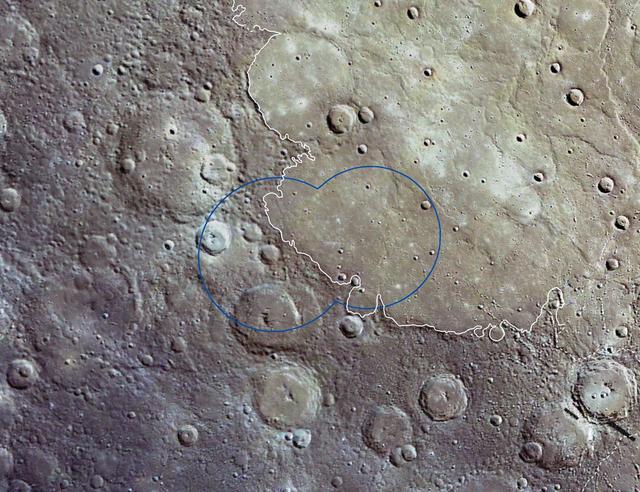
A Northern Footprint

WAC Changing Footprint

Footprints from Above

Satellite Footprints Seen in Jupiter Aurora
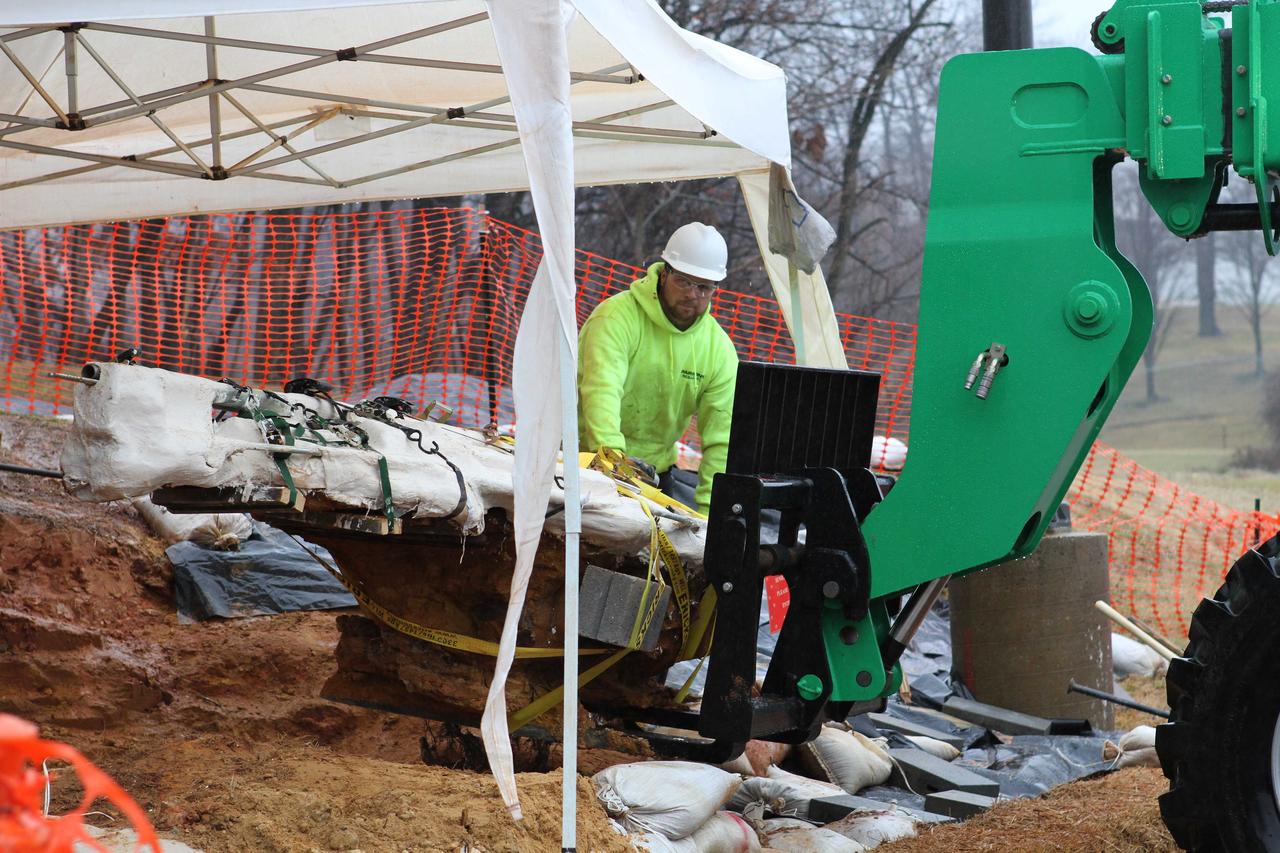

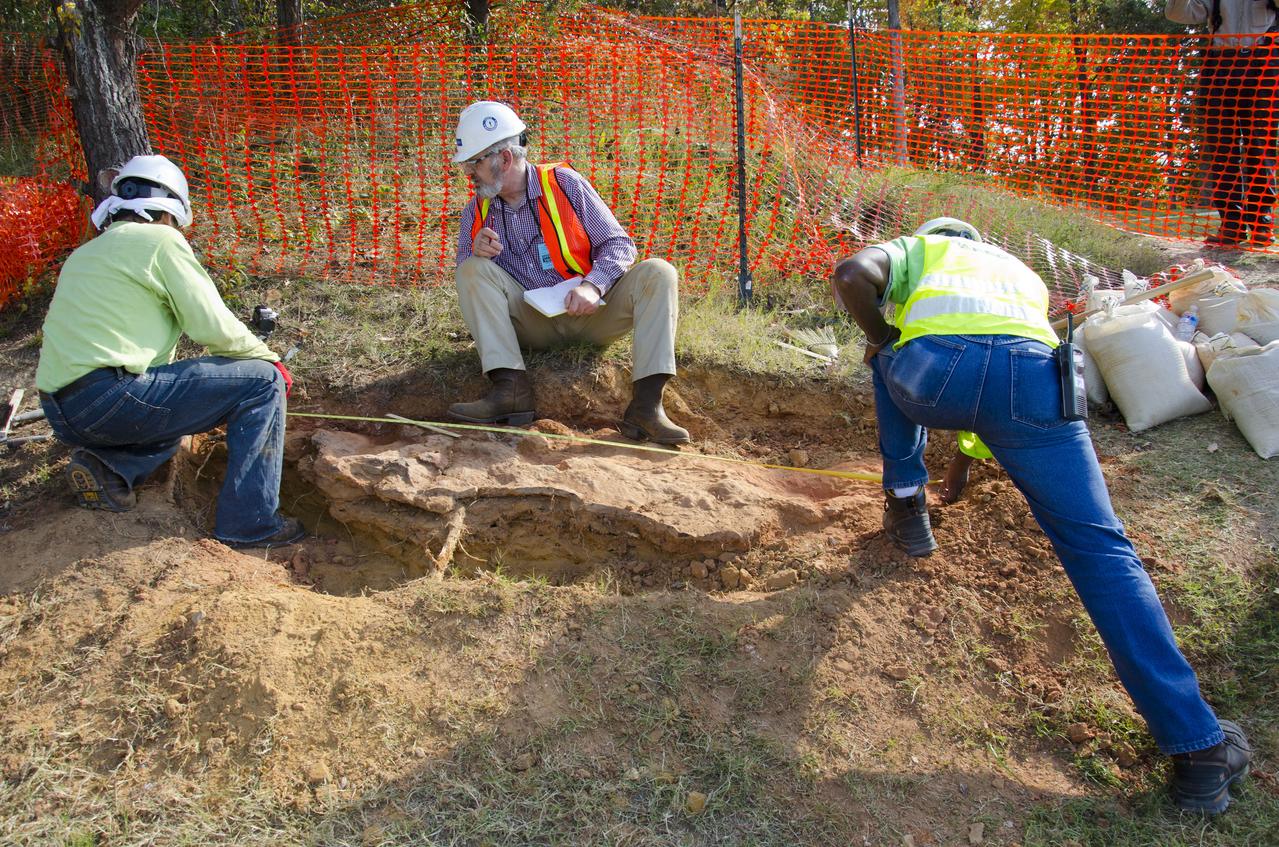
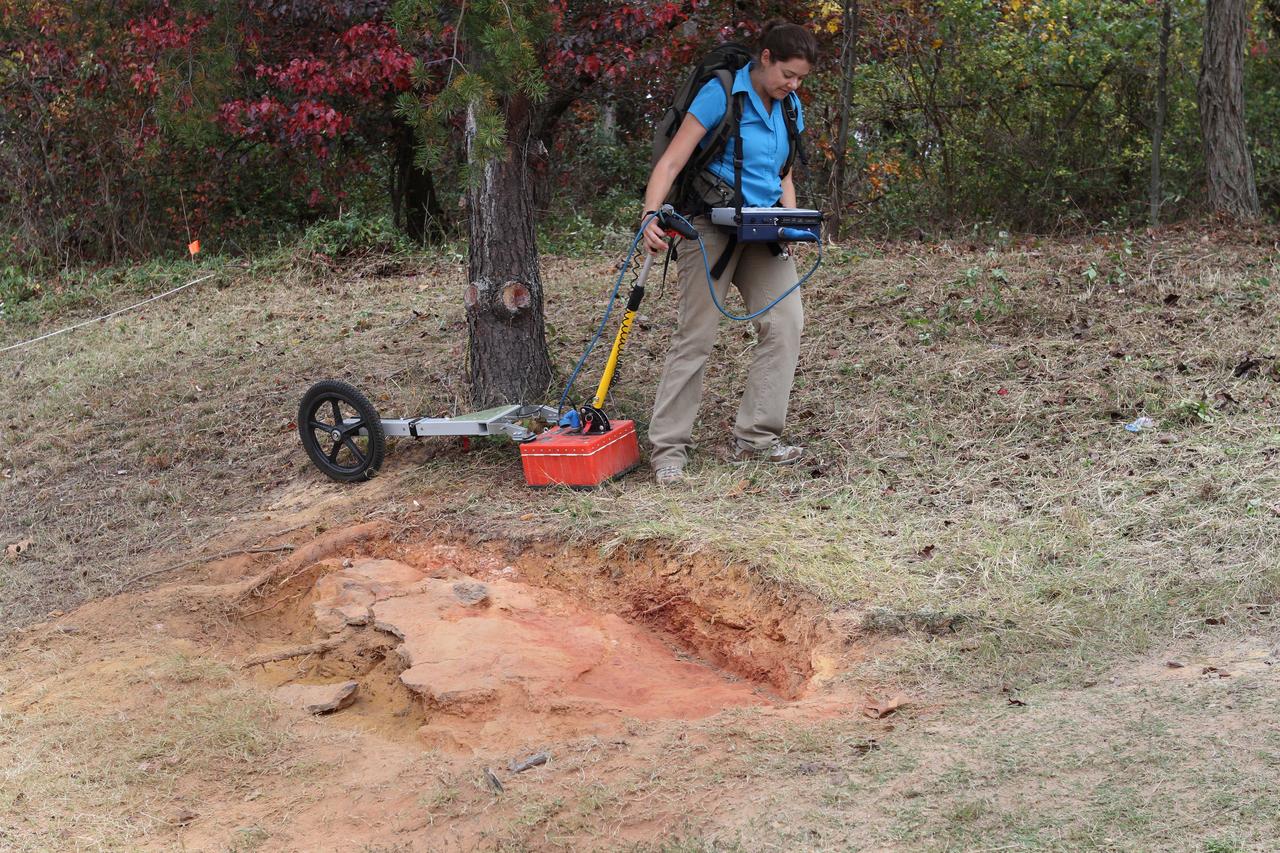
The entire find, containing at least three dinosaur footprints, is approximately seven feet long and three feet across at its widest point. Additionally, the footprint-rich layer is bonded to a separate layer of iron-rich sandstone that complicated the efforts to extract and preserve it. Before removing the rock layer, Godfrey made a silicon-rubber cast of the prints, then jacketed the entire find in multiple layers of plaster-soaked burlap (i.e. just like a cast) to add rigidity and to further ward against breakage during transport. Galvanized steel pipes wrapped into the jacket acted like splints to provide additional structural support. The combined weight of the footprint, field jacket material and surrounding soil that was removed was estimated to be approximately 3,000 pounds, so extra care was taken in moving it to avoid damaging the rather extraordinary find. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Michelle Handleman <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

About 110 million light years away, the bright, barred spiral galaxy NGC3259 was just forming stars in dark bands of dust and gas. On Earth, a plant-eating dinosaur left footprints in the Cretaceous mud of what would later become the grounds of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. A model of a Nodosaur dinosaur sits inside what is believed to be the fossil of a Nodosaur footprint. The footprint was found by Ray Stanford a local dinosaur hunter. <b>To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur....</a></b> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
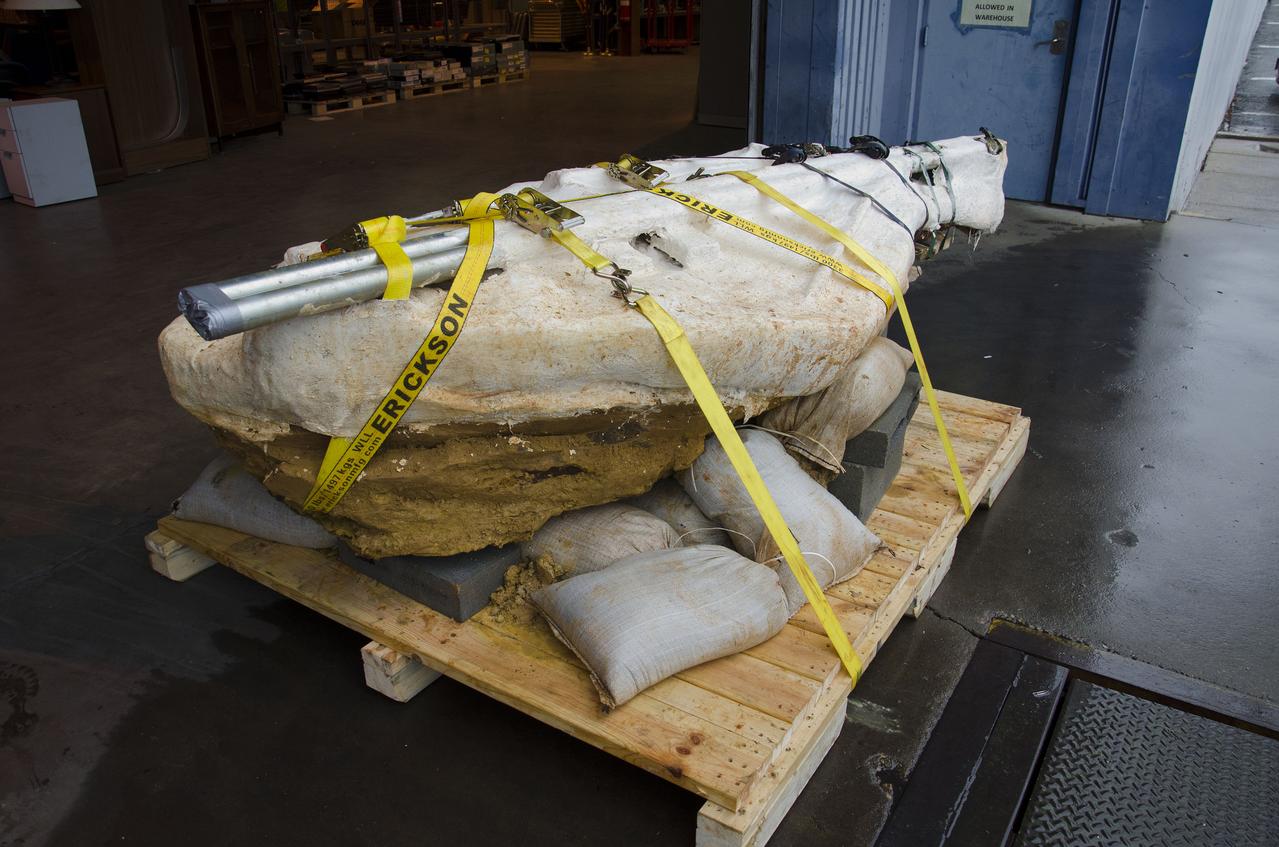

The entire find, containing at least three dinosaur footprints, is approximately seven feet long and three feet across at its widest point. Additionally, the footprint-rich layer is bonded to a separate layer of iron-rich sandstone that complicated the efforts to extract and preserve it. Before removing the rock layer, Godfrey made a silicon-rubber cast of the prints, then jacketed the entire find in multiple layers of plaster-soaked burlap (i.e. just like a cast) to add rigidity and to further ward against breakage during transport. Galvanized steel pipes wrapped into the jacket acted like splints to provide additional structural support. The combined weight of the footprint, field jacket material and surrounding soil that was removed was estimated to be approximately 3,000 pounds, so extra care was taken in moving it to avoid damaging the rather extraordinary find. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
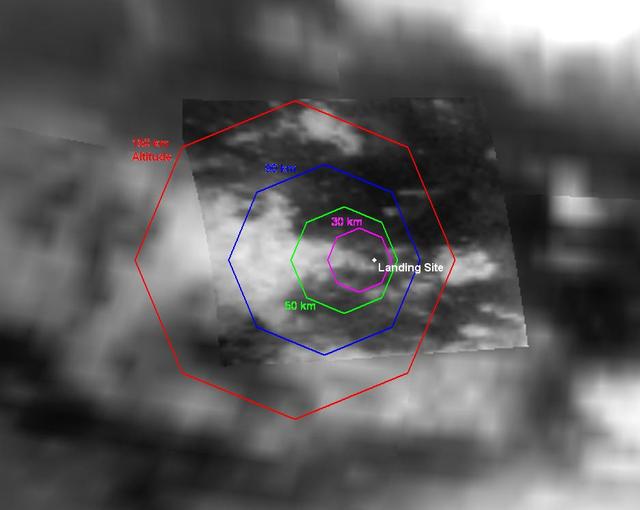
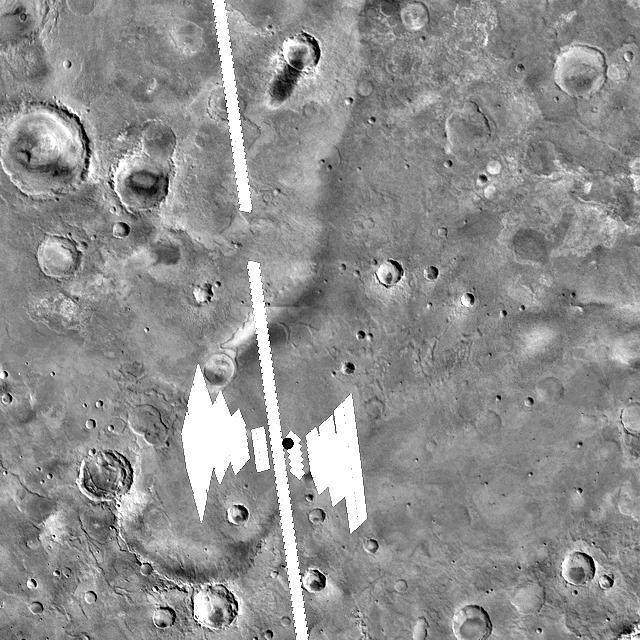
Expected Footprints of 36-Image Panoramas from Huygens Camera

Michael Godfrey beginning the process of quarrying down around the footprint bearing layer. Photo taken December 31, 2012. Image courtesy Stephen Godfrey <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

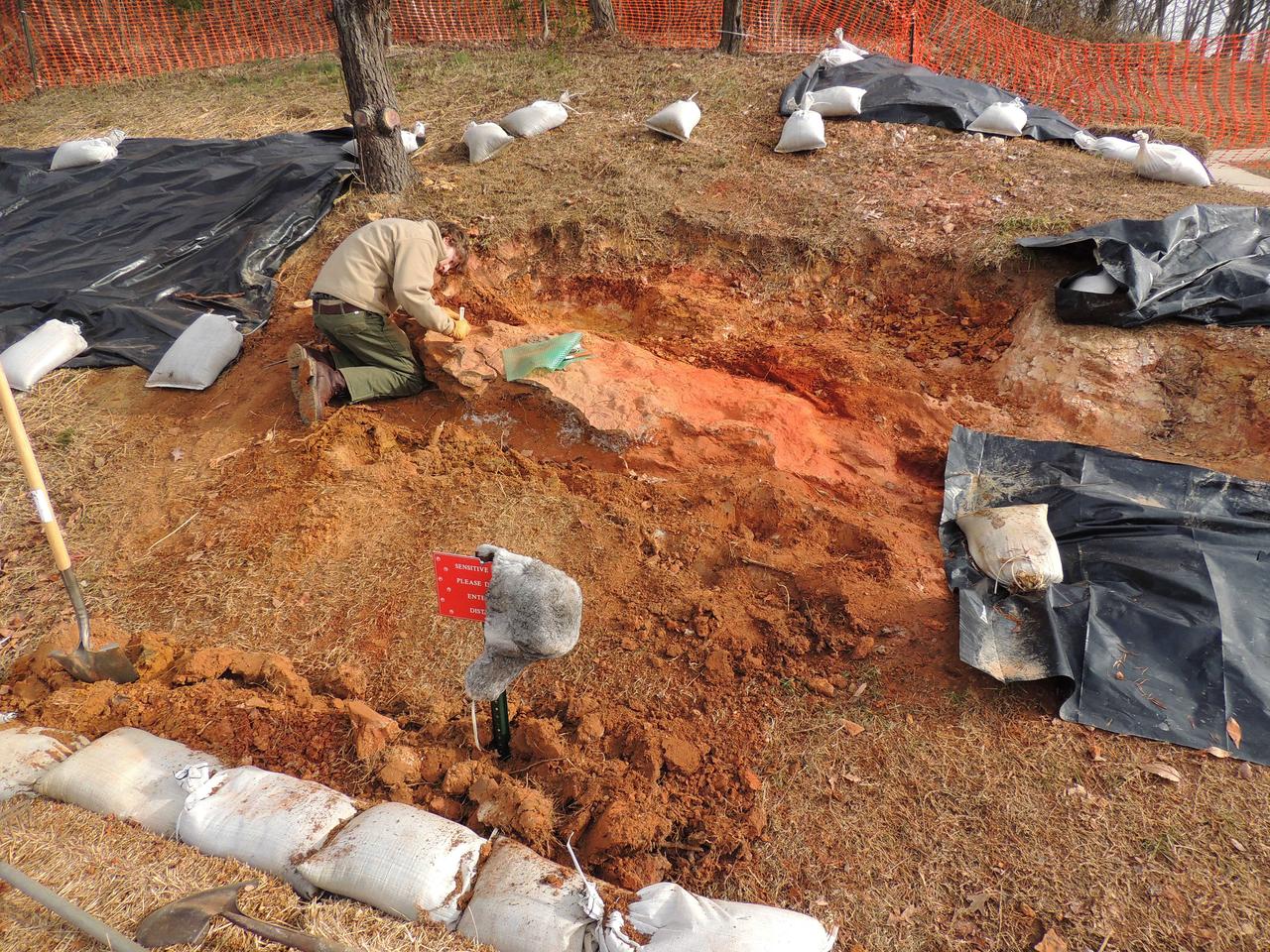
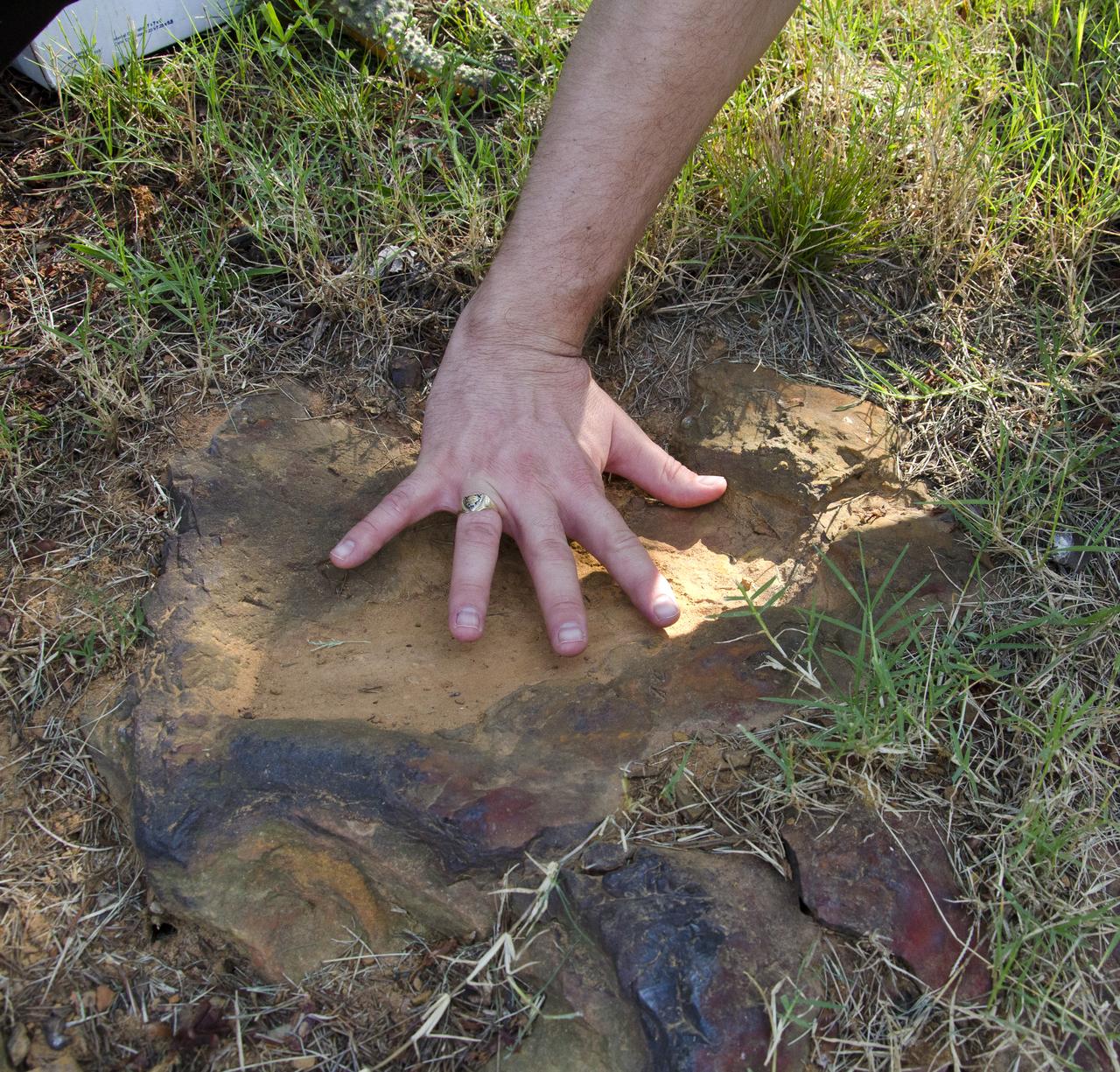
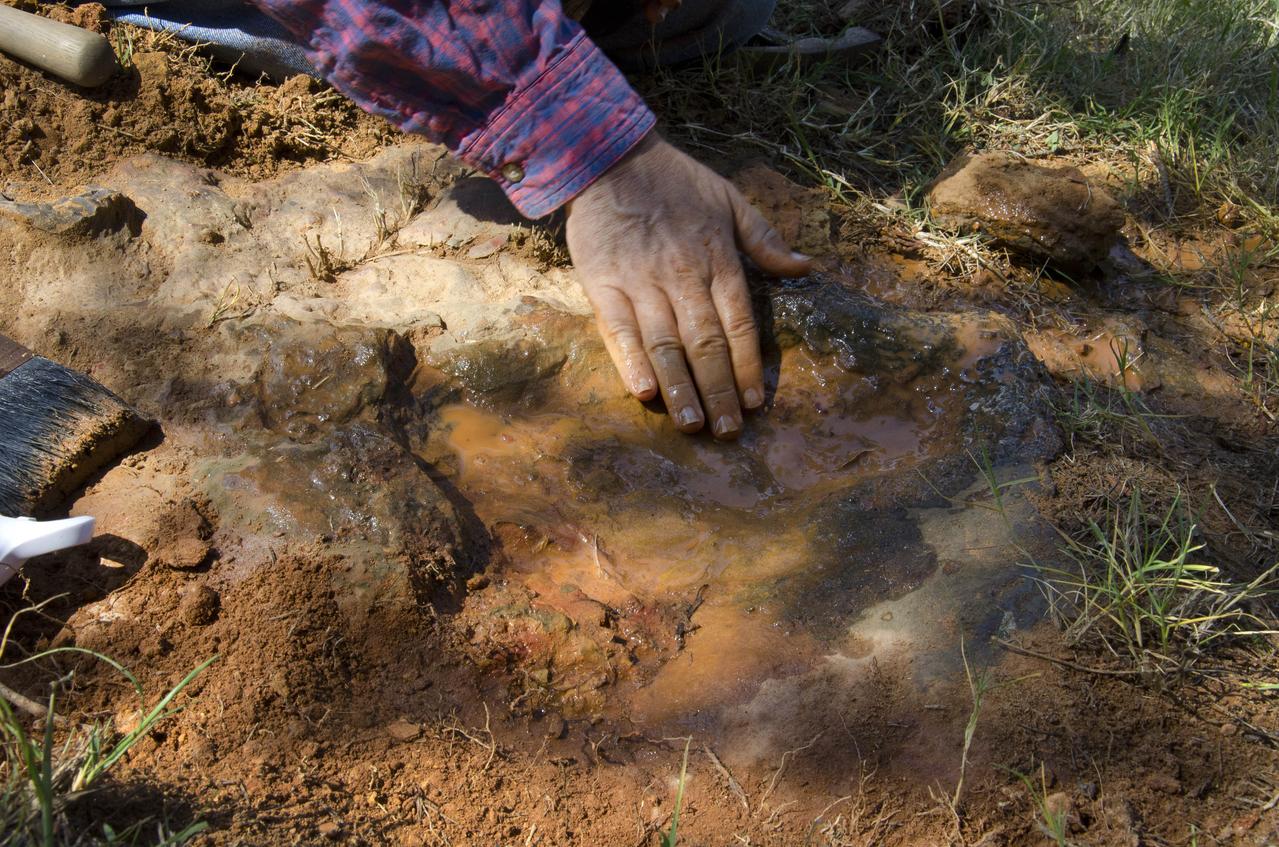
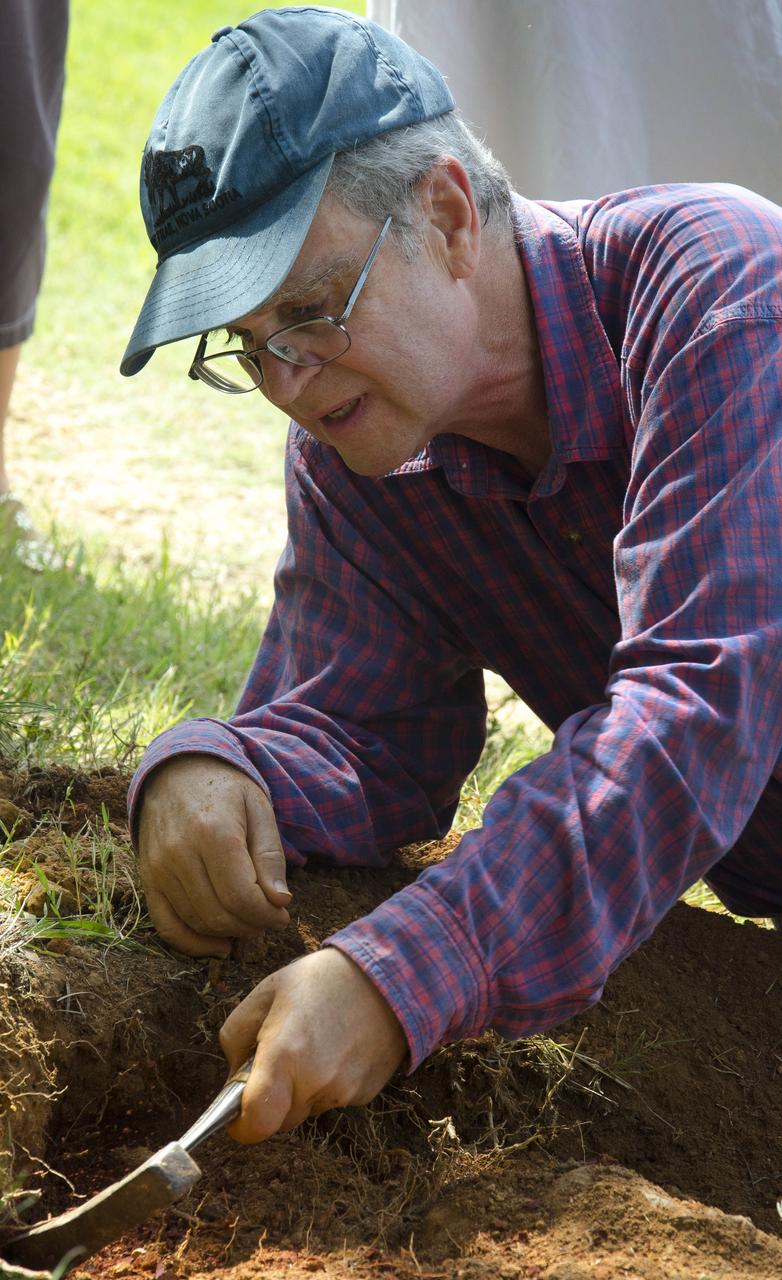
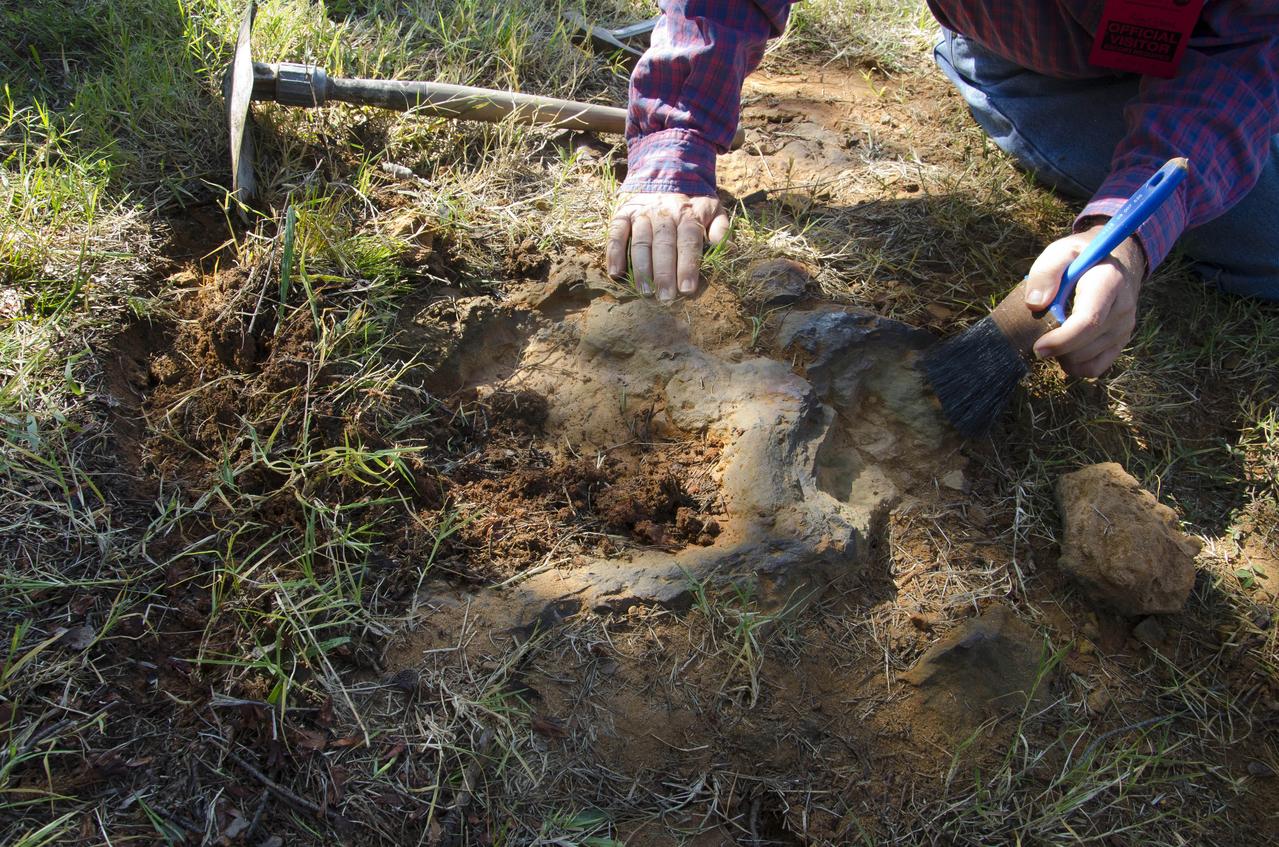
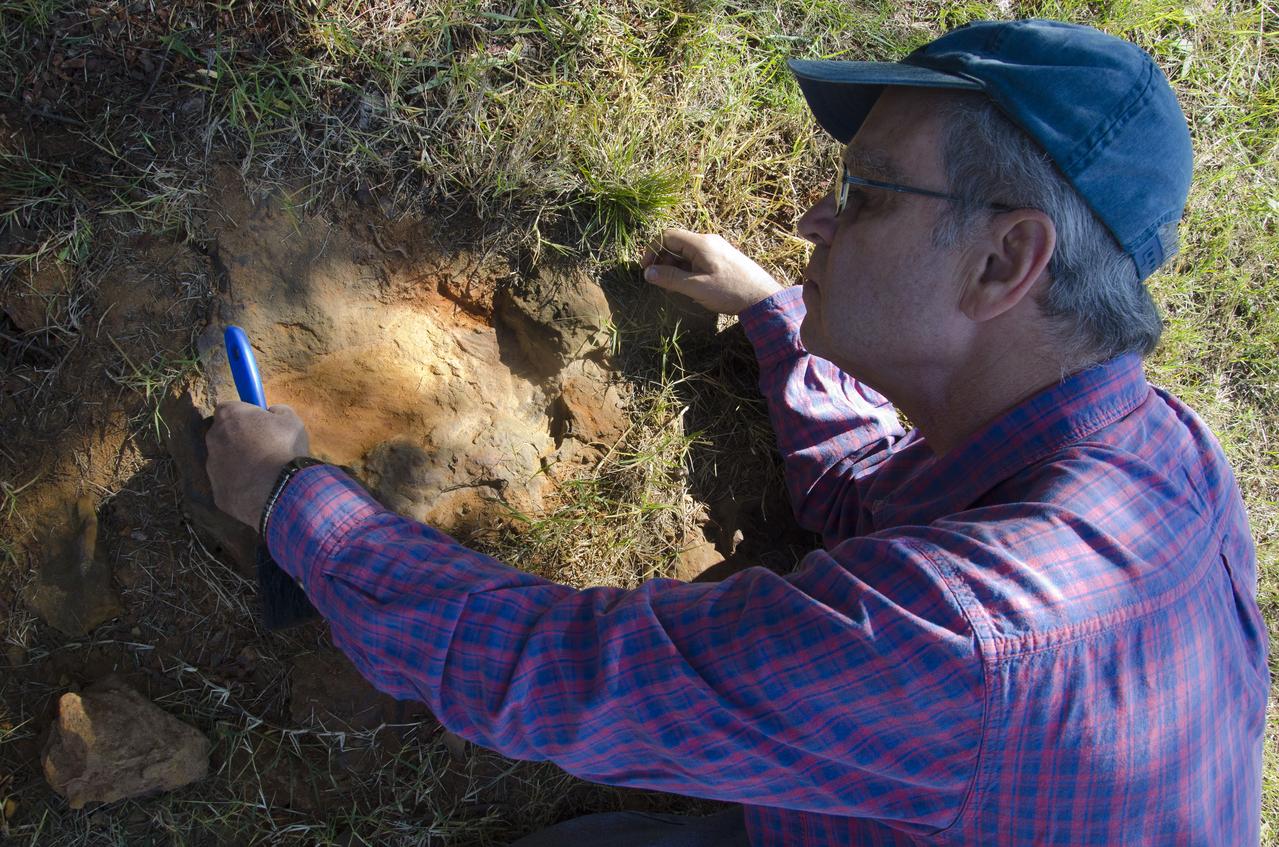
Goddard's consultant paleontologist Dr. Lee Monnens verified the track and discovered additional footprints hiding under a thin layer of topsoil in the same rock layer on October 23, 2012. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
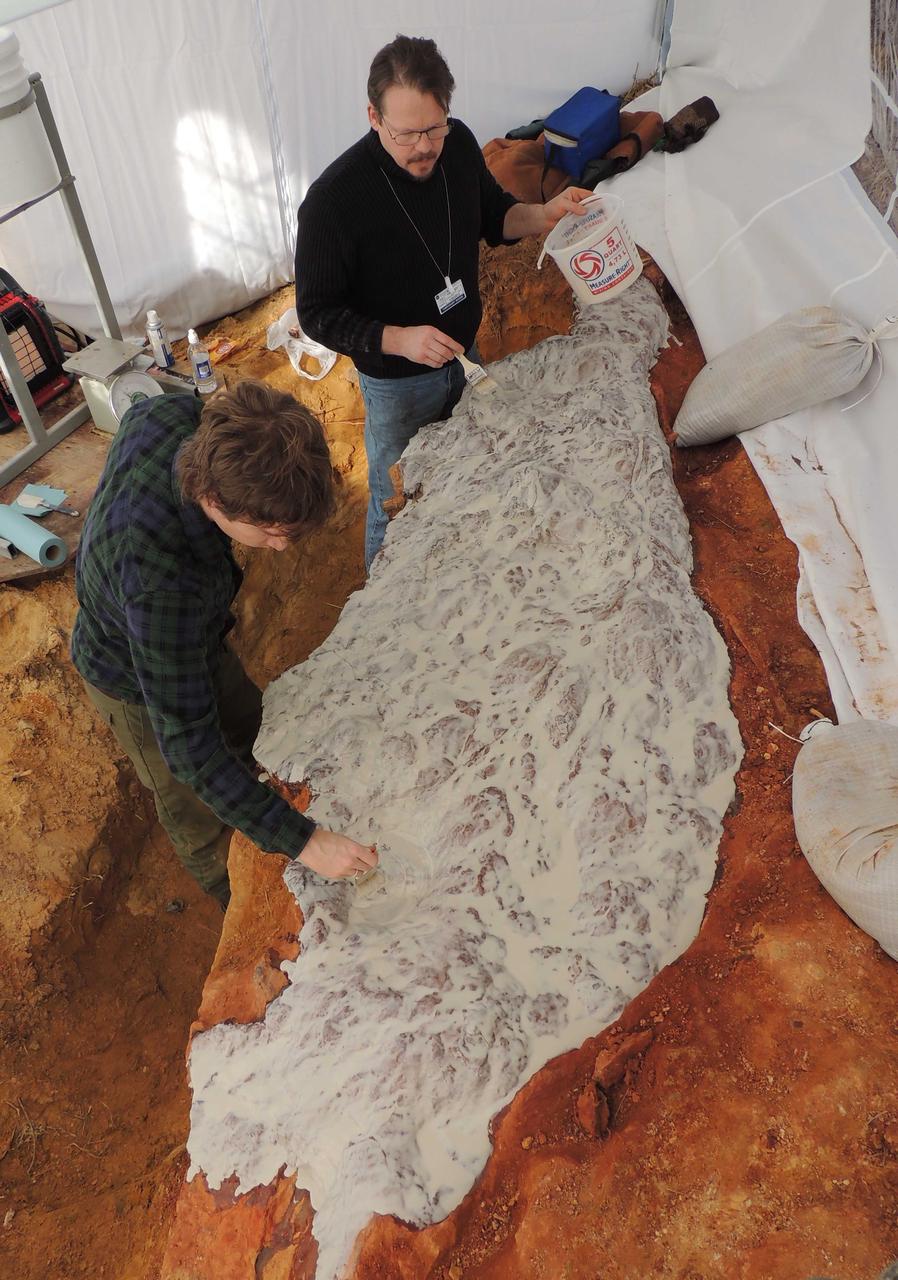

