First Image of MESSENGER Extended Mission
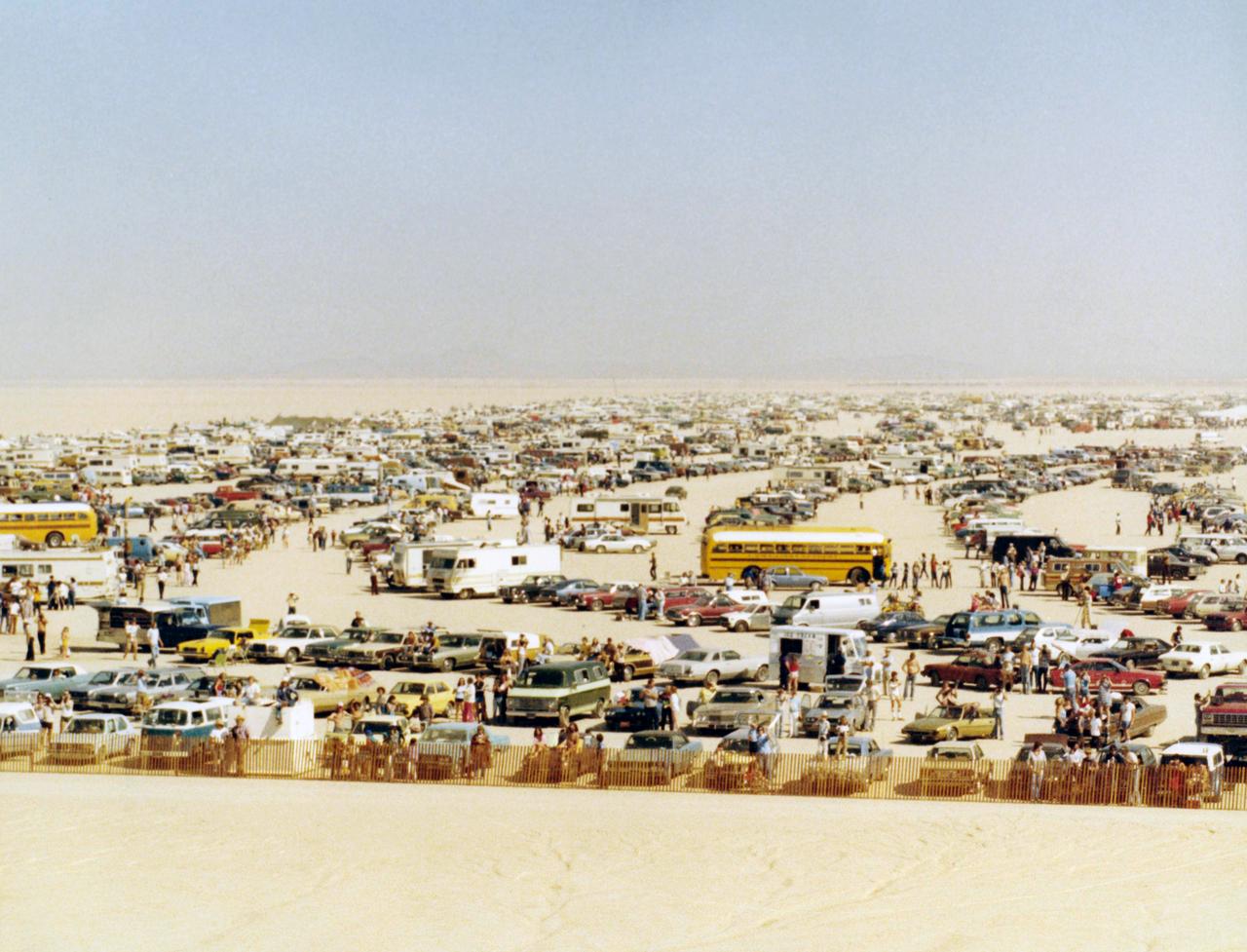

Large crowds gathered on Rogers Dry Lake at Edwards AFB to see the first landing of the Space Shuttle Columbia, completing its first orbital mission.
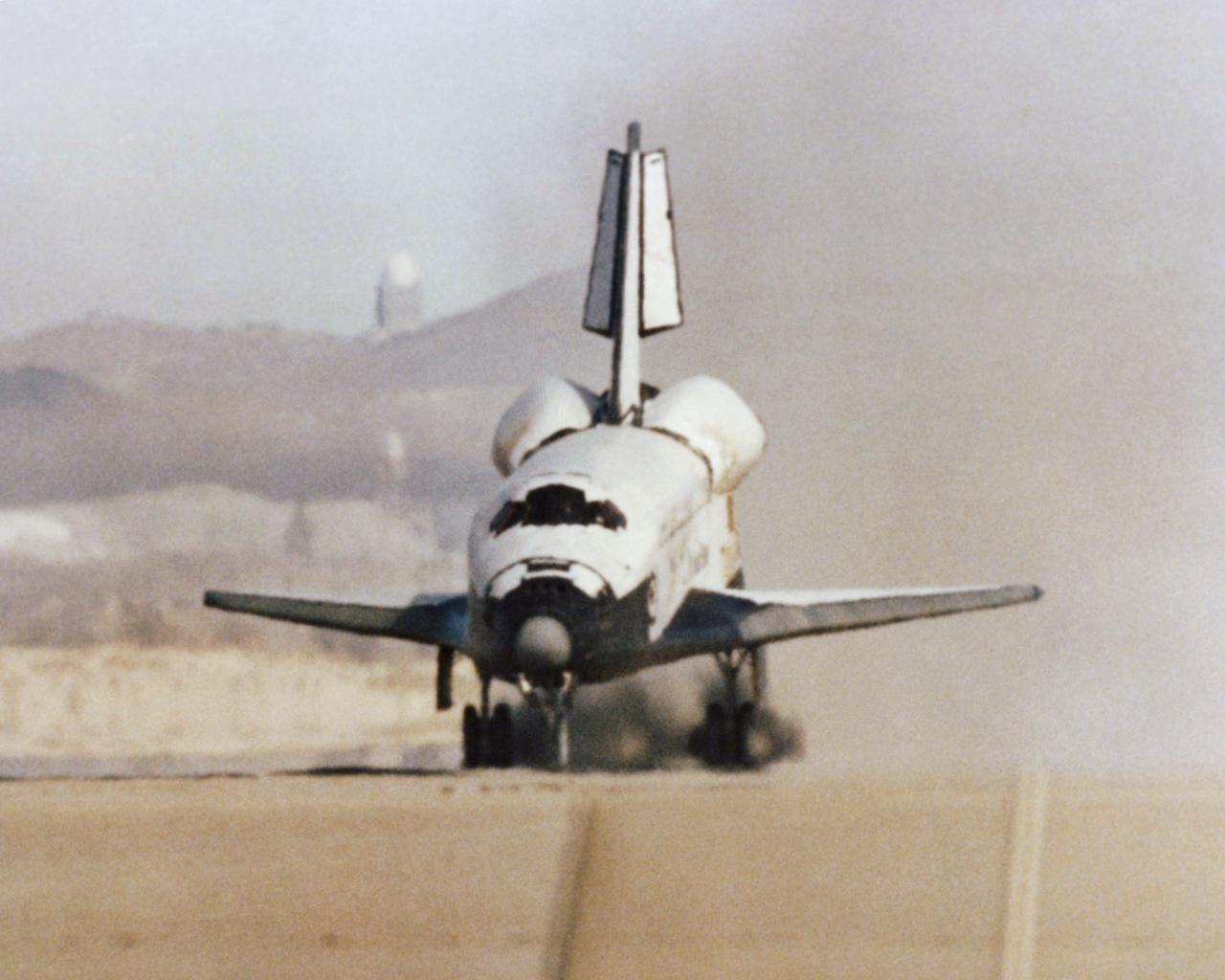

The Space Shuttle Columbia touches down on lakebed runway 23 at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., to conclude the first orbital shuttle mission.
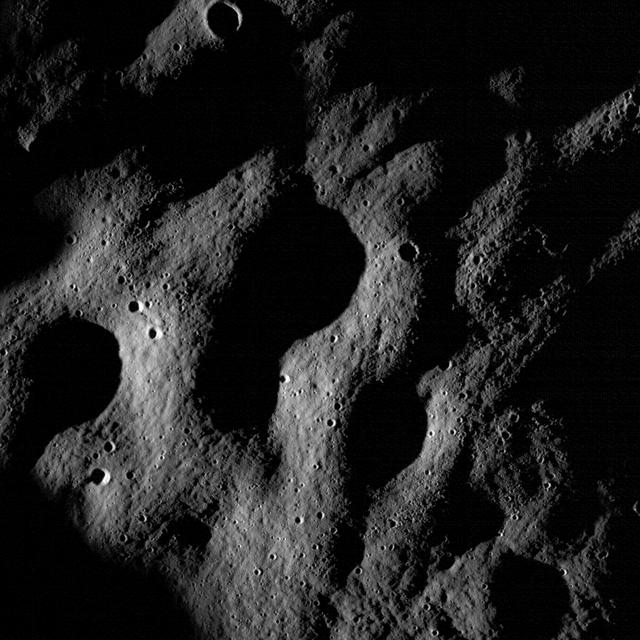

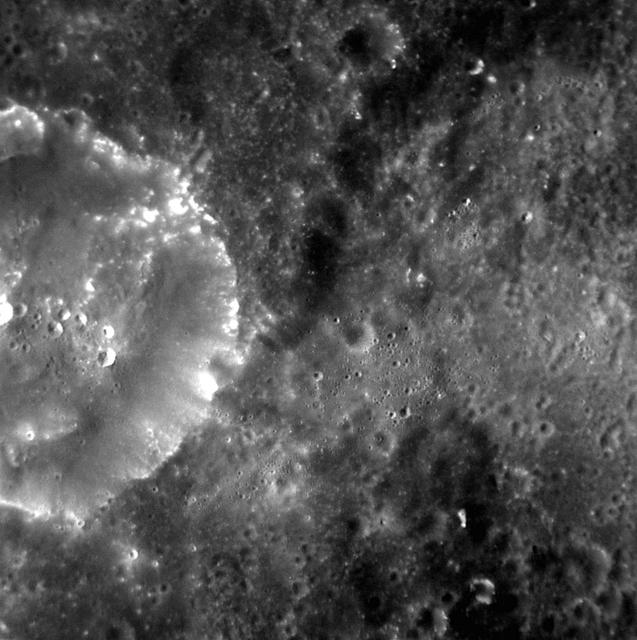
These images show cratered regions near the moon's Mare Nubium region, as photographed by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter's LROC instrument. Each image shows a region 1,400 meters (0.87 miles) wide. the bottoms of both images face lunar north. The image below shows the location of these two images in relation to each other. Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/Arizona State University
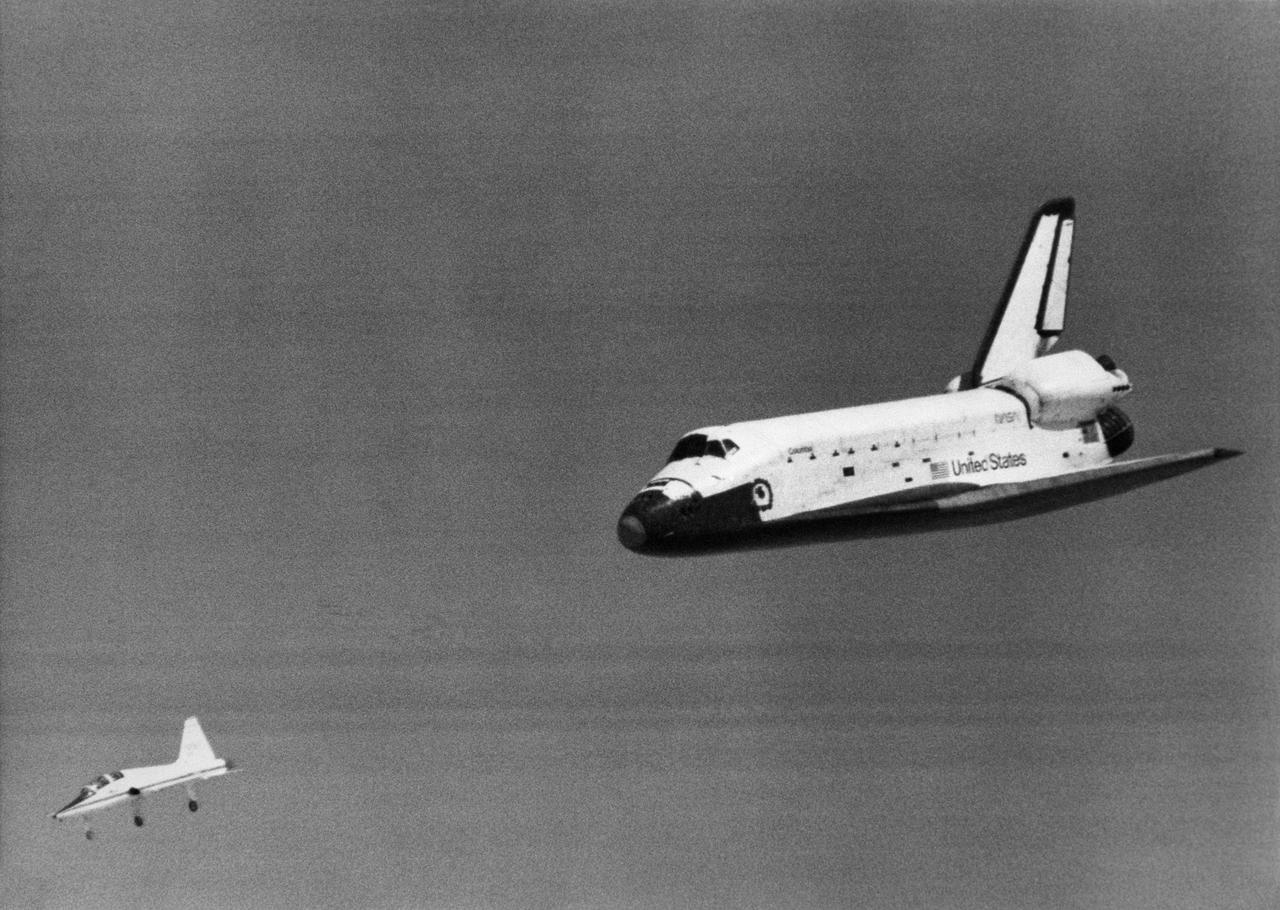

The Space Shuttle Columbia glides down over Rogers Dry Lake as it heads for a landing at Edwards Air Force Base at the conclusion of its first orbital mission on April 14, 1981.
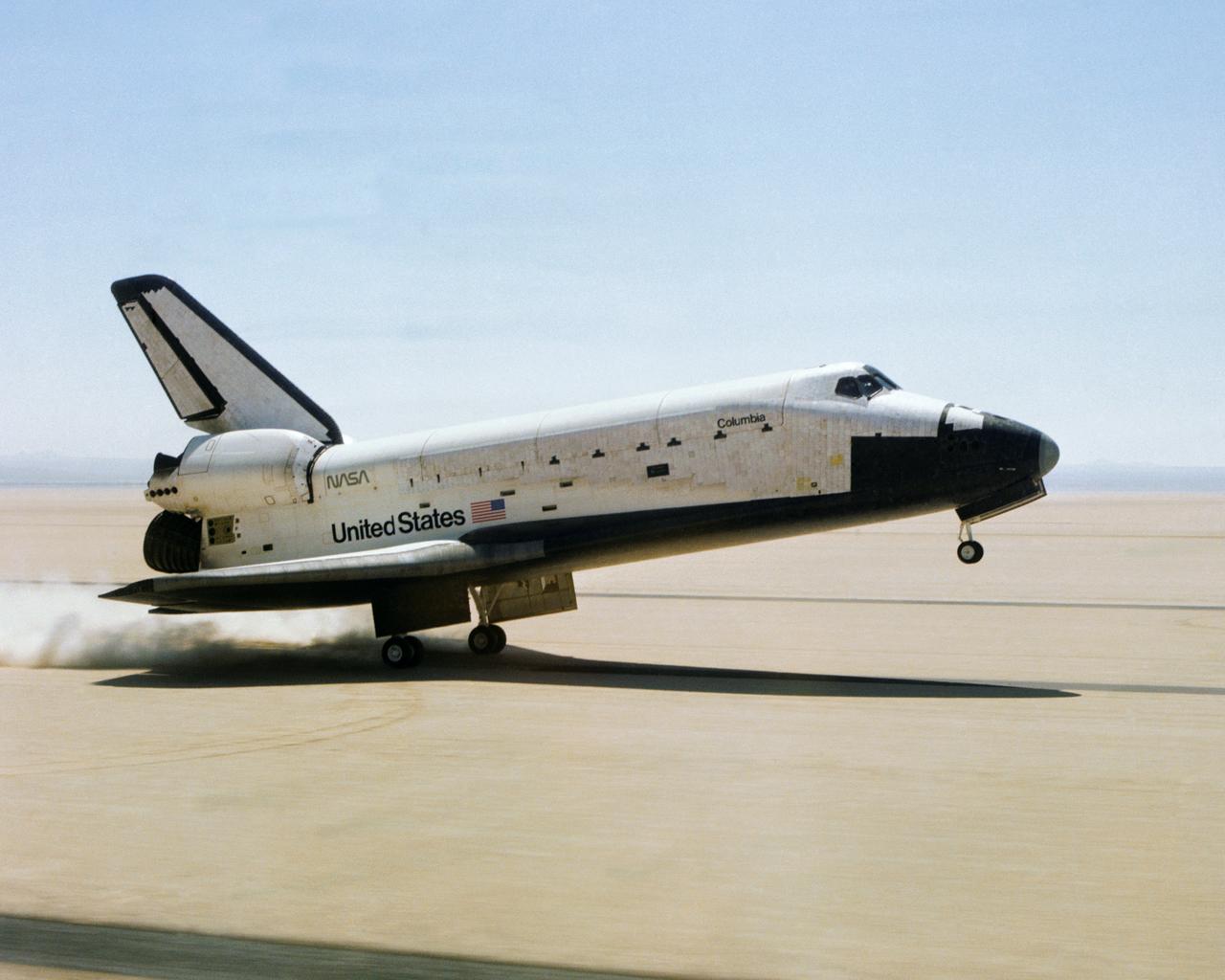

The Space Shuttle Columbia touches down on lakebed runway 23 at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., to conclude the first orbital shuttle mission. (JSC photo # S81-30734)
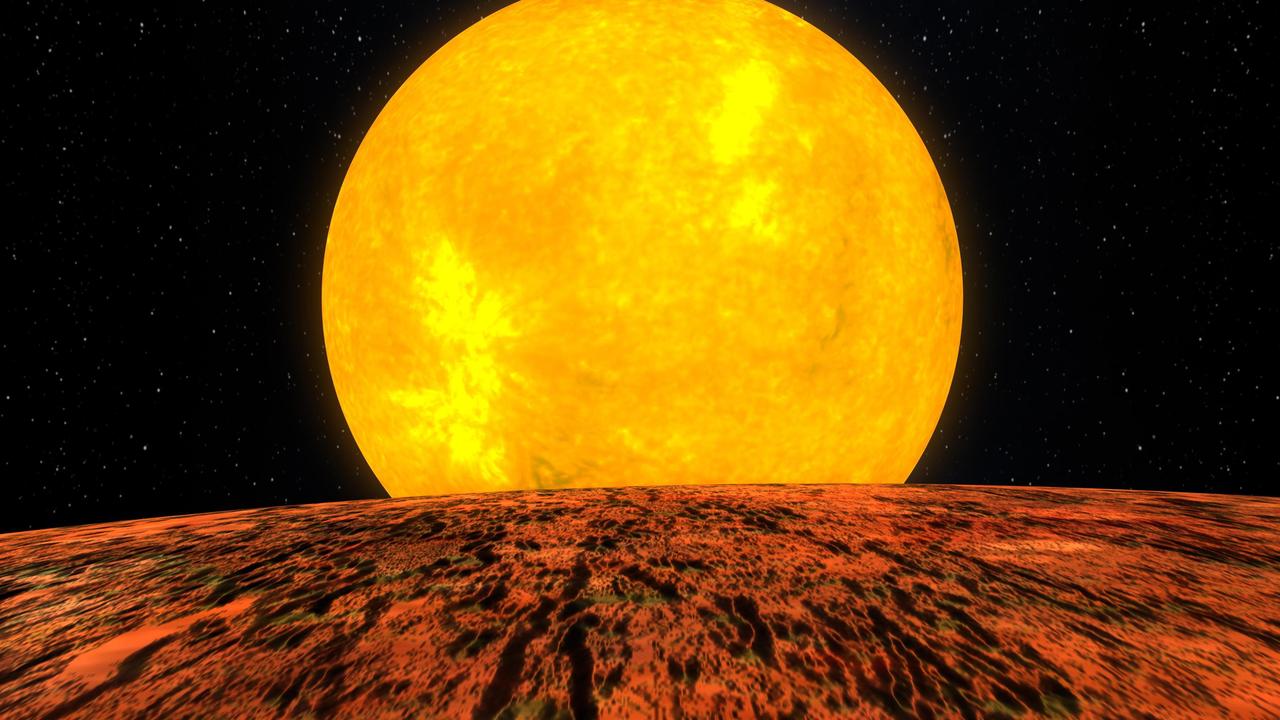

Artist concept of the first rocky world discovered by NASA Kepler mission. The planet, called Kepler 10-b, is shown in front of its host star.
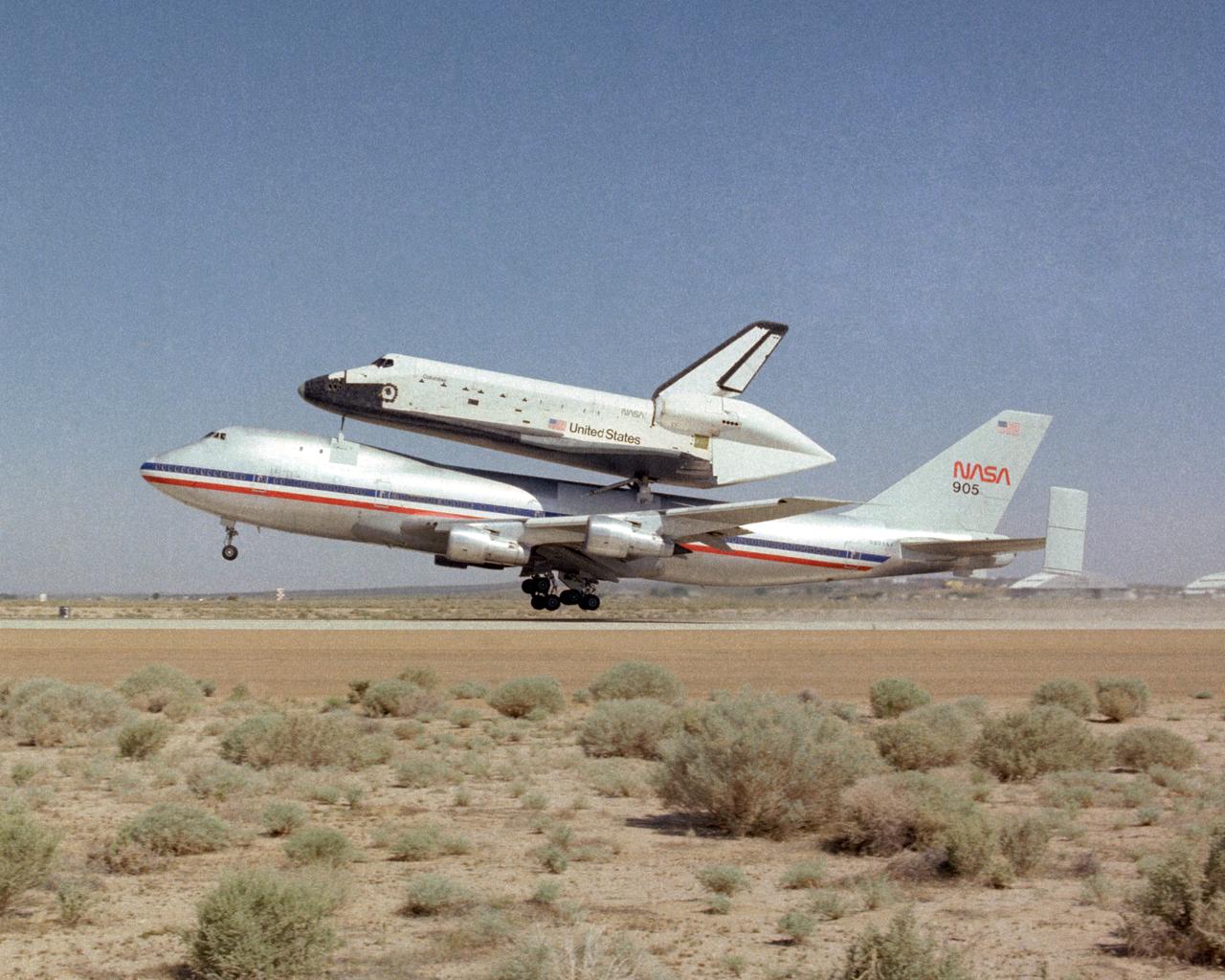

NASA's specially modified 747 with the Space Shuttle Columbia atop takes off to ferry the Shuttle back to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Columbia had recently completed its first orbital mission with a landing at Edwards Air Force Base in California.
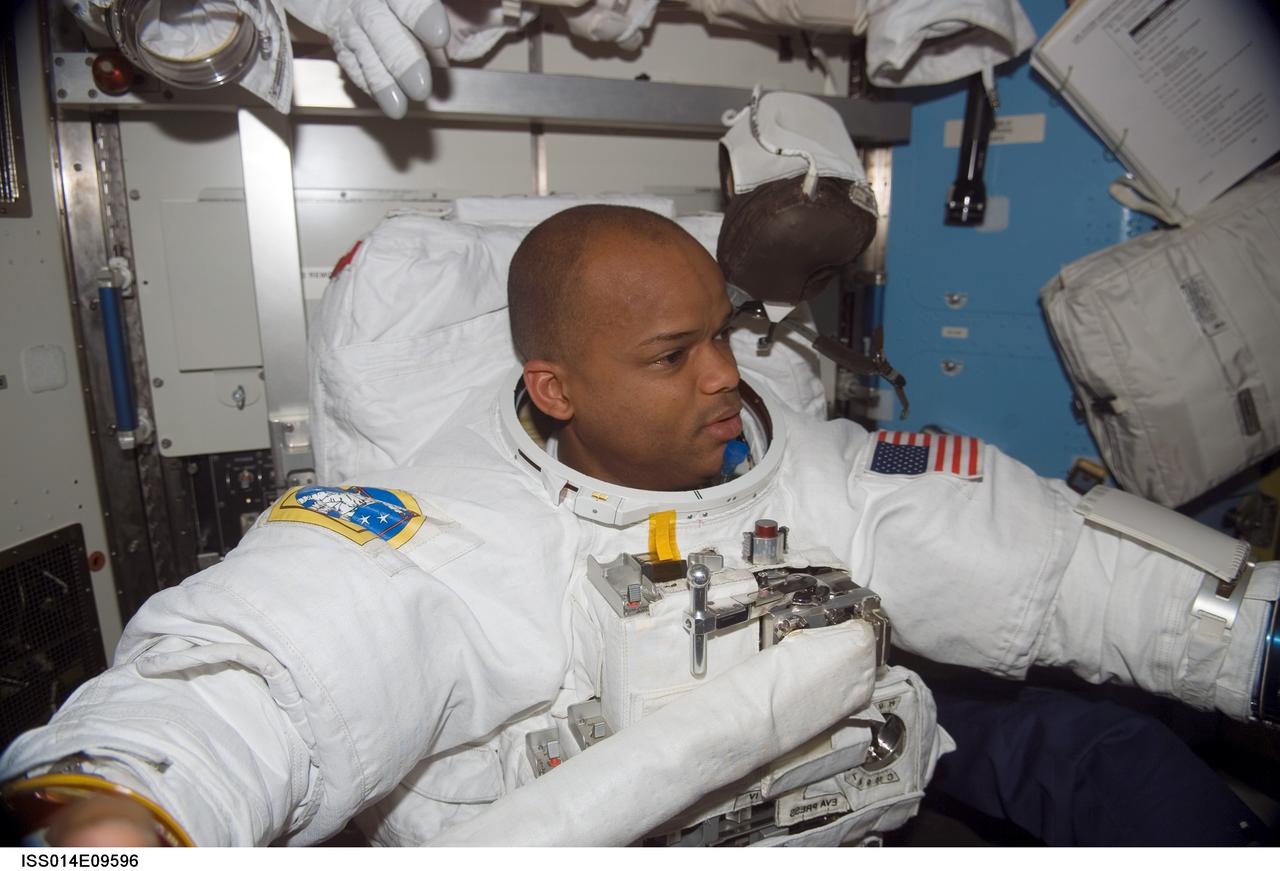

ISS014-E-09596 (12 Dec. 2006) --- Attired in his extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit, astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., STS-116 mission specialist, prepares for the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) in the Quest Airlock of the International Space Station while Space Shuttle Discovery was docked with the station.
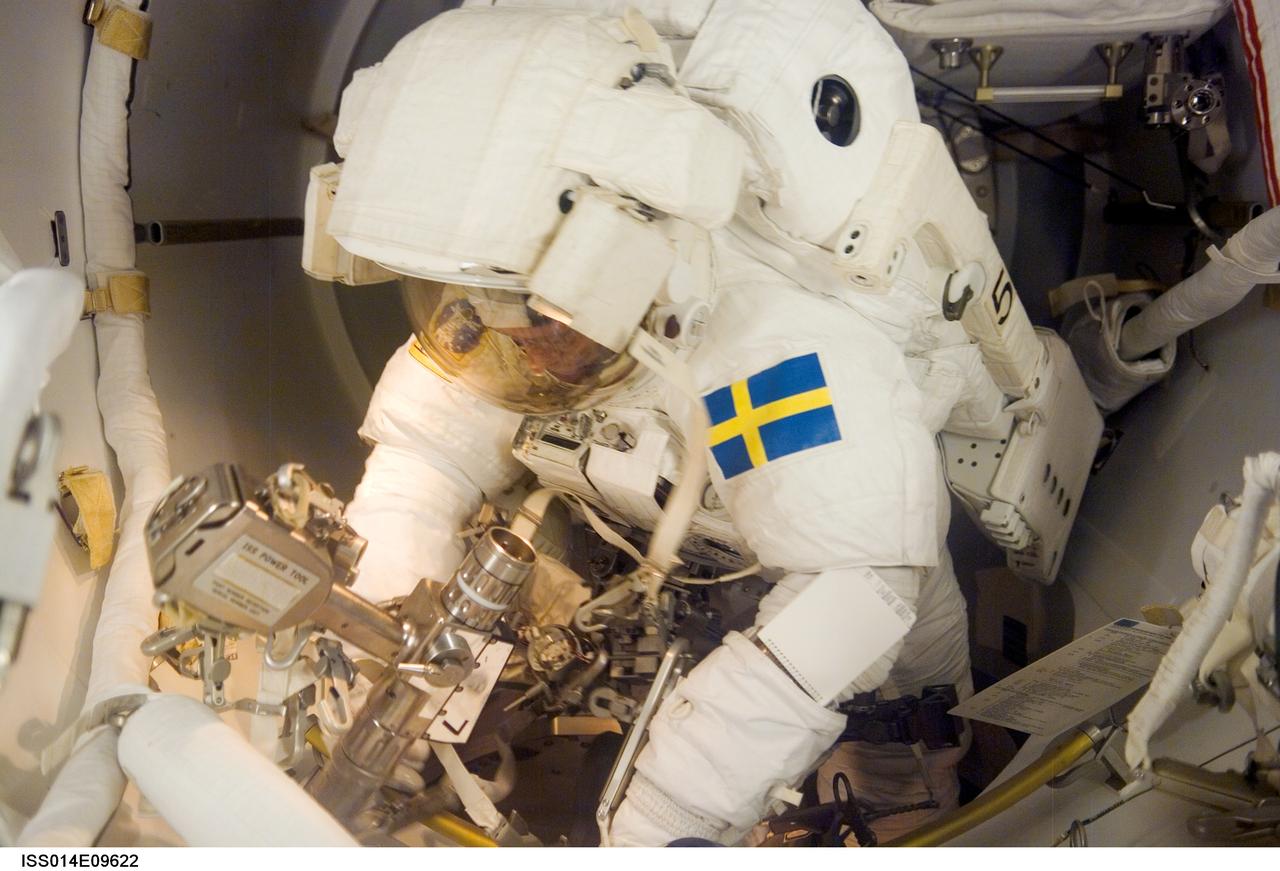

ISS014-E-09622 (12 Dec. 2006) --- Attired in his extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit, European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Christer Fuglesang, STS-116 mission specialist, makes final preparations for the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) in the Quest Airlock of the International Space Station.
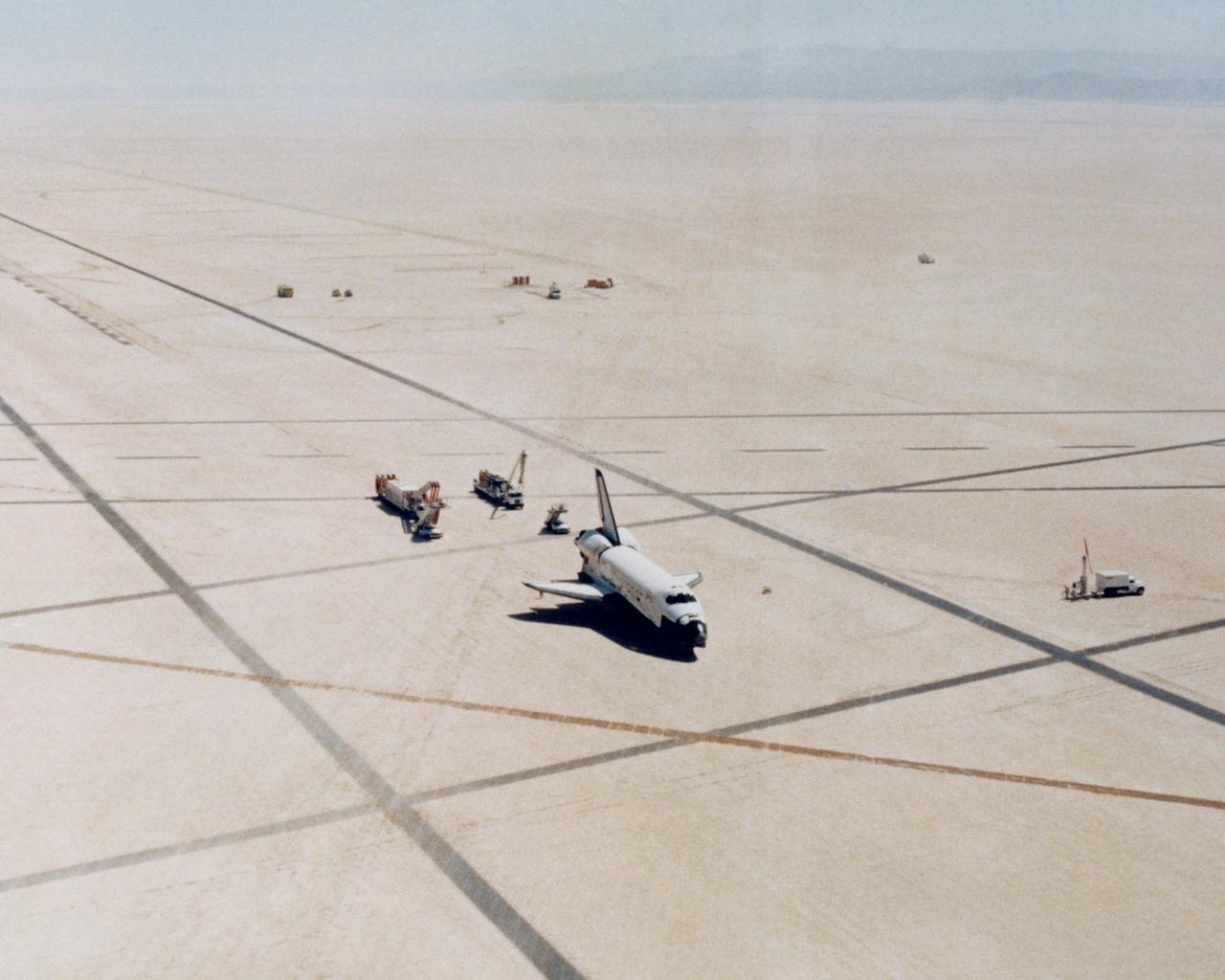

The Space Shuttle Columbia on Rogers Dry lakebed at Edwards AFB after landing to complete its first orbital mission on April 14, 1981. Technicians towed the Shuttle back to the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center for post-flight processing and preparation for a return ferry flight atop a modified 747 to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. (JSC photo # S81-30749)
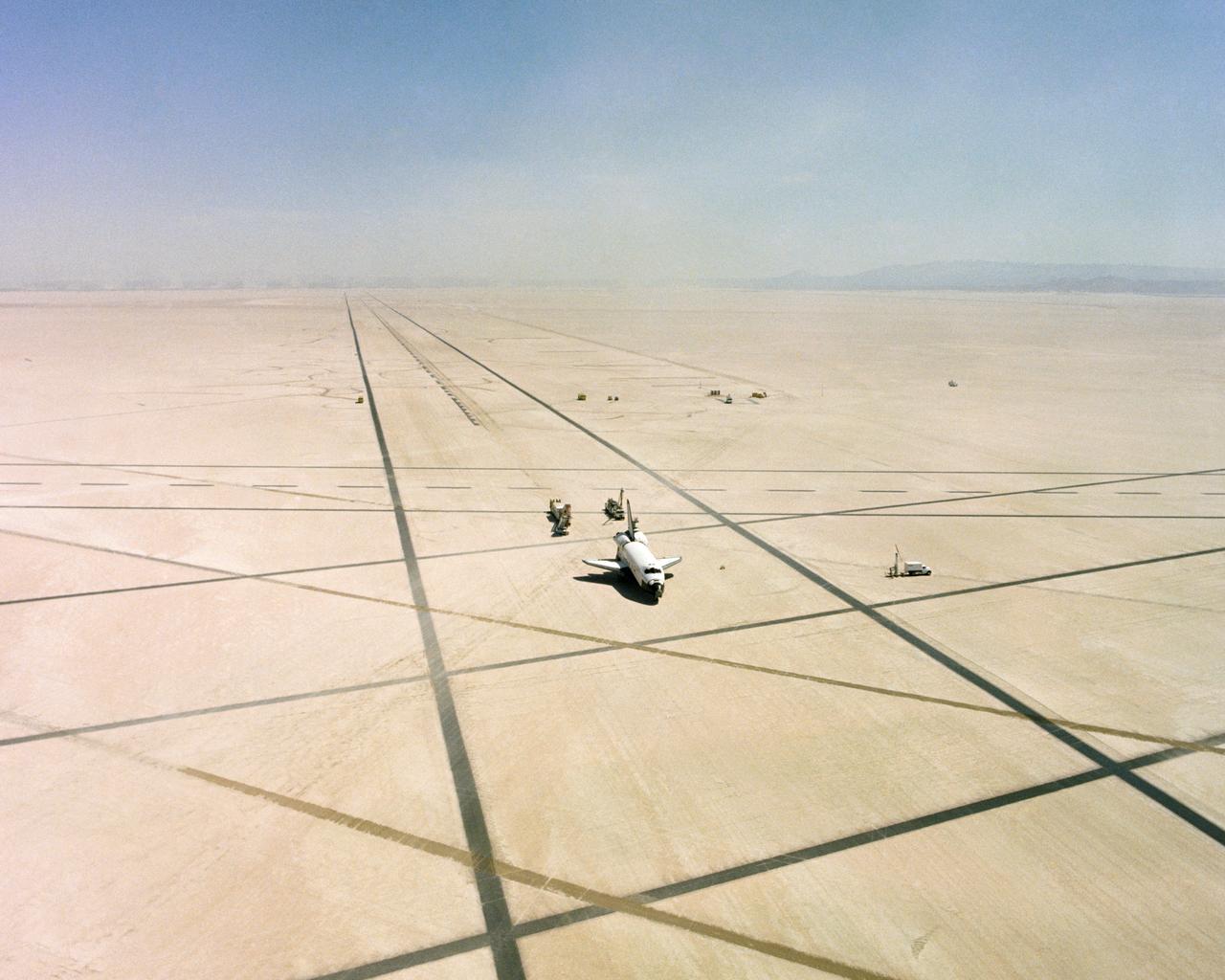

The Space Shuttle Columbia on Rogers Dry lakebed at Edwards AFB after landing to complete its first orbital mission on April 14, 1981. Technicians towed the Shuttle back to the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center for post-flight processing and preparation for a return ferry flight atop a modified 747 to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. (JSC photo # S81-31163)
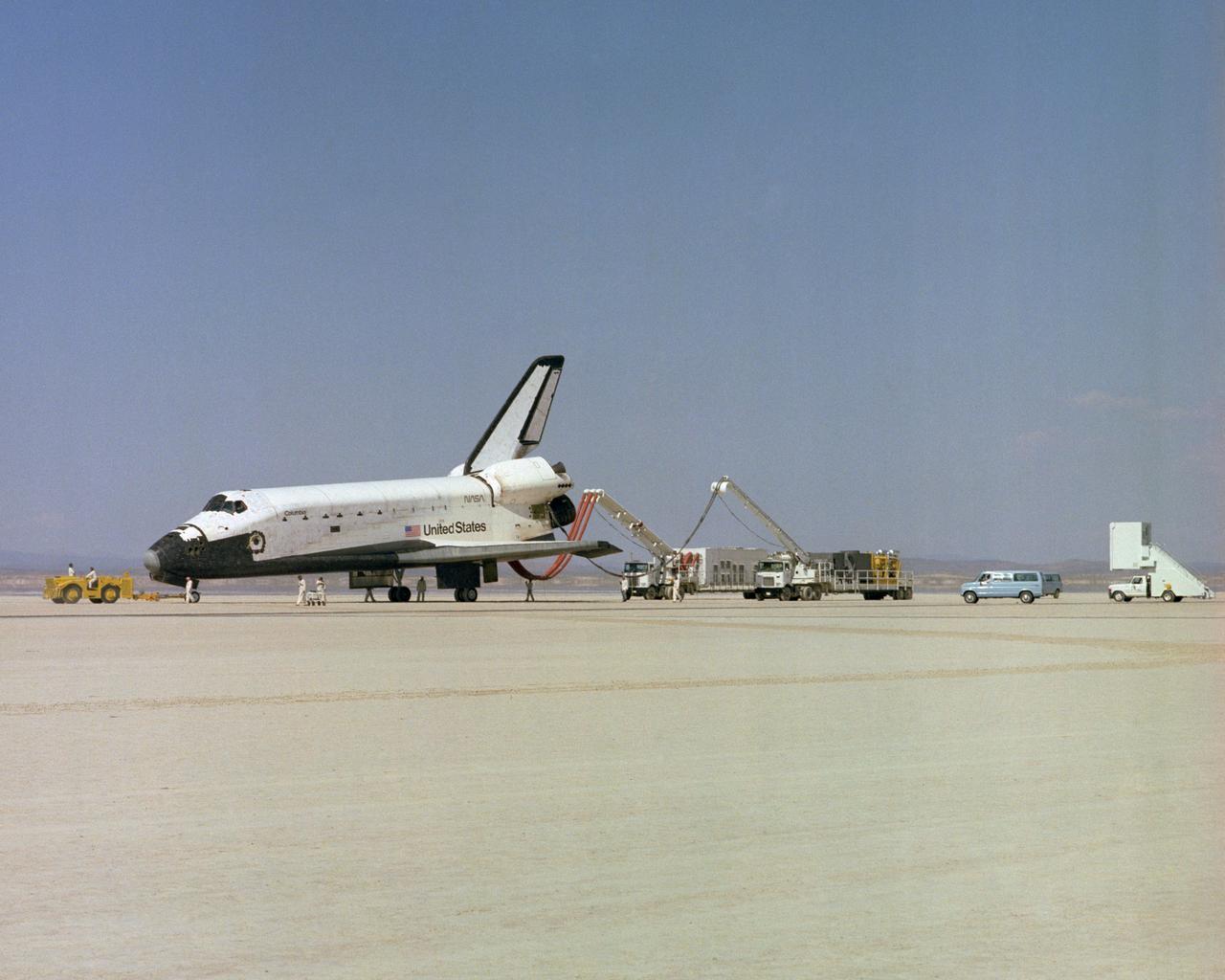

