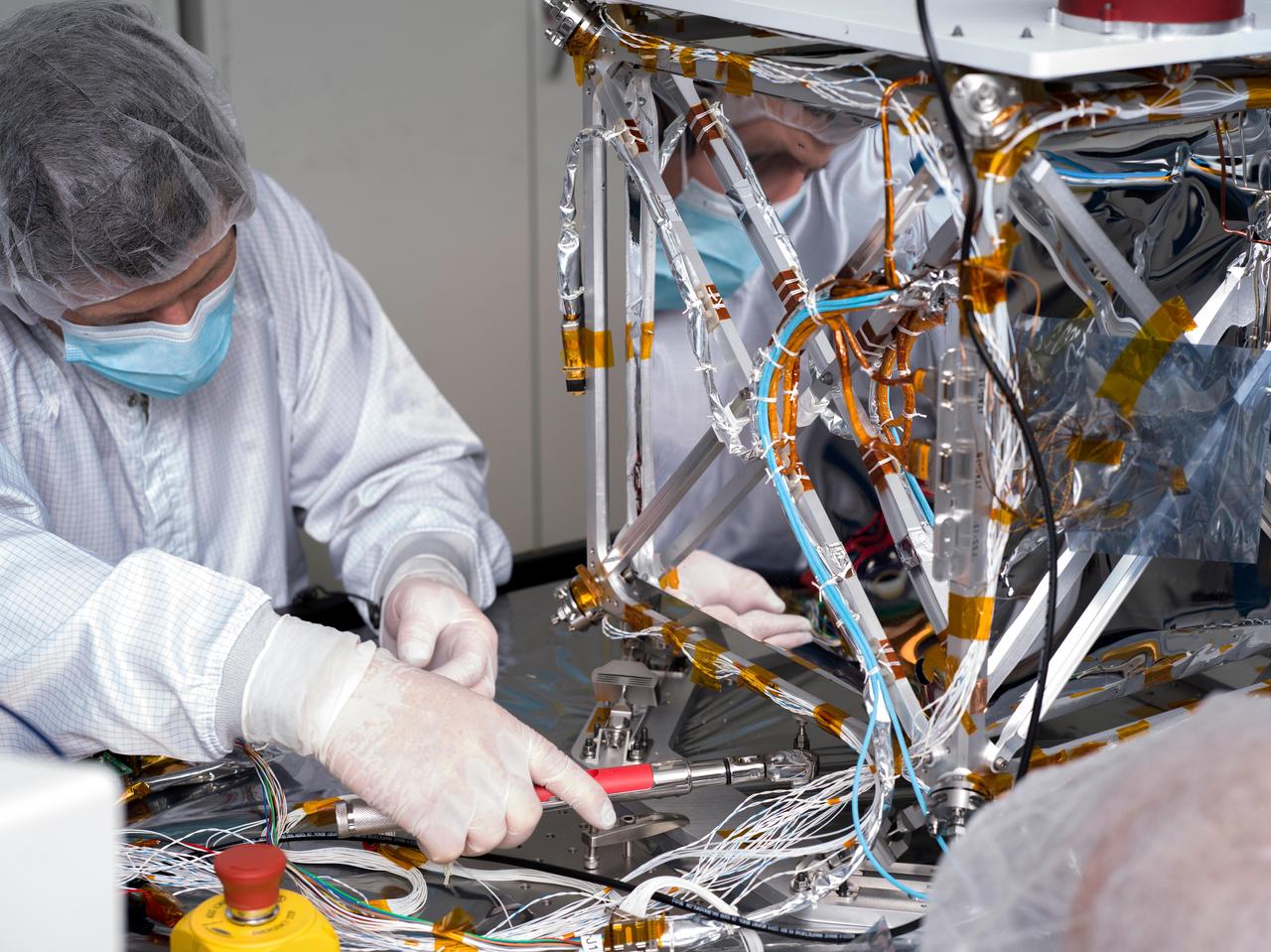
In a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in March 2024, technician Nik Schwarz prepares the agency's Farside Seismic Suite (FSS) for testing. The cube-shaped payload contains two instruments that will gather NASA's first seismic data from the Moon in nearly 50 years and take the first-ever seismic measurements from the Moon's far side. FSS will operate continuously for at least 4½ months, working through the long, cold lunar nights. The two seismometers are packaged together with a large battery, a computer, and electronics inside a cube structure that's surrounded by several layers of insulation (the shiny, reflective material seen here) and suspended within an outer protective cube, which is in turn covered with a shiny insulating blanket. A technician is here attaching a stiffening brace to the bottom of the FSS outer cube structure. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26341

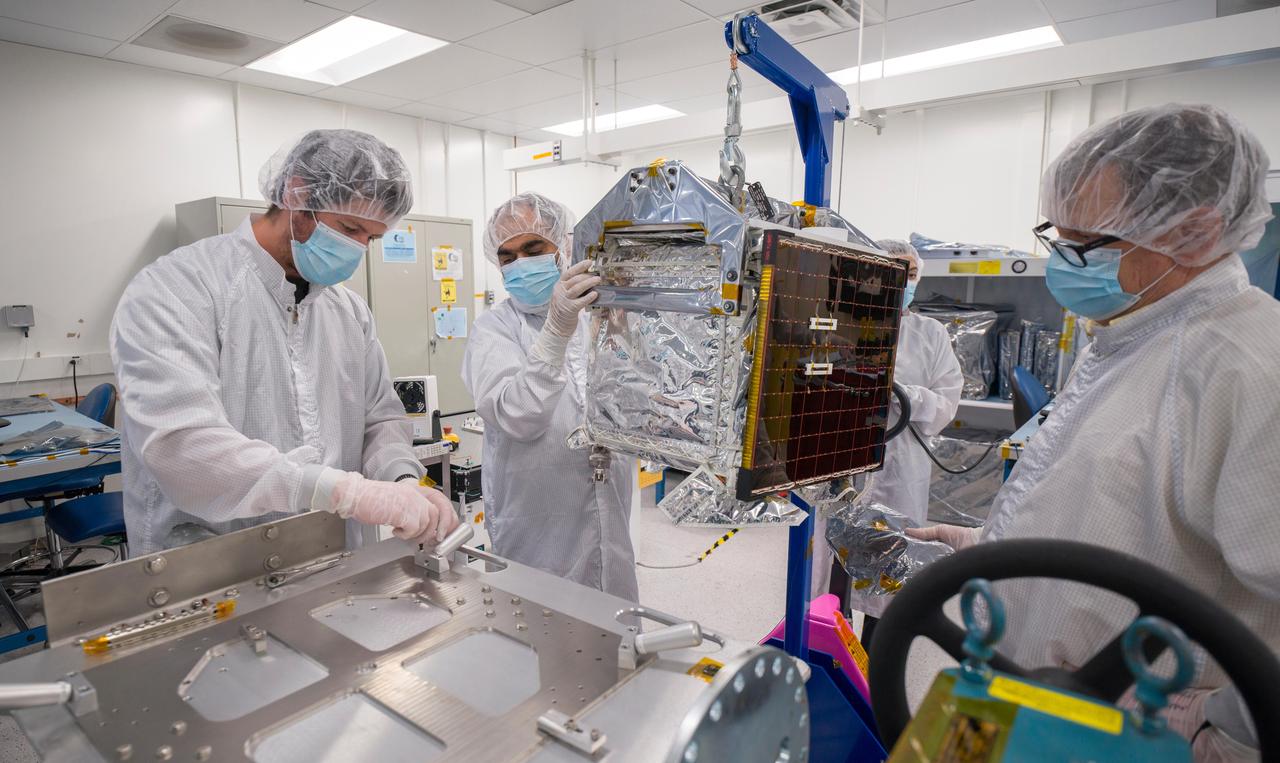
In a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in March 2024, engineers and technicians work to prepare the agency's Farside Seismic Suite (FSS) for environmental testing to simulate conditions it will encounter in space. Along with being placed in a vacuum chamber and subjected to extreme temperatures, the instrument suite will undergo severe shaking that mimics the rocket's motion during launch. The cube-shaped payload contains two instruments that will gather NASA's first seismic data from the Moon in nearly 50 years and take the first-ever seismic measurements from the Moon's far side. FSS will operate continuously for at least 4½ months, working through the long, cold lunar nights. The two seismometers are packaged together with a large battery, a computer, and electronics inside a cube structure that's surrounded by several layers of insulation and suspended within an outer protective cube, which is in turn covered with a shiny insulating blanket. The suite's single solar panel can be seen at center. On top is a white radiator that will allow the suite to shed heat generated by its electronics during the hot lunar daytime hours. The puck-like object atop the radiator is the suite's antenna, for communicating with two small relay satellites that will orbit the Moon and send data to Earth. Pictured (from left): Joanna Farias, and Bert Turney, and Hsin-Yi Hao. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26299

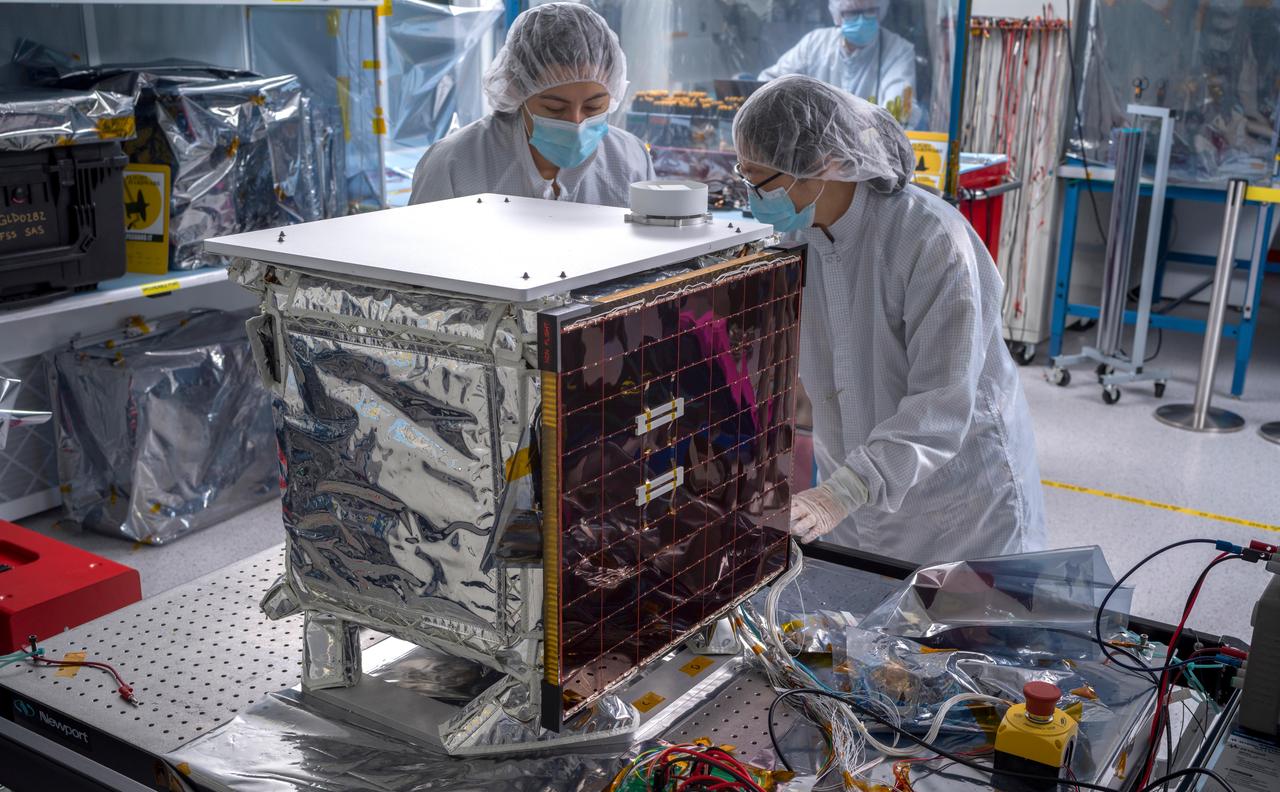
In a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in March 2024, engineers and technicians prepare the agency's Farside Seismic Suite (FSS) for testing. The cube-shaped payload contains two instruments that will gather NASA's first seismic data from the Moon in nearly 50 years and take the first-ever seismic measurements from the Moon's far side. FSS will operate continuously for at least 4½ months, working through the long, cold lunar nights. Here, engineers move FSS onto a fixture that will allow them to tilt the payload, simulating the pull of lunar gravity in the direction at which one of the instrument's two seismometers is sensitive to motion. (The Moon's gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's.) Called an ambient tilt test, this activity allows engineers to check the seismometers' performance. The two seismometers are packaged together with a large battery, a computer, and electronics inside a cube structure that's surrounded by several layers of insulation and suspended within an outer protective cube, which is in turn covered with a shiny insulating blanket. The suite's single solar panel can be seen right of center. Surrounding the instrument are (from left): Nik Schwarz, Vik Singh, Joanna Farias, and Bert Turney. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26298
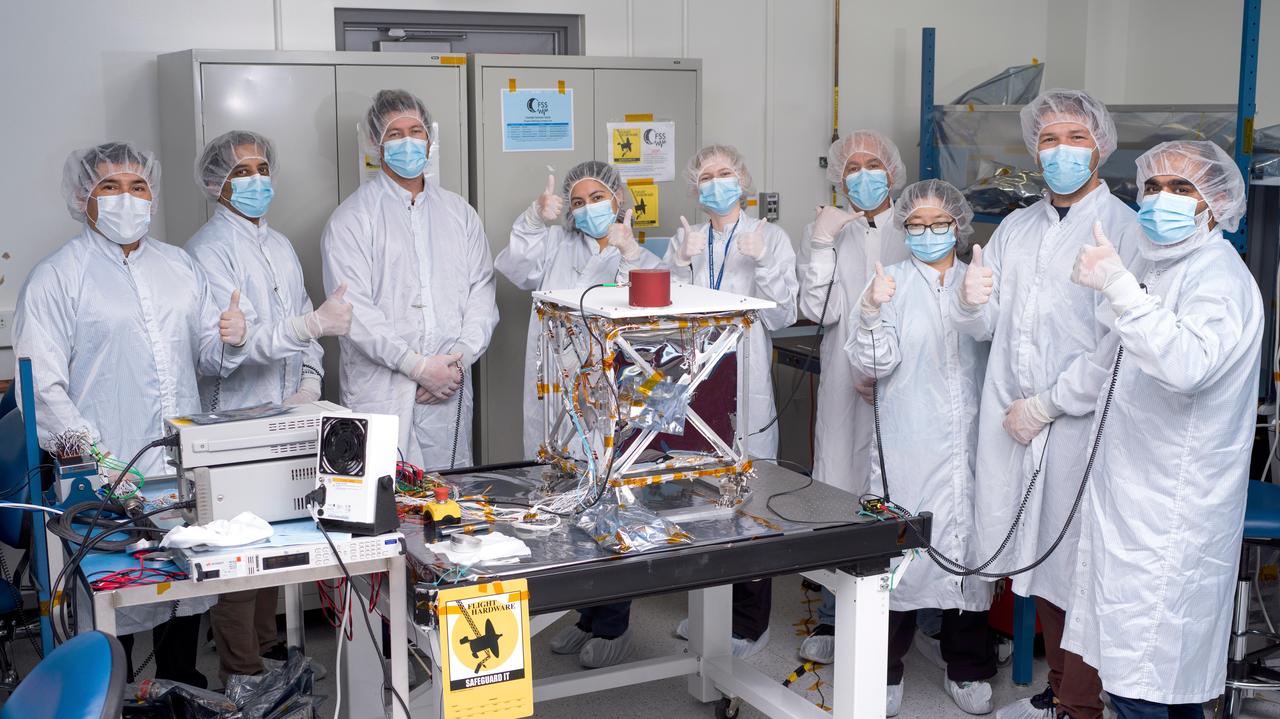

In a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in March 2024, engineers and technicians pose with the agency's Farside Seismic Suite while the payload is readied for testing. The suite contains two instruments that will gather NASA's first seismic data from the Moon in nearly 50 years and take the first-ever seismic measurements from the Moon's far side. FSS will operate continuously for at least 4½ months, working through the long, cold lunar nights. The two seismometers are packaged together with a large battery, a computer, and electronics inside a cube structure that's surrounded by several layers of insulation (the shiny material at center) and suspended within a protective outer cube, which is, in turn, covered with an insulating blanket. In this photo, the blanket has not yet been attached. Members of the FSS integration team pictured are (from left) Salvador Ramirez, Asad Aboobaker, Nik Schwarz, Joanna Farias, Clara MacFarland, Frank Barone, Hsin-Yi Hao, Nicholas Roy-Steier, and Vik Singh. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26342
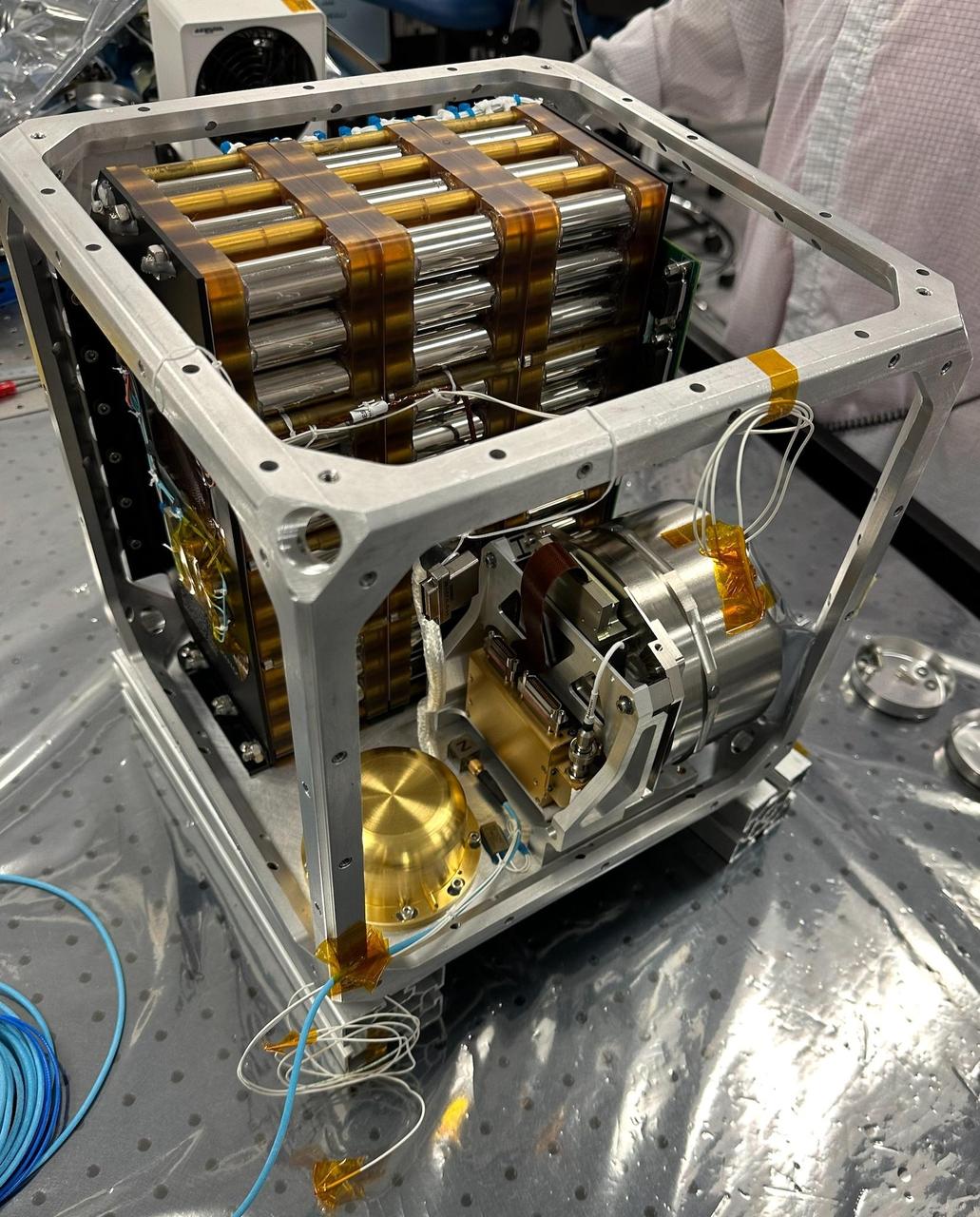
NASA's Farside Seismic Suite (FSS) is assembled in a clean room at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in November 2023. Two sensitive seismometers packaged in the suite's cube-within-a-cube structure will gather NASA's first seismic data from the Moon in nearly 50 years and take the first-ever seismic measurements from the Moon's far side. FSS will operate continuously for at least 4½ months, working through the long, cold lunar nights. Seen here is the inner cube structure, with the suite's large battery at rear. The gold, puck-shaped device at left is the Short Period sensor, or SP, which measures motion in three directions using sensors etched into a trio of square silicon chips, each about 1 inch (25 millimeters) wide. At right, within the silver cylindrical enclosure, is the Very Broadband seismometer, or VBB, the most sensitive seismometer ever built for use in space exploration. It can detect ground motions smaller than the size of a single hydrogen atom, measuring up-and-down movement using a pendulum held in place by a spring. Constructed as a backup instrument (a "flight spare") for NASA's InSight Mars lander by the French space agency, CNES (Centre National d'Études Spatiales), the VBB was slightly modified and packaged in a new enclosure for lunar use. The suite's computer and electronics are packed alongside the battery and seismometers. After being encased in insulation, this inner cube was suspended within a protective outer cube, which was in turn covered with a shiny insulating blanket. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26300

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson and President of the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES) Dr. Philippe Baptiste sign an agreement for the Farside Seismic Suite (FSS), Wednesday, Nov. 30, 2022 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The FSS will return the first lunar seismic data from the far side of the Moon. CNES is contributing one of the seismometers to this payload, which will be delivered via NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payloads Services (CLPS) initiative, based on heritage capabilities from the Mars InSight mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
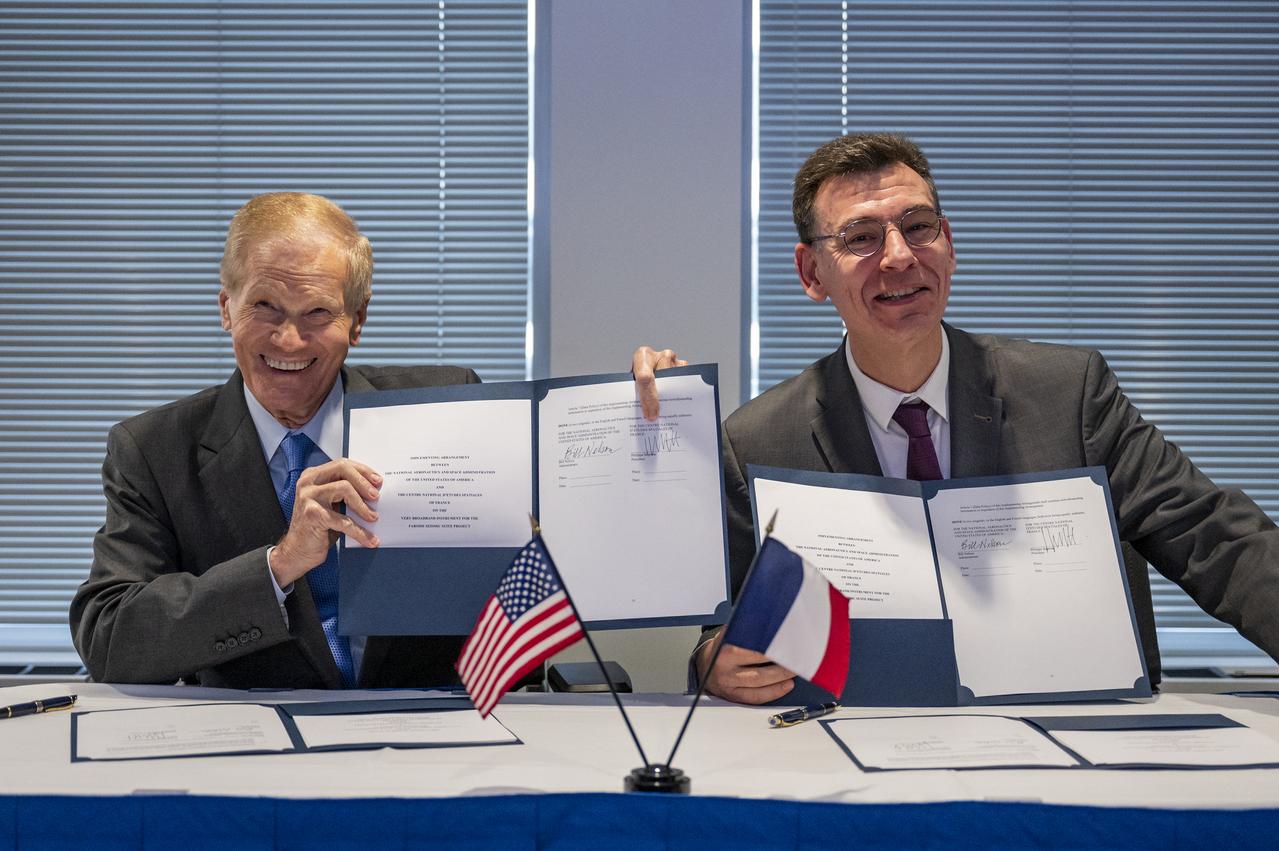

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson and President of the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES) Dr. Philippe Baptiste sign an agreement for the Farside Seismic Suite (FSS), Wednesday, Nov. 30, 2022 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The FSS will return the first lunar seismic data from the far side of the Moon. CNES is contributing one of the seismometers to this payload, which will be delivered via NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payloads Services (CLPS) initiative, based on heritage capabilities from the Mars InSight mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
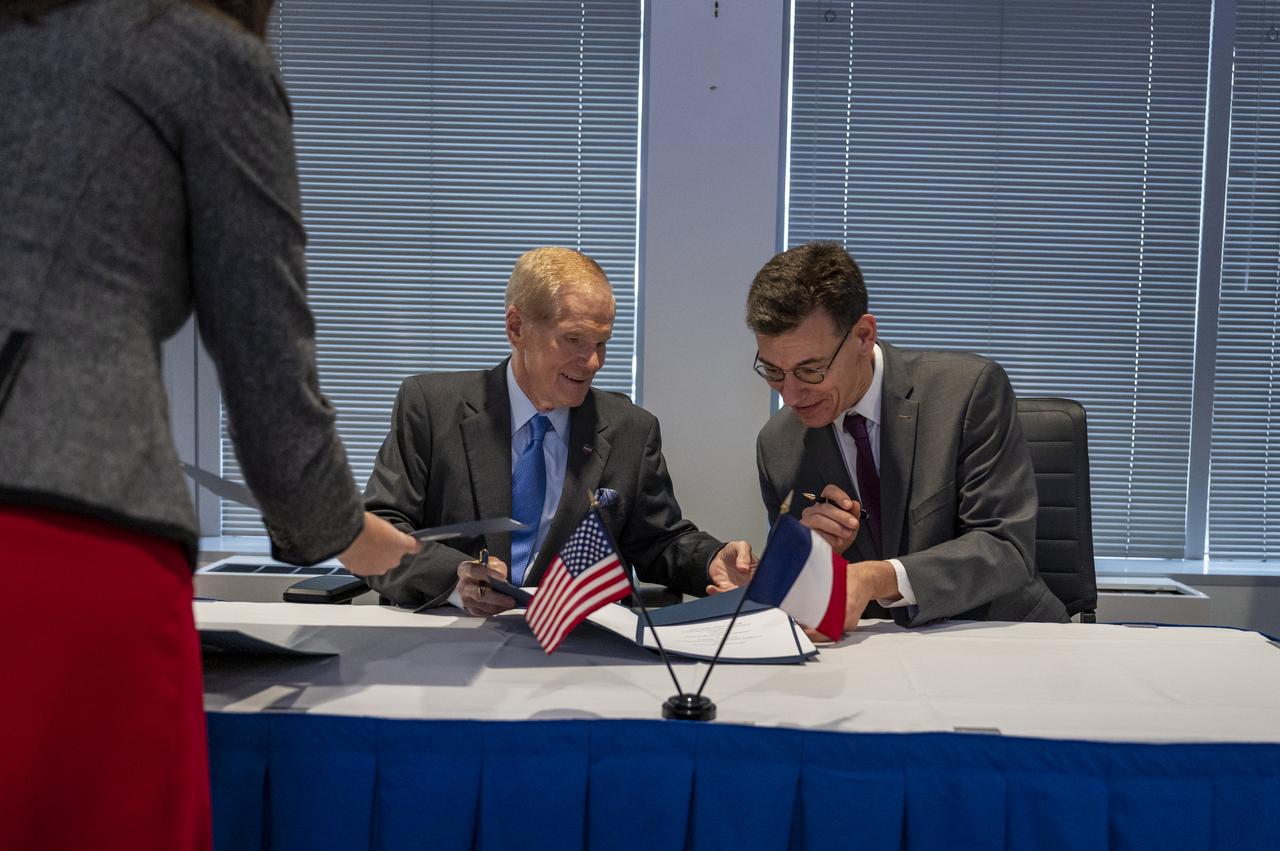

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson and President of the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES) Dr. Philippe Baptiste sign an agreement for the Farside Seismic Suite (FSS), Wednesday, Nov. 30, 2022 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The FSS will return the first lunar seismic data from the far side of the Moon. CNES is contributing one of the seismometers to this payload, which will be delivered via NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payloads Services (CLPS) initiative, based on heritage capabilities from the Mars InSight mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)