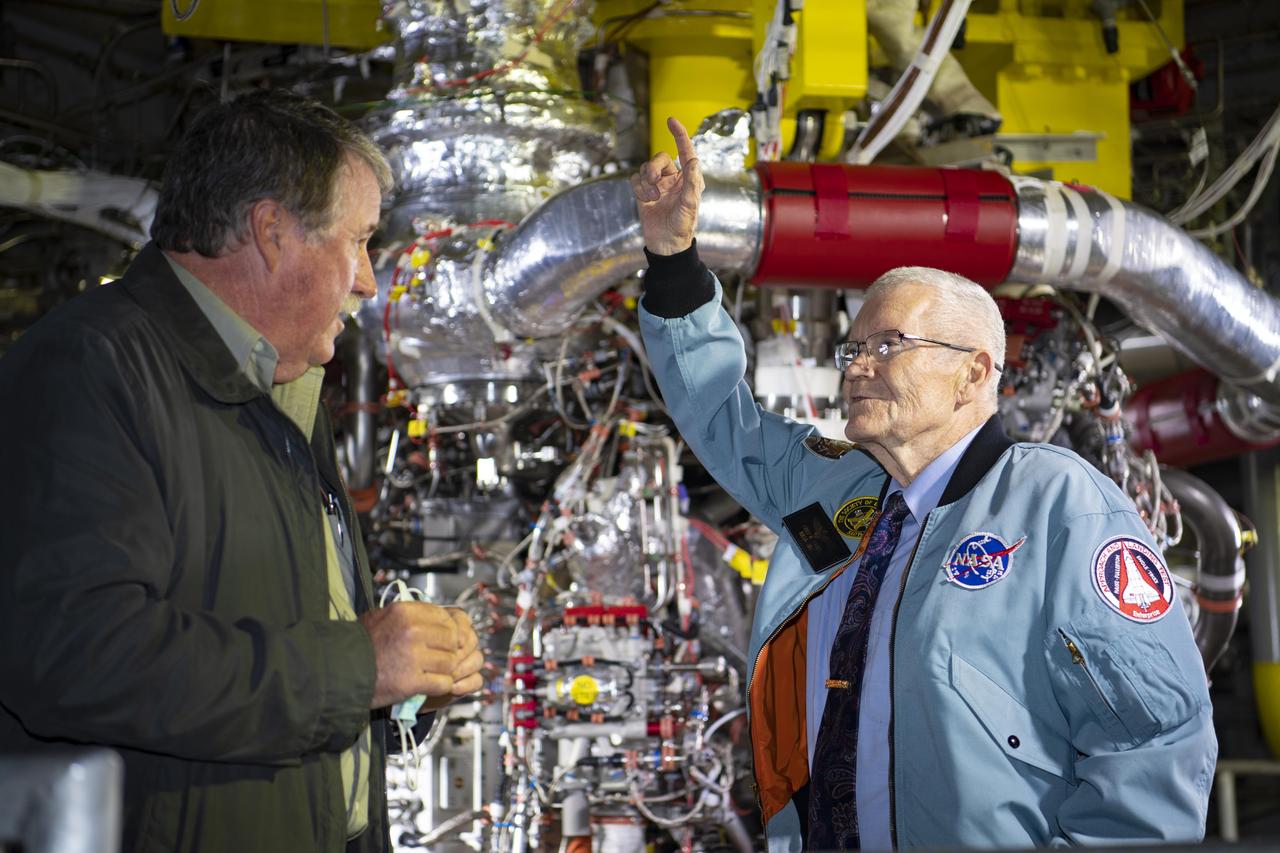

Apollo 13 Astronaut Fred Haise, right, stands in front of an RS-25 rocket engine installed on the A-1 Test Stand along with Jeff Henderson, test director at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The A-1 stand was dedicated to the former astronaut on Dec. 7, 2021 and is now officially known as the Fred Haise Test Stand.
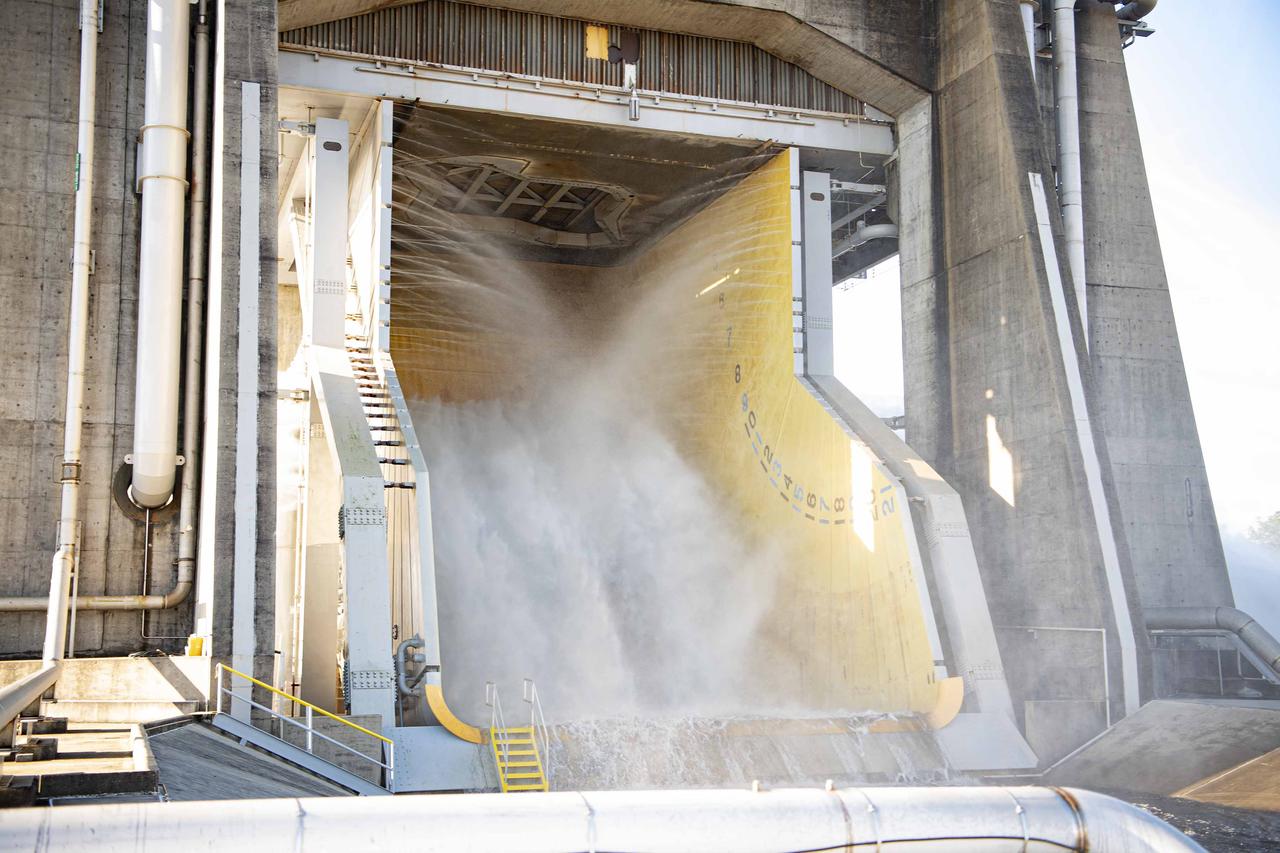

Crews conduct a planned flame deflector water flow system flush on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center on Oct. 22, following the recent completion of upgrades to the High Pressure Industrial Water Facility’s underground piping network. The flush, a periodic procedure to ensure system functionality and performance, involves flowing 150,000 gallons or more per minute from the High Pressure Industrial Water Facility to the stand. It also continues stand preparations for testing RS-25 flight engines for use on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.

Crews conduct a planned flame deflector water flow system flush on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center on Oct. 22, following the recent completion of upgrades to the High Pressure Industrial Water Facility’s underground piping network. The flush, a periodic procedure to ensure system functionality and performance, involves flowing 150,000 gallons or more per minute from the High Pressure Industrial Water Facility to the stand. It also continues stand preparations for testing RS-25 flight engines for use on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
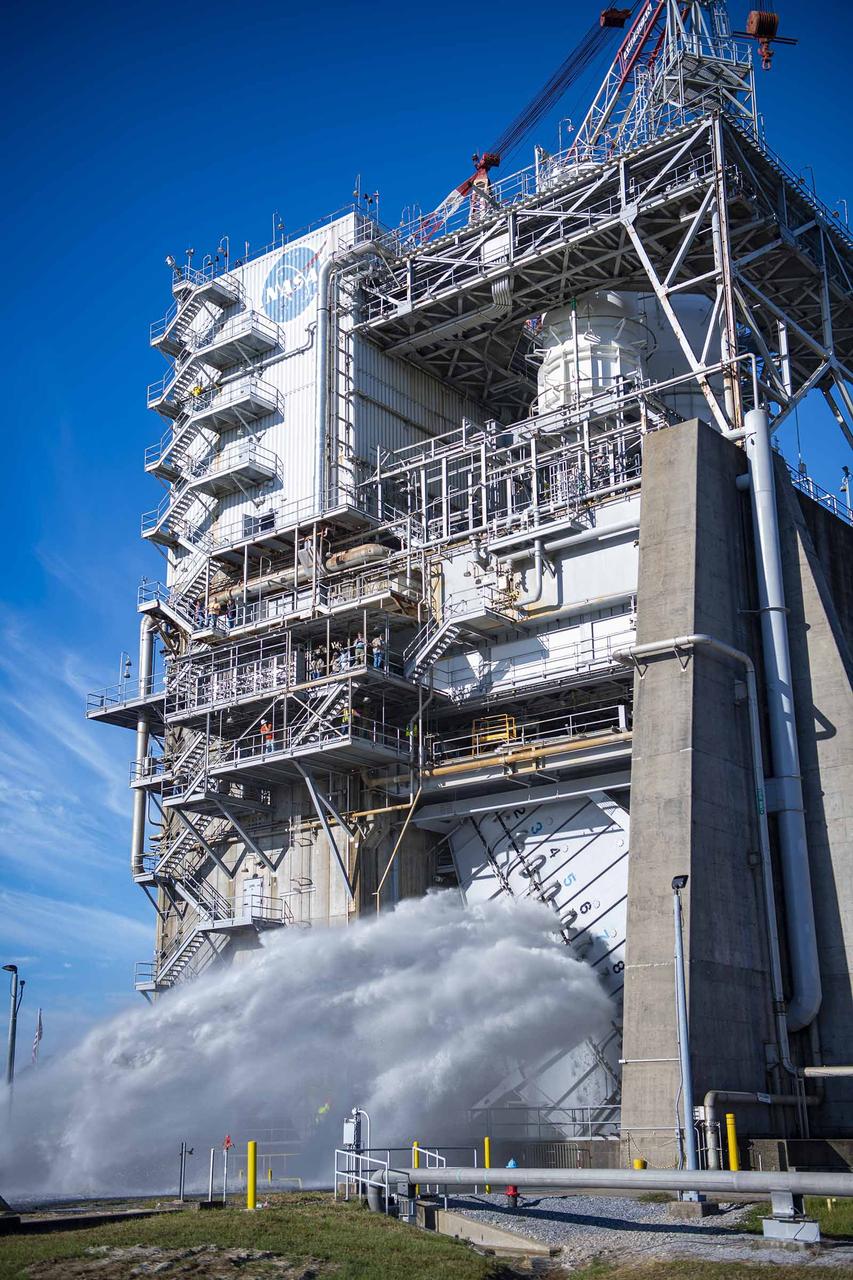

Crews conduct a planned flame deflector water flow system flush on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center on Oct. 22, following the recent completion of upgrades to the High Pressure Industrial Water Facility’s underground piping network. The flush, a periodic procedure to ensure system functionality and performance, involves flowing 150,000 gallons or more per minute from the High Pressure Industrial Water Facility to the stand. It also continues stand preparations for testing RS-25 flight engines for use on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
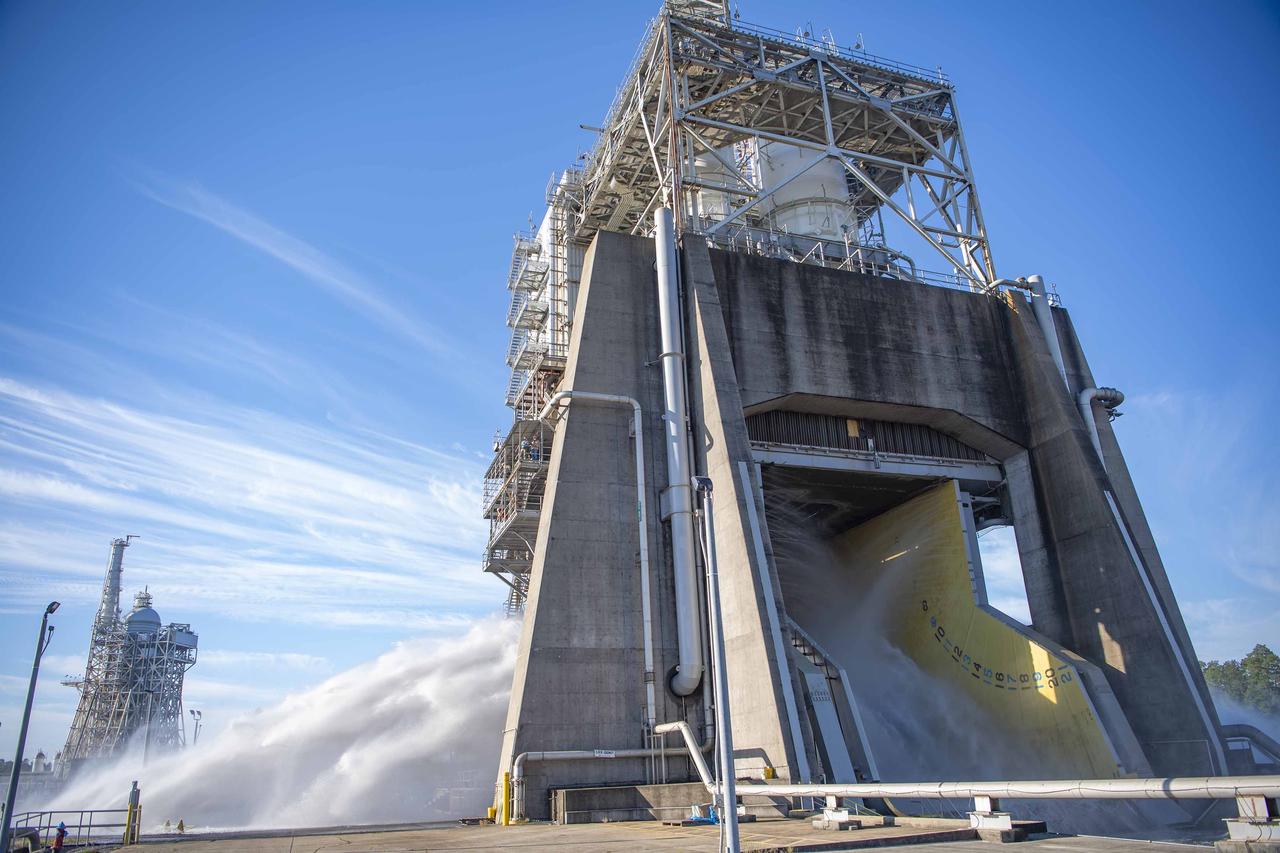

Crews conduct a planned flame deflector water flow system flush on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center on Oct. 22, following the recent completion of upgrades to the High Pressure Industrial Water Facility’s underground piping network. The flush, a periodic procedure to ensure system functionality and performance, involves flowing 150,000 gallons or more per minute from the High Pressure Industrial Water Facility to the stand. It also continues stand preparations for testing RS-25 flight engines for use on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
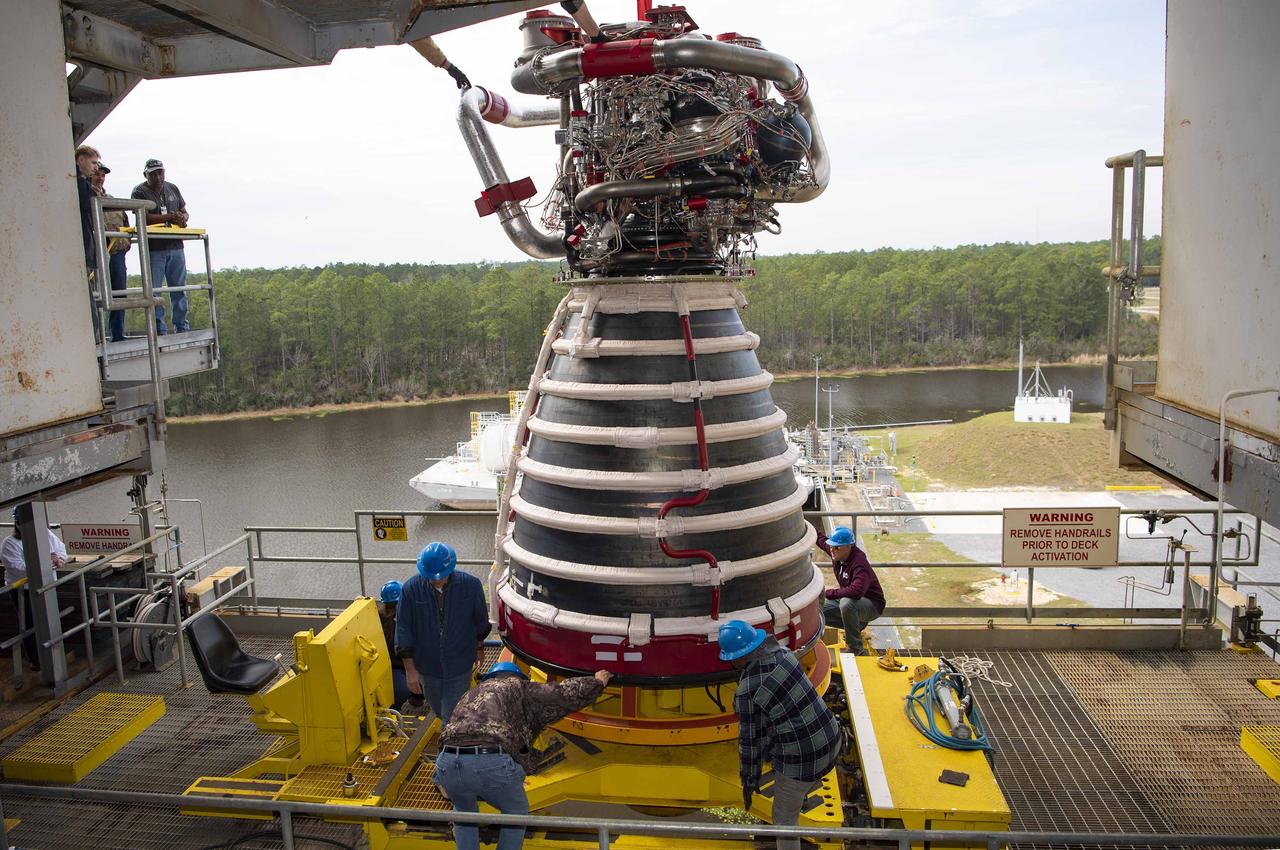

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.
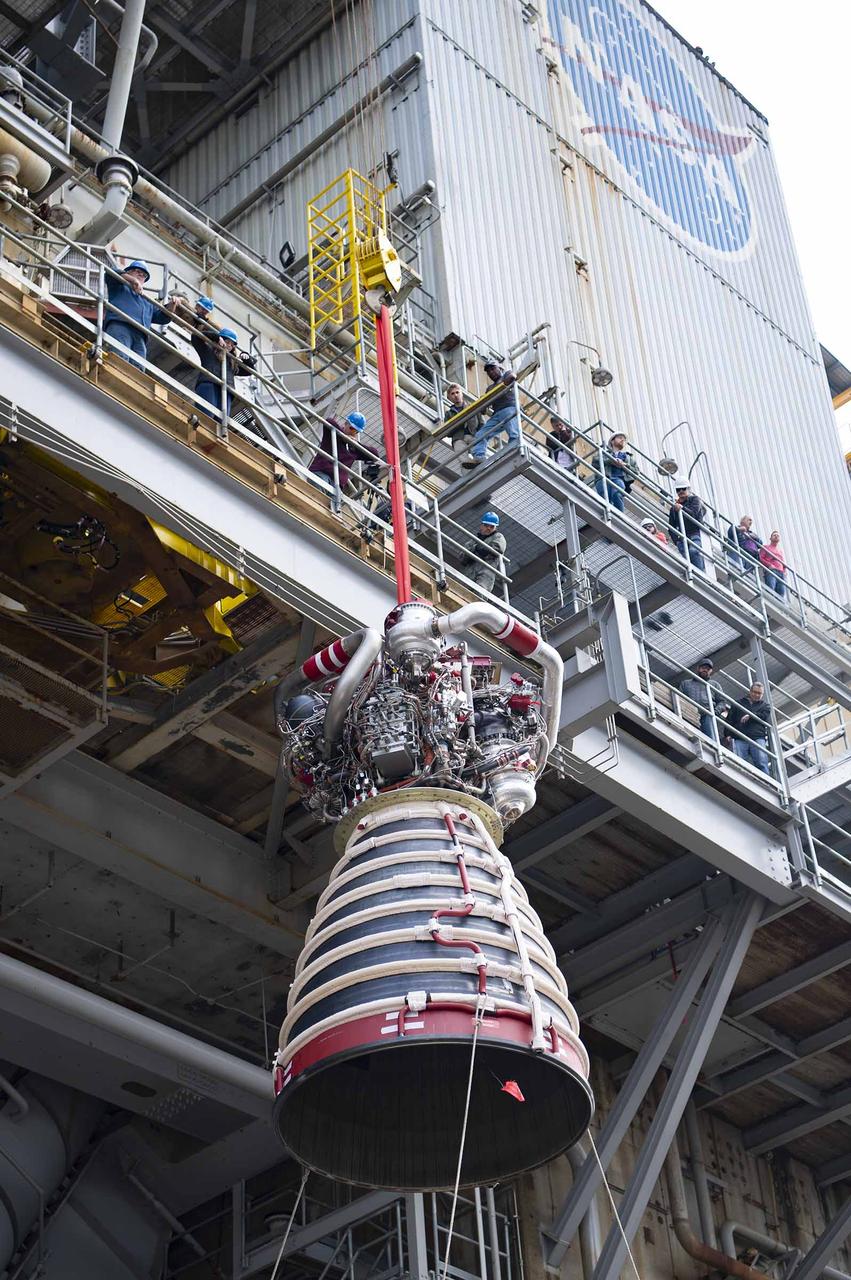