Michael Godfrey (left) and Perry Carsley (center) are coating the dinosaur footprints with a silicone rubber molding compound. A mold was made of the prints so that in addition to preserving the original rocky surface, cast replicas of the surface could also be made. Photo taken January 5, 2013. Image courtesy Stephen Godfrey <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
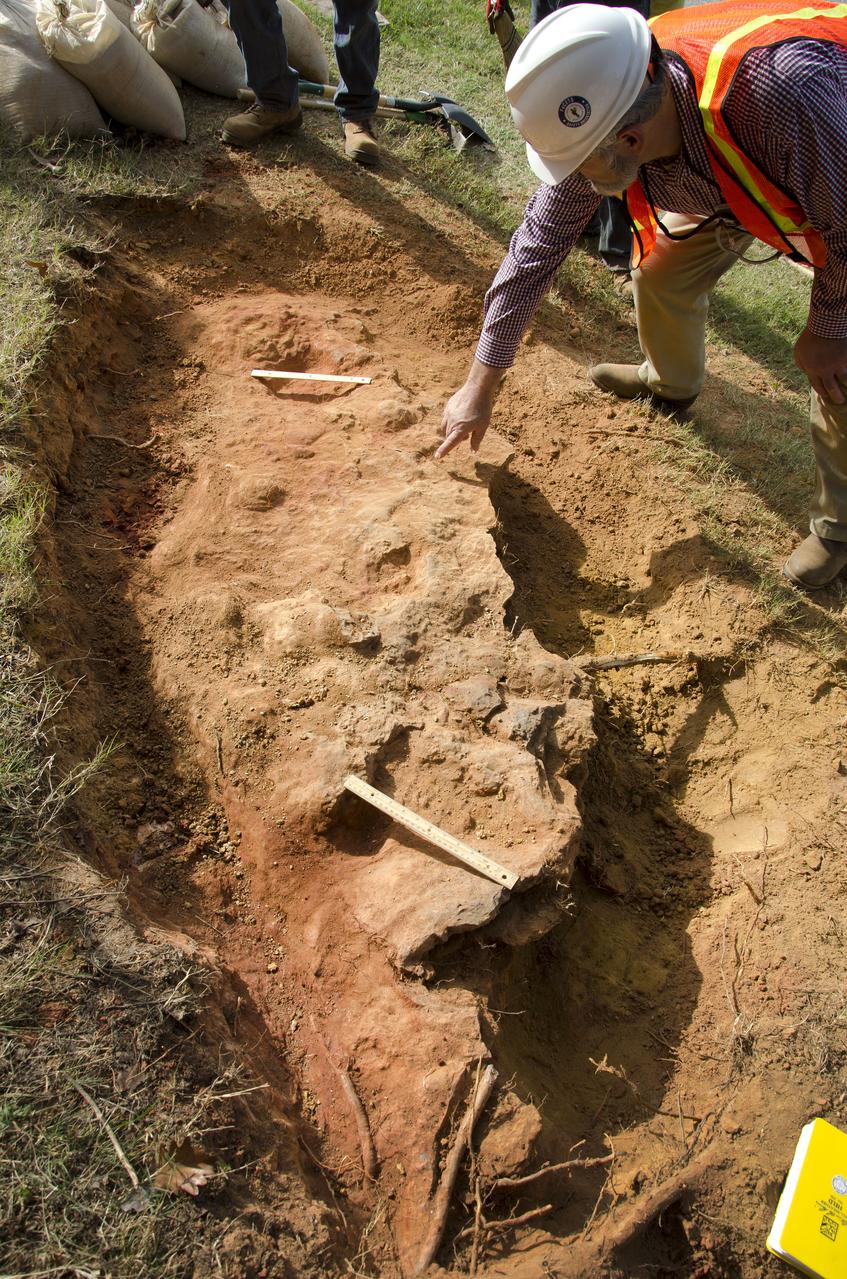

Goddard's consultant paleontologist Dr. Lee Monnens verified the track and discovered additional footprints hiding under a thin layer of topsoil in the same rock layer on October 23, 2012. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Goddard's consultant paleontologist Dr. Lee Monnens verified the track and discovered additional footprints hiding under a thin layer of topsoil in the same rock layer on October 23, 2012. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
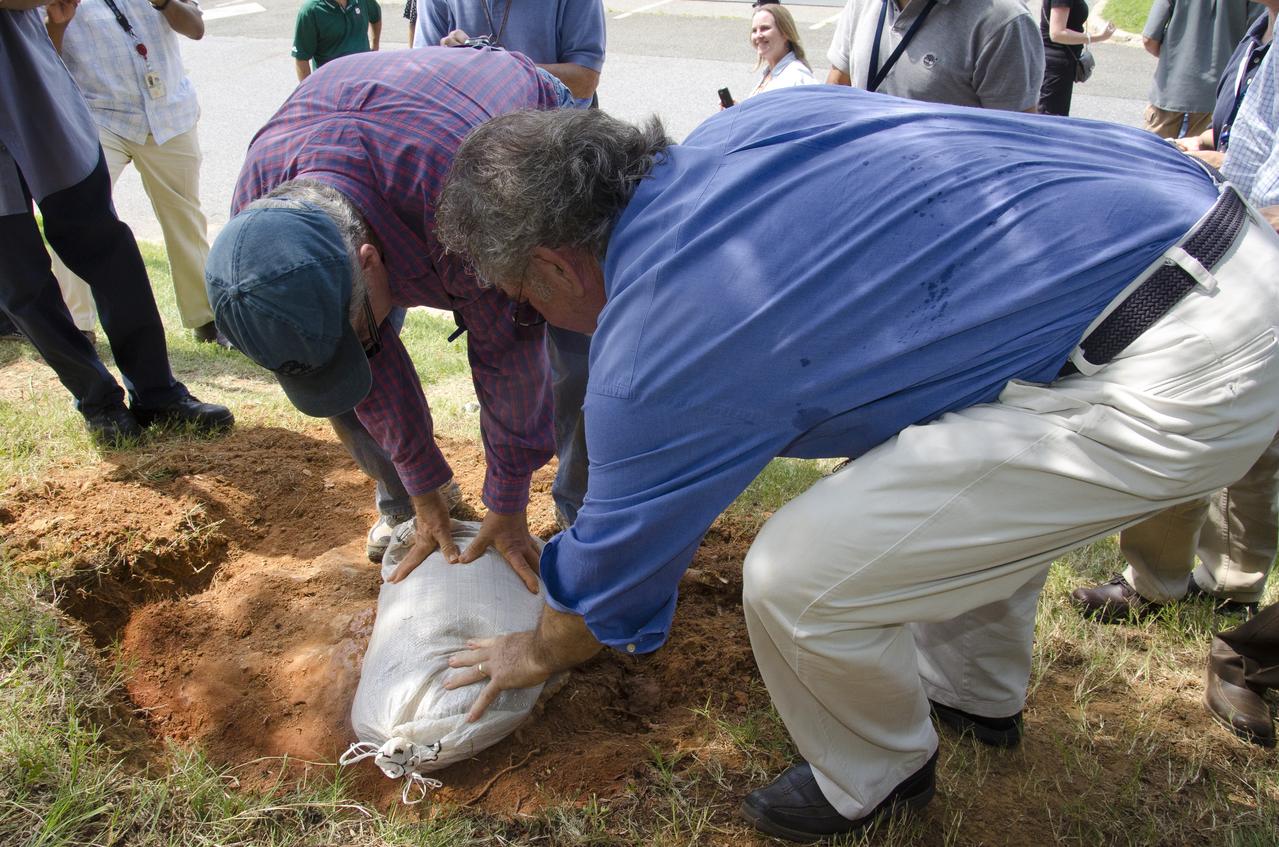

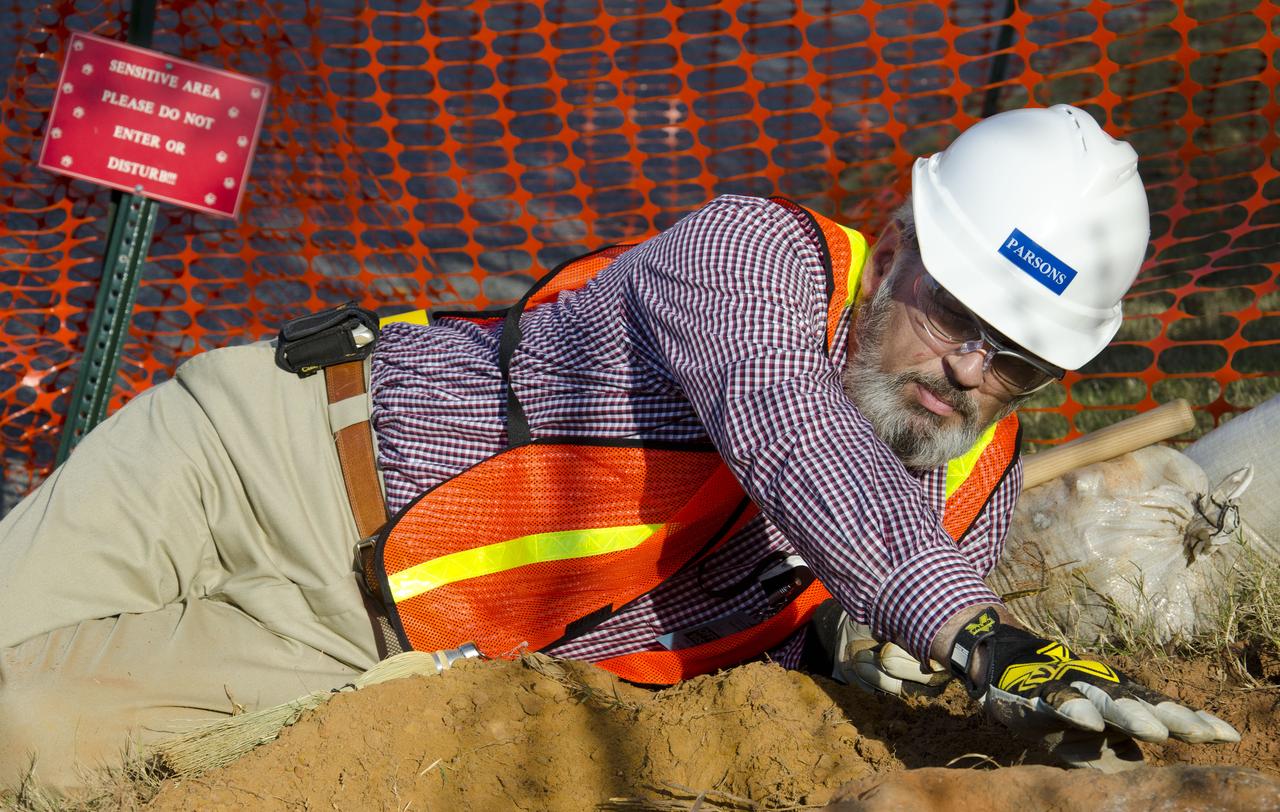
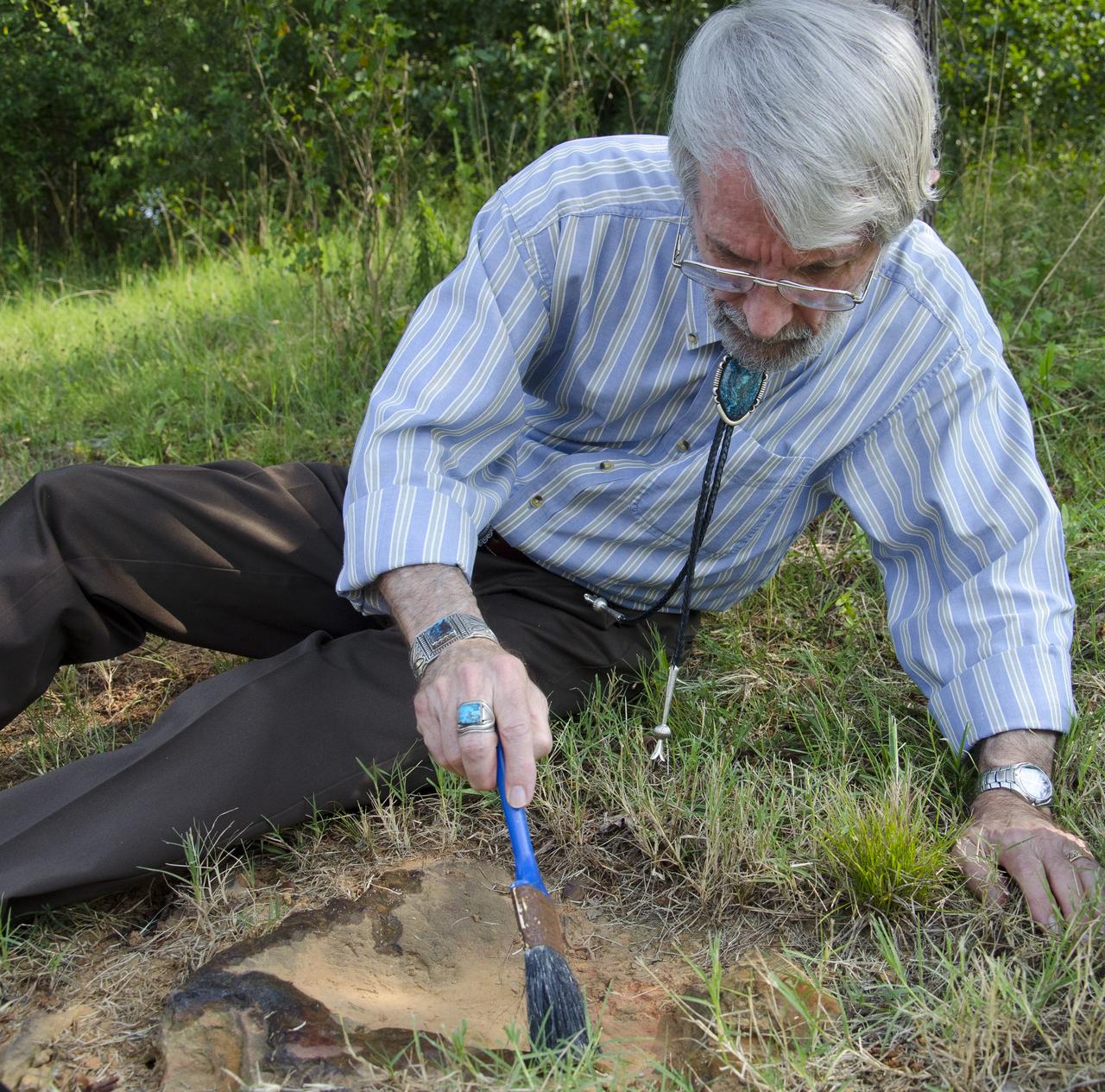
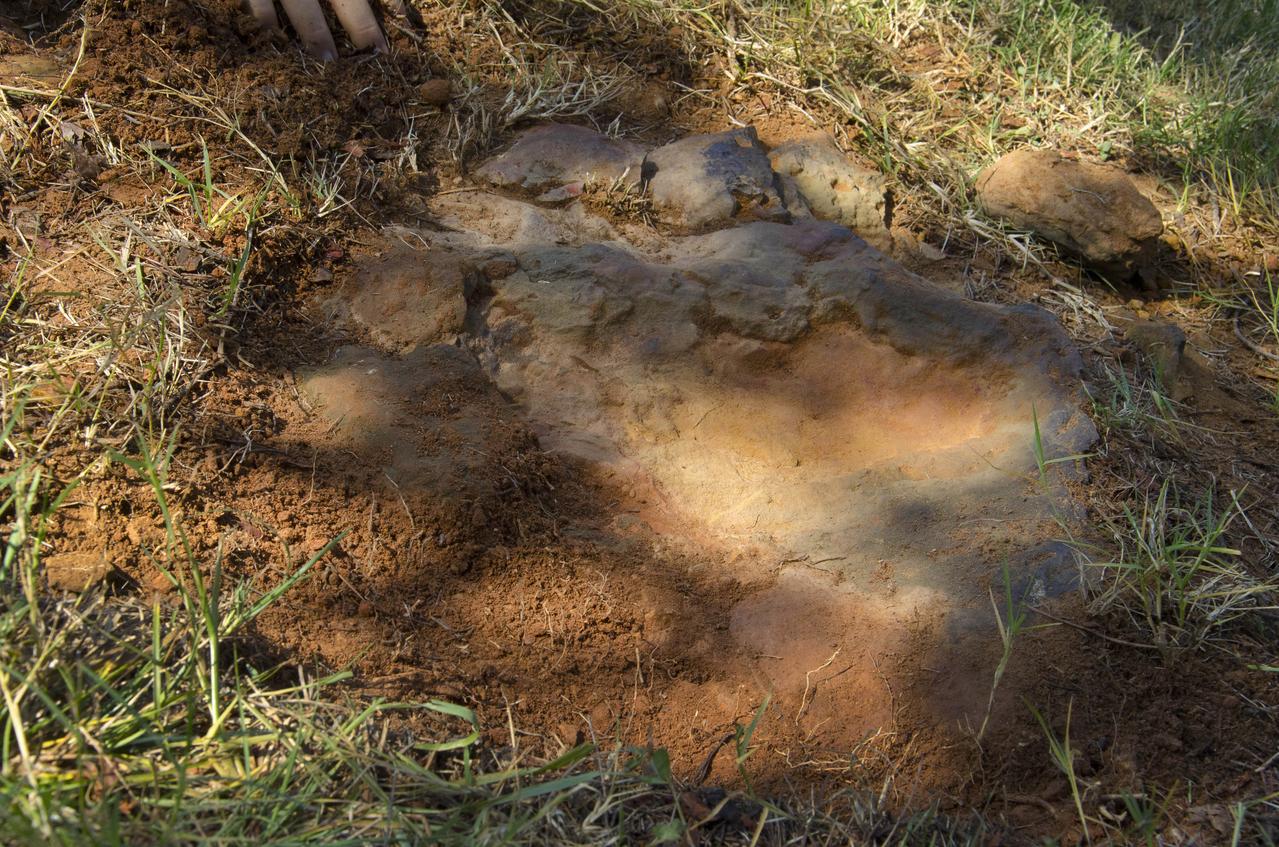
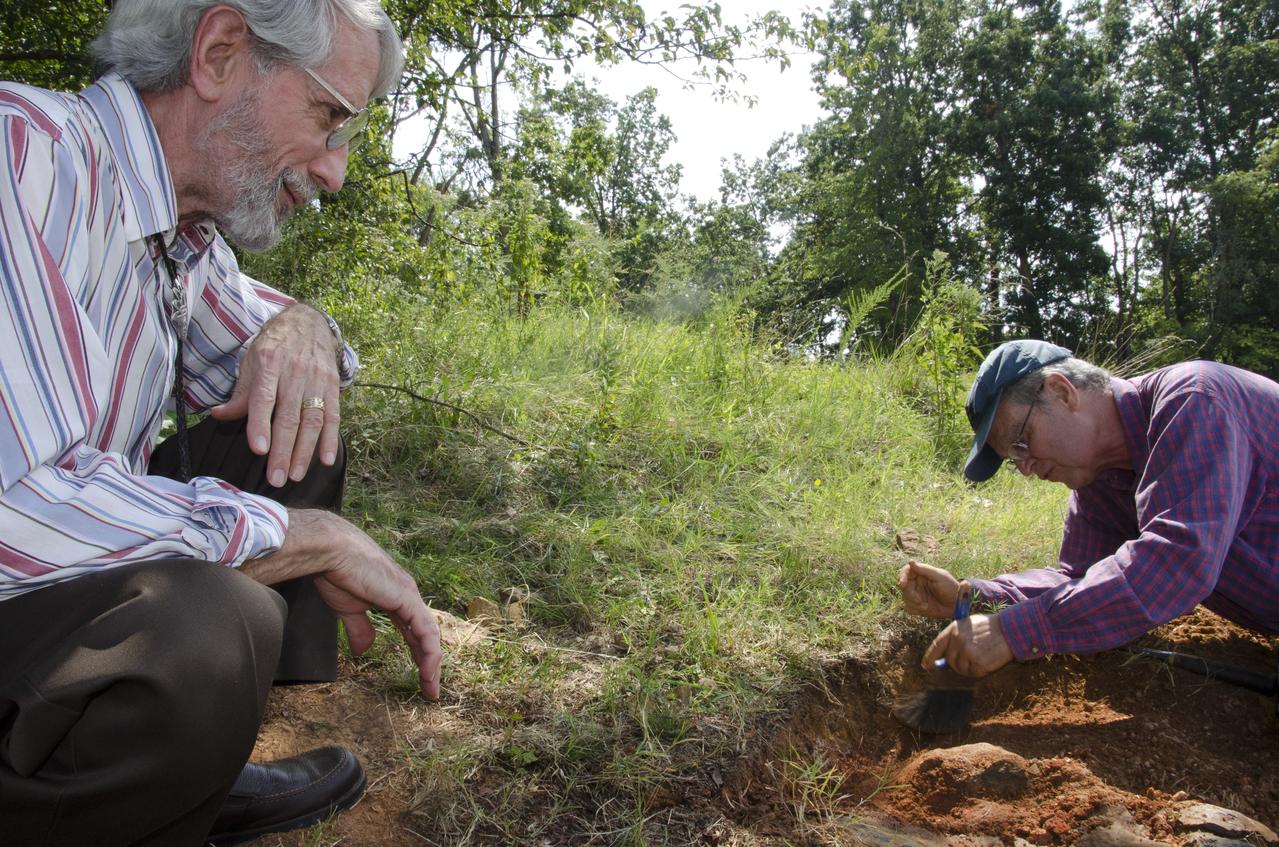
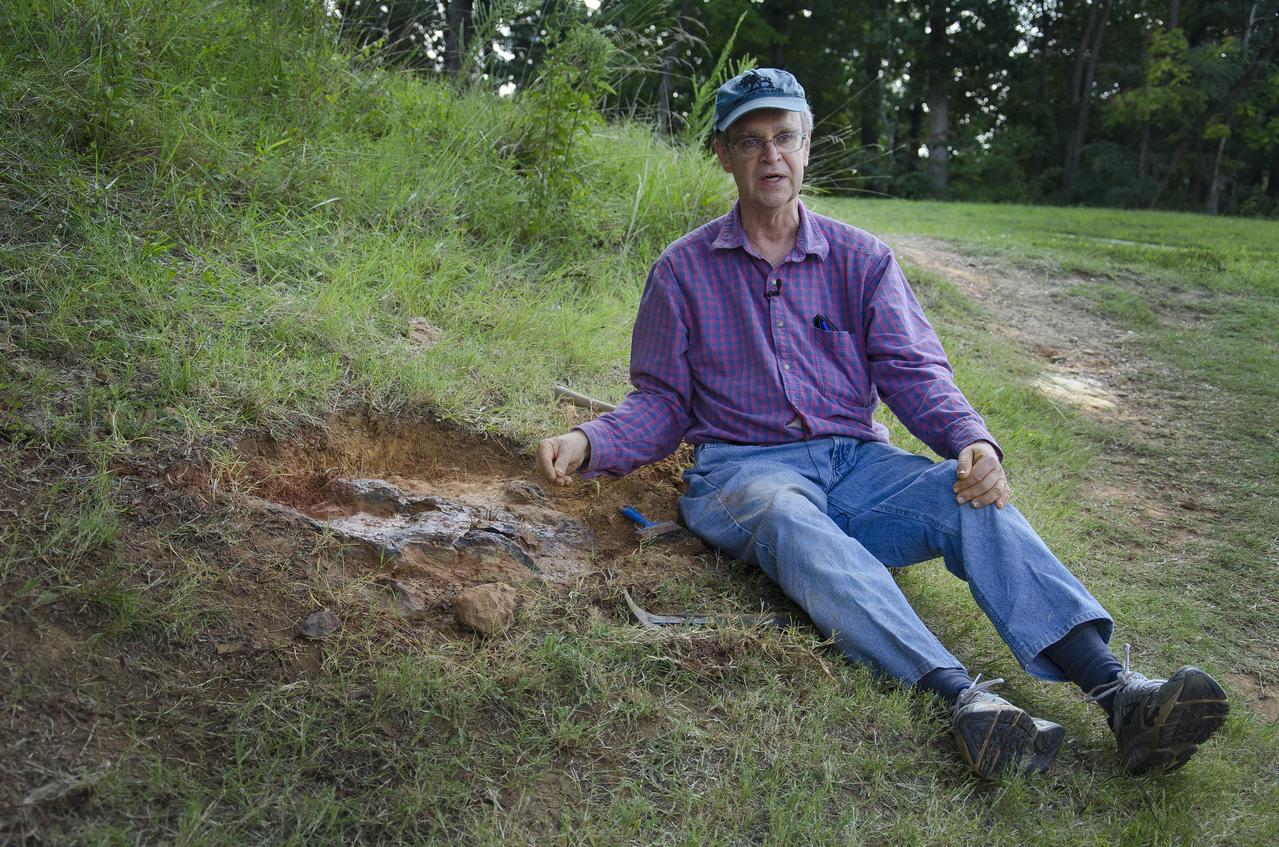
On Friday, Aug. 17, 2012, noted dinosaur hunter Ray Stanford shared the location of that footprint with Goddard’s facility management. The imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. Picuted here are Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS and Goddard Facilities Planner Alan Binstock, covering the newly discover nodosaur imprint with a sandbag to help preserve the imprecision. To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

