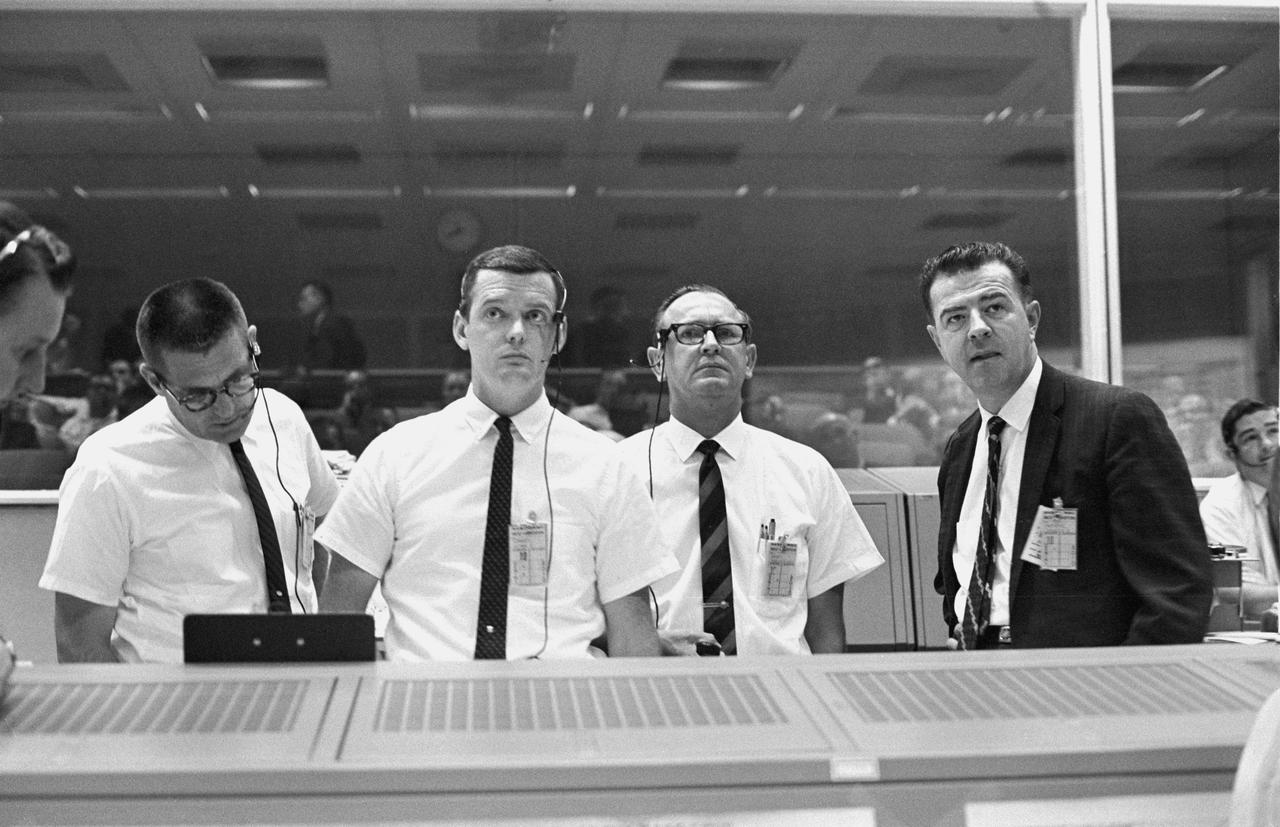

S66-43377 (18 July 1966) --- Standing at the flight director's console, viewing the Gemini-10 flight display in the Mission Control Center, are (left to right) William C. Schneider, Mission Director; Glynn Lunney, Prime Flight Director; Christopher C. Kraft Jr., MSC Director of Flight Operations; and Charles W. Mathews, Manager, Gemini Program Office. Photo credit: NASA

S66-39691 (18 June 1966) --- Astronaut John W. Young, prime crew command pilot for the Gemini-10 spaceflight, sits in Static Article 5 during water egress training activity onboard the NASA Motor Vessel Retriever. The SA-5 will be placed in the water and he and astronaut Michael Collins will then practice egress and water survival techniques. At right is Gordon Harvey, Spacecraft Operations Branch, Flight Crew Support Division. Photo credit: NASA
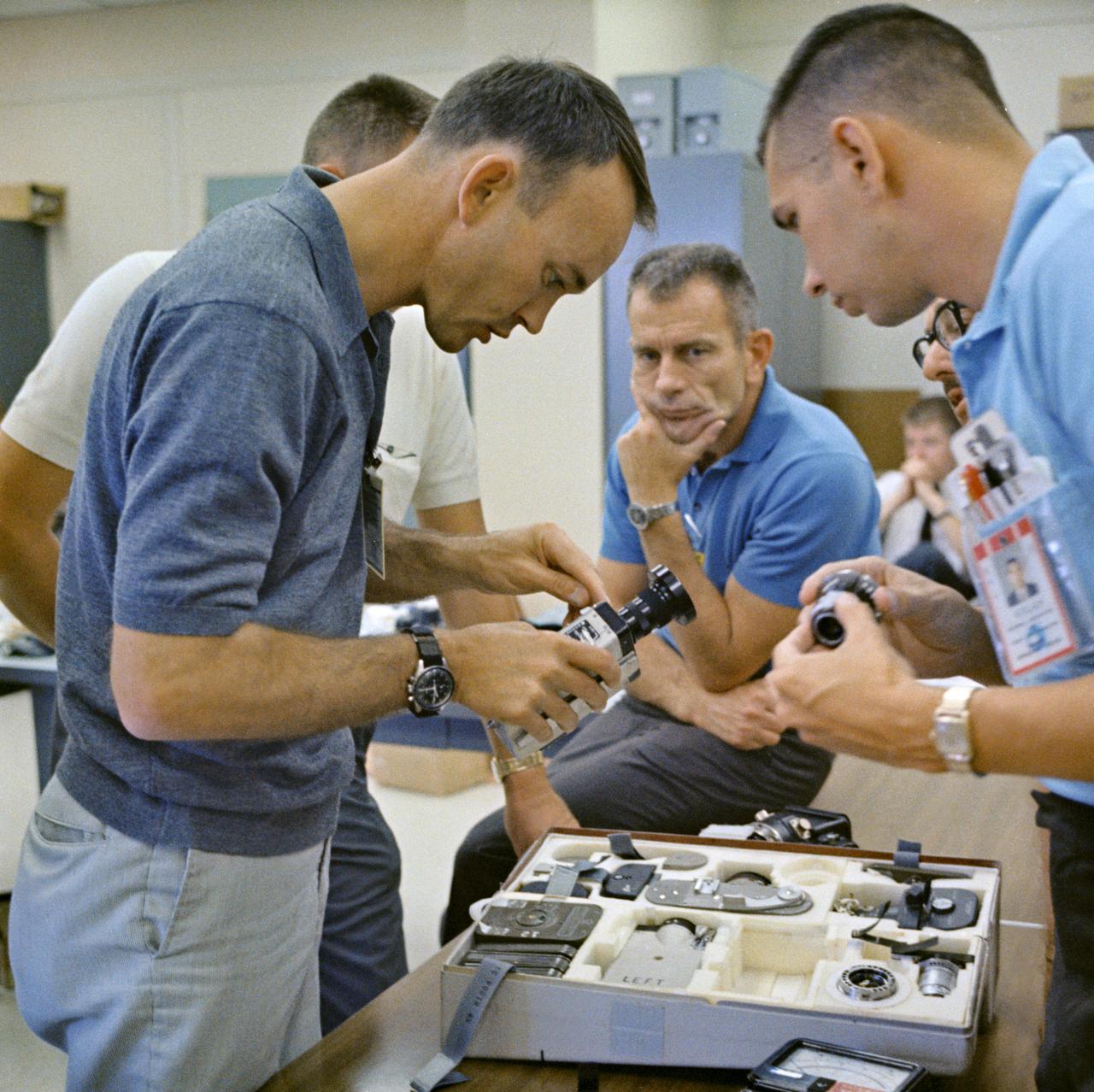

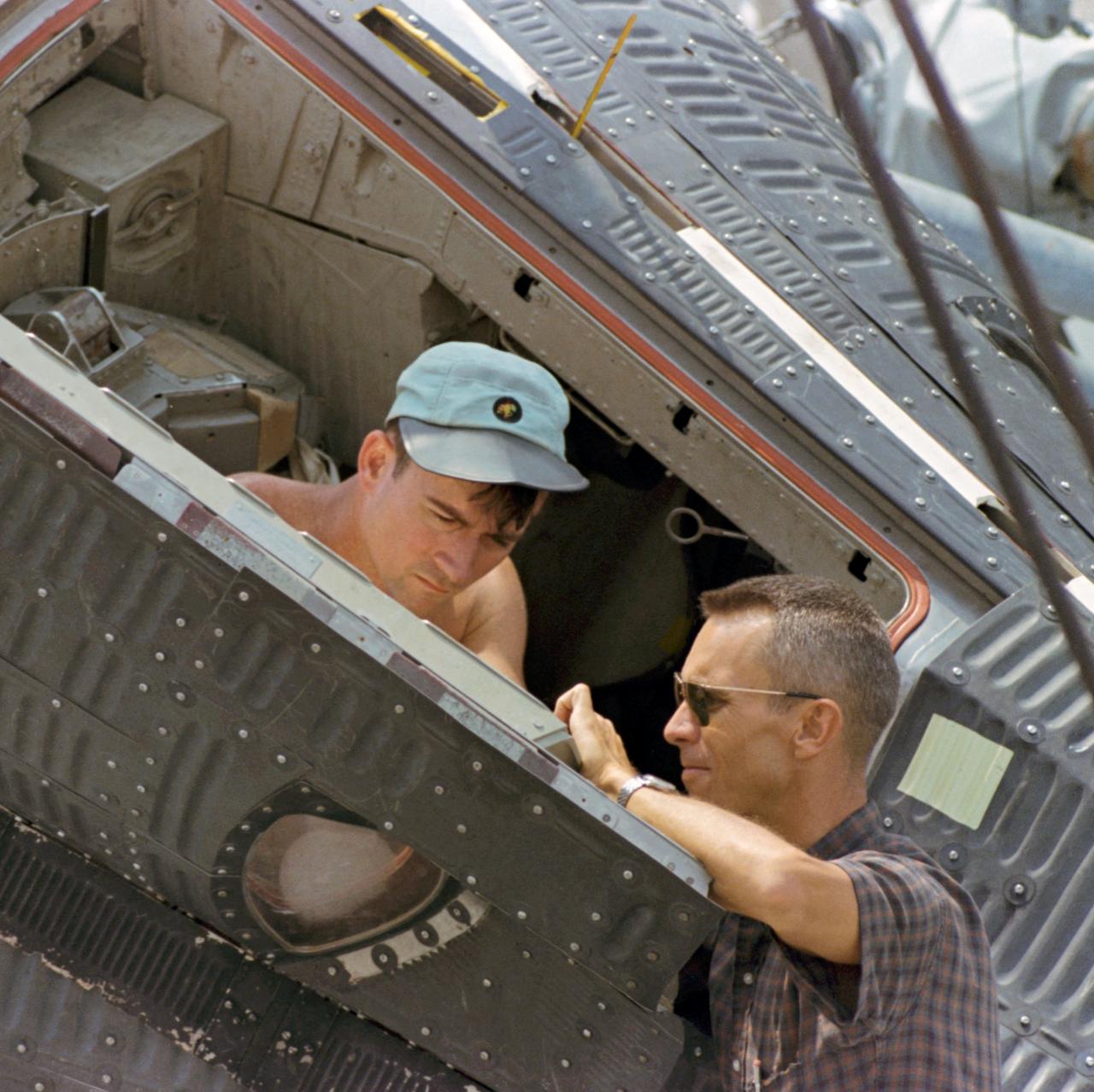
S66-42763 (18 July 1966) --- Astronaut Michael Collins (left), Gemini-10 prime crew pilot, inspects a camera during prelaunch activity at Cape Kennedy, Florida. In center background is Dr. Donald K. Slayton, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Director of Flight Crew Operations. Photo credit: NASA
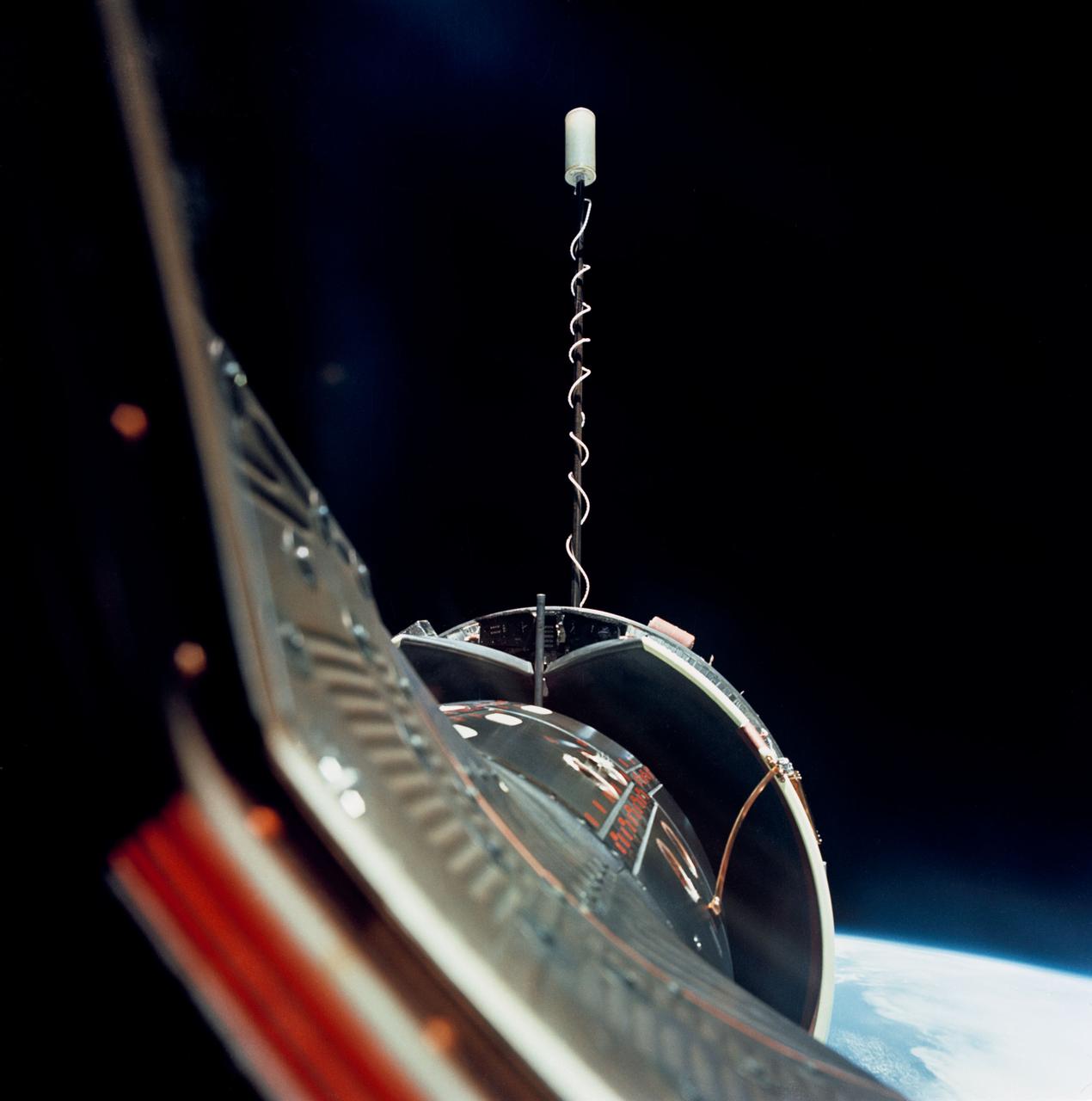

S66-46144 (18 July 1966) --- The Gemini-10 spacecraft is successfully docked with the Agena Target Docking Vehicle 5005. The Agena display panel is clearly visible. After docking with the Agena, astronauts John W. Young, command pilot, and Michael Collins, pilot, fired the 16,000-pound thrust engine of Agena-10's primary propulsion system to boost the combined vehicles into an orbit with an apogee of 413 nautical miles to set a new altitude record for manned spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA
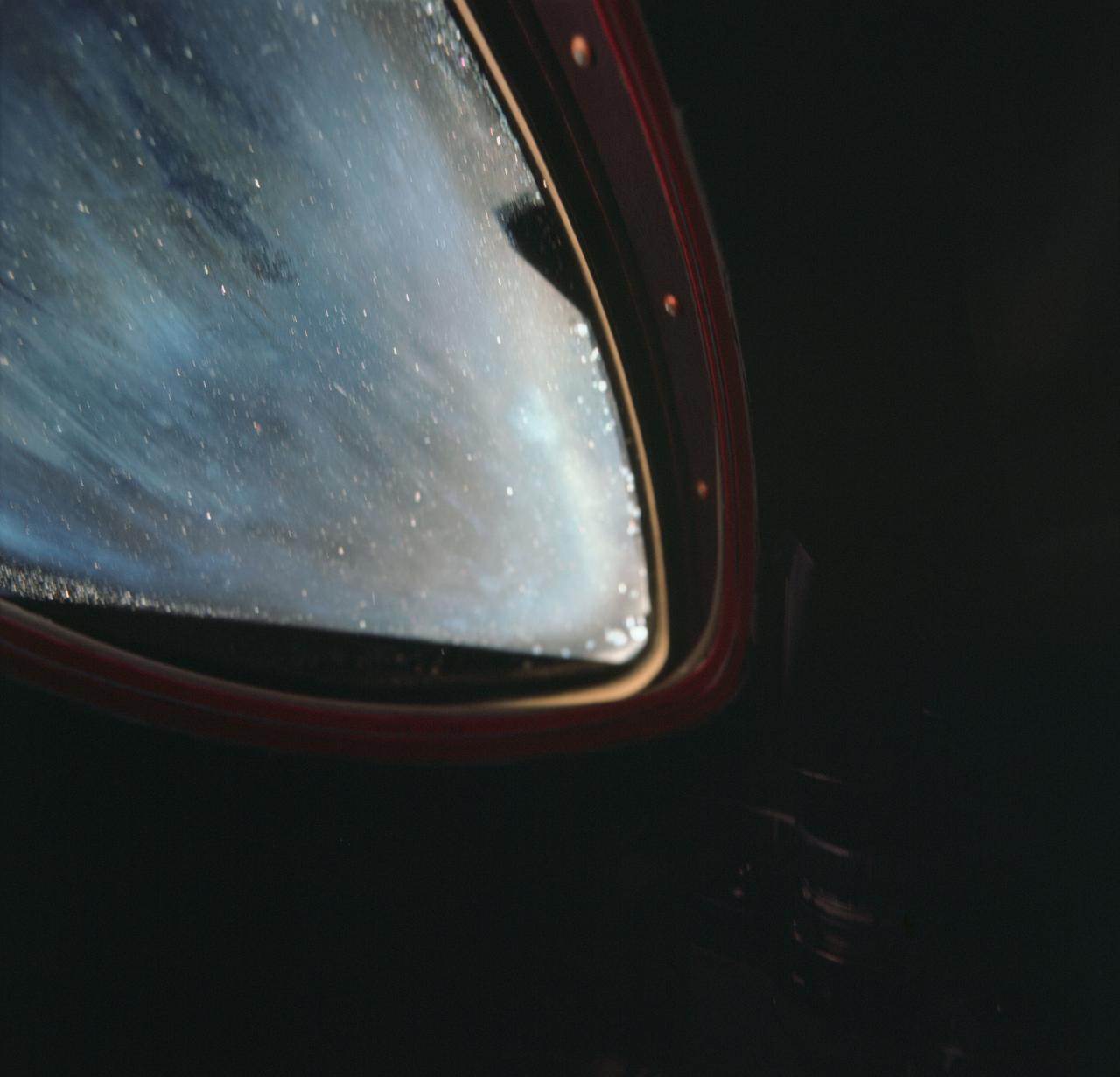

