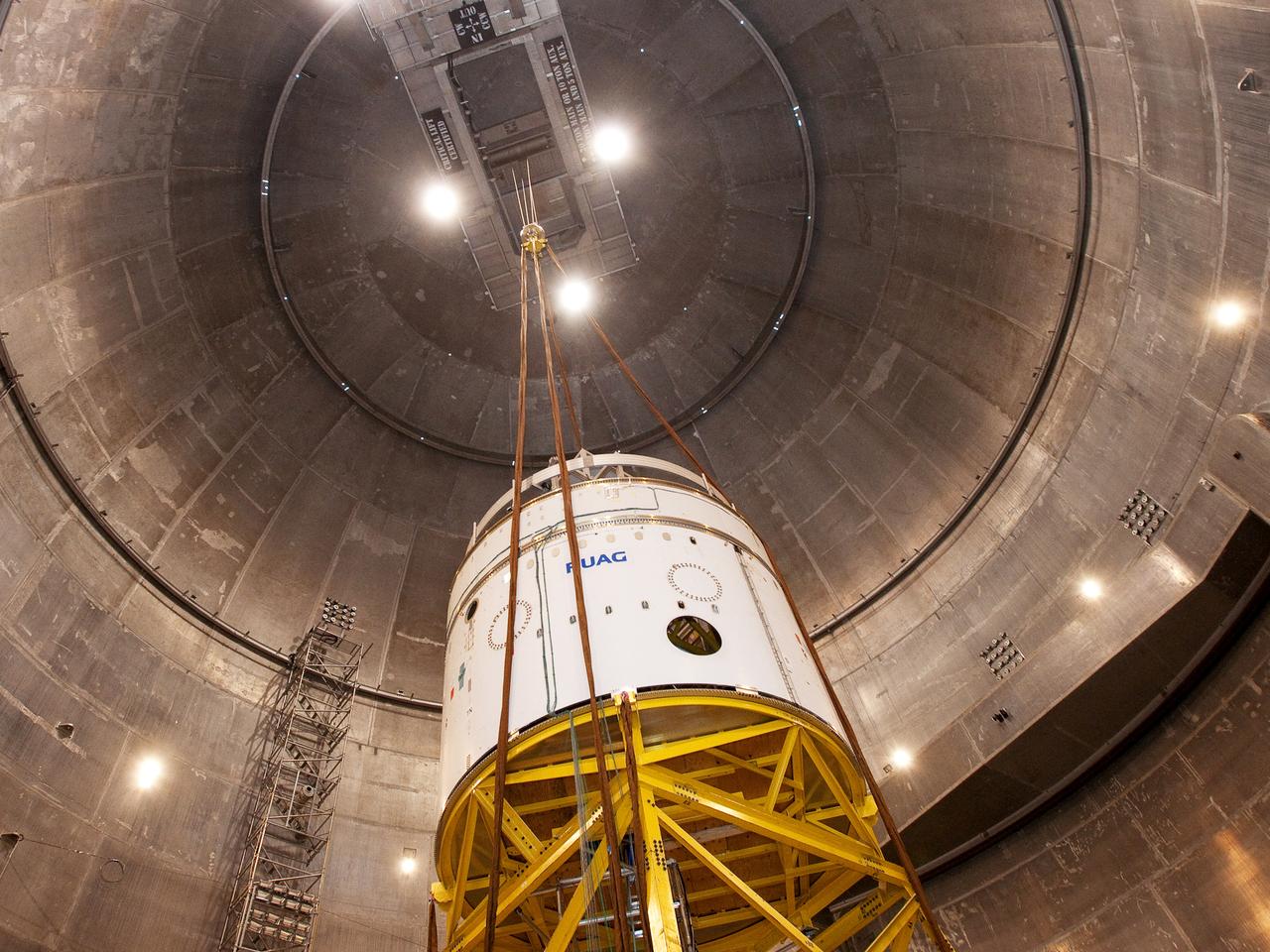

NASA Glenn conducted a test on the Ariane 5 Payload Fairing at Plum Brook’s Space Power Facility (SPF). The test was to qualify a new horizontal pyrotechnic separation system, which blew the two fairing halves apart and away from the payload during flight.
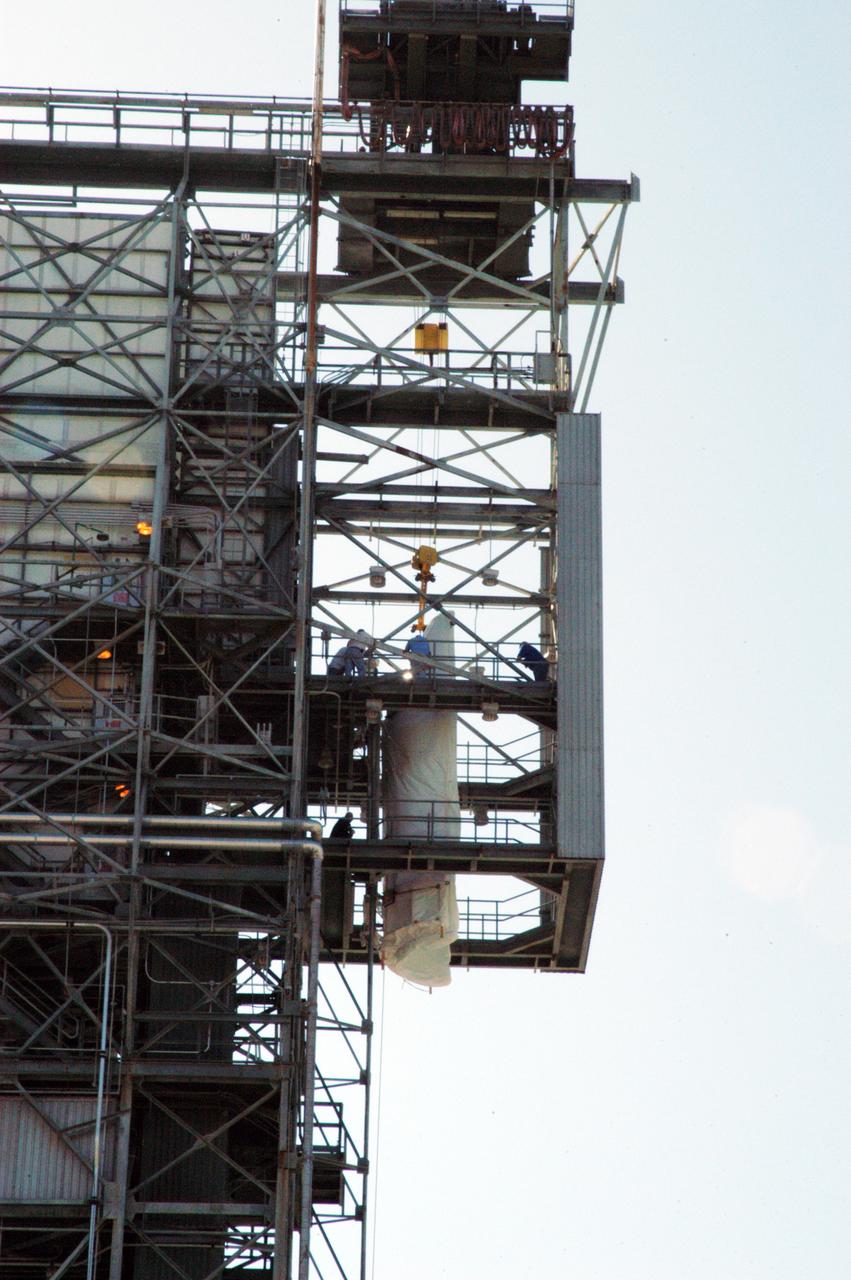

Fairing lift at CX-17, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, FL.
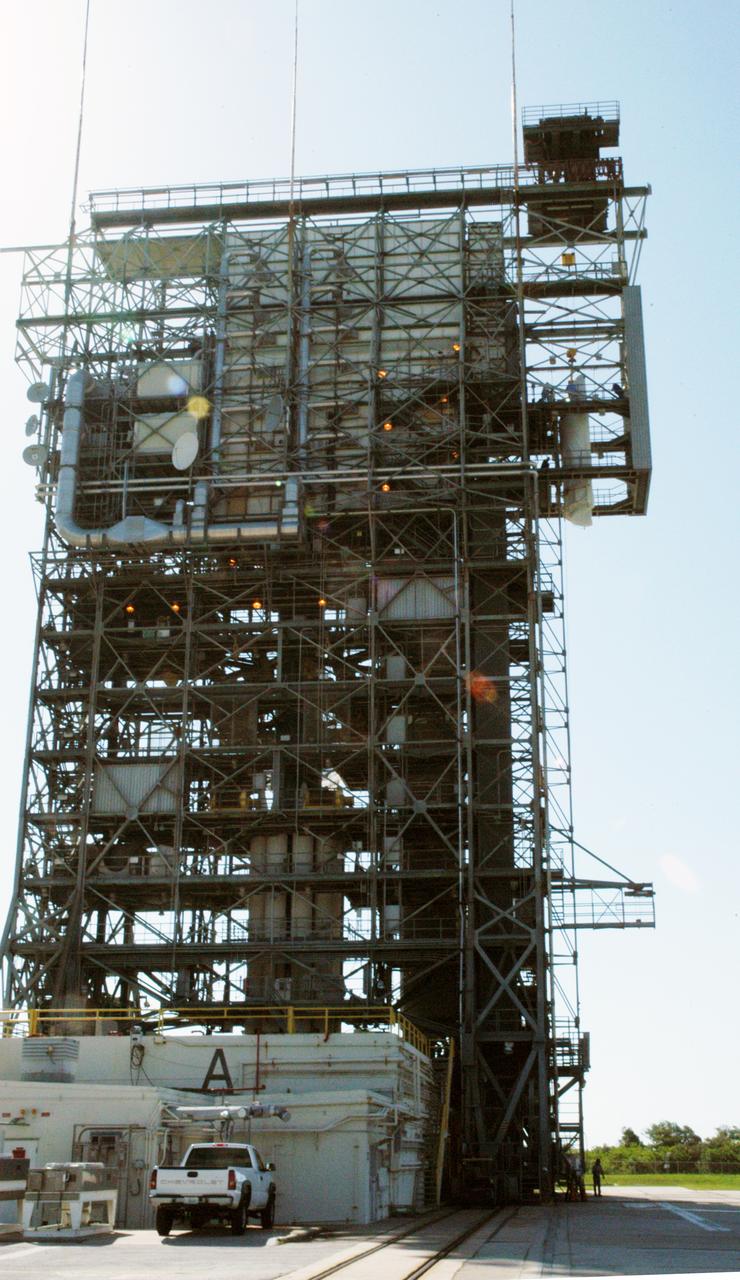

Fairing lift at CX-17, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, FL.
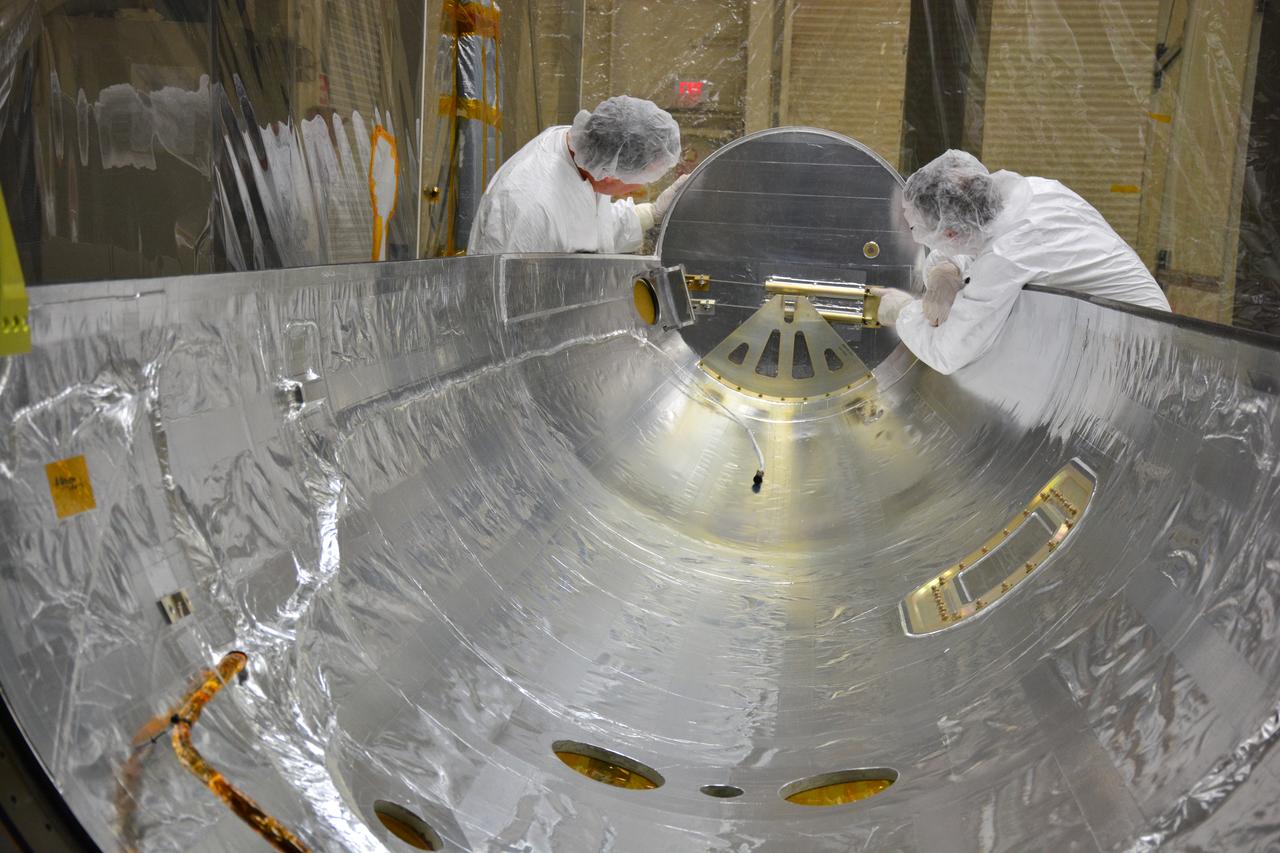

The payload fairing for an Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket is inspected in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect NASA's Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) spacecraft during launch. The rocket and spacecraft are being prepared at Vandenberg, then will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft and transported to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
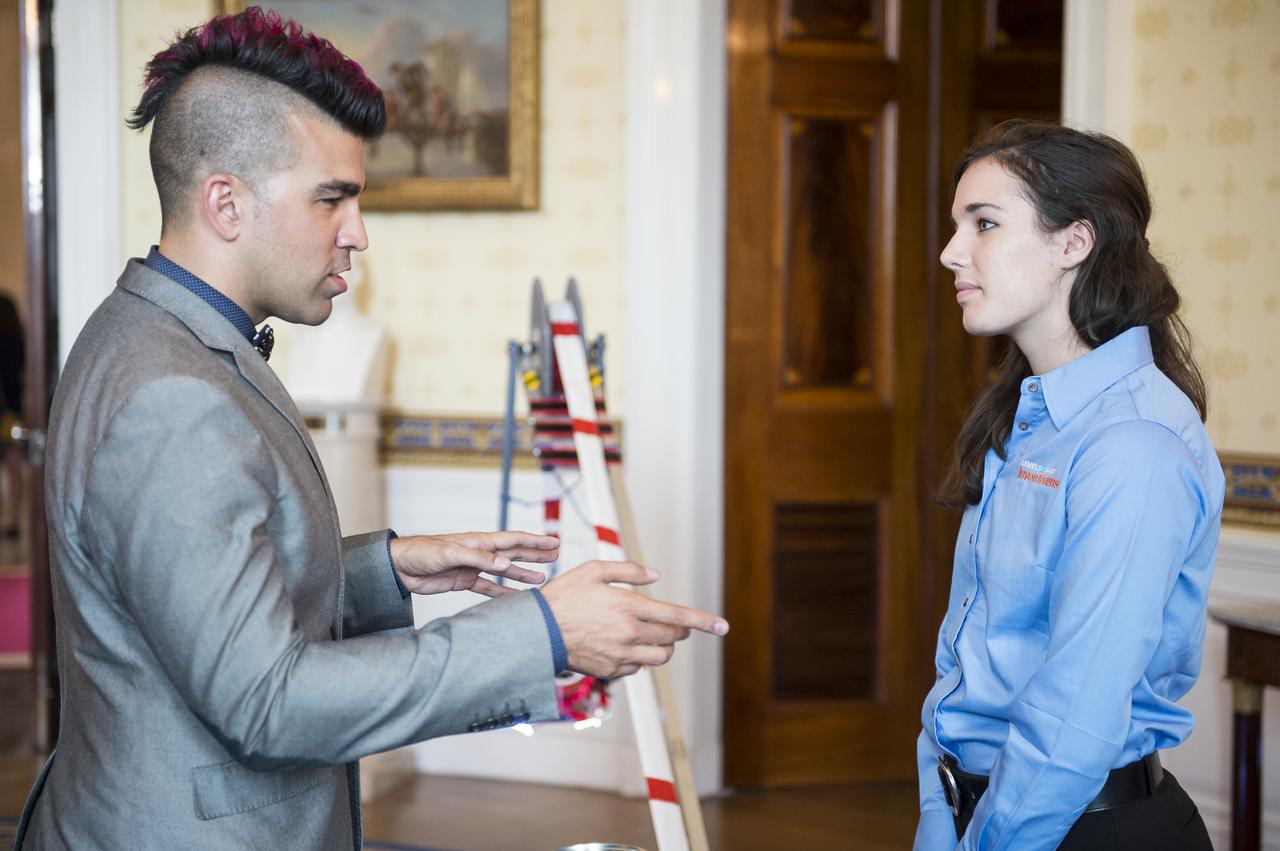

Bobak Ferdowsi, a system's engineer at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory who became widely known for his mohawk hairstyle during the broadcast of the Curiosity landing on Mars, is seen here discussing a project with a participant in the White House Science Fair. The fourth White House Science Fair was held at the White House and included 100 students from more than 30 different states who competed in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) competitions. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
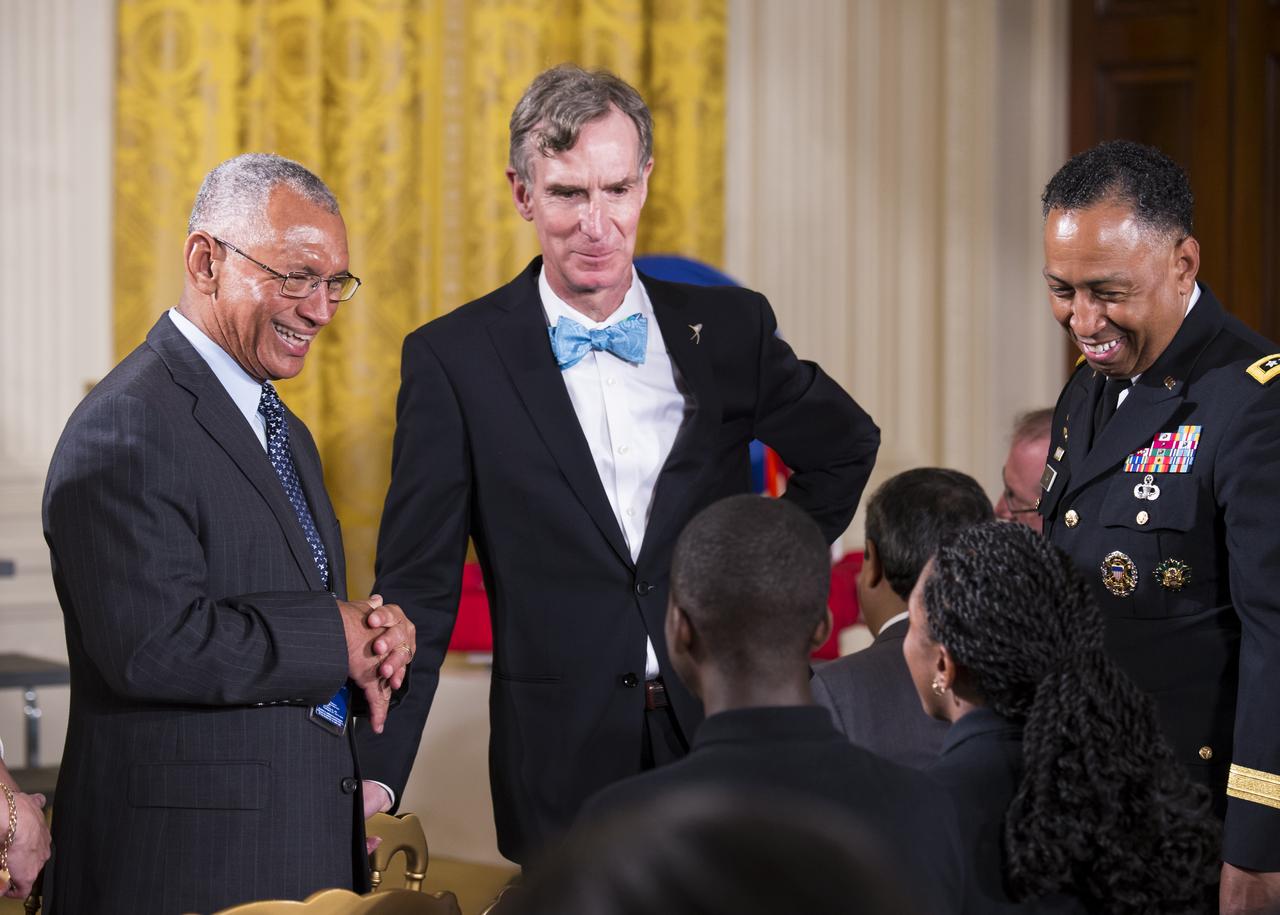

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden (left) and Bill Nye, The Science Guy, speak with some students that participated in the White House Science Fair. The fourth White House Science Fair was held at the White House on May 27, 2014 and included 100 students from more than 30 different states who competed in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) competitions. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

The Maker Faire trailer is seen outside the rose garden during the first ever White House Maker Faire, which brings together students, entrepreneurs, and everyday citizens who are using new tools and techniques to launch new businesses, learn vital skills in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), and fuel the renaissance in American manufacturing, at the White House, Wednesday, June 18, 2014 in Washington. The President announced new steps the Administration and its partners are taking to support the ability of more Americans, young and old, to have to access to these tools and techniques and brings their ideas to life. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Both halves of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, are delivered to Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations have begun to hoist the sections of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the pad's tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A crane is employed to lift half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into a vertical position at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to hoist this section of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
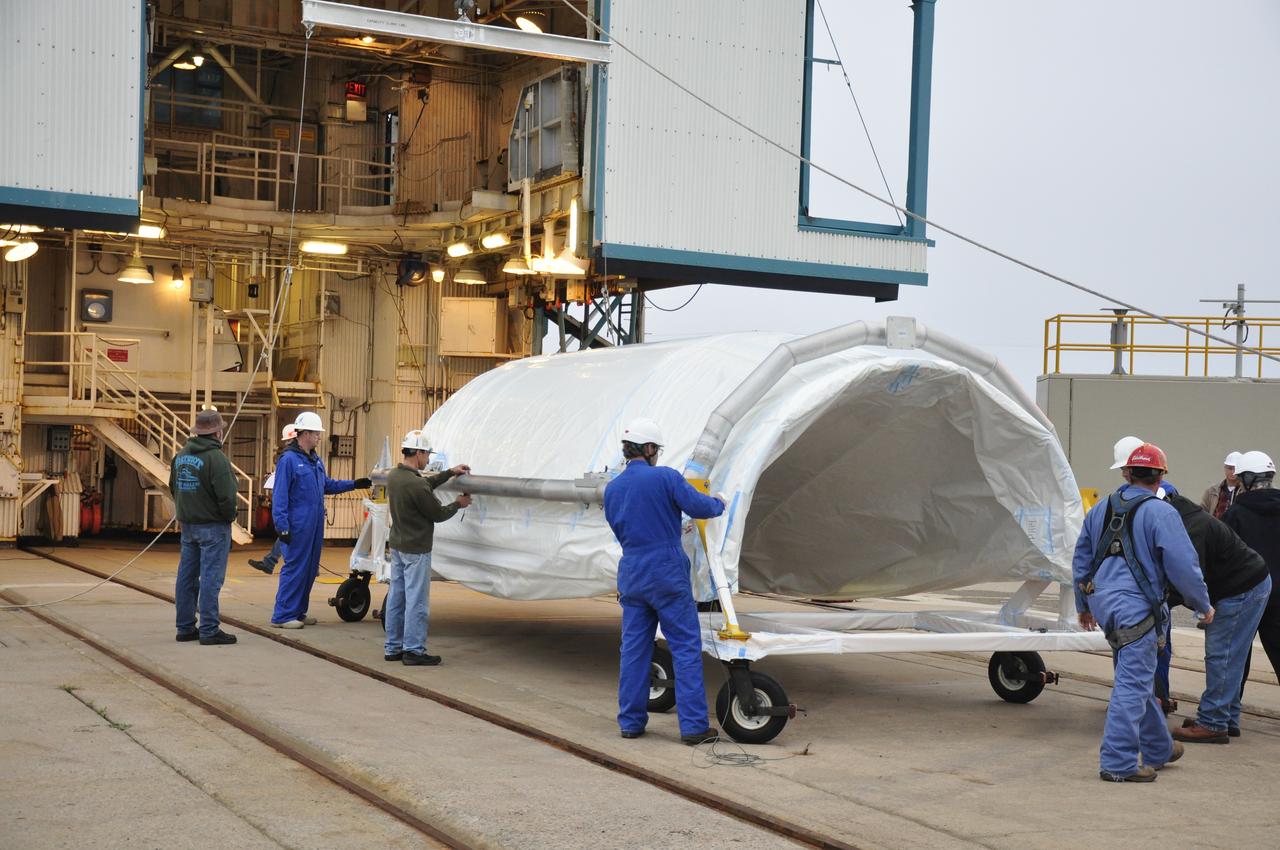

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers remove the protective wrap from half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, newly arrived at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to hoist this section of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
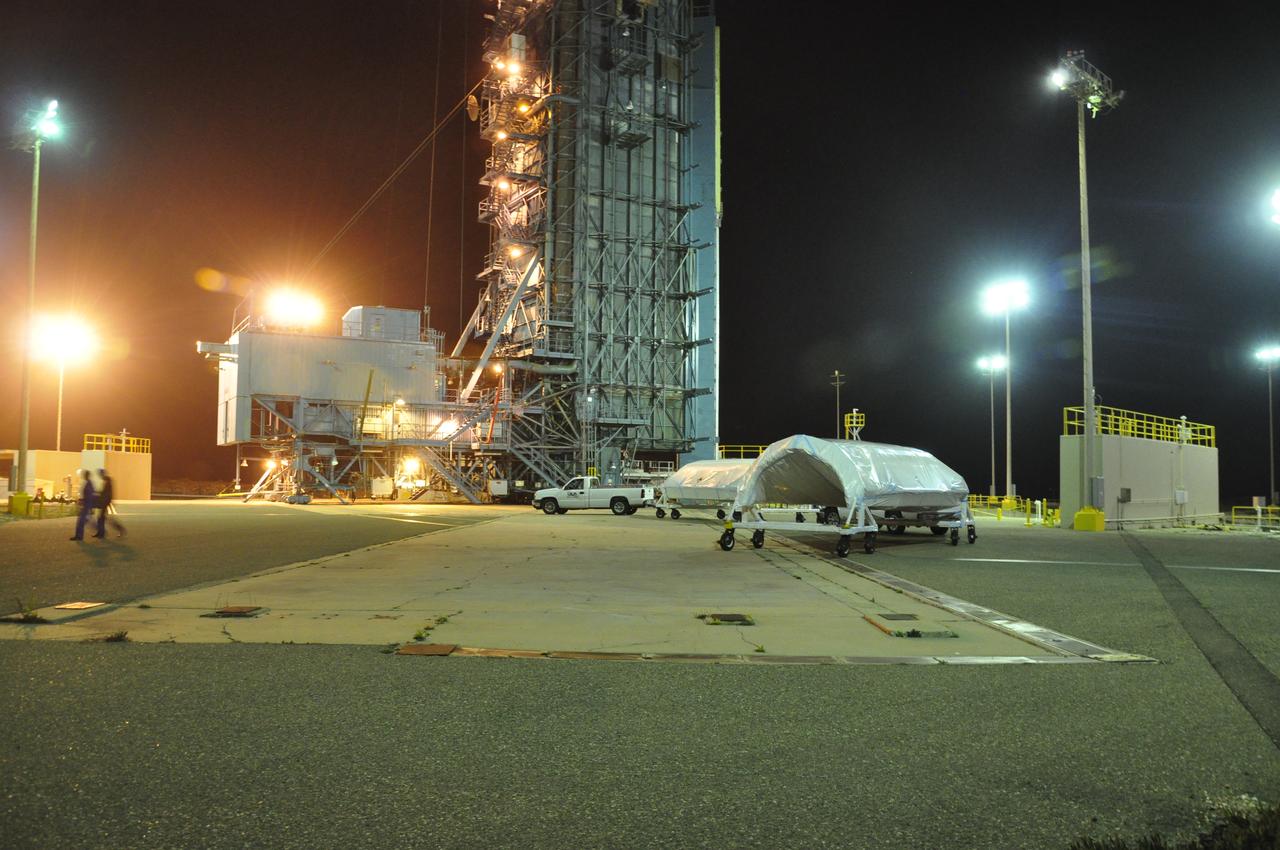

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Both halves of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, arrive at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations have begun to hoist the sections of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the pad's tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
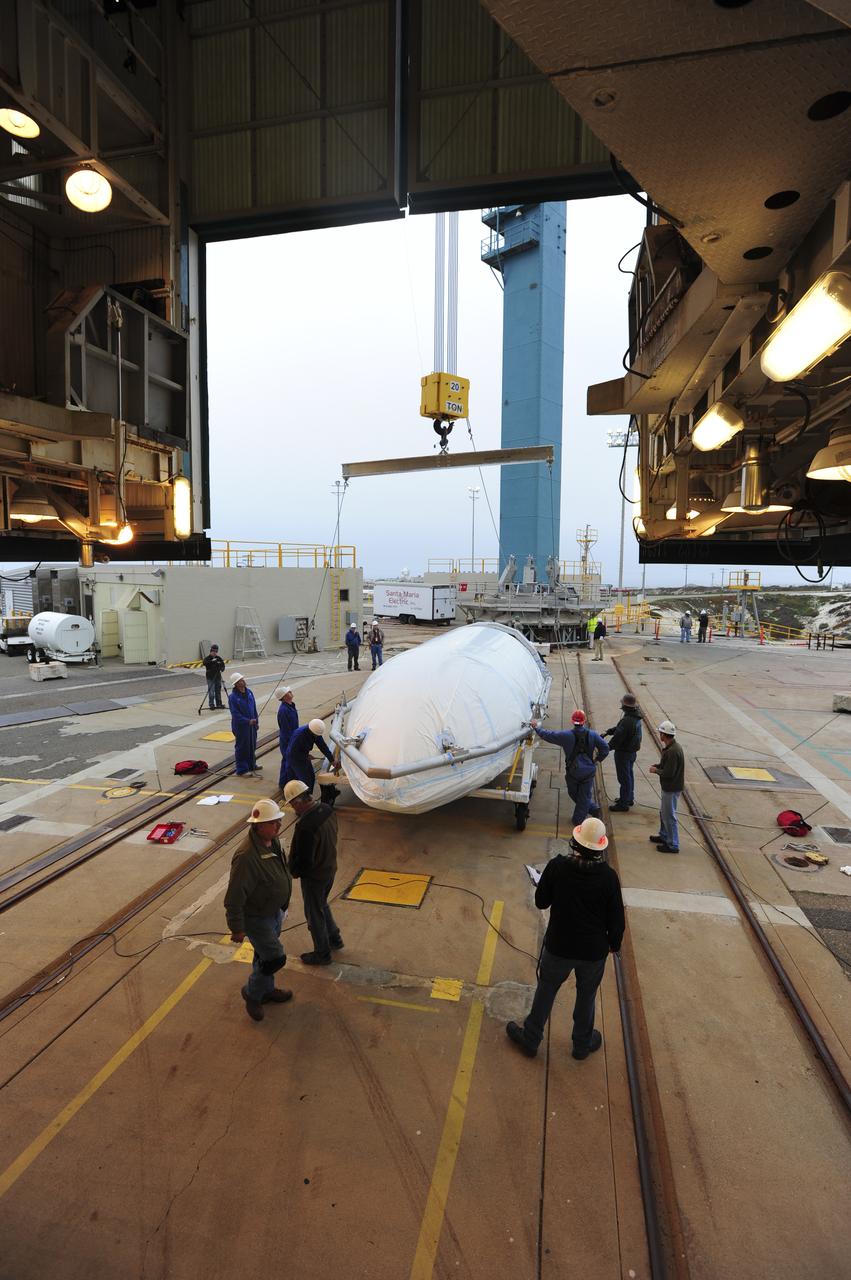

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers attach half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to a crane at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations have begun to hoist the sections of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the pad's mobile service tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/30th Space Wing, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Both halves of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, are towed from the Building 836 hangar to Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations have begun to hoist the sections of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the pad's tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
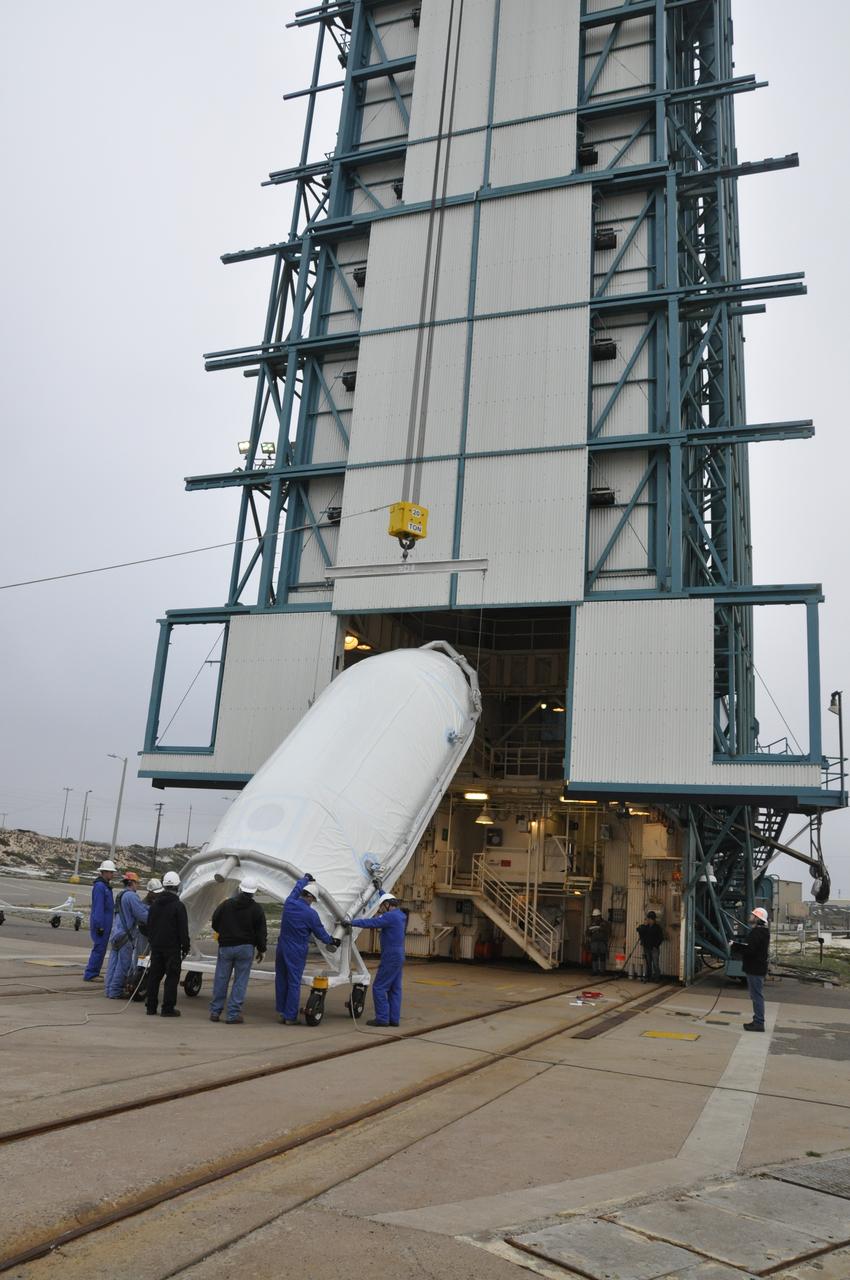

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted into a vertical position at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to hoist this section of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
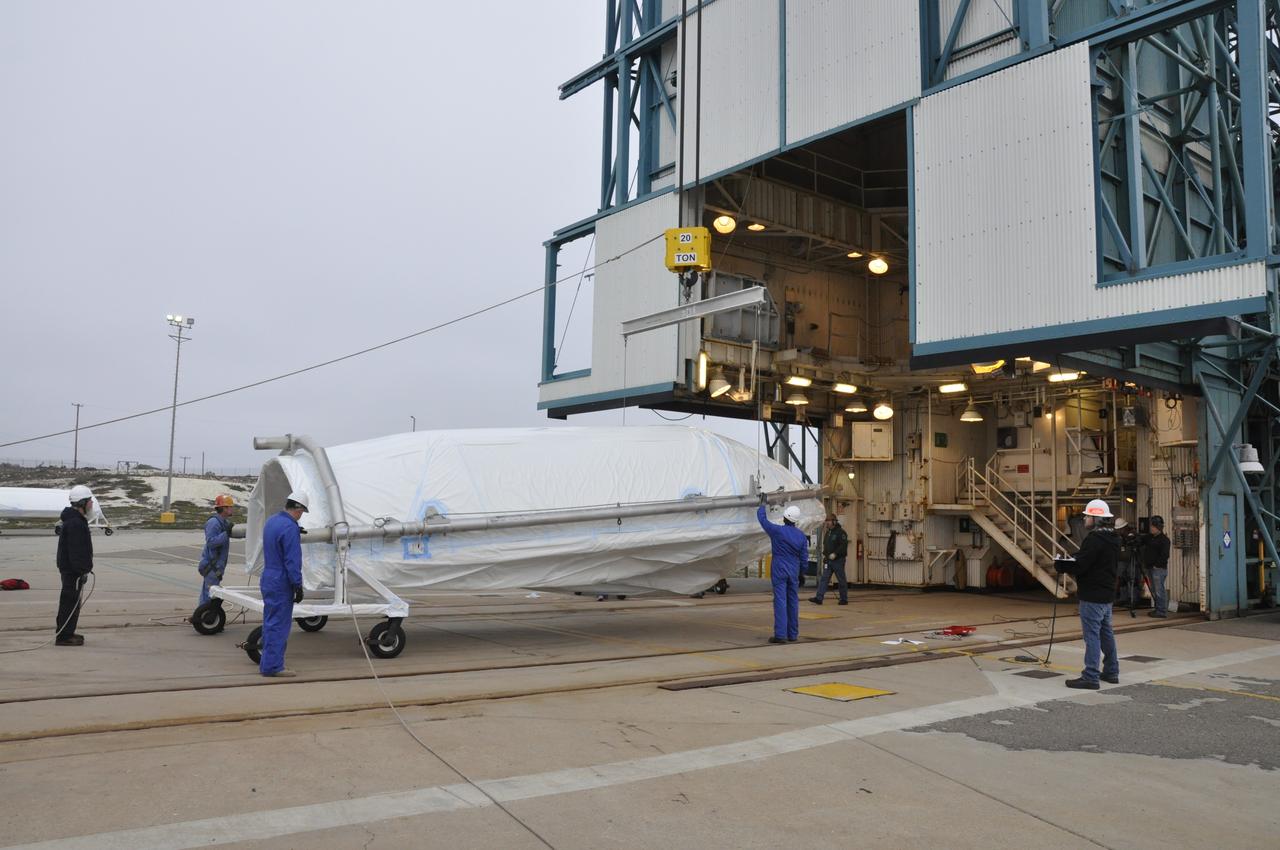

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Preparations are underway to lift half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into a vertical position at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to hoist this section of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The second half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, arrives at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to hoist this section of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower where the other half already is in position. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
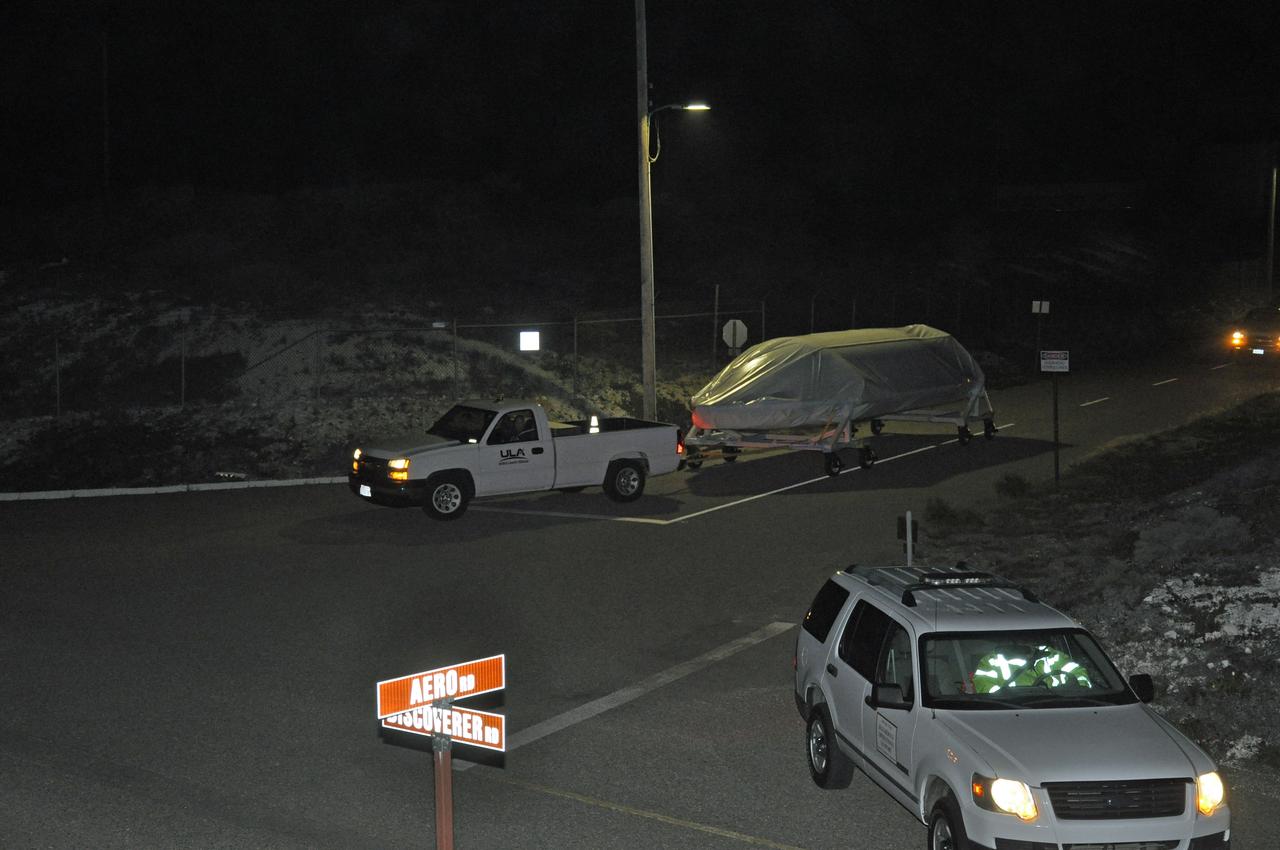

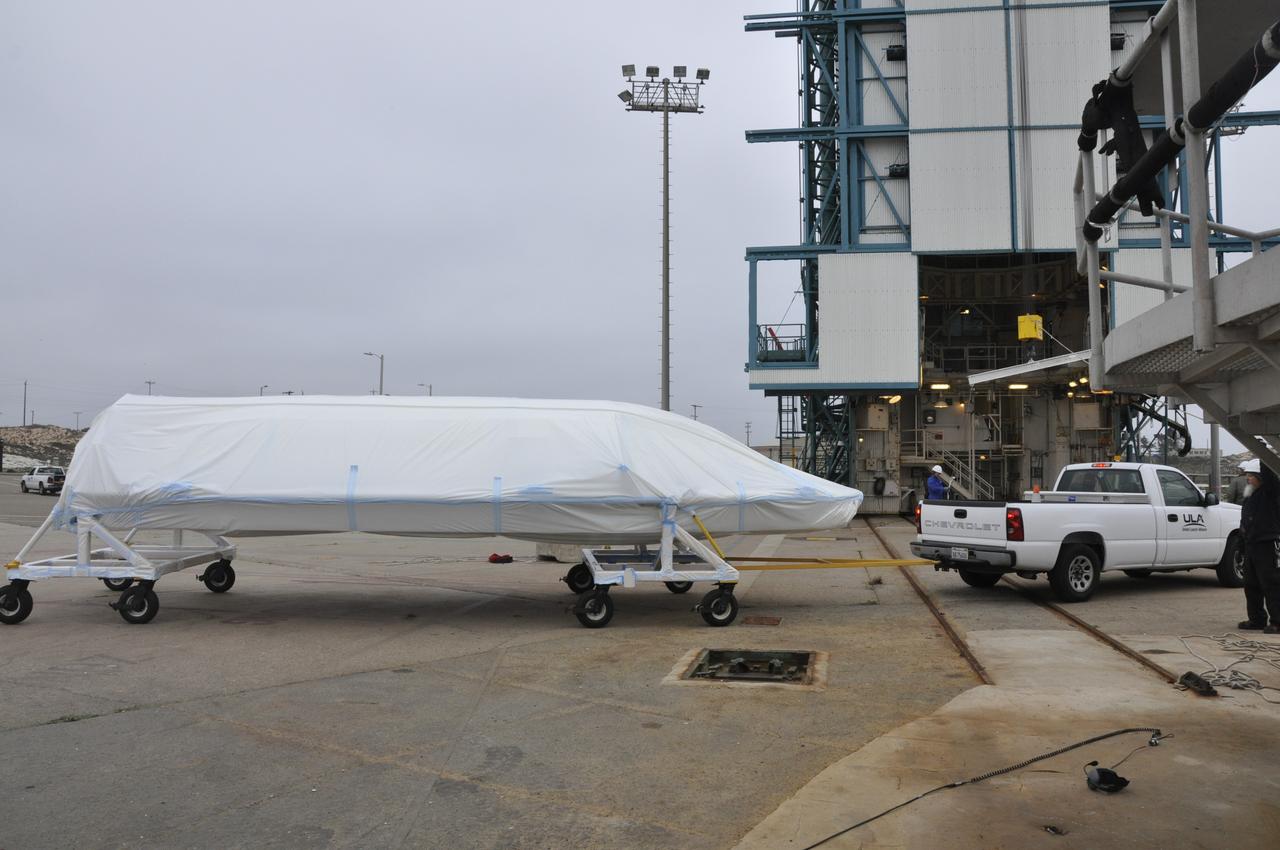
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is towed from the Building 836 hangar to Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations have begun to hoist the sections of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the pad's tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
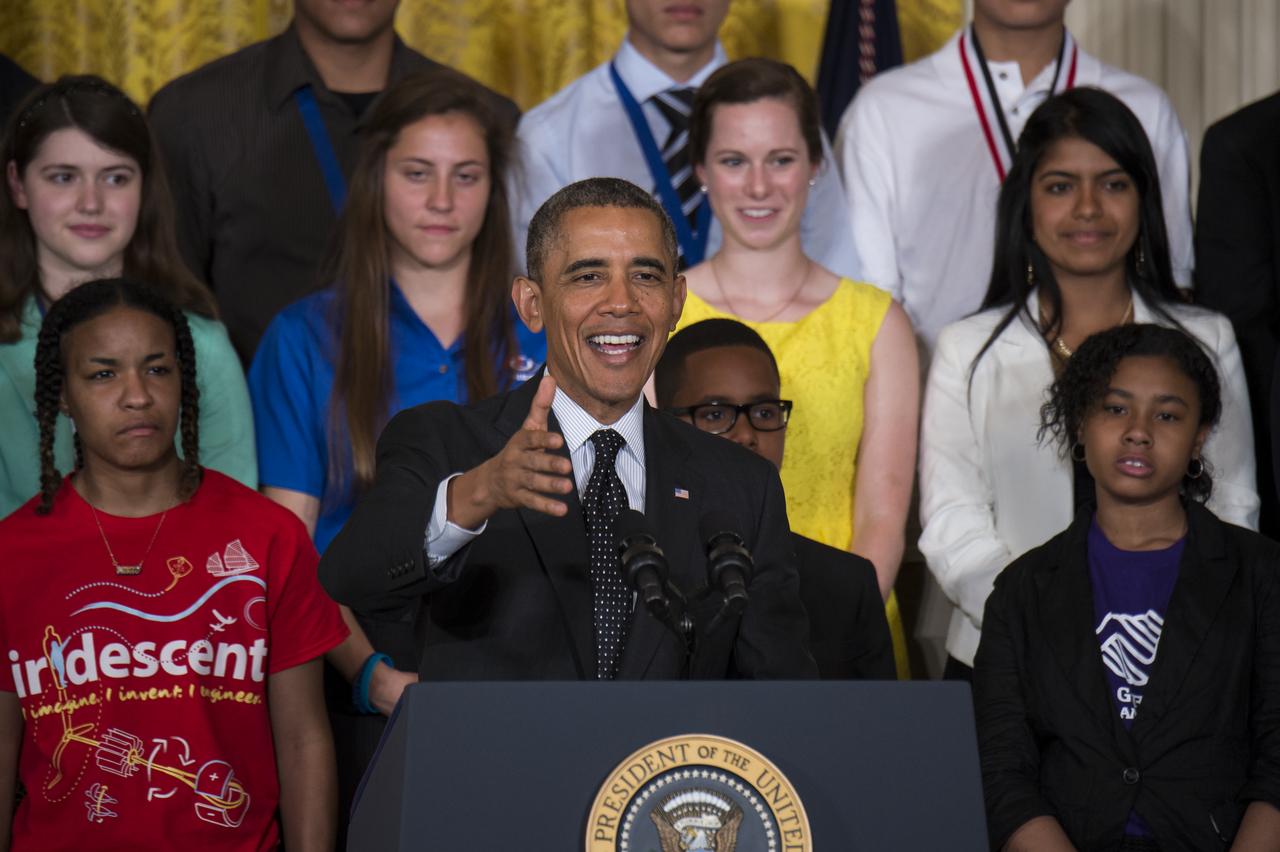

President Barack Obama spoke at the White House Science Fair Tuesday, May 27, 2014 at the White House. NASA Administrator Charles Bolden attended and was recognized by the President at the fourth White House Science Fair, which included 100 students from more than 30 different states who competed in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) competitions. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
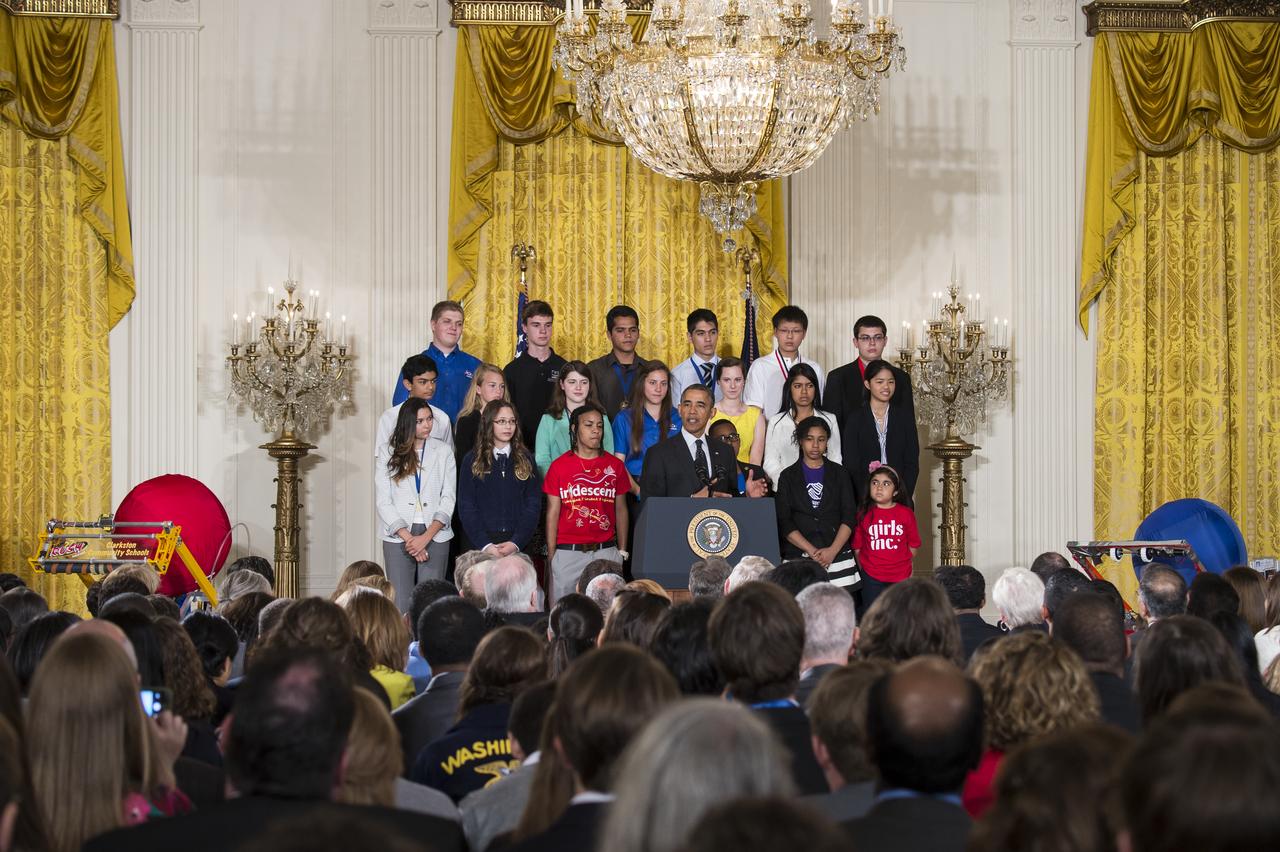

President Barack Obama spoke at the White House Science Fair Tuesday, May 27, 2014 at the White House. NASA Administrator Charles Bolden attended and was recognized by the President at the fourth White House Science Fair, which included 100 students from more than 30 different states who competed in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) competitions. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
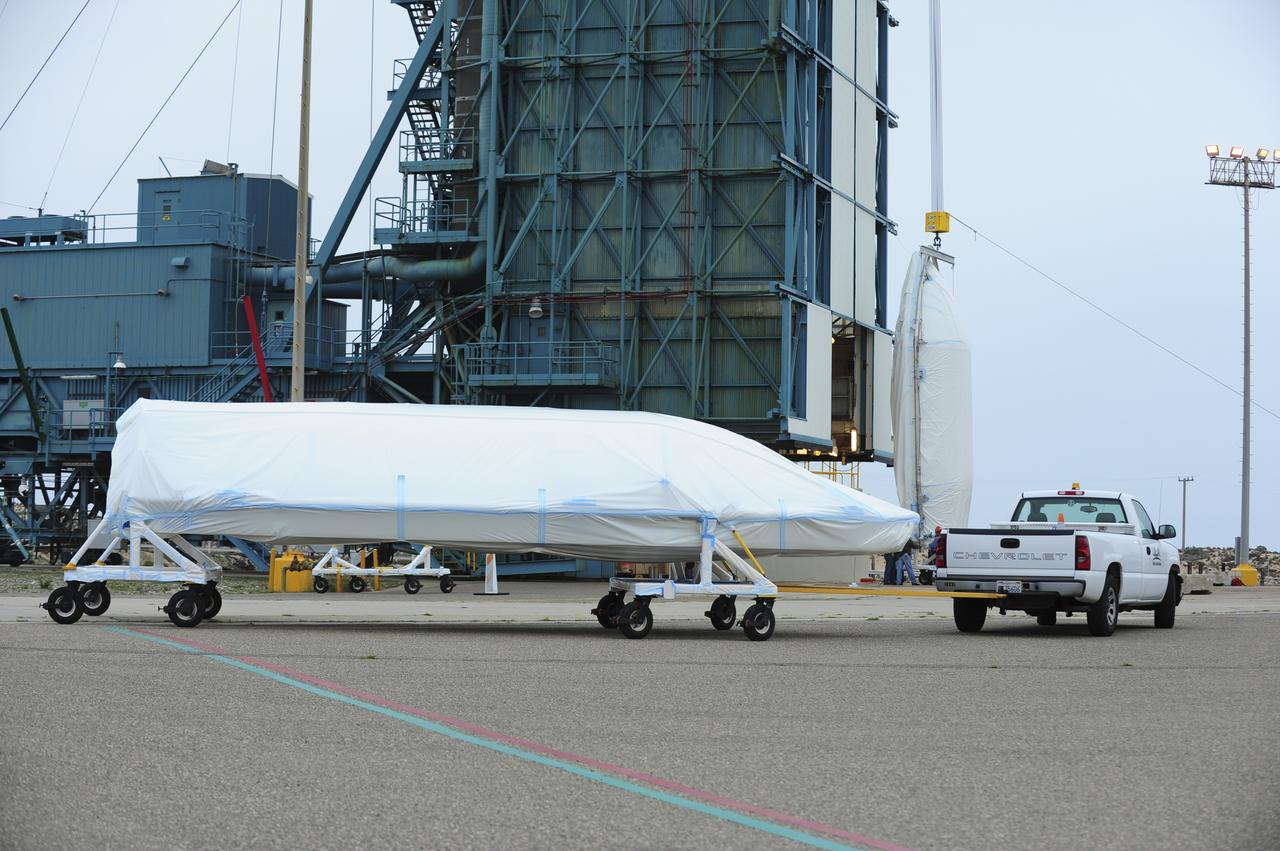

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is towed from the Building 836 hangar to Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations have begun to hoist the sections of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the pad's mobile service tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/30th Space Wing, VAFB
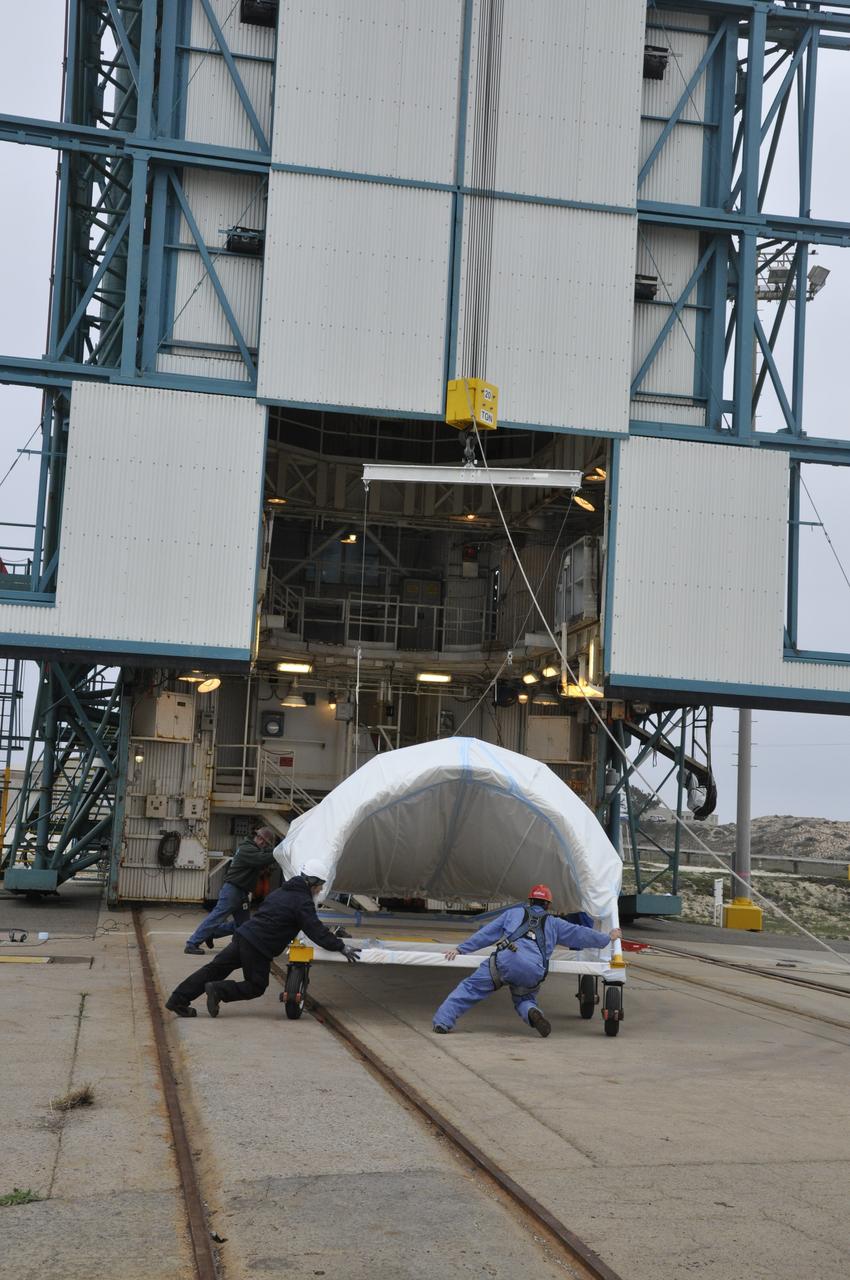

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers maneuver half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, newly arrived at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, into position underneath the crane. Operations are underway to hoist this section of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower where the other half already is in position. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
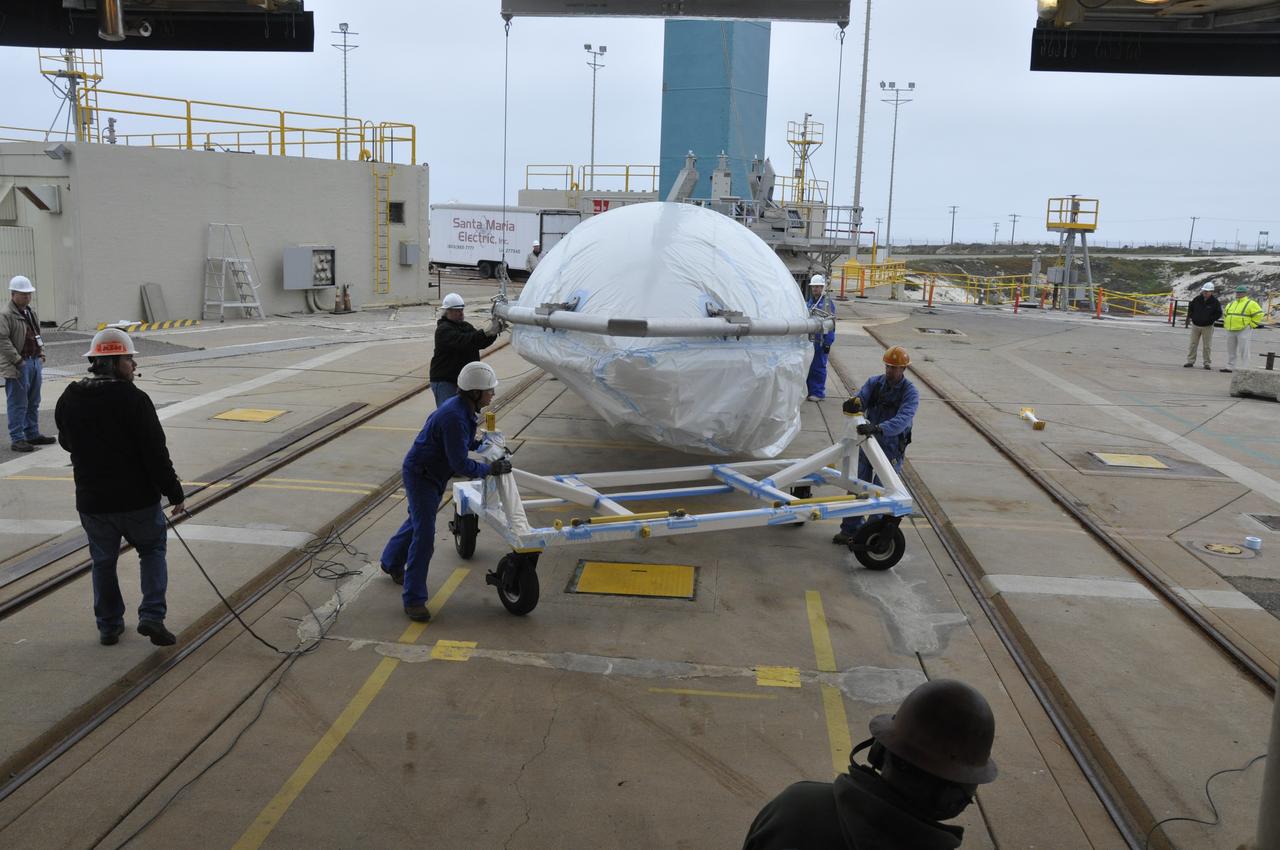

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers maneuver half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, newly arrived at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, into position underneath the crane. Operations are underway to hoist this section of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower where the other half already is in position. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers attach a crane onto half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, newly arrived at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to hoist this section of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower where the other half already is in position. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
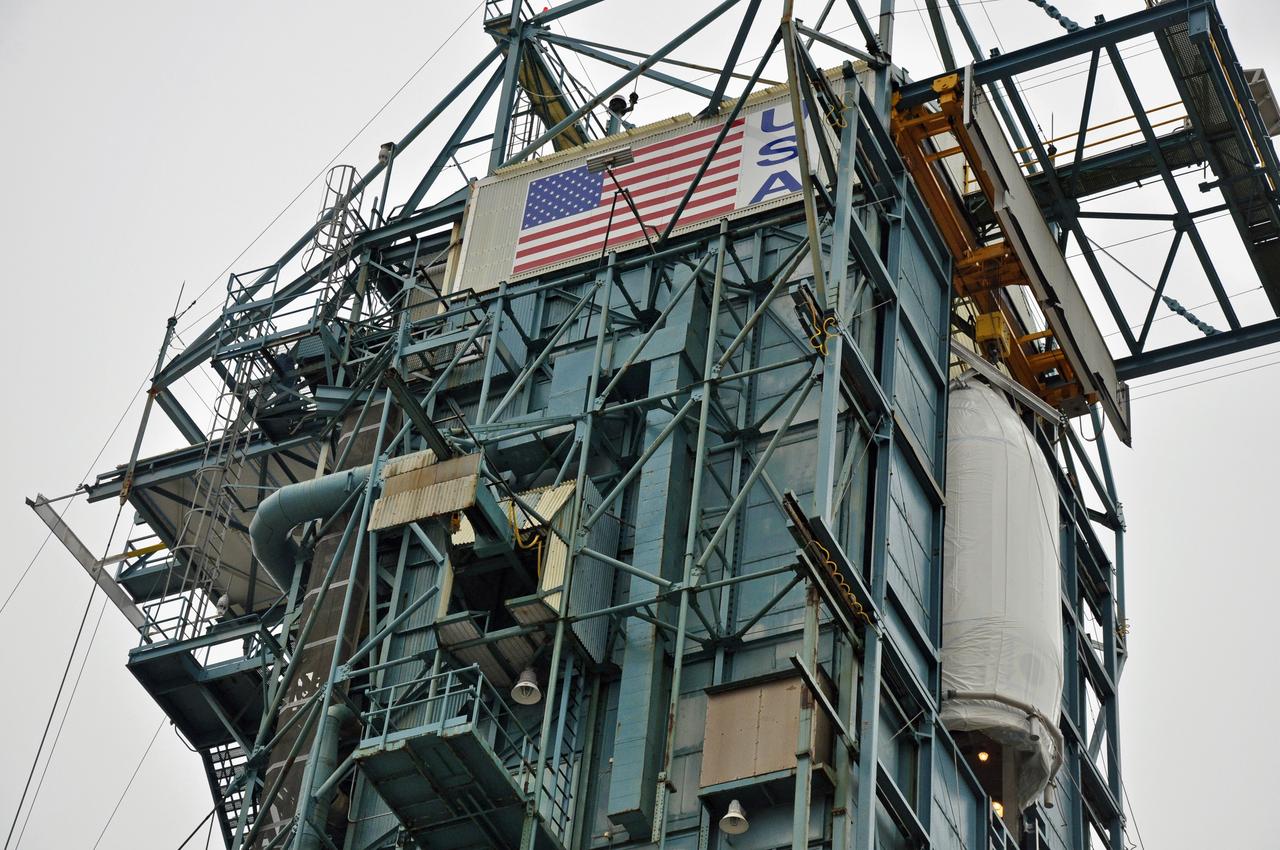

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is transferred through the portal into the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the Delta II launcher at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
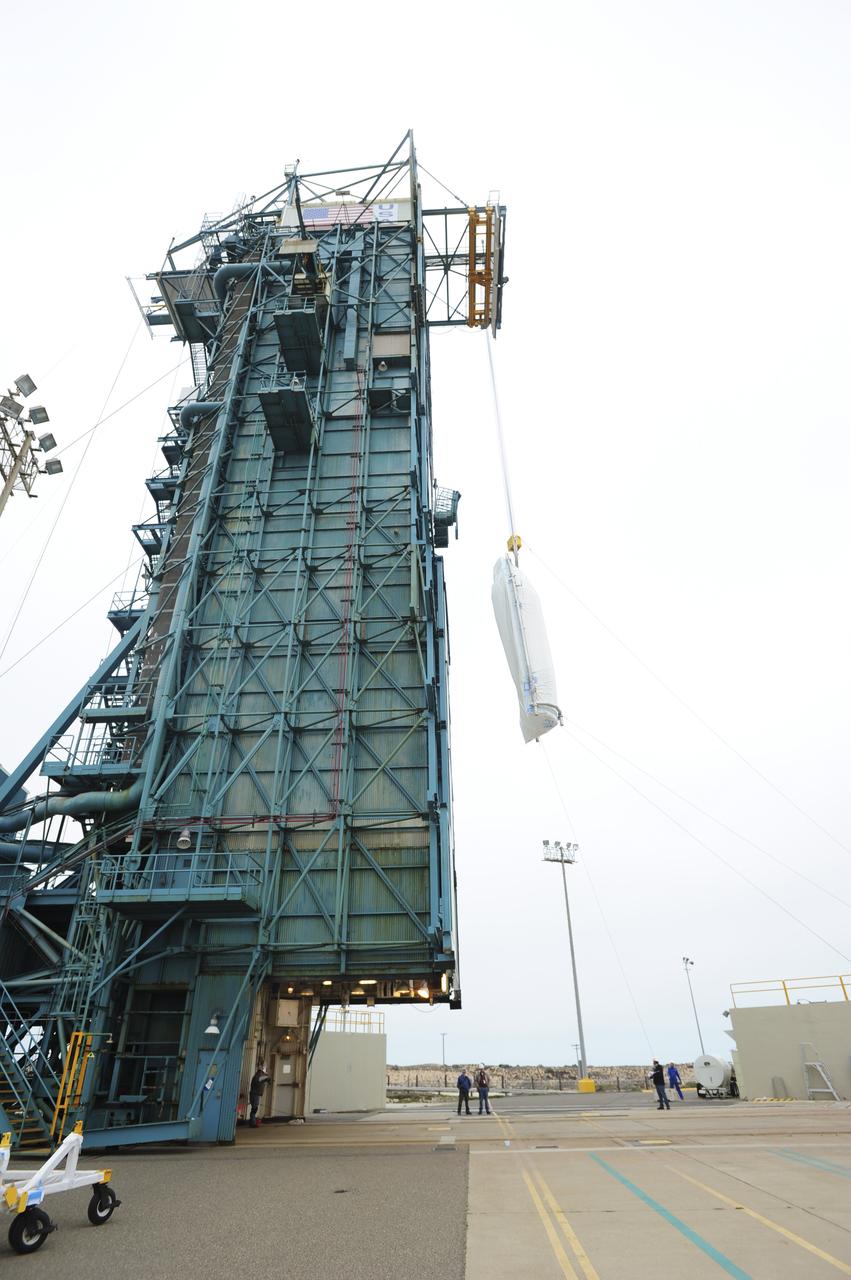

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted up the side of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California toward the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/30th Space Wing, VAFB
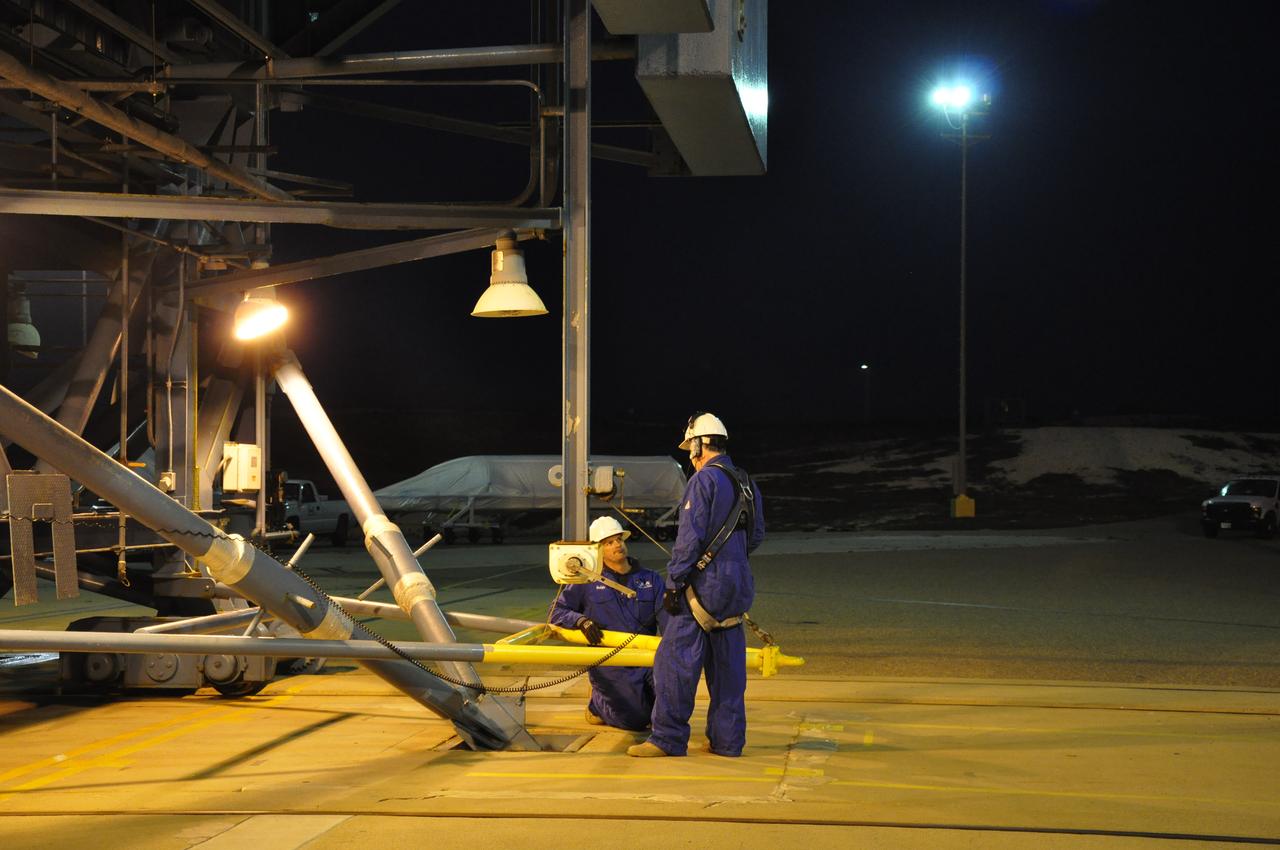

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers prepare to hoist the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, seen in the background, into the gantry's environmental enclosure, or clean room, following the rollback of the mobile service tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The mobile service tower is rolled away from the Delta II launcher at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California in preparation for hoisting the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into the gantry's environmental enclosure, or clean room. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
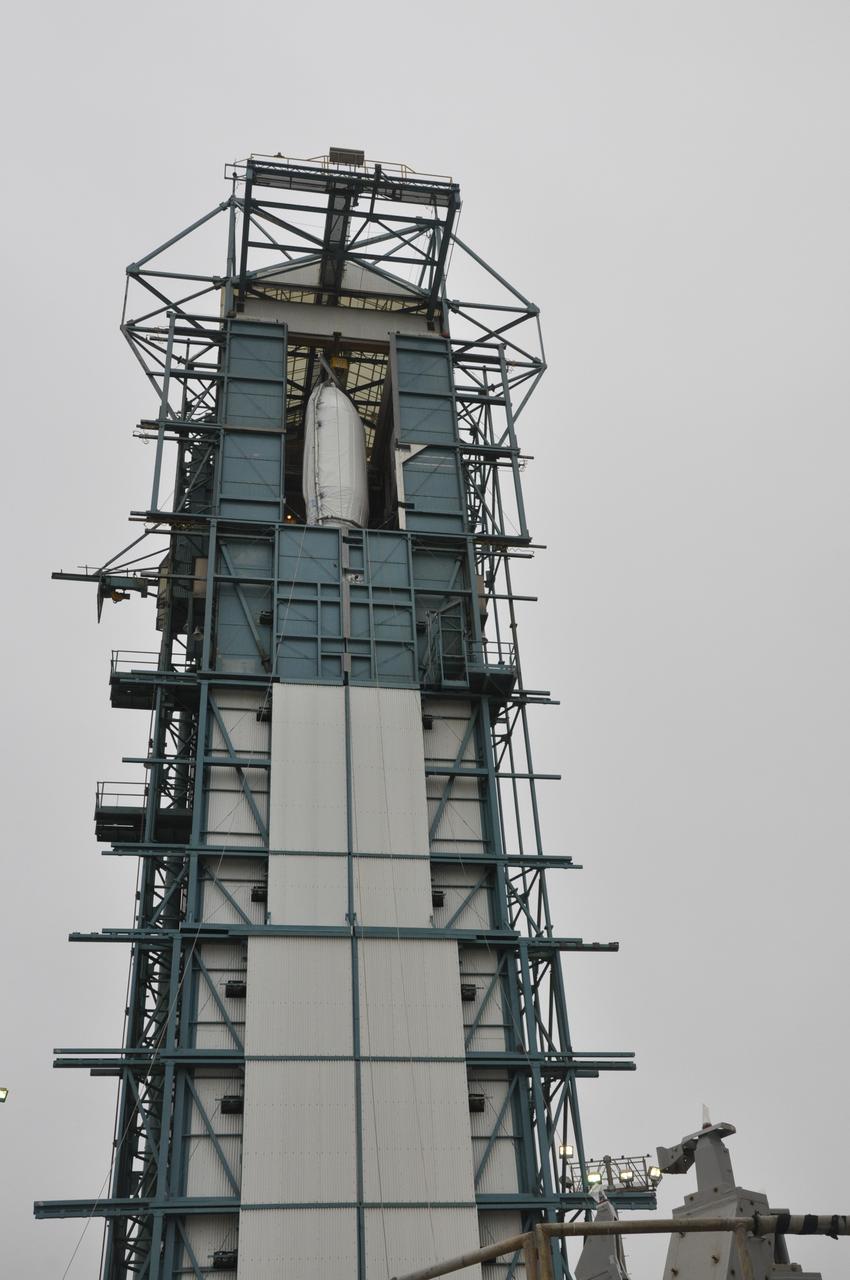

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is positioned into the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the Delta II launcher at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
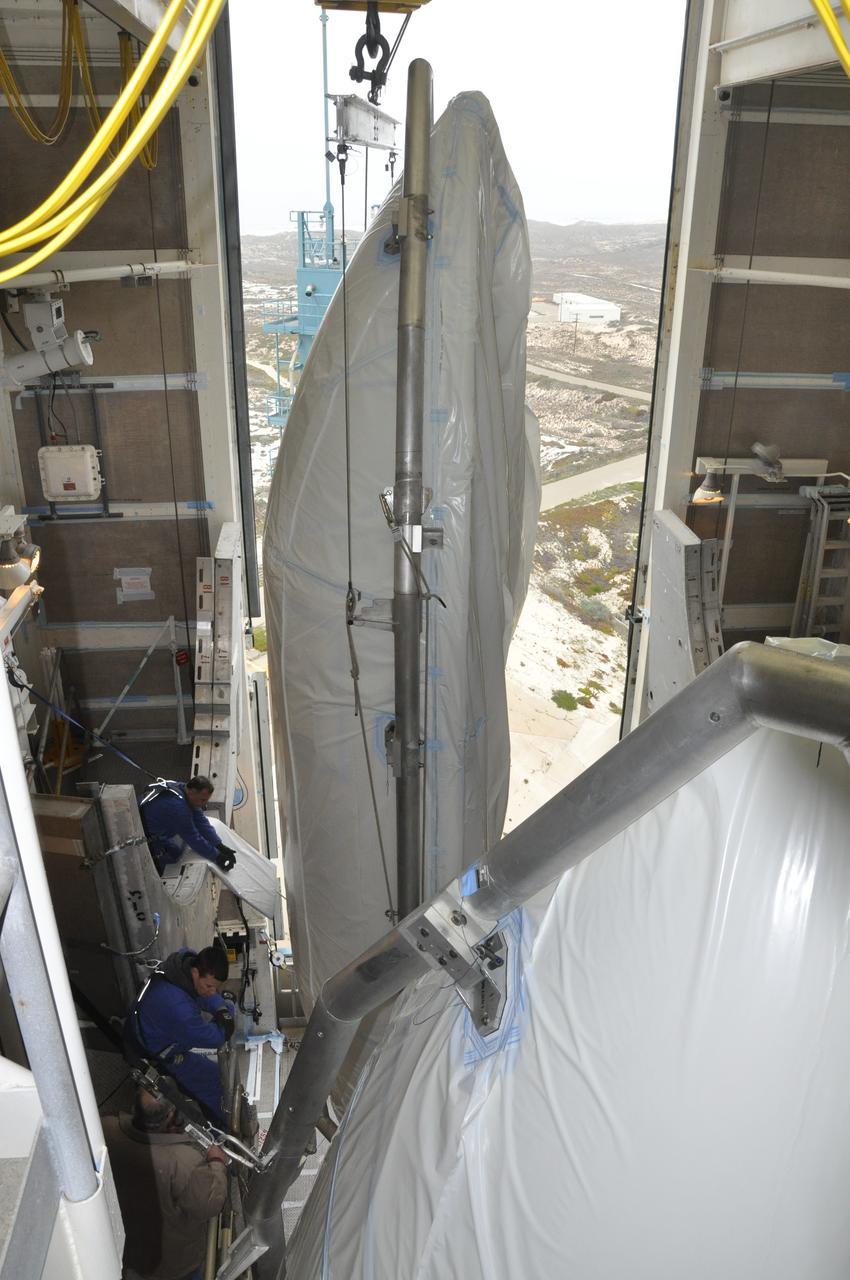

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers transfer half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the Delta II launcher at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
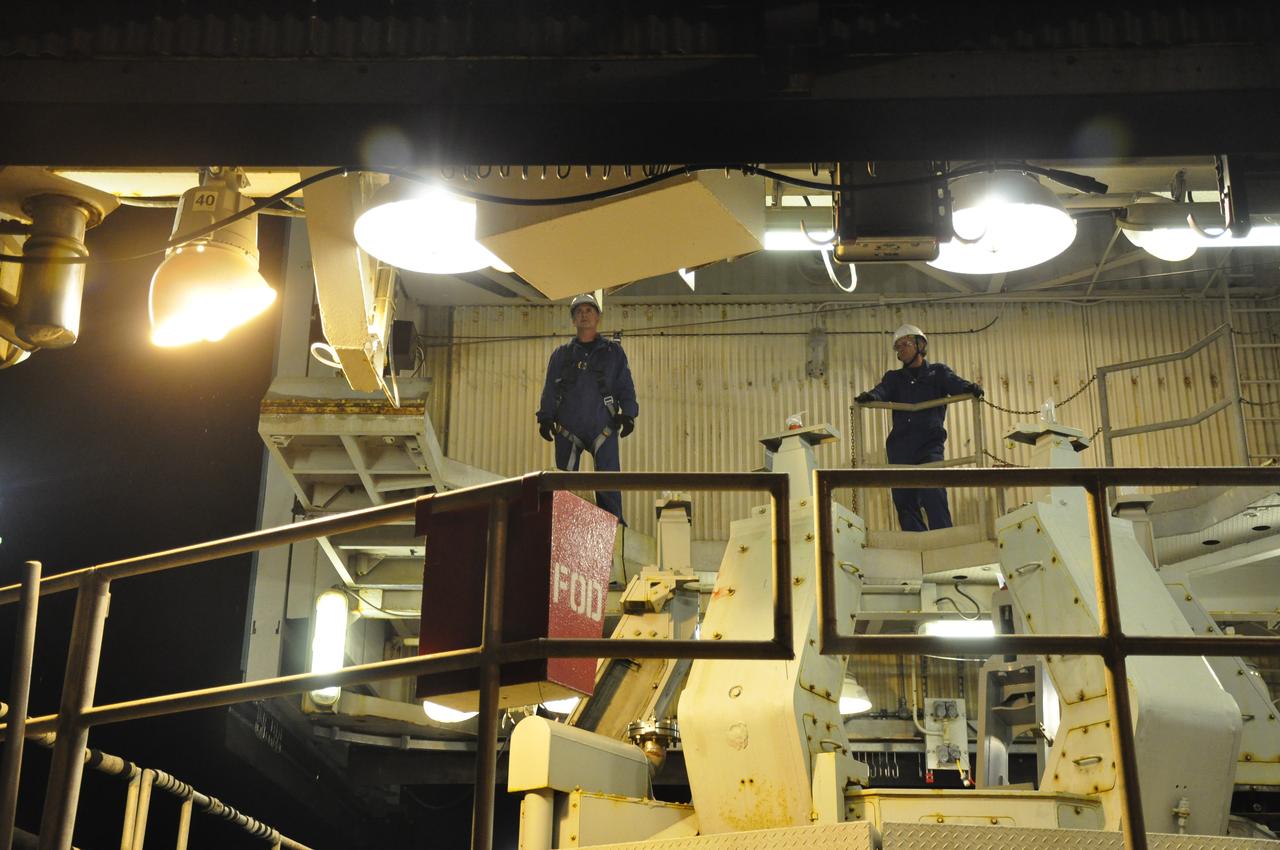

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers roll the mobile service tower away from the Delta II launcher behind them at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California in preparation for hoisting the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into the gantry's environmental enclosure, or clean room. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
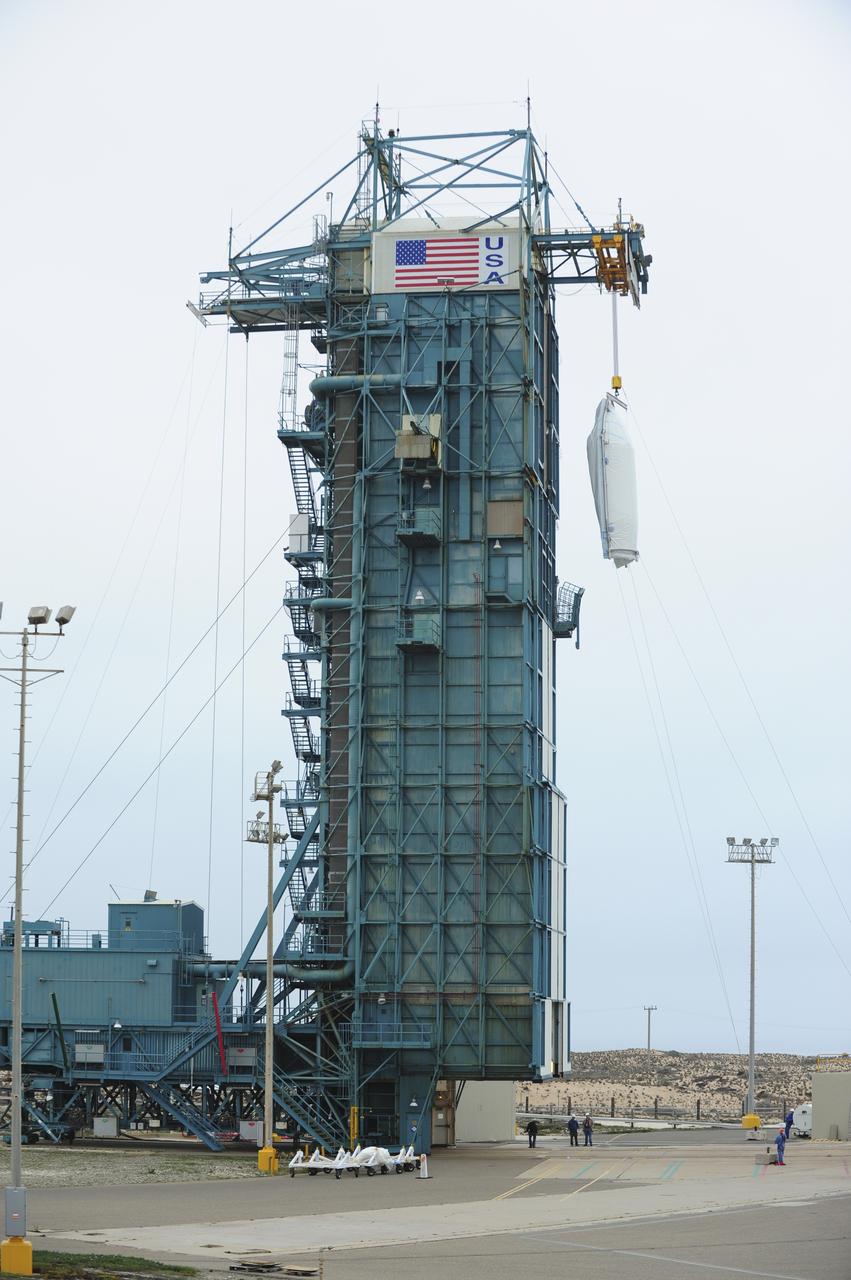

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted up the side of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California toward the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/30th Space Wing, VAFB
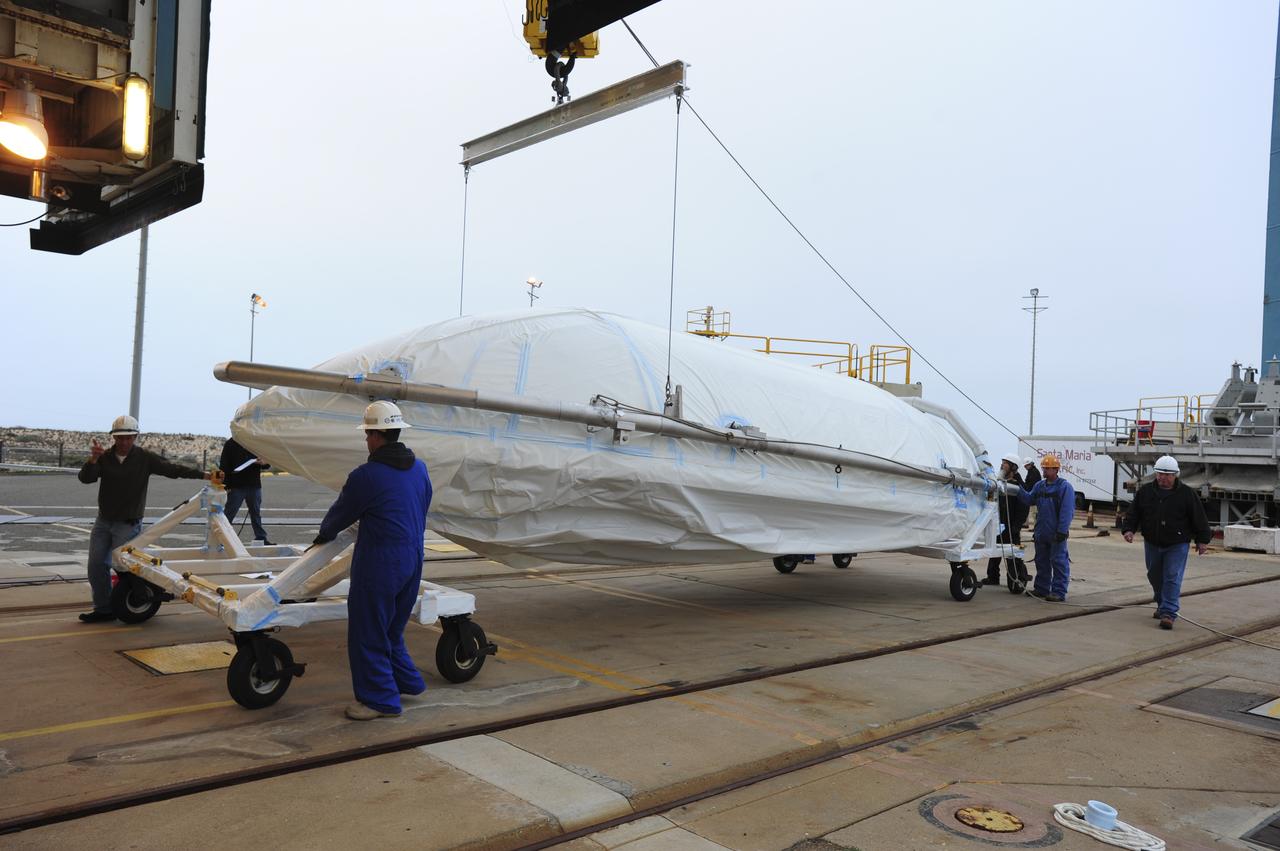

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is attached to a crane for its lift into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/30th Space Wing, VAFB
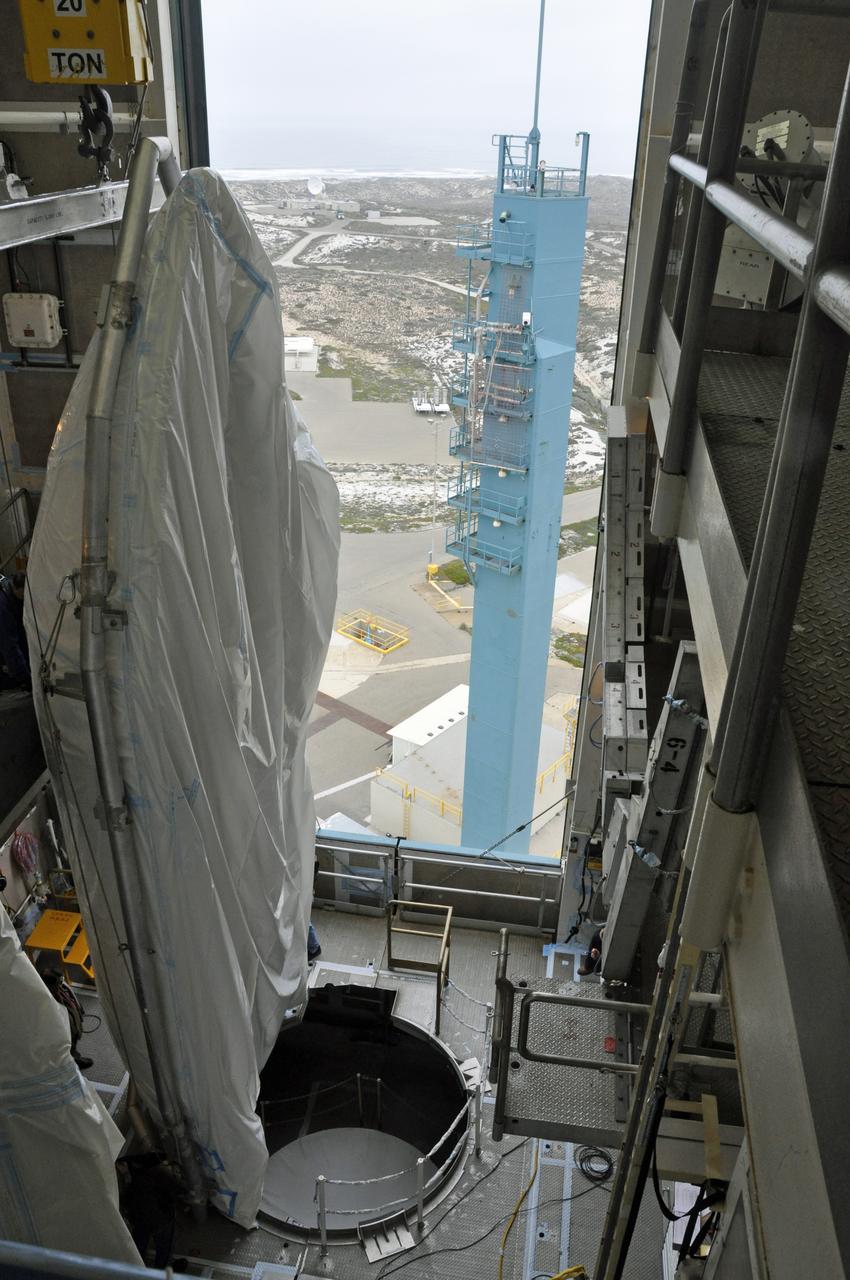

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Both halves of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, have arrived in the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the Delta II launcher at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
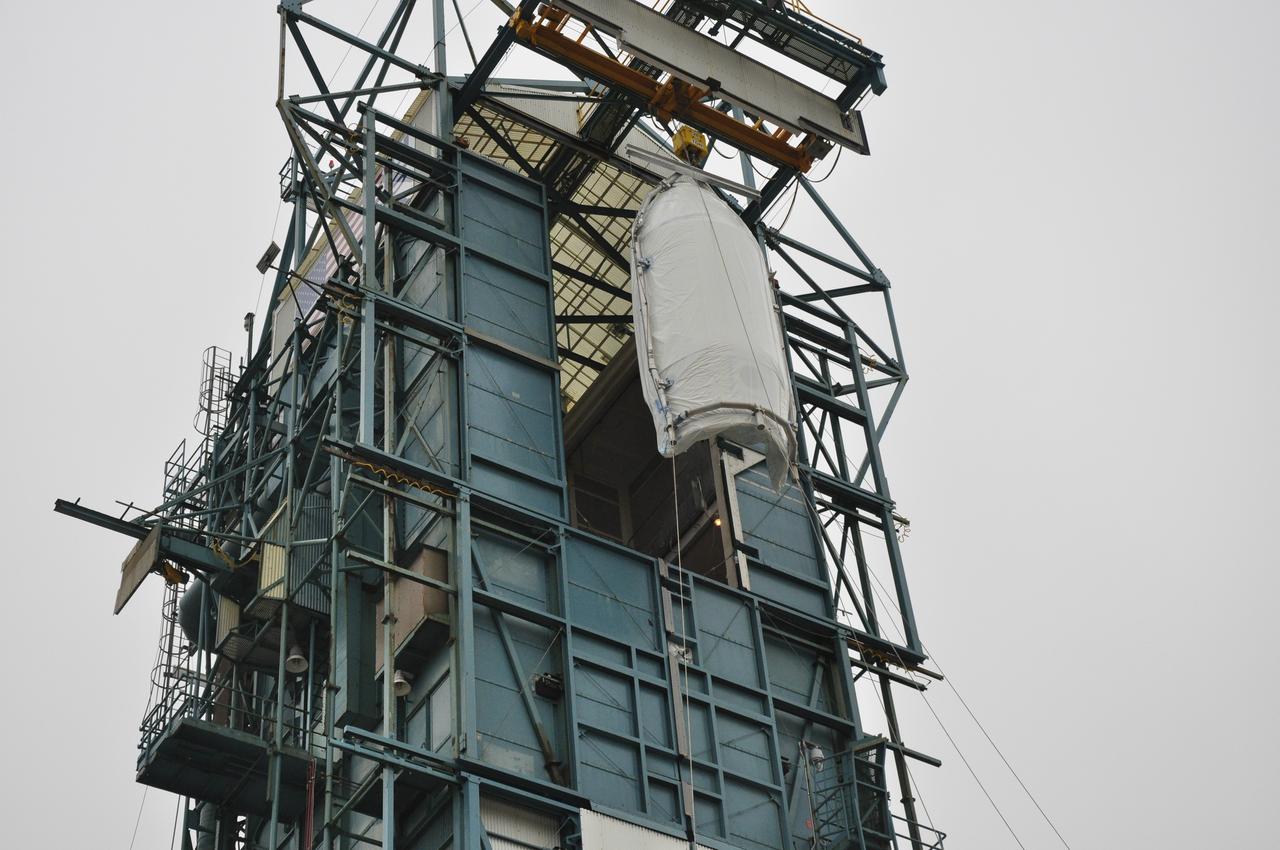

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, arrives at the portal to the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the Delta II launcher at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
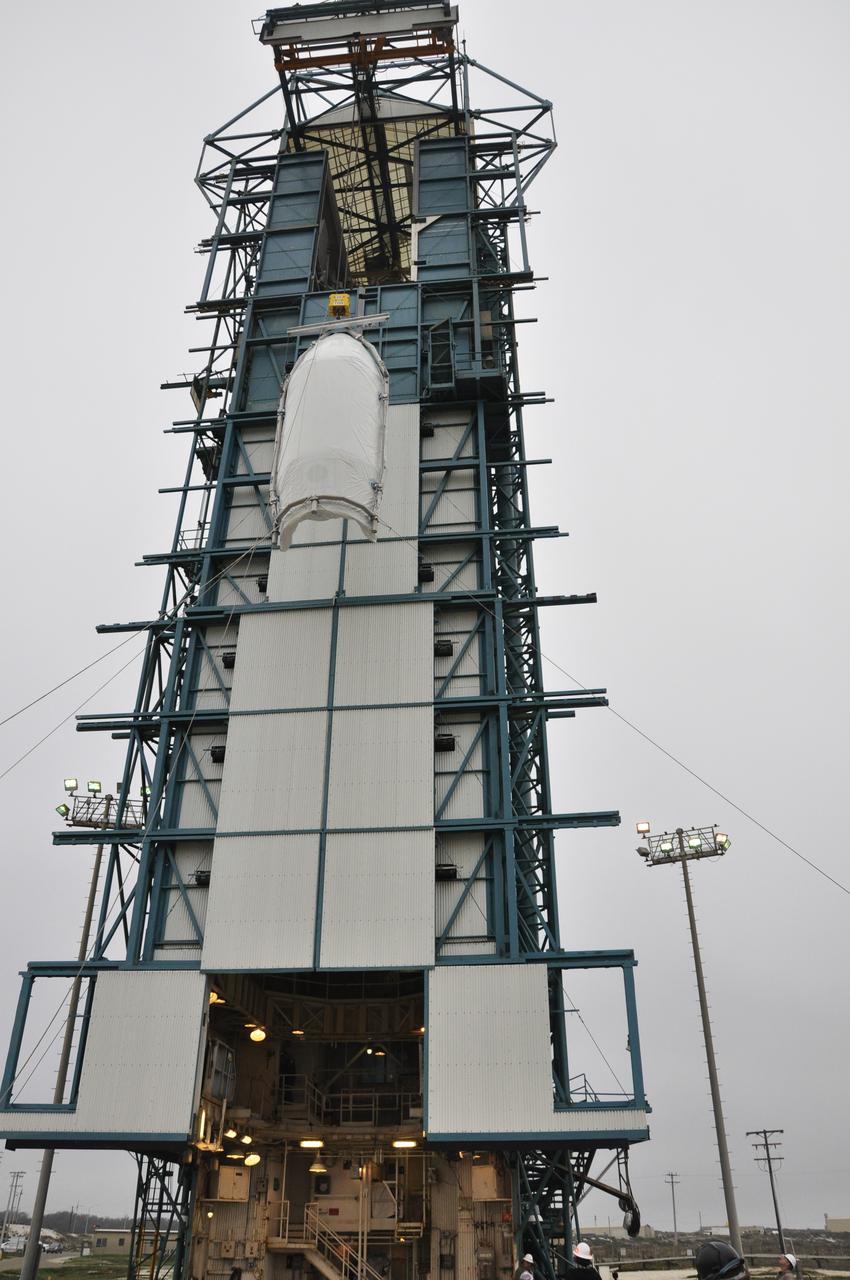

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted toward the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the Delta II launcher at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
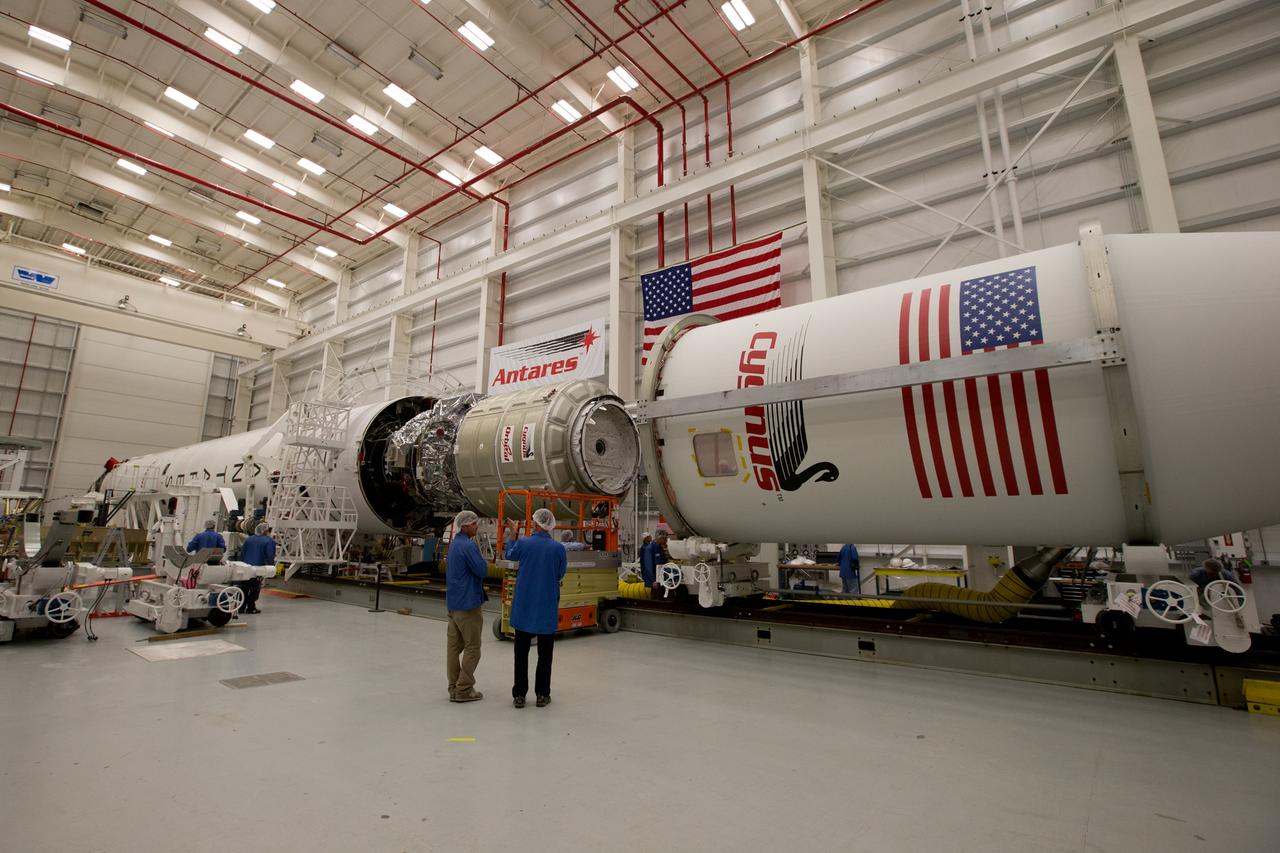

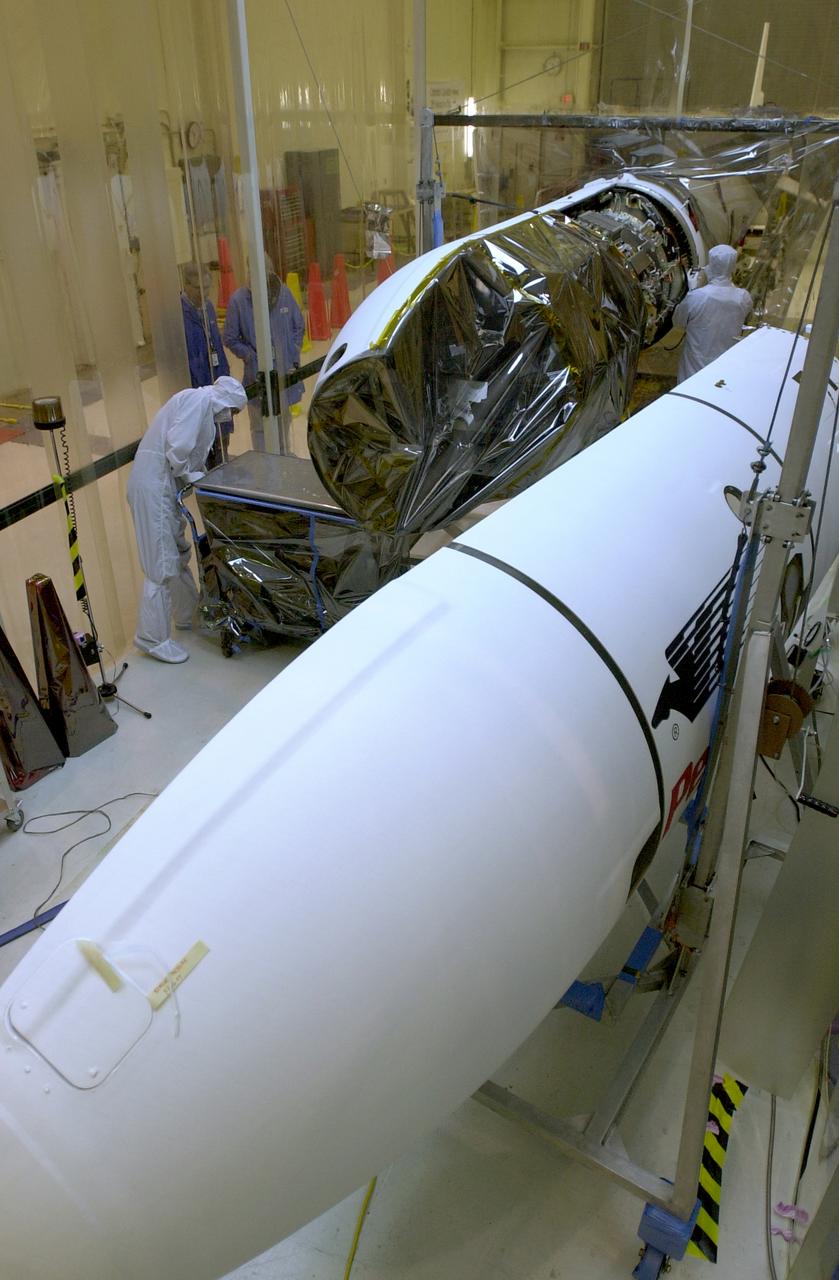
The payload fairing is installed on the Orbital Sciences Antares rocket at the Horizontal Integration Facility at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility on Virginia's Eastern Shore, Tuesday, July 8, 2014. The Antares rocket is scheduled to roll-out to Virginia's Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport Pad 0A Wednesday, July 9, ahead of its scheduled launch July 11. The Antares rocket will carry Orbital's unmanned Cygnus spacecraft to the International Space Station. This Orbital-2 mission's cargo is more than 3,000 pounds of supplies for the station, including science experiments to expand the research capability of the Expedition 40 crew members aboard the orbiting laboratory, crew provisions, spare parts and experiment hardware. Credit: NASA's Wallops Flight Facility <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
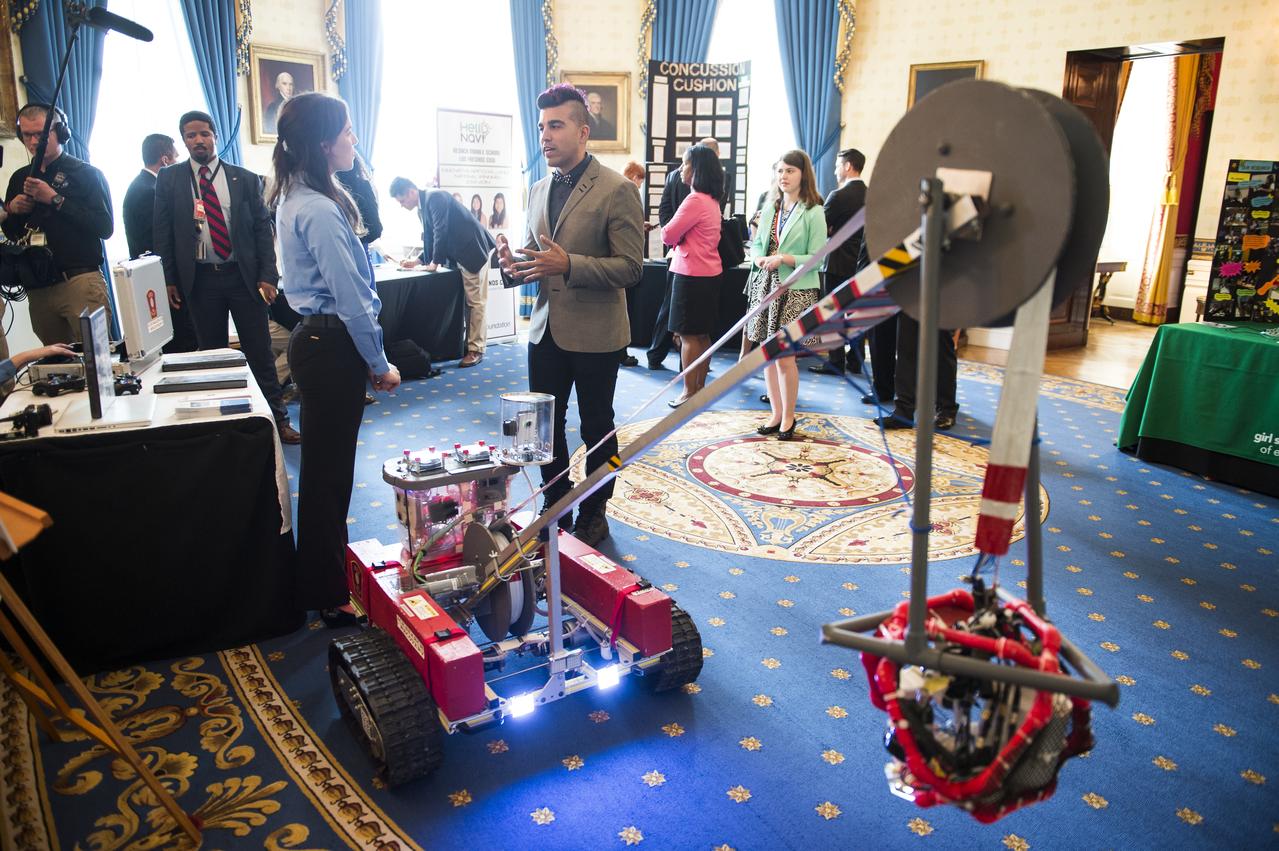

Bobak Ferdowsi, a system's engineer at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, speaks with a member of "invenTeam" at the White House Science Fair. Olivia Van Amsterdam, 16, Katelyn Sweeney, 17, and their team of student engineers from Natick, MA, invented a 120 lb remotely operated vehicle (ROV) that can help search-and-rescue dive teams search for bodies in dangerous, icy waters. The fourth White House Science Fair was held at the White House and included 100 students from more than 30 different states who competed in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) competitions. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
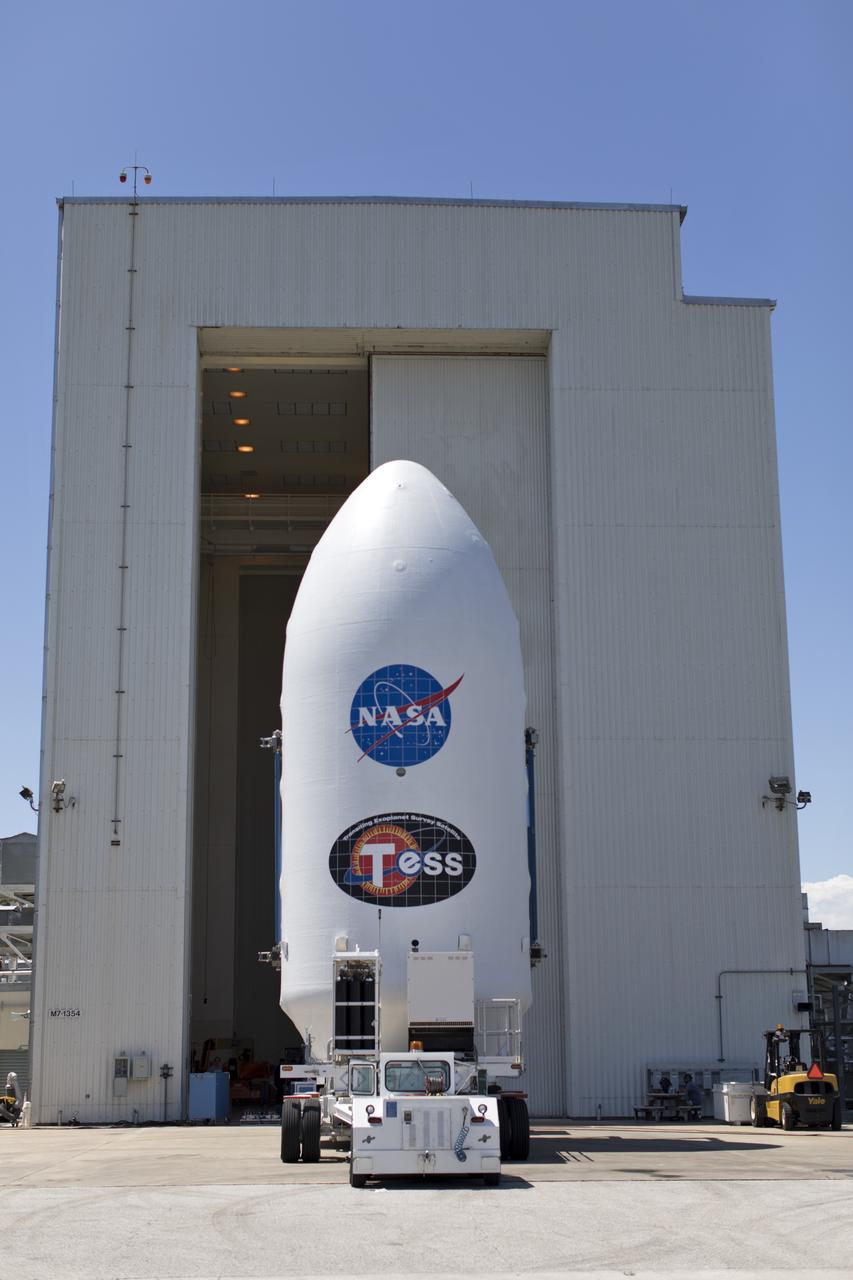

The payload fairing for NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is moved to the entrance of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the facility, TESS will be encapsulated in the payload fairing. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
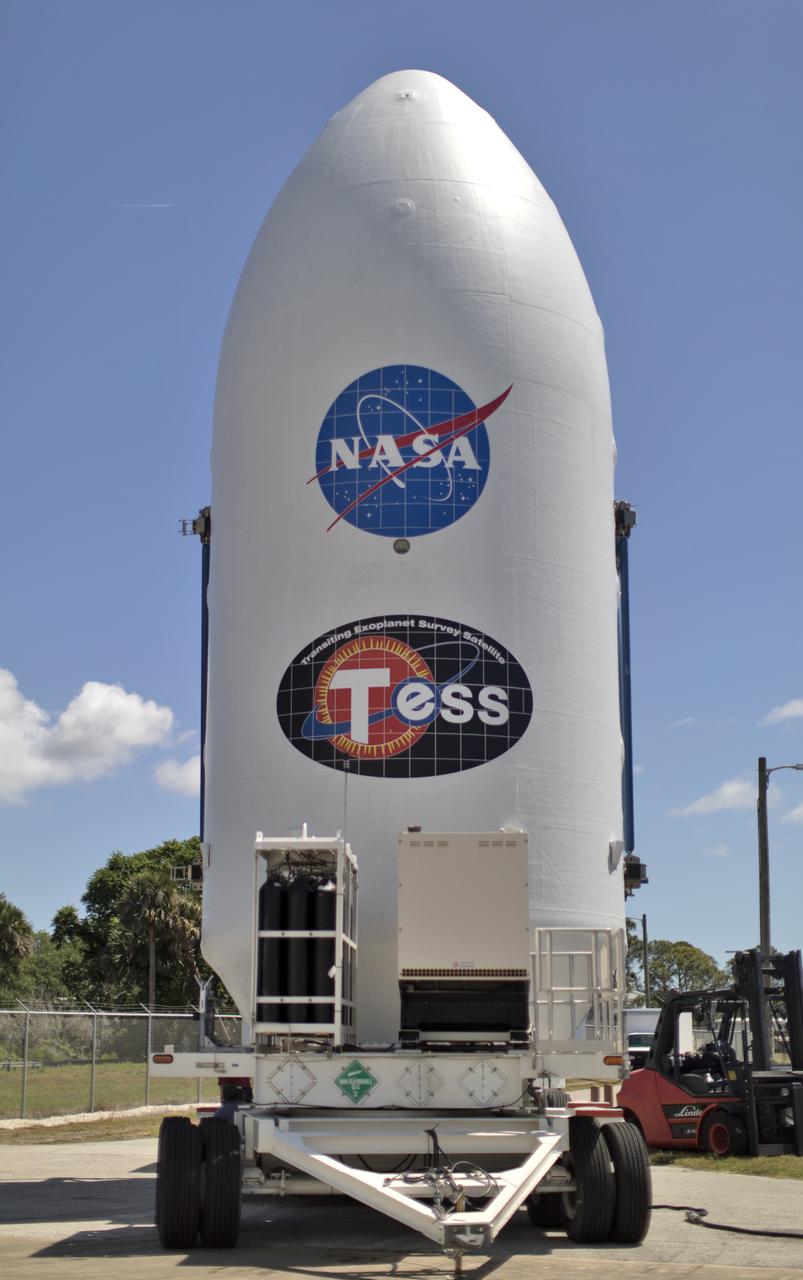

The payload fairing for NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is being prepared for the move to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the facility, TESS will be encapsulated in the payload fairing. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
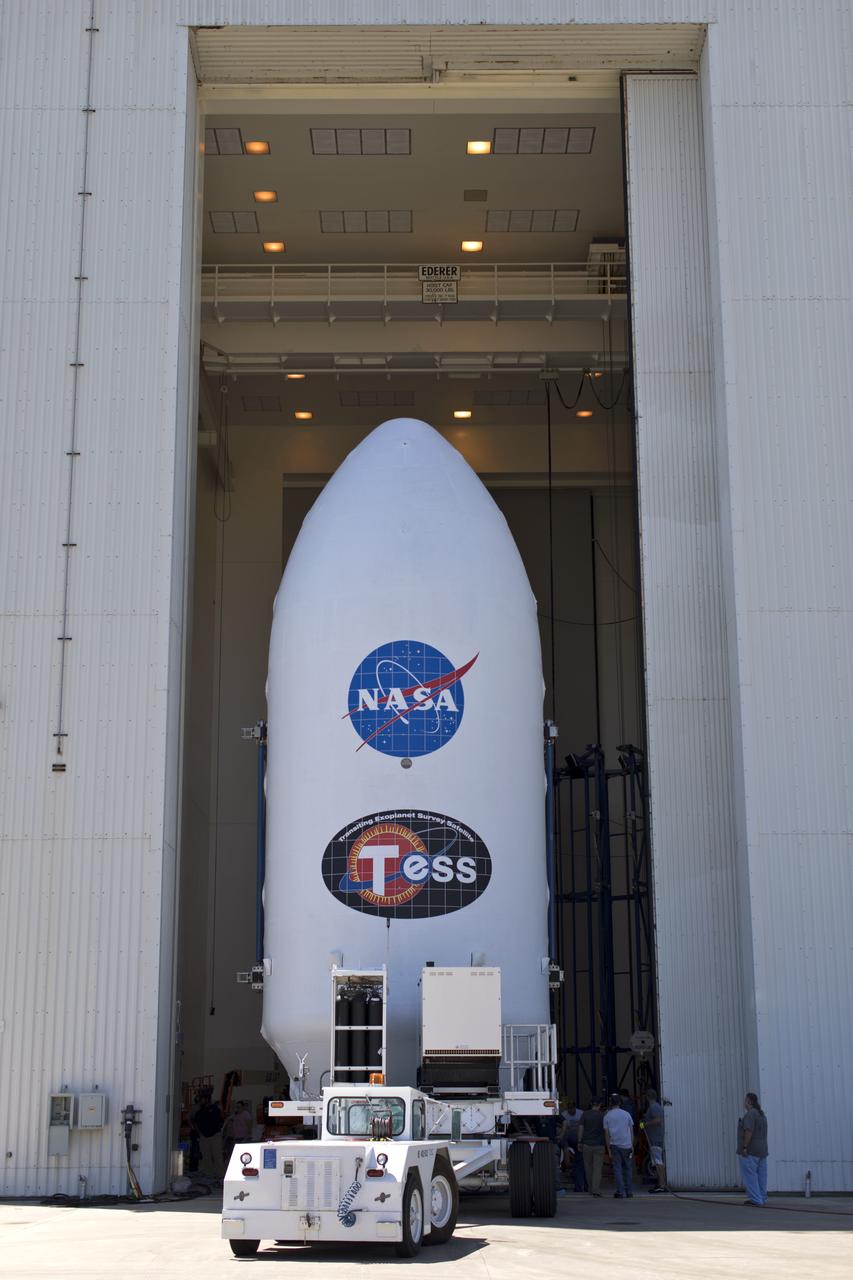

The payload fairing for NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is moved inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the facility, TESS will be encapsulated in the payload fairing. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.

The payload fairing for NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is moved inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the facility, TESS will be encapsulated in the payload fairing. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.

The payload fairing for NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is being moved to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the facility, TESS will be encapsulated in the payload fairing. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
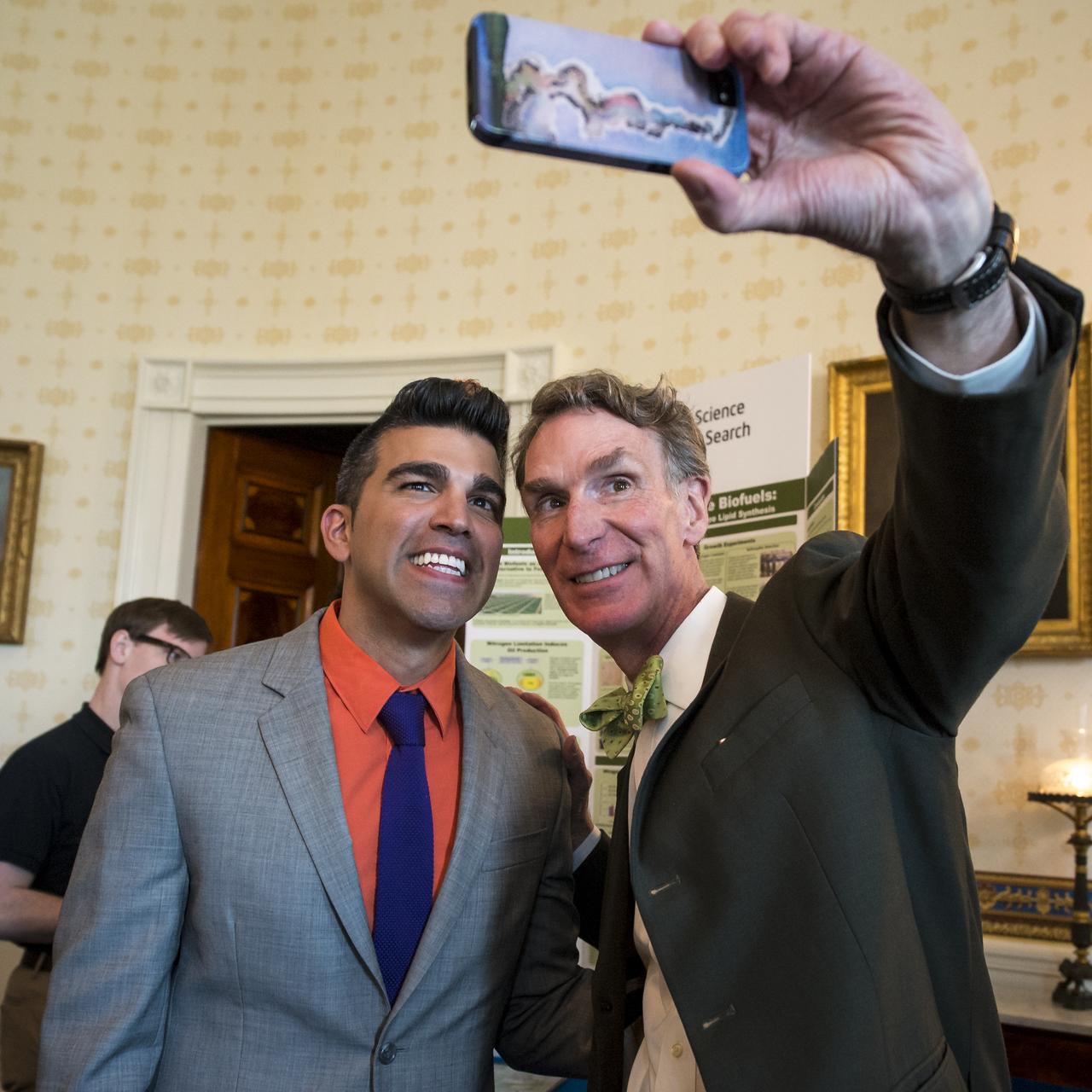

Planetary Society Executive Director and “Bill Nye the Science Guy” host Bill Nye, right, photographs himself with NASA Mars Curiosity Landing mission controller, Bobak "Mohawk Guy" Ferdowsi, during the White House Science Fair held at the White House, April 22, 2013. The science fair celebrated student winners of a broad range of science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) competitions from across the country. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
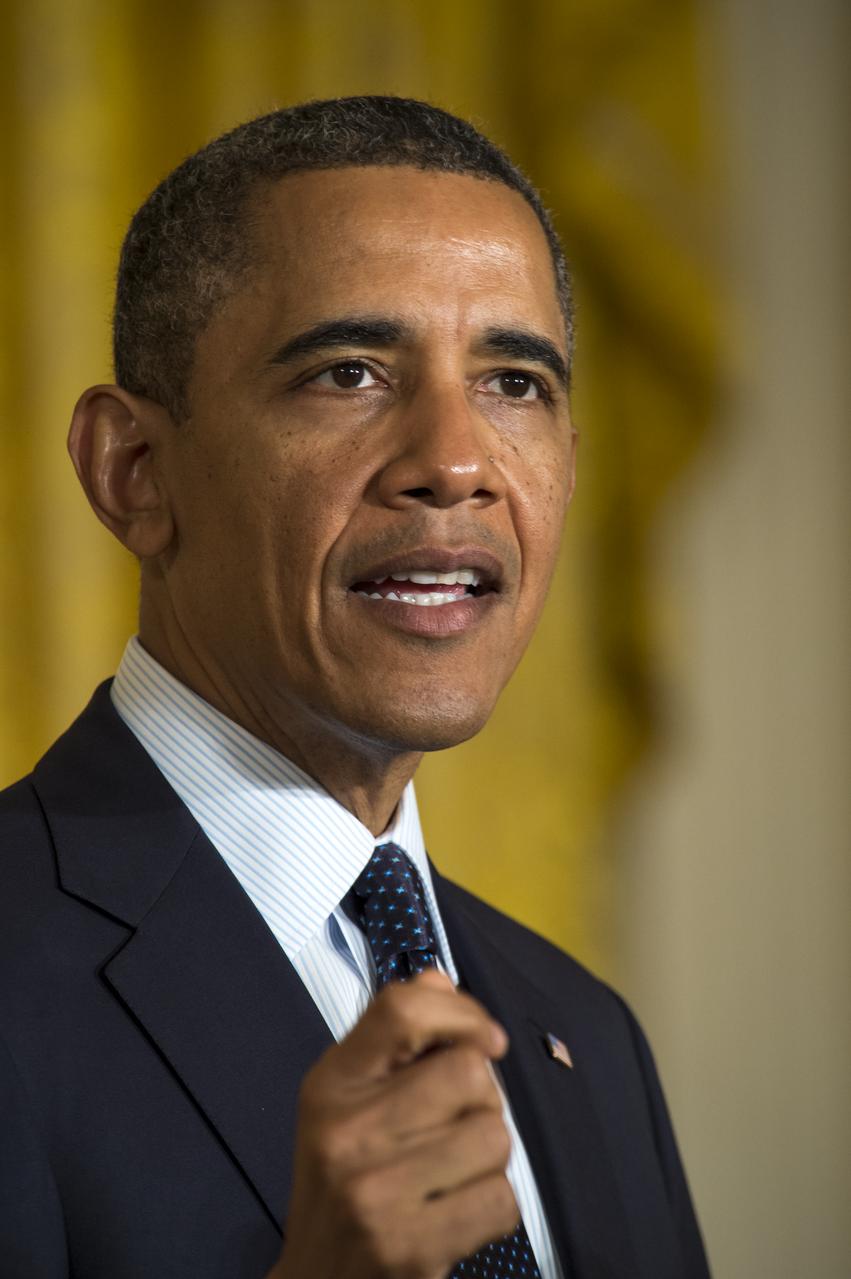

U.S. President Barack Obama speaks as he hosts the third-ever White House Science Fair in the East Room at the White House in Washington, April 22, 2013. The science fair celebrated student winners of a broad range of science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) competitions from across the country. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
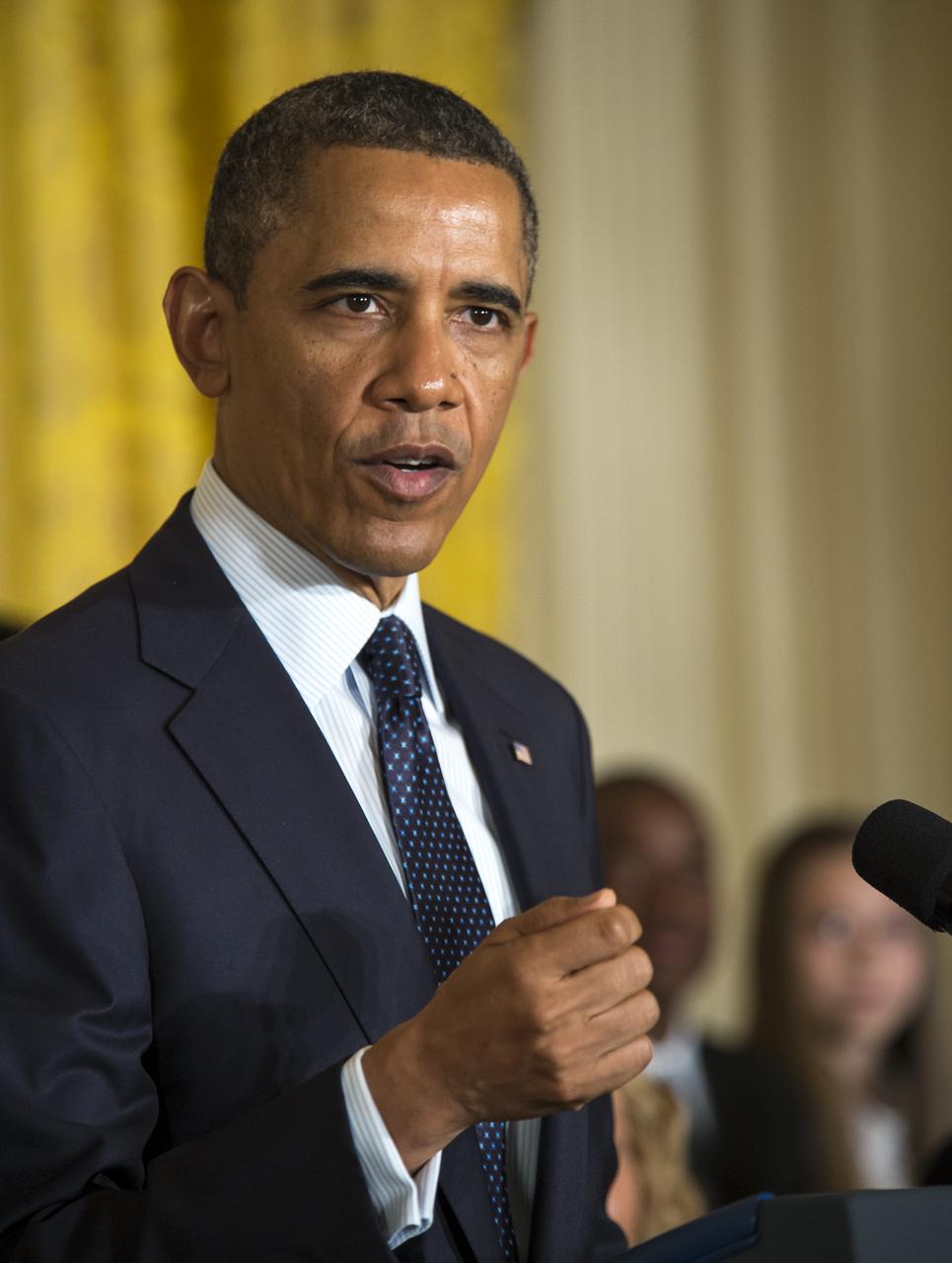

U.S. President Barack Obama speaks as he hosts the third-ever White House Science Fair in the East Room at the White House in Washington, April 22, 2013. The science fair celebrated student winners of a broad range of science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) competitions from across the country. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
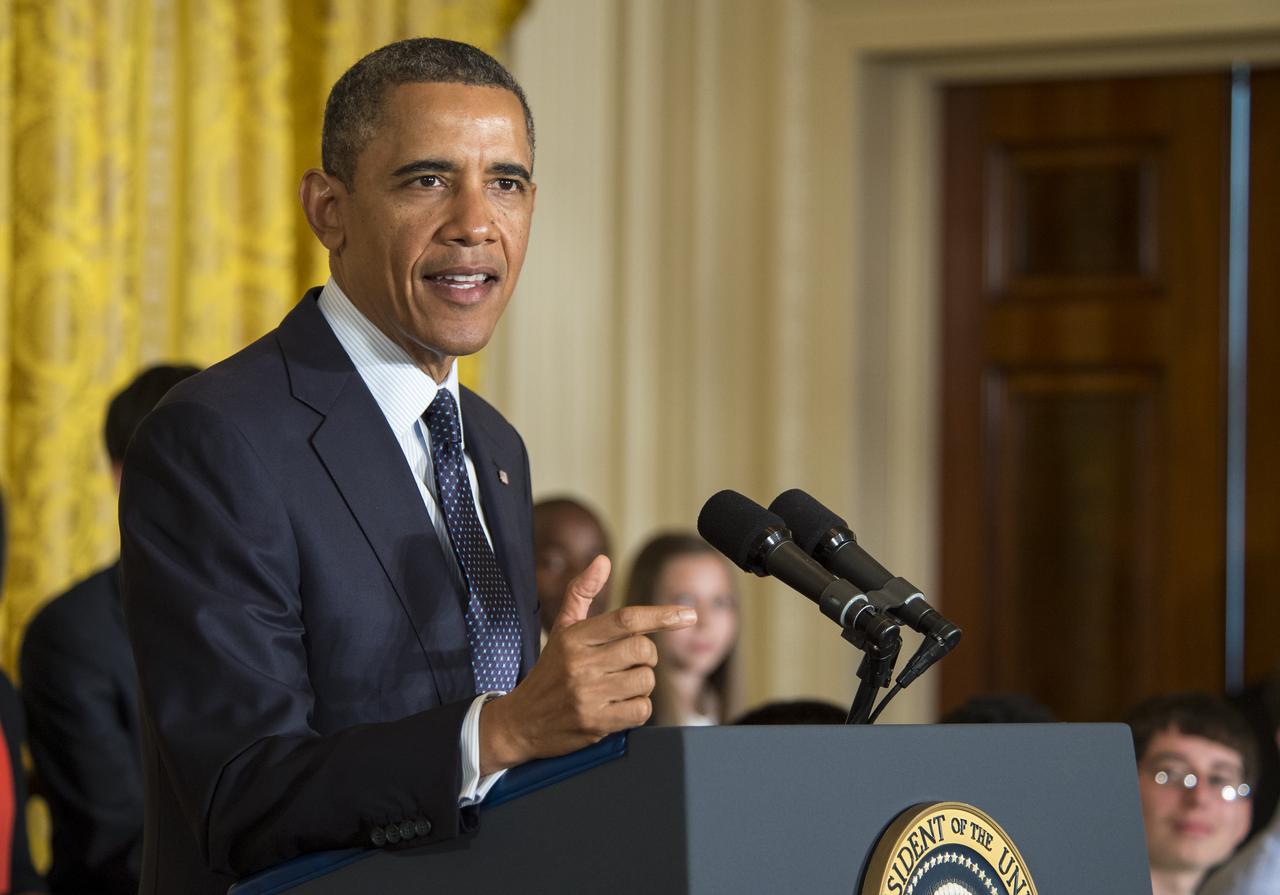

U.S. President Barack Obama speaks as he hosts the third-ever White House Science Fair in the East Room at the White House in Washington, April 22, 2013. The science fair celebrated student winners of a broad range of science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) competitions from across the country. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
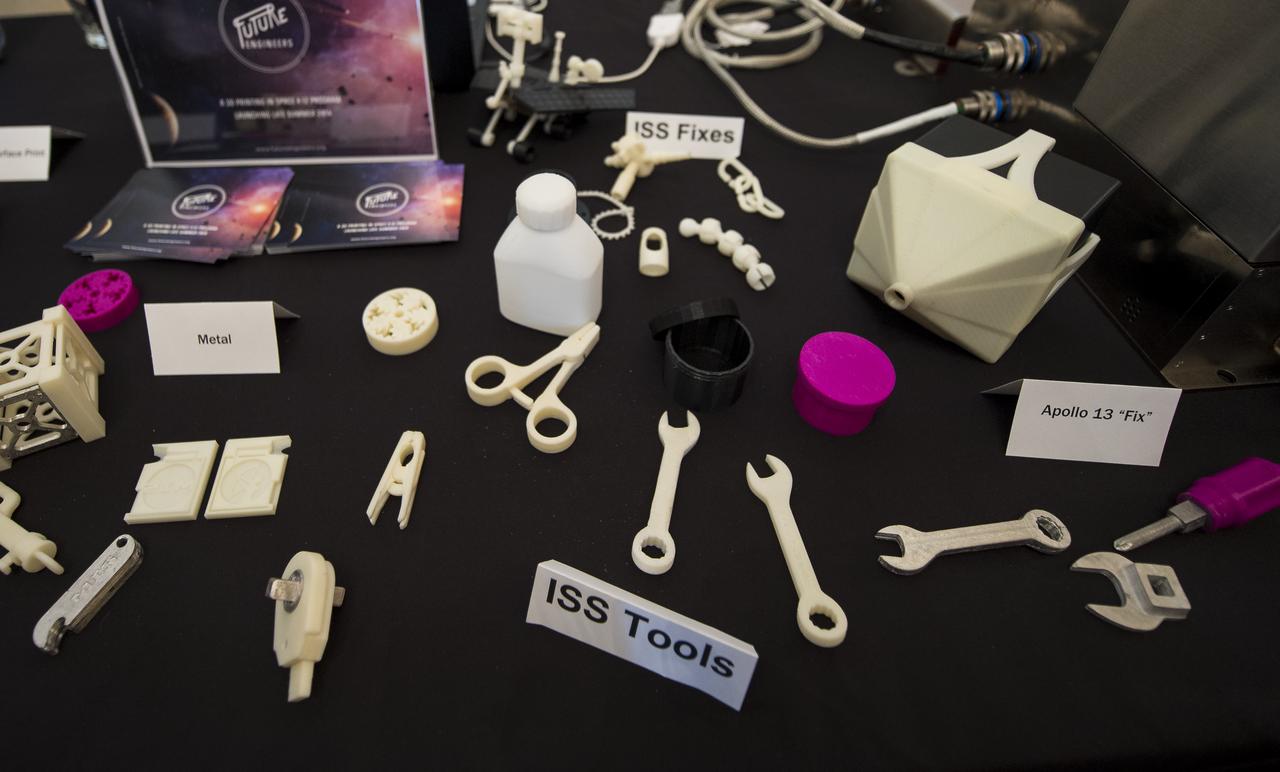

The Made In Space company displays some of the tools that can be made by their 3D printer during the first ever White House Maker Faire which brings together students, entrepreneurs, and everyday citizens who are using new tools and techniques to launch new businesses, learn vital skills in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), and fuel the renaissance in American manufacturing, at the White House, Wednesday, June 18, 2014 in Washington. The Made In Space 3D printer was just approved by NASA to be tested onboard the International Space Station (ISS), and NASA announced a challenge for students to design items that would be printed by this first 3D printer to fly in space. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
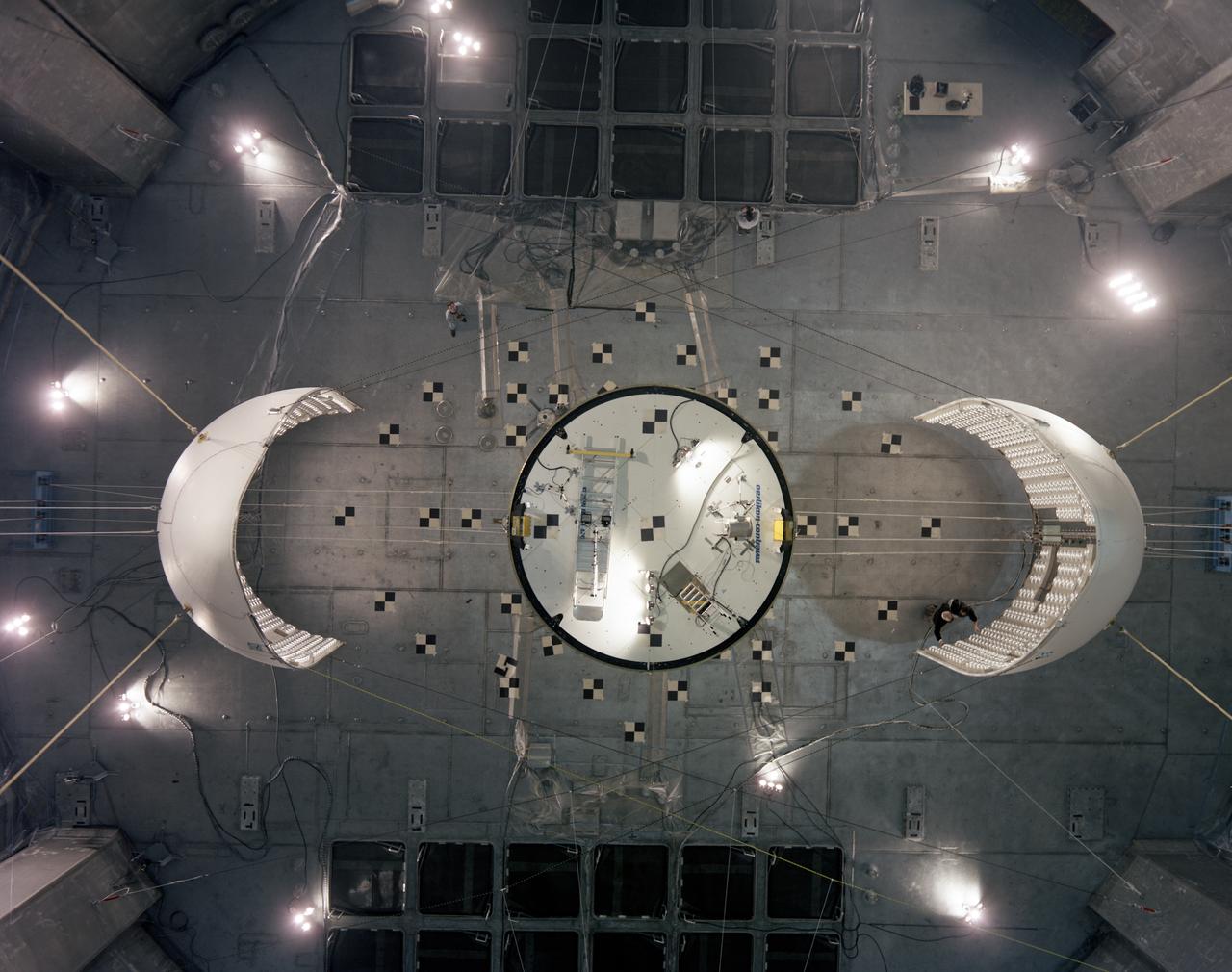
Top down photograph showing separation of the Ariane V fairing after testing in the vacuum chamber at SEC
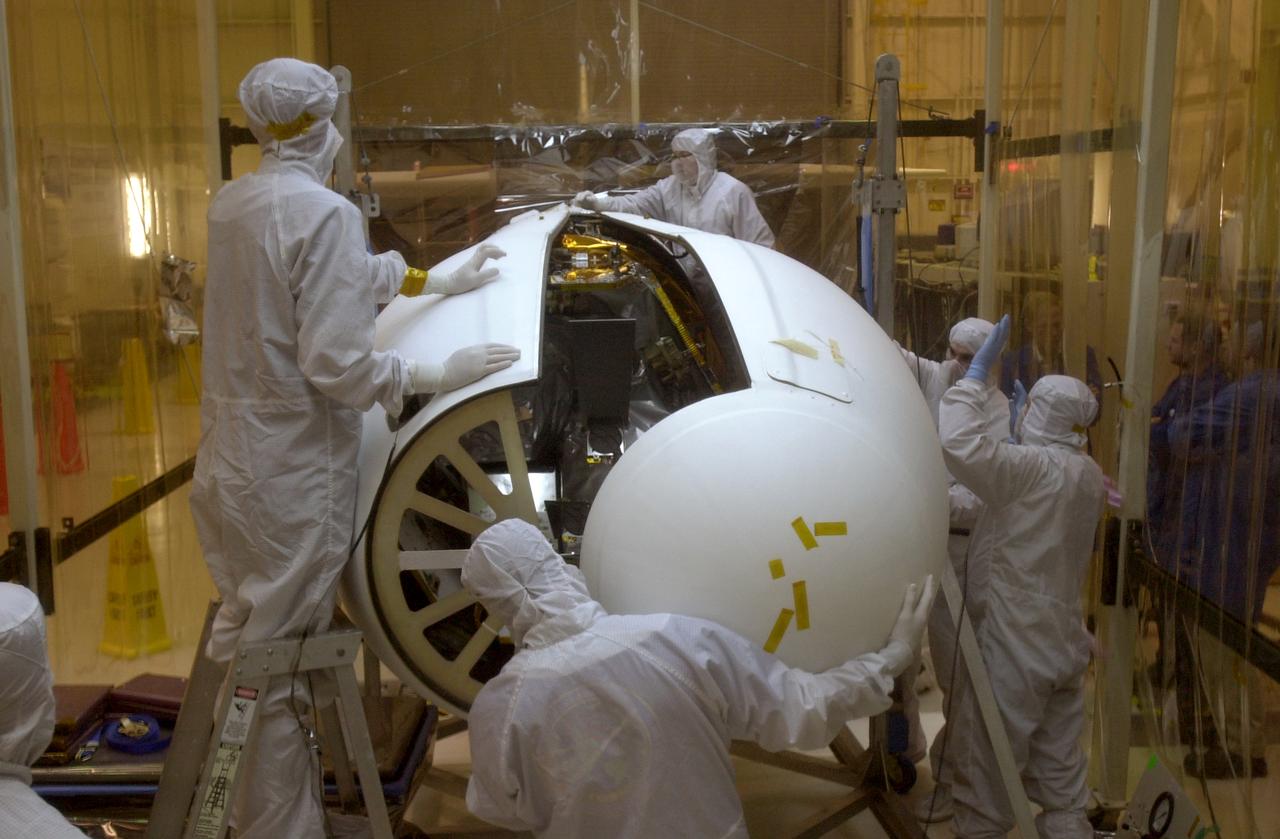

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, under the protective clean tent, technicians move the second half of the fairing into place around the AIM spacecraft. The fairing is a molded structure that fits around the spacecraft and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch. Launch will be from a Pegasus XL rocket, carried and released by Orbital Sciences L-1011 jet aircraft. AIM, which stands for Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, is being prepared for integrated testing and a flight simulation. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. Launch is scheduled for April 25.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, under the protective clean tent, technicians begin installing the fairing around the AIM spacecraft. The fairing is a molded structure that fits around the spacecraft and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch. Launch will be from a Pegasus XL rocket, carried and released by Orbital Sciences L-1011 jet aircraft. AIM, which stands for Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, is being prepared for integrated testing and a flight simulation. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. Launch is scheduled for April 25.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, under the protective clean tent, technicians maneuver the second half of the fairing into place around the AIM spacecraft. The fairing is a molded structure that fits around the spacecraft and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch. Launch will be from a Pegasus XL rocket, carried and released by Orbital Sciences L-1011 jet aircraft. AIM, which stands for Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, is being prepared for integrated testing and a flight simulation. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. Launch is scheduled for April 25.
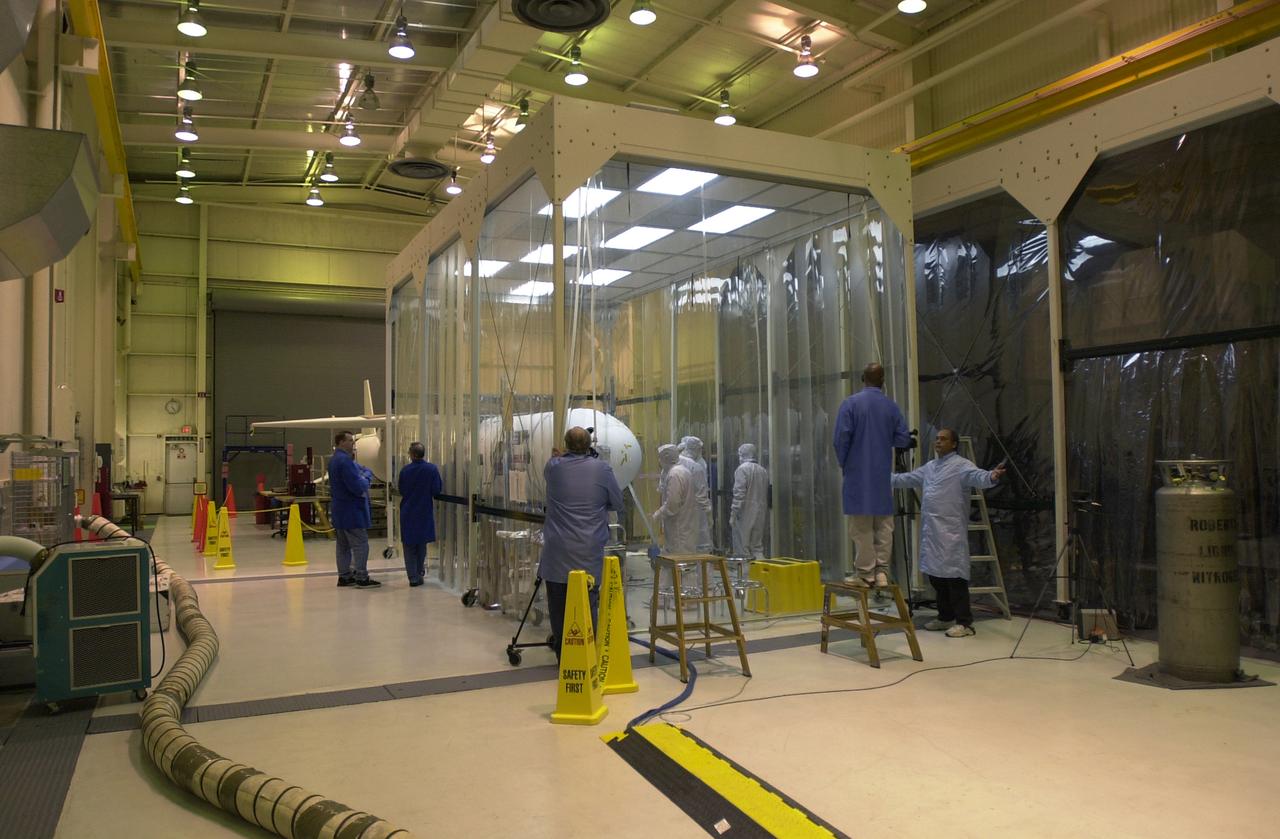

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, under the protective clean tent, technicians examine the installation of the fairing around the AIM spacecraft. The fairing is a molded structure that fits around the spacecraft and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch. Launch will be from a Pegasus XL rocket, carried and released by Orbital Sciences L-1011 jet aircraft. AIM, which stands for Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, is being prepared for integrated testing and a flight simulation. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. Launch is scheduled for April 25.
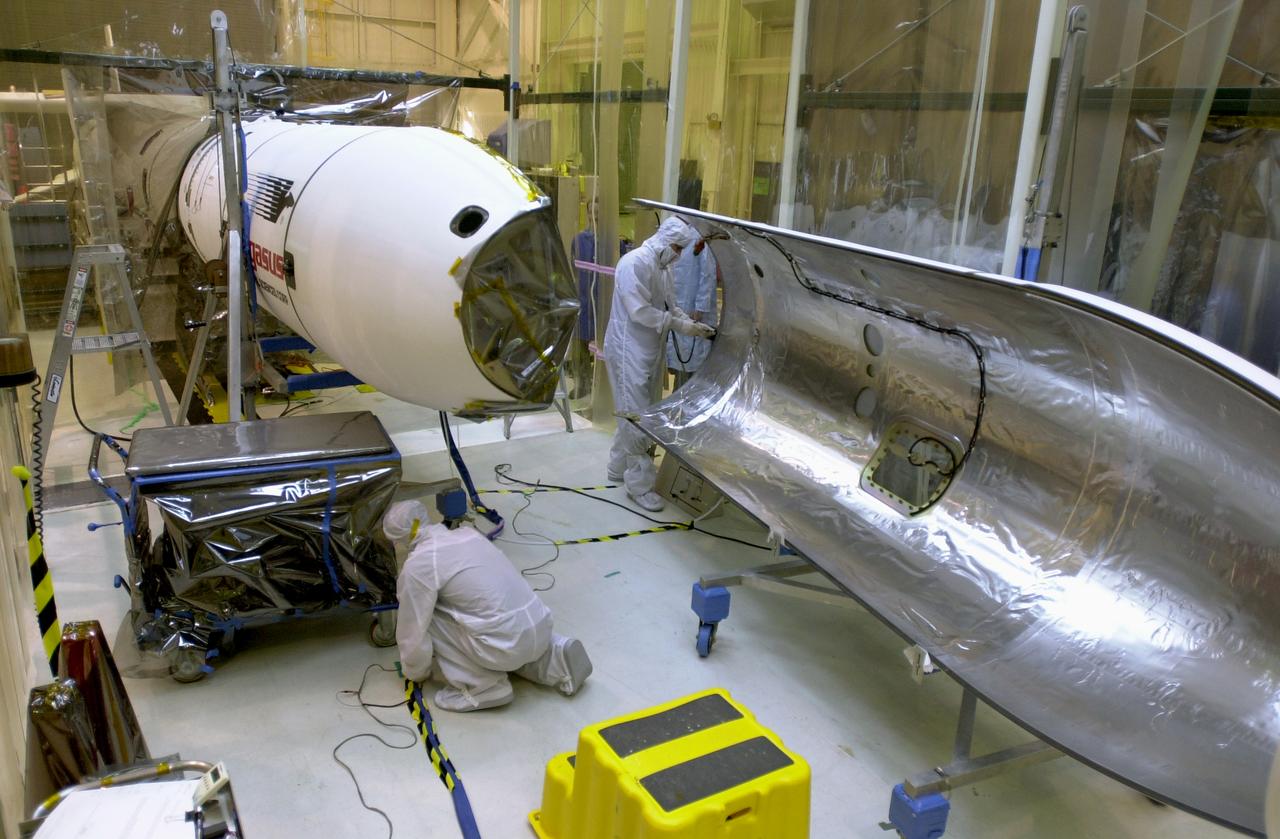

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, under the protective clean tent, technicians work on the second half of the fairing to be installed around the AIM spacecraft. The fairing is a molded structure that fits around the spacecraft and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch. Launch will be from a Pegasus XL rocket, carried and released by Orbital Sciences L-1011 jet aircraft. AIM, which stands for Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, is being prepared for integrated testing and a flight simulation. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. Launch is scheduled for April 25.
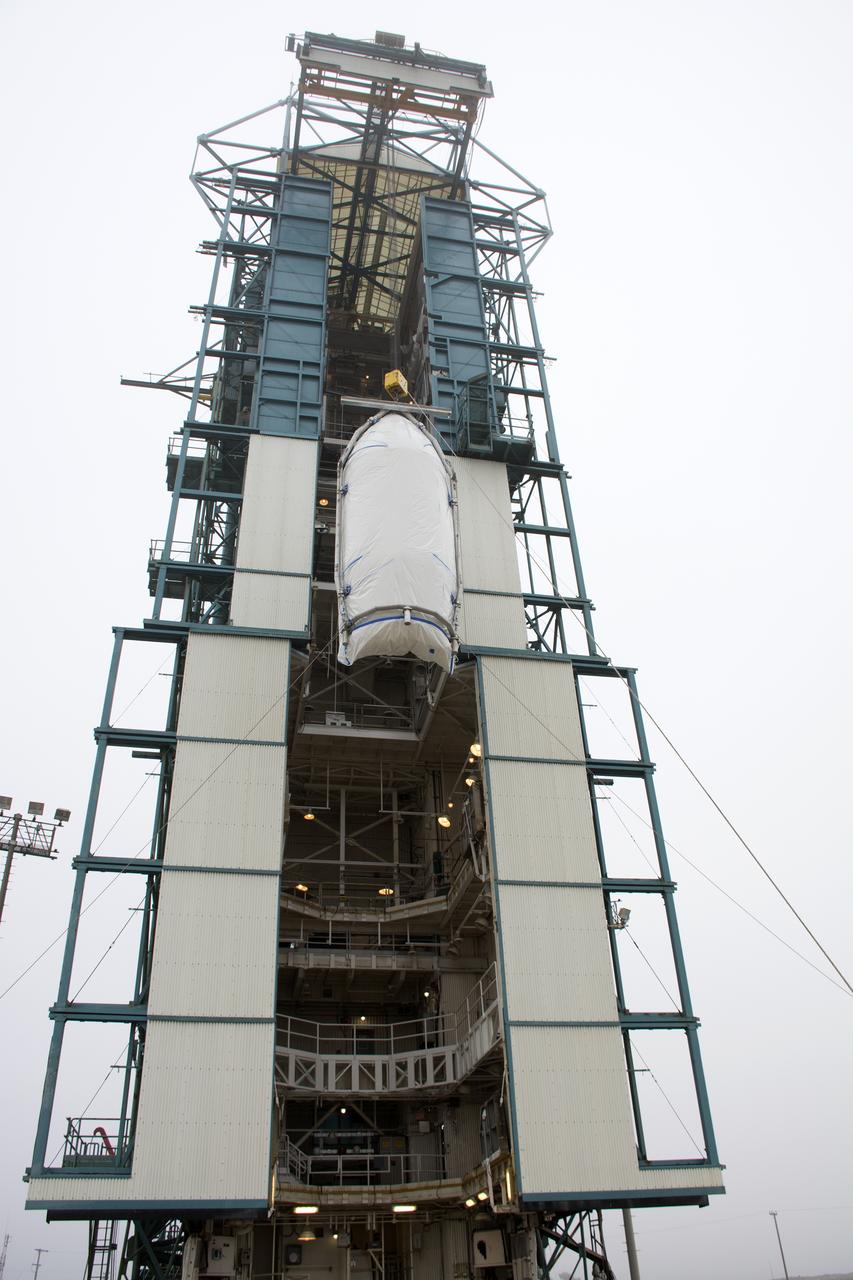

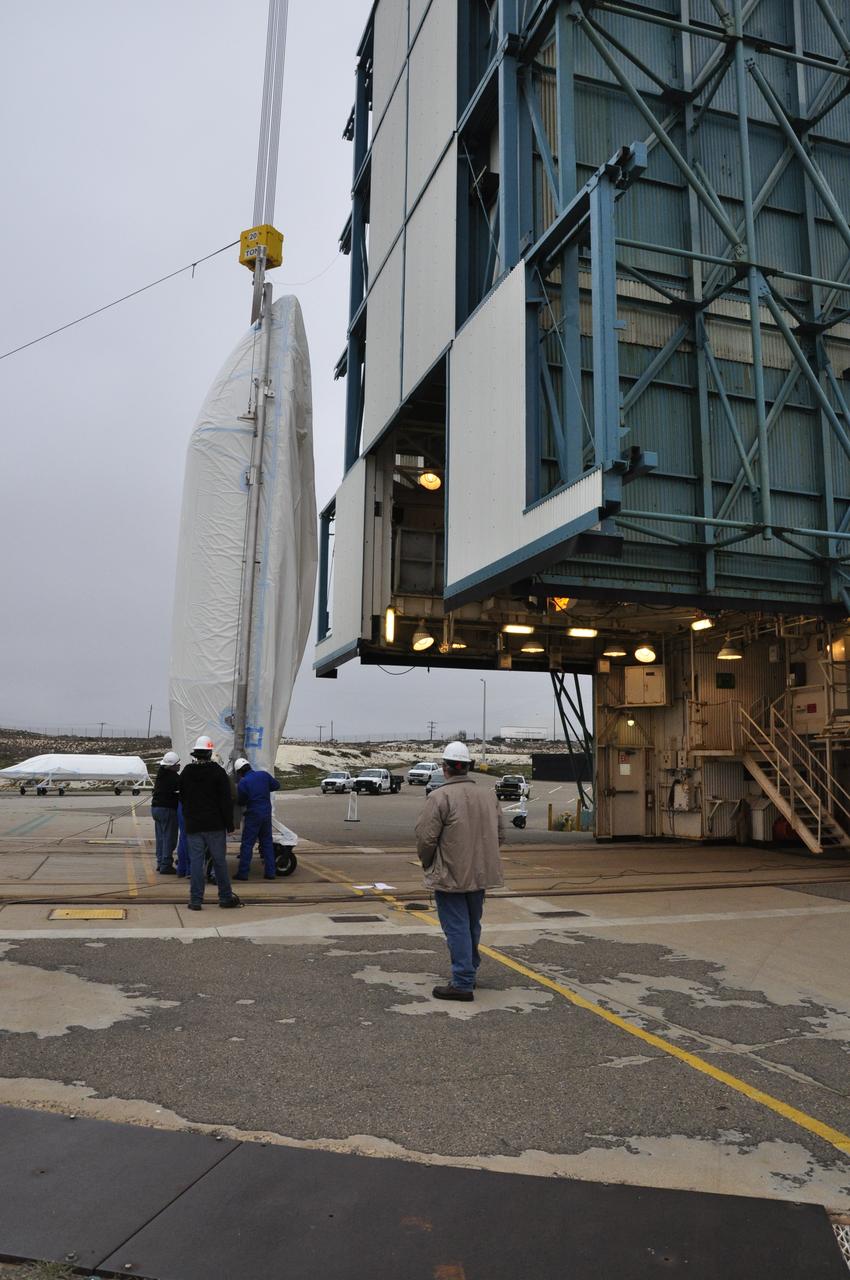
A bi-sector half of the payload fairing for a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is lifted toward level 4 of the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Preparations are underway for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft in 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA. To learn more about JPSS-1, visit http://www.jpss.noaa.gov.
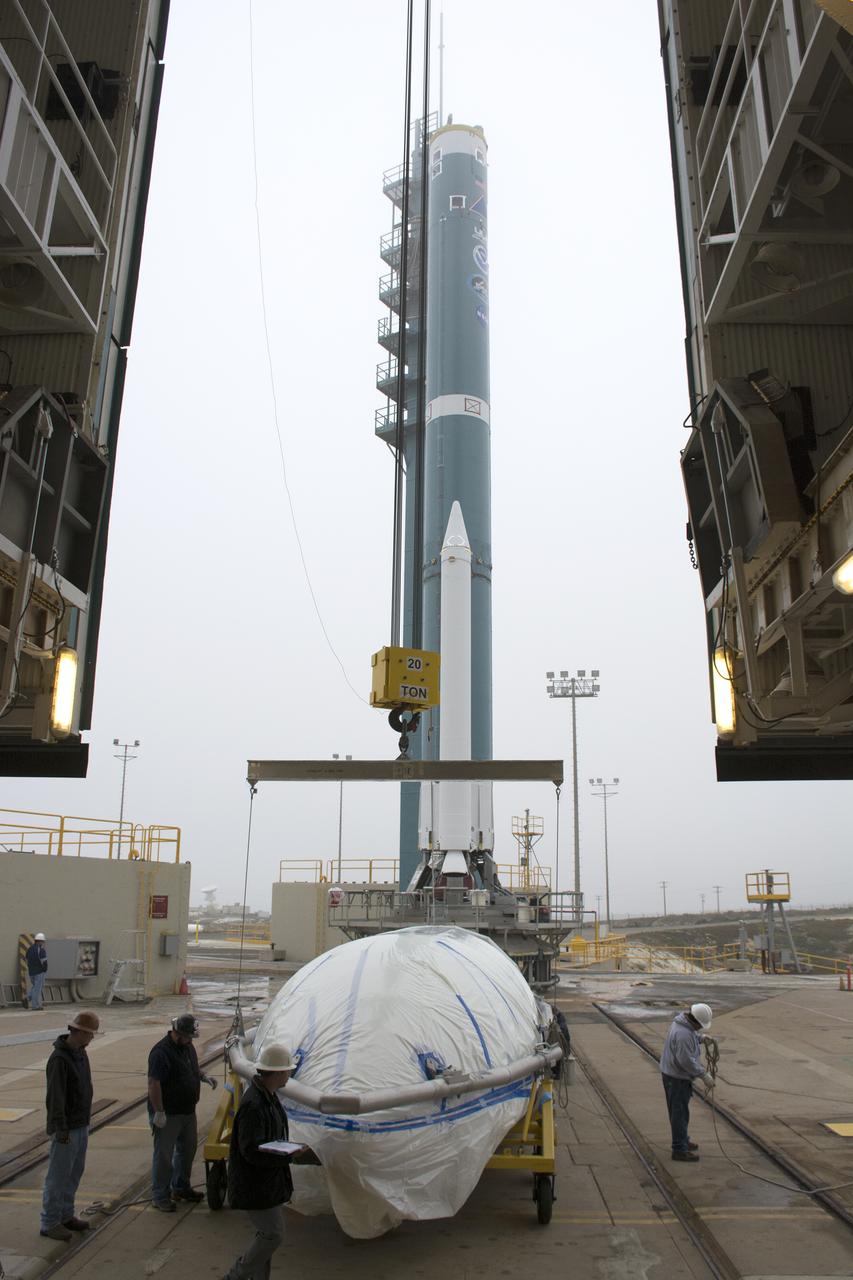

A bi-sector half of the payload fairing for a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is prepared for lifting into the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Preparations are underway for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft in 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA. To learn more about JPSS-1, visit http://www.jpss.noaa.gov.
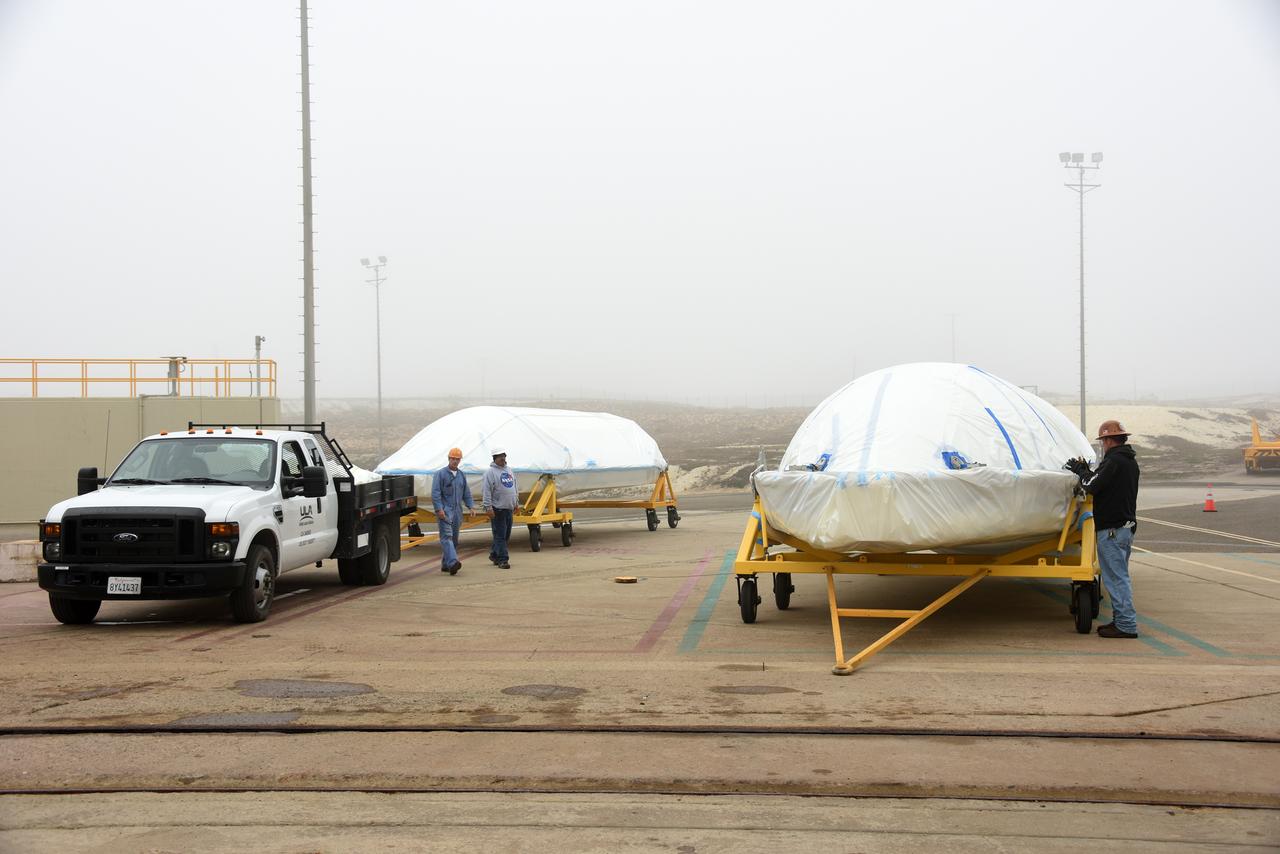

Bi-sector halves of the payload fairing for a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket arrive at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Preparations are underway for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft in 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA. To learn more about JPSS-1, visit http://www.jpss.noaa.gov.
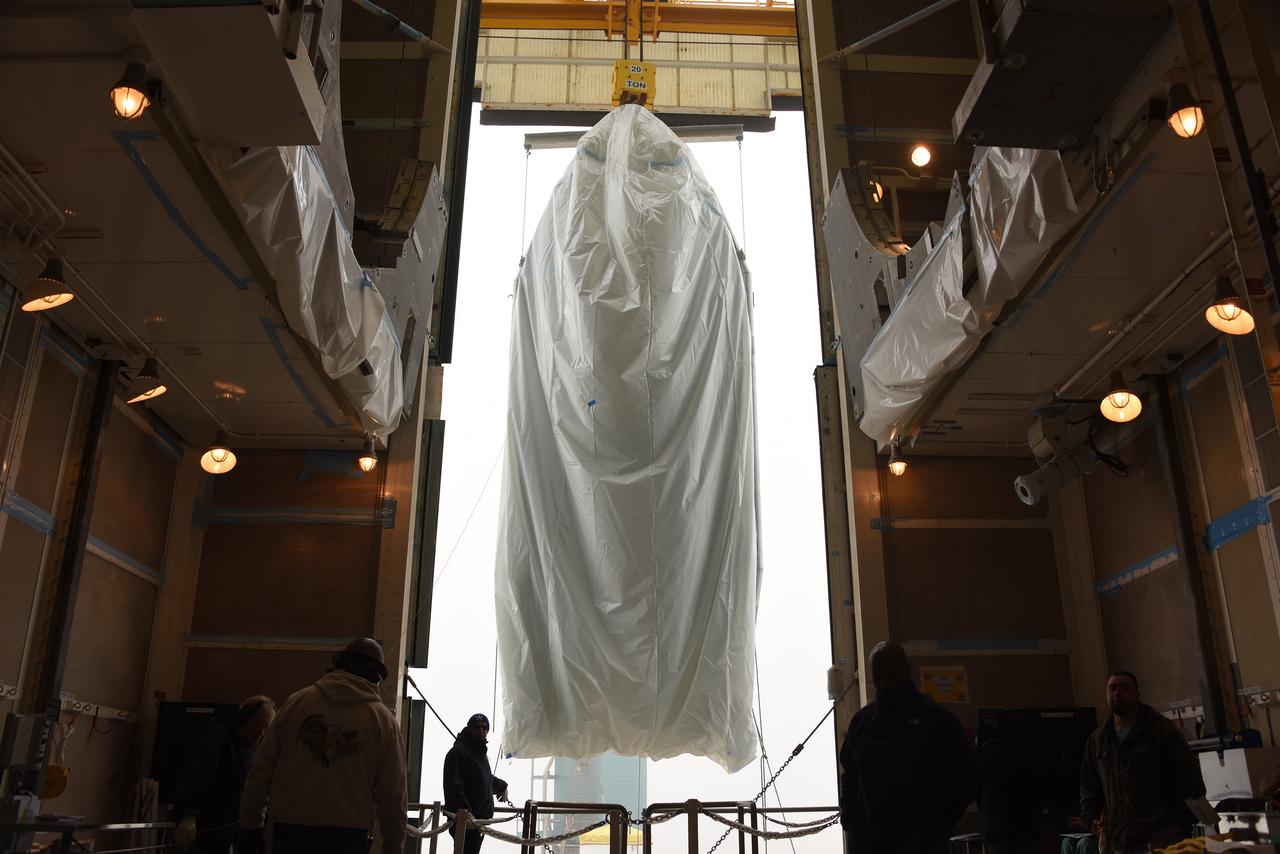

A bi-sector half of the payload fairing for a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket glides into the clean room on level 4 of the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Preparations are underway for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft in 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA. To learn more about JPSS-1, visit http://www.jpss.noaa.gov.
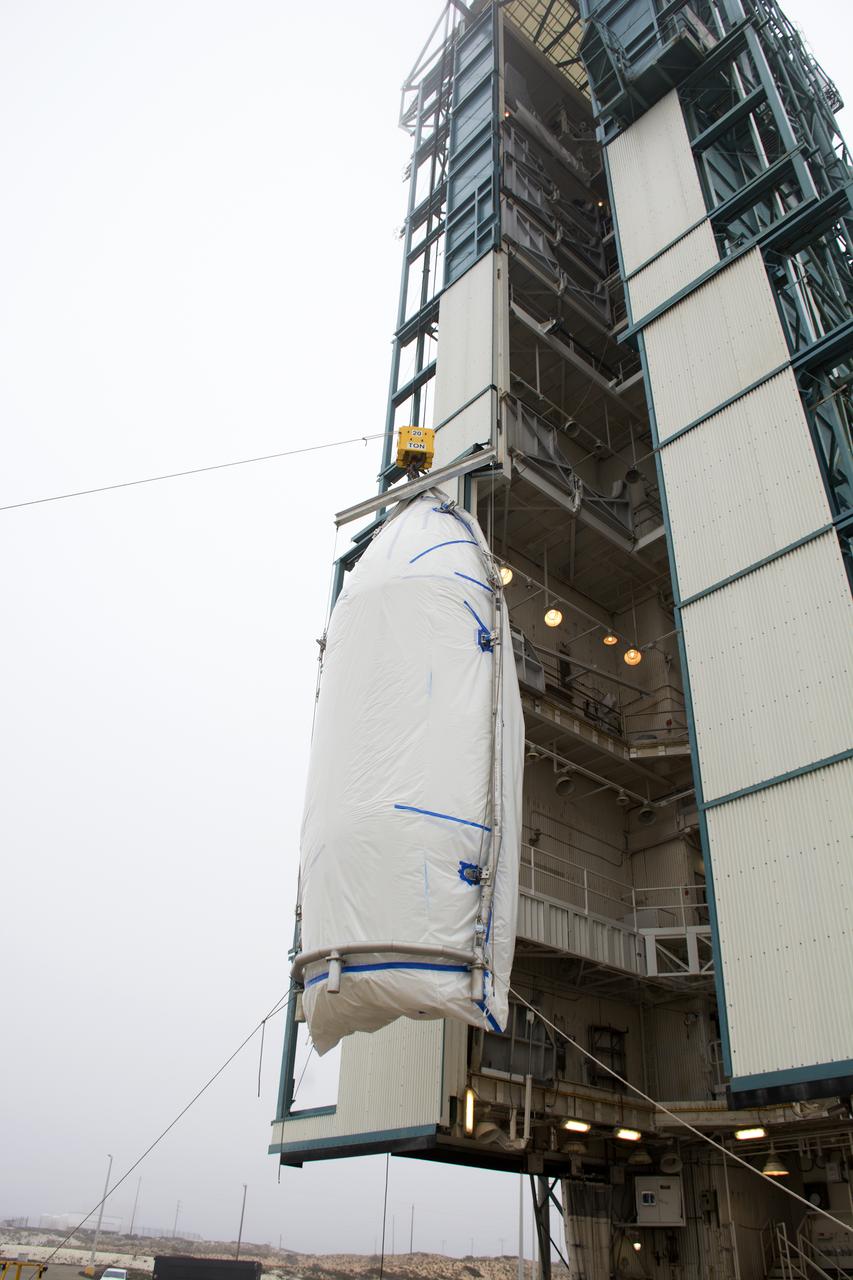

A bi-sector half of the payload fairing for a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is lifted up the side of the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Preparations are underway for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft in 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA. To learn more about JPSS-1, visit http://www.jpss.noaa.gov.
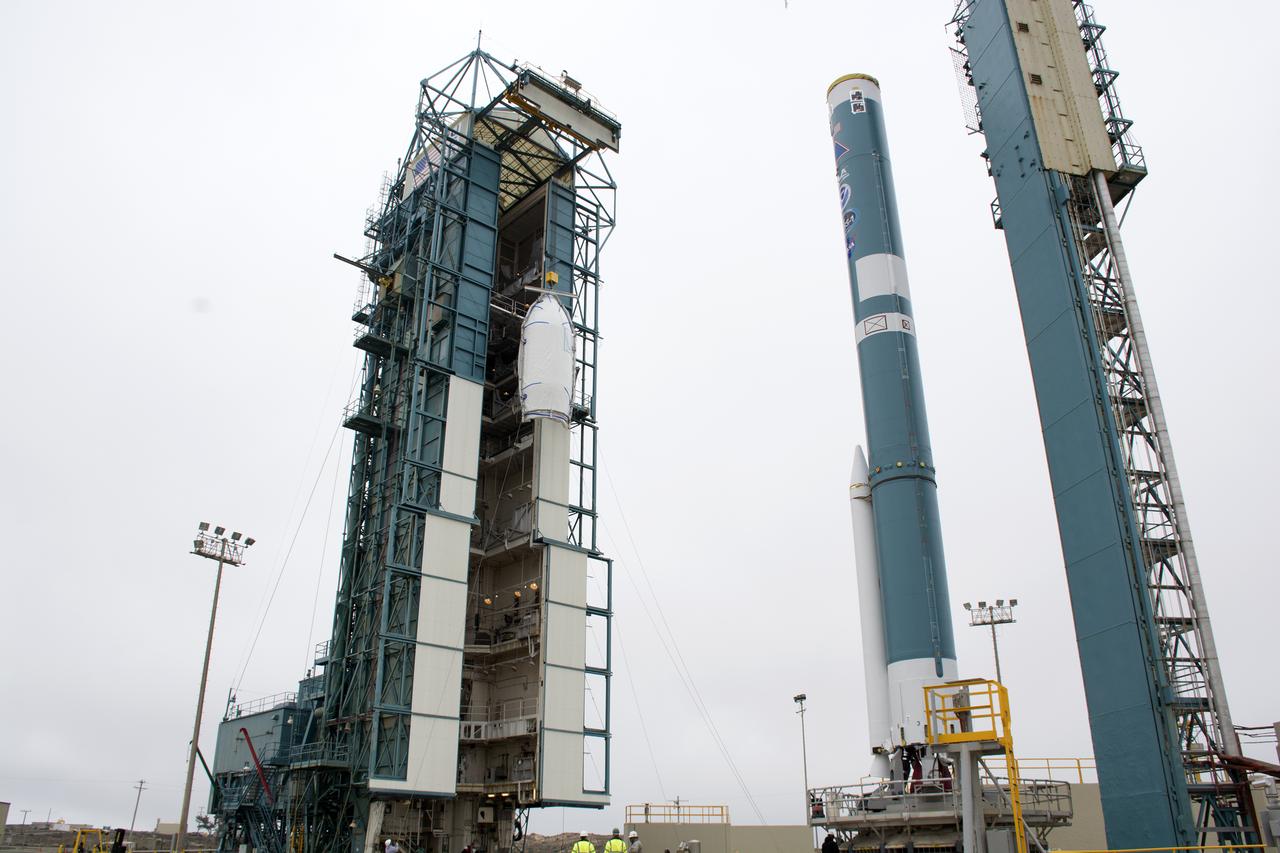

A bi-sector half of the payload fairing for a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is lifted toward level 4 of the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Preparations are underway for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft in 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA. To learn more about JPSS-1, visit http://www.jpss.noaa.gov.
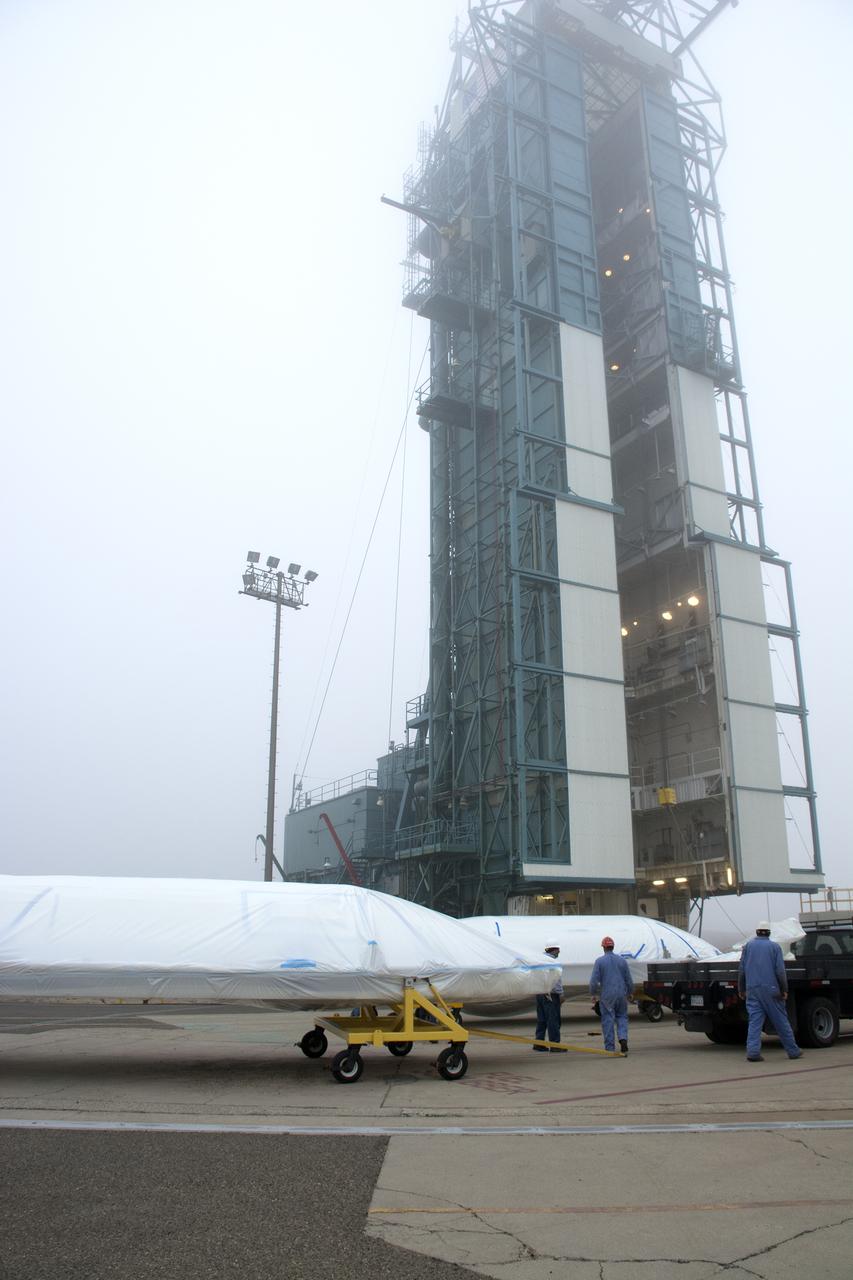

Bi-sector halves of the payload fairing for a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket arrive at the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Preparations are underway for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft in 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA. To learn more about JPSS-1, visit http://www.jpss.noaa.gov.
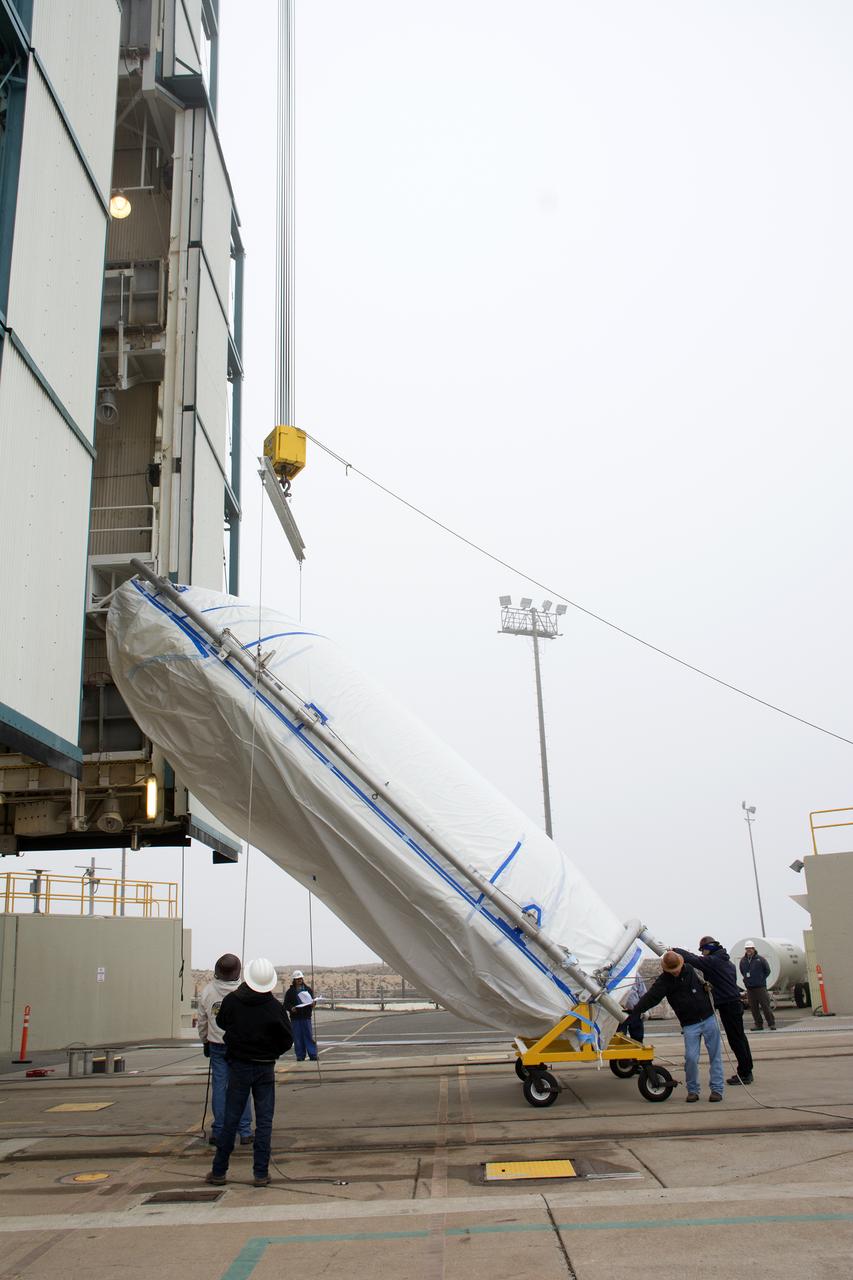

A bi-sector half of the payload fairing for a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is lifted upright for its move into the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Preparations are underway for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft in 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA. To learn more about JPSS-1, visit http://www.jpss.noaa.gov.
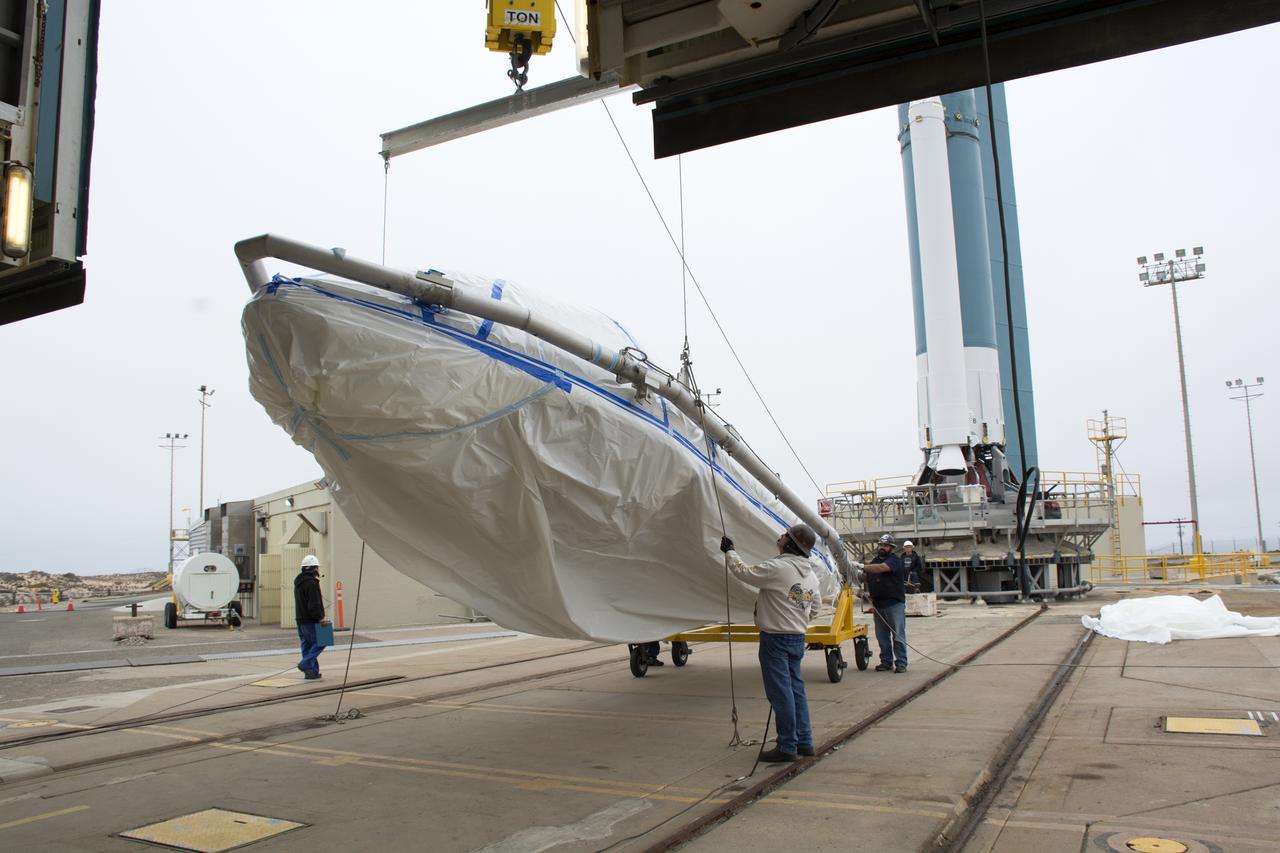

A bi-sector half of the payload fairing for a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is lifted upright for its move into the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Preparations are underway for launch of the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS-1) spacecraft in 2017. JPSS-1 is part of the next-generation environmental satellite system, a collaborative program between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA. To learn more about JPSS-1, visit http://www.jpss.noaa.gov.
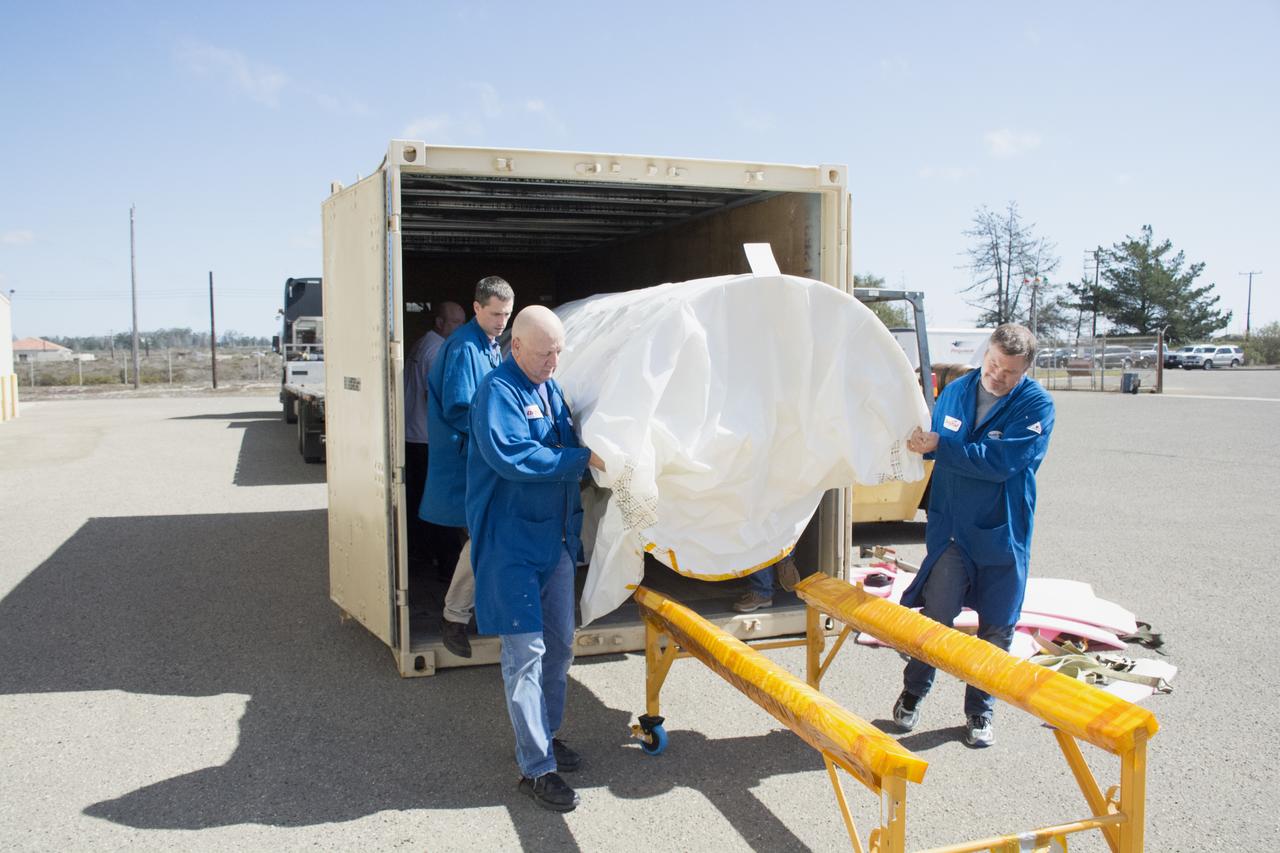

Technicians with Orbital ATK remove the first half of the Pegasus payload fairing for NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) from its shipping container near Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. CYGNSS is being prepared at Vandenberg, and then will be transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket which will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
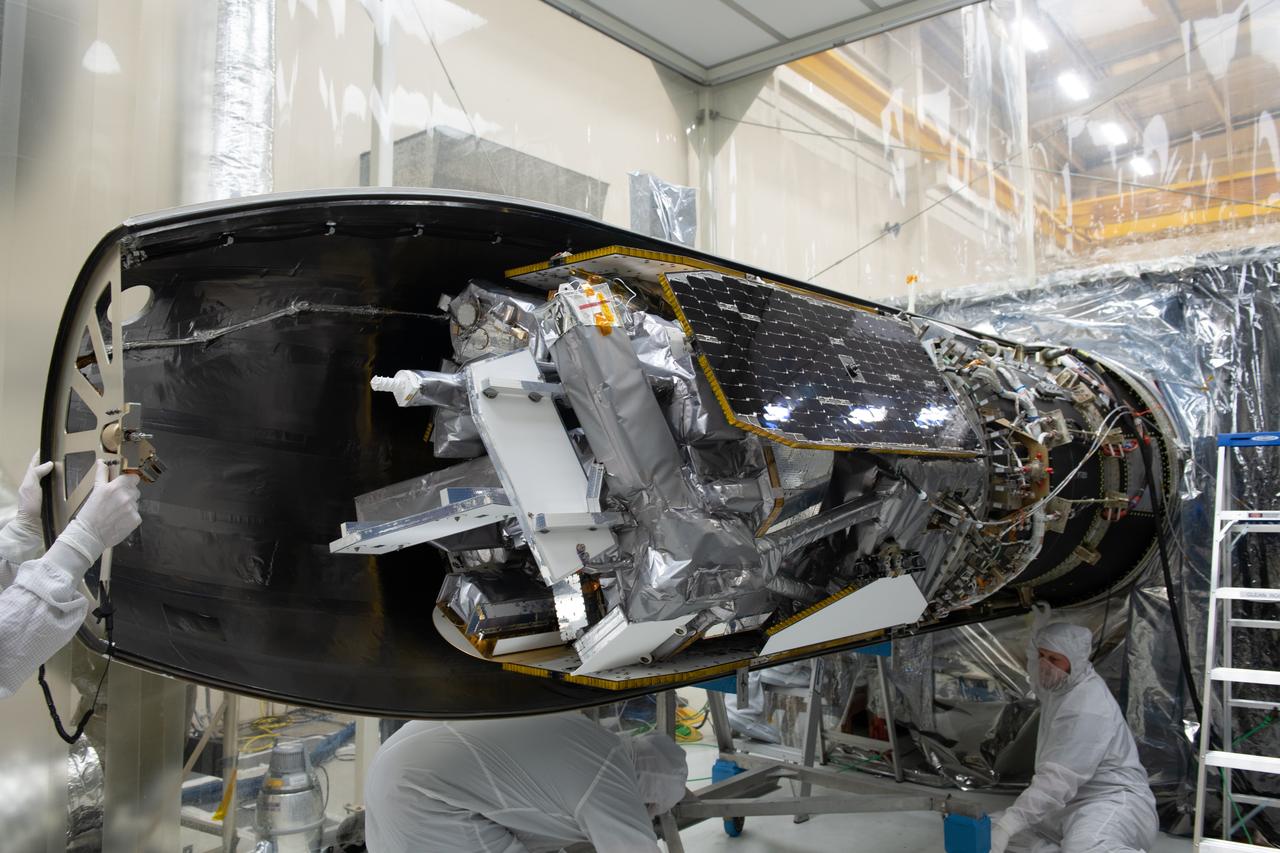

The starboard side of the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket’s payload fairing has been installed around NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 17, 2019. ICON launched on the Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
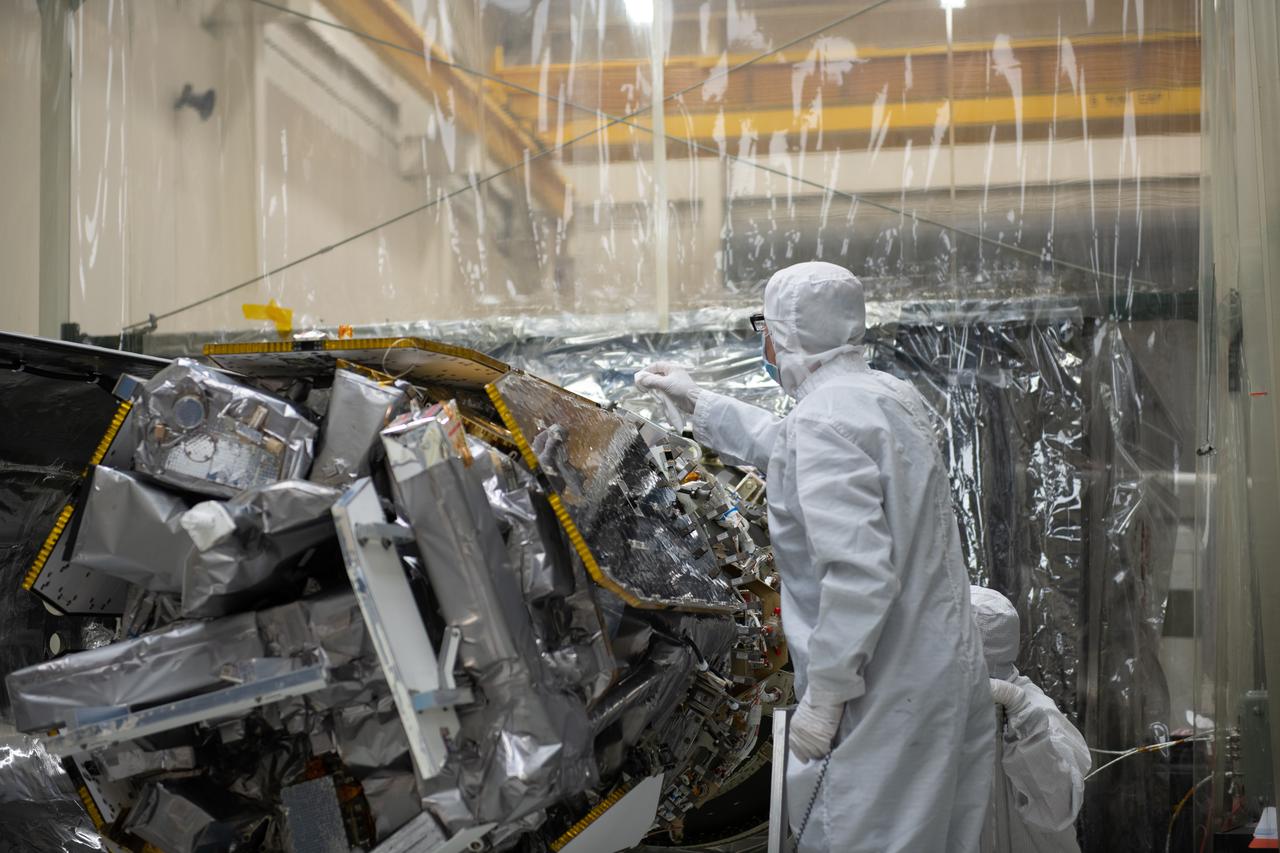

Technicians prepare to install the starboard side of the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket’s payload fairing around NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 17, 2019. ICON launched on the Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
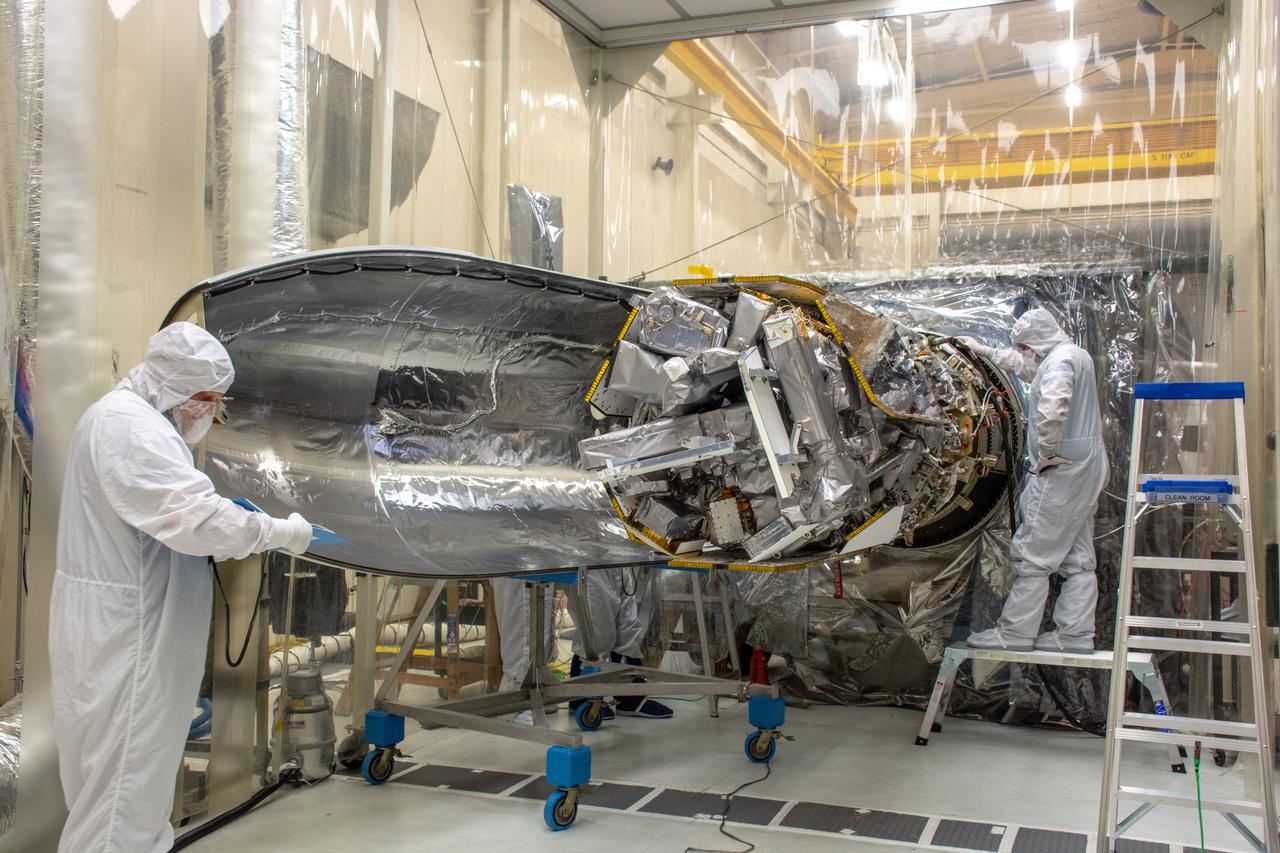

Technicians install the starboard side of the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket’s payload fairing around NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 17, 2019. ICON launched on the Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
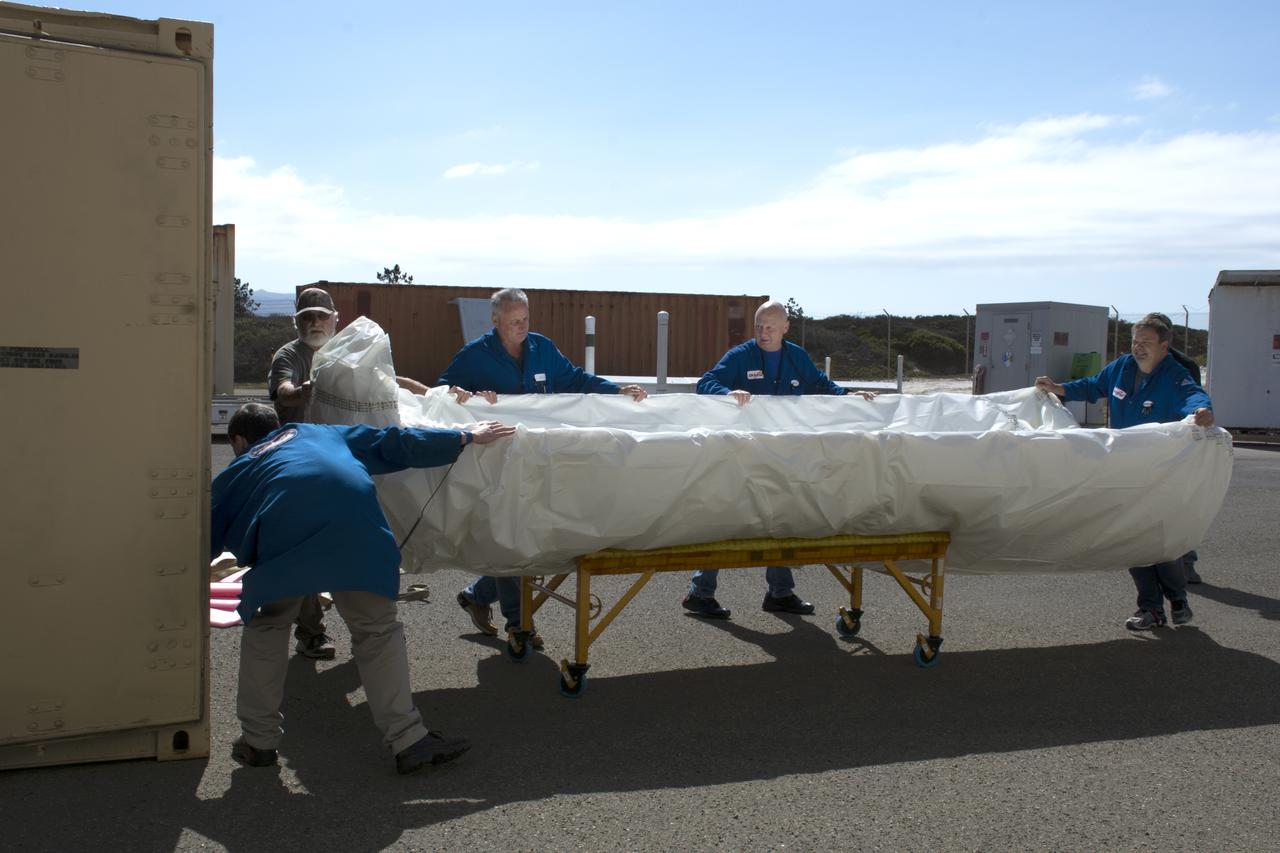

Technicians with Orbital ATK remove the first half of the Pegasus payload fairing for NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) from its shipping container and prepare it for the move to nearby Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. CYGNSS is being prepared at Vandenberg, and then will be transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket which will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
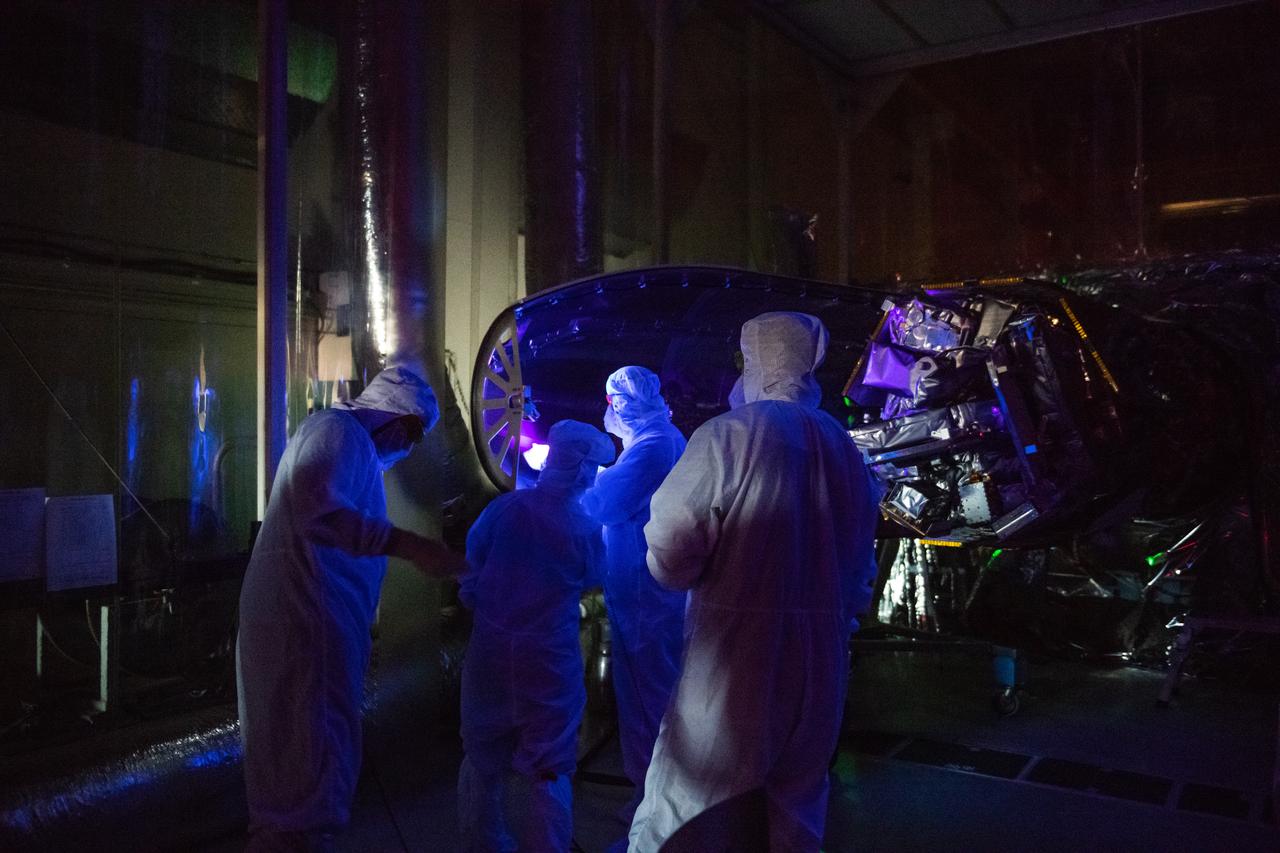
Technicians install the starboard side of the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket’s payload fairing around NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 17, 2019. ICON launched on the Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
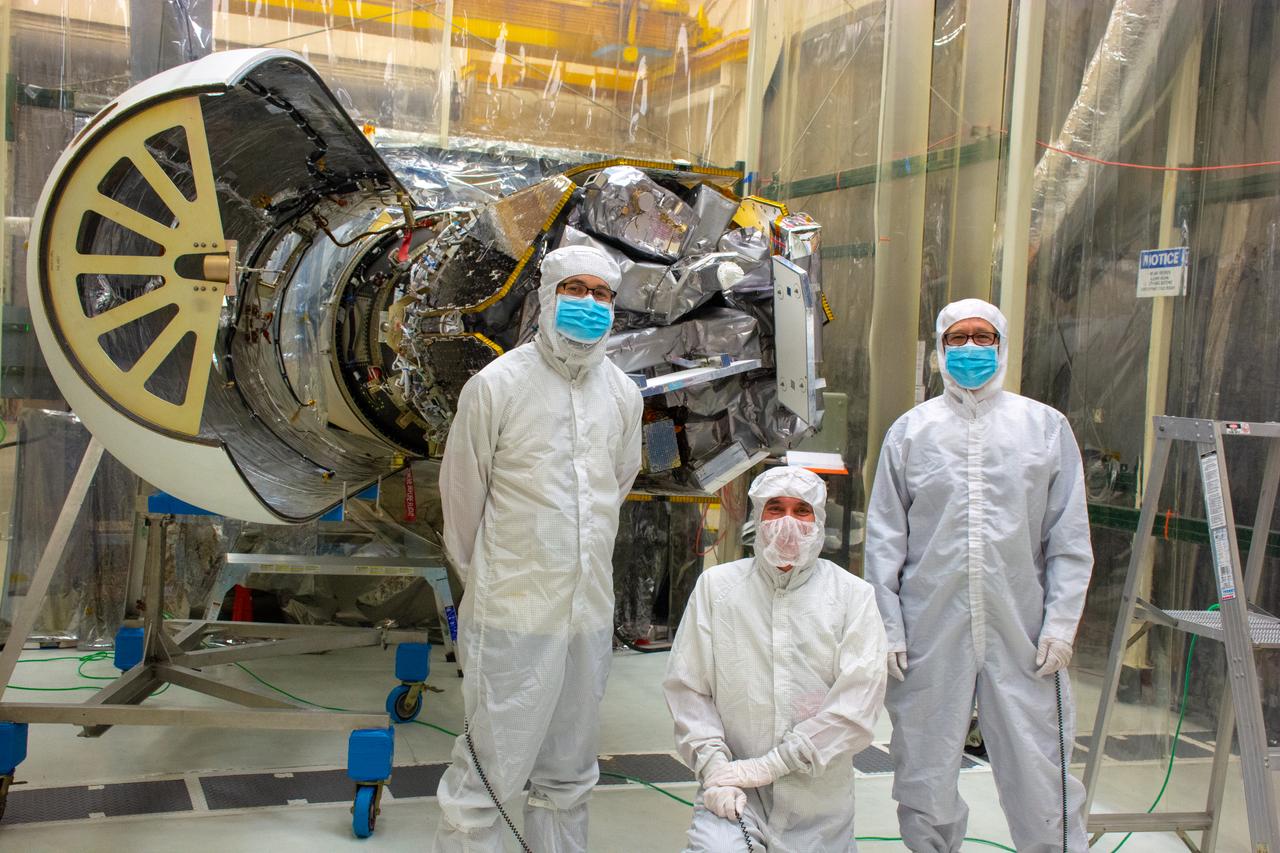

Technicians pose for a photo after the starboard side of the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket’s payload fairing was installed around NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 17, 2019. ICON launched on the Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
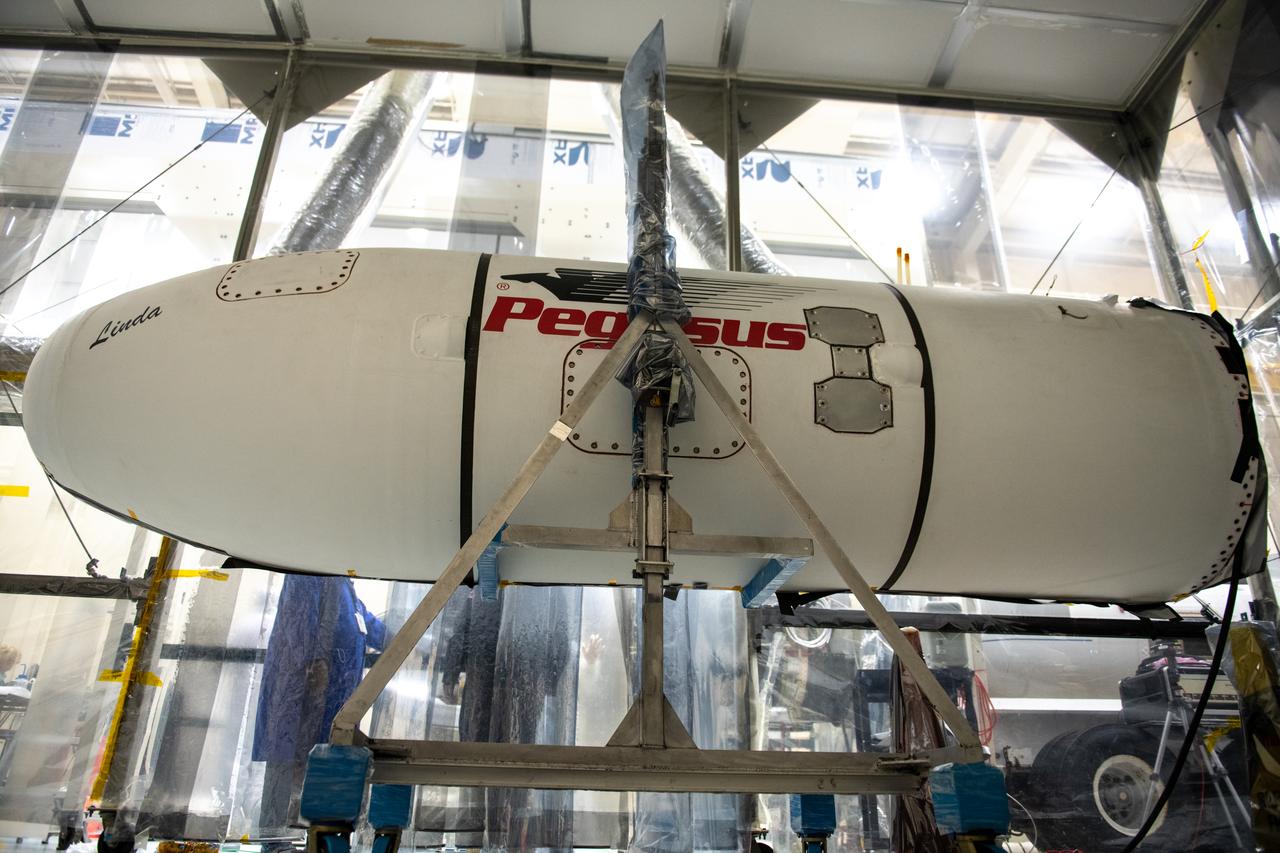

The starboard side of the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket’s payload fairing is ready for installation around NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 17, 2019. ICON launched on the Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
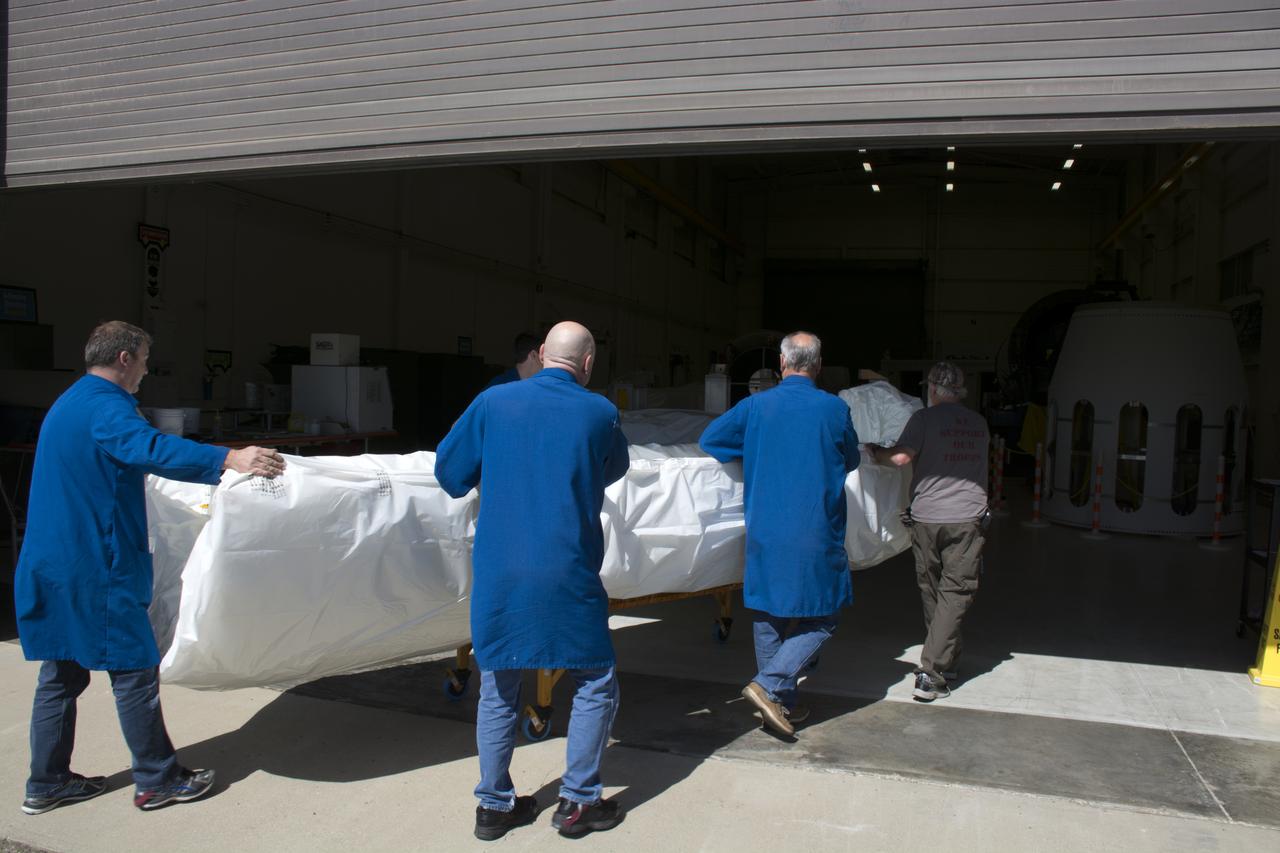

Technicians with Orbital ATK move the first half of the Pegasus payload fairing for NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) from into Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. CYGNSS is being prepared at Vandenberg, and then will be transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket which will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
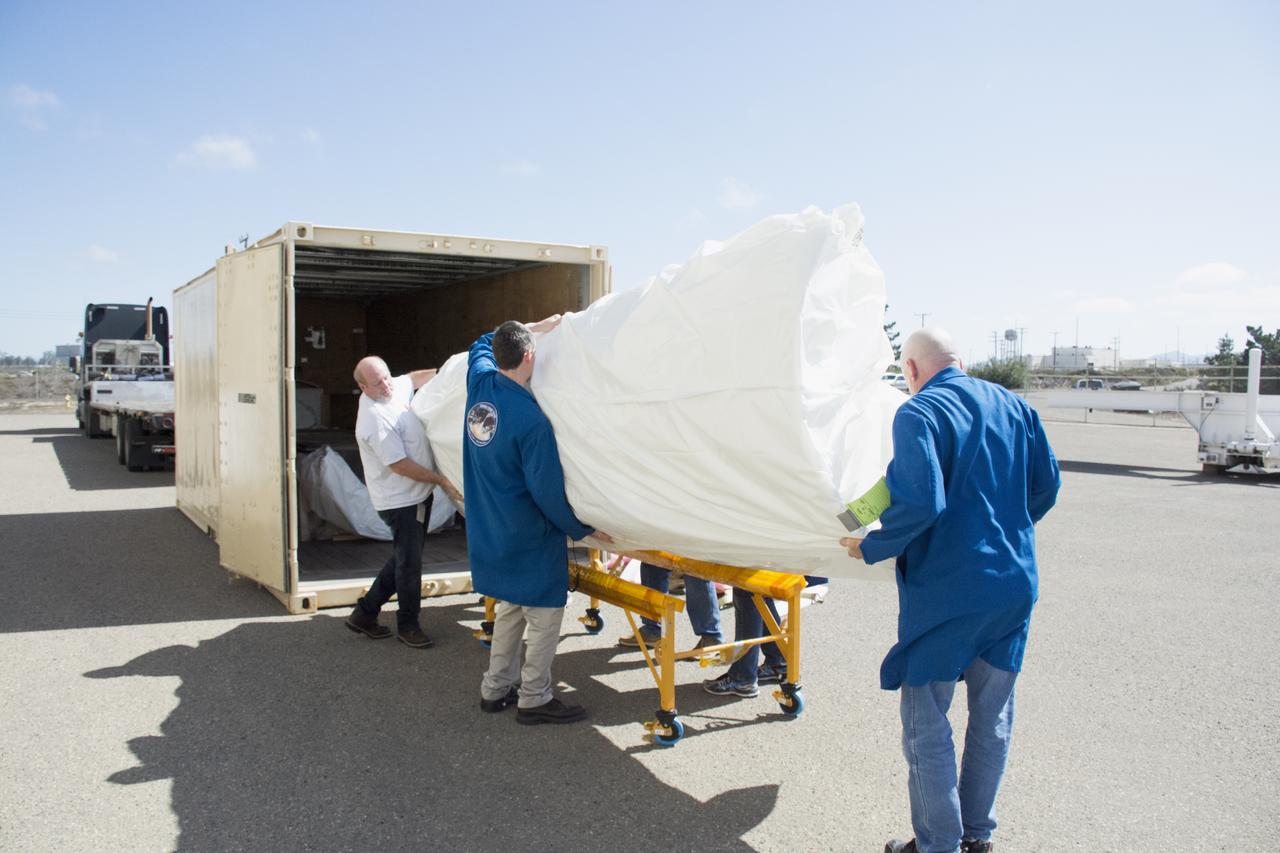

Technicians with Orbital ATK remove the first half of the Pegasus payload fairing for NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) from its shipping container near Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. CYGNSS is being prepared at Vandenberg, and then will be transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket which will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
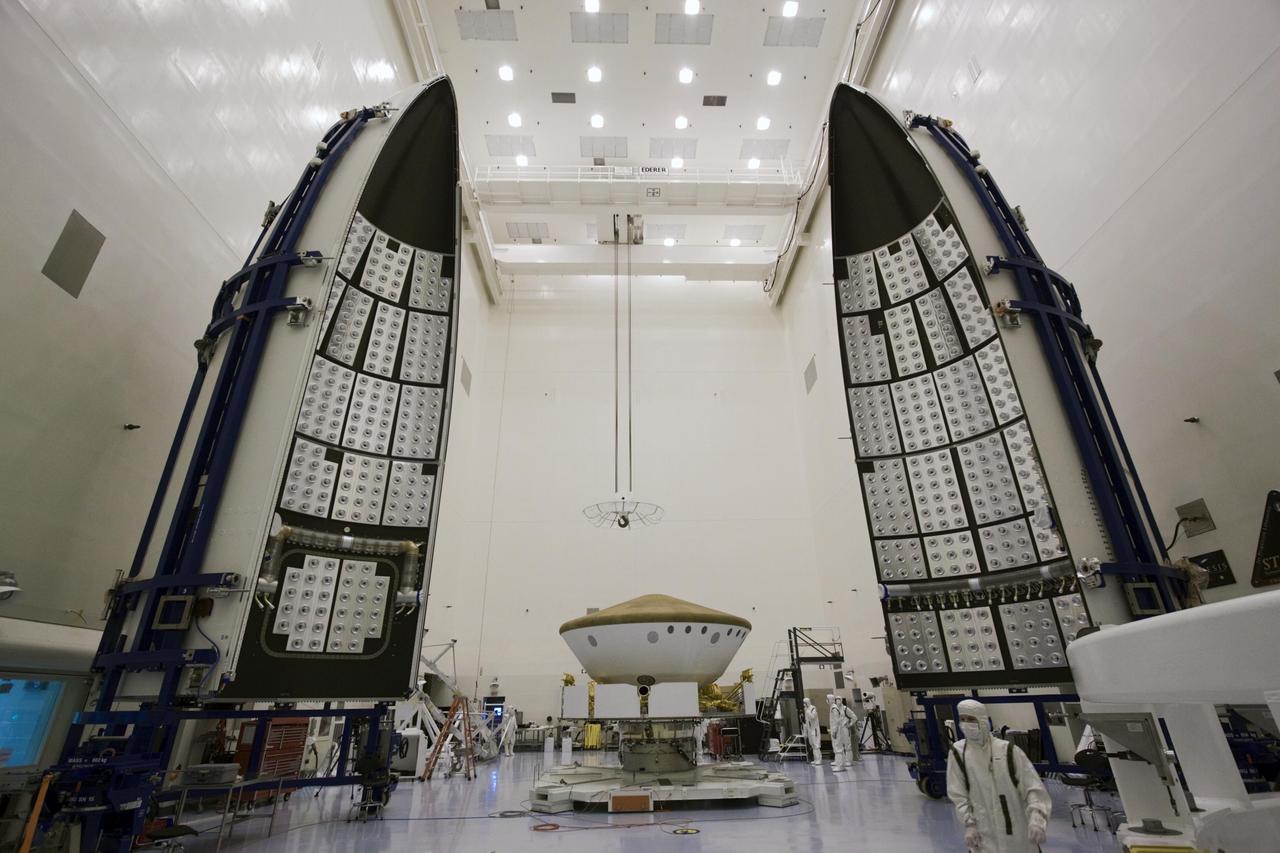

Preparations are under way to enclose NASA Mars Science Laboratory in an Atlas V rocket payload fairing. The fairing protects the spacecraft from the impact of aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent.
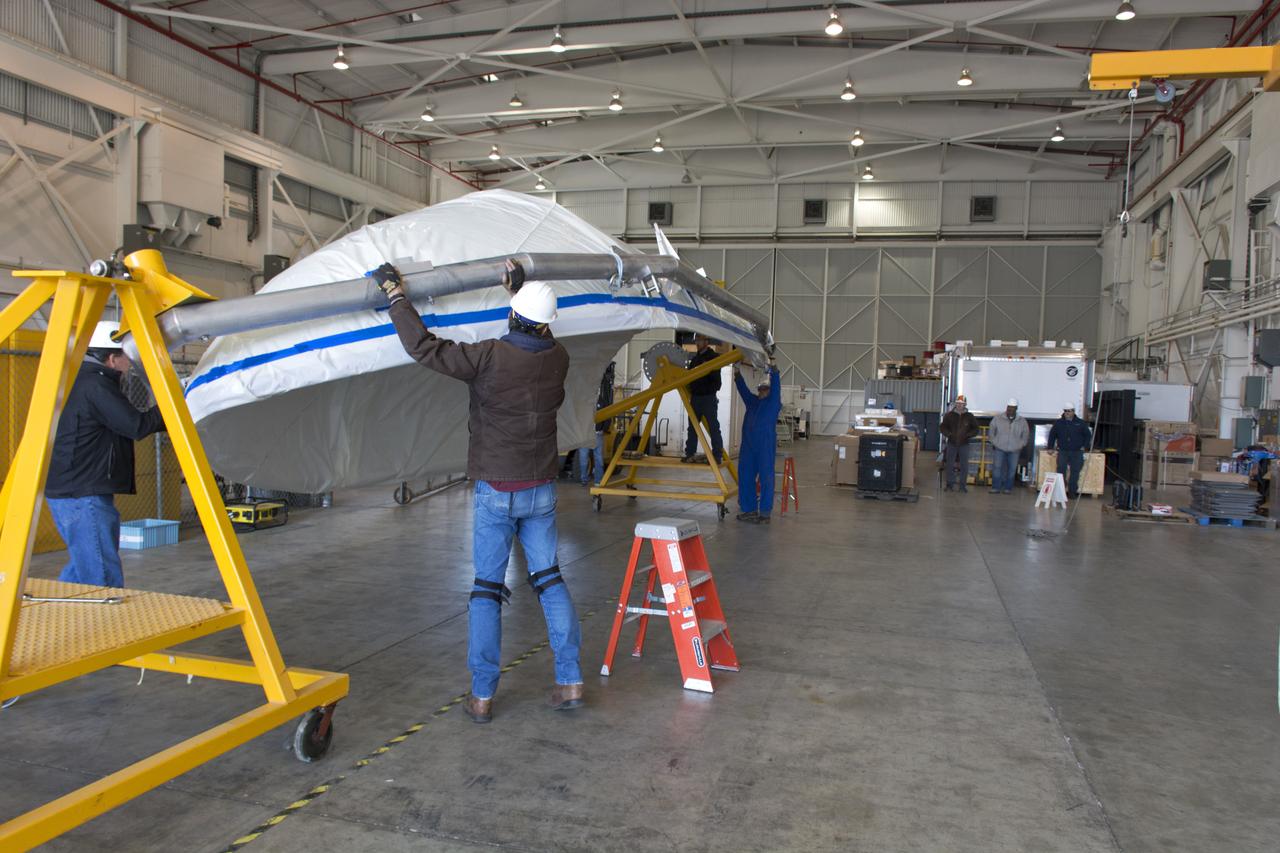

Inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the first half of the payload fairing for the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket has been lifted out of its shipping container. The metal framing around it is being secured on a stand that allows the fairing to be rotated. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is scheduled to launch on the final ULA Delta II rocket later this year. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

U.S. President Obama recognizes NASA Administrator Charles Bolden during his remarks at the 3rd Annual White House Science Fair in the East Room of the White House on Monday, April 22, 2013. The science fair celebrated student winners of a broad range of science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) competitions from across the country. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
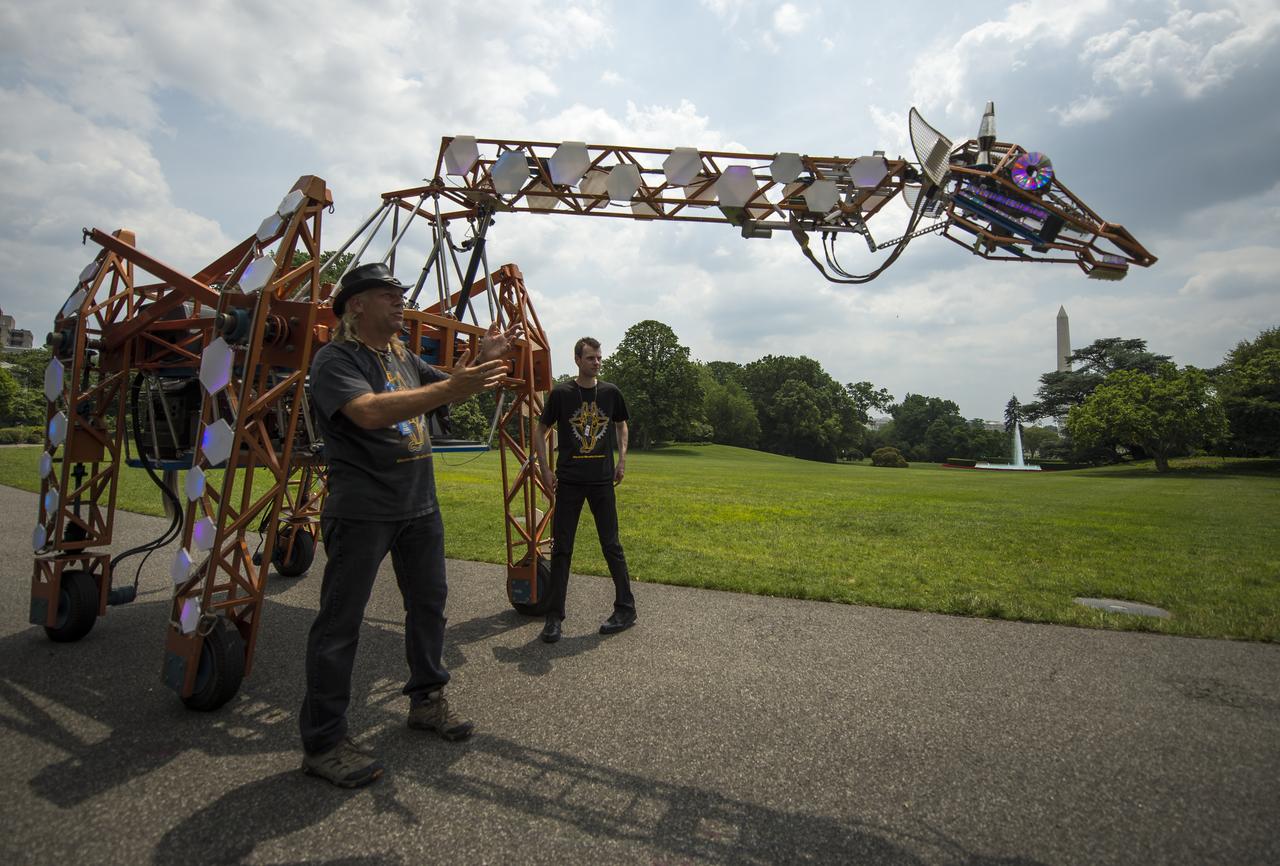

Lindsay Lawlor, of San Diego, Calif., left, demonstrates his creation, a 17-foot-tall, robotic giraffe that "walks" on wheels and is powered by a 12-horsepower hybrid fuel-engine motor, during the first ever White House Maker Faire, which brings together students, entrepreneurs, and everyday citizens who are using new tools and techniques to launch new businesses, learn vital skills in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), and fuel the renaissance in American manufacturing, at the White House, Wednesday, June 18, 2014 in Washington. The President announced new steps the Administration and its partners are taking to support the ability of more Americans, young and old, to have to access to these tools and techniques and brings their ideas to life. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
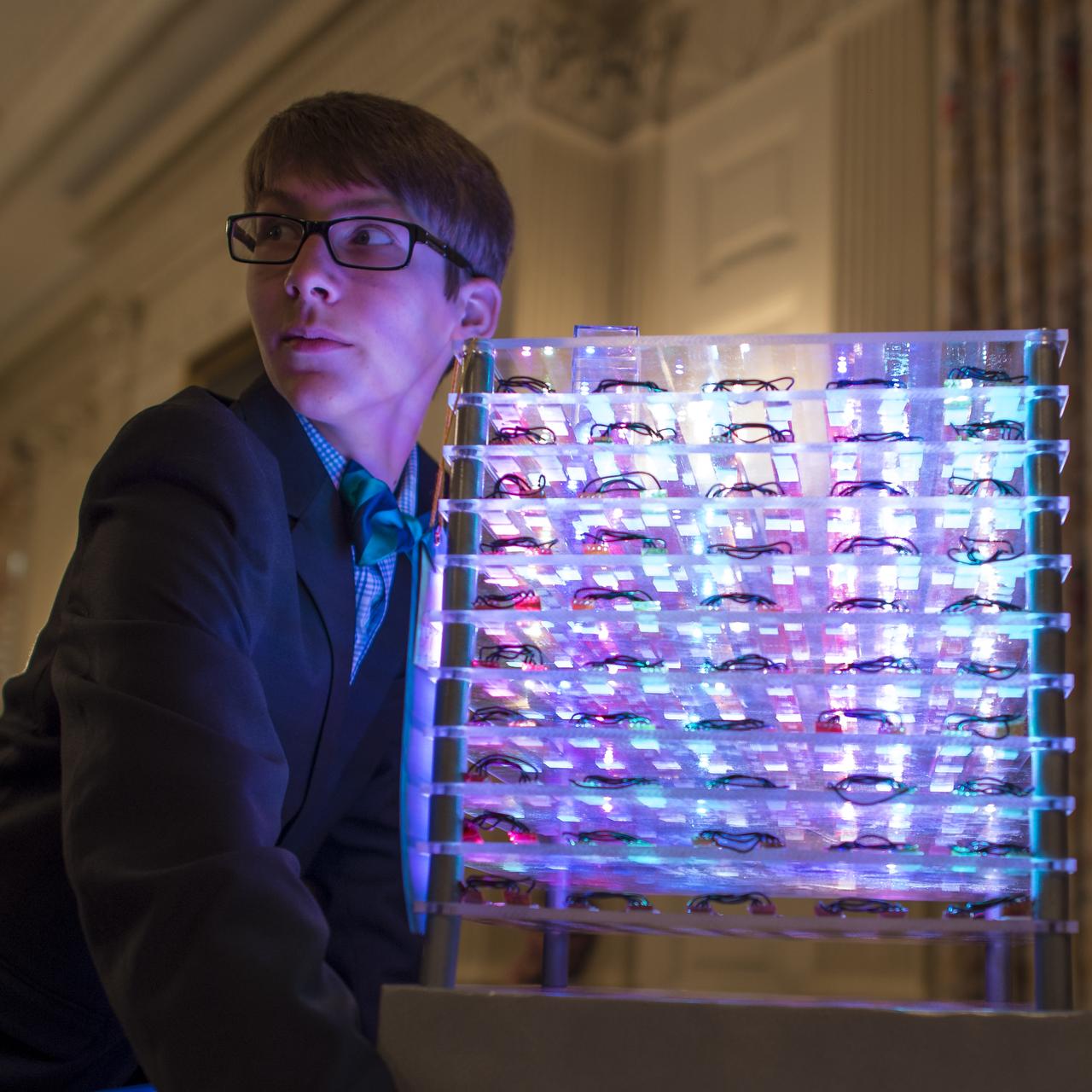

Joey Hudy demonstrates his Intel Galileo-based 10x10x10 LED Cube during the first ever White House Maker Faire which brings together students, entrepreneurs, and everyday citizens who are using new tools and techniques to launch new businesses, learn vital skills in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), and fuel the renaissance in American manufacturing, at the White House, Wednesday, June 18, 2014 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
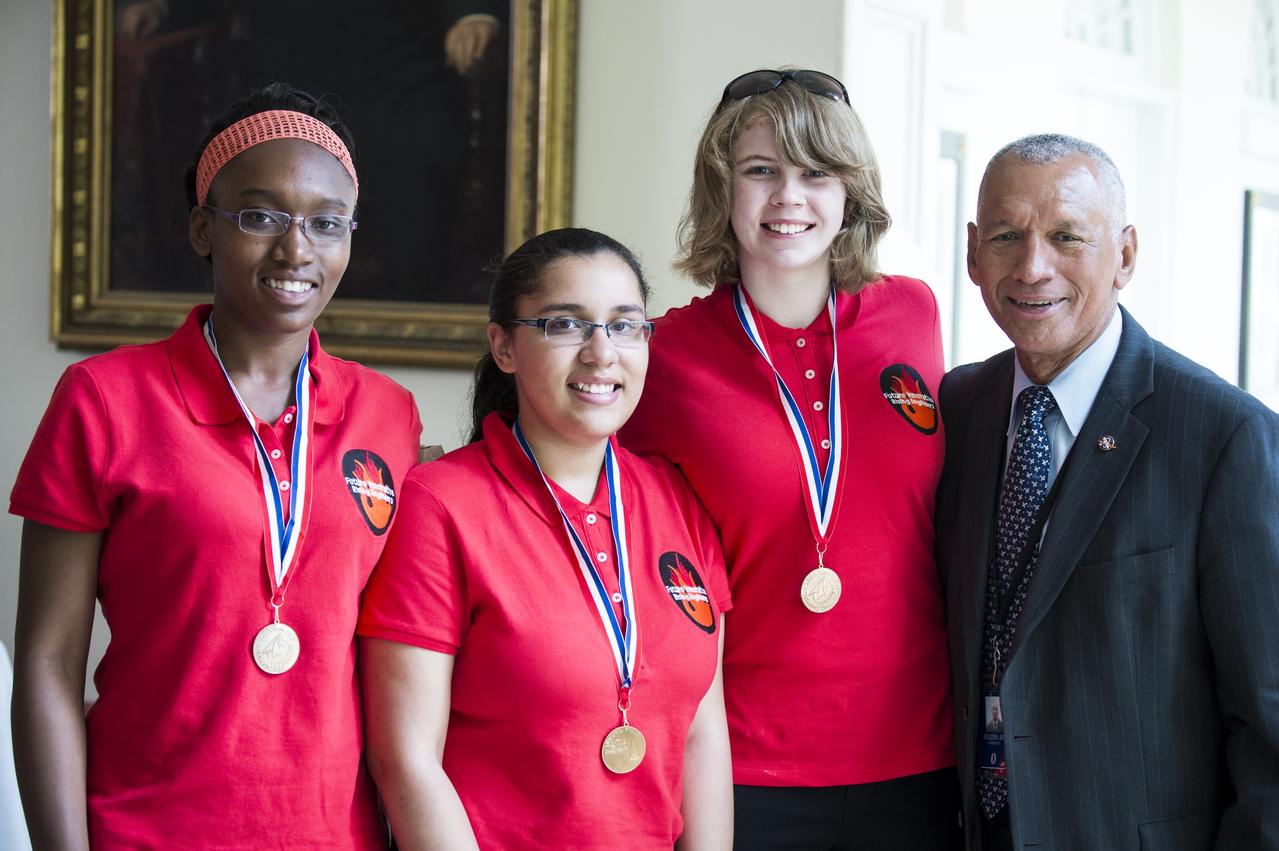

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden poses with an all-girl engineering team that participated in the White House Science Fair. "Team Rocket Power" was one of 100 teams that qualified for last year’s Team America Rocketry Challenge (TARC). Nia'mani Robinson, 15, Jasmyn Logan, 15, and Rebecca Chapin-Ridgely, 17, gave up their weekends and free time after school to build and test their bright purple rocket, which is designed to launch to an altitude of about 750 ft, and then return a “payload” (an egg) to the ground safely. The fourth White House Science Fair was held at the White House on May 27, 2014 and included 100 students from more than 30 different states who competed in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) competitions. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
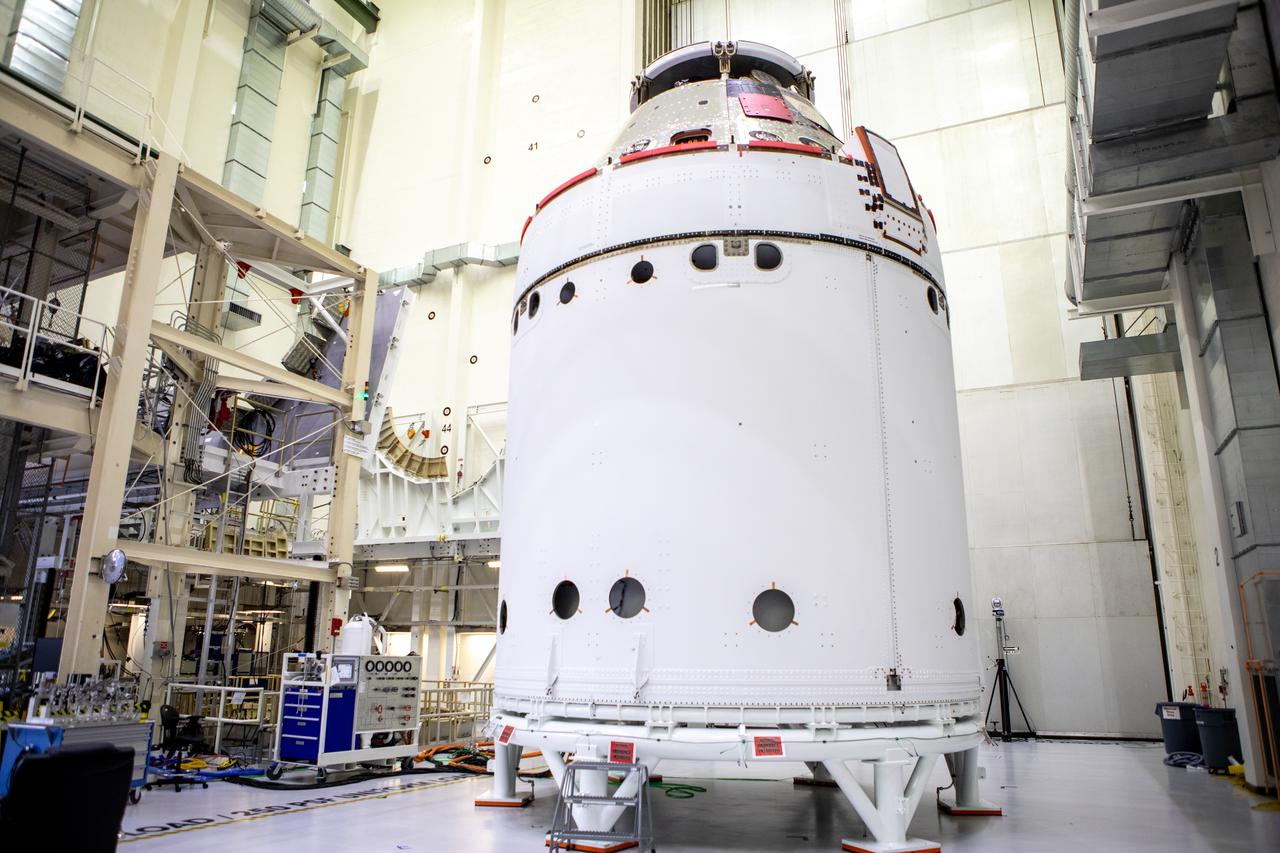
The spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels are secured onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 27, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The three panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
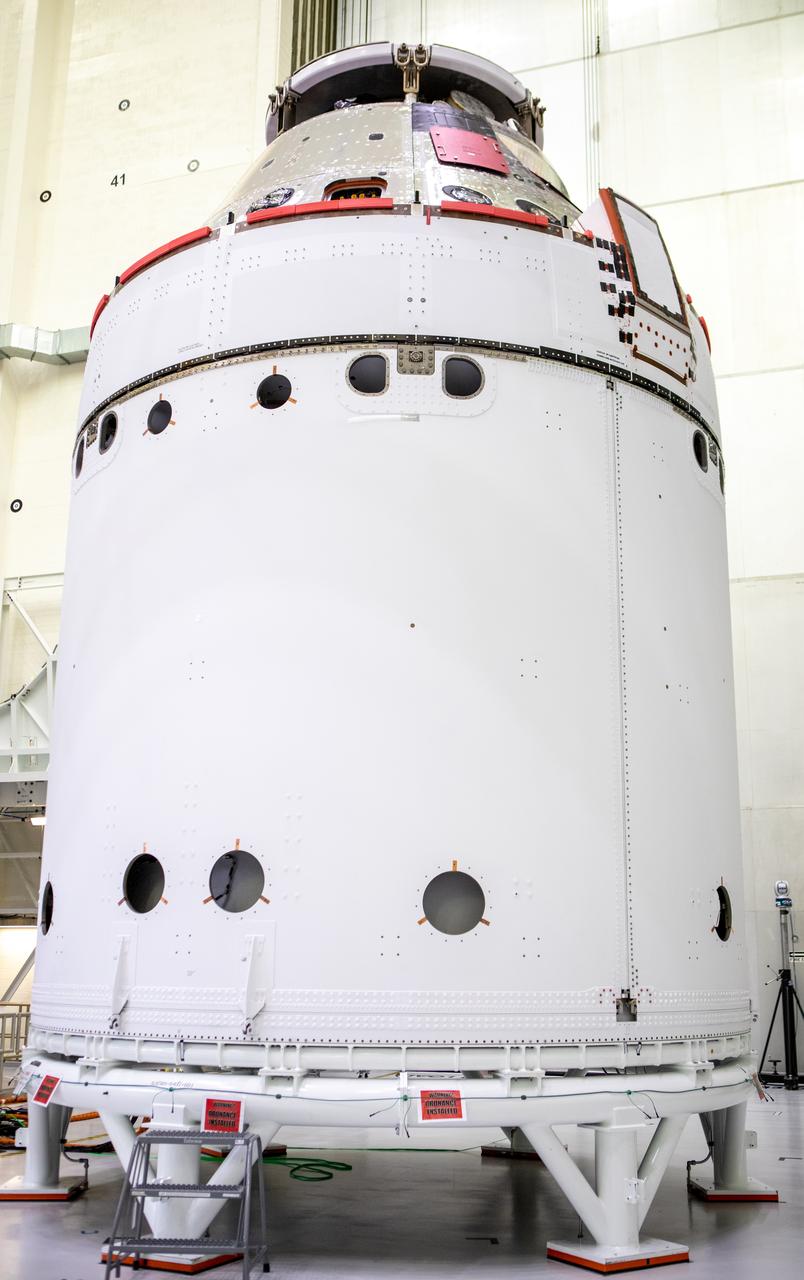
The spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels are secured onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 27, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The three panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
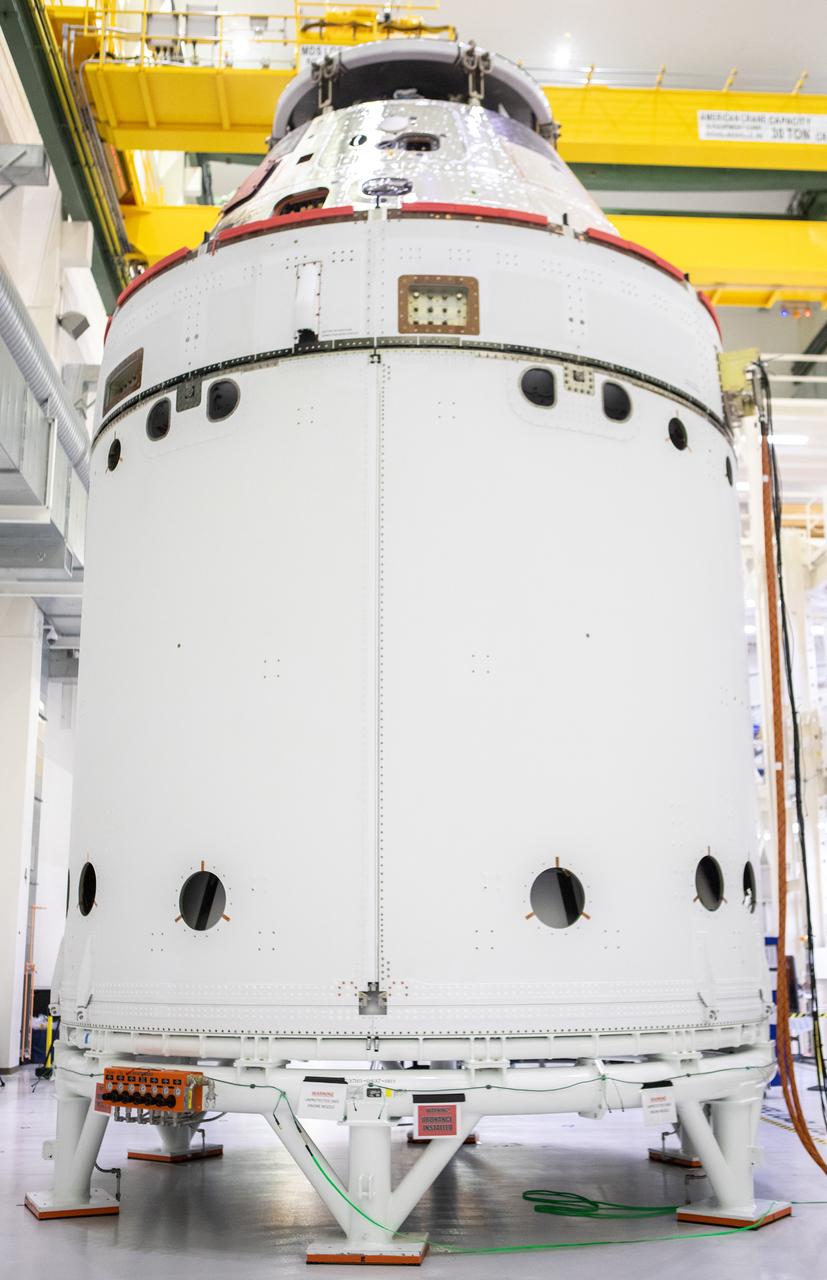

The spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels are secured onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 27, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The three panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
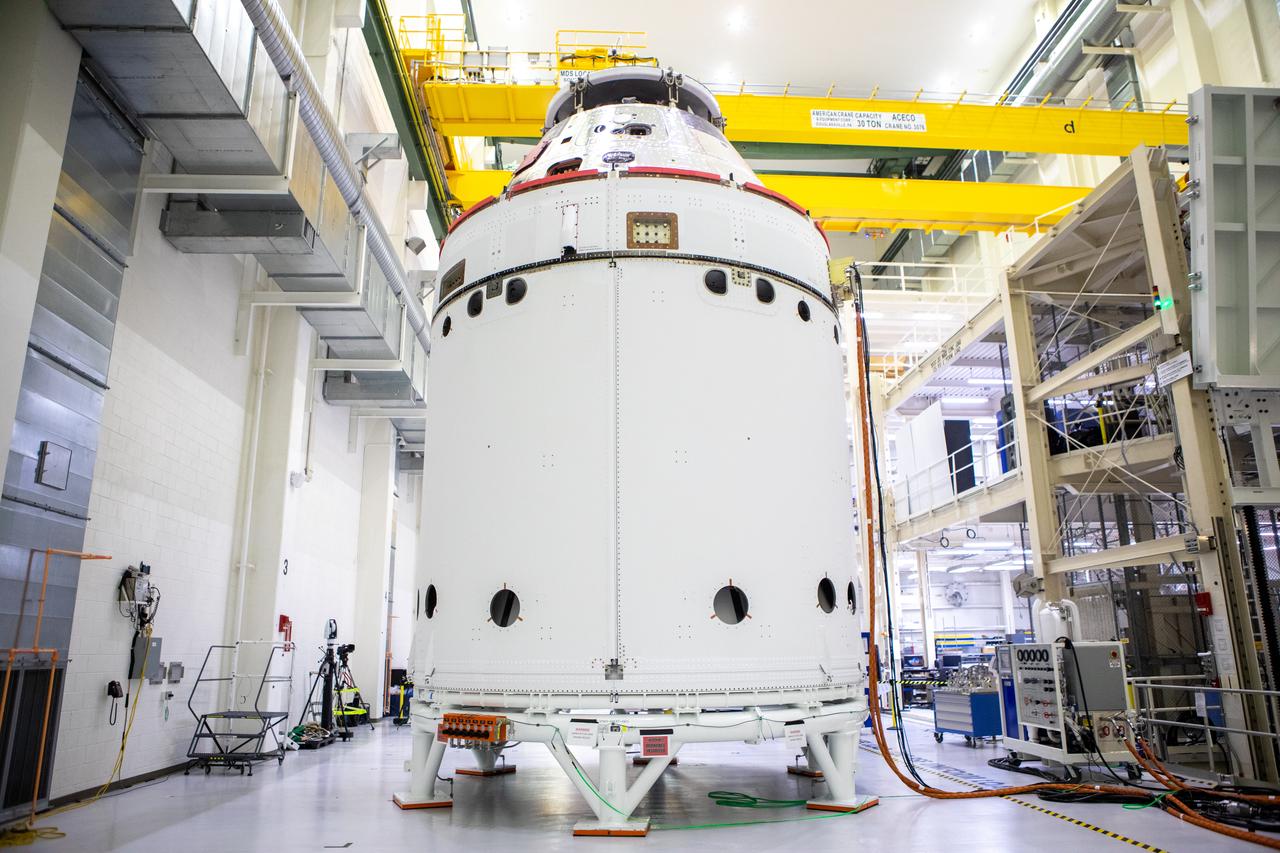

The spacecraft adapter jettison fairing panels are secured onto Orion’s European Service Module (ESM) on Oct. 27, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The three panels were inspected and moved into place for installation by technicians with Lockheed Martin. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
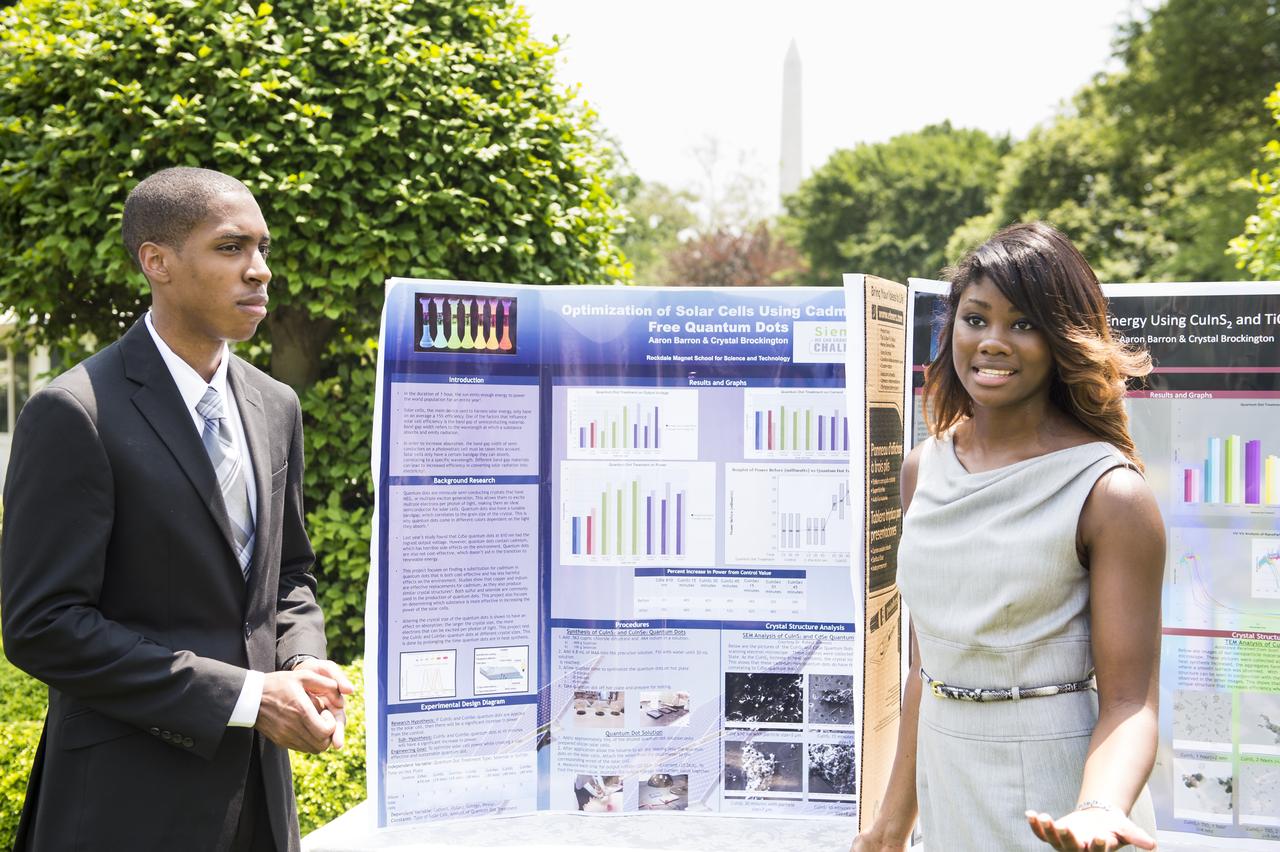

Crystal Brockington and Aaron Barron, both 18 years old, designed a more efficient and cost effective solar cell that harnesses energy without cadmium, which has been shown to be harmful to the environment. They were selected to participate in the White House Science Fair after they were awarded the High School Grand Prize at the Siemens We Can Change the World Challenge. The fourth White House Science Fair was held at the White House on May 27, 2014 and included 100 students from more than 30 different states who competed in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) competitions. (Photo Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
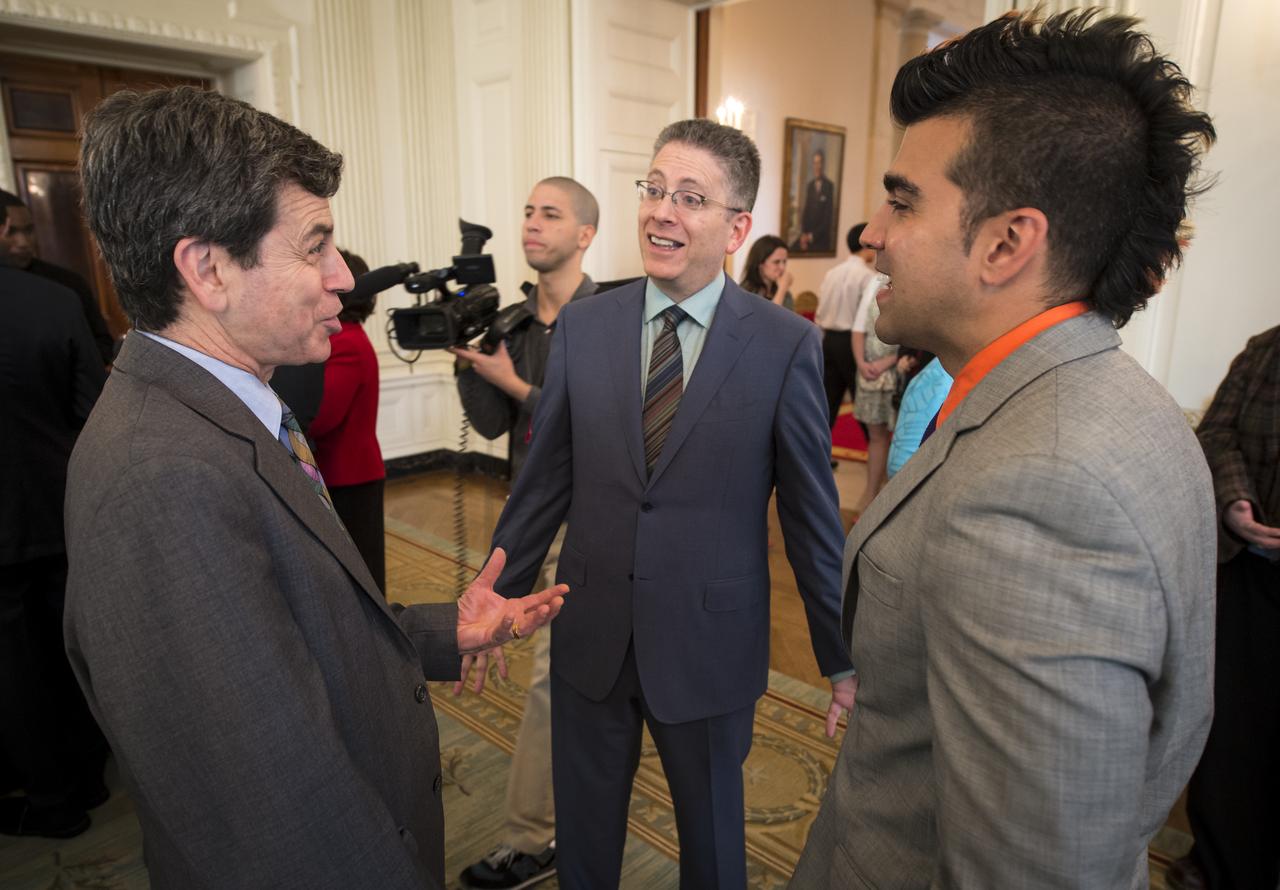

Director of Strategic Communications and Senior Science and Technology Policy Analyst, Office of Science and Technology Policy, Executive Office of the President, Rick Weiss, left, “Big Bang Theory” co-creator Bill Prady, center, and NASA Mars Curiosity Landing mission controller, Bobak "Mohawk Guy" Ferdowsi talk during the White House Science Fair held at the White House, April 22, 2013. The science fair celebrated student winners of a broad range of science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) competitions from across the country. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
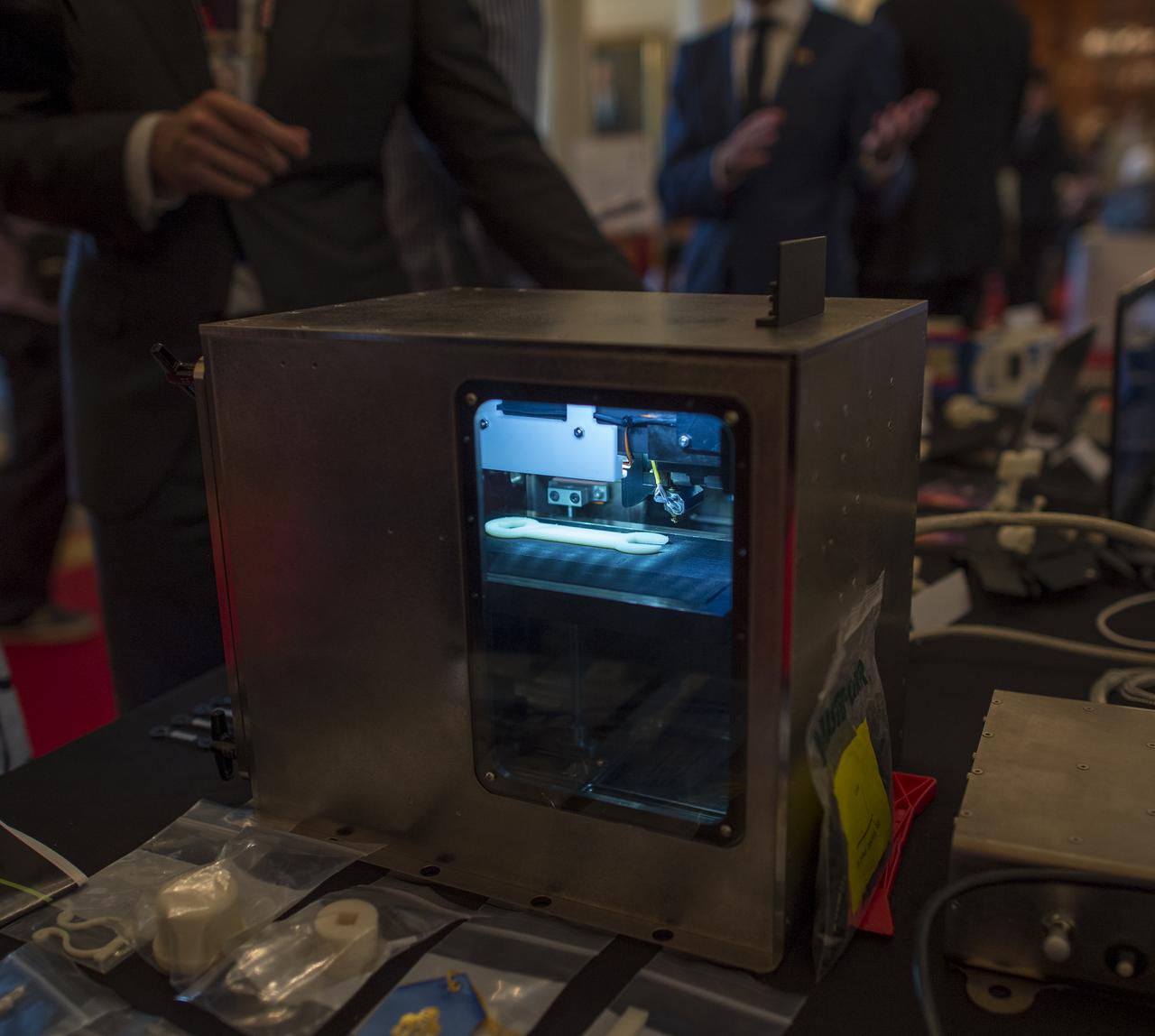

A prototype model of the Made In Space 3D printer is on display during the first ever White House Maker Faire which brings together students, entrepreneurs, and everyday citizens who are using new tools and techniques to launch new businesses, learn vital skills in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), and fuel the renaissance in American manufacturing, at the White House, Wednesday, June 18, 2014 in Washington. The Made In Space 3D printer was just approved by NASA to be tested onboard the International Space Station (ISS), and NASA announced a challenge for students to design items that would be printed by this first 3D printer to fly in space. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
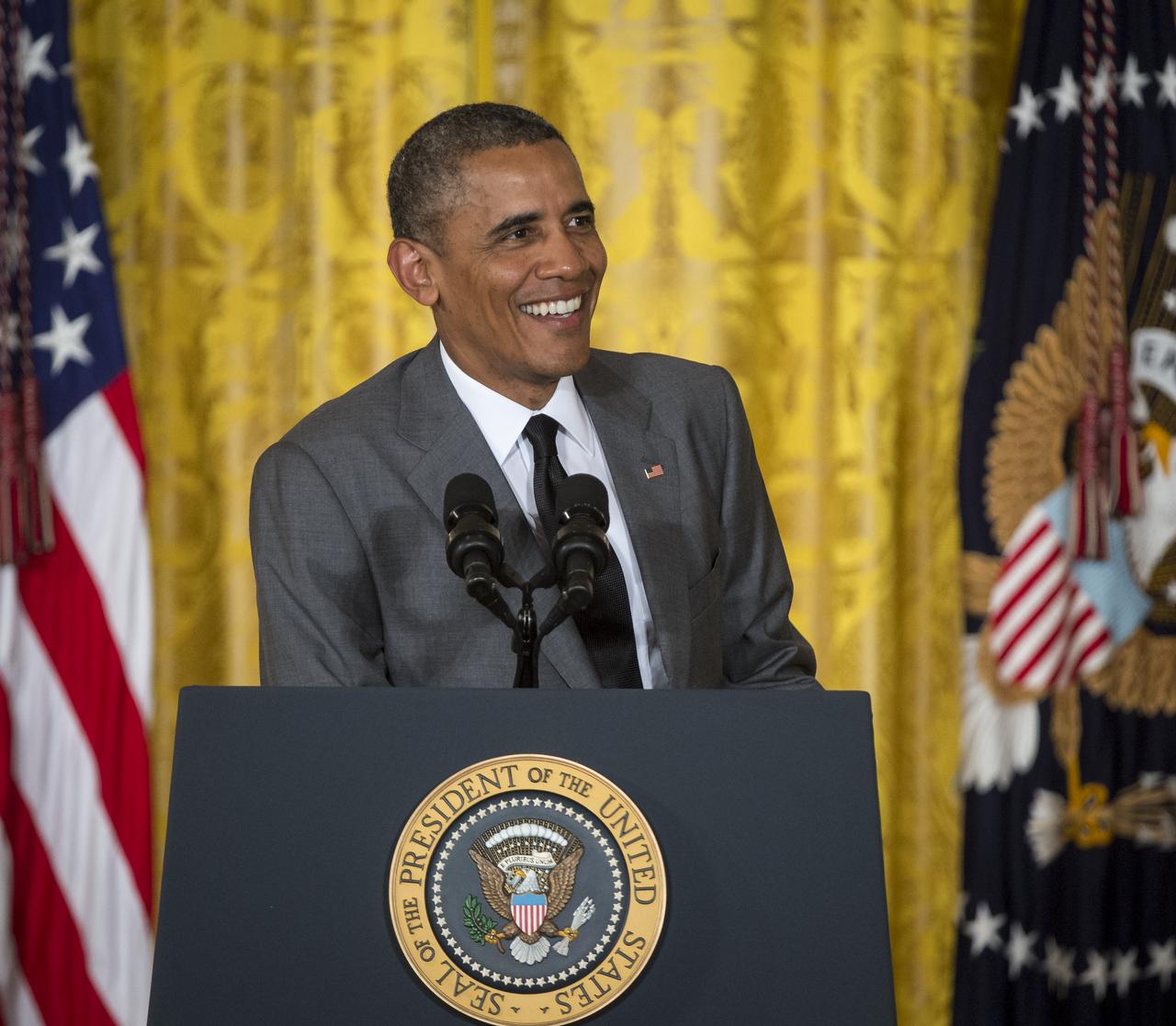

President Barack Obama delivers his remarks at the first ever White House Maker Faire, which brings together students, entrepreneurs, and everyday citizens who are using new tools and techniques to launch new businesses, learn vital skills in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), and fuel the renaissance in American manufacturing, at the White House, Wednesday, June 18, 2014 in Washington. The President announced new steps the Administration and its partners are taking to support the ability of more Americans, young and old, to have to access to these tools and techniques and brings their ideas to life. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
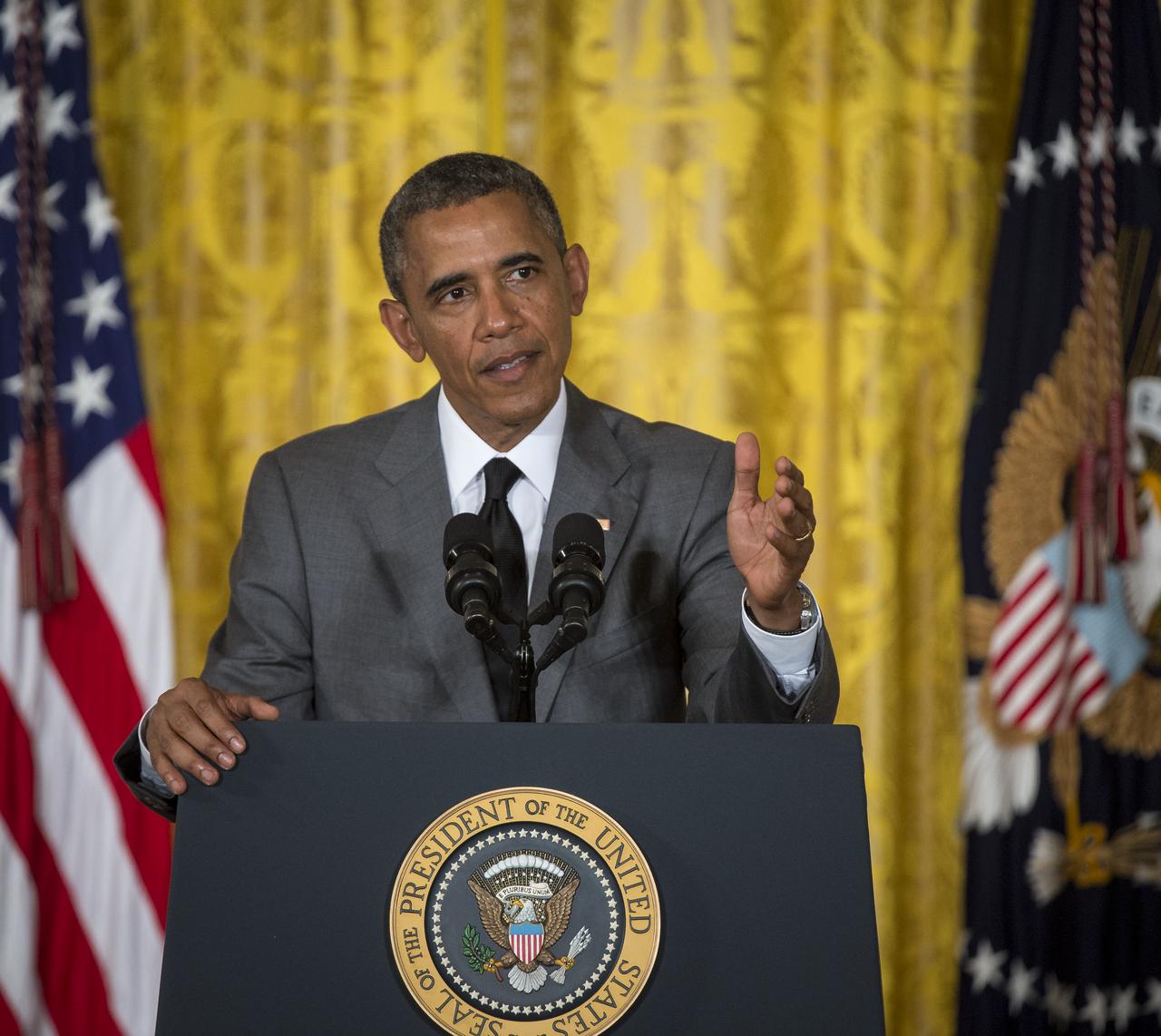

President Barack Obama delivers his remarks at the first ever White House Maker Faire, which brings together students, entrepreneurs, and everyday citizens who are using new tools and techniques to launch new businesses, learn vital skills in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), and fuel the renaissance in American manufacturing, at the White House, Wednesday, June 18, 2014 in Washington. The President announced new steps the Administration and its partners are taking to support the ability of more Americans, young and old, to have to access to these tools and techniques and brings their ideas to life. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
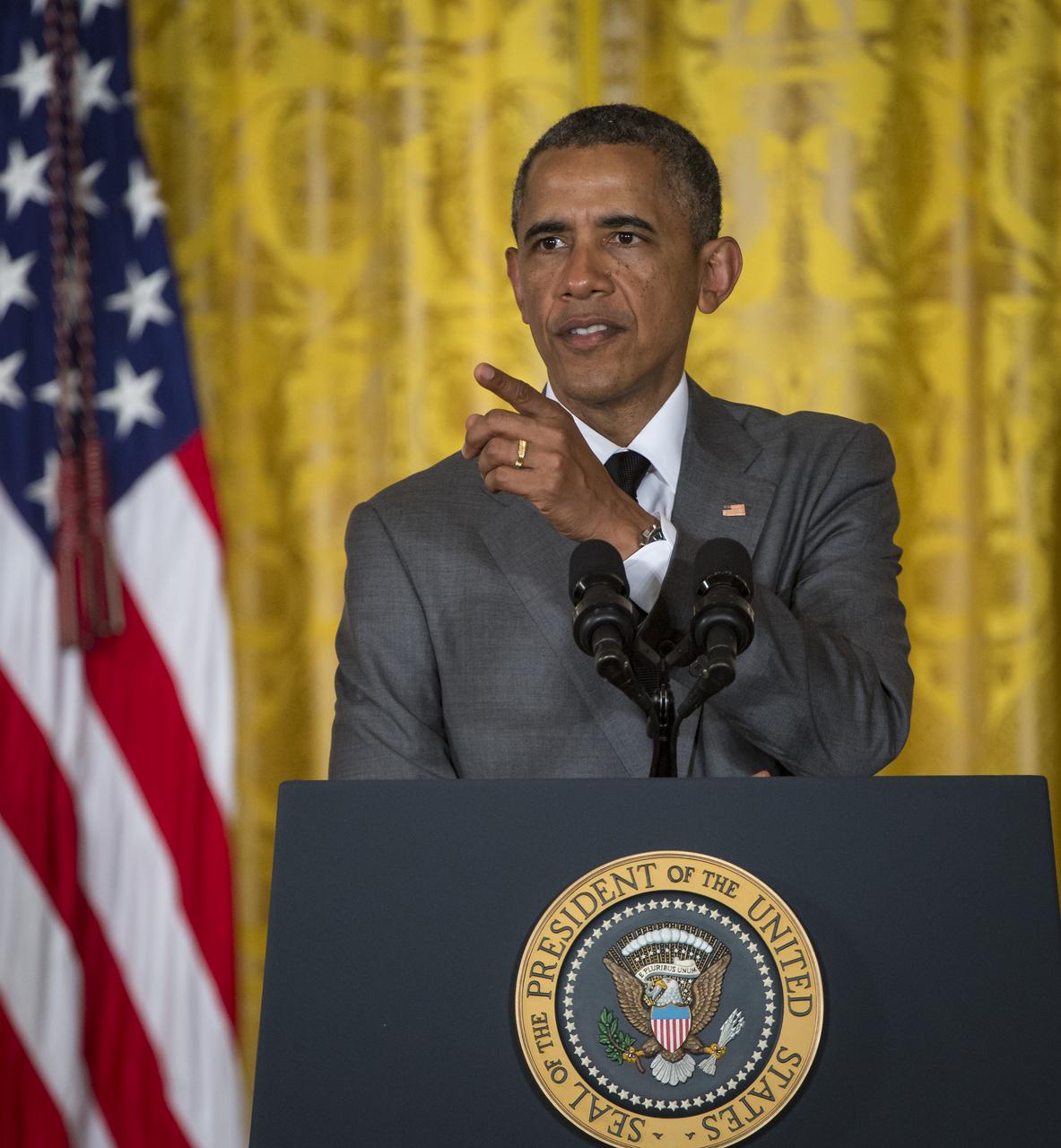

President Barack Obama delivers his remarks at the first ever White House Maker Faire, which brings together students, entrepreneurs, and everyday citizens who are using new tools and techniques to launch new businesses, learn vital skills in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), and fuel the renaissance in American manufacturing, at the White House, Wednesday, June 18, 2014 in Washington. The President announced new steps the Administration and its partners are taking to support the ability of more Americans, young and old, to have to access to these tools and techniques and brings their ideas to life. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The Voyager 2 spacecraft, encapsulated within its payload fairing, is seen in August 1977, as it was being hoisted upward for attachment to its launch vehicle at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21727
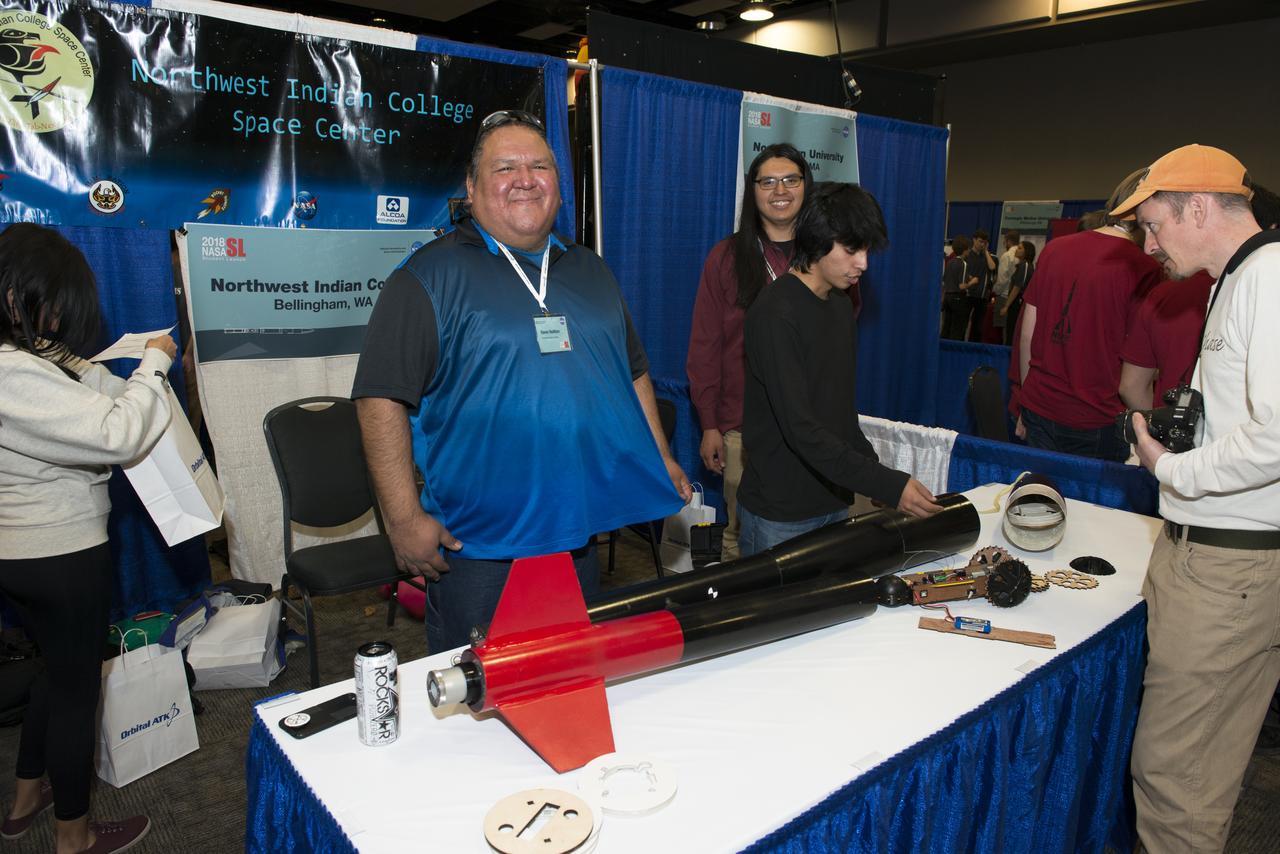

Students from 23 states display their rockets and talk about what they did to make them fly at the NASA Student Launch Rocket Fair on Friday, April 6. Over 800 students traveled to Huntsville, Alabama, to participate in a week of activities as part of NASA Student Launch.
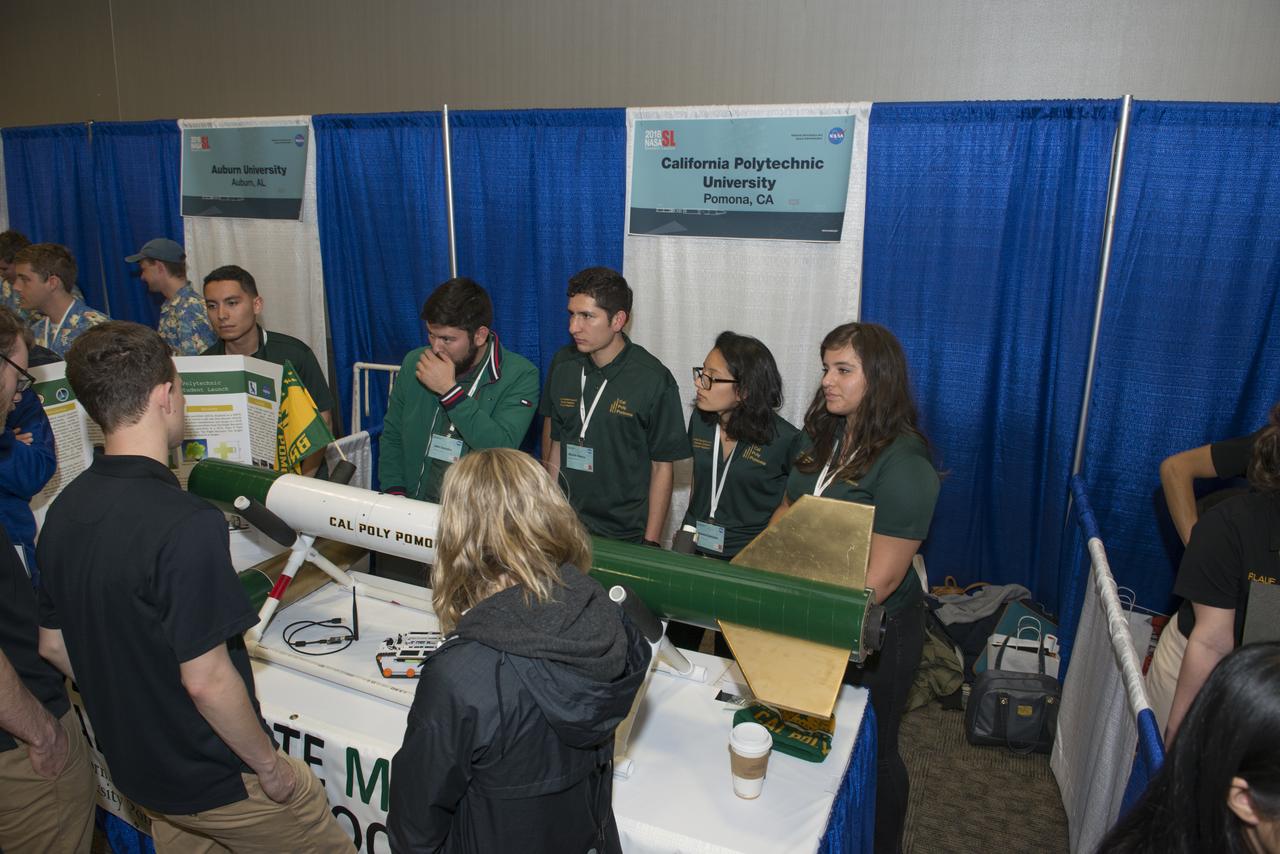
Students from 23 states display their rockets and talk about what they did to make them fly at the NASA Student Launch Rocket Fair on Friday, April 6. Over 800 students traveled to Huntsville, Alabama, to participate in a week of activities as part of NASA Student Launch.
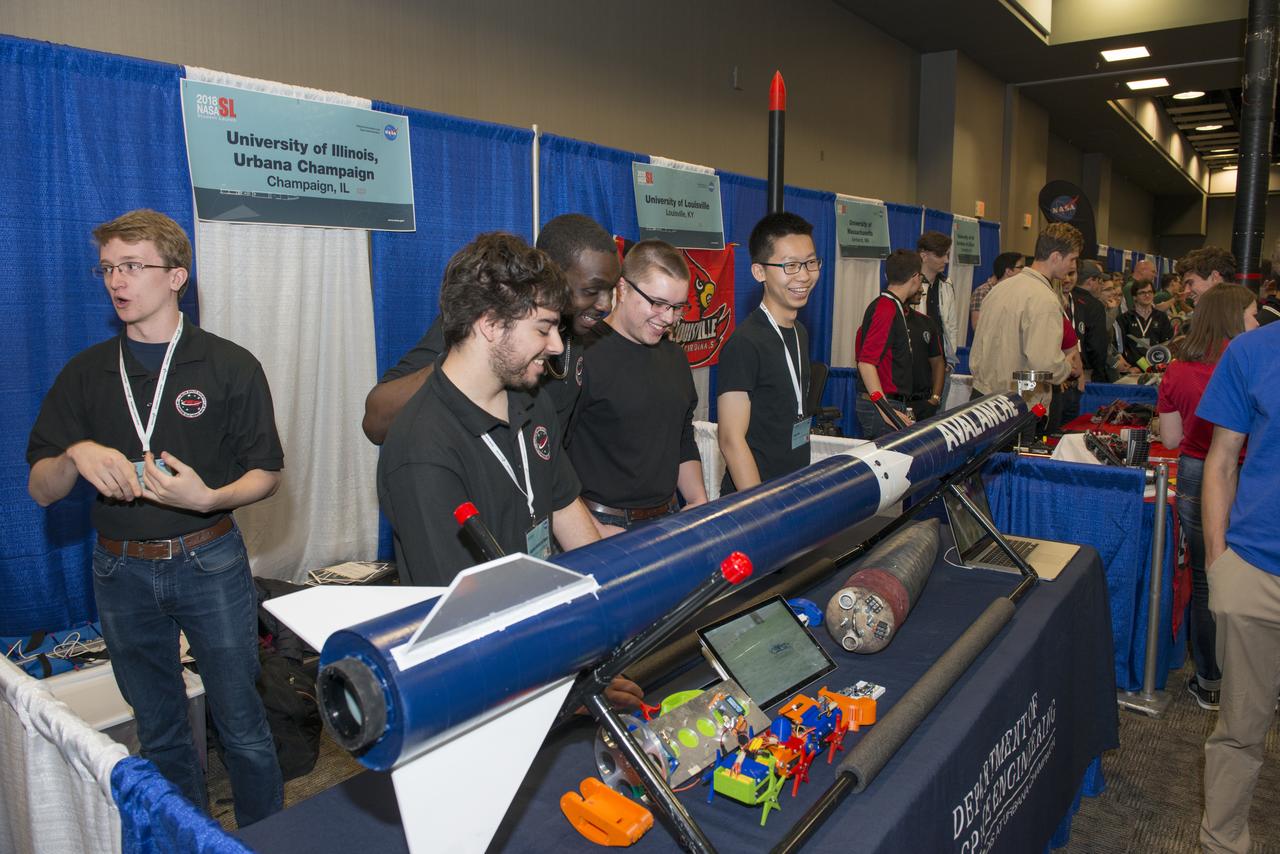

Students from 23 states display their rockets and talk about what they did to make them fly at the NASA Student Launch Rocket Fair on Friday, April 6. Over 800 students traveled to Huntsville, Alabama, to participate in a week of activities as part of NASA Student Launch.
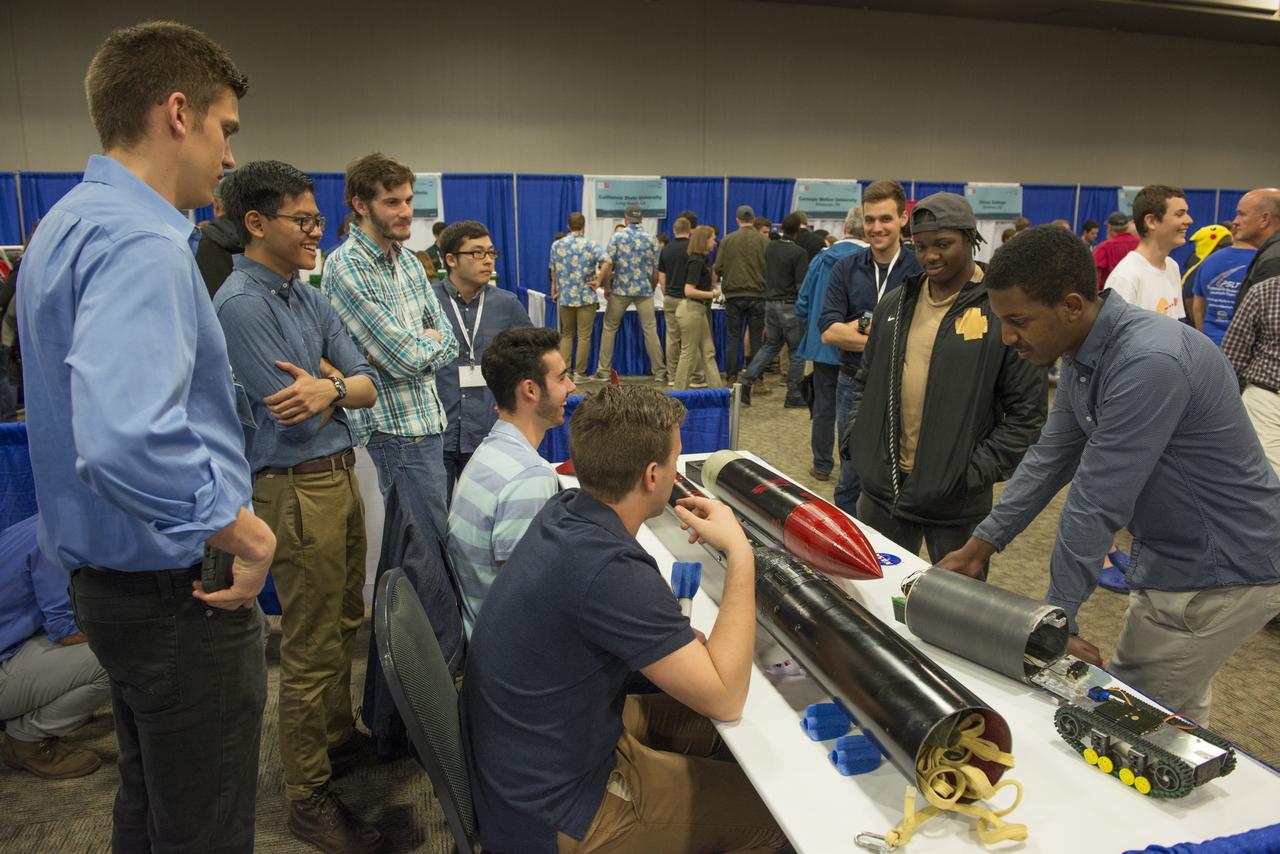

Students from 23 states display their rockets and talk about what they did to make them fly at the NASA Student Launch Rocket Fair on Friday, April 6. Over 800 students traveled to Huntsville, Alabama, to participate in a week of activities as part of NASA Student Launch.

Students from 23 states display their rockets and talk about what they did to make them fly at the NASA Student Launch Rocket Fair on Friday, April 6. Over 800 students traveled to Huntsville, Alabama, to participate in a week of activities as part of NASA Student Launch.

Students from 23 states display their rockets and talk about what they did to make them fly at the NASA Student Launch Rocket Fair on Friday, April 6. Over 800 students traveled to Huntsville, Alabama, to participate in a week of activities as part of NASA Student Launch.
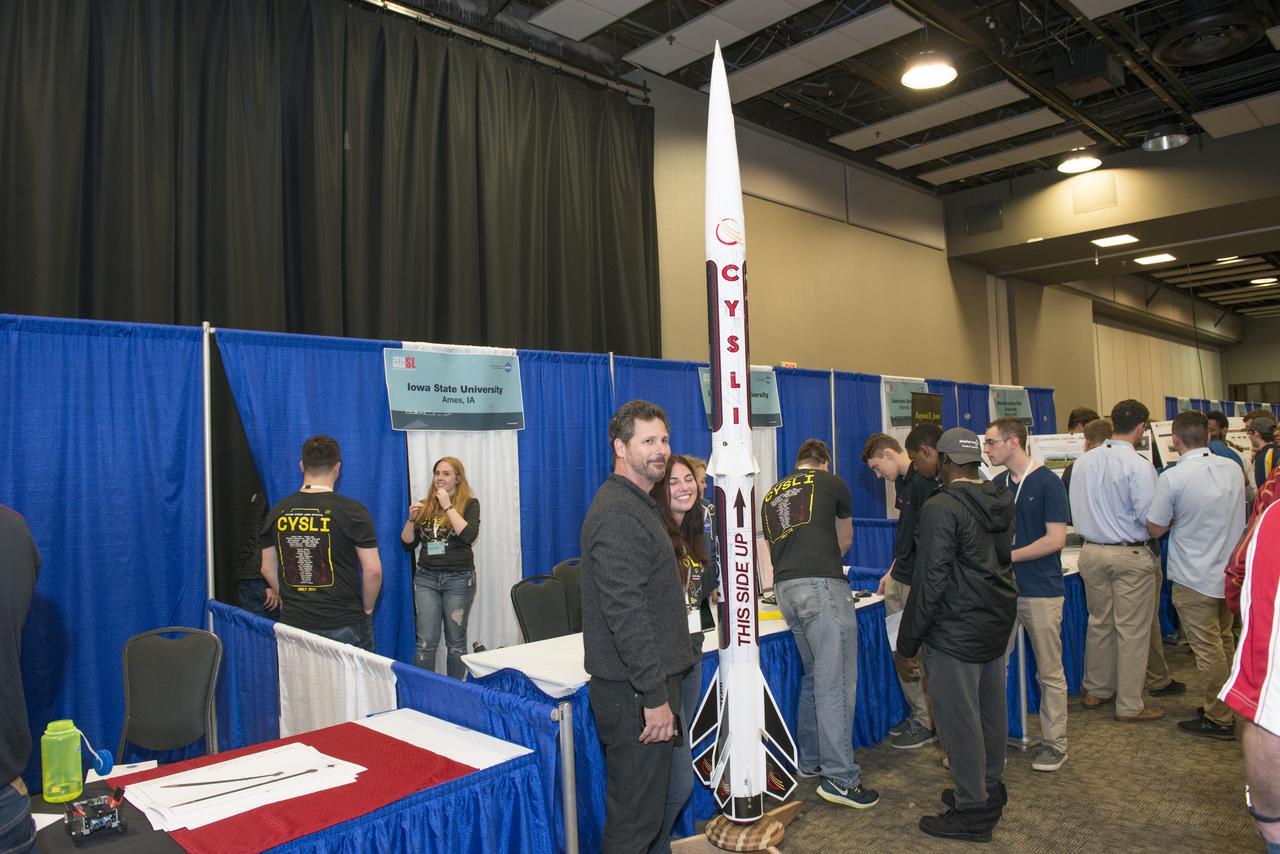

Students from 23 states display their rockets and talk about what they did to make them fly at the NASA Student Launch Rocket Fair on Friday, April 6. Over 800 students traveled to Huntsville, Alabama, to participate in a week of activities as part of NASA Student Launch.

Students from 23 states display their rockets and talk about what they did to make them fly at the NASA Student Launch Rocket Fair on Friday, April 6. Over 800 students traveled to Huntsville, Alabama, to participate in a week of activities as part of NASA Student Launch.

Students from 23 states display their rockets and talk about what they did to make them fly at the NASA Student Launch Rocket Fair on Friday, April 6. Over 800 students traveled to Huntsville, Alabama, to participate in a week of activities as part of NASA Student Launch.

Students from 23 states display their rockets and talk about what they did to make them fly at the NASA Student Launch Rocket Fair on Friday, April 6. Over 800 students traveled to Huntsville, Alabama, to participate in a week of activities as part of NASA Student Launch.
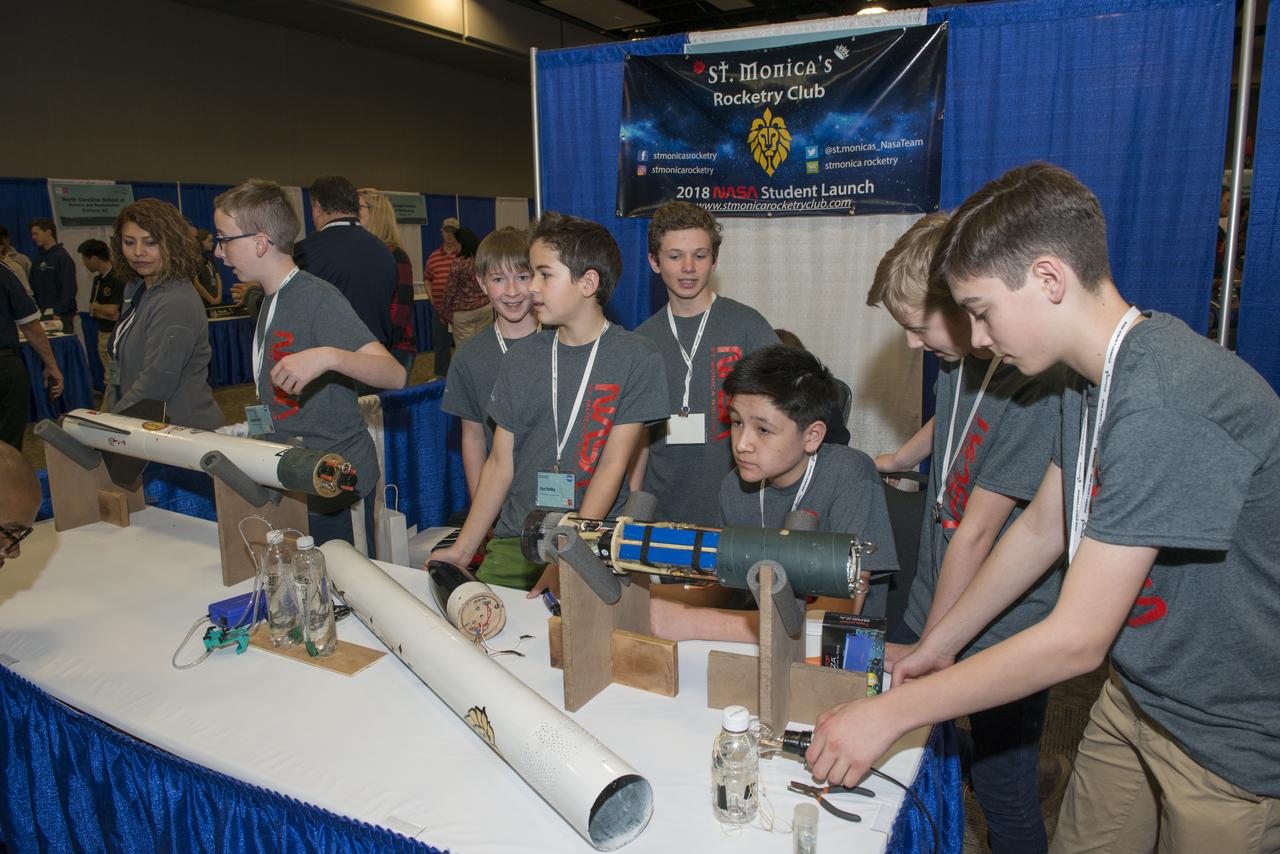

Students from 23 states display their rockets and talk about what they did to make them fly at the NASA Student Launch Rocket Fair on Friday, April 6. Over 800 students traveled to Huntsville, Alabama, to participate in a week of activities as part of NASA Student Launch.