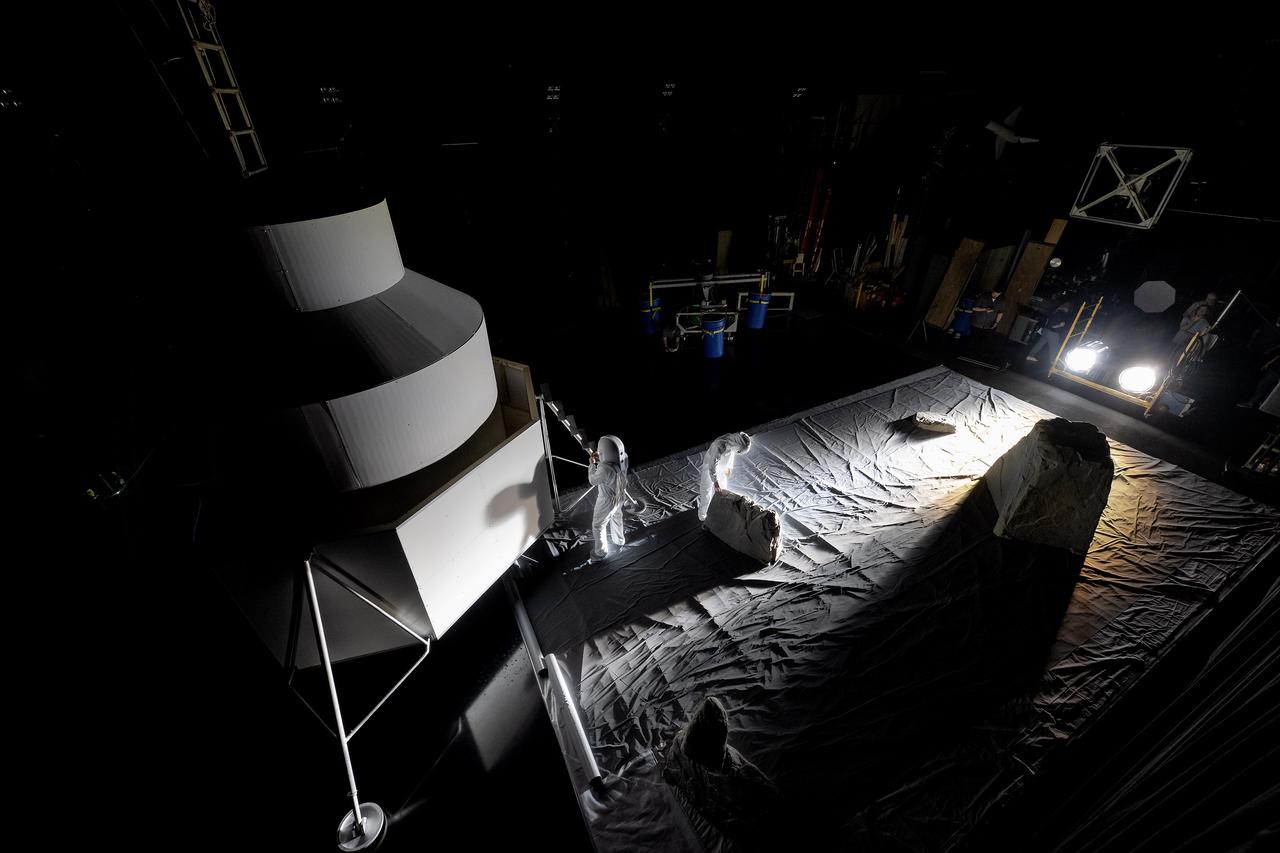

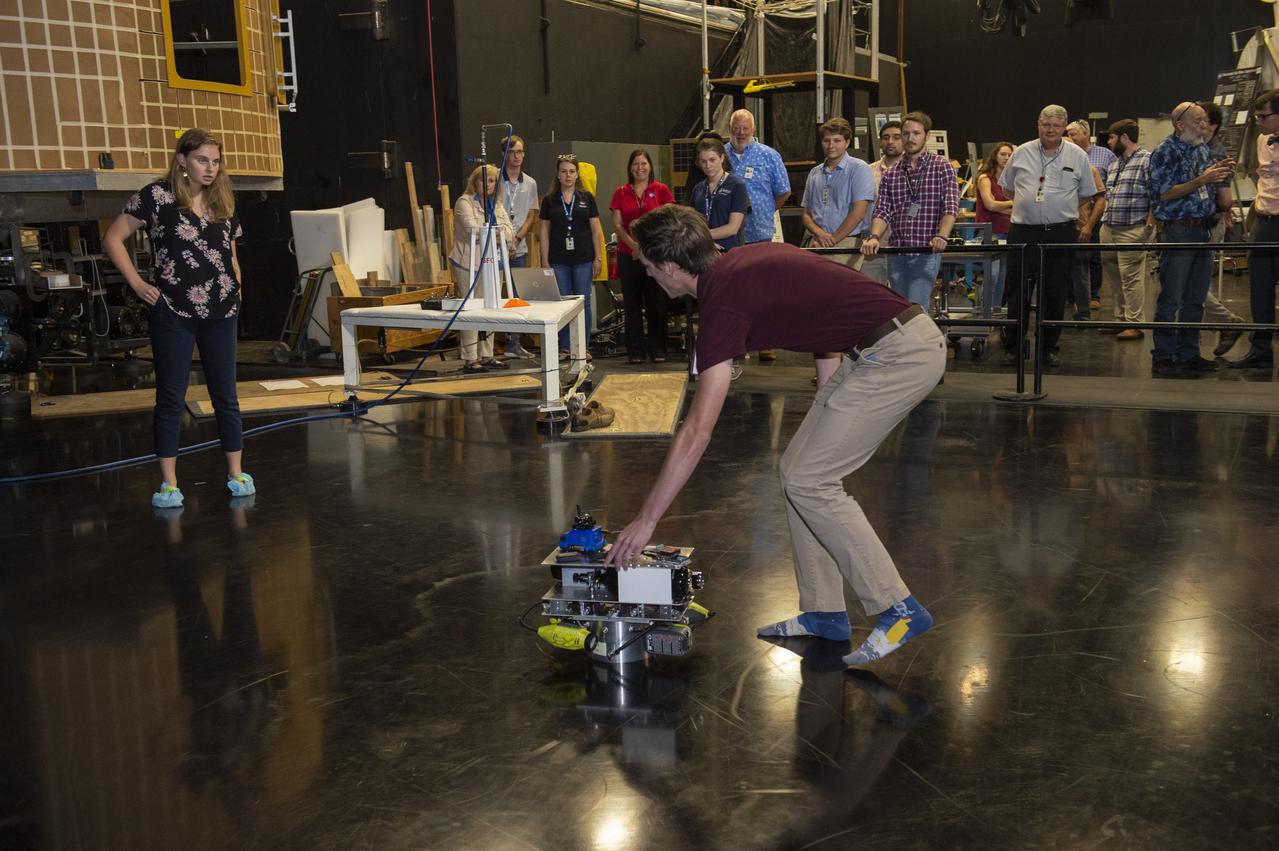
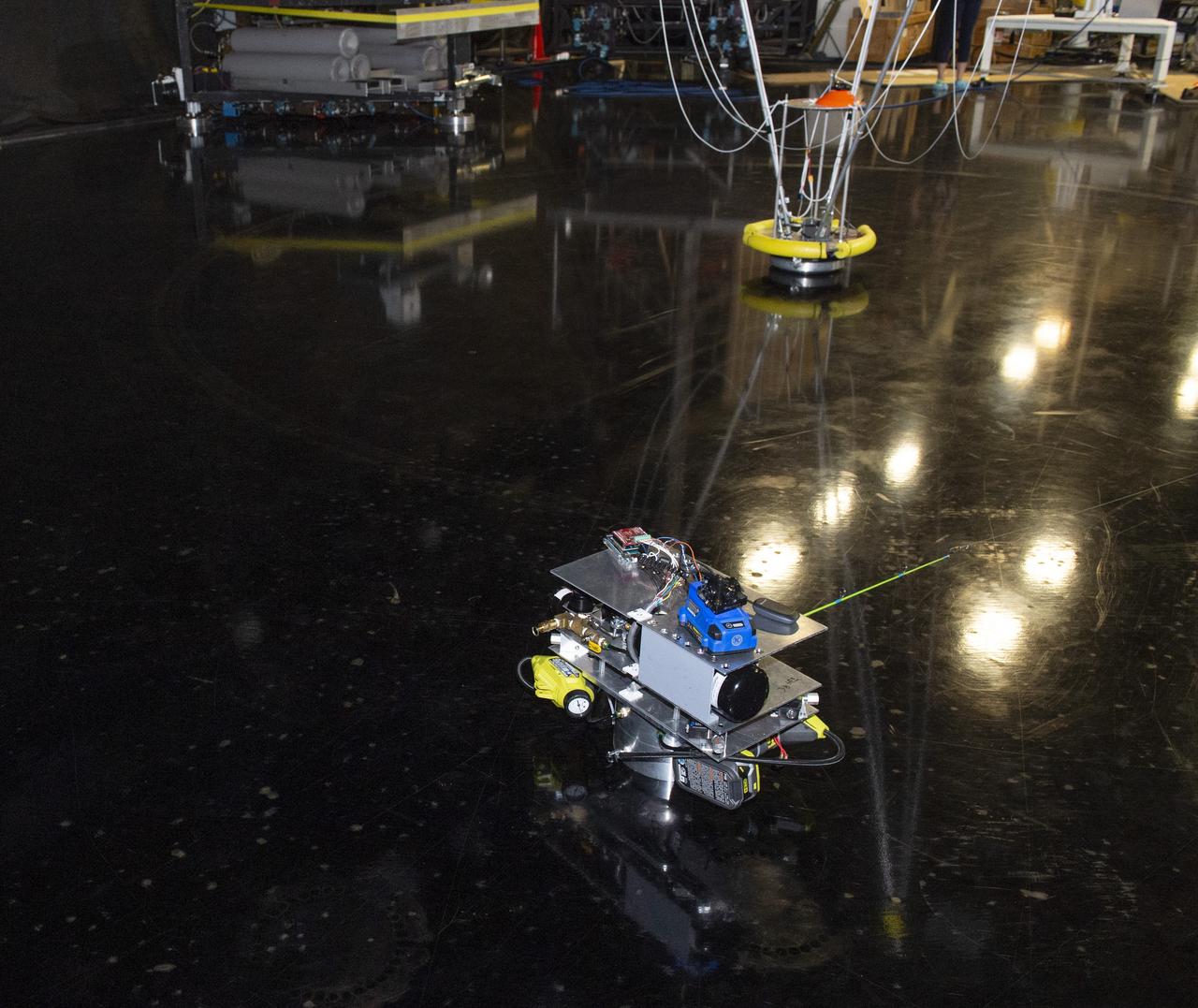
These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
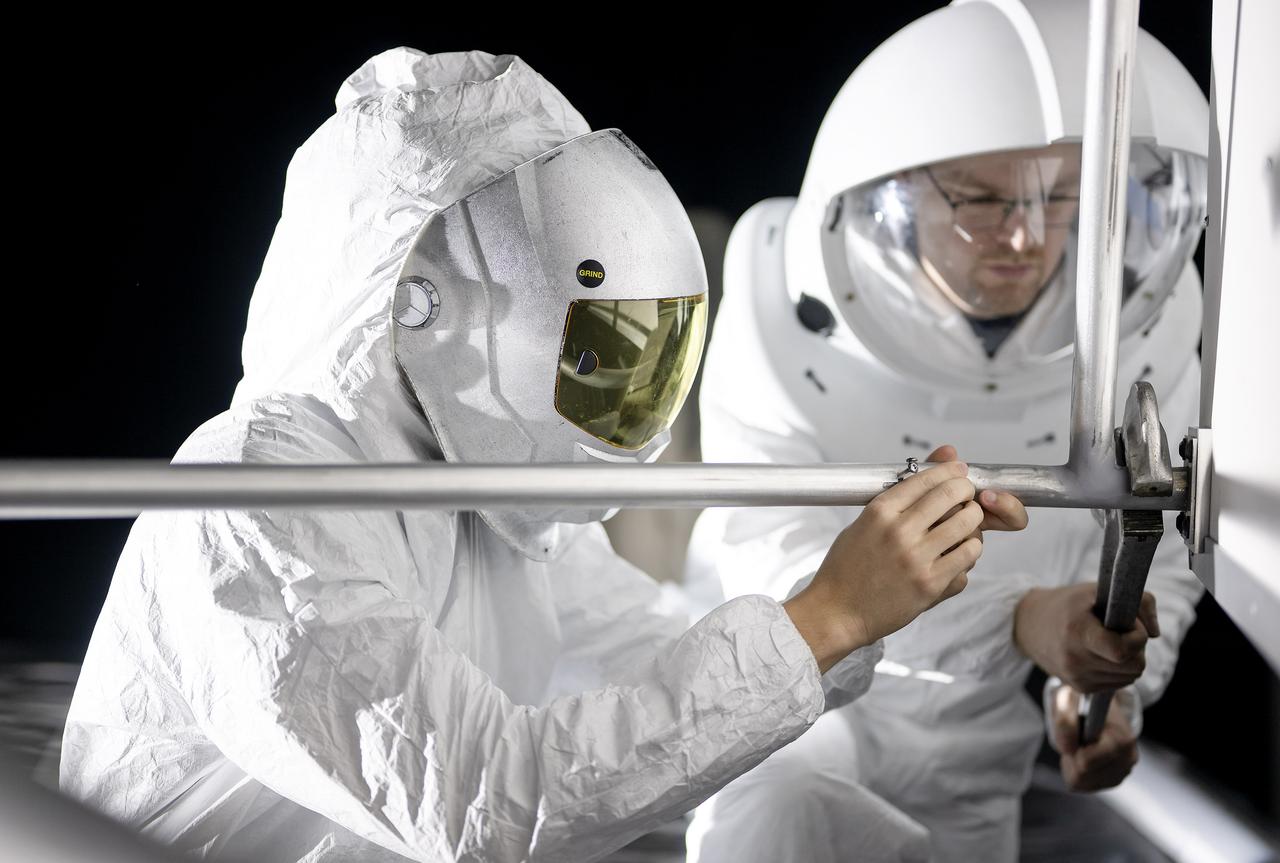

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
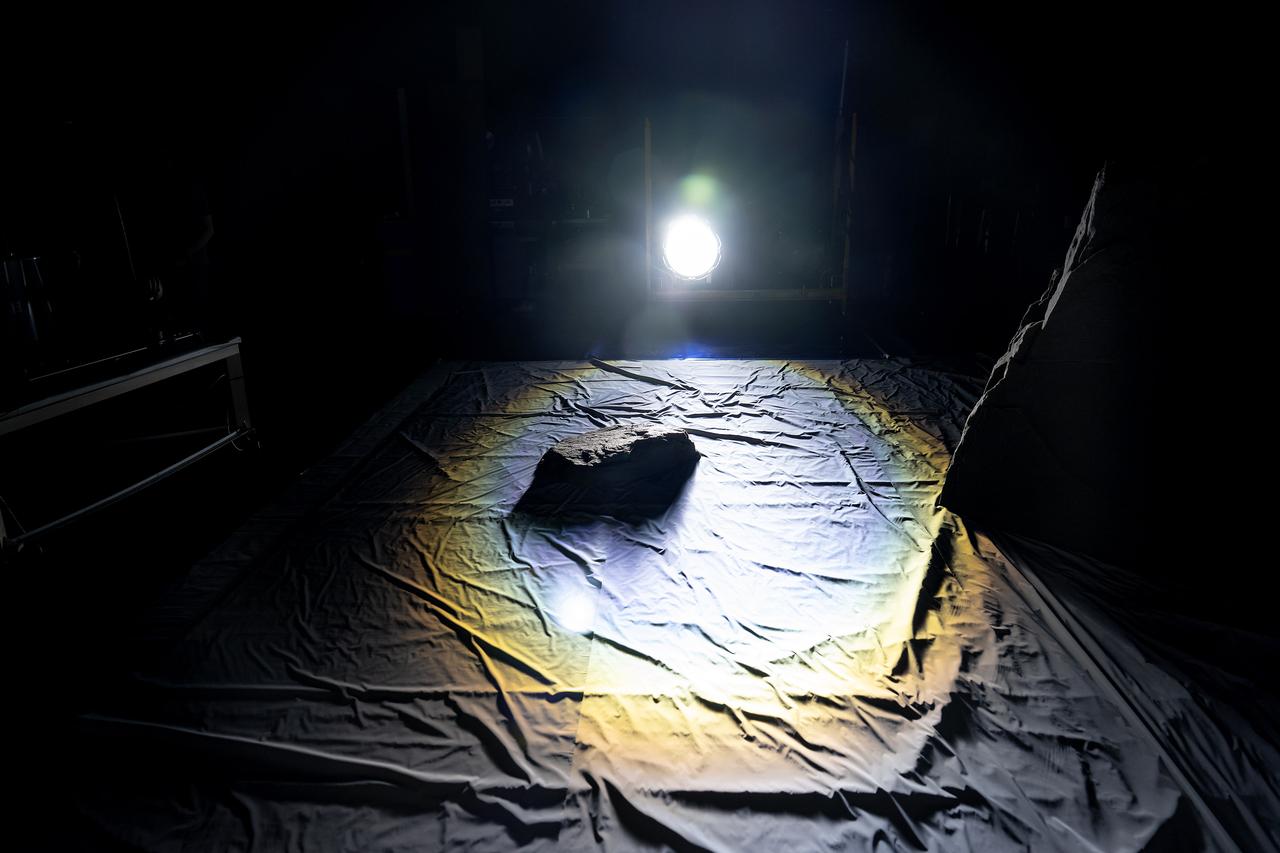

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
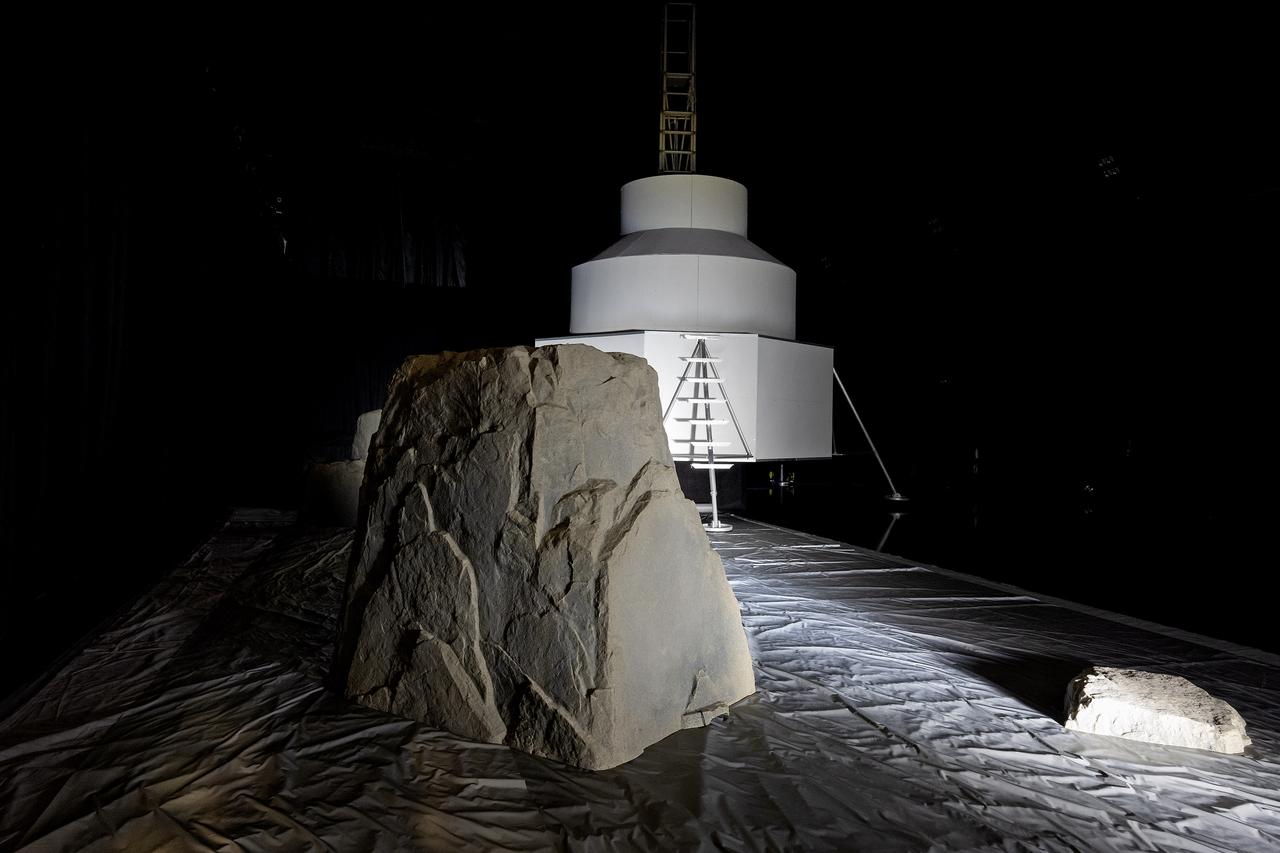

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
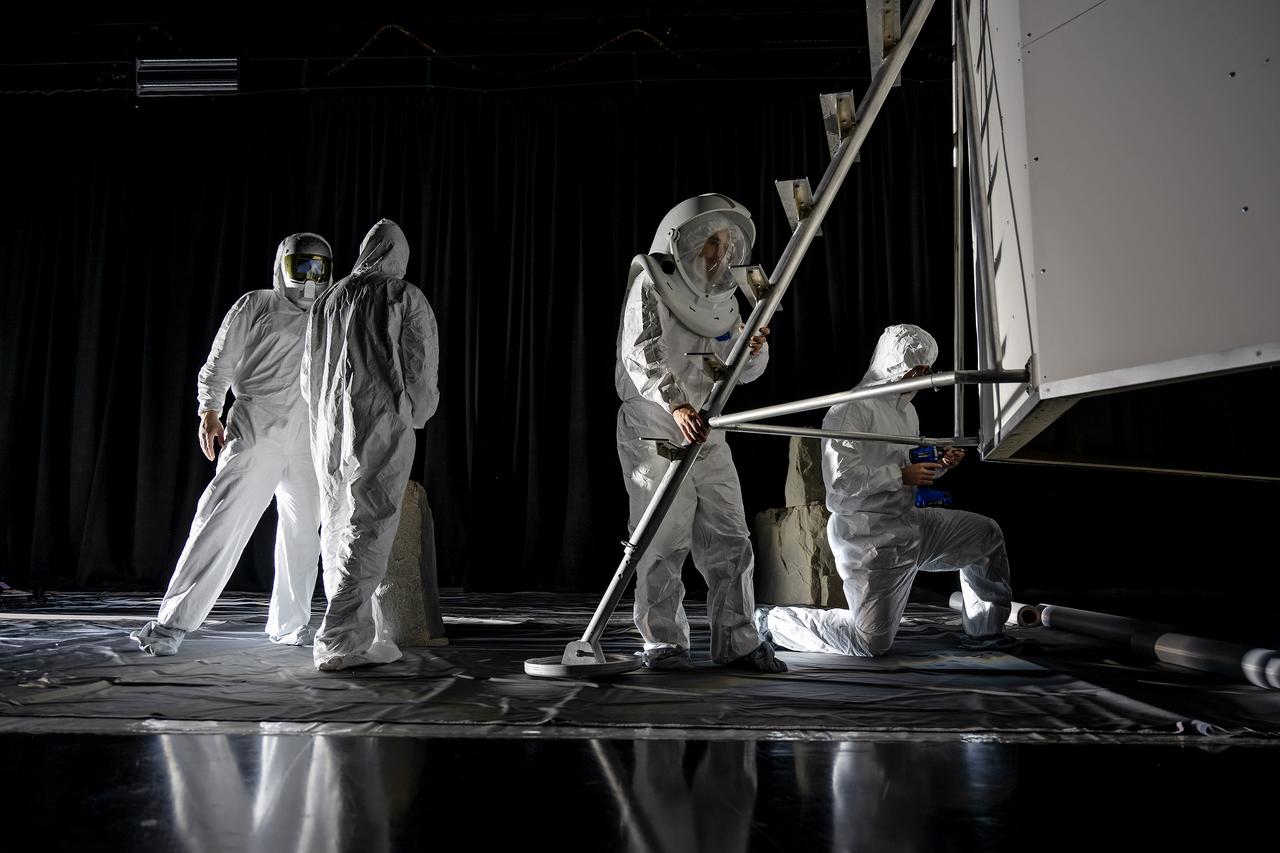

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
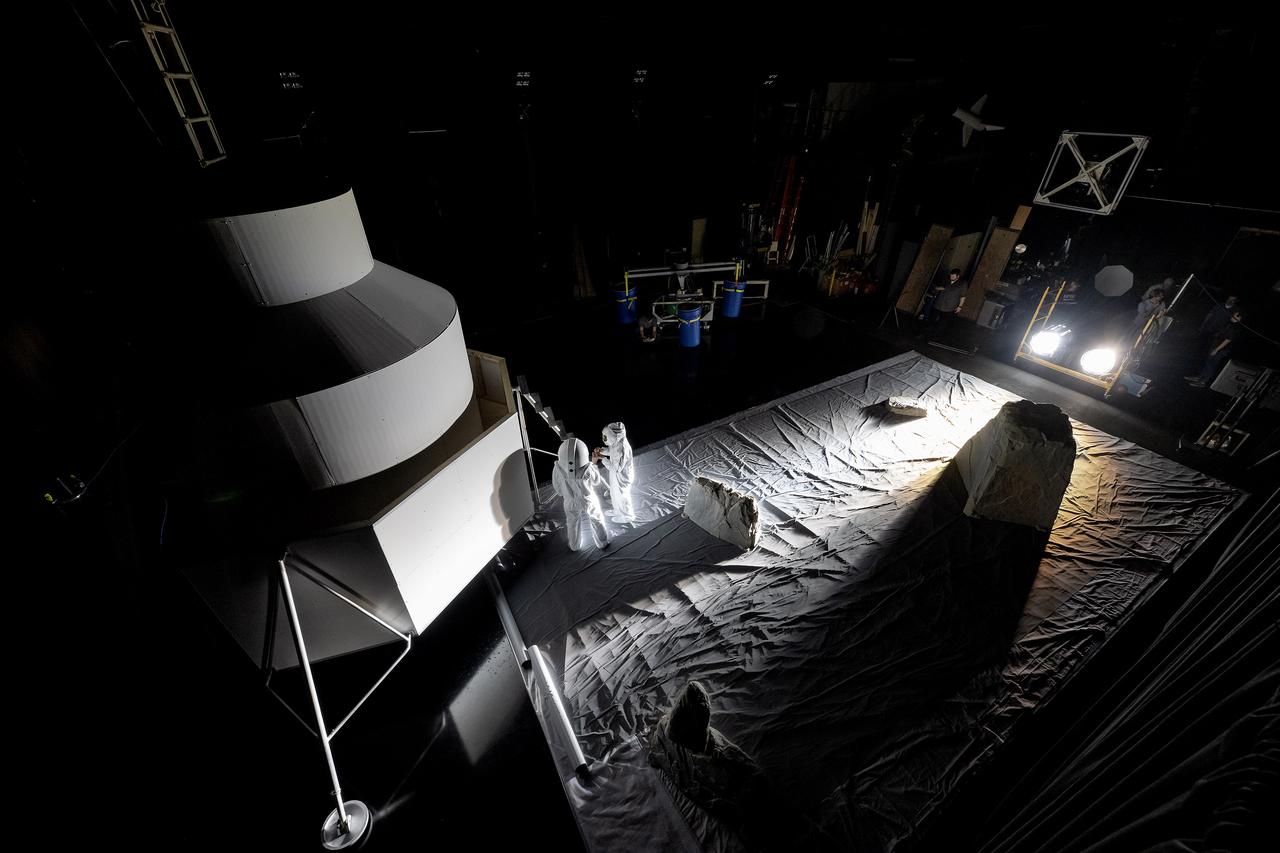