The Space Shuttle Columbia on Rogers Dry lakebed at Edwards AFB after landing to complete its first orbital mission on April 14, 1981. Technicians towed the Shuttle back to the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center for post-flight processing and preparation for a return ferry flight atop a modified 747 to Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
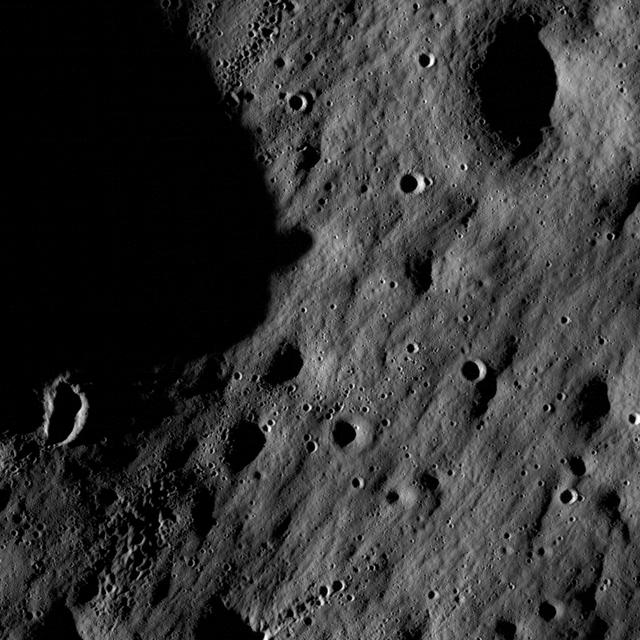

These images show cratered regions near the moon's Mare Nubium region, as photographed by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter's LROC instrument. Each image shows a region 1,400 meters (0.87 miles) wide. the bottoms of both images face lunar north. The image below shows the location of these two images in relation to each other. Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/Arizona State University
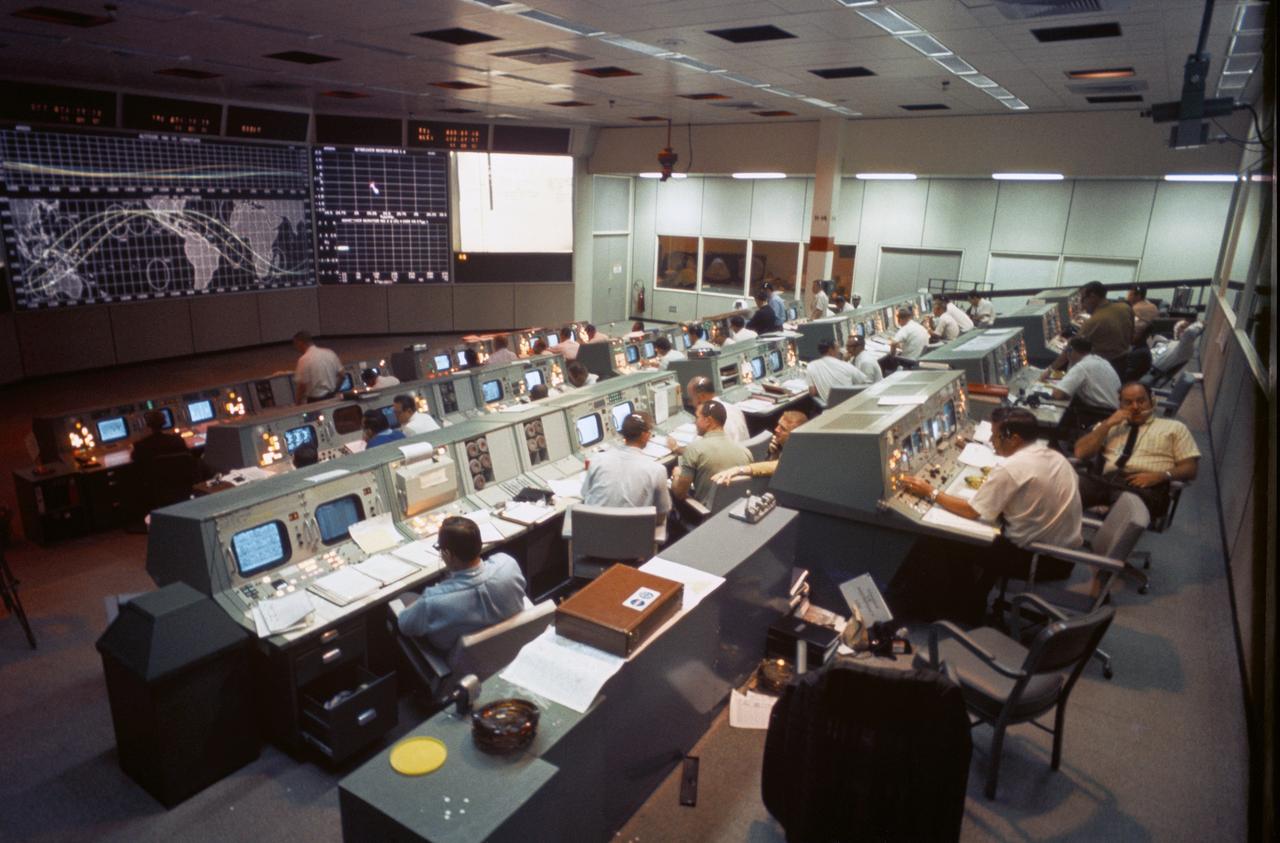

Overall view of activity in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center, Bldg 30, on the first day of the Apollo 7 space mission.
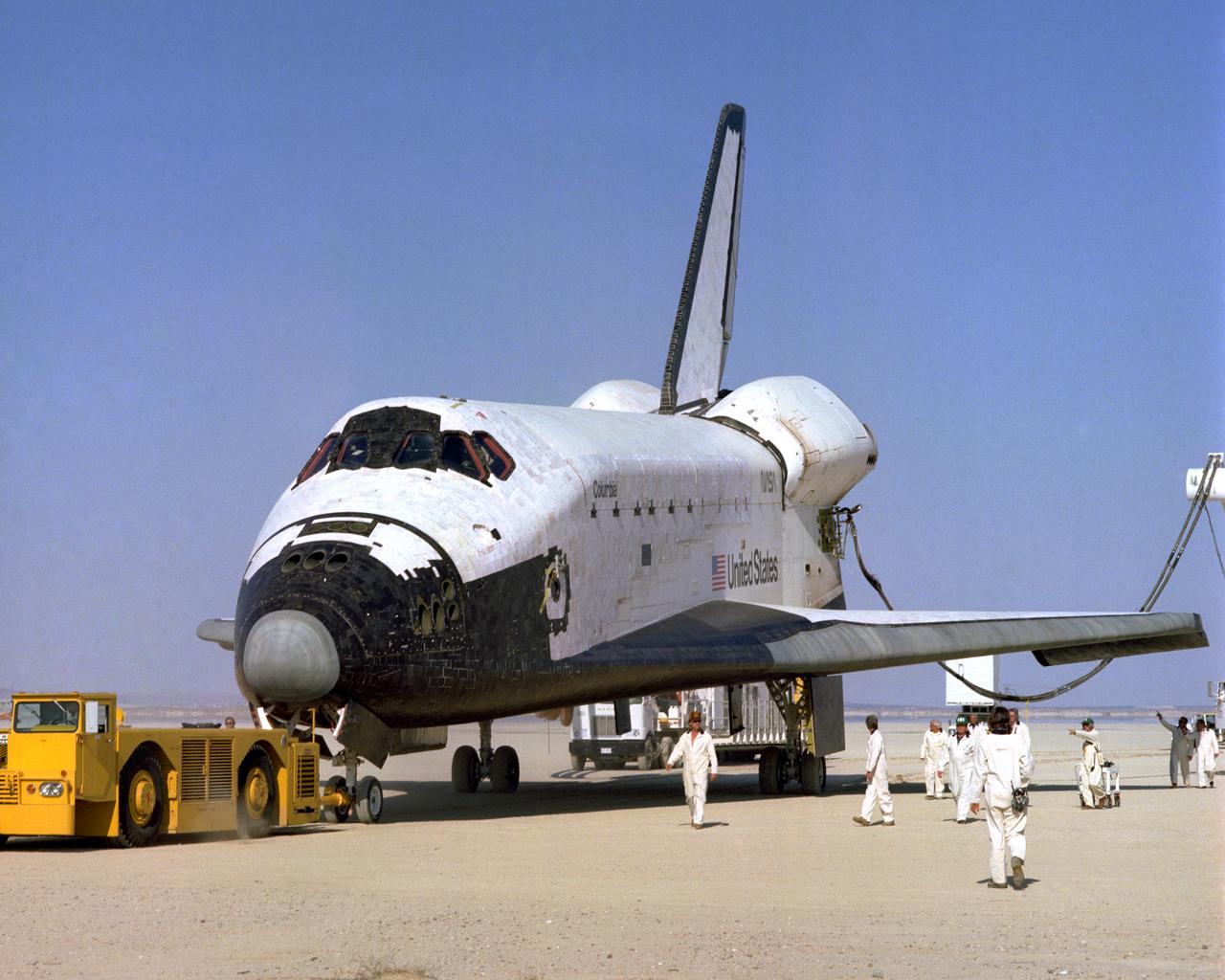

The Space Shuttle Columbia on Rogers Dry lakebed at Edwards AFB after landing to complete its first orbital mission on April 14, 1981. Technicians towed the Shuttle back to the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center for post-flight processing and preparation for a return ferry flight atop a modified 747 to Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
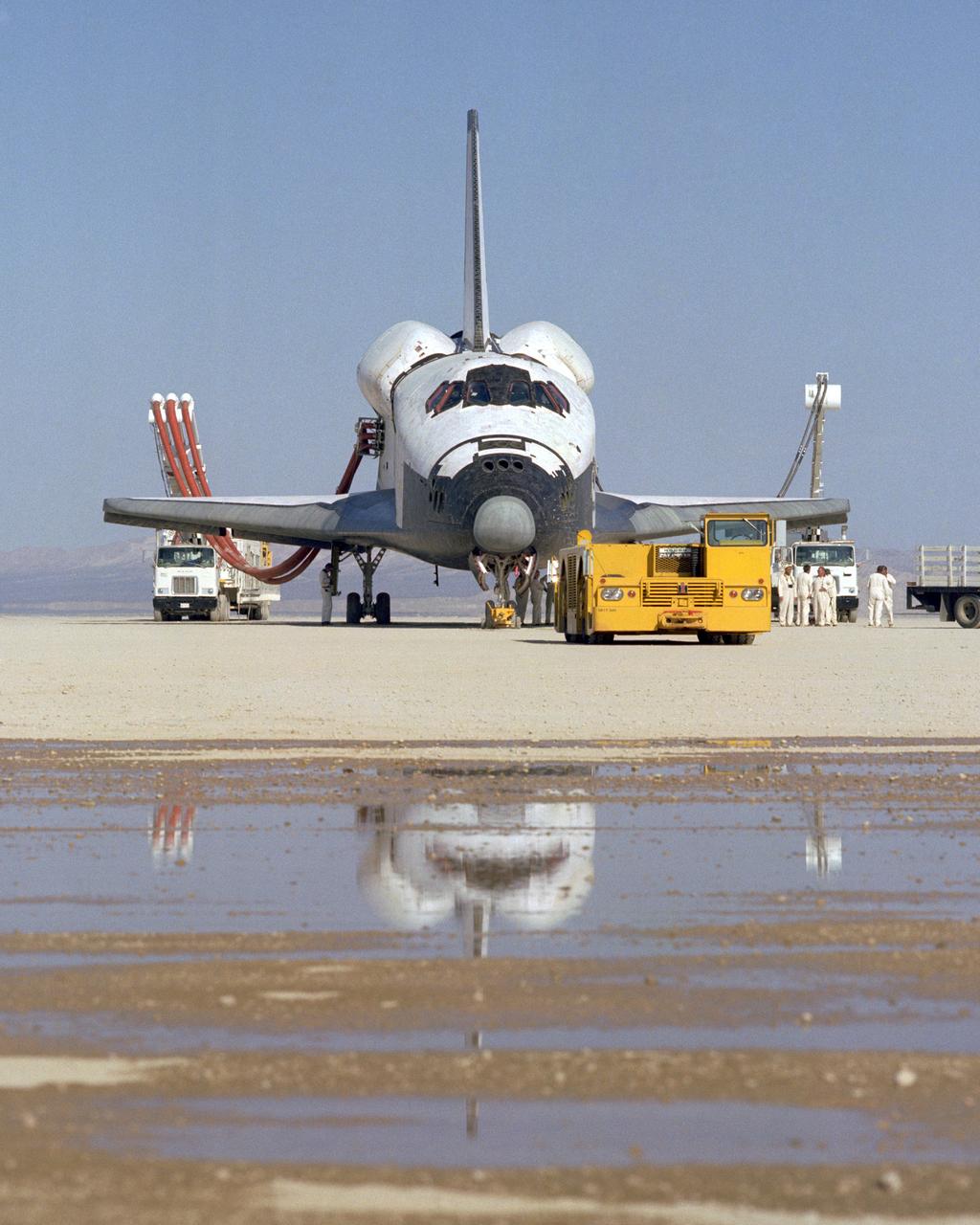

The Space Shuttle Columbia on Rogers Dry lakebed at Edwards AFB after landing to complete its first orbital mission on April 14, 1981. Technicians towed the Shuttle back to the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center for post-flight processing and preparation for a return ferry flight atop a modified 747 to Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
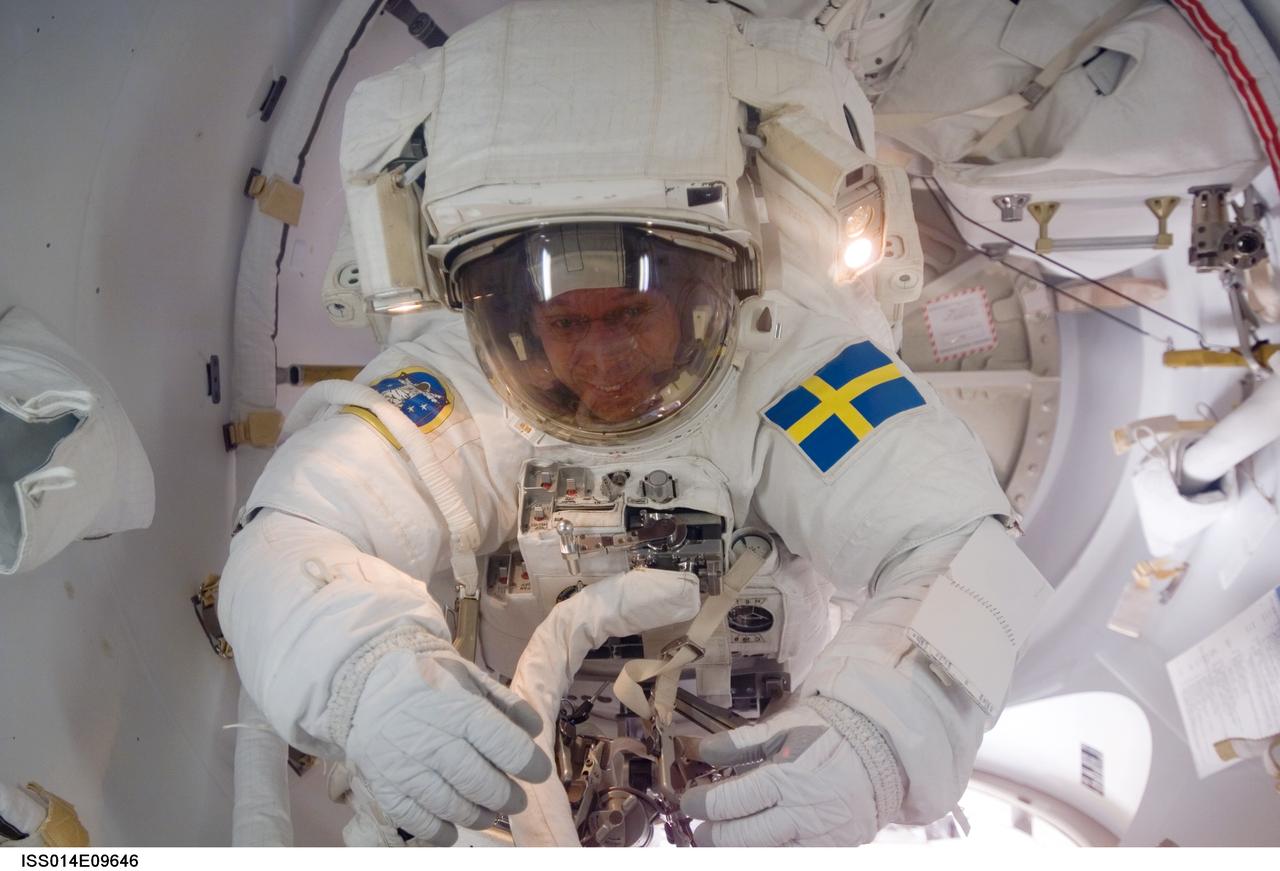

ISS014-E-09646 (12 Dec. 2006) --- As the mission's first spacewalk draws to a close, European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Christer Fuglesang, STS-116 mission specialist, moves through the Quest Airlock as he returns to the International Space Station.
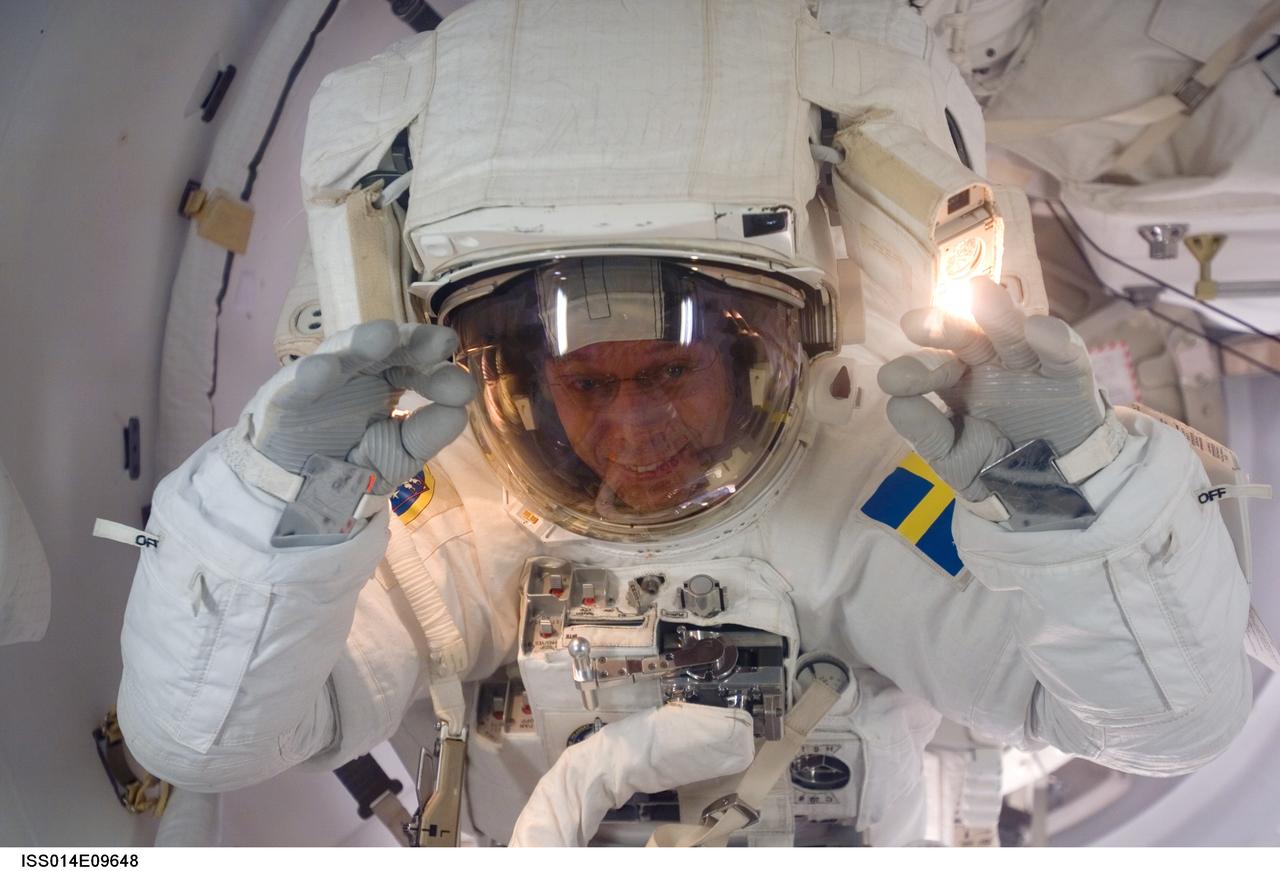

ISS014-E-09648 (12 Dec. 2006) --- As the mission's first spacewalk draws to a close, European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Christer Fuglesang, STS-116 mission specialist, moves through the Quest Airlock as he returns to the International Space Station.
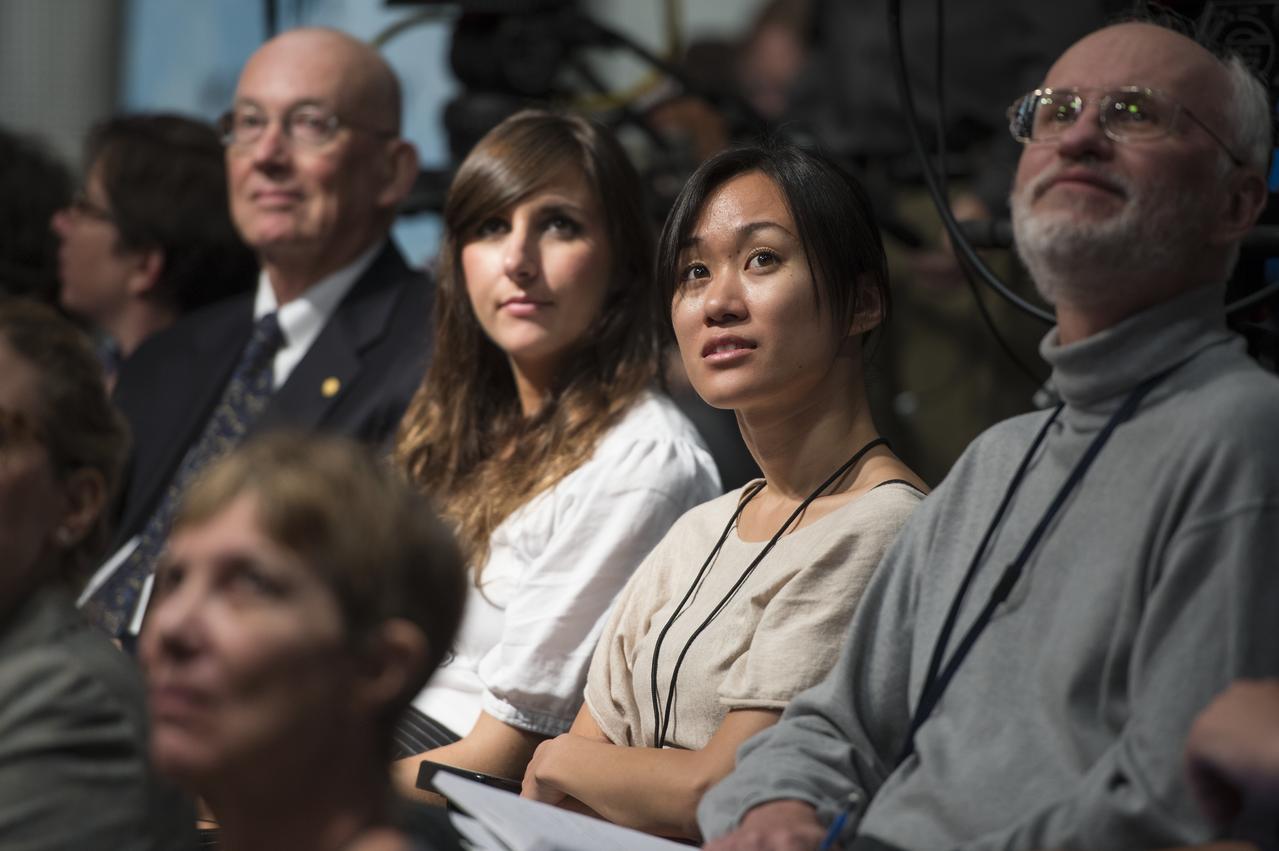

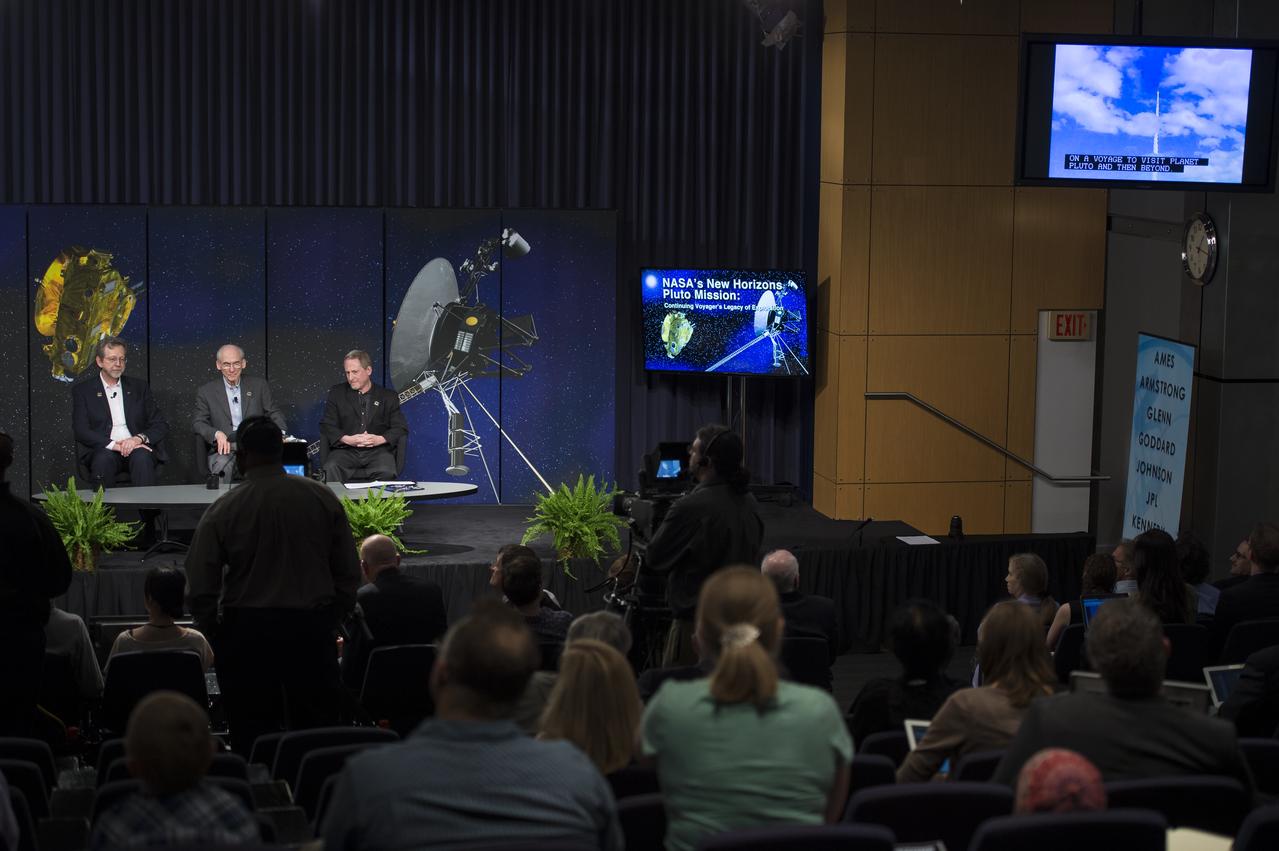
Audience members view images of Neptune taken by Voyager while scientists discuss how the first images of Pluto and its moons will be captured during the "New Horizons: The First Mission to the Pluto System and the Kuiper Belt" Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Monday, August 25, 2014. The New Horizons spacecraft launched on January 19, 2006 will conduct a five month long reconnaissance flyby study of Pluto and its moons starting in the summer of 2015. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
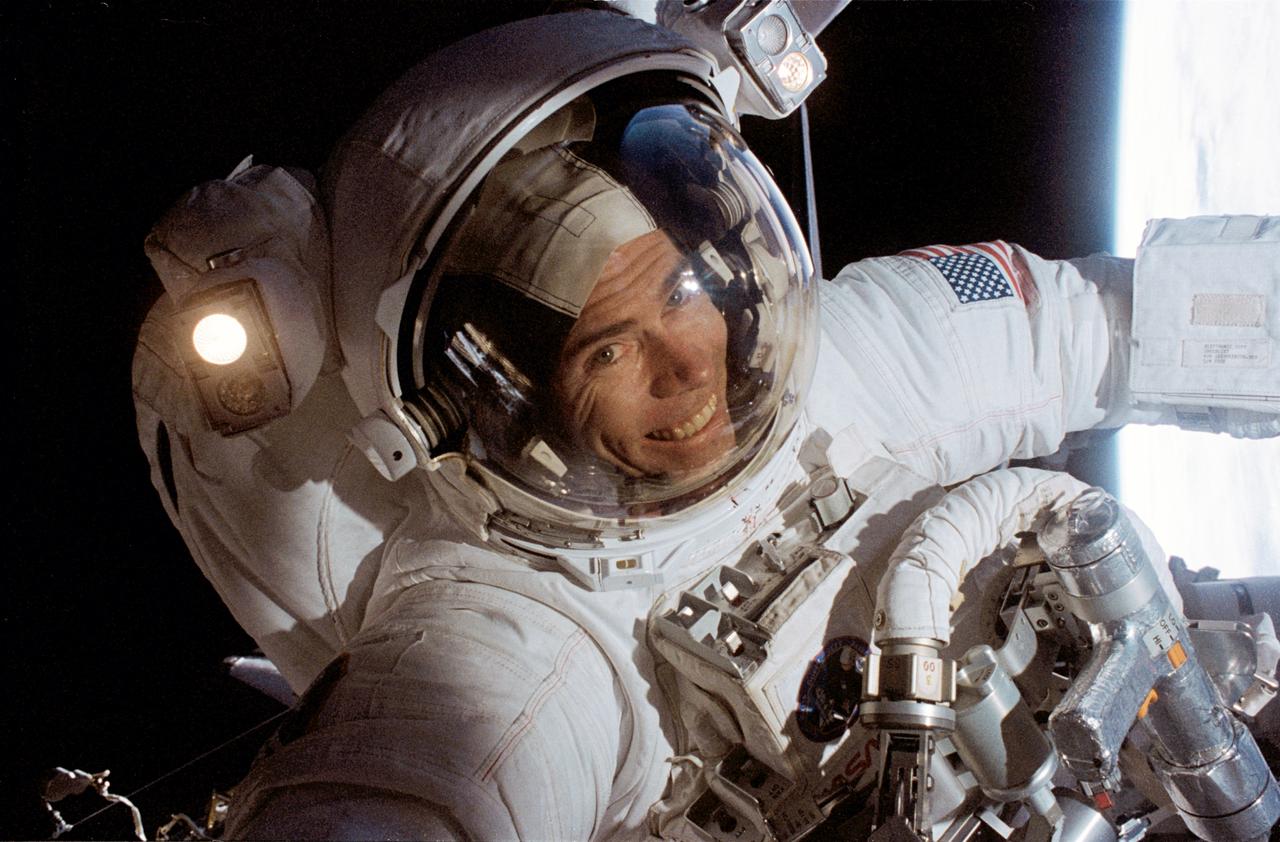

STS072-305-034 (15 Jan. 1996) --- Astronaut Daniel T. Barry, mission specialist, works in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Endeavour during the first of two extravehicular activities (EVA). Barry was joined by astronaut Leroy Chiao for the EVA. The two joined four other NASA astronauts for a week and a half aboard Endeavour.

Dr. Jim Green, Dr. Ed Stone, and Dr. Alan Stern speak on a panel at the "New Horizons: The First Mission to the Pluto System and the Kuiper Belt" Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Monday, August 25, 2014. They discussed how the first images of Pluto and its moons would be captured by the New Horizons spacecraft during a five month long reconnaissance flyby study starting in the summer of 2015. New Horizons launched on January 19, 2006 and is scheduled to make its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
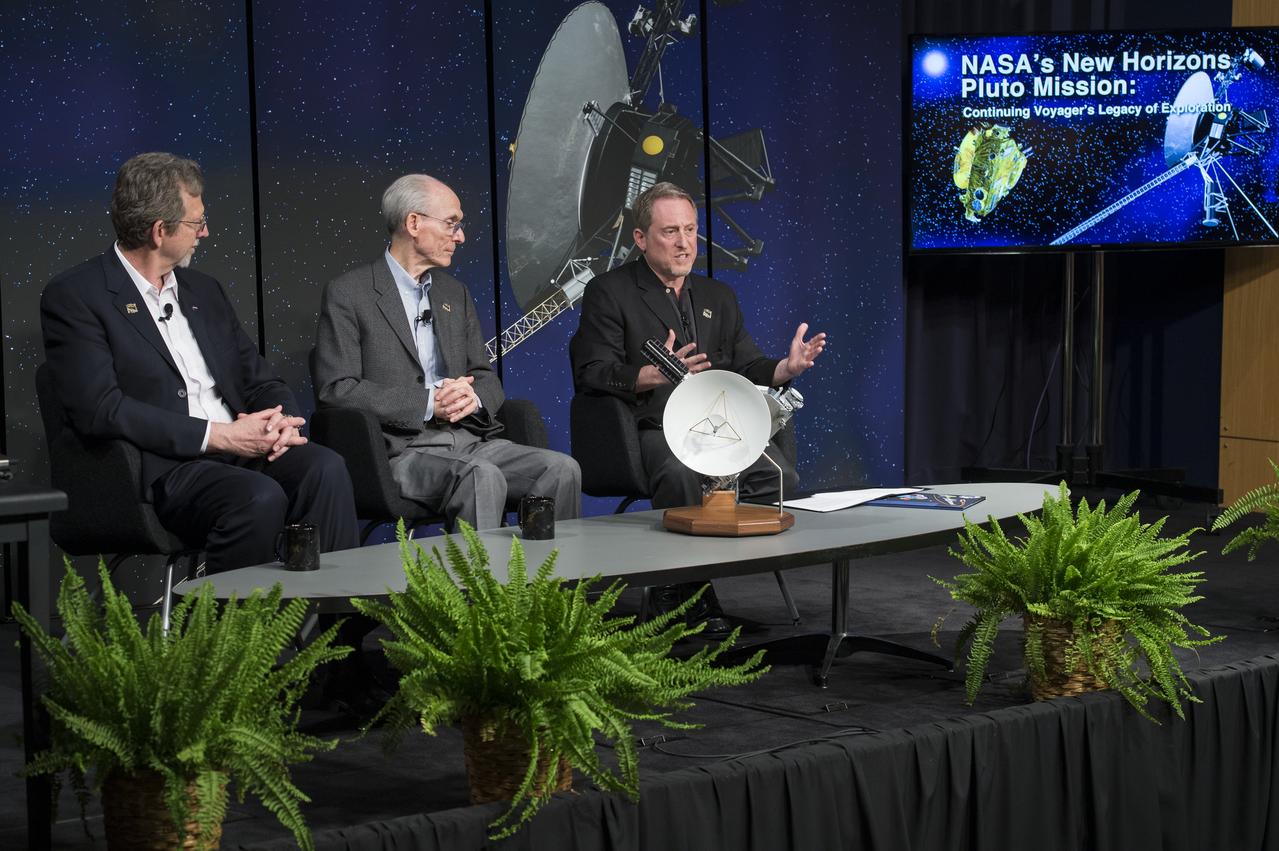

Dr. Jim Green, Dr. Ed Stone, and Dr. Alan Stern speak on a panel at the "New Horizons: The First Mission to the Pluto System and the Kuiper Belt" Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Monday, August 25, 2014. They discussed how the first images of Pluto and its moons would be captured by the New Horizons spacecraft during a five month long reconnaissance flyby study starting in the summer of 2015. New Horizons launched on January 19, 2006 and is scheduled to make its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
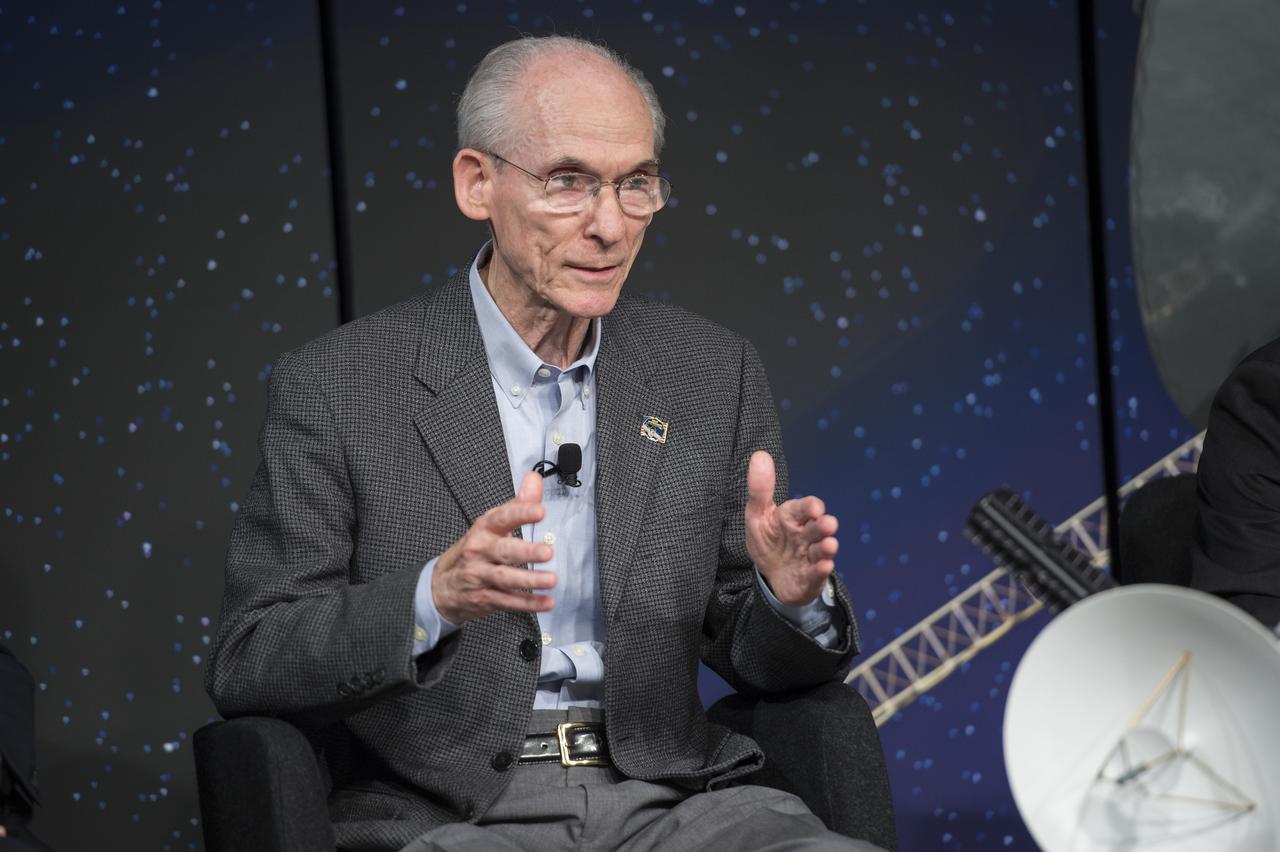

Dr. Ed Stone, Voyager project scientist, speaks on a panel at the "New Horizons: The First Mission to the Pluto System and the Kuiper Belt" Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Monday, August 25, 2014. Scientists discussed how the first images of Pluto and its moons would be captured by the New Horizons spacecraft during a five month long reconnaissance flyby study starting in the summer of 2015. New Horizons launched on January 19, 2006 and is scheduled to make its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Dr. Alan Stern, New Horizons principal investigator, speaks on a panel at the "New Horizons: The First Mission to the Pluto System and the Kuiper Belt" Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Monday, August 25, 2014. Scientists discussed how the first images of Pluto and its moons would be captured by the New Horizons spacecraft during a five month long reconnaissance flyby study starting in the summer of 2015. New Horizons launched on January 19, 2006 and is scheduled to make its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
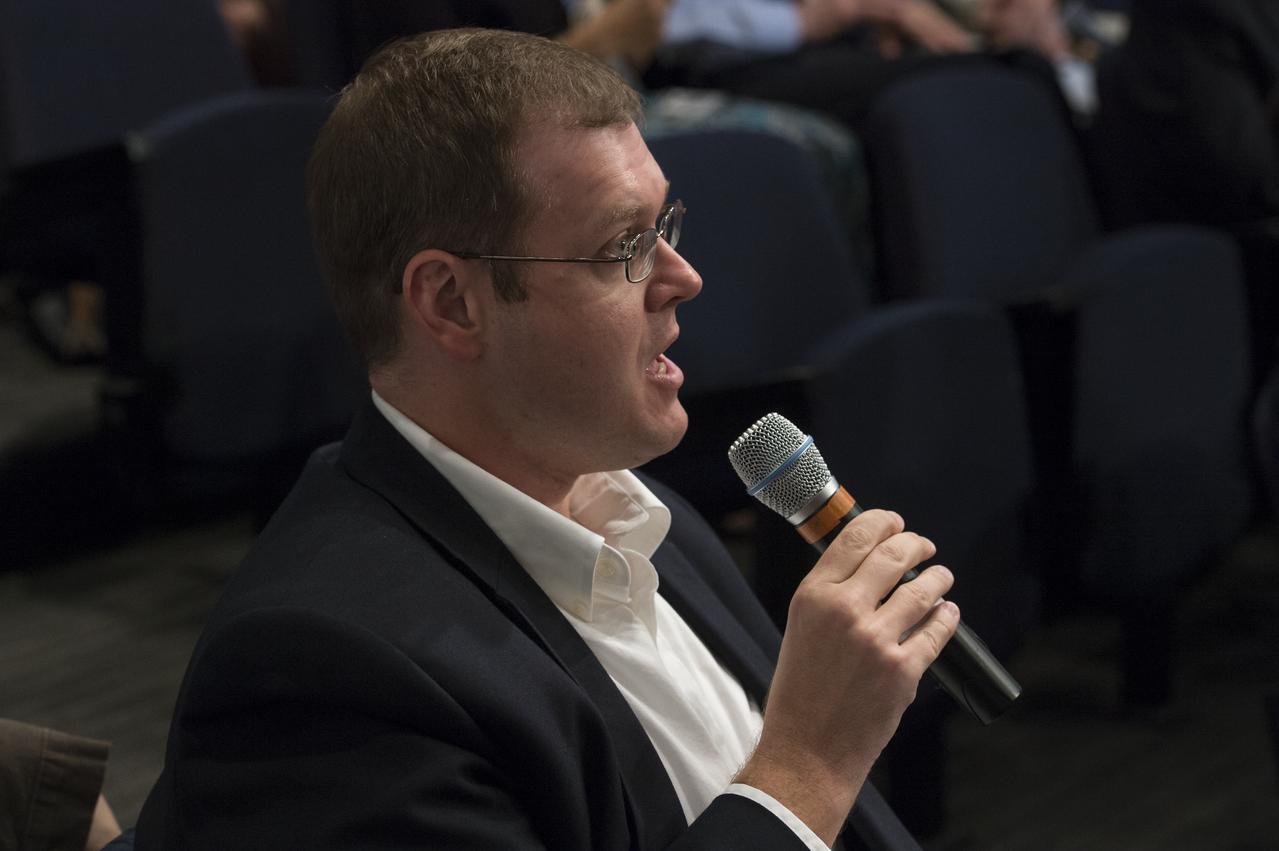

An audience member asks the panelists a question at the "New Horizons: The First Mission to the Pluto System and the Kuiper Belt" Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Monday, August 25, 2014. Scientists discussed how the first images of Pluto and its moons would be captured by the New Horizons spacecraft during a five month long reconnaissance flyby study starting in the summer of 2015. New Horizons launched on January 19, 2006 and is scheduled to make its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
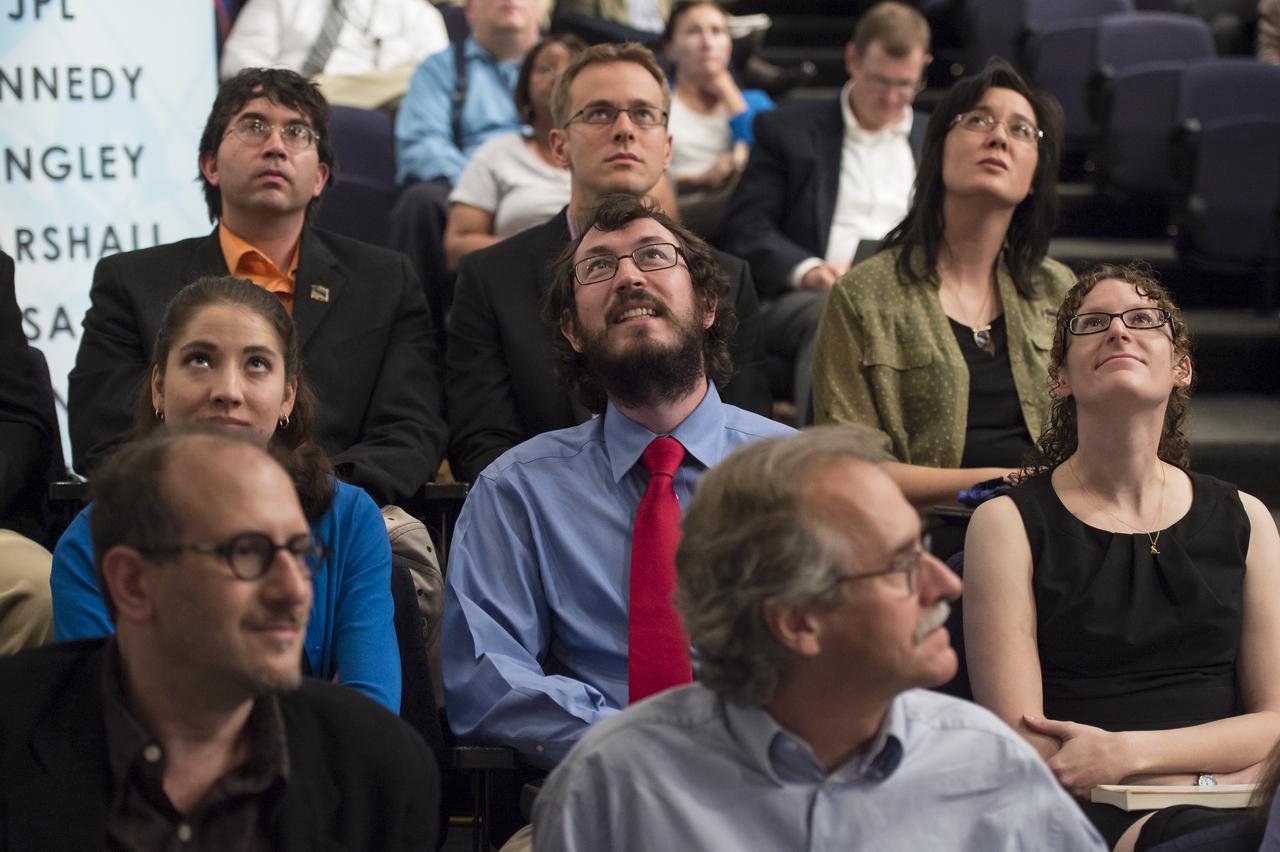

Audience members view slides from a presentation by Dr. Jim Green, Dr. Ed Stone, and Dr. Alan Stern at the "New Horizons: The First Mission to the Pluto System and the Kuiper Belt" Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Monday, August 25, 2014. They discussed how the first images of Pluto and its moons would be captured by the New Horizons spacecraft during a five month long reconnaissance flyby study starting in the summer of 2015. New Horizons launched on January 19, 2006 and is scheduled to make its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
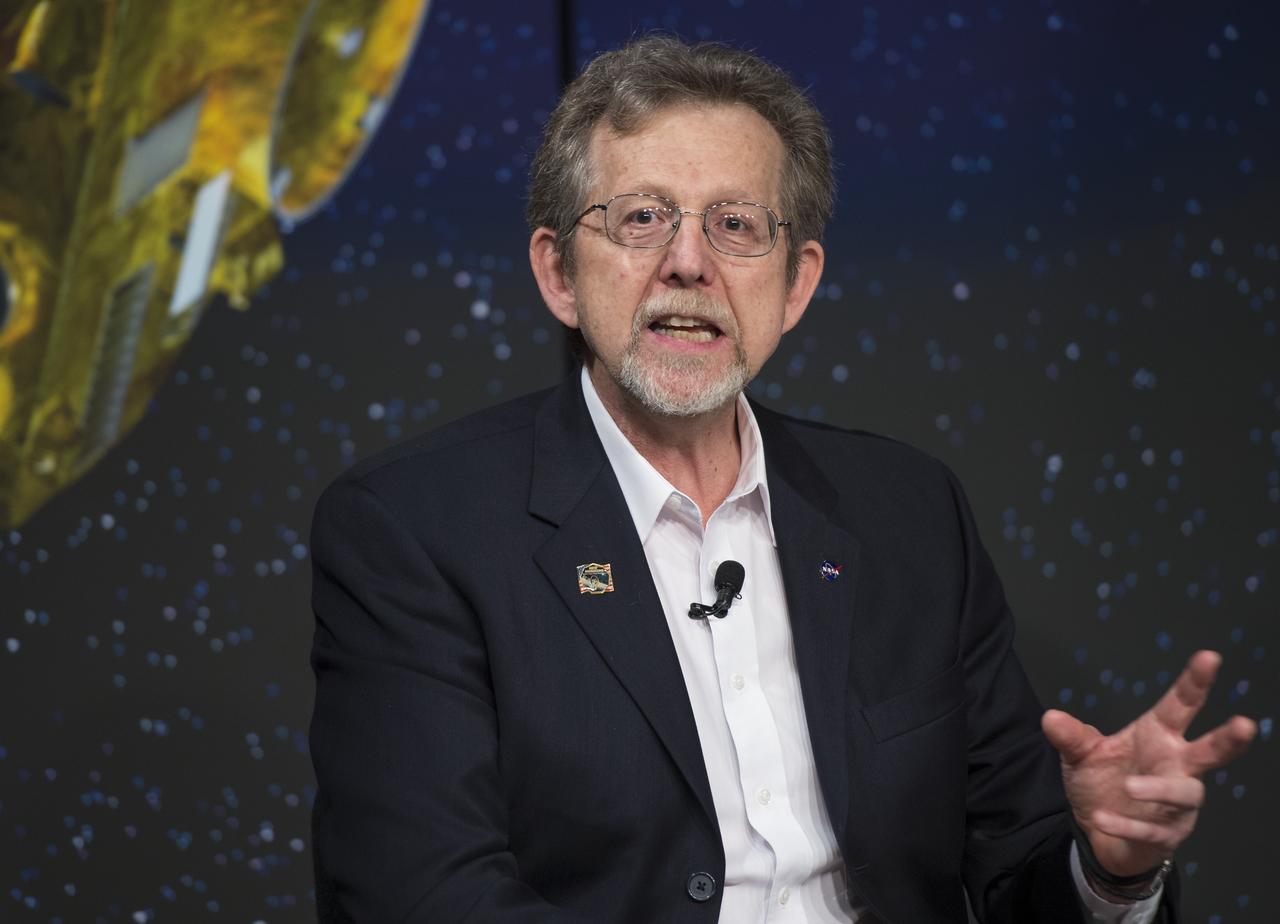

Dr. Jim Green, Director of NASA’s Planetary Division, speaks on a panel at the "New Horizons: The First Mission to the Pluto System and the Kuiper Belt" Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Monday, August 25, 2014. Scientists discussed how the first images of Pluto and its moons would be captured by the New Horizons spacecraft during a five month long reconnaissance flyby study starting in the summer of 2015. New Horizons launched on January 19, 2006 and is scheduled to make its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
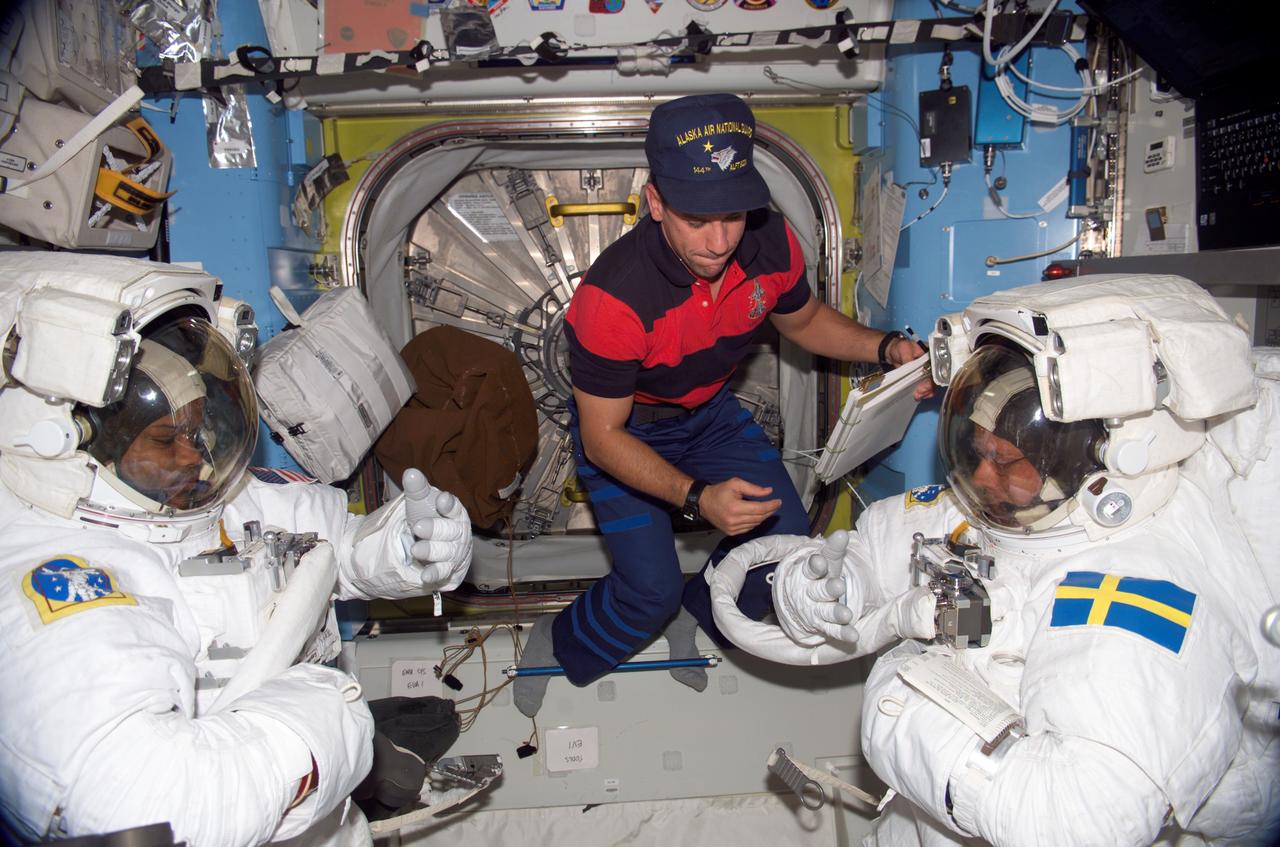

ISS014-E-09608 (12 Dec. 2006) --- Attired in their extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuits, astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. (left) and European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Christer Fuglesang, both STS-116 mission specialists, prepare for the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) in the Quest Airlock of the International Space Station while Space Shuttle Discovery was docked with the station. Astronaut William A. (Bill) Oefelein (center), pilot, assisted Curbeam.

S72-52630 (February 1972) --- This is the emblem for the first manned Skylab mission. It will be a mission of up to 28 days. Skylab is an experimental space station consisting of a 100-ton laboratory complex in which medical, scientific and technological experiments will be performed in Earth orbit. The prime crew of this mission will be astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander; scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot; and astronaut Paul J. Weits, pilot. The patch, designed by artist Kelly Freas, shows the Skylab silhouetted against the Earth's globe, which in turn is eclipsing the sun--showing the brilliant signet-ring pattern of the instant before the total eclipse. Photo credit: NASA
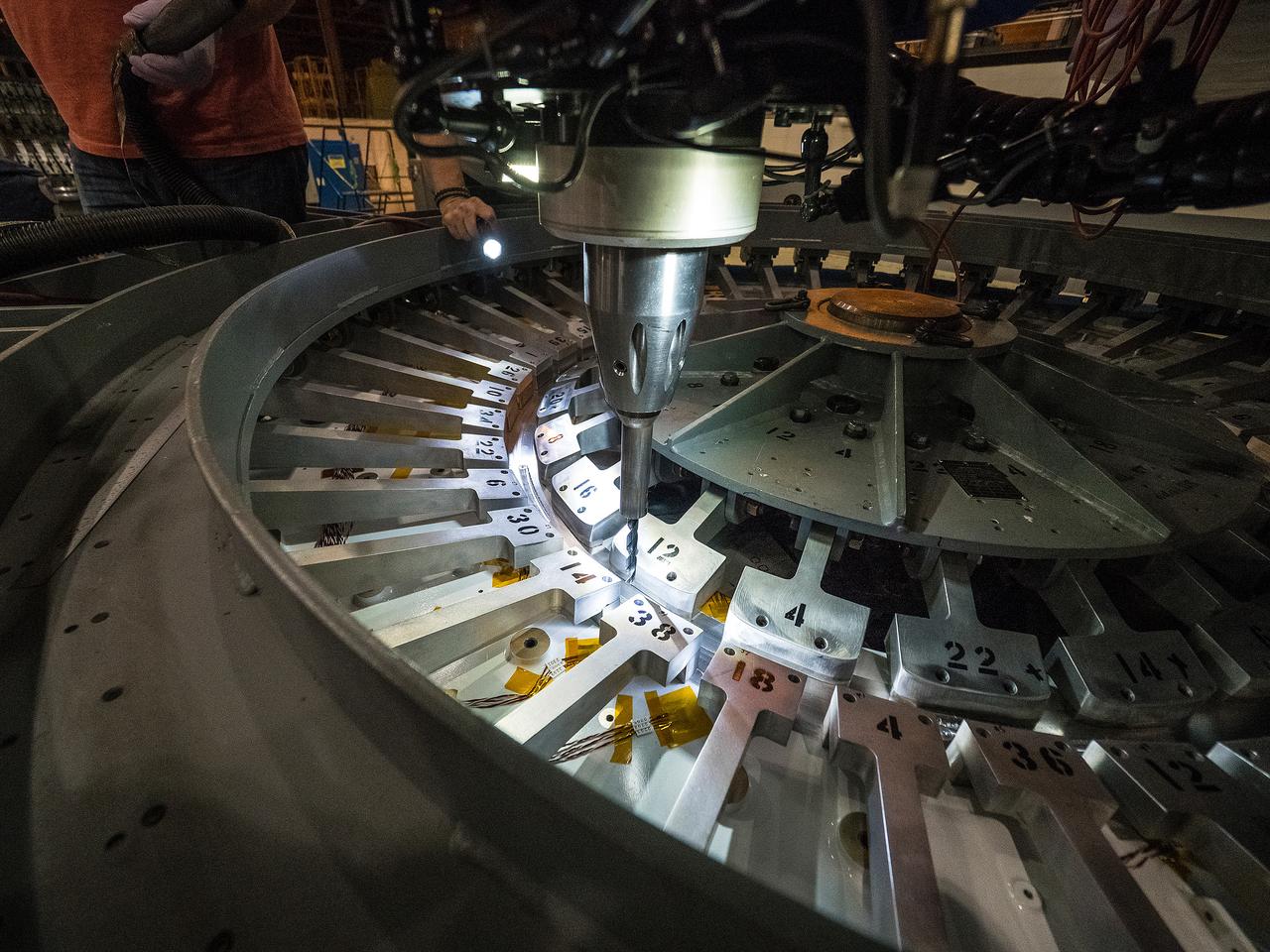

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
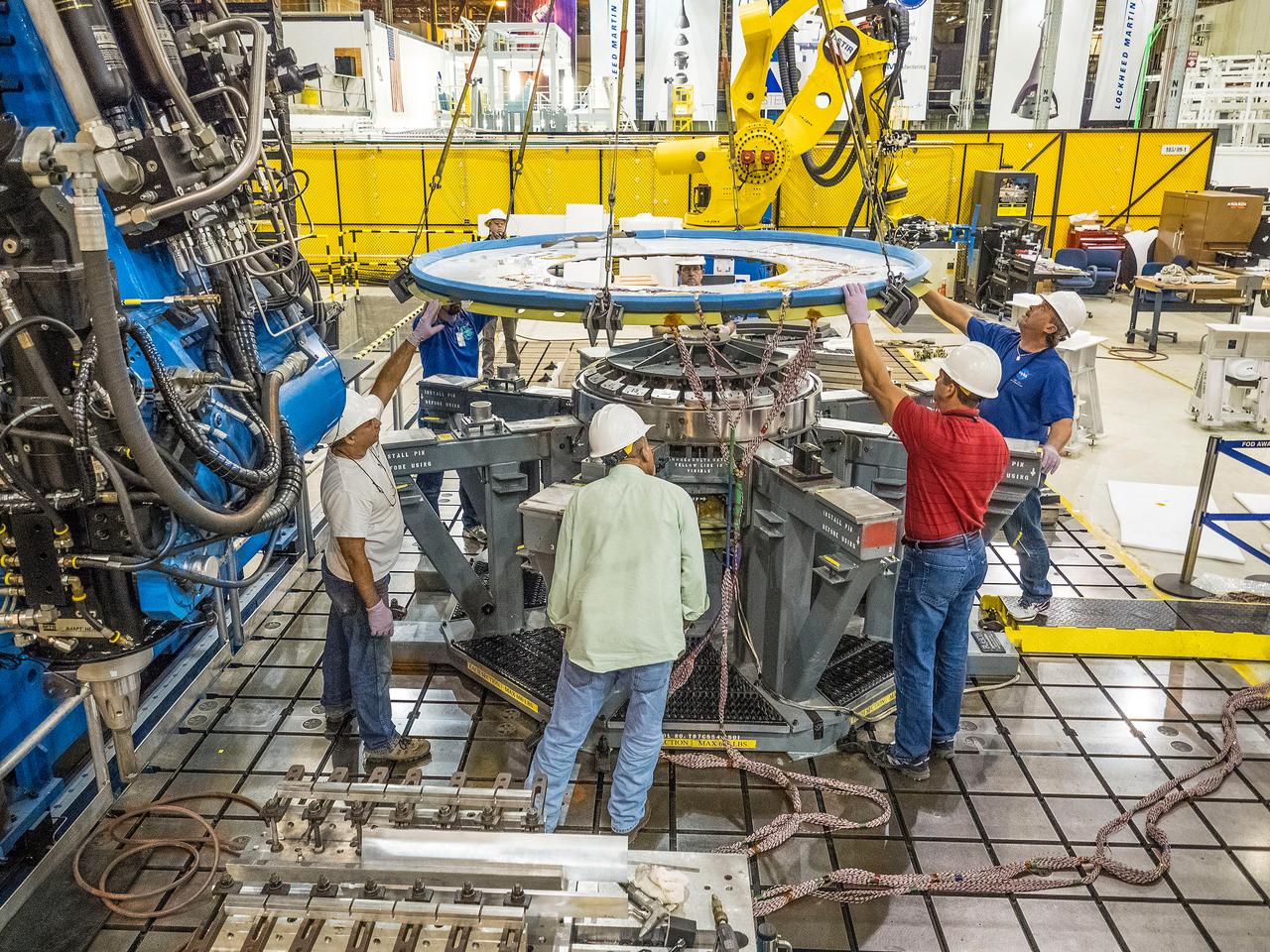

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
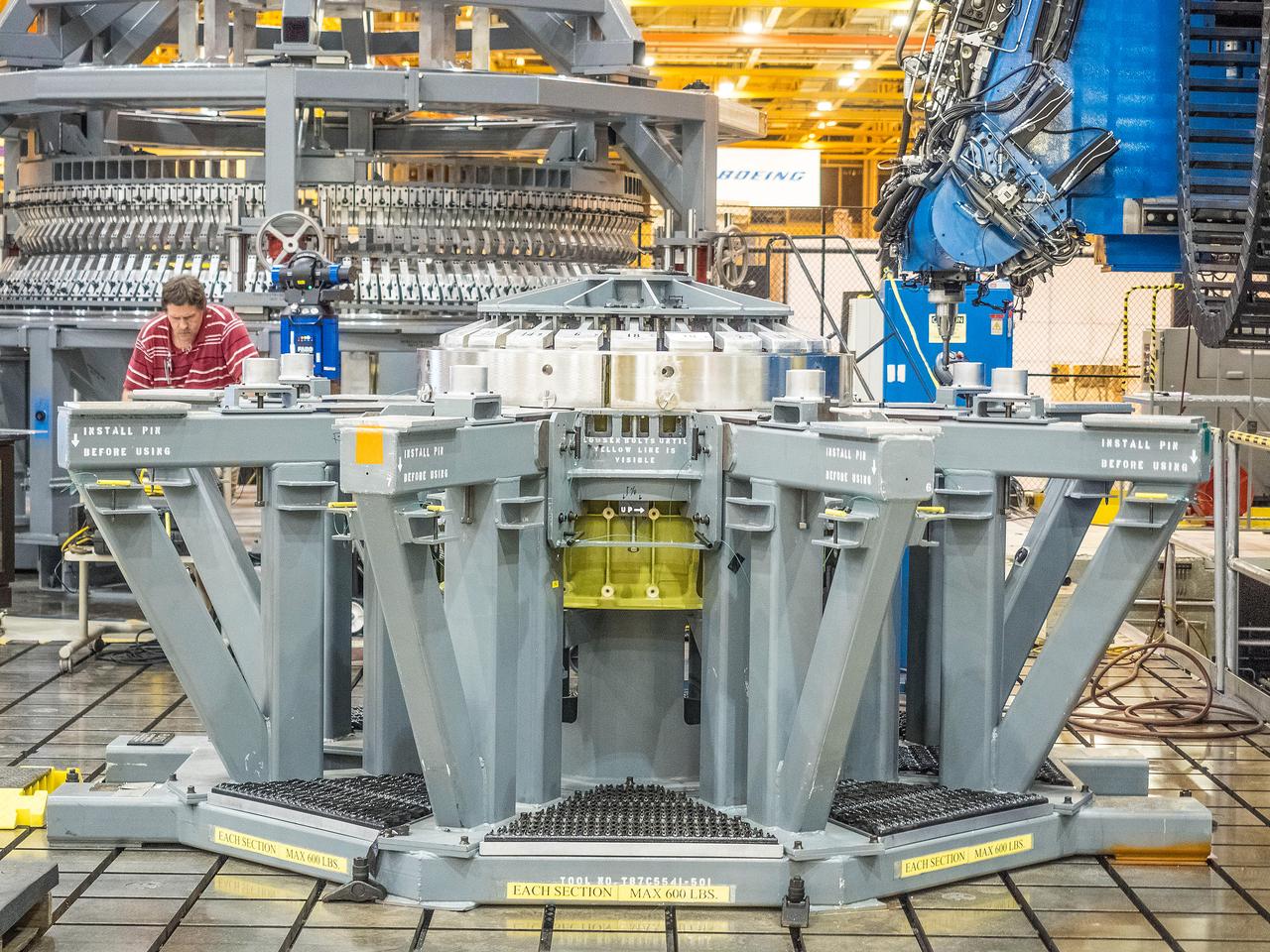
First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
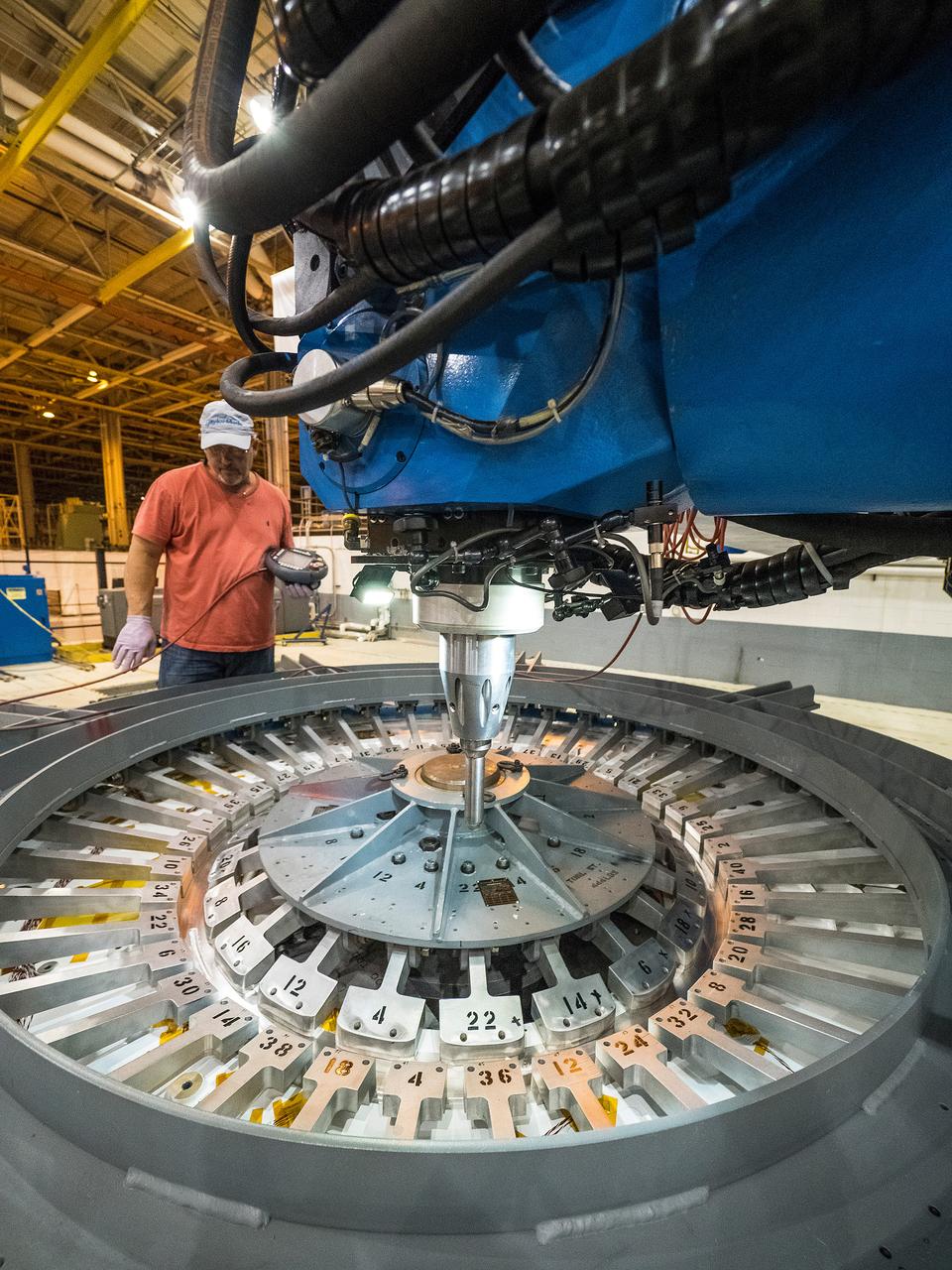

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
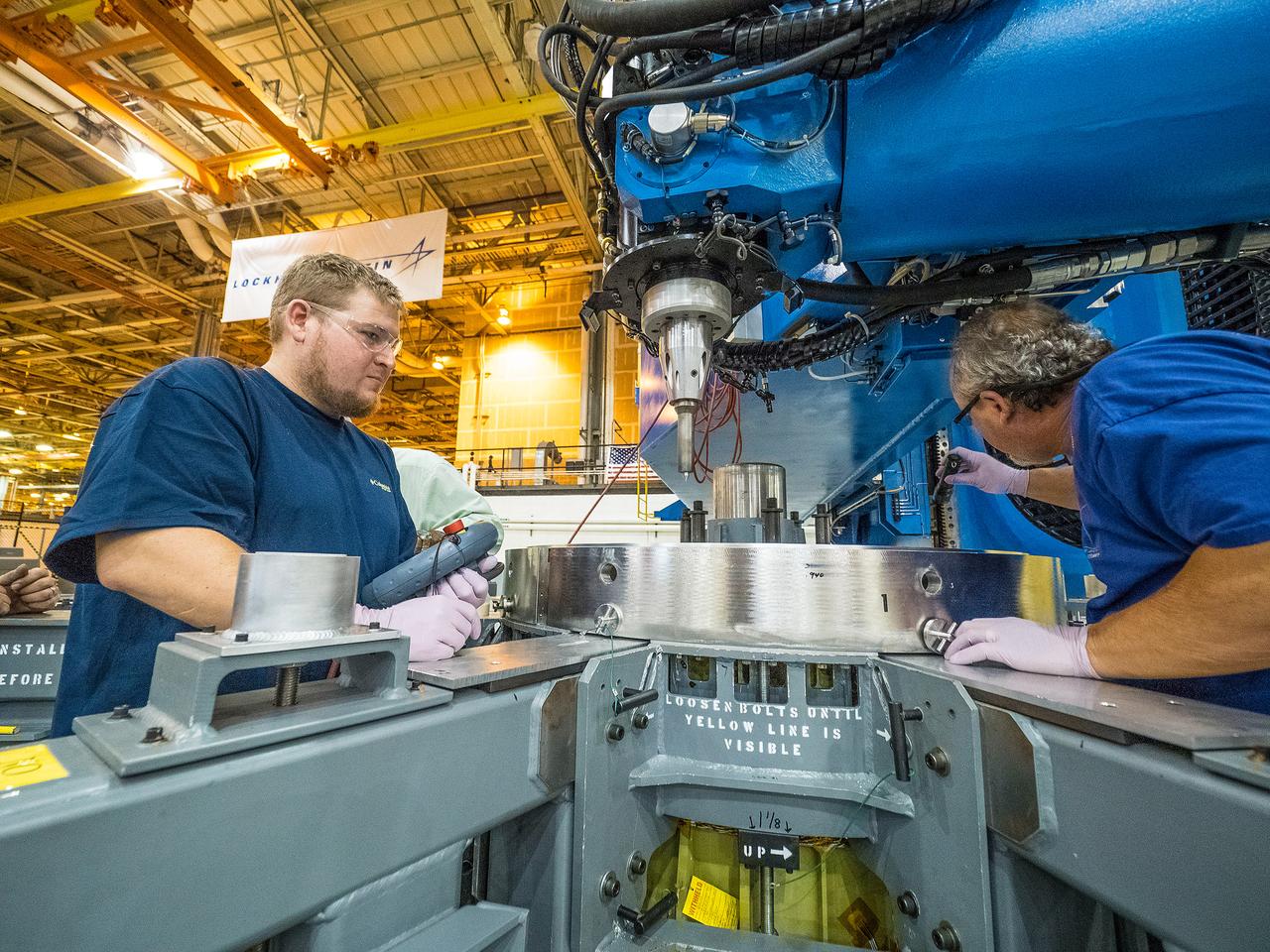

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
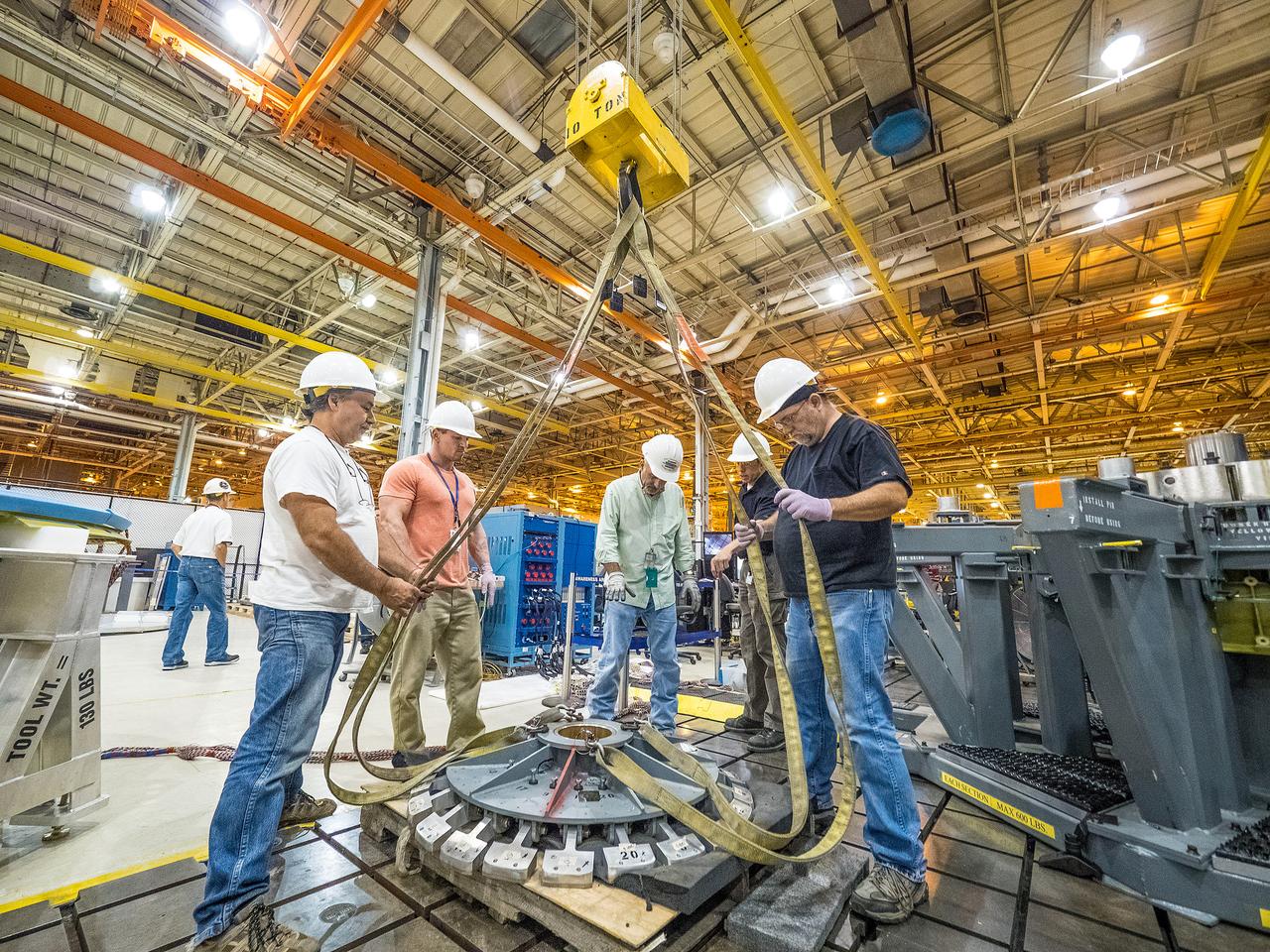

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
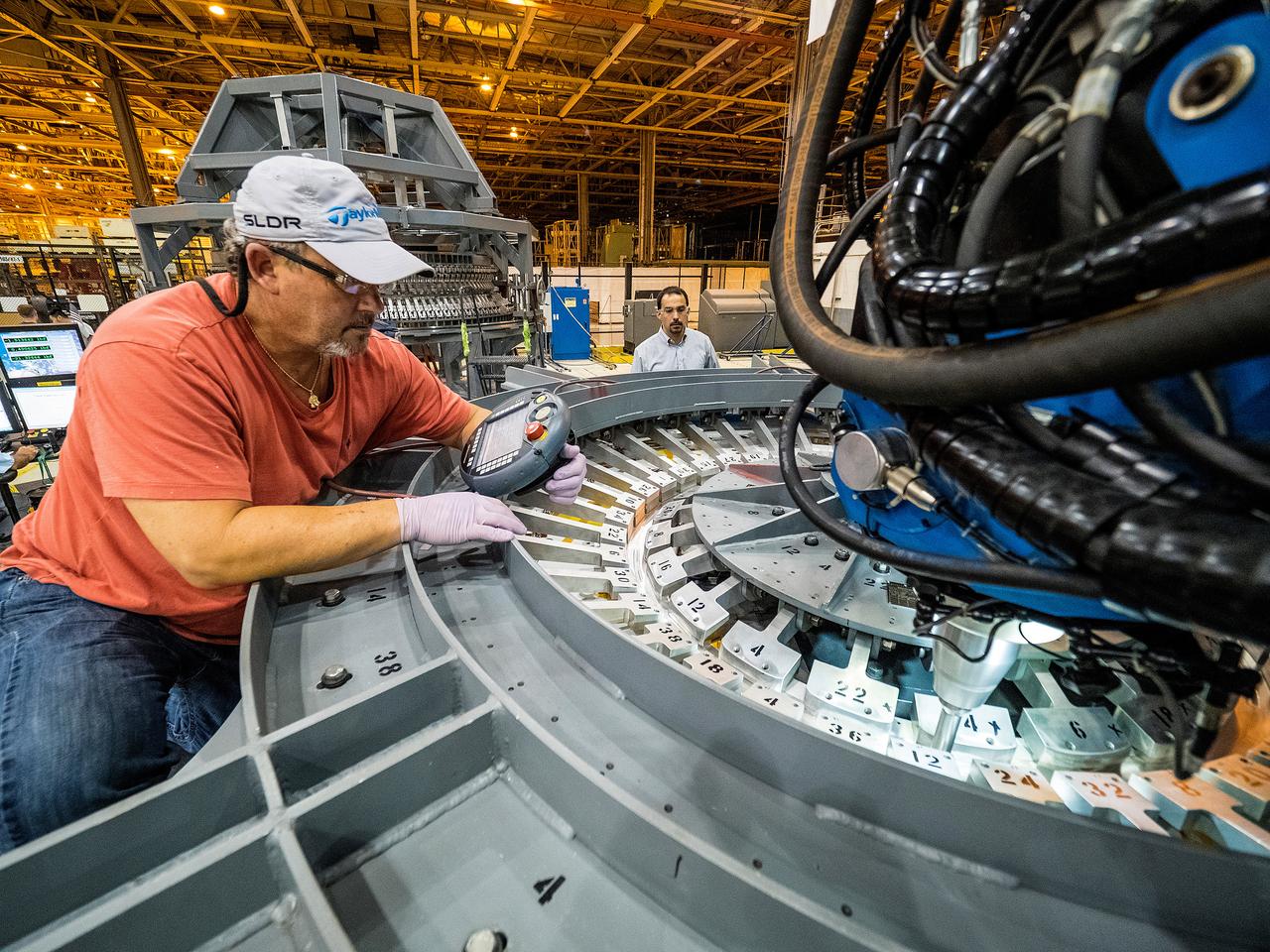

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
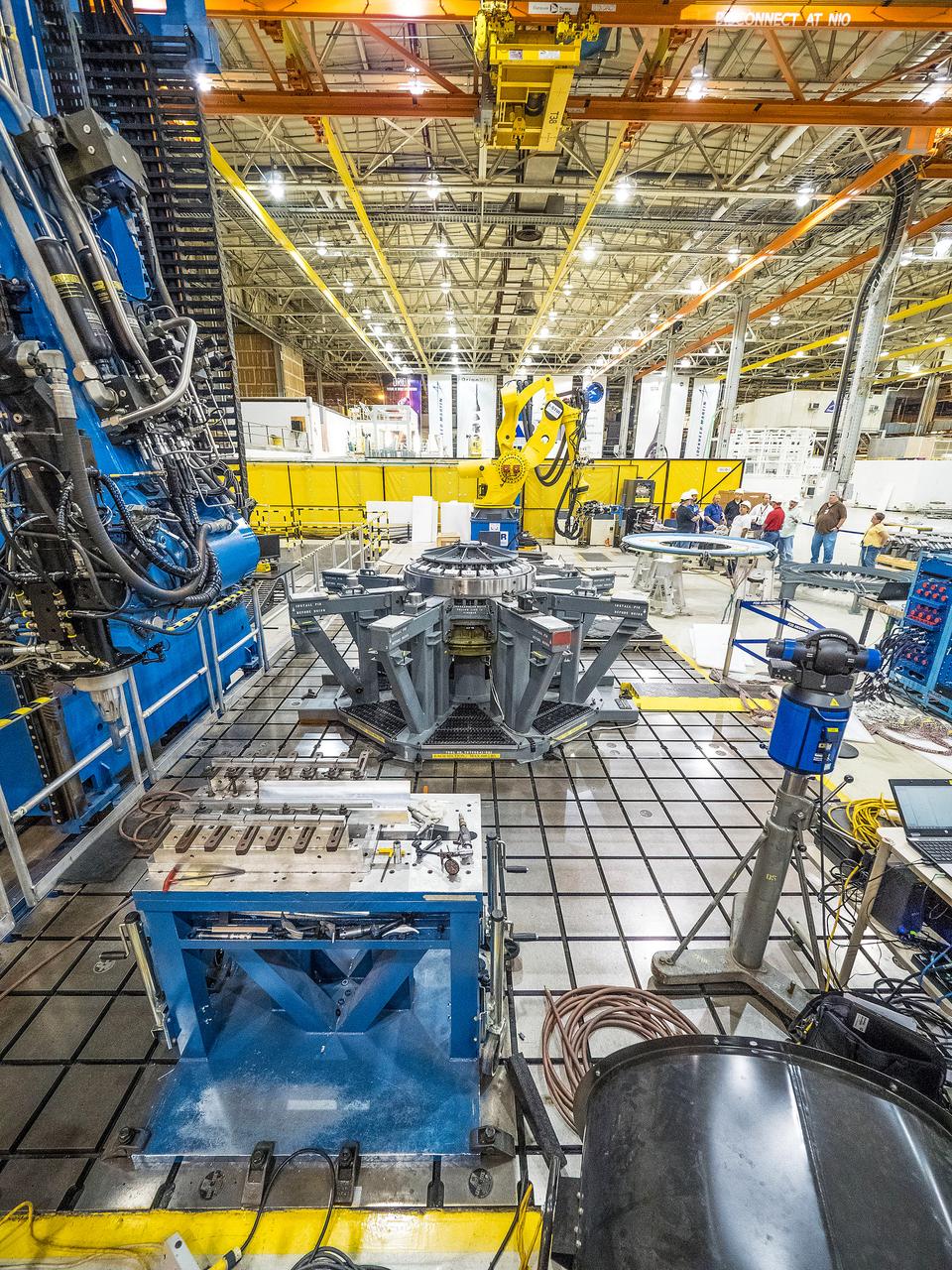
First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
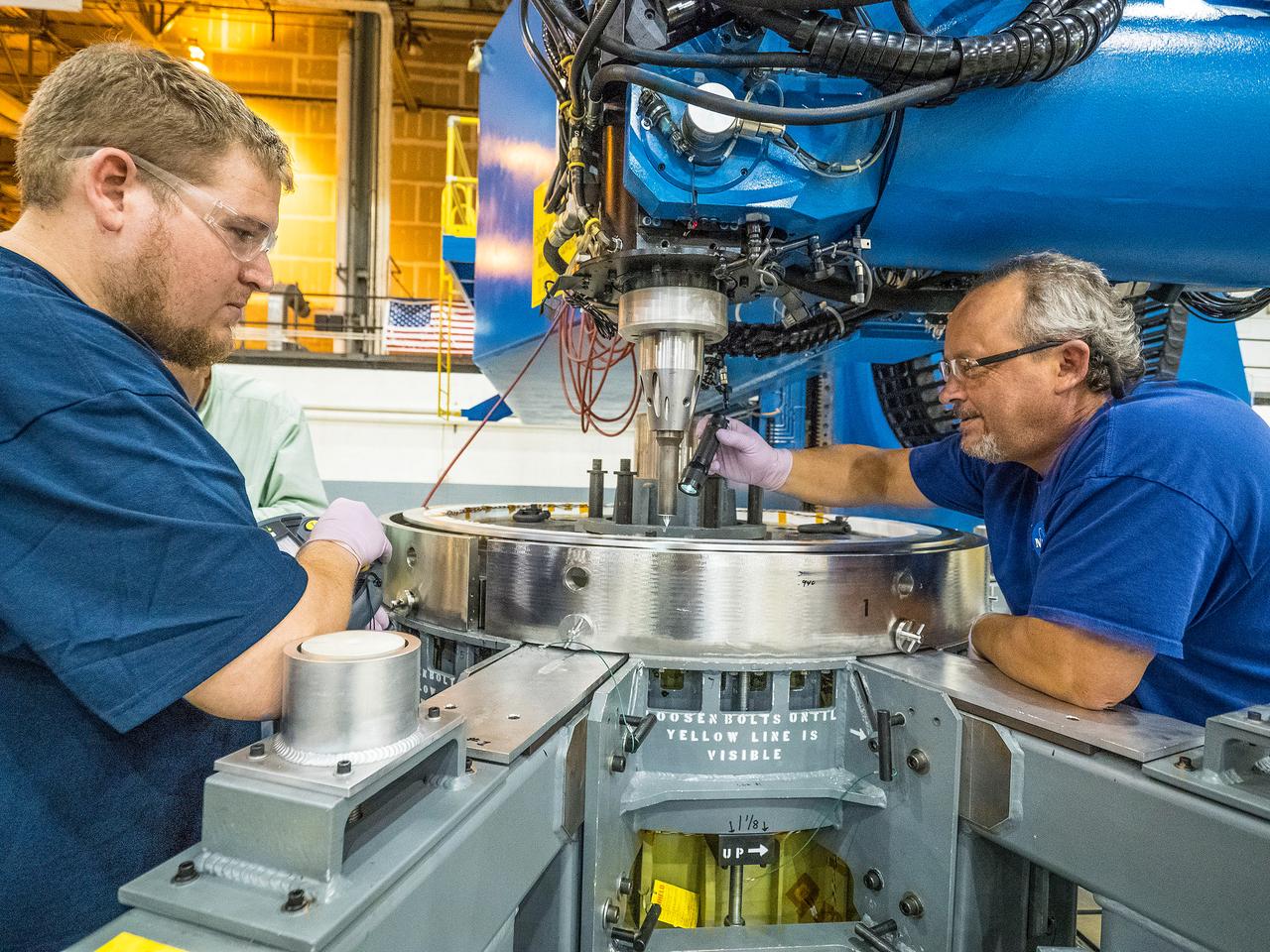

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
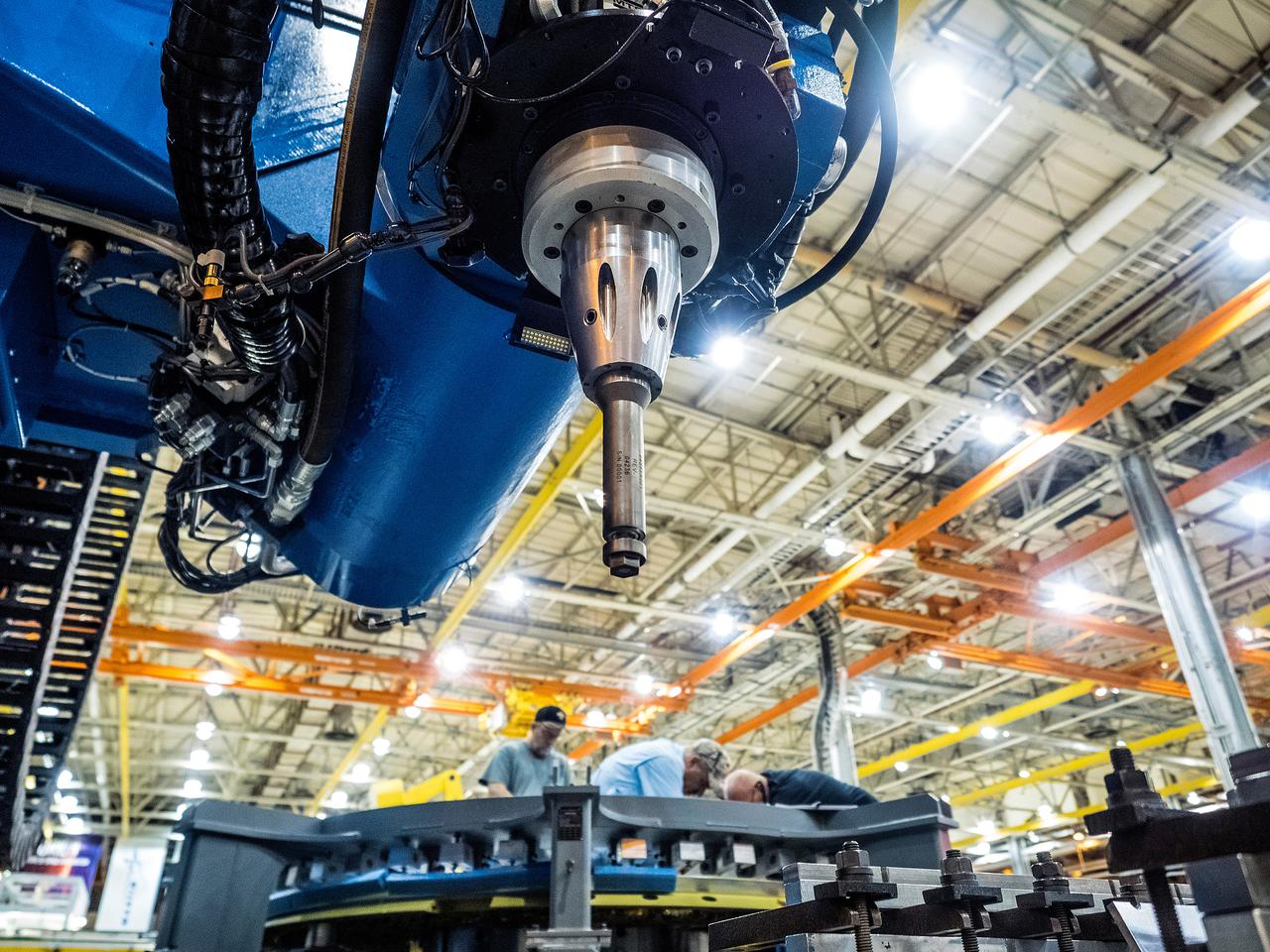

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
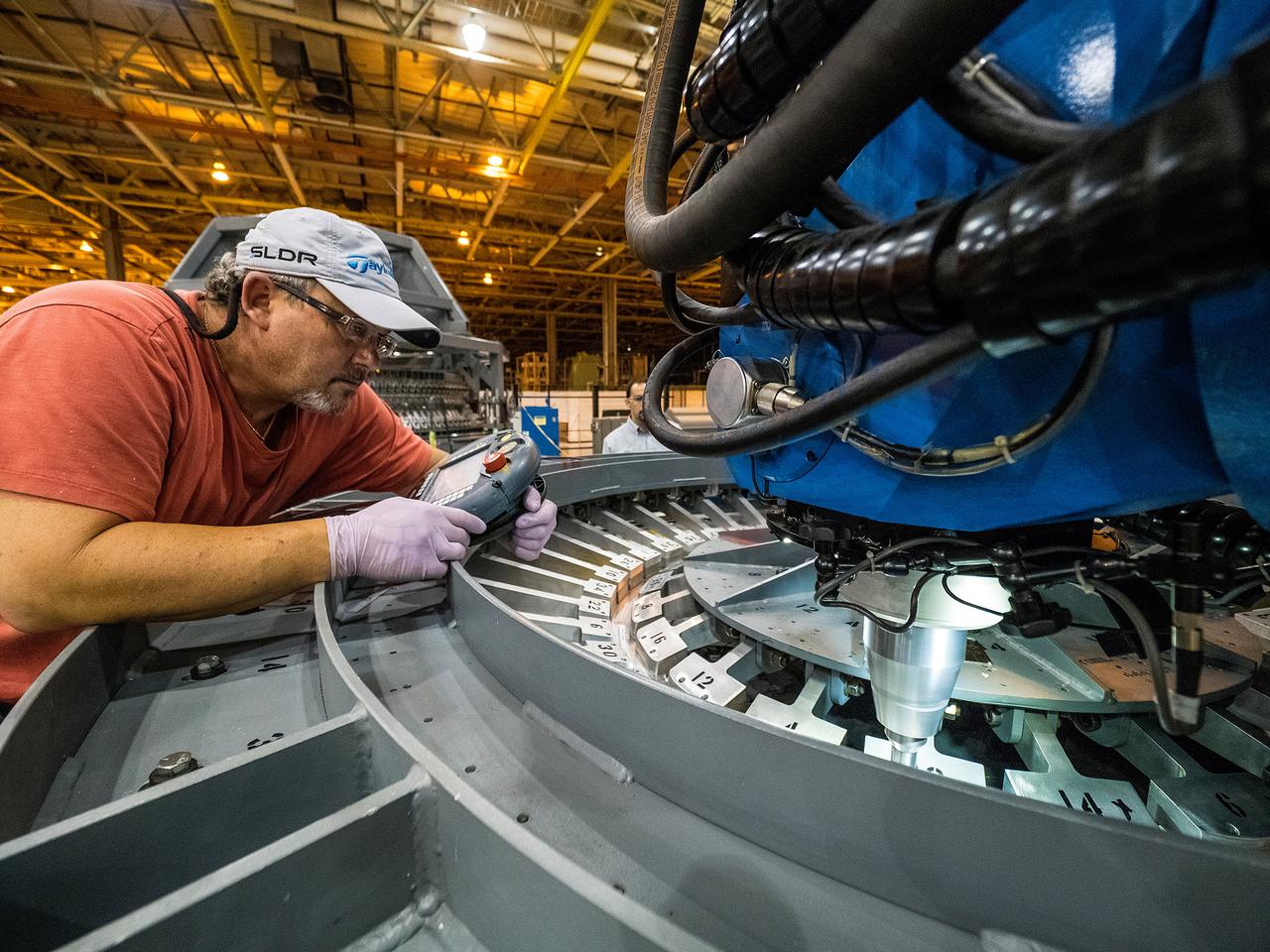

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
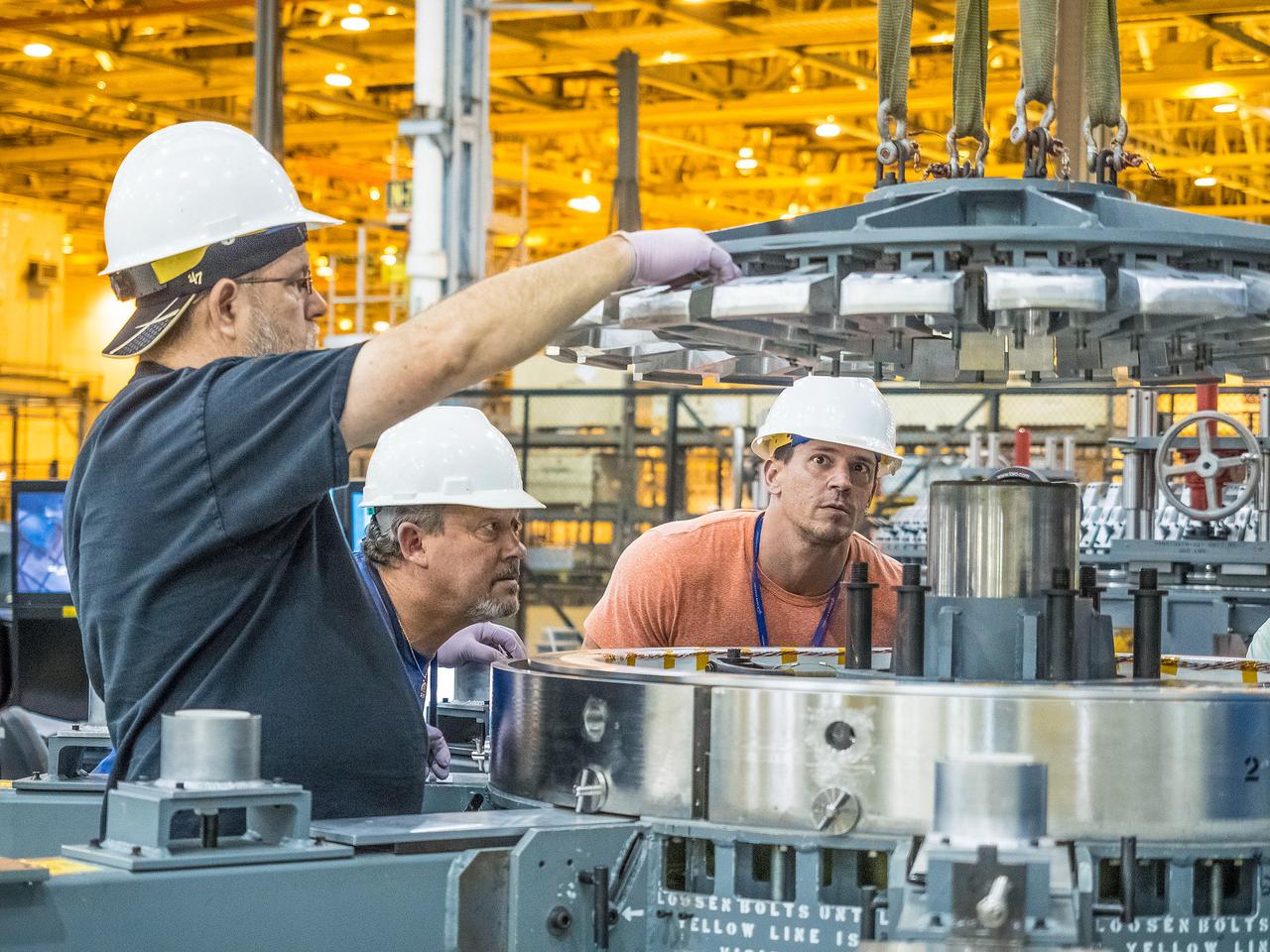

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
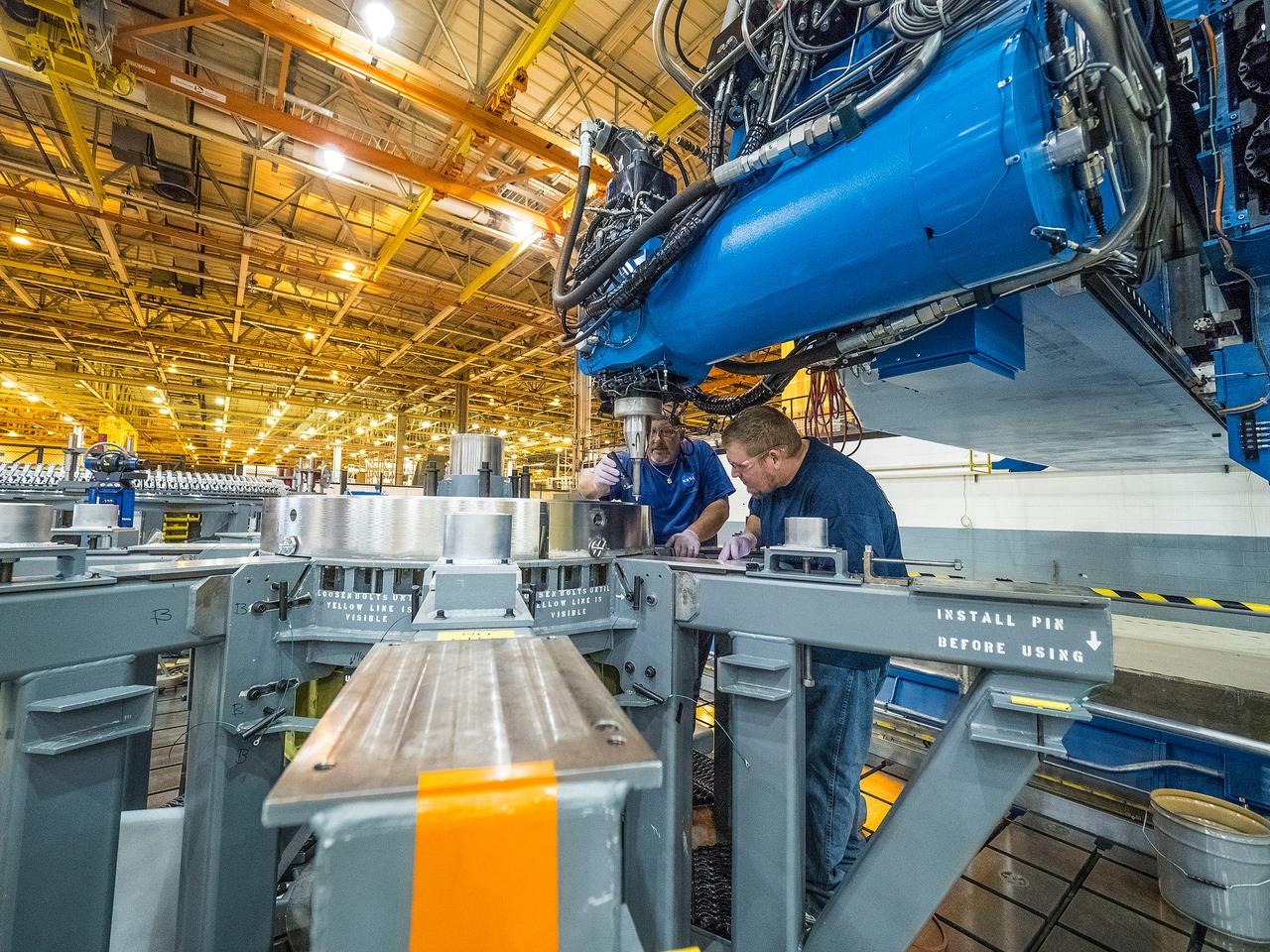

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
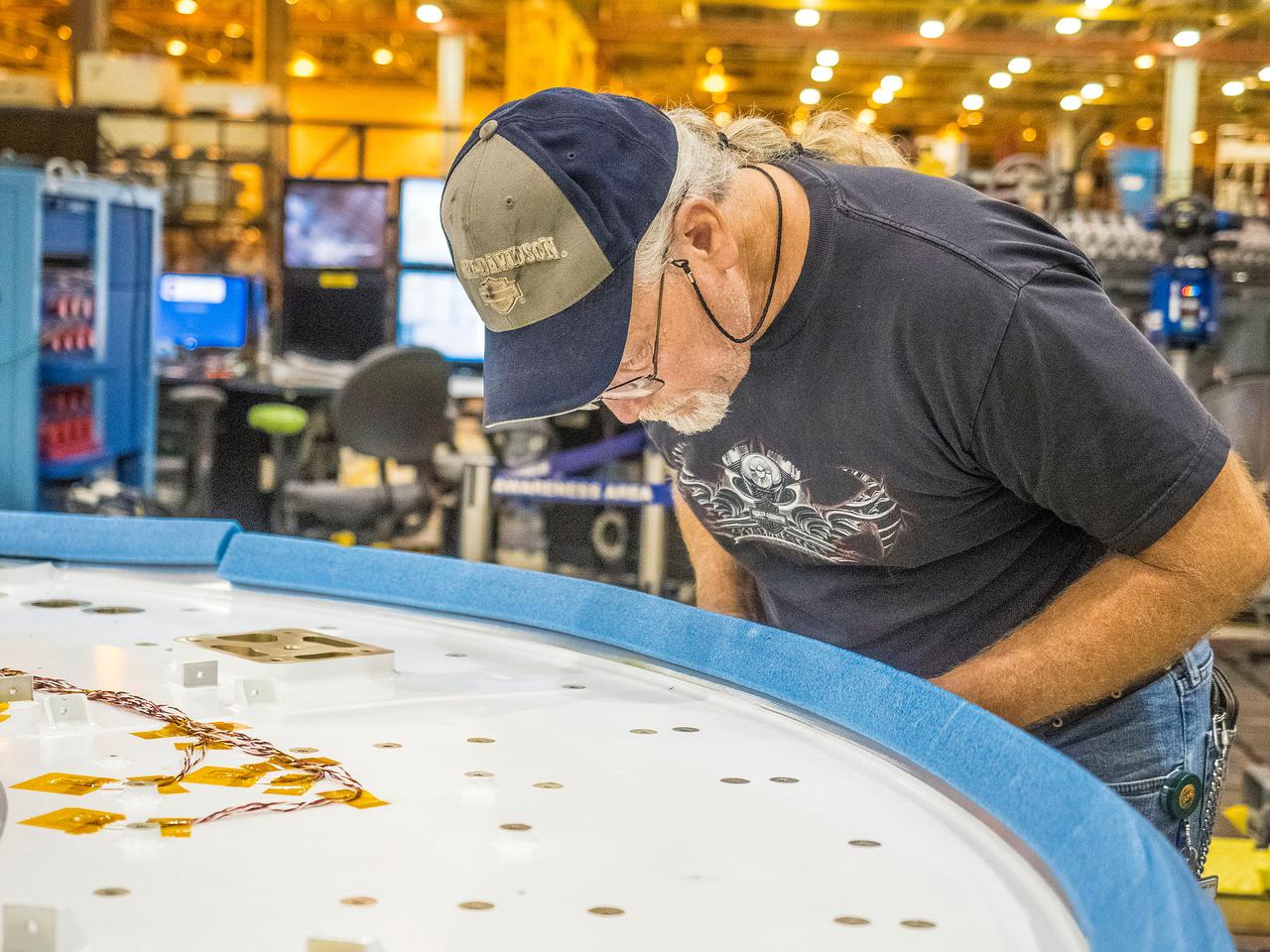

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
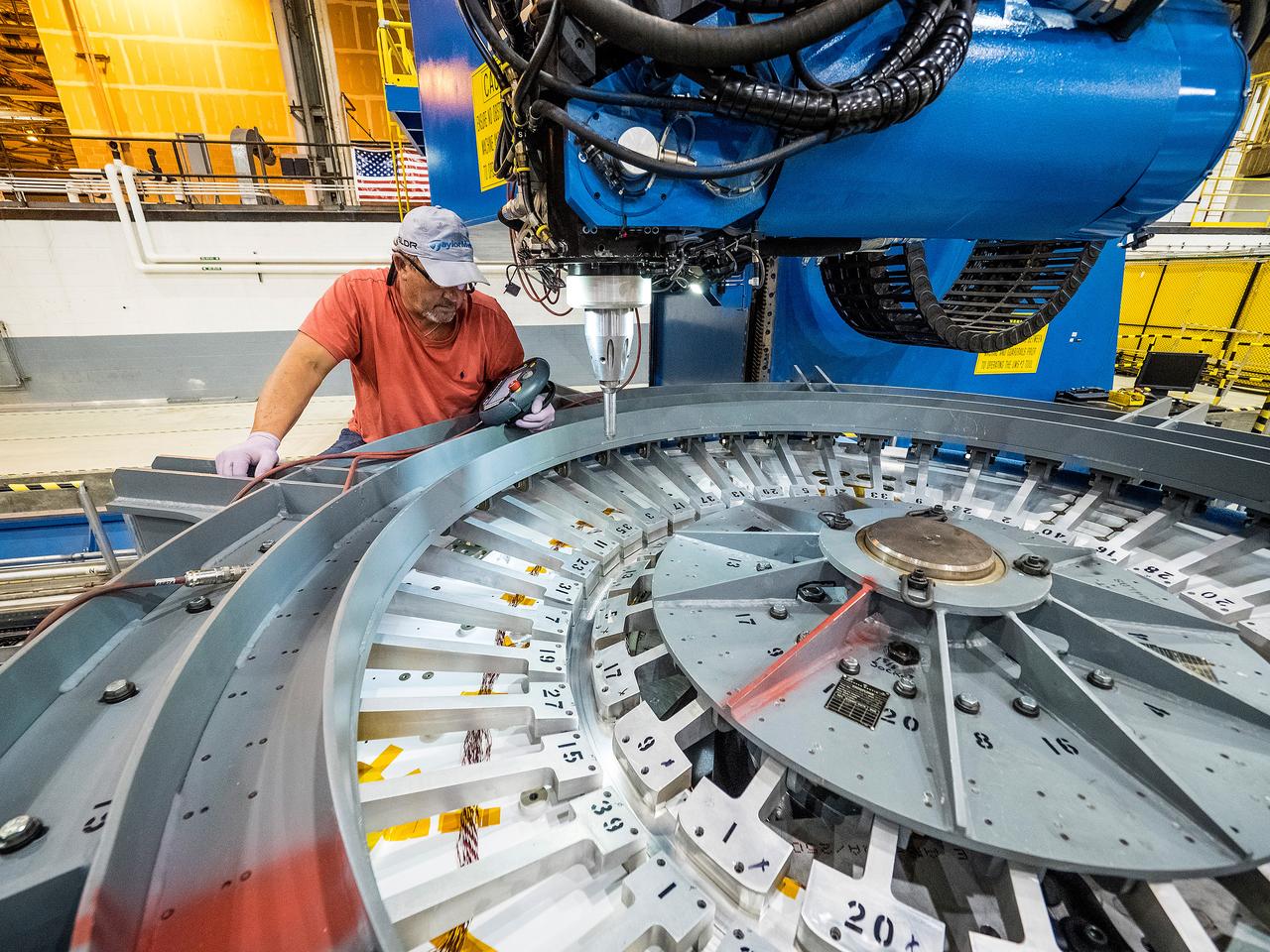
First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
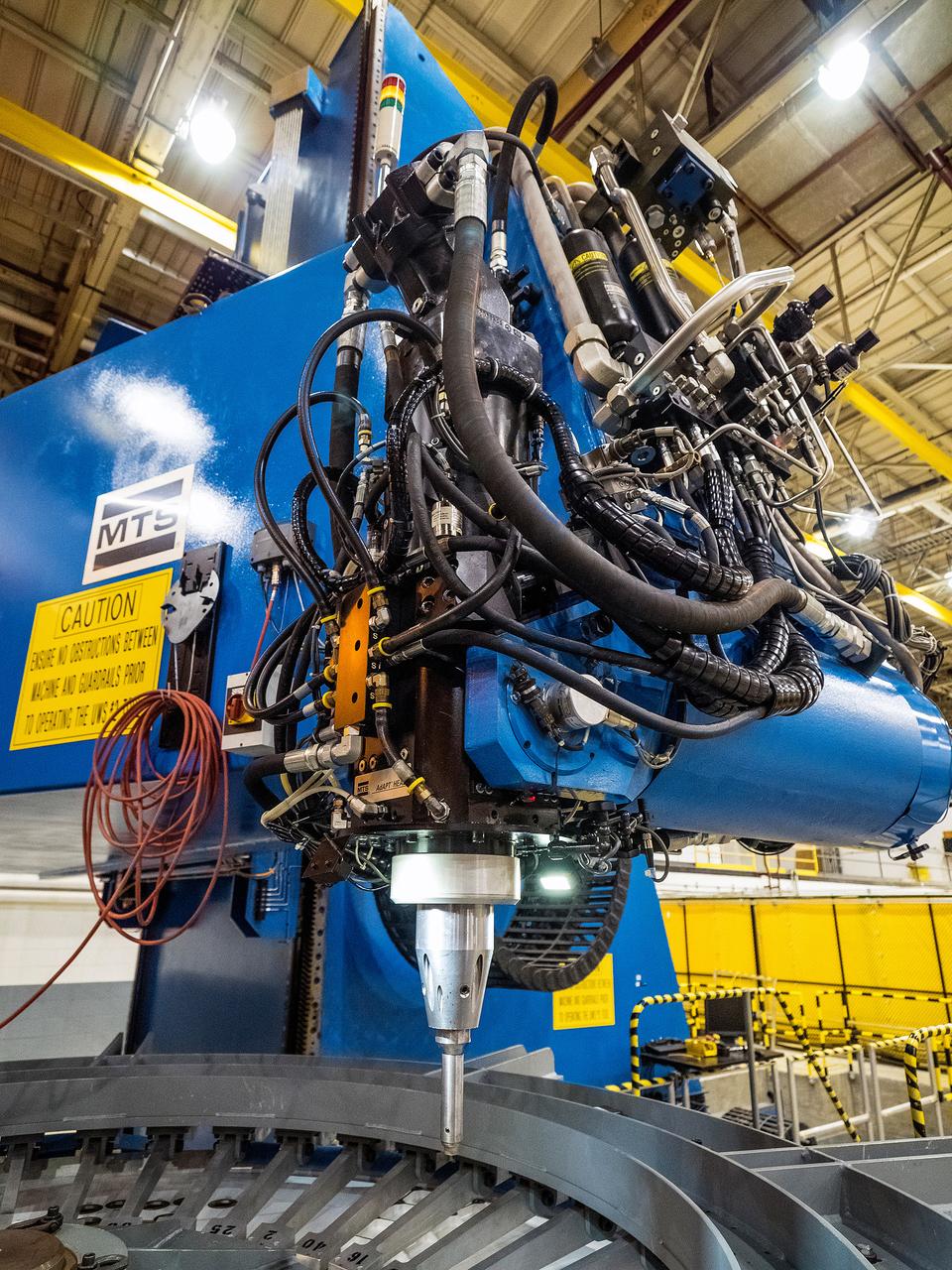

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
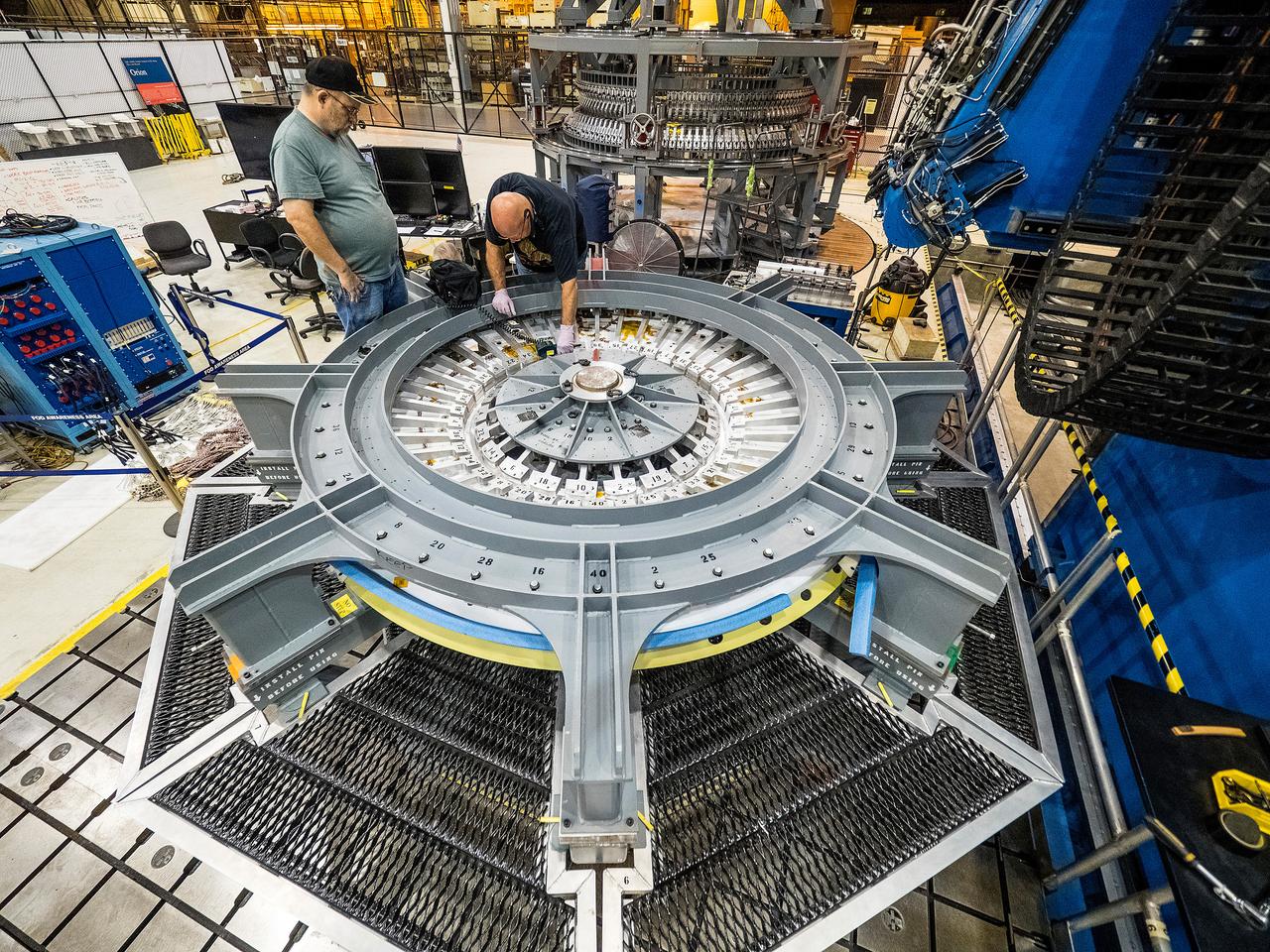
First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
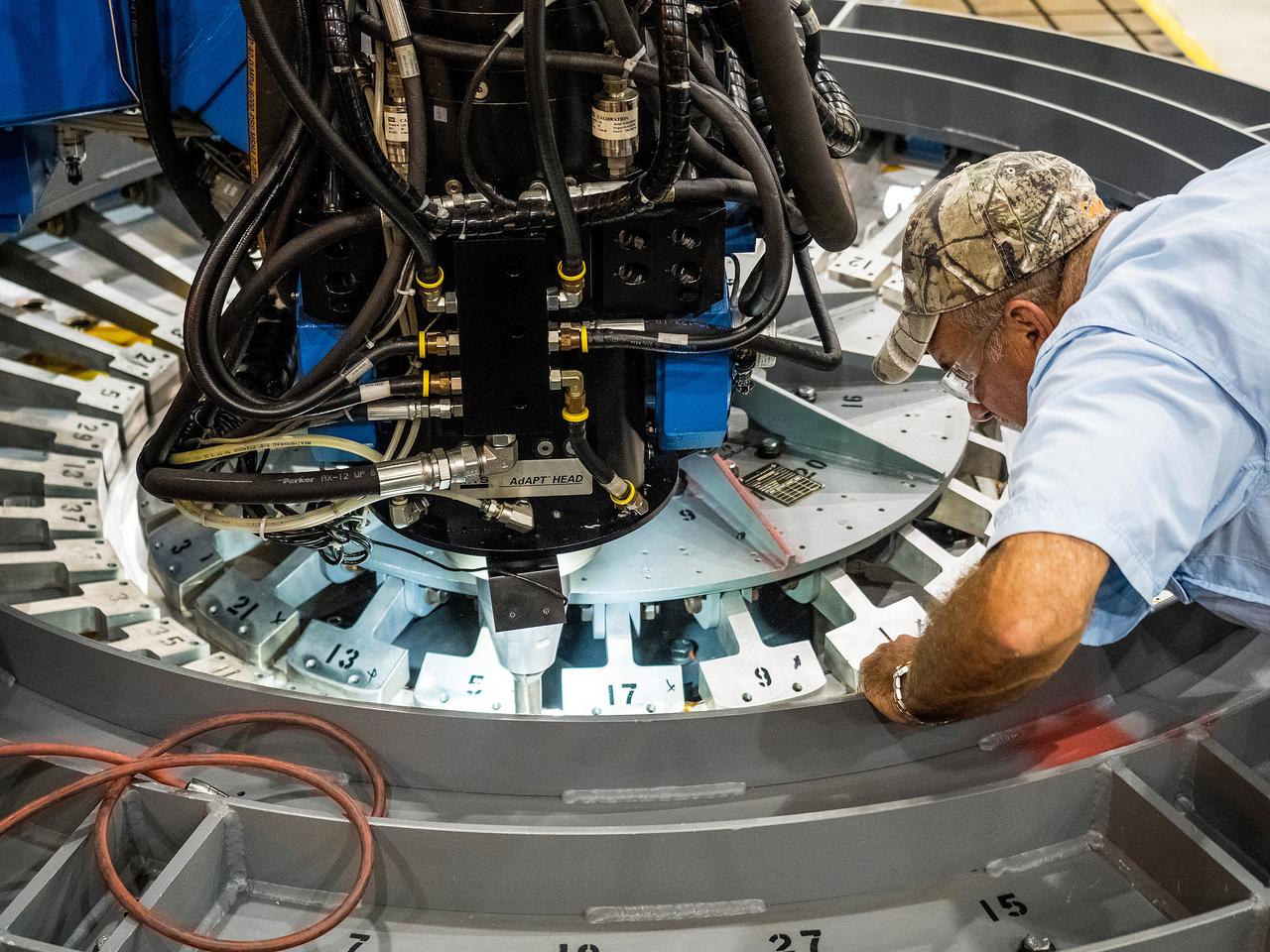
First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
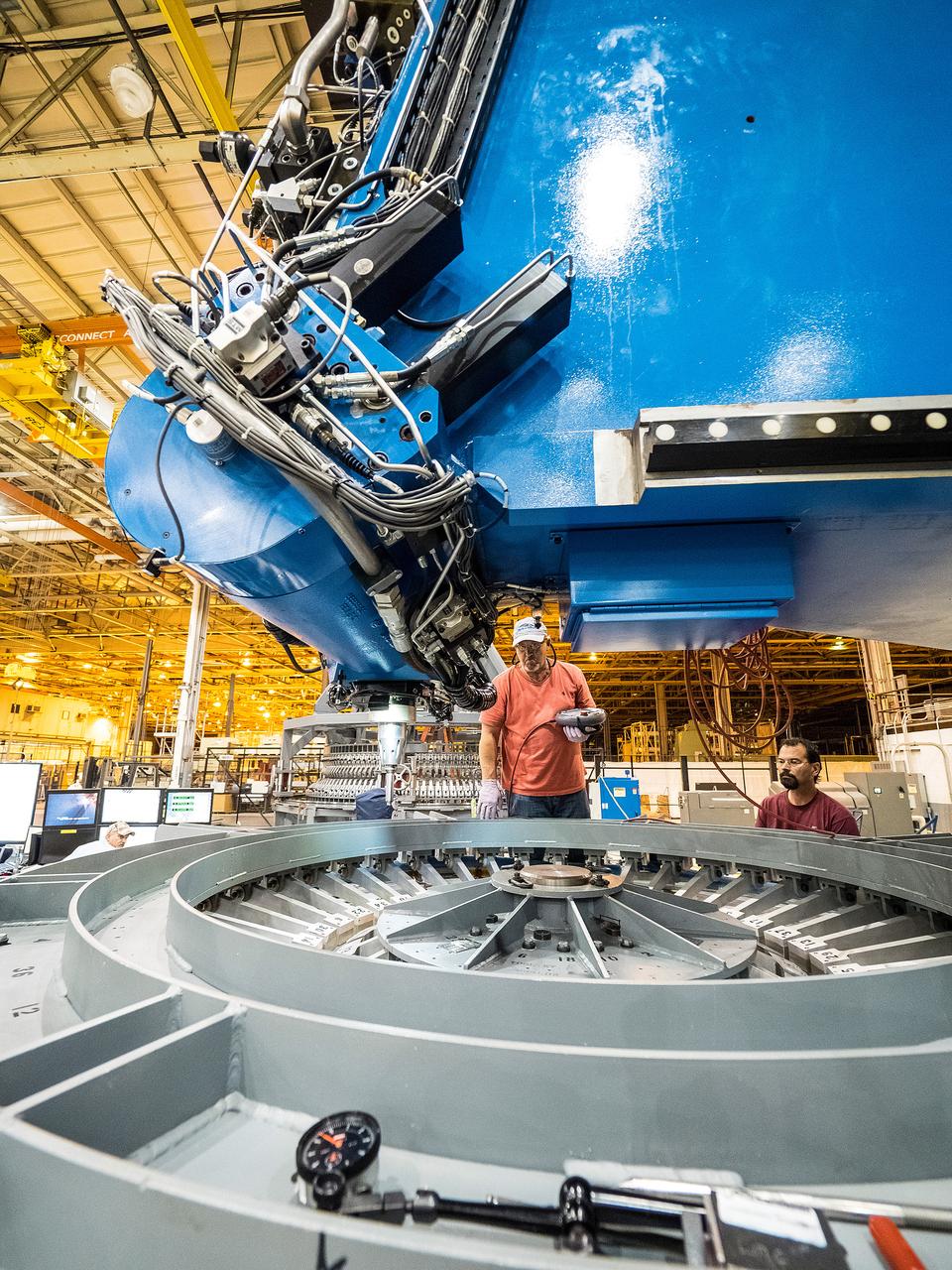

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module

First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
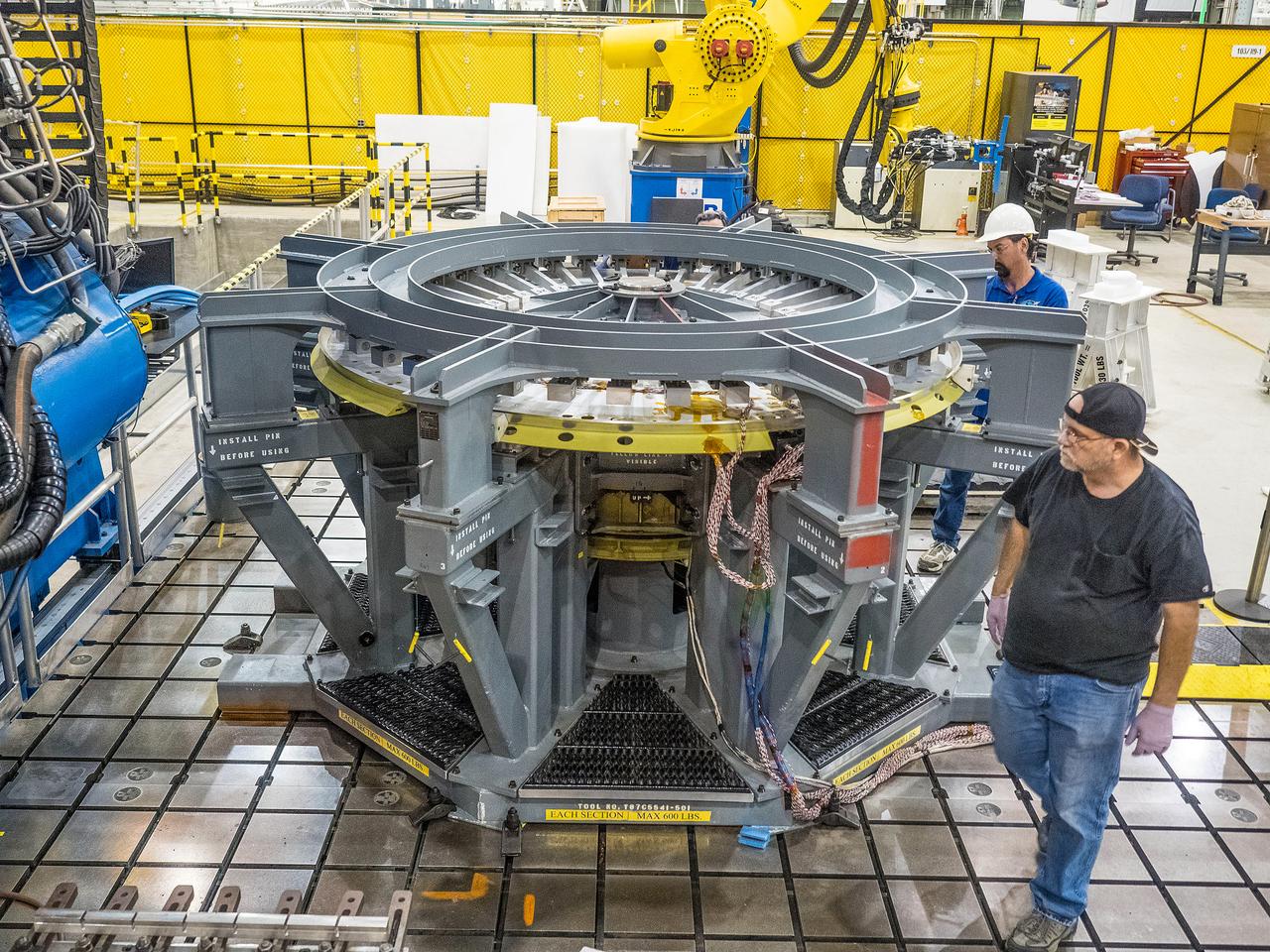
First weld of Orion Exploration Mission 1 crew module
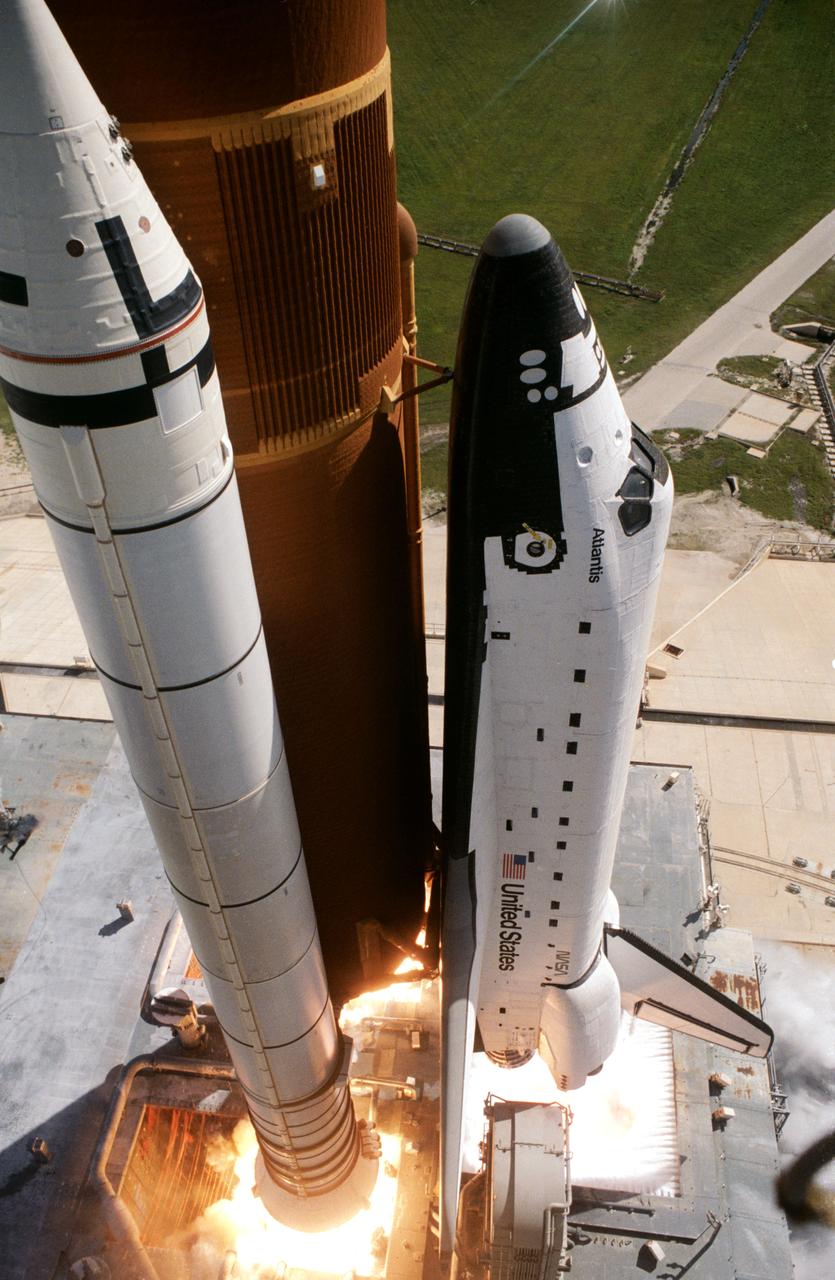

Liftoff of first flight of Atlantis and the STS 51-J mission. Mid-day skies of Florida form the backdrop for this smokey scene of the 51-J launch (001); This photograph, taken from the support structure at Launch Pad 39A, captures the first moments of the initial blastoff of the shuttle Atlantis (002); This frame was taken moments after the Atlantis cleared the launch tower. The view is from the below the orbiter and show its solid rocket boosters firing (003).
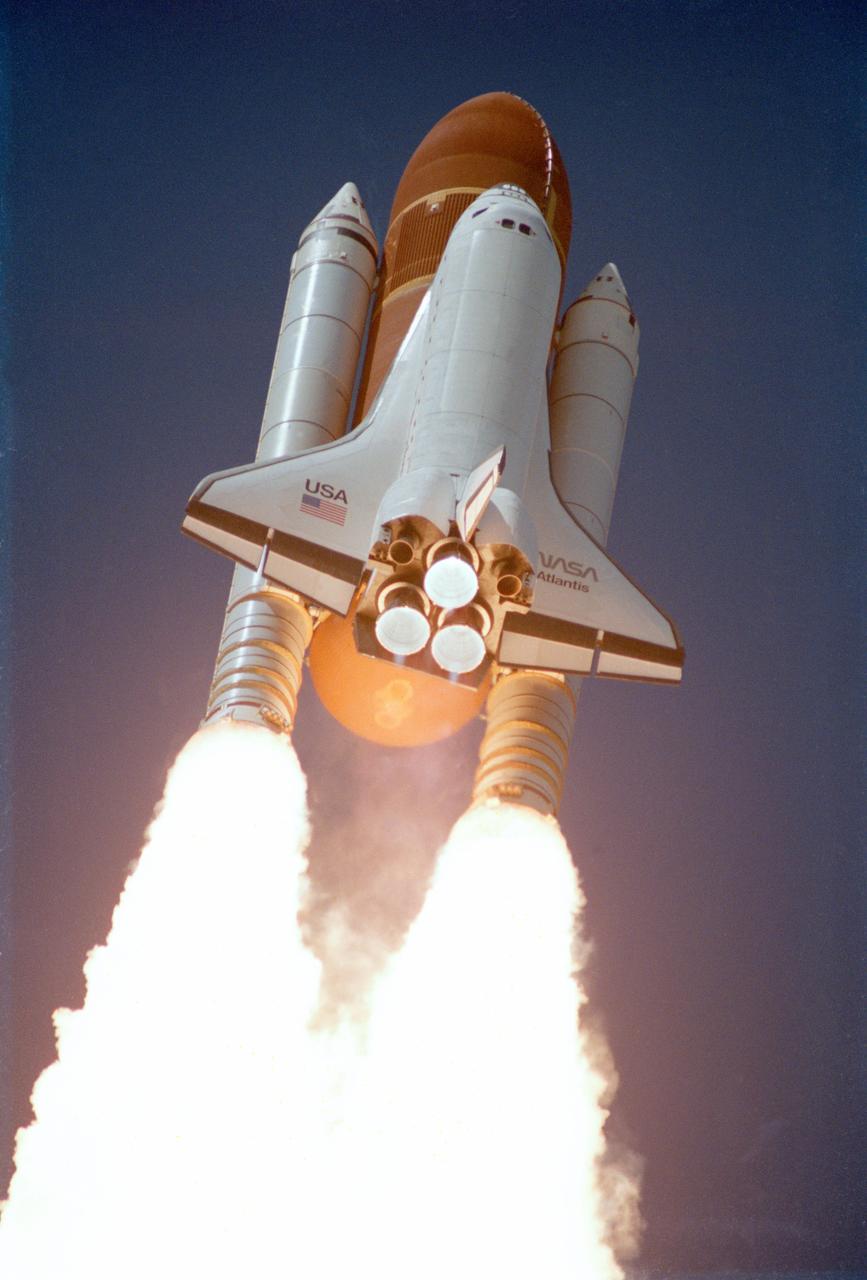

51J-S-003 (3 Oct 1985) --- This 35mm frame was taken moments after the Space Shuttle Atlantis cleared the launch tower to begin its first mission in space. Onboard, ready to carry out STS-51J mission were astronauts Karol J. Bobko, commander; Ronald J. Grabe, pilot; Robert L. Stewart and David C. Hilmers, mission specialist; and U.S.A.F. Major William A. Pailes, payload specialist.

51J-S-001 (3 Oct 1985) --- This 35mm frame was taken moments after the Space Shuttle Atlantis cleared the launch tower to begin its first mission in space. Onboard, ready to carry out STS-51J mission were astronauts Karol J. Bobko, commander; Ronald J. Grabe, pilot; Robert L. Stewart and David C. Hilmers, mission specialist; and United States Air Force Major William A. Pailes, payload specialist.
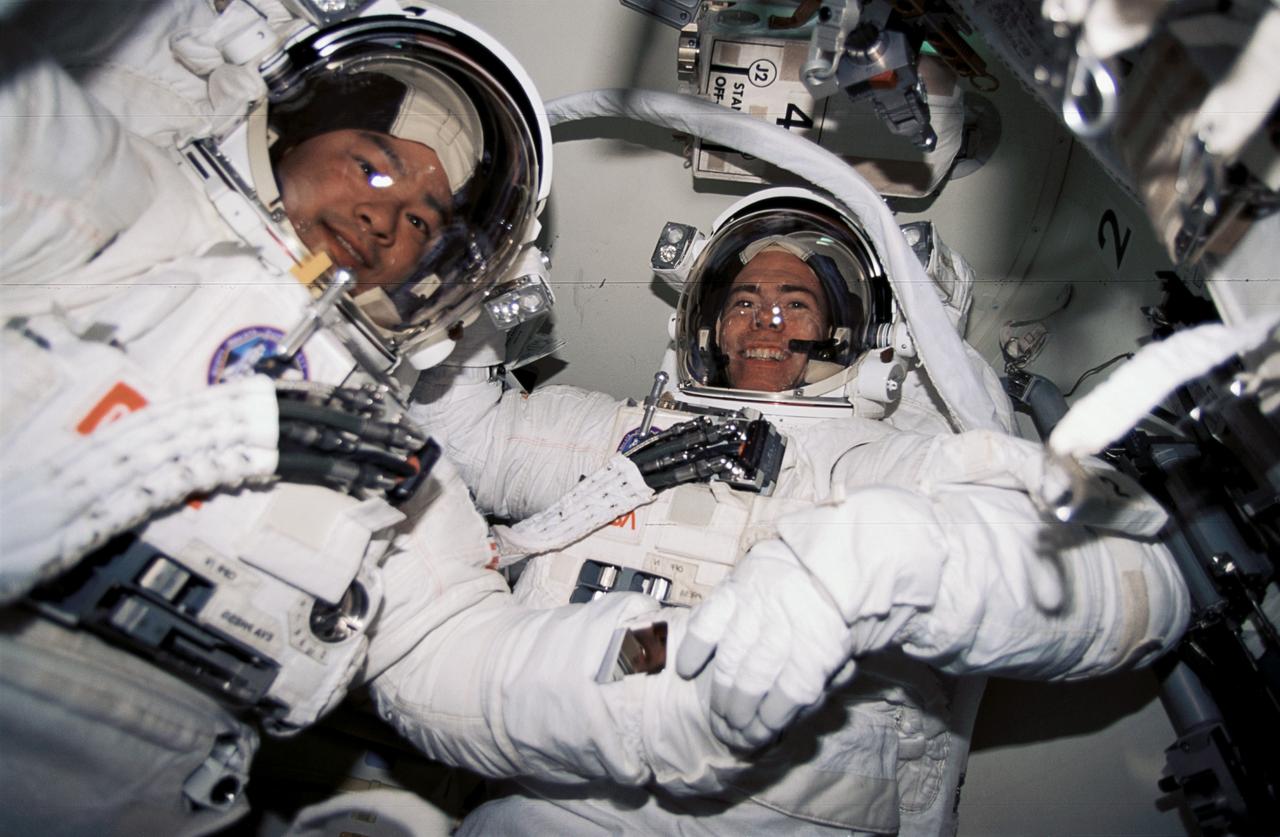

STS072-391-009 (15 Jan. 1996) --- In the Space Shuttle Endeavour's airlock, astronauts Leroy Chiao (left) and Daniel T. Barry prepare for the first extravehicular activity (EVA) scheduled on the mission. The two EVA's were scheduled to evaluate space station assembly techniques.
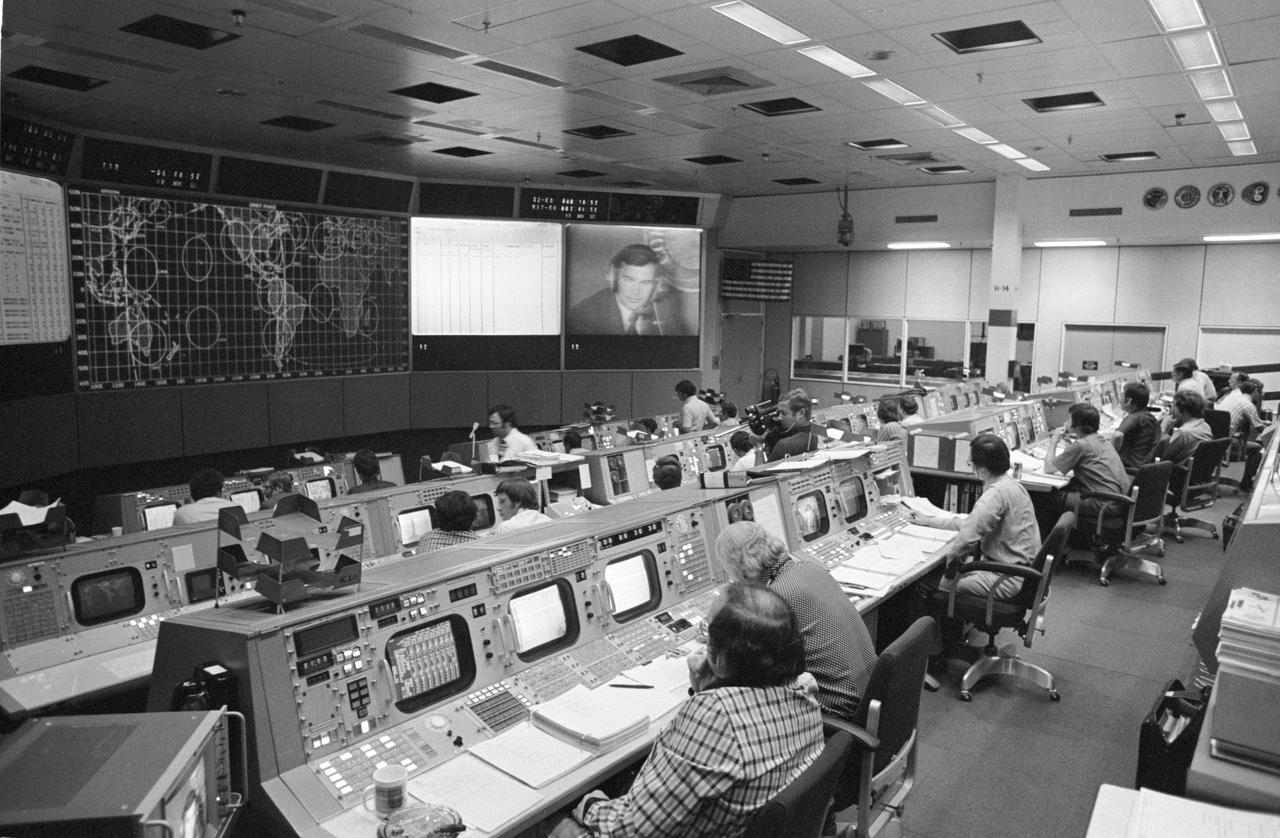

S75-28483 (15 July 1975) --- An overall view of the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center on the first day of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. The American ASTP flight controllers at NASA's Johnson Space Center were monitoring the progress of the Soviet ASTP launch when this photograph was taken. The television monitor shows cosmonaut Yuri V. Romanenko at his spacecraft communicator?s console in the ASTP mission control center in the Soviet Union. The American ASTP liftoff followed the Soviet ASTP launch by seven and one-half hours.
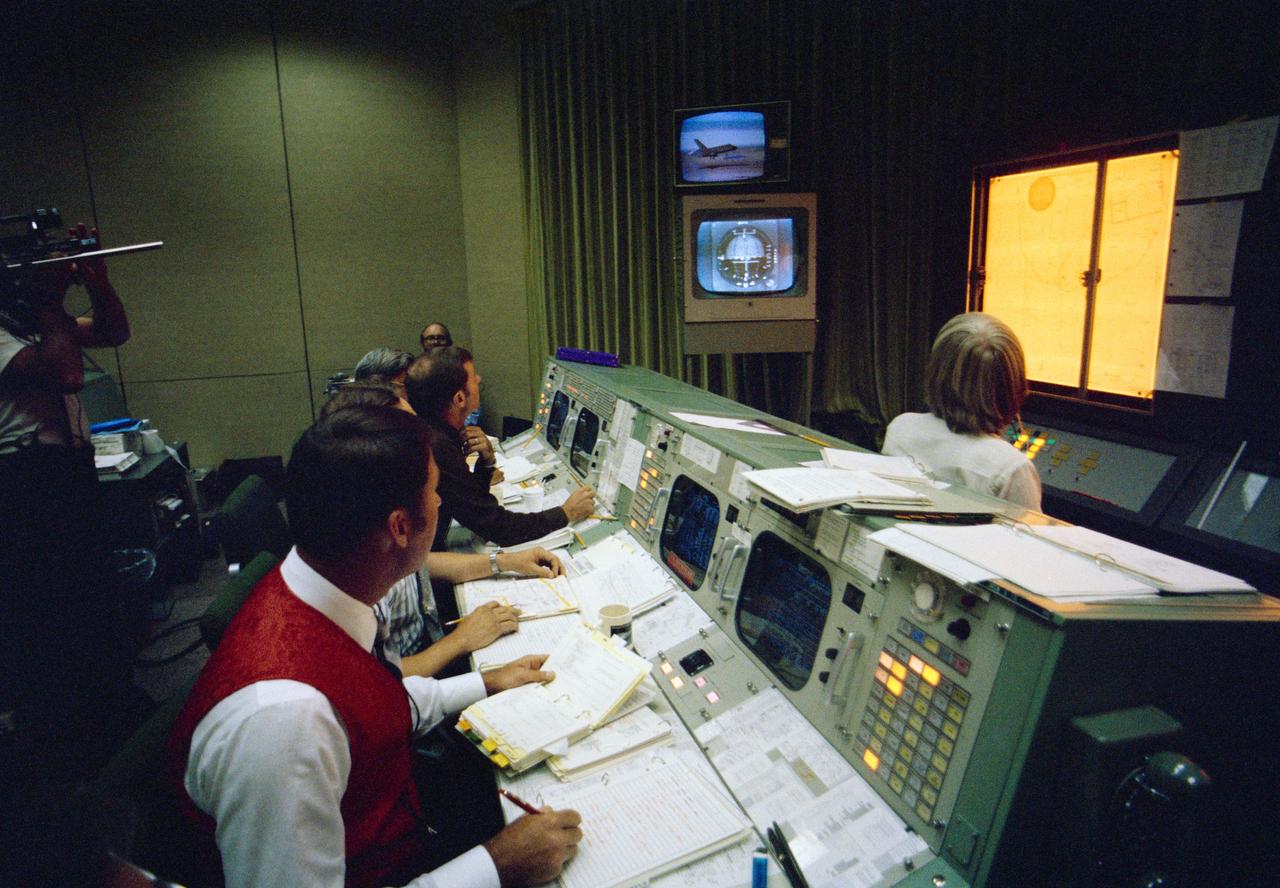

S77-27546 (12 Aug 1977) --- An overall view of Mission Control Operations in the Mission Control Center, bldg 30, at JSC, during the first free flight of the Shuttle Approach and Landing Tests (ALTs) conducted on August 12, 1977 at the Dryden Flight Research Center in Southern California. This view is looking across the console of flight director Donald R. Puddy. The television monitor in the background shows the Orbiter 101 "Enterprise" landing following its five minute 23-second unpowered free flight.
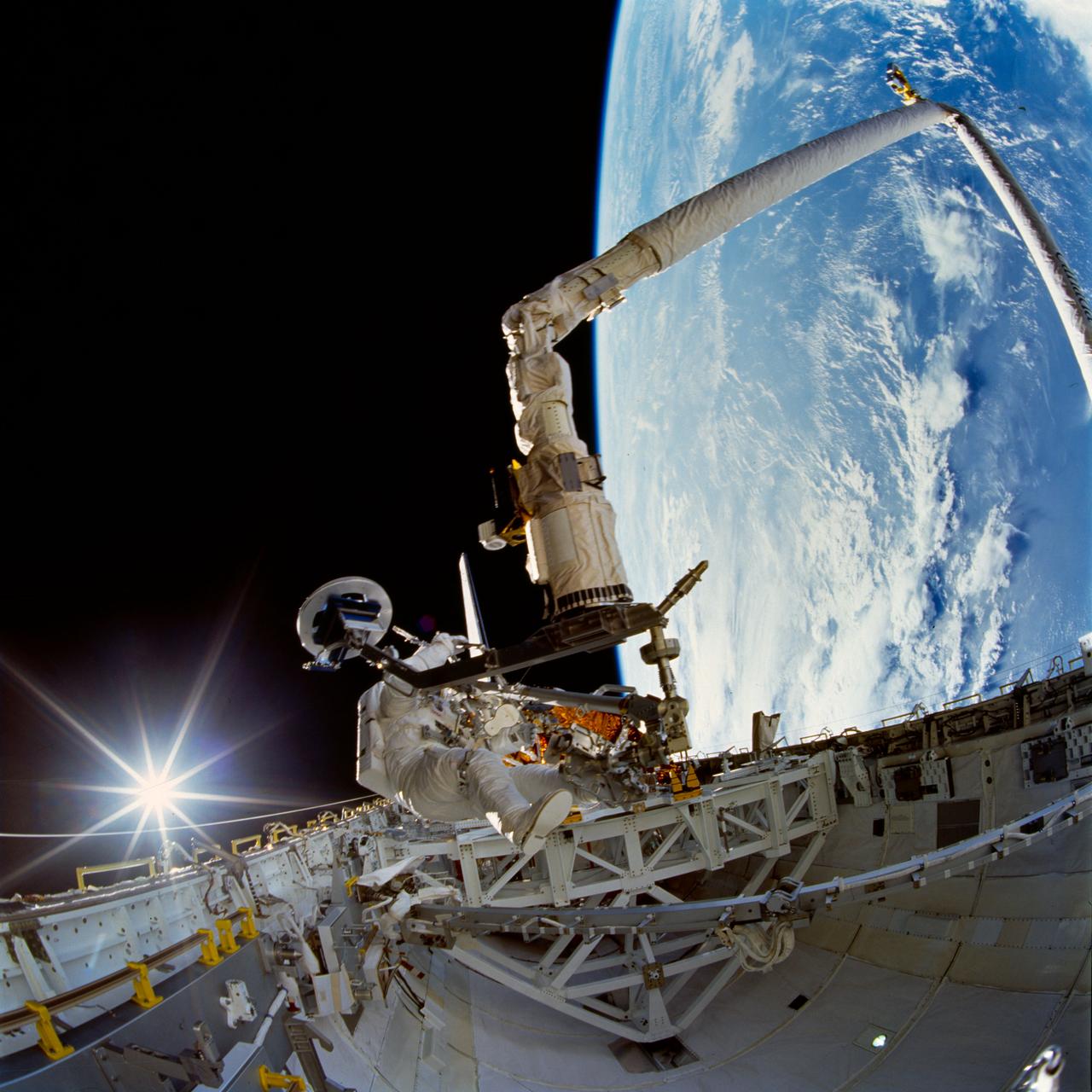

STS072-742-004 (15 Jan. 1996) --- Astronaut Daniel T. Barry, STS-72 mission specialist, tests a Temporary Equipment Restraint Aid (TERA) in the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Endeavour. A reflection of the sun’s rays beam off Endeavour’s aft flight deck window in the “fish-eye” image. Barry was joined by astronaut Leroy Chiao for this first of two extravehicular activities (EVA) on the mission. A good part of the EVA was spent evaluating EVA hardware for future scheduled missions. Astronauts Chiao and Winston E. Scott participated in the second EVA two days later. Photo credit: NASA

S68-26668 (June 1968) --- The official emblem of Apollo 7, the first manned Apollo space mission. The crew will consist of astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr., Donn F. Eisele, and Walter Cunningham. The NASA insignia design for Apollo flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for the official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced.
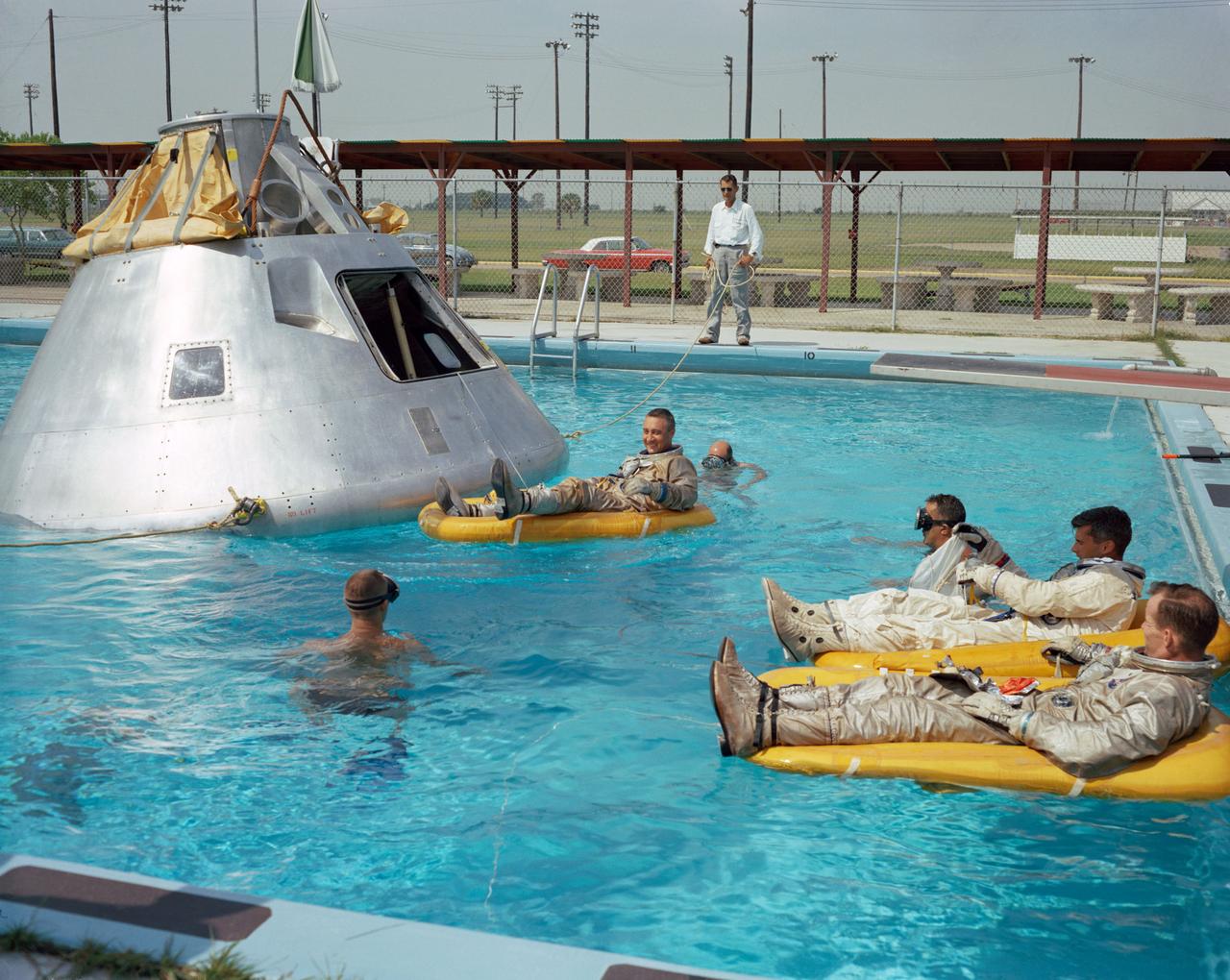

S66-51581 (June 1966) --- Prime crew for the first manned Apollo mission practice water egress procedures with full scale boilerplate model of their spacecraft. In the water at right is astronaut Edward H. White (foreground) and astronaut Roger B. Chaffee. In raft near the spacecraft is astronaut Virgil I. Grissom. NASA swimmers are in the water to assist in the practice session that took place at Ellington AFB, near the Manned Spacecraft Center, Houston.
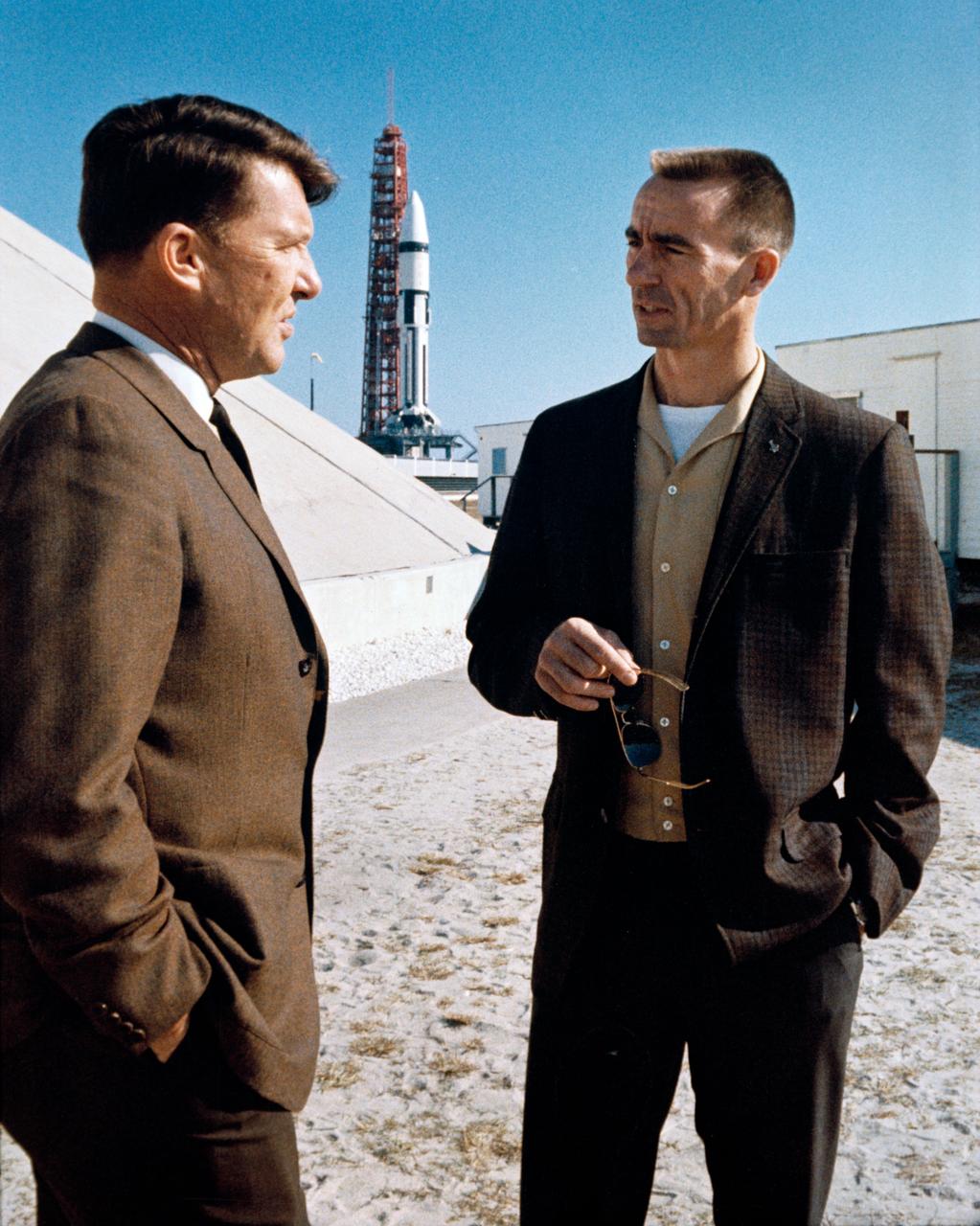

S68-18700 (22 Jan. 1968) --- Two prime crew members of the first manned Apollo space flight were present at Cape Kennedy for the launch of the Apollo V (LM-1/Saturn 204) unmanned space mission. On left is astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr.; and on right is astronaut R. Walter Cunningham. In background is the Apollo V stack at Launch Complex 37 ready for launch.
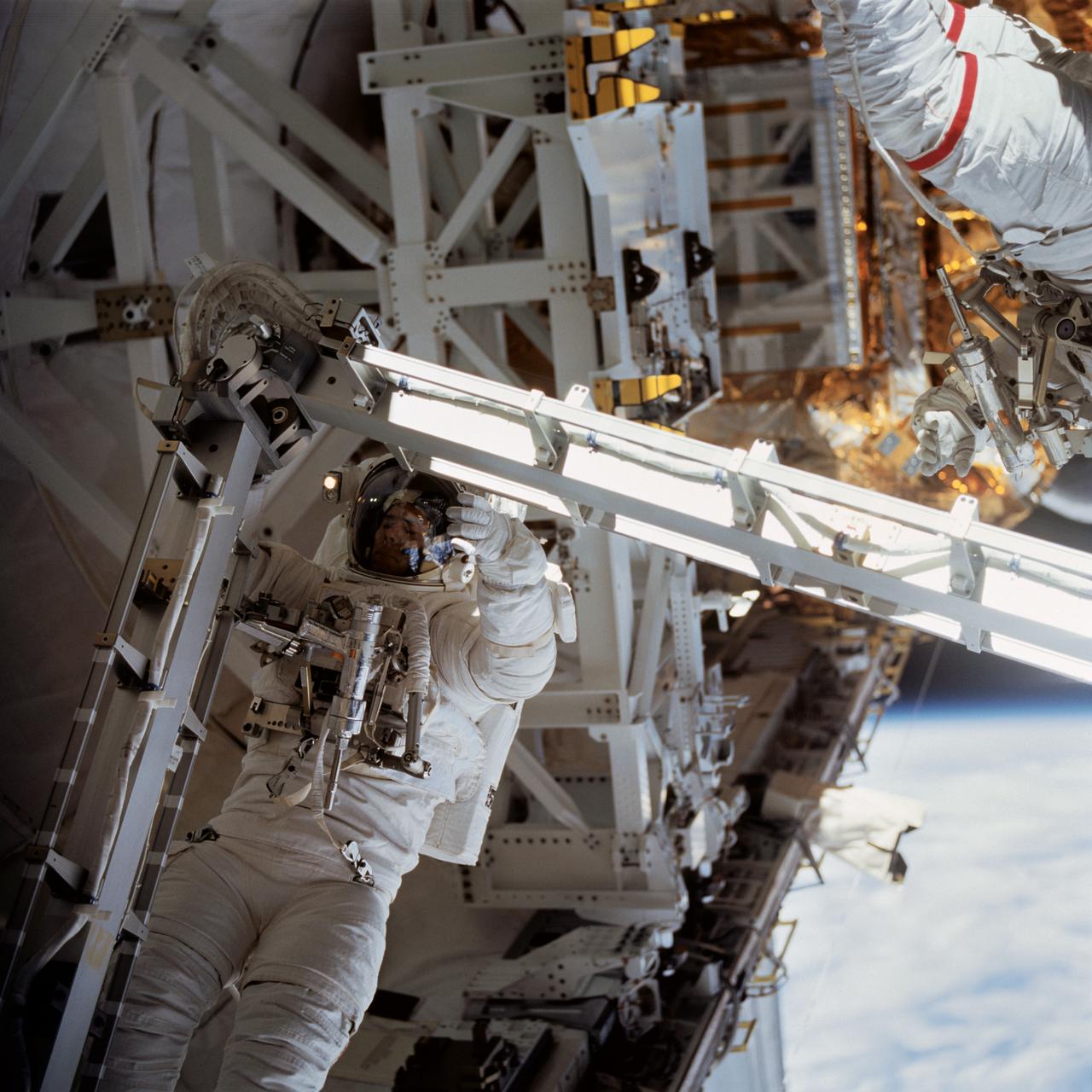

STS072-735-093 (15 Jan. 1996) --- Astronaut Daniel T. Barry, STS-72 mission specialist, works in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Endeavour during the first of two extravehicular activities (EVA). Barry unfolds the rigid umbilical as astronaut Leroy Chiao (partially visible at top) assists. The two joined four other NASA astronauts for a week and a half aboard Endeavour.
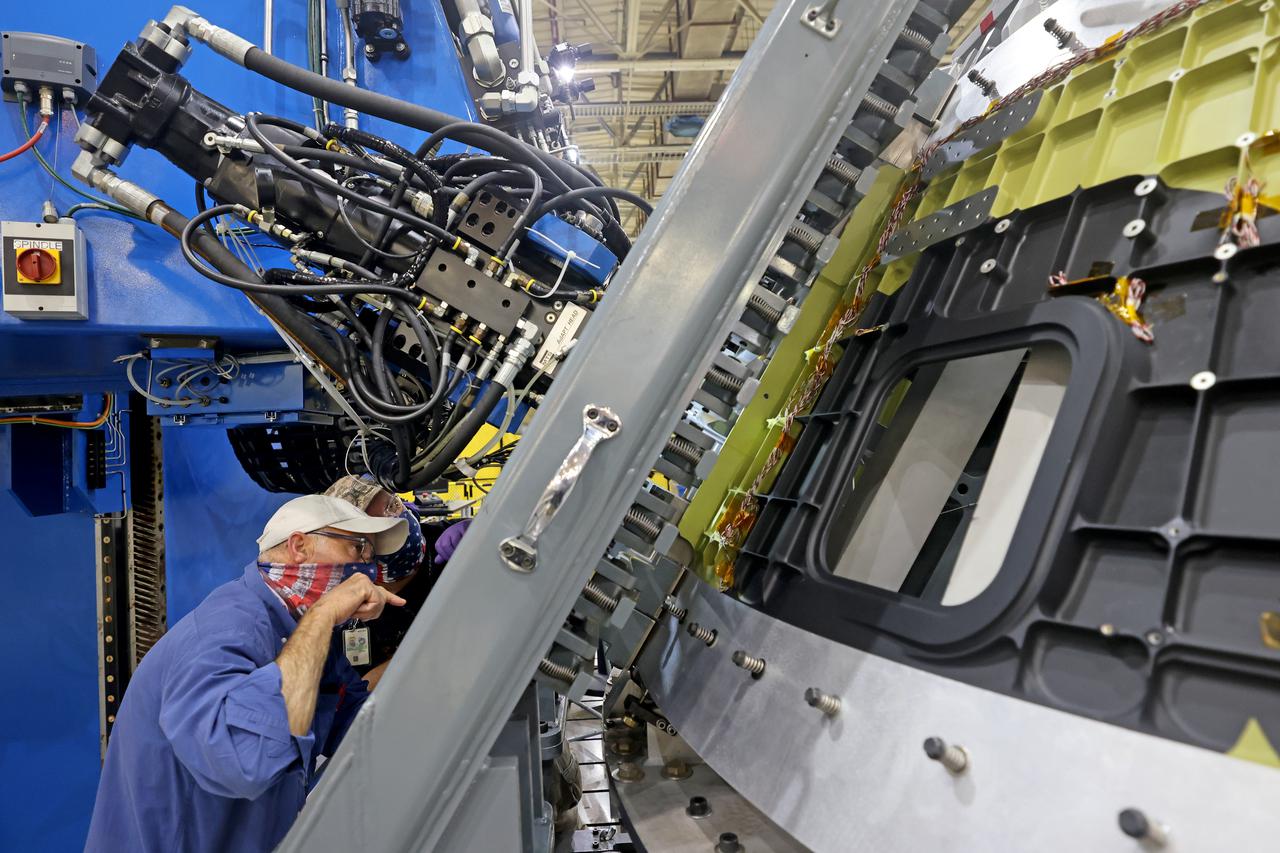

