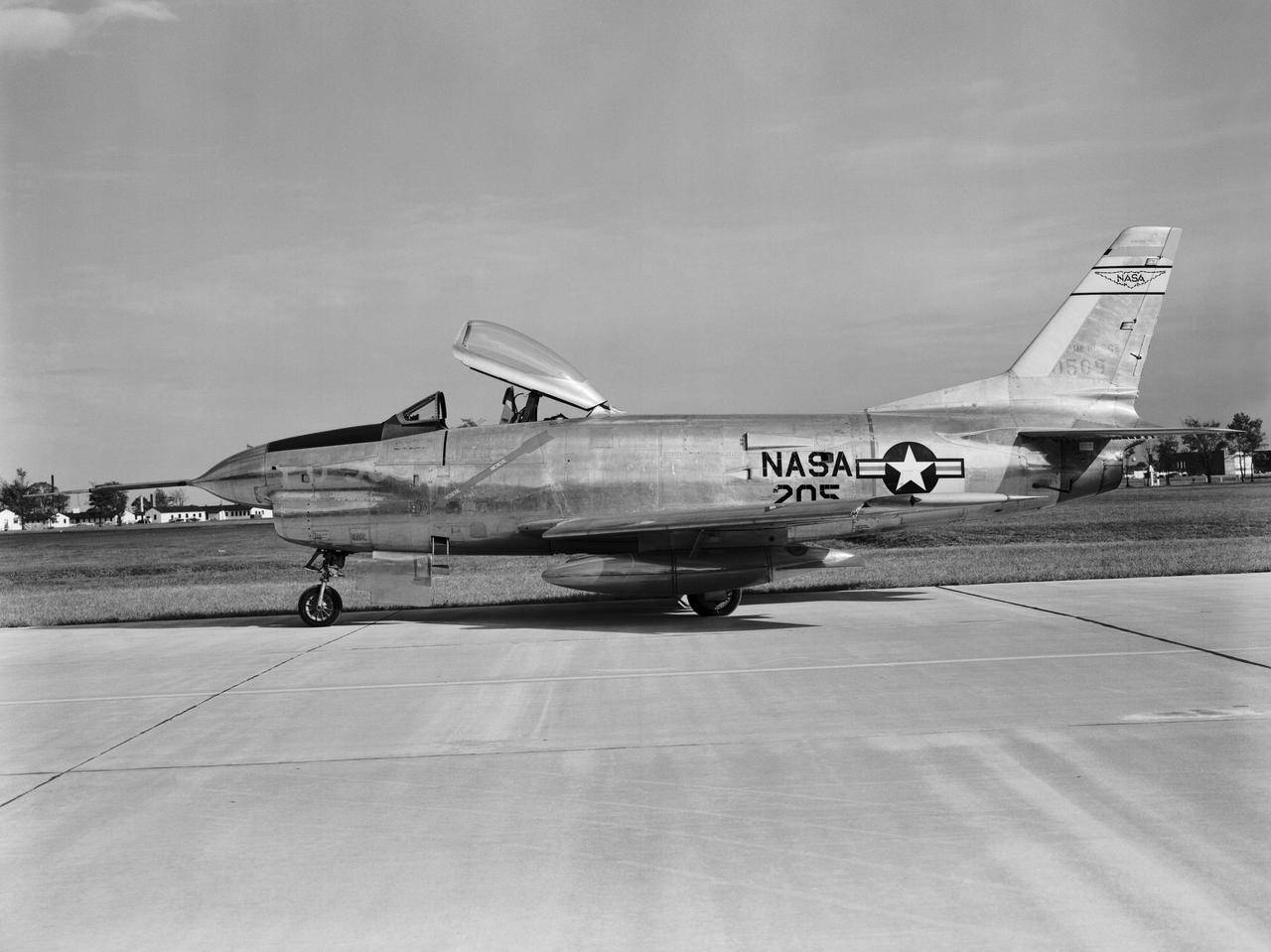

F-86 D NASA 205
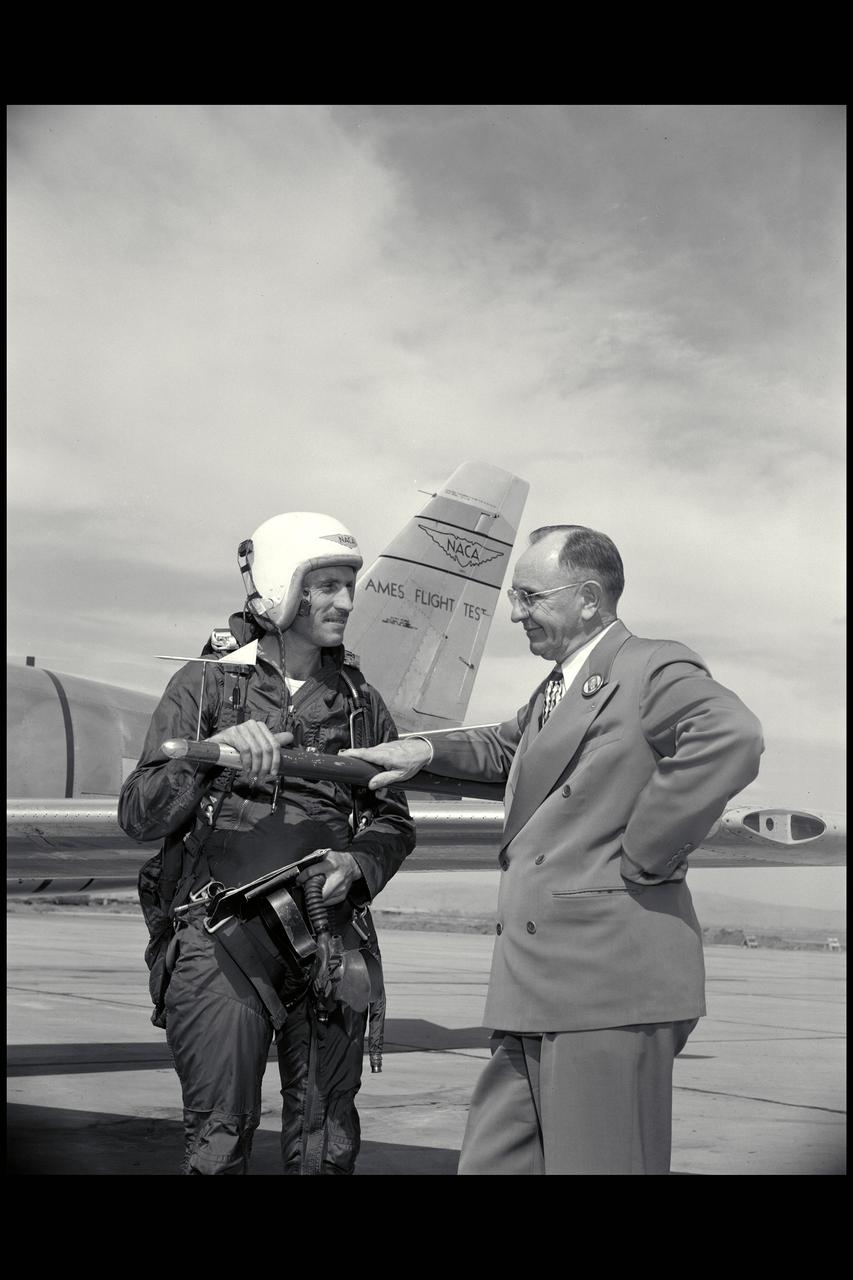

Ames Pilot George Cooper (l) and Ames Director Smith DeFrance discuss F-86 flight test
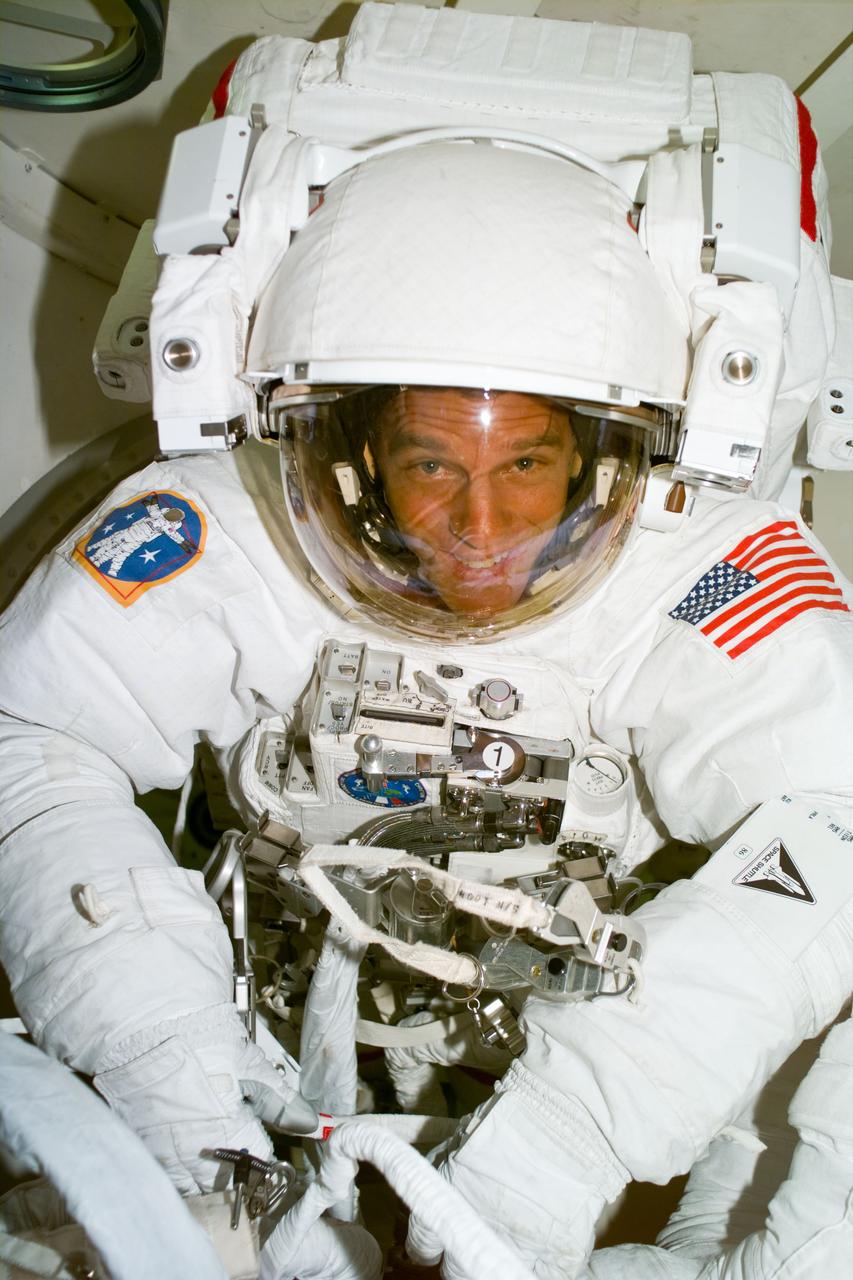

STS086E5383 (1 Oct. 1997) --- This still photo shows Scott F. Parazynski, mission specialist, still suited up after performing an Extravehicular Activity during the STS-86 mission. Parazynski was joined in the EVA by Vladimir G. Titov, mission specialist representing the Russian Space Agency (RSA), out of frame. It was the first U.S. vehicle-based spacewalk involving an international astronaut. The view was captured at 23:11:05 GMT on October 1, 1997.