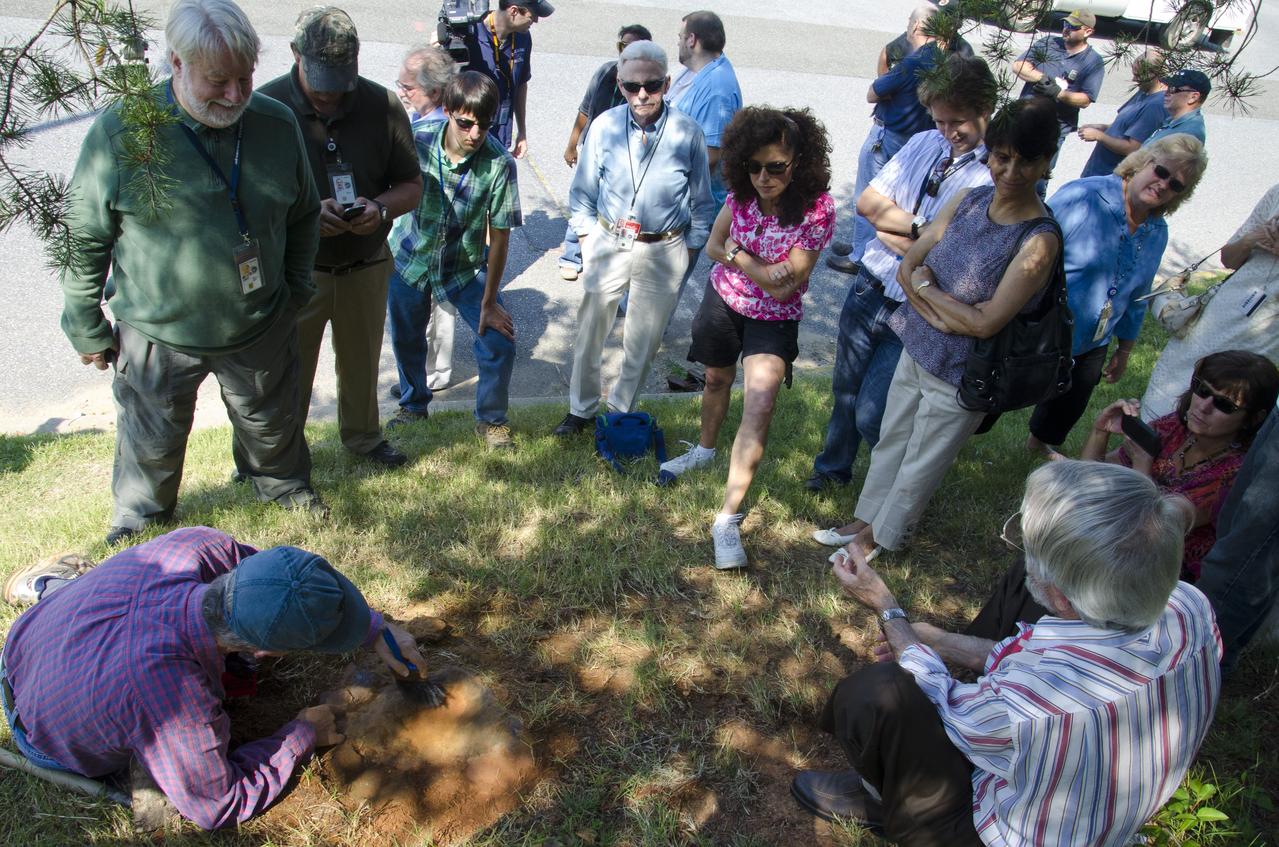
About 110 million light years away, the bright, barred spiral galaxy NGC3259 was just forming stars in dark bands of dust and gas. On Earth, a plant-eating dinosaur left footprints in the Cretaceous mud of what would later become the grounds of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Local dinosaur hunter Ray Stanford speaks to local press and Goddard officials about this discovery. <b>To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur....</a></b> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

About 110 million light years away, the bright, barred spiral galaxy NGC3259 was just forming stars in dark bands of dust and gas. On Earth, a plant-eating dinosaur left footprints in the Cretaceous mud of what would later become the grounds of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Local dinosaur hunter Ray Stanford points out the impression to Goddard officials and members of local media. <b>To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur....</a></b> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
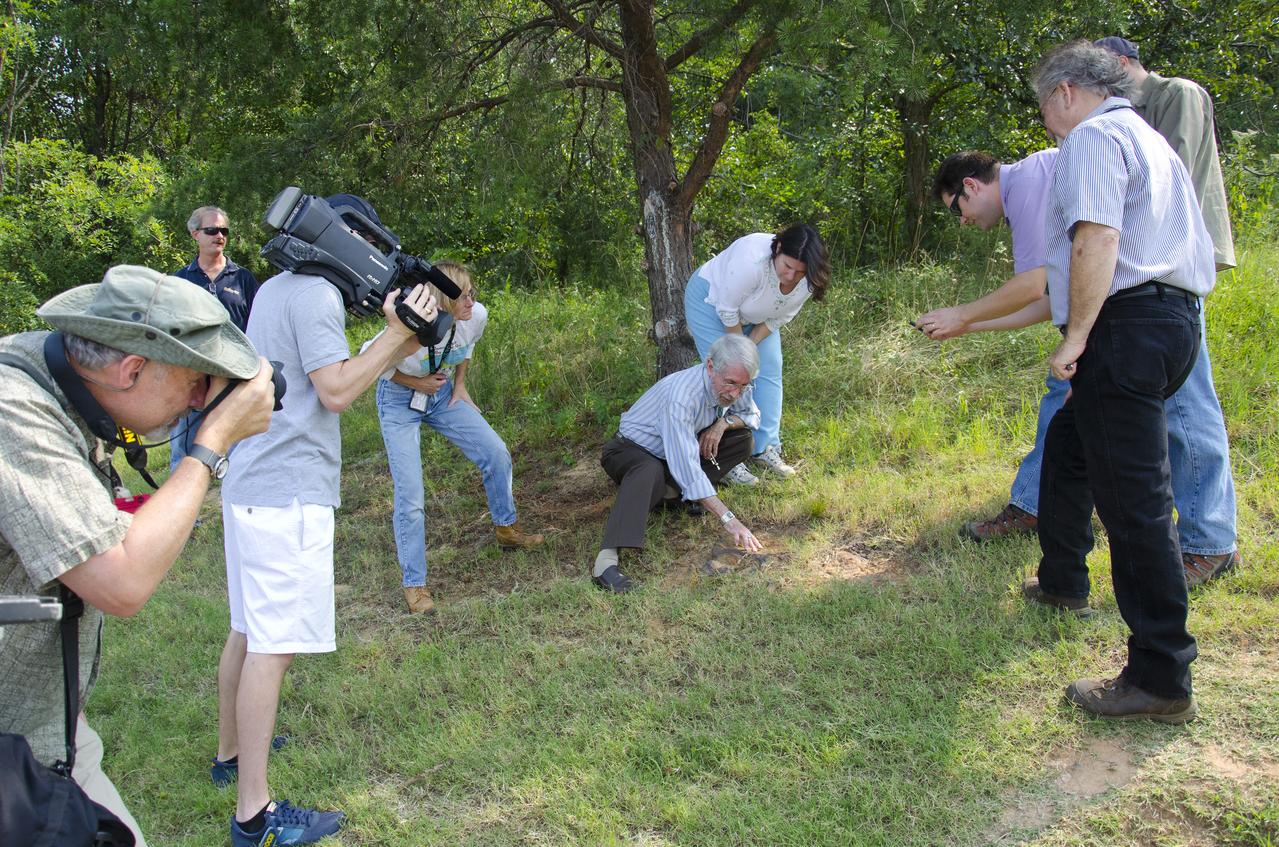

About 110 million light years away, the bright, barred spiral galaxy NGC3259 was just forming stars in dark bands of dust and gas. On Earth, a plant-eating dinosaur left footprints in the Cretaceous mud of what would later become the grounds of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Local dinosaur hunter Ray Stanford points out the impression to Goddard officials and members of local media. <b>To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur....</a></b> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

About 110 million light years away, the bright, barred spiral galaxy NGC3259 was just forming stars in dark bands of dust and gas. On Earth, a plant-eating dinosaur left footprints in the Cretaceous mud of what would later become the grounds of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Local dinosaur hunter Ray Stanford reviews a fossil found at the site. <b>To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur....</a></b> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

About 110 million light years away, the bright, barred spiral galaxy NGC3259 was just forming stars in dark bands of dust and gas. On Earth, a plant-eating dinosaur left footprints in the Cretaceous mud of what would later become the grounds of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Local dinosaur hunter Ray Stanford points out the impression to Goddard officials and members of local media. <b>To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur....</a></b> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

About 110 million light years away, the bright, barred spiral galaxy NGC3259 was just forming stars in dark bands of dust and gas. On Earth, a plant-eating dinosaur left footprints in the Cretaceous mud of what would later become the grounds of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. <b>To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2012/nodosaur....</a></b> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
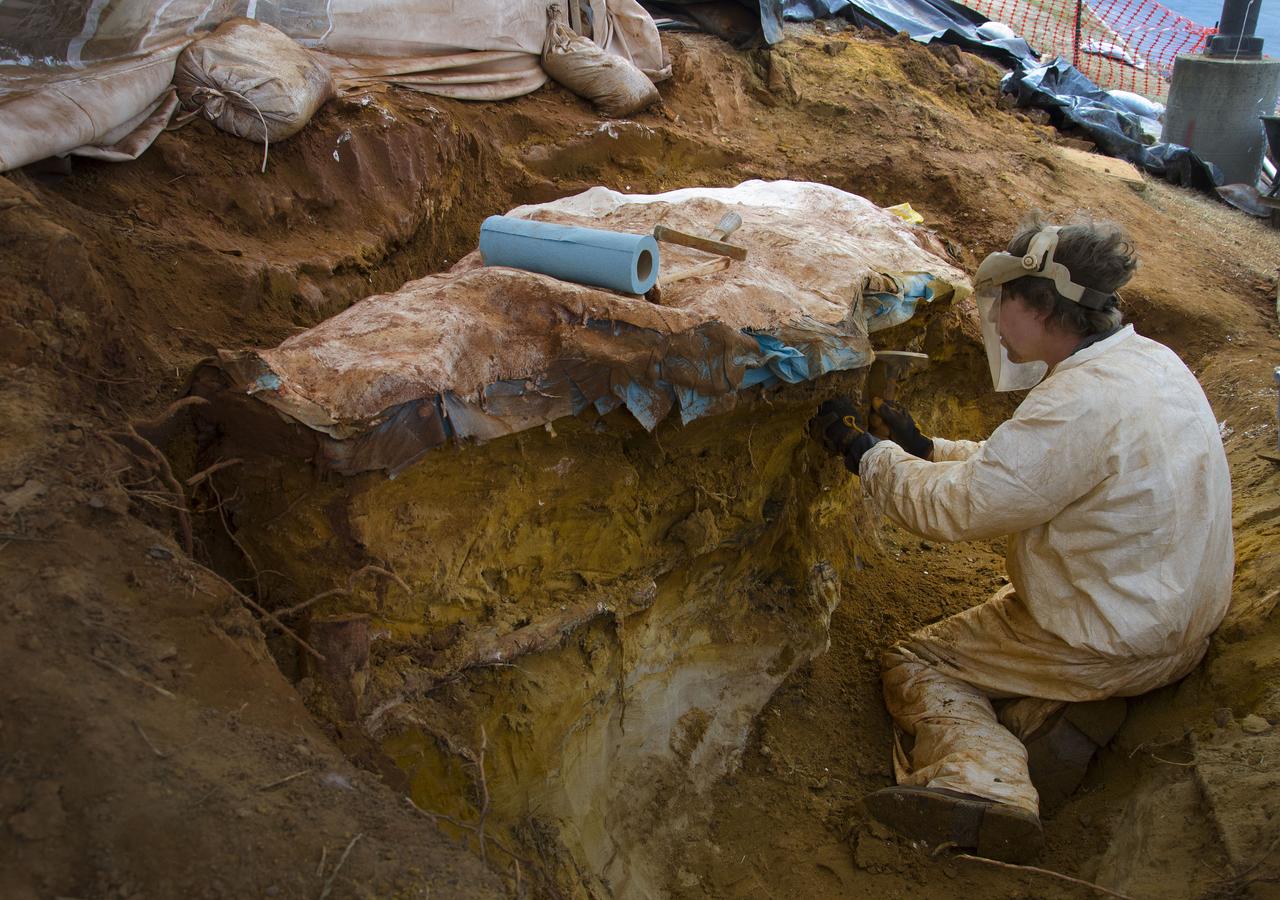

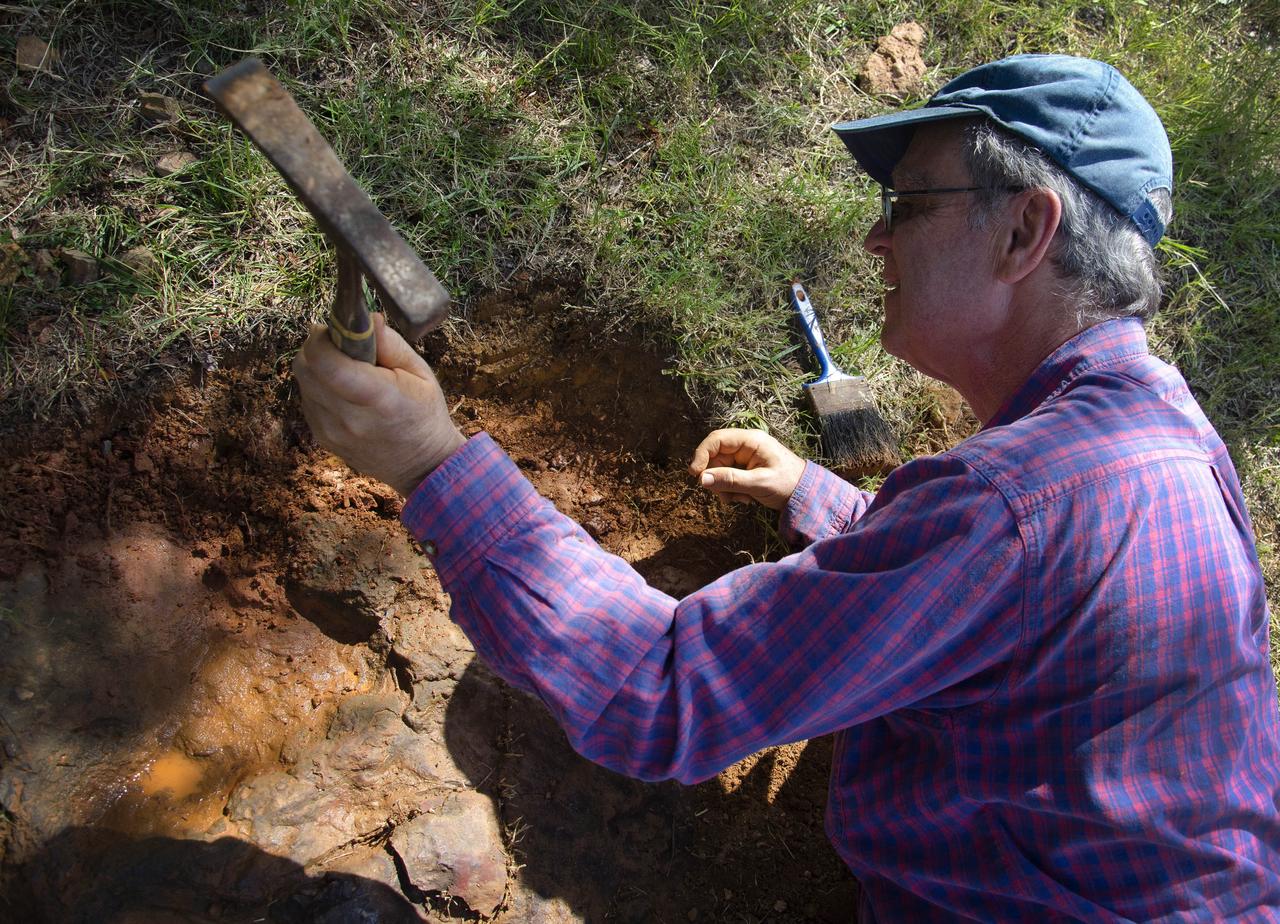
Seen here we have started to encase the dinosaur footprints in what is known as a field jacket. A field jacket is much like a cast that a doctor would place on a broken arm or leg. Our field jacket consisted of many layers of burlap soaked in plaster-of-Paris into which we also laminate metal pipes to act like splints for additional support. Here Michael is working to remove the very hard sandstone layer below the iron-rich clay layer in which the prints were preserved. Photo taken on January 7, 2013. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
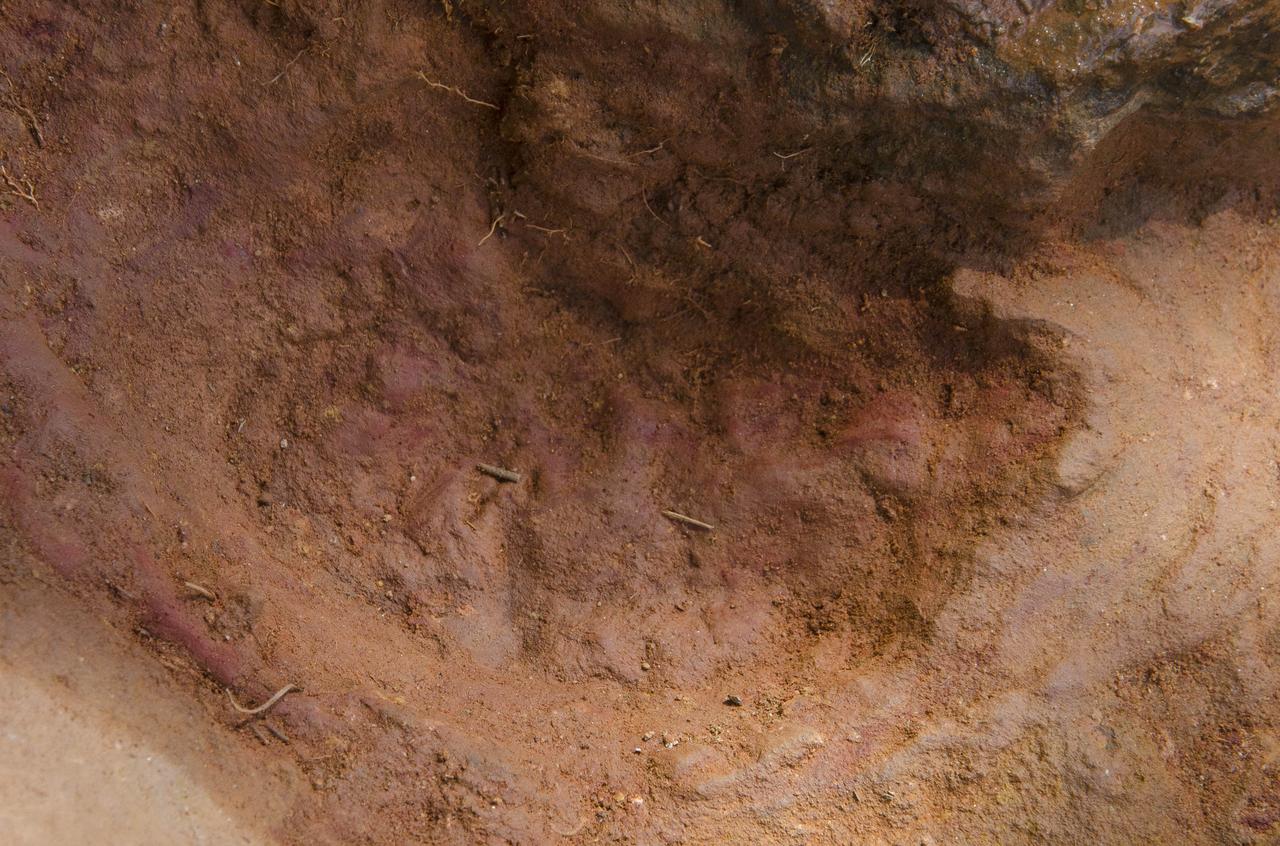

Not one, but two nodosaurs passed through the Goddard campus 110 to 112 million years ago, a USGS paleontologist confirmed. Pictured here the second track, overlapping the first, looks to be a young version of the same creature, perhaps following and sniffing along after, said Rob Weems, emeritus paleontologist and stratigrapher with the USGS. “It’s definitely a track.” To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
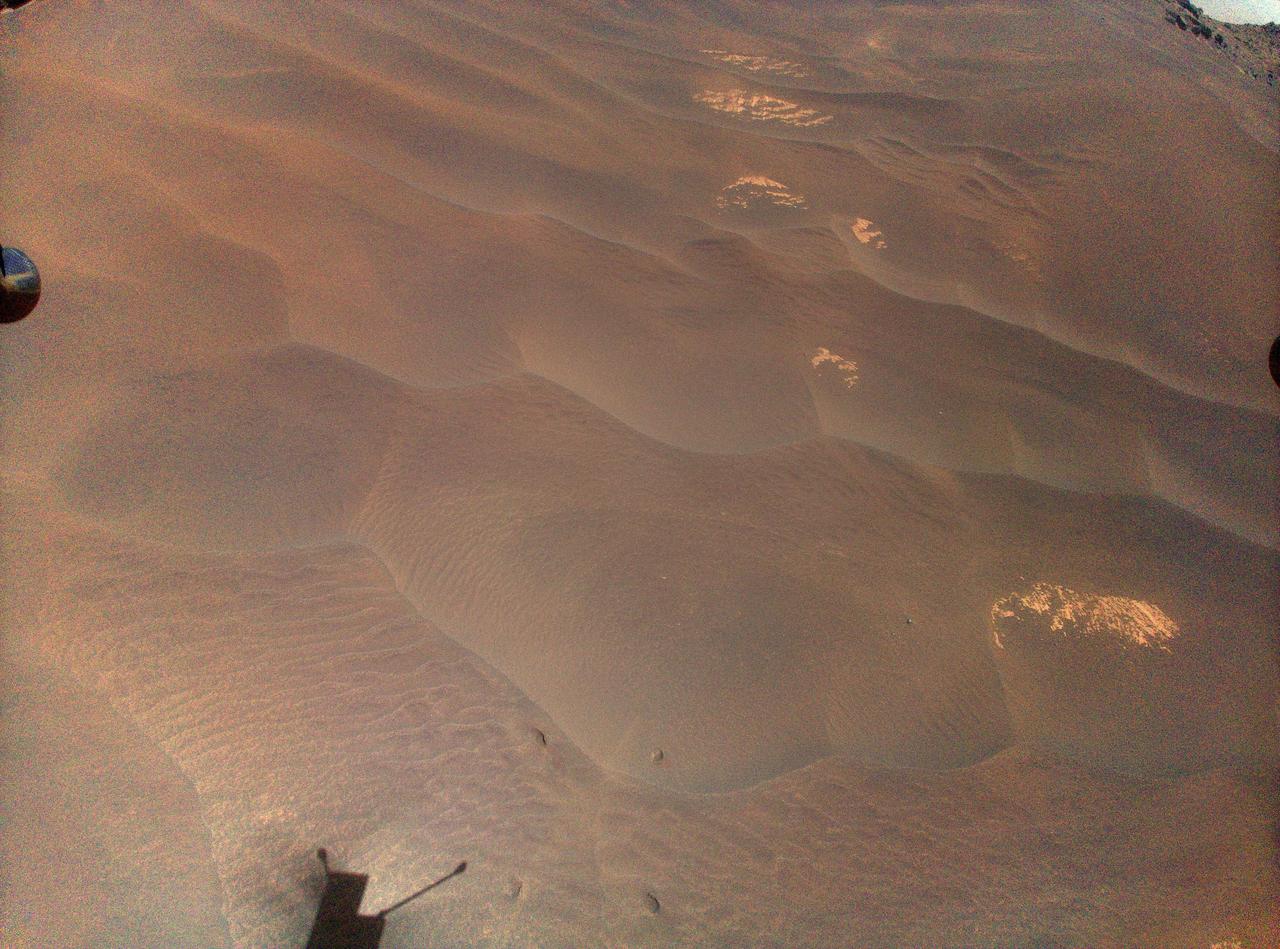

NASA's Ingenuity Mars helicopter captured this view of its "footprints" during Flight 66 on Nov. 3, 2023. The helicopter was being repositioned to the spot where it will spend several weeks during Mars solar conjunction. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26049

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

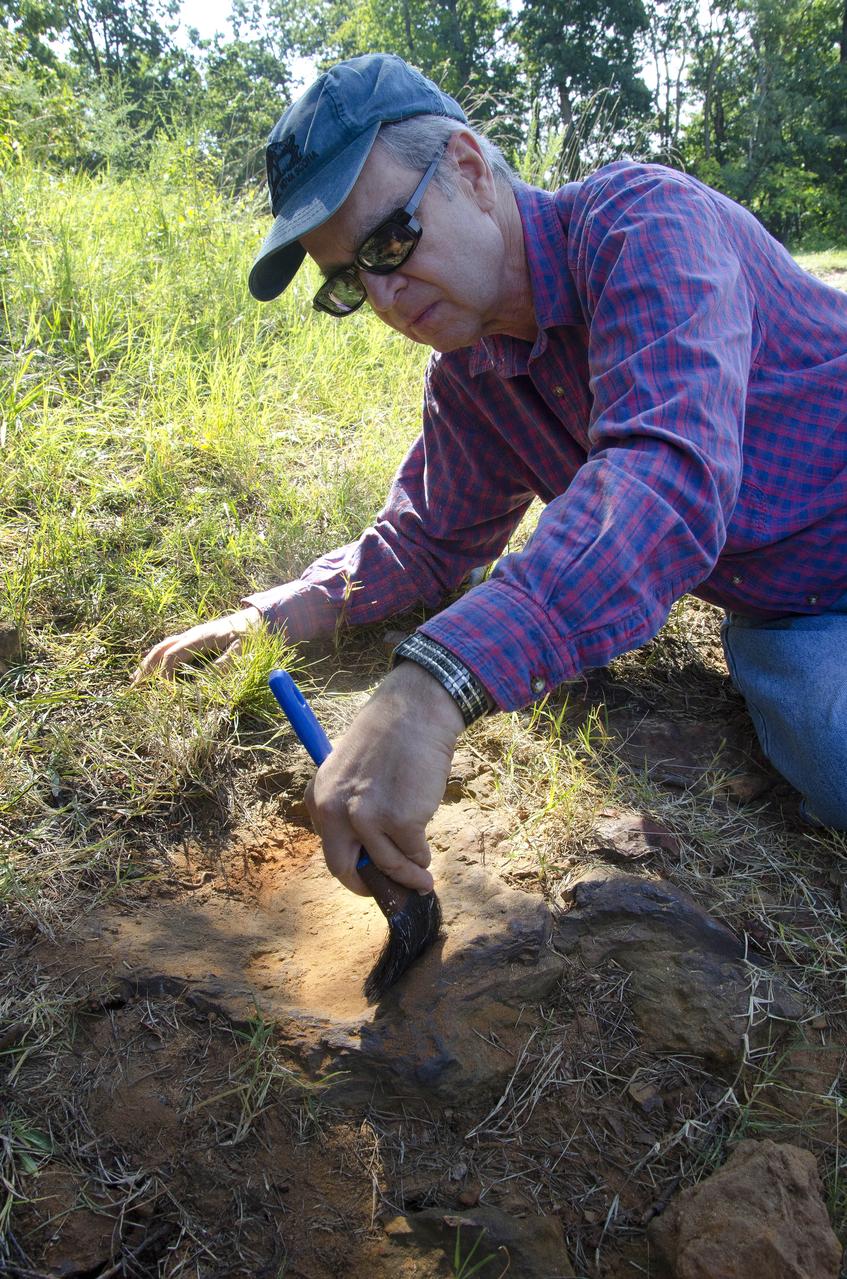
This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
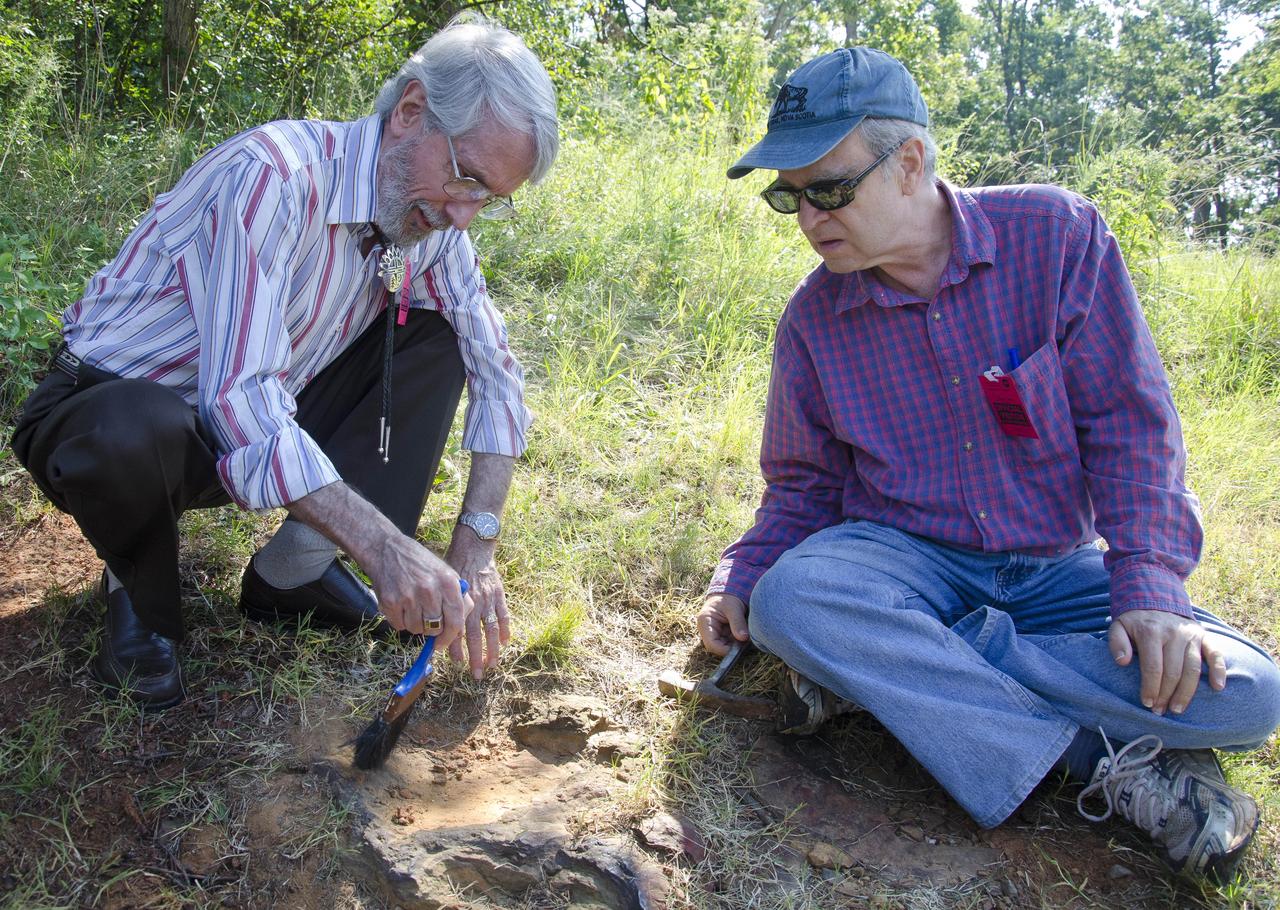

Dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford describes the cretaceous-era nodosaur track he found on the Goddard Space Flight Center campus with Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS who verified his discovery. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford describes the cretaceous-era nodosaur track he found on the Goddard Space Flight Center campus with Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS who verified his discovery. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
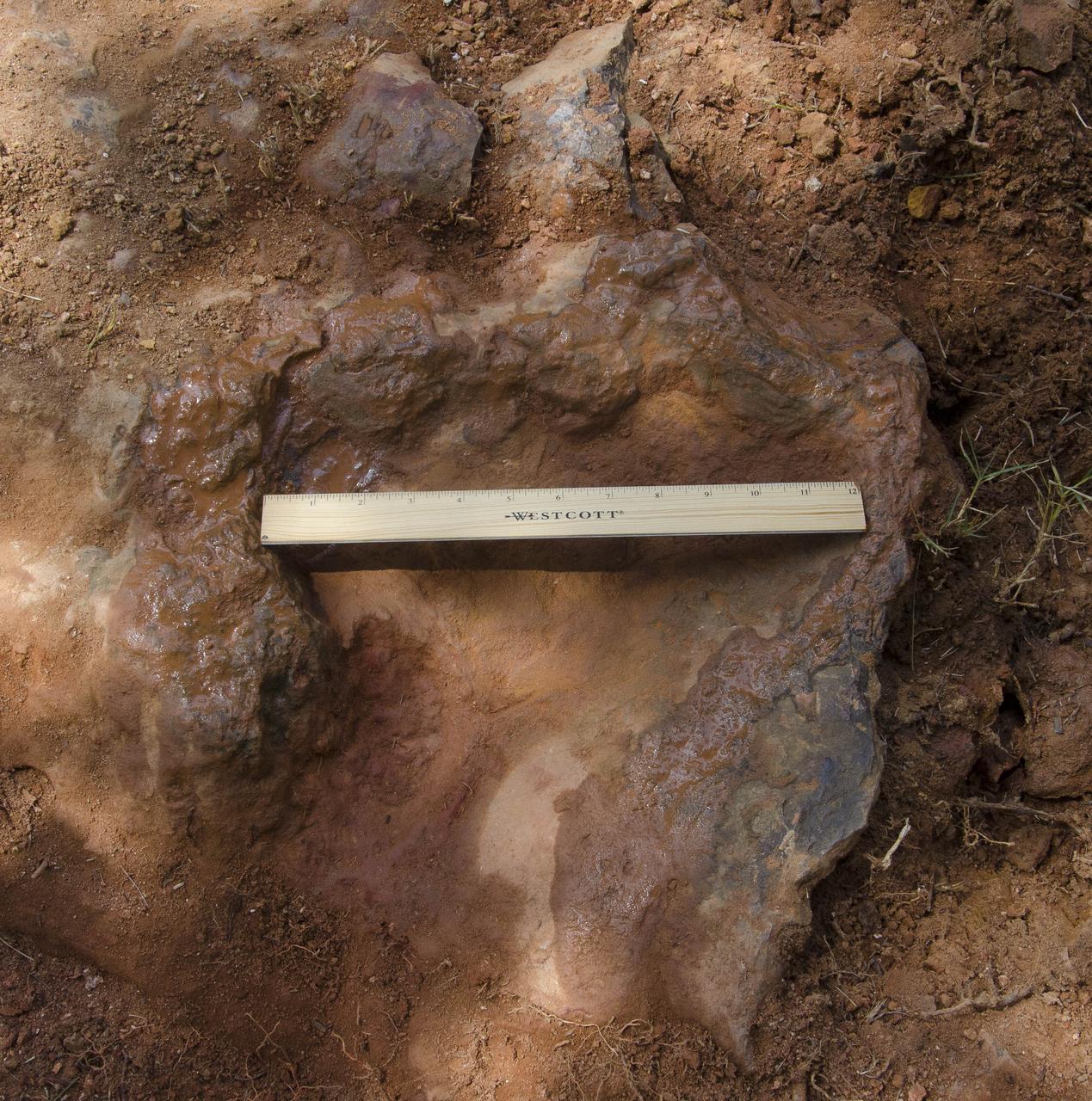