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
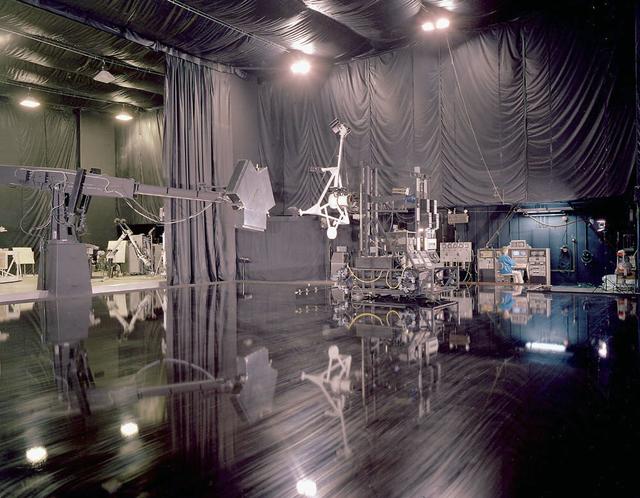

Marshall employees conduct tests on the simulated rendezvous docking mechanism (SRDM)as depicted in this photo of the flat floor area in building 4619.
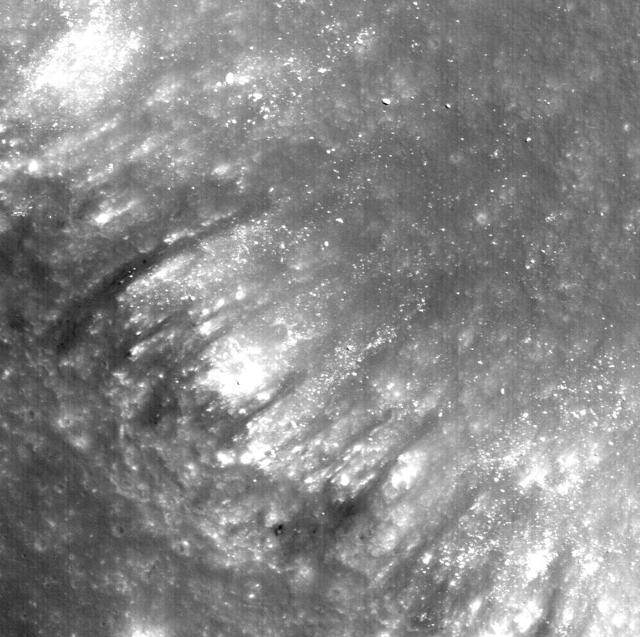

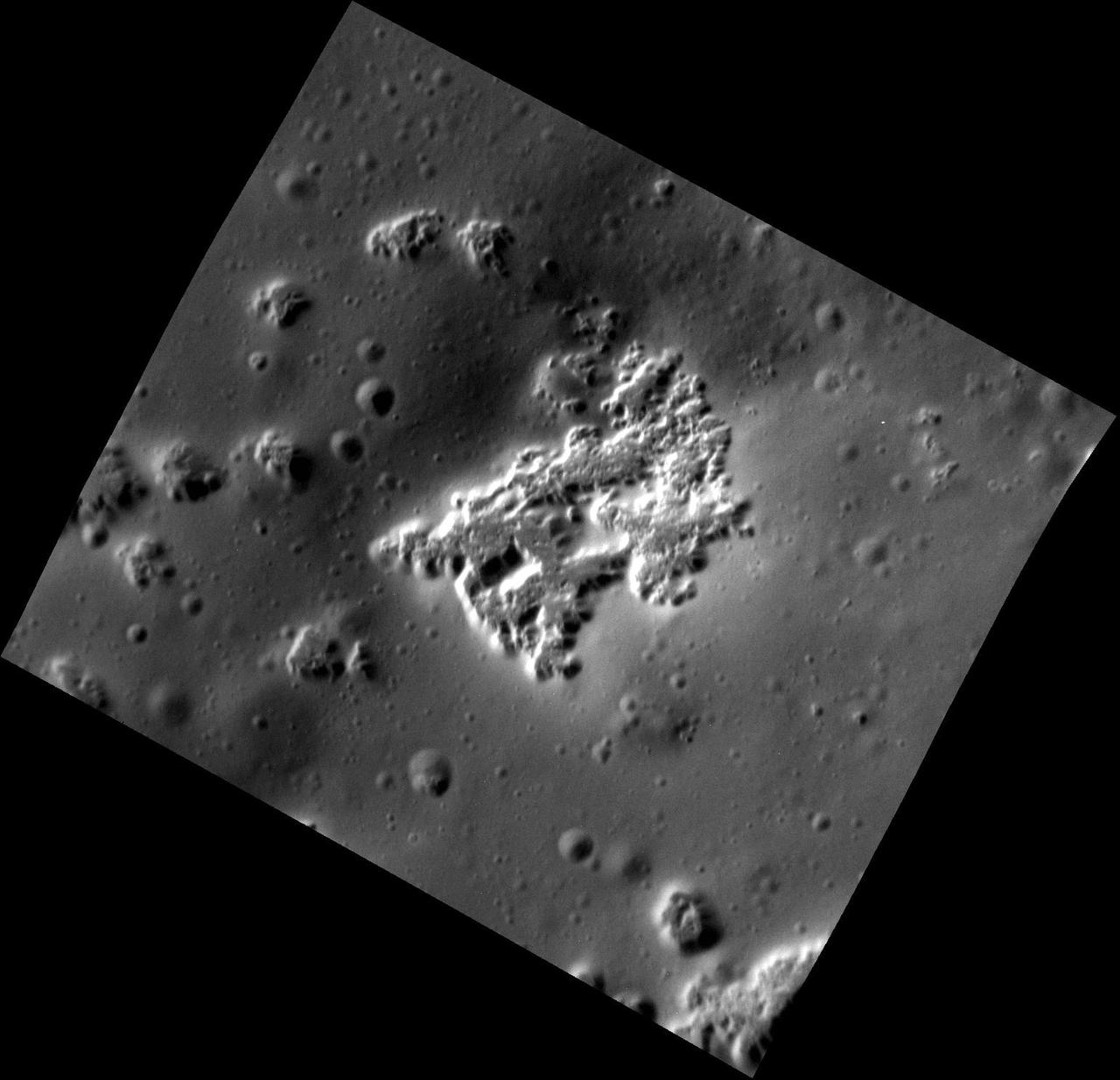
Many fractures on the Moon are seen in the floors of ancient, flat-floored highlands craters in this image taken by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.

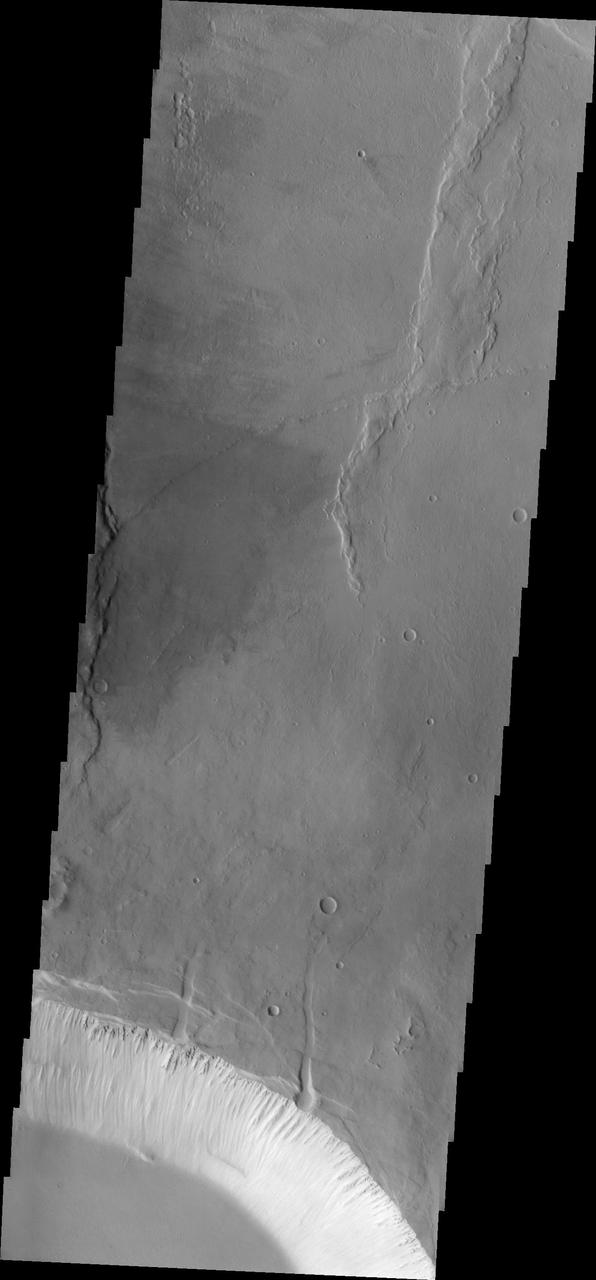
The impact crater observed in this NASA Mars Odyssey image taken in Terra Cimmeria suggests sediments have filled the crater due to the flat and smooth nature of the floor compared to rougher surfaces at higher elevations.

The relatively flat floor and terrace walls of this impact crater imaged by NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft suggest the crater was partly infilled with sediment and subsequently eroded to its present day form.

Surface textures vary in relation to topography on the south polar cap. Trough sides and floors are different from the flat top surface of the cap. This image was captured by NASA Mars Odyssey.

Chasma Boreale is a long, flat-floored valley that cuts deep into Mars north polar icecap. This image is part of an All Star set marking the occasion of NASA Mars Odyssey as the longest-working Mars spacecraft in history.

This image, from NASA Mariner 10 spacecraft which launched in 1974, shows young craters superposed on smooth plains. Larger young craters have central peaks, flat floors, terraced walls, and radial ejecta deposits.

The fluidized impact crater ejecta and flat crater floors observed in this image from NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft suggest near-surface volatiles once played an important role in modifying the Martian surface.

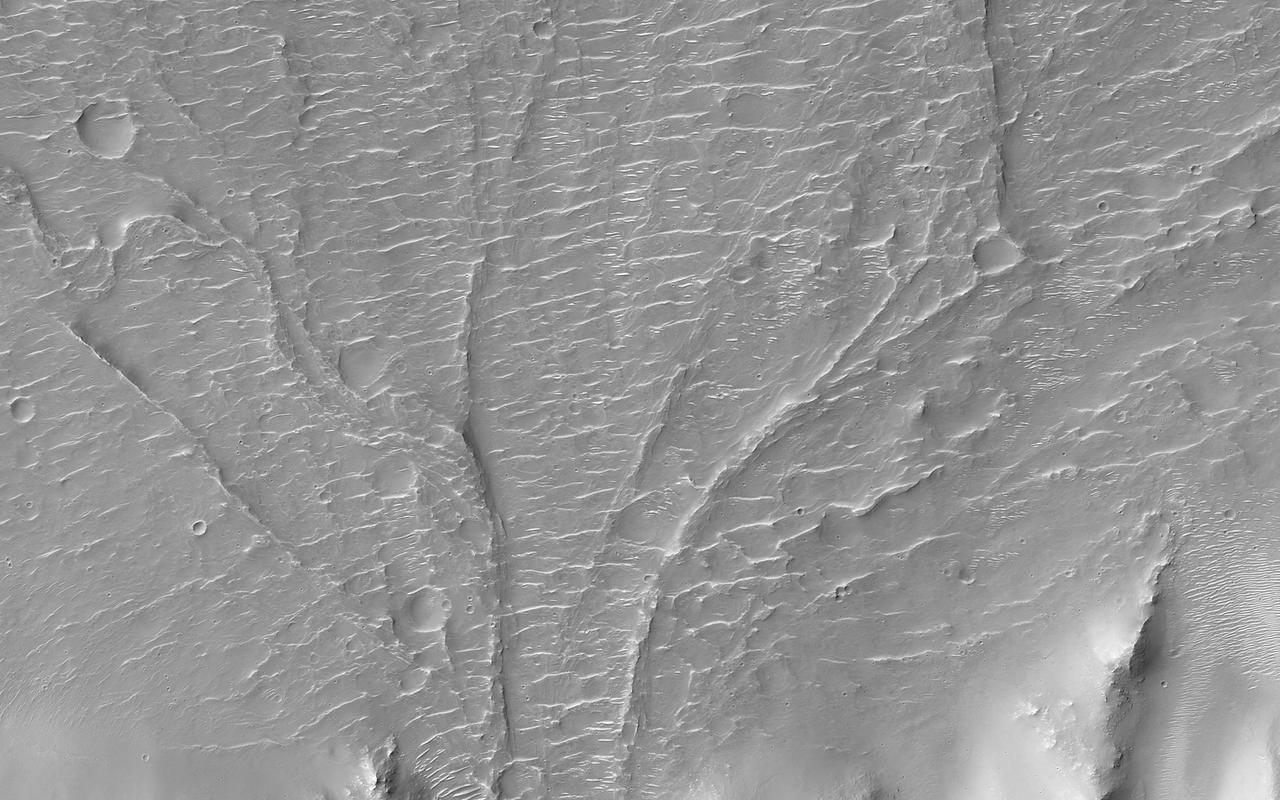
This MOC image shows a wide, flat-floored trough flanked by several smaller, branching troughs in the Olympica Fossae region of Mars. Dark- and intermediate-toned slope streaks -- created by dry avalanches of dust -- occur on the trough walls

On Mars, alluvial fans are sometimes visible in impact crater basins, as material from the steep rims is transported radially inward to the relatively flat floor. This image is from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.

Impact crater floors are commonly flat and relatively smooth, the result of the cooling and solidification of impact melt generated by the impact event itself. Often, the pool of impact melt cracks as it cools, a process well illustrated by the striking Abedin crater. Although not visible in the frame above, this crater also hosts cooling cracks on its floor. It also boasts numerous terraces along its inner wall, which likely formed after the impact melt solidified. Note how the fine-grained texture of the inner walls contrasts with the crater's floor. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19231

This high-resolution view shows hollows on the southwestern peak ring of the Scarlatti basin. The hollows are the irregularly shaped, flat-floored depressions. The image is striking because it shows that there are abundant small impact craters on the surface surrounding the hollows. But there are few if any within the hollows themselves. Since impacts occur randomly over Mercury's surface and accumulate with time, the lack of craters on the hollows indicates that they must be very young relative to the rest of Mercury's surface. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19246

Crater floors can have a range of features, from flat to a central peak or a central pit. This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows an unnamed crater in Terra Sabaea has a central pit. This unnamed crater in Terra Sabaea has a central pit. The different floor features develop do due several factors, including the size of the impactor, the geology of the surface material and the geology of the materials at depth. Orbit Number: 60737 Latitude: 22.3358 Longitude: 61.2019 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2015-08-23 20:13 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20092

This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft shows an interesting collection of kilometer-scale craters with flat and smooth floors. The craters themselves may be the result of secondary impacts, craters caused by debris from a distant larger impact. Since then, the surface has been significantly modified and reworked, muting the craters and flattening their floors. Presently, there are a few sand dunes and a broad overlay of a dusty soil mantle. This soil mantle occurs over much of the middle latitudes of Mars. Here, as elsewhere, the mantle covers these craters, but a closer inspection reveals that its smooth texture becomes significantly pitted and bumpy on the pole facing slopes of each crater interior wall. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20288
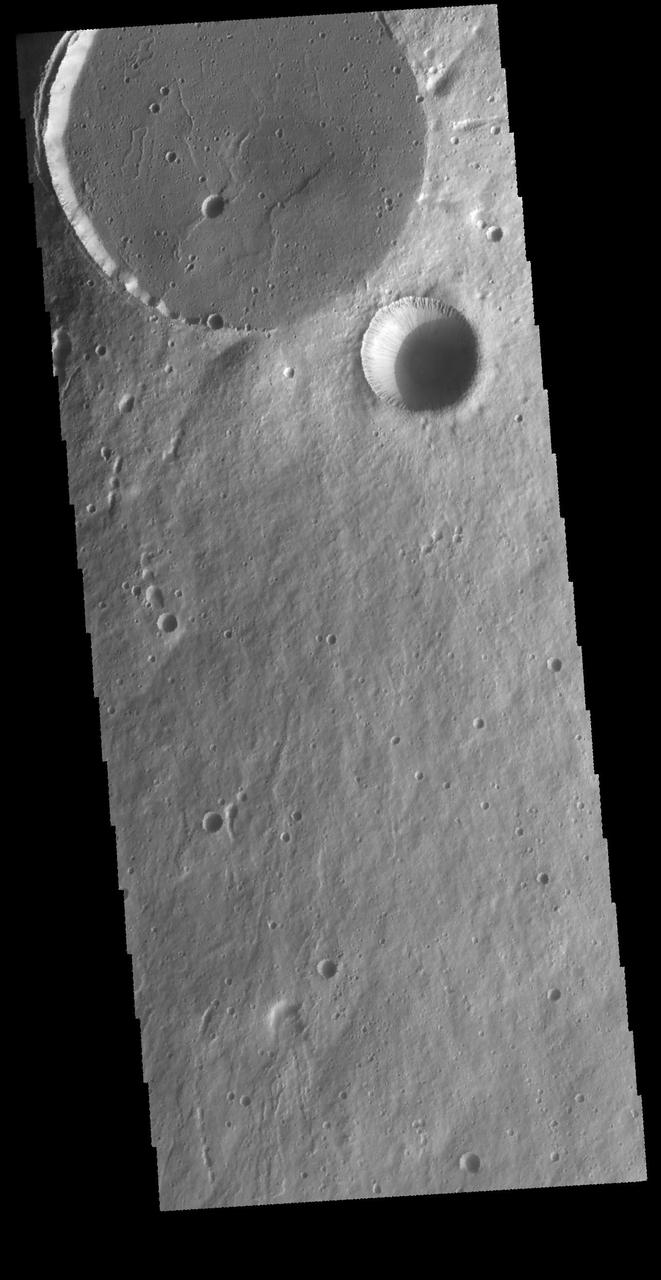

This VIS image shows two circular features. The flat floored feature at the top of the image is the summit caldera of Elysium Mons and was formed by volcanic activity. The bowl-shaped feature next to the caldera is an impact crater. Orbit Number: 65587 Latitude: 24.3248 Longitude: 146.842 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2016-09-26 07:14 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21159

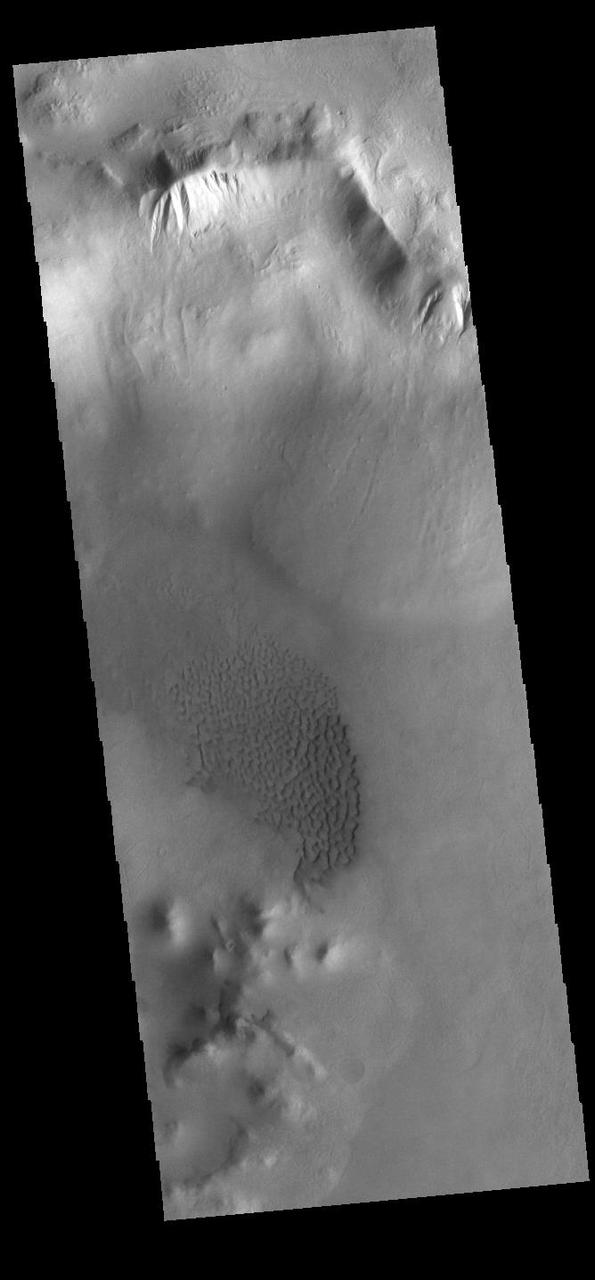
Today's VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Dunes cover the majority of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated more than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 90256 Latitude: -43.5412 Longitude: 34.6619 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-04-19 23:24 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25470

Today's VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Dunes cover halp of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated more than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 84884 Latitude: -43.4896 Longitude: 34.4426 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-02-01 15:04 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24736
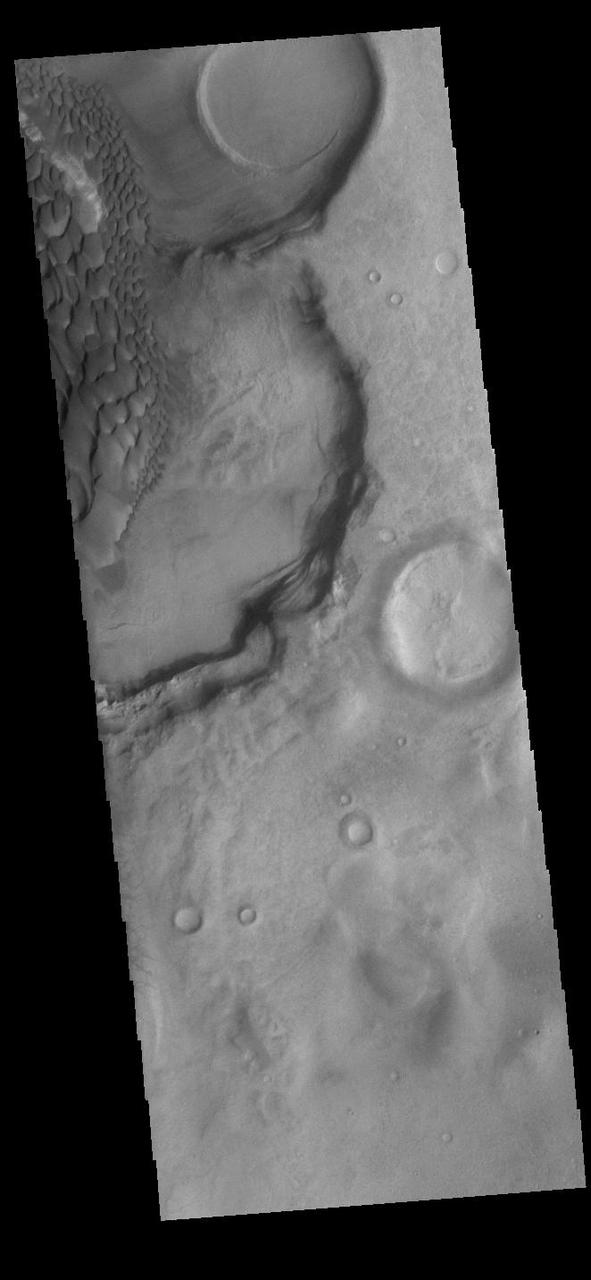

Today's VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Dunes cover only the very upper left of this image of Rabe Crater. The sand is likely derived by erosion into the deposit that fills most of the crater floor, creating a pit which hosts the dunes. The lower elevations at the top of this image are the eroded pit. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated less than the longer side. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming sand dunes. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 91404 Latitude: -43.8048 Longitude: 35.2382 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-07-23 12:03 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25547

Today's VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater, including the large dune field. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 93332 Latitude: -43.7011 Longitude: 34.9216 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-12-29 05:34 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25851
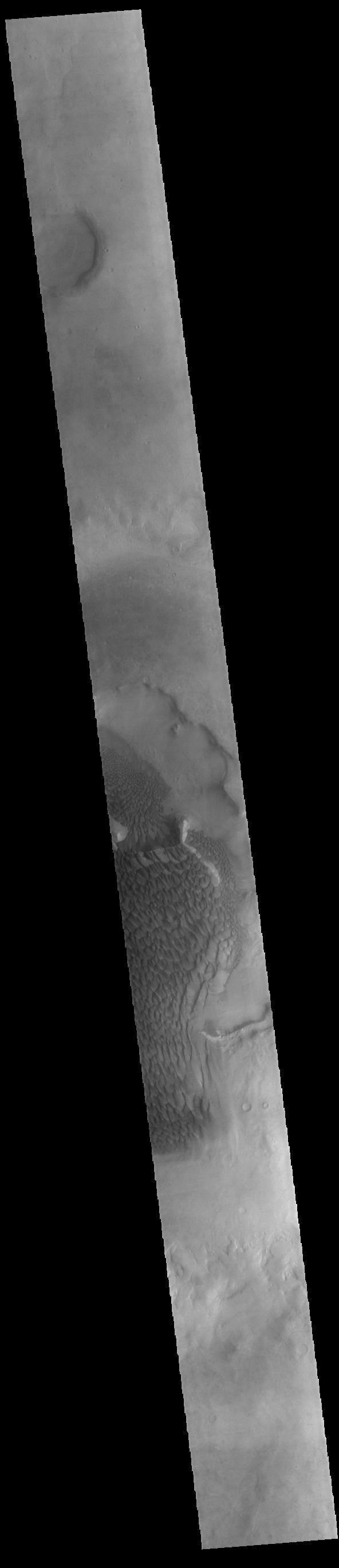