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.
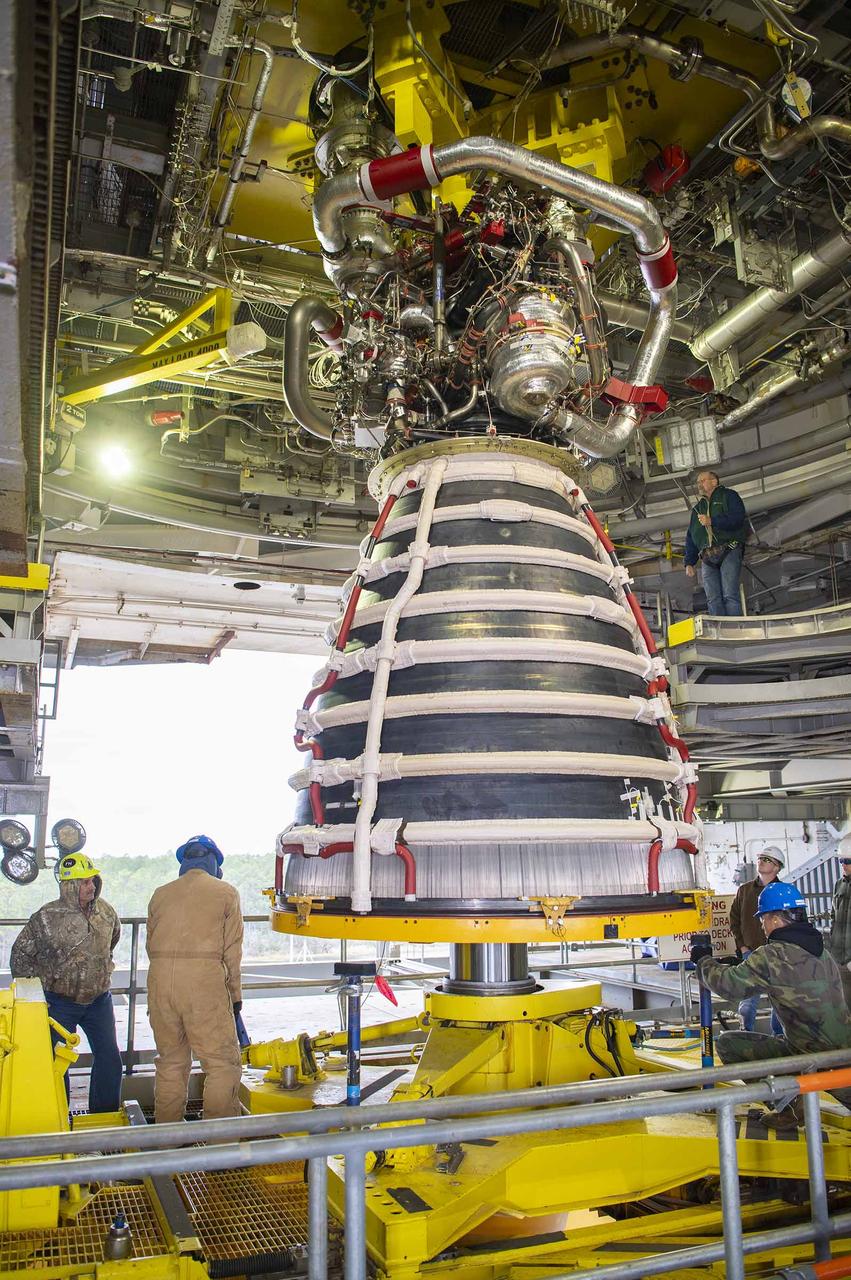

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.
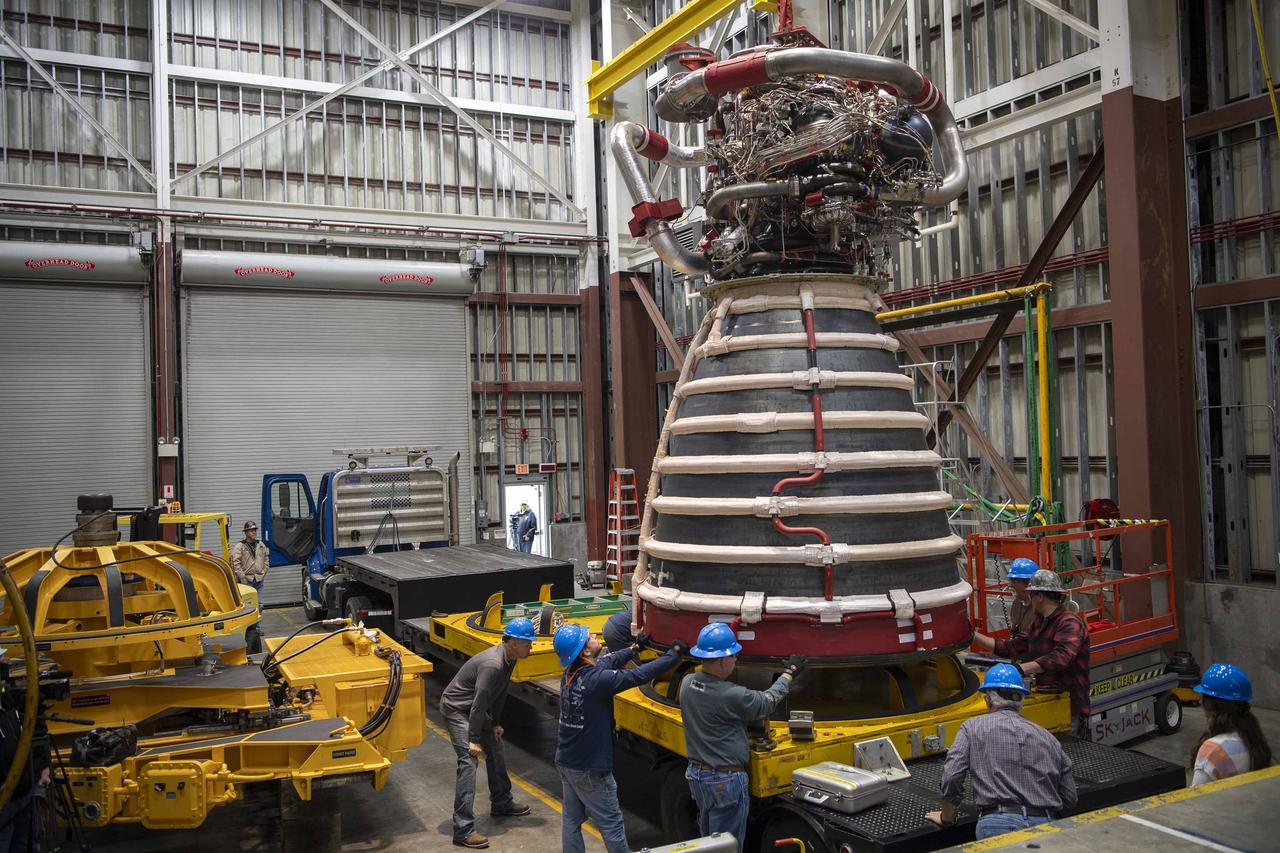

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.
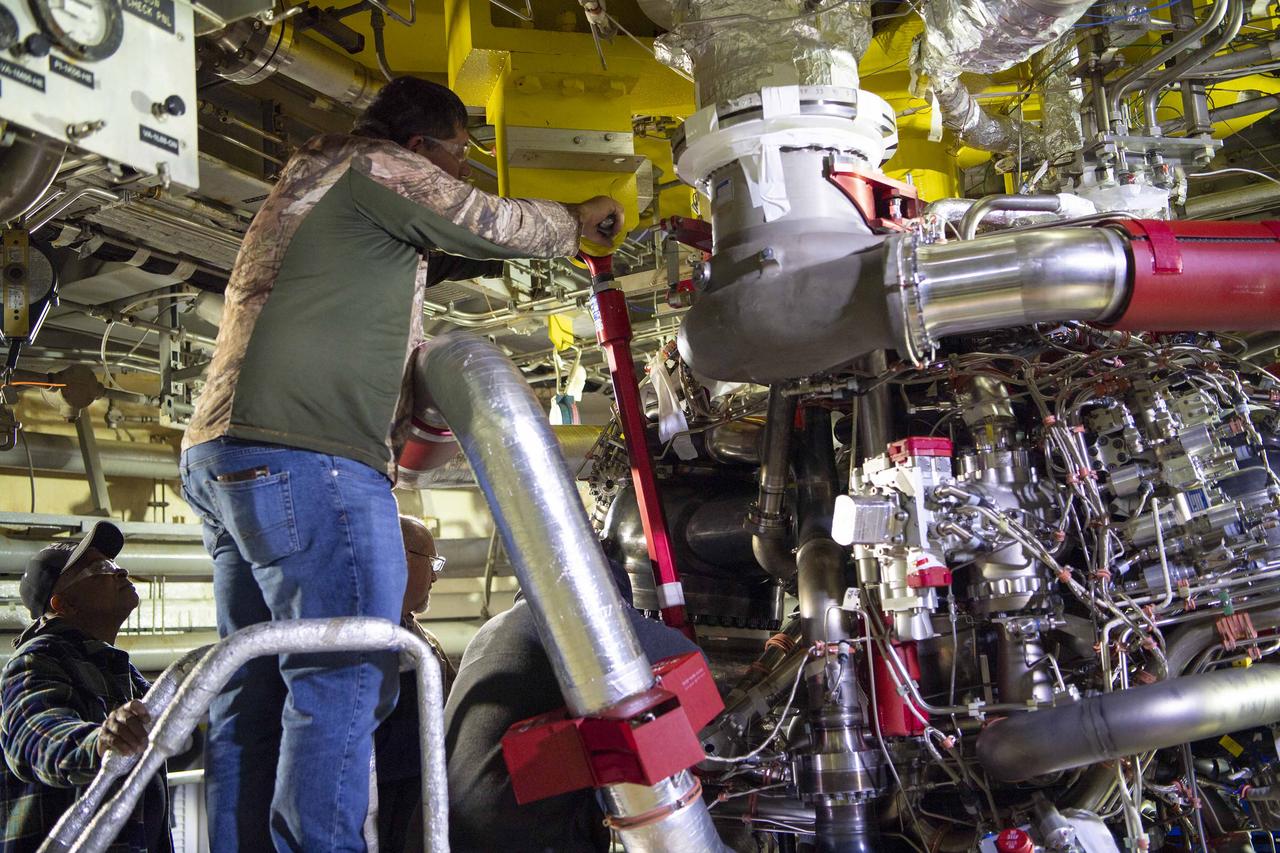

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.
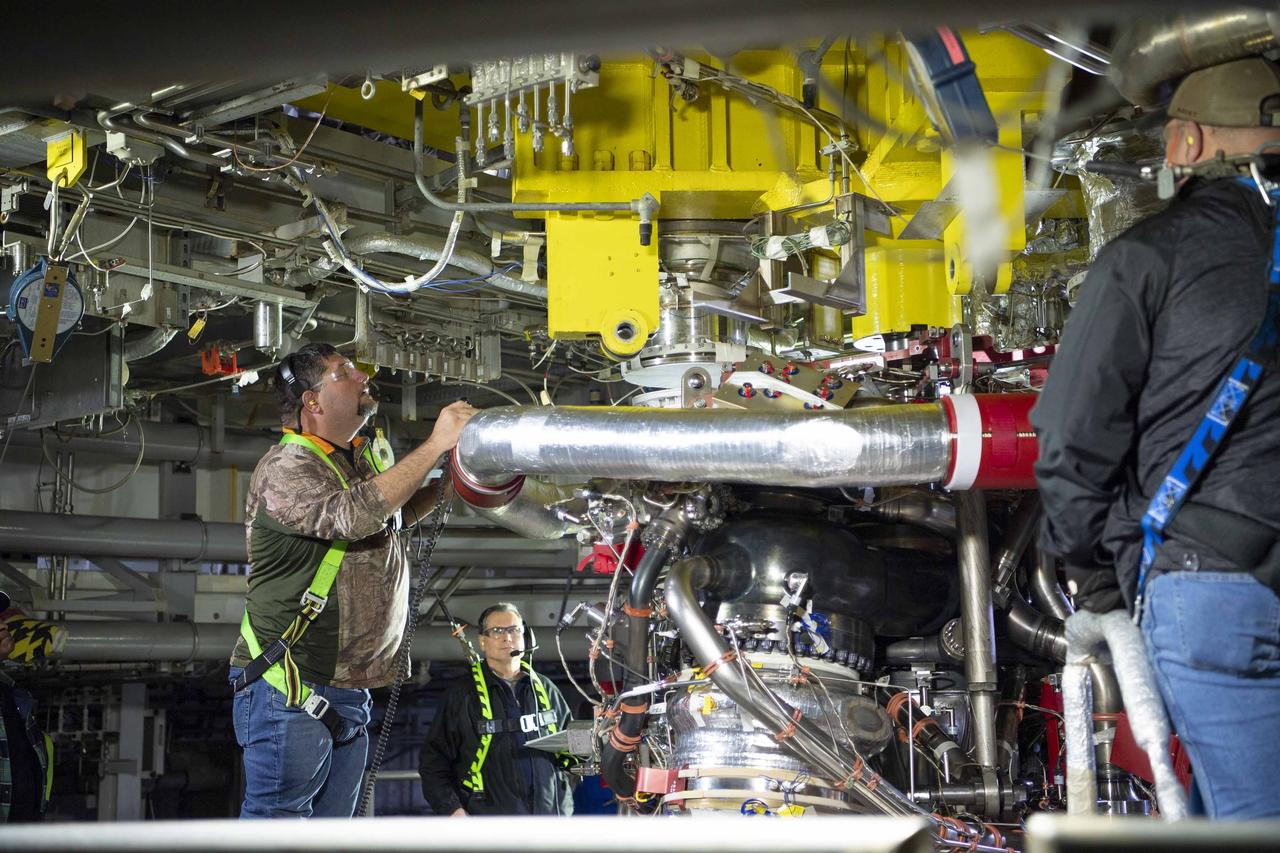

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.
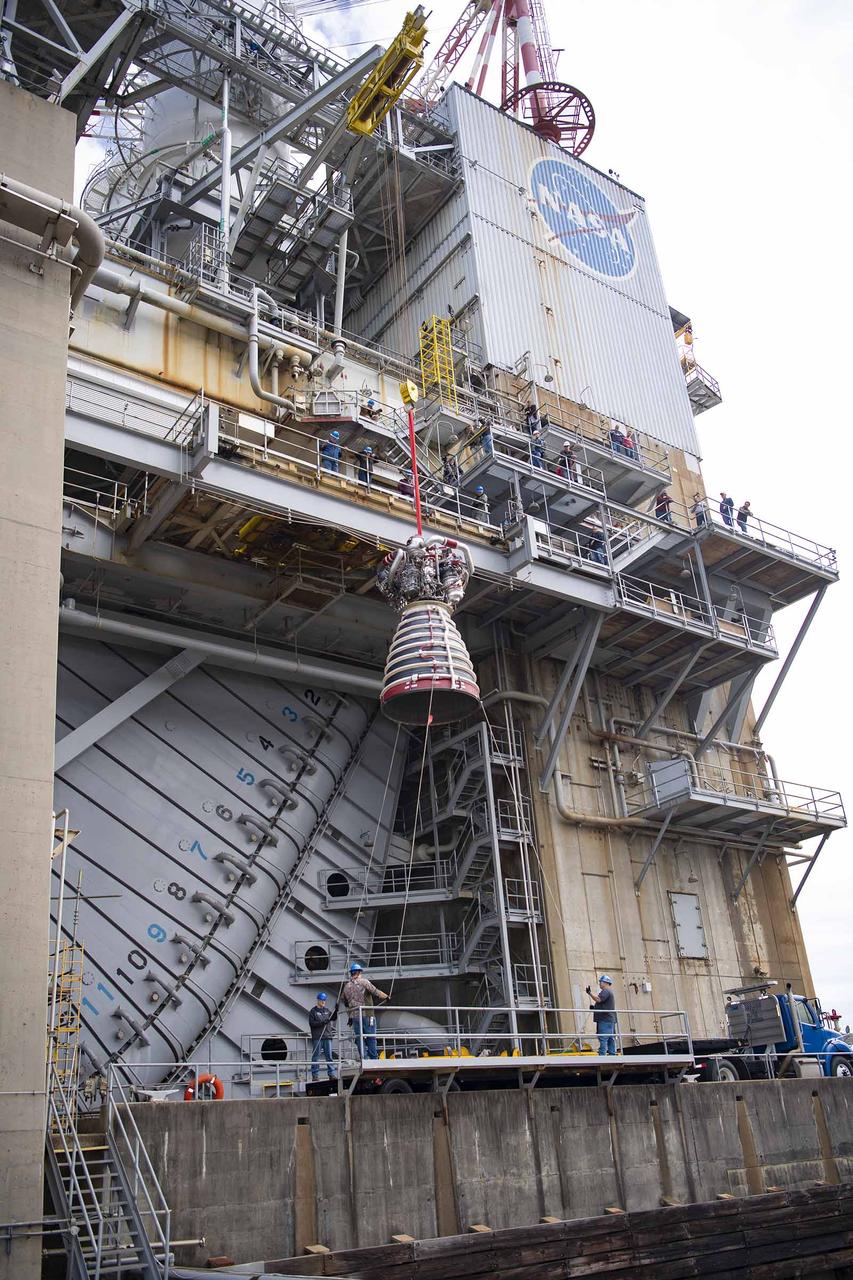

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.
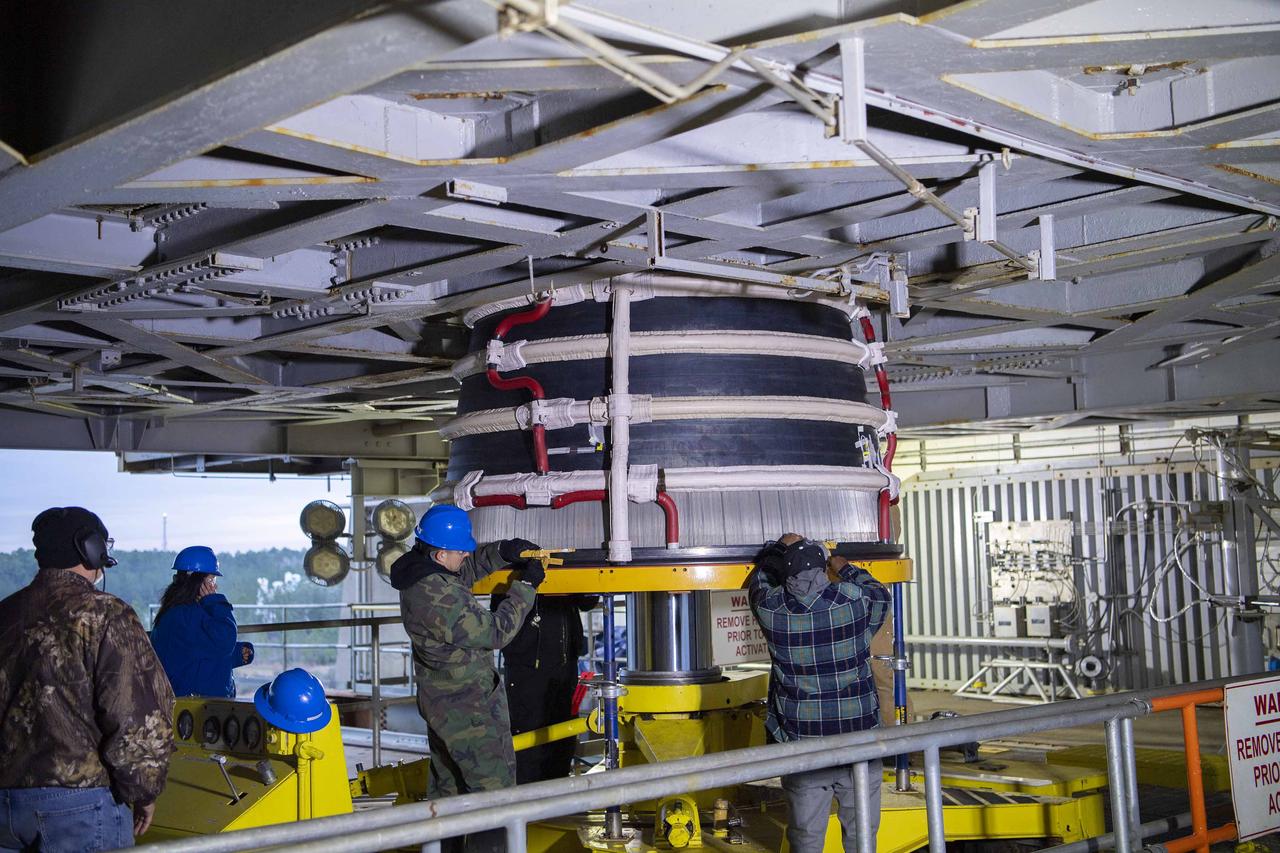

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.
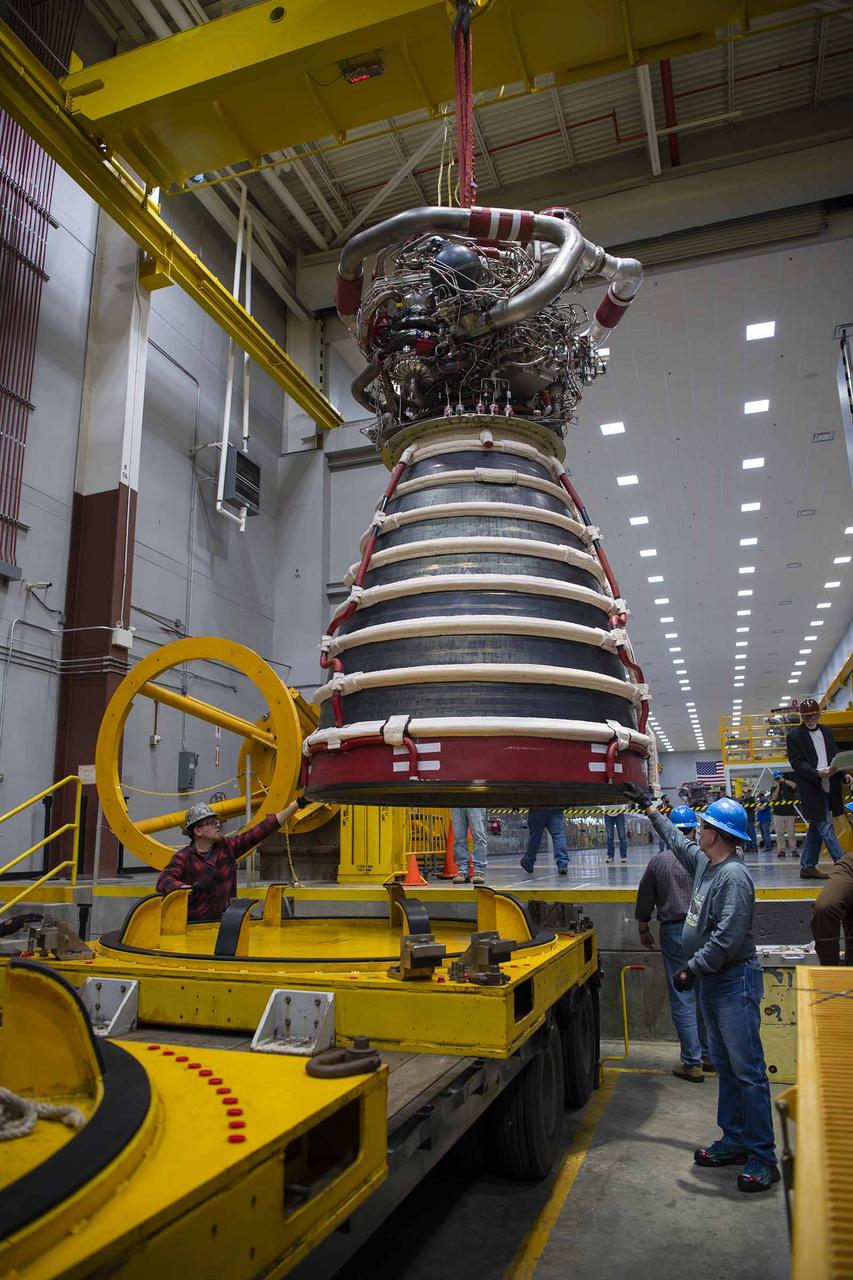

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.
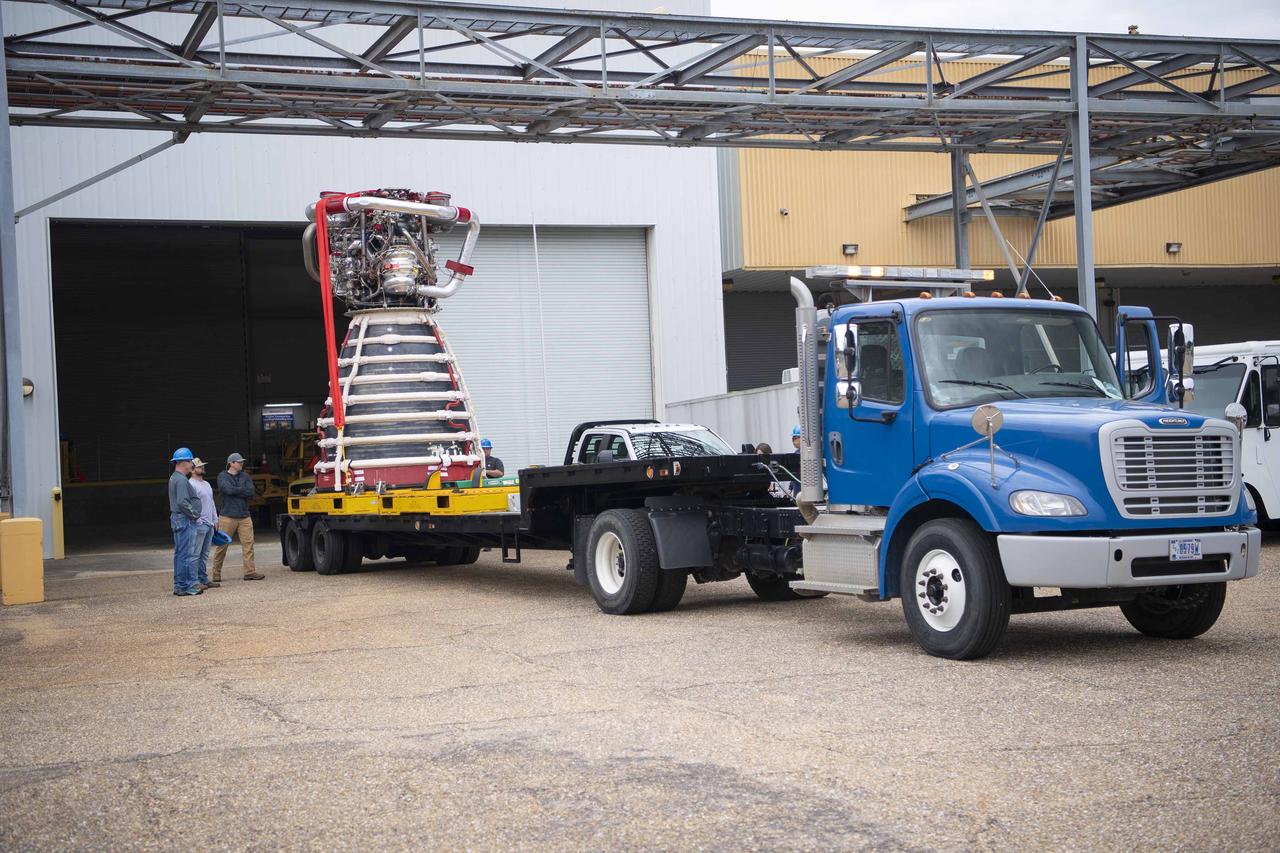

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center deliver, lift, and install the first new production RS-25 engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand on Feb. 18.
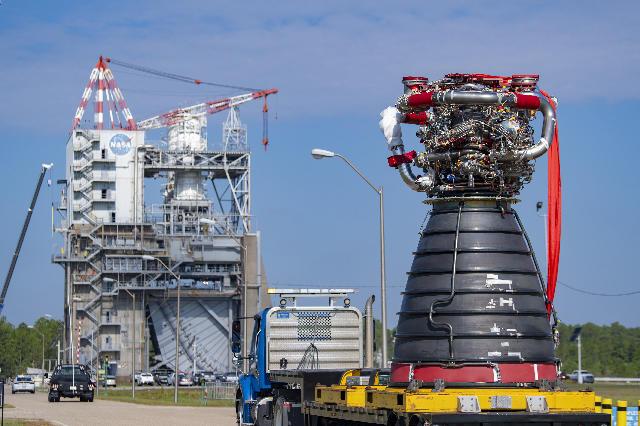

Crews bring RS-25 developmental engine E0525 to the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center on Aug. 30 for the second and final certification test series.
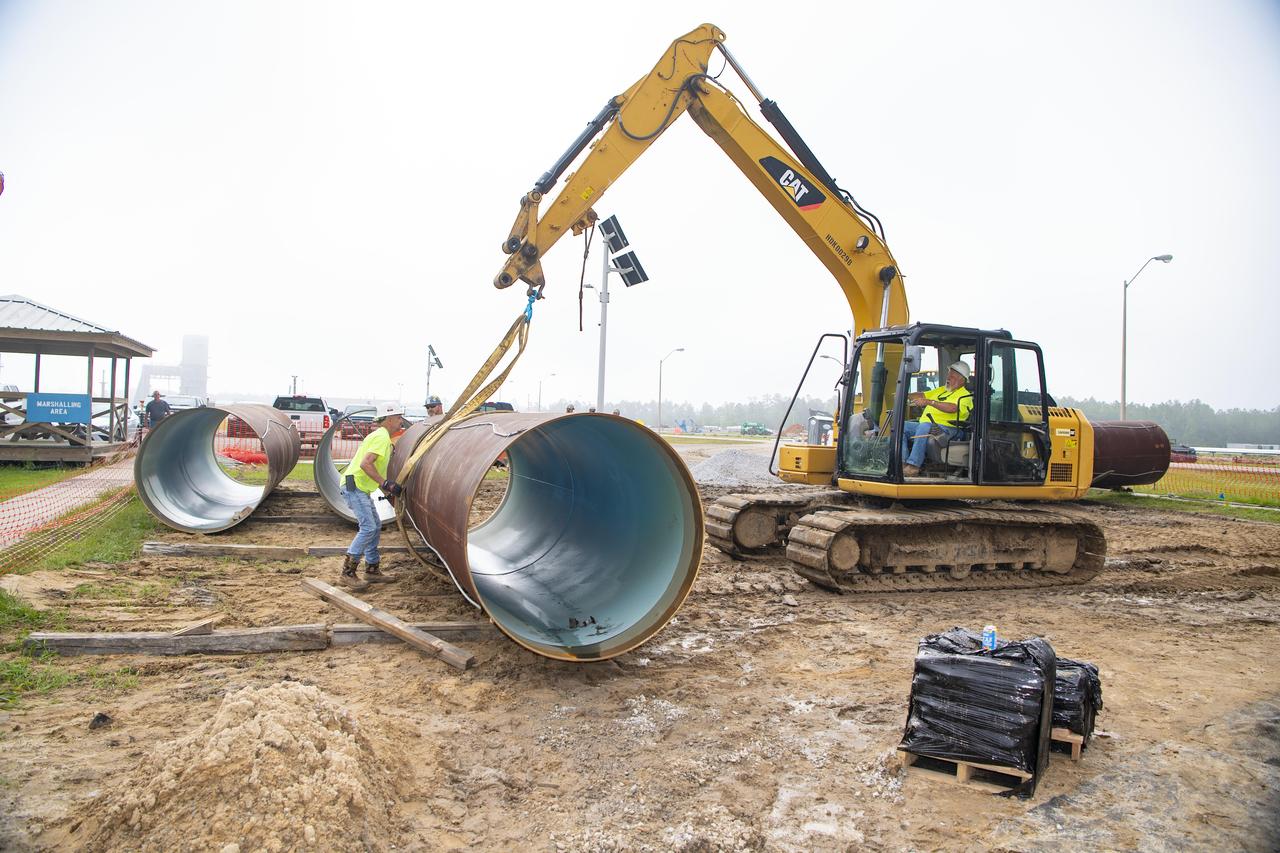

Crews lift a new pipeline liner section near the Fred Haise Test Stand on May 1 in the last phase of updating the original test complex water system at NASA’s Stennis Space Center.
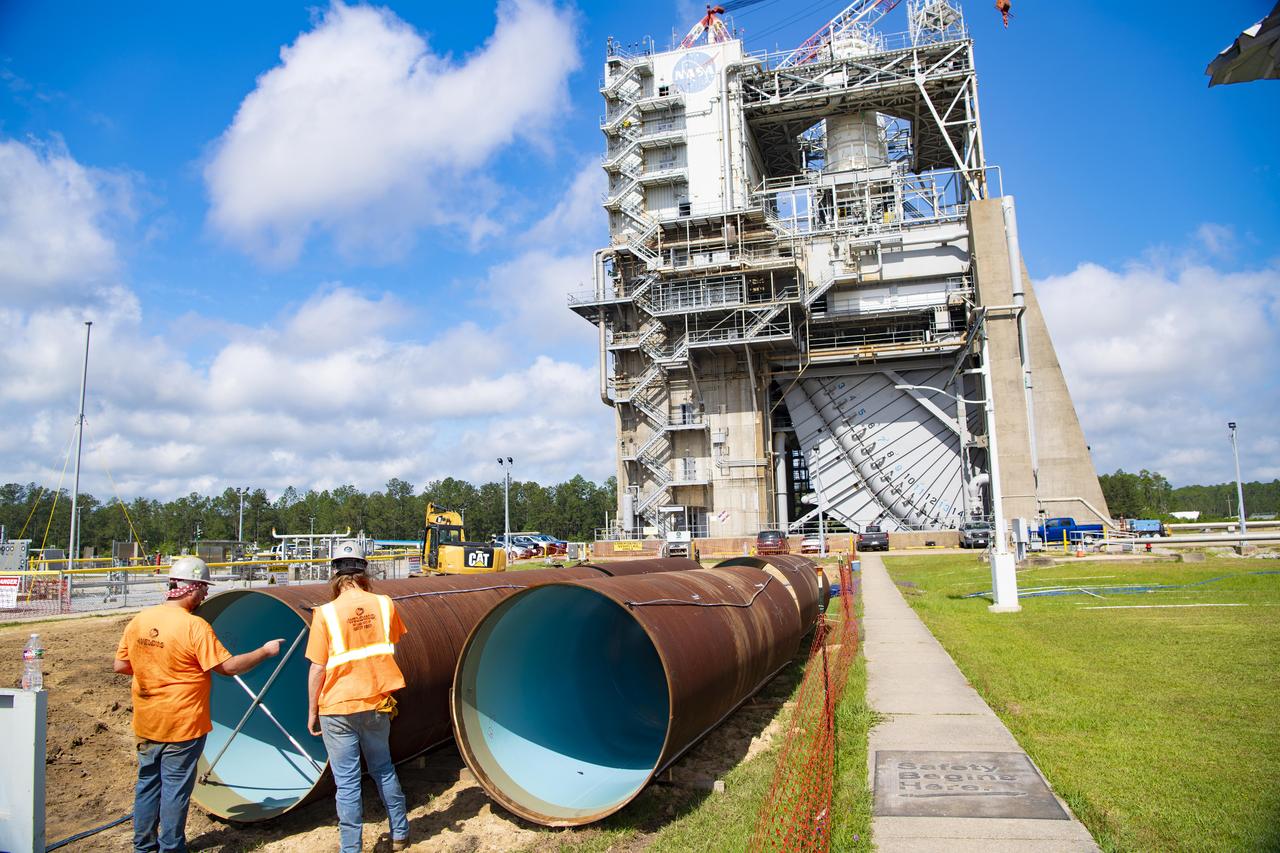

Crews prepare new pipeline liner sections for installation near the Fred Haise Test Stand on May 1 in the last phase of updating the original test complex industrial water system at NASA’s Stennis Space Center.
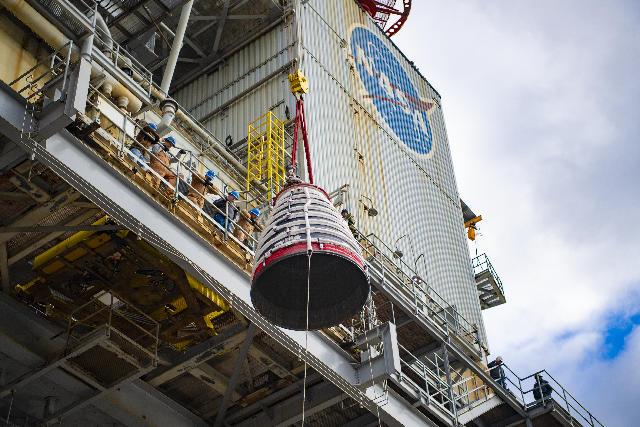

The new production nozzle is lifted on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center on Feb. 6. Crews used specially adapted procedures and tools to swap out the nozzles with the engine in place.
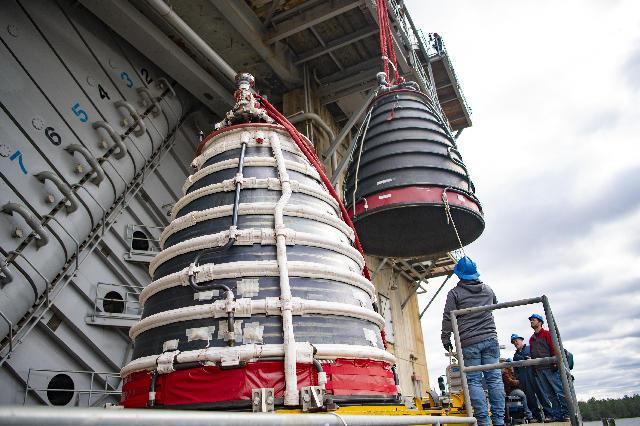

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center install a second production nozzle, left, on Feb. 6 to gather additional performance data on the RS-25 certification engine at the Fred Haise Test Stand.
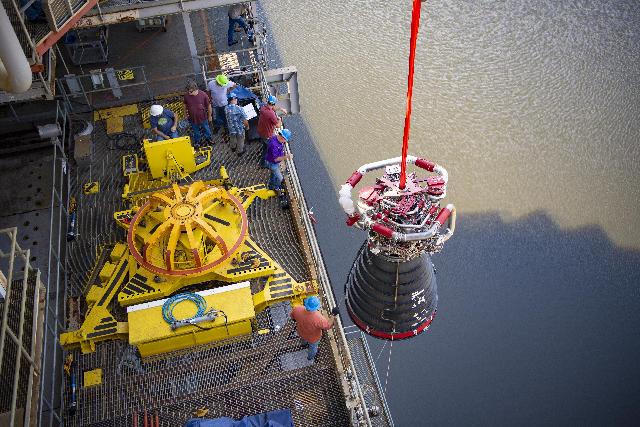

Crews prepare to place the RS-25 engine on the engine vertical installer, which raises the engine, so technicians can attach the engine on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center on Aug. 30.
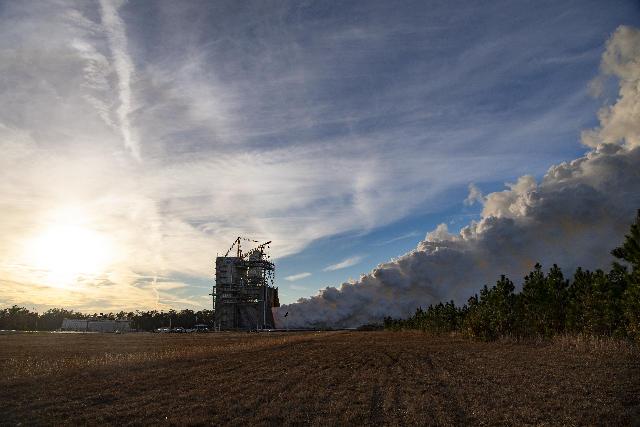

The first hot fire of 2024 takes place on Jan. 17 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center when crews complete a 500-second hot fire on the Fred Haise Test Stand.
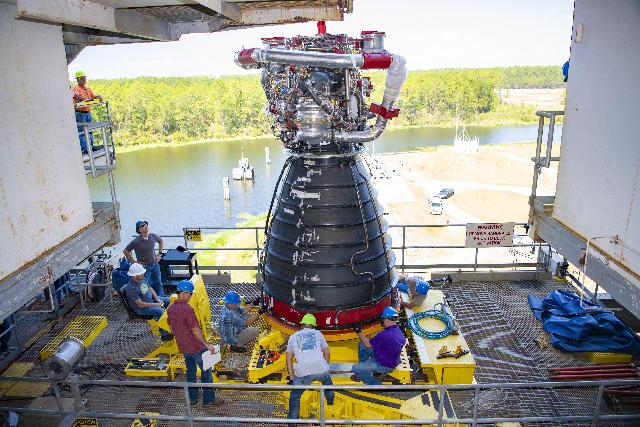

Once crews place the RS-25 engine on the engine vertical installer and it is attached to the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center, the installer moves away, and technicians ensure all connections to the test facility are complete for the second certification test series to collect data for the final RS-25 design certification review.
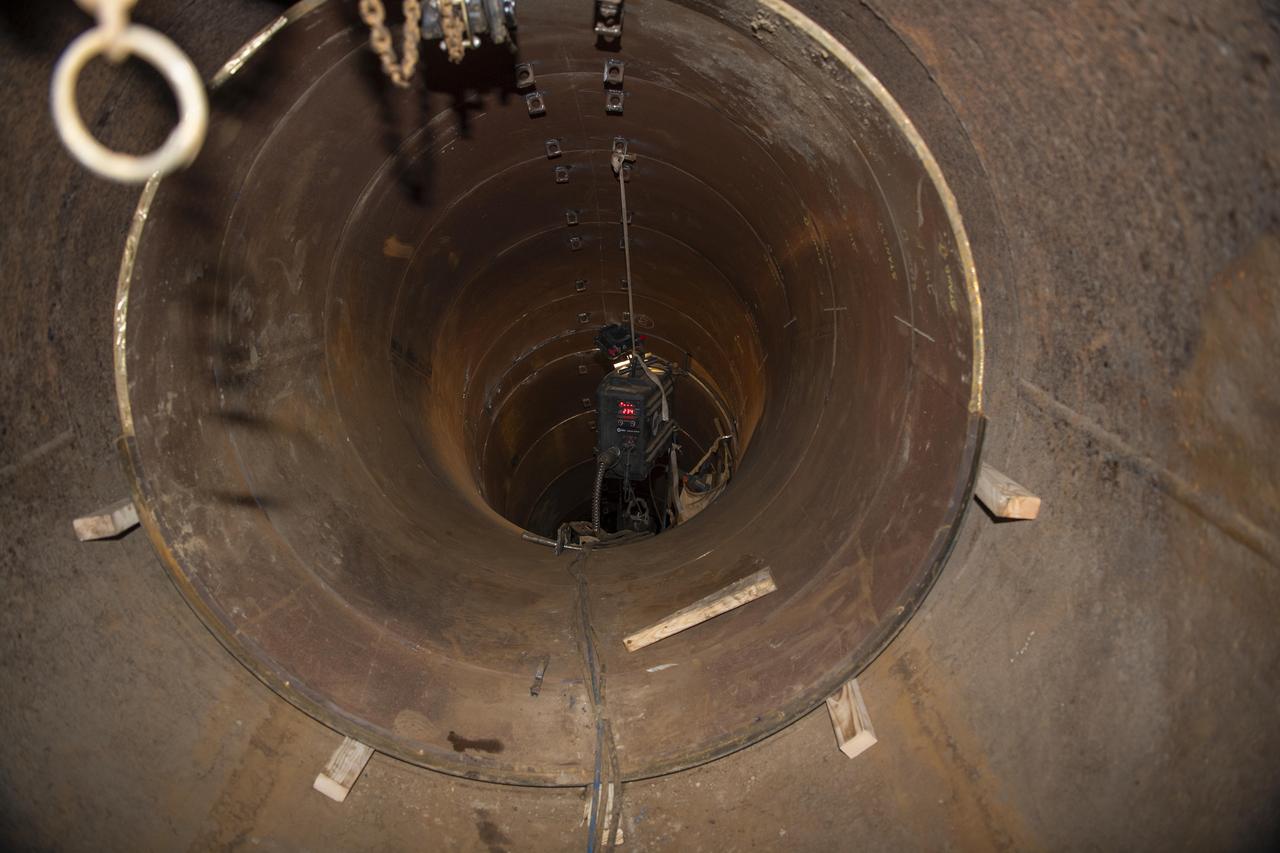

An image shows a new pipeline liner section being place inside the existing carrier pipe near the Fred Haise Test Stand on May 1 in the last phase of updating the original test complex industrial water system at NASA’s Stennis Space Center.
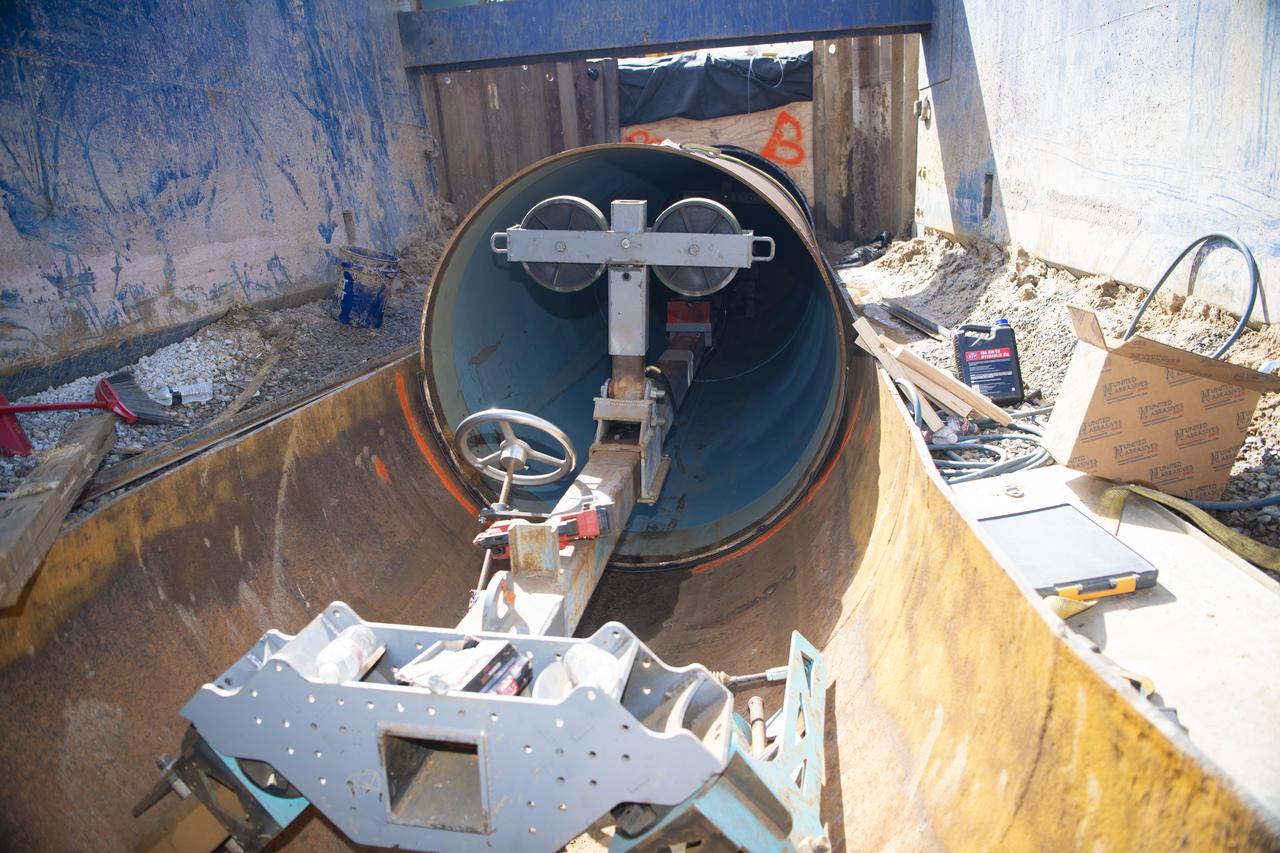

