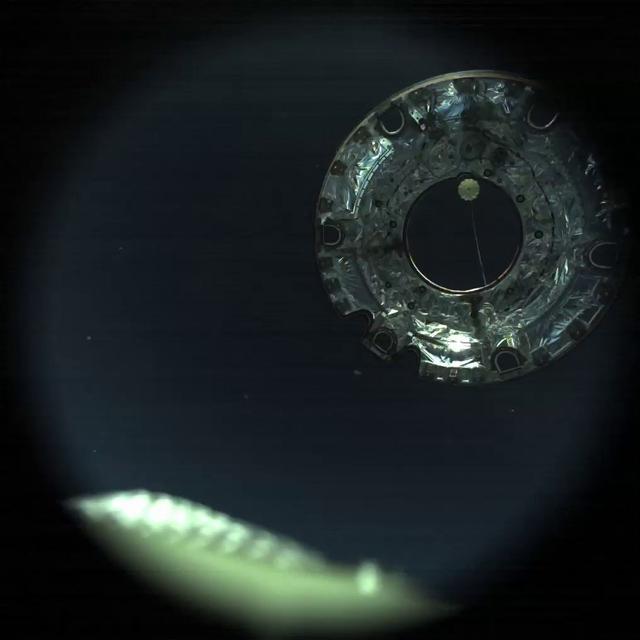

Orion's forward bay cover is jettisoned on its first flight test, Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1), on December 5, 2014.

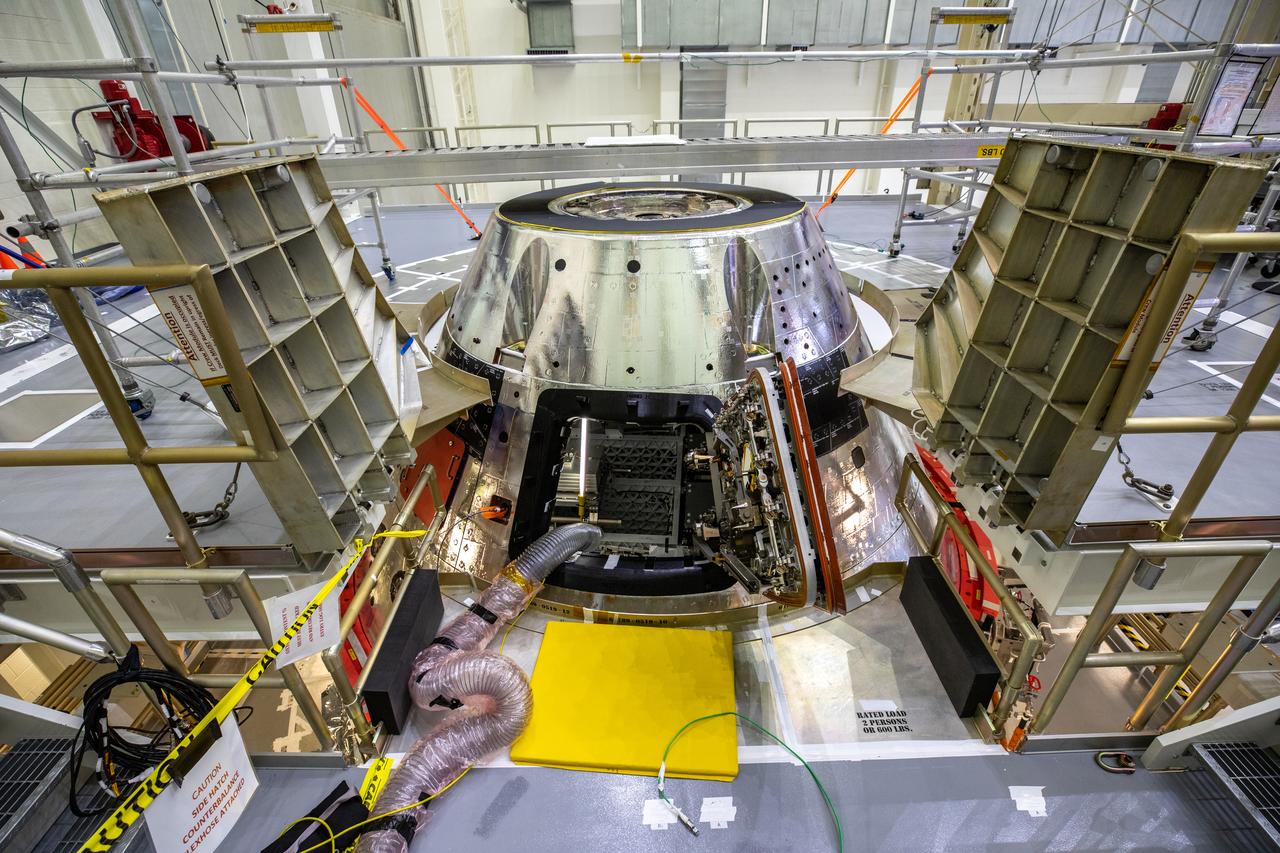
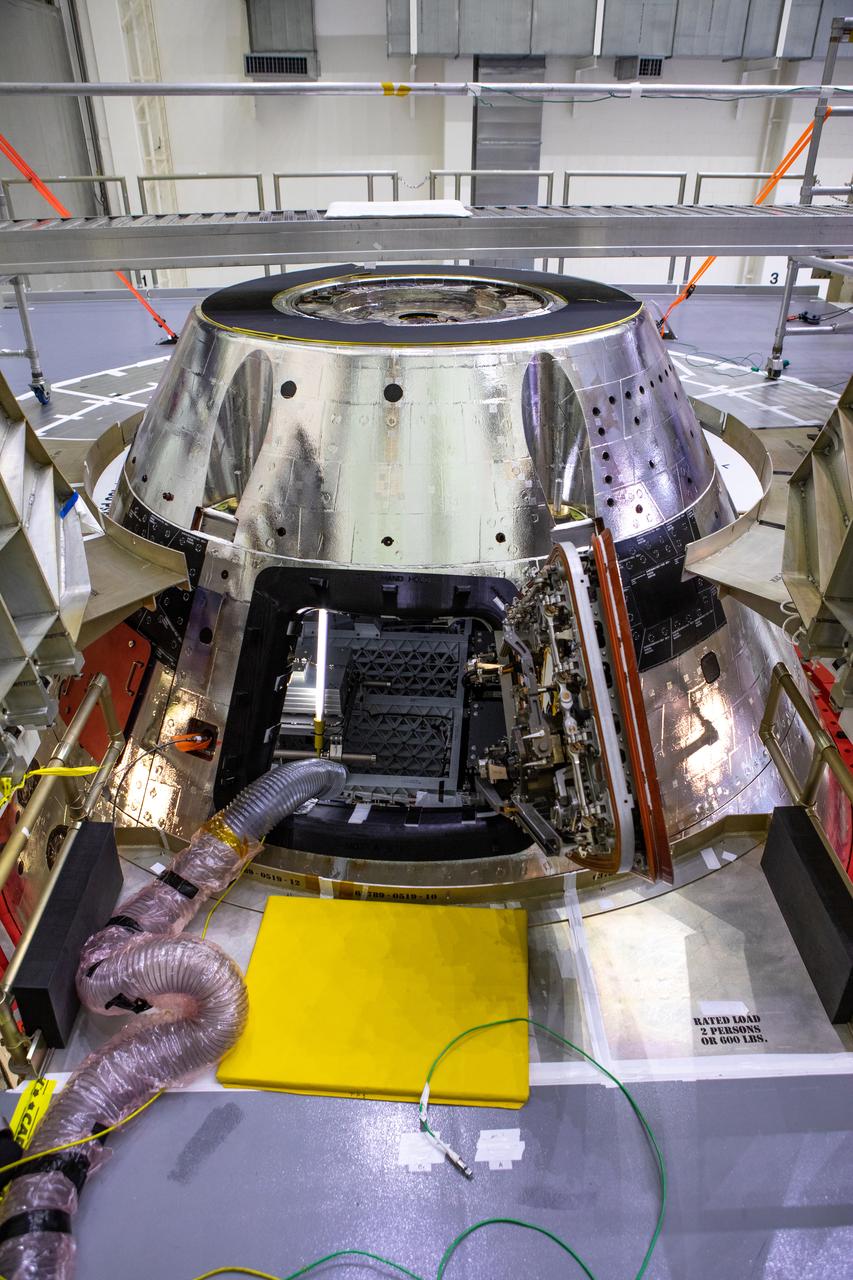
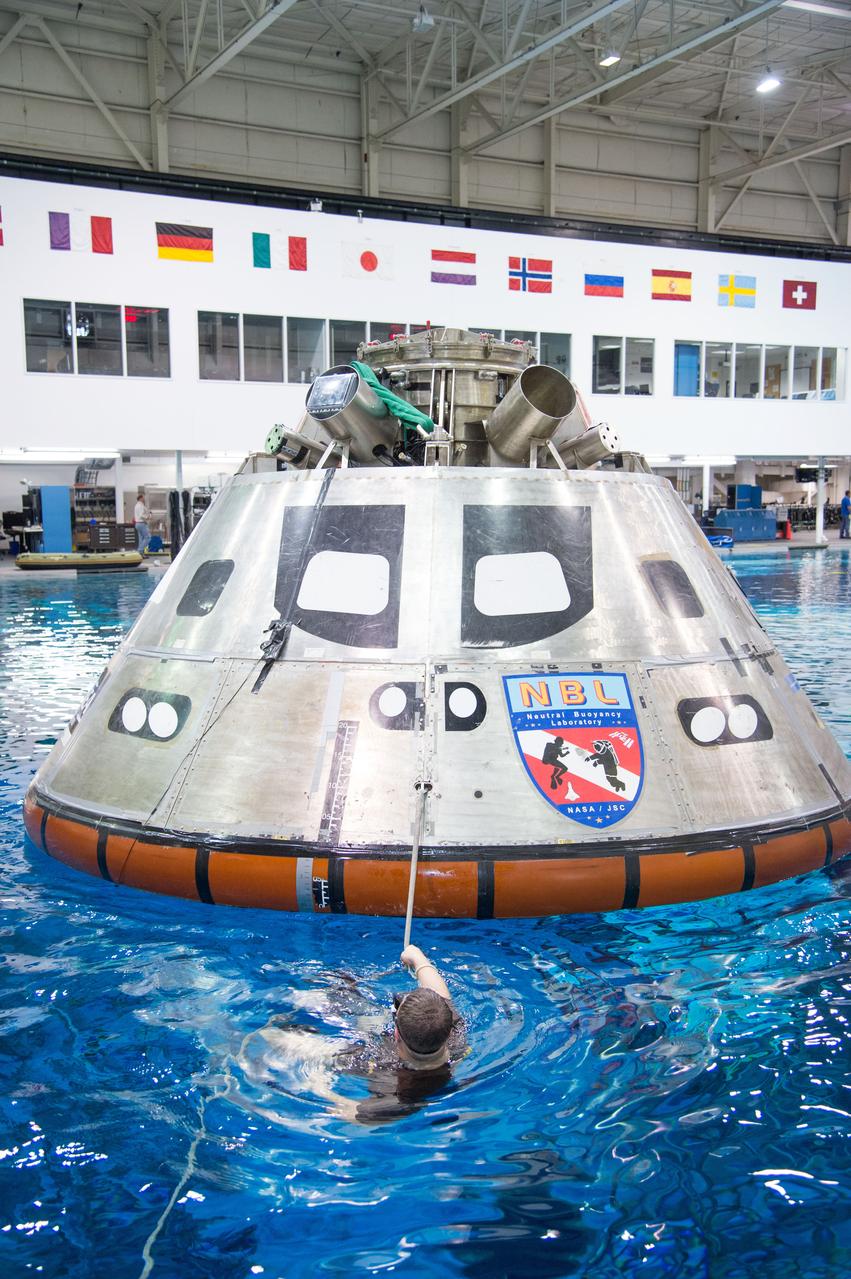
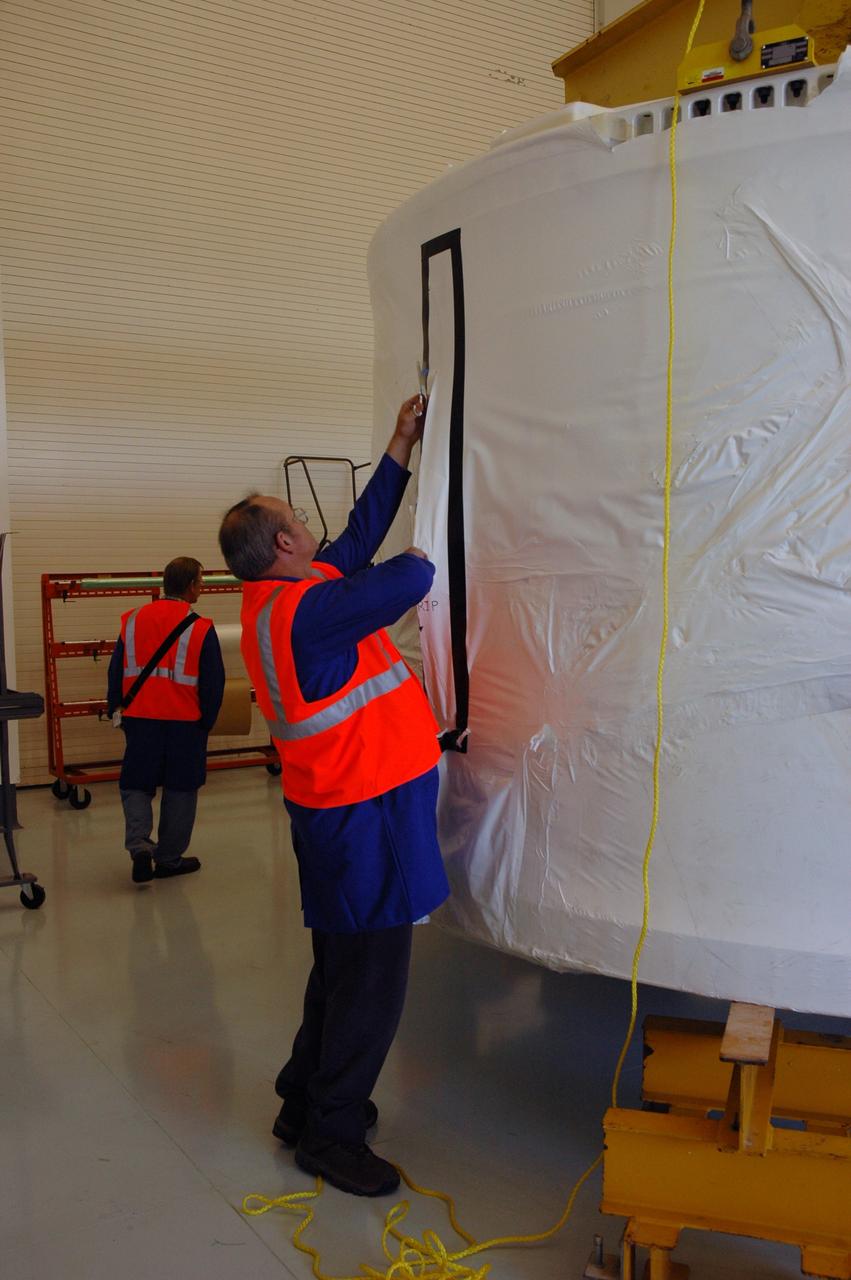
The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy. This image shows the setup right before the FBC deployment test. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
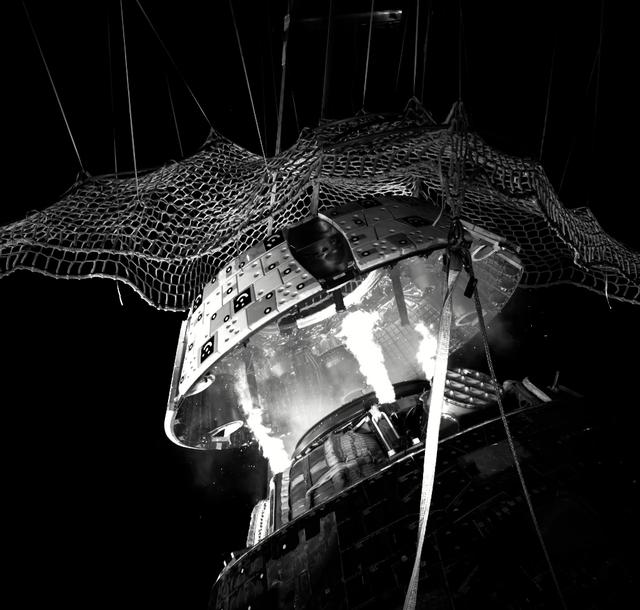

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy. Photo Credit: (NASA/Quentin Schwinn and Jordan Salkin)
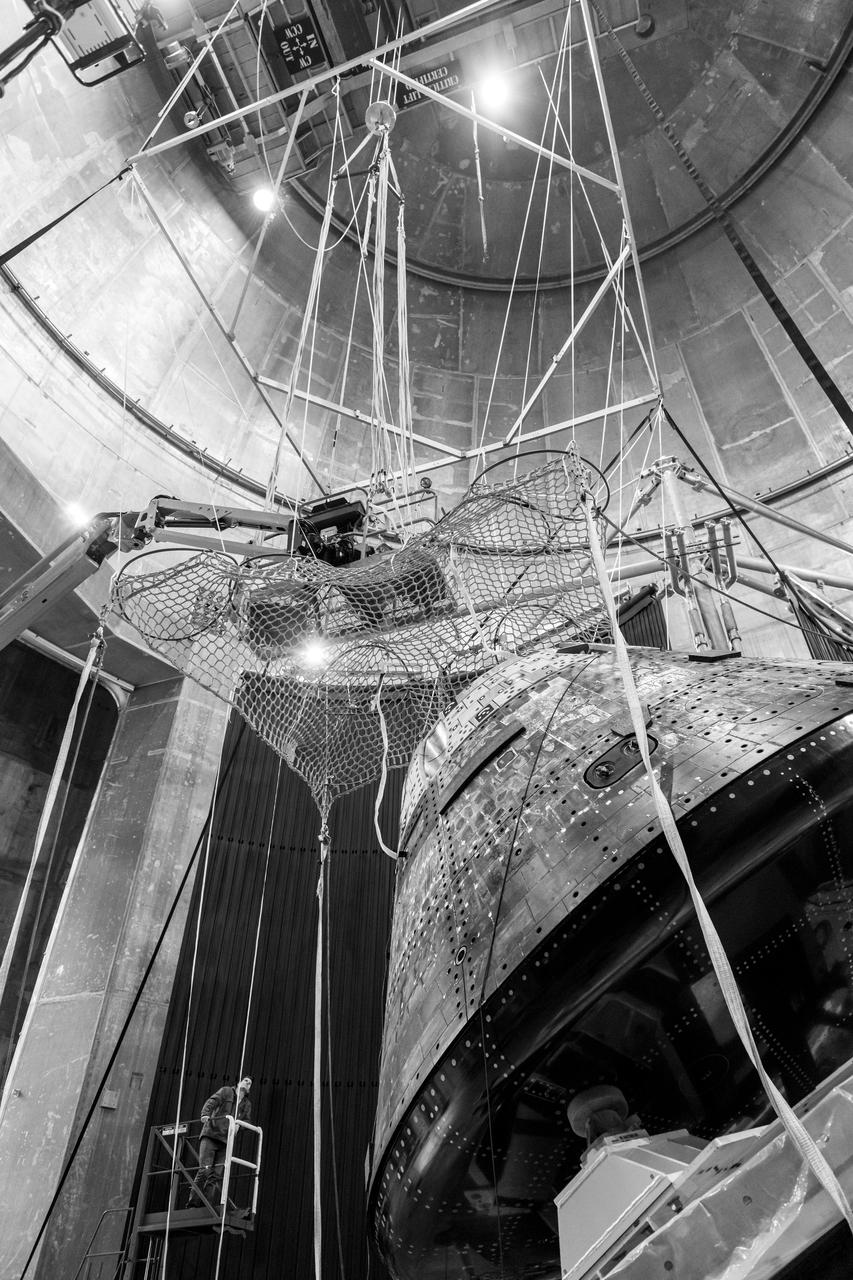

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy. This image shows the setup right before the FBC deployment test. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
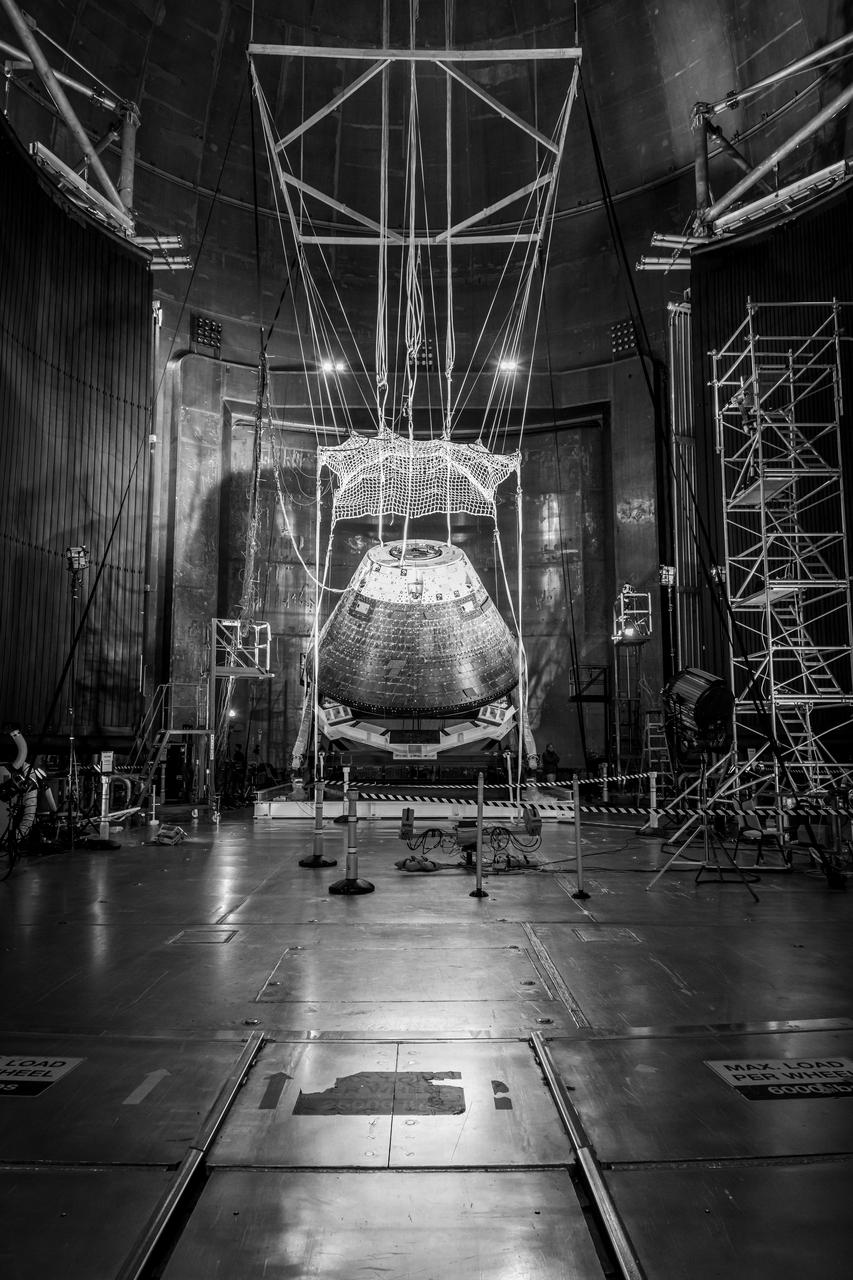

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy. This image shows the setup right before the FBC deployment test. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
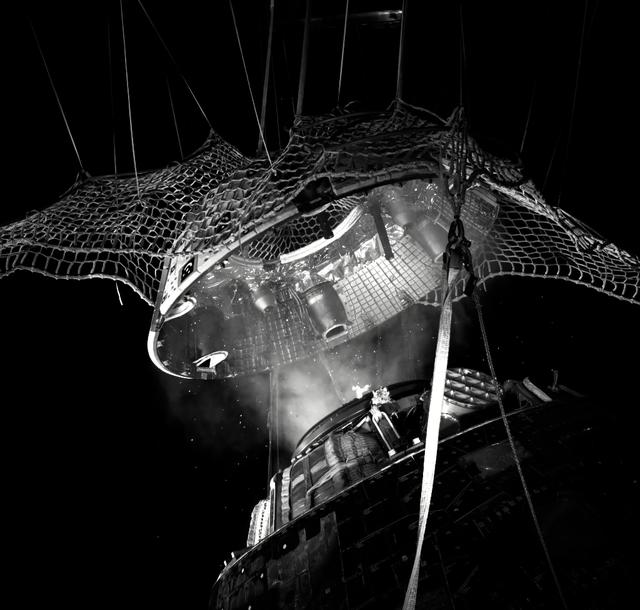

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy.
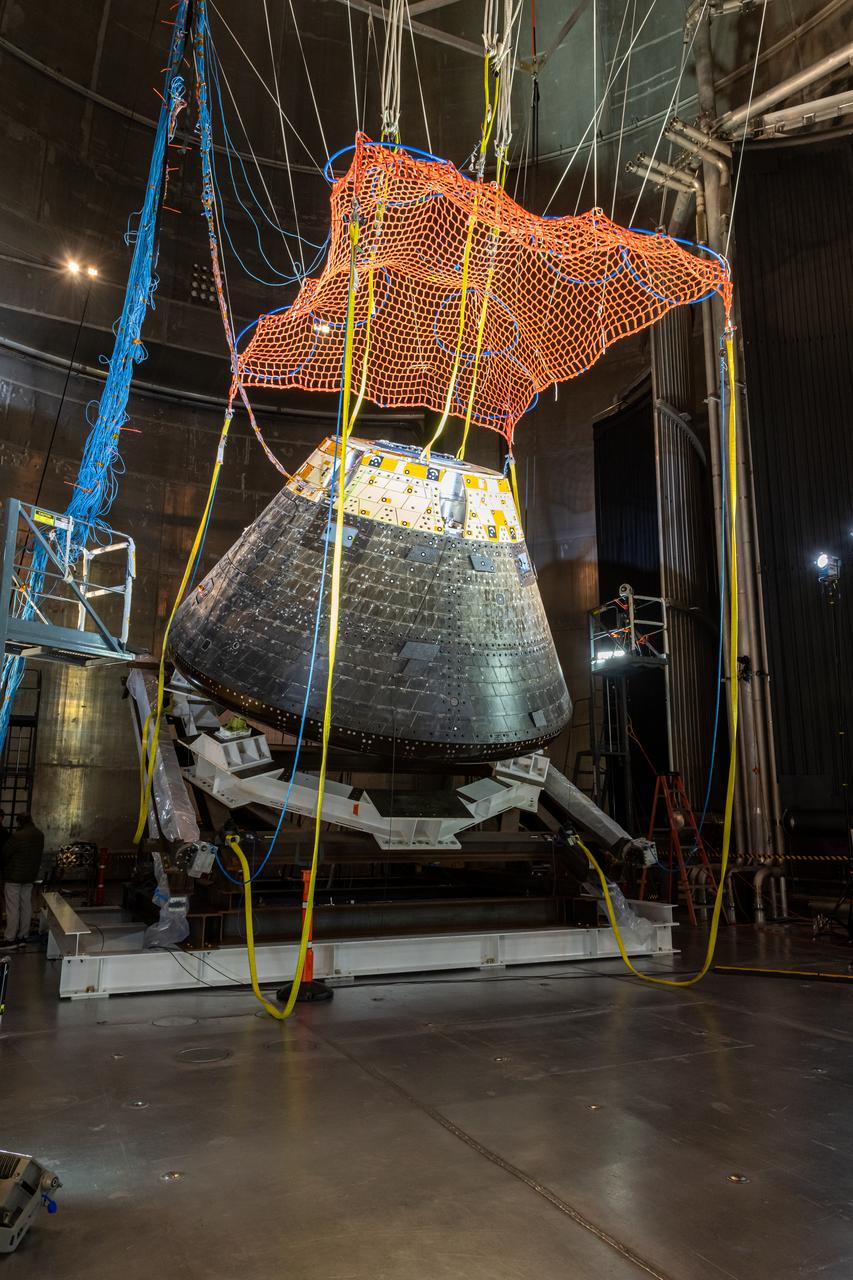

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy. This image shows the setup right before the FBC deployment test. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
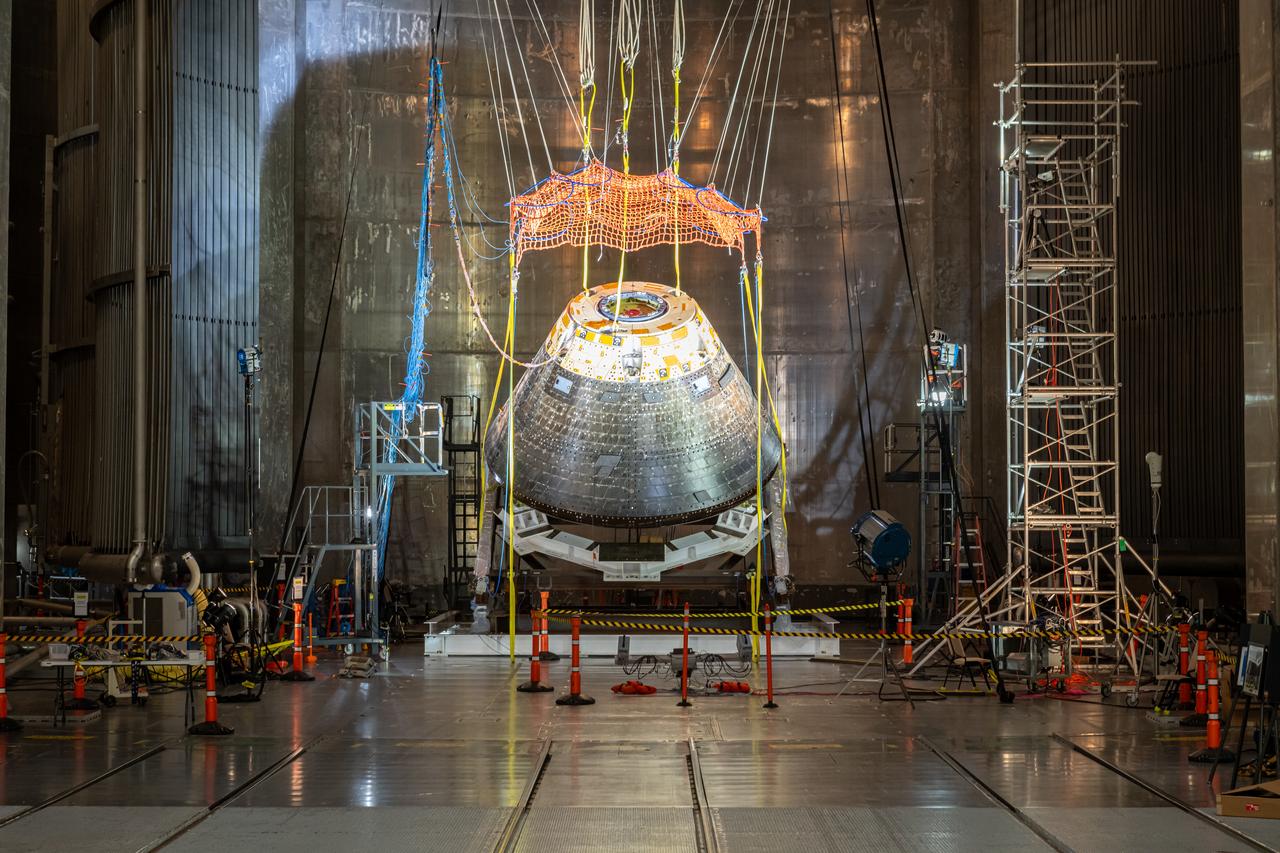

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy. This image shows the setup right before the FBC deployment test. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
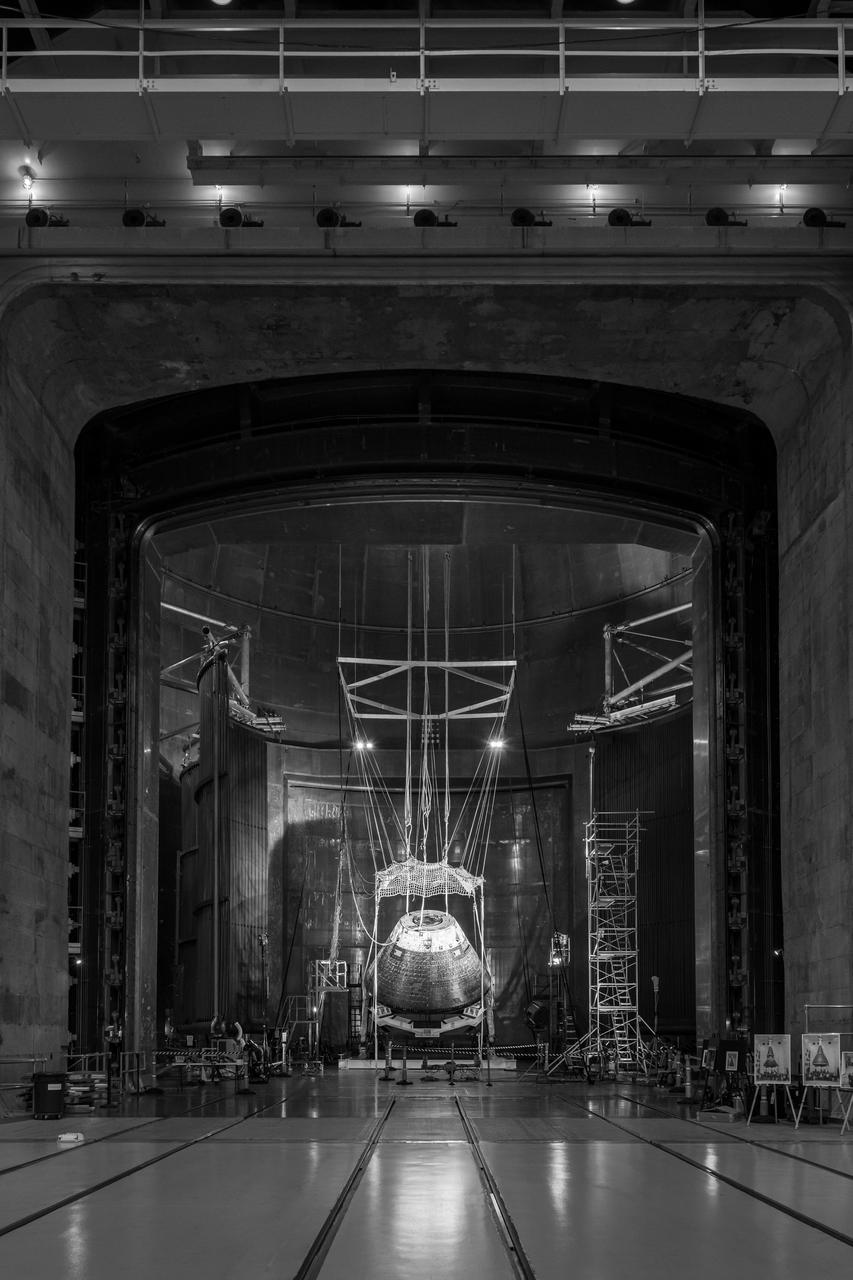

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy. This image shows the setup right before the FBC deployment test. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
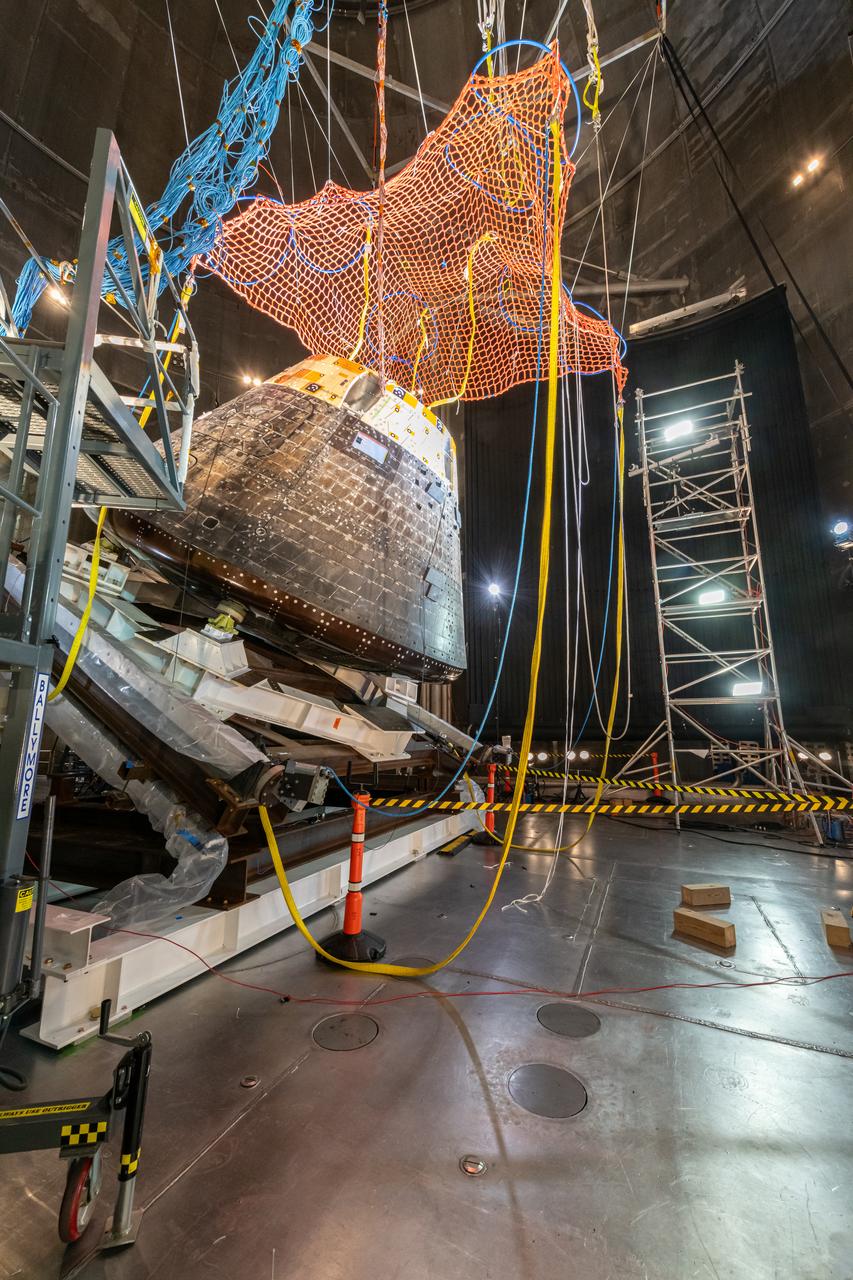

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy. This image shows the setup right before the FBC deployment test. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
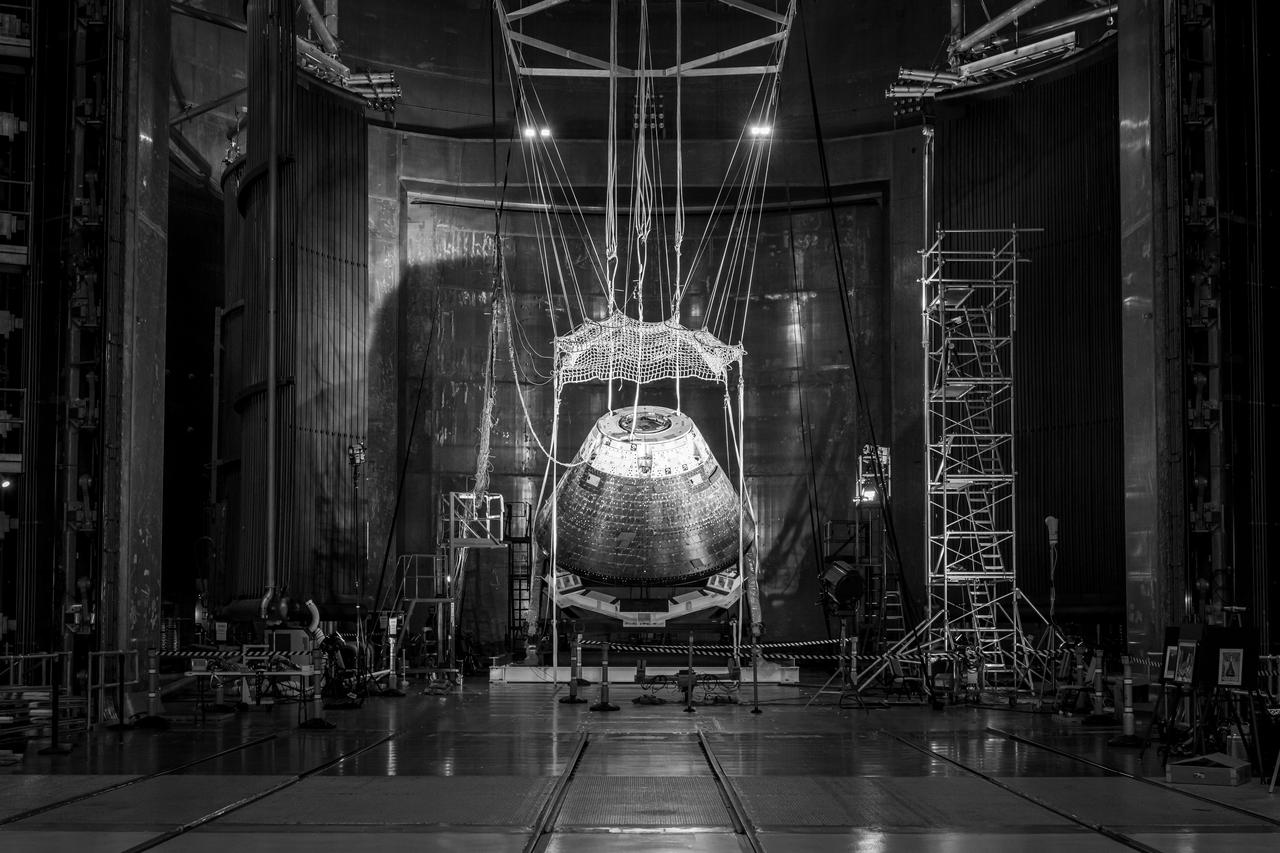