S66-46241 (18 July 1966) --- Debris on spacecraft window in picture taken from inside the Gemini-10 spacecraft. At this time Gemini-10 was docked with the Agena Target Docking Vehicle 5005. Taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome, MS (S.O. 217) color film. The Gemini-10 crew is astronaut John W. Young, command pilot, and Michael Collins, pilot. Photo credit: NASA
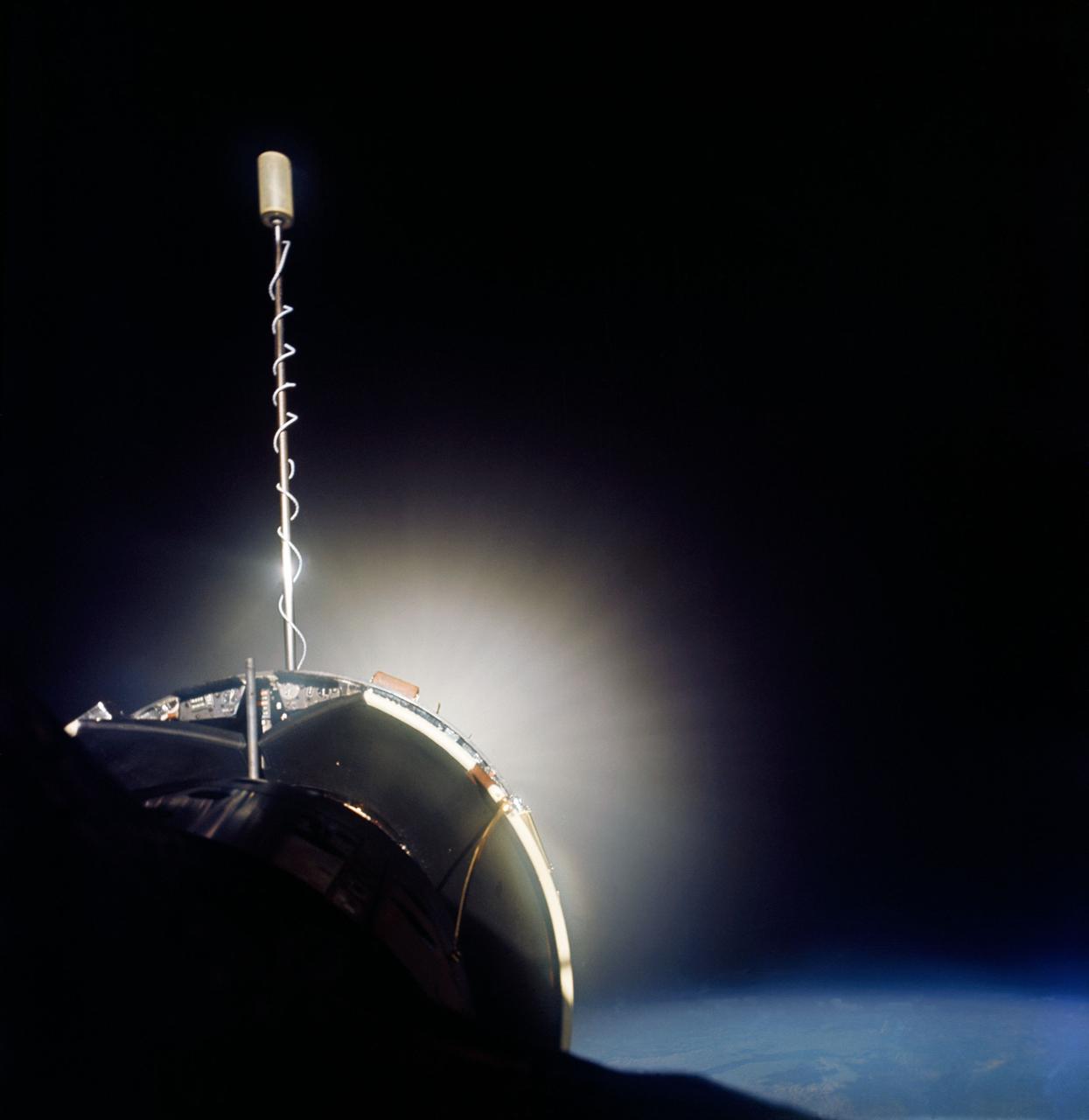

S66-46249 (18-21 July 1966) --- Agena Target Docking Vehicle docked to Gemini-10 spacecraft. Excellent view of Agena display panel. Glow from Agena's primary propulsion system. Photo credit: NASA
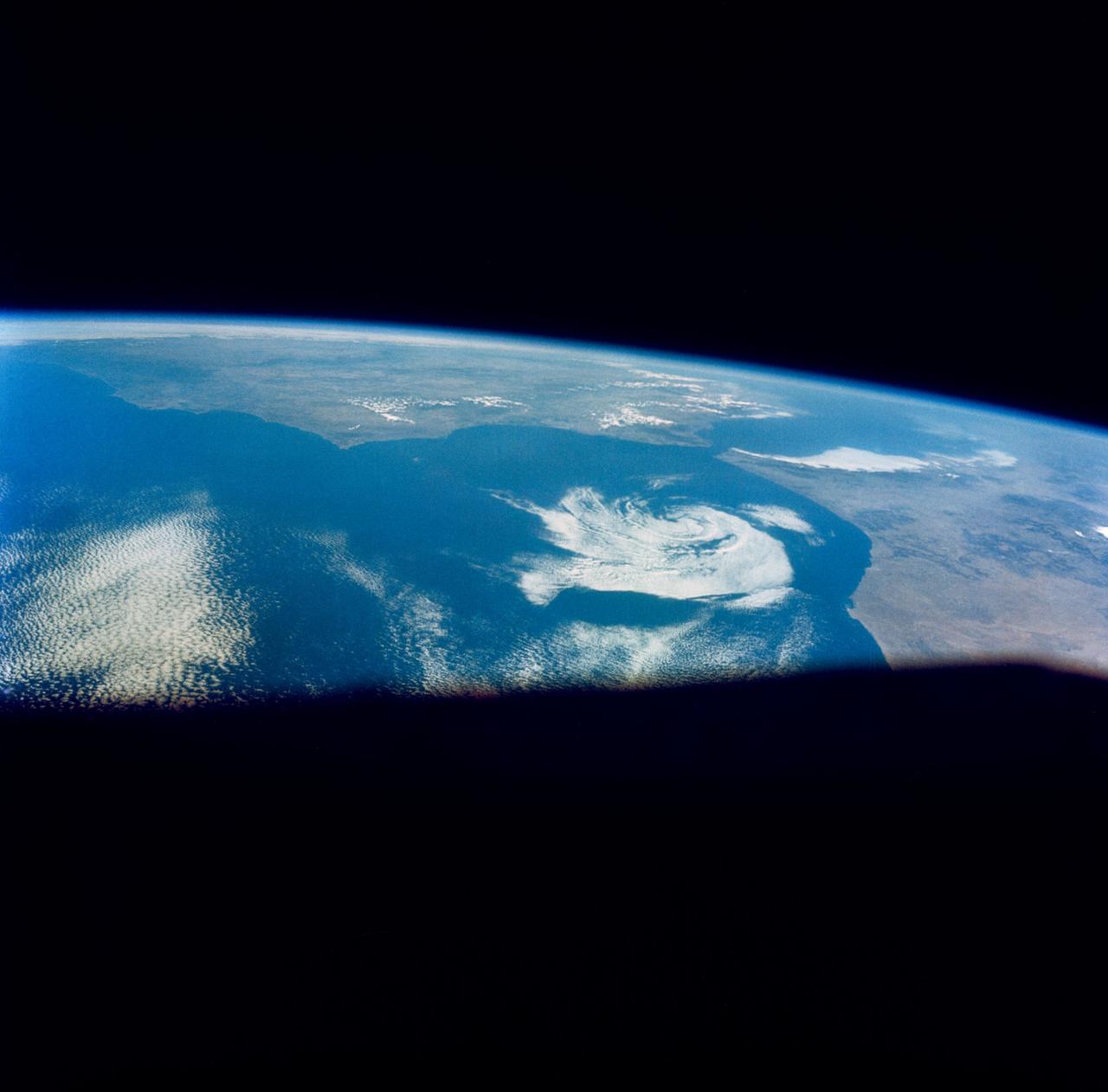

S66-46044 (18-21 July 1966) --- Straits of Gibraltar and Spain ? Portugal (left), Morocco (right), Atlantic Ocean (foreground), and unique vortex, as seen from the Gemini-10 spacecraft. Taken with J.A. Maurer 70mm camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome, MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
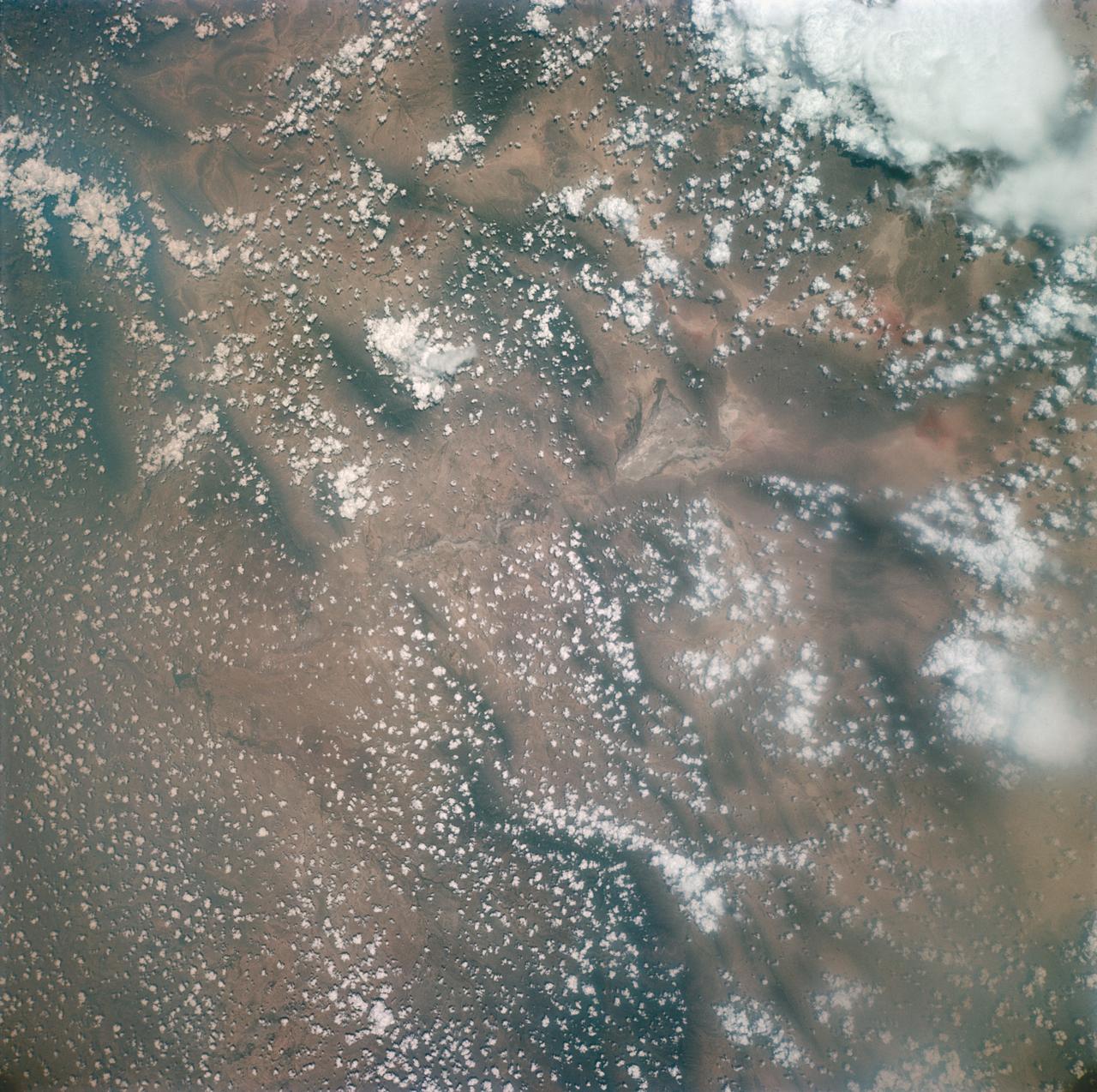

S66-45763 (18-21 July 1966) --- Don Martin Reservoir and Sabinas River Valley area of the States of Coahuila and Nuevo Leon, Mexico, as seen from the Gemini-10 spacecraft. Taken with a J. A. Maurer 70mm camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome, MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA

S66-46122 (18 July 1966) --- Agena Target Docking Vehicle 5005 is photographed from the Gemini-Titan 10 (GT-10) spacecraft during rendezvous in space. The two spacecraft are about 38 feet apart. After docking with the Agena, astronauts John W. Young, command pilot, and Michael Collins, pilot, fired the 16,000 pound thrust engine of Agena X's primary propulsion system to boost the combined vehicles into an orbit with an apogee of 413 nautical miles to set a new altitude record for manned spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA
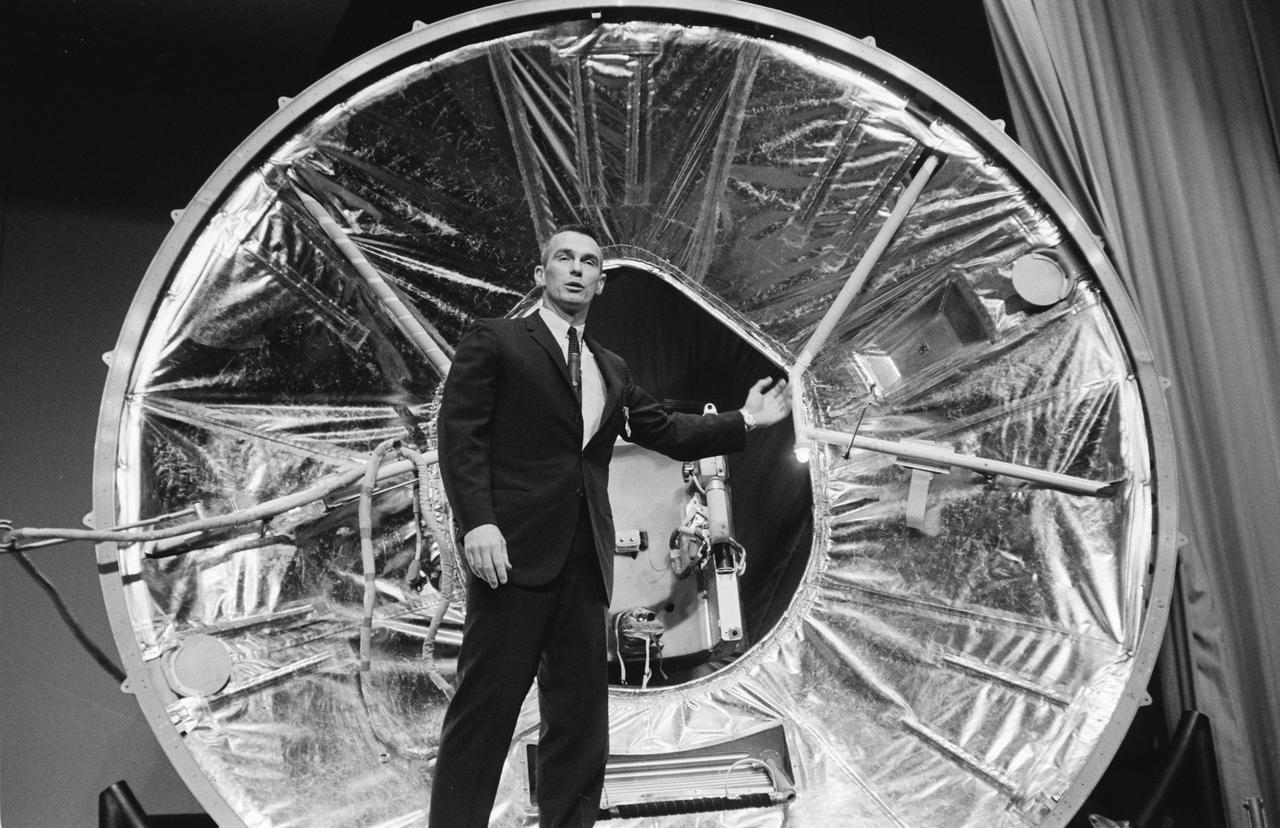

S66-32698 (17 June 1966) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan discusses his Gemini-9A extravehicular activity before a gathering of news media representatives in the MSC auditorium. In the background is an Astronaut Maneuvering Unit (AMU) mock-up mounted in a mock-up of a Gemini spacecraft adapter equipment section. Astronauts Cernan and Thomas P. Stafford completed their three-day mission in space on June 6, 1966. Photo credit: NASA
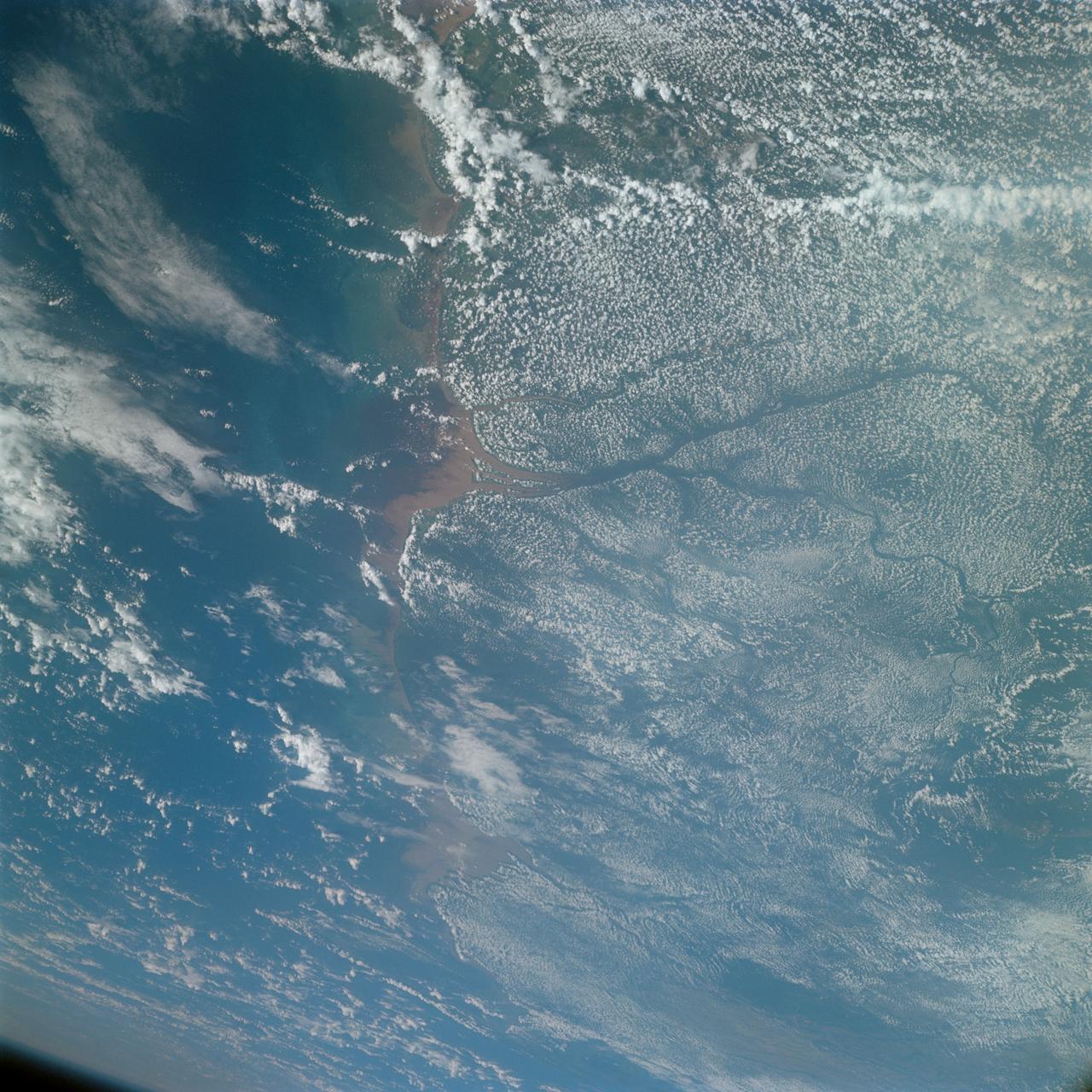

S66-46054 (18 July 1966) --- Venezuela, British Guyana, Surinam and Trinidad, as seen from the Gemini-10 spacecraft. On the left is the mouth of the Orinoco River in Venezuela. Mouth of Essequibo River in British Guyana is in right center. Photo credit: NASA
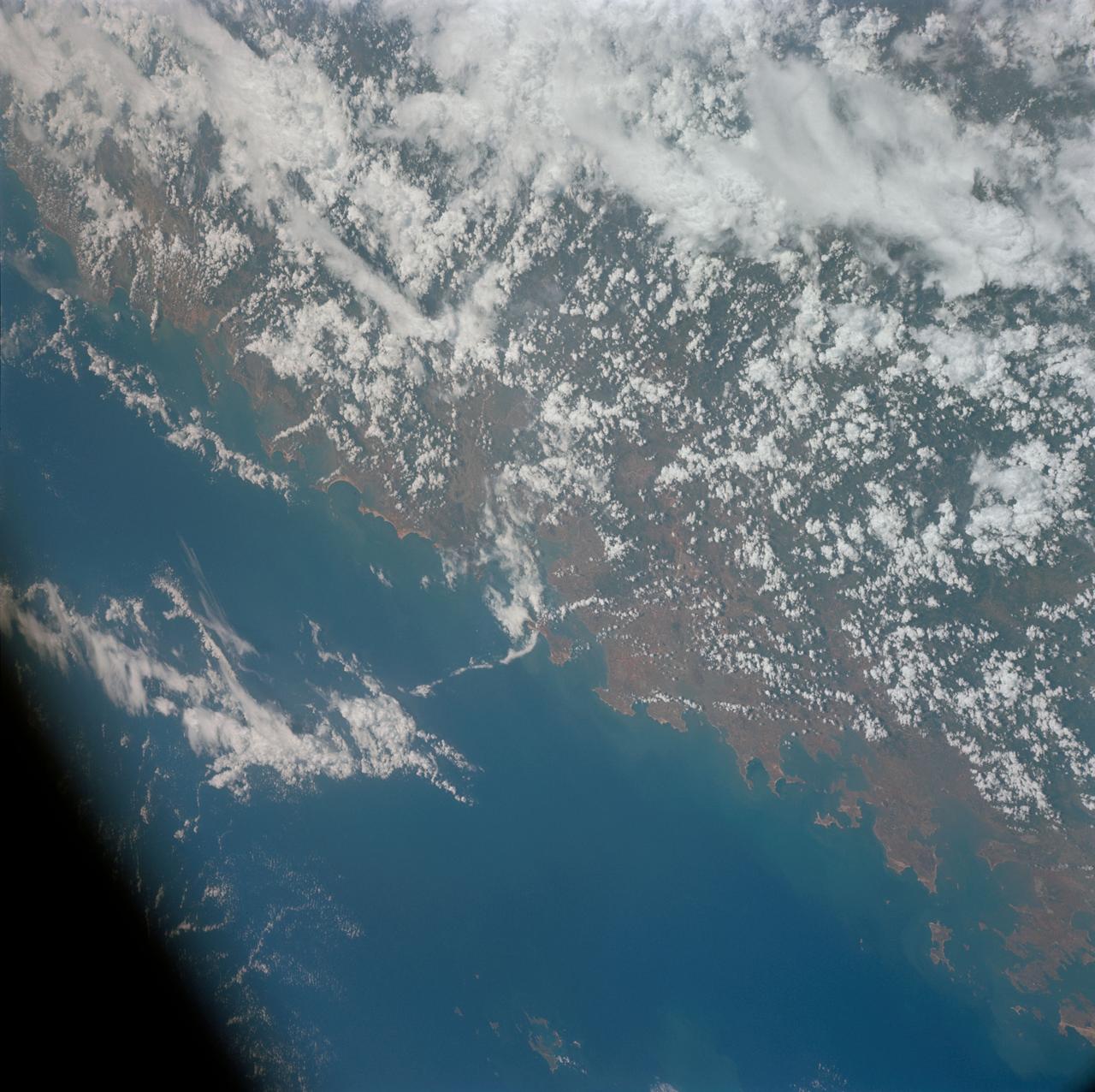