This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford describes the cretaceous-era nodosaur track he found on the Goddard Space Flight Center campus this year. The imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
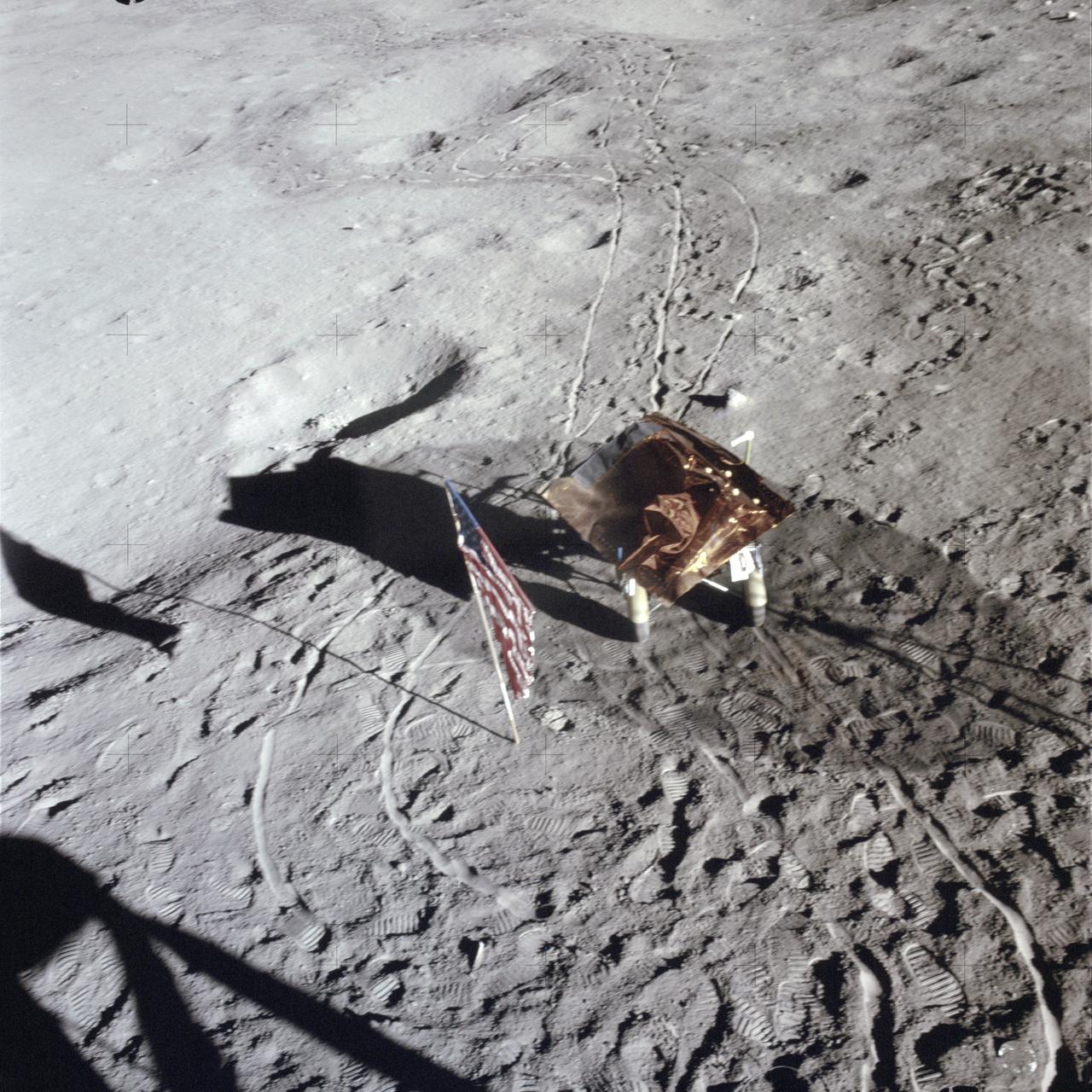

AS14-66-9325 (5 Feb. 1971) --- The third United States flag to be deployed on the lunar surface, footprints, wheel tracks and the "Rickshaw"-type portable workbench, as seen by the two moon-exploring astronauts from inside the Lunar Module (LM), give evidence of a busy first extravehicular activity (EVA) period. The two-wheeled cart is the Apollo modularized equipment transporter (MET), covered with a sheet of foil material to protect the cameras and rock box between EVAs. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

In December, 2012, Goddard scientists using ground penetrating radar showed that the sedimentary rock layer bearing these prints was preserved in its original location, but that investigation found no additional indications of locations of dinosaur track specimens of scientific value. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Michelle Handleman <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
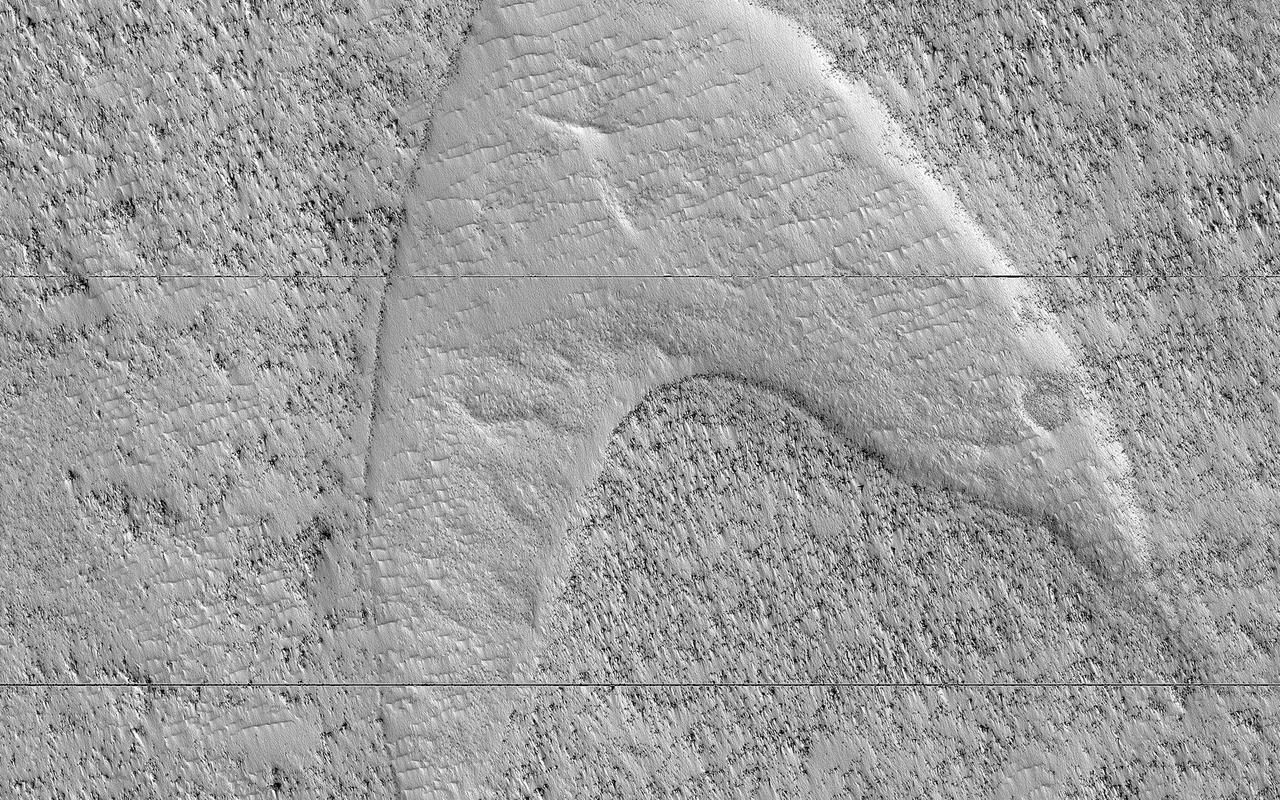

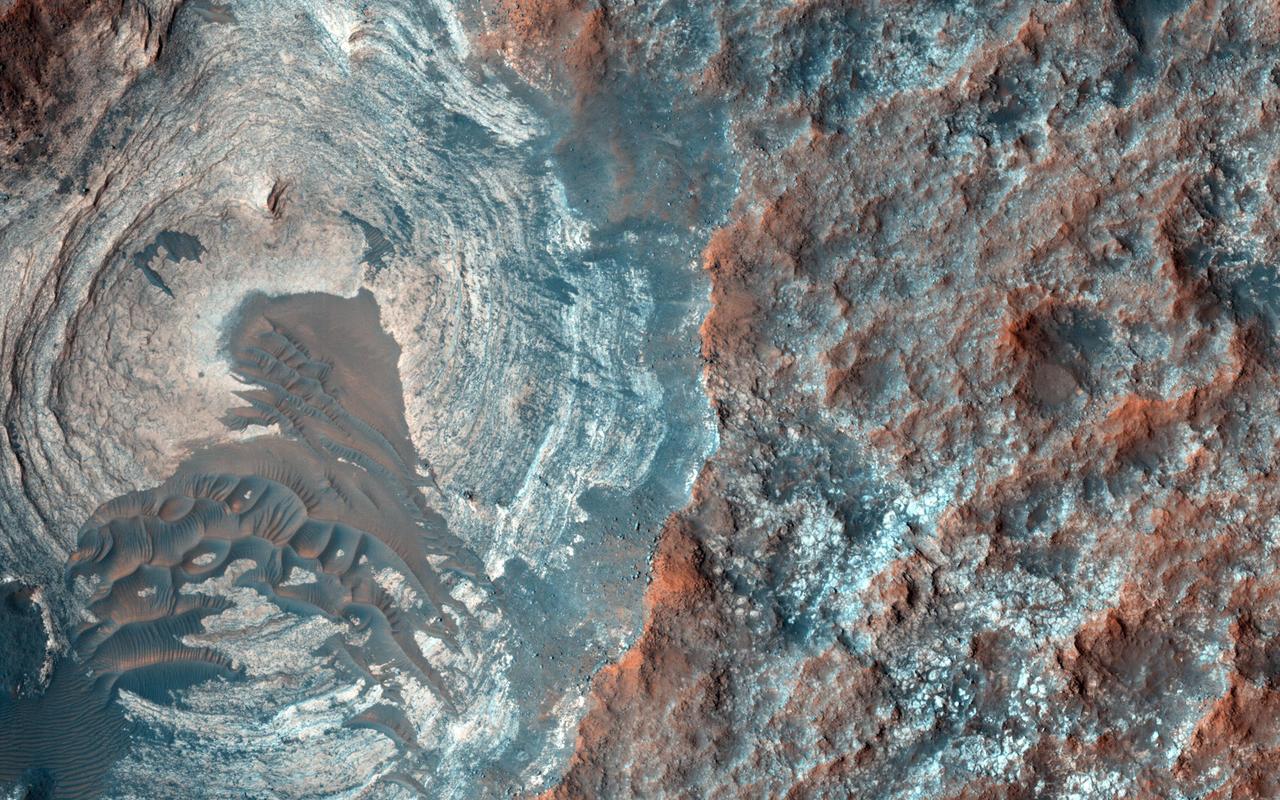
These curious chevron shapes in southeast Hellas Planitia are the result of a complex story of dunes, lava, and wind. Long ago, there were large crescent-shaped (barchan) dunes that moved across this area, and at some point, there was an eruption. The lava flowed out over the plain and around the dunes, but not over them. The lava solidified, but these dunes still stuck up like islands. However, they were still just dunes, and the wind continued to blow. Eventually, the sand piles that were the dunes migrated away, leaving these "footprints" in the lava plain. These are also called "dune casts" and record the presence of dunes that were surrounded by lava. Enterprising viewers will make the discovery that these features look conspicuously like a famous logo: and you'd be right, but it's only a coincidence. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23288
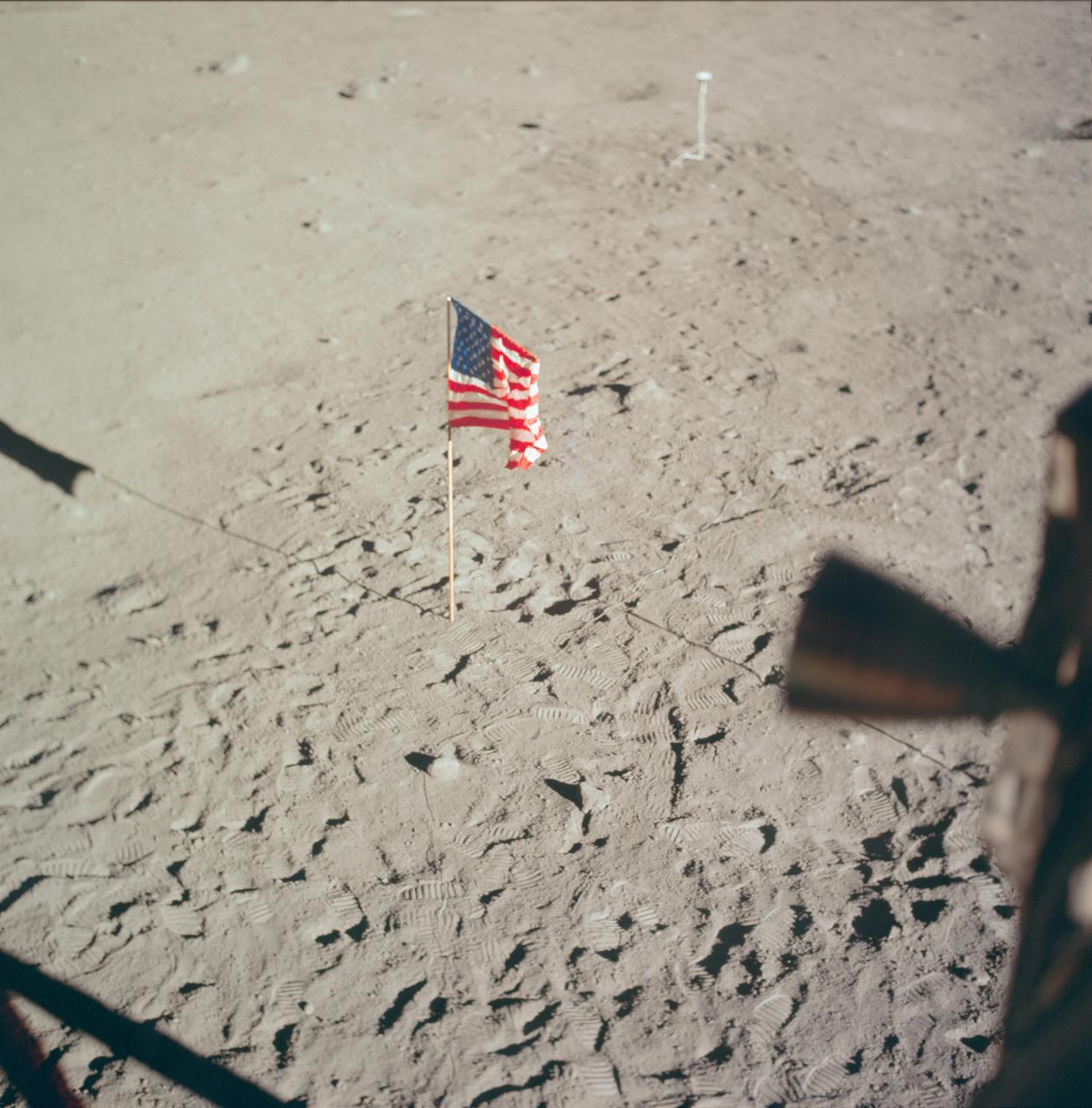
AS11-37-5545 (20 July 1969) --- The flag of the United States, deployed on the surface of the moon, dominates this photograph taken from inside the Lunar Module (LM). The footprints of astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. stand out very clearly. In the far background is the deployed black and white lunar surface television camera which televised the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Armstrong, commander, and Aldrin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
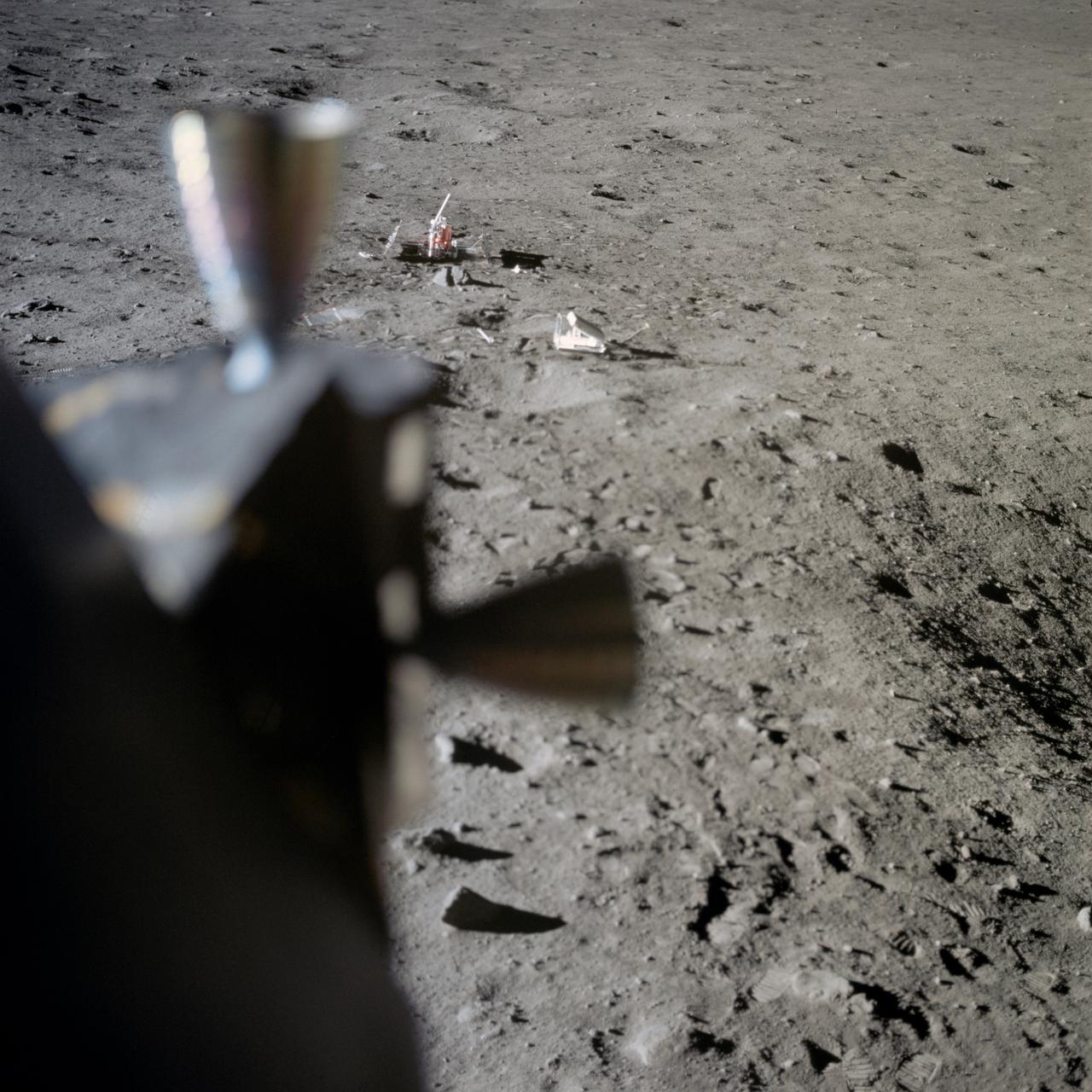

AS11-37-5551 (20 July 1969) --- Two components of the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP) are seen deployed on the lunar surface in this view photographed from inside the Lunar Module (LM). In the far background is the Passive Seismic Experiment Package (PSEP); and to the right and closer to the camera is the Laser Ranging Retro-Reflector (LR-3). The footprints of Apollo 11 astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. are very distinct in the lunar soil.
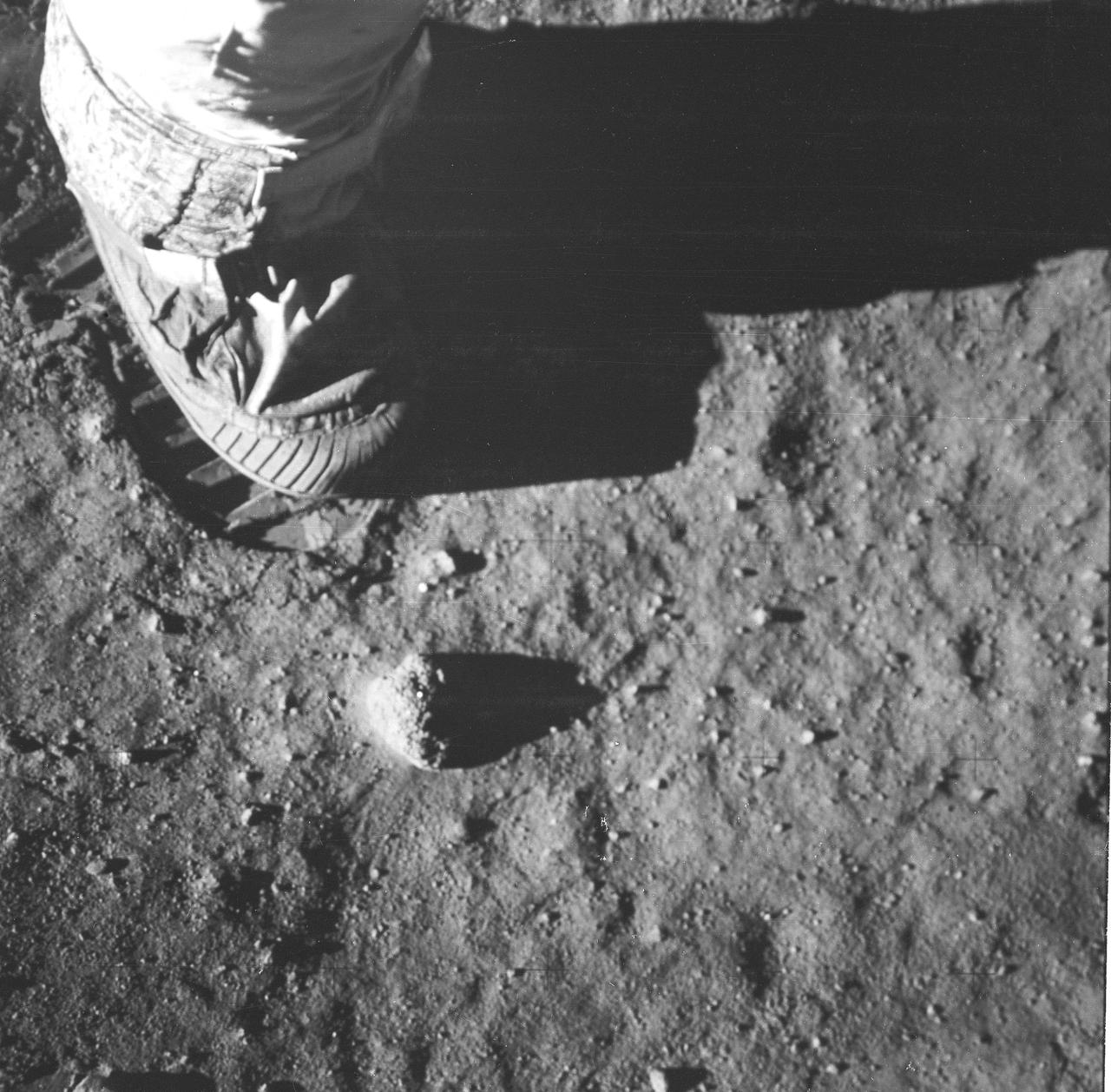

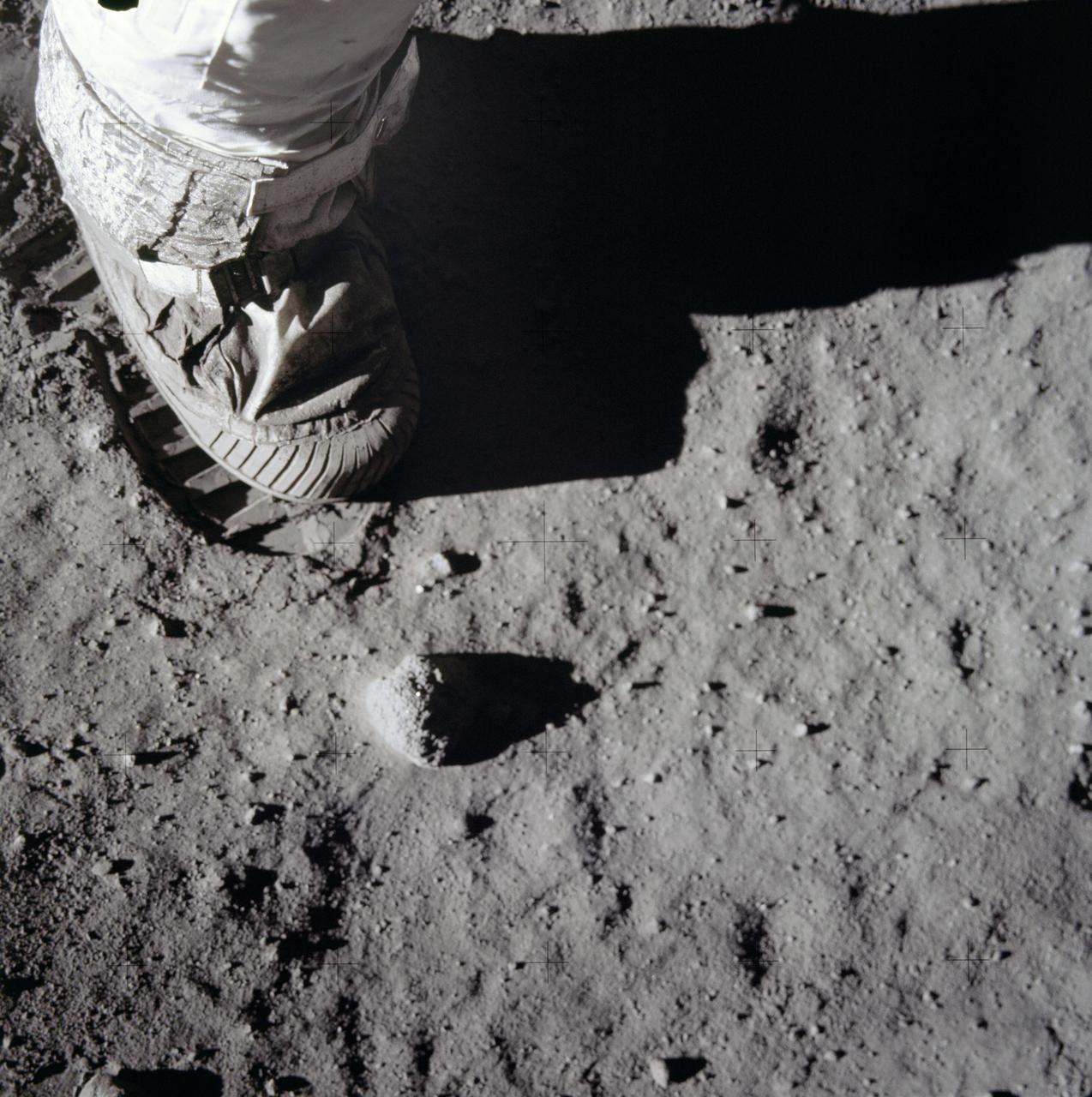
This is a close-up view of an astronaut’s foot and footprint in the lunar soil, photographed by a 70 mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). The first manned lunar mission launched via a Saturn V launch vehicle from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. The 3-man crew aboard the flight consisted of astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, mission commander; Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr., Lunar Module (LM) Pilot; and Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot. The LM landed on the moon’s surface on July 20, 1969 in the region known as Mare Tranquilitatis (the Sea of Tranquility). Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface. As he stepped off the LM, Armstrong proclaimed, “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind”. He was followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin, describing the lunar surface as magnificent desolation. Astronaut Collins piloted the CM in a parking orbit around the Moon. During a 2½ hour surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material which was returned to Earth for analysis. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.

This is a close-up view of an astronaut’s footprint in the lunar soil, photographed by a 70 mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity. The first manned lunar mission, the Apollo 11 launched aboard a Saturn V launch vehicle from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The 3-man crew aboard the flight consisted of Neil A, Armstrong, mission commander; Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr., Lunar Module Pilot; and Michael Collins, Command Module pilot. The LM landed on the moon’s surface on July 20, 1969 in the region known as Mare Tranquilitatis (the Sea of Tranquility). Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface. As he stepped off the LM, Armstrong proclaimed, “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind”. He was followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin, describing the lunar surface as Magnificent desolation. Astronaut Collins piloted the Command Module in a parking orbit around the Moon. The crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material which was returned to Earth for analysis. The surface exploration was concluded in 2½ hours. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. von Braun.

AS11-40-5878 (20 July 1969) --- A close-up view of an astronaut's bootprint in the lunar soil, photographed with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
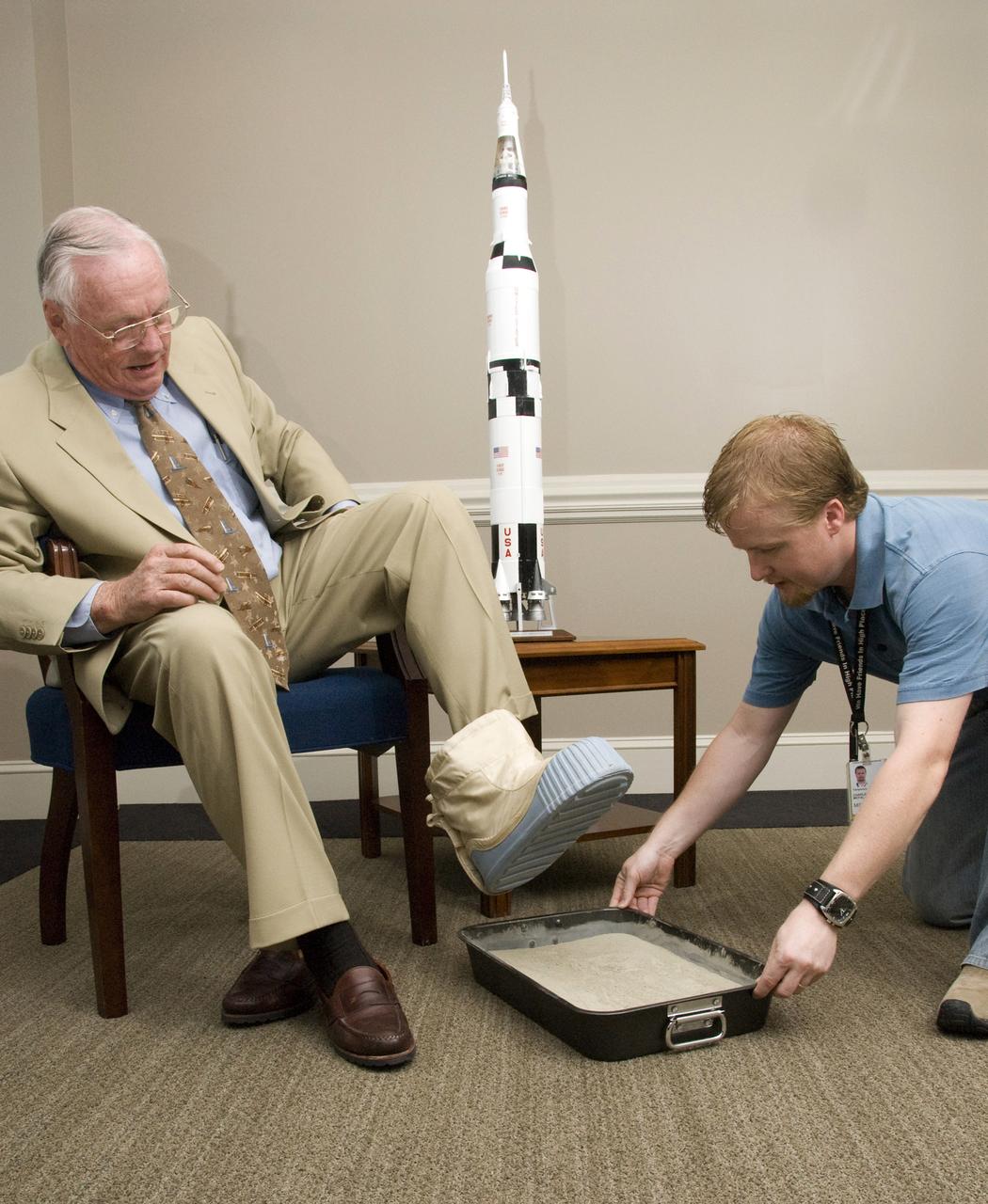

Among several other NASA dignitaries, former astronaut Neil A. Armstrong visited the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in attendance of the annual NASA Advisory Council Meeting. While here, Mr. Armstrong was gracious enough to allow the casting of his footprint. This casting will join those of other astronauts on display at the center. Armstrong was first assigned to astronaut status in 1962. He served as command pilot for the Gemini 8 mission, launched March 16, 1966, and performed the first successful docking of two vehicles in space. In 1969, Armstrong was commander of Apollo 11, the first manned lunar landing mission, and gained the distinction of being the first man to land a craft on the Moon and the first man to step on its surface. Armstrong subsequently held the position of Deputy Associate Administrator for Aeronautics, NASA Headquarters Office of Advanced Research and Technology, from 1970 to 1971. He resigned from NASA in 1971. Pictured with Armstrong is MSFC employee Daniel McFall, who assisted with the casting procedure.