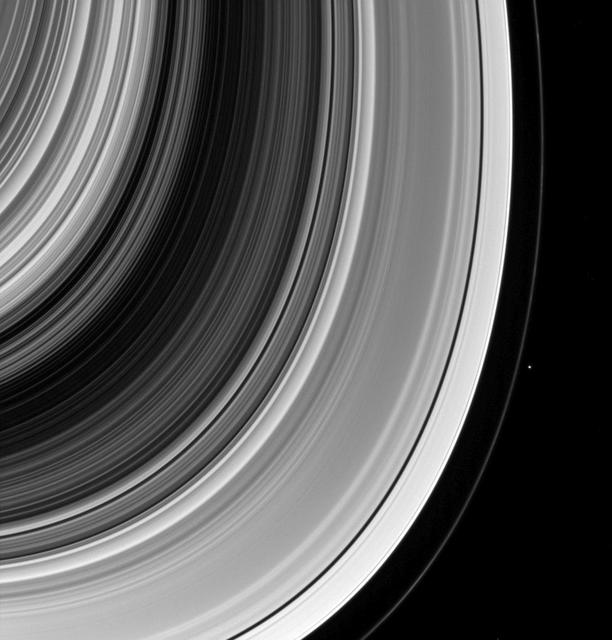
Saturn's moon Prometheus, seen here looking suspiciously blade-like, is captured near some of its sculpting in the F ring. Prometheus' (53 miles or 86 kilometers across) orbit sometimes takes it into the F ring. When it enters the ring, it leaves a gore where its gravitational influence clears out some of the smaller ring particles. Below Prometheus, the dark lanes interior to the F ring's bright core provide examples of previous ring-moon interactions. This view looks toward the unilluminated side of the rings from about 7 degrees below the ring plane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on March 15, 2015. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 286,000 miles (461,000 kilometers) from Saturn and at a Sun-Saturn-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 115 degrees. Image scale is 1.7 miles (2.8 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18324

The F ring shepherd Pandora is captured here by NASA Cassini spacecraft along with other well-known examples of Saturn moons shaping the rings. From the narrow F ring, to the gaps in the A ring, to the Cassini Division, Saturn's rings are a masterpiece of gravitational sculpting by the moons. Pandora (50 miles, or 81 kilometers across), along with its fellow shepherd Prometheus (53 miles, or 86 kilometers across), helps confine the F ring and keep it from spreading. This view looks toward the unilluminated side of the rings from about 31 degrees below the ringplane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft wide-angle camera on March 8, 2014. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 533,000 miles (858,000 kilometers) from Saturn and at a Sun-Saturn-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 63 degrees. Image scale is 32 miles (51 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18271

Seen by NASA Cassini spacecraft within the vast expanse of Saturn rings, Prometheus appears as little more than a dot. But that little moon still manages to shape the F ring, confining it to its narrow domain. Prometheus (53 miles, or 86 kilometers across) and its fellow moon Pandora (50 miles, or 81 kilometers across) orbit beside the F ring and keep the ring from spreading outward through a process dubbed "shepherding." This view looks toward the unilluminated side of the rings from about 45 degrees below the ringplane. The image was taken in green light with the Cassini spacecraft wide-angle camera on March 8, 2014. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 533,000 miles (858,000 kilometers) from Prometheus and at a Sun-Prometheus-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 90 degrees. Image scale is 32 miles (51 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18272
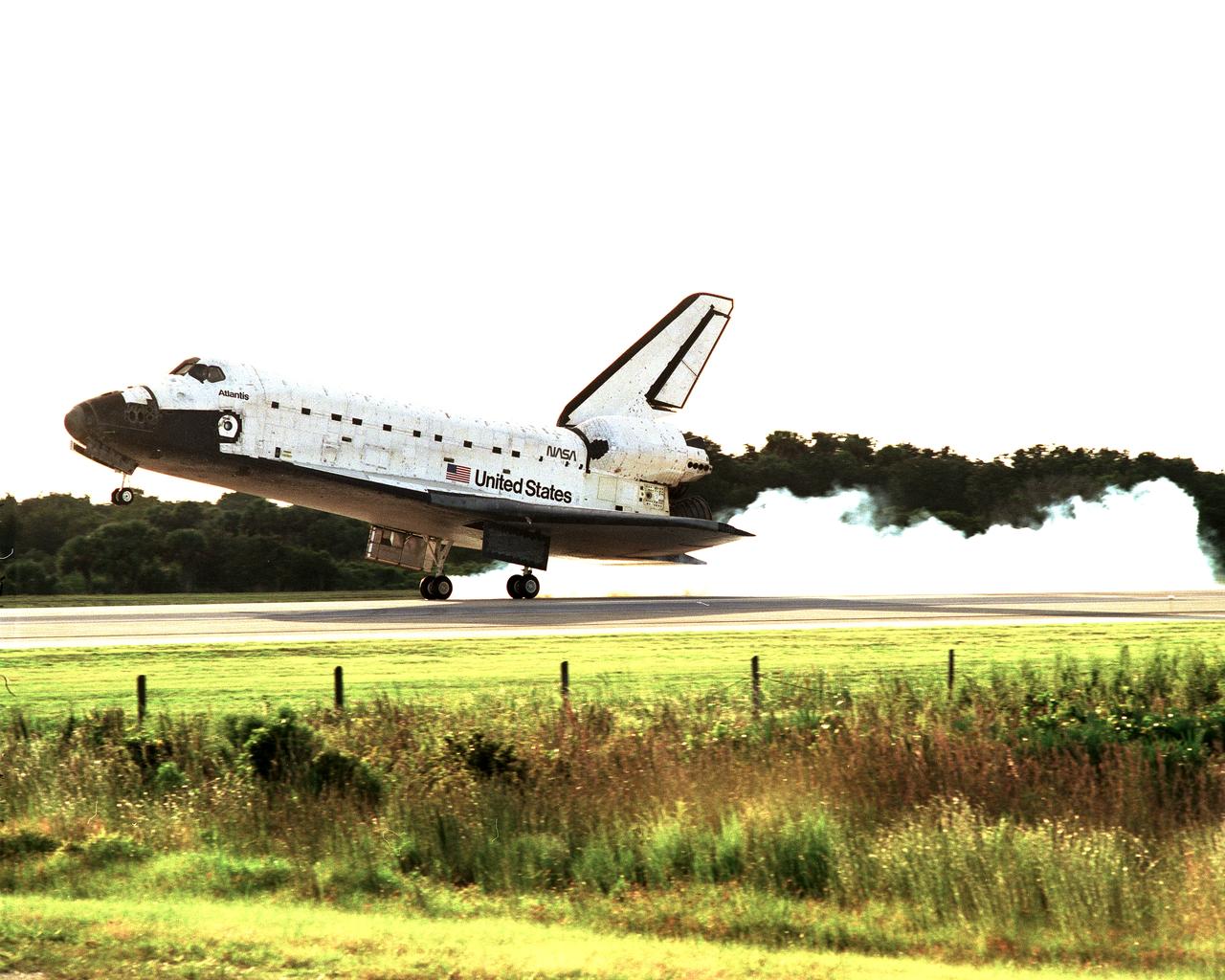

STS086-S-015 (6 Oct 1997) --- The main landing gear of the Space Shuttle Atlantis touches down on the Kennedy Space Center?s (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility to complete the STS-86 mission. Touchdown occurred at 5:55:09 p.m. (EDT), October 6, 1997. Onboard were astronauts James D. Wetherbee, Michael J. Bloomfield, Wendy B. Lawrence, Scott F. Parazynski, Vladimir G. Titov, C. Michael Foale and Jean-Loup J. M. Chretien. Chretien and Titov represent the French Space Agency (CNES) and the Russian Space Agency (RSA), respectively.
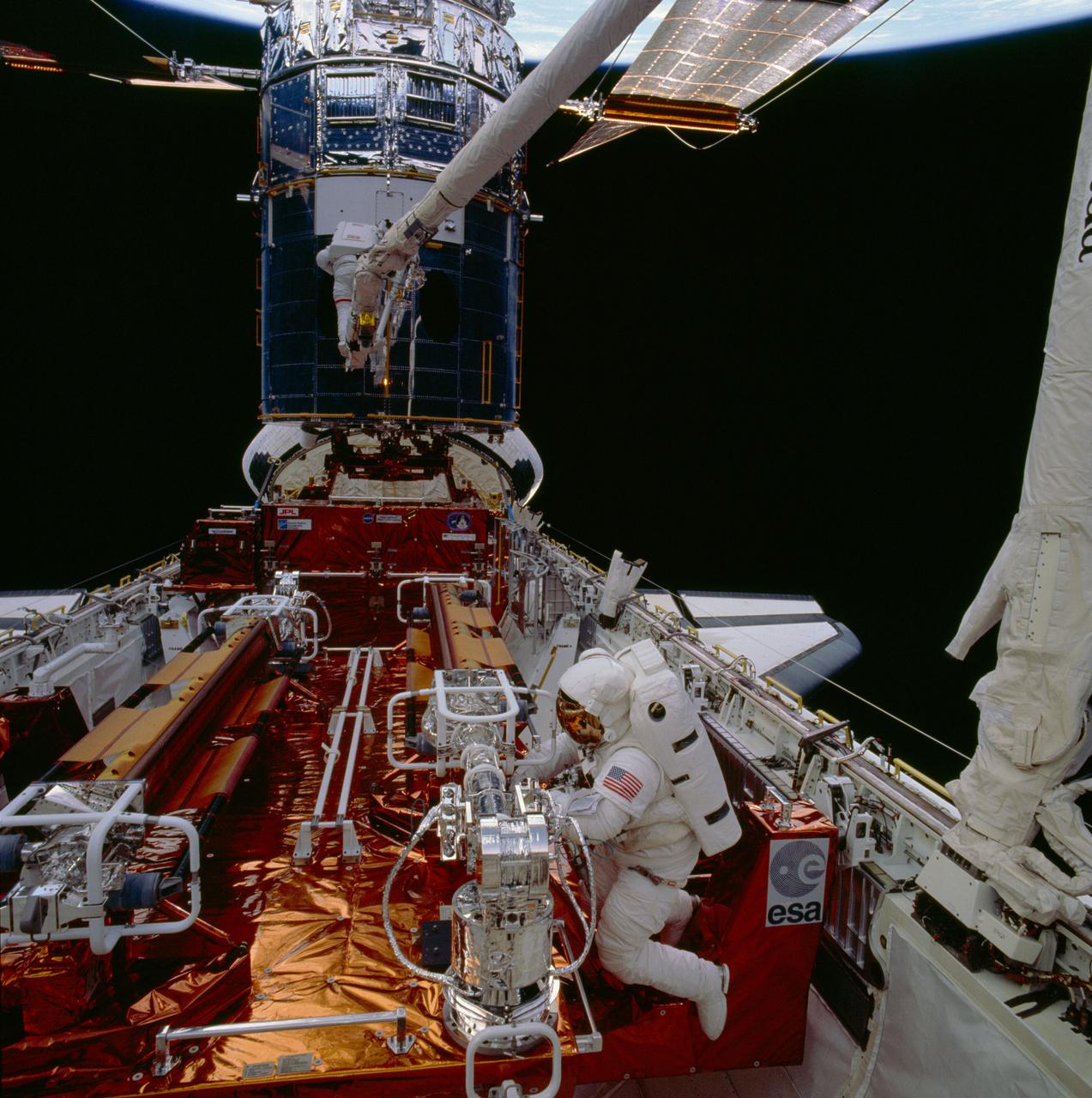
STS061-86-048 (5 Dec 1993) --- Astronauts F. Story Musgrave (foreground) and Jeffrey A. Hoffman are pictured near the end of the first of five extravehicular activity?s (EVA). Musgrave works at the Solar Array Carrier (SAC) in the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cargo bay. Hoffman, anchored to a foot restraint mounted on the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, waits to be maneuvered to the forward payload bay. The original solar array panels are partially visible at top, while their replacements remain stowed in foreground. The crew's second pair of space walkers -- astronauts Kathryn C. Thornton and Thomas D. Akers -- later changed the solar arrays on the mission's second EVA.
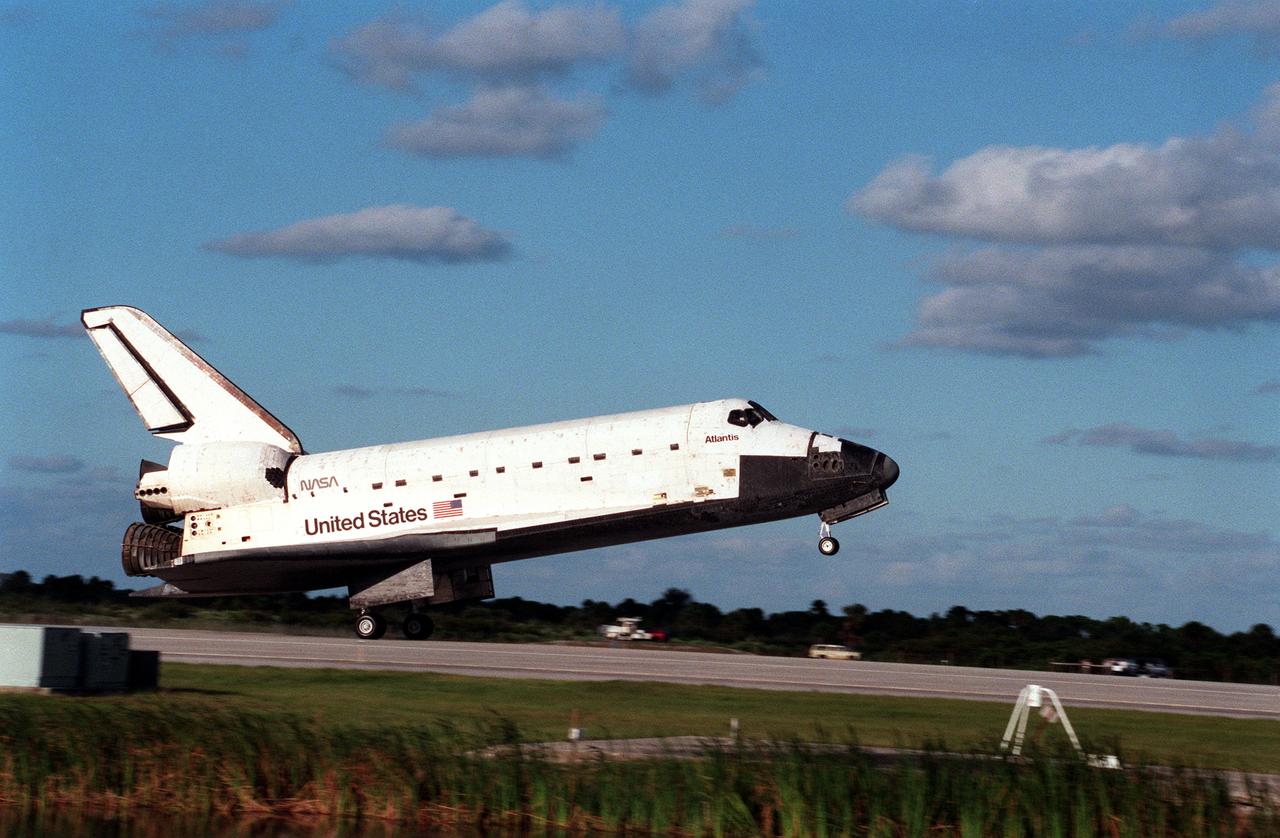

STS086-S-014 (6 Oct 1997) --- The main landing gear of the Space Shuttle Atlantis is about to touch down on the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility to complete the STS-86 mission. Touchdown occurred at 5:55:09 p.m. (EDT), October 6, 1997. Onboard were astronauts James D. Wetherbee, Michael J. Bloomfield, Wendy B. Lawrence, Scott F. Parazynski, Vladimir G. Titov, C. Michael Foale and Jean-Loup J. M. Chretien. Chretien and Titov represent the French Space Agency (CNES) and the Russian Space Agency (RSA), respectively.
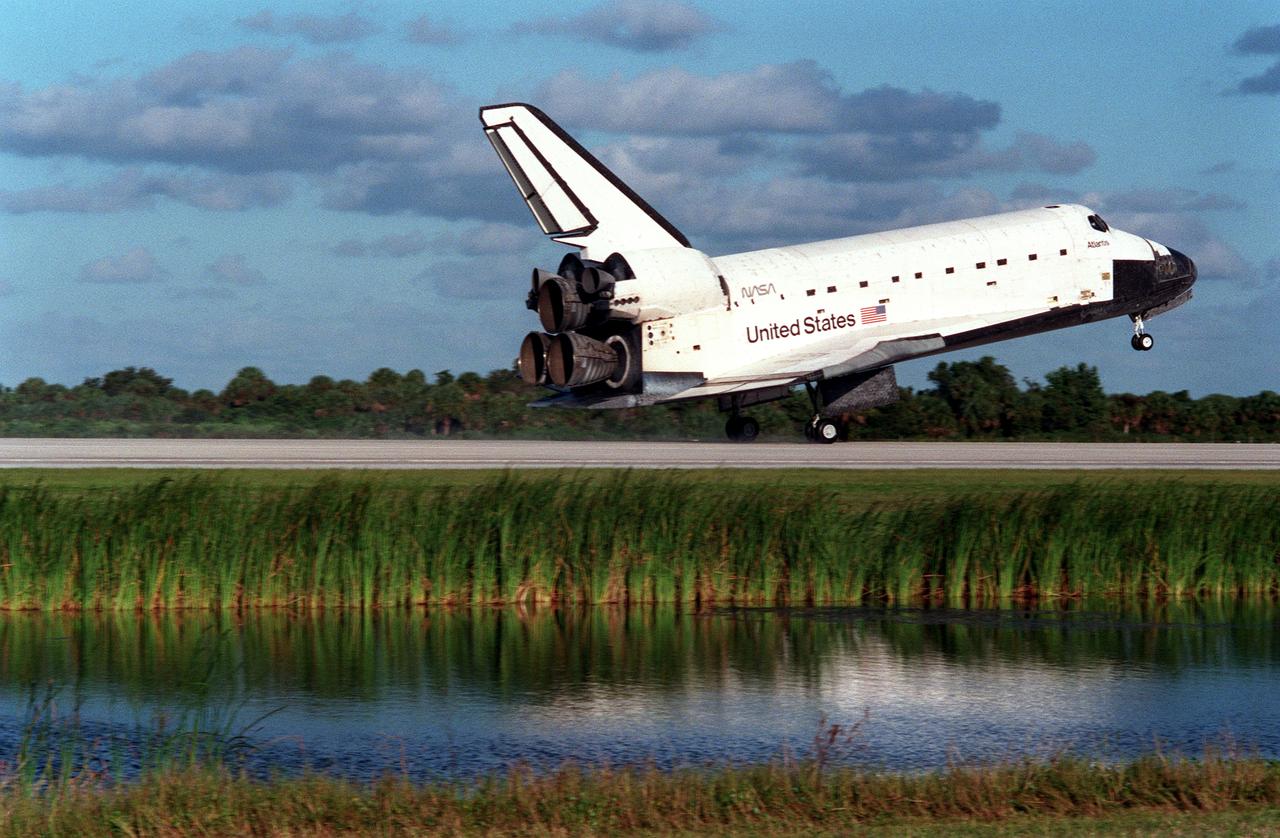

STS086-S-013 (6 Oct 1997) --- The main landing gear of the Space Shuttle Atlantis is about to touch down on the Kennedy Space Center?s (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility to complete the STS-86 mission. Touchdown occurred at 5:55:09 p.m. (EDT), October 6, 1997. Onboard were astronauts James D. Wetherbee, Michael J. Bloomfield, Wendy B. Lawrence, Scott F. Parazynski, Vladimir G. Titov, C. Michael Foale and Jean-Loup J. M. Chretien. Chretien and Titov represent the French Space Agency (CNES) and the Russian Space Agency (RSA), respectively.
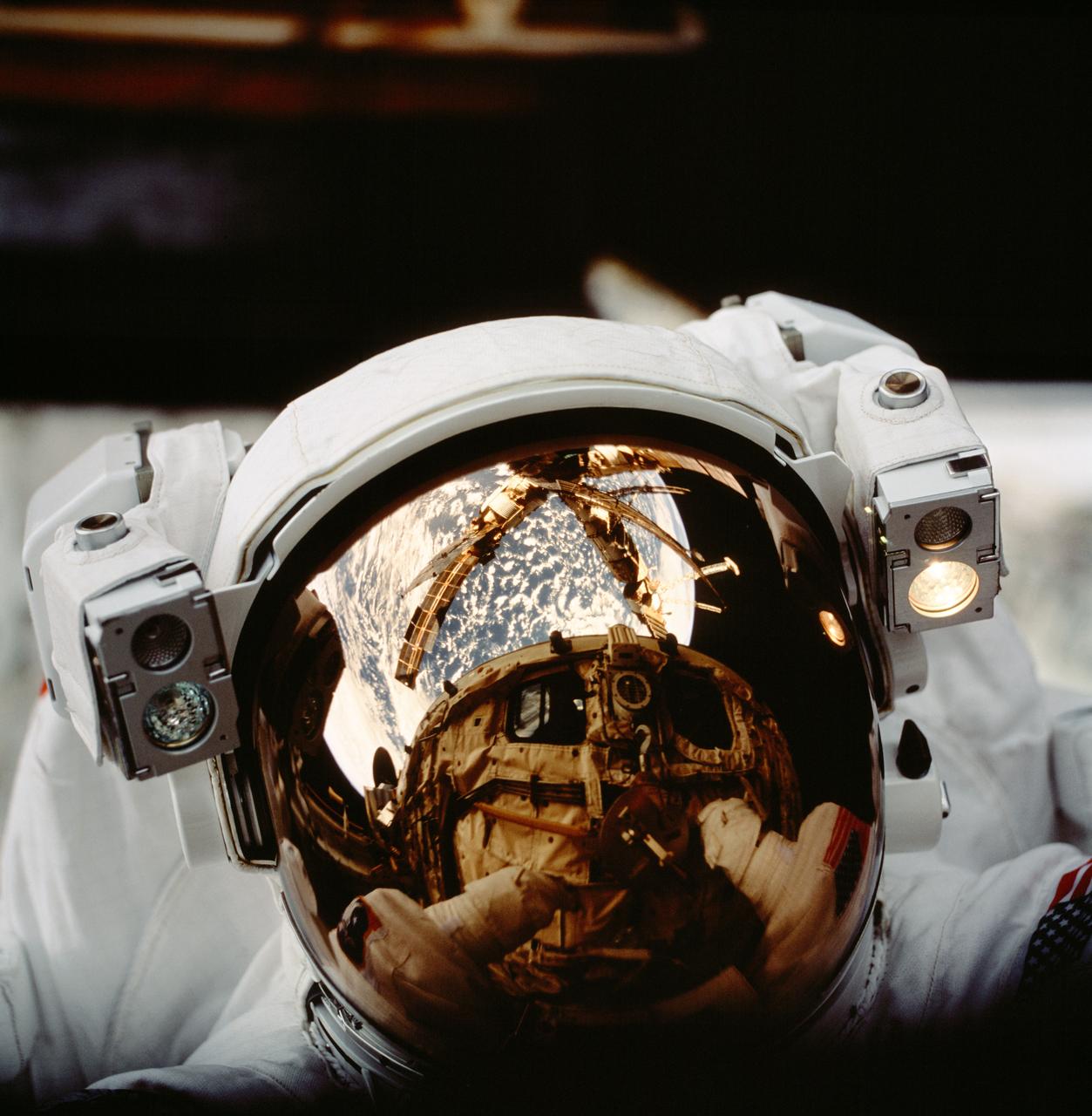

STS086-729-076 (25 Sept-6 Oct. 1997) --- The helmet visor of astronaut Scott F. Parazynski reflects the space shuttle Atlantis’ cargo bay and Russia’s Mir Space Station as well as Earth’s horizon. Astronauts Parazynski and Vladimir G. Titov, both STS-86 mission specialists, spent several hours retrieving Mir Environmental Effects Packages (MEEP) which had been exposed to the space environment around Mir’s permanent Docking Module (DM) since September of 1996. Titov is representing the Russian Space Agency (RSA). Photo credit: NASA
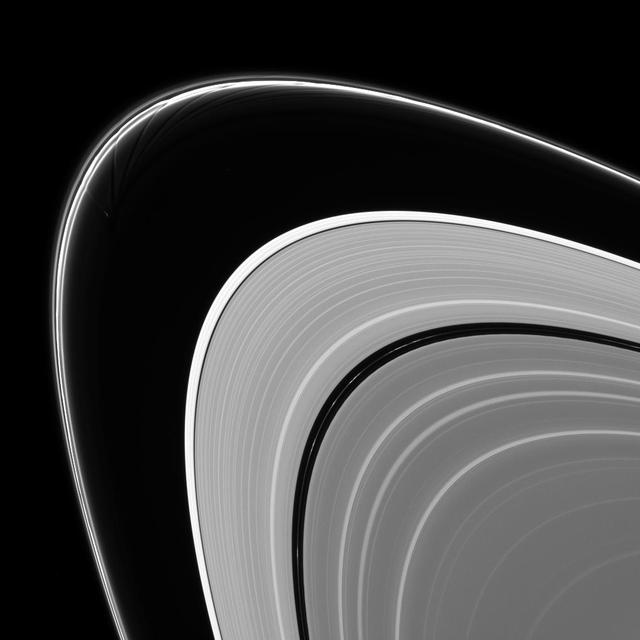
Prometheus is caught in the act of creating gores and streamers in the F ring. Scientists believe that Prometheus and its partner-moon Pandora are responsible for much of the structure in the F ring as shown by NASA Cassini spacecraft. The orbit of Prometheus (53 miles, or 86 kilometers across) regularly brings it into the F ring. When this happens, it creates gores, or channels, in the ring where it entered. Prometheus then draws ring material with it as it exits the ring, leaving streamers in its wake. This process creates the pattern of structures seen in this image. This process is described in detail, along with a movie of Prometheus creating one of the streamer/channel features, in PIA08397. This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 8.6 degrees above the ringplane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on Feb. 11, 2014. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 1.3 million miles (2.1 million kilometers) from Saturn and at a Sun-Saturn-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 147 degrees. Image scale is 8 miles (13 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18270
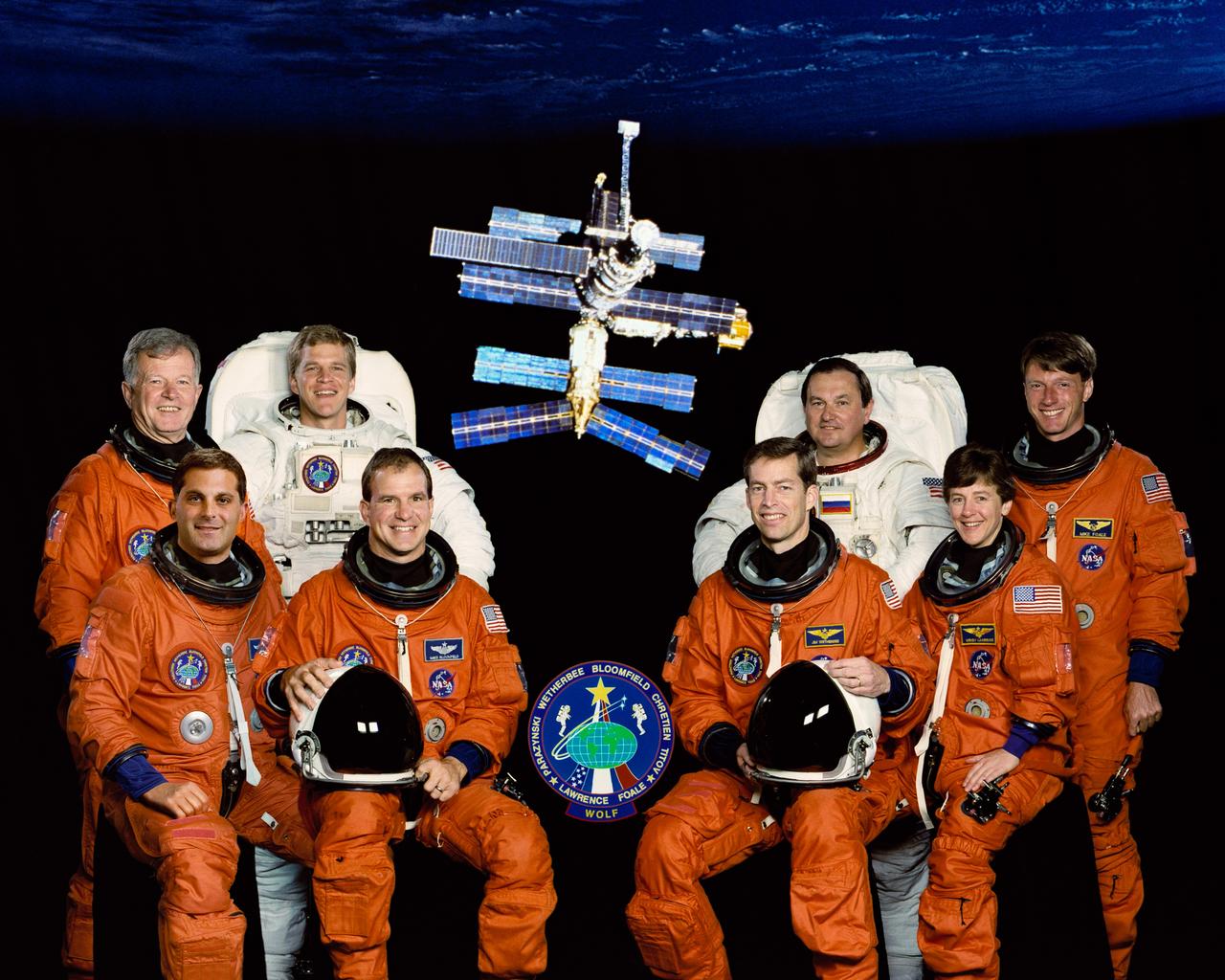

STS086-S-002 (May 1997) --- These eight astronauts have been assigned as the crew for the STS-86 mission, scheduled for a September 1997 launch and visit to Russia's Mir space station. Wearing the partial pressure launch and entry suits are, from the left, Jean-Loup J.M. Chretien, mission specialist; David A. Wolf, mission specialist; Michael J. Bloomfield, pilot; James D. Wetherbee, mission commander; and Wendy B. Lawrence and C. Michael Foale, both mission specialists. Wearing the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) space suits are Scott F. Parazynski (left) and Vladimir G. Titov, both mission specialists. Chretien and Titov are international mission specialists, representing the French Space Agency (CNES) and Russian Space Agency (RSA), respectively.
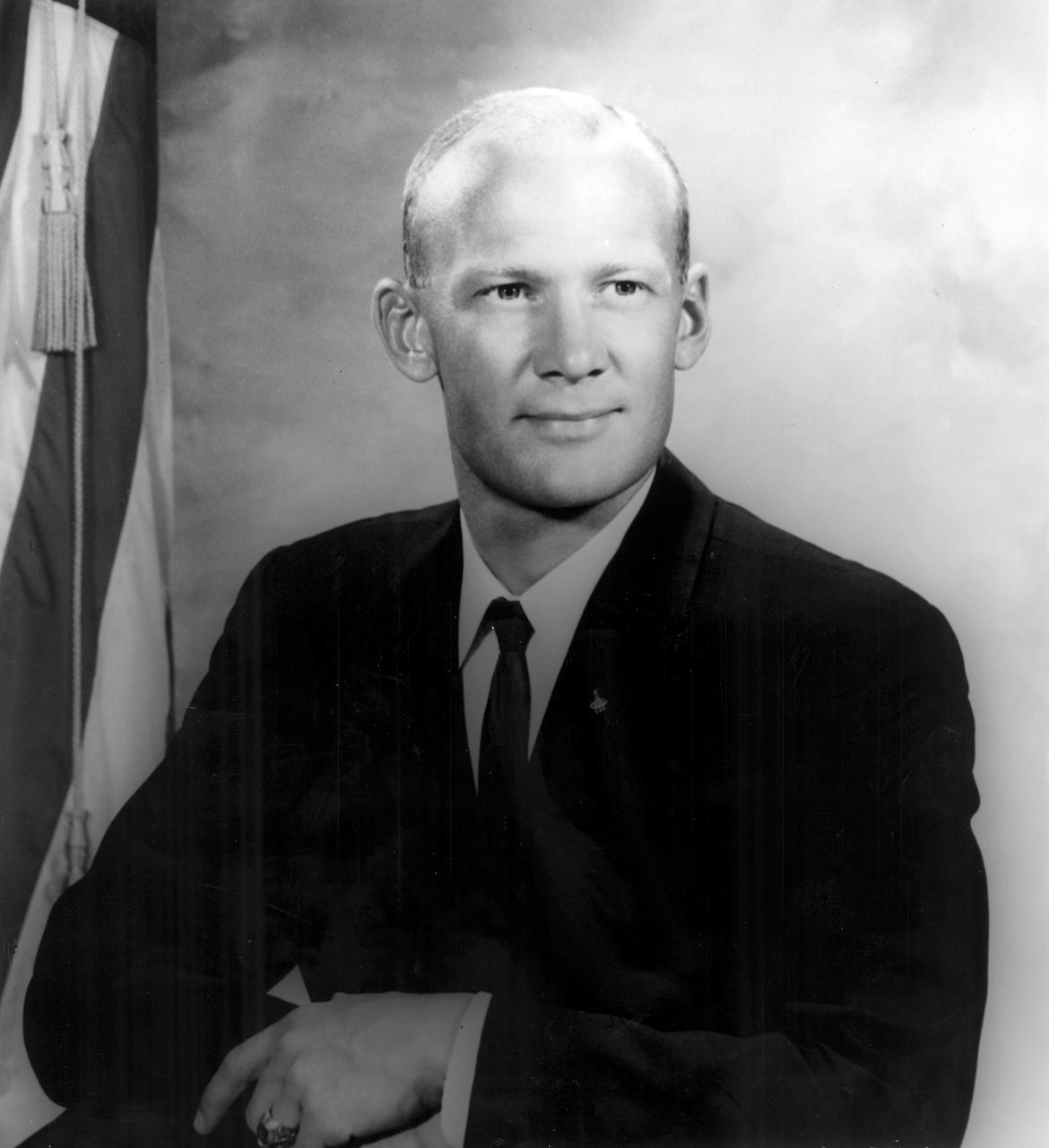

This is the official NASA portrait of astronaut Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin. Prior to joining NASA, Aldrin flew 66 combat missions in F-86s while on duty in Korea. At Nellis Air Force Base, Nevada, he served as an aerial gunnery instructor. Following his assignment as aide to the dean of faculty at the Air Force Academy, Aldrin flew F-100s as a flight commander at Bitburg, Germany. Aldrin was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963 and has logged 289 hours and 53 minutes in space, of which, 7 hours and 52 minutes were spent in Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA). On November 11, 1966, he launched into space aboard the Gemini 12 spacecraft on a 4-day flight, which brought the Gemini program to a successful close. During that mission, Aldrin established a new record for EVA, spending 5-1/2 hours outside the spacecraft. July 16-24, 1969, Aldrin served as lunar module pilot for Apollo 11, the first manned lunar landing mission. Aldrin followed Neil Armstrong onto the lunar surface on July 20, 1969, completing a 2-hour and 15 minute lunar EVA. Aldrin resigned from NASA in July 1971.
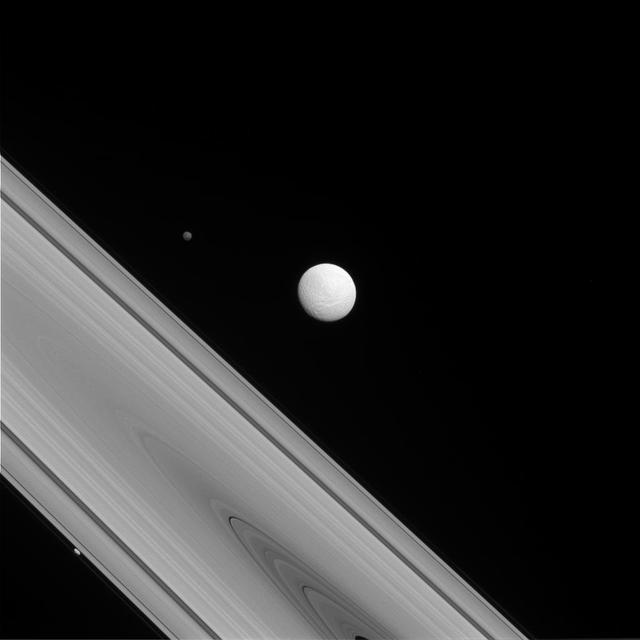

The Cassini spacecraft captures a rare family photo of three of Saturn's moons that couldn't be more different from each other! As the largest of the three, Tethys (image center) is round and has a variety of terrains across its surface. Meanwhile, Hyperion (to the upper-left of Tethys) is the "wild one" with a chaotic spin and Prometheus (lower-left) is a tiny moon that busies itself sculpting the F ring. To learn more about the surface of Tethys (660 miles, or 1,062 kilometers across), see PIA17164 More on the chaotic spin of Hyperion (168 miles, or 270 kilometers across) can be found at PIA07683 And discover more about the role of Prometheus (53 miles, or 86 kilometers across) in shaping the F ring in PIA12786. This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 1 degree above the ringplane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on July 14, 2014. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 1.2 million miles (1.9 million kilometers) from Tethys and at a Sun-Tethys-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 22 degrees. Image scale is 7 miles (11 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18283
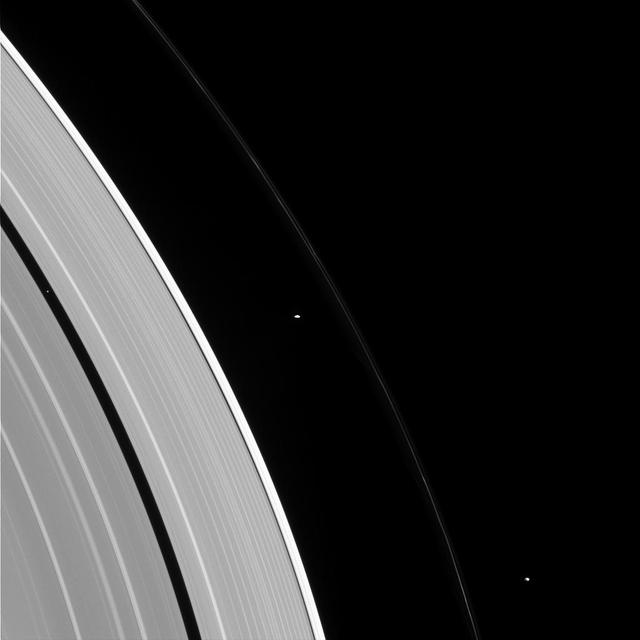

People with similar jobs or interests hold conventions and meetings, so why shouldn't moons? Pandora, Prometheus, and Pan -- seen here, from right to left -- also appear to be holding some sort of convention in this image. Some moons control the structure of nearby rings via gravitational "tugs." The cumulative effect of the moon's tugs on the ring particles can keep the rings' edges from spreading out as they are naturally inclined to do, much like shepherds control their flock. Pan is a prototypical shepherding moon, shaping and controlling the locations of the inner and outer edges of the Encke gap through a mechanism suggested in 1978 to explain the narrow Uranian rings. However, though Prometheus and Pandora have historically been called "the F ring shepherd moons" due to their close proximity to the ring, it has long been known that the standard shepherding mechanism that works so well for Pan does not apply to these two moons. The mechanism for keeping the F ring narrow, and the roles played -- if at all -- by Prometheus and Pandora in the F ring's configuration are not well understood. This is an ongoing topic for study by Cassini scientists. This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 29 degrees above the ringplane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on Jan. 2, 2015. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 1.6 million miles (2.6 million kilometers) from the rings and at a Sun-ring-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 86 degrees. Image scale is 10 miles (15 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/pia18306
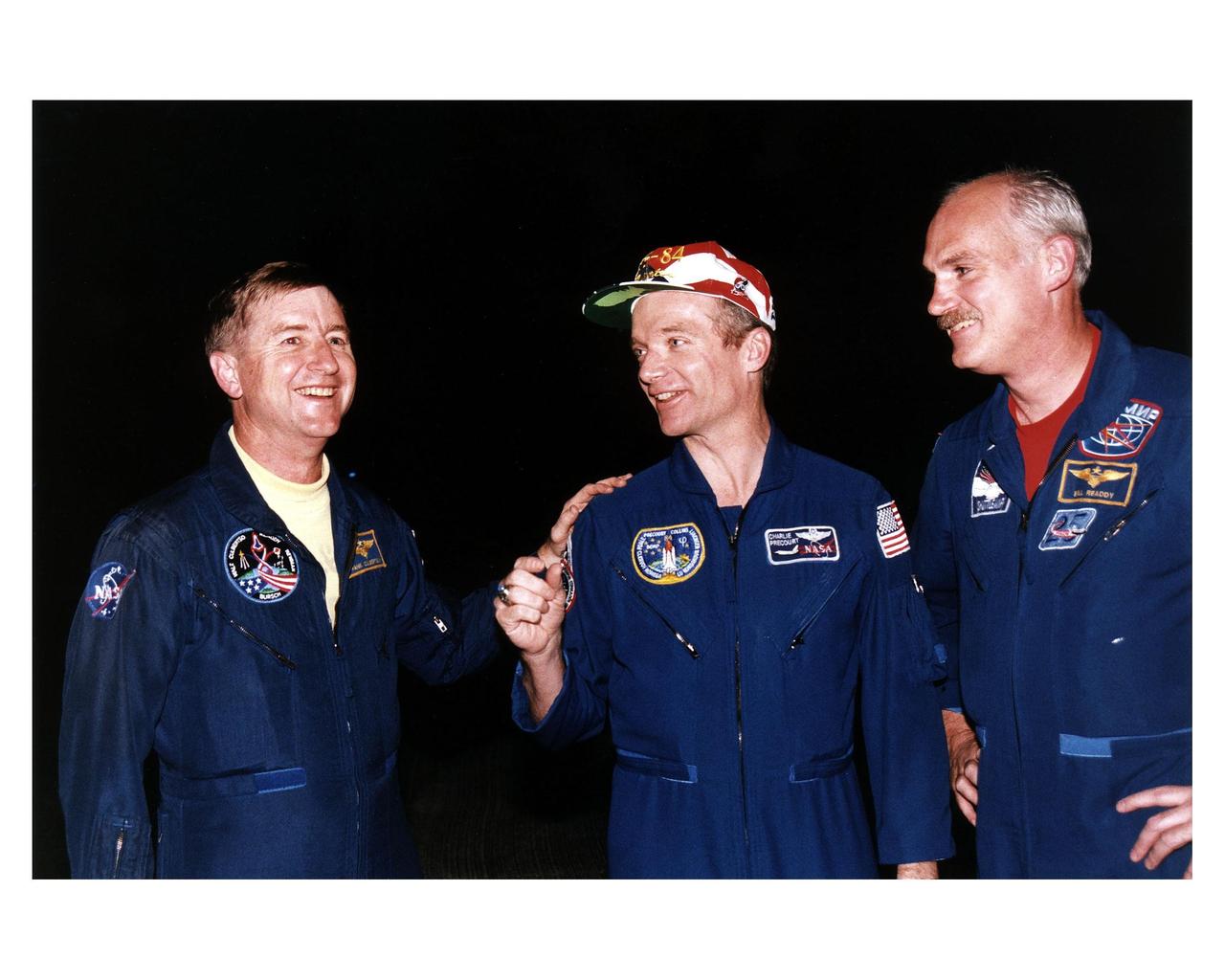

STS-84 Commander Charles J. Precourt talks with fellow astronauts Frank Culbertson, at left, and William F. Readdy after their arrival at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facilty. Culbertson, NASA director of the Phase One Program of the International Space Station, and Readdy, manager, program development, in the Space Shuttle Program Office at Johnson Space Center, were the pilots of T-38 jets which brought STS-84 crew members to KSC for the launch. Culbertson’s passenger was STS-84 Mission Specialist Carlos I. Noriega; Readdy’s passenger was Mission Specialist C. Michael Foale. Liftoff of Space Shuttle Mission STS-84 is scheduled May 15. STS-84 will be the sixth docking of the Space Shuttle with the Russian Space Station Mir. During the docking, Foale will transfer to the Russian space station to become a member of the Mir 23 crew, replacing U.S. astronaut Jerry M. Linenger, who will return to Earth on Atlantis. Foale is scheduled to remain on Mir about four months until his replacement arrives on STS-86 in September
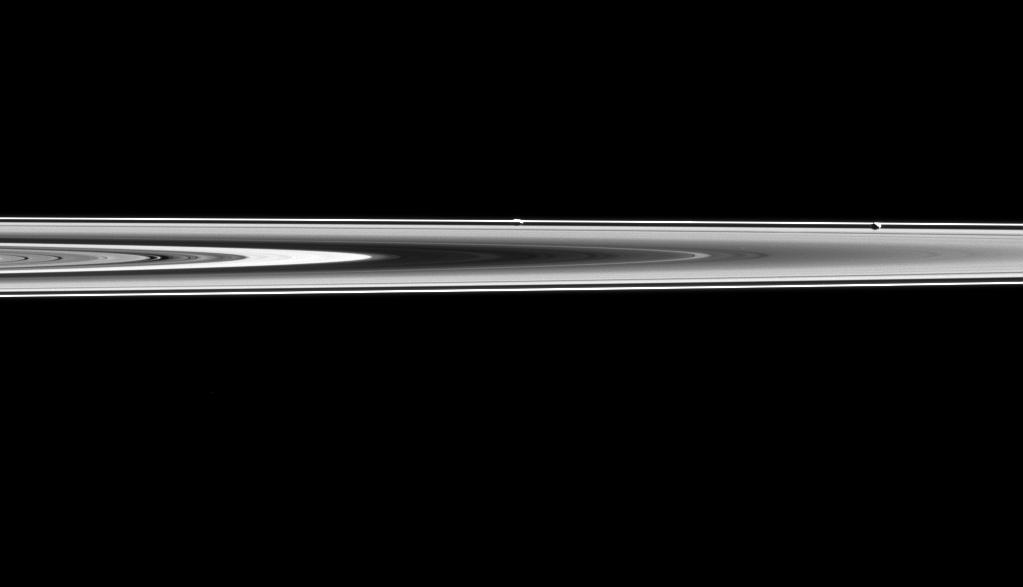

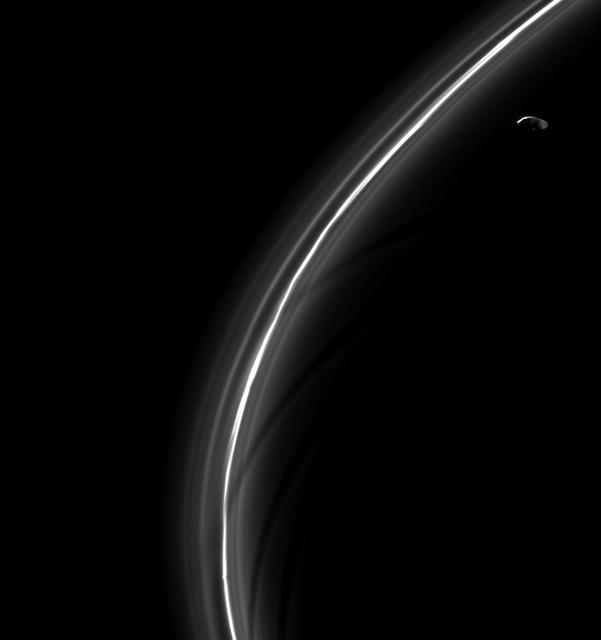
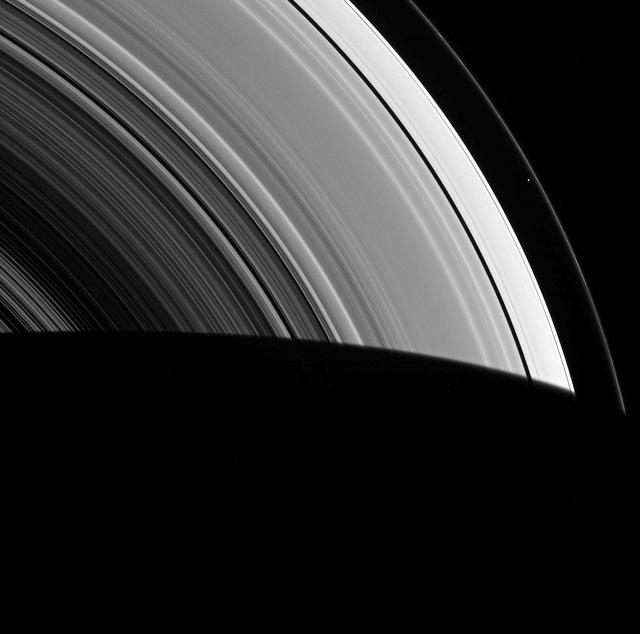
Prometheus and Pandora are almost hidden in Saturn's rings in this image. Prometheus (53 miles or 86 kilometers across) and Pandora (50 miles or 81 kilometers across) orbit along side Saturn's narrow F ring, which is shaped, in part, by their gravitational influences help to shape that ring. Their proximity to the rings also means that they often lie on the same line of sight as the rings, sometimes making them difficult to spot. In this image, Prometheus is the left most moon in the ring plane, roughly in the center of the image. Pandora is towards the right. This view looks toward the unilluminated side of the rings from about 0.3 degrees below the ring plane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on May 6, 2015. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 994,000 miles (1.6 million kilometers) from Prometheus and at a Sun-Prometheus-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 106 degrees. Image scale is 6 miles (10 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18334
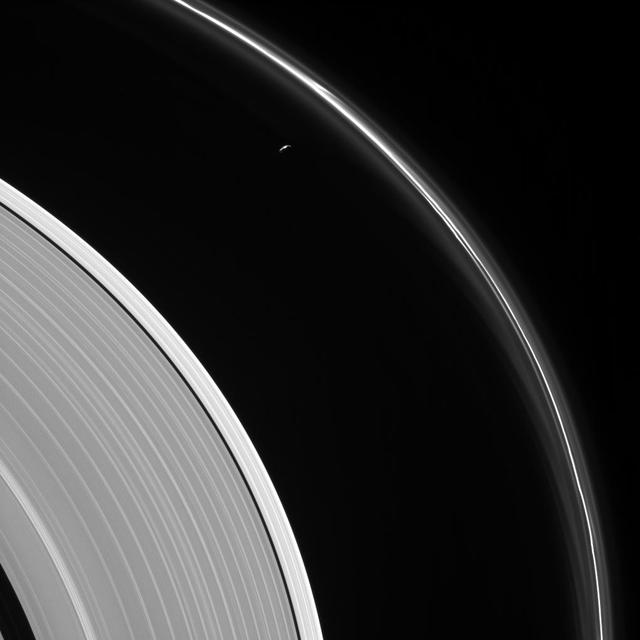

The thin sliver of Saturn's moon Prometheus lurks near ghostly structures in Saturn's narrow F ring in this view from NASA's Cassini spacecraft. Many of the narrow ring's faint and wispy features result from its gravitational interactions with Prometheus (86 kilometers, or 53 miles across). Most of the small moon's surface is in darkness due to the viewing geometry here. Cassini was positioned behind Saturn and Prometheus with respect to the sun, looking toward the moon's dark side and just a bit of the moon's sunlit northern hemisphere. Also visible here is a distinct difference in brightness between the outermost section of Saturn's A ring (left of center) and rest of the ring, interior to the Keeler Gap (lower left). This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 13 degrees above the ring plane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on May 13, 2017. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 680,000 miles (1.1 million kilometers) from Saturn. Image scale is 4 miles (6 kilometers) per pixel. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21340
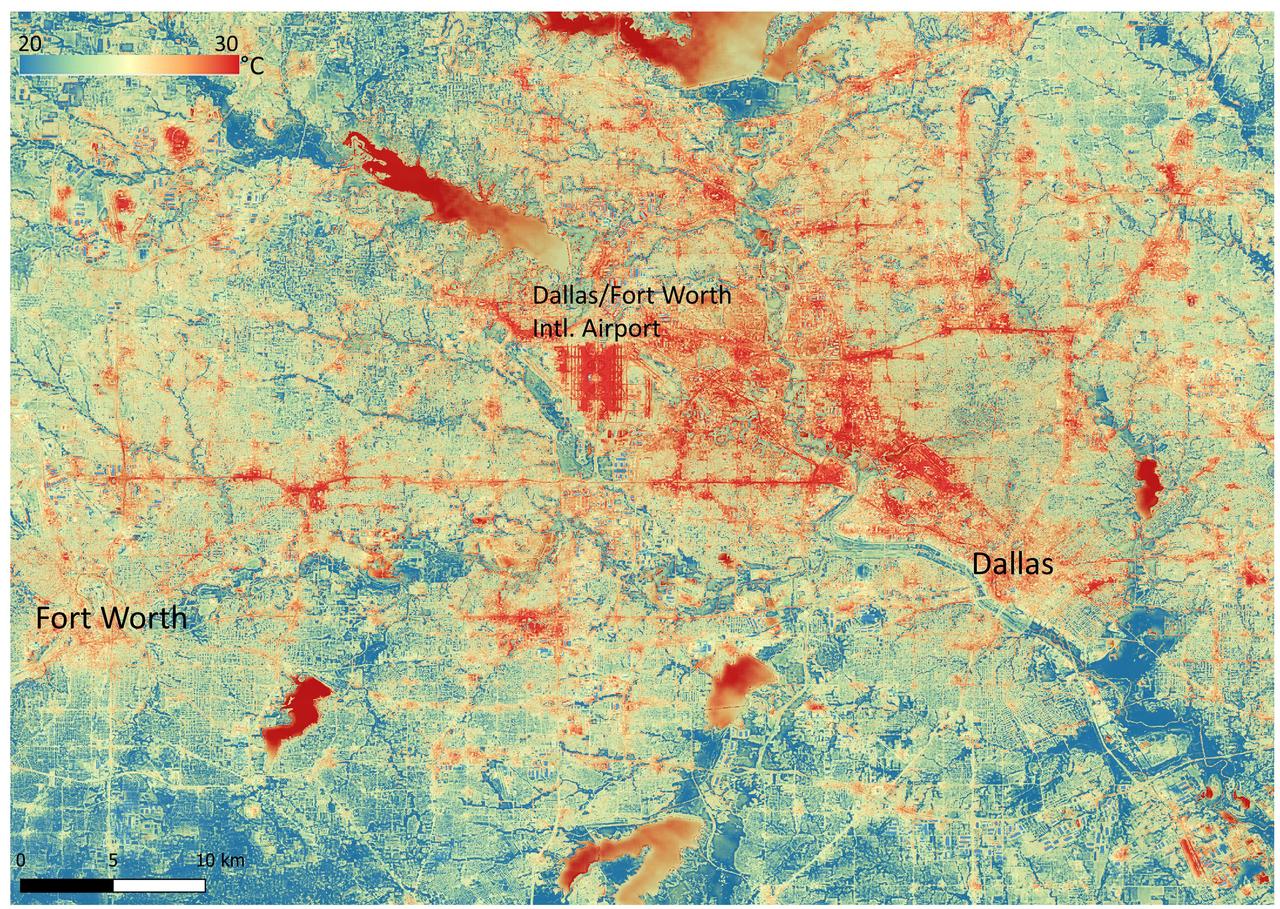
NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station (ECOSTRESS) instrument recorded this image of ground surface temperatures in Dallas and Fort Worth, Texas, on June 20, 2022, at 7:17 a.m. Central Daylight Time. Even early in the day, manmade urban surfaces near city centers and transportation networks – streets, roads, and highways shown in red and orange – are warmer than the outskirts by up to 18 degrees Fahrenheit (10 degrees Celsius). The paved surfaces at Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport, shown in red near the top-center of the image, had the warmest temperatures, exceeding 86 F (30 C). Natural land surfaces such as vegetation and streams in rural areas, shown in green and blue, are cooler than nearby large bodies of water, shown in red and yellow, that tend to retain more heat overnight due to their higher heat capacity. Cities are usually warmer than open land because of human activities and the materials used in building and construction. Streets are often the hottest part of the built environment due to asphalt paving. Dark-colored surfaces absorb more heat from the Sun than lighter-colored ones; asphalt absorbs up to 95% of solar radiation and retains the heat for hours into the nighttime. ECOSTRESS measures the temperature of the ground, which is hotter than the air temperature during the daytime. The instrument launched to the space station in 2018. Its primary mission is to identify plants' thresholds for water use and water stress, giving insight into their ability to adapt to a warming climate. However, ECOSTRESS is also useful for documenting other heat-related phenomena, like patterns of heat absorption and retention. Its high-resolution images, with a pixel size of about 225 feet (70 meters) by 125 feet (38 meters), are a powerful tool for understanding our environment. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25422
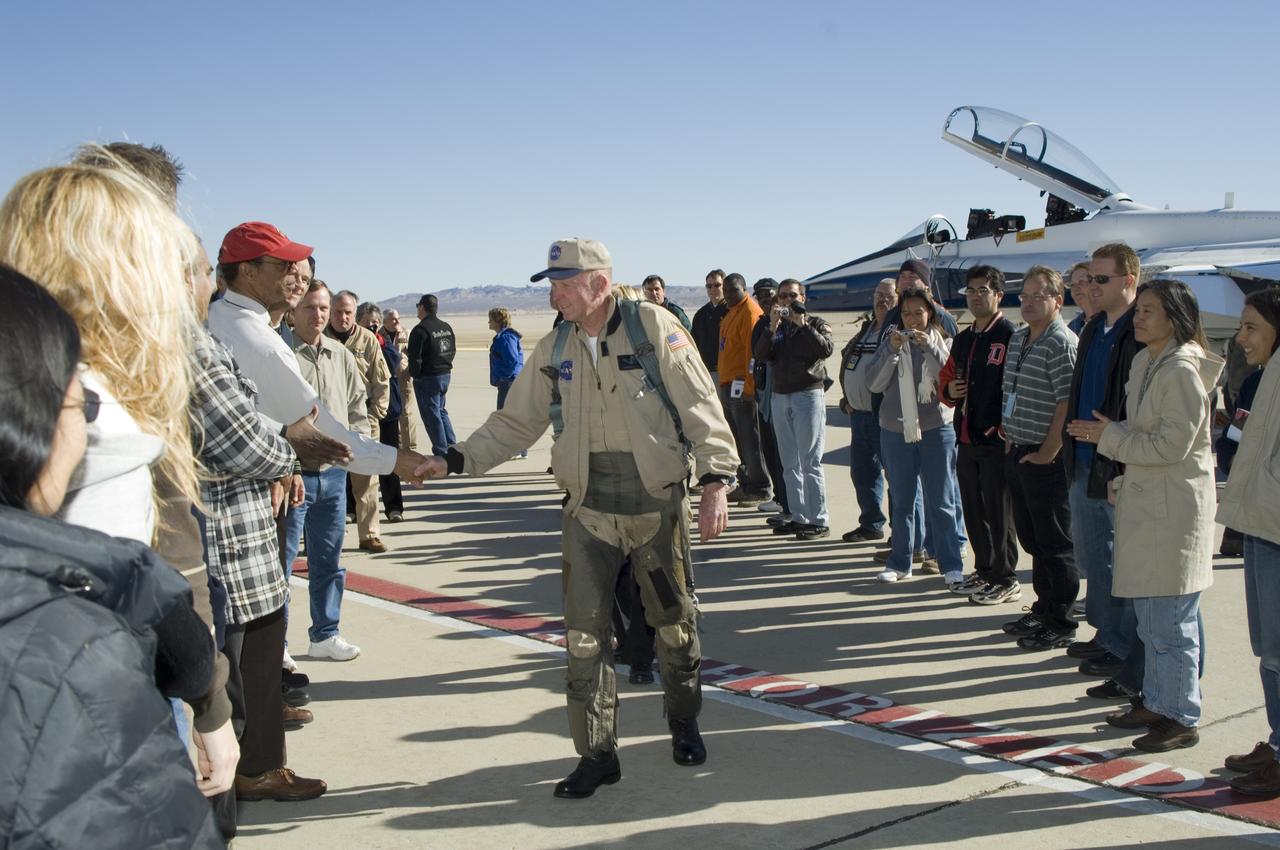

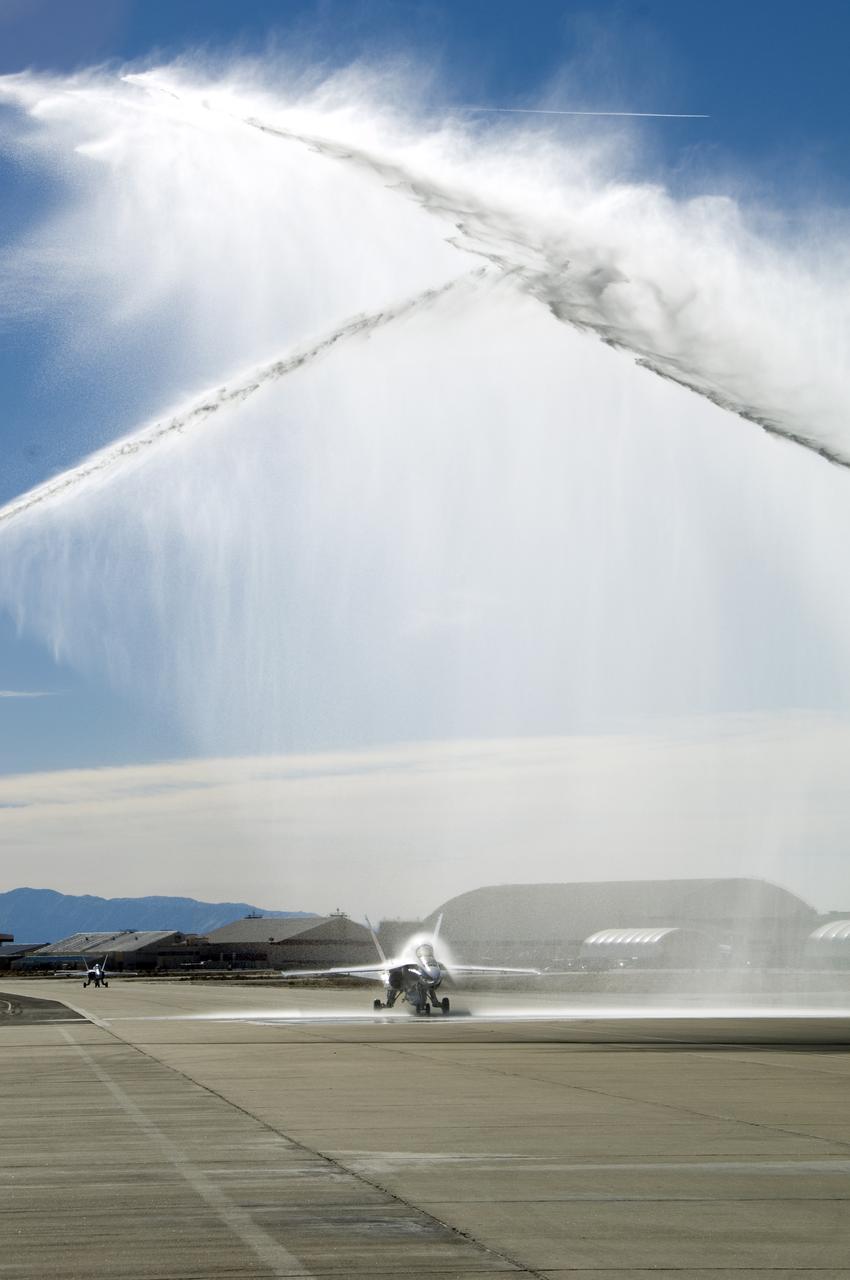
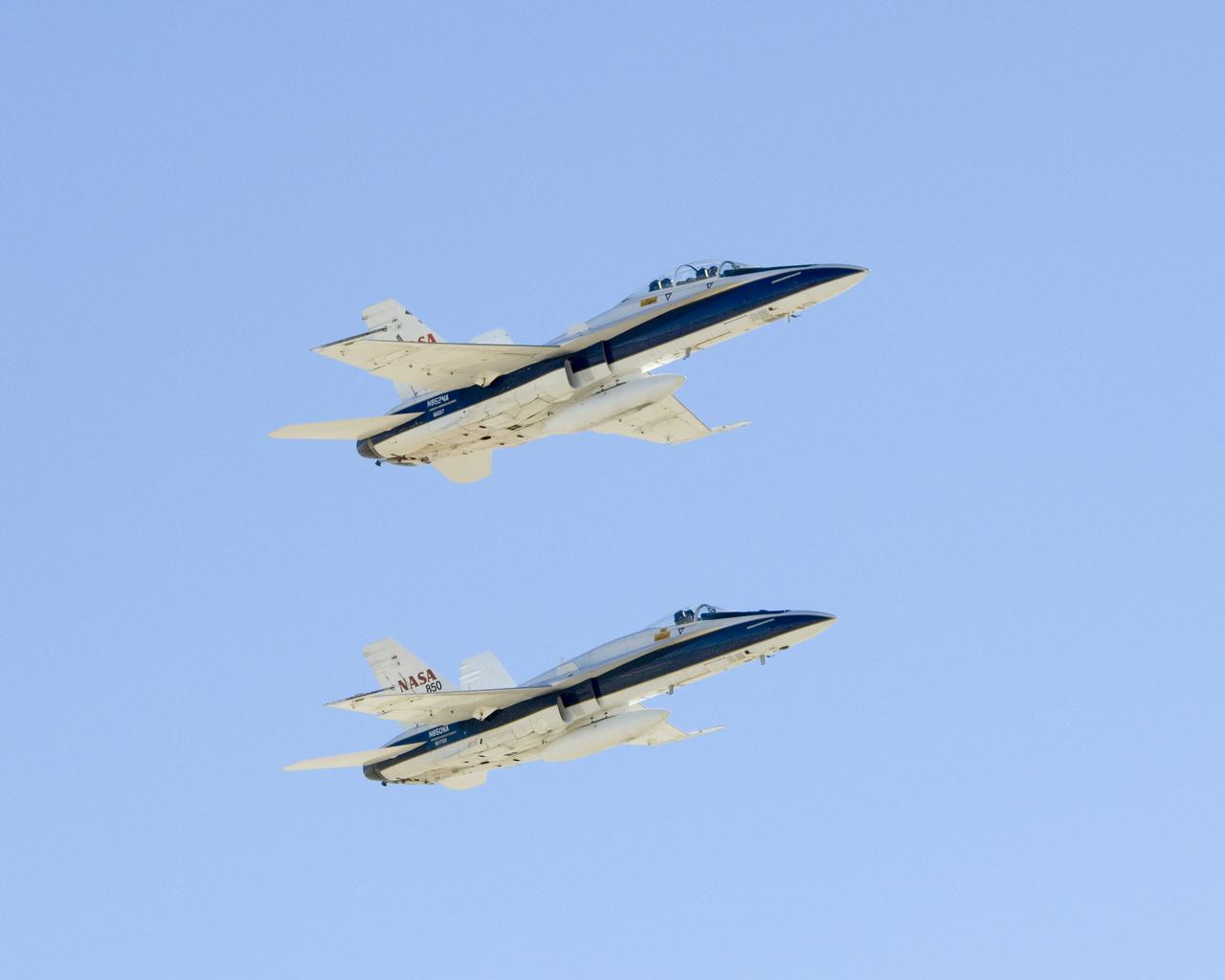
Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
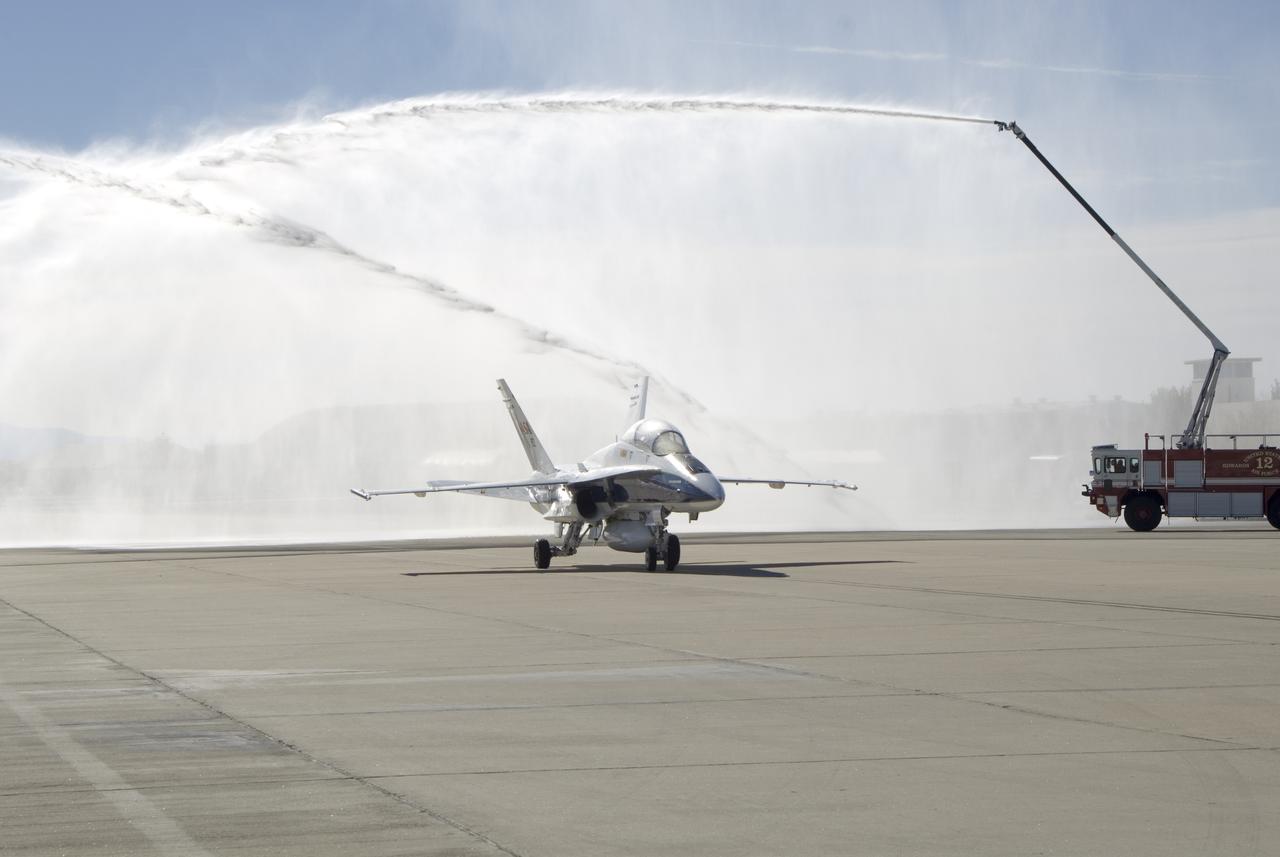

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of sp

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of

Long-time NASA Dryden research pilot and former astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton capped an almost 50-year flying career, including more than 38 years with NASA, with a final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007. Fullerton and Dryden research pilot Jim Smolka flew a 90-minute pilot proficiency formation aerobatics flight with another Dryden F/A-18 and a Dryden T-38 before concluding with two low-level formation flyovers of Dryden before landing. Fullerton was honored with a water-cannon spray arch provided by two fire trucks from the Edwards Air Force Base fire department as he taxied the F/A-18 up to the Dryden ramp, and was then greeted by his wife Marie and several hundred Dryden staff after his final flight. Fullerton began his flying career with the U.S. Air Force in 1958 after earning bachelor's and master's degrees in mechanical engineering from the California Institute of Technology. Initially trained as a fighter pilot, he later transitioned to multi-engine bombers and became a bomber operations test pilot after attending the Air Force Aerospace Research Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. He then was assigned to the flight crew for the planned Air Force Manned Orbital Laboratory in 1966. Upon cancellation of that program, the Air Force assigned Fullerton to NASA's astronaut corps in 1969. He served on the support crews for the Apollo 14, 15, 16 and 17 lunar missions, and was later assigned to one of the two flight crews that piloted the space shuttle prototype Enterprise during the Approach and Landing Test program at Dryden. He then logged some 382 hours in space when he flew on two early space shuttle missions, STS-3 on Columbia in 1982 and STS-51F on Challenger in 1985. He joined the flight crew branch at NASA Dryden after leaving the astronaut corps in 1986. During his 21 years at Dryden, Fullerton was project pilot on a number of high-profile research efforts, including the Propulsion Controlled Aircraft, the high-speed landing tests of
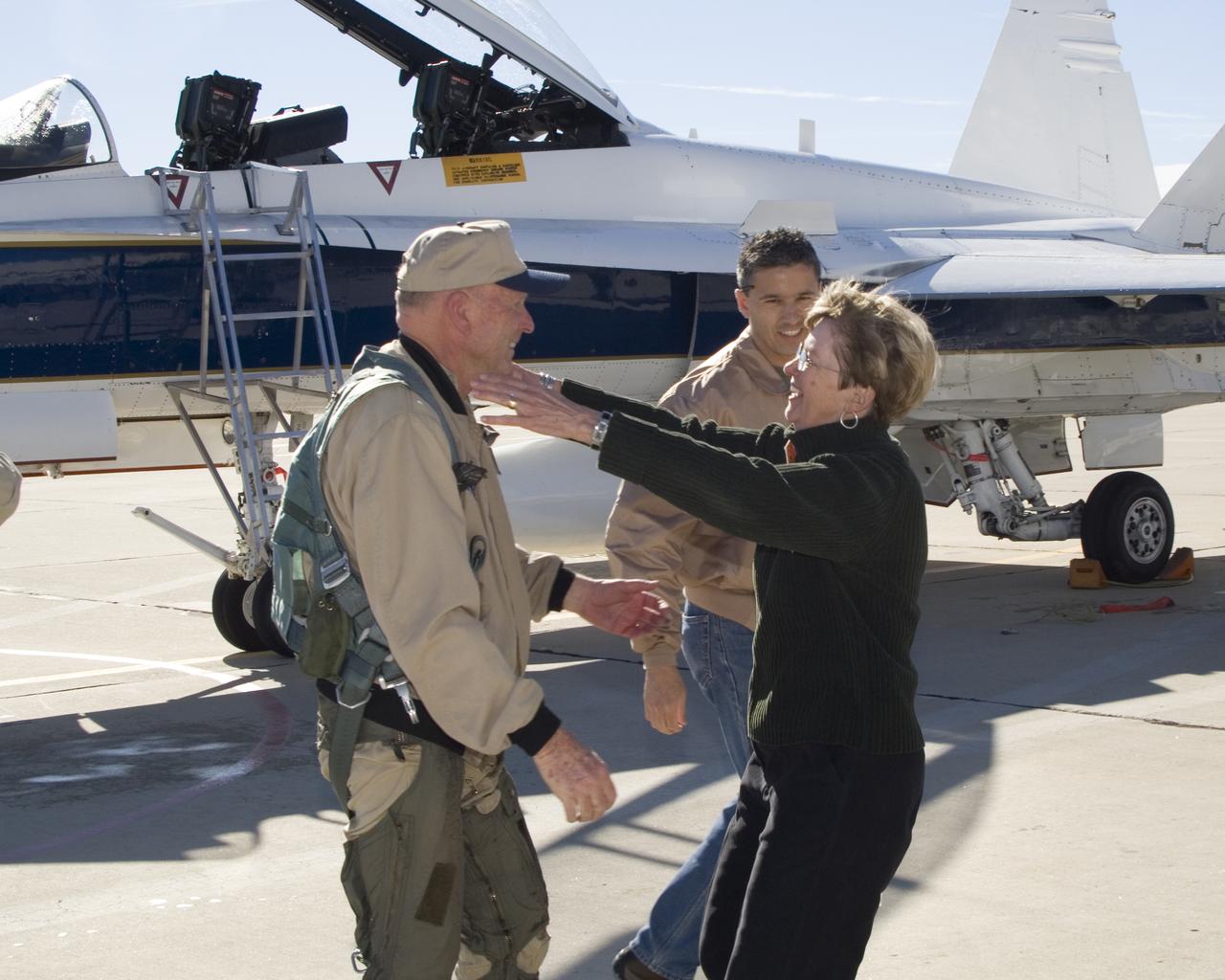

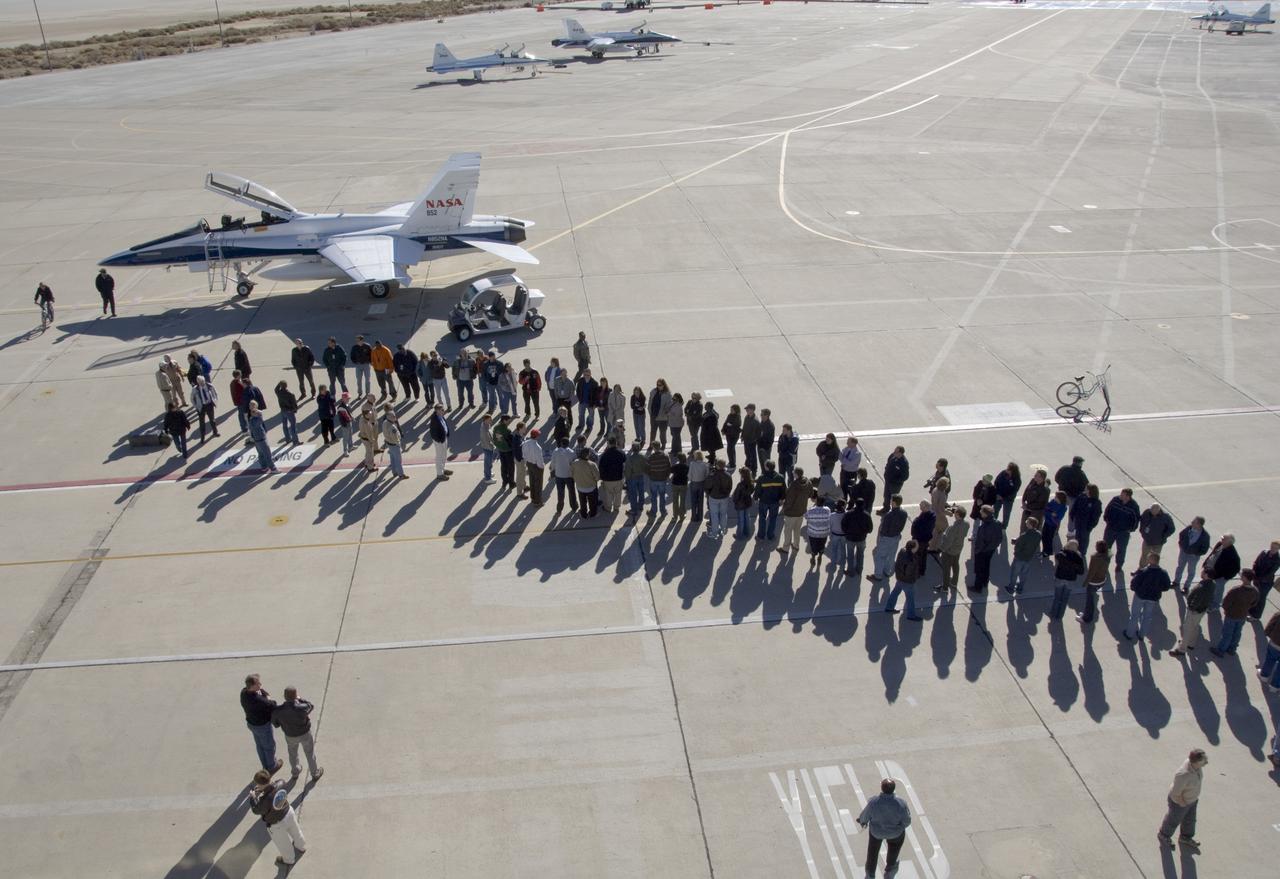
NASA Dryden research pilot Gordon Fullerton is greeted by his wife Marie on the Dryden ramp after his final flight in a NASA F/A-18 on Dec. 21, 2007.

On July 19, 2013, in an event celebrated the world over, NASA's Cassini spacecraft slipped into Saturn's shadow and turned to image the planet, seven of its moons, its inner rings -- and, in the background, our home planet, Earth. With the sun's powerful and potentially damaging rays eclipsed by Saturn itself, Cassini's onboard cameras were able to take advantage of this unique viewing geometry. They acquired a panoramic mosaic of the Saturn system that allows scientists to see details in the rings and throughout the system as they are backlit by the sun. This mosaic is special as it marks the third time our home planet was imaged from the outer solar system; the second time it was imaged by Cassini from Saturn's orbit; and the first time ever that inhabitants of Earth were made aware in advance that their photo would be taken from such a great distance. With both Cassini's wide-angle and narrow-angle cameras aimed at Saturn, Cassini was able to capture 323 images in just over four hours. This final mosaic uses 141 of those wide-angle images. Images taken using the red, green and blue spectral filters of the wide-angle camera were combined and mosaicked together to create this natural-color view. A brightened version with contrast and color enhanced (Figure 1), a version with just the planets annotated (Figure 2), and an annotated version (Figure 3) are shown above. This image spans about 404,880 miles (651,591 kilometers) across. The outermost ring shown here is Saturn's E ring, the core of which is situated about 149,000 miles (240,000 kilometers) from Saturn. The geysers erupting from the south polar terrain of the moon Enceladus supply the fine icy particles that comprise the E ring; diffraction by sunlight gives the ring its blue color. Enceladus (313 miles, or 504 kilometers, across) and the extended plume formed by its jets are visible, embedded in the E ring on the left side of the mosaic. At the 12 o'clock position and a bit inward from the E ring lies the barely discernible ring created by the tiny, Cassini-discovered moon, Pallene (3 miles, or 4 kilometers, across). (For more on structures like Pallene's ring, see PIA08328). The next narrow and easily seen ring inward is the G ring. Interior to the G ring, near the 11 o'clock position, one can barely see the more diffuse ring created by the co-orbital moons, Janus (111 miles, or 179 kilometers, across) and Epimetheus (70 miles, or 113 kilometers, across). Farther inward, we see the very bright F ring closely encircling the main rings of Saturn. Following the outermost E ring counter-clockwise from Enceladus, the moon Tethys (662 miles, or 1,066 kilometers, across) appears as a large yellow orb just outside of the E ring. Tethys is positioned on the illuminated side of Saturn; its icy surface is shining brightly from yellow sunlight reflected by Saturn. Continuing to about the 2 o'clock position is a dark pixel just outside of the G ring; this dark pixel is Saturn's Death Star moon, Mimas (246 miles, or 396 kilometers, across). Mimas appears, upon close inspection, as a very thin crescent because Cassini is looking mostly at its non-illuminated face. The moons Prometheus, Pandora, Janus and Epimetheus are also visible in the mosaic near Saturn's bright narrow F ring. Prometheus (53 miles, or 86 kilometers, across) is visible as a faint black dot just inside the F ring and at the 9 o'clock position. On the opposite side of the rings, just outside the F ring, Pandora (50 miles, or 81 kilometers, across) can be seen as a bright white dot. Pandora and Prometheus are shepherd moons and gravitational interactions between the ring and the moons keep the F ring narrowly confined. At the 11 o'clock position in between the F ring and the G ring, Janus (111 miles, or 179 kilometers, across) appears as a faint black dot. Janus and Prometheus are dark for the same reason Mimas is mostly dark: we are looking at their non-illuminated sides in this mosaic. Midway between the F ring and the G ring, at about the 8 o'clock position, is a single bright pixel, Epimetheus. Looking more closely at Enceladus, Mimas and Tethys, especially in the brightened version of the mosaic, one can see these moons casting shadows through the E ring like a telephone pole might cast a shadow through a fog. In the non-brightened version of the mosaic, one can see bright clumps of ring material orbiting within the Encke gap near the outer edge of the main rings and immediately to the lower left of the globe of Saturn. Also, in the dark B ring within the main rings, at the 9 o'clock position, one can see the faint outlines of two spoke features, first sighted by NASA's Voyager spacecraft in the early 1980s and extensively studied by Cassini. Finally, in the lower right of the mosaic, in between the bright blue E ring and the faint but defined G ring, is the pale blue dot of our planet, Earth. Look closely and you can see the moon protruding from the Earth's lower right. (For a higher resolution view of the Earth and moon taken during this campaign, see PIA14949.) Earth's twin, Venus, appears as a bright white dot in the upper left quadrant of the mosaic, also between the G and E rings. Mars also appears as a faint red dot embedded in the outer edge of the E ring, above and to the left of Venus. For ease of visibility, Earth, Venus, Mars, Enceladus, Epimetheus and Pandora were all brightened by a factor of eight and a half relative to Saturn. Tethys was brightened by a factor of four. In total, 809 background stars are visible and were brightened by a factor ranging from six, for the brightest stars, to 16, for the faintest. The faint outer rings (from the G ring to the E ring) were also brightened relative to the already bright main rings by factors ranging from two to eight, with the lower-phase-angle (and therefore fainter) regions of these rings brightened the most. The brightened version of the mosaic was further brightened and contrast-enhanced all over to accommodate print applications and a wide range of computer-screen viewing conditions. Some ring features -- such as full rings traced out by tiny moons -- do not appear in this version of the mosaic because they require extreme computer enhancement, which would adversely affect the rest of the mosaic. This version was processed for balance and beauty. This view looks toward the unlit side of the rings from about 17 degrees below the ring plane. Cassini was approximately 746,000 miles (1.2 million kilometers) from Saturn when the images in this mosaic were taken. Image scale on Saturn is about 45 miles (72 kilometers) per pixel. This mosaic was made from pictures taken over a span of more than four hours while the planets, moons and stars were all moving relative to Cassini. Thus, due to spacecraft motion, these objects in the locations shown here were not in these specific places over the entire duration of the imaging campaign. Note also that Venus appears far from Earth, as does Mars, because they were on the opposite side of the sun from Earth. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA17172
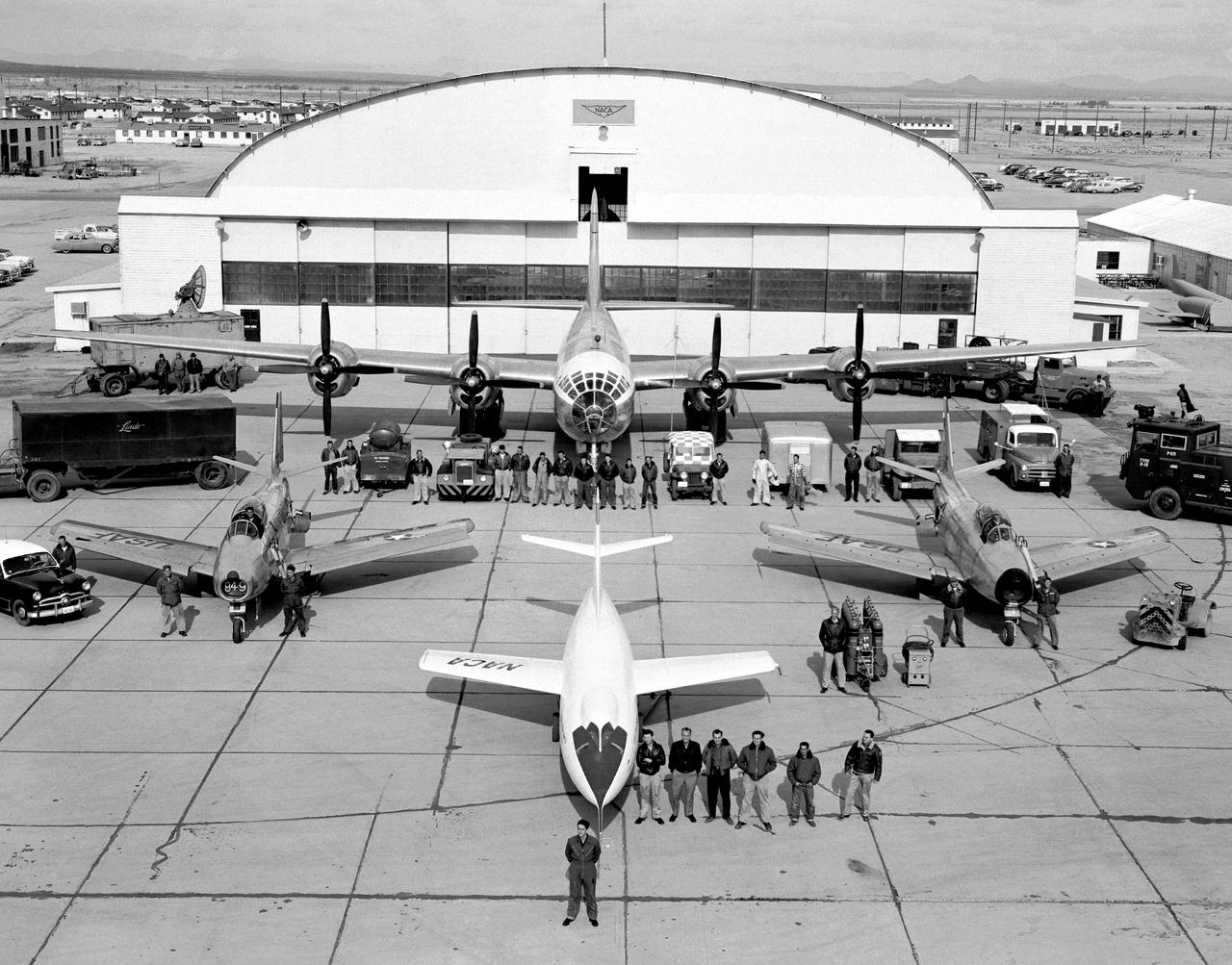

These people and this equipment supported the flight of the NACA D-558-2 Skyrocket at the High-Speed Flight Station at South Base, Edwards AFB. Note the two Sabre chase planes, the P2B-1S launch aircraft, and the profusion of ground support equipment, including communications, tracking, maintenance, and rescue vehicles. Research pilot A. Scott Crossfield stands in front of the Skyrocket.