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy. This image shows the setup right before the FBC deployment test. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
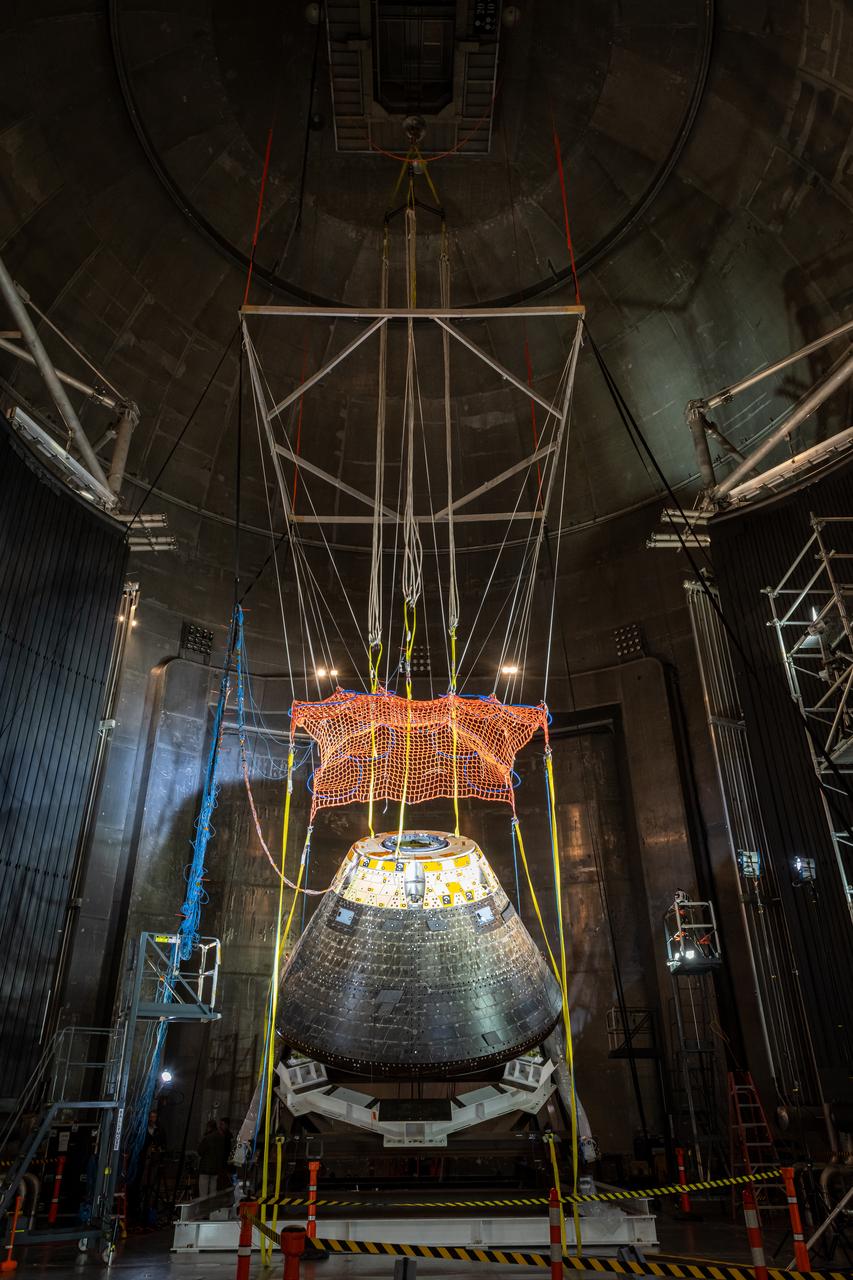

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy. This image shows the setup right before the FBC deployment test. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
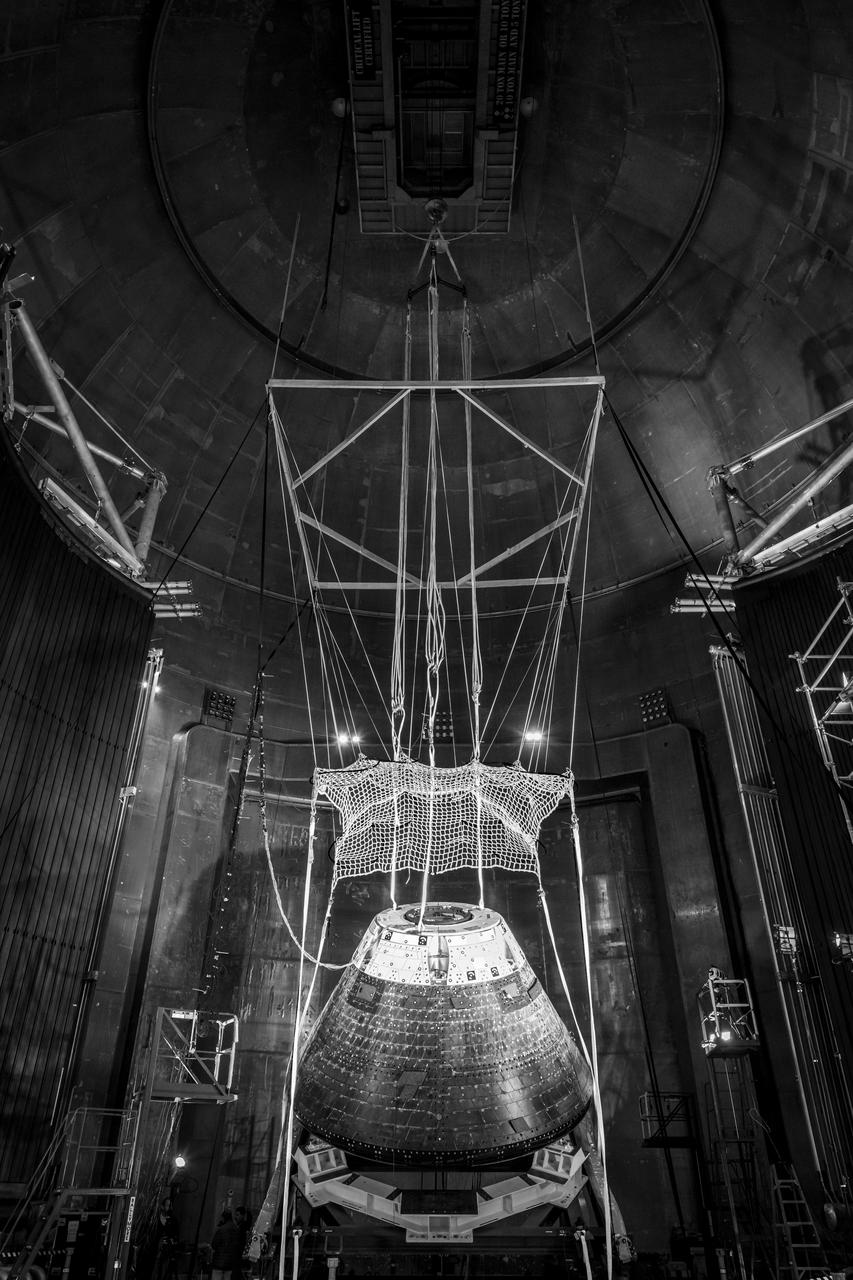

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy. This image shows the setup right before the FBC deployment test. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
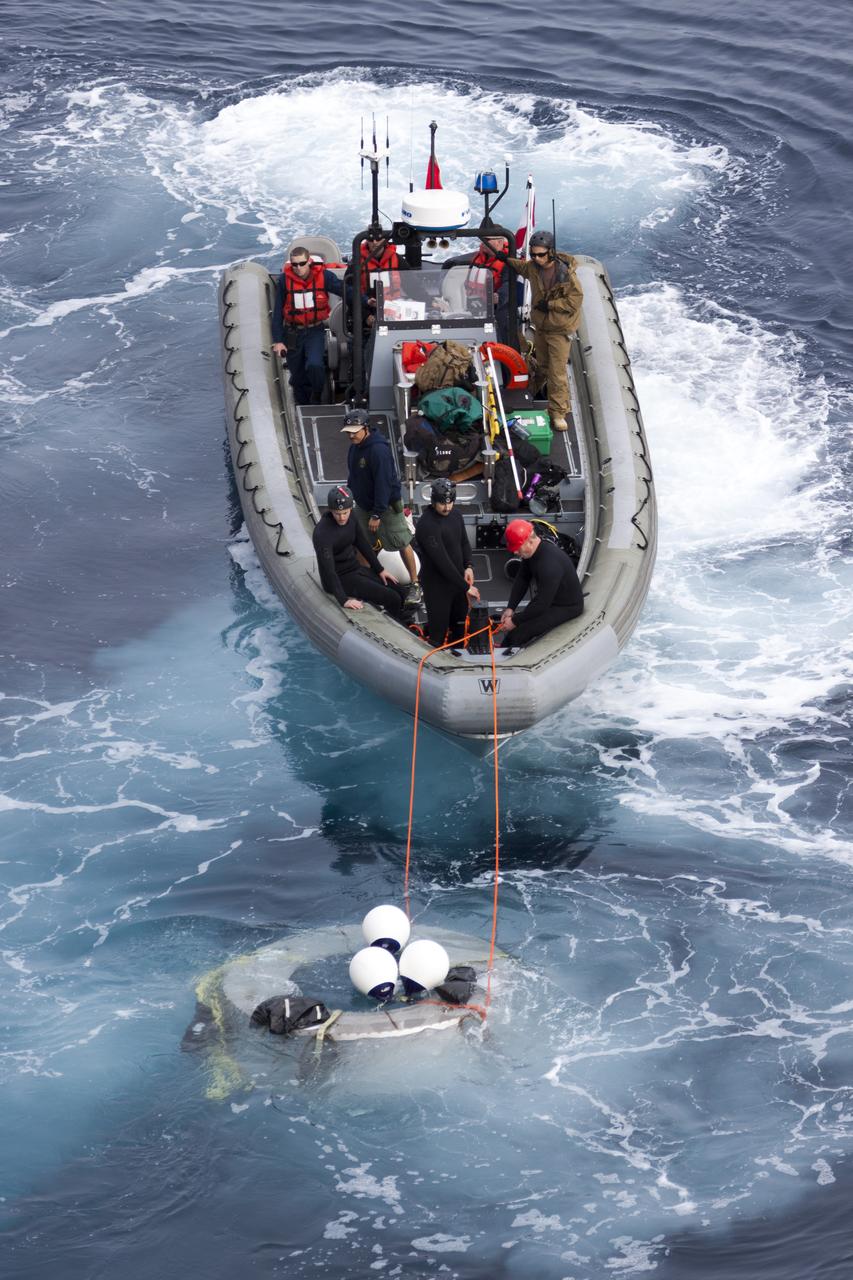

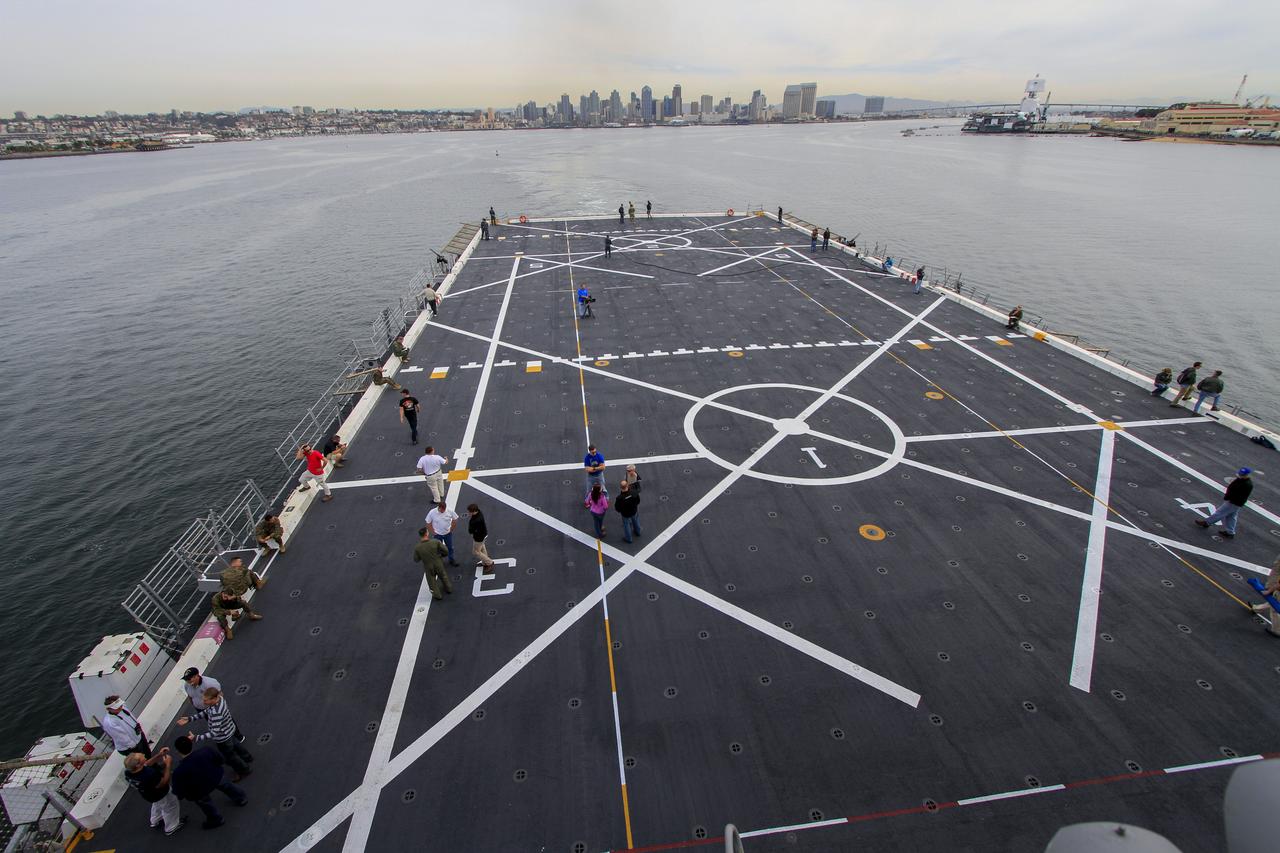
SAN DIEGO, Calif. – Using a rigid hull inflatable boat, NASA and the U.S. Navy practice retrieving the Orion forward bay cover from the Pacific Ocean as part of the Orion underway recovery test. The Orion boilerplate test vehicle and other hardware are secured in the well deck of the USS San Diego nearby in preparation for the test about 100 miles off the coast of San Diego, California. NASA and the U.S. Navy conducted tests to prepare for the recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. During the testing, the tether lines were unable to support the tension caused by crew module motion that was driven by wave turbulence in the well deck of the ship. NASA and the U.S. Navy called off the week’s remaining testing to allow engineers to evaluate the next steps The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program conducted the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
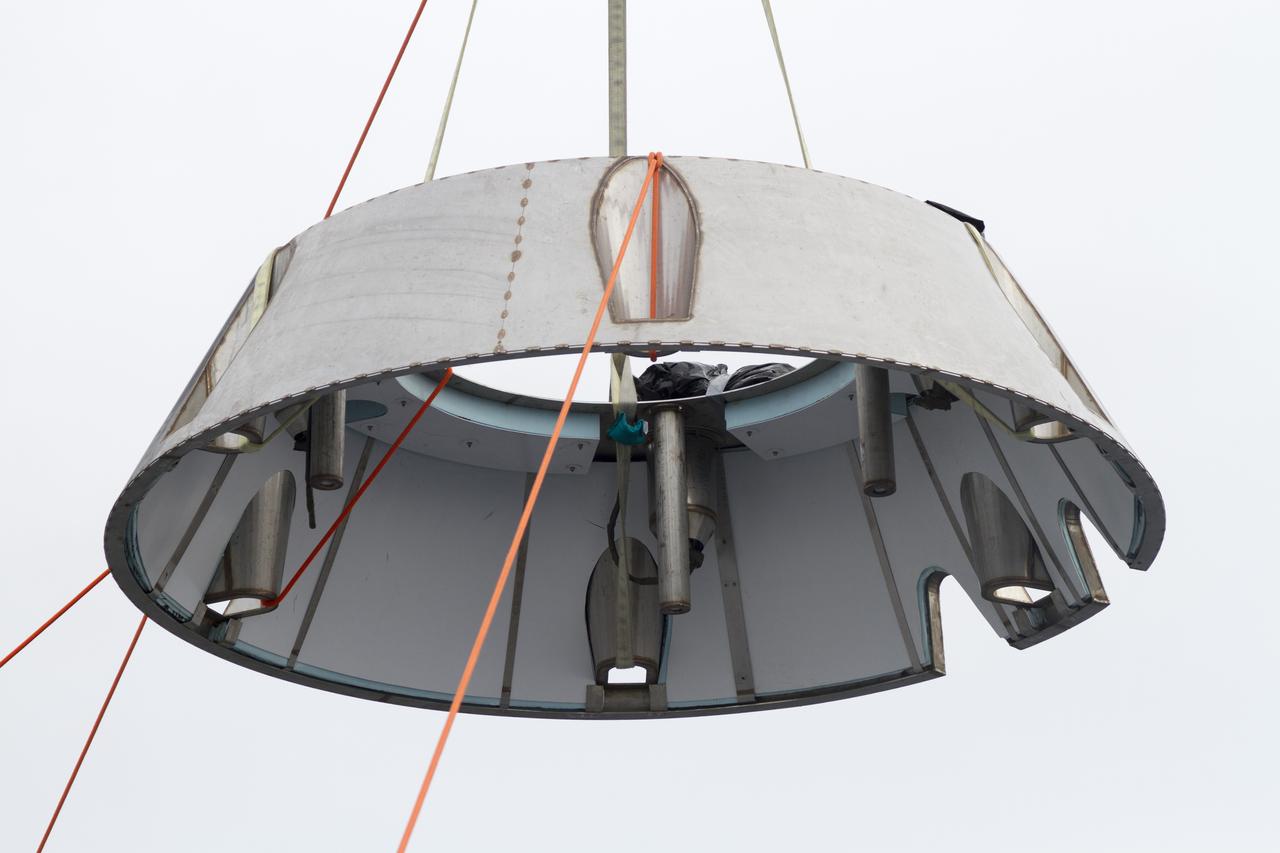

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion forward bay cover is lowered into the water using a crane and tether lines as part of the Orion underway recovery test. The Orion boilerplate test vehicle and other hardware are secured in the well deck of the USS San Diego in preparation for the test about 100 miles off the coast of San Diego, California. NASA and the U.S. Navy conducted tests to prepare for the recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. During the testing, the tether lines were unable to support the tension caused by crew module motion that was driven by wave turbulence in the well deck of the ship. NASA and the U.S. Navy are reviewing the testing data collected to evaluate the next steps. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program conducted the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
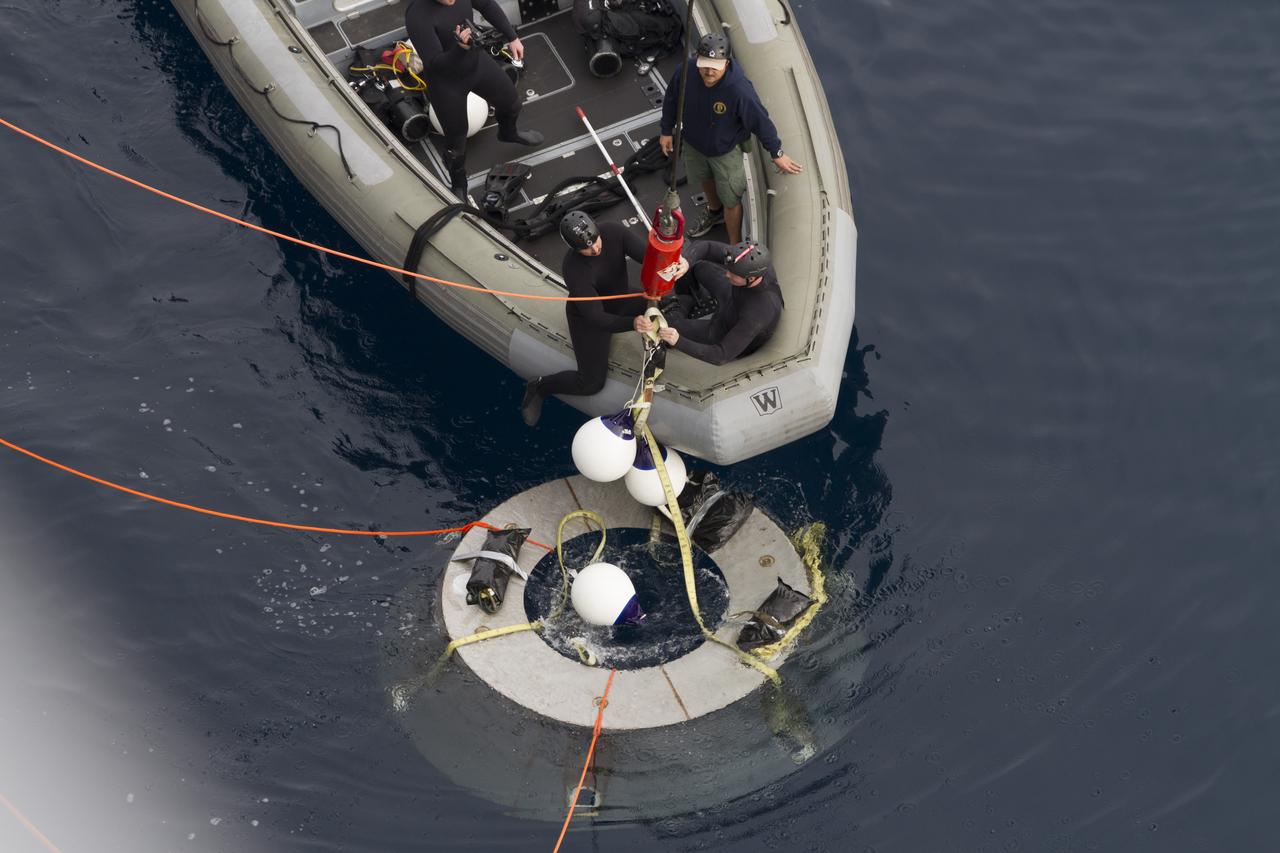

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – NASA and U.S. Navy personnel practice retrieving the Orion forward bay cover from the water during the Orion underway recovery test. The Orion boilerplate test vehicle and other hardware are secured in the well deck of the USS San Diego nearby in preparation for the test about 100 miles off the coast of San Diego, California. NASA and the U.S. Navy conducted tests to prepare for the recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. During the testing, the tether lines were unable to support the tension caused by crew module motion that was driven by wave turbulence in the well deck of the ship. NASA and the U.S. Navy are reviewing the testing data collected to evaluate the next steps. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program conducted the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – At the U.S. Naval Base San Diego in California, the USS San Diego heads out to sea with the Orion boilerplate test vehicle and other hardware in its well deck for an underway recovery test. On the top deck is the Orion forward bay cover. About 100 miles offshore, NASA and the U.S. Navy conducted tests to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. During the testing, the tether lines were unable to support the tension caused by crew module motion that was driven by wave turbulence in the well deck of the ship. NASA and the U.S. Navy are reviewing the testing data collected to evaluate the next steps. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program conducted the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
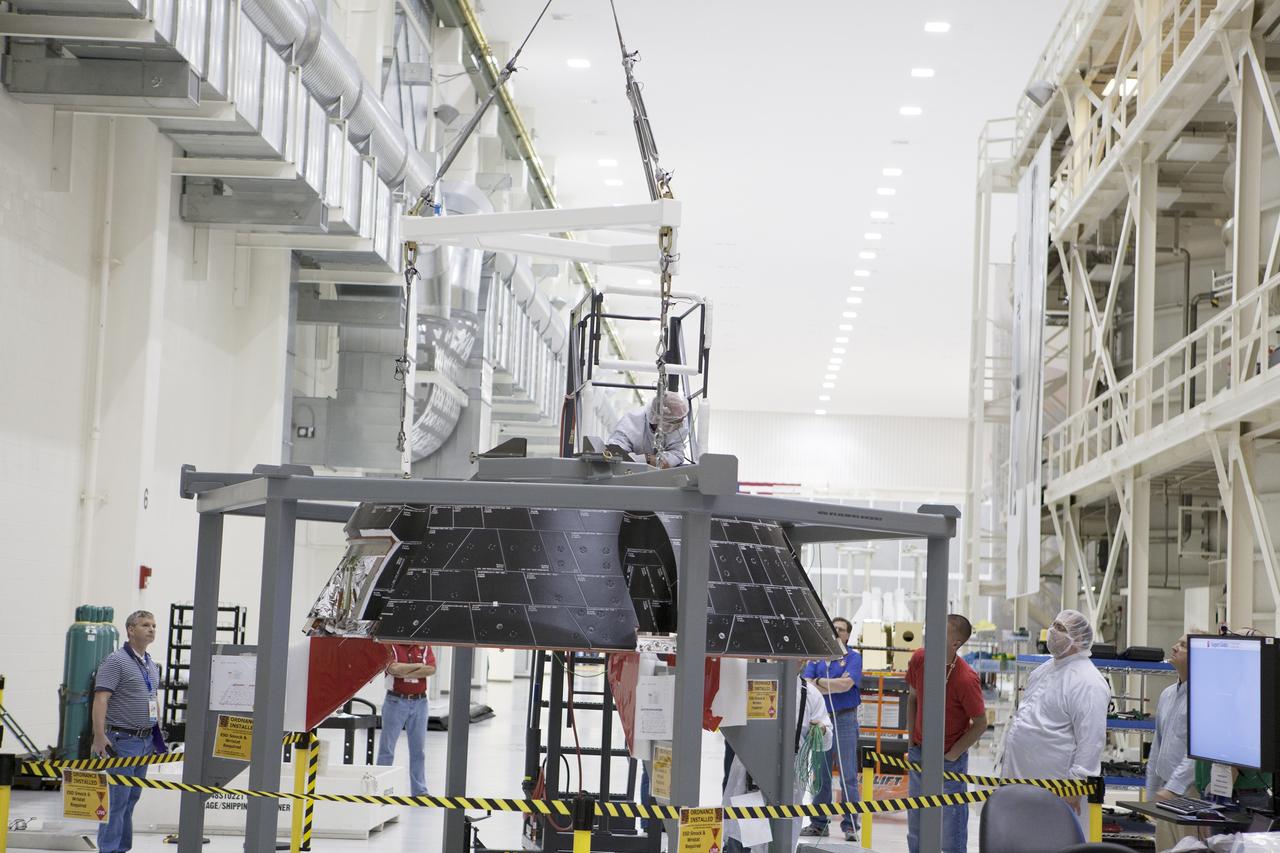

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians prepare to do a fit check of the forward bay cover for the Orion crew module. The cover is a shell that fits over Orion's crew module to protect the spacecraft during launch, orbital flight and re-entry into Earth's atmosphere. When Orion returns from space, the cover must be jettisoned high above the ground so that the parachutes can deploy and unfurl. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
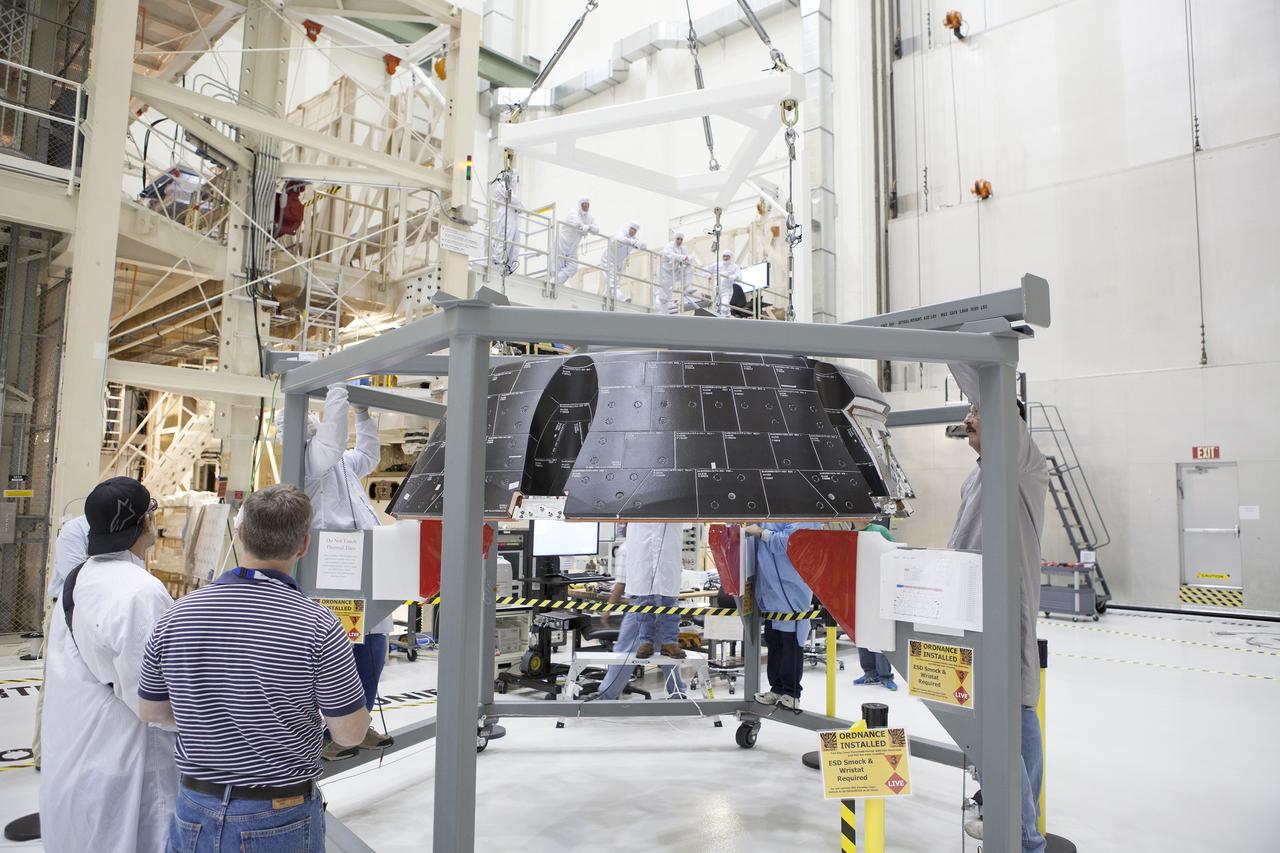

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians prepare to do a fit check of the forward bay cover for the Orion crew module. The cover is a shell that fits over Orion's crew module to protect the spacecraft during launch, orbital flight and re-entry into Earth's atmosphere. When Orion returns from space, the cover must be jettisoned high above the ground so that the parachutes can deploy and unfurl. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the progress as a crane lifts the forward bay cover for a fit check on the Orion crew module. The cover is a shell that fits over Orion's crew module to protect the spacecraft during launch, orbital flight and re-entry into Earth's atmosphere. When Orion returns from space, the cover must be jettisoned high above the ground so that the parachutes can deploy and unfurl. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
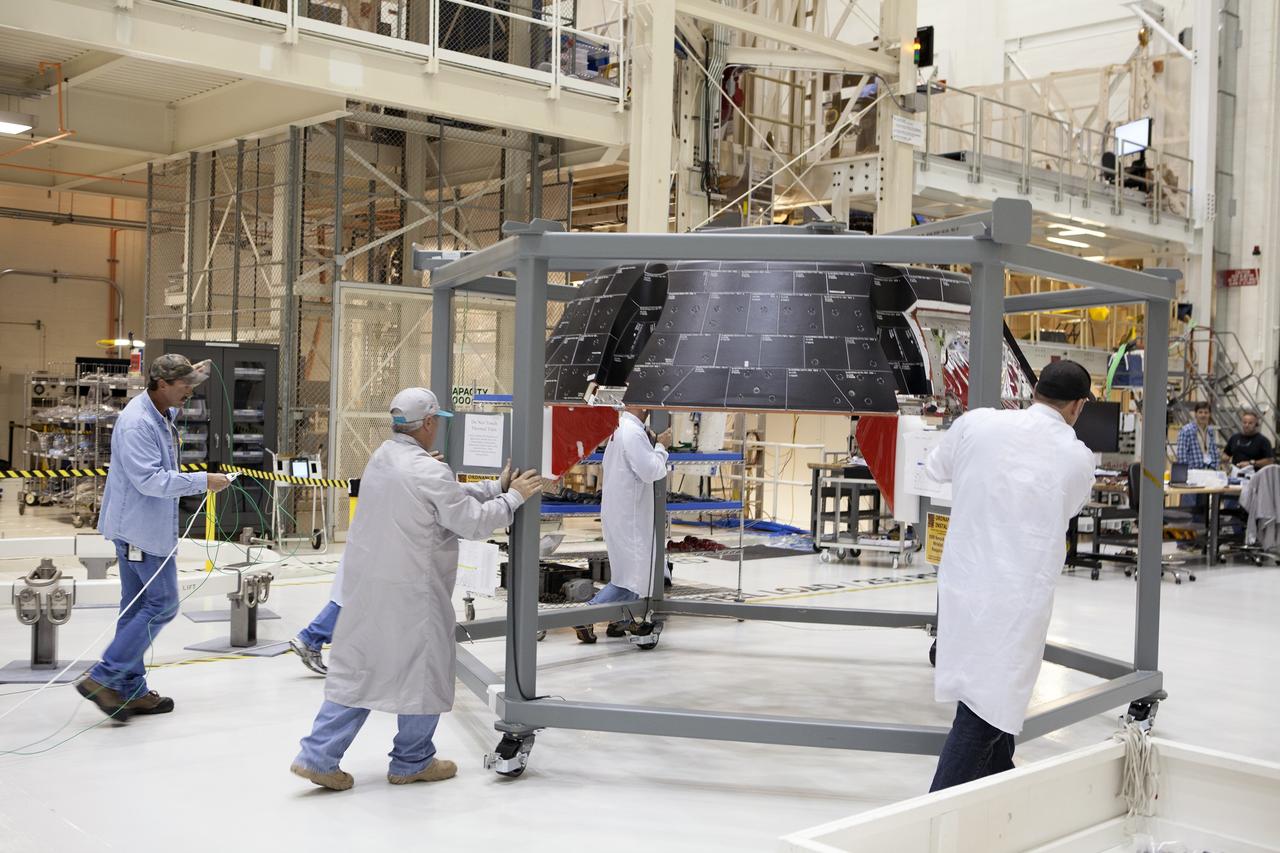

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians prepare to do a fit check of the forward bay cover for the Orion crew module. The cover is a shell that fits over Orion's crew module to protect the spacecraft during launch, orbital flight and re-entry into Earth's atmosphere. When Orion returns from space, the cover must be jettisoned high above the ground so that the parachutes can deploy and unfurl. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
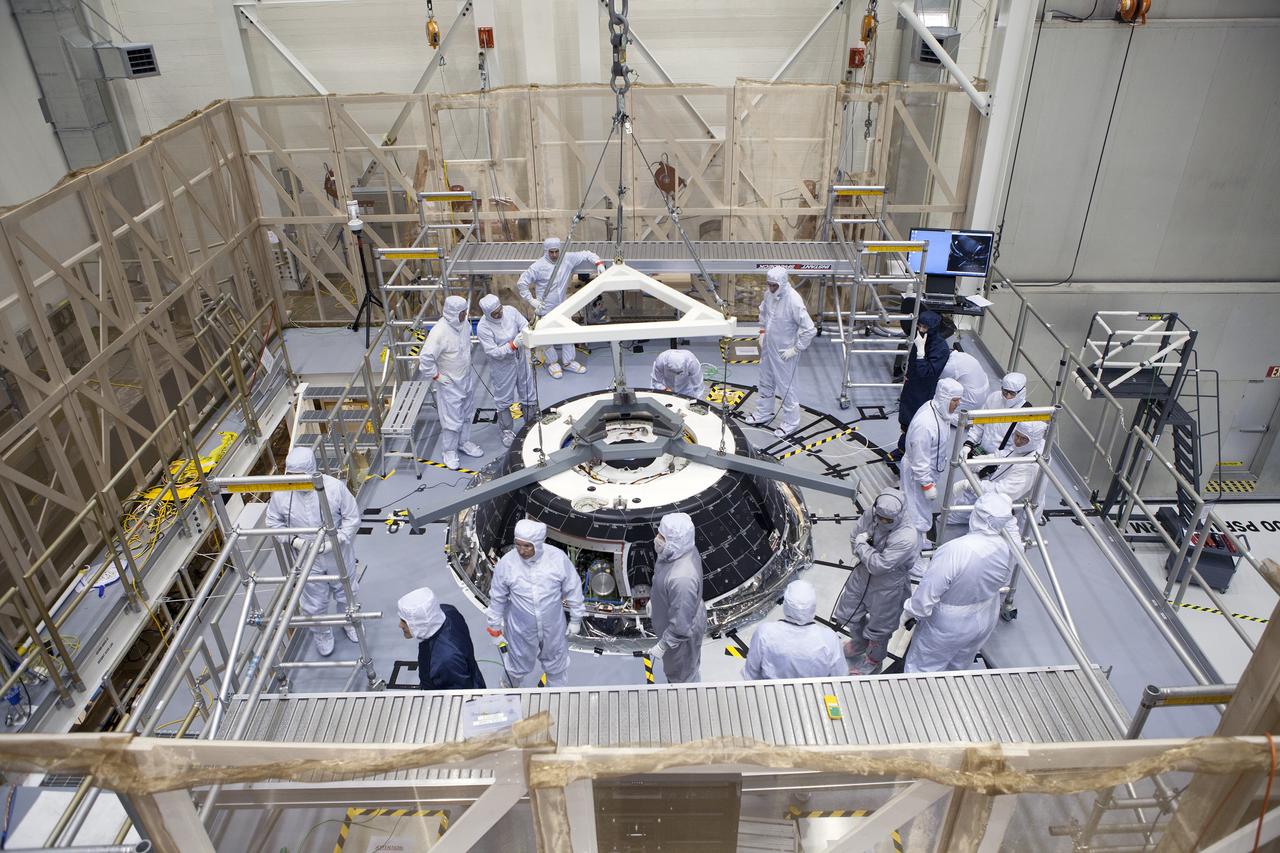

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians on a work platform monitor the progress as a crane lowers the forward bay cover onto the Orion crew module for a fit check. The cover is a shell that fits over Orion's crew module to protect the spacecraft during launch, orbital flight and re-entry into Earth's atmosphere. When Orion returns from space, the cover must be jettisoned high above the ground so that the parachutes can deploy and unfurl. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
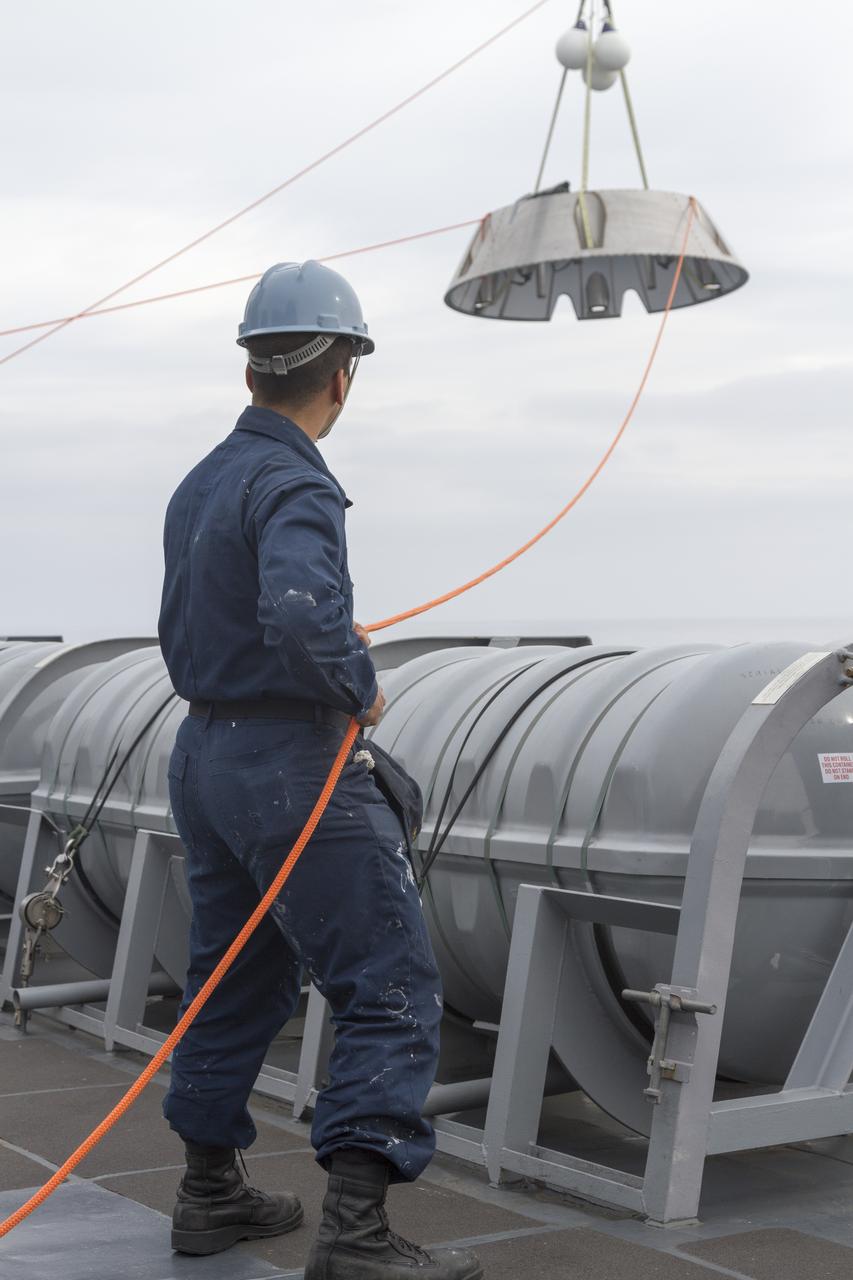

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The Orion forward bay cover is lowered into the water using a crane and tether lines as part of the Orion underway recovery test. The Orion boilerplate test vehicle and other hardware are secured in the well deck of the USS San Diego in preparation for the test about 100 miles off the coast of San Diego, California. NASA and the U.S. Navy conducted tests to prepare for the recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. During the testing, the tether lines were unable to support the tension caused by crew module motion that was driven by wave turbulence in the well deck of the ship. NASA and the U.S. Navy are reviewing the testing data collected to evaluate the next steps. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program conducted the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
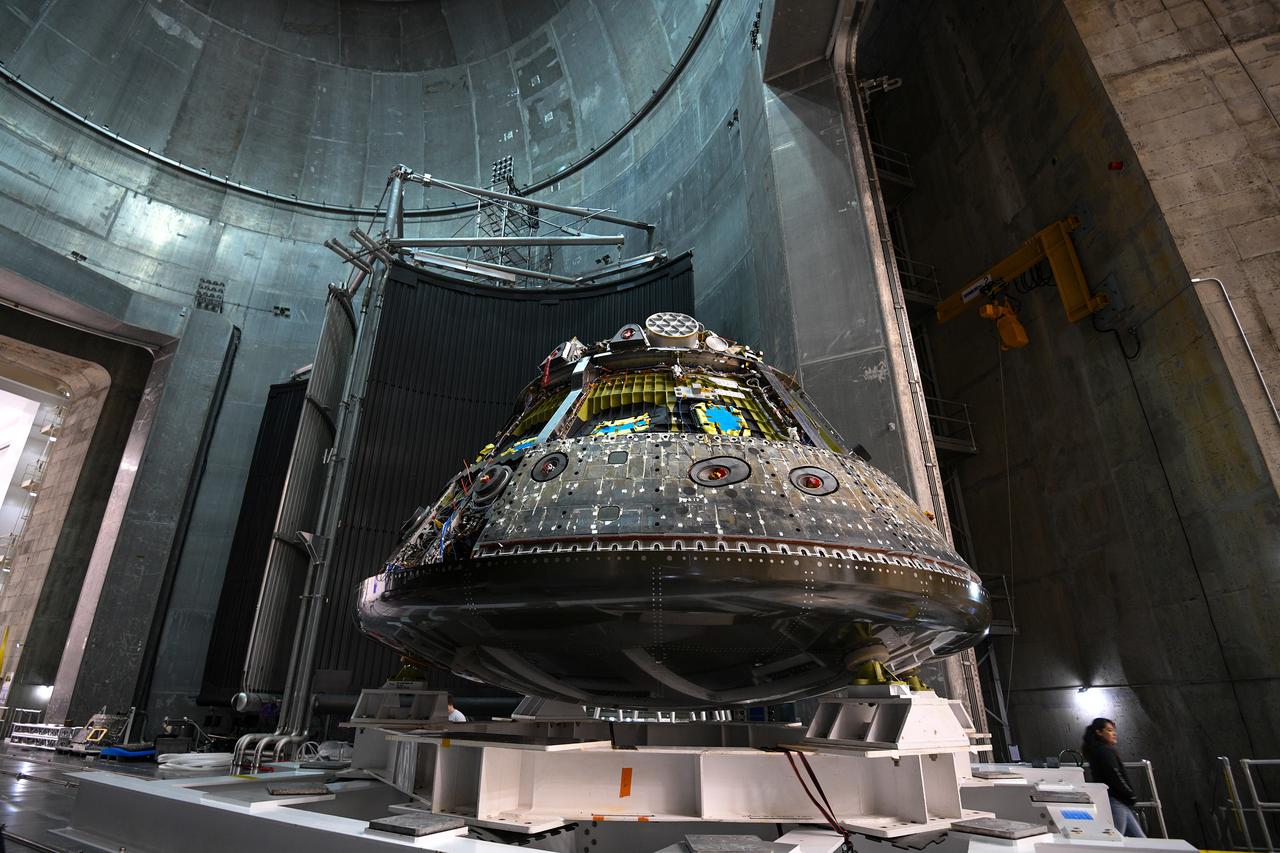