S66-45951 (18-21 July 1966) --- China, Fukien and Kwangtung provinces, Formosa Strait, Pescadores Island, Quemoy Island, as seen from the Gemini-10 spacecraft. Taken with a J.A. Maurer 70mm camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome, MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
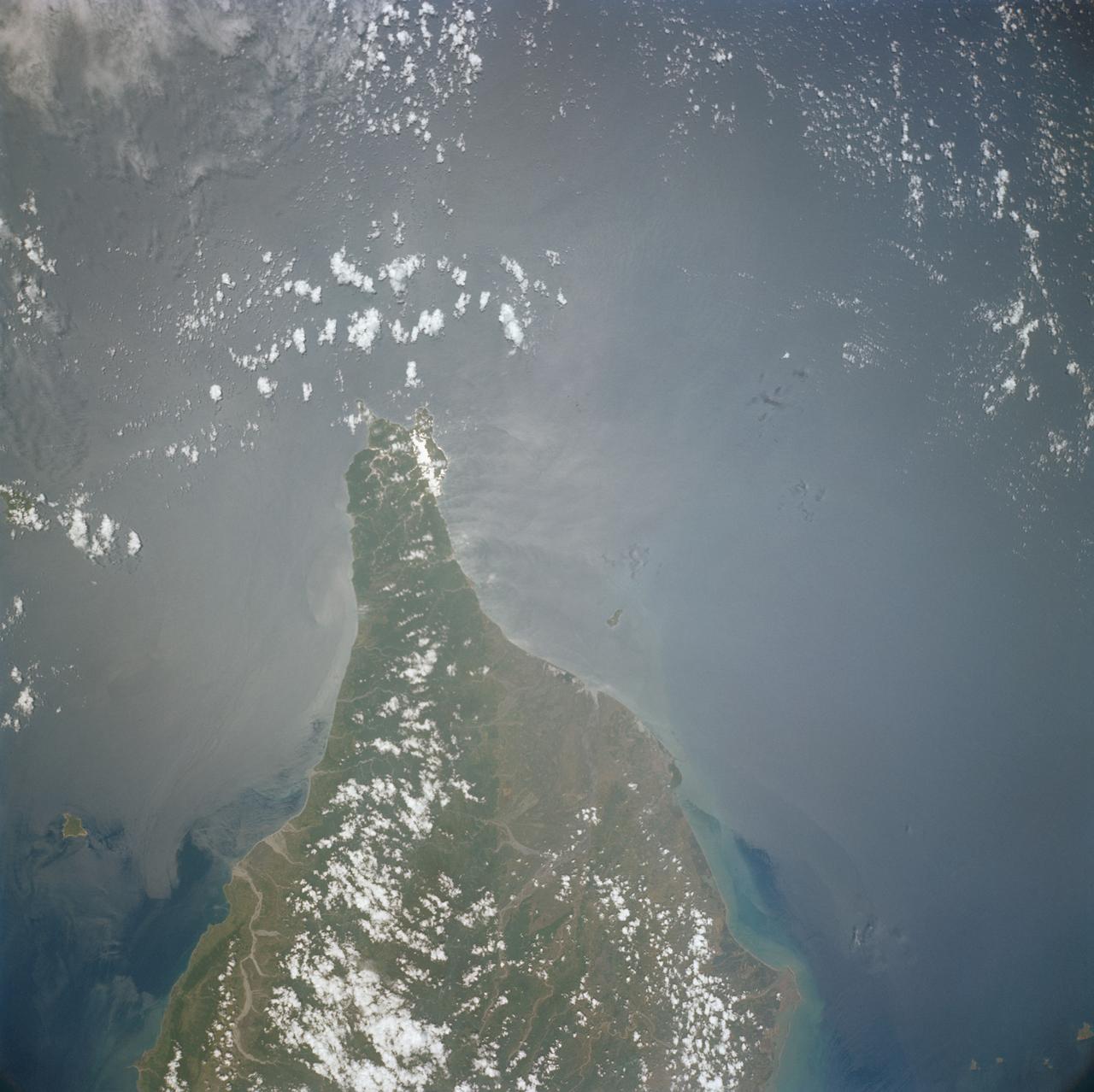

S66-45868 (18-21 July 1966) --- Southern half of the island of Taiwan (Formosa) as seen from the Gemini-10 spacecraft. Taken with a J.A. Maurer 70mm camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome, MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
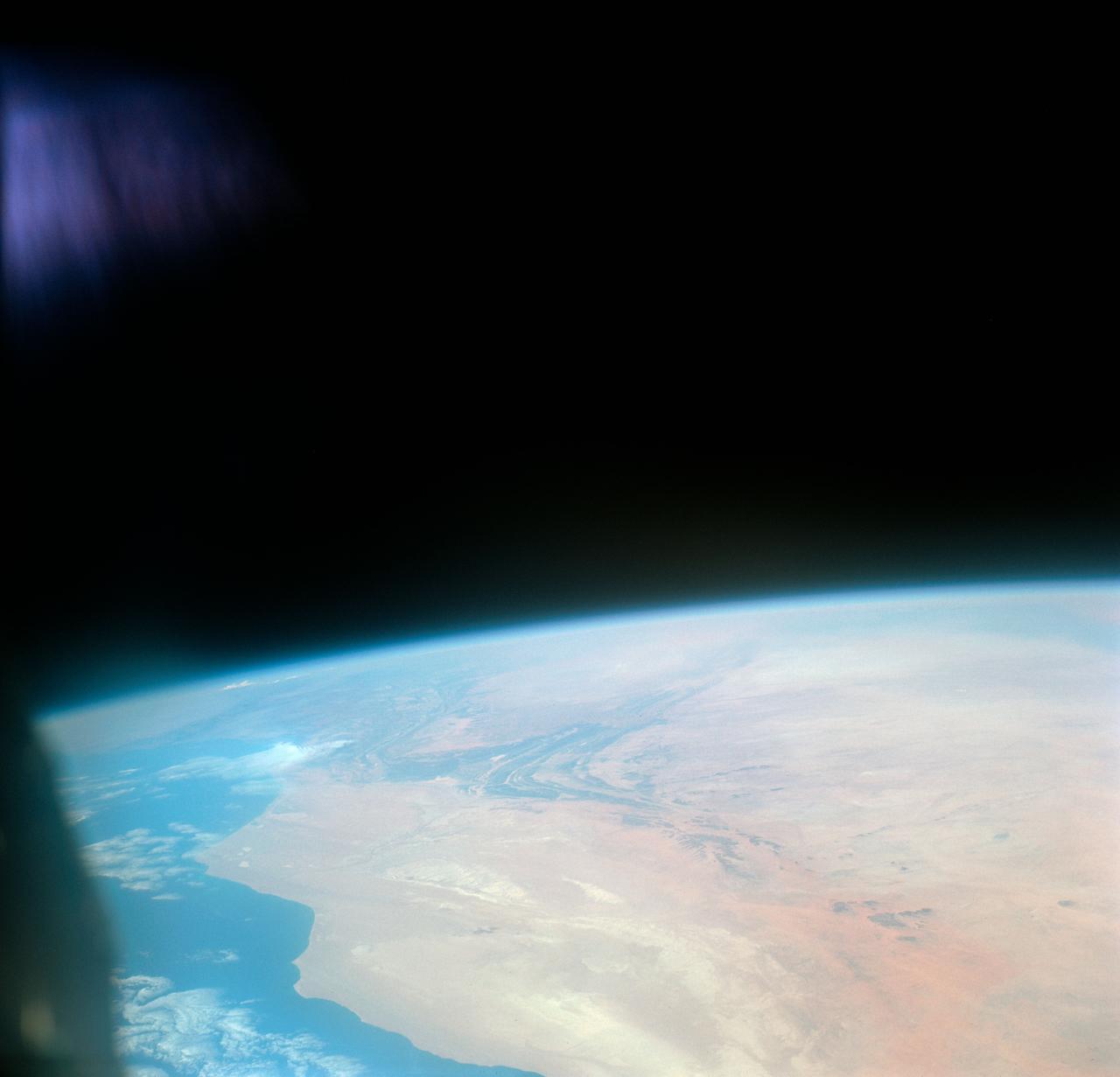

S66-46062 (18-21 July 1966) --- Area of the Spanish Sahara--Mauritania--Algeria--Morocco, looking north into Hamada Du Dra, as seen from the Gemini-10 spacecraft. Taken with a J.A. Maurer 70mm camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome, MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
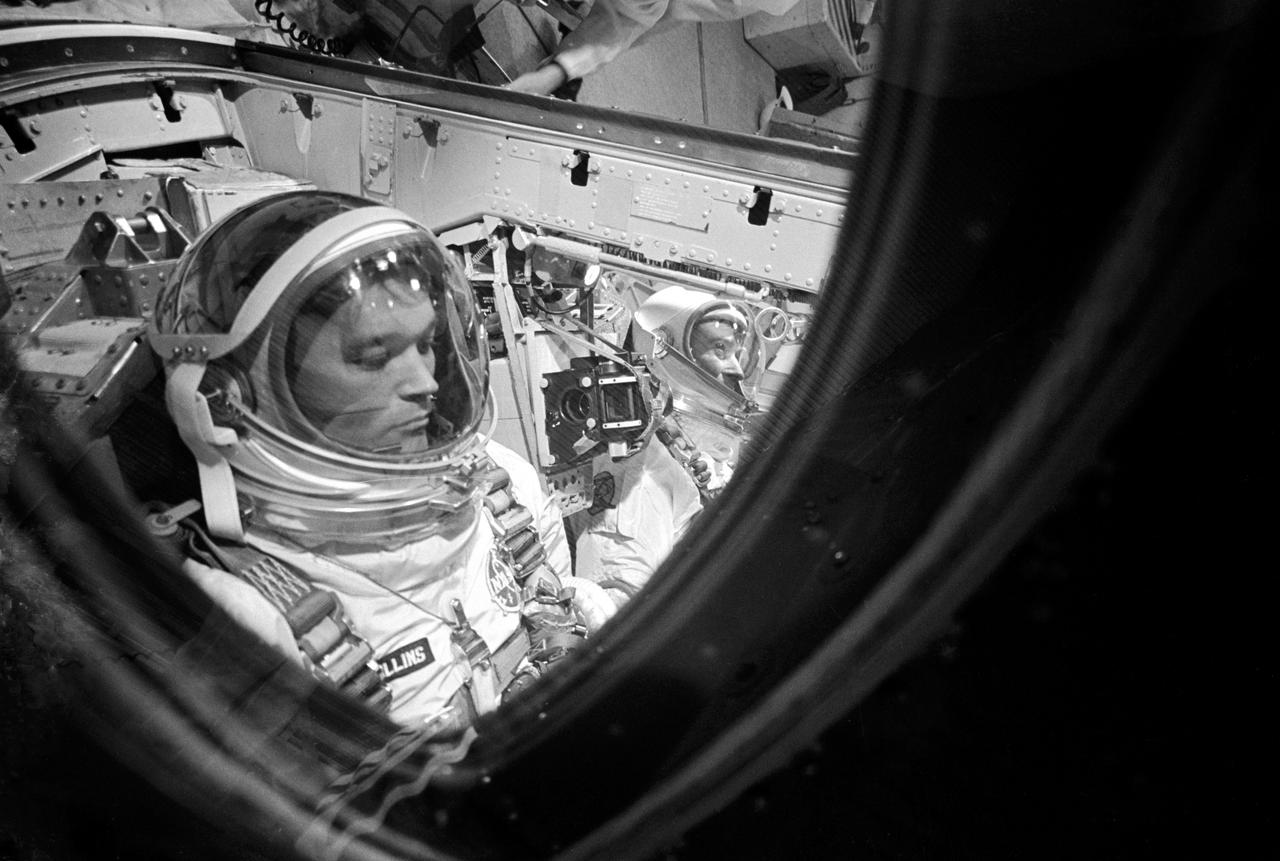

S66-46477 (18 July 1966) --- Close-up of astronaut Michael Collins, Gemini-10 pilot, making final adjustments and checks in the Gemini spacecraft during prelaunch countdown. In right background is astronaut John W. Young, command pilot. Photo credit: NASA
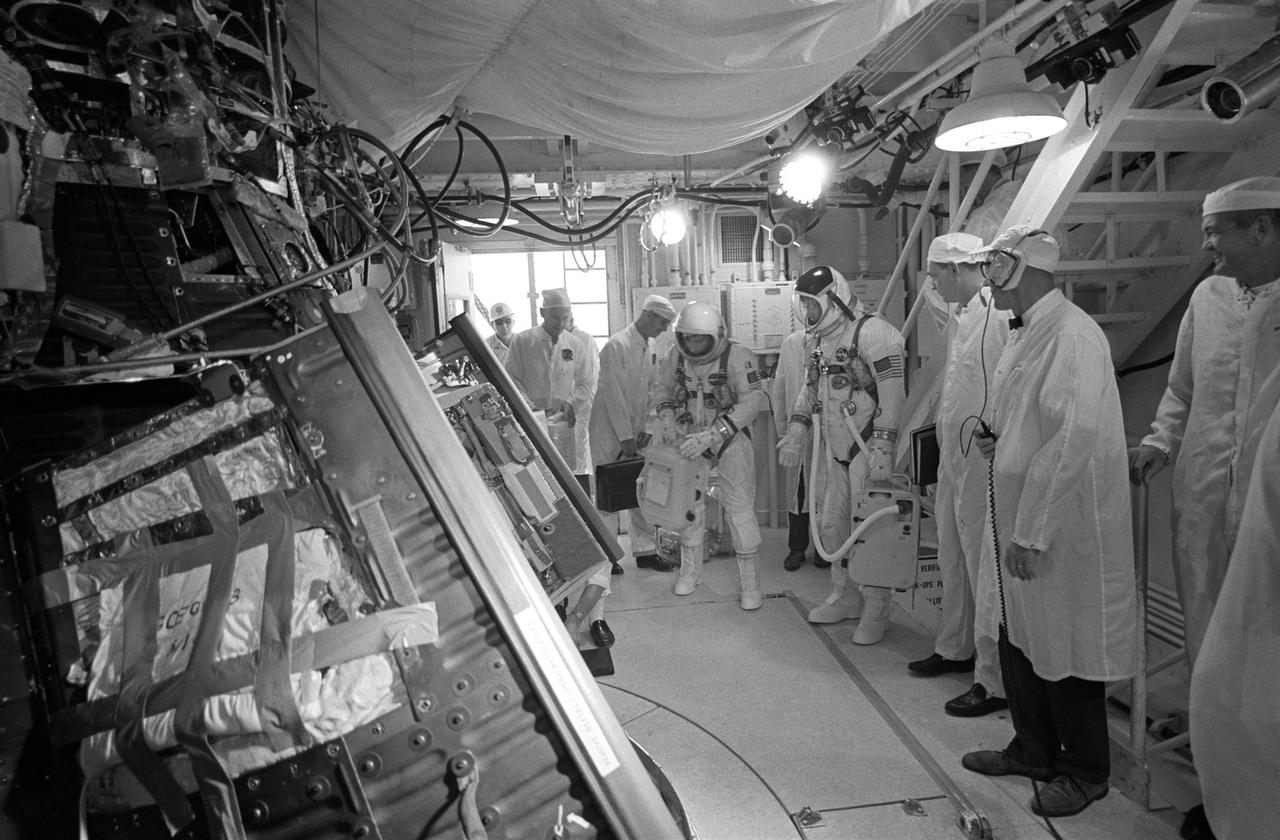

S66-42702 (12 July 1966) --- Gemini-10 prime crew, astronauts John W. Young (left), command pilot, and Michael Collins (right), pilot, check equipment in the White Room atop Pad 19 where they participated in a Simultaneous Launch Demonstration. Photo credit: NASA
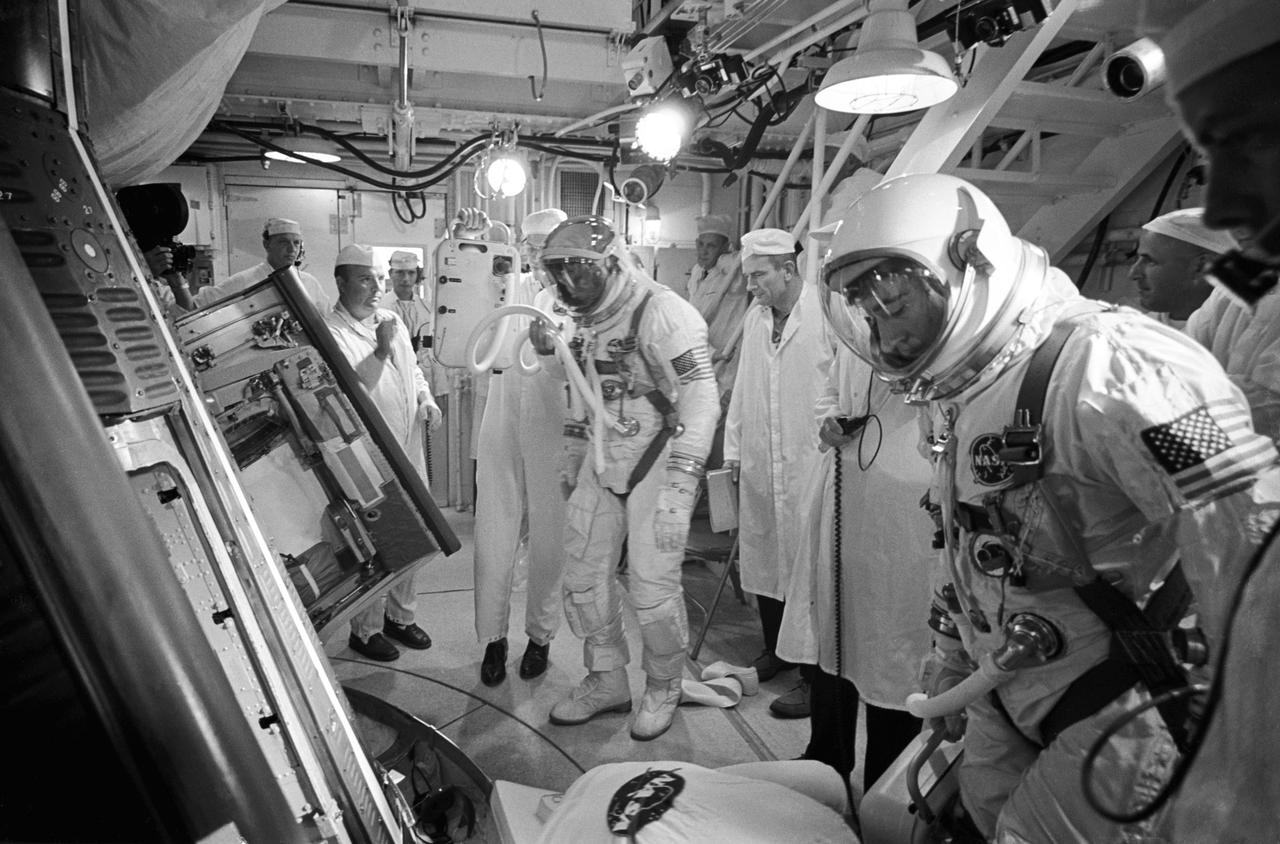
S66-42737 (18 July 1966) --- In the White Room atop the Gemini launch vehicle, astronauts Michael Collins (left), pilot, and John W. Young (right), command pilot, prepare to enter the Gemini-10 spacecraft. Engineers and technicians stand by to assist in the insertion. Photo credit: NASA
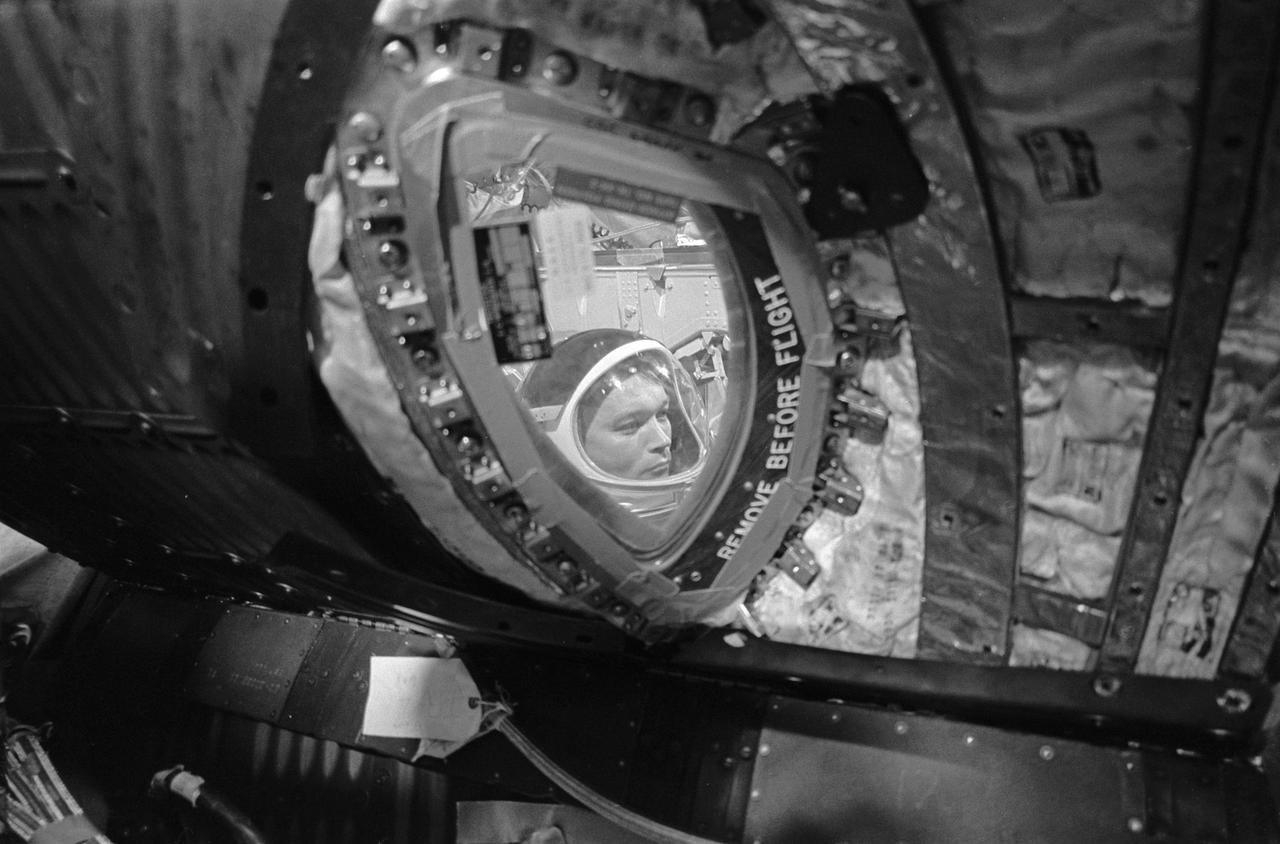

S66-42704 (12 July 1966) --- Astronaut Michael Collins, prime crew pilot for the Gemini-10 spaceflight, is seen through a hatch in the spacecraft during a Simultaneous Launch Demonstration in the White Room atop Pad 19, Cape Kennedy, Florida. Photo credit: NASA
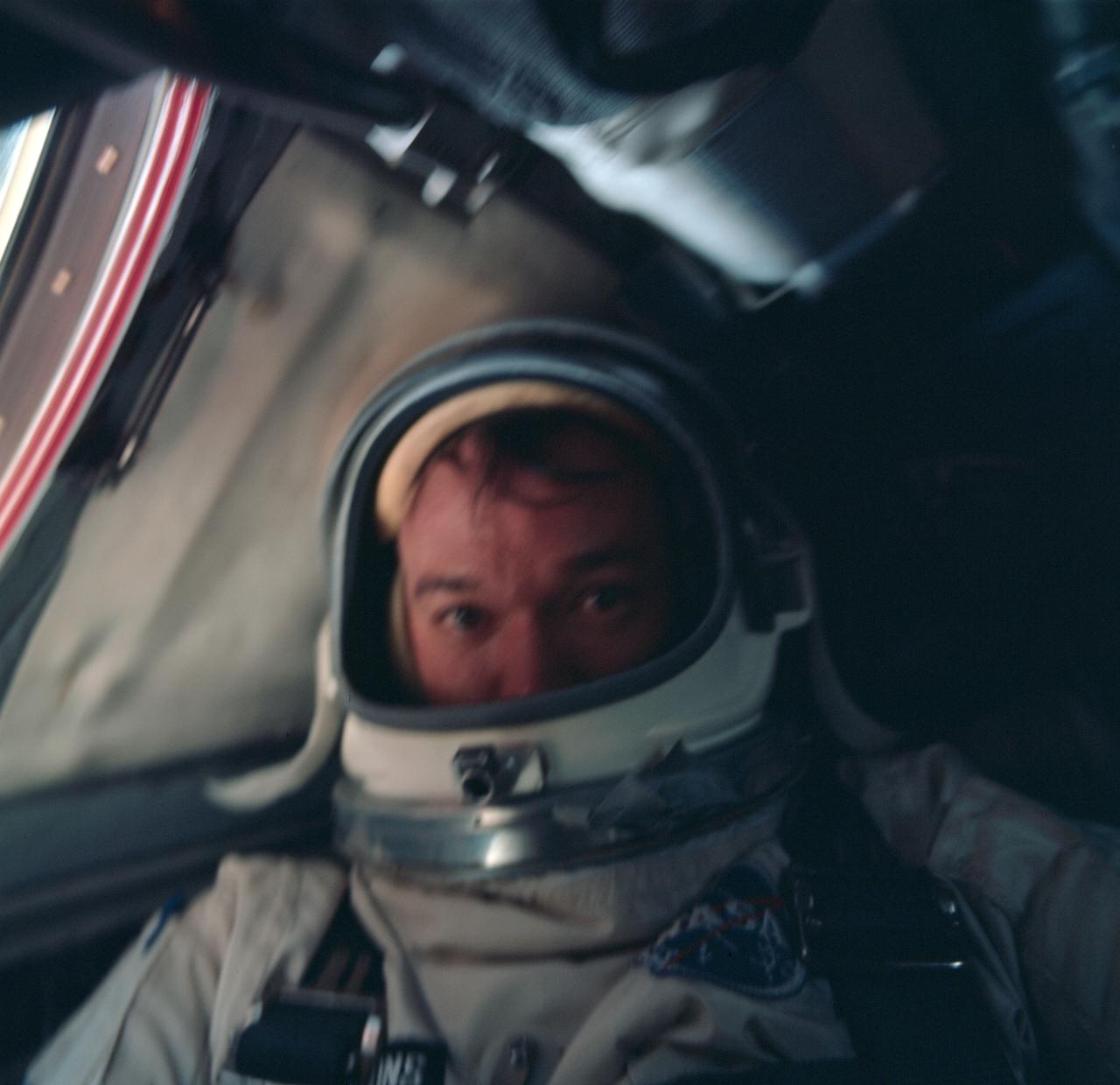

S66-46270 (18 July 1966) --- Astronaut Michael Collins is photographed inside the spacecraft during the Gemini-10 mission. Photo credit: NASA
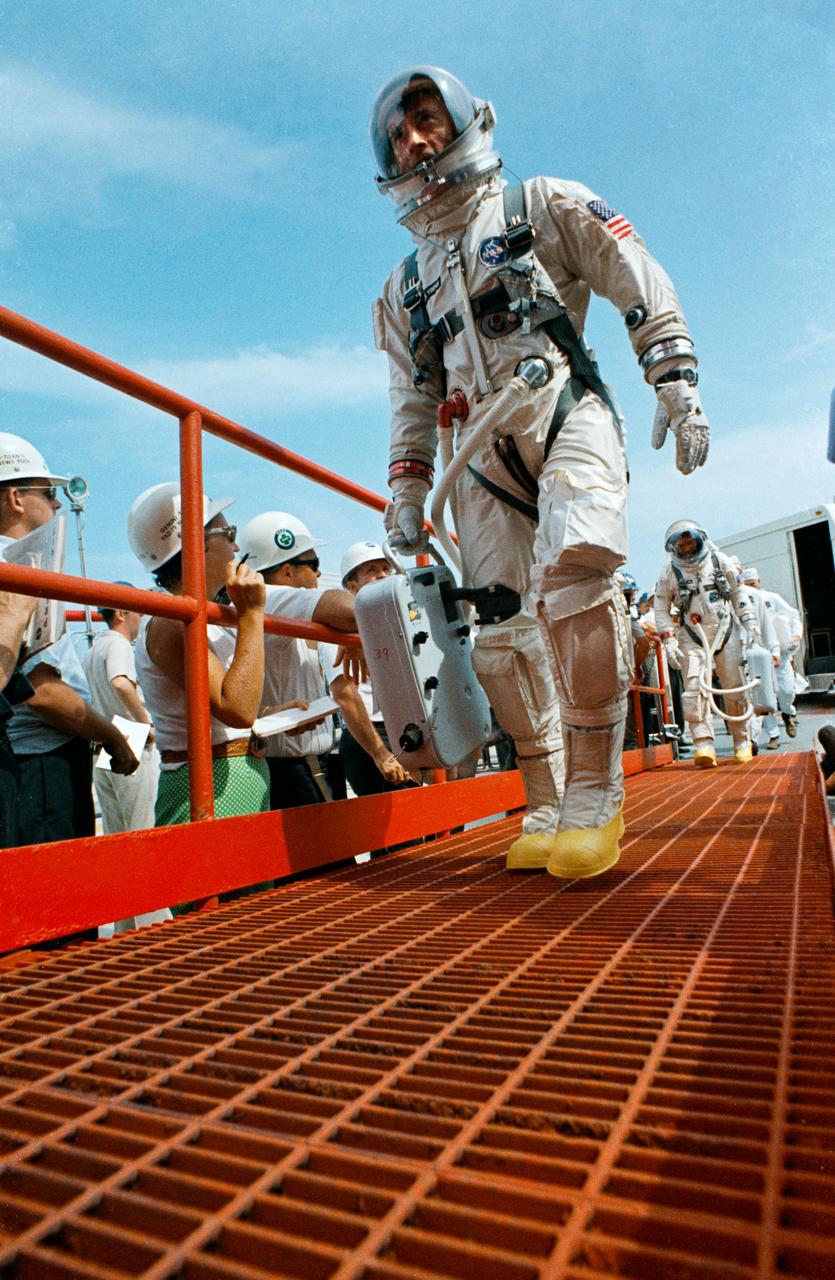

S66-42754 (18 July 1966) --- Astronauts John W. Young (leading), command pilot, and Michael Collins, pilot, walk up the ramp at Pad 19 after arriving from the Launch Complex 16 suiting trailer during the prelaunch countdown. Moments later they entered the elevator which took them to the white room and the waiting Gemini-10 spacecraft. Liftoff was at 5:20 p.m. (EST), July 18, 1966. Photo credit: NASA
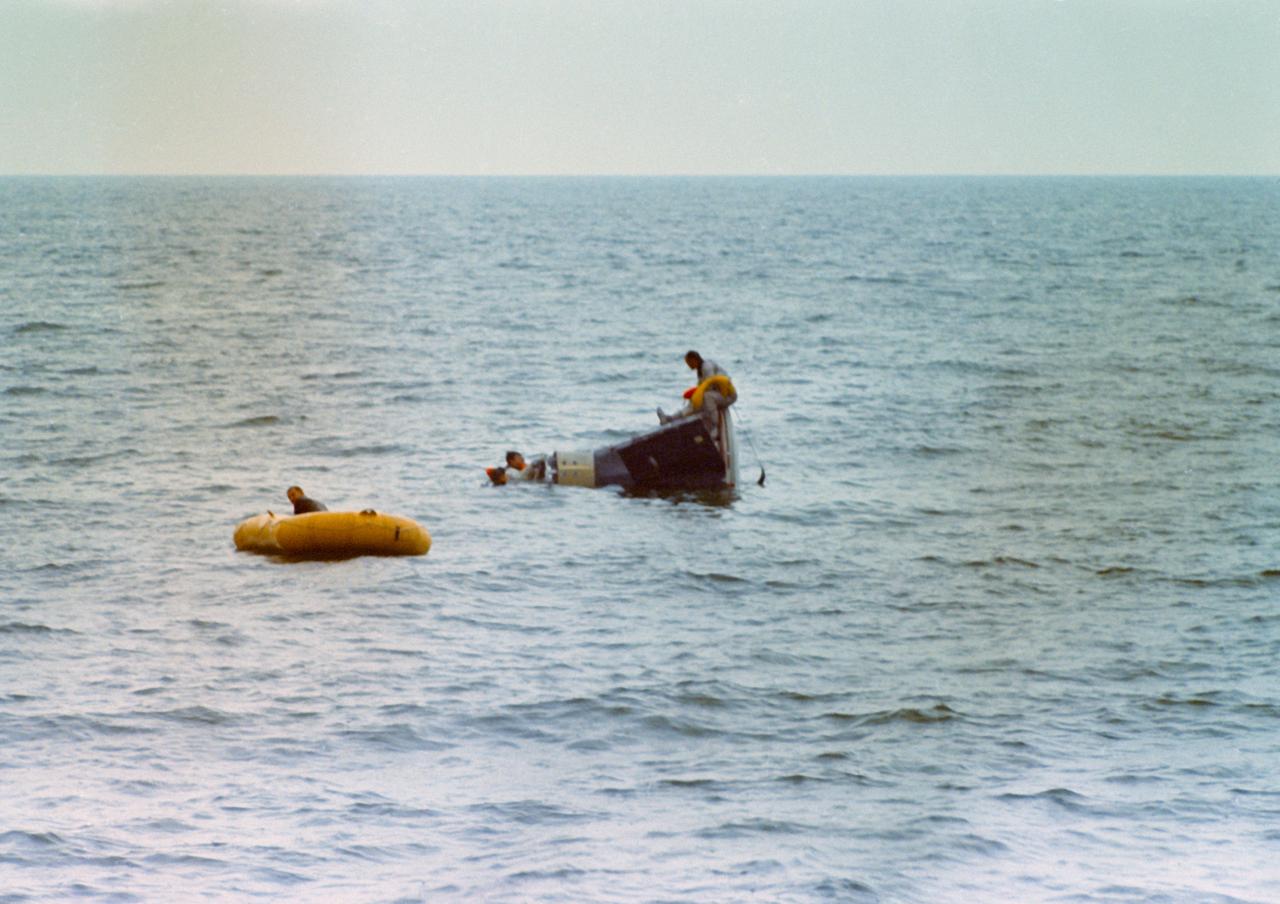

S66-39699 (18 June 1966) --- Astronauts John W. Young (in water, nose of spacecraft), Gemini-10 command pilot, and Michael Collins (sitting on spacecraft), pilot, use Static Article 6 spacecraft during water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. A team of Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) swimmers assisted in the training exercise. Photo credit: NASA
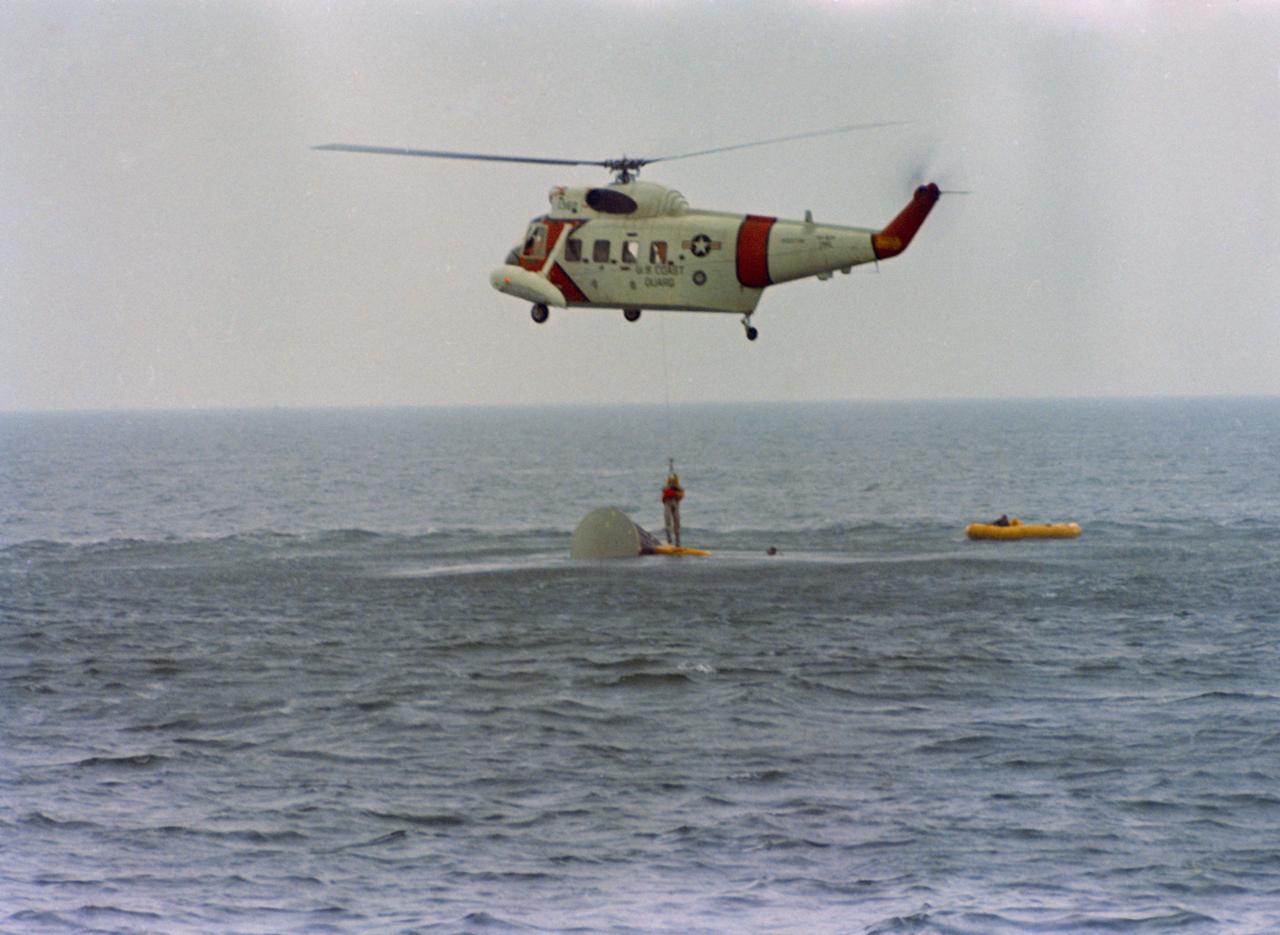

S66-39713 (18 June 1966) --- Astronaut John W. Young, Gemini-10 command pilot, is hoisted up to a U.S. Coast Guard helicopter during water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. A team of Manned Spaceflight Center (MSC) swimmers assists in the exercise. The Static Article 5 spacecraft can be seen in the water. Photo credit: NASA
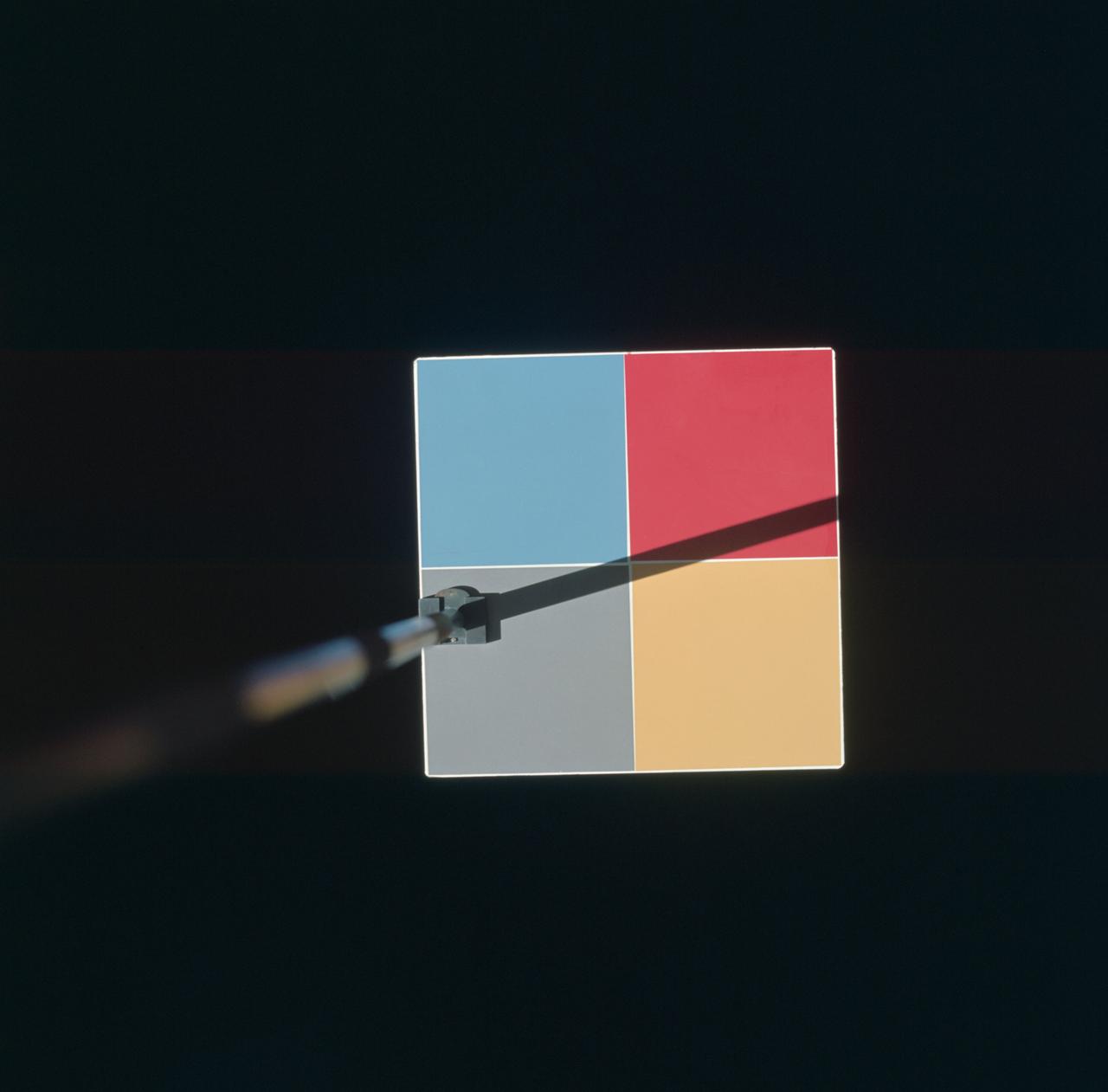