A dying star, called the Helix nebula, is shown surrounded by the tracks of asteroids in an image captured by NASA WISE. Skirting around the edges of the Helix nebula are the footprints of asteroids marching across the field of view.

This artist concept based on data from NASA Cassini spacecraft, shows a glowing patch of ultraviolet light near Saturn north pole that occurs at the footprint of the magnetic connection between Saturn and its moon Enceladus.
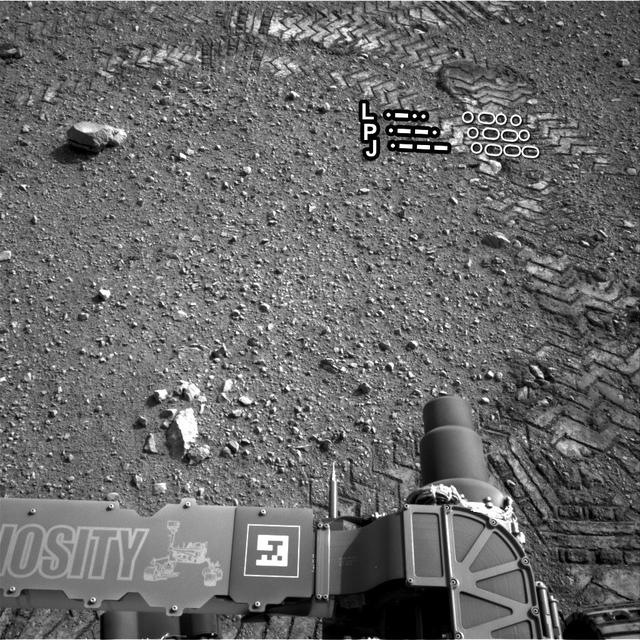

The straight lines in Curiosity zigzag track marks are Morse code for JPL. The footprint is an important reference mark that the rover can use to drive more precisely via a system called visual odometry.
As we head into the 21st Century, it seems hard to believe that human beings have been sending spacecraft toward Mars for more than 3 decades already. The first spacecraft to reach Mars was Mariner 4 in 1965. This success was followed by two spacecraft in 1969, Mariners 6 and 7. Now the wonders and alien beauty of Mars continue to unfold with each day that the Mars Global Surveyor -- which arrived in September 1997 -- continues to radio its data to Earth. Mars exploration was always difficult and each bit of data returned from the planet is a marvel. On August 5, 1969, the Mariner 7 spacecraft flew past Mars at a minimum altitude of about 4200 km. It acquired 14 wide/narrow angle image pairs during the few minutes of the "near encounter" flyby. One of these image pairs, 7N19/7N20, shows the south polar region and contains a feature that at the time was nicknamed "the Giant's Footprint." Shown in the first two pictures, above, the feature consists of two adjoining craters, one about 80 km (50 mi) in diameter and the other about 50 km (31 mi) across near latitude 76°S, longitude 276°W. The oblique geometry of the Mariner 7 image enhances the impression of a footprint. The "Giant's Footprint" was almost missed when Mariner 7 suffered a near-catastrophic battery failure just a few days before the encounter -- on July 30 -- that put the spacecraft sporadically out of contact with Earth for two days. Ground controllers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL)recovered the spacecraft, re-planned its imaging sequence based on results from the Mariner 6 flyby on July 31, and salvaged all of the mission's science goals in under a week! In the 1970's, the larger crater in "giant's footprint" was named "Vishniac" in honor of Wolf Vishniac, an American microbiologist of the University of Rochester who was instrumental in the development of methods to search for life on Mars. Vishniac was tragically killed in a fall in Antarctica in 1973 while retrieving a life detection experiment, and the crater was named in honor of this "giant" in the search for life on Mars. More than three decades after the Mariner 7 flyby, Mars Global Surveyor's Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) acquired a commemorative view of the interior of Vishniac Crater on October 25, 1999. The context image and the 3-meters (9.8 feet)-per-pixel narrow angle view are shown above (in the lower image pair). Mariner 7's 7N20 has a nominal resolution of about 180 meters (591 feet) per pixel, while the MOC high resolution view is about 60 times higher (in actuality, the lower quality of the Mariner 7 images makes the resolution gain even more dramatic). The MOC high resolution view (lower right, above) shows a 1.5 kilometer-(0.9 mile)-wide portion of the floor of Vishniac in the process of defrosting during southern spring. The bright areas are still frost-covered, while the darker areas are either defrosted or composed of darkened or "dirty" frost. The dark patches in the image seem to serve as sources for dark streaks of material that has either been blown across the landscape by wind, or has somehow caused the erosion of frost to create the streaks. Dark streaks follow the local topography, as might the wind that blew across this landscape. This pattern of spots and streaks was quite common on the defrosting south polar cap during the spring that lasted from early August 1999 to late December 1999. All images shown here are illuminated by sunlight from the lower right. Image orientation with north toward the bottom was selected in order to show the "footprint" visible in Mariner 7 image 7N20. The Mariner 7 images were recovered at Malin Space Science Systems from the original 7-track magnetic tapes, archived on CD-ROM by the JPL Data Preservation activity. More images relating to the release can be viewed at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02365
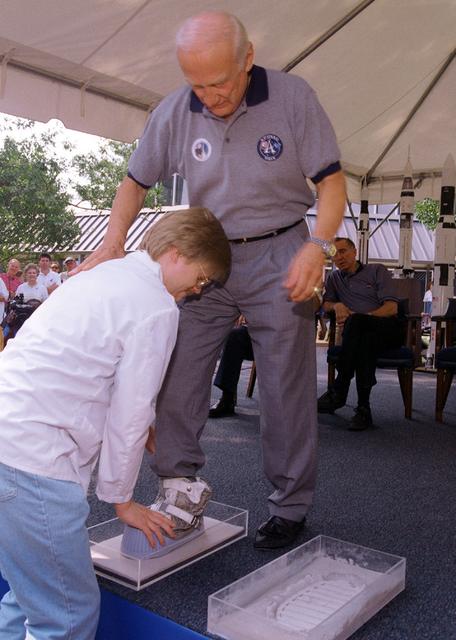

Apollo 11 Astronaut Buzz Aldrin has his footprints casted during the dedication ceremony of the rocket fountain at Building 4200 at Marshall Space Flight Center. The casts of Aldrin's footprints will be placed in the newly constructed Von Braun courtyard representing the accomplishments of the Apollo 11 lunar landing.
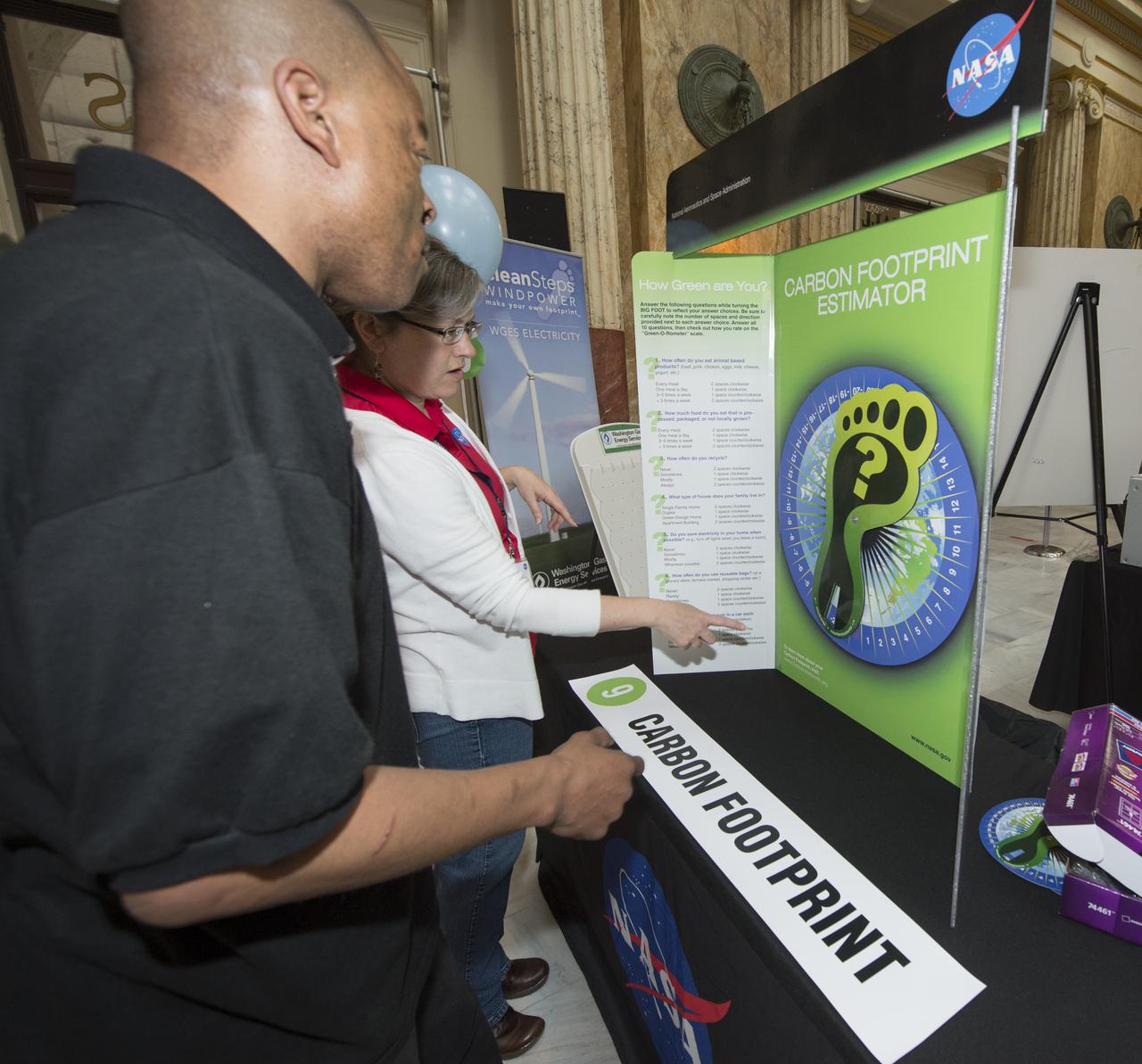

A participant at NASA's Earth Day Science Gallery Exhibit calculates his carbon footprint at the Carbon Footprint Estimator, Monday, April 22, 2013 at Union Station in Washington. The NASA Science Gallery exhibits are being sponsored by NASA in honor of Earth Day. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)
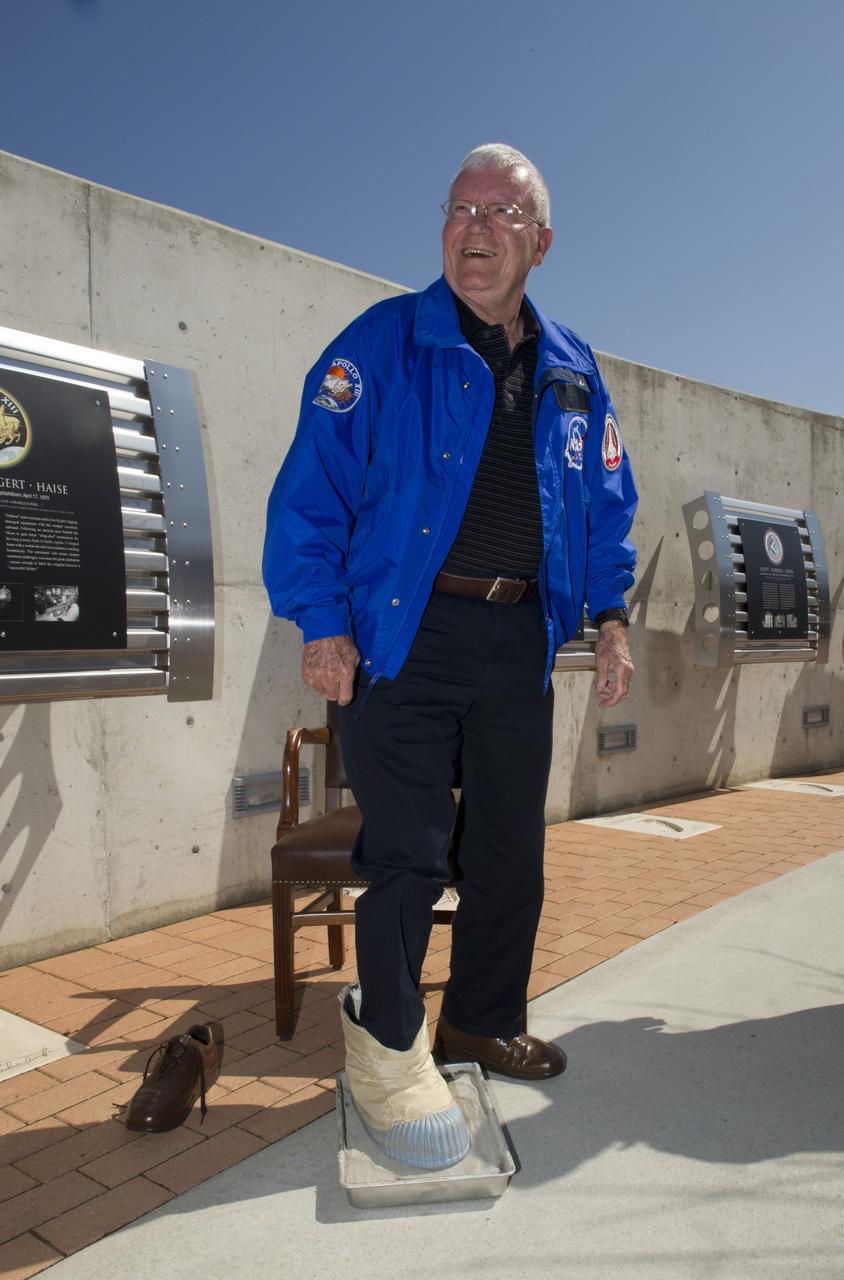

APOLLO 13 ASTRONAUT FRED HAISE CASTS FOOTPRINT AT USSRC DAVIDSON CENTER

AS12-48-7160 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- This view of the lunar surface was taken by one of the two astronauts on the Apollo 12 mission during their extravehicular activity. Seen in this view are the U.S. flag, several astronaut footprints, and a small crater near their Lunar Module landing site. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the lunar surface. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.
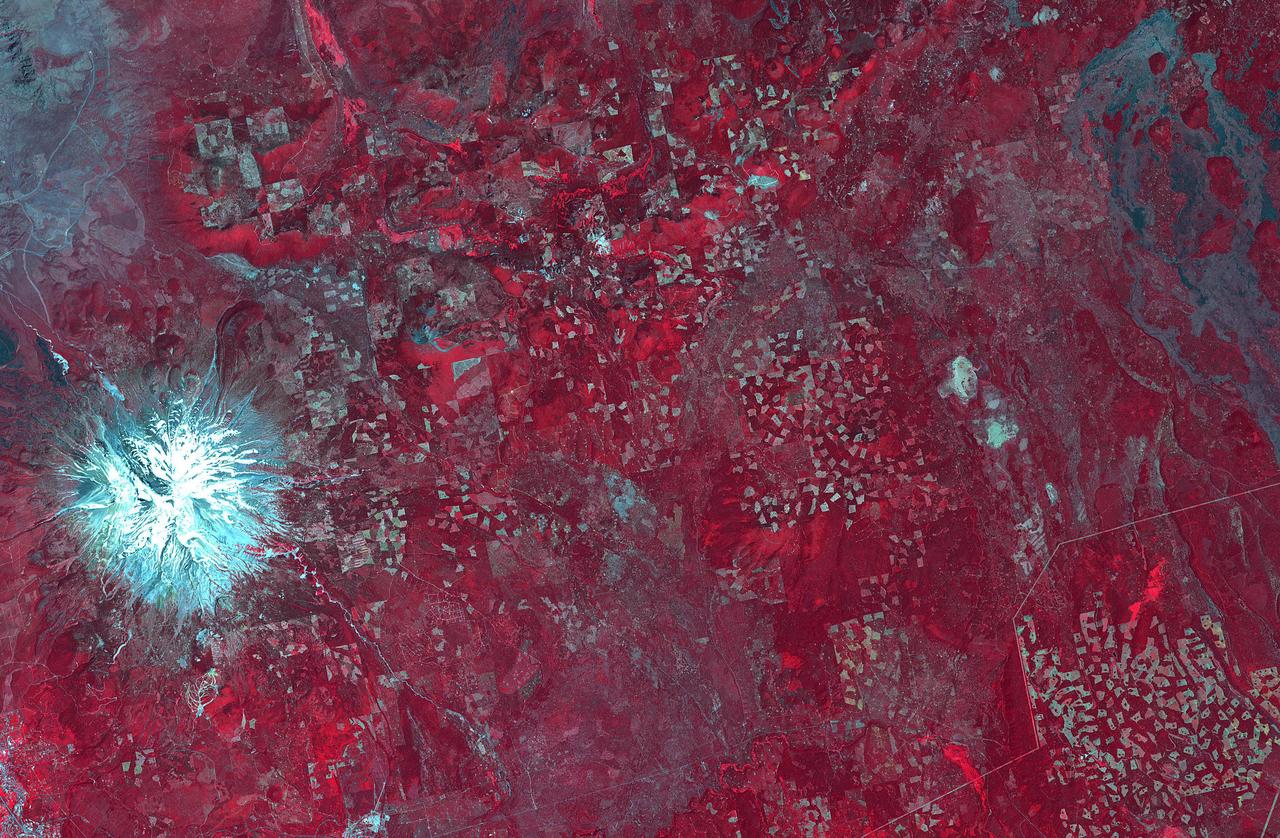
In northern California, east of Mt. Shasta, the footprints of clear-cut logging activities are evident in this ASTER image. Newer logged-out parcels are brighter blue-green. Where secondary growth has started, the logged tracts appear "fuzzy." Note that some of the logged-out tracts are located within the Shasta National Forest. The image was acquired July 2, 2018, covers an area of 37 by 56.5 kilometers, and is located at 42.5 degrees north, 122 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22613

AS11-40-5880 (20 July 1969) --- A close-up view of an astronaut's boot and bootprint in the lunar soil, photographed with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin A. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM)" Columbia" in lunar orbit.
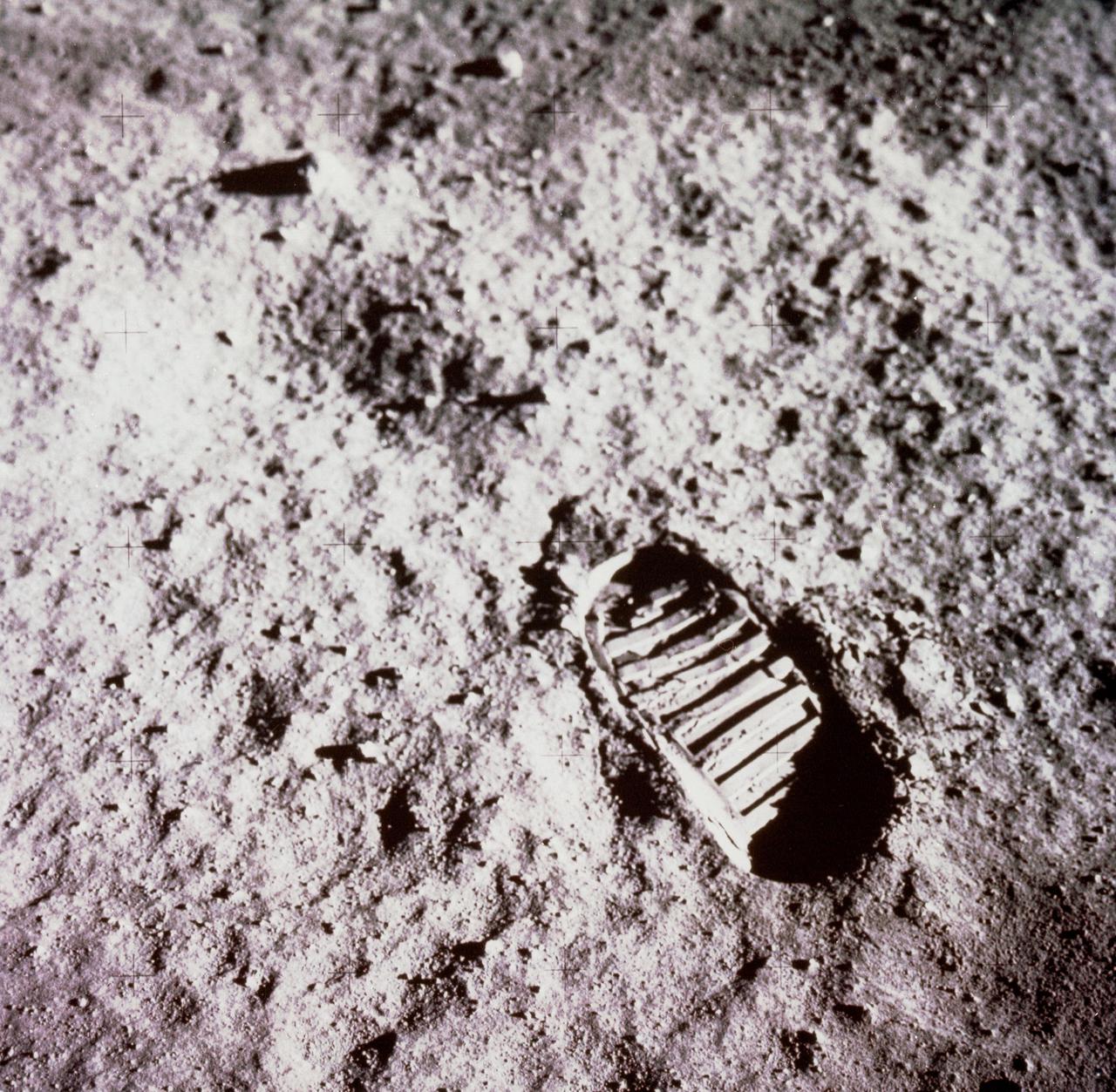

Buzz Aldrin took this iconic image of a bootprint on the Moon during the Apollo 11 moonwalk on July 20, 1969. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24439
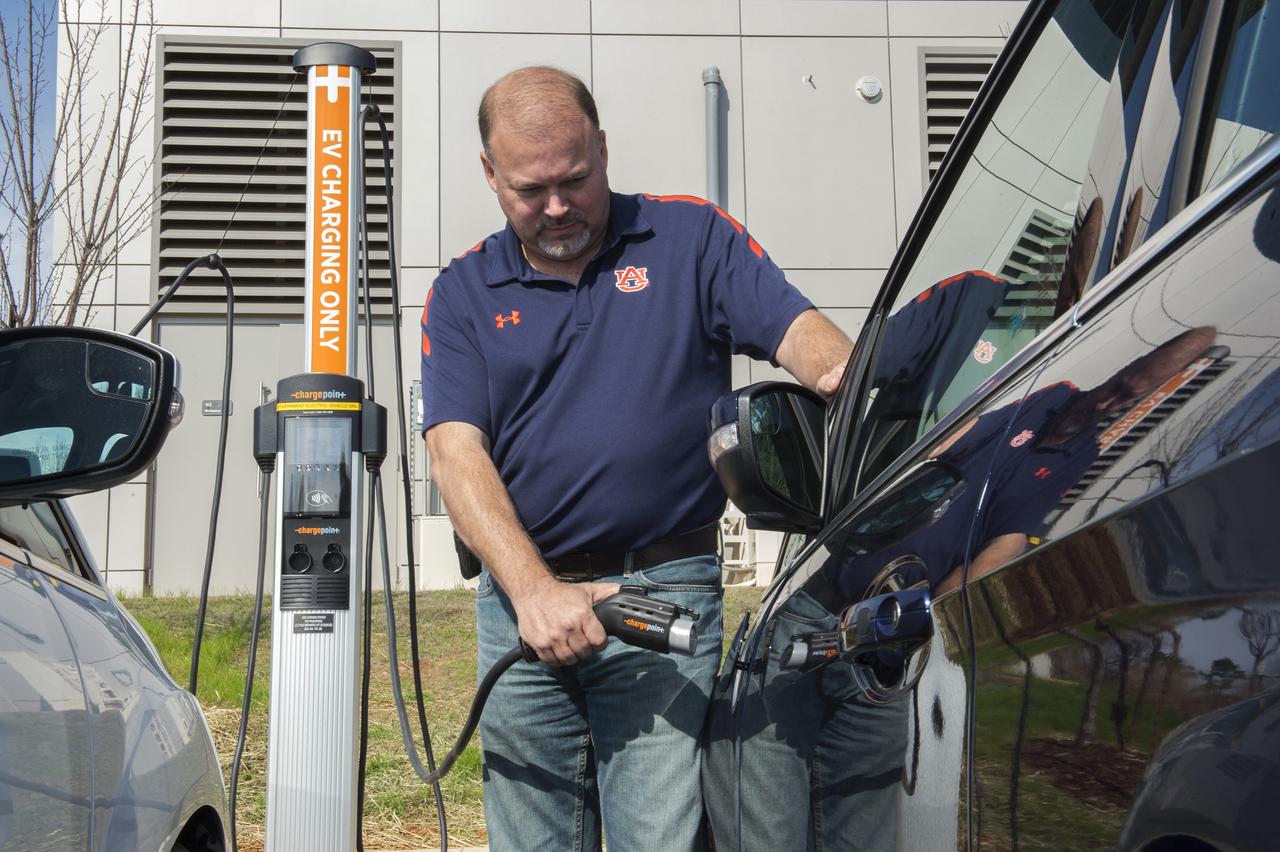

TRANSPORTATION SPECIALIST DAVID NORRIS DEMONSTRATES MARSHALL'S FIRST ELECTRIC VEHICLE CHARGING STATION, WHICH IS PART OF A PROGRAM DESIGNED TO REDUCE THE AGENCY'S ENVIRONMENTAL FOOTPRINT.
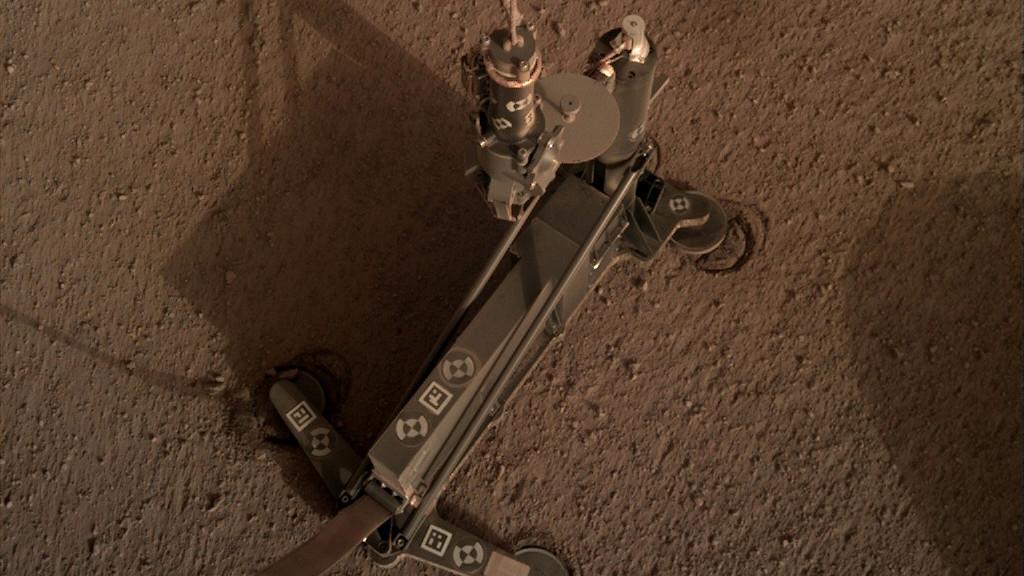

The support structure of the Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP3) instrument moved slightly during hammering, as indicated by the circular "footprints" that can be seen around the instrument's footpads. These marks indicate the instrument's self-hammering mole wasn't digging as expected. This image was taken on March 4, 2019 (the 94th Martian day, or sol, of the mission). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23271
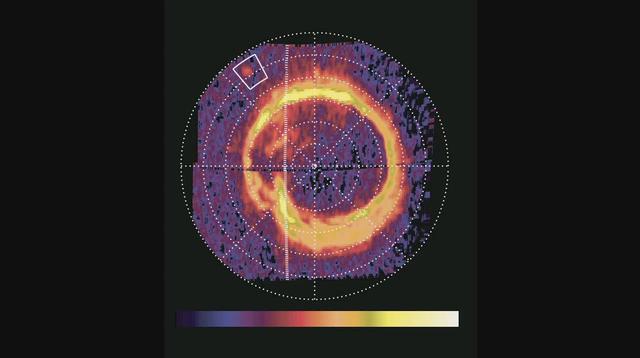
NASA Cassini spacecraft has spotted a glowing patch of ultraviolet light near Saturn north pole that marks the presence of an electrical circuit that connects Saturn with its moon Enceladus. Movie available at the Photojournal.
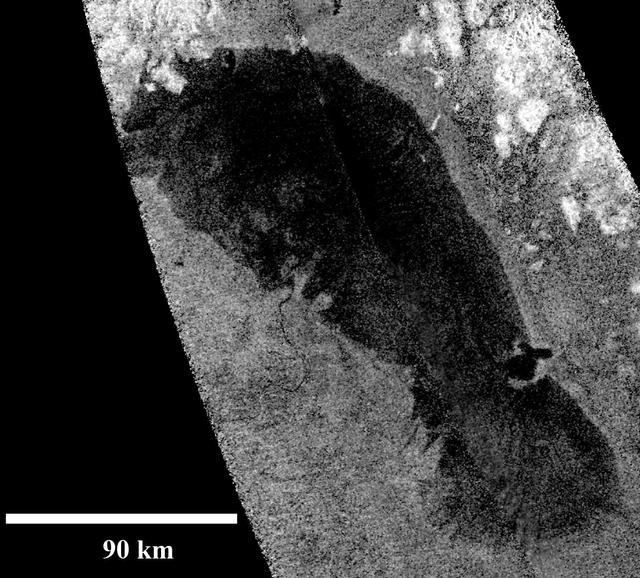

This image of Ontario Lacus, the largest lake on the southern hemisphere of Saturn moon Titan, was obtained by NASA Cassini spacecraft. The lake surface appears dark because it is smooth.
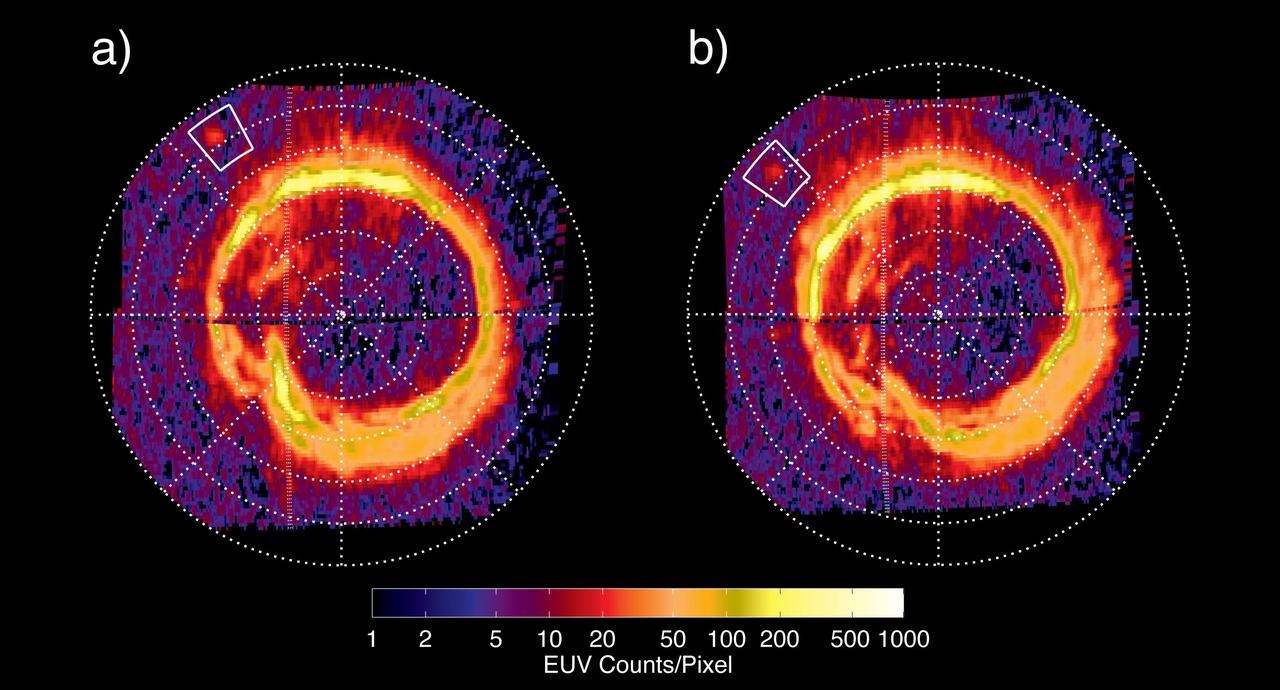
NASA Cassini spacecraft has spotted a glowing patch of ultraviolet light near Saturn north pole that marks the presence of an electrical circuit that connects Saturn with its moon Enceladus.
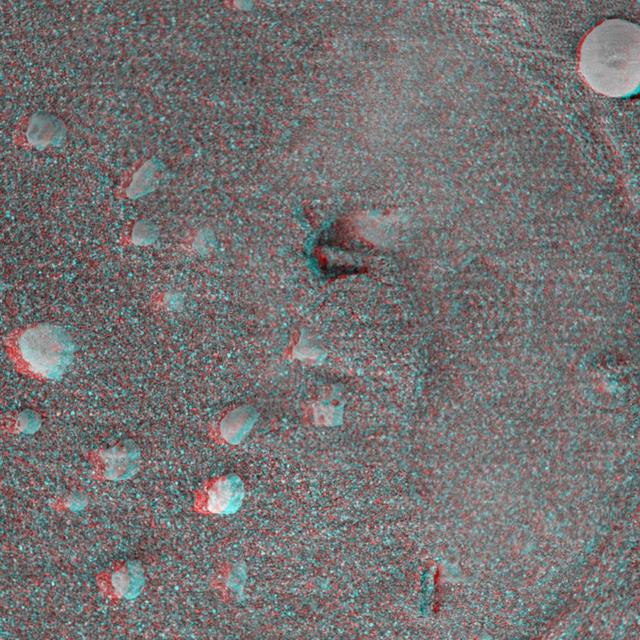

This 3-D anaglyph, from NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit, shows a circular imprint left in the Meridiani Planum soil by the rover Moessbauer spectrometer. 3D glasses are necessary.