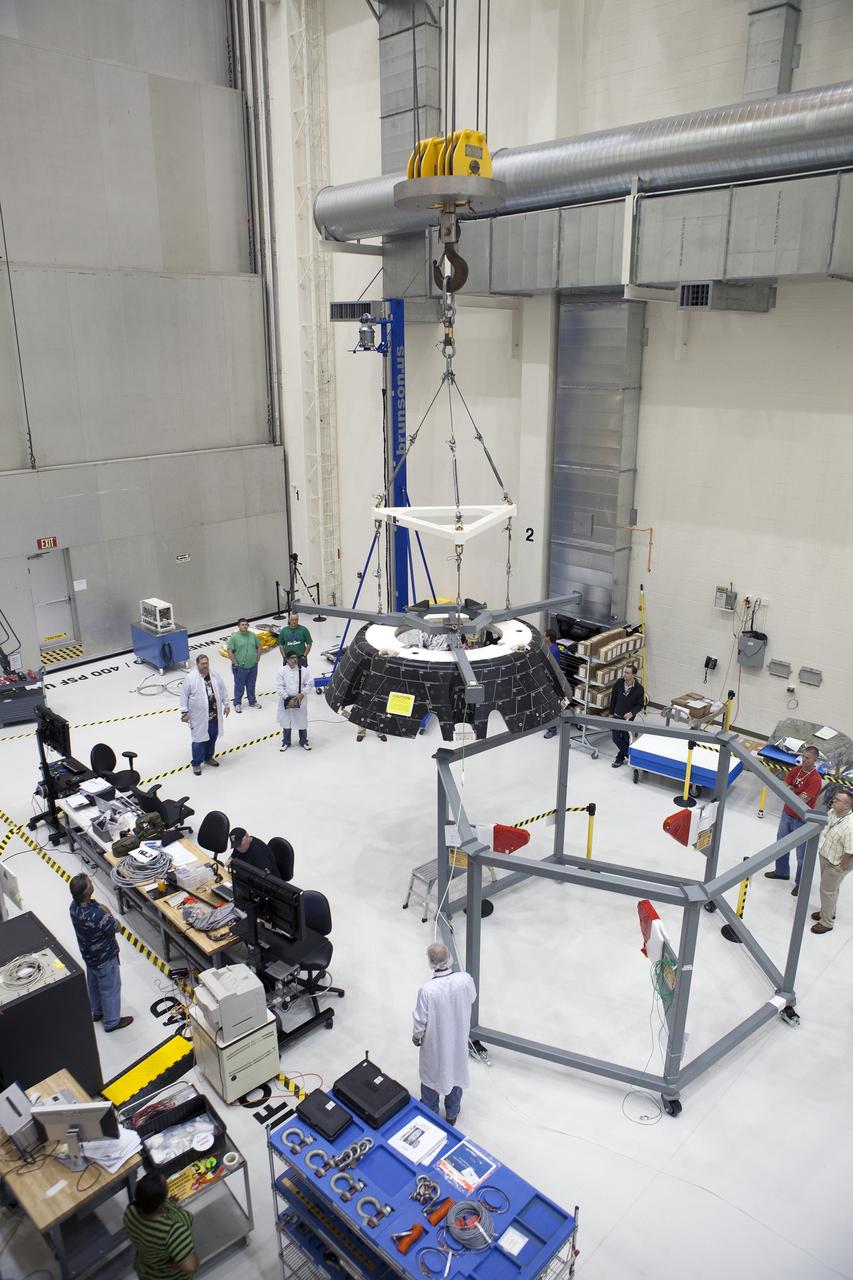
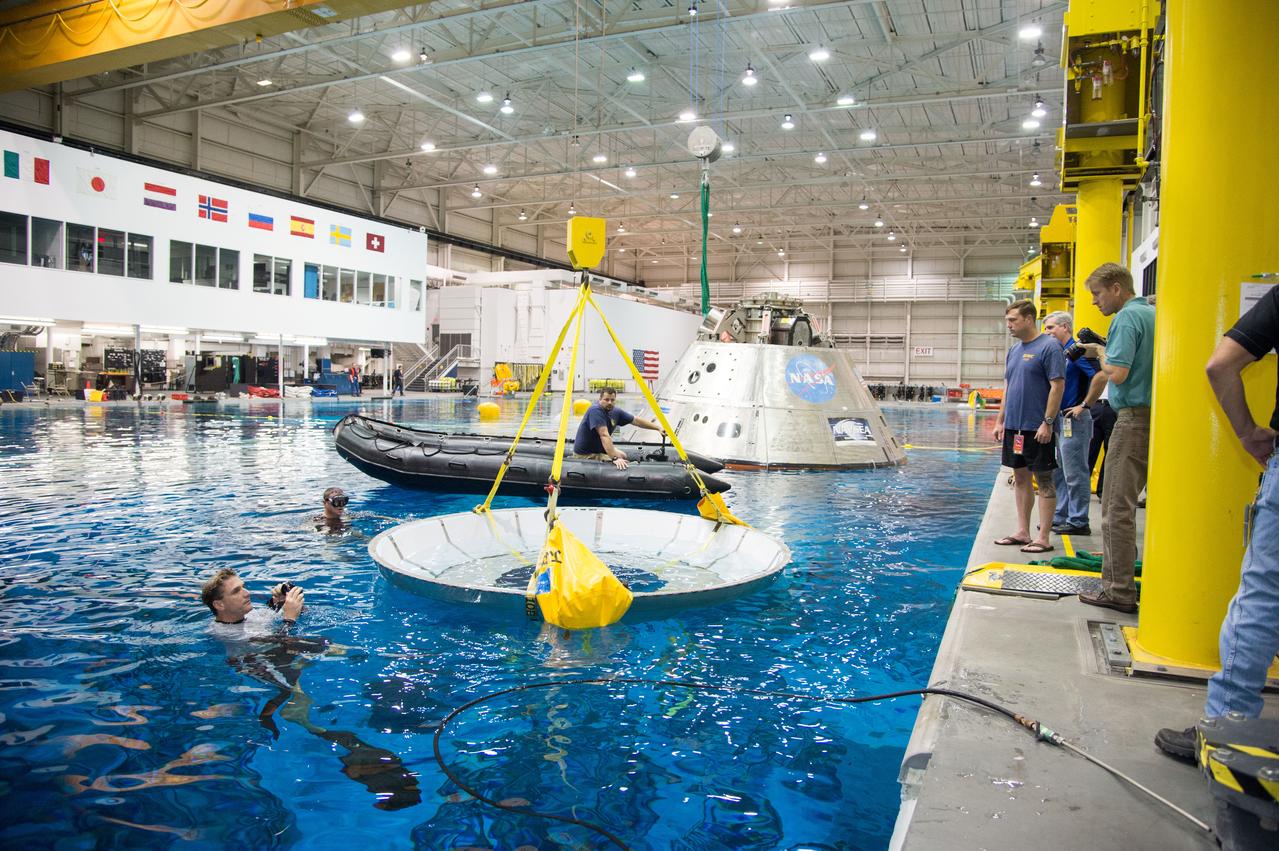
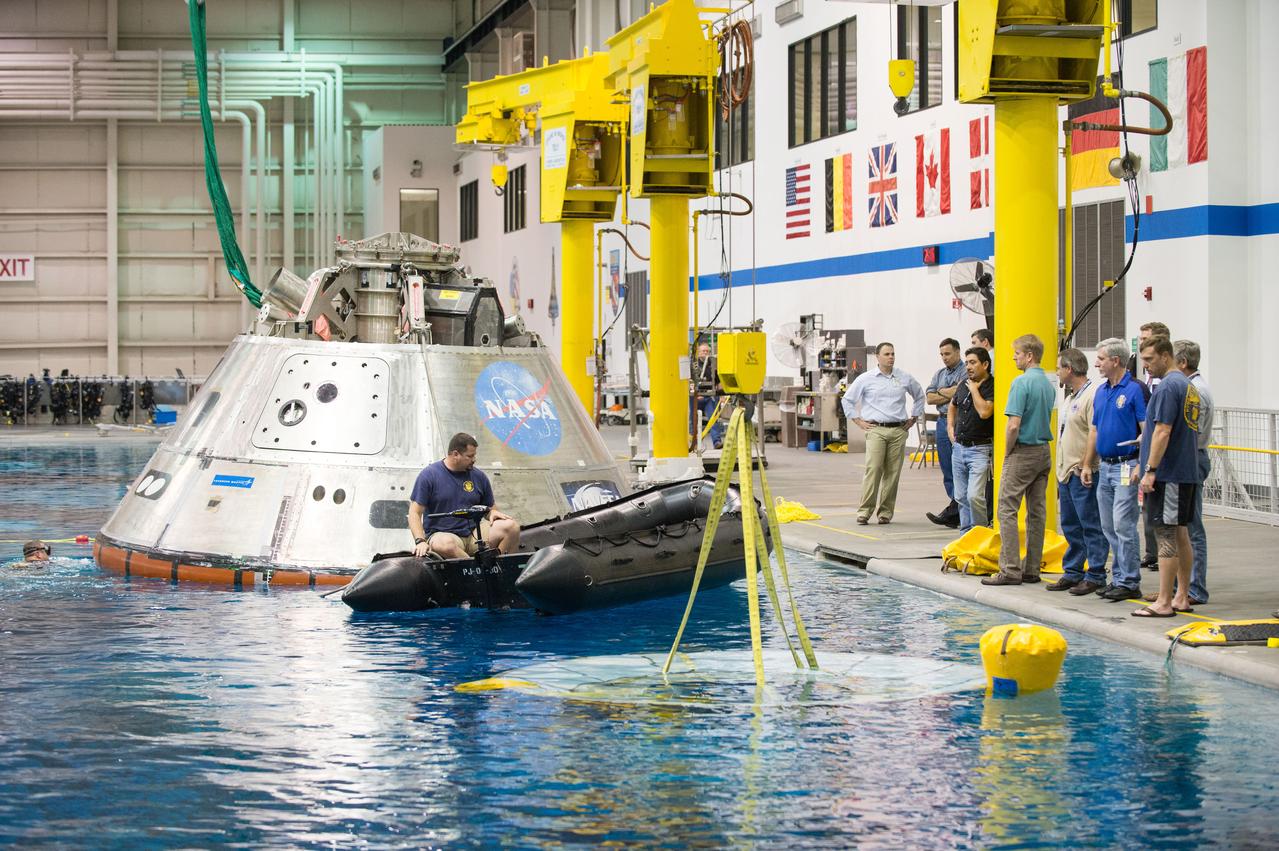
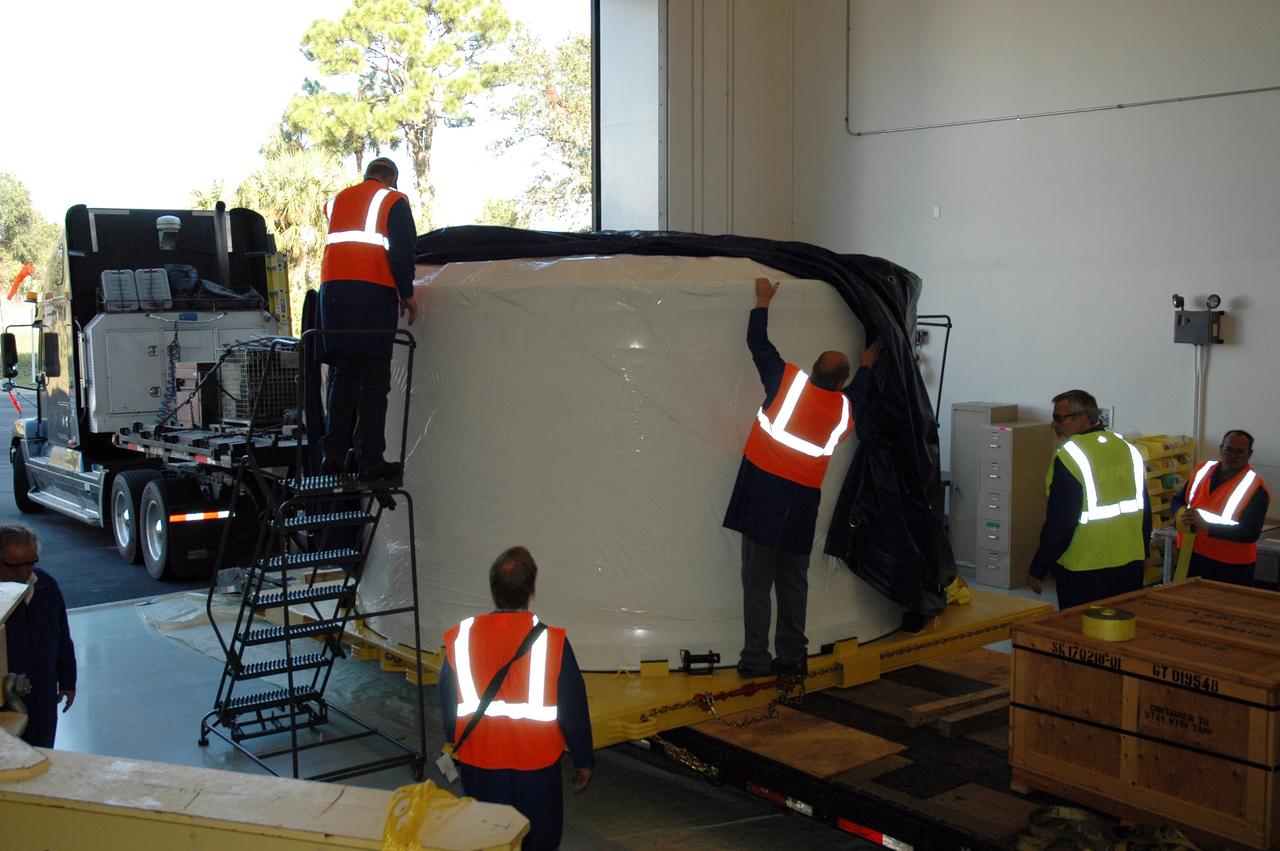
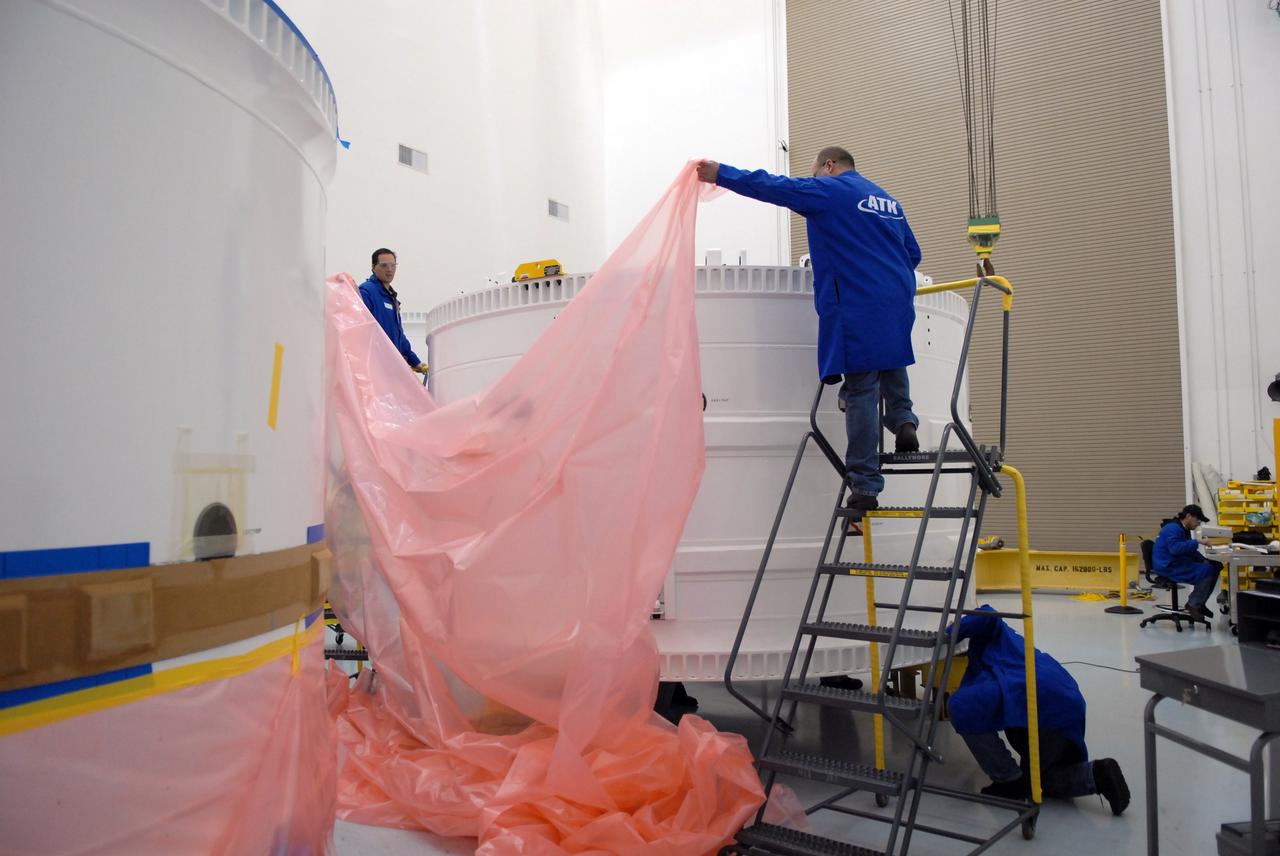
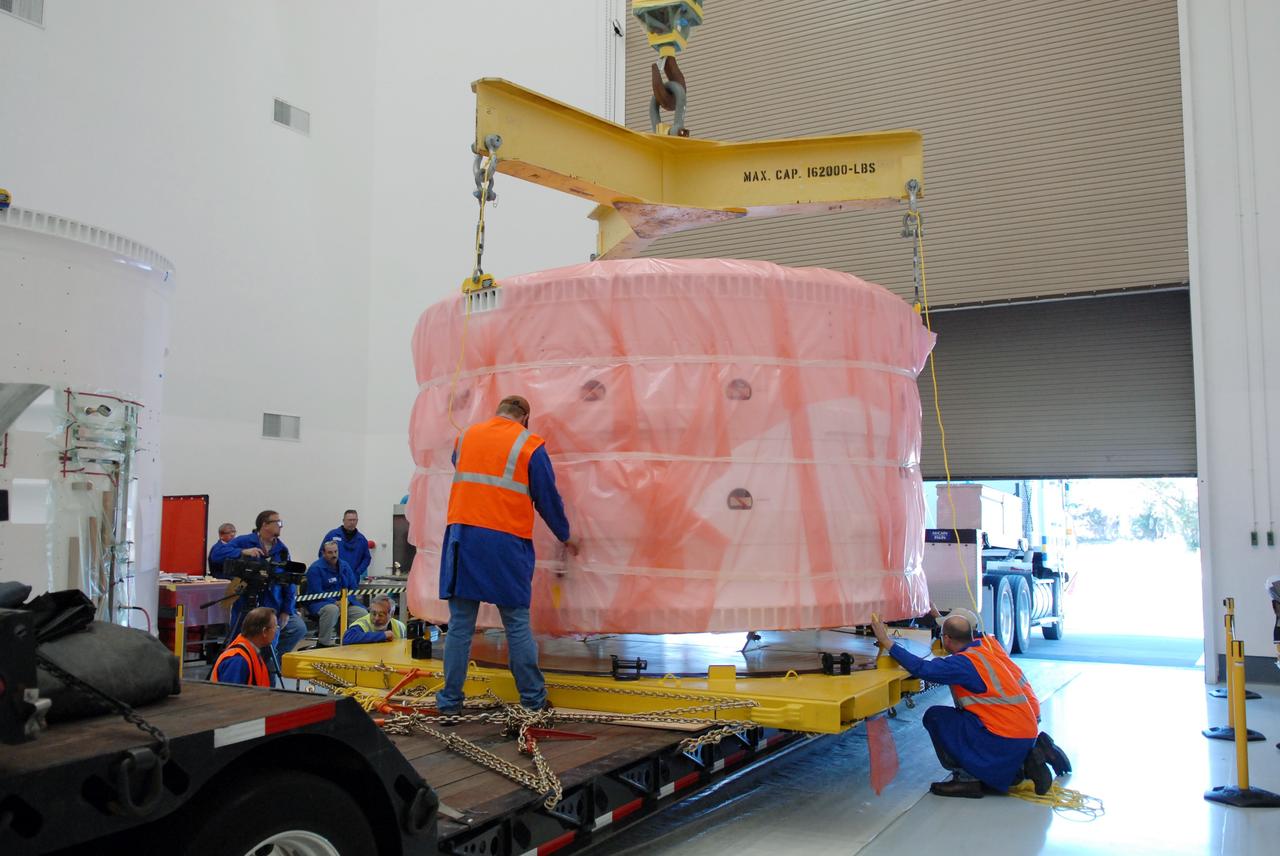
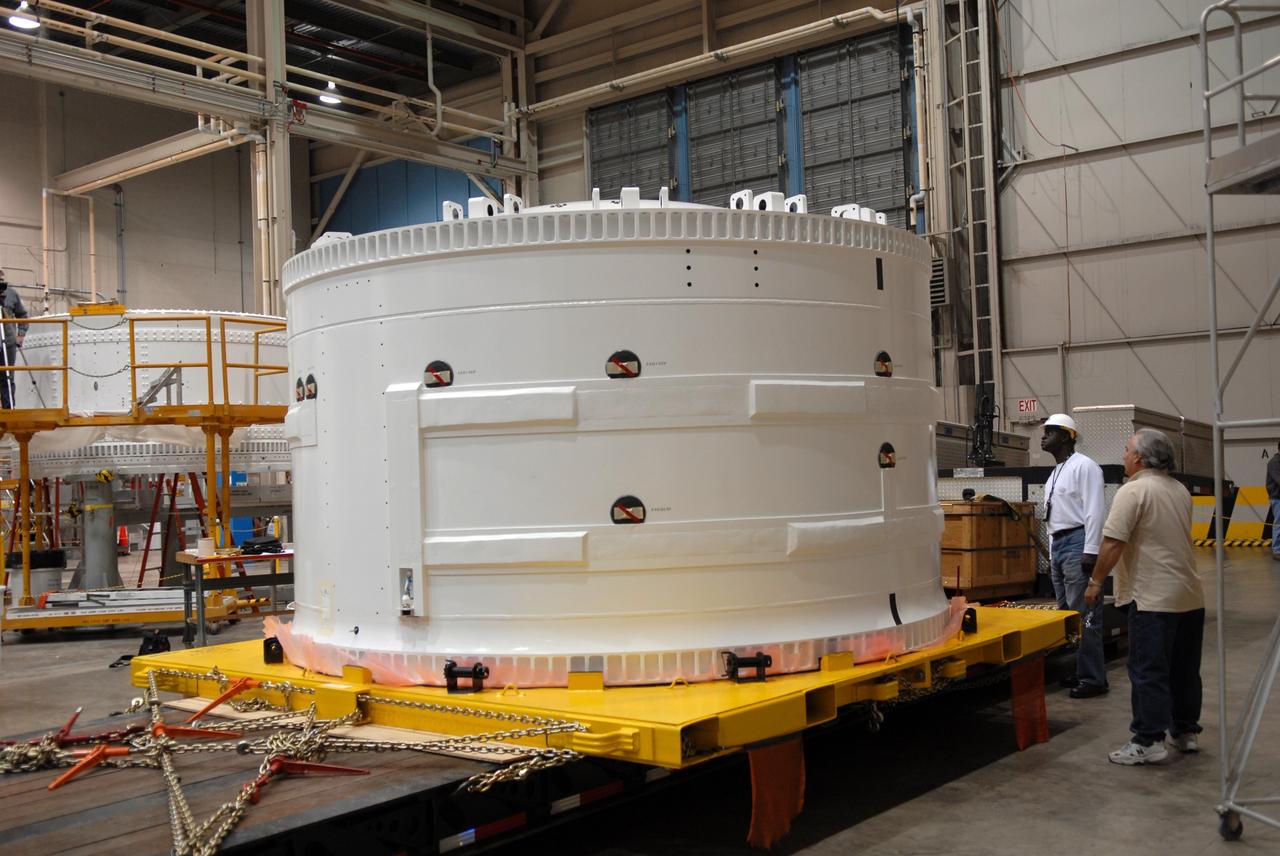
The Orion CM (Crew Module) or Orion ETA (Environmental Test Article) is passed through the vacuum chamber on its way to get ready for two critical tests in preparation for the Artemis II flight. There will be a jettison test of the Docking Module and a jettison test of the Forward Bay Cover.
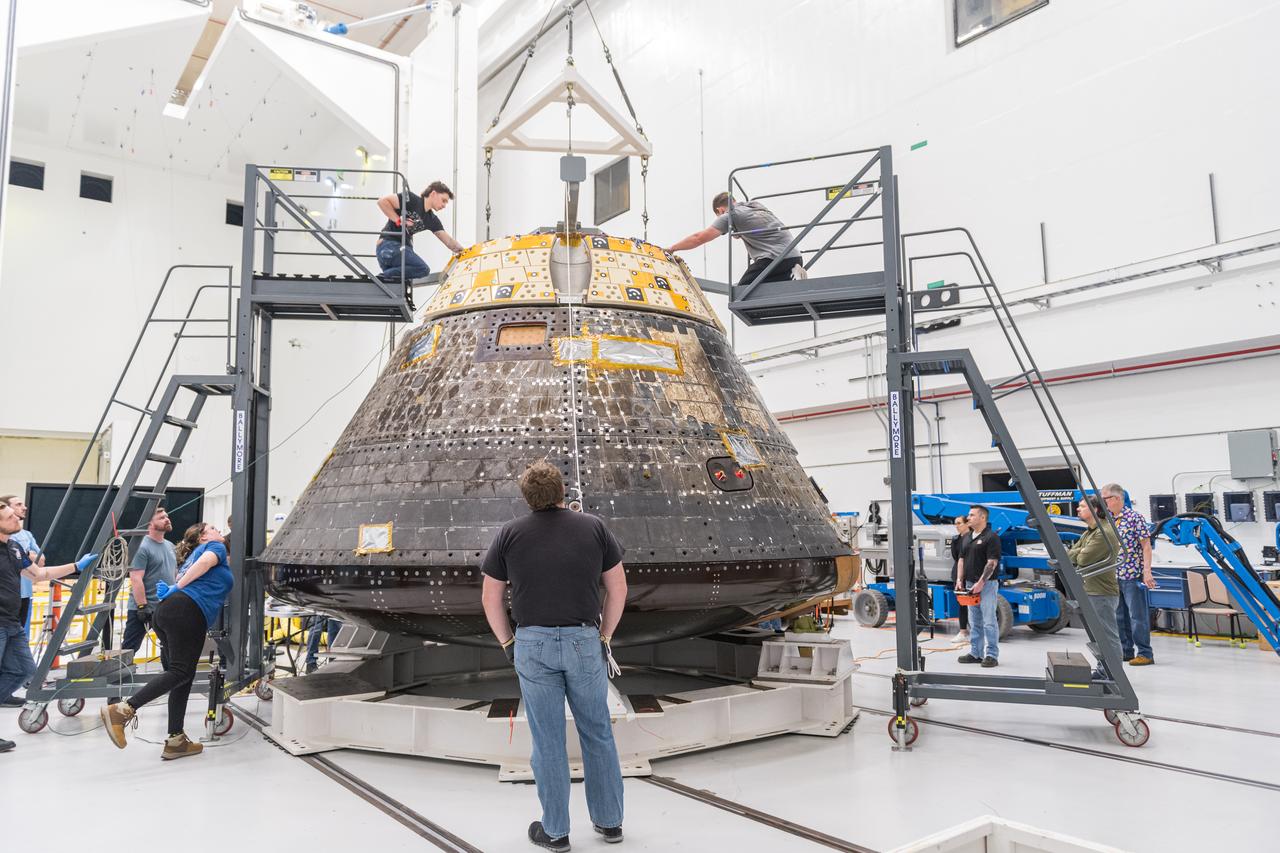

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), prepares for testing by installing the Forward Bay Cover. The Crew Module returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
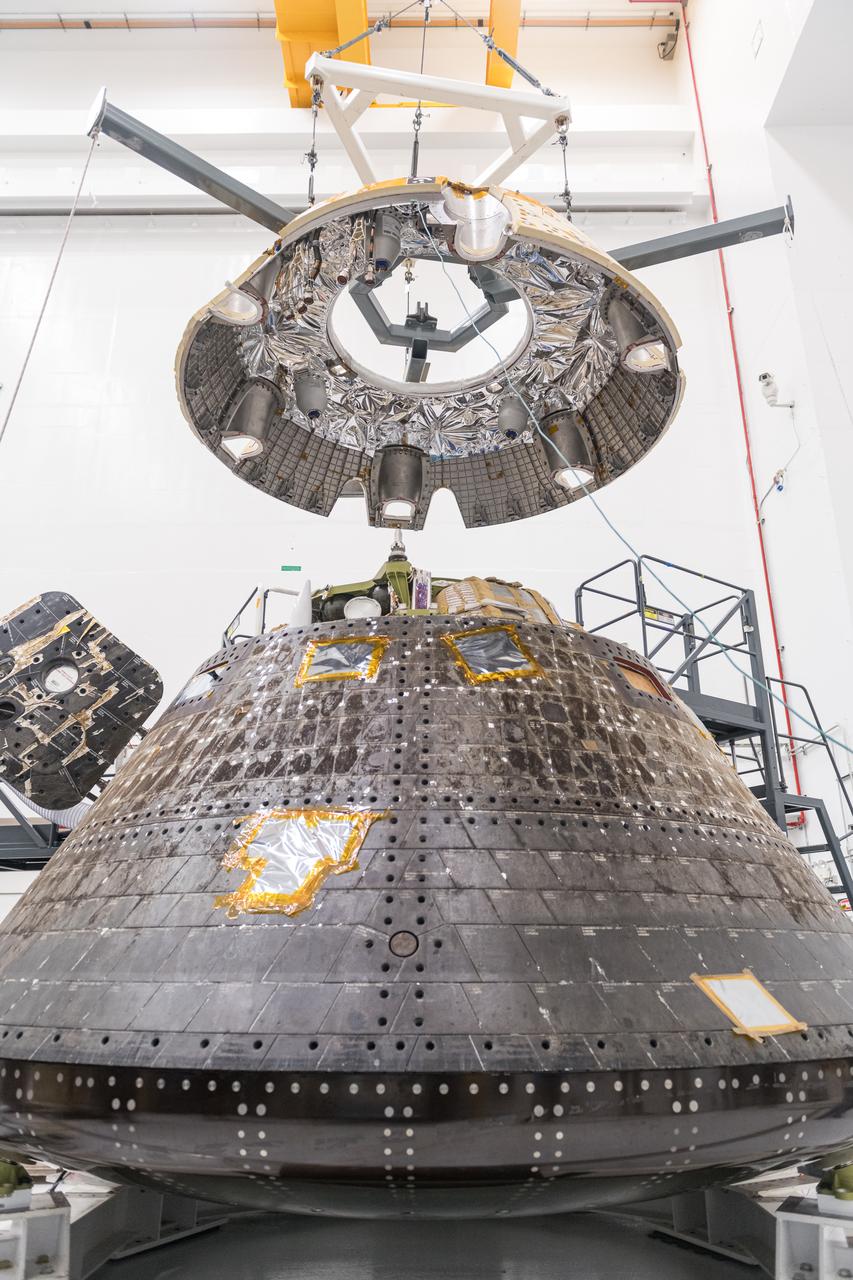

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), prepares for testing by installing the Forward Bay Cover. The Crew Module returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
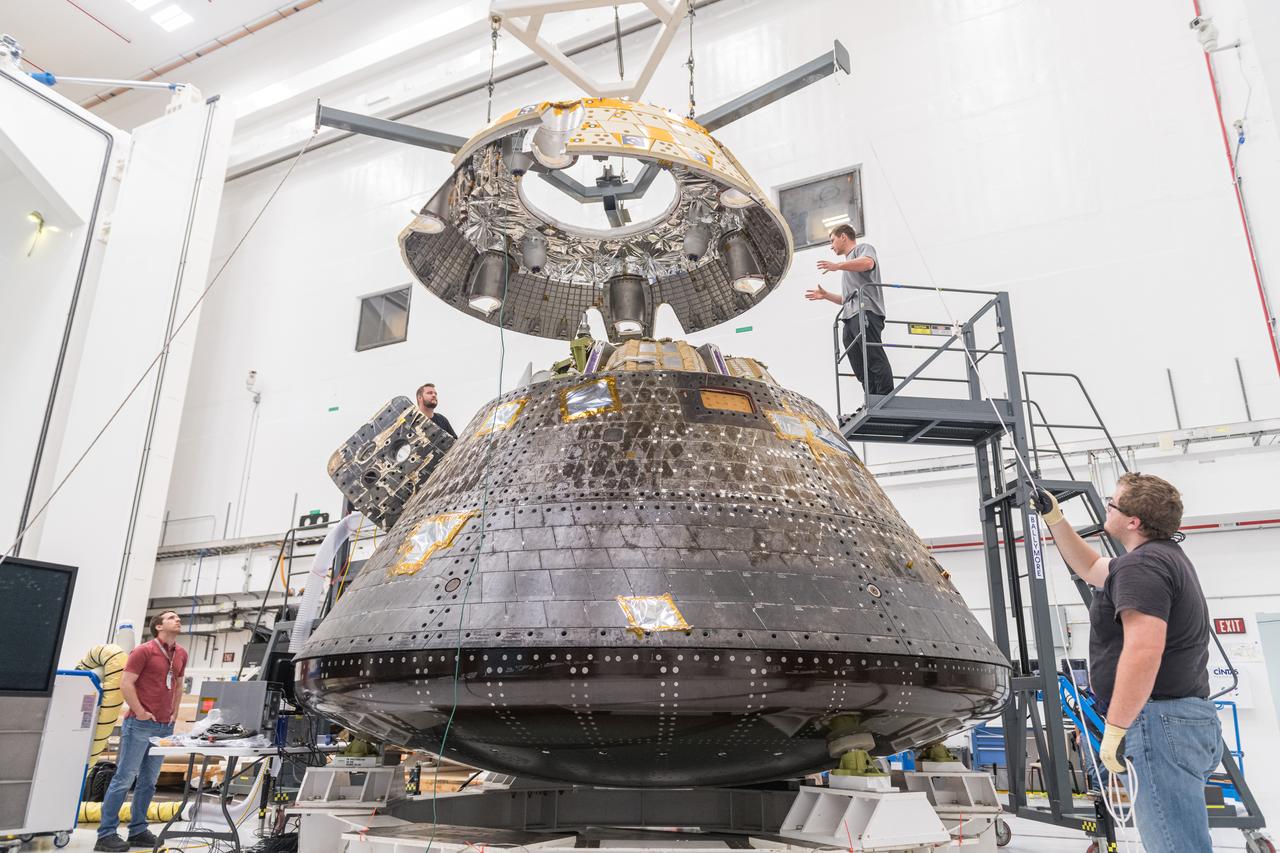

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), prepares for testing by installing the Forward Bay Cover. The Crew Module returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
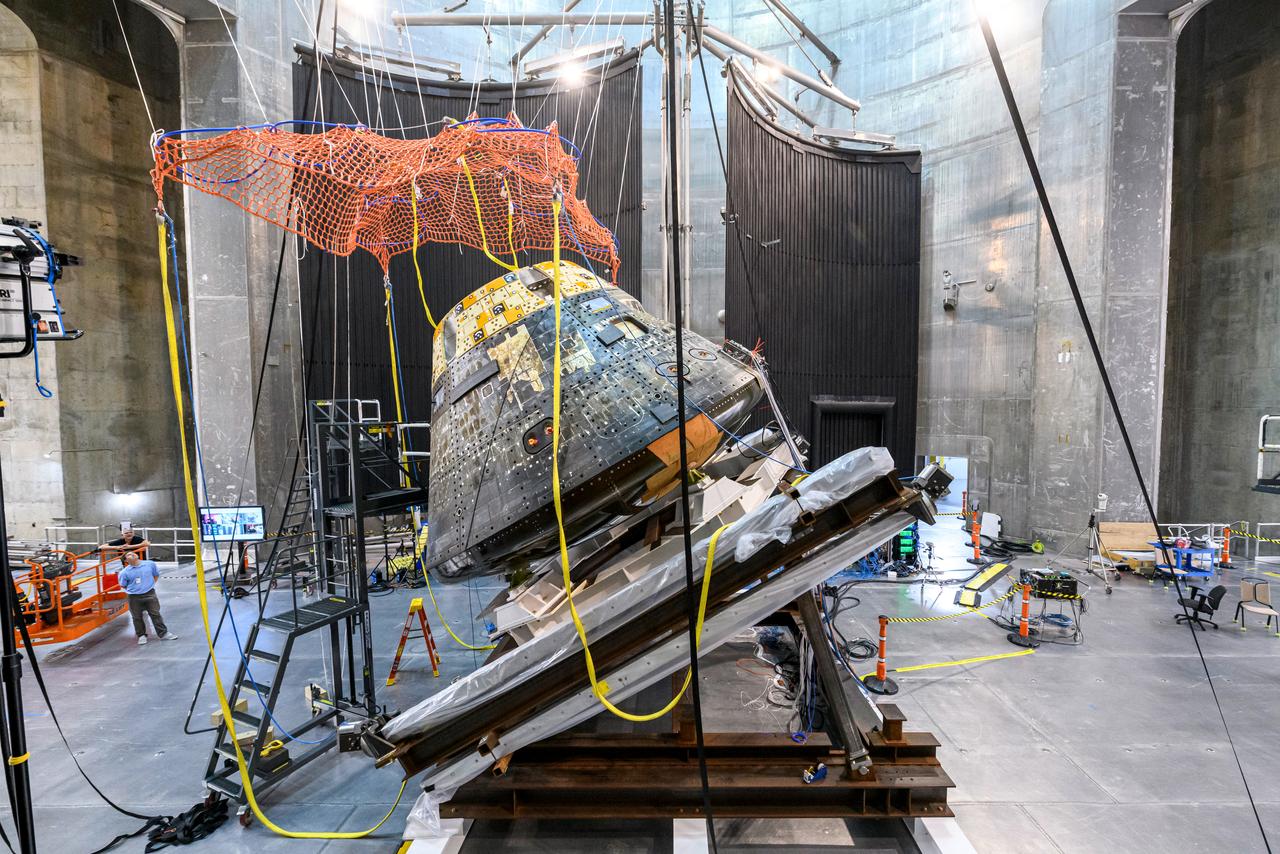

The Orion Crew Module, also known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), returned to NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio, in January 2024 and completed an 11-month test campaign necessary for the safety and success of Artemis II. In November 2024, experts completed the Forward Bay Cover jettison test, which is the last piece that must eject right before parachutes deploy. This image shows the setup right before the FBC deployment test. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
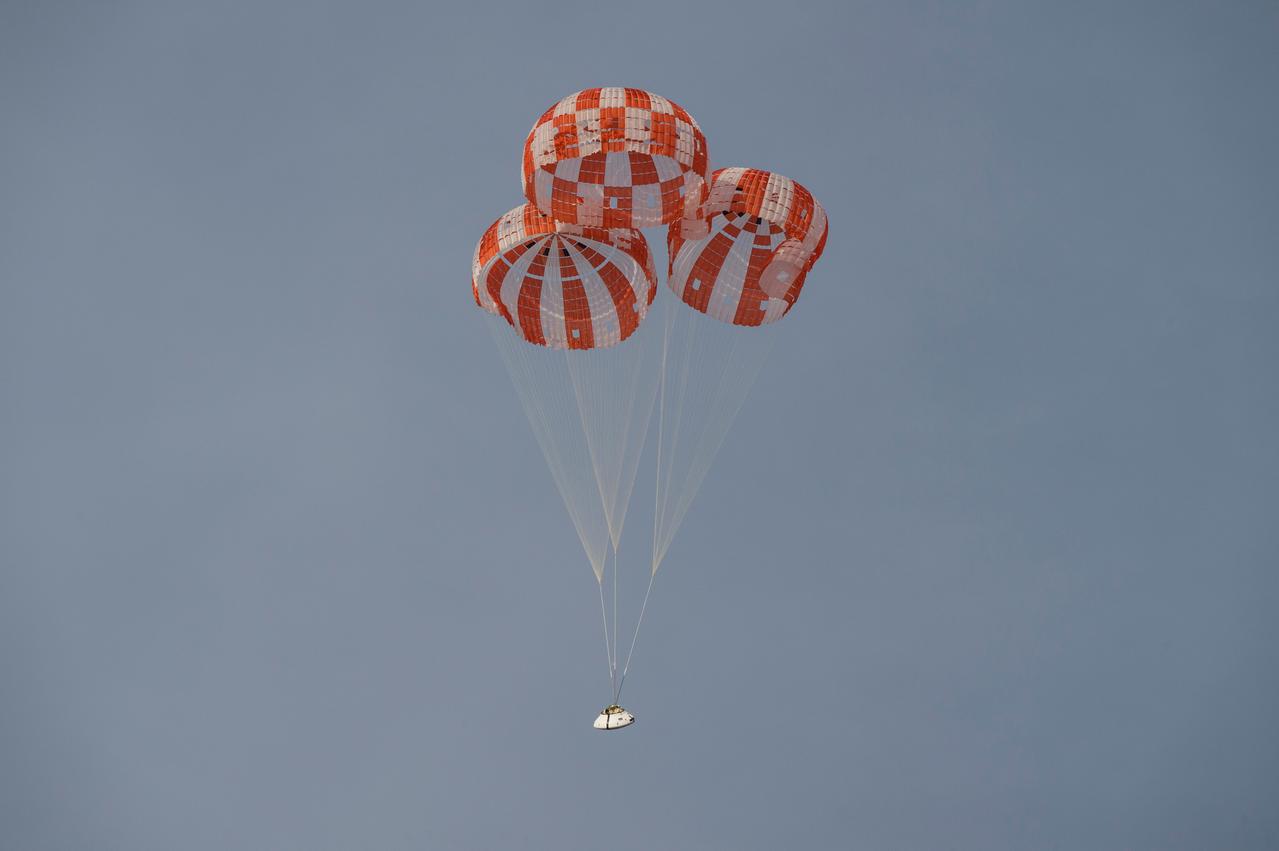

NASA successfully tested the Orion spacecraft’s parachute system on March 16, 2018 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma, Arizona. It was the first time engineers intentionally failed one of the system’s three Forward Bay Cover parachutes. The Forward Bay Cover protects the upper part of Orion throughout its mission, but must be jettisoned during landing so the rest of Orion’s parachutes can deploy. Engineers are nearing completion of the series of tests to qualify the parachute system for flights with crew.
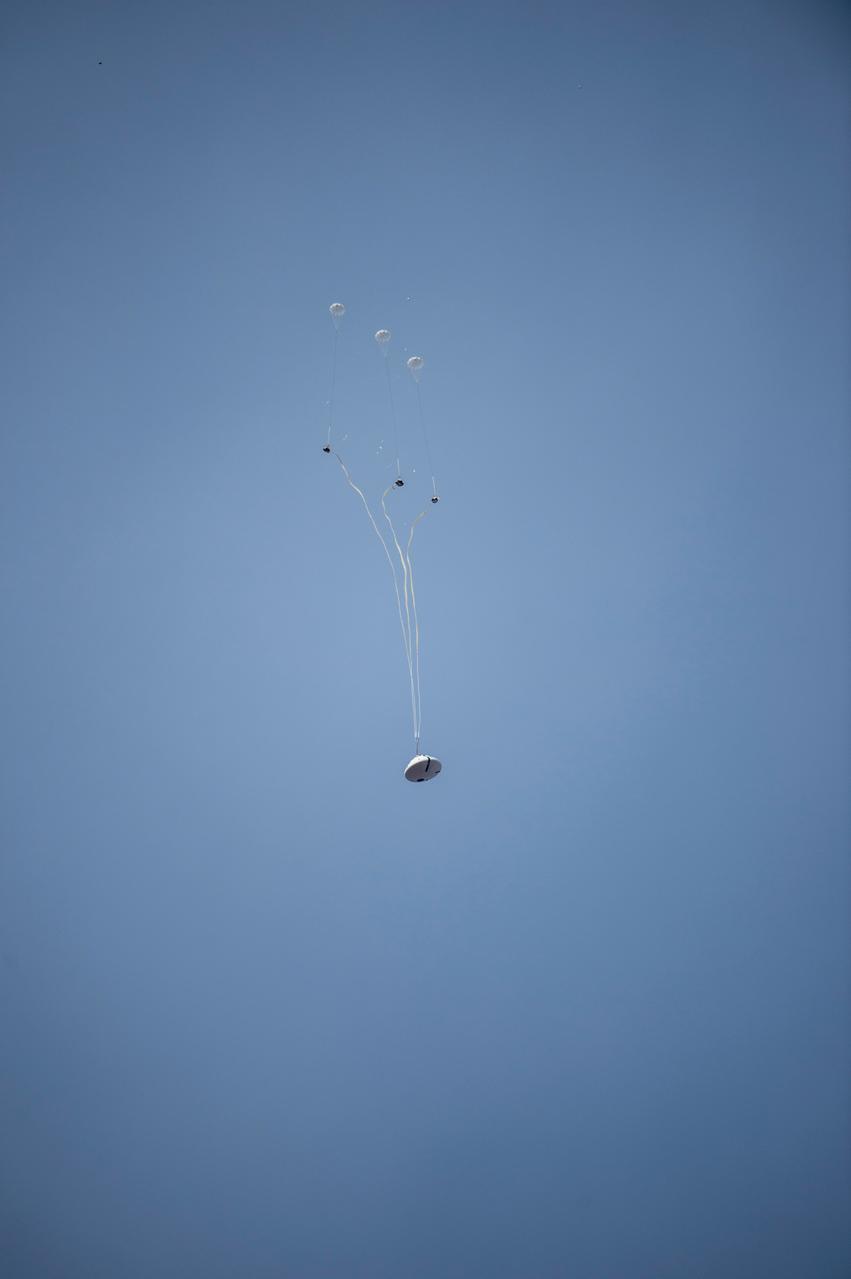

NASA successfully tested the Orion spacecraft’s parachute system on March 16, 2018 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma, Arizona. It was the first time engineers intentionally failed one of the system’s three Forward Bay Cover parachutes. The Forward Bay Cover protects the upper part of Orion throughout its mission, but must be jettisoned during landing so the rest of Orion’s parachutes can deploy. Engineers are nearing completion of the series of tests to qualify the parachute system for flights with crew.
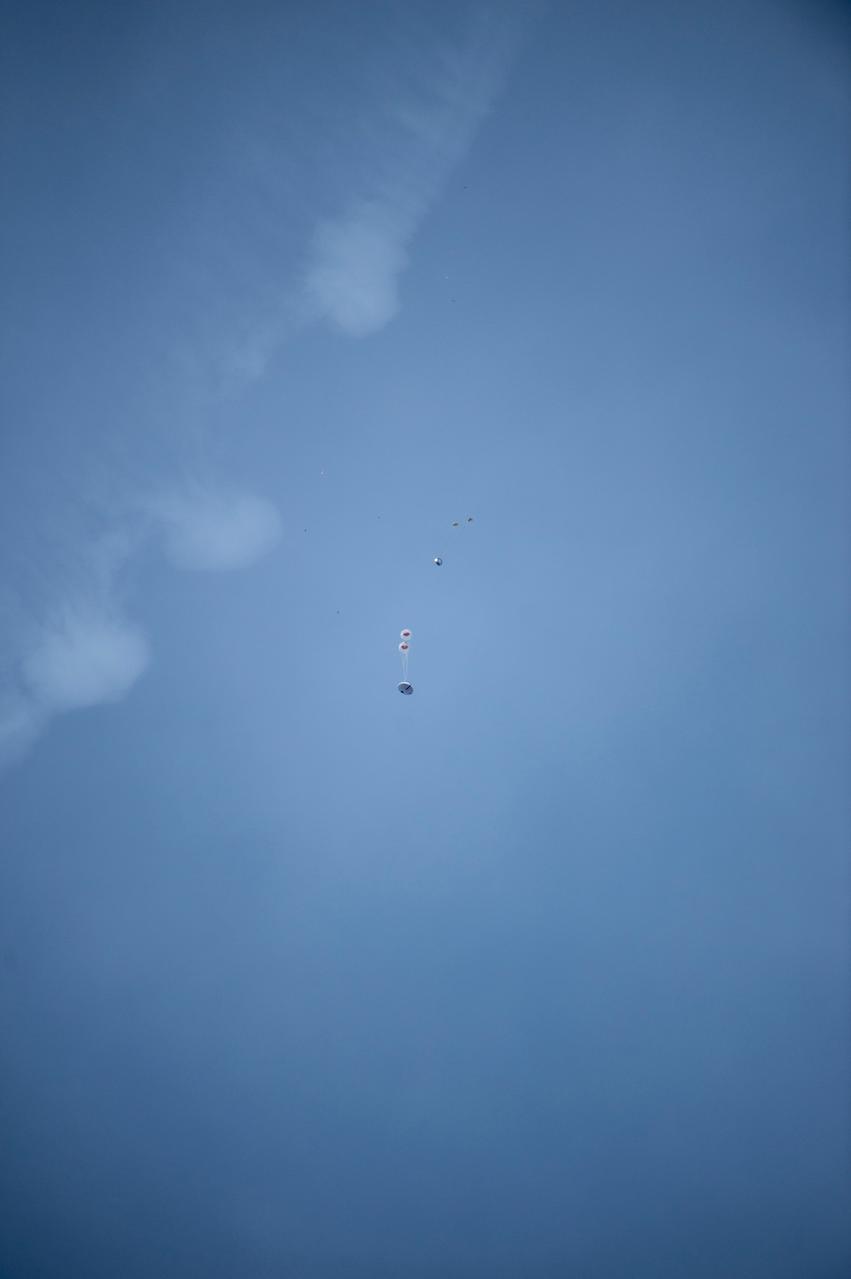

NASA successfully tested the Orion spacecraft’s parachute system on March 16, 2018 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma, Arizona. It was the first time engineers intentionally failed one of the system’s three Forward Bay Cover parachutes. The Forward Bay Cover protects the upper part of Orion throughout its mission, but must be jettisoned during landing so the rest of Orion’s parachutes can deploy. Engineers are nearing completion of the series of tests to qualify the parachute system for flights with crew.
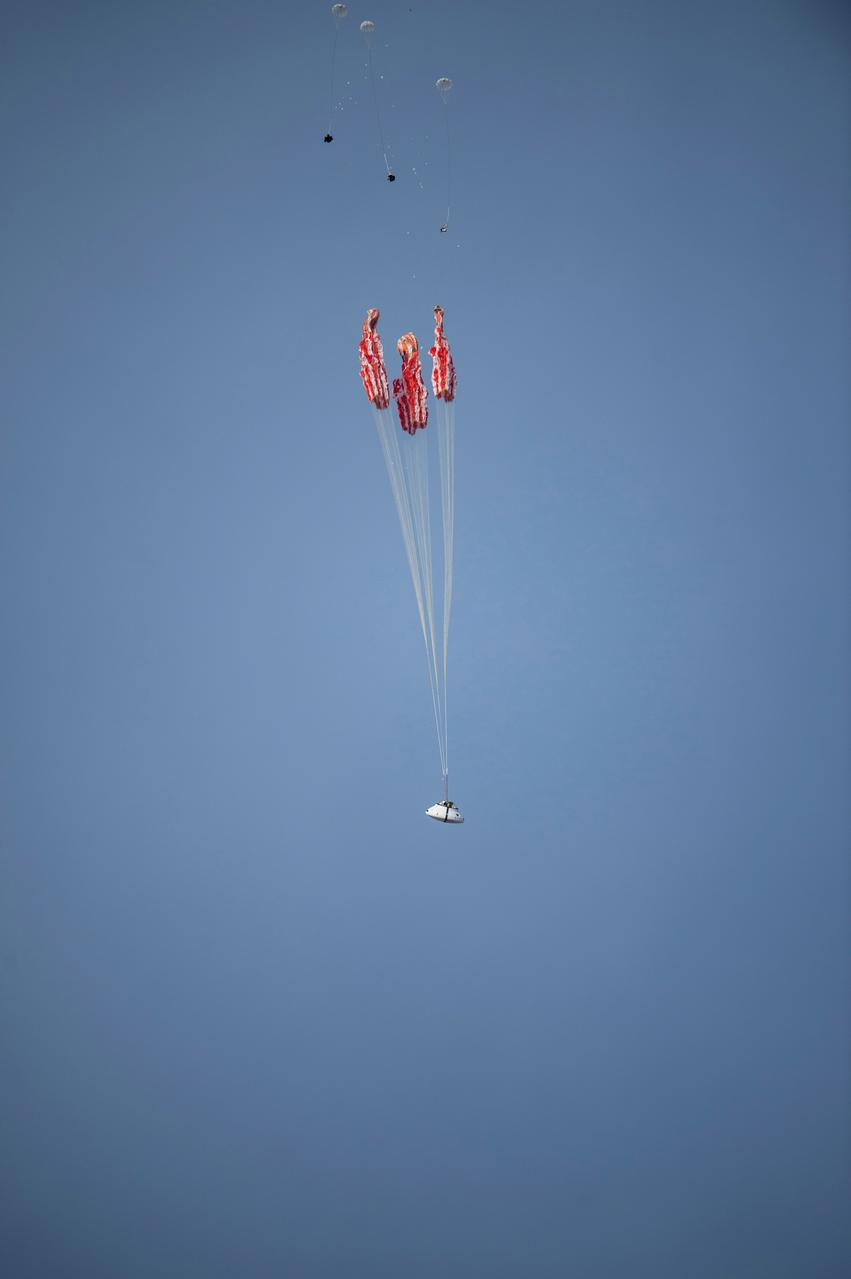

NASA successfully tested the Orion spacecraft’s parachute system on March 16, 2018 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma, Arizona. It was the first time engineers intentionally failed one of the system’s three Forward Bay Cover parachutes. The Forward Bay Cover protects the upper part of Orion throughout its mission, but must be jettisoned during landing so the rest of Orion’s parachutes can deploy. Engineers are nearing completion of the series of tests to qualify the parachute system for flights with crew.

NASA successfully tested the Orion spacecraft’s parachute system on March 16, 2018 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma, Arizona. It was the first time engineers intentionally failed one of the system’s three Forward Bay Cover parachutes. The Forward Bay Cover protects the upper part of Orion throughout its mission, but must be jettisoned during landing so the rest of Orion’s parachutes can deploy. Engineers are nearing completion of the series of tests to qualify the parachute system for flights with crew.
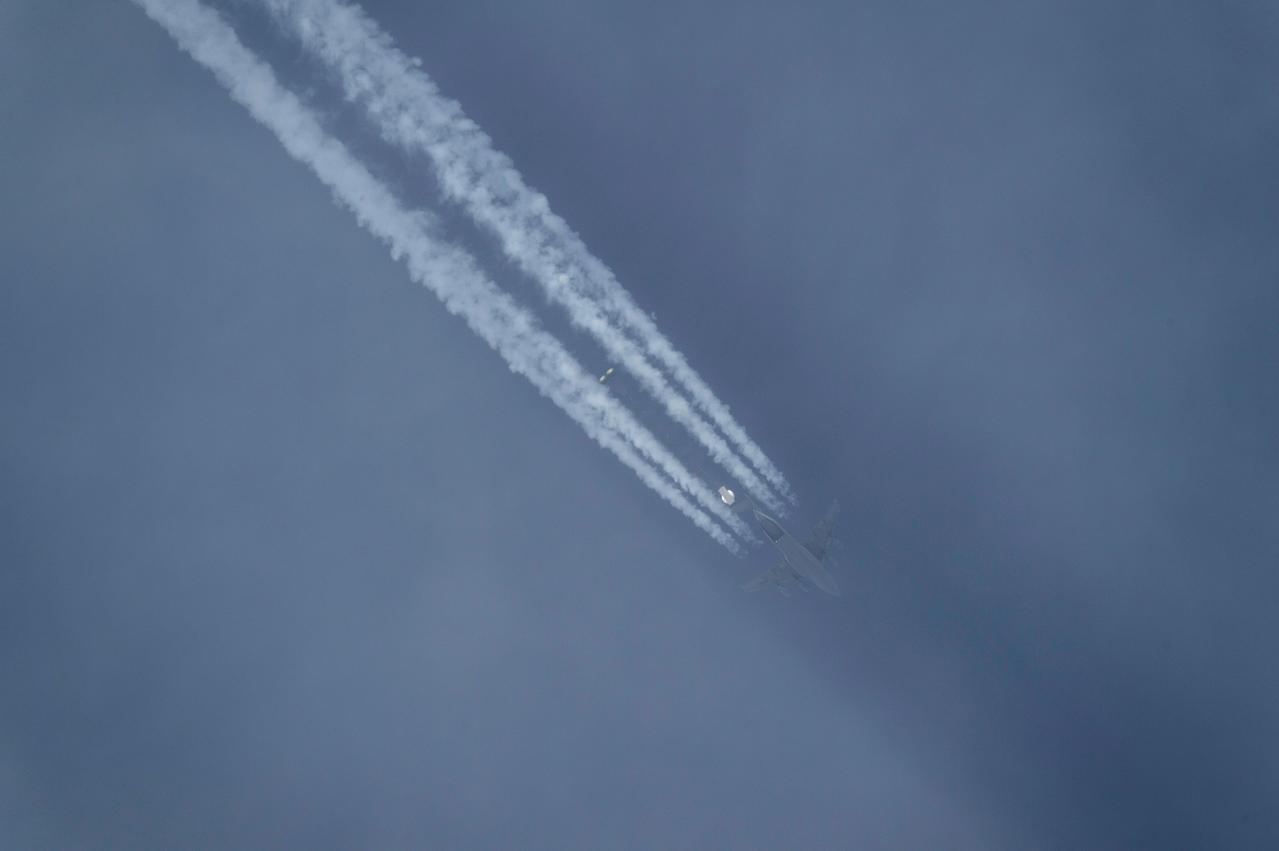

NASA successfully tested the Orion spacecraft’s parachute system on March 16, 2018 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma, Arizona. It was the first time engineers intentionally failed one of the system’s three Forward Bay Cover parachutes. The Forward Bay Cover protects the upper part of Orion throughout its mission, but must be jettisoned during landing so the rest of Orion’s parachutes can deploy. Engineers are nearing completion of the series of tests to qualify the parachute system for flights with crew.
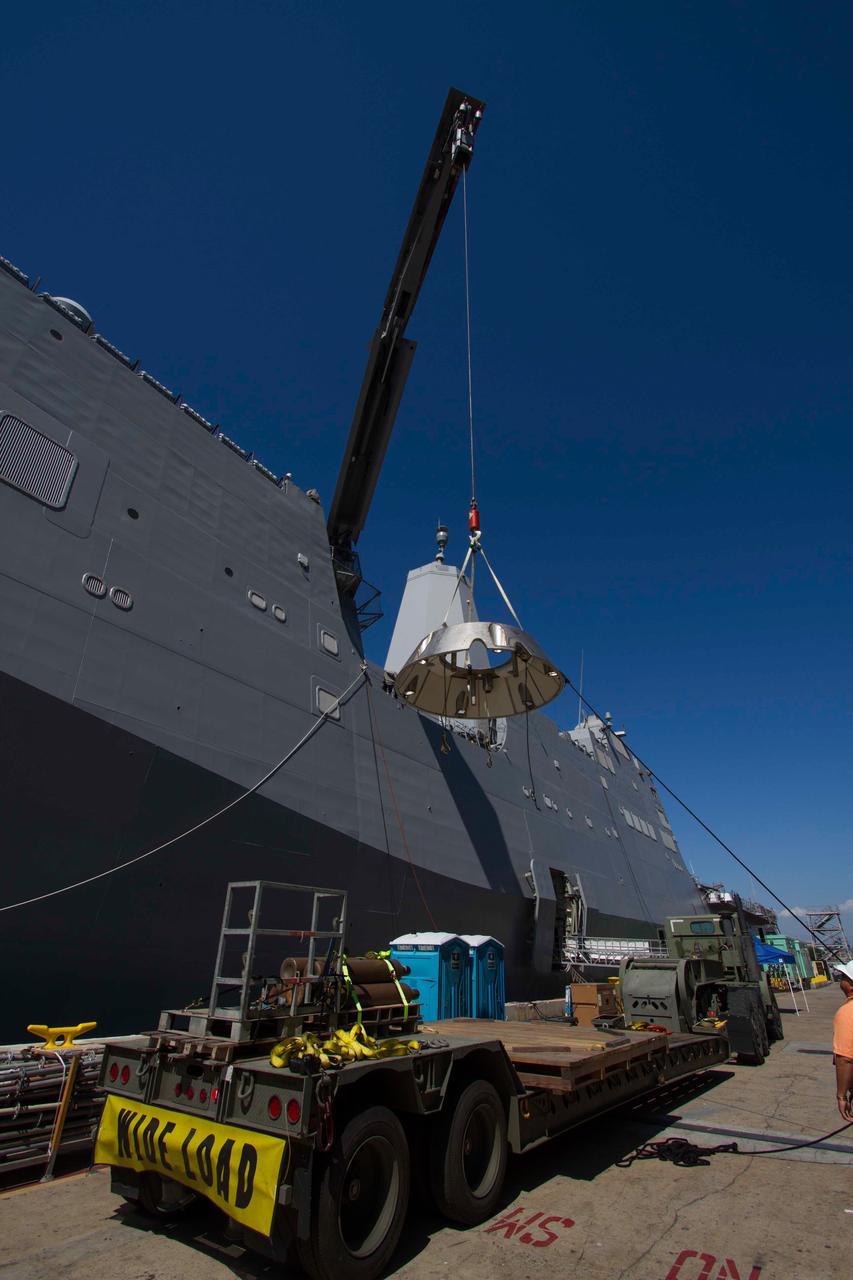

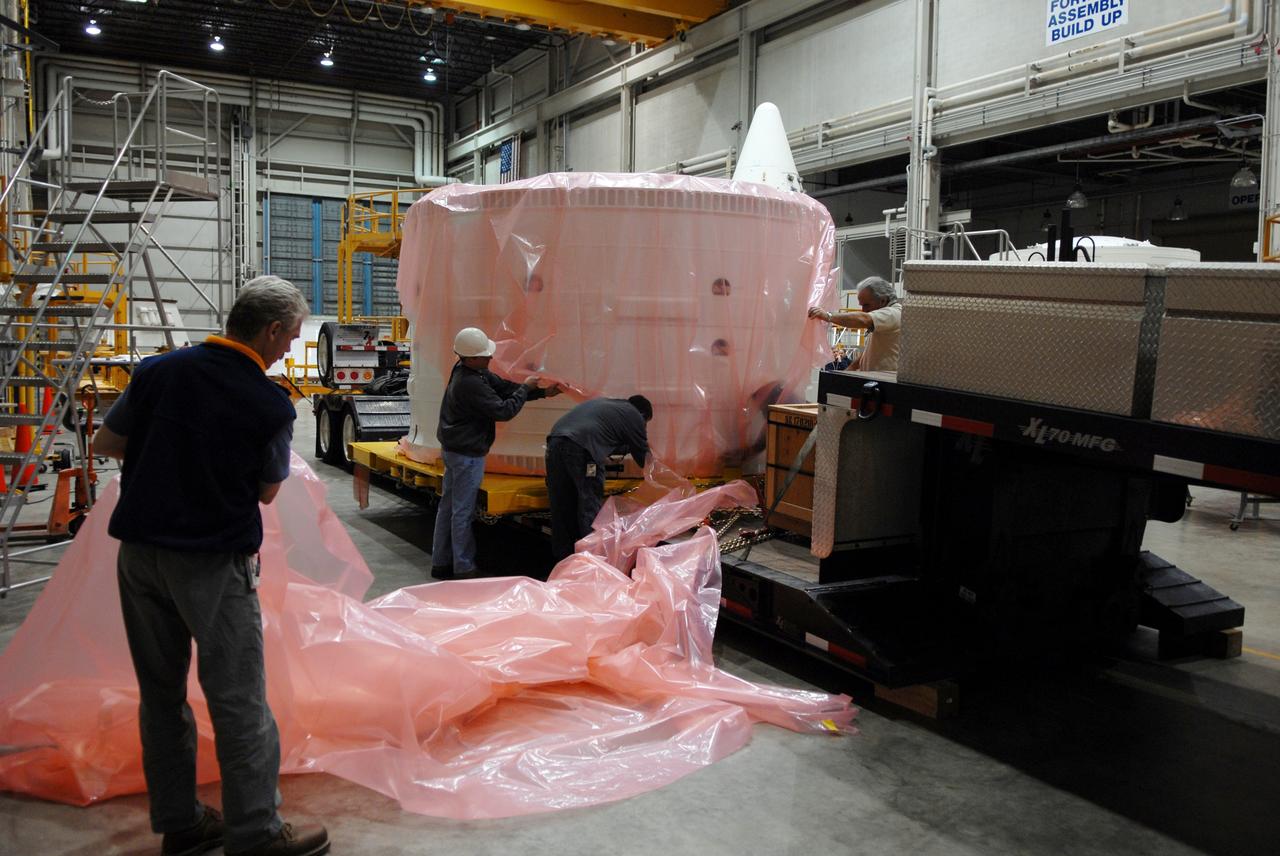
A test version of Orion's forward bay cover is loaded onto the Navy's USS Anchorage in preparation for testing Orion recovery tools and techniques in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego on Sept. 12, 2014. The forward bay cover protects the top section of Orion's crew module until the spacecraft is almost ready to land. It is jettisoned to allow Orion's parachutes to deploy and must be recovered separately from the crew module. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
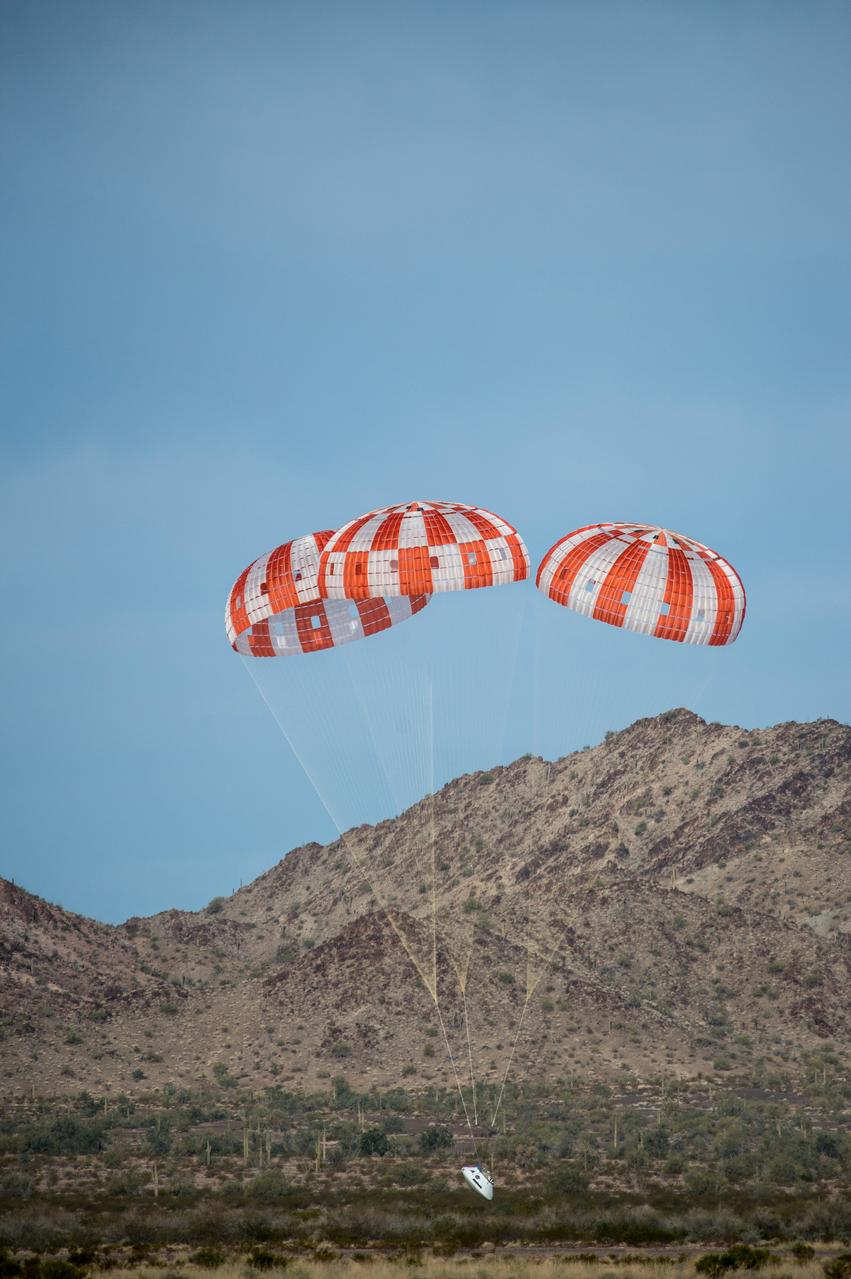

NASA successfully tested the Orion spacecraft’s parachute system on March 16, 2018 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma, Arizona. It was the first time engineers intentionally failed one of the system’s three Forward Bay Cover parachutes. The Forward Bay Cover protects the upper part of Orion throughout its mission, but must be jettisoned during landing so the rest of Orion’s parachutes can deploy. Engineers are nearing completion of the series of tests to qualify the parachute system for flights with crew.
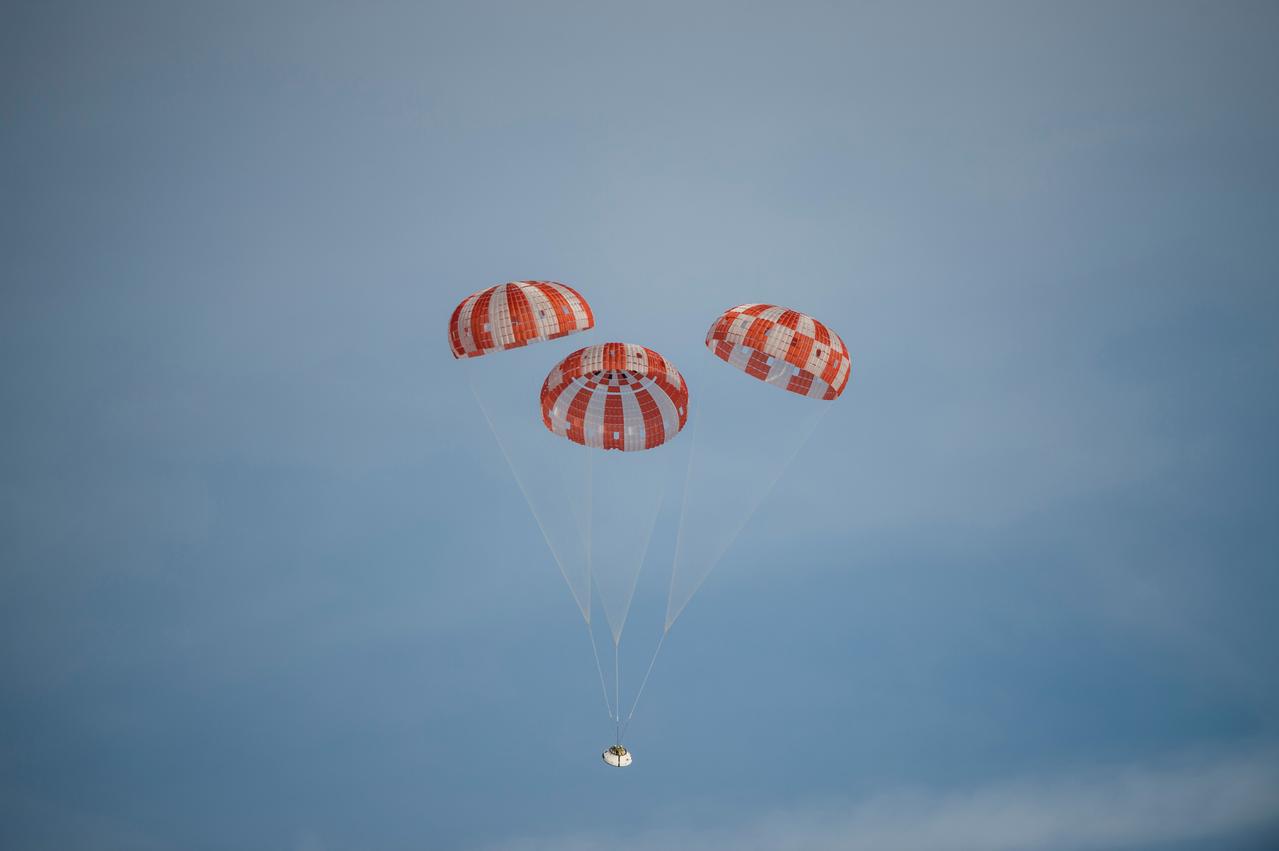

NASA successfully tested the Orion spacecraft’s parachute system on March 16, 2018 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma, Arizona. It was the first time engineers intentionally failed one of the system’s three Forward Bay Cover parachutes. The Forward Bay Cover protects the upper part of Orion throughout its mission, but must be jettisoned during landing so the rest of Orion’s parachutes can deploy. Engineers are nearing completion of the series of tests to qualify the parachute system for flights with crew.
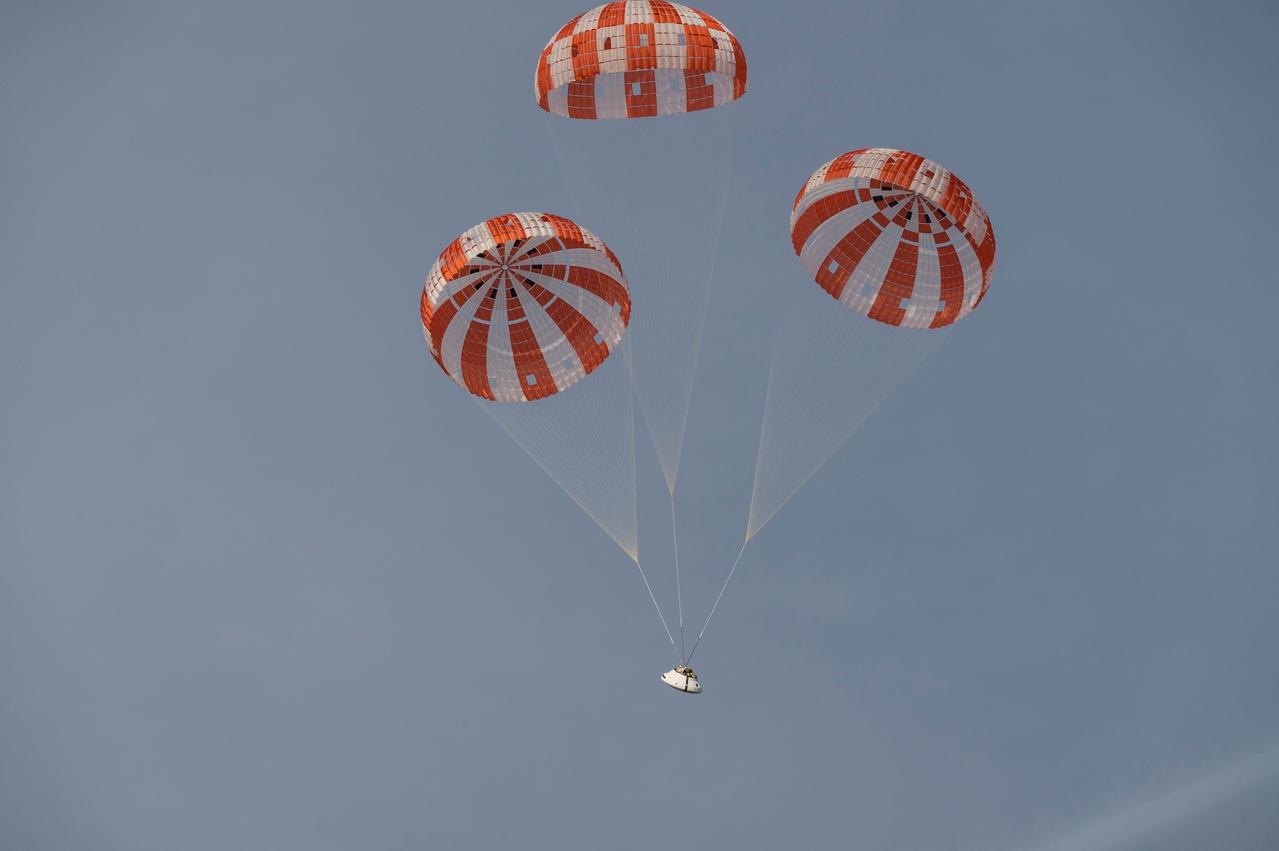

NASA successfully tested the Orion spacecraft’s parachute system on March 16, 2018 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma, Arizona. It was the first time engineers intentionally failed one of the system’s three Forward Bay Cover parachutes. The Forward Bay Cover protects the upper part of Orion throughout its mission, but must be jettisoned during landing so the rest of Orion’s parachutes can deploy. Engineers are nearing completion of the series of tests to qualify the parachute system for flights with crew.
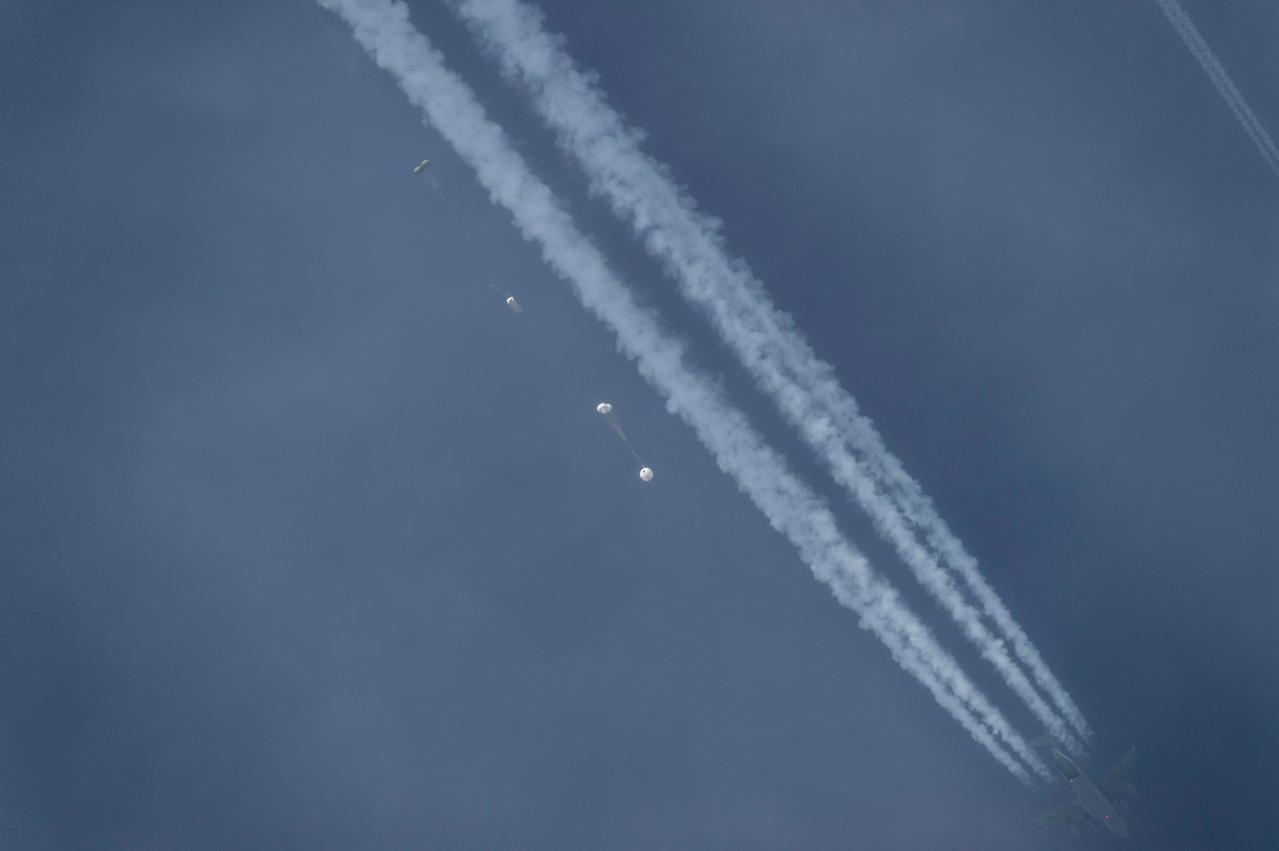

NASA successfully tested the Orion spacecraft’s parachute system on March 16, 2018 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma, Arizona. It was the first time engineers intentionally failed one of the system’s three Forward Bay Cover parachutes. The Forward Bay Cover protects the upper part of Orion throughout its mission, but must be jettisoned during landing so the rest of Orion’s parachutes can deploy. Engineers are nearing completion of the series of tests to qualify the parachute system for flights with crew.
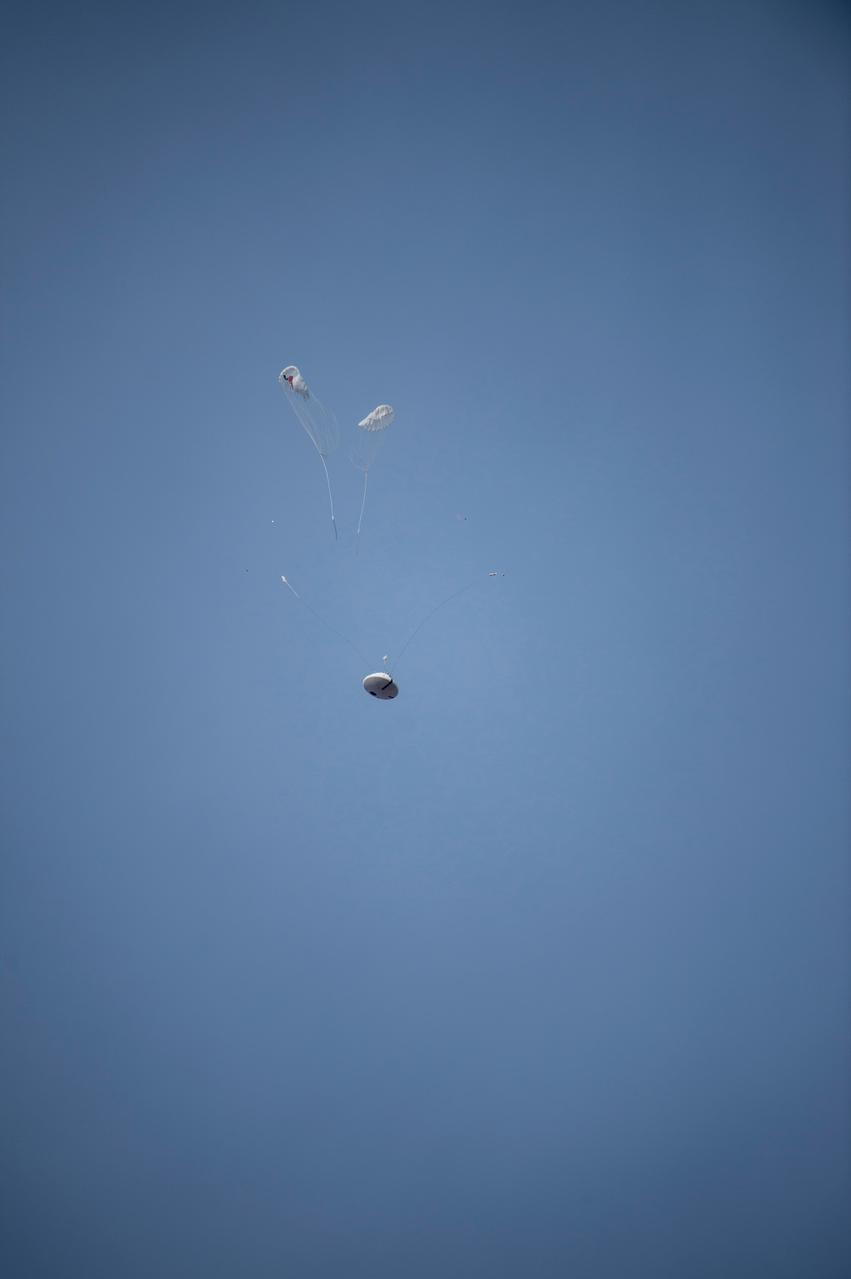

