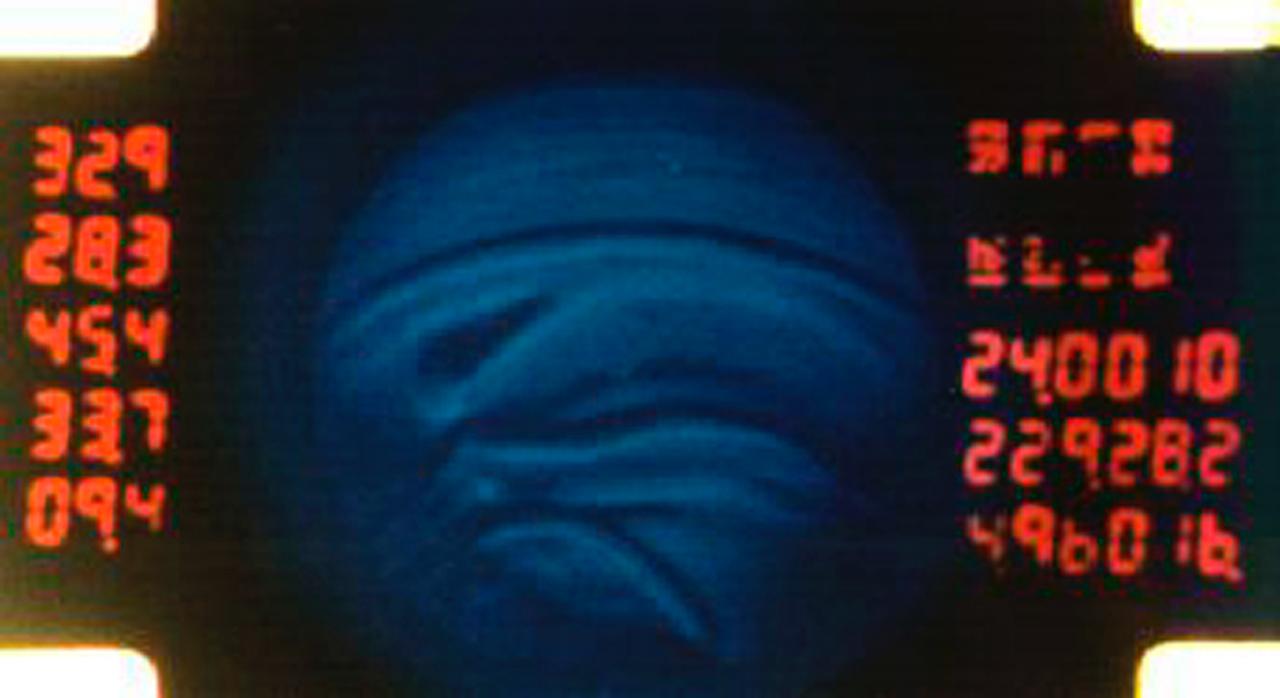

A 16mm film frame shows convective regions inside silicone oil playing the part of a stellar atmosphere in the Geophysical Fluid Flow Cell (GFFC). An electrostatic field pulled the oil inward to mimic gravity's effects during the experiments. The GFFC thus produced flow patterns that simulated conditions inside the atmospheres of Jupiter and the Sun and other stars. Numbers of the frame indicate temperatures and other conditions. This image is from the Spacelab-3 flight in 1985. GFFC was reflown on U.S. Microgravity Laboratory-2 in 1995. The principal investigator was John Hart of the University of Colorado at Boulder. It was managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. (Credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center)
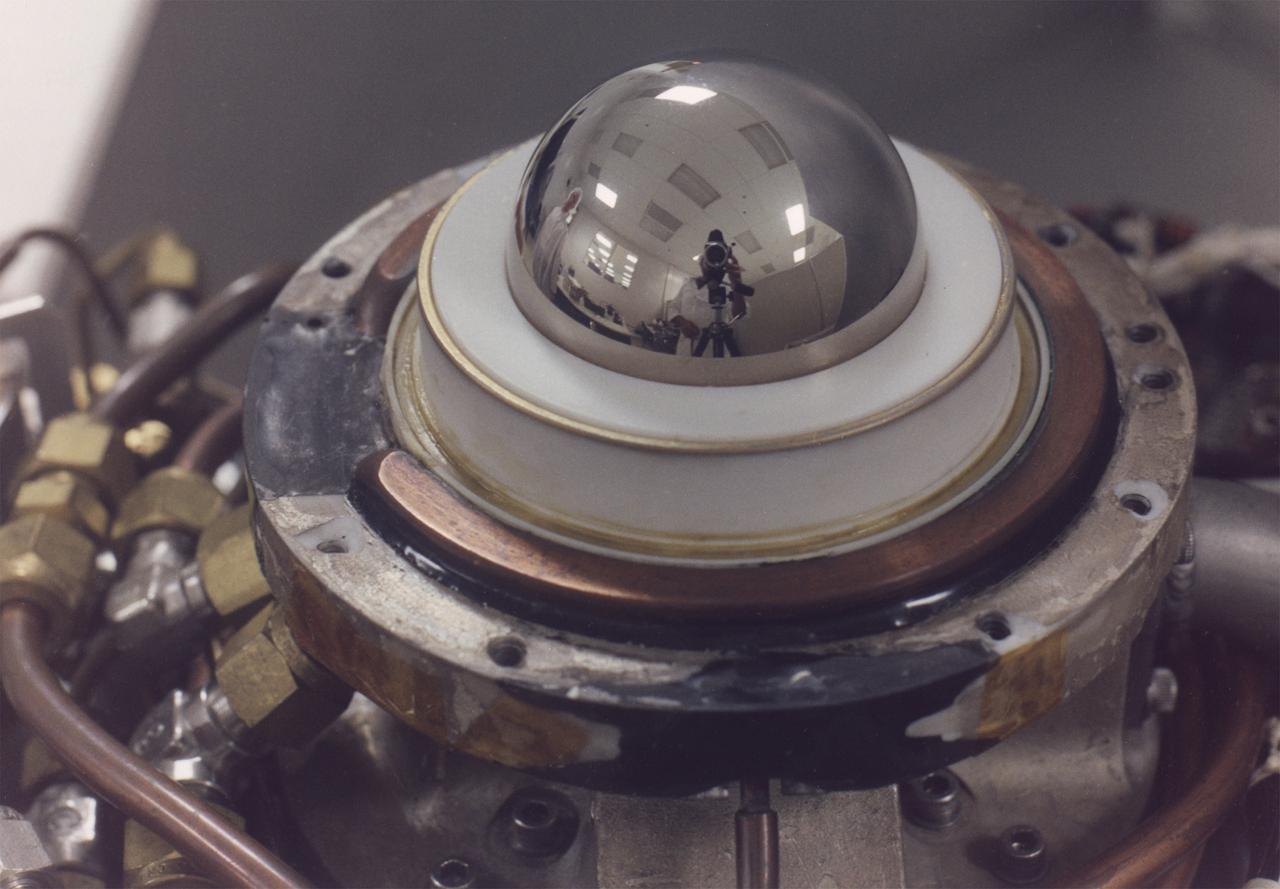
A steel hemisphere was at the core of the Geophysical Fluid Flow Cell (GFFC) that flew on two Spacelab missions. It was capped by a sapphire dome. Silicone oil between the two played the part of a steller atmosphere. An electrostatic field pulled the oil inward to mimic gravity's effects during the experiments. The GFFC thus produced flow patterns that simulated conditions inside the atmospheres of Jupiter and the Sun and other stars. GFFC flew on Spacelab-3 in 1985 and U.S. Microgravity Laboratory-2 in 1995. The principal investigator was John Hart of the University of Colorado at Boulder. It was managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. (Credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center)
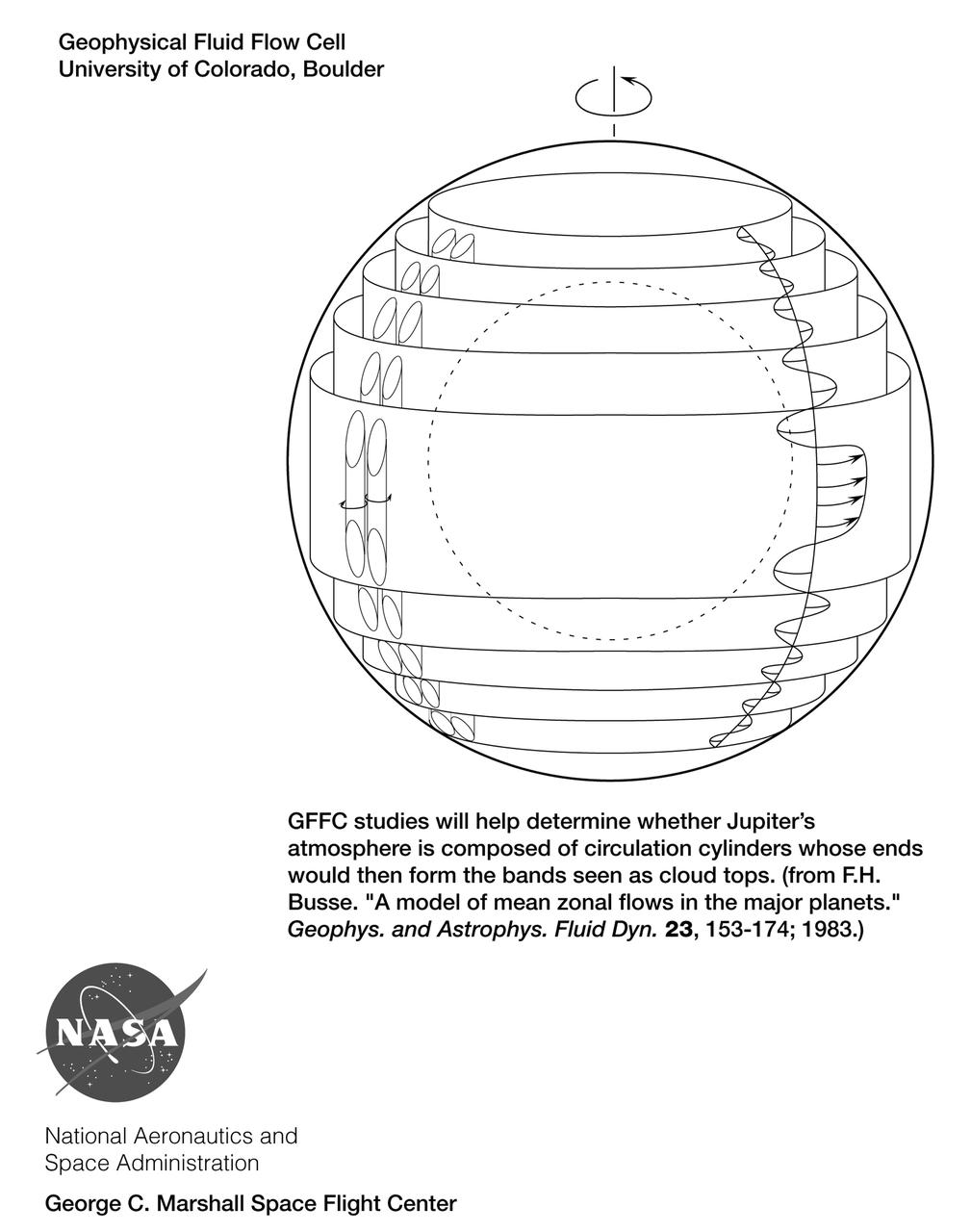
This drawing depicts one set of flow patterns simulated in the Geophysical Fluid Flow Cell (GFFC) that flew on two Spacelab missions. Silicone oil served as the atmosphere around a rotating steel hemisphere (dotted circle) and an electrostatic field pulled the oil inward to mimic gravity's effects during the experiments. The GFFC thus produced flow patterns that simulated conditions inside the atmospheres of Jupiter and the Sun and other stars. The principal investigator was John Hart of the University of Colorado at Boulder. It was managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). An Acrobat PDF copy of this drawing is available at http://microgravity.nasa.gov/gallery. (Credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center)
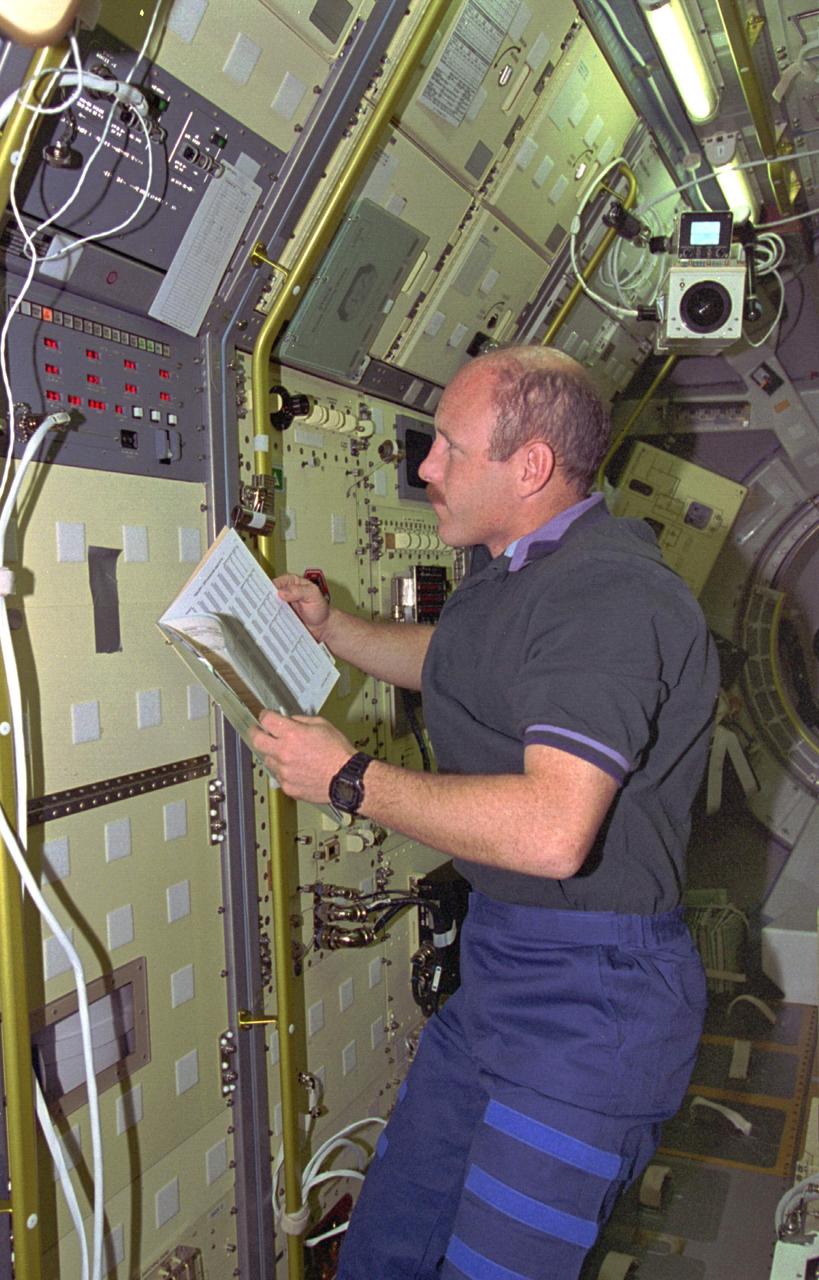

STS073-363-032 (20 October - 5 November 1995) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, STS-73 mission commander, studies the movement of fluids in microgravity at the Geophysical Fluid Flow Cell (GFFC) workstation in the science module of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Bowersox was joined by four other NASA astronauts and two guest researchers for almost 16-days of Earth-orbit research in support of the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission.
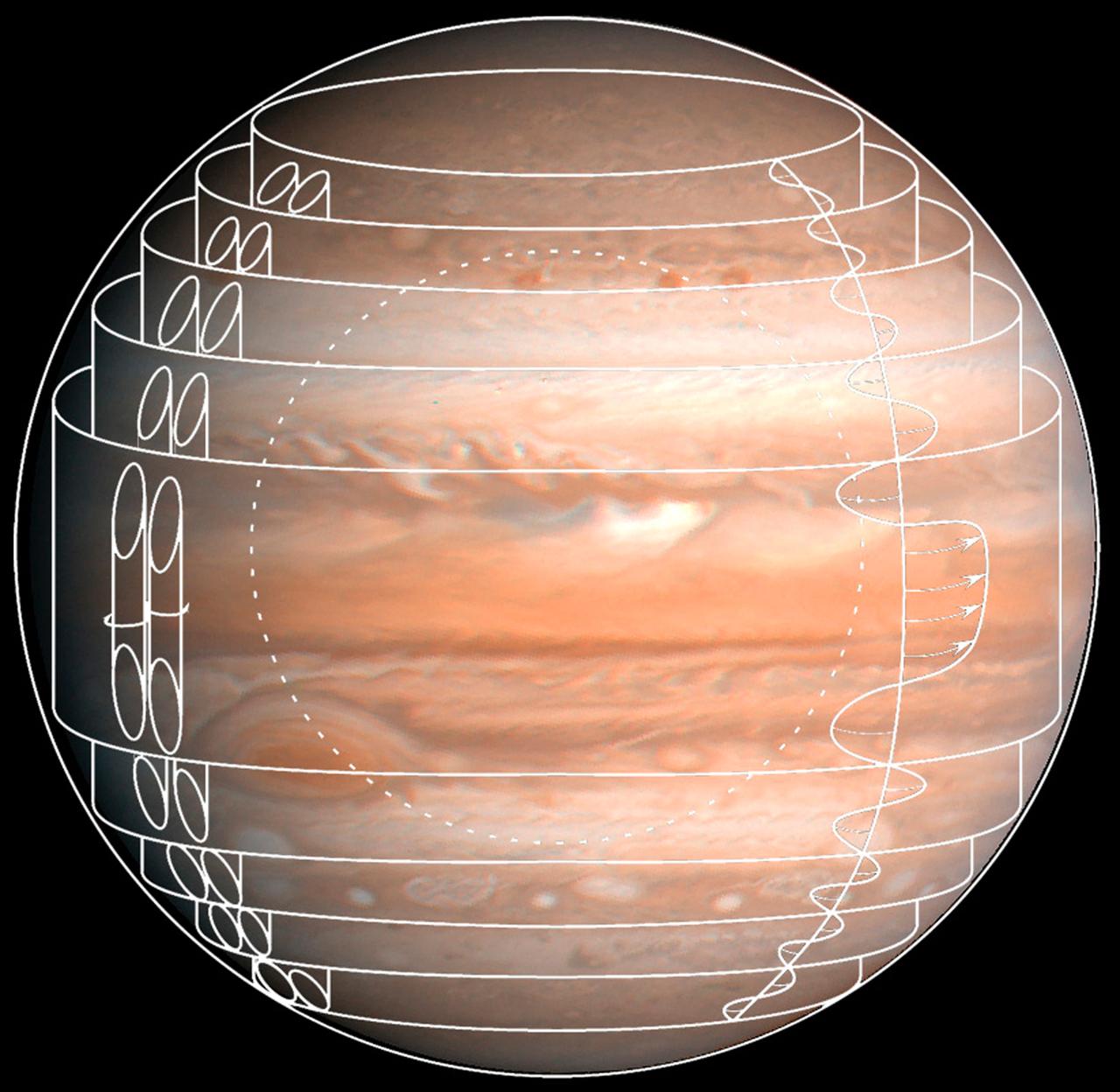
This composite image depicts one set of flow patterns simulated in the Geophysical Fluid Flow Cell (GFFC) that flew on two Spacelab missions. Silicone oil served as the atmosphere around a rotating steel hemisphere (dotted circle) and an electrostatic field pulled the oil inward to mimic gravity's effects during the experiments. The GFFC thus produced flow patterns that simulated conditions inside the atmospheres of Jupiter and the Sun and other stars. GFFC flew on Spacelab-3 in 1985 and U.S. Microgravity Laboratory-2 in 1995. The principal investigator was John Hart of the University of Colorado at Boulder. It was managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. (Credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center)
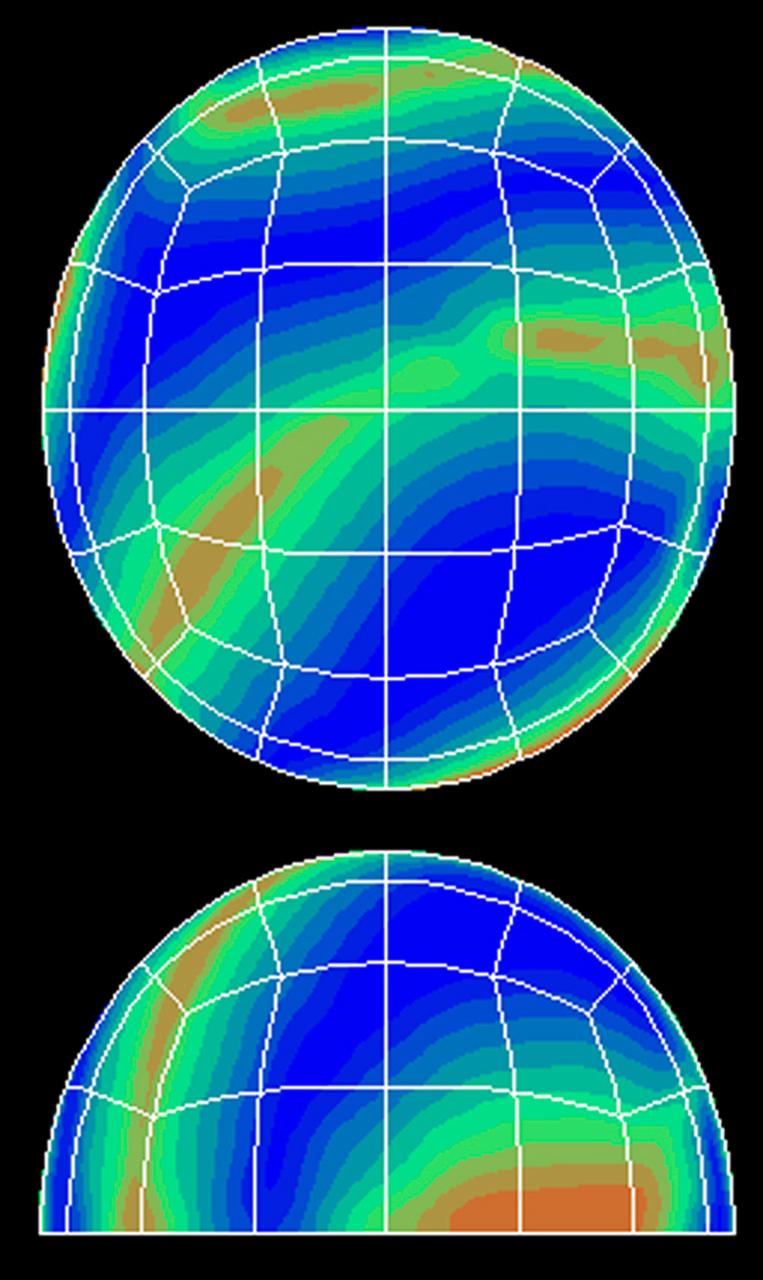
Computer simulation of atmospheric flow corresponds well to imges taken during the second Geophysical Fluid Flow Cell (BFFC) mission. The top shows a view from the pole, while the bottom shows a view from the equator. Red corresponds to hot fluid rising while blue shows cold fluid falling. This simulation was developed by Anil Deane of the University of Maryland, College Park and Paul Fischer of Argorne National Laboratory. Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center