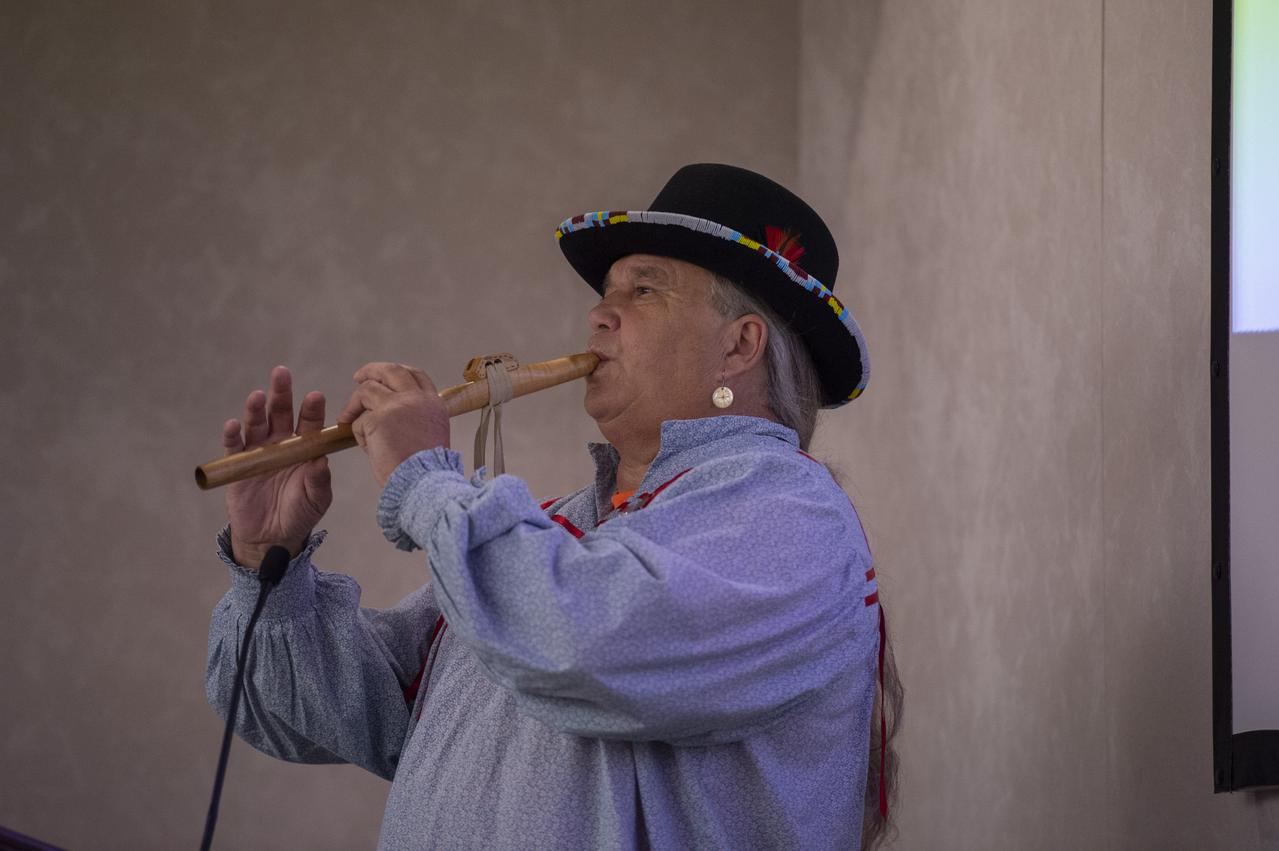

JIMMY YELLOWHORSE, FROM DECATUR, ALABAMA, PLAYS A HAND-CARVED FLUTE DURING THE NATIVE AMERICAN HERITAGE MONTH PROGRAM NOV. 13 AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER. YELLOWHORSE CRAFTED THE FLUTE HIMSELF FROM CEDAR, WALNUT AND MAHOGANY, USING TRADITIONAL CHEROKEE TECHNIQUES. THE ANNUAL OBSERVANCE, COORDINATED BY MARSHALL'S OFFICE OF DIVERSITY AND EQUAL OPPORTUNITY, HONORS THE CULTURE AND CONTRIBUTIONS OF NATIVE AMERICANS THROUGH STORYTELLING AND ETHNIC FOOD SAMPLINGS.
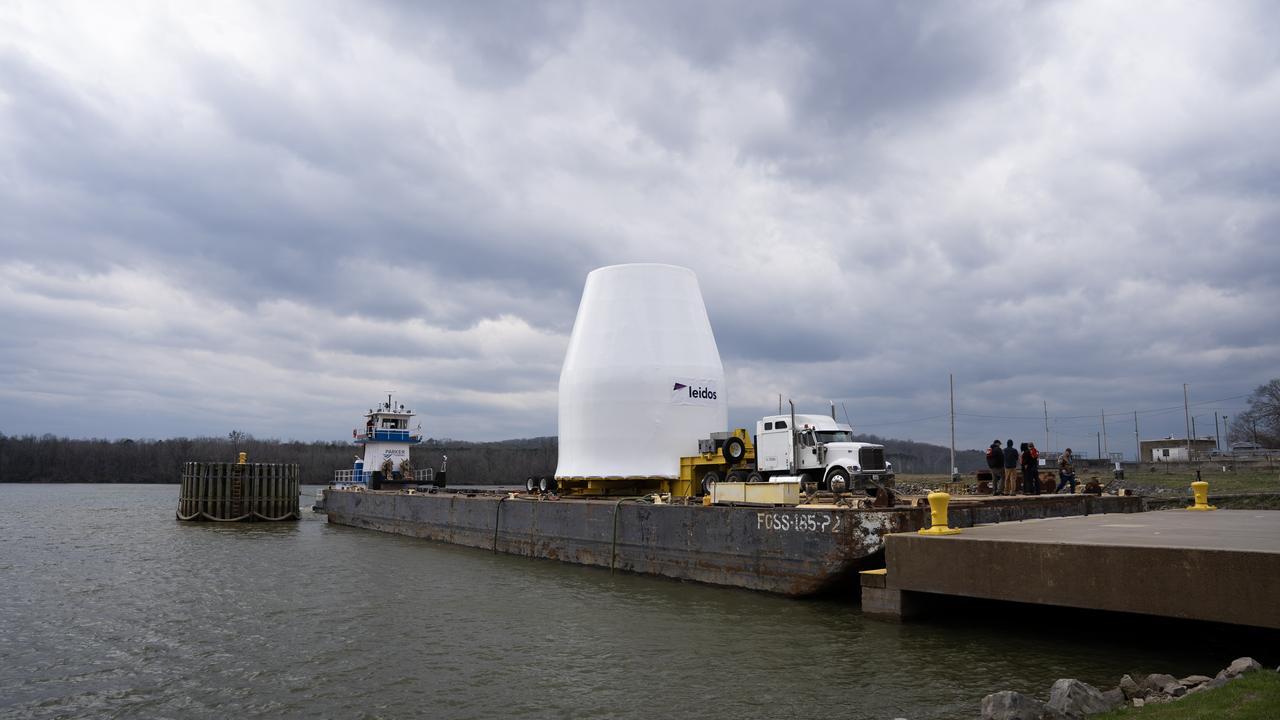

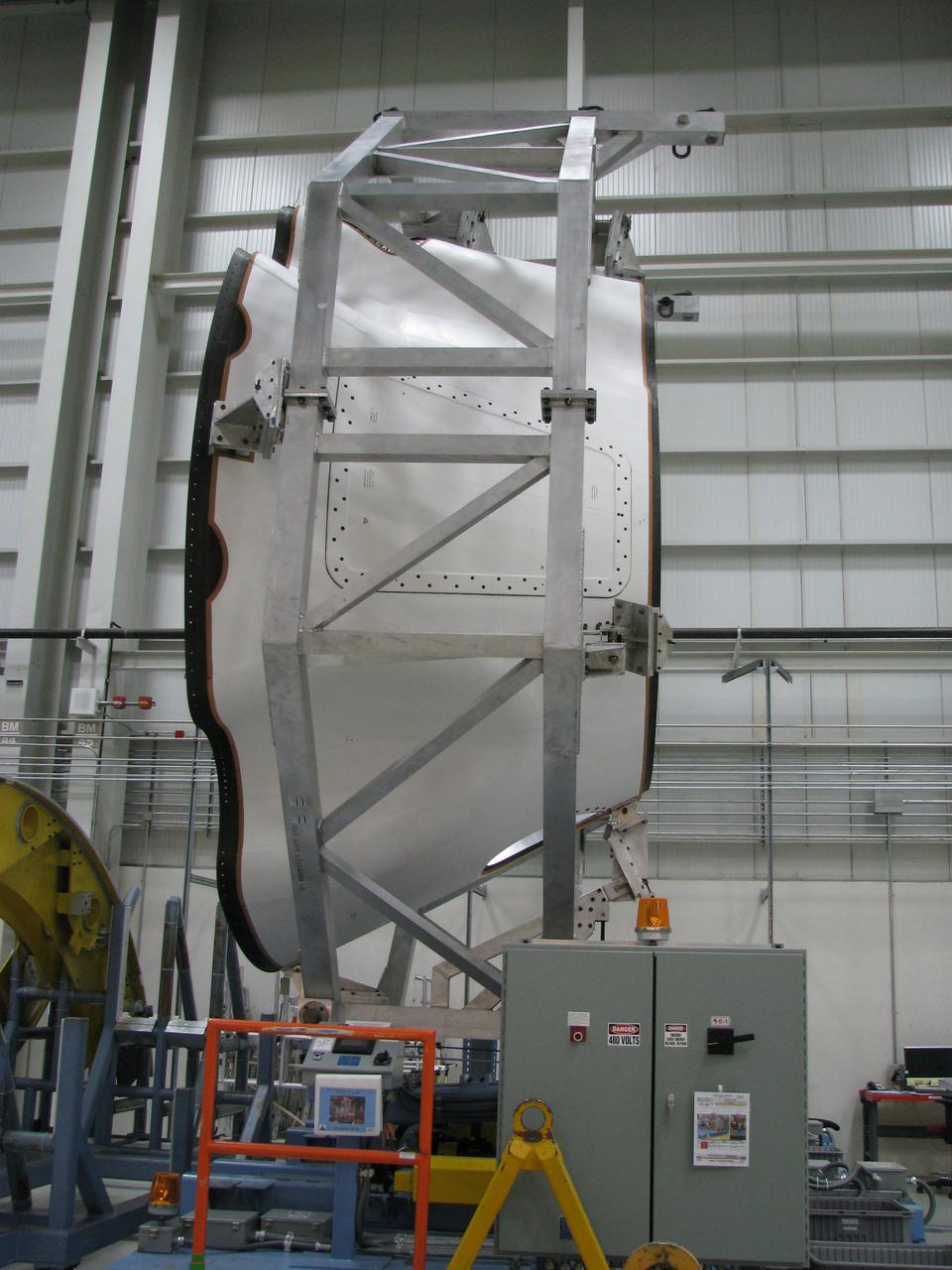
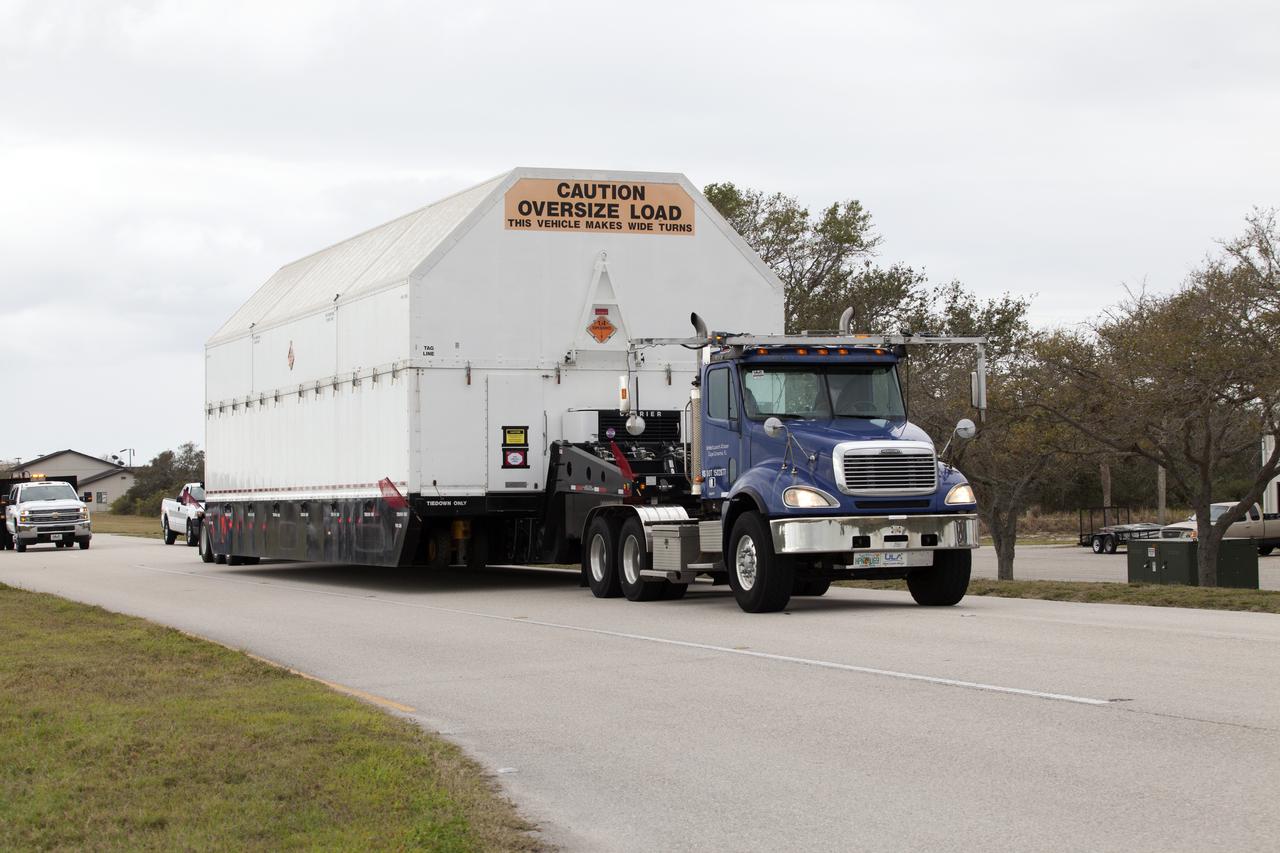
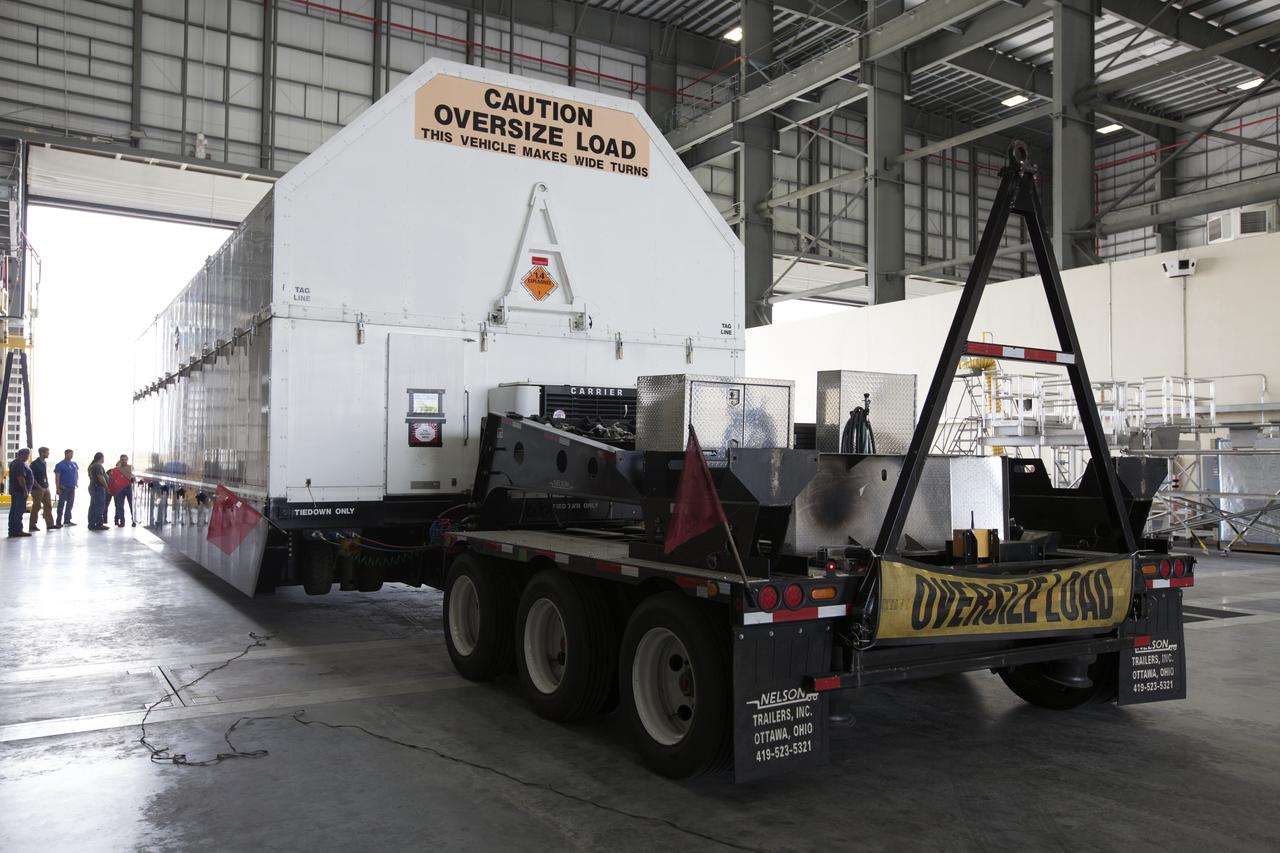
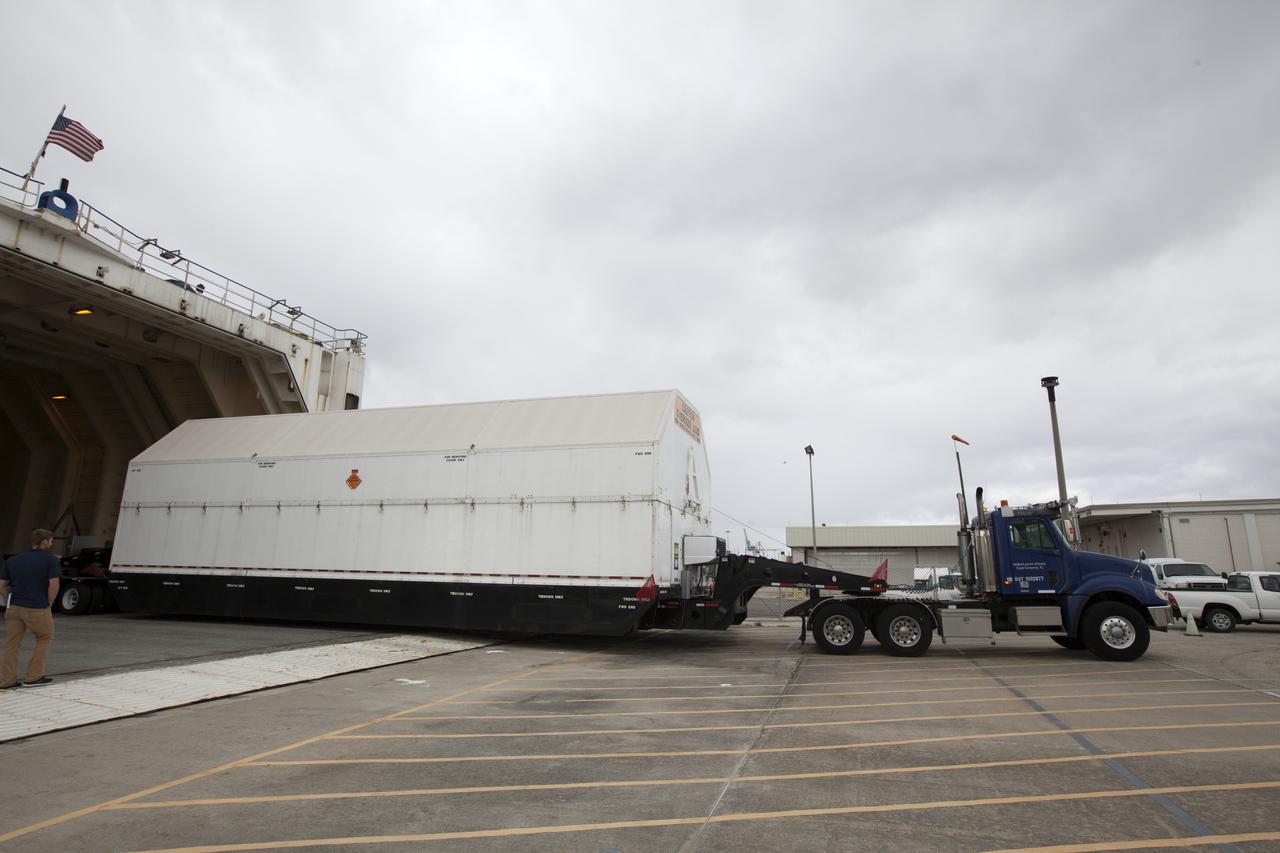
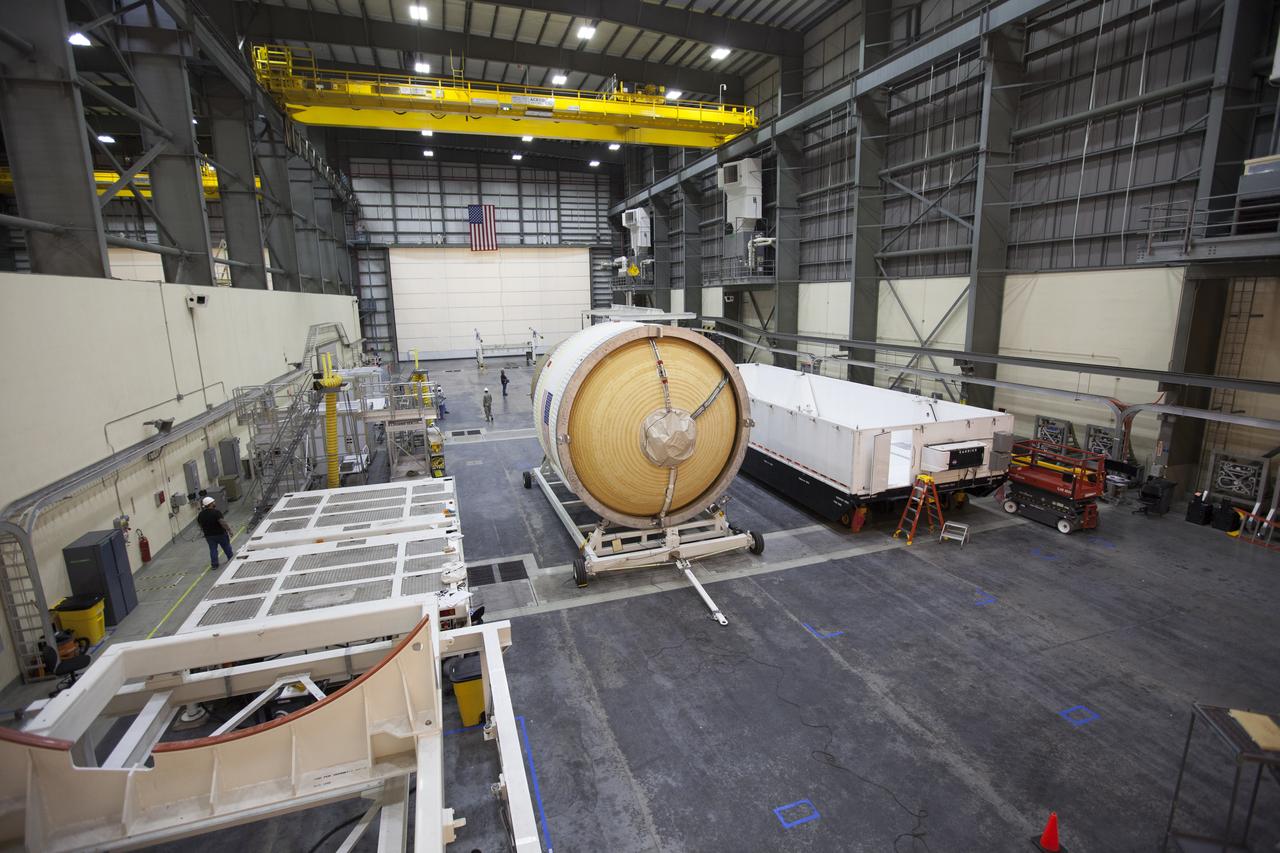
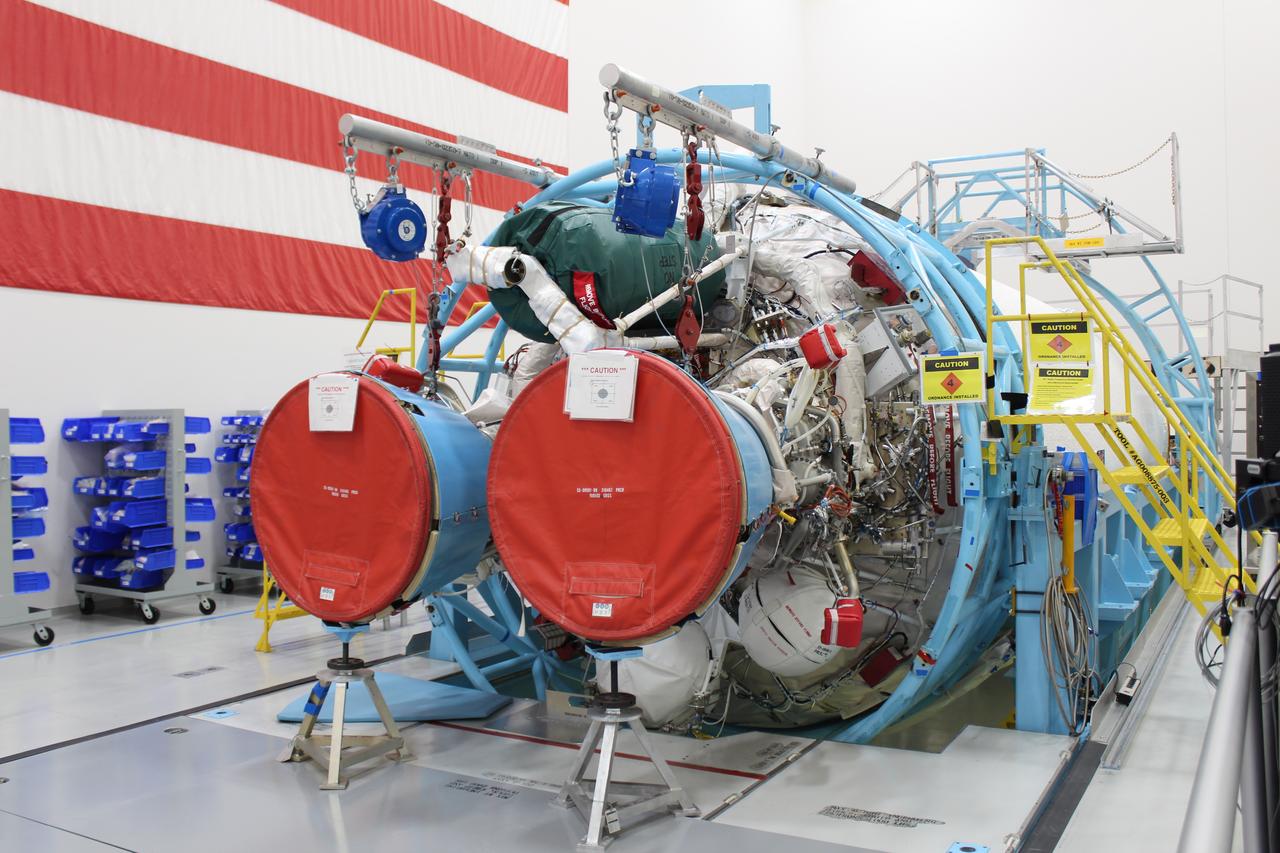
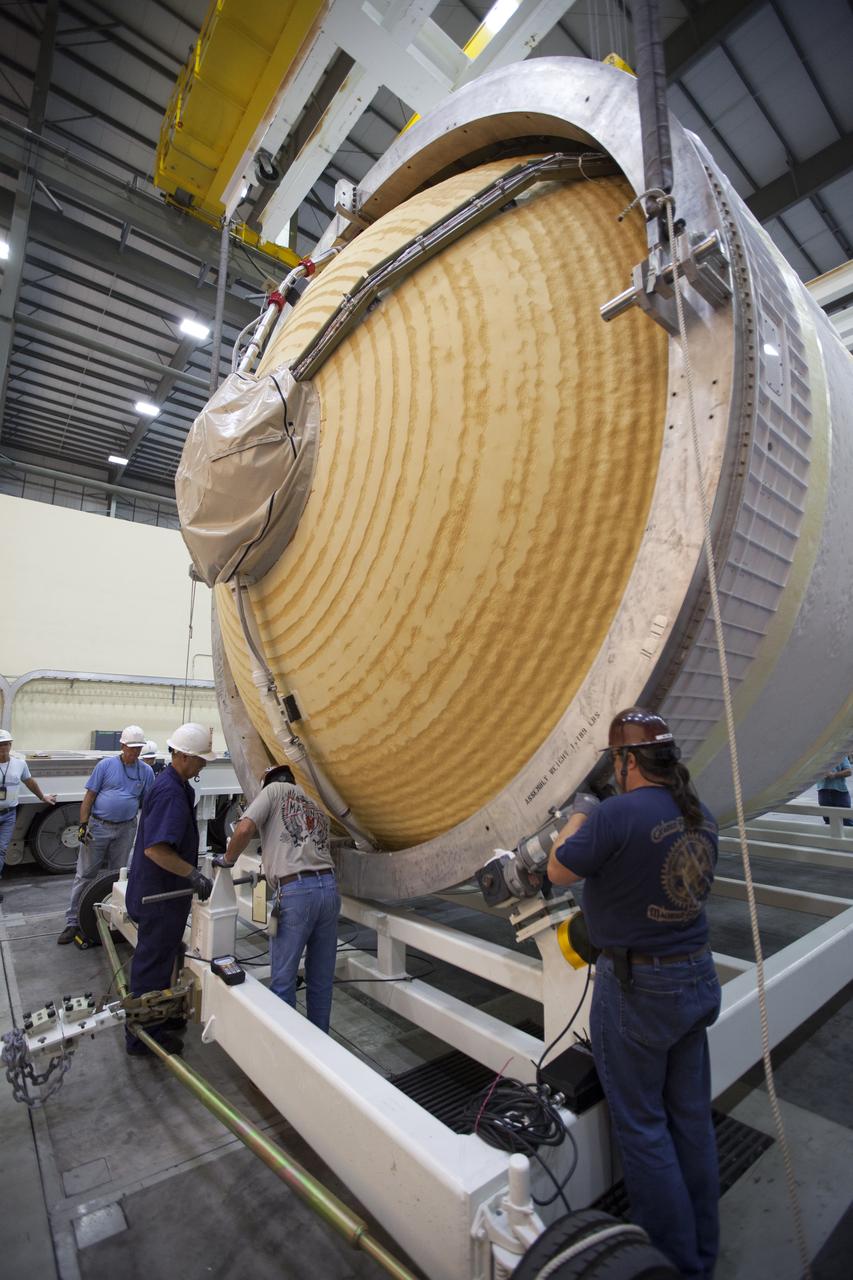
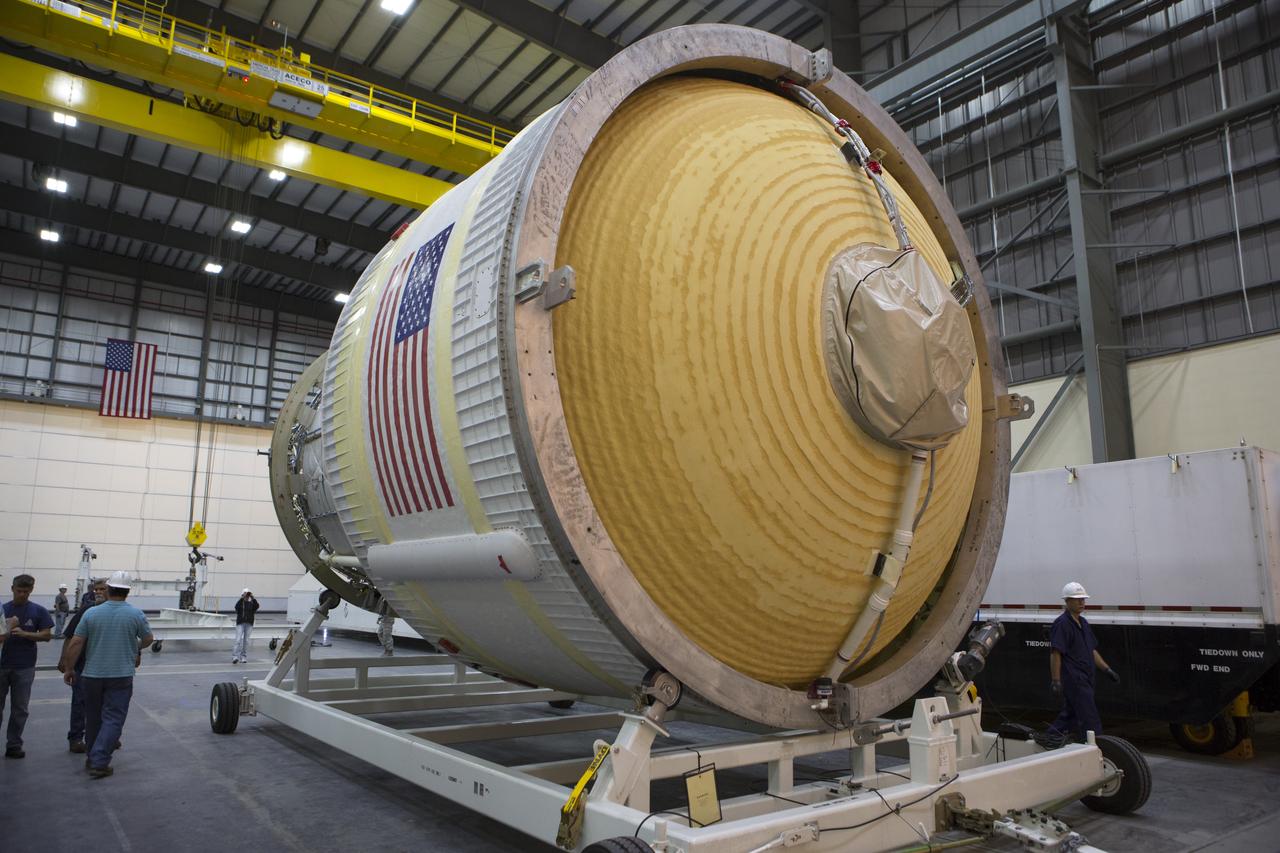
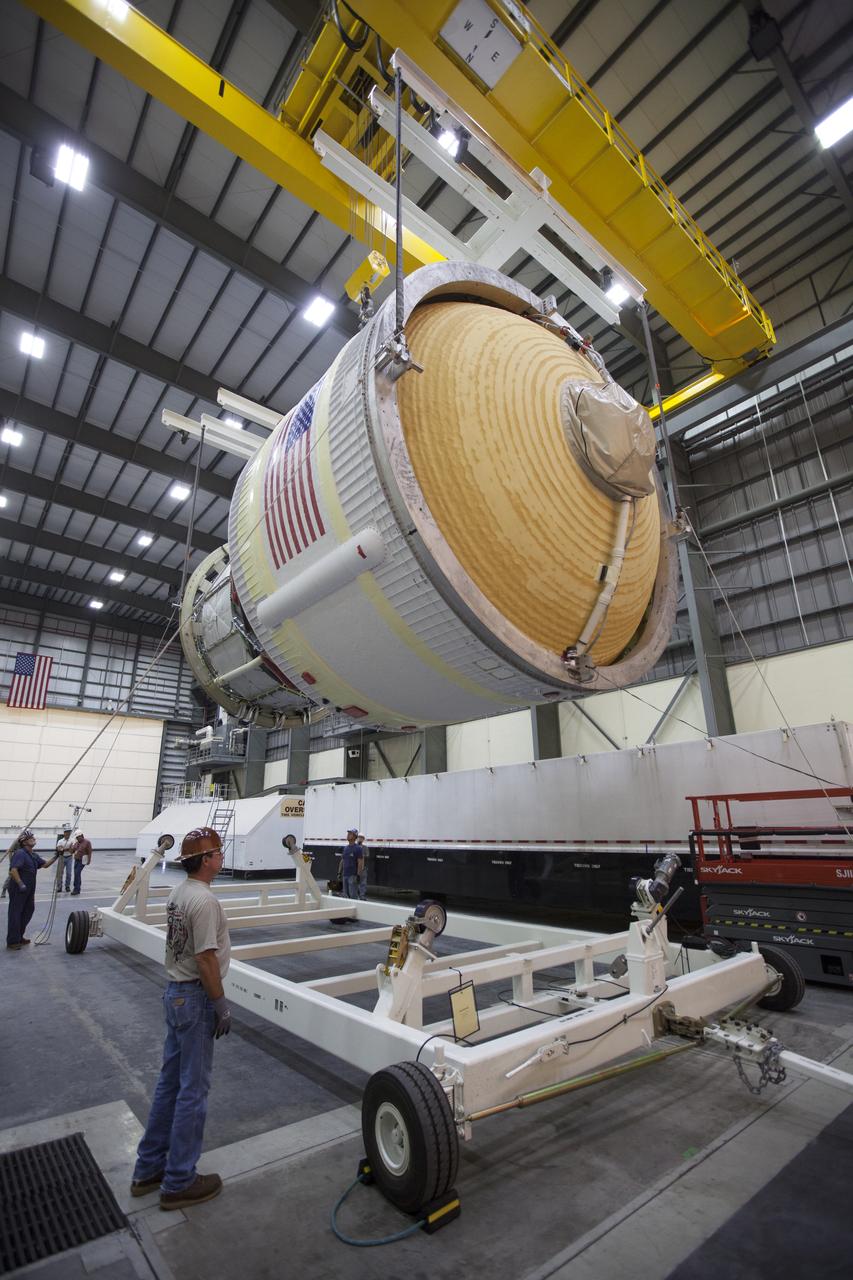
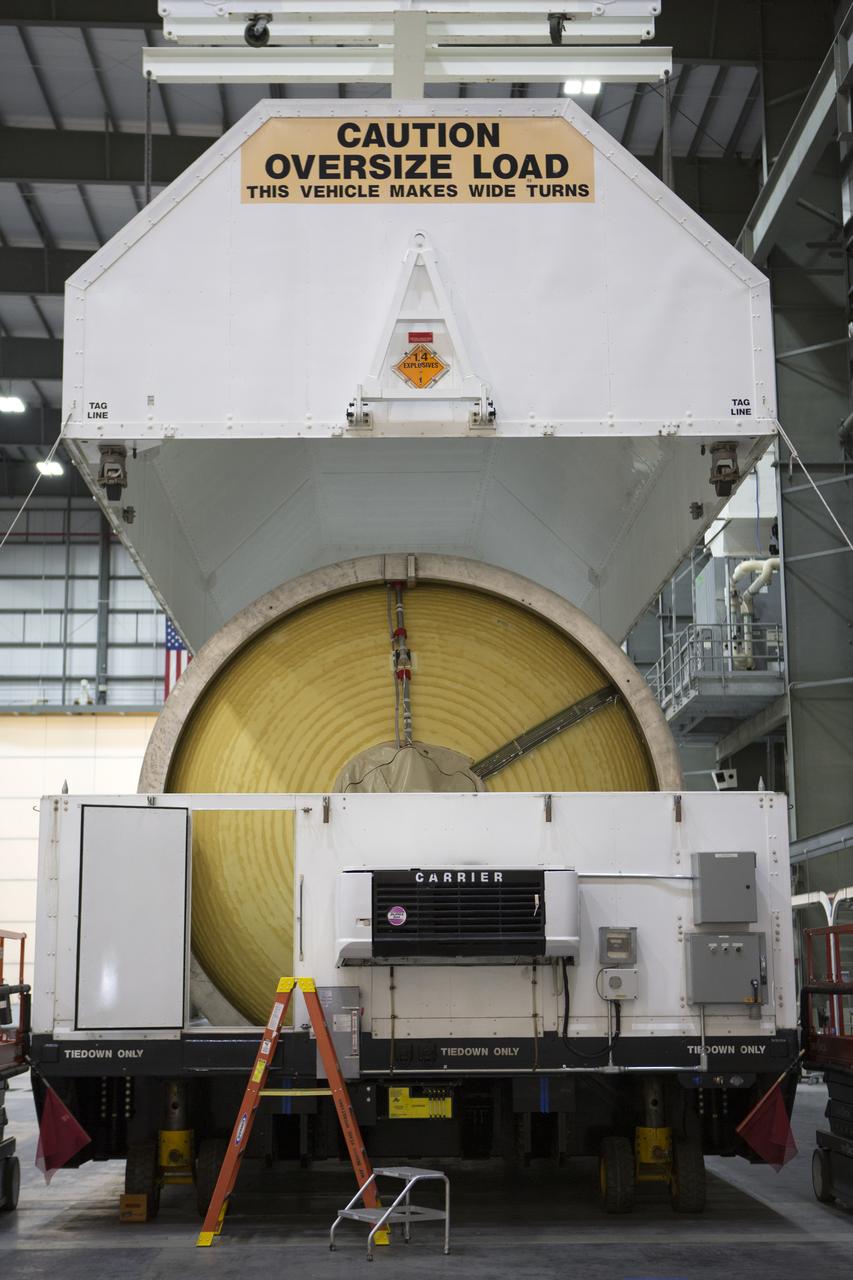
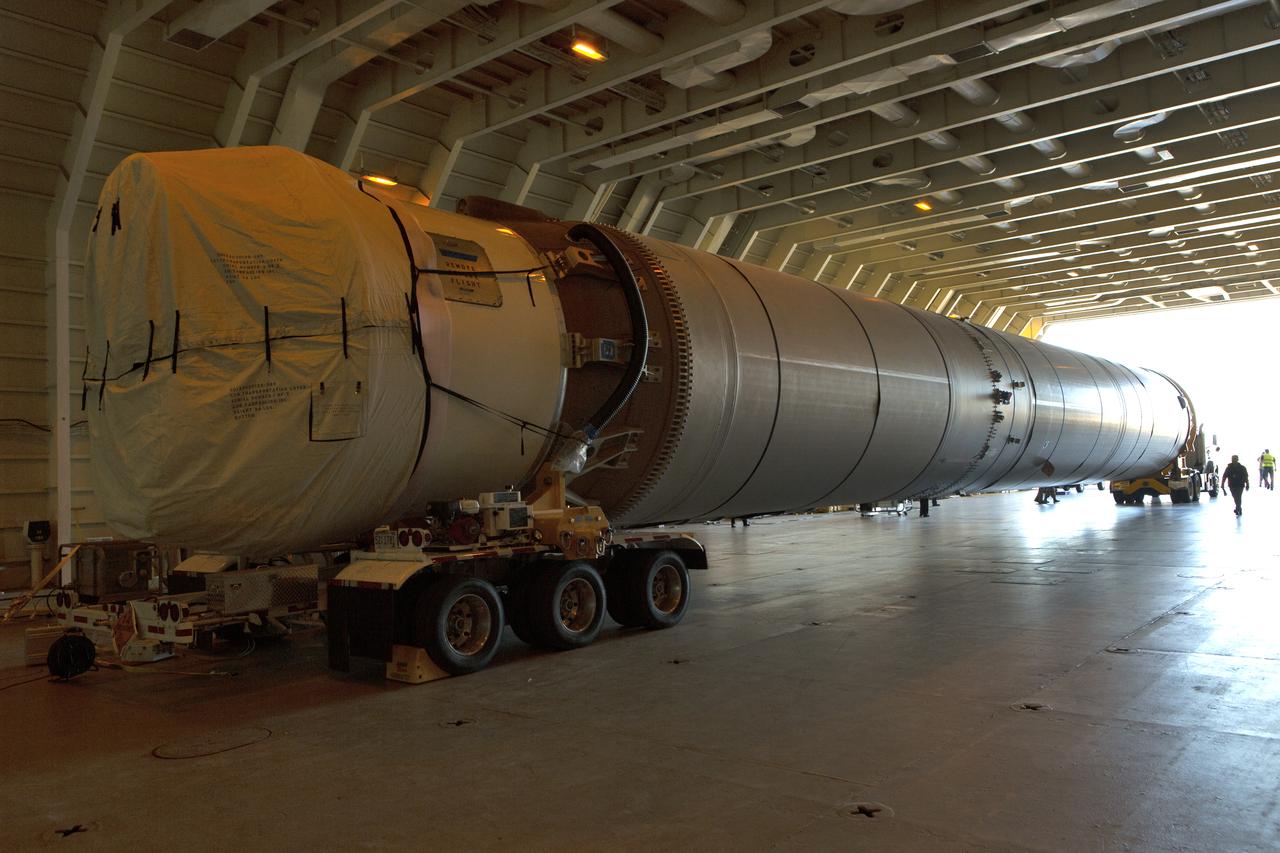
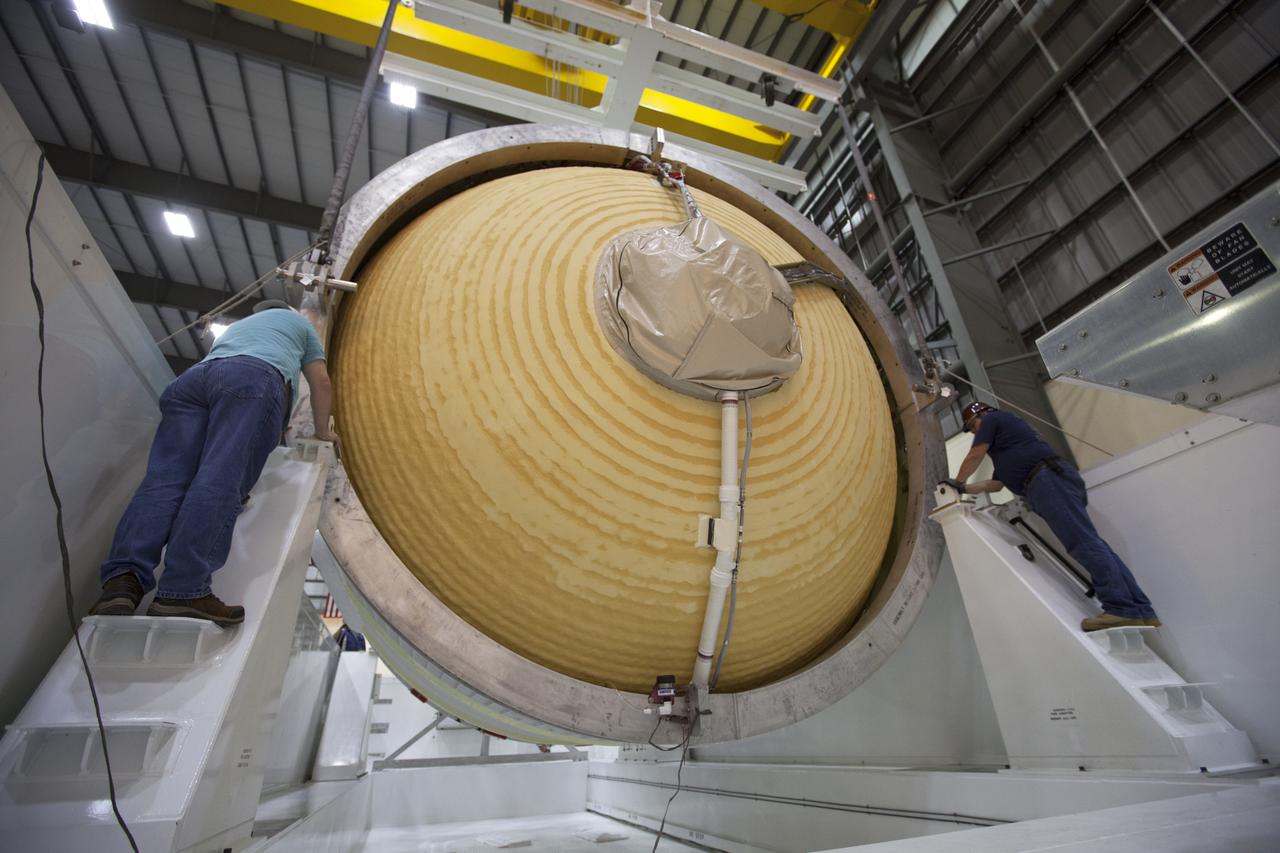
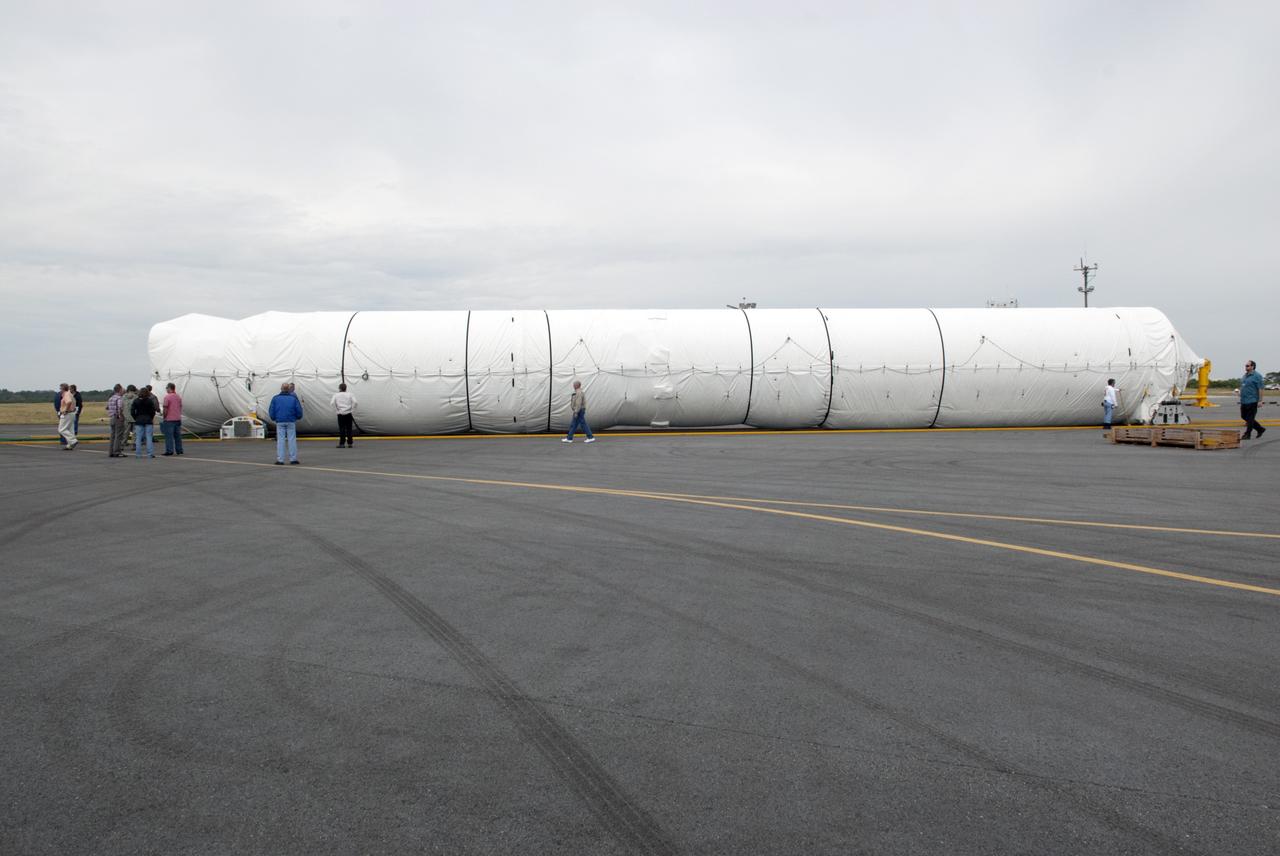
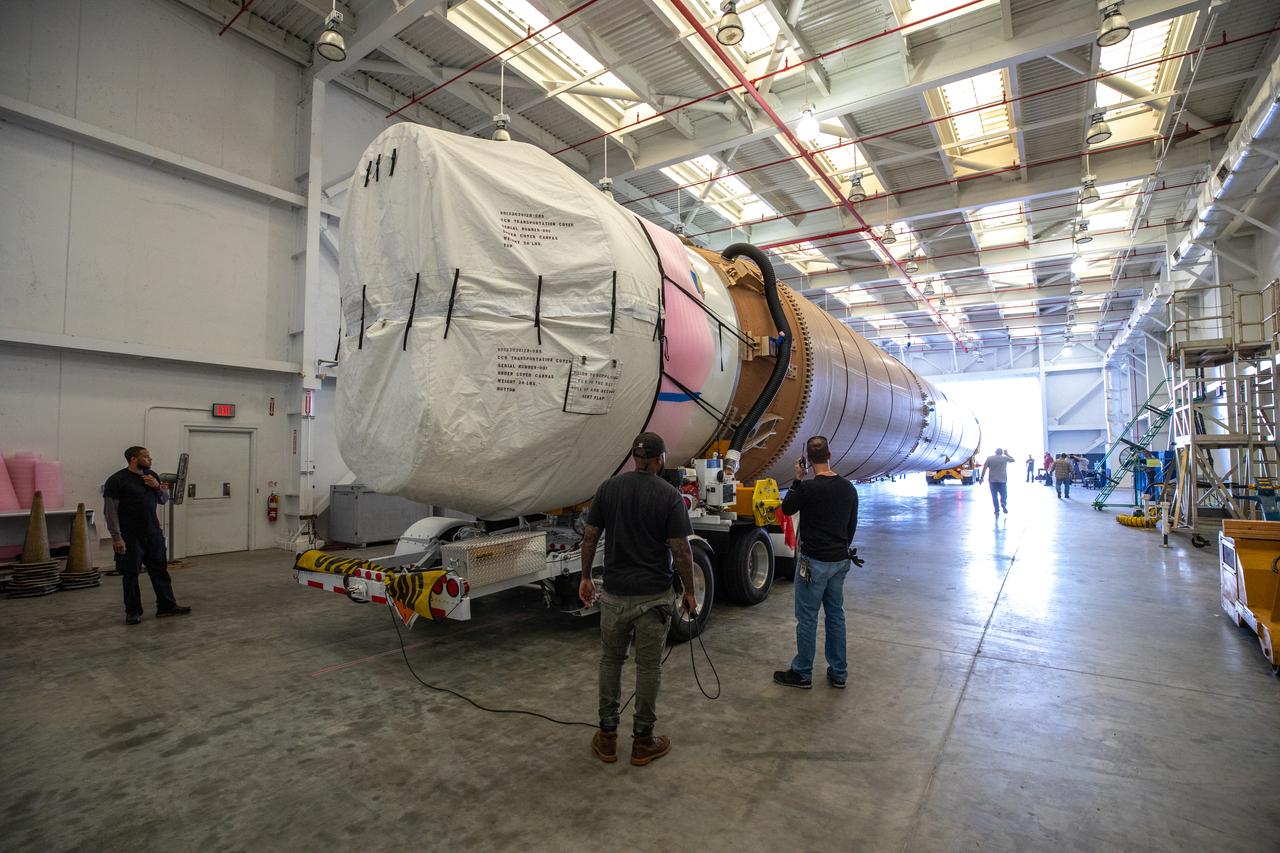
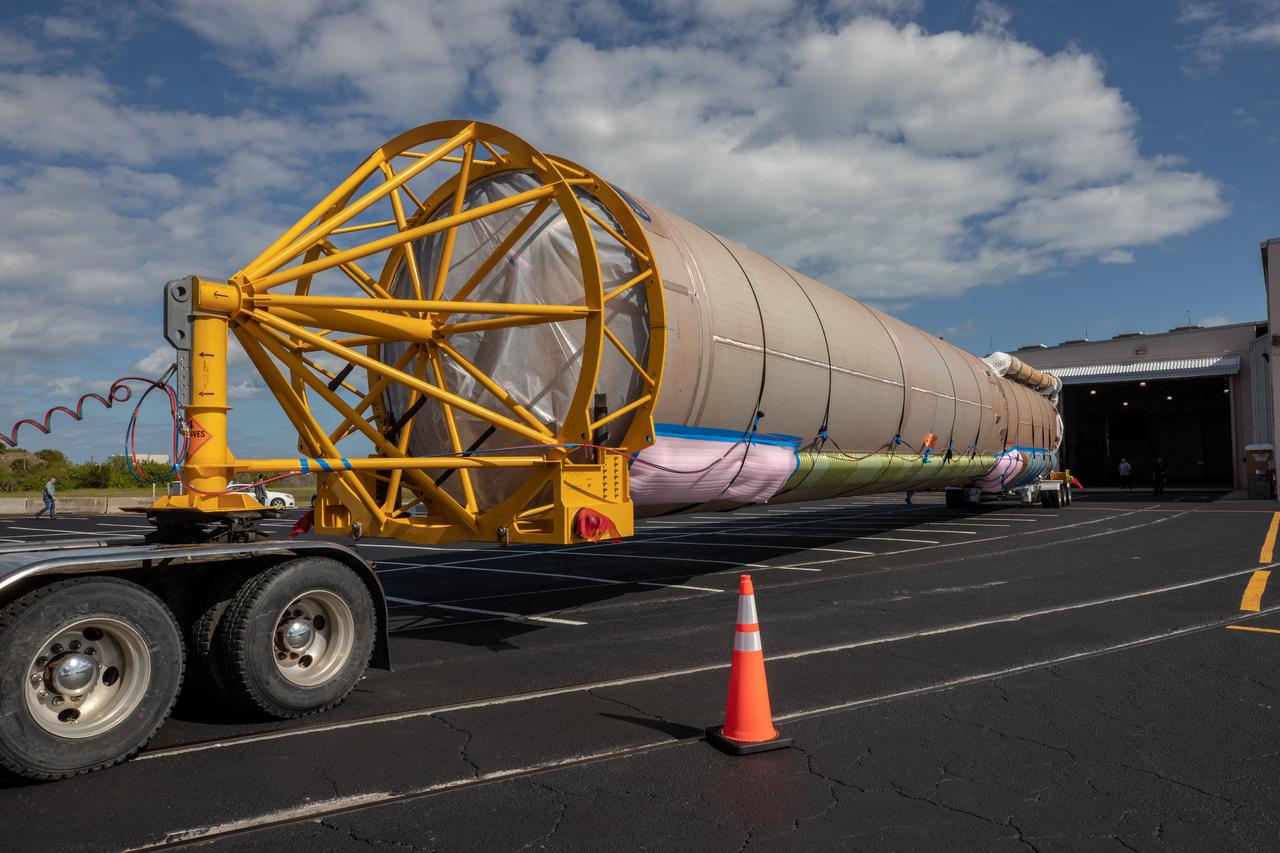
These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
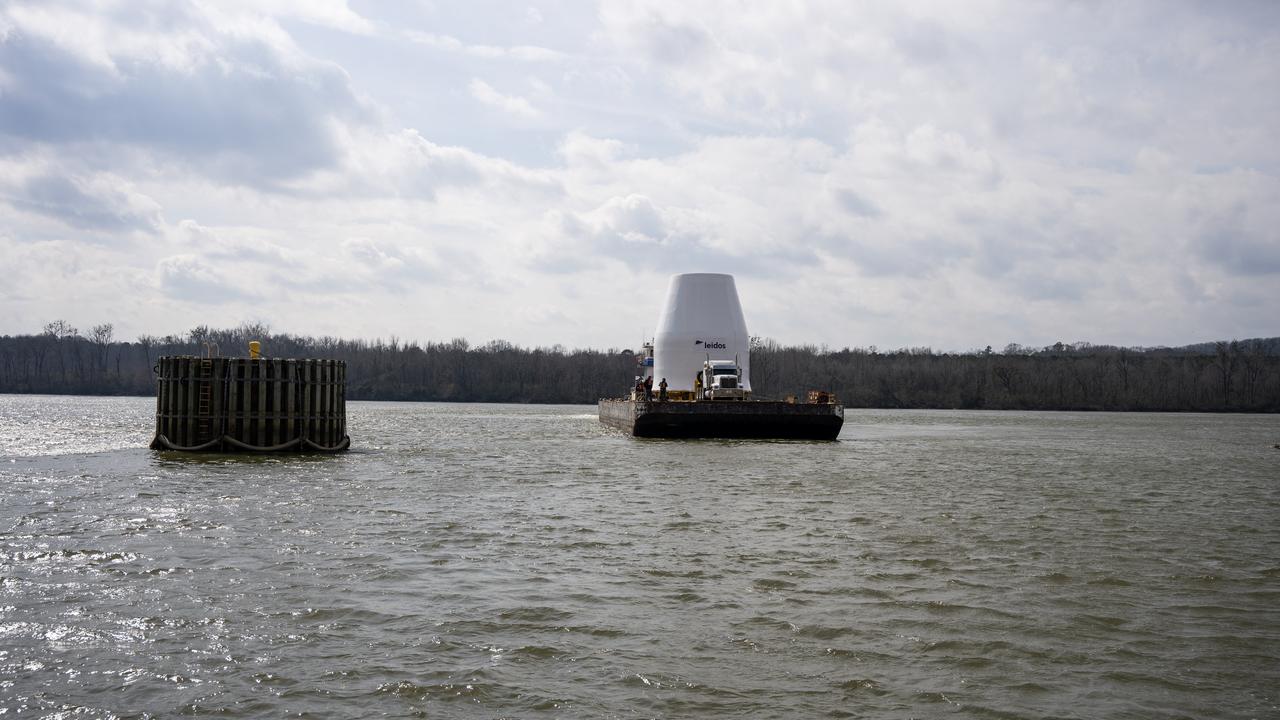