NASA successfully tested the Orion spacecraft’s parachute system on March 16, 2018 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma, Arizona. It was the first time engineers intentionally failed one of the system’s three Forward Bay Cover parachutes. The Forward Bay Cover protects the upper part of Orion throughout its mission, but must be jettisoned during landing so the rest of Orion’s parachutes can deploy. Engineers are nearing completion of the series of tests to qualify the parachute system for flights with crew.
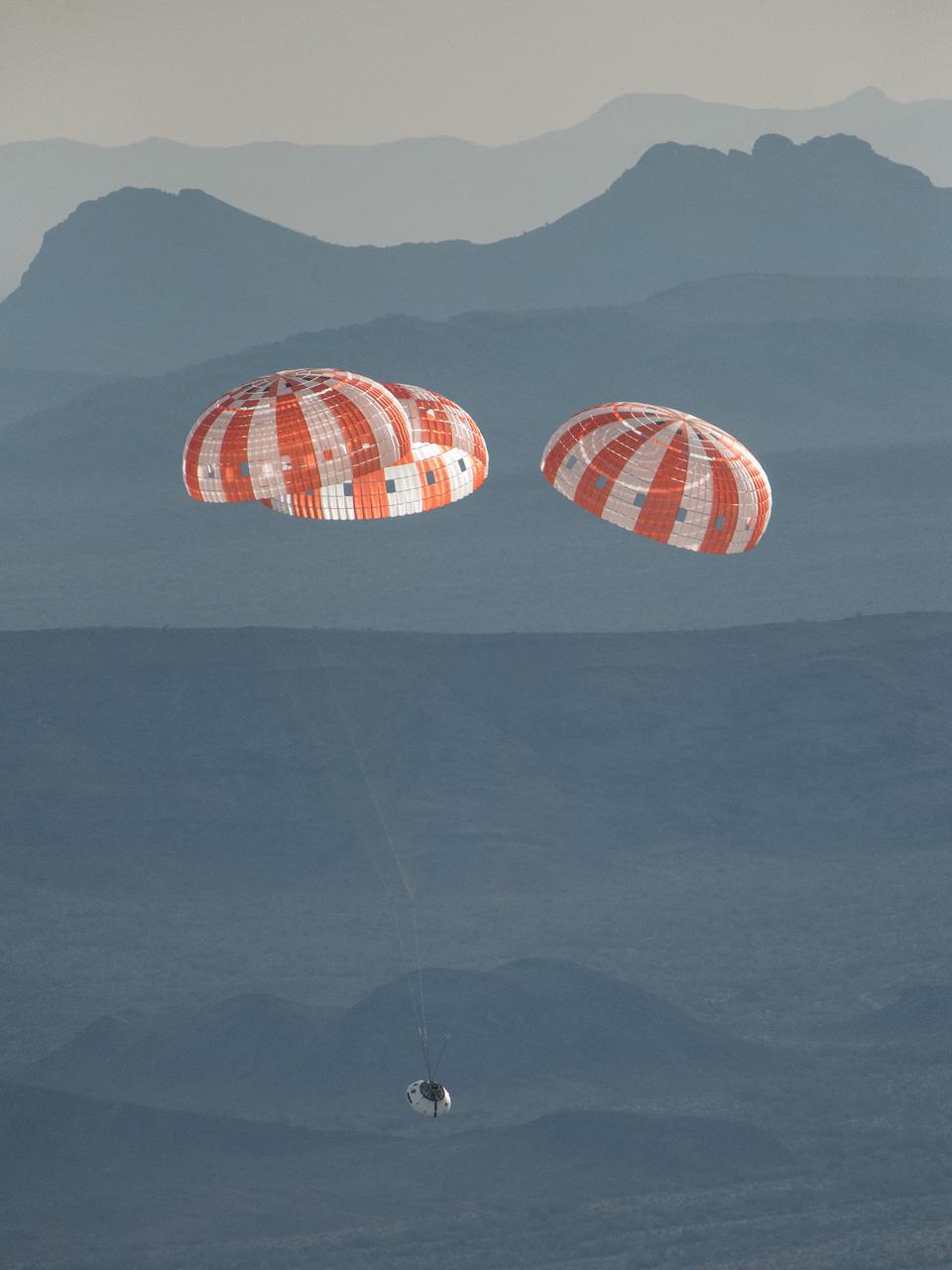

NASA successfully tested the Orion spacecraft’s parachute system on March 16, 2018 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma, Arizona. It was the first time engineers intentionally failed one of the system’s three Forward Bay Cover parachutes. The Forward Bay Cover protects the upper part of Orion throughout its mission, but must be jettisoned during landing so the rest of Orion’s parachutes can deploy. Engineers are nearing completion of the series of tests to qualify the parachute system for flights with crew.
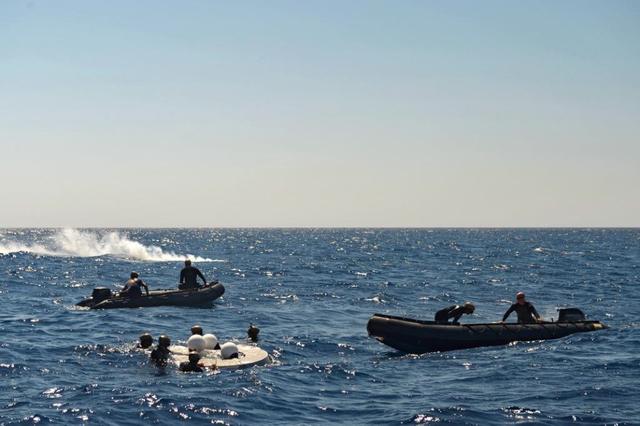

Recovery team members work to retrieve a test version of Orion's forward bay cover from the Pacific Ocean on Sept. 16, 2014. NASA and the Navy are working together this week to test tools and techniques that will be used to recover the spacecraft once it splashes down following Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). The forward bay cover protects the top section of Orion's crew module until the spacecraft is almost ready to land. It is jettisoned to allow Orion's parachutes to deploy and must be recovered separately from the crew module. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
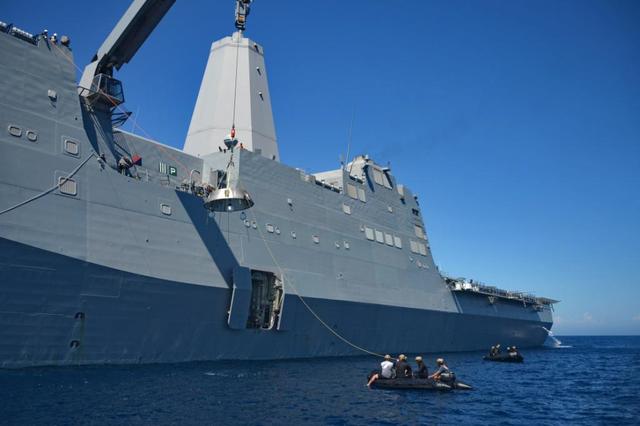

Recovery team members work to lift a test version of Orion's forward bay cover out of the Pacific Ocean using a crane on board the USS Anchorage on Sept. 16, 2014. NASA and the Navy are working together this week to test tools and techniques that will be used to retrieve the spacecraft once it splashes down following Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). The forward bay cover protects the top section of Orion's crew module until the spacecraft is almost ready to land. It is jettisoned to allow Orion's parachutes to deploy and must be recovered separately from the crew module. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
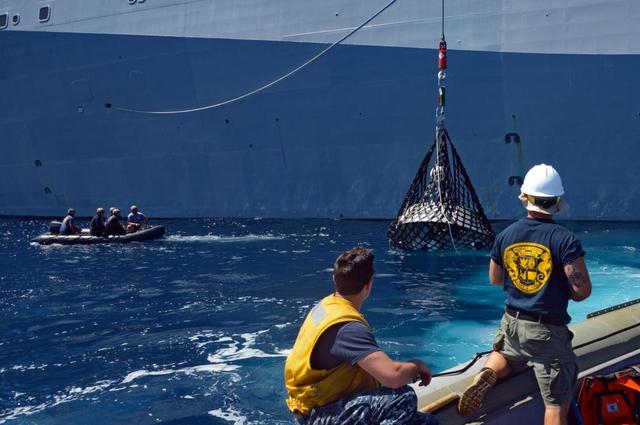

Recovery team members work to lift a test version of Orion's forward bay cover out of the Pacific Ocean using a crane on board the USS Anchorage on Sept. 16, 2014. NASA and the Navy are working together this week to test tools and techniques that will be used to retrieve the spacecraft once it splashes down following Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). The forward bay cover protects the top section of Orion's crew module until the spacecraft is almost ready to land. It is jettisoned to allow Orion's parachutes to deploy and must be recovered separately from the crew module. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
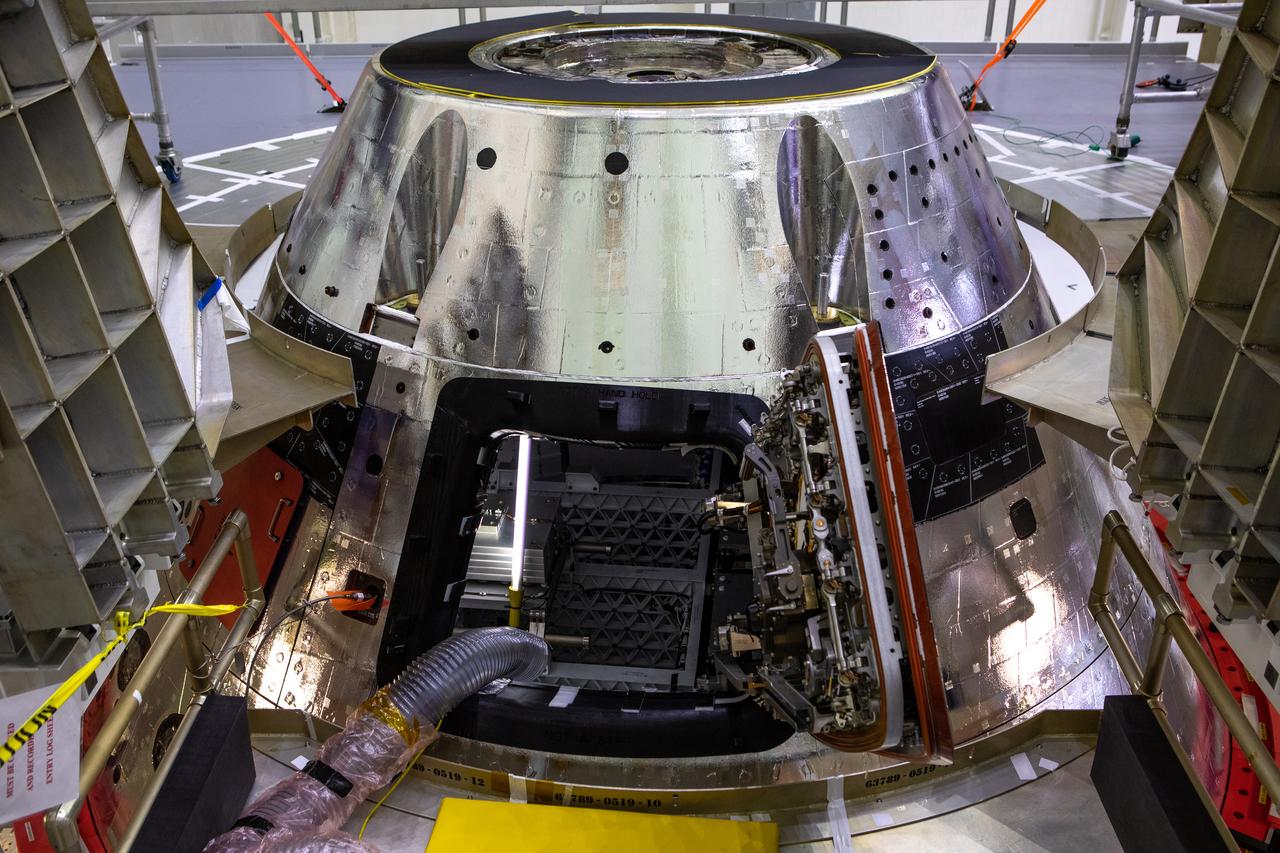

The forward bay cover is installed on the Artemis I spacecraft in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 23, 2020. It protects the upper part of Orion during the mission and, upon reentry into Earth’s atmosphere, jettison mechanisms will push the forward bay cover a safe distance from the spacecraft, allowing the three main parachutes to unfurl and slow Orion to a safe speed for splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The first in a series of increasingly complex mission, Artemis I will test the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA is planning to land the first woman and next man on the lunar surface by 2024.
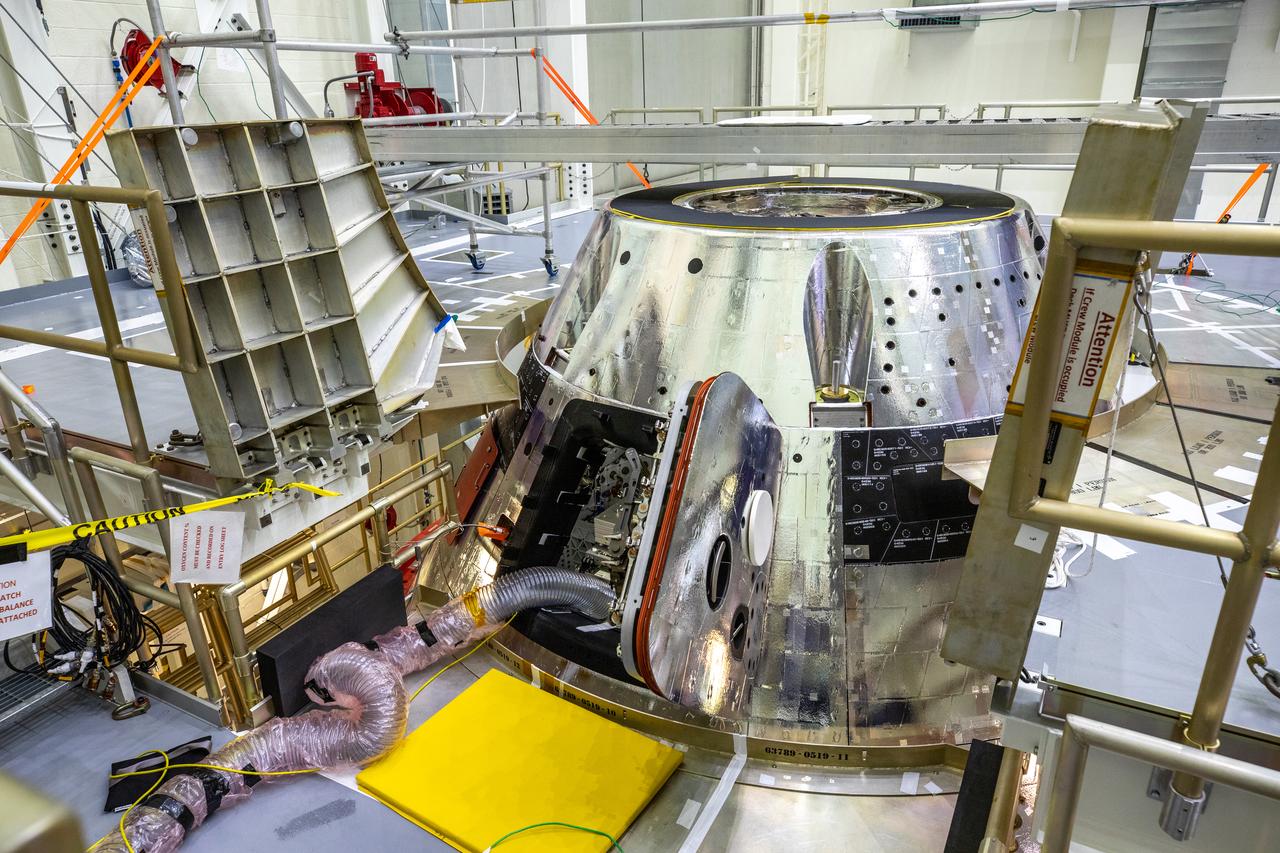

The forward bay cover is installed on the Artemis I spacecraft in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 23, 2020. It protects the upper part of Orion during the mission and, upon reentry into Earth’s atmosphere, jettison mechanisms will push the forward bay cover a safe distance from the spacecraft, allowing the three main parachutes to unfurl and slow Orion to a safe speed for splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The first in a series of increasingly complex mission, Artemis I will test the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA is planning to land the first woman and next man on the lunar surface by 2024.

The forward bay cover is installed on the Artemis I spacecraft in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 23, 2020. It protects the upper part of Orion during the mission and, upon reentry into Earth’s atmosphere, jettison mechanisms will push the forward bay cover a safe distance from the spacecraft, allowing the three main parachutes to unfurl and slow Orion to a safe speed for splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The first in a series of increasingly complex mission, Artemis I will test the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA is planning to land the first woman and next man on the lunar surface by 2024.

The forward bay cover is installed on the Artemis I spacecraft in the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 23, 2020. It protects the upper part of Orion during the mission and, upon reentry into Earth’s atmosphere, jettison mechanisms will push the forward bay cover a safe distance from the spacecraft, allowing the three main parachutes to unfurl and slow Orion to a safe speed for splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The first in a series of increasingly complex mission, Artemis I will test the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA is planning to land the first woman and next man on the lunar surface by 2024.
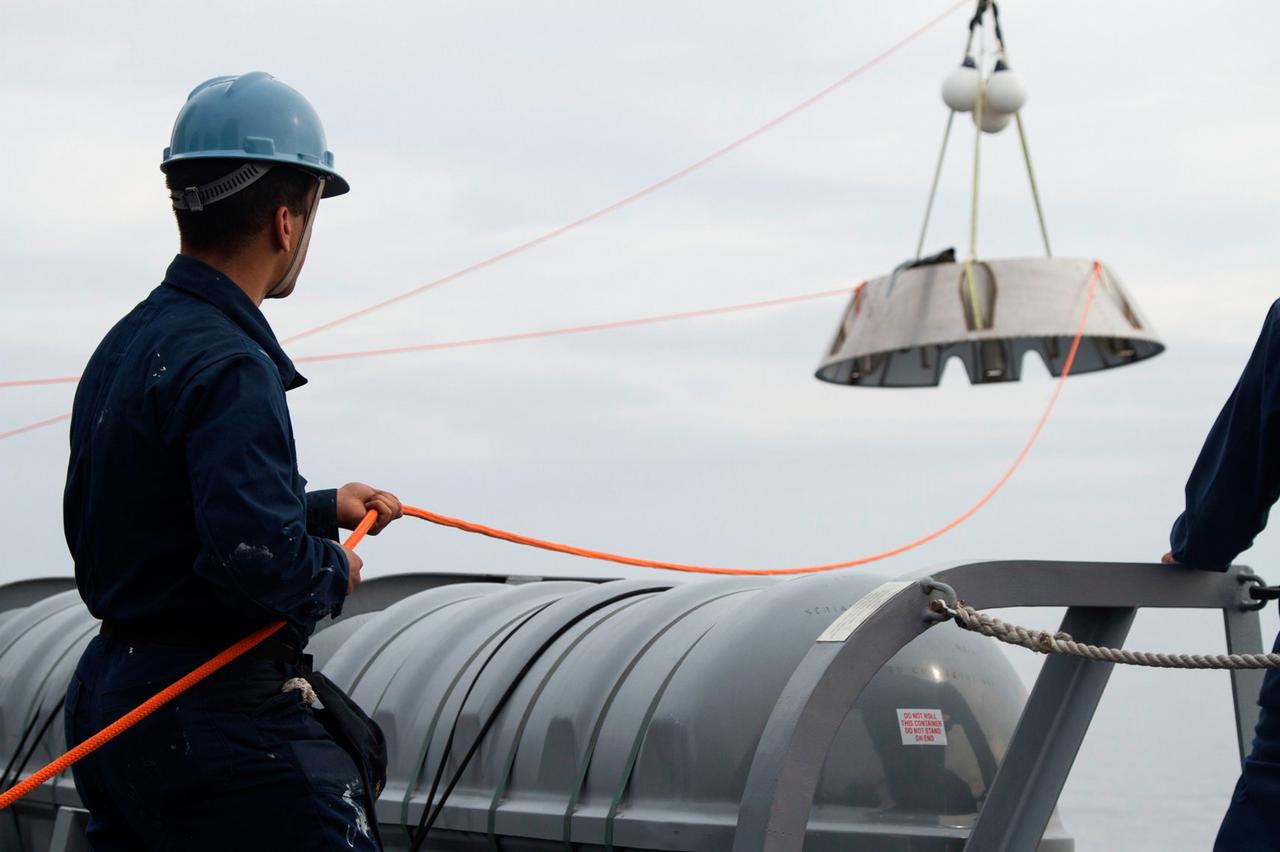

On the deck of the USS San Diego, NASA and U.S. Navy personnel monitor the process as a crane is used to lower Orion's forward bay cover into the Pacific Ocean as part of a Orion underway recovery test on Feb. 18, 2014. The Orion boilerplate test vehicle and other hardware were secured in the well deck of the ship in preparation for the test about 100 miles off the coast of San Diego, California. NASA and the U.S. Navy conducted tests to prepare for the recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover, and parachutes on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery tests allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
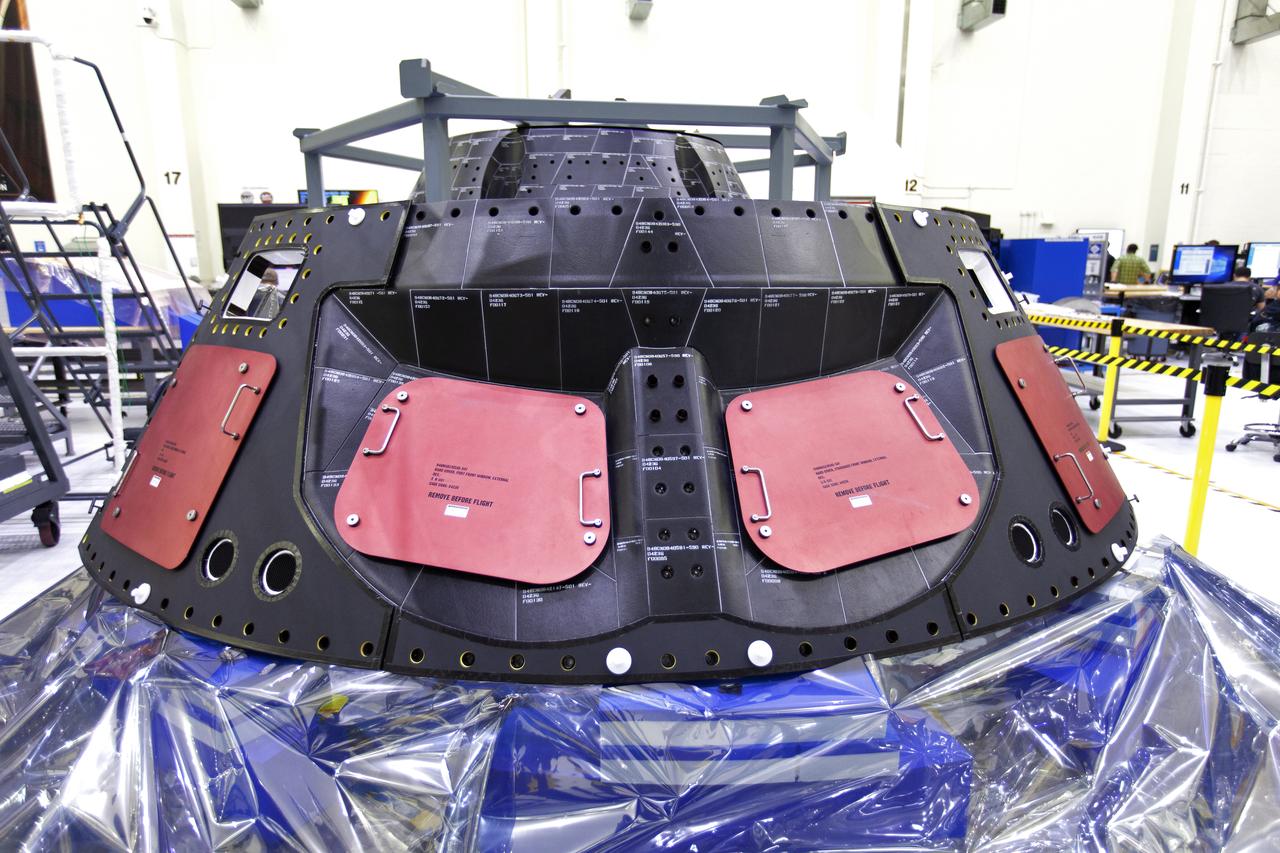
The forward bay cover for Orion for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) is in view inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on March 21, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. For EM-1, Orion will launch atop the Space Launch System rocket from Launch Pad 39B. The spacecraft will travel thousands of miles past the Moon on an approximately three-week test flight. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
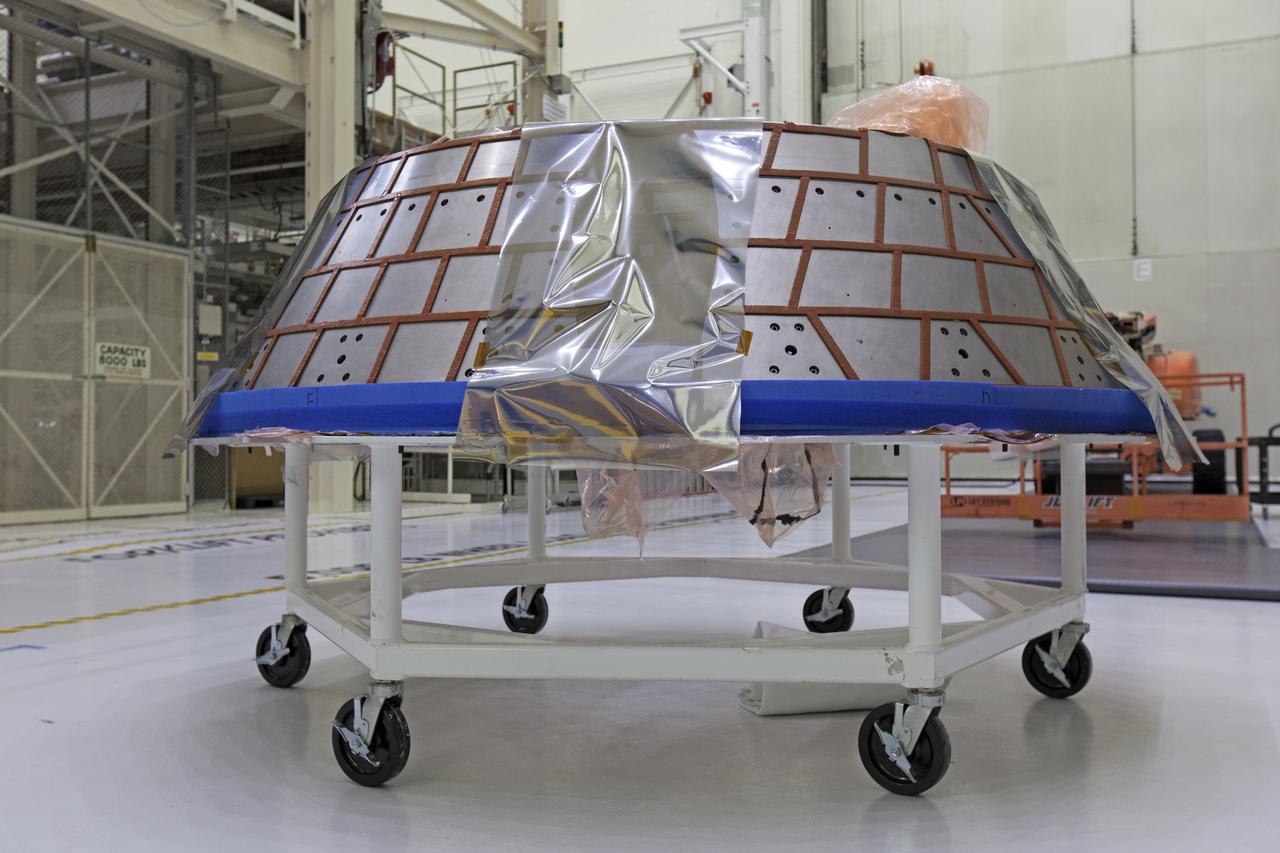

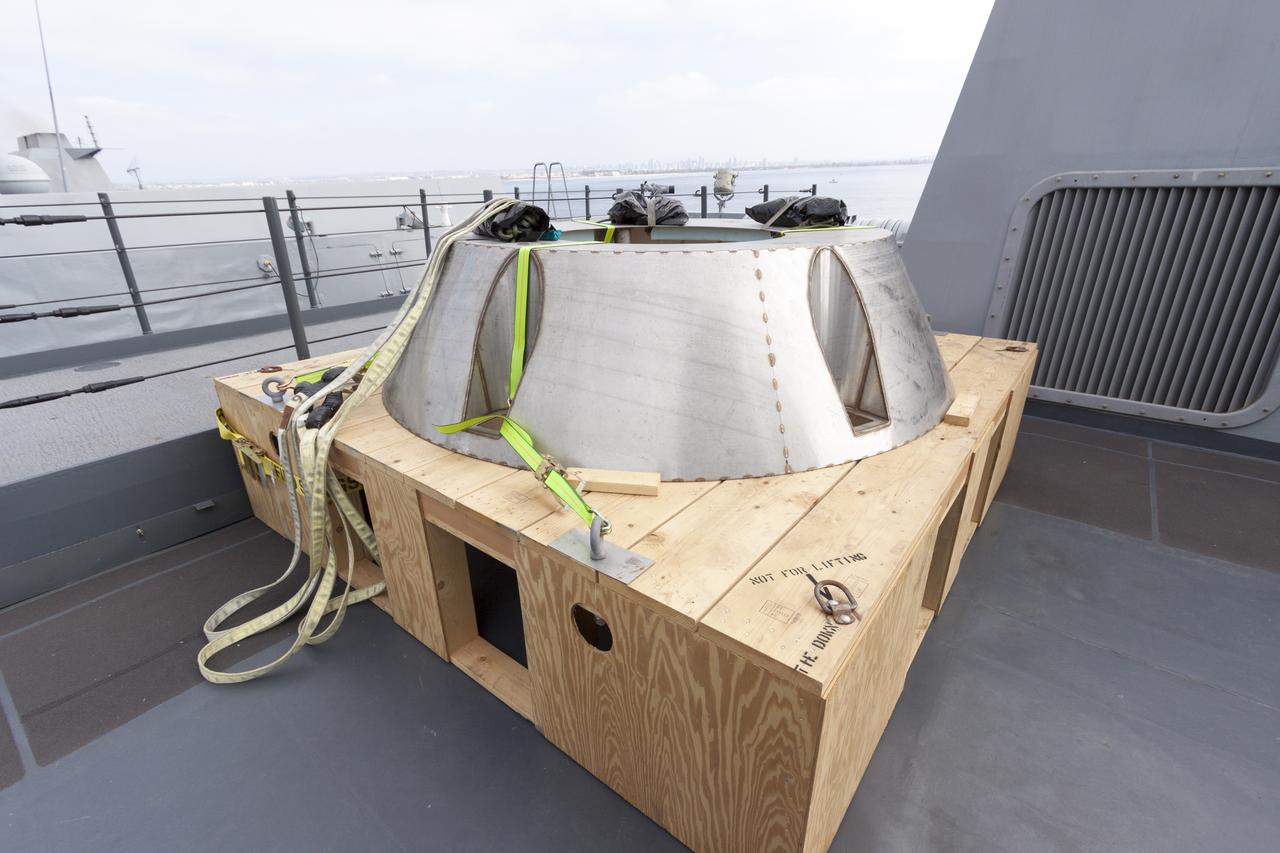
The forward bay cover for the Orion crew module is secured on a movable stand in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The space hardware for Orion is undergoing processing to prepare it for launch. Orion is being prepared for its first uncrewed integrated flight atop the Space Launch System rocket on Exploration Mission-1.
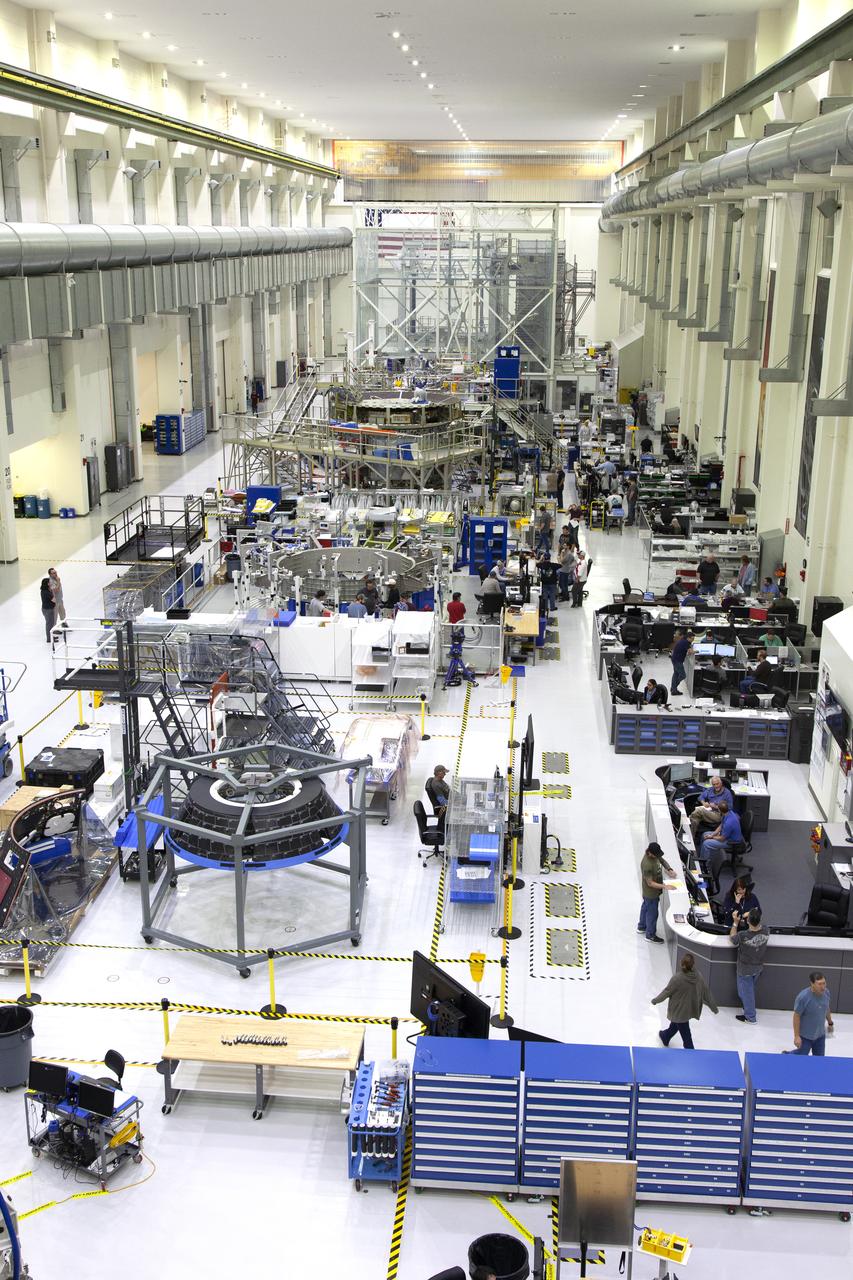

The Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay is filled with various pieces of flight hardware for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) and Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In this view taken on March 21, 2019, the forward bay cover for Orion (EM-1) is at far left in the foreground. Just to its right is the bay cover (EM-1). Behind these two pieces is the crew module adapter for EM-2. Further back, secured on a test stand is the European Service Module that will serve as the powerhouse for Orion. For EM-1, Orion will launch atop the Space Launch System rocket from Launch Pad 39B. The spacecraft will travel thousands of miles past the Moon on an approximately three-week test flight. Orion will return to Earth and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California, where it will be retrieved and returned to Kennedy.
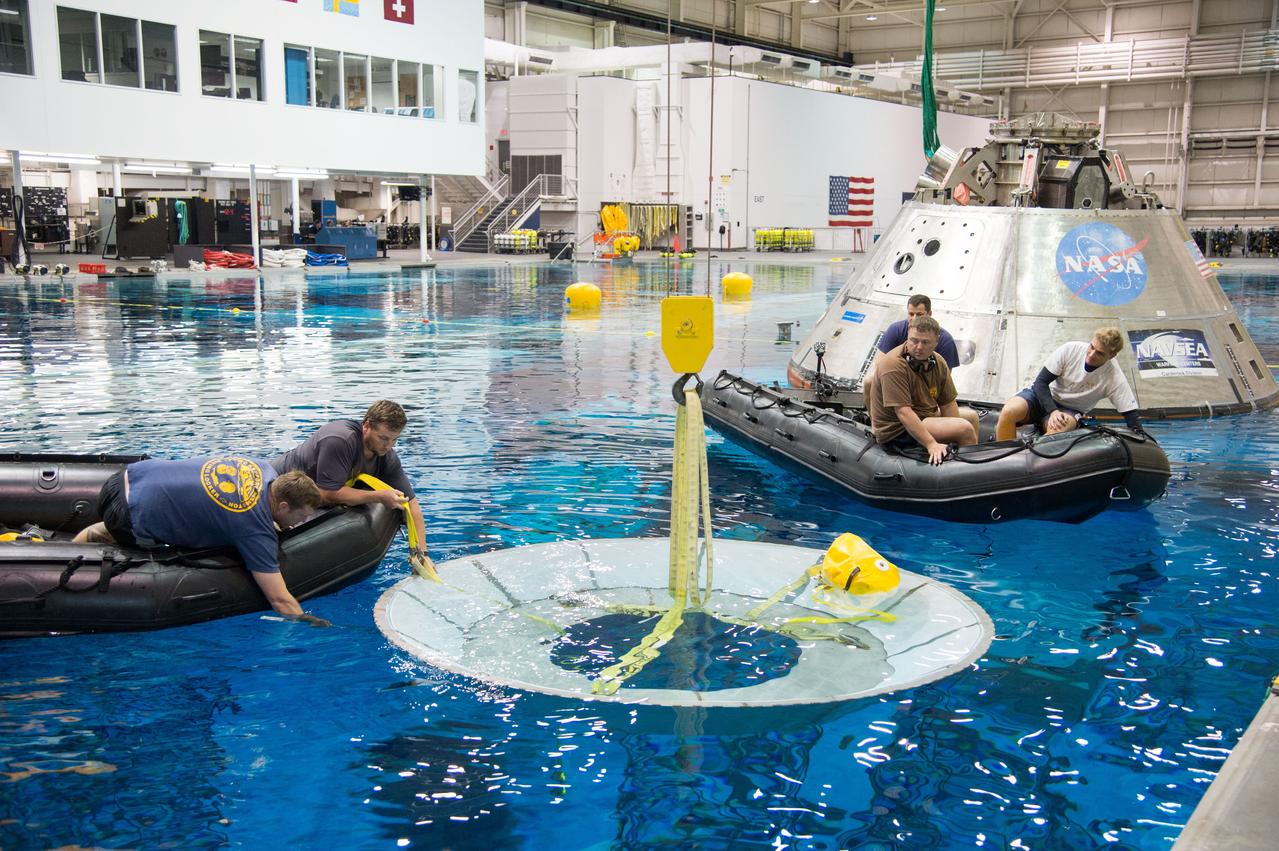
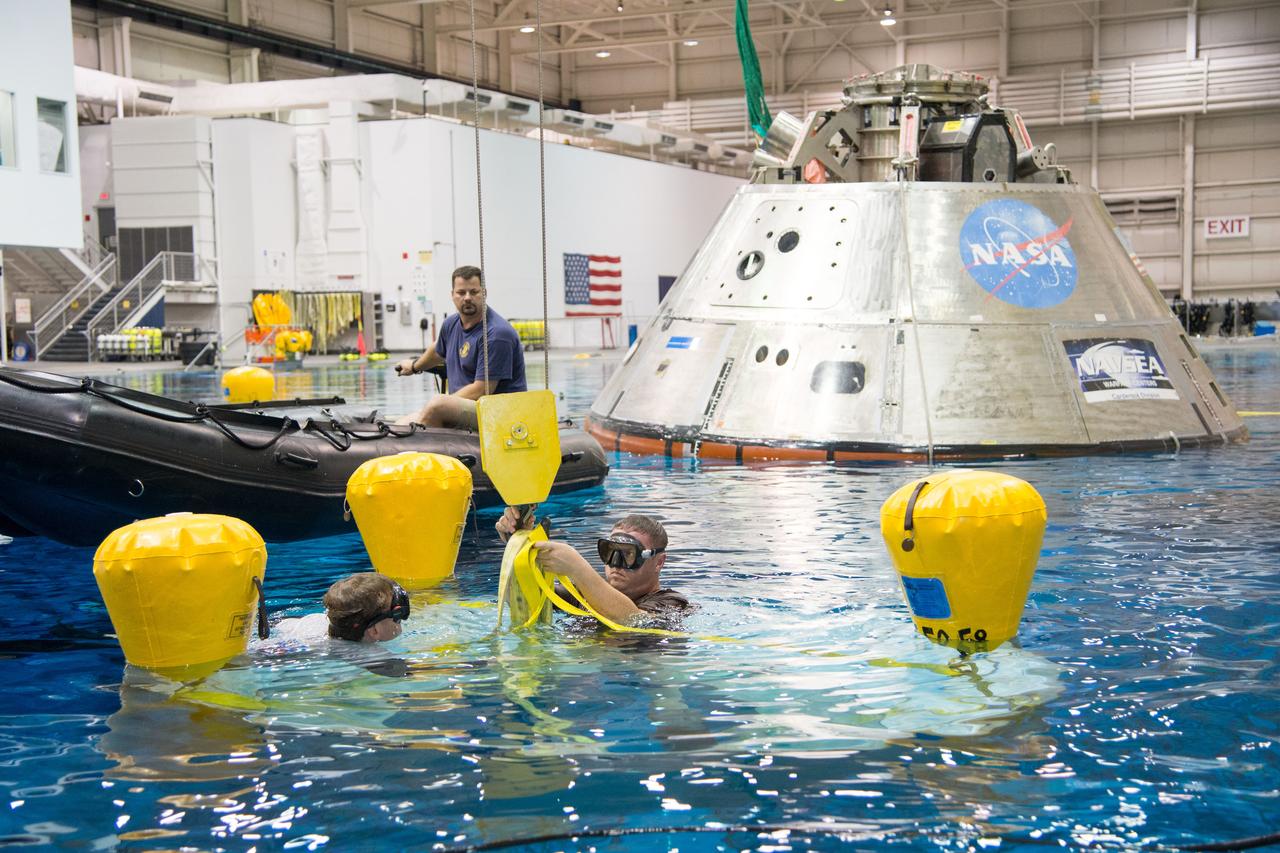
NASA, Department of Defense personnel from Detachment 3 out of Patrick Air Force Base, and the Mobile Diving Salvage Unit based in San Diego conduct a testing session at the Neutral Buoyancy Lab in Houston on Dec. 5, 2012 to evaluate procedures, mockups, and prototype hardware used to train personnel in recovery of the Orion crew module and the forward bay cover for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
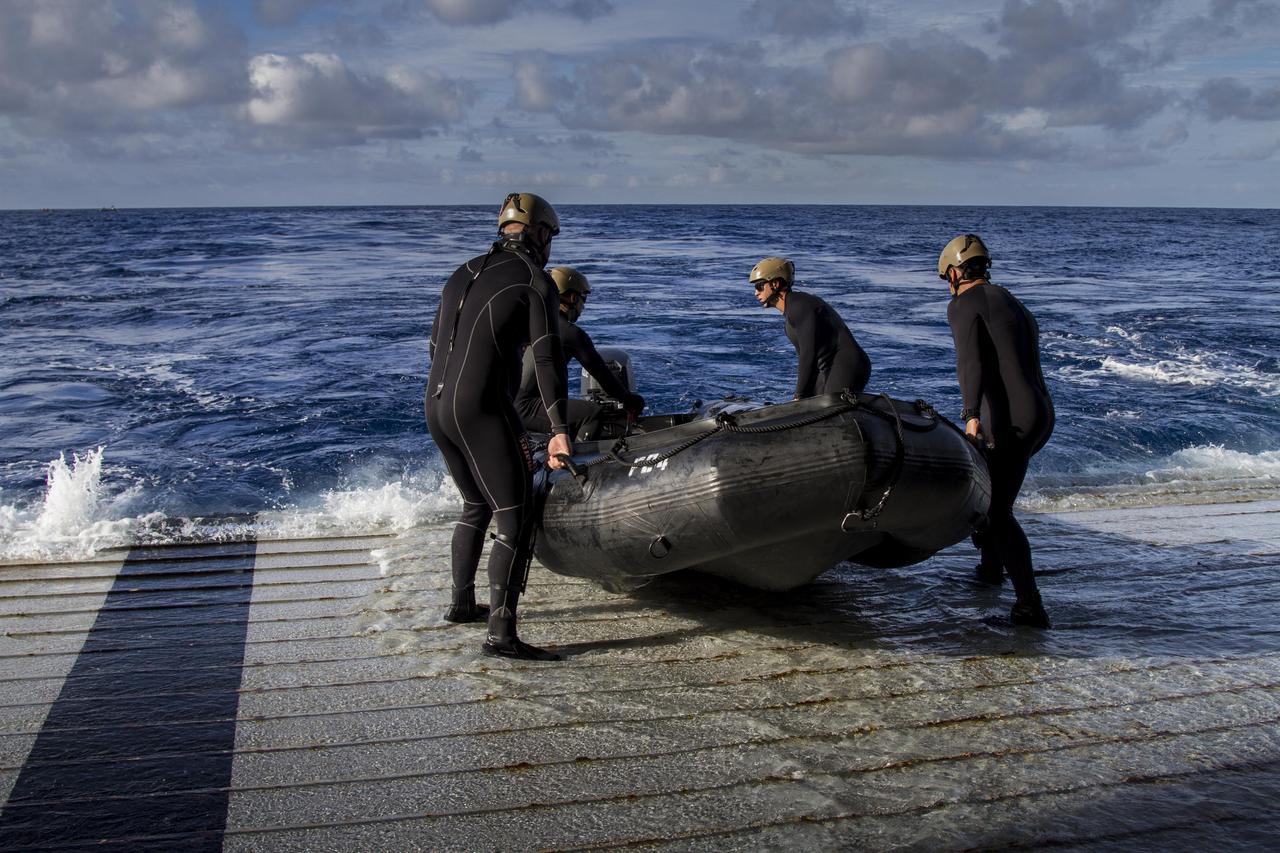

On the third day of preparations for recovery of Orion after its splashdown in the Pacific Ocean, U.S. Navy Divers prepare to embark from the well deck of the USS Anchorage in a rigid hull Zodiac boat about 600 miles off the coast of Baja, California. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are preparing for recovery of the crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.
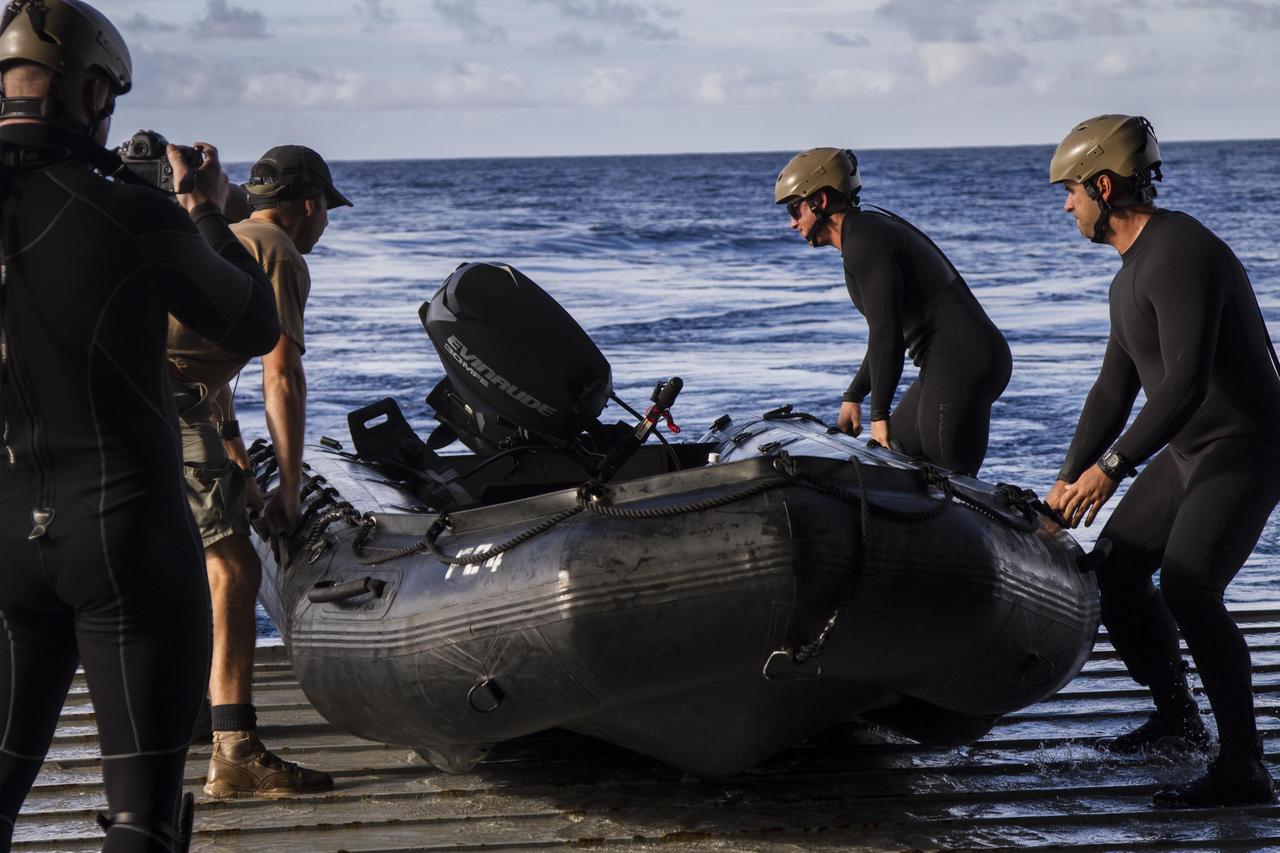

On the third day of preparations for recovery of Orion after its splashdown in the Pacific Ocean, U.S. Navy Divers prepare to embark from the well deck of the USS Anchorage in a rigid hull Zodiac boat about 600 miles off the coast of Baja, California. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are preparing for recovery of the crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.

NASA, Department of Defense personnel from Detachment 3 out of Patrick Air Force Base, and the Mobile Diving Salvage Unit based in San Diego conduct a testing session at the Neutral Buoyancy Lab in Houston on Dec. 5, 2012 to evaluate procedures, mockups, and prototype hardware used to train personnel in recovery of the Orion crew module and the forward bay cover for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

NASA, Department of Defense personnel from Detachment 3 out of Patrick Air Force Base, and the Mobile Diving Salvage Unit based in San Diego conduct a testing session at the Neutral Buoyancy Lab in Houston on Dec. 5, 2012 to evaluate procedures, mockups, and prototype hardware used to train personnel in recovery of the Orion crew module and the forward bay cover for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
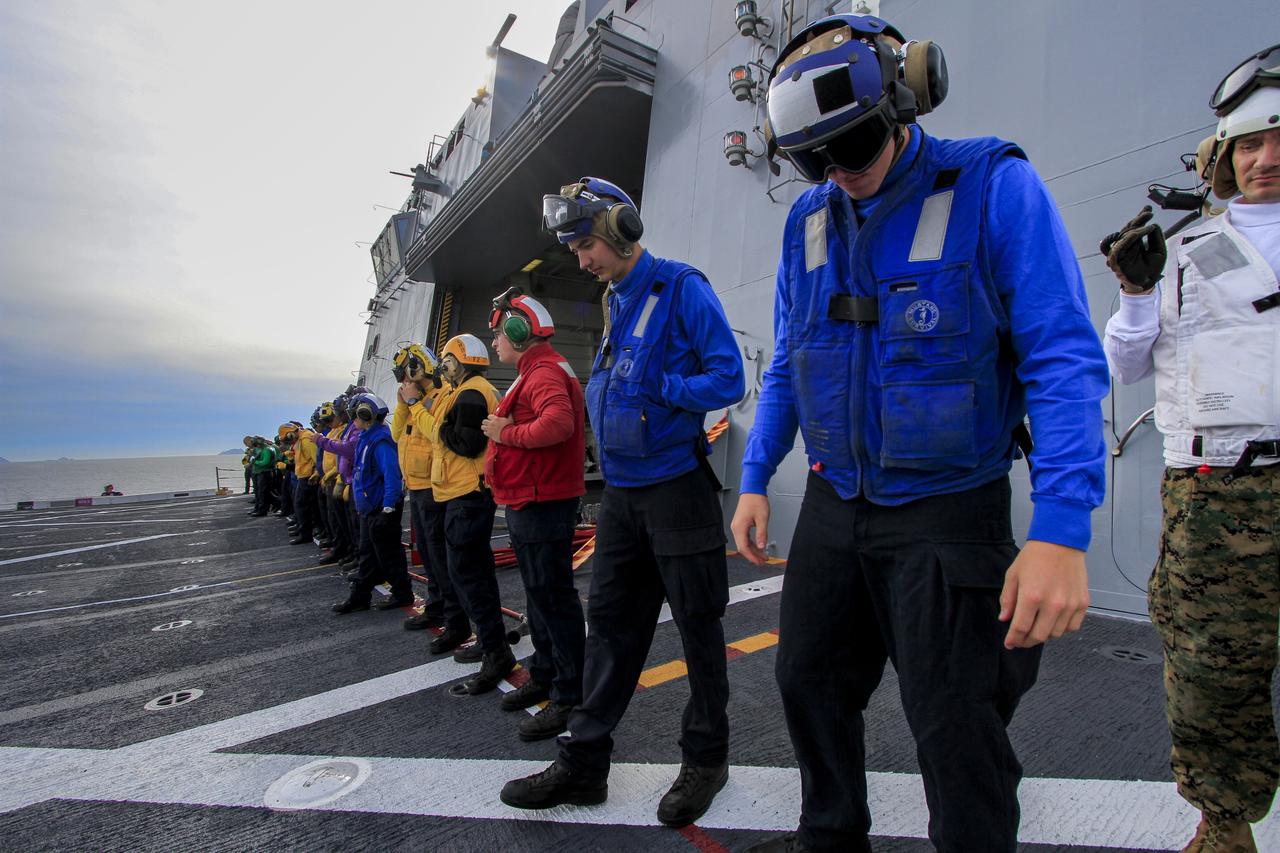

Helicopter Sea Combat Squadron 8 personnel review procedures on the deck of the USS Anchorage as the ship departs Naval Base San Diego in California for the open waters of the Pacific Ocean. NASA and the U.S. Navy are making preparations ahead of Orion's flight test for recovery of the crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.
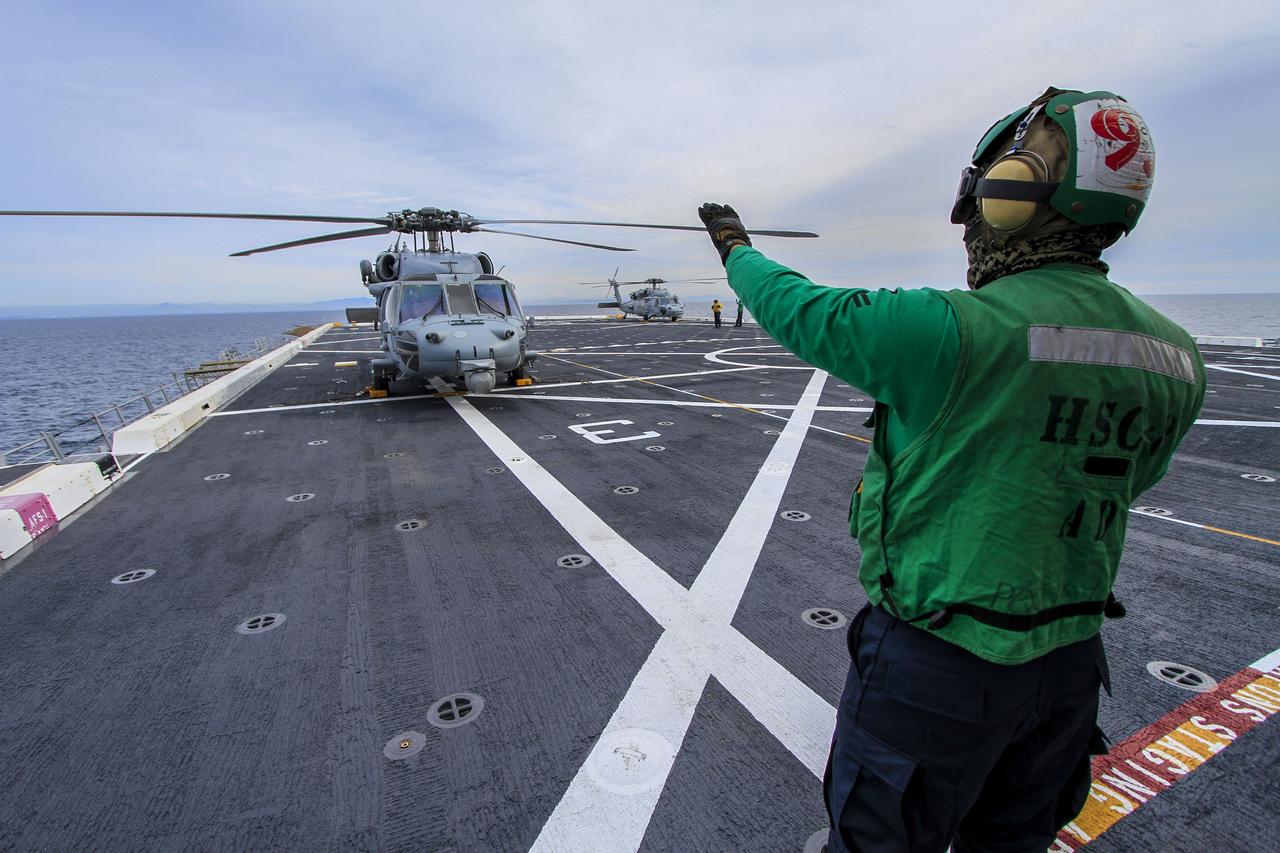

A member of the Helicopter Sea Combat Squadron 8 signals to the pilot in an H60-S Seahawk helicopter on the deck of the USS Anchorage as the ship departs Naval Base San Diego in California for the open waters of the Pacific Ocean. NASA and the U.S. Navy are making preparations ahead of Orion's flight test for recovery of the crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.
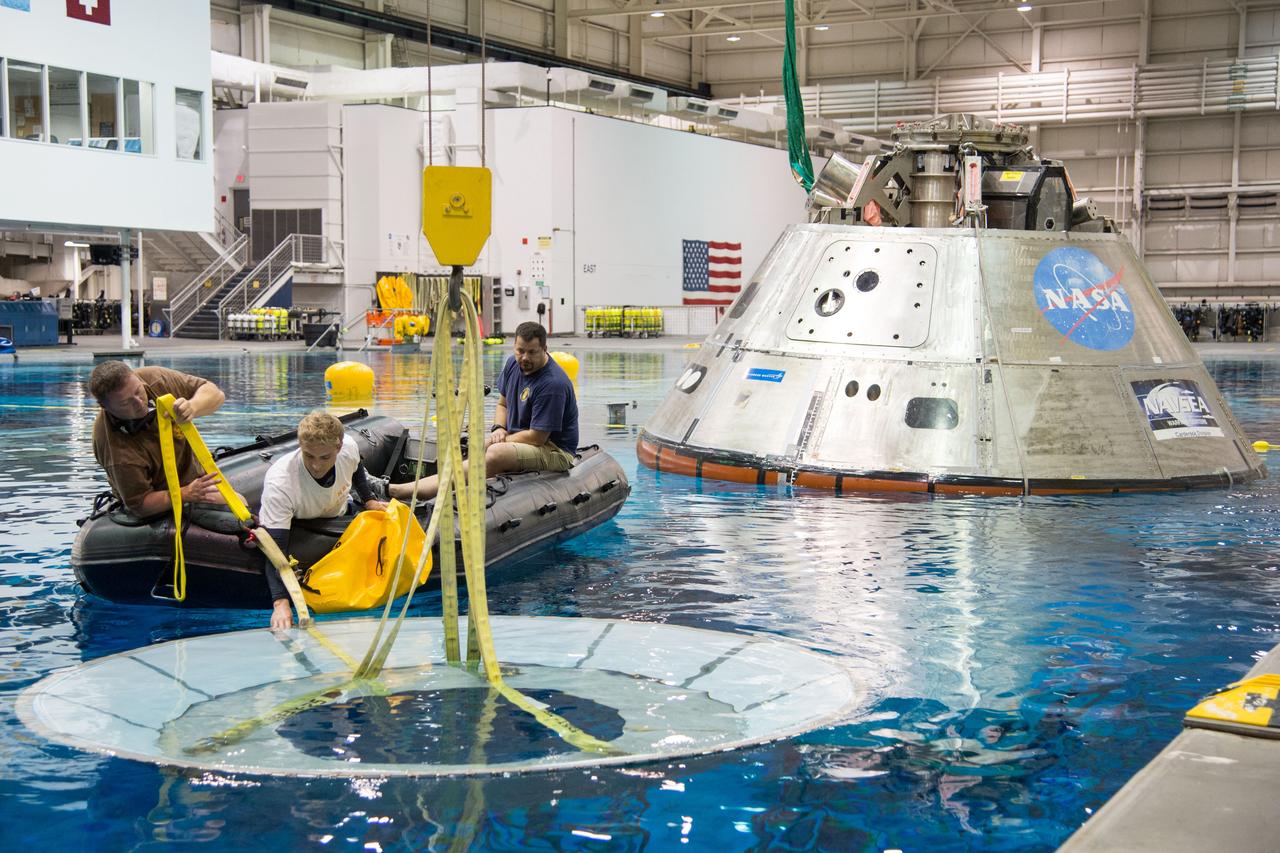

NASA, Department of Defense personnel from Detachment 3 out of Patrick Air Force Base, and the Mobile Diving Salvage Unit based in San Diego conduct a testing session at the Neutral Buoyancy Lab in Houston on Dec. 5, 2012 to evaluate procedures, mockups, and prototype hardware used to train personnel in recovery of the Orion crew module and the forward bay cover for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
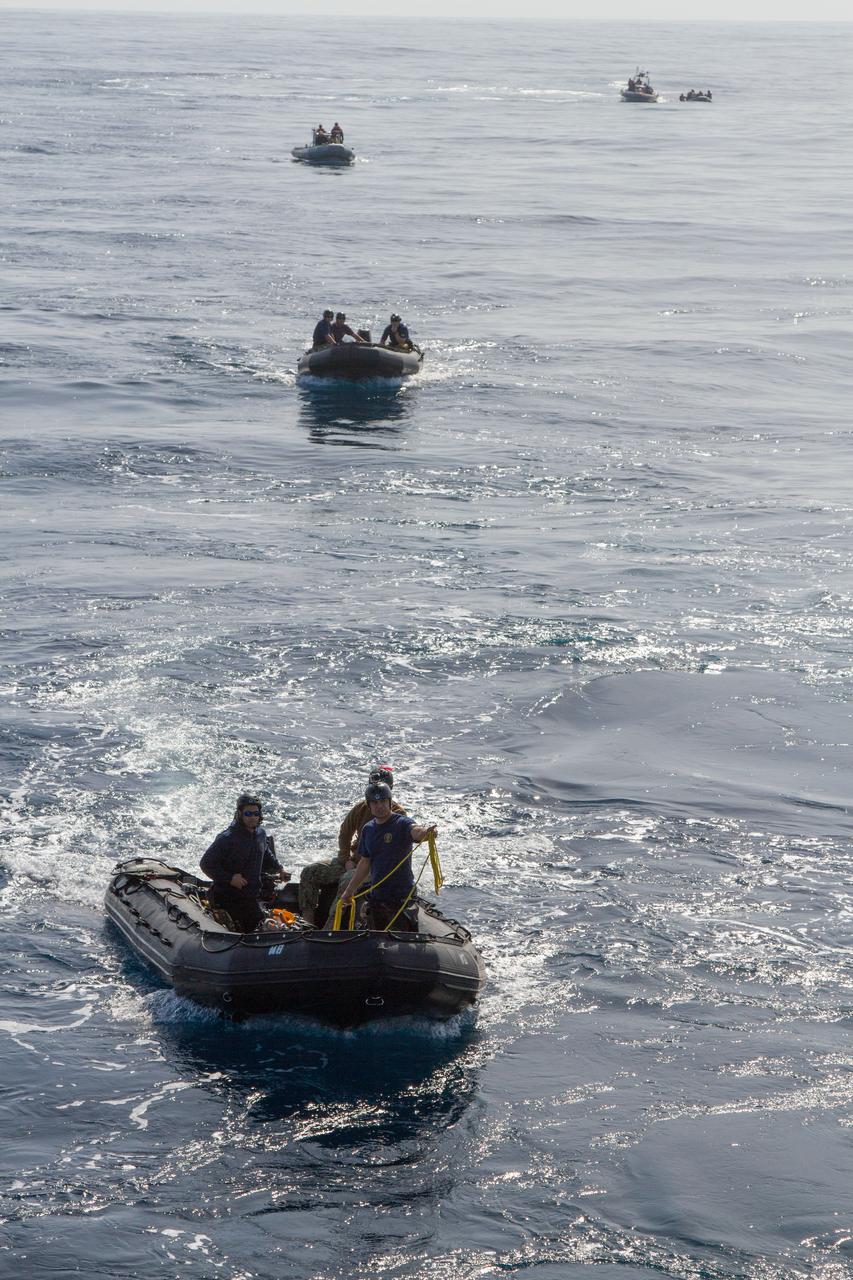

NASA and the U.S. Navy conduct a test on Feb. 20, 2014 in the Pacific Ocean, about 100 miles off the coast of San Diego, California, to prepare for the recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
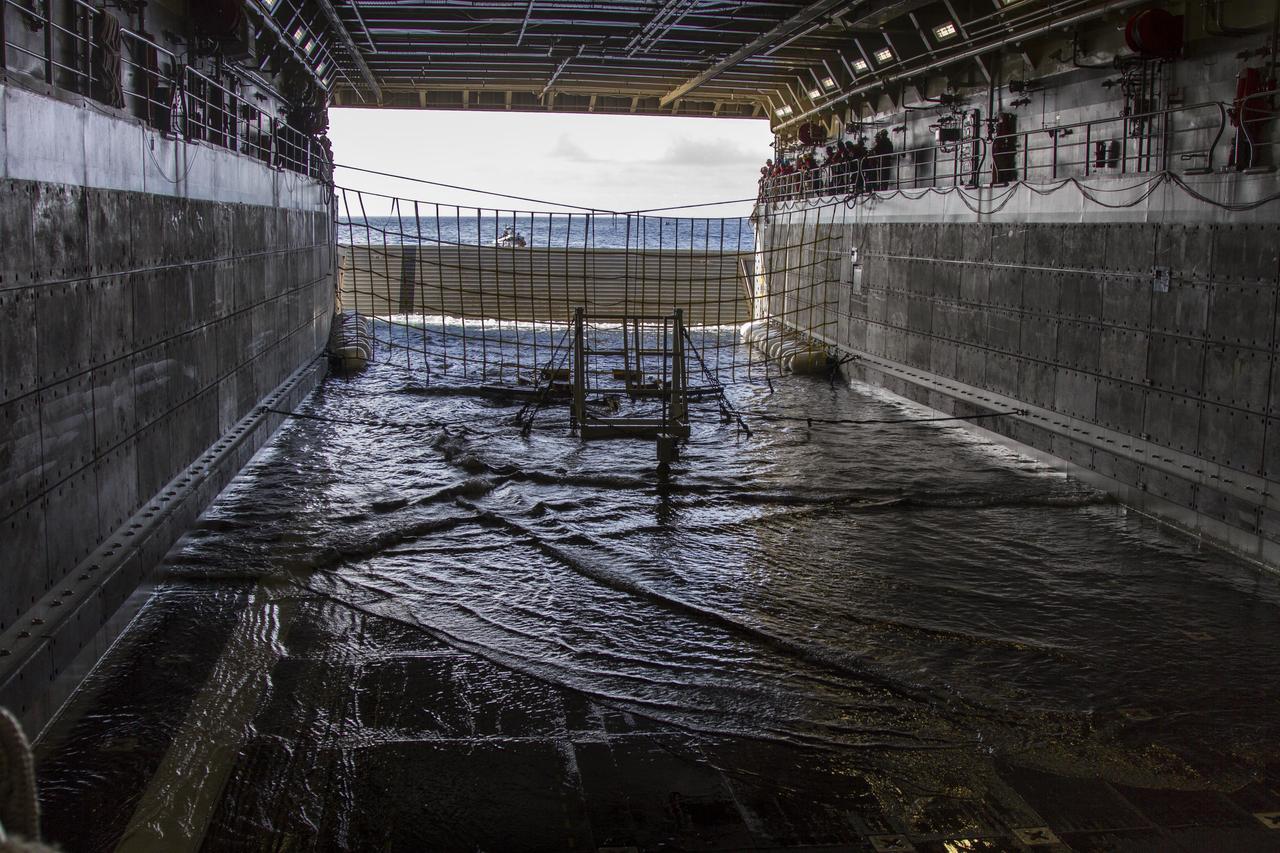

On the third day of preparations for recovery of Orion after its splashdown in the Pacific Ocean, the well deck of the USS Anchorage has been filled with water and recovery hardware is in place. The ship is about 600 miles off the coast of Baja, California. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are preparing for recovery of the crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.
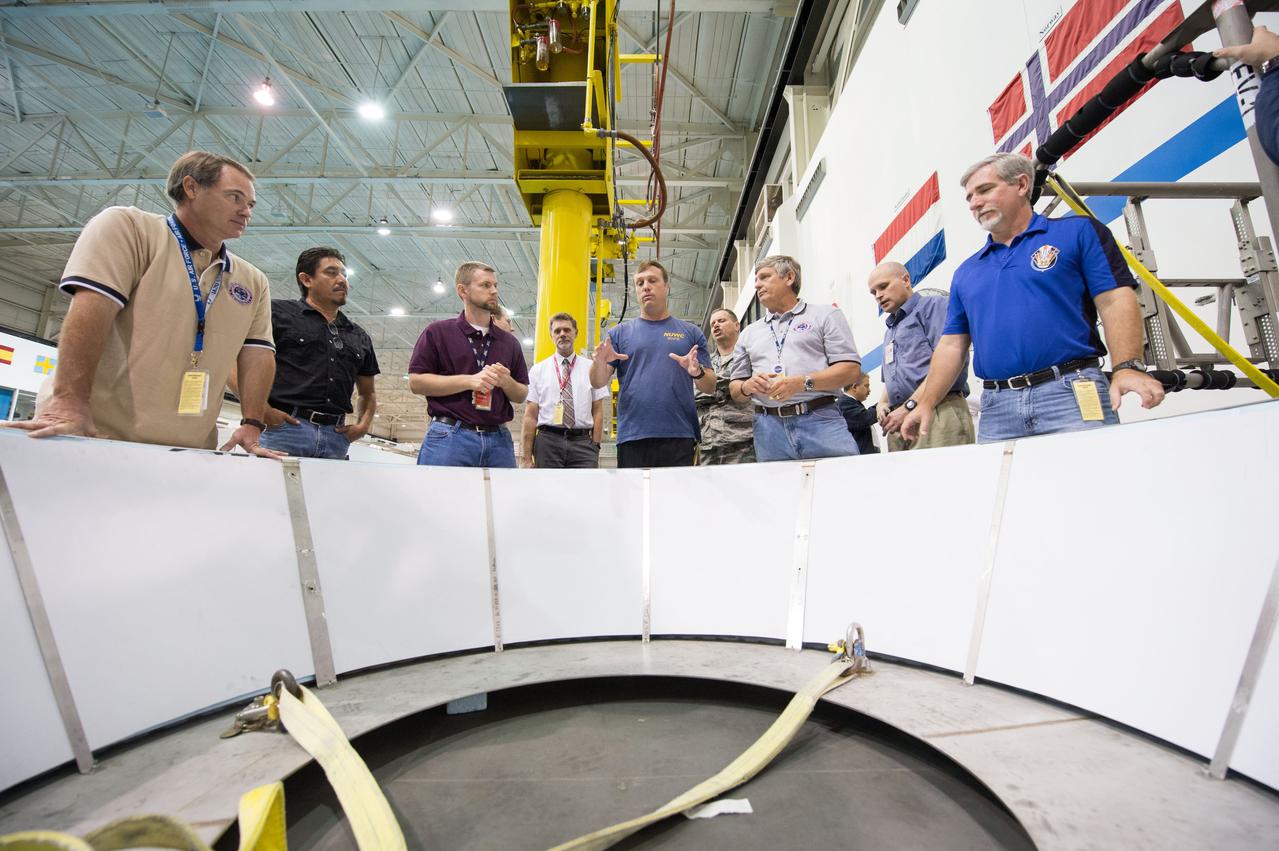

NASA, Department of Defense personnel from Detachment 3 out of Patrick Air Force Base, and the Mobile Diving Salvage Unit based in San Diego conduct a testing session at the Neutral Buoyancy Lab in Houston on Dec. 5, 2012 to evaluate procedures, mockups, and prototype hardware used to train personnel in recovery of the Orion crew module and the forward bay cover for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

NASA and U.S. Navy personnel are on the deck of the USS Anchorage as the ship departs Naval Base San Diego and heads out to sea in the Pacific Ocean. NASA and the U.S. Navy are making preparations ahead of Orion's flight test for recovery of the crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.
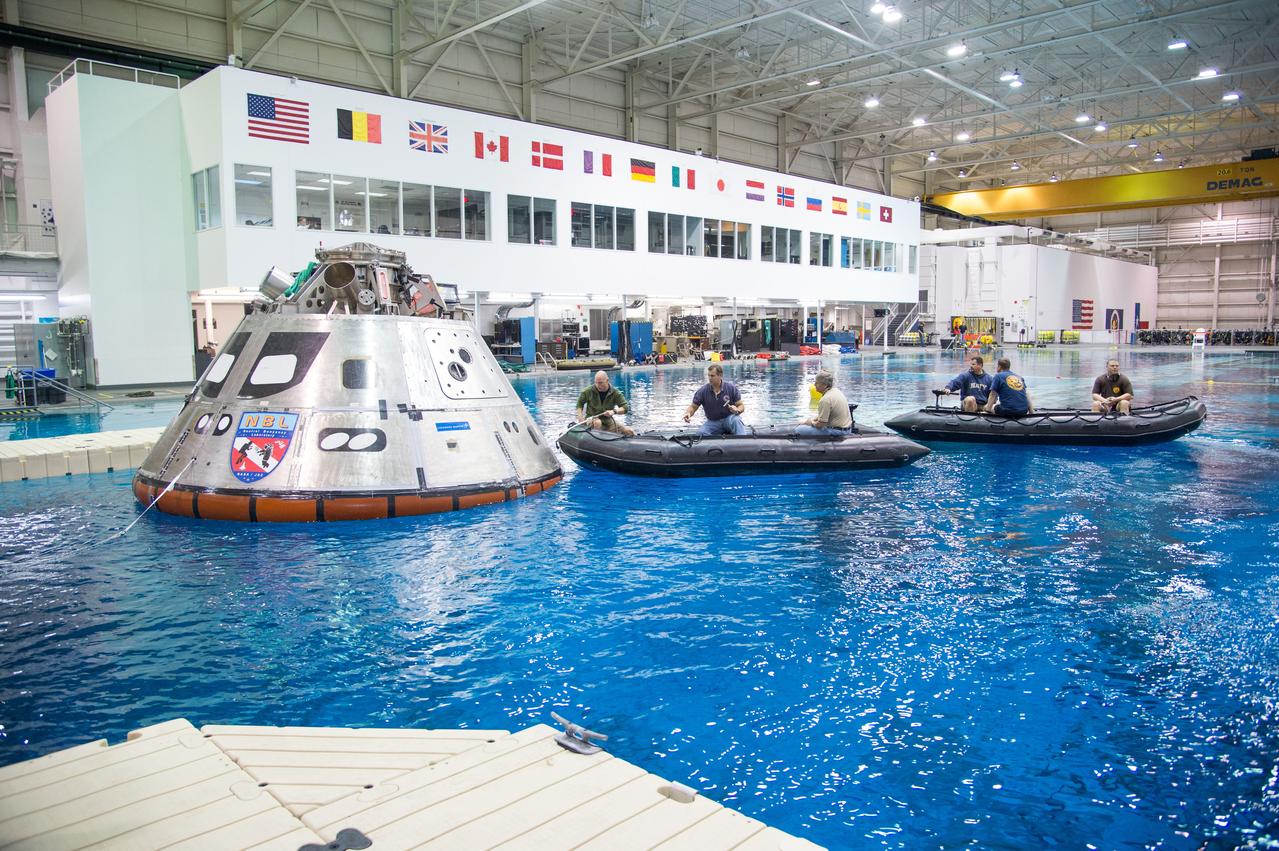

NASA, Department of Defense personnel from Detachment 3 out of Patrick Air Force Base, and the Mobile Diving Salvage Unit based in San Diego conduct a testing session at the Neutral Buoyancy Lab in Houston on Dec. 5, 2012 to evaluate procedures, mockups, and prototype hardware used to train personnel in recovery of the Orion crew module and the forward bay cover for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

On the third day of preparations for recovery of Orion, pilots in two H60-S Seahawk helicopters practice take-off and search from the deck of the USS Anchorage in the Pacific Ocean about 600 miles off the coast of Baja, California. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are preparing to recover the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes after the spacecraft's return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.
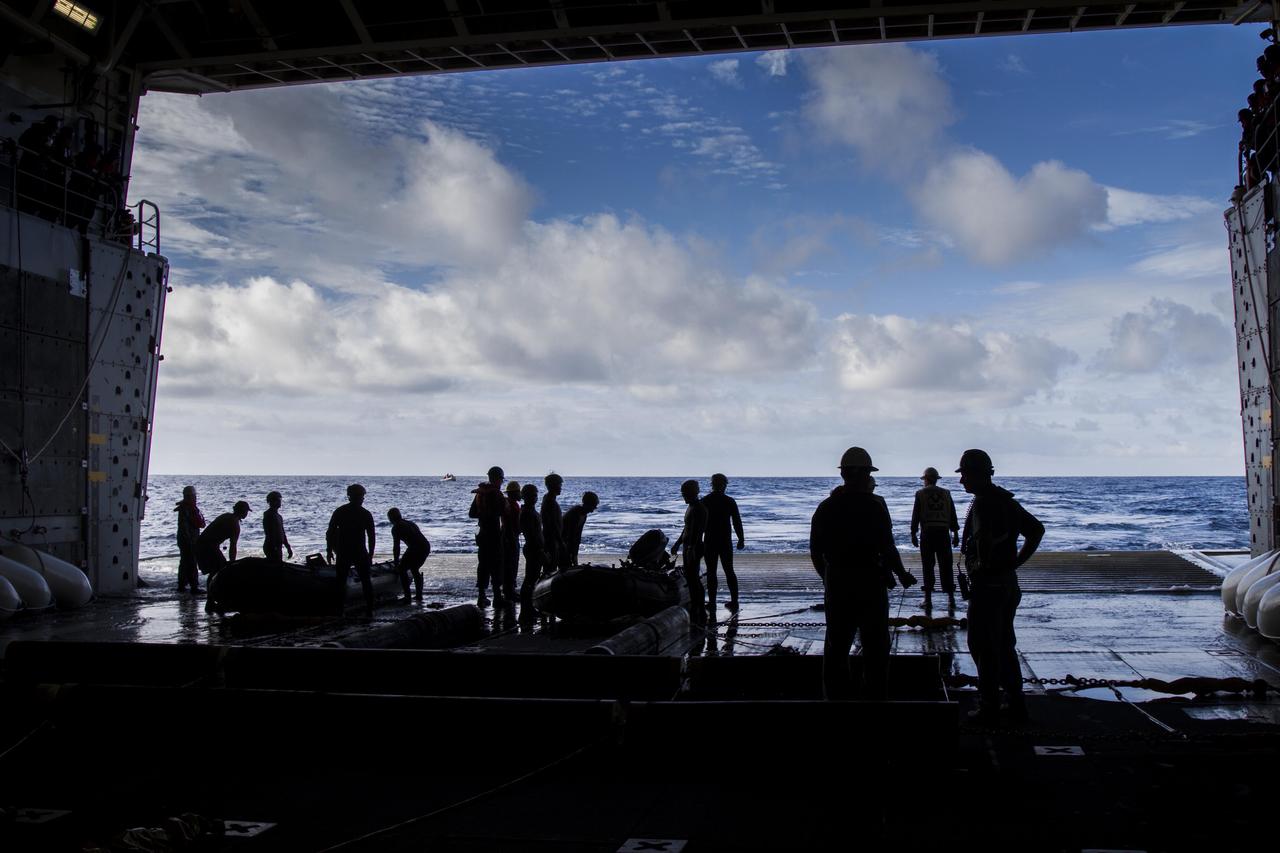

On the third day of preparations for recovery of Orion after its splashdown in the Pacific Ocean, U.S. Navy Divers prepare to embark from the well deck of the USS Anchorage in two rigid hull Zodiac boats about 600 miles off the coast of Baja, California. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are preparing for recovery of the crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.
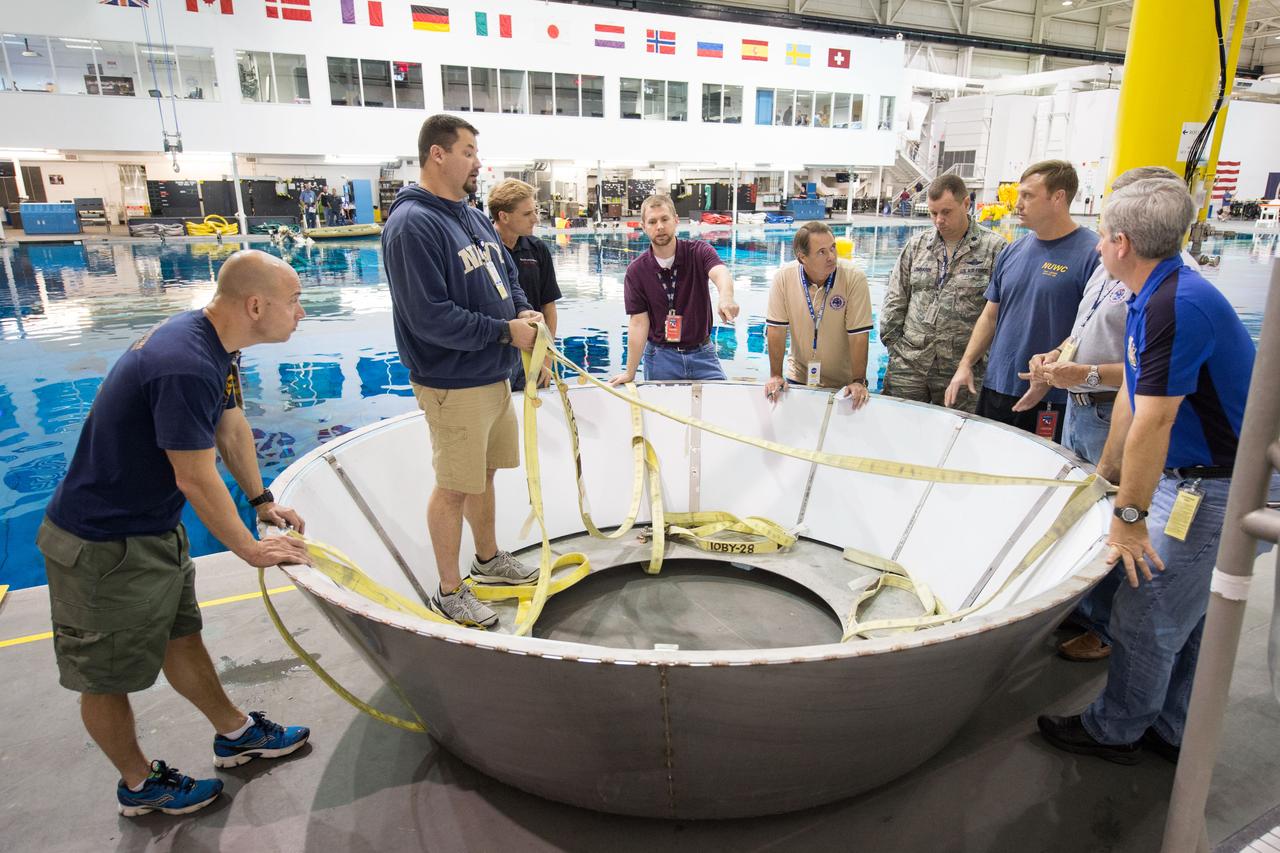

NASA, Department of Defense personnel from Detachment 3 out of Patrick Air Force Base, and the Mobile Diving Salvage Unit based in San Diego conduct a testing session at the Neutral Buoyancy Lab in Houston on Dec. 5, 2012 to evaluate procedures, mockups, and prototype hardware used to train personnel in recovery of the Orion crew module and the forward bay cover for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
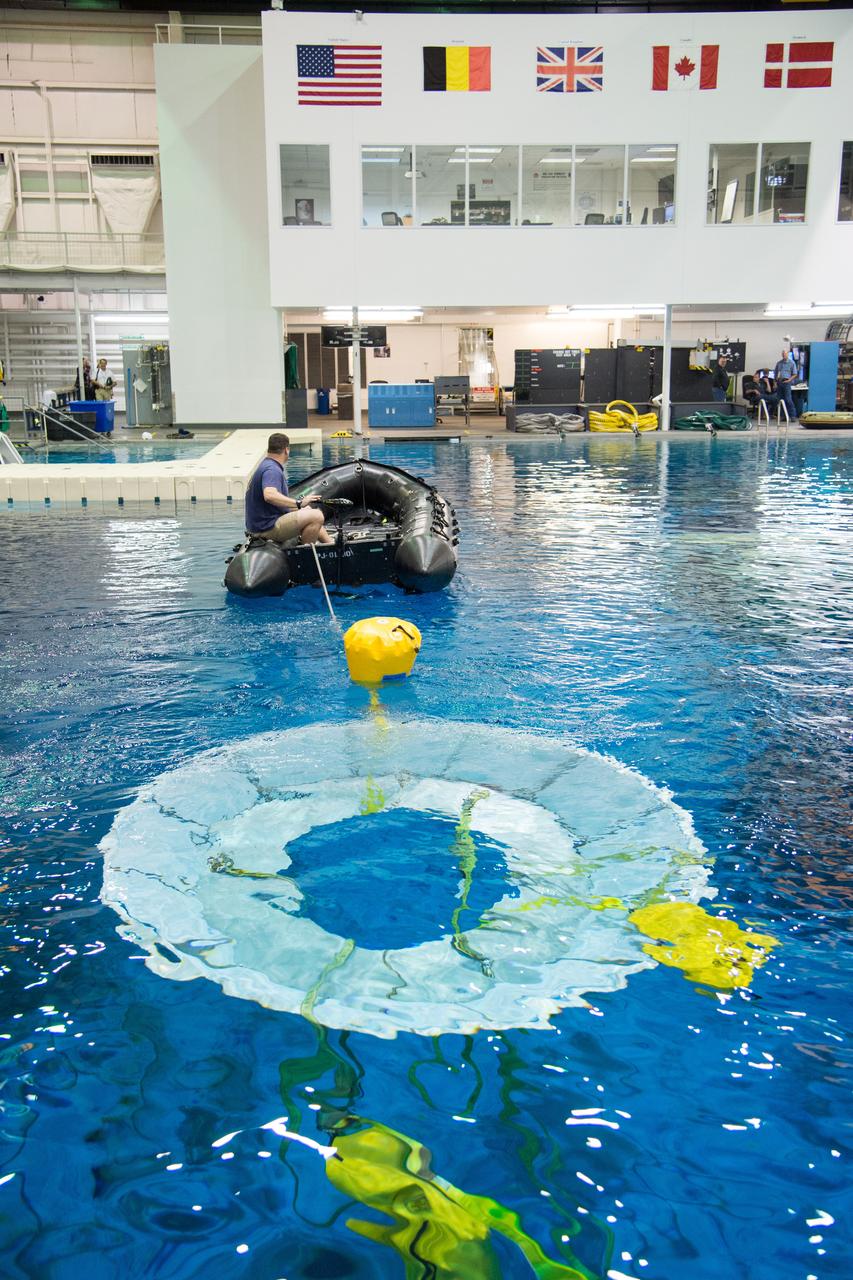

NASA, Department of Defense personnel from Detachment 3 out of Patrick Air Force Base, and the Mobile Diving Salvage Unit based in San Diego conduct a testing session at the Neutral Buoyancy Lab in Houston on Dec. 5, 2012 to evaluate procedures, mockups, and prototype hardware used to train personnel in recovery of the Orion crew module and the forward bay cover for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
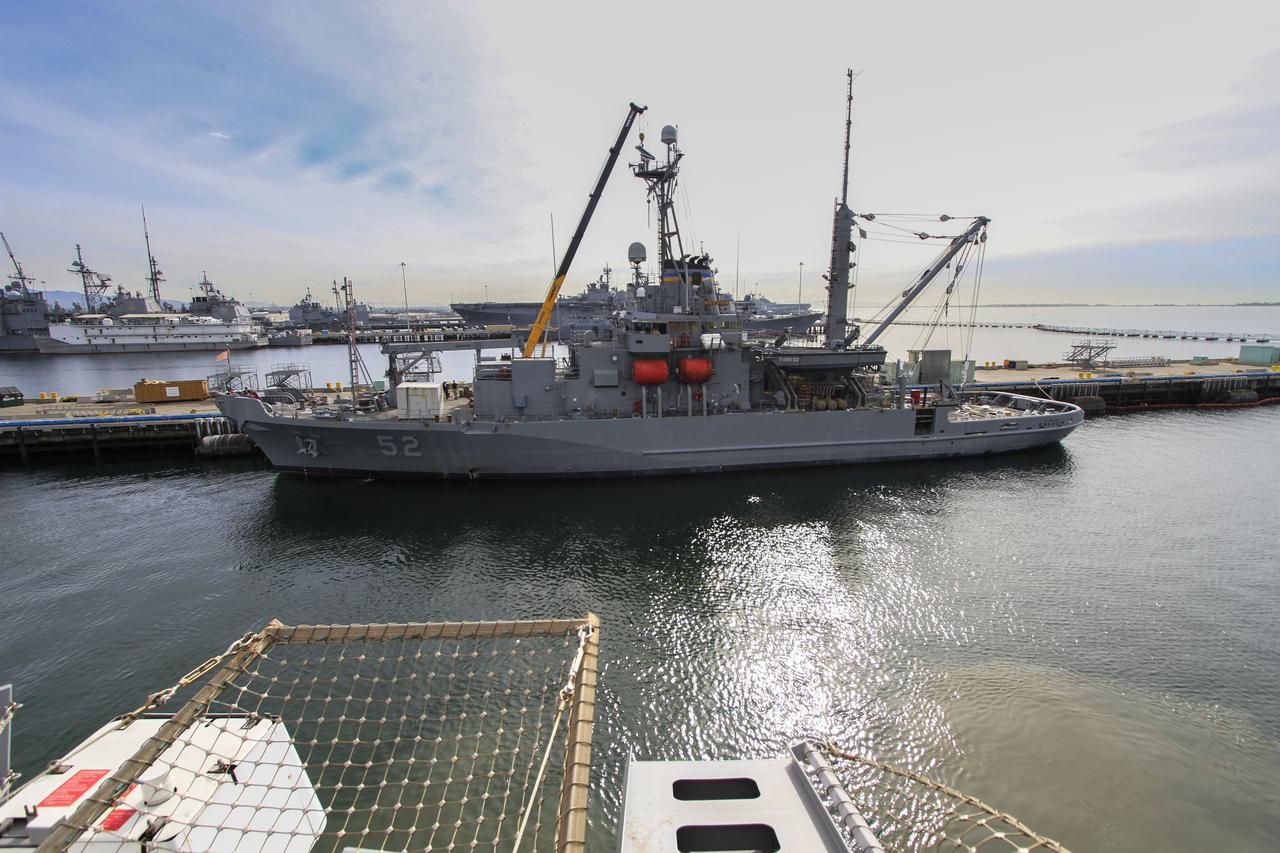

The USNS Salvor, a safeguard-class rescue and salvage ship, is docked at Naval Base San Diego in California. The ship will head out to sea along with the USS Anchorage ahead of Orion's first flight test. NASA and U.S. Navy personnel are making preparations ahead of Orion's flight test for recovery of the crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. If needed, the Salvor would be used for an alternate recovery method. Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.

NASA, Department of Defense personnel from Detachment 3 out of Patrick Air Force Base, and the Mobile Diving Salvage Unit based in San Diego conduct a testing session at the Neutral Buoyancy Lab in Houston on Dec. 5, 2012 to evaluate procedures, mockups, and prototype hardware used to train personnel in recovery of the Orion crew module and the forward bay cover for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
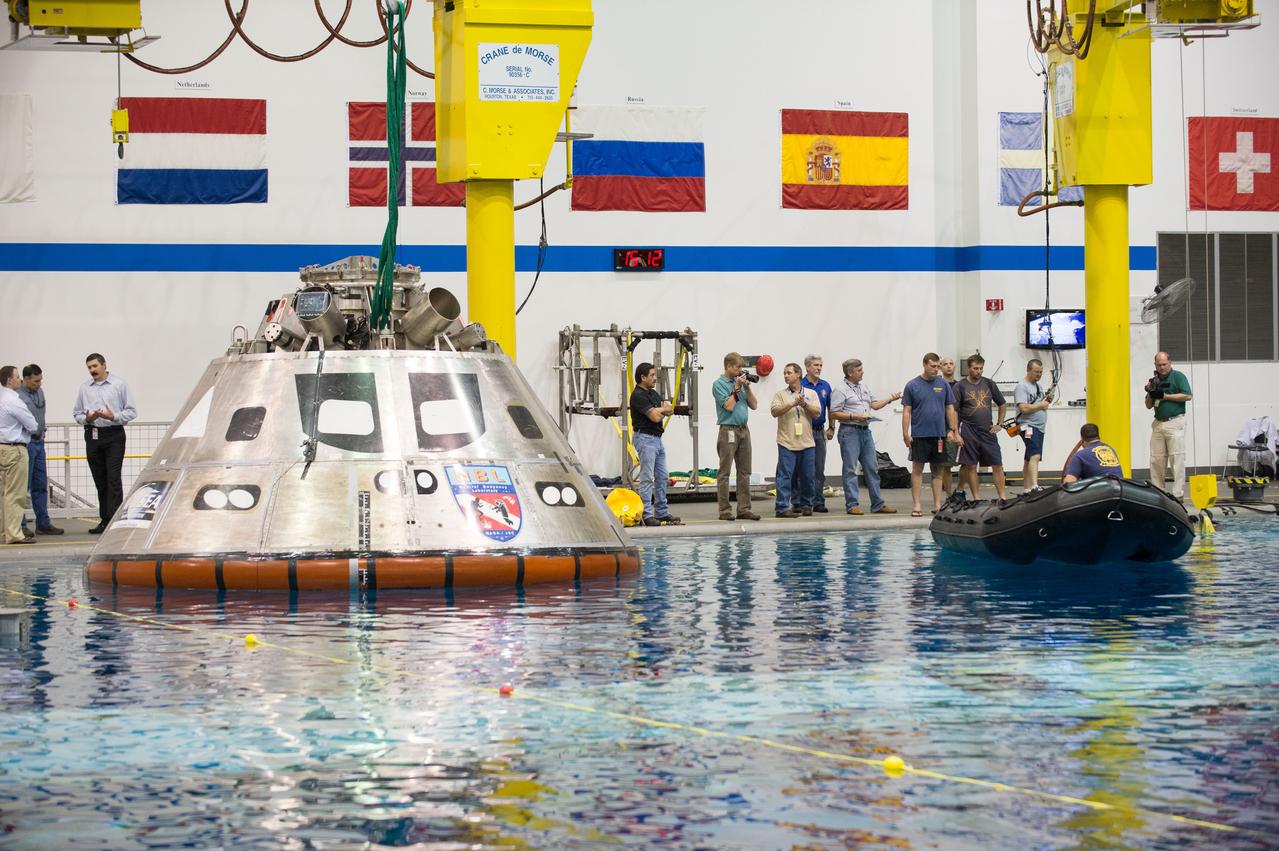

NASA, Department of Defense personnel from Detachment 3 out of Patrick Air Force Base, and the Mobile Diving Salvage Unit based in San Diego conduct a testing session at the Neutral Buoyancy Lab in Houston on Dec. 5, 2012 to evaluate procedures, mockups, and prototype hardware used to train personnel in recovery of the Orion crew module and the forward bay cover for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
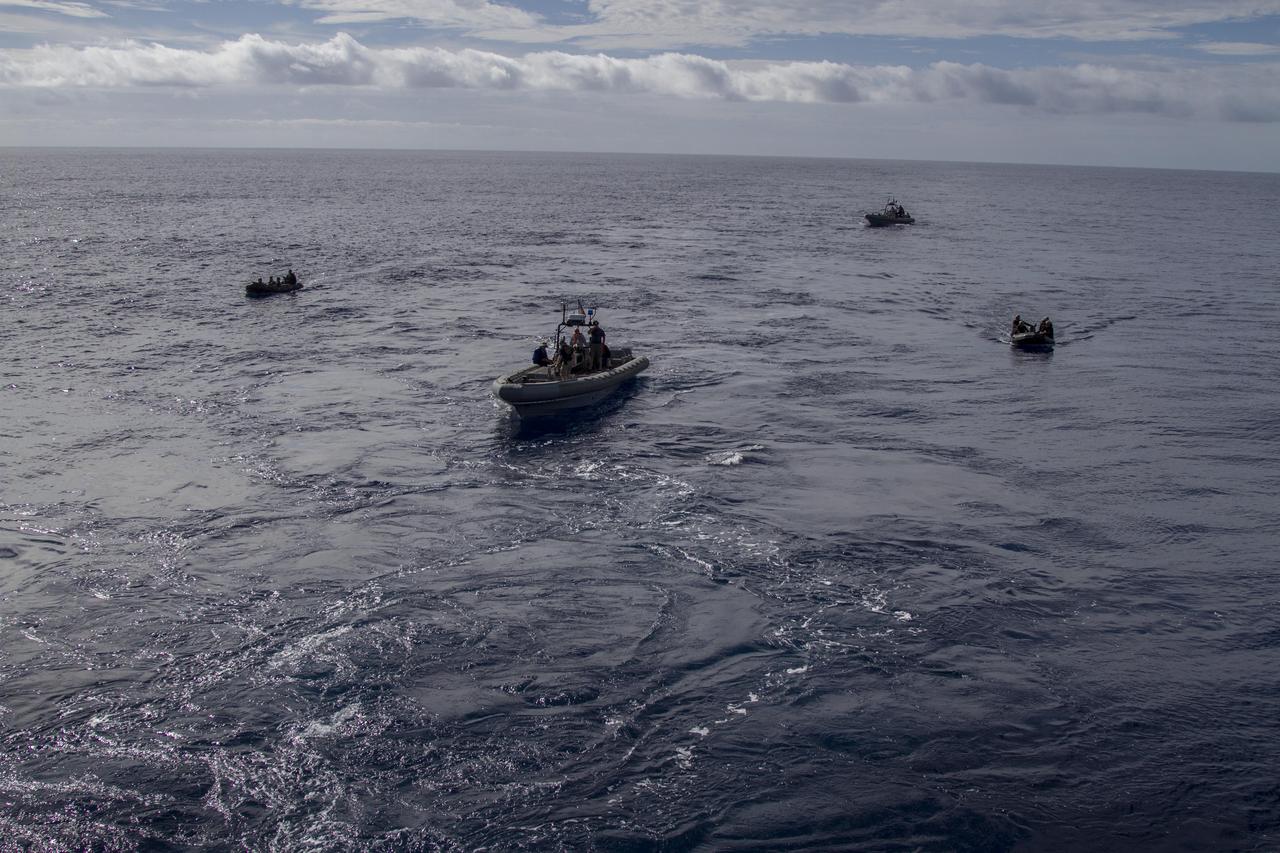

On the third day of preparations for recovery of Orion, U.S. Navy divers in two rigid hull inflatable boats and two Zodiac boats practice recovery procedures nearby the USS Anchorage in the Pacific Ocean about 600 miles off the coast of Baja, California. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are preparing for recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes after its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.
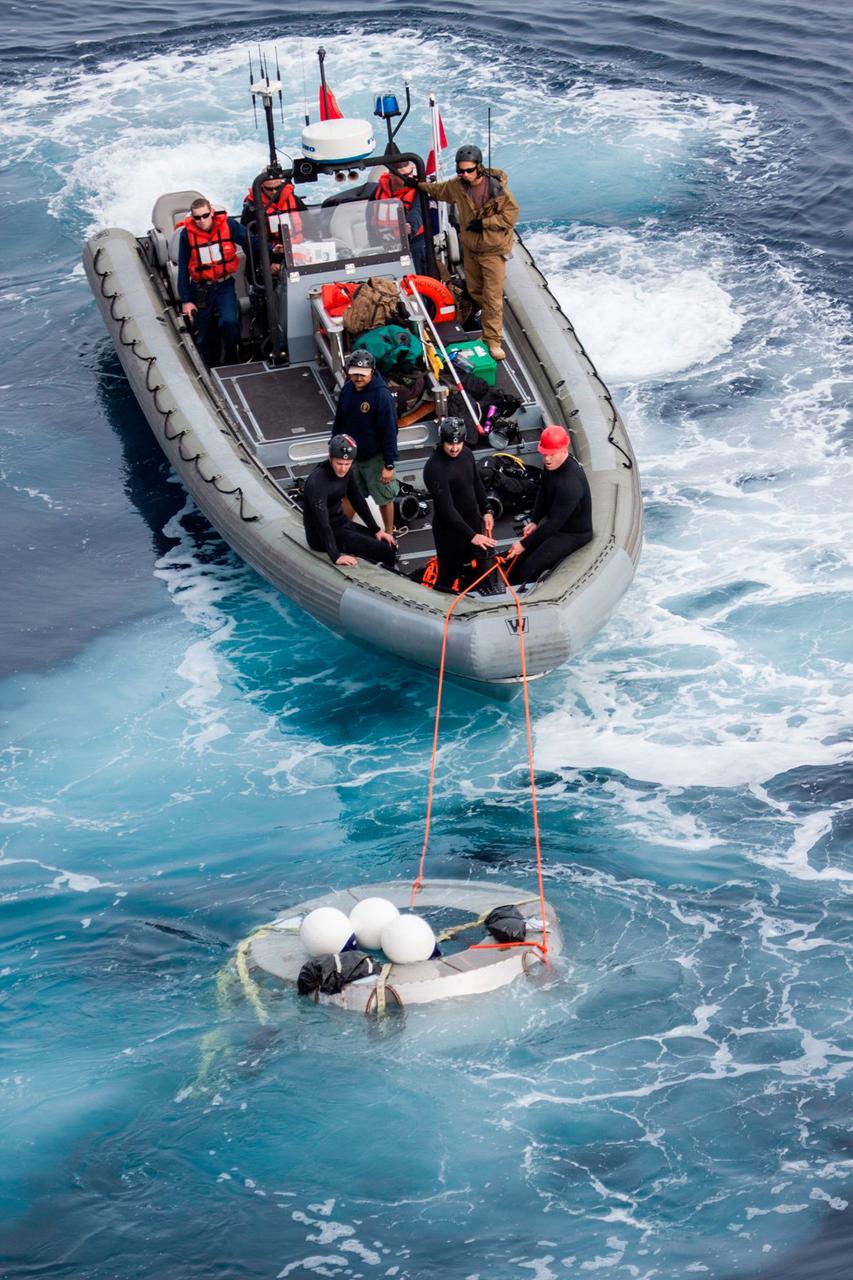

Members of the Orion recovery team work to retrieve a test version of Orion's forward bay cover, a protective shell that fits on top of the crew module, from the Pacific Ocean on Feb. 18, 2014, during an Underway Recovery Test. NASA and U.S. Navy personnel came together on board the USS San Diego, off the coast of California, to practice the processes they used to recover Orion after its splashdown following Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

NASA, Department of Defense personnel from Detachment 3 out of Patrick Air Force Base, and the Mobile Diving Salvage Unit based in San Diego conduct a testing session at the Neutral Buoyancy Lab in Houston on Dec. 5, 2012 to evaluate procedures, mockups, and prototype hardware used to train personnel in recovery of the Orion crew module and the forward bay cover for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
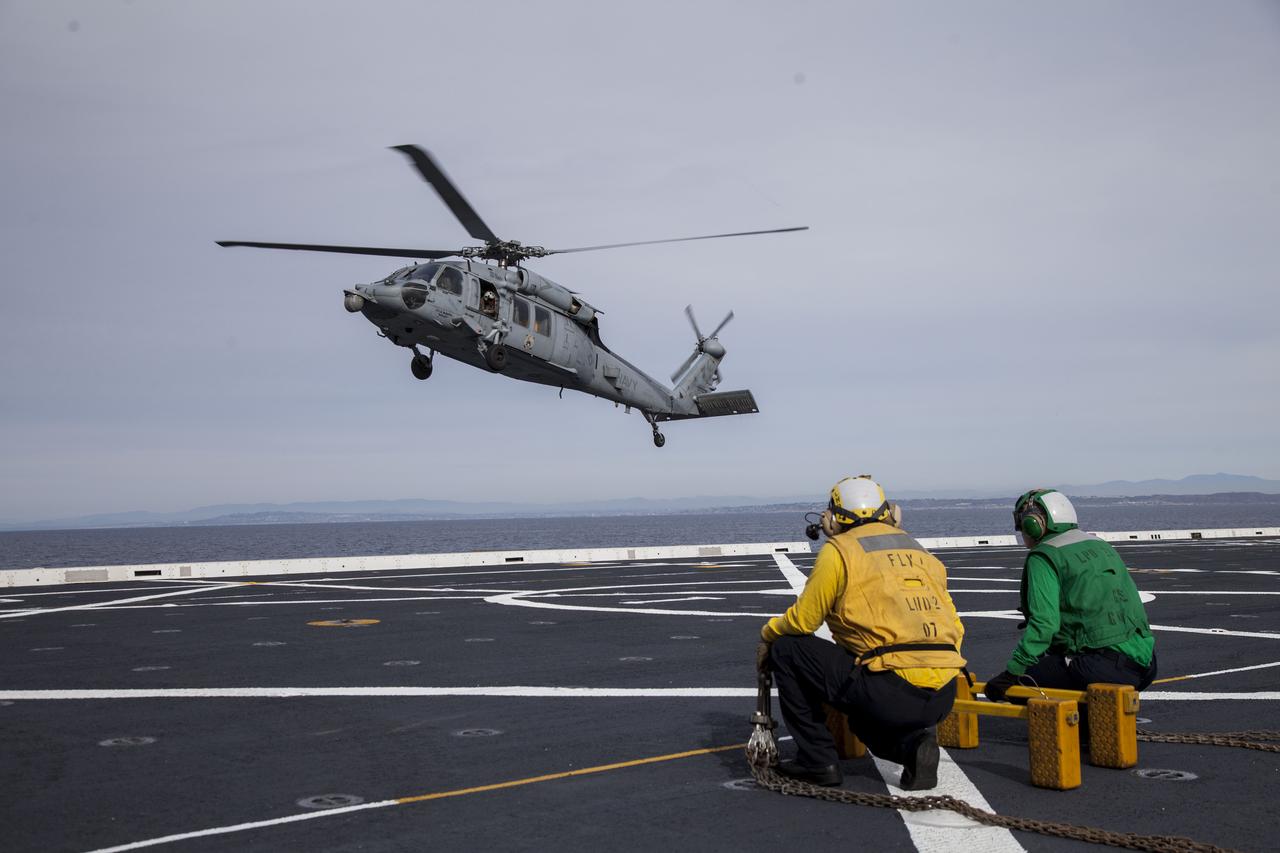

An H60-S Seahawk helicopter lands on the deck of the USS Anchorage in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California. NASA and the U.S. Navy are heading out to sea ahead of Orion's flight test to prepare for recovery of the crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.
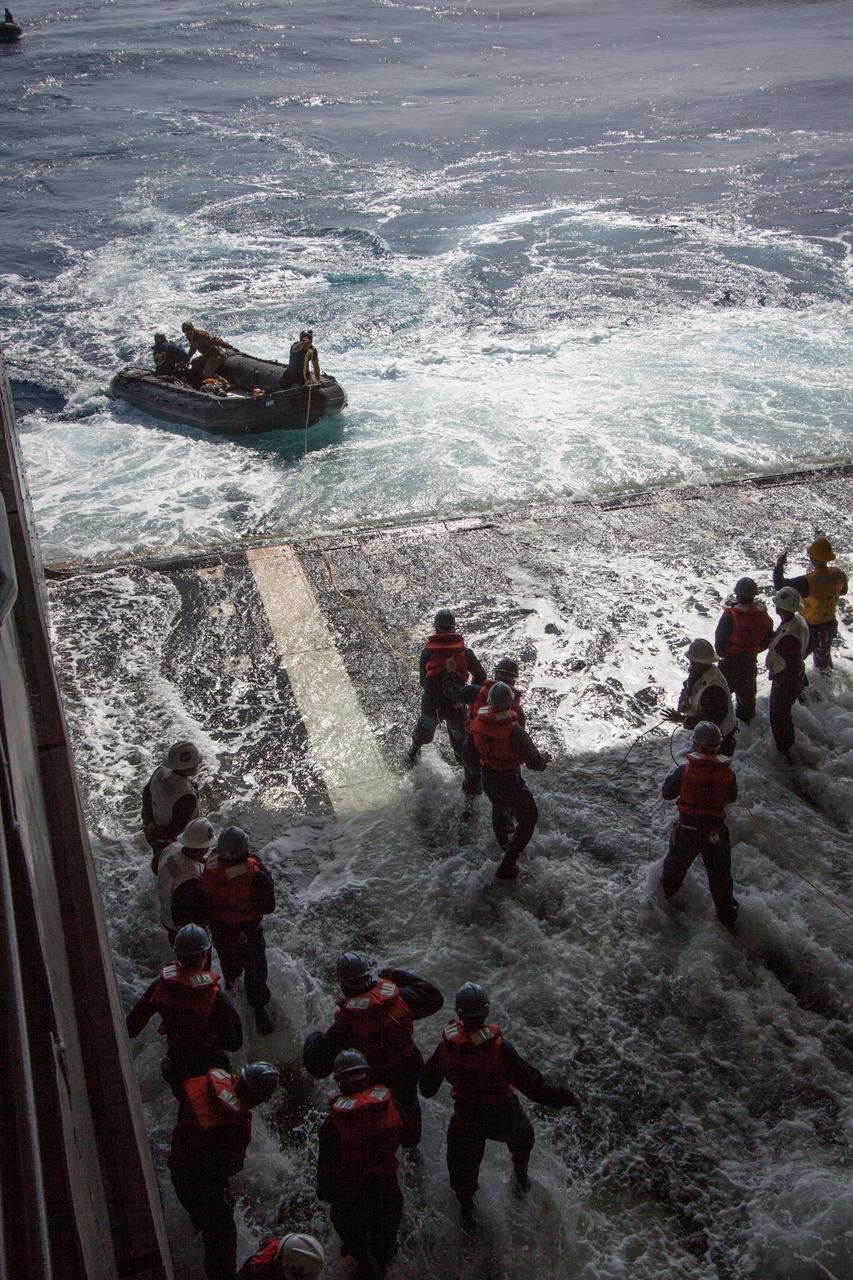

NASA and the U.S. Navy conduct a test on Feb. 20, 2014 in the Pacific Ocean, about 100 miles off the coast of San Diego, California, to prepare for the recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
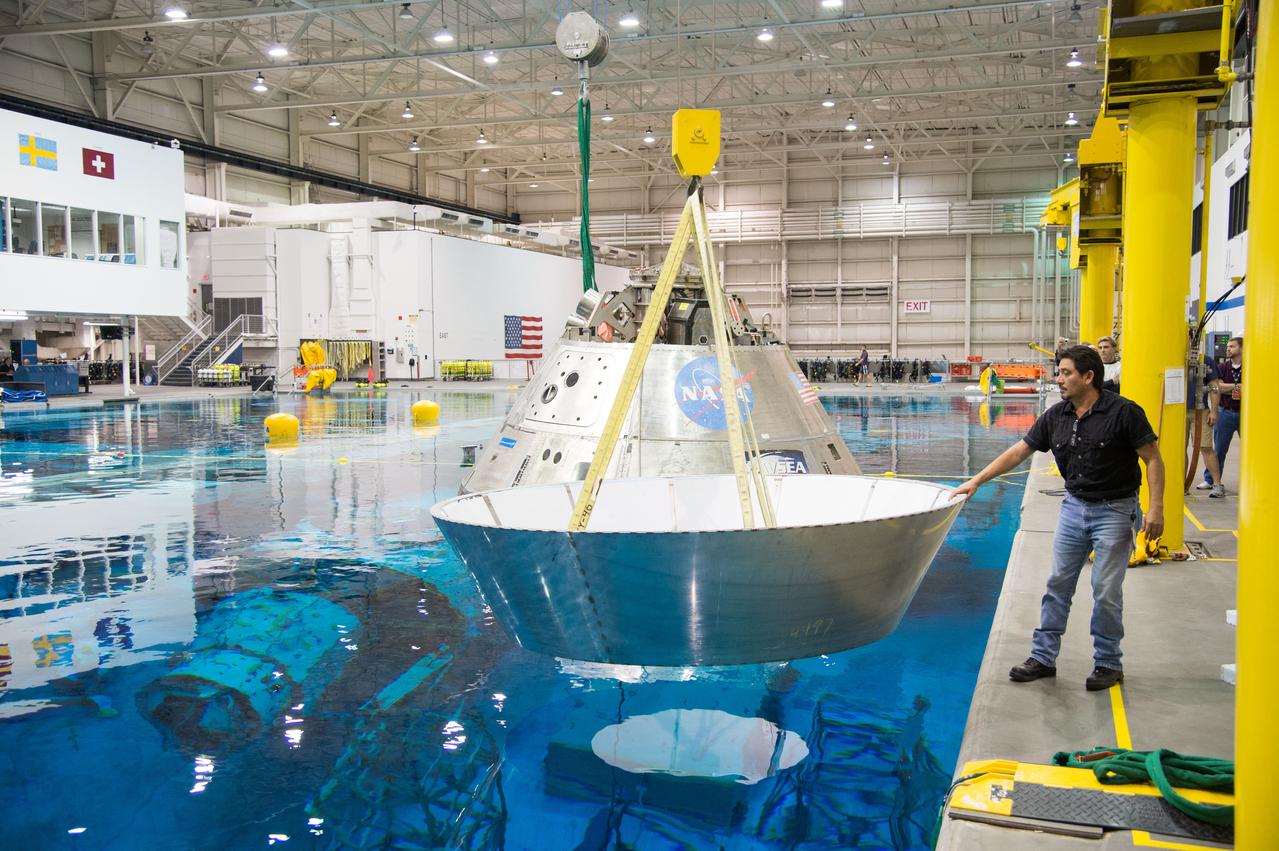

NASA, Department of Defense personnel from Detachment 3 out of Patrick Air Force Base, and the Mobile Diving Salvage Unit based in San Diego conduct a testing session at the Neutral Buoyancy Lab in Houston on Dec. 5, 2012 to evaluate procedures, mockups, and prototype hardware used to train personnel in recovery of the Orion crew module and the forward bay cover for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
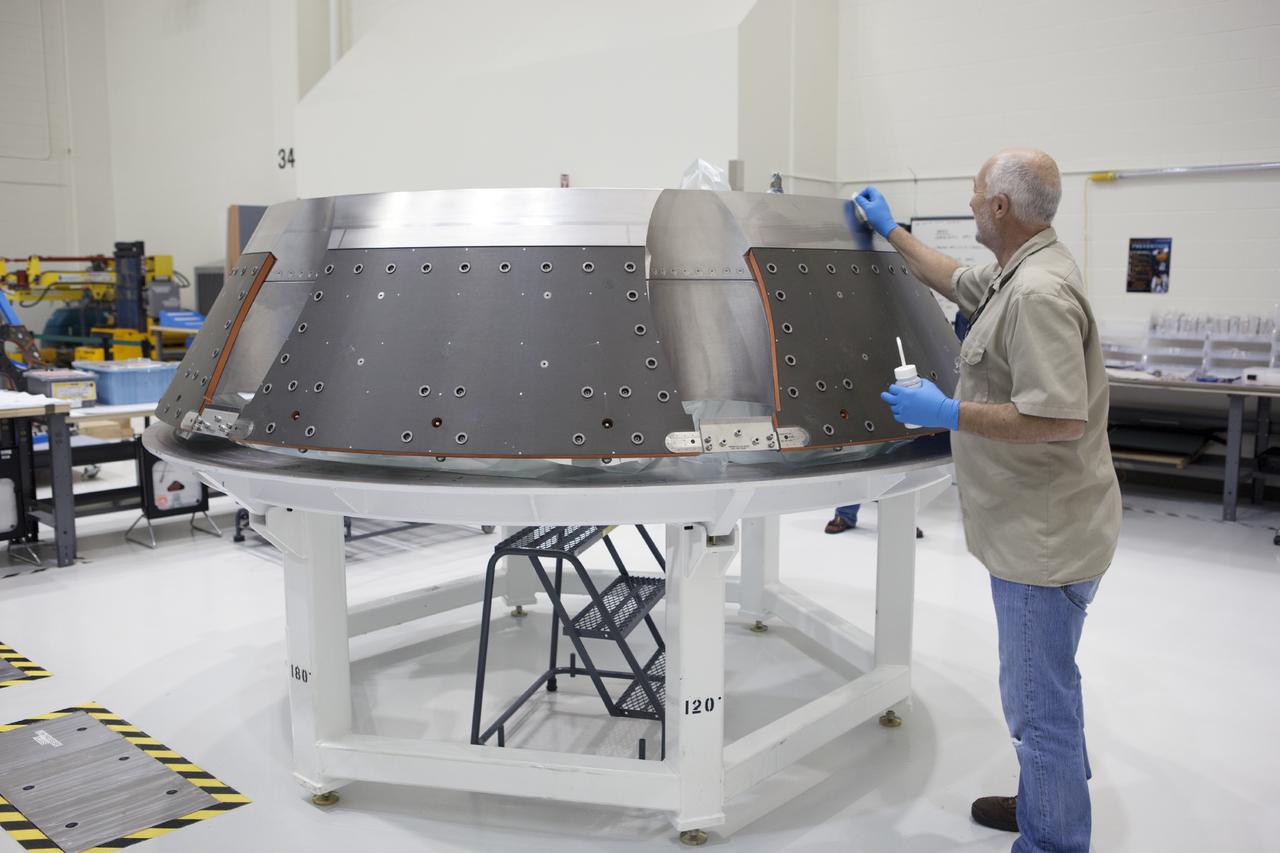

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician prepares the forward bay cover for the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
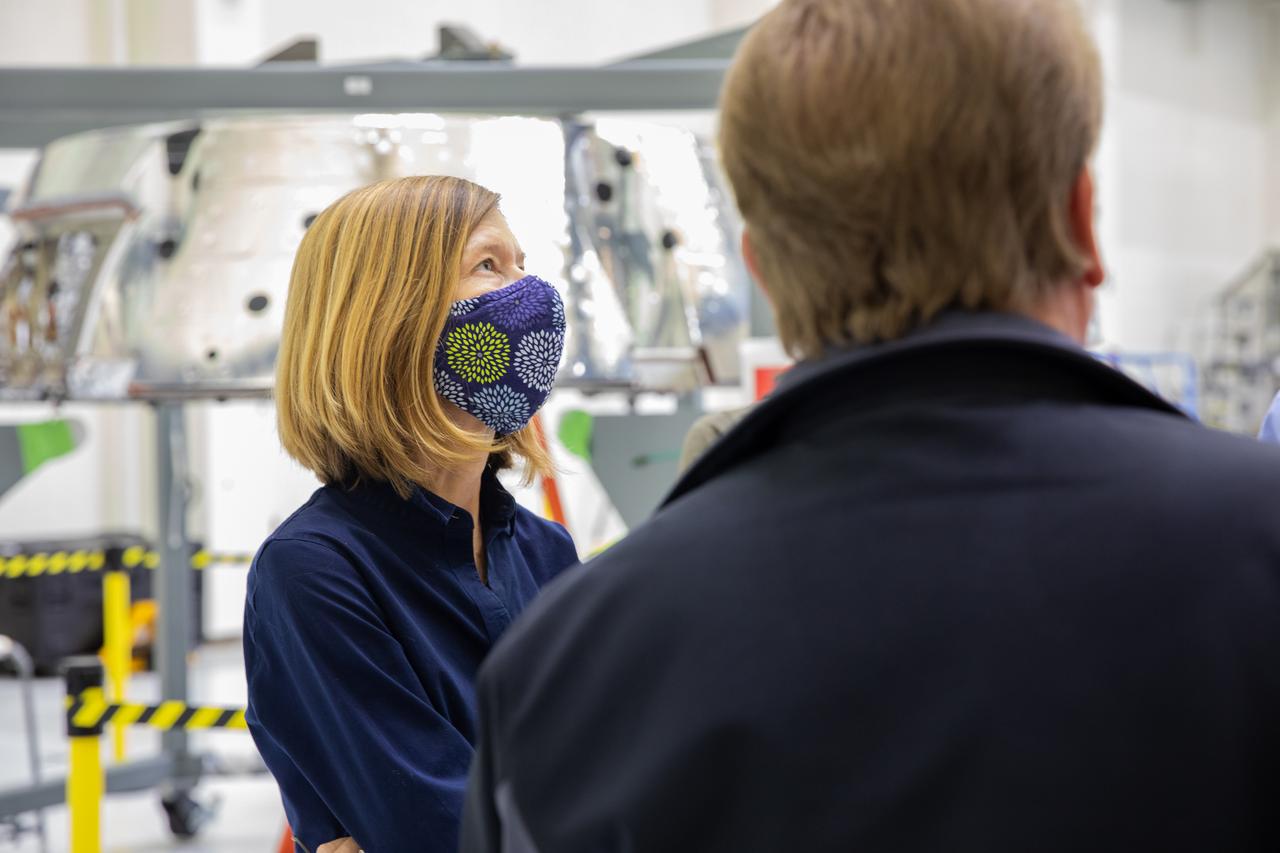

Kathy Lueders, associate administrator of NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate, visits the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 5, 2020. In the background is the Orion spacecraft’s forward bay cover for Artemis I. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA is planning to land the first woman and the next man on the lunar surface by 2024.
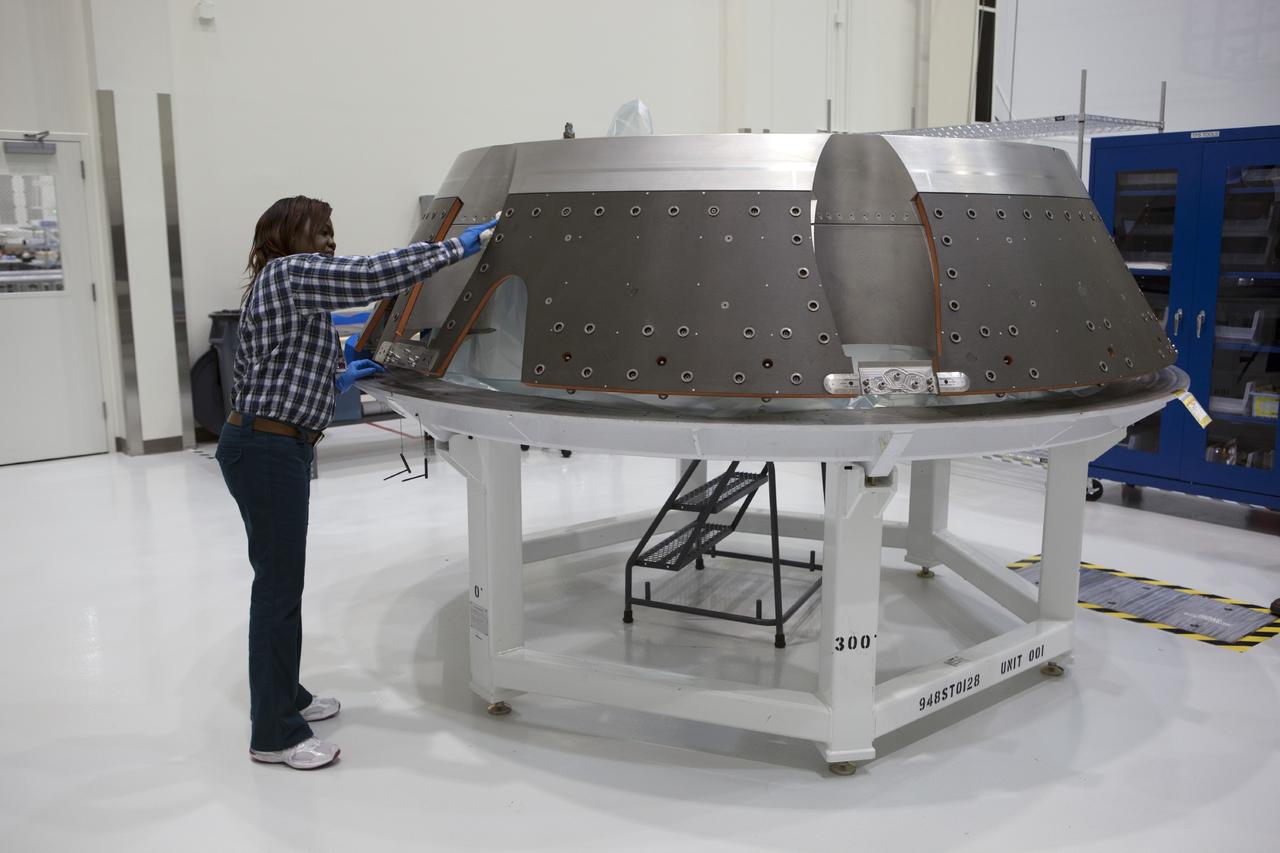

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician prepares the forward bay cover for the Orion crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
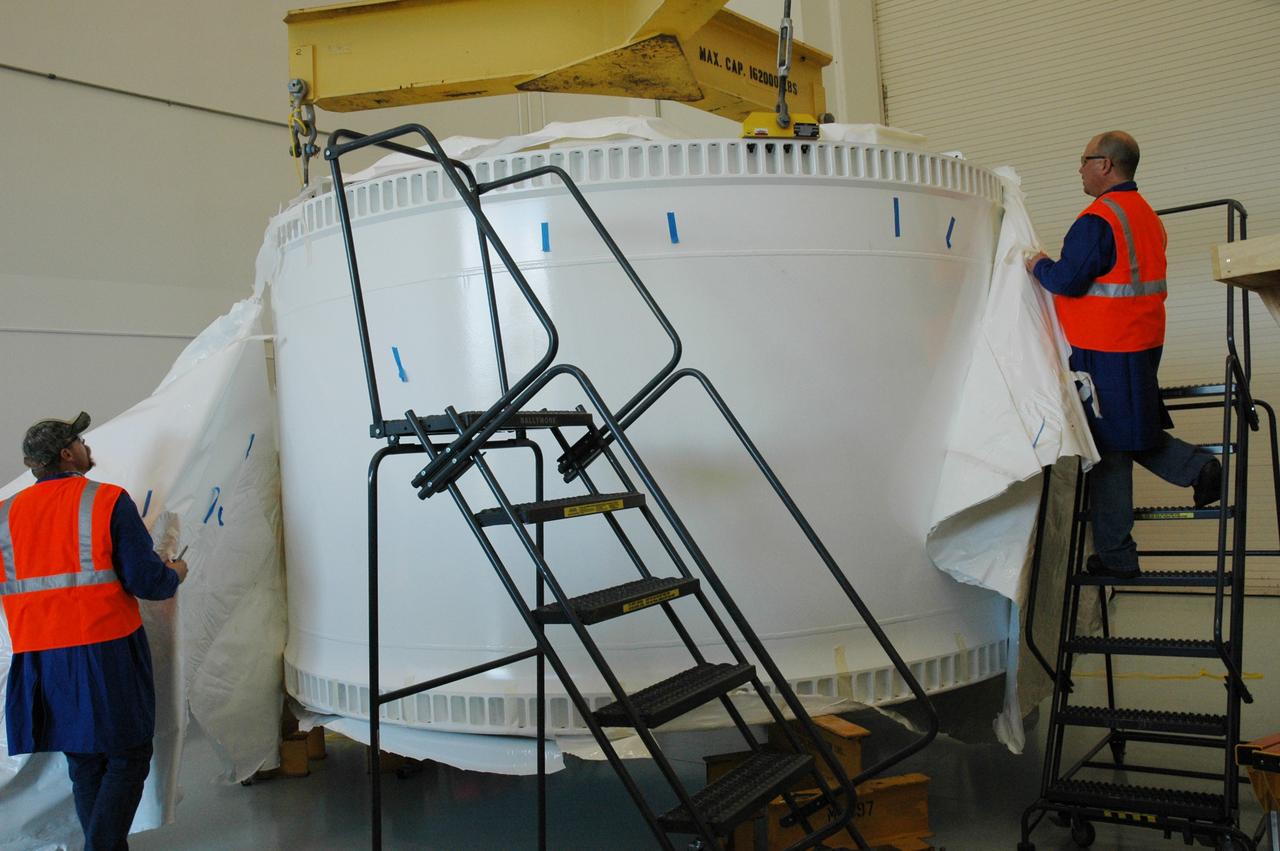