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. walks on the surface of the Moon near a leg of the Lunar Module during the Apollo 11 EVA. Armstrong also took this picture with the 70-mm lunar surface camera. Note footprints in the foreground.

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - Surrounded by Man's footprints on the lunar surface, Apollo 11 Lunar Module Pilot Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. erects a solar wind experiment near the Tranquility Base established by the Lunar Module, Eagle.
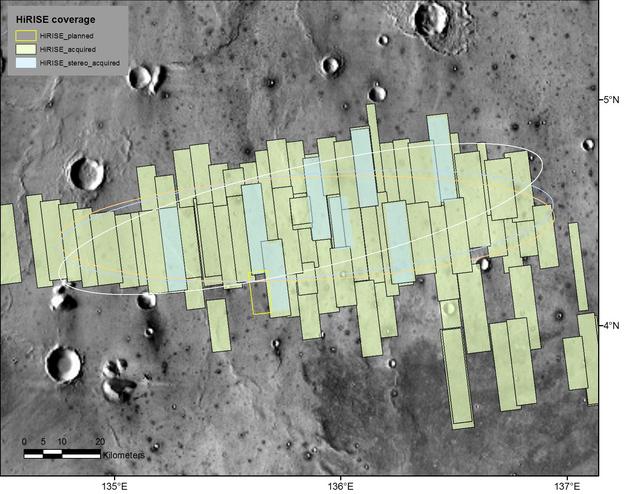
This map shows footprints of images taken from Mars orbit by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera as part of advance analysis of the area where NASA's InSight mission will land in 2018. The final planned image of the set is targeted to fill in the yellow-outlined rectangle on March 30, 2017. HiRISE is one of six science instruments on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, which reached Mars in 2006 and surpassed 50,000 orbits on March 27, 2017. The map covers an area about 100 miles (160 kilometers) across. HiRISE has been used since 2006 to inspect dozens of candidate landing sites on Mars, including the sites where the Phoenix and Curiosity missions landed in 2008 and 2012. The site selected for InSight's Nov. 26, 2018, landing is on a flat plain in the Elysium Planitia region of Mars, between 4 and 5 degrees north of the equator. HiRISE images are detailed enough to reveal individual boulders big enough to be a landing hazard. The March 30 observation that completes the planned advance imaging of this landing area brings the number of HiRISE images of the area to 73. Some are pairs covering the same ground. Overlapping observations provide stereoscopic, 3-D information for evaluating characteristics such as slopes. On this map, coverage by stereo pairs is coded in pale blue, compared to the gray-green of single HiRISE image footprints. The ellipses on the map are about 81 miles (130 kilometers) west-to-east by about 17 miles (27 kilometers) north-to-south. InSight has about 99 percent odds of landing within the ellipse for which it is targeted. The three ellipses indicate landing expectations for three of the possible InSight launch dates: white outline for launch at the start of the launch period, on May 5, 2018; blue for launch on May 26, 2018; orange for launch on June 8, 2018. InSight -- an acronym for "Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport" -- will study the deep interior of Mars to improve understanding about how rocky planets like Earth formed and evolved. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21489

The target of this observation as seen by ASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter is a circular depression in a dark-toned unit associated with a field of cones to the northeast. At the image scale of a Context Camera image, the depression appears to expose layers especially on the sides or walls of the depression, which are overlain by dark sands presumably associated with the dark-toned unit. HiRISE resolution, which is far higher than that of the Context Camera and its larger footprint, can help identify possible layers. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19358

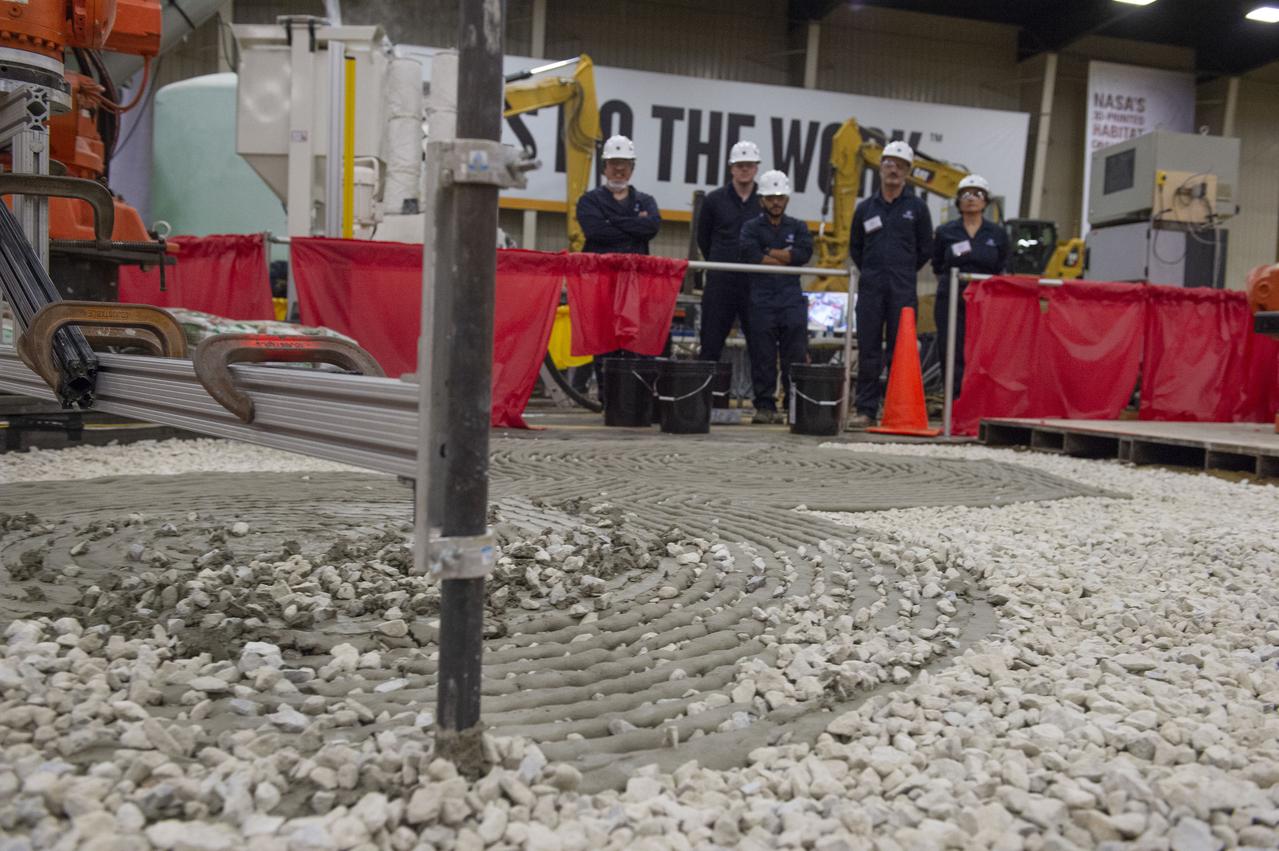
AI. SpaceFactory of New York and Pennsylvania State University of College Park print subscale habitat structures at NASA's 3D-Printed Habitat Challenge, held at the Caterpillar Edwards Demonstration & Learning Center in Edwards, Illinois, May 1-4, 2019. The habitat print is the final level of the multi-phase competition, which began in in 2015. The challenge is managed by NASA's Centennial Challenges program, and partner Bradley University of Peoria, Illinois. Initial footprint of 3D material laydown for Penn State habitat.
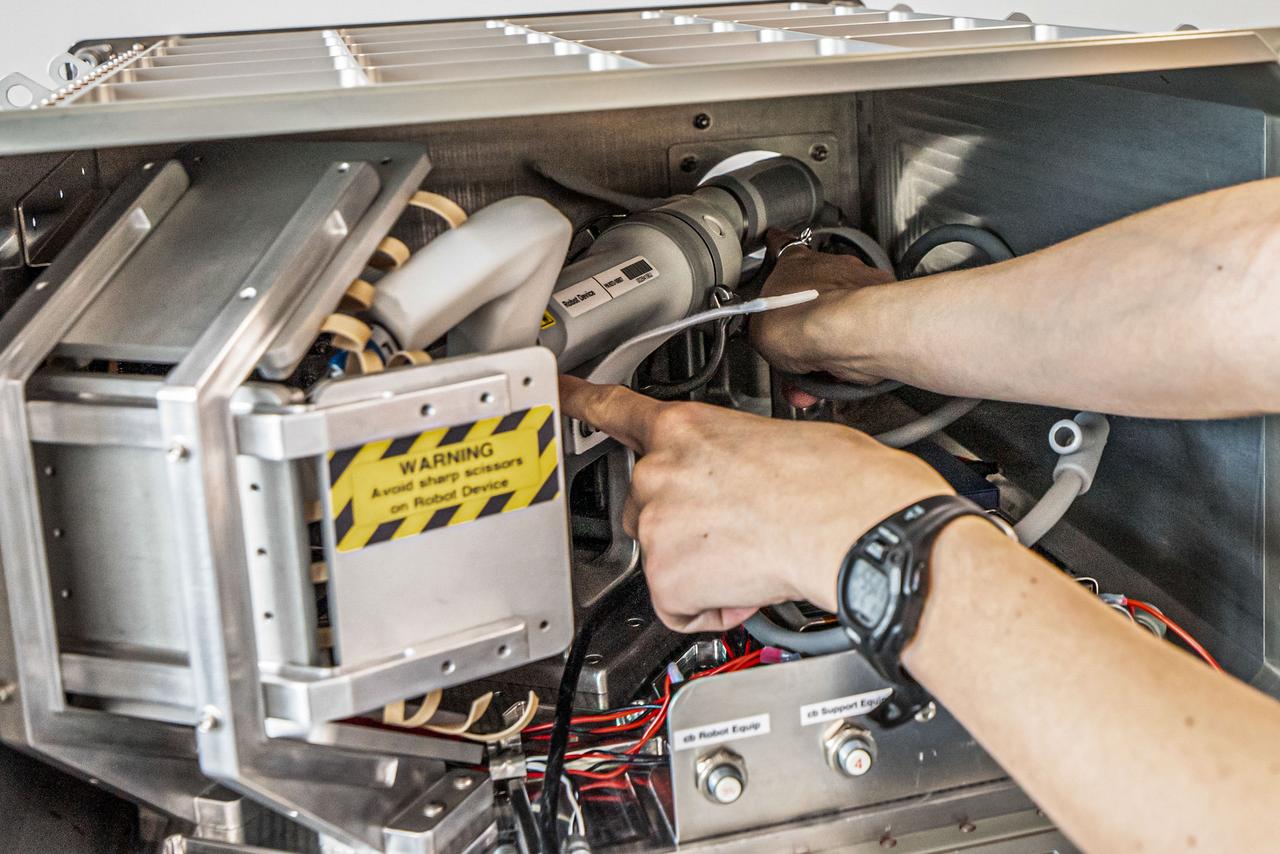
jsc2024e005981 (9/15/2023) --- The robotic surgery device is shown positioned inside the science locker, with the instrument arms and camera oriented toward the simulated surgical tissue on the experiment board. The unique small footprint makes it possible to transport the minibot anywhere, even to space. Robotic Surgery Tech Demo flies a special iteration of MIRA, Virtual Incision’s miniaturized robotic assisted surgery system. Image courtesy of Virtual Incision.

Sarah Manning, an aerospace engineer at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, is part of a team that operates “Sasquatch,” an important software tool created specifically for the agency’s Orion spacecraft. Sasquatch will be used to predict large footprints of the various debris that will be released from Orion before splashdown into the Pacific Ocean. The Landing and Recovery team, based out of Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, will be aboard a Navy ship, ready to retrieve Orion and some of the intentionally released debris.

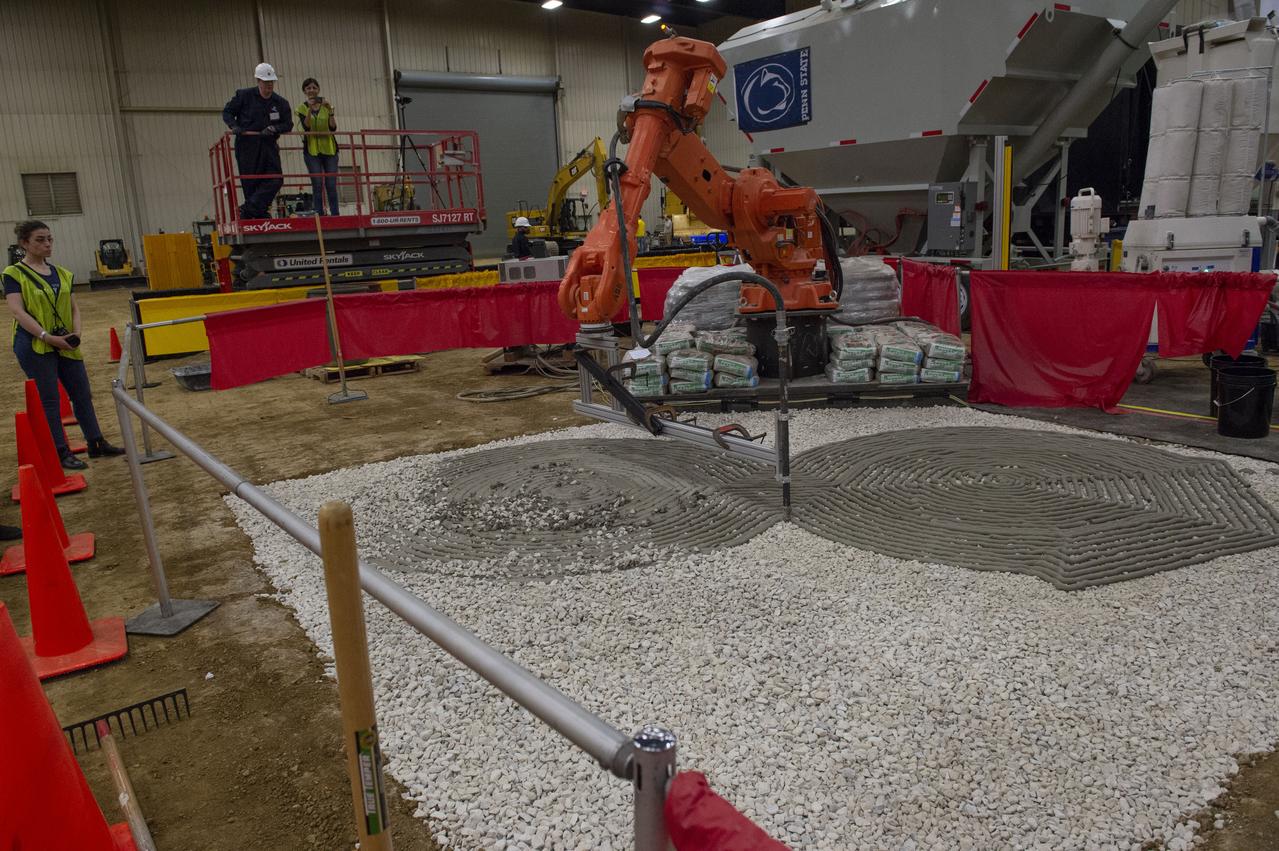
AI. SpaceFactory of New York and Pennsylvania State University of College Park print subscale habitat structures at NASA's 3D-Printed Habitat Challenge, held at the Caterpillar Edwards Demonstration & Learning Center in Edwards, Illinois, May 1-4, 2019. The habitat print is the final level of the multi-phase competition, which began in in 2015. The challenge is managed by NASA's Centennial Challenges program, and partner Bradley University of Peoria, Illinois. Initial footprint of 3D material laydown for Penn State habitat.

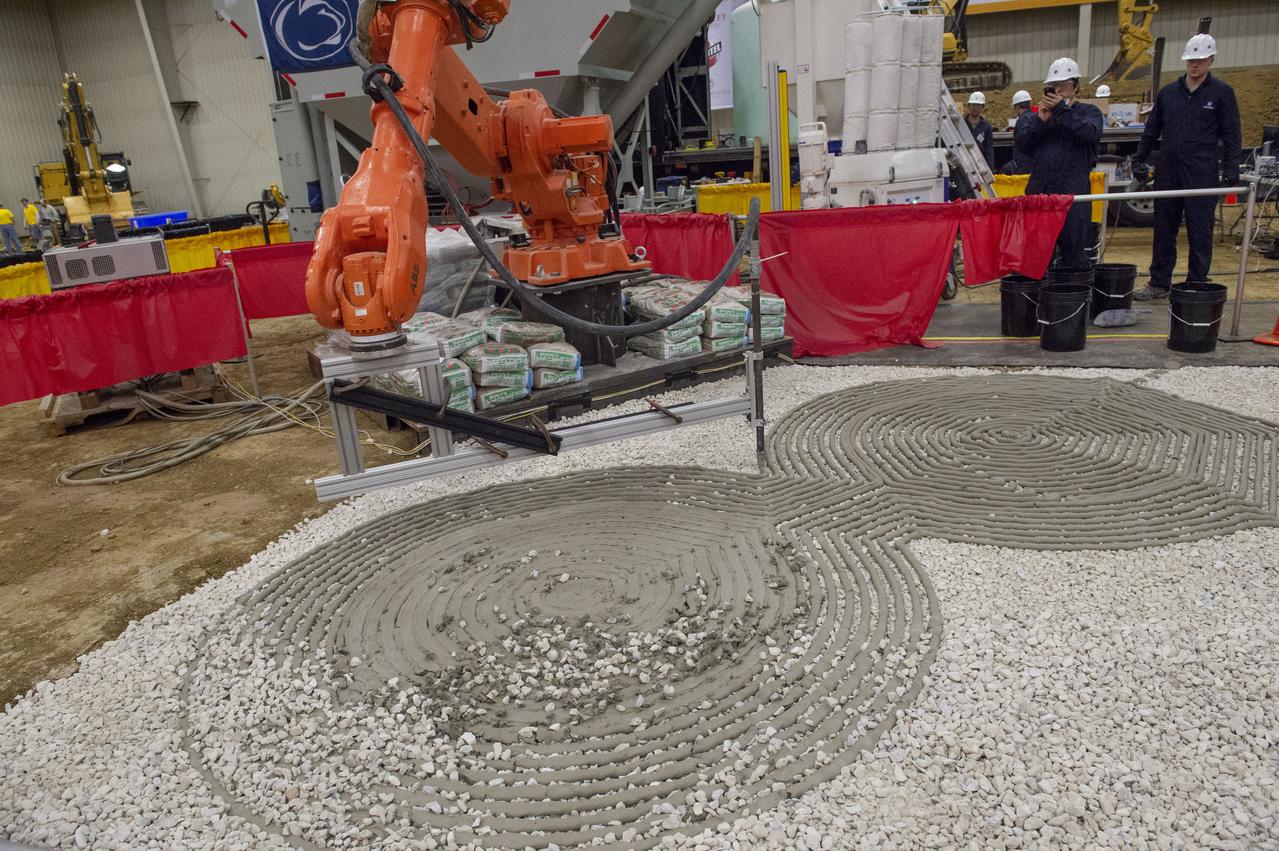
AI. SpaceFactory of New York and Pennsylvania State University of College Park print subscale habitat structures at NASA's 3D-Printed Habitat Challenge, held at the Caterpillar Edwards Demonstration & Learning Center in Edwards, Illinois, May 1-4, 2019. The habitat print is the final level of the multi-phase competition, which began in in 2015. The challenge is managed by NASA's Centennial Challenges program, and partner Bradley University of Peoria, Illinois. Initial footprint of 3D material laydown for Penn State habitat.

AI. SpaceFactory of New York and Pennsylvania State University of College Park print subscale habitat structures at NASA's 3D-Printed Habitat Challenge, held at the Caterpillar Edwards Demonstration & Learning Center in Edwards, Illinois, May 1-4, 2019. The habitat print is the final level of the multi-phase competition, which began in in 2015. The challenge is managed by NASA's Centennial Challenges program, and partner Bradley University of Peoria, Illinois. Initial footprint of 3D material laydown for Penn State habitat.

In this rare image taken on July 19, 2013, the wide-angle camera on NASA's Cassini spacecraft has captured Saturn's rings and our planet Earth and its moon in the same frame. It is only one footprint in a mosaic of 33 footprints covering the entire Saturn ring system (including Saturn itself). At each footprint, images were taken in different spectral filters for a total of 323 images: some were taken for scientific purposes and some to produce a natural color mosaic. This is the only wide-angle footprint that has the Earth-moon system in it. The dark side of Saturn, its bright limb, the main rings, the F ring, and the G and E rings are clearly seen; the limb of Saturn and the F ring are overexposed. The "breaks" in the brightness of Saturn's limb are due to the shadows of the rings on the globe of Saturn, preventing sunlight from shining through the atmosphere in those regions. The E and G rings have been brightened for better visibility. Earth, which is 898 million miles (1.44 billion kilometers) away in this image, appears as a blue dot at center right; the moon can be seen as a fainter protrusion off its right side. An arrow indicates their location in the annotated version. (The two are clearly seen as separate objects in the accompanying composite image PIA14949.) The other bright dots nearby are stars. This is only the third time ever that Earth has been imaged from the outer solar system. The acquisition of this image, along with the accompanying composite narrow- and wide-angle image of Earth and the moon and the full mosaic from which both are taken, marked the first time that inhabitants of Earth knew in advance that their planet was being imaged. That opportunity allowed people around the world to join together in social events to celebrate the occasion. This view looks toward the unilluminated side of the rings from about 20 degrees below the ring plane. Images taken using red, green and blue spectral filters were combined to create this natural color view. The images were obtained with the Cassini spacecraft wide-angle camera on July 19, 2013 at a distance of approximately 753,000 miles (1.212 million kilometers) from Saturn, and approximately 898.414 million miles (1.445858 billion kilometers) from Earth. Image scale on Saturn is 43 miles (69 kilometers) per pixel; image scale on the Earth is 53,820 miles (86,620 kilometers) per pixel. The illuminated areas of neither Earth nor the Moon are resolved here. Consequently, the size of each "dot" is the same size that a point of light of comparable brightness would have in the wide-angle camera. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA17171
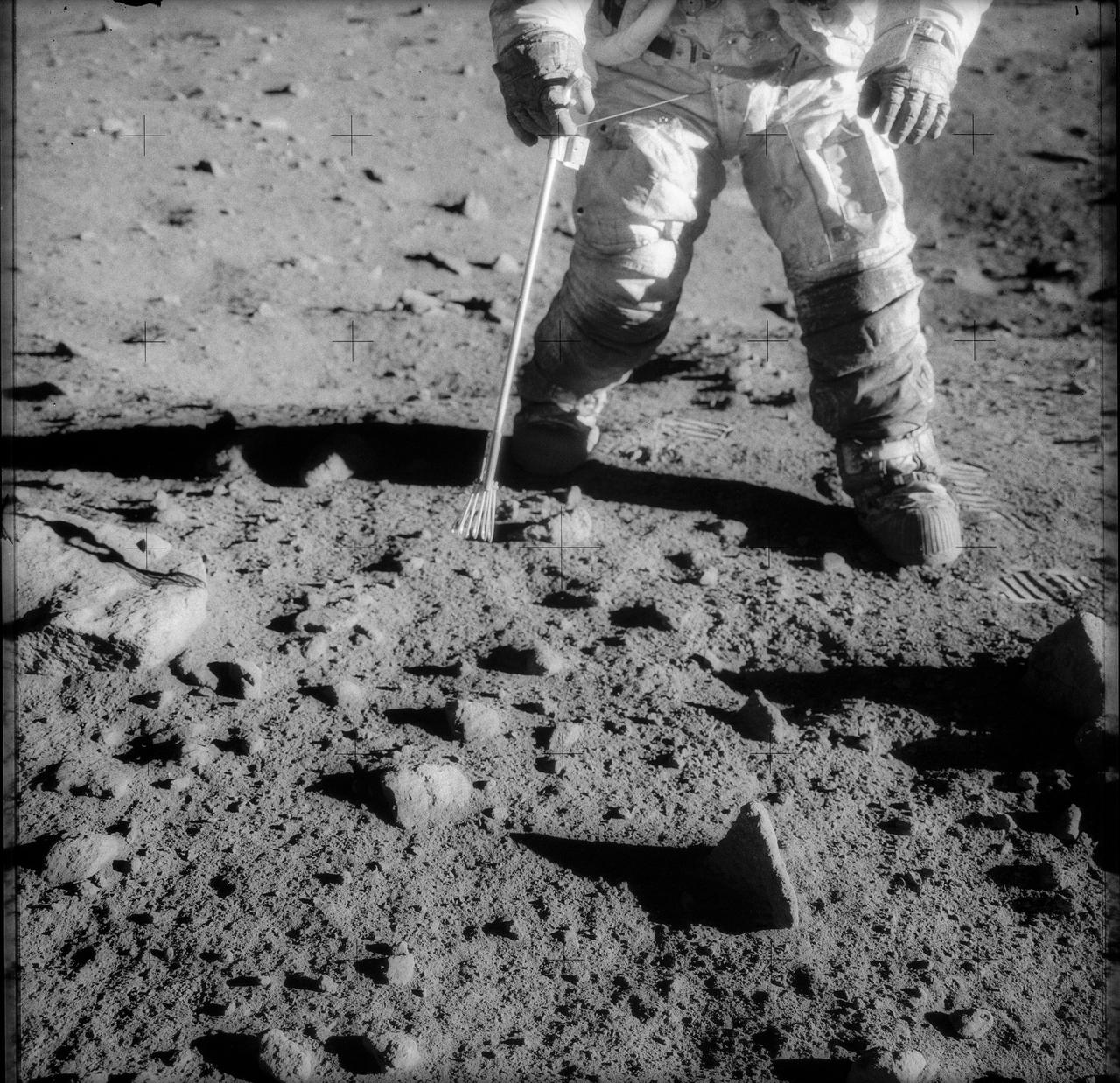

AS12-48-7149 (20 Nov. 1969) --- A close-up view of astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, photographed during the extravehicular activity (EVA) on the surface of the moon. An EVA checklist is on Conrad's left wrist. A set of tongs, an Apollo Lunar Hand Tool (ALHT), is held in his right hand. Several footprints can be seen. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Conrad and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon. Note lunar soil on the suit of Conrad, especially around the knees and below.
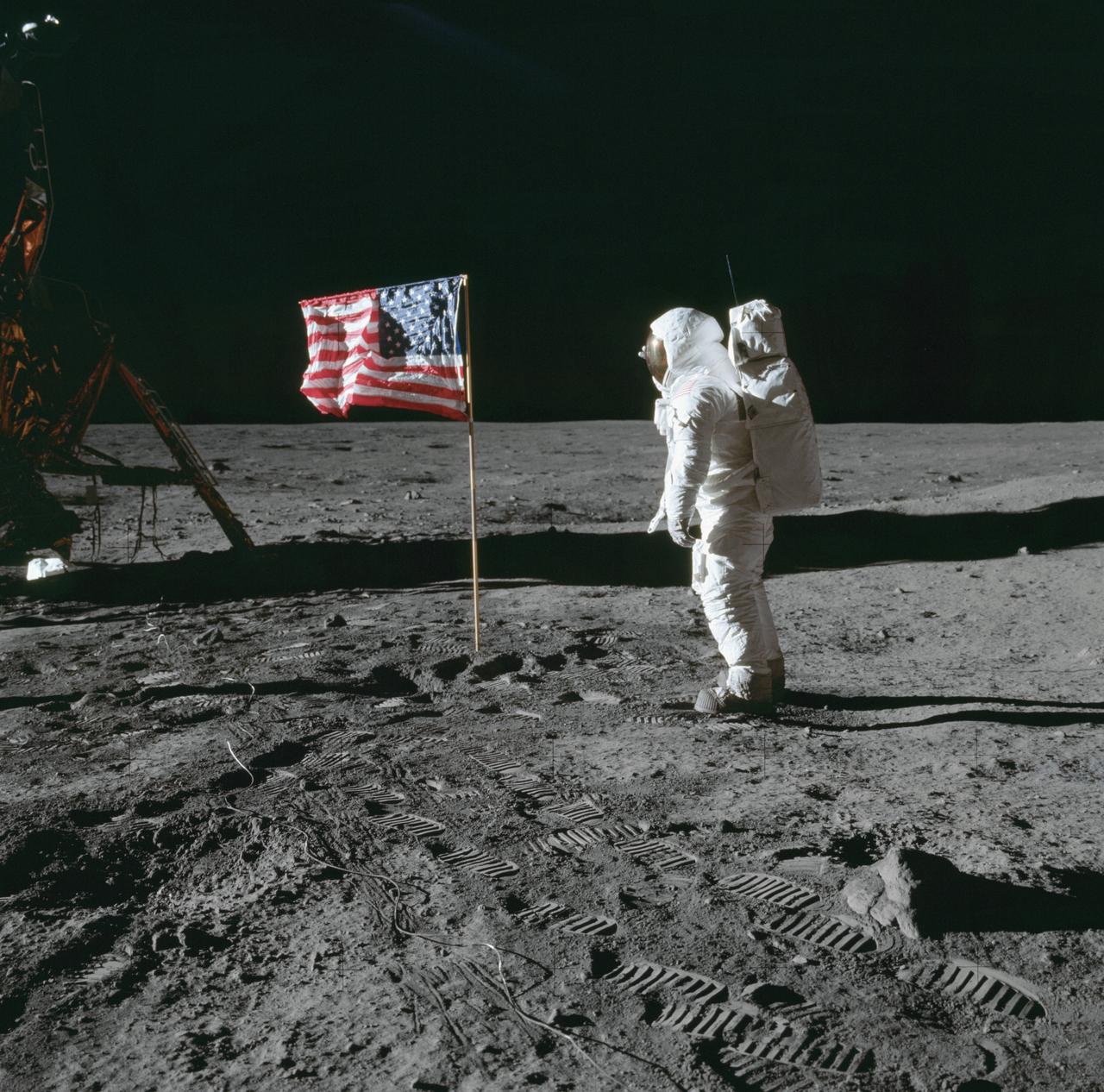

AS11-40-5874 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, poses for a photograph beside the deployed United States flag during Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The Lunar Module (LM) is on the left, and the footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil of the moon. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM the "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
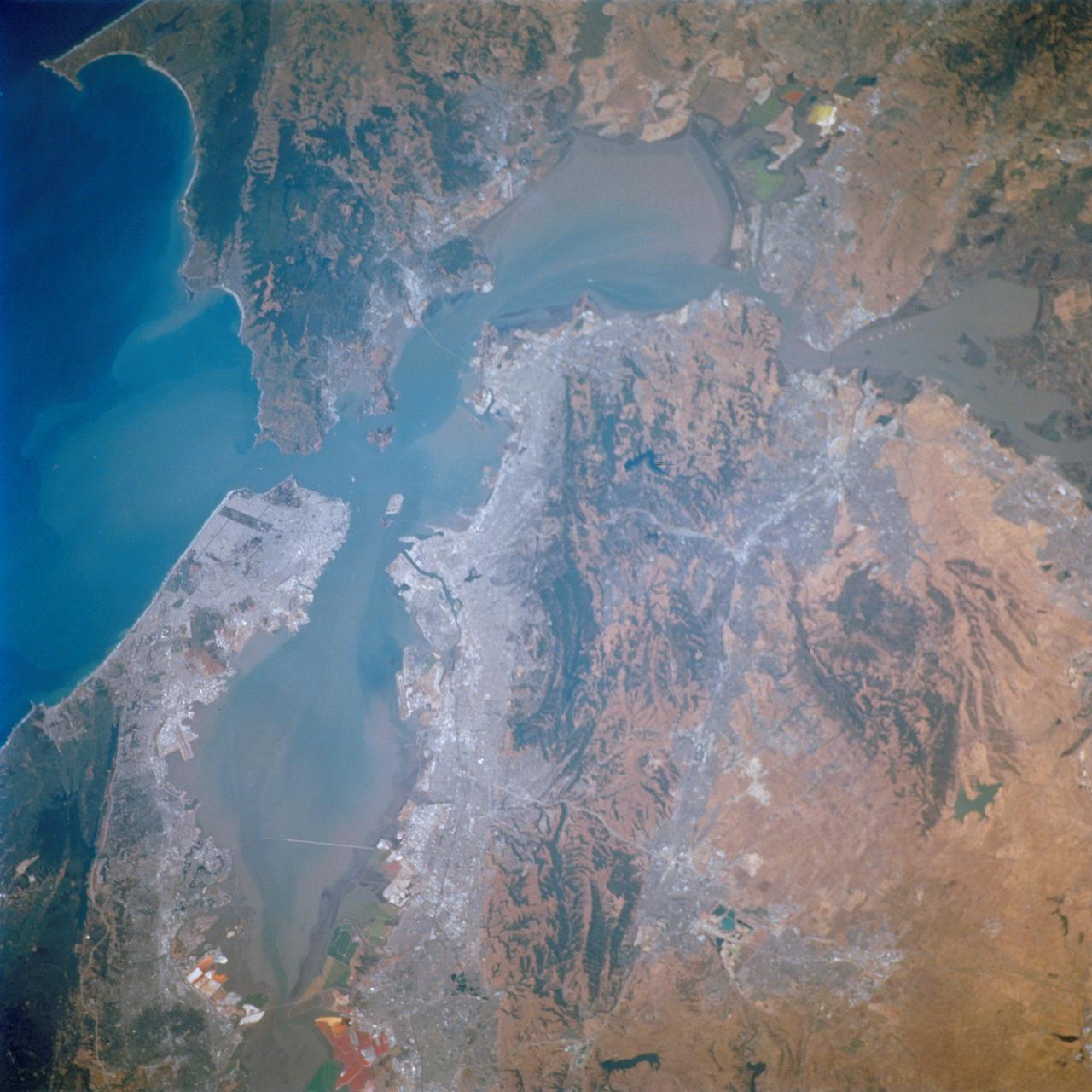

STS111-712-028 (5-19 June 2002) --- This photo featuring the San Francisco Bay area in California was photographed by one of the STS-111 crewmembers aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. The gray urban footprint of San Francisco, Oakland, San Jose, and the surrounding suburbs contrasts strongly with the brown and green vegetation in the hillsides. At the top and bottom of the picture the green, red and yellow pools are impoundments and salt evaporation ponds. The Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth (link to http://eol.jsc.nasa.gov/sseop/) provides searchable access to other photographs of Earth taken by astronauts.

AS11-40-5875 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, poses for a photograph beside the deployed United States flag during an Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The Lunar Module (LM) is on the left, and the footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil of the moon. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM, the "Eagle", to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA
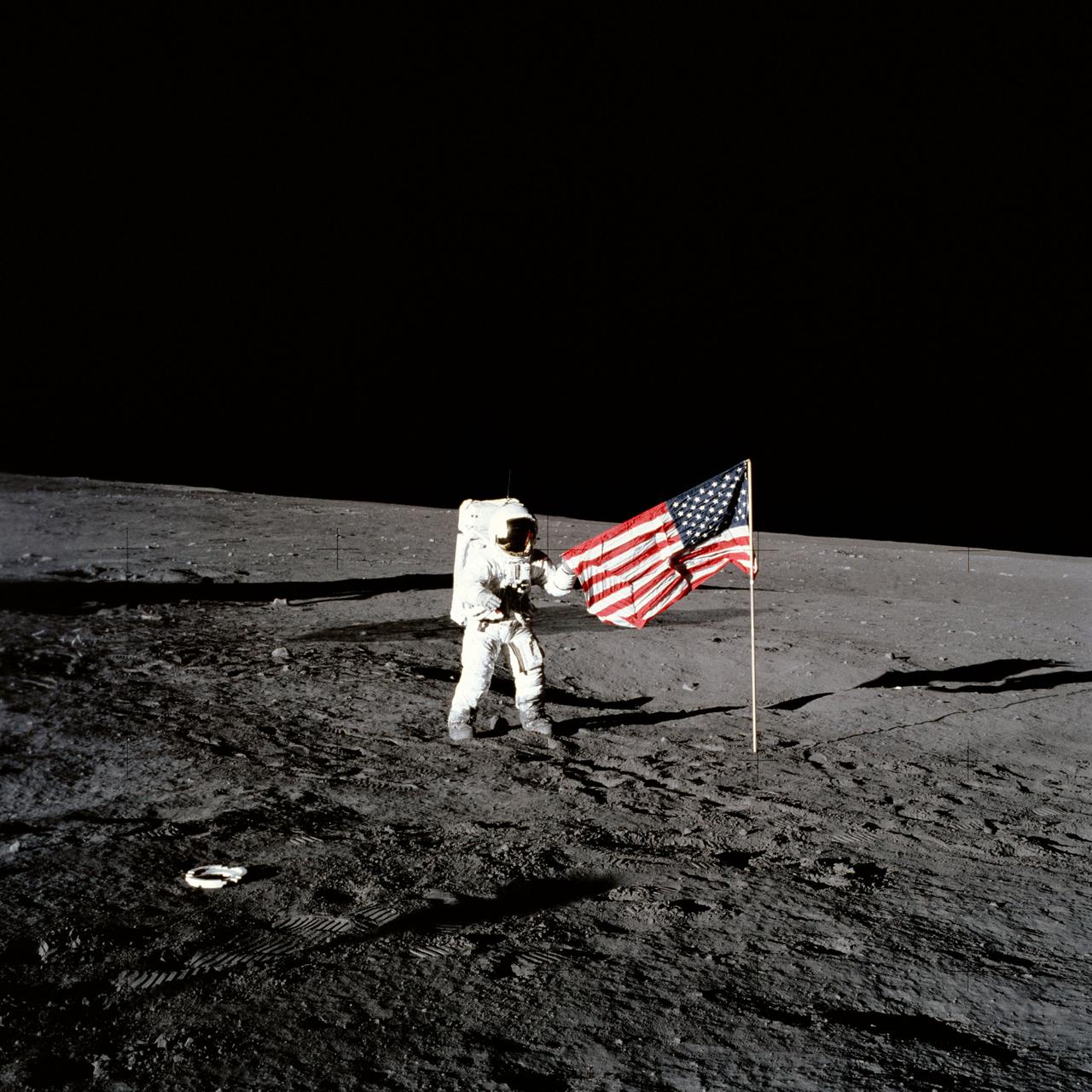

AS12-47-6897 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., Apollo 12 commander, stands beside the United States flag after it was unfurled on the lunar surface during the first extravehicular activity (EVA), on Nov. 19, 1969. Several footprints made by the crewmembers can be seen in the photograph. While astronauts Conrad and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Intrepid" to explore the Ocean of Storms region of the moon, astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Yankee Clipper" in lunar orbit.
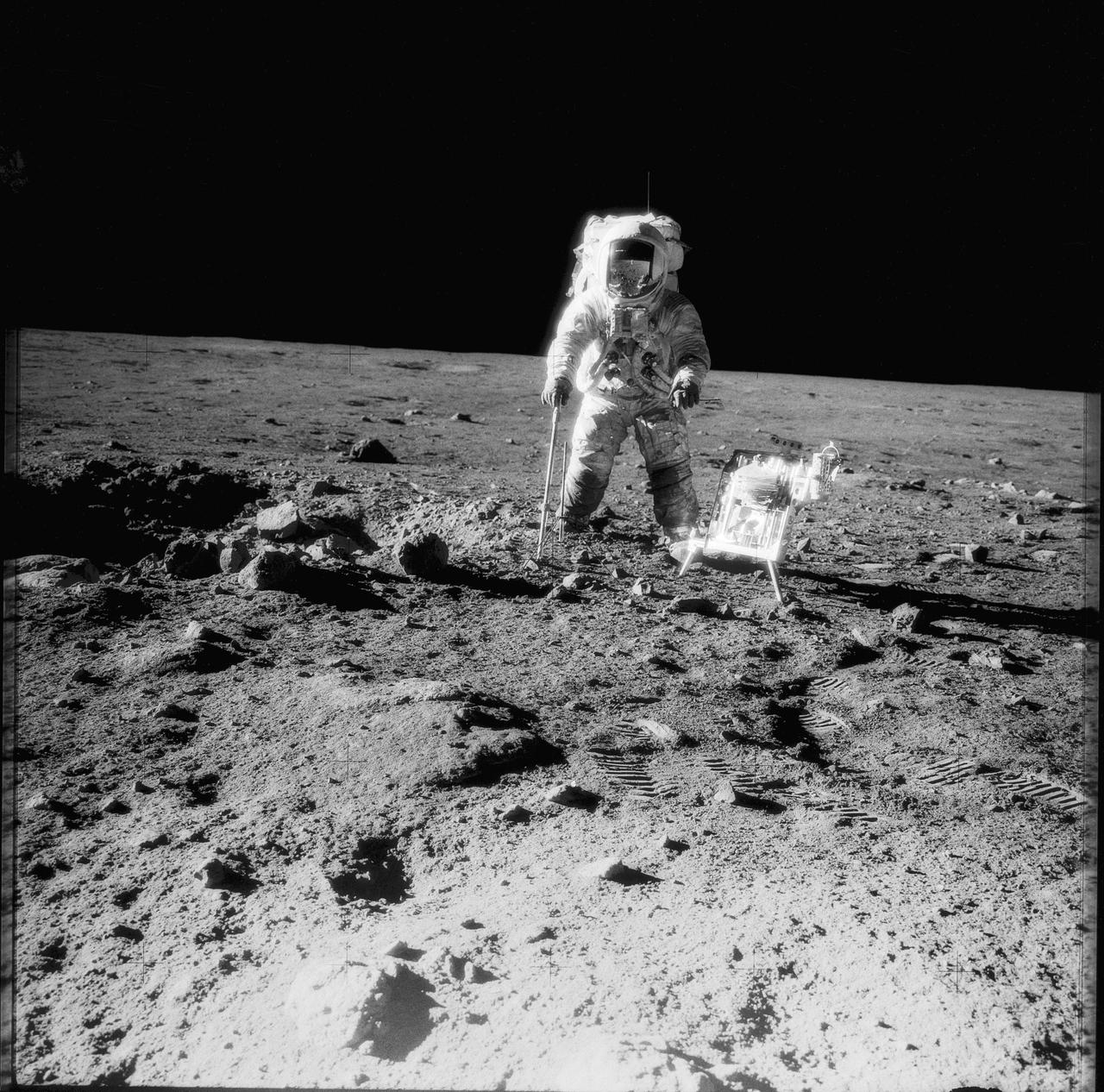

AS12-49-7318 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- One of the Apollo 12 crew members is photographed with the tools and carrier of the Apollo Lunar Hand Tools (ALHT) during extravehicular activity (EVA) on the surface of the moon. Several footprints made by the two crew members during their EVA are seen in the foreground. While astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Intrepid" to explore the Ocean of Storms region of the moon, astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Yankee Clipper" in lunar orbit.
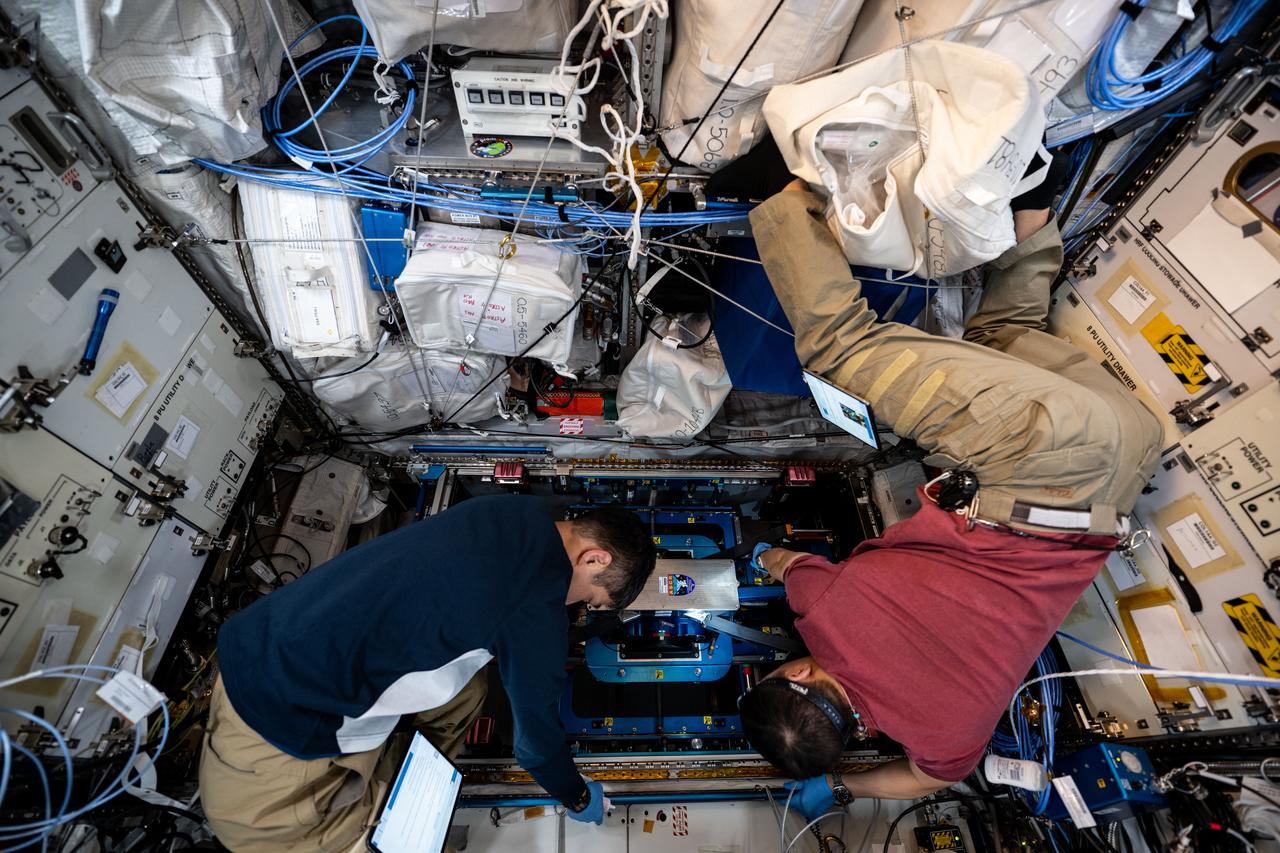

iss073e0177115 (6/9/2025) --- NASA astronaut Jonny Kim and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Takuya Onishi work on a vibration isolation system for the new European Enhanced Exploration Exercise Device (E4D) on the International Space Station. The E4D combines resistive and aerobic capabilities in a small footprint, important for future long-term exploration missions. Once the device is operating, researchers plan to acquire and evaluate data on its function and feedback from multiple crew members. The system adds new exercises to the current portfolio, such as targeting muscle groups essential for activities like leaving a spacecraft after landing.
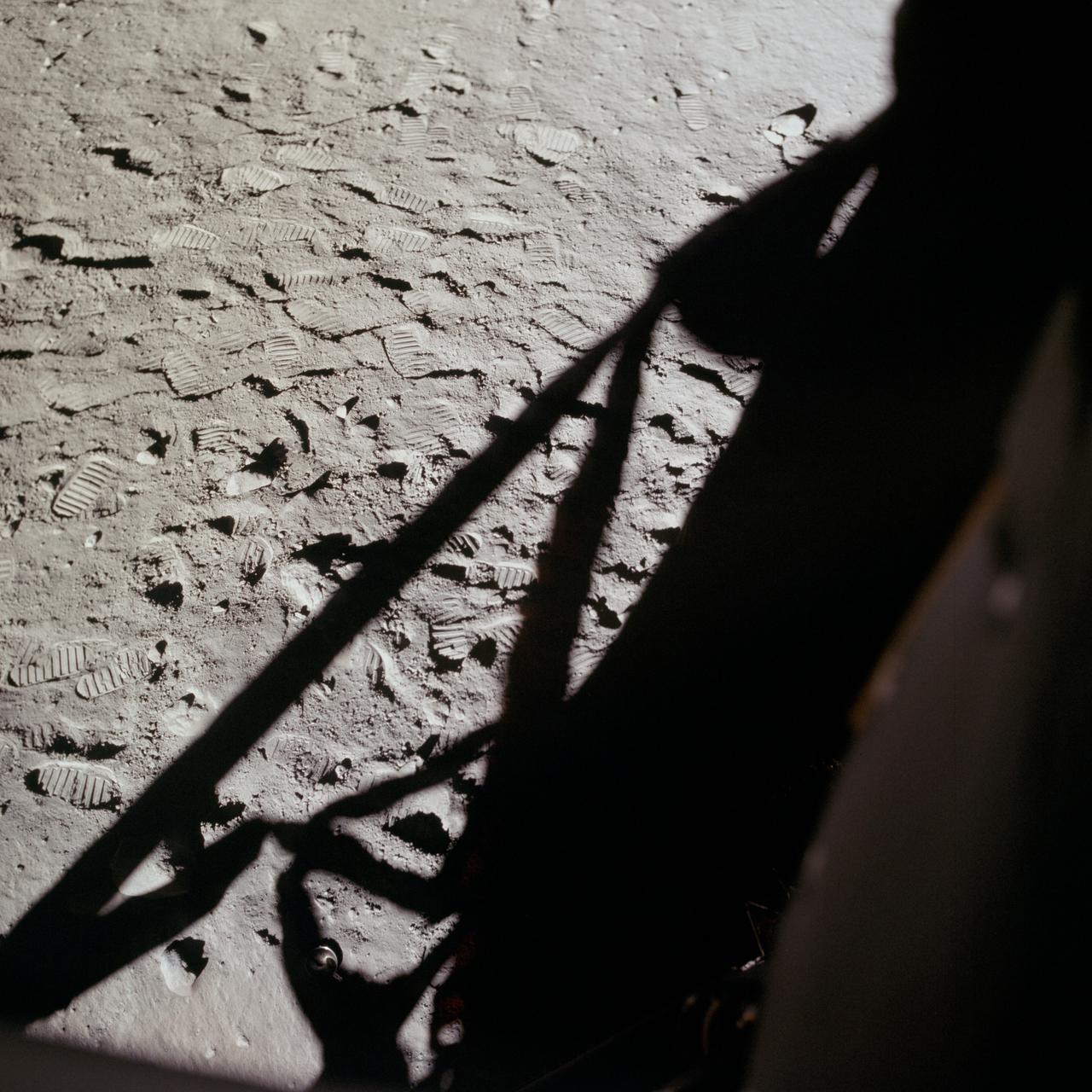

AS11-37-5505 (20 July 1969) --- This photograph shows in fine detail the impressions in the lunar soil made by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Armstrong, commander, and Aldrin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
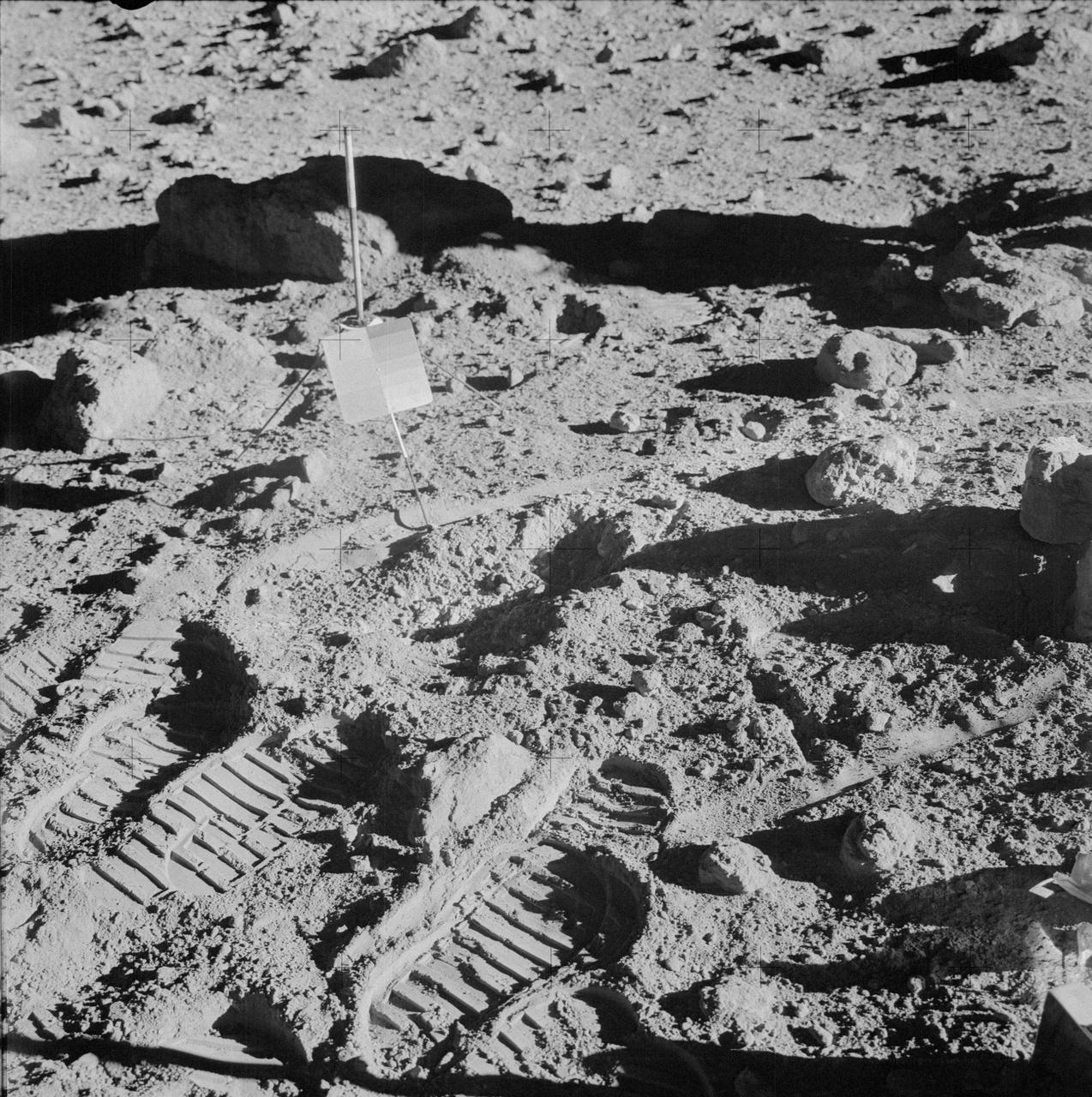

AS14-64-9127 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of lunar soil, showing bootprints made by the Apollo 14 astronauts during extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. Also visible are tracks made by the modularized equipment transporter (MET) and deployed gnomon. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
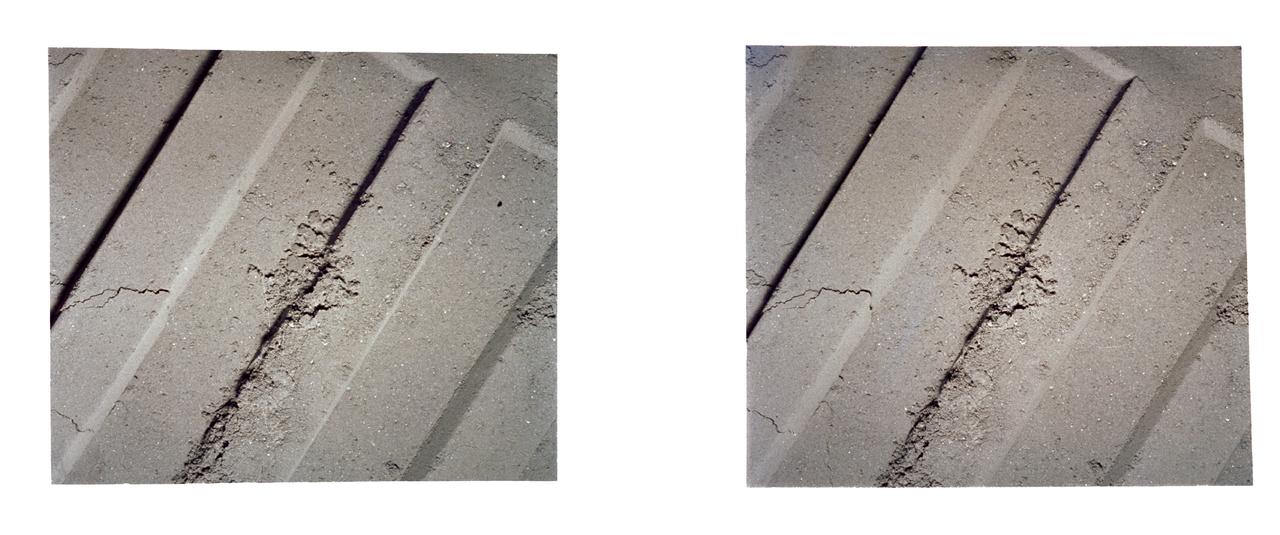

AS12-57-8448 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- An Apollo 12 stereo view showing a three-inch square of the lunar surface upon which an astronaut had stepped. Taken during extravehicular activity of astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. and Alan L. Bean, the exposure of the boot imprint was made with an Apollo 35mm stereo close-up camera. The camera was developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. The three-inch square is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. While astronauts Conrad and Bean descended in their Apollo 12 Lunar Module to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.
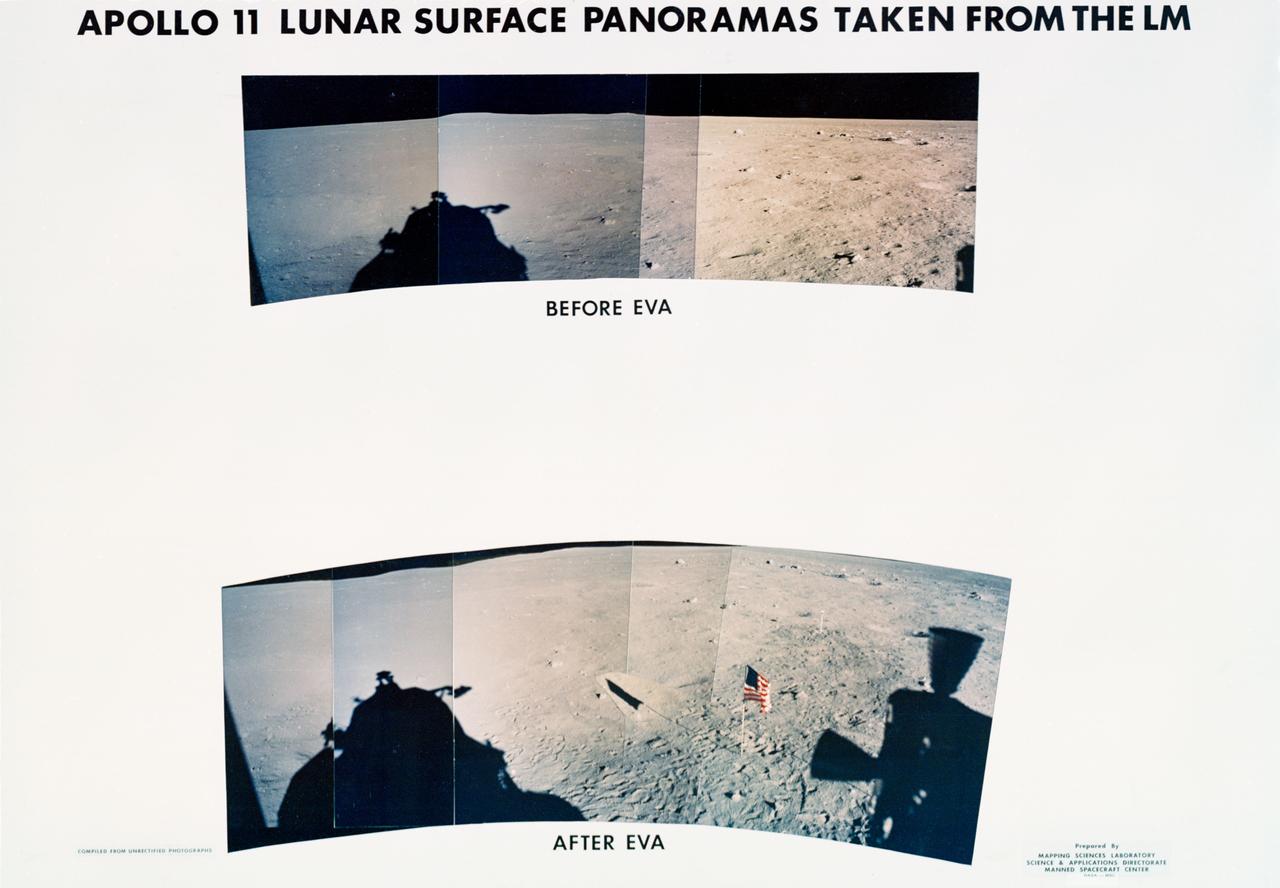

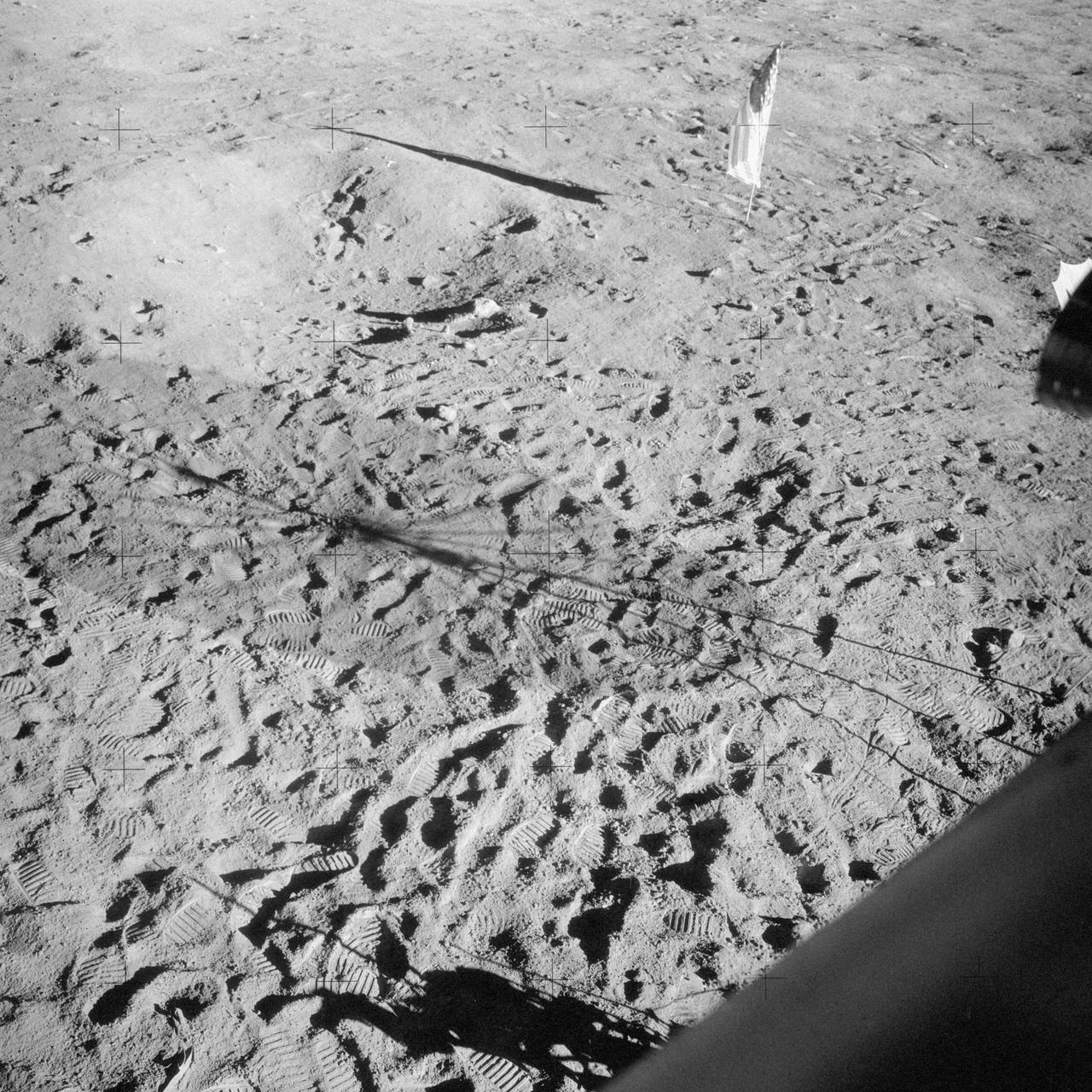
S69-44465 (20 July 1969) --- These panoramic views of the lunar surface, photographed from the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) as it rested on the lunar surface. The views reveal the surface near where the LM touched down, in the southeastern Sea of Tranquility. The views are as it looked before and after astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. participated in extravehicular activity (EVA). The United States flag is pictured in the bottom or "after" photo with the black and white lunar surface television camera pictured at the right of flag. Shadows of the LM are visible in the two panoramic views and a silhouette of part of a Reaction Control Subsystem thruster is seen in the bottom picture. Note the numerous footprints made by the two crewmen during the EVA period.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Construction of an exercise pad is underway beside the new fitness trail next to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The one-mile-long track will provide employees with a safe place off Kennedy's roadways to walk or run. The more than 6 tons of green waste removed to create the trail's footprint will be mulched and used for cover at Kennedy's landfill. Approximately 1,594 tons of crawler fines -- ground-up crawler rock removed from the crawlerway in the Launch Complex 39 area -- was used for the foundation of the trail. Fitness equipment has been ordered and will be installed on a concrete slab at the trail's west end. After the equipment has been installed, the slab will be coated to provide a rubberized exercise pad. At Kennedy Space Center, the health and safety of every employee is paramount. To learn more about Kennedy, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
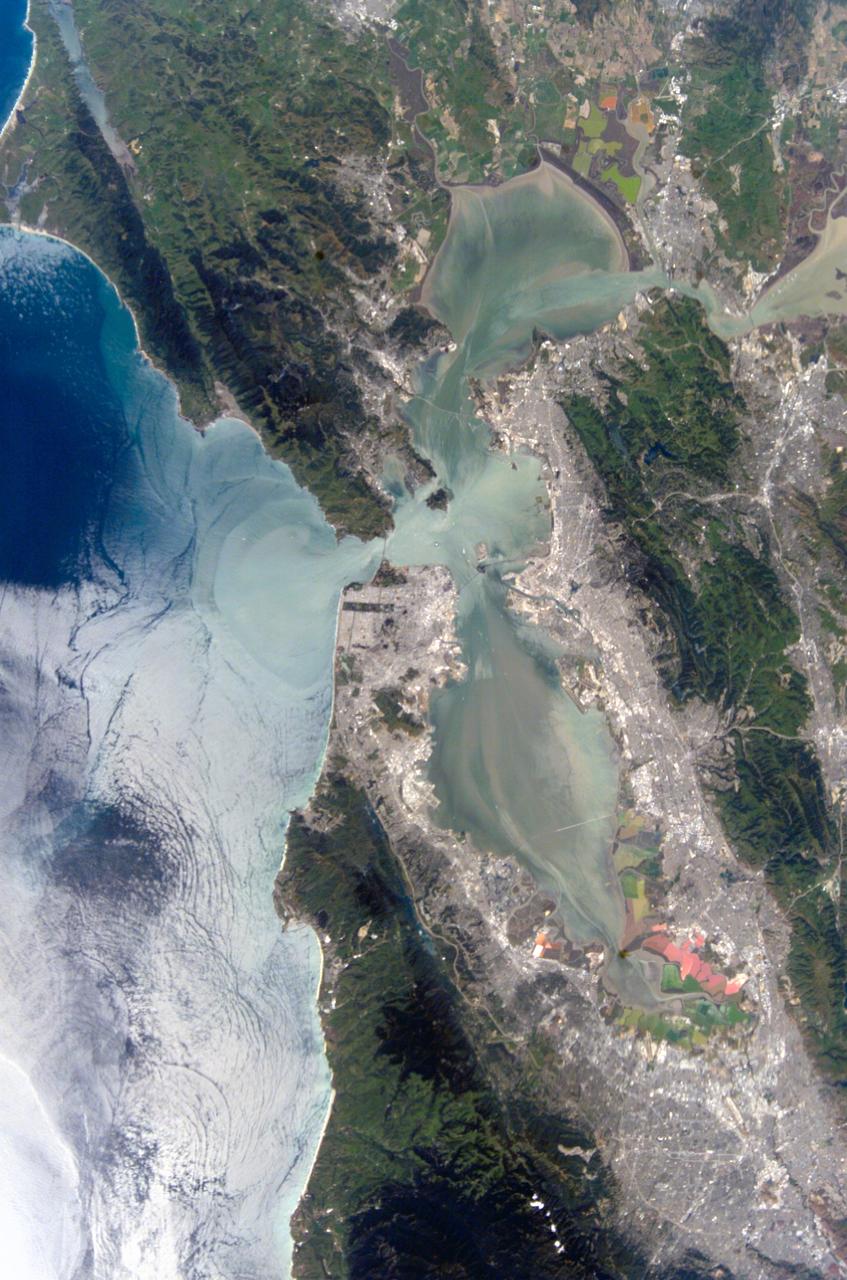

ISS004-E-10288 (21 April 2002) --- This view featuring the San Francisco Bay Area was photographed by an Expedition 4 crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS). The gray urban footprint of San Francisco, Oakland, San Jose, and their surrounding suburbs contrasts strongly with the green hillsides. Of particular note are the Pacific Ocean water patterns that are highlighted in the sun glint. Sets of internal waves traveling east impinge on the coastline south of San Francisco. At the same time, fresher bay water flows out from the bay beneath the Golden Gate Bridge, creating a large plume traveling westward. Tidal current channels suggest the tidal flow deep in the bay. Because the ISS orbits are not synchronous with the sun, station crewmembers view Earth with variable solar illumination angles. This allows them to document phenomena such as the sun reflecting differentially off surface waters in a way that outlines complicated water structures.
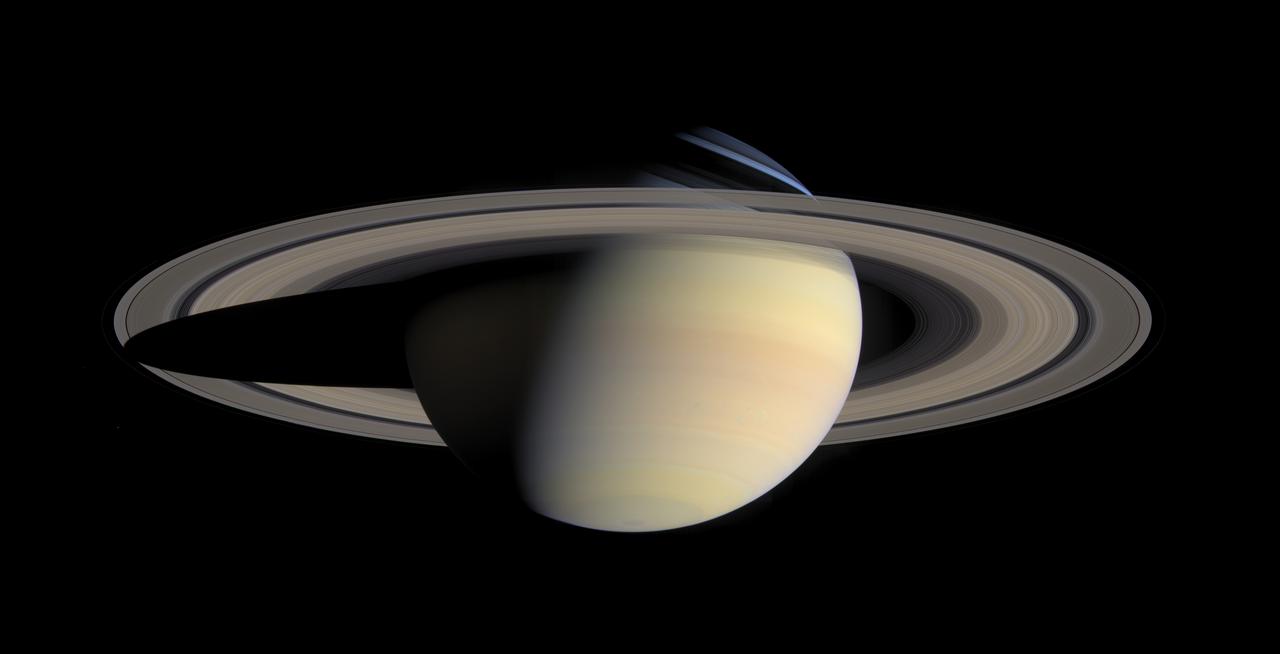

While cruising around Saturn in early October 2004, Cassini captured a series of images that have been composed into the largest, most detailed, global natural color view of Saturn and its rings ever made. This grand mosaic consists of 126 images acquired in a tile-like fashion, covering one end of Saturn's rings to the other and the entire planet in between. The images were taken over the course of two hours on Oct. 6, 2004, while Cassini was approximately 6.3 million kilometers (3.9 million miles) from Saturn. Since the view seen by Cassini during this time changed very little, no re-projection or alteration of any of the images was necessary. Three images (red, green and blue) were taken of each of 42 locations, or "footprints," across the planet. The full color footprints were put together to produce a mosaic that is 8,888 pixels across and 4,544 pixels tall. The smallest features seen here are 38 kilometers (24 miles) across. Many of Saturn's splendid features noted previously in single frames taken by Cassini are visible in this one detailed, all-encompassing view: subtle color variations across the rings, the thread-like F ring, ring shadows cast against the blue northern hemisphere, the planet's shadow making its way across the rings to the left, and blue-grey storms in Saturn's southern hemisphere to the right. Tiny Mimas and even smaller Janus are both faintly visible at the lower left. The Sun-Saturn-Cassini, or phase, angle at the time was 72 degrees; hence, the partial illumination of Saturn in this portrait. Later in the mission, when the spacecraft's trajectory takes it far from Saturn and also into the direction of the Sun, Cassini will be able to look back and view Saturn and its rings in a more fully-illuminated geometry. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06193
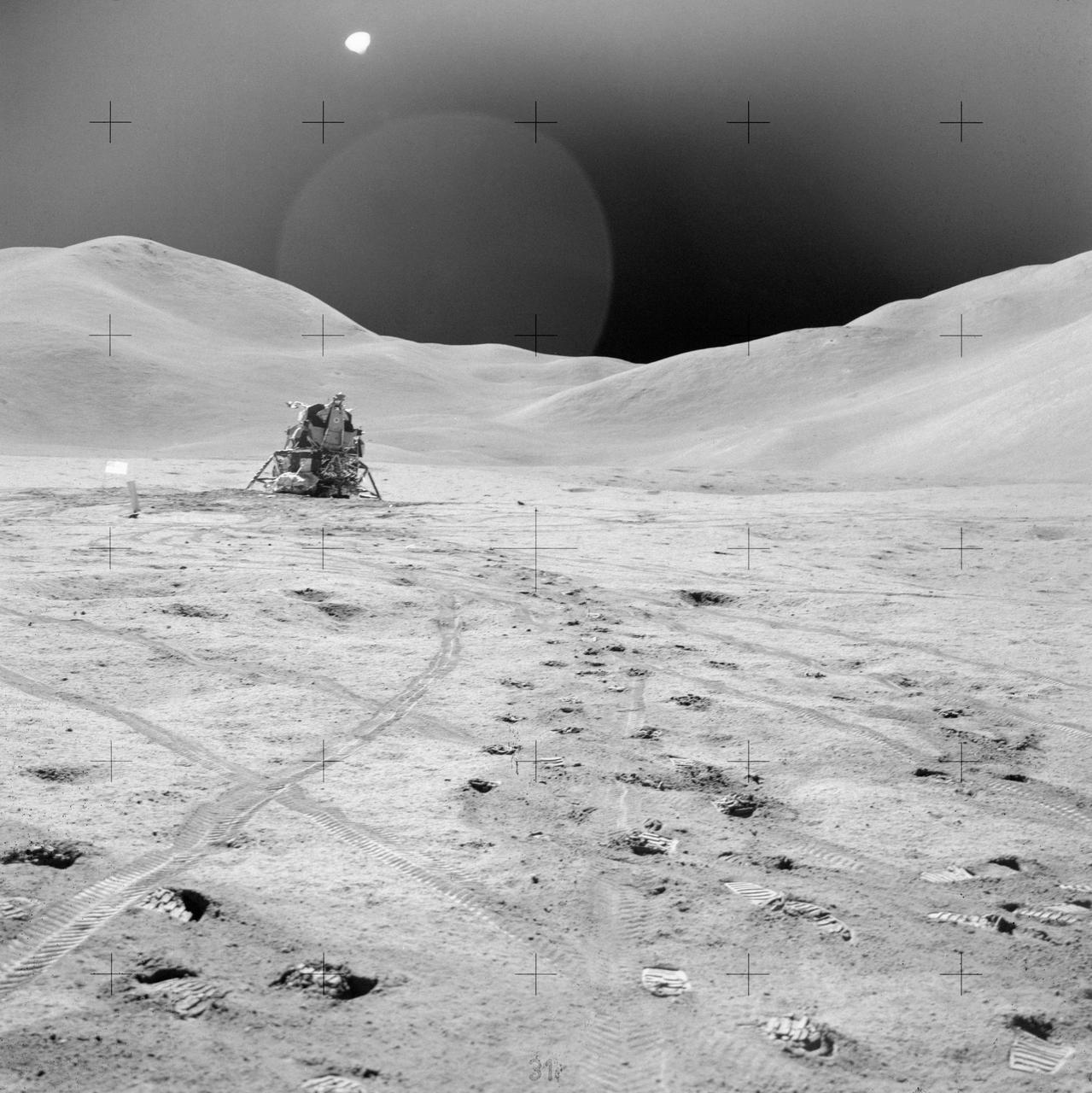

AS15-82-11057 (2 Aug. 1971) --- The Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" is photographed against the barren lunarscape during the third Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site on the lunar nearside. This view is looking southeast. The Apennine Front is in the left background; and Hadley Delta Mountain is in the right background. The object next to the United States flag is the Solar Wind Composition (SWC) experiment. Last Crater is to the right of the LM. Note bootprints and tracks of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The light spherical object at the top is a reflection in the lens of the camera. While astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

This image from NASA's Dawn spacecraft showing the northern part of Hanami Planum on Ceres honors the Japanese cherry blossom festival, or "Hanami," which is a long-standing Japanese tradition of welcoming spring. Hanami Planum is the third largest geological feature on Ceres, after Vendimia Planitia and the Samhain Catenae. It extends over 345 miles (555 kilometers). This image shows familiar features, such as Occator Crater, characterized both by bright material inside the crater and dark ejecta material outside. Several parallel linear features, called Junina Catenae, can be seen departing from Occator and extending toward the top of the image. These catenae are chains of small craters formed by the impact and scouring of material ejected when large craters are formed. Scientists were able to relate these crater chains to Urvara and Yalode. Even though these are located in the southern hemisphere, some of their ejecta could reach the northern hemisphere, thanks to Ceres' fast rotation and small size. This image was obtained by Dawn on June 15, 2015. The spacecraft was then in its survey orbit (2,700 miles, or 4,400 kilometers high), when the footprint of Dawns framing camera on Ceres surface was about 260 miles (420 kilometers). The resolution is 1,400 feet (410 meters) per pixel. The central coordinates of the picture are 14 degrees north latitude, 213 degrees east in longitude. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21921

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Director of Center Operations Nancy Bray welcomes the employees who turned out during their lunchtime for a ribbon-cutting ceremony opening the new fitness trail next to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The one-mile-long track will provide employees with a safe place off Kennedy's roadways to walk or run. The more than 6 tons of green waste removed to create the trail's footprint will be mulched and used for cover at Kennedy's landfill. Approximately 1,594 tons of crawler fines -- ground-up crawler rock removed from the crawlerway in the Launch Complex 39 area -- was used for the foundation of the trail. Fitness equipment has been ordered and will be installed on a concrete slab at the trail's west end. After the equipment has been installed, the slab will be coated to provide a rubberized exercise pad. At Kennedy Space Center, the health and safety of every employee is paramount. To learn more about Kennedy, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Employees turn out during their lunchtime for a ribbon-cutting ceremony opening the new fitness trail next to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Director of Center Operations Nancy Bray, at left, encourages the employees to join her in putting the trail to good use. The one-mile-long track will provide employees with a safe place off Kennedy's roadways to walk or run. The more than 6 tons of green waste removed to create the trail's footprint will be mulched and used for cover at Kennedy's landfill. Approximately 1,594 tons of crawler fines -- ground-up crawler rock removed from the crawlerway in the Launch Complex 39 area -- was used for the foundation of the trail. Fitness equipment has been ordered and will be installed on a concrete slab at the trail's west end. After the equipment has been installed, the slab will be coated to provide a rubberized exercise pad. At Kennedy Space Center, the health and safety of every employee is paramount. To learn more about Kennedy, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers lift one of the walls of the Propellants North Administrative and Maintenance Facility into an upright position. A tilt-up construction method is being used to erect a THERMOMASS concrete wall insulation system for the facility's walls. In this approach, the exterior layer of concrete for the wall panels is poured and leveled on the building's footprint. Then, prefabricated, predrilled insulation sheets are arranged on top of the unhardened concrete, and connectors, designed to hold the sandwiched layers of concrete and insulation secure, are inserted through the predrilled holes. Next, the structural wythe is poured. Once cured, these panels are lifted upright to form the building's envelope. The facility will have a two-story administrative building to house managers, mechanics and technicians who fuel spacecraft at Kennedy adjacent to an 1,800-square-foot single-story shop to store cryogenic fuel transfer equipment. The new facility will feature high-efficiency roofs and walls, “Cool Dry Quiet” air conditioning with energy recovery technology, efficient lighting, and other sustainable features. The facility is striving to qualify for the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, or LEED, Platinum certification. If successful, Propellants North will be the first Kennedy facility to achieve this highest of LEED ratings after it is completed in the summer of 2010. The facility was designed for NASA by Jones Edmunds and Associates. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
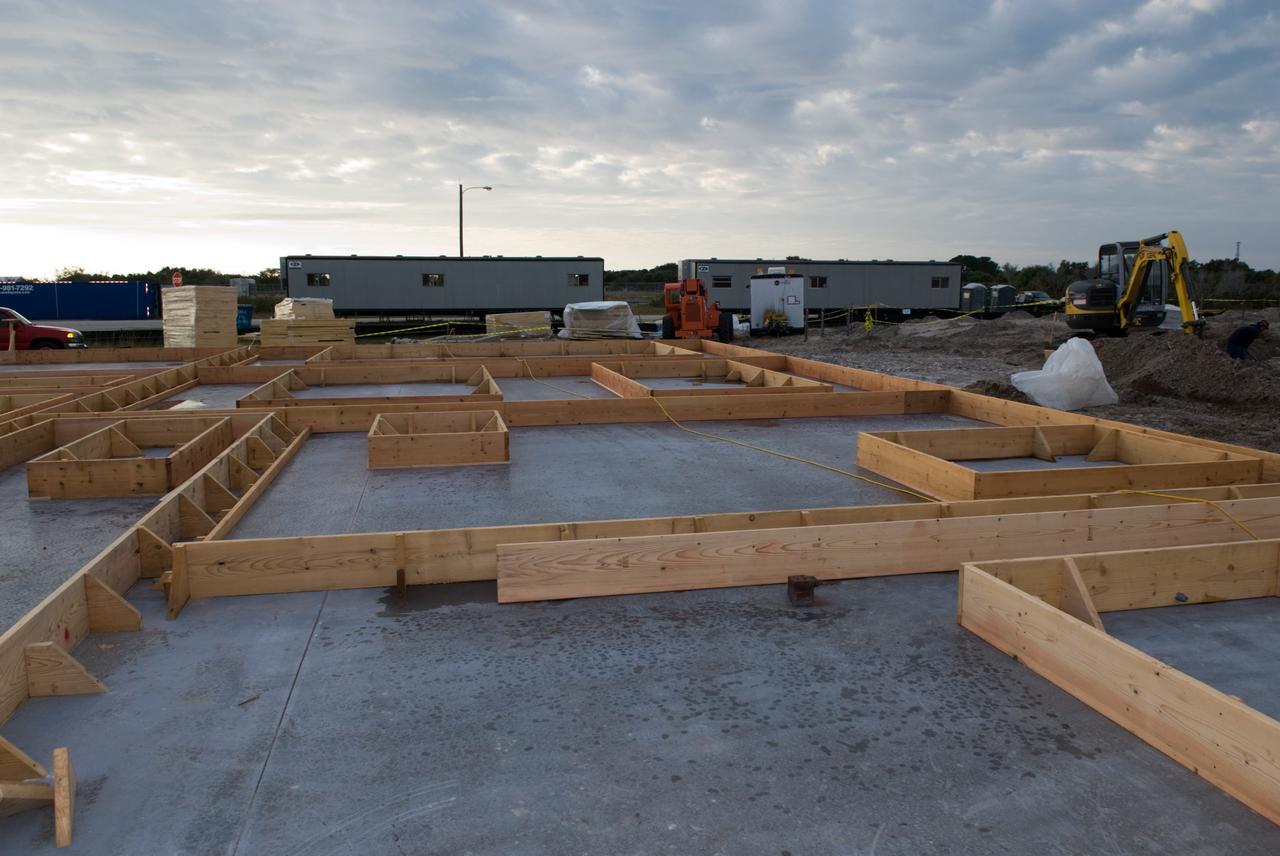

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Concrete covers the insulation in the walls for the Propellants North Administrative and Maintenance Facility in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A tilt-up construction method is being used to erect a THERMOMASS concrete wall insulation system for the facility's walls. In this approach, the exterior layer of concrete for the wall panels is poured and leveled on the building's footprint. Then, prefabricated, predrilled insulation sheets are arranged on top of the unhardened concrete, and connectors, designed to hold the sandwiched layers of concrete and insulation secure, are inserted through the predrilled holes. Next, the structural wythe is poured. Once cured, these panels are lifted upright to form the building's envelope. The facility will have a two-story administrative building to house managers, mechanics and technicians who fuel spacecraft at Kennedy adjacent to an 1,800-square-foot single-story shop to store cryogenic fuel transfer equipment. The new facility will feature high-efficiency roofs and walls, “Cool Dry Quiet” air conditioning with energy recovery technology, efficient lighting, and other sustainable features. The facility is striving to qualify for the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, or LEED, Platinum certification. If successful, Propellants North will be the first Kennedy facility to achieve this highest of LEED ratings after it is completed in the summer of 2010. The facility was designed for NASA by Jones Edmunds and Associates. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
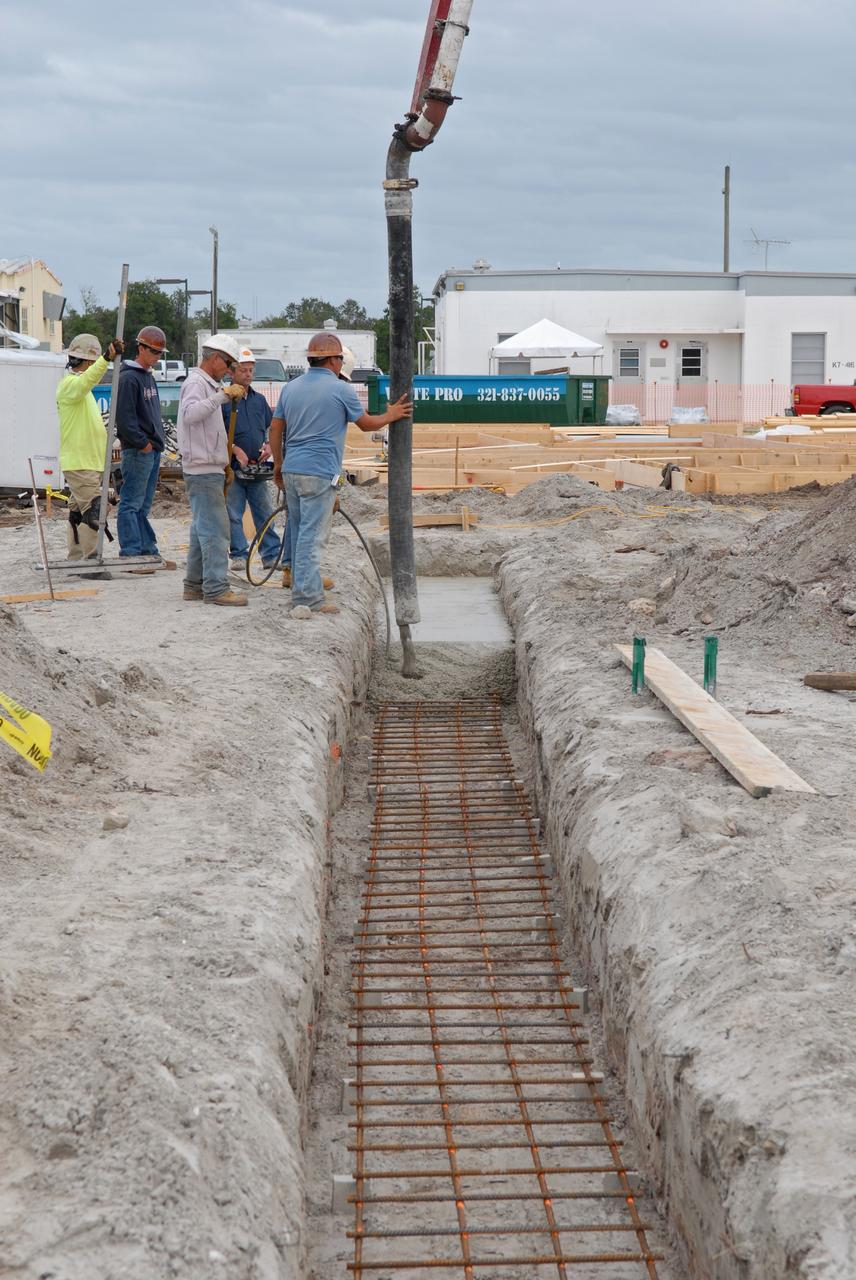

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Insulation is placed in the walls for the Propellants North Administrative and Maintenance Facility in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A tilt-up construction method is being used to erect a THERMOMASS concrete wall insulation system for the facility's walls. In this approach, the exterior layer of concrete for the wall panels is poured and leveled on the building's footprint. Then, prefabricated, predrilled insulation sheets are arranged on top of the unhardened concrete, and connectors, designed to hold the sandwiched layers of concrete and insulation secure, are inserted through the predrilled holes. Next, the structural wythe is poured. Once cured, these panels are lifted upright to form the building's envelope. The facility will have a two-story administrative building to house managers, mechanics and technicians who fuel spacecraft at Kennedy adjacent to an 1,800-square-foot single-story shop to store cryogenic fuel transfer equipment. The new facility will feature high-efficiency roofs and walls, “Cool Dry Quiet” air conditioning with energy recovery technology, efficient lighting, and other sustainable features. The facility is striving to qualify for the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, or LEED, Platinum certification. If successful, Propellants North will be the first Kennedy facility to achieve this highest of LEED ratings after it is completed in the summer of 2010. The facility was designed for NASA by Jones Edmunds and Associates. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
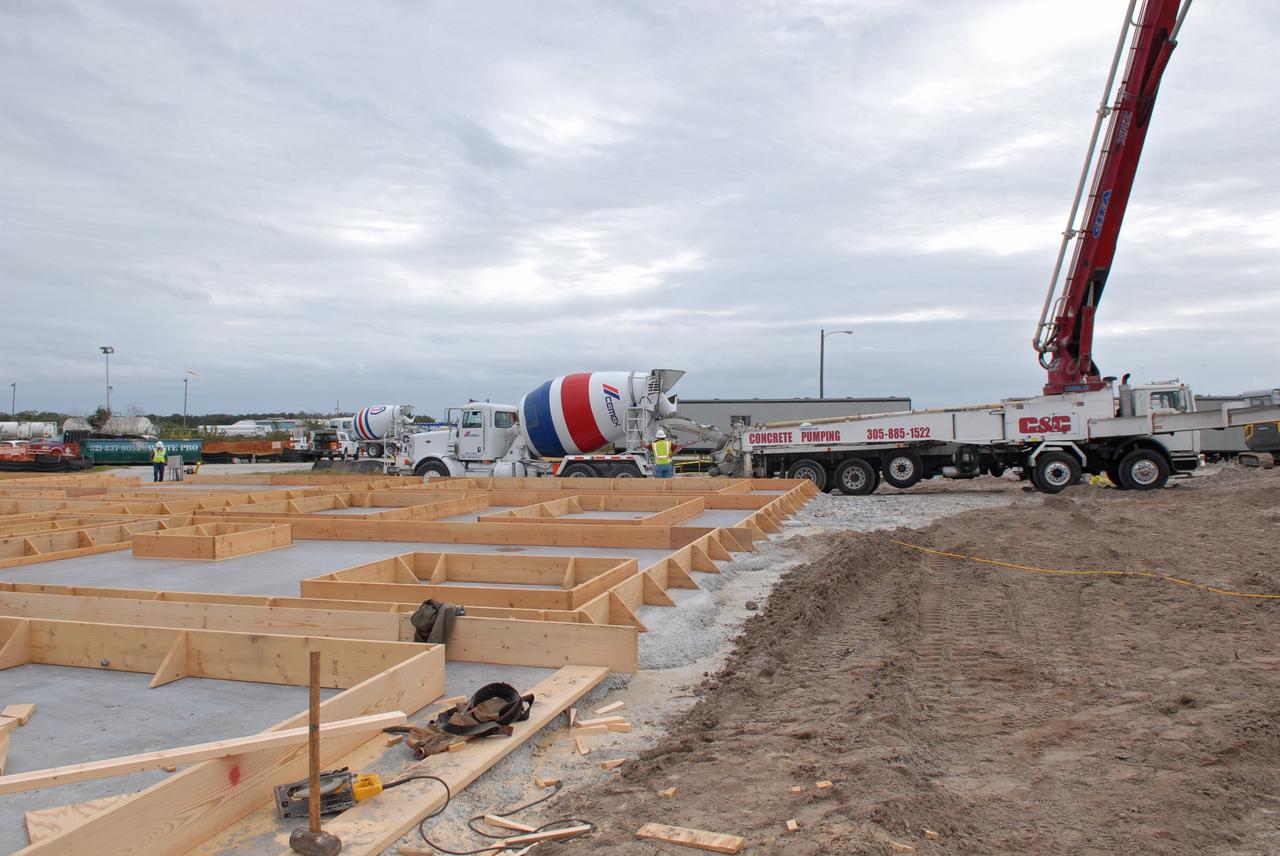

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Construction of the walls for the Propellants North Administrative and Maintenance Facility begins in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A tilt-up construction method is being used to erect a THERMOMASS concrete wall insulation system for the facility's walls. In this approach, the exterior layer of concrete for the wall panels is poured and leveled on the building's footprint. Then, prefabricated, predrilled insulation sheets are arranged on top of the unhardened concrete, and connectors, designed to hold the sandwiched layers of concrete and insulation secure, are inserted through the predrilled holes. Next, the structural wythe is poured. Once cured, these panels are lifted upright to form the building's envelope. The facility will have a two-story administrative building to house managers, mechanics and technicians who fuel spacecraft at Kennedy adjacent to an 1,800-square-foot single-story shop to store cryogenic fuel transfer equipment. The new facility will feature high-efficiency roofs and walls, “Cool Dry Quiet” air conditioning with energy recovery technology, efficient lighting, and other sustainable features. The facility is striving to qualify for the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, or LEED, Platinum certification. If successful, Propellants North will be the first Kennedy facility to achieve this highest of LEED ratings after it is completed in the summer of 2010. The facility was designed for NASA by Jones Edmunds and Associates. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
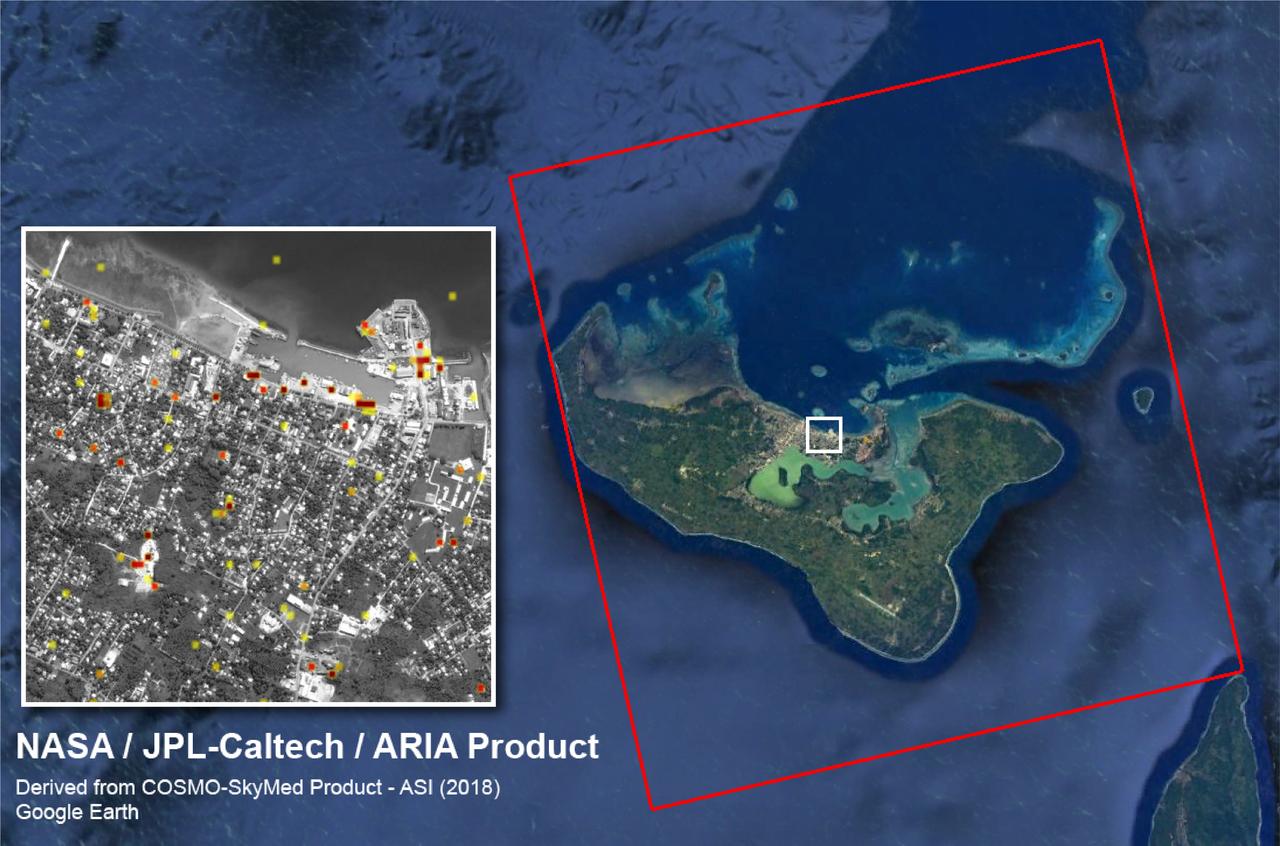
The Advanced Rapid Imaging and Analysis (ARIA) team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory created this Damage Proxy Map (DPM) of Tongatapu, the main island of Tonga, following the landfall of Cyclone Gita, a Category 4 storm that hit Tonga on Feb. 12-13, 2018. The map depicts areas that are likely damaged from the storm, shown by red and yellow pixels. The map was produced by comparing two pairs of interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) images from the COSMO-SkyMed satellites, operated by the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The pre- and post-cyclone images were acquired on Jan. 19 and Feb. 13, 2018, respectively. The later image was acquired just 4-1/2 hours after the peak damage by the cyclone. The map covers the entire island of Tongatapu (the 25-by-25-mile, or 40-by-40 kilometer SAR image footprint indicated with the large red polygon). Each pixel measures about 98 feet (30 meters) across. The color variation from yellow to red indicates increasingly more significant ground surface change. Preliminary validation of the SAR data was done by comparing them with high-resolution optical imagery acquired by DigitalGlobe. This Damage Proxy Map should be used as guidance to identify damaged areas and may be less reliable over vegetated and flooded areas. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22257

Zella Morewitz poses with a model of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory, currently the NASA Glenn Research Center. The model was displayed in the Administration Building during the construction of the laboratory in the early 1940s. Detailed models of the individual test facilities were also fabricated and displayed in the facilities. The laboratory was built on a wedge of land between the Cleveland Municipal Airport on the far side and the deep curving valley etched by the Rocky River on the near end. Roughly only a third of the laboratory's semicircle footprint was initially utilized. Additional facilities were added to the remaining areas in the years after World War II. In the late 1950s the site was supplemented by the acquisition of additional adjacent land. Morewitz joined the NACA in 1935 as a secretary in the main office at the Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory. In September 1940 she took on the task of setting up and guiding an office dedicated to the design of the NACA’s new engine research laboratory. Morewitz and the others in the design office transferred to Cleveland in December 1941 to expedite the construction. Morewitz served as Manager Ray Sharp’s secretary for six years and was a popular figure at the new laboratory. In December 1947 Morewitz announced her engagement to Langley researcher Sidney Batterson and moved back to Virginia.
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Dressed for a little exercise, Deputy Program Manager of Launch Services Chuck Dovale addresses the employees who have turned out during their lunchtime for a ribbon-cutting ceremony opening the new fitness trail next to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The one-mile-long track will provide employees with a safe place off Kennedy's roadways to walk or run. The more than 6 tons of green waste removed to create the trail's footprint will be mulched and used for cover at Kennedy's landfill. Approximately 1,594 tons of crawler fines -- ground-up crawler rock removed from the crawlerway in the Launch Complex 39 area -- was used for the foundation of the trail. Fitness equipment has been ordered and will be installed on a concrete slab at the trail's west end. After the equipment has been installed, the slab will be coated to provide a rubberized exercise pad. At Kennedy Space Center, the health and safety of every employee is paramount. To learn more about Kennedy, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin