This photograph shows Skylab's Galactic X-Ray Mapping facility (S150), an astrophysics and space sciences investigation. An objective of this experiment was to extend the search for the origin of galactic x-rays beyond the sensitivity possible with short flights of small research rockets. This was accomplished by placing a large-area, soft x-ray detector in orbit to collect data for a much longer time. The S150 instrument was not in Skylab but in the instrument unit of the second stage of the Skylab-3 Saturn IB rocket.
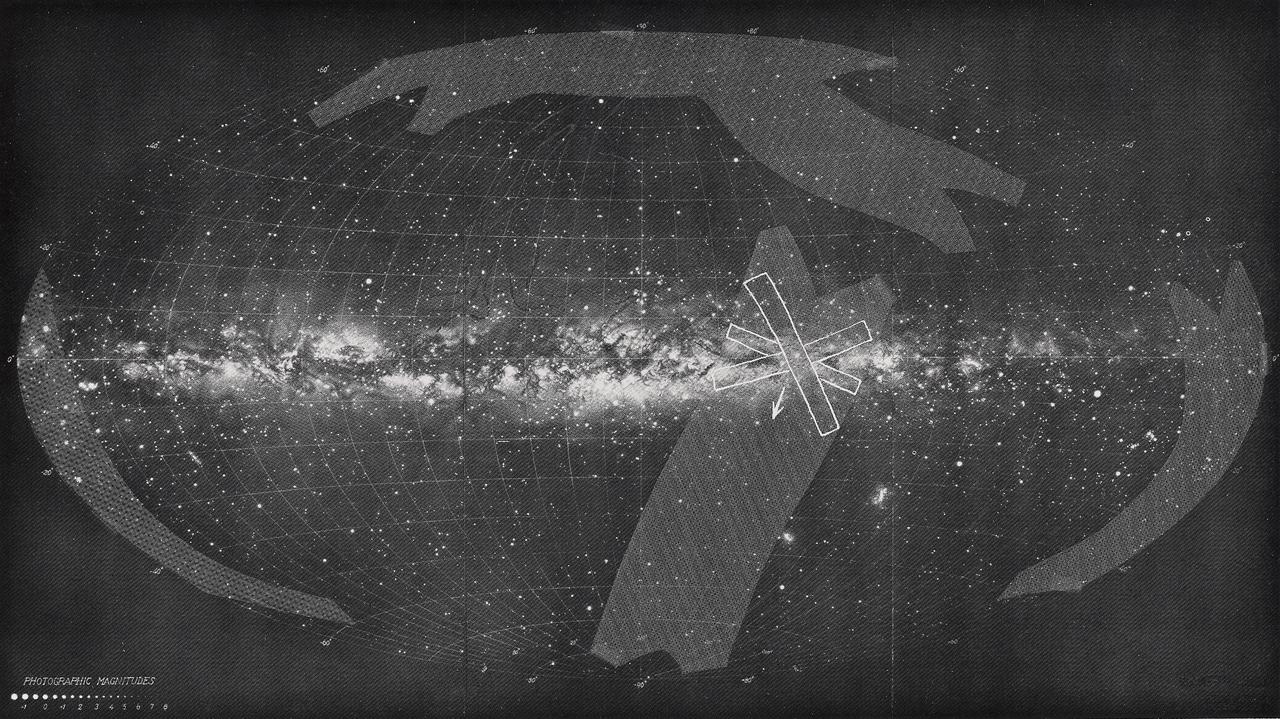

This image shows the Milky Way as seen from the solar system. The shaded regions are those scanned by the Skylab experiment Galactic X-Ray Mapping (S150). The galactic center is approximately at the center of the map. The three overlapping rectangles illustrate the fields of view of the three collimators in one instant of time. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
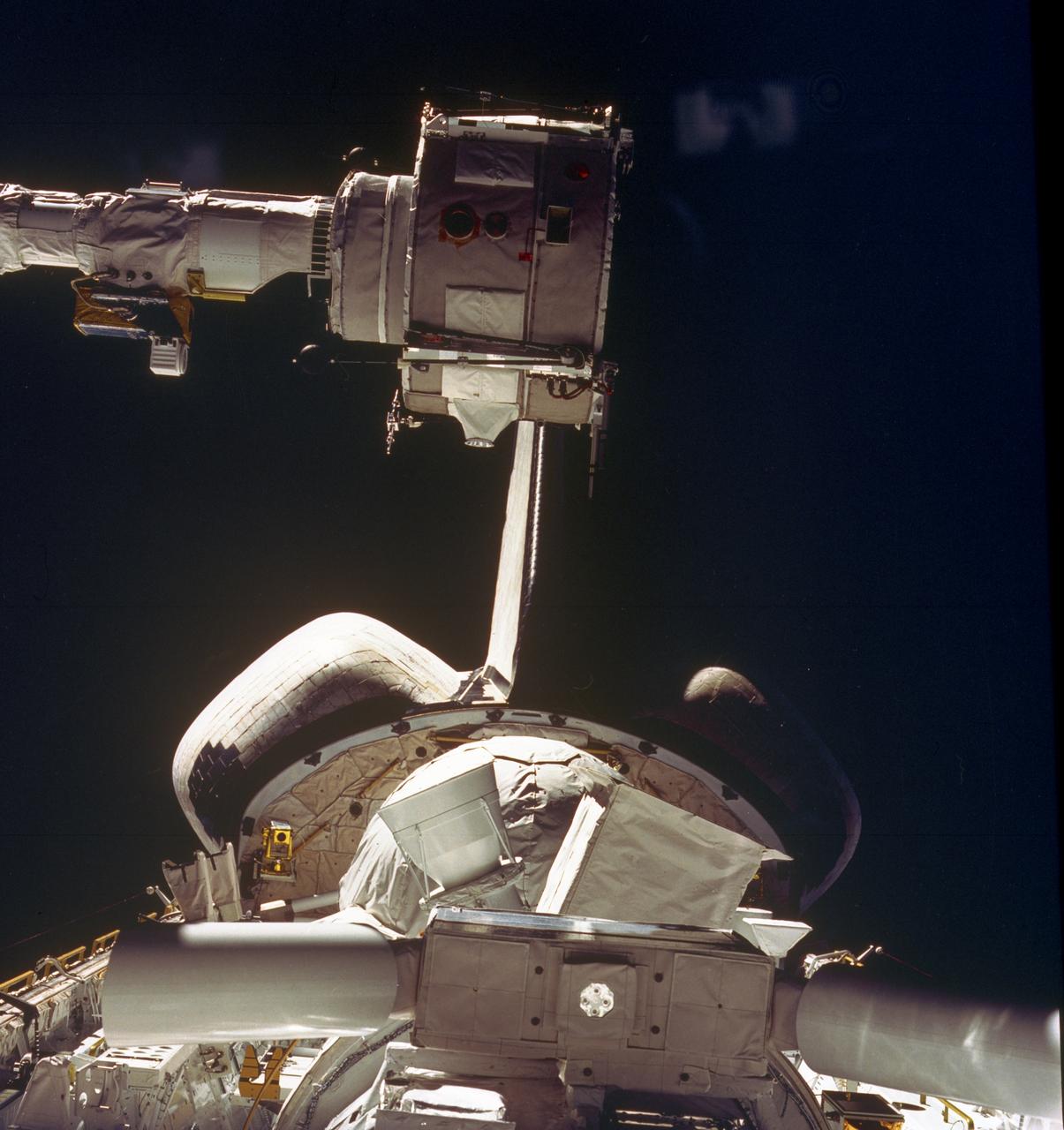

This STS-51F mission onboard Photograph shows some of the Spacelab-2 instruments in the cargo bay of the Orbiter Challenger. The Plasma Diagnostics Package (PDP). shown at the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), used instruments on a subsatellite to study natural plasma processes, orbiter-induced plasma processes, and beam plasma physics. Fourteen instruments were mounted on the PDP for measurements of various plasma characteristics. The X-ray Telescope (XRT), is at the front. The goal of this investigation was to image and examine the X-ray emissions from clusters of galaxies in order to study the mechanisms that cause high-temperature emissions and to determine the weight of galactic clusters. The Small Helium-Cooled Infrared Telescope (IRT) is at the right behind the XRT. The objective of this investigation was to measure and map diffused and discrete infrared astronomical sources while evaluating the Space Shuttle as a platform for infrared astronomy. At the same time, a new large superfluid helium dewar system for cooling the telescope was evaluated. The egg-shaped Cosmic Ray Nuclei experiment (CRNE) is shown at the rear. This investigation was to study the composition of high-energy cosmic rays by using a large instrument exposed to space for a considerable period of time. Spacelab-2 (STS-51F, 19th Shuttle mission) was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on July 29, 1985.

Matthew Mullin and Bobby Meazell, Orbital ATK/Columbia Scientific Balloon Facility technicians, conduct compatibility testing on NASA Langley Research Center’s Radiation Dosimetry Experiment payload Wednesday, Sept. 9, at Fort Sumner, N.M. The successful compatibility test was a key milestone in ensuring the flight readiness of RaD-X, which is scheduled to launch on an 11-million-cubic-foot NASA scientific balloon no earlier than Friday, Sept. 11, from the agency’s balloon launching facility in Fort Sumner. RaD-X will measure cosmic ray energy at two separate altitude regions in the stratosphere—above 110,000 feet and between 69,000 to 88,500 feet. The data is key to confirming Langley’s Nowcast of Atmospheric Ionizing Radiation for Aviation Safety (NAIRAS) model, which is a physics-based model that determines solar radiation and galactic cosmic ray exposure globally in real-time. The NAIRAS modeling tool will be used to help enhance aircraft safety as well as safety procedures for the International Space Station. In addition to the primary payload, 100 small student experiments will fly on the RaD-X mission as part of the Cubes in Space program. The program provides 11- to 18-year-old middle and high school students a no-cost opportunity to design and compete to launch an experiment into space or into the near-space environment. The cubes measure just 4 centimeters by 4 centimeters. NASA’s scientific balloons offer low-cost, near-space access for scientific payloads weighing up to 8,000 pounds for conducting scientific investigations in fields such as astrophysics, heliophysics and atmospheric research. NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia manages the agency’s scientific balloon program with 10 to 15 flights each year from launch sites worldwide. Orbital ATK provides program management, mission planning, engineering services and field operations for NASA’s scientific balloon program. The program is executed from the Columbia Scientific Balloon Facility in Palestine, Texas. The Columbia team has launched more than 1,700 scientific balloons in over 35 years of operation. Anyone may track the progress of the Fort Sumner flights, which includes a map showing the balloon’s real-time location, at: <a href="http://towerfts.csbf.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">towerfts.csbf.nasa.gov/</a> For more information on the balloon program, see: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/scientificballoons" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/scientificballoons</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>