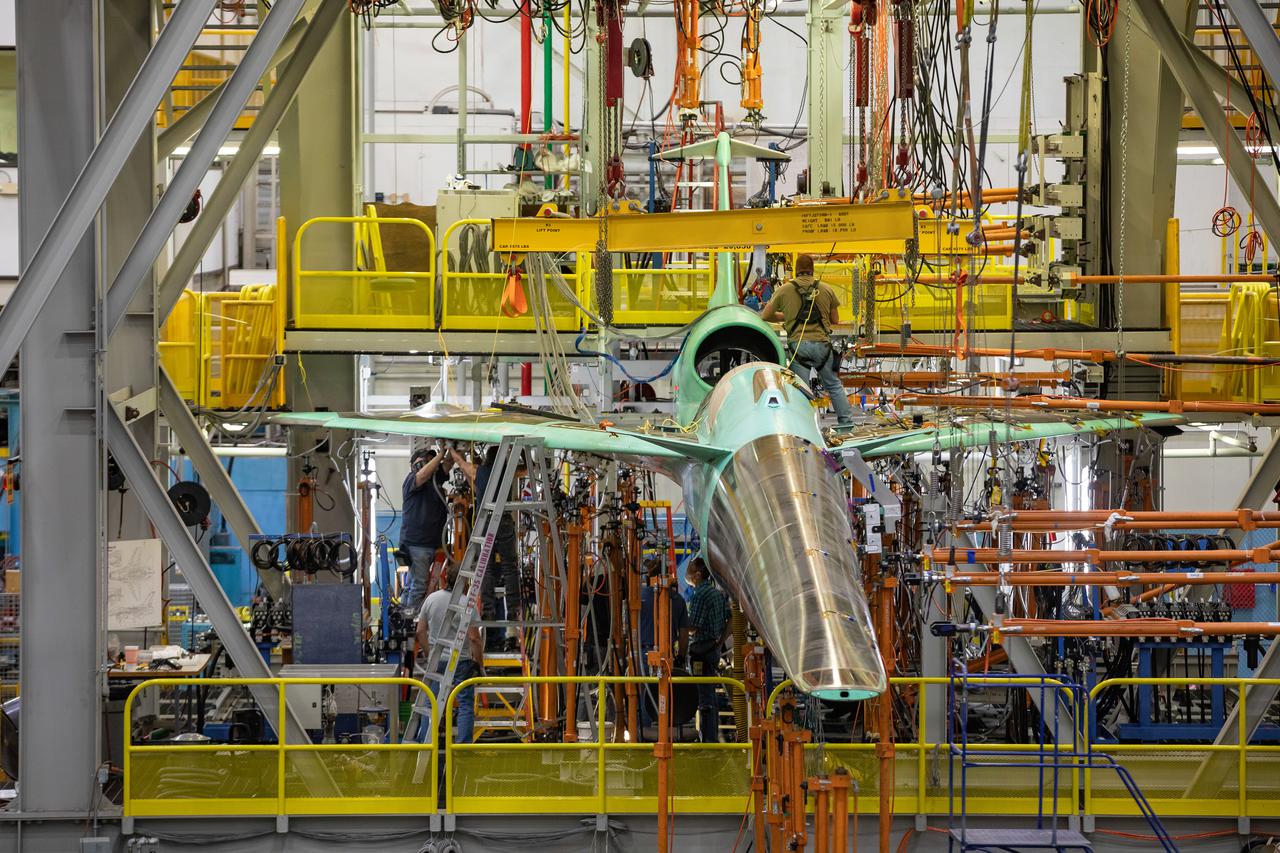

NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology airplane undergoes structural stress tests at a Lockheed Martin facility in Fort Worth, Texas. Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company - Fort Worth - Chris Hanoch Subject: X-59 - Various Angles in Test Fixture FP#: 21-03420 POC: Analiese Smith, Chris Higgins Other info: X-59 in Fort Worth, testing; high angle shots in fixture 1-10-22
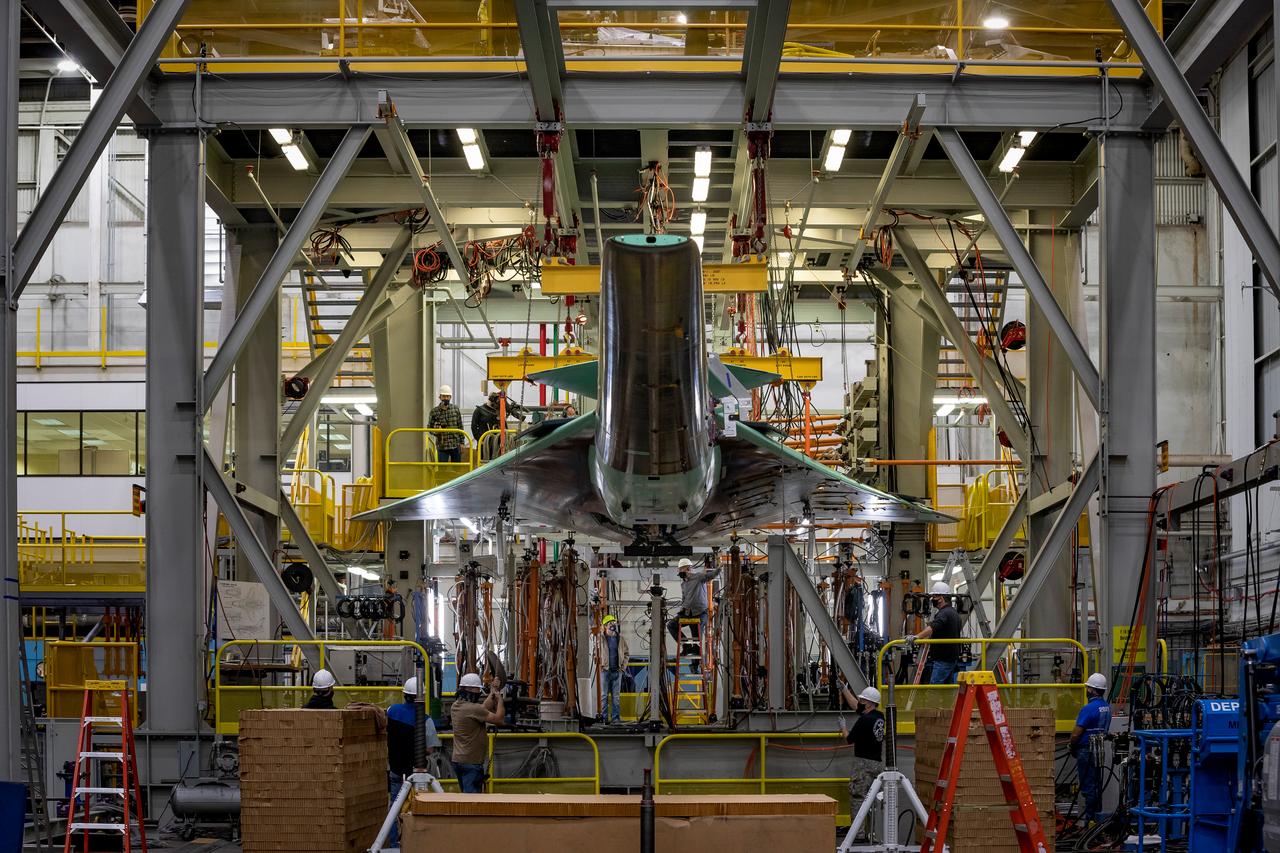

NASA’s X-59 is lowered into the test fixture as it prepares to undergo structural stress tests at Lockheed Martin in Fort Worth, Texas. The X-59 is a one-of-a-kind airplane designed to fly at supersonic speeds without making a startling sonic boom sound for the communities below. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to help enable supersonic air travel over land.

Orion technicians at the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Facility at the Kennedy Space Center move the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module from the clean room into the birdcage fixture on Dec. 5, 2012. The fixture is designed to enable precise pre-launch processing of the Orion spacecraft.
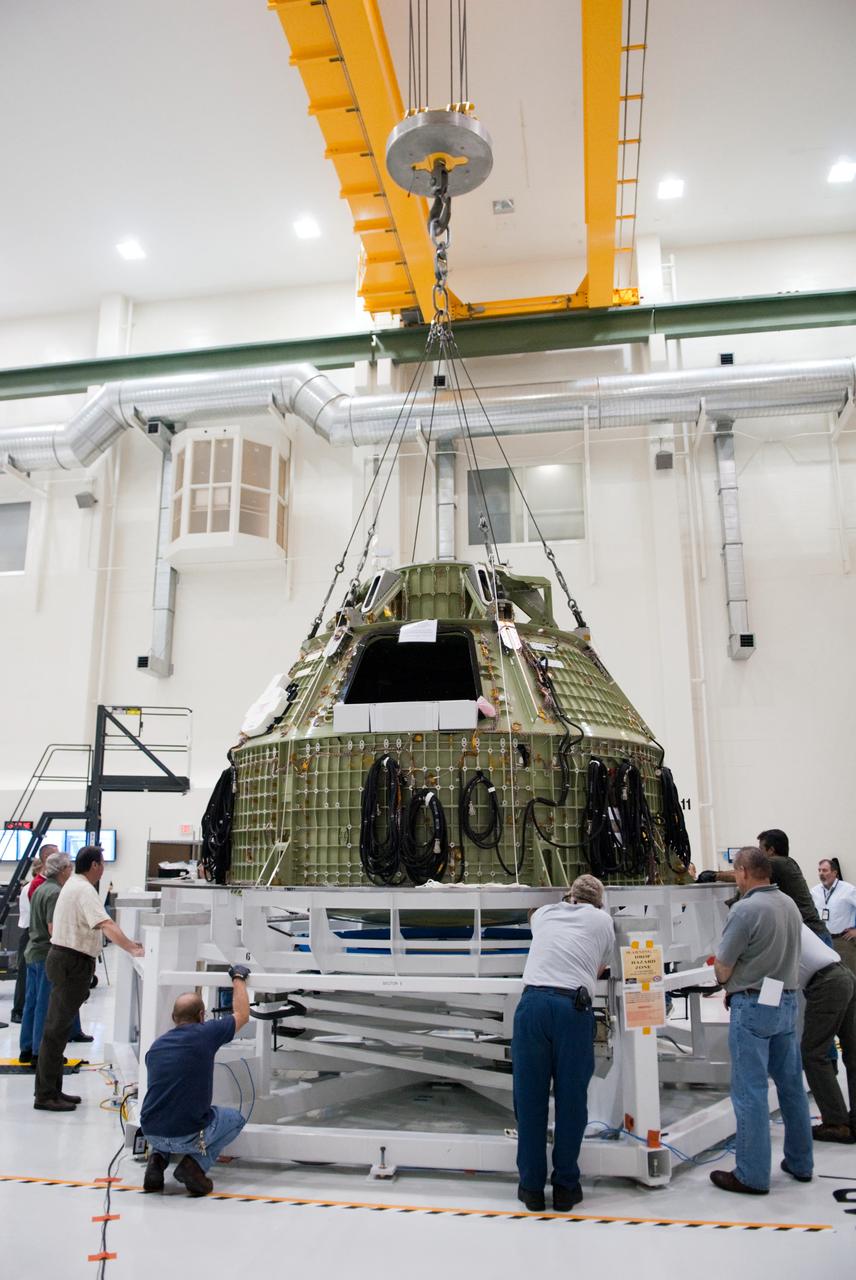

Orion technicians at the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Facility at the Kennedy Space Center move the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module from the clean room into the birdcage fixture on Dec. 5, 2012. The fixture is designed to enable precise pre-launch processing of the Orion spacecraft.

Orion technicians at the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Facility at the Kennedy Space Center move the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module from the clean room into the birdcage fixture on Dec. 5, 2012. The fixture is designed to enable precise pre-launch processing of the Orion spacecraft.
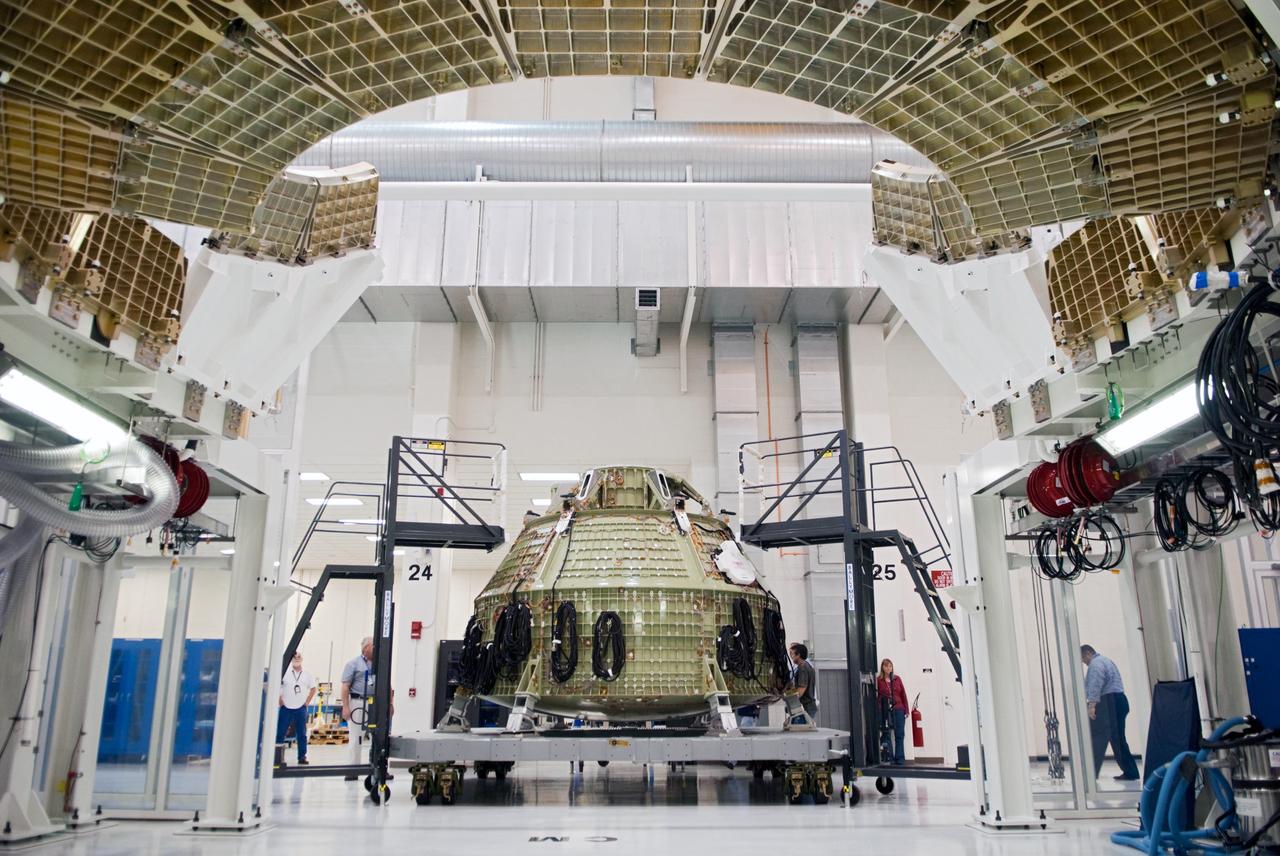

Orion technicians at the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Facility at the Kennedy Space Center move the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module from the clean room into the birdcage fixture on Dec. 5, 2012. The fixture is designed to enable precise pre-launch processing of the Orion spacecraft.
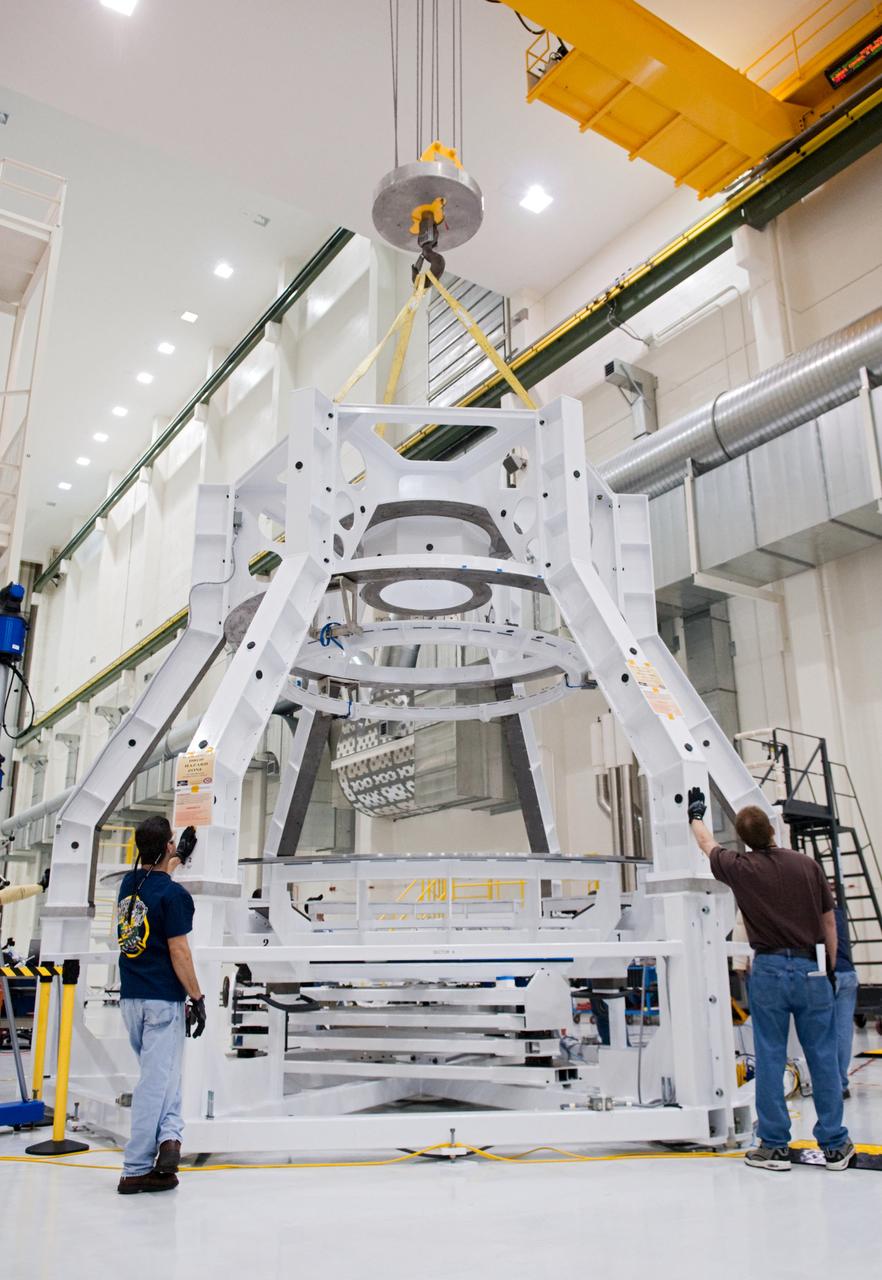

Orion technicians at the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Facility at the Kennedy Space Center move the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module from the clean room into the birdcage fixture on Dec. 5, 2012. The fixture is designed to enable precise pre-launch processing of the Orion spacecraft.
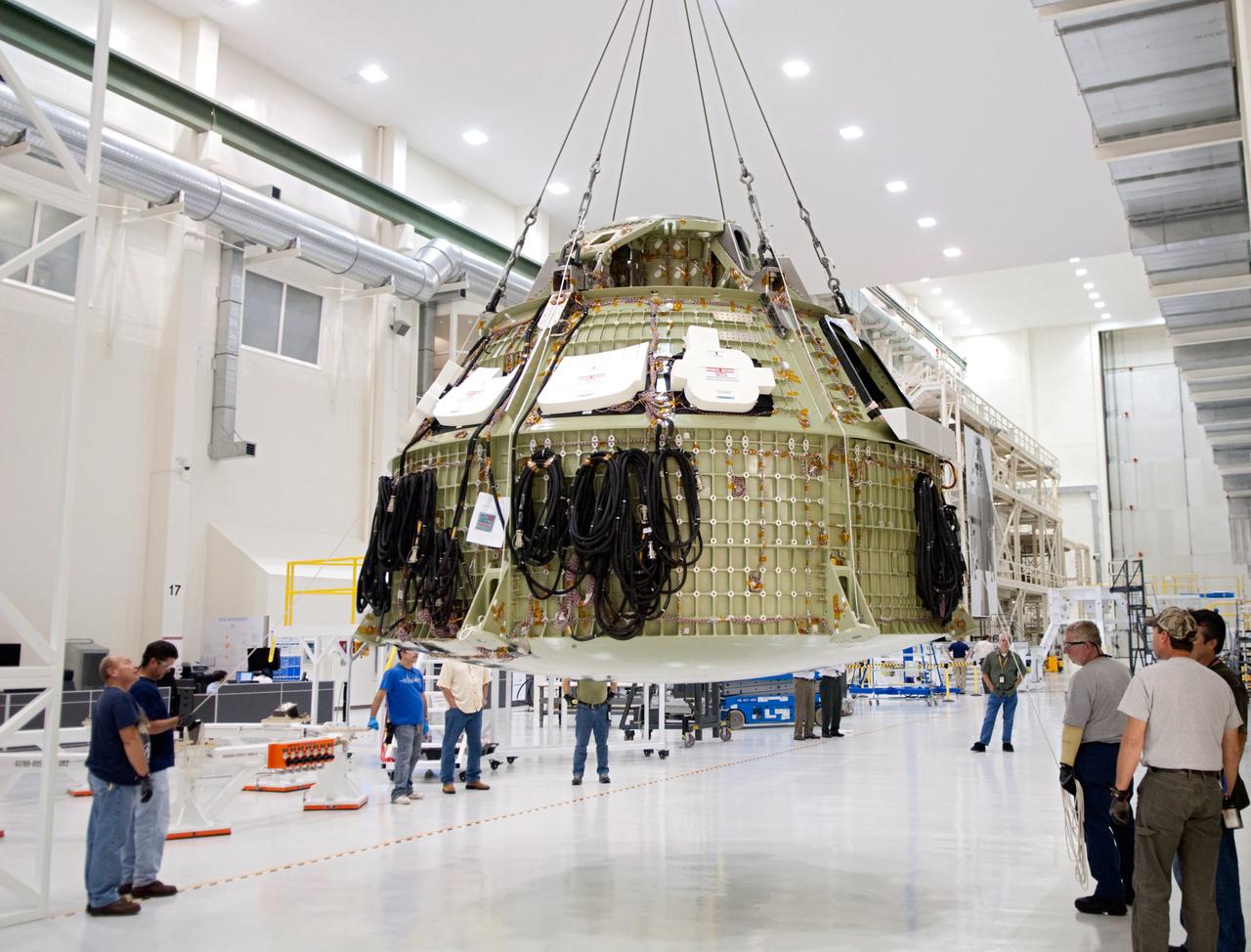

Orion technicians at the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Facility at the Kennedy Space Center move the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module from the clean room into the birdcage fixture on Dec. 5, 2012. The fixture is designed to enable precise pre-launch processing of the Orion spacecraft.
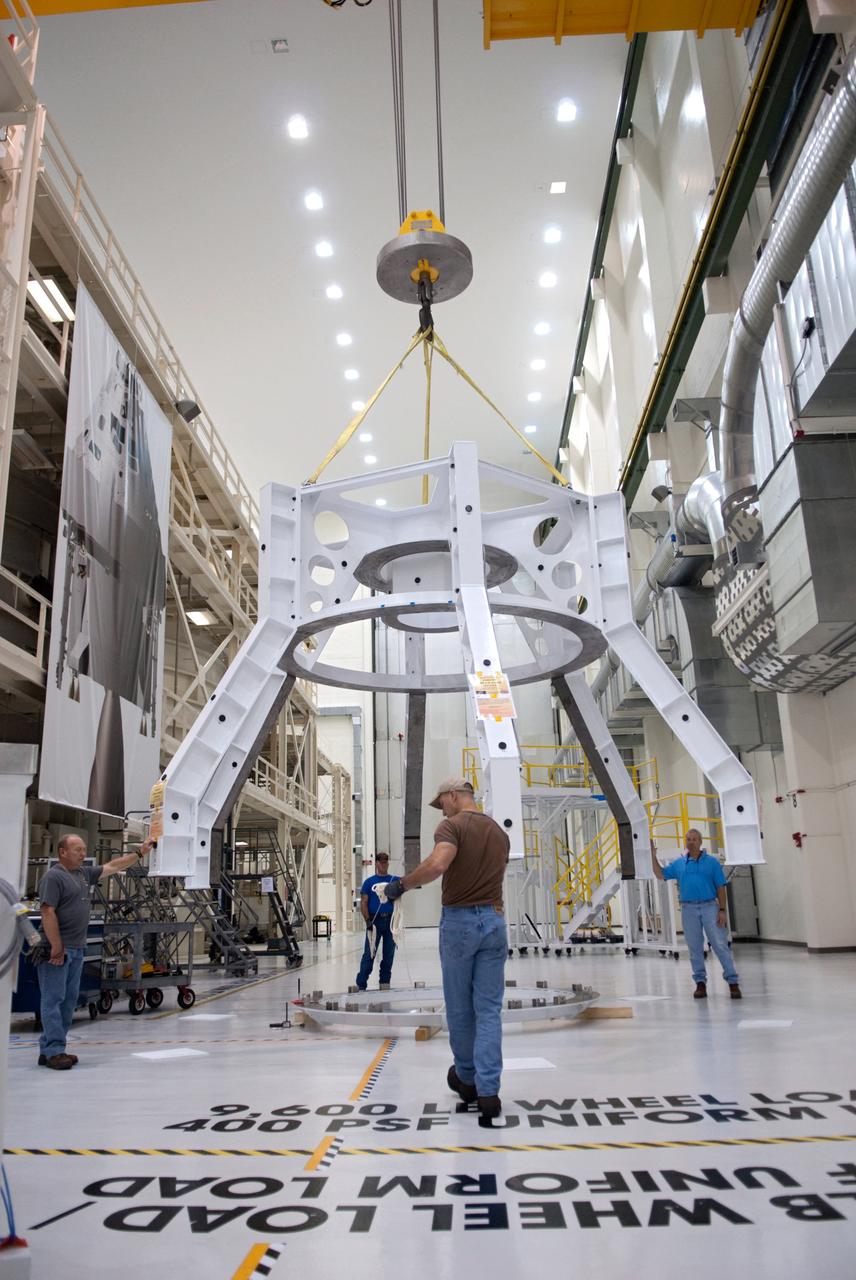

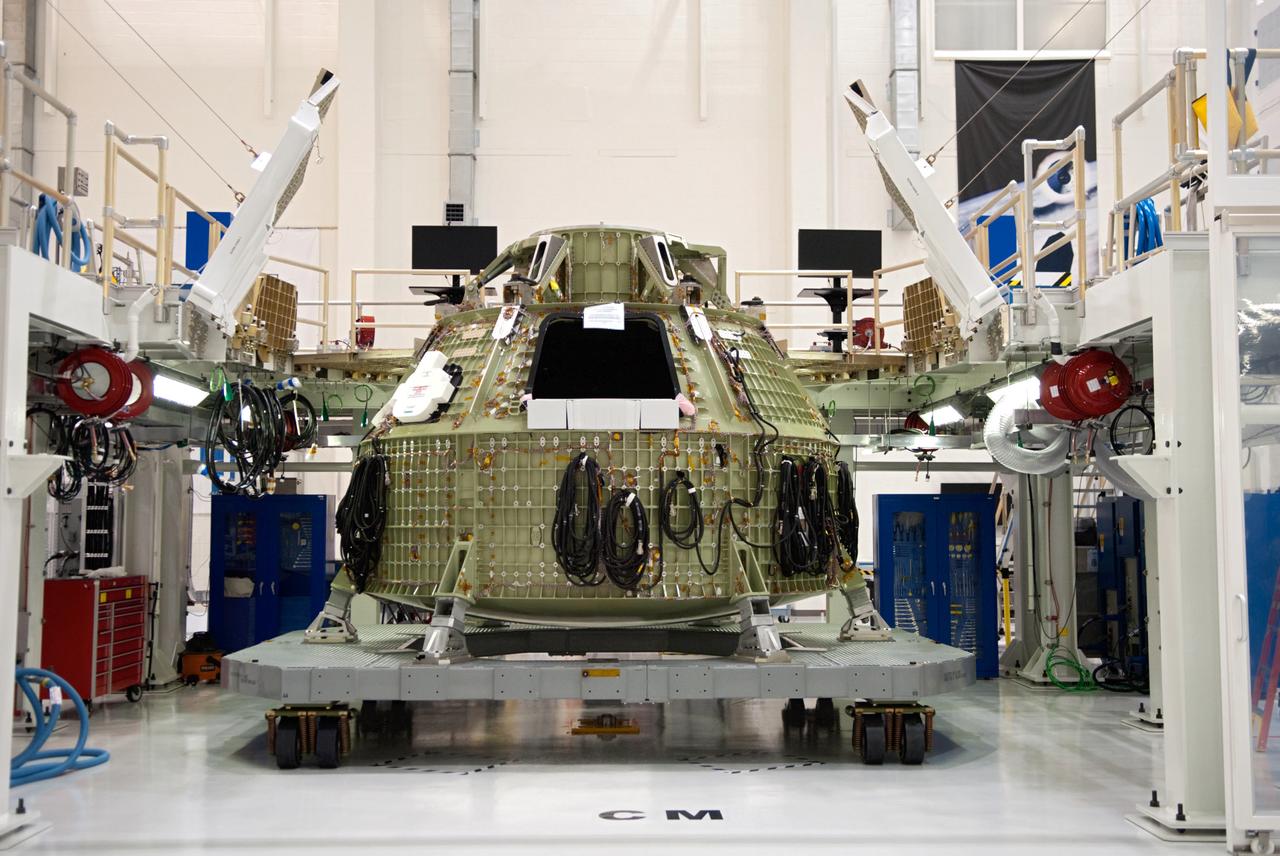
Orion technicians at the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Facility at the Kennedy Space Center move the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module from the clean room into the birdcage fixture on Dec. 6, 2012. The fixture is designed to enable precise pre-launch processing of the Orion spacecraft. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
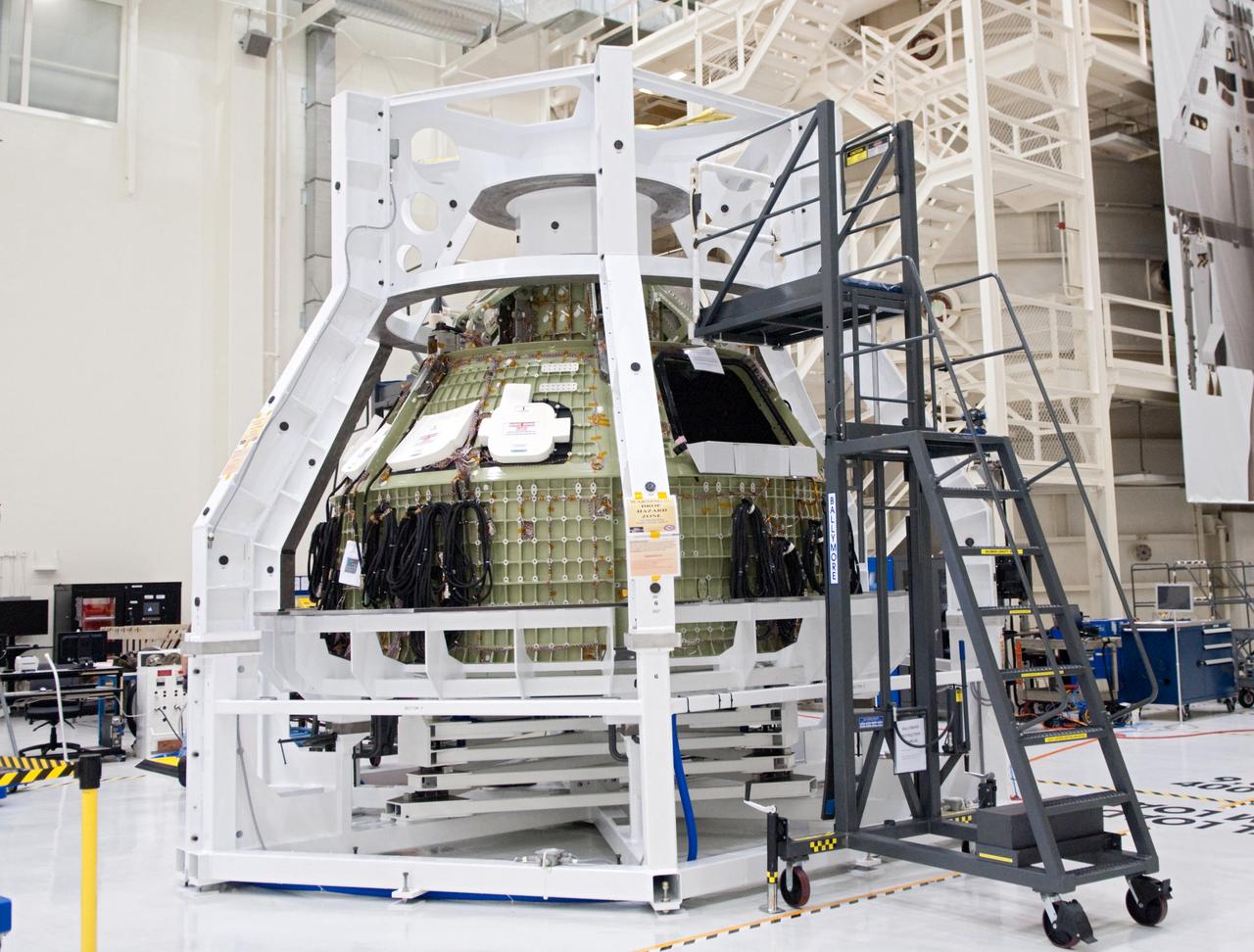

Orion technicians at the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Facility at the Kennedy Space Center move the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module from the clean room into the birdcage fixture on Dec. 6, 2012. The fixture is designed to enable precise pre-launch processing of the Orion spacecraft. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
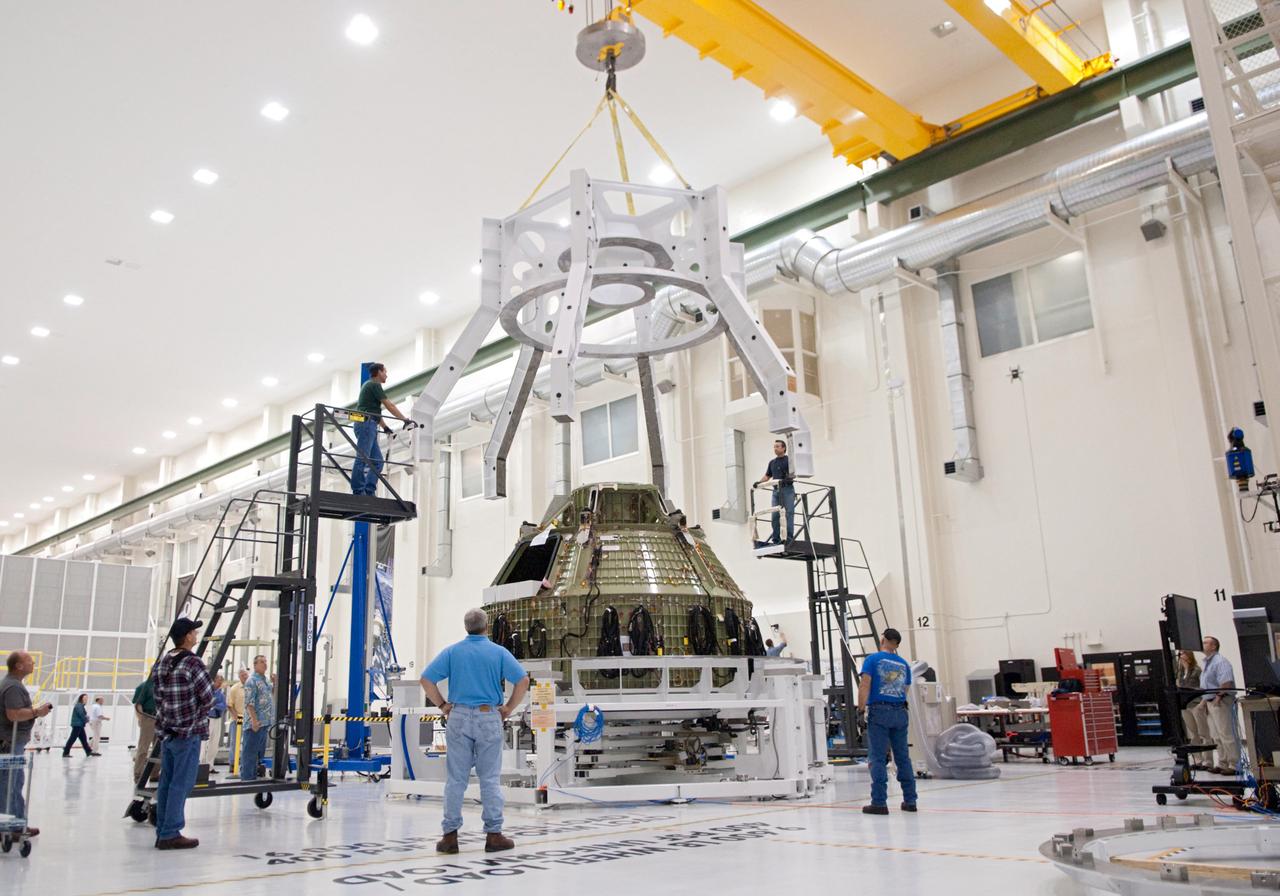

Orion technicians at the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Facility at the Kennedy Space Center move the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module from the clean room into the birdcage fixture on Dec. 6, 2012. The fixture is designed to enable precise pre-launch processing of the Orion spacecraft. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
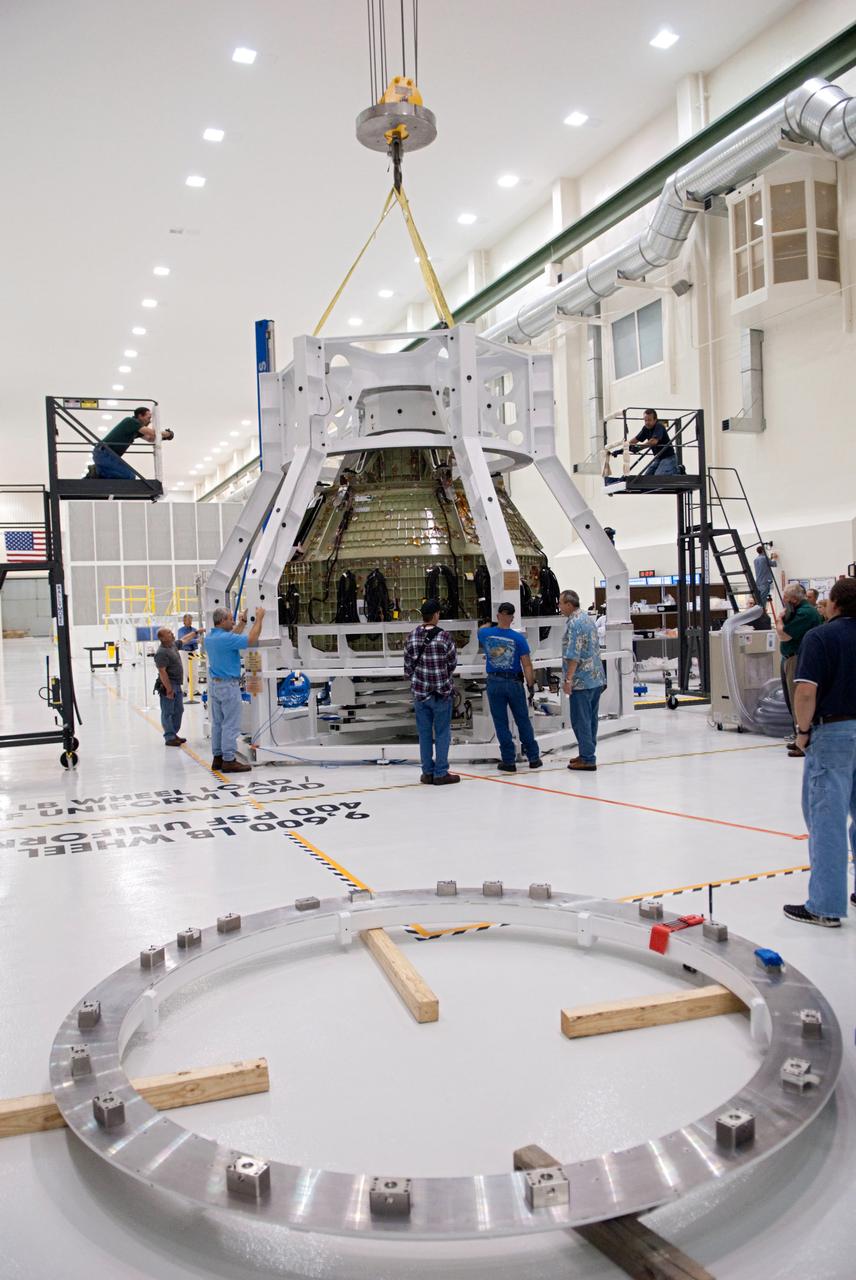

Orion technicians at the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Facility at the Kennedy Space Center move the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module from the clean room into the birdcage fixture on Dec. 6, 2012. The fixture is designed to enable precise pre-launch processing of the Orion spacecraft. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
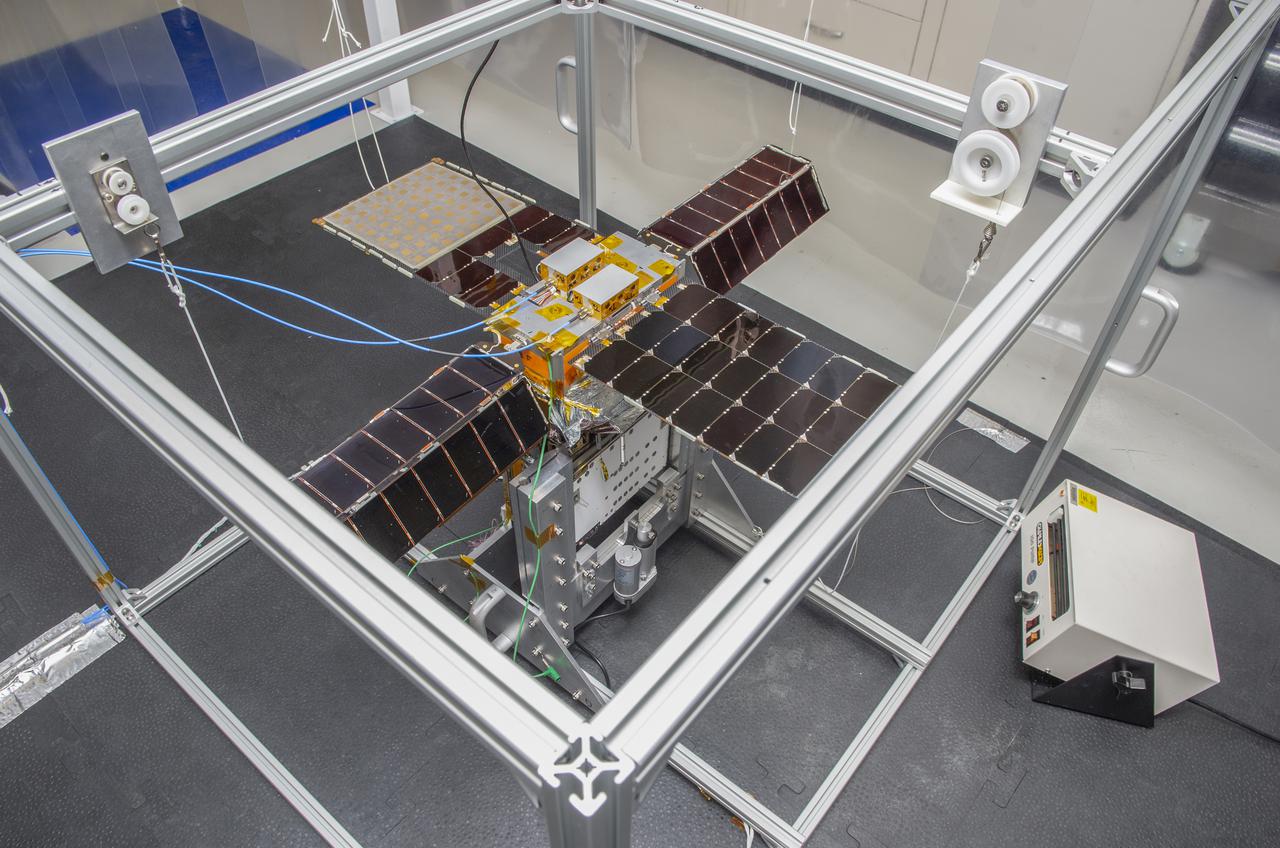
Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
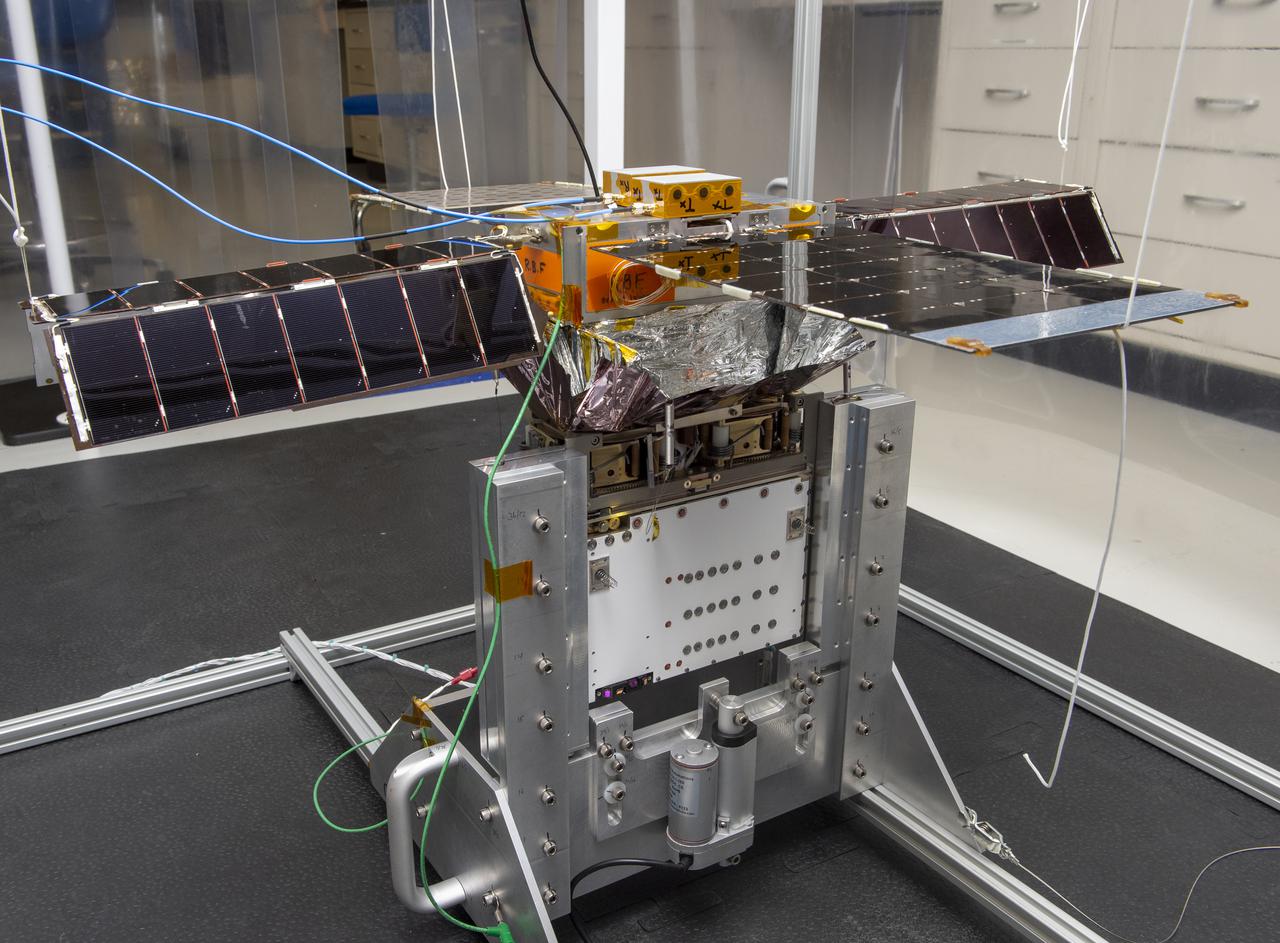

Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer

Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
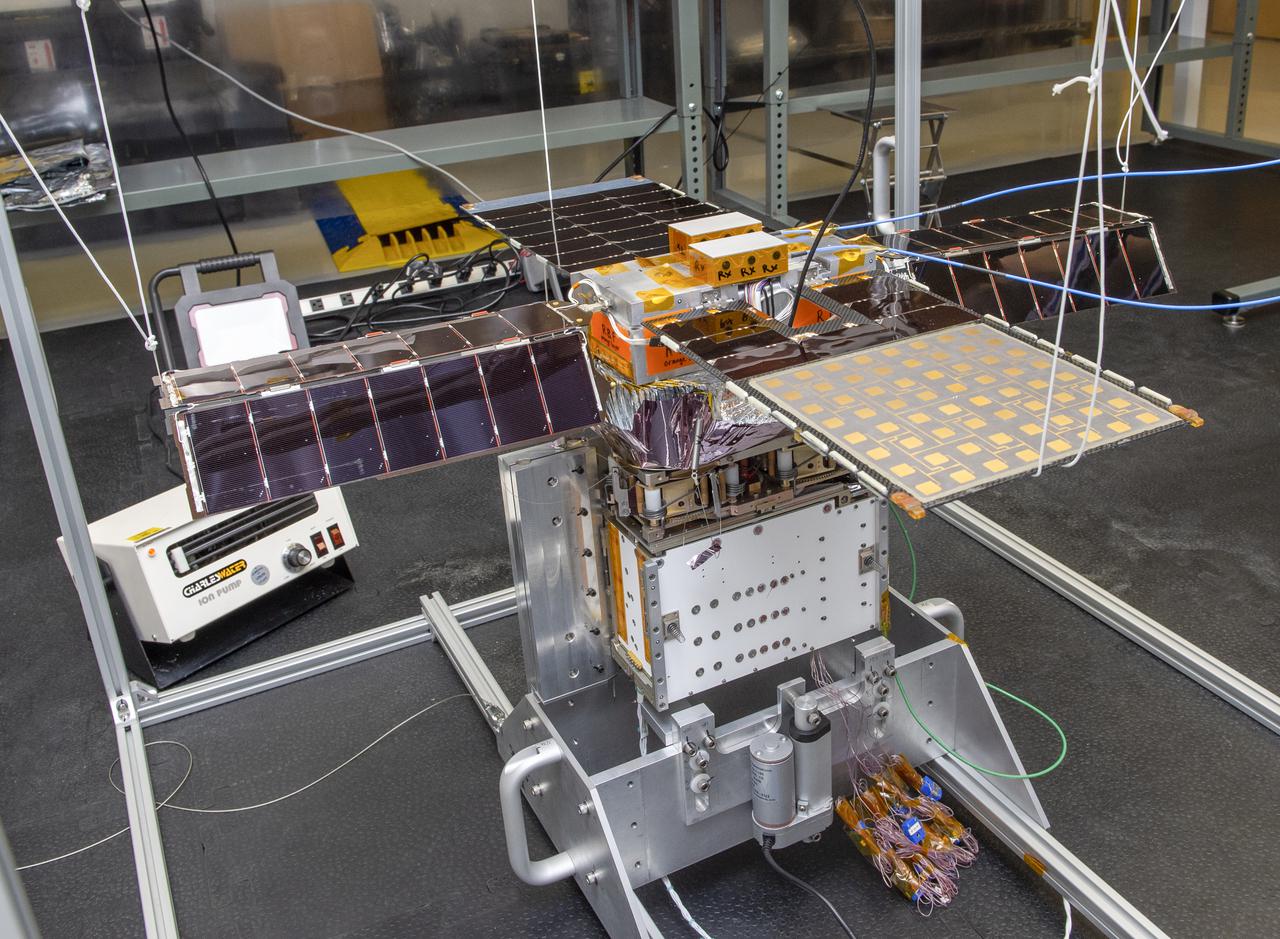
Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
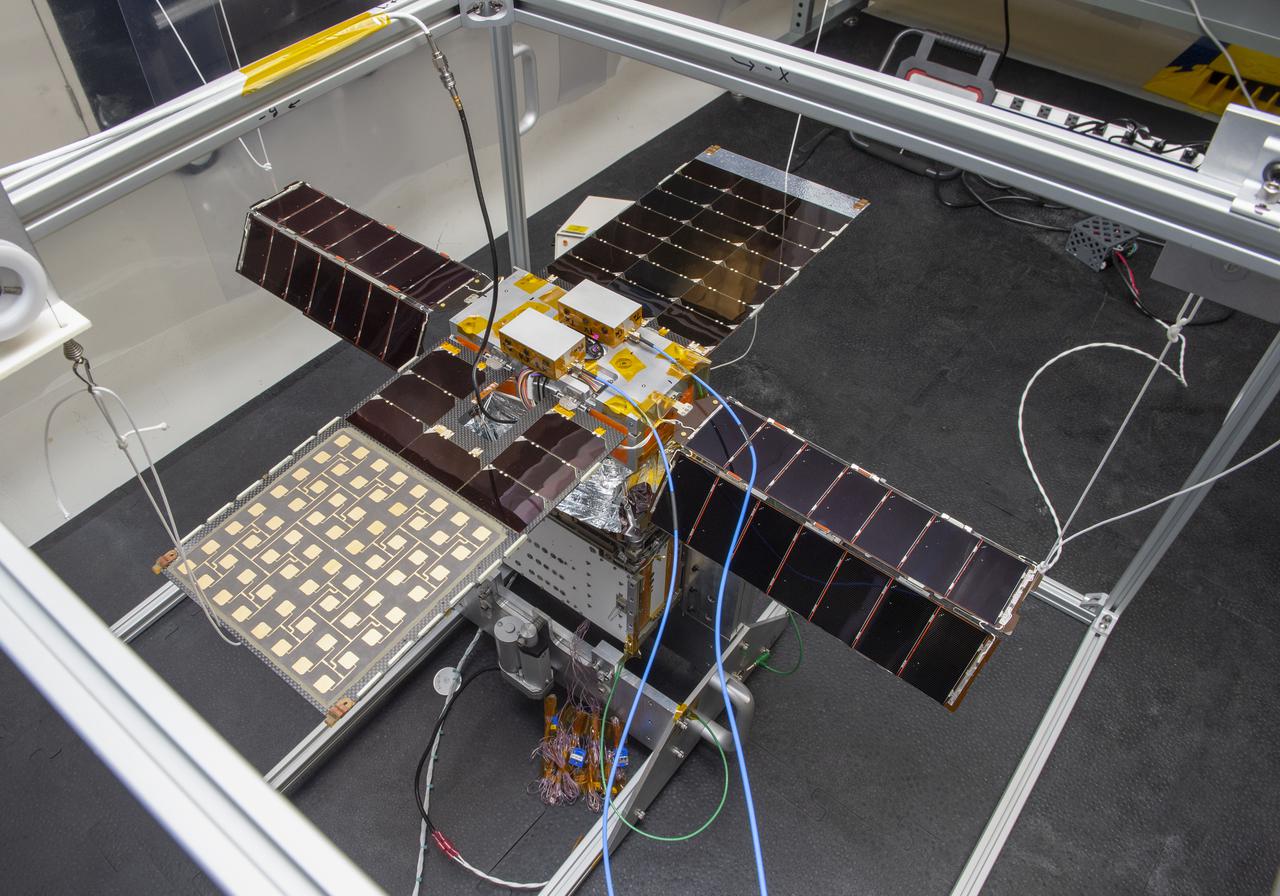
Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
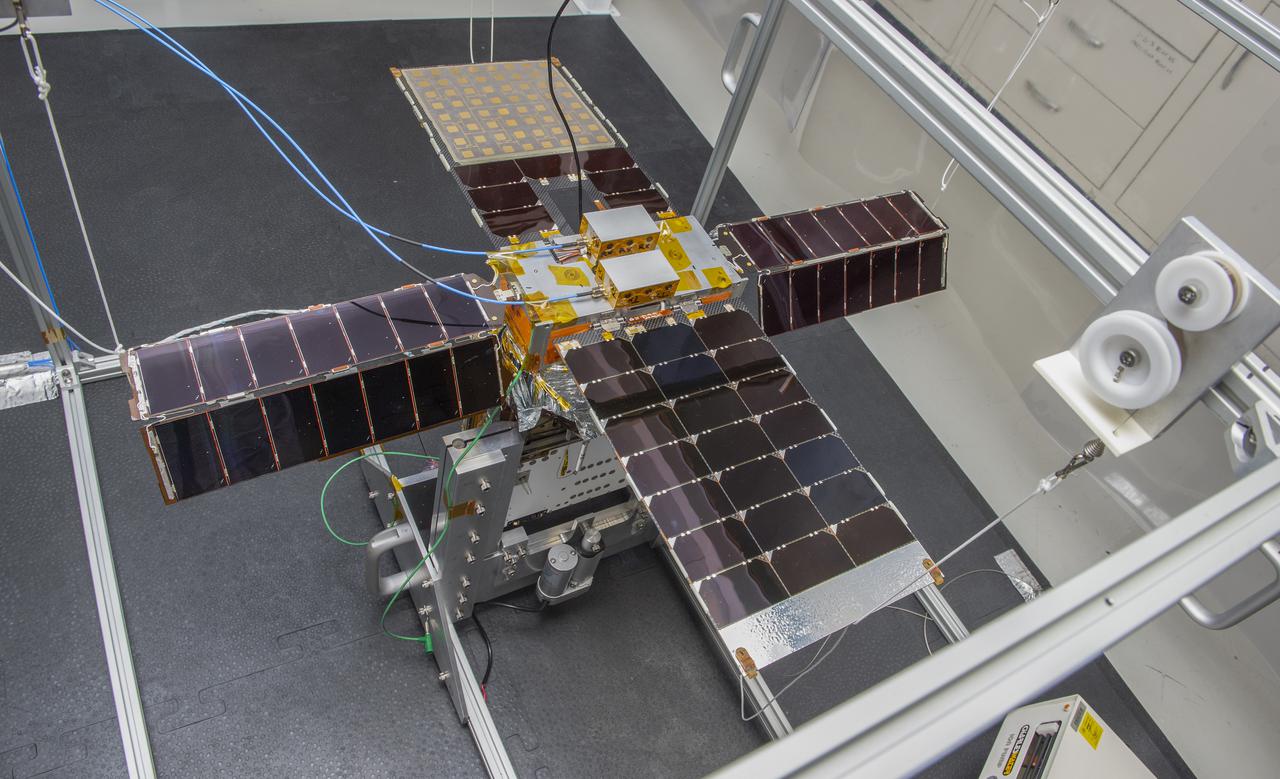

Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
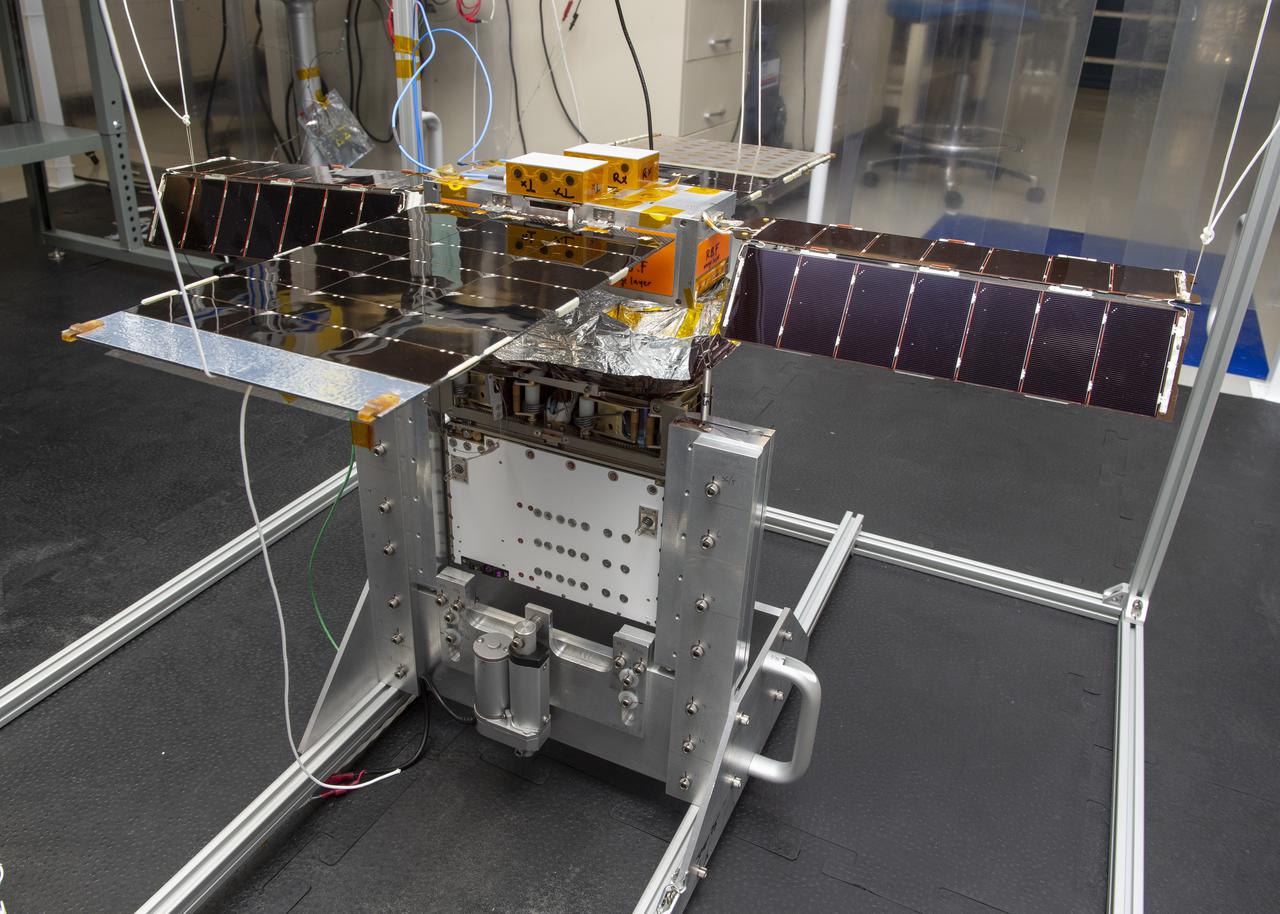
Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
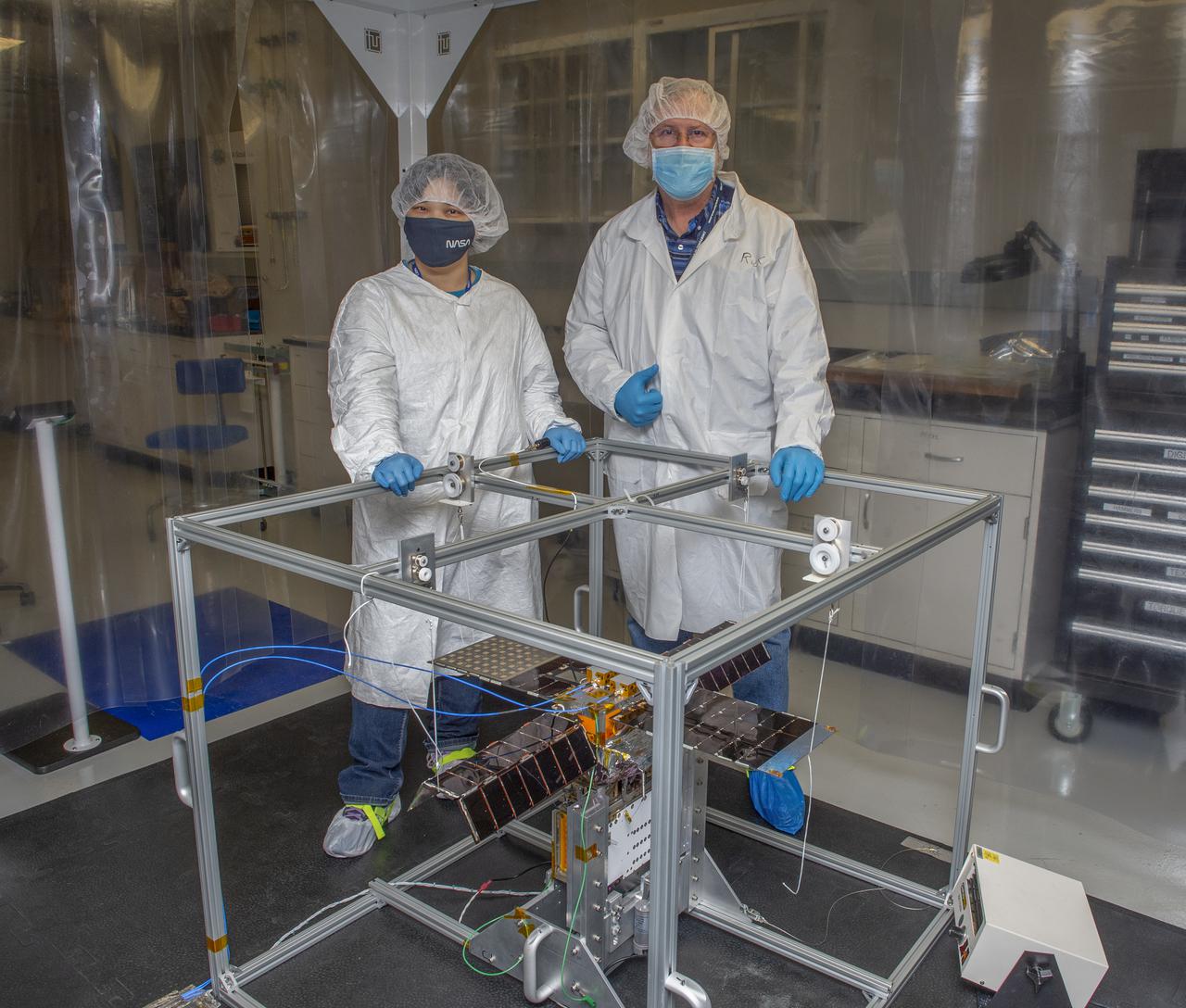

Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
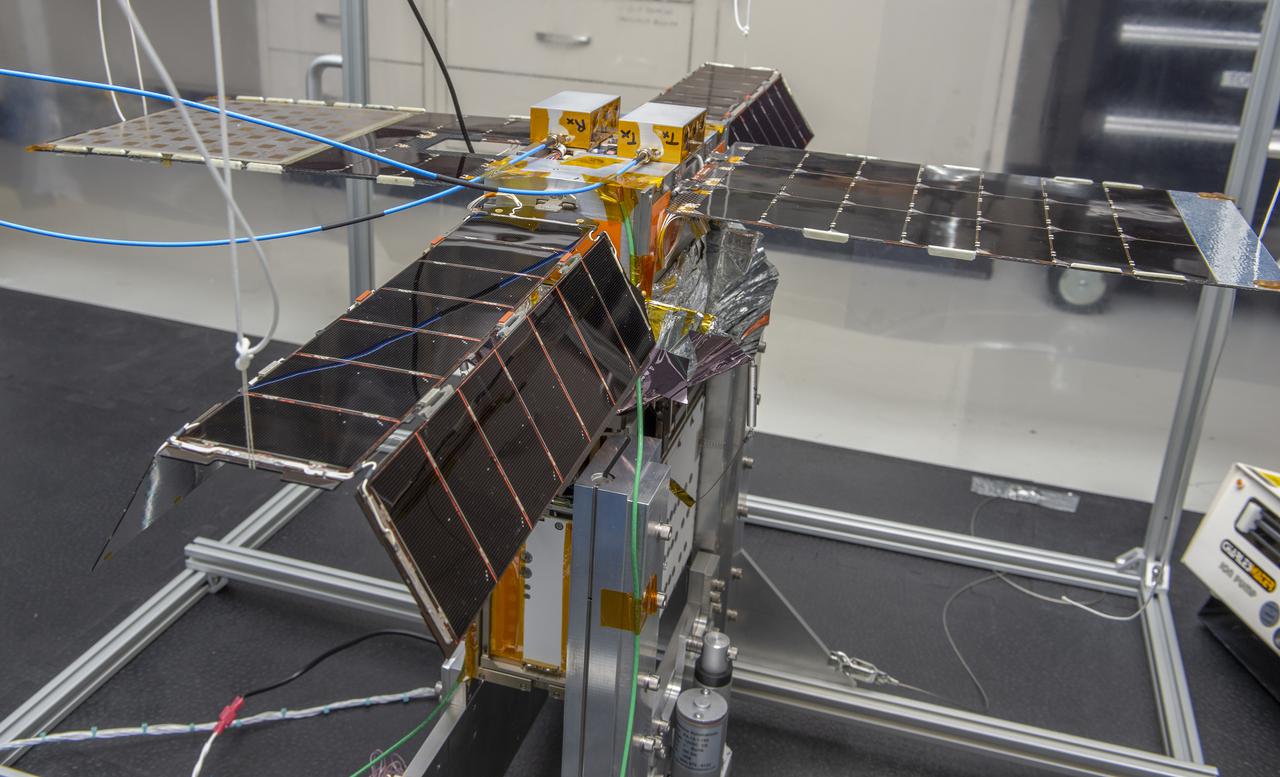

Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
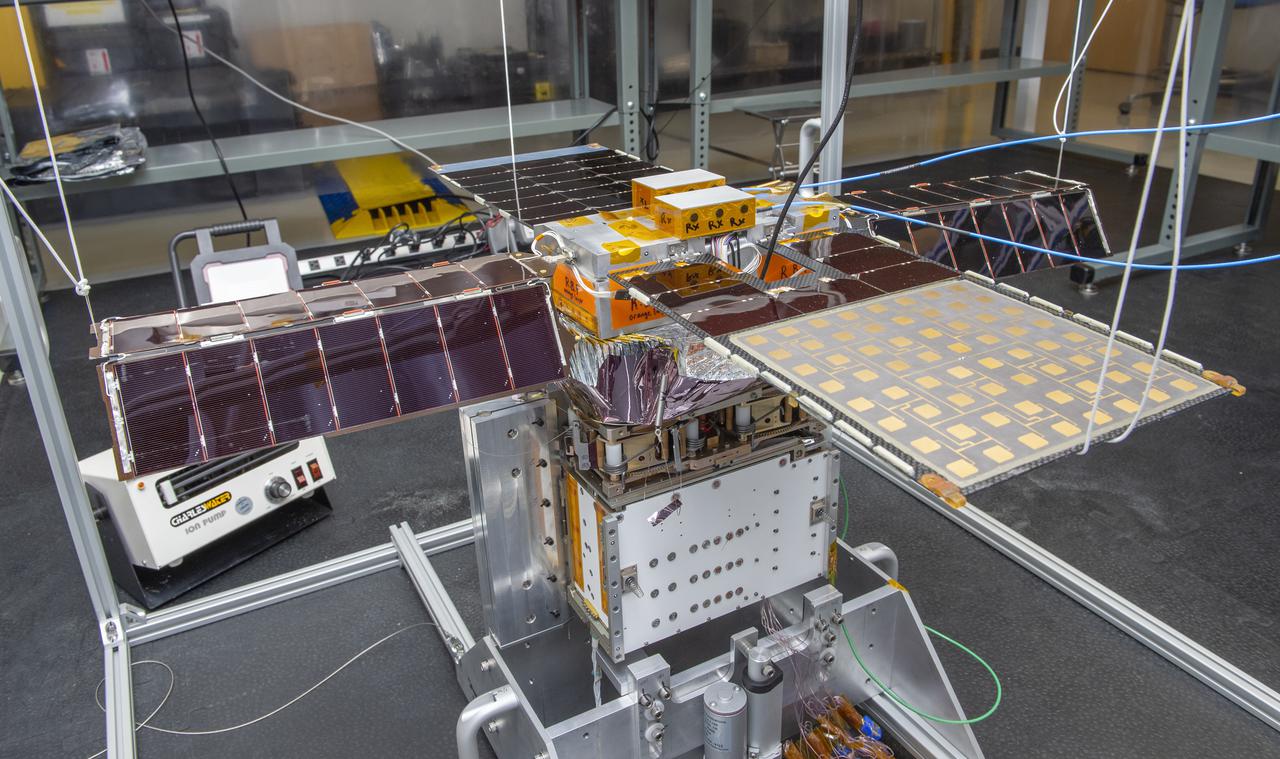
Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
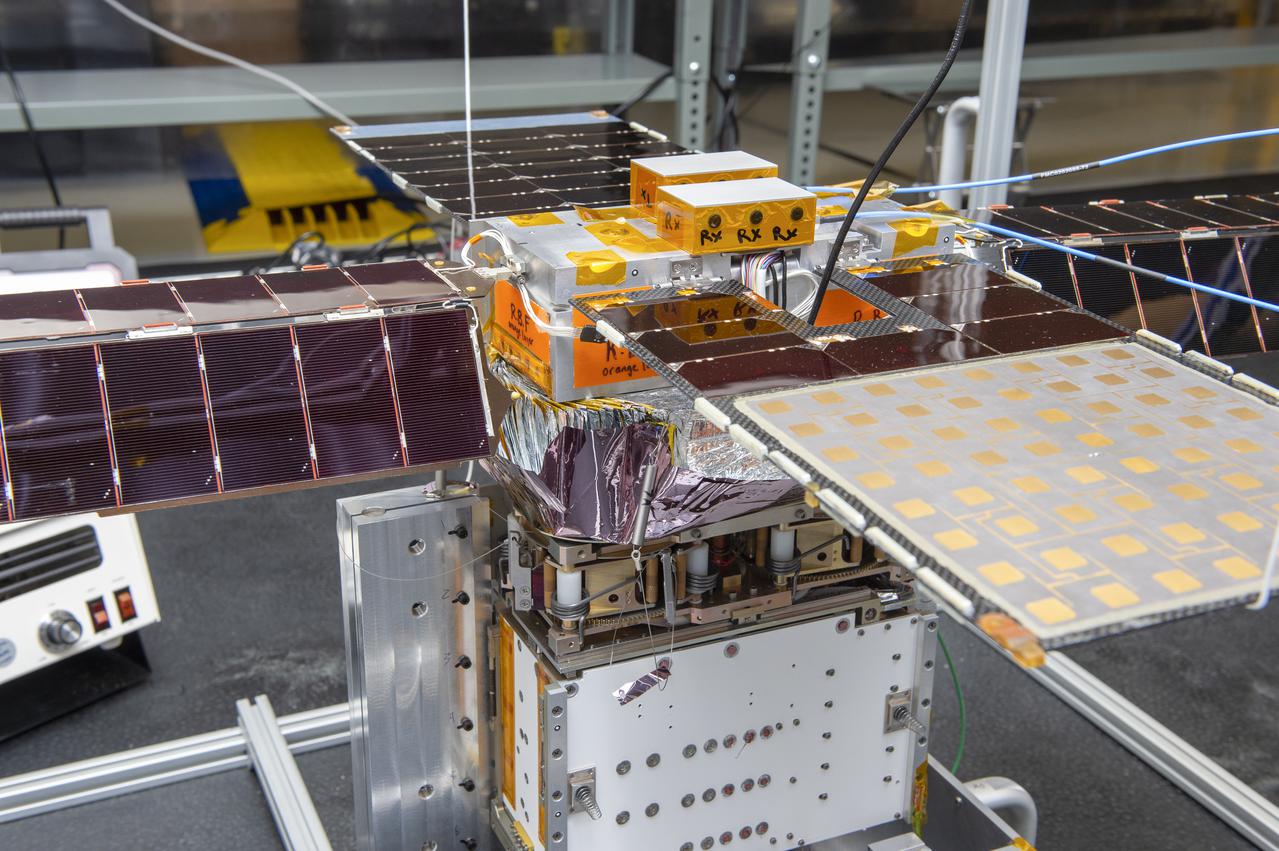
Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
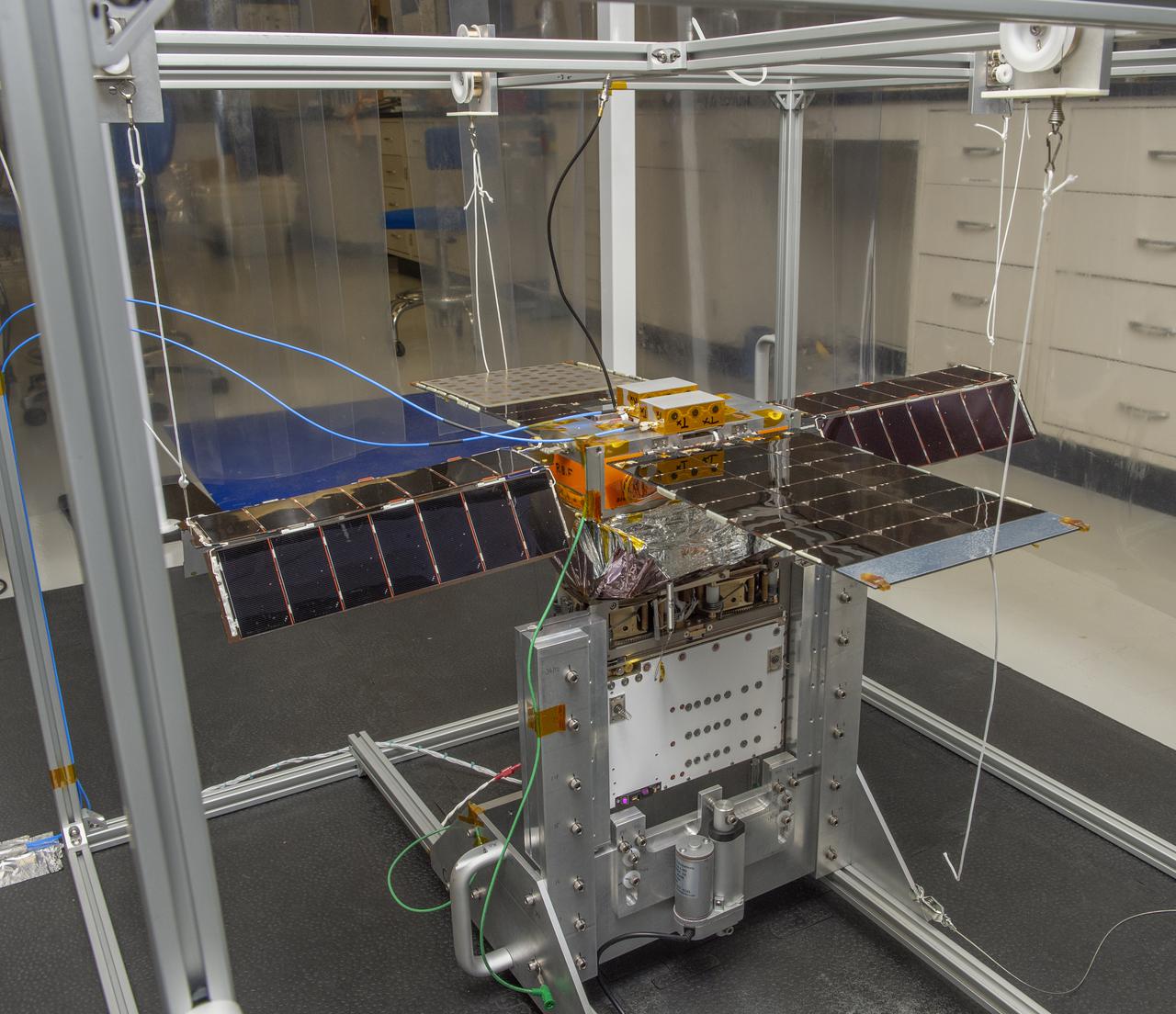

Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
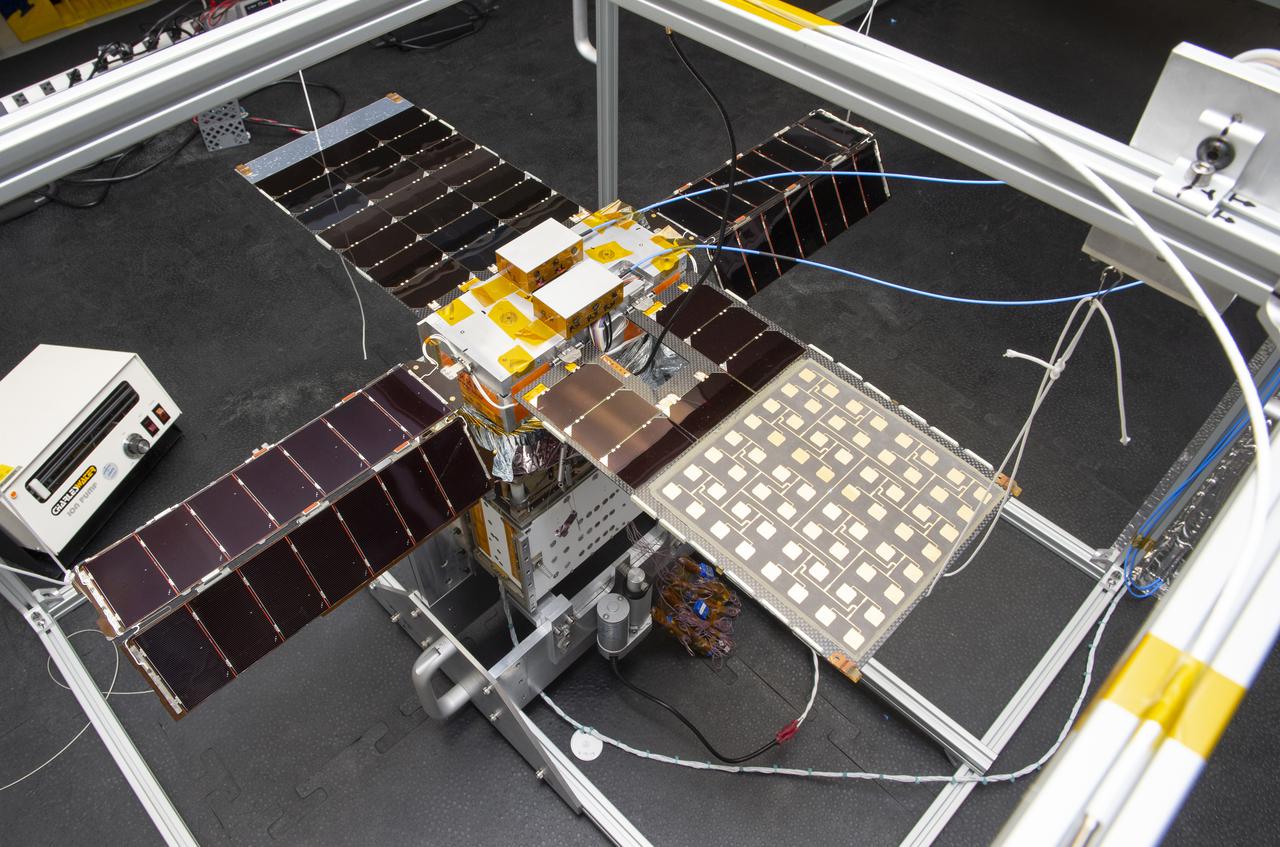
Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
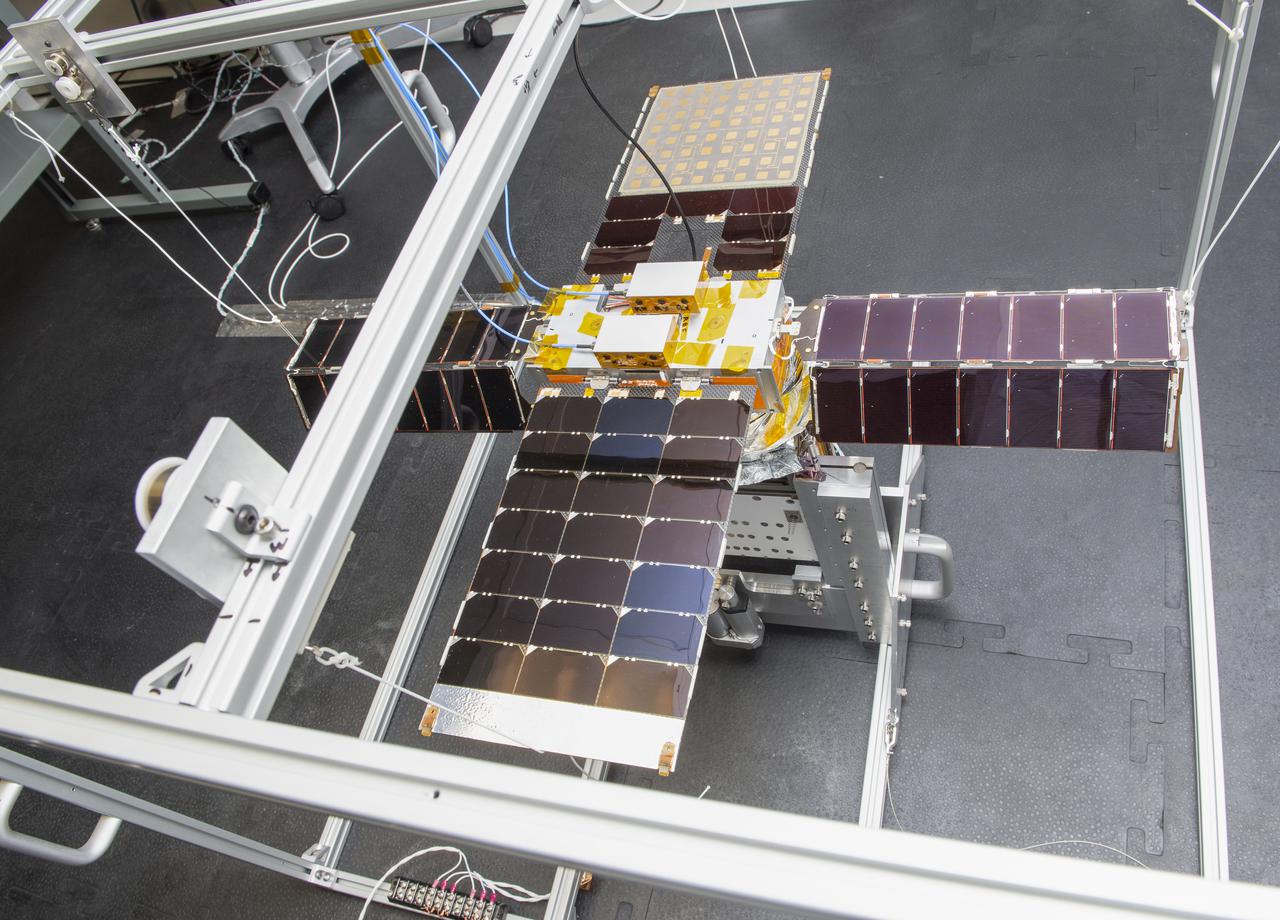
Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer

Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
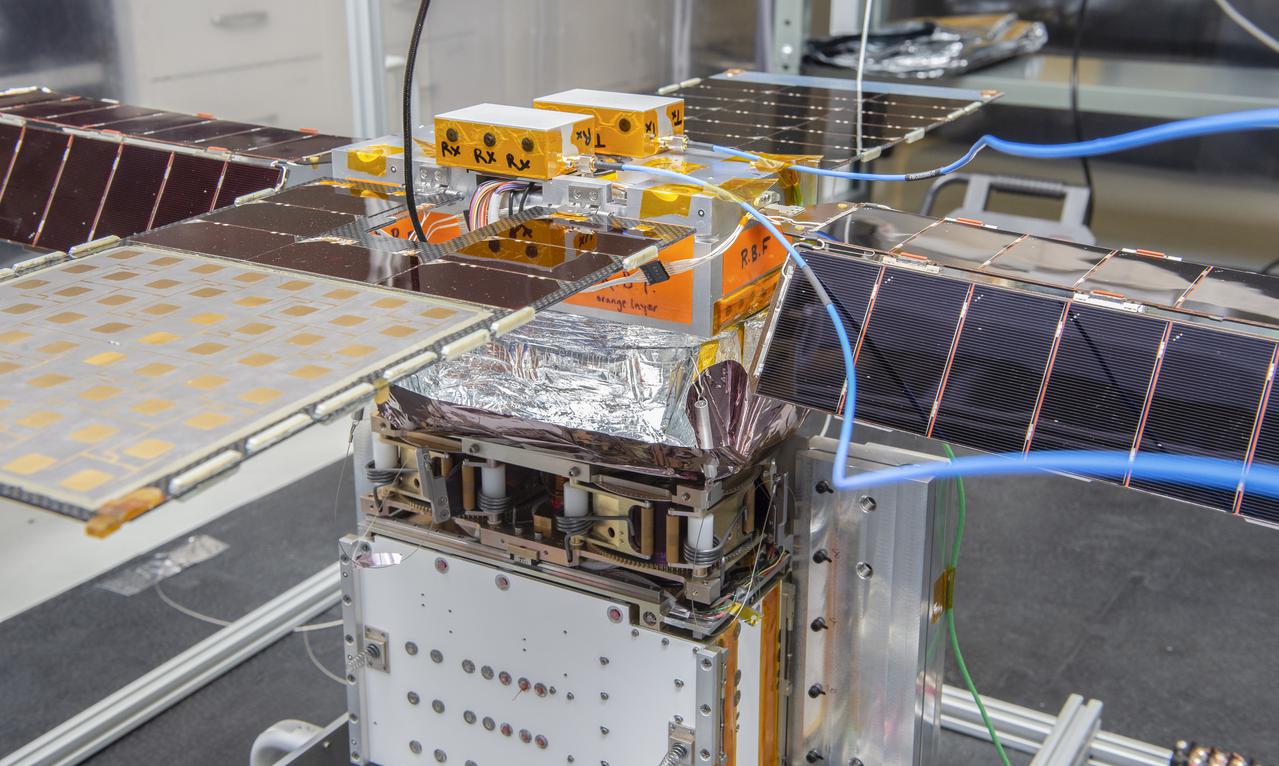
Spacecraft in Gravity Off-load Fixture (GOLF), System Test configuration - Arisa Waddle – Test Engineer, Rick Wilson – Lead Test Engineer
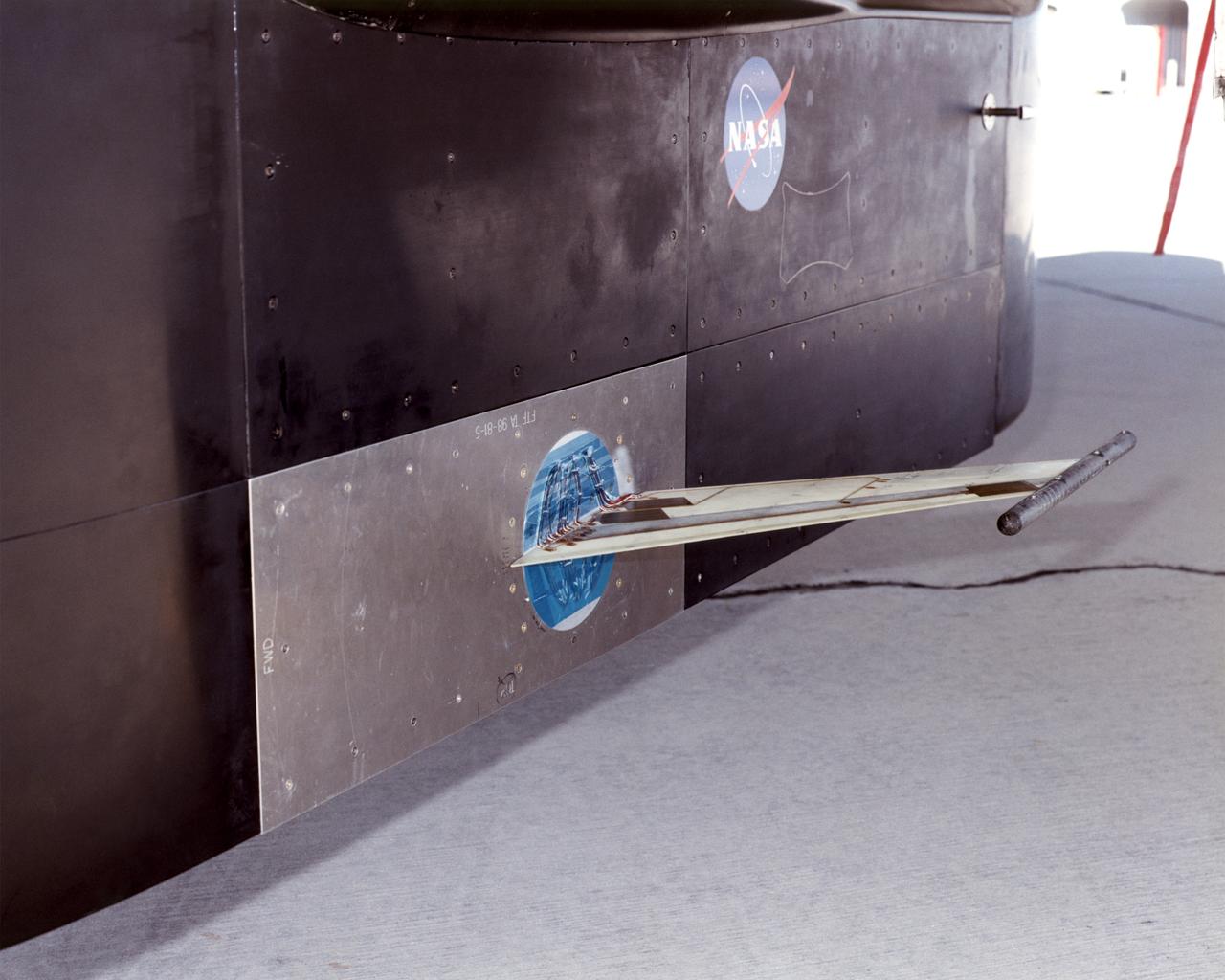

The Aerostructures Test Wing (ATW), which consisted of an 18-inch carbon fiber test wing with surface-mounted piezoelectric strain actuators, was mounted on a special ventral flight test fixture and flown on Dryden's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft
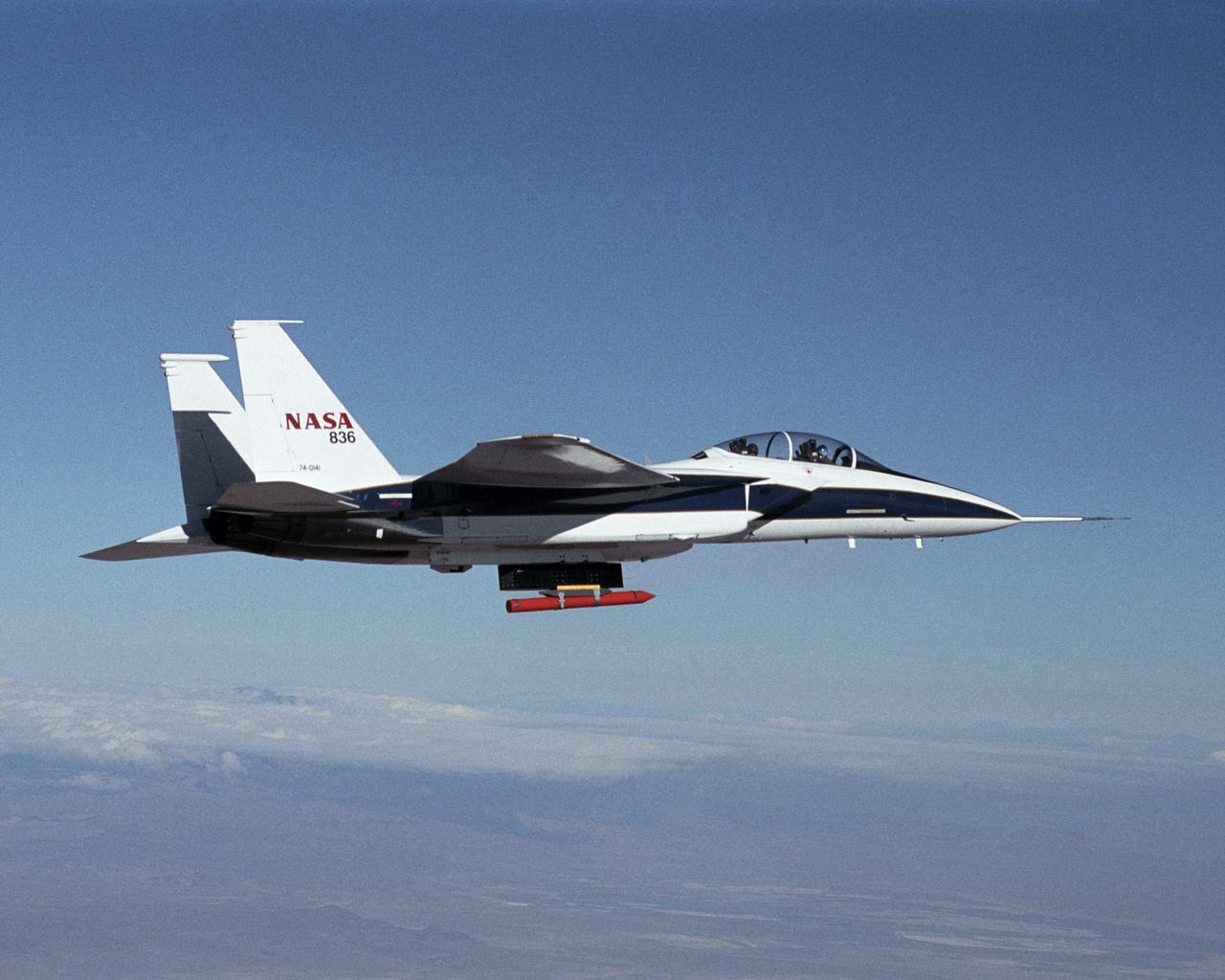

NASA Dryden's new in-house designed Propulsion Flight Test Fixture (PFTF) flew mated to a specially-equipped supersonic F-15B research aircraft during December 2001 and January 2002.
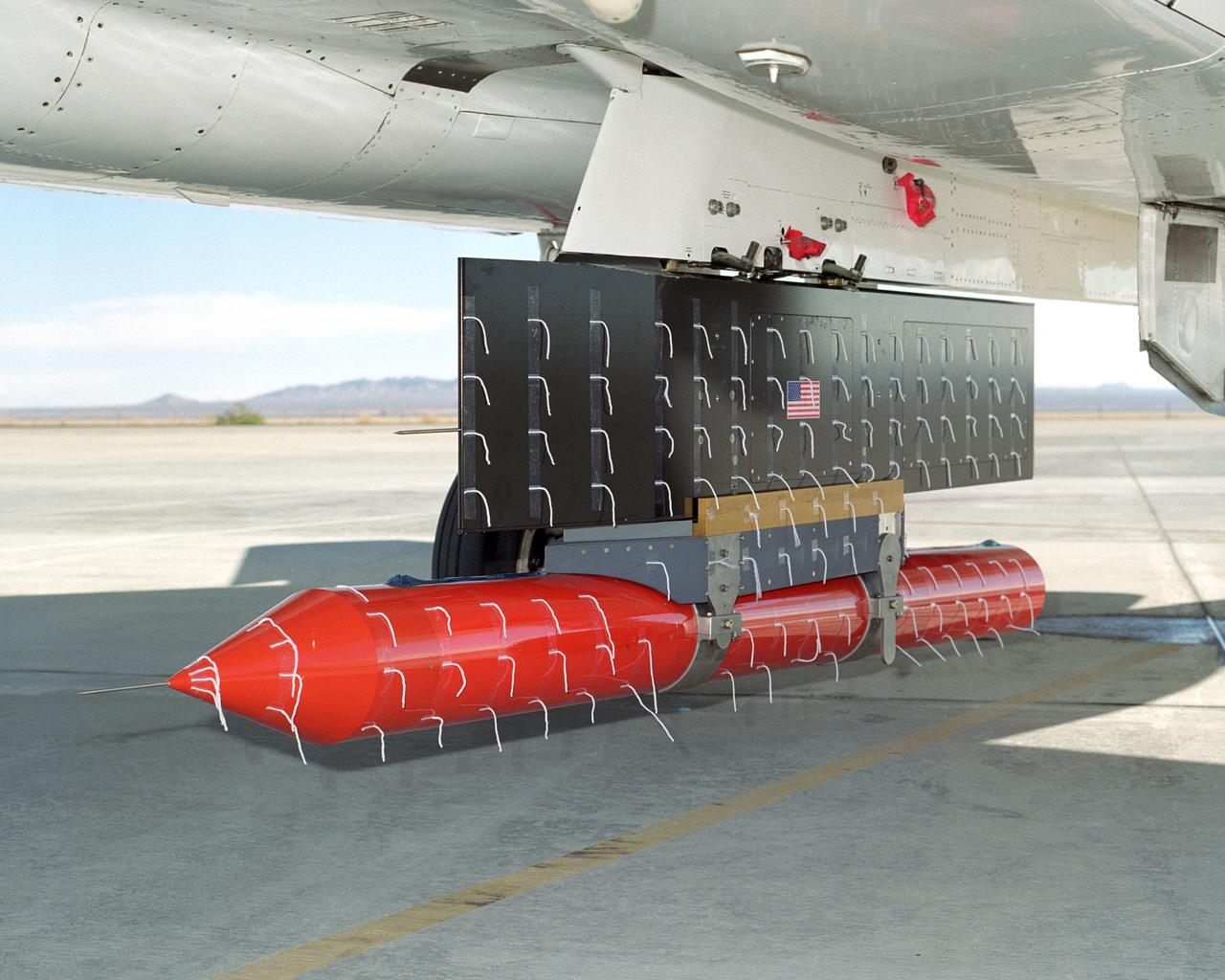

NASA Dryden's new in-house designed Propulsion Flight Test Fixture (PFTF), carried on an F-15B's centerline attachment point, underwent flight envelope expansion in order to verify its design and capabilities.
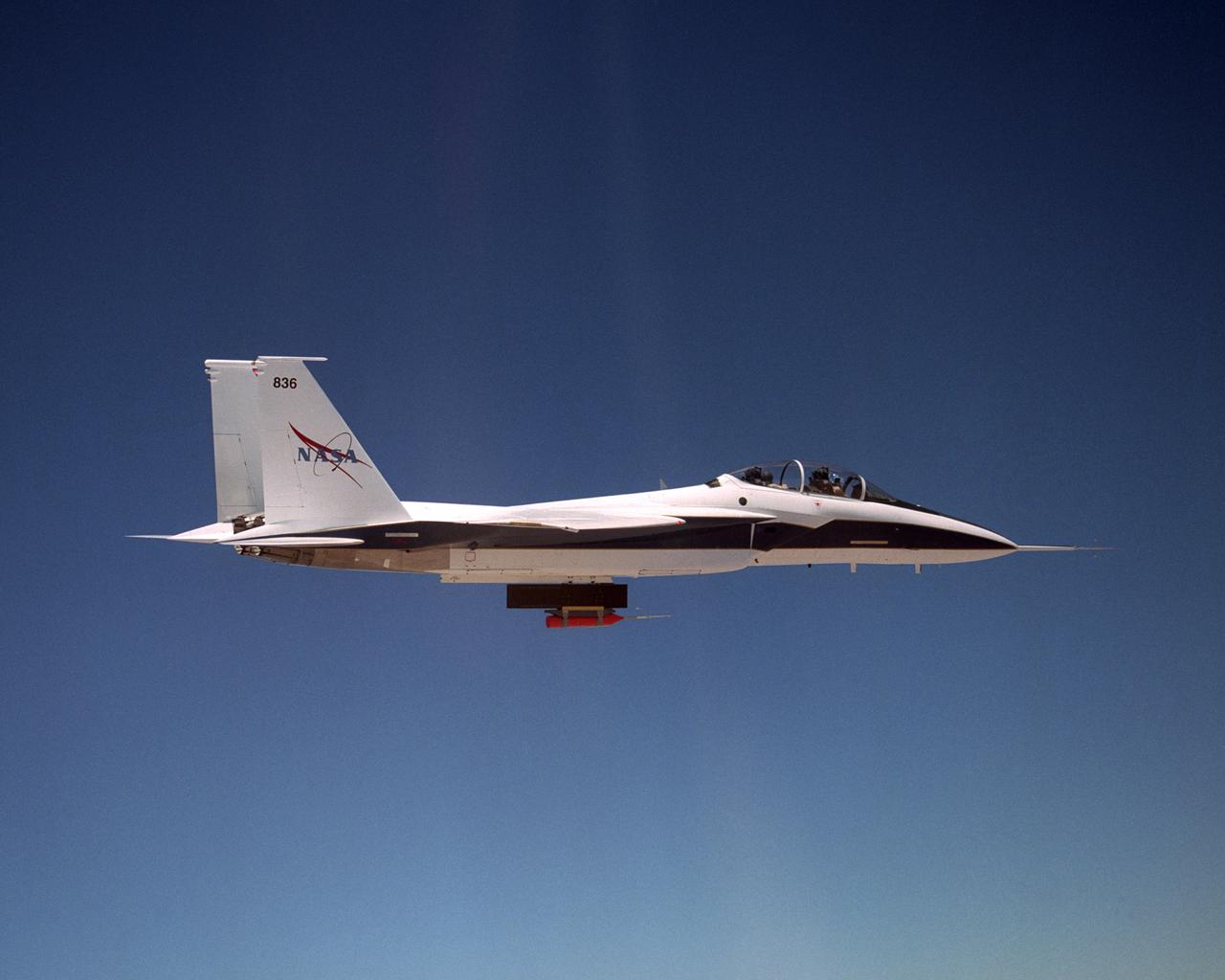

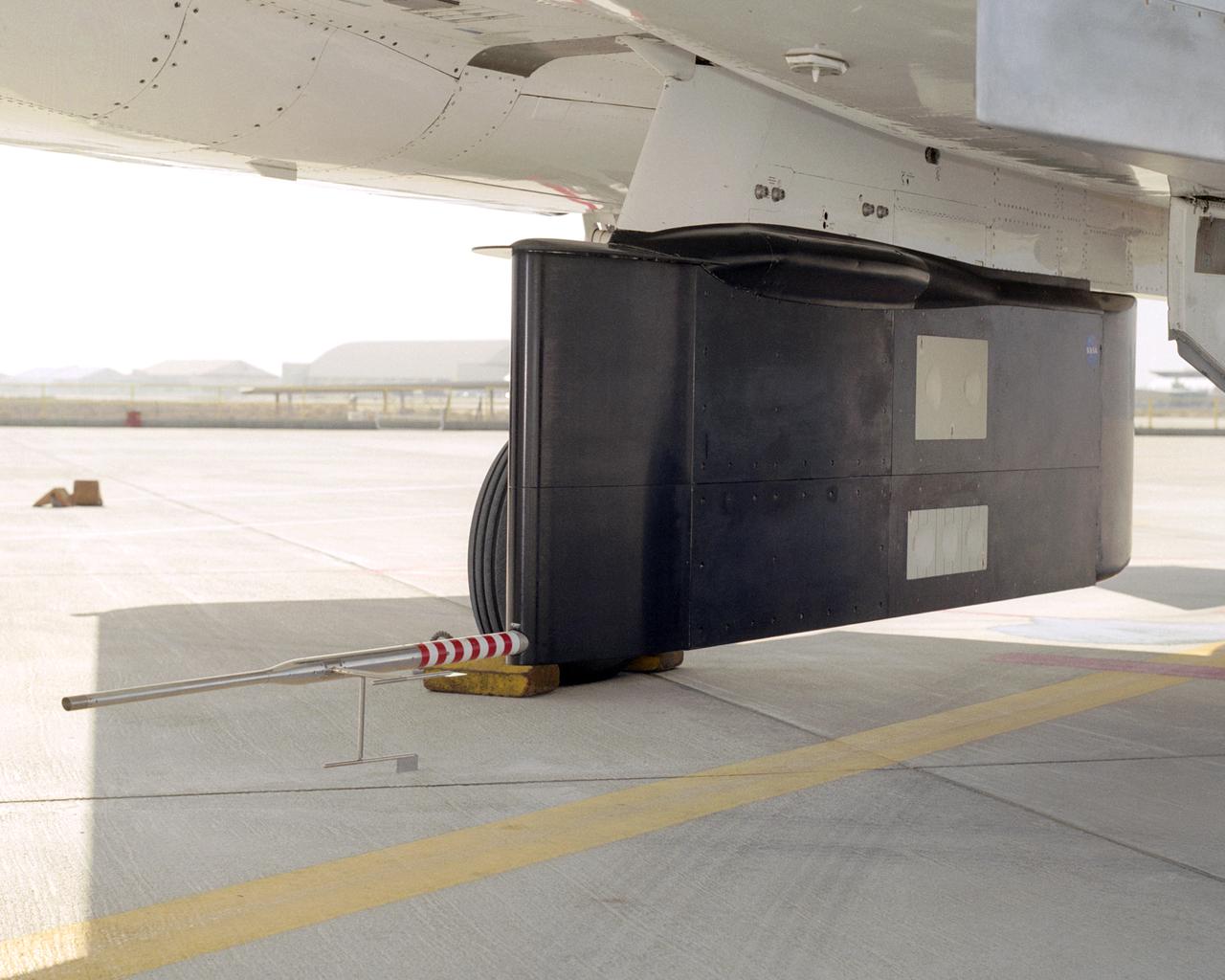
NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft flew instrumentation in June 2004 called the Local Mach Investigation (LMI), designed to gather local airflow data for future research projects using the aircraft's Propulsion Flight Test Fixture (PFTF). The PFTF is the black rectangular fixture attached to the aircraft's belly. The LMI package was located in the orange device attached to the PFTF.
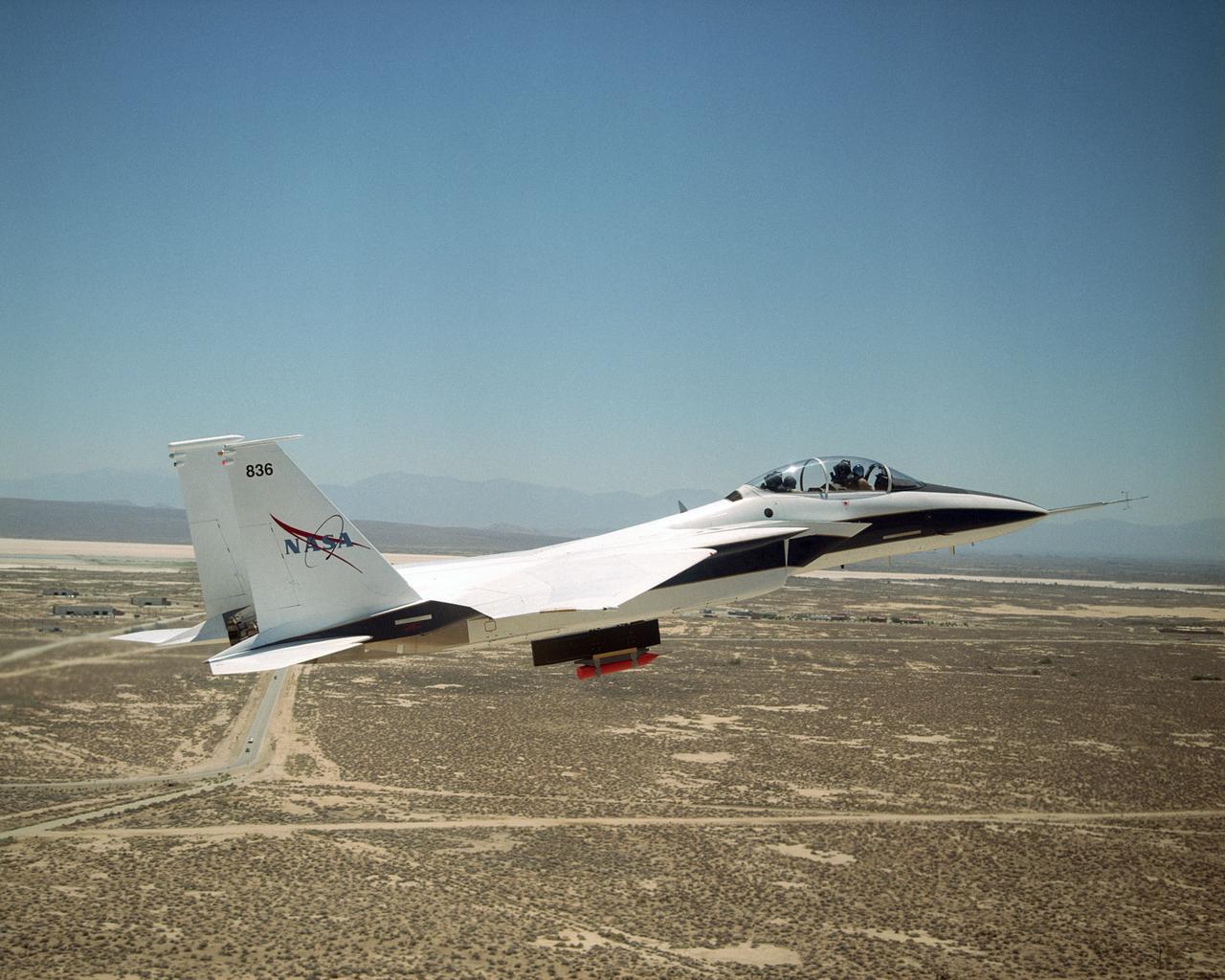

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft flew instrumentation in June 2004 called the Local Mach Investigation (LMI), designed to gather local airflow data for future research projects using the aircraft's Propulsion Flight Test Fixture (PFTF). The PFTF is the black rectangular fixture attached to the aircraft's belly. The LMI package was located in the orange device attached to the PFTF.

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft flew instrumentation in June 2004 called the Local Mach Investigation (LMI), designed to gather local airflow data for future research projects using the aircraft's Propulsion Flight Test Fixture (PFTF). The PFTF is the black rectangular fixture attached to the aircraft's belly. The LMI package was located in the orange device attached to the PFTF.
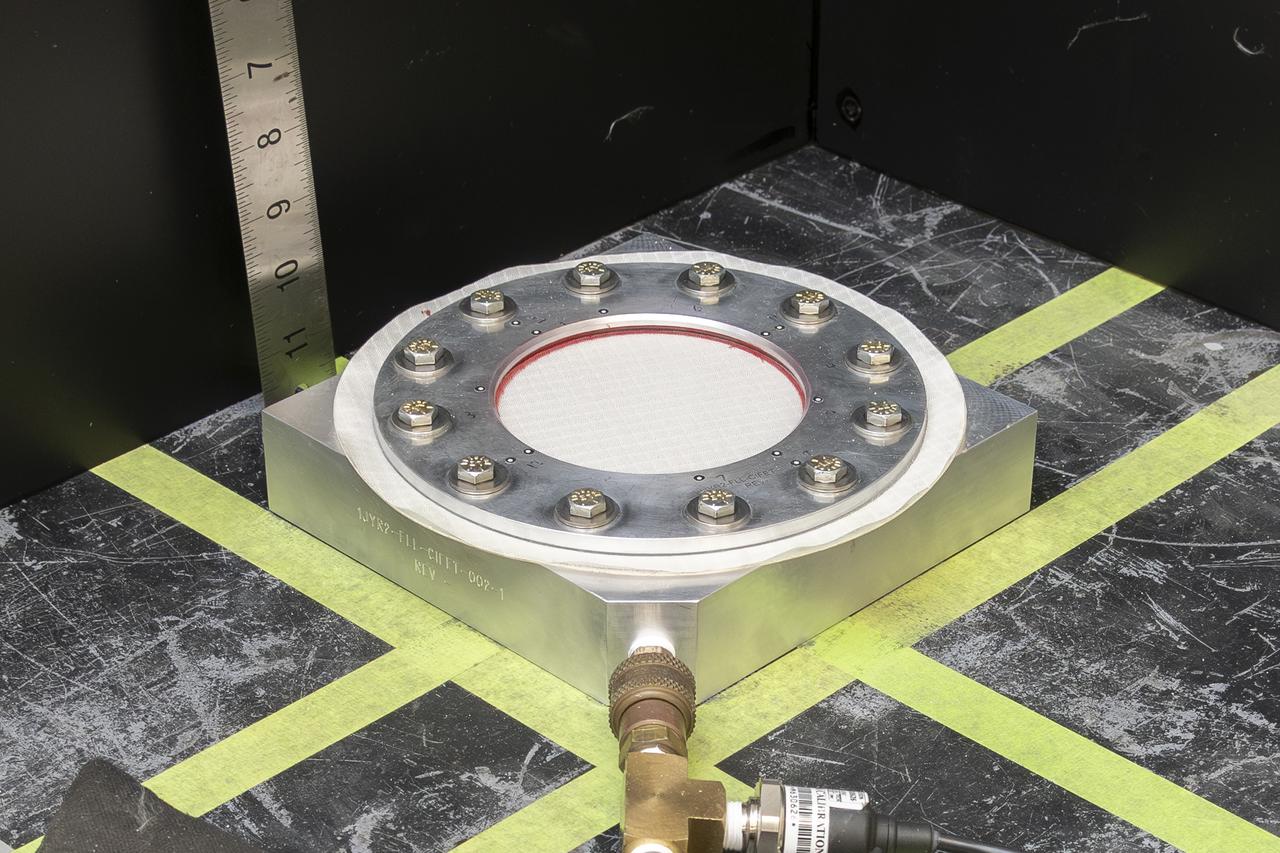
The test team prepares a test fixture with a nylon fabric sample at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The fabric in the test fixture forms a bubble when pressure is applied to the silicone bladder underneath. A similar test can be performed with a sensor on the fabric to verify the sensor will work when stretched in three dimensions.
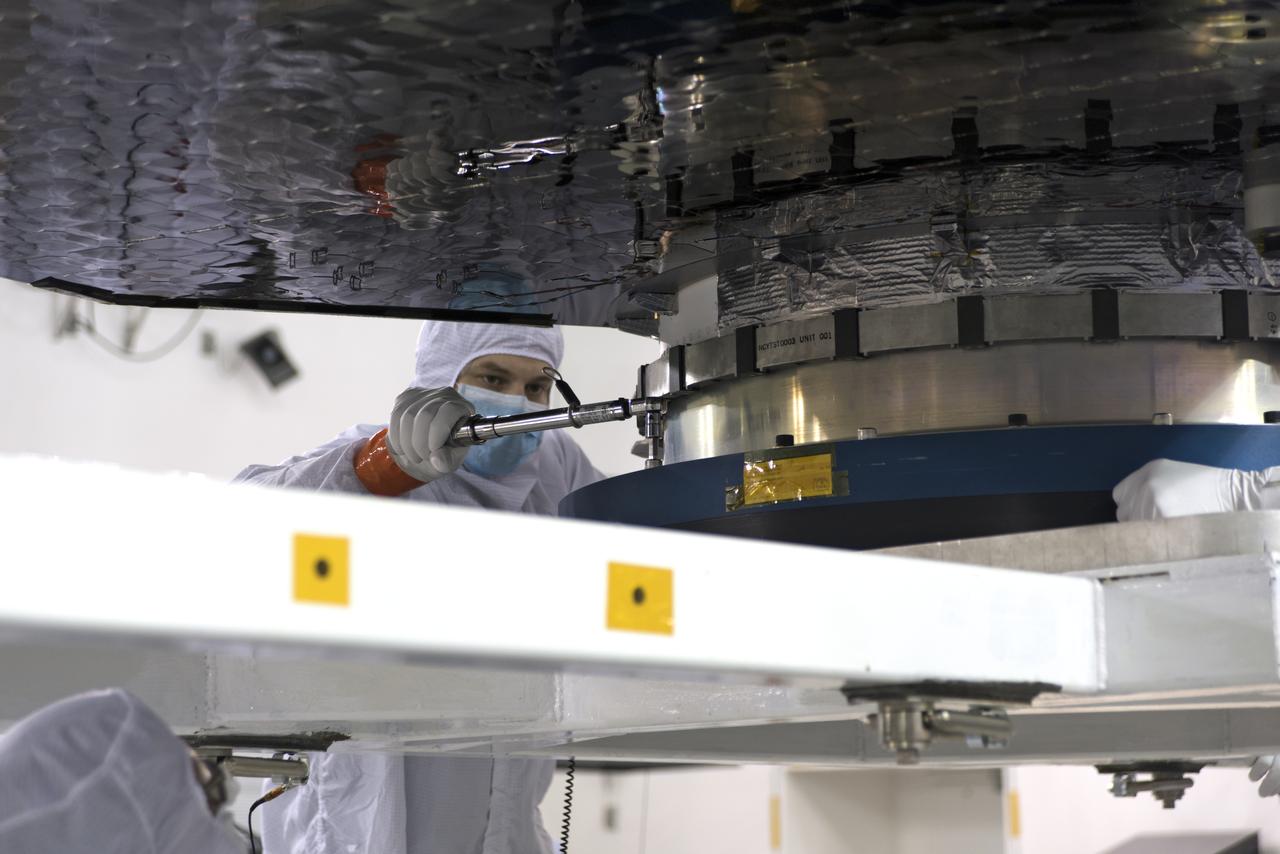

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft has been mounted on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
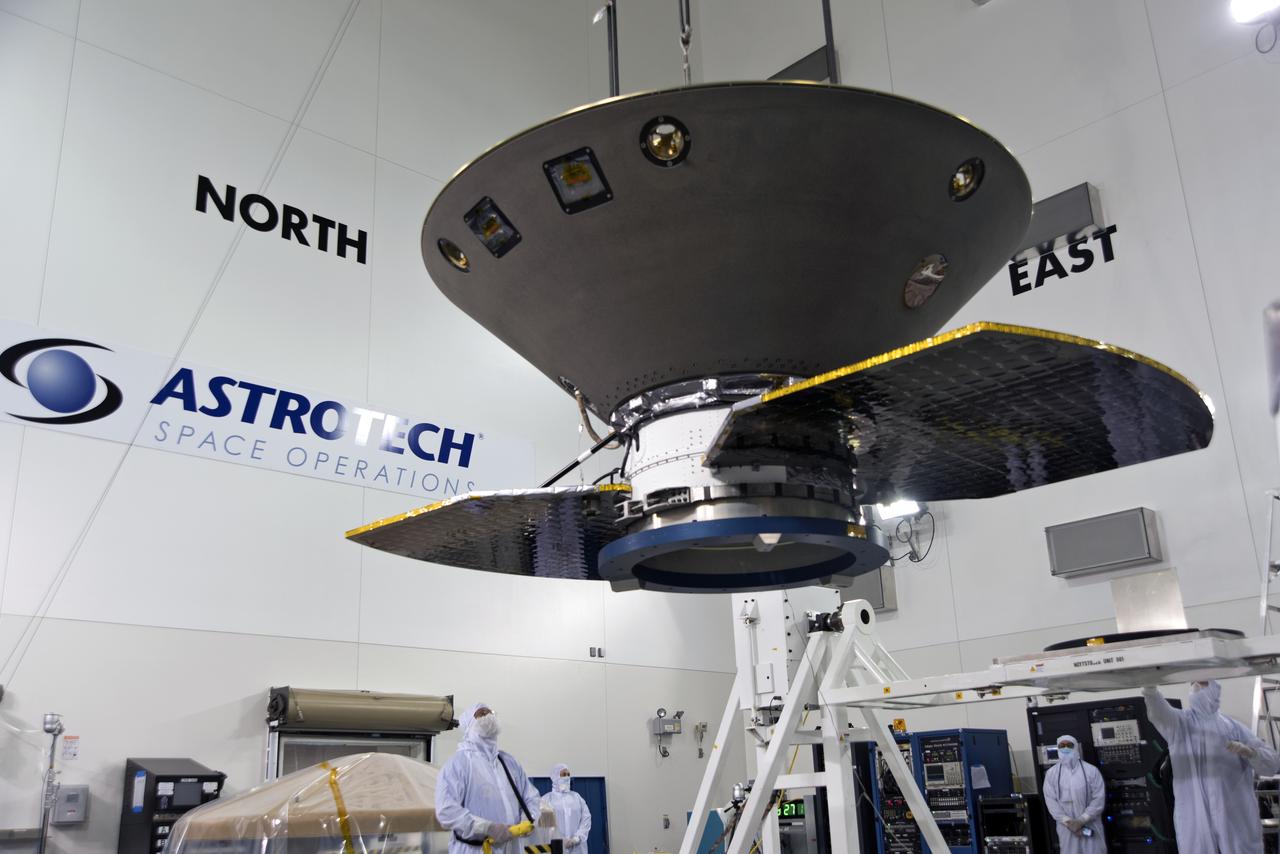

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is lifted for mounting on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
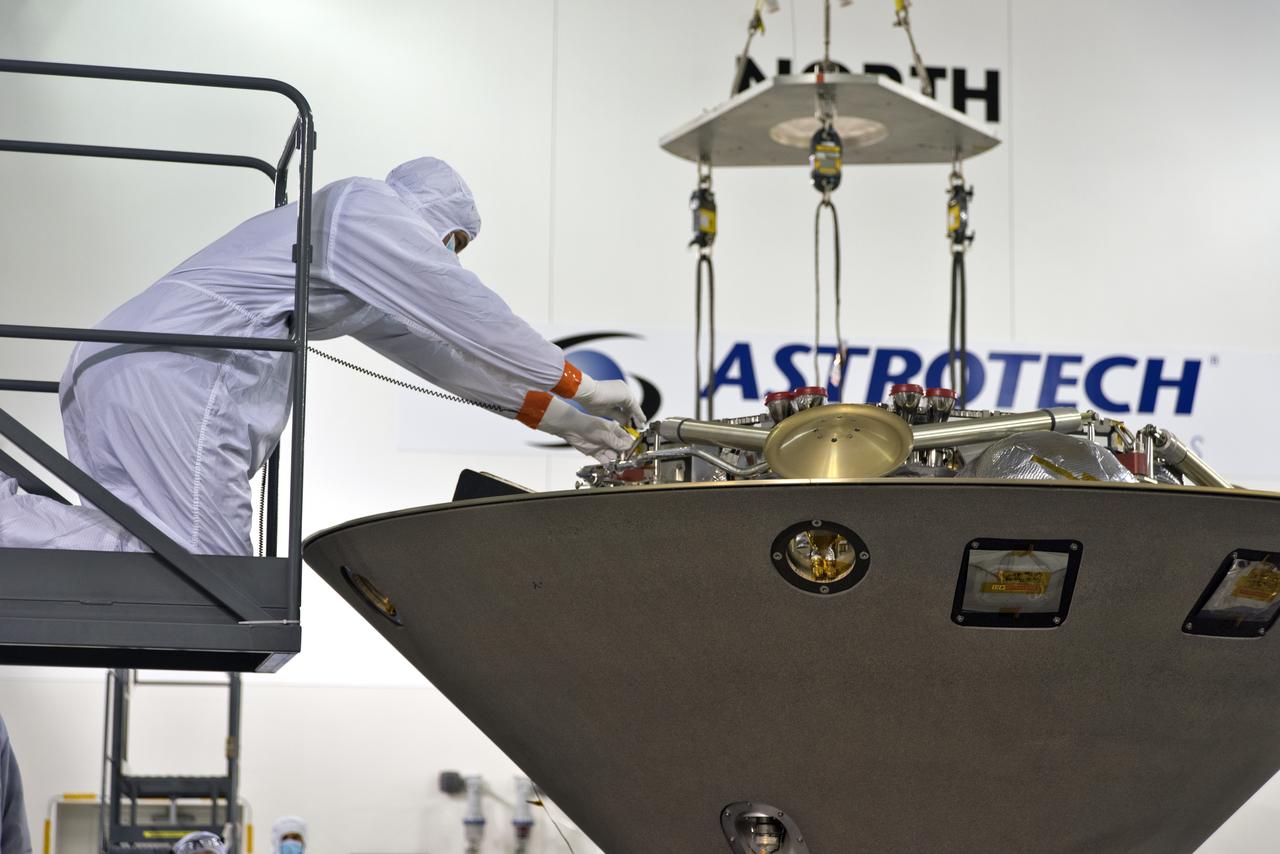

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is prepared to be lifted on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
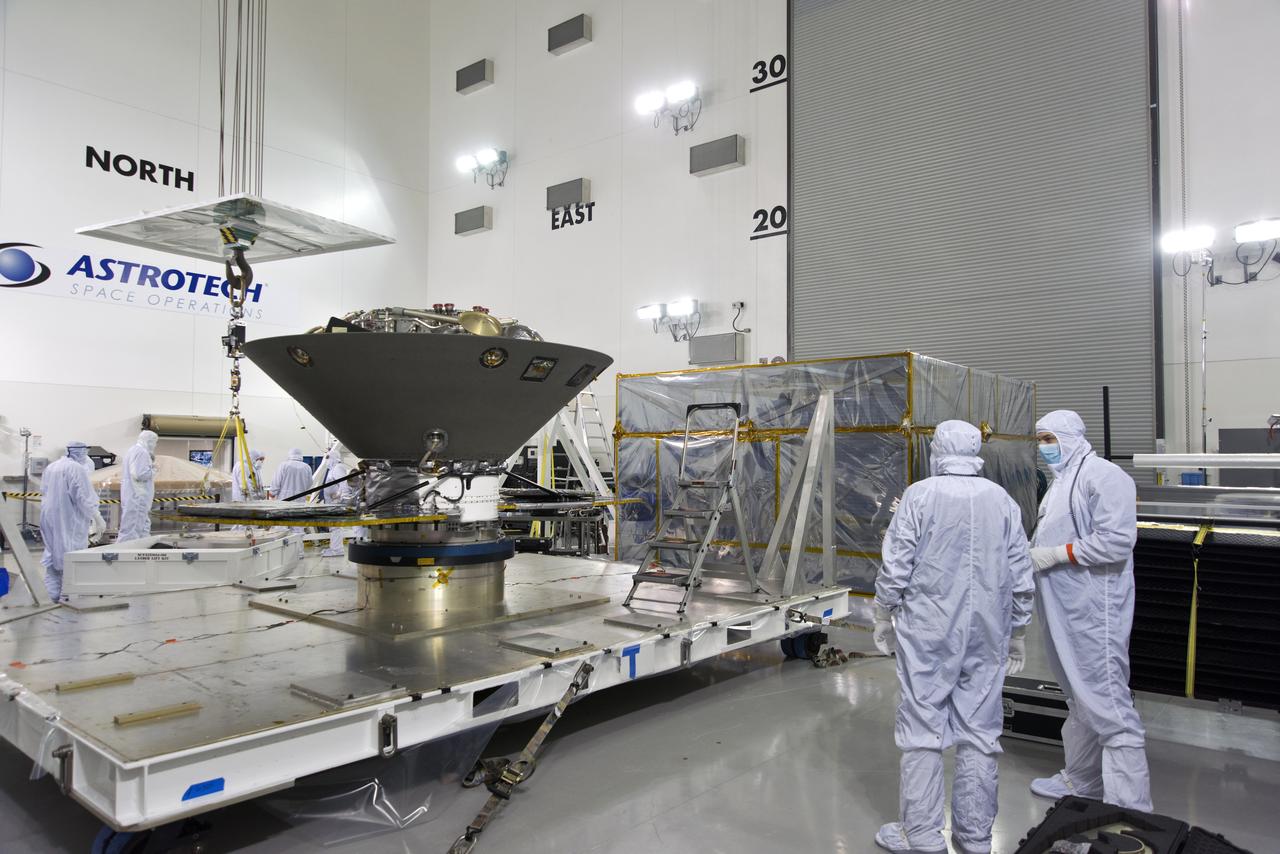

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is prepared to be lifted on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
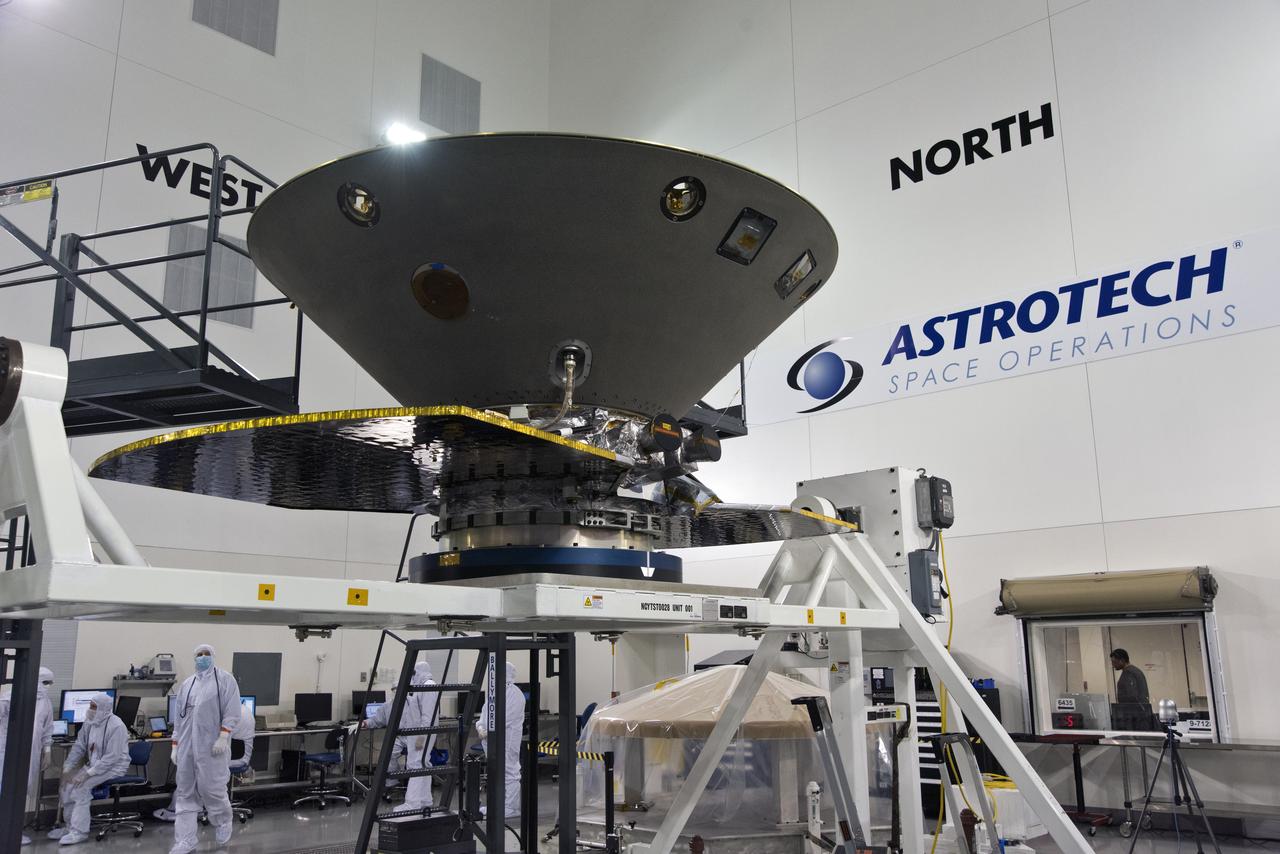

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft has been mounted on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
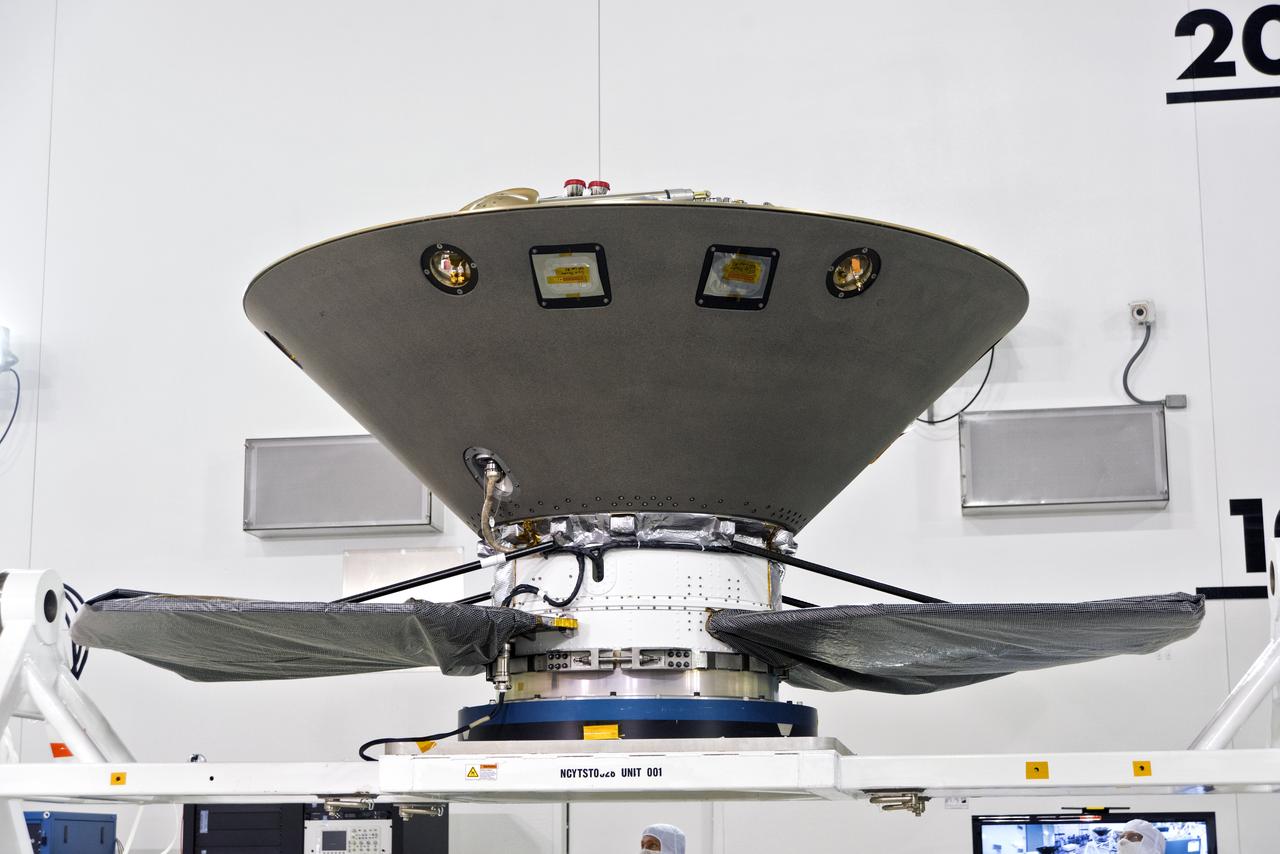

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft has been mounted on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
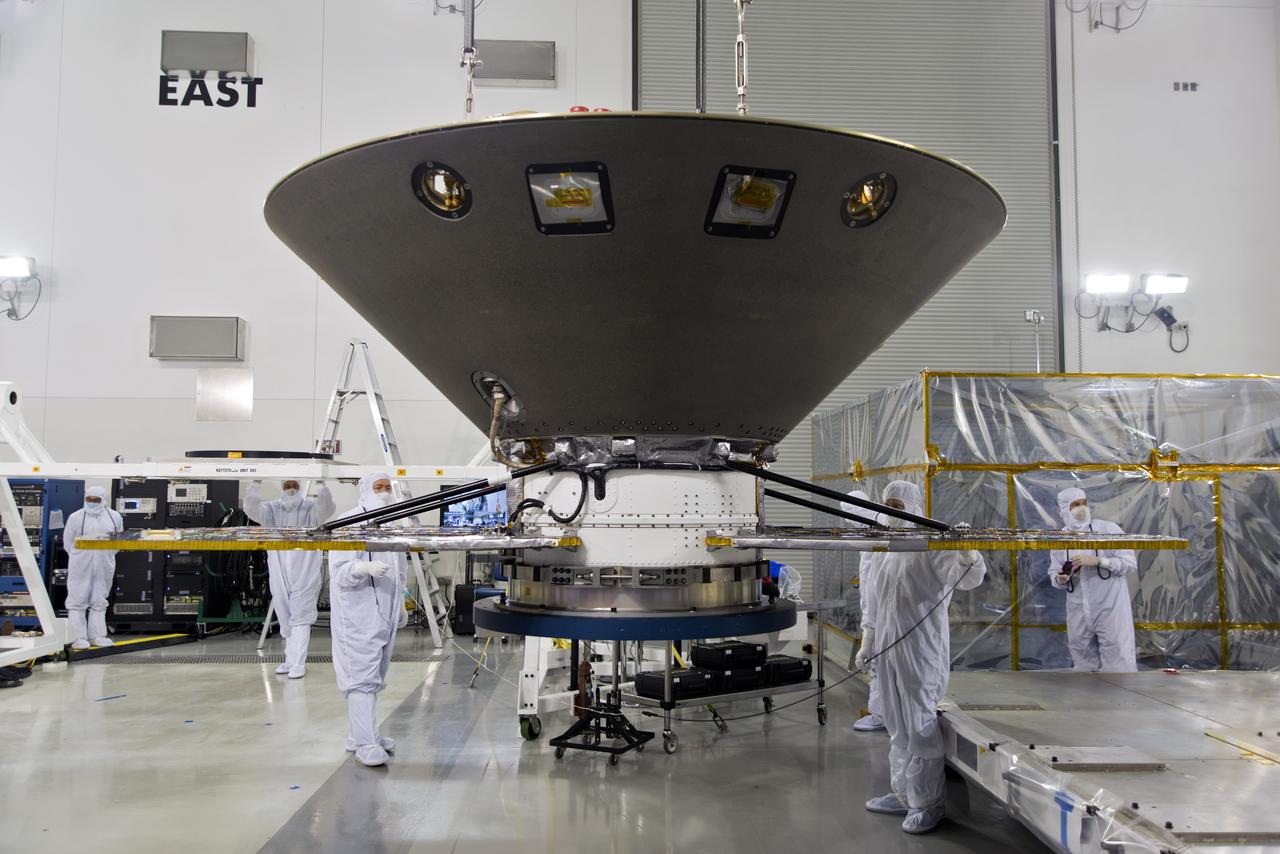

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is prepared to be lifted on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is rotated on a fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
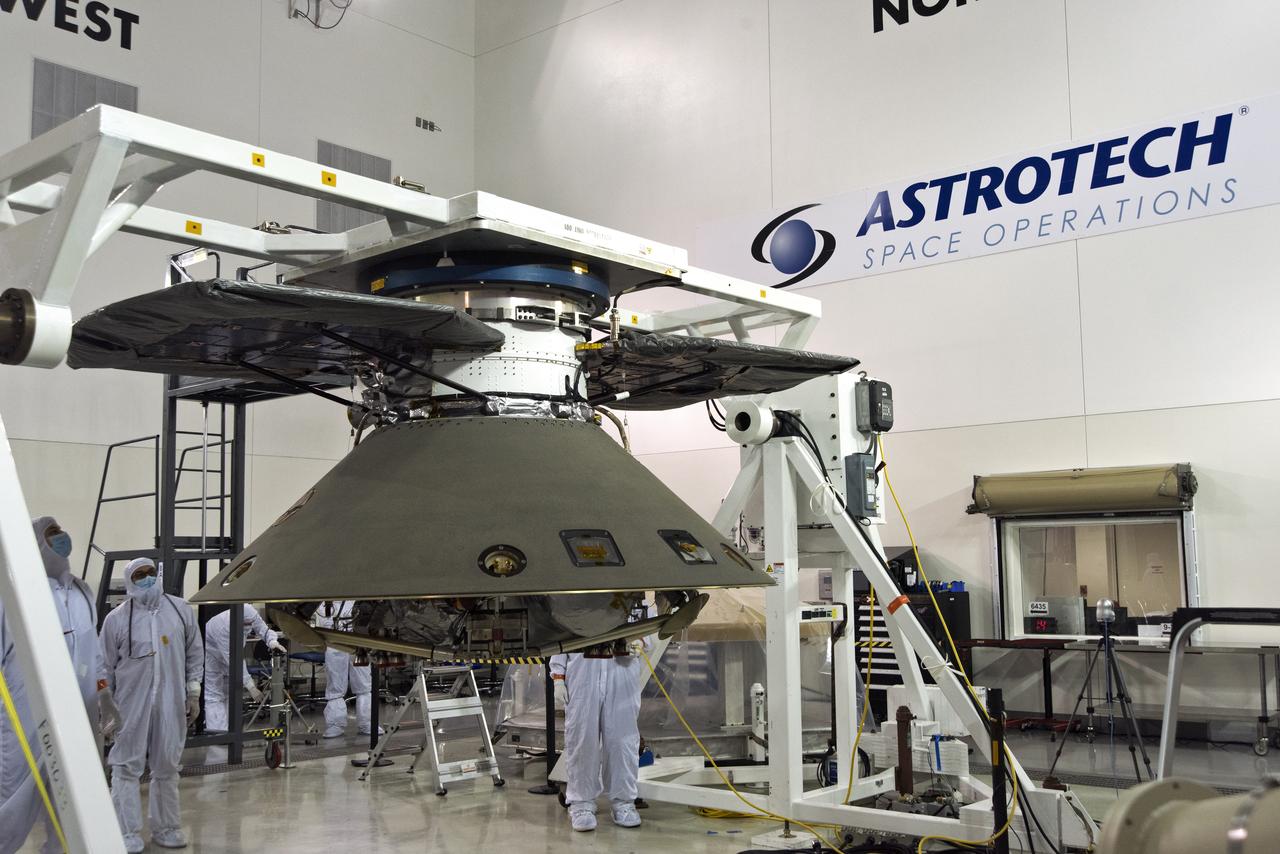

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft has been rotated on a fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
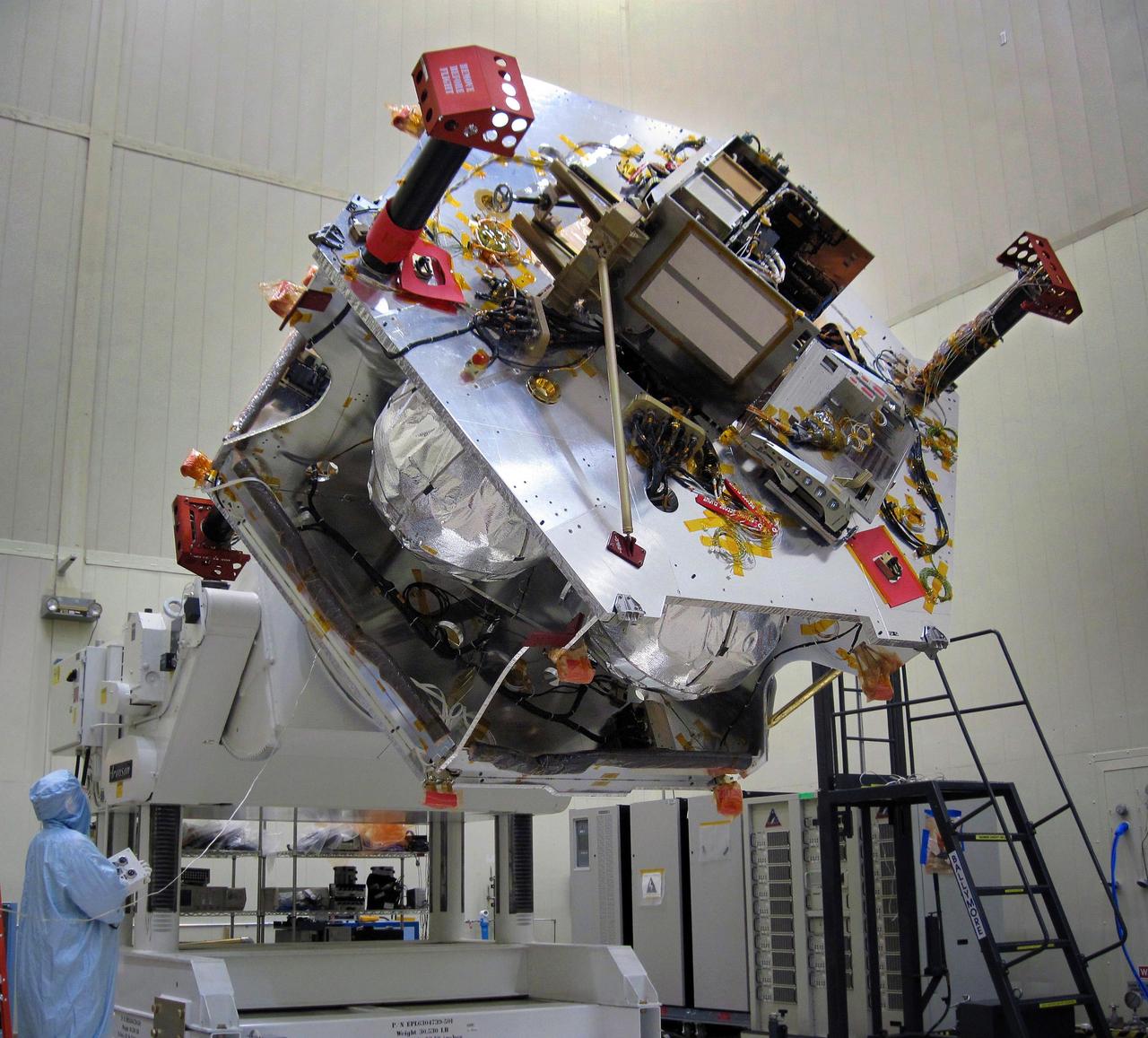

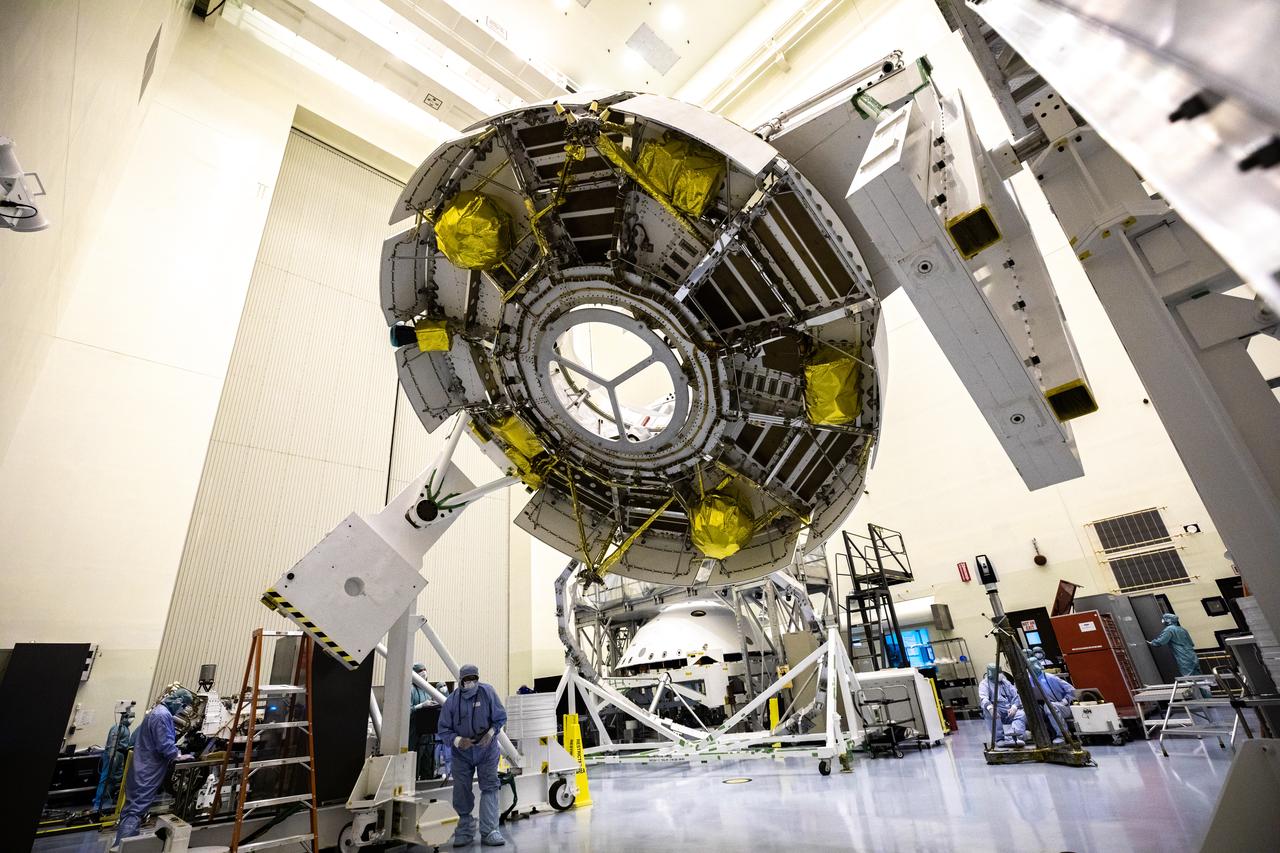
Once the radiation vault was installed on top of the propulsion module, NASA Juno spacecraft was lifted onto a large rotation fixture. The fixture allows the spacecraft to be turned for convenient access for integrating and testing instruments.
Engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida remove the vibration fixture on the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument on Aug. 4, 2022. The activity followed a vibration test in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
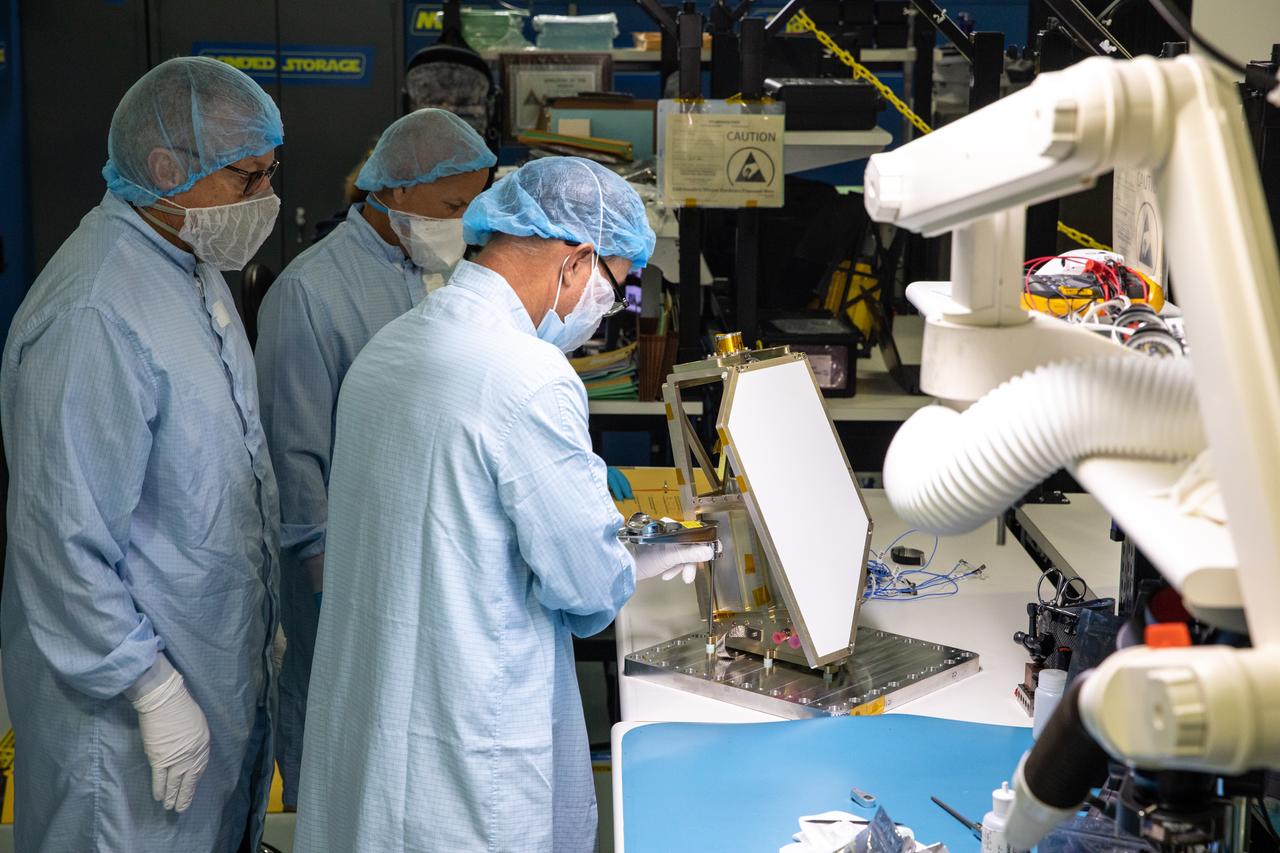
Engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida remove the vibration fixture on the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument on Aug. 4, 2022. The activity followed a vibration test in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.

Engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida remove the vibration fixture on the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument on Aug. 4, 2022. The activity followed a vibration test in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.

Engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida remove the vibration fixture on the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument on Aug. 4, 2022. The activity followed a vibration test in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
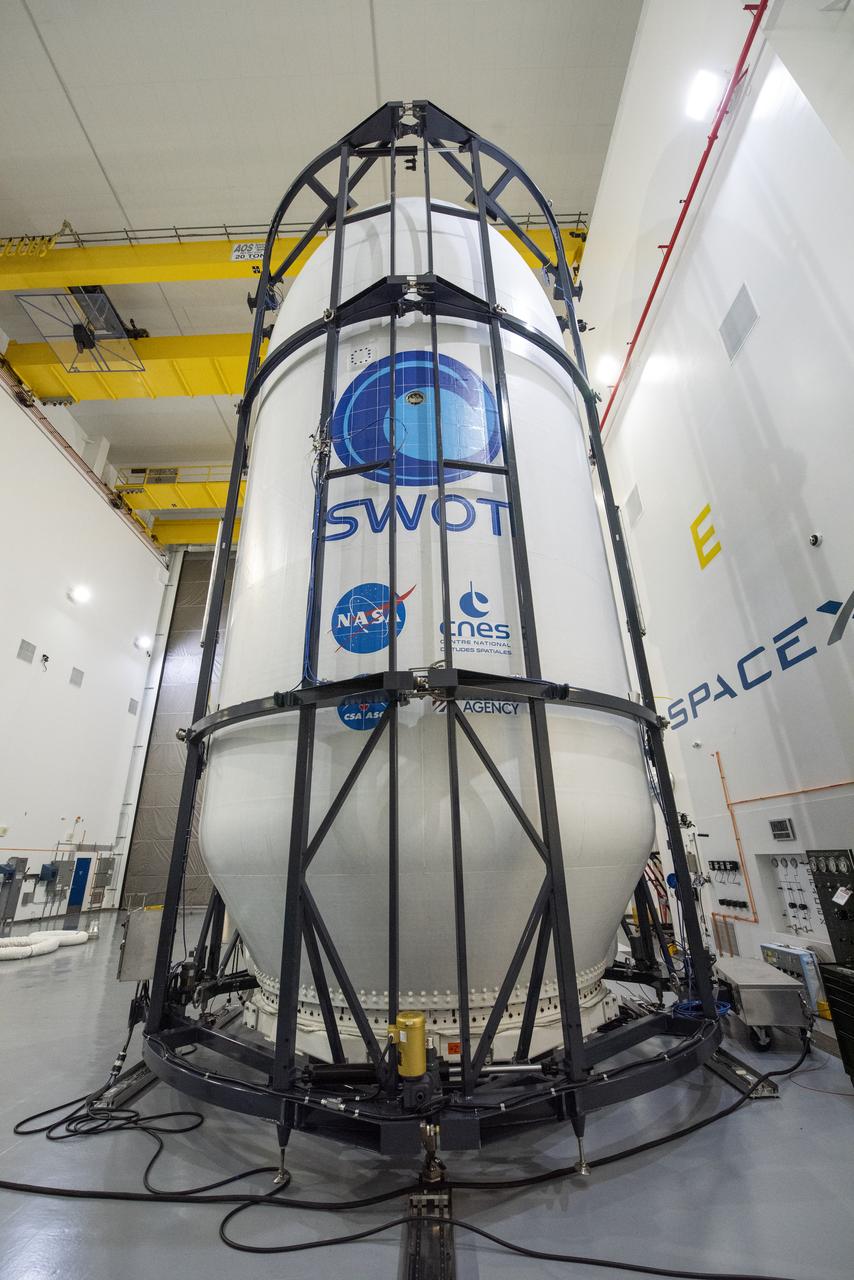

Inside the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, decal fixtures are placed on the SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite on Dec. 9, 2022. A collaboration between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency, SWOT will be the first satellite to survey nearly all water on Earth’s surface. SWOT is scheduled to lift off aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST.
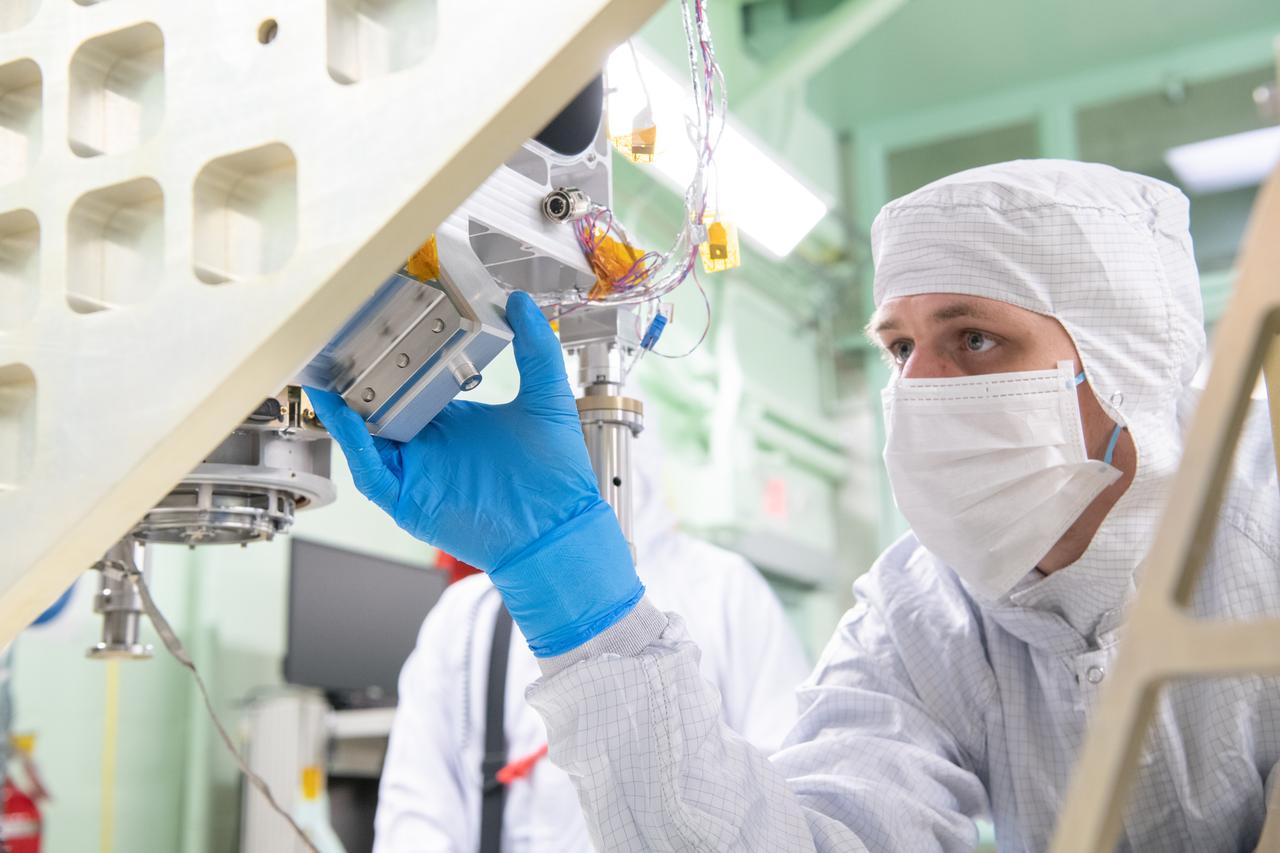

Mechanical technician, Joseph Eddy, carefully guides the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) Main Optics Bench (MOB) during a crane lift onto its turnover fixture. This fixture allows the team to integrate additional components multiple different orientations. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
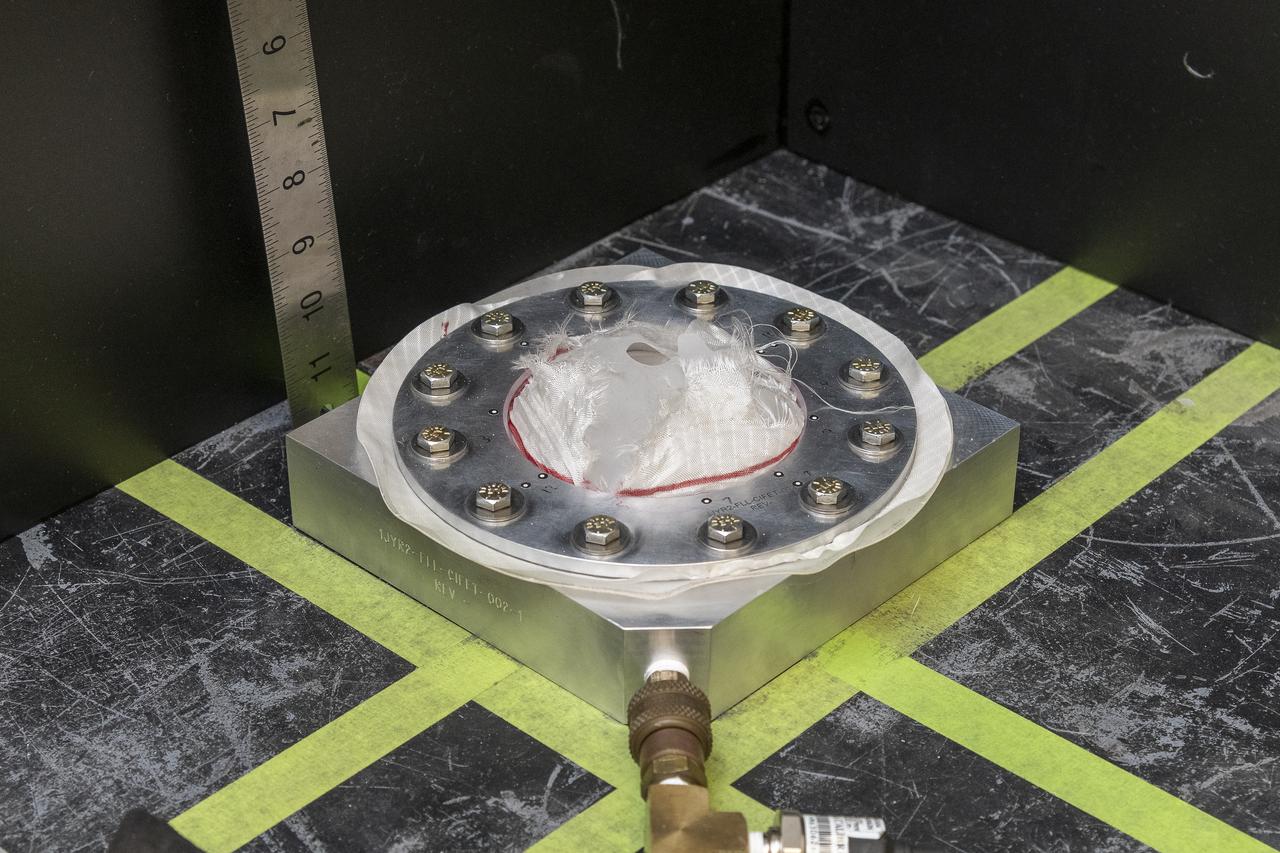
Pressure is applied to a test fixture with a nylon fabric sample until it fails at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The fabric in the test fixture forms a bubble when pressure is applied to the silicone bladder underneath. In this frame, the silicone bladder is visible underneath the torn fabric after it was inflated to failure. A similar test can be performed with a sensor on the fabric to verify the sensor will work when stretched in three dimensions.

This photo shows the Shuttle tile flight test fixture under the wing of a National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration WP-3D aircraft.
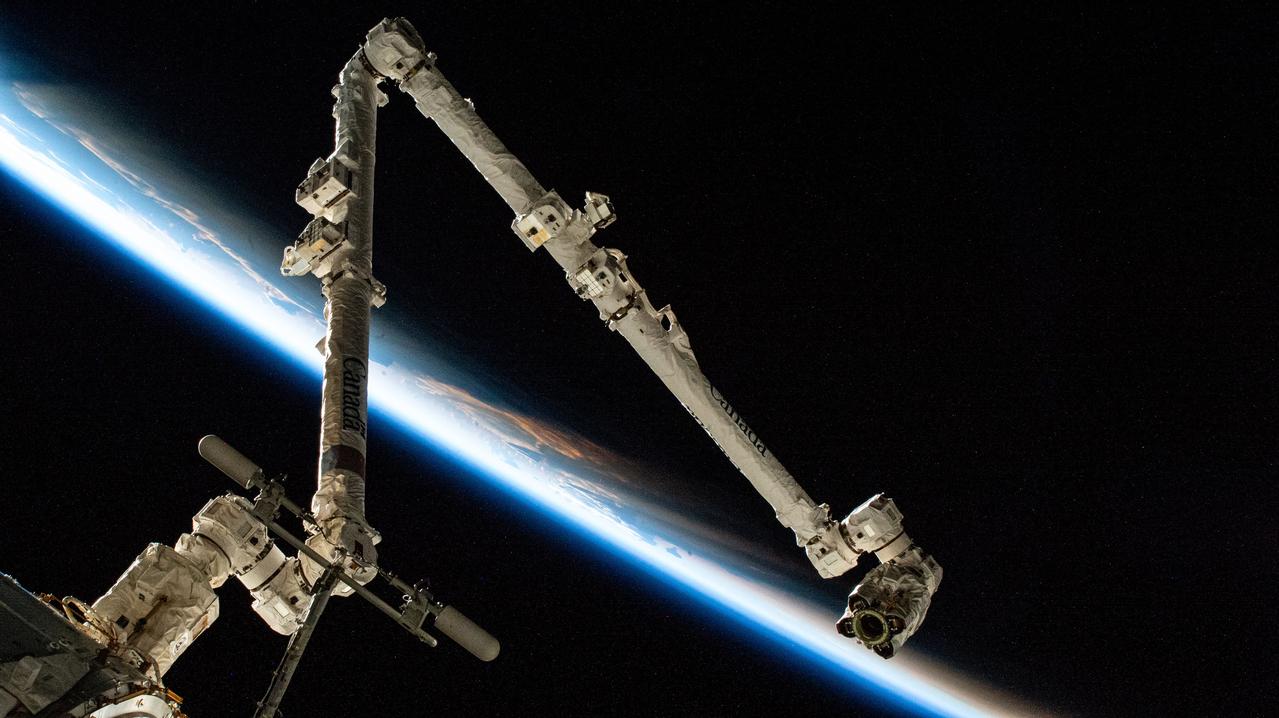

iss073e0657546 (Sept. 8, 2025) --- The 57.7-foot-long Canadarm2 robotic arm extends from a grapple fixture on the International Space Station as it soared into an orbital sunrise 260 miles above the Philippine Sea at approximately 4:04 a.m. local time.
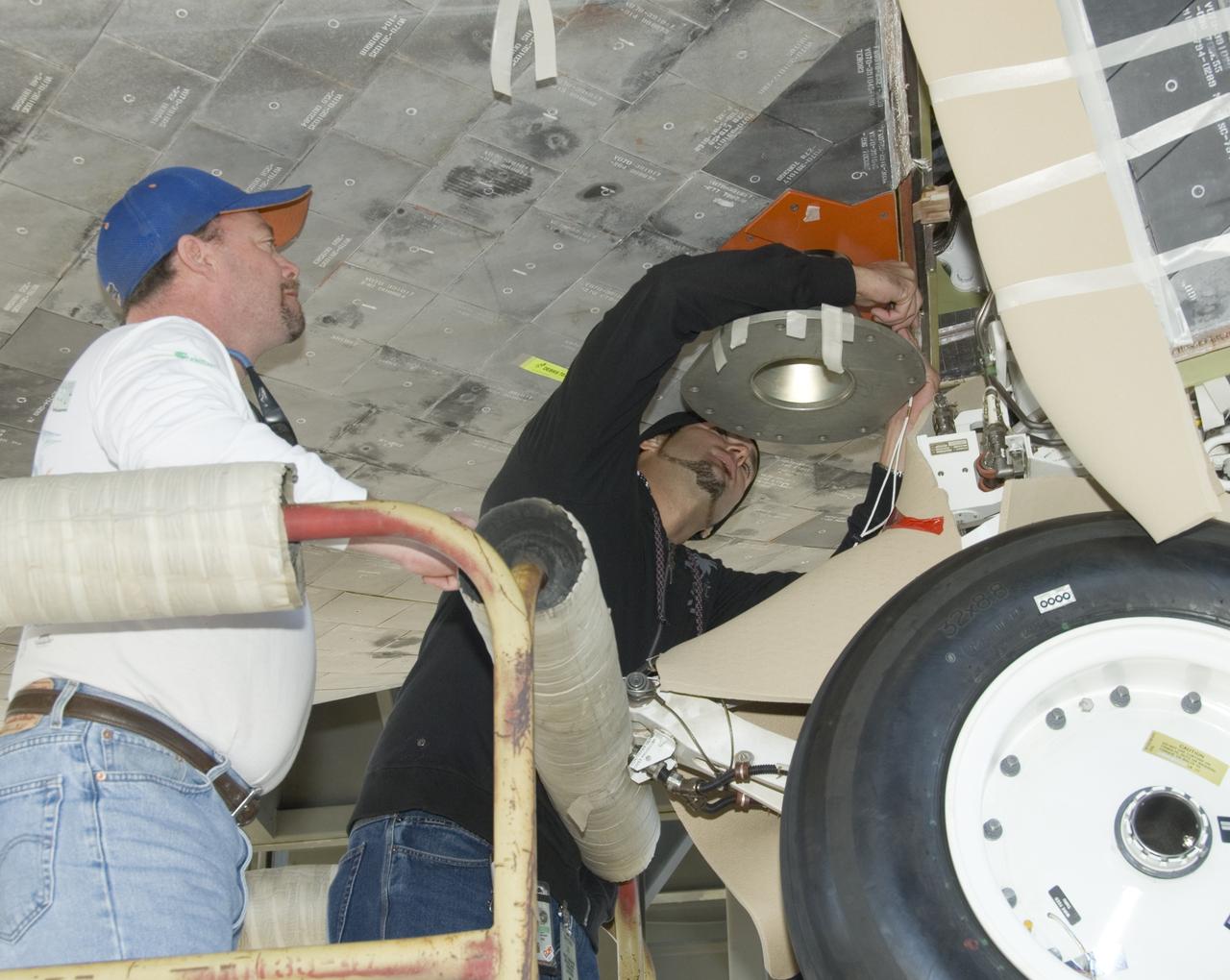

United Space Alliance employees Mark Burton and Russell Wazniak attach the forward mount fixture to Shuttle Endeavour for mounting the orbiter to the 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft.
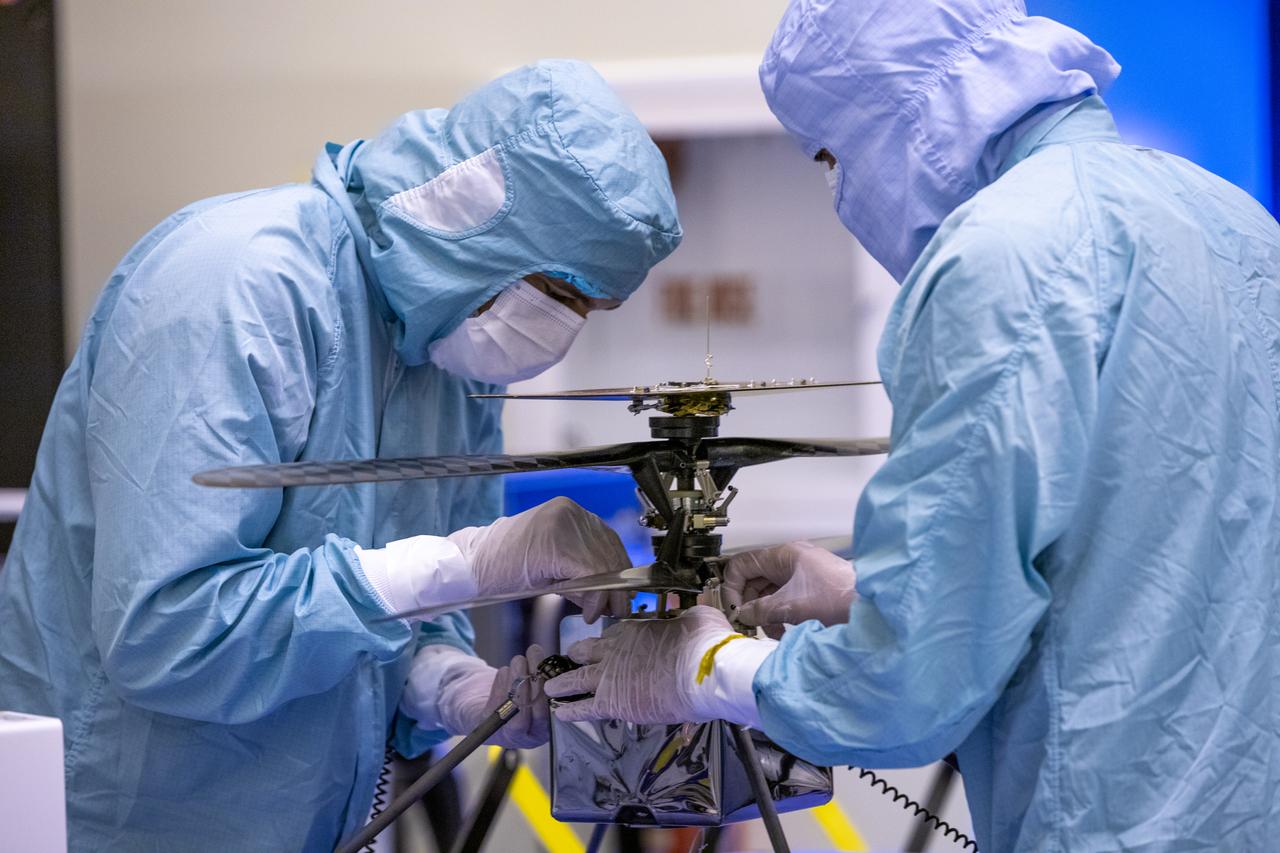

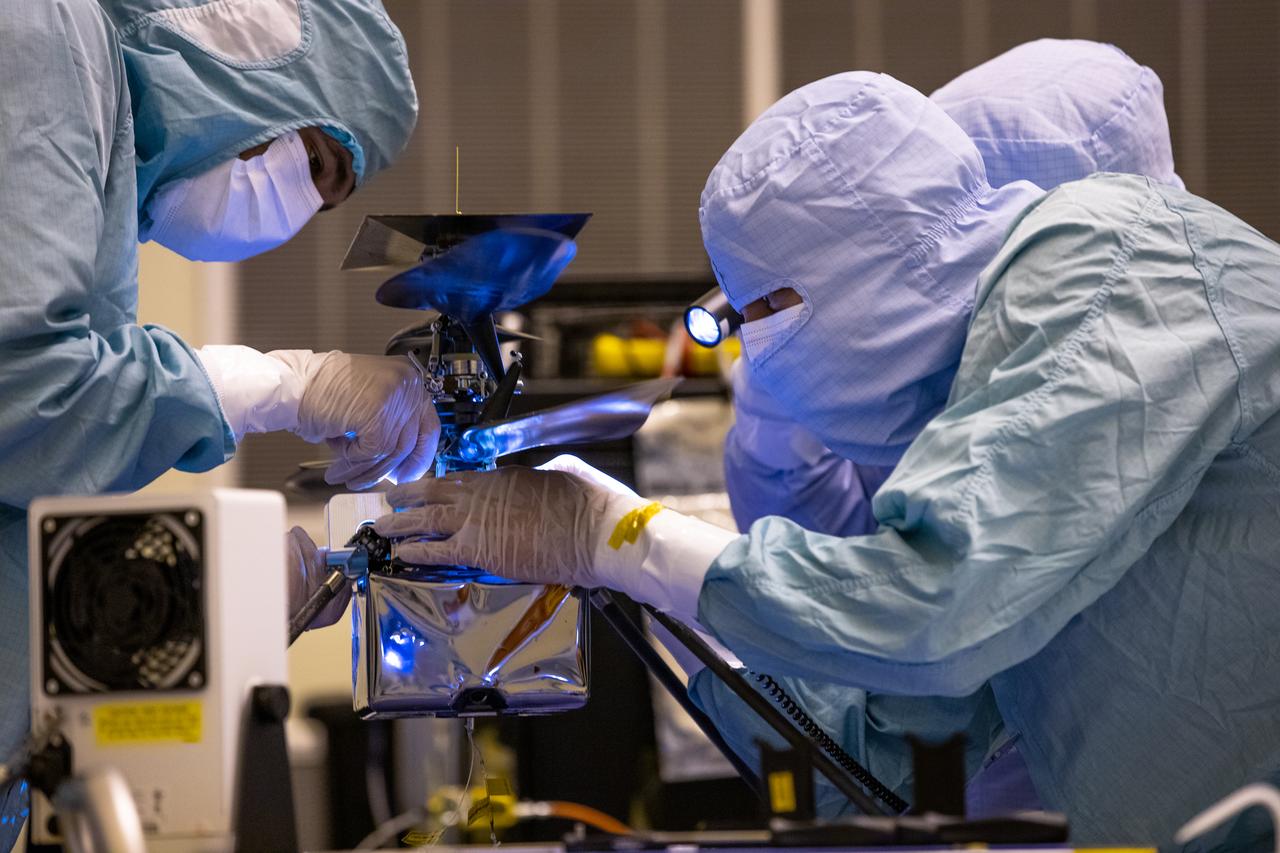
Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
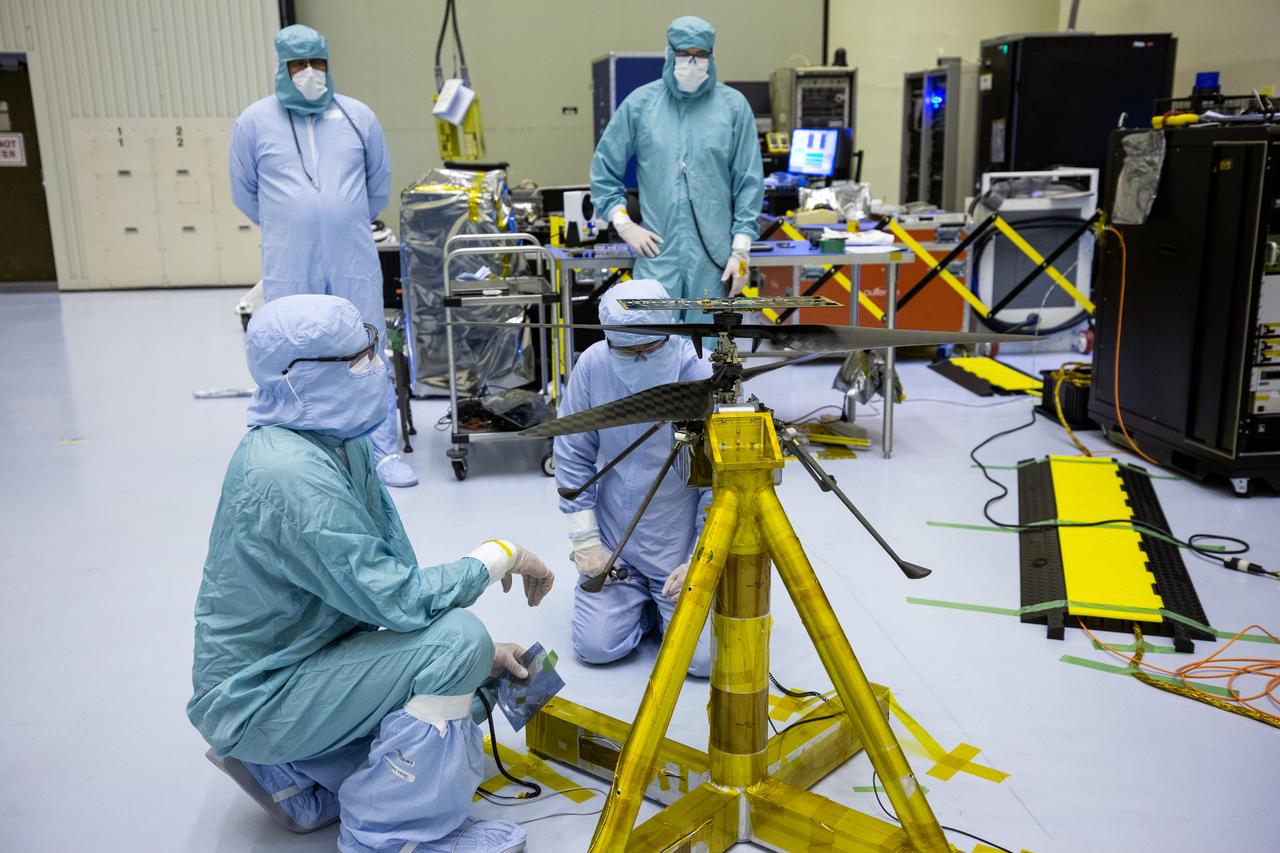

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
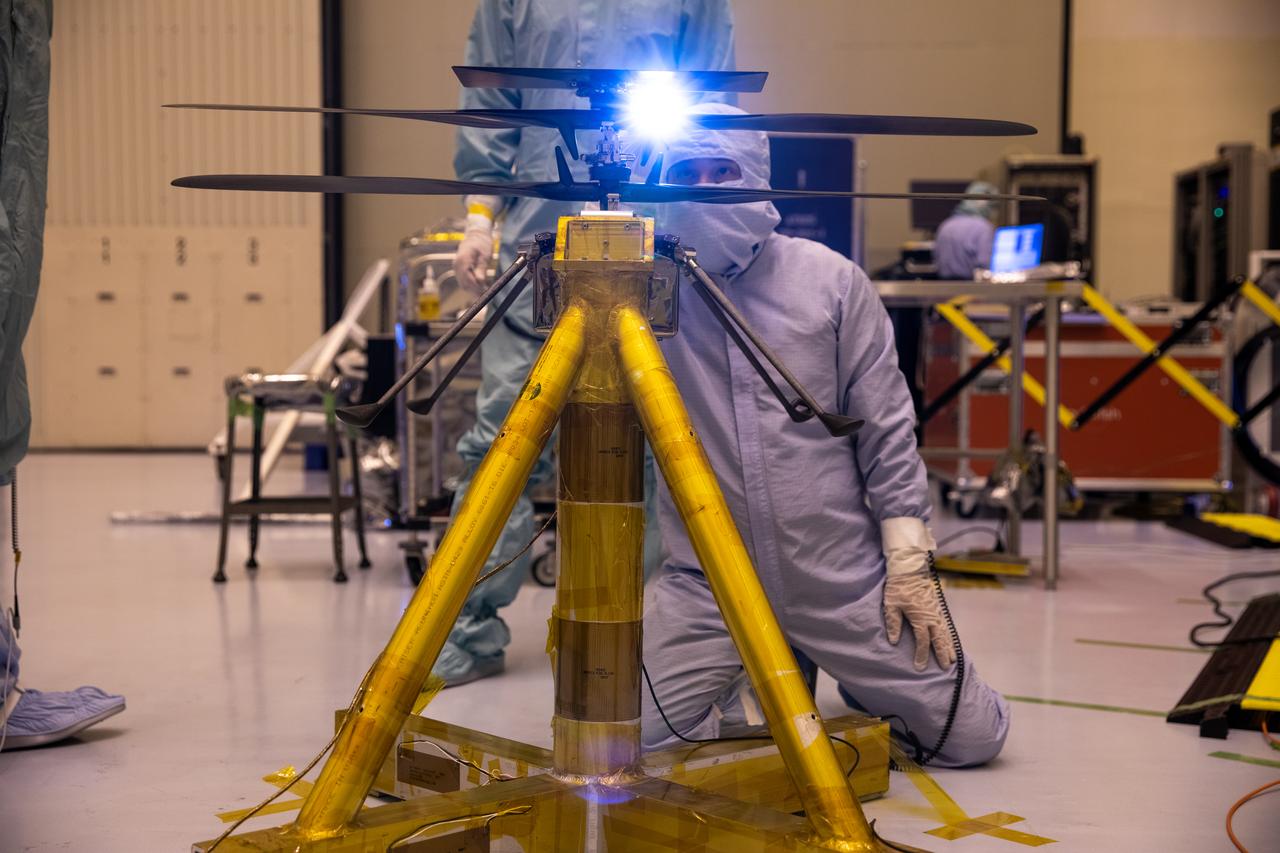

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
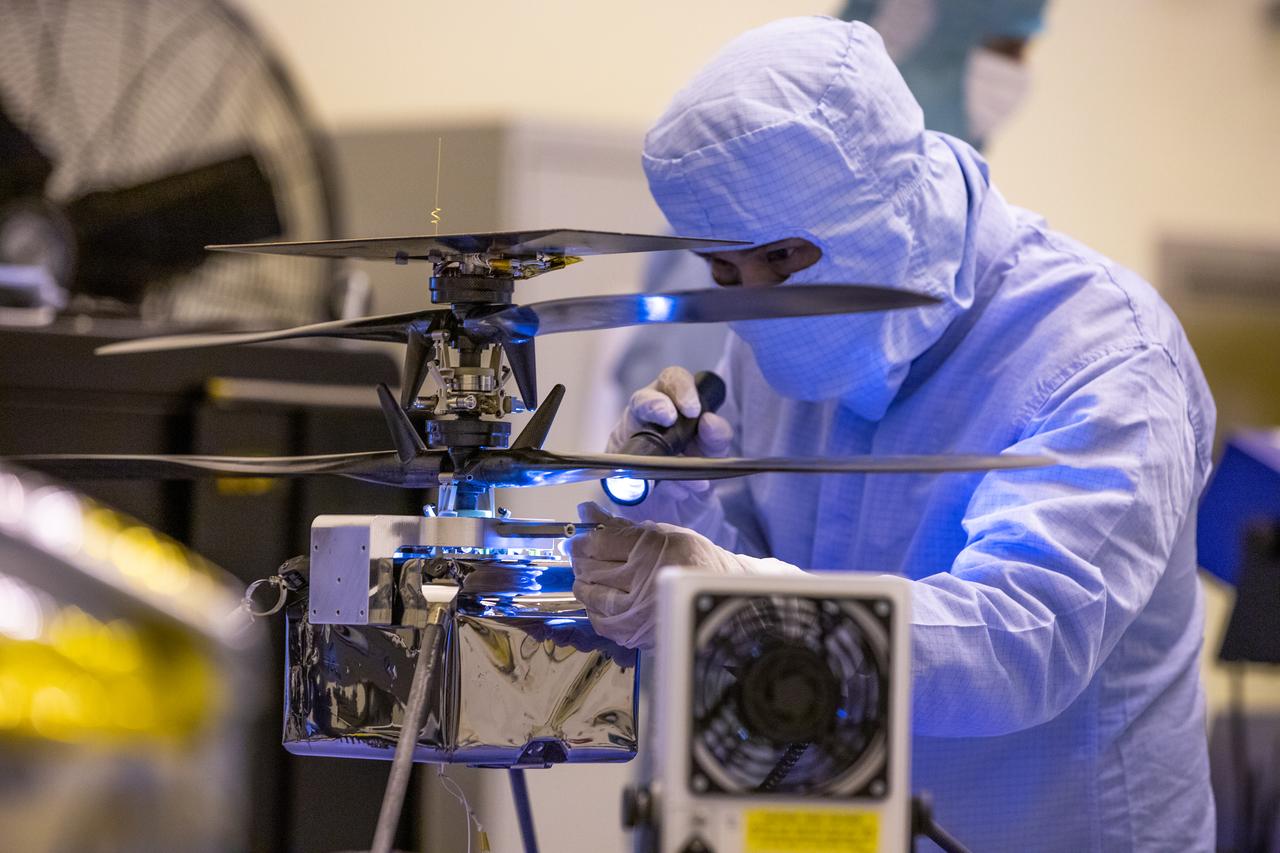

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
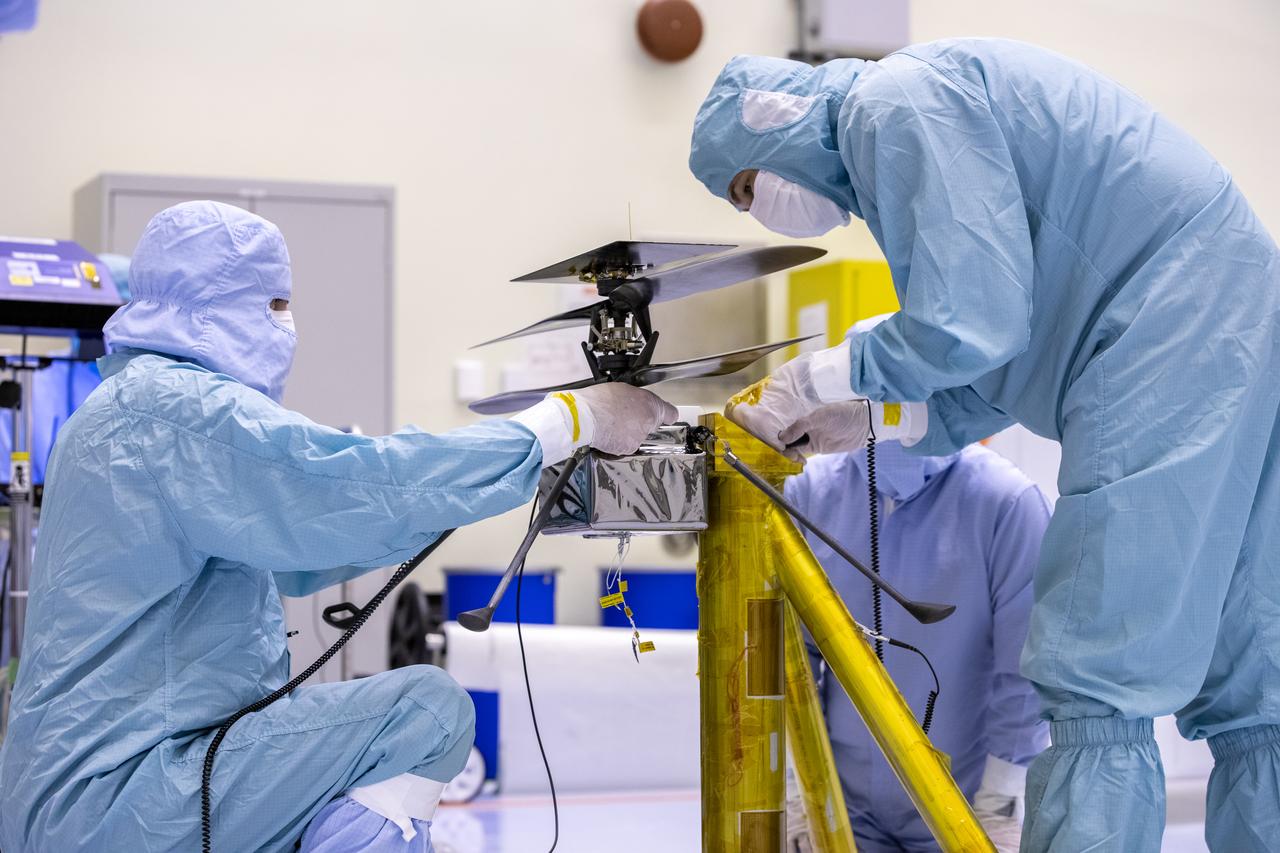

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
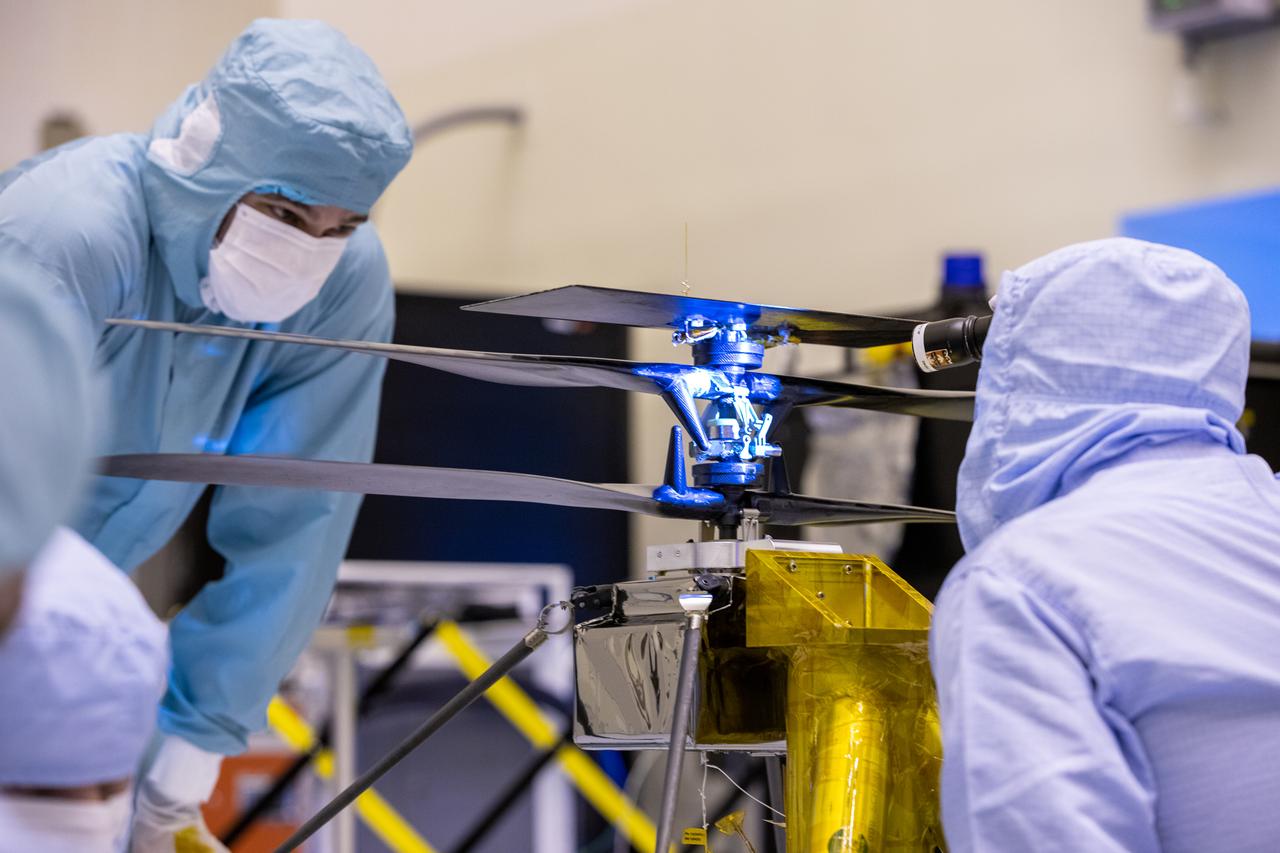

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
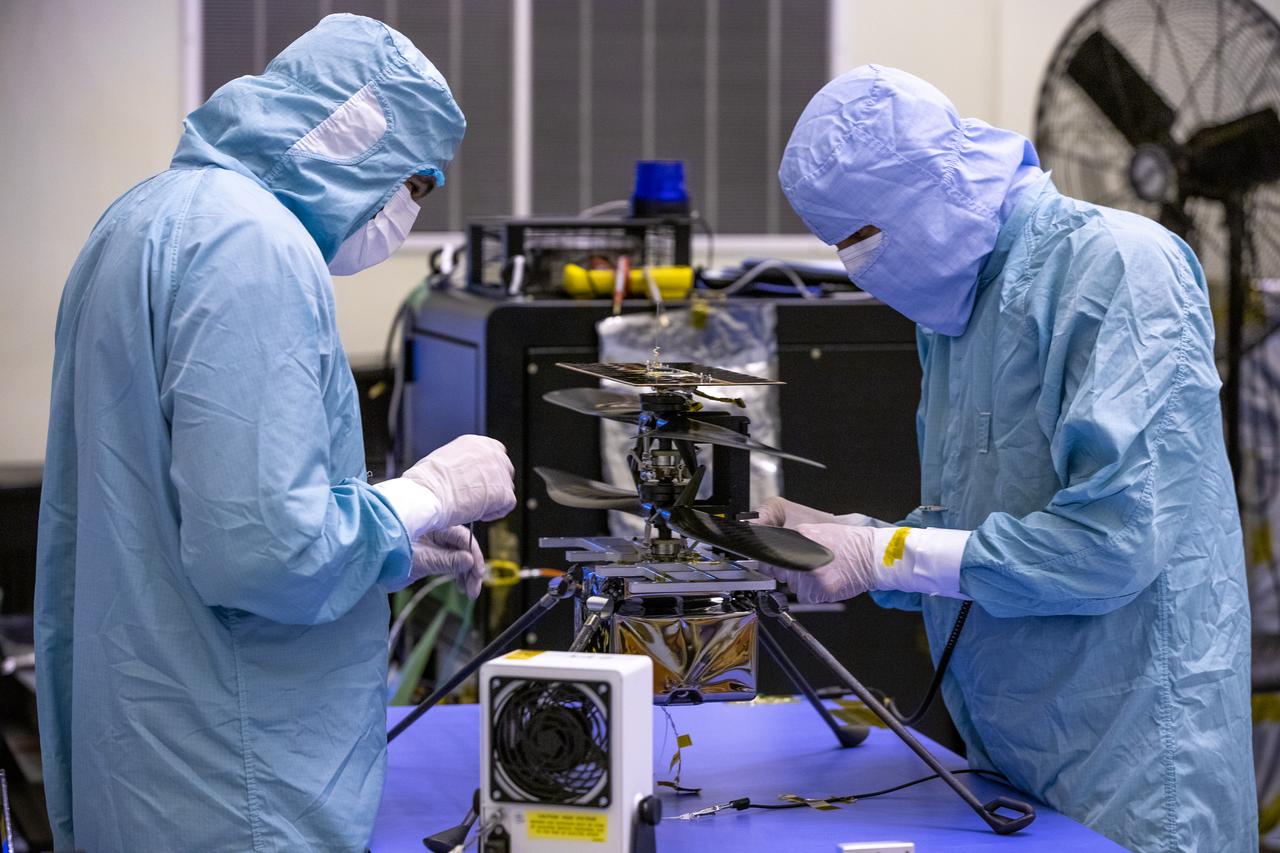

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
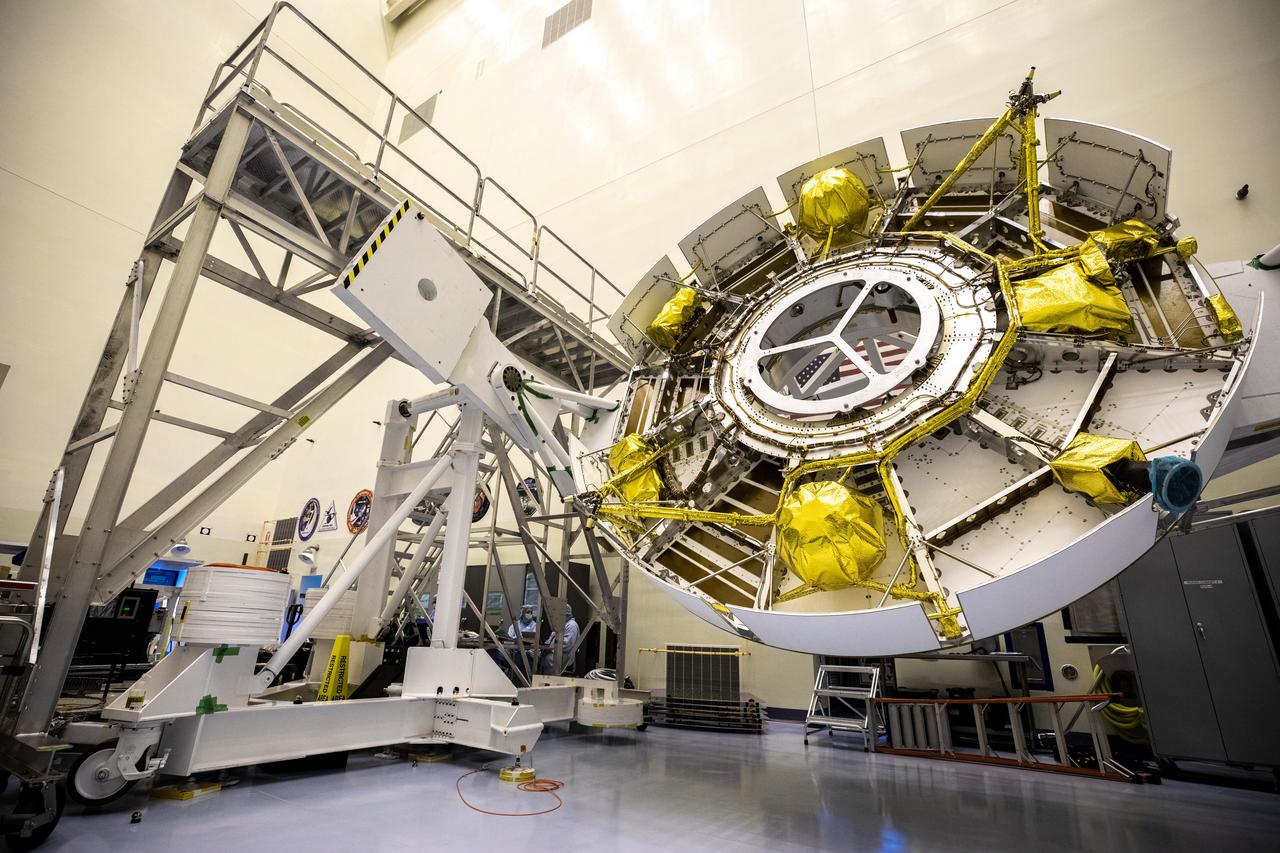

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
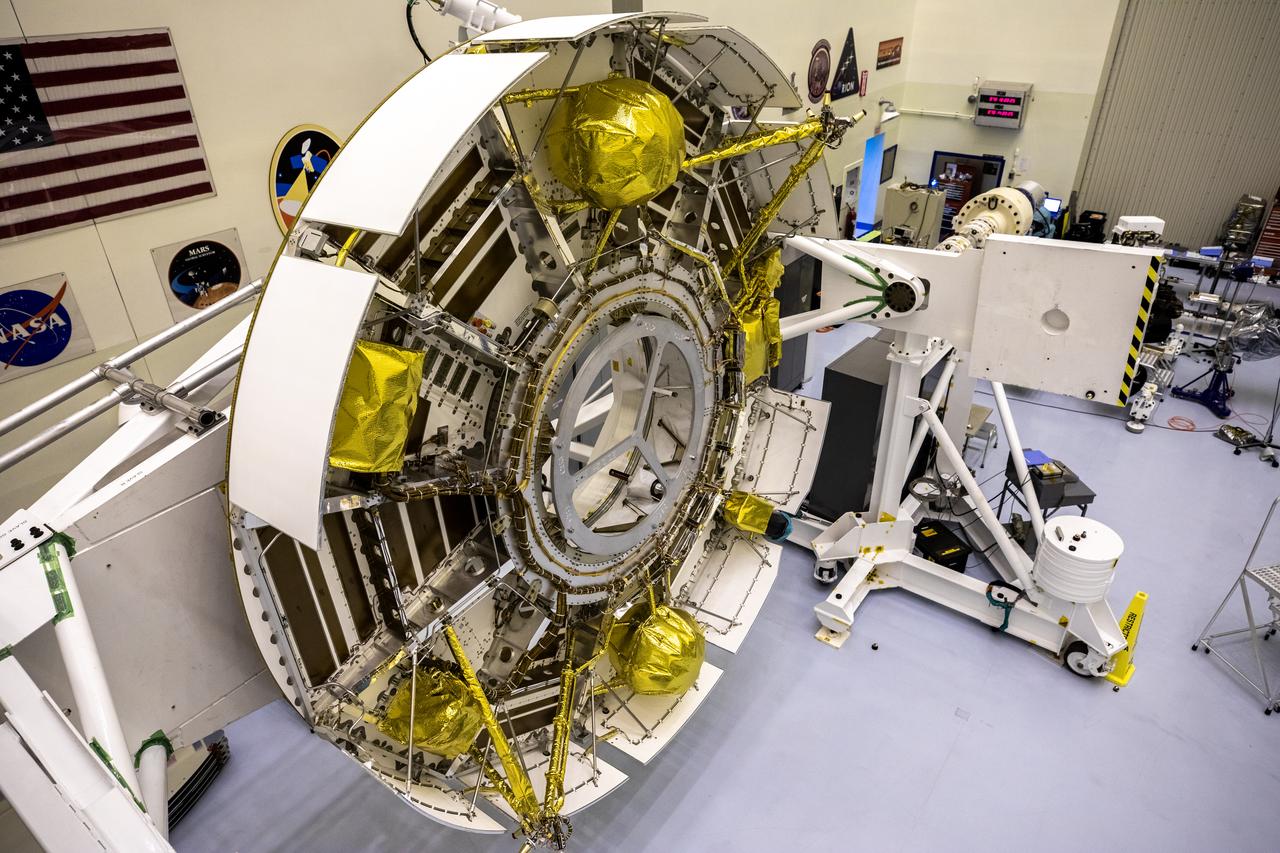
Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
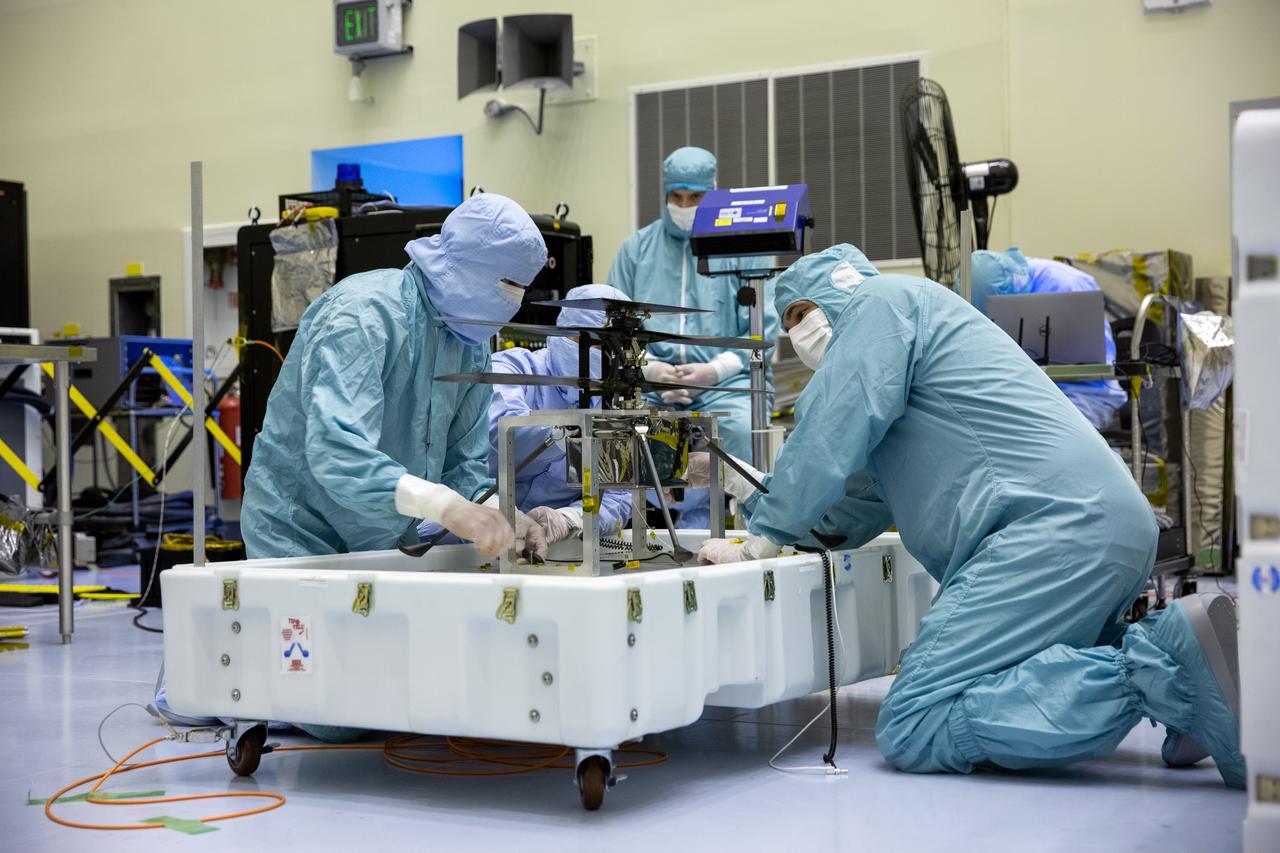
Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
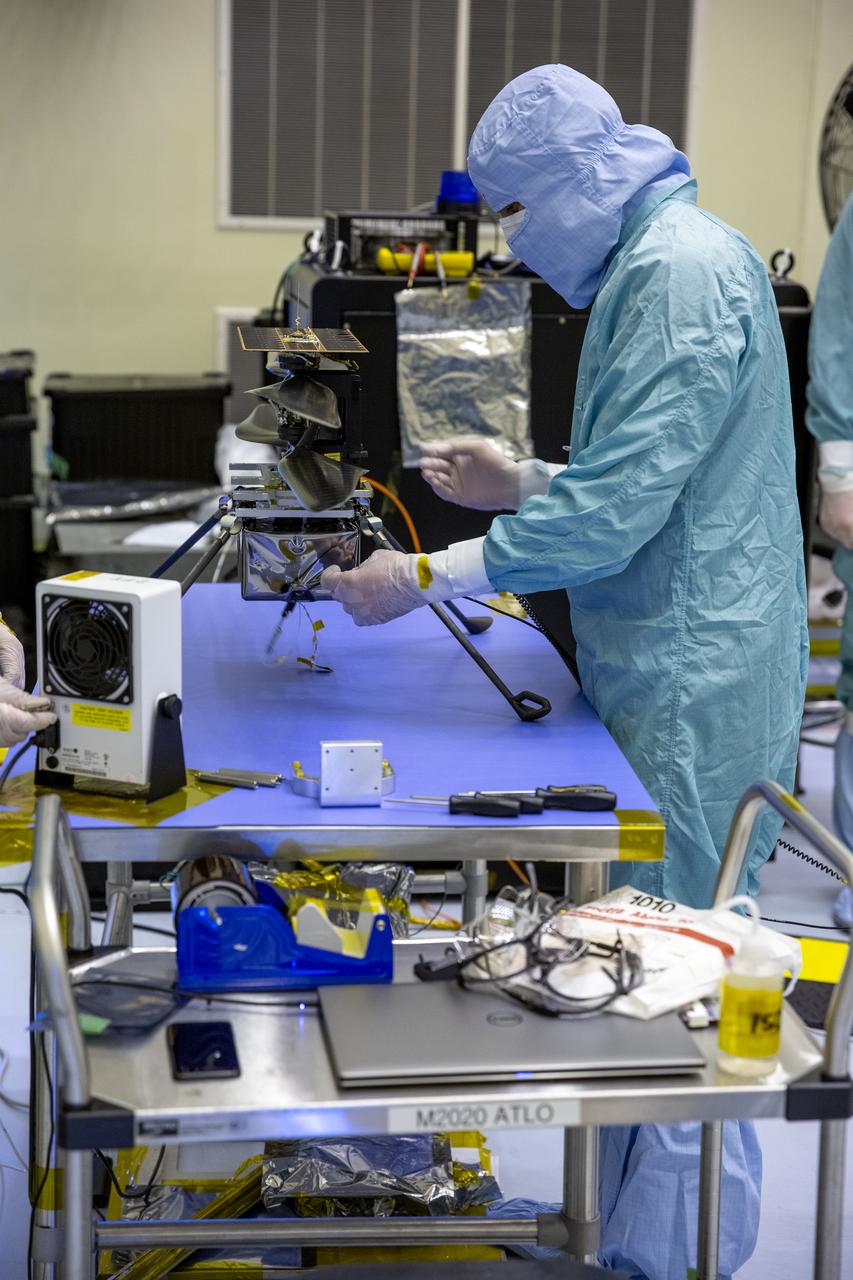

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
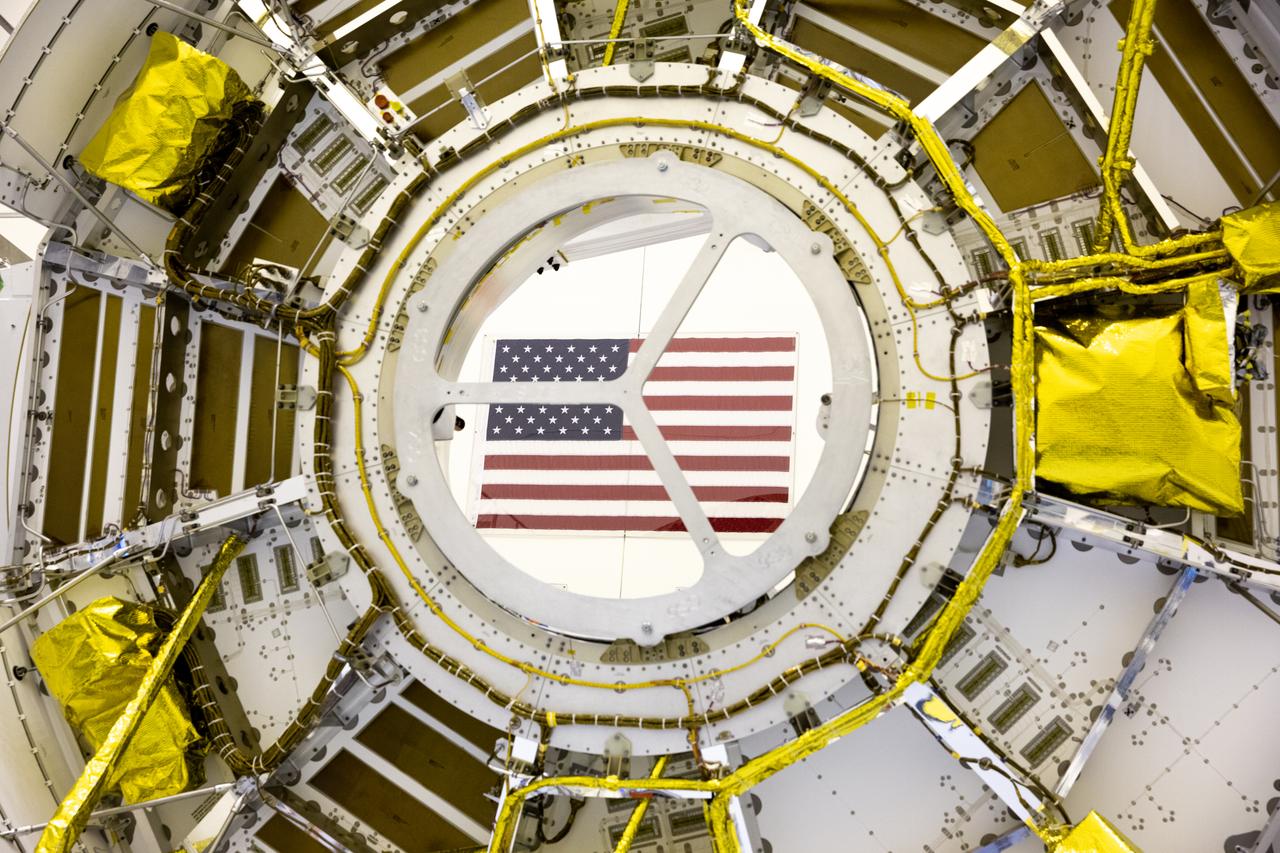
Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
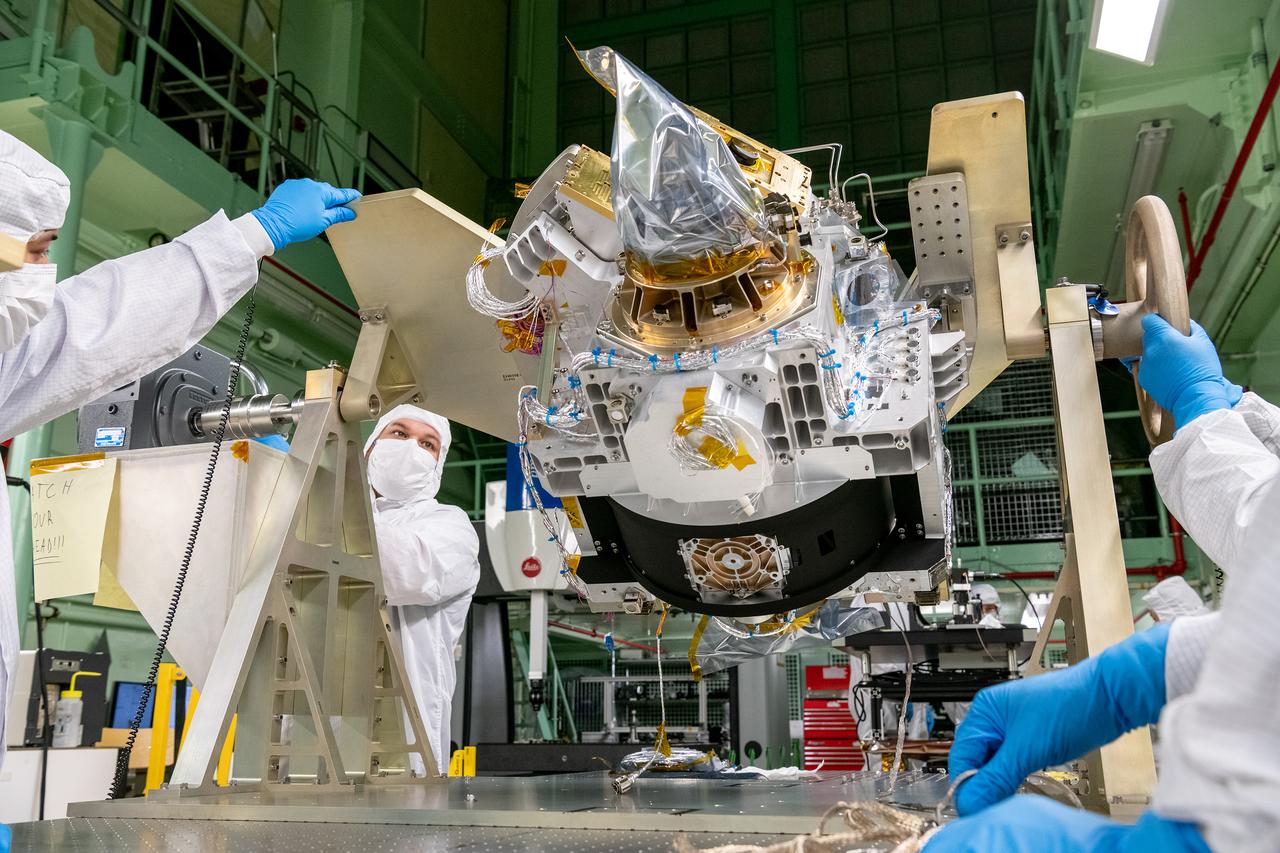

Mechanical technicians reorient the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) Optical Module on a rotation fixture to allow for additional hardware integration. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
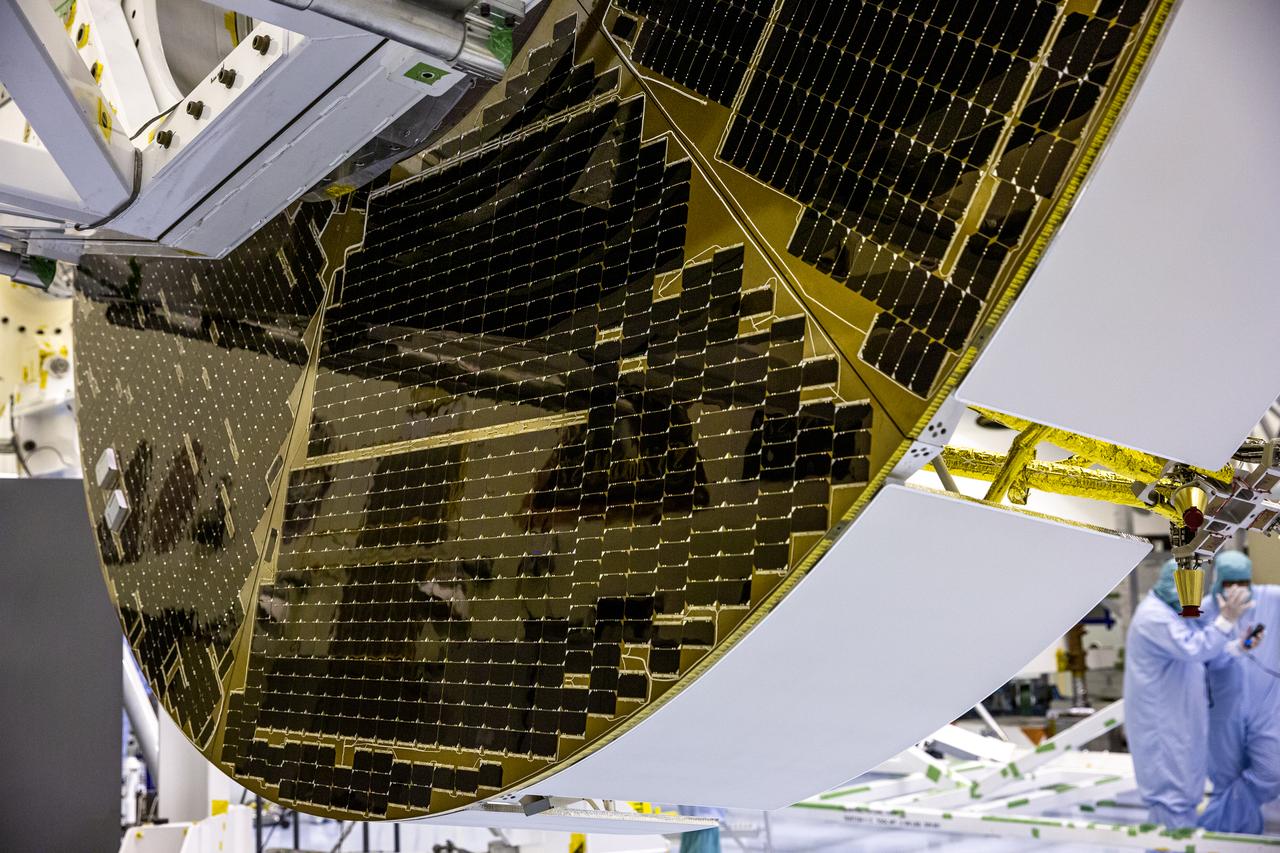

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
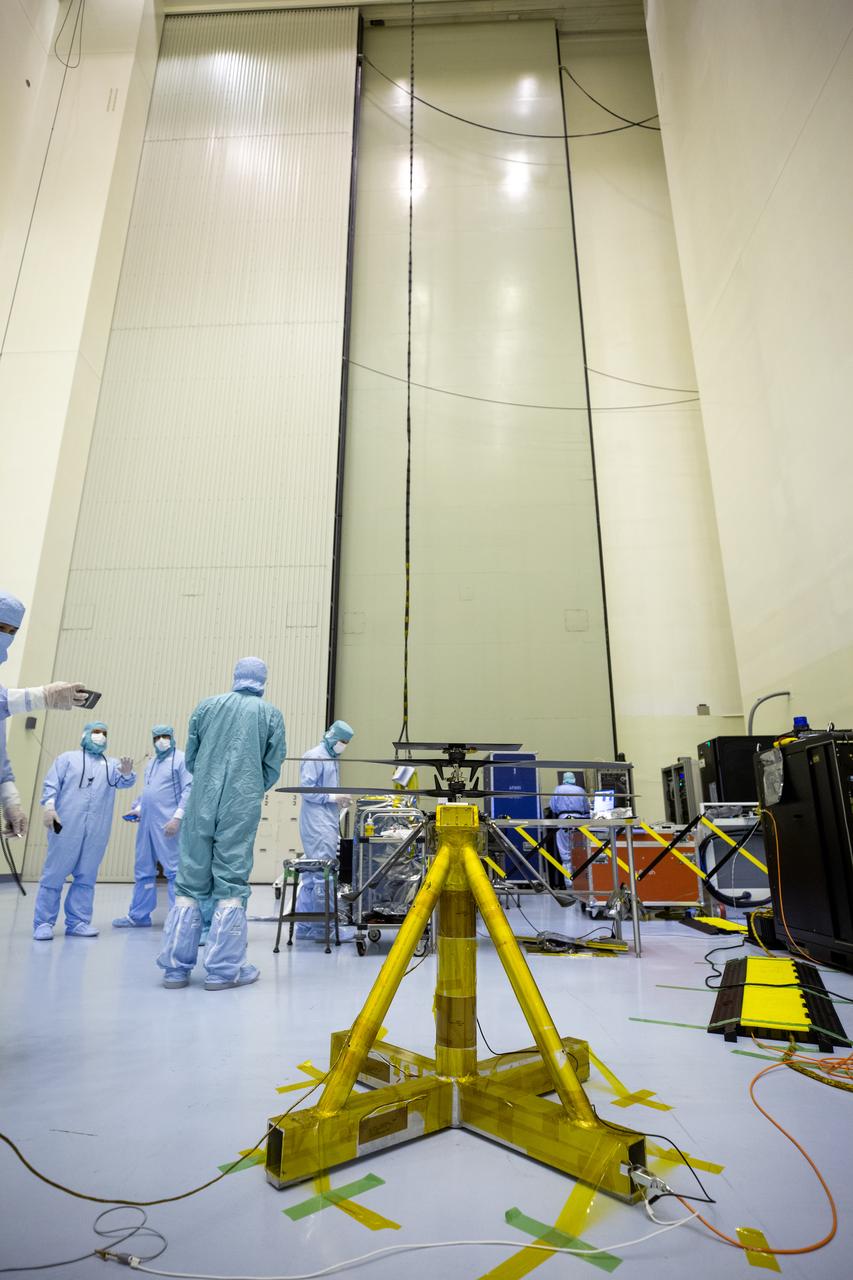

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
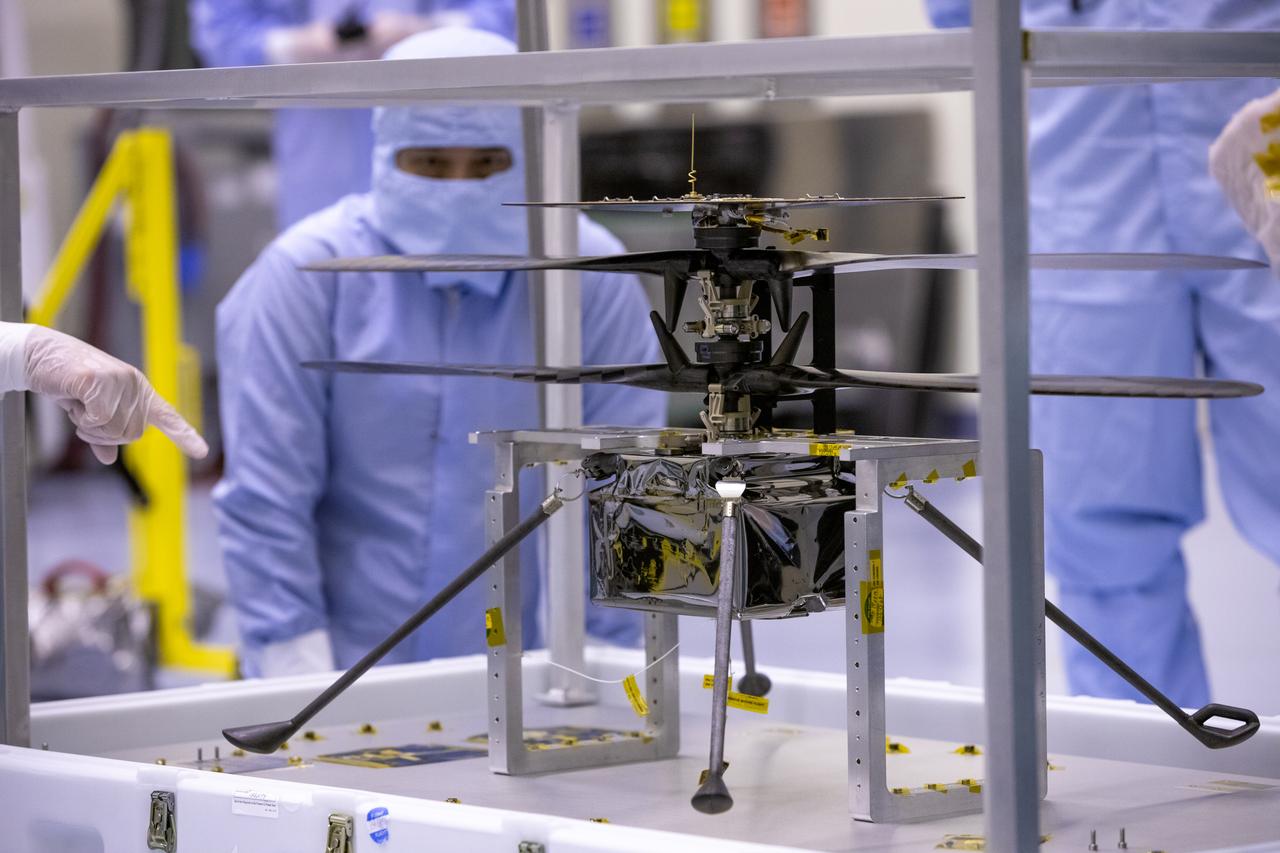
Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
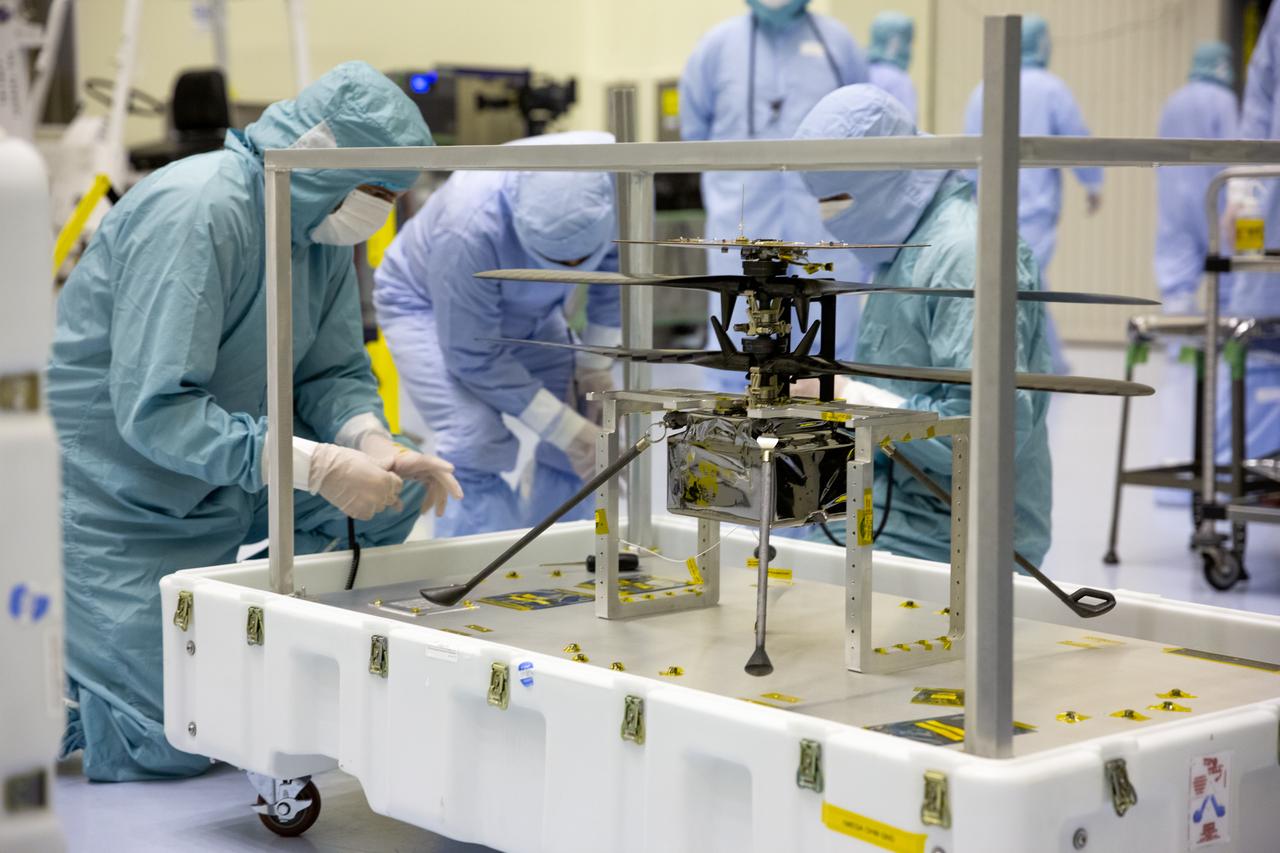

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
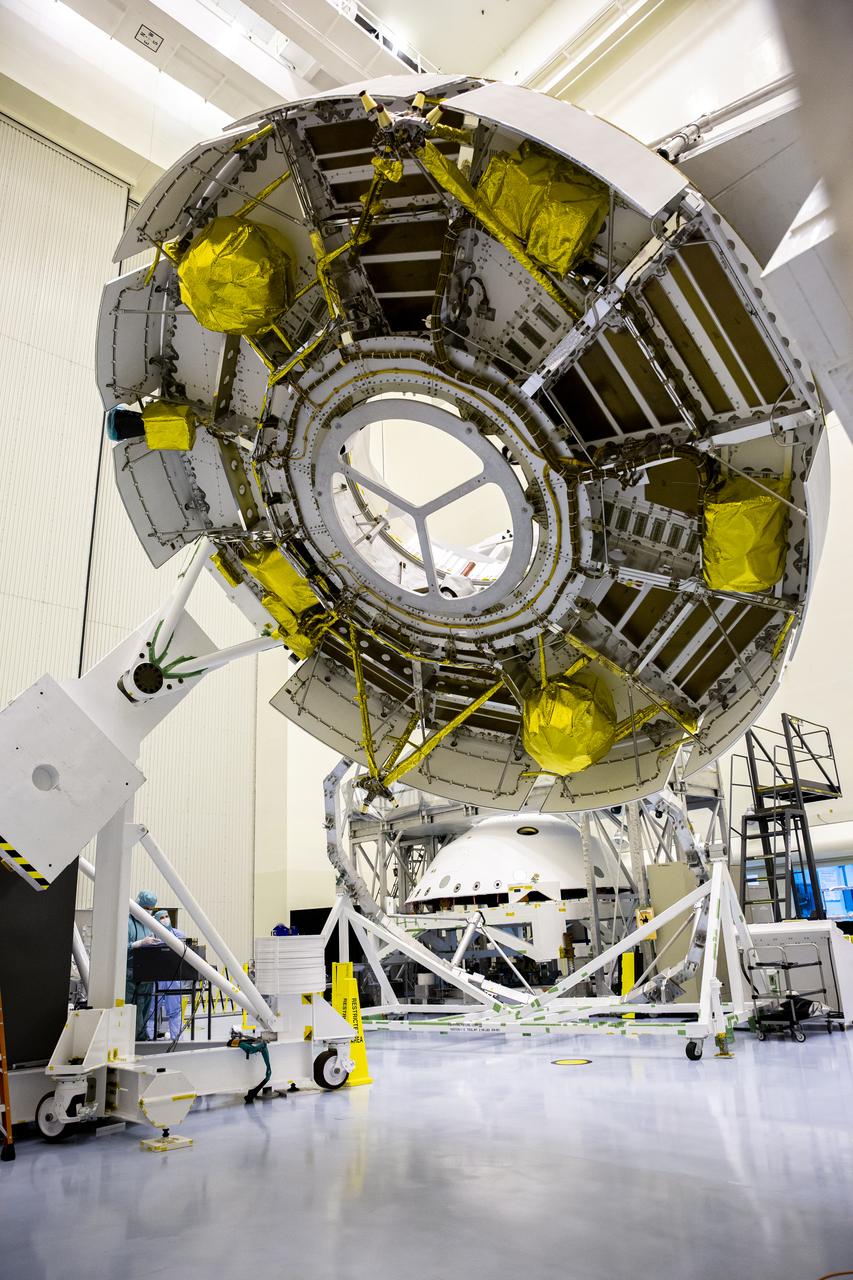

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
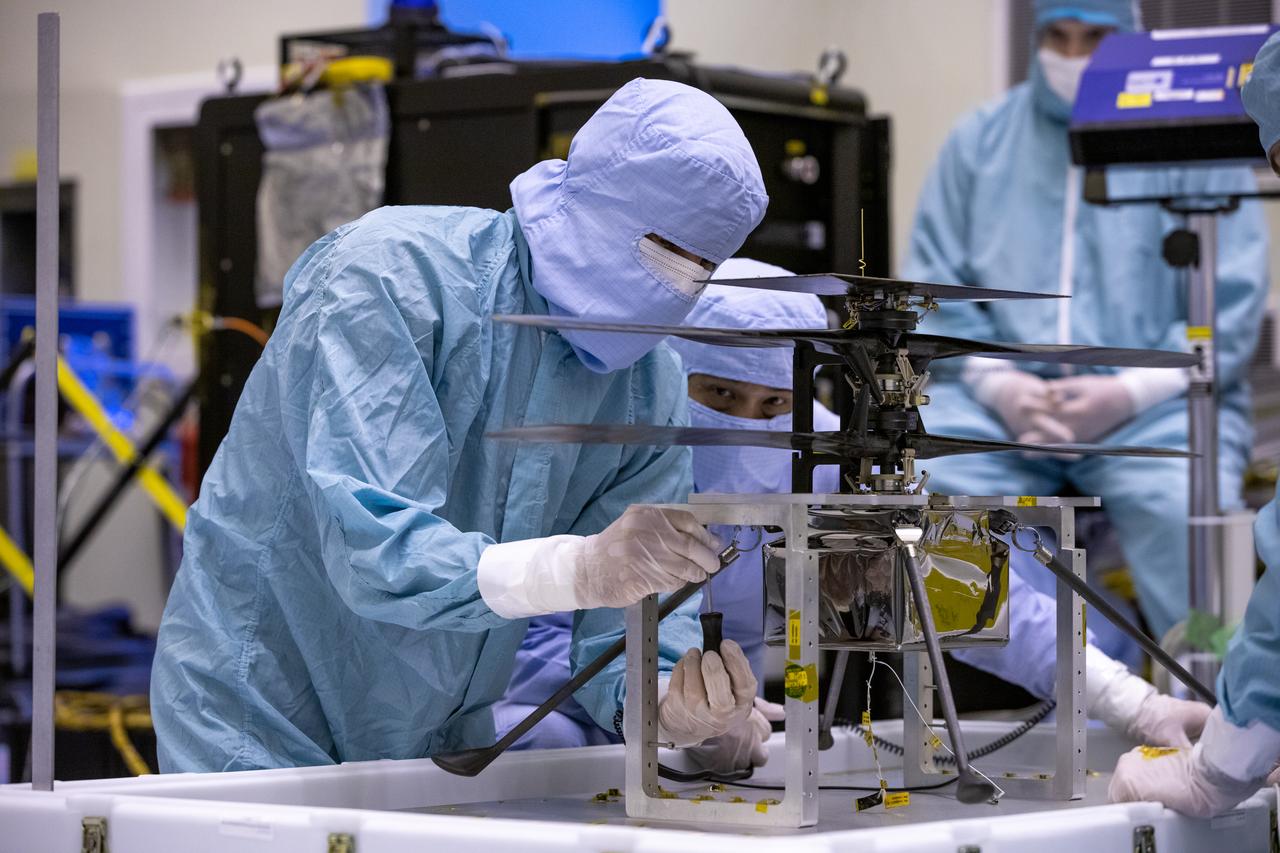

Functional testing of NASA’s Mars Helicopter and its cruise stage occurred in the airlock inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on March 10, 2020. The helicopter was tested on a stand while the cruise stage was tested on the rotation fixture. The helicopter will be attached to the Mars Perseverance rover during its mission, which is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program. Perseverance will land on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted for mid-July from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.

A close up of the Flight Test Fixture II, mounted on the underside of the F-15B Aerodynamic Flight Facility aircraft. The Thermal Protection System (TPS) samples, which included metallic Inconel tiles, soft Advanced Flexible Reusable Surface Insulation tiles, and sealing materials, were attached to the forward-left side position of the test fixture. In-flight video from the aircraft's on-board video system, as well as chase aircraft photos and video footage, documented the condition of the TPS during flights. Surface pressures over the TPS was measured by thermocouples contained in instrumentation "islands," to document shear and shock loads.
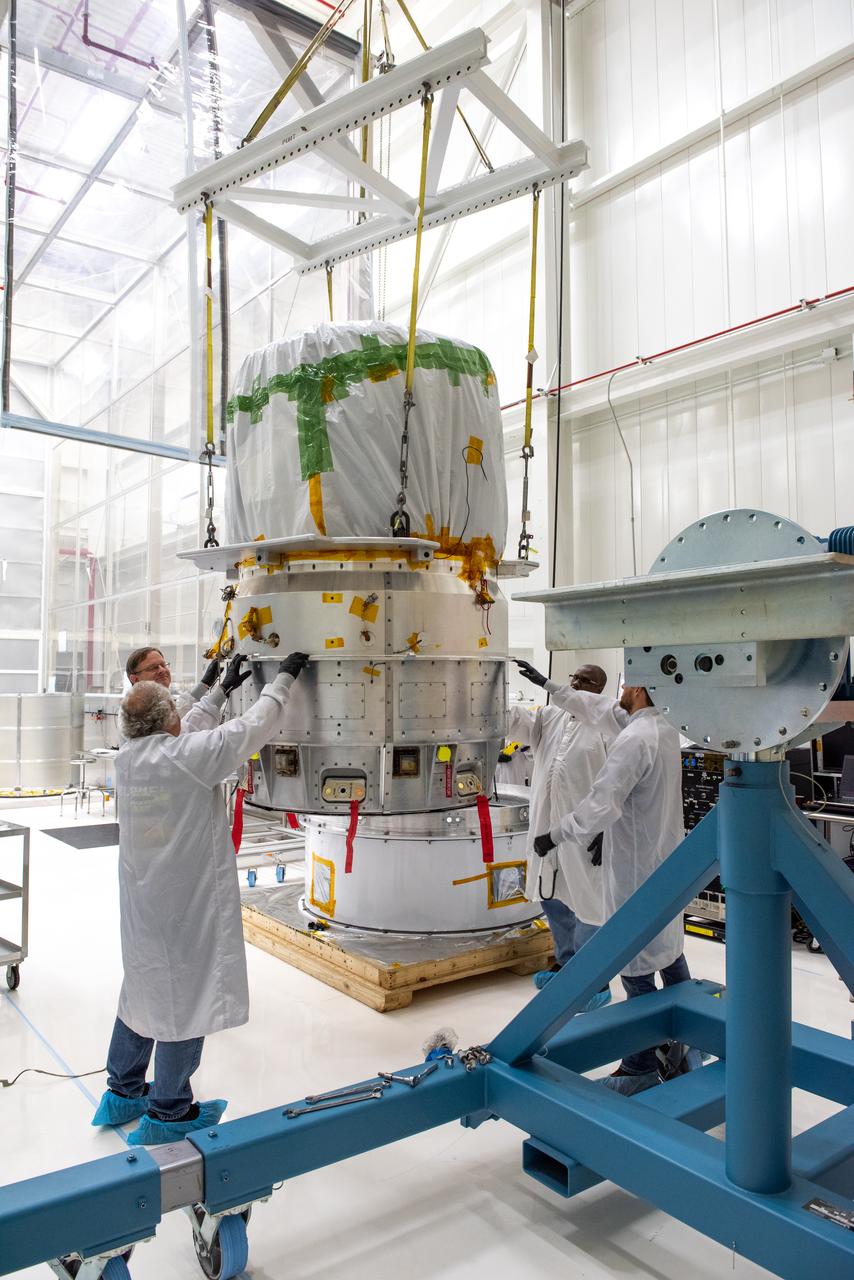

Technicians move NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) re-entry vehicle over to a turnover fixture for prelaunch processing inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Aug. 19, 2022. Dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter, LOFTID is a technology demonstration mission aimed at validating inflatable heat shield technology for atmospheric re-entry. This technology could enable missions to other planetary bodies, as well as allow NASA to return heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit. LOFTID is a rideshare launching with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite. NASA and NOAA are targeting Nov. 1, 2022, for the launch of JPSS-2 on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex-3 at Vandenberg.

Technicians move NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) re-entry vehicle onto a turnover fixture for prelaunch processing inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Aug. 19, 2022. Dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter, LOFTID is a technology demonstration mission aimed at validating inflatable heat shield technology for atmospheric re-entry. This technology could enable missions to other planetary bodies, as well as allow NASA to return heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit. LOFTID is a rideshare launching with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite. NASA and NOAA are targeting Nov. 1, 2022, for the launch of JPSS-2 on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex-3 at Vandenberg.
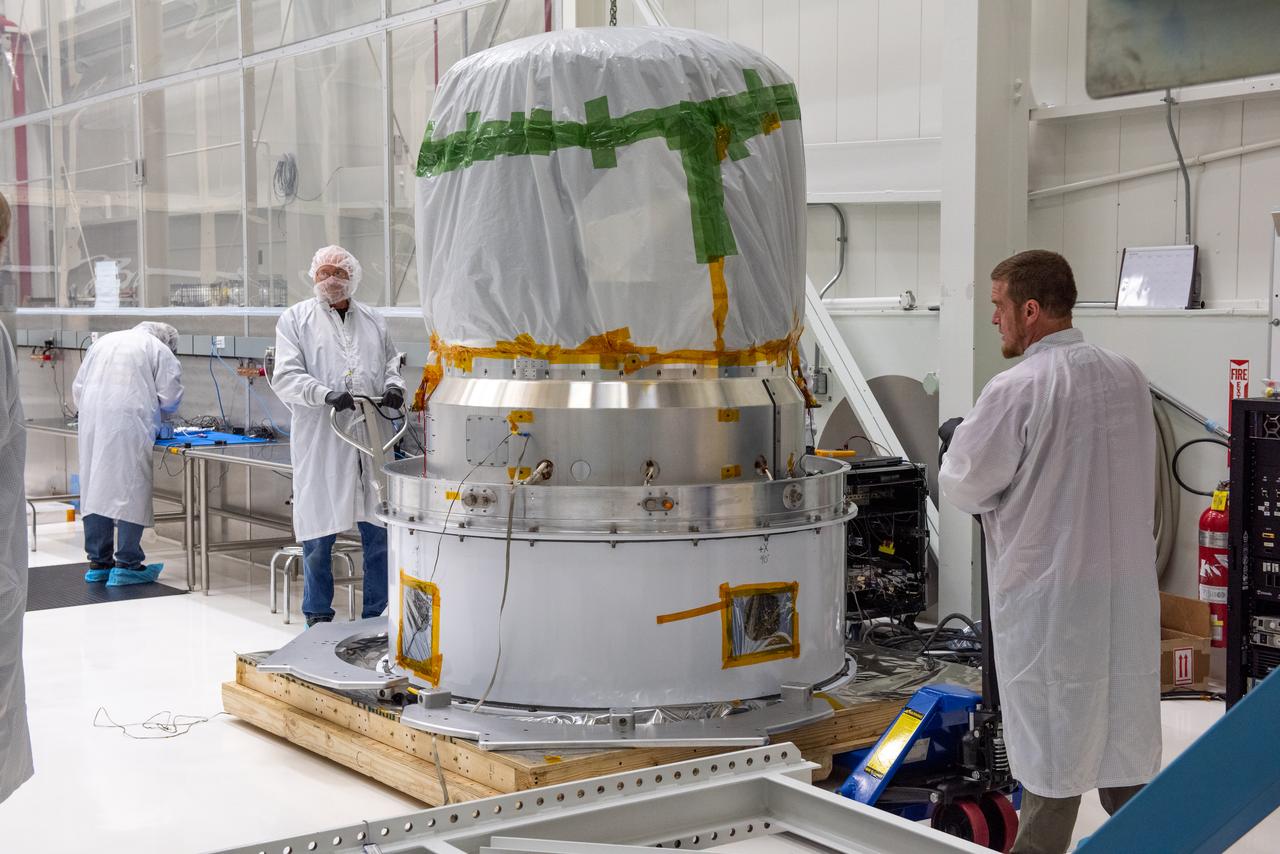

Technicians prepare to move NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) re-entry vehicle onto a turnover fixture for prelaunch processing inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Aug. 19, 2022. Dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter, LOFTID is a technology demonstration mission aimed at validating inflatable heat shield technology for atmospheric re-entry. This technology could enable missions to other planetary bodies, as well as allow NASA to return heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit. LOFTID is a rideshare launching with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite. NASA and NOAA are targeting Nov. 1, 2022, for the launch of JPSS-2 on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex-3 at Vandenberg.
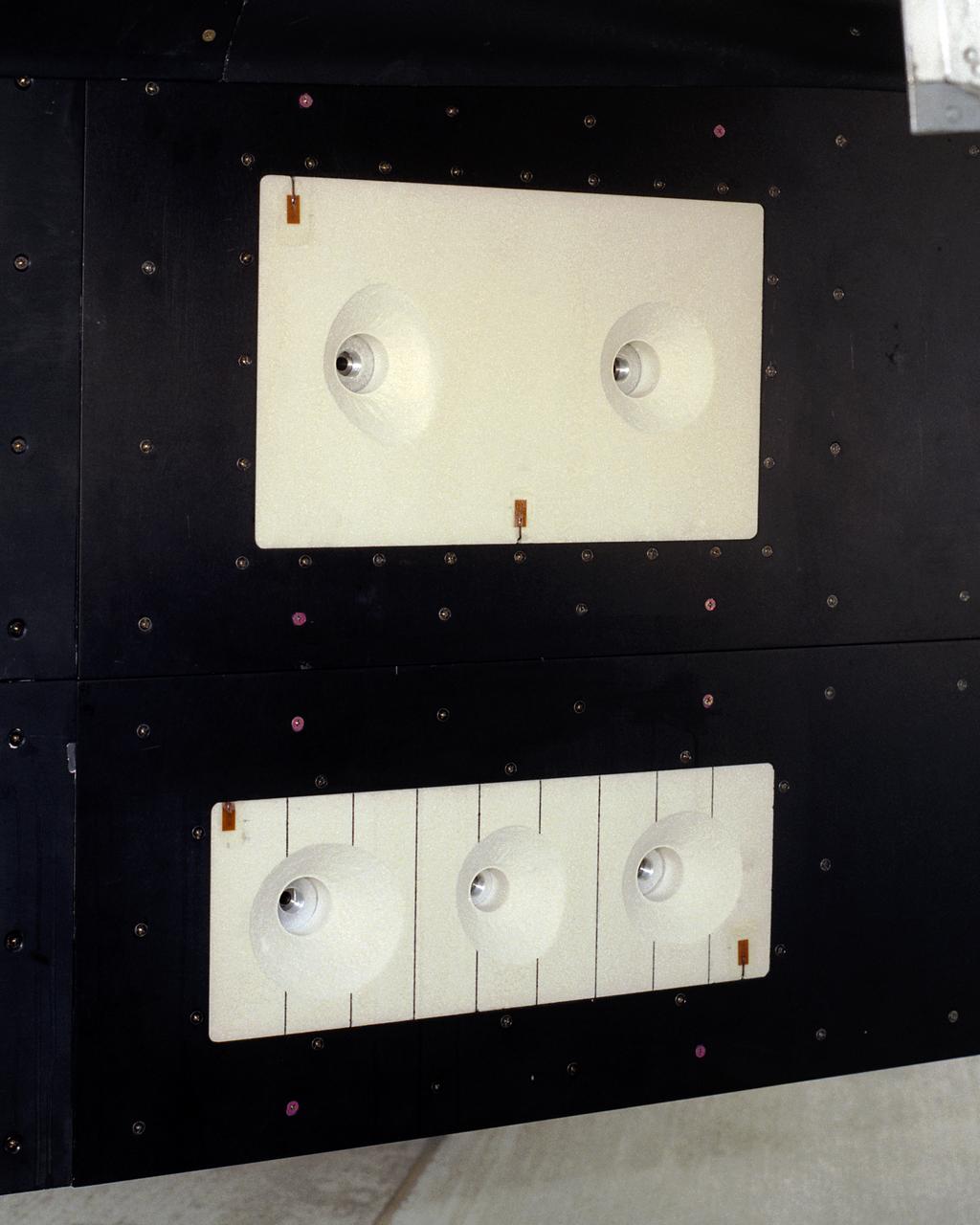

A close-up of the panels on the F-15B's flight test fixture shows five divots of TPS foam were successfully ejected during the LIFT experiment flight #2, the first flight with TPS foam.

A post-flight inspection of the panels on the F-15B's flight test fixture shows five divots of TPS foam were successfully ejected during the LIFT experiment flight #2, the first flight with TPS foam.
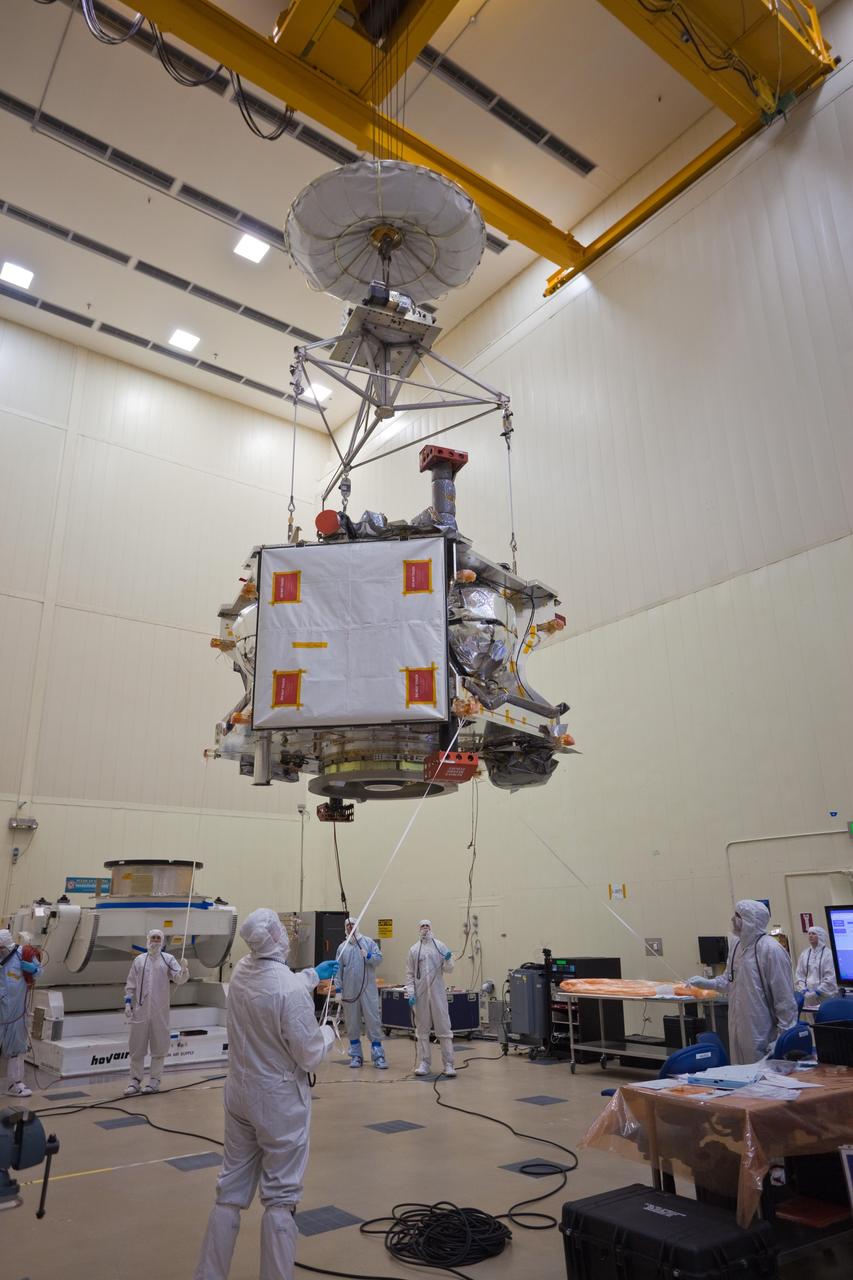

Technicians transfer NASA Juno spacecraft from its rotation fixture to the base of its shipping container in preparation for a move to environmental testing facilities.
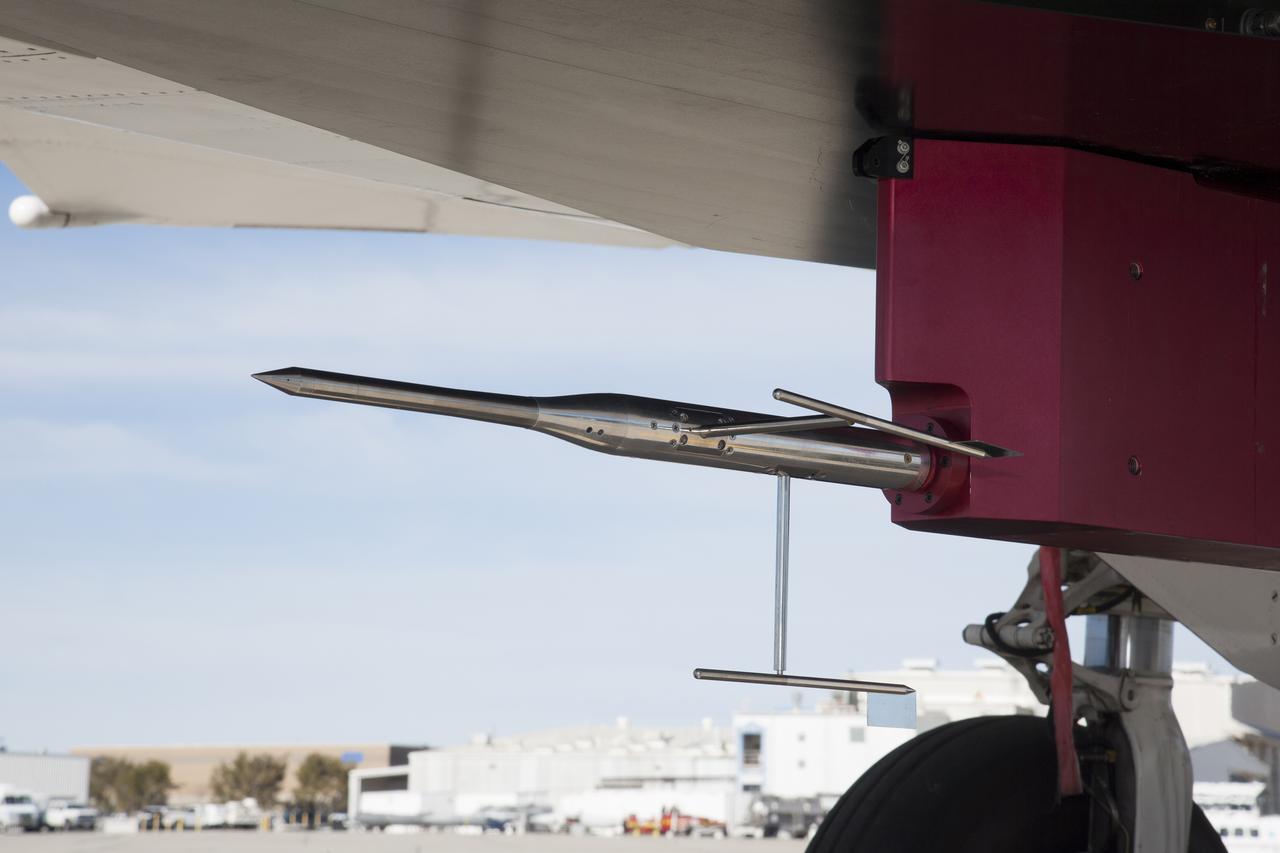

A new supersonic probe seen affixed to a F-15B flight test fixture might one day measure the sonic booms of a new generation of supersonic aircraft.
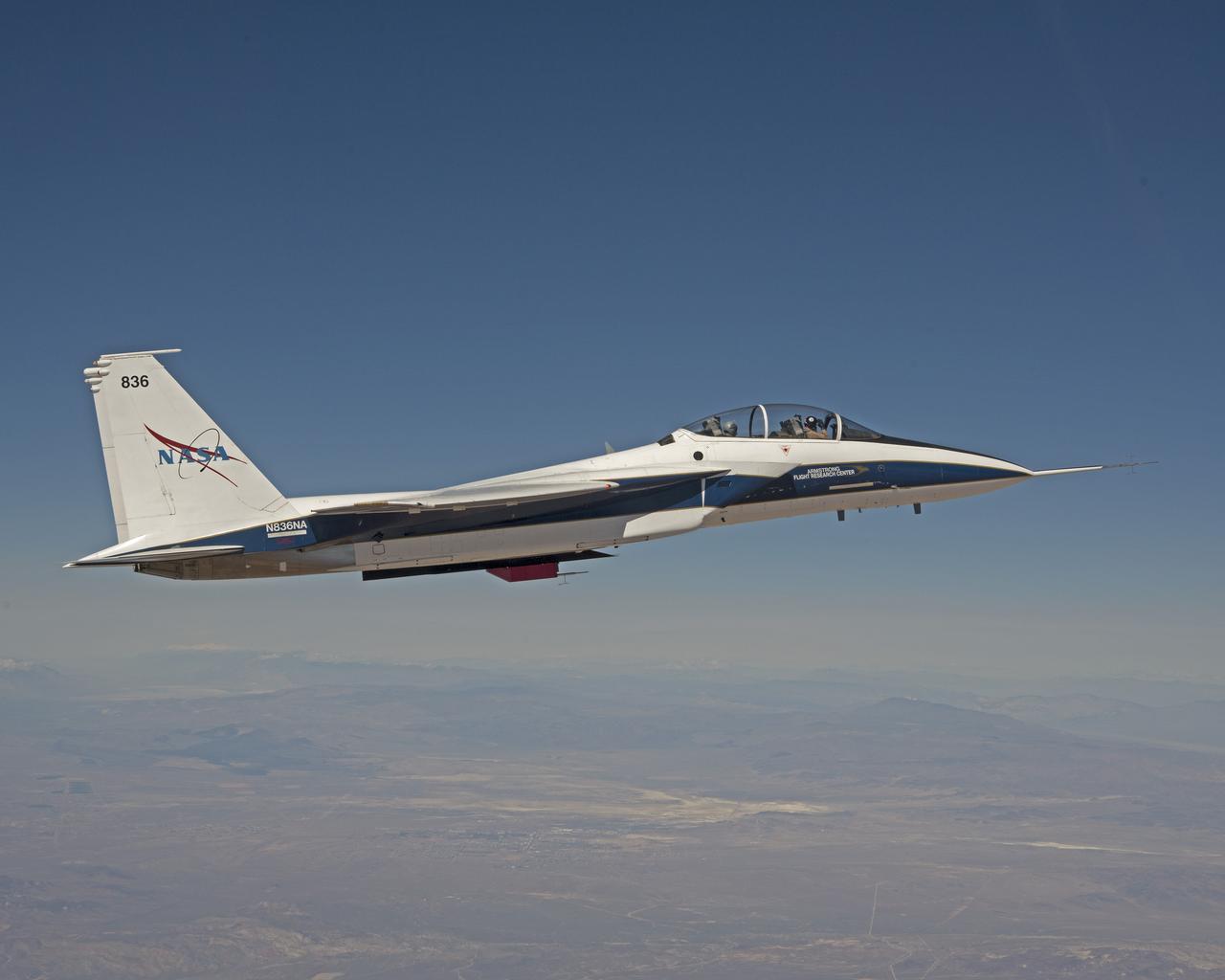

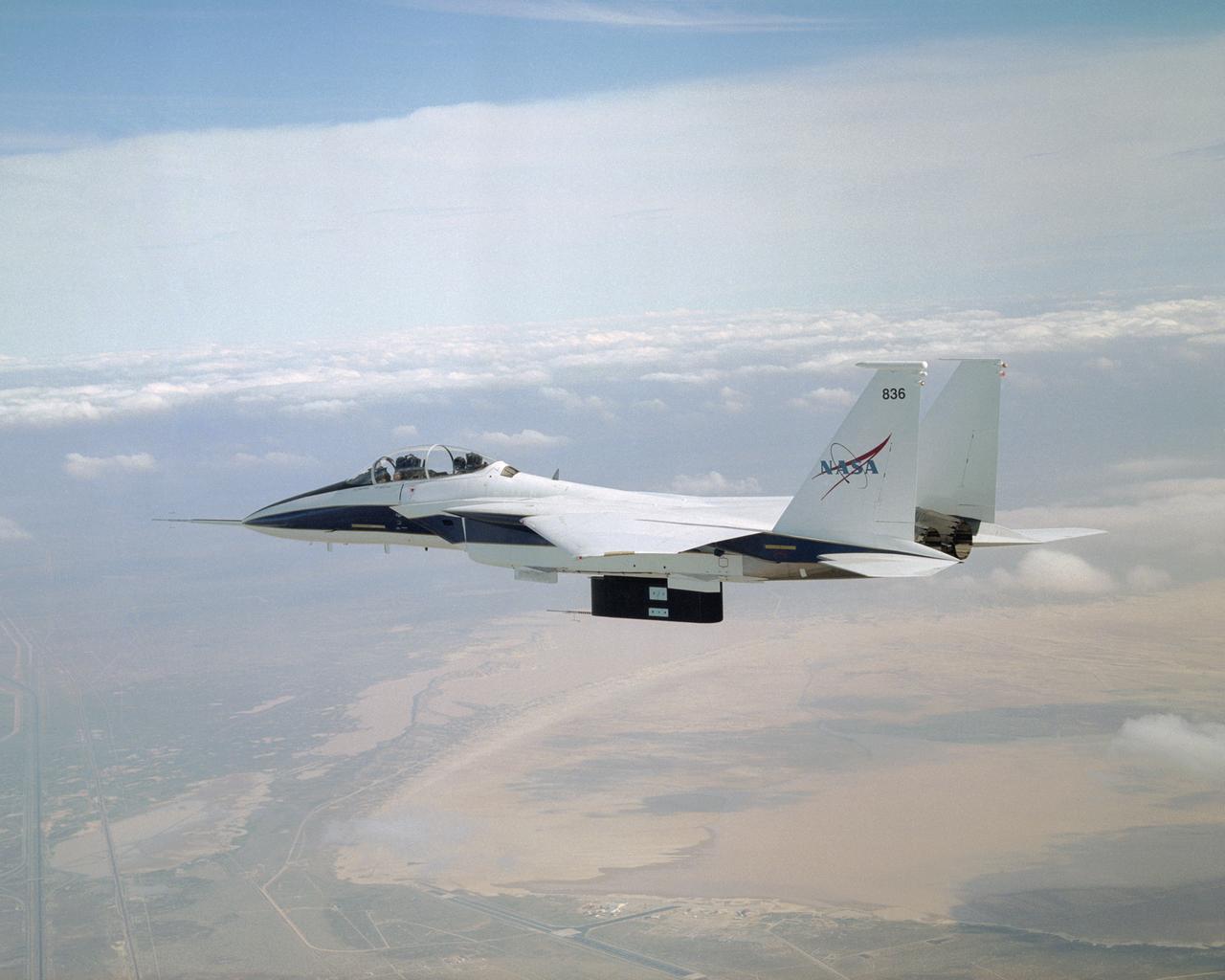
Research on the Eagle Aero Probe is ongoing from an F-15B flight test fixture, as the aircraft flies missions over the high desert.
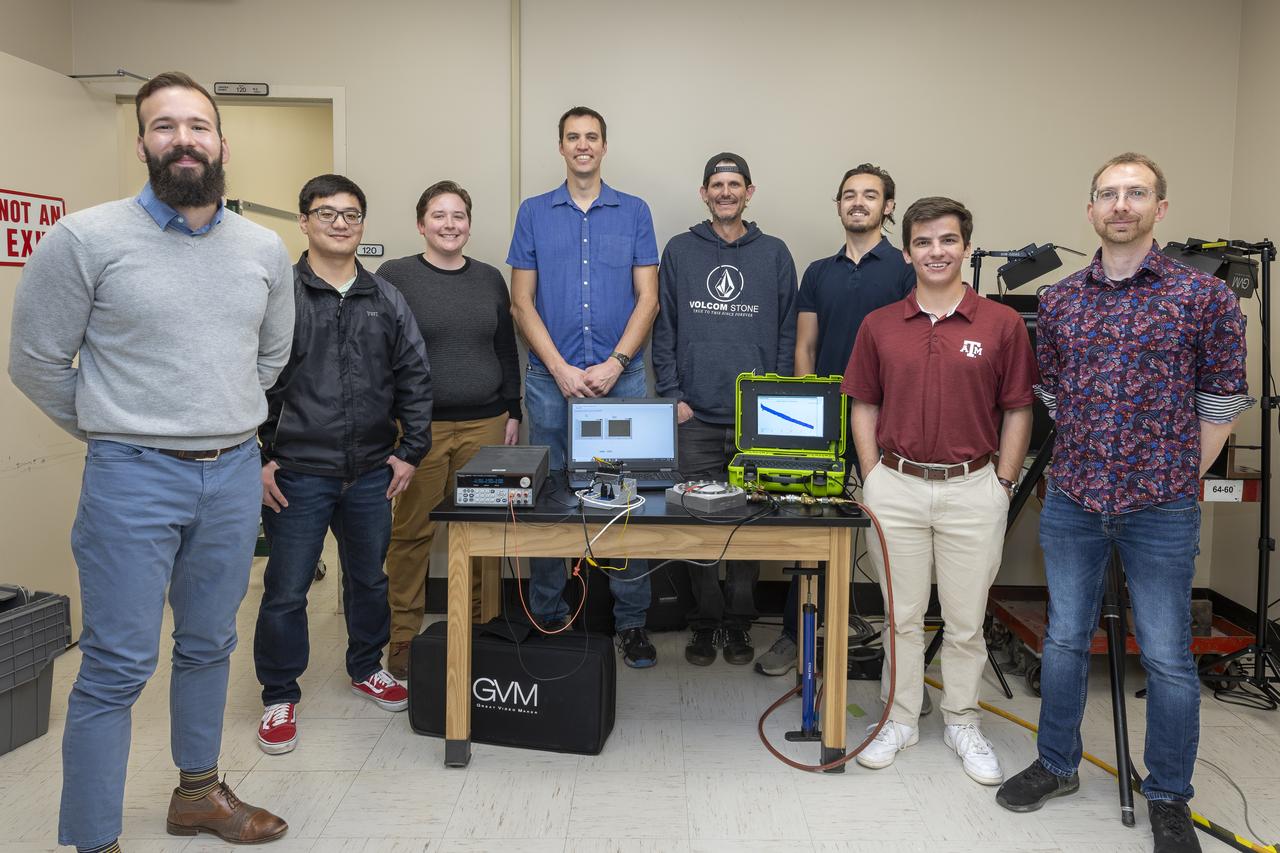

Erick Rossi De La Fuente, from left, John Rudy, L. J. Hantsche, Adam Curry, Jeff Howell, Coby Asselin, Benjamin Mayeux, and Paul Bean pose with a test fixture, material, sensor, and data acquisition systems at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The sensor tests seek to quantify the limits of the material to improve computer models and make more reliable supersonic parachutes.

All six divots of thermal insulation foam have been ejected from the flight test fixture on NASA's F-15B testbed as it returns from a LIFT experiment flight.
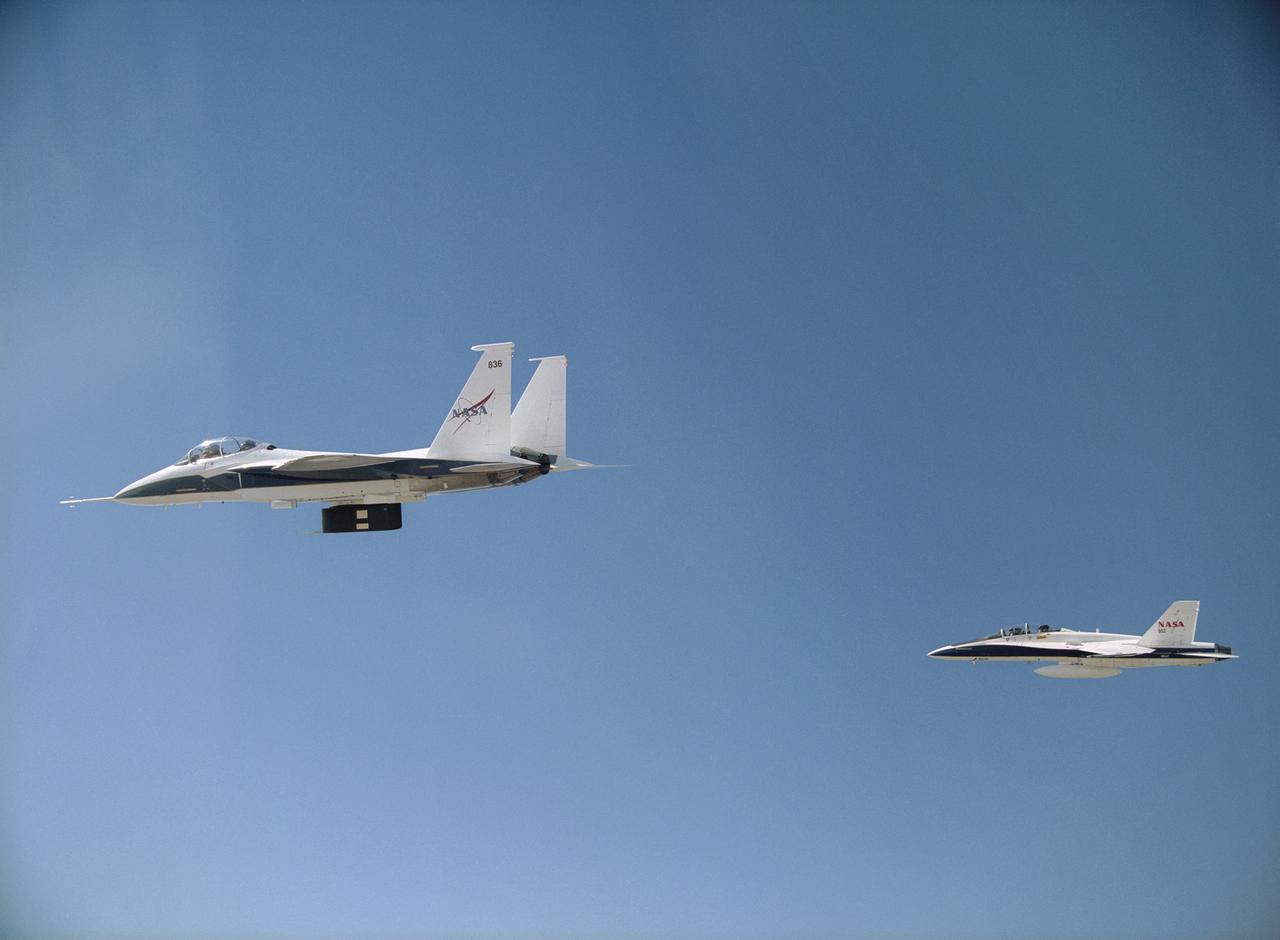

NASA's F-15B carrying thermal insulation foam on its flight test fixture is shadowed by a NASA F-18B chase aircraft during a LIFT experiment research flight.
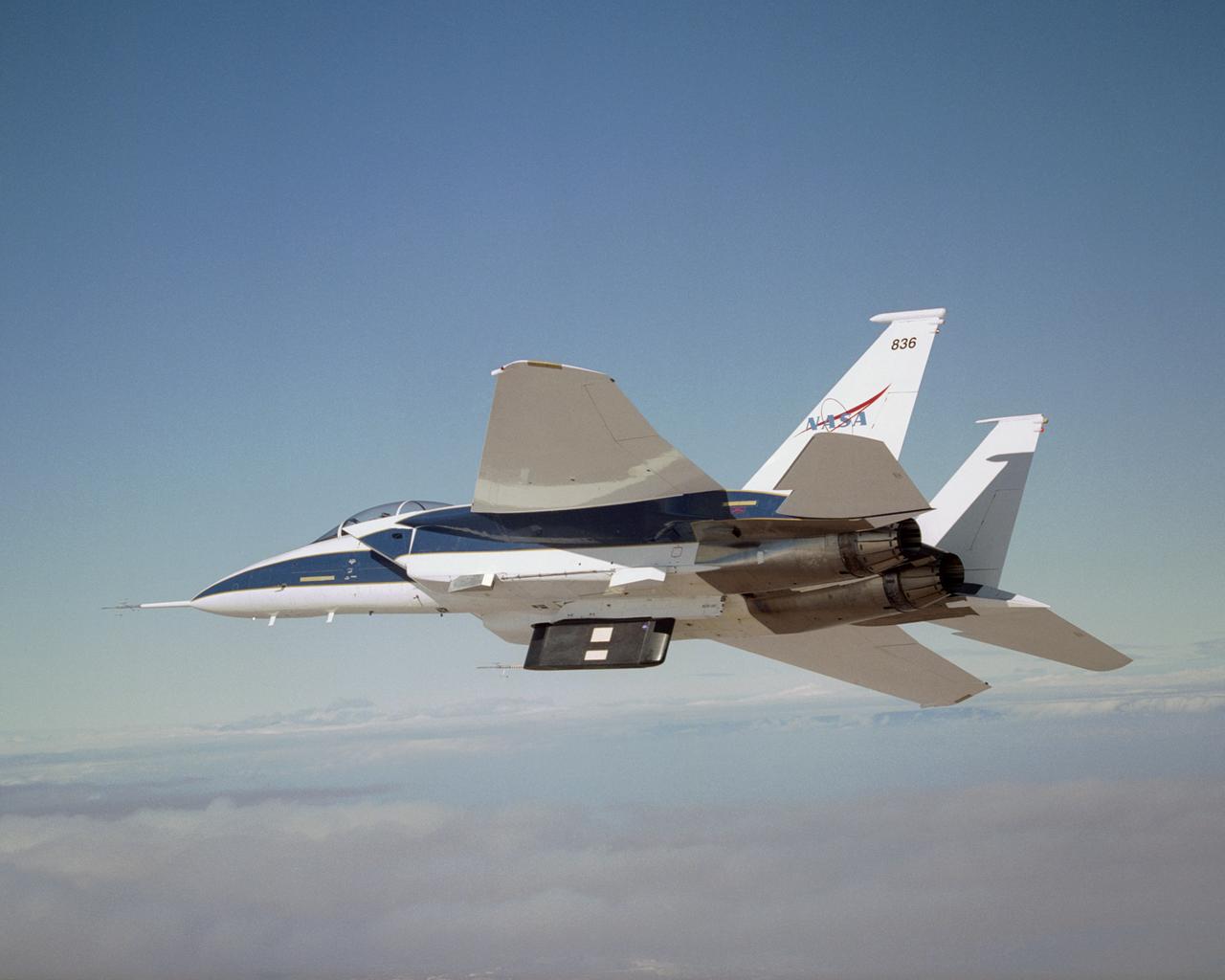

Two panels of Space Shuttle TPS insulation were mounted on the flight test fixture underneath NASA's F-15B during the Lifting Foam Trajectory flight test series.
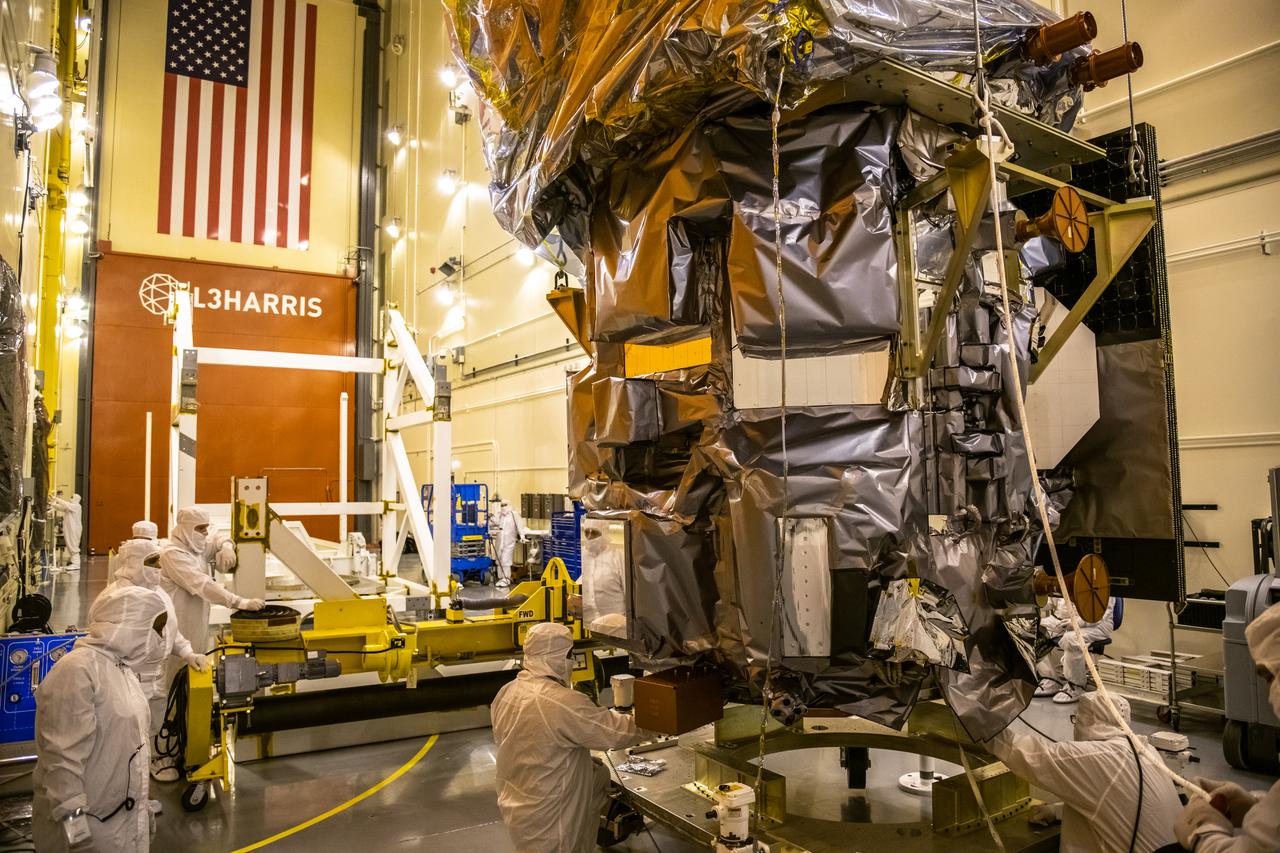

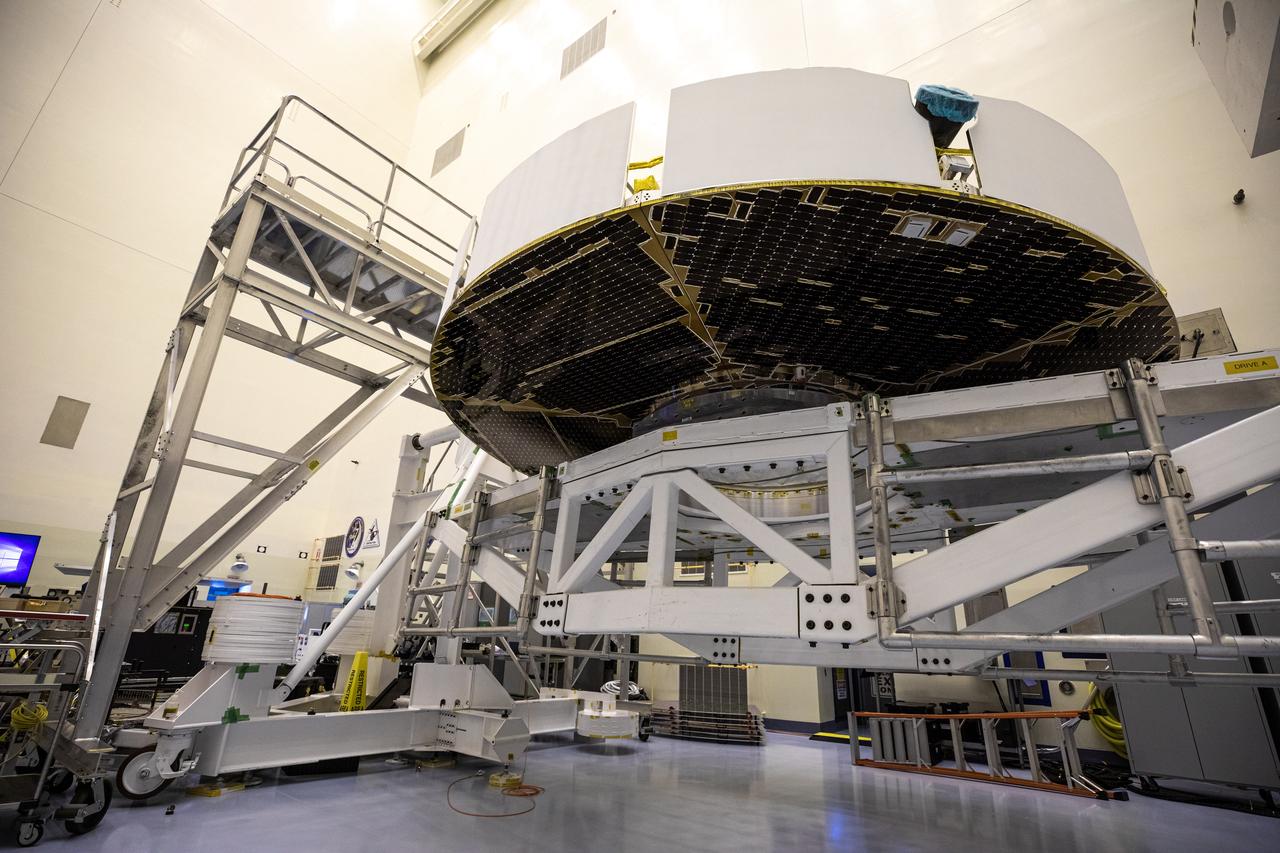
Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, NASA’s Landsat 9 observatory is lowered onto a fixture structure on July 12, 2021. Landsat 9 will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
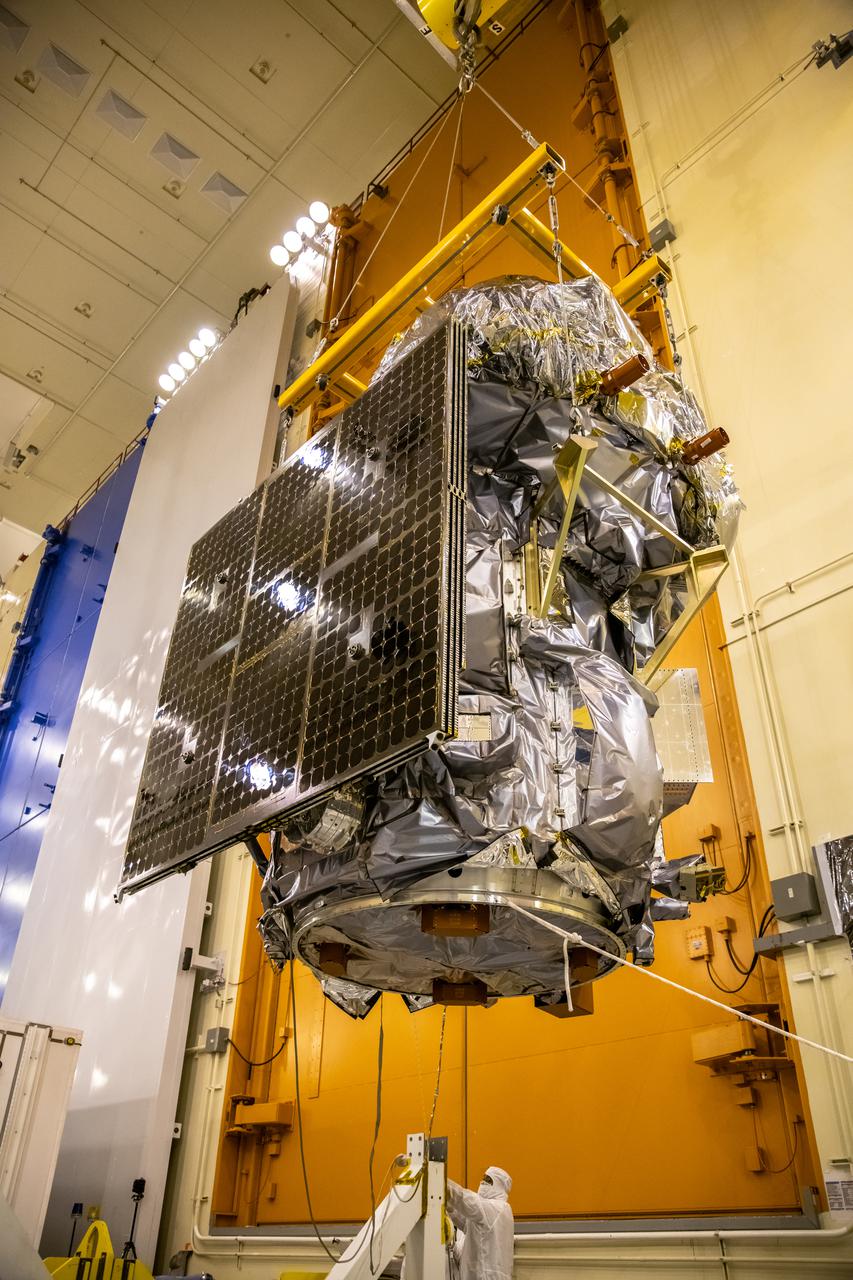

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, NASA’s Landsat 9 observatory is lifted for its move to a fixture structure on July 12, 2021. Landsat 9 will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
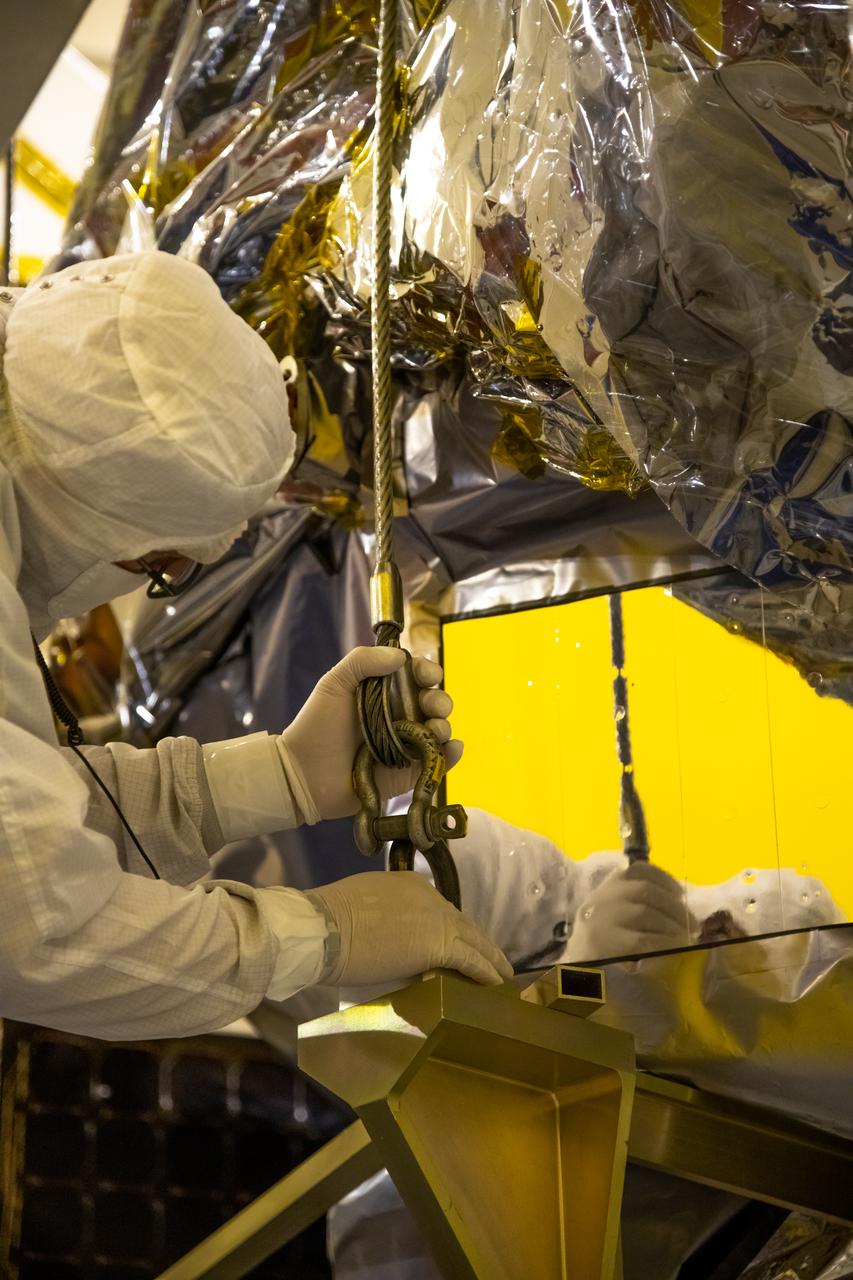

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians attach a crane to NASA’s Landsat 9 observatory for its lift to a fixture structure on July 12, 2021. Landsat 9 will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
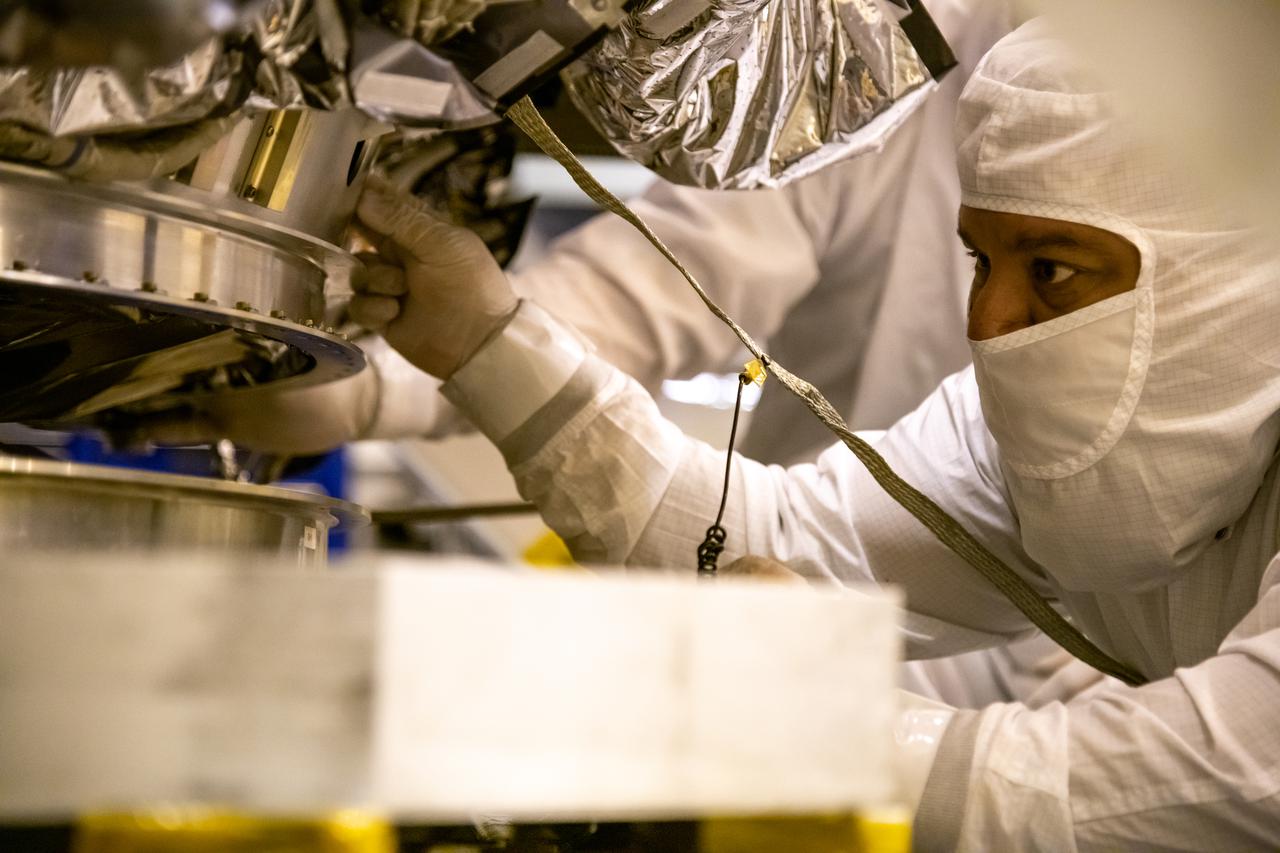

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians prepare NASA’s Landsat 9 observatory for its lift to a fixture structure on July 12, 2021. Landsat 9 will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
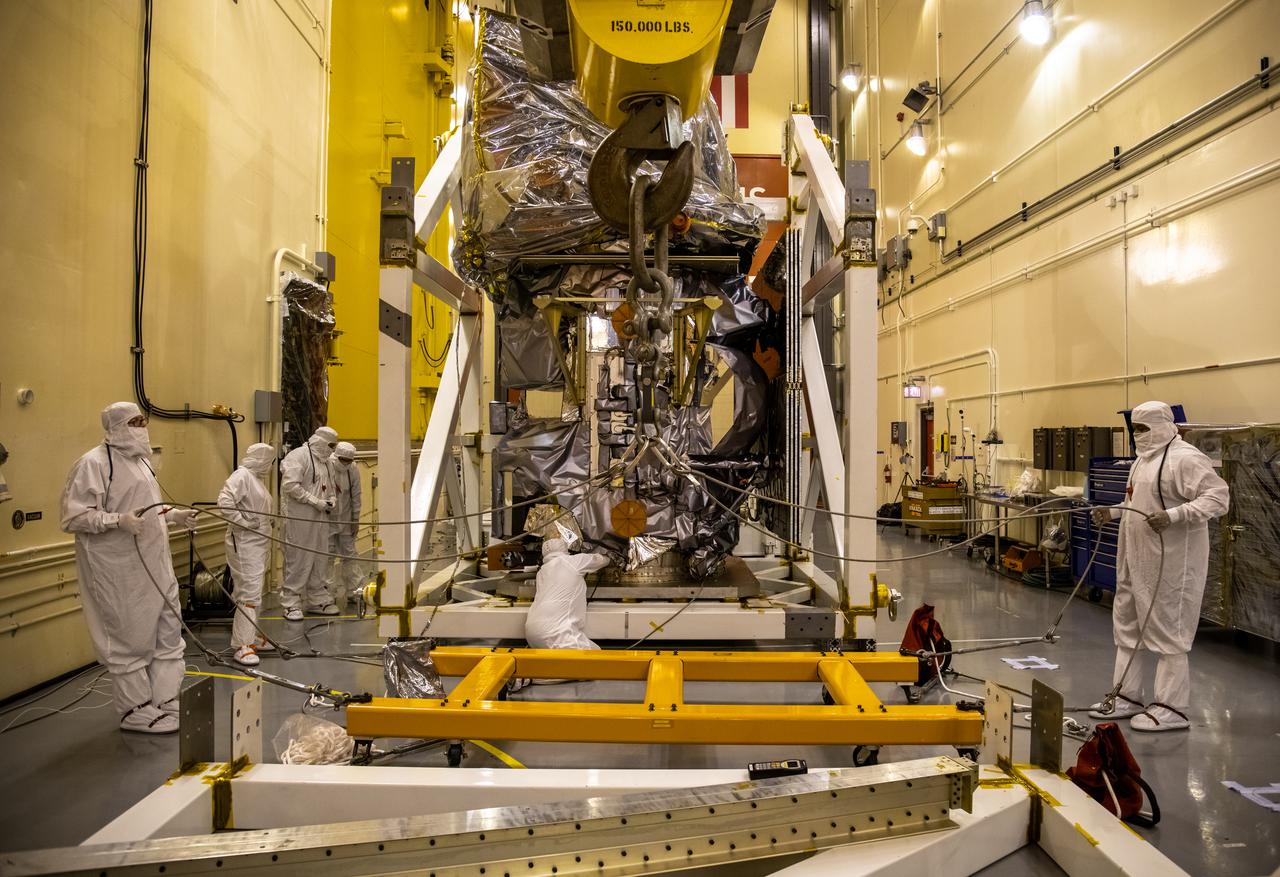

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians prepare NASA’s Landsat 9 observatory for its lift to a fixture structure on July 12, 2021. Landsat 9 will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
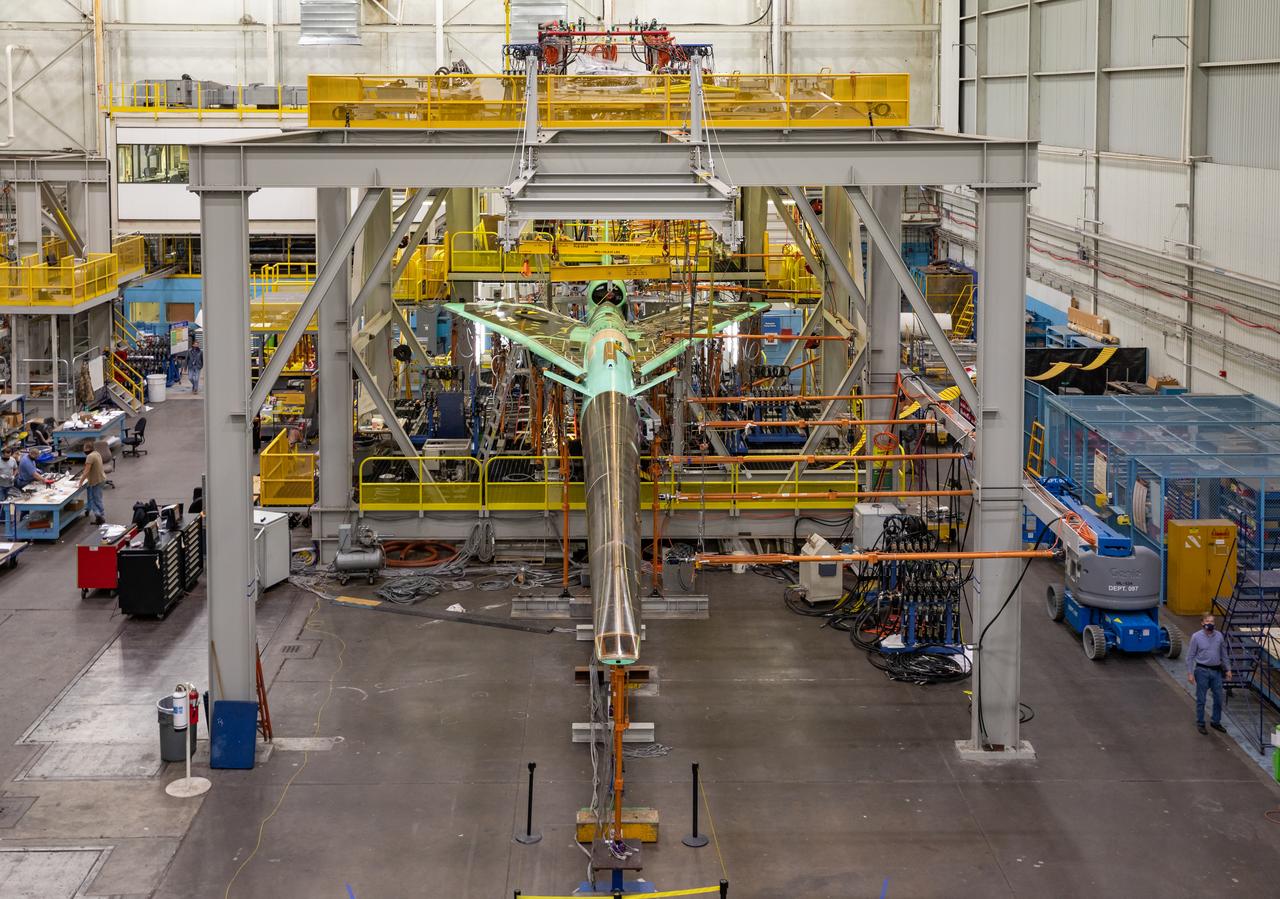

NASA’s X-59 undergoes a structural stress test at Lockheed Martin’s facility at Fort Worth, Texas. The X-59 is a one-of-a-kind airplane designed to fly at supersonic speeds without making a startling sonic boom sound for the communities below. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission, which plans to help enable supersonic air travel over land.

NASA’s X-59 undergoes a structural stress test at Lockheed Martin’s facility at Fort Worth, Texas. The X-59 is a one-of-a-kind airplane designed to fly at supersonic speeds without making a startling sonic boom sound for the communities below. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission, which plans to help enable supersonic air travel over land.