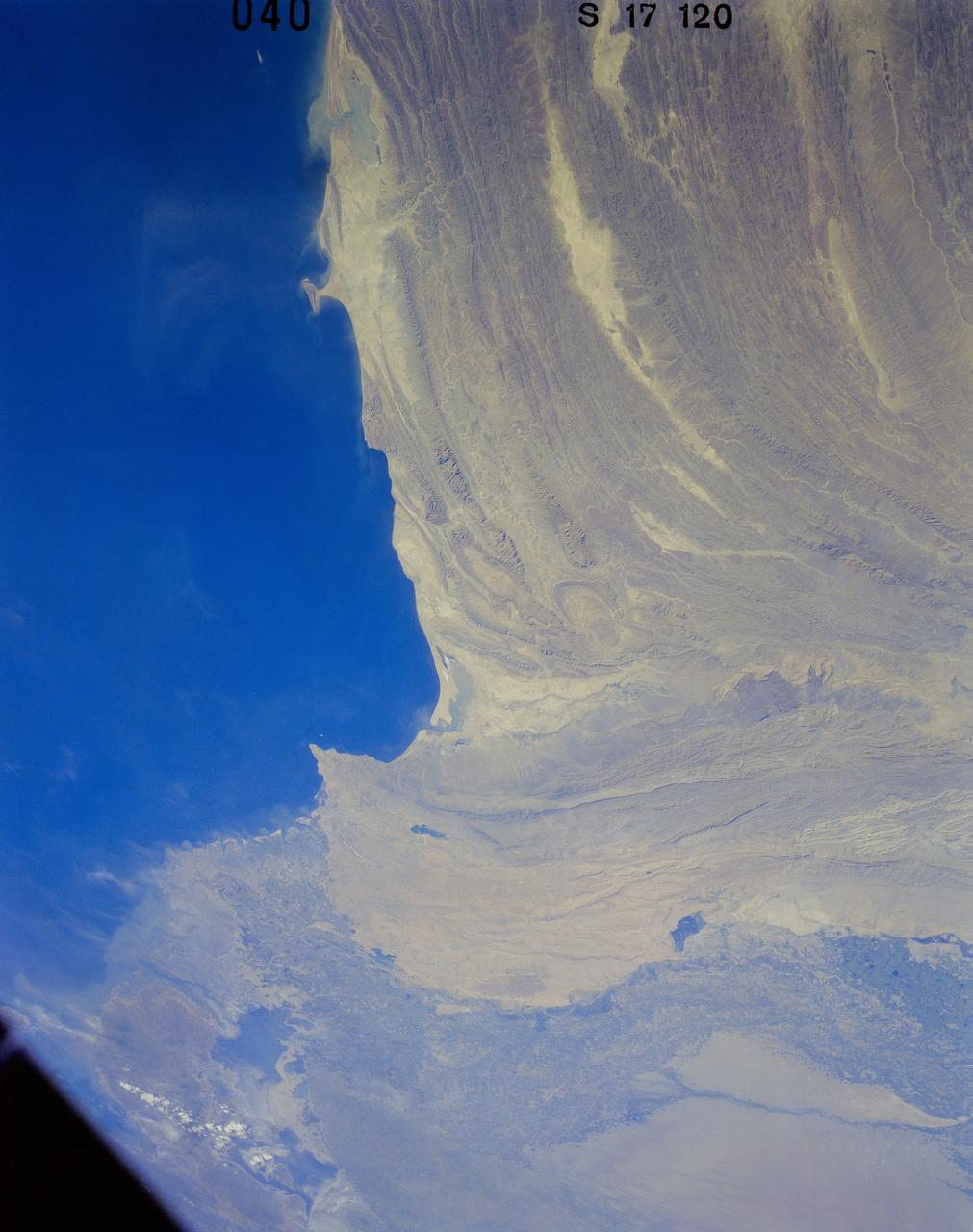

41G-120-040 (5-13 Oct. 1984) --- Pakistan, featuring the city of Karachi, the Makran mountain range, the mouth of the Indus River and the North Arabian Sea were photographed with a medium format camera aboard the space shuttle Challenger during the 41-G mission. Photo credit: NASA
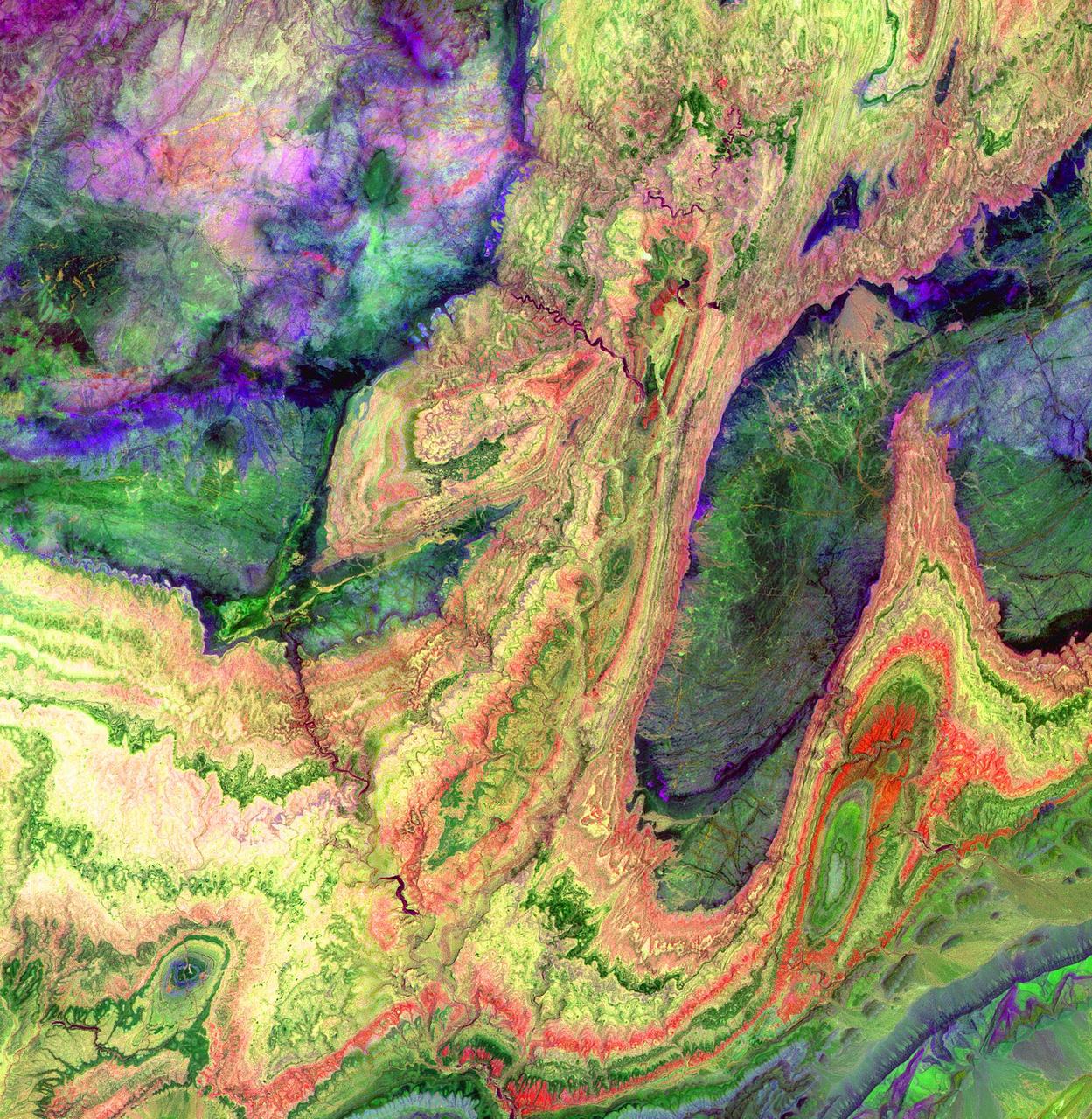
The Anti-Atlas Mountains of Morocco formed as a result of the collision of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates about 80 million years ago. This collision destroyed the Tethys Ocean; the limestone, sandstone, claystone, and gypsum layers that formed the ocean bed were folded and crumpled to create the Atlas and Anti-Atlas Mountains. In this ASTER image, short wavelength infrared bands are combined to dramatically highlight the different rock types, and illustrate the complex folding. The yellowish, orange and green areas are limestones, sandstones and gypsum; the dark blue and green areas are underlying granitic rocks. The ability to map geology using ASTER data is enhanced by the multiple short wavelength infrared bands, that are sensitive to differences in rock mineralogy. This image was acquired on June 13, 2001 by the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA's Terra satellite. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region, and its high spatial resolution of 15 to 90 meters (about 50 to 300 feet), ASTER images Earth to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03893
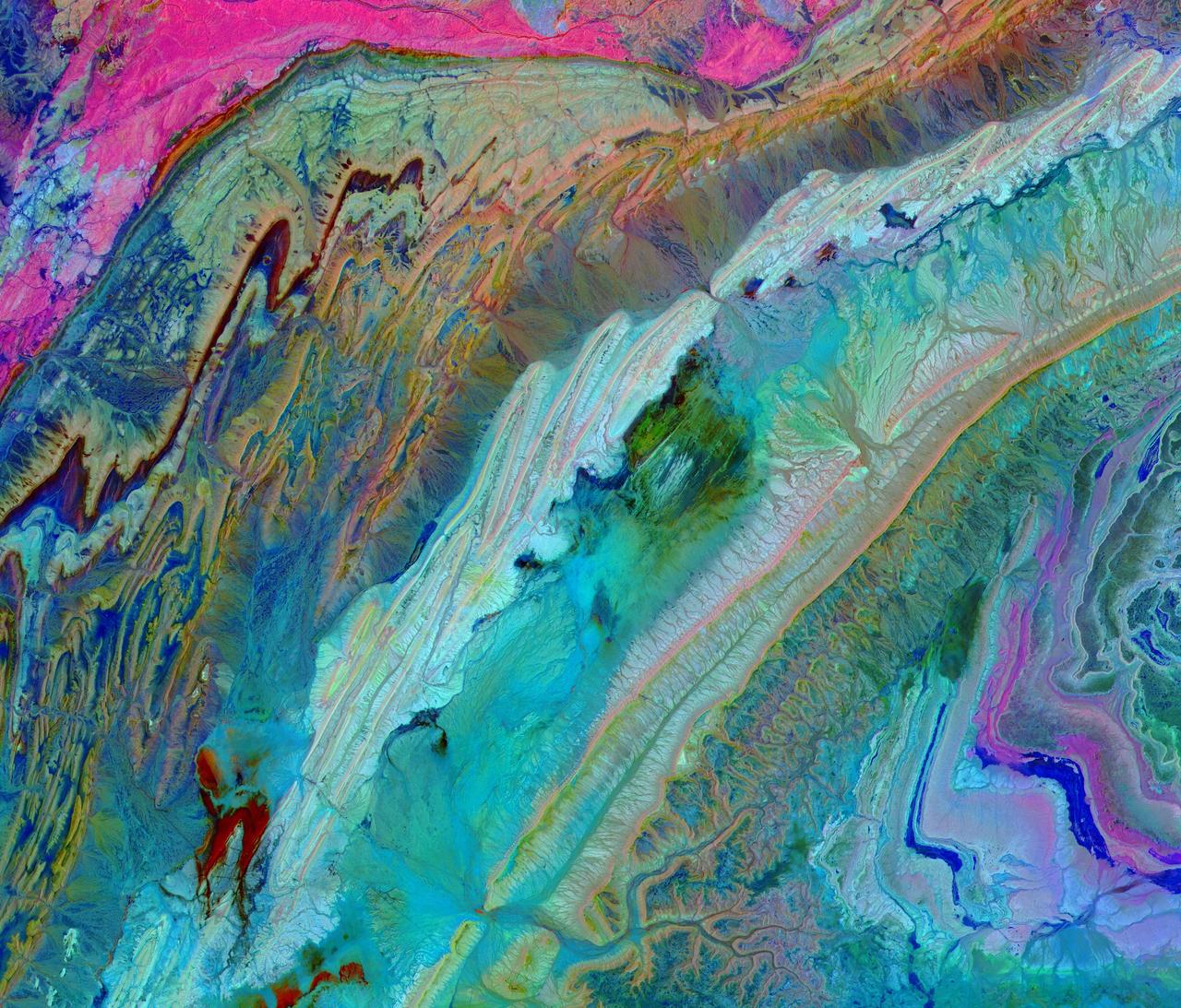

The Anti-Atlas Mountains of Morocco formed as a result of the collision of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates about 80 million years ago. This collision destroyed the Tethys Ocean; the limestone, sandstone, claystone, and gypsum layers that formed the ocean bed were folded and crumpled to create the Anti-Atlas Mountains. In this ASTER image of southwest Morocco, visible, near infrared, and short wavelength infrared bands are combined to dramatically highlight the different rock types, and illustrate the complex folding. The ability to map geology using ASTER data is enhanced by bands that are sensitive to differences in rock mineralogy. The image was acquired on November 5, 2007, covers an area of 51.9 by 60.8 km, and is located at 28.1 degrees north and 10.7 degrees west. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region and its high spatial resolution of about 50 to 300 feet (15 to 90 meters), ASTER images Earth to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. ASTER is one of five Earth-observing instruments launched Dec. 18, 1999, on Terra. The instrument was built by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. A joint U.S./Japan science team is responsible for validation and calibration of the instrument and data products. The broad spectral coverage and high spectral resolution of ASTER provides scientists in numerous disciplines with critical information for surface mapping and monitoring of dynamic conditions and temporal change. Example applications are monitoring glacial advances and retreats; monitoring potentially active volcanoes; identifying crop stress; determining cloud morphology and physical properties; wetlands evaluation; thermal pollution monitoring; coral reef degradation; surface temperature mapping of soils and geology; and measuring surface heat balance. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23533

ISS040-E-027042 (30 June 2014) --- Kulunda Steppe, Siberia in central Russia is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 40 crew member on the International Space Station. The crew on the station called down to Houston to ask for an explanation of this strange pattern of spikes crossing the Kulunda Steppe in central Russia. The ?spikes? are a prominent visual feature (center) visible from the top of the ISS orbit (approximately 52 degrees north), the highest latitude flown over by the spacecraft. In fact these linear zones are gentle folds in the surface rocks of the area, lying slightly lower than the surrounding lighter-toned agricultural lands. The dark zones are forested with pines and dotted with salt-rich lakes. The image width (left to right edge) represents more than 300 kilometers ground distance, and the forested spikes are nearly that length. The green floodplain of the famous Ob River (right) is the westernmost of Siberia?s three great rivers (the others being the Yenisei and Lena). The Ob flows north (towards the top of the image) for another 2,000 kilometers to the Arctic Ocean. The city of Barnaul (population 612,000), a major center of industry, trade and culture in Siberia, lies on the banks of the river with riverboat, air and rail links to the rest of the country. A broader, winter image of the Kulunda geology and the Ob River can be seen here.
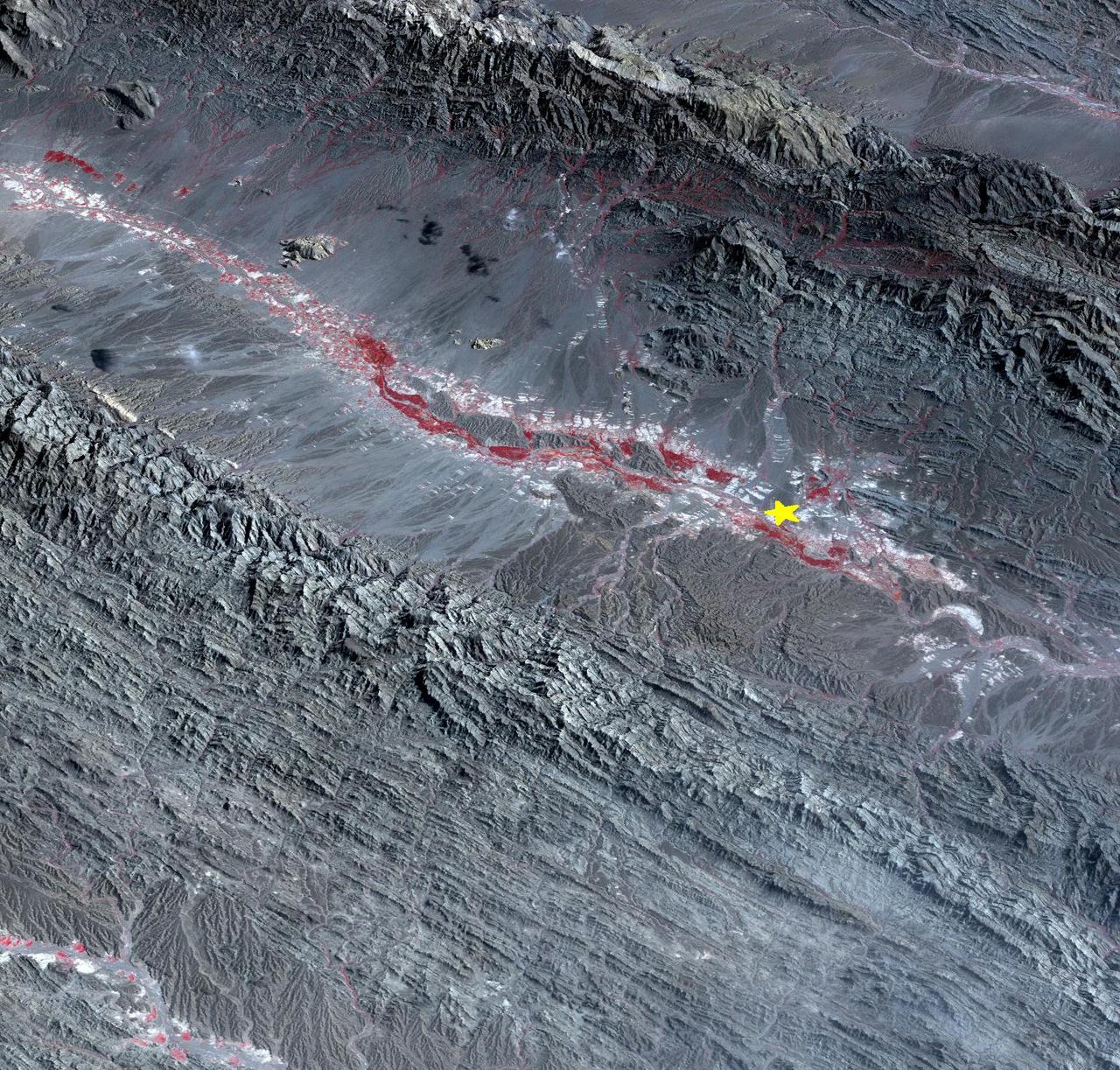
On September 24 at 11:29 GMT, a magnitude 7.7 earthquake struck in south-central Pakistan at a relatively shallow depth of 20 kilometers. The earthquake occurred as the result of oblique strike-slip motion, consistent with rupture within the Eurasian tectonic plate. Tremors were felt as far away as New Delhi as well as Karachi in Pakistan. Even though the immediate area to the epicenter is sparsely populated, the majority of houses are of mud brick construction and damage is expected to be extensive. The perspective view, looking to the east, shows the location of the epicenter in Pakistan's Makran fold belt. The image is centered near 27 degrees north latitude, 65.5 degrees east longitude, and was acquired December 13, 2012. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region and its high spatial resolution of 15 to 90 meters (about 50 to 300 feet), ASTER images Earth to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. ASTER is one of five Earth-observing instruments launched Dec. 18, 1999, on Terra. The instrument was built by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. A joint U.S./Japan science team is responsible for validation and calibration of the instrument and data products. The broad spectral coverage and high spectral resolution of ASTER provides scientists in numerous disciplines with critical information for surface mapping and monitoring of dynamic conditions and temporal change. Example applications are: monitoring glacial advances and retreats; monitoring potentially active volcanoes; identifying crop stress; determining cloud morphology and physical properties; wetlands evaluation; thermal pollution monitoring; coral reef degradation; surface temperature mapping of soils and geology; and measuring surface heat balance. The U.S. science team is located at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. The Terra mission is part of NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. More information about ASTER is available at <a href="http://asterweb.jpl.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">asterweb.jpl.nasa.gov/</a>. Image Credit: NASA/GSFC/METI/ERSDAC/JAROS, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team Image Addition Date: 2013-09-24 <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>