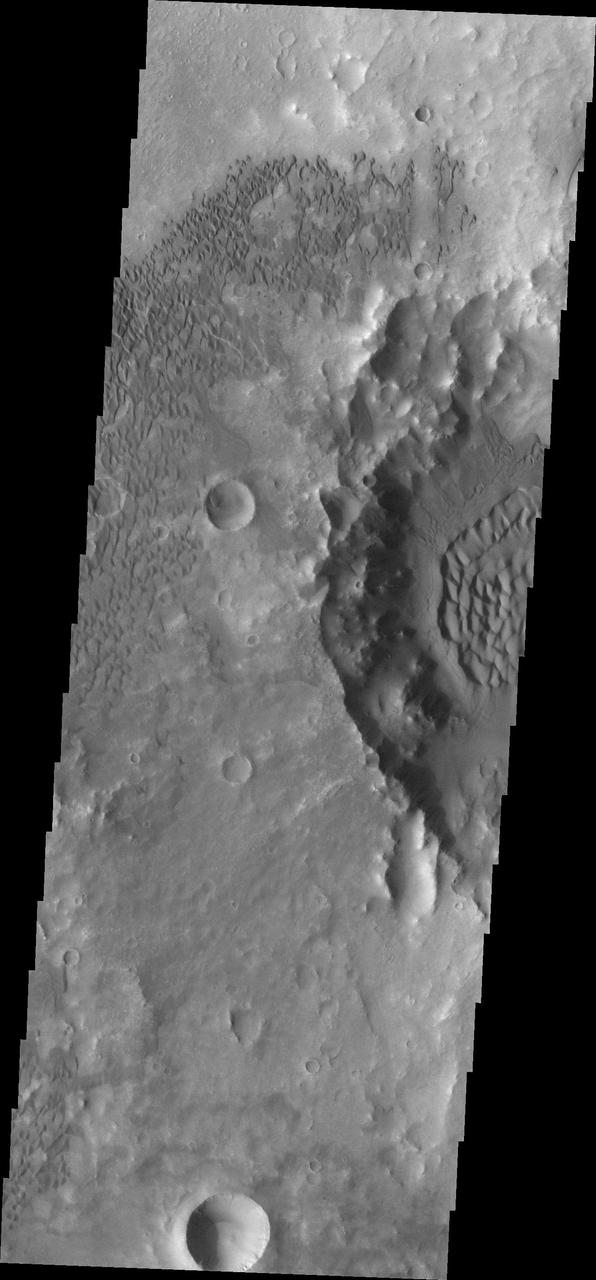

Dunes Galore
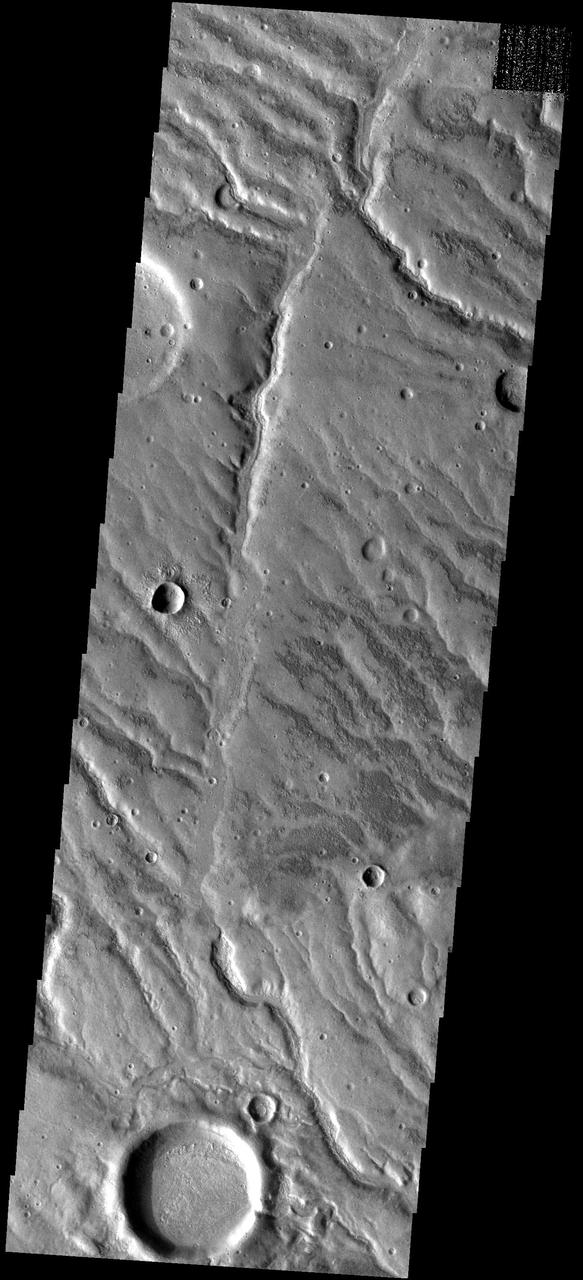

Channels Galore
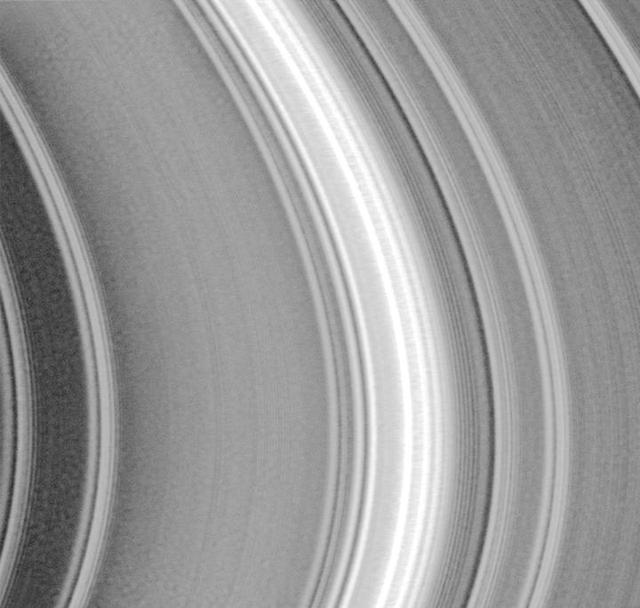
Rings Galore

Shapes Galore

Gullies Galore!
Dunes Galore
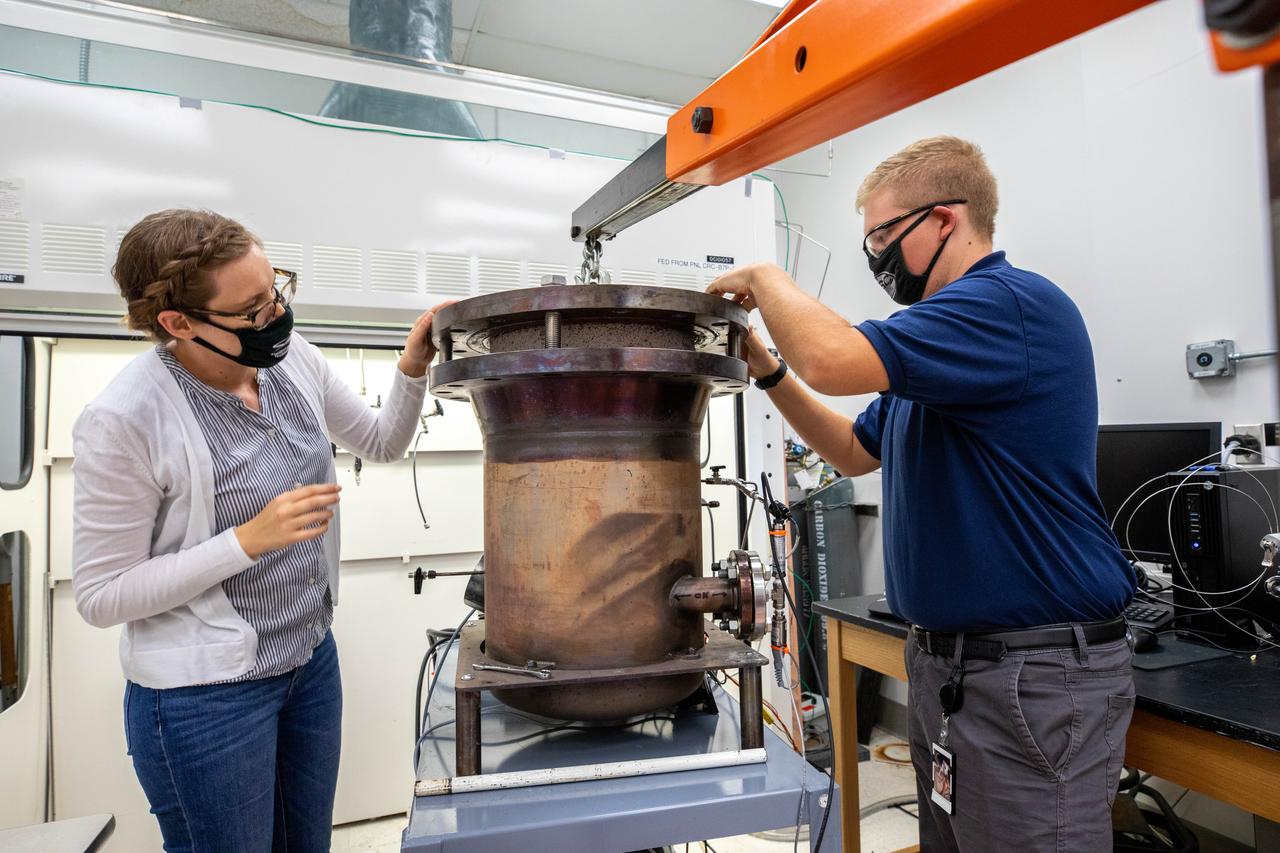

Elspeth Petersen, left, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and Evan Bell, GaLORE mechanical engineer, inspect hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – stimulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
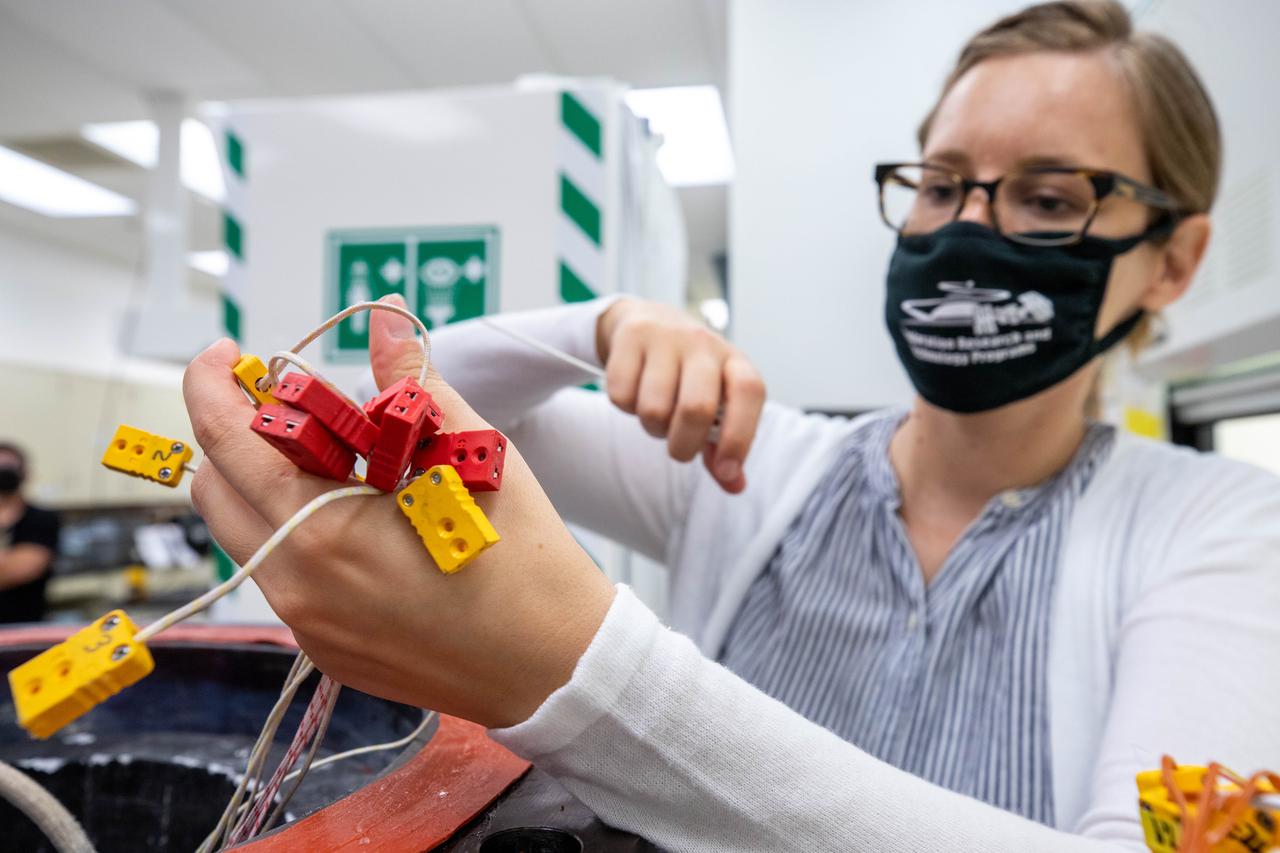

Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects some of the GaLORE hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
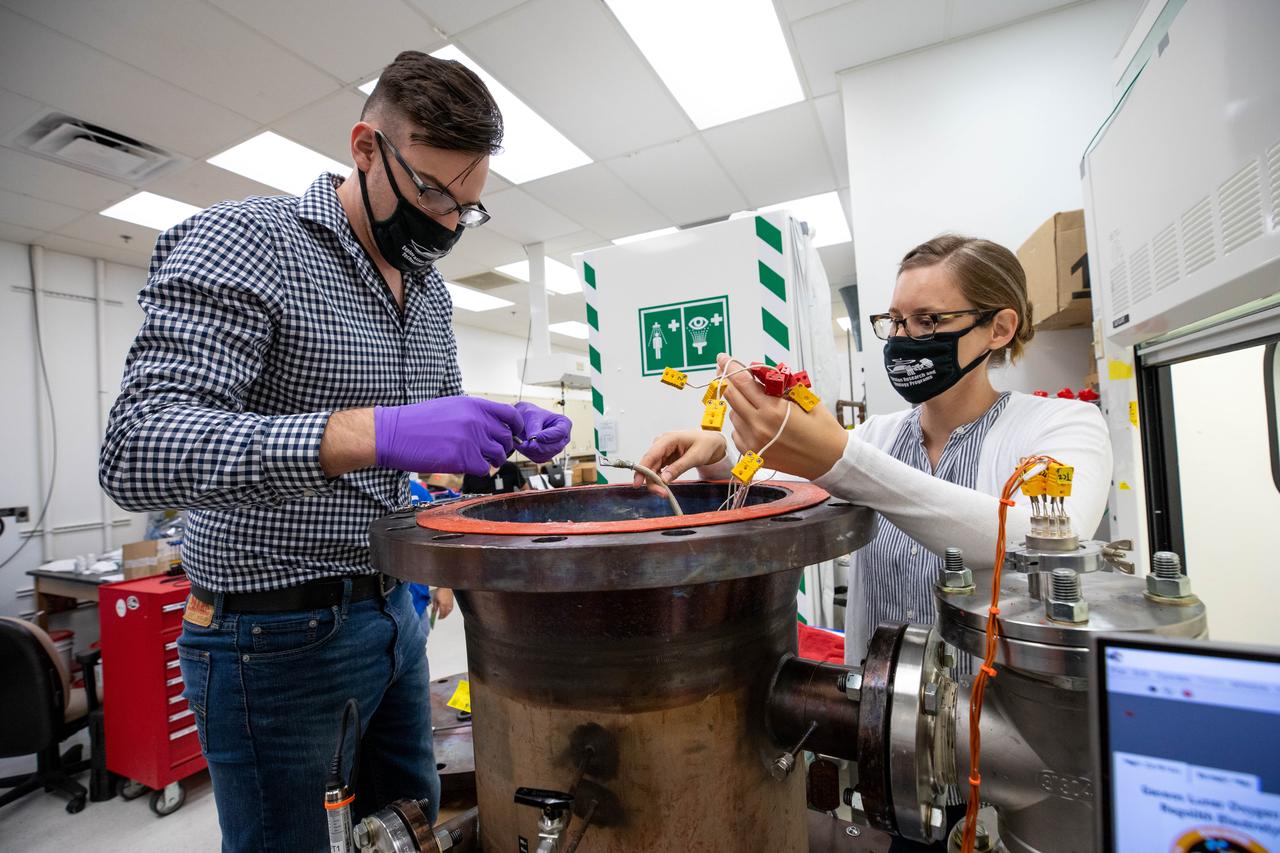

Kevin Grossman, left, principal investigator of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project, and Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the GaLORE team, check some of the project’s hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
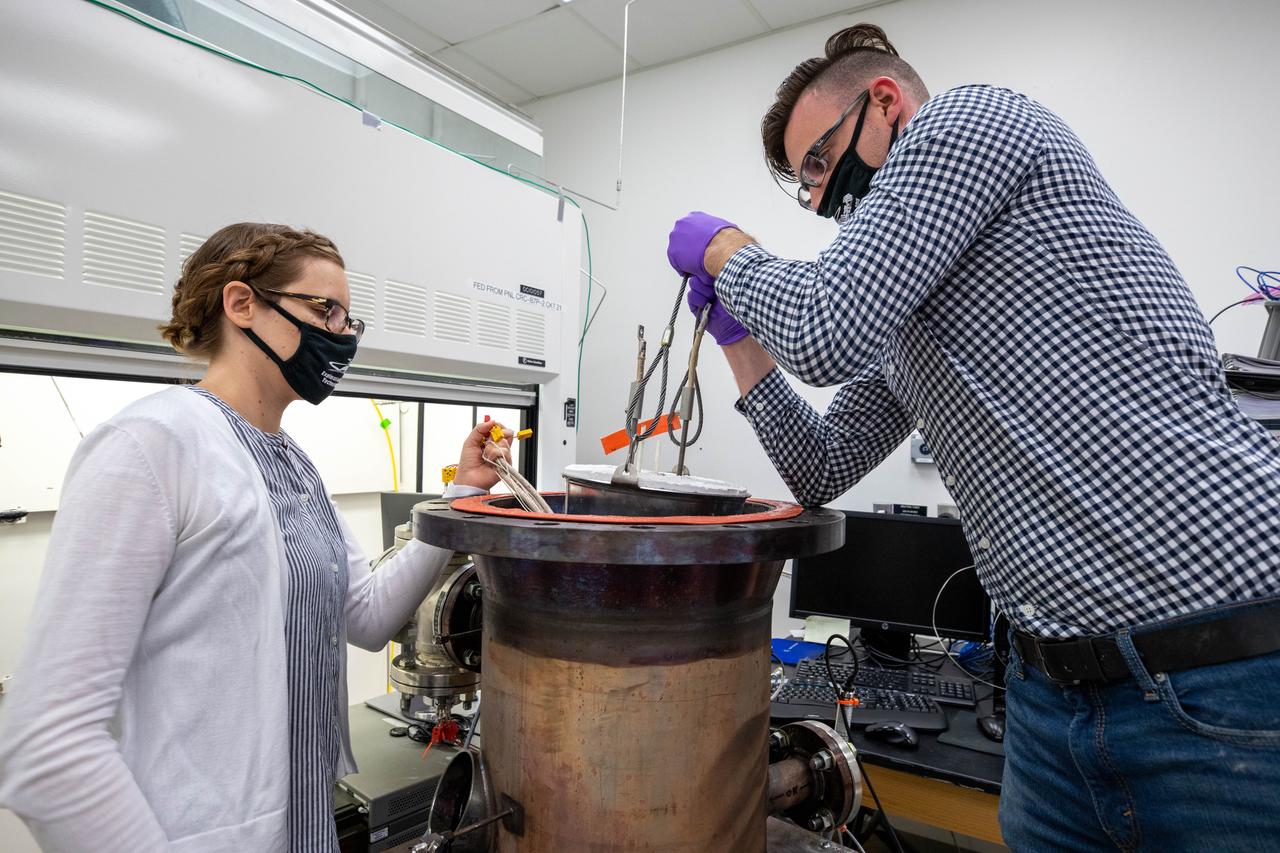

Elspeth Petersen, left, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team, and Kevin Grossman, GaLORE principal investigator, inspect a reactor before a test to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
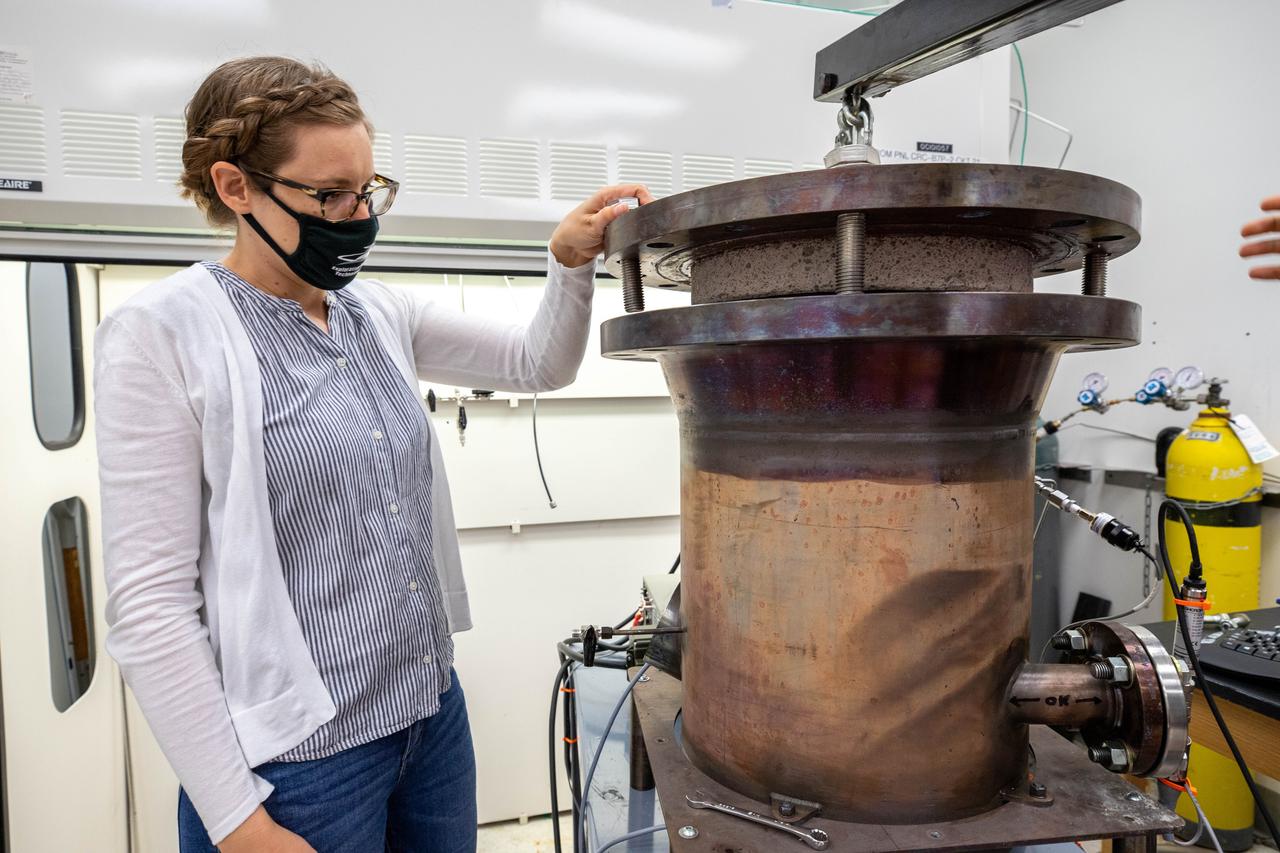

Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects the GaLORE hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
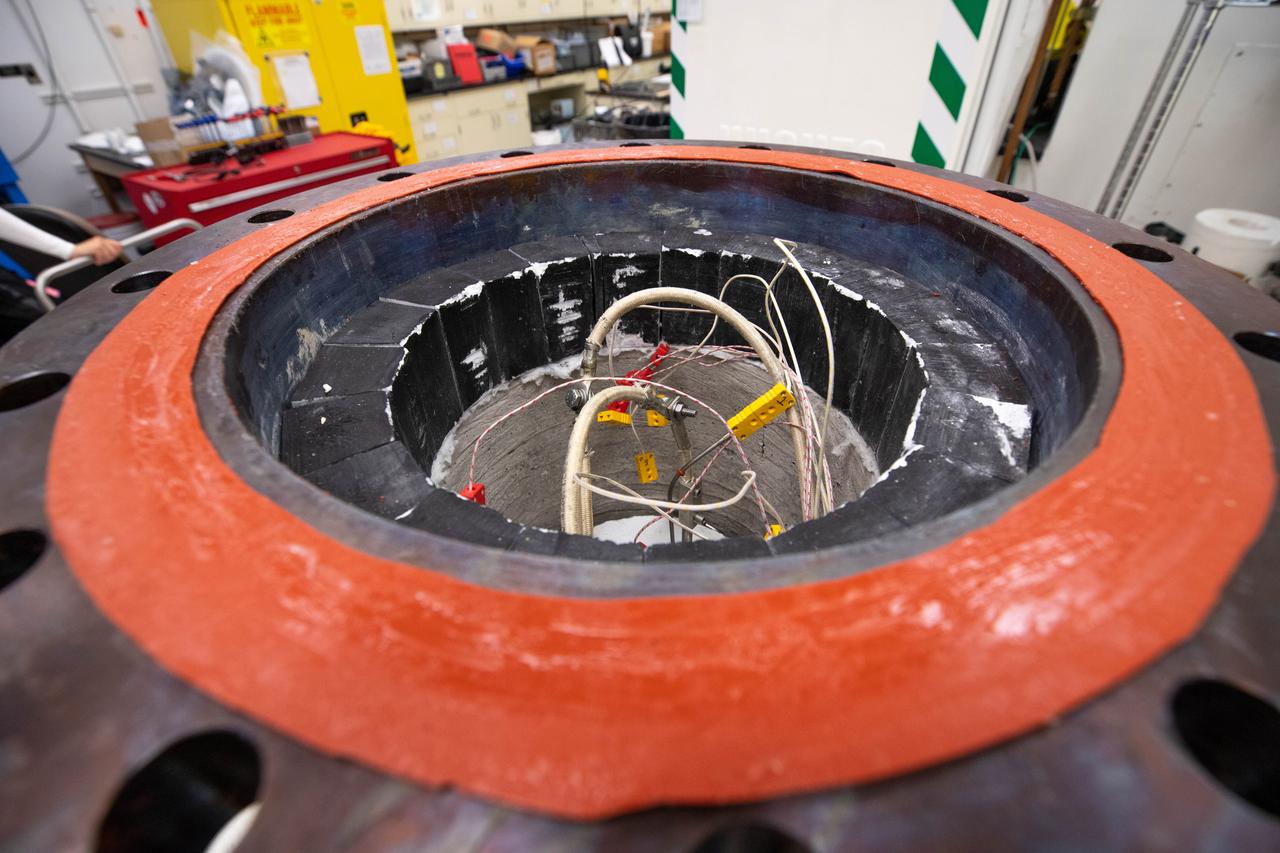

A team investigating molten regolith electrolysis prepares to test a reactor inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 29, 2020. The Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project seeks to develop technology to extract oxygen and metals from the crushed rock, or regolith, that covers the Moon’s surface. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
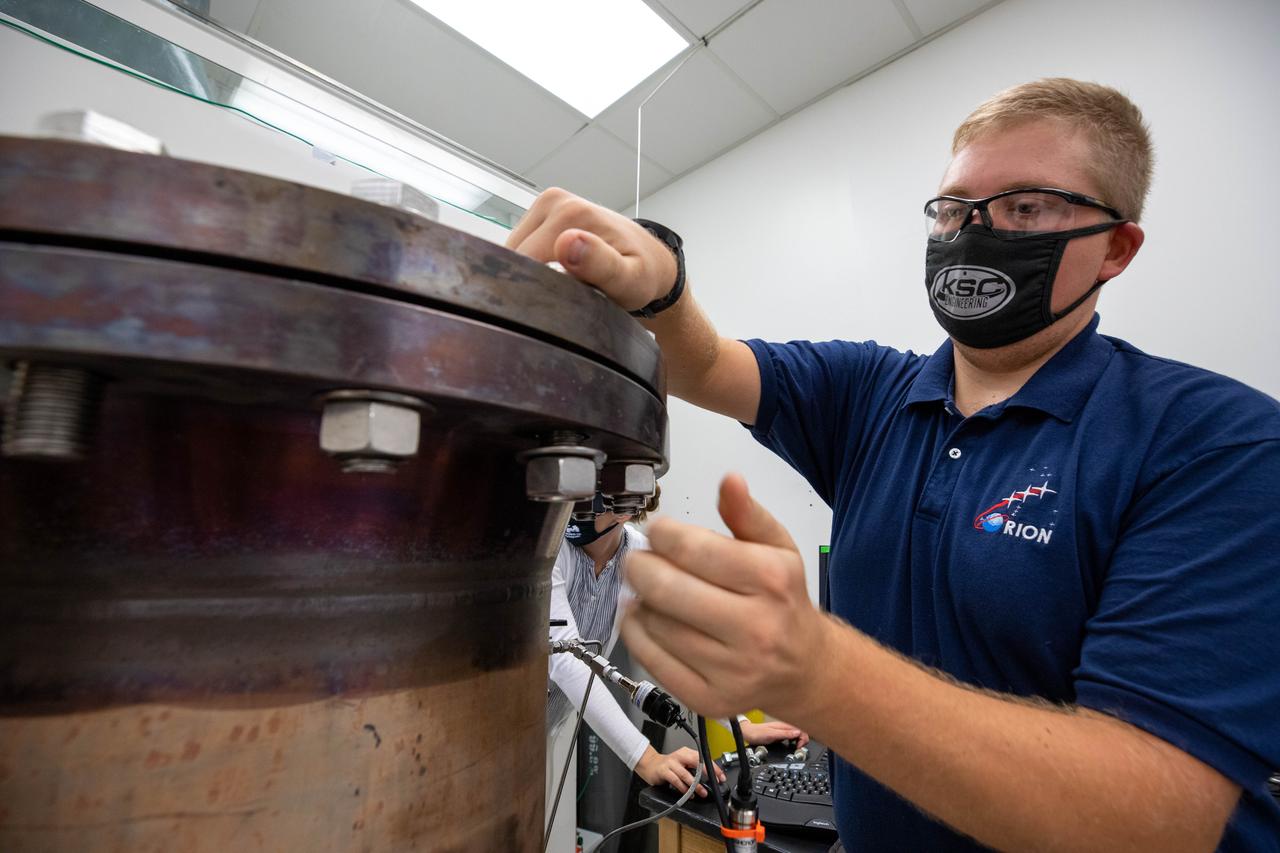

Evan Bell, a mechanical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
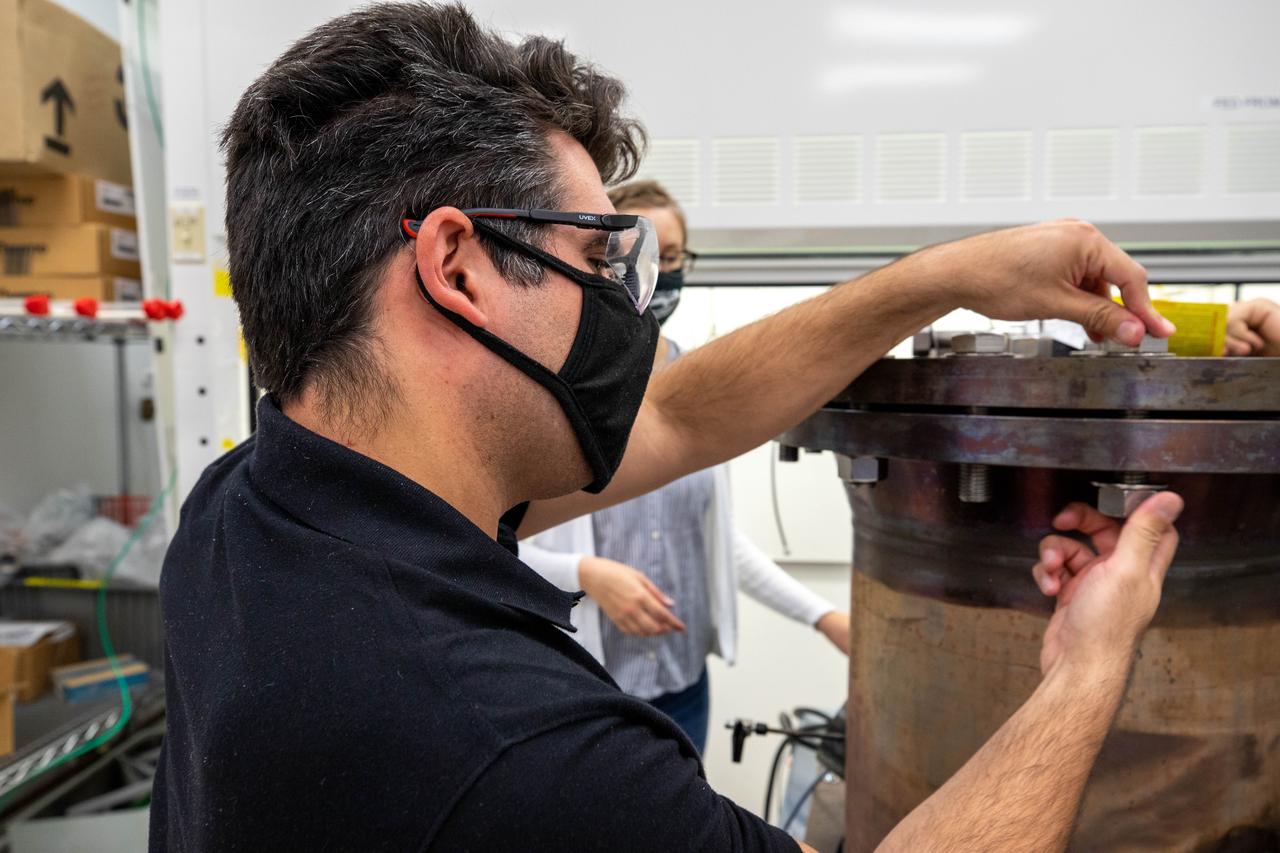

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
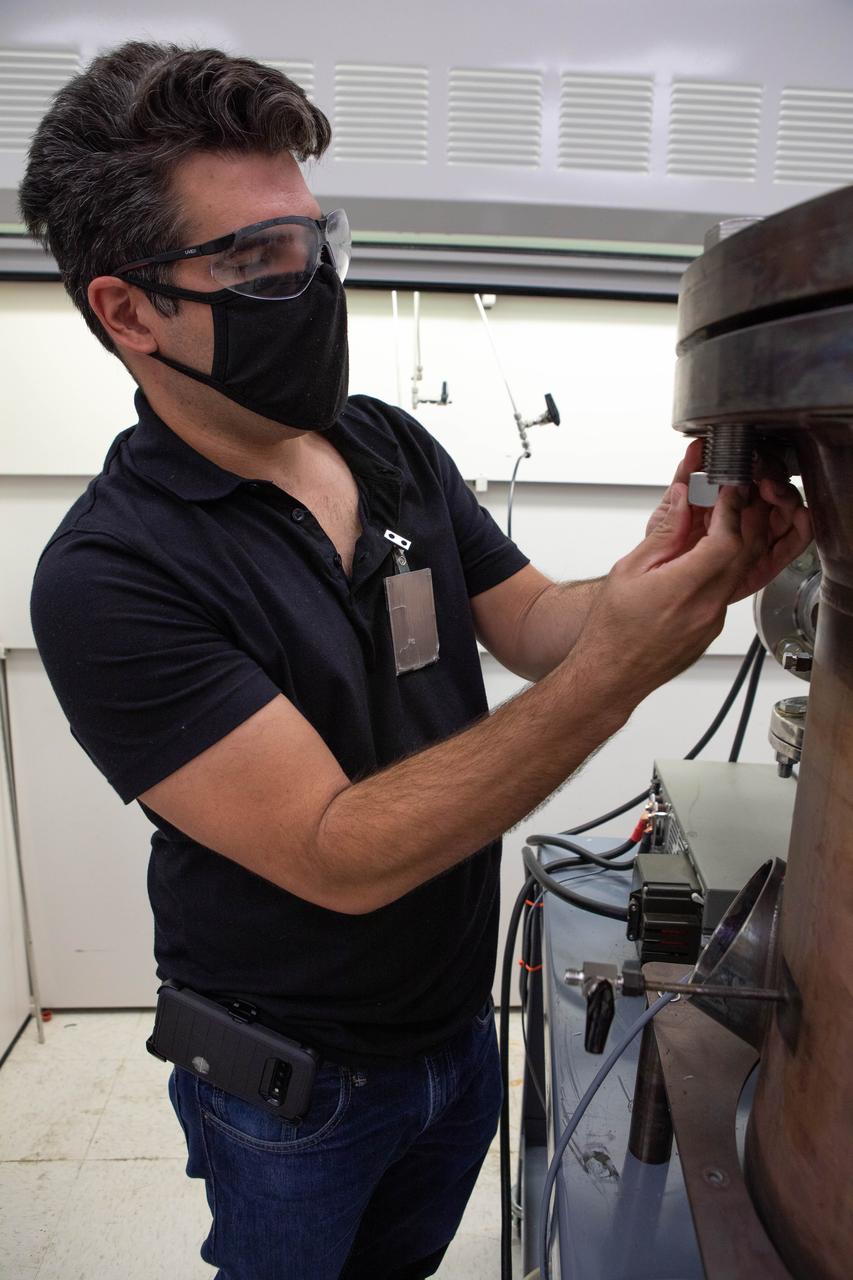