Crews use a special tool to place a new pipeline liner section inside the existing carrier pipe near the Fred Haise Test Stand on May 1 in the last phase of updating the original test complex industrial water system at NASA’s Stennis Space Center.
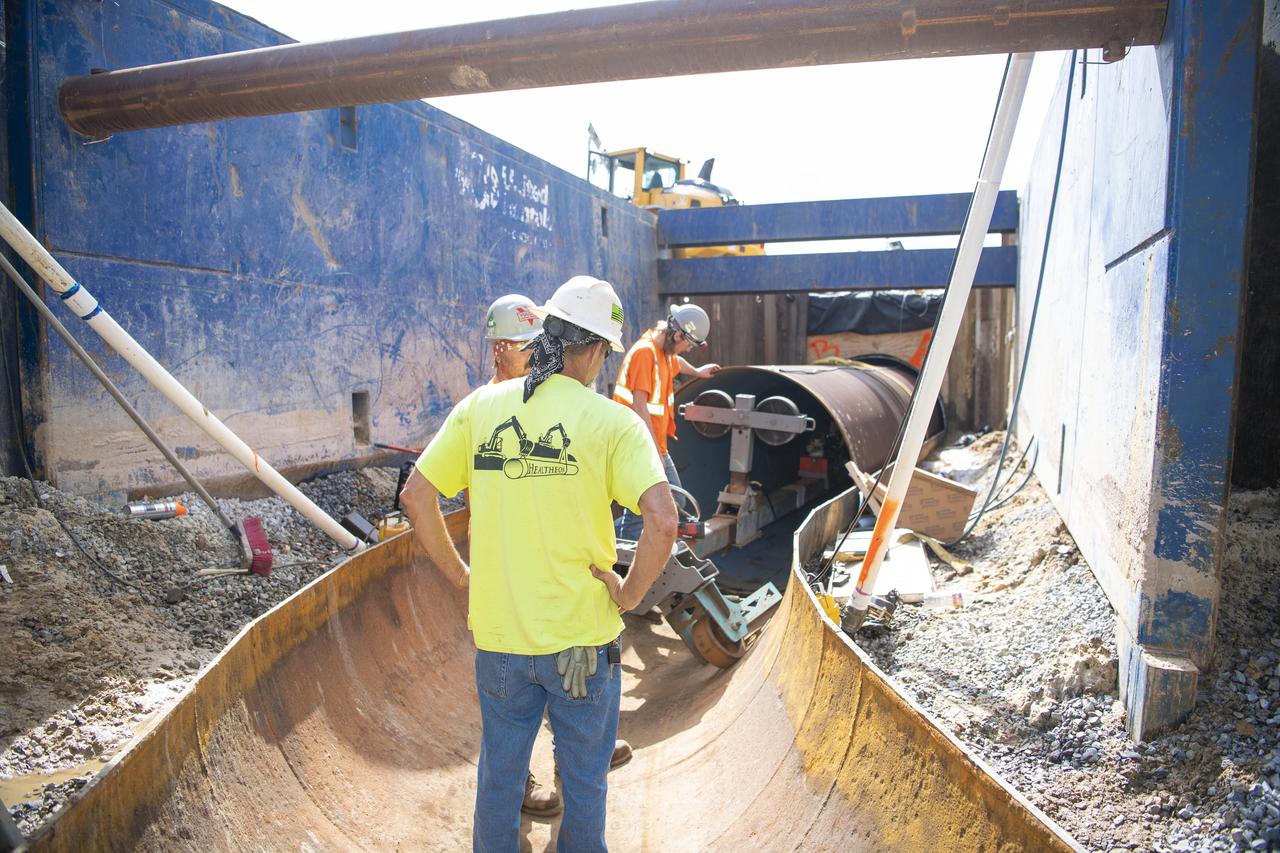

Crews use a special tool to place a new pipeline liner inside the existing carrier pipe near the Fred Haise Test Stand on May 1 in the last phase of updating the original test complex industrial water system at NASA’s Stennis Space Center.
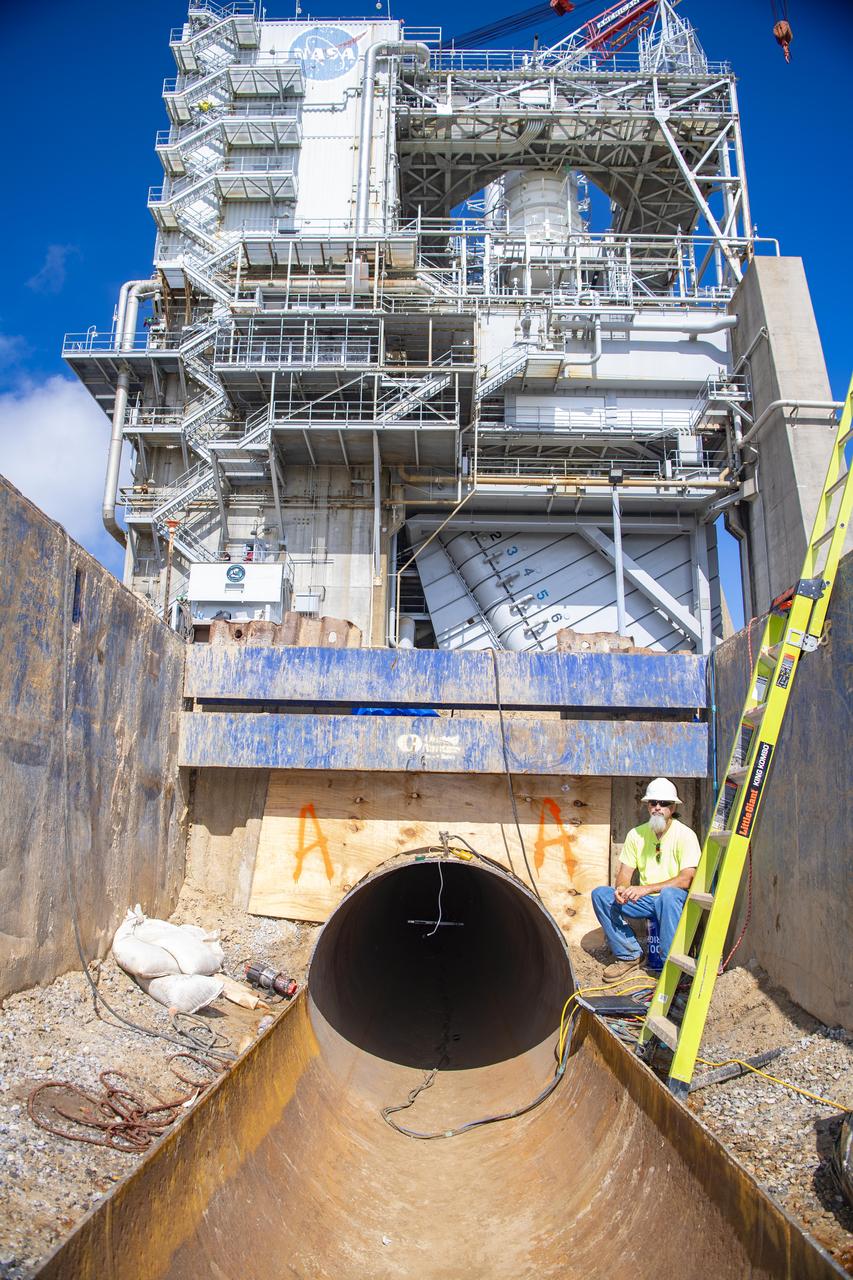

: An image shows the entry location of the existing carrier pipe where new liner sections are being placed at the base of the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center in the last phase of updating the original test complex industrial water system.
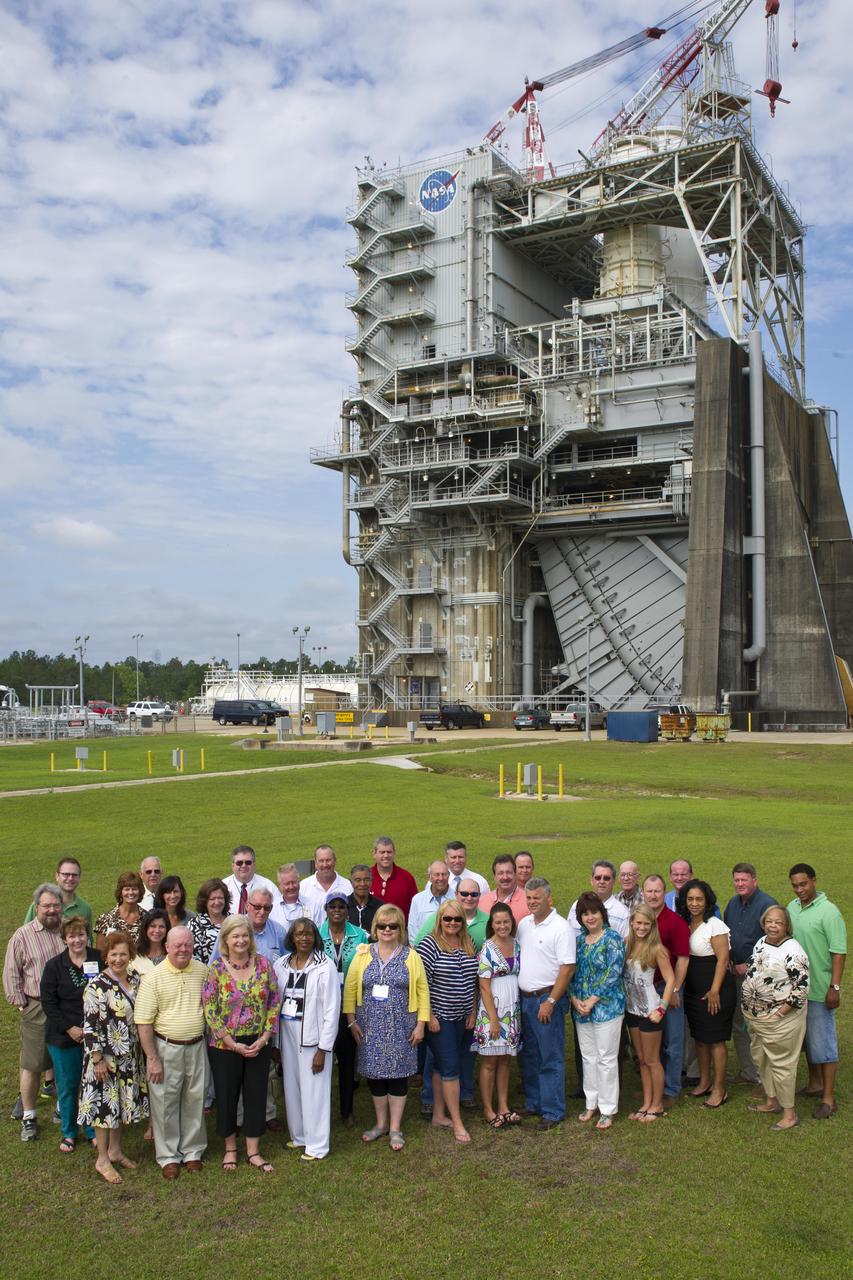

Legislators from across Mississippi visited Stennis Space Center on May 7, 2012, touring various facilities, including the A-1 Test Stand, and learning about work under way at the facility. The legislators also toured the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility and met with Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise.
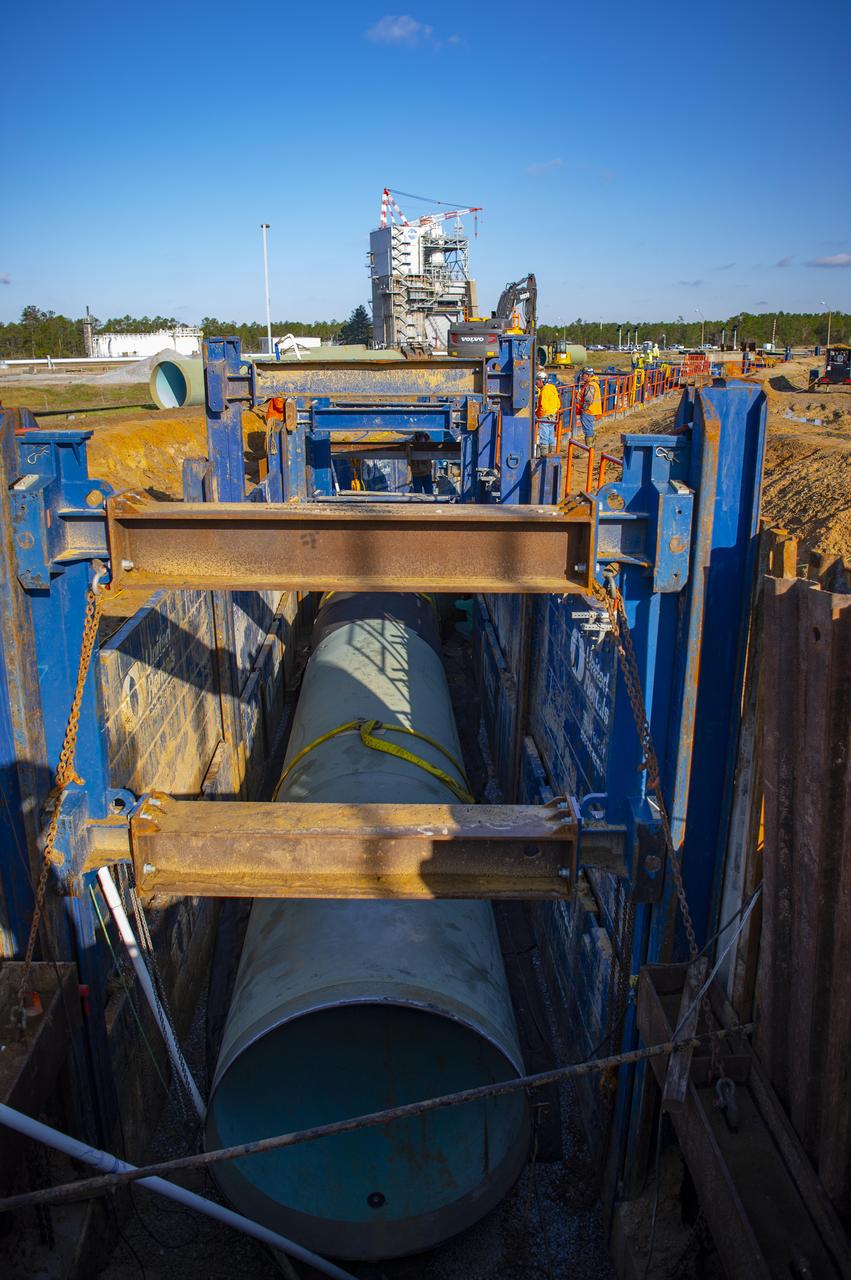

In this March 2022 photo, crews use a shoring system to hold back soil as they install new 75-inch piping leading from the NASA Stennis High Pressure Industrial Water Facility to the valve vault pit serving the Fred Haise Test Stand.
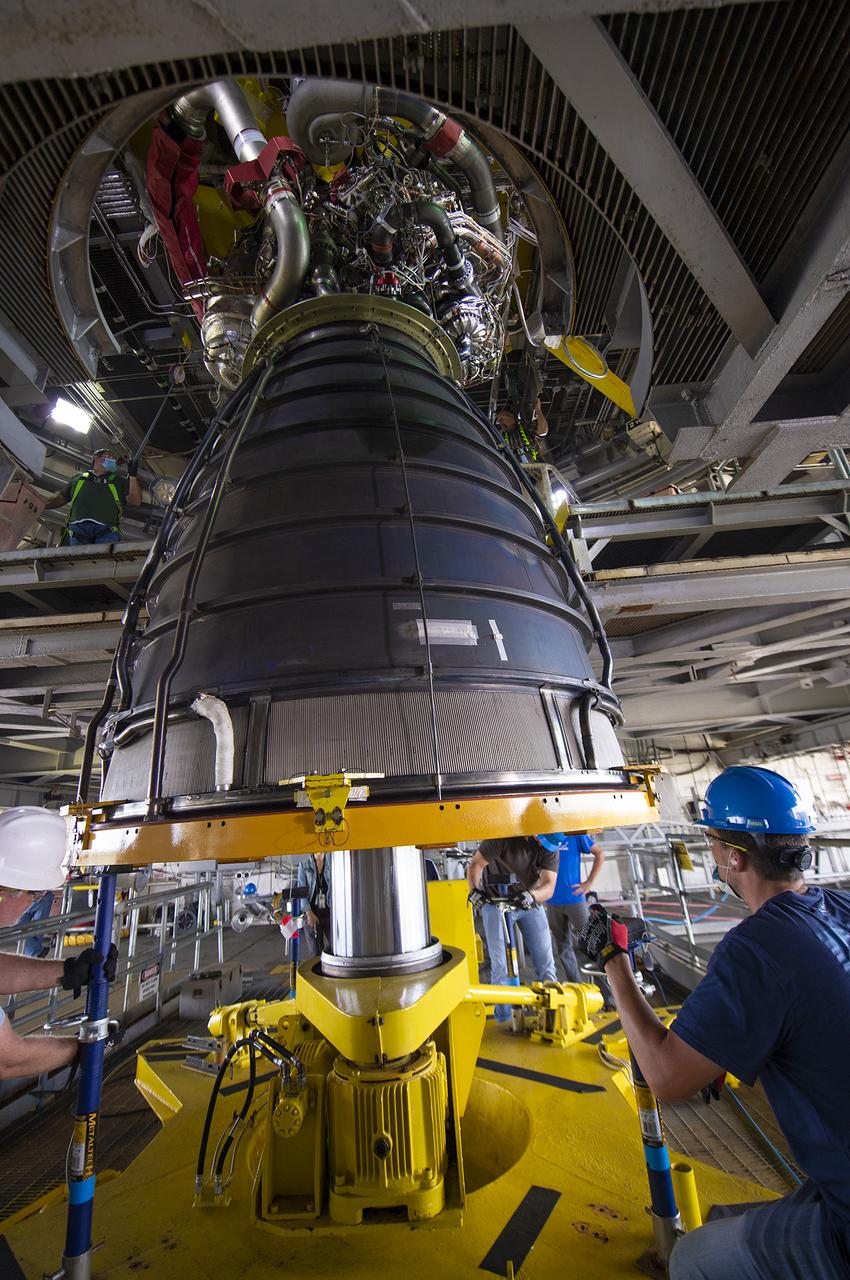

Crews at NASA’s Stennis Space Center remove an RS-25 rocket engine from the A-1 test stand on Nov. 1, 2021, following a series of successful tests.

NASA marks the halfway point of the RS-25 certification series four days later on Jan. 27 with the sixth test of the series on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. For each Artemis mission, four RS-25 engines, along with a pair of solid rocket boosters, power the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, producing more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust at liftoff.
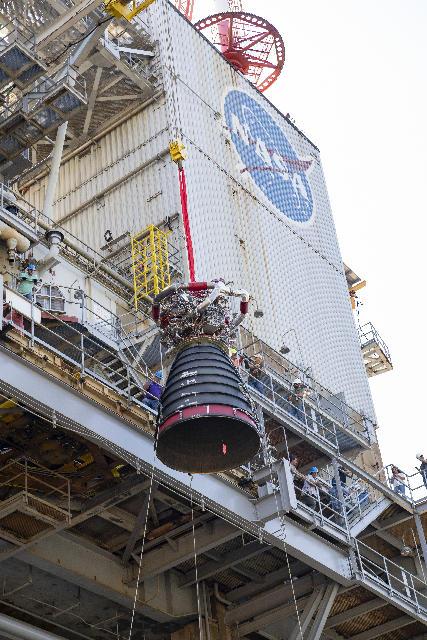

A crane lifts developmental engine E0525 on the west side of the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center on Aug. 30 in preparation for a series of 12 tests that are a key step for lead SLS (Space Launch System) engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to produce engines that will help power the SLS rocket, beginning with Artemis V.
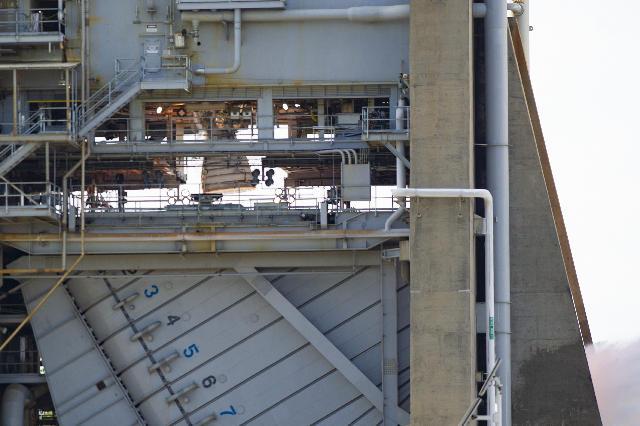

NASA demonstrates a key capability necessary for flight of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket during the hot fire on Nov. 29, 2023. Crews gimbal, or pivot, the RS-25 engine around a central point during the almost 11-minute (650 seconds) hot fire on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center.
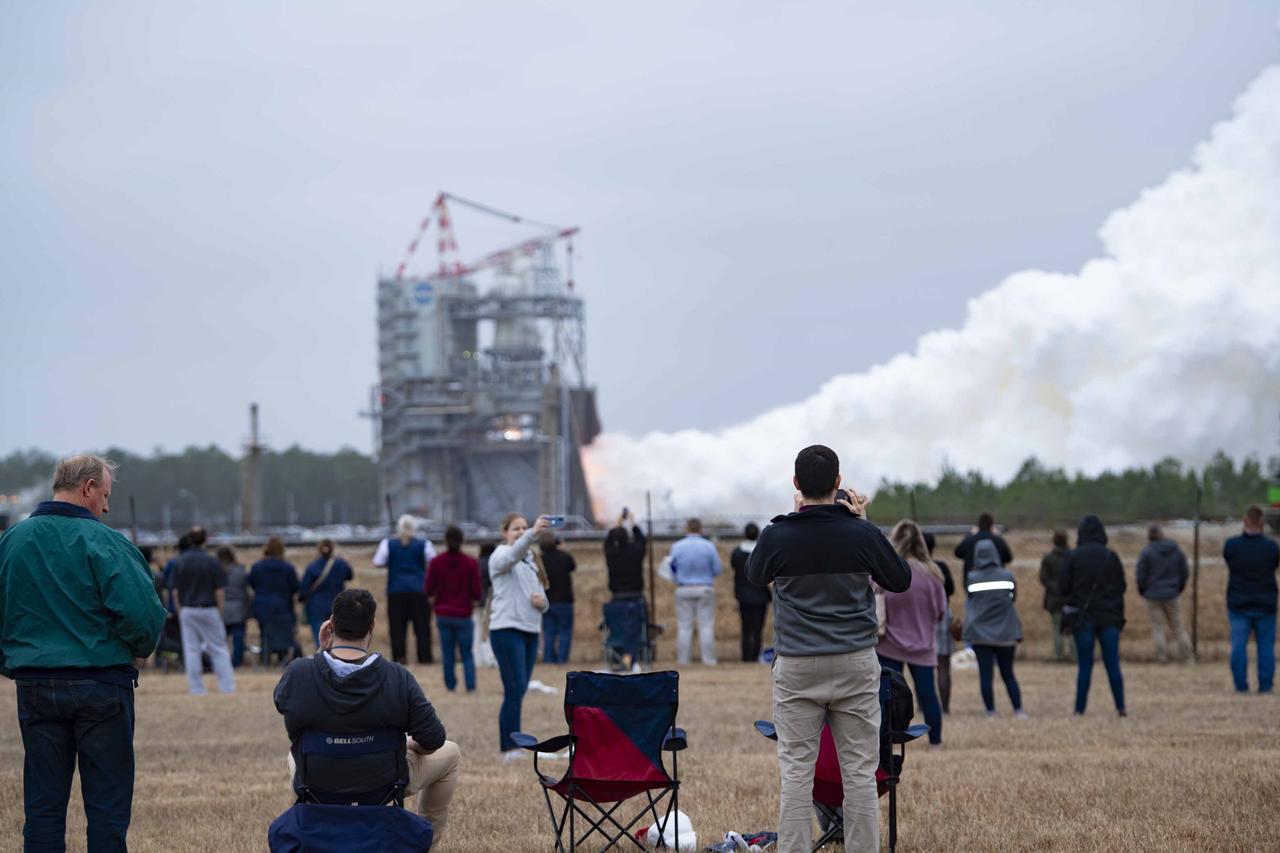

Sitewide employees at NASA’s Stennis Space Center watch the RS-25 test conducted on Jan. 23 as NASA continued a critical test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The full-duration hot fire on the Fred Haise Test Stand is part of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company. The new engines will help power SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
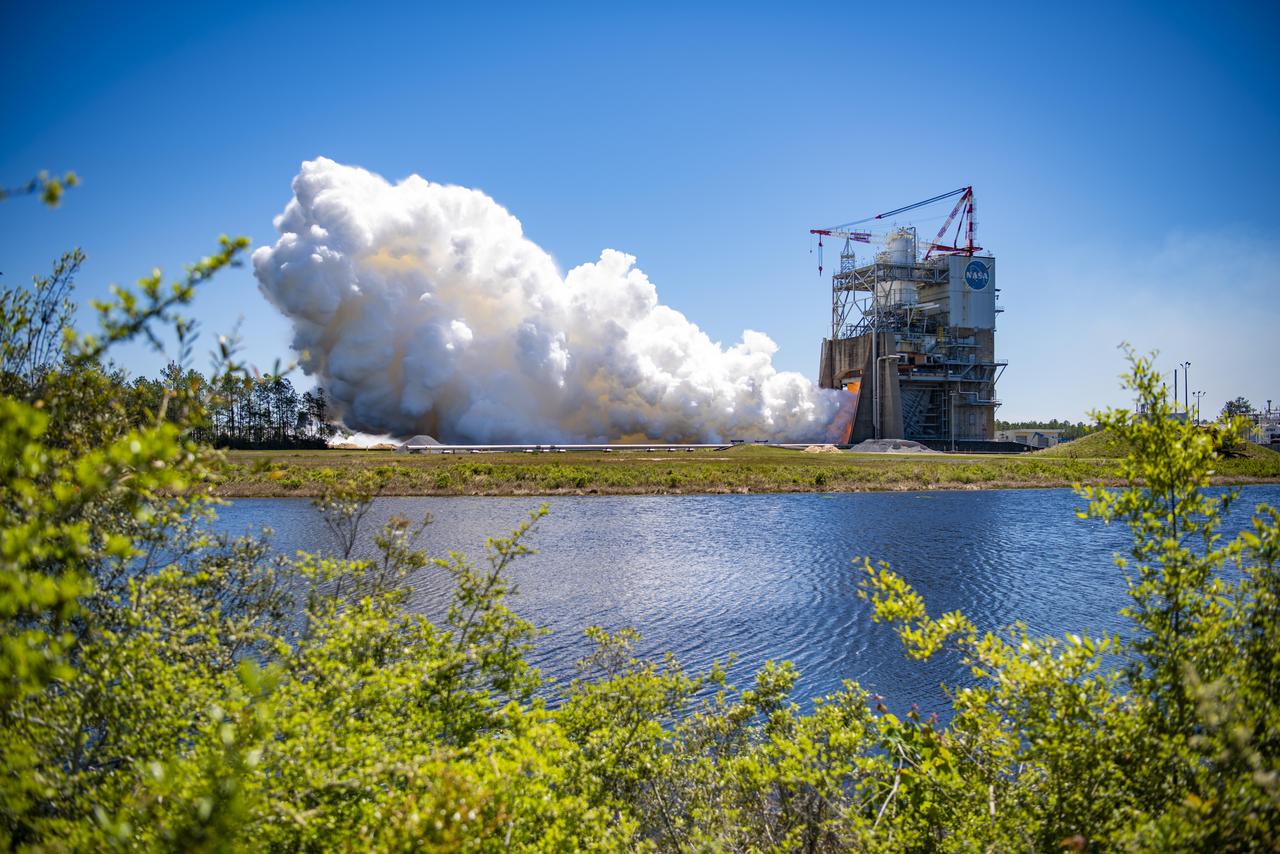

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
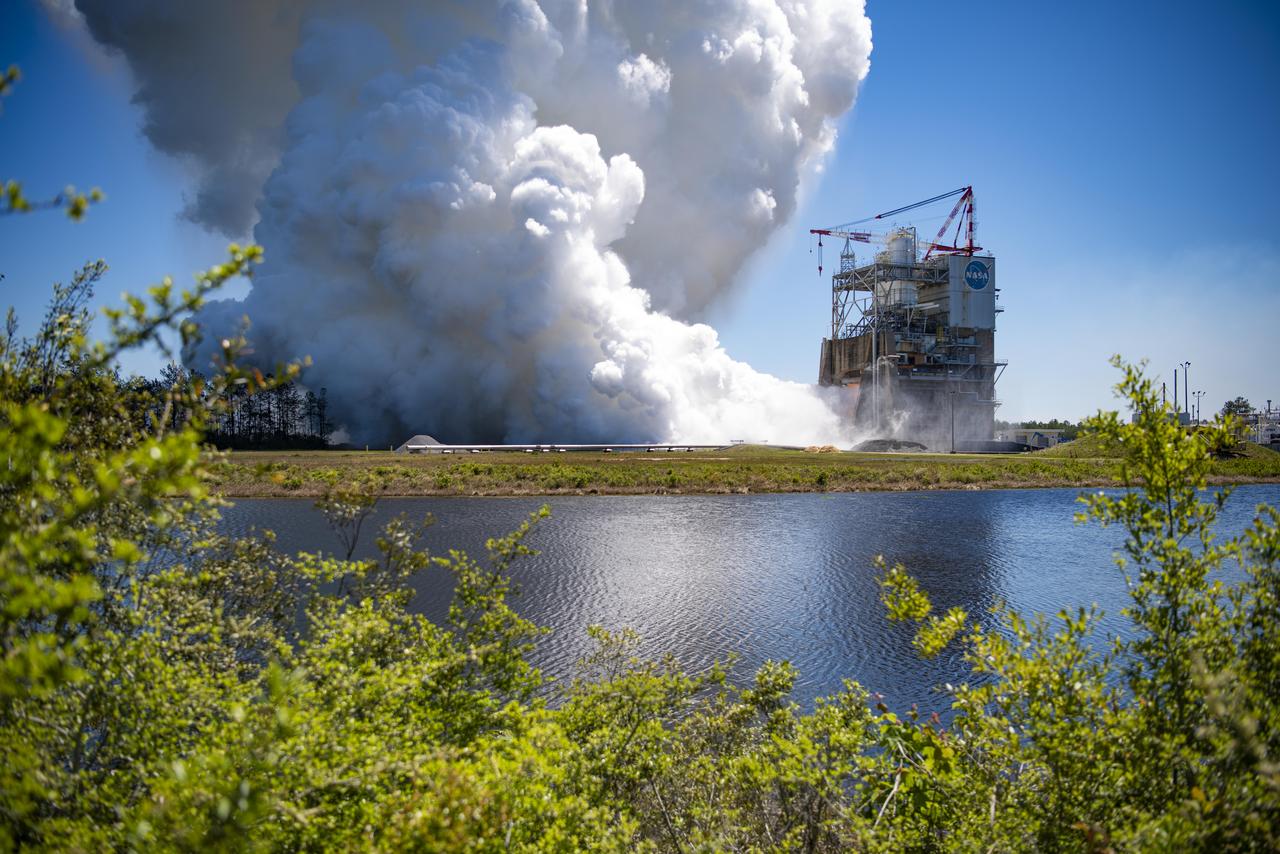

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
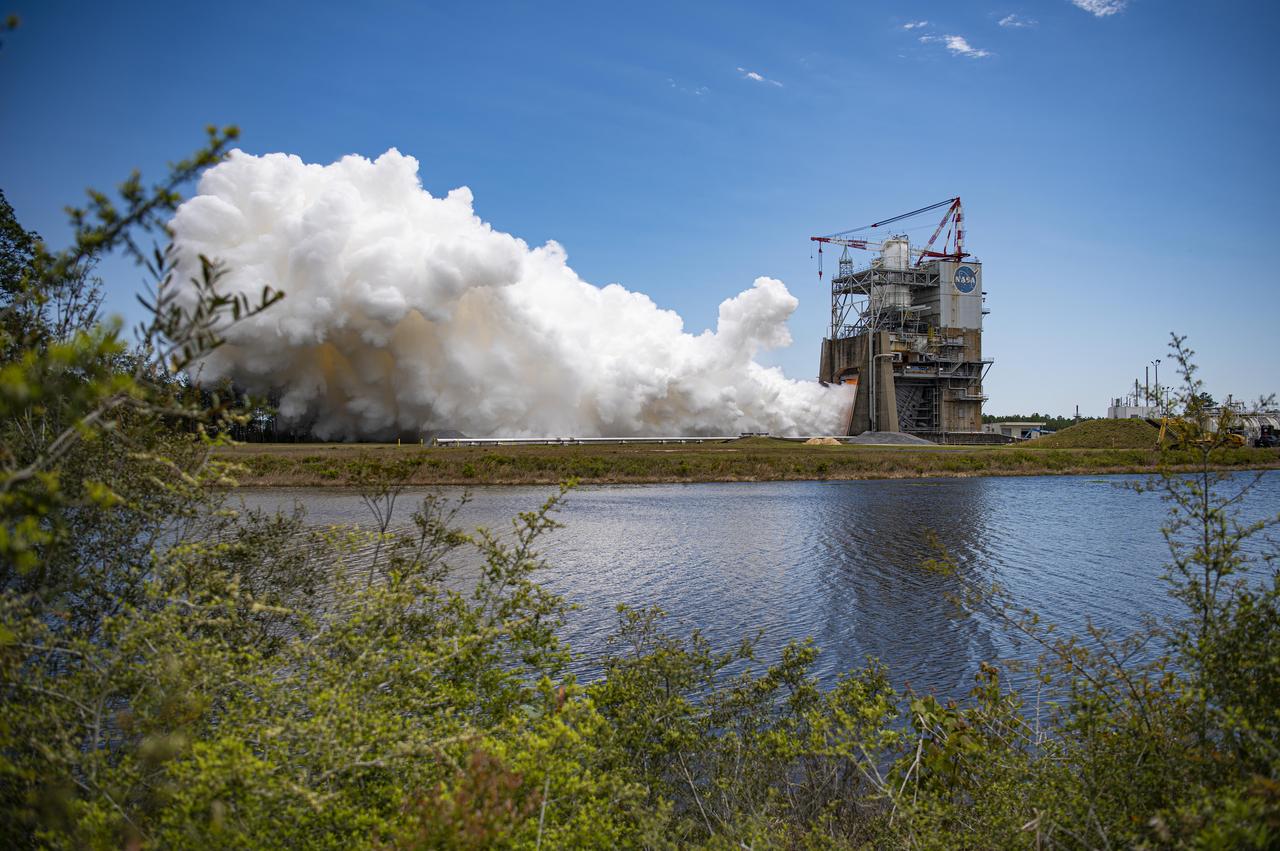

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
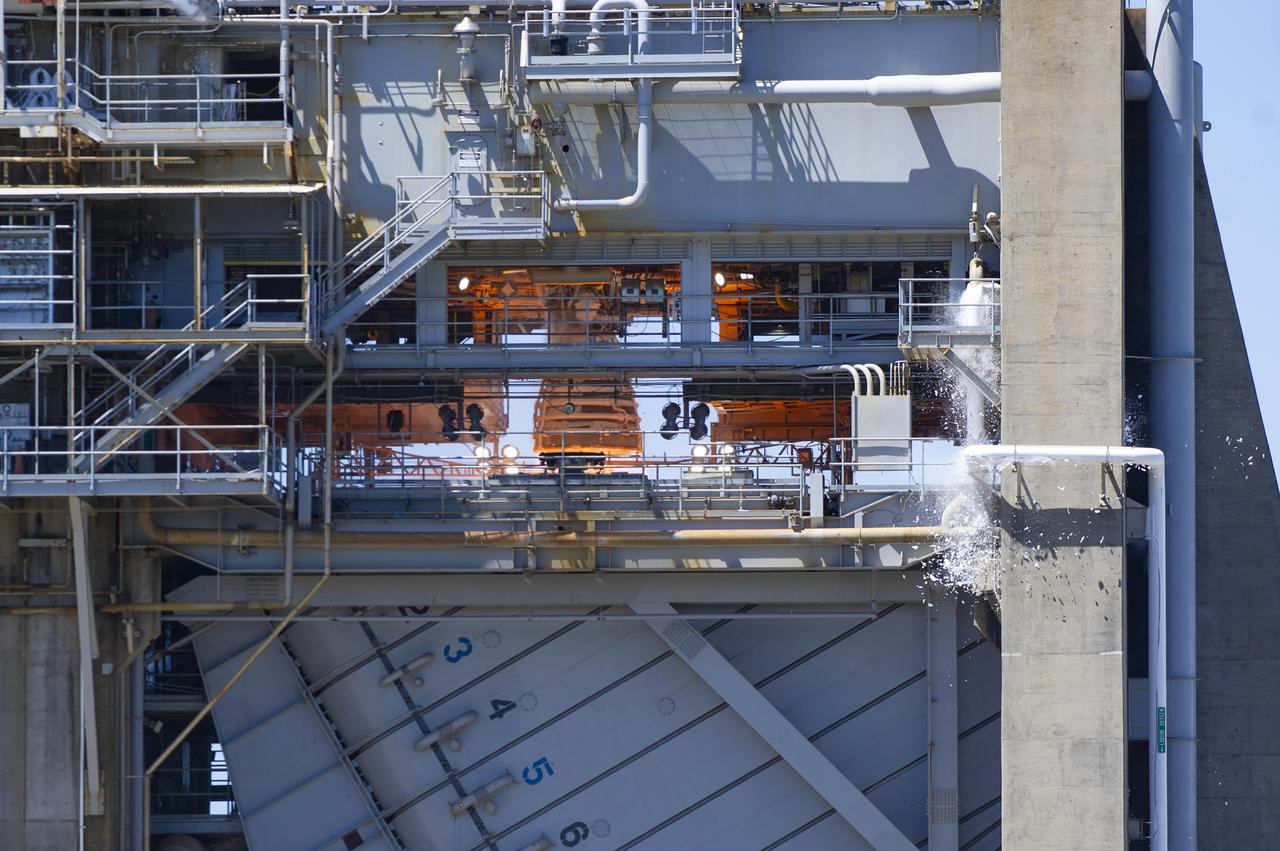

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V
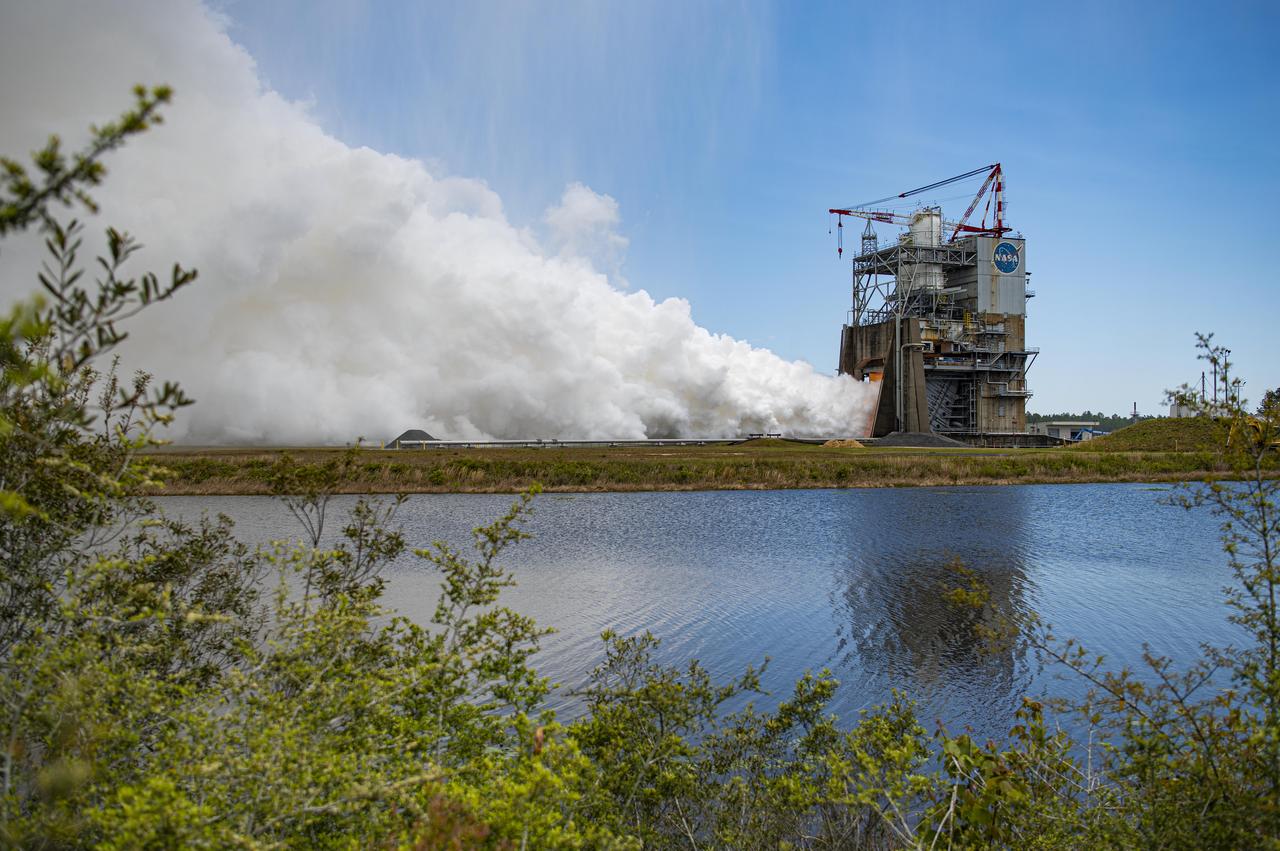

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
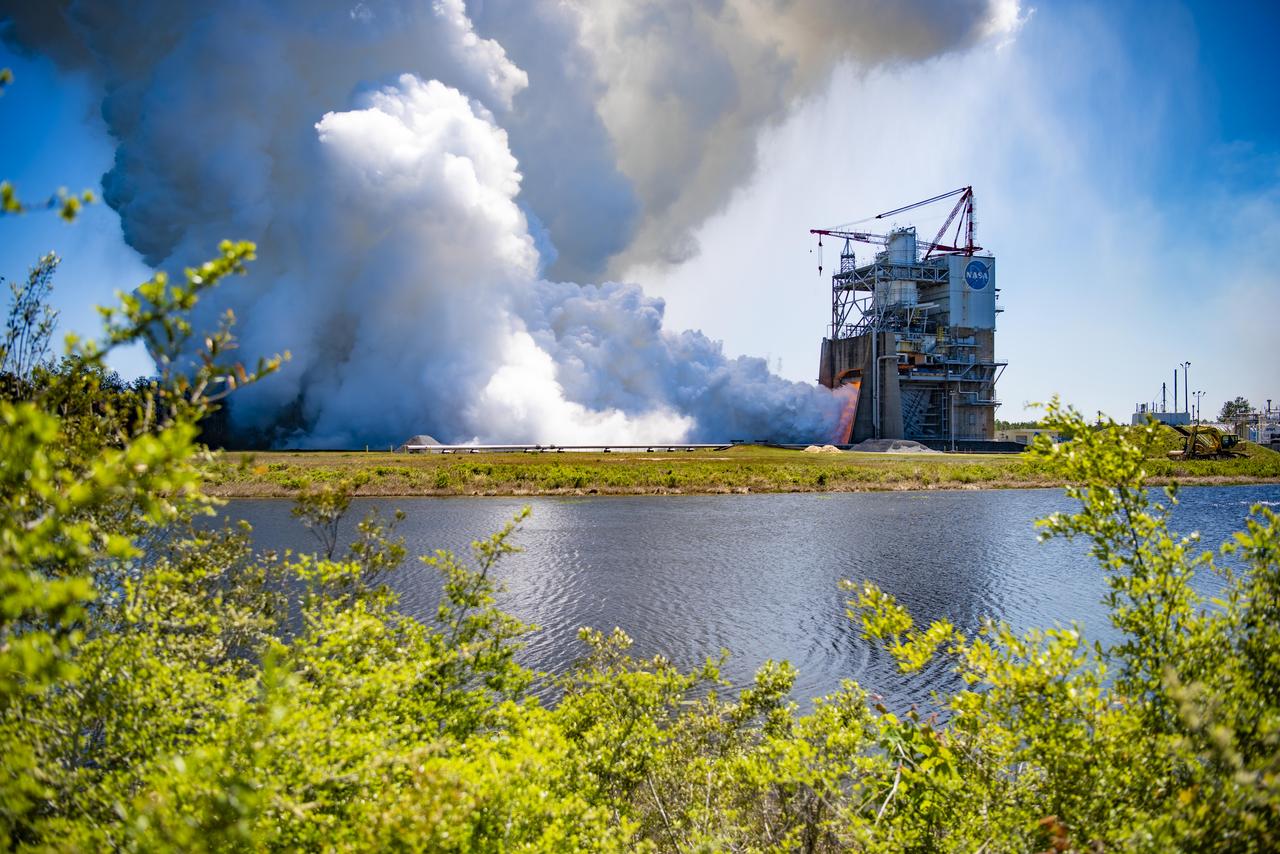

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
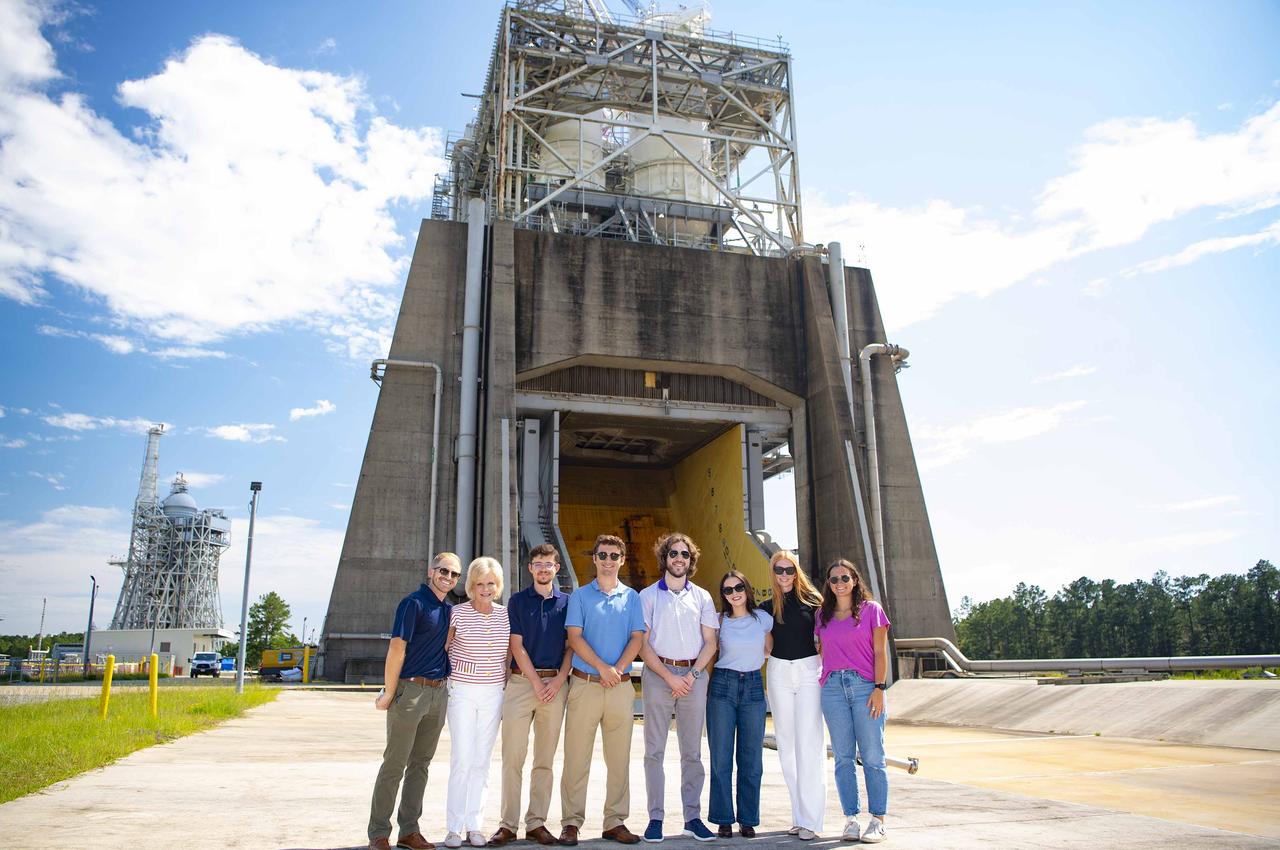

Legislative staff and interns from the office of U.S. Rep. Garrett Graves of Louisiana are pictured at the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA Stennis on July 11. During the visit to the south Mississippi site, the group learned more about internship opportunities with NASA and NASA Stennis. In addition to touring the test complex where RS-25 engines are tested for future Artemis missions, the group visited the Aerojet Rocketdyne Engine Assembly Facility onsite. Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, manufactures RS-25 engines to help power NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
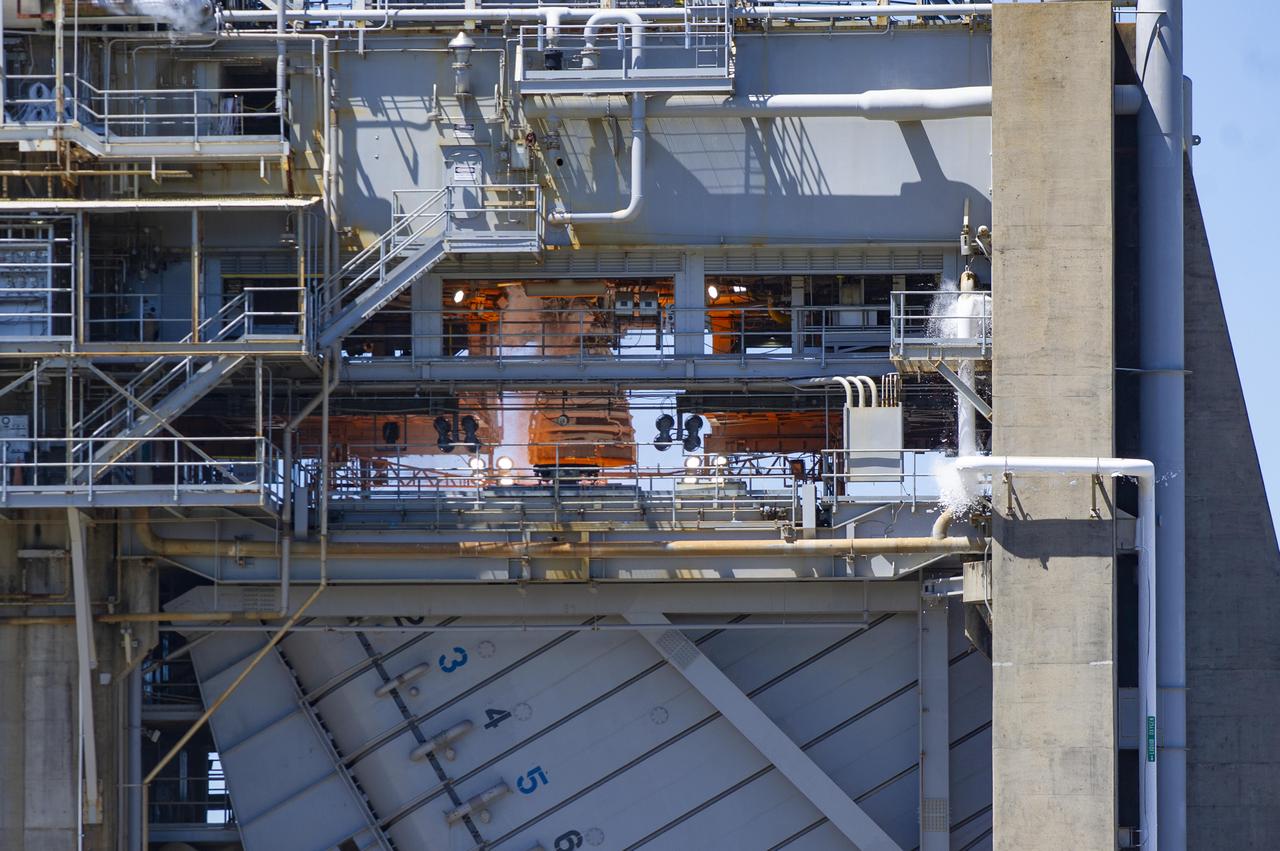

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
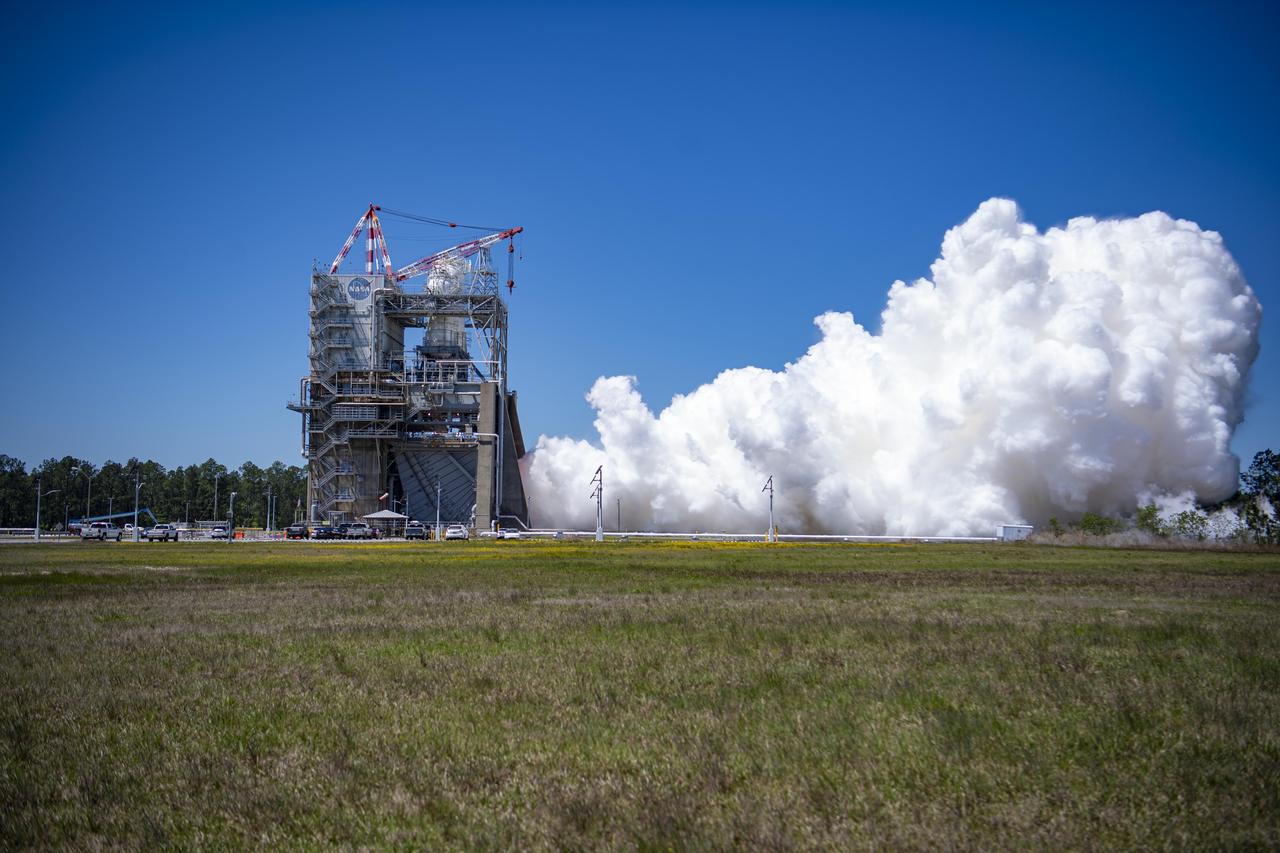

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
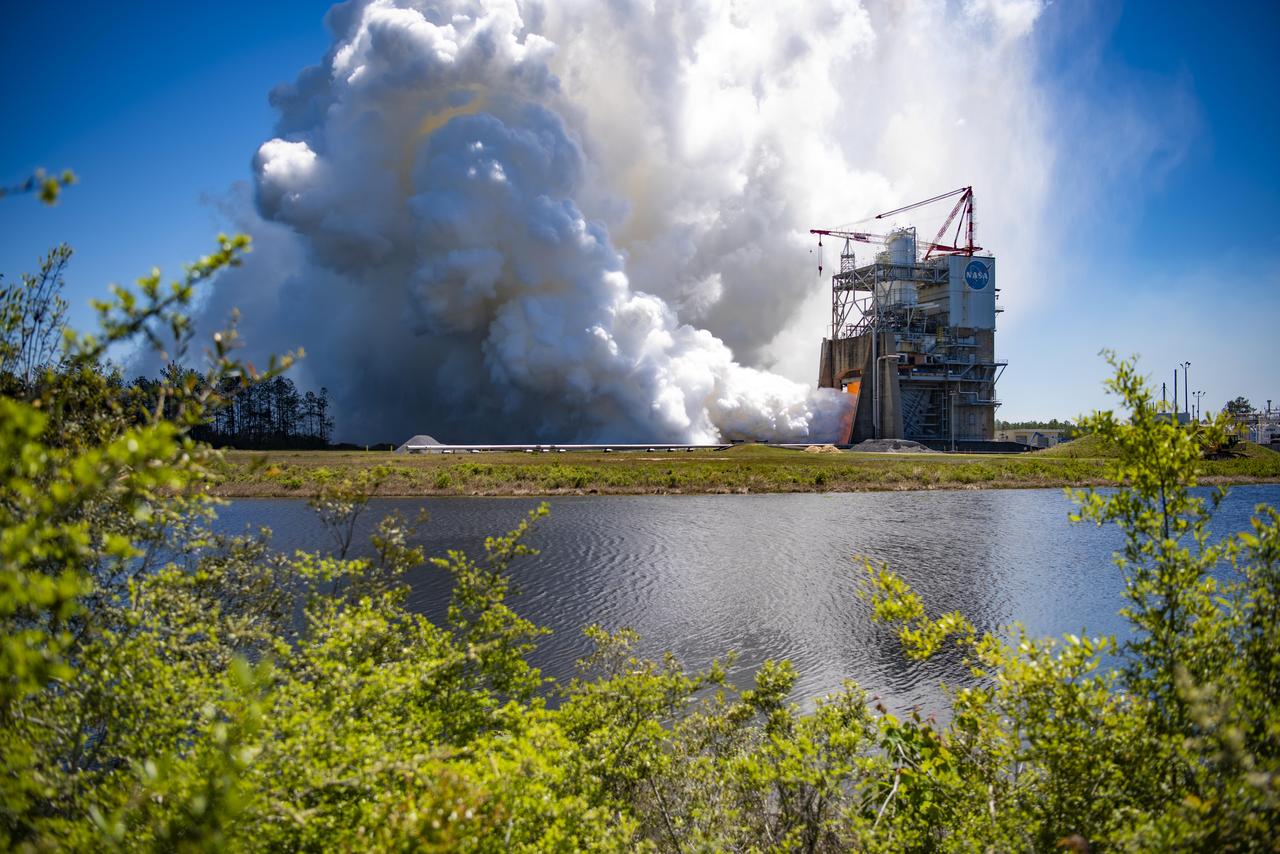

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
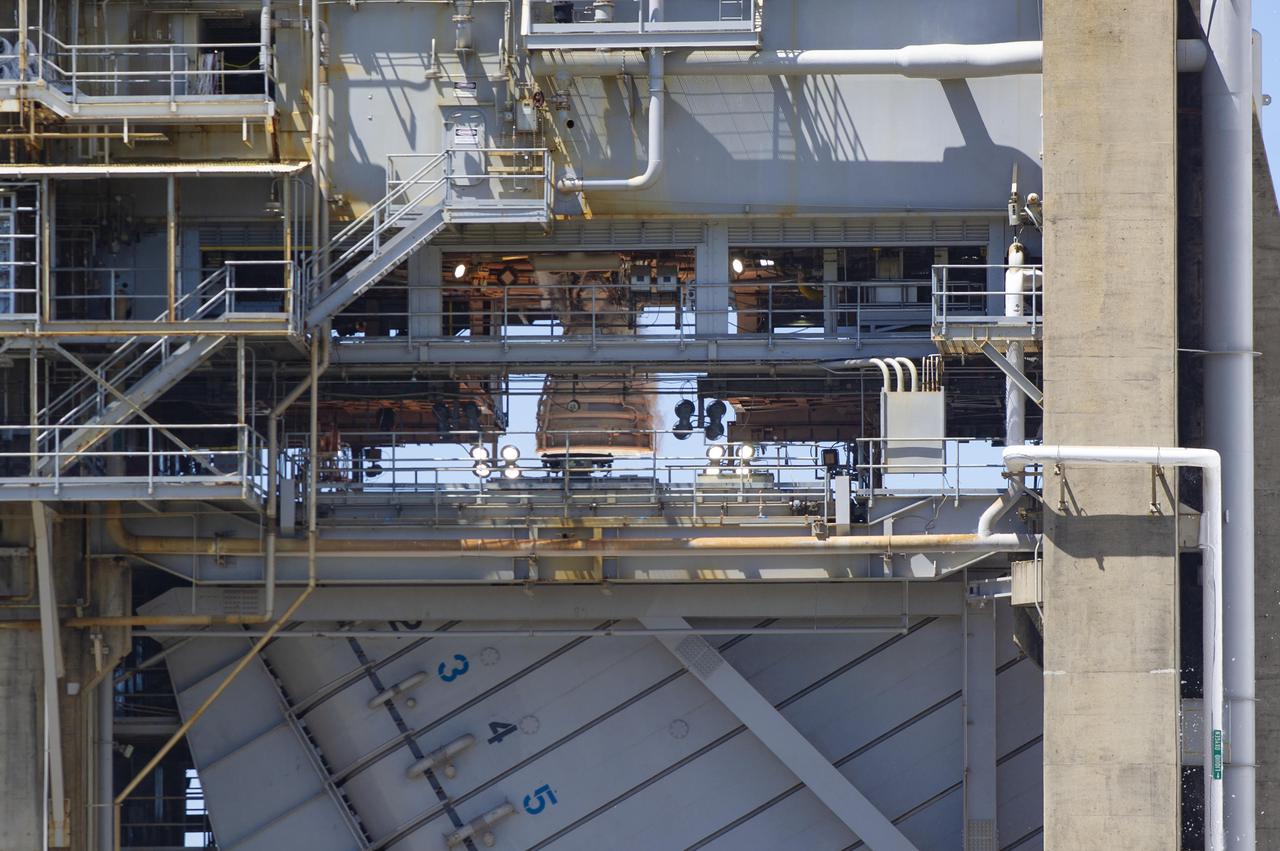

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
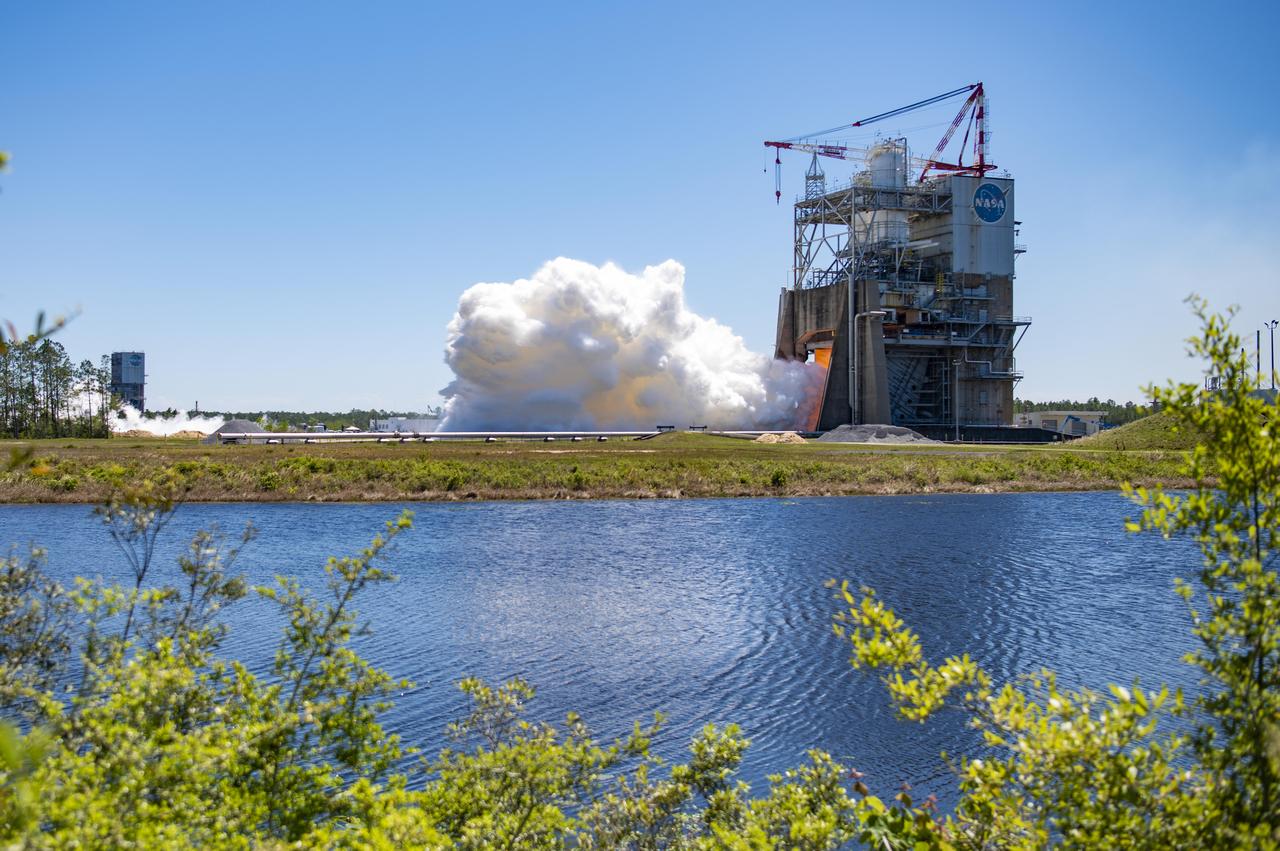