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
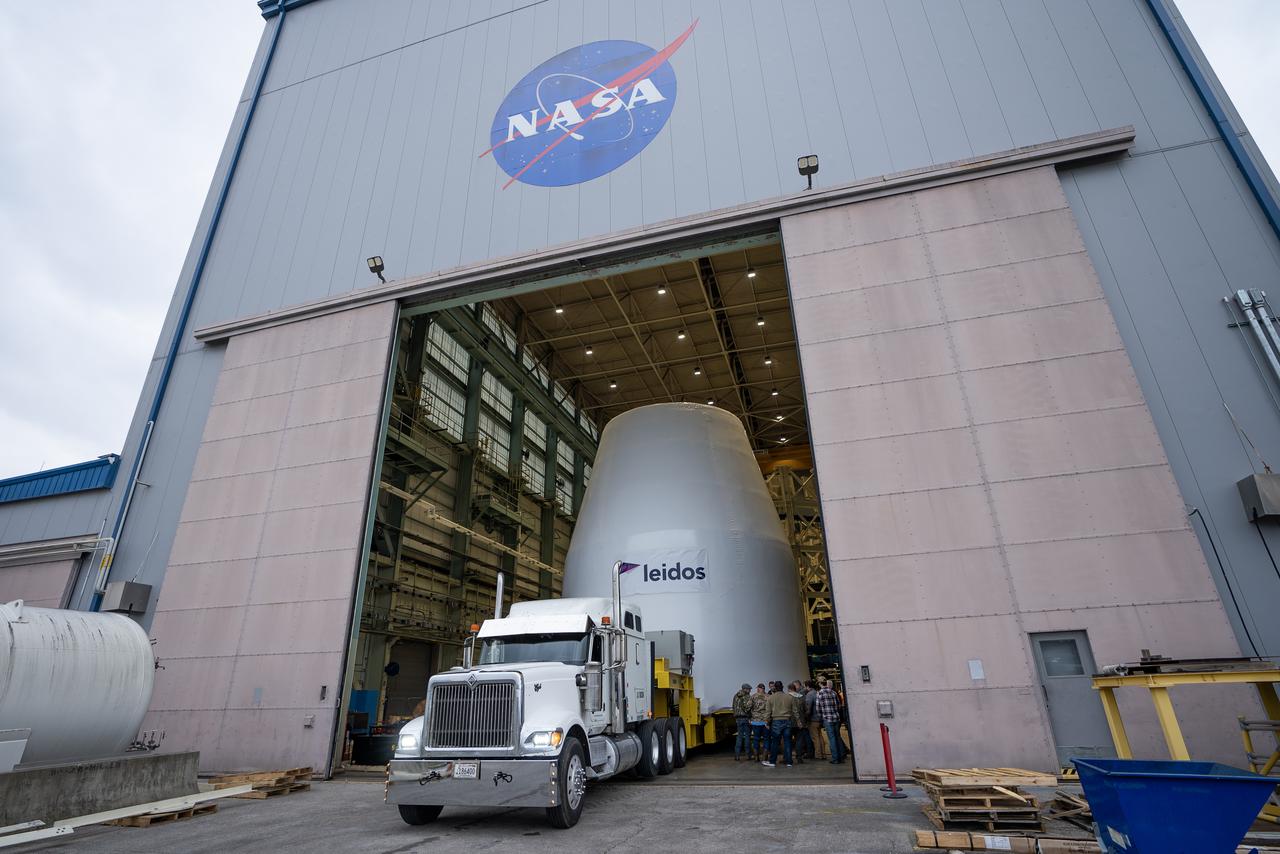

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
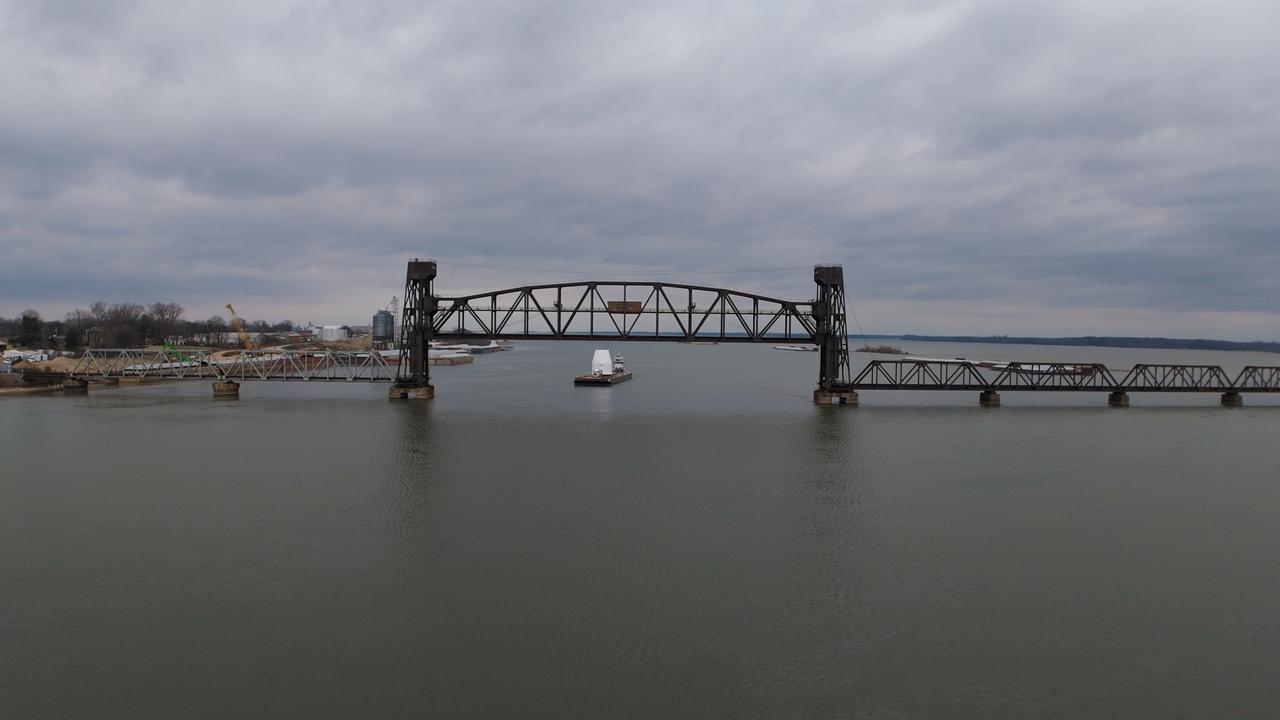

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
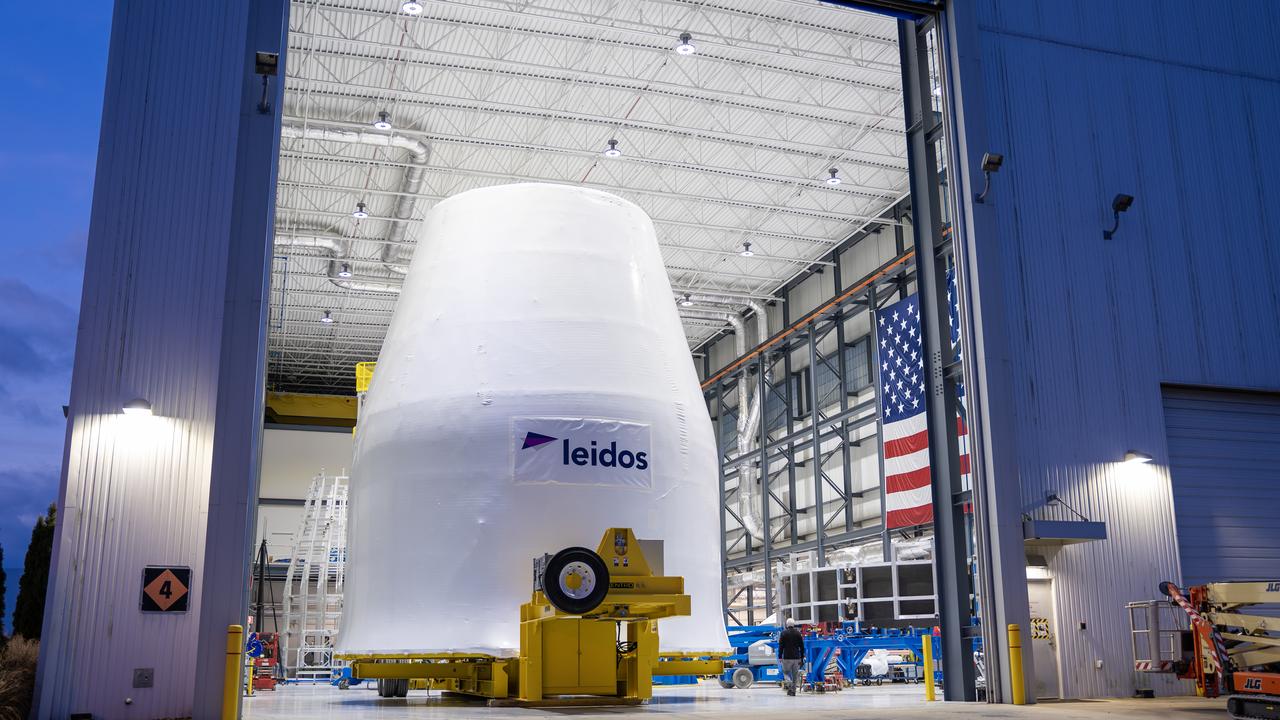

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
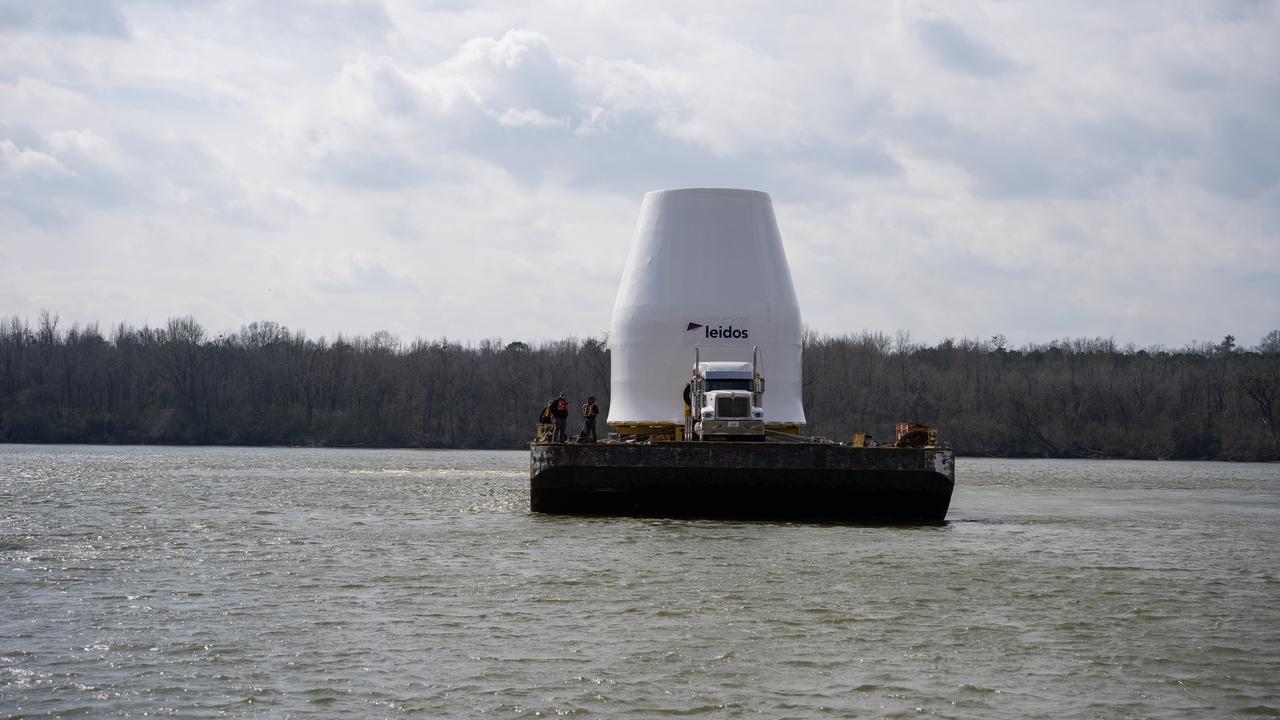

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
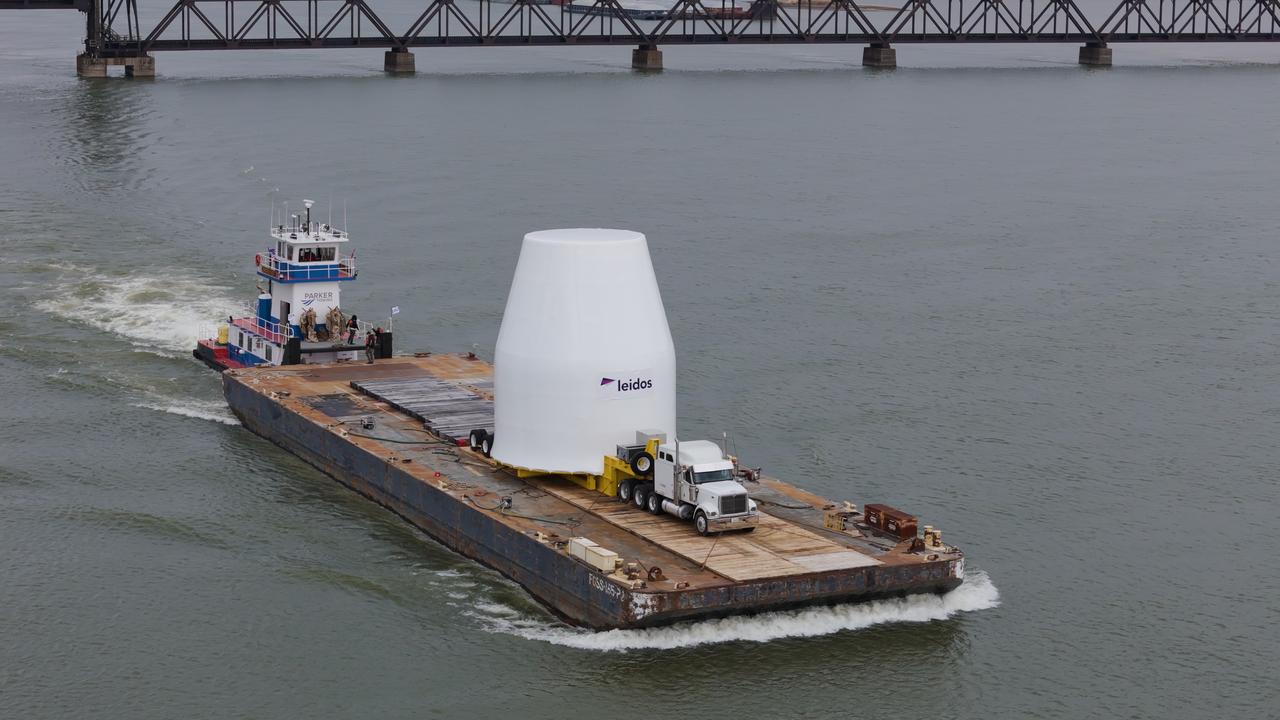

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
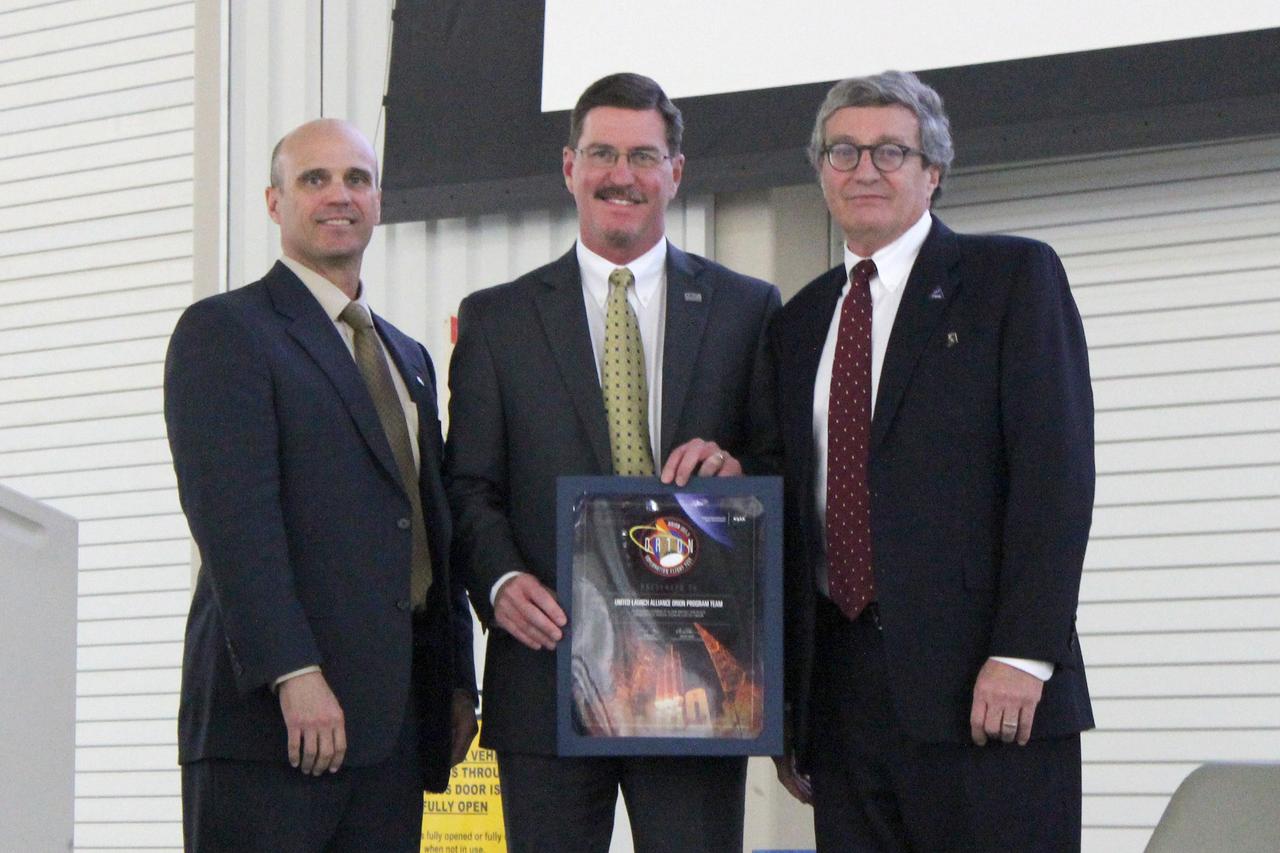

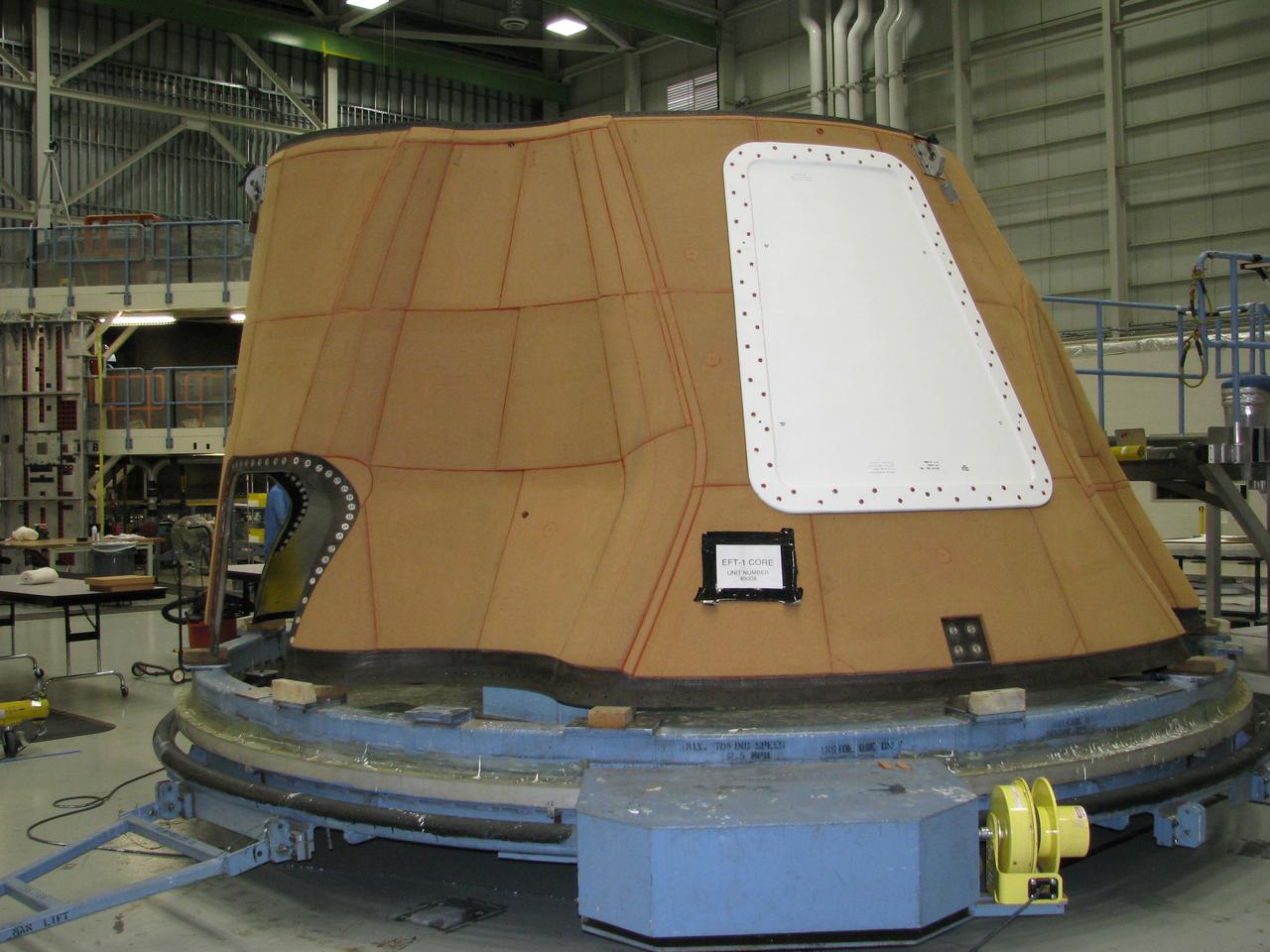
The Orion team recognizes the contributions to Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) by United Launch Alliance in Decatur, Alabama on March 18, 2015. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Orion team recognizes the contributions to Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) by United Launch Alliance in Decatur, Alabama on March 18, 2015. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
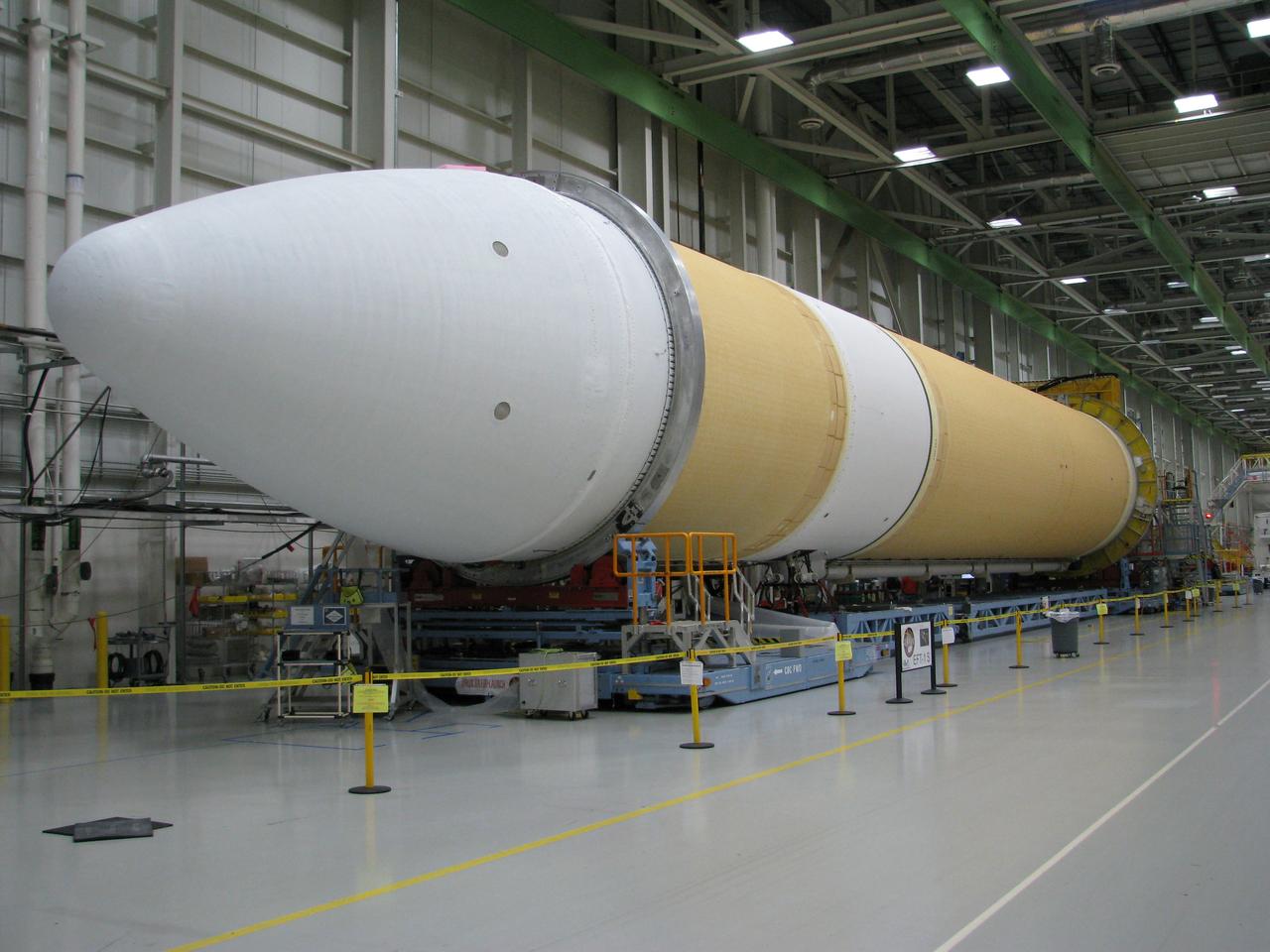

The Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle used to launch Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled at the United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, AL on Dec. 11, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
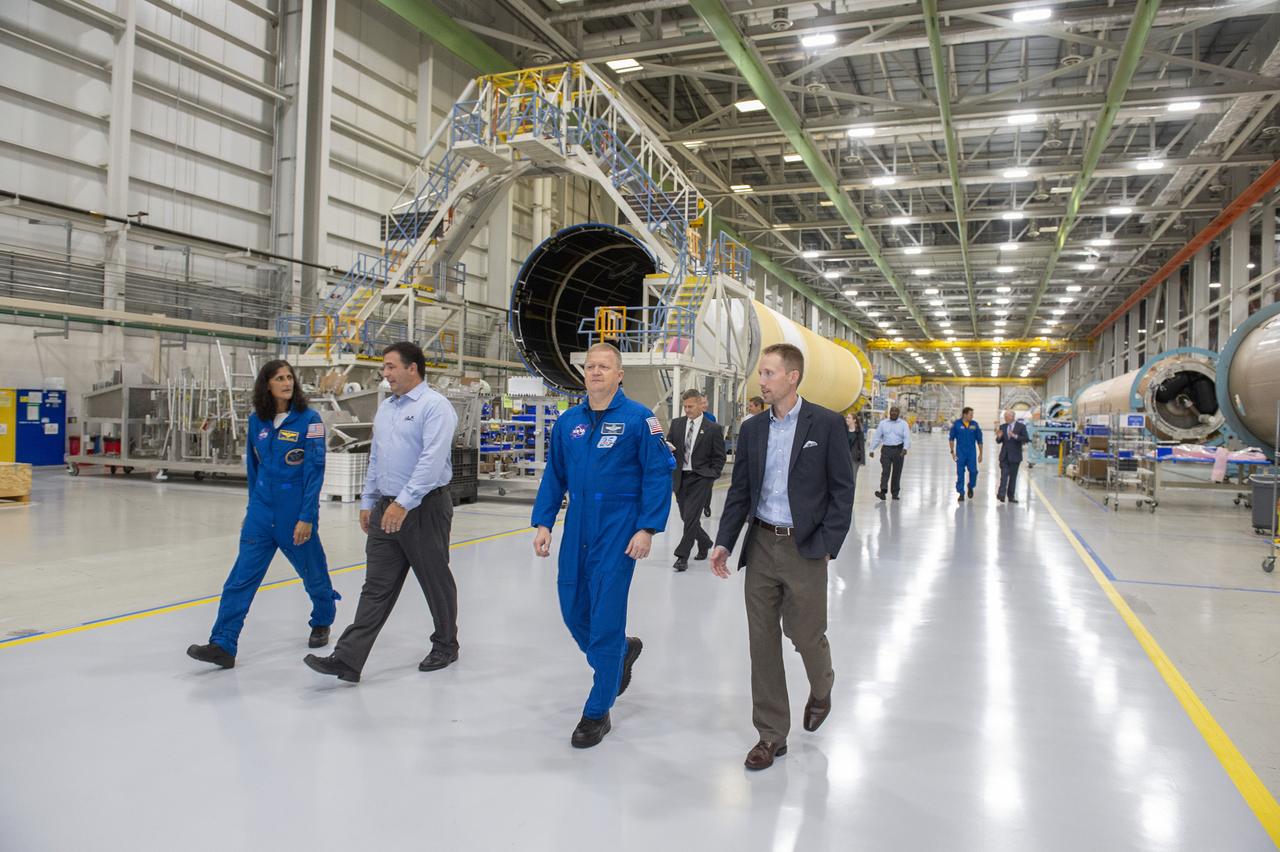

Commercial Crew astronauts toured the United Launch Alliance factory in Decatur, Alabama, on July 17, 2018. They viewed hardware to be used for upcoming commercial crew missions. At far left is Suni Williams, second from right is Eric Boe. Behind them, at right, is Josh Cassada.
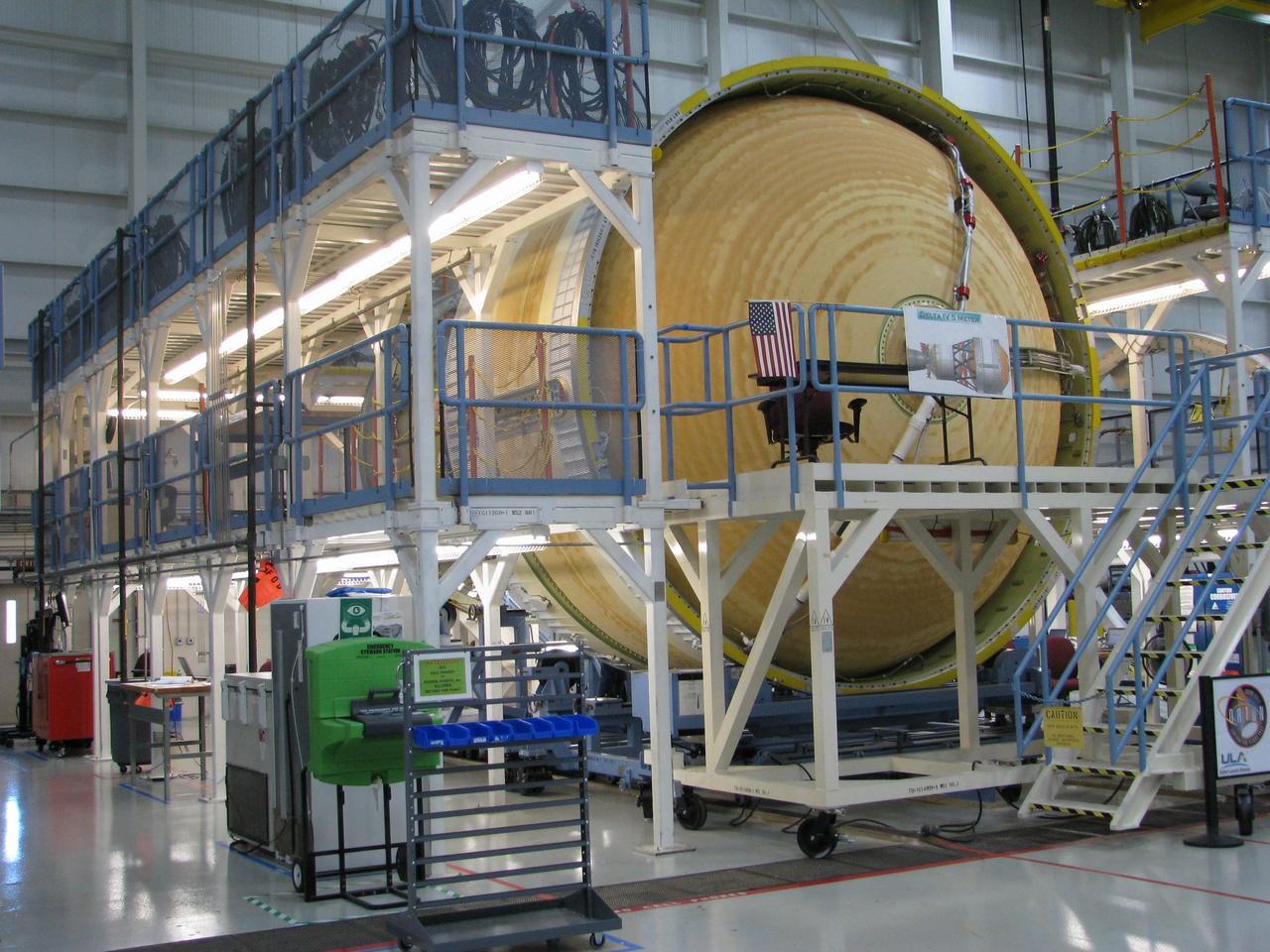

The Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle used to launch Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled at the United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, AL on Nov. 1, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
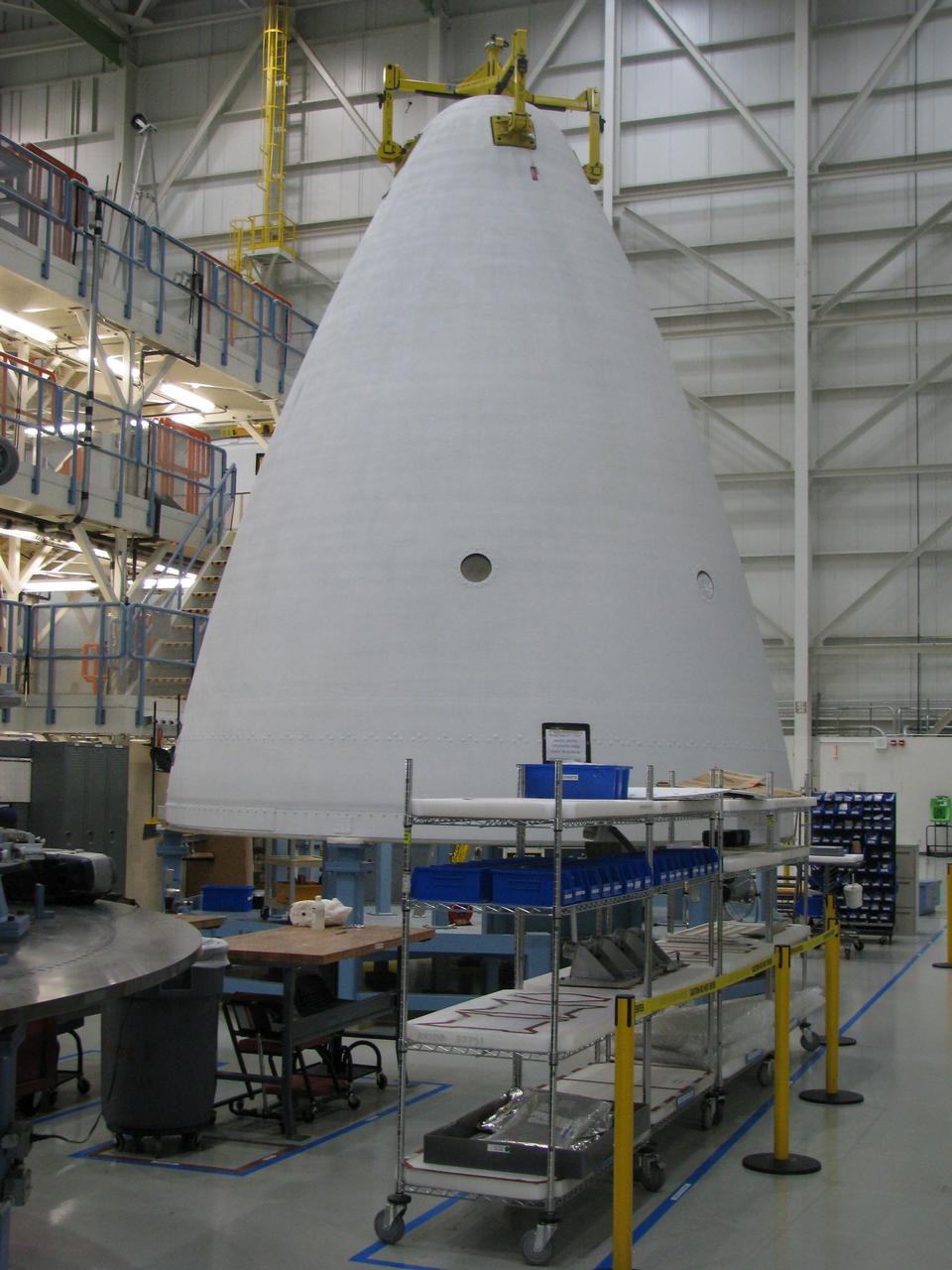

The Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle used to launch Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled at the United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, AL on Nov. 1, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
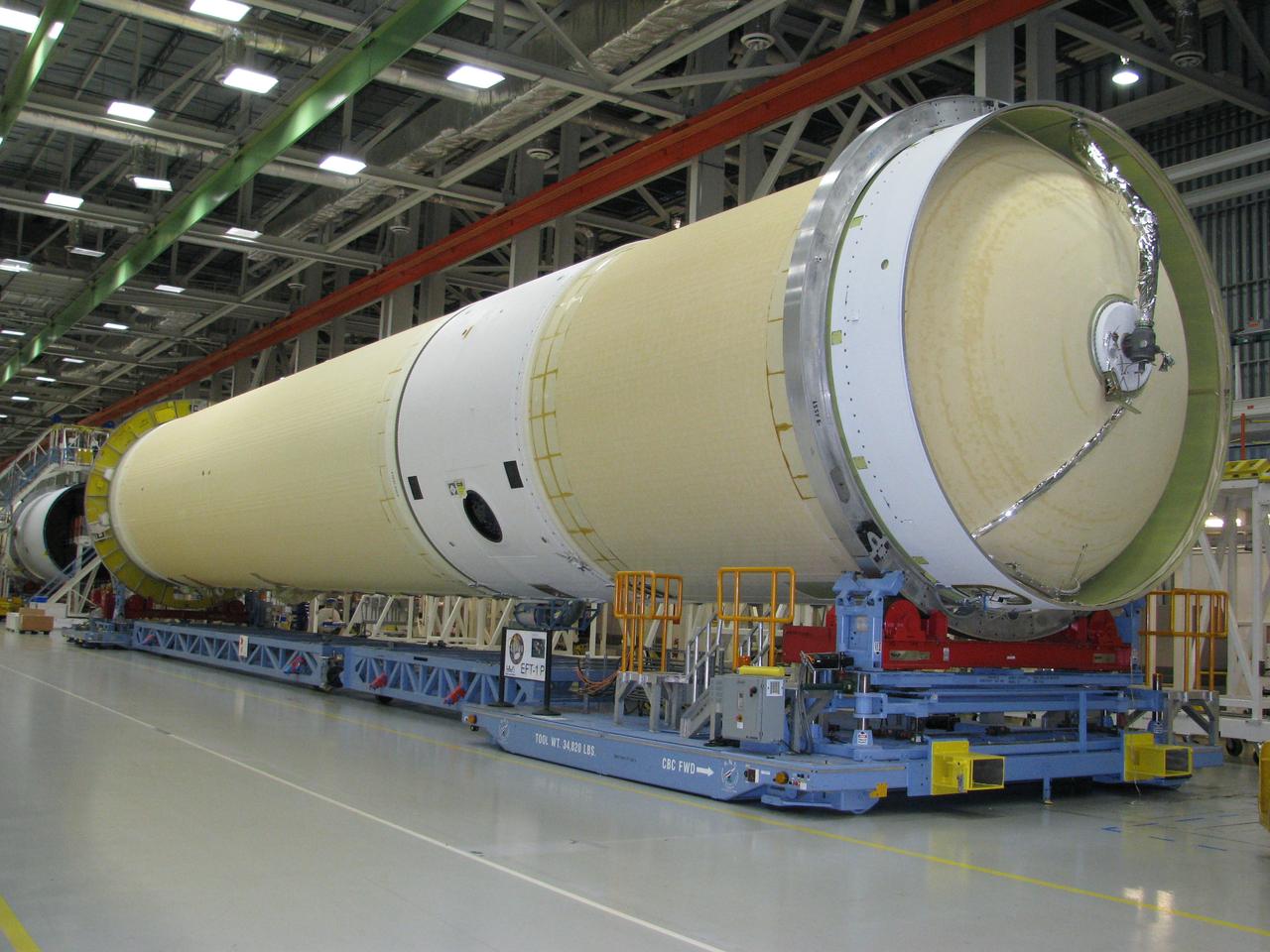

The Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle used to launch Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled at the United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, AL on Dec. 11, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
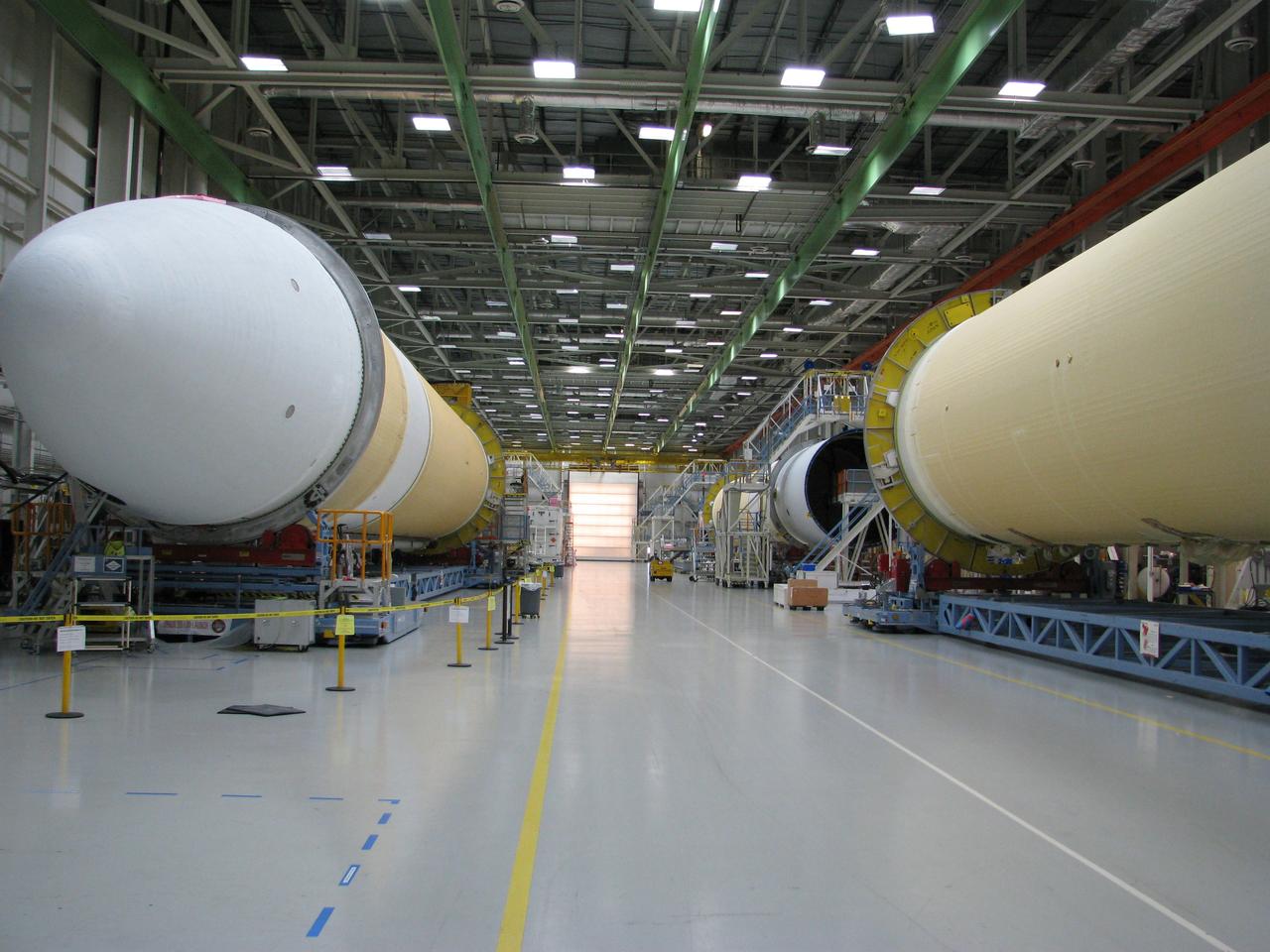

The Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle used to launch Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled at the United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, AL on Dec. 11, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle used to launch Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled at the United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, AL on Dec. 11, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle used to launch Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled at the United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, AL on Dec. 11, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
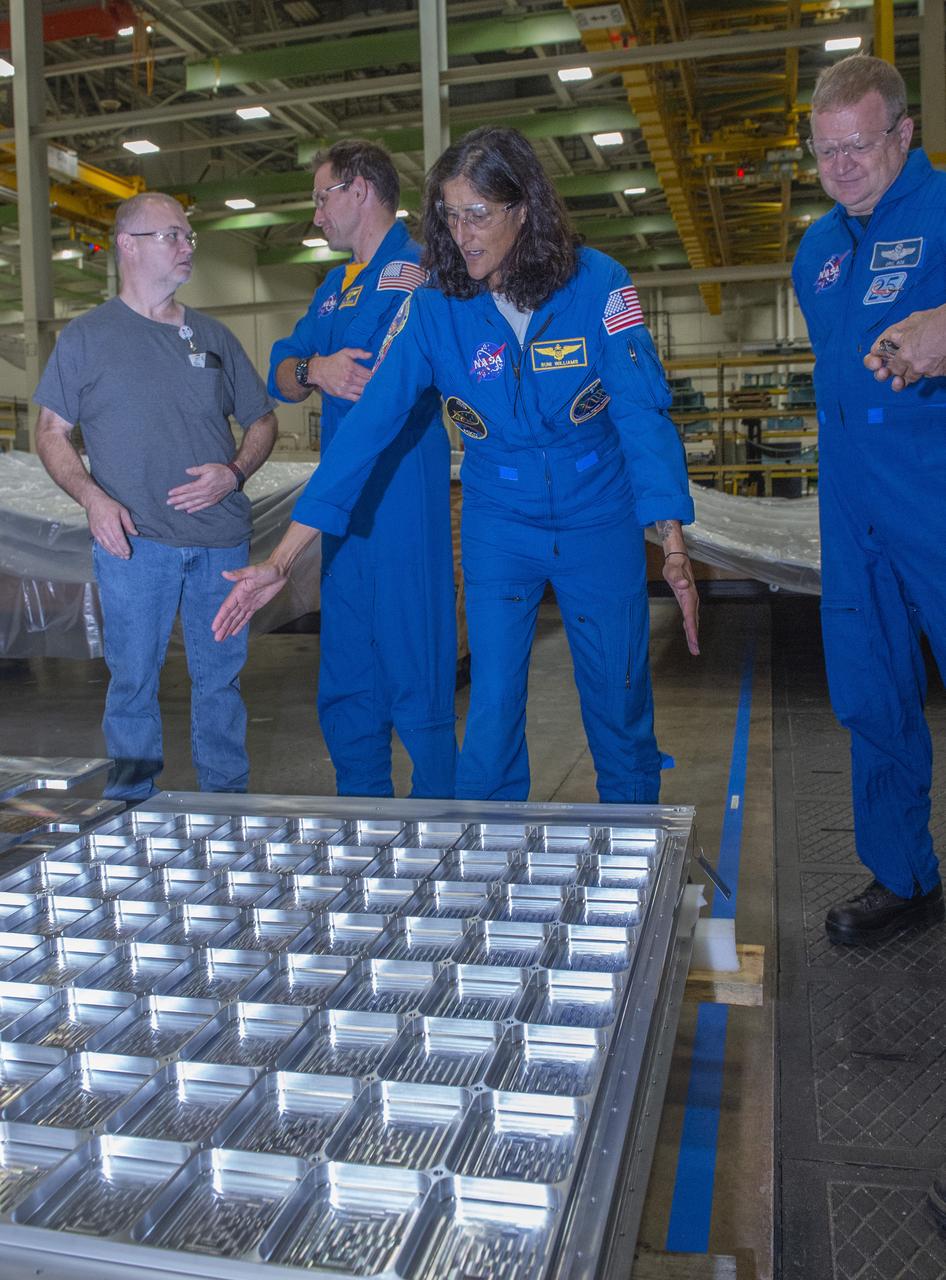

Commercial Crew astronauts toured the United Launch Alliance factory in Decatur, Alabama, on July 17, 2018. Viewing hardware to be used for upcoming commercial crew missions are, second from left, Josh Cassada, Suni Williams and Eric Boe.
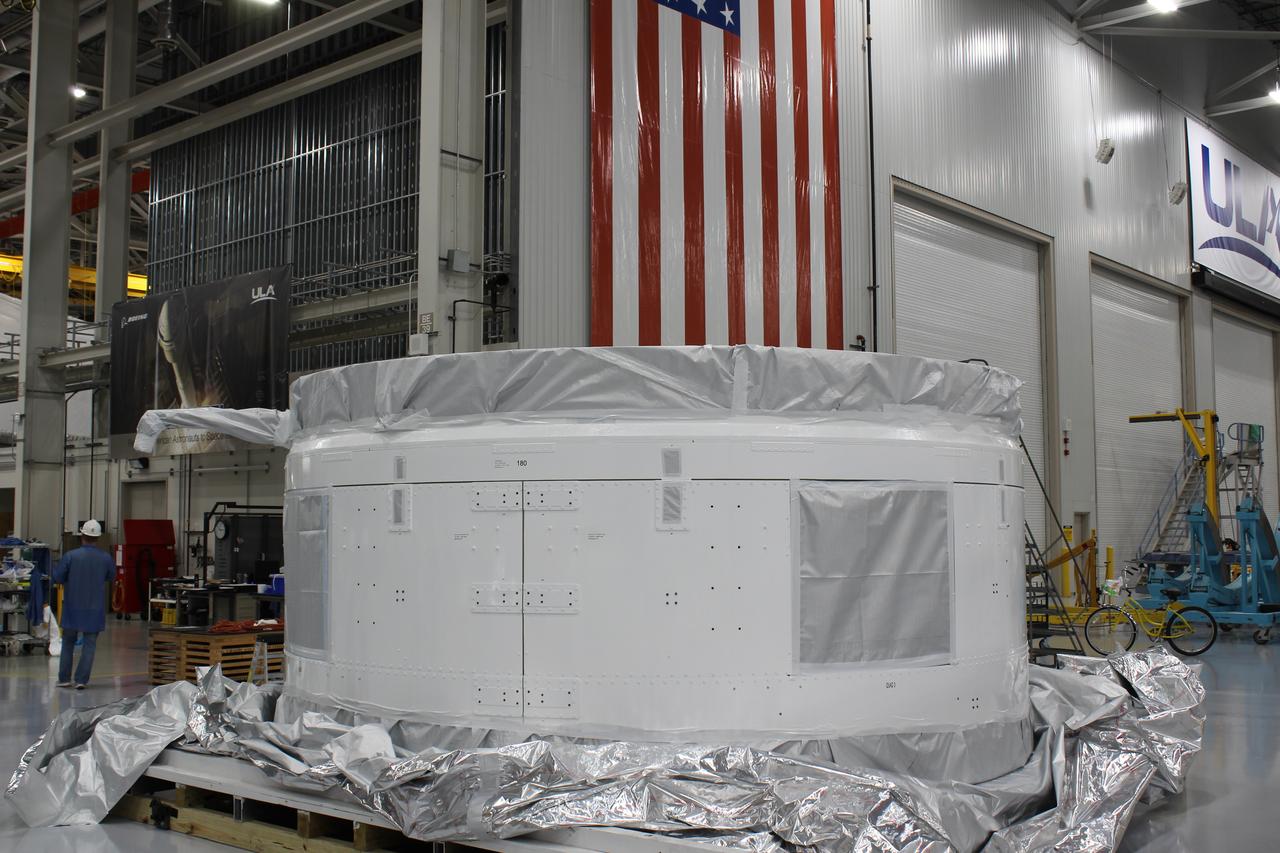

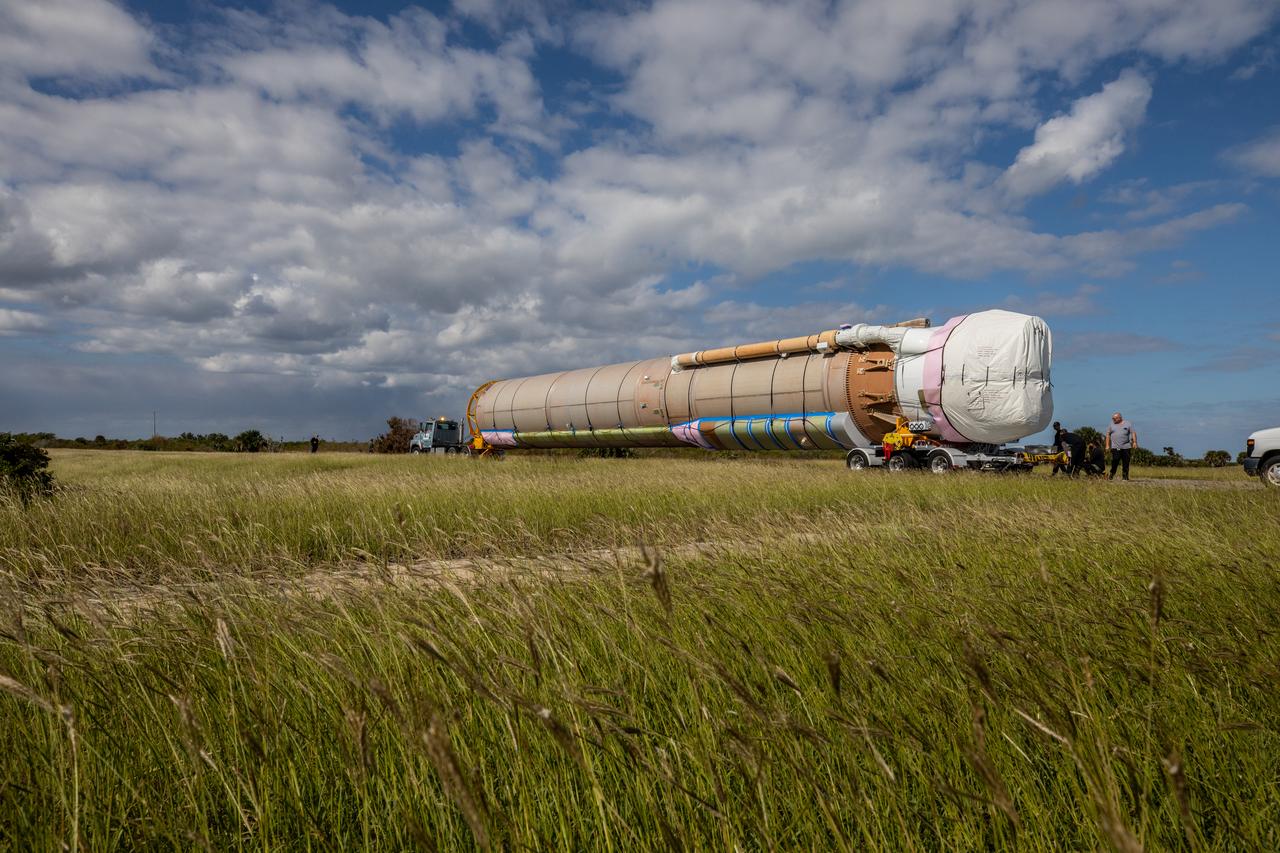
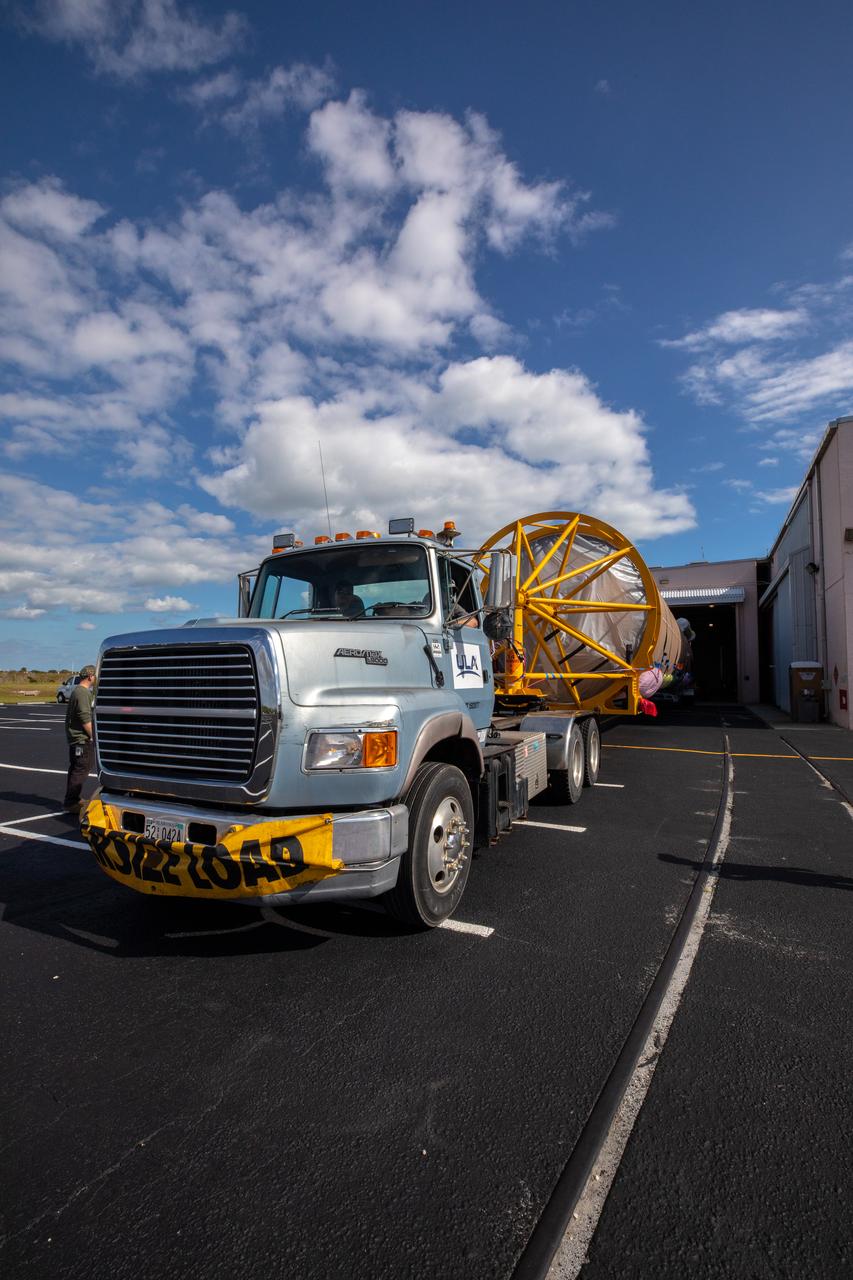
The Launch Vehicle Adapter (LVA) that will attach Boeing’s first Starliner spacecraft to the Atlas V launch vehicle is ready for transport from United Launch Alliance's manufacturing factory in Decatur, Alabama to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
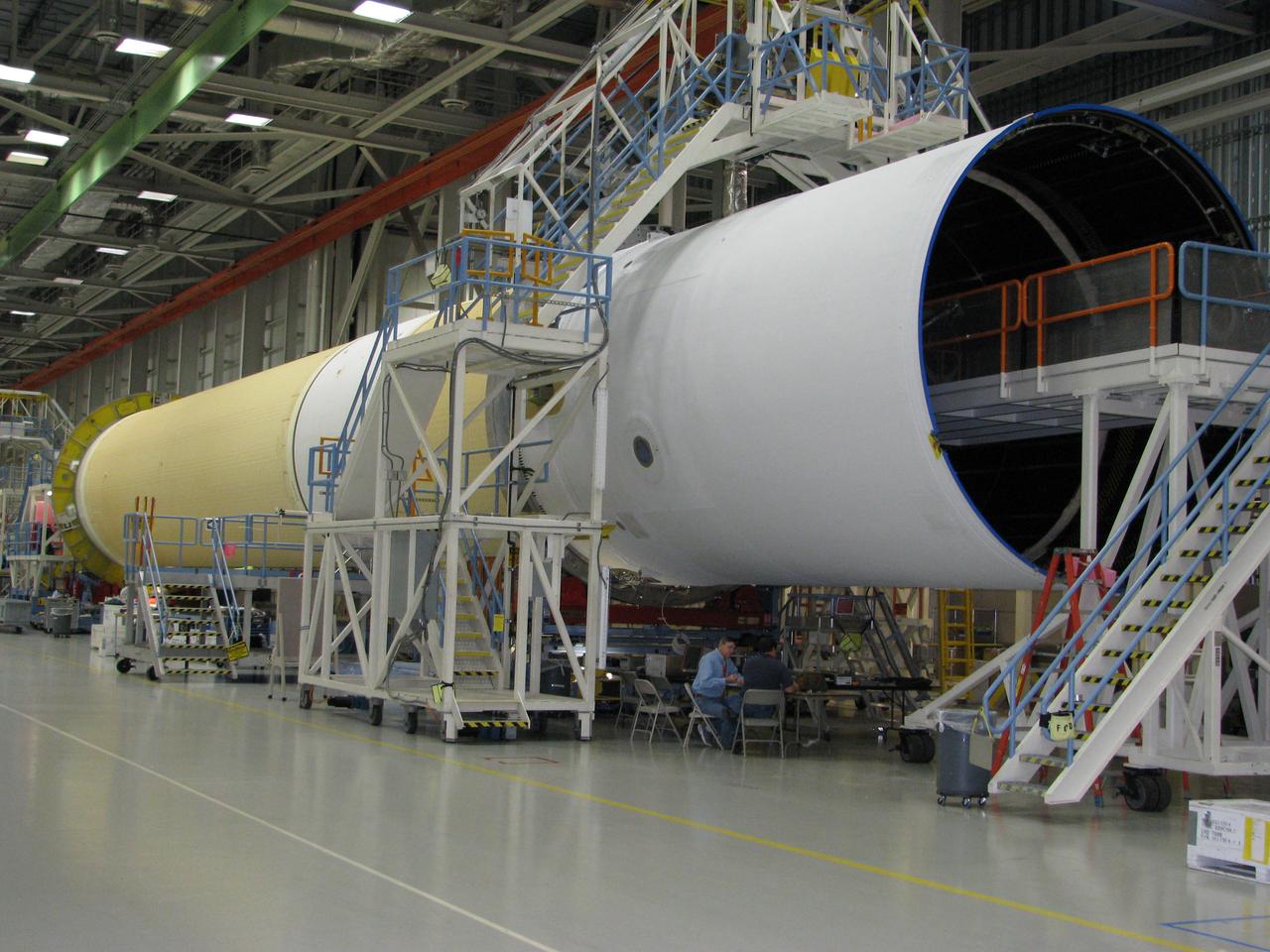

The Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle used to launch Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled at the United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, AL on Dec. 11, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
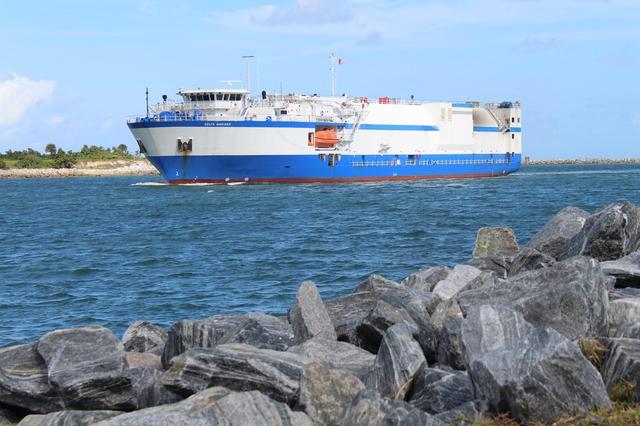

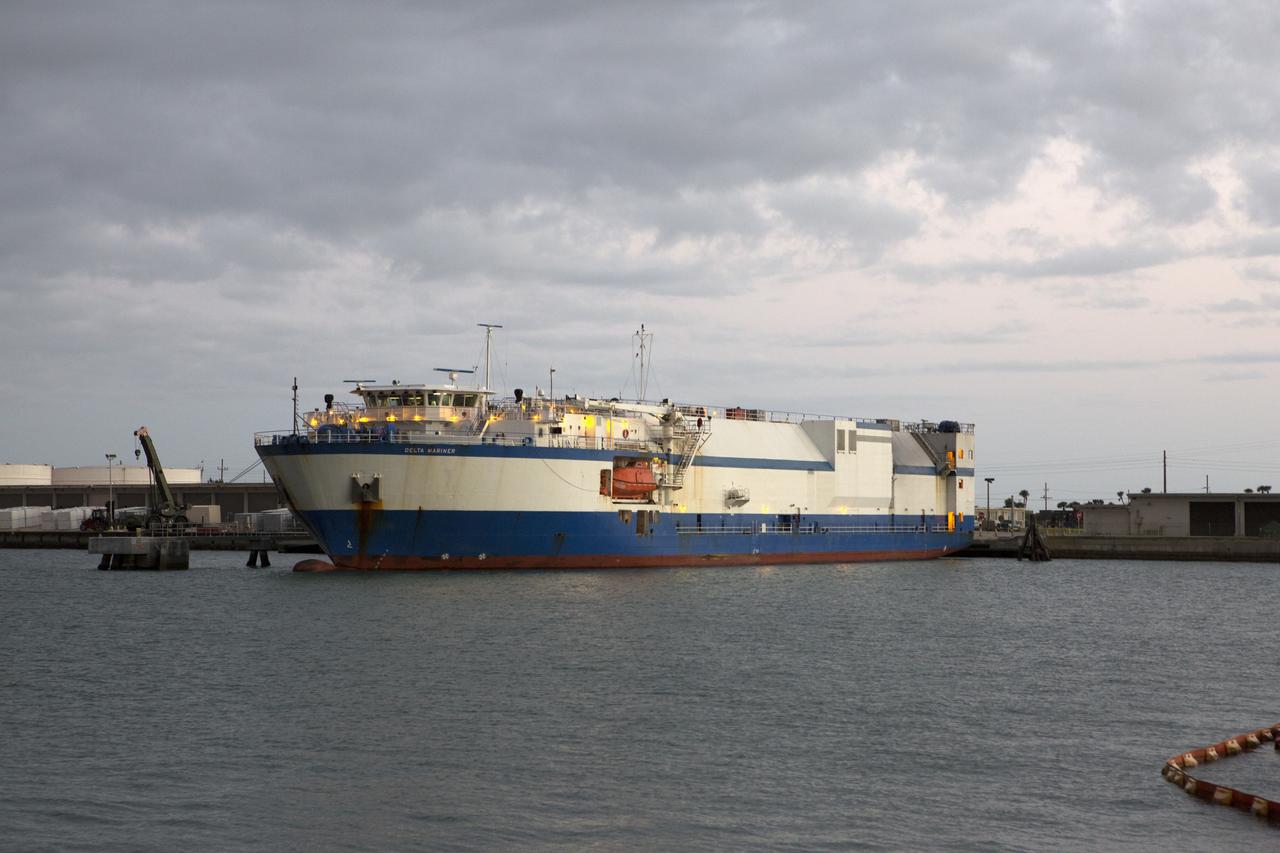
The Launch Vehicle Adapter (LVA) that will attach Boeing’s first Starliner spacecraft to the Atlas V launch vehicle arrived at Cape Canaveral in Florida on November 11, 2018. The Mariner cargo vessel brought the LVA and two stages of a Delta IV rocket from United Launch Alliance's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama.

The Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle used to launch Orion on Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled at the United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, AL on Dec. 11, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
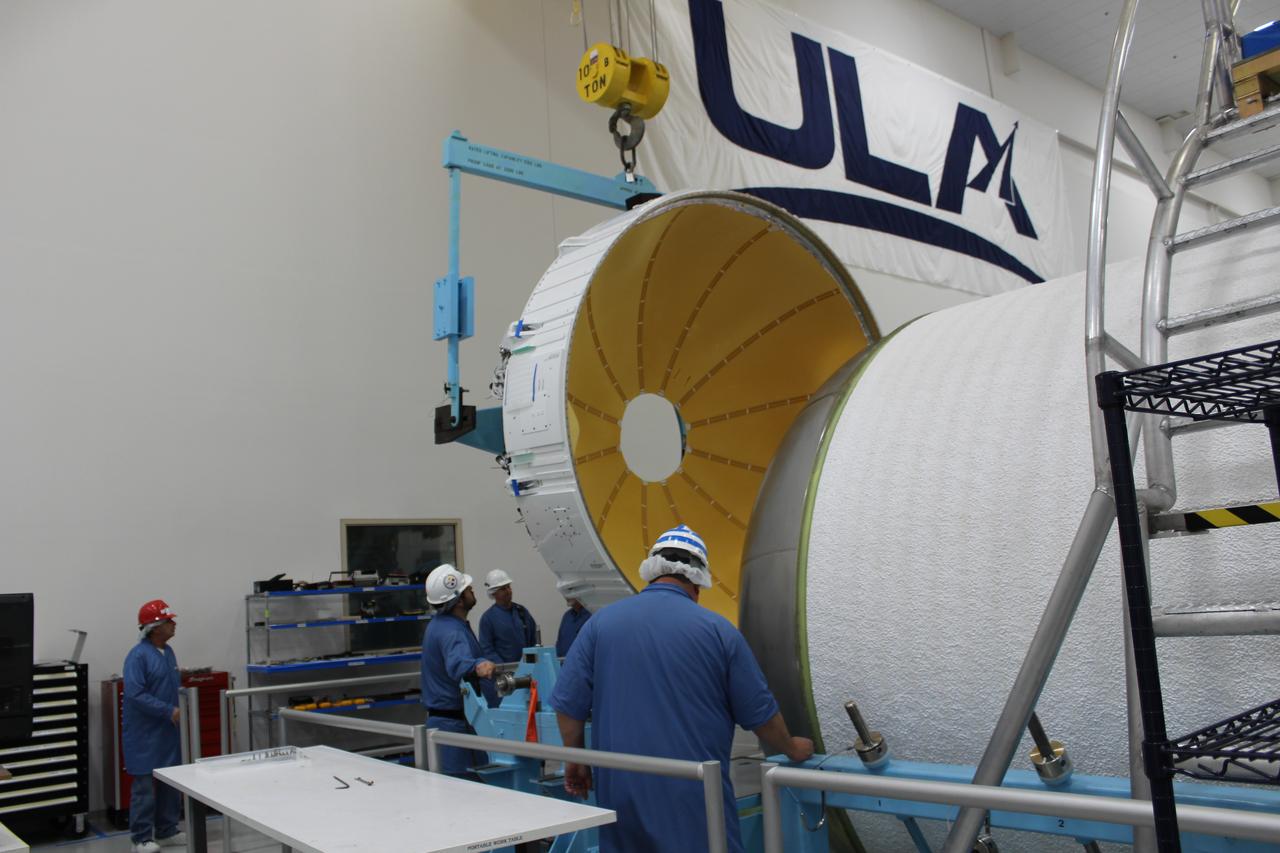

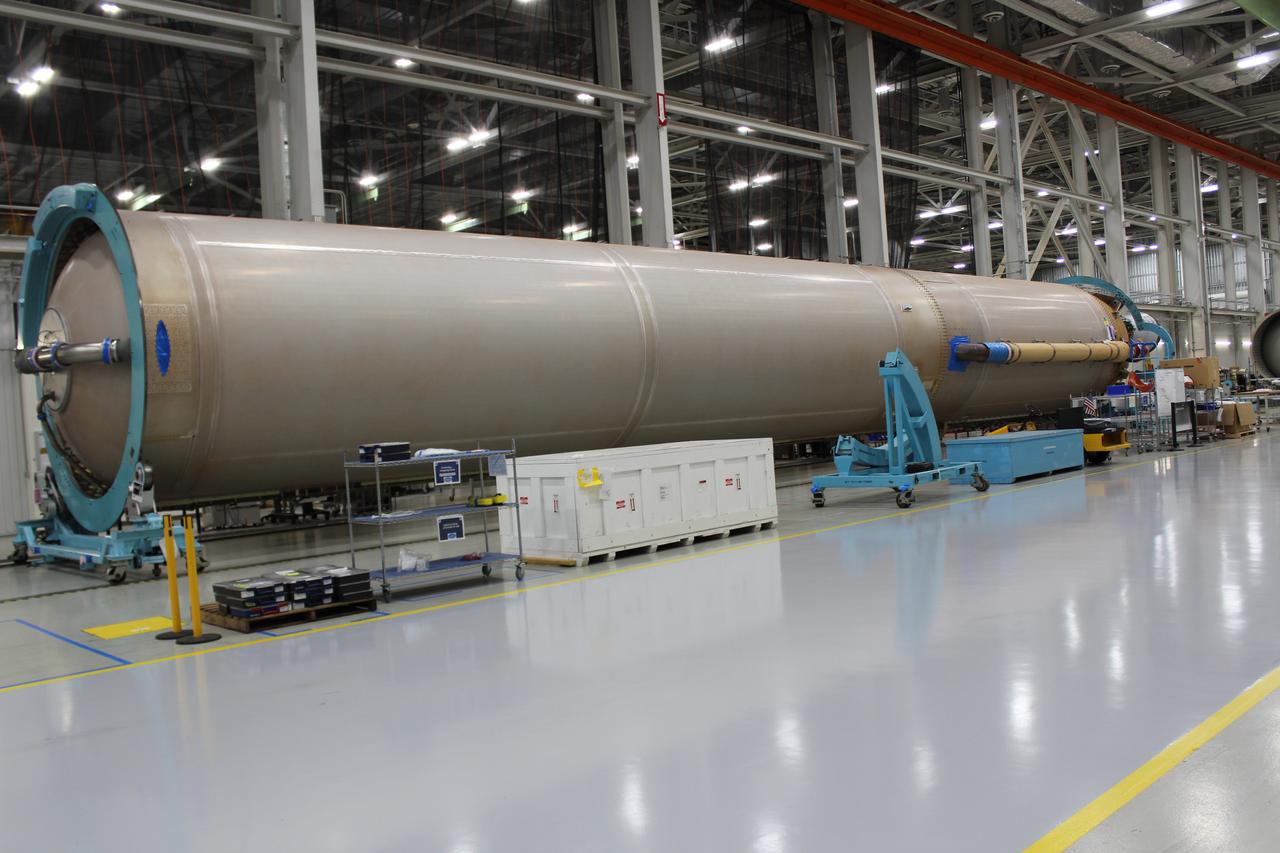
Workers assemble a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stage in ULA’s factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 29, 2019. The dual engine upper stage is being prepared for the first crew rotation mission of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner to the International Space Station. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key elements of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program to restore the capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil.
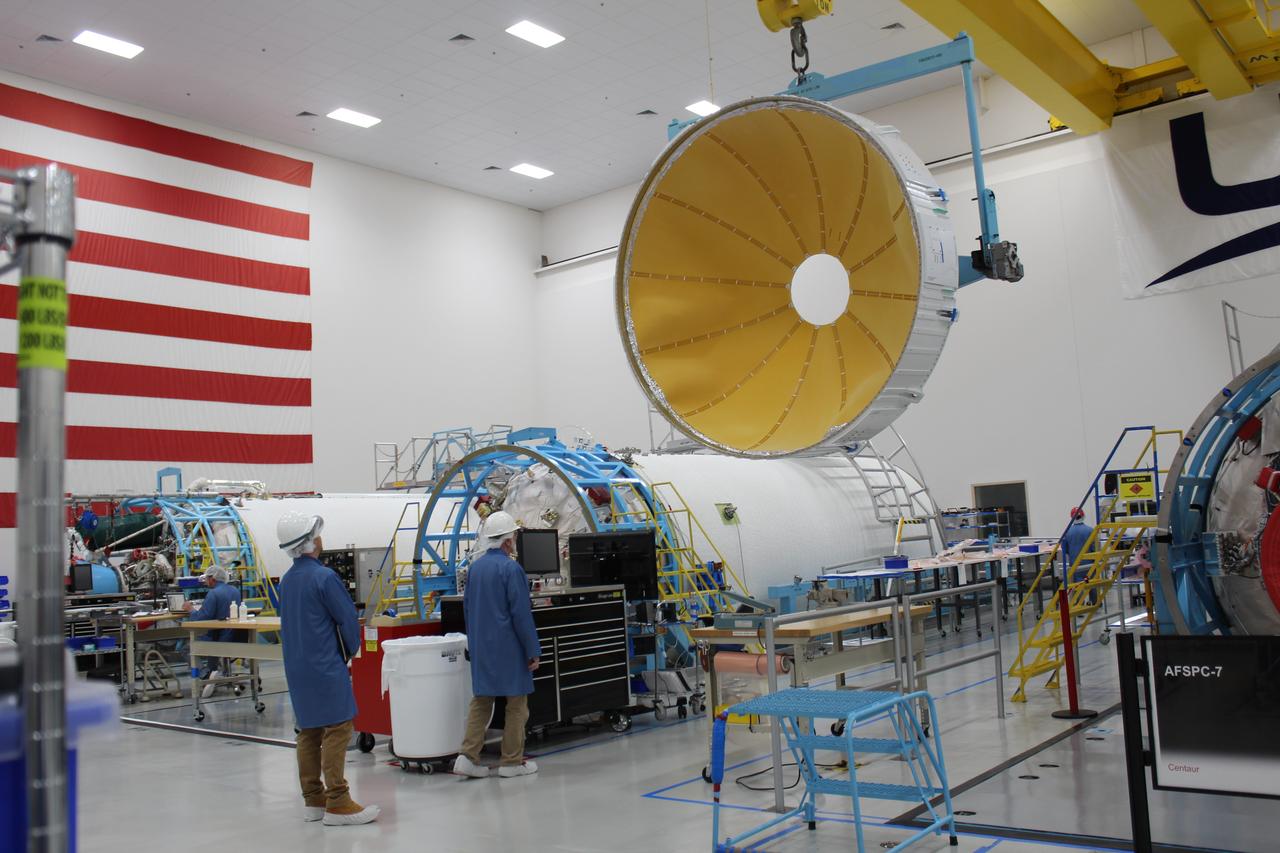

Workers assemble a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stage in ULA’s factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 29, 2019. The dual engine upper stage is being prepared for the first crew rotation mission of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner to the International Space Station. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key elements of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program to restore the capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil.

The first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) was offloaded from the Mariner barge at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, and is being transported to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS was shipped from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) was offloaded from the Mariner barge at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, and transported to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) is offloaded from the Mariner barge at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS will be transported to the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

Inside the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) for NASA's Space Launch System rocket was removed from its shipping container and then lowered and secured onto a movable transport stand. The ICPS is the first integrated piece of flight hardware to arrive for the SLS. The ICPS arrived from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
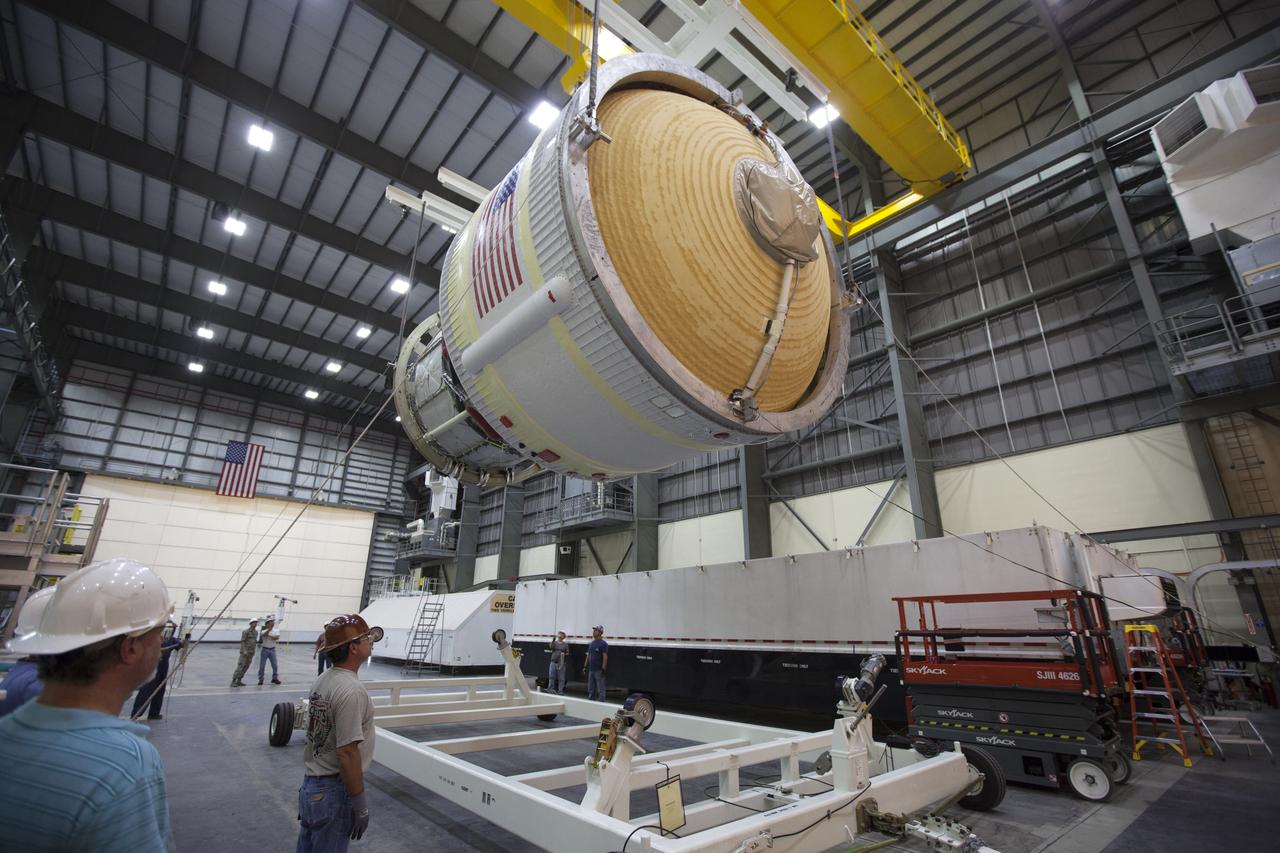

Inside the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a crane lifts the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) for NASA's Space Launch System rocket away from the base of its shipping container. The ICPS is the first integrated piece of flight hardware to arrive for the SLS. The ICPS arrived from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
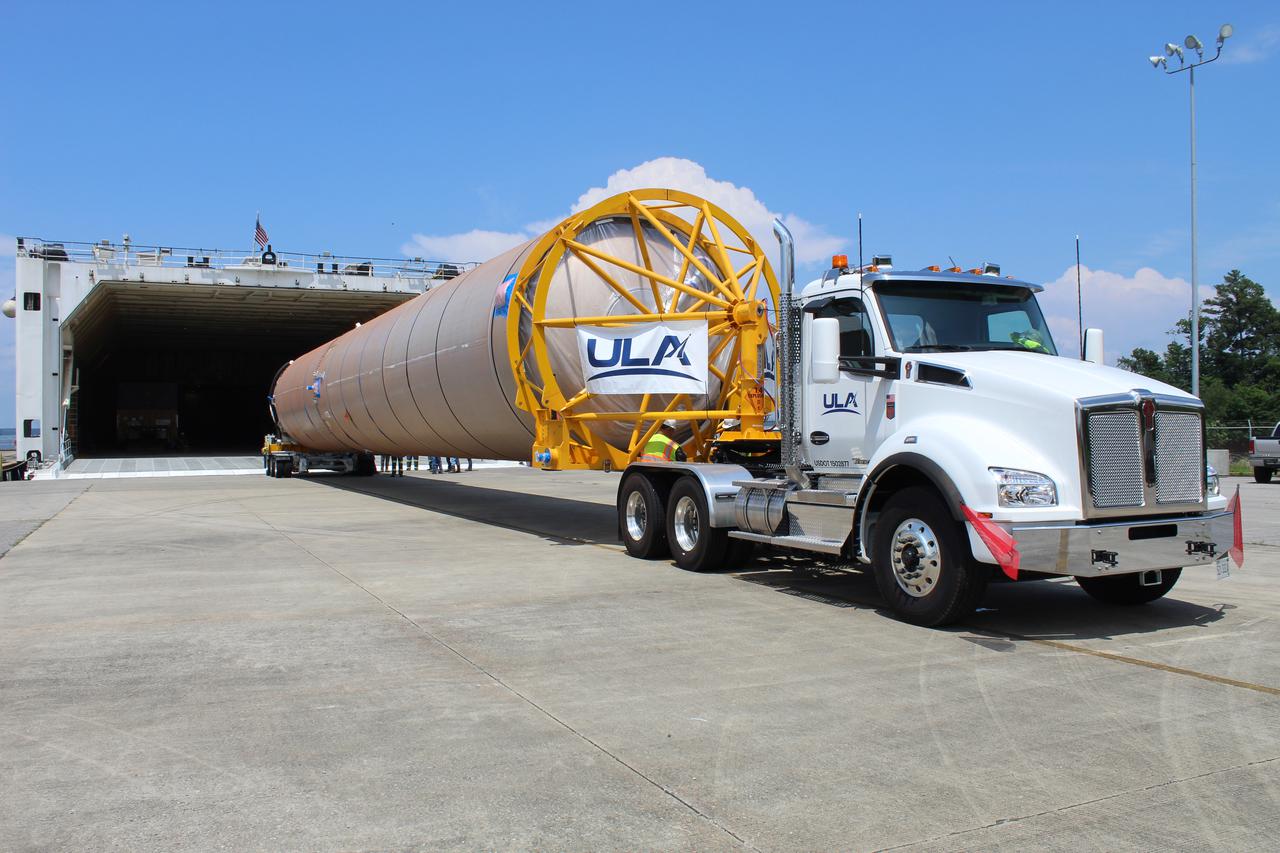

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster for Boeing's CST-100 Starliner Crew Flight Test (CFT) is loaded onto a rocket-delivery ship at ULA’s manufacturing factory in Decatur, Alabama, on June 11, 2021, to begin its journey to Cape Canaveral, Florida. Starliner’s first flight with astronauts aboard, CFT will launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The flight test will demonstrate the ability of the Atlas V and Starliner to safely carry astronauts to and from the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
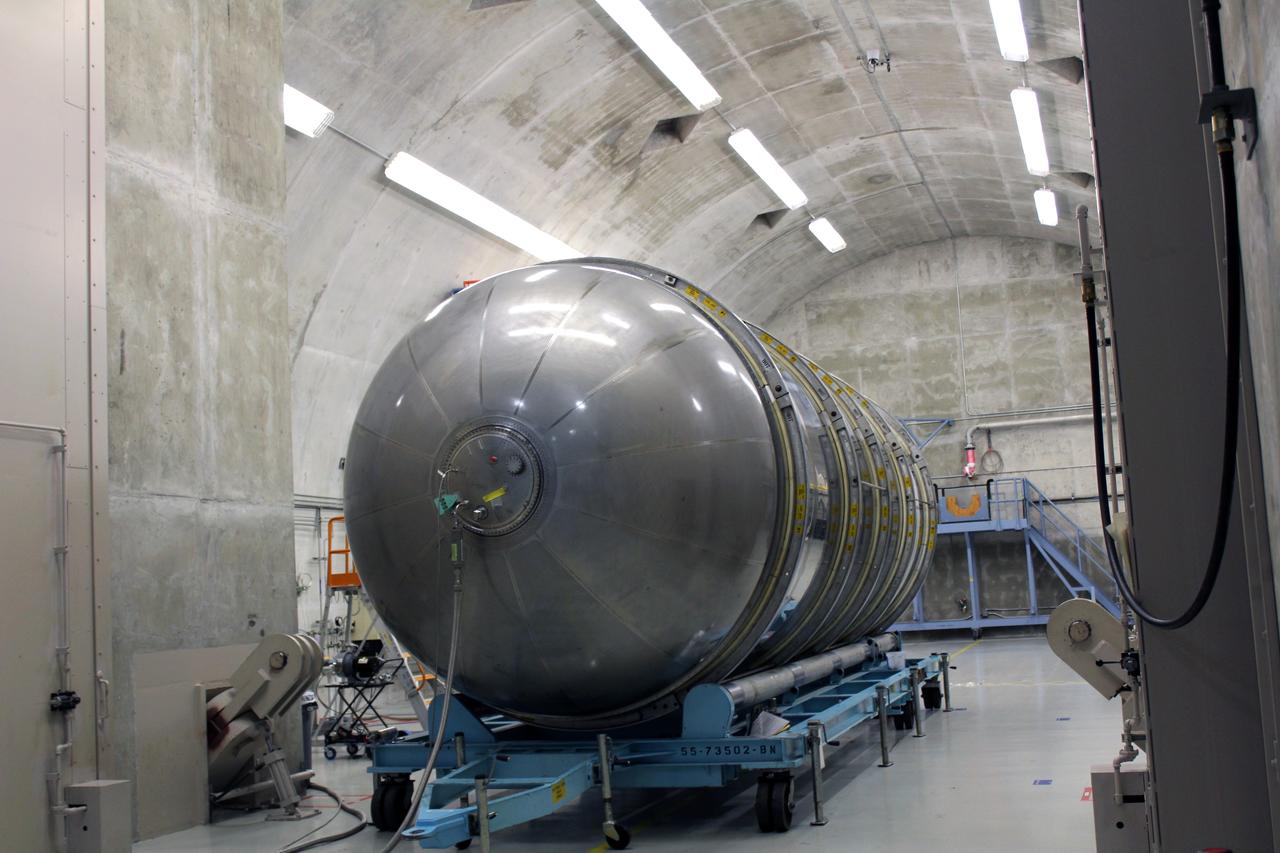

The Atlas V rocket that will launch Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft on the company’s uncrewed Orbital Flight Test for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program is coming together inside a United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, Alabama. The flight test is intended to prove the design of the integrated space system prior to the Crew Flight Test. These events are part of NASA’s required certification process as the company works to regularly fly astronauts to and from the International Space Station. Boeing's Starliner will launch on the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
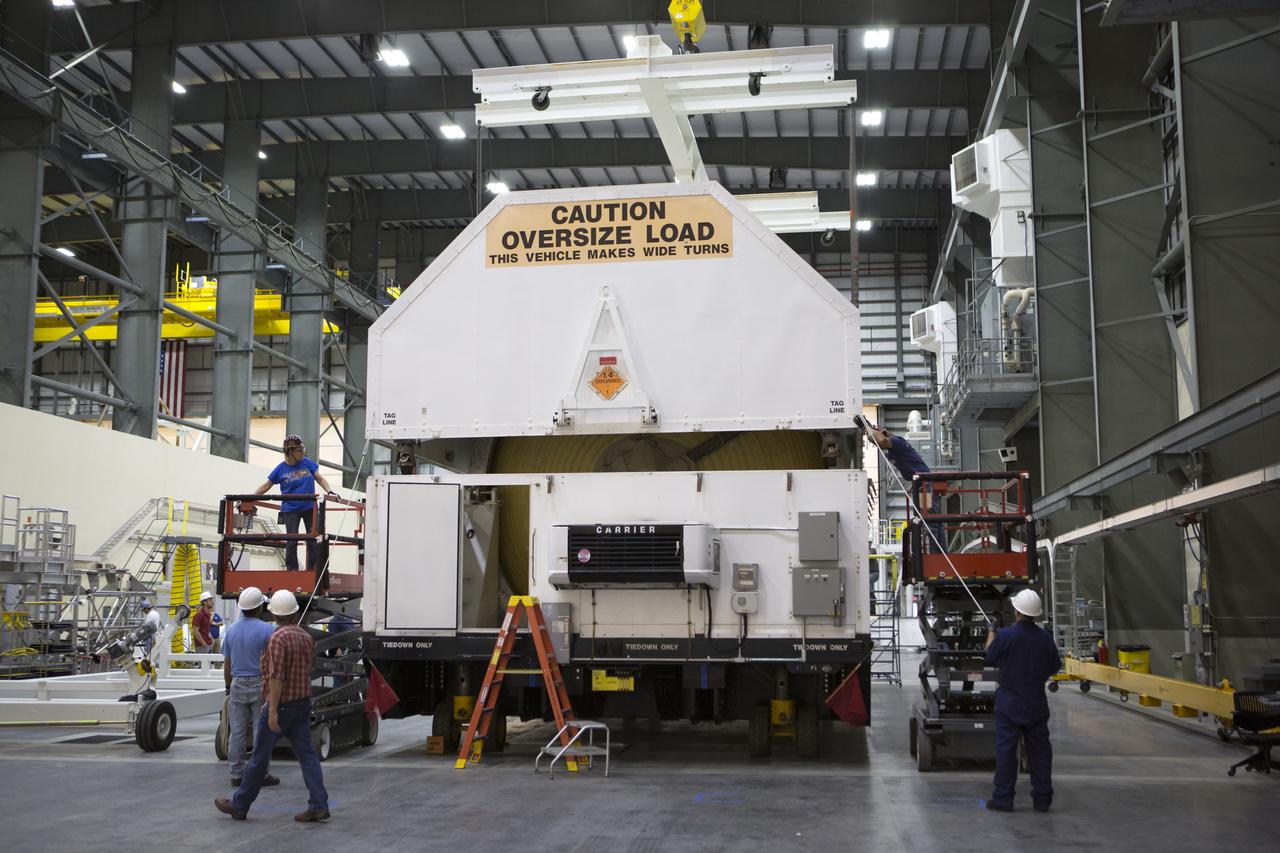

Inside the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, technicians prepare to remove the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) for NASA's Space Launch System rocket from its shipping container. The ICPS is the first integrated piece of flight hardware to arrive for the SLS. The ICPS arrived from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
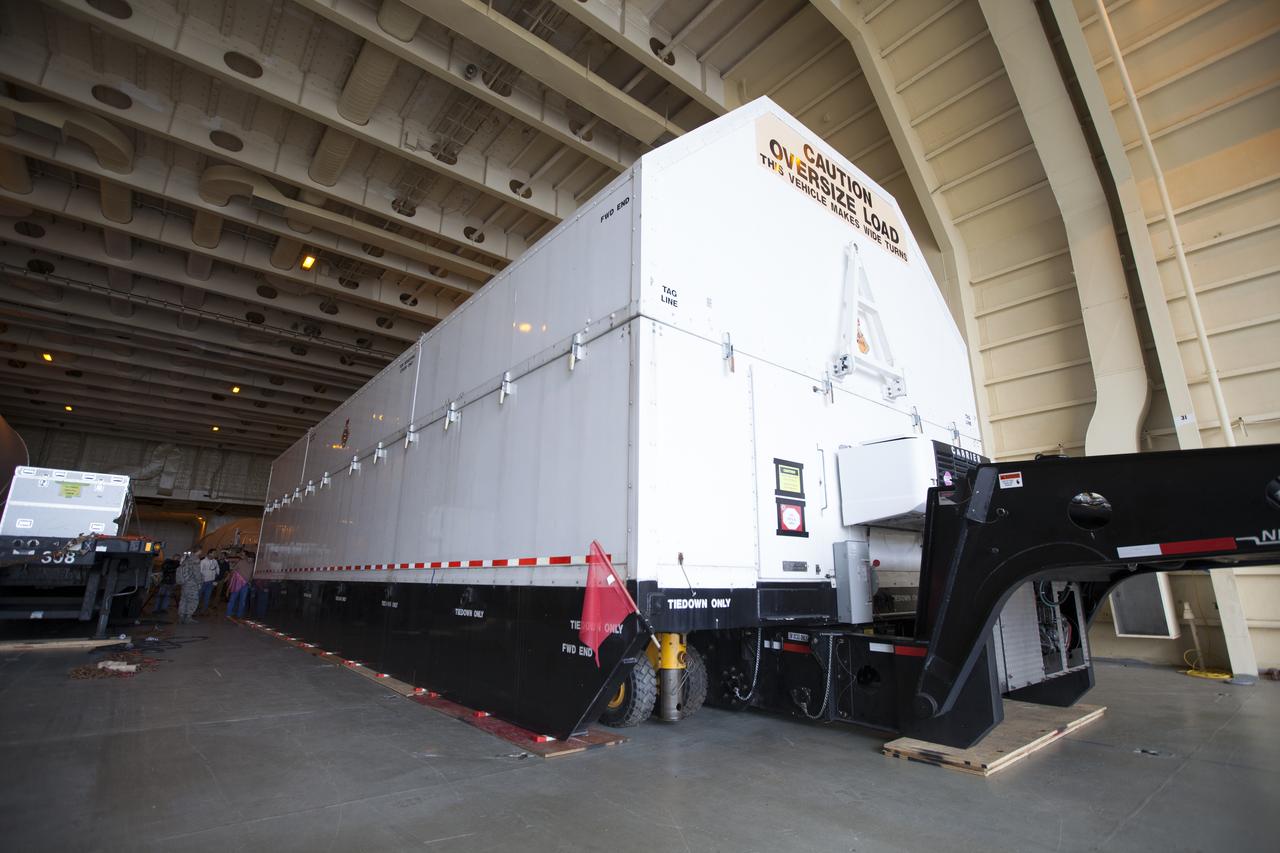

The first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) has arrived aboard the Mariner barge at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. Preparations are underway to offload the ICPS and transport it to the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The Mariner barge arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying the first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS). The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS will be offloaded and transported to the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
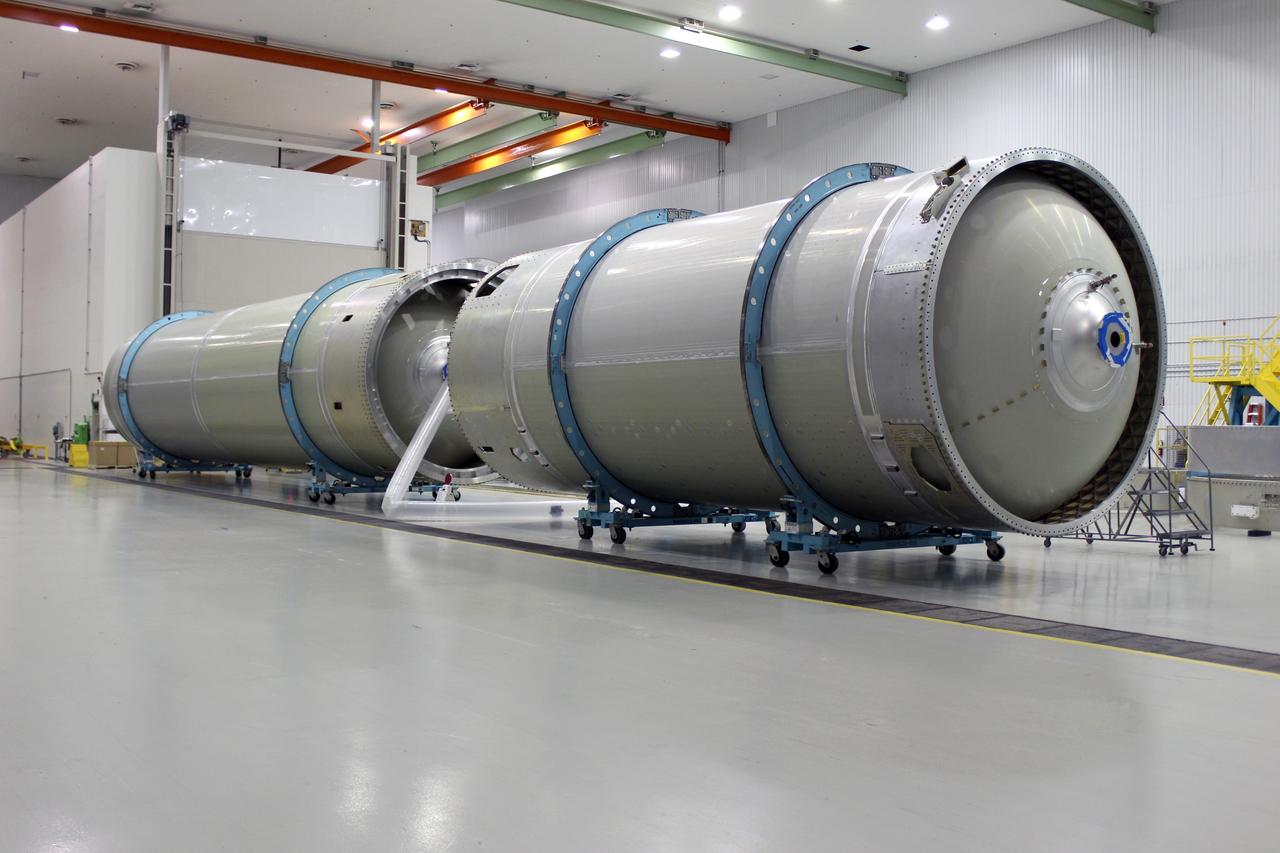

The Atlas V rocket that will launch Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft on the company’s uncrewed Orbital Flight Test for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program is coming together inside a United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, Alabama. The flight test is intended to prove the design of the integrated space system prior to the Crew Flight Test. These events are part of NASA’s required certification process as the company works to regularly fly astronauts to and from the International Space Station. Boeing's Starliner will launch on the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
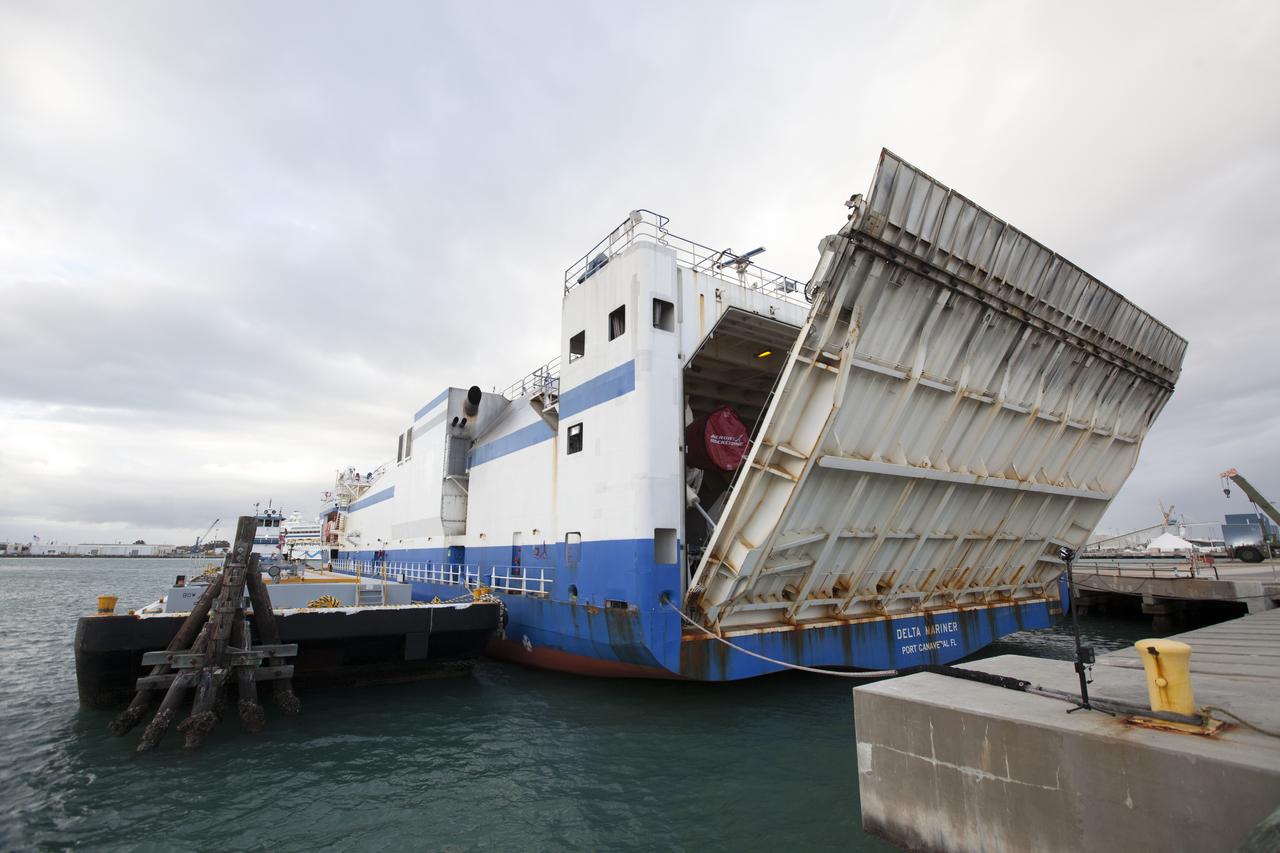

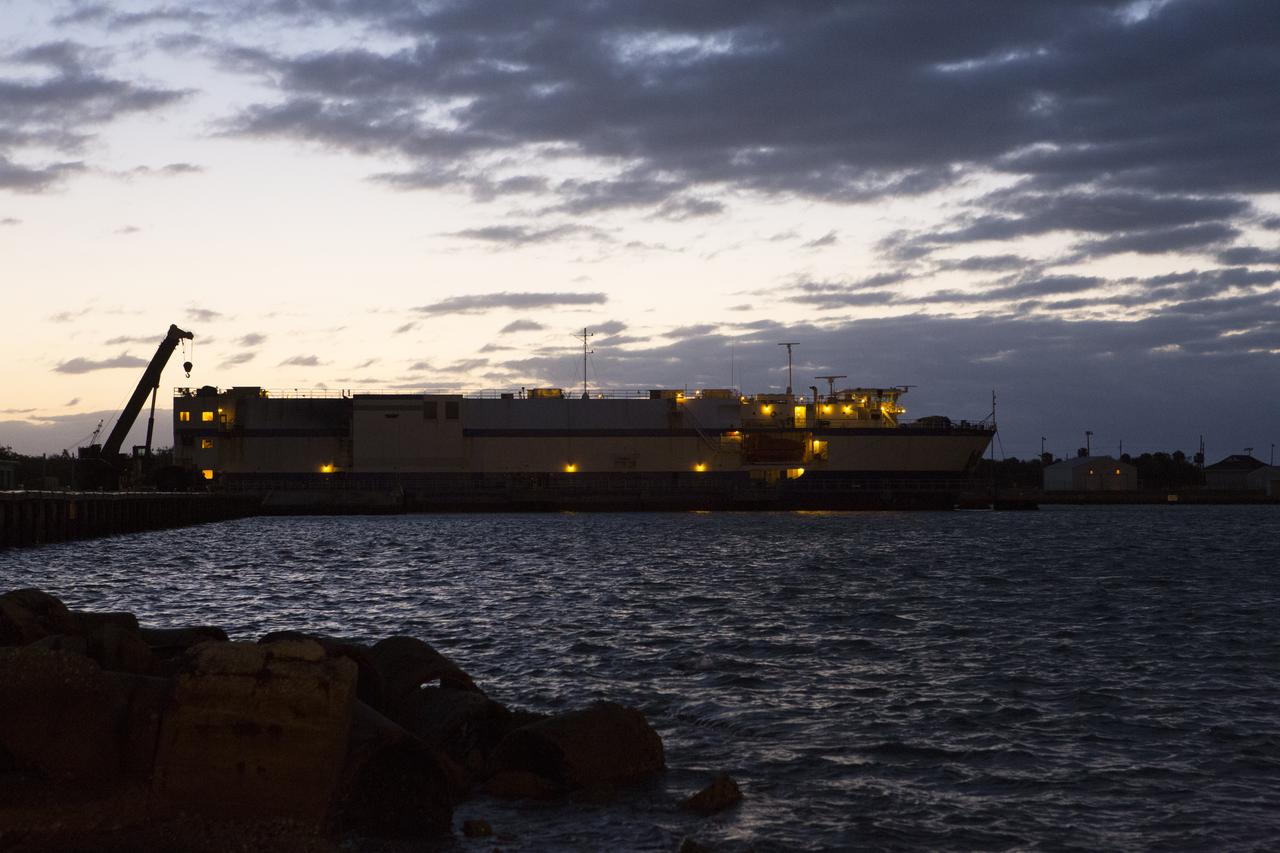
The Mariner barge arrives at a dock at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying the first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS). The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS will be offloaded and transported to the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The Mariner barge is docked at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, with the first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) inside, at right. The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS will be offloaded and transported to the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
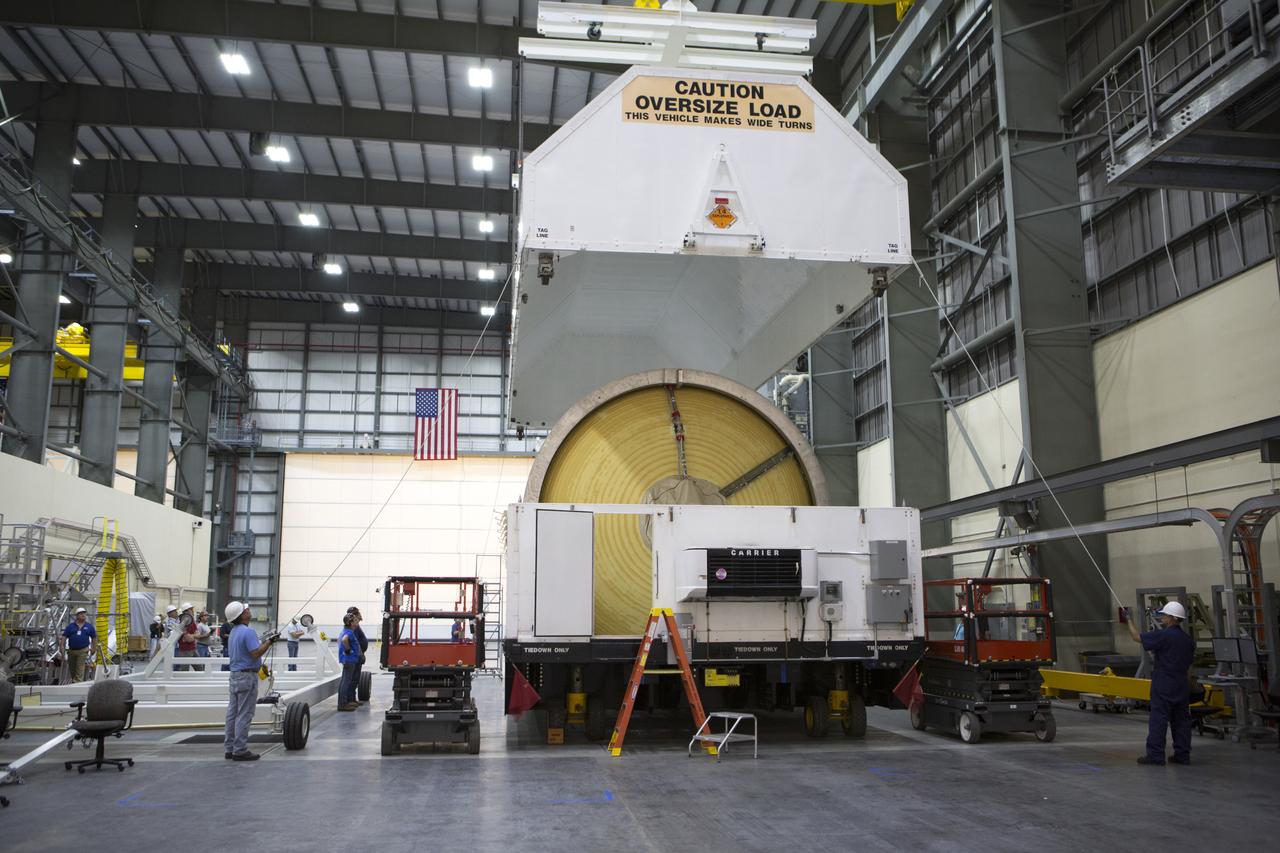

Inside the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, technicians assists as a crane lifts the shipping container cover away from the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) for NASA's Space Launch System rocket. The ICPS is the first integrated piece of flight hardware to arrive for the SLS. The ICPS arrived from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The Mariner barge arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying the first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS). The ICPS was shipped from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS will be offloaded and transported to the ULA Horizontal Integration Facility where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
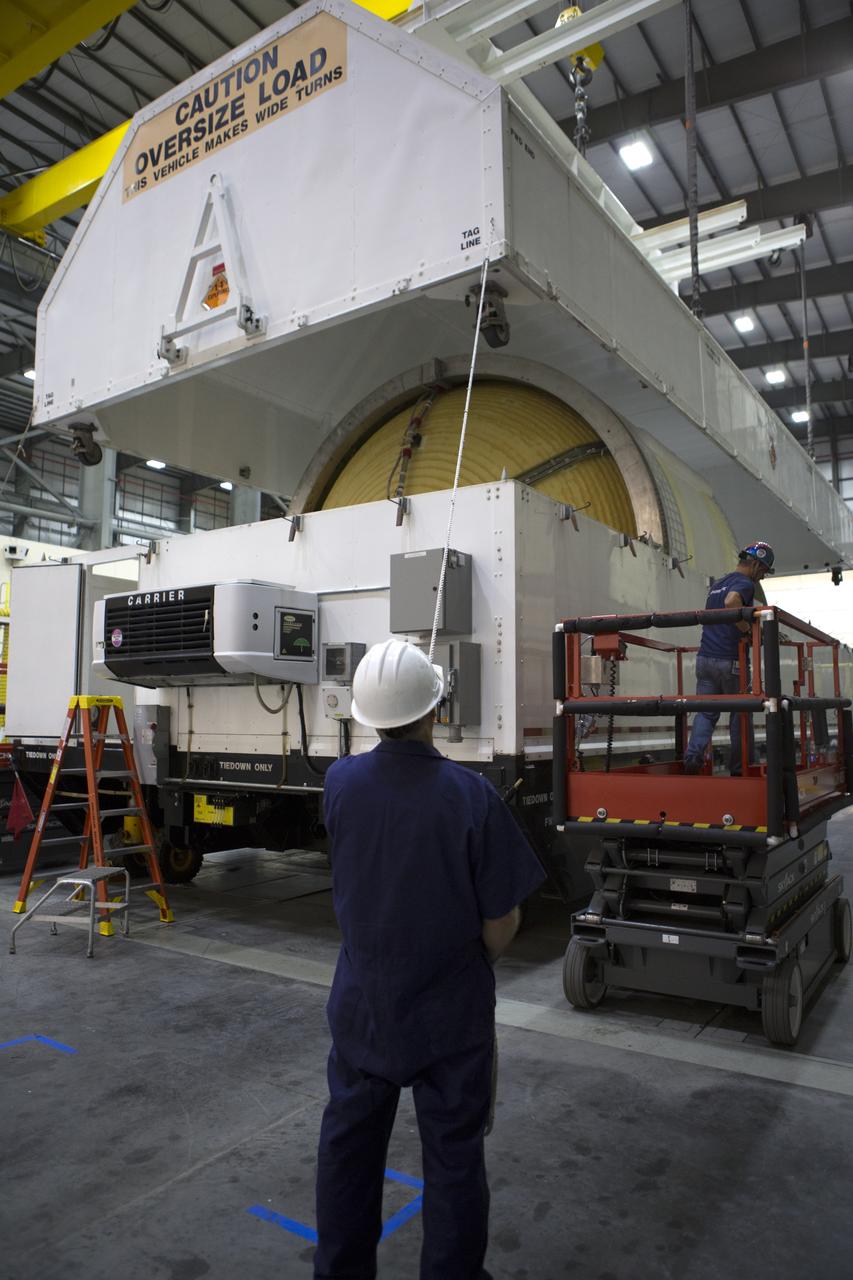

Inside the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a technician assists as a crane lifts the top of the shipping container cover away from the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) for NASA's Space Launch System rocket. The ICPS is the first integrated piece of flight hardware to arrive for the SLS. The ICPS arrived from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) arrives at the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS was shipped aboard the Mariner barge from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
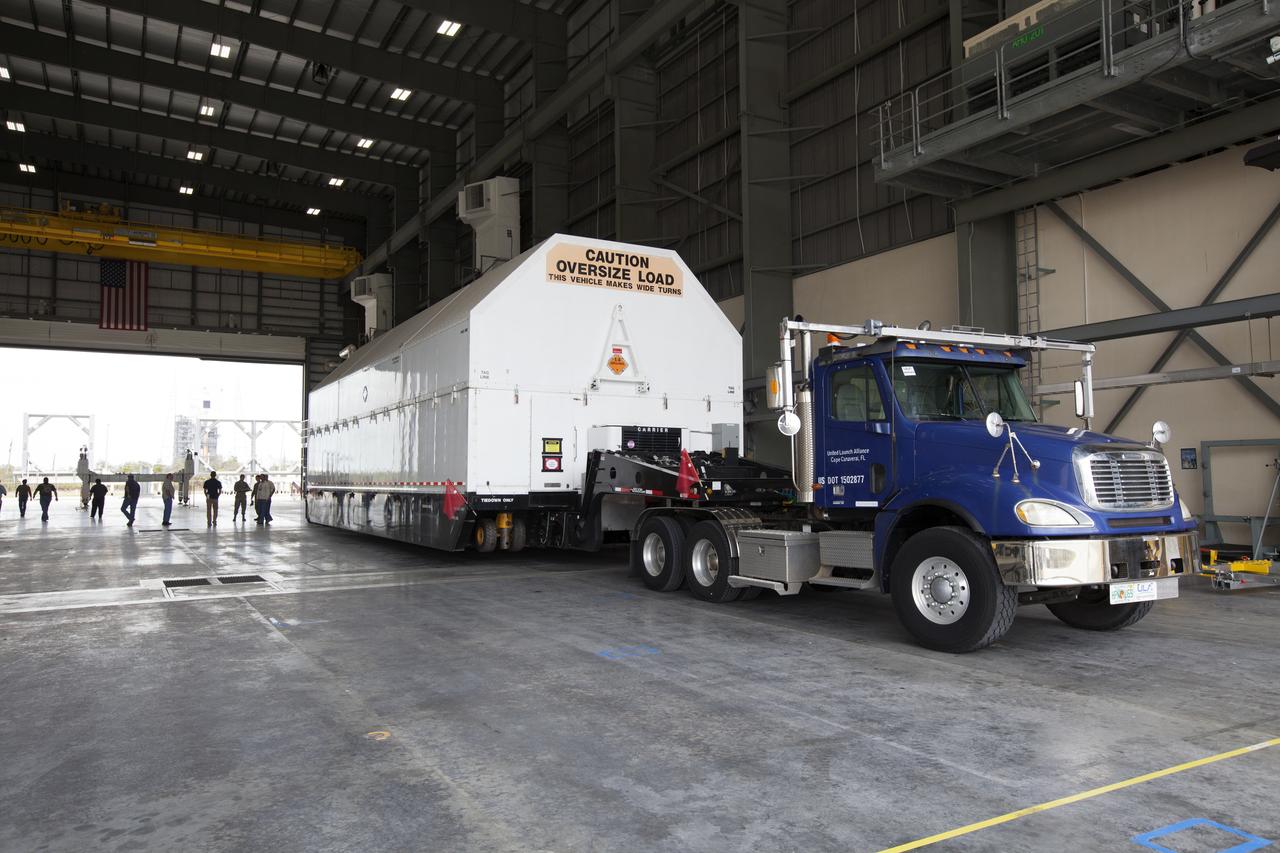

The first integrated piece of flight hardware for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) arrives at the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, where it will be removed from its flight case. The ICPS arrived aboard the Mariner barge from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
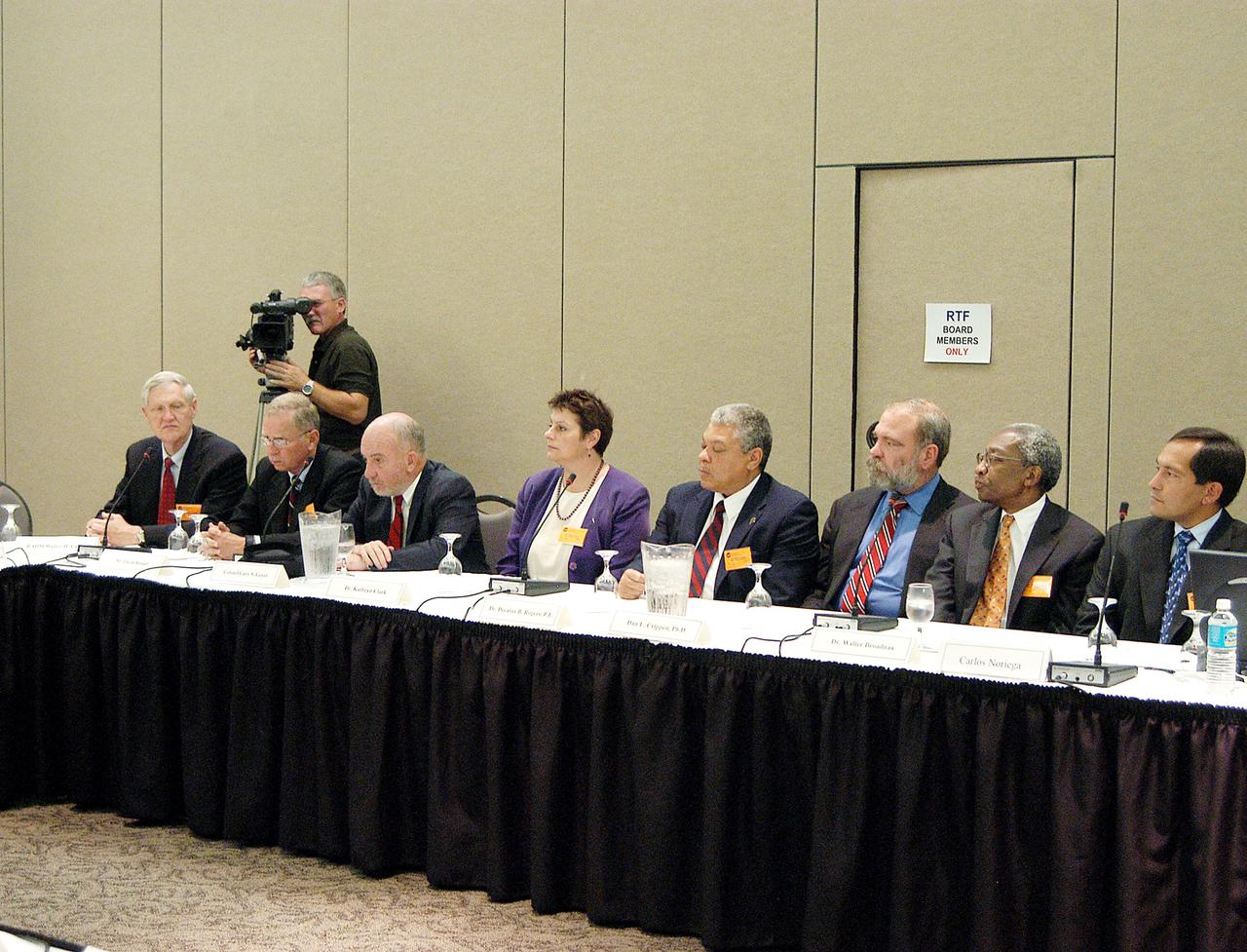

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Return To Flight Task Group (RTFTG) holds the first public meeting at the Debus Center, KSC Visitor Complex. Members and staff at the table, from left, are retired Navy Rear Adm. Walter H. Cantrell, David Raspet, retired Air Force Col. Gary S. Geyer, Dr. Kathryn Clark, Dr. Decatur B. Rogers, Dr. Dan L. Crippen, Dr. Walter Broadnax and astronaut Carlos Noriega. The RTFTG was at KSC to conduct organizational activities, tour Space Shuttle facilities and receive briefings on Shuttle-related topics. The task group was chartered by NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe to perform an independent assessment of NASA’s implementation of the final recommendations of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. The group is co-chaired by former Shuttle commander Richard O. Covey and retired Air Force Lt. Gen. Thomas P. Stafford, who was an Apollo commander.
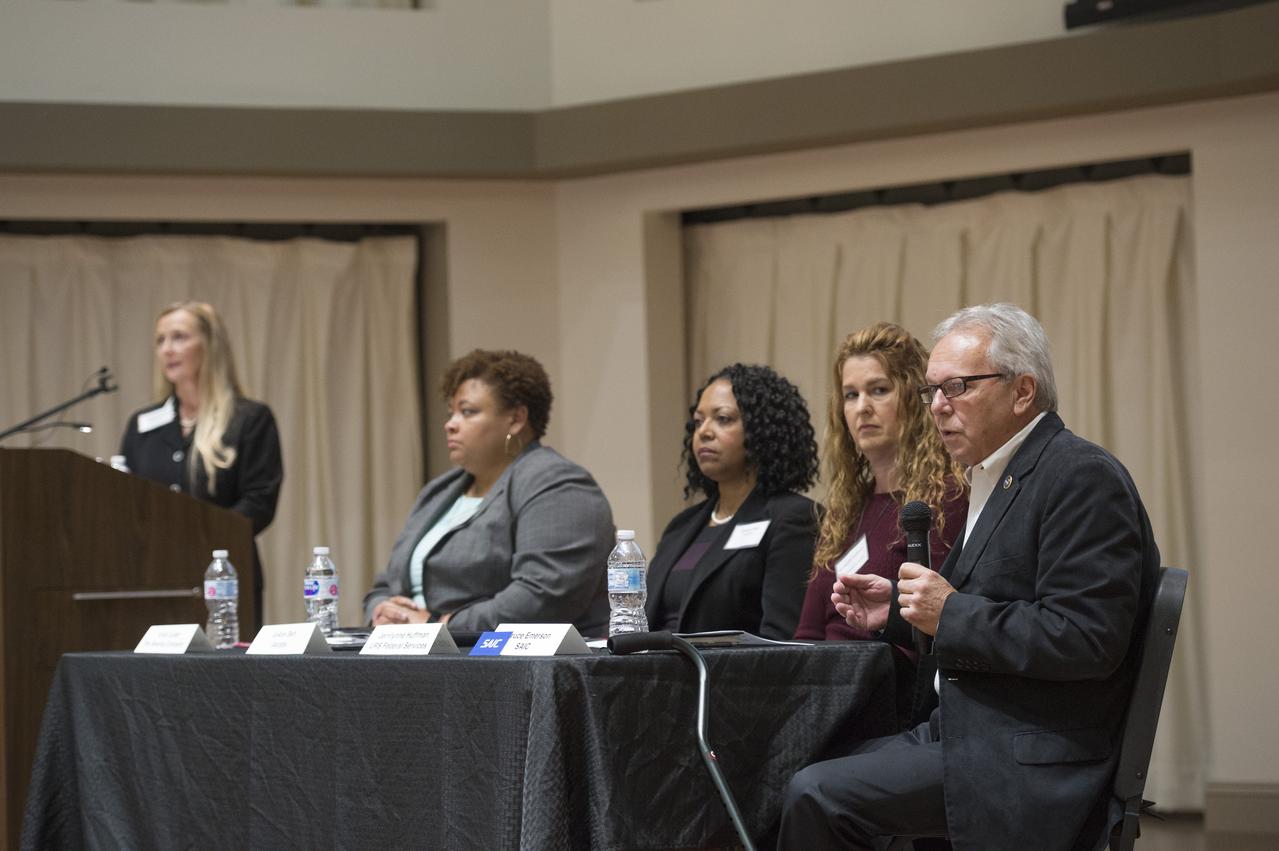

The Morgan County Economic Development Association and the City of Decatur, in Partnership with the NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), hosted a business forum on, How to Launch Your Business with NASA, Wednesday, October 18, 2017, at the Alabama Center for the Arts in downtown Decatur, AL. The event was open to all businesses allowed them to connect with Senior NASA representatives and their prime contractors. The program guided businesses through the process of working with NASA as a supplier, subcontractor, and/or a service provider. The Marshall Space Flight Center’s projected procurement budget in FY 2018 is approximately $2.2 billion and numerous procurement opportunities are available for small business participation each fiscal year. The program included Todd May, Director of Marshall Space Flight Center; Johnny Stephenson, Director of Marshall Space Flight Center’s Office of Strategic Analysis and Communication; David Brock, Small Business Specialist with Marshall Space Flight Center; and Lynn Garrison, Small Business Specialist Technical Advisor with Marshall Space Flight Center. Additionally, there was a prime contractor panel consisting of representatives from five NASA prime contractors. The event included a dedicated networking session with those prime contractors. The “Launch Your Business With NASA” event provides those in attendance the opportunity to network with key Marshall Space Flight Center procurement and technical personnel, and representatives of several major Marshall Space Flight Center prime contractors.Arts.
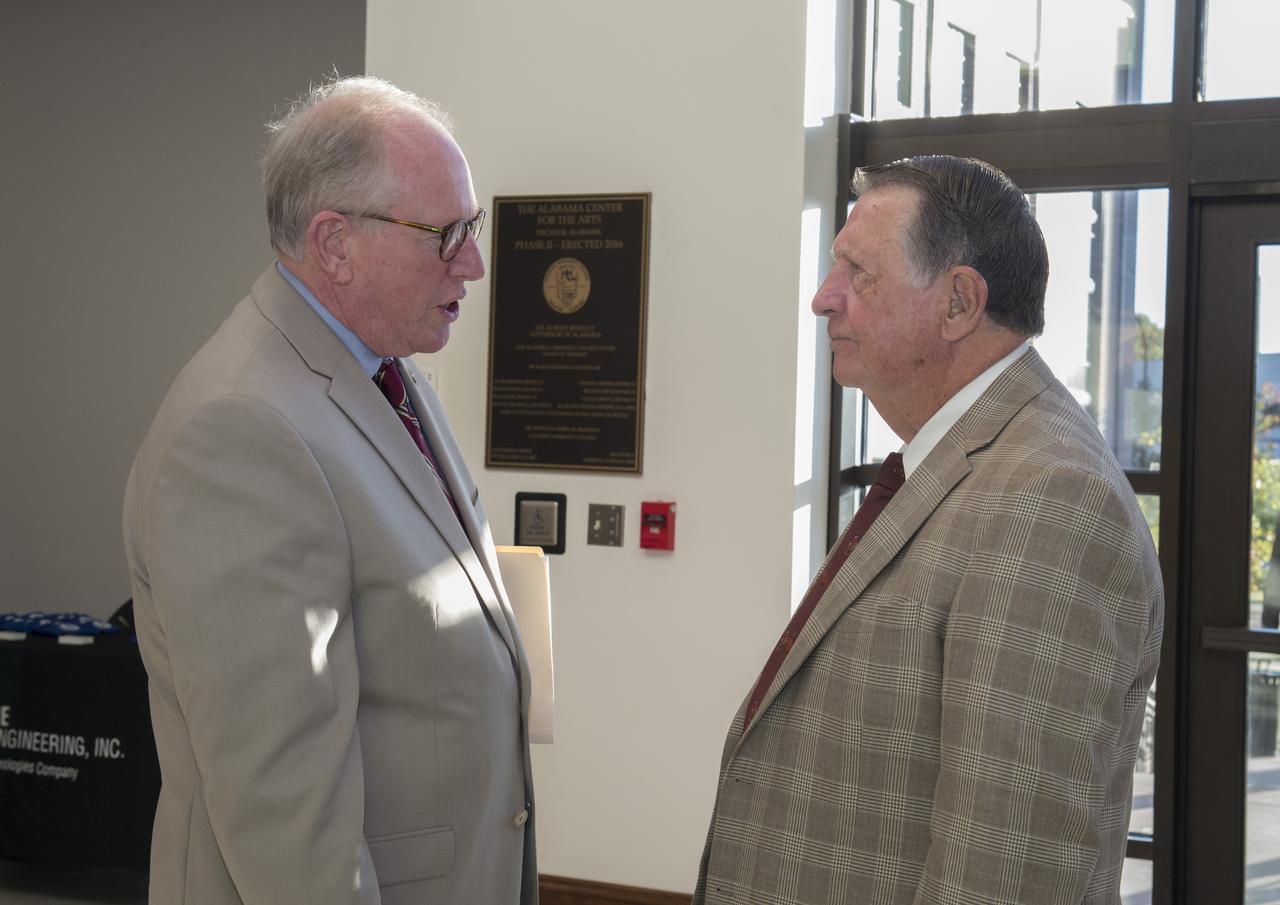

The Morgan County Economic Development Association and the City of Decatur, in Partnership with the NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), hosted a business forum on, How to Launch Your Business with NASA, Wednesday, October 18, 2017, at the Alabama Center for the Arts in downtown Decatur, AL. The event was open to all businesses allowed them to connect with Senior NASA representatives and their prime contractors. The program guided businesses through the process of working with NASA as a supplier, subcontractor, and/or a service provider. The Marshall Space Flight Center’s projected procurement budget in FY 2018 is approximately $2.2 billion and numerous procurement opportunities are available for small business participation each fiscal year. The program included Todd May, Director of Marshall Space Flight Center; Johnny Stephenson, Director of Marshall Space Flight Center’s Office of Strategic Analysis and Communication; David Brock, Small Business Specialist with Marshall Space Flight Center; and Lynn Garrison, Small Business Specialist Technical Advisor with Marshall Space Flight Center. Additionally, there was a prime contractor panel consisting of representatives from five NASA prime contractors. The event included a dedicated networking session with those prime contractors. The “Launch Your Business With NASA” event provides those in attendance the opportunity to network with key Marshall Space Flight Center procurement and technical personnel, and representatives of several major Marshall Space Flight Center prime contractors. Decatur Mayor Tab Bowling chats with NASA retiree Don Odum
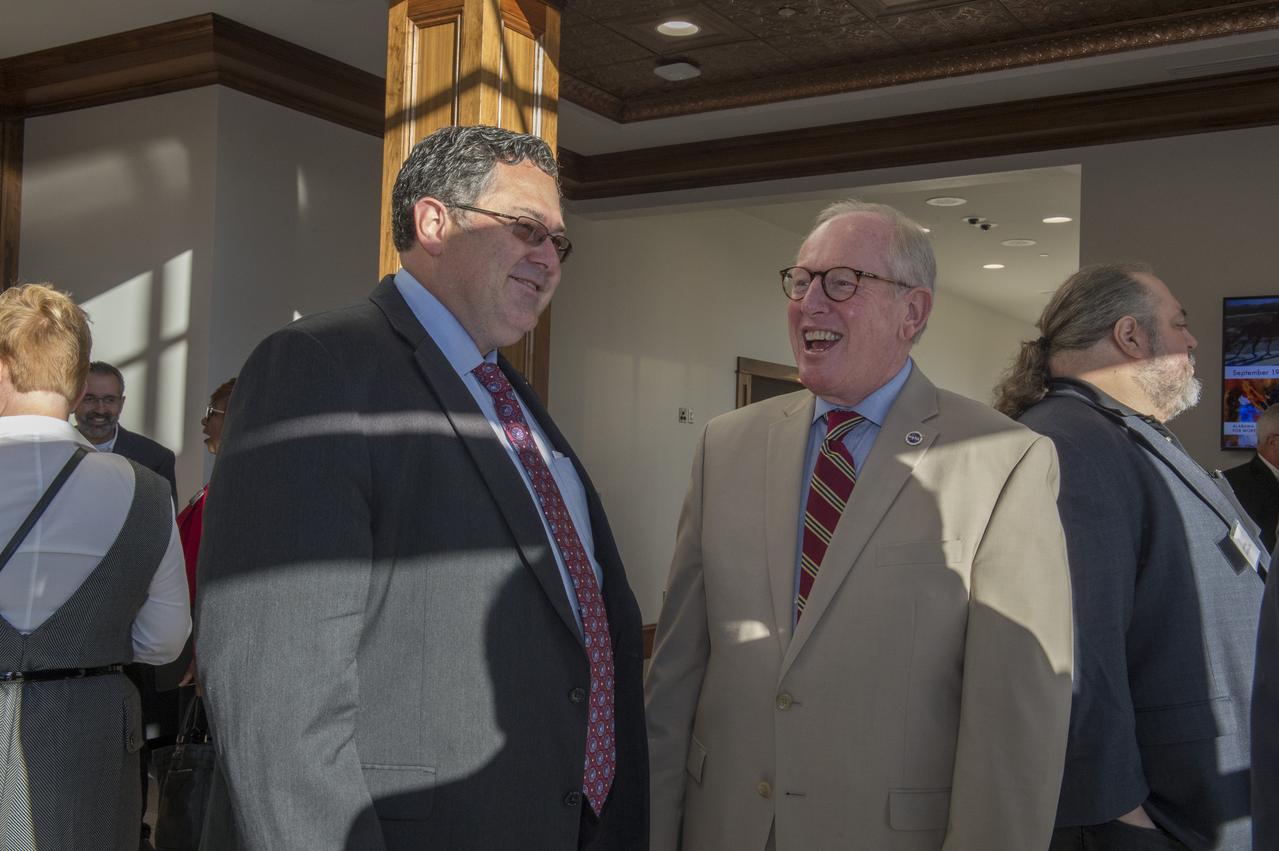

The Morgan County Economic Development Association and the City of Decatur, in Partnership with the NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), hosted a business forum on, How to Launch Your Business with NASA, Wednesday, October 18, 2017, at the Alabama Center for the Arts in downtown Decatur, AL. The event was open to all businesses allowed them to connect with Senior NASA representatives and their prime contractors. The program guided businesses through the process of working with NASA as a supplier, subcontractor, and/or a service provider. The Marshall Space Flight Center’s projected procurement budget in FY 2018 is approximately $2.2 billion and numerous procurement opportunities are available for small business participation each fiscal year. The program included Todd May, Director of Marshall Space Flight Center; Johnny Stephenson, Director of Marshall Space Flight Center’s Office of Strategic Analysis and Communication; David Brock, Small Business Specialist with Marshall Space Flight Center; and Lynn Garrison, Small Business Specialist Technical Advisor with Marshall Space Flight Center. Additionally, there was a prime contractor panel consisting of representatives from five NASA prime contractors. The event included a dedicated networking session with those prime contractors. The “Launch Your Business With NASA” event provides those in attendance the opportunity to network with key Marshall Space Flight Center procurement and technical personnel, and representatives of several major Marshall Space Flight Center prime contractors.Arts. MSFC Director Todd May and Decatur Mayor Tab Bowling enjoy a light moment.

The Morgan County Economic Development Association and the City of Decatur, in Partnership with the NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), hosted a business forum on, How to Launch Your Business with NASA, Wednesday, October 18, 2017, at the Alabama Center for the Arts in downtown Decatur, AL. The event was open to all businesses allowed them to connect with Senior NASA representatives and their prime contractors. The program guided businesses through the process of working with NASA as a supplier, subcontractor, and/or a service provider. The Marshall Space Flight Center’s projected procurement budget in FY 2018 is approximately $2.2 billion and numerous procurement opportunities are available for small business participation each fiscal year. The program included Todd May, Director of Marshall Space Flight Center; Johnny Stephenson, Director of Marshall Space Flight Center’s Office of Strategic Analysis and Communication; David Brock, Small Business Specialist with Marshall Space Flight Center; and Lynn Garrison, Small Business Specialist Technical Advisor with Marshall Space Flight Center. Additionally, there was a prime contractor panel consisting of representatives from five NASA prime contractors. The event included a dedicated networking session with those prime contractors. The “Launch Your Business With NASA” event provides those in attendance the opportunity to network with key Marshall Space Flight Center procurement and technical personnel, and representatives of several major Marshall Space Flight Center prime contractors.Arts.. Decatur Mayor Tab Bowling welcomes attendees.
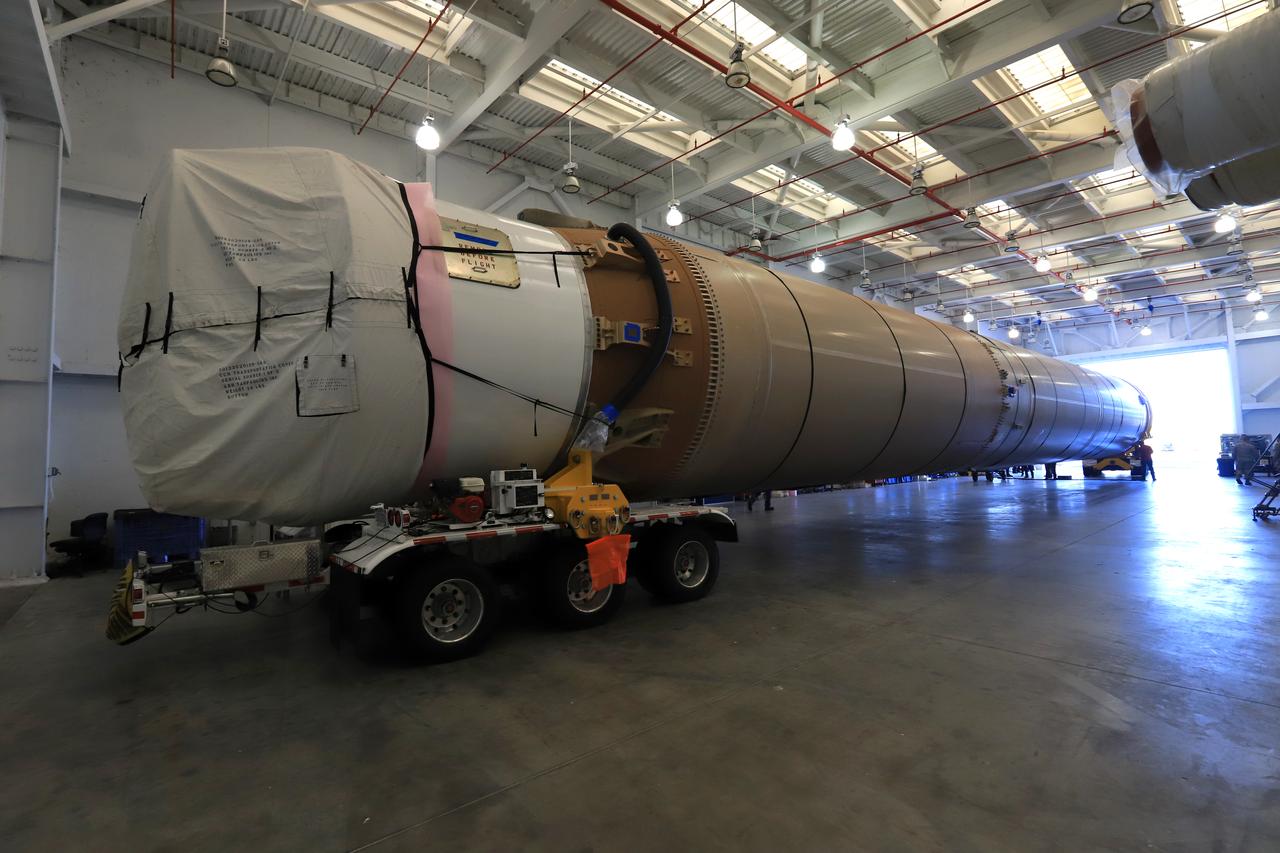

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrives at the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrived at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard ULA's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.
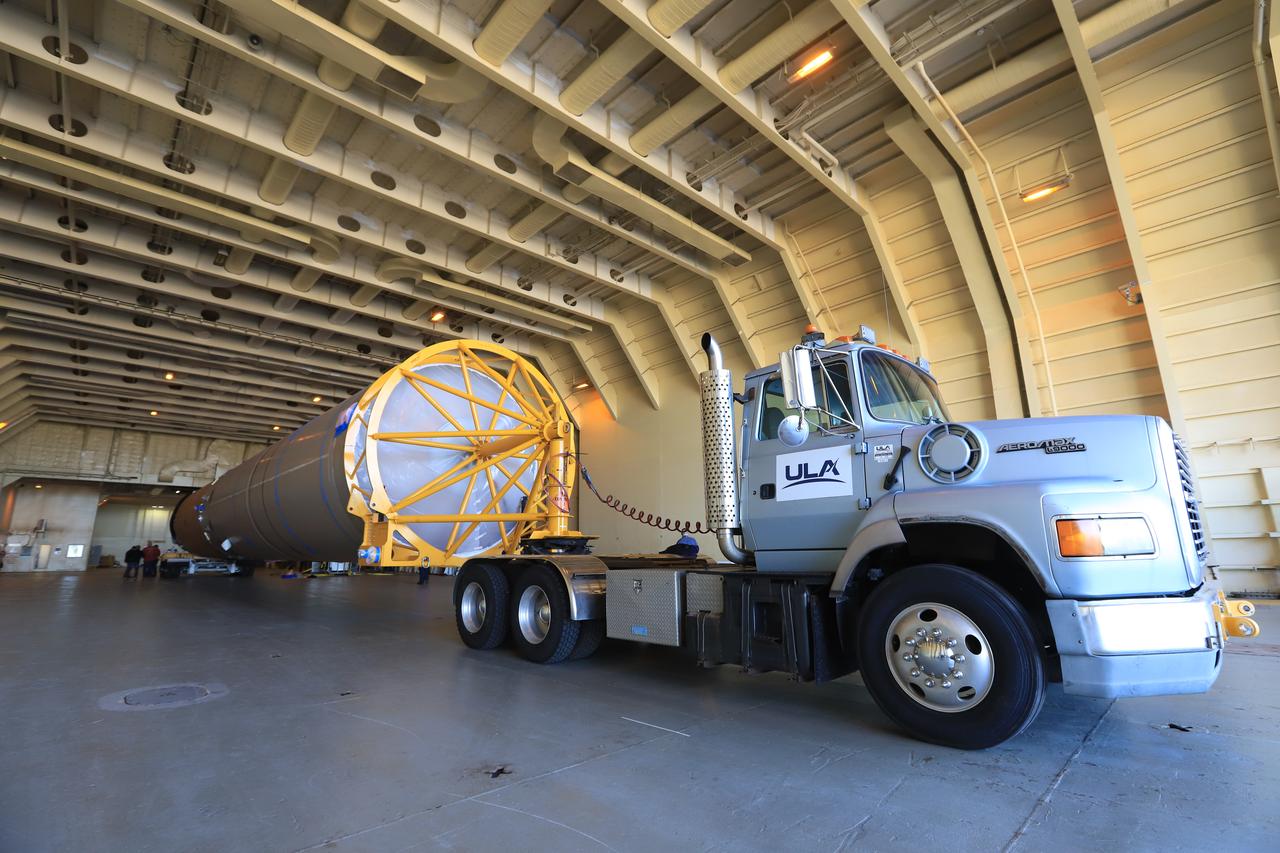
A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stage is in ULA’s factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 29, 2019. The dual engine upper stage is being prepared for Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner Crew Flight Test. Soon the upper stage will be assembled with the first stage booster and shipped aboard the company’s Mariner cargo ship to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key elements of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program to restore the capability to send astronauts to the International Space Station from U.S. soil.
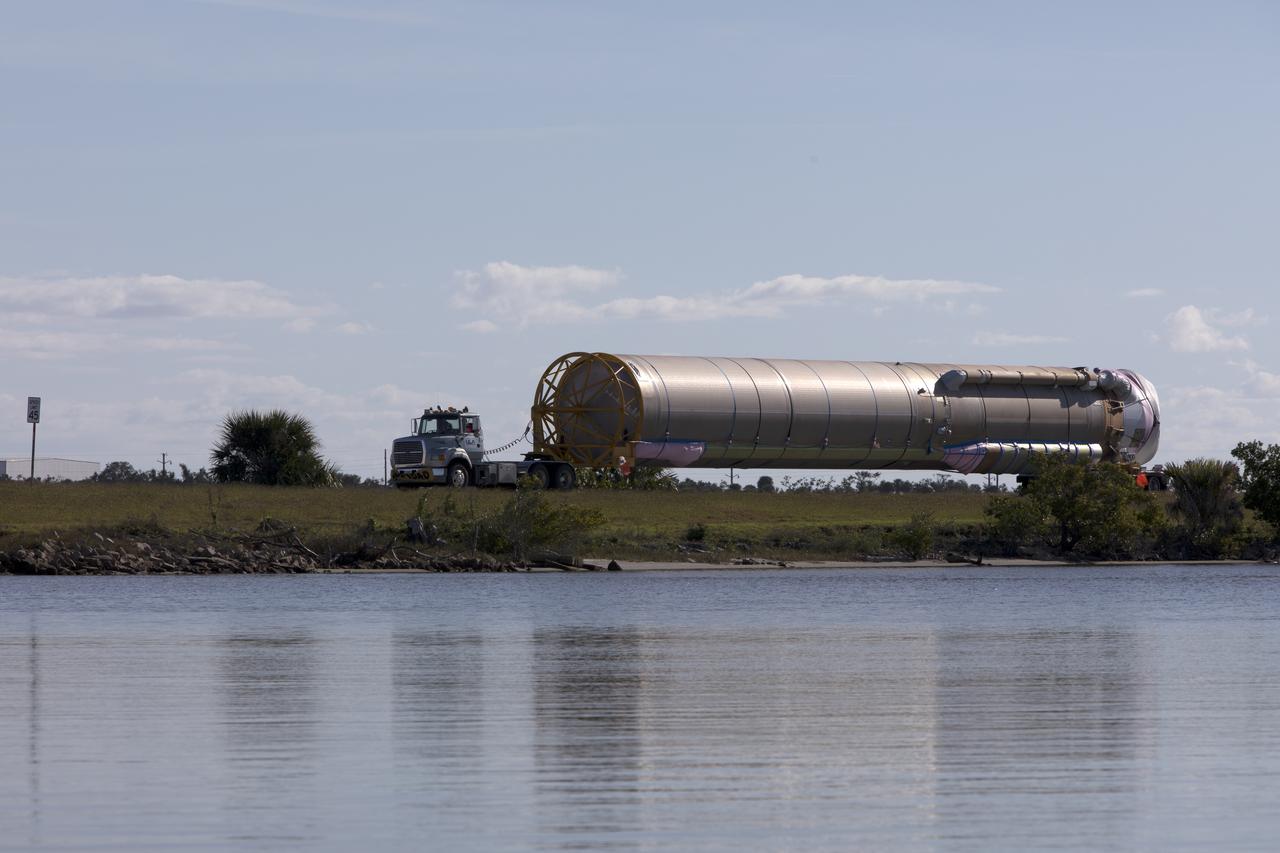

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is on its way to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.

Inside the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, technicians help to secure the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) for NASA's Space Launch System rocket onto a movable transport stand. The ICPS is the first integrated piece of flight hardware to arrive for the SLS. The ICPS arrived from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

Inside the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) for NASA's Space Launch System rocket is secured on a movable transport stand. The ICPS is the first integrated piece of flight hardware to arrive for the SLS. The ICPS arrived from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

Inside the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a crane lowers the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) for NASA's Space Launch System rocket to a movable transport stand. The ICPS is the first integrated piece of flight hardware to arrive for the SLS. The ICPS arrived from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

Inside the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a technician assists as a crane lifts the container cover off of the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) for NASA's Space Launch System rocket. The ICPS is the first integrated piece of flight hardware to arrive for the SLS. The ICPS arrived from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.
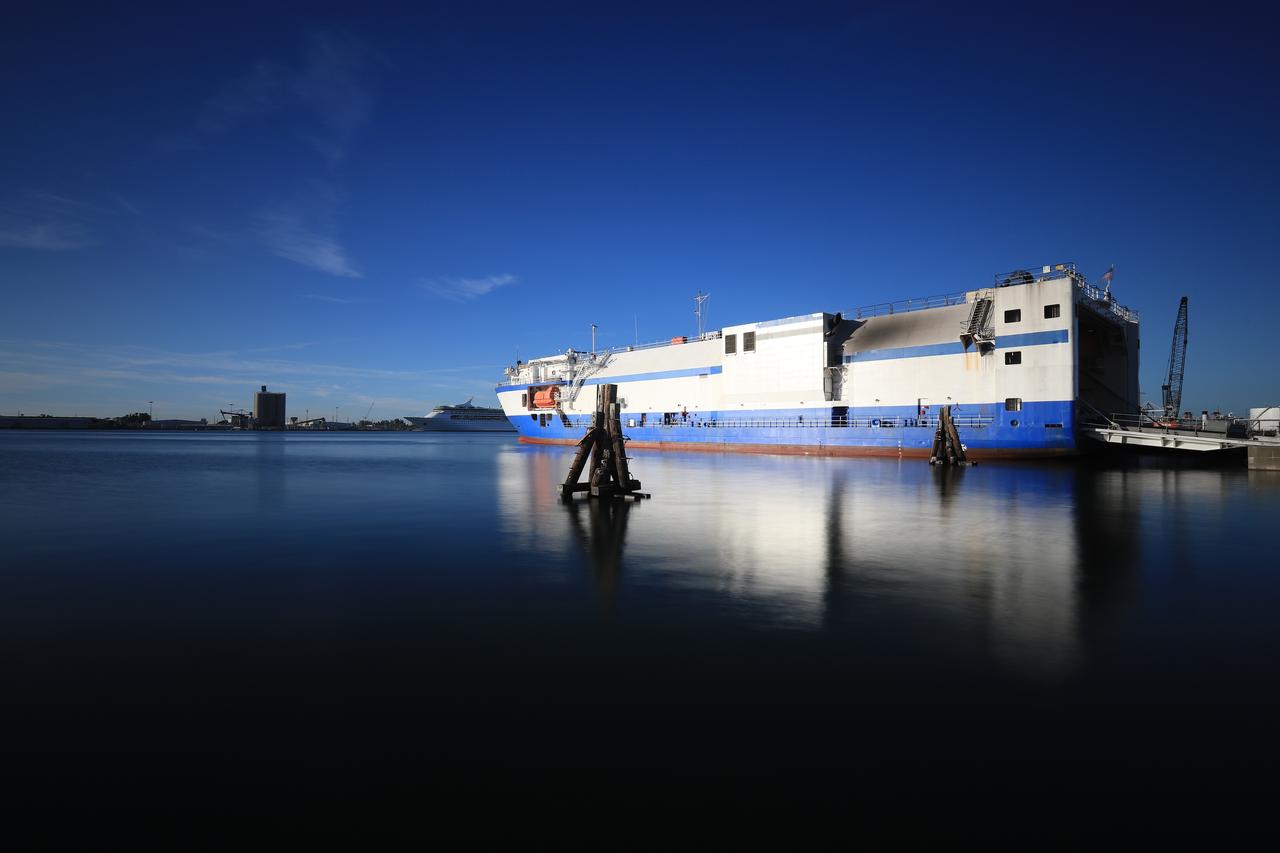

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner cargo vessel arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018, carrying the first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard ULA's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.
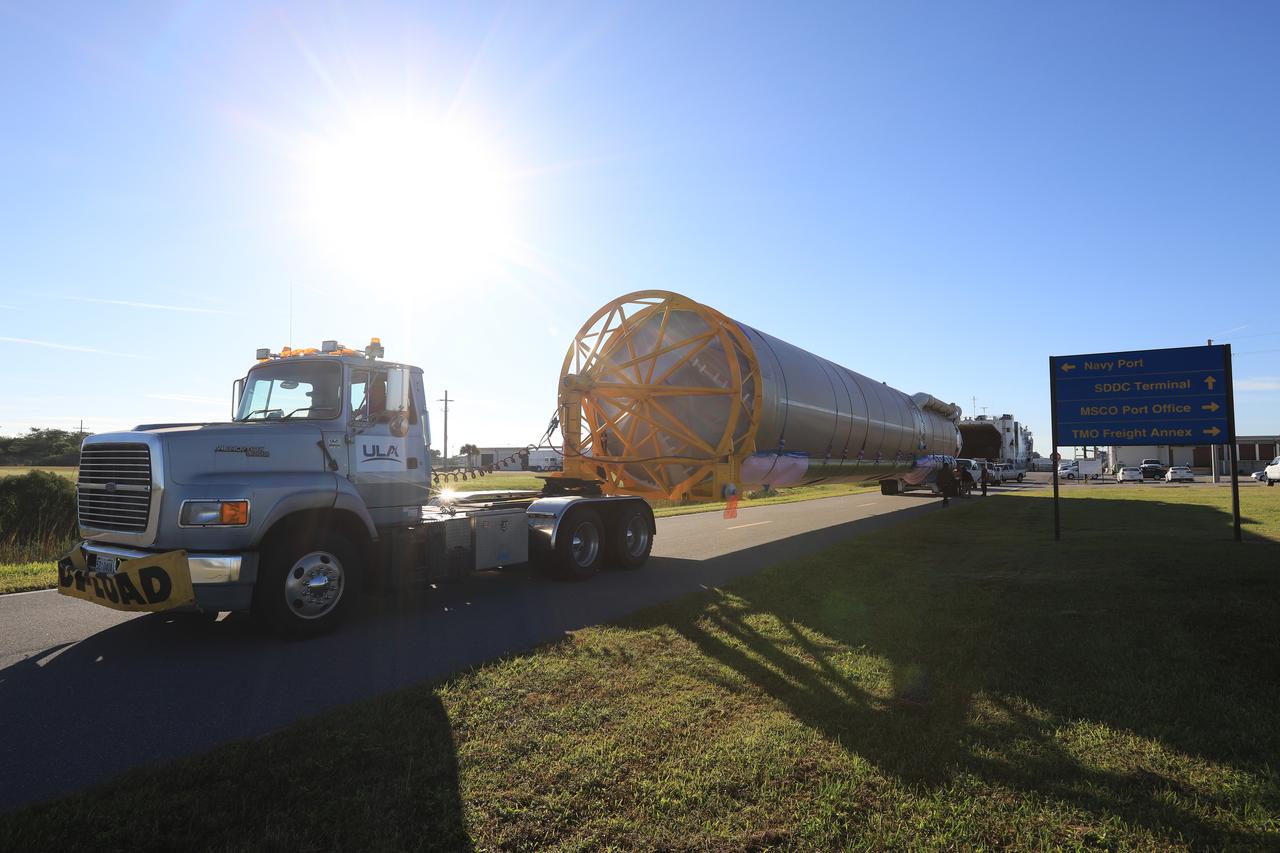

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is on its way to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.
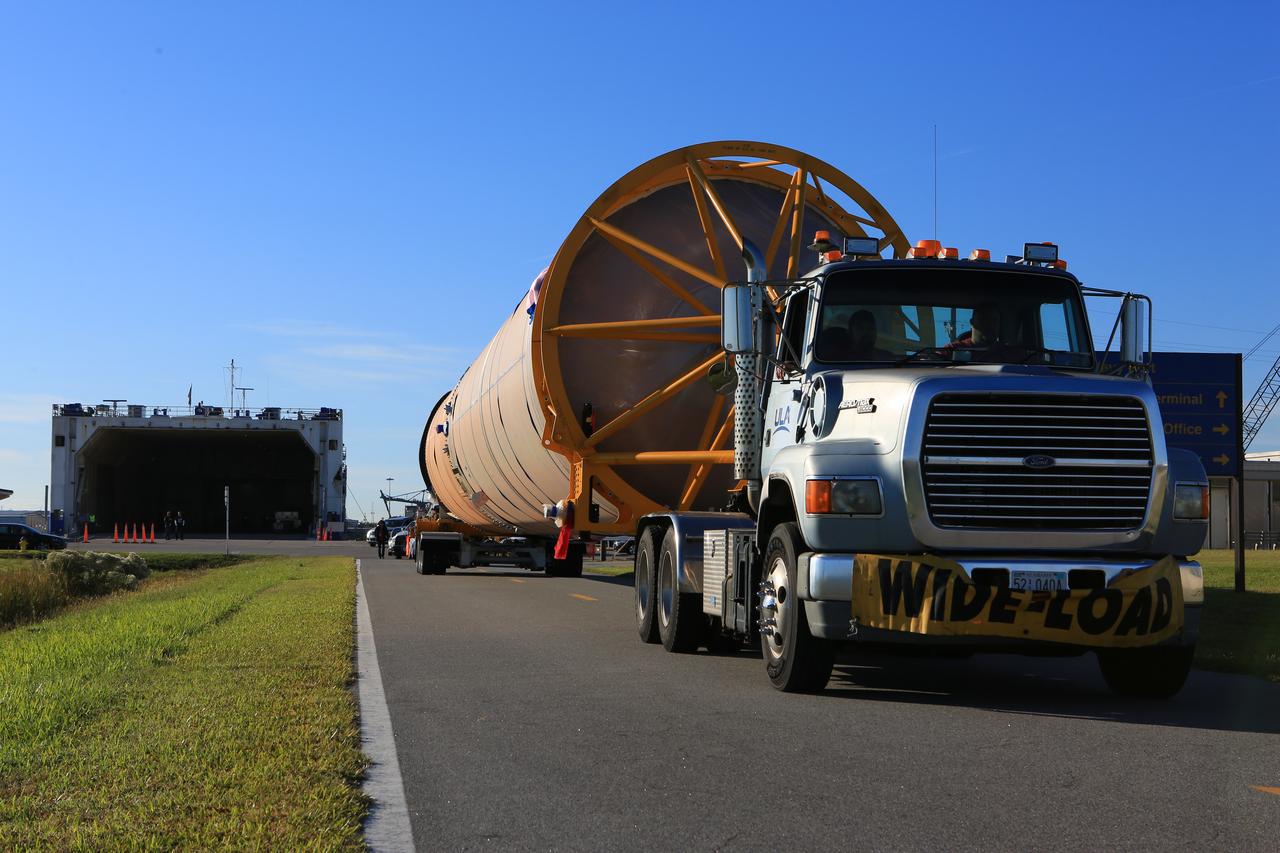

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard ULA's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is on its way to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.

Inside the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Horizontal Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, technicians attach a crane to the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) for NASA's Space Launch System rocket. The ICPS is the first integrated piece of flight hardware to arrive for the SLS. The ICPS arrived from the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. The ICPS is the in-space stage that is located toward the top of the rocket, between the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter and the Orion Spacecraft Adapter. It will provide some of the in-space propulsion during Orion's first flight test atop the SLS on Exploration Mission 1.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster for the Crew Flight Test of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner is in production in ULA's factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 1, 2019. Soon the booster will be assembled with the dual engine Centaur upper stage. They will be shipped aboard the company’s Mariner cargo ship to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key to restoring the nation’s capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann, and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will launch to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Crew Flight Test.

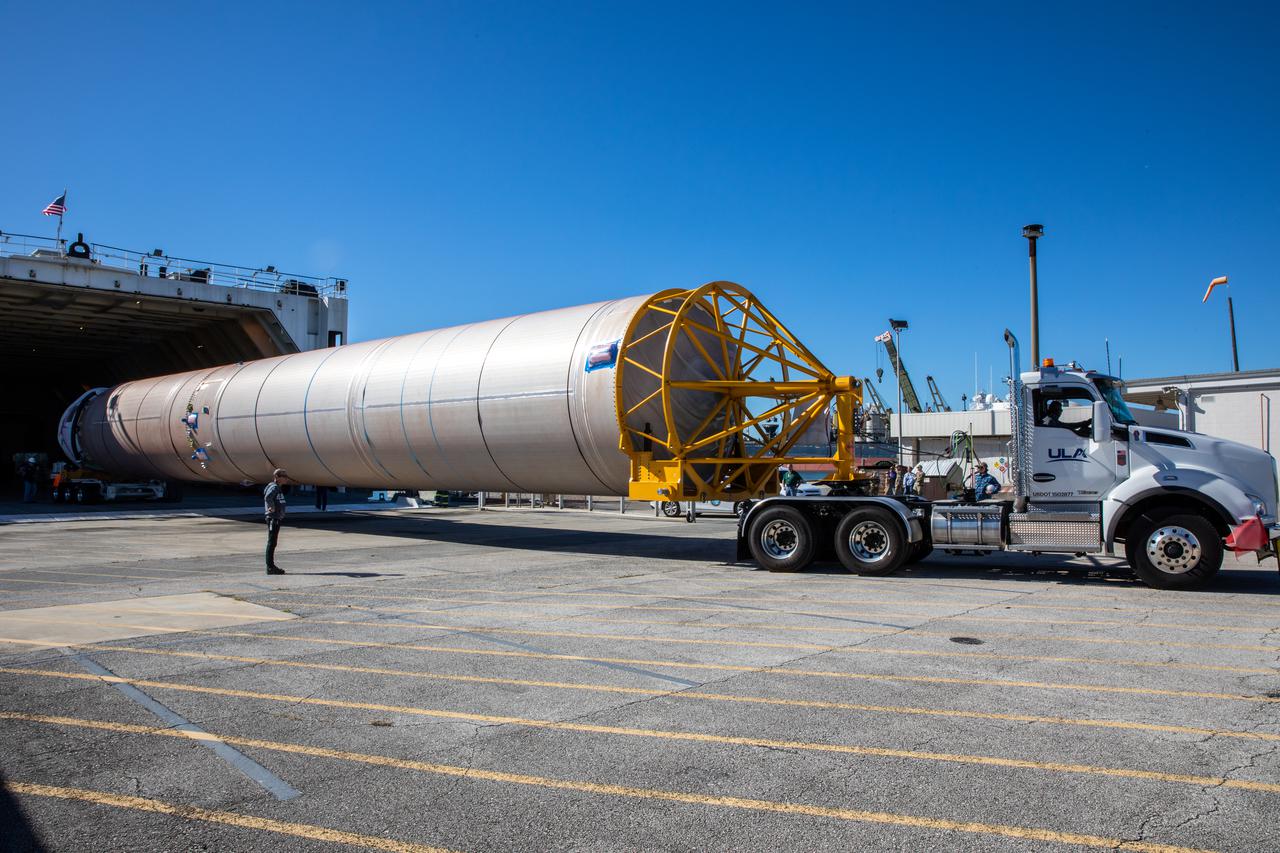
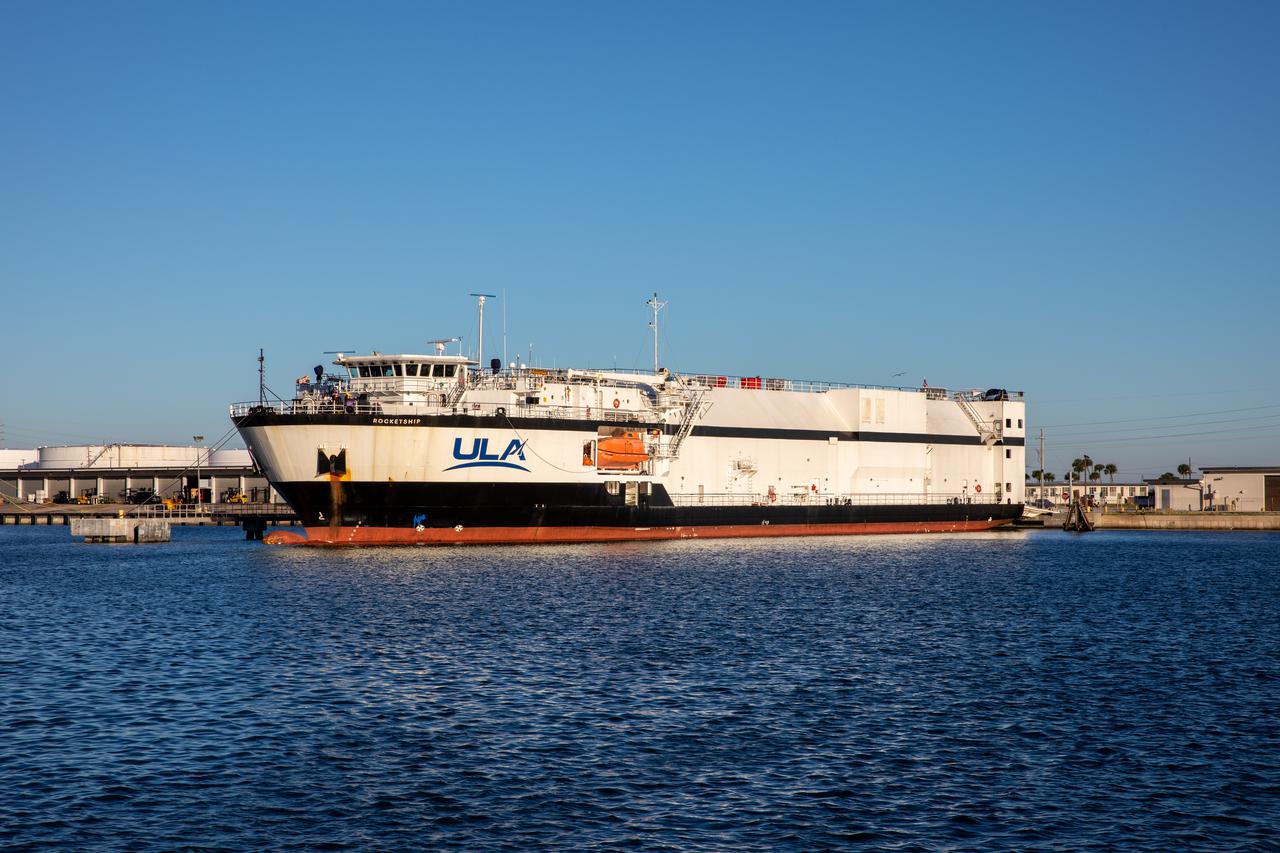
The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is transported by truck from Port Canaveral to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. The company’s Rocketship vessel carried the booster from its manufacturing facility in Decatur, Alabama, to the port. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard the ULA Atlas V rocket.

United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) first stage of the Atlas V 541 rocket is offloaded from the company’s transport boat at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 16, 2021. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
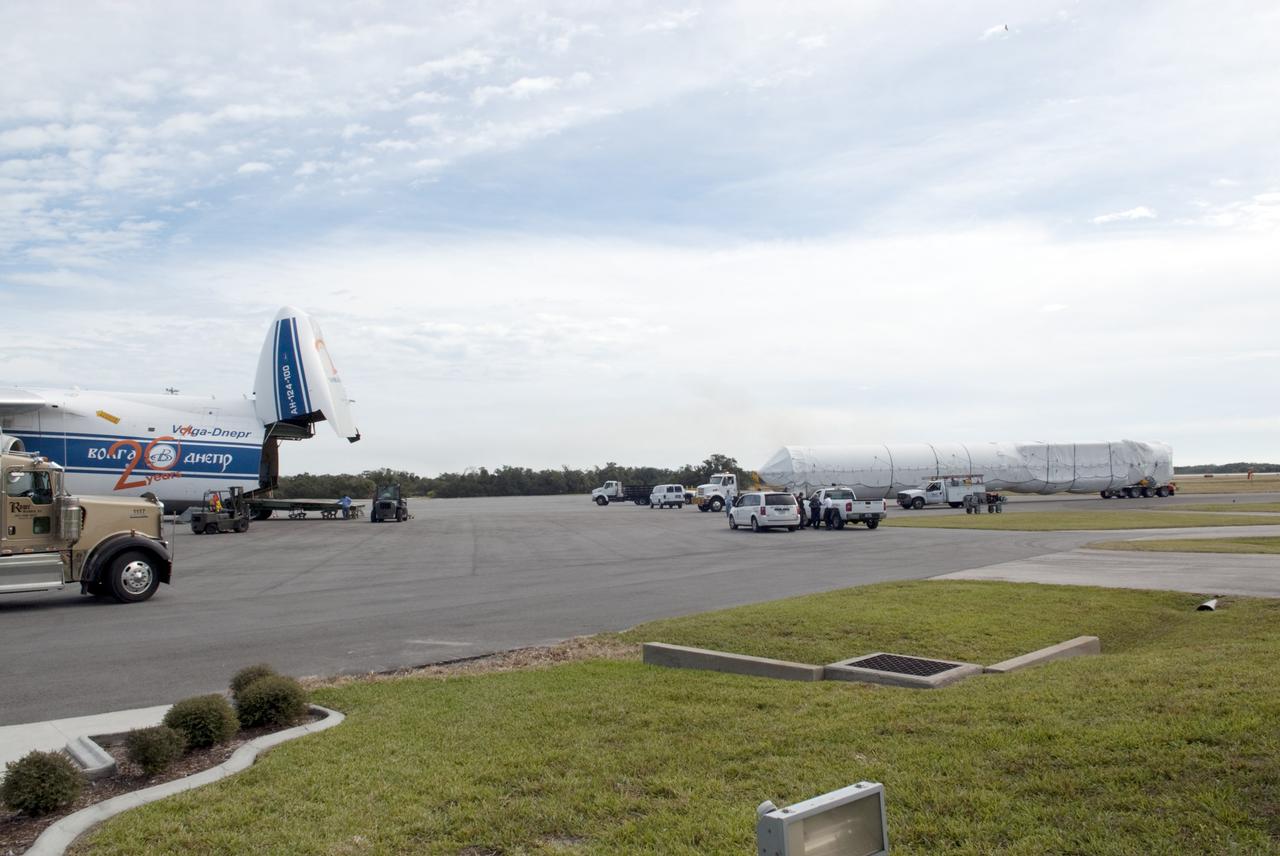

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The first stage of the Atlas V rocket that will carry the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-K, into orbit has been off loaded from a Ukrainian Antonov-124 transport aircraft after its arrival at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The booster stage was delivered from the United Launch Alliance manufacturing plant in Decatur, Ala., and will be taken to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral to begin processing. Launch of the TDRS-K on the Atlas V rocket is planned for January 2013 from Space Launch Complex 41. The TDRS-K spacecraft is part of the next-generation series in the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System, a constellation of space-based communication satellites providing tracking, telemetry, command and high-bandwidth data return services. For more information, visit http://tdrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
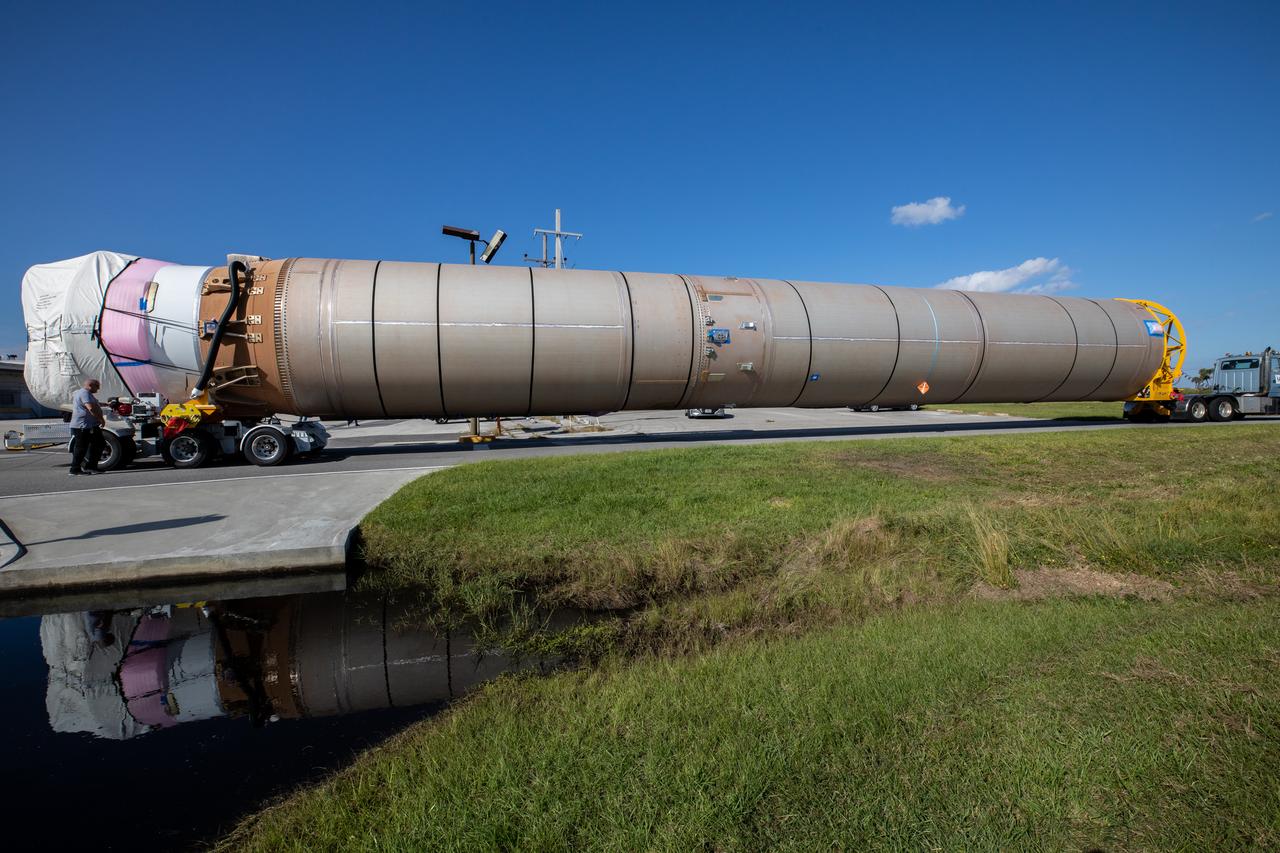

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is transported by truck from Port Canaveral to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. The company’s Rocketship vessel carried the booster from its manufacturing facility in Decatur, Alabama, to the port. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard the ULA Atlas V rocket.
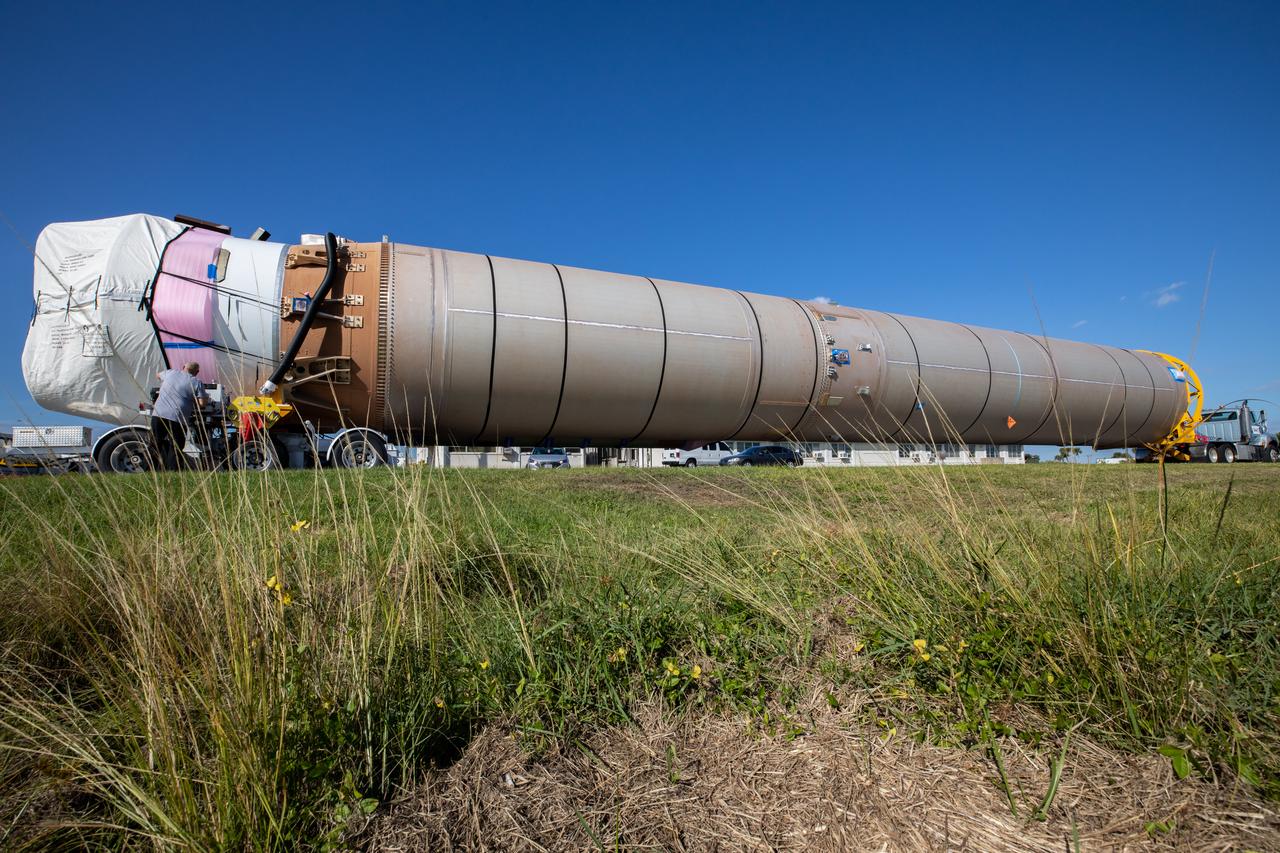

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is transported by truck from Port Canaveral to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. The company’s Rocketship vessel carried the booster from its manufacturing facility in Decatur, Alabama, to the port. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard the ULA Atlas V rocket.
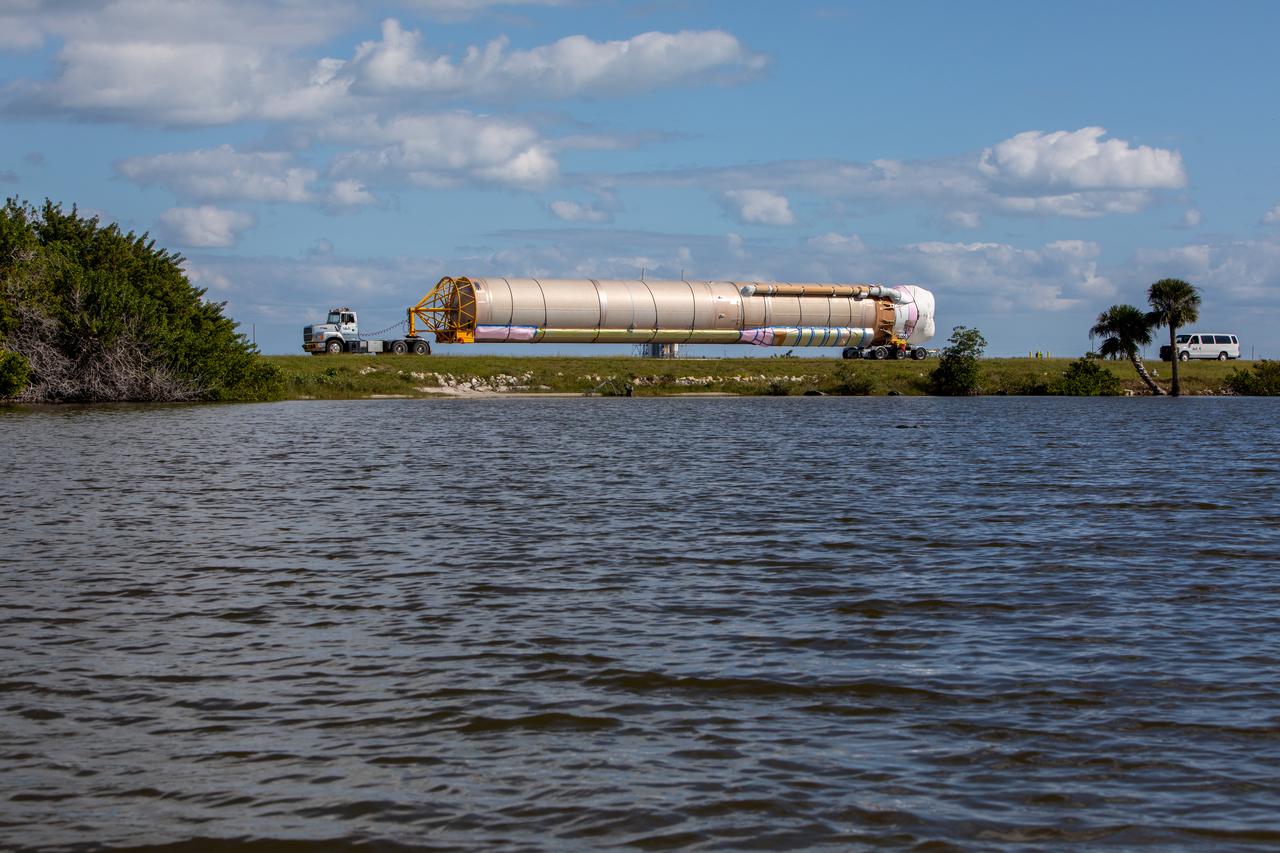

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is transported by truck from Port Canaveral to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. The company’s Rocketship vessel carried the booster from its manufacturing facility in Decatur, Alabama, to the port. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard the ULA Atlas V rocket.

United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) first and second stages of the Atlas V 541 rocket are offloaded from the company’s transport boat at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 16, 2021. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The first stage of the Atlas V rocket that will carry the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-K, into orbit is off loaded from a Ukrainian Antonov-124 transport aircraft after its arrival at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The booster stage was delivered from the United Launch Alliance manufacturing plant in Decatur, Ala., and will be taken to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral to begin processing. Launch of the TDRS-K on the Atlas V rocket is planned for January 2013 from Space Launch Complex 41. The TDRS-K spacecraft is part of the next-generation series in the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System, a constellation of space-based communication satellites providing tracking, telemetry, command and high-bandwidth data return services. For more information, visit http://tdrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
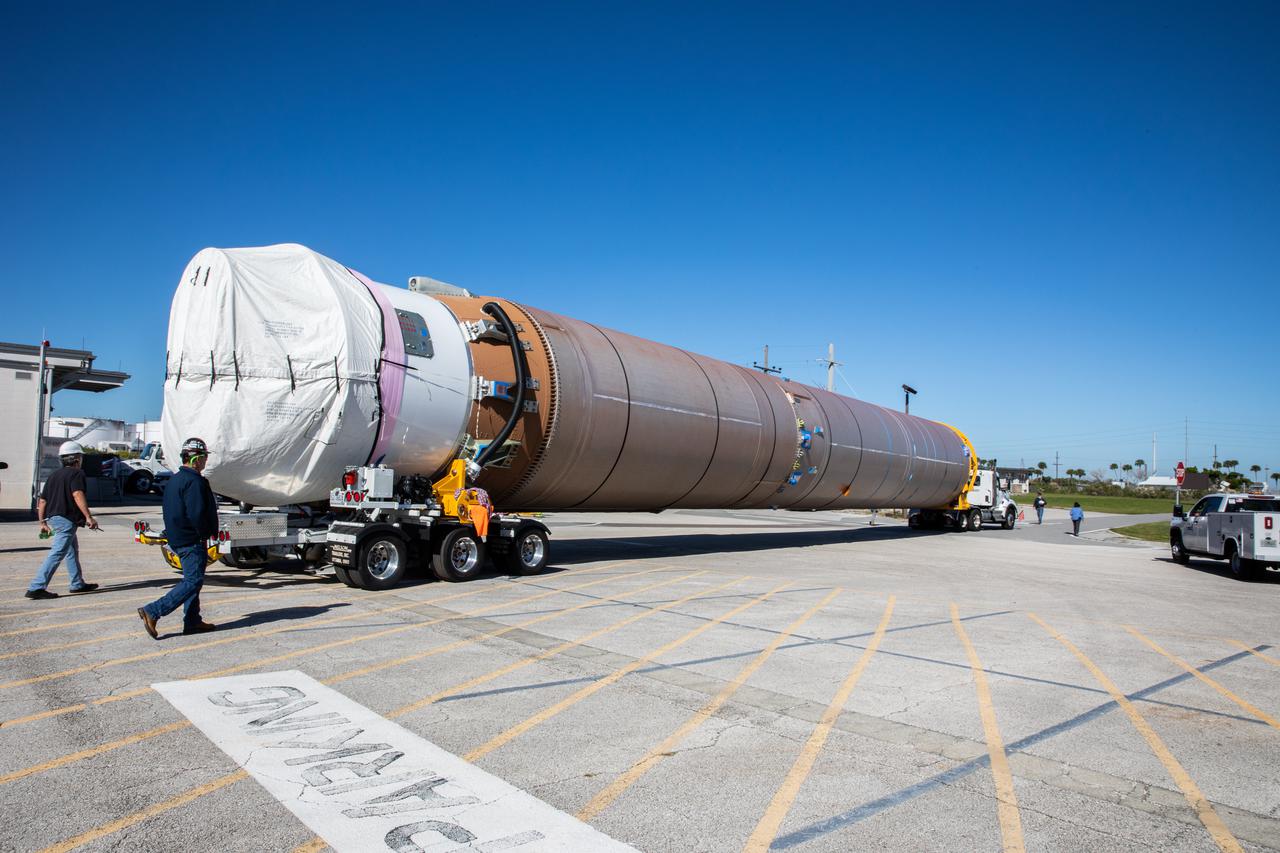

United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) first stage of the Atlas V 541 rocket is offloaded from the company’s transport boat at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 16, 2021. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
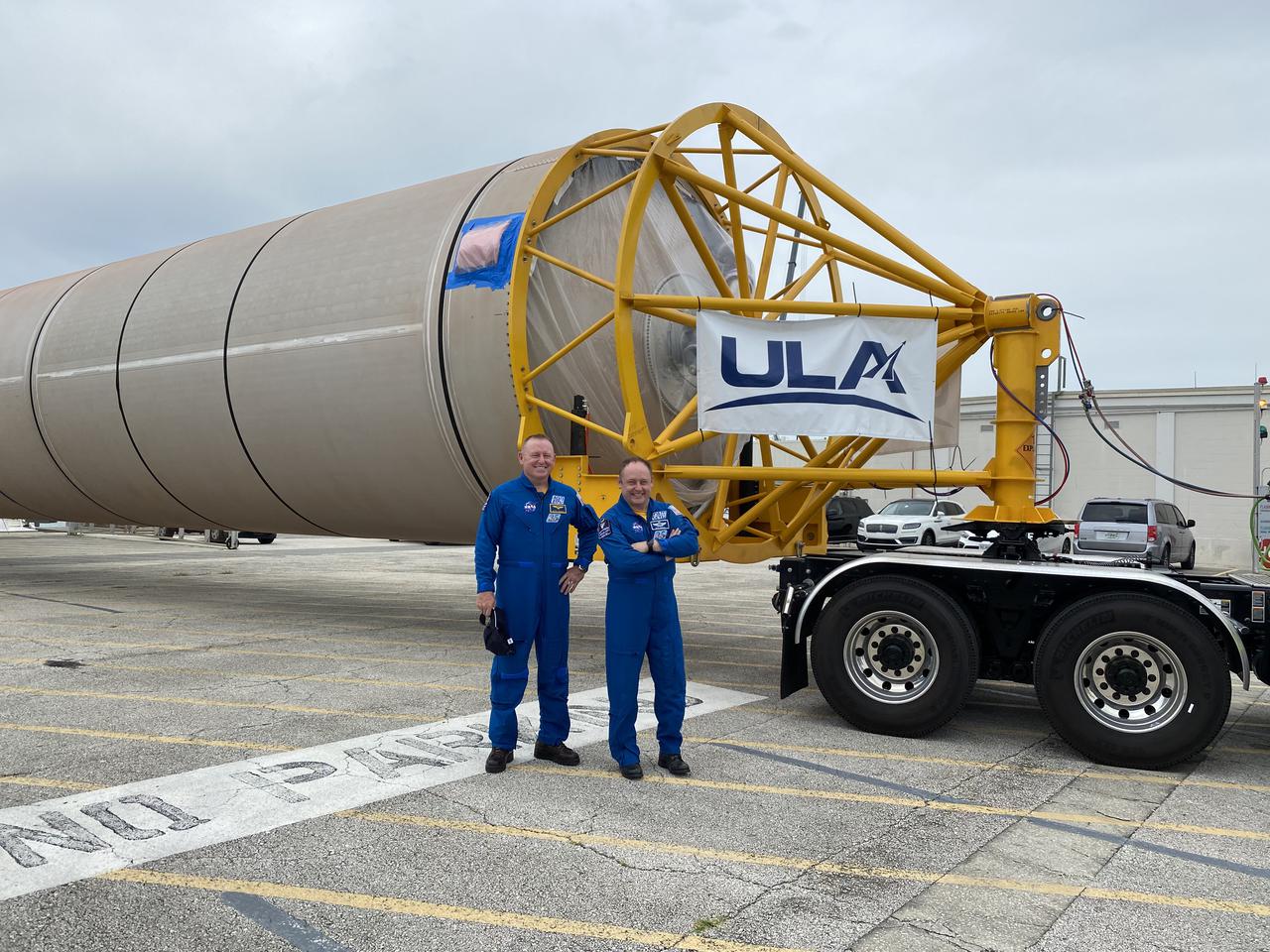

NASA astronauts Barry “Butch” Wilmore, left, Mike Fincke, right, welcome the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will transport them and NASA astronaut Nicole Mann to the International Space Station on Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft for the company’s Crew Flight Test (CFT). The Atlas V rocket arrived at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS), Florida on June 21, 2021, after its journey on a rocket-delivery ship from ULA’s manufacturing factory in Decatur, Alabama. Starliner’s first flight with astronauts aboard, CFT will launch from Space Launch Complex-41 at CCSFS. The flight test will demonstrate the ability of the Atlas V and Starliner to safely carry astronauts to and from the space station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
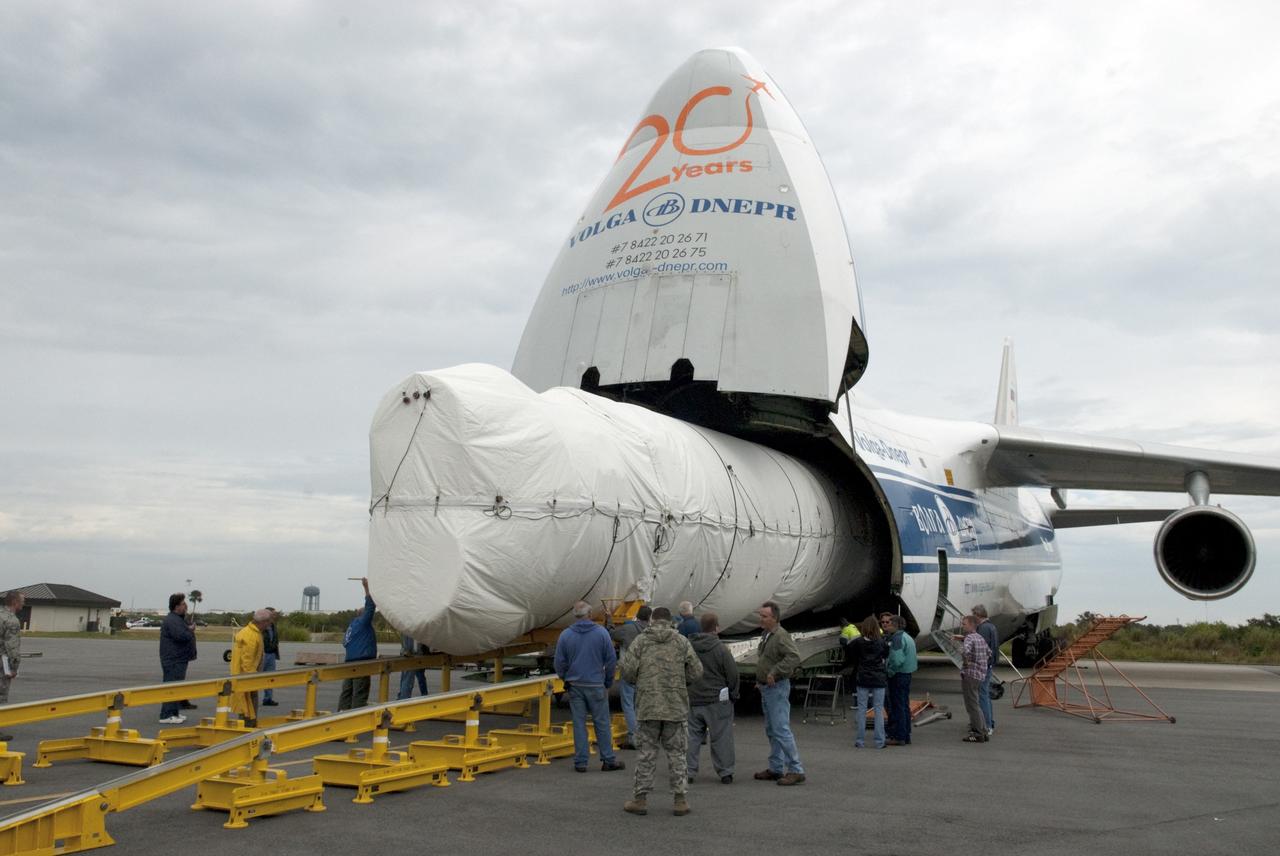

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The first stage of the Atlas V rocket that will carry the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-K, into orbit is off loaded from a Ukrainian Antonov-124 transport aircraft after its arrival at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The booster stage was delivered from the United Launch Alliance manufacturing plant in Decatur, Ala., and will be taken to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral to begin processing. Launch of the TDRS-K on the Atlas V rocket is planned for January 2013 from Space Launch Complex 41. The TDRS-K spacecraft is part of the next-generation series in the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System, a constellation of space-based communication satellites providing tracking, telemetry, command and high-bandwidth data return services. For more information, visit http://tdrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
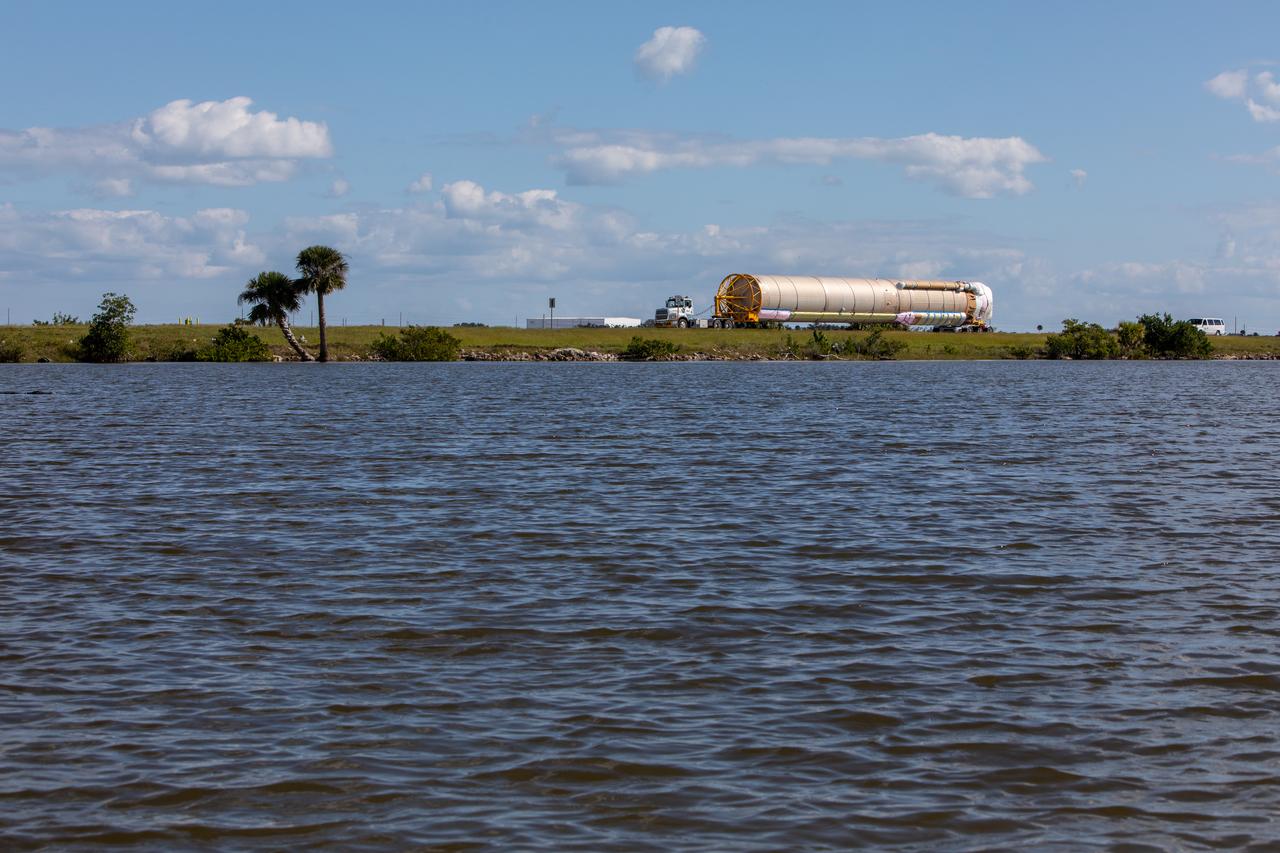

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is transported by truck from Port Canaveral to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. The company’s Rocketship vessel carried the booster from its manufacturing facility in Decatur, Alabama, to the port. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard the ULA Atlas V rocket.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The first stage of the Atlas V rocket that will carry the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-K, into orbit has been off loaded from a Ukrainian Antonov-124 transport aircraft after its arrival at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The booster stage was delivered from the United Launch Alliance manufacturing plant in Decatur, Ala., and will be taken to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral to begin processing. Launch of the TDRS-K on the Atlas V rocket is planned for January 2013 from Space Launch Complex 41. The TDRS-K spacecraft is part of the next-generation series in the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System, a constellation of space-based communication satellites providing tracking, telemetry, command and high-bandwidth data return services. For more information, visit http://tdrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is delivered by truck to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. The company’s Rocketship vessel carried the booster from its manufacturing facility in Decatur, Alabama, to Port Canaveral. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard the ULA Atlas V rocket.

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) transport boat carrying the first and second stages of the company’s Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 15, 2021. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is delivered by truck to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. The company’s Rocketship vessel carried the booster from its manufacturing facility in Decatur, Alabama, to Port Canaveral. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard the ULA Atlas V rocket.
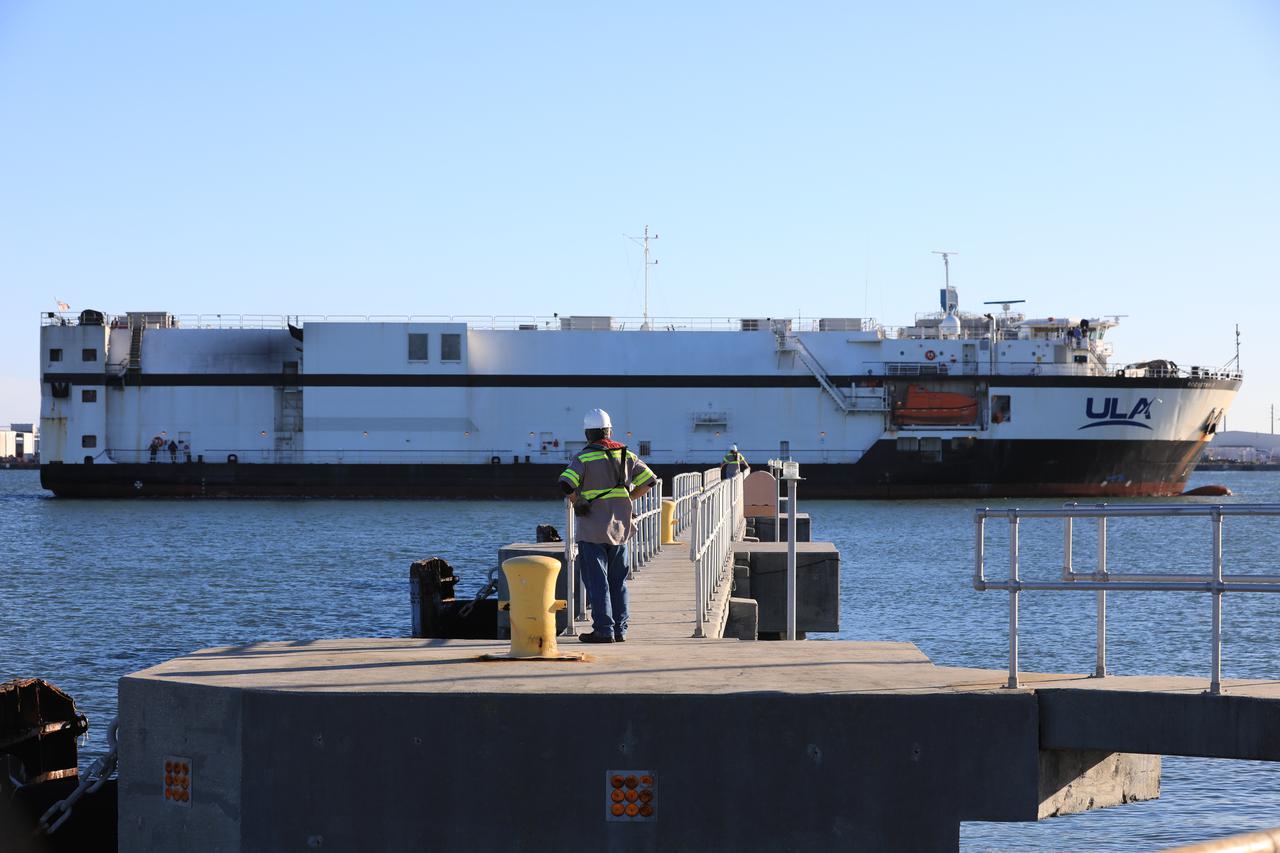

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) transport boat carrying the first and second stages of the company’s Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 15, 2021. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
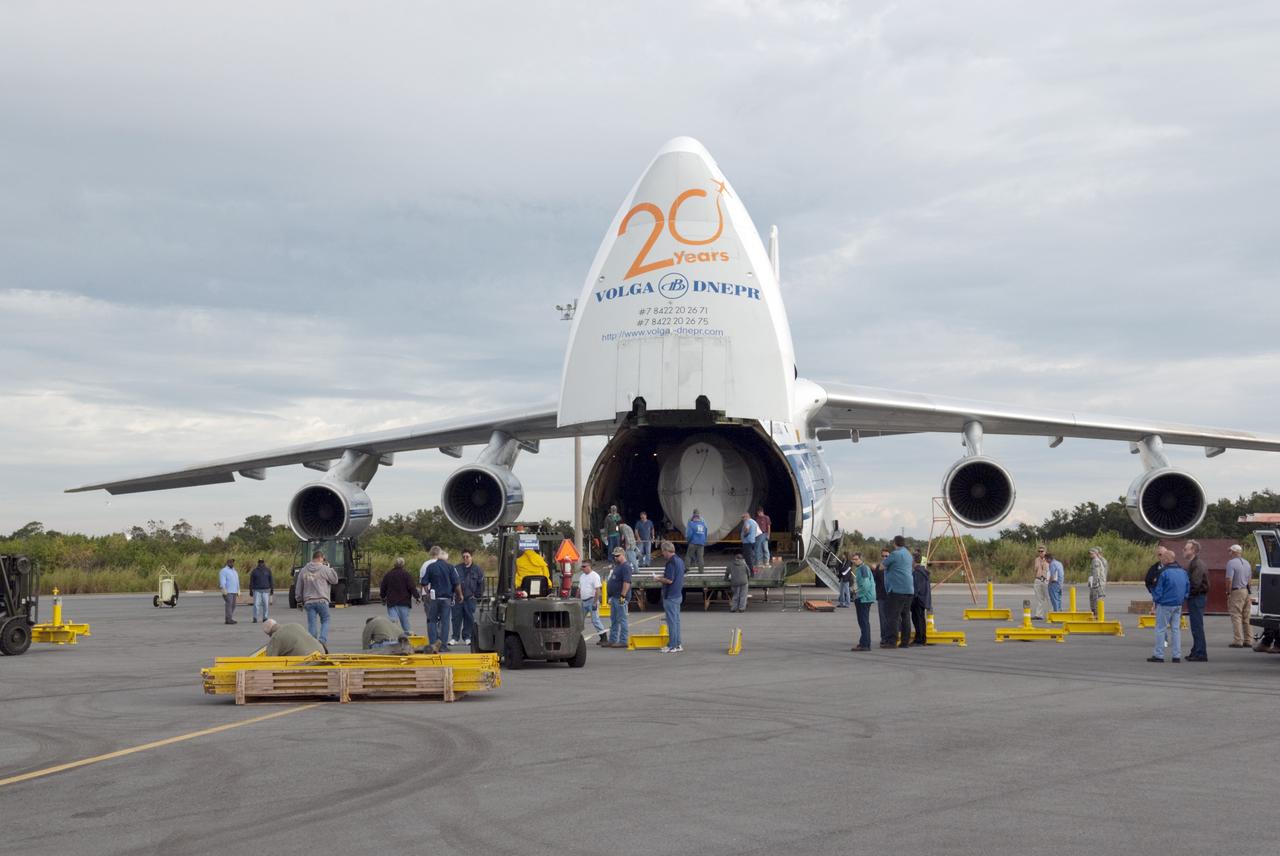

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Ukrainian Antonov-124 transport aircraft arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida with the first stage of the Atlas V rocket that will carry the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-K, into orbit. The booster stage, arriving from the United Launch Alliance manufacturing plant in Decatur, Ala., will be taken to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral to begin processing. Launch of the TDRS-K on the Atlas V rocket is planned for January 2013 from Space Launch Complex 41. The TDRS-K spacecraft is part of the next-generation series in the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System, a constellation of space-based communication satellites providing tracking, telemetry, command and high-bandwidth data return services. For more information, visit http://tdrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) transport boat carrying the first and second stages of the company’s Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 16, 2021. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is delivered by truck to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. The company’s Rocketship vessel carried the booster from its manufacturing facility in Decatur, Alabama, to Port Canaveral. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard the ULA Atlas V rocket.
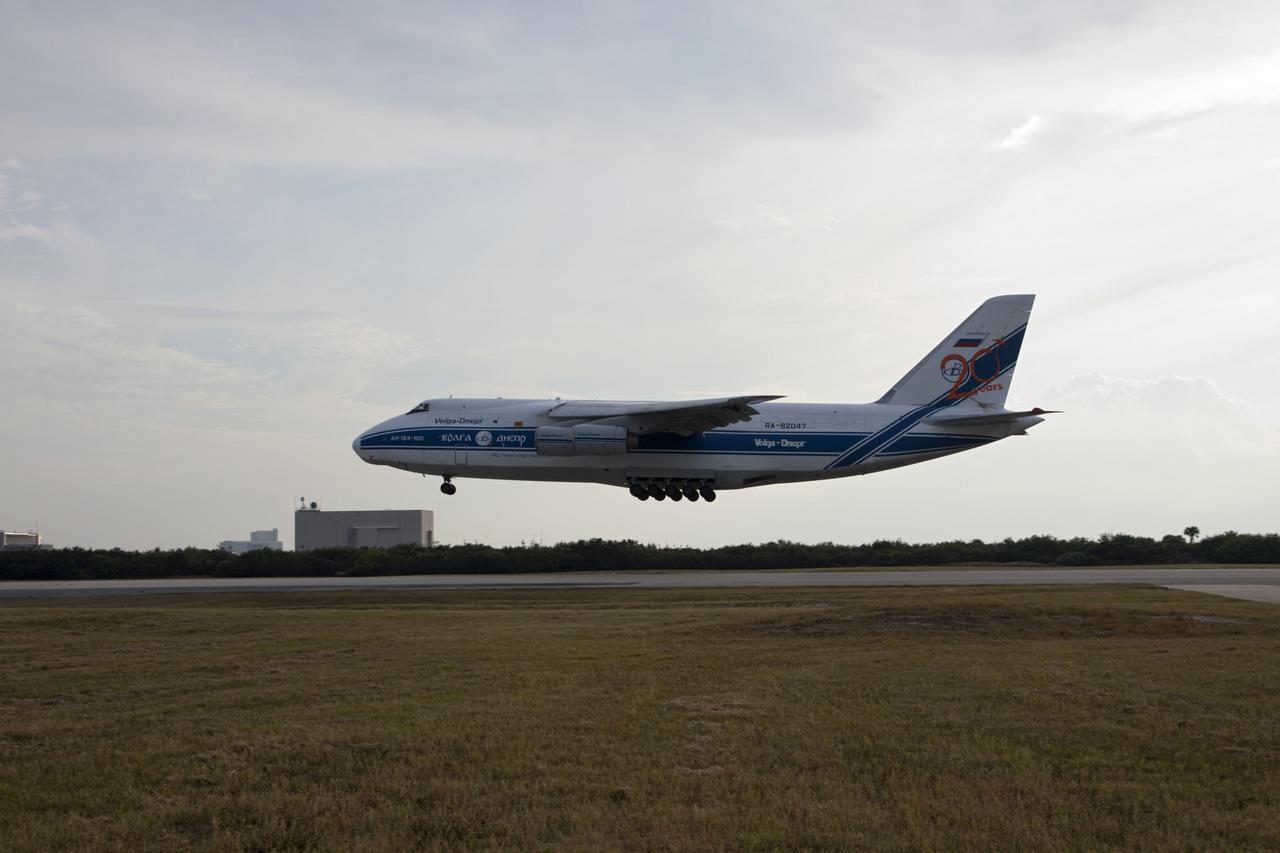

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Ukrainian Antonov-124 transport aircraft prepares to touch down at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida with the first stage of the Atlas V rocket that will carry the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-K, into orbit. The booster stage, arriving from the United Launch Alliance manufacturing plant in Decatur, Ala., will be taken to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral. Launch of the TDRS-K on the Atlas V rocket is planned for January 2013 from Space Launch Complex 41. The TDRS-K spacecraft is part of the next-generation series in the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System, a constellation of space-based communication satellites providing tracking, telemetry, command and high-bandwidth data return services. For more information, visit http://tdrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
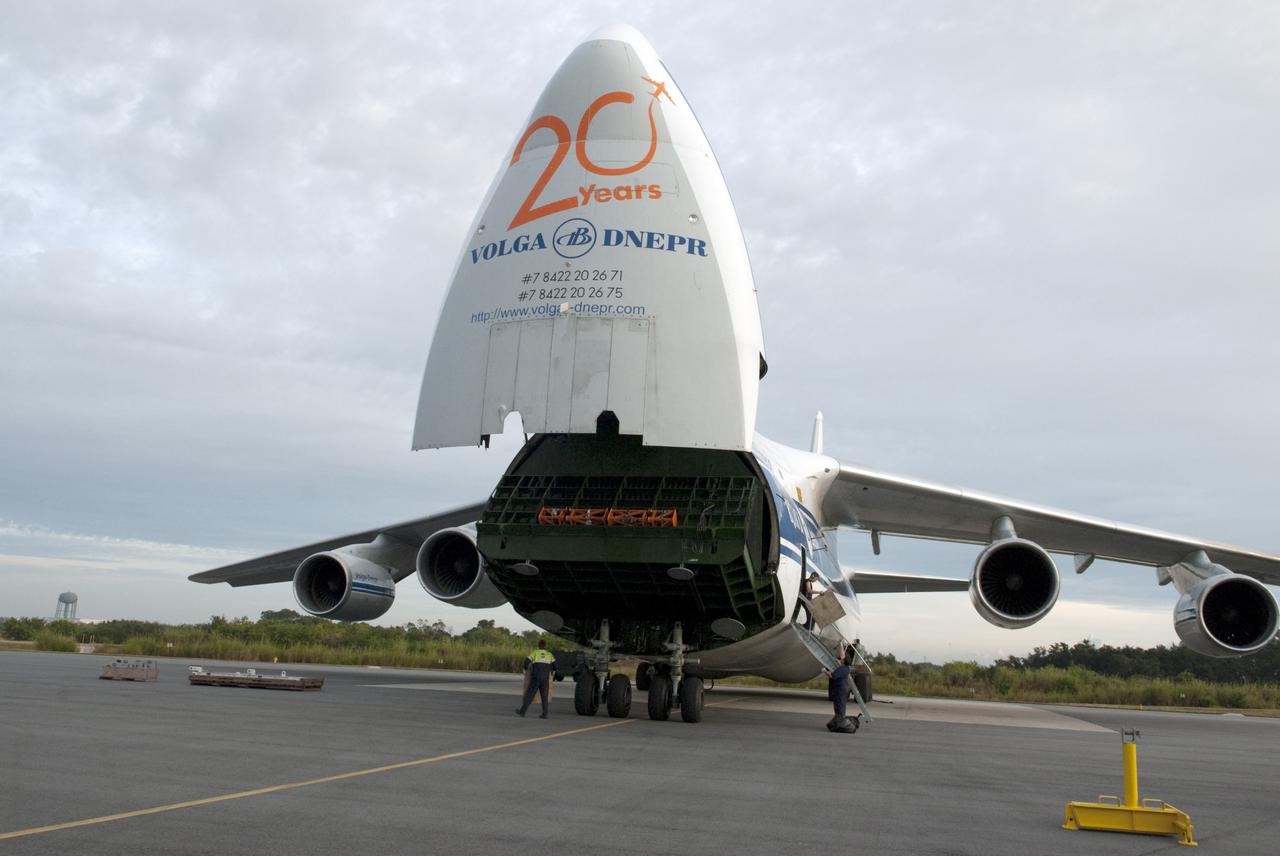

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Ukrainian Antonov-124 transport aircraft arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida with the first stage of the Atlas V rocket that will carry the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-K, into orbit. The booster stage, arriving from the United Launch Alliance manufacturing plant in Decatur, Ala., will be taken to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral to begin processing. Launch of the TDRS-K on the Atlas V rocket is planned for January 2013 from Space Launch Complex 41. The TDRS-K spacecraft is part of the next-generation series in the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System, a constellation of space-based communication satellites providing tracking, telemetry, command and high-bandwidth data return services. For more information, visit http://tdrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) first stage of the Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at the horizontal processing facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 16, 2021, after arriving on the company’s transport boat. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
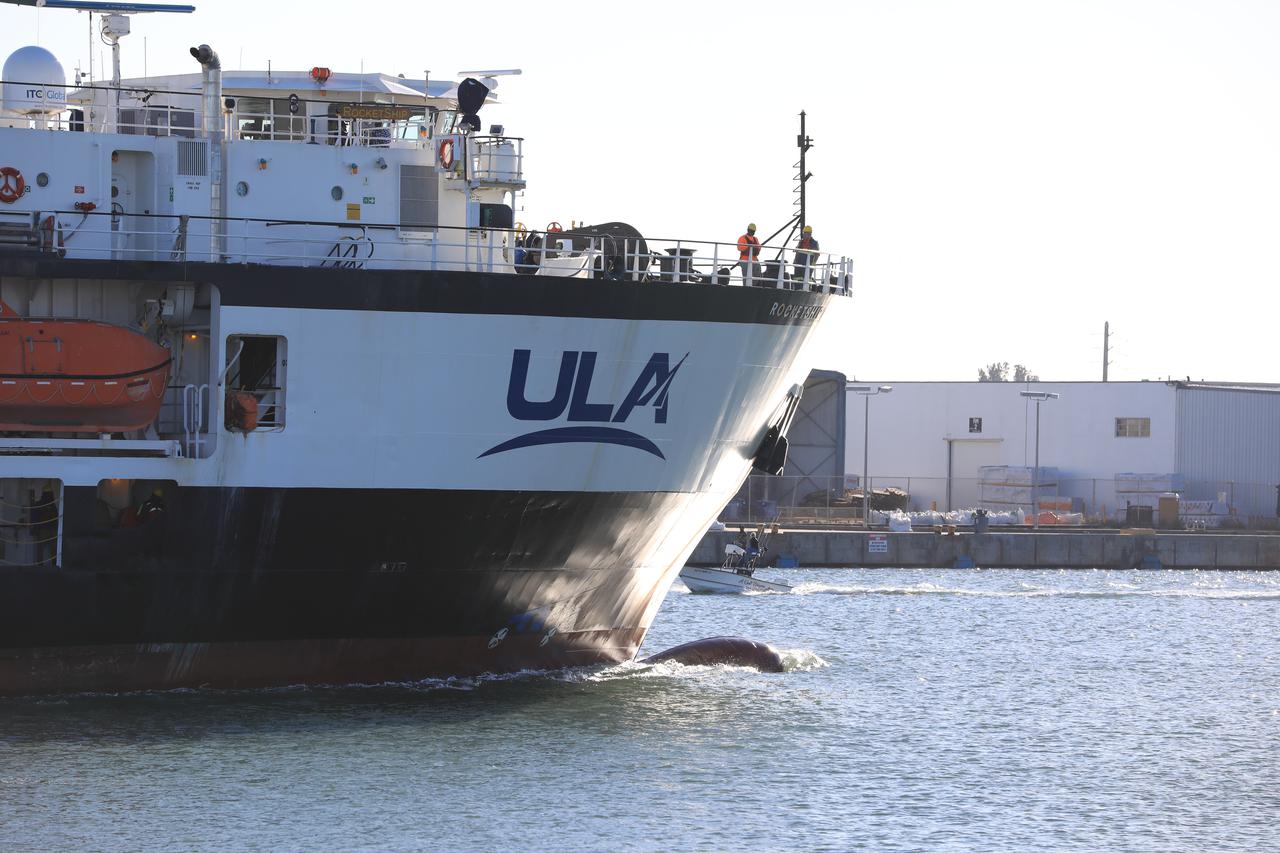

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) transport boat carrying the first and second stages of the company’s Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 15, 2021. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
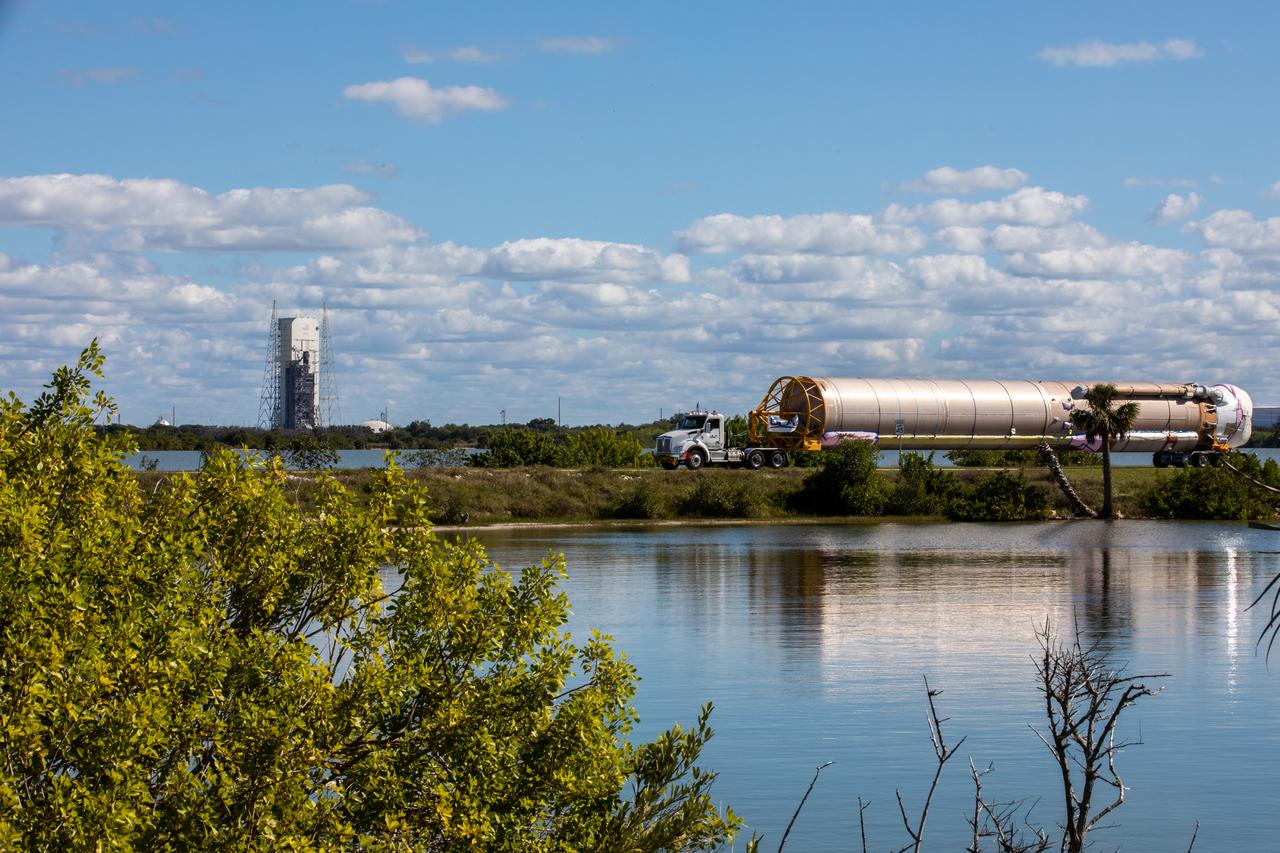

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) first stage of the Atlas V 541 rocket is transported to the horizontal processing facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 16, 2021, after arriving on the company’s transport boat. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
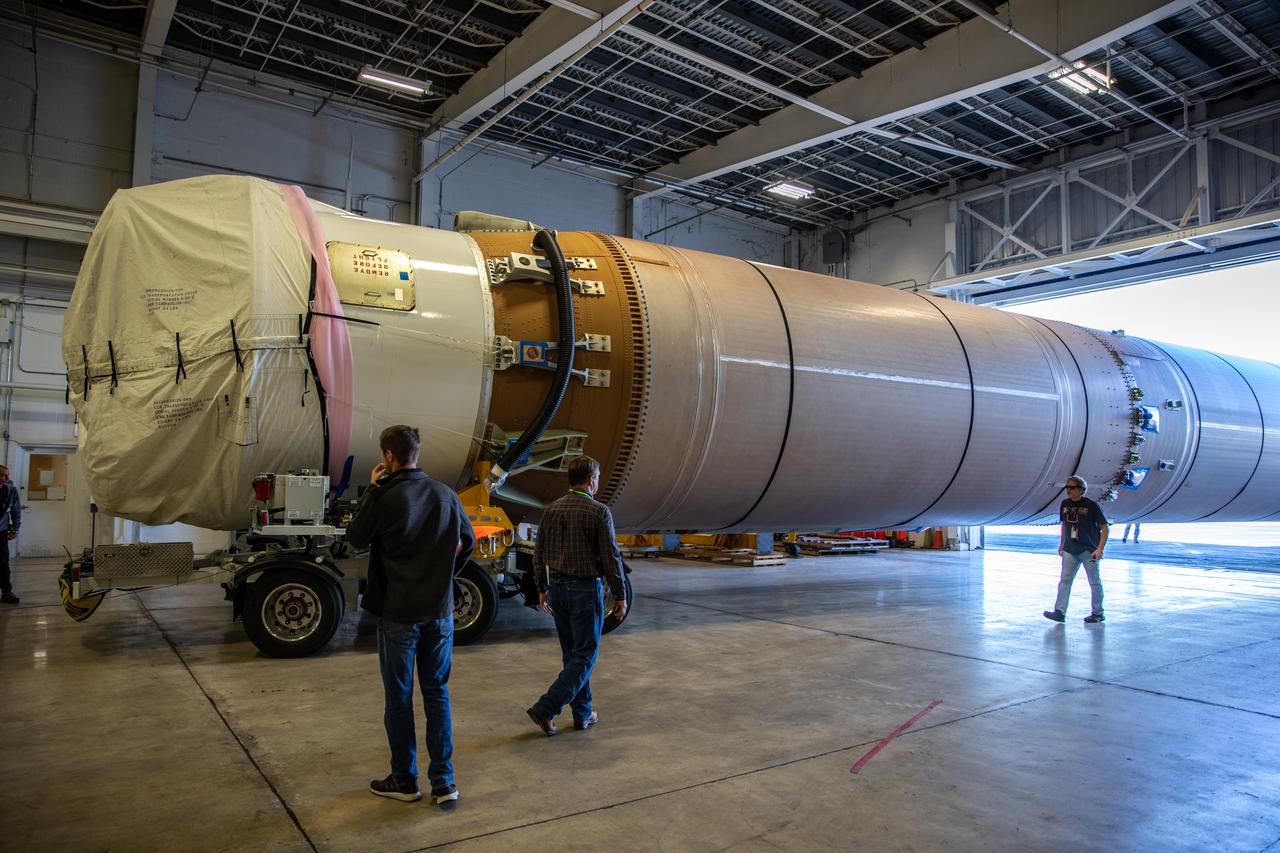

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) first stage of the Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at the horizontal processing facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 16, 2021, after arriving on the company’s transport boat. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
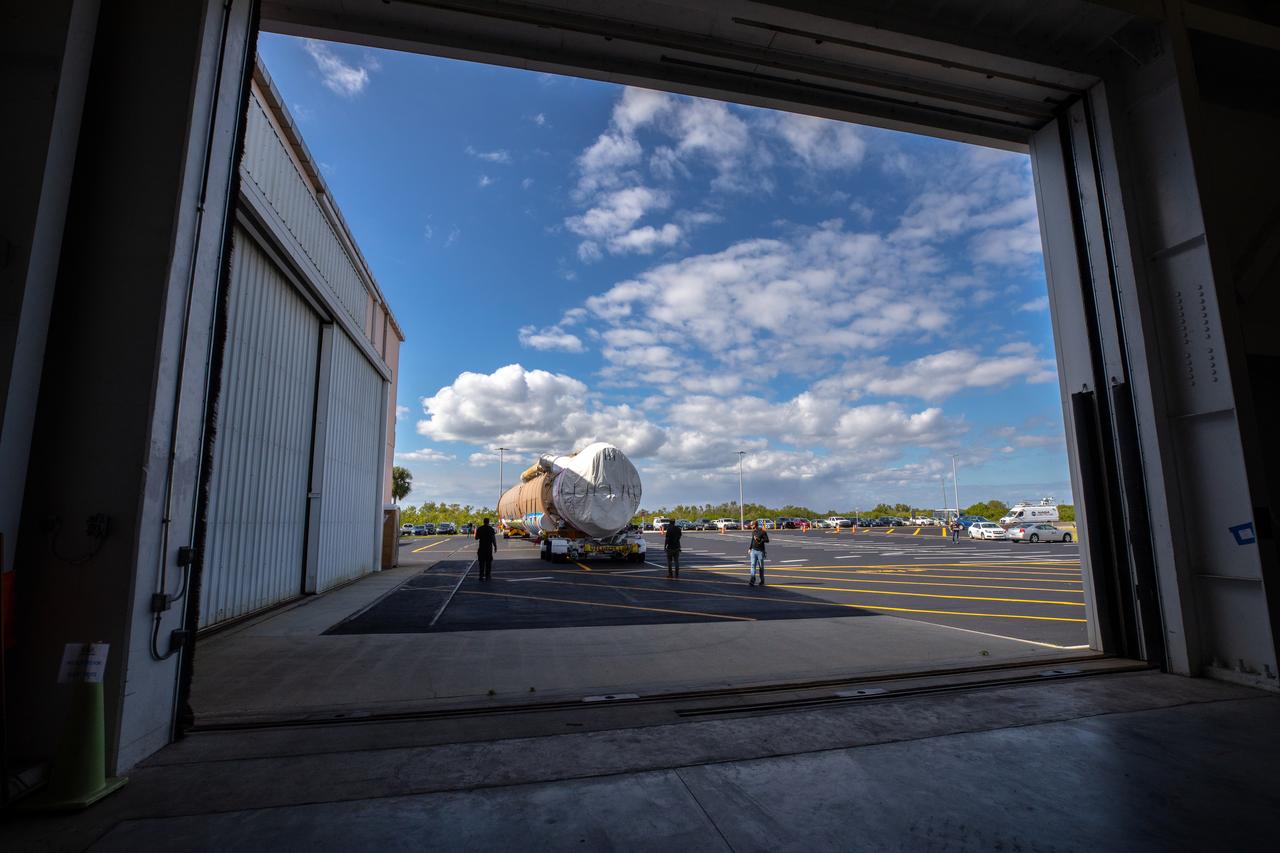

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is delivered by truck to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. The company’s Rocketship vessel carried the booster from its manufacturing facility in Decatur, Alabama, to Port Canaveral. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard the ULA Atlas V rocket.
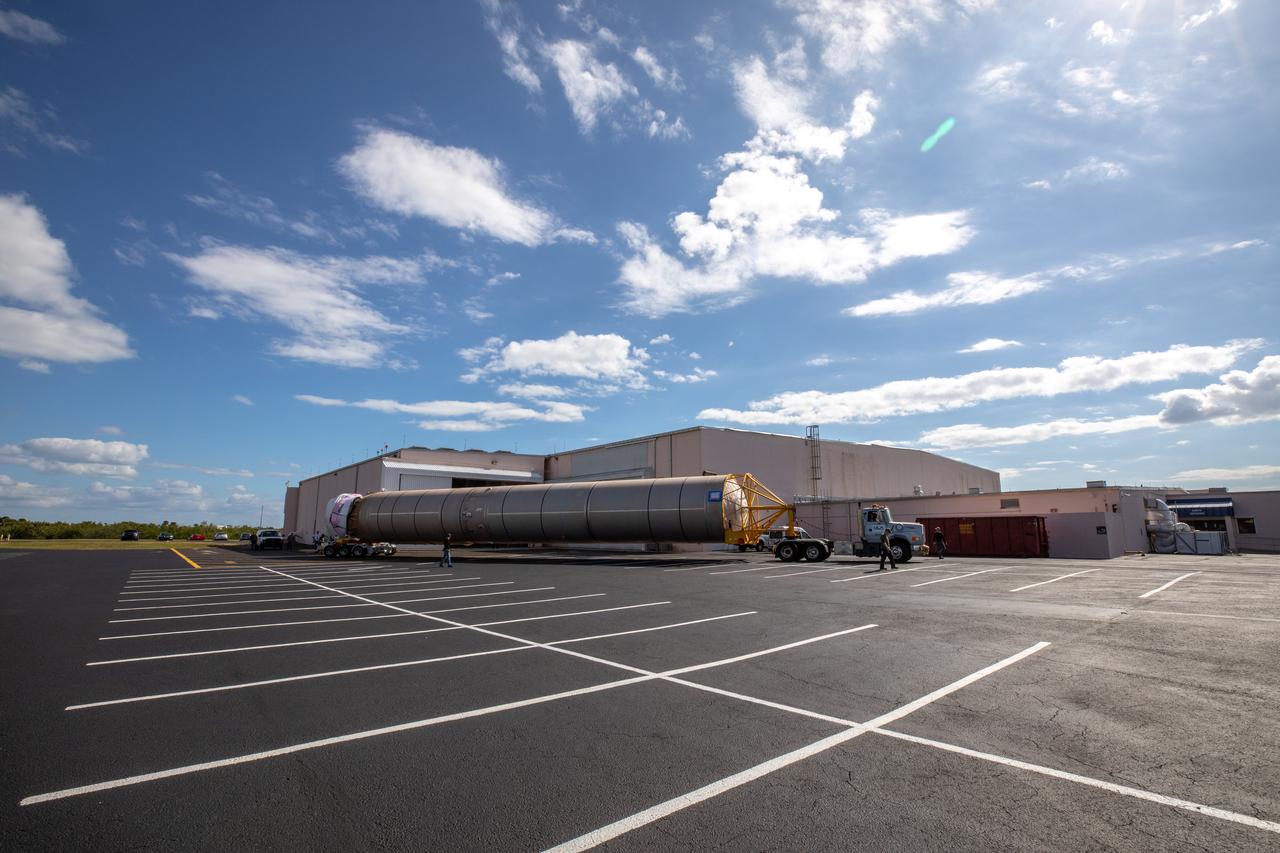

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is delivered by truck to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. The company’s Rocketship vessel carried the booster from its manufacturing facility in Decatur, Alabama, to Port Canaveral. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard the ULA Atlas V rocket.
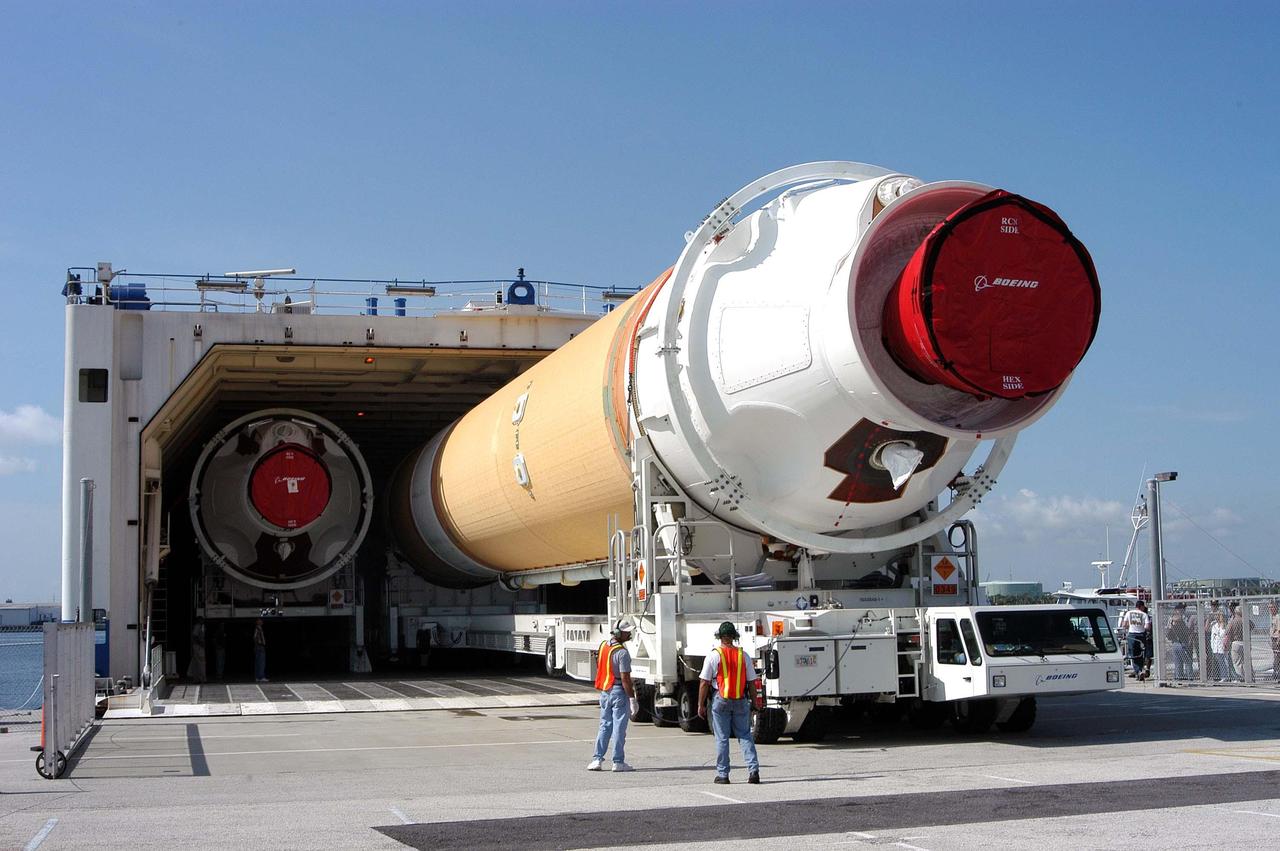

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Boeing Delta IV first stage, called a Common Booster Core, is offloaded from the Delta Mariner at Port Canaveral. It is one of two shipped from Decatur, Ala., and is being transported to the Horizontal Integration Facility at Launch Complex 37, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket will be used for the December launching of the GOES-N weather satellite for NASA and NOAA. The GOES-N is the first in a series of three advanced weather satellites including GOES-O and GOES-P. This satellite will provide continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. It will provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric “triggers” of severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. When these conditions develop, GOES-N will be able to monitor storm development and track their movements.
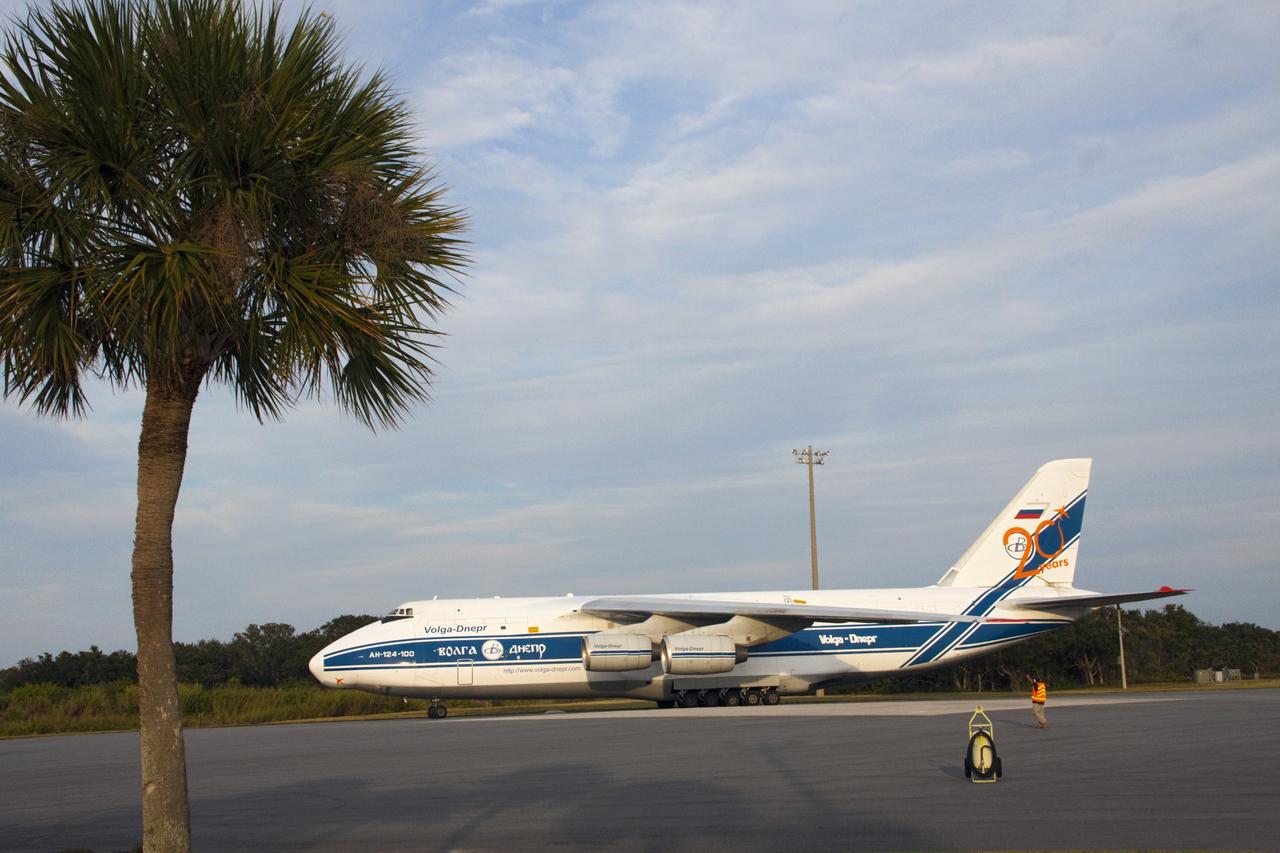

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Ukrainian Antonov-124 transport aircraft arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida with the first stage of the Atlas V rocket that will carry the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-K, into orbit. The booster stage, arriving from the United Launch Alliance manufacturing plant in Decatur, Ala., will be taken to the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral. Launch of the TDRS-K on the Atlas V rocket is planned for January 2013 from Space Launch Complex 41. The TDRS-K spacecraft is part of the next-generation series in the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System, a constellation of space-based communication satellites providing tracking, telemetry, command and high-bandwidth data return services. For more information, visit http://tdrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
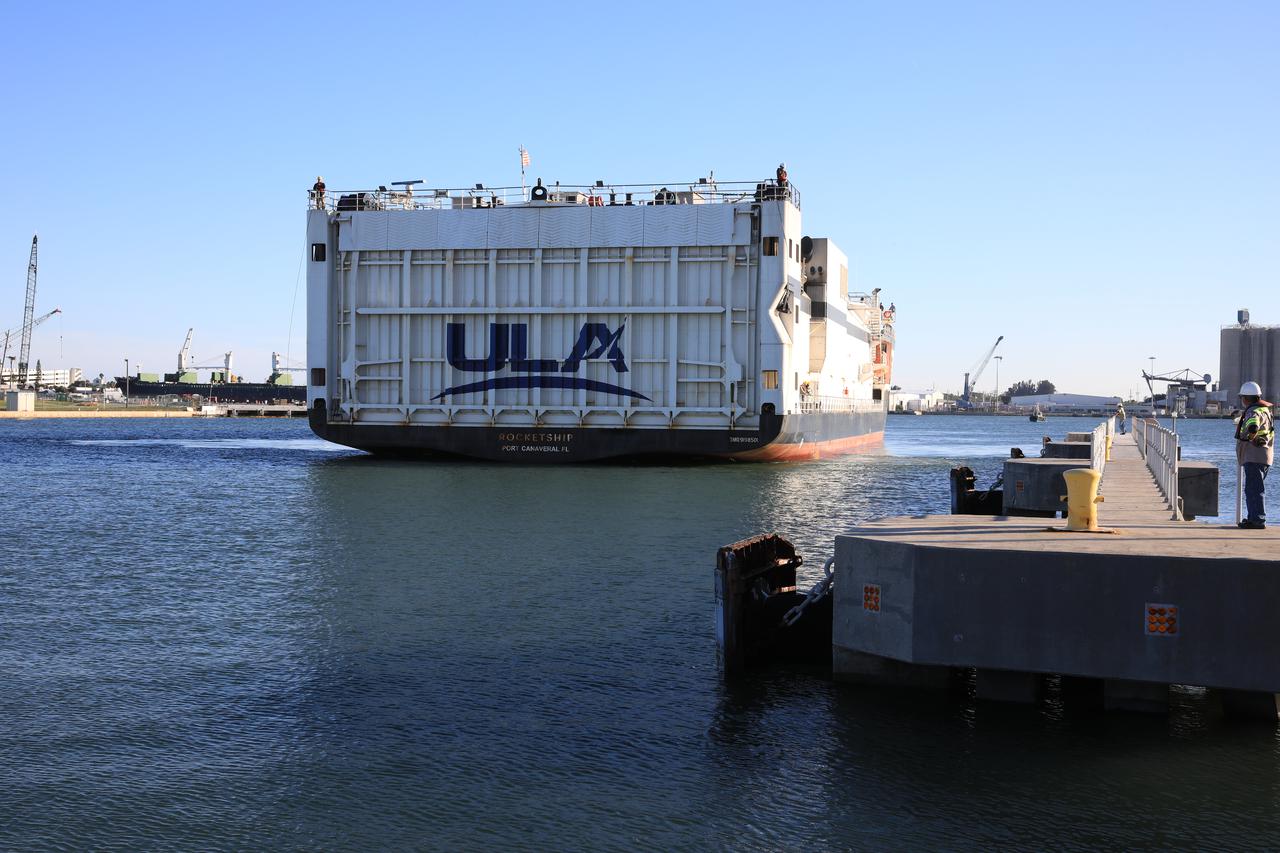

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) transport boat carrying the first and second stages of the company’s Atlas V 541 rocket arrives at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) in Florida on Nov. 15, 2021. The ship journeyed from ULA’s manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama, to deliver the rocket that will launch NASA and the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 41 at CCSFS on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
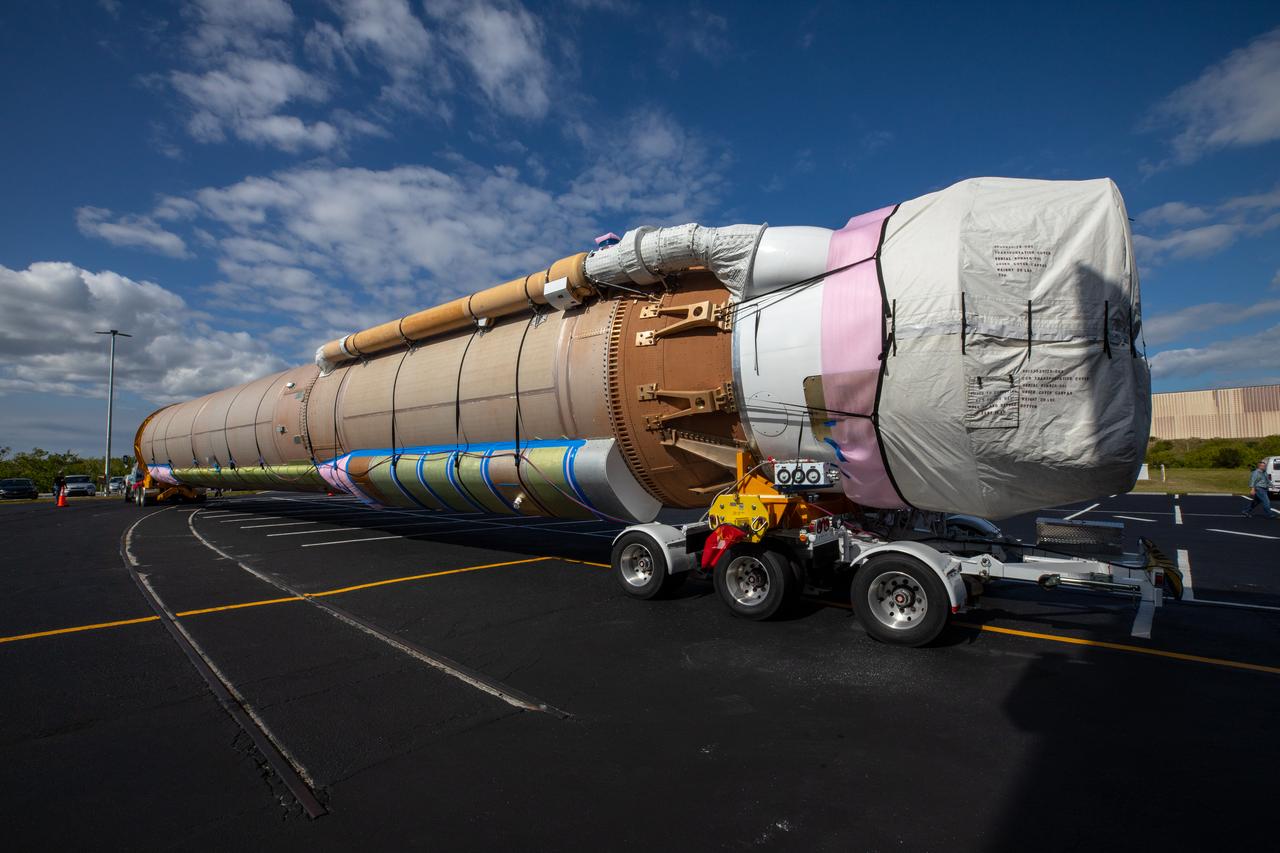

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster that will launch the Solar Orbiter spacecraft is delivered by truck to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. The company’s Rocketship vessel carried the booster from its manufacturing facility in Decatur, Alabama, to Port Canaveral. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard the ULA Atlas V rocket.
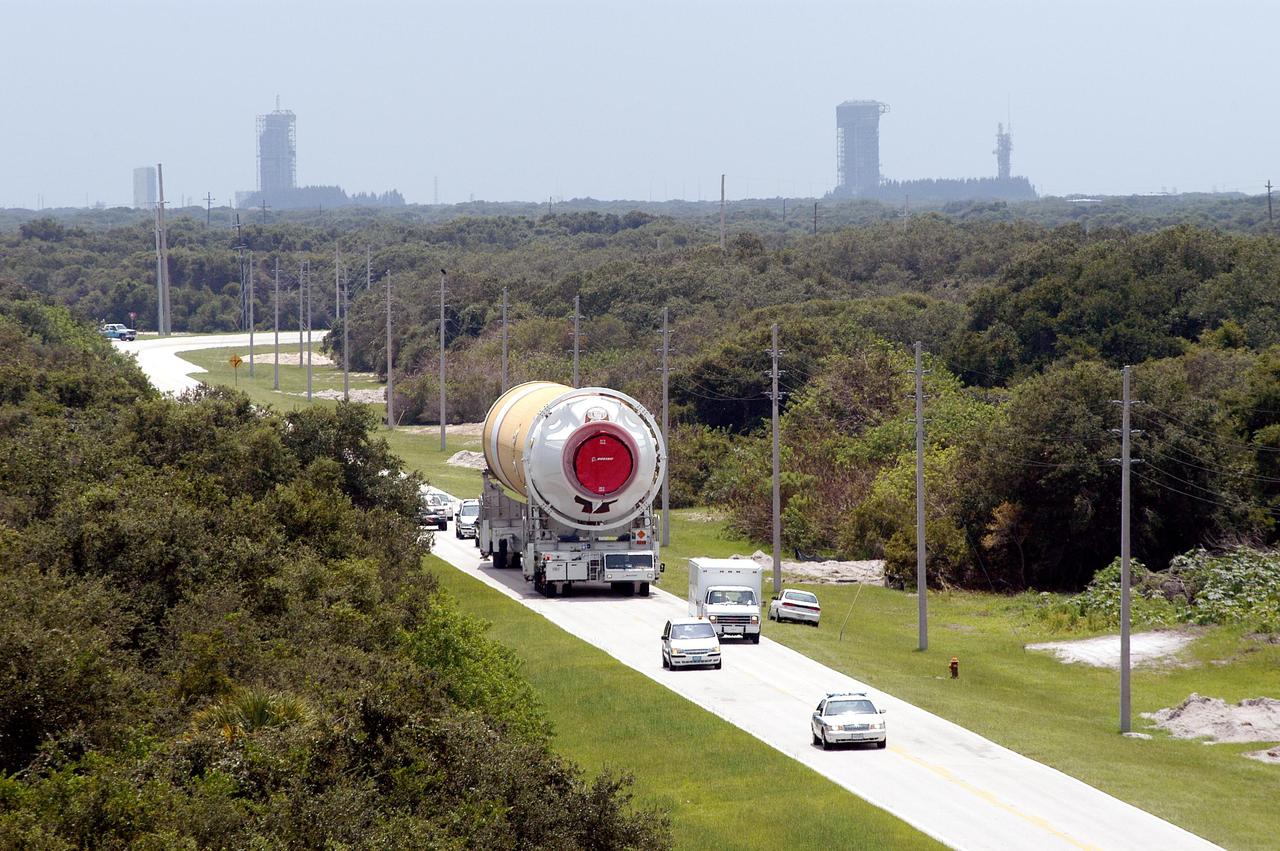

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Security escort leads the way as this Boeing Delta IV first stage heads to the Horizontal Integration Facility at Launch Complex 37, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Two of the launch pads on Cape Canaveral’s coast can be seen in the background. Two rockets were shipped by barge from Decatur, Ala., to Port Canaveral and offloaded onto Elevating Platform Transporters. A Boeing Delta IV will be used for the December launching of the GOES-N weather satellite for NASA and NOAA. The GOES-N is the first in a series of three advanced weather satellites including GOES-O and GOES-P. This satellite will provide continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. It will provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric “triggers” of severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. When these conditions develop, GOES-N will be able to monitor storm development and track their movements.
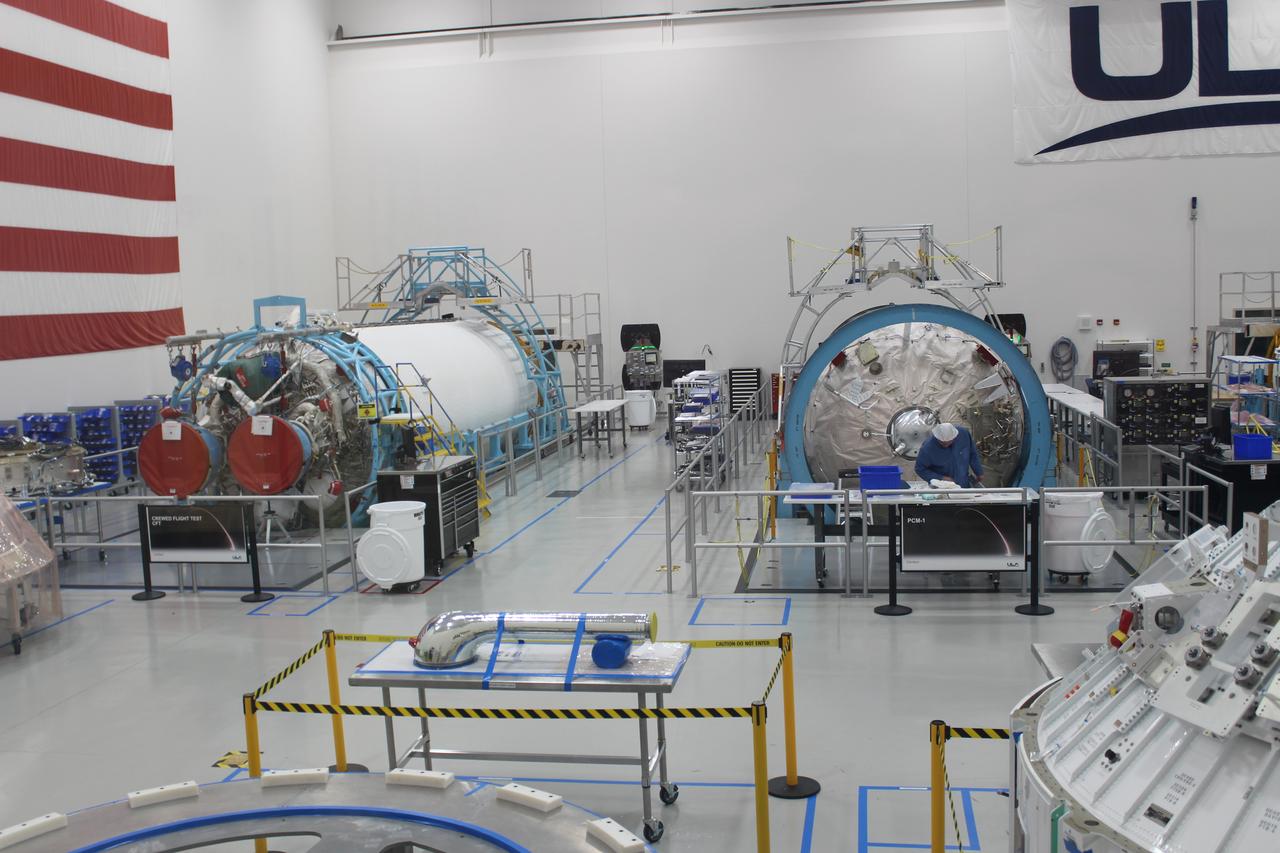

Two United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stages are in production in ULA's factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 1, 2019. One is for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test on the CST-100 Starliner, and the other will be used for the first crew rotation mission on the Starliner. One of the Centaur upper stages will be assembled to the first stage booster. They will be shipped aboard the company’s Mariner cargo ship to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key to restoring the nation’s capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann, and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will launch to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Crew Flight Test.
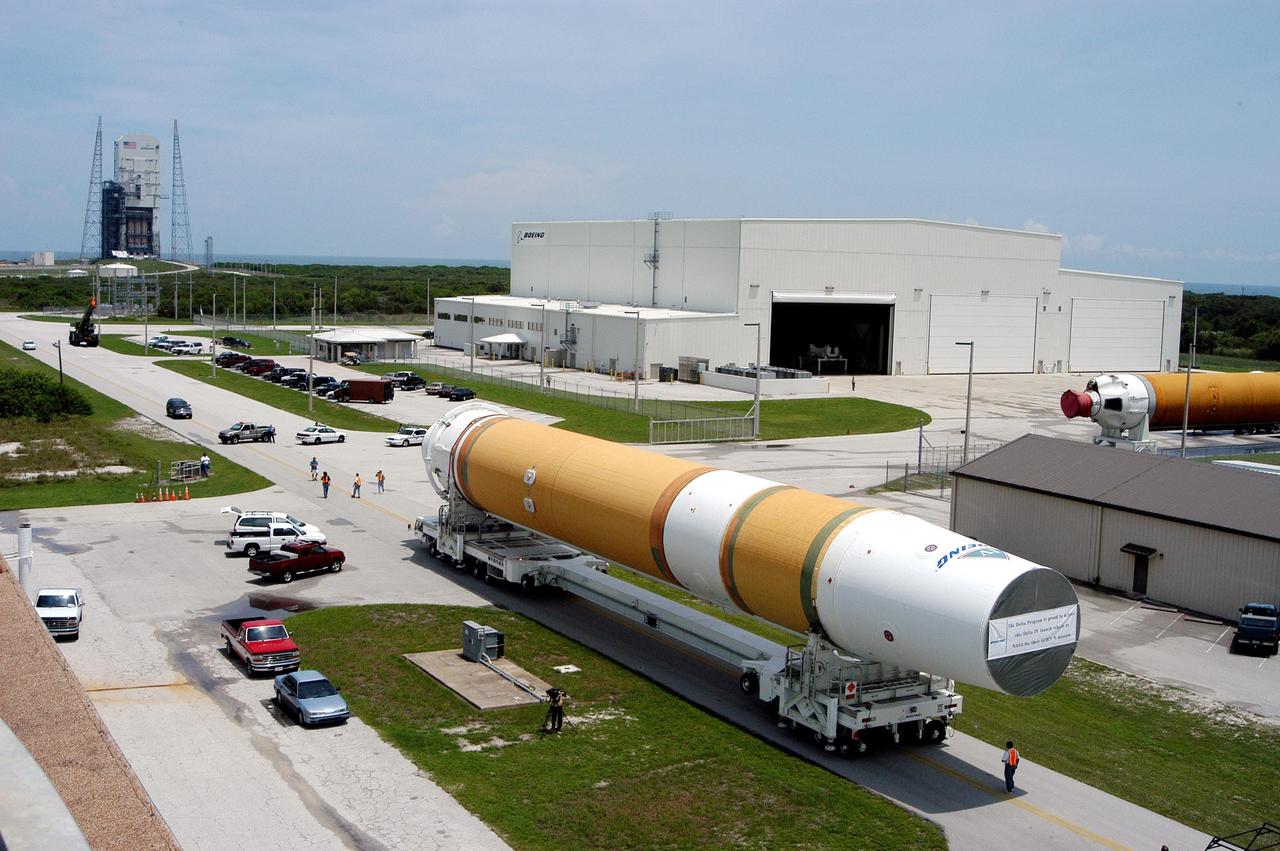

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Two Boeing Delta IV first stages head to the Horizontal Integration Facility (upper right) at Launch Complex 37, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rockets were shipped by barge from Decatur, Ala., to Port Canaveral and offloaded onto Elevating Platform Transporters. A Boeing Delta IV will be used for the December launching of the GOES-N weather satellite for NASA and NOAA. The GOES-N is the first in a series of three advanced weather satellites including GOES-O and GOES-P. This satellite will provide continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. It will provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric “triggers” of severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. When these conditions develop, GOES-N will be able to monitor storm development and track their movements.
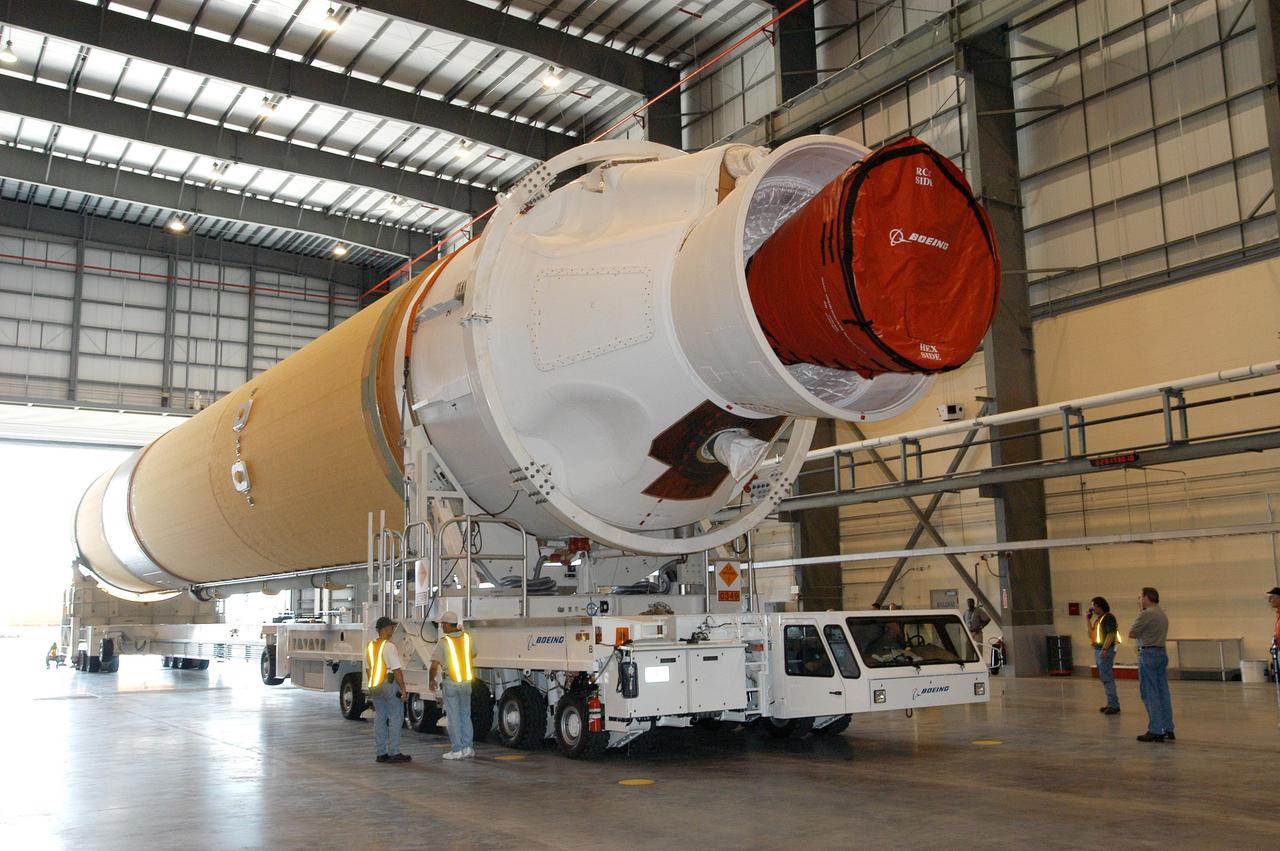

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first of two Boeing Delta IV first stages is moved inside the Horizontal Integration Facility at Launch Complex 37, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rockets were shipped by barge from Decatur, Ala., to Port Canaveral and offloaded onto Elevating Platform Transporters. . A Boeing Delta IV will be used for the December launching of the GOES-N weather satellite for NASA and NOAA. The GOES-N is the first in a series of three advanced weather satellites including GOES-O and GOES-P. This satellite will provide continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. It will provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric “triggers” of severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. When these conditions develop, GOES-N will be able to monitor storm development and track their movements.

The Morgan County Economic Development Association and the City of Decatur, in Partnership with the NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), hosted a business forum on, How to Launch Your Business with NASA, Wednesday, October 18, 2017, at the Alabama Center for the Arts in downtown Decatur, AL. The event was open to all businesses allowed them to connect with Senior NASA representatives and their prime contractors. The program guided businesses through the process of working with NASA as a supplier, subcontractor, and/or a service provider. The Marshall Space Flight Center’s projected procurement budget in FY 2018 is approximately $2.2 billion and numerous procurement opportunities are available for small business participation each fiscal year. The program included Todd May, Director of Marshall Space Flight Center; Johnny Stephenson, Director of Marshall Space Flight Center’s Office of Strategic Analysis and Communication; David Brock, Small Business Specialist with Marshall Space Flight Center; and Lynn Garrison, Small Business Specialist Technical Advisor with Marshall Space Flight Center. Additionally, there was a prime contractor panel consisting of representatives from five NASA prime contractors. The event included a dedicated networking session with those prime contractors. The “Launch Your Business With NASA” event provides those in attendance the opportunity to network with key Marshall Space Flight Center procurement and technical personnel, and representatives of several major Marshall Space Flight Center prime contractors.Arts.. OSAC Director Johnny Stephenson talks about Marshall's Mission areas to audience