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
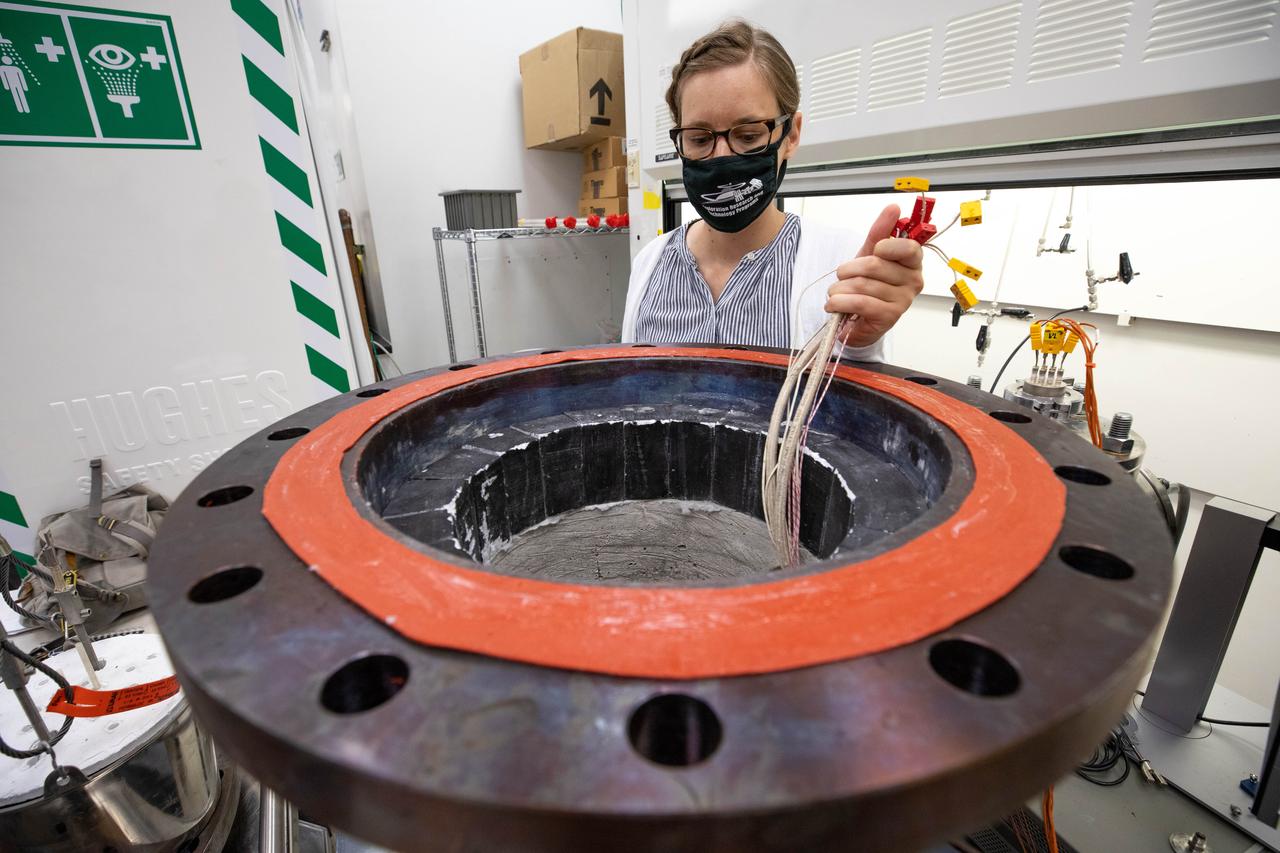

Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects hardware before a test to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
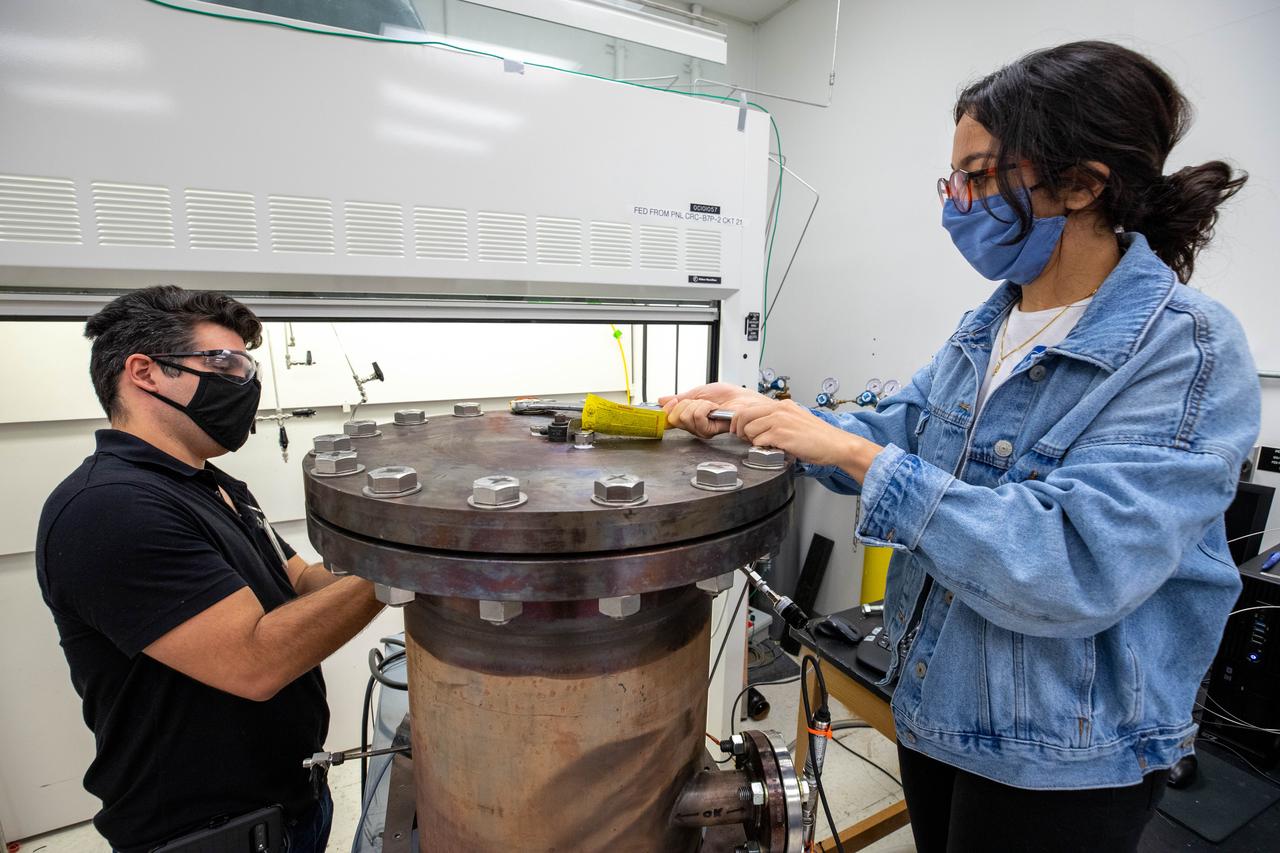

Members of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team inspect hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
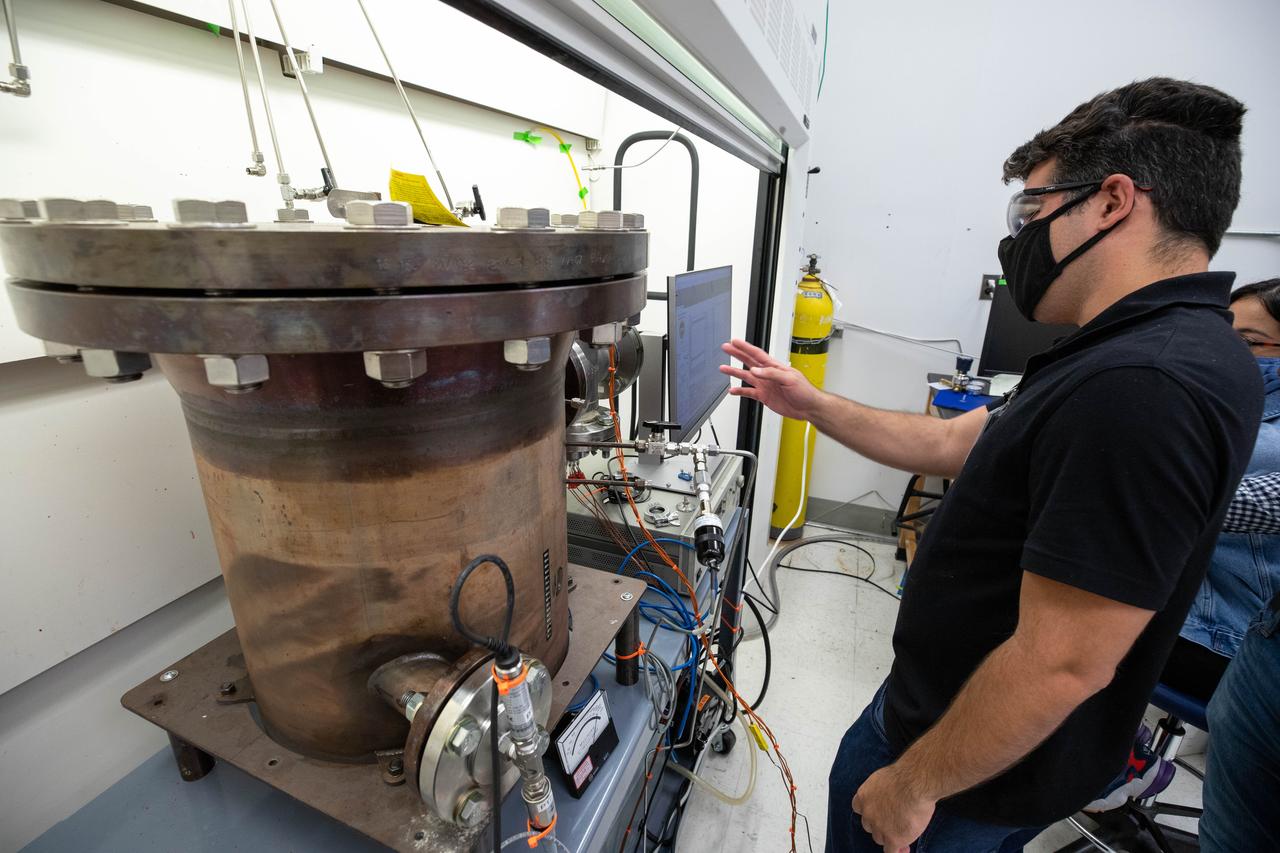

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
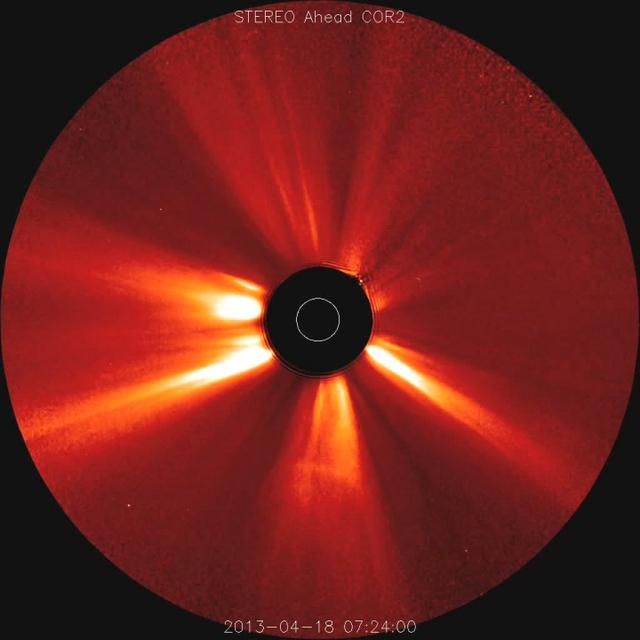

Coronal mass ejections were popping out from the Sun at a pace of two per day on average (Apr. 18-23, 2013). We counted ten CMEs for the five days, but some of the eruptions were complex and difficult to differentiate from one another. Almost all of them blew particles out to the left, most of them probably originating from the same active region. These were taken by the STEREO (Ahead) spacecraft?s coronagraph, in which the black disk blocks the Sun (represented by the white circle) so that we can observe the fainter features beyond it. Credit: NASA/Goddard/STEREO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
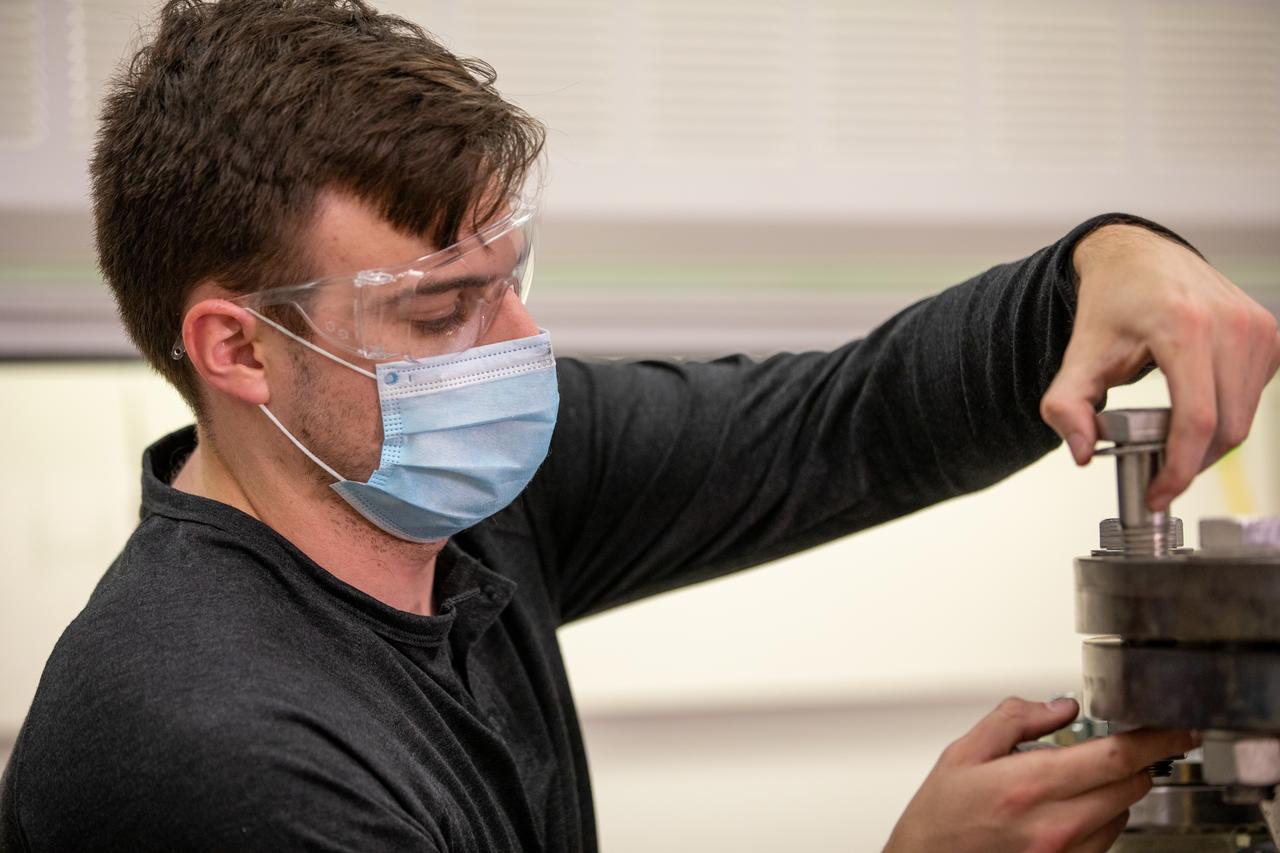
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
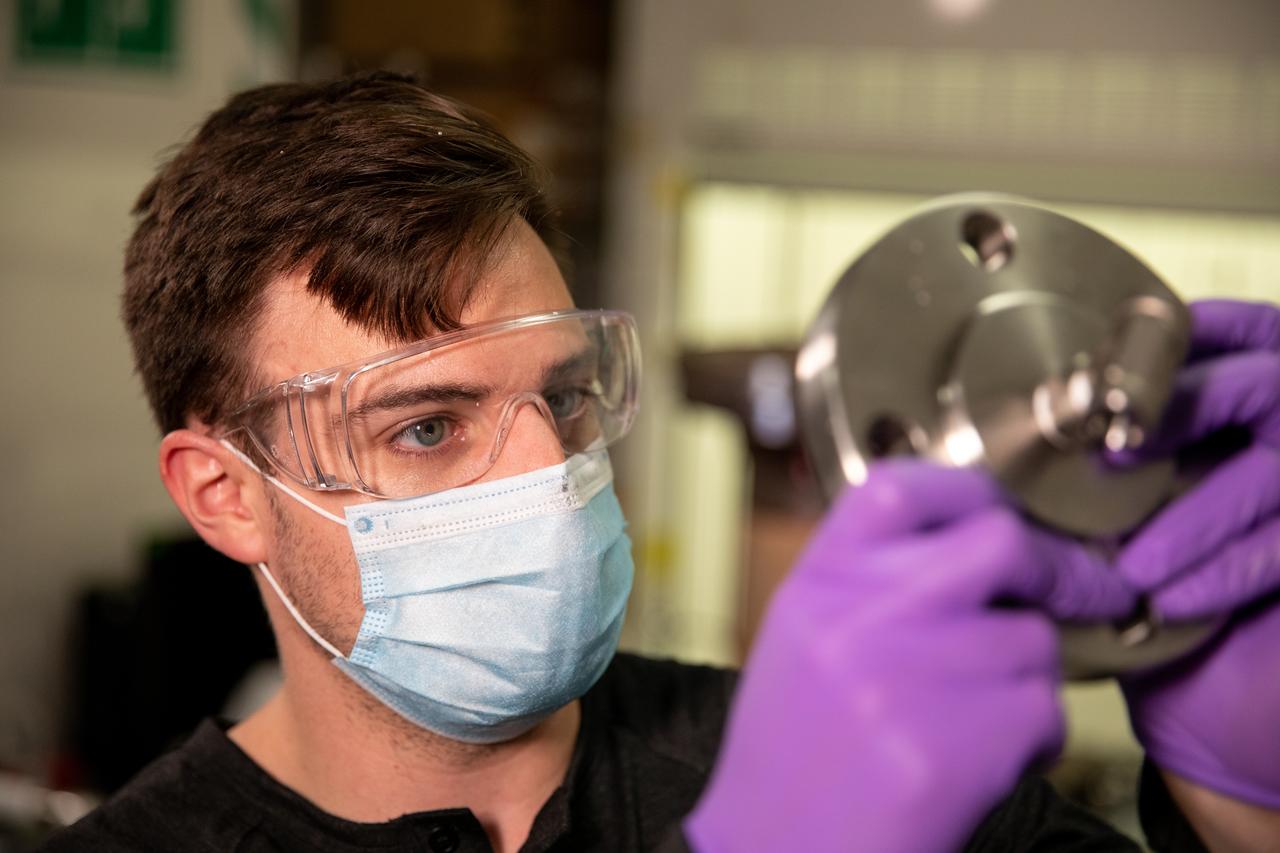

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
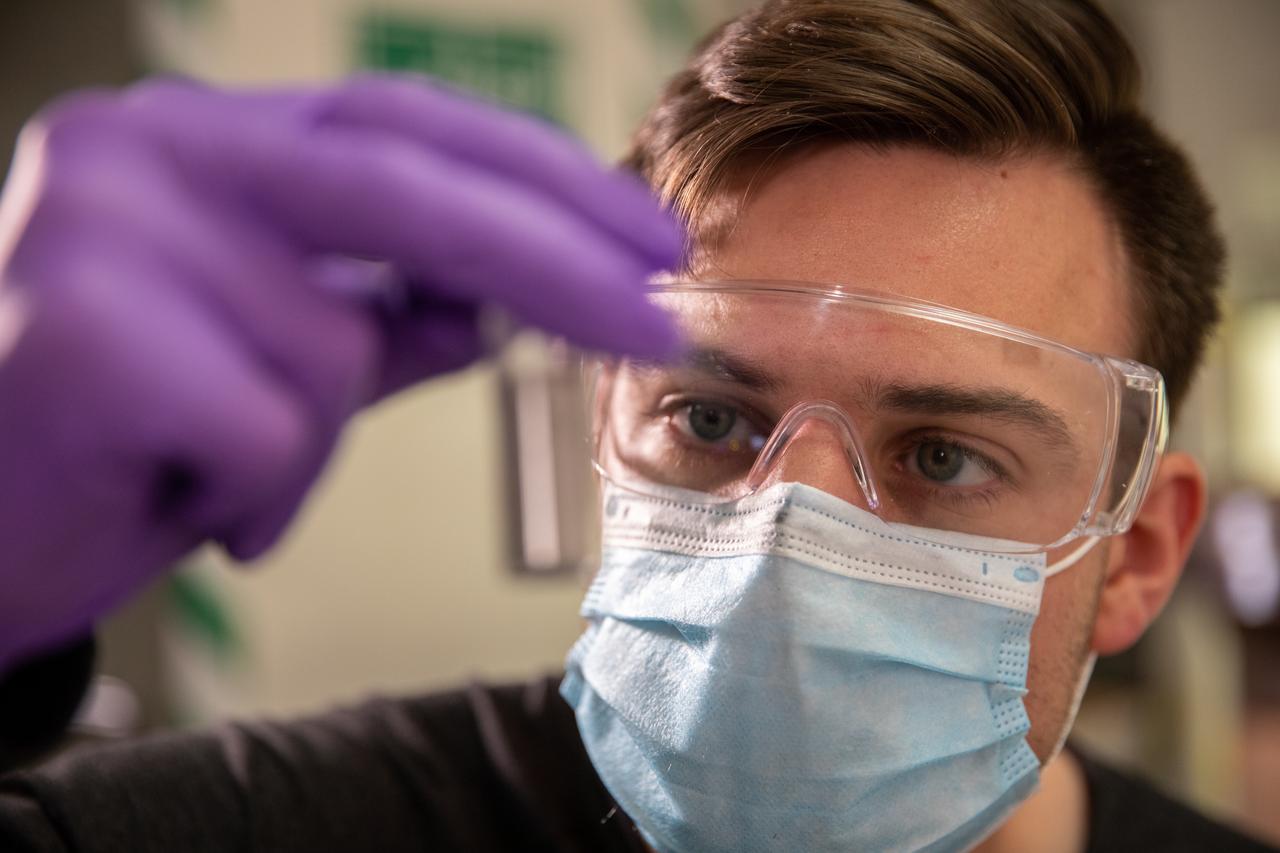
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
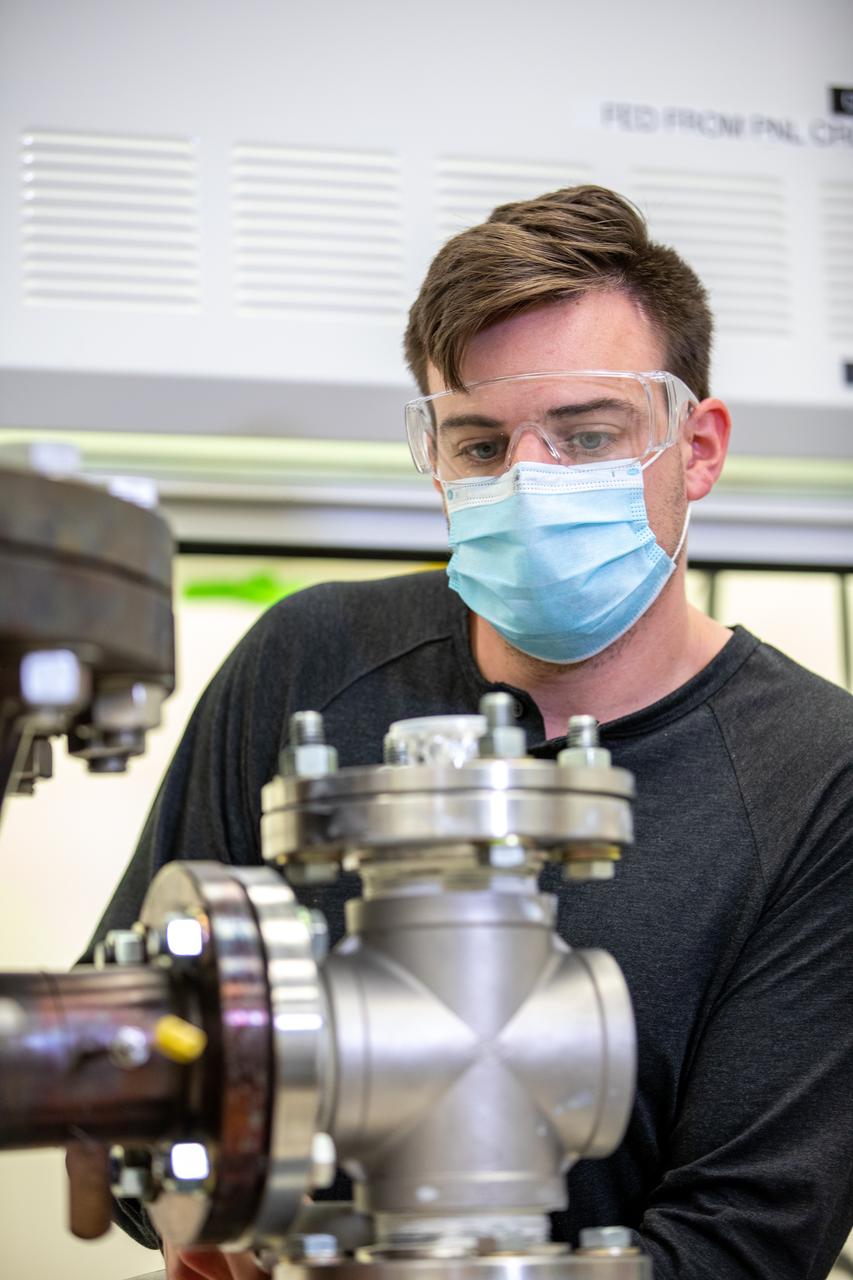

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
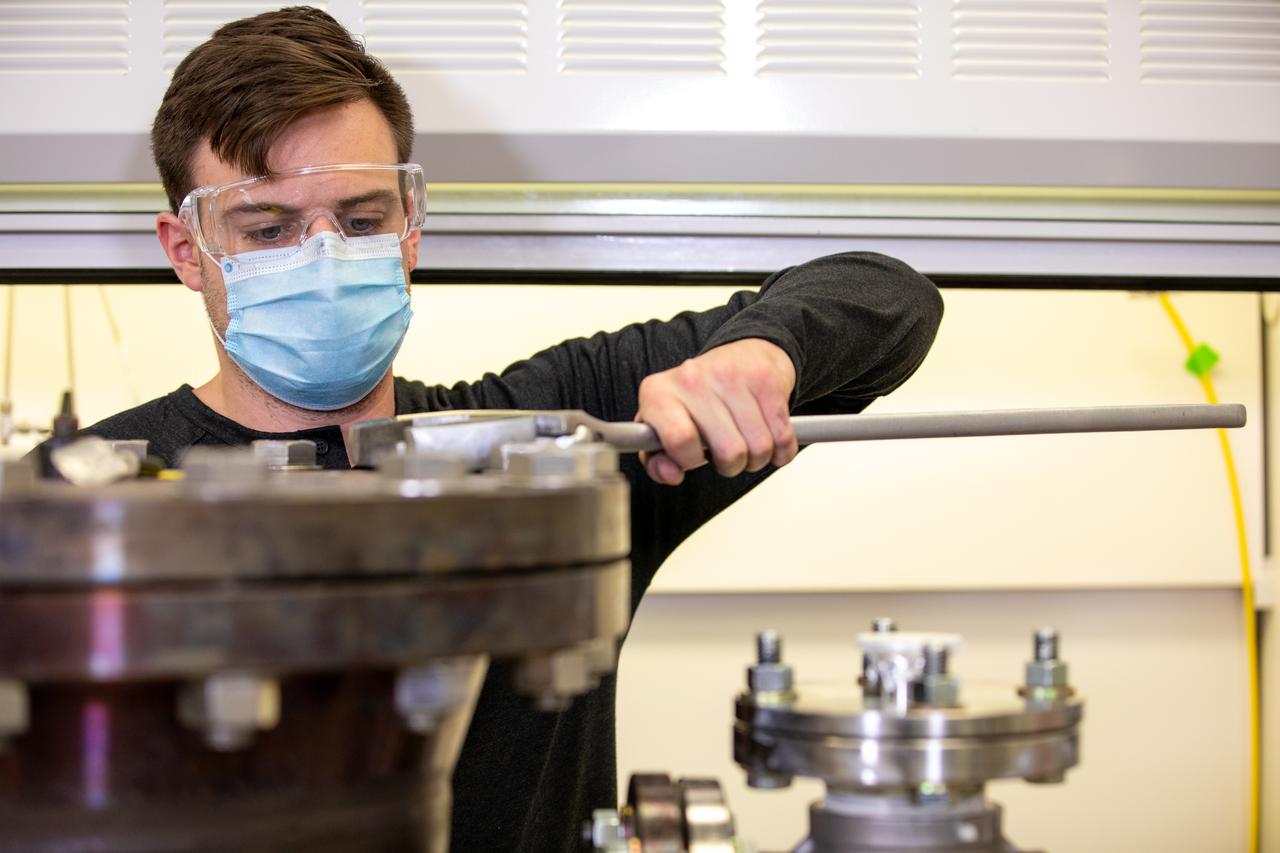

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
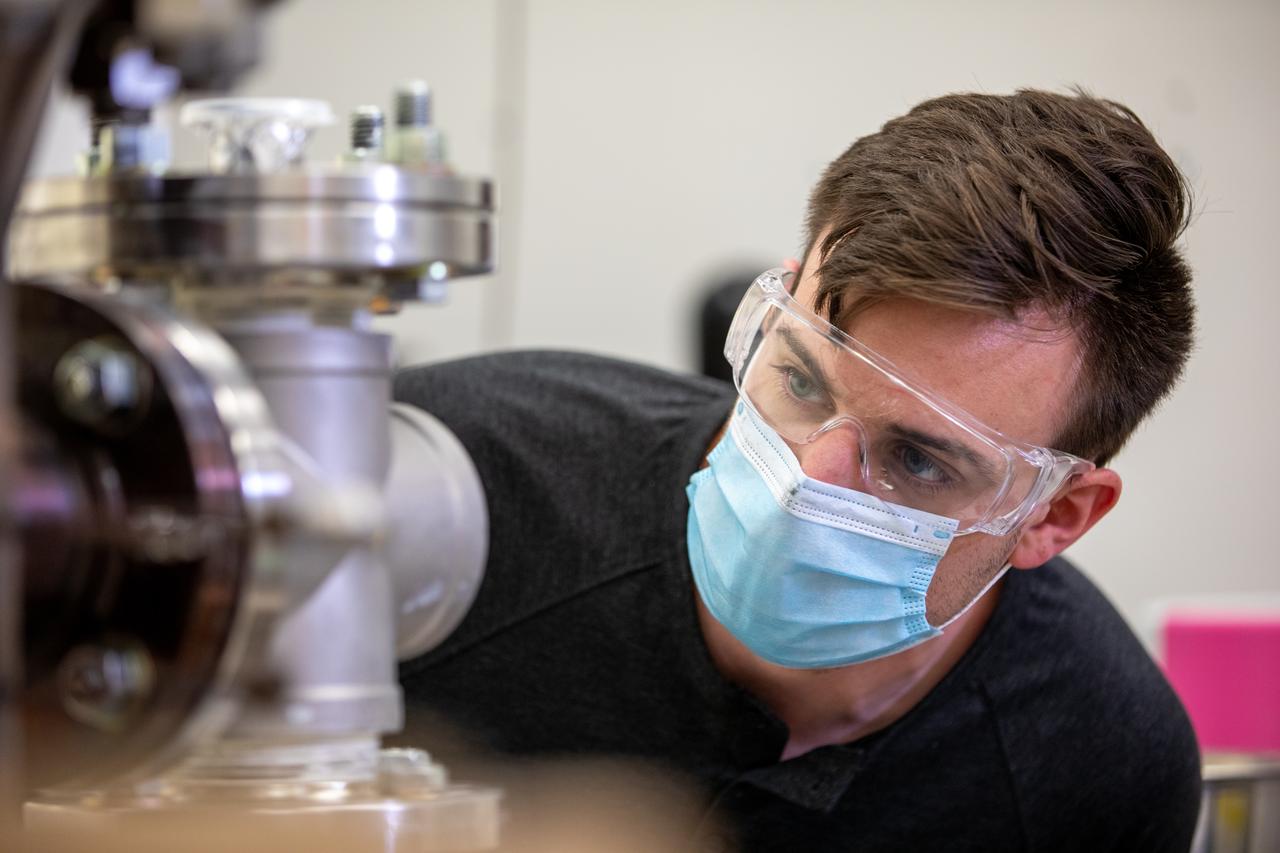

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
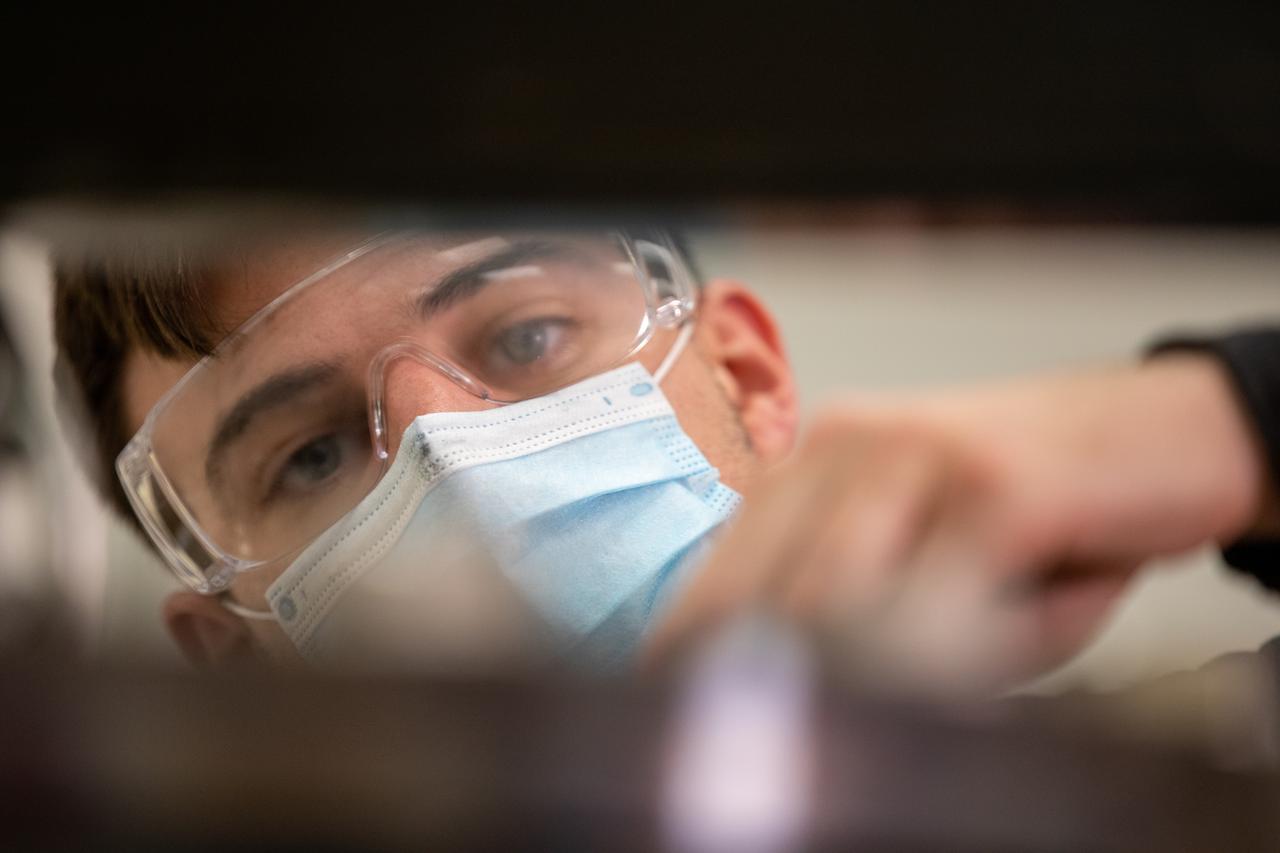