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Alliant Techsystems Inc. workers at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., remove an internal cover from around the Ares I-X forward skirt. The hardware was delivered from Major Tool & Machine Inc. in Indiana. Major Tool is subcontractor to Ares I prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, in Utah. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will integrate and assemble the forward skirt components in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
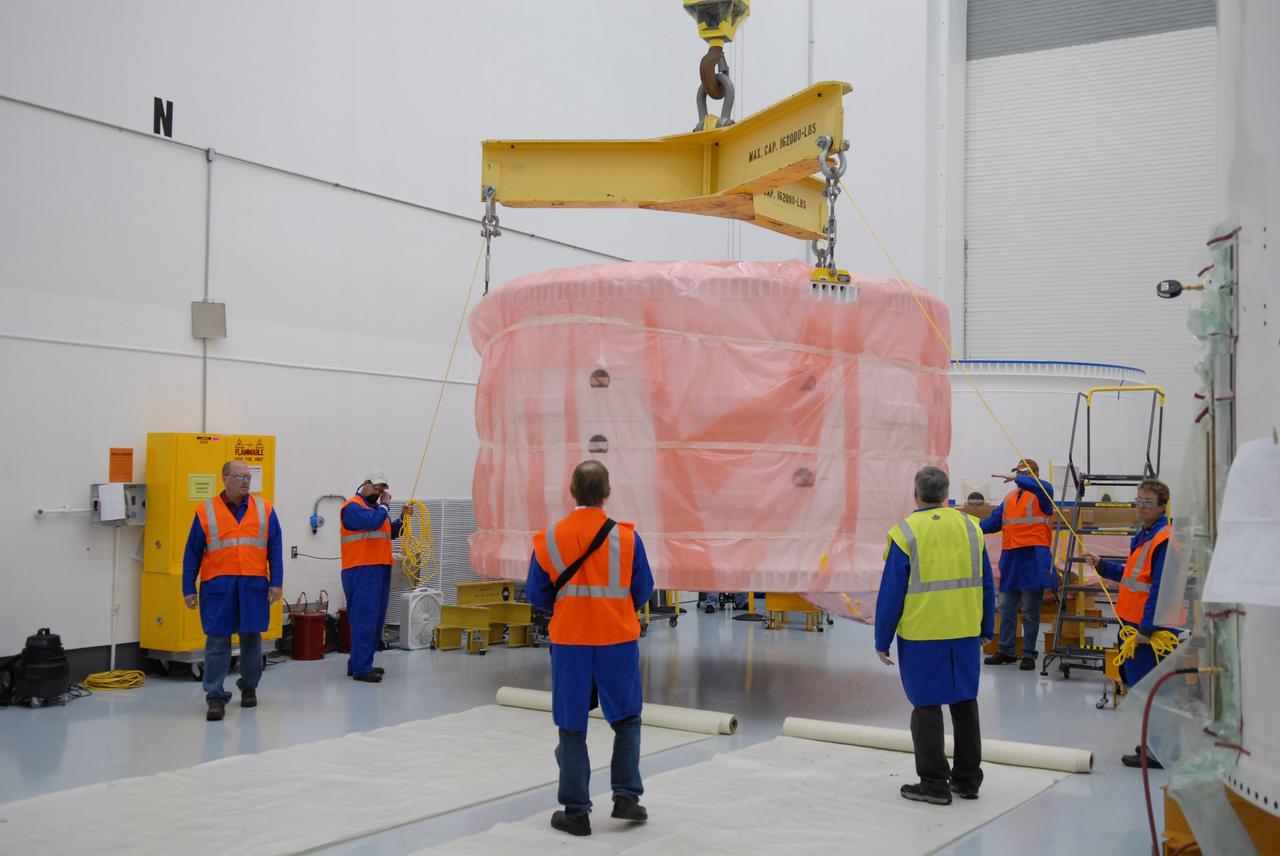

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., the Ares I-X forward skirt, wrapped in a protective cover, is lifted by a crane for a move to a transporter. The segment will be transferred to the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Alliant Techsystems Inc. workers at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., remove the protective outer shipping cover from the Ares I-X forward skirt after its arrival from Major Tool & Machine Inc. in Indiana. Major Tool is subcontractor to Ares I prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, in Utah. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will integrate and assemble the forward skirt components in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., workers place protective covers around the Ares I-X forward skirt. The segment will be transferred to the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Alliant Techsystems Inc. workers at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., begin removing an internal cover from around the Ares I-X forward skirt. The hardware was delivered from Major Tool & Machine Inc. in Indiana. Major Tool is subcontractor to Ares I prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, in Utah. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will integrate and assemble the forward skirt components in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., the Ares I-X forward skirt, wrapped in a protective cover, is lowered by crane onto a transporter. The segment will be transferred to the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers begin removing the protective cover from around the Ares I-X forward skirt. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the pristine Ares I-X forward skirt is examined by workers after the protective cover was removed. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
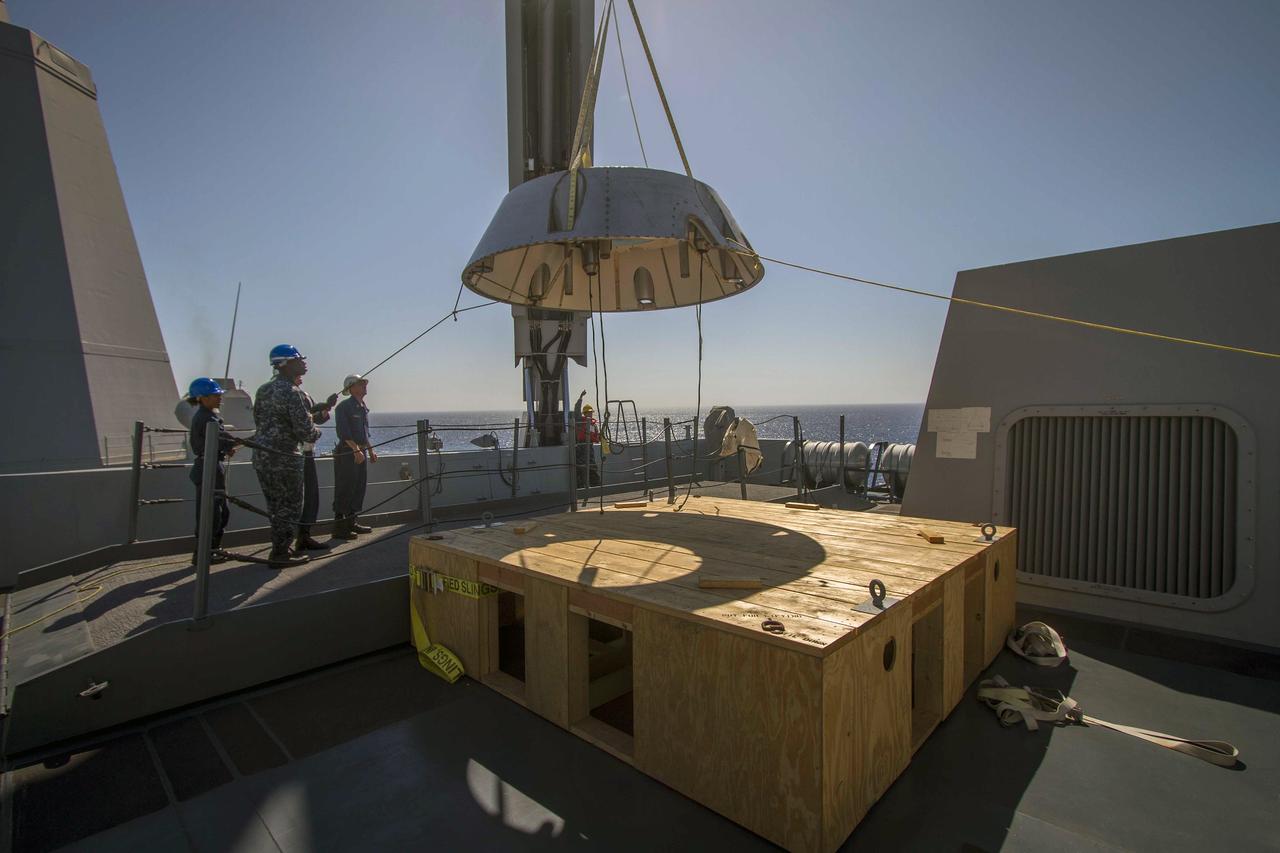

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – A mock-up of the Orion forward bay cover is being lifted by crane on the USS Anchorage during the second day of Orion Underway Recovery Test 3 in the Pacific Ocean. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test using the Orion boilerplate test vehicle and mock-up forward bay cover to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – A mock-up of the Orion forward bay cover is being lifted by crane on the USS Anchorage during the second day of Orion Underway Recovery Test 3 in the Pacific Ocean. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test using the Orion boilerplate test vehicle and mock-up forward bay cover to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
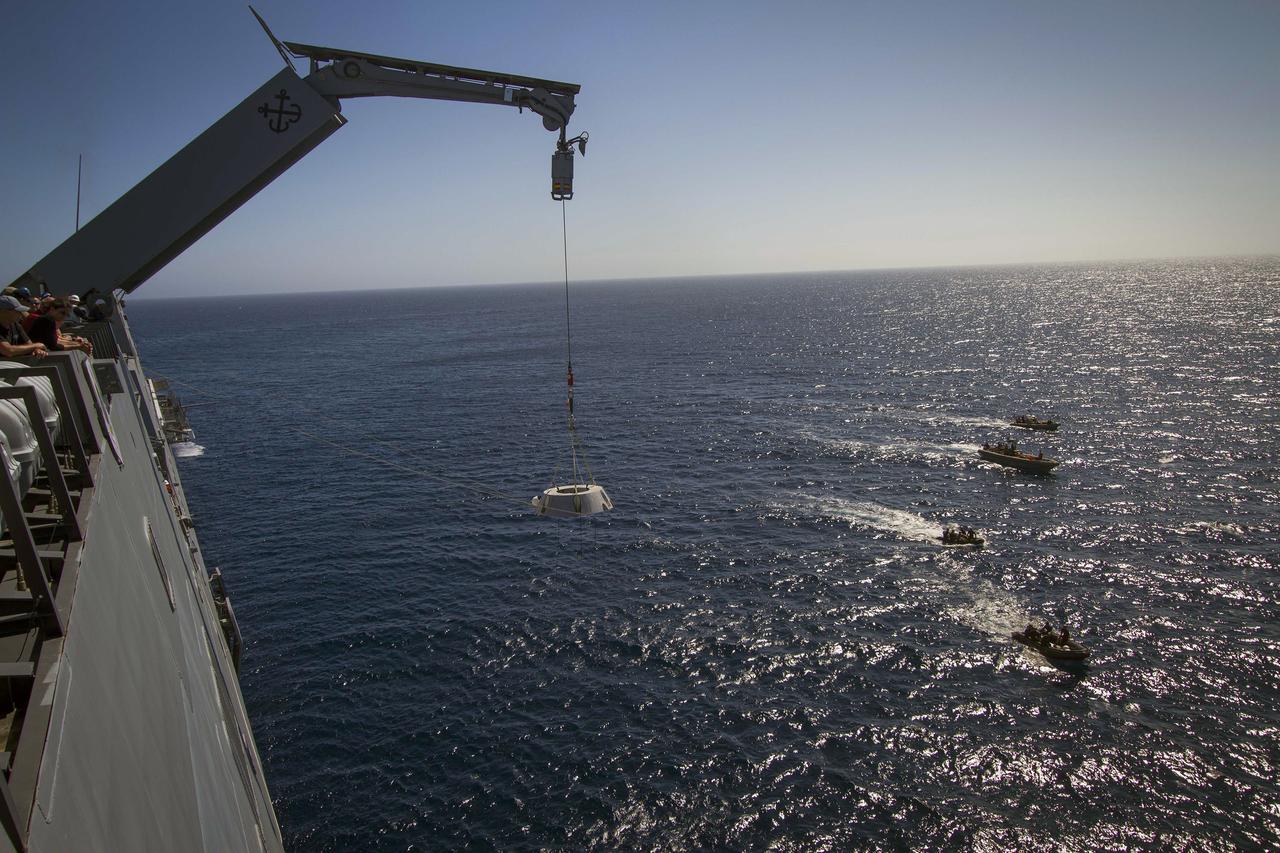

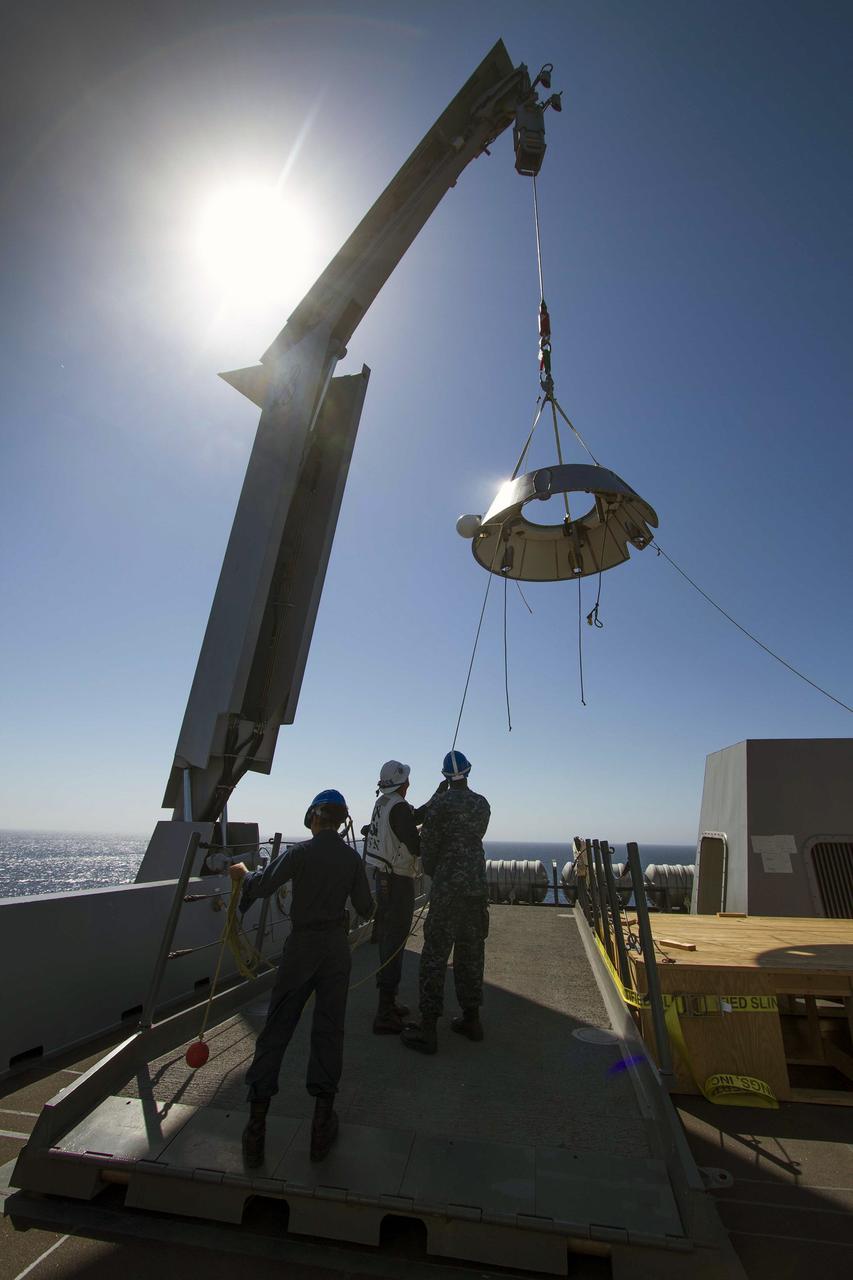
SAN DIEGO, Calif. – A mock-up of the Orion forward bay cover is being lowered by crane from the USS Anchorage into the water during the second day of Orion Underway Recovery Test 3 in the Pacific Ocean. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test using the Orion boilerplate test vehicle and mock-up forward bay cover to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
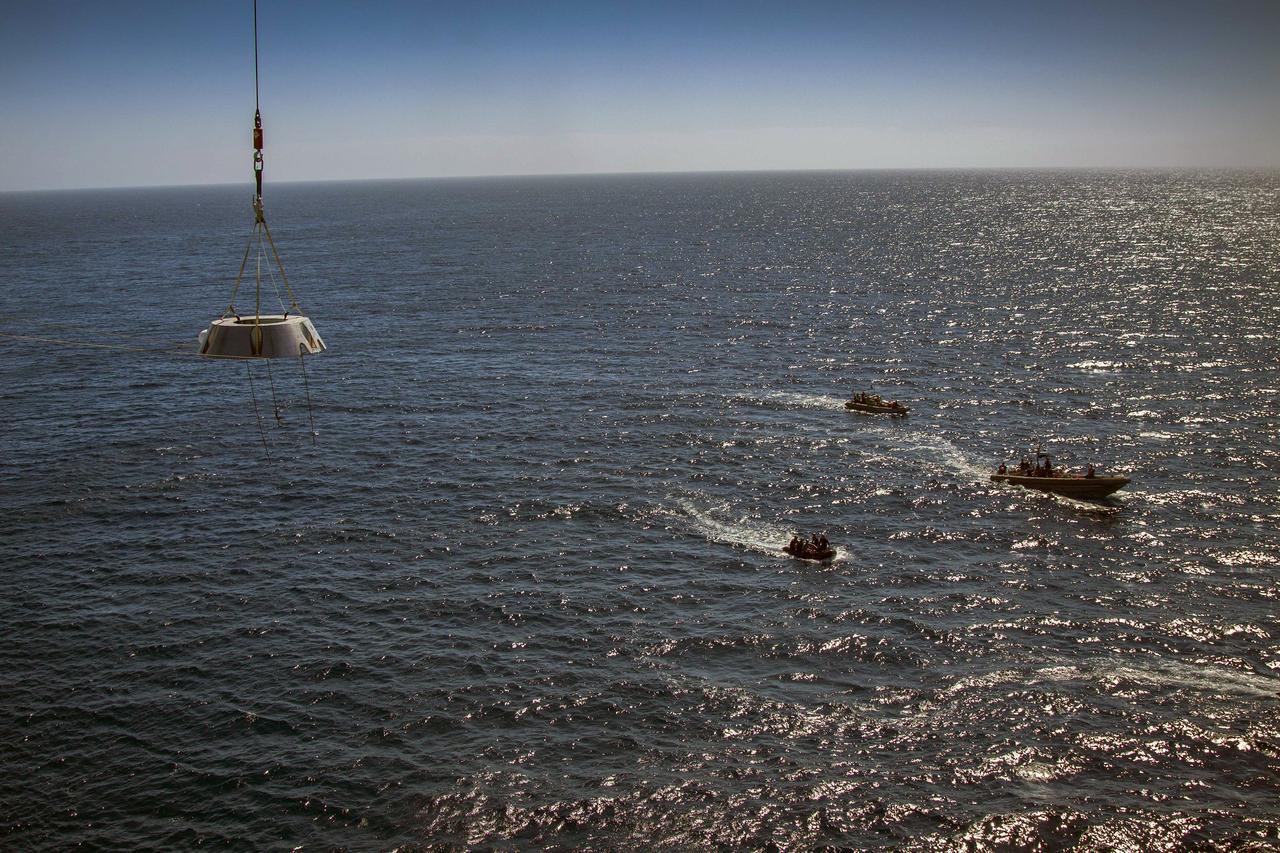

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – A mock-up of the Orion forward bay cover is lowered by crane from the USS Anchorage into the water during the second day of Orion Underway Recovery Test 3 in the Pacific Ocean. Nearby, U.S. navy divers in two Zodiac boats and other team members in a rigid hull inflatable boat, wait to practice recovery procedures. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test using the Orion boilerplate test vehicle and mock-up forward bay cover to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
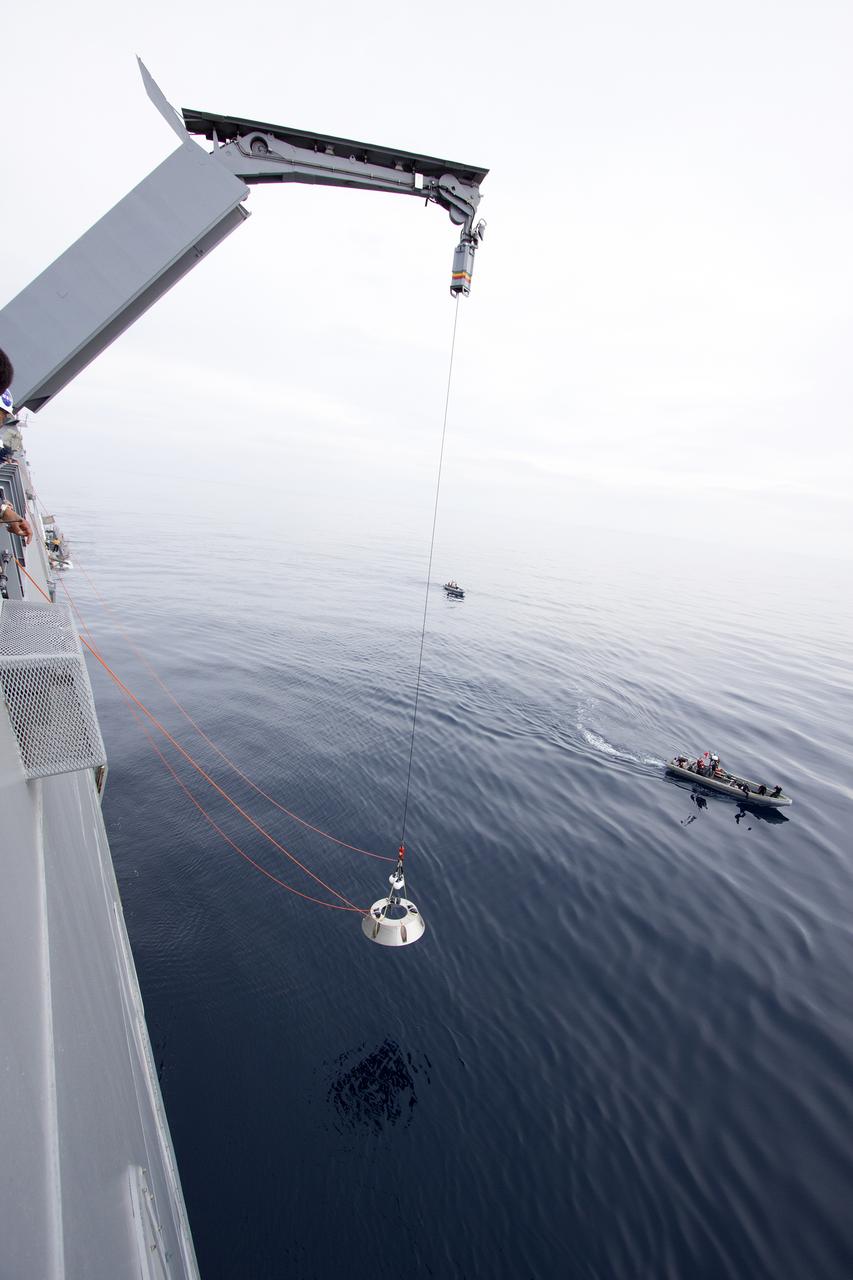

On the deck of the USS San Diego, NASA and U.S. Navy personnel monitor the process as a crane is used to lower the forward bay cover into the Pacific Ocean as part of the Orion underway recovery test on March 6, 2014. The Orion boilerplate test vehicle and other hardware are secured in the well deck of the ship in preparation for the test about 100 miles off the coast of San Diego, California. NASA and the U.S. Navy conducted tests to prepare for the recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. During the testing, the tether lines were unable to support the tension caused by crew module motion that was driven by wave turbulence in the well deck of the ship. NASA and the U.S. Navy are reviewing the testing data collected to evaluate the next steps. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program conducted the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.
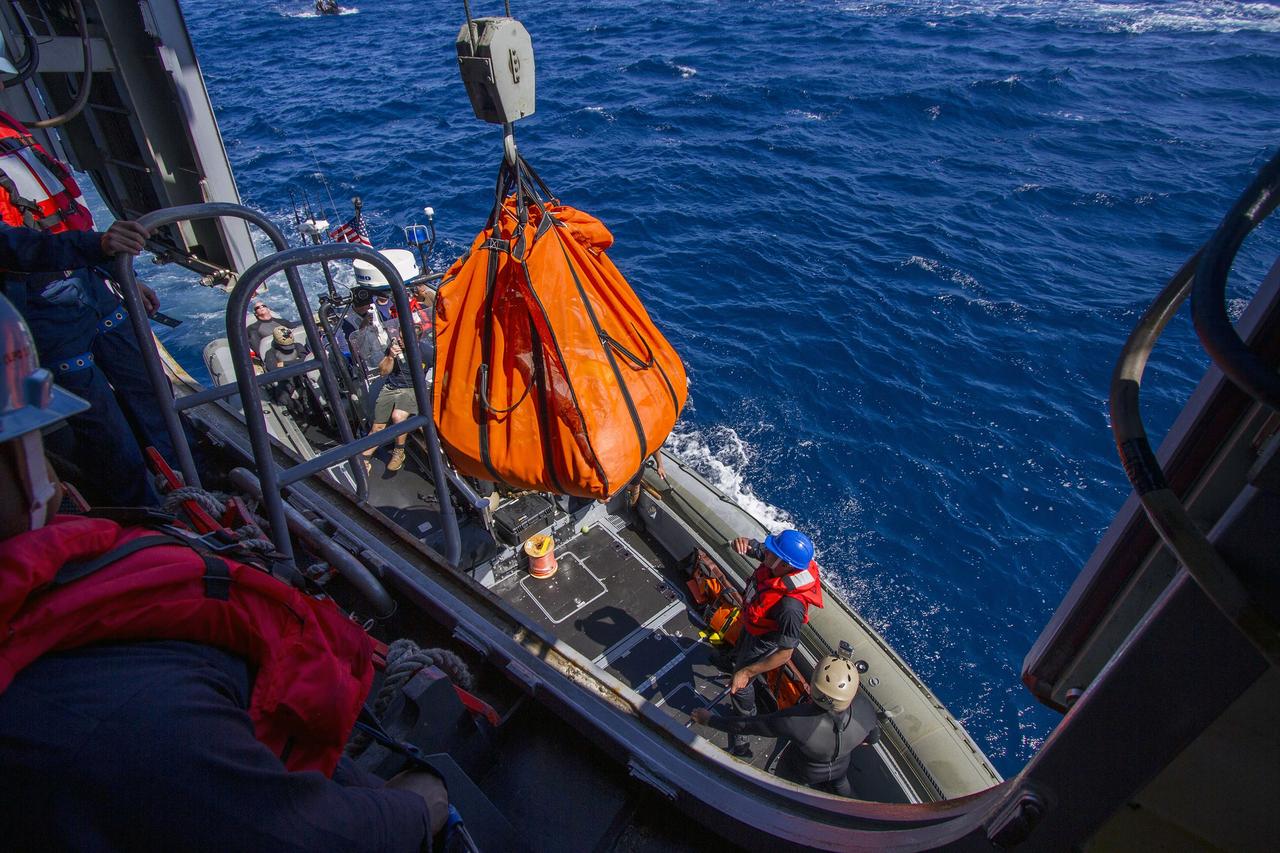

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – A crane lifts a mock-up of the Orion forward bay cover in its net from a boat docked near the well deck of the USS Anchorage during the second day of Orion Underway Recovery Test 3 in the Pacific Ocean. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are conducting the recovery test using the Orion boilerplate test vehicle and mock-up forward bay cover to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module on its return from a deep space mission. The test allows the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is conducting the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
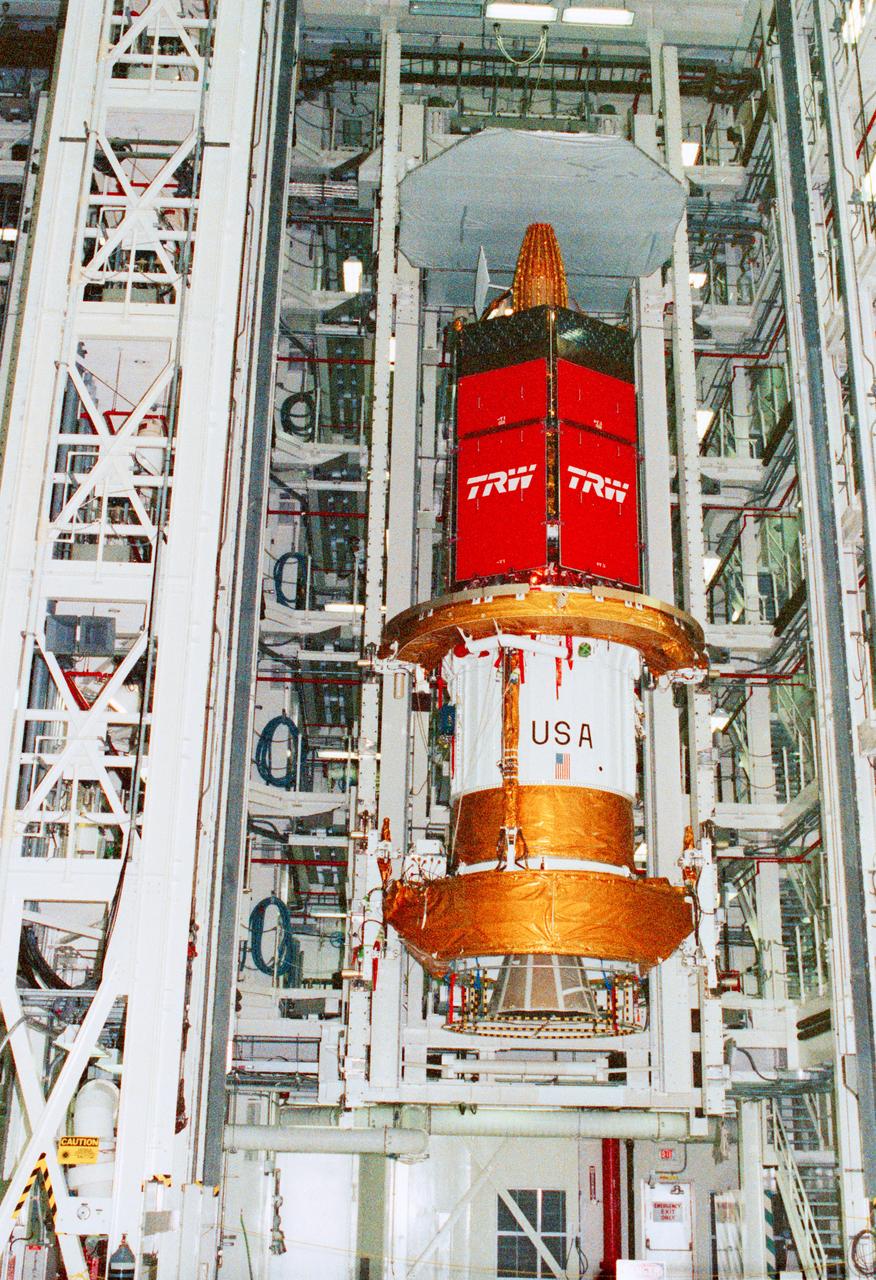
STS-43 Tracking and Data Relay Satellite E (TDRS-E) undergoes preflight processing in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC's) Vertical Processing Facility (VPF) before being loaded into a payload canister for transfer to the launch pad and eventually into Atlantis', Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104's, payload bay (PLB). This side of the TDRS-E will rest at the bottom of the PLB therefore the airborne support equipment (ASE) forward frame keel pin (at center of spacecraft) and the umbilical boom running between the two ASE frames are visible. The solar array panels are covered with protective TRW shields. Above the shields the stowed antenna and solar sail are visible. The inertial upper stage (IUS) booster is the white portion of the spacecraft and rests in the ASE forward frame and ASE aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) frame (at the bottom of the IUS). The IUS booster nozzle extends beyond the AFTA frame. View provided by KSC with alternate number KSC-91PC-1079.
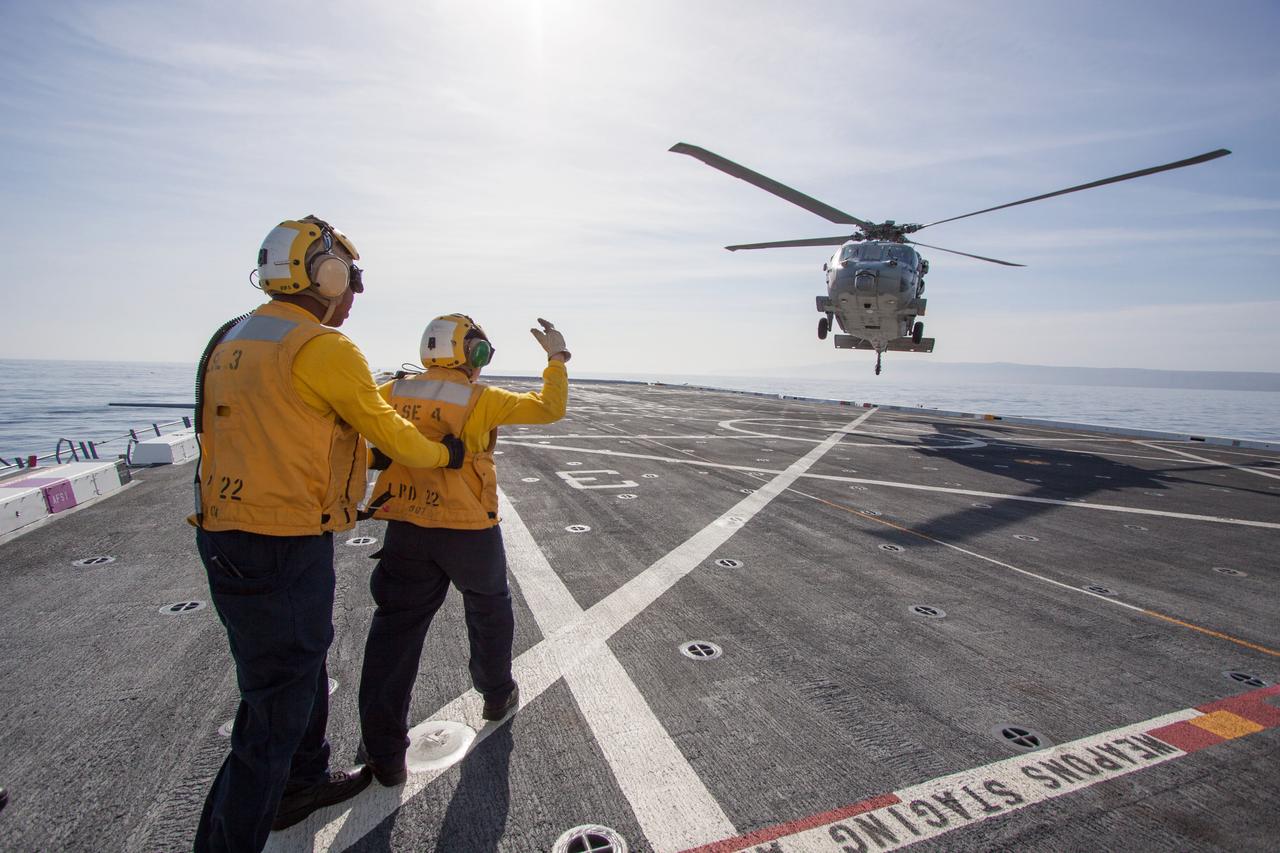

On the top deck of the USS San Diego, a helicopter flies overhead to monitor conditions as the Orion underway recovery test begins in the Pacific Ocean, about 100 miles off the coast of San Diego, California on Feb. 20, 2014. The Orion boilerplate test vehicle and other hardware are secured in the well deck of the ship in preparation for the test. NASA and the U.S. Navy conducted tests to prepare for the recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Orion boilerplate test vehicle is secured in the well deck of the USS San Diego at the U.S. Naval Base San Diego in California on Feb. 20, 2014. Orion was transported about 100 miles offshore for an underway recovery test. NASA and the U.S. Navy conducted tests to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
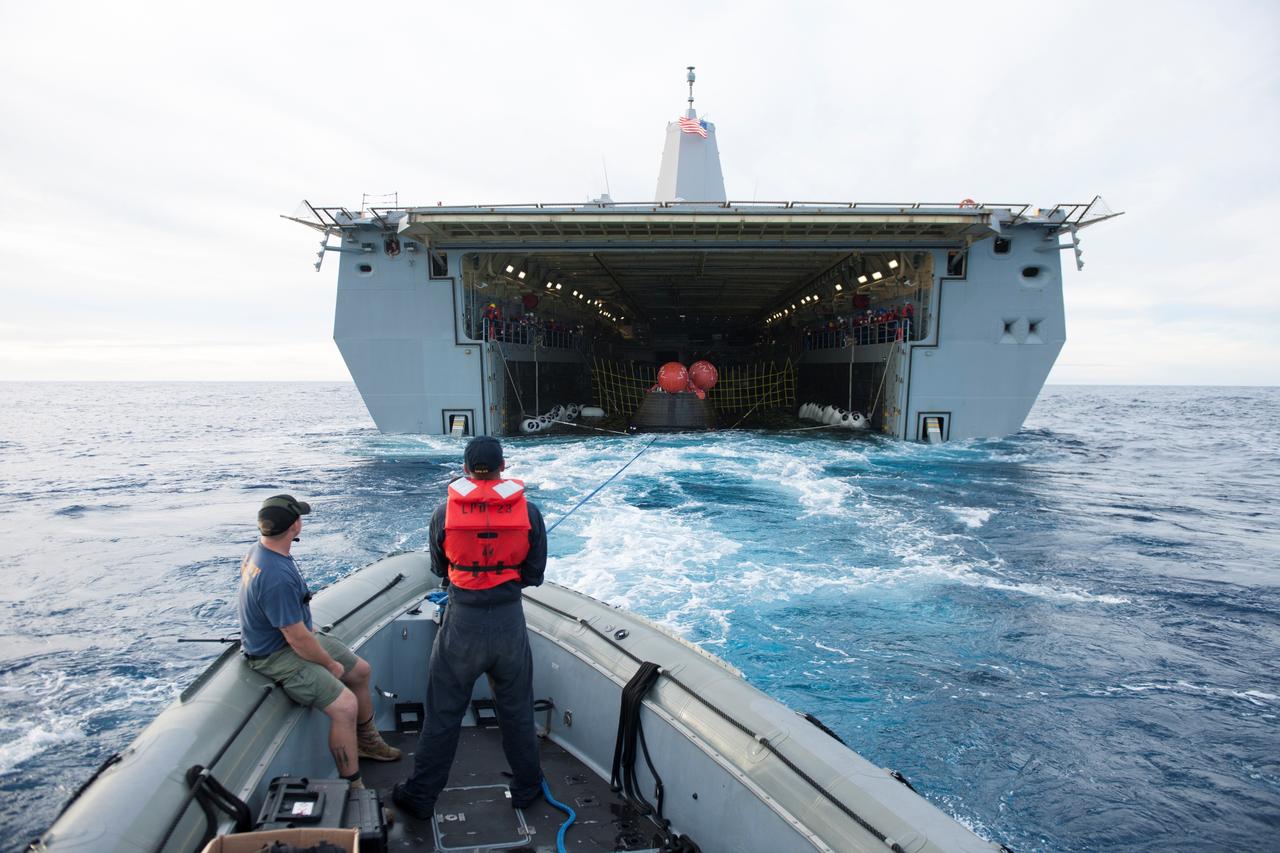

U.S. Navy personnel aboard a rigid hull inflatable boat help recover NASA's Orion spacecraft following its splashdown in the Pacific Ocean after its first flight test in Earth orbit. Orion is towed into the flooded well deck of the USS Anchorage. NASA, the U.S. Navy and Lockheed Martin coordinated efforts to recover Orion, the forward bay cover and main parachutes. Orion completed a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission, to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.
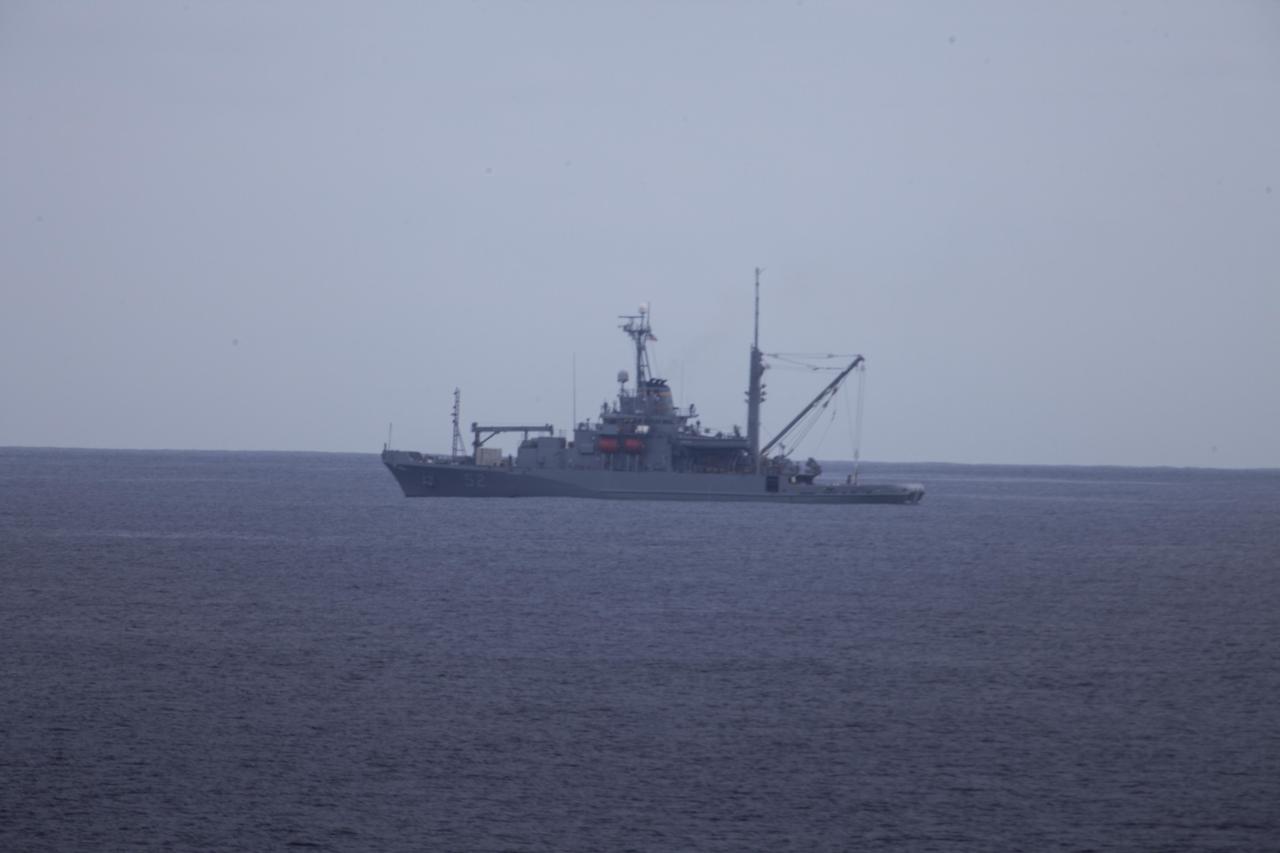

On the third day of preparations for recovery of Orion after its splashdown in the Pacific Ocean, the USNS Salvor is in the Pacific Ocean, nearby the USS Anchorage, about 600 miles off the coast of Baja, California. The Salvor will be used to recover Orion in the event that the spacecraft cannot be recovered using the well deck of the USS Anchorage. NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel are preparing for recovery of the crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes after the spacecraft's return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts.