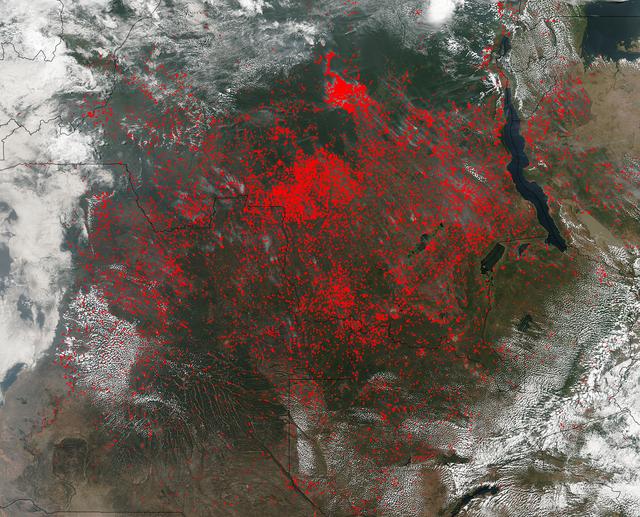
The Suomi NPP satellite's Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument captured a look at huge numbers of fires burning and the resulting smoke in central Africa on June 27, 2017. Actively burning areas, detected by VIIRS are outlined in red. The fires obscure most of the landscape in central Africa. June heralds the end of the crop season in this part of the world, and these fires may be intentional agricultural fires set by people to rid the area of left over crops and get it ready for the next season. So too some of these may also be lightning strike fires or they may be accidental fires which may have gotten out of control. The Suomi NPP satellite is a joint mission between NASA and NOAA. NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
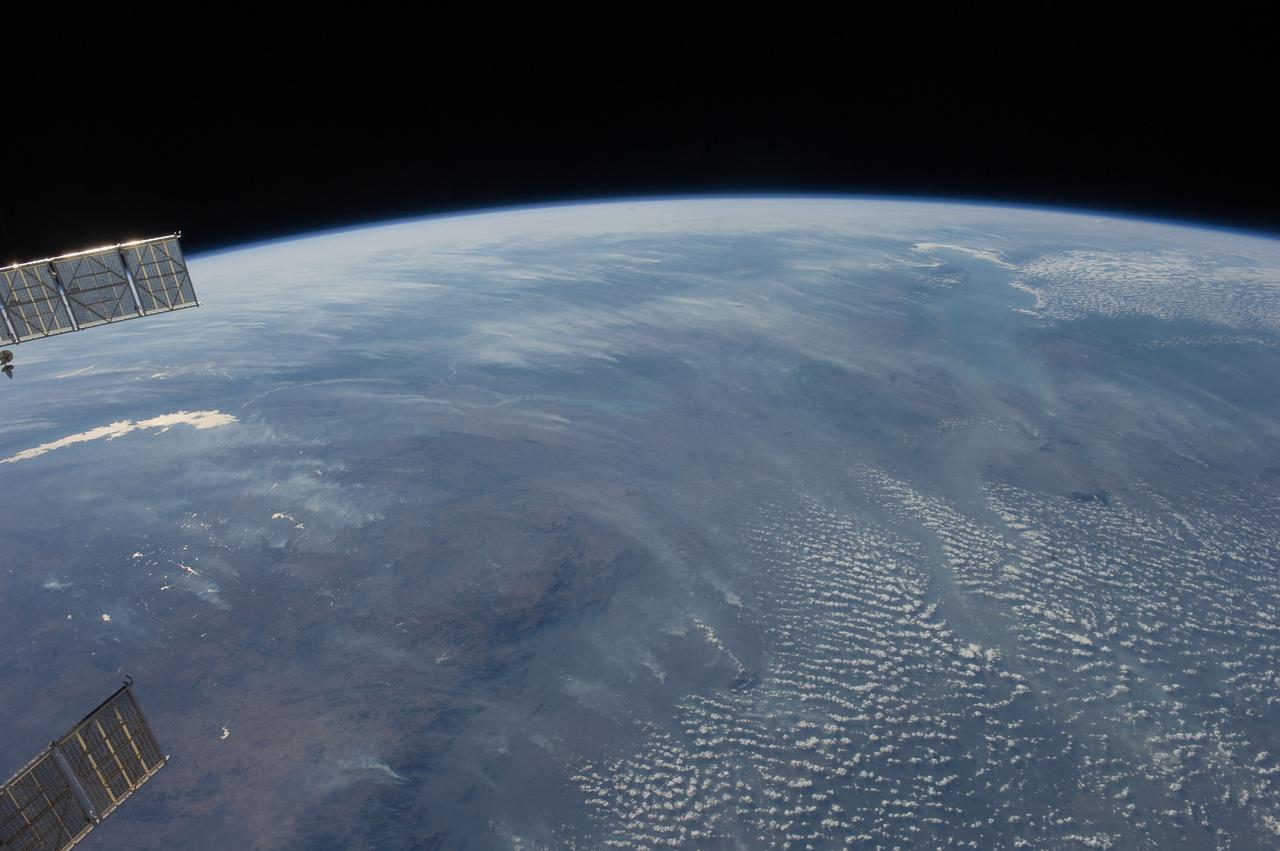

ISS028-E-018675 (23 July 2011) --- Biomass burning in southern Africa is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 28 crew member on the International Space Station. A smoke pall of subcontinental proportions dominates this view of tropical southern Africa. In what has been described as the most fire-prone part of the world, numerous fires give rise to regional smoke palls every dry season. Fires are both natural and set by local people to clear woodland for agricultural fields. This recent, oblique, northwest-looking view taken in July 2011 at the end of the dry season shows the extent of the smoke on the African plateau?from central Zimbabwe (lower left) to northern Malawi more than 1,000 kilometers away (top right)?and in the wide coastal plains of the lower Zambezi River valley of Mozambique (lower right). Here smoke can be seen blowing inland (left to right), channeled up the Zambezi River valley and contributing to the pall on the plateau. The light gray smoke plumes contrast with higher altitude, brighter patchy cloud cover at lower right. The smoke palls obscure much surface detail, so that Lake Malawi, one of Africa?s Great Lakes, is barely visible, as is Lake Cahora Bassa, Africa?s fourth largest reservoir, in the Zambezi valley. The sun?s reflection off its surface (sunglint) makes Lake Kariba most prominent in the view at left. Kariba is the world?s largest artificial reservoir by volume, and is 220 kilometers long, giving a sense of the scale of the view. The steep, shadowed, mid-afternoon faces of the Inyanga Mountains on the Mozambique-Zimbabwe border protrude above the smoke layer at lower left. Solar panels extending from Russian spacecraft docked at the International Space Station are visible in the foreground at left.