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
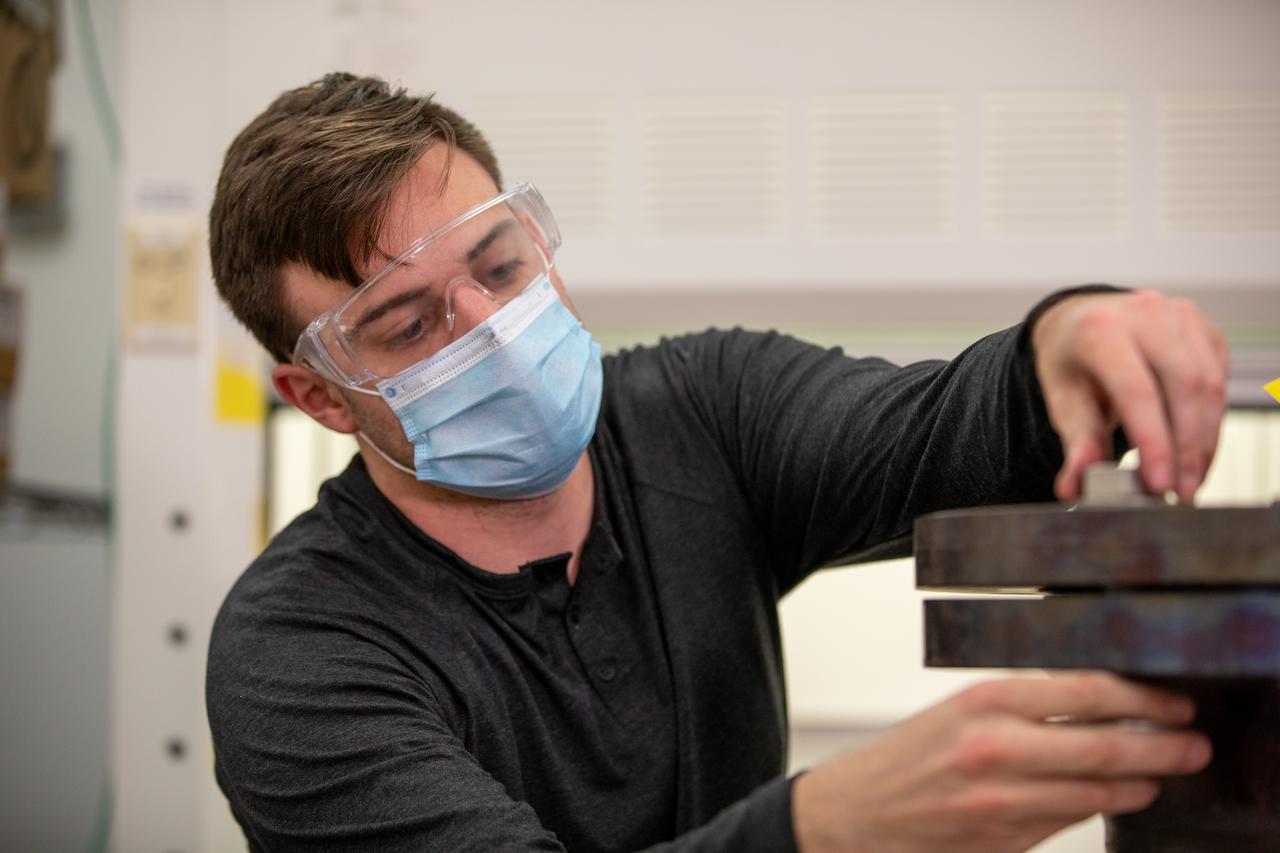

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
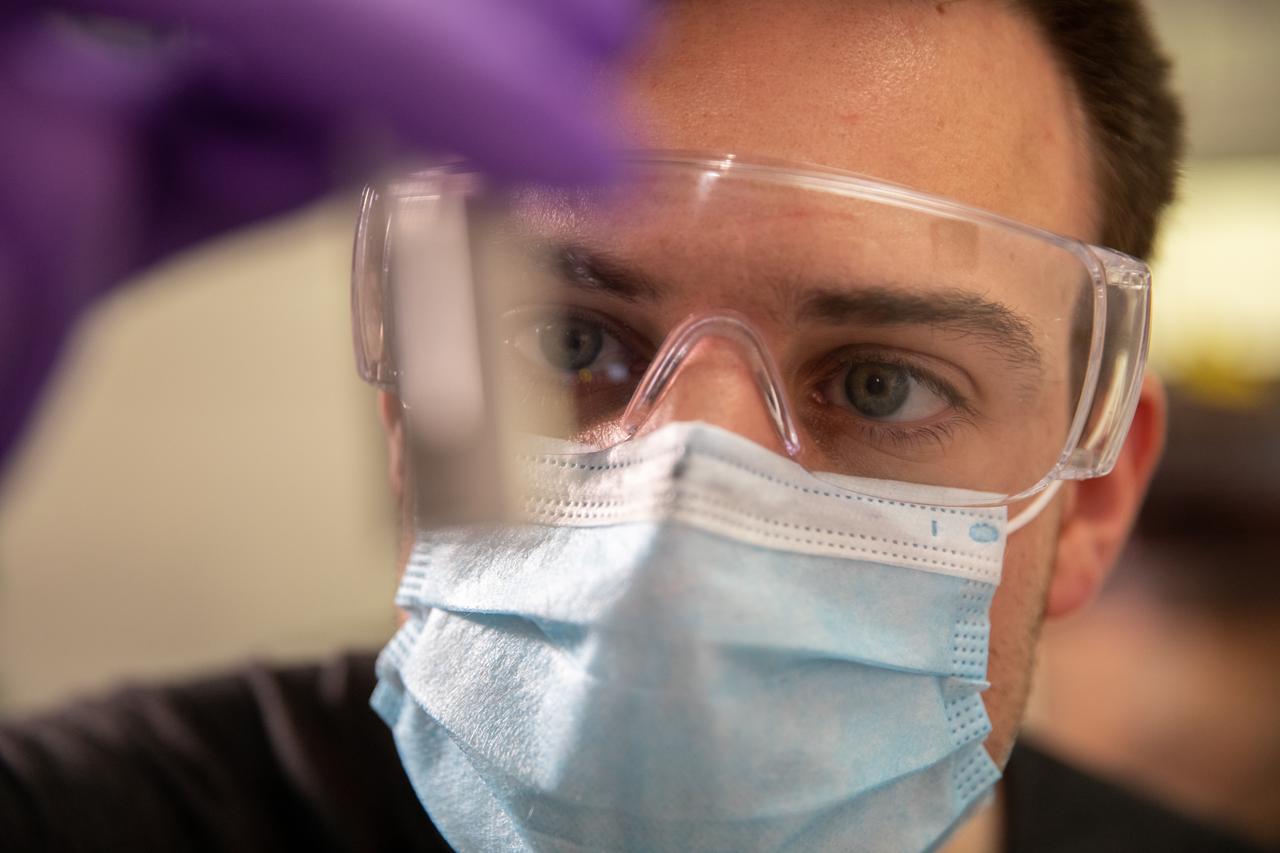
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
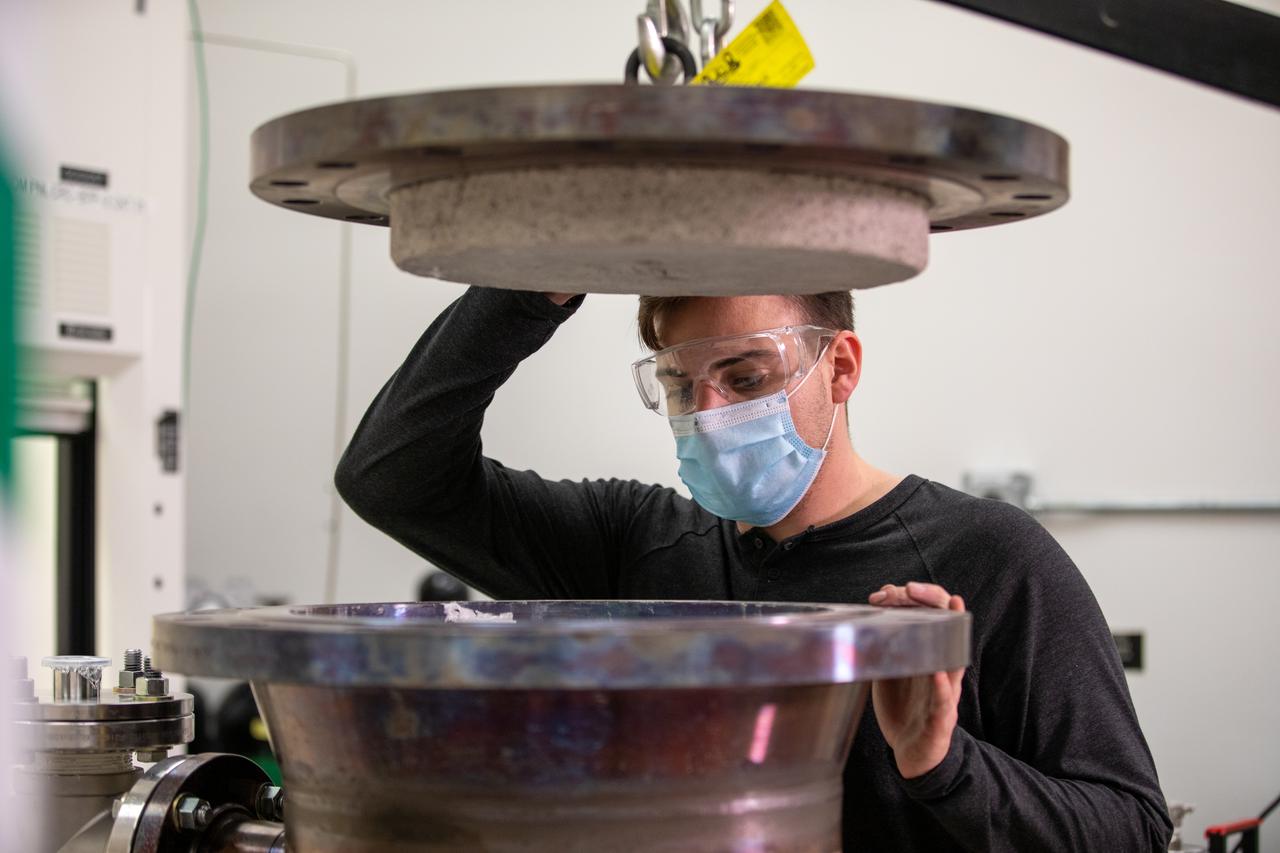

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
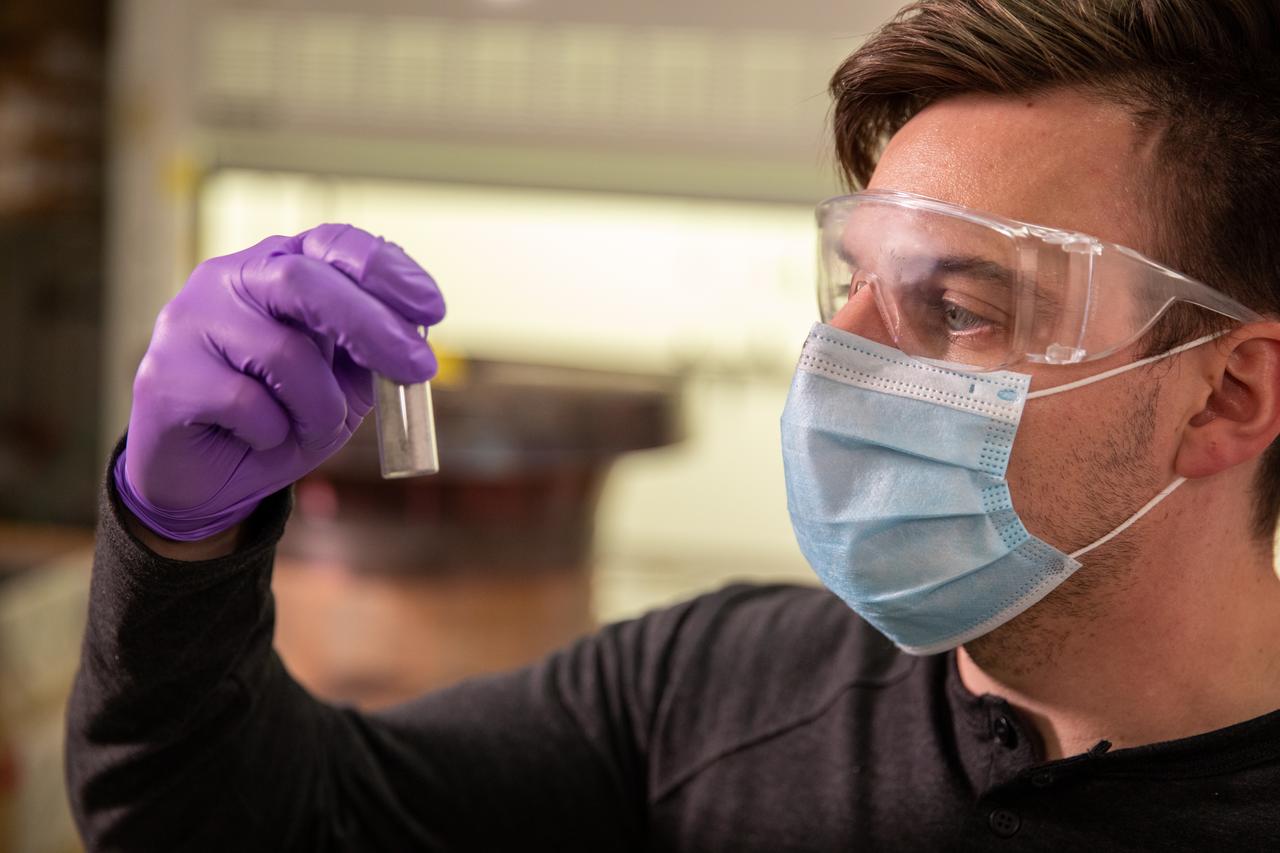

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
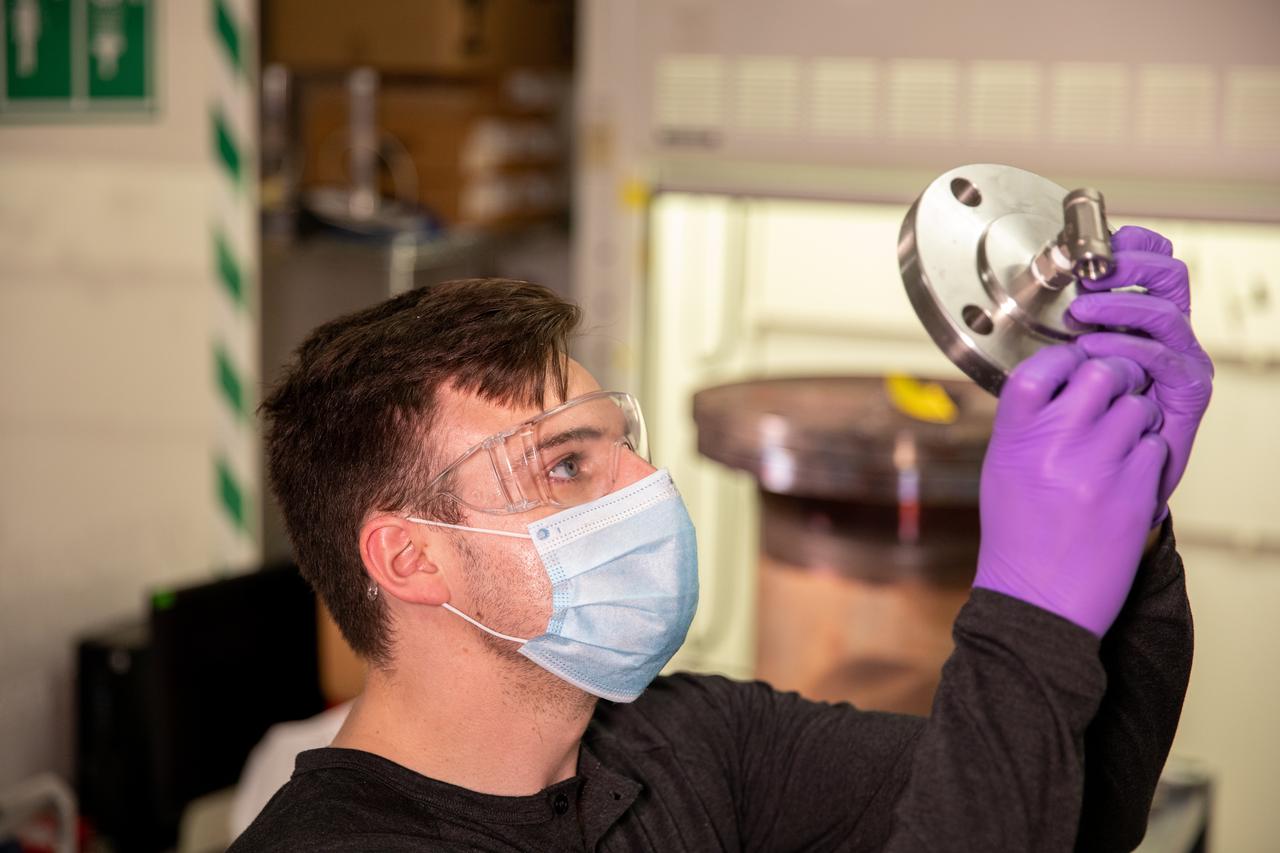

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
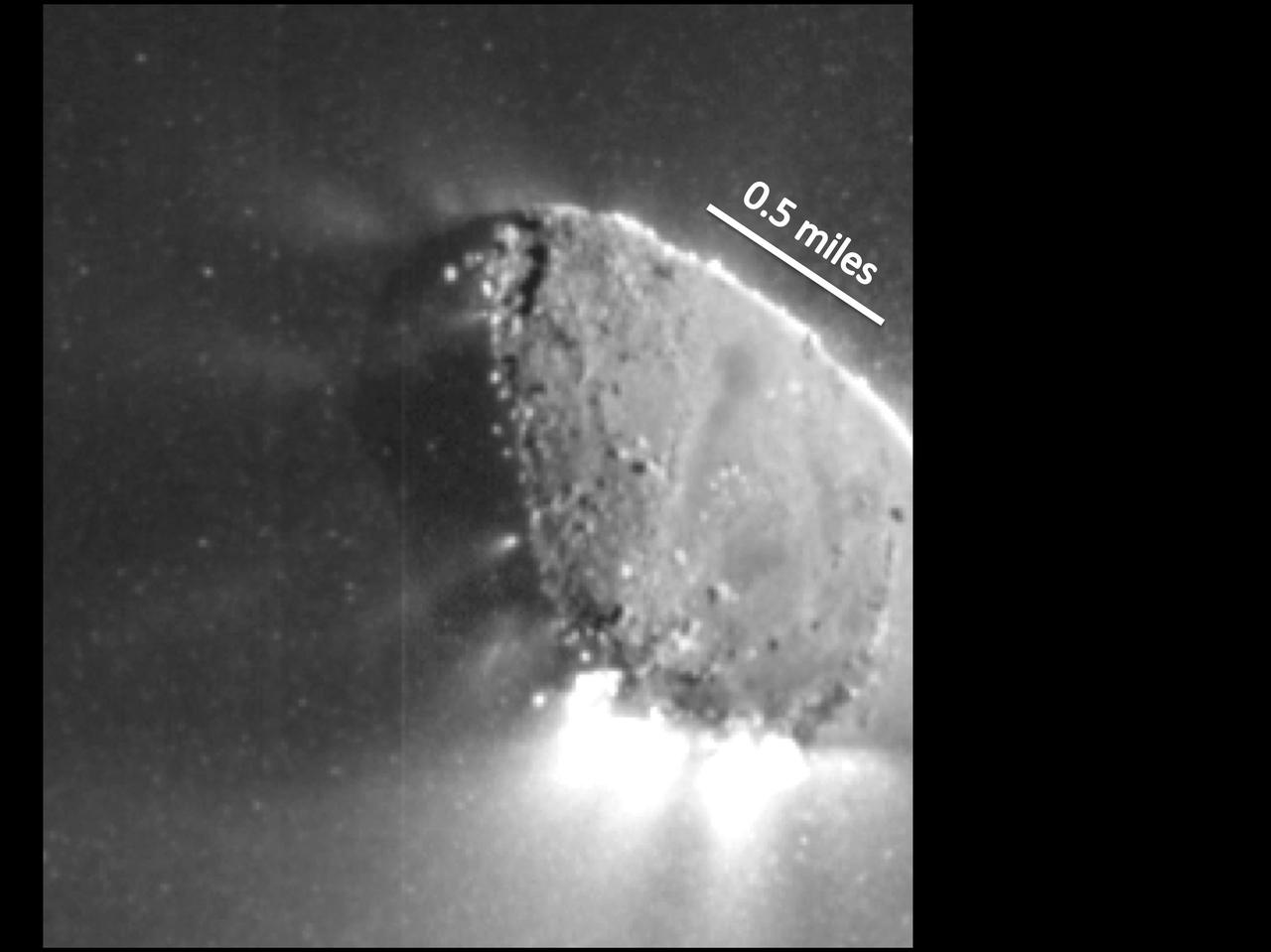
This enhanced image, one of the closest taken of comet Harley 2 by NASA EPOXI mission, shows jets and where they originate from the surface. There are jets outgassing from the sunward side, the night side, and along the terminator.
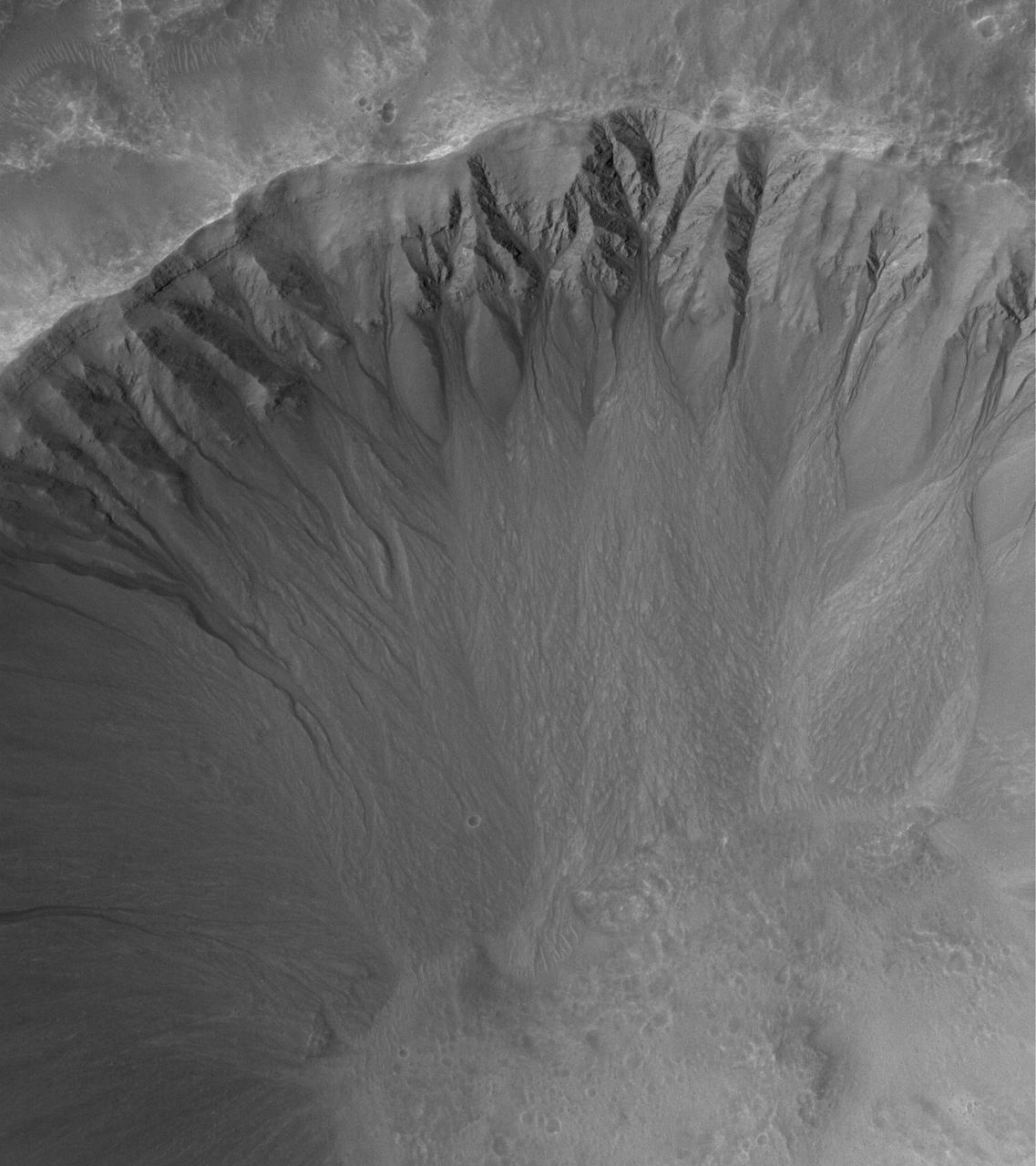

This MOC image shows an array of gullies in the north-northwest wall of a crater in Terra Cimmeria