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
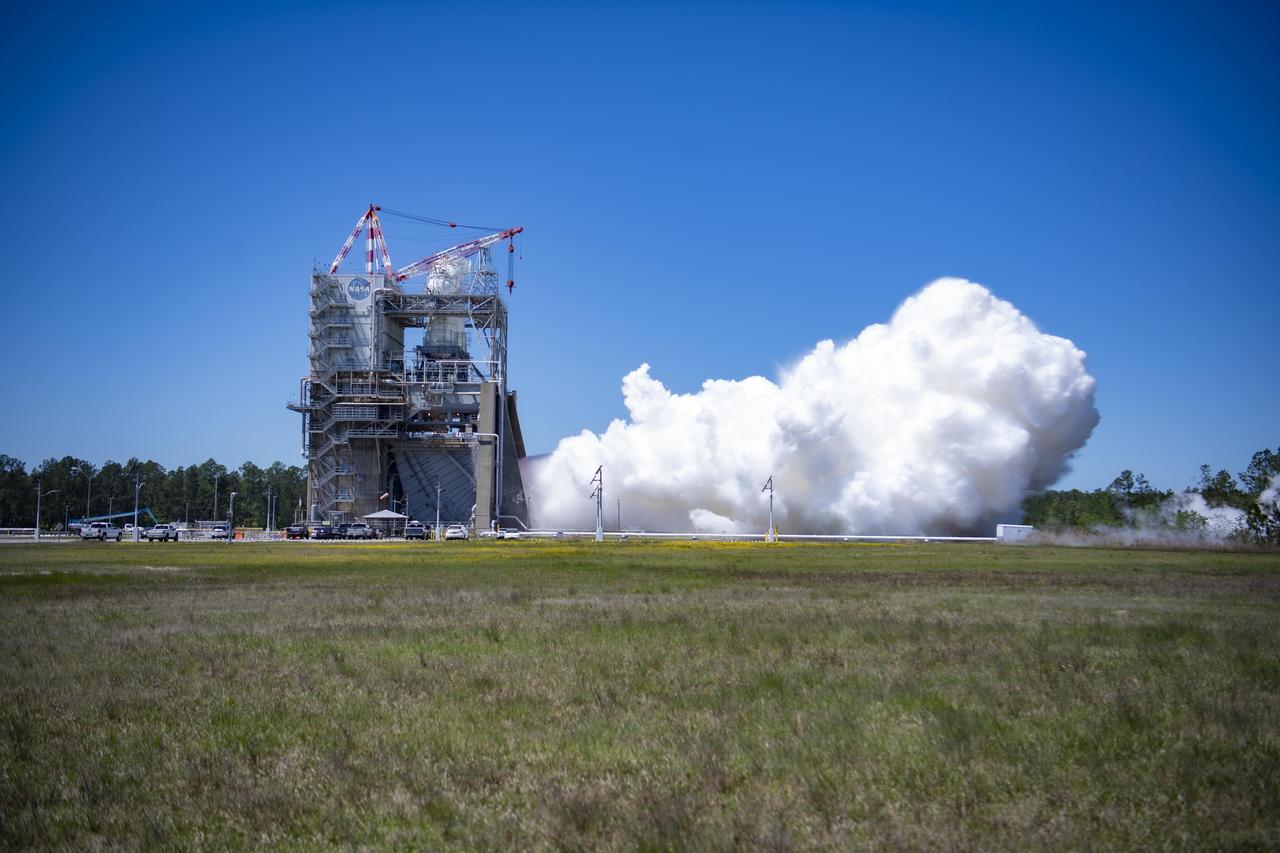

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire April 3 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, achieving a major milestone for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It marked the final test of a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V.
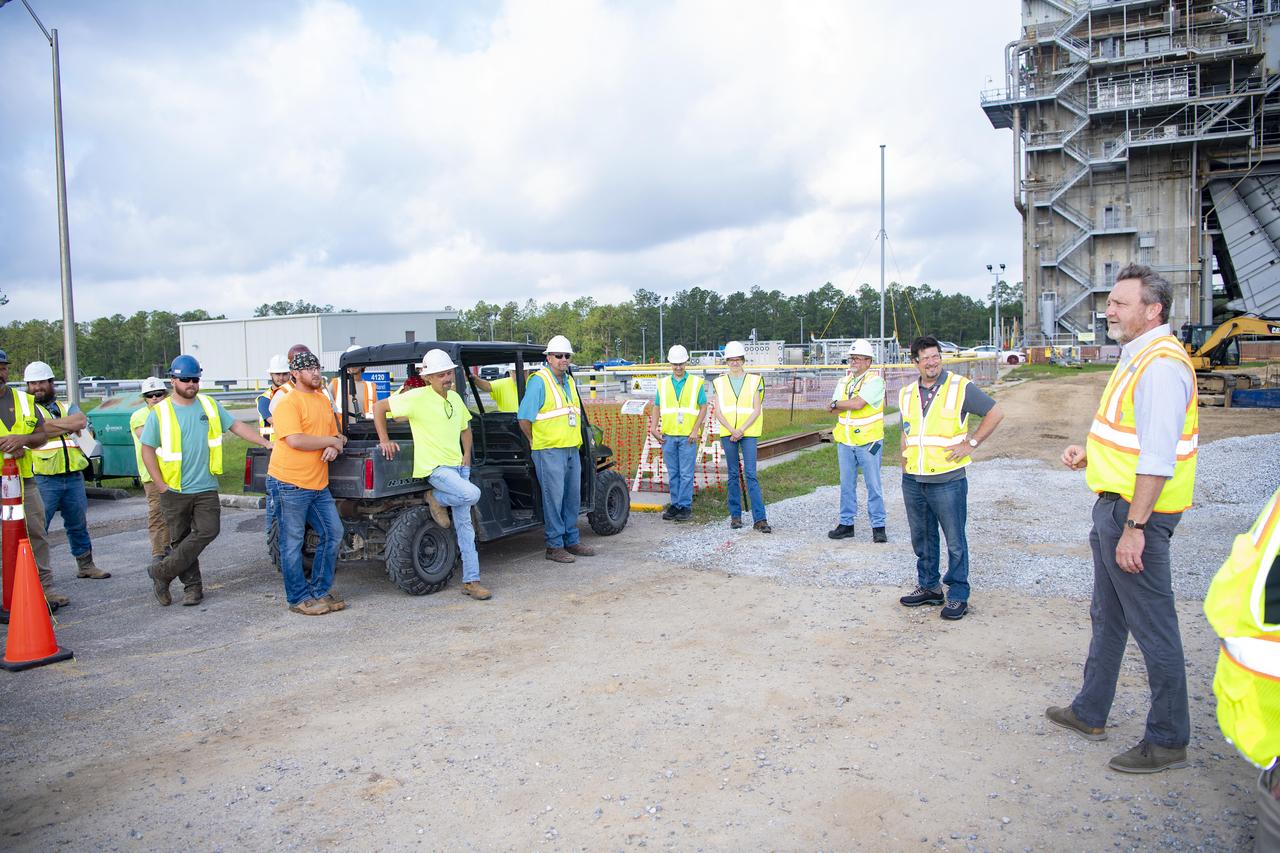

Rodney McKellip, associate director of NASA’s Stennis Space Center, and Gary Benton, director of the NASA Stennis Safety and Mission Assurance Directorate, are shown, from right to left, with employees working on the High Pressure Industrial Water Facility project near the Fred Haise Test Stand. The NASA Stennis leaders visited work sites on May 8 to recognize employees with NASA SHAKERS (Smart Human Actions Keep Everyone Really Safe) Awards for conducting work in a safe manner. NASA’s constant attention to safety, one of the agency’s five core values, is the cornerstone for mission success.
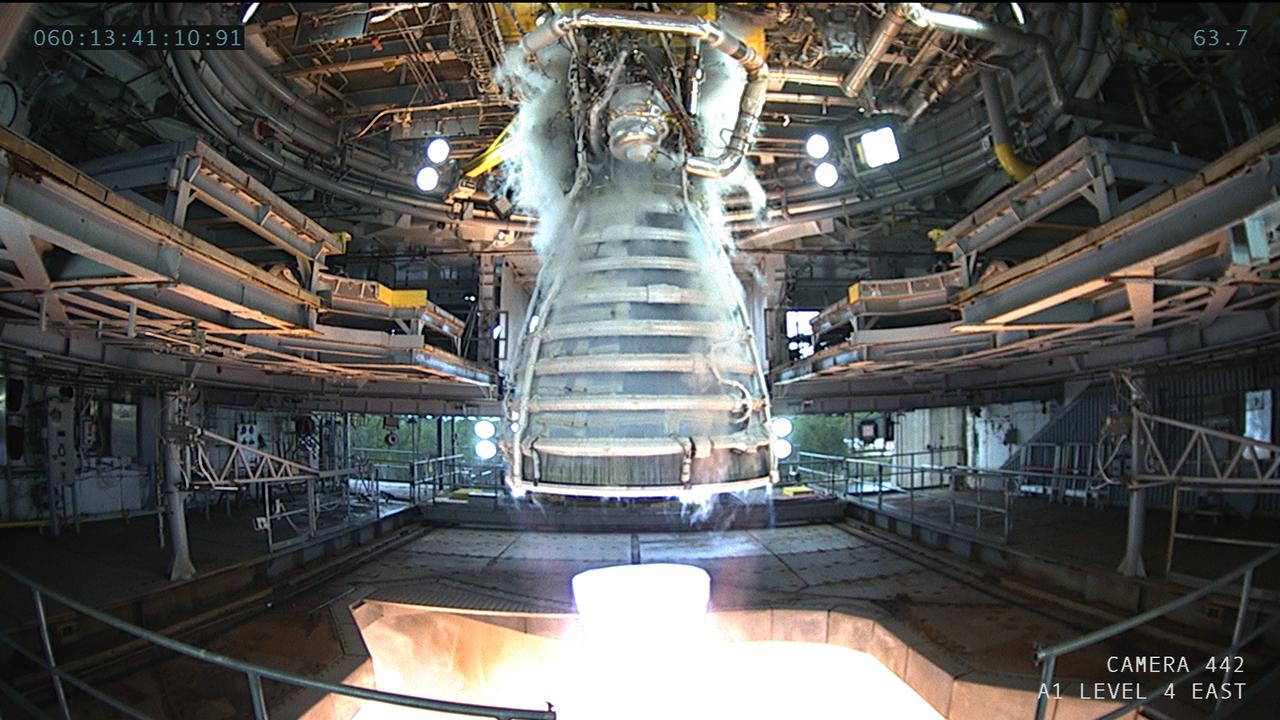

NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire Feb. 29 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, continuing a key test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The hot fire to certify new production RS-25 engines for SLS marked only the second ever Leap Day engine test. Fourty-four years ago on Feb. 29, 1980, before the first space shuttle launch, a test-fire occurred for RS-25 engine #0009. Both tests were conducted on the Fred Haise Test, previously known as the A-1 Test Stand at NASA Stennis. The Feb. 29, 2024, hot fire is the second test following installation of a second production engine nozzle that will provide additional performance data on the upgraded unit. It also marked the eighth in a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V. The current series is the second and final series to certify restart production of the upgraded engines. NASA completed an initial 12-test certification series with the upgraded components in June 2023. Four RS-25 engines fire simultaneously to help launch each SLS rocket, producing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust.
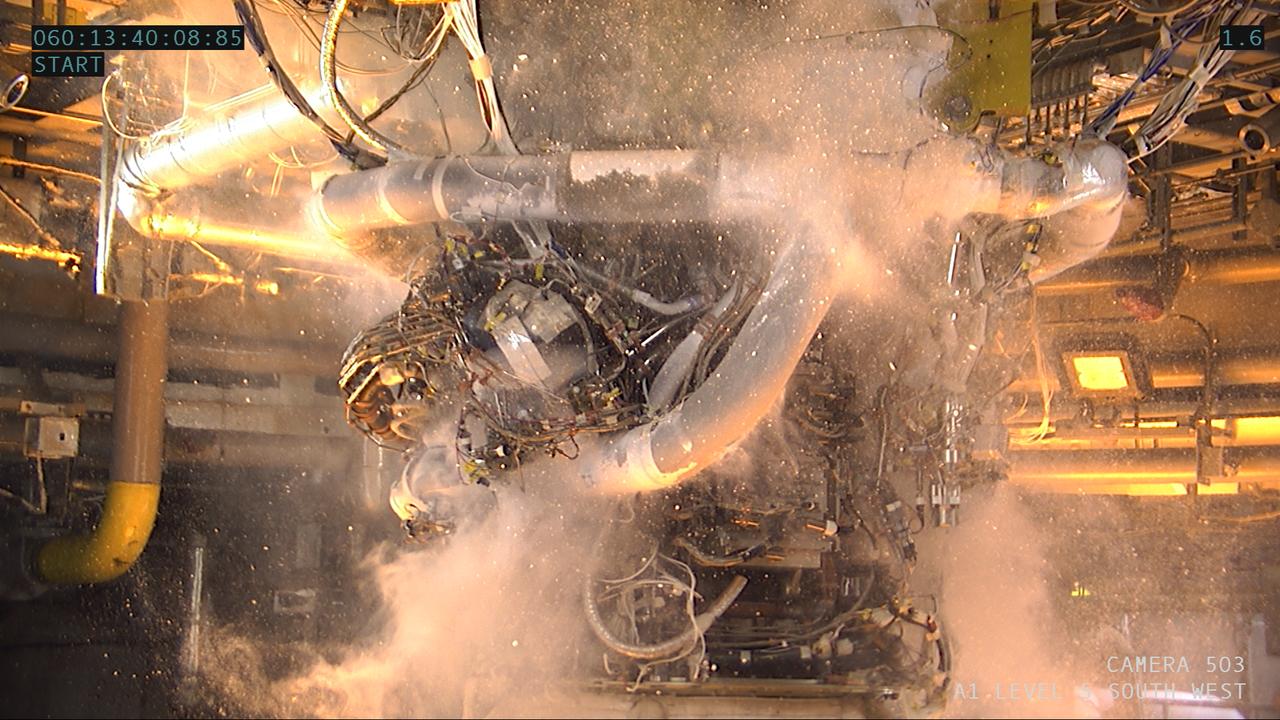
NASA conducted a full-duration RS-25 hot fire Feb. 29 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, continuing a key test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The hot fire to certify new production RS-25 engines for SLS marked only the second ever Leap Day engine test. Fourty-four years ago on Feb. 29, 1980, before the first space shuttle launch, a test-fire occurred for RS-25 engine #0009. Both tests were conducted on the Fred Haise Test, previously known as the A-1 Test Stand at NASA Stennis. The Feb. 29, 2024, hot fire is the second test following installation of a second production engine nozzle that will provide additional performance data on the upgraded unit. It also marked the eighth in a 12-test series to certify production of new RS-25 engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V. The current series is the second and final series to certify restart production of the upgraded engines. NASA completed an initial 12-test certification series with the upgraded components in June 2023. Four RS-25 engines fire simultaneously to help launch each SLS rocket, producing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust.
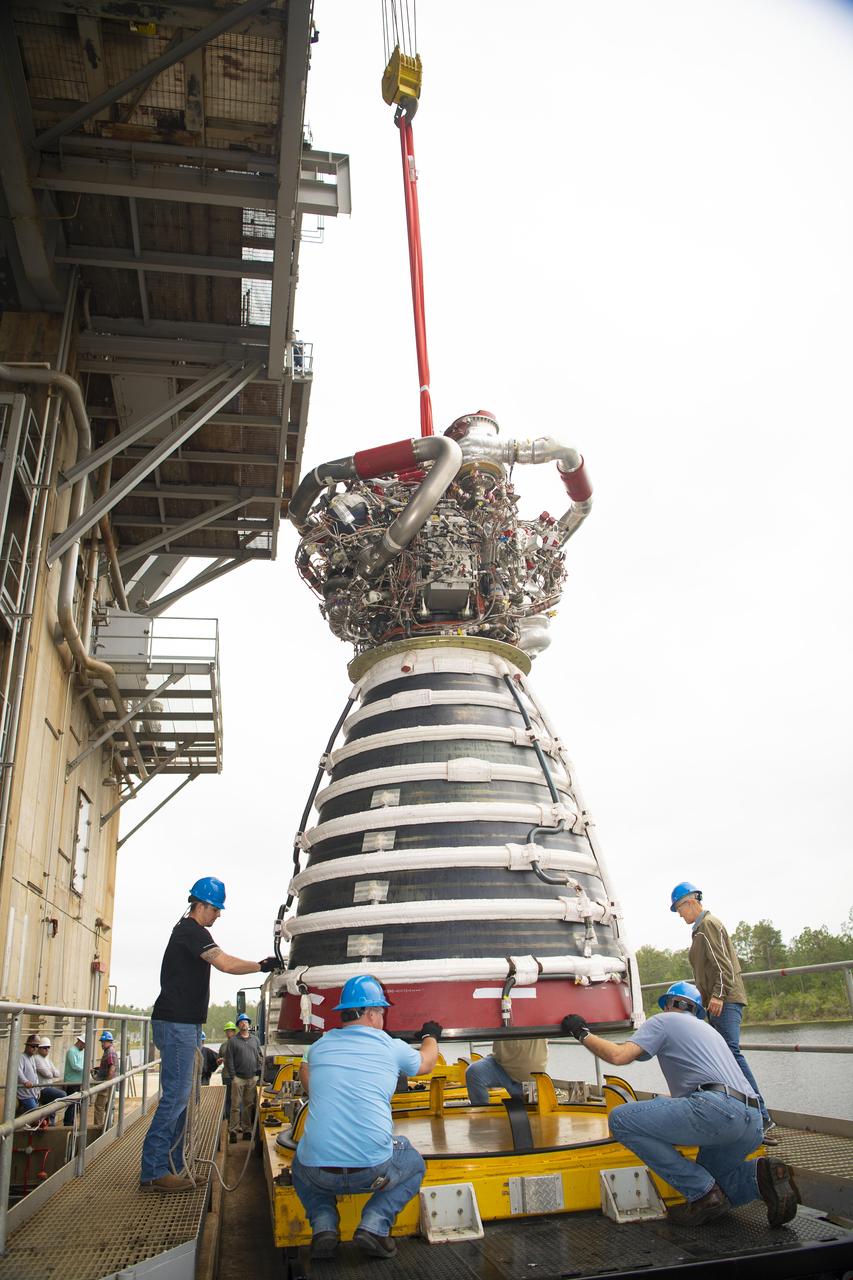

A work crew at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi removes RS-25 developmental engine E0525 from the Fred Haise Test Stand on April 9. Removal of the engine follows completion of the second and final 12-test series for lead engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to certify and build new RS-25 engines for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rockets that will power future lunar missions, beginning with Artemis V. Through Artemis, NASA will establish the foundation for long-term scientific exploration at the Moon; land the first woman, first person of color, and first international partner astronaut on the lunar surface; and prepare for human expeditions to Mars for the benefit of all.
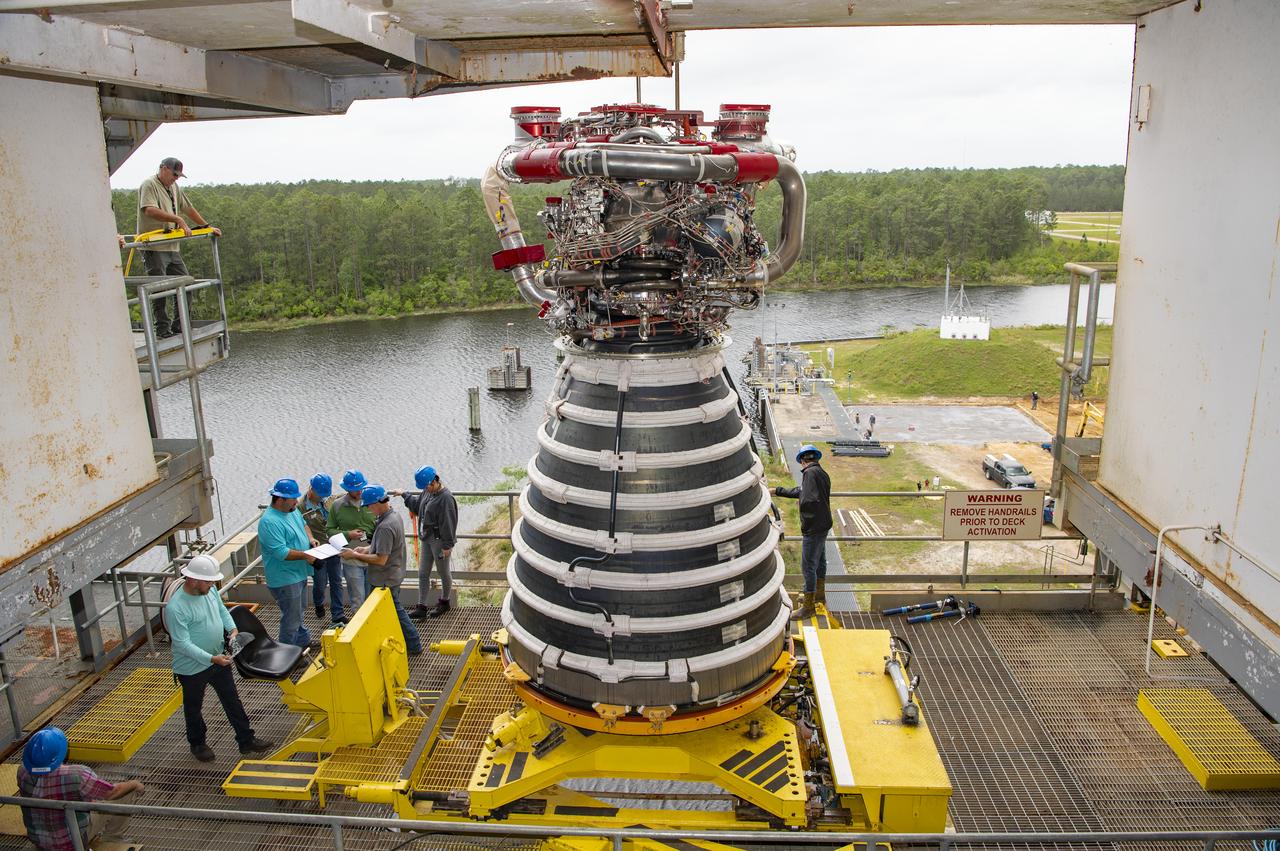

A work crew at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi removes RS-25 developmental engine E0525 from the Fred Haise Test Stand on April 9. Removal of the engine follows completion of the second and final 12-test series for lead engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to certify and build new RS-25 engines for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rockets that will power future lunar missions, beginning with Artemis V. Through Artemis, NASA will establish the foundation for long-term scientific exploration at the Moon; land the first woman, first person of color, and first international partner astronaut on the lunar surface; and prepare for human expeditions to Mars for the benefit of all.
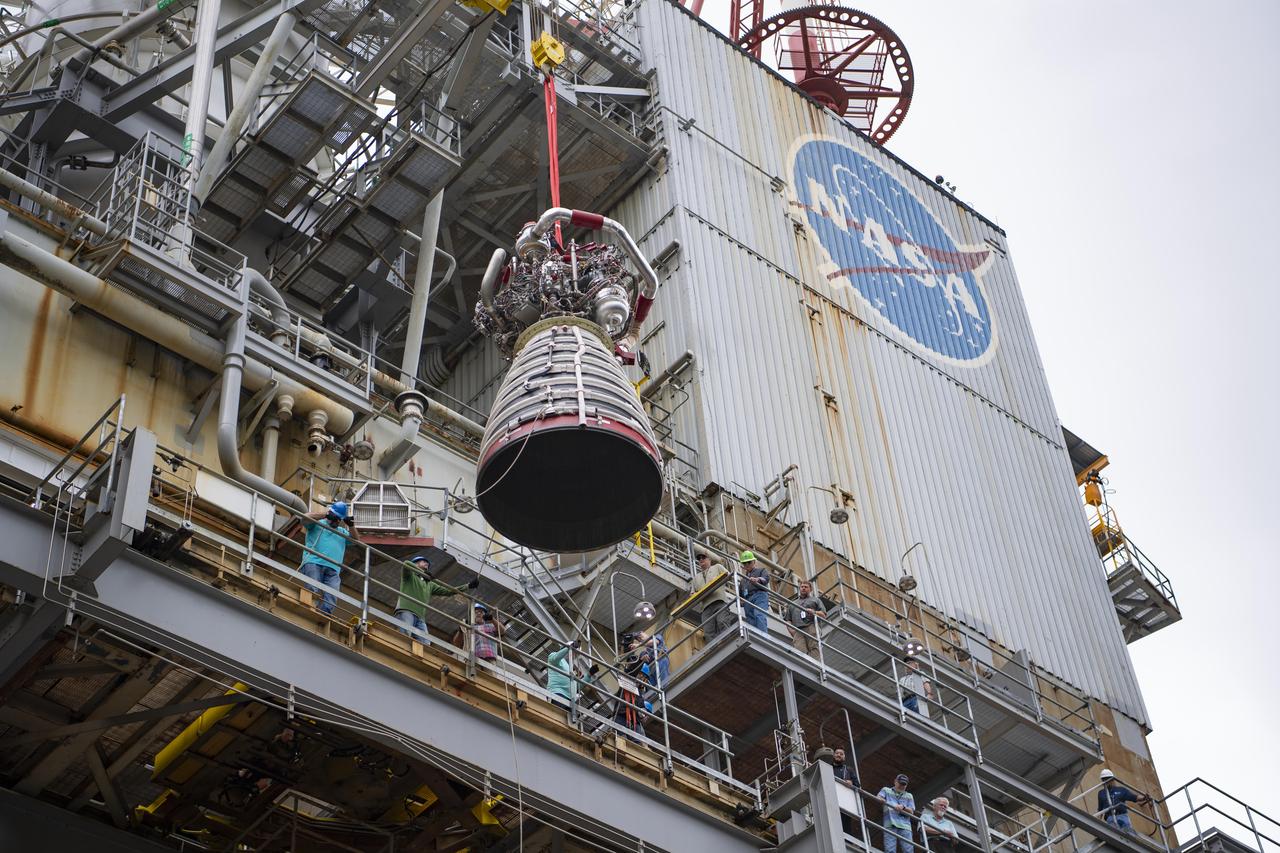

A work crew at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi removes RS-25 developmental engine E0525 from the Fred Haise Test Stand on April 9. Removal of the engine follows completion of the second and final 12-test series for lead engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to certify and build new RS-25 engines for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rockets that will power future lunar missions, beginning with Artemis V. Through Artemis, NASA will establish the foundation for long-term scientific exploration at the Moon; land the first woman, first person of color, and first international partner astronaut on the lunar surface; and prepare for human expeditions to Mars for the benefit of all.
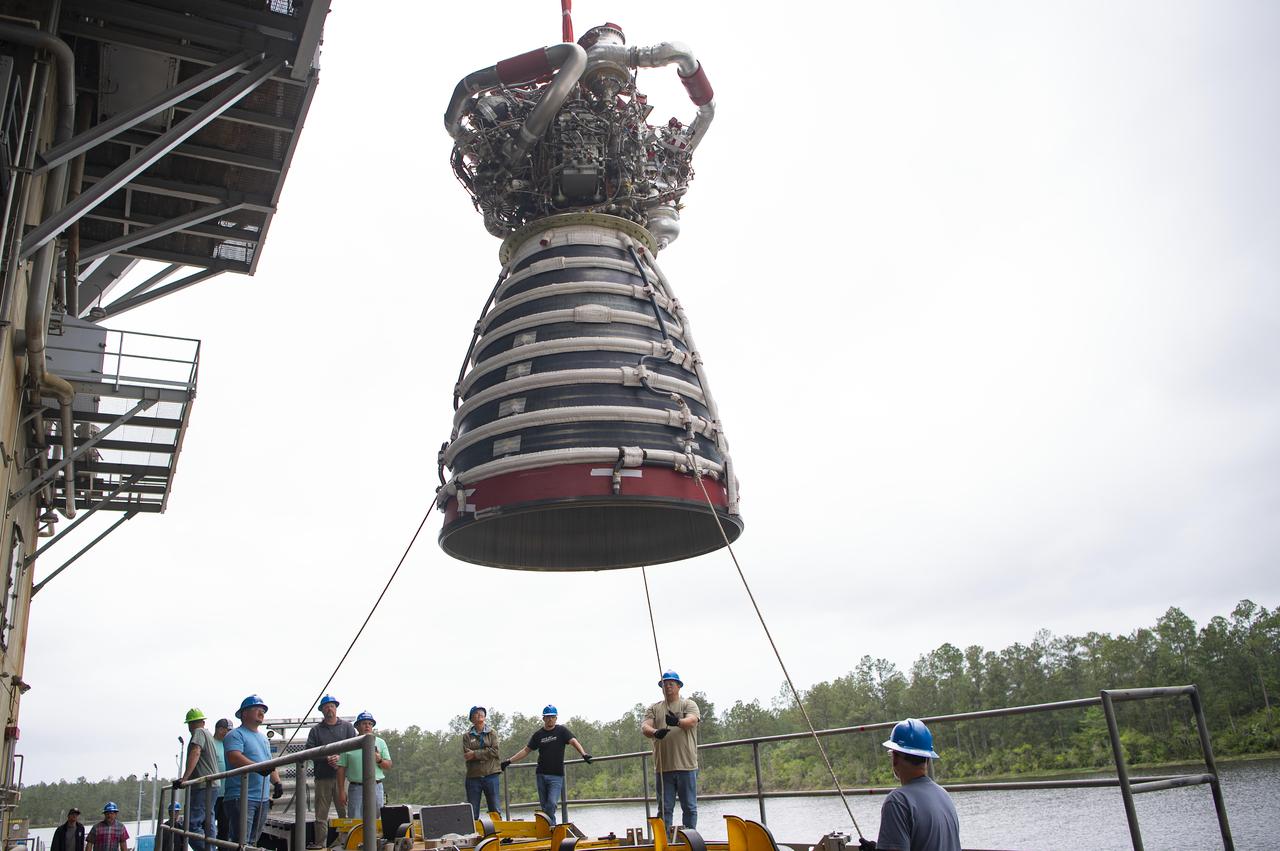

A work crew at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi removes RS-25 developmental engine E0525 from the Fred Haise Test Stand on April 9. Removal of the engine follows completion of the second and final 12-test series for lead engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, to certify and build new RS-25 engines for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rockets that will power future lunar missions, beginning with Artemis V. Through Artemis, NASA will establish the foundation for long-term scientific exploration at the Moon; land the first woman, first person of color, and first international partner astronaut on the lunar surface; and prepare for human expeditions to Mars for the benefit of all.
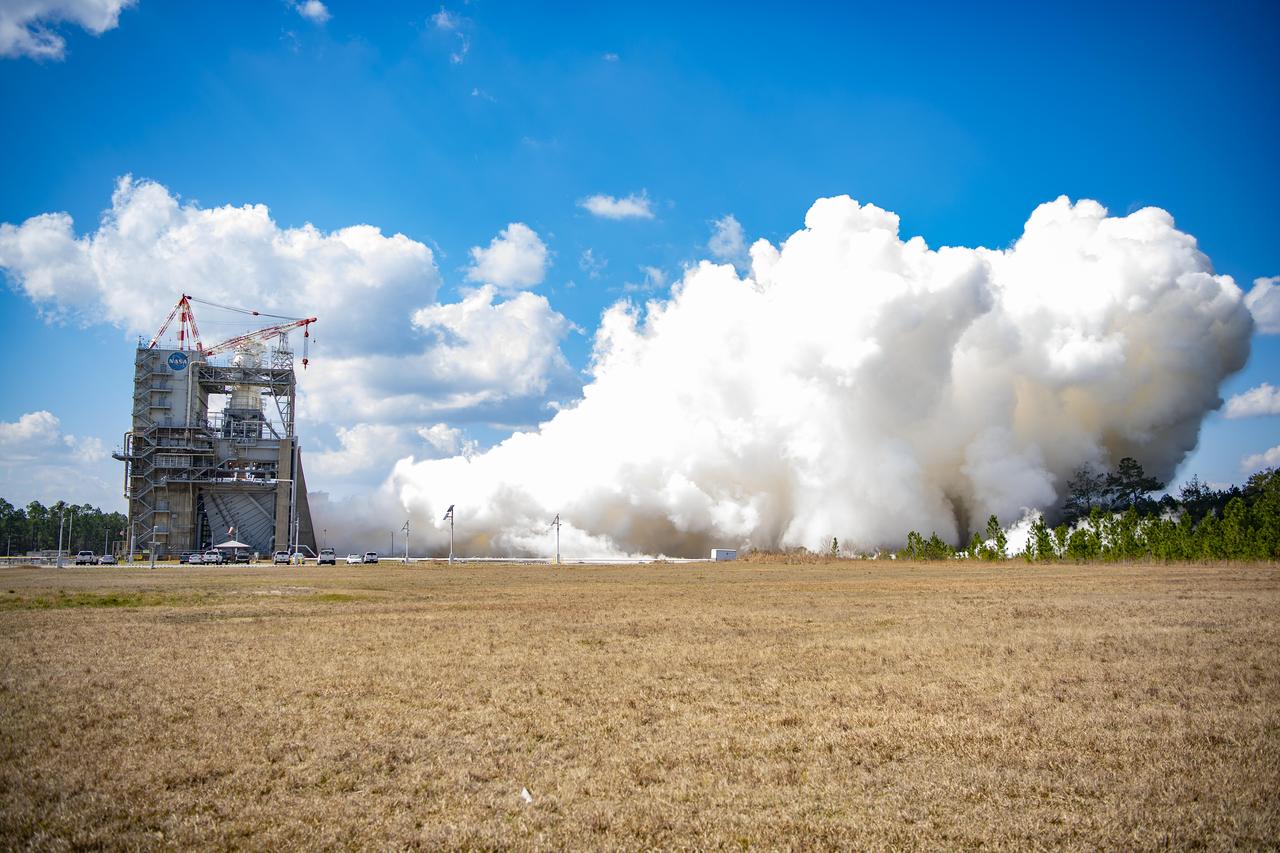

NASA conducts a full-duration RS-25 hot fire Feb. 23 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, continuing a key test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. During the seventh test of the 12-test series, operators fired the certification engine for 550 seconds and up to a 113% power level. The hot fire followed installation of a second production engine nozzle that will provide additional performance data on the upgraded unit. The test series is the second, and final, series to certify restart production of the upgraded engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company. New engines will help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V. NASA and Aerojet Rocketdyne modified 16 former space shuttle engines for use on Artemis missions I through IV. NASA completed an initial 12-test certification series with the upgraded components in June 2023. Four RS-25 engines fire simultaneously to help launch each SLS rocket, producing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust.

NASA conducts a full-duration RS-25 hot fire Feb. 23 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, continuing a key test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. During the seventh test of the 12-test series, operators fired the certification engine for 550 seconds and up to a 113% power level. The hot fire followed installation of a second production engine nozzle that will provide additional performance data on the upgraded unit. The test series is the second, and final, series to certify restart production of the upgraded engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company. New engines will help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V. NASA and Aerojet Rocketdyne modified 16 former space shuttle engines for use on Artemis missions I through IV. NASA completed an initial 12-test certification series with the upgraded components in June 2023. Four RS-25 engines fire simultaneously to help launch each SLS rocket, producing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust.
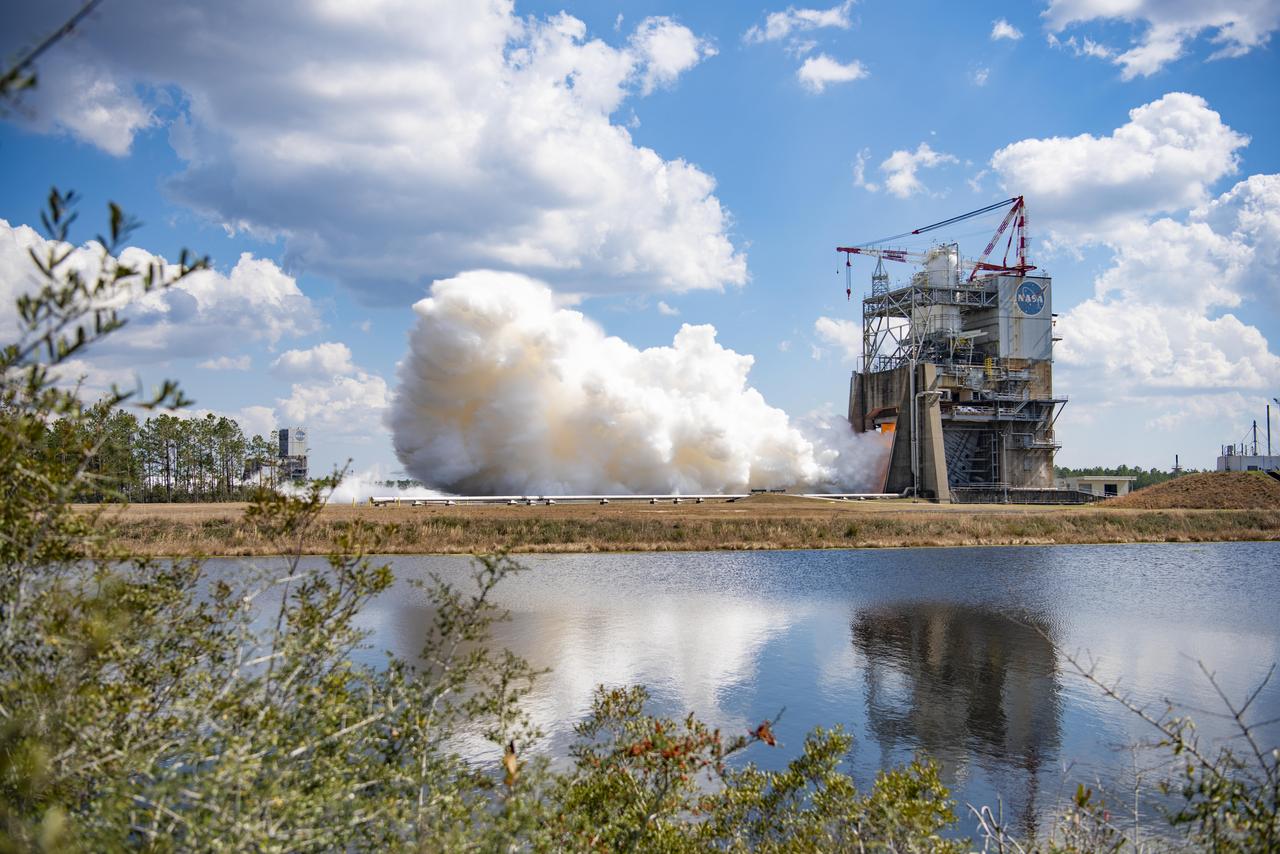

NASA conducts a full-duration RS-25 hot fire Feb. 23 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, continuing a key test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. During the seventh test of the 12-test series, operators fired the certification engine for 550 seconds and up to a 113% power level. The hot fire followed installation of a second production engine nozzle that will provide additional performance data on the upgraded unit. The test series is the second, and final, series to certify restart production of the upgraded engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company. New engines will help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V. NASA and Aerojet Rocketdyne modified 16 former space shuttle engines for use on Artemis missions I through IV. NASA completed an initial 12-test certification series with the upgraded components in June 2023. Four RS-25 engines fire simultaneously to help launch each SLS rocket, producing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust.
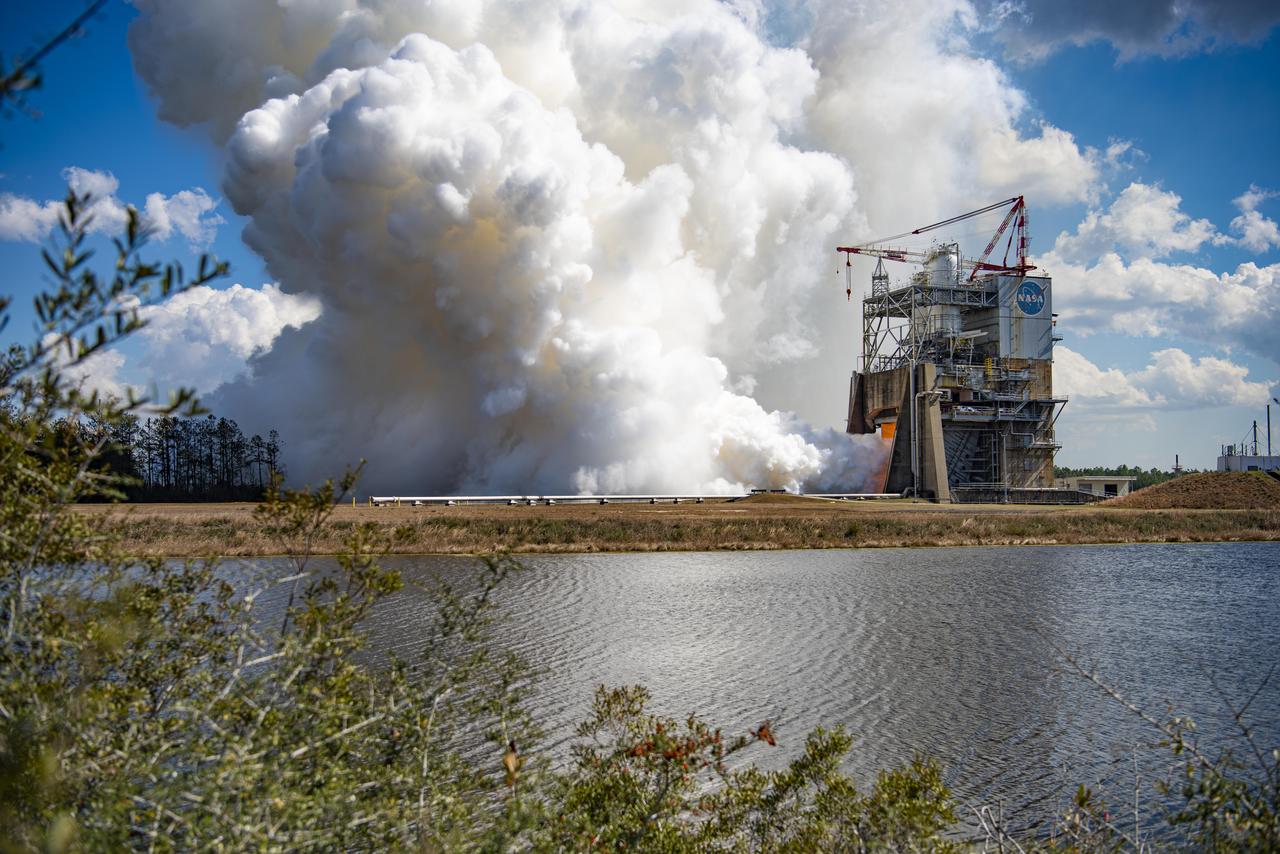

NASA conducts a full-duration RS-25 hot fire Feb. 23 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, continuing a key test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. During the seventh test of the 12-test series, operators fired the certification engine for 550 seconds and up to a 113% power level. The hot fire followed installation of a second production engine nozzle that will provide additional performance data on the upgraded unit. The test series is the second, and final, series to certify restart production of the upgraded engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company. New engines will help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V. NASA and Aerojet Rocketdyne modified 16 former space shuttle engines for use on Artemis missions I through IV. NASA completed an initial 12-test certification series with the upgraded components in June 2023. Four RS-25 engines fire simultaneously to help launch each SLS rocket, producing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust.
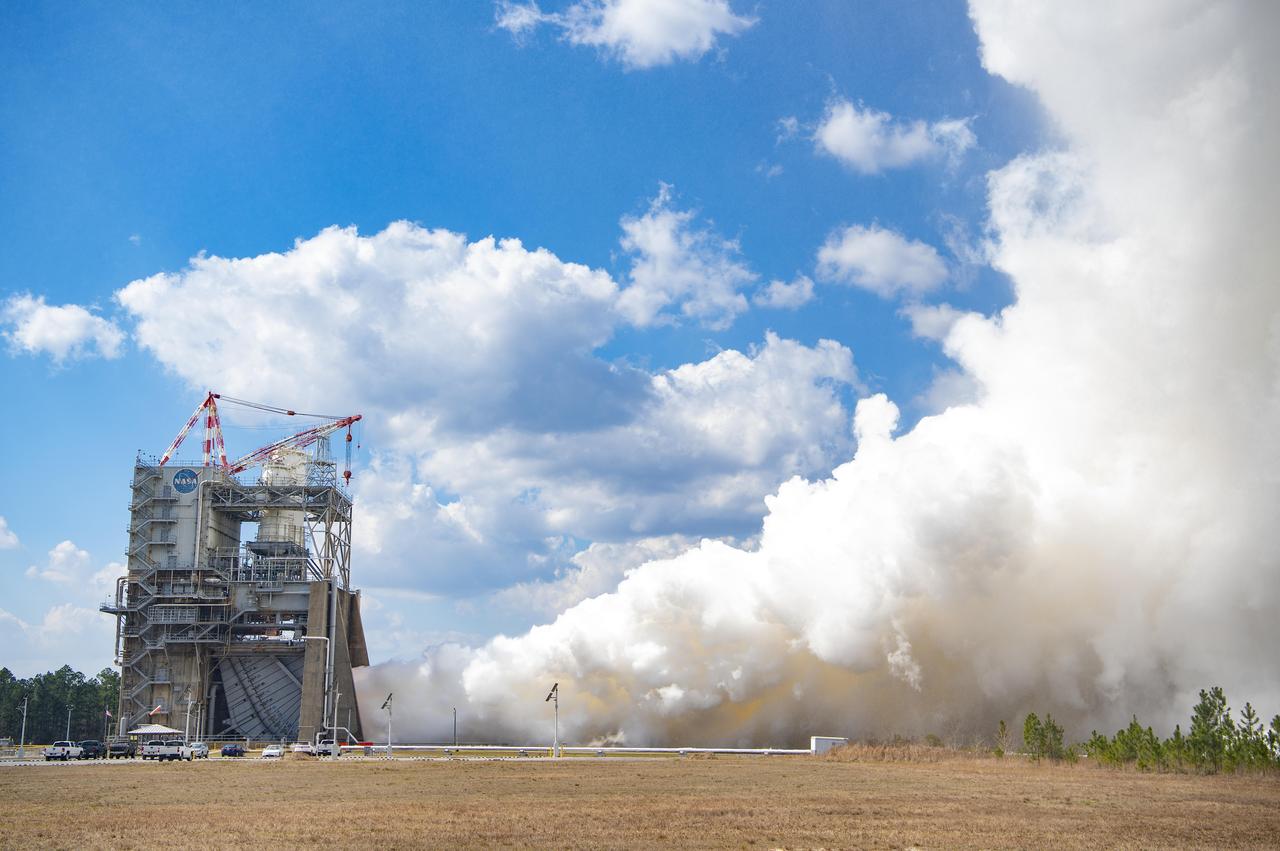

NASA conducts a full-duration RS-25 hot fire Feb. 23 on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, continuing a key test series for future Artemis flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. During the seventh test of the 12-test series, operators fired the certification engine for 550 seconds and up to a 113% power level. The hot fire followed installation of a second production engine nozzle that will provide additional performance data on the upgraded unit. The test series is the second, and final, series to certify restart production of the upgraded engines by lead contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company. New engines will help power NASA’s SLS rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond, beginning with Artemis V. NASA and Aerojet Rocketdyne modified 16 former space shuttle engines for use on Artemis missions I through IV. NASA completed an initial 12-test certification series with the upgraded components in June 2023. Four RS-25 engines fire simultaneously to help launch each SLS rocket, producing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust.