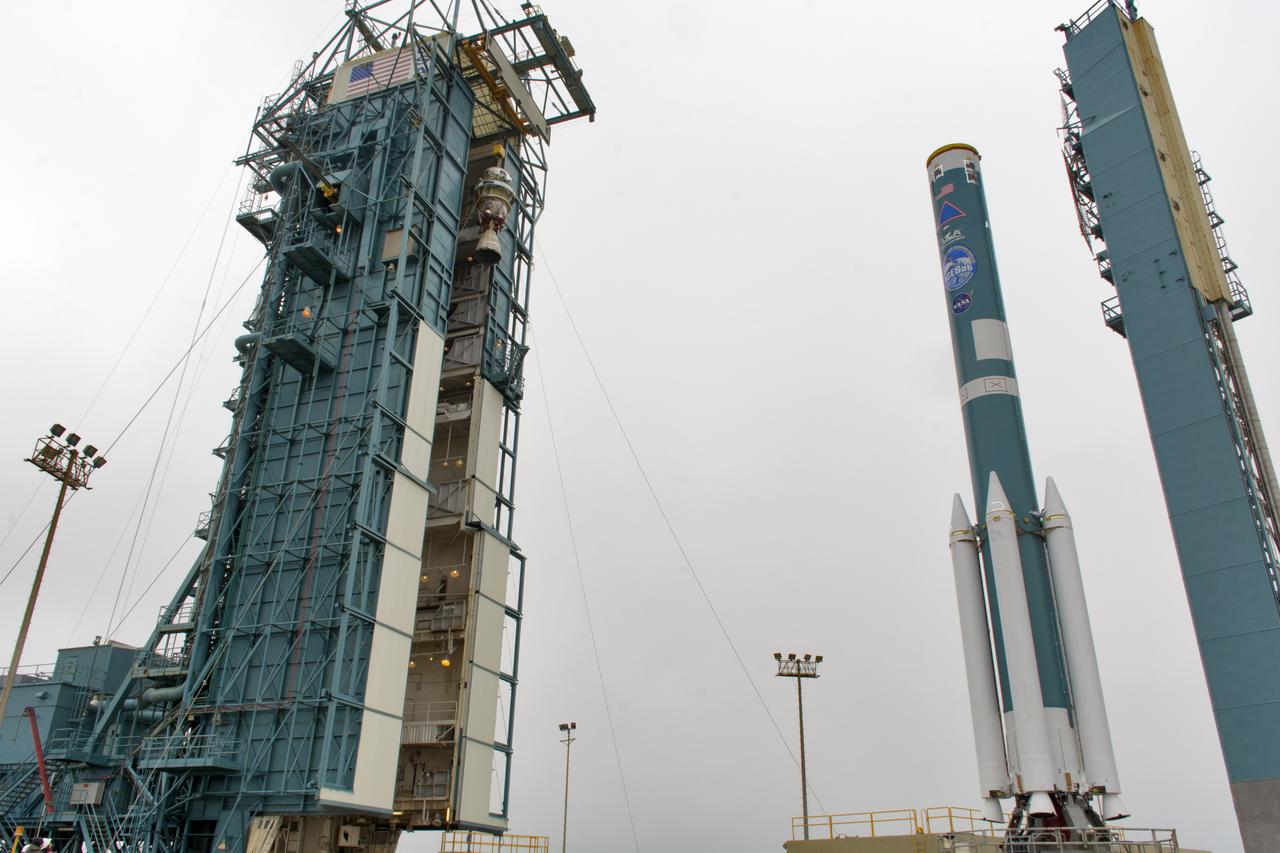

The second stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is lifted high up at the Vertical Integration Facility, at left, at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 21, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The second stage will be attached to the top of the booster, or first stage of the rocket, which is being moved out of the Mobile Service Tower, at right. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
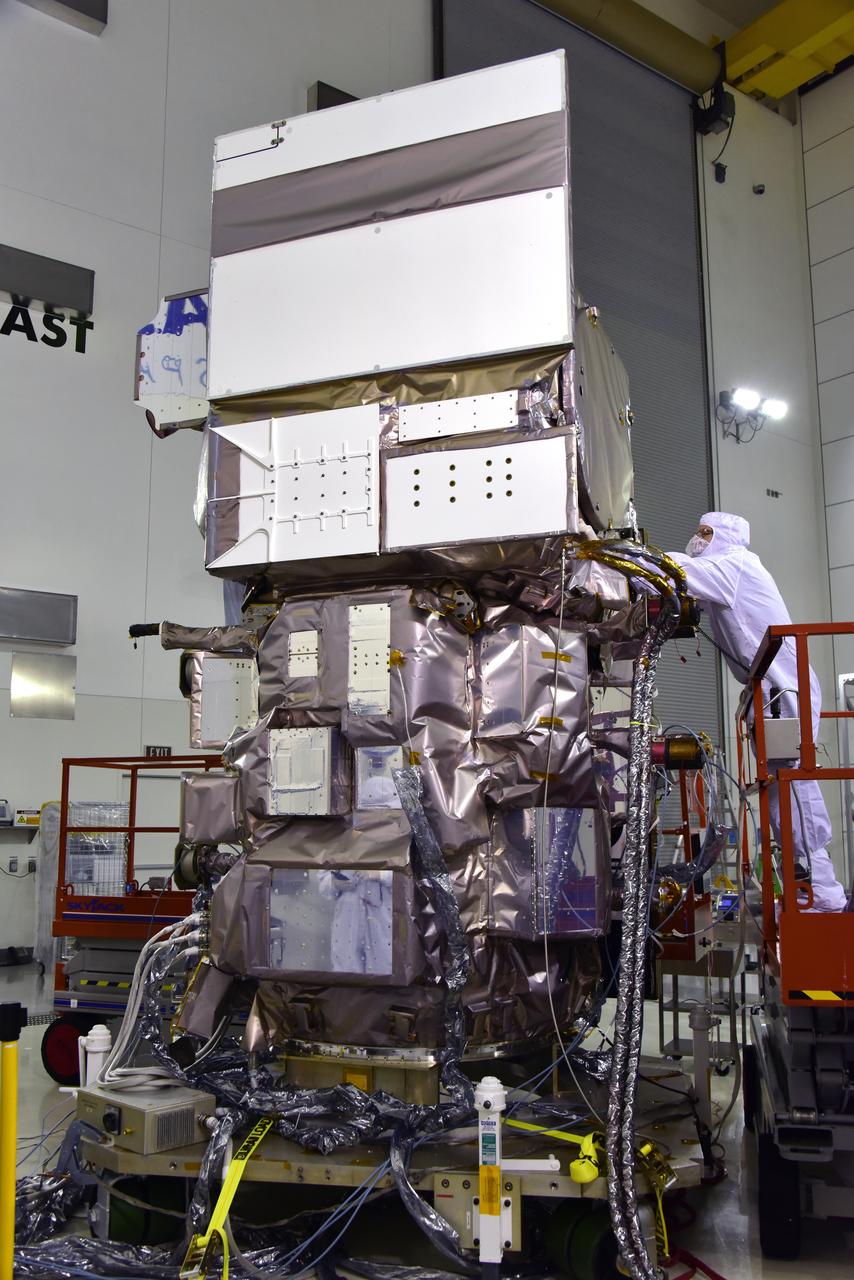

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician checks the flight door for the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS) on NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on June 21, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry ATLAS. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
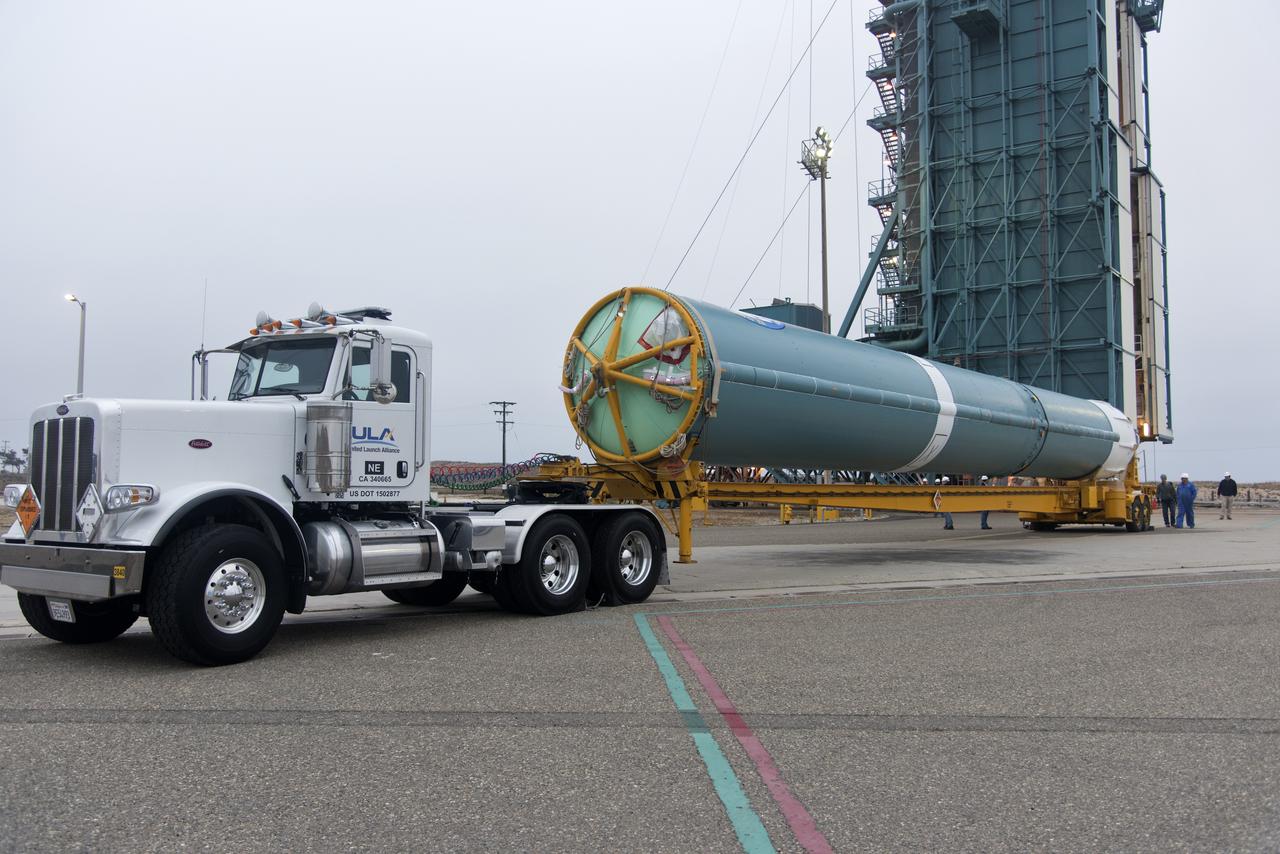

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage arrives at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be lifted to vertical and moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
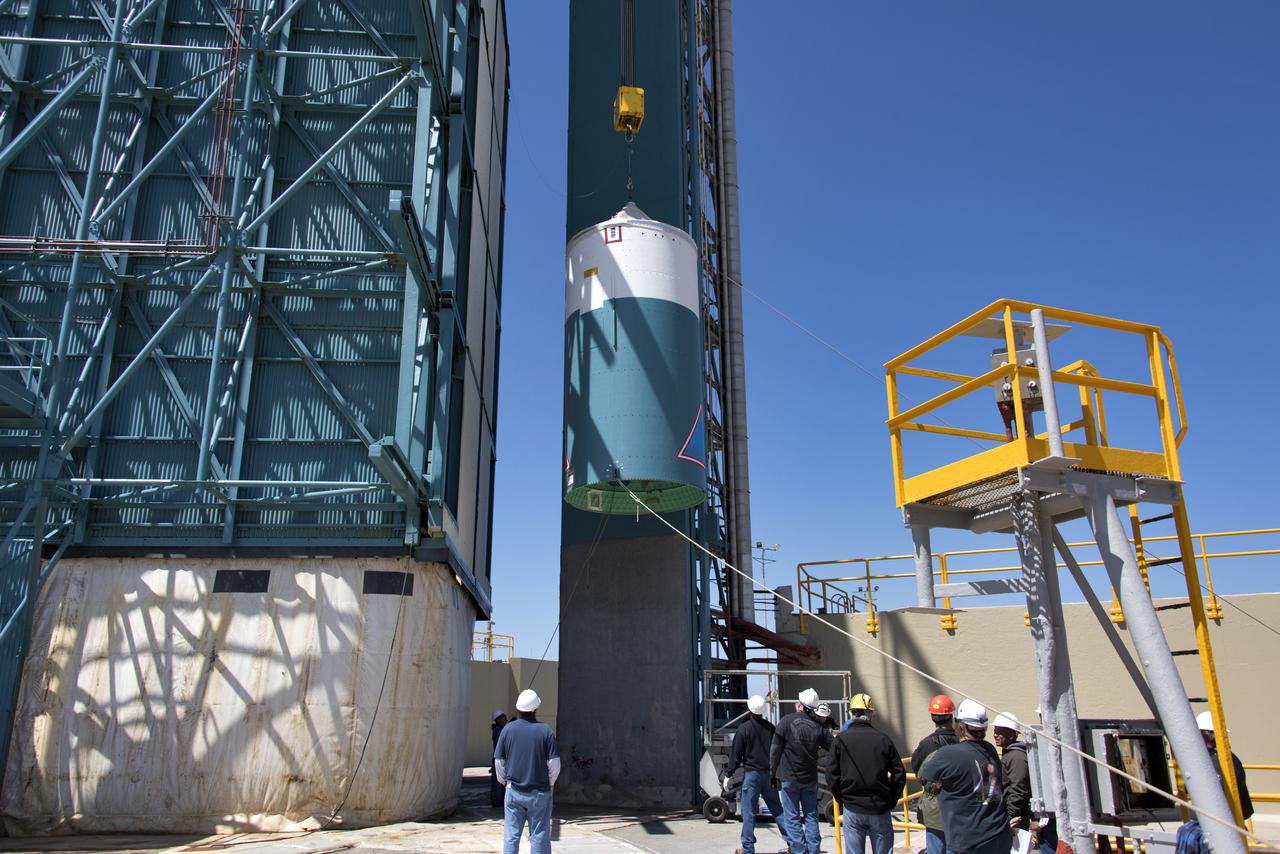

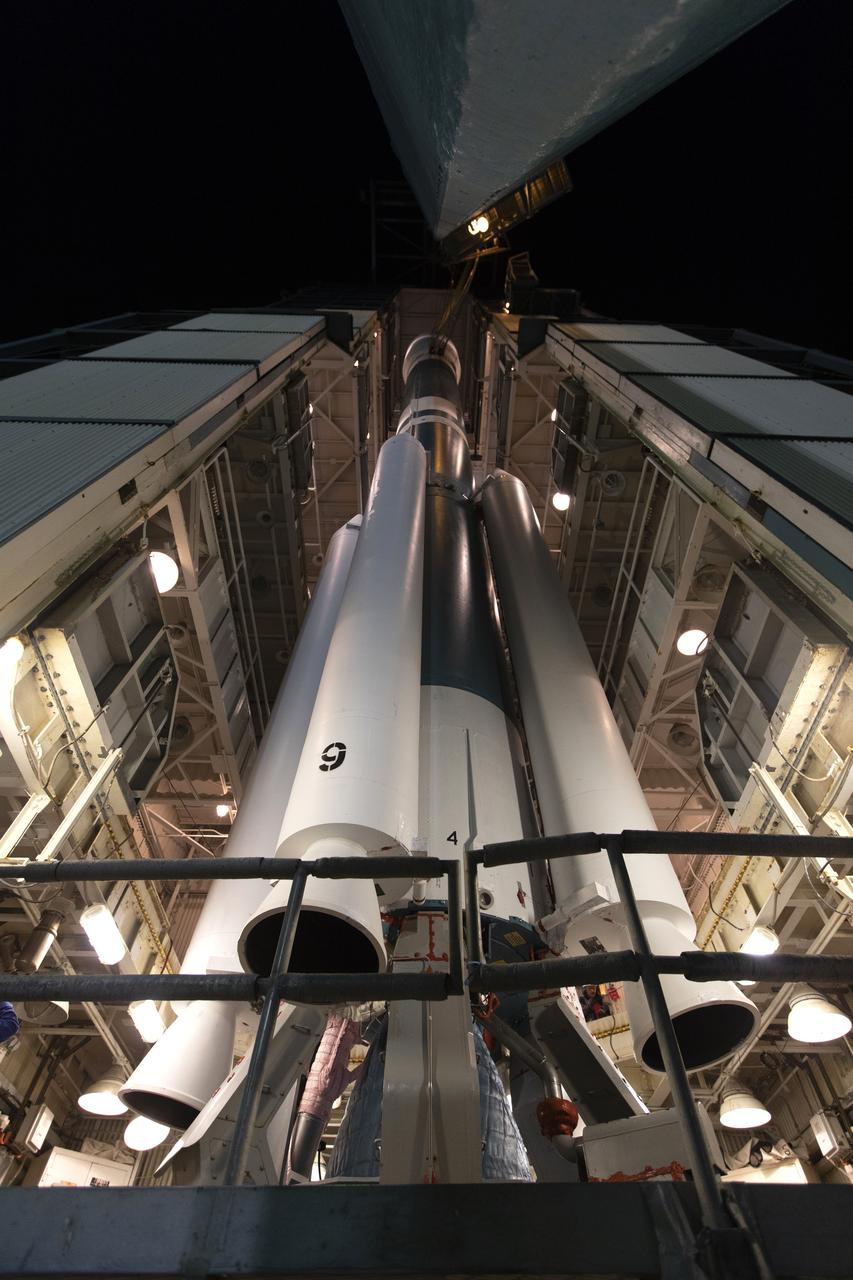
The United Launch Alliance Delta II interstage is lifted up at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 12, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The interstage will be moved in and mated to the top of the booster, or first stage of the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
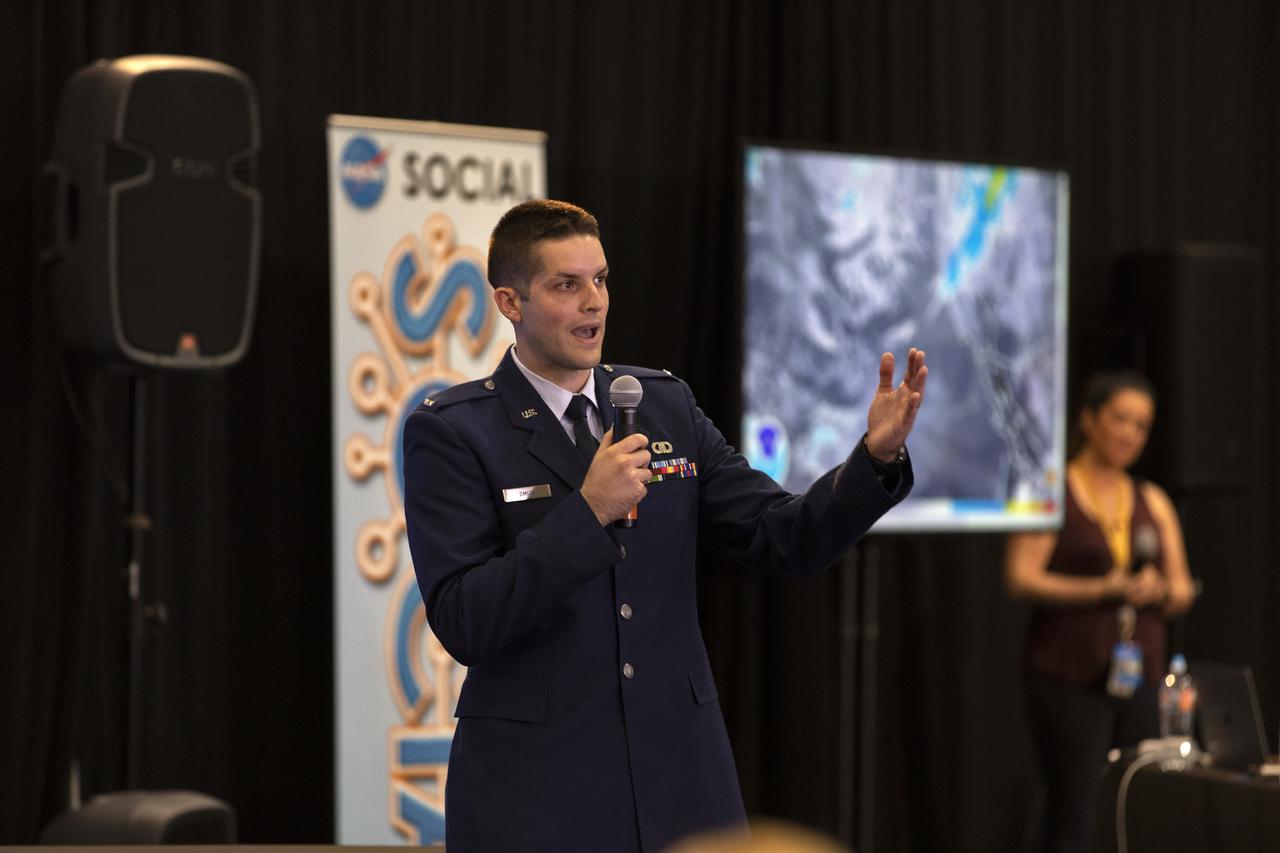

1st Lt. Daniel Smith, launch weather officer, 30th Space Wing, Vandenberg Air Force Base, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
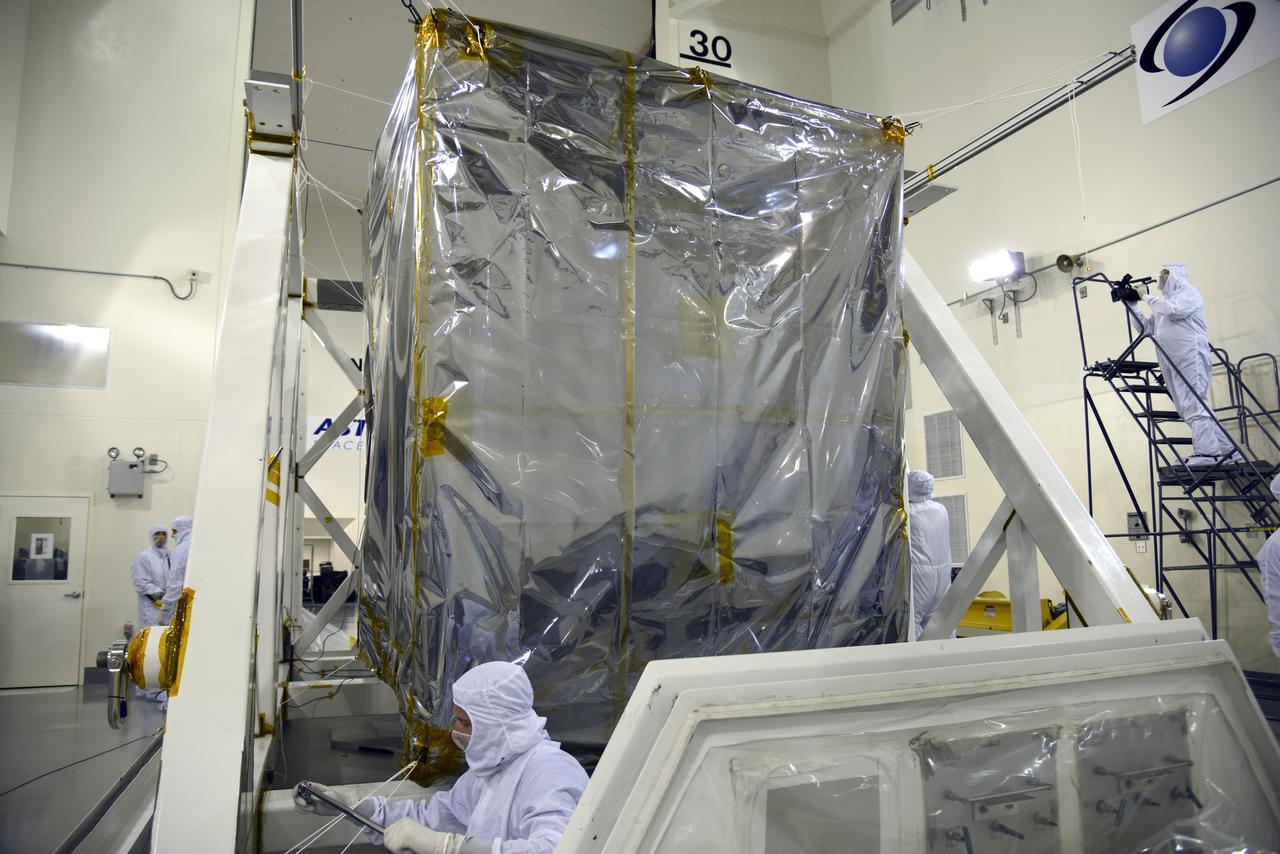

NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is uncrated inside the airlock of the Astrotech processing facility on June 13, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
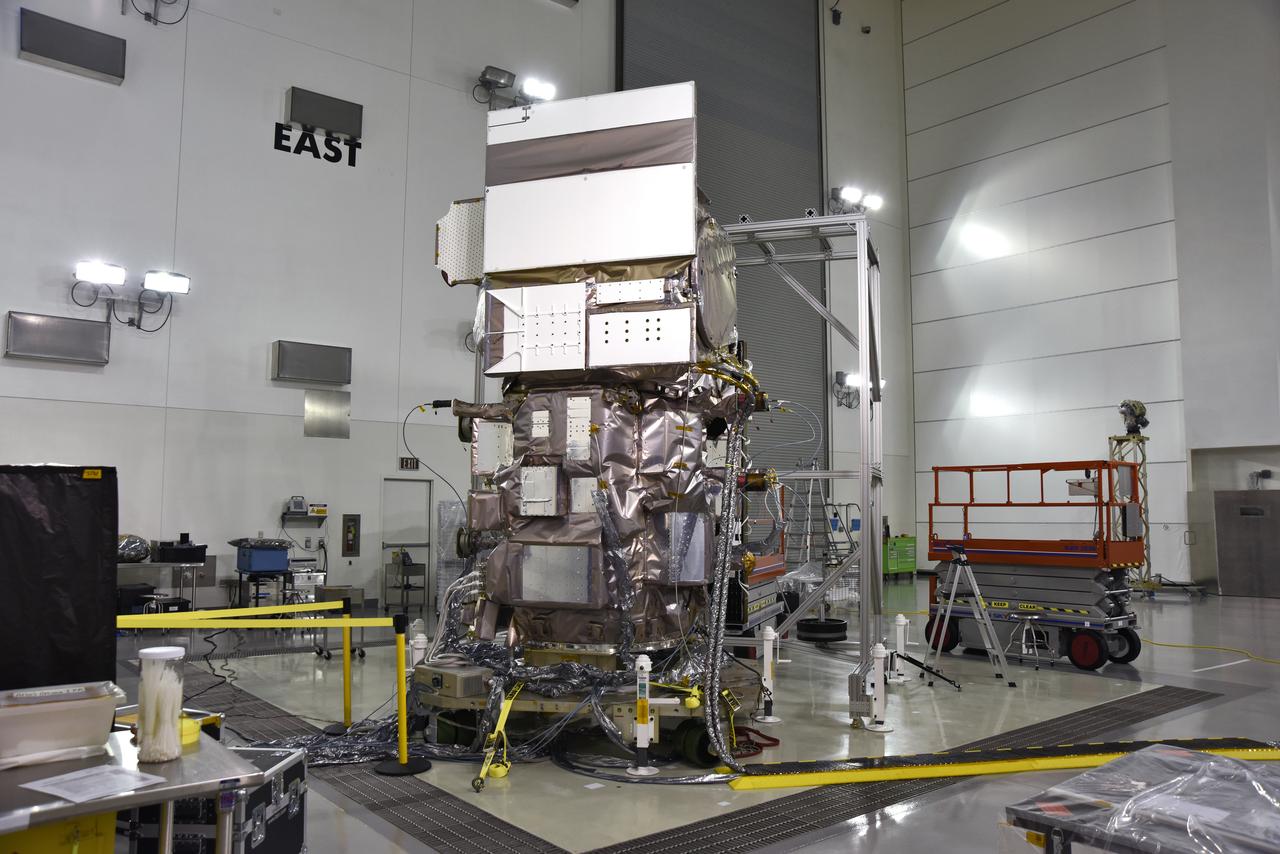

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solar array first motion test is in progress on NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on June 18, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
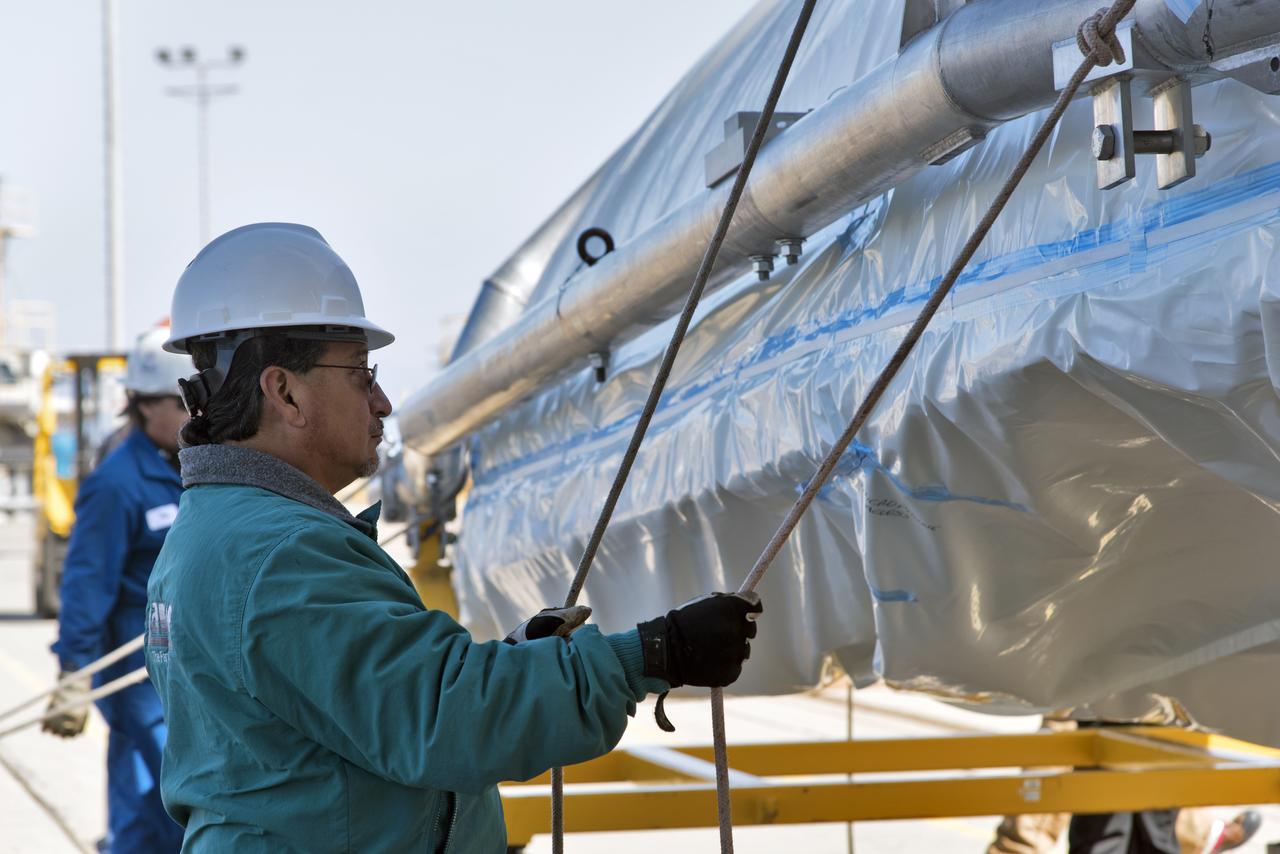

The second half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket payload fairing is being prepared for the move to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on June 4, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch later this year on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
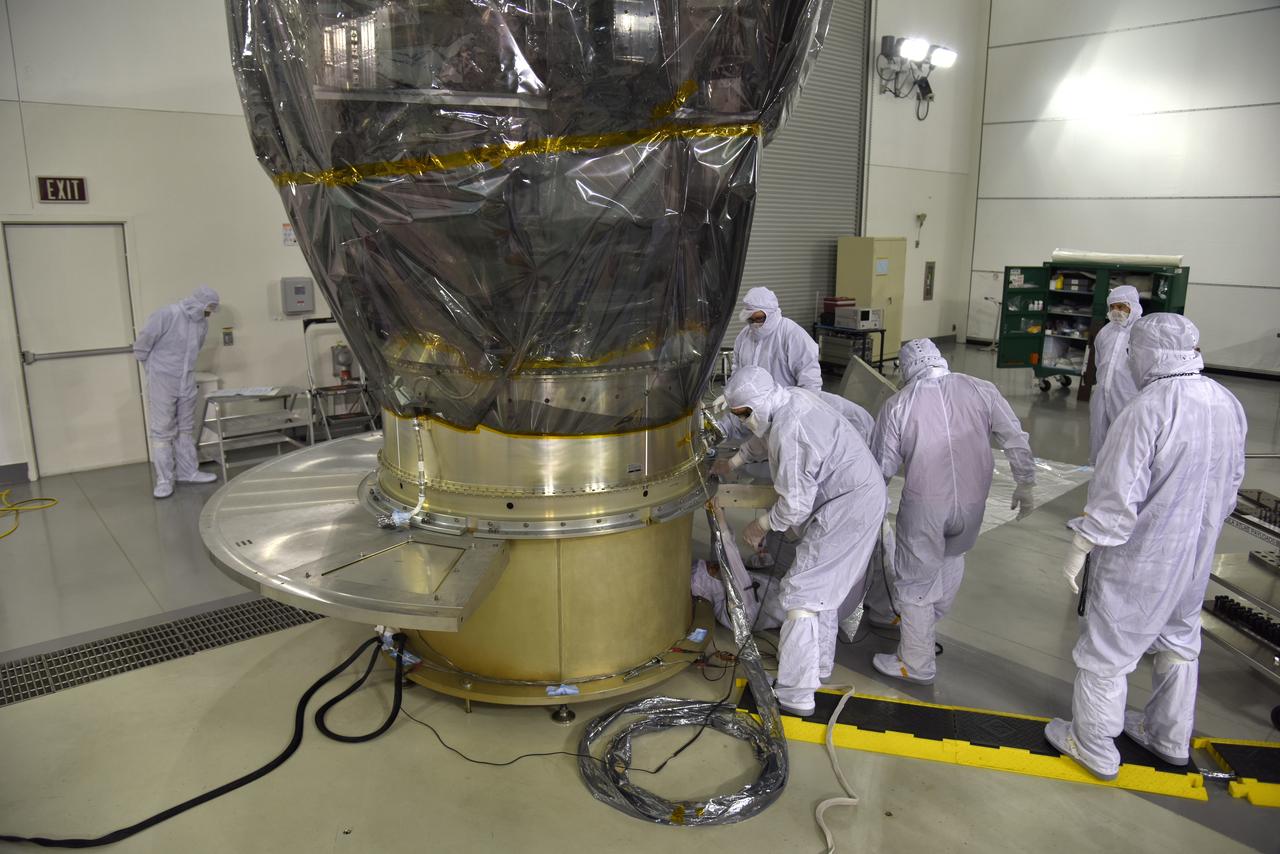

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians attach NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) to the payload direct mate adapter, on Aug. 24, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
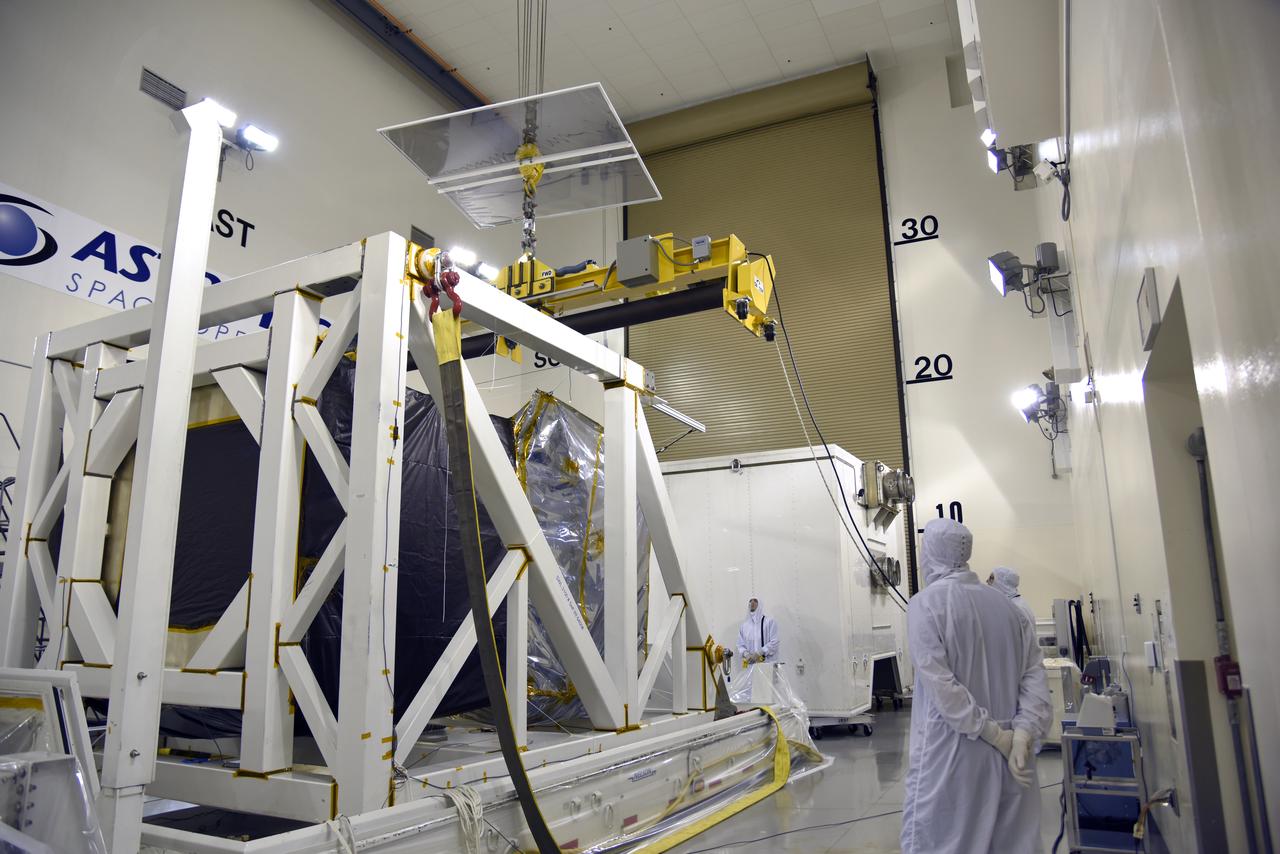

NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is uncrated and is being prepared for its move to the high bay of the Astrotech processing facility on June 13, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
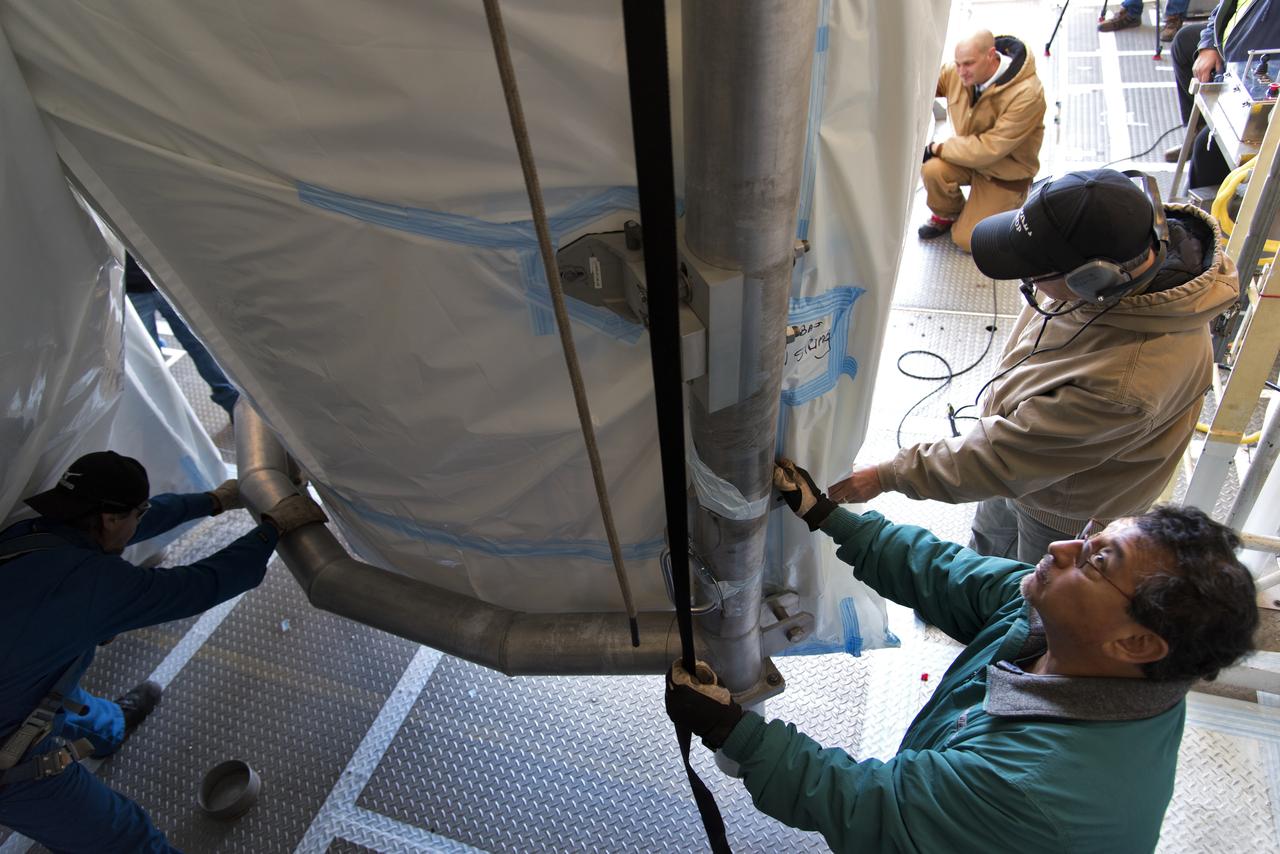

Technicians assist as the second half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket payload fairing is lifted up into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on June 4, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch later this year on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
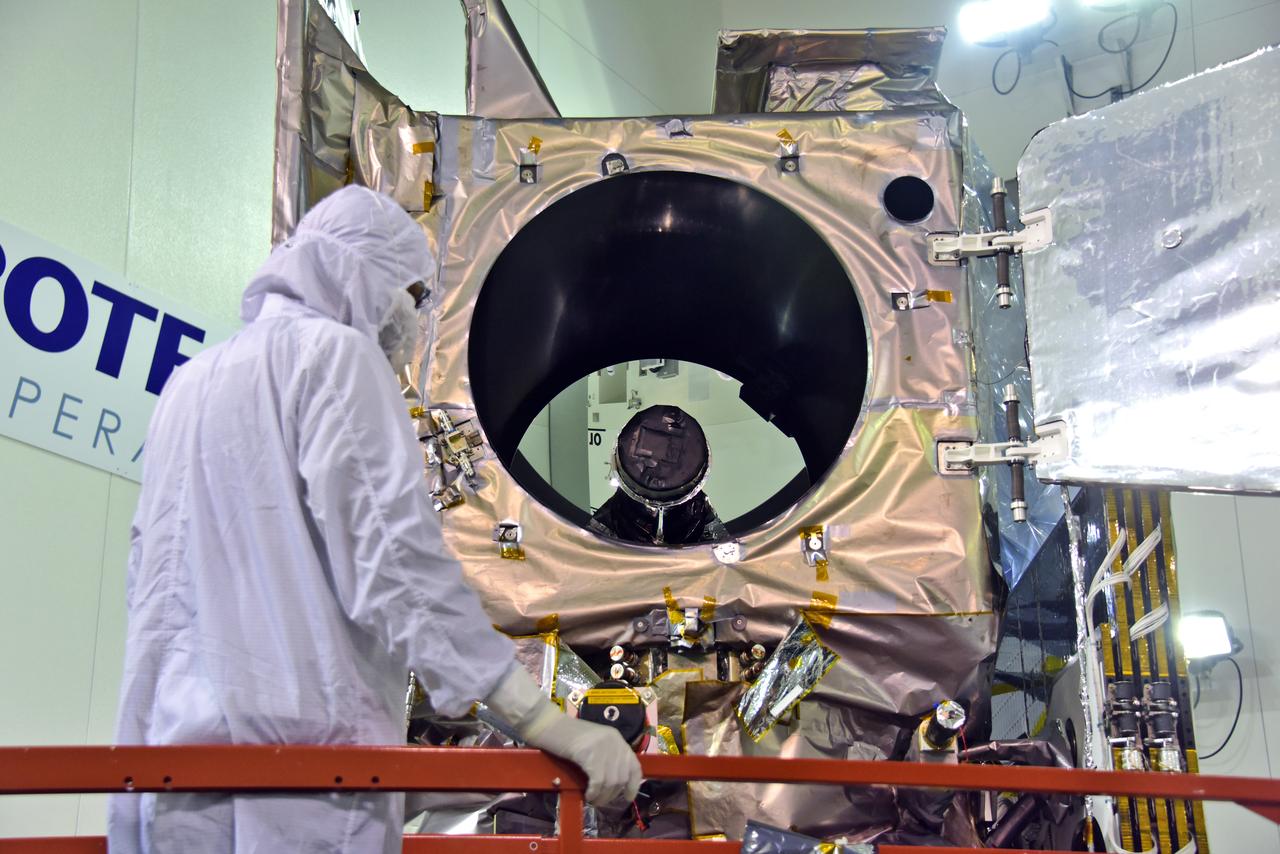

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician opens and checks the flight door for the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS) on NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on June 21, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry ATLAS. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
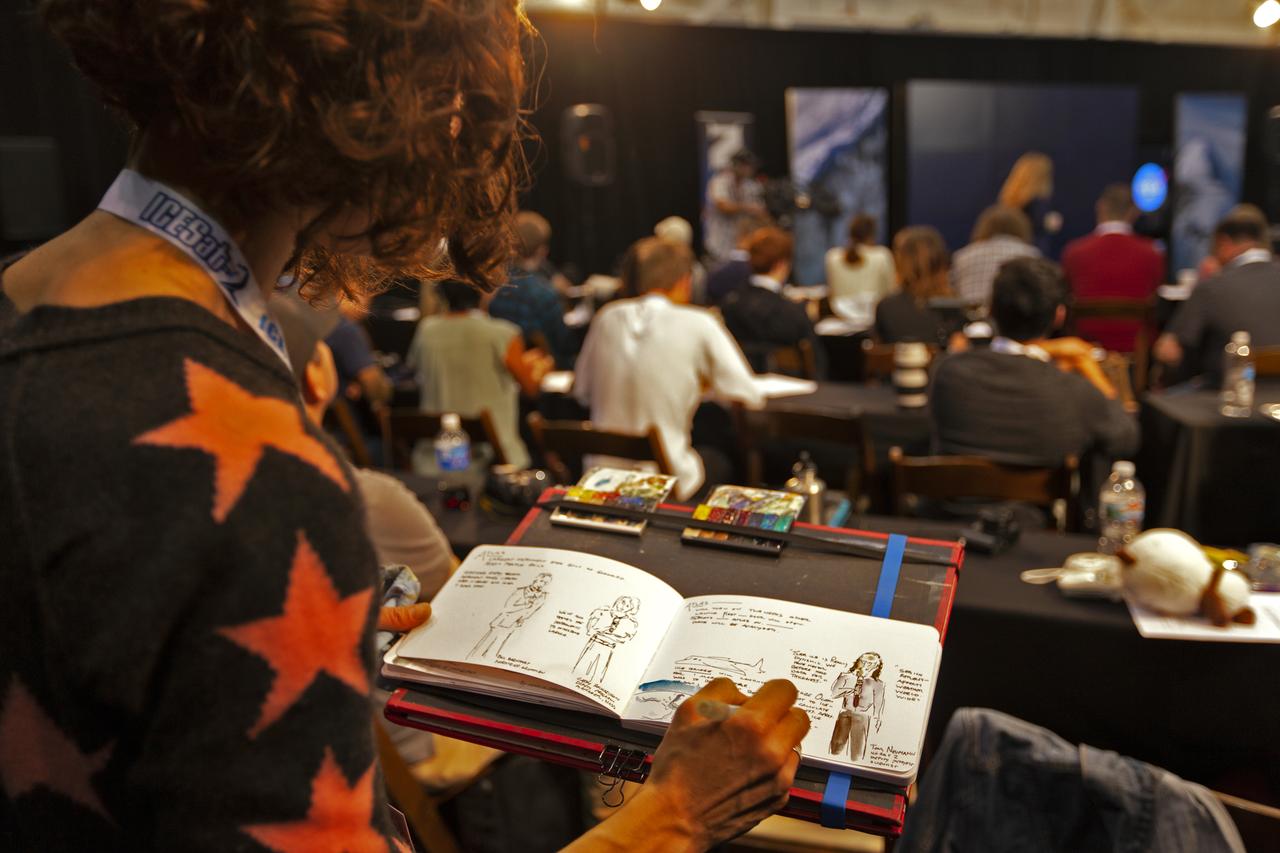

Social media participant sketches NASA and industry leaders speaking to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on Sept. 13, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.

United Launch Alliance workers prepare the first stage of the Delta II second stage to be lifted up in the Vertical Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 21, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The second stage will be attached to the top of the booster, or first stage, of the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
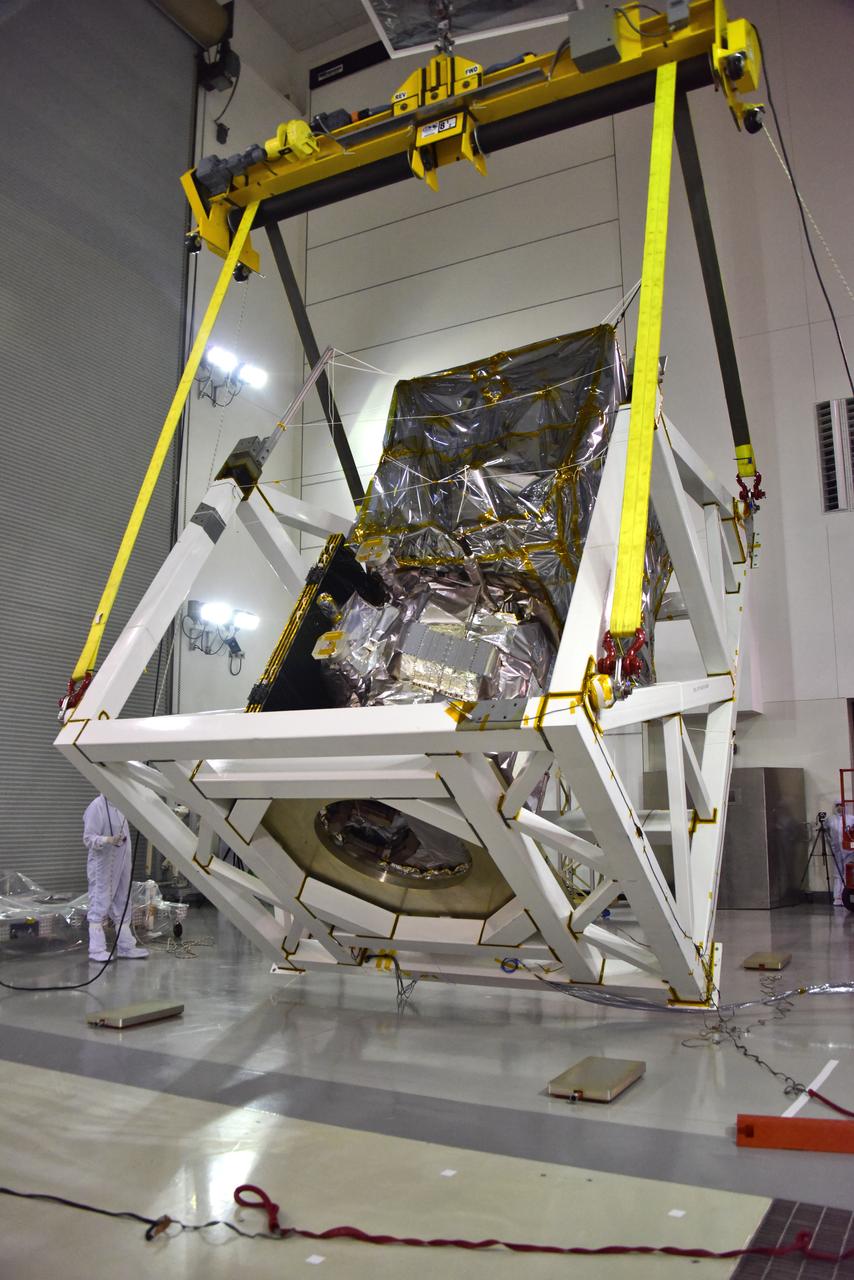

A crane is used to rotate NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) in its fixture inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The United Launch Alliance Delta II interstage is lifted high up at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 12, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The interstage will be moved in and mated to the top of the booster, or first stage of the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

Helen Fricker, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, California, ICESat-2 science definition team member, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
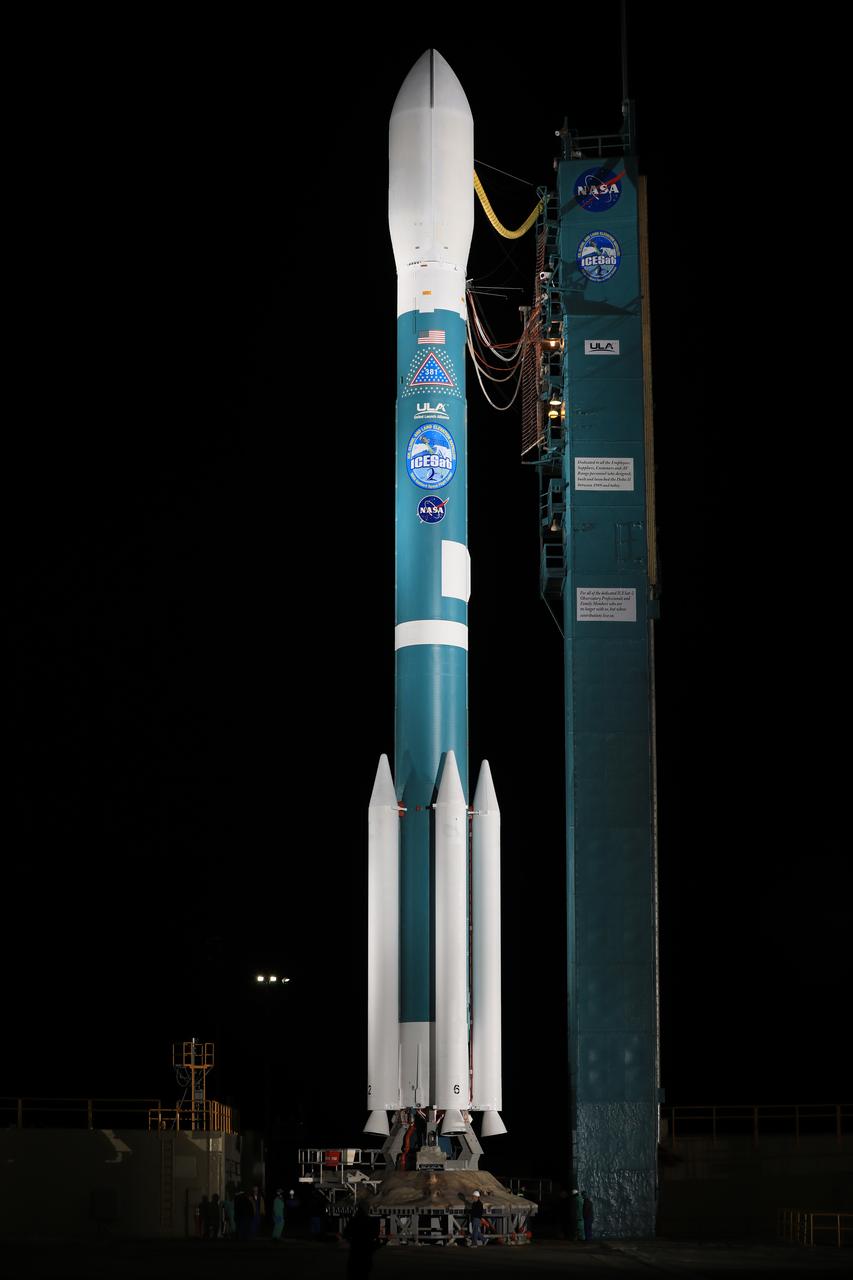

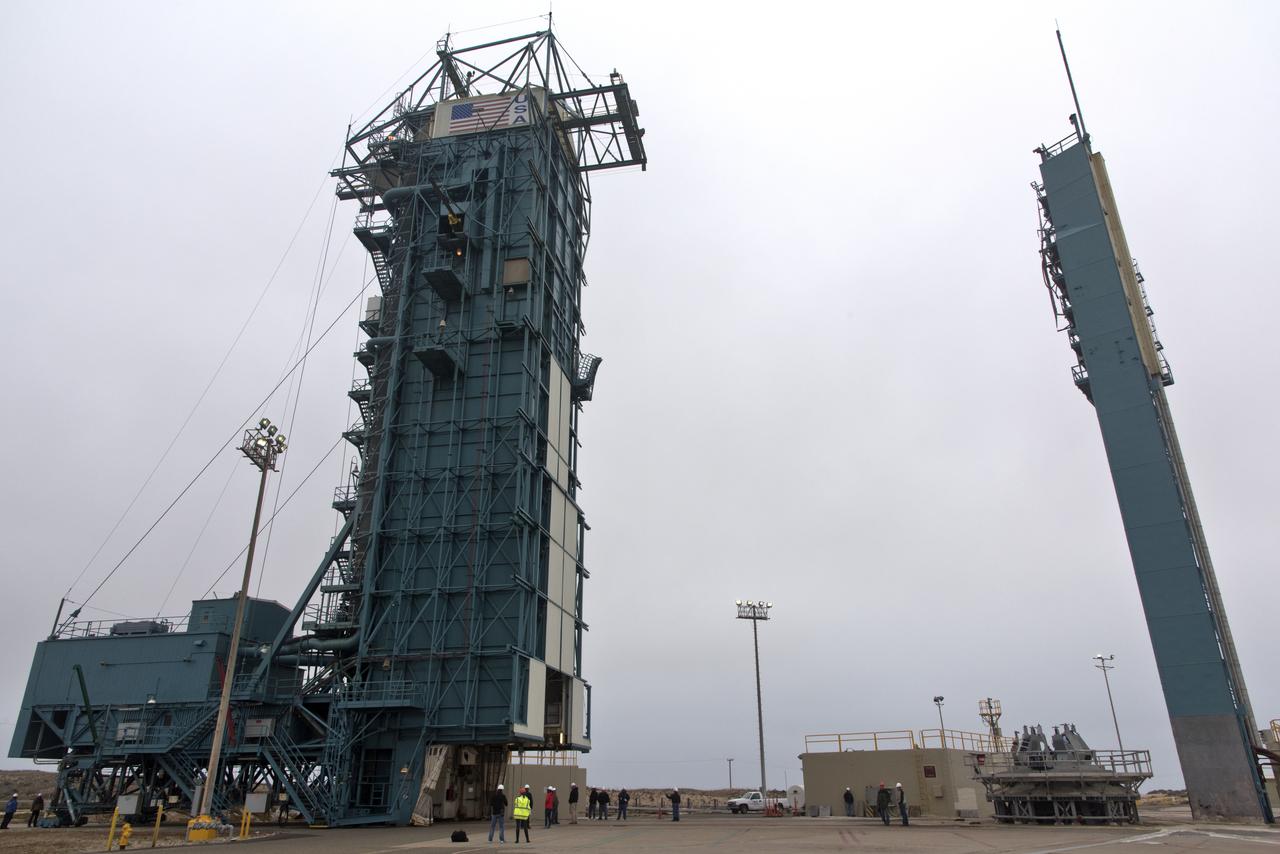
The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.
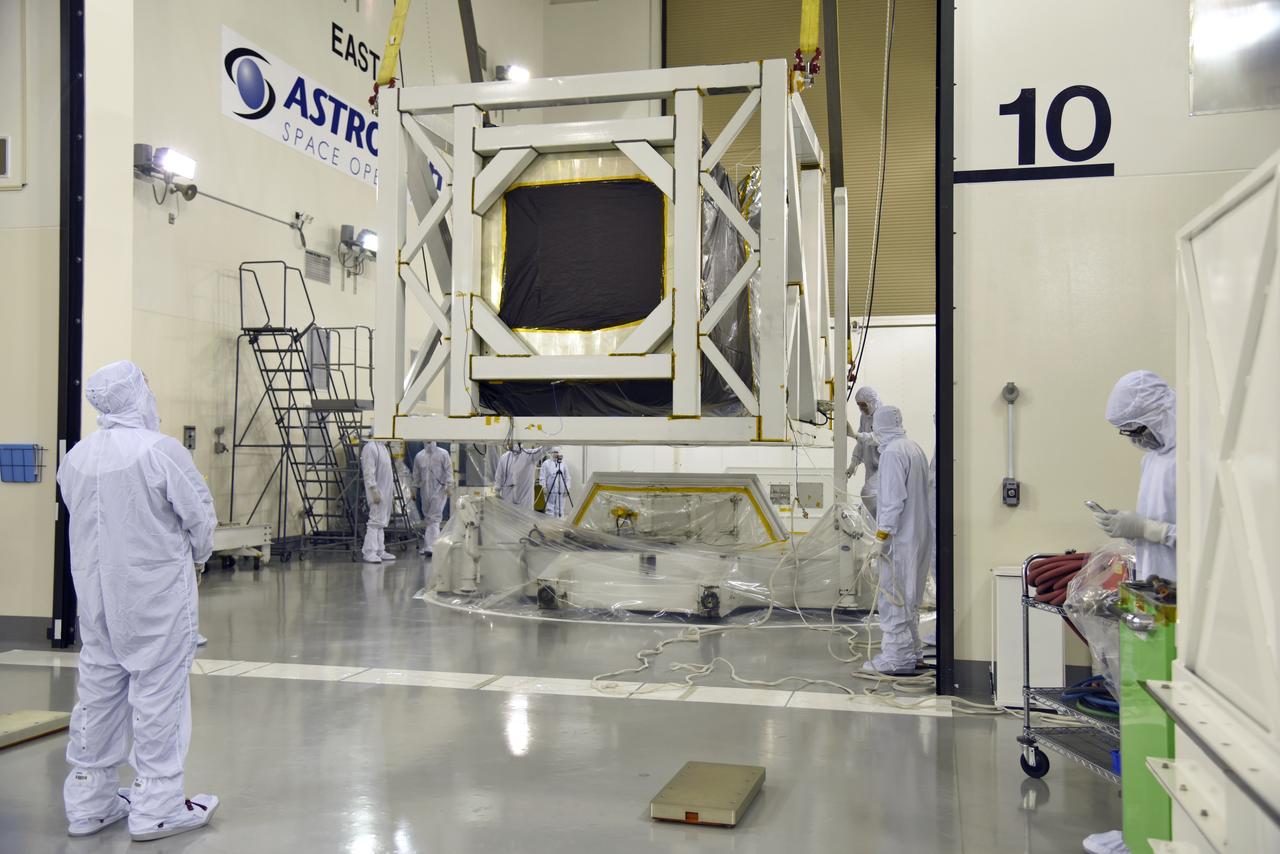

A crane is used to move NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) into the high bay of the Astrotech processing facility on June 13, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
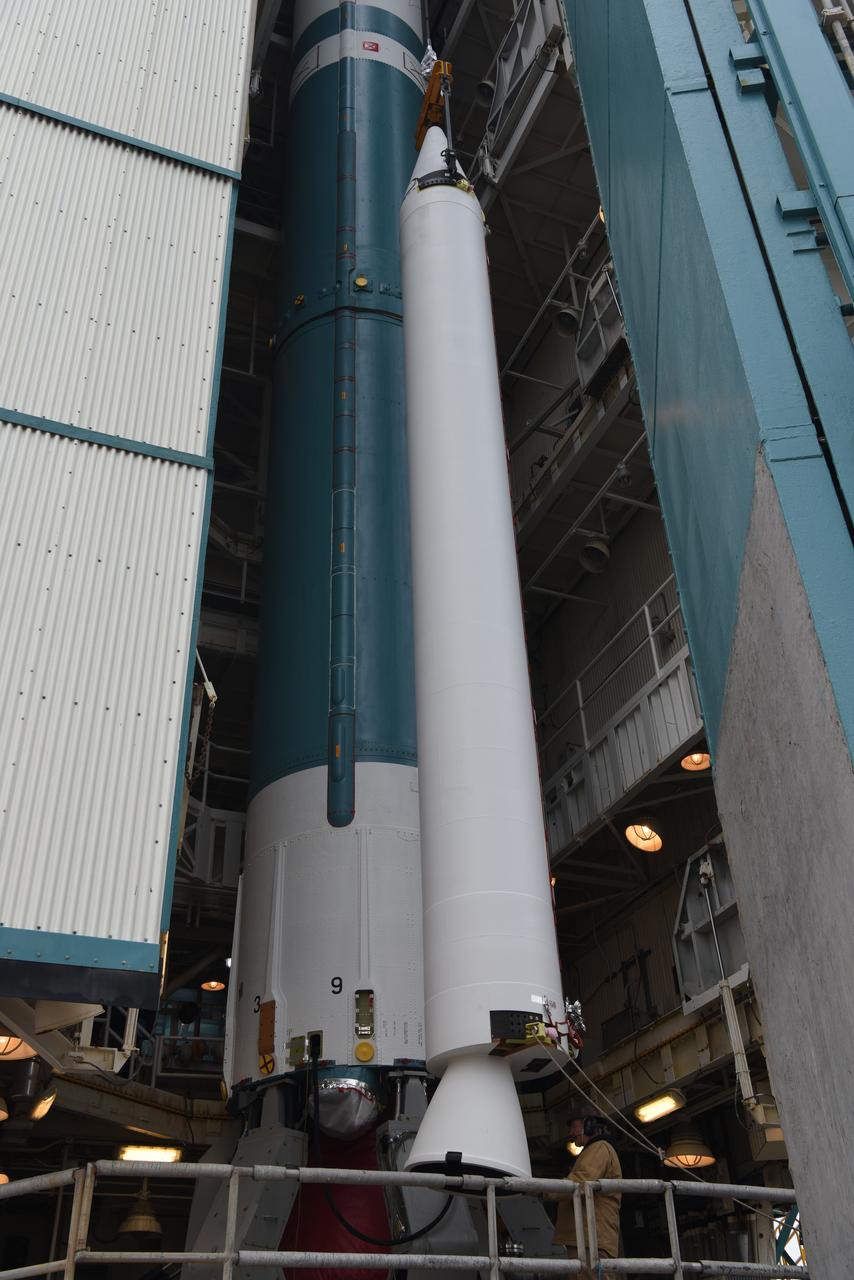

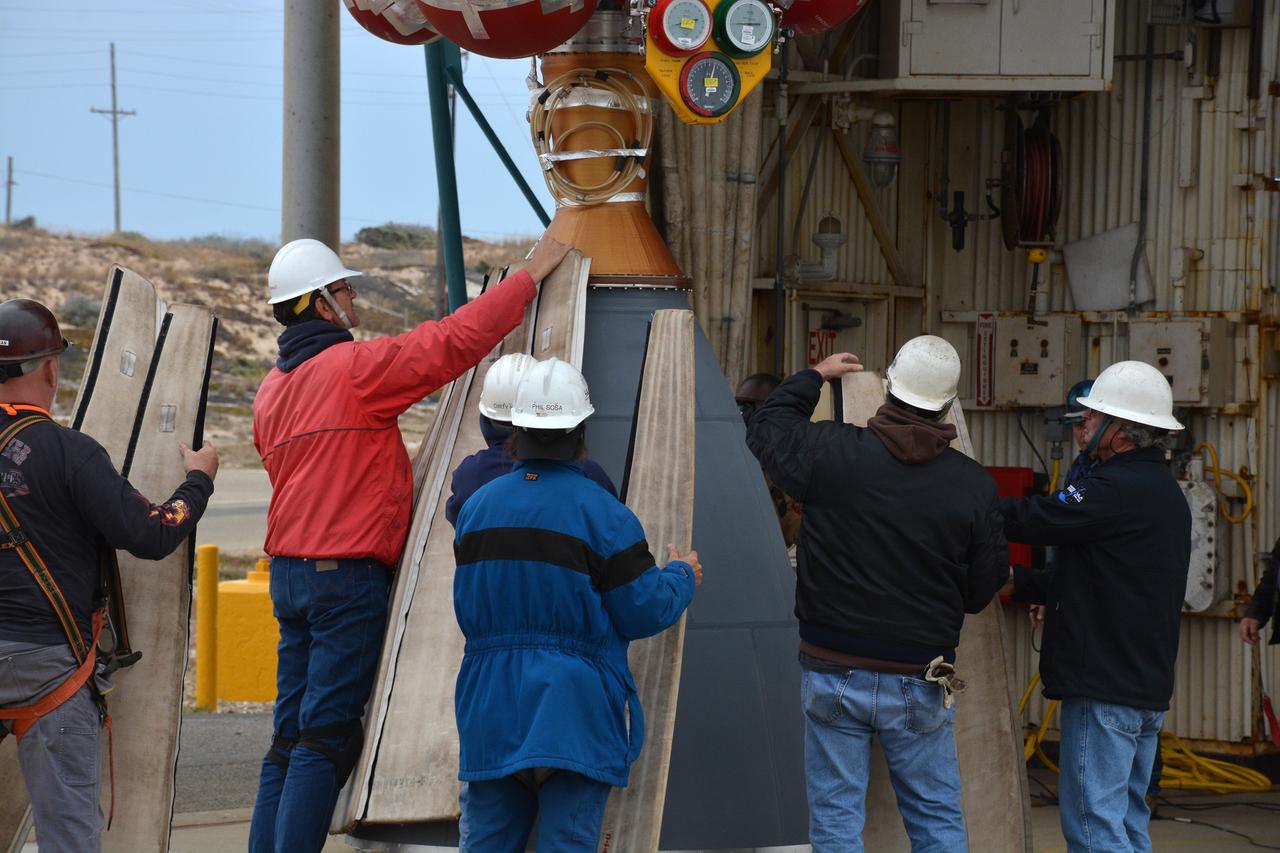
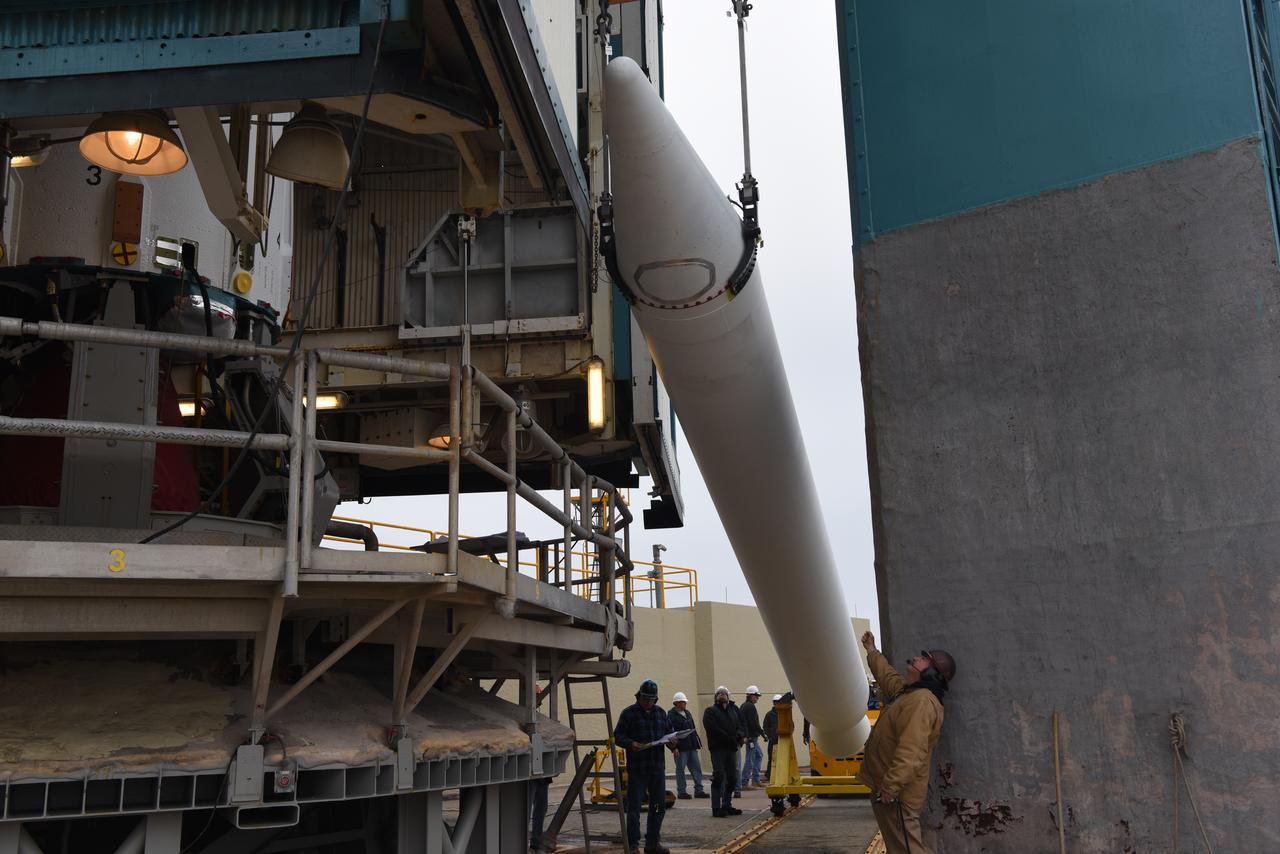
The solid rocket motor for mating to the United Launch Alliance Delta II launch vehicle is lifted up at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

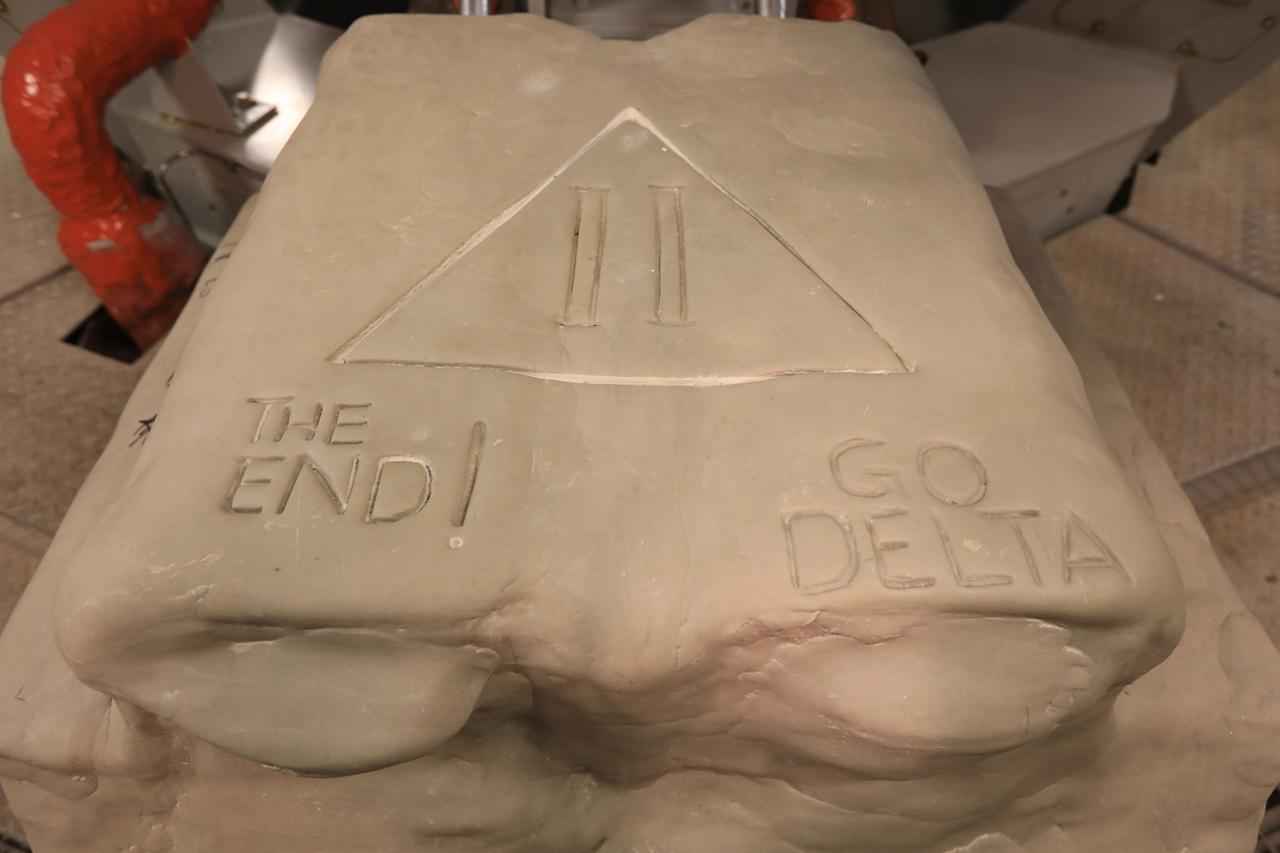
Stars are in view on the first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 13, 2018. Historically, each Delta rocket used to notate the number of launches within the program, beginning in May, 1960, with the first Delta I. This practice was brought back for the final Delta II launch of ICESat-2. The “381” on the rocket signifies that this will be the 381st flight in the Delta family. A star traditionally was placed on the rocket to recognize each mission. For the final Delta II, stars were sent to team members and partners throughout the nation. This rocket boasts more than 150 stars with over 800 signatures of people who have been part of the Delta II program.

A photon demonstration was conducted in front of news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.
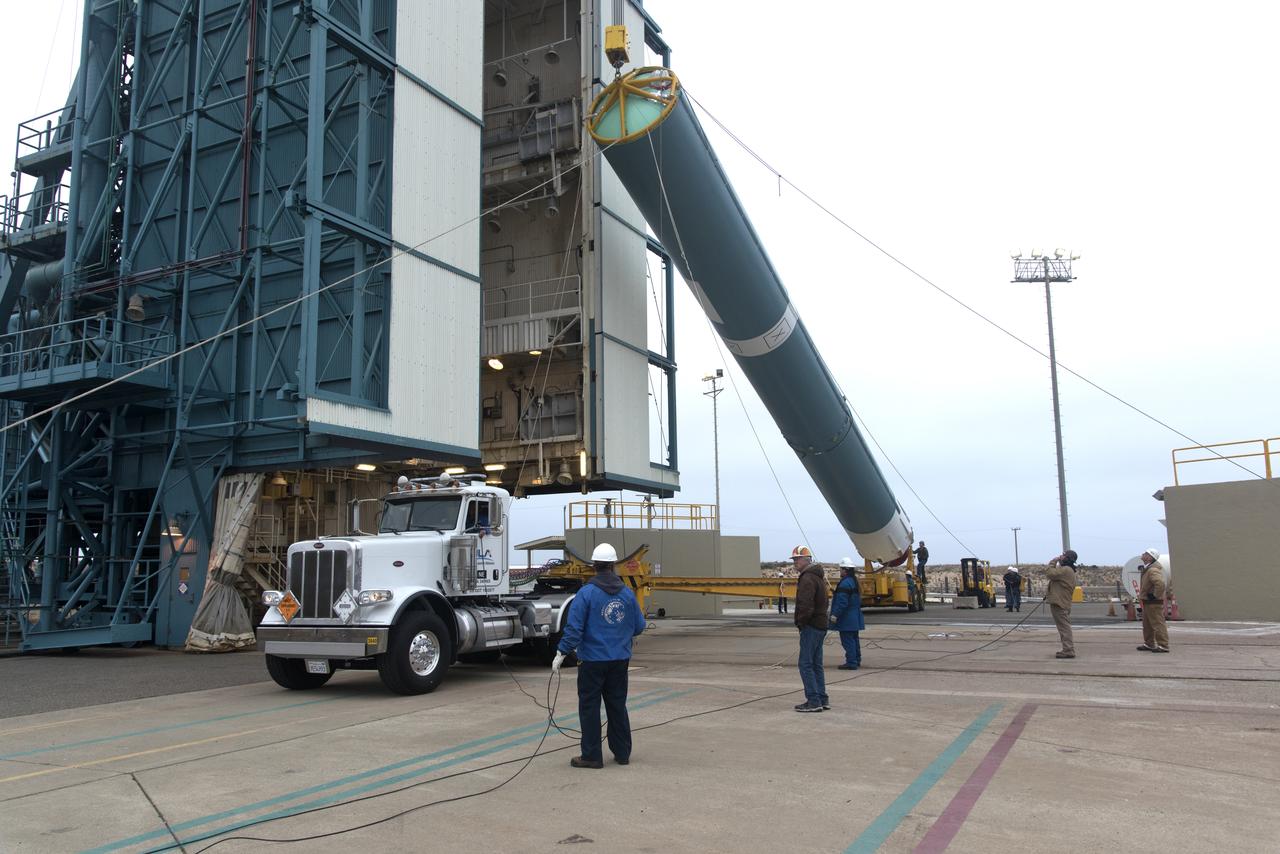

United Launch Alliance (ULA) workers assist as the Delta II first stage is lifted to vertical at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
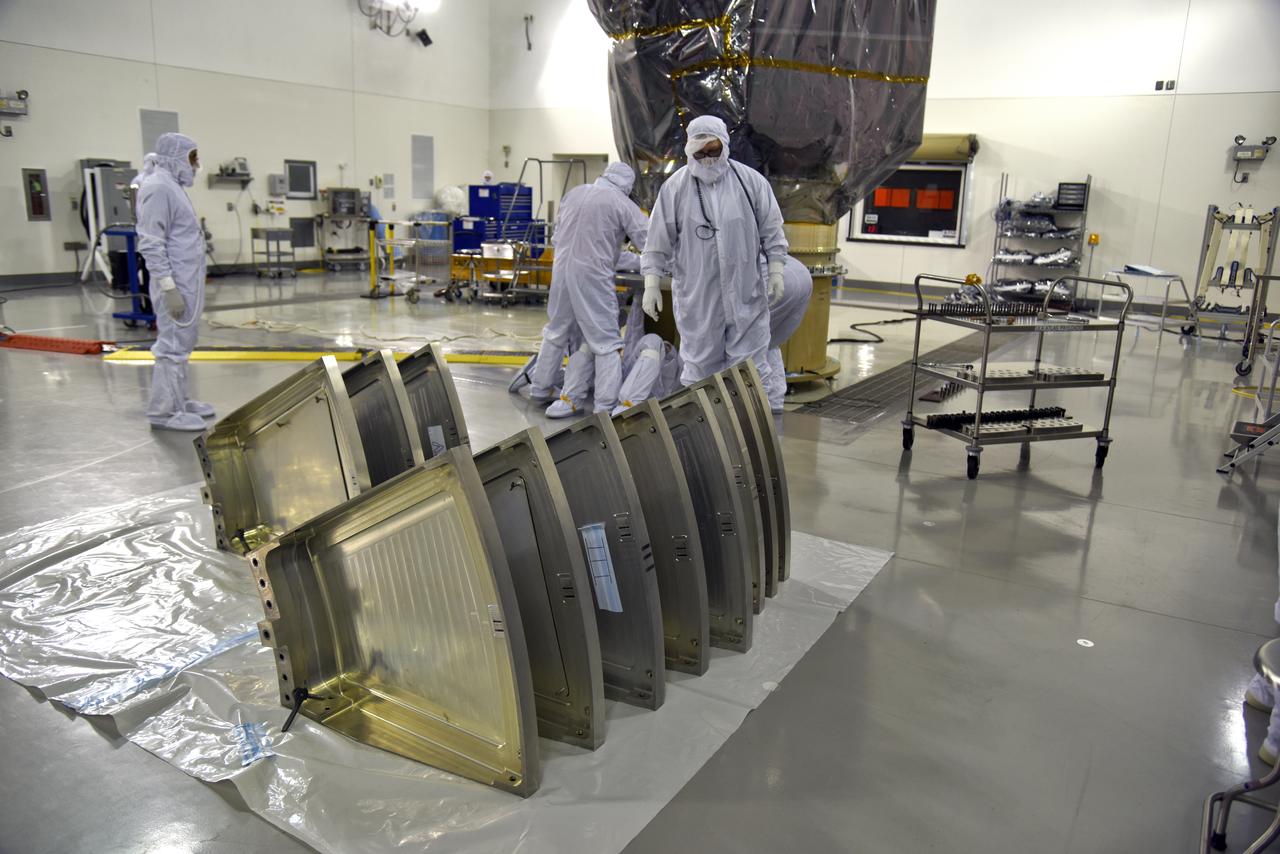

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians attach NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) to the payload direct mate adapter, on Aug. 24, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
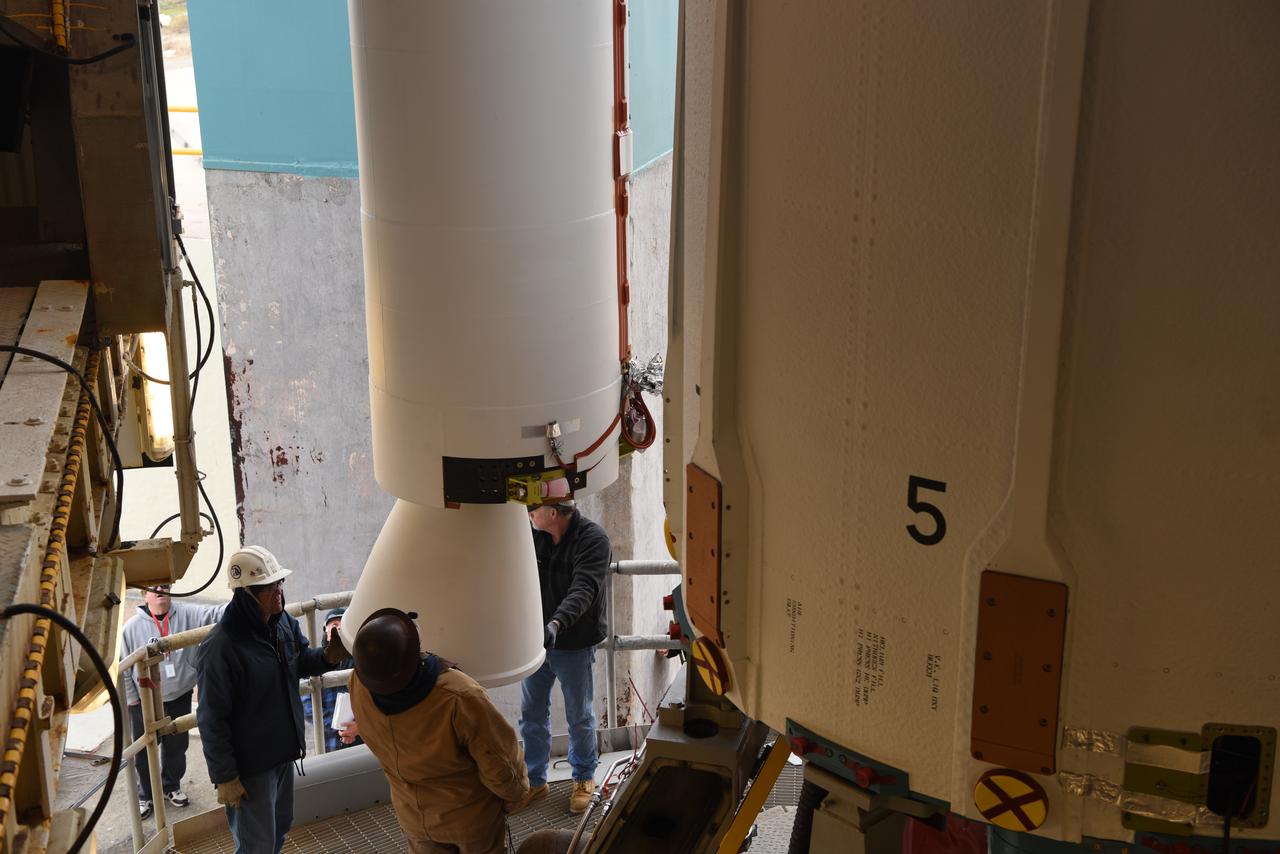

United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians assist as the solid rocket motor is lifted up and moved toward the Delta II launch vehicle in the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final ULA Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.
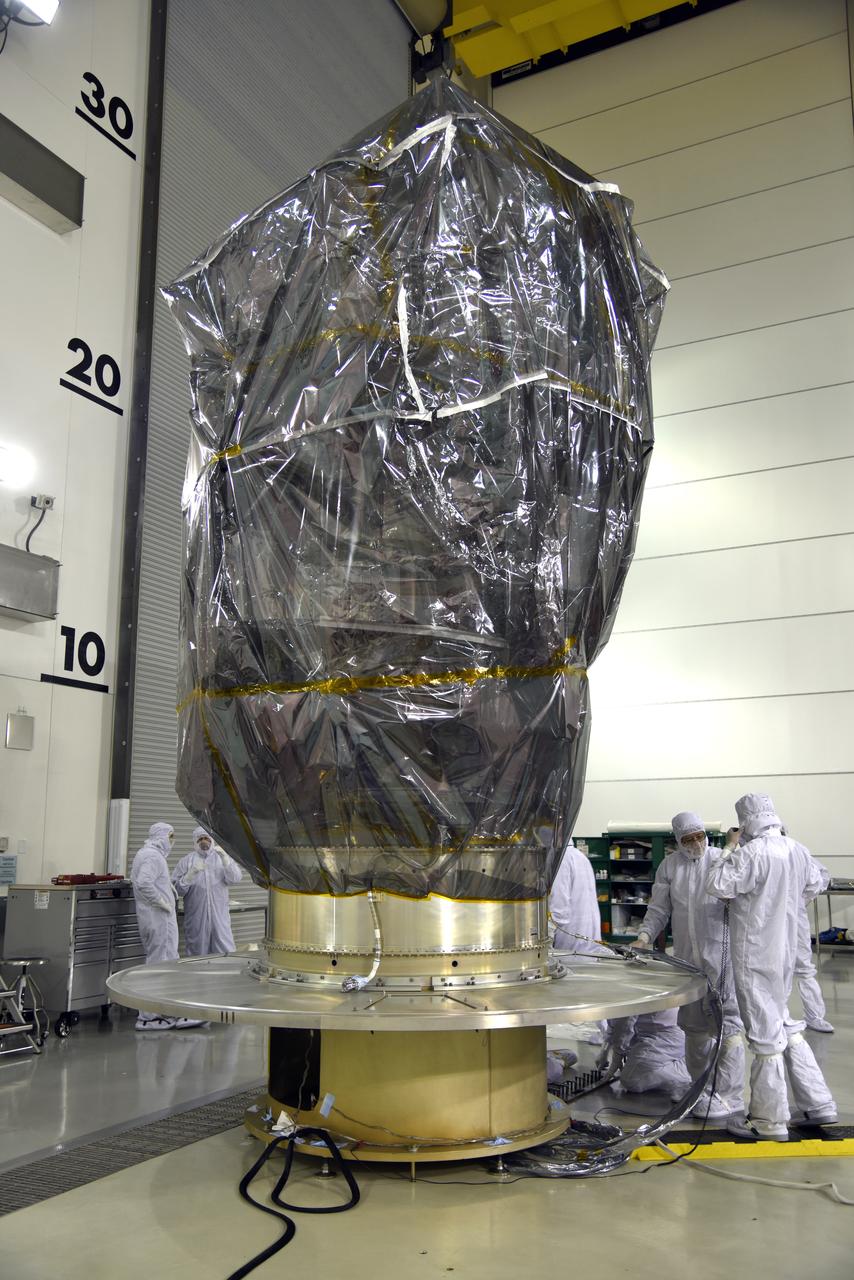

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians attach NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) to the payload direct mate adapter, on Aug. 24, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.

The solid rocket motor for mating to the United Launch Alliance Delta II launch vehicle is lifted up at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

Tim Dunn, launch director, NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).

The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.
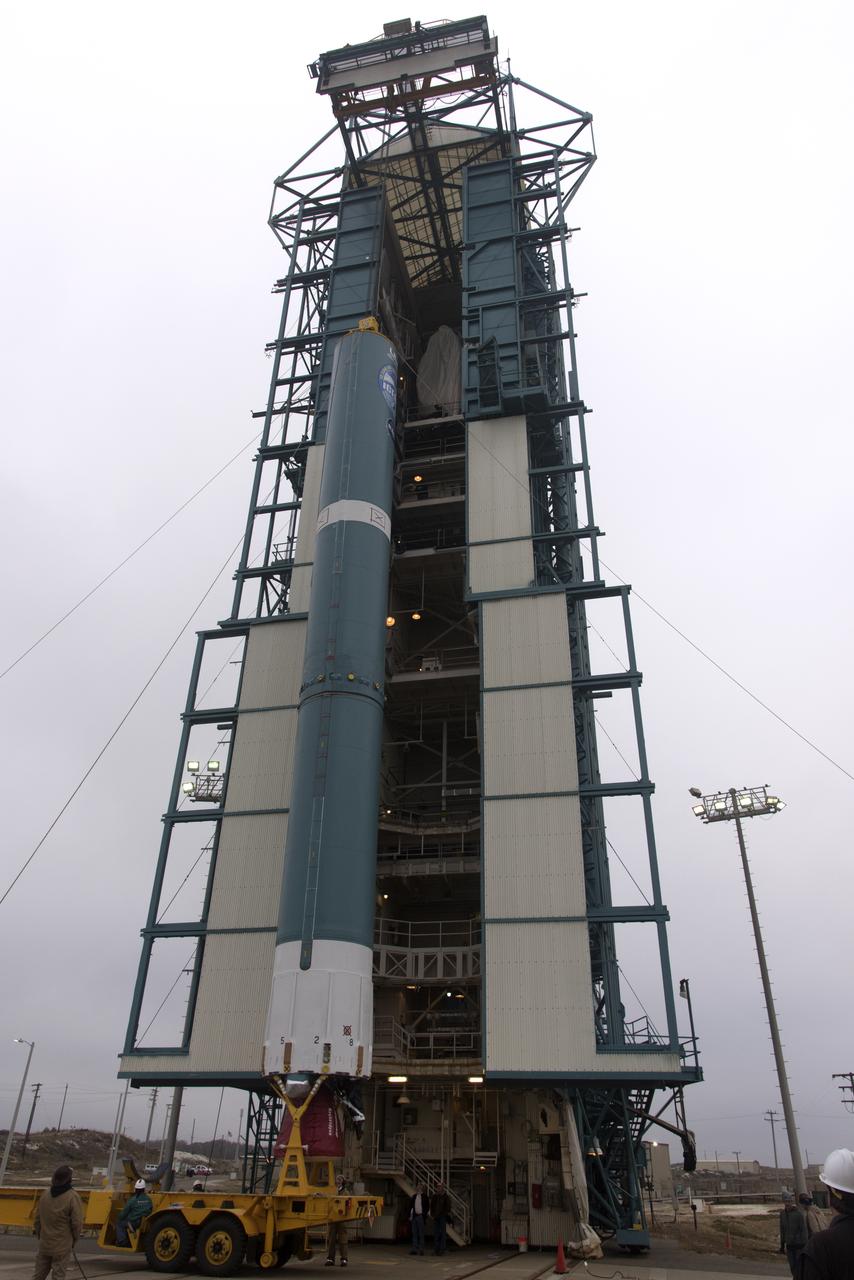

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted to vertical on the stand at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be lifted and moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

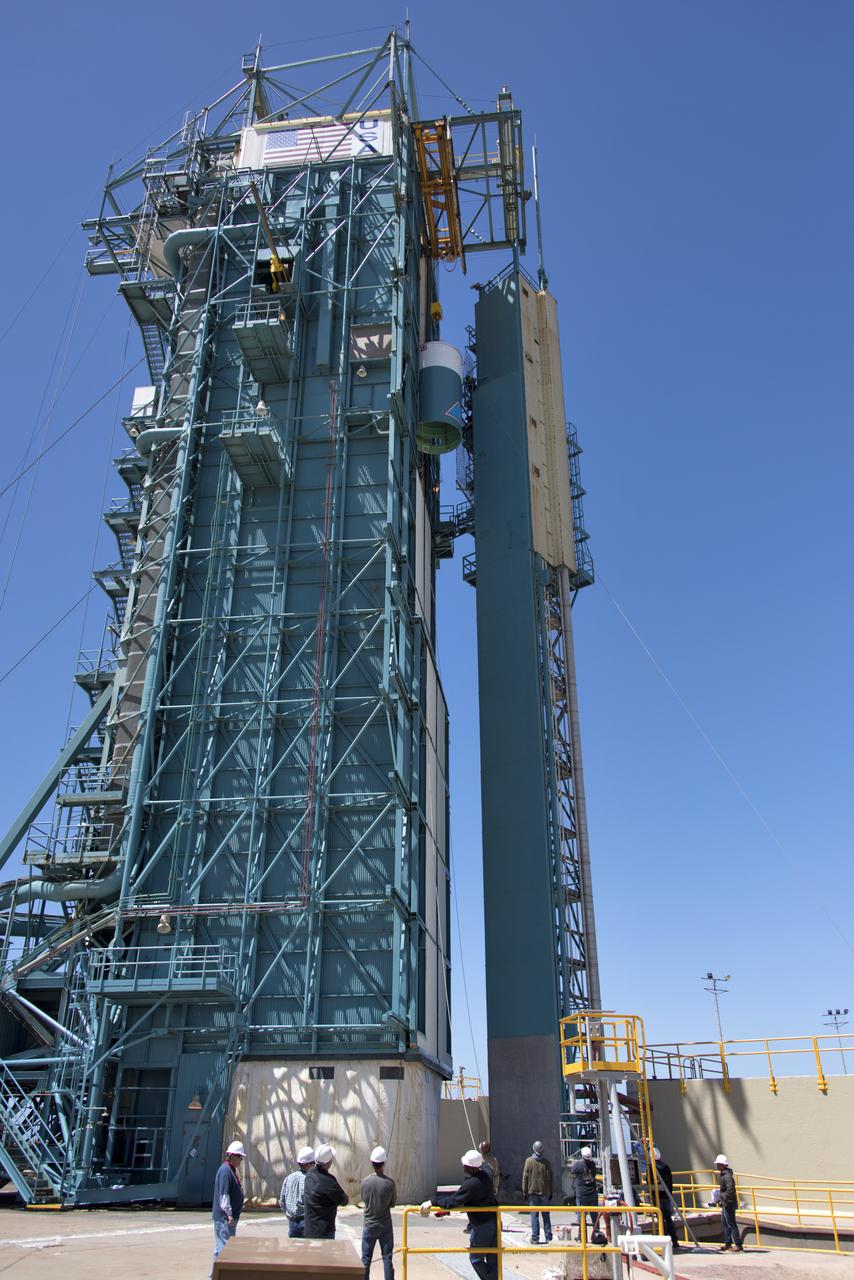
Protective doors have been closed on the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on June 8, 2018. The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted up and secured inside the tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.

The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.
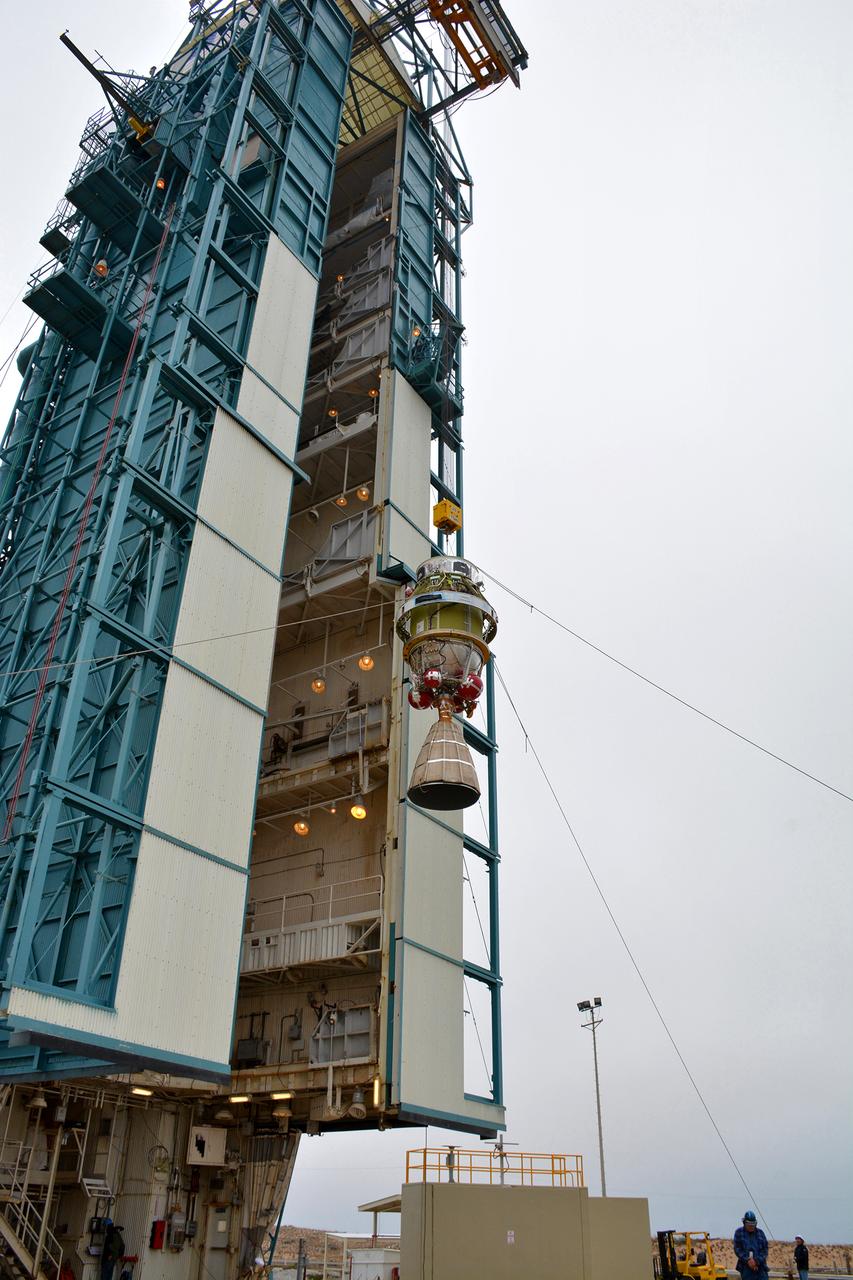

The United Launch Alliance Delta II second stage is lifted high up at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 12, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The second stage will be attached to the top of the booster, or first stage of the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
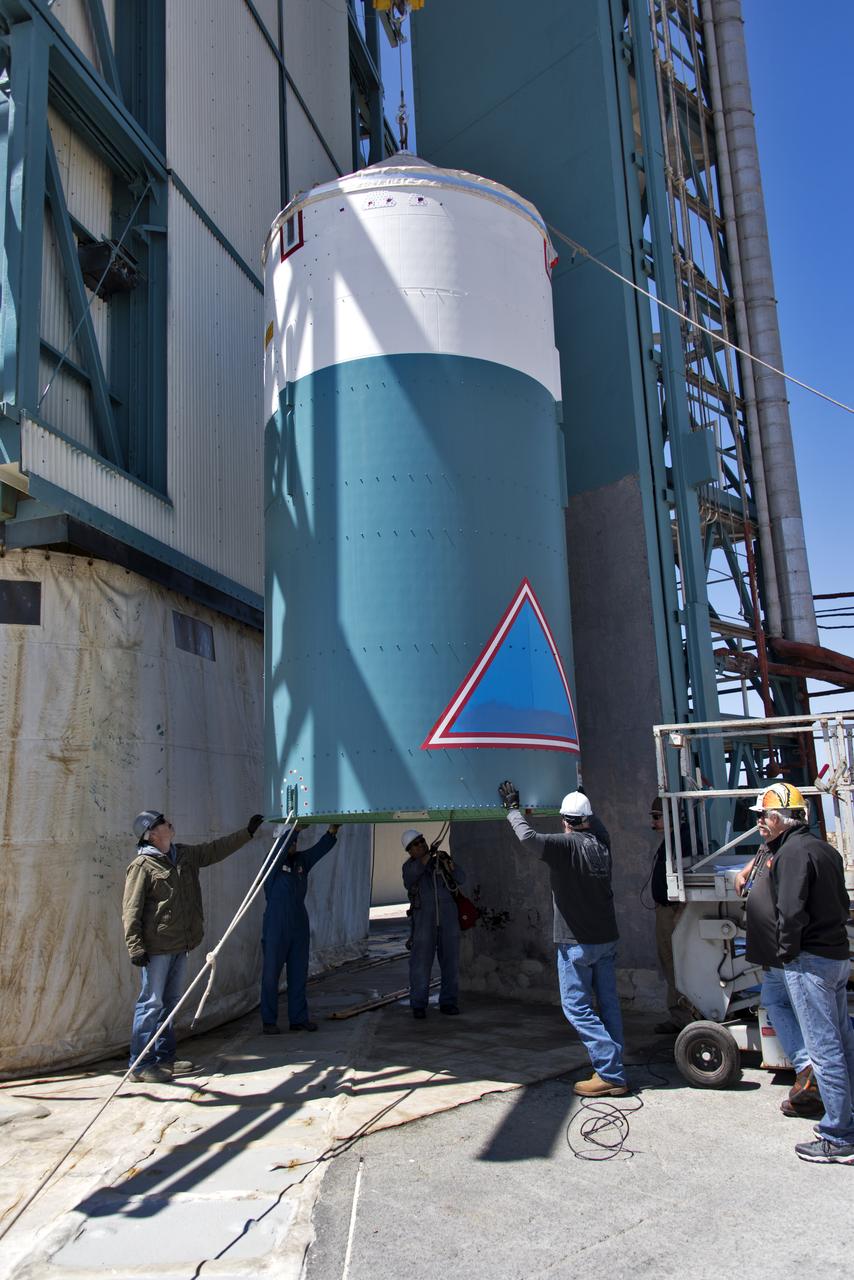

The United Launch Alliance Delta II interstage is lifted up at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 12, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The interstage will be moved in and mated to the top of the booster, or first stage of the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
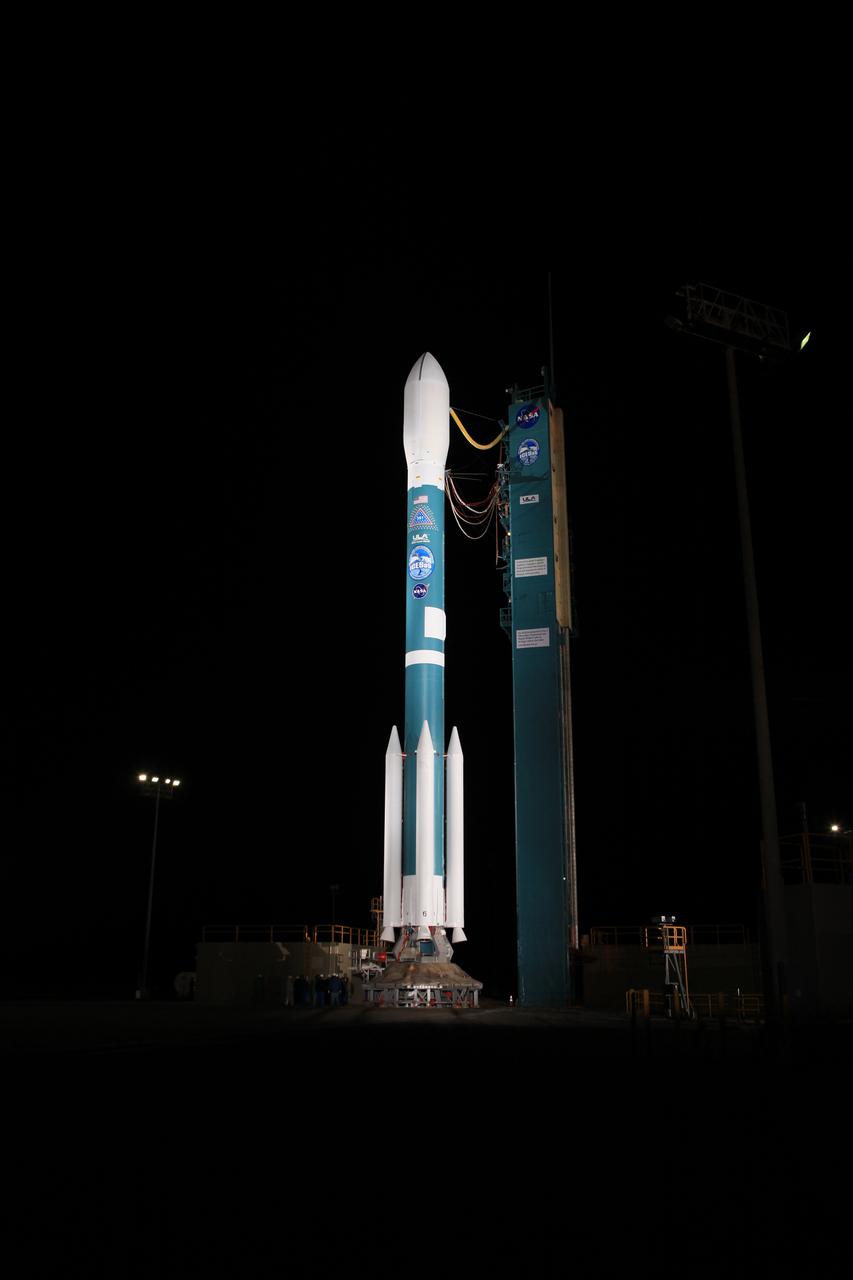

The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.

Technicians remove NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) from its fixture inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The satellite will be secured on a work stand for processing. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
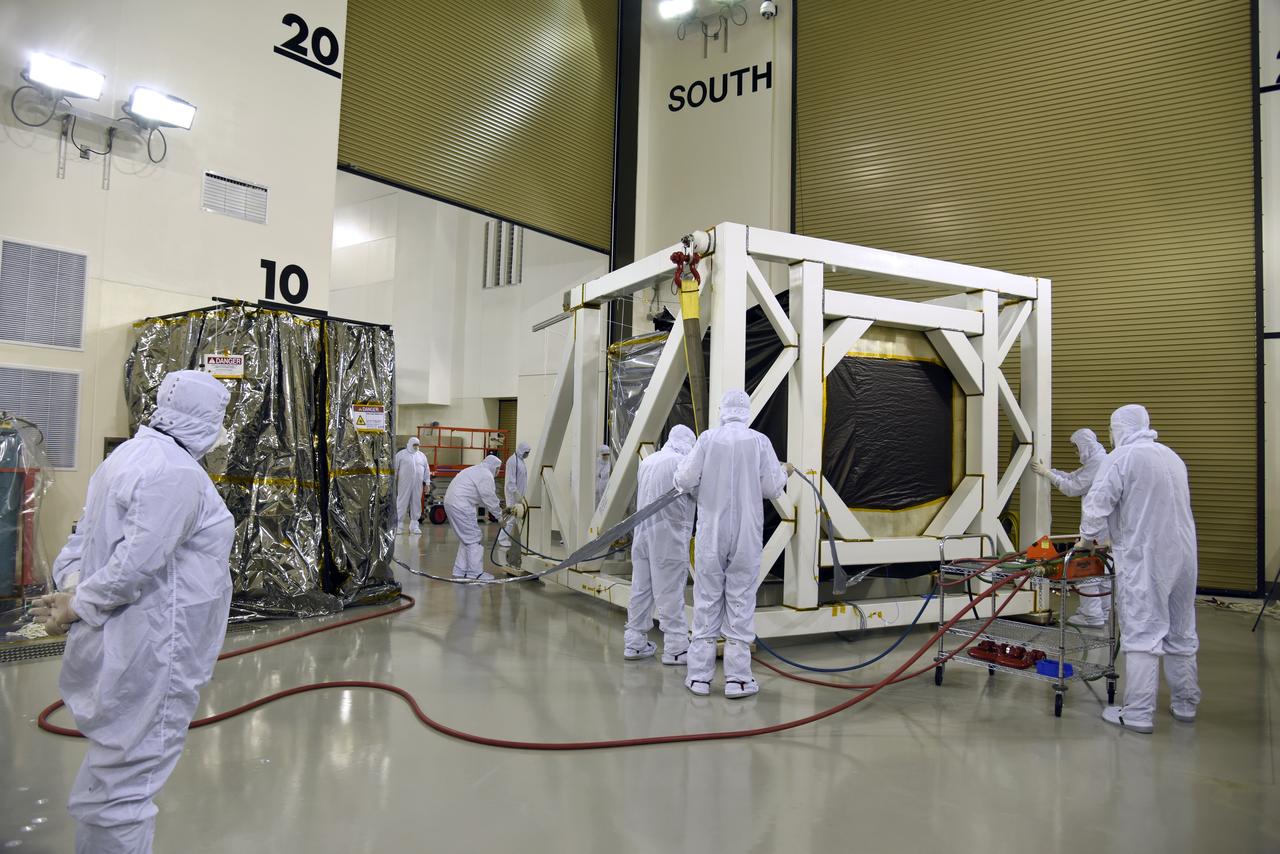

NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is moved into the high bay of the Astrotech processing facility on June 13, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
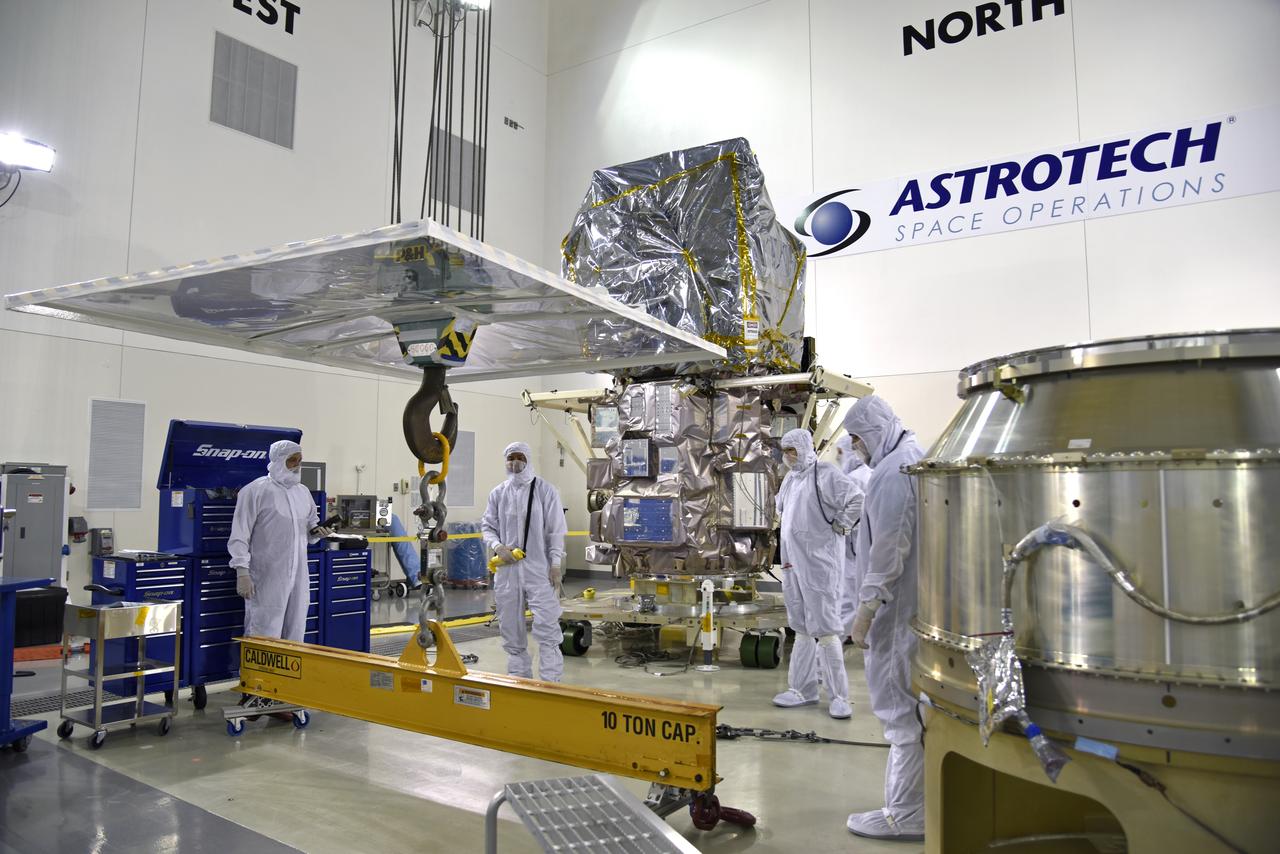

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to attach NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) to the payload adapter, on Aug. 20, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
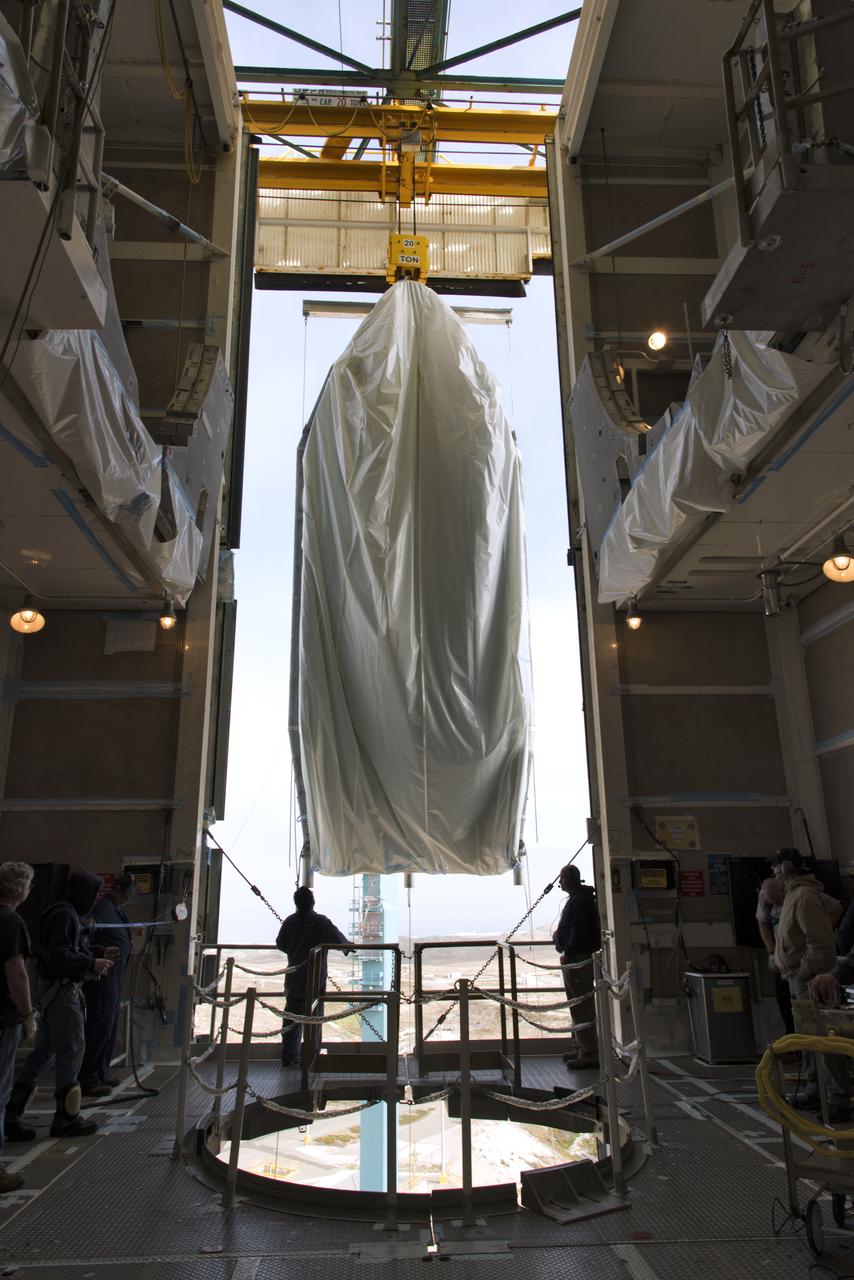

The first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket payload fairing is lifted up and into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on June 4, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch later this year on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted up from its stand and moved into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
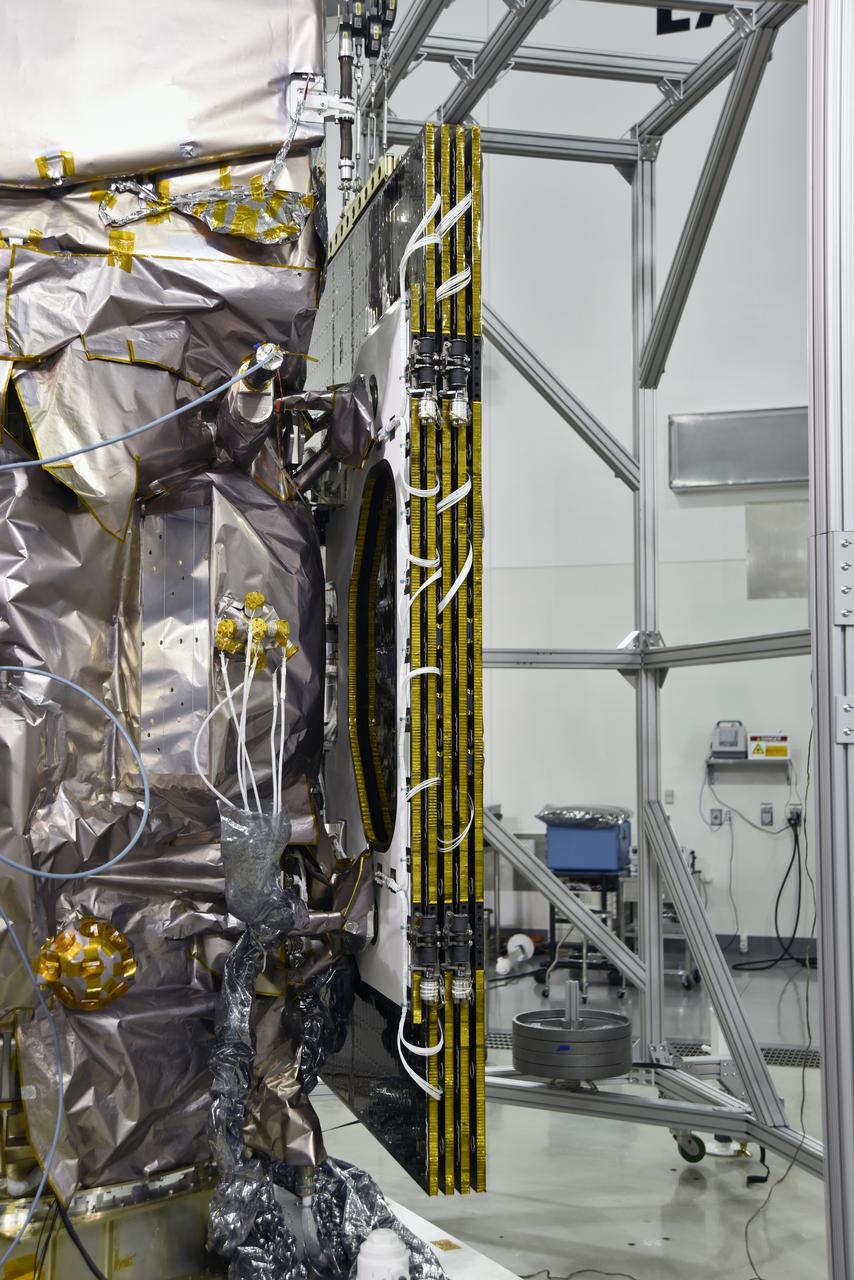

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solar array first motion test is in progress on NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on June 18, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
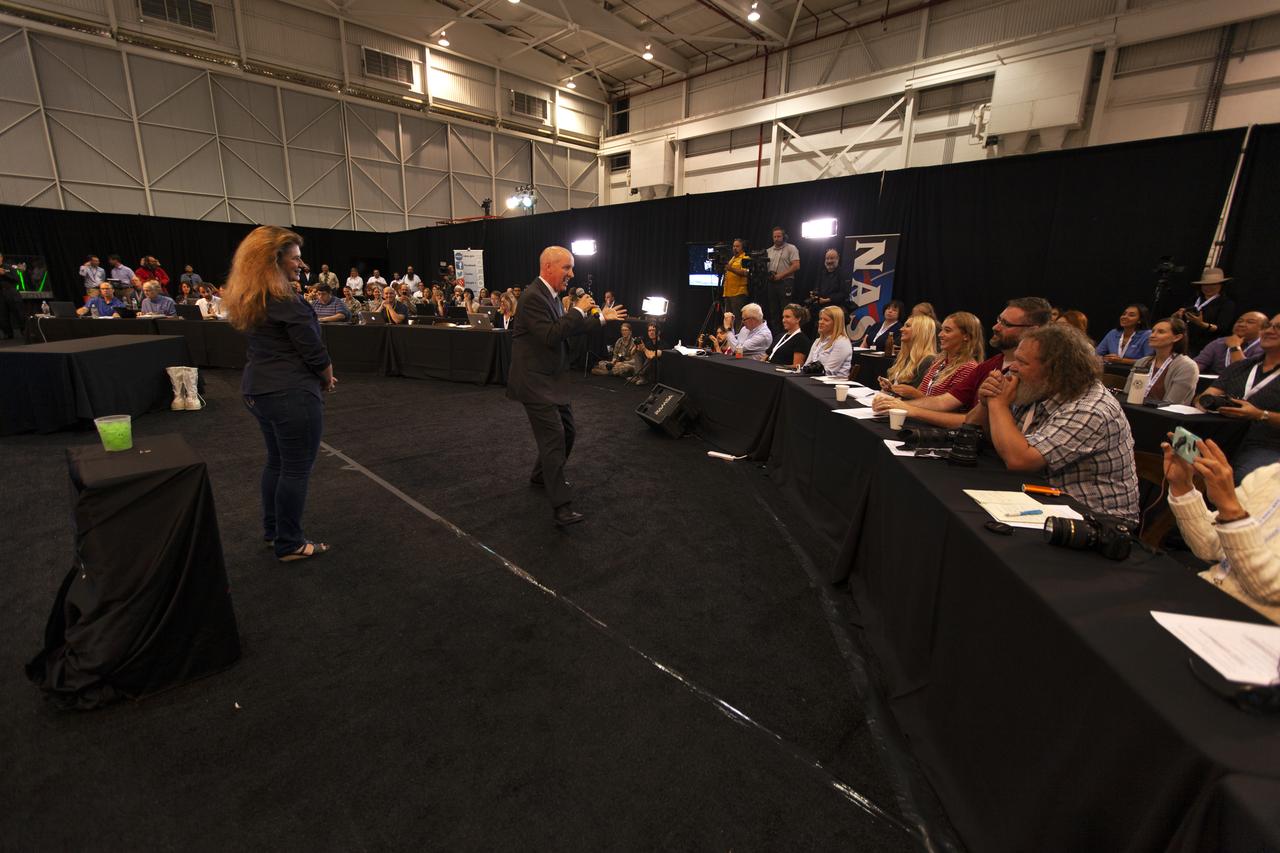

Tim Dunn, launch director, NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
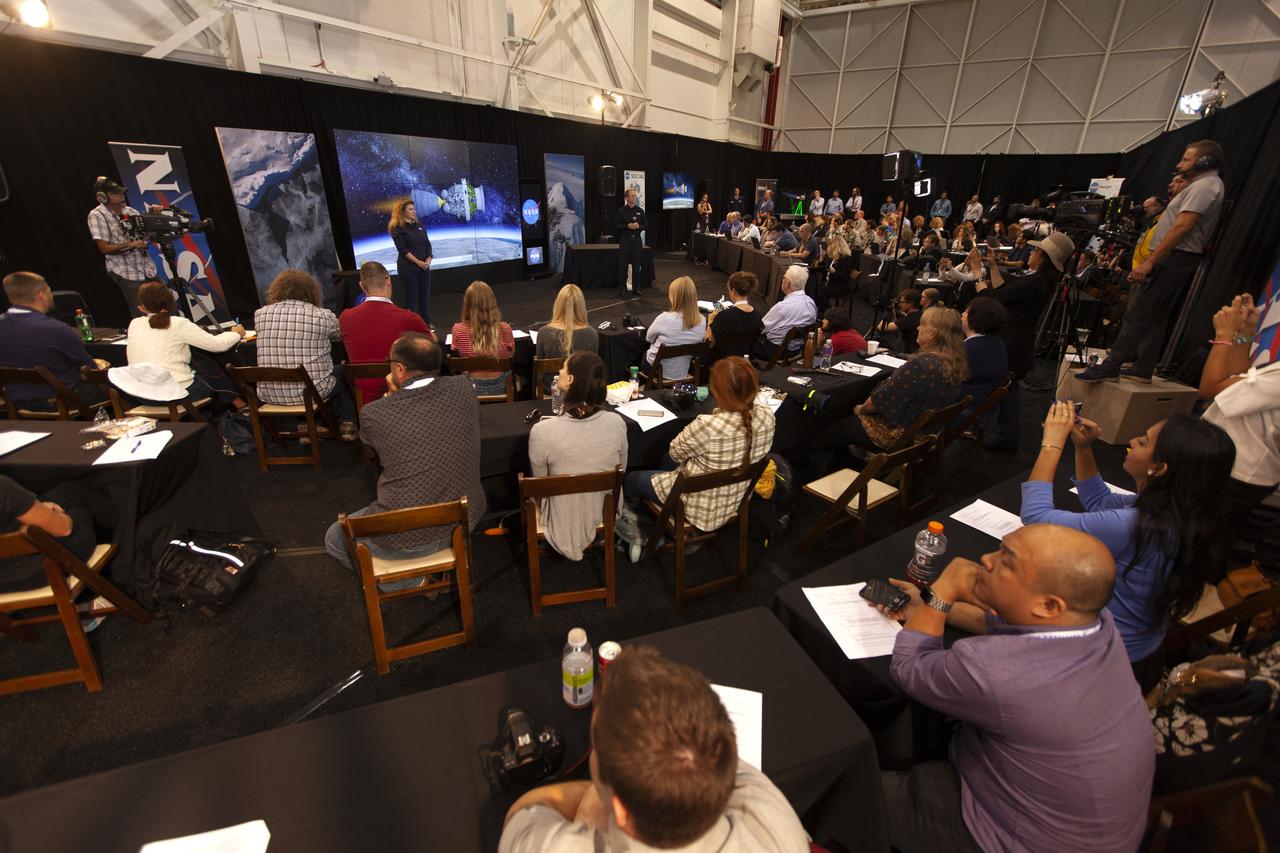

NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on Sept. 13, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.

The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.
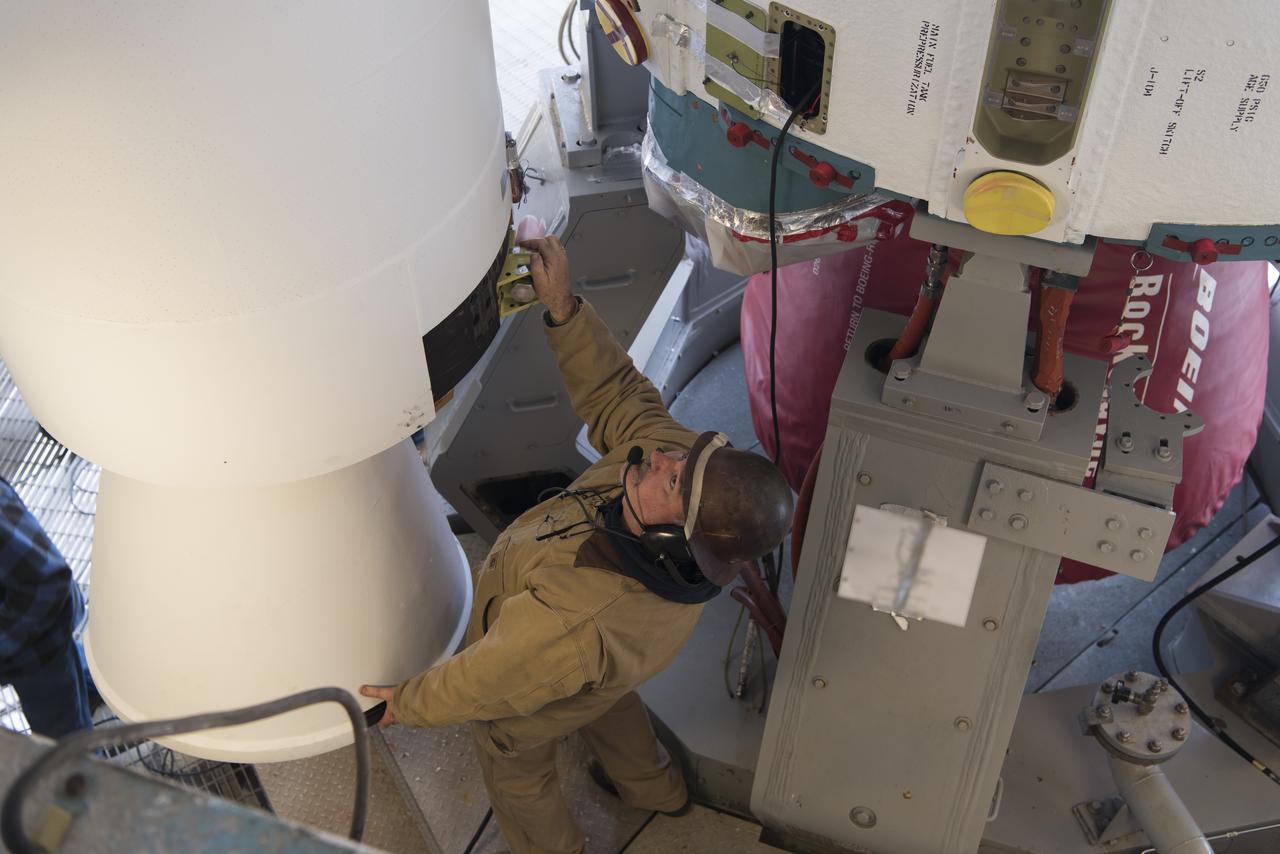

United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians assist as the solid rocket motor is moved toward the Delta II launch vehicle in the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final ULA Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted to vertical at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be lifted and moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
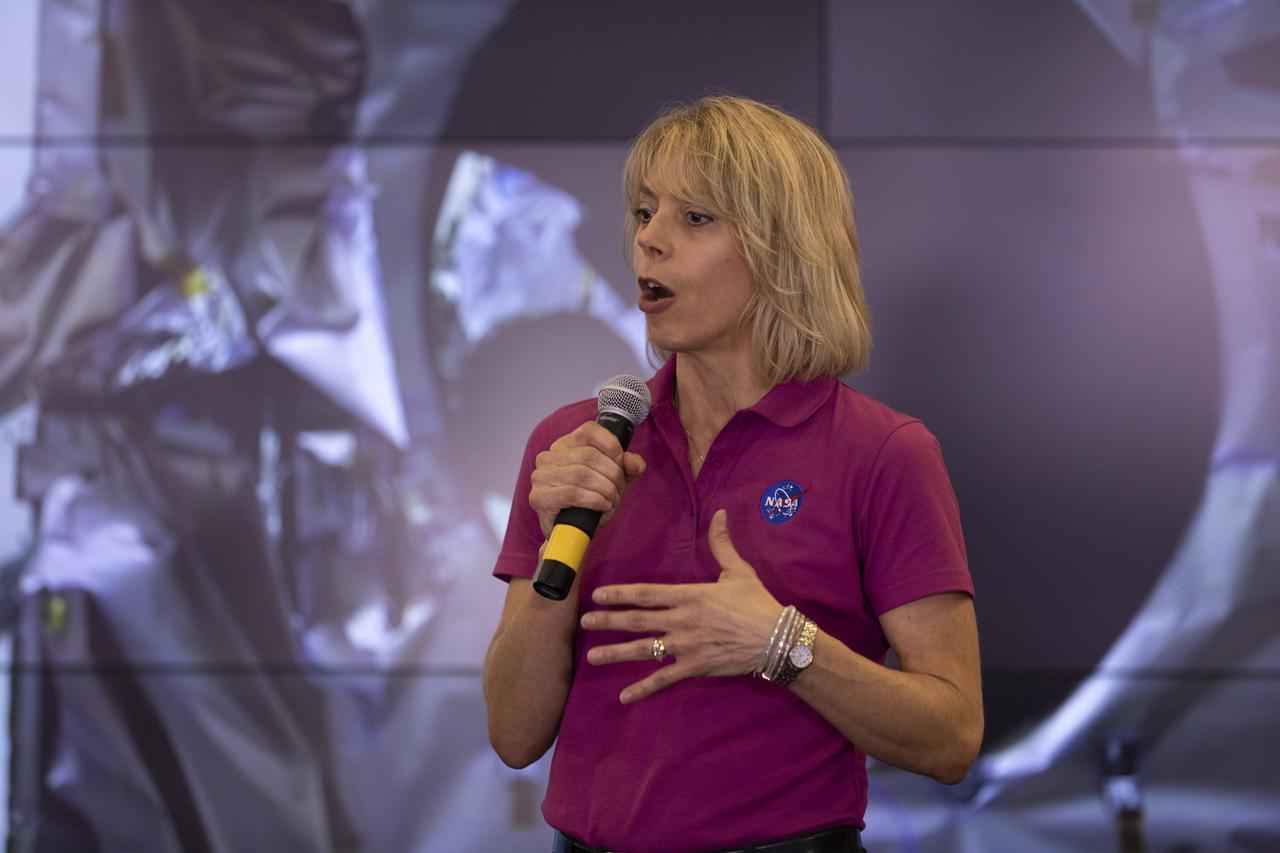

Cathy Richardson, Deputy Program Manager, Earth Science Projects Division, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
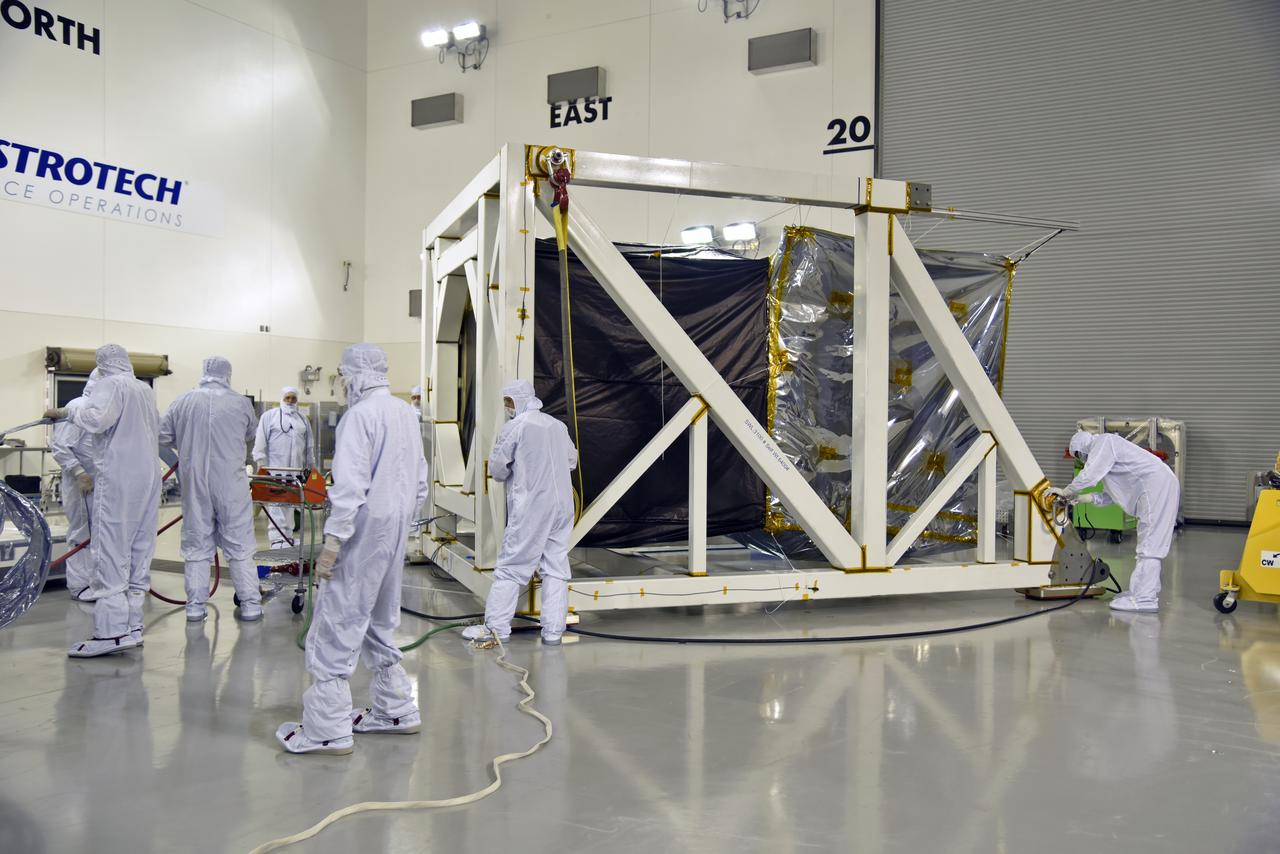

NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is being secured in the high bay of the Astrotech processing facility on June 13, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
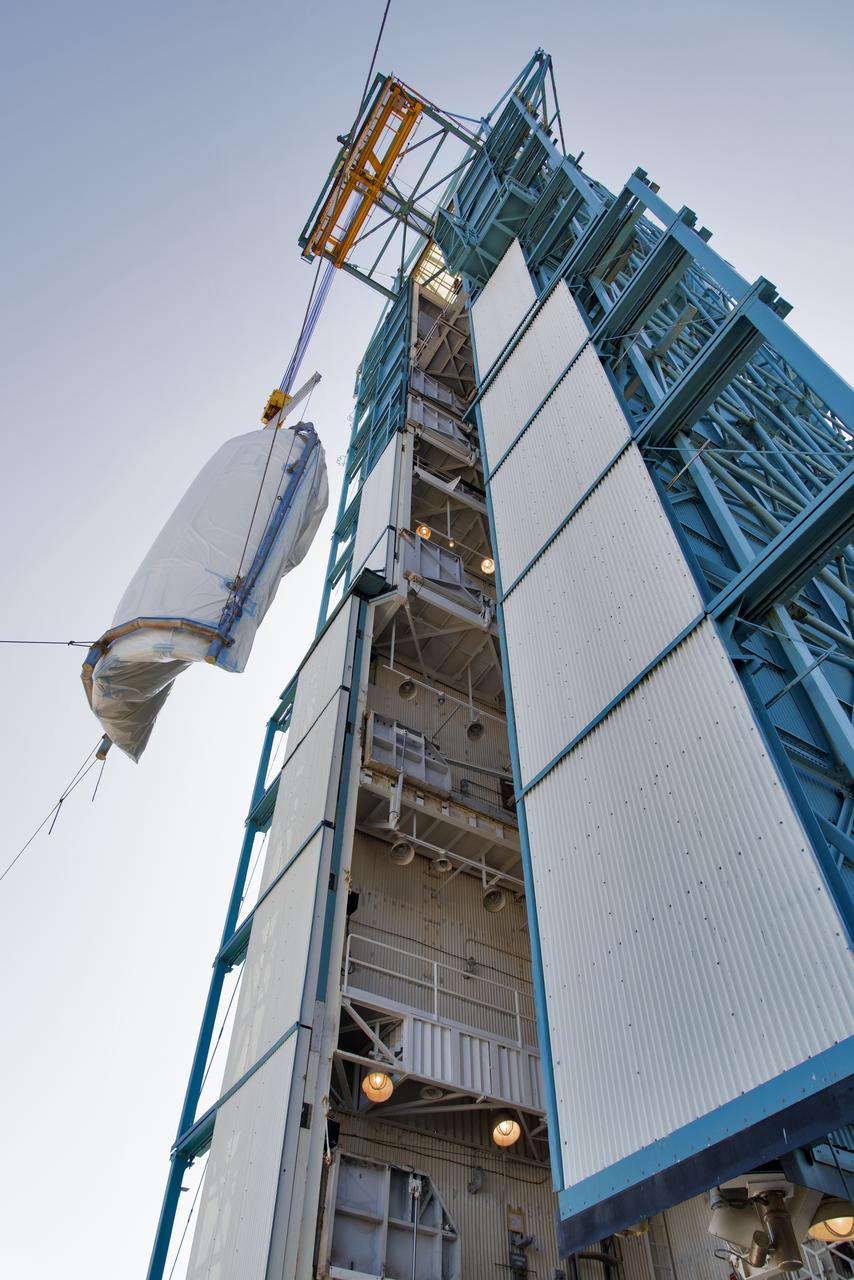

The second half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket payload fairing is lifted up into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on June 4, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch later this year on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
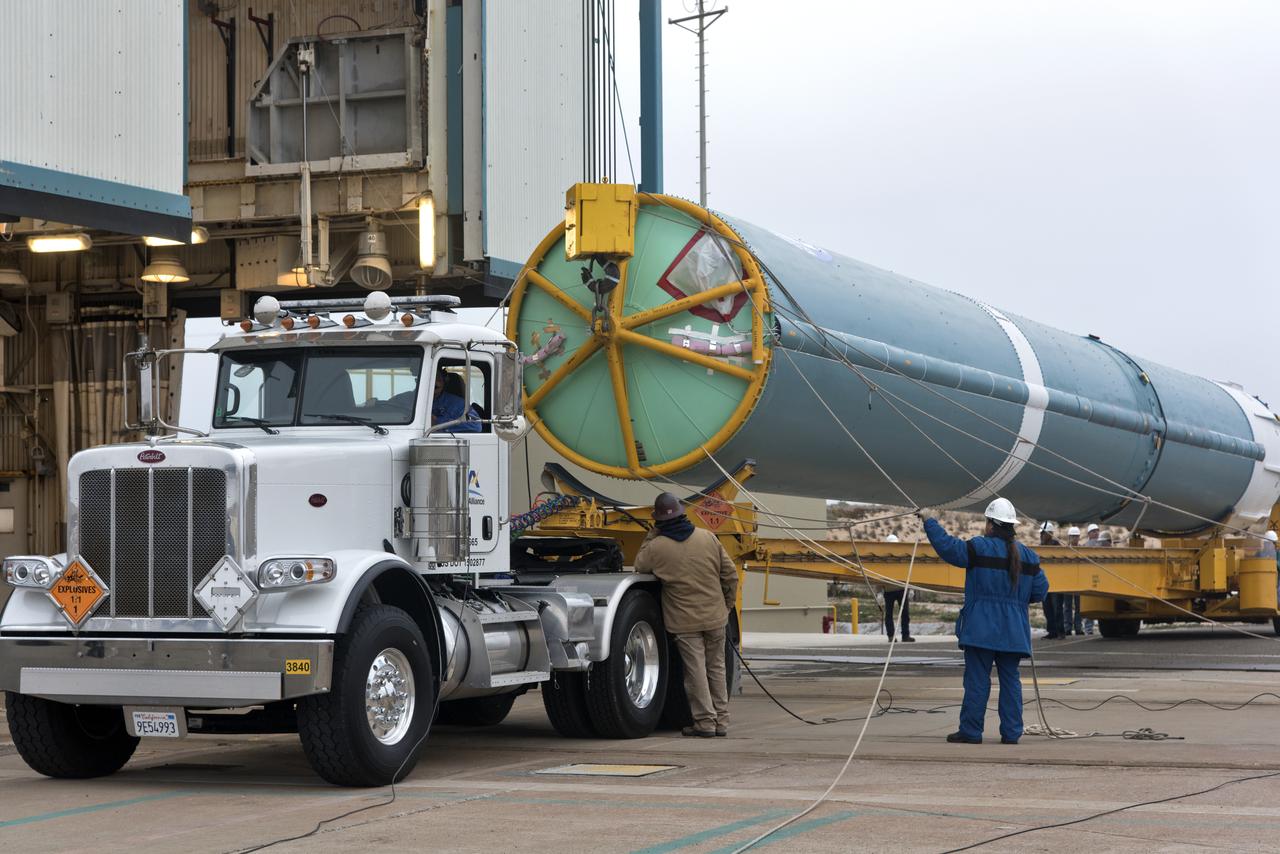

United Launch Alliance (ULA) workers assist as the Delta II first stage is lifted to vertical at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The solid rocket motor for mating to the United Launch Alliance Delta II launch vehicle is lifted up at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
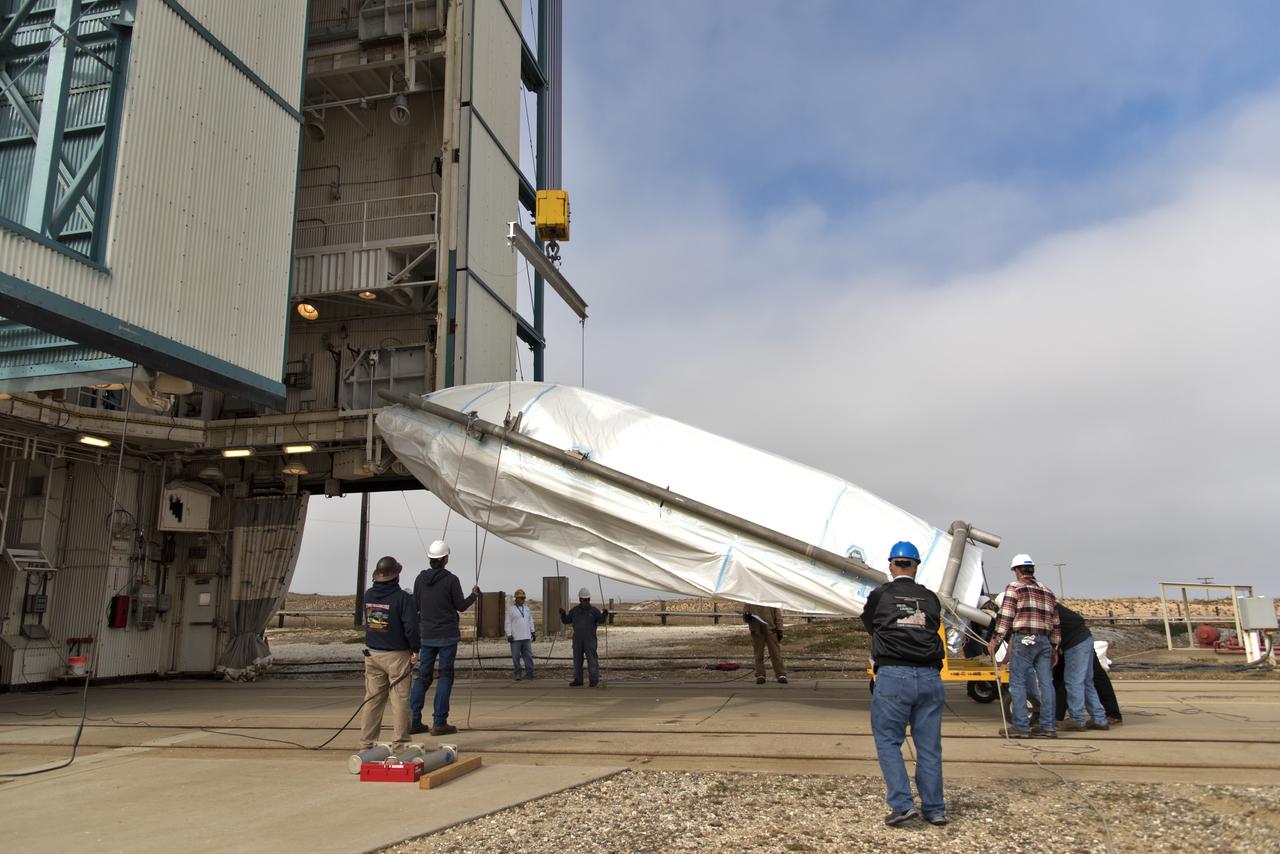

The first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket payload fairing is transported to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on June 4, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch later this year on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
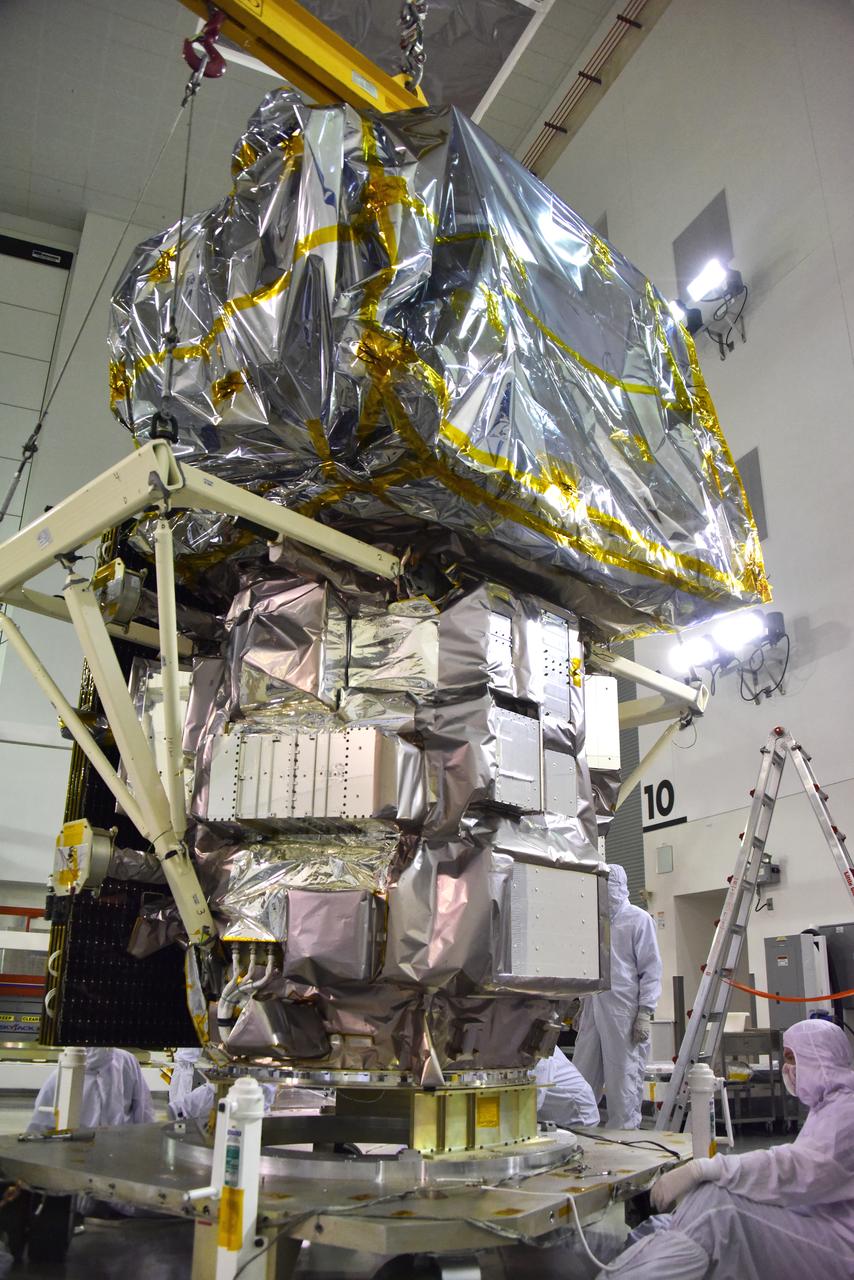

Technicians assist as a crane lowers NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onto a work stand in the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
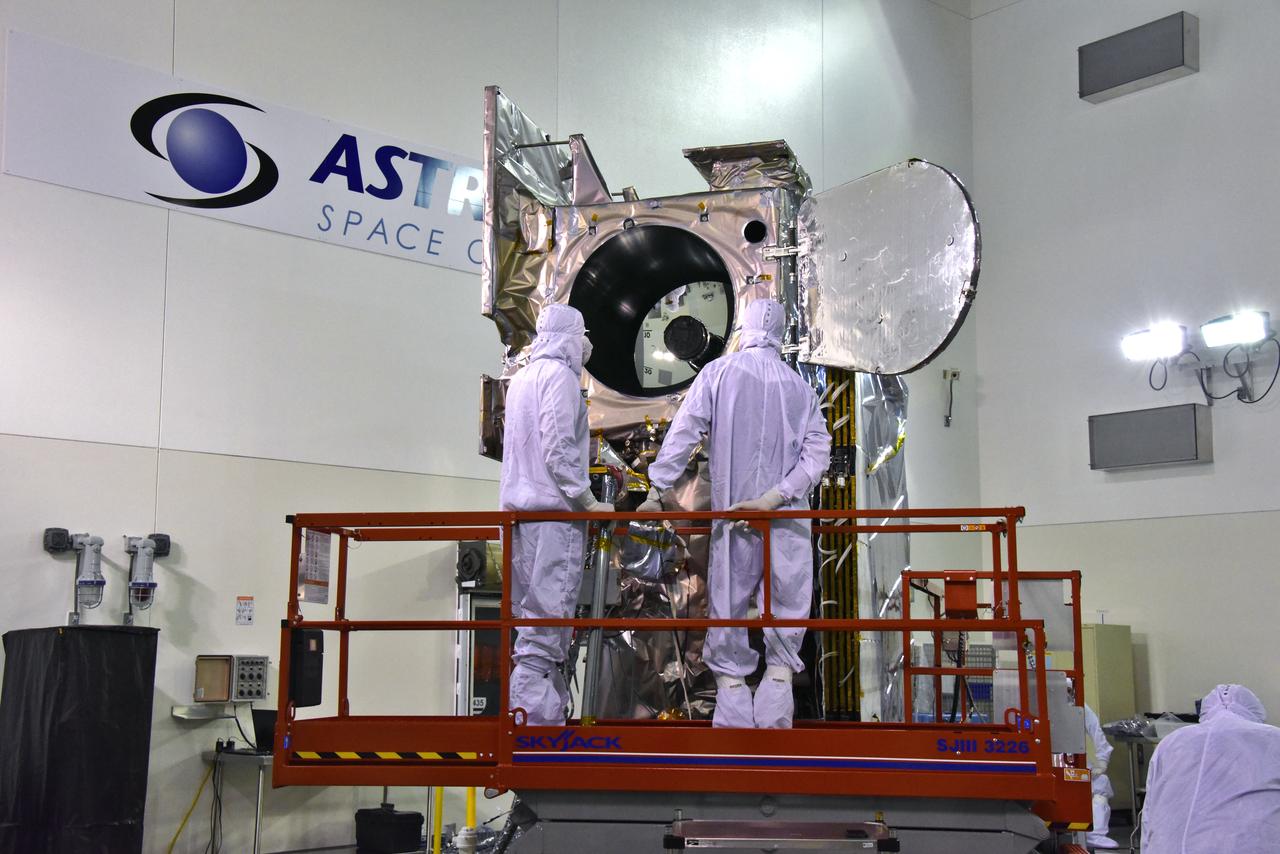

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians open and check the flight door for the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS) on NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on June 18, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry ATLAS. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
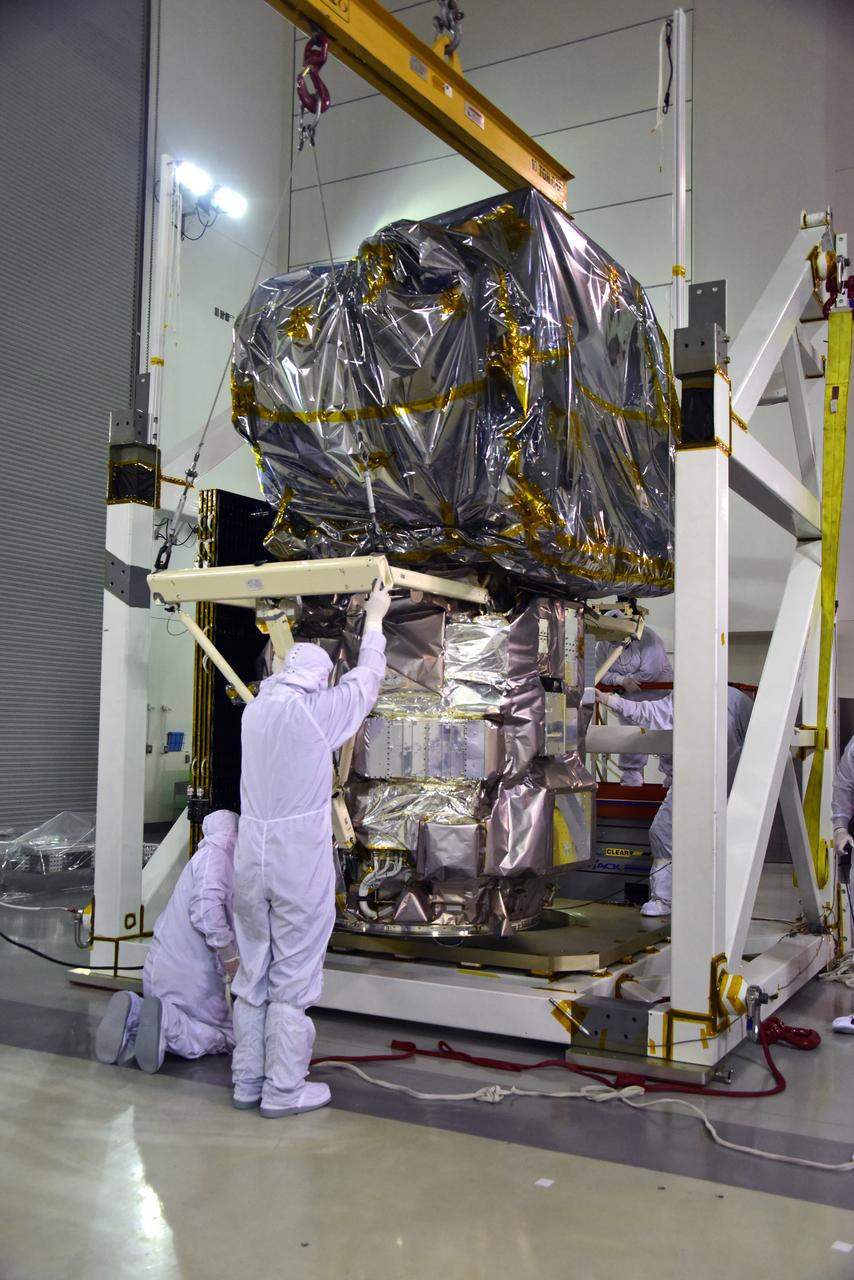

Technicians assist as a crane rotates NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) into position for removal and lift to a work stand in the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
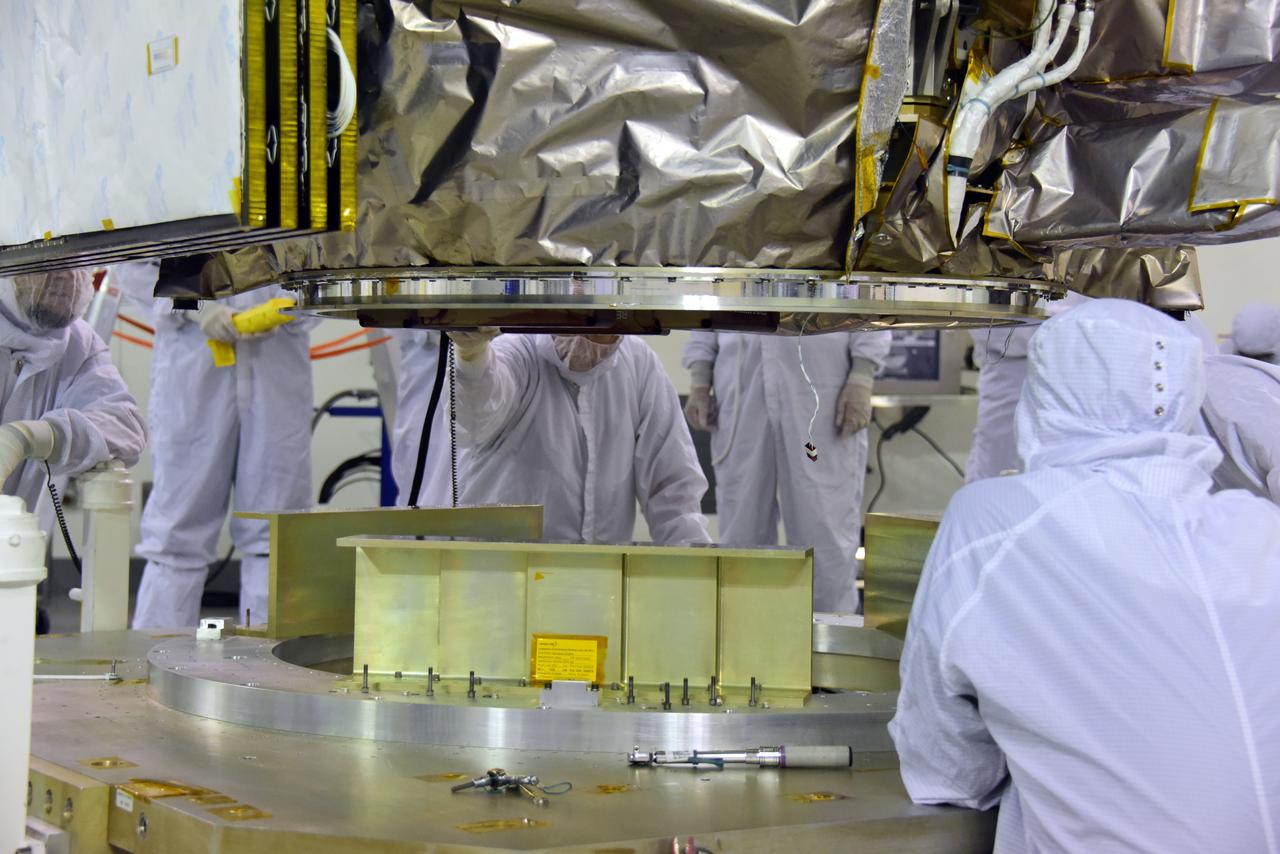

Technicians assist as a crane lowers NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onto a work stand in the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.
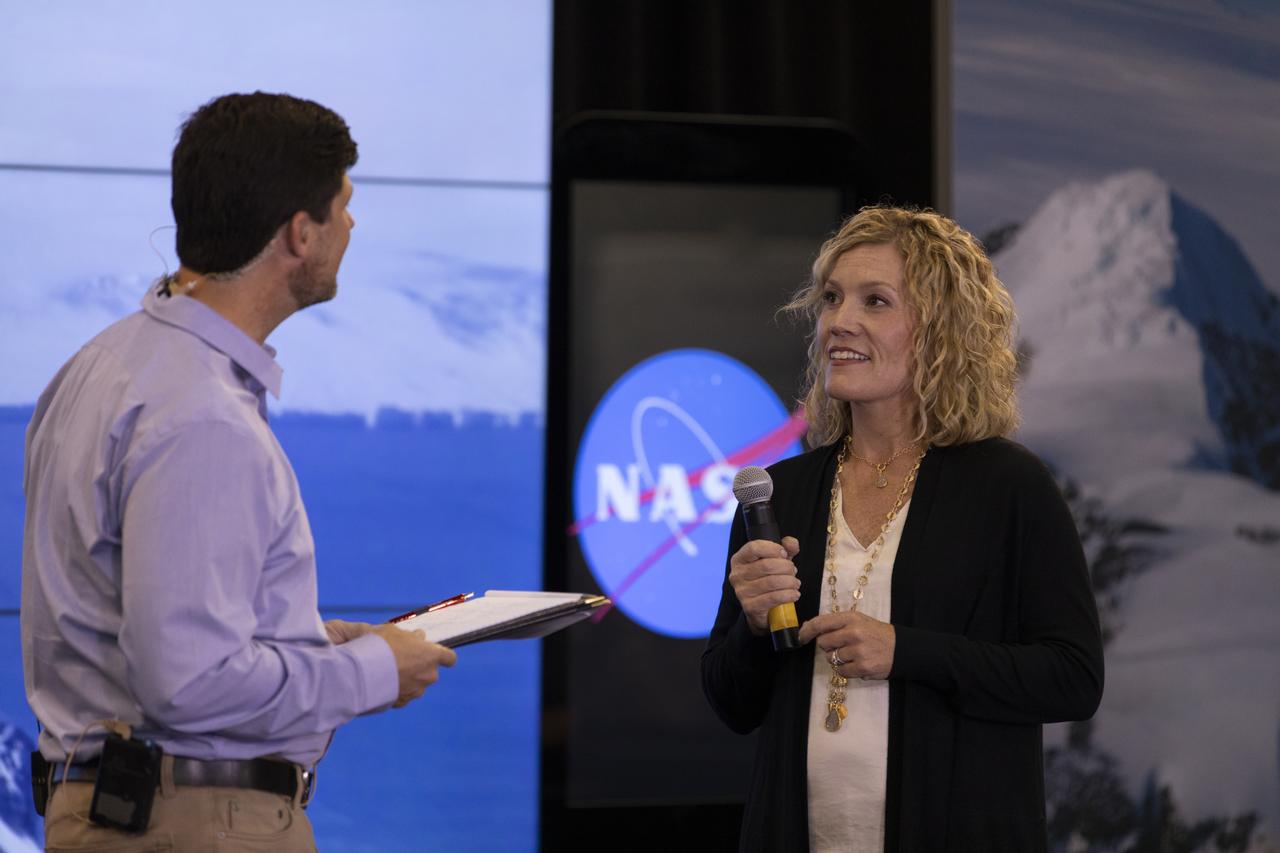

Lori Magruder, University of Texas at Austin, ICESat-2 science definition team lead, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
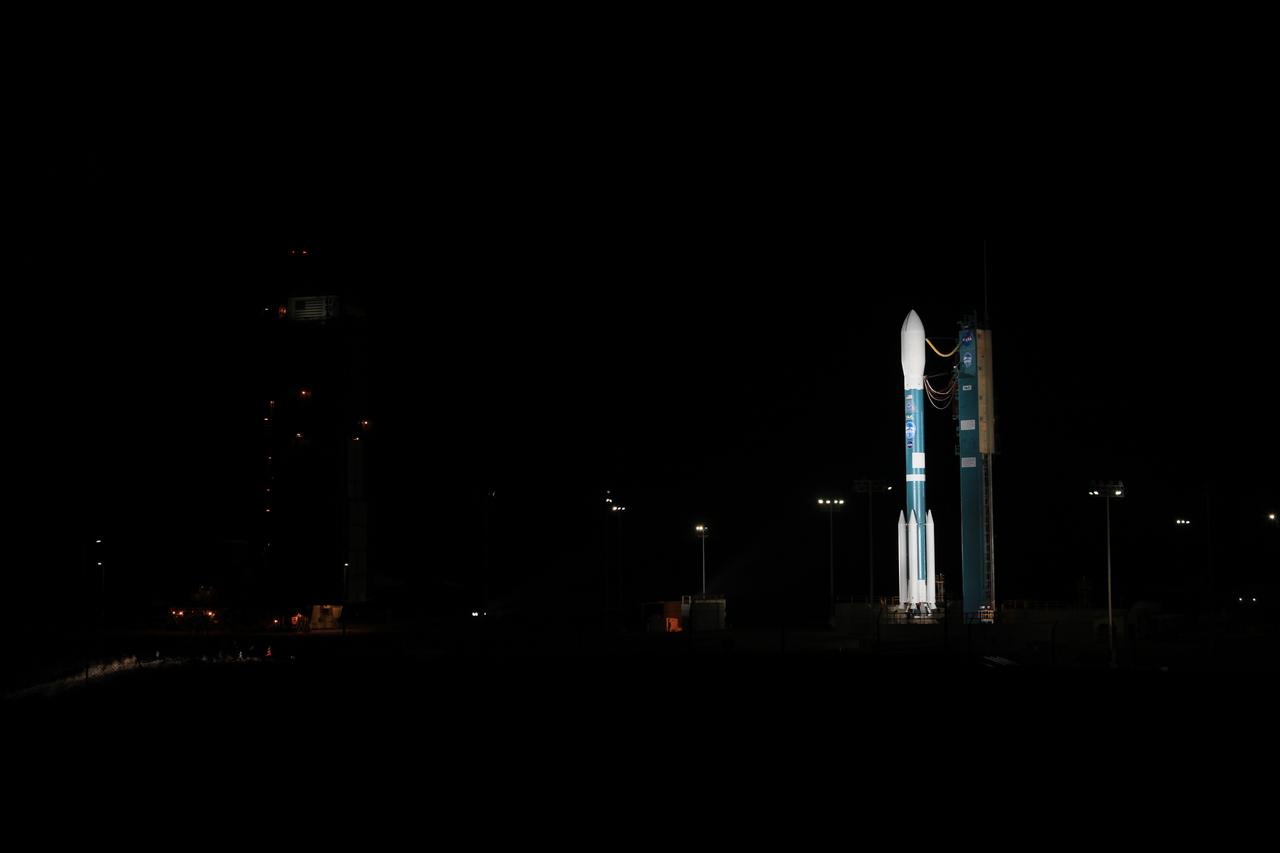

The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.
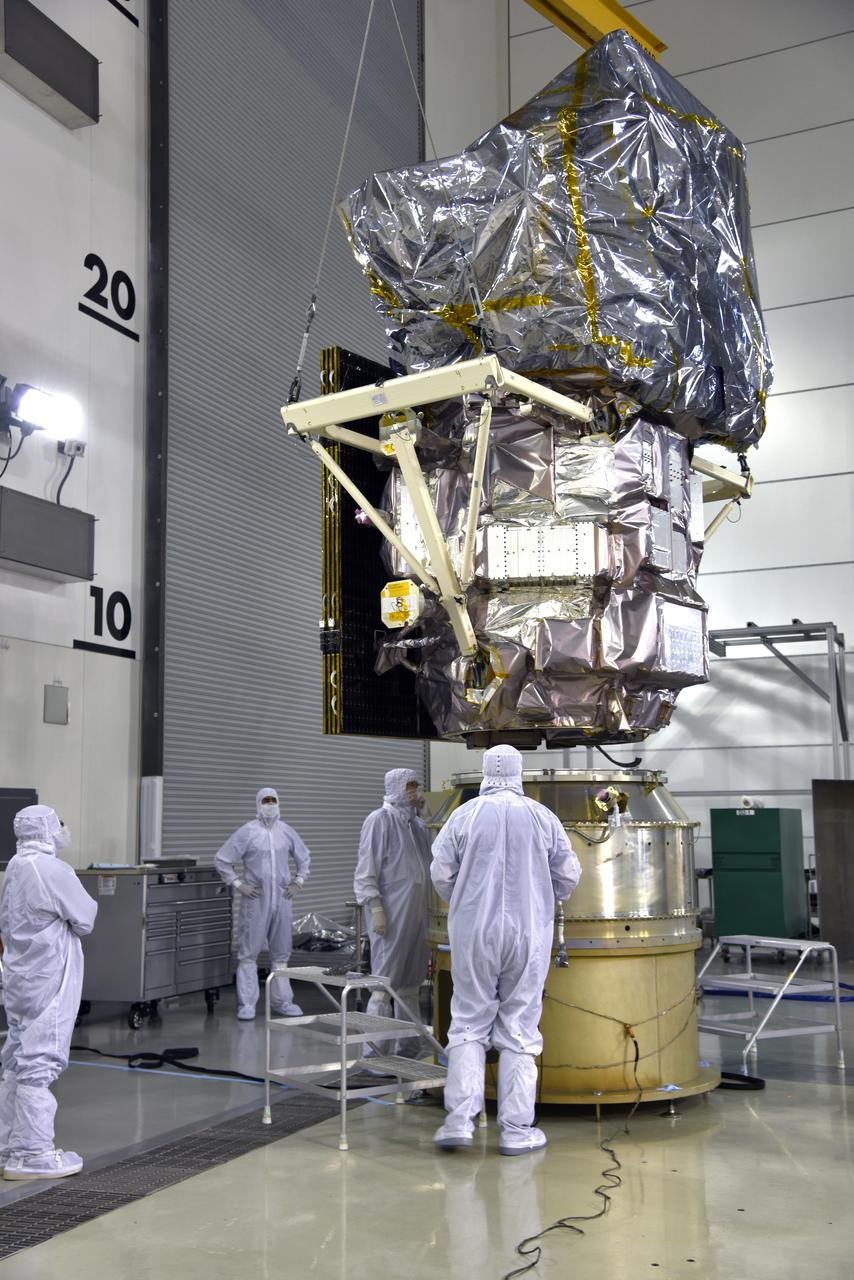

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane lifts and moves NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) over the payload adapter on Aug. 30, 2018. The satellite will be attached to the adapter. ICESat-2 is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
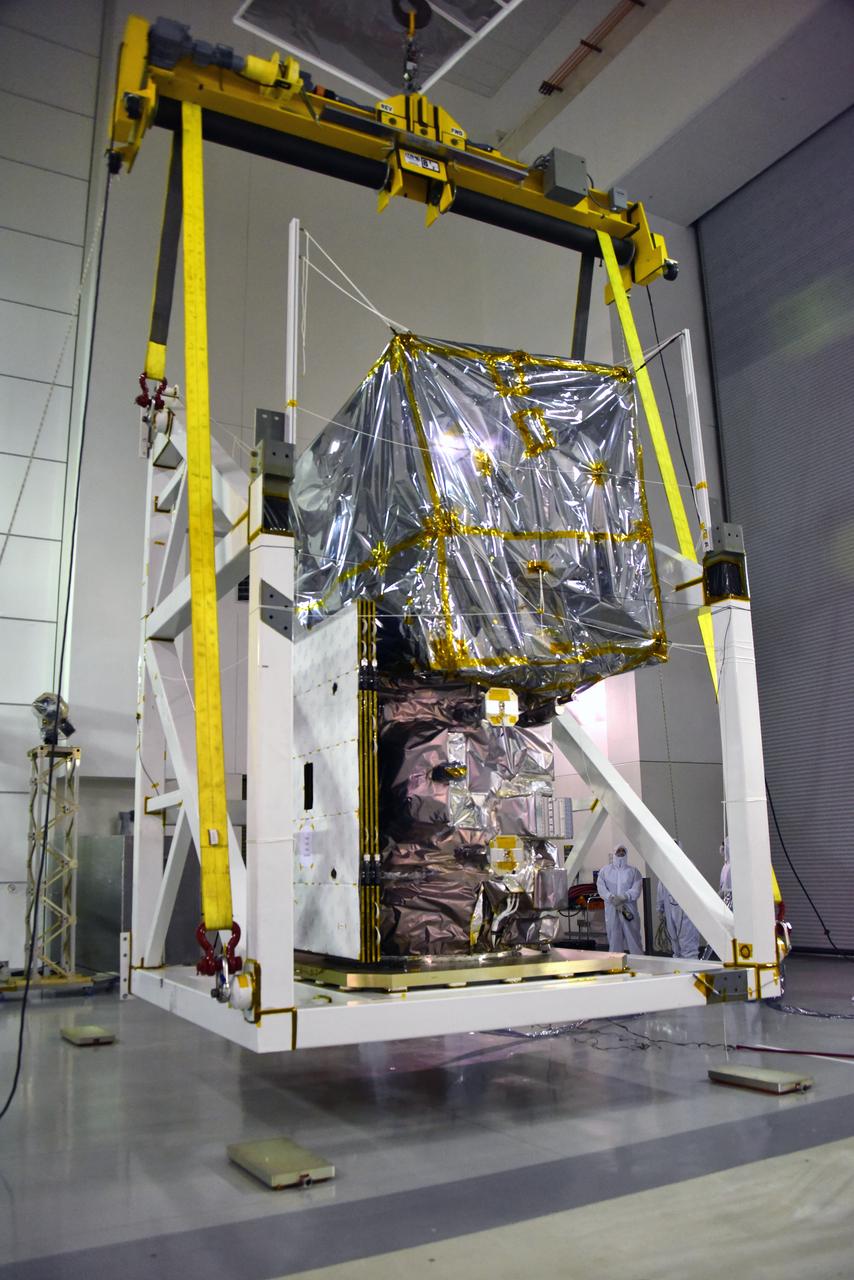

A crane rotates NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) in its fixture inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
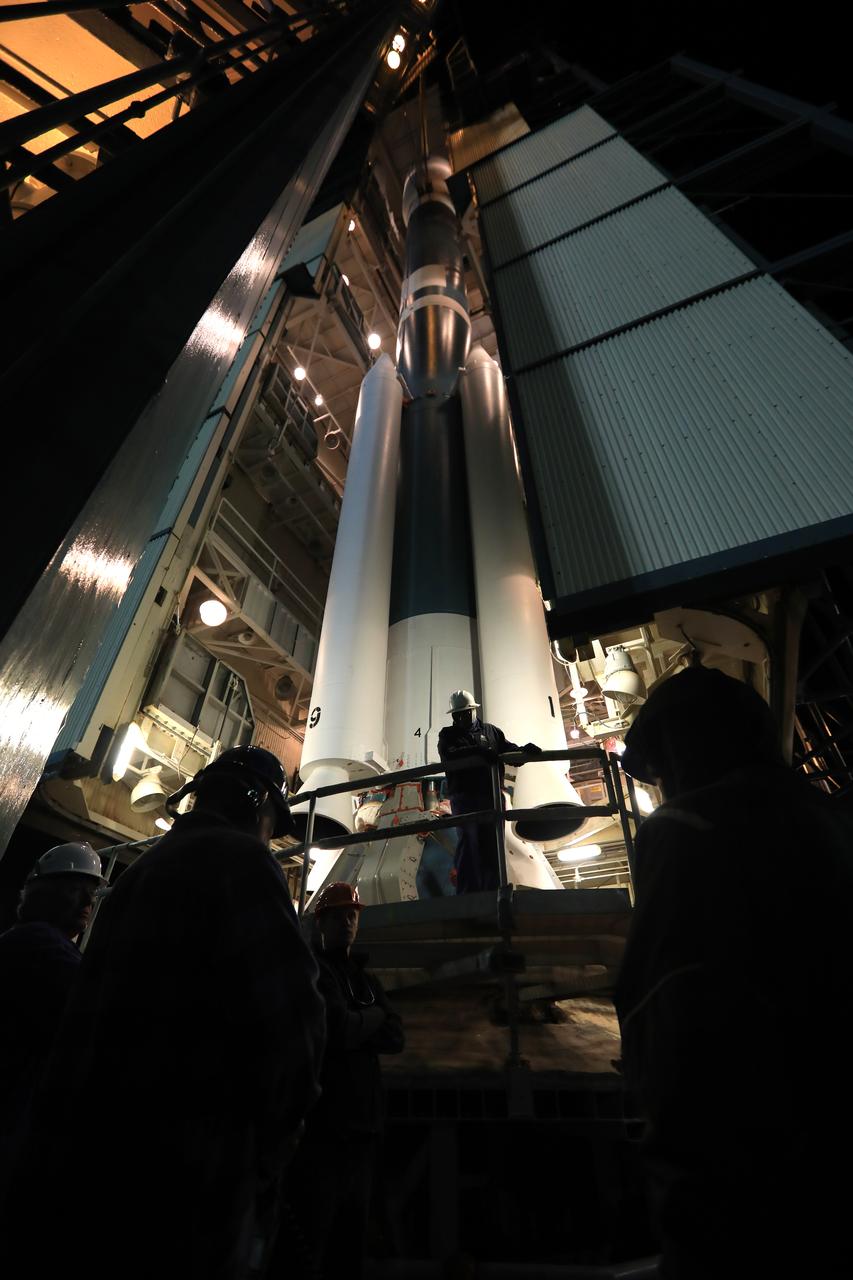

The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.
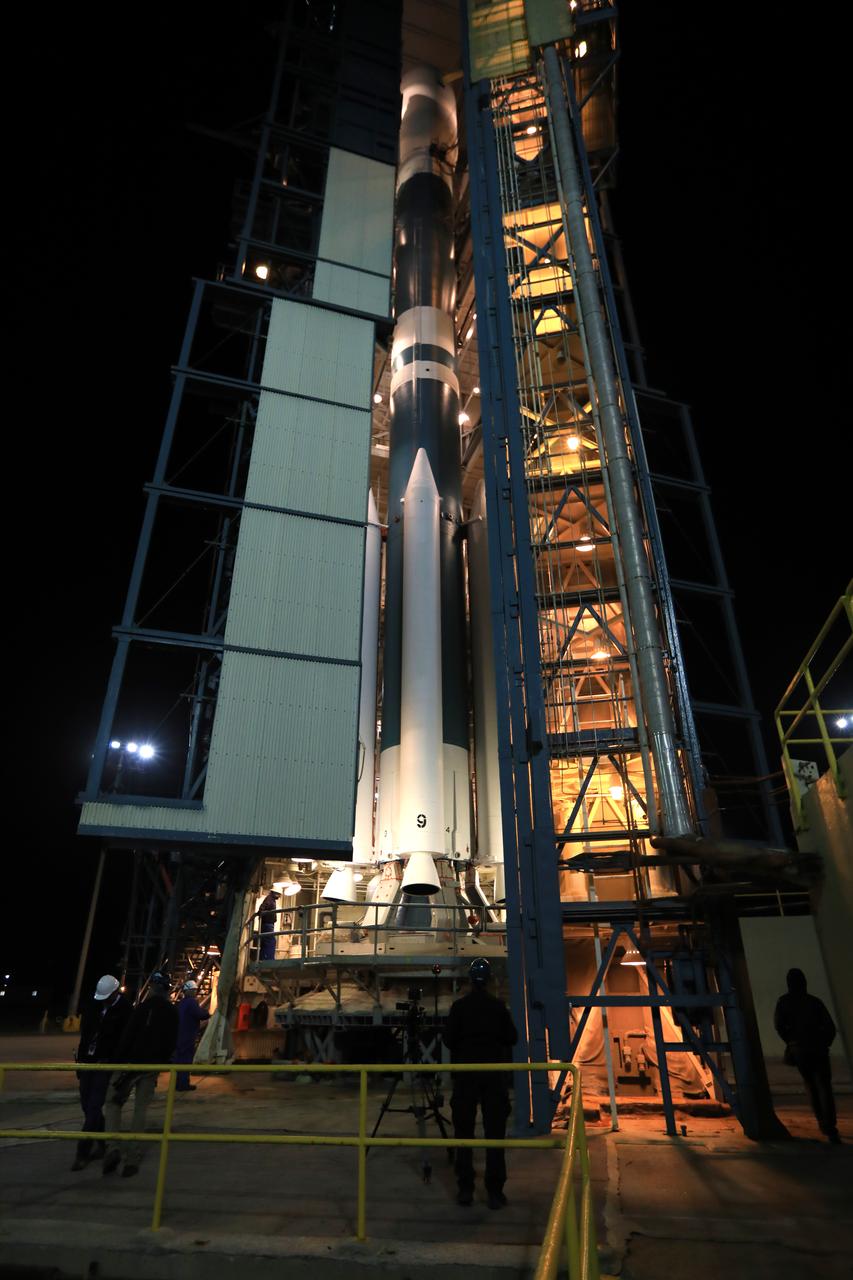

The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.
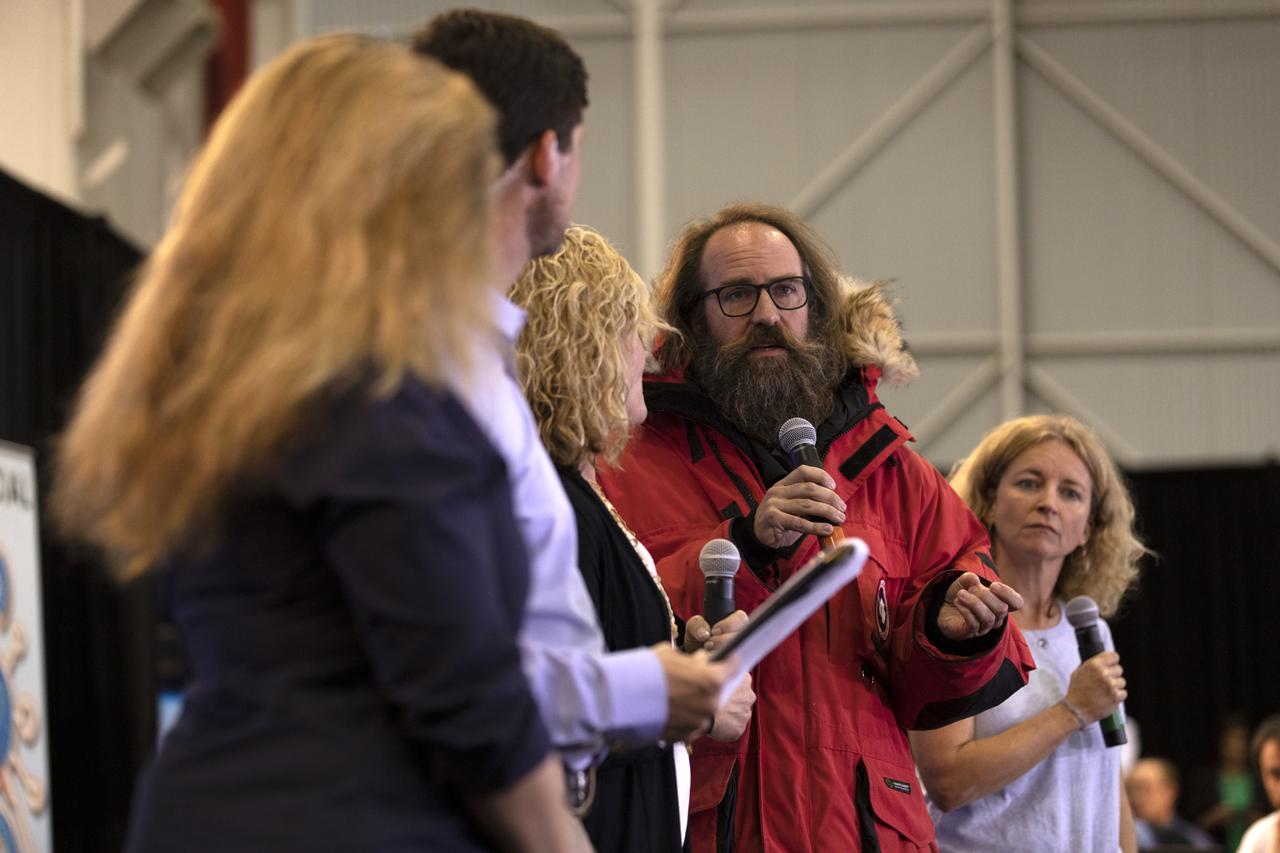

Tom Neumann, ICESat-2 deputy project scientist, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
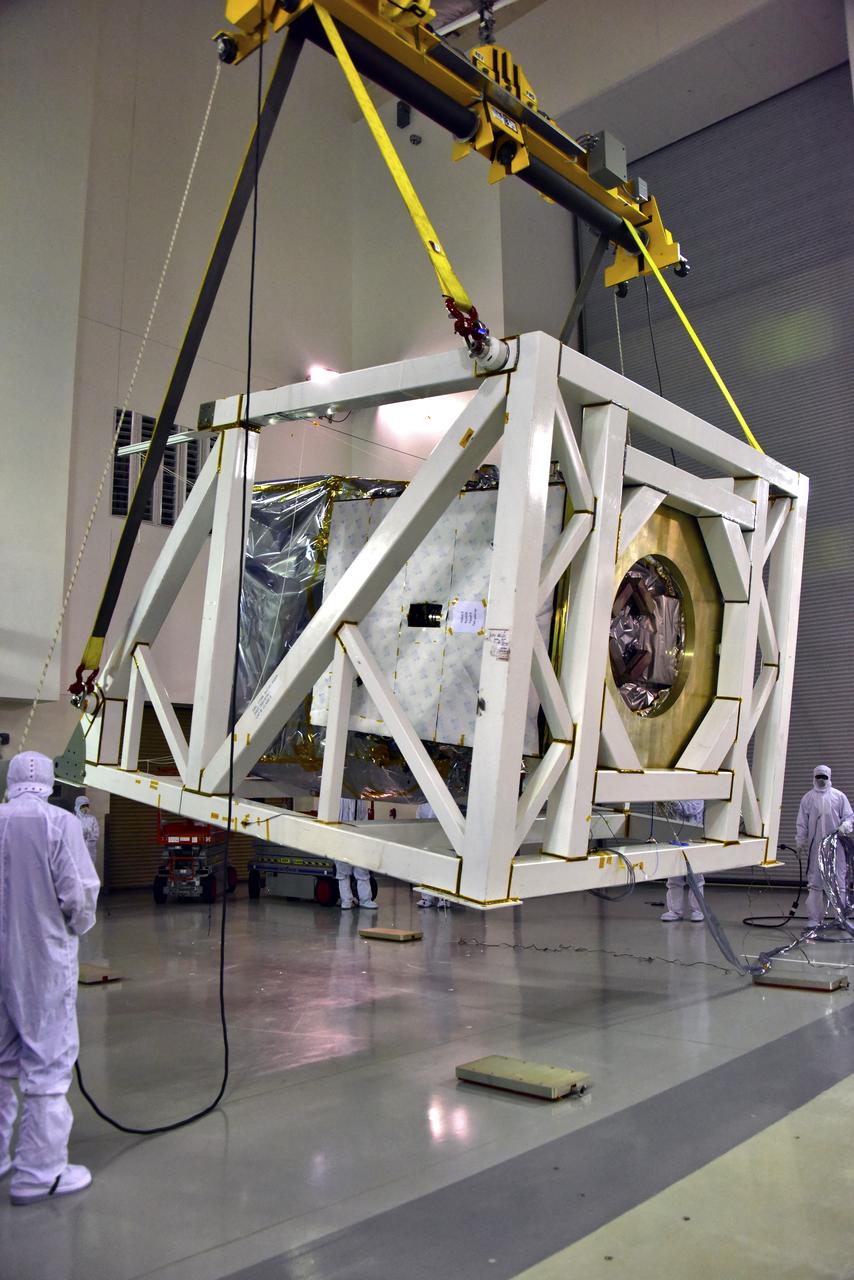

NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is lifted in its fixture inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.
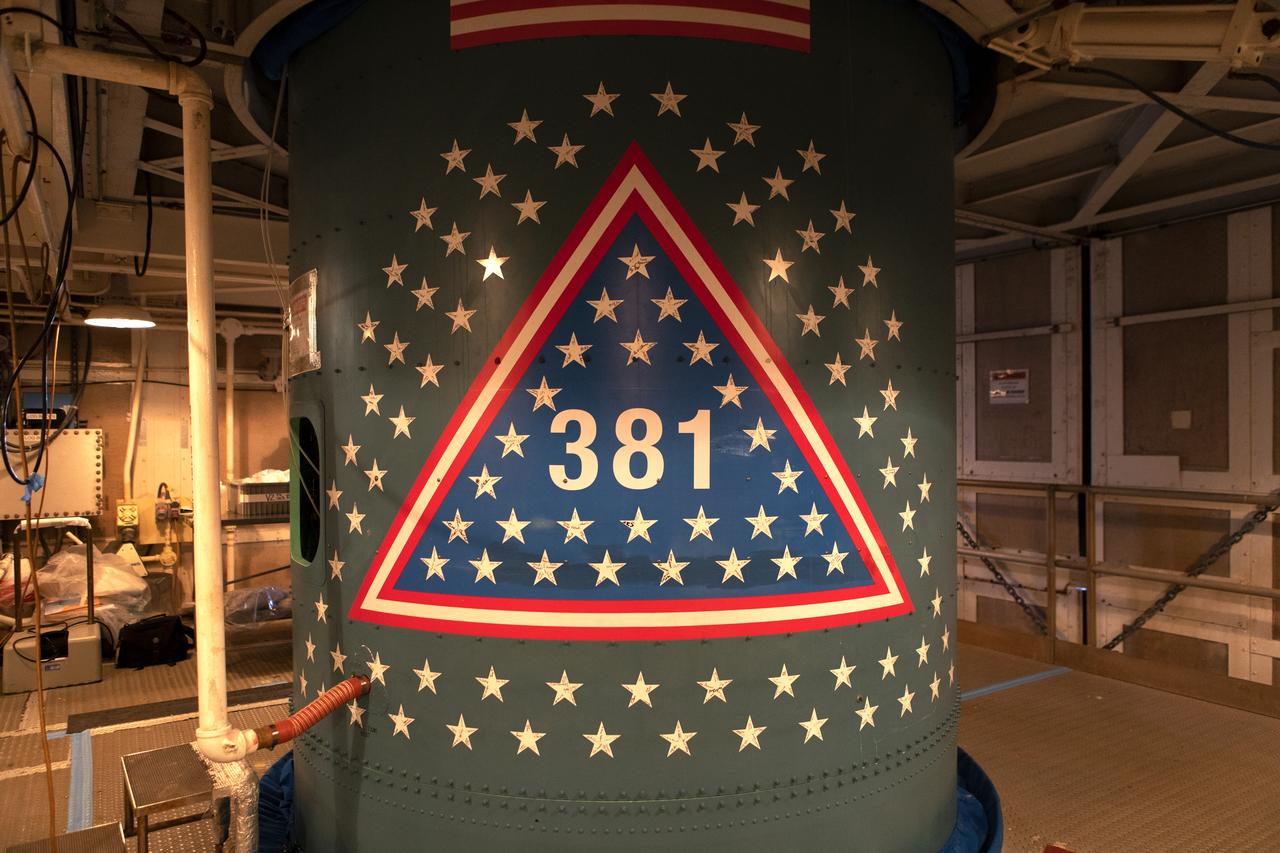

Stars are in view on the first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 13, 2018. Historically, each Delta rocket used to notate the number of launches within the program, beginning in May, 1960, with the first Delta I. This practice was brought back for the final Delta II launch of ICESat-2. The “381” on the rocket signifies that this will be the 381st flight in the Delta family. A star traditionally was placed on the rocket to recognize each mission. For the final Delta II, stars were sent to team members and partners throughout the nation. This rocket boasts more than 150 stars with over 800 signatures of people who have been part of the Delta II program.
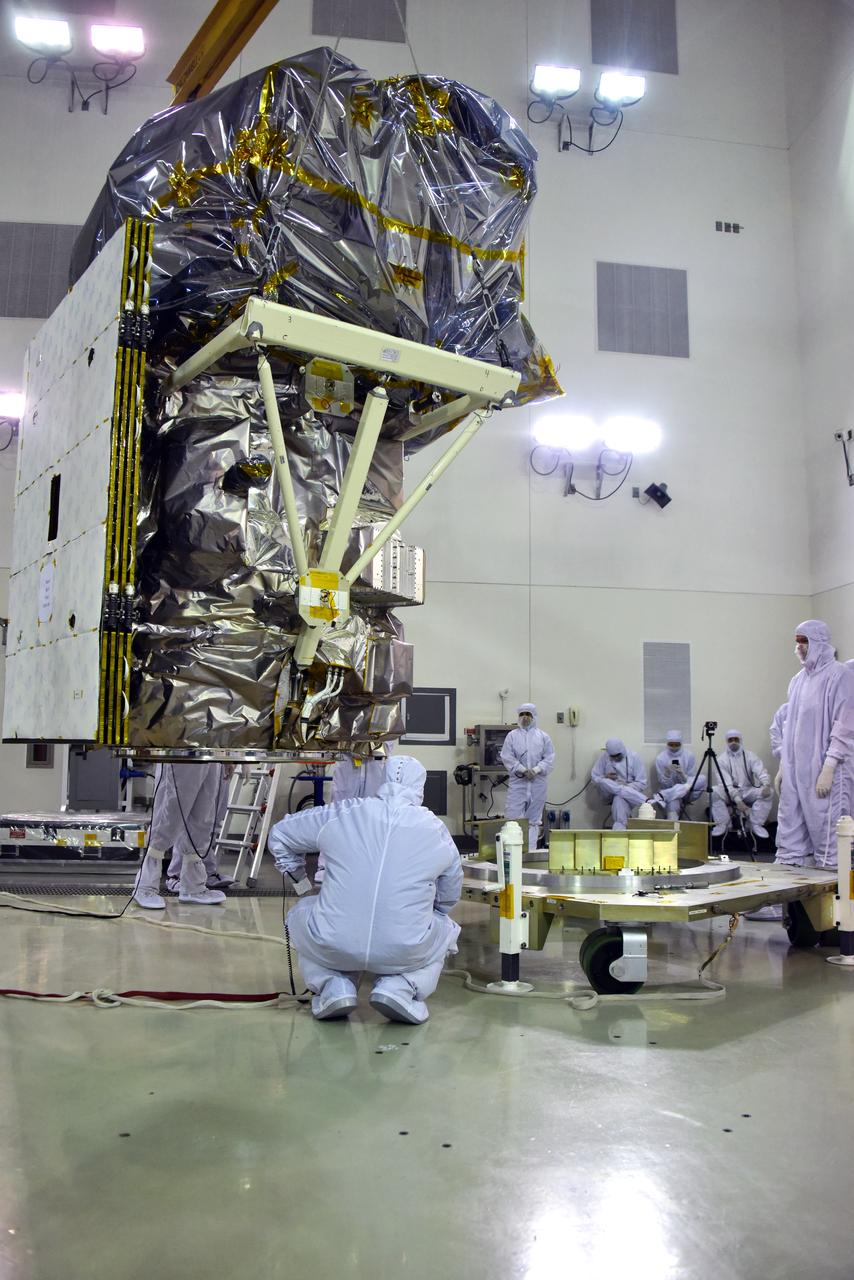

Technicians monitor the progress as NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is removed from its fixture in the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The satellite will be secured on a work stand for processing. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solar array first motion test is underway on NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on June 18, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
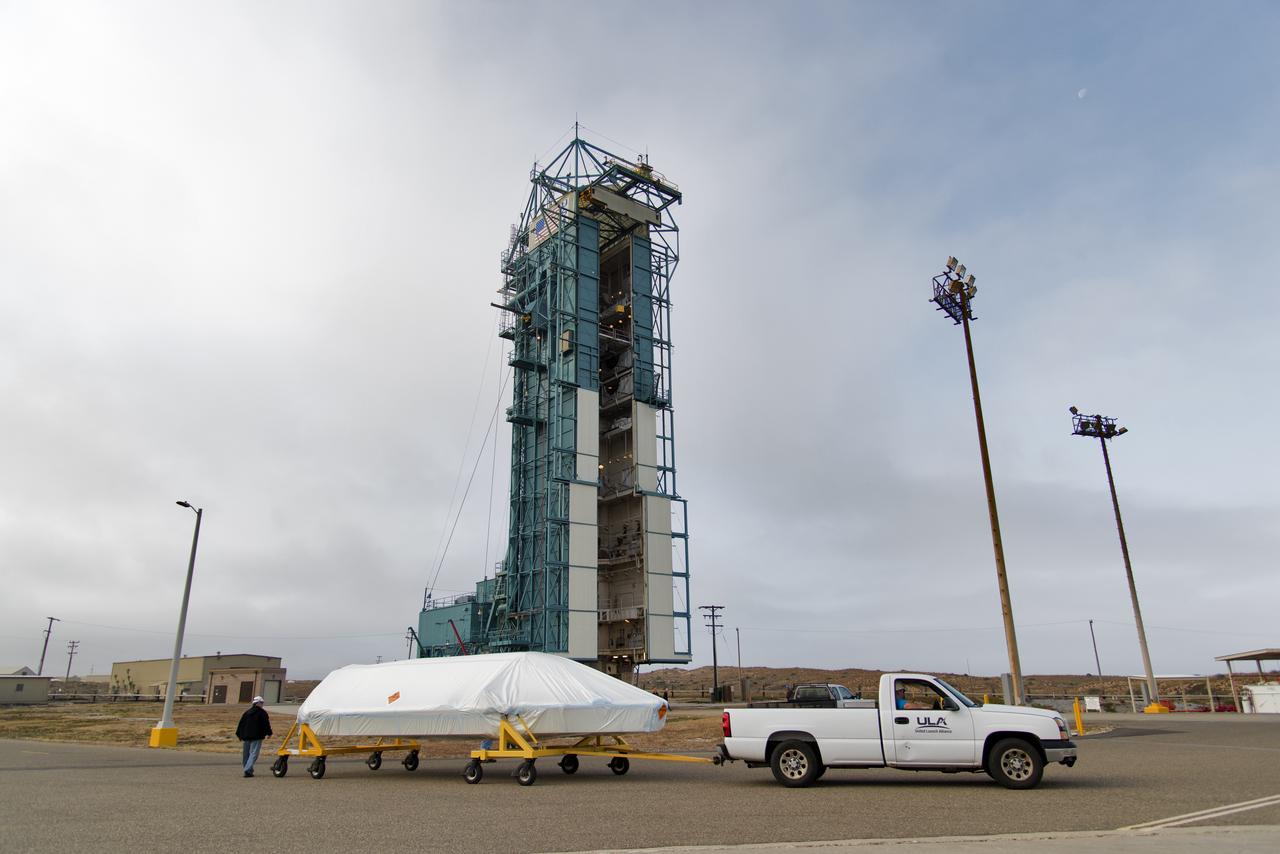

The first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket payload fairing is transported to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on June 4, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch later this year on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
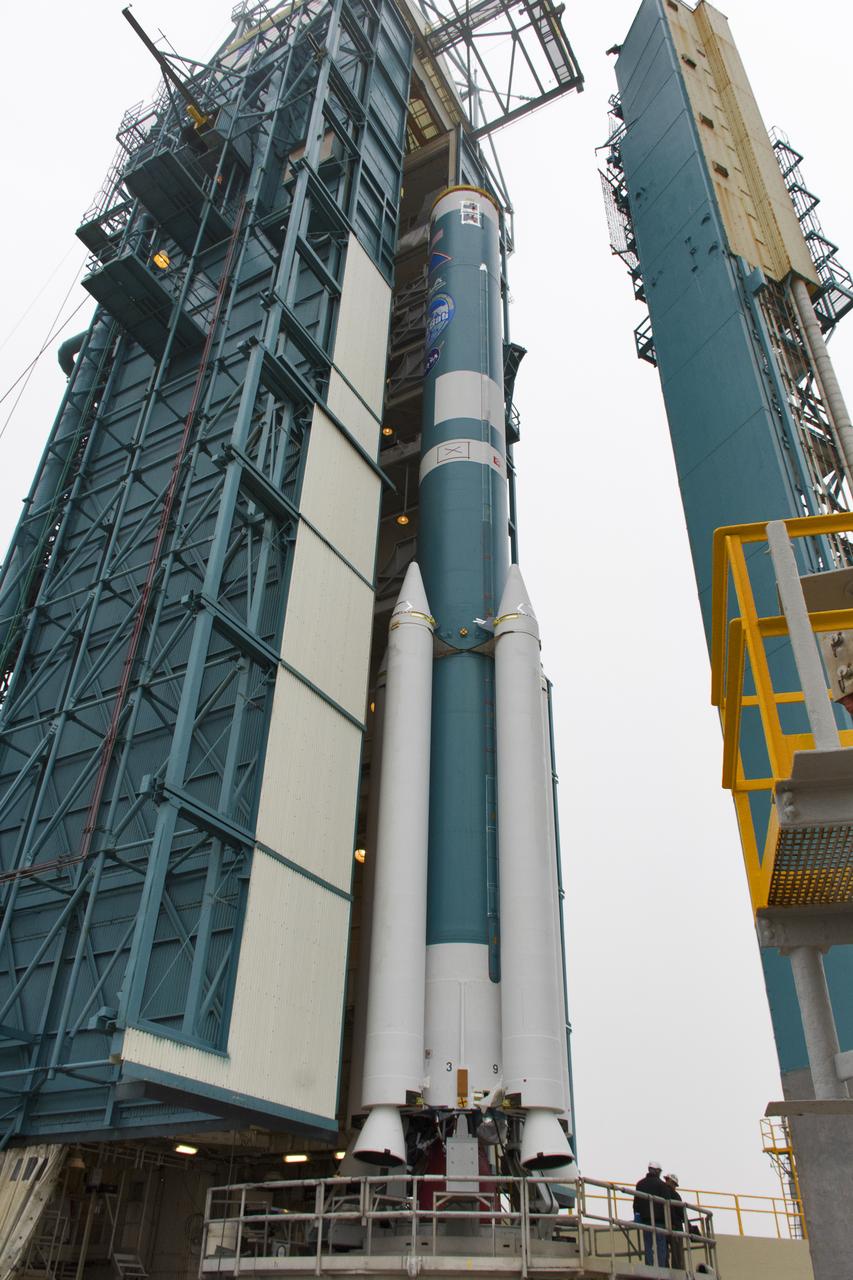

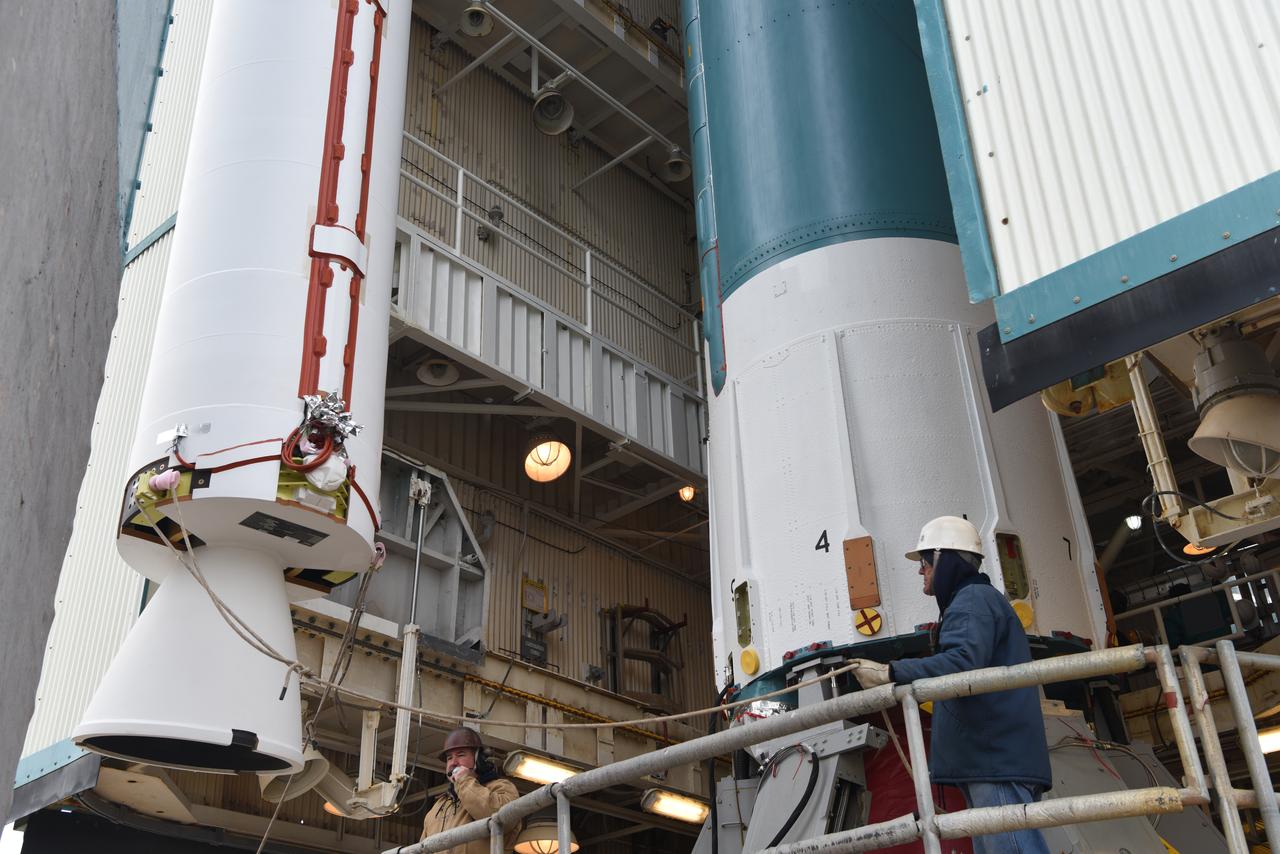
The United Launch Alliance Delta II booster, or first stage, with the interstage attached on top is moved out of the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 21, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The second stage will be lifted up at the VIF. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

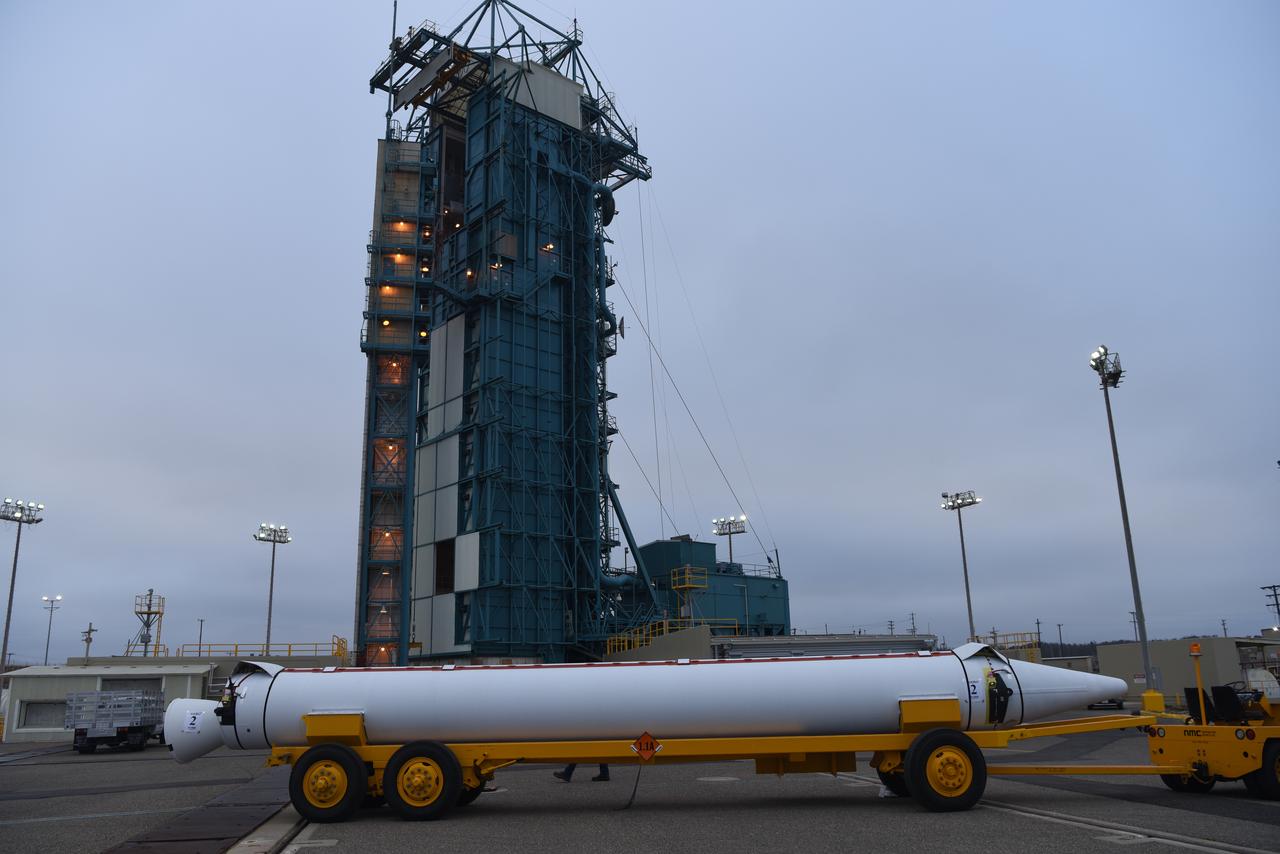
The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted to vertical at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ULA workers make adjustments so the booster can be lifted up from its stand and moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

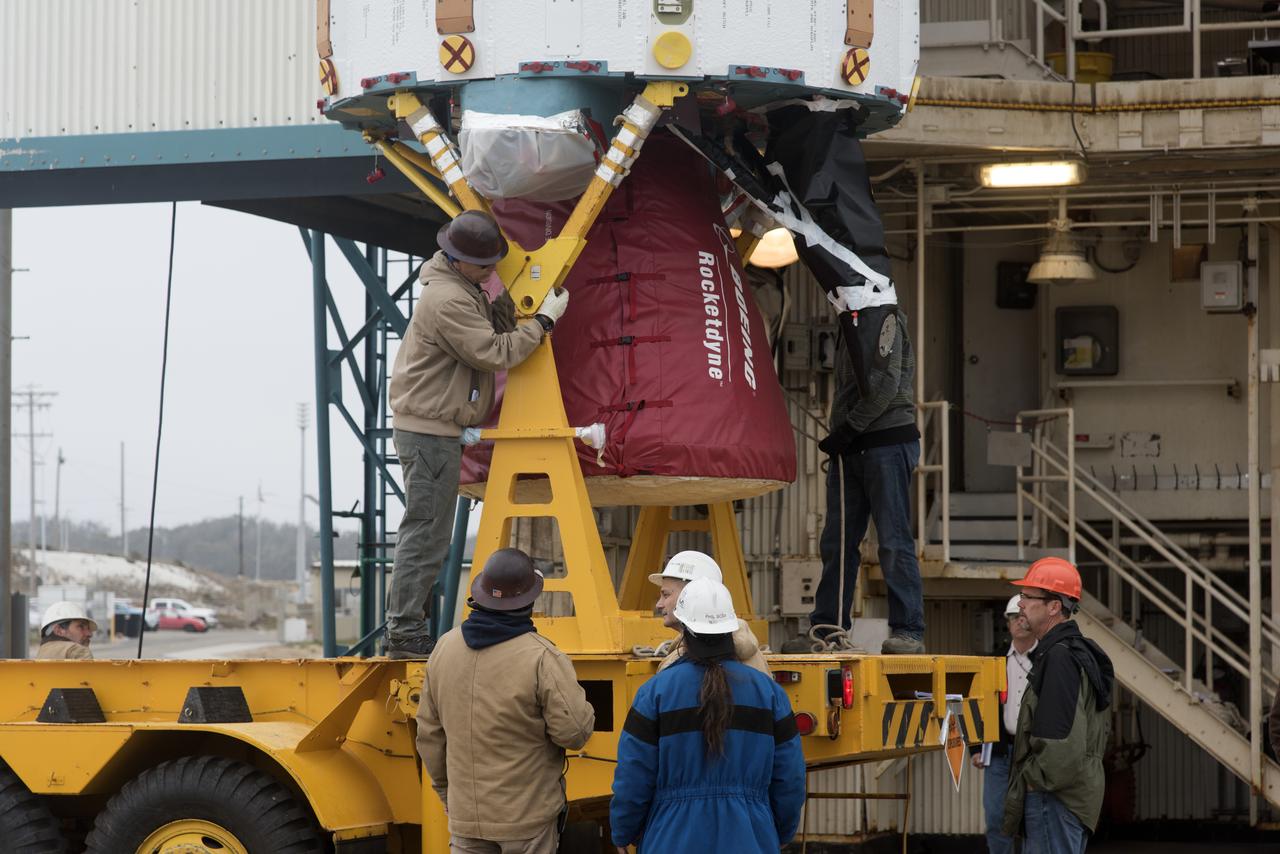
The solid rocket motor for mating to the United Launch Alliance Delta II launch vehicle arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be lifted up and attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
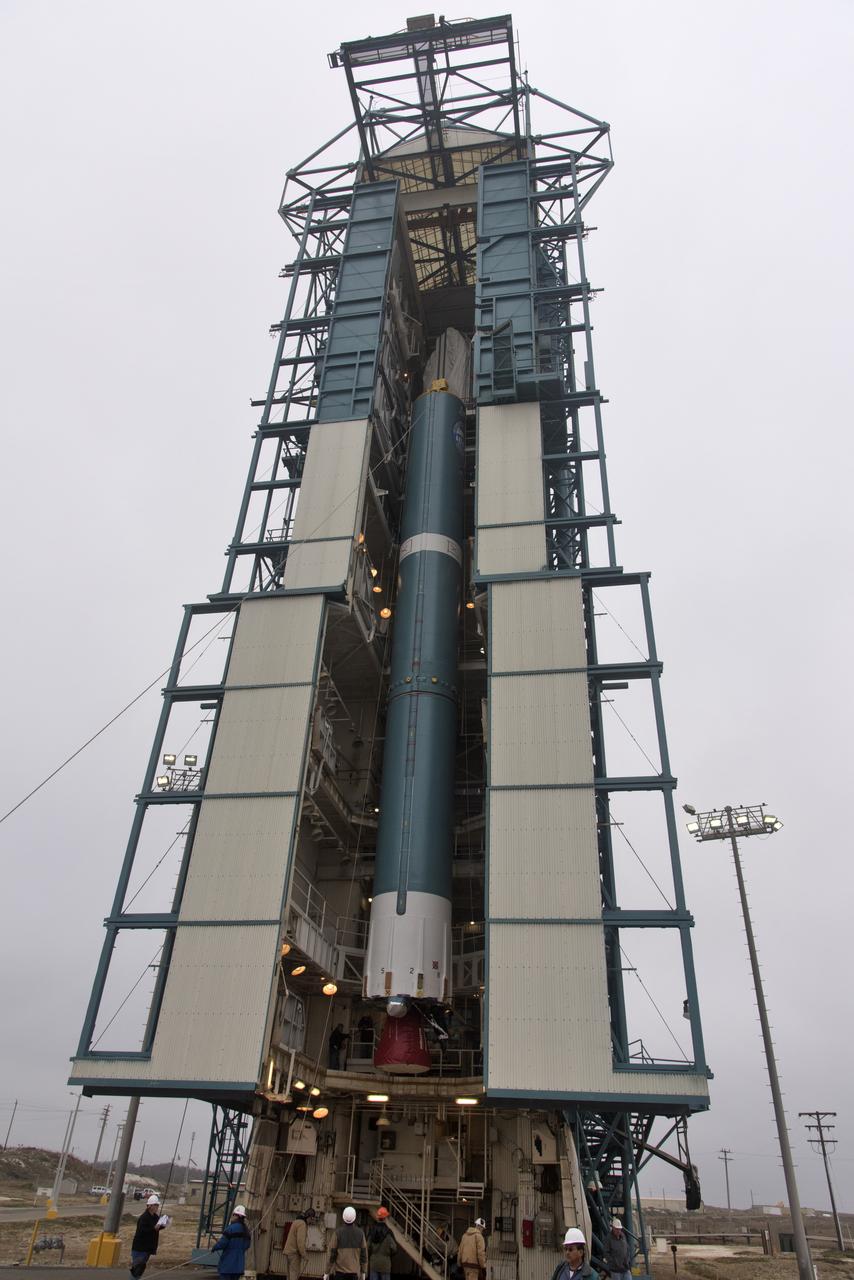

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted up in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

Michelle Thaller, NASA Communications (left), and Tom Wagner, ICESat-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters (right) speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).

The gantry rolls back at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 14, 2018, for the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket which will carry NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2). Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018, at 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT). The satellite will measure the height of our changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses per second. ICESat-2 will provide scientists with height measurements that create a global portrait of Earth's third dimension, gathering date that can precisely track changes of terrain, including glaciers, sea ice and forests.
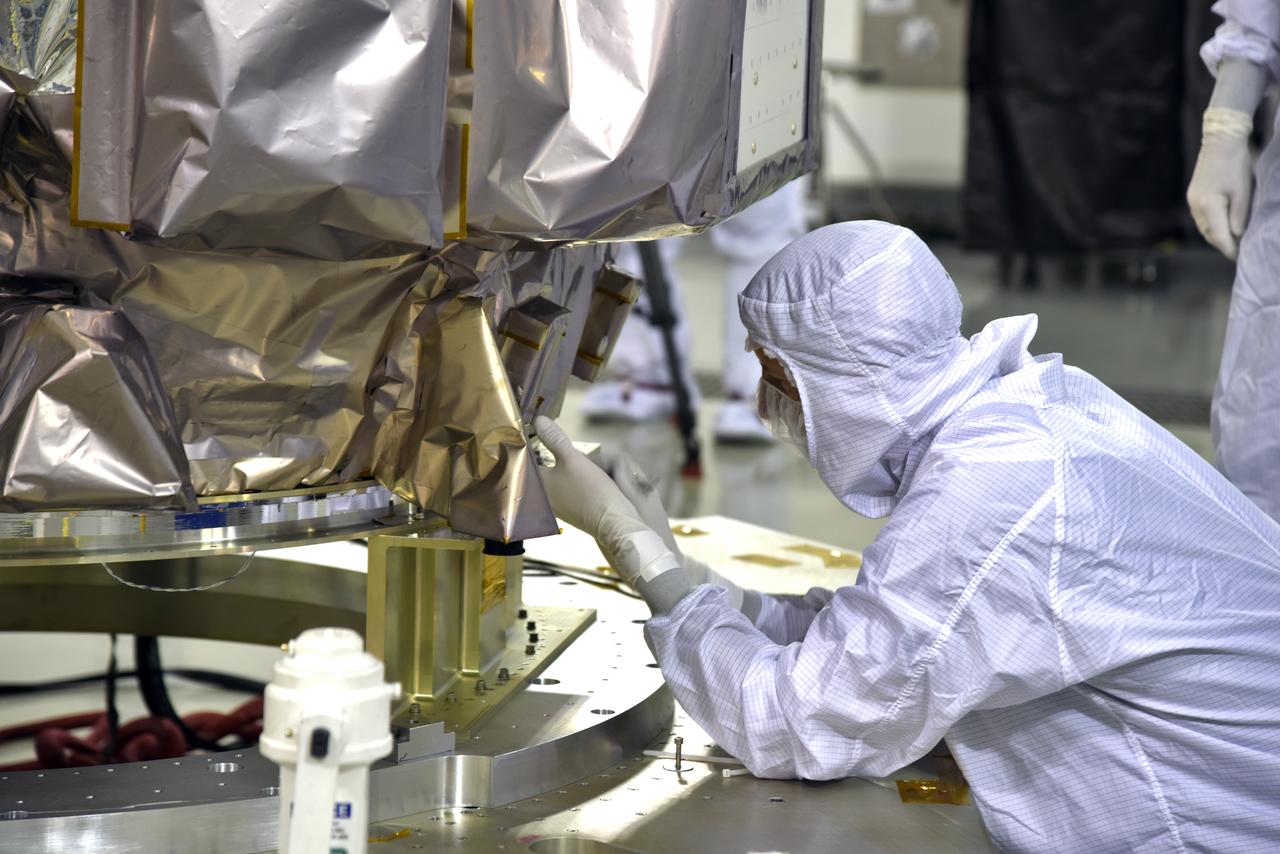

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician prepares NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) to be attached to the payload adapter, on Aug. 20, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
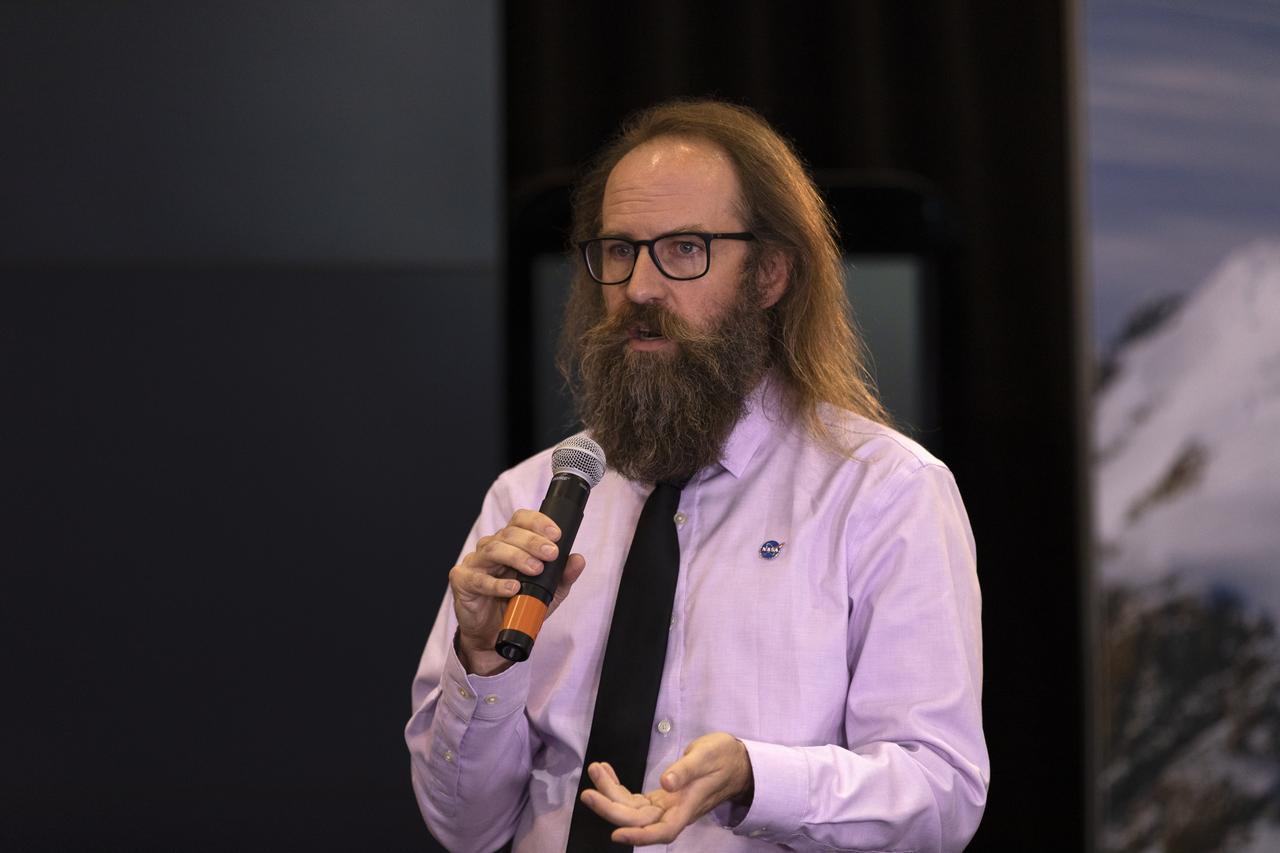

Tom Neumann, ICESat-2 deputy project scientist, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
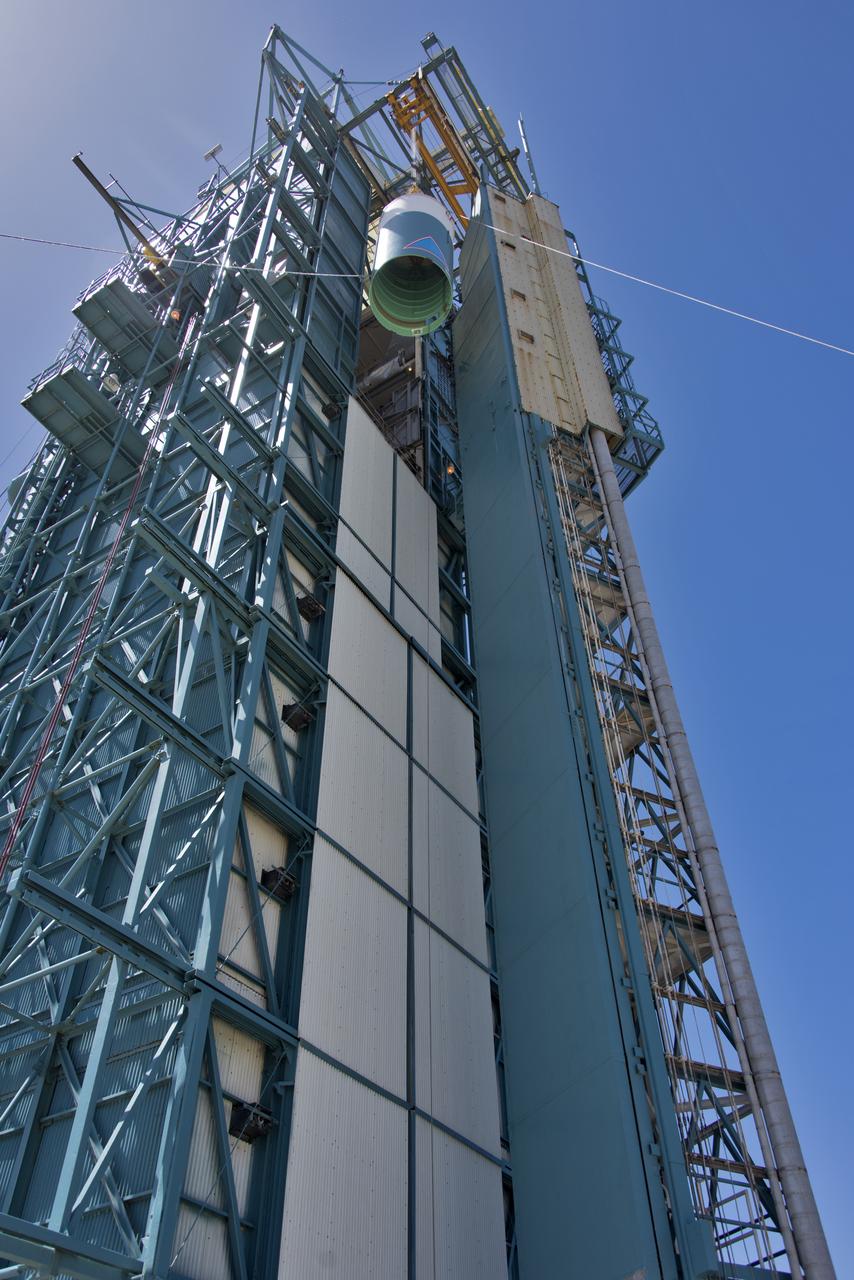

The United Launch Alliance Delta II interstage is lifted high up at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 12, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The interstage will be moved in and mated to the top of the booster, or first stage of the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
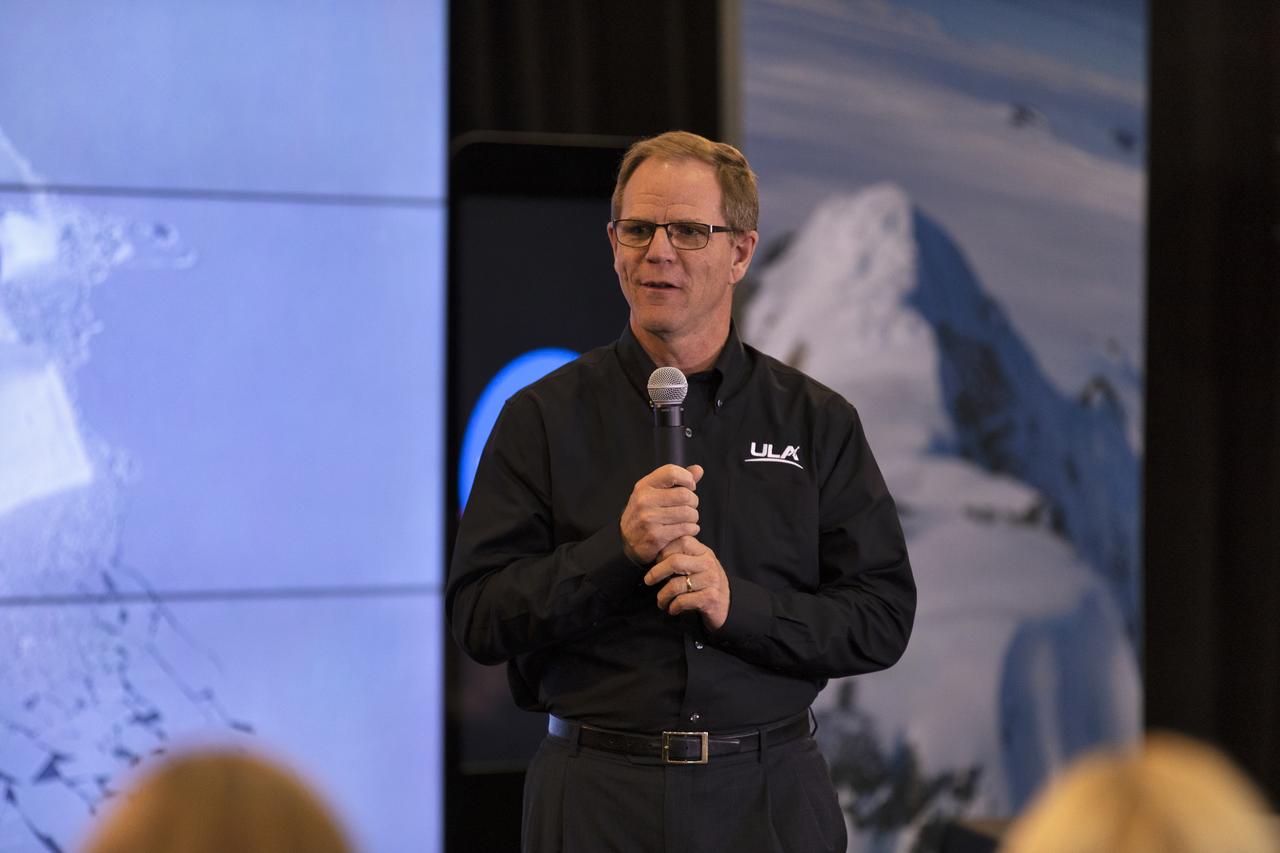

Scott Messer, program manager, NASA Programs, United Launch Alliance, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane lifts and moves NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on Aug. 30, 2018. The satellite will be attached to the payload adapter. ICESat-2 is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician checks the flight door for the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS) on NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on June 21, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry ATLAS. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
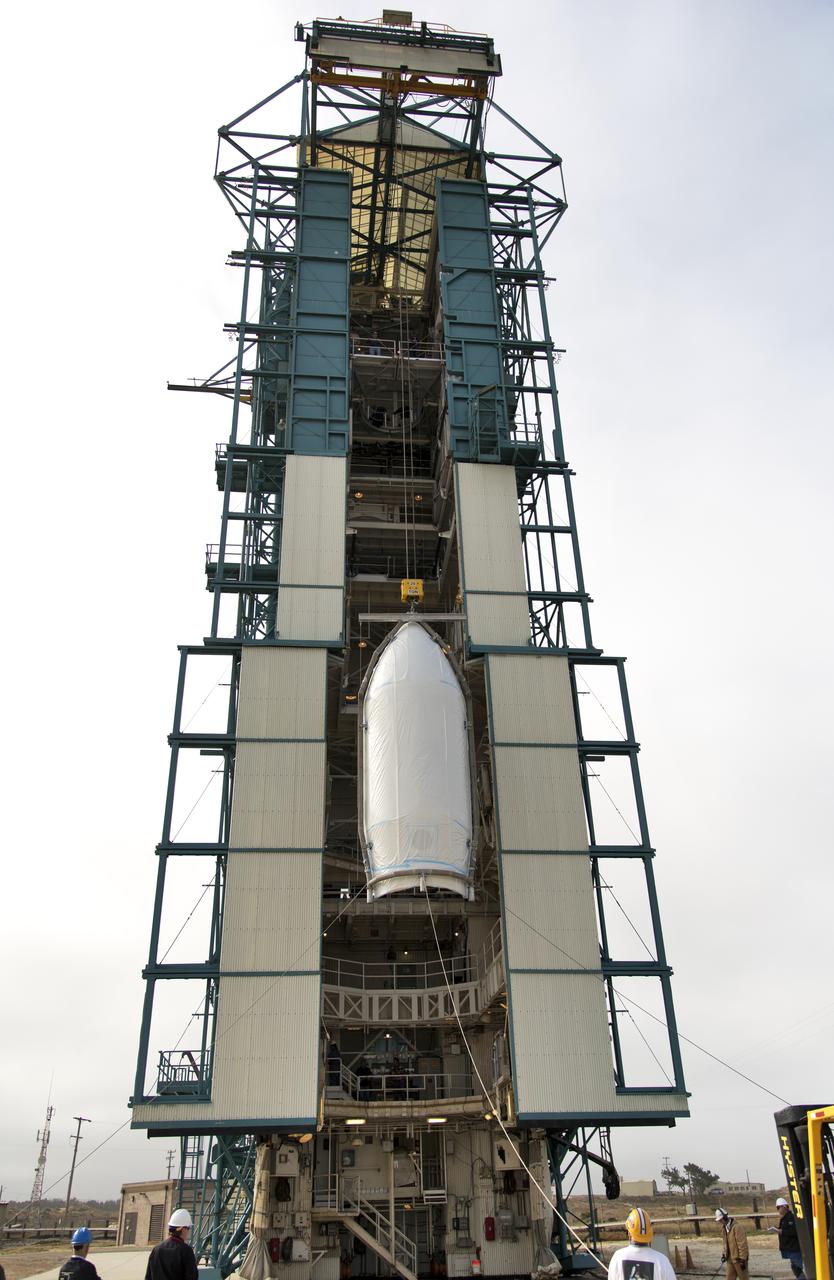

The first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket payload fairing is lifted up and into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on June 4, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch later this year on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
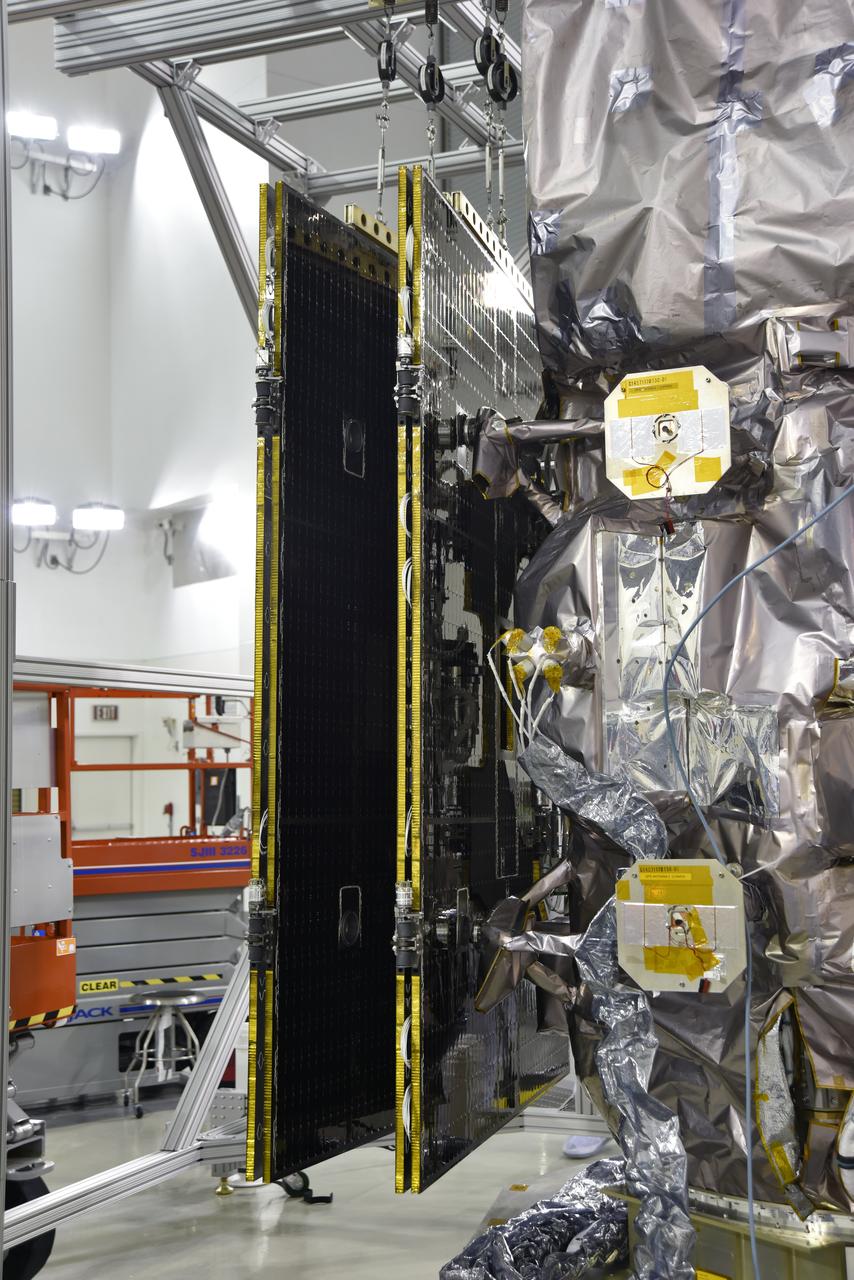

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solar array first motion test is underway on NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on June 18, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solar array first motion test is in progress on NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on June 18, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
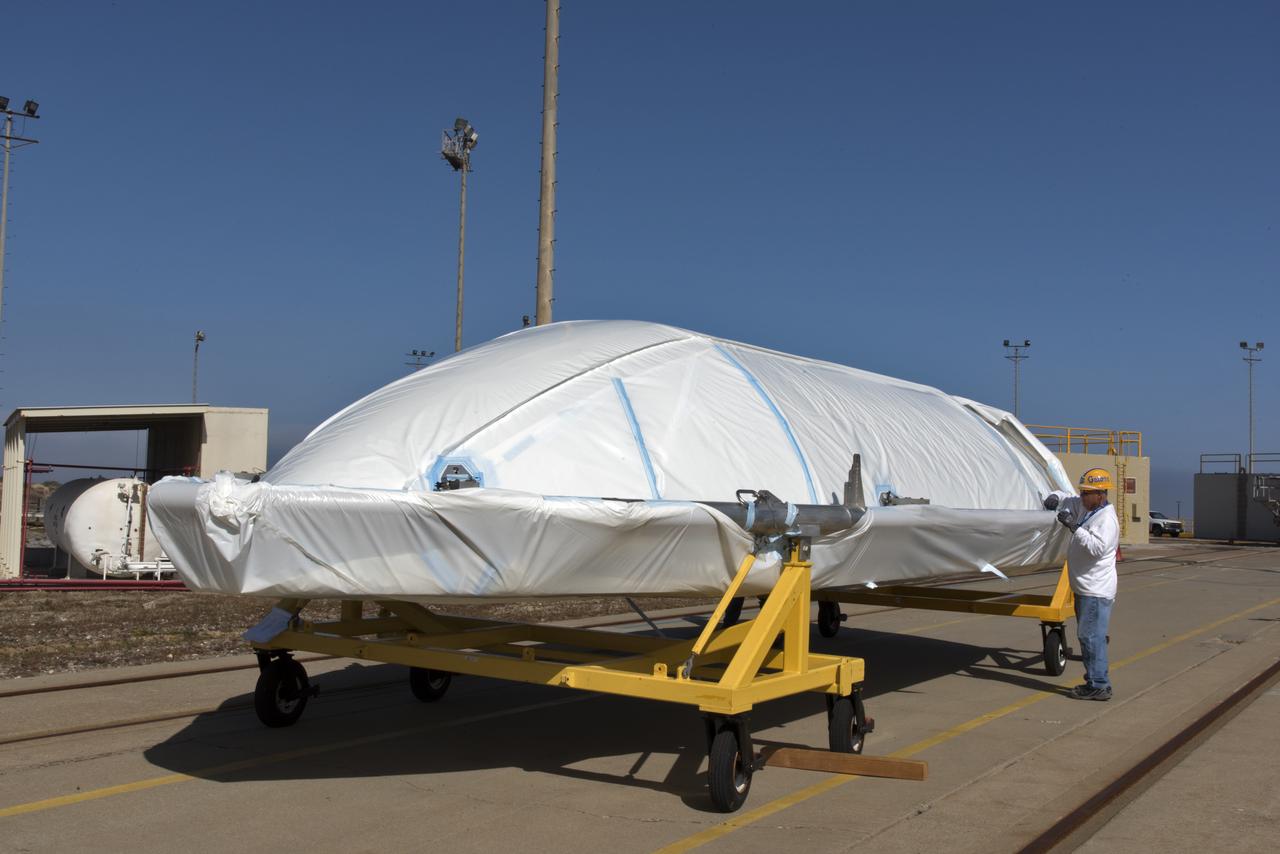

The second half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket payload fairing is being prepared for the move to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on June 4, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch later this year on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
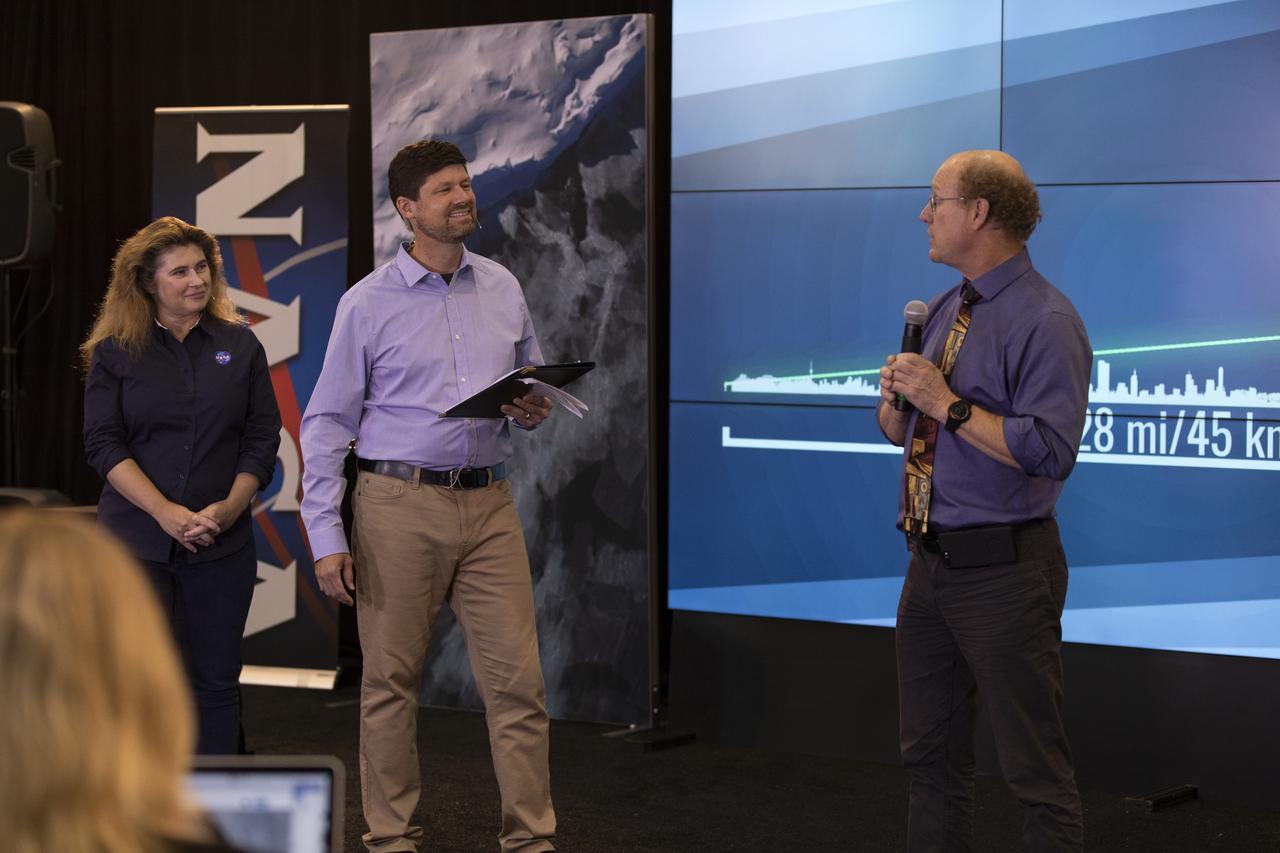

Doug McLennan, ICESat-2 project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).
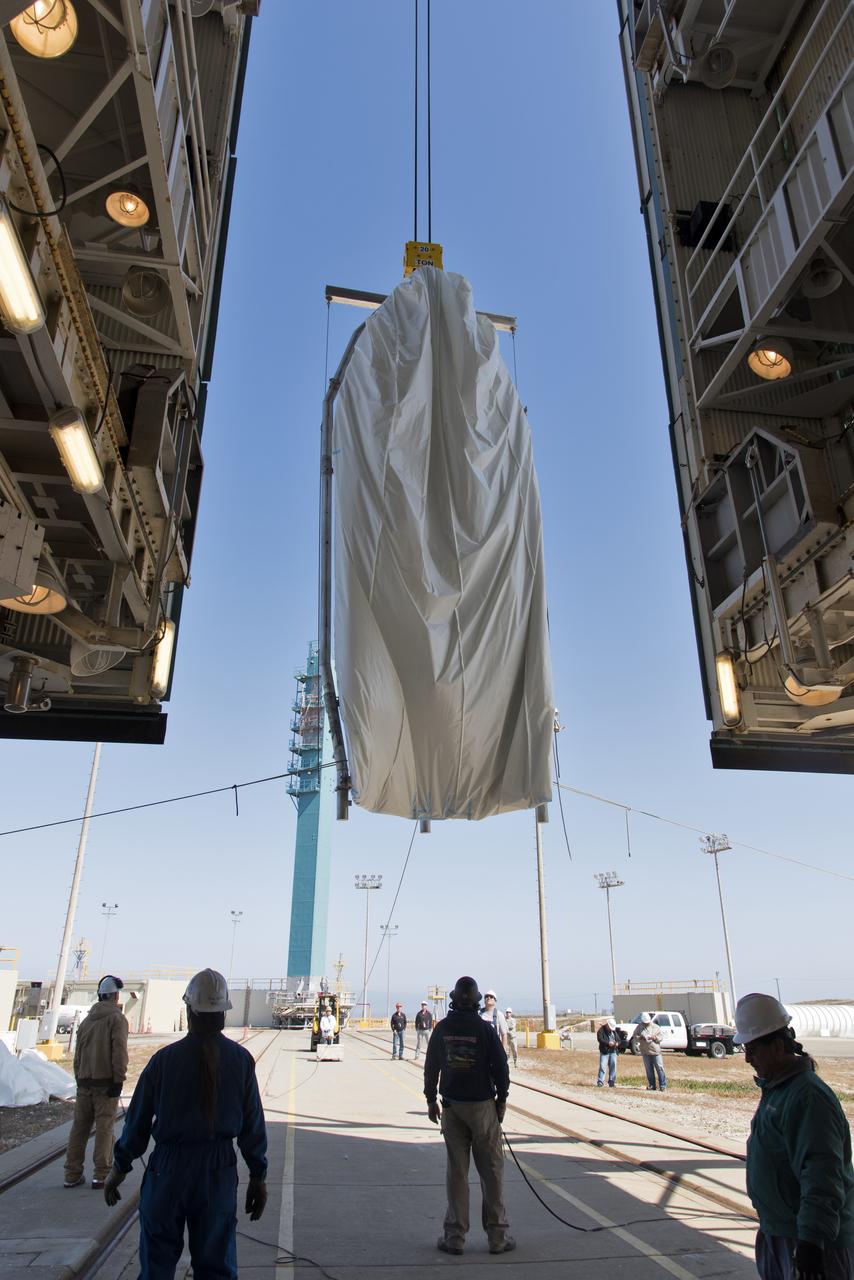

The second half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta II rocket payload fairing is lifted up into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on June 4, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch later this year on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
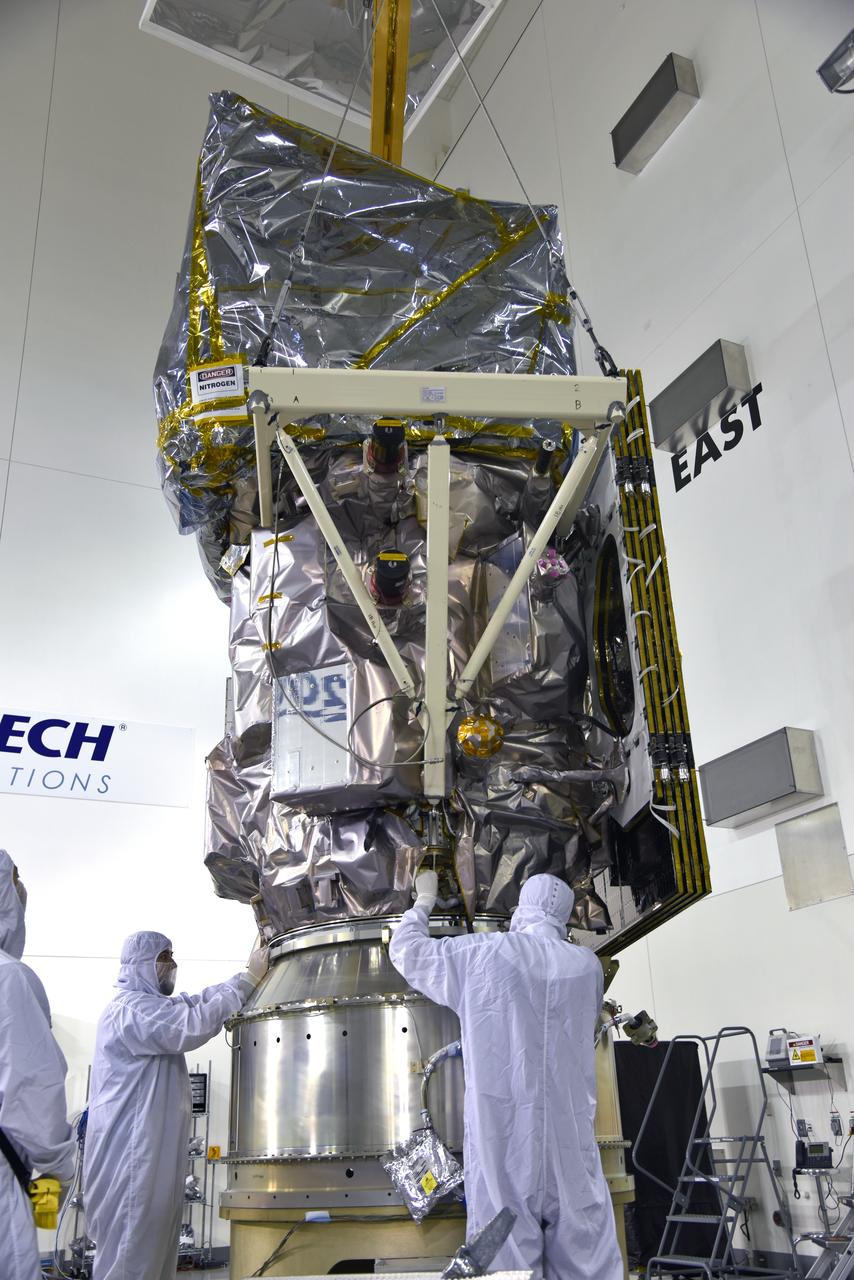

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians help secure NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) to the payload adapter on Aug. 30, 2018. ICESat-2 is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.

Bill Barnhart, ICESat-2 program manager, Northrop Grumman, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage arrives at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be lifted to vertical and moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to attach NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) to the payload adapter, on Aug. 20, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
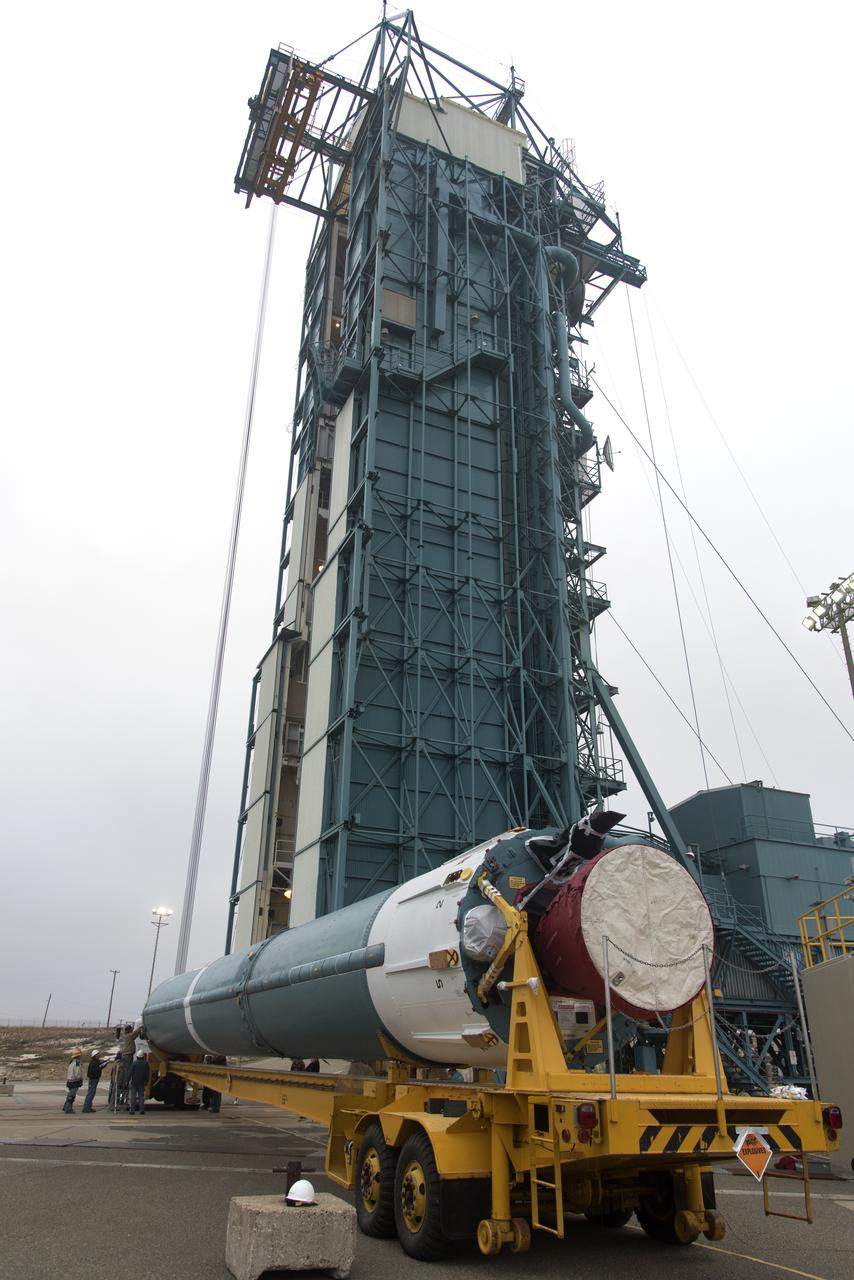

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage arrives at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be lifted to vertical and moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The solid rocket motor for mating to the United Launch Alliance Delta II launch vehicle is lifted up at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The solid rocket motor will be attached to the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
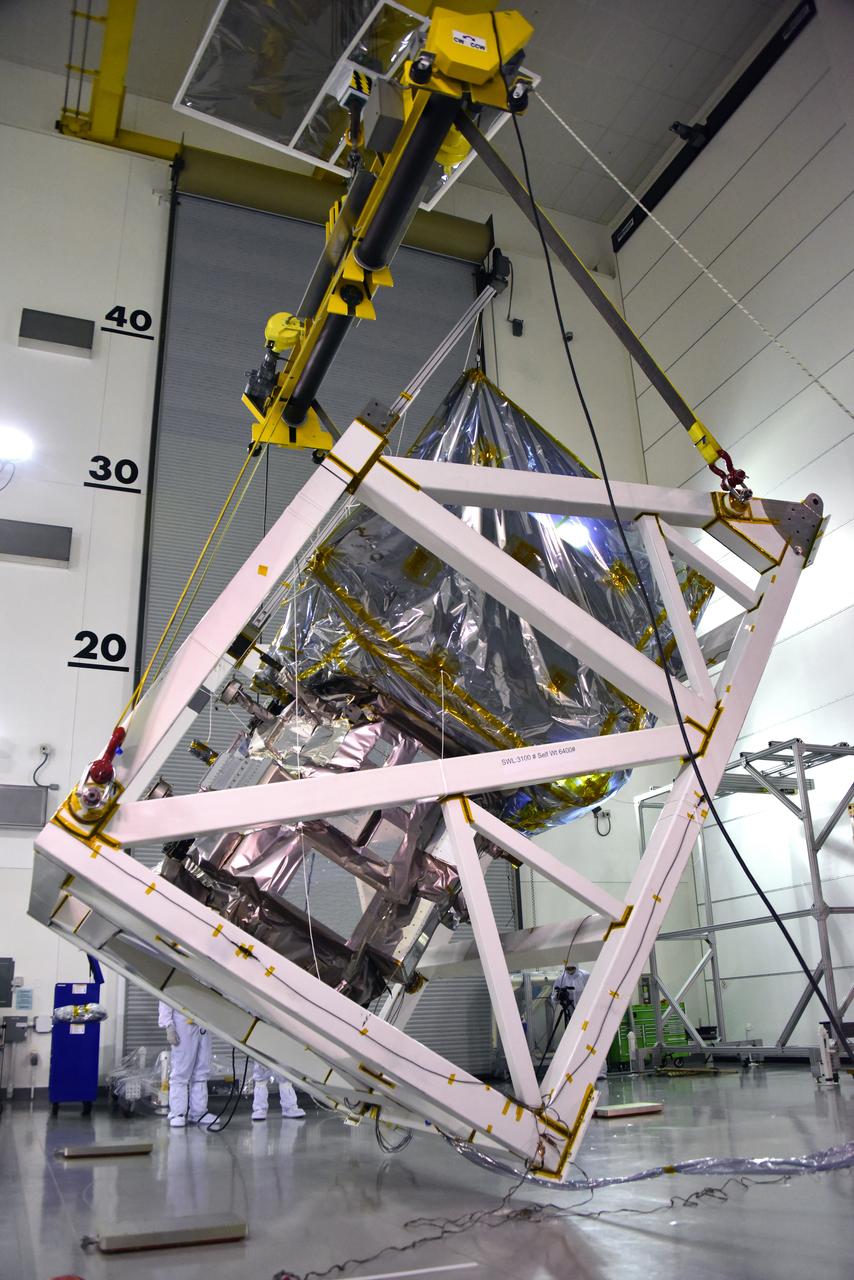
A crane is used to rotate NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) in its fixture inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility on June 14, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
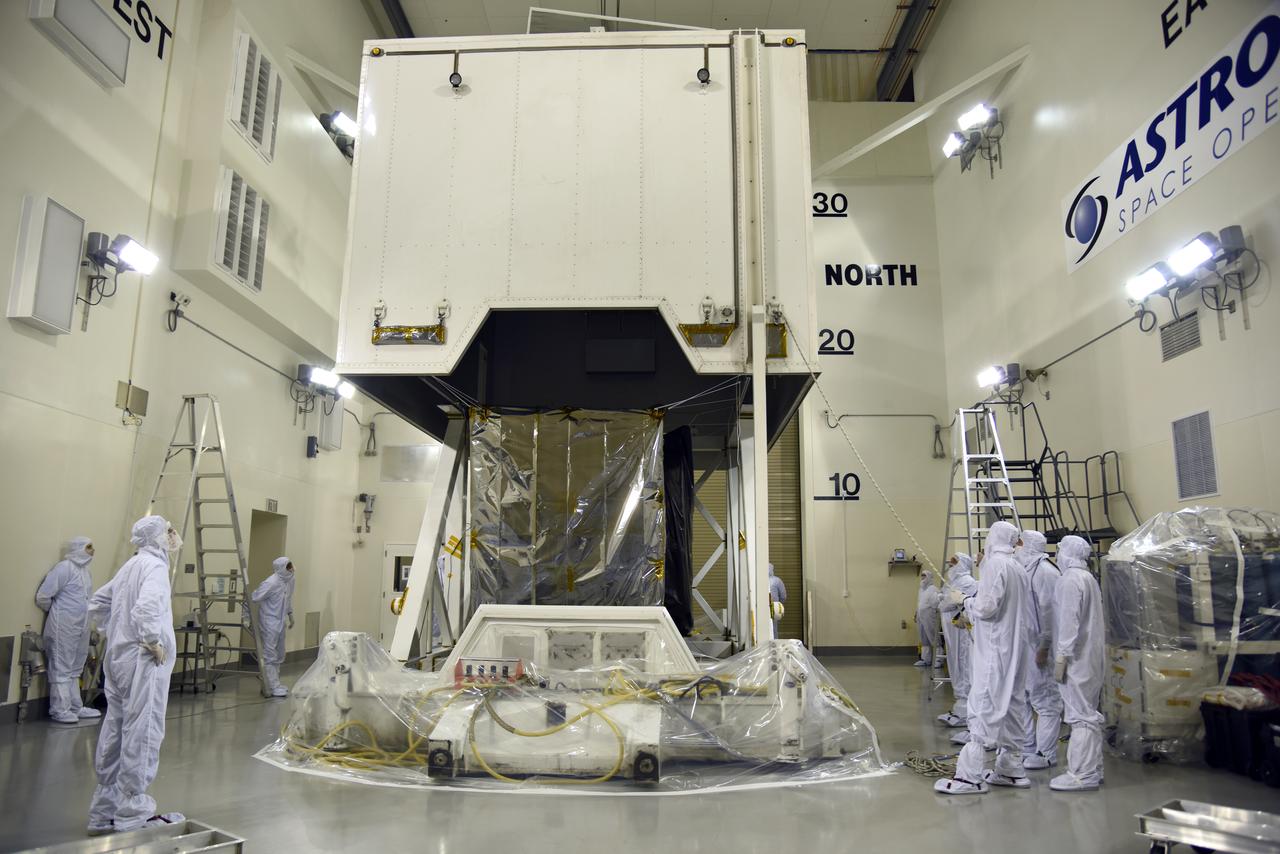

NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is uncrated inside the airlock of the Astrotech processing facility on June 13, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICESat-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. The satellite is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
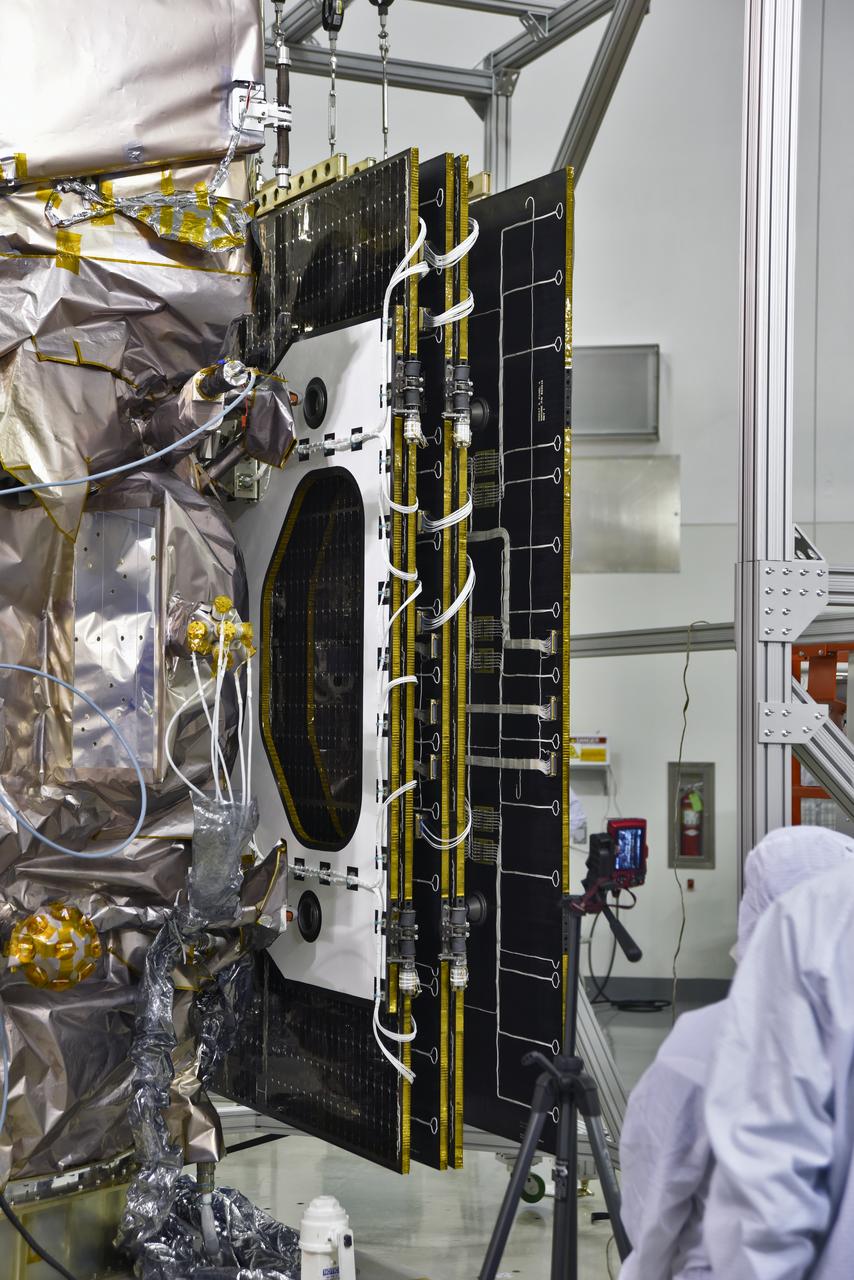

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a solar array first motion test is underway on NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on June 18, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted up and into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.