S66-46025 (18 July 1966) --- Astronaut Michael Collins, Gemini-10 pilot, photographed this MSC-8 color patch outside the spacecraft during the Gemini-10/Agena docking mission. The experiment was for the purpose of showing what effect the environment of space will have upon the color photography taken in cislunar space and on the lunar surface during an Apollo mission. Photo credit: NASA
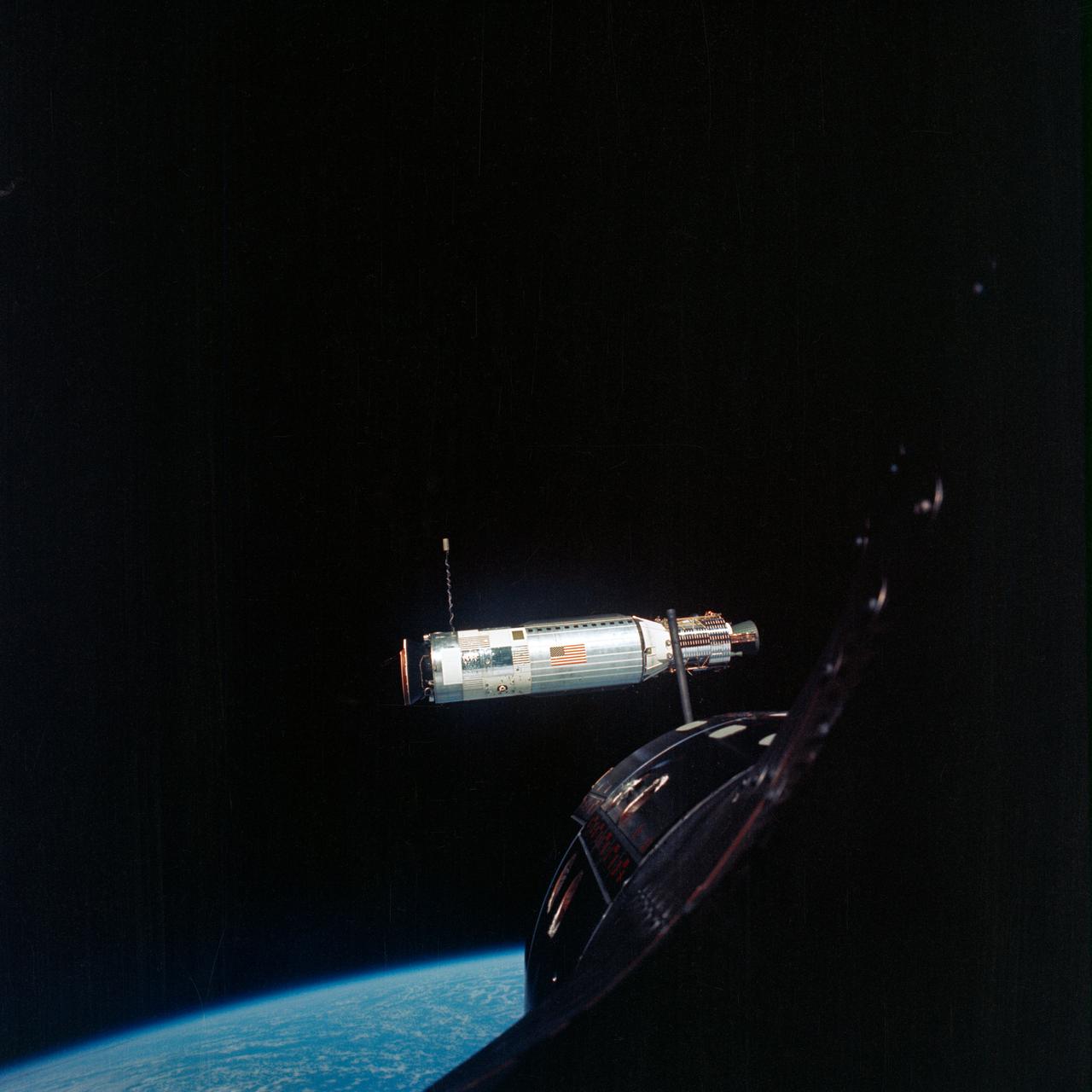

S66-46124 (18 July 1966) --- Agena Target Docking Vehicle 5005 is photographed from the Gemini-10 spacecraft during rendezvous in space. The two spacecraft are about 41 feet apart. After docking with the Agena, astronauts John W. Young, command pilot, and Michael Collins, pilot, fired the 16,000-pound thrust engine of Agena-10's primary propulsion system to boost the combined vehicles into an orbit with an apogee of 413 nautical miles to set a new altitude record for manned spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA
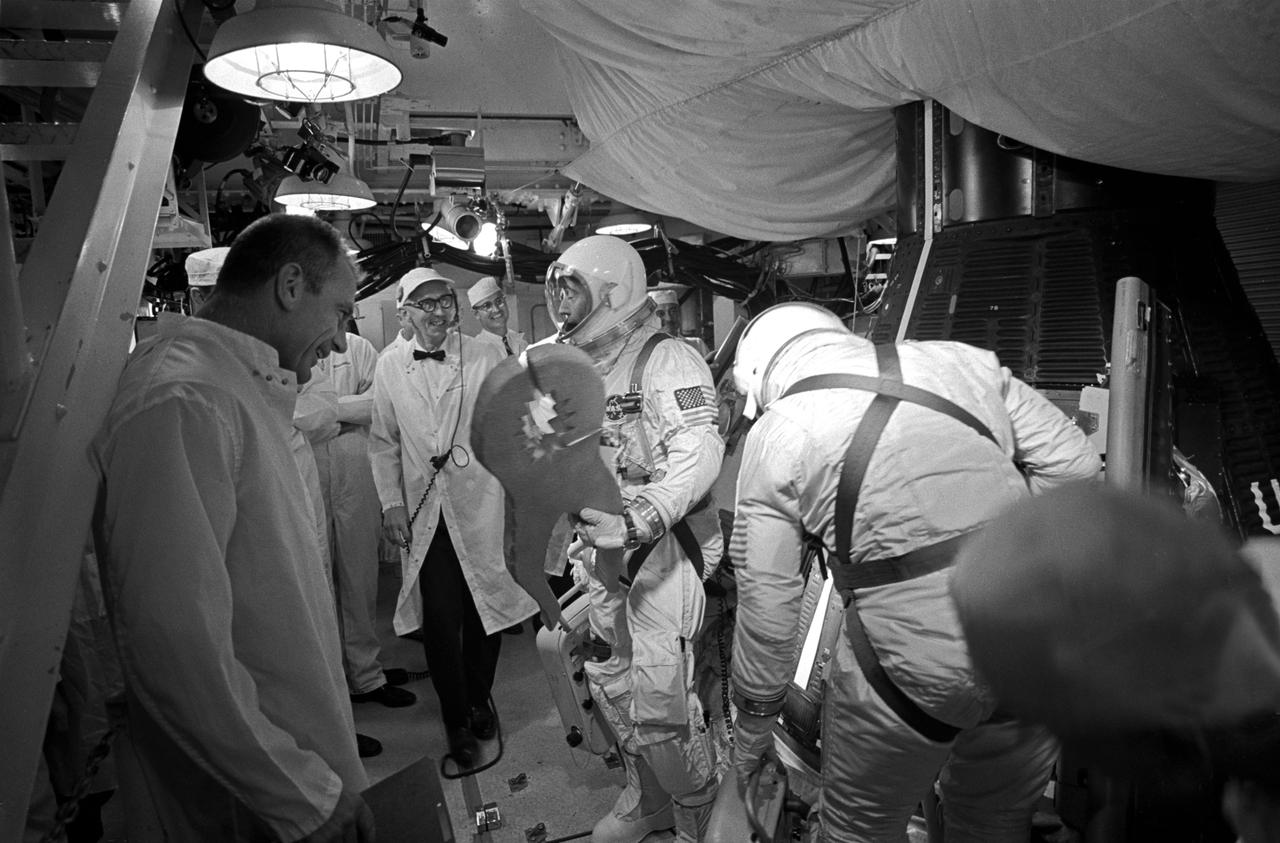

S66-42738 (18 July 1966) --- Astronaut John W. Young, Gemini-10 command pilot, holds a pair of king-size pliers presented to him by the crew at Pad 19 for in-flight first-echelon maintenance of a spacecraft utility power cord Young earlier had difficulty in connecting. Gunther Wendt (right center background), Pad 19 leader, jokes with Young about the pliers. At right is Dr. Donald K. Slayton, MSC Director of Flight Crew Operations. At left is astronaut Michael Collins, Gemini-10 pilot. Photo credit: NASA
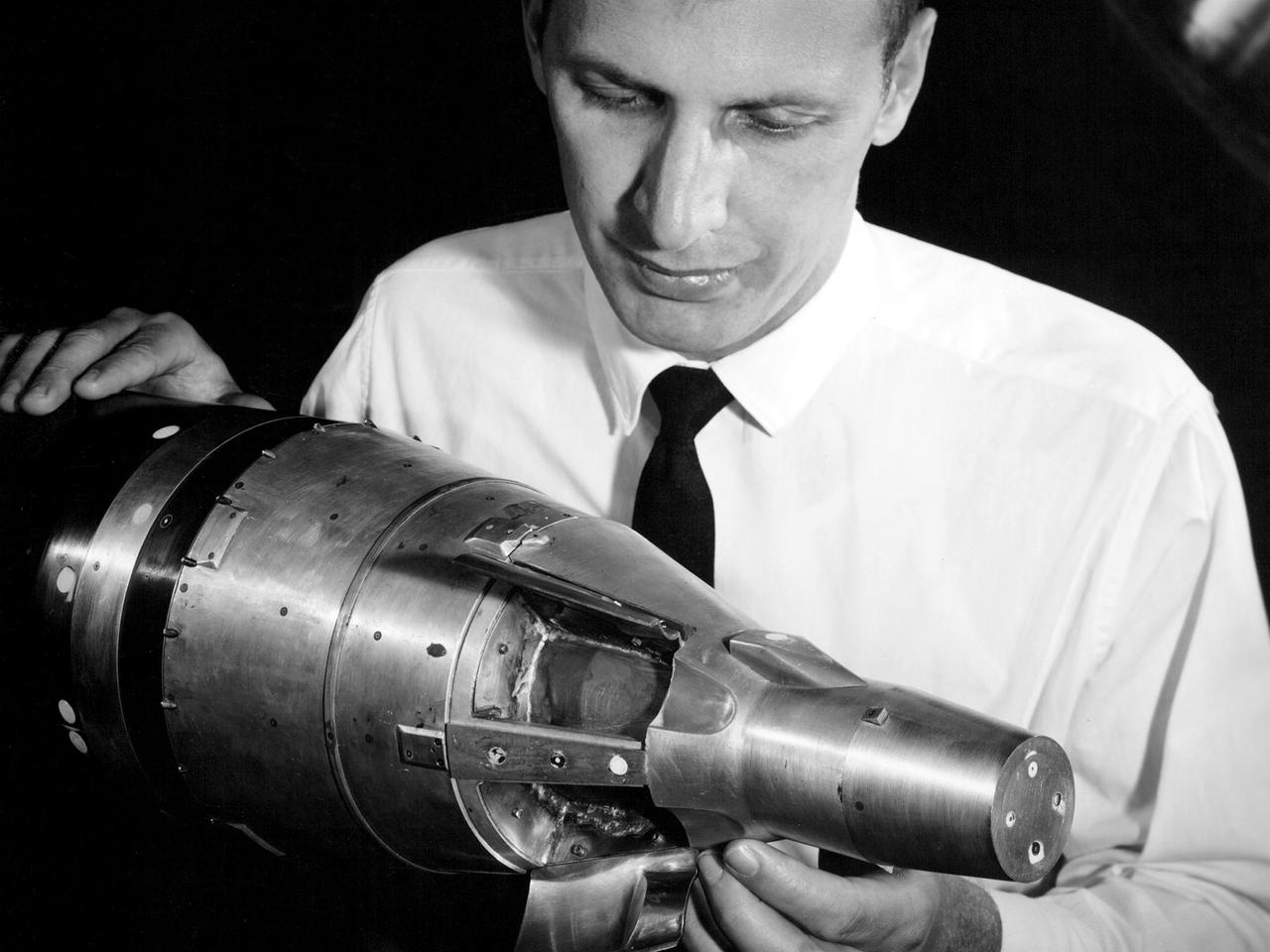

A researcher at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center examines a small-scale model of the Gemini capsule in the 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel test section. Gemini was added to NASA’s manned space program after its predecessor, Mercury, and its antecedent, Apollo, were already established. Gemini was a transitional mission designed provide the astronauts with practice docking with other spacecraft and withstanding durations in space up to two weeks. The program was officially announced on December 7, 1961, but planning began in mid-1959. It was named Gemini after the zodiac twins because of the spacecraft’s two passenger capacity. The Gemini Program was the first program to start at the new Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, now the Johnson Space Center. Unlike Mercury and Apollo, Lewis had very little involvement with the Gemini Program. This model was tested in the 10- by 10 tunnel for several weeks in September 1962. Lewis began managing the Agena second-stage rocket program shortly after this photograph was taken. Agenas were used to launch a variety of spacecraft and satellites in the 1960s. They were also used on several Gemini missions to provide targets for the astronauts to practice their rendezvous maneuvers. Gemini had two unmanned and ten manned flights in 1965 and 1966. These yielded the first spacewalks, long-duration space missions, first onboard computer, docking with a second spacecraft, and rendezvous maneuvers.

Project Gemini: On Jan. 3, 1962, NASA announced the advanced Mercury Mark II project had been named "Gemini." After 12 missions – 2 uncrewed and 10 crewed – Project Gemini ended Nov. 15, 1966, following a nearly four-day, 59 orbit-flight. Its achievements included long-duration spaceflight, rendezvous and docking of two spacecraft in Earth orbit, extravehicular activity, and precision-controlled re-entry and landing of the spacecraft. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
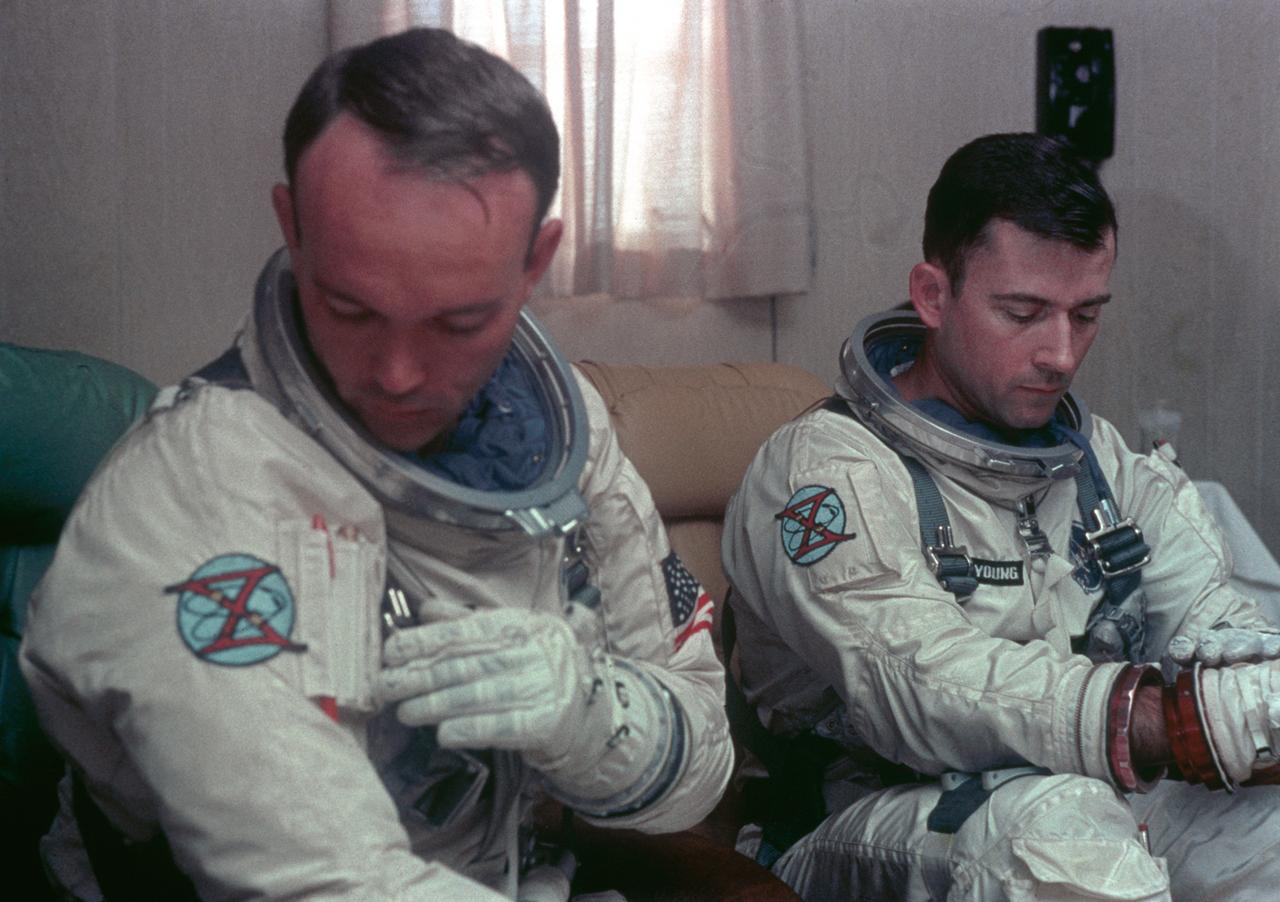

S66-42424 (18 July 1966) --- Astronauts John W. Young (right), command pilot, and Michael Collins (left), pilot, prime crew for the Gemini-10 spaceflight, undergo suiting up operations in the Launch Complex 16 suiting trailer. Photo credit: NASA
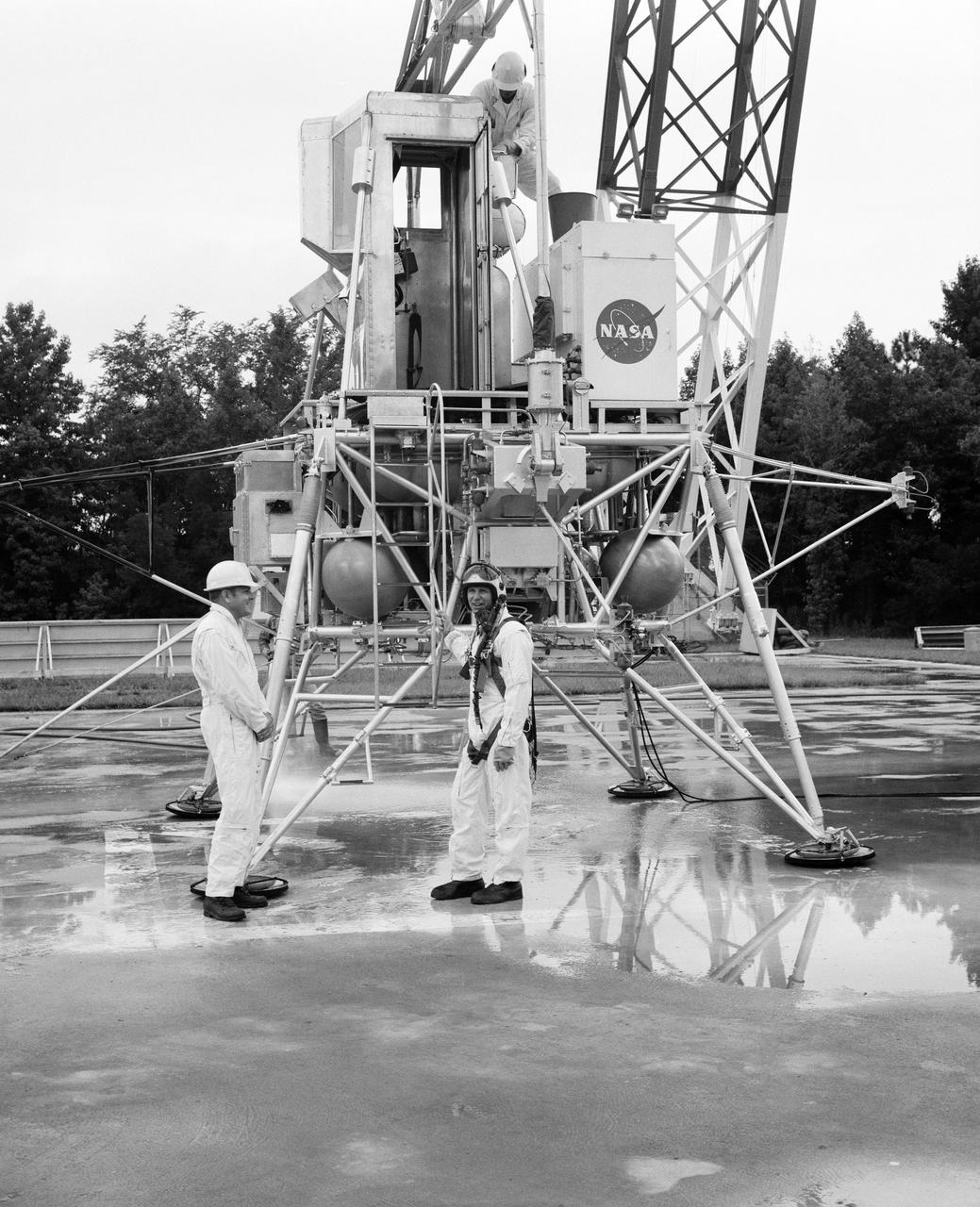

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
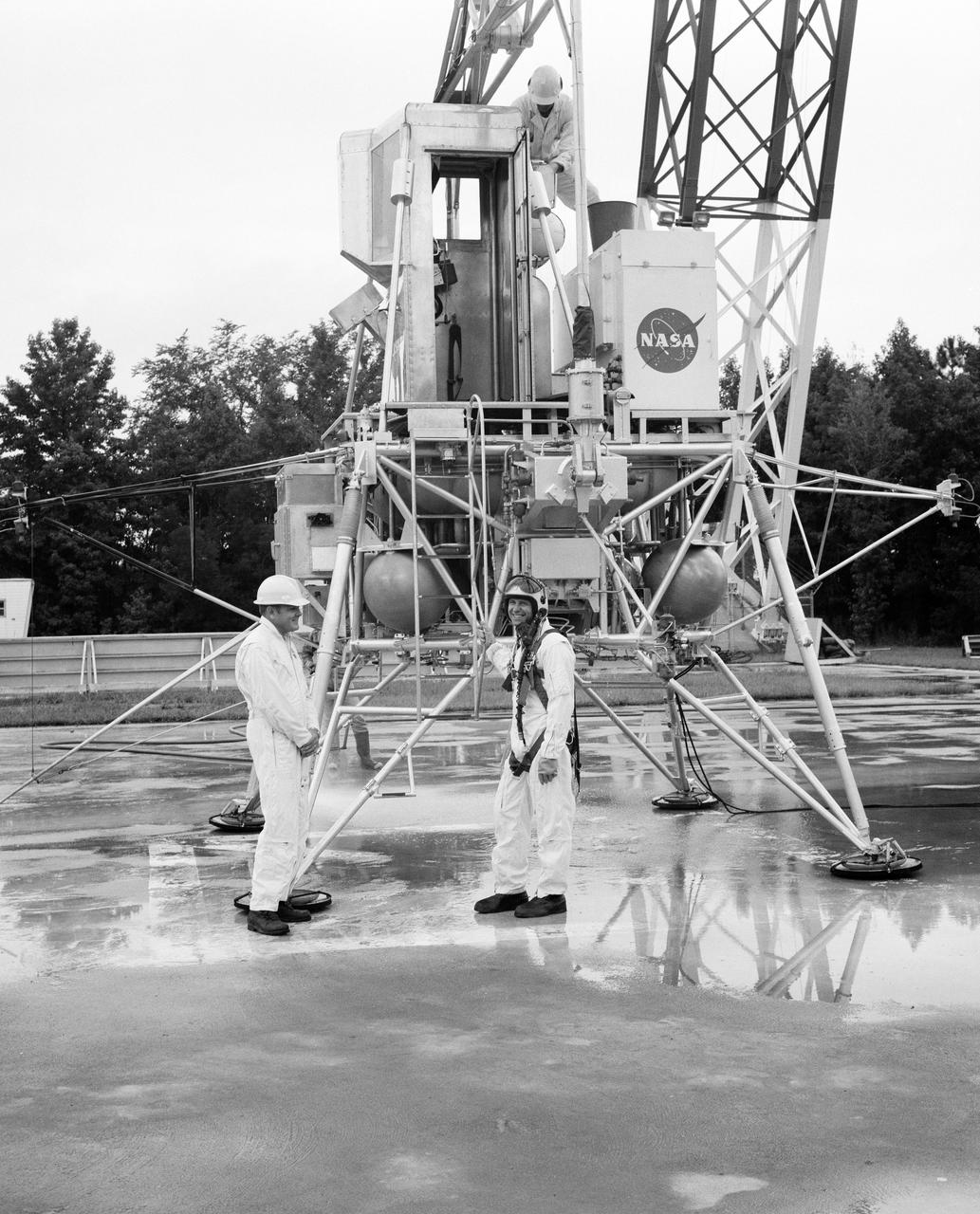

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
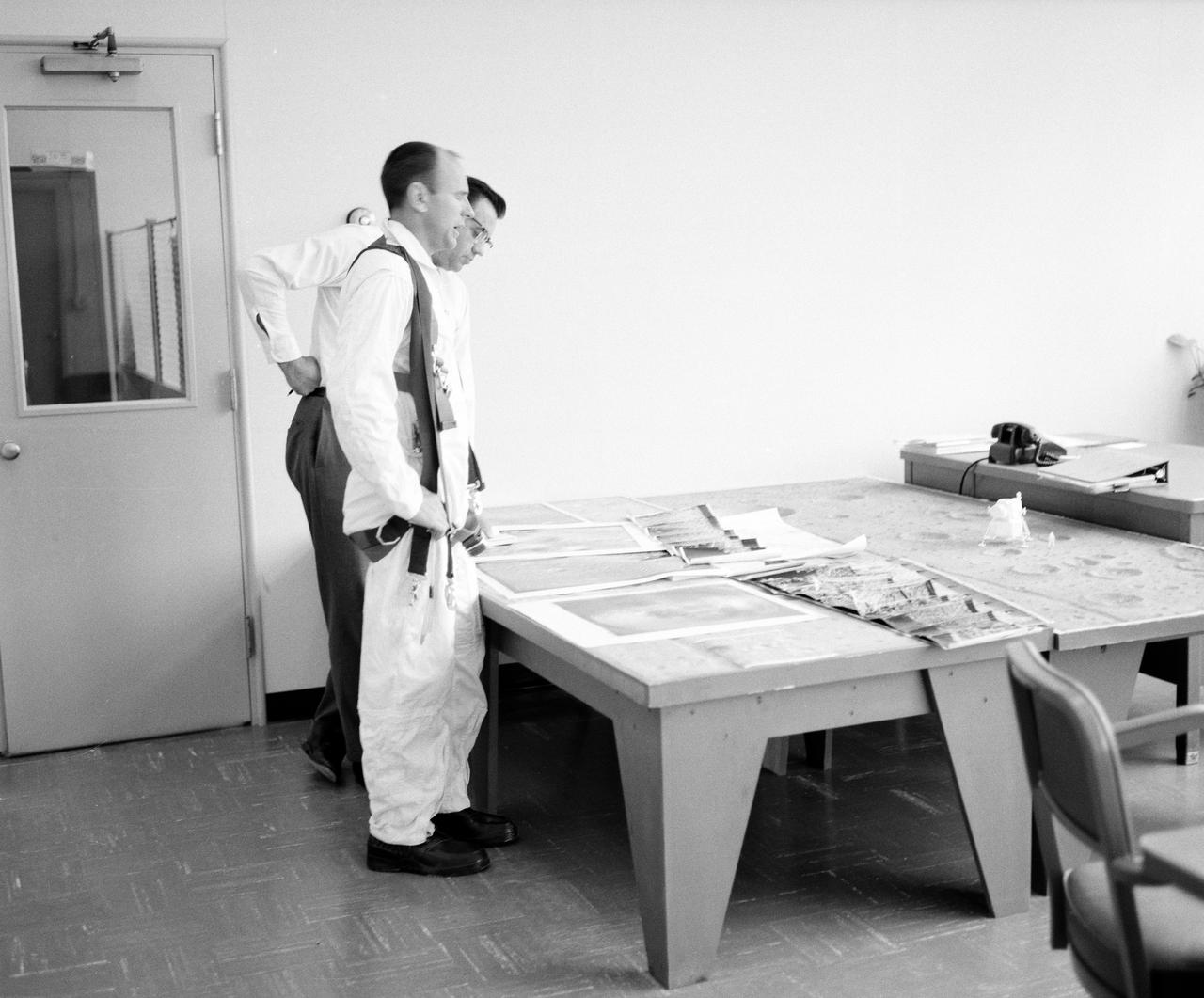

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
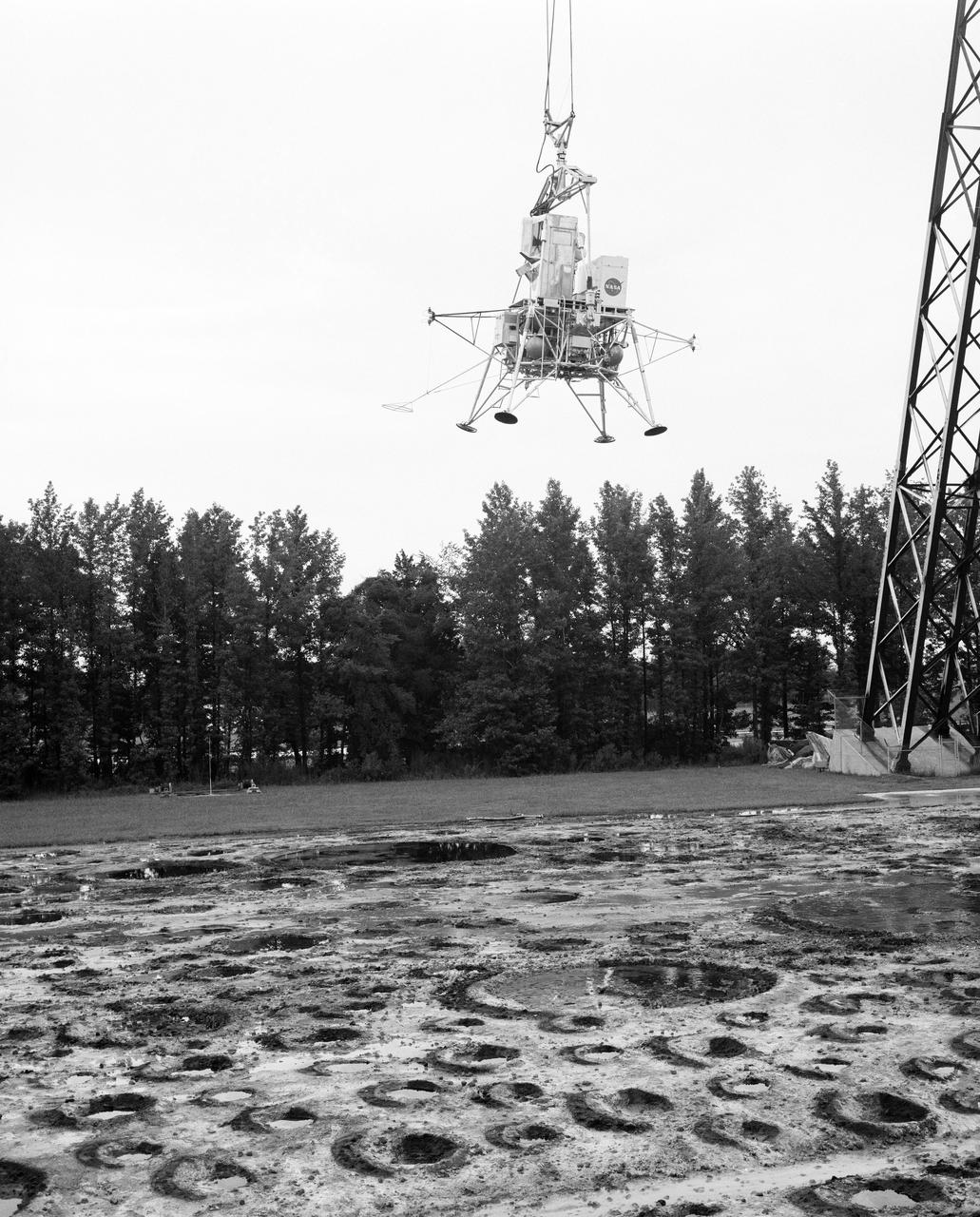

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
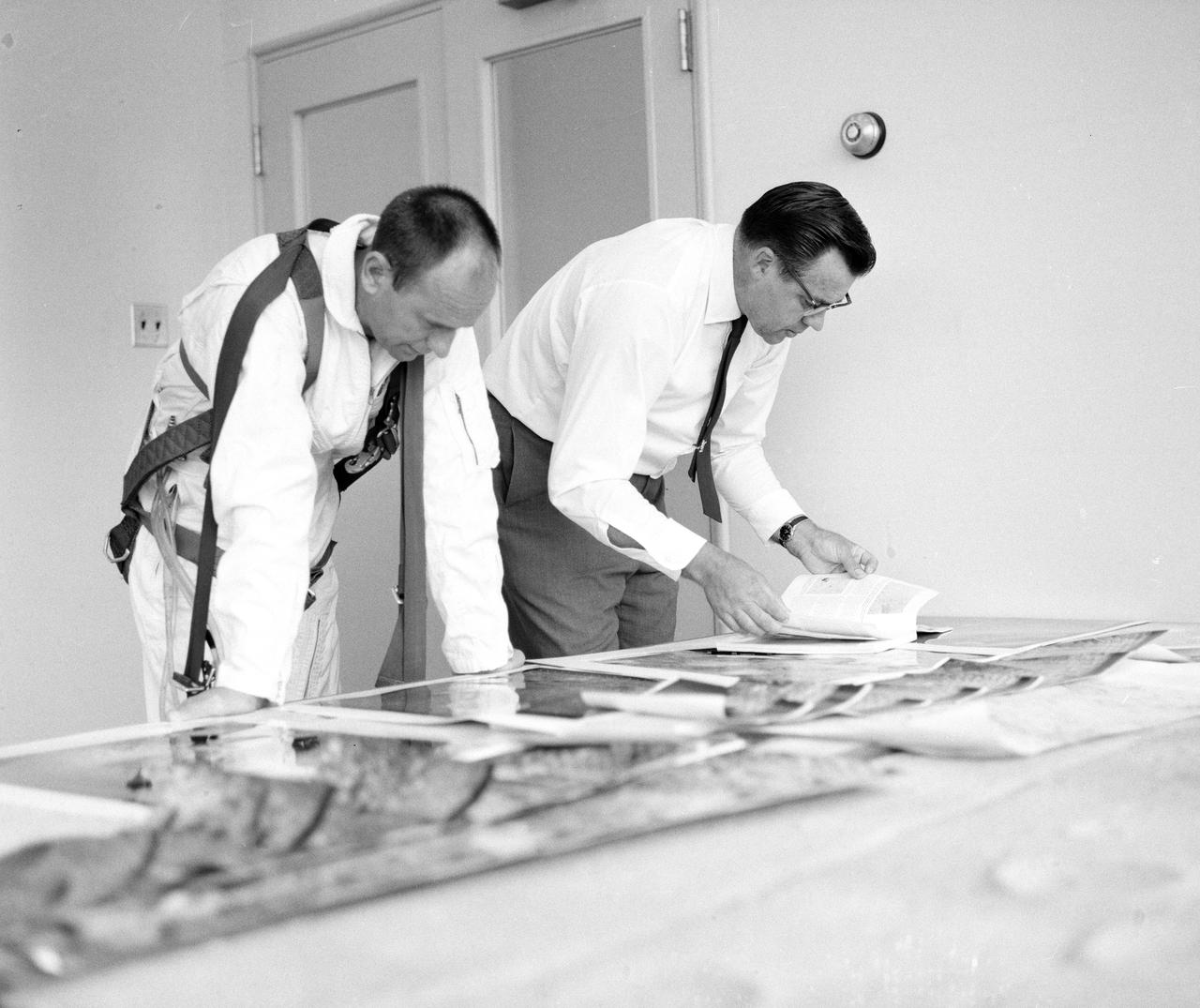

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
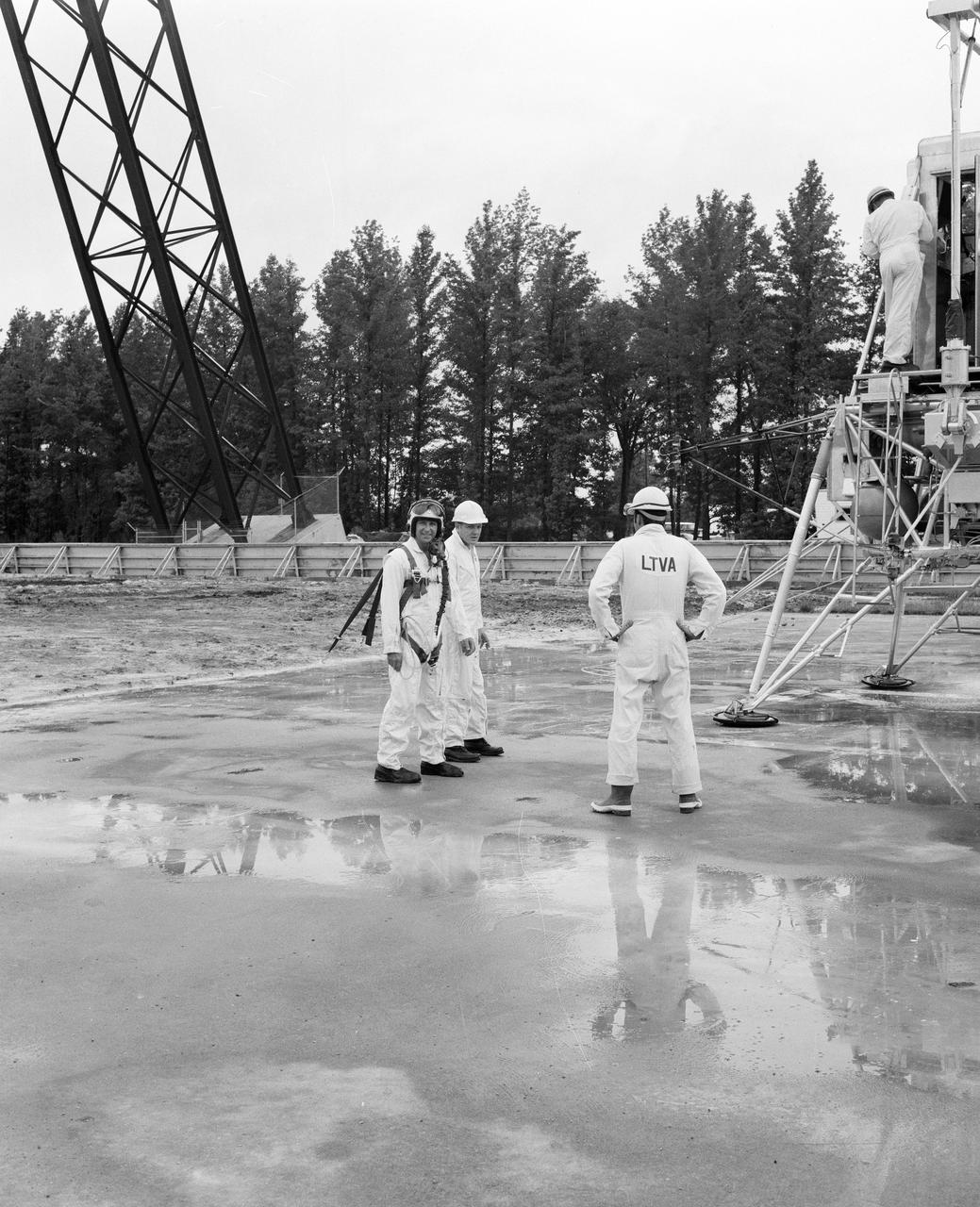

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
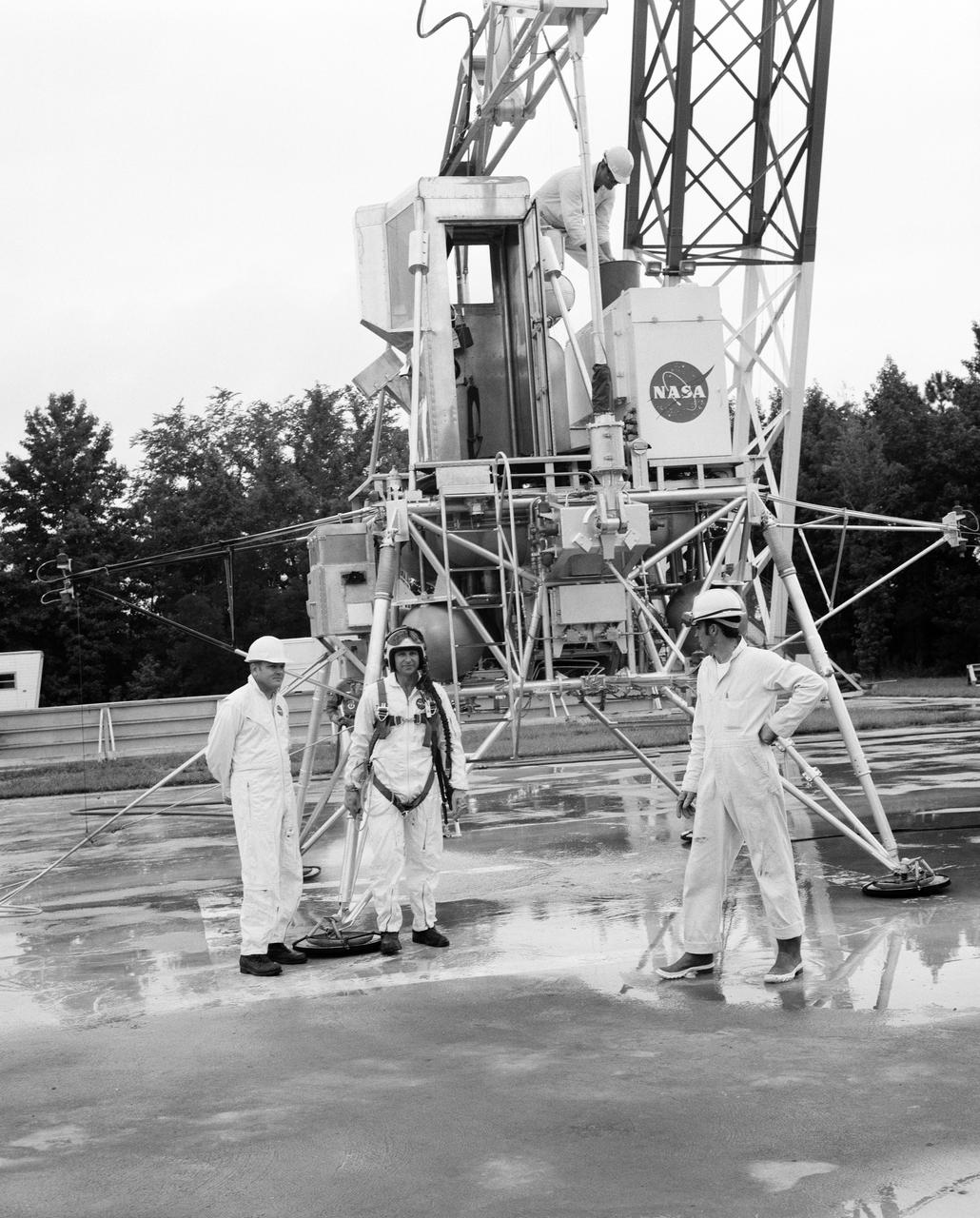

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
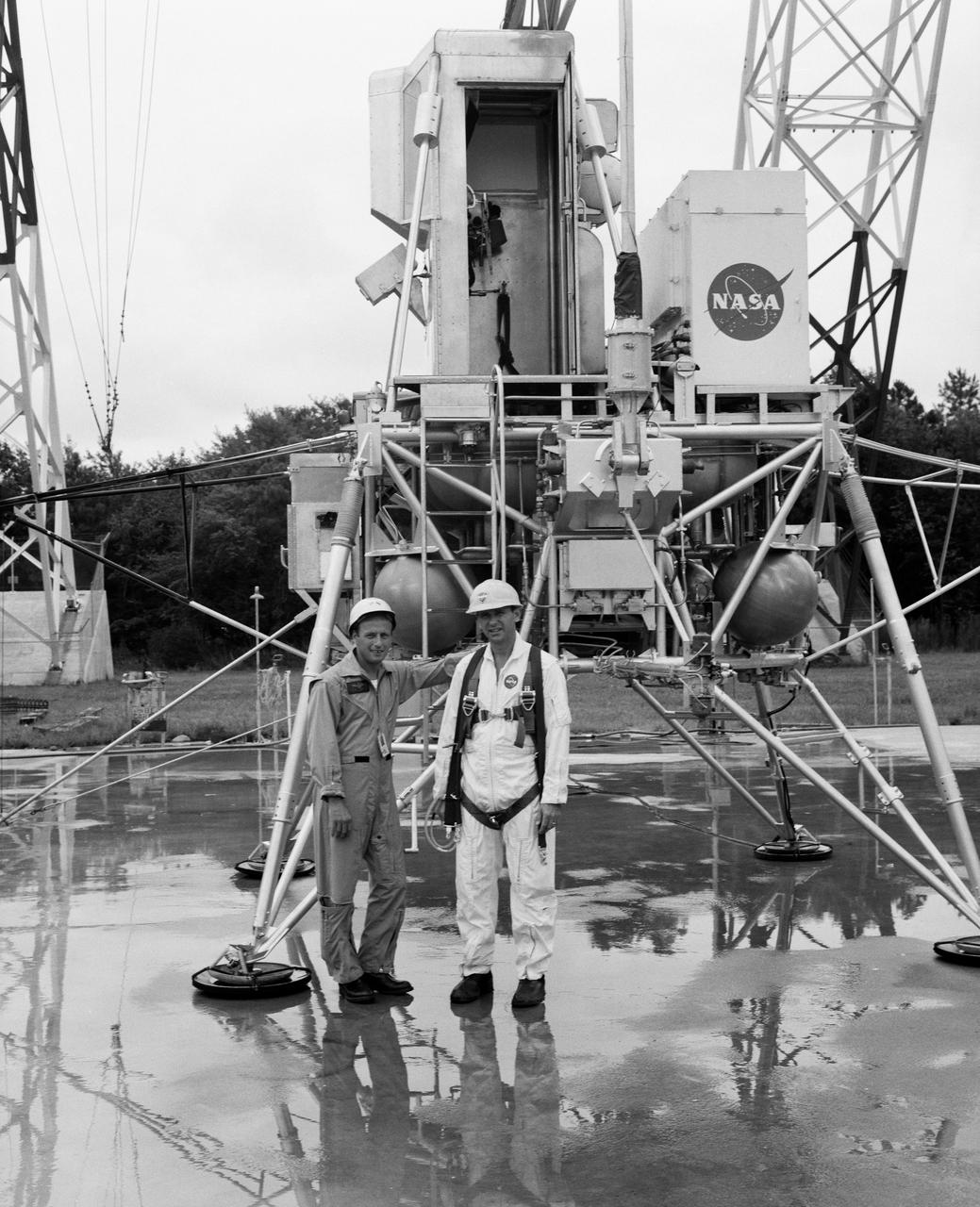

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
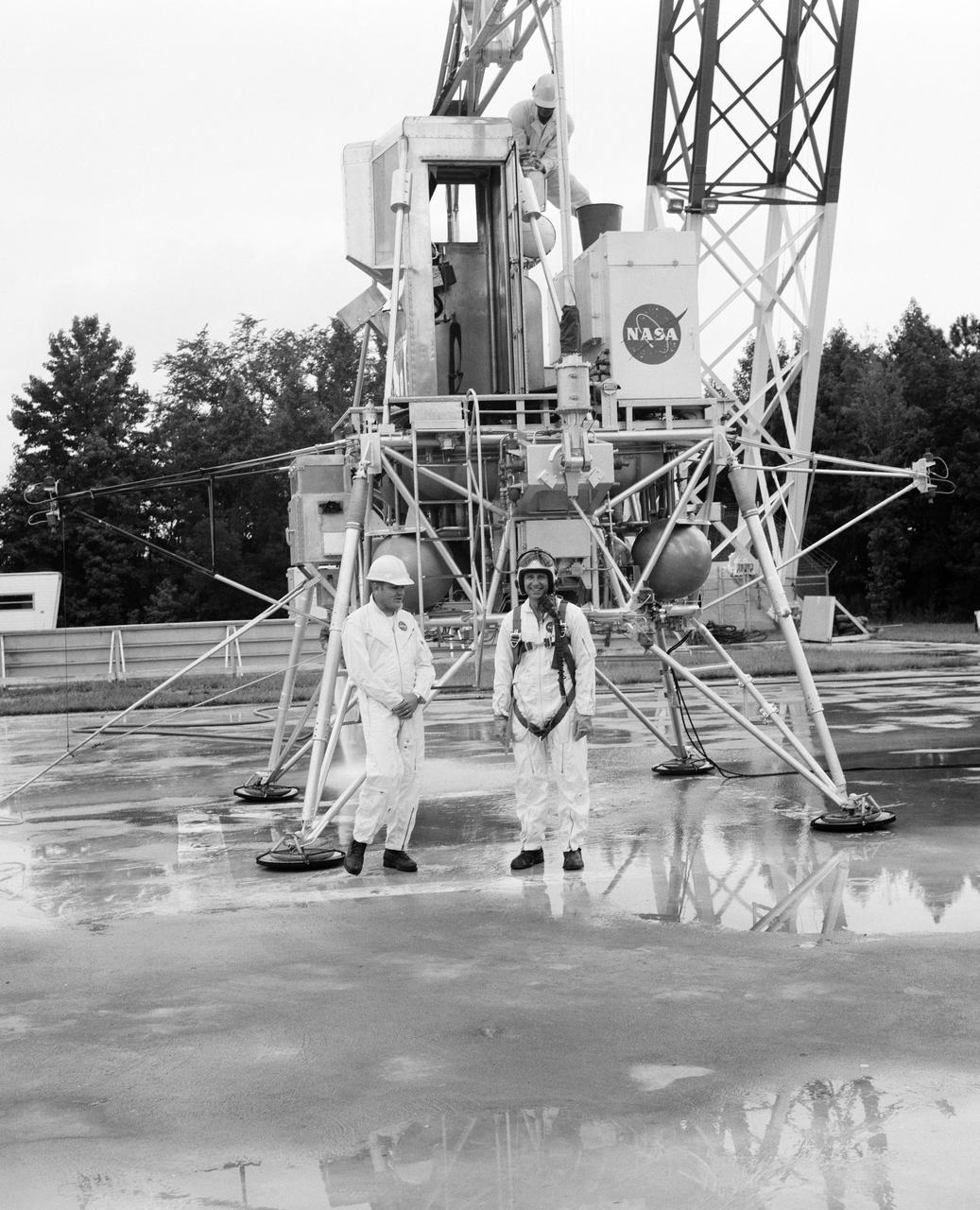

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
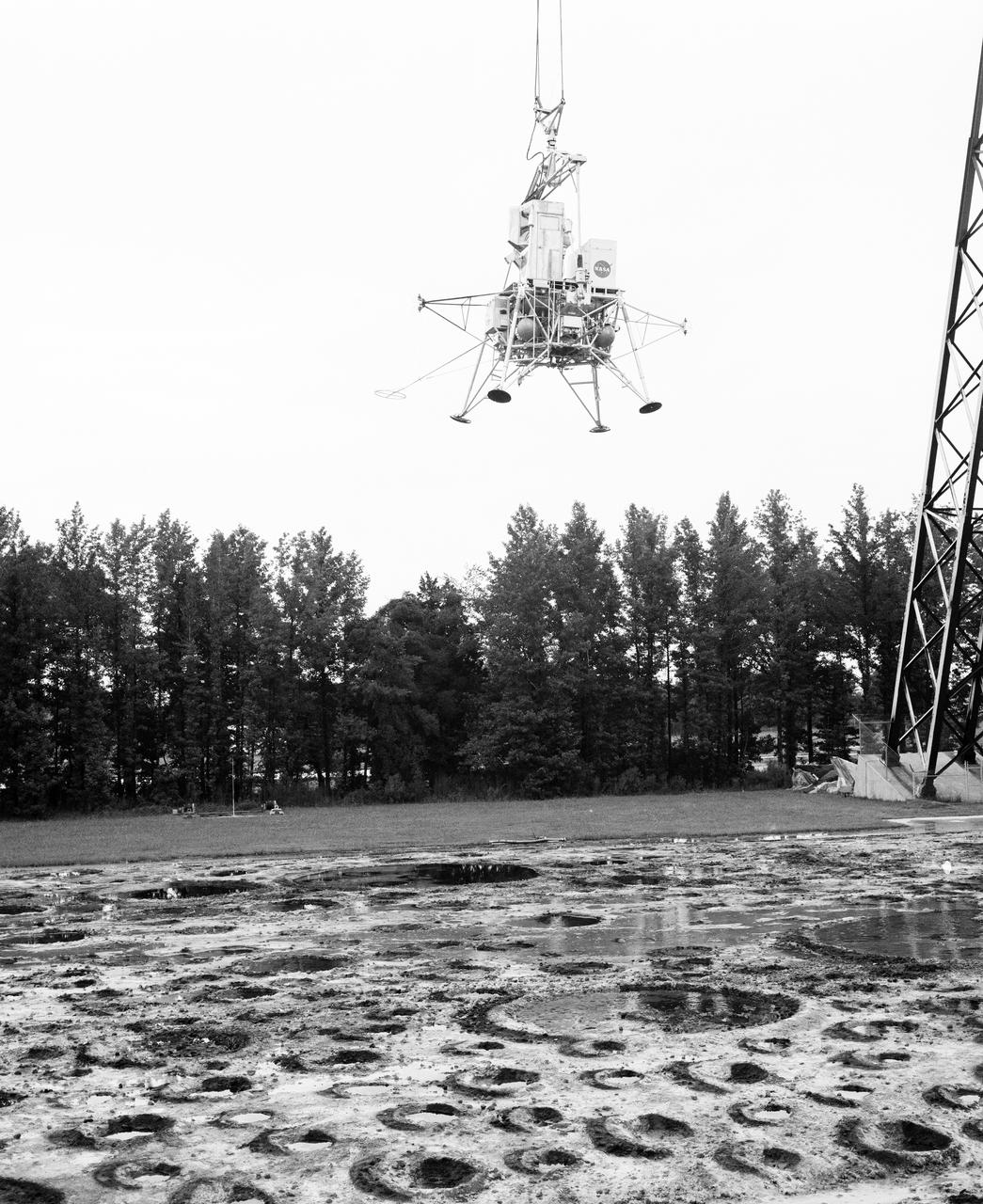

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
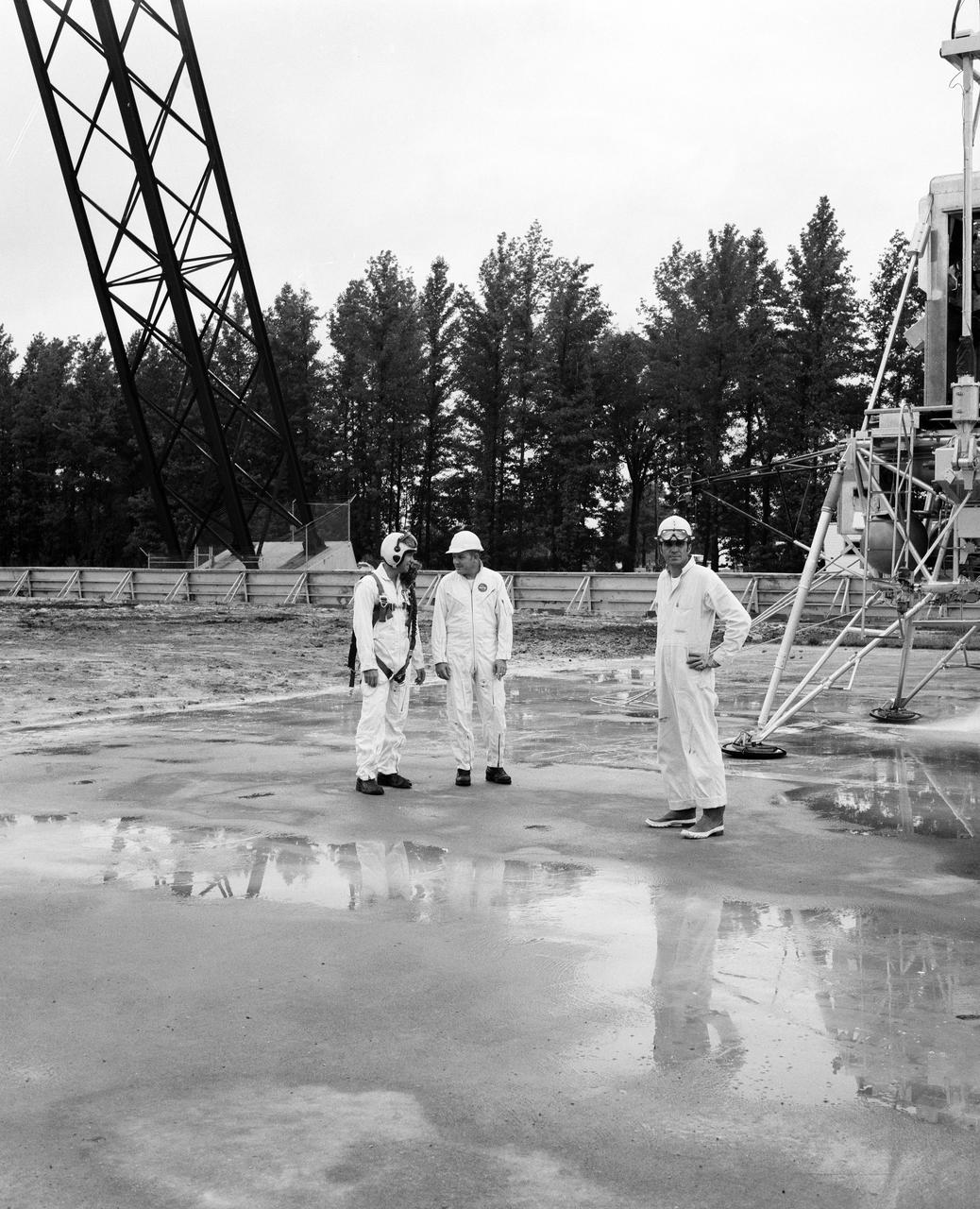

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
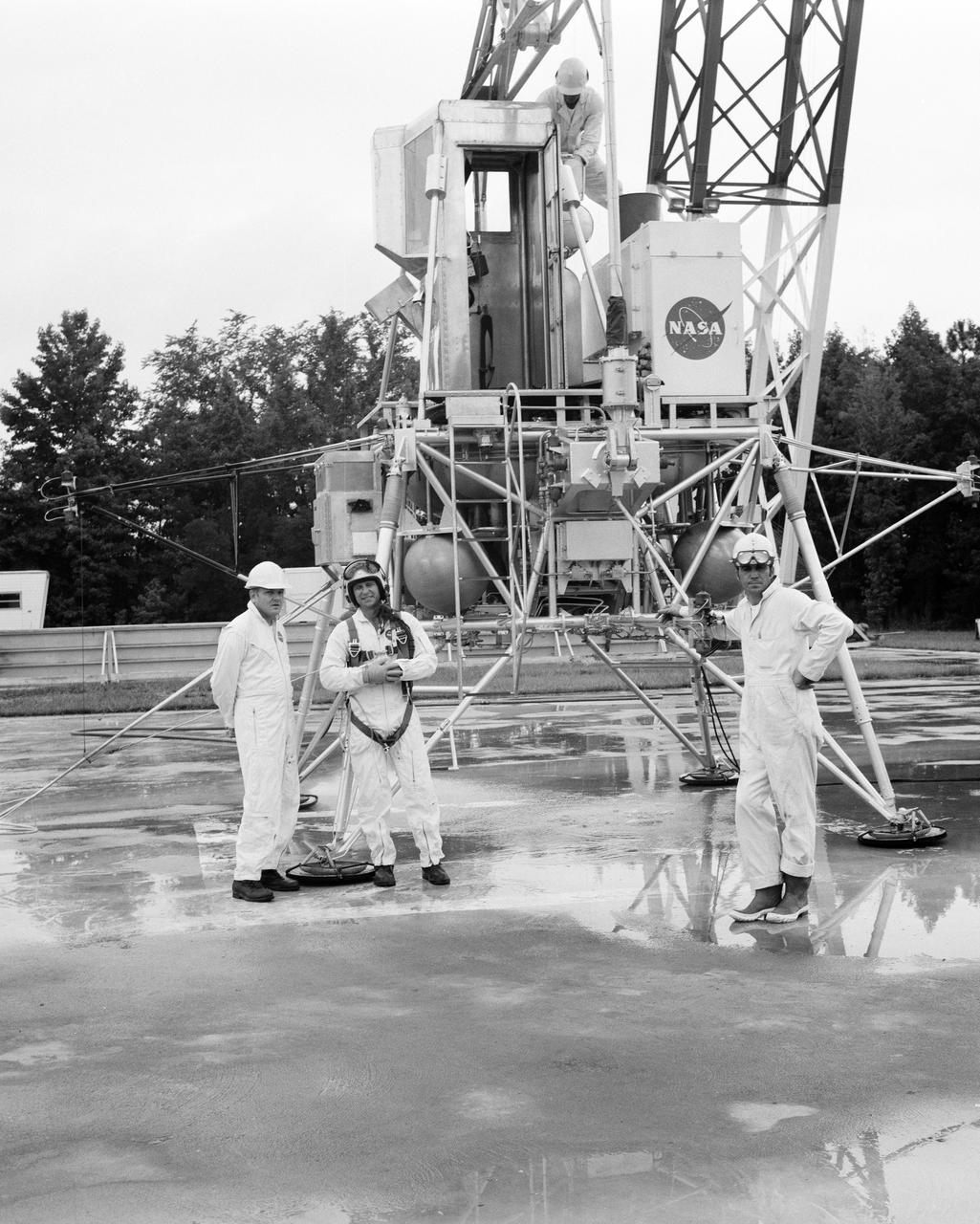

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
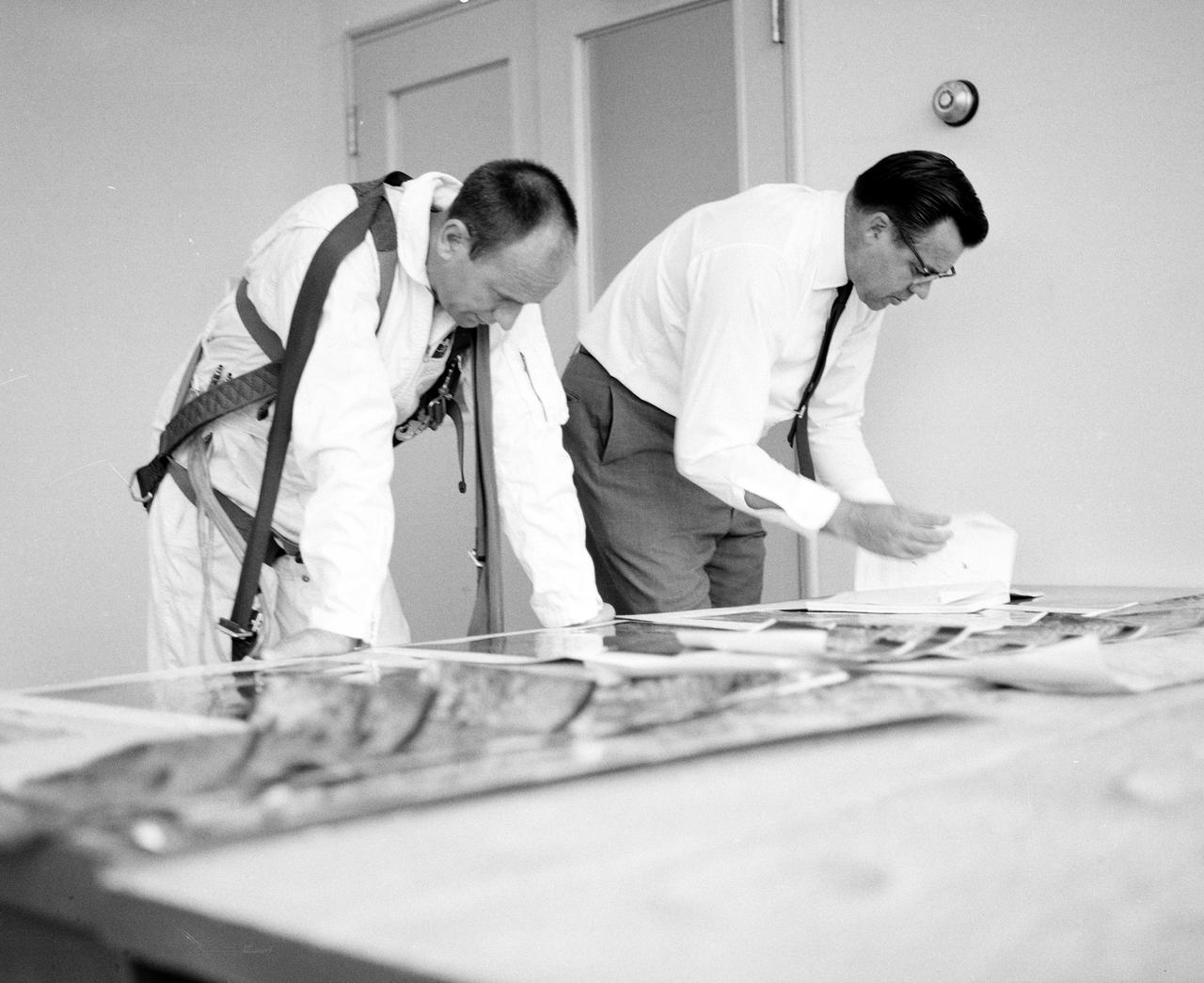

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
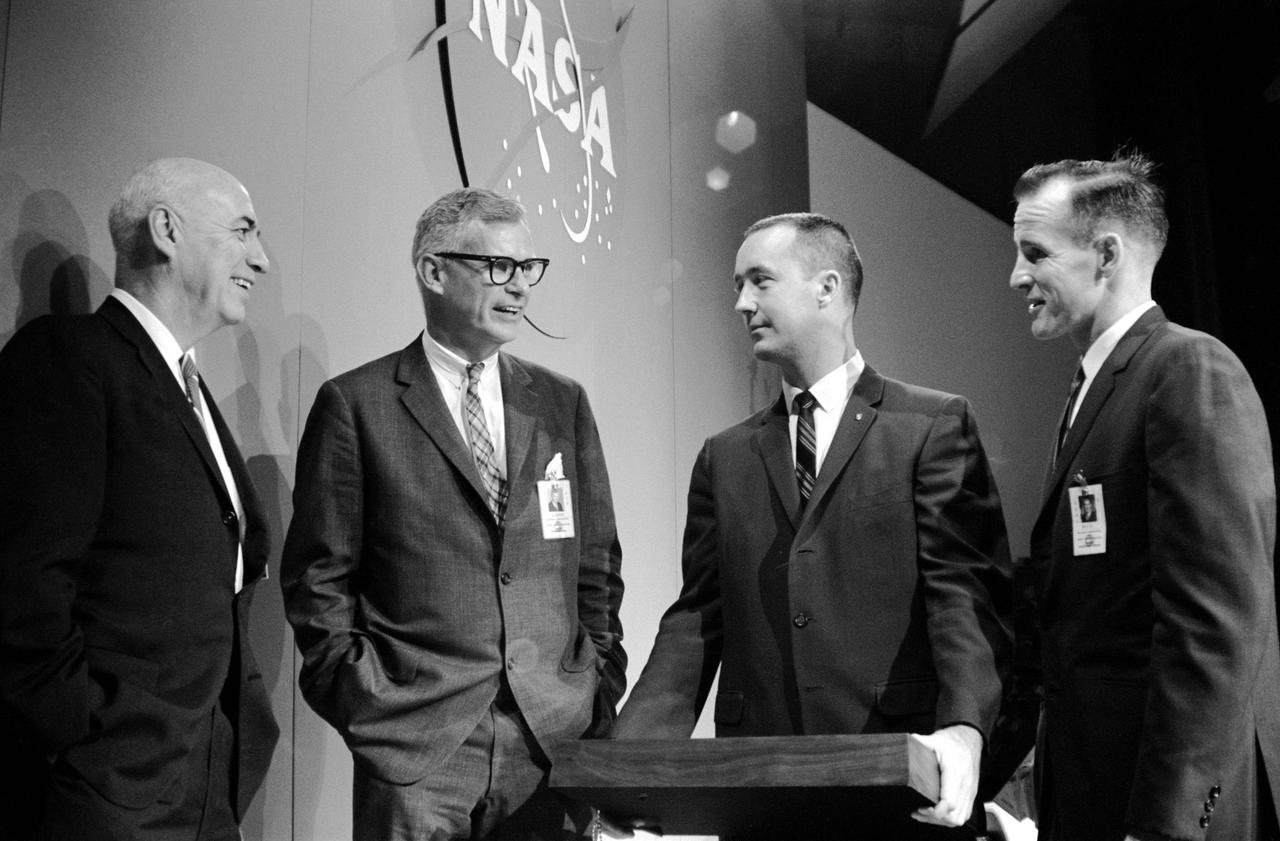

S65-33352 (11 June 1965) --- The Gemini-4 prime crew pose with two NASA officials after a press conference in the MSC auditorium. Left to right, are Dr. Robert R. Gilruth, MSC director; Dr. Robert C. Seamans Jr., associate administrator, National Aeronautics and Space Administration; astronaut James A. McDivitt, command pilot of the Gemini-4 flight; and astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot of the mission. The two astronauts had just returned to Houston following their debriefings at Cape Kennedy. The Gt-4 liftoff was at 10:16 a.m. (EST) on June 3, 1965. Time of splashdown ending the four-day, 62-revolution mission was at 12:12 p.m. on June 7, 1965.
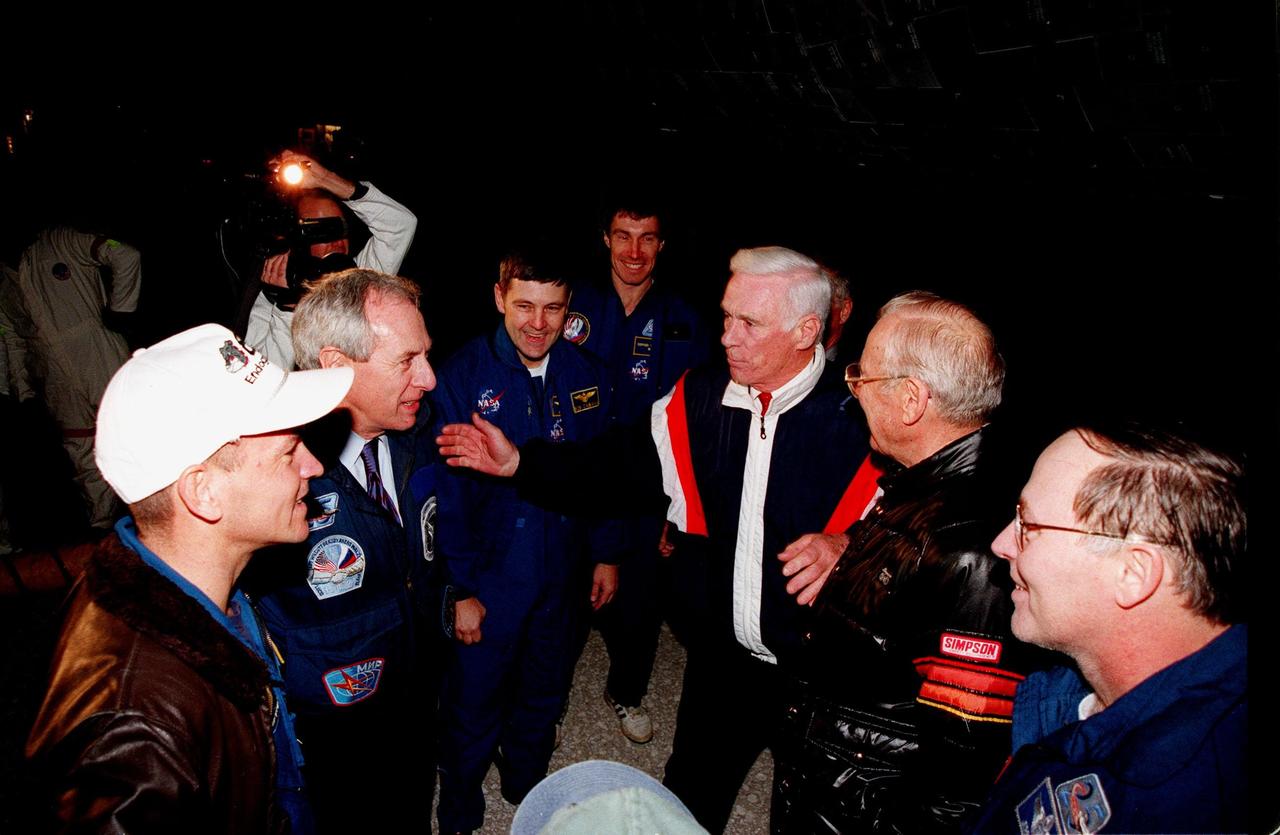

Following their touchdown on Runway 15 at 10:53:29 p.m. EST, STS-88 crew members are greeted by NASA Administrator Daniel Goldin and former astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and James A. Lovell Jr. From left are Pilot Frederick W. "Rick" Sturckow, Goldin , Commander Robert D. Cabana, Mission Specialist Sergei Konstantinovich Krikalev, Cernan, Lovell and Mission Specialist Jerry L. Ross. Cernan flew on Gemini 9, Apollo 10 and 17 and has more than 566 cumulative hours of space flight. Lovell flew on Gemini 7 and 12, Apollo 8 and 13. His cumulative hours of space flight are more than 715. On the 4.6-million-mile, nearly 12-day STS-88 mission, Endeavour carried the U.S.-built Unity connecting module to begin construction of the International Space Station. The crew successfully mated Unity with the Russian-built Zarya control module during three space walks. With this mission, Ross completed seven space walks totaling 44 hours and 9 minutes, more than any other American space walker. Newman moved into third place for U.S. space walks with a total of 28 hours and 27 minutes on four excursions
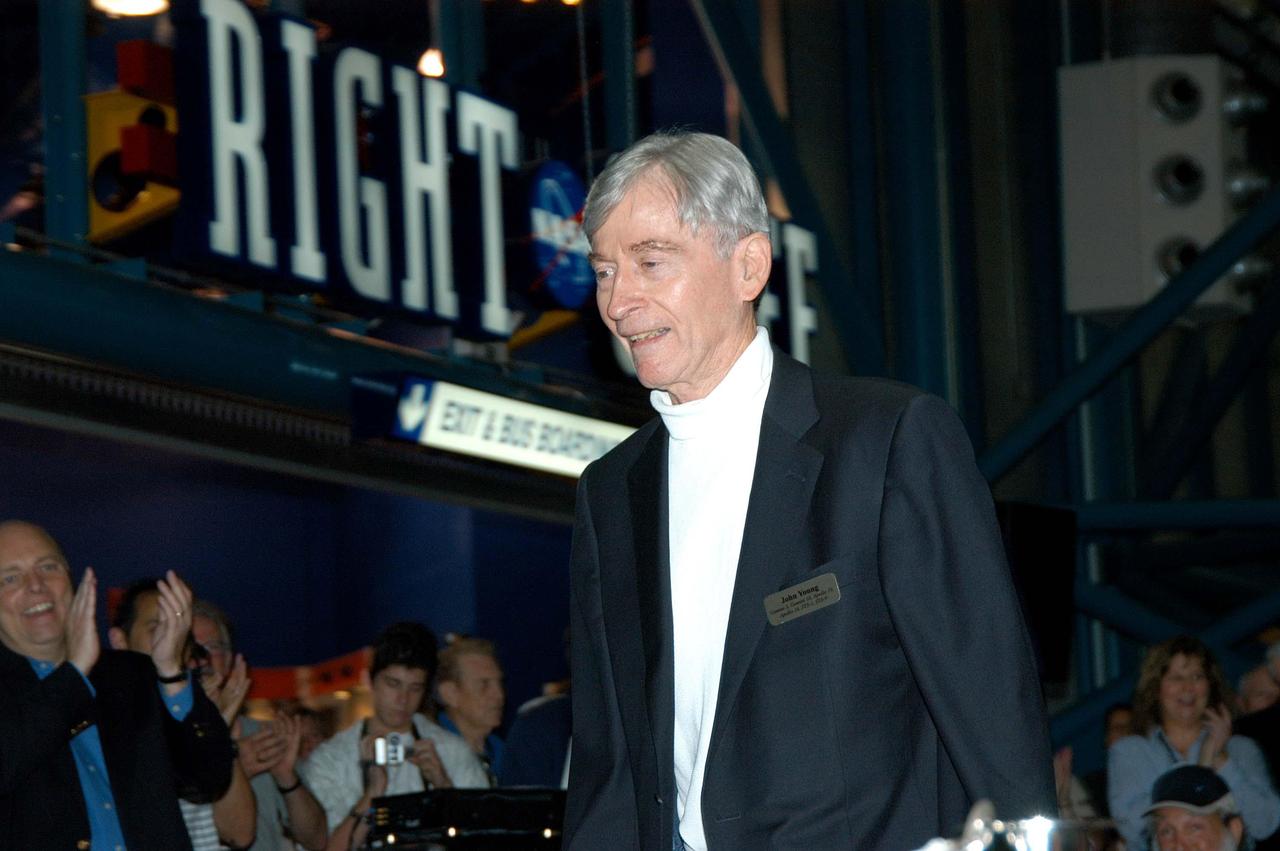

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Before the induction ceremony of five space program heroes into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame, astronaut John Young is warmly greeted as he is introduced as a previous inductee. Co-holder of a record for the most space flights, six, he flew on Gemini 3 and 10, orbited the Moon on Apollo 10, walked on the Moon on Apollo 16, and commanded two space shuttle missions, STS-1 and STS-9. Young currently serves as associate director, technical, at Johnson Space Center. The induction ceremony was held at the Apollo/Saturn V Center at KSC. New inductees are Richard O. Covey, commander of the Hubble Space Telescope repair mission; Norman E. Thagard, the first American to occupy Russia’s Mir space station; the late Francis R. "Dick" Scobee, commander of the ill-fated 1986 Challenger mission; Kathryn D. Sullivan, the first American woman to walk in space; and Frederick D. Gregory, the first African-American to command a space mission and the current NASA deputy administrator. The U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame opened in 1990 to provide a place where space travelers could be remembered for their participation and accomplishments in the U.S. space program. The five inductees join 52 previously honored astronauts from the ranks of the Gemini, Apollo, Skylab, Apollo-Soyuz, and Space Shuttle programs.
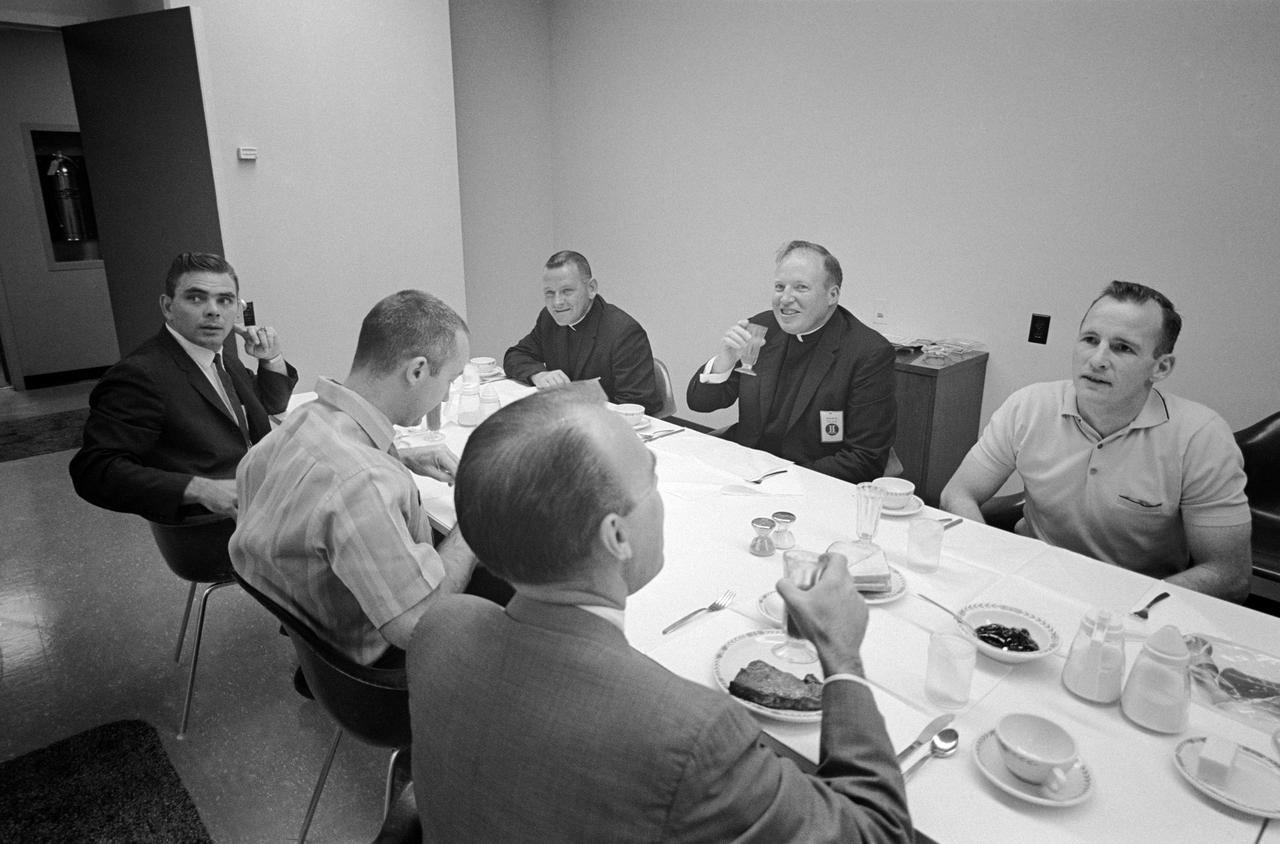

S65-19600 (3 June 1965) --- The prime crew for the Gemini-Titan 4 mission have an early morning breakfast prior to their historic flight which was launched at 10:16 a.m. (EST) on June 3, 1965. Shown here seated around the table (clockwise starting front center) are Dr. D. Owens Coons, chief, MSC Center Medical Office; astronaut James A. McDivitt, GT-4 command pilot; Dr. Eugene F. Tubbs, Kennedy Space Center; Rt. Rev. James Heiliky, McDivitt's priest at Cocoa Beach, Florida; Msgr. Irvine J. Nugent and astronaut Edward H. White II, GT-4 pilot. The group had a breakfast of tomato juice, broiled sirloin steak, poached eggs, toast, strawberry gelatin and coffee.

This is an illustration of a supermassive black hole, weighing as much as 21 million suns, located in the middle of the ultradense galaxy M60-UCD1. The dwarf galaxy is so dense that millions of stars fill the sky as seen by an imaginary visitor. Because no light can escape from the black hole, it appears simply in silhouette against the starry background. The black hole's intense gravitational field warps the light of the background stars to form ring-like images just outside the dark edges of the black hole's event horizon. Combined observations by the Hubble Space Telescope and Gemini North telescope determined the presence of the black hole inside such a small and dense galaxy. More info: Astronomers using data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and ground observation have found an unlikely object in an improbable place -- a monster black hole lurking inside one of the tiniest galaxies ever known. The black hole is five times the mass of the one at the center of our Milky Way galaxy. It is inside one of the densest galaxies known to date -- the M60-UCD1 dwarf galaxy that crams 140 million stars within a diameter of about 300 light-years, which is only 1/500th of our galaxy’s diameter. If you lived inside this dwarf galaxy, the night sky would dazzle with at least 1 million stars visible to the naked eye. Our nighttime sky as seen from Earth’s surface shows 4,000 stars. The finding implies there are many other compact galaxies in the universe that contain supermassive black holes. The observation also suggests dwarf galaxies may actually be the stripped remnants of larger galaxies that were torn apart during collisions with other galaxies rather than small islands of stars born in isolation. “We don’t know of any other way you could make a black hole so big in an object this small,” said University of Utah astronomer Anil Seth, lead author of an international study of the dwarf galaxy published in Thursday’s issue of the journal Nature. Seth’s team of astronomers used the Hubble Space Telescope and the Gemini North 8-meter optical and infrared telescope on Hawaii’s Mauna Kea to observe M60-UCD1 and measure the black hole’s mass. The sharp Hubble images provide information about the galaxy’s diameter and stellar density. Gemini measures the stellar motions as affected by the black hole’s pull. These data are used to calculate the mass of the black hole. Black holes are gravitationally collapsed, ultra-compact objects that have a gravitational pull so strong that even light cannot escape. Supermassive black holes -- those with the mass of at least one million stars like our sun -- are thought to be at the centers of many galaxies. The black hole at the center of our Milky Way galaxy has the mass of four million suns. As heavy as that is, it is less than 0.01 percent of the Milky Way’s total mass. By comparison, the supermassive black hole at the center of M60-UCD1, which has the mass of 21 million suns, is a stunning 15 percent of the small galaxy’s total mass. “That is pretty amazing, given that the Milky Way is 500 times larger and more than 1,000 times heavier than the dwarf galaxy M60-UCD1,” Seth said. One explanation is that M60-UCD1 was once a large galaxy containing 10 billion stars, but then it passed very close to the center of an even larger galaxy, M60, and in that process all the stars and dark matter in the outer part of the galaxy were torn away and became part of M60. The team believes that M60-UCD1 may eventually be pulled to fully merge with M60, which has its own monster black hole that weighs a whopping 4.5 billion solar masses, or more than 1,000 times bigger than the black hole in our galaxy. When that happens, the black holes in both galaxies also likely will merge. Both galaxies are 50 million light-years away. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington. For images and more information about Hubble, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This computer-simulated image shows a supermassive black hole at the core of a galaxy. The black region in the center represents the black hole’s event horizon, where no light can escape the massive object’s gravitational grip. The black hole’s powerful gravity distorts space around it like a funhouse mirror. Light from background stars is stretched and smeared as the stars skim by the black hole. Credits: NASA, ESA, and D. Coe, J. Anderson, and R. van der Marel (STScI) More info: Astronomers have uncovered a near-record breaking supermassive black hole, weighing 17 billion suns, in an unlikely place: in the center of a galaxy in a sparsely populated area of the universe. The observations, made by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the Gemini Telescope in Hawaii, may indicate that these monster objects may be more common than once thought. Until now, the biggest supermassive black holes – those roughly 10 billion times the mass of our sun – have been found at the cores of very large galaxies in regions of the universe packed with other large galaxies. In fact, the current record holder tips the scale at 21 billion suns and resides in the crowded Coma galaxy cluster that consists of over 1,000 galaxies. More: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/behemoth-black-hole-found-in-an-unlikely-place" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/behemoth-black-hole-fou...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>