Today's VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Dunes cover the majority of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated more than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 84990 Latitude: -43.3123 Longitude: 34.9141 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-02-10 09:02 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24739
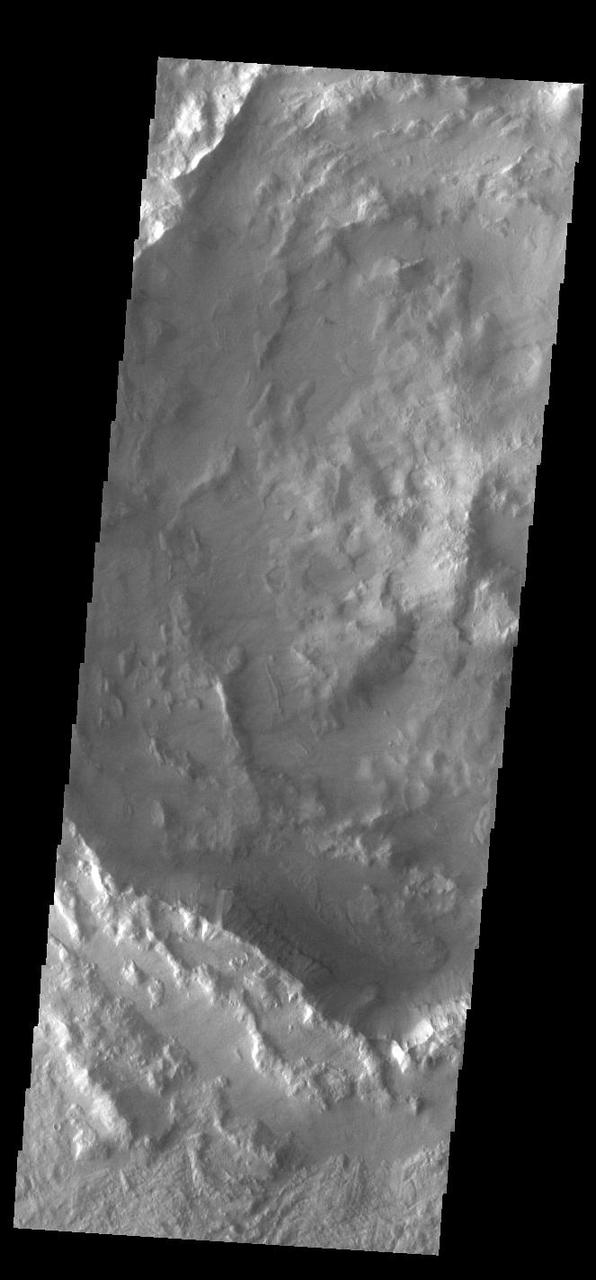

Today's VIS image shows part of an unnamed crater located in Noachis Terra. Unlike most Martian craters, this one has a very rugged floor. Most craters have flat floors, having been filled with materials such as sand blown into the crater, layered deposits from short term lakes, and volcanic materials from nearby flows. The morphology of the crater floor indicates that this is a relatively young crater, with the original floor created during the impact event. Orbit Number: 93133 Latitude: -41.7607 Longitude: 16.3316 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-12-12 20:18 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25841
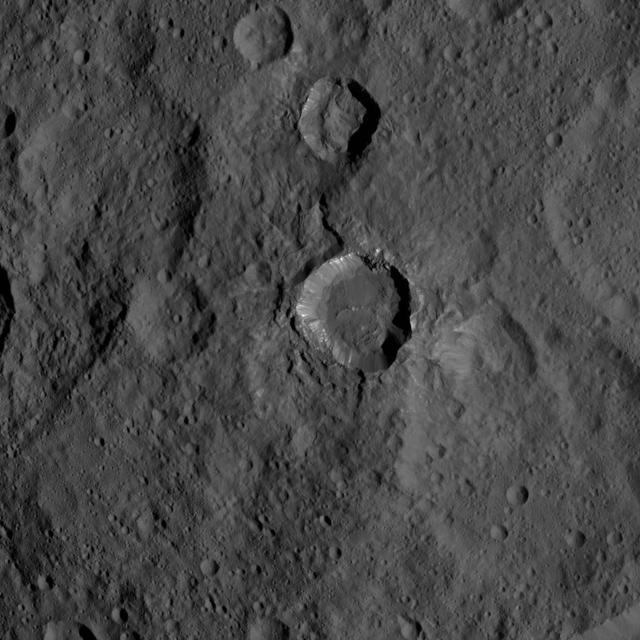

This view of Ceres from NASA's Dawn spacecraft shows a fresh impact crater with a flat floor. The crater is surrounded by smooth, flow-like ejecta that covers adjacent older impact craters. The crater is about 16 miles (26 kilometers) in diameter. The image was taken Oct. 9, 2015, from an altitude of 915 miles (1,470 kilometers). It has a resolution of 450 feet (140 meters) per pixel. The image is located at 31 degrees south latitude, 176 degrees east longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20124
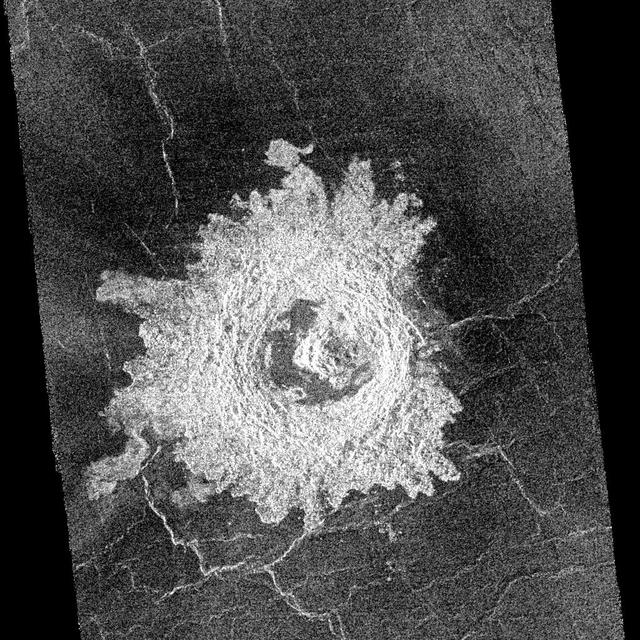
This complex crater in the Navka region of Venus was mapped by Magellan on September 26-27, 1990 during orbits 459 and 460. The crater has a diameter of 22 kilometers (13.6 miles) and is located at latitude 5.75 degrees south, longitude 349.6 degrees east. It has the terraced walls, flat radar-dark floor, and central peak that are characteristic of craters classified as 'complex.' The central peak on its floor is unusually large. Flow-like deposits extend beyond the limits of the coarser rim deposits on its west and southwest. Like about half of the craters mapped by Magellan to date, it is surrounded by a local, radar-dark halo. Buck, the proposed name for this crater honors Pearl S. Buck, American author (1892-1973). Proposed names for all features on planetary bodies are provisional until formally adopted by the International Astronomical Union. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00470

This is a false color image of Rabe Crater. In this combination of filters "blue" typically means basaltic sand. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 52231 Latitude: -43.6665 Longitude: 34.2627 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2013-09-22 14:29 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22146
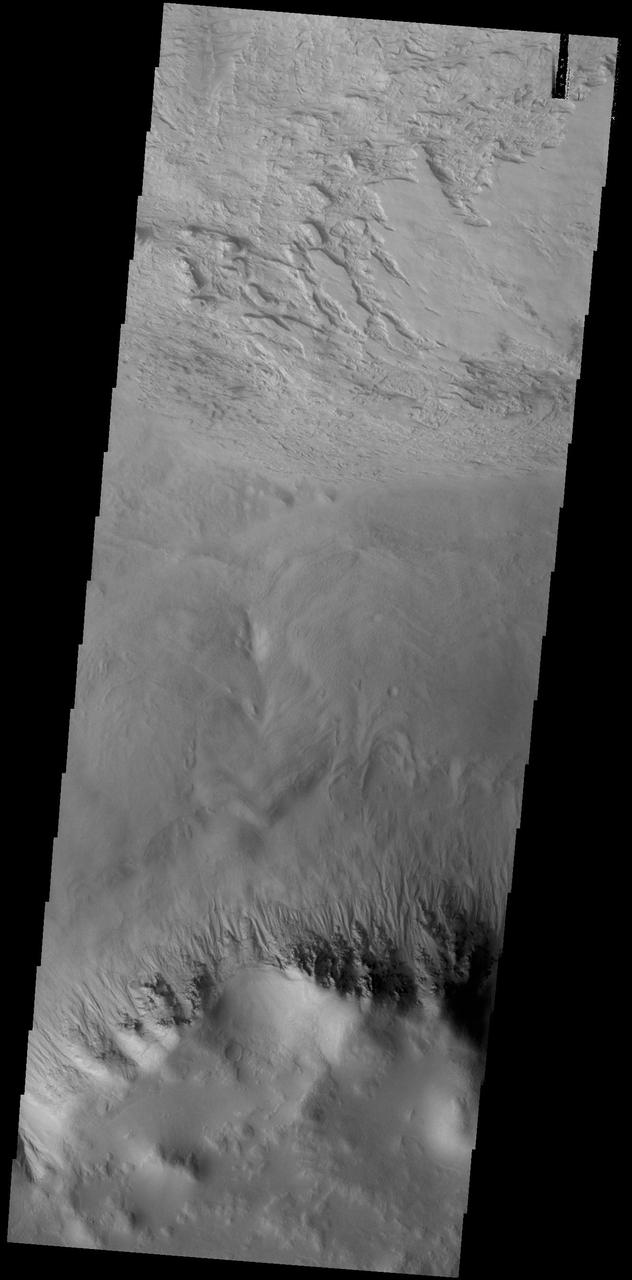

This VIS image shows a small portion of the floor of Galle Crater. This large crater is located on the eastern side of Argyre Planitia. The floor of Galle Crater contains many different features, including fluvial, glacial and aeolian derived products. The steep crater rim is toward the bottom of the image. The incised, flat laying materials at the top of the image are probably eroded layered deposits. Orbit Number: 74804 Latitude: -52.1339 Longitude: 329.267 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2018-10-25 14:28 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22884
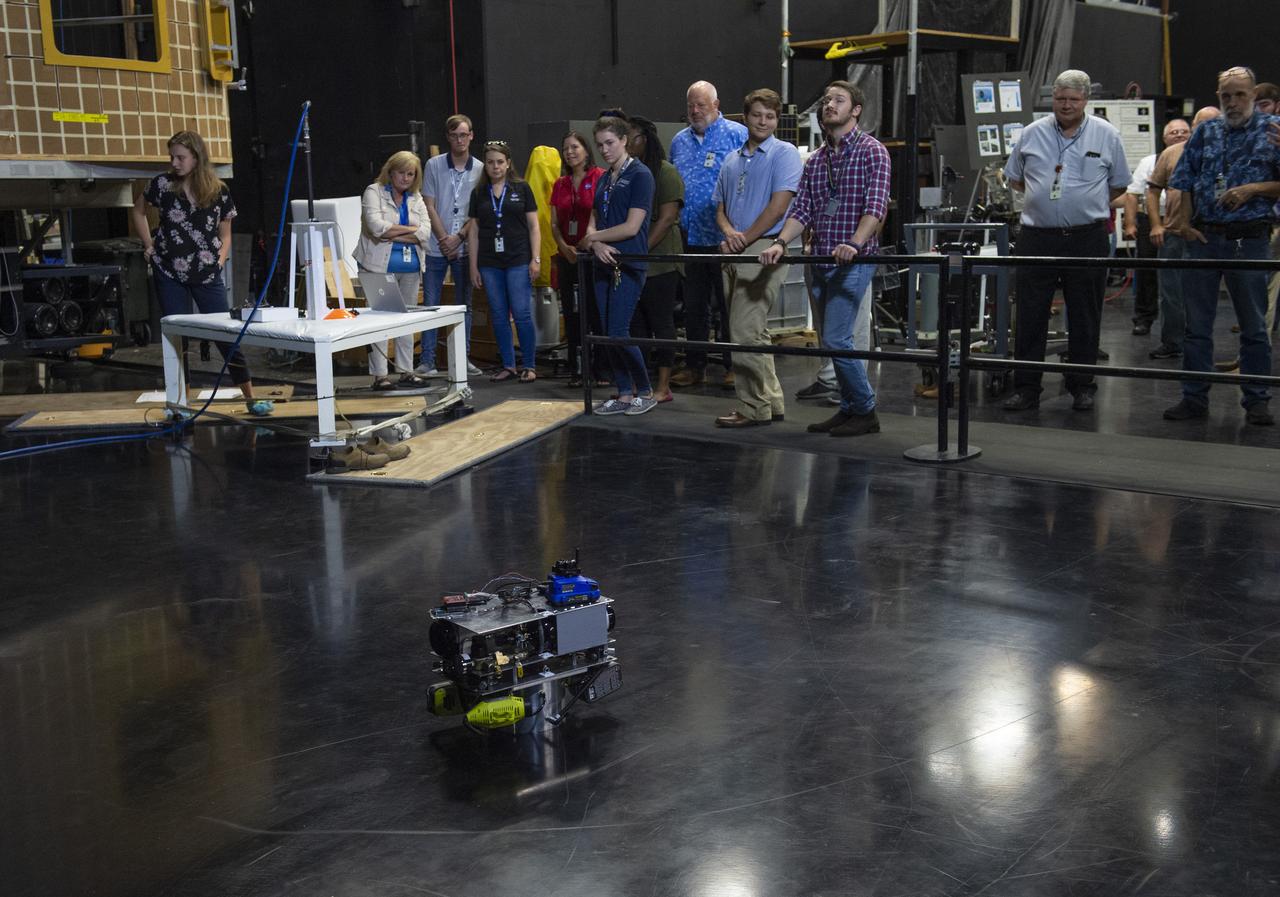
PATHWAYS INTERN ALEXANDRA BOEHM, AND JACOBS INTERN, PEYTON NELSON DEMONSTRATE STEERABLE AIR BEARING TETHER DEPLOYMENT SYSTEM TO MSFC SENIOR MANAGEMENT. ALSO WORKING ON THE PROJECT BUT NOT PICTURED WERE SUMMER INTERN ALI BERTELSMAN, PATHWAYS INTERN ANNA SHIPMAN, AND JACOBS FULL-TIME EMPLOYEE BRANDON MOORE.
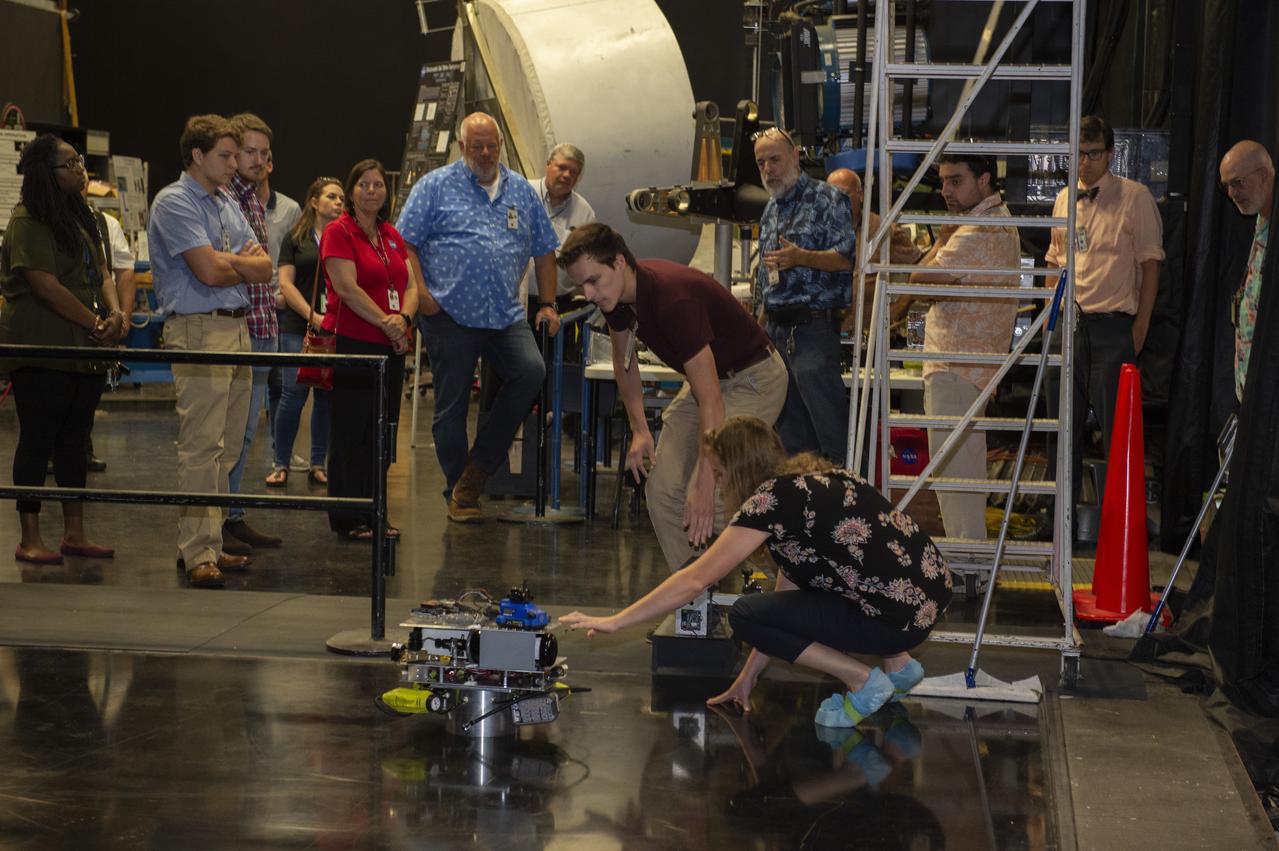
PATHWAYS INTERN ALEXANDRA BOEHM, AND JACOBS INTERN, PEYTON NELSON DEMONSTRATE STEERABLE AIR BEARING TETHER DEPLOYMENT SYSTEM TO MSFC SENIOR MANAGEMENT. ALSO WORKING ON THE PROJECT BUT NOT PICTURED WERE SUMMER INTERN ALI BERTELSMAN, PATHWAYS INTERN ANNA SHIPMAN, AND JACOBS FULL-TIME EMPLOYEE BRANDON MOORE.
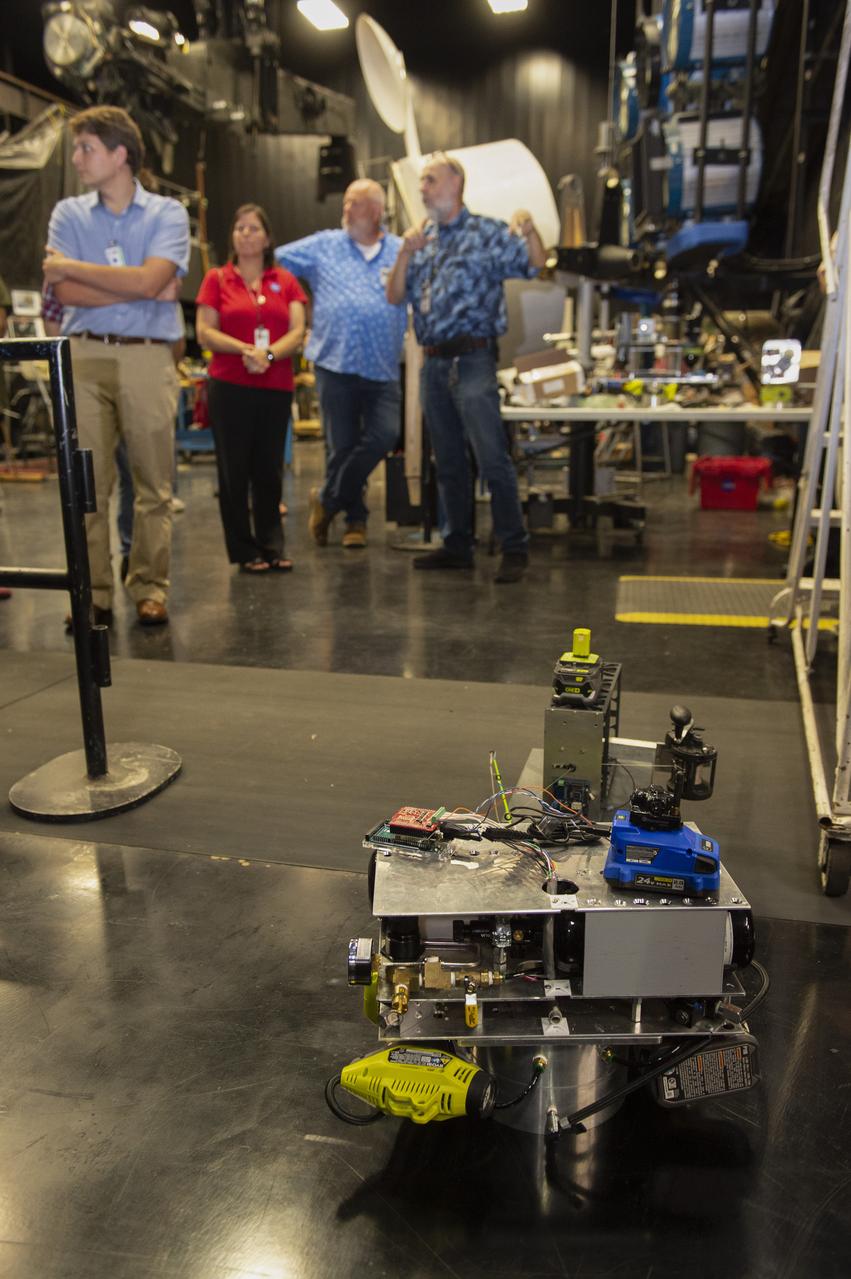
PATHWAYS INTERN ALEXANDRA BOEHM, AND JACOBS INTERN, PEYTON NELSON DEMONSTRATE STEERABLE AIR BEARING TETHER DEPLOYMENT SYSTEM TO MSFC SENIOR MANAGEMENT. ALSO WORKING ON THE PROJECT BUT NOT PICTURED WERE SUMMER INTERN ALI BERTELSMAN, PATHWAYS INTERN ANNA SHIPMAN, AND JACOBS FULL-TIME EMPLOYEE BRANDON MOORE.
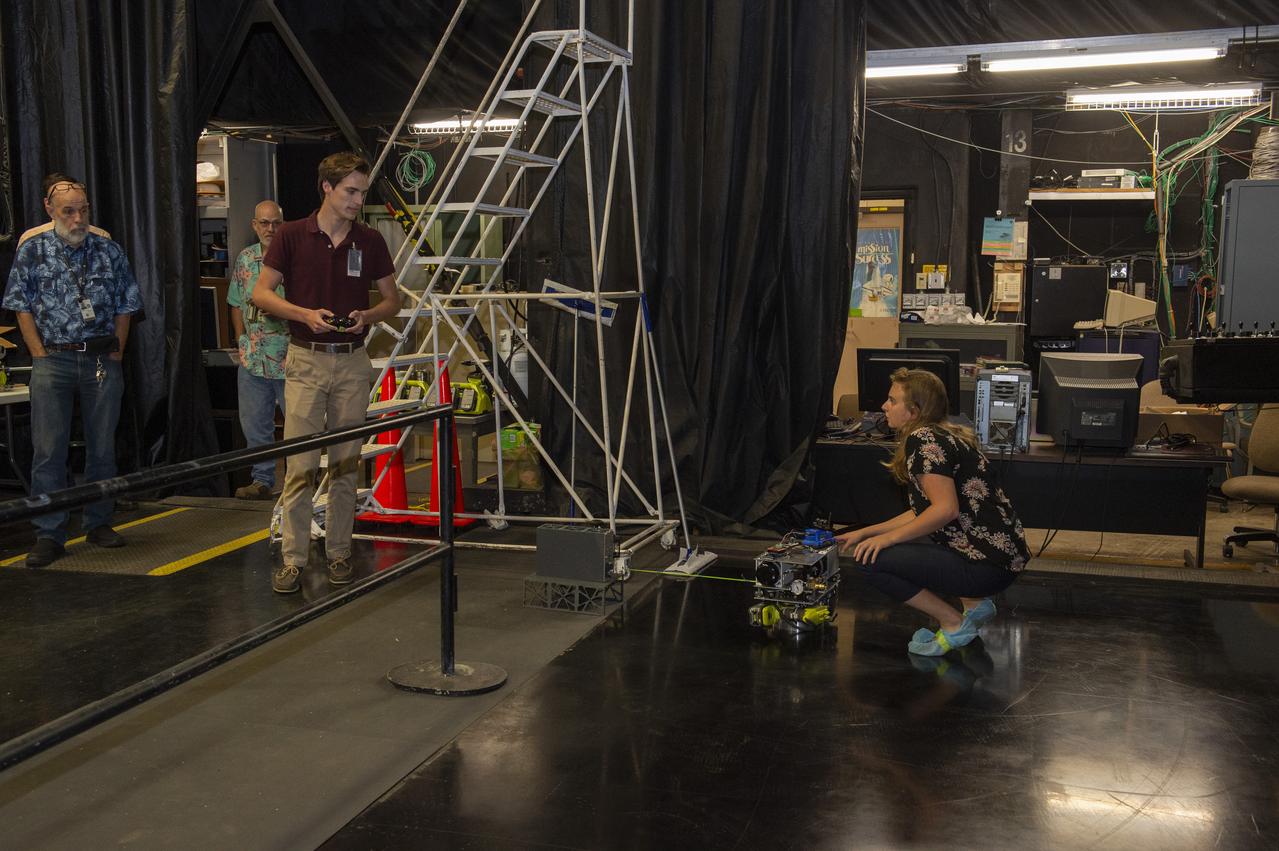

PATHWAYS INTERN ALEXANDRA BOEHM, AND JACOBS INTERN, PEYTON NELSON DEMONSTRATE STEERABLE AIR BEARING TETHER DEPLOYMENT SYSTEM TO MSFC SENIOR MANAGEMENT. ALSO WORKING ON THE PROJECT BUT NOT PICTURED WERE SUMMER INTERN ALI BERTELSMAN, PATHWAYS INTERN ANNA SHIPMAN, AND JACOBS FULL-TIME EMPLOYEE BRANDON MOORE.
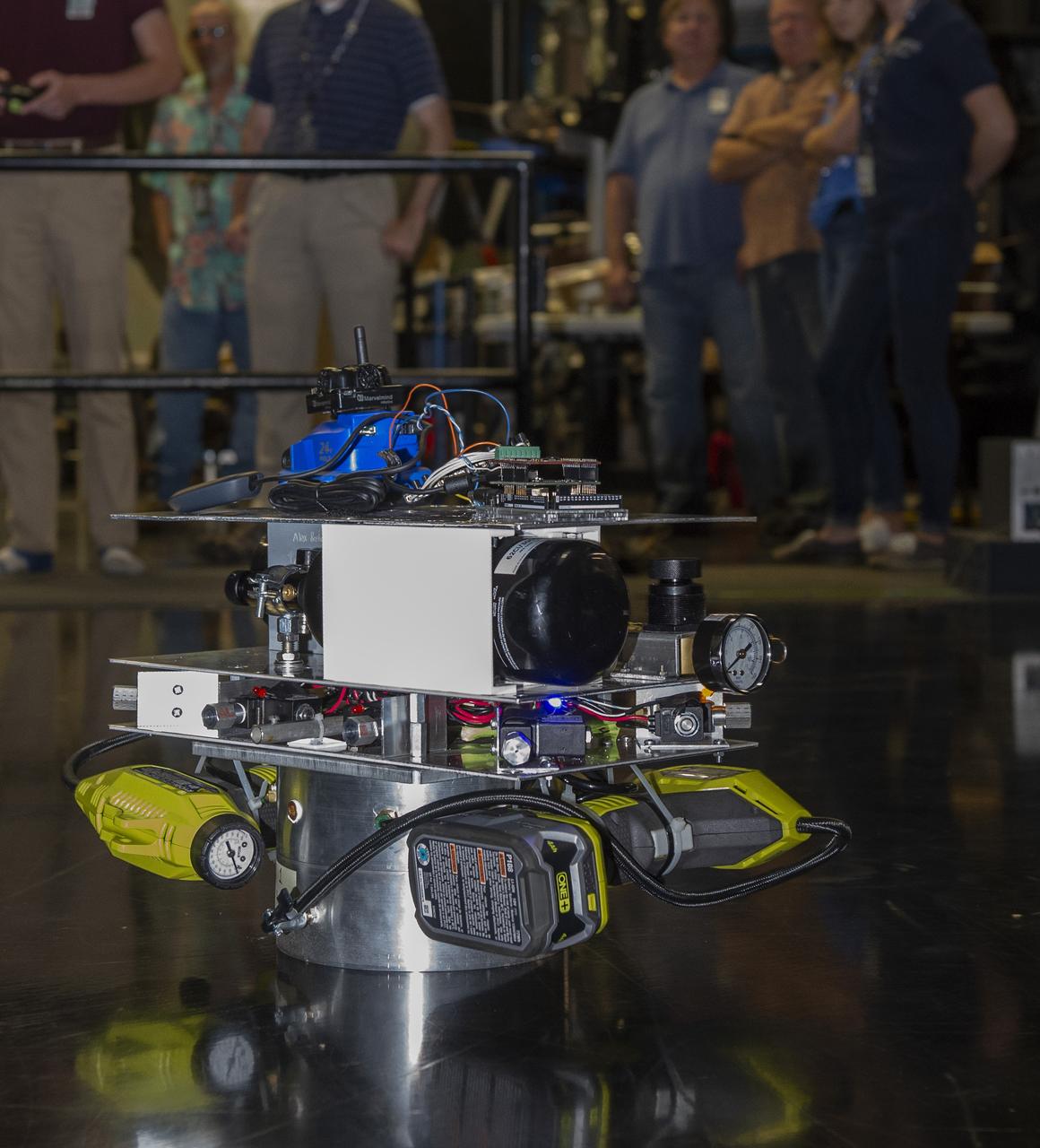
PATHWAYS INTERN ALEXANDRA BOEHM, AND JACOBS INTERN, PEYTON NELSON DEMONSTRATE STEERABLE AIR BEARING TETHER DEPLOYMENT SYSTEM TO MSFC SENIOR MANAGEMENT. ALSO WORKING ON THE PROJECT BUT NOT PICTURED WERE SUMMER INTERN ALI BERTELSMAN, PATHWAYS INTERN ANNA SHIPMAN, AND JACOBS FULL-TIME EMPLOYEE BRANDON MOORE.
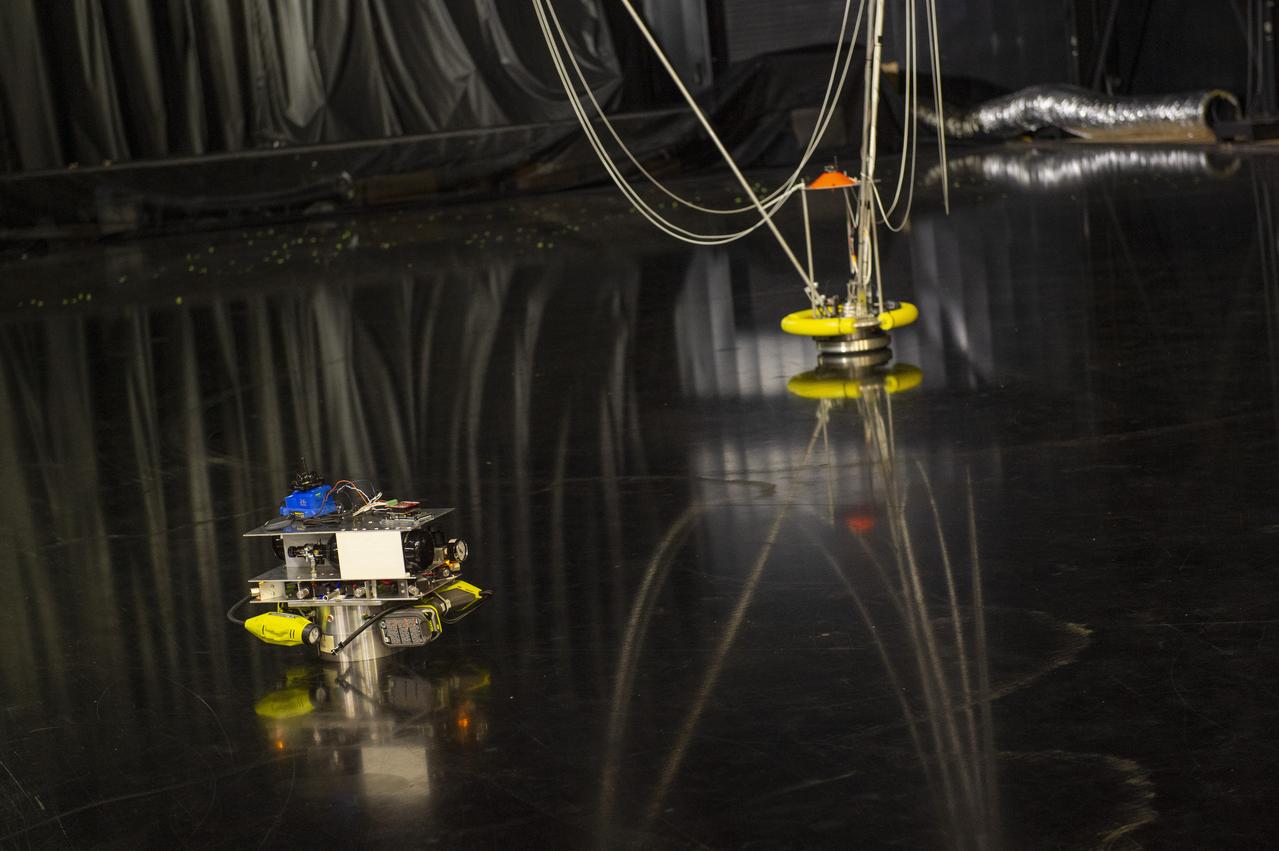
PATHWAYS INTERN ALEXANDRA BOEHM, AND JACOBS INTERN, PEYTON NELSON DEMONSTRATE STEERABLE AIR BEARING TETHER DEPLOYMENT SYSTEM TO MSFC SENIOR MANAGEMENT. ALSO WORKING ON THE PROJECT BUT NOT PICTURED WERE SUMMER INTERN ALI BERTELSMAN, PATHWAYS INTERN ANNA SHIPMAN, AND JACOBS FULL-TIME EMPLOYEE BRANDON MOORE.
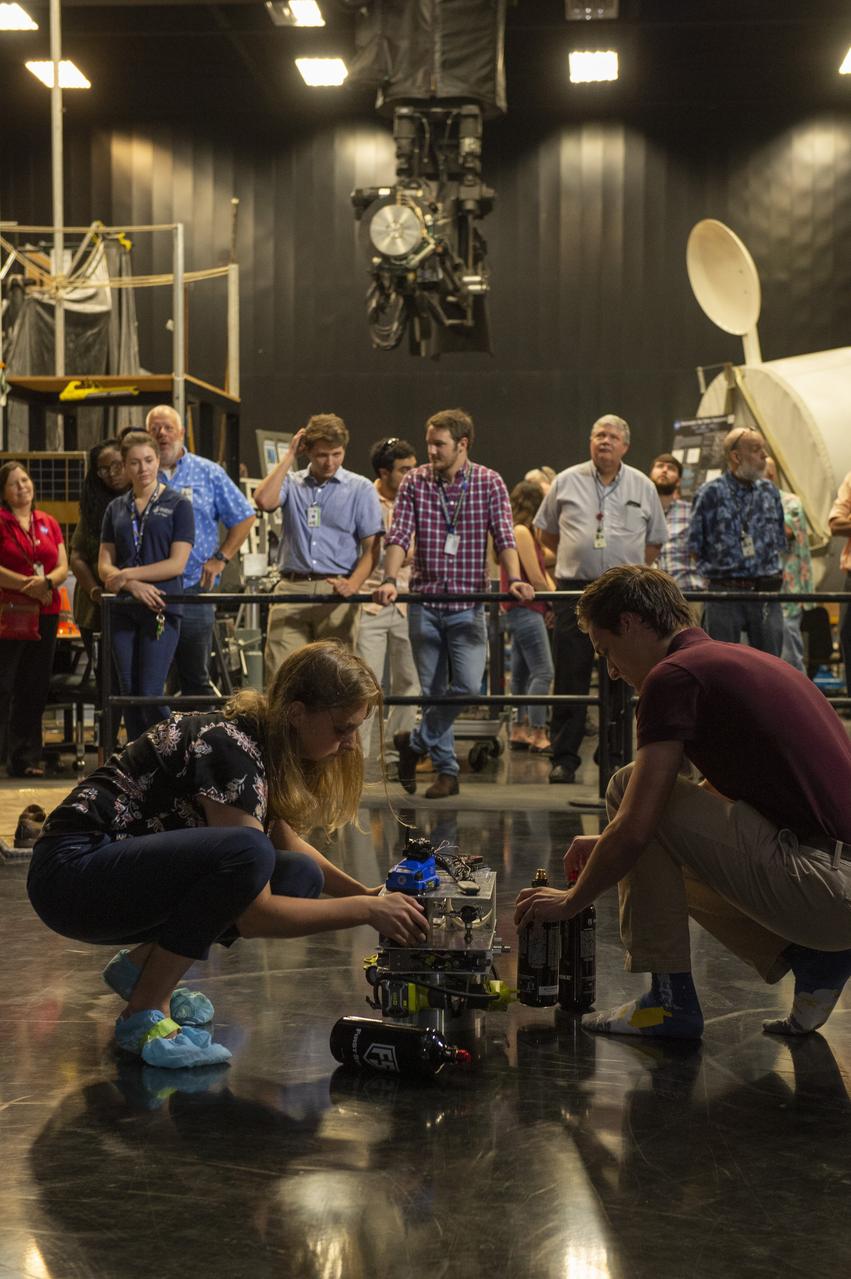

PATHWAYS INTERN ALEXANDRA BOEHM, AND JACOBS INTERN, PEYTON NELSON DEMONSTRATE STEERABLE AIR BEARING TETHER DEPLOYMENT SYSTEM TO MSFC SENIOR MANAGEMENT. ALSO WORKING ON THE PROJECT BUT NOT PICTURED WERE SUMMER INTERN ALI BERTELSMAN, PATHWAYS INTERN ANNA SHIPMAN, AND JACOBS FULL-TIME EMPLOYEE BRANDON MOORE.
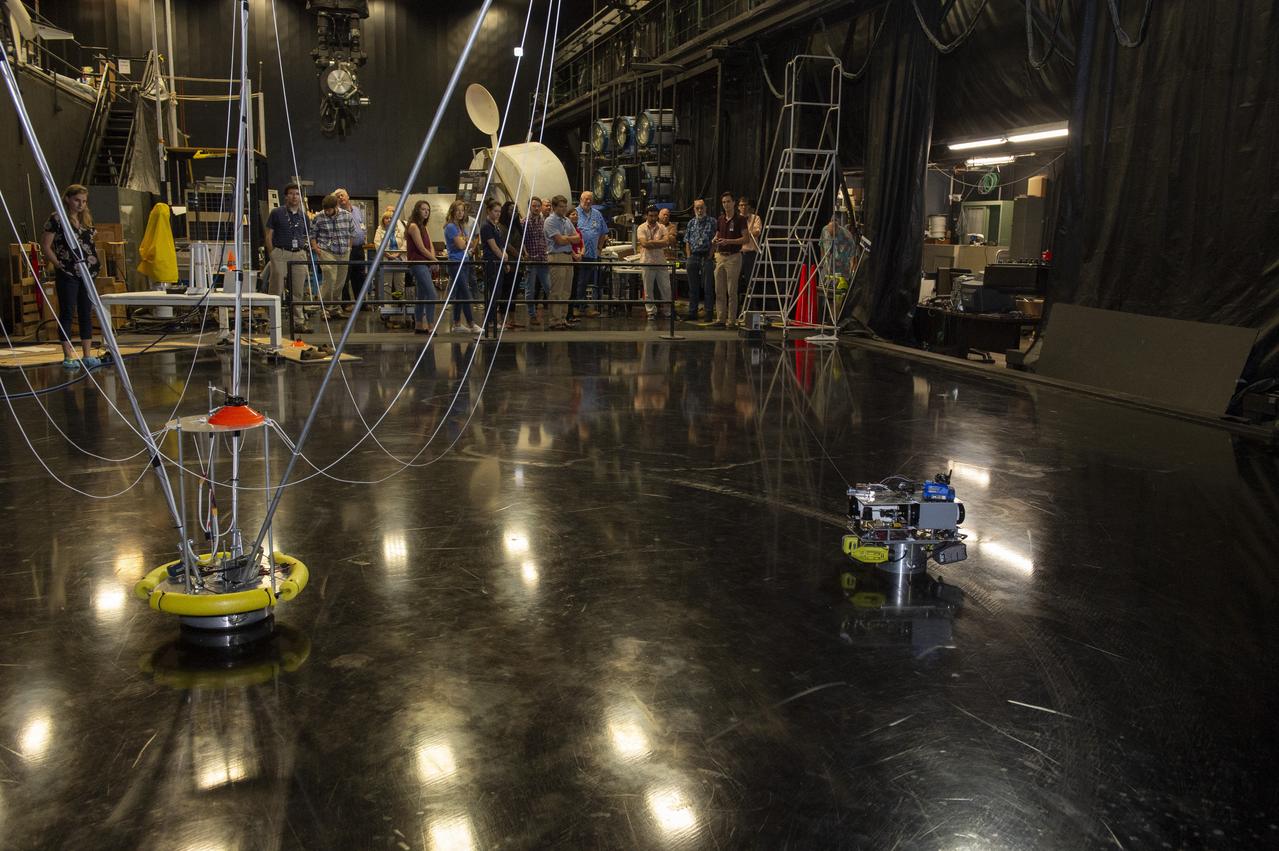

PATHWAYS INTERN ALEXANDRA BOEHM, AND JACOBS INTERN, PEYTON NELSON DEMONSTRATE STEERABLE AIR BEARING TETHER DEPLOYMENT SYSTEM TO MSFC SENIOR MANAGEMENT. ALSO WORKING ON THE PROJECT BUT NOT PICTURED WERE SUMMER INTERN ALI BERTELSMAN, PATHWAYS INTERN ANNA SHIPMAN, AND JACOBS FULL-TIME EMPLOYEE BRANDON MOORE.
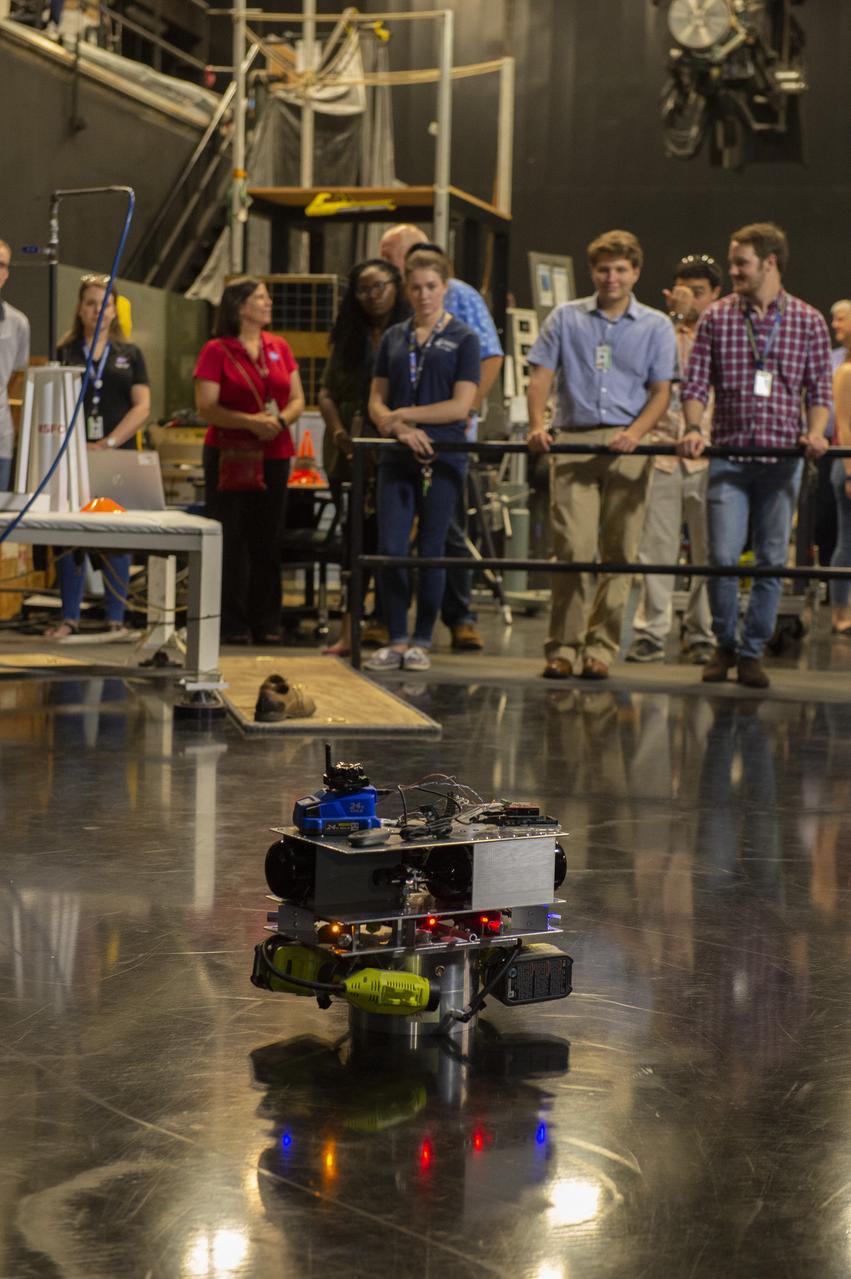
PATHWAYS INTERN ALEXANDRA BOEHM, AND JACOBS INTERN, PEYTON NELSON DEMONSTRATE STEERABLE AIR BEARING TETHER DEPLOYMENT SYSTEM TO MSFC SENIOR MANAGEMENT. ALSO WORKING ON THE PROJECT BUT NOT PICTURED WERE SUMMER INTERN ALI BERTELSMAN, PATHWAYS INTERN ANNA SHIPMAN, AND JACOBS FULL-TIME EMPLOYEE BRANDON MOORE.

PATHWAYS INTERN ALEXANDRA BOEHM, AND JACOBS INTERN, PEYTON NELSON DEMONSTRATE STEERABLE AIR BEARING TETHER DEPLOYMENT SYSTEM TO MSFC SENIOR MANAGEMENT. ALSO WORKING ON THE PROJECT BUT NOT PICTURED WERE SUMMER INTERN ALI BERTELSMAN, PATHWAYS INTERN ANNA SHIPMAN, AND JACOBS FULL-TIME EMPLOYEE BRANDON MOORE.

PATHWAYS INTERN ALEXANDRA BOEHM, AND JACOBS INTERN, PEYTON NELSON DEMONSTRATE STEERABLE AIR BEARING TETHER DEPLOYMENT SYSTEM TO MSFC SENIOR MANAGEMENT. ALSO WORKING ON THE PROJECT BUT NOT PICTURED WERE SUMMER INTERN ALI BERTELSMAN, PATHWAYS INTERN ANNA SHIPMAN, AND JACOBS FULL-TIME EMPLOYEE BRANDON MOORE.

PATHWAYS INTERN ALEXANDRA BOEHM, AND JACOBS INTERN, PEYTON NELSON DEMONSTRATE STEERABLE AIR BEARING TETHER DEPLOYMENT SYSTEM TO MSFC SENIOR MANAGEMENT. ALSO WORKING ON THE PROJECT BUT NOT PICTURED WERE SUMMER INTERN ALI BERTELSMAN, PATHWAYS INTERN ANNA SHIPMAN, AND JACOBS FULL-TIME EMPLOYEE BRANDON MOORE.

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Rabe Crater. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The movement of the sand is from the lower right towards the upper left. In this combination of filters "blue" typically means basaltic sand. Orbit Number: 67013 Latitude: -43.2572 Longitude: 34.5875 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-01-21 18:25 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24055
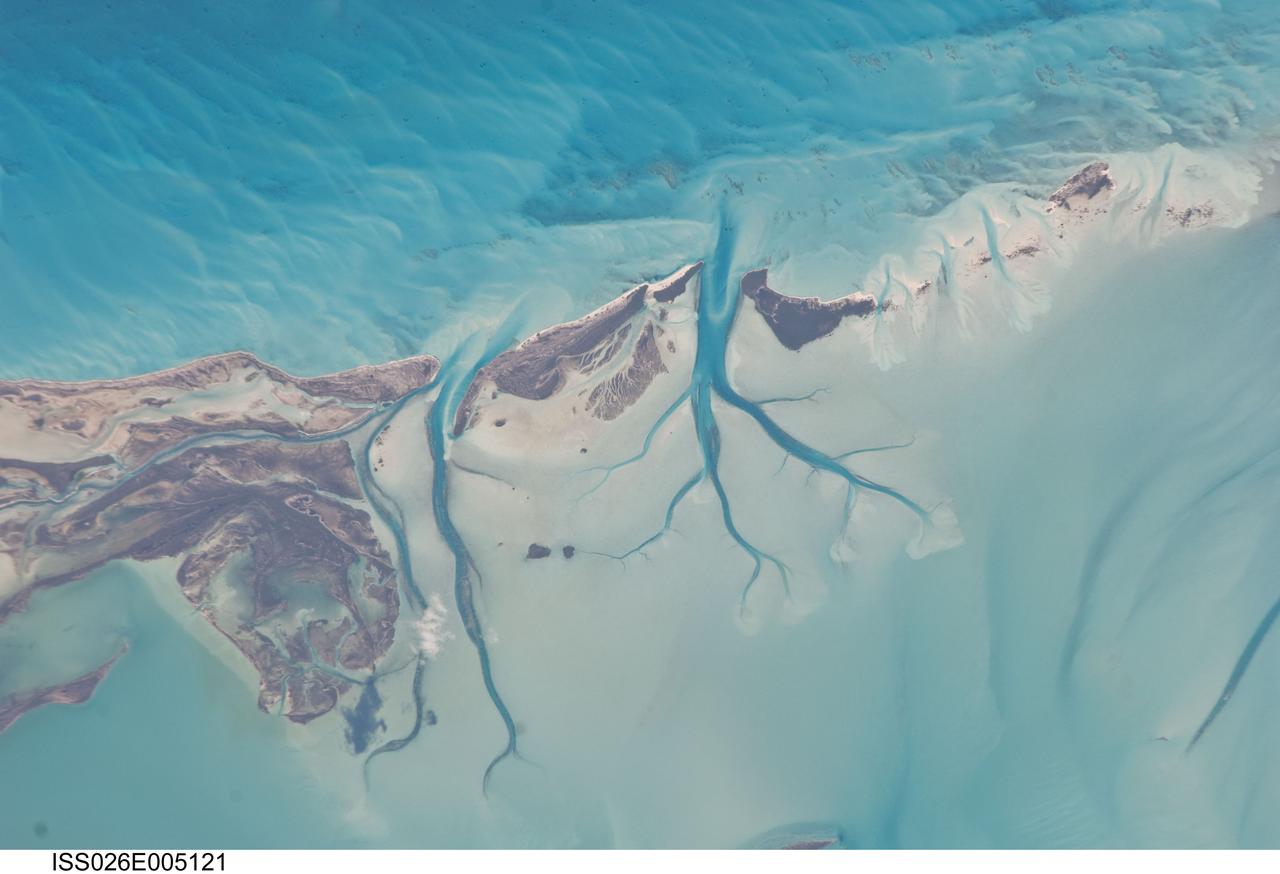
ISS026-E-005121 (27 Nov. 2010) --- Tidal flats and channels on Long Island, Bahamas are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 26 crew member on the International Space Station. The islands of the Bahamas in the Caribbean Sea are situated on large depositional platforms (the Great and Little Bahama Banks) composed mainly of carbonate sediments ringed by fringing reefs – the islands themselves are only the parts of the platform currently exposed above sea level. The sediments are formed mostly from the skeletal remains of organisms settling to the sea floor; over geologic time, these sediments will consolidate to form carbonate sedimentary rocks such as limestone. This detailed photograph provides a view of tidal flats and tidal channels near Sandy Cay on the western side of Long Island, located along the eastern margin of the Great Bahama Bank. The continually exposed parts of the island have a brown coloration in the image, a result of soil formation and vegetation growth (left). To the north of Sandy Cay an off-white tidal flat composed of carbonate sediments is visible; light blue-green regions indicate shallow water on the tidal flat. Tidal flow of seawater is concentrated through gaps in the anchored land surface, leading to formation of relatively deep tidal channels that cut into the sediments of the tidal flat. The channels, and areas to the south of the island, have a vivid blue coloration that provides a clear indication of deeper water (center).

This VIS image of Rabe Crater is dominated by the extensive dunes that cover the crater floor. To the top of the image part of the pit is visible, as well as a small peninsula that has been eroded into the upper level floor materials. On the upper elevation on the side left of the peninsula the dunes cascade onto the lower pit elevation. There is also a slight arc to the dunes on the pit floor due to how the peninsula changed the wind pattern. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 52206 Latitude: -43.6573 Longitude: 34.9551 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2013-09-20 13:07 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22142

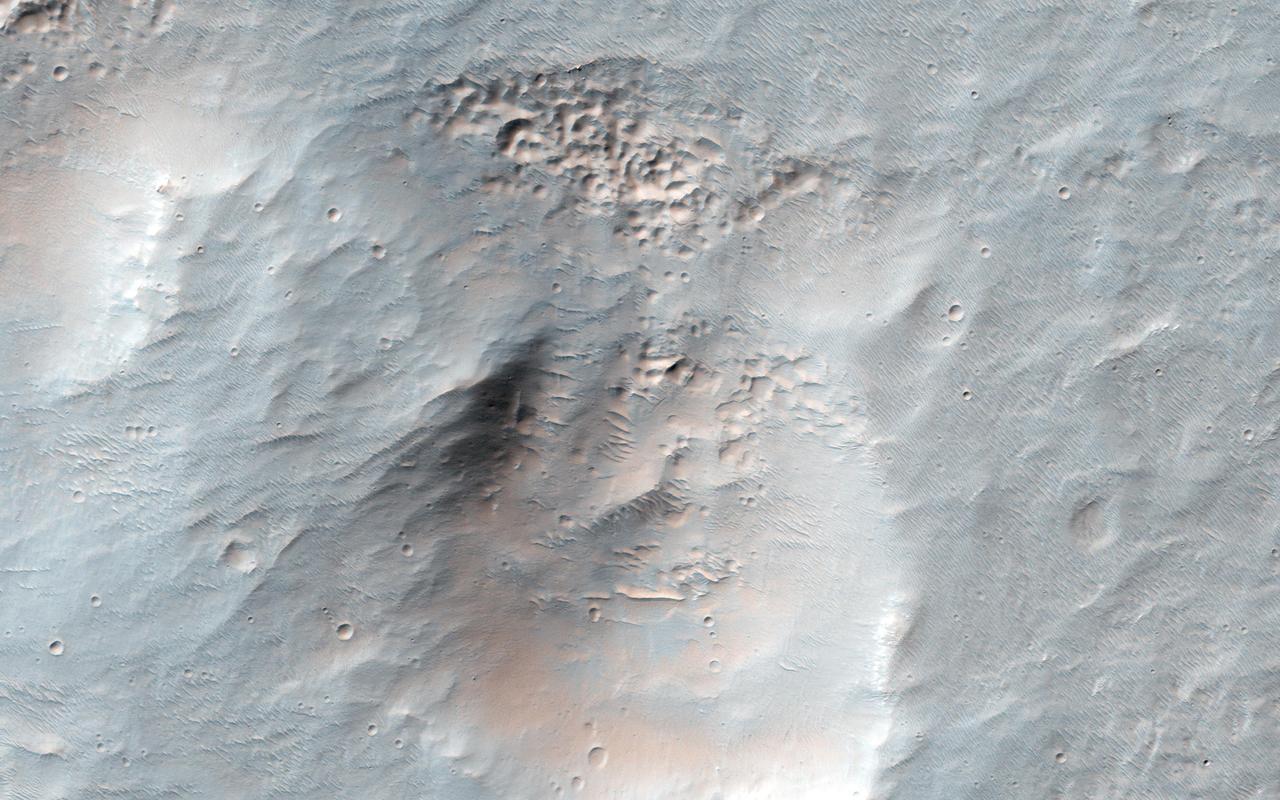
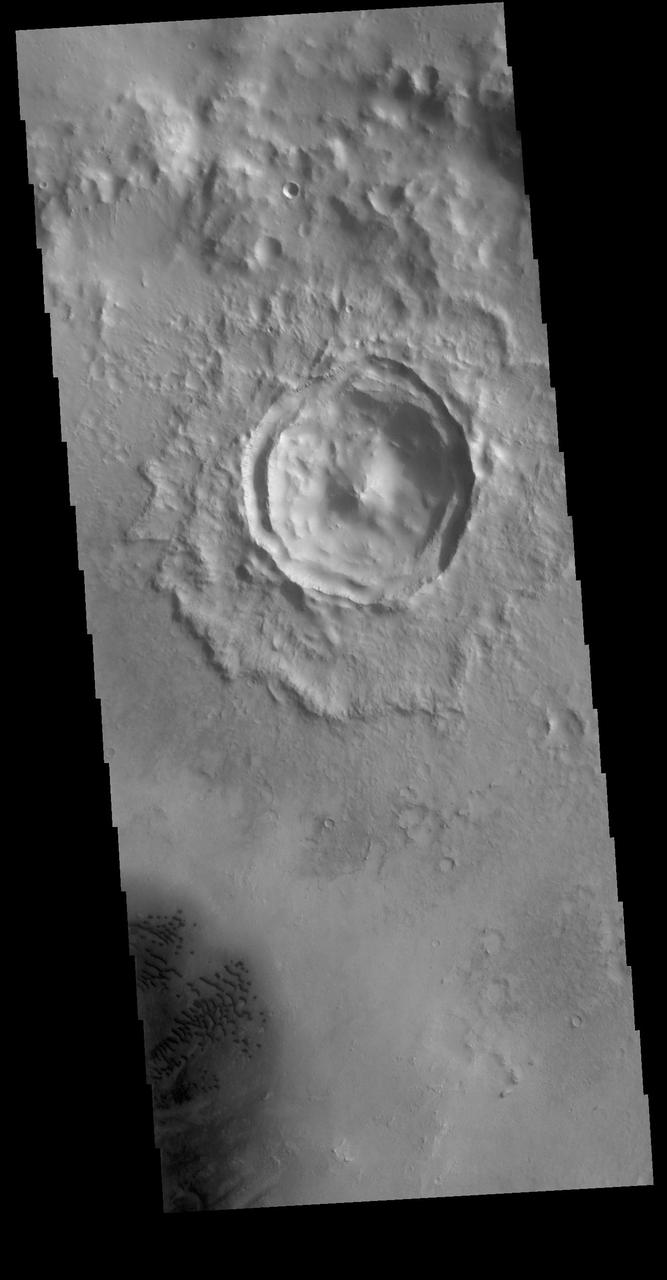
This VIS image shows an unnamed crater in Noachis Terra. The crater is relatively young, with several different structures on the floor and rim still visible. The inner rim of the crater has series of concentric benches, formed by collapse of the impacted surface into the bowl shaped interior. The crater floor is not flat, with several mounds created by rebound of melted material inside the crater. One of the more interesting features is that the crater is not round, as would be expected. The straight rims likely mean the there was a pre-existing tectonic fracture system, where the forces of the blast aligned with the fractures. Orbit Number: 72453 Latitude: -19.7034 Longitude: 317.572 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2018-04-14 23:14 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22608

Today's VIS image shows a cross section of Coprates Chasma. In this region the chasma has two sections – a deep, flat floored canyon at the top of the image, and a shallower section in the lower part of the image. The sections are divided by a large ridge. The floor of the bottom canyon is covered by large landslide deposits. Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Orbit Number: 91988 Latitude: -12.6995 Longitude: 293.287 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-09-09 13:27 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25717
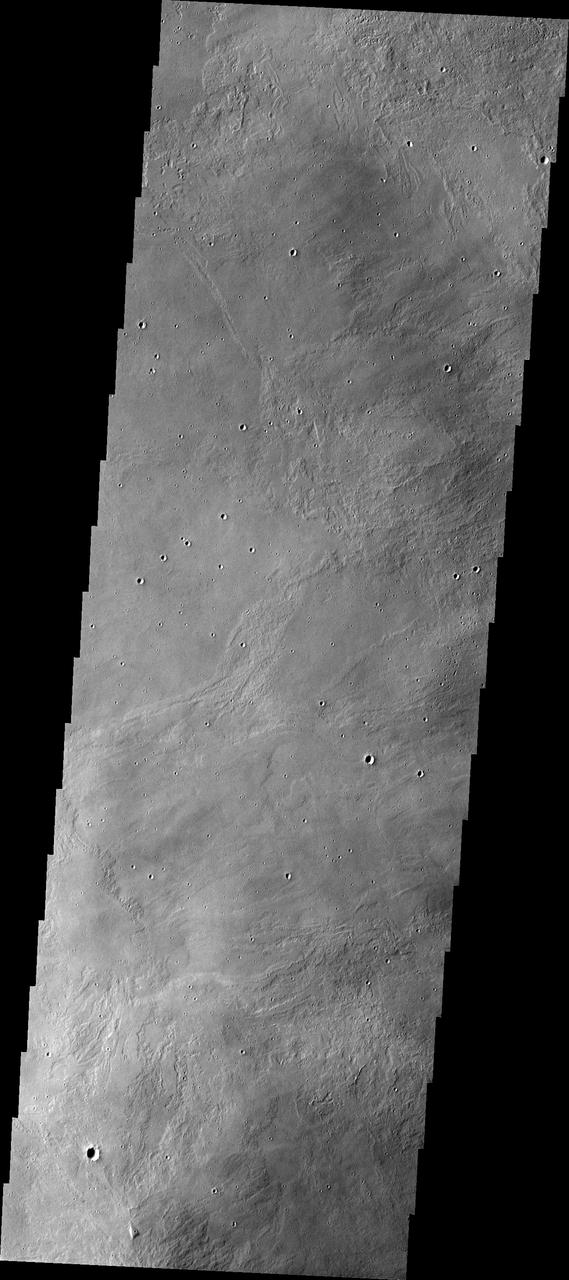

This THEMIS image shows part of the caldera floor of Arsia Mons. It is not uncommon for calderas to have "flat" floors after the final explosive eruption that empties the subsurface magma chamber. There may still be some magma or superheated rock left after the collapse that will fill in part of the depression. Additionally, over time erosion will work to level the topography. Within Arsia Mons there was renewed activity that occurred within the caldera along the alignment of the NE/SW trend of the three large volcanoes. This ongoing, low volume actitivity is similar to the lava lake in Kilauea in Hawaii. Small flows are visible throughout this image. Arsia Mons is the southernmost of the Tharsis volcanoes. It is 270 miles (450km) in diameter, almost 12 miles (20km) high, and the summit caldera is 72 miles (120km) wide. For comparison, the largest volcano on Earth is Mauna Loa. From its base on the sea floor, Mauna Loa measures only 6.3 miles high and 75 miles in diameter. A large volcanic crater known as a caldera is located at the summit of all of the Tharsis volcanoes. These calderas are produced by massive volcanic explosions and collapse. The Arsia Mons summit caldera is larger than many volcanoes on Earth. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 19588 Latitude: -9.19485 Longitude: 239.276 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2006-05-15 03:33 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22156
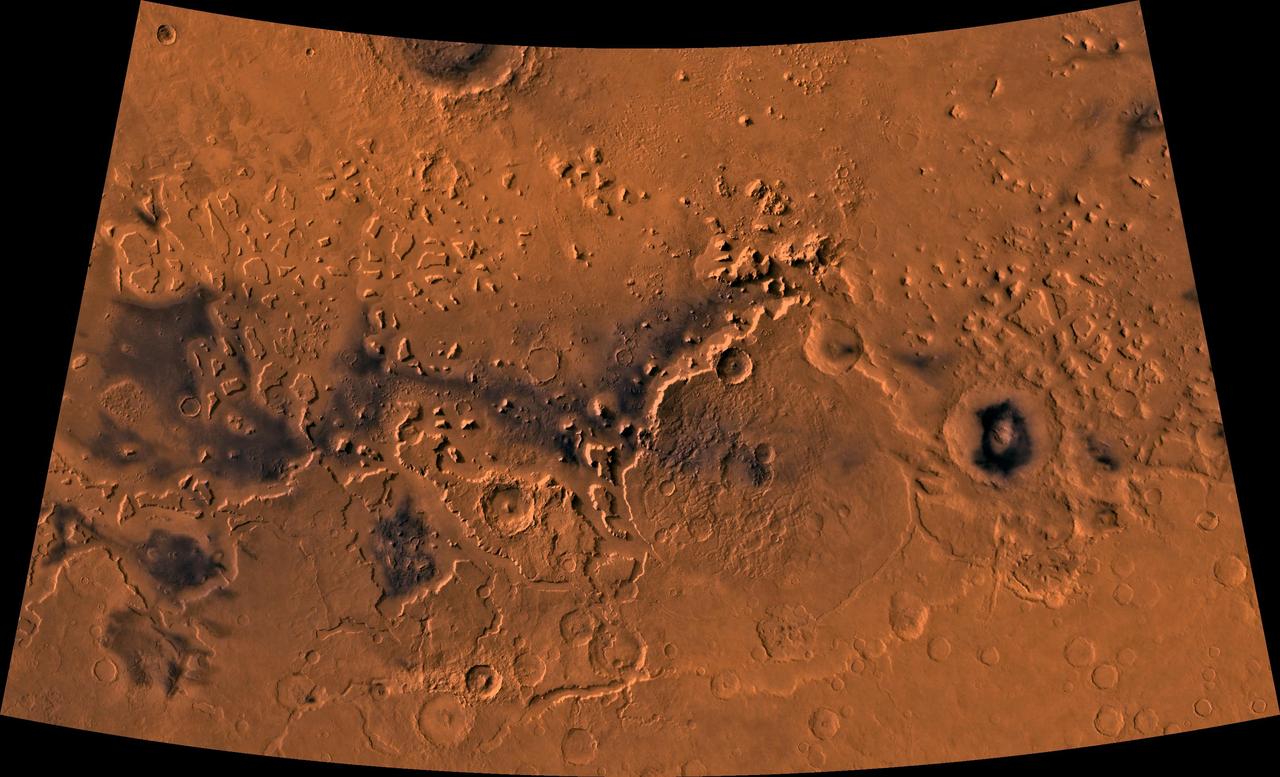
Color image of part of the Ismenius Lacus region of Mars (MC-5 quadrangle) containing the impact crater Moreux (right center); north toward top. The scene shows heavily cratered highlands in the south on relatively smooth lowland plains in the north separated by a belt of dissected terrain, containing flat-floored valleys, mesas, and buttes. This image is a composite of Viking medium-resolution images in black and white and low-resolution images in color. The image extends from latitude 36 degrees N. to 50 degrees N. and from longitude 310 degrees to 340 degrees; Lambert conformal conic projection. The dissected terrain along the highlands/lowlands boundary consists of the flat-floored valleys of Deuteronilus Mensae (on left) and Prontonilus Mensae (on right) and farther north the small, rounded hills of knobby terrain. Flows on the mensae floors contain striae that run parallel to valley walls; where valleys meet, the striae merge, similar to medial moraines on glaciers. Terraces within the valley hills have been interpreted as either layered rocks or wave terraces. The knobby terrain has been interpreted as remnants of the old, densely cratered highland terrain perhaps eroded by mass wasting. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00420
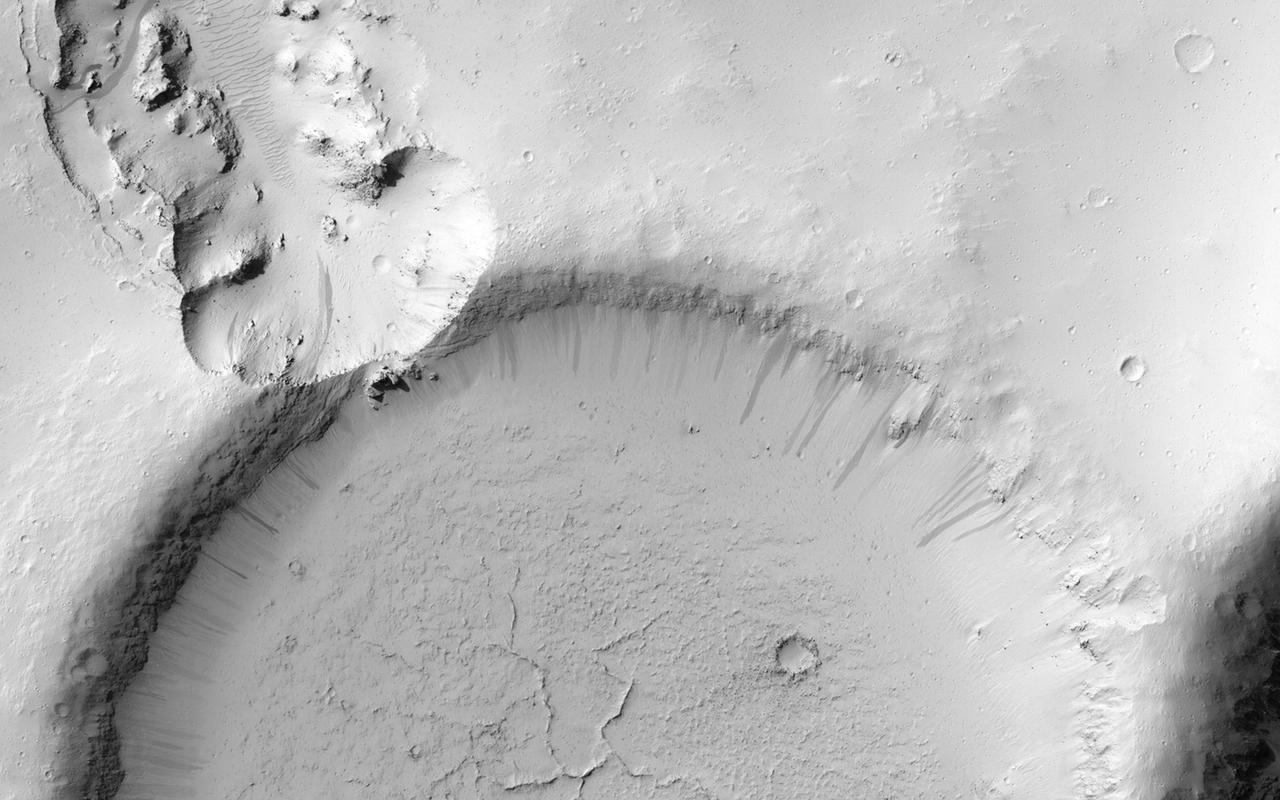

This image NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows an impact crater that was cut by lava in the Elysium Planitia region of Mars. It looks relatively flat, with a shallow floor, rough surface texture, and possible cooling cracks seem to indicate that the crater was partially filled with lava. The northern part of the image also shows a more extensive lava flow deposit that surrounds the impact ejecta of the largest impact crater in the image. Which way did the lava flow? It might appear that the lava flowed from the north through the channel into the partially filled crater. However, if you look at the anaglyph with your red and blue 3D glasses, it becomes clear that the partially filled crater sits on top of the large crater's ejecta blanket, making it higher than the lava flow to the north. Since lava does not flow uphill, that means the explanation isn't so simple. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18887
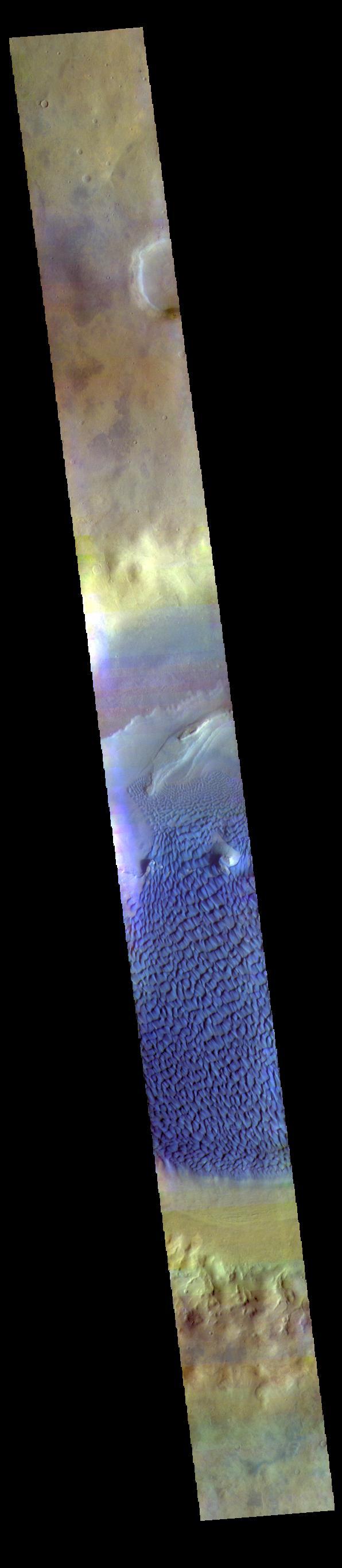

This is a false color image of Rabe Crater. In this combination of filters "blue" typically means basaltic sand. This VIS image crosses the entire crater and demonstrates how extensive the dunes are on the floor of Rabe Crater. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 67013 Latitude: -43.2572 Longitude: 34.5875 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-01-21 18:25 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22147

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Dunes cover the majority of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated more than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 83505 Latitude: -43.6272 Longitude: 34.5903 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-10-11 02:34 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24709

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Dunes cover the majority of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated more than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 67144 Latitude: -43.5512 Longitude: 34.5951 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-02-01 12:57 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24056
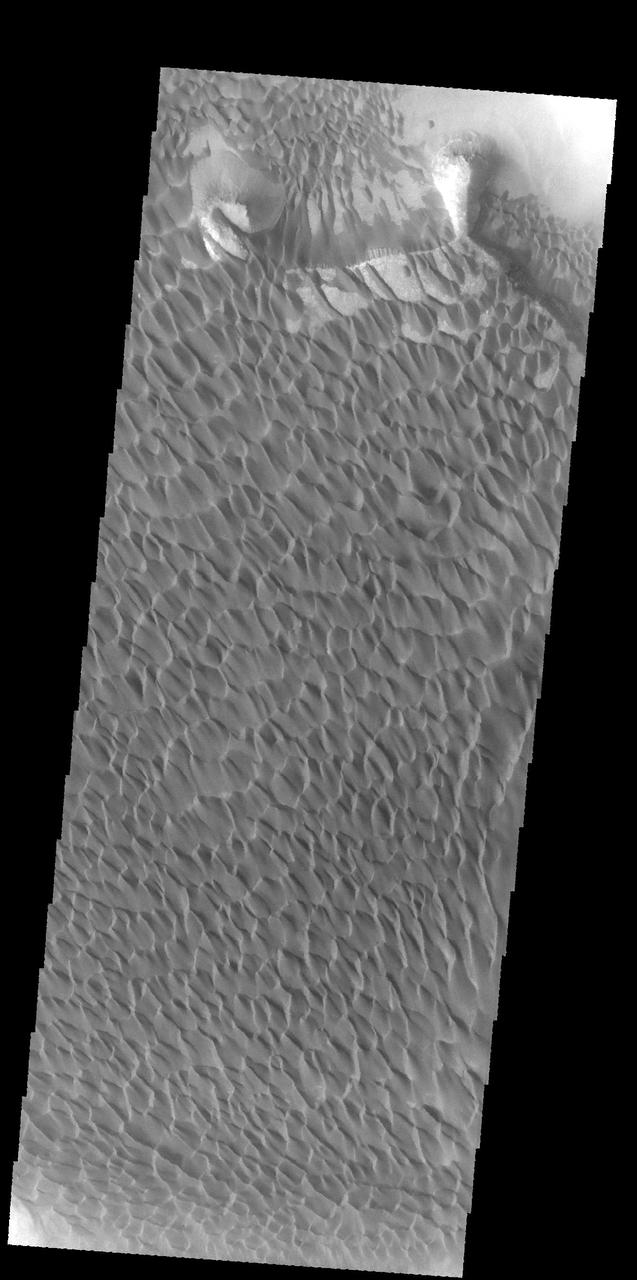

The majority of the dune field in Rabe Crater consists of a sand sheet with dune forms on the surface. The sand sheet is where a thick layer of sand has been concentrated. As continued winds blow across the sand surface it creates dune forms. The depth of the sand sheet prevents excavation to the crater floor and the dune forms all appear connected. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 58024 Latitude: -43.6954 Longitude: 34.8236 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2015-01-12 09:48 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22144
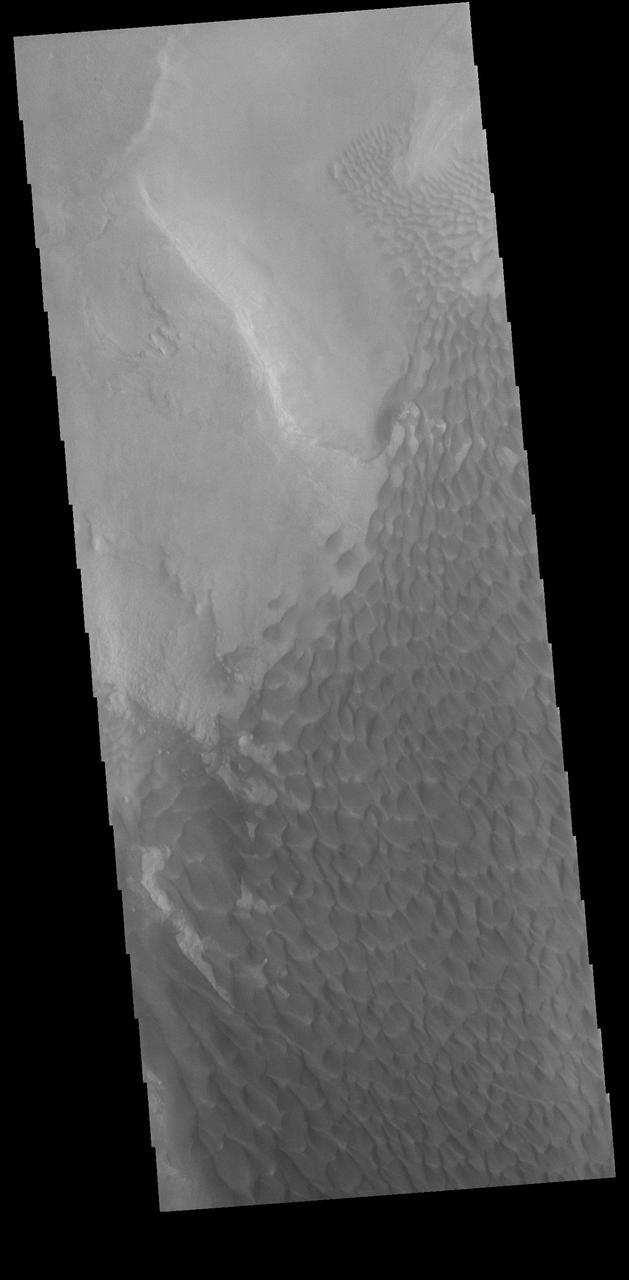

Today's VIS image shows part of the floor of Rabe Crater. Located in Noachis Terra, Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Sand dunes cover the half of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated less than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Craters of similar size as Rabe Crater often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. Several other craters in this region have complex floors with pits. Orbit Number: 89682 Latitude: -43.5957 Longitude: 34.446 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-03-03 17:05 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25458
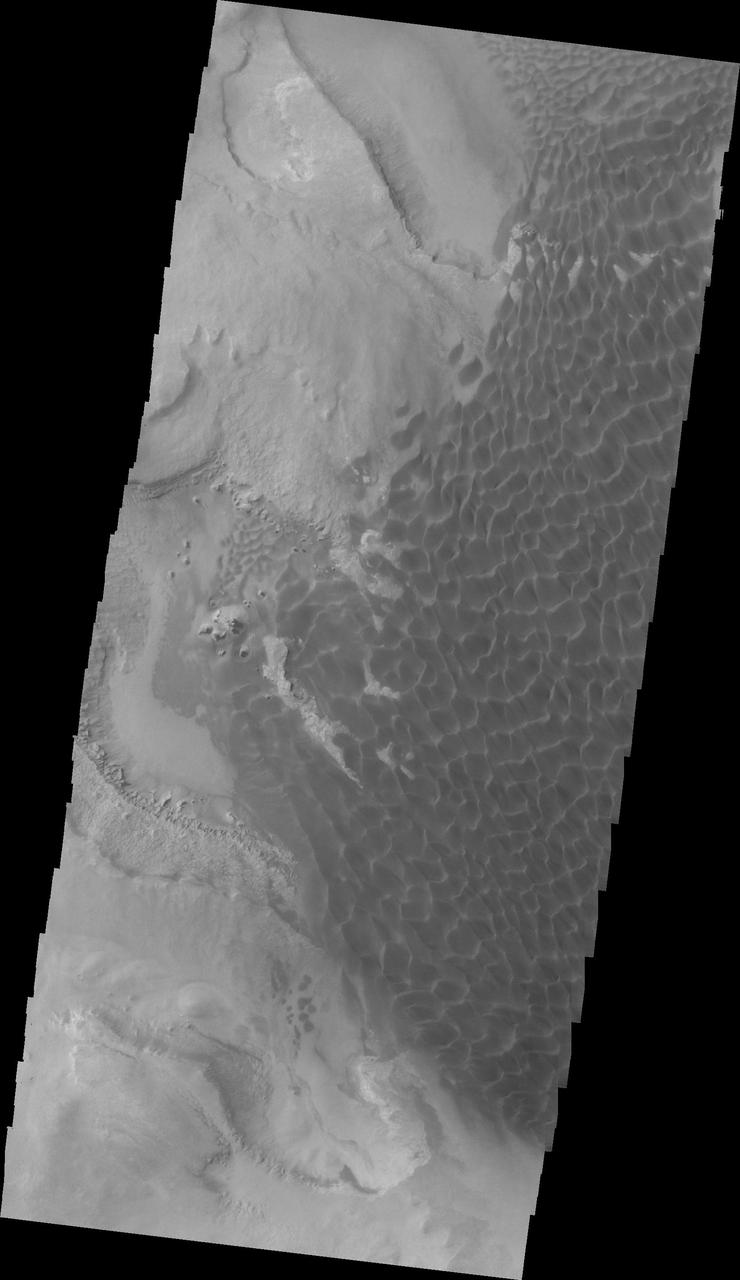

In this VIS image of the floor of Rabe Crater the step down into the pit is visible in the sinuous ridges on the left side of the image. The appearance of the exposed side of the cliffs does not look like a volcanic, difficult to erode material, but rather an easy to erode material such as layered sediments. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 34456 Latitude: -43.7164 Longitude: 34.4056 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2009-09-20 09:38 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22140
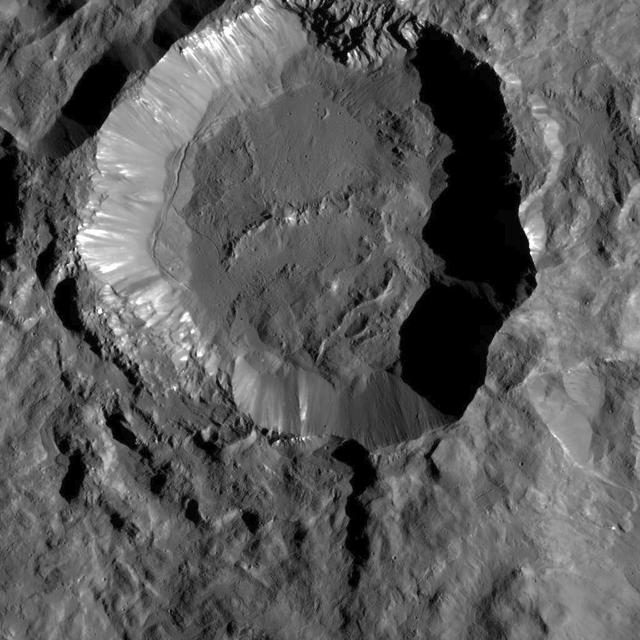

This image from NASA's Dawn spacecraft shows Kupalo Crater, one of the youngest craters on Ceres. The crater has bright material exposed on its rim and walls, which could be salts. Its flat floor likely formed from impact melt and debris. Kupalo, which measures 16 miles (26 kilometers) across and is located at southern mid-latitudes, is named for the Slavic god of vegetation and harvest. Kupalo was imaged earlier in Dawn's science mission at Ceres -- during Survey orbit (see PIA19624) and from the high altitude mapping orbit, or HAMO (see PIA20124). Dawn took this image on Dec. 21 from its low-altitude mapping orbit (LAMO) at an approximate altitude of 240 miles (385 kilometers) above Ceres. The image resolution is 120 feet (35 meters) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20192

This is a false color image of Rabe Crater. In this combination of filters "blue" typically means basaltic sand. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 67144 Latitude: -43.5512 Longitude: 34.5951 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2017-02-01 12:57 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22148
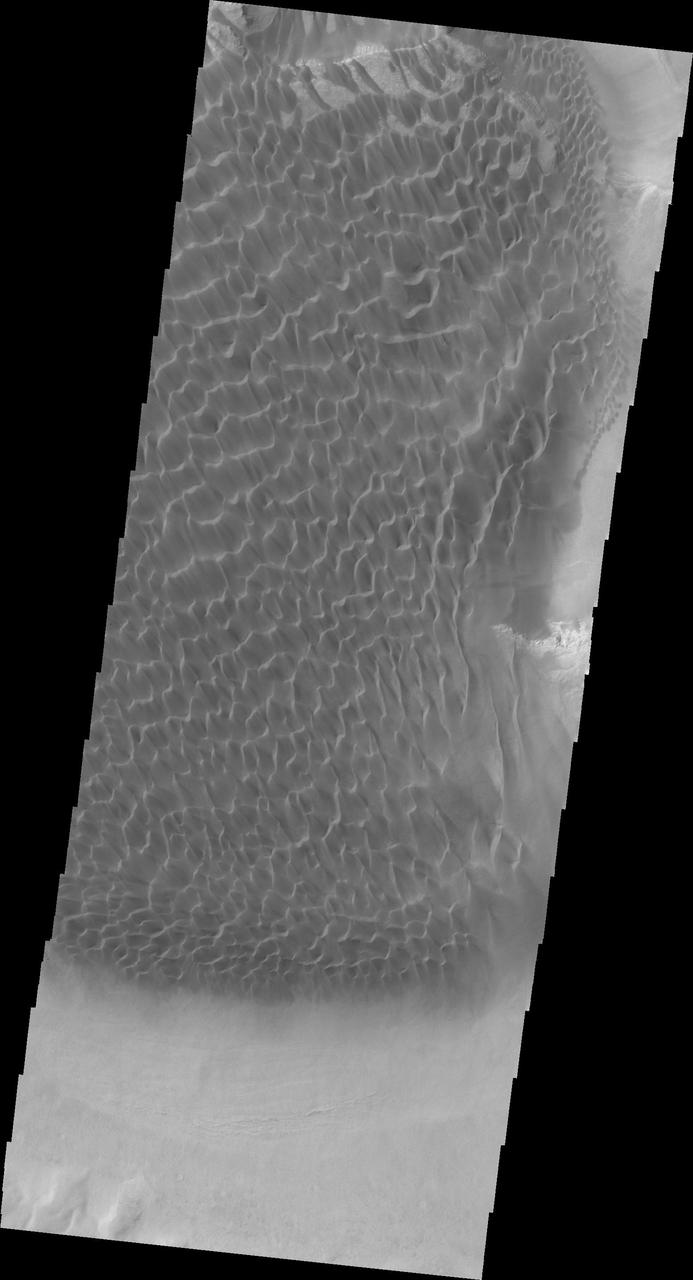
Dunes cover the majority of this image of Rabe Crater. As the dunes are created by wind action the forms of the dunes record the wind direction. Dunes will have a long low angle component and a short high angle side. The steep side is called the slip face. The wind blows up the long side of the dune. In this VIS image the slip faces are illuminated more than the longer side. In this part of the crater the winds were generally moving from the lower right corner of the image towards the upper left. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 35105 Latitude: -43.8533 Longitude: 34.8802 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2009-11-12 19:59 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22141
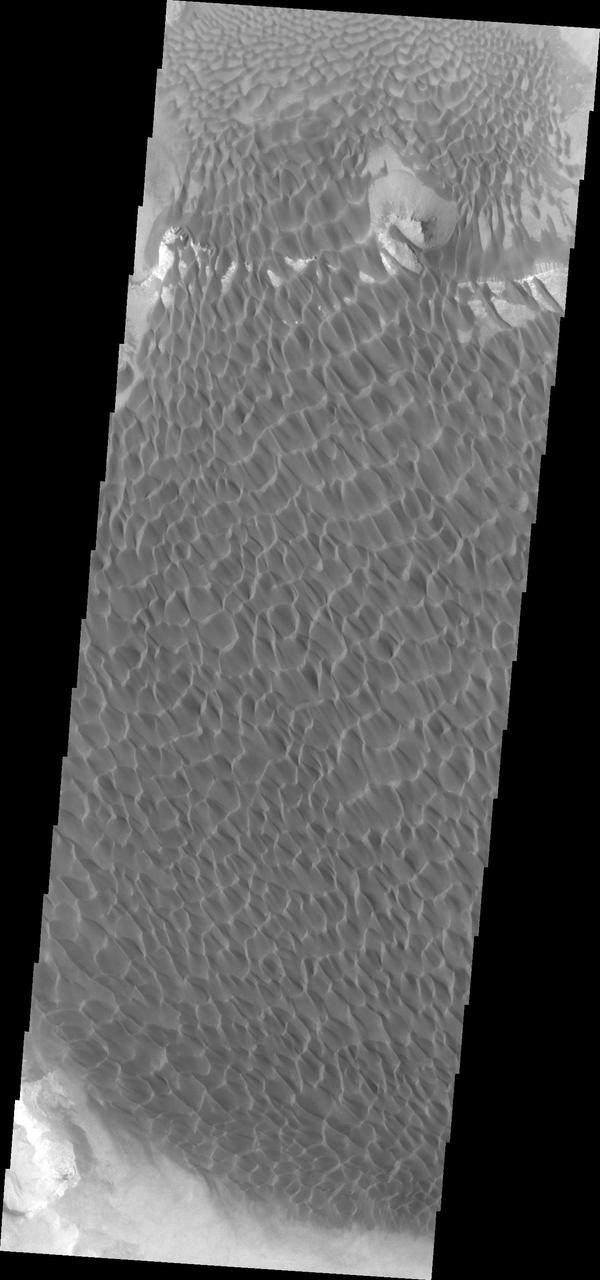
Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. In this VIS image the rim of the pit is visible near the top of the image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 17074 Latitude: -43.6954 Longitude: 34.66 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-10-20 04:05 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22139
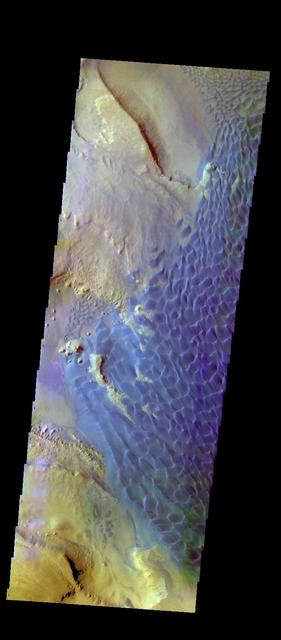
This is a false color image of Rabe Crater. In this combination of filters "blue" typically means basaltic sand. Rabe Crater is 108 km (67 miles) across. Craters of similar size often have flat floors. Rabe Crater has some areas of flat floor, but also has a large complex pit occupying a substantial part of the floor. The interior fill of the crater is thought to be layered sediments created by wind and or water action. The pit is eroded into this material. The eroded materials appear to have stayed within the crater forming a large sand sheet with surface dune forms as well as individual dunes where the crater floor is visible. The dunes also appear to be moving from the upper floor level into the pit. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 51157 Latitude: -43.6787 Longitude: 34.3985 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2013-06-26 05:33 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22145
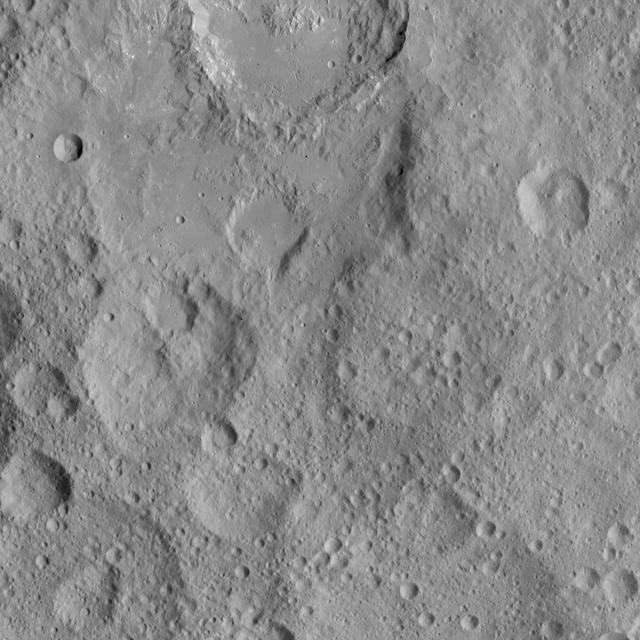

This view shows cratered terrain in the northern hemisphere of Ceres. Ikapati crater is partially cut off at the top of the scene. It appears to have flat plains in its interior that were filled by flows, and it is surrounded by smooth material and ejecta from the crater’s interior. On the crater floor are clusters of small pits, some surrounded by bright material. NASA's Dawn spacecraft took this image on Oct. 6, 2015, from an altitude of 915 miles (1,470 kilometers). It has a resolution of 450 feet (140 meters) per pixel. The image is located at 36 degrees north latitude, 43 degrees east longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20127
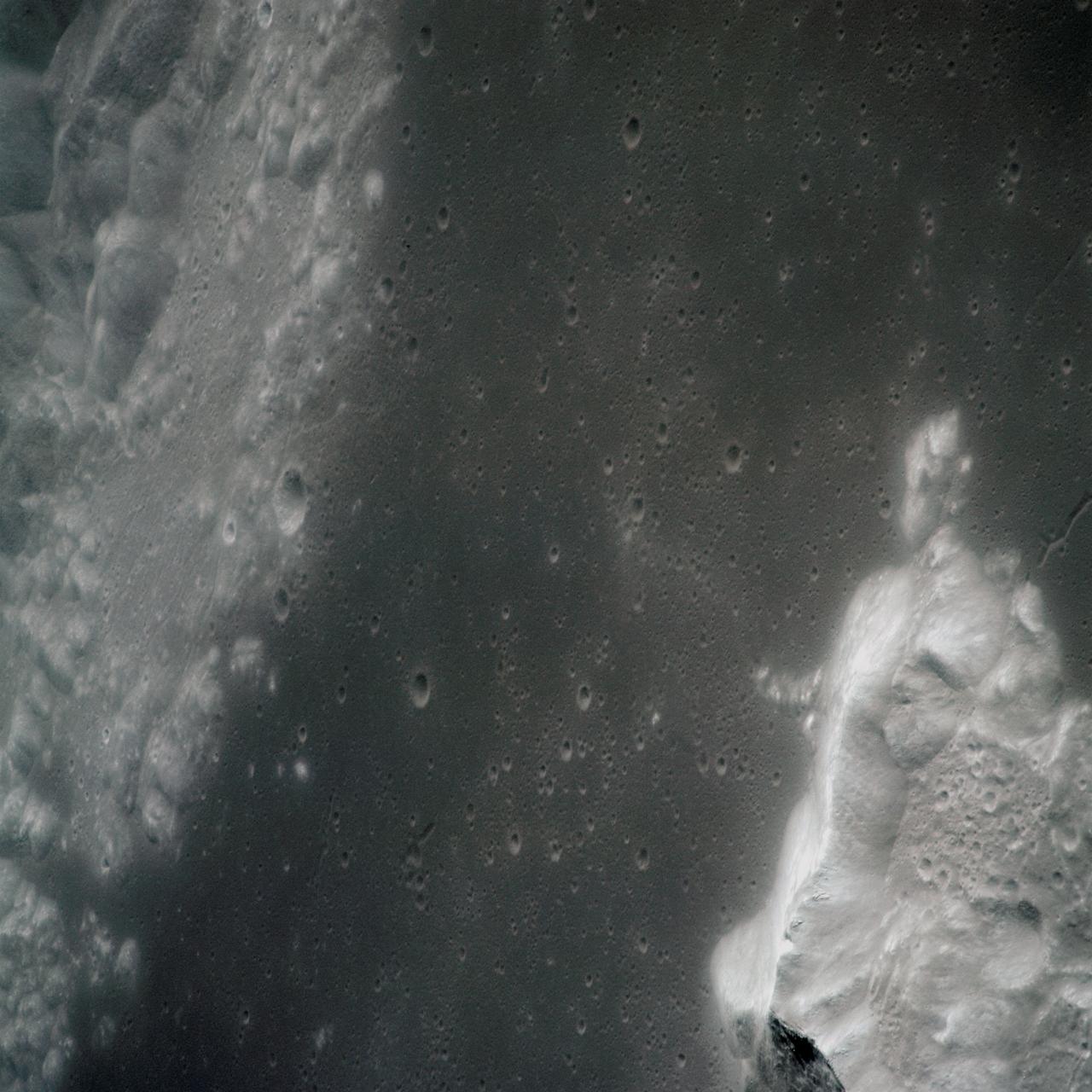

AS15-97-13160 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- A view of a portion of the crater Tsiolkovsky located in the highlands on the farside of the moon, as photographed from the Apollo 15 Command and Service Modules (CSM) by astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot. Note the dark, flat crater floor surrounding the very prominent central mountains. The mountains are in the northeastern corner of the photograph. The other upland area comprises part of the southwestern edge of the crater. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Worden remained with the CSM in lunar orbit.
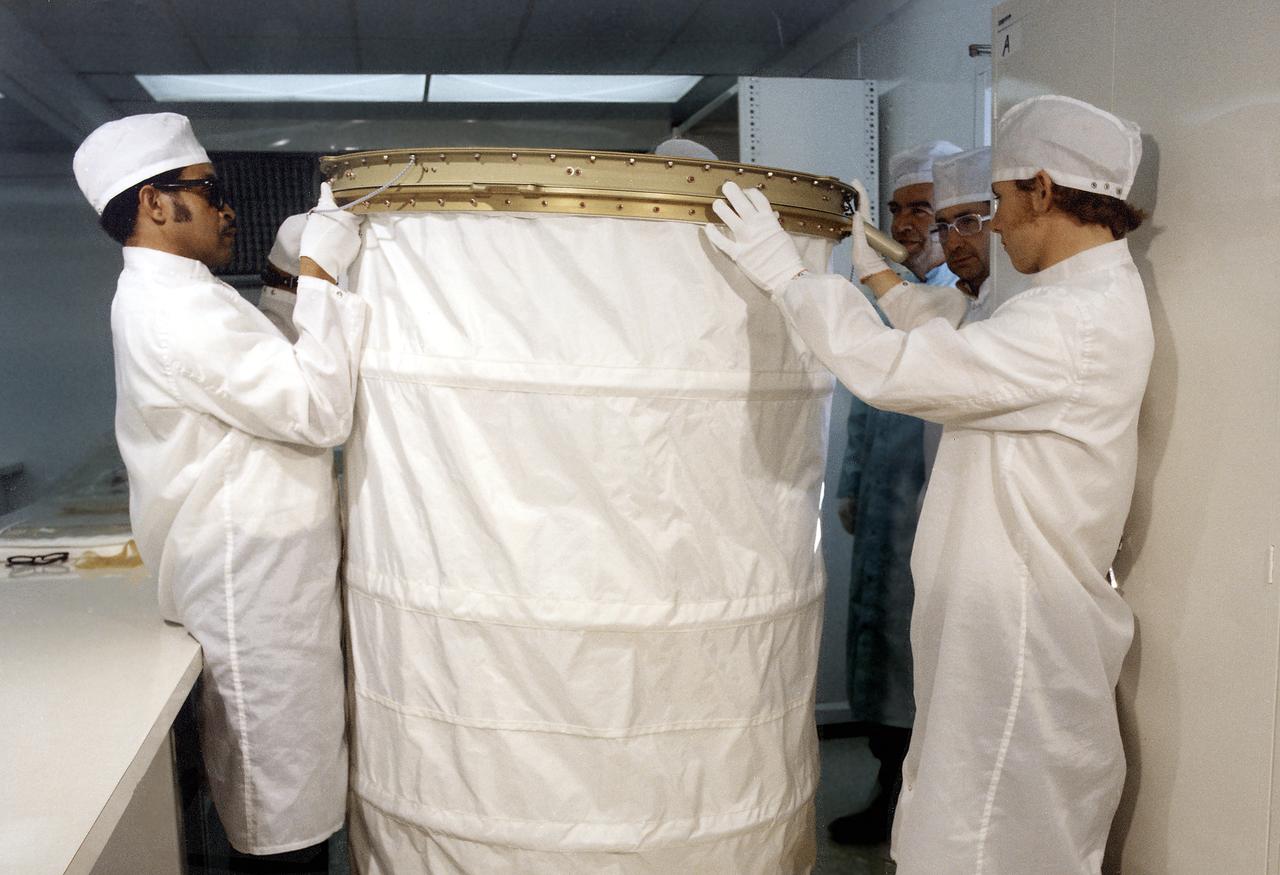

In this photograph, the Orbital Workshop shower compartment was unfolded by technicians for inspection. The shower compartment was a cylindrical cloth enclosure that was folded flat when not in use. The bottom ring of the shower was fastened to the floor and contained foot restraints. The upper ring contained the shower head and hose. To use the shower, the astronaut filled a pressurized portable bottle with heated water and attached the bottle to the ceiling. A flexible hose cornected the water bottle to a handheld shower head. The astronaut pulled the cylindrical shower wall up into position and bathed, using liquid soap. Both soap and water were carefully rationed, having been premeasured for economical use.
During orbits 423 through 424 on 22 September 1990, NASA's Magellan imaged this impact crater that is located at latitude 10.7 degrees north and longitude 340.7 degrees east. This crater is shown as a representative of Venusian craters that are of the proper diameter (about 15 kilometers) to be 'transitional' in their morphology between 'complex' and irregular' craters. Complex craters account for about 96 percent of all craters on Venus with diameters larger than about 15 kilometers; they are thought to have been formed by the impact of a large, more or less intact, mass of asteroidal material that has not been excessively effected during its passage through the dense Venusian atmosphere. Complex craters are characterized by circular rims, terraced inner wall slopes, well developed ejecta deposits, and flat floors with a central peak or peak ring. Irregular craters make up about 60 percent of the craters with diameters less than about 15 kilometers. Irregular craters are thought to form as the result of the impact of asteroidal projectiles that have been aerodynamically crushed and fragmented during their passage through the atmosphere. Irregular craters are characterized by irregular and/or discontinuous rims and hummocky or multiple floors. The 'transitional' crater shown here has a somewhat circular rim like larger complex craters, but has the hummocky floor and asymmetric ejecta characteristic of smaller irregular craters. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00468

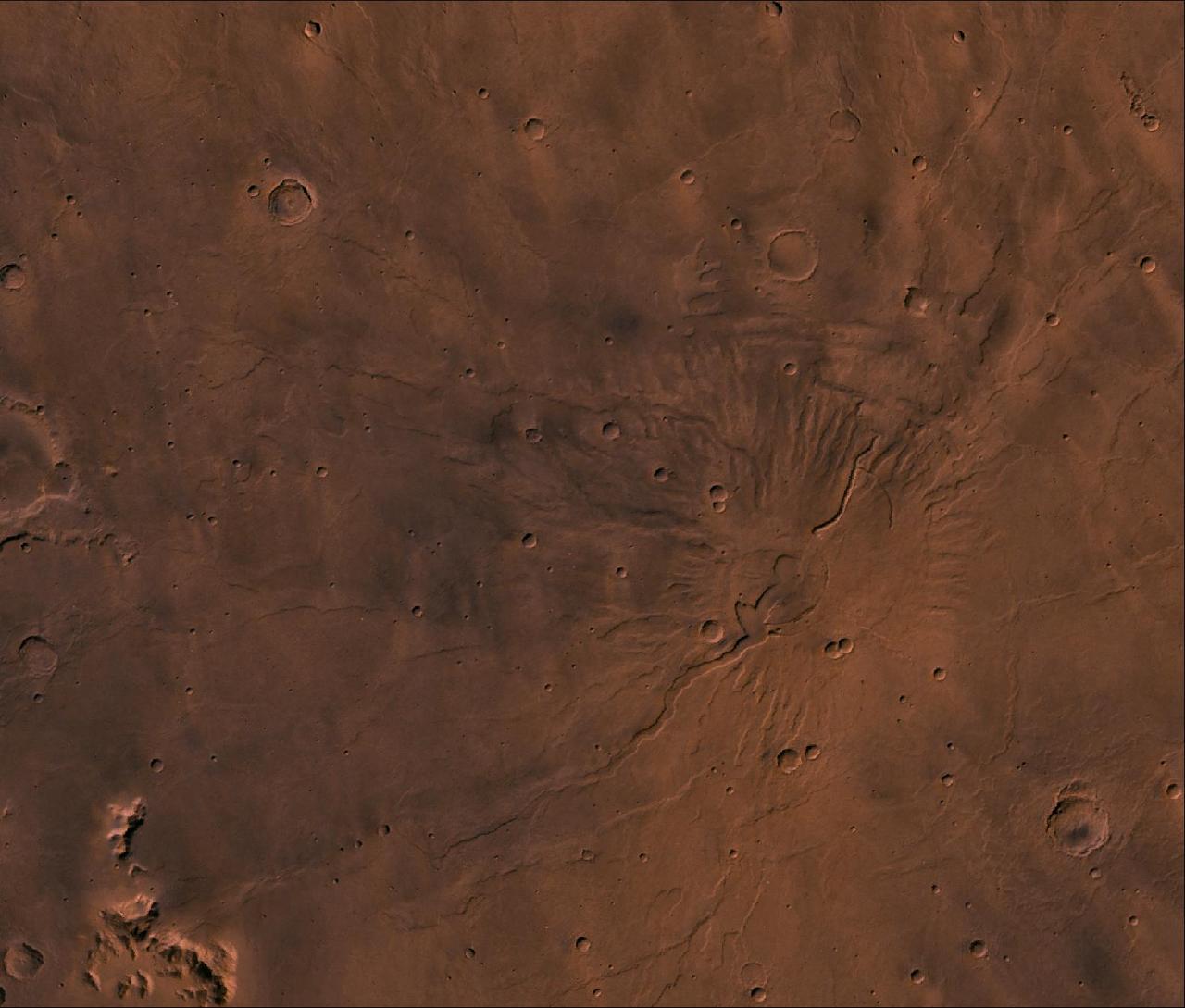
McLaughlin Crater (21.9 N, 337.6 E) is a large, approximately 95-kilometer diameter impact crater located north of Mawrth Vallis, in Arabia Terra, a region that was made famous by the book and movie "The Martian" by Andy Weir. McLaughlin Crater straddles three major terrain types: the Northern lowlands, the Southern highlands and the Mawrth Vallis region. The crater floor is thought to be covered by clays and carbonates that were deposited in a deep lake at least 3.8 billion years ago perhaps by ground water upwelling from beneath the crater floor (Michalski et al., 2013, Nature Geoscience). McLaughlin Crater is listed as a candidate landing site for the 2020 Mars surface mission. Although it is described as a "flat, low-risk and low-elevation landing zone," the region in this image on the southern floor of the crater shows a complex surface of eroded layers that are rough in places. An unusual feature is a straight fracture cutting diagonally across the layered material at the bottom portion of the image that may be a fault line. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20338
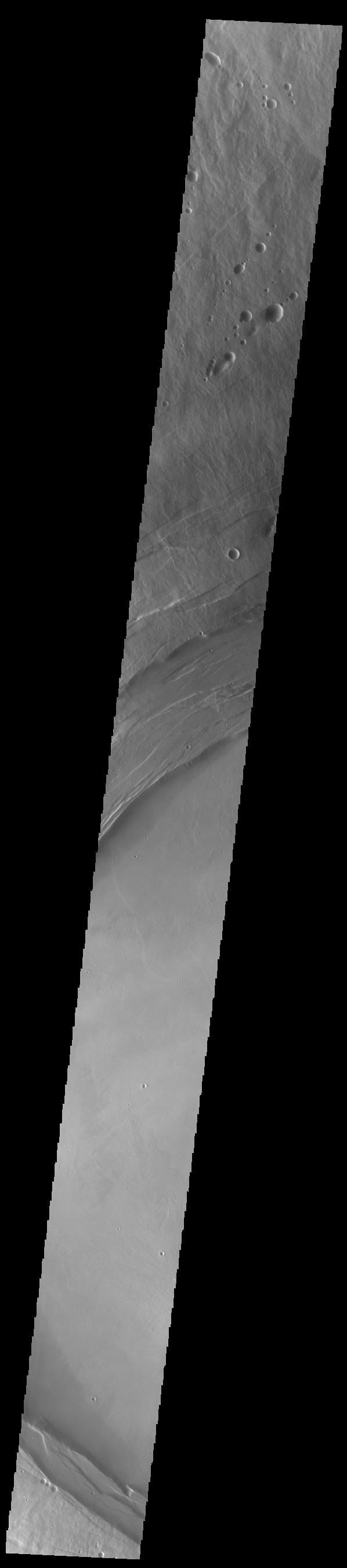

A large volcanic crater known as a caldera is located at the summit of all of the Tharsis volcanoes. These calderas are produced by massive volcanic explosions and collapse.Today's VIS image shows the summit caldera of Arsia Mons. Several small volcanic vents are visible on the caldera floor. It is not uncommon for calderas to have "flat" floors after the final explosive eruption the empties the subsurface magma chamber. There may still be some magma or superheated rock left after the collapse that will fill in part of the depression. Additionally, over time erosion will work to level the topography. Within the Arsia Mons caldera there was renewed activity from several small vents that occurred along the alignment of the NE/SW trend of the three large volcanoes. This ongoing, low volume activity is similar to the lava lake in Kilauea in Hawaii. Arsia Mons is the southernmost of the Tharsis volcanoes. It is 450 km (270 miles) in diameter, almost 20 km (12 miles) high, and the summit caldera is 120 km (72 miles) wide. For comparison, the largest volcano on Earth is Mauna Loa. From its base on the sea floor, Mauna Loa measures only 6.3 miles high and 75 miles in diameter.The Arsia Mons summit caldera is larger than many volcanoes on Earth. Orbit Number: 84328 Latitude: -8.58304 Longitude: 239.166 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-12-17 20:11 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24393

Today's VIS image shows a cross section of Coprates Chasma. In this region the chasma has two sections – a deep, flat floored canyon at the top of the image (the northern cliff face is not visible in this image), and the second section below that separated by a large ridge. Paralleling it to the south runs a narrower and shallower chain of linked pits and depressions called Coprates Catena. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. The brighter materials at the top of the image are layered deposits. It is unknown how deep these canyon deposits were when they formed. The layering is only visible due to erosion, making it difficult to estimate the original thickness. While layered deposits can be found on the floor of Coprates Chasma, they are most commonly found along the lower elevations and at the bottom of the cliff faces in the canyon. Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Orbit Number: 93111 Latitude: -14.0758 Longitude: 295.079 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-12-11 00:40 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25816

This image shows a bright, rectangular-looking landform surrounded by a dark floor. How did this feature get here if it looks so different than its surroundings? The feature resembles a plateau. Dark streaks mark steep slopes on its sides while the top appears flat. The slope streaks are not all the same age, as we see a variation in colors from faint to dark. Craters in a variety of sizes and ages pepper the entire rectangle, but the dark, textured floor has very few noticeable craters. The evidence suggests that this rectangular feature is a high-standing "island" of older land surrounded by one or more younger lava flows. This landmass is located in Amazonis Planitia, a smooth plains area potentially formed by large-scale lava floods between the Tharsis and Elysium volcanic regions. As lava flowed into this area, the rectangular plateau was too high to cover completely, leaving a bright spot sticking out of the dark basalt floor for us to find. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22725

A large volcanic crater known as a caldera is located at the summit of all of the Tharsis volcanoes. These calderas are produced by massive volcanic explosions and collapse.Today's VIS image shows the summit caldera of Arsia Mons. Several small volcanic vents are visible on the caldera floor. It is not uncommon for calderas to have "flat" floors after the final explosive eruption the empties the subsurface magma chamber. There may still be some magma or superheated rock left after the collapse that will fill in part of the depression. Additionally, over time erosion will work to level the topography. Within the Arsia Mons caldera there was renewed activity from several small vents that occurred along the alignment of the NE/SW trend of the three large volcanoes. This ongoing, low volume activity is similar to the lava lake in Kilauea in Hawaii. Arsia Mons is the southernmost of the Tharsis volcanoes. It is 450 km (270 miles) in diameter, almost 20 km (12 miles) high, and the summit caldera is 120 km (72 miles) wide. For comparison, the largest volcano on Earth is Mauna Loa. From its base on the sea floor, Mauna Loa measures only 6.3 miles high and 75 miles in diameter.The Arsia Mons summit caldera is larger than many volcanoes on Earth. Orbit Number: 79230 Latitude: -9.4441 Longitude: 239.984 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2019-10-25 02:43 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23639

This image shows part of the two summit calderas of Pavonis Mons. The surface in the majority of the image is the floor of the larger caldera. The smaller caldera occupies the bottom of the image. In both calderas the floor is predominately flat. The final summit flow would have pooled in the caldera and cooled forming the flat floor. Pavonis Mons is one of the three aligned Tharsis Volcanoes. The four Tharsis volcanoes are Ascreaus Mons, Pavonis Mons, Arsia Mons, and Olympus Mars. All four are shield type volcanoes. Shield volcanoes are formed by lava flows originating near or at the summit, building up layers upon layers of lava. The Hawaiian islands on Earth are shield volcanoes. The three aligned volcanoes are located along a topographic rise in the Tharsis region. Along this trend there are increased tectonic features and additional lava flows. Pavonis Mons is the smallest of the four volcanoes, rising 14km above the mean Mars surface level with a width of 375km. It has a complex summit caldera, with the smallest caldera deeper than the larger caldera. Like most shield volcanoes the surface has a low profile. In the case of Pavonis Mons the average slope is only 4 degrees. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 17590 Latitude: 1.13446 Longitude: 247.411 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-12-01 17:26 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22020

A color image of the Tyrrhena Patera Region of Mars; north toward top. The scene shows a central circular depression surrounded by circular fractures and highly dissected horizontal sheets. A patera (Latin for shallow dish or saucer) is a volcano of broad areal extent with little vertical relief. This image is a composite of Viking medium-resolution images in black and white and low-resolution images in color. The image extends from latitude 17 degrees S. to 25 degrees S. and from longitude 250 degrees to 260 degrees; Mercator projection. Tyrrhena Patera has a 12-km-diameter caldera at its center surrounded by a 45-km-diameter fracture ring. Around the fracture ring, the terrain is highly eroded forming ragged outward-facing cliffs, as though successive flat-lying layers had been eroded back. Cut into the sequence are several flat-floored channels that extend outward as far as 200 km from the center of the volcano. The structure may be composed of highly erodible ash layers and the channels may be fluvial, with the release of water being triggered by volcanic activity (Carr, 1981, The surface of Mars, Yale Univ. Press, New Haven, 232 p.). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00421
![Hellas is an ancient impact structure and is the deepest and broadest enclosed basin on Mars. It measures about 2,300 kilometers across and the floor of the basin, Hellas Planitia, contains the lowest elevations on Mars. The Hellas region can often be difficult to view from orbit due to seasonal frost, water-ice clouds and dust storms, yet this region is intriguing because of its diverse, and oftentimes bizarre, landforms. This image from eastern Hellas Planitia shows some of the unusual features on the basin floor. These relatively flat-lying "cells" appear to have concentric layers or bands, similar to a honeycomb. This "honeycomb" terrain exists elsewhere in Hellas, but the geologic process responsible for creating these features remains unresolved. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 52.2 centimeters (20.6 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 157 centimeters (61.8 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21570](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA21570/PIA21570~medium.jpg)
Hellas is an ancient impact structure and is the deepest and broadest enclosed basin on Mars. It measures about 2,300 kilometers across and the floor of the basin, Hellas Planitia, contains the lowest elevations on Mars. The Hellas region can often be difficult to view from orbit due to seasonal frost, water-ice clouds and dust storms, yet this region is intriguing because of its diverse, and oftentimes bizarre, landforms. This image from eastern Hellas Planitia shows some of the unusual features on the basin floor. These relatively flat-lying "cells" appear to have concentric layers or bands, similar to a honeycomb. This "honeycomb" terrain exists elsewhere in Hellas, but the geologic process responsible for creating these features remains unresolved. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 52.2 centimeters (20.6 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 157 centimeters (61.8 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21570
![Holden Crater in southern Margaritifer Terra displays a series of finely layered deposits on its floor. The layered deposits are especially well exposed in the southwestern section of the crater where erosion by water flowing through a breach in the crater rim created spectacular outcrops. In this location, the deposits appear beneath a cap of alluvial fan materials (tan to brown in this image). Within the deposits, individual layers are nearly flat-lying and can be traced for hundreds of meters to kilometers. Information from the CRISM instrument on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter suggests that at least some of these beds contain clays. By contrast, the beds in the overlying alluvial fan are less continuous and dip in varying directions, showing less evidence for clays. Collectively, the characteristics of the finely bedded deposits suggest they may have been deposited into a lake on the crater floor, perhaps fed by runoff related to formation of the overlying fans. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 25.9 centimeters (10.2 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 78 centimeters (30.7 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21561](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA21561/PIA21561~medium.jpg)
Holden Crater in southern Margaritifer Terra displays a series of finely layered deposits on its floor. The layered deposits are especially well exposed in the southwestern section of the crater where erosion by water flowing through a breach in the crater rim created spectacular outcrops. In this location, the deposits appear beneath a cap of alluvial fan materials (tan to brown in this image). Within the deposits, individual layers are nearly flat-lying and can be traced for hundreds of meters to kilometers. Information from the CRISM instrument on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter suggests that at least some of these beds contain clays. By contrast, the beds in the overlying alluvial fan are less continuous and dip in varying directions, showing less evidence for clays. Collectively, the characteristics of the finely bedded deposits suggest they may have been deposited into a lake on the crater floor, perhaps fed by runoff related to formation of the overlying fans. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 25.9 centimeters (10.2 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 78 centimeters (30.7 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21561

Today's VIS image shows part of an unnamed crater in Aonia Terra. At the top of the image numerous gullies dissect the crater rim. These channels are called gullies due to being on a steep slope rather than a flat river plain. In some images it is possible to see a boundary layer between the upper incised gully and a lower deposition region. The boundary marks a change in slope, the steep upper portion supports fast moving fluid that carves into the rim, eroding materials. The change to a flatter slope causes the fluid to slow down and as it slows the materials carried by the fluid are deposited. Sand dunes cover part of the crater floor. Orbit Number: 91821 Latitude: -52.412 Longitude: 246.698 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-08-26 20:03 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25648

Today's image shows an unnamed crater located in Arabia Terra. The small crater seen in the image is located on the floor of a much larger crater. The details visible in the crater indicate that it is a relatively youthful crater exhibiting pre-erosion morphology. This crater shape is a central peak with two rims that are close together. The inner ring is actually part of the original rim that slumped downward during the impact event. The inner rim is mostly a flat terrace, giving this a crater morphology type the name terraced wall crater. Small dark dunes are visible in the lower left corner of the image. Orbit Number: 78901 Latitude: 10.8884 Longitude: 9.16256 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2019-09-28 00:39 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23537
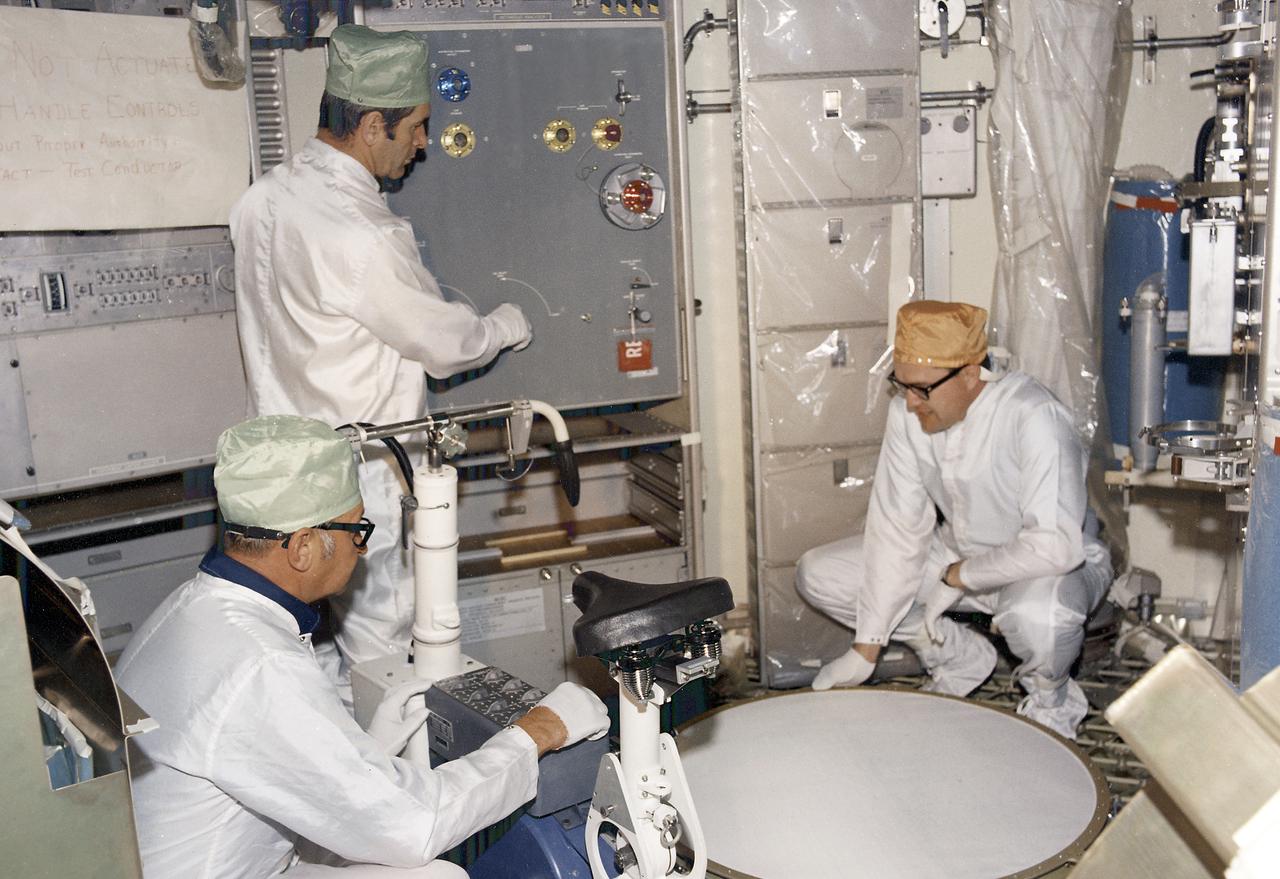

This photograph shows technicians performing a checkout of the Metabolic Analyzer (center background) and the Ergometer (foreground) in the Orbital Workshop (OWS). The shower compartment is at right. The Ergometer (Skylab Experiment M171) evaluated man's metabolic effectiveness and cost of work in space environment. Located in the experiment and work area of the OWS, the shower compartment was a cylindrical cloth enclosure that was folded flat when not in use. The bottom ring of the shower was fastened to the floor and contained foot restraints. The upper ring contained the shower head and hose. To use the shower, the astronaut filled a pressurized portable bottle with heated water and attached the bottle to the ceiling. A flexible hose cornected the water bottle to a handheld shower head. The astronaut pulled the cylindrical shower wall up into position and bathed, using liquid soap. Both soap and water were carefully rationed, having been premeasured for economical use.
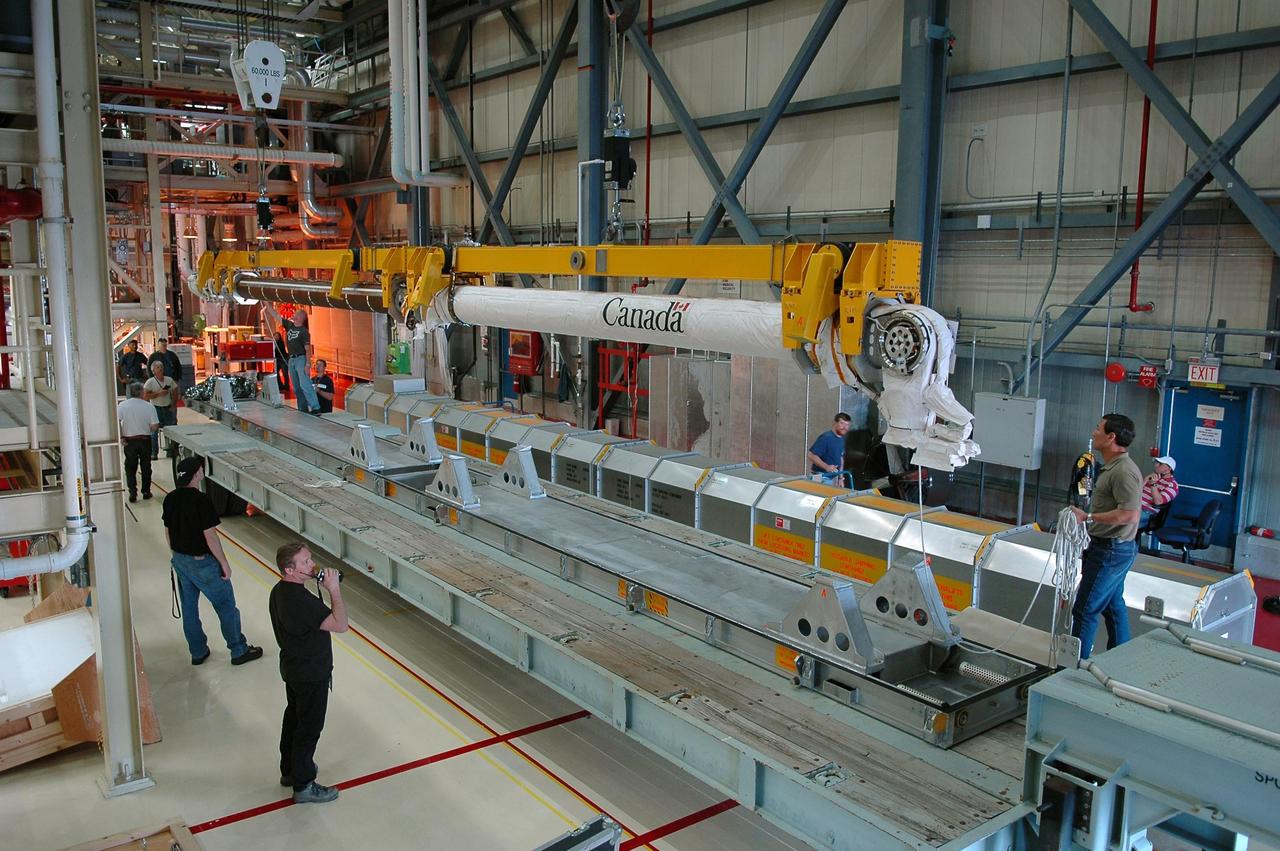

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers lower Discovery's robotic arm onto a flat bed in a work area. The arm was removed from Discovery's payload bay. The arm was removed due to damage found on the arm after it was accidentally bumped by a bridge bucket in the payload bay. Ultrasound inspections revealed a small crack, measuring 1.25 inches by 0.015 inch deep. The arm will be sent back to the vendor for repair. The bucket was being used by technicians cleaning the area and was in the process of being stowed. A bridge bucket is a personnel transport device that is suspended from an overhead bridge that moves back and forth above the shuttle's mid-body. It allows workers to access the payload bay area without walking or standing on the payload bay floor or on the fixed platforms. Space Shuttle Discovery is scheduled for launch on mission STS-121 during a launch planning window of July 1-19. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

This image of the floor of Jezero Crater was taken by one of the Navcam imagers aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover on Feb. 5, 2023, the 698th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The rover's tracks can be seen disappearing into the distance. The flat-topped hill that the science team refers to as "Kodiak," a remnant of Jezero Crater's river delta, is in the upper right of image, about 0.6 miles (1 kilometer) away. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25684
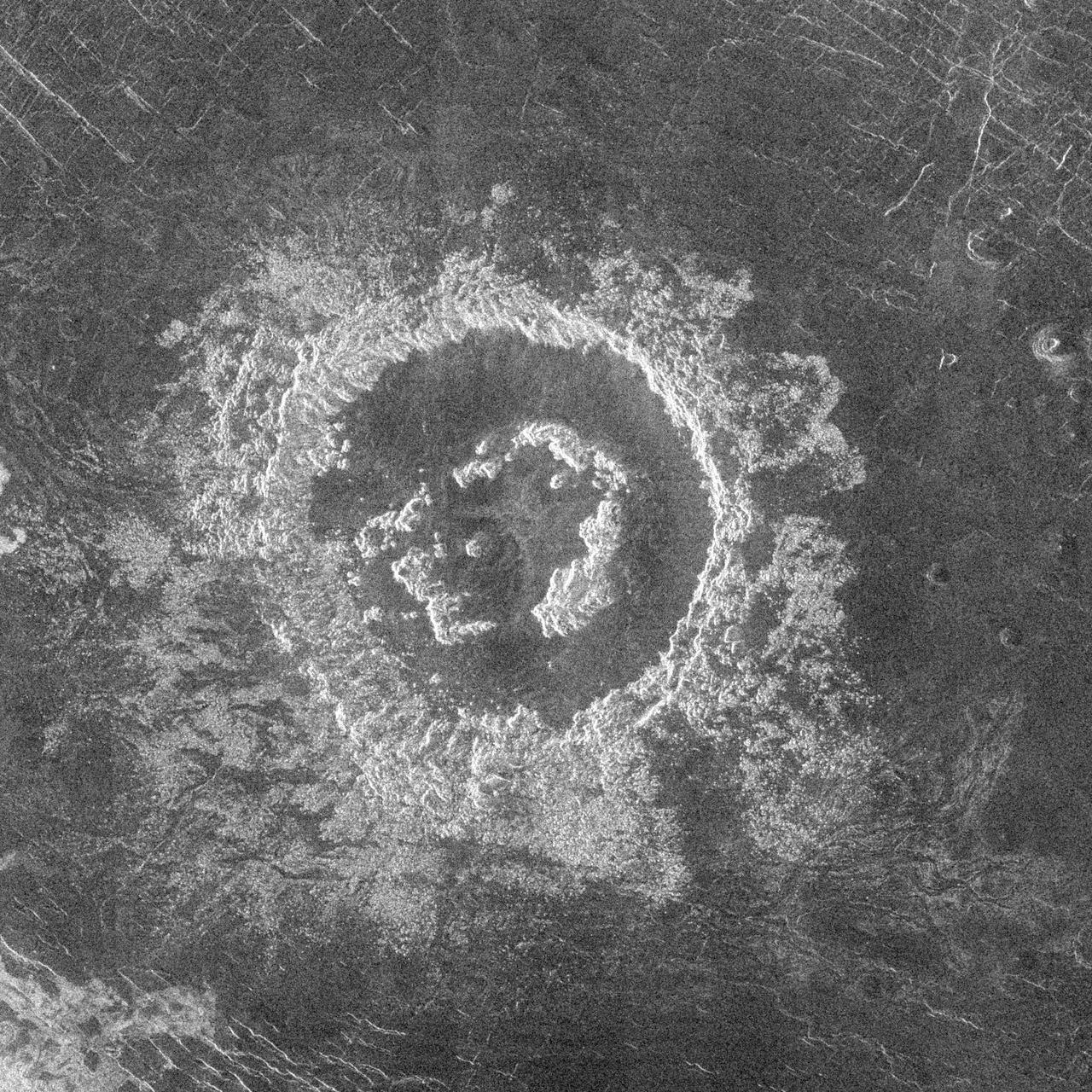
During orbits 404 through 414 on 19-20 September 1990, NASA's Magellan imaged a peak-ring crater that is 50 kilometers in diameter located at latitude 27.4 degrees north and longitude 337.5 degrees east. The name Barton has been proposed by the Magellan Science Team for this crater, after Clara Barton, founder of the Red Cross; however, the name is tentative pending approval by the International Astronomical Union. Barton is just at the diameter size that Venus craters appear to begin to possess peak-rings instead of a single central peak or central peak complex like does 75 percent of the craters with diameters between 50 and about 15 kilometers. The floor of the crater is flat and radar-dark, indicating possible infilling by volcanic deposits sometime following the impact event. Barton's central peak ring is discontinuous and appears to have been disrupted or separated during or following the cratering process. The extremely blocky crater deposits (ejecta) surrounding Barton appear to be most extensive on the southwest to southeast (lower left to right) side of the crater. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00463

This image from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows a location on Mars associated with the best-selling novel and Hollywood movie, "The Martian." It is the science-fiction tale's planned landing site for the Ares 4 mission. The novel placed the Ares 4 site on the floor of a very shallow crater in the southwestern corner of Schiaparelli Crater. This HiRISE image shows a flat region there entirely mantled by bright Martian dust. There are no color variations, just uniform reddish dust. A pervasive, pitted texture visible at full resolution is characteristic of many dust deposits on Mars. No boulders are visible, so the dust is probably at least a meter thick. Past Martian rover and lander missions from NASA have avoided such pervasively dust-covered regions for two reasons. First, the dust has a low thermal inertia, meaning that it gets extra warm in the daytime and extra cold at night, a thermal challenge to survival of the landers and rovers (and people). Second, the dust hides the bedrock, so little is known about the bedrock composition and whether it is of scientific interest. This view is one image product from HiRISE observation ESP_042014_1760, taken July 14, 2015, at 3.9 degrees south latitude, 15.2 degrees east longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19914

The robotic arm on NASA's Perseverance rover reached out to examine rocks in an area on Mars nicknamed the "Cratered Floor Fractured Rough" area in this image captured on July 10, 2021 (the 138th sol, or Martian day, of its mission). The image was taken by one of the rover's hazard cameras. An additional set of images from July 10-12 have been compiled into a GIF. Scientists are particularly interested in the flat rocks that appear light in color (nicknamed "paver rocks"). This image was processed to enhance contrast. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24748

This wide view of Mars' Jezero Crater was taken by NASA's Perseverance rover on July 15, 2021 (the 143rd sol, or Martian day, of its mission). The rover has driven nearly a mile (1.5 kilometers) south of its landing site, "Octavia E. Butler Landing," into a region the team has nicknamed the "Crater Floor Fractured Rough" unit. The stones that appear light-colored and flat in this image are informally referred to as the "paver rocks" and will be the first type from which Perseverance will collect a sample for planned return to Earth by subsequent missions. Small hills to the south of the rover and the sloping inner walls of the Jezero Crater rim fill the distant background of this view. Five images from the rover's Mastcam-Z instrument were calibrated and combined to make this mosaic. Perseverance has been exploring the floor of Jezero since landing on Feb. 18, 2021. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24745
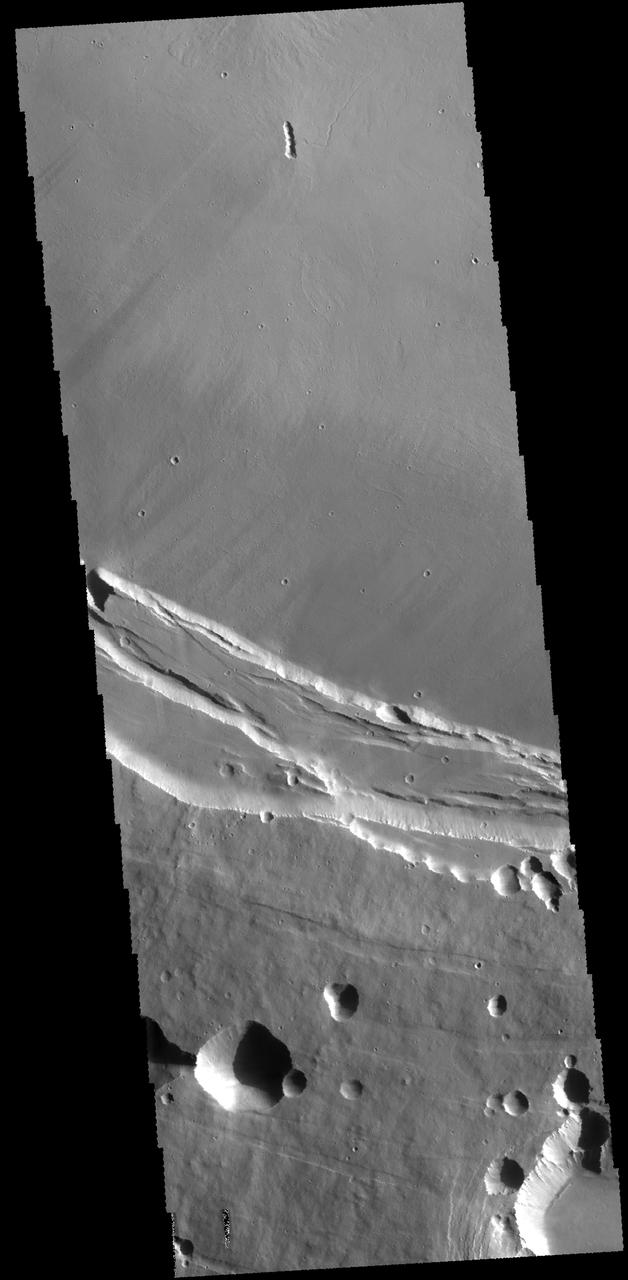

This THEMIS image shows part of the southern margin of the summit caldera. This image contains a variety of features representing the major events related to the formation of the volcano. At the top of the image a small linear vent has produced lava flows increasing the elevation of the surface around it. The flat floor of the caldera surrounds the vent and the cliff faces at the center of the image were created during the collapse event that formed the caldera. Depressions at the bottom illustrate collapse into empty voids like lava tubes. Arsia Mons is the southernmost of the Tharsis volcanoes. It is 270 miles (450 km) in diameter, almost 12 miles (20 km) high, and the summit caldera is 72 miles (120 km) wide. For comparison, the largest volcano on Earth is Mauna Loa. From its base on the sea floor, Mauna Loa measures only 6.3 miles high and 75 miles in diameter. A large volcanic crater known as a caldera is located at the summit of all of the Tharsis volcanoes. These calderas are produced by massive volcanic explosions and collapse. The Arsia Mons summit caldera is larger than many volcanoes on Earth. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 63900 Latitude: -10.0873 Longitude: 239.197 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2016-05-10 07:58 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22159
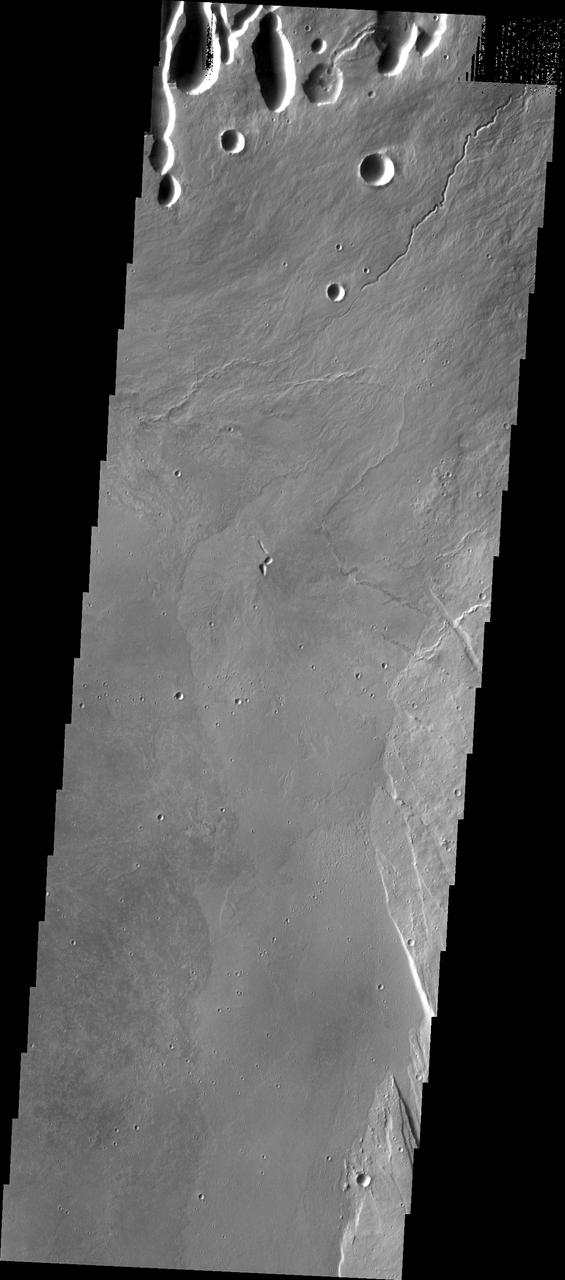

This THEMIS image shows part of the caldera floor of Arsia Mons. It is not uncommon for calderas to have "flat" floors after the final explosive eruption the empties the subsurface magma chamber. There may still be some magma or superheated rock left after the collapse that will fill in part of the depression. Additionally, over time erosion will work to level the topography. Within Arsia Mons there was renewed activity that occurred within the caldera along the alignment of the NE/SW trend of the three large volcanoes. This ongoing, low volume actitivity is similar to the lava lake in Kilauea in Hawaii. Small flows are visible throughout this image. In the center of the image is a small "L" shaped feature. This is the summit vent for the volcanic flows around it. The flows have lapped up against the caldera wall, filling in faults left by the caldera formation and increasing the elevation of the surface in this region of the caldera. Arsia Mons is the southernmost of the Tharsis volcanoes. It is 270 miles (450km) in diameter, almost 12 miles (20km) high, and the summit caldera is 72 miles (120km) wide. For comparison, the largest volcano on Earth is Mauna Loa. From its base on the sea floor, Mauna Loa measures only 6.3 miles high and 75 miles in diameter. A large volcanic crater known as a caldera is located at the summit of all of the Tharsis volcanoes. These calderas are produced by massive volcanic explosions and collapse. The Arsia Mons summit caldera is larger than many volcanoes on Earth. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 19874 Latitude: -8.57834 Longitude: 240.452 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2006-06-07 18:39 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22157

Completed: 07-16-2009 Straddling the equator approximately 1000 kilometers to the west of the South American mainland, the Galapagos Islands lie within the heart of the equatorial current system. Rising from the sea floor, the volcanic islands of the Galapagos are set on top of a large submarine platform. The main portion of the Galapagos platform is relatively flat and less than 1000 meters in depth. The steepest slopes are found along the western and southern flanks of the platform with a gradual slope towards the east. The interactions of the Galapagos and the oceanic currents create vastly different environmental regimes which not only isolates one part of the Archipelago from the other but allows penguins to live along the equator on the western part of the Archipelago and tropical corals around the islands to the north. The islands are relatively new in geologic terms with the youngest islands in the west still exhibiting periodic eruptions from their massive volcanic craters. Please give credit for this item to: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, The SeaWiFS Project and GeoEye, Scientific Visualization Studio. NOTE: All SeaWiFS images and data presented on this web site are for research and educational use only. All commercial use of SeaWiFS data must be coordinated with GeoEye (http://www.geoeye.com). To download this video go to: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?3628" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?3628</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.

ISS014-E-15732 (1 March 2007) --- Salt ponds of Botswana are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 14 crewmember on the International Space Station. This recent, detailed view shows the salt ponds of one of Africa's major producers of soda ash (sodium carbonate) and salt. Soda ash is used for glass making, in metallurgy, in the detergent industry, and in chemical manufacture. The image shows a small part of the great salt flats of central Botswana known as the Makgadikgadi Salt Pans. The soda ash and salt are both mainly exported (since 1989) to most countries in southern and central Africa. Brines from just beneath the pan floor are evaporated to produce the soda ash and salt -- a process for which the semiarid climate of Botswana is ideal. Red salt-loving algae in the ponds indicate that the salinity of the evaporating brines is medium to high. The salt pans of Botswana--a prominent visual photo target of interest for astronauts aboard the station--lie at the low point of a vast shallow continental basin. Rivers draining from as far away as central Angola - more than 1,000 kilometers away - supply water to the pans. According to scientists, during several wet climatic phases in the recent geological past the pans were permanently filled with water, for thousands of years, only to dry out when climates fluctuated to drier conditions. During dry phases water only reaches the pans underground. These are the brines that support the ash and salt industry. During wet phases when open water exists, beach ridges are constructed by wave action. One of these crosses the lower part of the view.

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera system to create this panorama of its first drill site. Scientists will be looking for a rock to drill somewhere in this. Perseverance's team has nicknamed this region the "Crater Floor Fractured Rough" unit. The flat, light-colored stones are informally referred to as "paver rocks" and will be the first type from which Perseverance will collect a sample for planned return to Earth by subsequent missions. Small hills to the south of the rover and the sloping inner walls of the Jezero Crater rim fill the distant background of this view. The panorama is stitched together from 70 individual images taken on July 28, 2021, the 155th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This panorama is seen here in natural color. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24765
This area is south of Pluto's dark equatorial band informally named Cthulhu Regio, and southwest of the vast nitrogen ice plains informally named Sputnik Planitia. North is at the top; in the western portion of the image, a chain of bright mountains extends north into Cthulhu Regio. New Horizons compositional data indicate the bright snowcap material covering these mountains isn't water, but atmospheric methane that has condensed as frost onto these surfaces at high elevation. Between some mountains are sharply cut valleysindicated by the white arrows. These valleys are each a few miles across and tens of miles long. A similar valley system in the expansive plains to the east (blue arrows) appears to be branched, with smaller valleys leading into it. New Horizons scientists think flowing nitrogen ice that once covered this area -- perhaps when the ice in Sputnik was at a higher elevation -- may have formed these valleys. The area is also marked by irregularly shaped, flat-floored depressions (green arrows) that can reach more than 50 miles (80 kilometers) across and almost 2 miles (3 kilometers) deep. The great widths and depths of these depressions suggest that they may have formed when the surface collapsed, rather than through the sublimation of ice into the atmosphere. This enhanced color image was obtained by New Horizons' Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC). The image resolution is approximately 2,230 feet (680 meters) per pixel. It was obtained at a range of approximately 21,100 miles (33,900 kilometers) from Pluto, about 45 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21026

This animated artist's concept depicts a scene of water breaking through the rim of Mars' Jezero Crater, which NASA's Perseverance rover is now exploring. Water entered the crater billions of years ago, depositing sediments that built up into a delta. Since the spacecraft's landing in February 2021, Perseverance's exploration of the crater floor and the delta have led to scientists developing a detailed timeline for the crater's formation. They now know there were three major periods after water began flooding through the crater rim. First, those waters brought fine-grained sand and mud (seen by Perseverance at "Hogwallow Flats") that is known for preserving fossilized life in comparable environments on Earth. Second, the crater's lake grew as wide as 22 miles (35 kilometers) in diameter and as deep as 100 feet (30 meters) – deep enough to lay down several sedimentary layers (like those seen at "Pinestand"). Finally, high-energy rivers brought in boulders that were rounded as they tumbled through water, as seen at "Castell Henllys." A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26207

This image shows part of the complex caldera at the summit of the volcano. Calderas are found at the tops of volcanoes and are the source region for magma that rises from an underground lava source to erupt at the surface. Volcanoes are formed by repeated flows from the central caldera. The final eruptions can pool within the summit caldera, leaving a flat surface as they cool. This image shows part of two of the summit calderas, each with a floor at different elevations. Calderas are also a location of collapse, creating rings of tectonic faults that form the caldera rim. Ascraeus Mons has several caldera features at its summit. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 63076 Latitude: 11.3749 Longitude: 255.364 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2016-03-03 11:14 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21830

ISS018-E-043947 (26 March 2009) --- Etosha Pan in Namibia is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 18 crewmember on the International Space Station. Etosha Pan is a large dry lake about 130 kilometers long that dominates Namibia?s Etosha National Park (the sharp edge of the park fence can be seen at right). Small related dry lake beds appear as bright shapes top left, a portion of the International Space Station appears at top right. This view shows the pan as it appeared almost ten years ago. The pan is the low point in a major inland basin in northern Namibia. During occasional flood events, such those experienced in the last nine months, rivers from Angola (the Namibia?Angola boundary lies just outside the top of the image) deliver large quantities of water to the pan. In this image flood water in the Oshigambo River, resulting from recent heavy rains in Angola, appears as a gray stream entering the northwest corner of the pan (top left). The floodwater becomes a thin sheet on the vast salt flat of the pan floor. Algae blooms in the warm water have produced a light-green tinge. Another image of the Oshigambo River mouth in flood can be seen here. Reports on the ground, augmented with orbital unmanned satellite imagery acquired subsequent to this photograph, show that the plains north of the pan are now flooded, causing damage to homesteads, crops and roads. More than 340,000 people have been affected in northern Namibia and approximately 250,000 in southern Angola.

This image shows the area on Mars from which NASA's Perseverance rover will collect its first rock sample. Scientists are particularly interested in the flat stones that appear light-colored (informally called "paver rocks"). The Perseverance team has nicknamed this area in Mars' Jezero Crater the "Crater Floor Fractured Rough" area. The 28 individual images that were combined to make the larger main image were taken by the rover's Mastcam-Z right-eye camera on July 8, 2021 (the 136th sol, or Martian day, of the mission). The images have been calibrated and are presented in natural color, simulating the approximate view that we would see with our own eyes if we were there. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24746
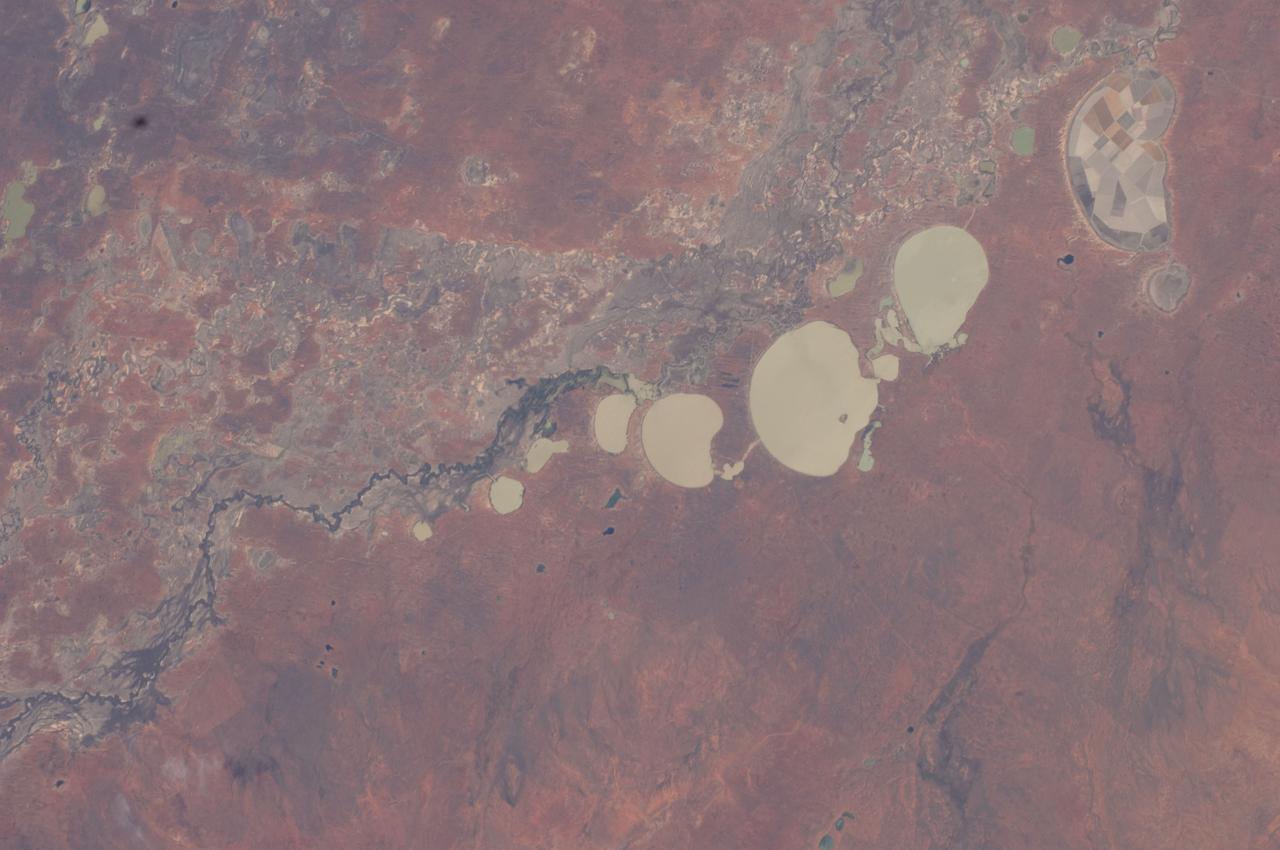

ISS030-E-009186 (3 Dec. 2011) --- The Menindee Lakes, New South Wales, Australia are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 30 crew member on the International Space Station. The Menindee Lakes comprise a system of ephemeral, freshwater lakes fed by the Darling River when it floods. The lakes lie in the far west of New South Wales, Australia, near the town of Menindee. The longest is Lake Tandou (18.6 kilometers north?south dimension), visible at the upper right of this photograph. The lakes appear to have a small amount of water flooding them. The Darling River itself was flowing, as indicated by the dark water and blackened mud along its course (left). The Darling River flows southwest in tortuous fashion (bottom left to upper right). In the flat landscapes of this part of Australia, the river has created several inland deltas in its course to the sea, with characteristic diverging channel patterns, marked by younger sediments, which appear grayer than the surrounding ancient red soils and rocks. One such inland delta appears at right where minor channels wind across the countryside. The apex of another inland delta appears at upper right. Some of the Menindee Lakes have been incorporated in an artificially regulated overflow system providing for flood control, water storage for domestic use and livestock, as well as downstream irrigation. The lakes are also important as wetlands supporting a rich diversity of birds. The floor of one lake, Lake Tandou, is also used as prime agricultural land, as can be seen by its patchwork of irrigated fields, and is protected from flooding.
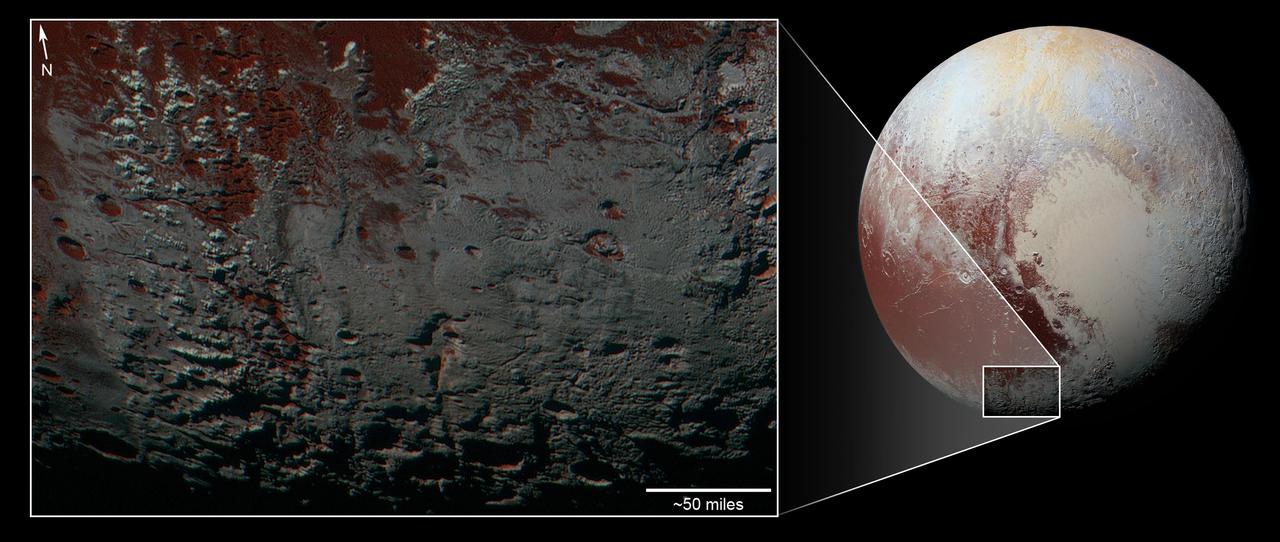

This area is south of Pluto's dark equatorial band informally named Cthulhu Regio, and southwest of the vast nitrogen ice plains informally named Sputnik Planitia. North is at the top; in the western portion of the image, a chain of bright mountains extends north into Cthulhu Regio. New Horizons compositional data indicate the bright snowcap material covering these mountains isn't water, but atmospheric methane that has condensed as frost onto these surfaces at high elevation. Between some mountains are sharply cut valleys -- indicated by the white arrows. These valleys are each a few miles across and tens of miles long. A similar valley system in the expansive plains to the east (blue arrows) appears to be branched, with smaller valleys leading into it. New Horizons scientists think flowing nitrogen ice that once covered this area -- perhaps when the ice in Sputnik was at a higher elevation -- may have formed these valleys. The area is also marked by irregularly shaped, flat-floored depressions (green arrows) that can reach more than 50 miles (80 kilometers) across and almost 2 miles (3 kilometers) deep. The great widths and depths of these depressions suggest that they may have formed when the surface collapsed, rather than through the sublimation of ice into the atmosphere. This enhanced color image was obtained by New Horizons' Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC). The image resolution is approximately 2,230 feet (680 meters) per pixel. It was obtained at a range of approximately 21,100 miles (33,900 kilometers) from Pluto, about 45 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21025
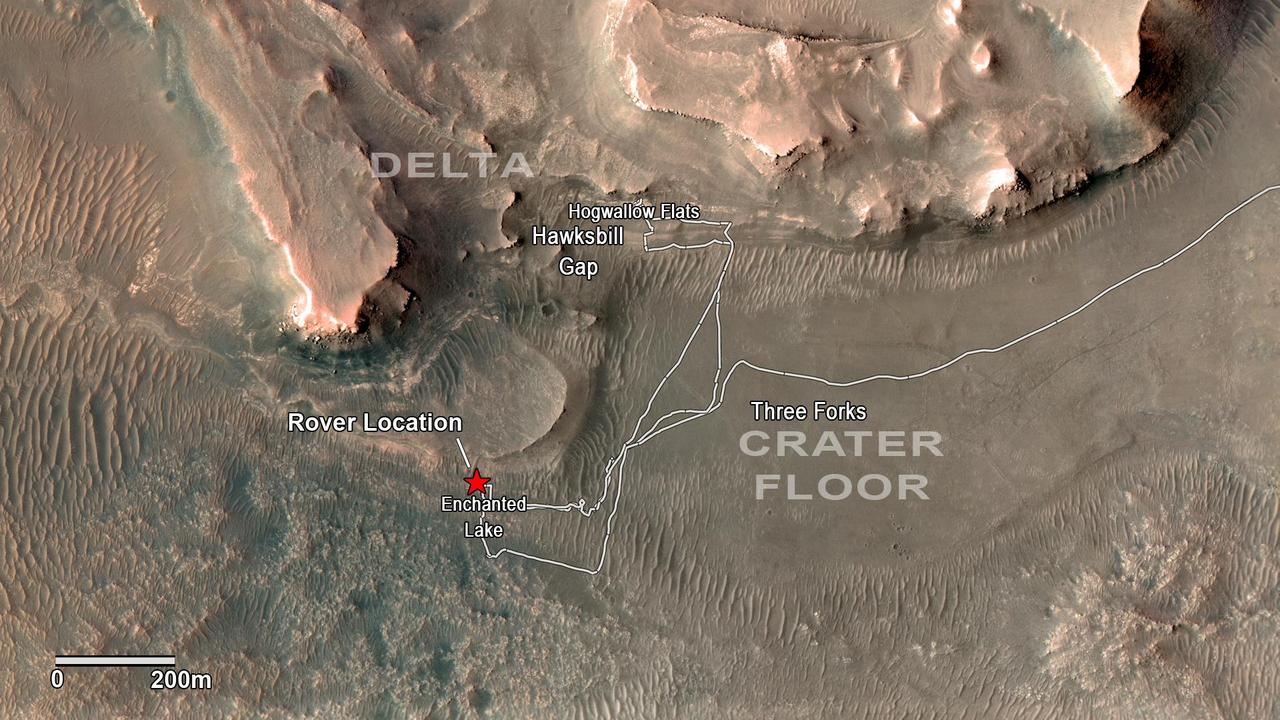
NASA's Perseverance rover has been investigating rocks at the front of the delta in Mars' Jezero Crater along the path indicated in this annotated image taken by the agency's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The red star indicates the location of the rover in September 2022. Perseverance touched down at "Octavia E. Butler Landing" on the floor of Jezero Crater on Feb. 18, 2021. It reached the delta in April 2022. The delta is a fan-shaped feature where, billions of years ago, a river flowed into a lake and deposited rocks and sediments. Scientists consider the delta one of the best places on Mars to search for potential signs of ancient microbial life. The annotations show the names of some of the key features Perseverance visited, such as "Enchanted Lake" and "Hogwallow Flats." Sample tubes already filled with rock are currently stored in the rover's Sampling and Caching System. Perseverance will deposit select samples in designated locations. MRO took this overhead image with its High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24923

OSAM-1 team members prepare a weight to be crane lifted onto the SPIKA work platform as part of its commissioning workmanship test inside the cleanroom at Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt Md., Mar 20, 2023. This photo has been reviewed by OSAM1 project management and the Export Control Office and is released for public view. NASA/Mike Guinto

This image shows part of the southeastern flank of Arsia Mons, including the flat lying flows around the base of the volcano. These flows are located at the bottom of the image. Numerous small lava channels are visible aligned sub-parallel to the base of the volcano. Several narrow, lobate flows show the downslope direction from the top left of the image towards the bottom right. Running against this elevation change are large paired faults called graben. Graben form by faults that have allowed the material between them to "slide" down. The resultant topography is a linear depression. None of the lobate flows enter and then run along the fault valley, indicating that the faulting occurred after the lava flows. Arsia Mons is the southernmost of the Tharsis volcanoes. It is 270 miles (450km) in diameter, almost 12 miles (20km) high, and the summit caldera is 72 miles (120km) wide. For comparison, the largest volcano on Earth is Mauna Loa. From its base on the sea floor, Mauna Loa measures only 6.3 miles high and 75 miles in diameter. A large volcanic crater known as a caldera is located at the summit of all of the Tharsis volcanoes. These calderas are produced by massive volcanic explosions and collapse. The Arsia Mons summit caldera is larger than many volcanoes on Earth. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 17691 Latitude: -11.2622 Longitude: 241 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-12-09 23:06 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22154