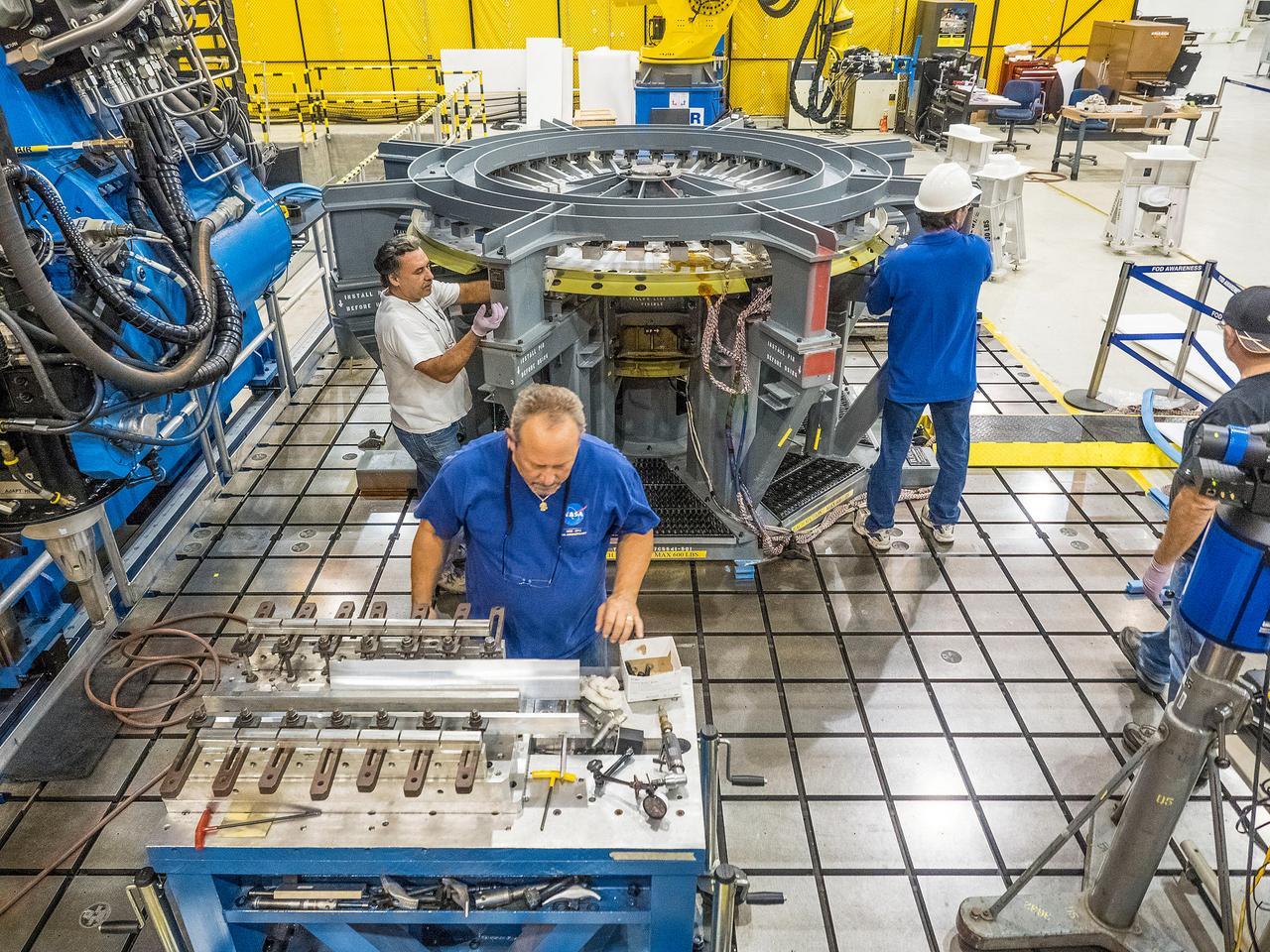
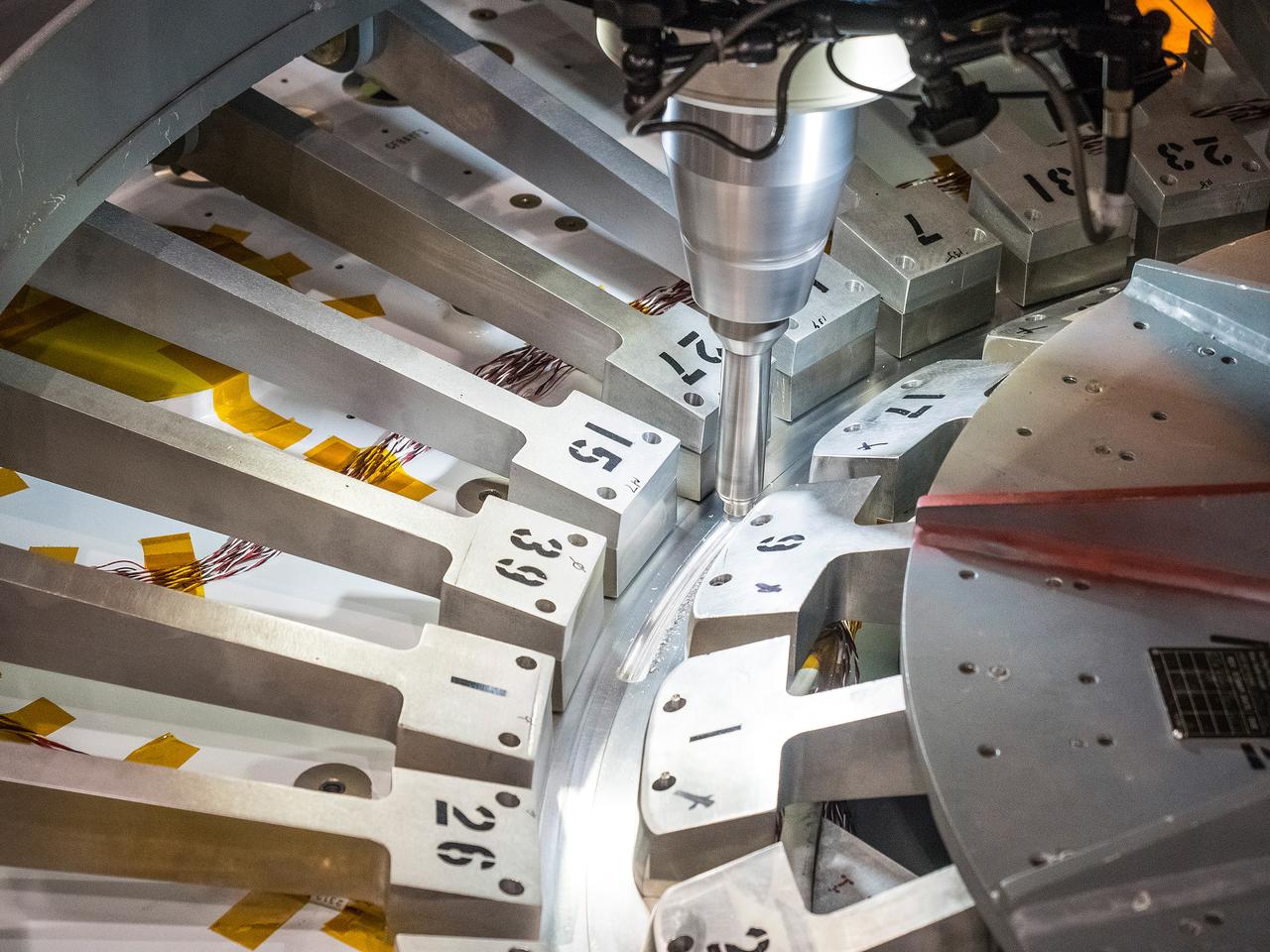
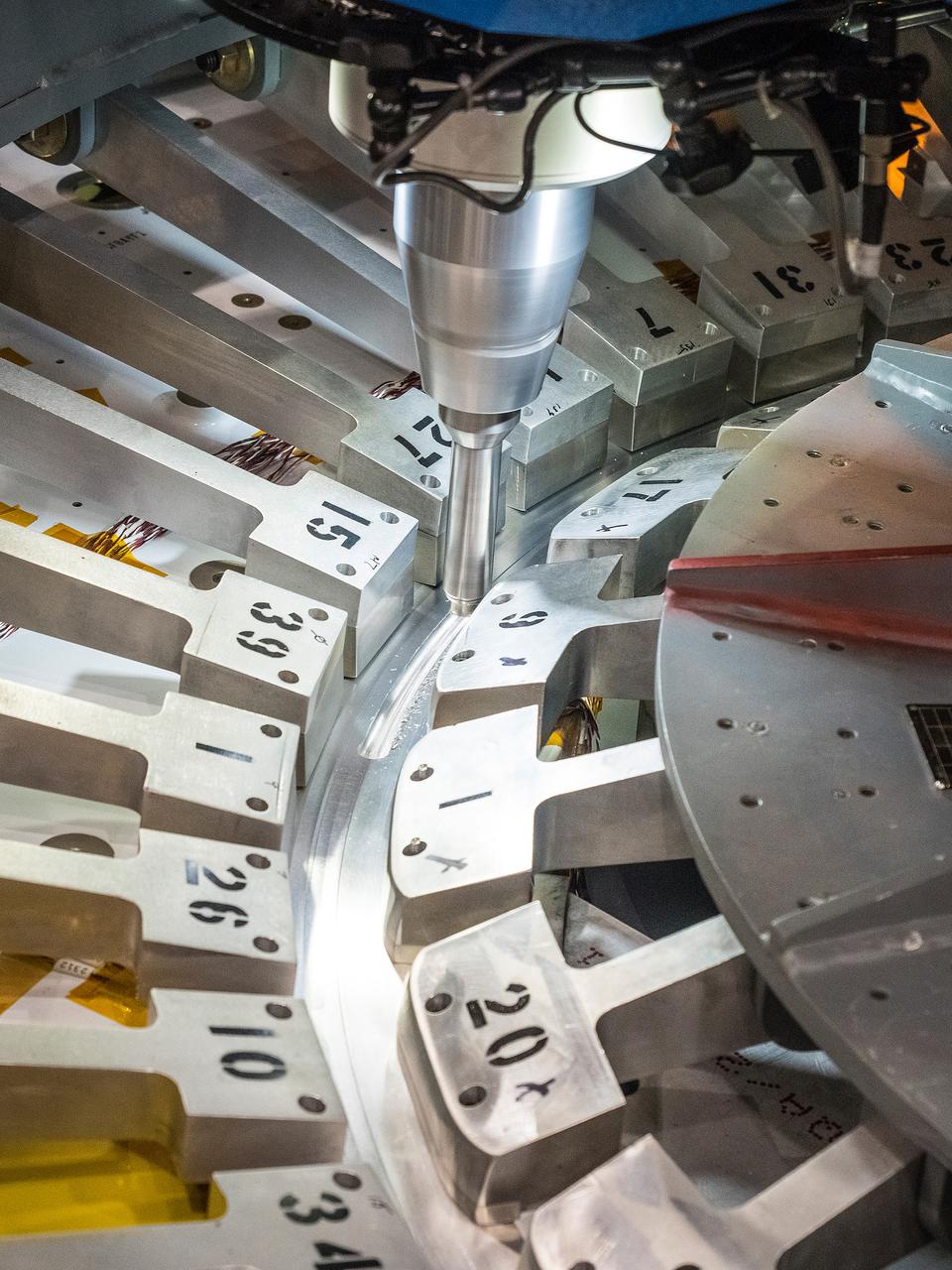
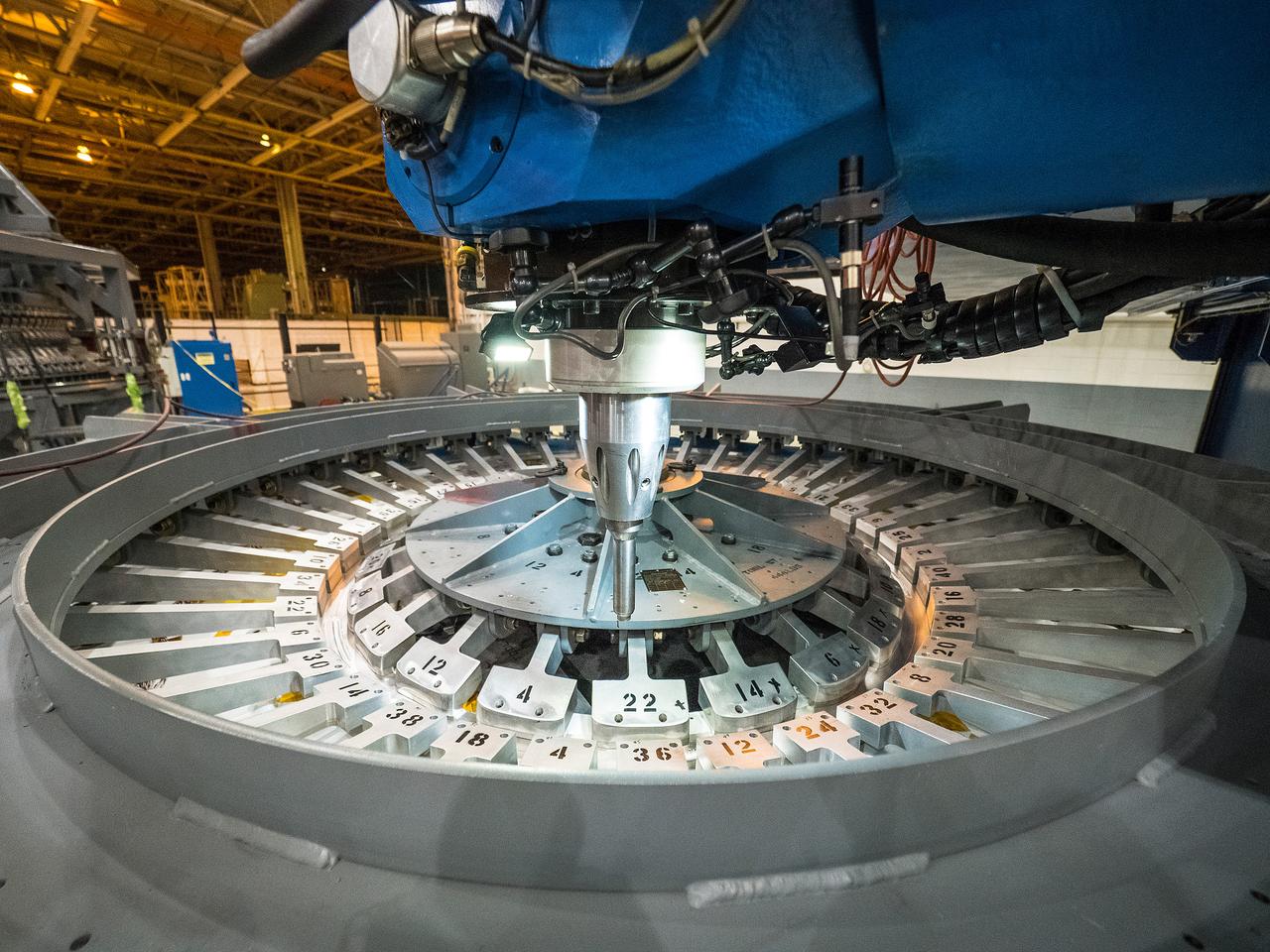
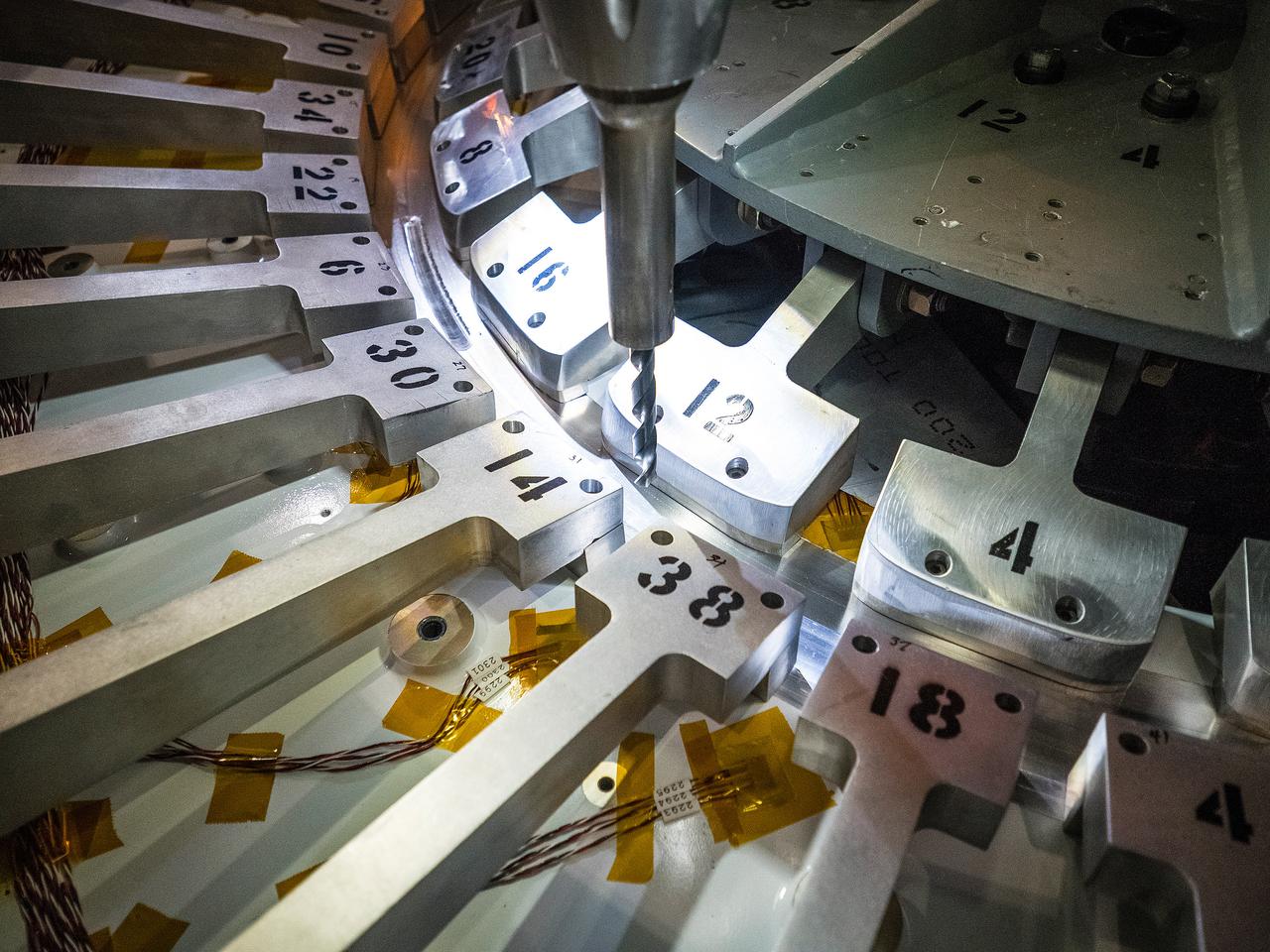
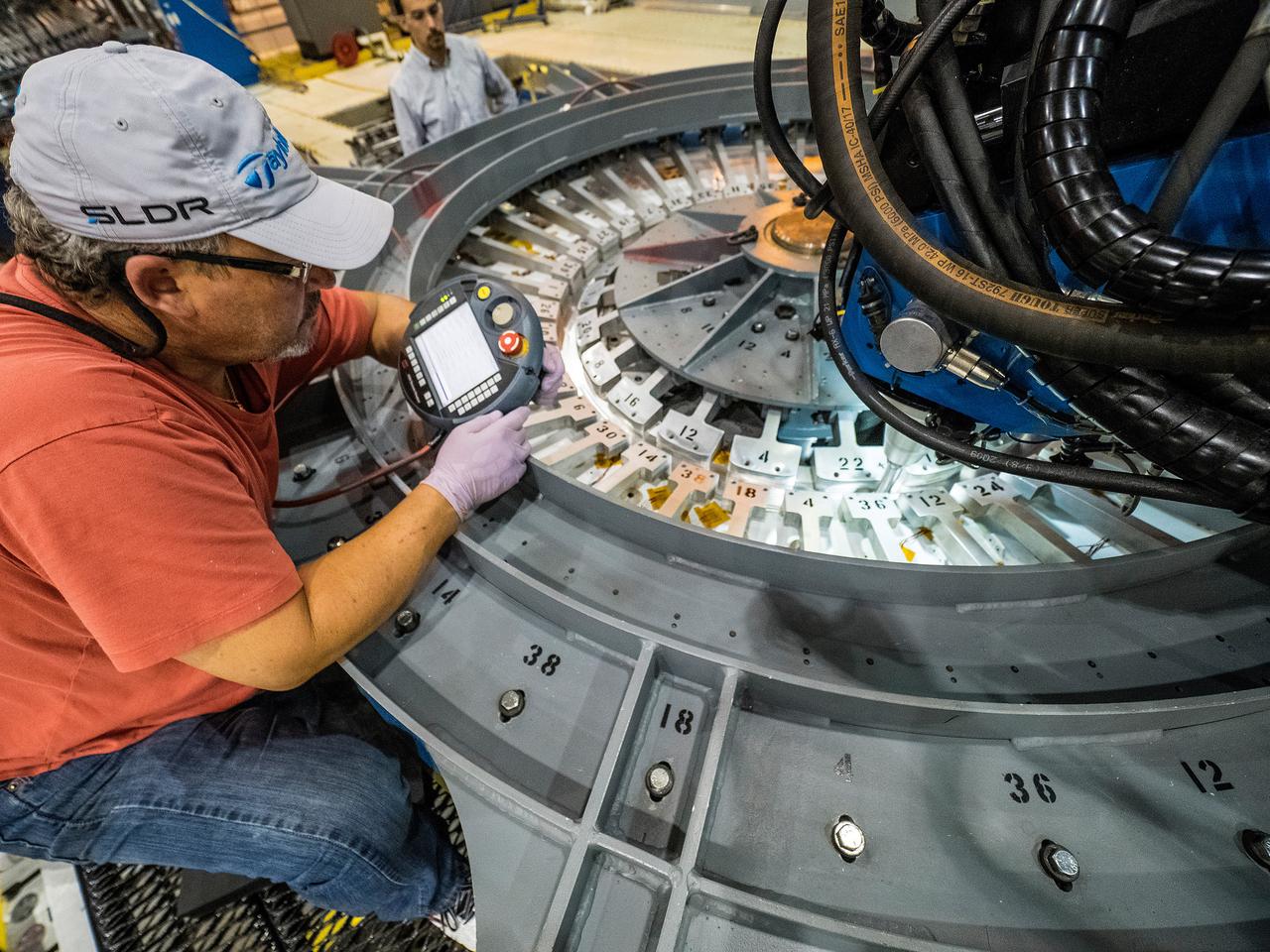
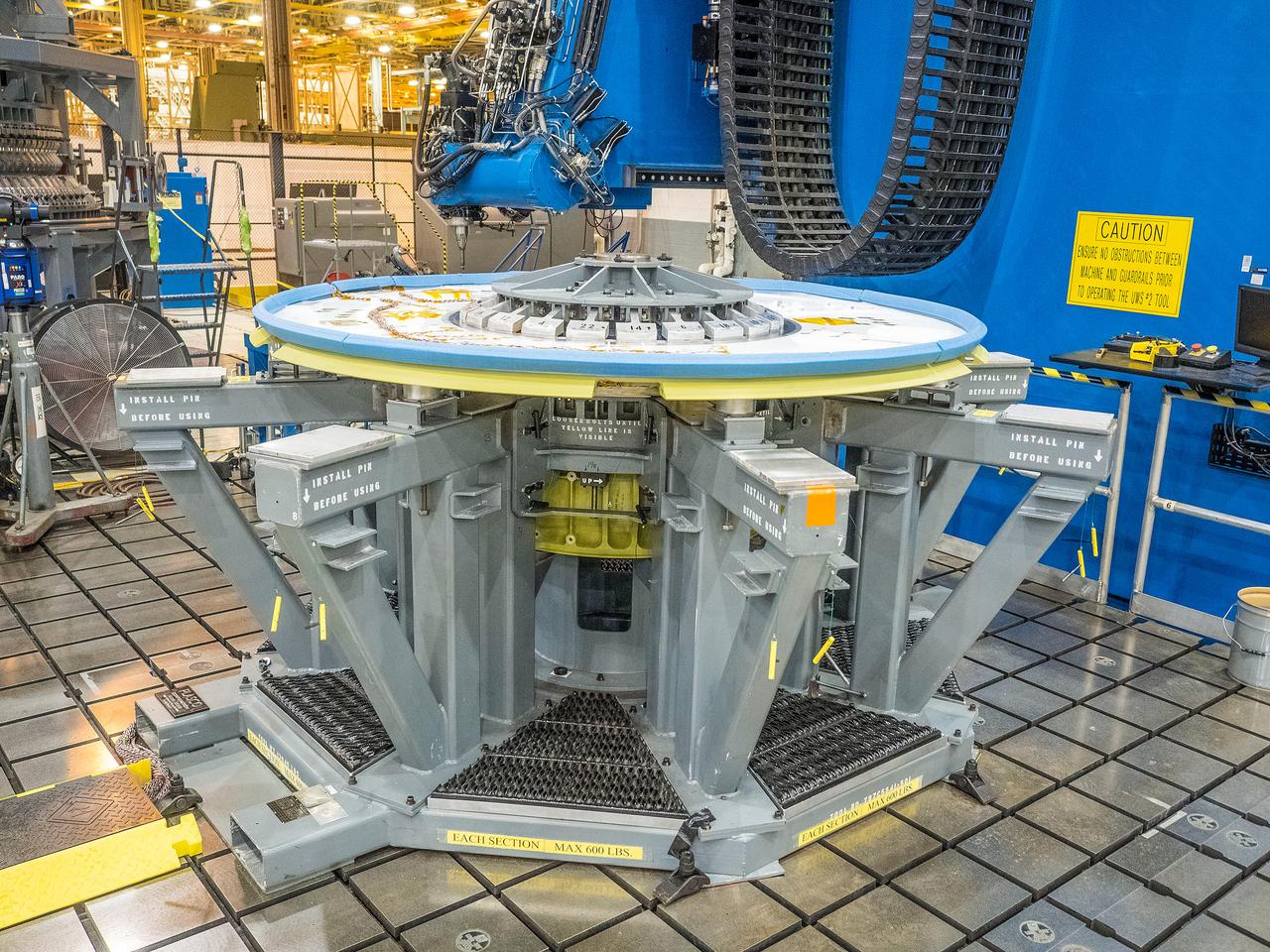
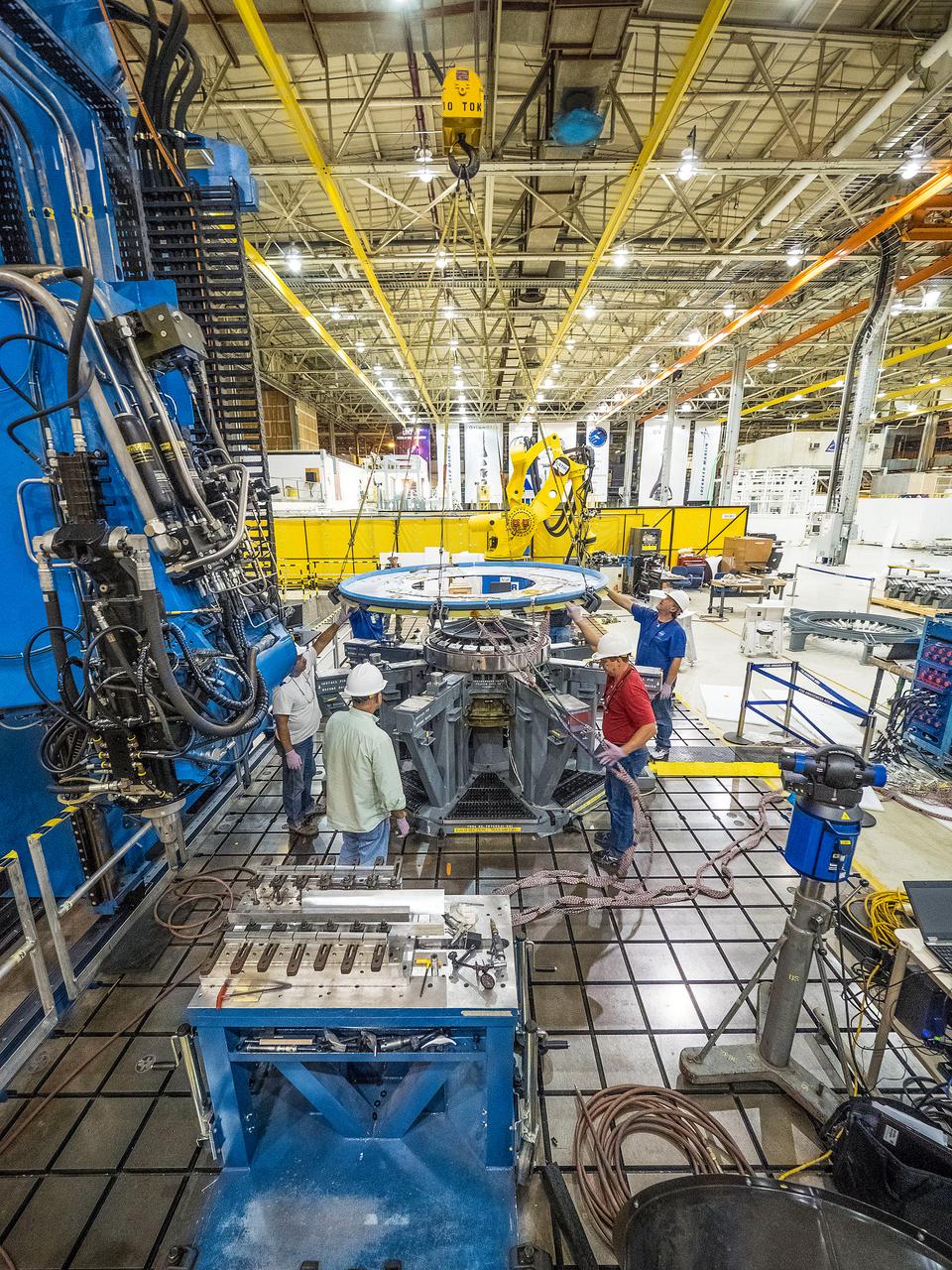
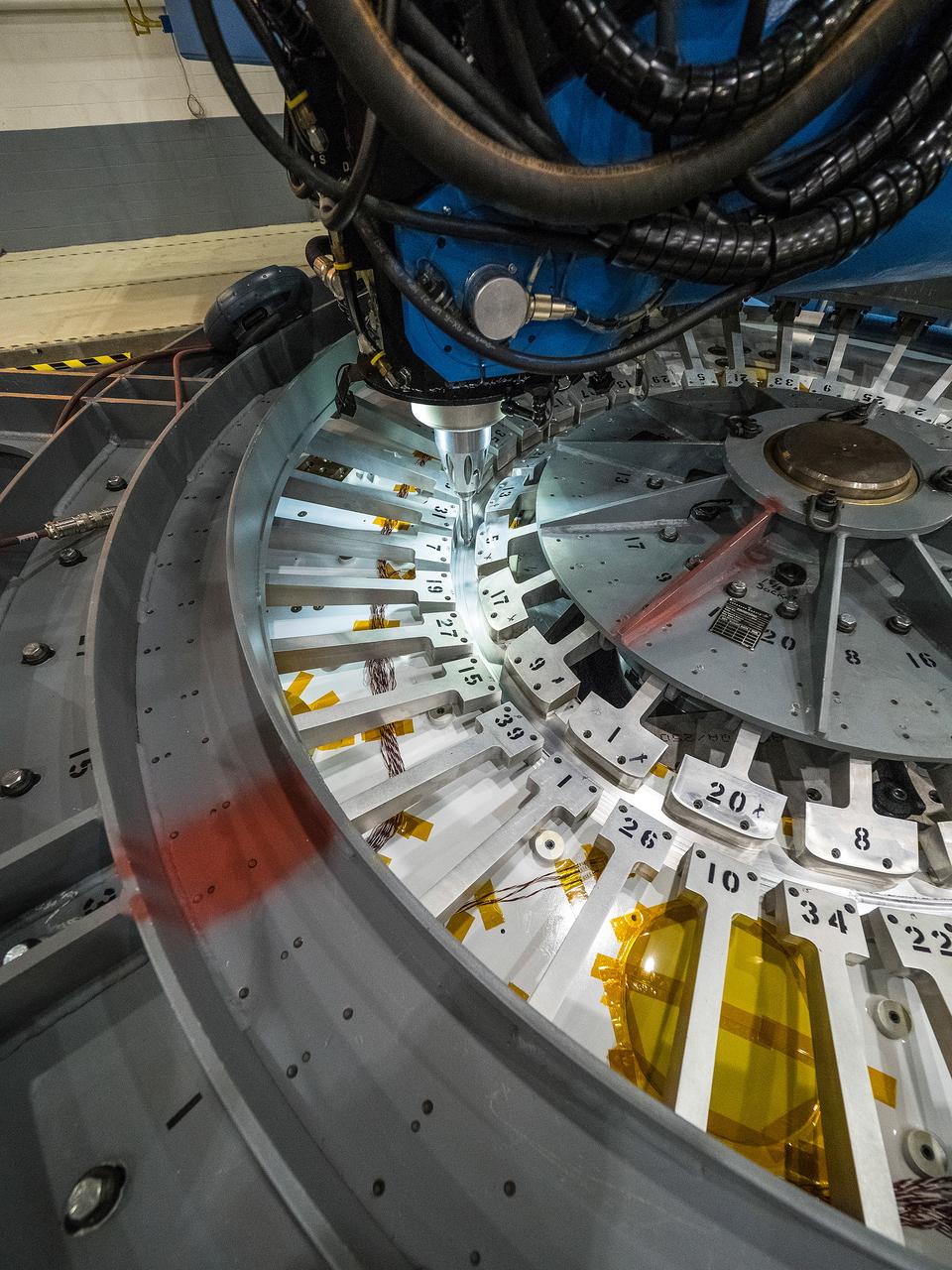
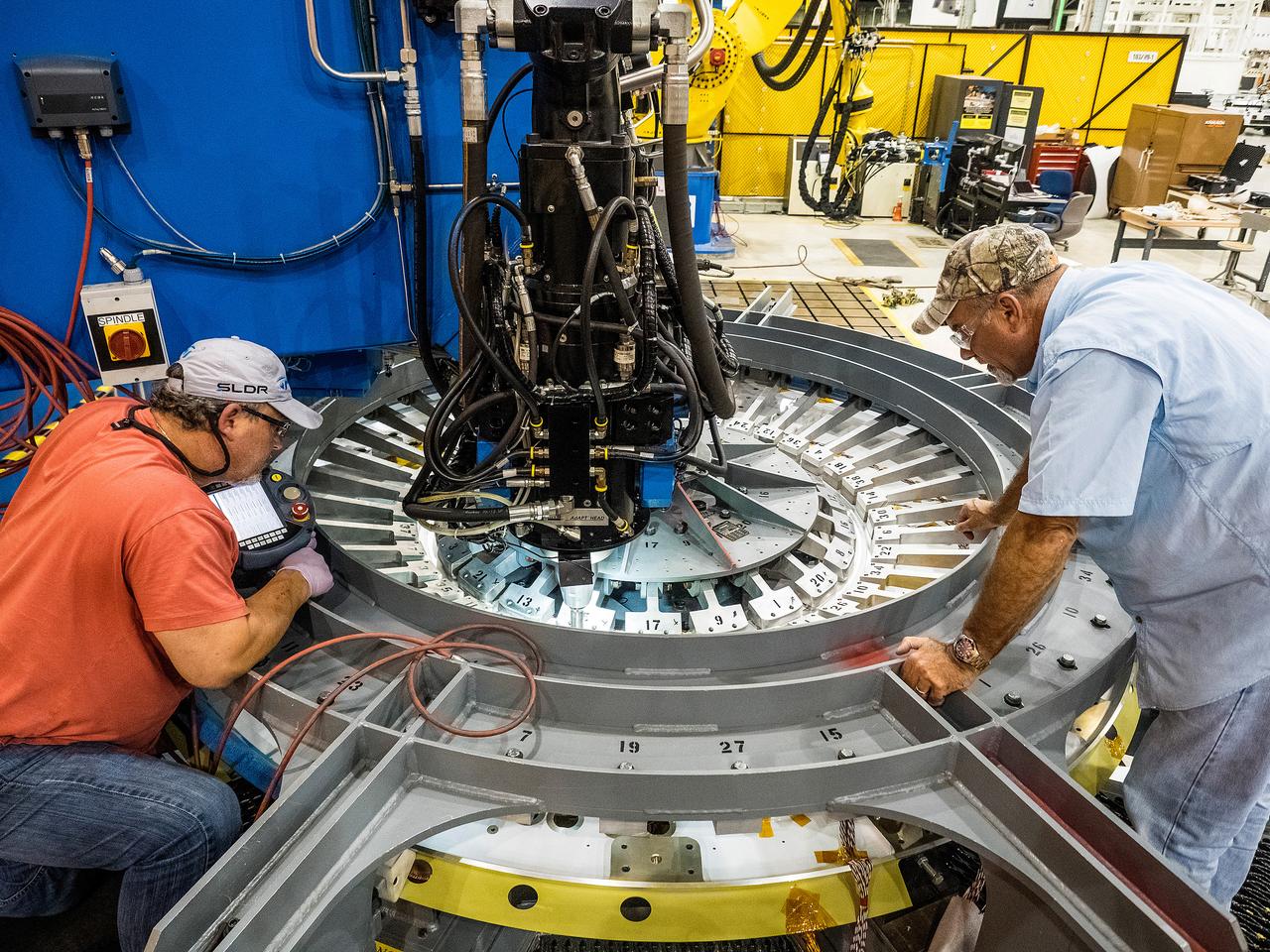
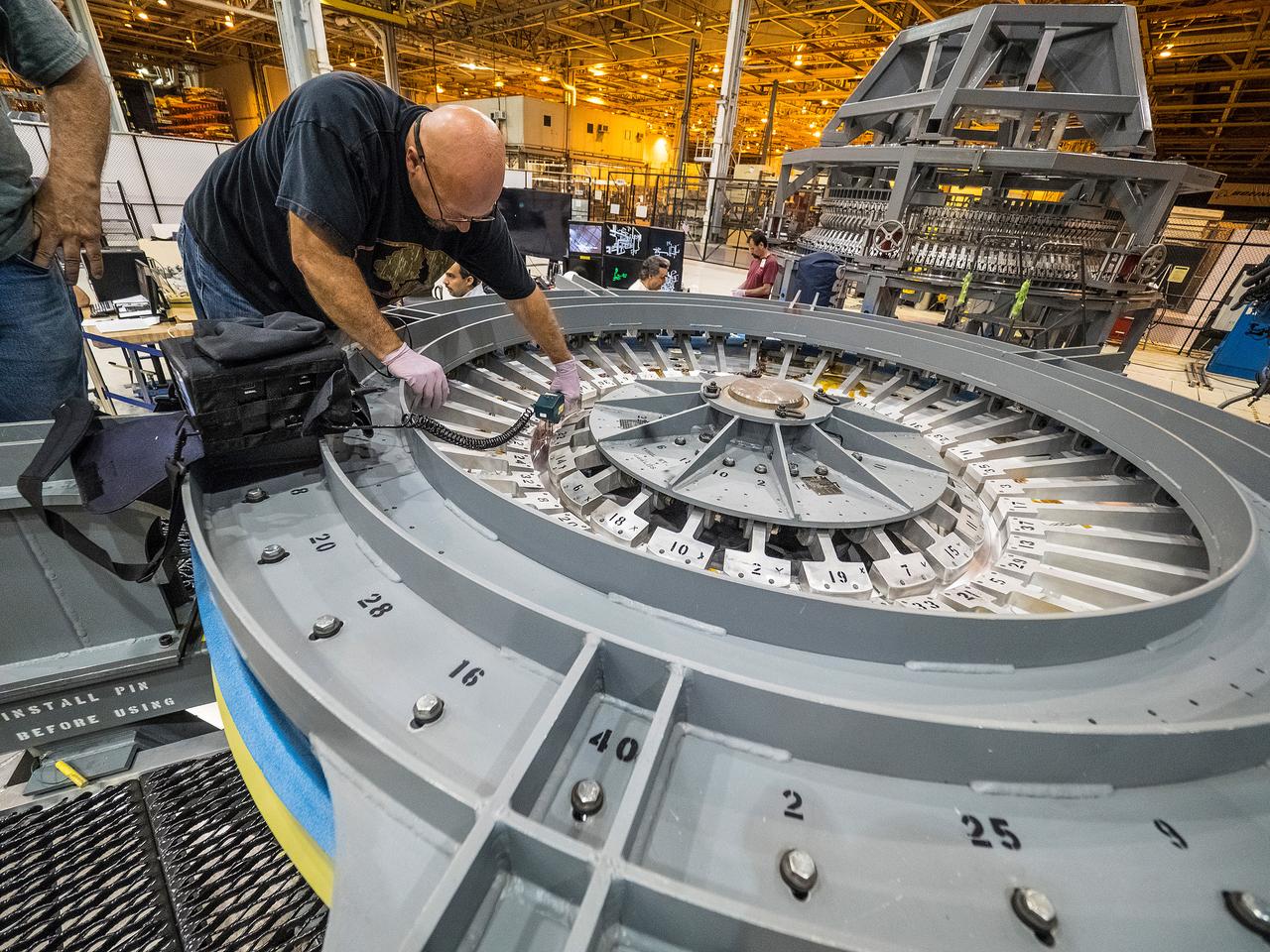
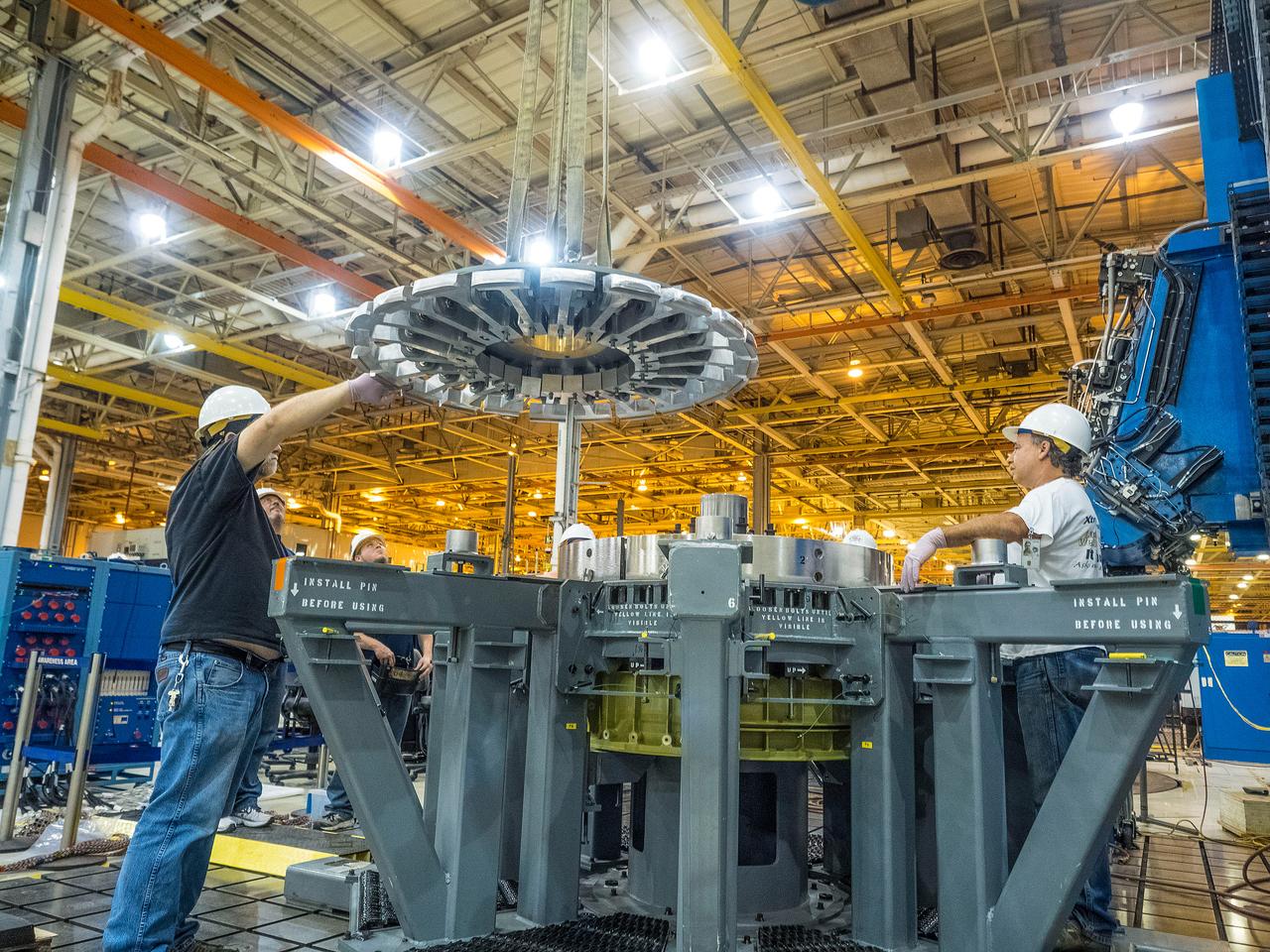
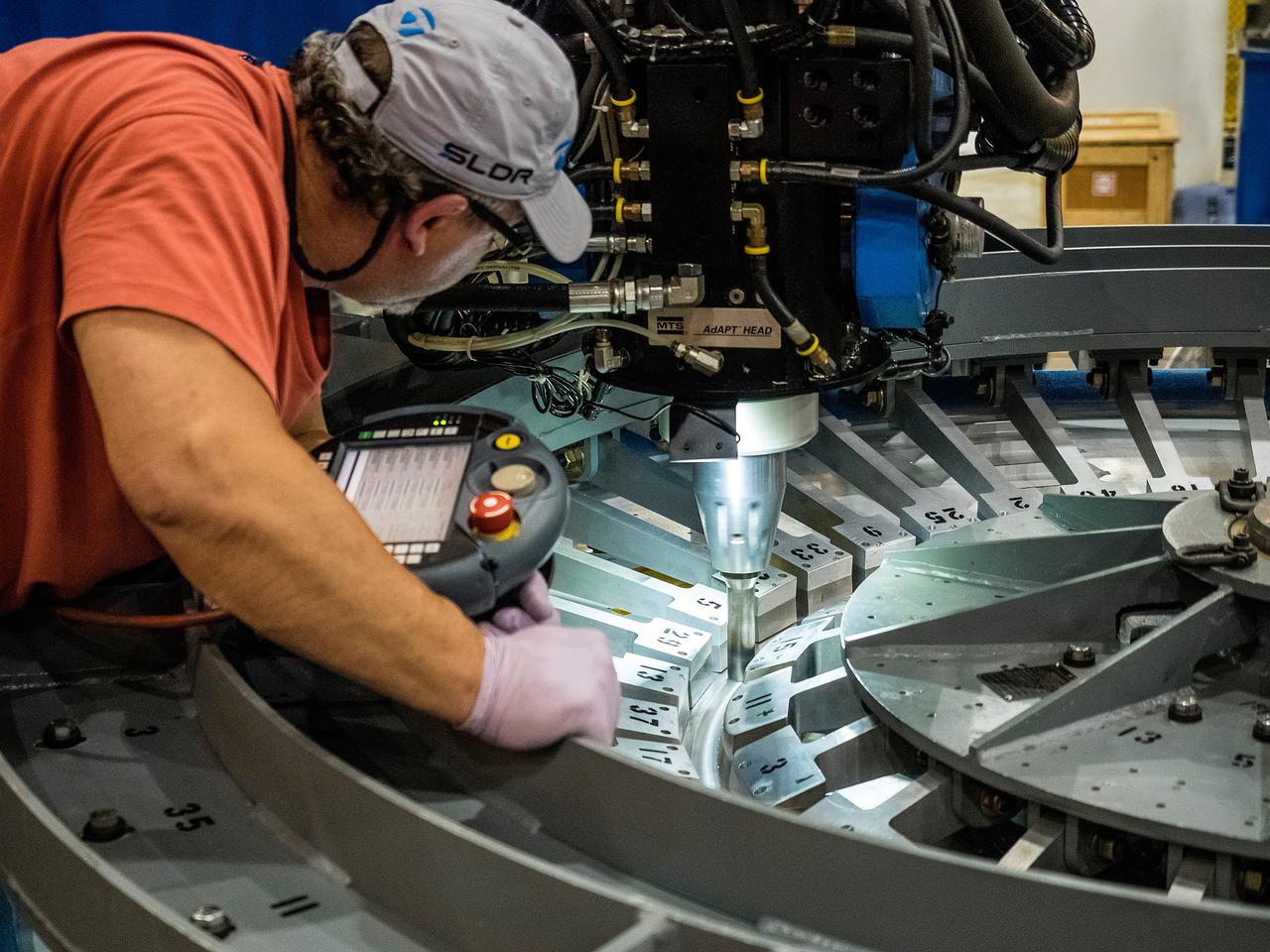
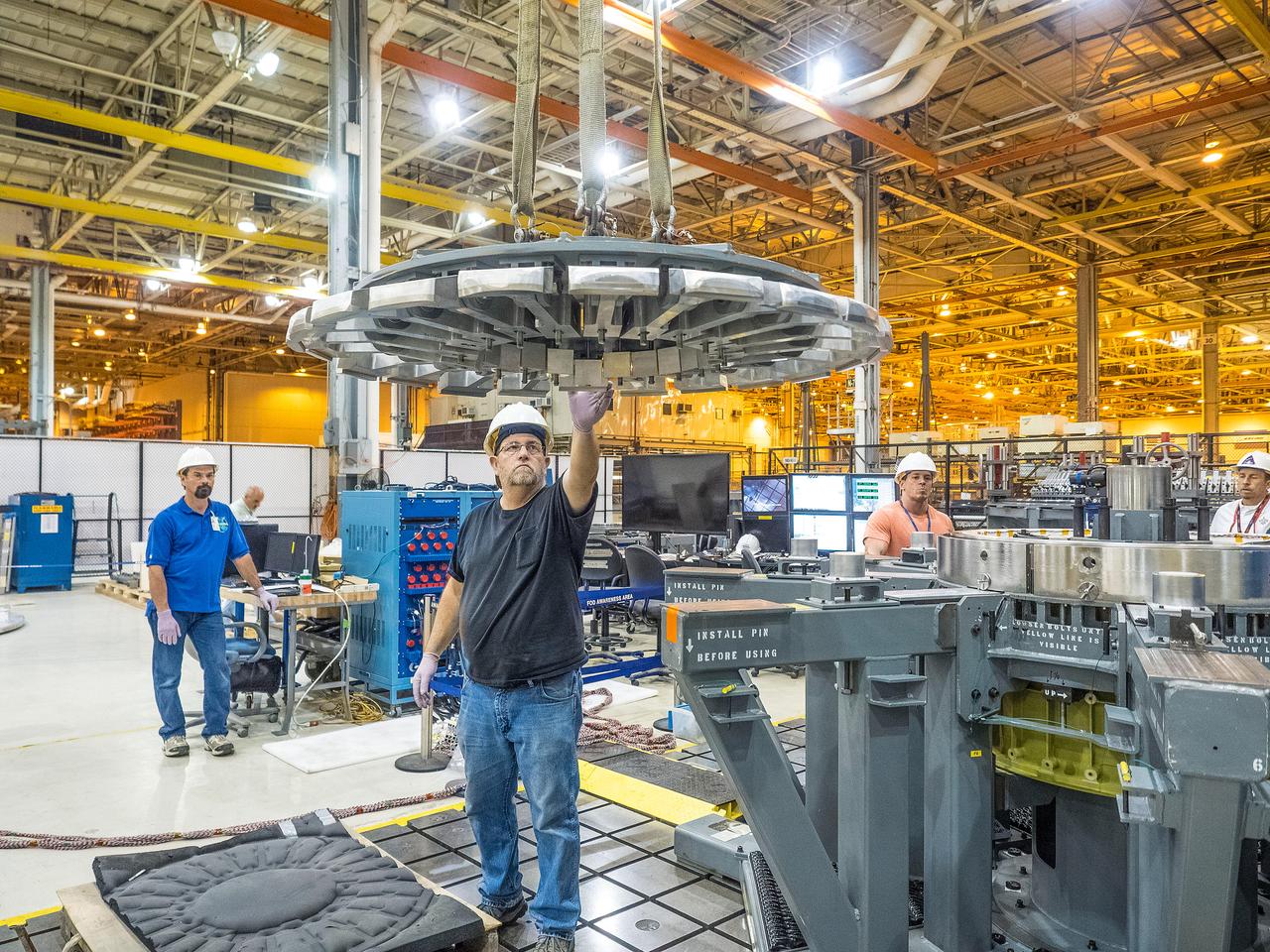
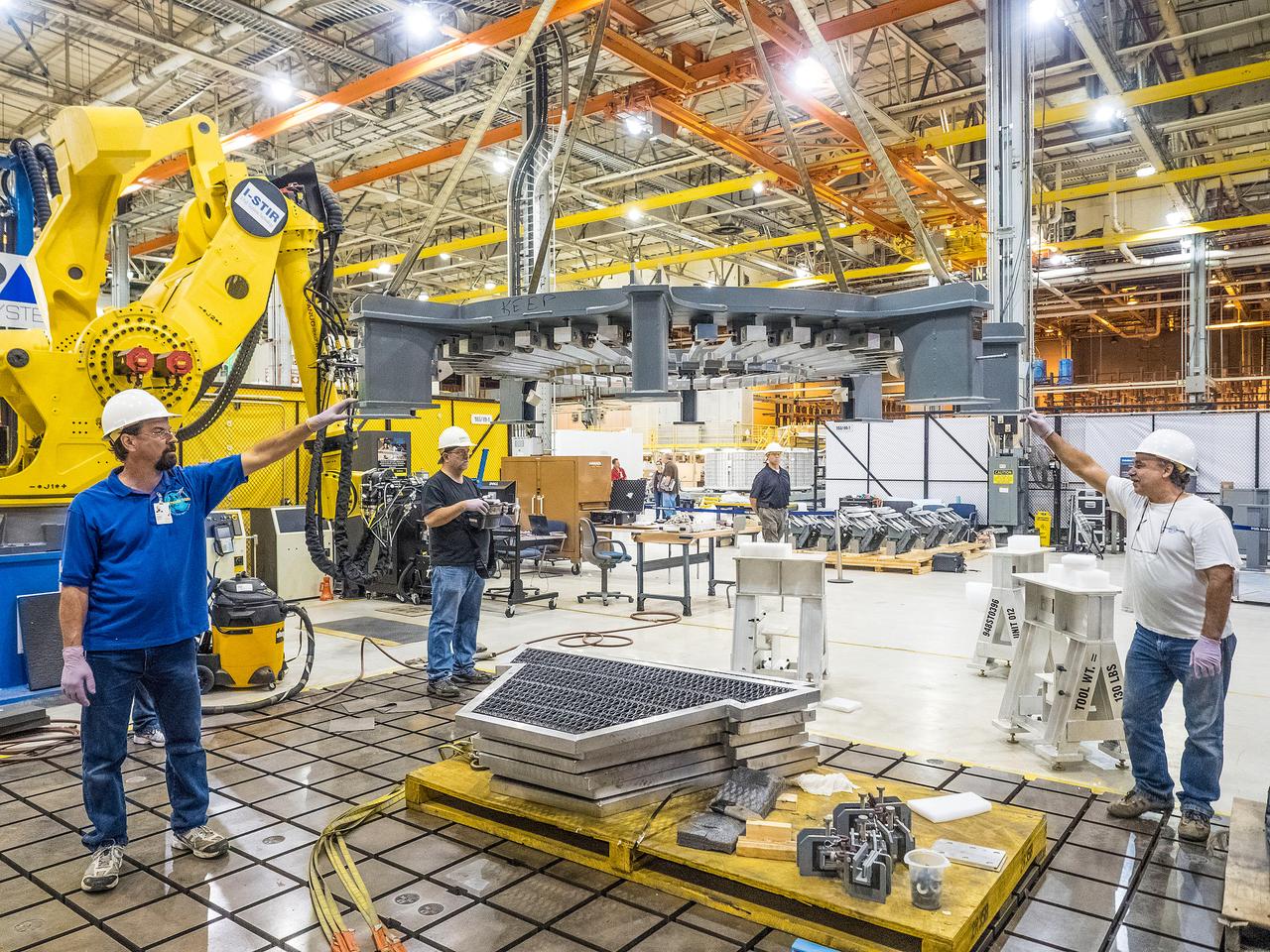
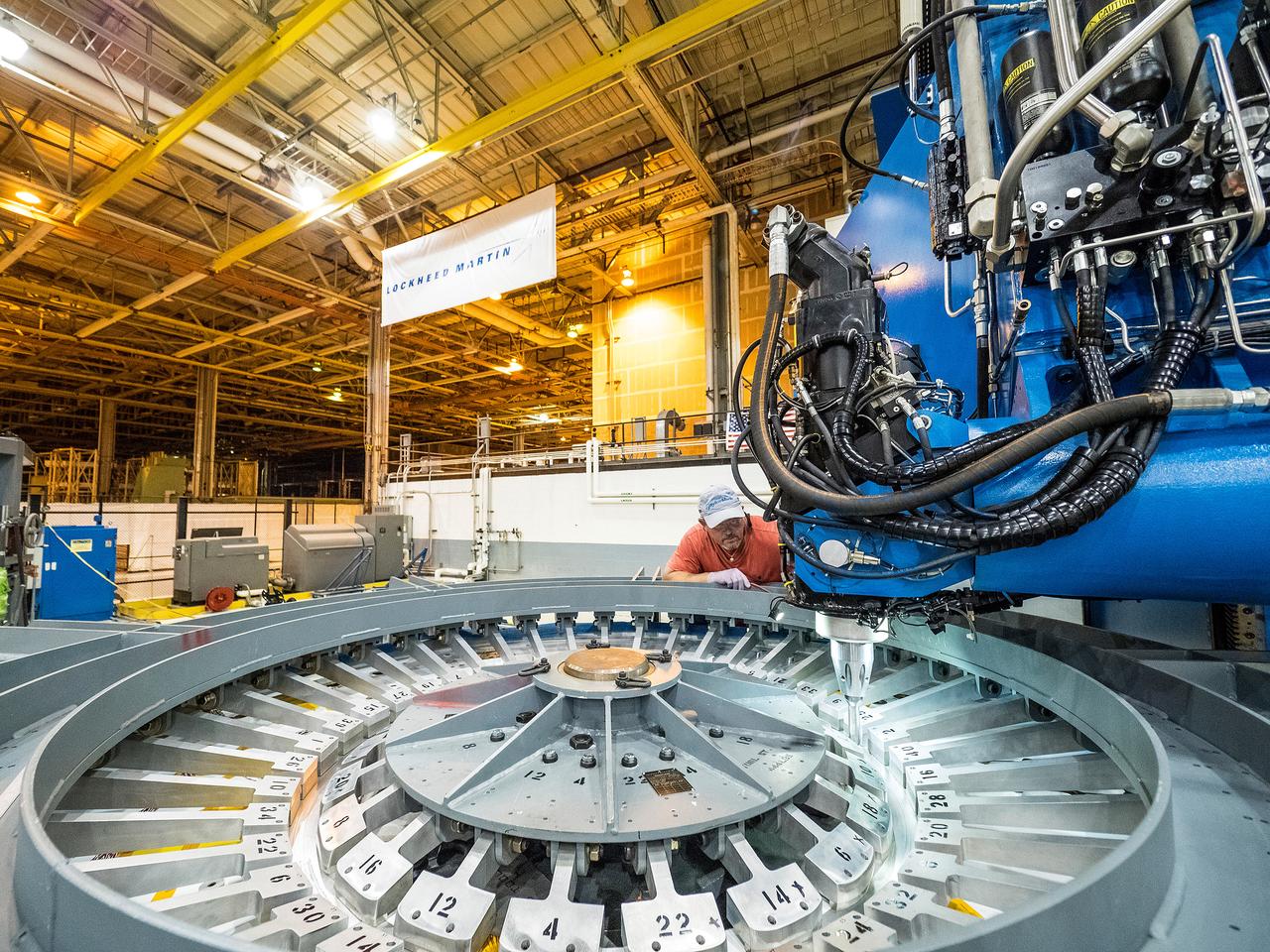
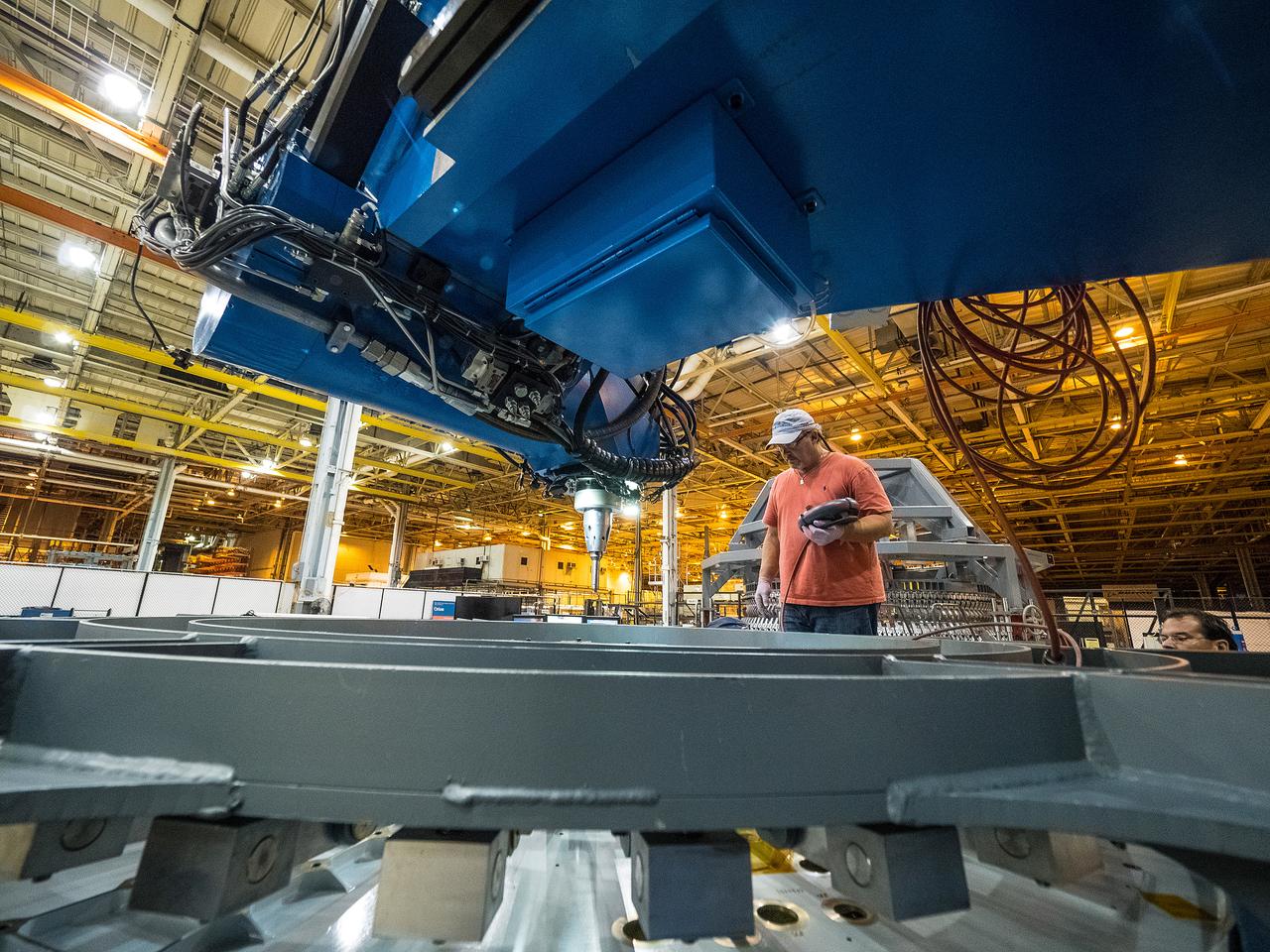
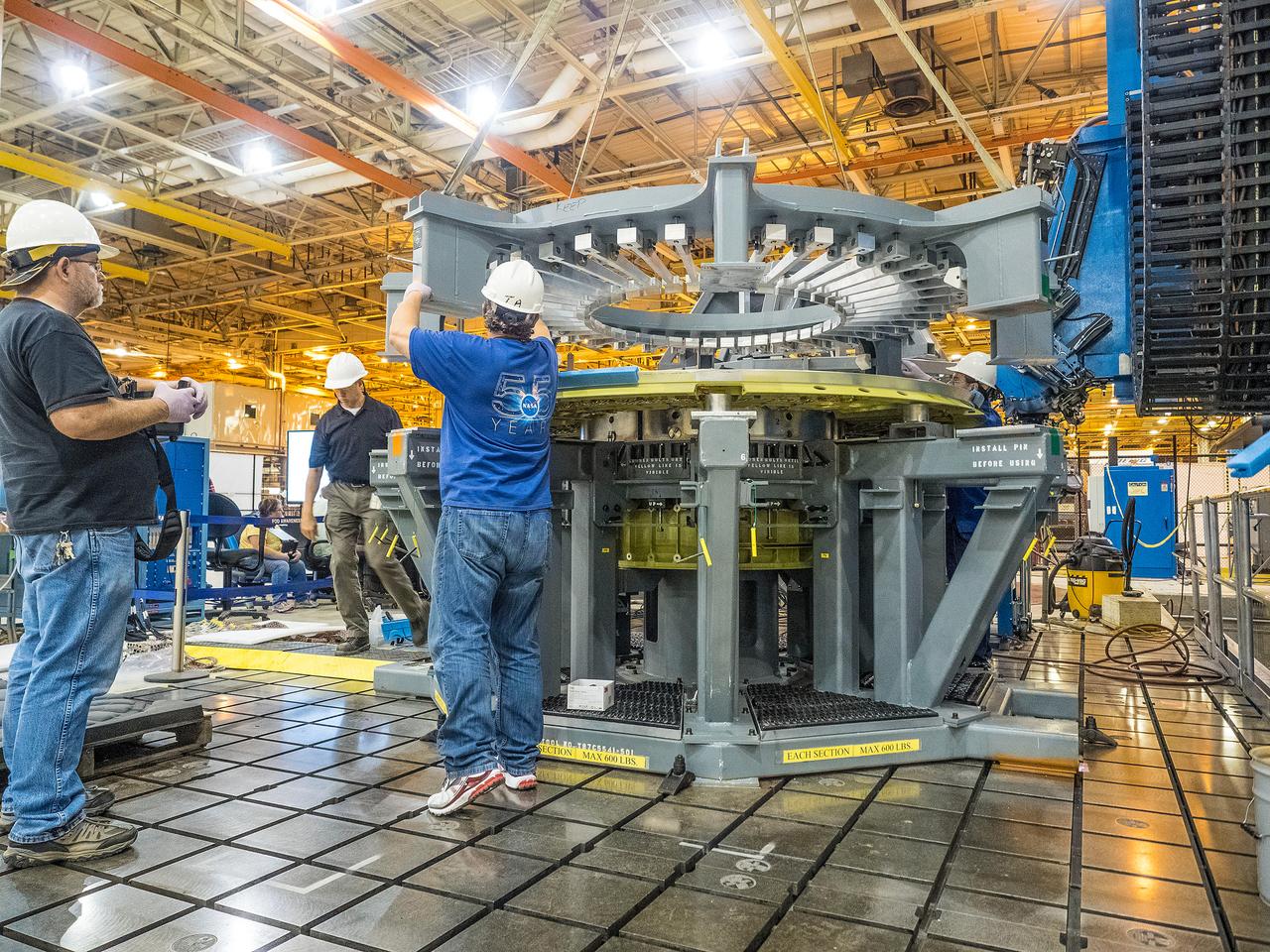
At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
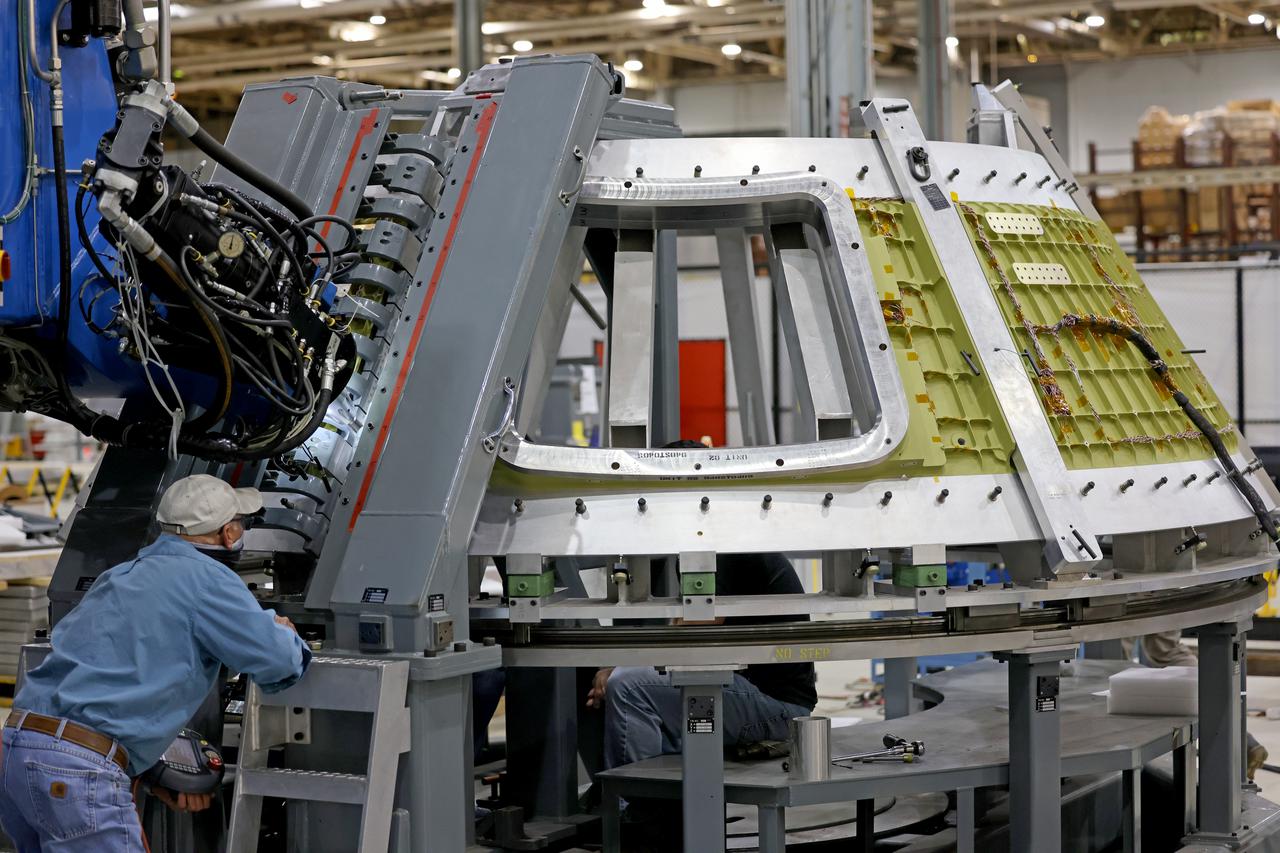
At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
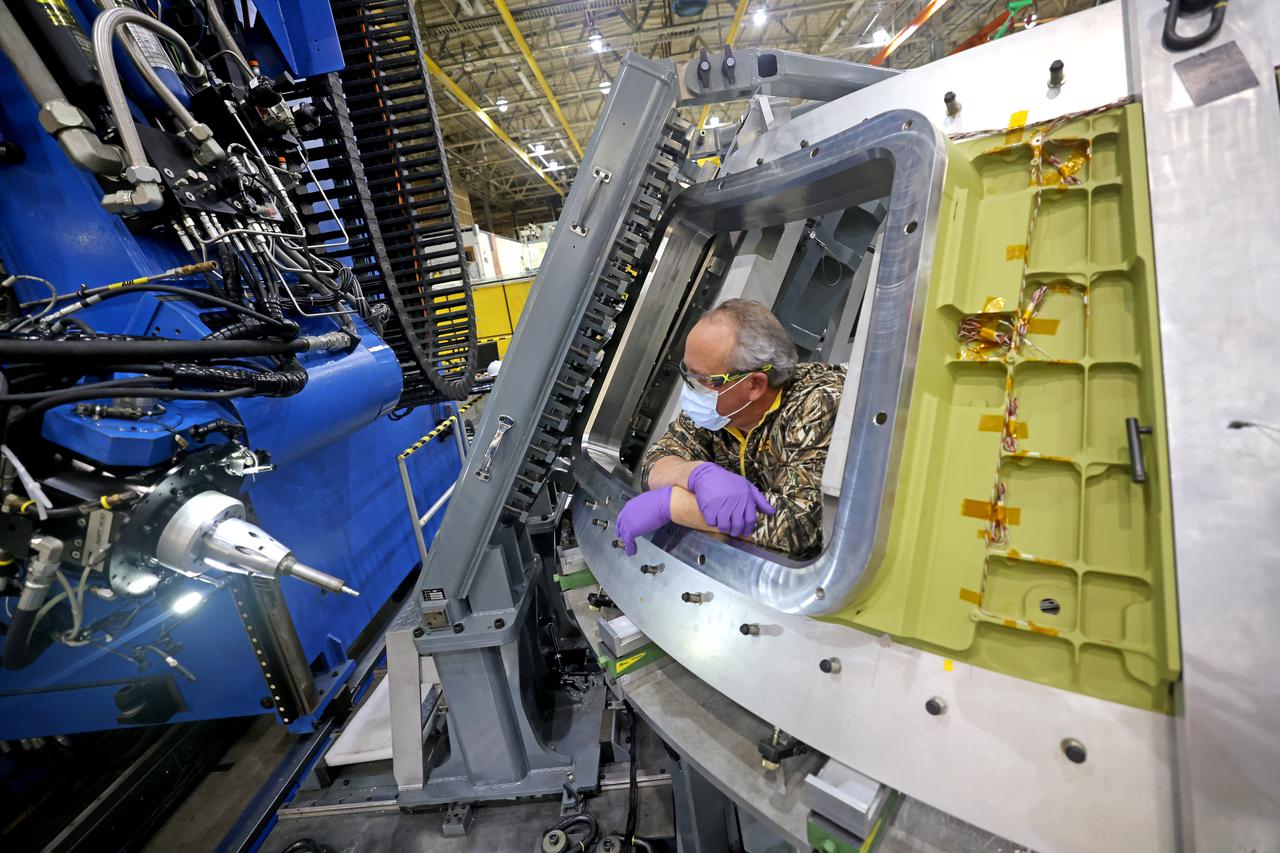

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
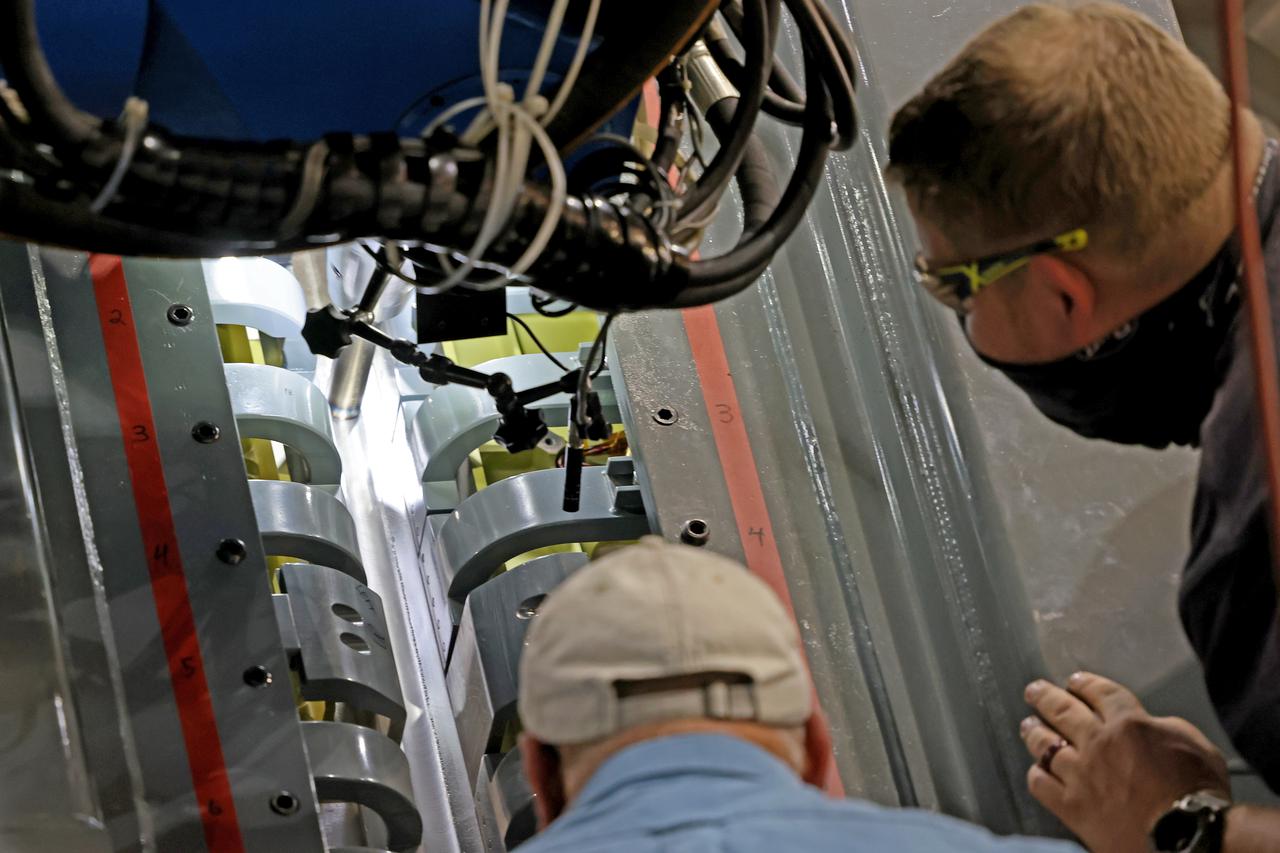

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
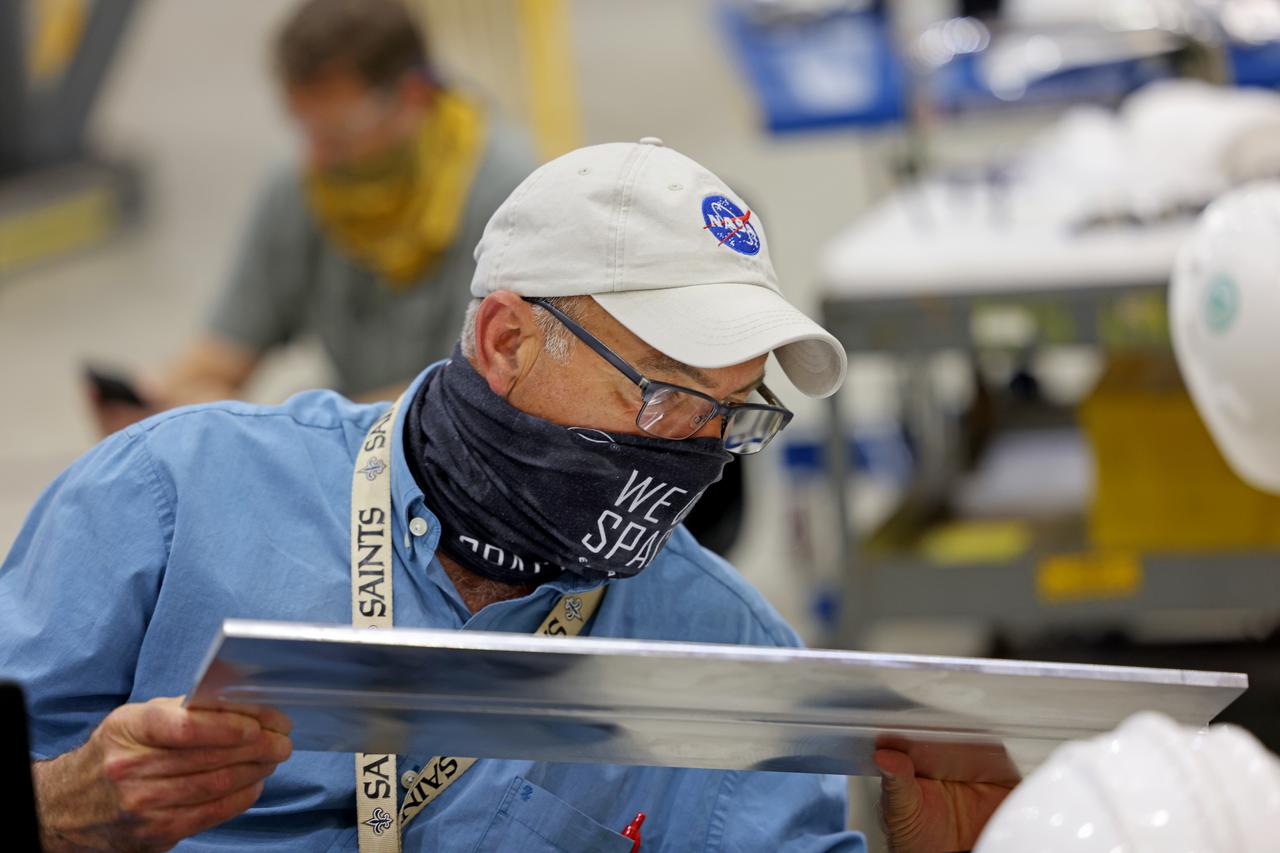

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
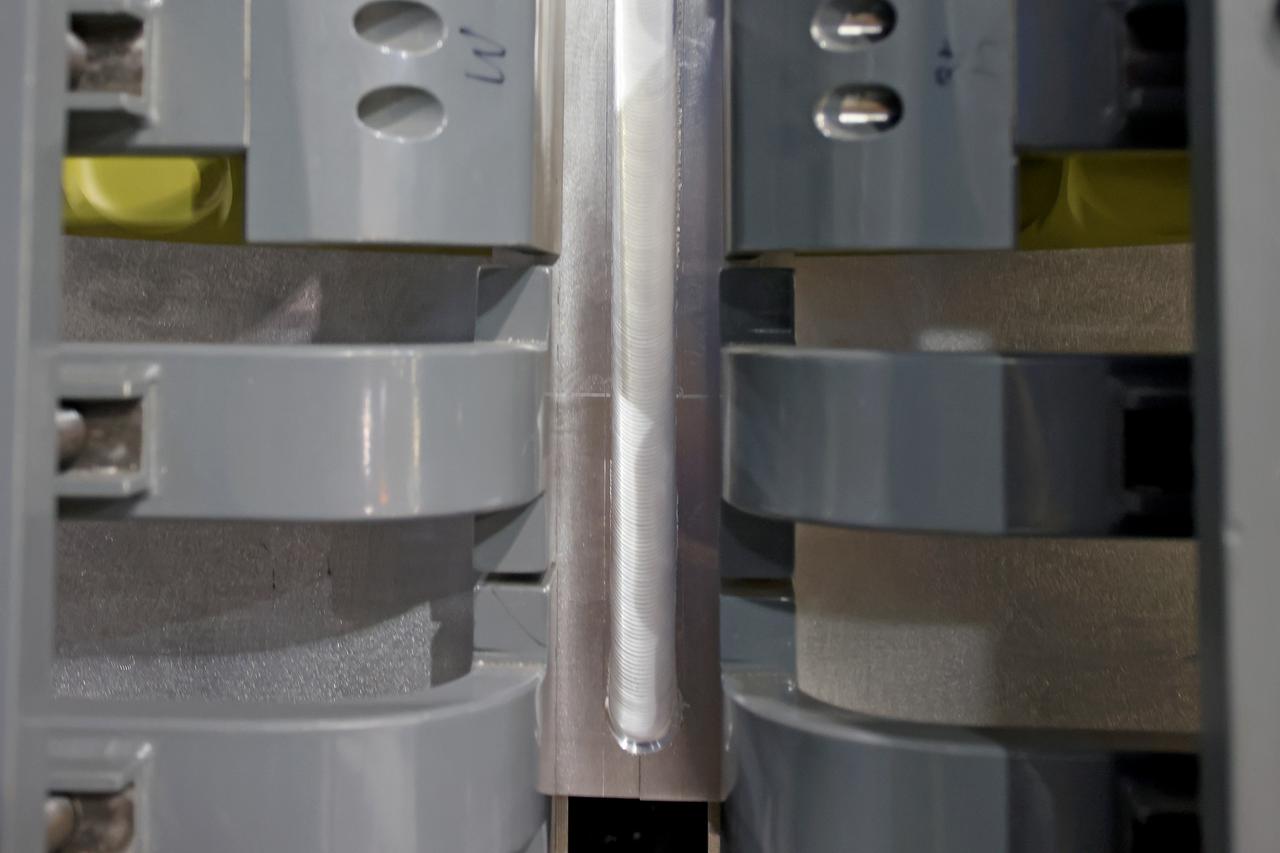

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
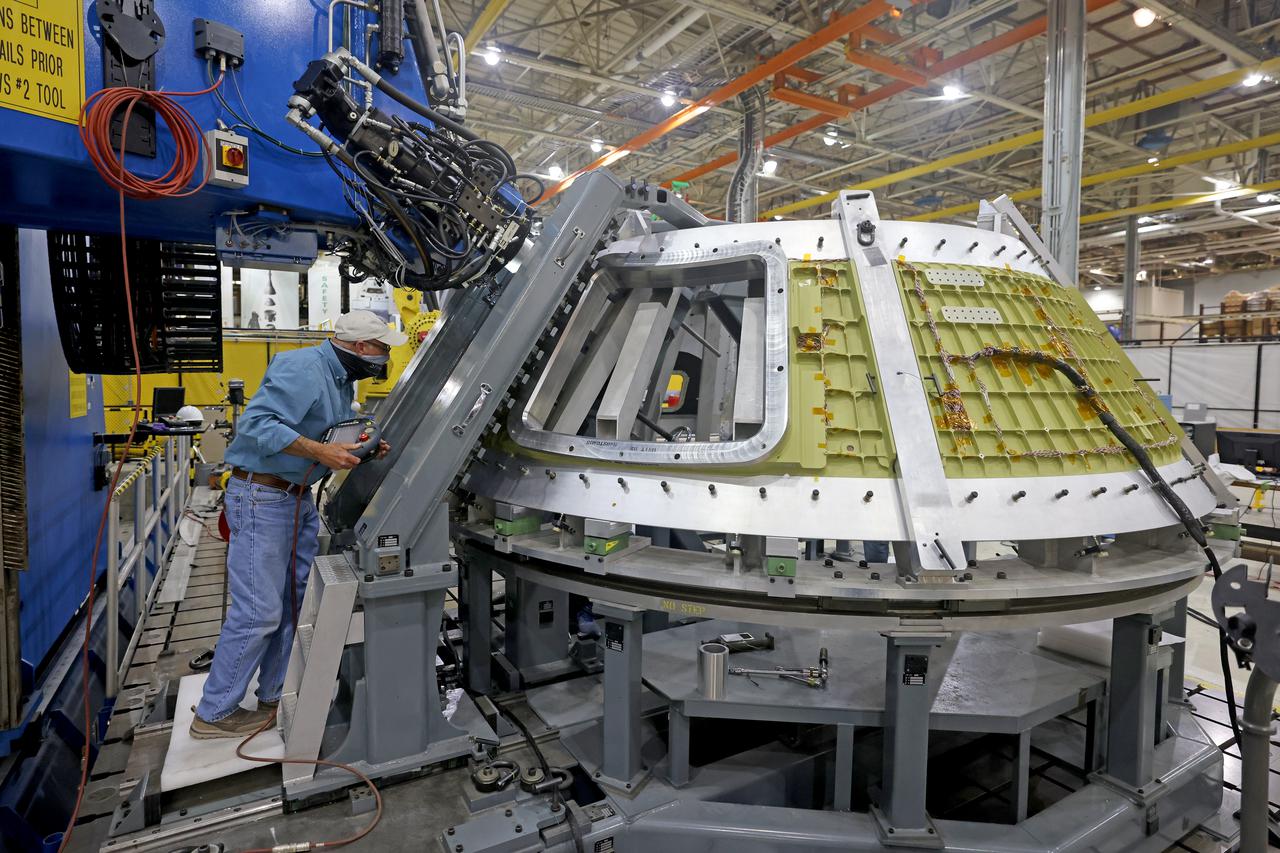

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
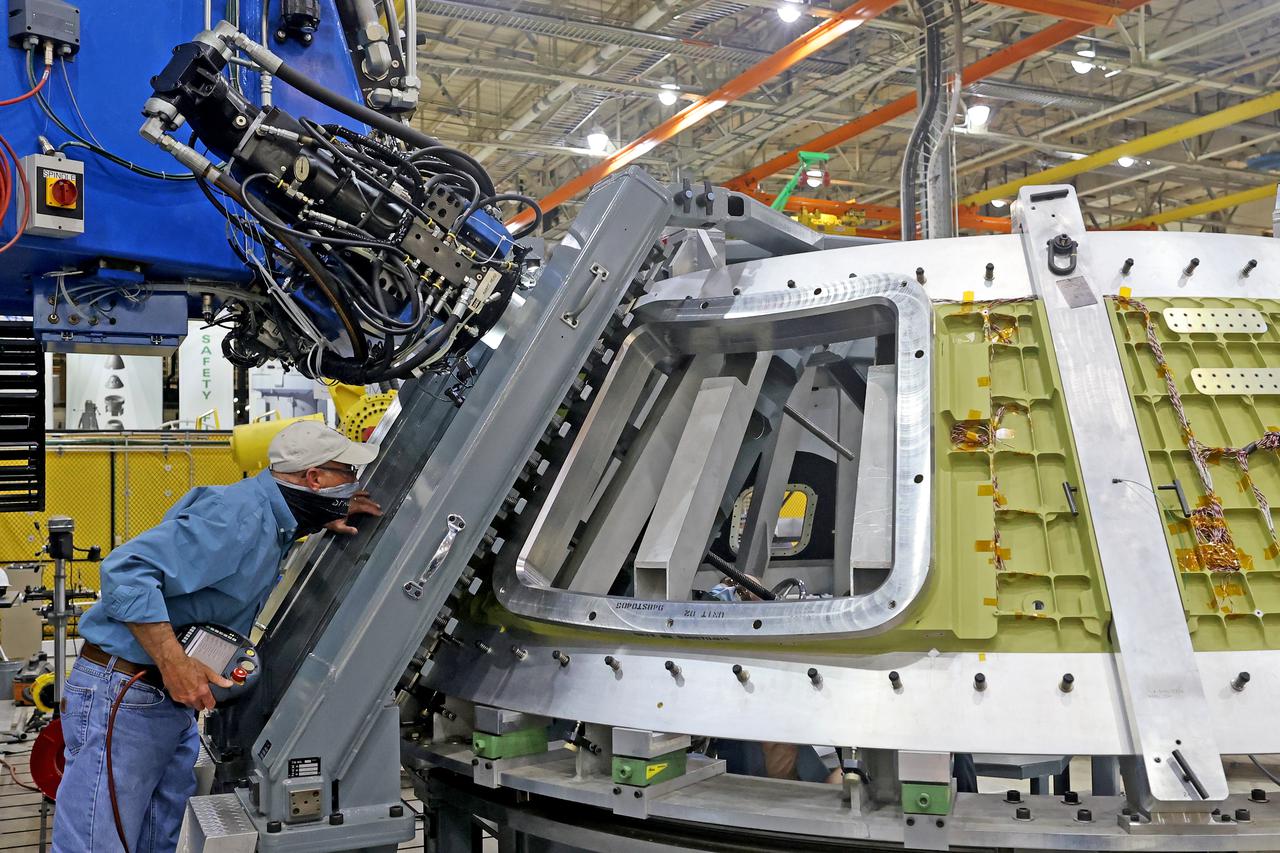

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
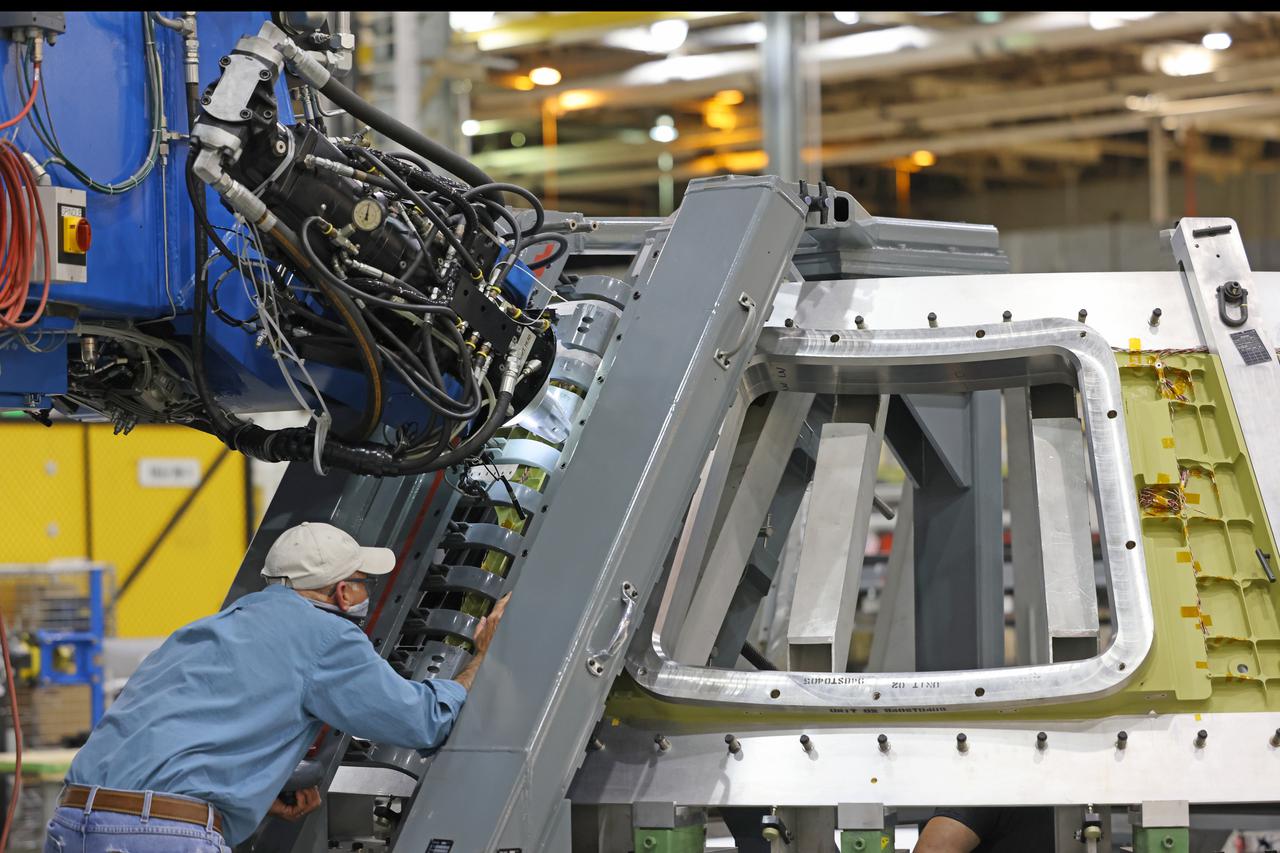

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
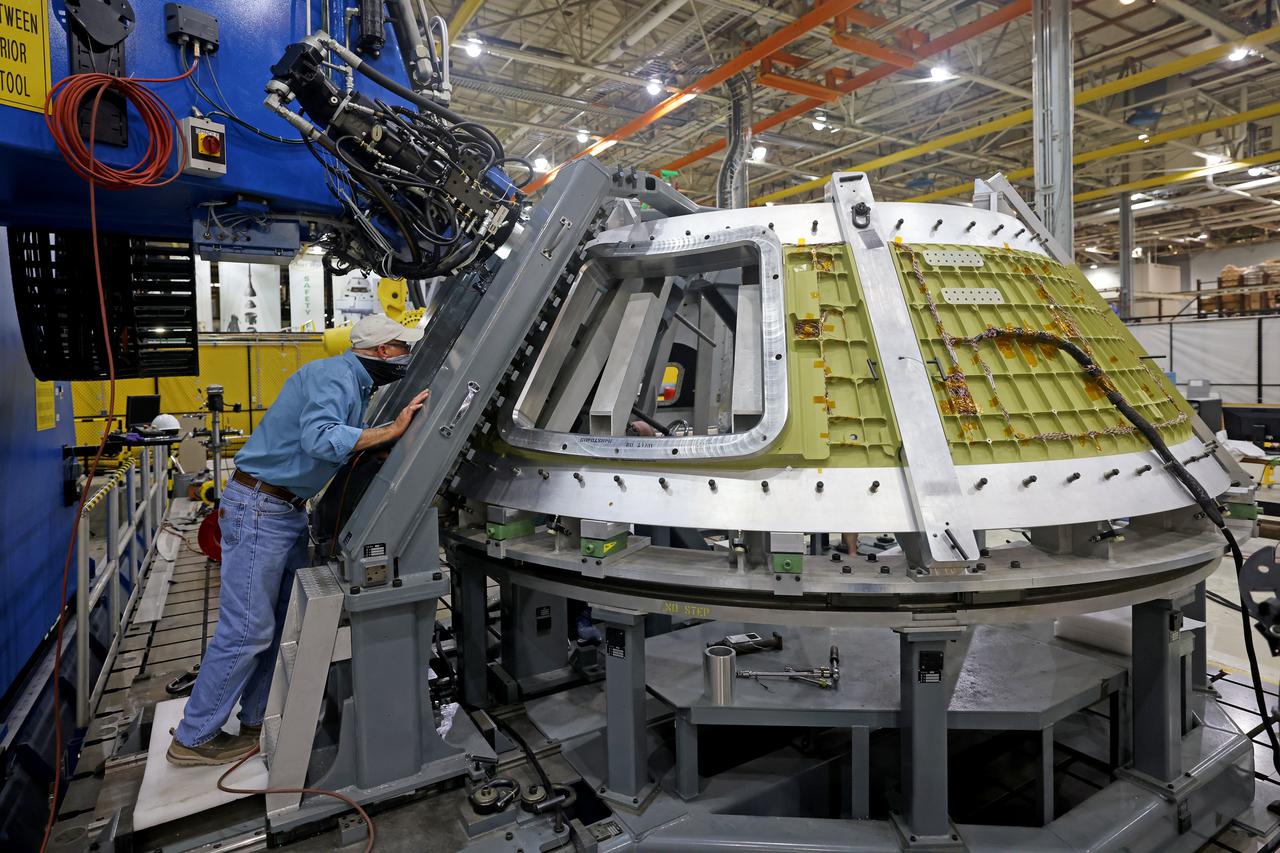

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
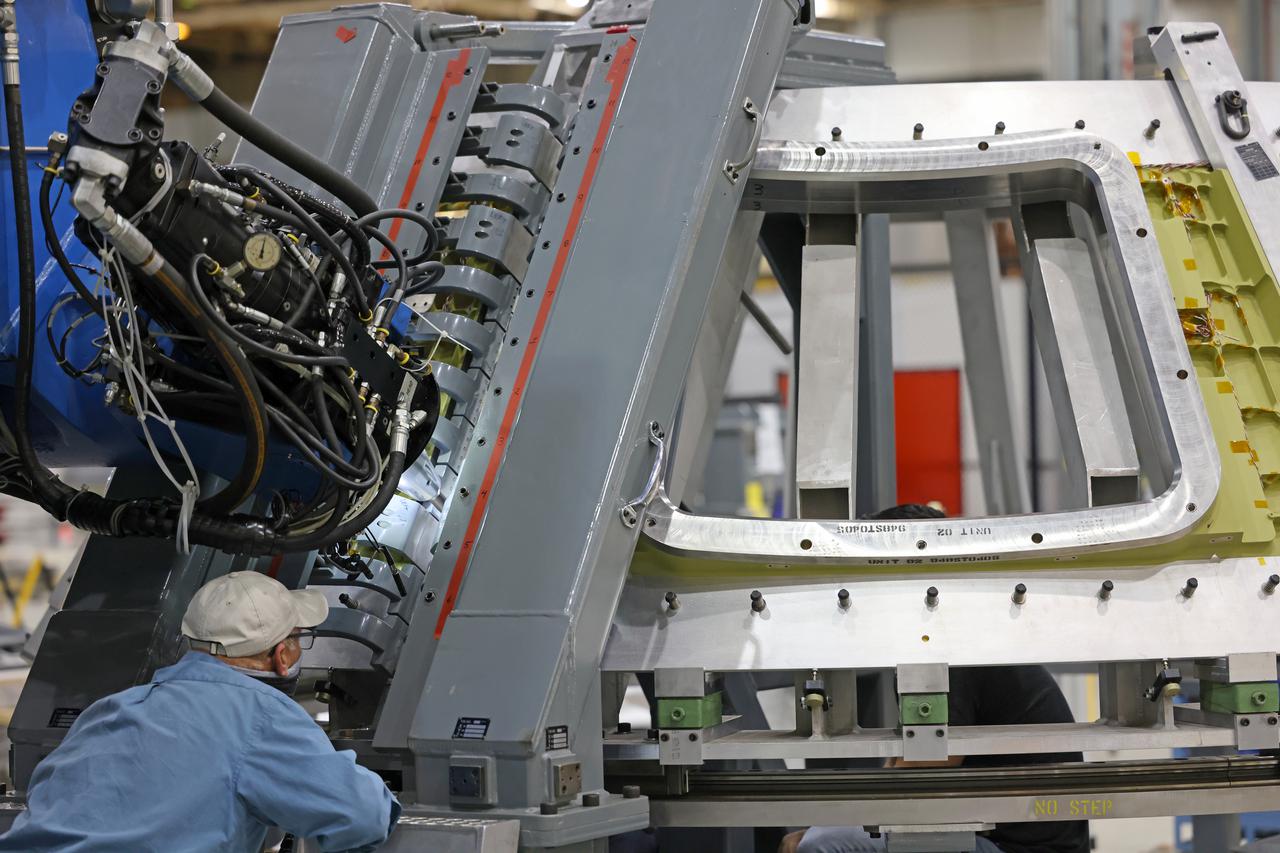
At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
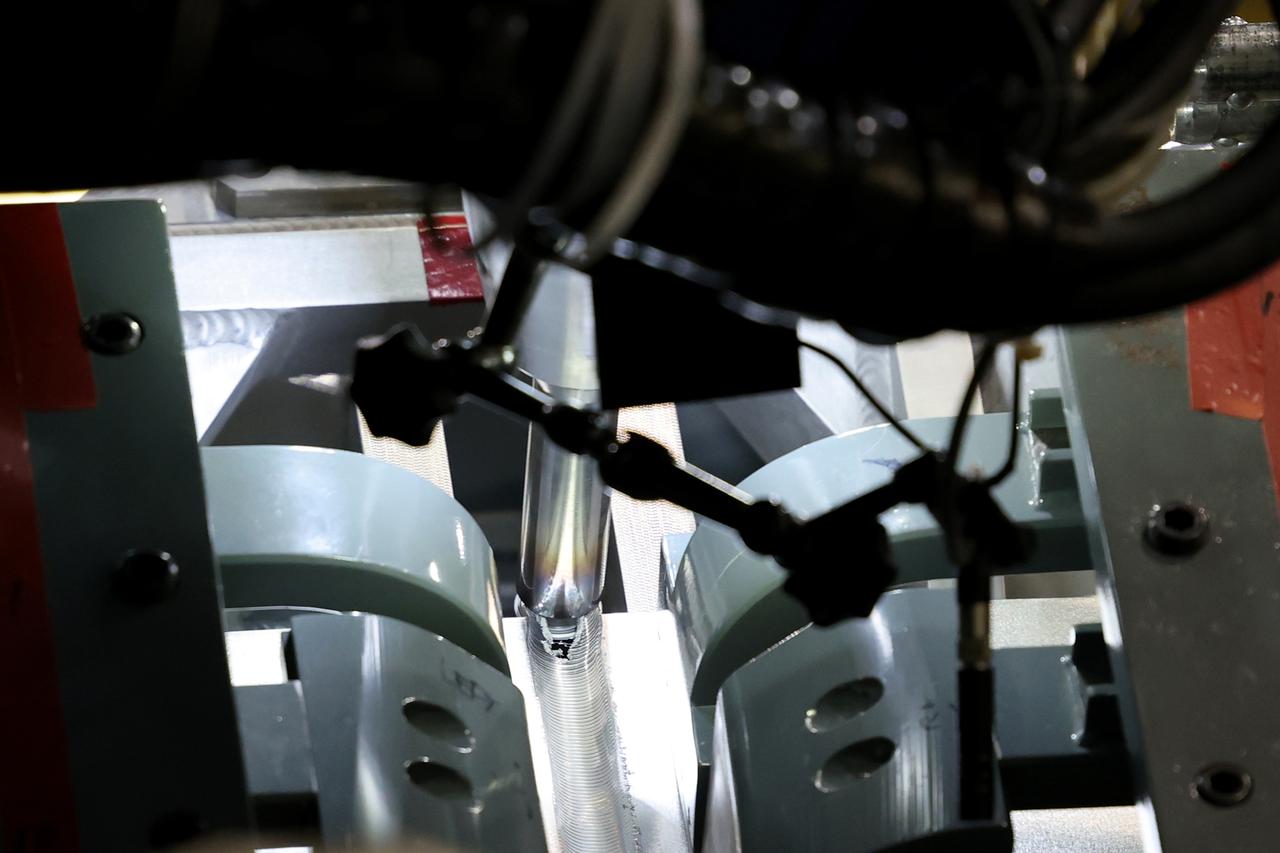

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
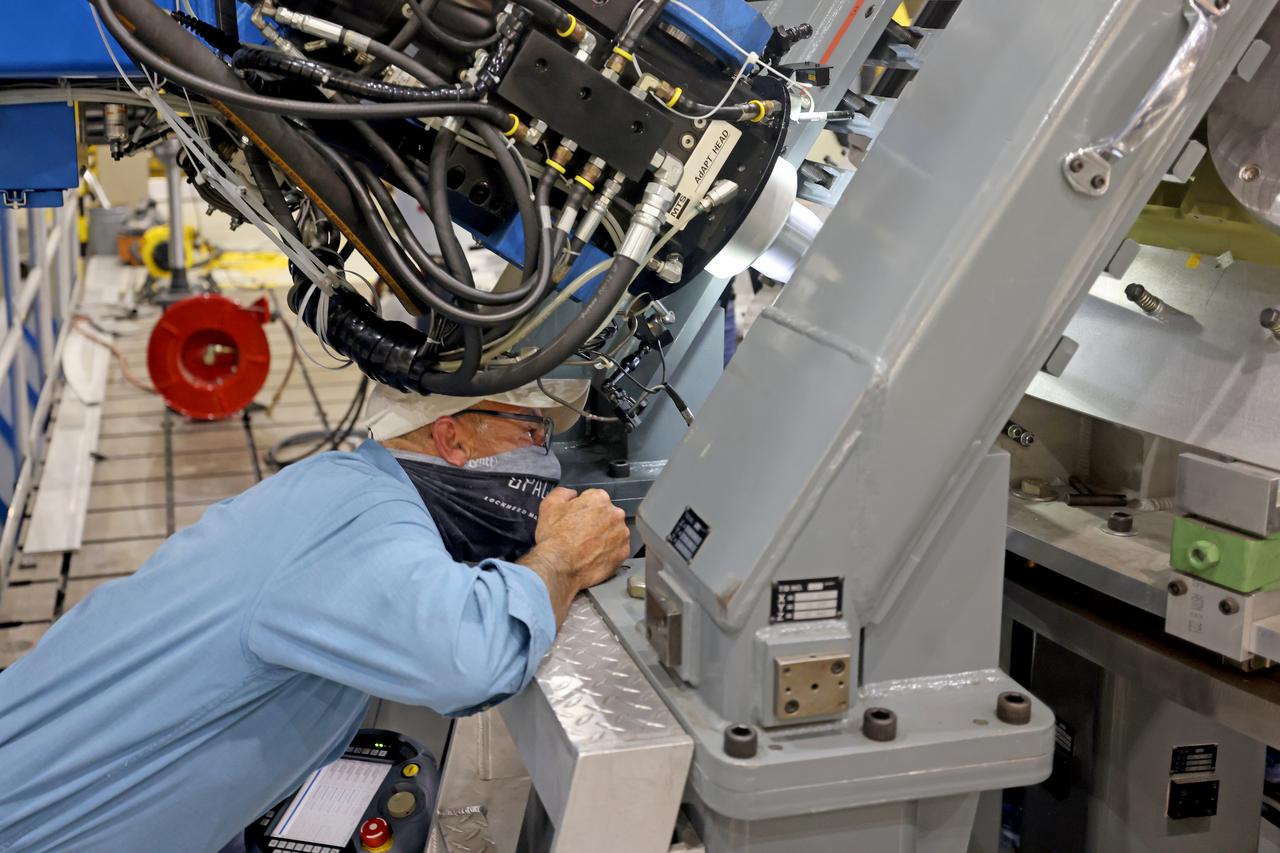

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
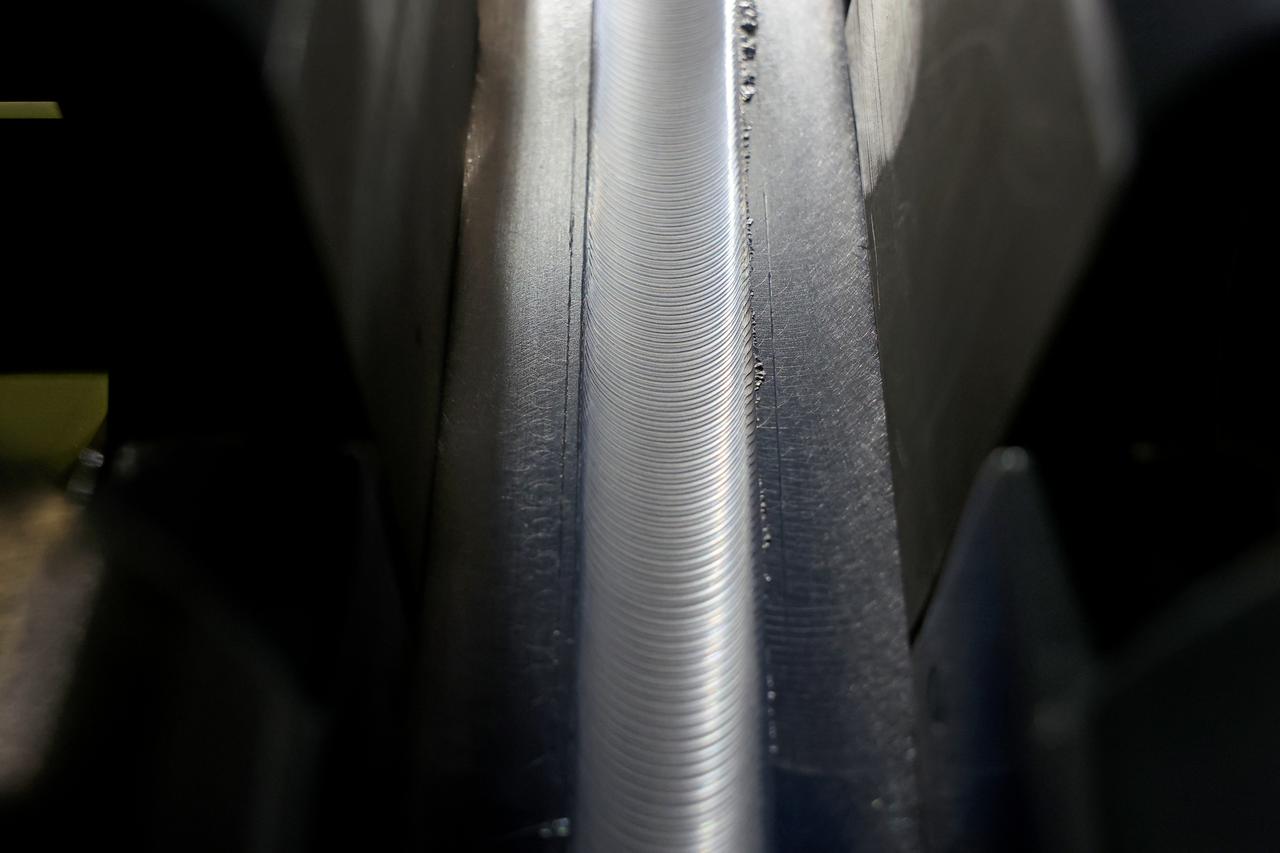

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
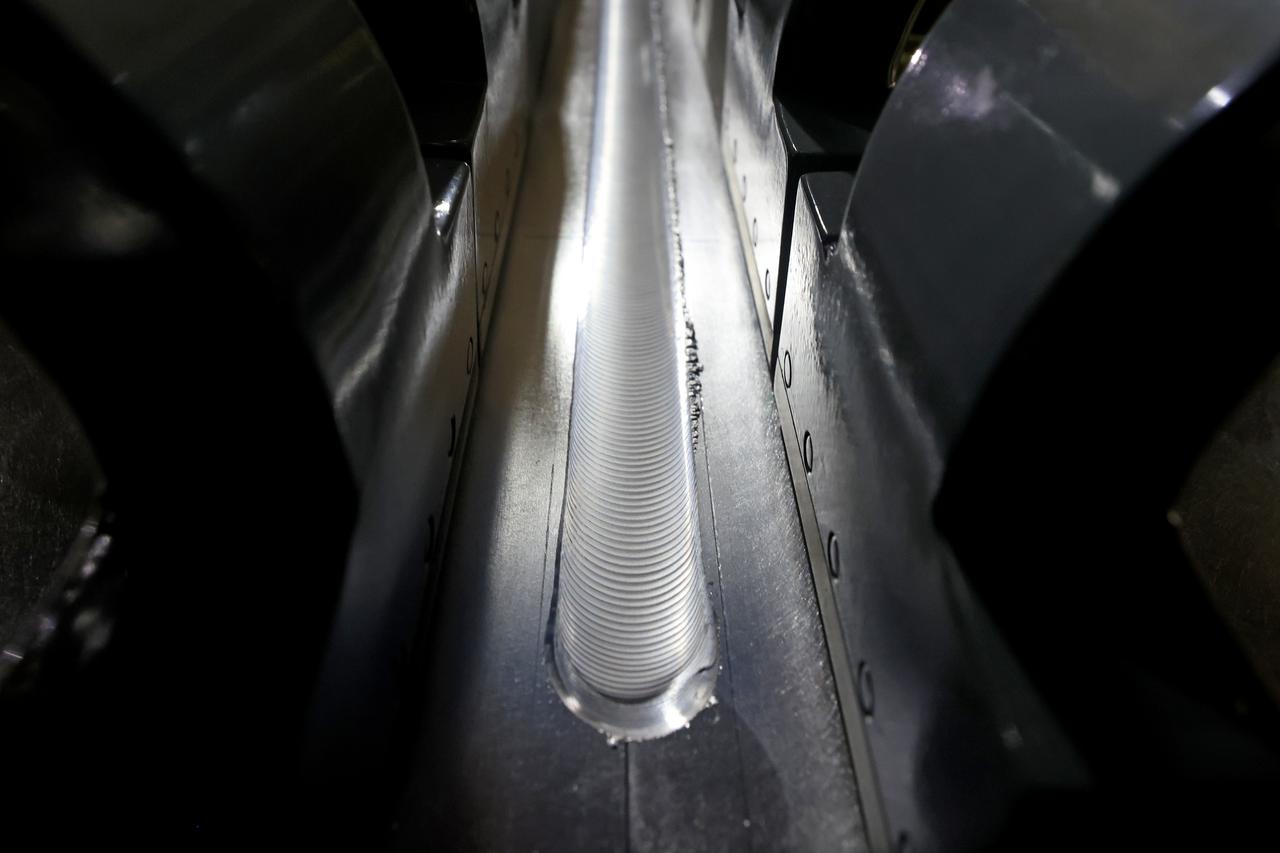

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
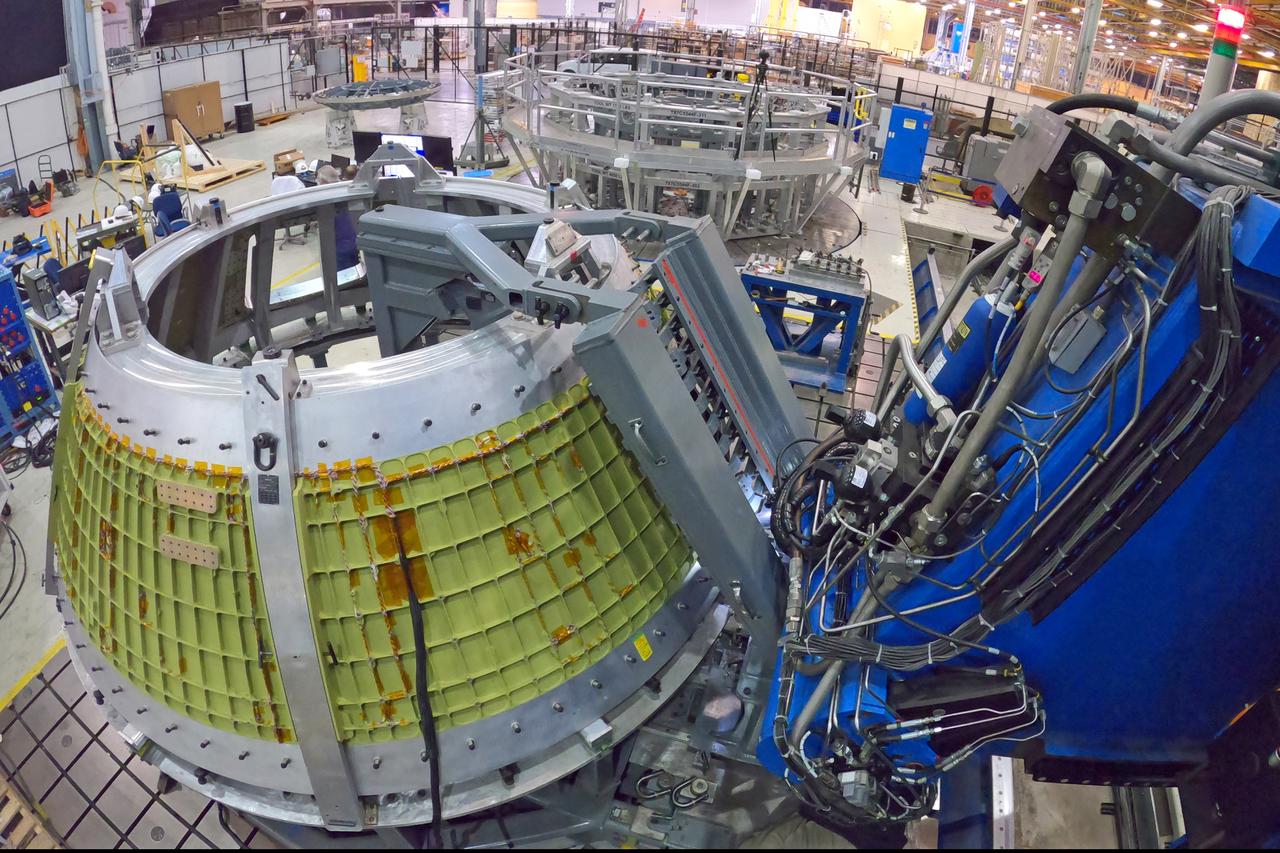
At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
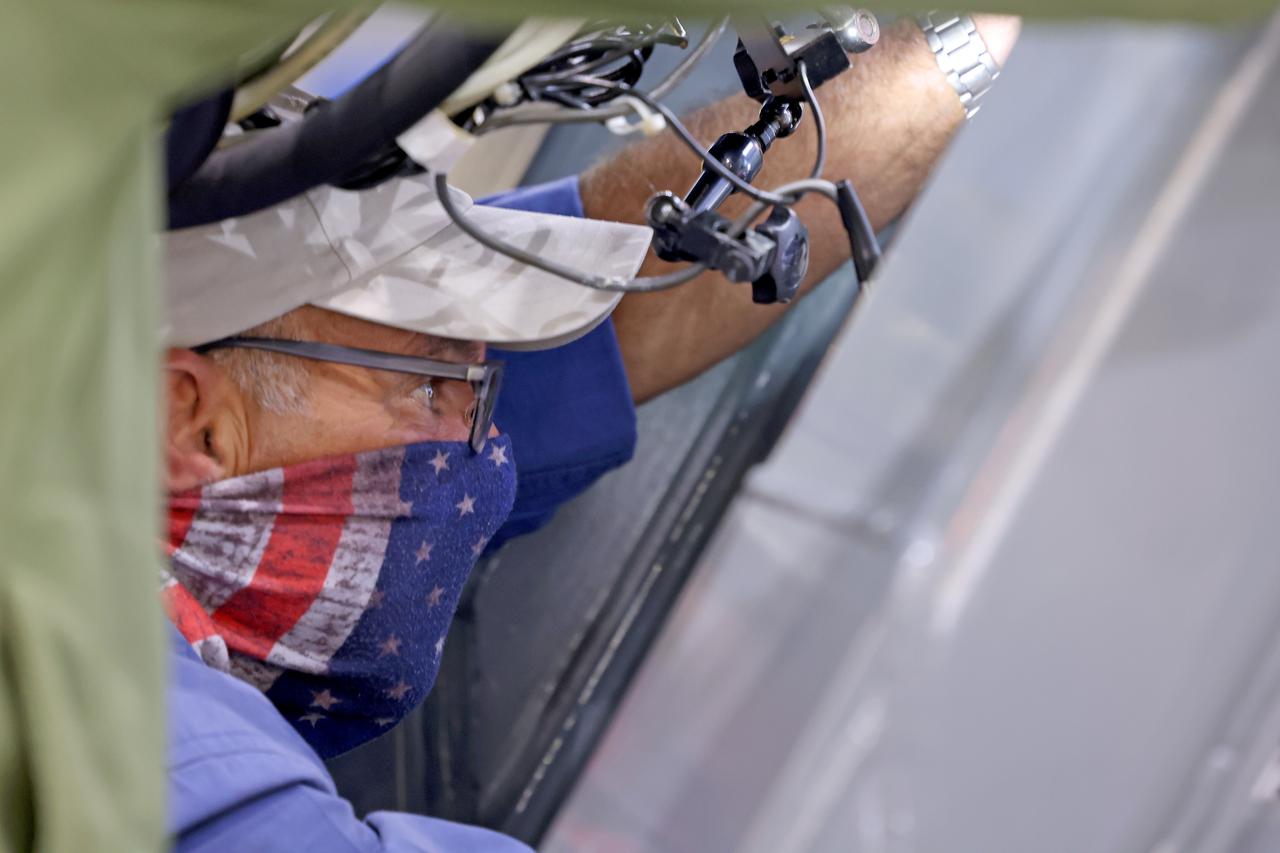

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
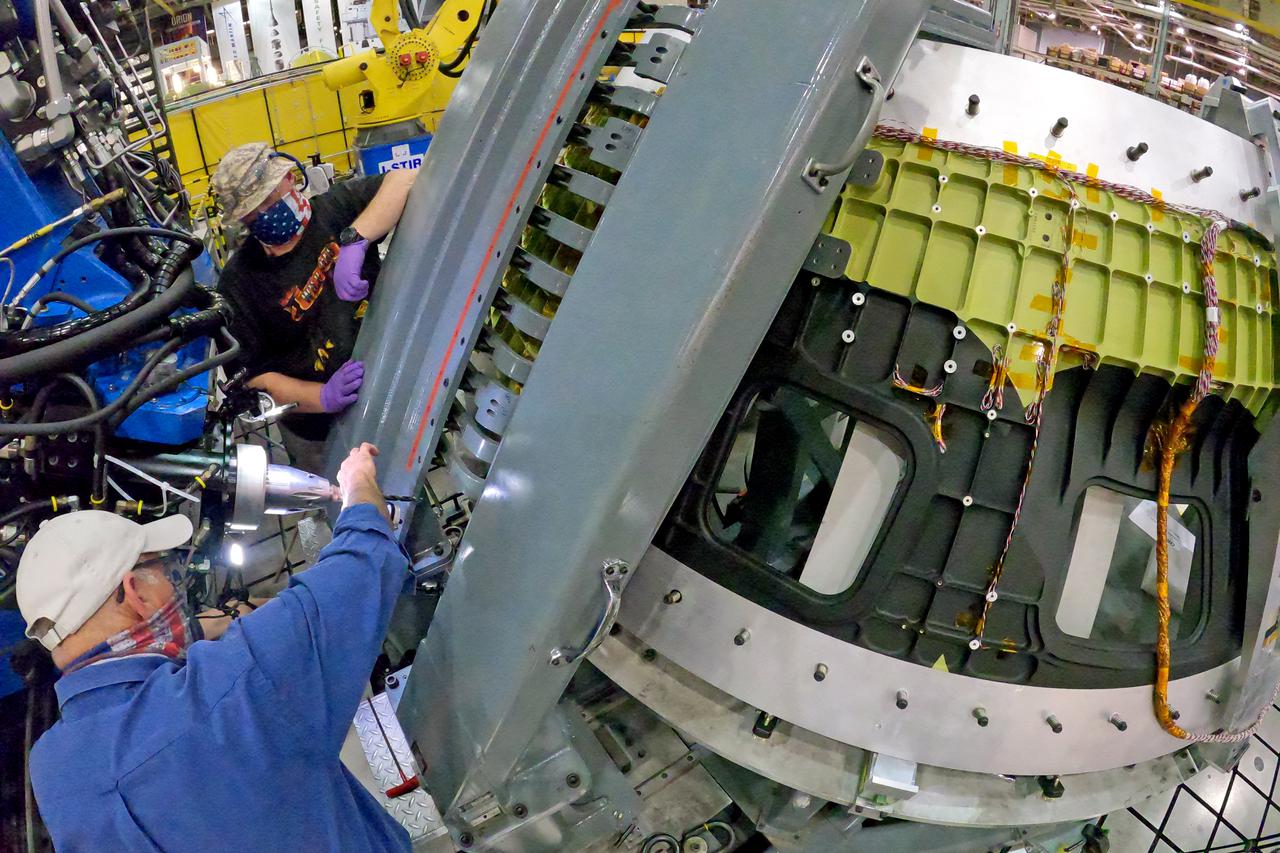

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker