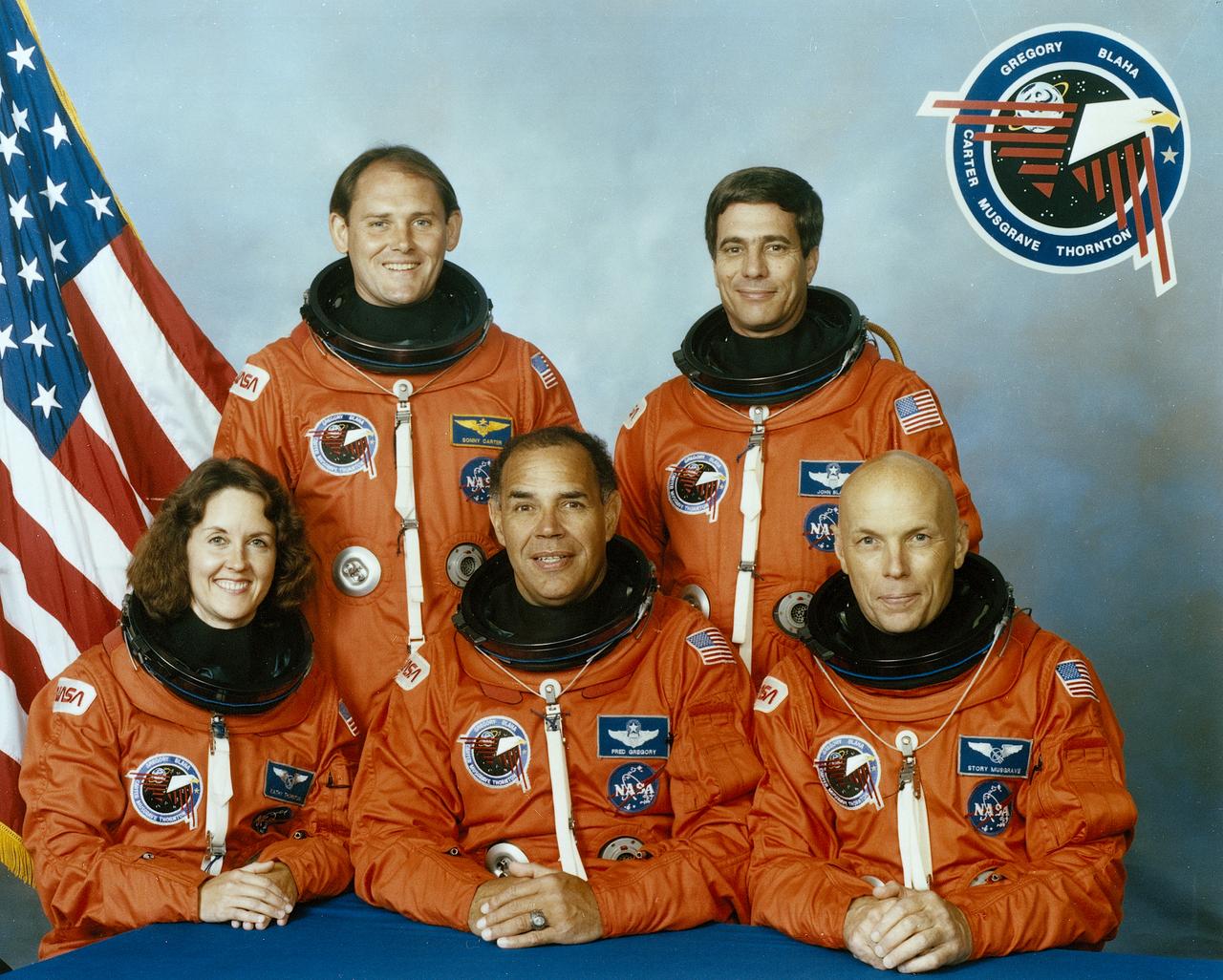

On November 22, 1989, at 7:23:30pm (EST), 5 astronauts were launched into space aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery for the 5th Department of Defense mission, STS-33. Photographed from left to right are Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialist 3; Manley L. (Sonny) Carter, mission specialist 2; Frederick D. Gregory, commander; John E. Blaha, pilot; and F. Story Musgrave, mission specialist 1.
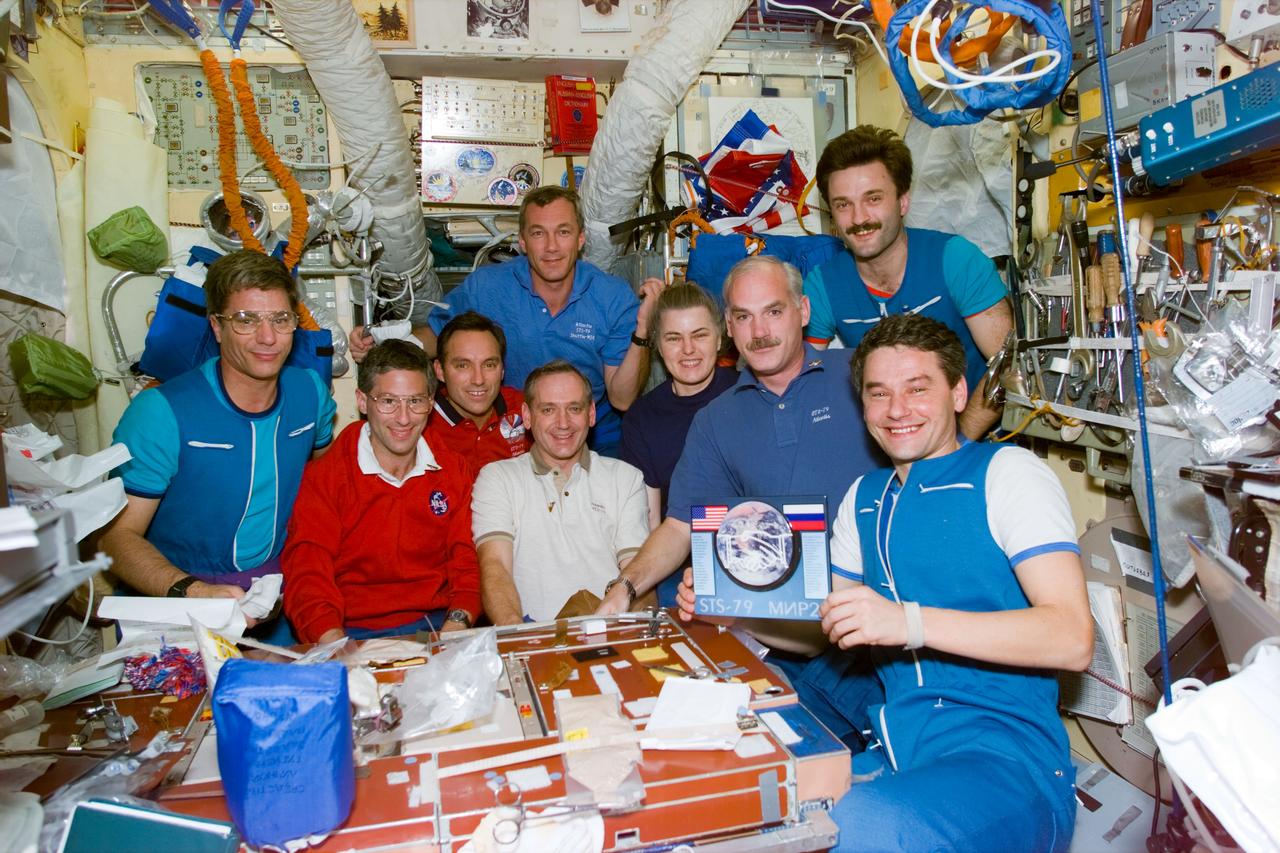

STS79-E-5180 (20 September 1996) --- The entire crews of STS-79 and Mir-22 are shown during a gift exchange ceremony aboard Russia's Mir Space Station's Base Block, during Flight Day 5. Front row, from the left, John E. Blaha, Jerome (Jay) Apt, Carl E. Walz, Thomas D. Akers, Shannon W. Lucid, William F. Readdy and Valeri G. Korzun. Back row: Terrence W. Wilcutt and Aleksandr Y. Kaleri.
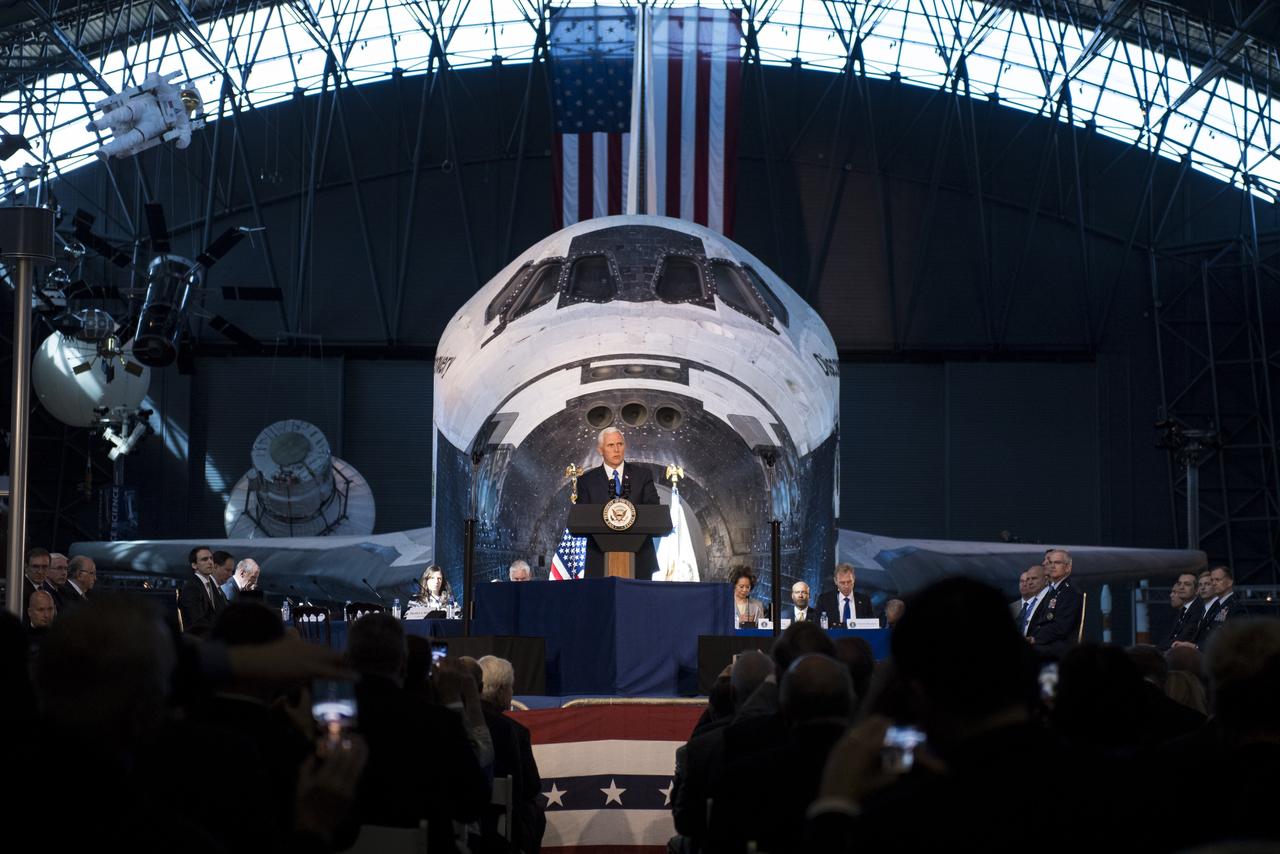

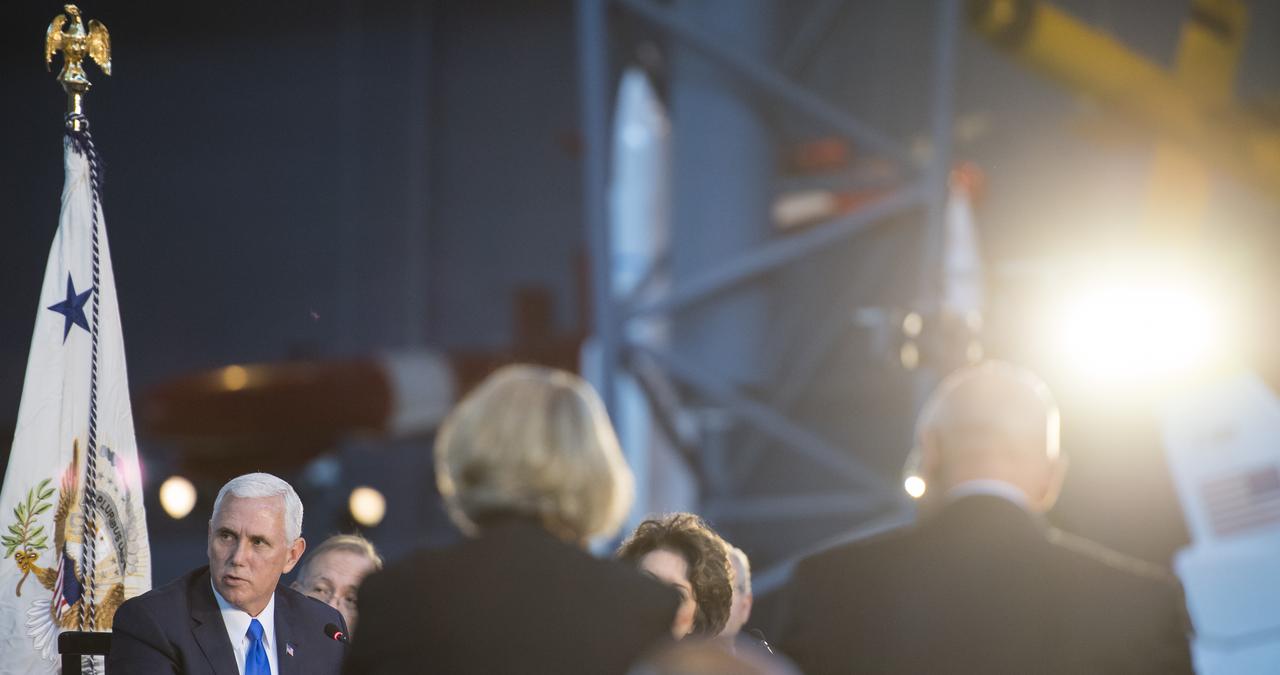
Vice President Mike Pence delivers opening remarks during the National Space Council's first meeting, Thursday, Oct. 5, 2017 at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. The National Space Council, chaired by Vice President Mike Pence heard testimony from representatives from civil space, commercial space, and national security space industry representatives. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
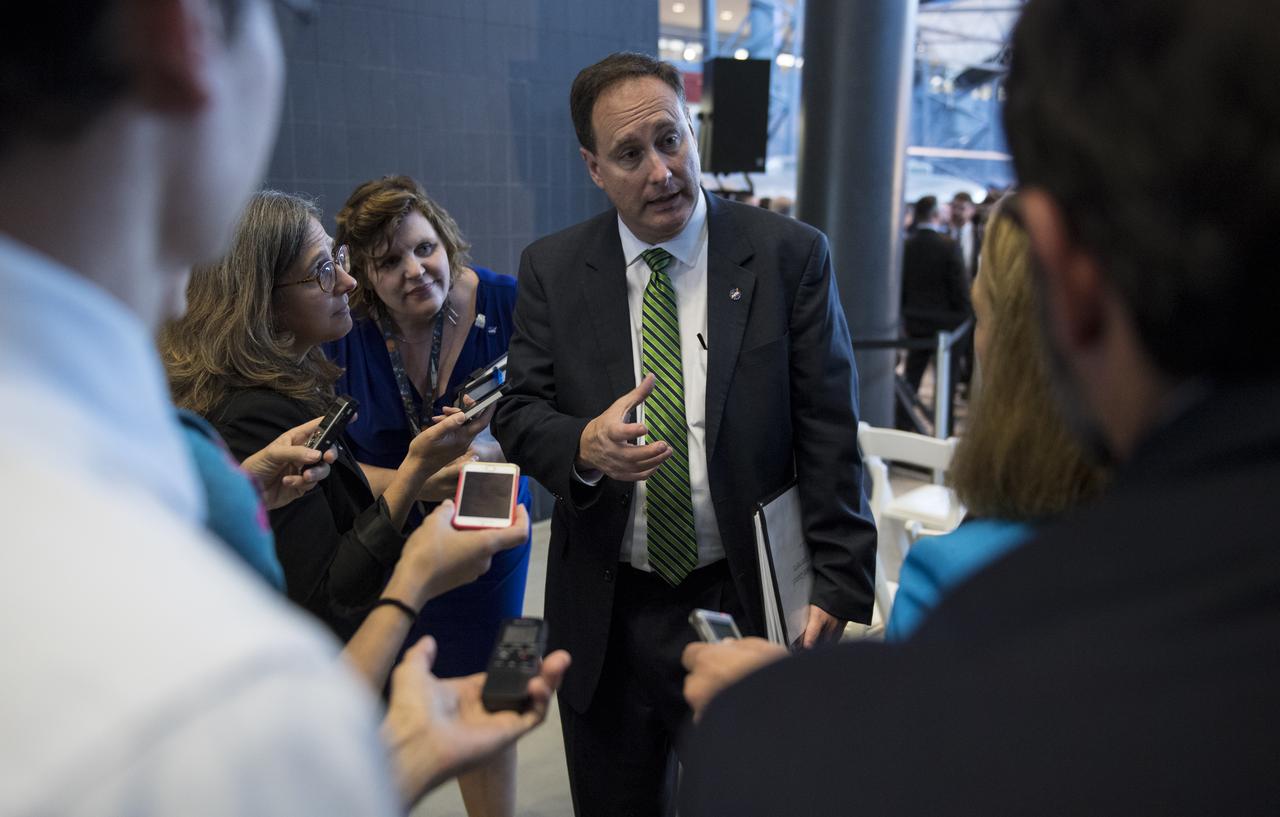

Acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot answers questions from reporters following the National Space Council's first meeting, Thursday, Oct. 5, 2017 at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. The National Space Council, chaired by Vice President Mike Pence heard testimony from representatives from civil space, commercial space, and national security space industry representatives. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

S85-40173 (5 Sept. 1985) --- In Johnson Space Center’s (JSC) Astronaut Office, astronaut F. Richard (Dick) Scobee, STS-51L mission commander, takes a break from training for his upcoming space mission. EDITOR’S NOTE: The STS-51L crew members lost their lives in the space shuttle Challenger accident moments after launch on Jan. 28, 1986 from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Photo credit: NASA
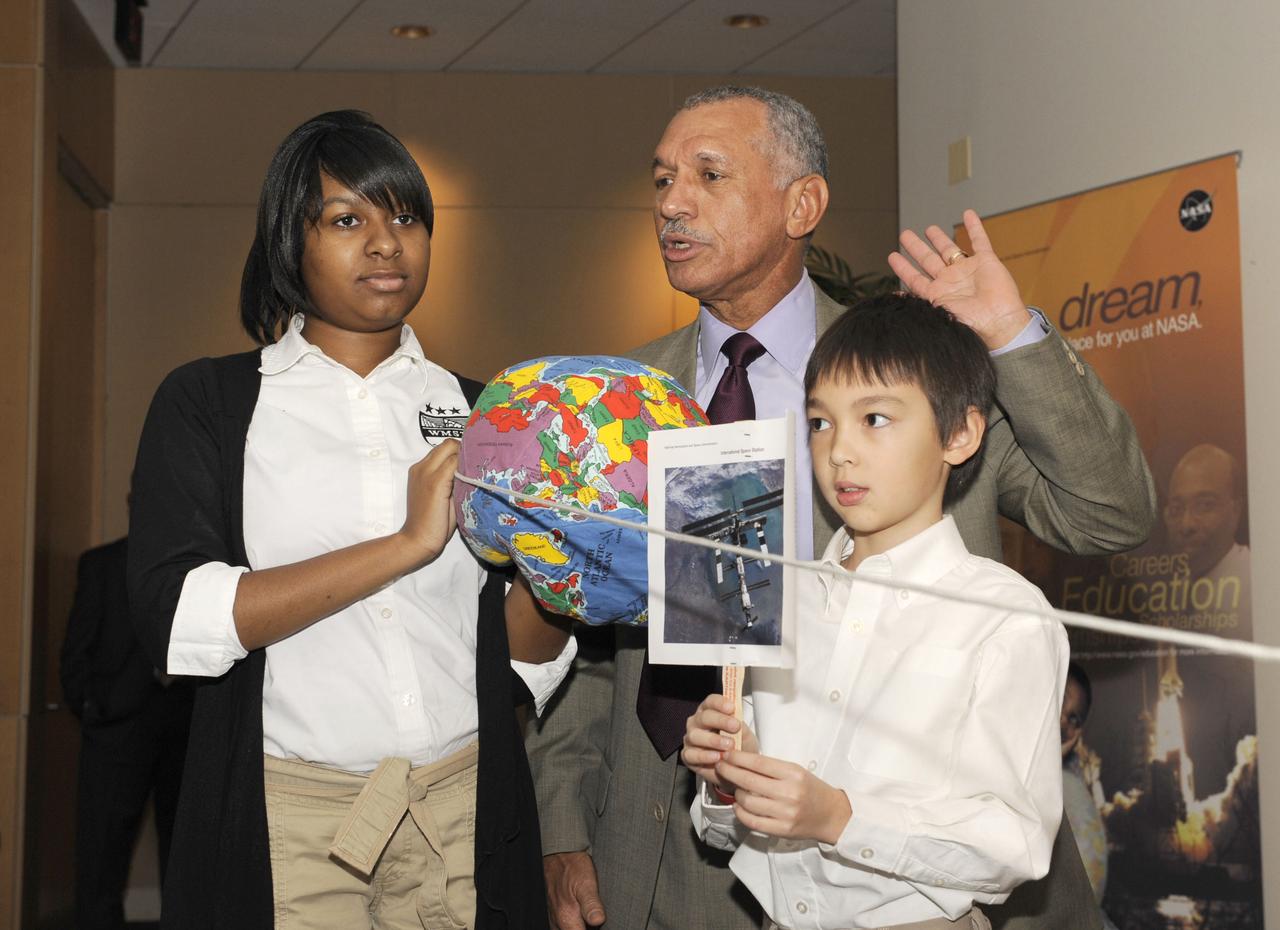

NASA Administrator Charles F. Bolden, center, stands with two unidentified students as he performs a demonstration to illustrate how far the International Space Station is from the Earth in comparison with the Moon, during an event where students spoke via downlink to astronauts on the ISS, Thursday, Nov. 5, 2009, at the U.S. Department of Education in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

51I-102-048 (4-5 Sept 1985) --- A 35mm frame showing astronaut William F. Fisher standing on the edge of Discovery's cargo bay (in foot restraint) during the second day of a two-day effort to capture, repair and re-release the Syncom IV-3 communications satellite. Astronaut James D. van Hoften, standing on the Discovery's RMS arm, exposed the frame.

During super-close flybys of Saturn's rings, NASA's Cassini spacecraft inspected the mini-moons Pan and Daphnis in the A ring; Atlas at the edge of the A ring; Pandora at the edge of the F ring; and Epimetheus, which is bathed in material that fans out from the moon Enceladus. The mini-moons' diameter ranges from 5 miles (8 kilometers) for Daphnis to 72 miles (116 kilometers) for Epimetheus. The rings and the moons depicted in this illustration are not to scale. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22772

Vice President Mike Pence is seen during the National Space Council's first meeting, Thursday, Oct. 5, 2017 at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. The National Space Council, chaired by Vice President Mike Pence heard testimony from representatives from civil space, commercial space, and national security space industry representatives. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
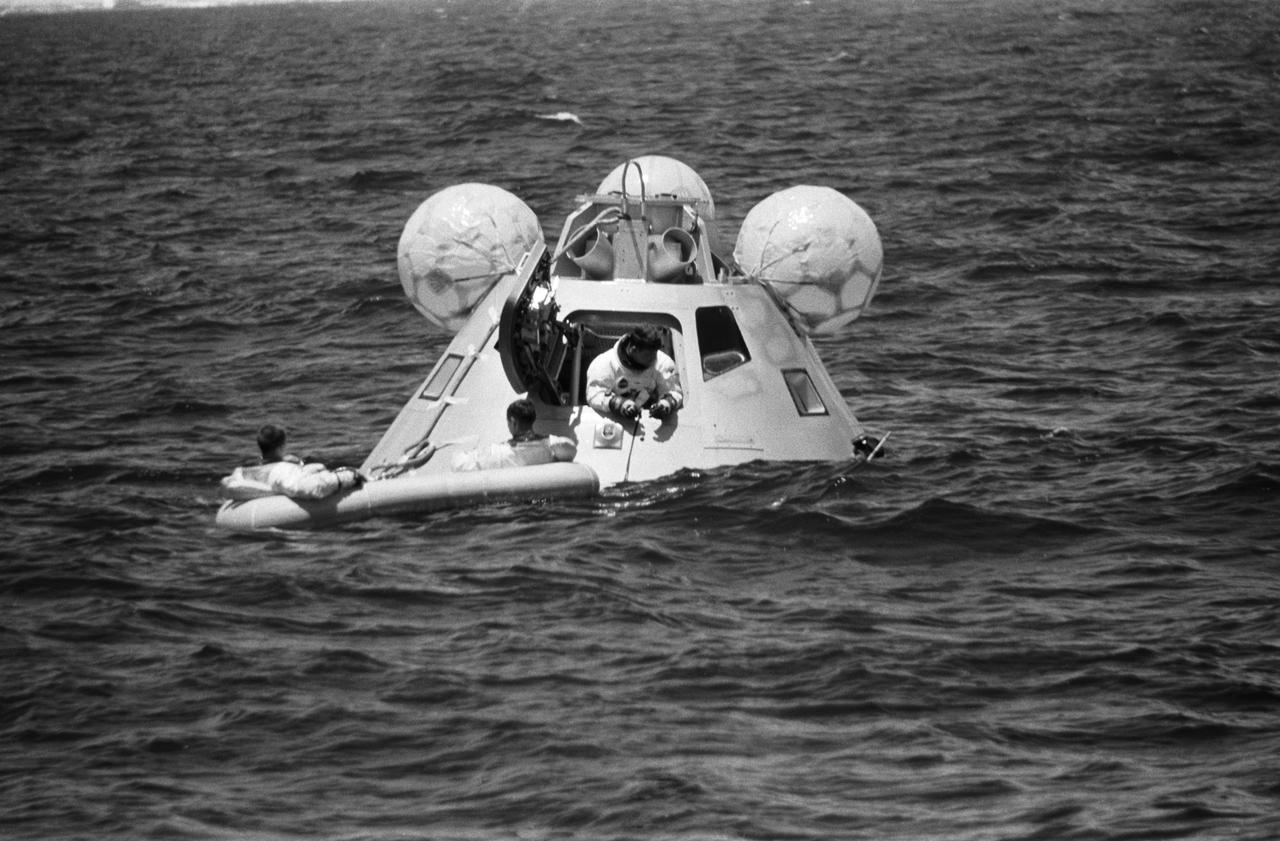

S68-42197 (5 Aug. 1968) --- The prime crew of the first manned Apollo space mission, Apollo 7, participates in water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. In hatch of the Apollo egress trainer (command module) is astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr. Sitting in life raft are astronauts Walter Cunningham (on left) and Donn F. Eisele. A team of MSC swimmers assisted with the training exercise. The inflated bags were used to upright the trainer prior to egress.
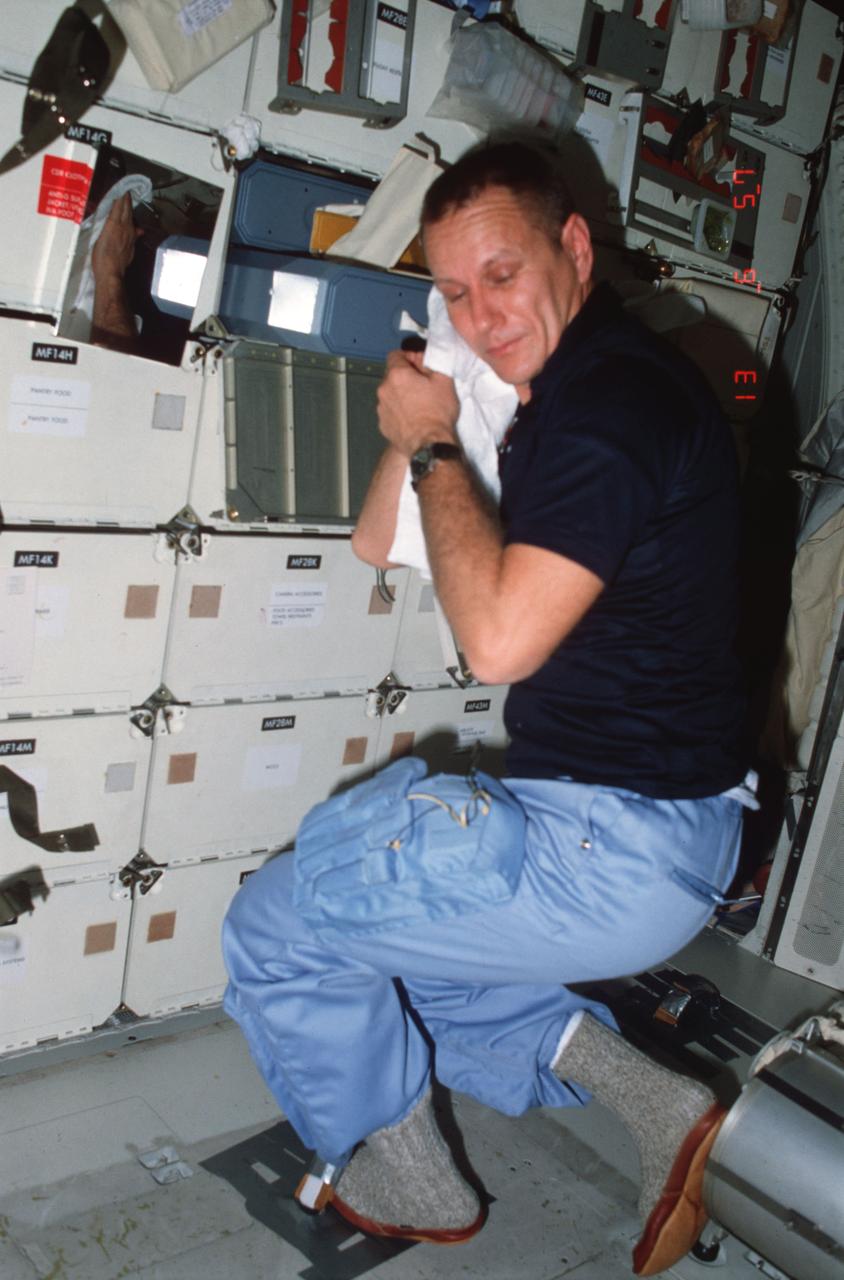

STS005-06-230 (11-16 Nov. 1982) --- On middeck, astronaut Robert F. Overmyer, STS-5 pilot, drying his face with a towel from forward single tray personal item stowage locker, completes personal hygiene activities (shaving) and demonstrates use of intravehicular activity (IVA) foot restraint on floor. Photo credit: NASA
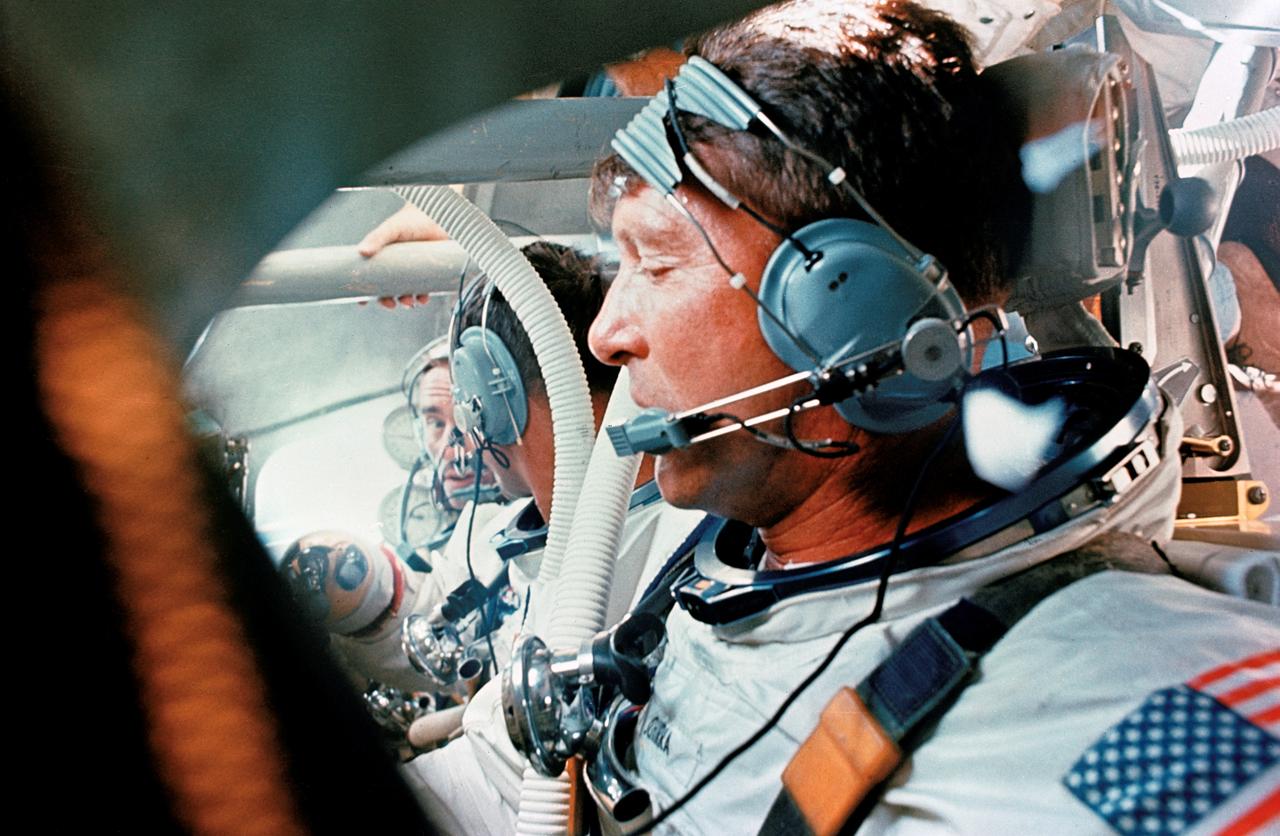

S68-46604 (5 Aug. 1968) --- The prime crew of the first manned Apollo mission (Spacecraft 101/Saturn 205) is seen in Apollo Command Module Boilerplate 1102 during water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. In foreground is astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr., in center is astronaut Donn F. Eisele, and in background is astronaut Walter Cunningham.

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, and Jeannie Schulz, widow of Peanuts gang creator Charles M. Schulz, left, are seen, Wednesday, April 5, 2023, Our Blue Planet concert at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts in Washington. Snoopy rode along as the zero gravity indicator on NASA’s Artemis I mission as part of a partnership with the agency and continues to help NASA inspire kids of all ages to follow along with Artemis missions. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)