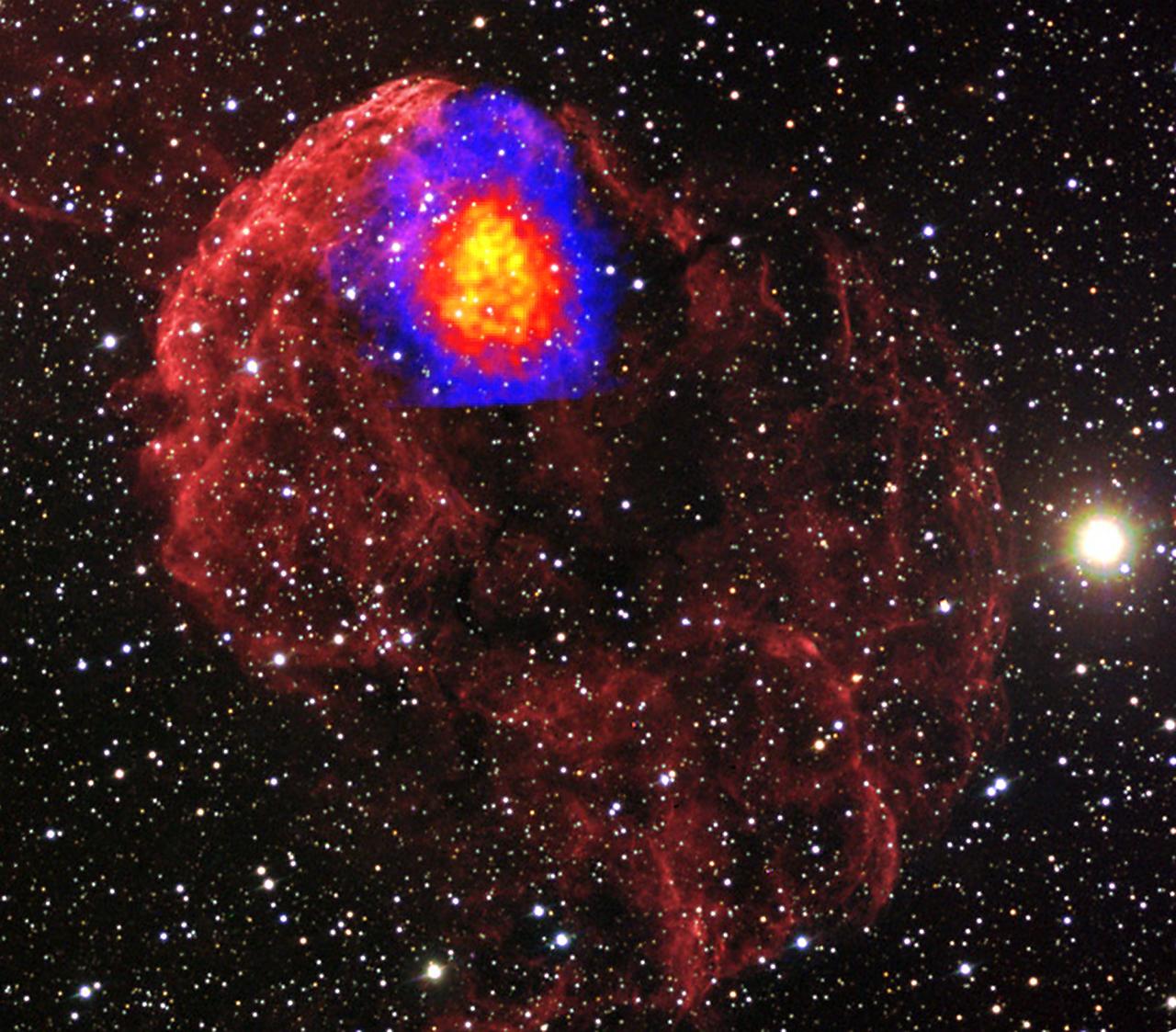

Suzaku Finds "Fossil" Fireballs from Supernovae In a supernova remnant known as the Jellyfish Nebula, Suzaku detected X-rays from fully ionized silicon and sulfur -- an imprint of higher-temperature conditions immediately following the star's explosion. The nebula is about 65 light-years across. (12/30/2009) Credit: JAXA/NASA/Suzaku To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/astro-e2/news/fossil-fireballs.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/astro-e2/news/fossil-fireballs...</a>
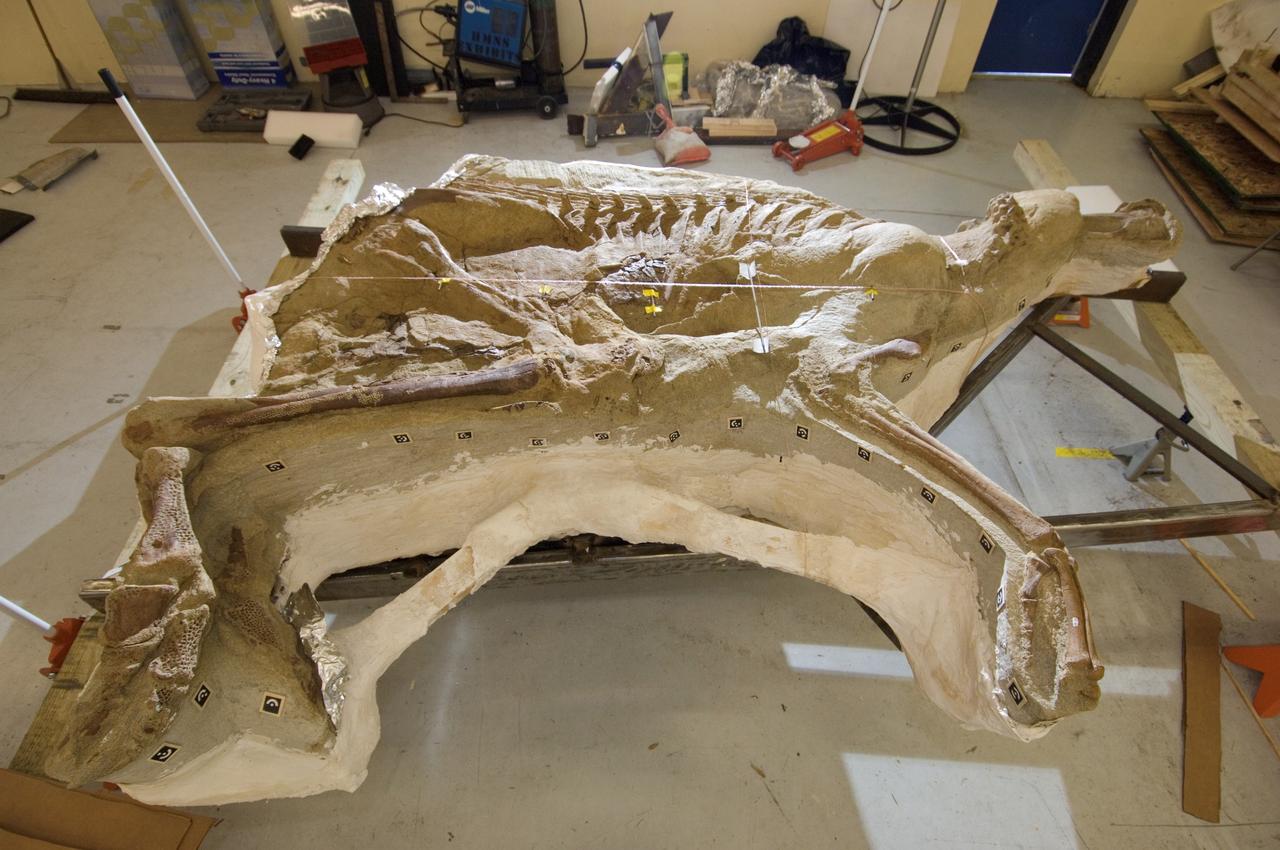

Documentation of NASA's partnership with the Houston Museum of Natural Science and Montana's Great Plains Dinosaur Museum to provide an insulated facility at Ellington Field in which the Leonardo Project Team was able to X-ray Leonardo, a 77 million year old dinosaur fossil. View of the Brachylophosaurus fossil called Leonardo.
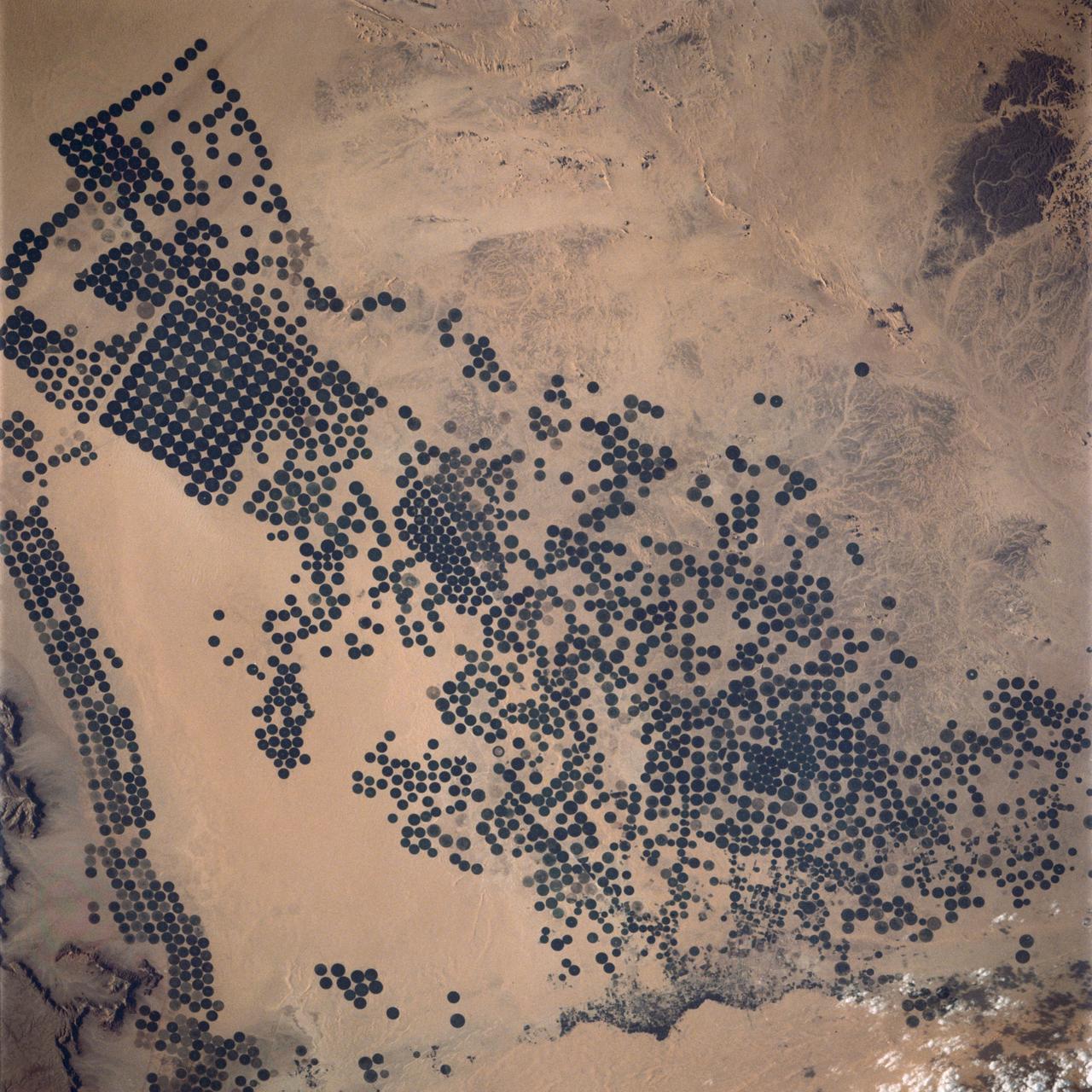

In Saudi Arabia, center-pivot, swing-arm irrigated agriculture complexes such as the one imaged at Jabal Tuwayq (20.5N, 45.0 E) extract deep fossil water reserves to achieve food crop production self sufficiency in this desert environment. The significance of the Saudi expanded irrigated agriculture is that the depletion of this finite water resource is a short term solution to a long term need that will still exist when the water has been extracted.
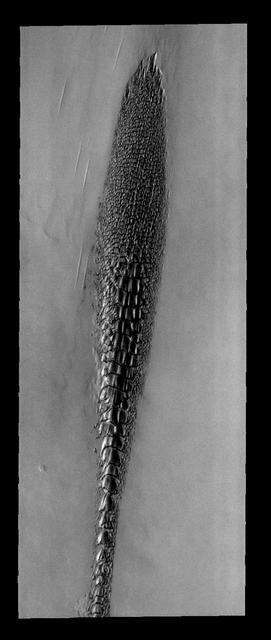
Back by popular demand: THEMIS ART IMAGE #73 These north polar dunes look odd -- like a plant, or fossil, or some alien creature
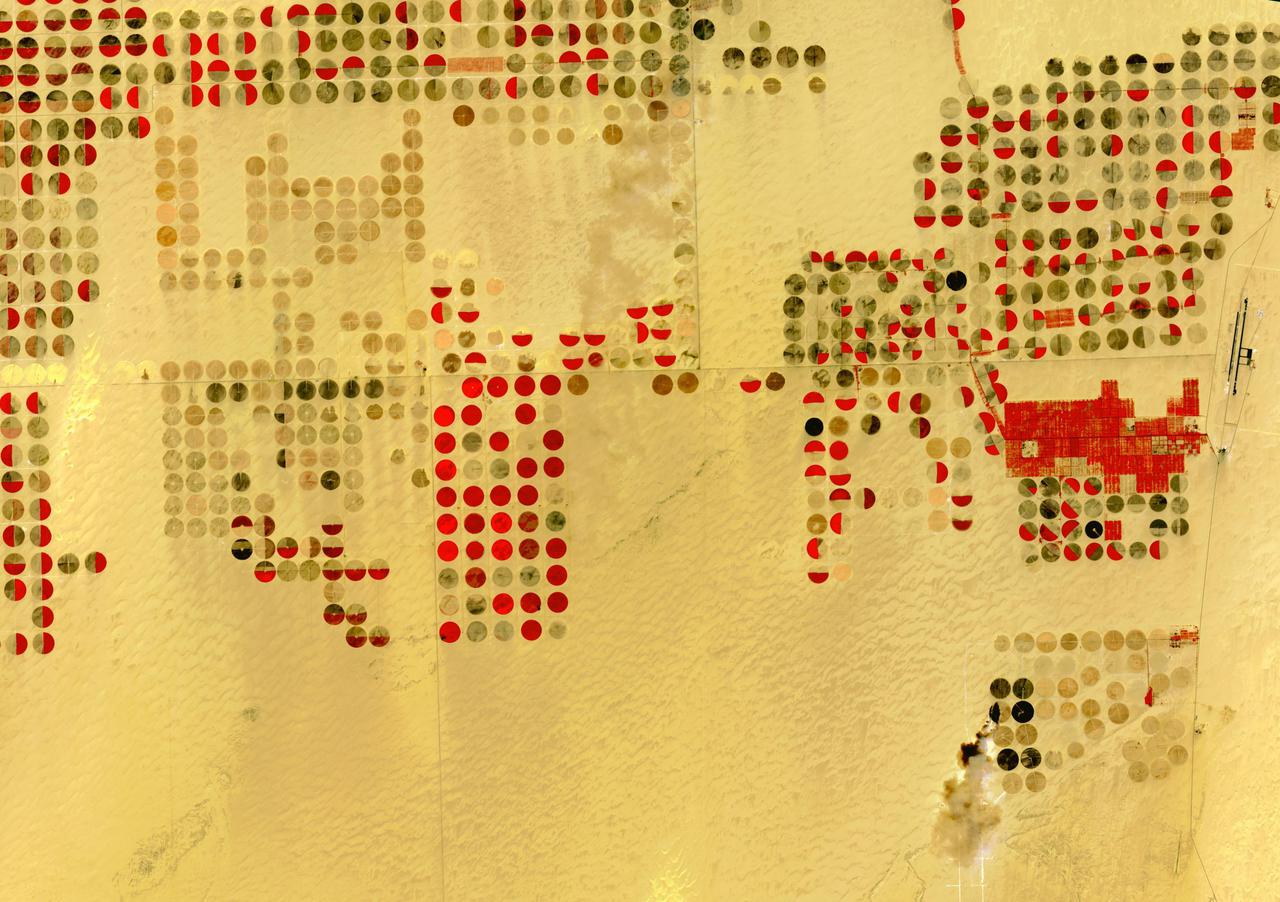
The Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System is the world's largest fossil water aquifer system. It covers an estimated area of 2.6 million square kilometers, including parts of Sudan, Chad, Libya, and most of Egypt. In the southwestern part of Egypt, the East Oweinat development project uses central pivot irrigation to mine the fossil water for extensive agricultural development. Crops include wheat and potatoes; they are transported via the airport on the eastern side. The image was acquired October 12, 2015, covers an area of 33.3 by 47.2 km, and is located near 22.6 degrees north, 28.5 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24616
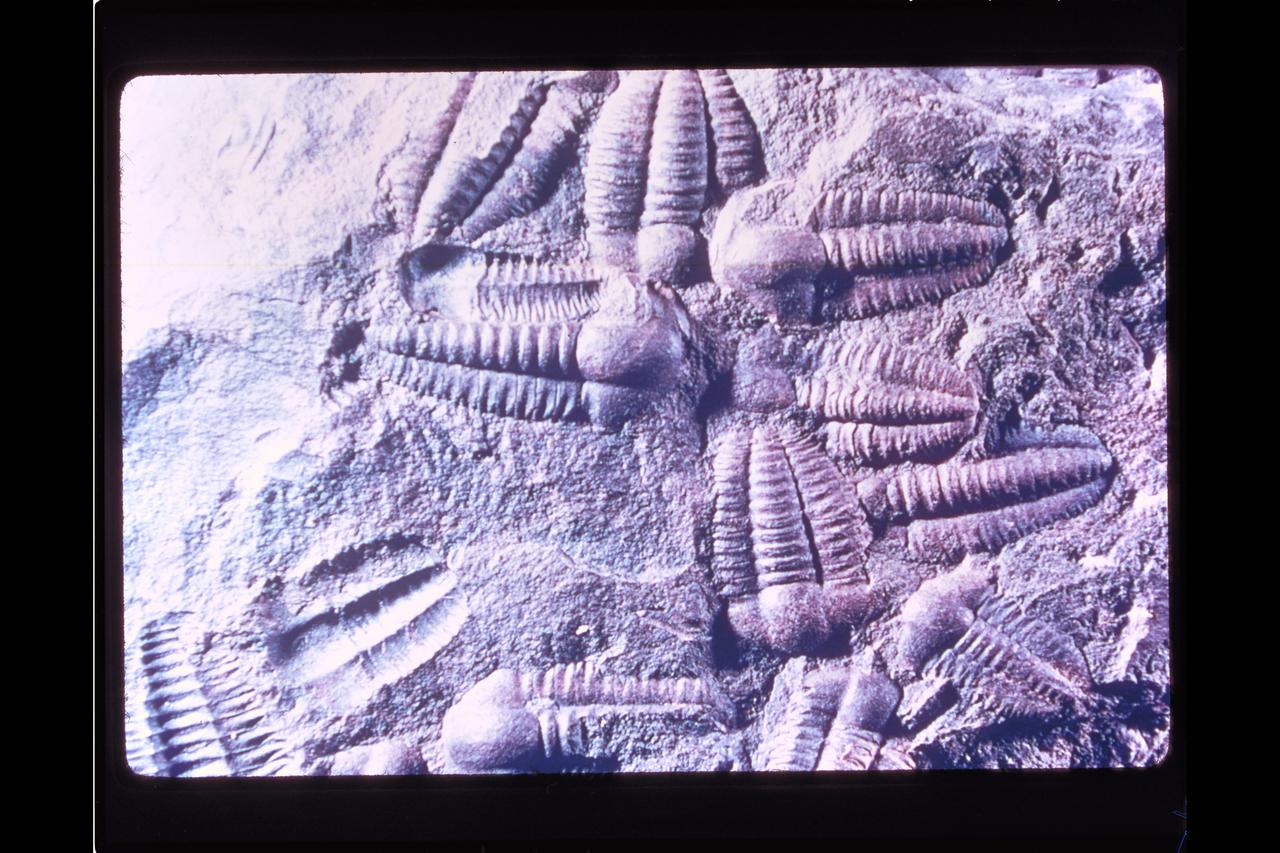

Origin of life (fossil)
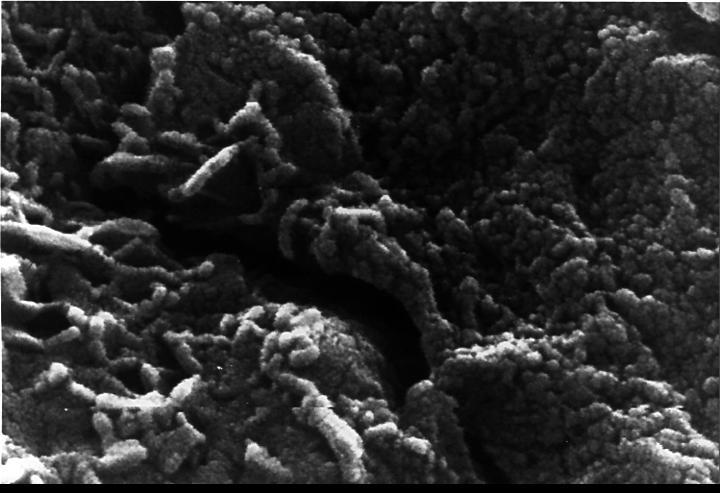

This electron microscope image shows extremely tiny tubular structures that are possible microscopic fossils of bacteria-like organisms that may have lived on Mars more than 3.6 billion years ago. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00285

Acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft on in 2011, this image shows the Wadi As-Sirhan Basin in northwest Saudi Arabia, which has been steadily developing agricultural fields using center pivot irrigation by tapping into fossil ground water.
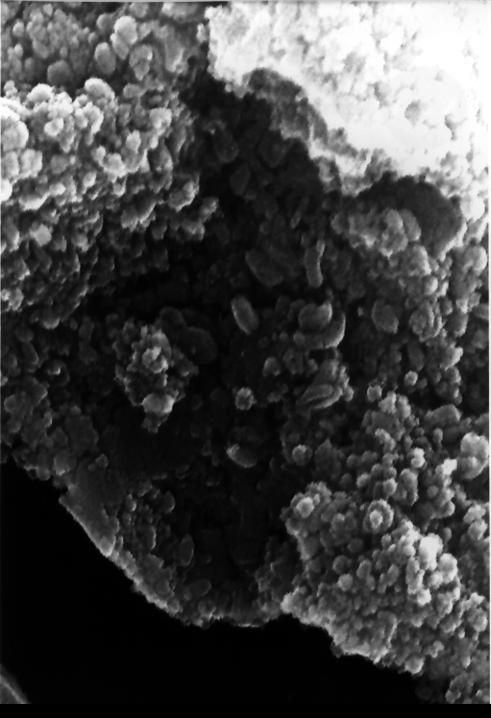
This electron microscope image shows egg-shaped structures, some of which may be possible microscopic fossils of Martian origin as discussed by NASA research published in the Aug. 16, 1996. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00286
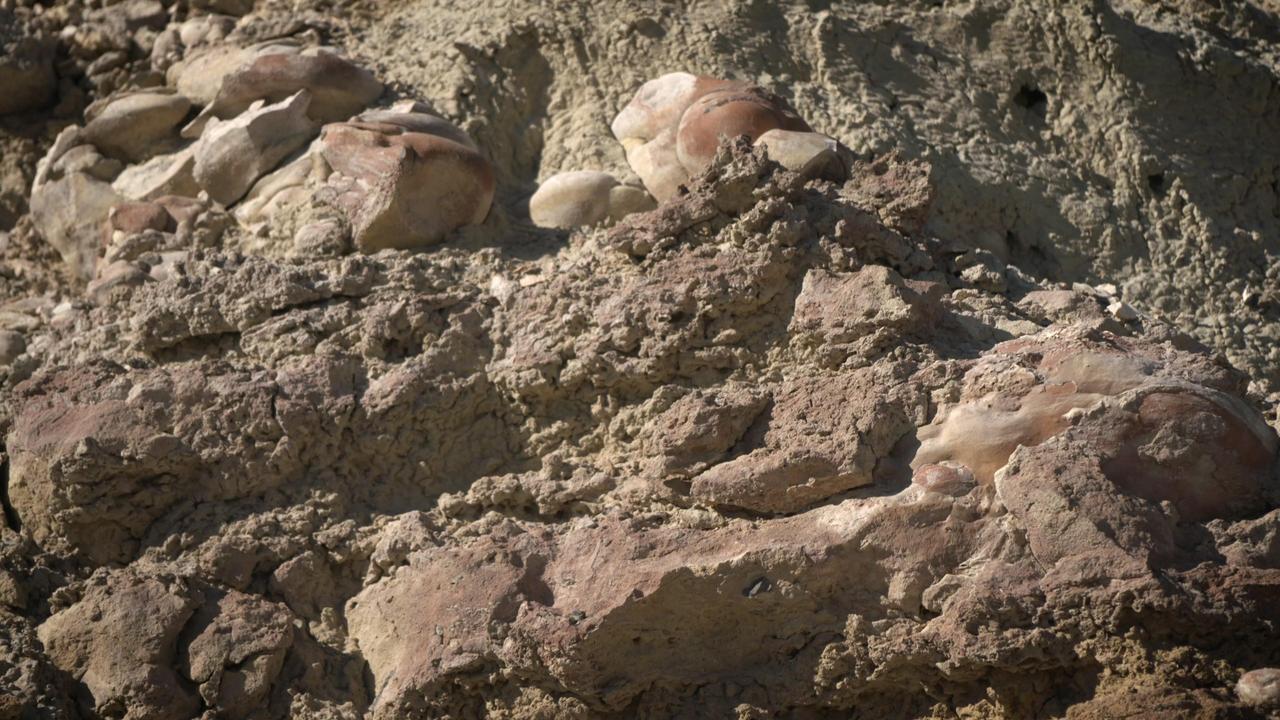

Made from fossilized microbes and sediment, these rounded rocks are stromatolites that were found in a dry lakebed during the field exercise. Scientists hope to find something similar in the dry lakebed Perseverance will be exploring on Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23779

Scientists from NASA's Mars 2020 and ESA's ExoMars projects study stromatolites, the oldest confirmed fossilized lifeforms on Earth, in the Pilbara region of North West Australia. The image was taken on Aug. 19, 2019. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23551
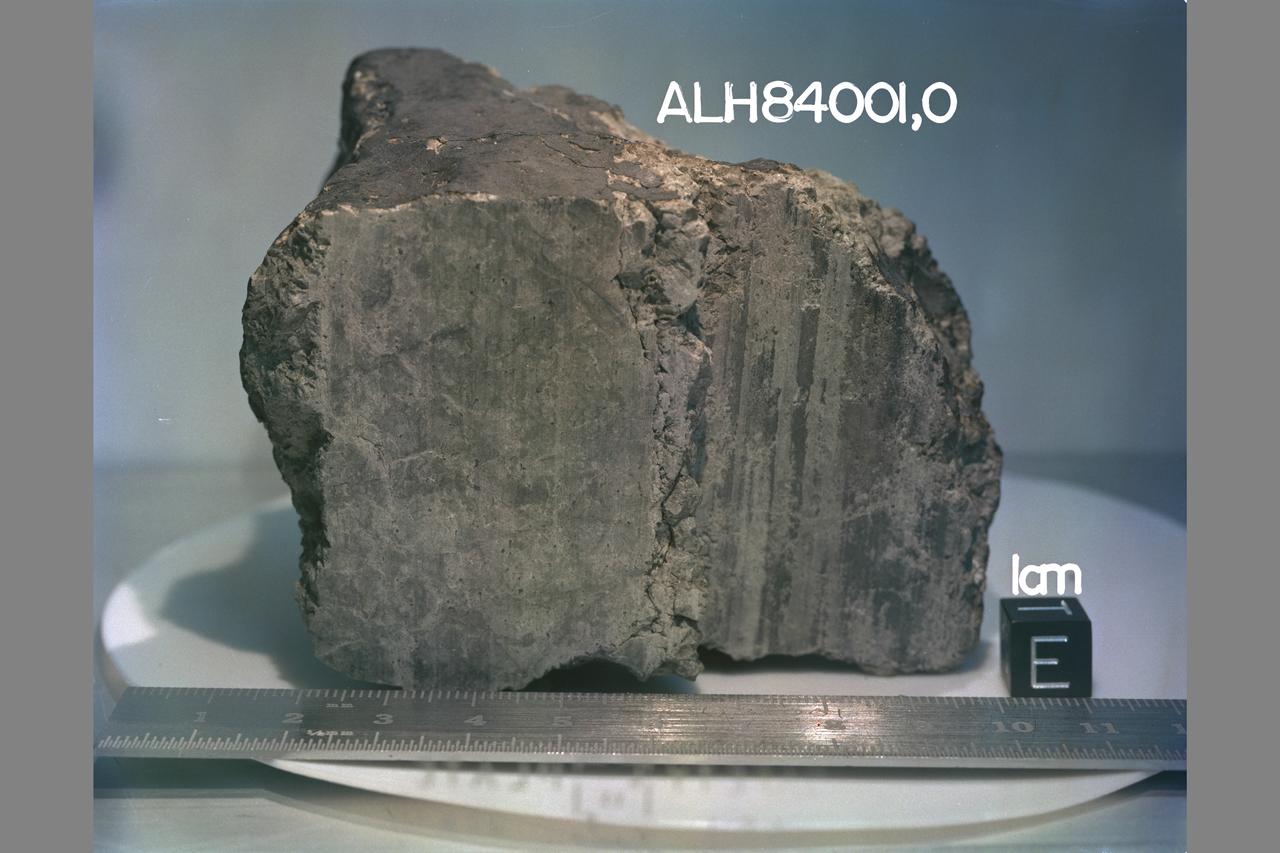

Martian Meteorite (ALH84001) Life on Mars? Microscopic Fossils

This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft was acquired near the Martian winter solstice, when the sun was low over the horizon at this location.
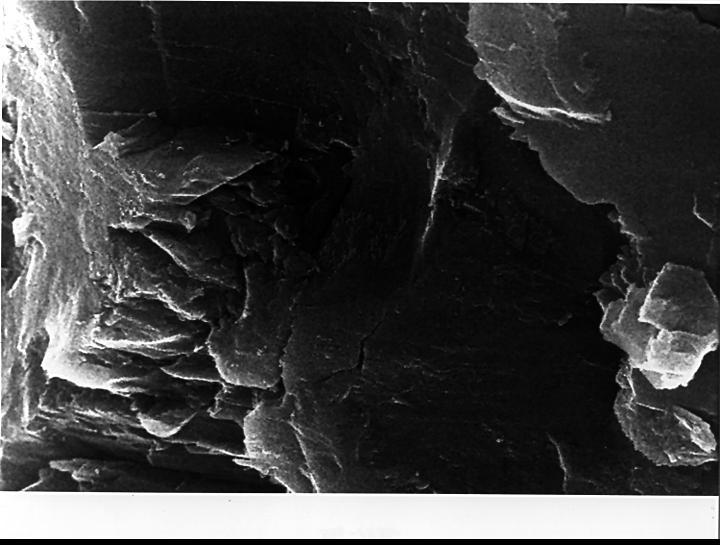
In the center of this electron microscope image of a small chip from a meteorite are several tiny structures that are possible microscopic fossils of primitive, bacteria-like organisms that may have lived on Mars more than 3.6 billion years ago. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00283
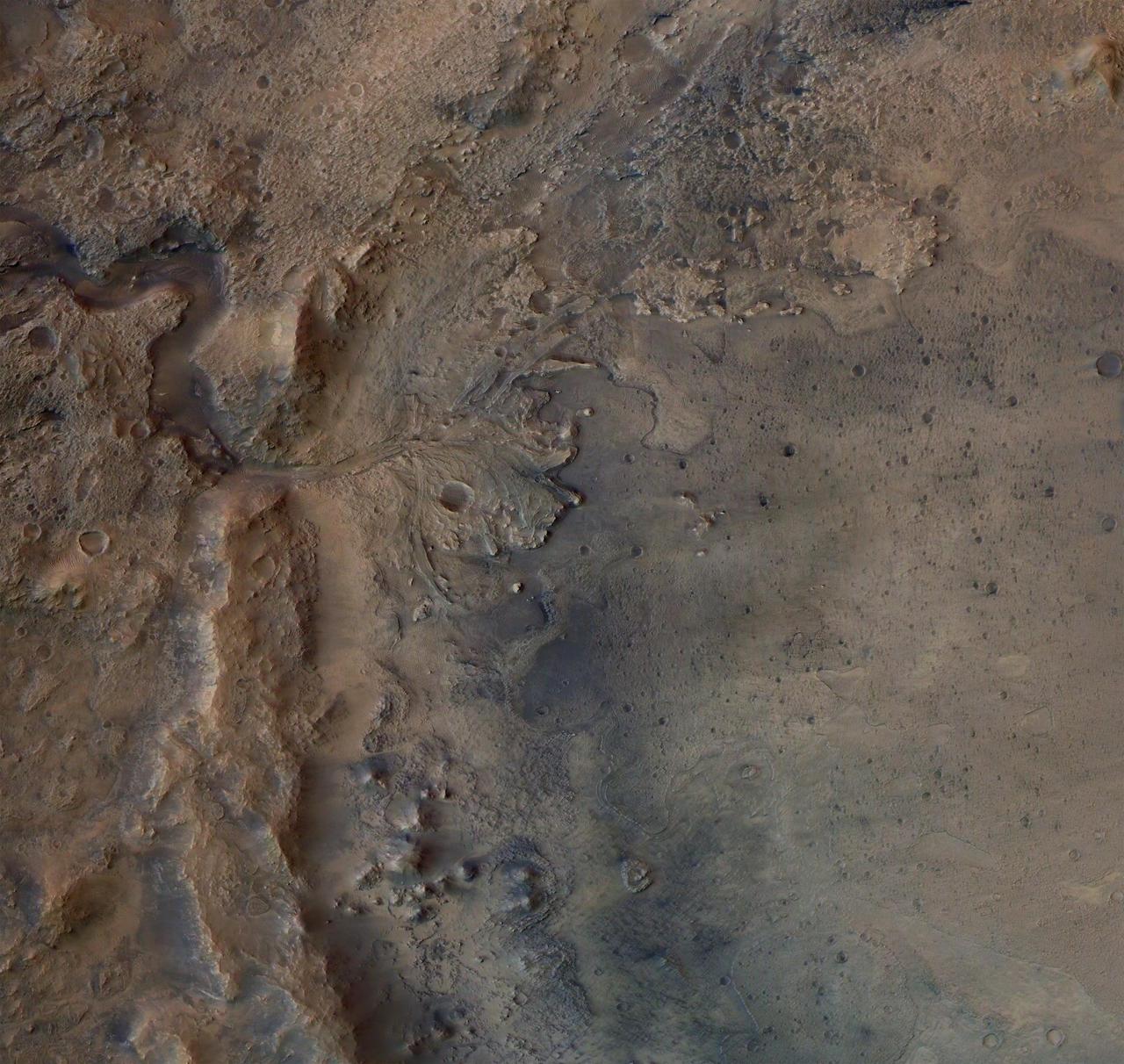

This image shows the remains of an ancient delta in Mars' Jezero Crater, which NASA's Perseverance Mars rover will explore for signs of fossilized microbial life. The image was taken by the High Resolution Stereo Camera aboard the ESA (European Space Agency) Mars Express orbiter. The European Space Operations Centre in Darmstadt, Germany, operates the ESA mission. The High Resolution Stereo Camera was developed by a group with leadership at the Freie Universitat Berlin. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24096
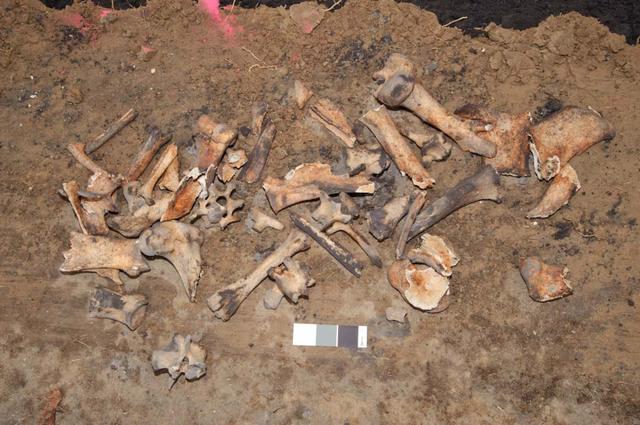

Bones found at the site of the Sustainability Base N-232. Later determined to be from a domestic animal, possibly a donkey or horse.
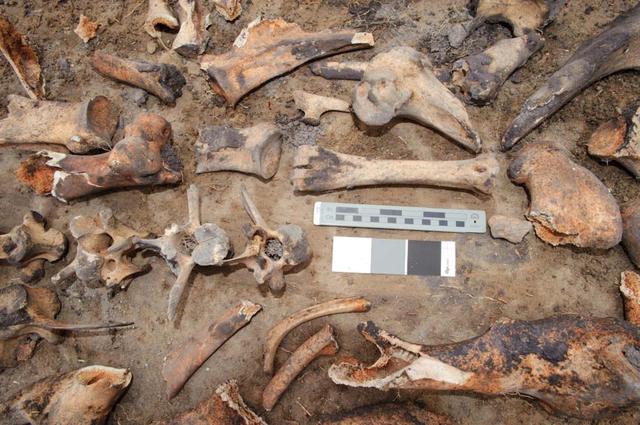

Bones found at the site of the Sustainability Base N-232. Later determined to be from a domestic animal, possibly a donkey or horse.
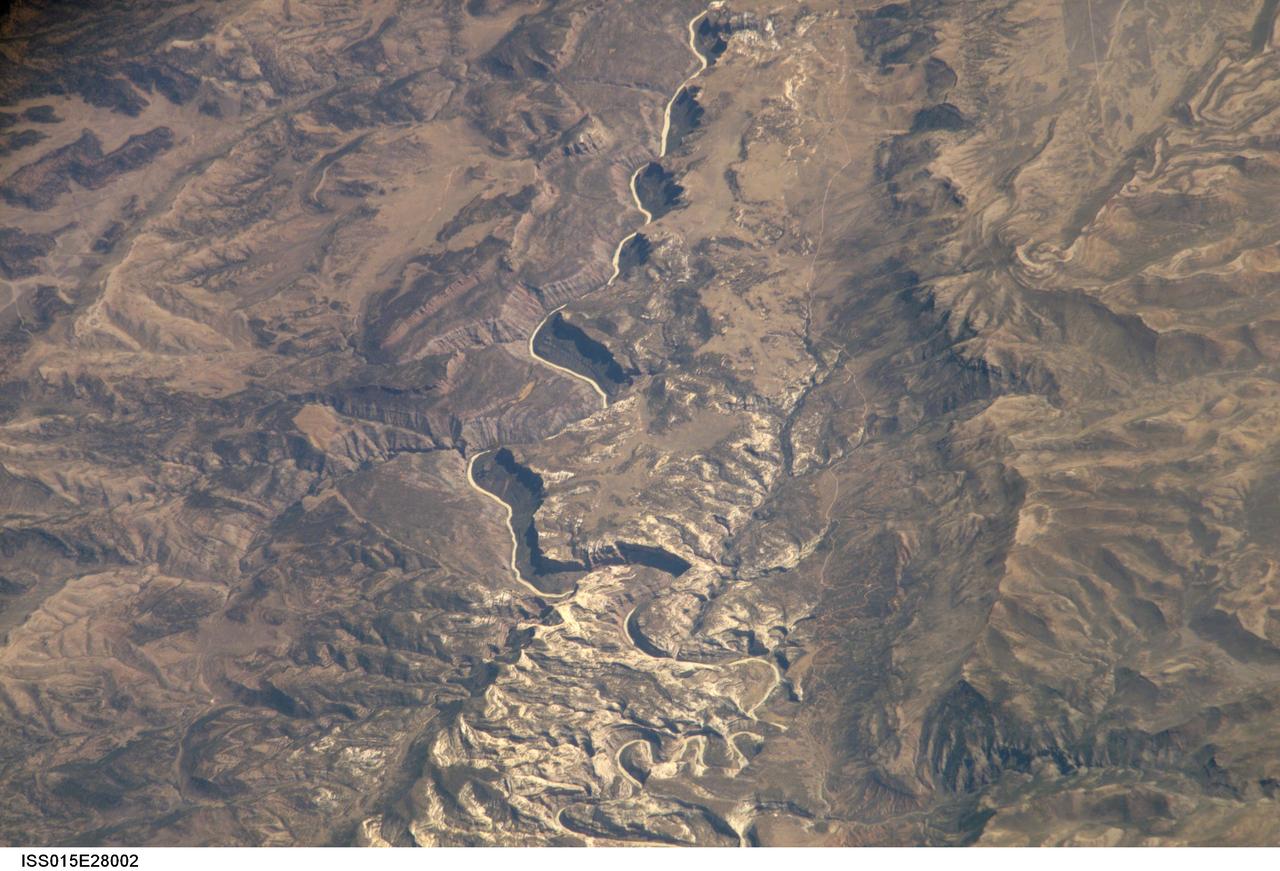
ISS015-E-28002 (12 Sept. 2007) --- A section of Dinosaur National Monument along the Yampa River in Colorado, which straddles the Colorado/Utah border, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 15 crewmember on the International Space Station. Dinosaur National Monument is perhaps best known for the abundant fossils found in the approximately 145 Ma (mega-annum, or millions of years old) Morrison Formation exposed in valleys and low ridges, according to scientists. The fossil assemblage is a unique record of terrestrial life of the period (dinosaurs, plants, and other animal species). Remains accumulated in streams and shallow lakes and were swiftly buried (and preserved) by sediments associated with those environments. Scientists believe these sediments in turn were lithified over many millions of years as they were buried under younger deposits -- forming the distinctive stratigraphy of the Monument. The generally flat-laying "layer cake" geology of the region -- similar to the Colorado Plateau to the south - is expressed in the image by parallel beds of tan, reddish-brown, and gray-brown sedimentary rocks cut by the Yampa River at the northern end of the Monument (top). Erosion by the Yampa River exposed the Morrison layer and its trove of fossil material. Together with other fossils found in both older and younger rock layers in the area, the Dinosaur National Monument remains an important scientific resource that continues to provide new insights into the geologic history and paleoecology of the region.
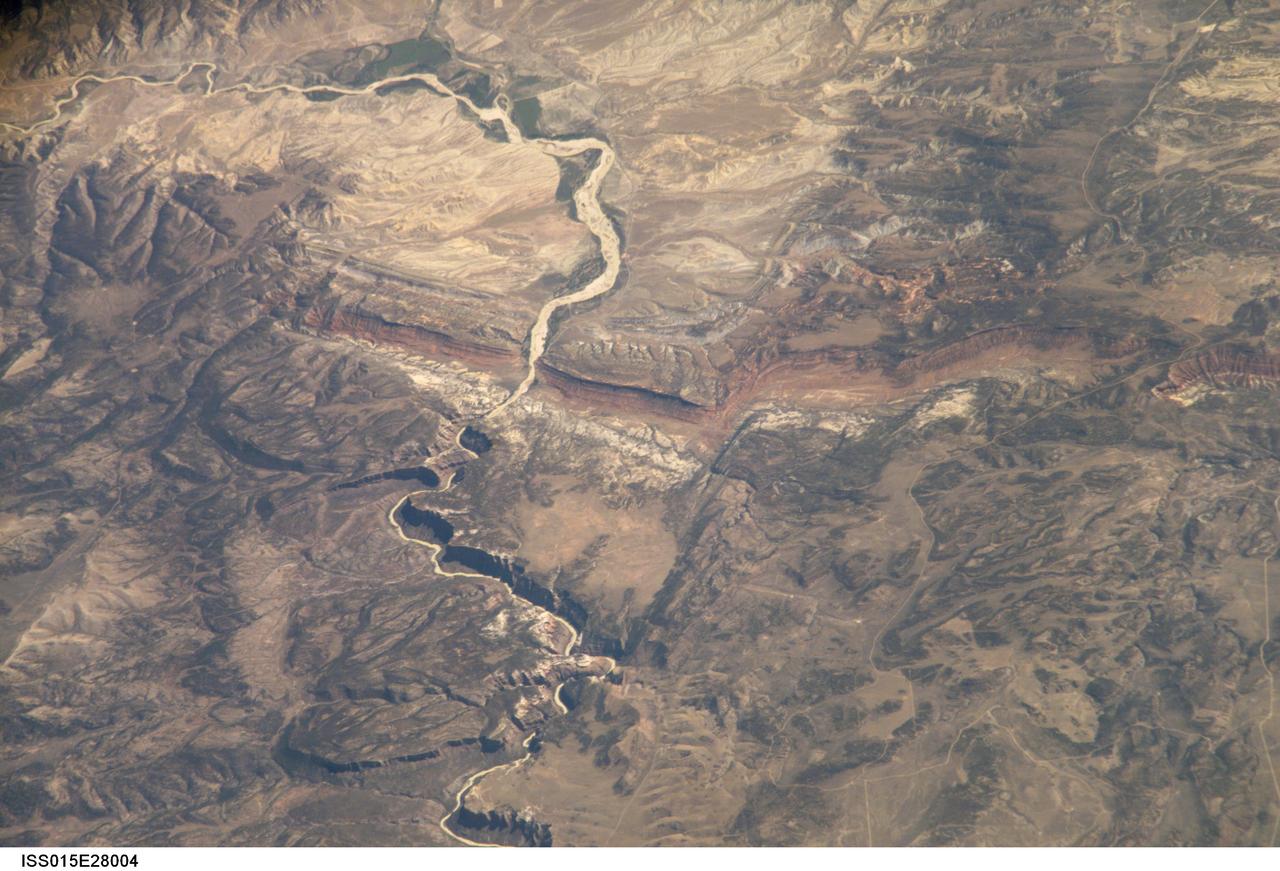

ISS015-E-28004 (12 Sept. 2007) --- A section of Dinosaur National Monument along the Yampa River in Colorado, which straddles the Colorado/Utah border, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 15 crewmember on the International Space Station. Dinosaur National Monument is perhaps best known for the abundant fossils found in the approximately 145 Ma (mega-annum, or millions of years old) Morrison Formation exposed in valleys and low ridges, according to scientists. The fossil assemblage is a unique record of terrestrial life of the period (dinosaurs, plants, and other animal species). Remains accumulated in streams and shallow lakes and were swiftly buried (and preserved) by sediments associated with those environments. Scientists believe these sediments in turn were lithified over many millions of years as they were buried under younger deposits -- forming the distinctive stratigraphy of the Monument. The generally flat-laying "layer cake" geology of the region -- similar to the Colorado Plateau to the south - is expressed in the image by parallel beds of tan, reddish-brown, and gray-brown sedimentary rocks cut by the Yampa River at the northern end of the Monument (top). Erosion by the Yampa River exposed the Morrison layer and its trove of fossil material. Together with other fossils found in both older and younger rock layers in the area, the Dinosaur National Monument remains an important scientific resource that continues to provide new insights into the geologic history and paleoecology of the region.

ISS015-E-28003 (12 Sept. 2007) --- A section of Dinosaur National Monument along the Yampa River in Colorado, which straddles the Colorado/Utah border, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 15 crewmember on the International Space Station. Dinosaur National Monument is perhaps best known for the abundant fossils found in the approximately 145 Ma (mega-annum, or millions of years old) Morrison Formation exposed in valleys and low ridges, according to scientists. The fossil assemblage is a unique record of terrestrial life of the period (dinosaurs, plants, and other animal species). Remains accumulated in streams and shallow lakes and were swiftly buried (and preserved) by sediments associated with those environments. Scientists believe these sediments in turn were lithified over many millions of years as they were buried under younger deposits -- forming the distinctive stratigraphy of the Monument. The generally flat-laying "layer cake" geology of the region -- similar to the Colorado Plateau to the south - is expressed in the image by parallel beds of tan, reddish-brown, and gray-brown sedimentary rocks cut by the Yampa River at the northern end of the Monument (top). Erosion by the Yampa River exposed the Morrison layer and its trove of fossil material. Together with other fossils found in both older and younger rock layers in the area, the Dinosaur National Monument remains an important scientific resource that continues to provide new insights into the geologic history and paleoecology of the region.

ISS015-E-28001 (12 Sept. 2007) --- A section of Dinosaur National Monument along the Yampa River in Colorado, which straddles the Colorado/Utah border, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 15 crewmember on the International Space Station. Dinosaur National Monument is perhaps best known for the abundant fossils found in the approximately 145 Ma (mega-annum, or millions of years old) Morrison Formation exposed in valleys and low ridges, according to scientists. The fossil assemblage is a unique record of terrestrial life of the period (dinosaurs, plants, and other animal species). Remains accumulated in streams and shallow lakes and were swiftly buried (and preserved) by sediments associated with those environments. Scientists believe these sediments in turn were lithified over many millions of years as they were buried under younger deposits -- forming the distinctive stratigraphy of the Monument. The generally flat-laying "layer cake" geology of the region -- similar to the Colorado Plateau to the south - is expressed in the image by parallel beds of tan, reddish-brown, and gray-brown sedimentary rocks cut by the Yampa River at the northern end of the Monument (top). Erosion by the Yampa River exposed the Morrison layer and its trove of fossil material. Together with other fossils found in both older and younger rock layers in the area, the Dinosaur National Monument remains an important scientific resource that continues to provide new insights into the geologic history and paleoecology of the region.
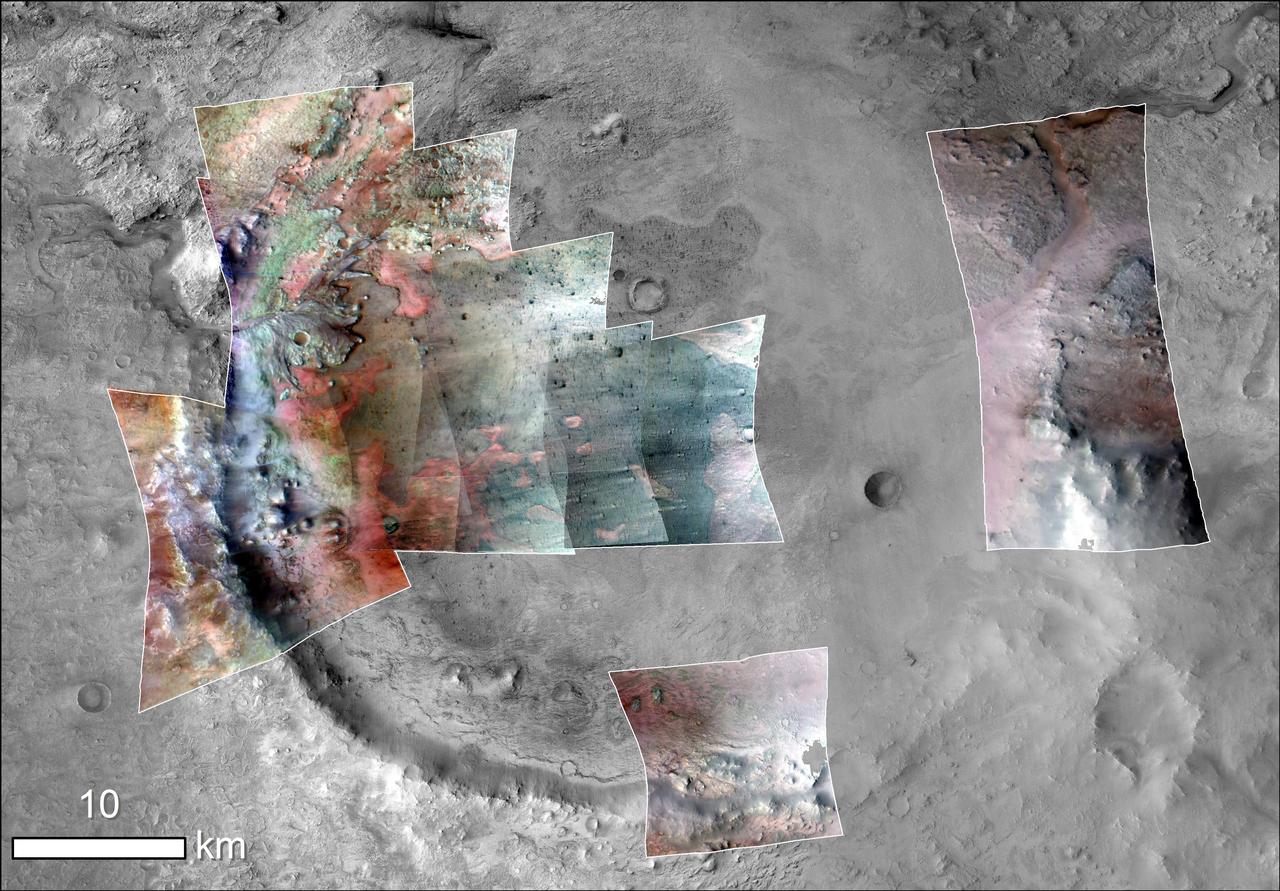
Color has been added to highlight minerals in this image of Jezero Crater on Mars, the landing site for NASA's Mars 2020 mission. The green color represents minerals called carbonates, which are especially good at preserving fossilized life on Earth. Red represents olivine sand eroding out of carbonate-containing rocks. The image was created using data taken by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and its Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) and Context Camera (CTX). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23380

Release date Dec. 30, 2009 In the supernova remnant W49B, Suzaku found another fossil fireball. It detected X-rays produced when heavily ionized iron atoms recapture an electron. This view combines infrared images from the ground (red, green) with X-ray data from NASA's Chandra X-Ray Observatory (blue). Credit: Caltech/SSC/J. Rho and T. Jarrett and NASA/CXC/SSC/J. Keohane et al. To learn more about this image go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/astro-e2/news/fossil-fireballs.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/astro-e2/news/fossil-fireballs...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
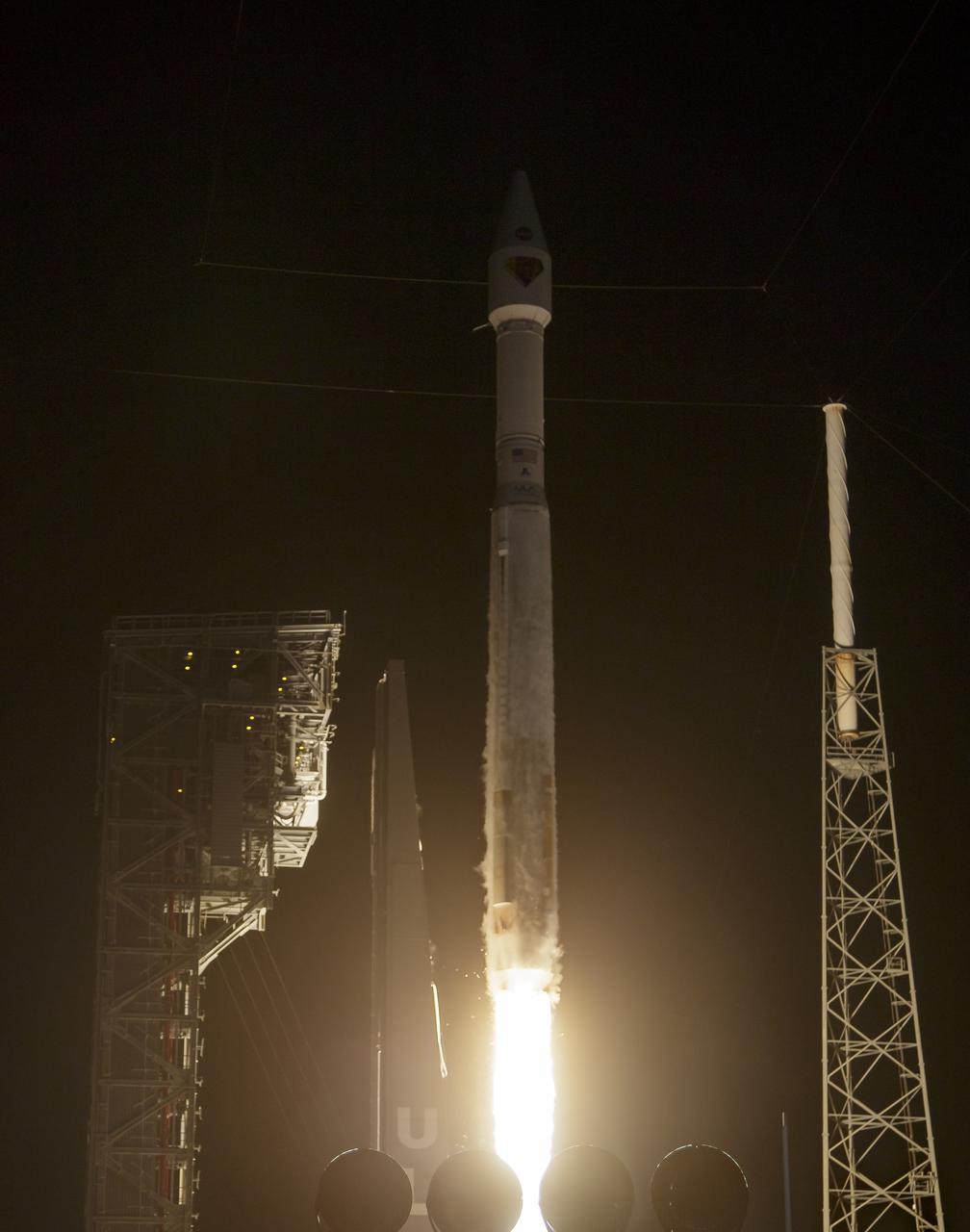

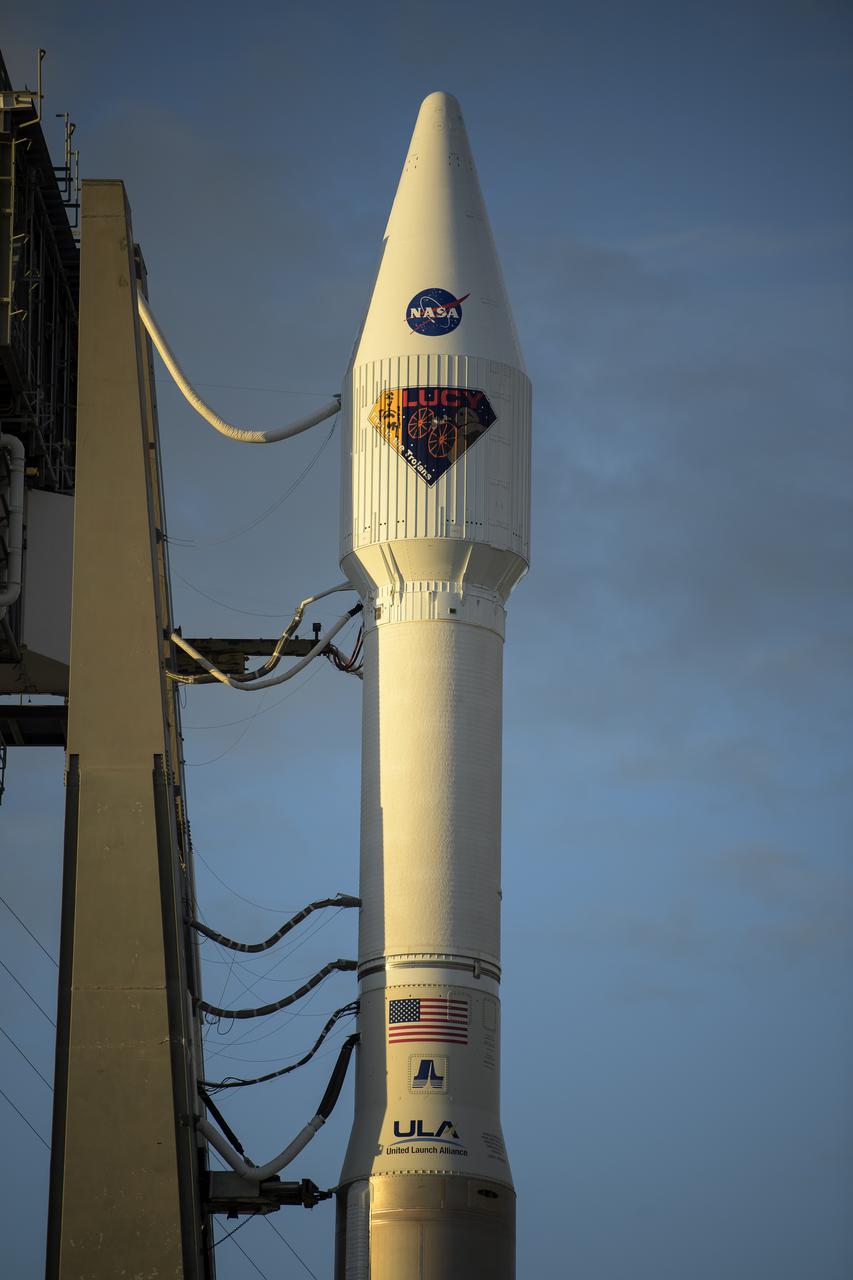
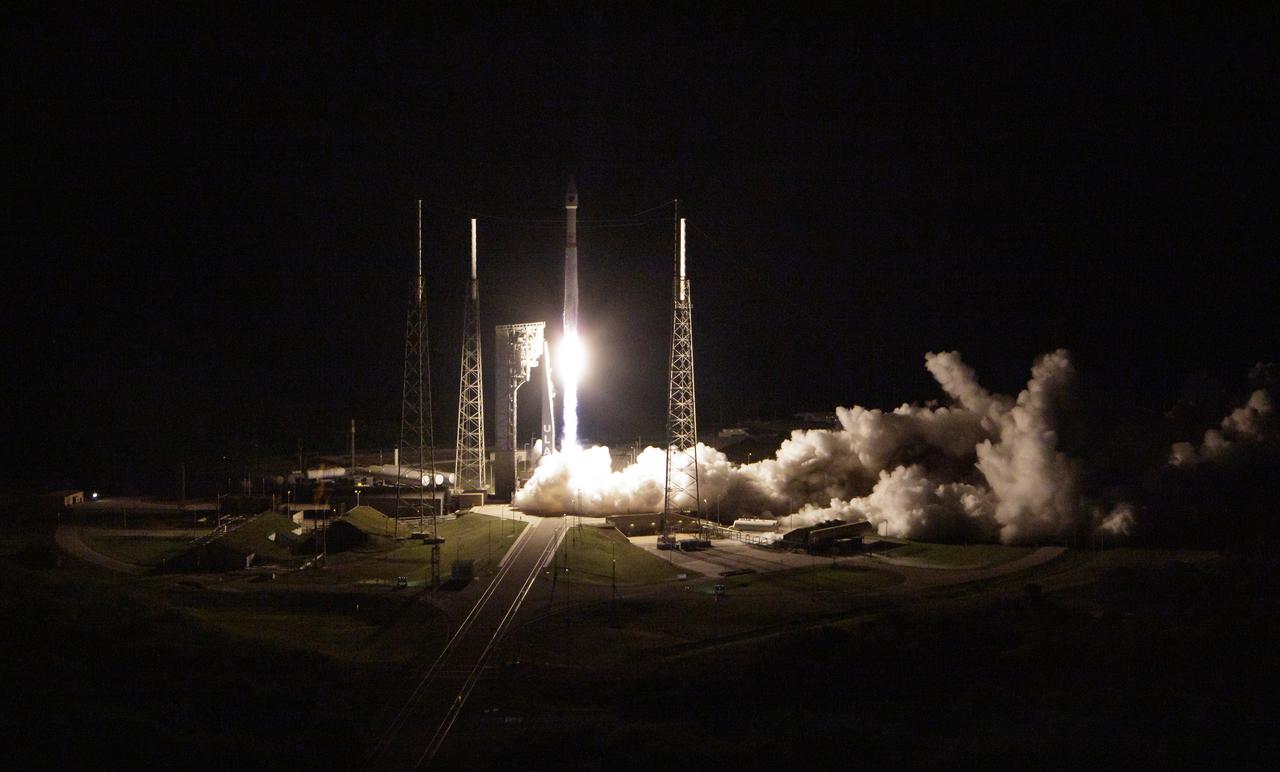
A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This photo shows the area within NASA's Kennedy Space Center where a solar photovoltaic power generation system will be built as the result of an agreement between NASA and Florida Power & Light. The agreement is part of a new initiative that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The major facility will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of electrical power, which can serve roughly 3,000 homes. A separate one-megawatt solar power facility will support the electrical needs of the center.
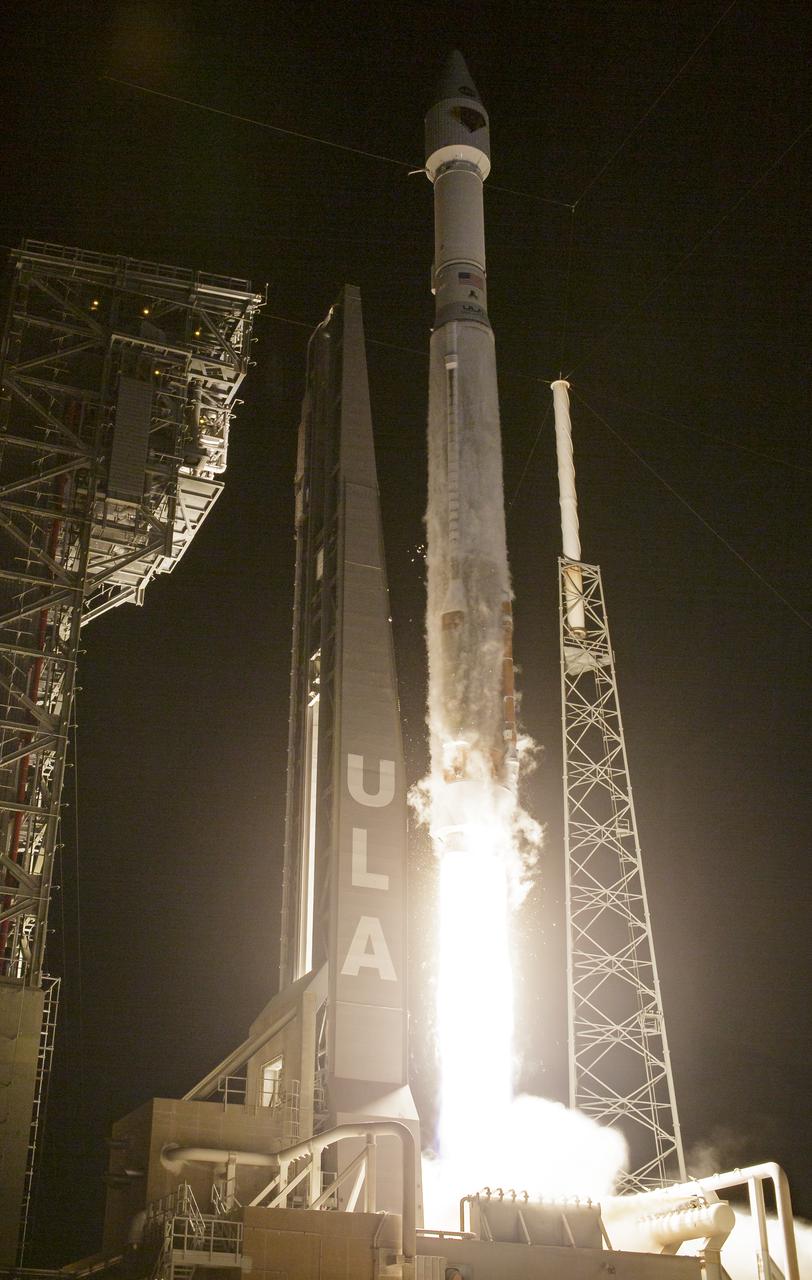

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
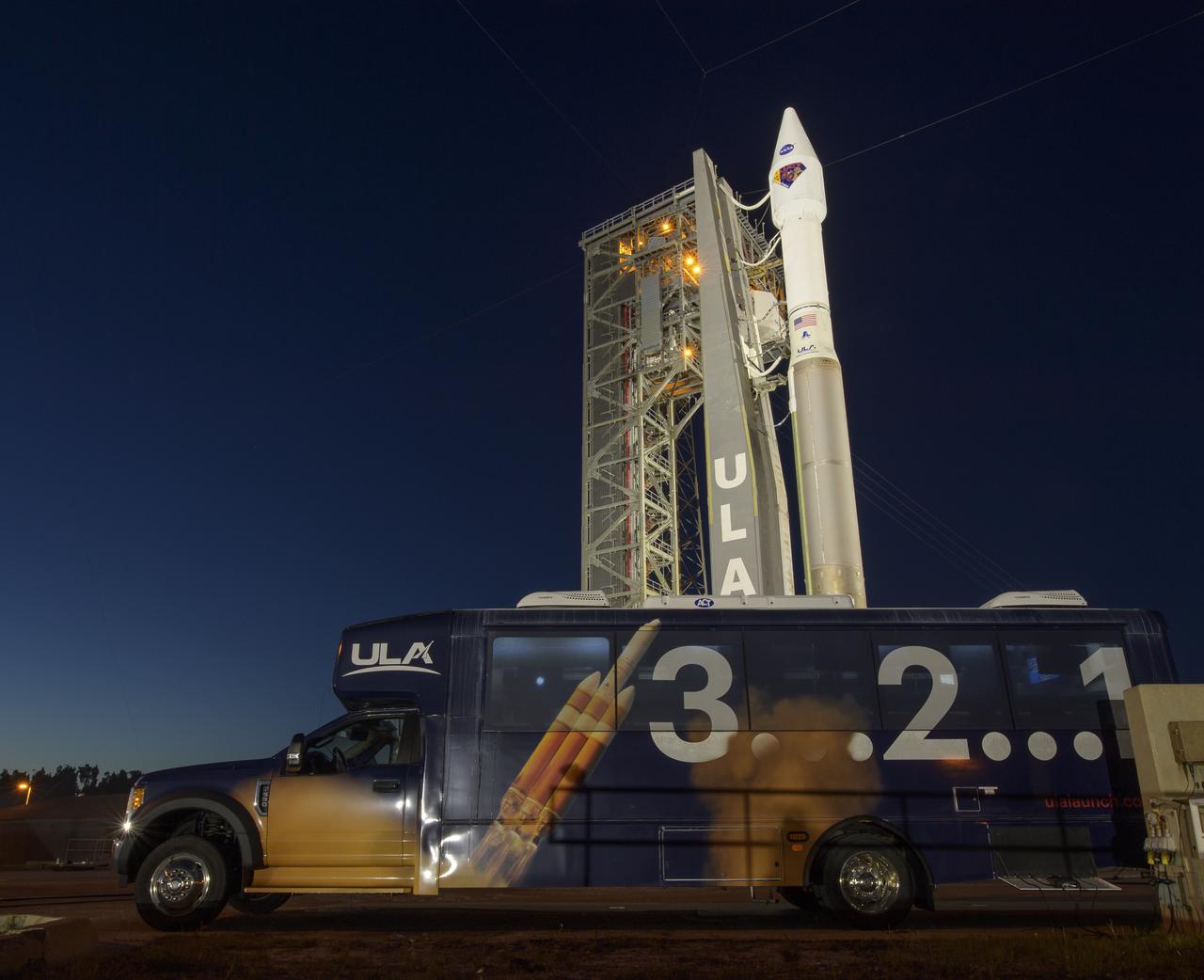

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

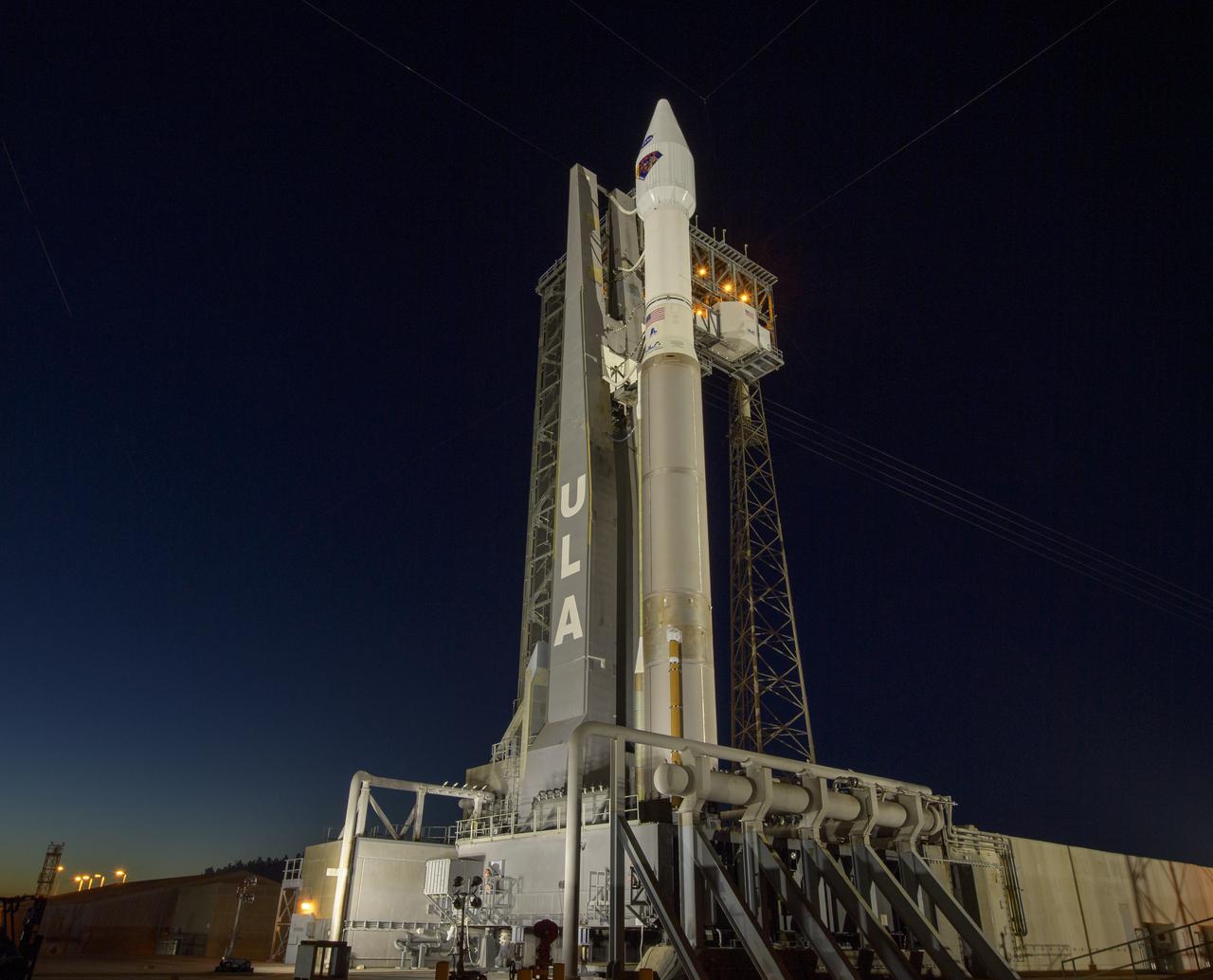
A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Friday, Oct. 15, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

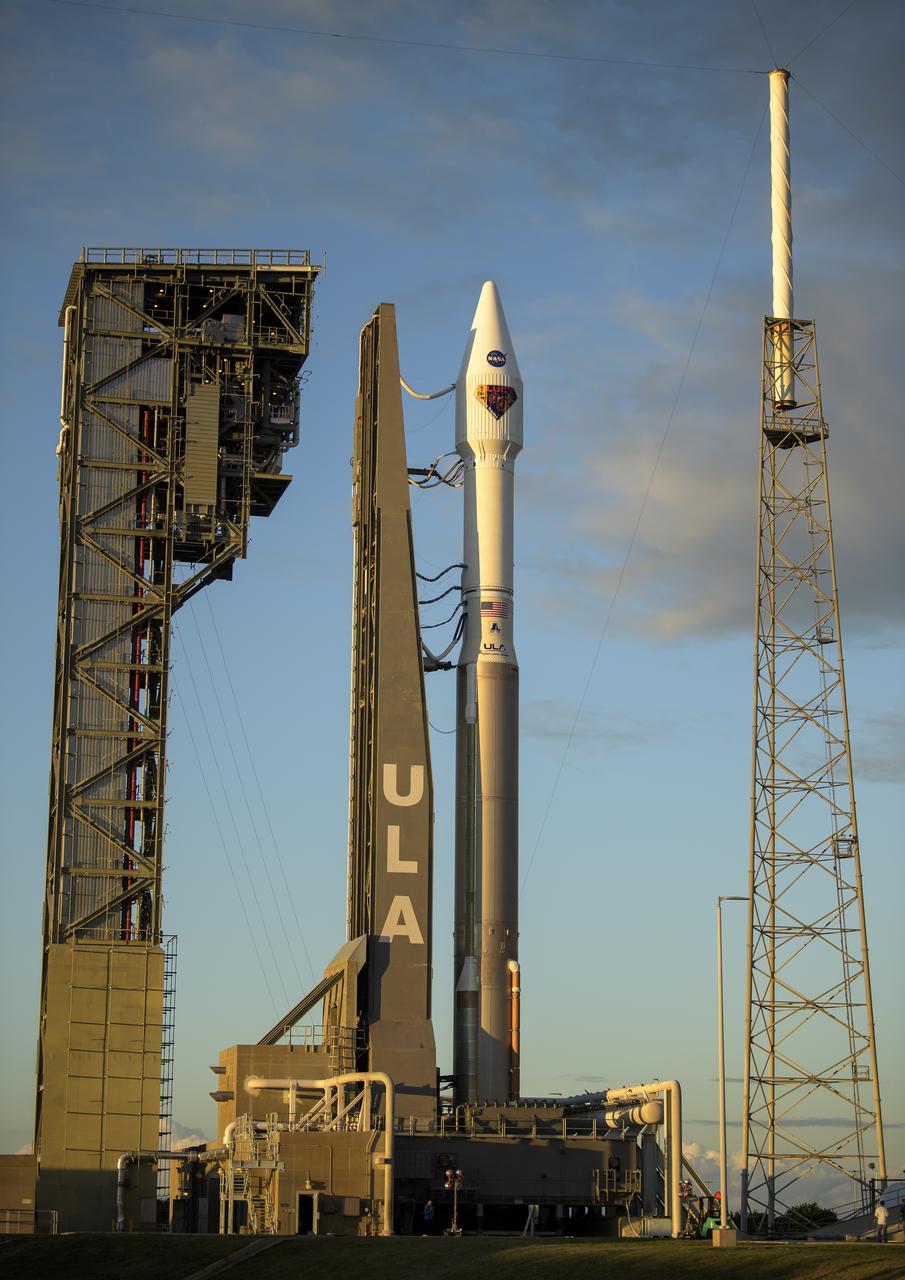
A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
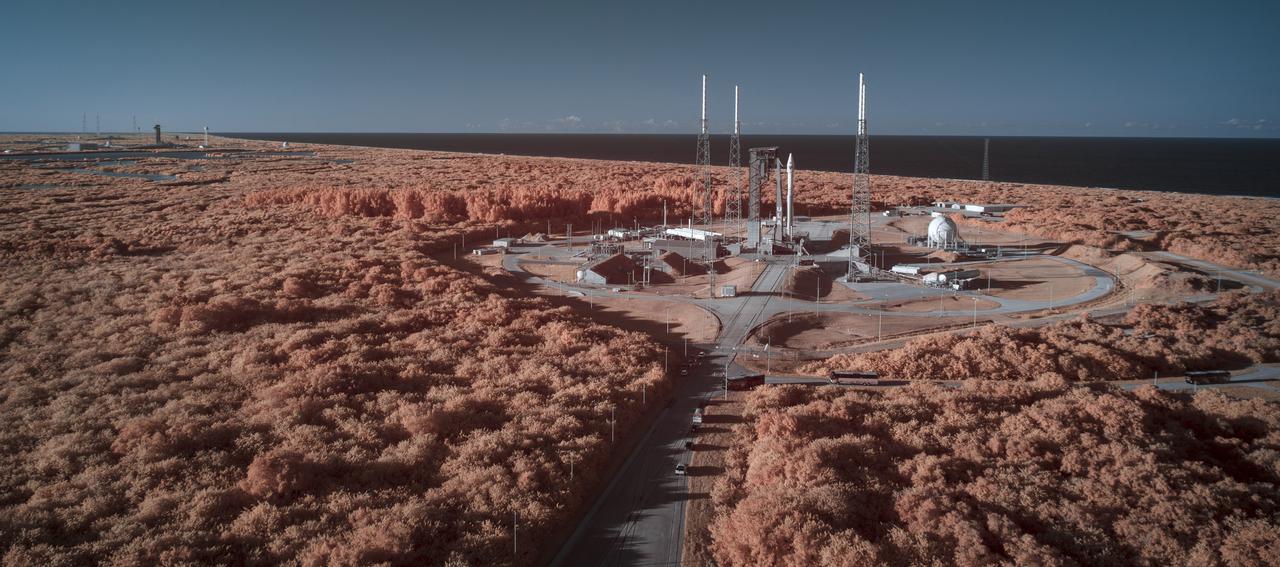

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen is seen in this false color infrared image at Space Launch Complex 41, Friday, Oct. 15, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
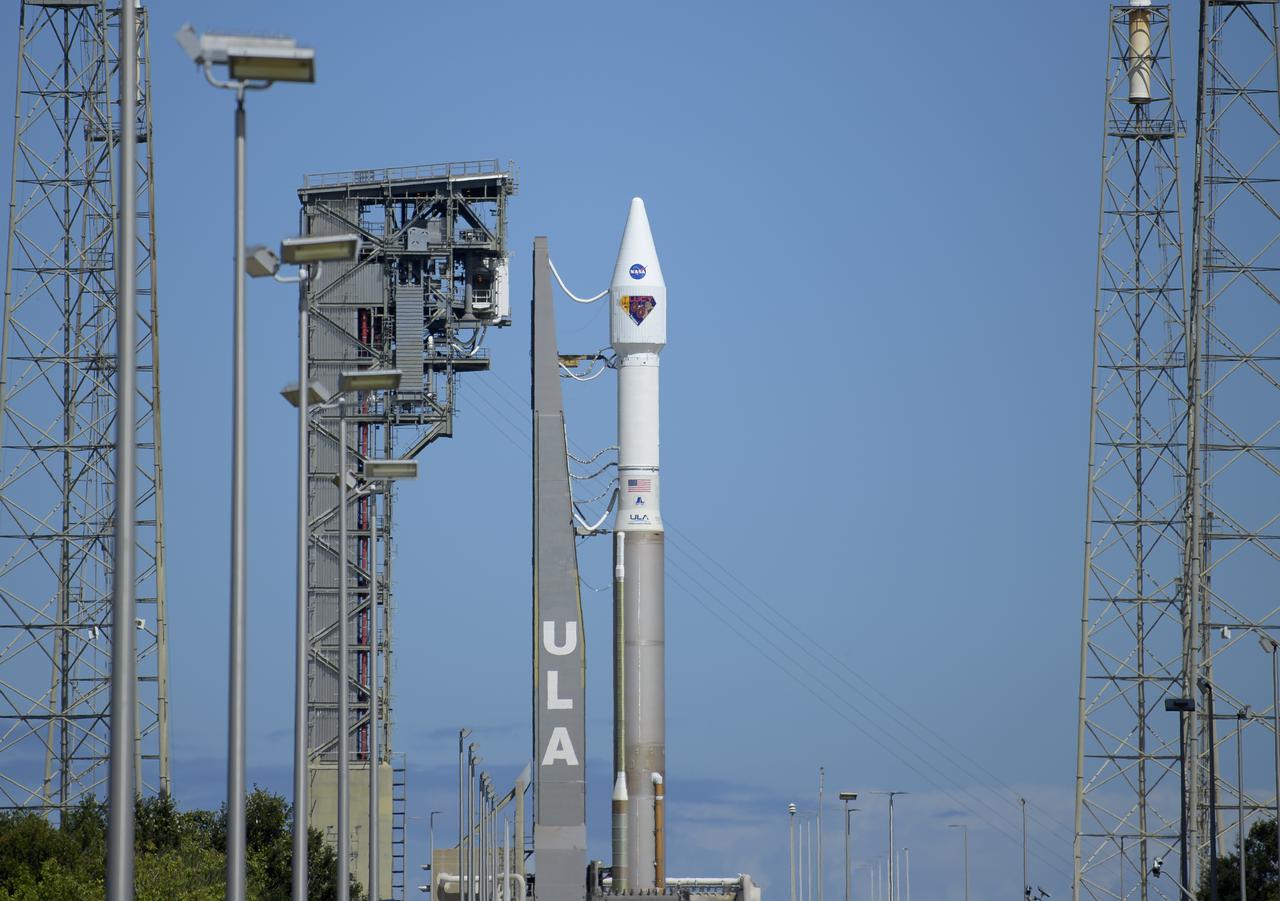

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
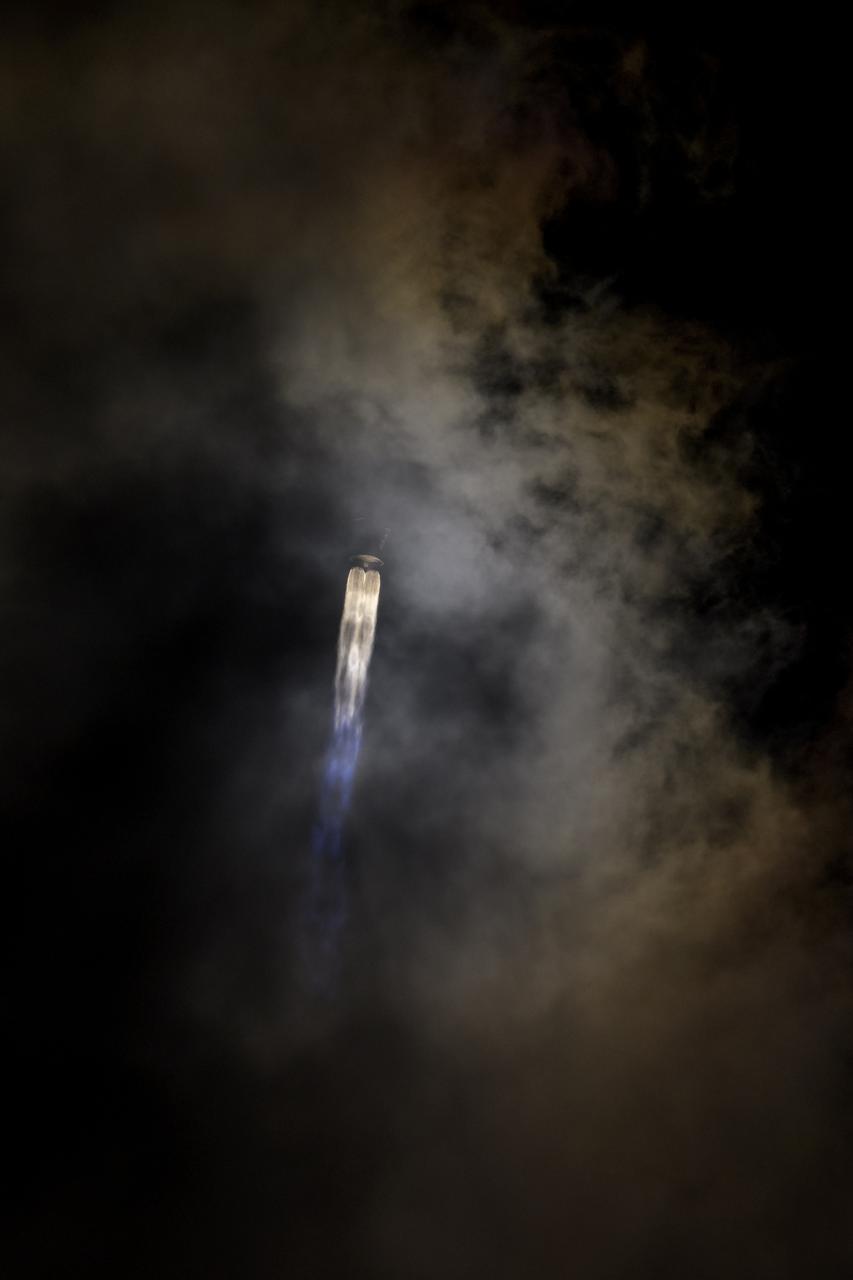

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
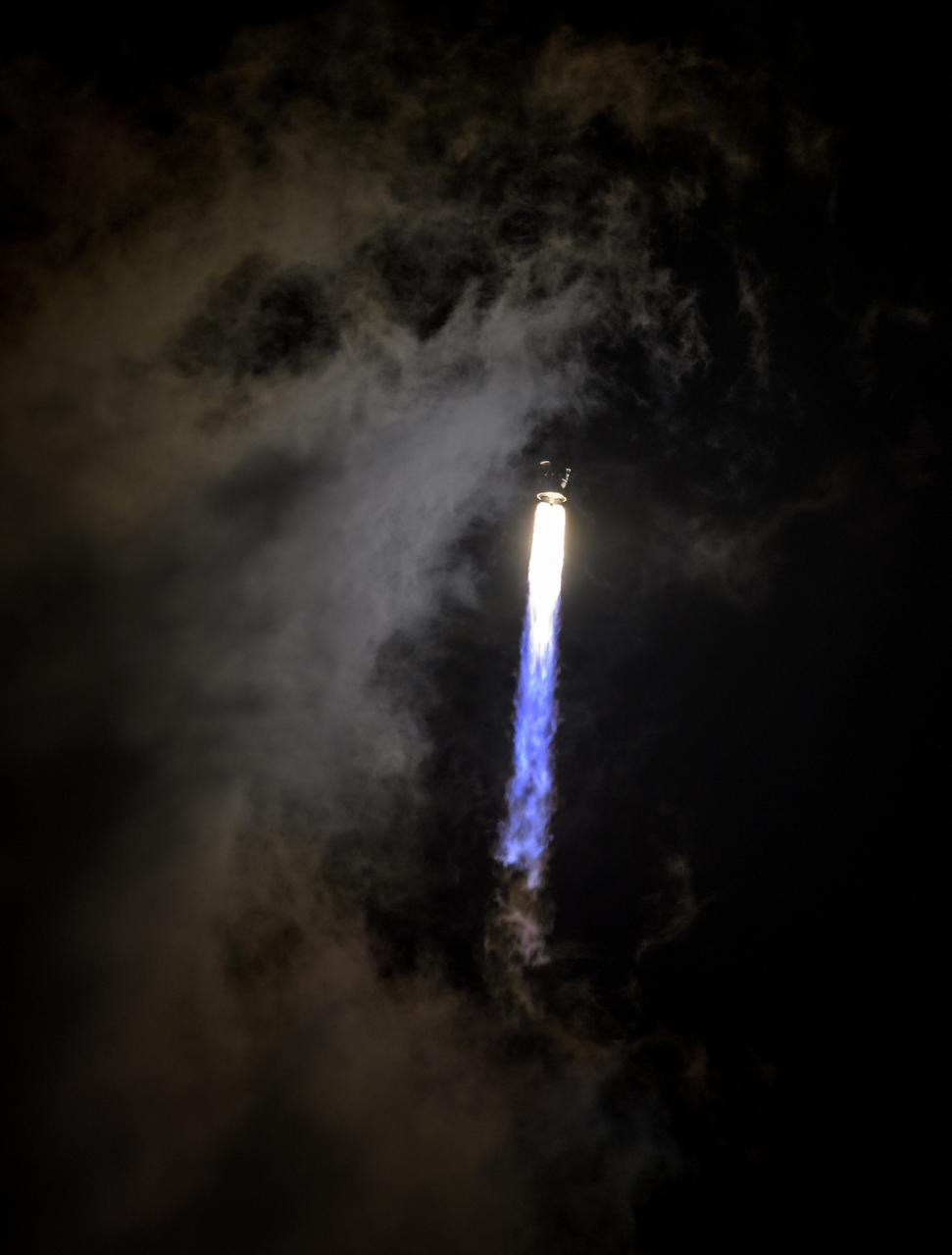

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
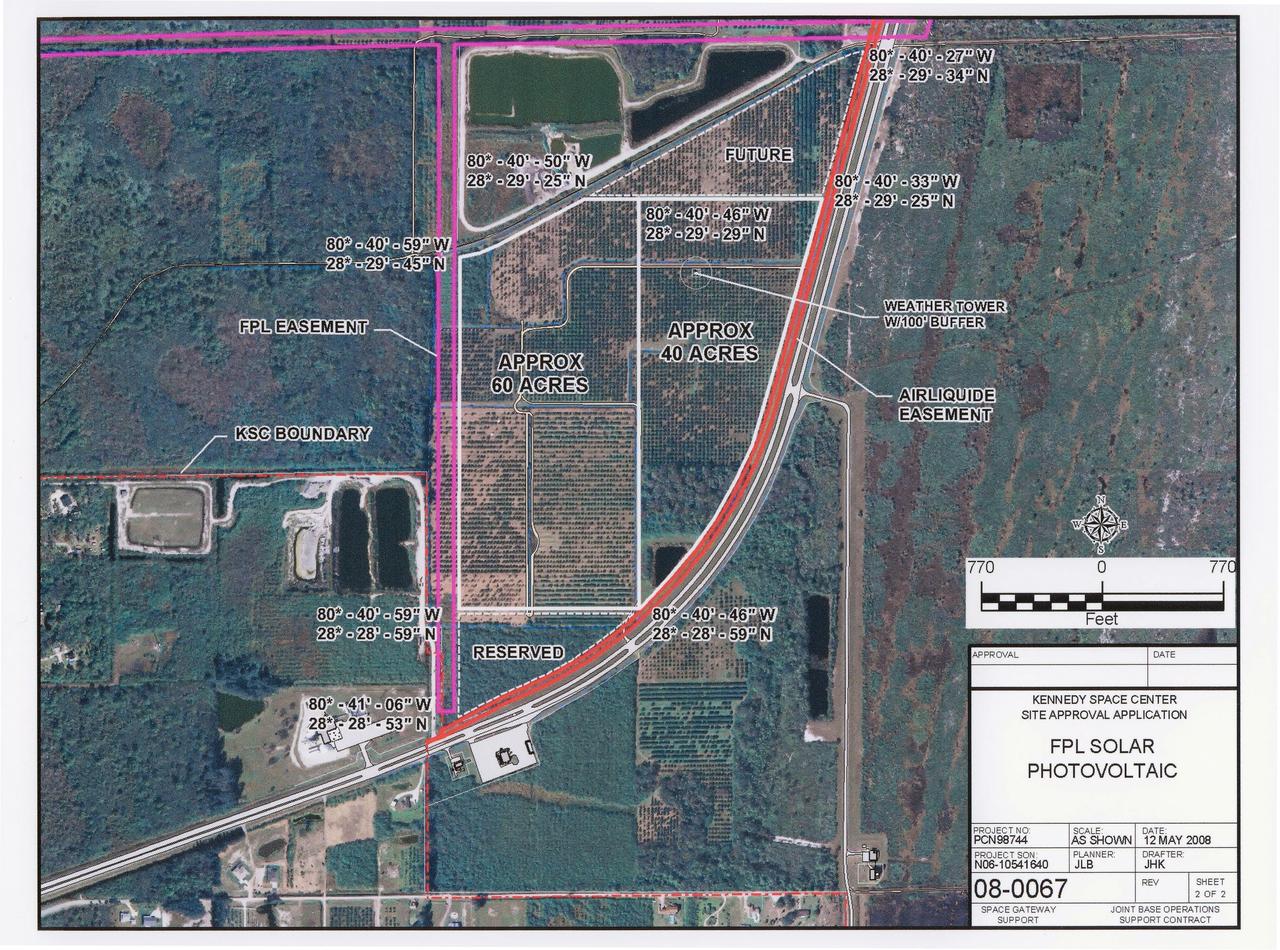
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This map shows the area within NASA's Kennedy Space Center where a solar photovoltaic power generation system will be built as the result of an agreement between NASA and Florida Power & Light. The agreement is part of a new initiative that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The major facility will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of electrical power, which can serve roughly 3,000 homes. A separate one-megawatt solar power facility will support the electrical needs of the center.

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
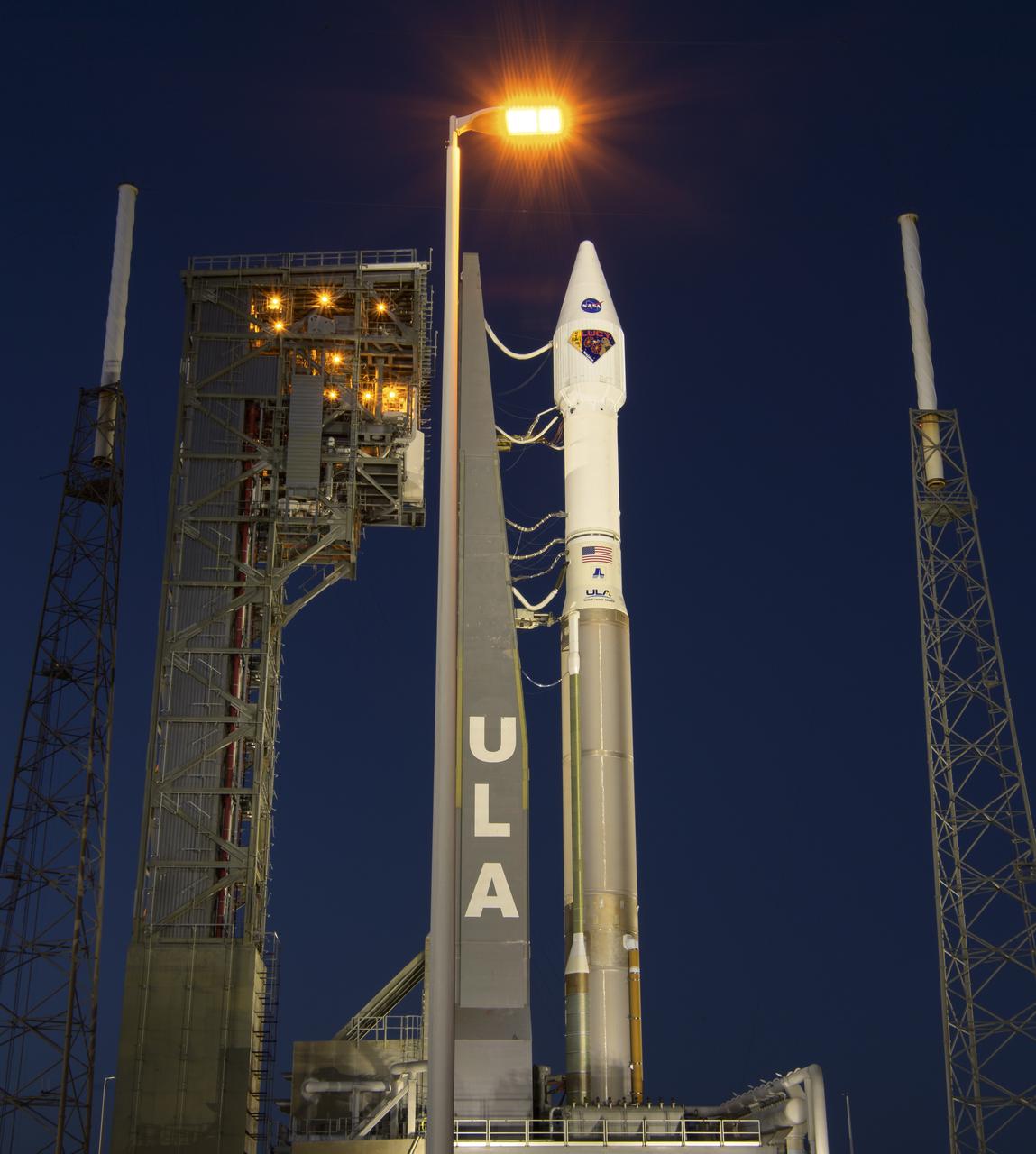

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
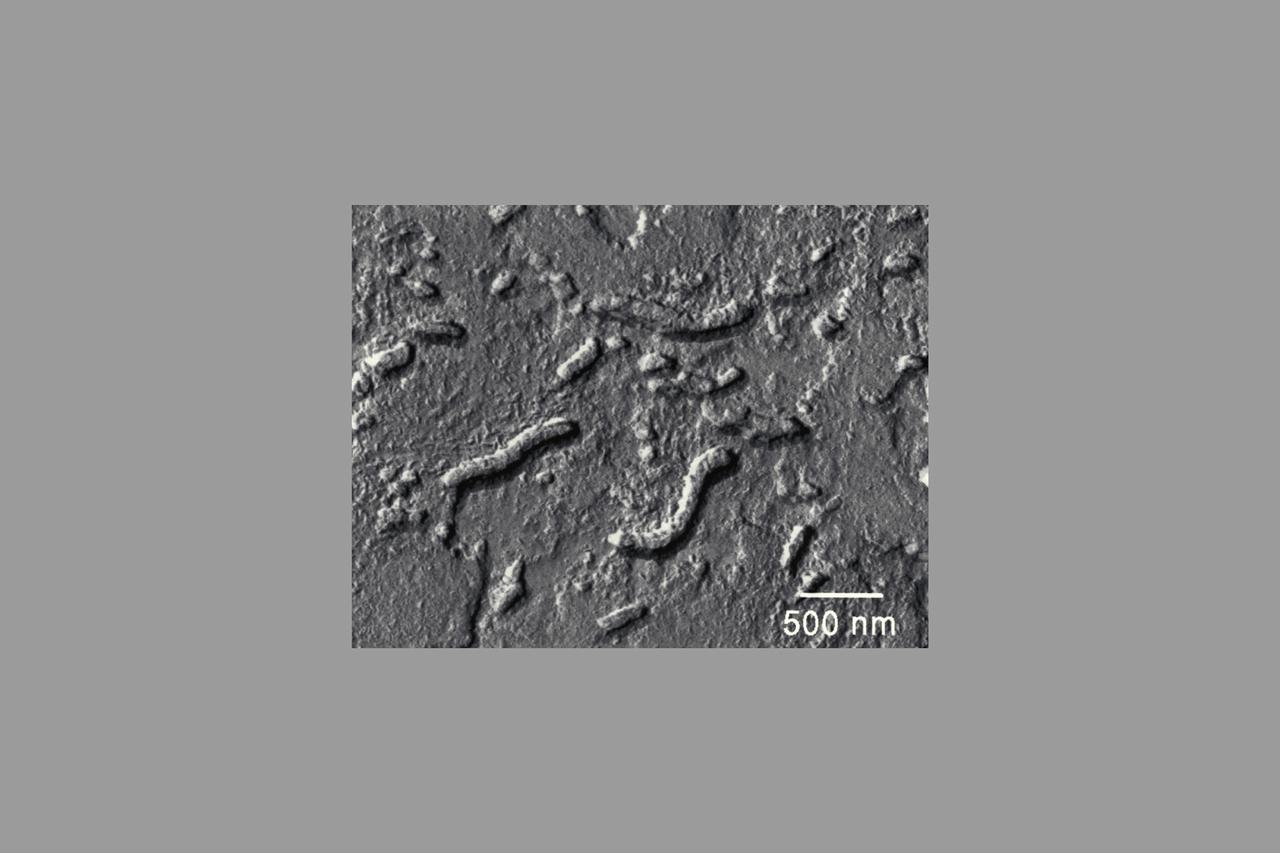
Martian Meteorite (ALH84001): This high resolution transmission electron microscope image is of a cast, or replica, from a chip of a Martian meteorite, labeled ALH84001, that shows the outline of what are believed to be possible microscopic fossils of bacteria-like organisms that may have lived on Mars more than 3.6 billion years ago. The tubular features in this image are less than a micrometer in size, or about 1/500th the diameter of a human hair. (JSC ref: S96-12637)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This photo shows the area within NASA's Kennedy Space Center where a solar photovoltaic power generation system will be built as the result of an agreement between NASA and Florida Power & Light. The agreement is part of a new initiative that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The major facility will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of electrical power, which can serve roughly 3,000 homes. A separate one-megawatt solar power facility will support the electrical needs of the center.

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
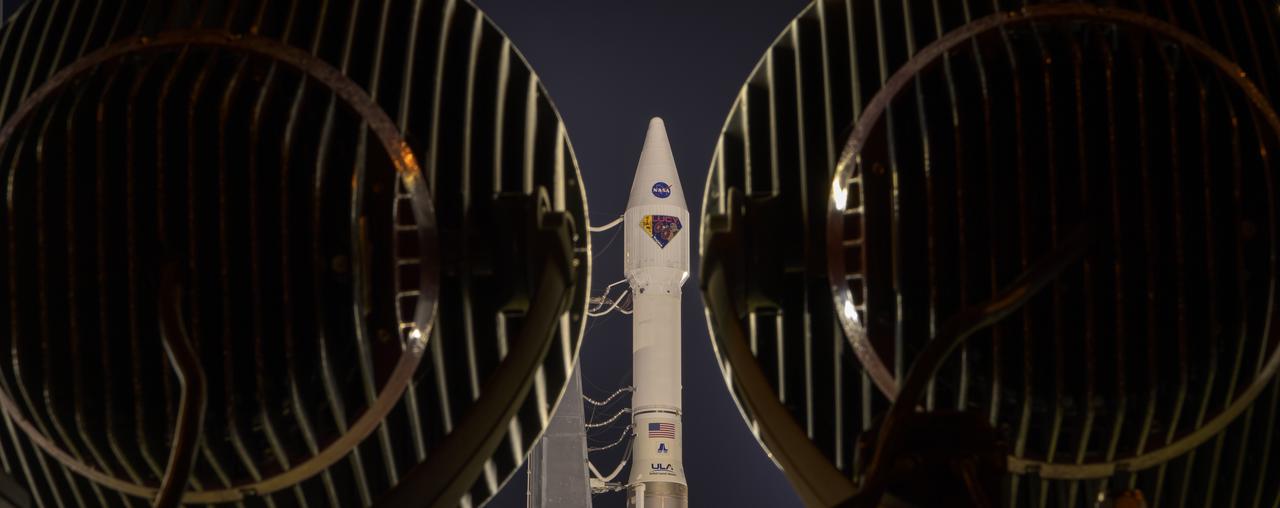

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
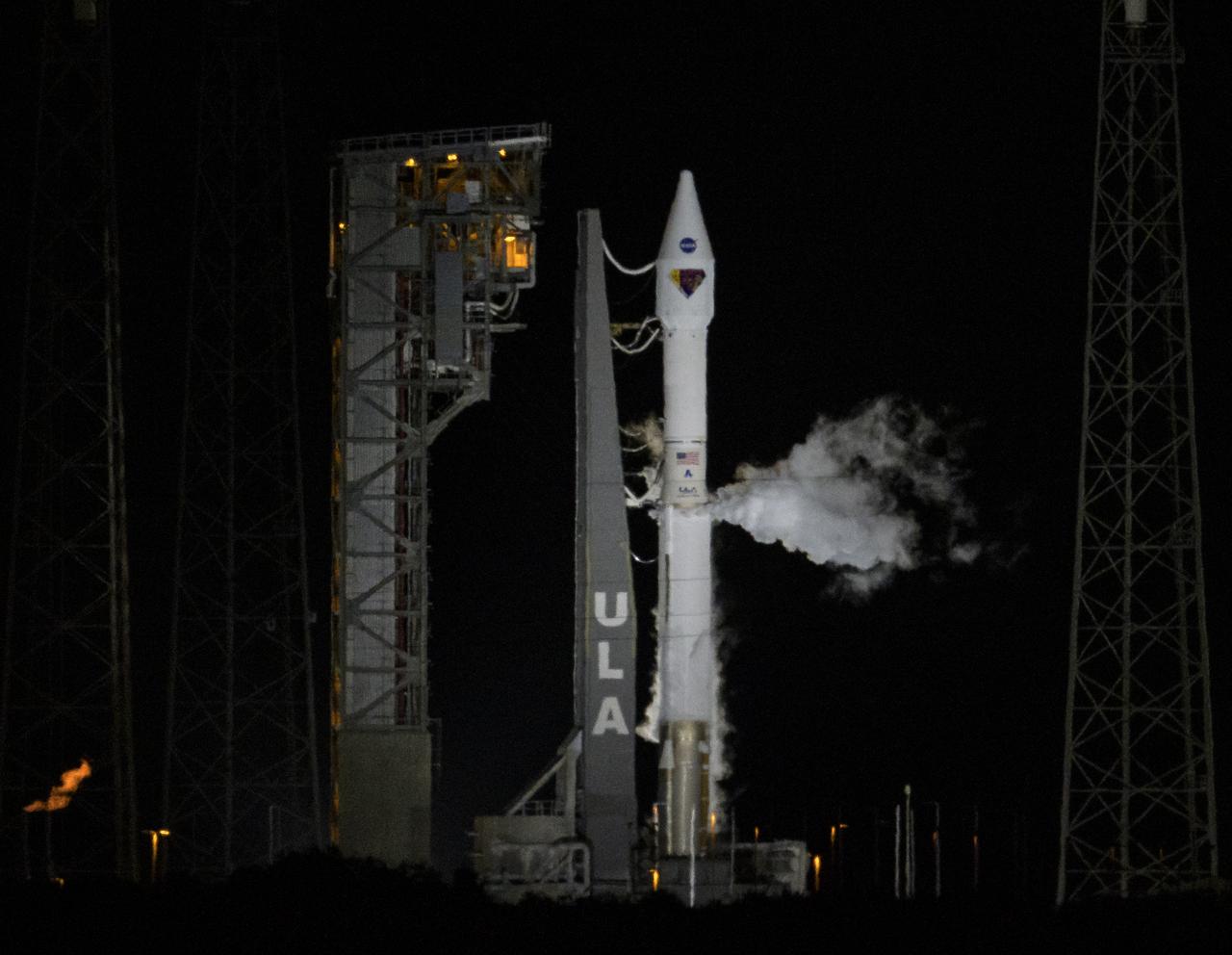

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft stands ready to launch from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
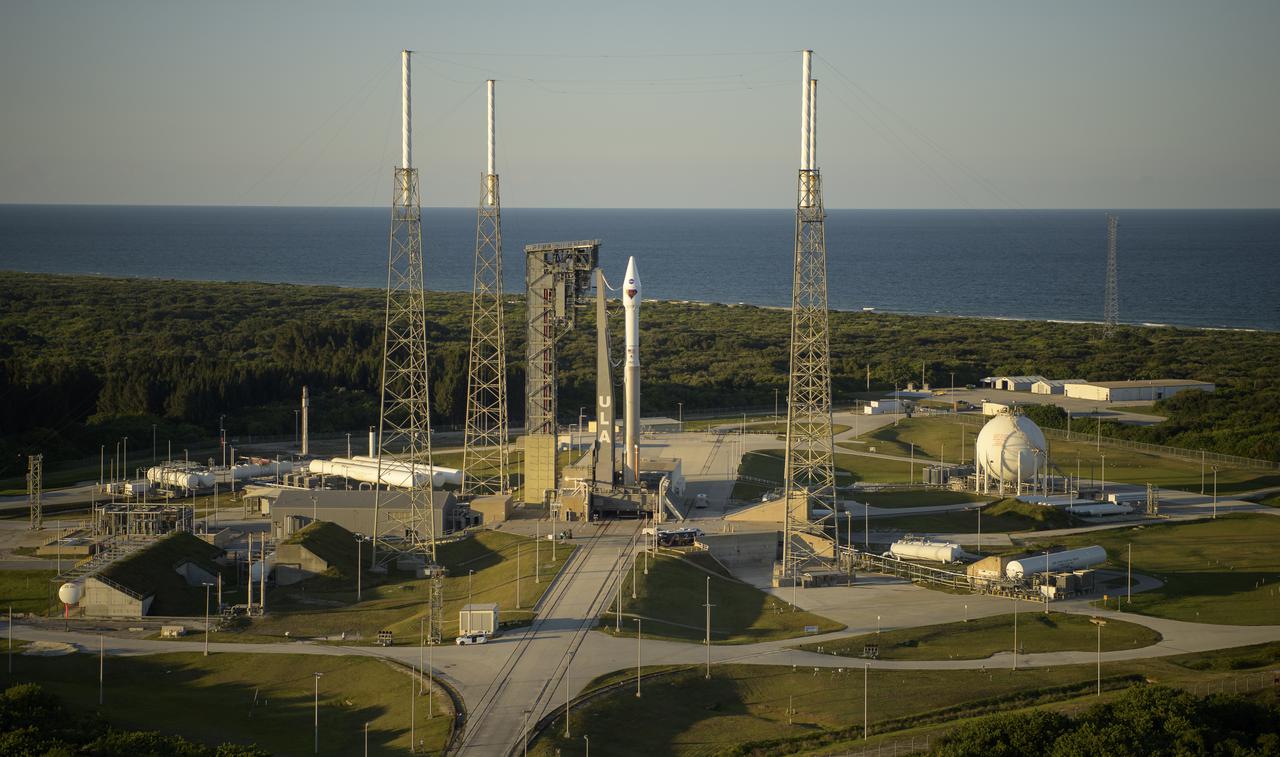

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Friday, Oct. 15, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
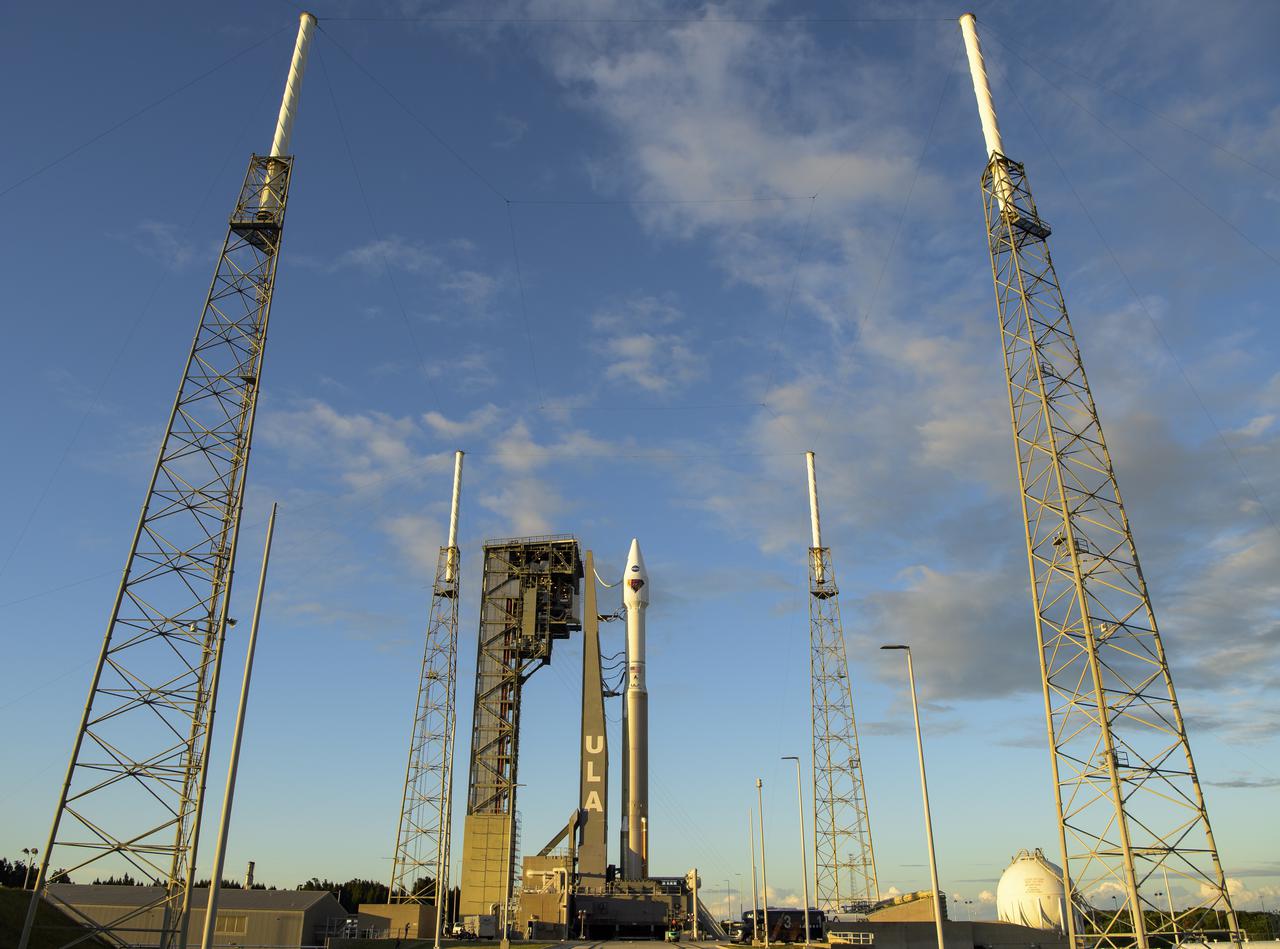

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
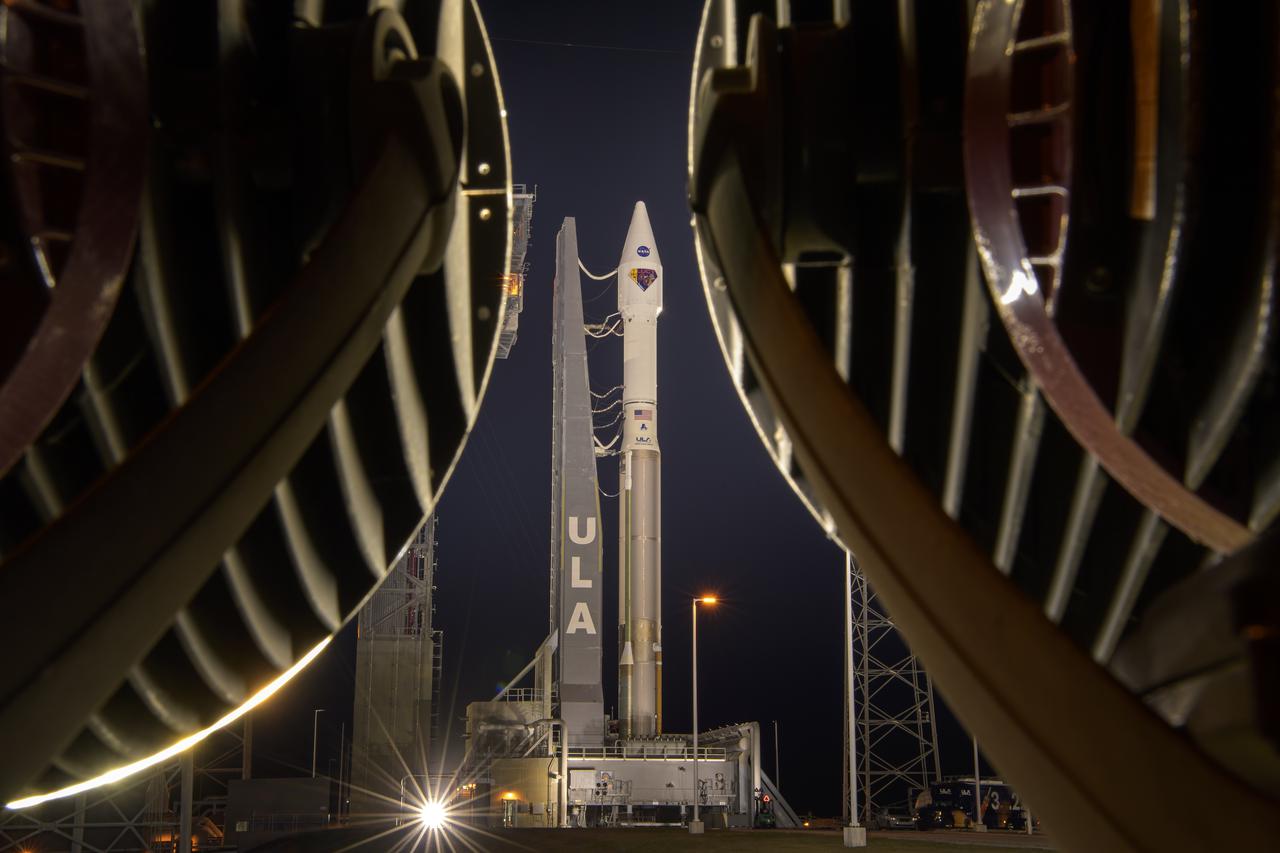

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
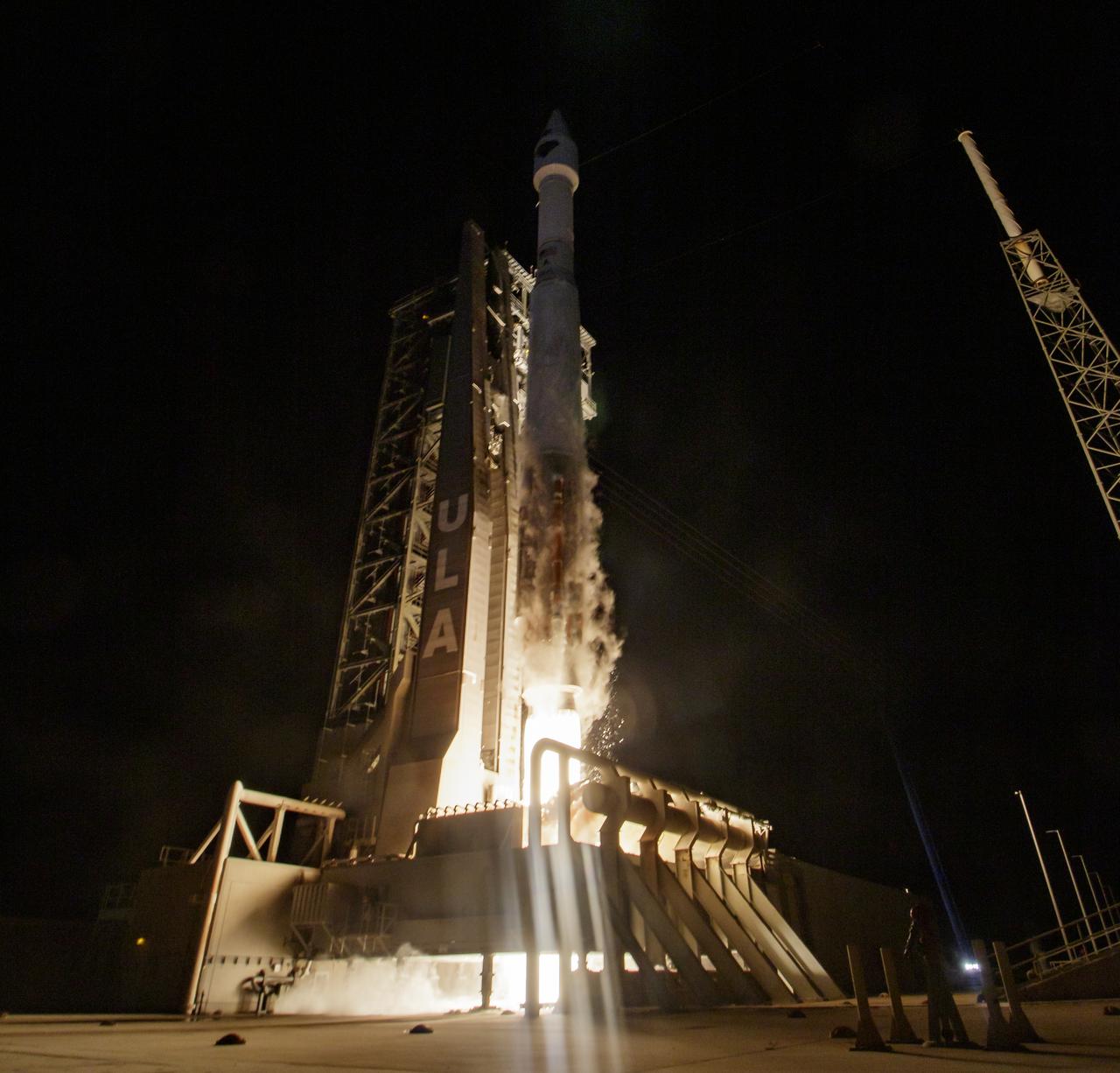

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
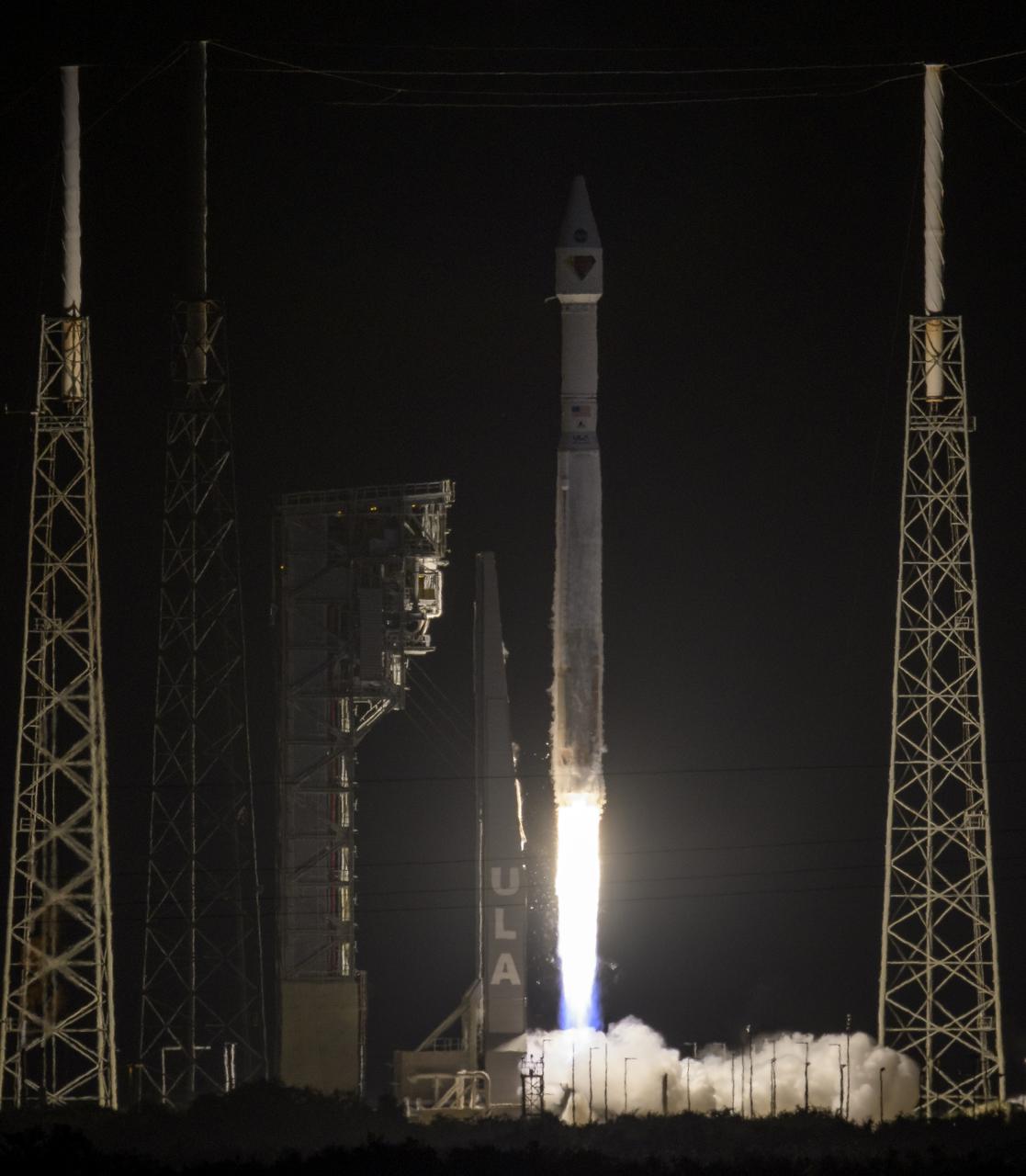

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
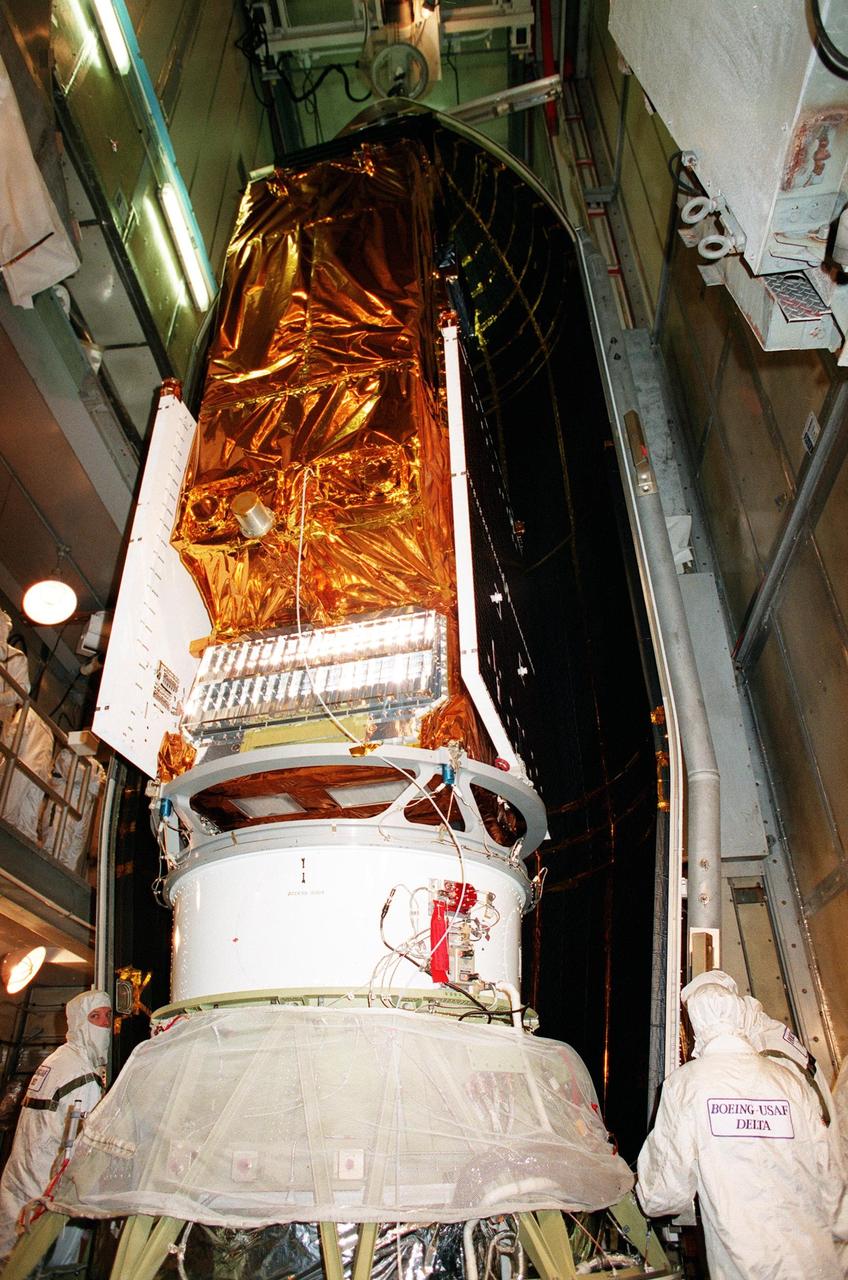

At Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite (foreground) is partially covered by half of the fairing (behind it) that will protect it during launch. The satellite is scheduled for launch June 24 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study those elements to unlock the secrets of how galaxies evolve and to discover what the Universe was like when it was only a few minutes old
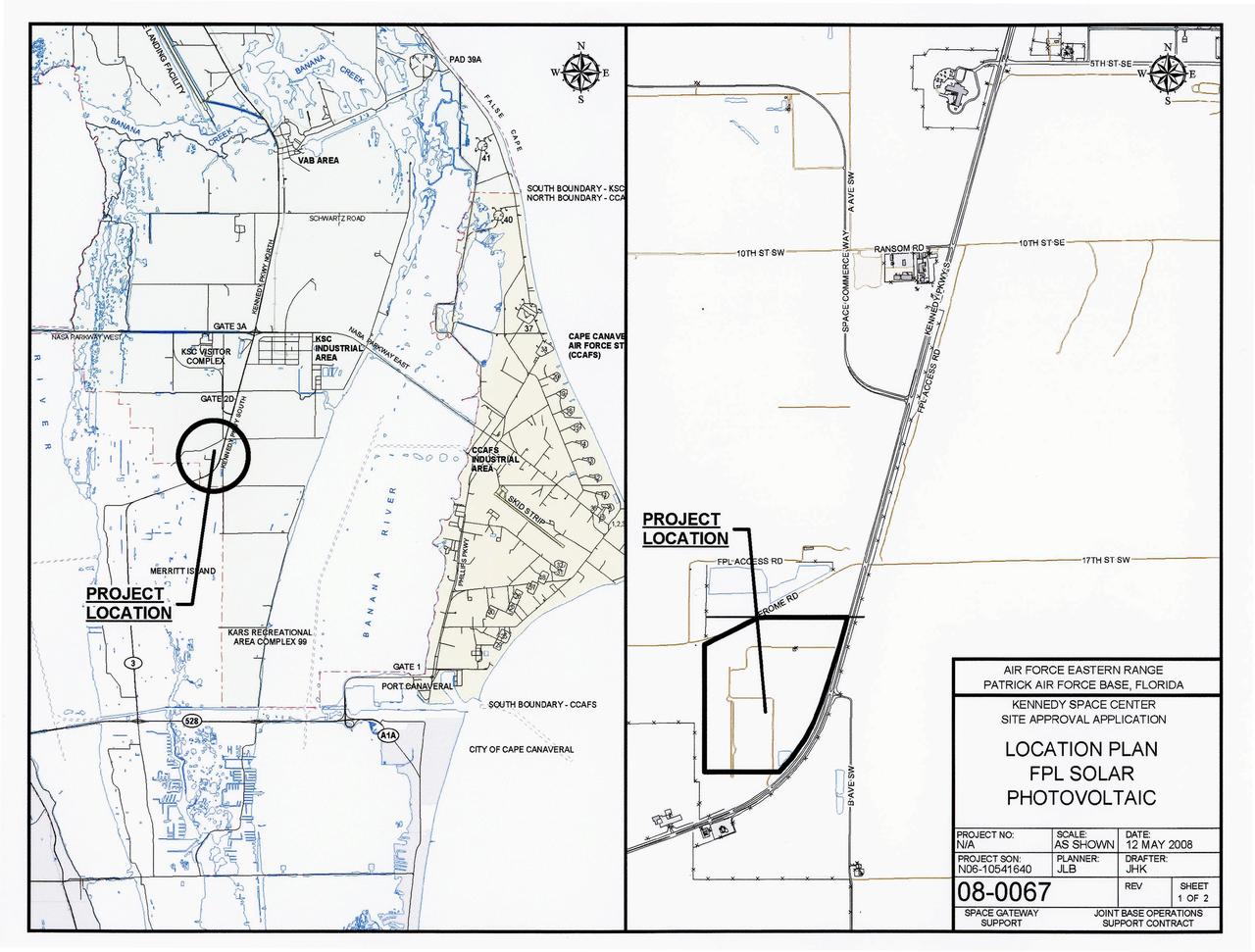
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This map shows the two sites within NASA's Kennedy Space Center where a solar photovoltaic power generation system will be built as the result of an agreement between NASA and Florida Power & Light. The agreement is part of a new initiative that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The major facility will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of electrical power, which can serve roughly 3,000 homes. A separate one-megawatt solar power facility will support the electrical needs of the center.
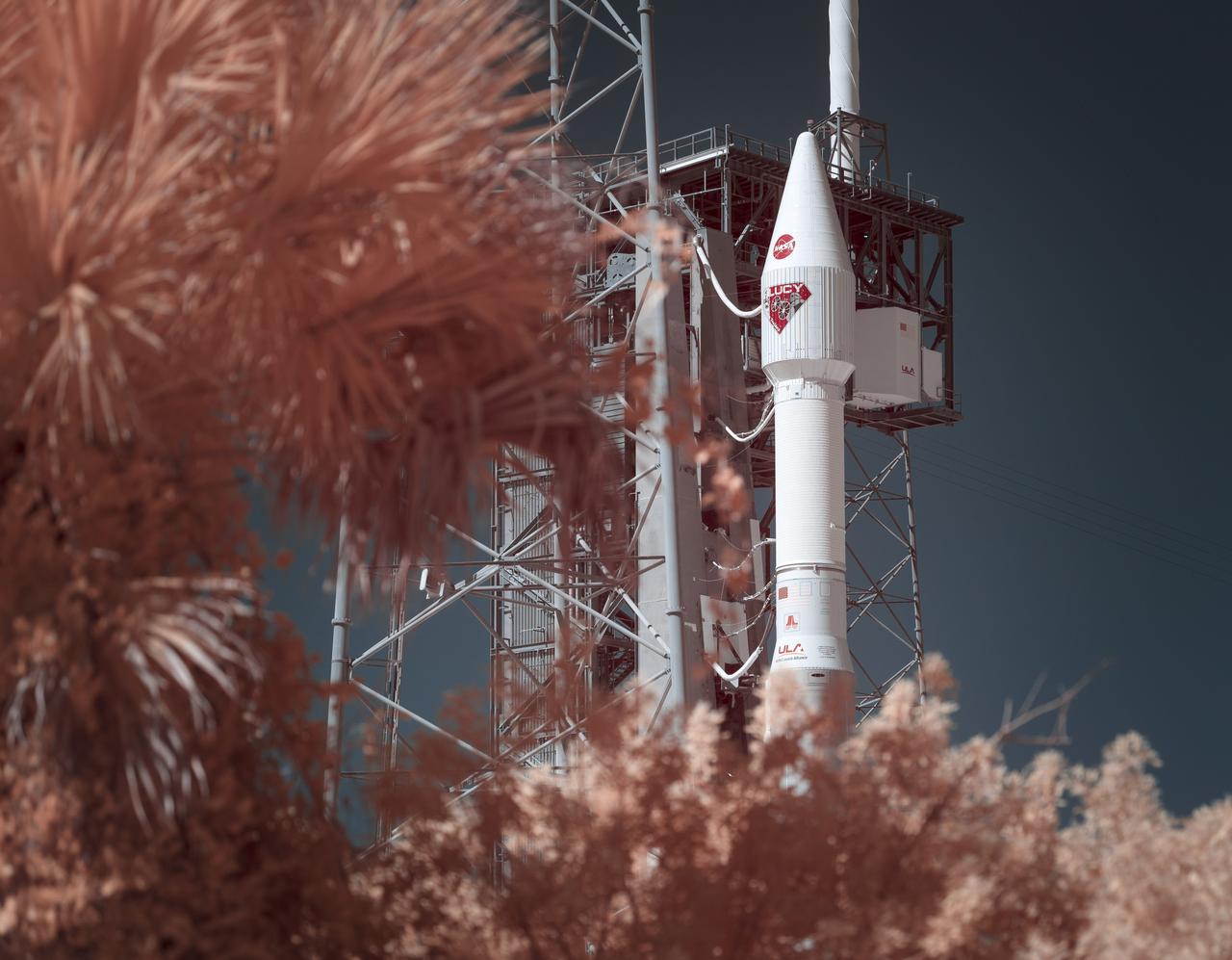

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen is seen in this false color infrared image at Space Launch Complex 41, Friday, Oct. 15, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
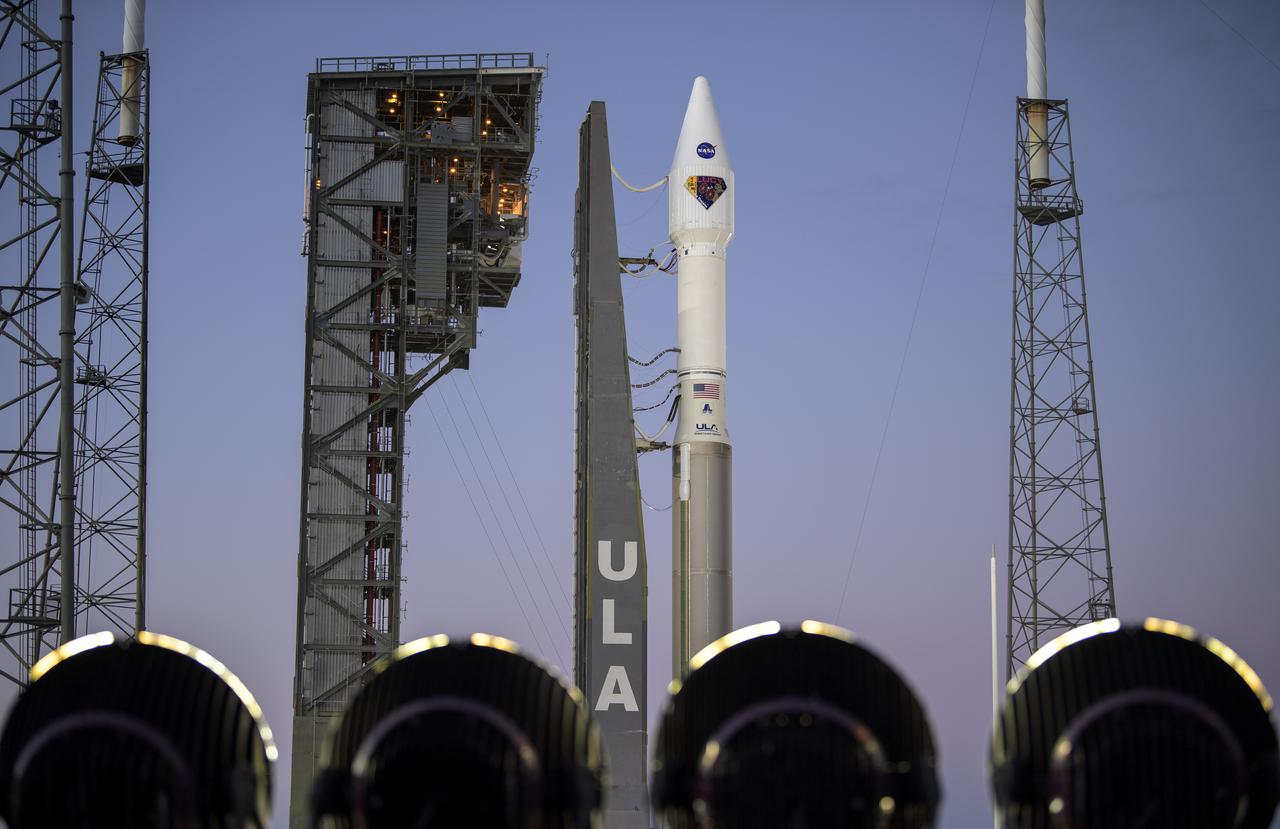

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
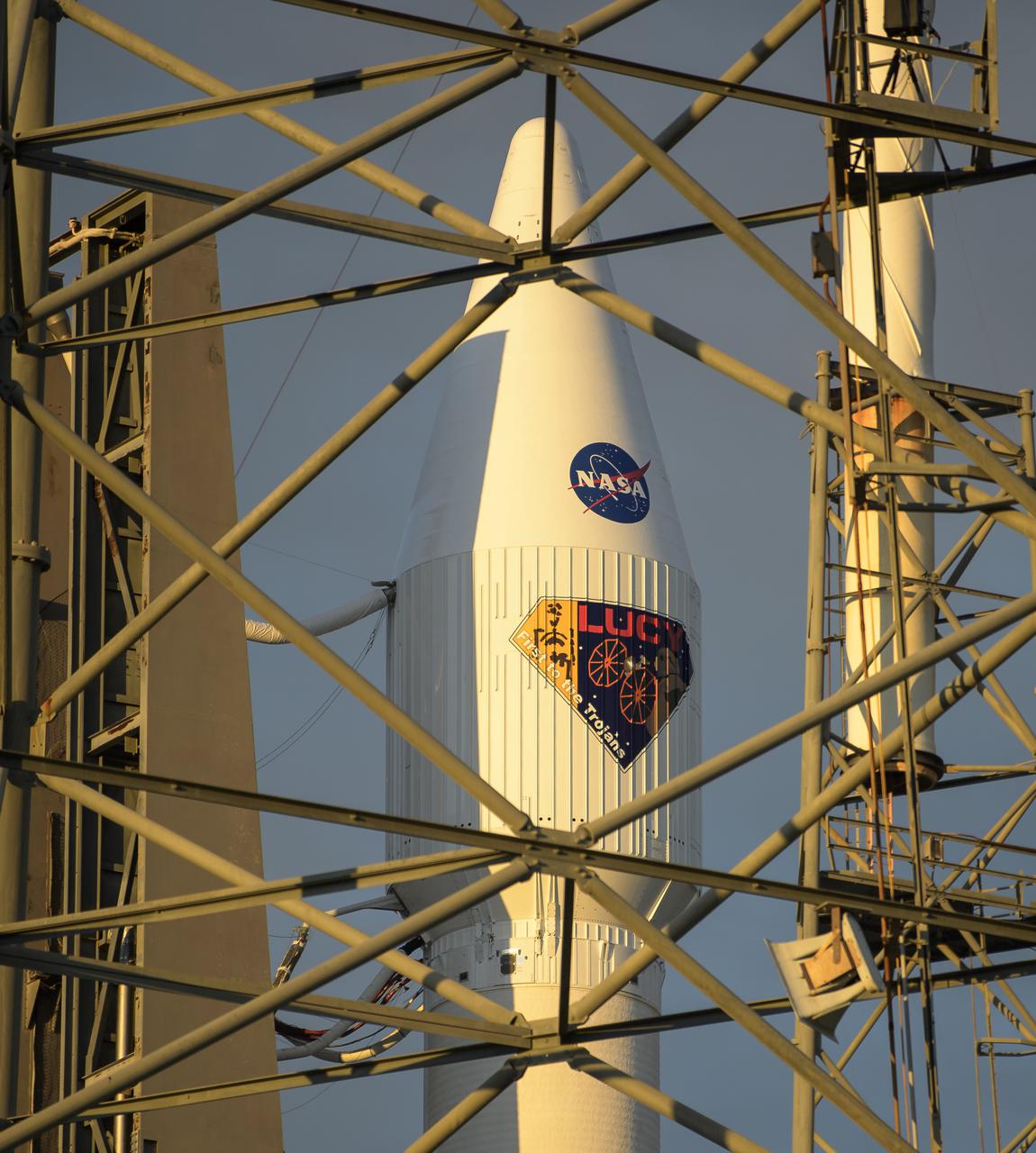

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
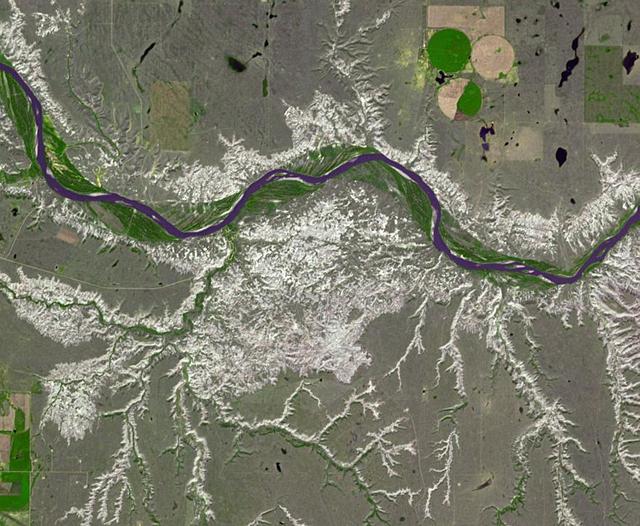
Dinosaur Provincial Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site east of Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Located in the Red River Valley, it is noted for its badland topography and rich abundance of dinosaur fossils. Found in Late Cretaceous rocks, over 60 dinosaur species have been discovered. The image was acquired June 6, 2018, covers an area of 10.9 by 13.2 km, and is located at 50.6 degrees north, 111.5 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26290
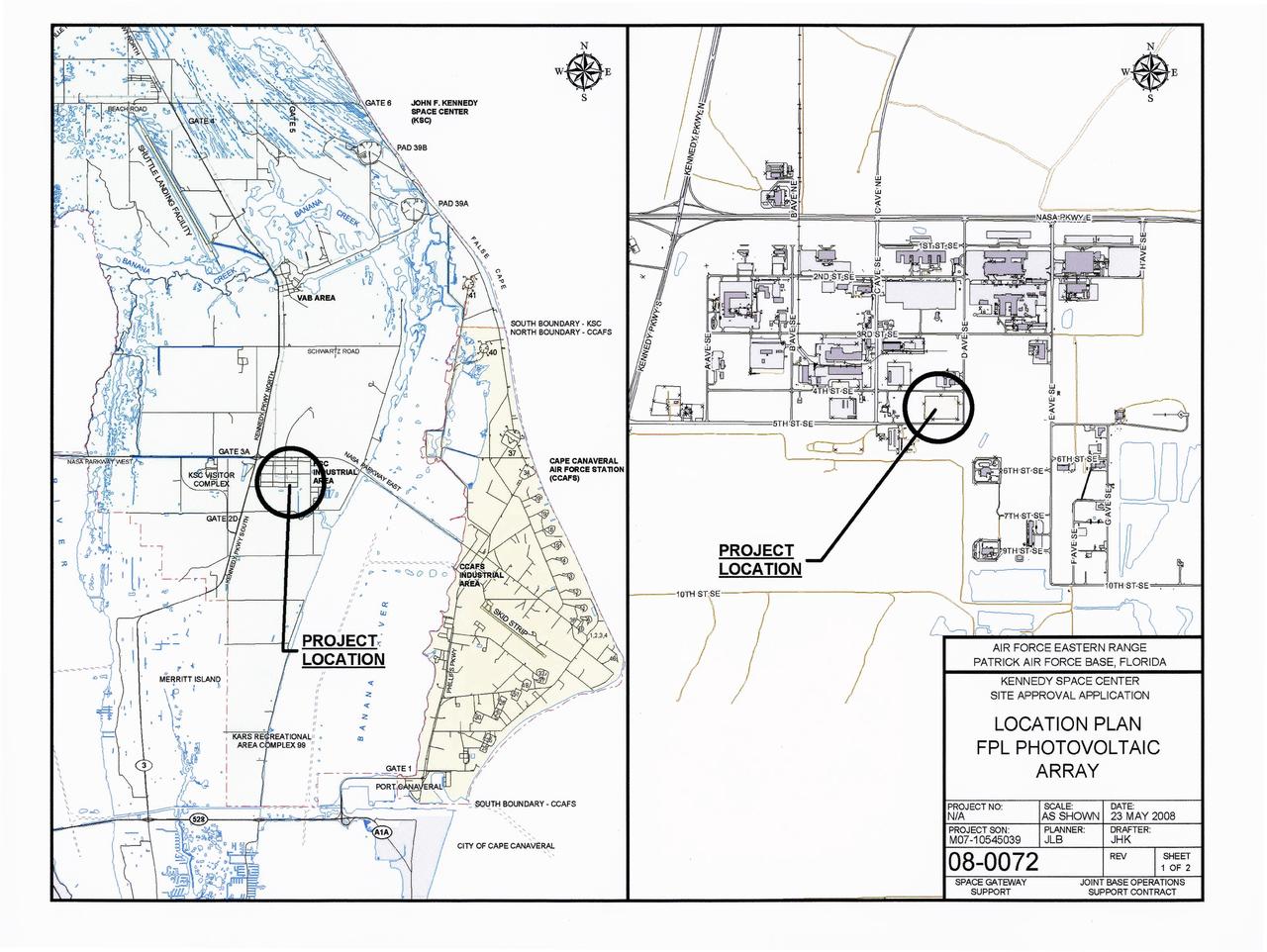
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This map shows the two sites within NASA's Kennedy Space Center where a solar photovoltaic power generation system will be built as the result of an agreement between NASA and Florida Power & Light. The agreement is part of a new initiative that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The major facility will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of electrical power, which can serve roughly 3,000 homes. A separate one-megawatt solar power facility will support the electrical needs of the center.
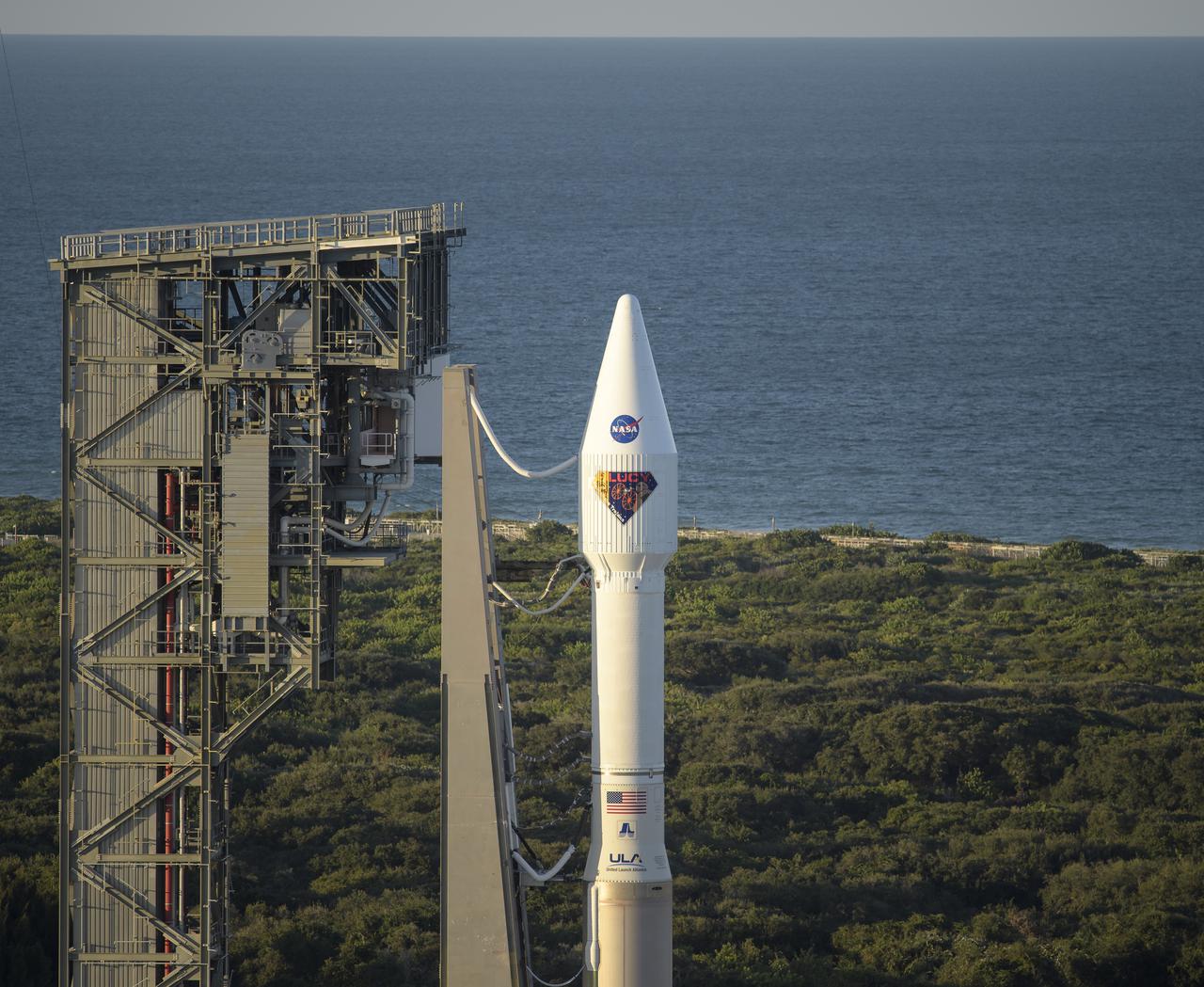

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Friday, Oct. 15, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
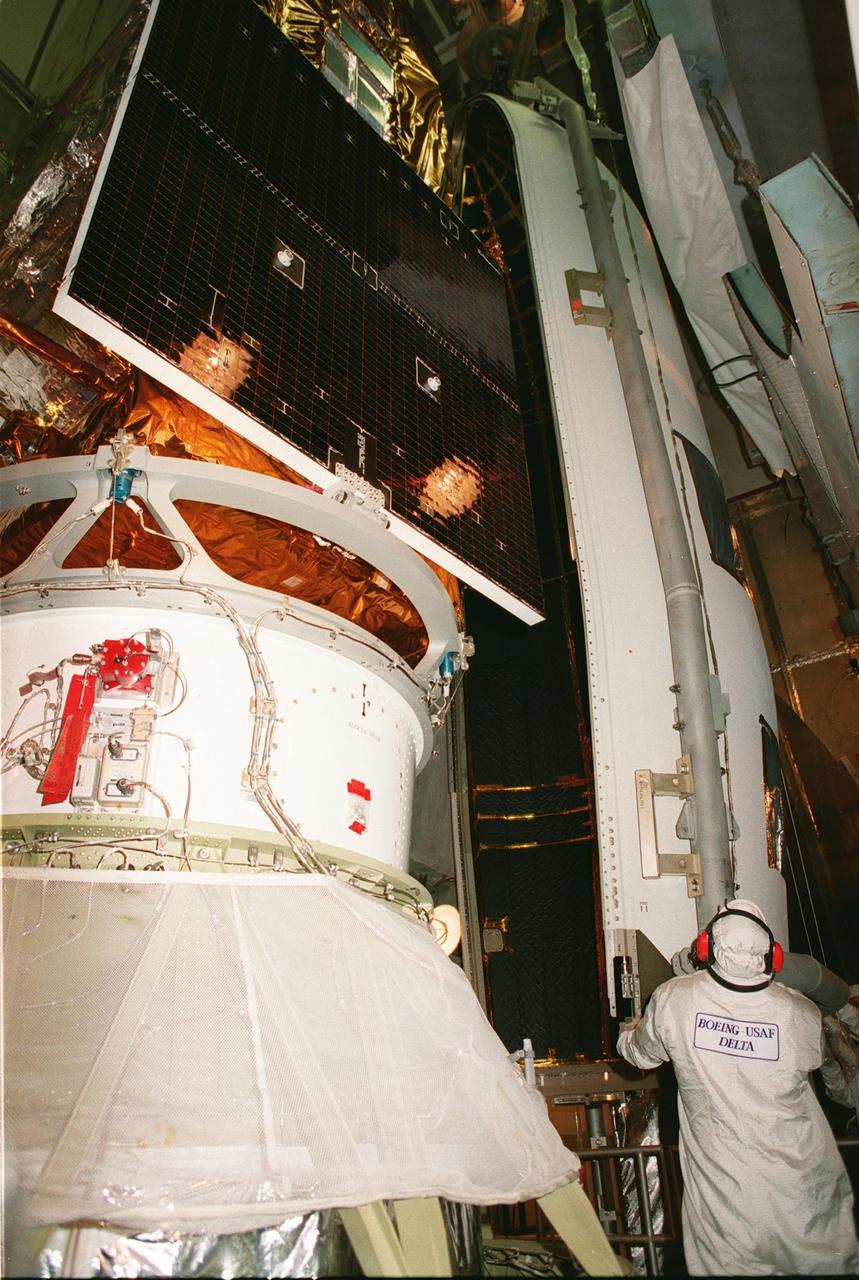

Workers in the launch tower at Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, help guide the first segment of the fairing around NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite. The satellite is scheduled for launch June 24 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study those elements to unlock the secrets of how galaxies evolve and to discover what the Universe was like when it was only a few minutes old
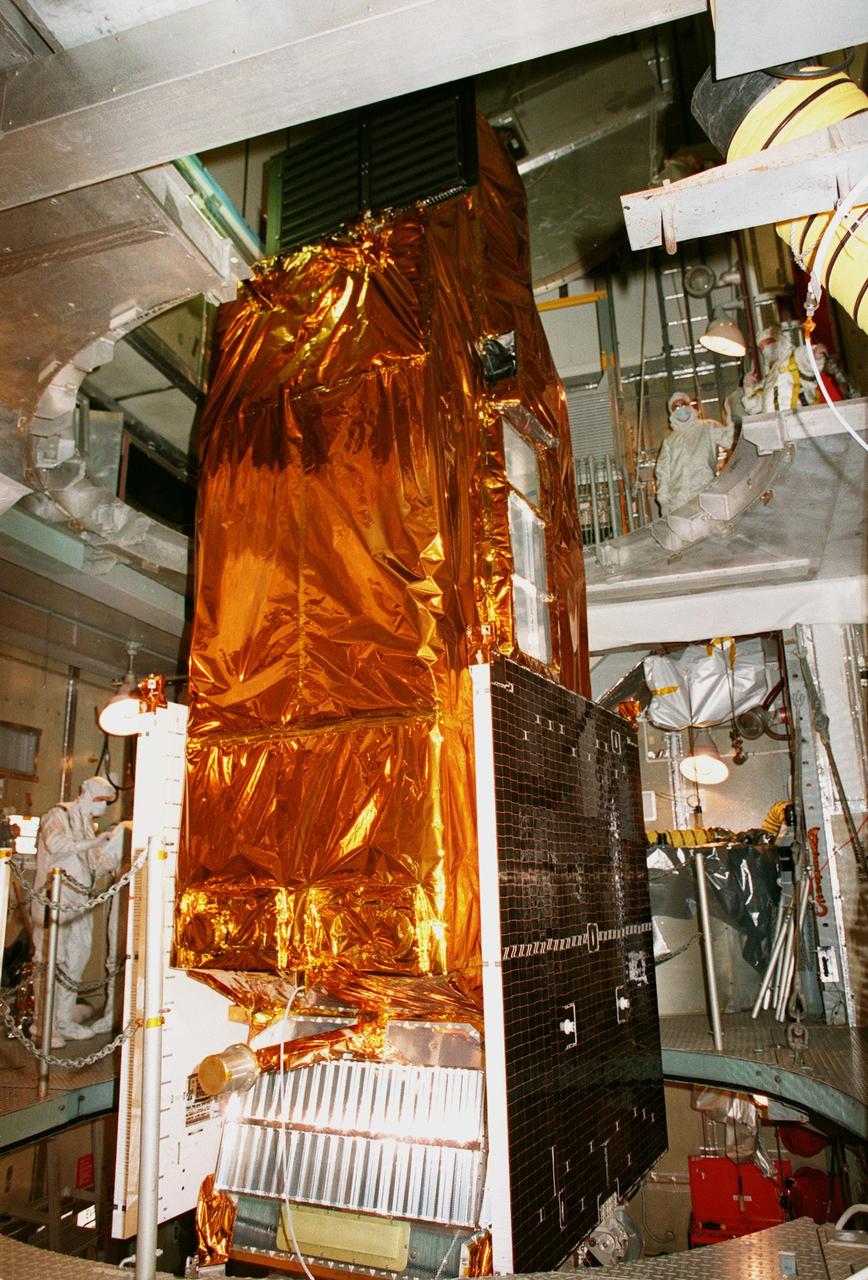

NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite sits ready for the fairing installation at Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station. The satellite is scheduled for launch June 24 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe
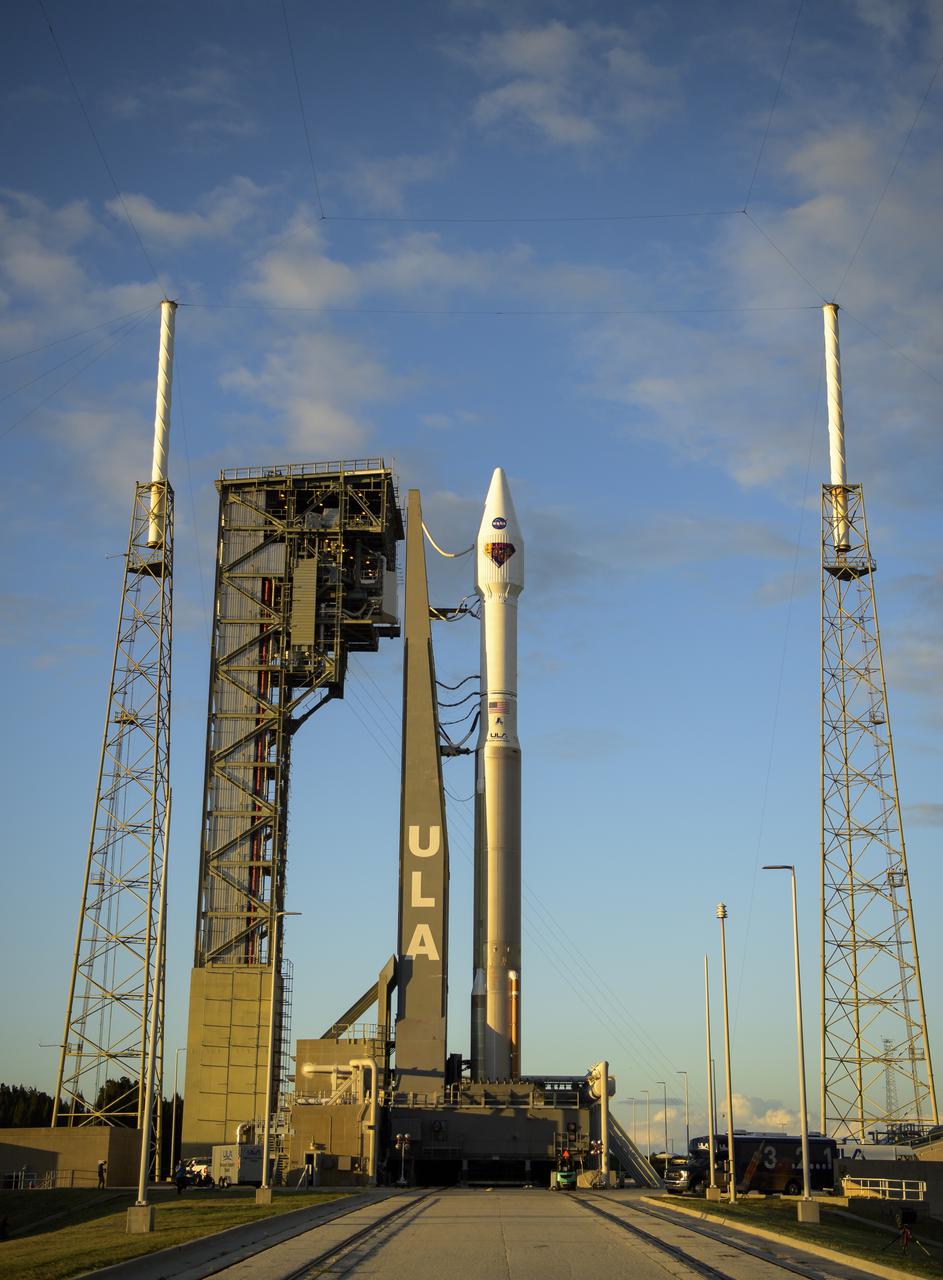

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
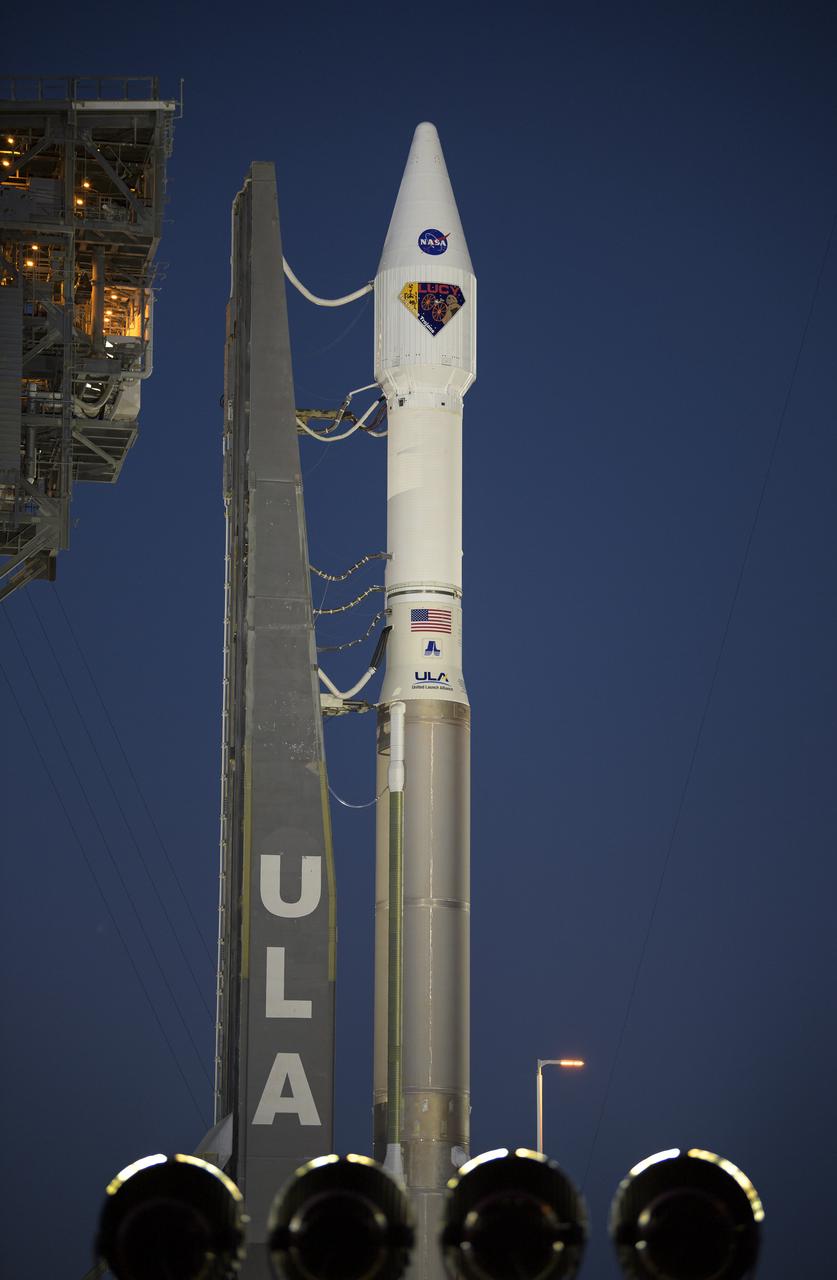

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
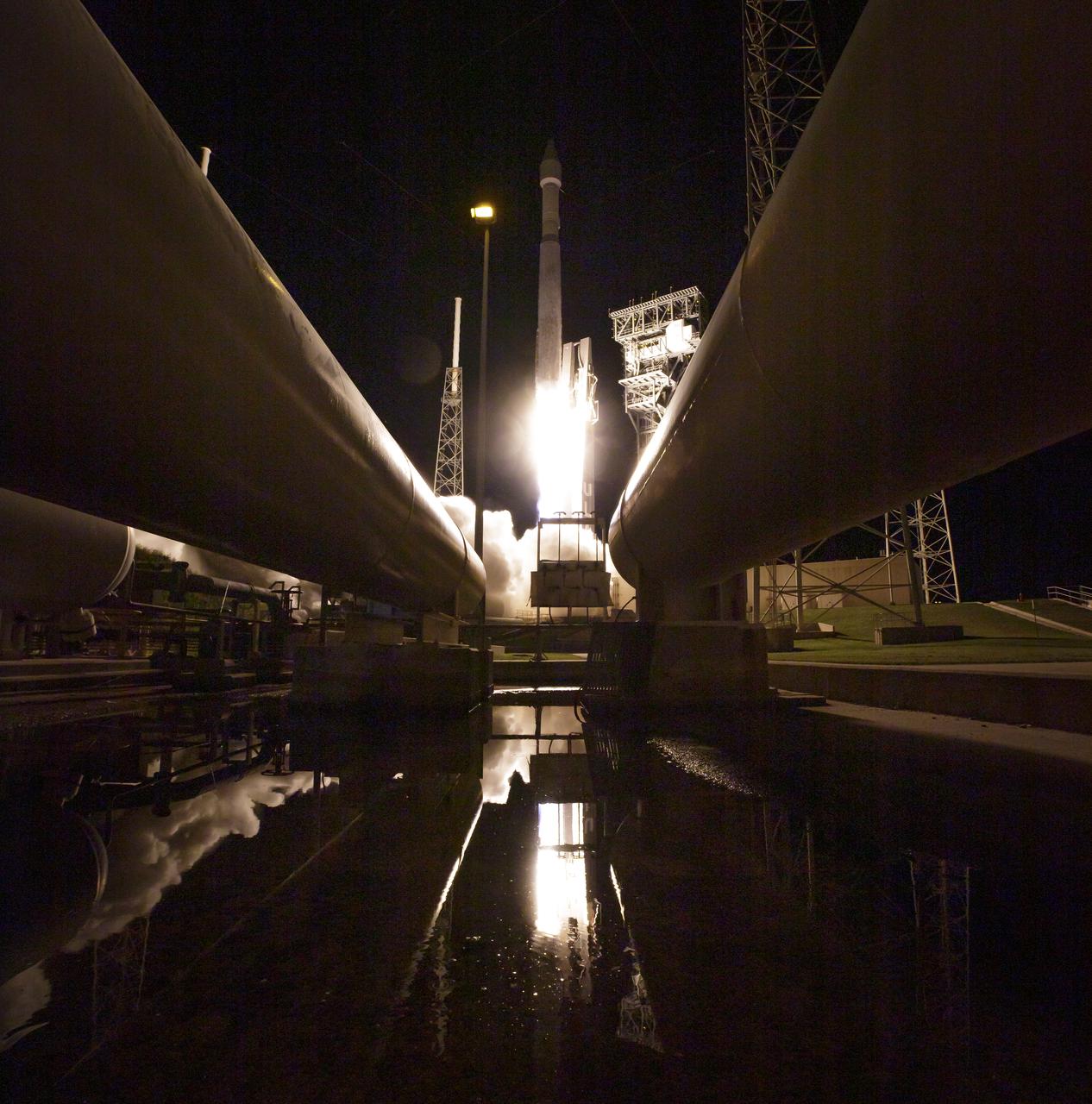

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
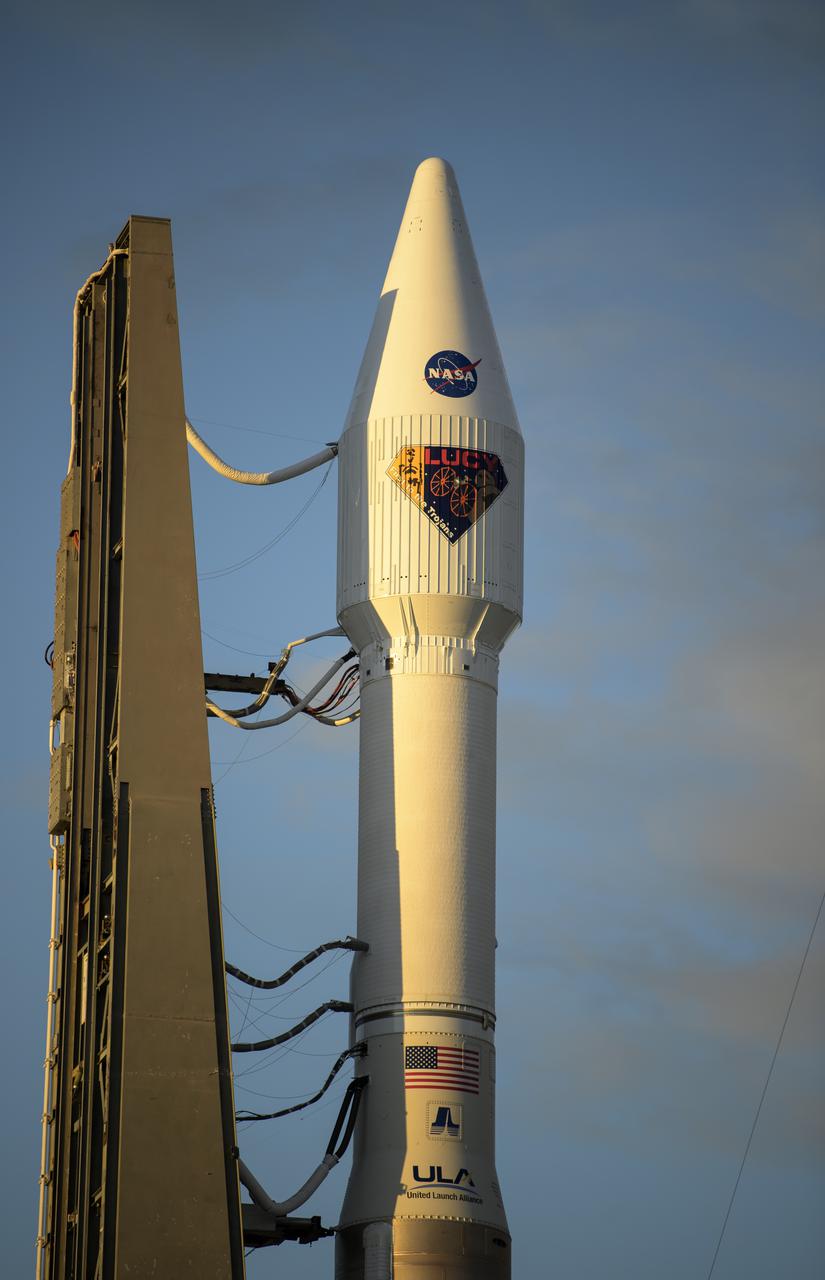

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen at Space Launch Complex 41, Friday, Oct. 15, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
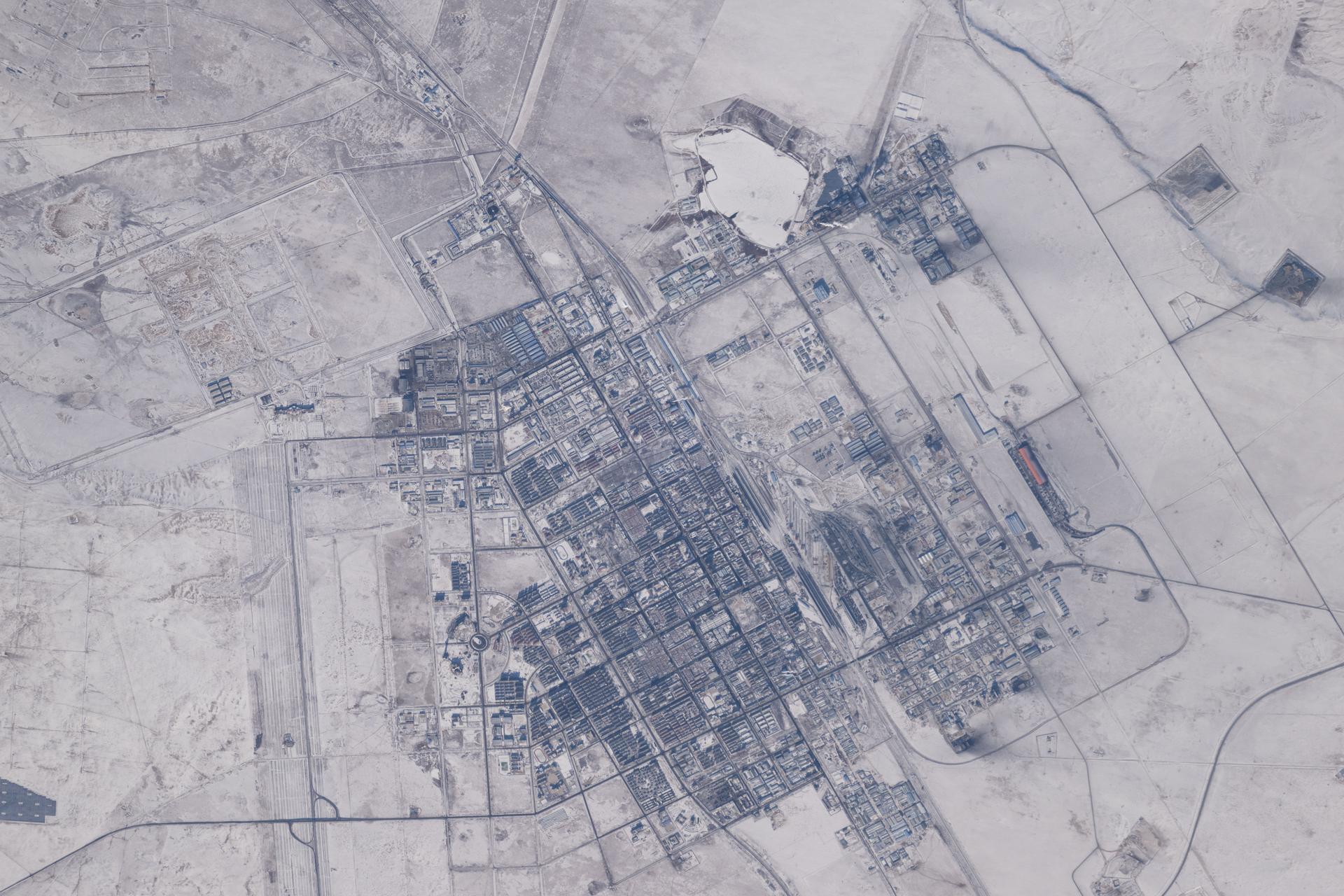

iss074e0000788 (Dec. 13, 2025) --- The county-level city of Erenhot in China's autonomous region of Inner Mongolia is pictured during a dry, deep winter from the International Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above Earth. Erenhot is a key border town for trade and international railway crossings between China and Mongolia. The city is also known for its paleontological history and numerous discoveries of dinosaur fossils.
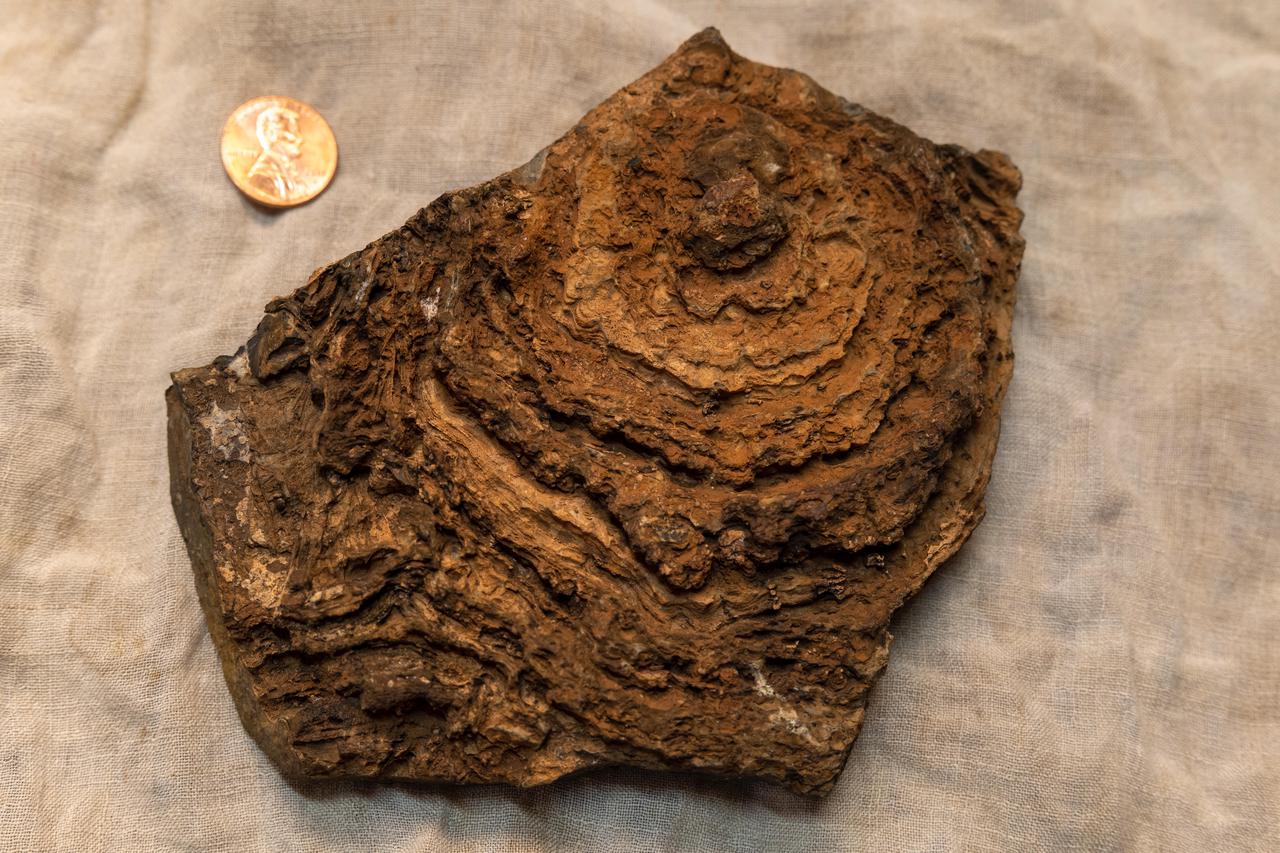

This image shows the finely layered internal structure of a stromatolite sample, with a U.S. penny for scale. This stromatolite formed about 2.7 billion years ago and was collected from an ancient lake environment preserved in the Tumbiana Formation, a succession of clastic and carbonate rocks outcropping along the southern margin of the Pilbara Craton in Western Australia. The view here is top down on what was once a dome that has been eroded flat, revealing the internal layering. Stromatolites form when communities of microorganisms organize into layered "microbial mats" that can trap and bind sediment or stimulate the precipitation of mineral grains from the water around them, both processes generating a kind of "living fossil." However, living stromatolites can rarely be found on Earth today. Stromatolite fossils are the dominant record of life for most of Earth's history prior to the appearance of complex, multicellular organisms. Scientists are seeking something similar to stromatolites in the dry lakebed Perseverance will be exploring on Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24240
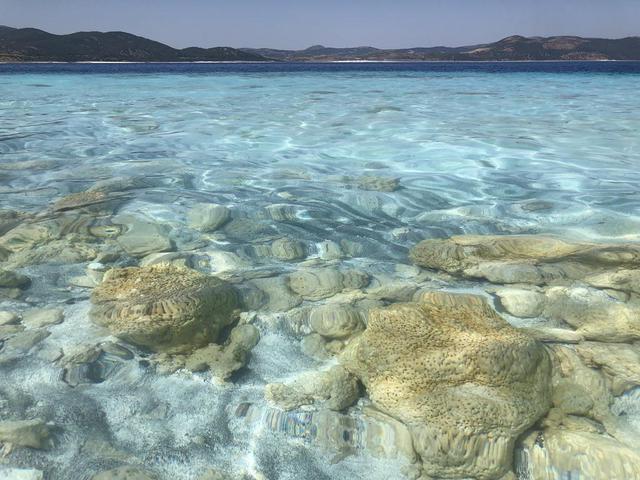

The rocks seen here along the shoreline of Lake Salda in Turkey were formed over time by microbes that trap minerals and sediments in the water. These so-called microbialites were once a major form of life on Earth and provide some of the oldest known fossilized records of life on our planet. NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance mission will search for signs of ancient life on the Martian surface. Studying these microbial fossils on Earth has helped scientists prepare for the mission. Today, the Martian surface is devoid of lakes and rivers, but billions of years ago it may have looked like this aqueous location on Earth. NASA's Perseverance Mars rover will land in Jezero Crater, which scientists believe was home to a lake and river delta about 3.5 billion years ago. Together, they could have collected and preserved ancient organic molecules and other potential signs of microbial life from the water and sediments that flowed into the crater billions of years ago. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24374
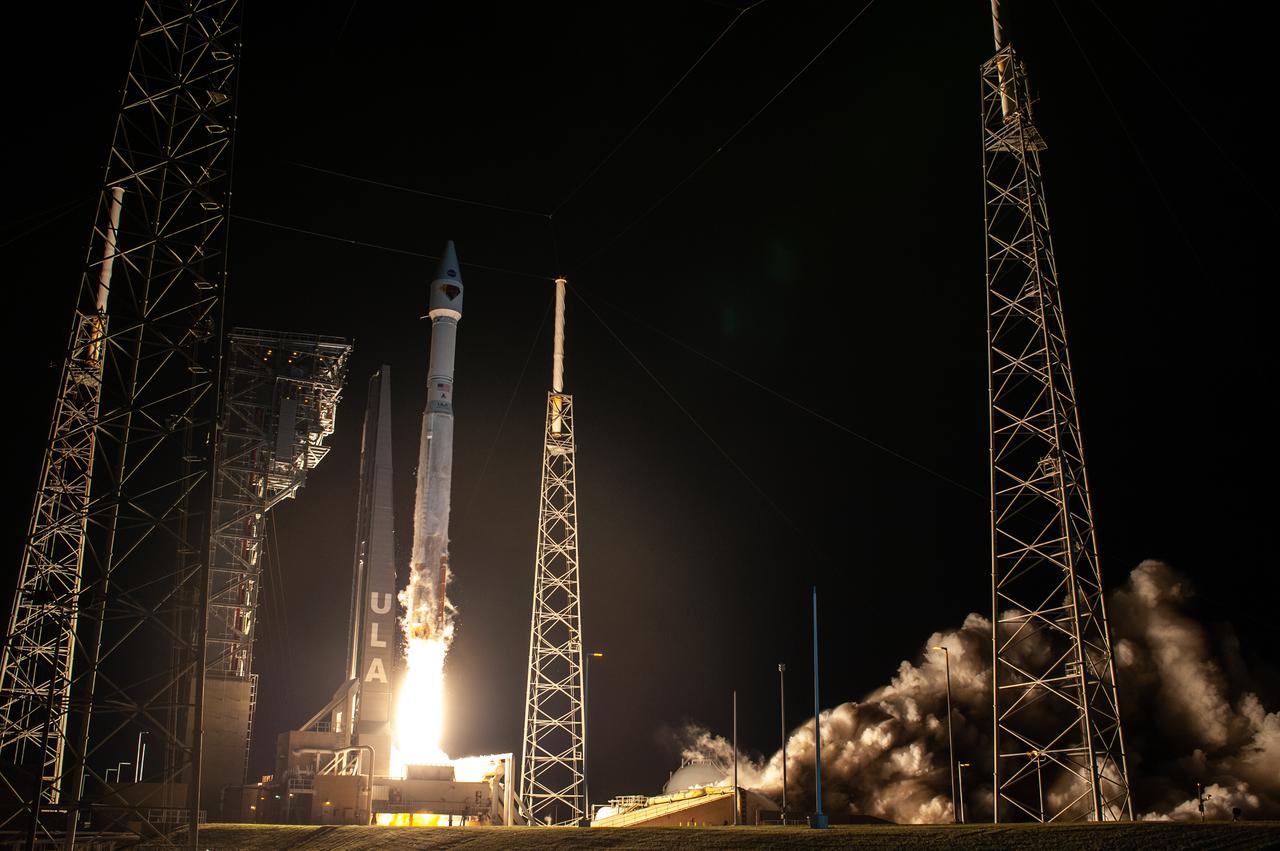

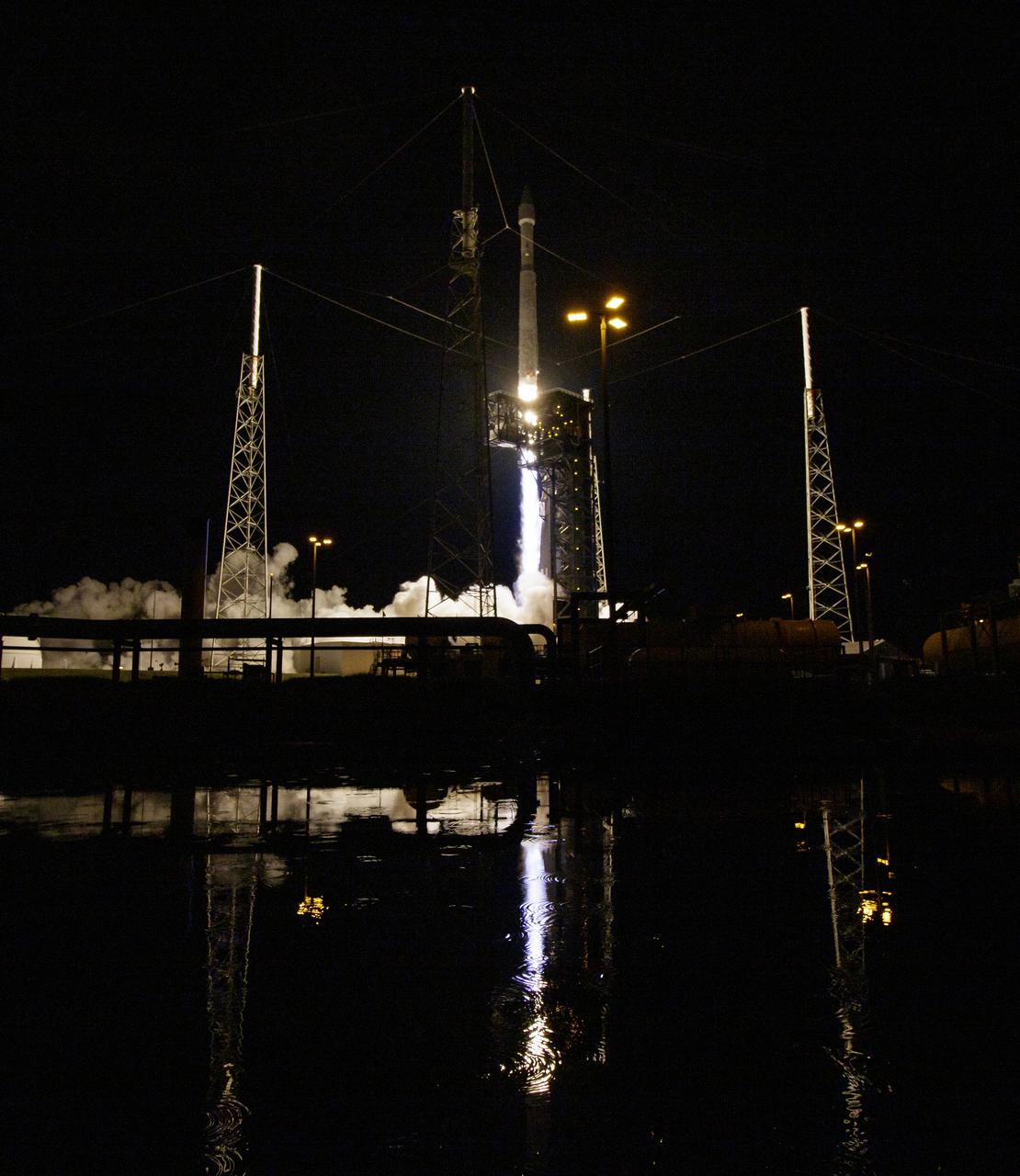
A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.

At Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), workers begin removing the lower sections of the canister surrounding NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe. FUSE is scheduled to be launched from CCAS June 23 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket
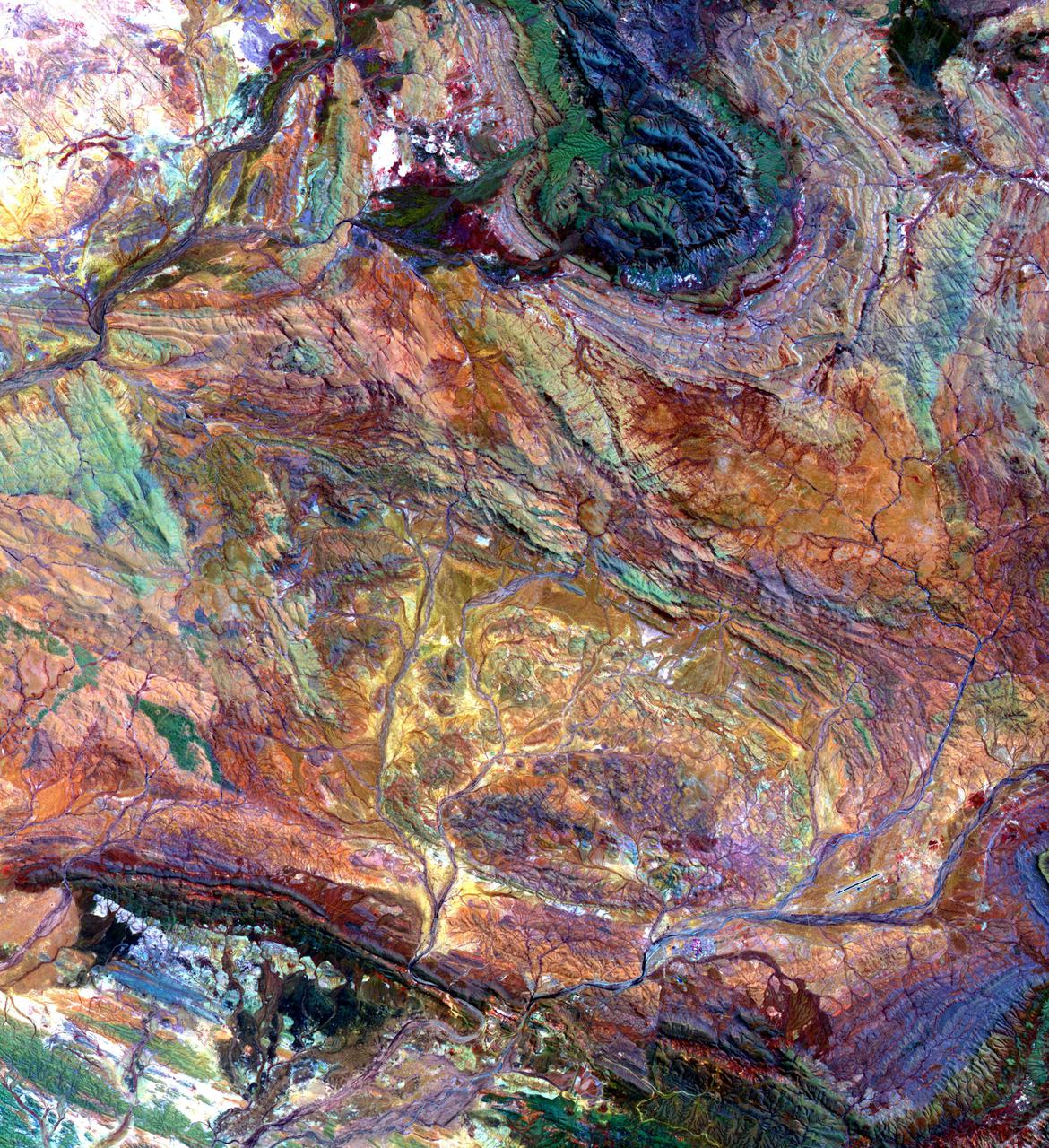

The Pilbara in northwestern Australia exposes some of the oldest rocks on Earth, over 3.6 billion years old. The iron-rich rocks formed before the presence of atmospheric oxygen, and life itself. Found upon these rocks are 3.45 billion-year-old fossil stromatolites, colonies of microbial cyanobacteria. The image is a composite of ASTER bands 4-2-1 displayed in RGB. The image was acquired October 12, 2004, covers an area of 49.1 by 55.2 km, and is located at 22.8 degrees south, 117.6 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25122
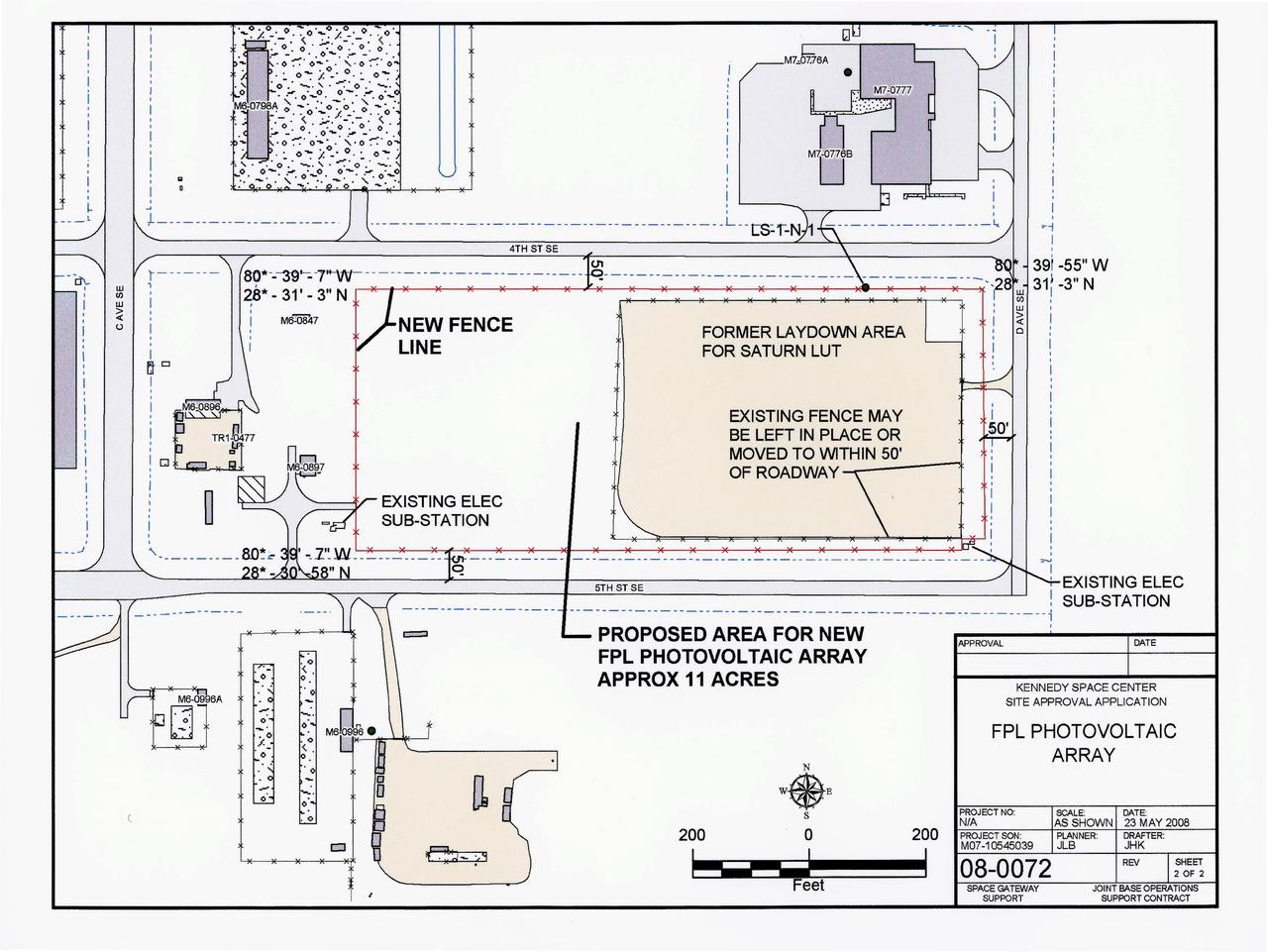
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This map shows the area within NASA's Kennedy Space Center where one of the two solar photovoltaic power generation systems will be built as the result of an agreement between NASA and Florida Power & Light. The agreement is part of a new initiative that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The major facility will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of electrical power, which can serve roughly 3,000 homes. A separate one-megawatt solar power facility will support the electrical needs of the center.
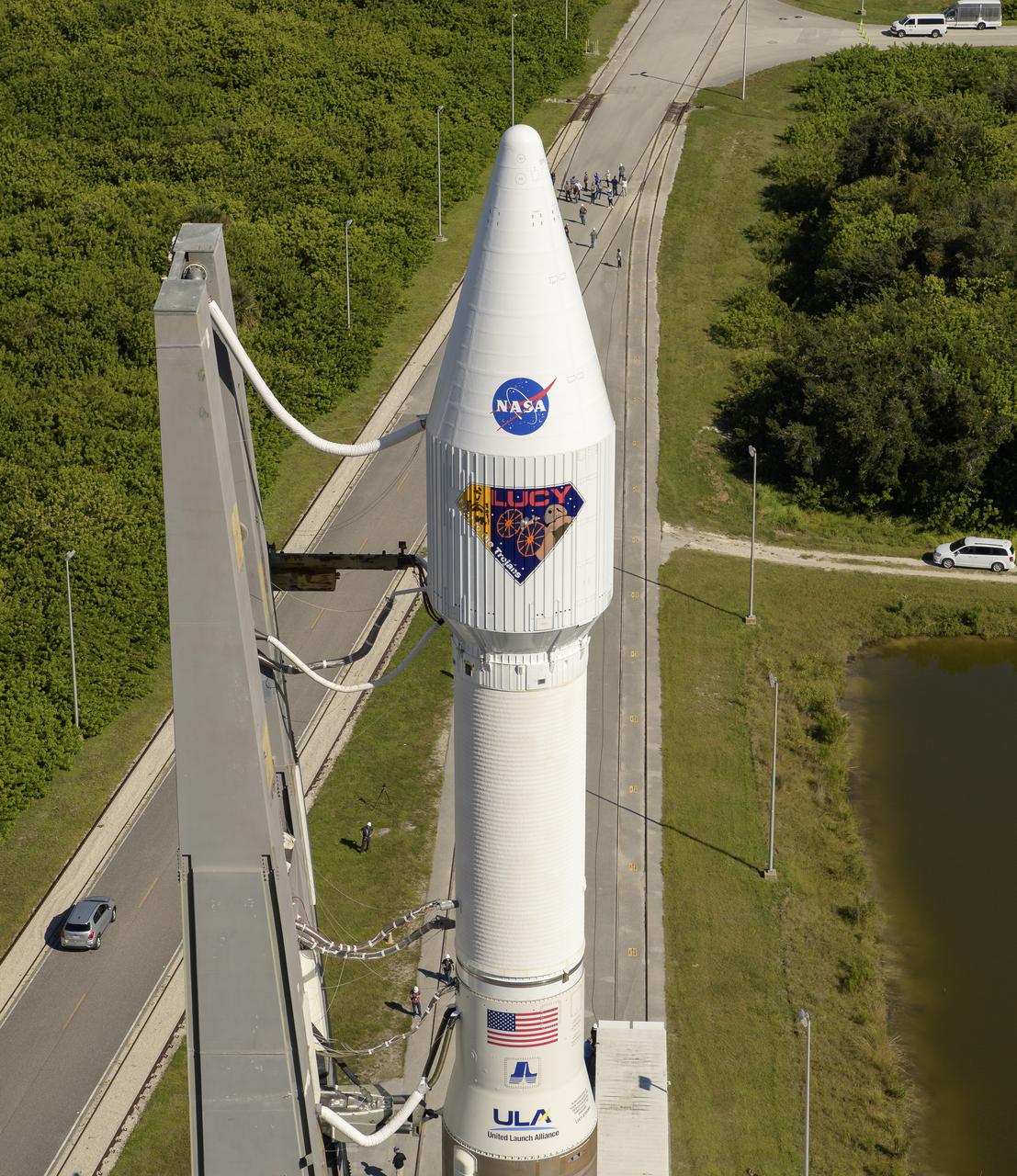

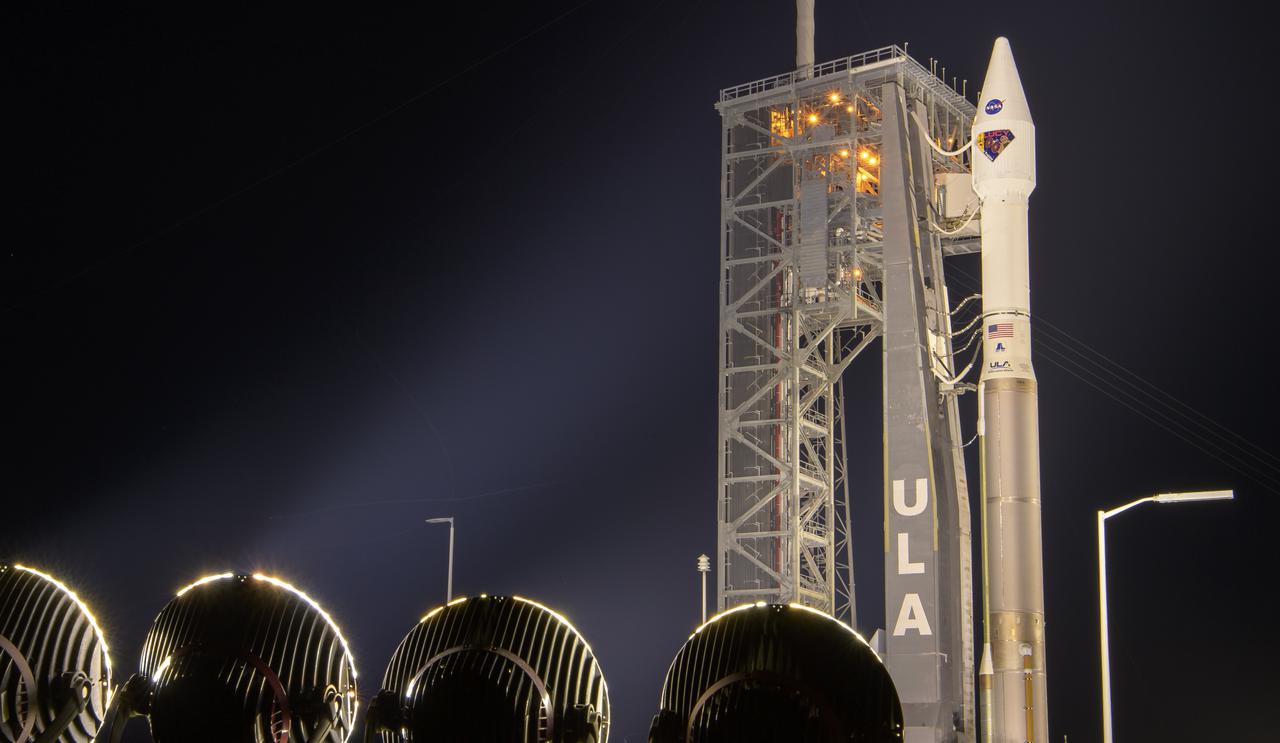
A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen as it is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
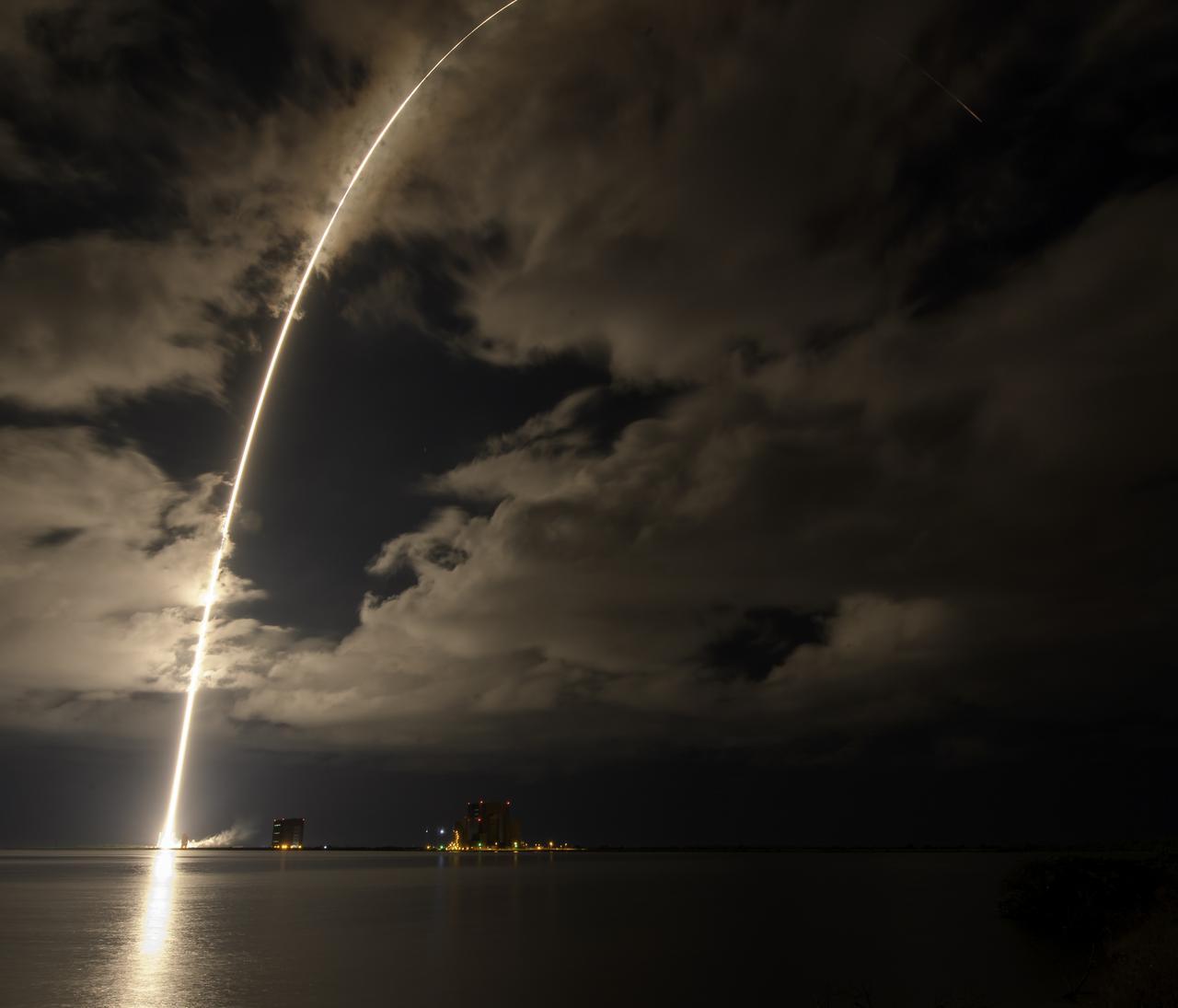

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen in this 2 minute and 30 second exposure photograph as it launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
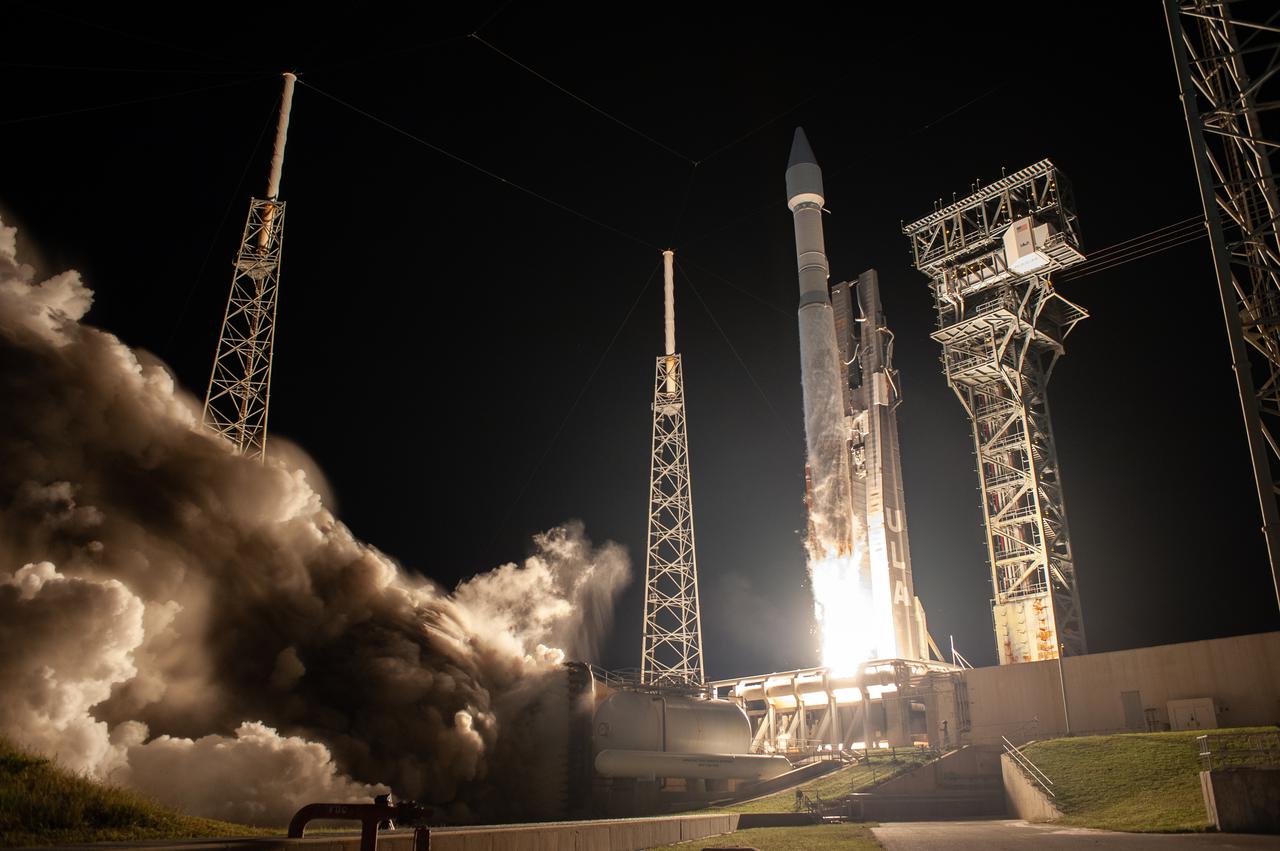

A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.
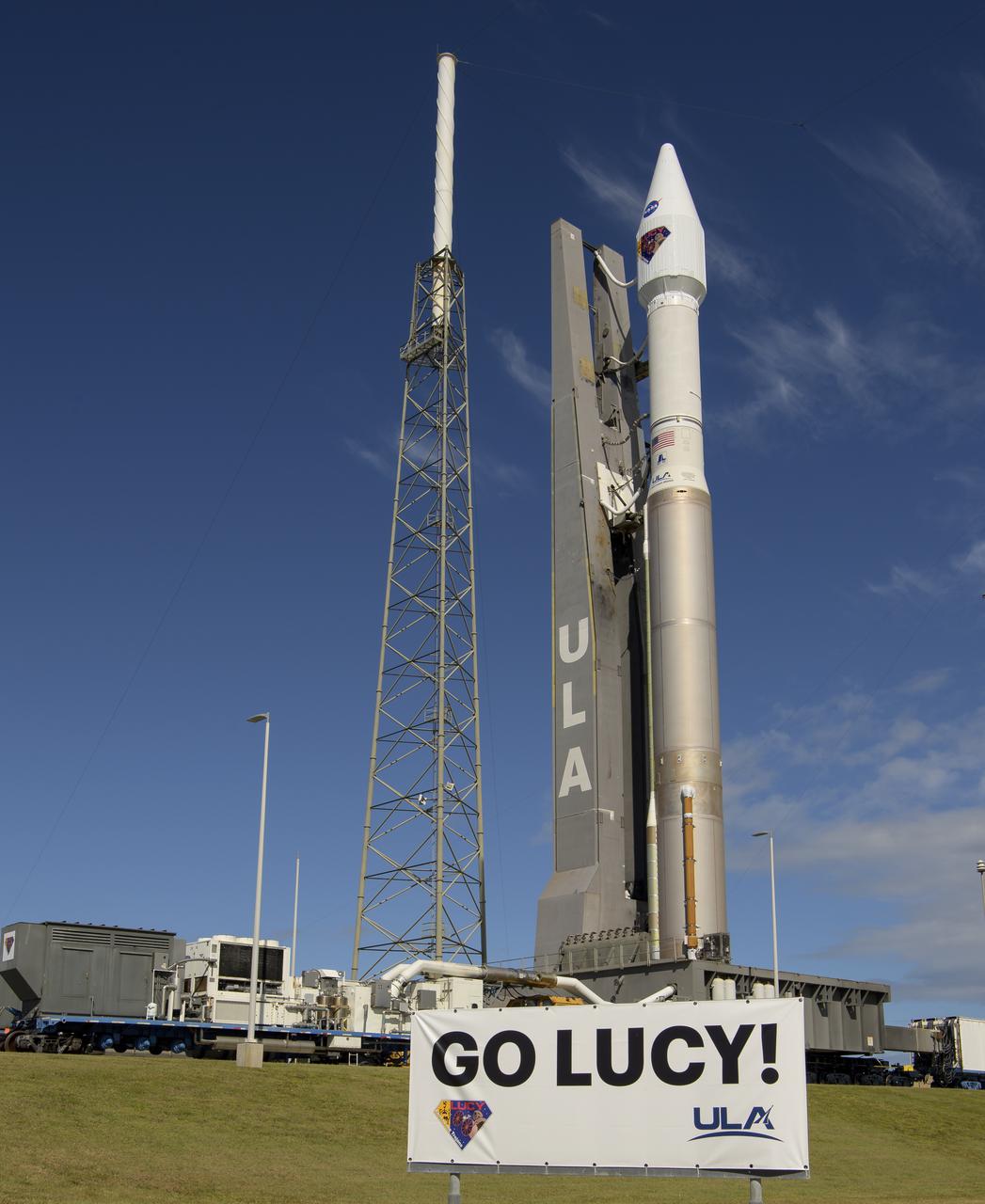

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen as it is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
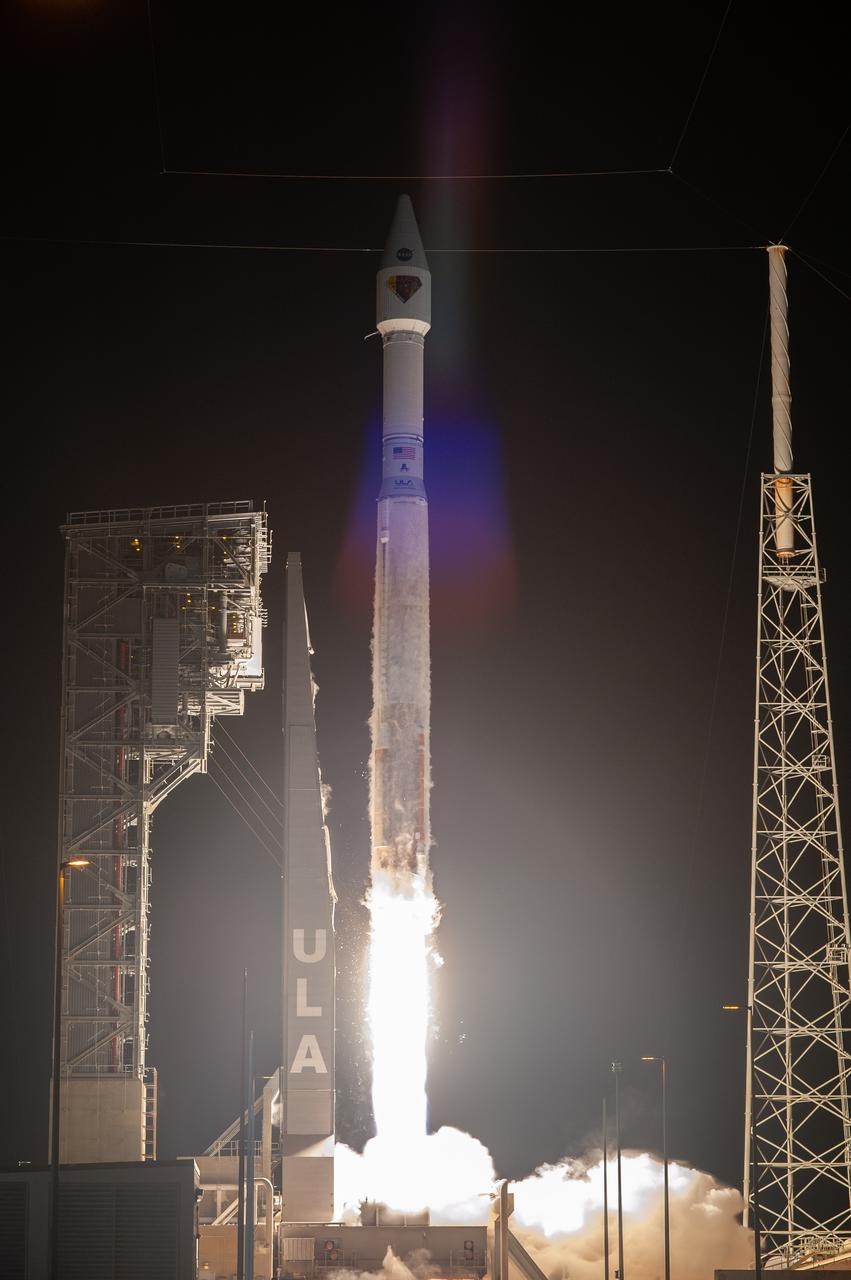

A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.
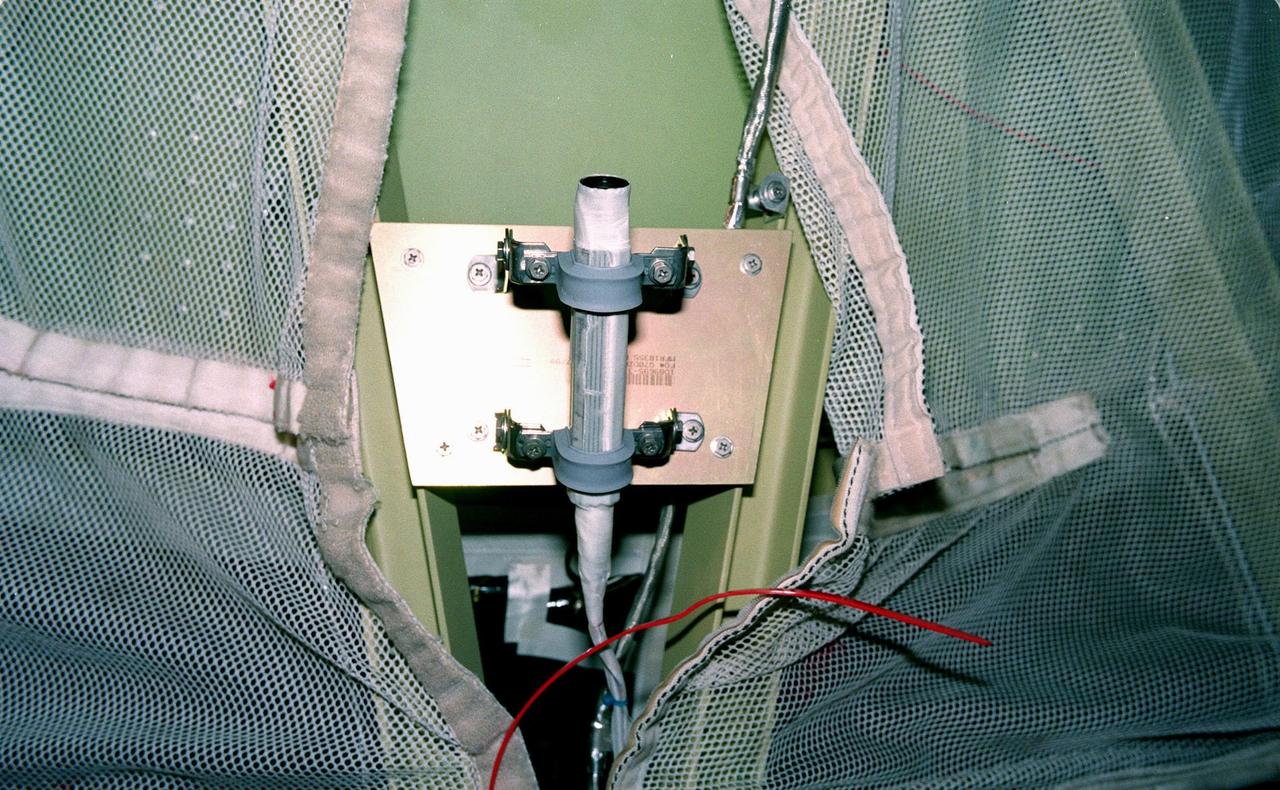
A camera is shown mounted on the second stage of the Boeing Delta II rocket scheduled to launch NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite June 24 from Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station. The camera will record the separation of the fairing encircling the satellite, which should occur several minutes after launch. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe
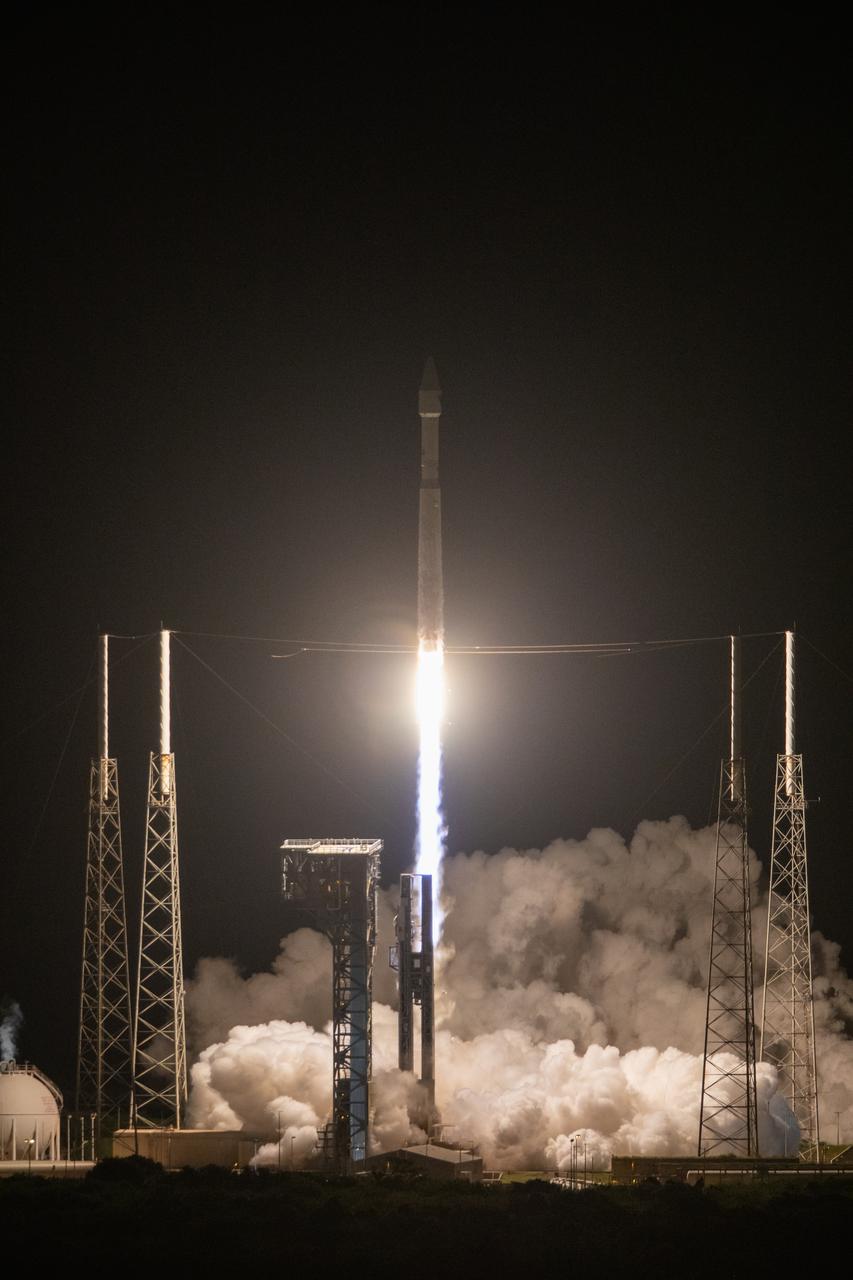

A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.
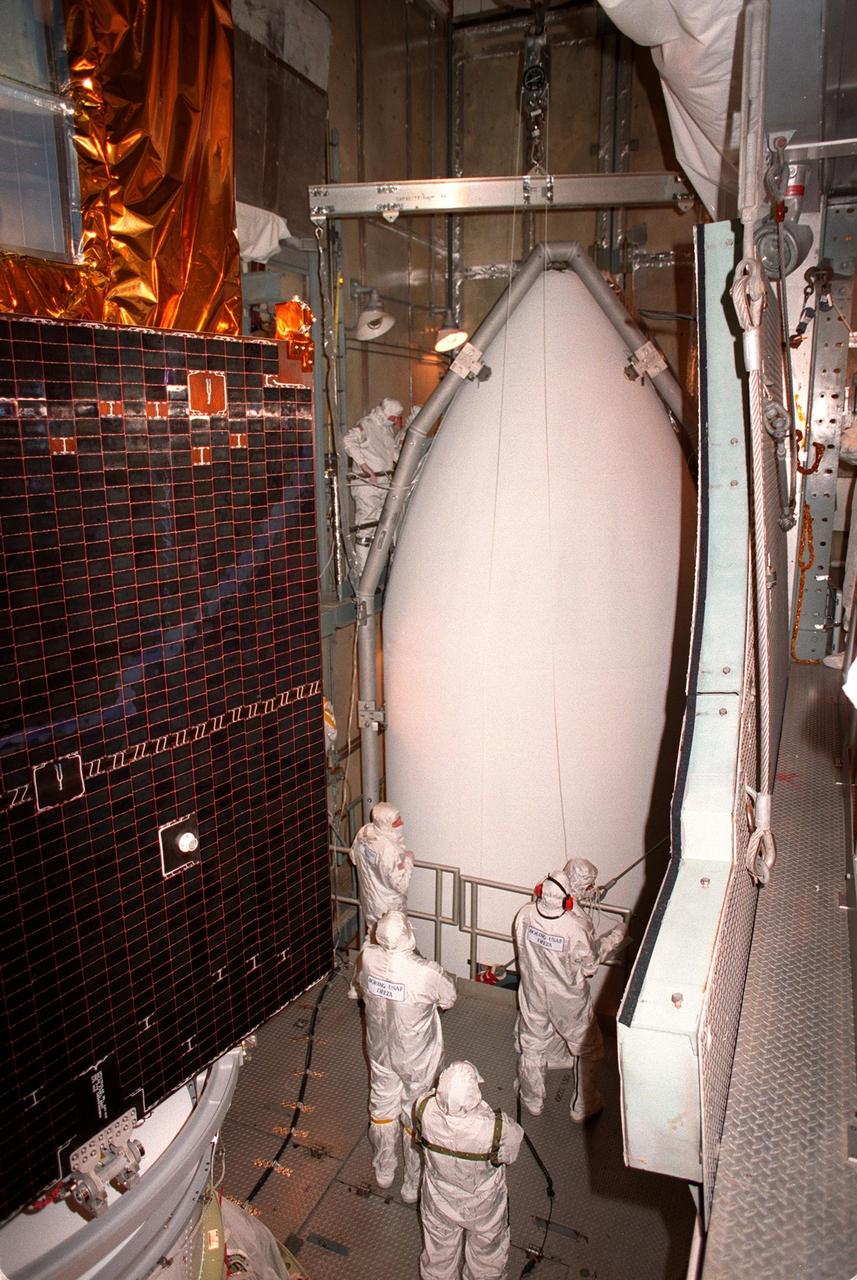

At Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, workers oversee the lifting of the fairing (right) into the tower. At left is NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite around which the fairing will be fitted. The satellite is scheduled for launch June 24 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe
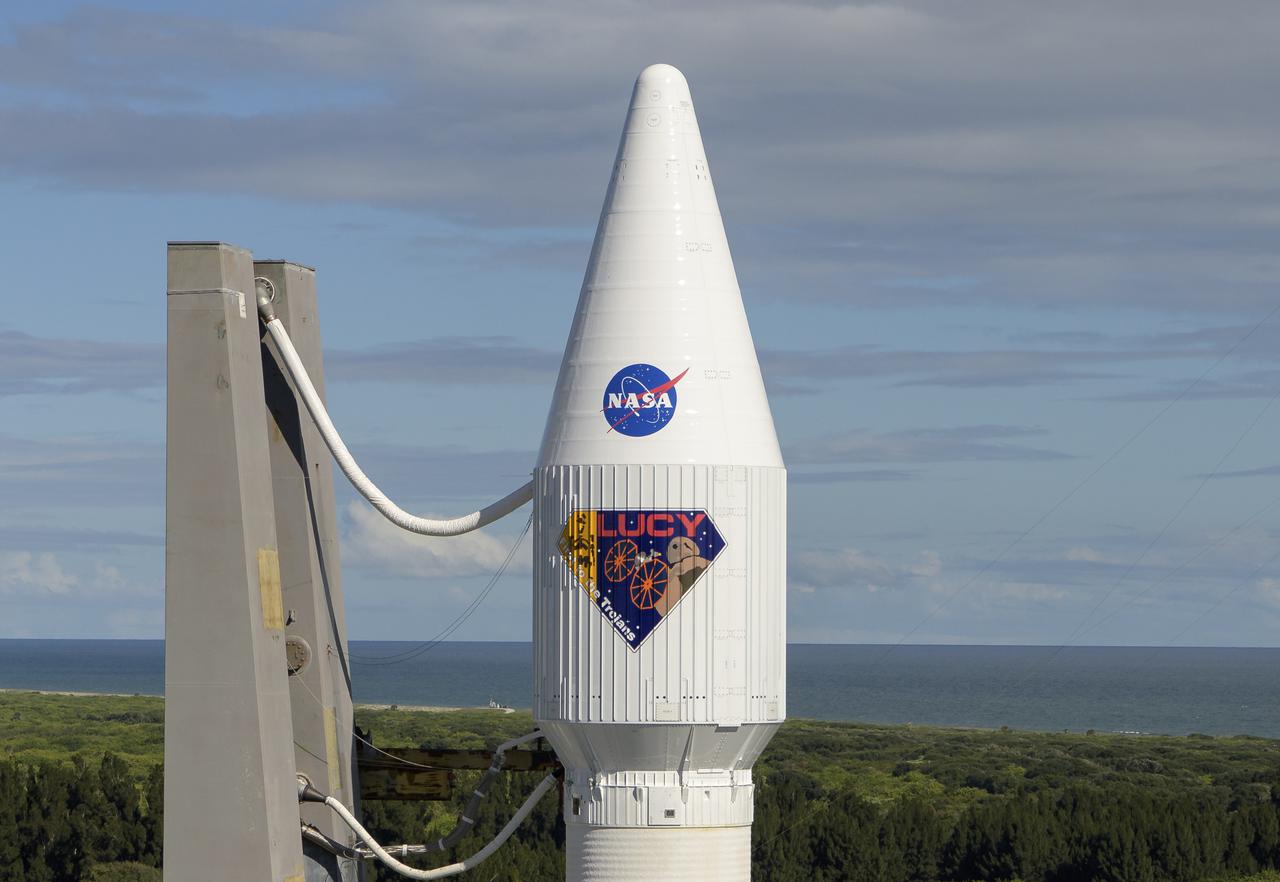

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen as it is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
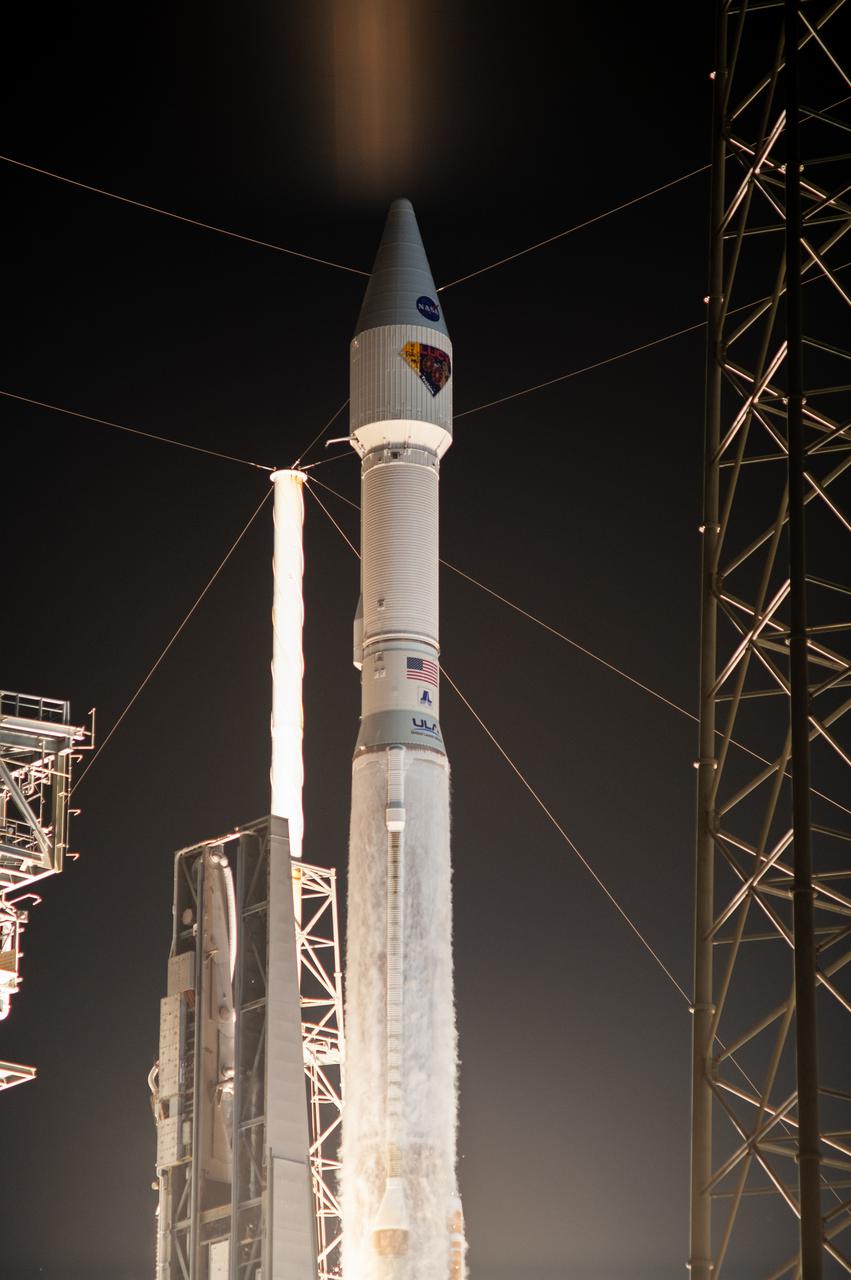

A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.

The Moon, lower left, and Jupiter, upper right, are seen the night before the planned launch of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft, Friday, Oct. 15, 2021, at Cape Canaveral, Florida. Scheduled to launch early Saturday morning, Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
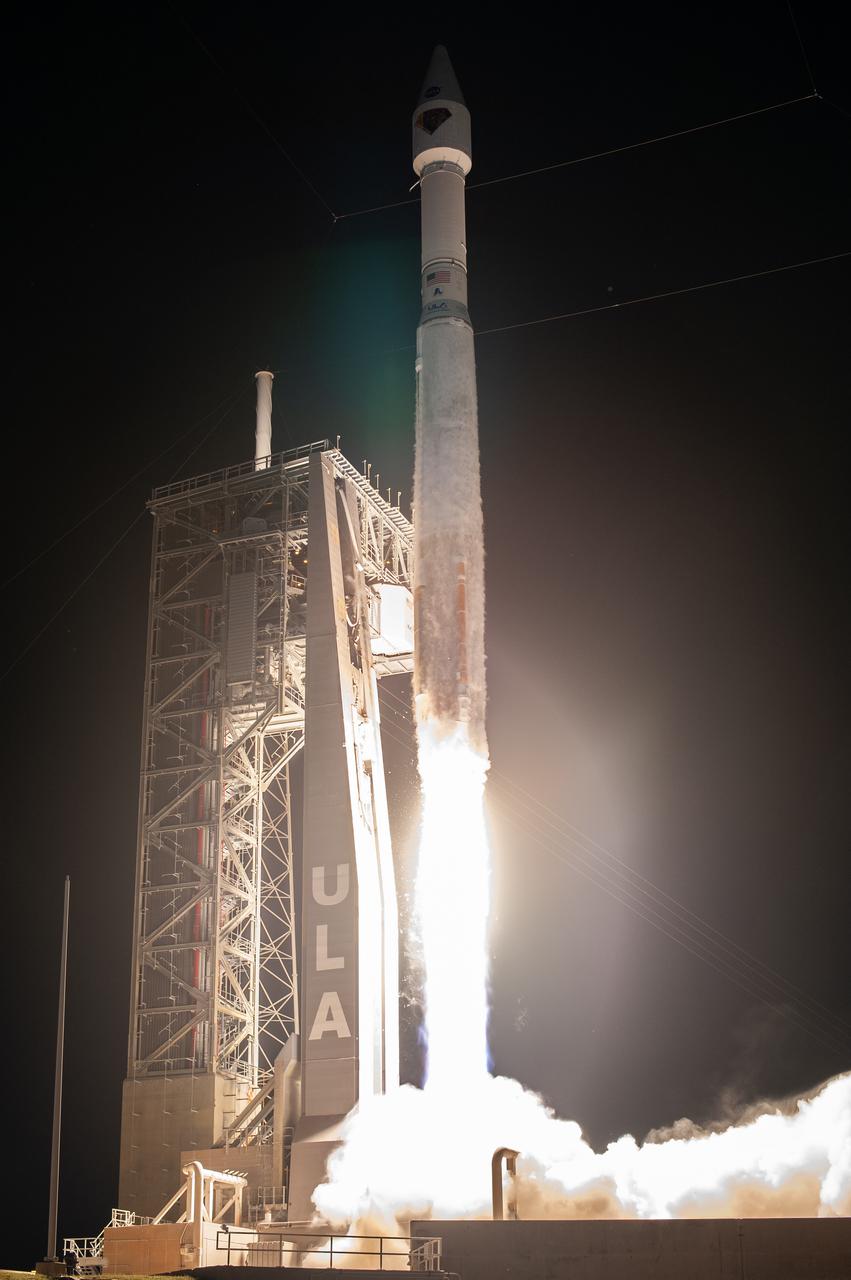

A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.
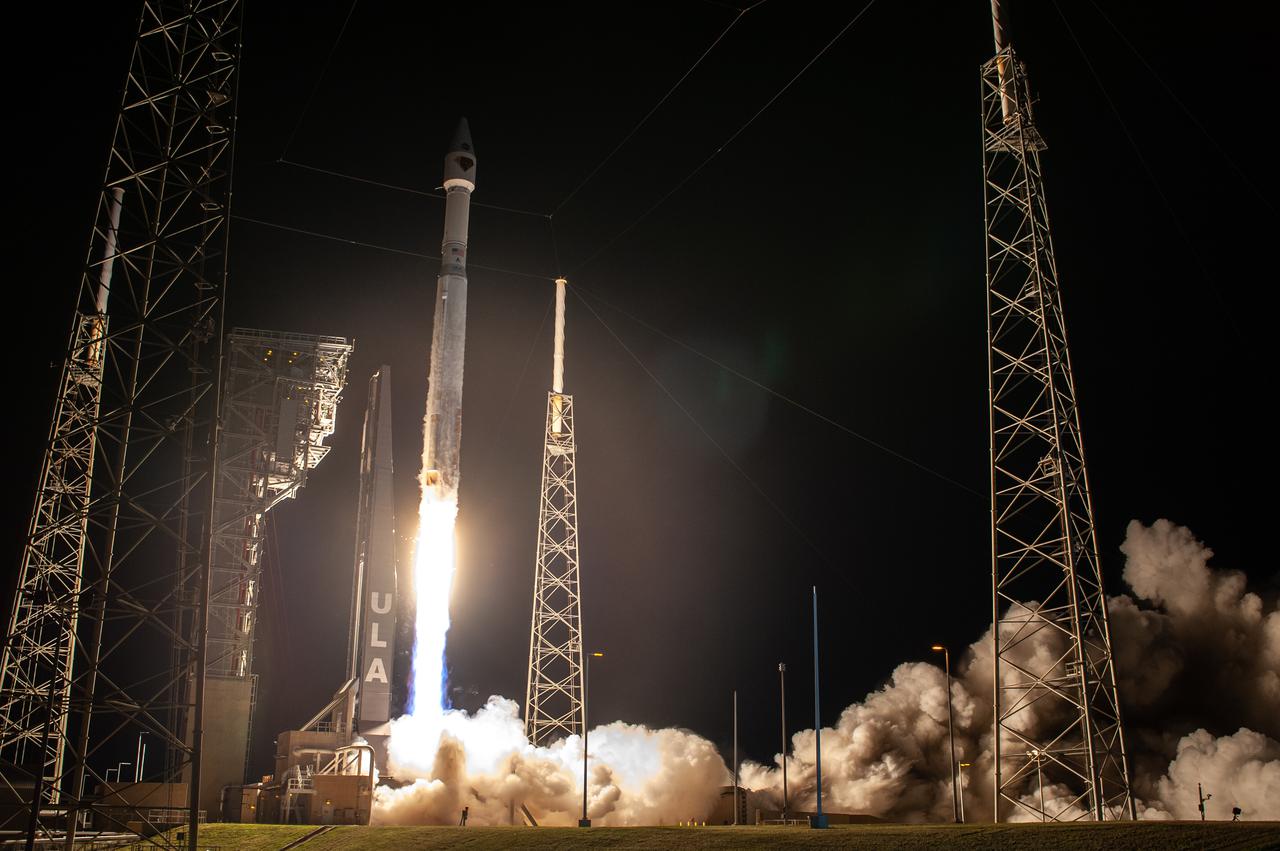

A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.
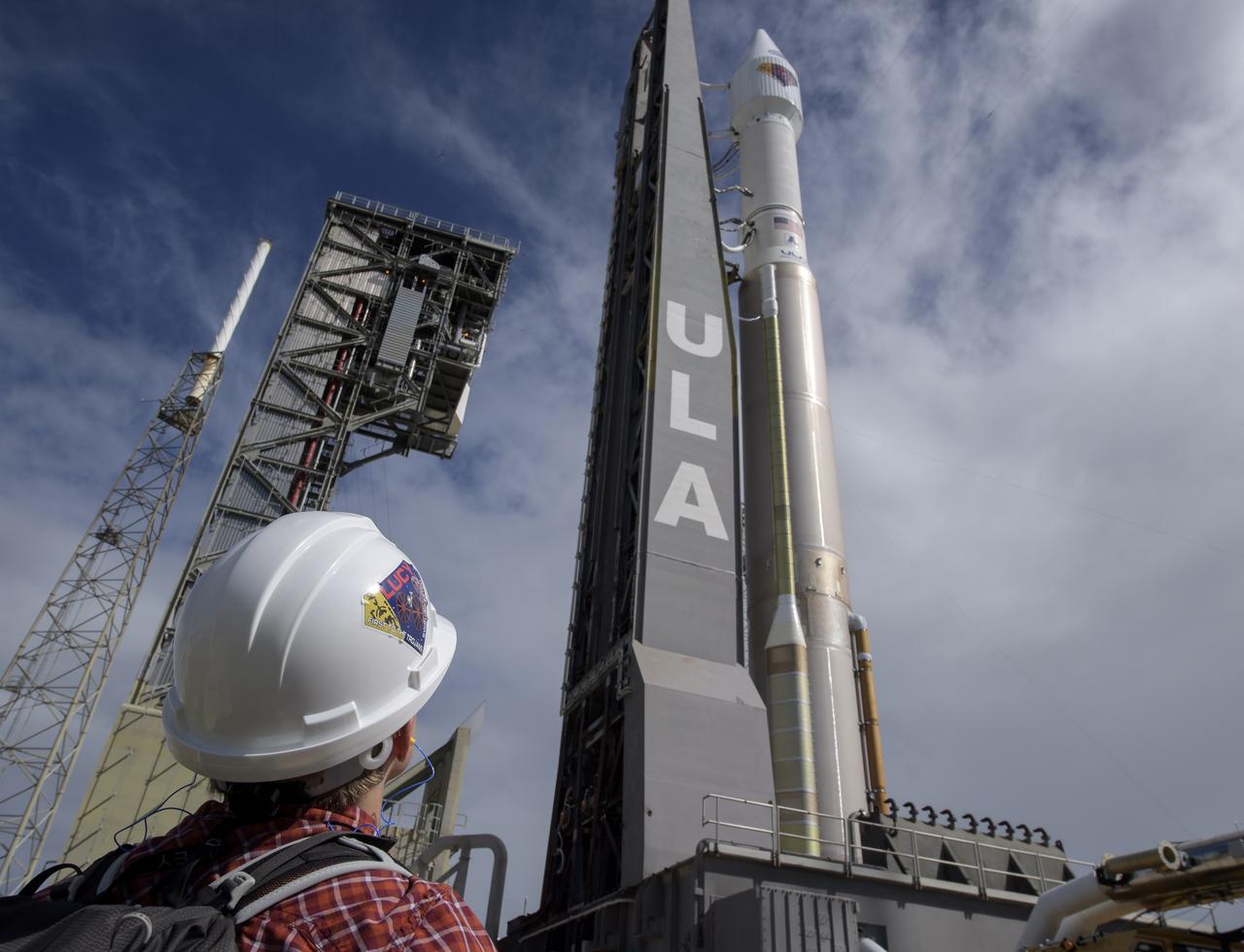

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen as it is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
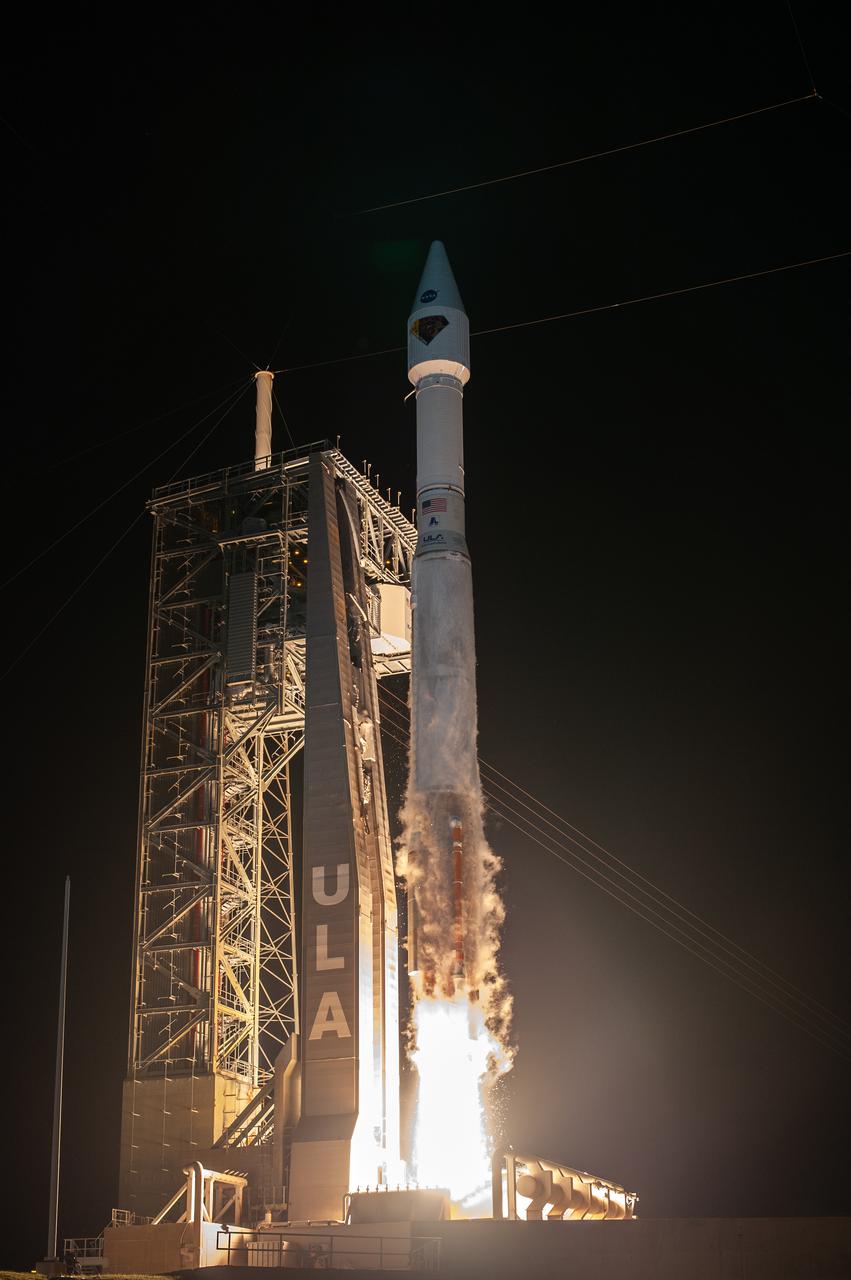

A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.
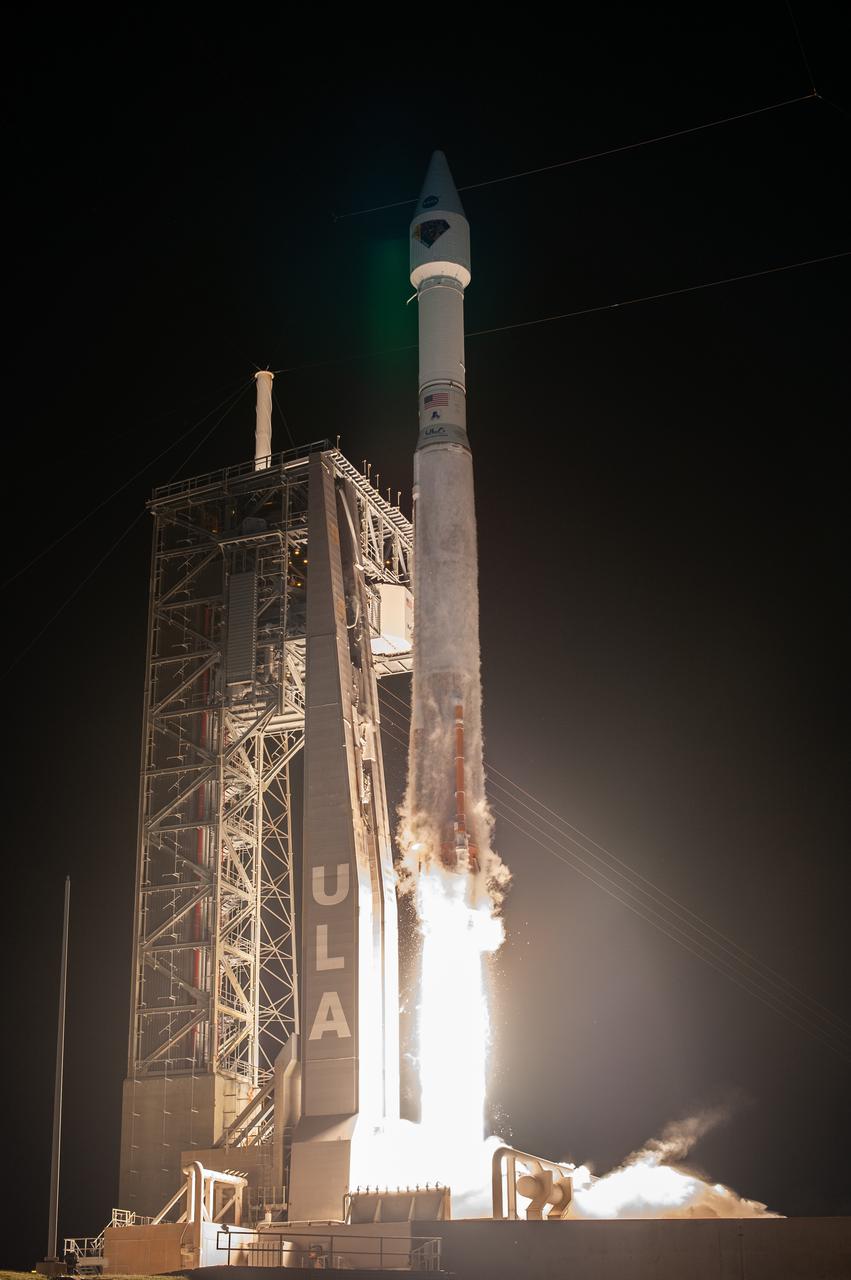

A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.
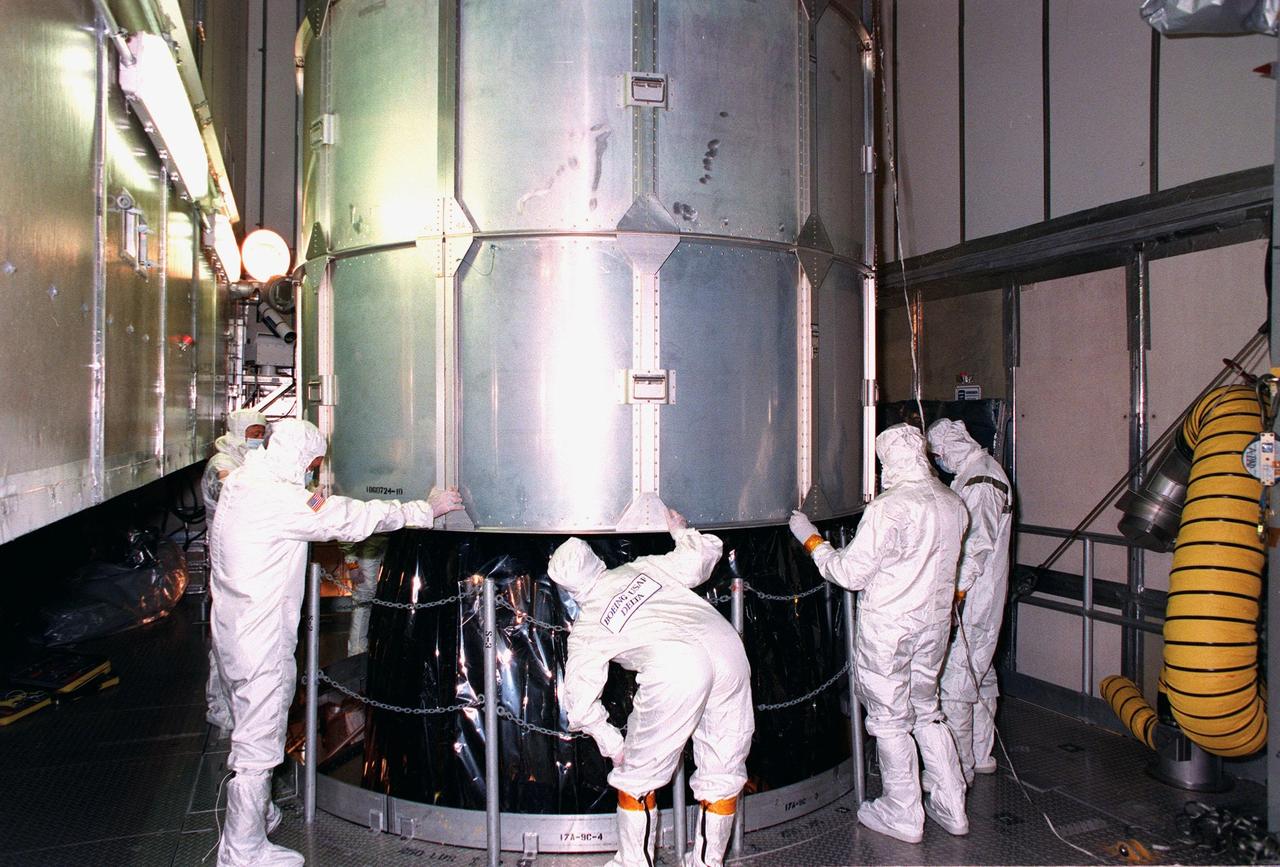

At Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), workers begin to remove the canister around the top of the NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe. FUSE is scheduled to be launched from CCAS June 23 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket
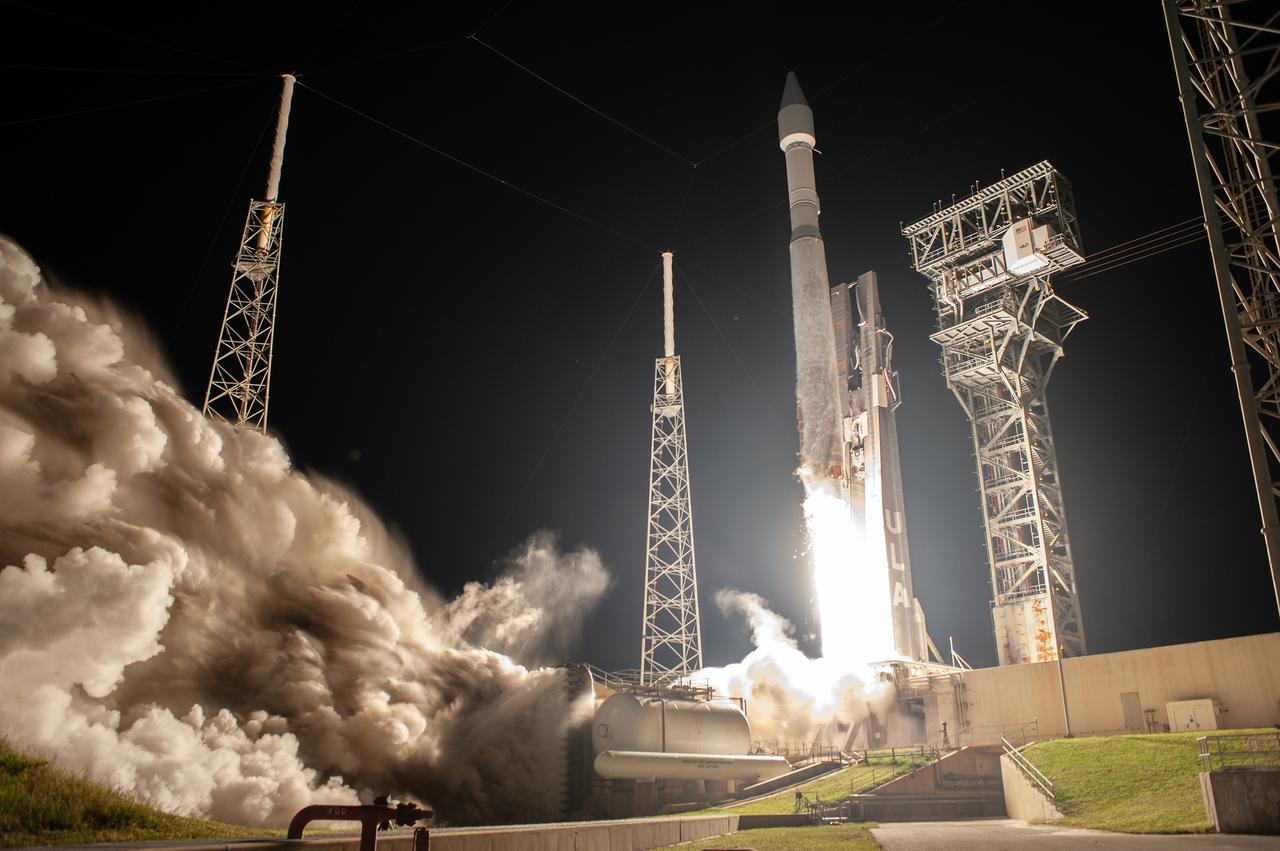

A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.
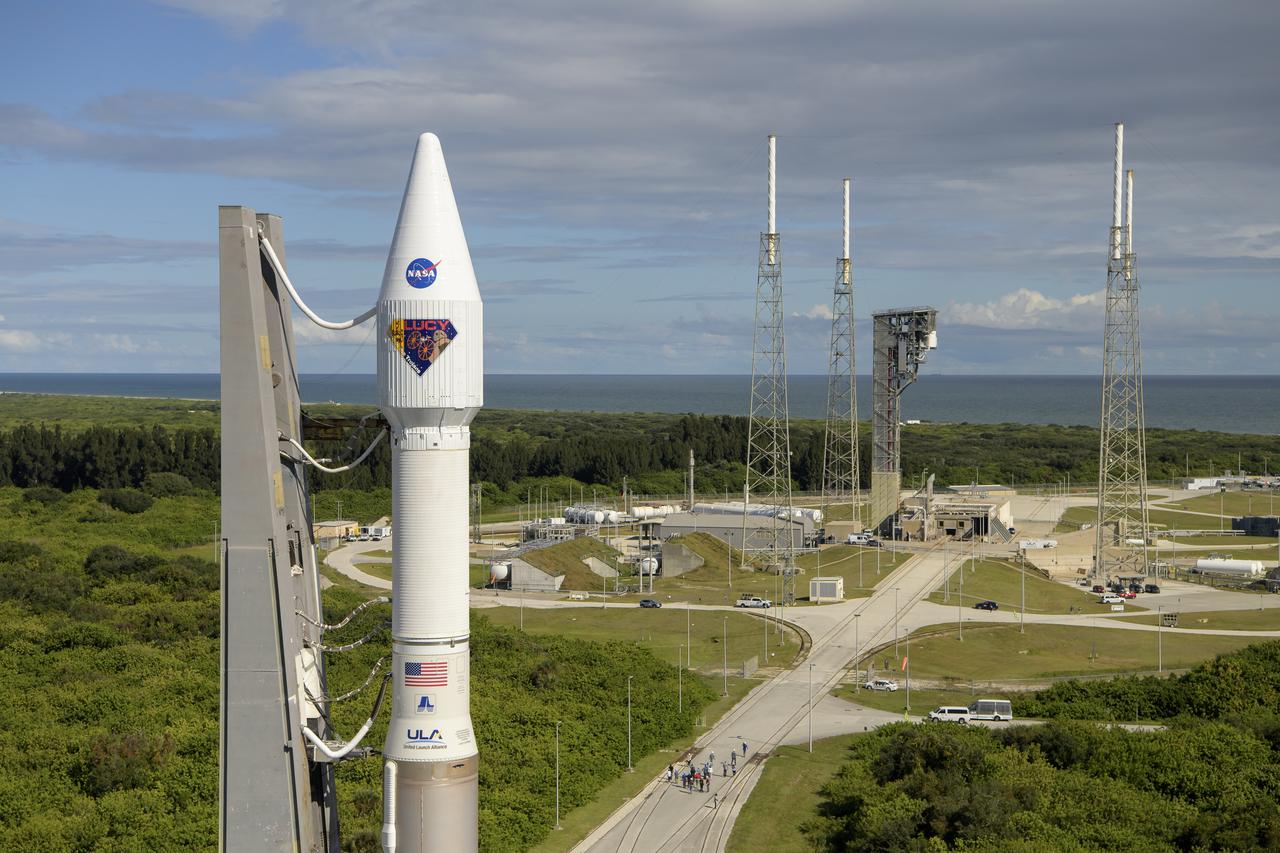

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen as it is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
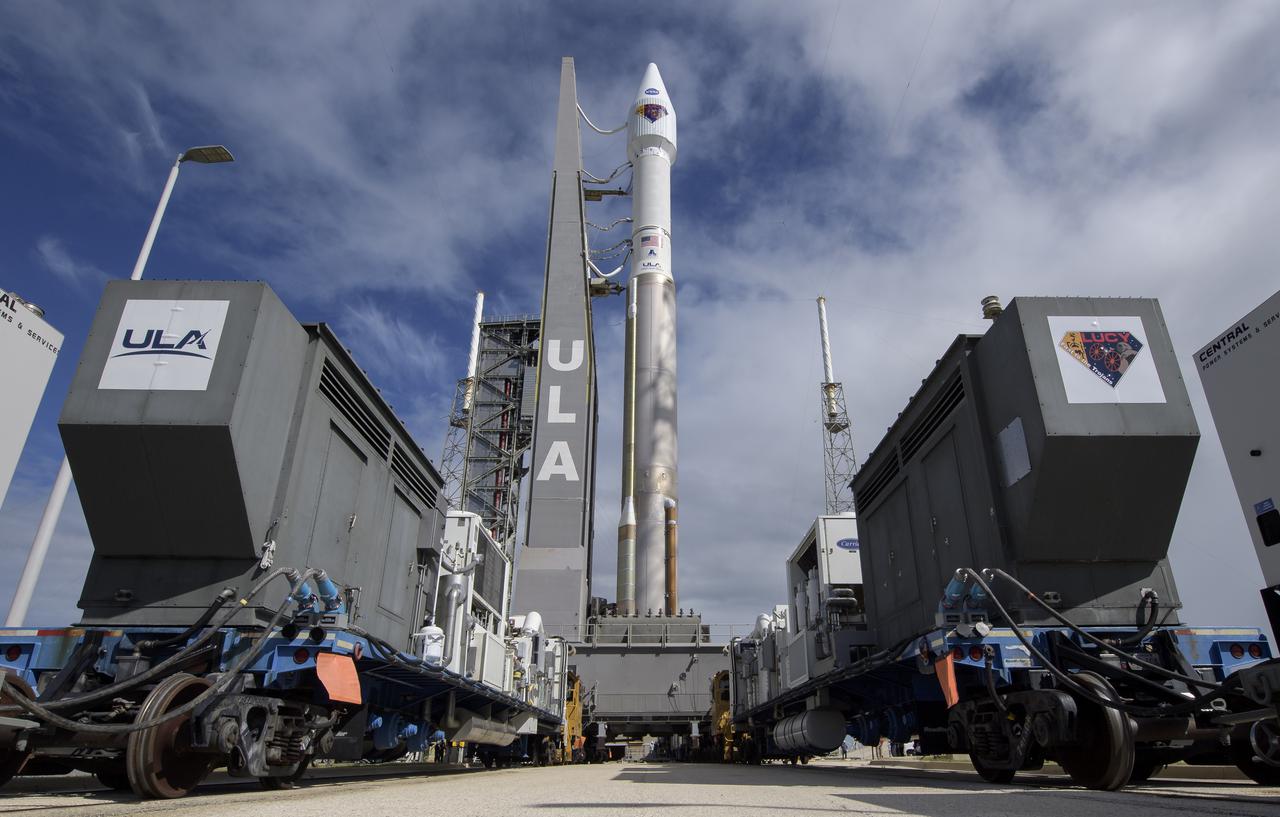

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen as it is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
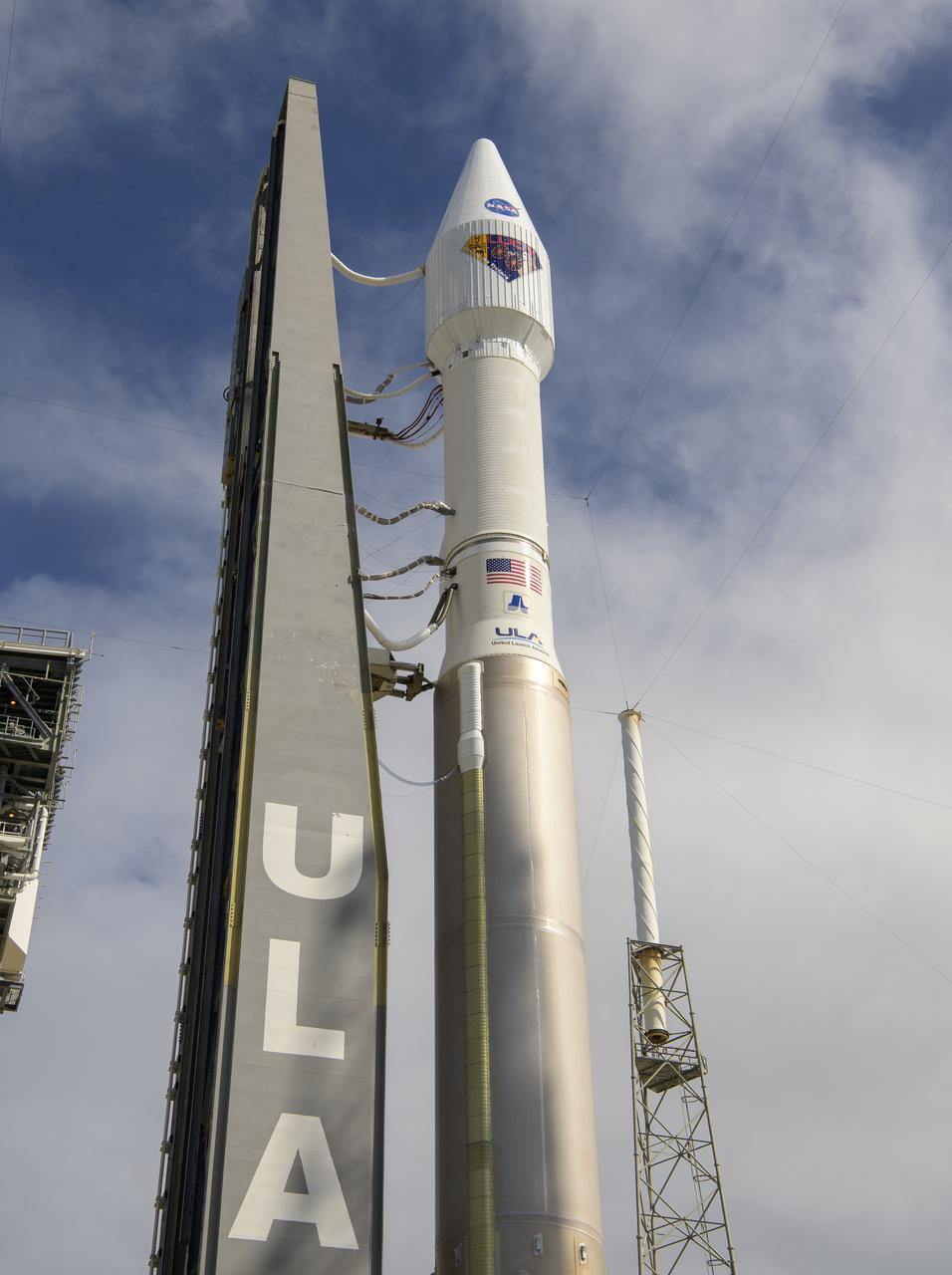

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen as it is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
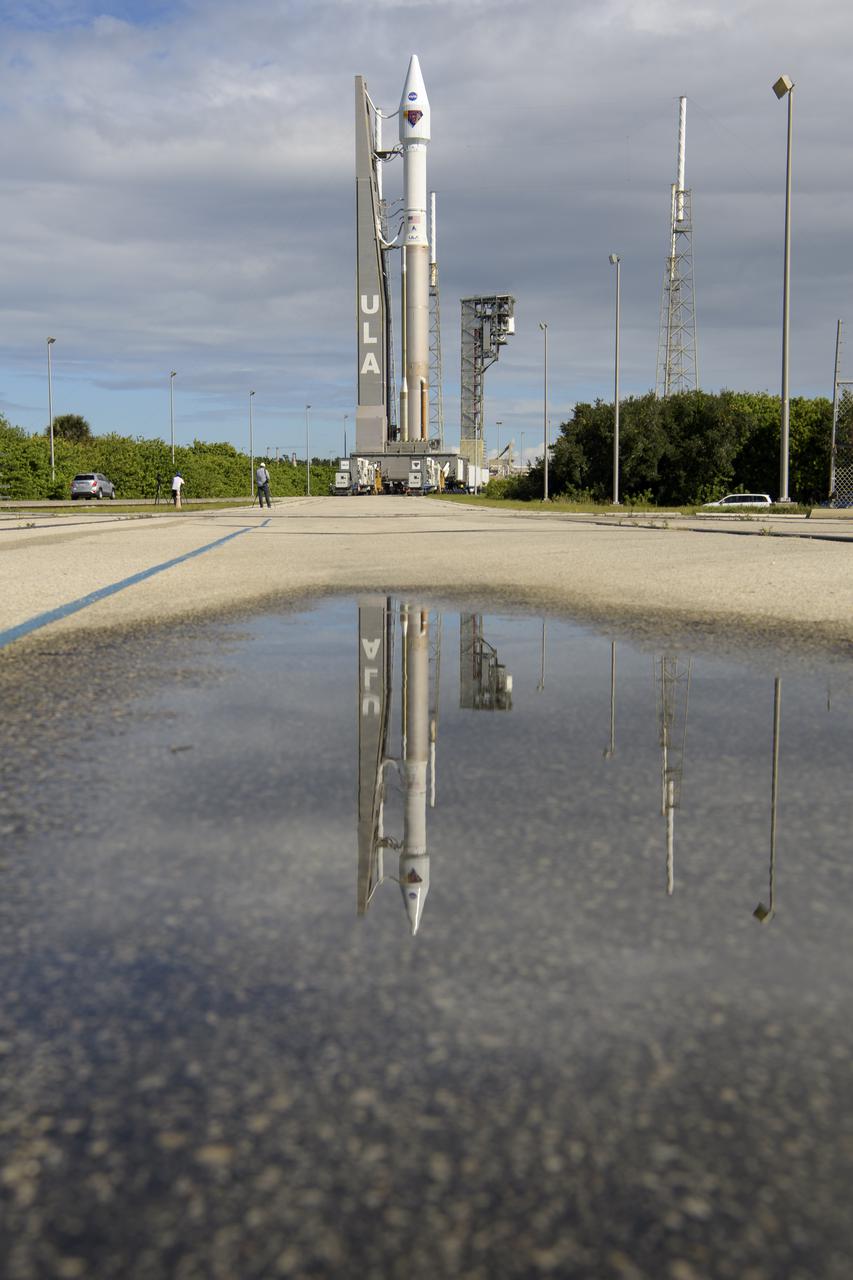

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen as it is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
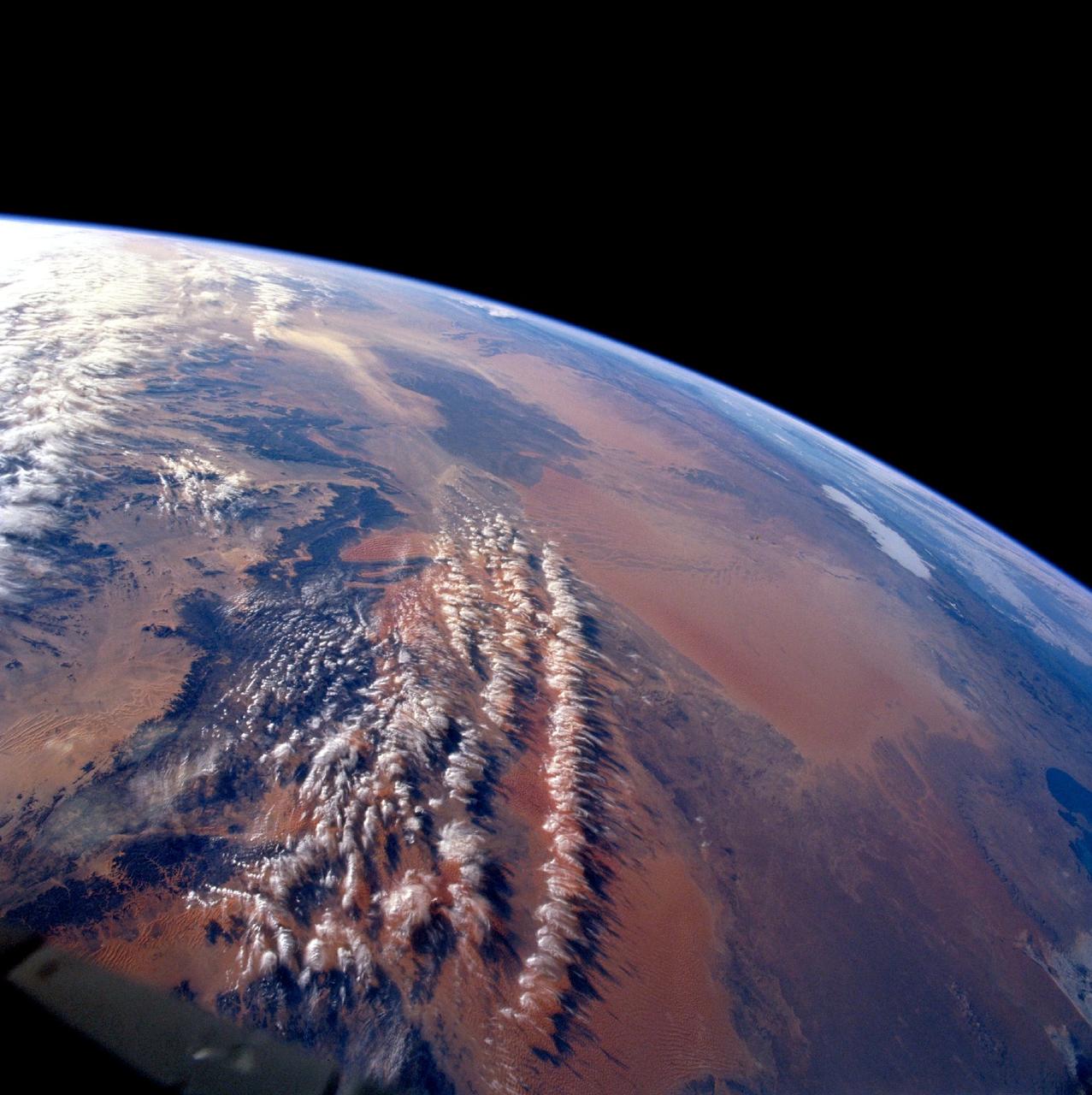

STS103-710-084 (19-27 December 1999)--- One of the astronauts aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery used a handheld 70mm camera to photograph the great sand seas which occupy northern Algeria. They are Grand Erg Oriental (Eastern Sand Sea) and Grand Erg Occidental (Western Sand Sea). Both sand seas occupy depressions that are separated by a north-south rise called Mizab. Ergs are areas of large accumulations of sand that take the form of actively shifting dunes, fossilized dunes, or extensive sand sheets.

A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.
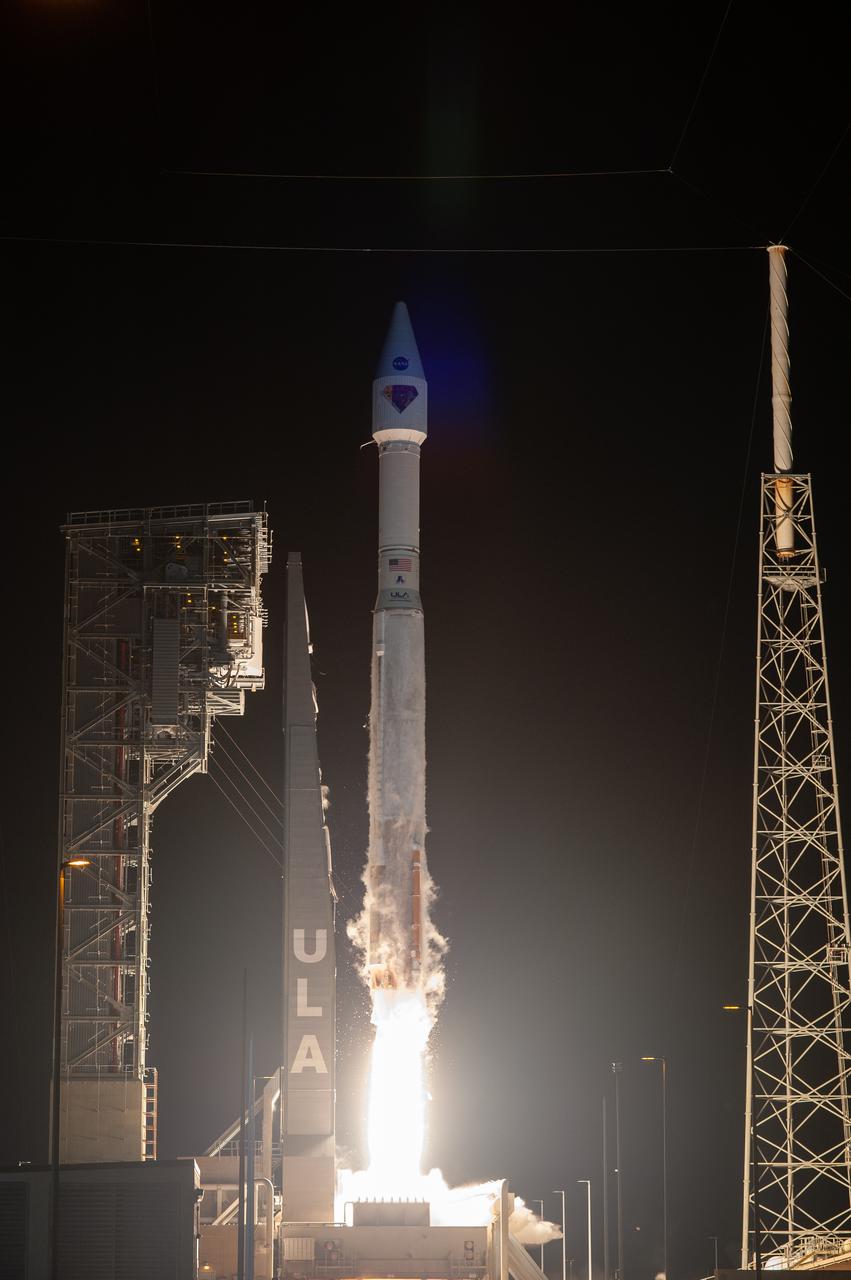

A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.
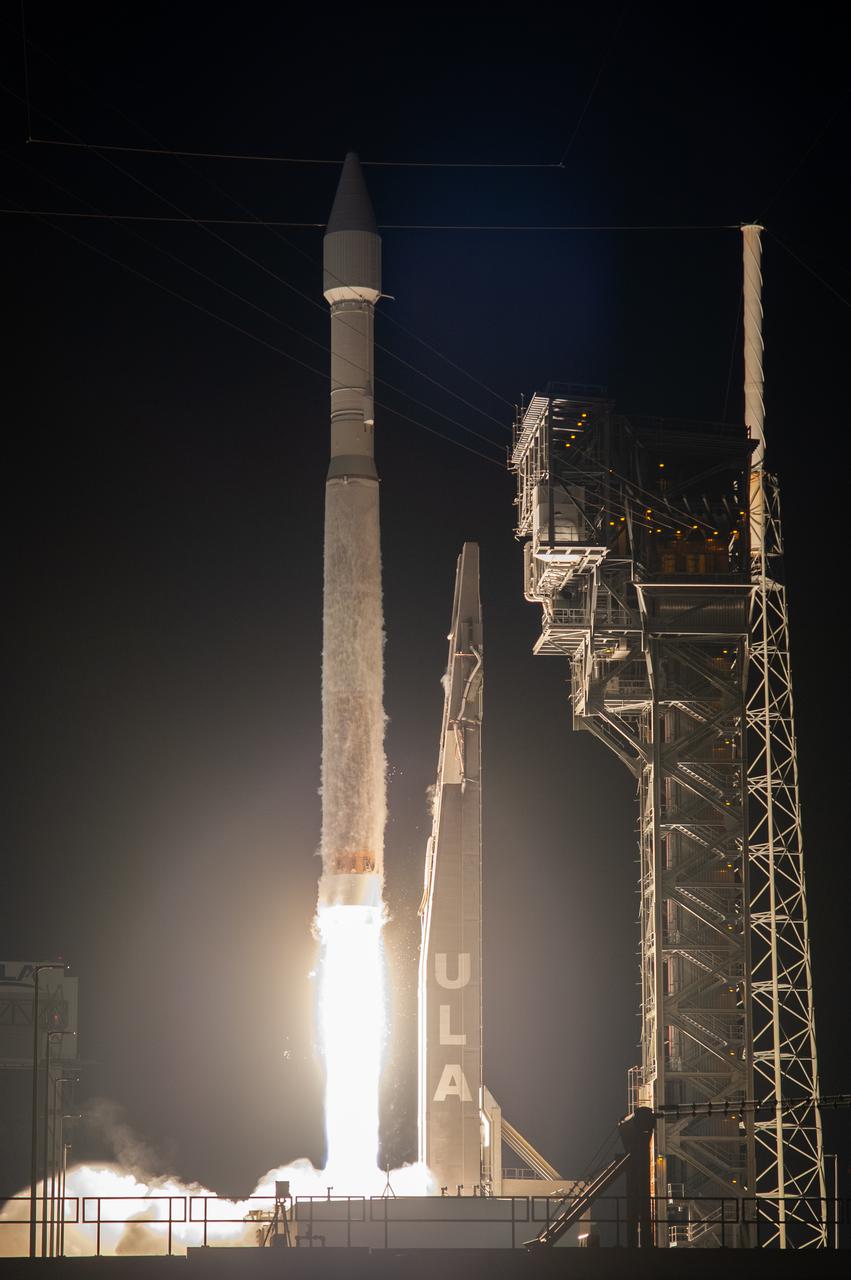

A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket, with NASA’s Lucy spacecraft atop, powers off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida at 5:34 a.m. EDT on Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center. Lucy will embark on a 12-year primary mission to explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, including the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. Named after a fossilized human ancestor whose skeleton provided discoverers insight into humanity’s evolution, the Lucy mission will do much of the same, providing scientists and researchers a look into the origins of our solar system.
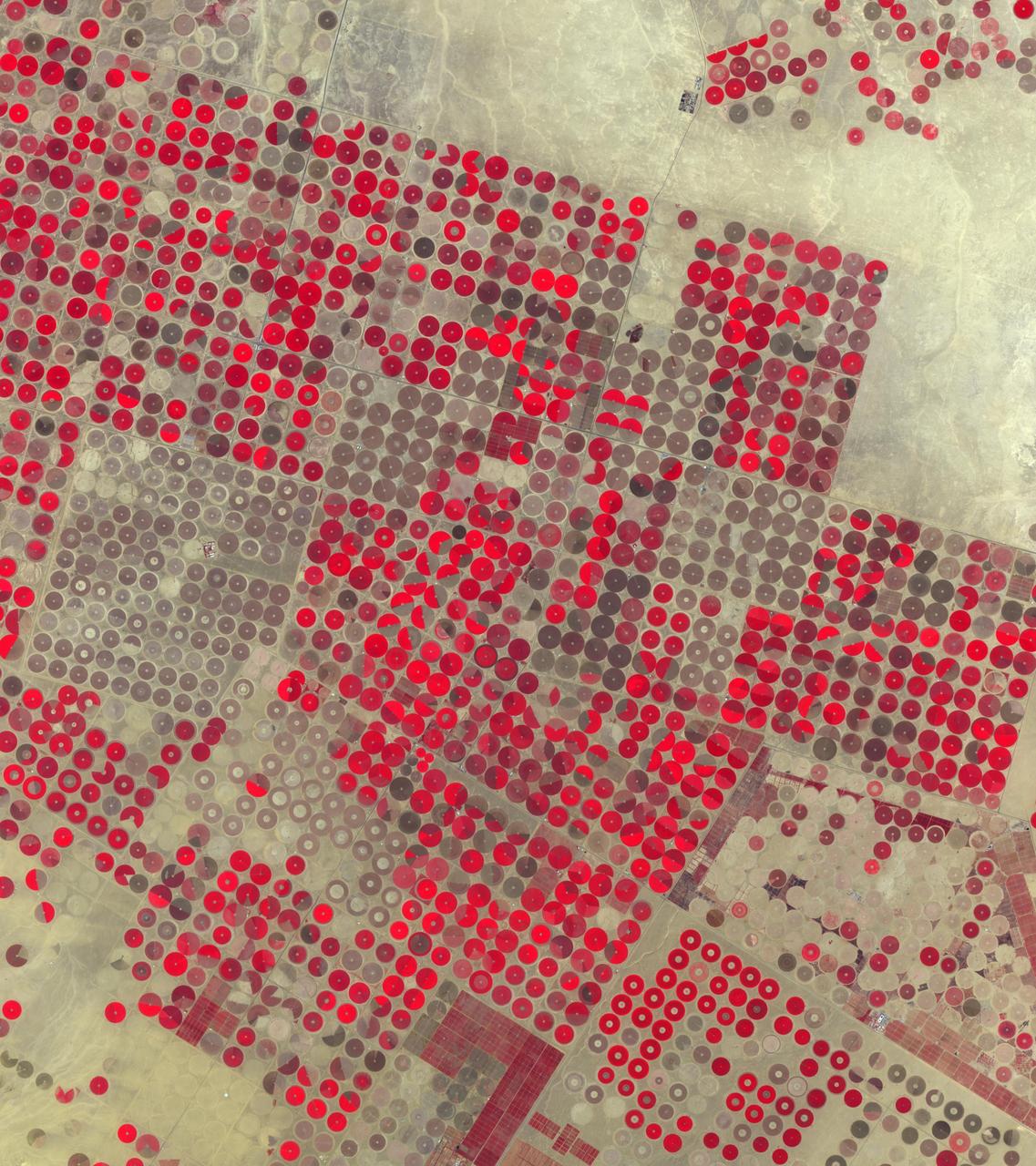

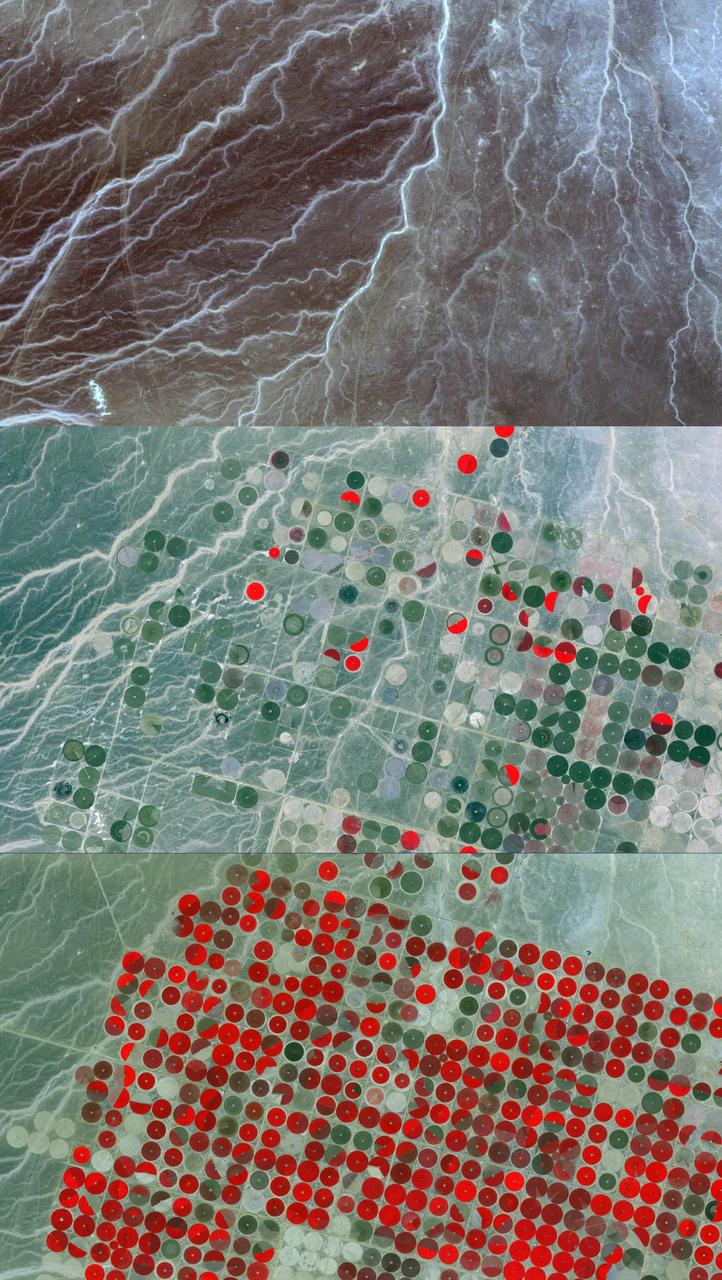
In the Al Jowf Province in northwestern Saudi Arabia, mining of fossil ground water has created an enormous agricultural enterprise, where tens of thousands of date palms and olive trees thrive in a hyper-arid environment. In a short 30-year period, the area has grown from 22 center-pivot irrigated fields to thousands. The Landsat TM image (Figure 1) was acquired March 30, 1989; the ASTER image on February 17, 2020. The images cover an area of 33.2 by 49 km, and are located at 30.1 degrees north, 38.3 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23955