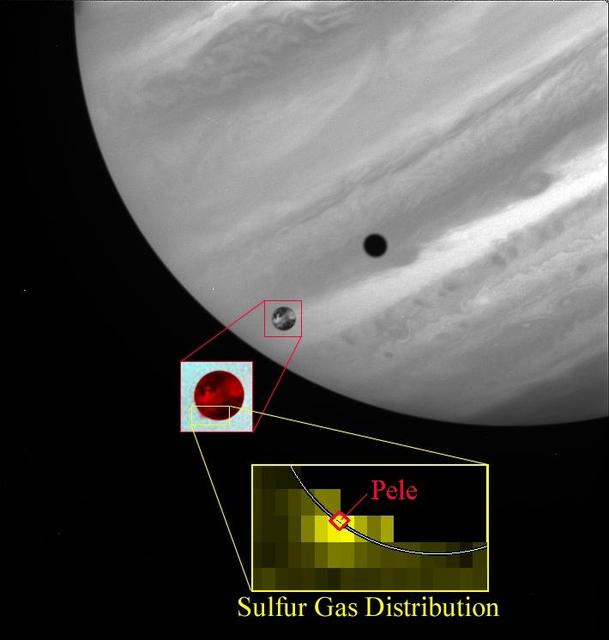
Sulfur Gas in Pele Plume

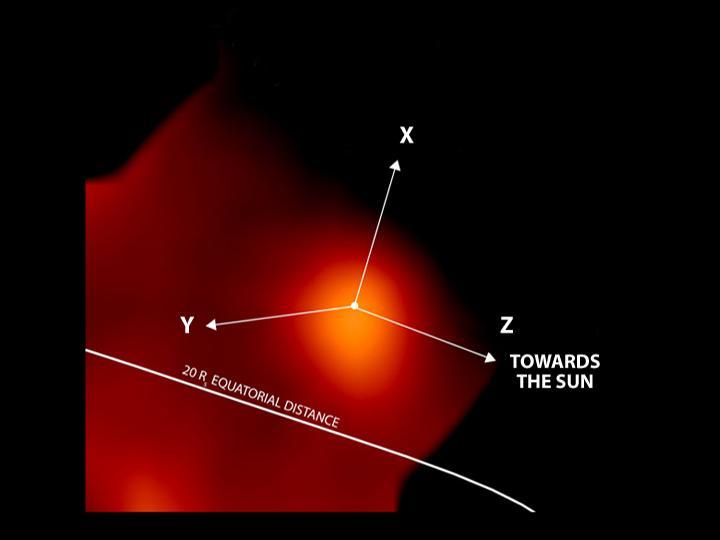
Massive Gas Cloud Around Jupiter
Neutral Gas Cloud Around Titan
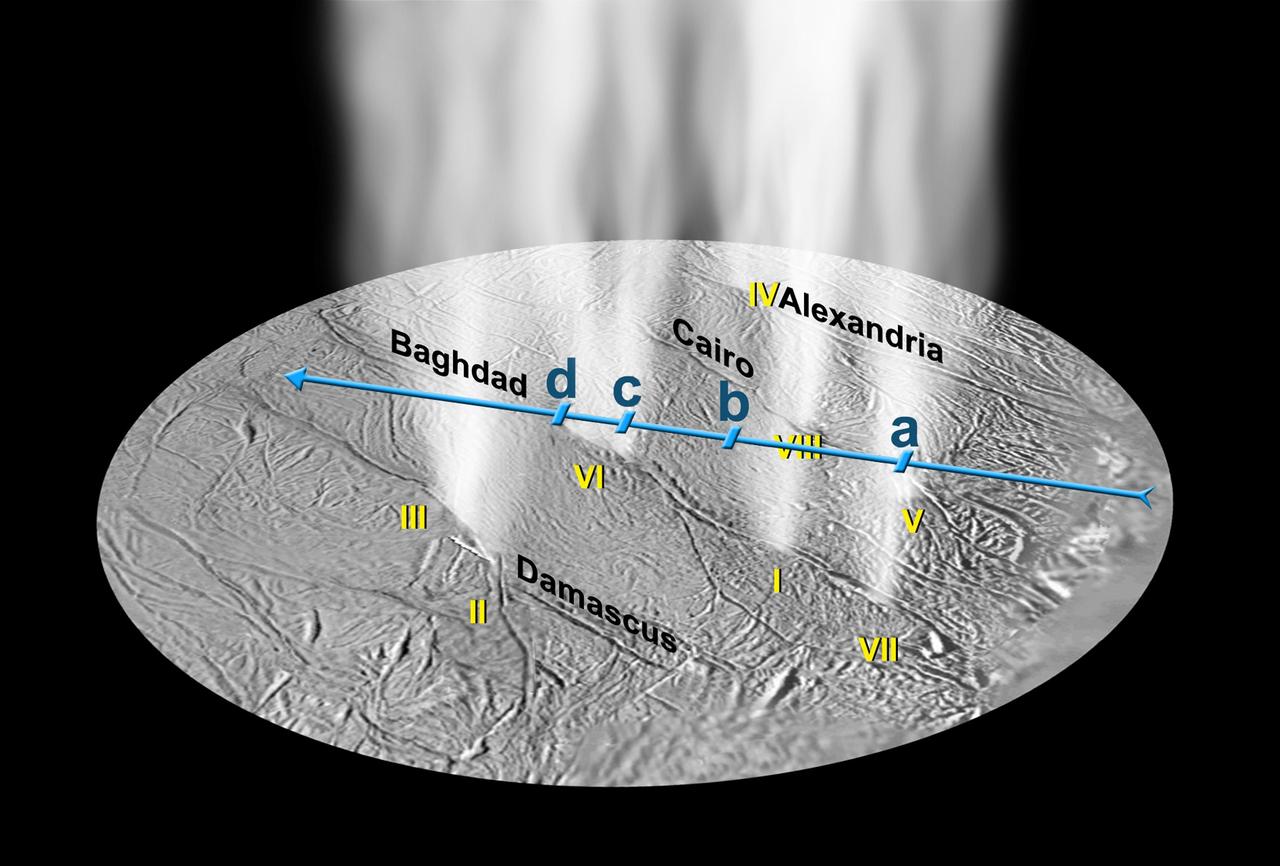
Gas and Dust Jets Match Up
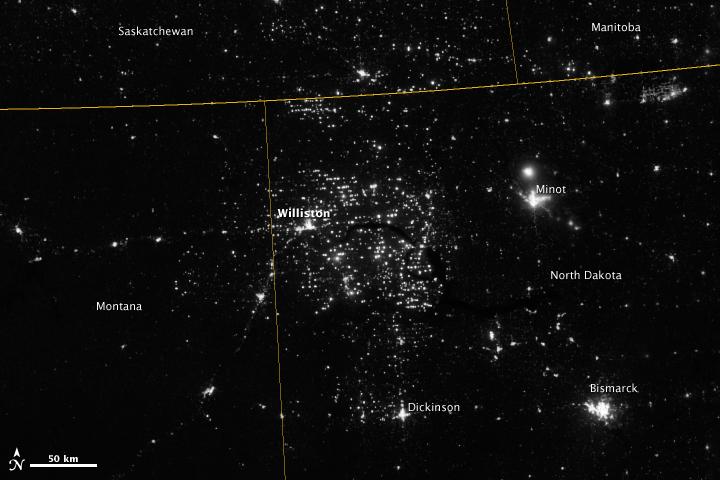
Northwestern North Dakota is one of the least-densely populated parts of the United States. Cities and people are scarce, but satellite imagery shows the area has been aglow at night in recent years. The reason: the area is home to the Bakken shale formation, a site where oil production is booming. Companies hoping to extract oil from the Bakken formation have drilled hundreds of new wells in the last few years; natural gas often bubbles up to the surface as part of the process. Lacking the infrastructure to pipe the gas away, many drillers simply burn it in a practice known as flaring. On November 12, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of widespread gas flaring throughout the area. Many of the specks of light are evidence of gas flaring, though others may be the lights around drilling equipment. Some of the brighter areas correspond to towns and cities including Williston, Minot, and Dickinson. The image was captured by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. When VIIRS acquired the image, the moon was in its waning crescent phase, meaning it was reflecting only a small amount of light. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, natural gas production from the Bakken shale has increased more than 20-fold between 2007 and 2010. Gas production averaged over 485 million cubic feet per day in September 2011, compared to the 2005 average of about 160 million cubic feet per day. Due to the lack of gas pipeline and processing facilities in the region, about 29 percent of that gas is flared. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79810" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Northwestern North Dakota is one of the least-densely populated parts of the United States. Cities and people are scarce, but satellite imagery shows the area has been aglow at night in recent years. The reason: the area is home to the Bakken shale formation, a site where gas and oil production are booming. On November 12, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of widespread drilling throughout the area. Most of the bright specks are lights associated with drilling equipment and temporary housing near drilling sites, though a few are evidence of gas flaring. Some of the brighter areas correspond to towns and cities including Williston, Minot, and Dickinson. The image was captured by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses “smart” light sensors to observe dim signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. When VIIRS acquired the image, the Moon was in its waning crescent phase, so the landscape was reflecting only a small amount of light. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, natural gas production from the Bakken shale has increased more than 20-fold between 2007 and 2010. Gas production averaged over 485 million cubic feet per day in September 2011, compared to the 2005 average of about 160 million cubic feet per day. Due to the lack of a gas pipeline and processing facilities in the region, about 29 percent of that gas is flared. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79810" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

THE GAS GENERATOR TO AN F-1 ENGINE, THE MOST POWERFUL ROCKET ENGINE EVER BUILT, IS TEST-FIRED AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA, ON SEPT. 3. ALTHOUGH THE ENGINE WAS ORIGINALLY BUILT TO POWER THE SATURN V ROCKETS DURING AMERICA'S MISSIONS TO THE MOON, THIS TEST ARTICLE HAD NEW PARTS CREATED USING ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING, OR 3-D PRINTING, TO TEST THE VIABILITY OF THE TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING NEW ENGINE DESIGNS.

THE GAS GENERATOR TO AN F-1 ENGINE, THE MOST POWERFUL ROCKET ENGINE EVER BUILT, IS TEST-FIRED AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA, ON SEPT. 3. ALTHOUGH THE ENGINE WAS ORIGINALLY BUILT TO POWER THE SATURN V ROCKETS DURING AMERICA'S MISSIONS TO THE MOON, THIS TEST ARTICLE HAD NEW PARTS CREATED USING ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING, OR 3-D PRINTING, TO TEST THE VIABILITY OF THE TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING NEW ENGINE DESIGNS.

THE GAS GENERATOR TO AN F-1 ENGINE, THE MOST POWERFUL ROCKET ENGINE EVER BUILT, IS TEST-FIRED AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA, ON SEPT. 3. ALTHOUGH THE ENGINE WAS ORIGINALLY BUILT TO POWER THE SATURN V ROCKETS DURING AMERICA'S MISSIONS TO THE MOON, THIS TEST ARTICLE HAD NEW PARTS CREATED USING ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING, OR 3-D PRINTING, TO TEST THE VIABILITY OF THE TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING NEW ENGINE DESIGNS.
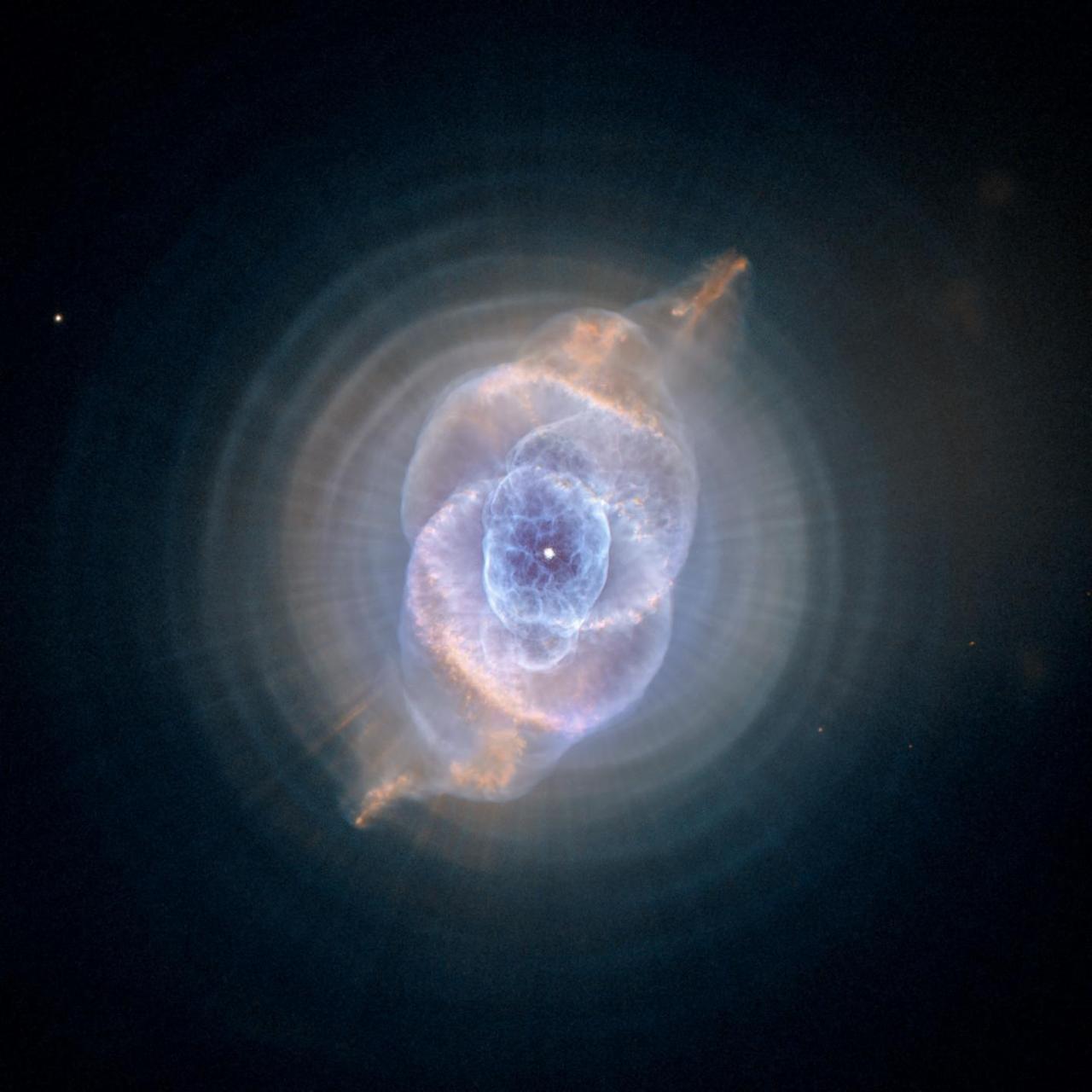

This detailed view of NGC 6543, the Cat Eye Nebula, from NASA Hubble Space Telescope includes intricate structures, including concentric gas shells, jets of high-speed gas, and unusual shock-induced knots of gas.
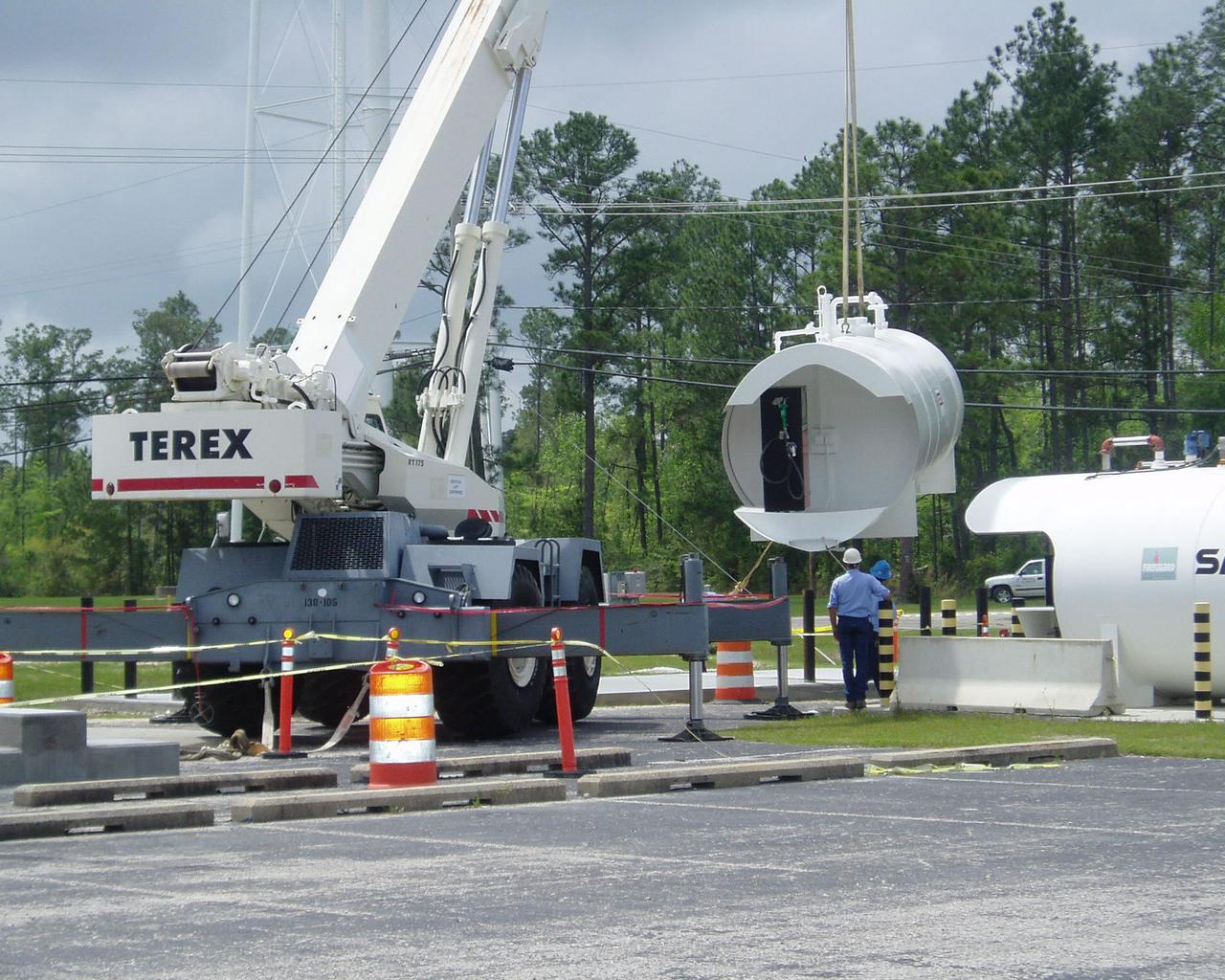

A worker pours concrete as part of a nitrogen risk mitigation project at the High Pressure Gas Facility at Stennis Space Center. The concrete slab will provide the foundation needed to place new pumps at the site and is part of ongoing hurricane-related mitigation work at Stennis.
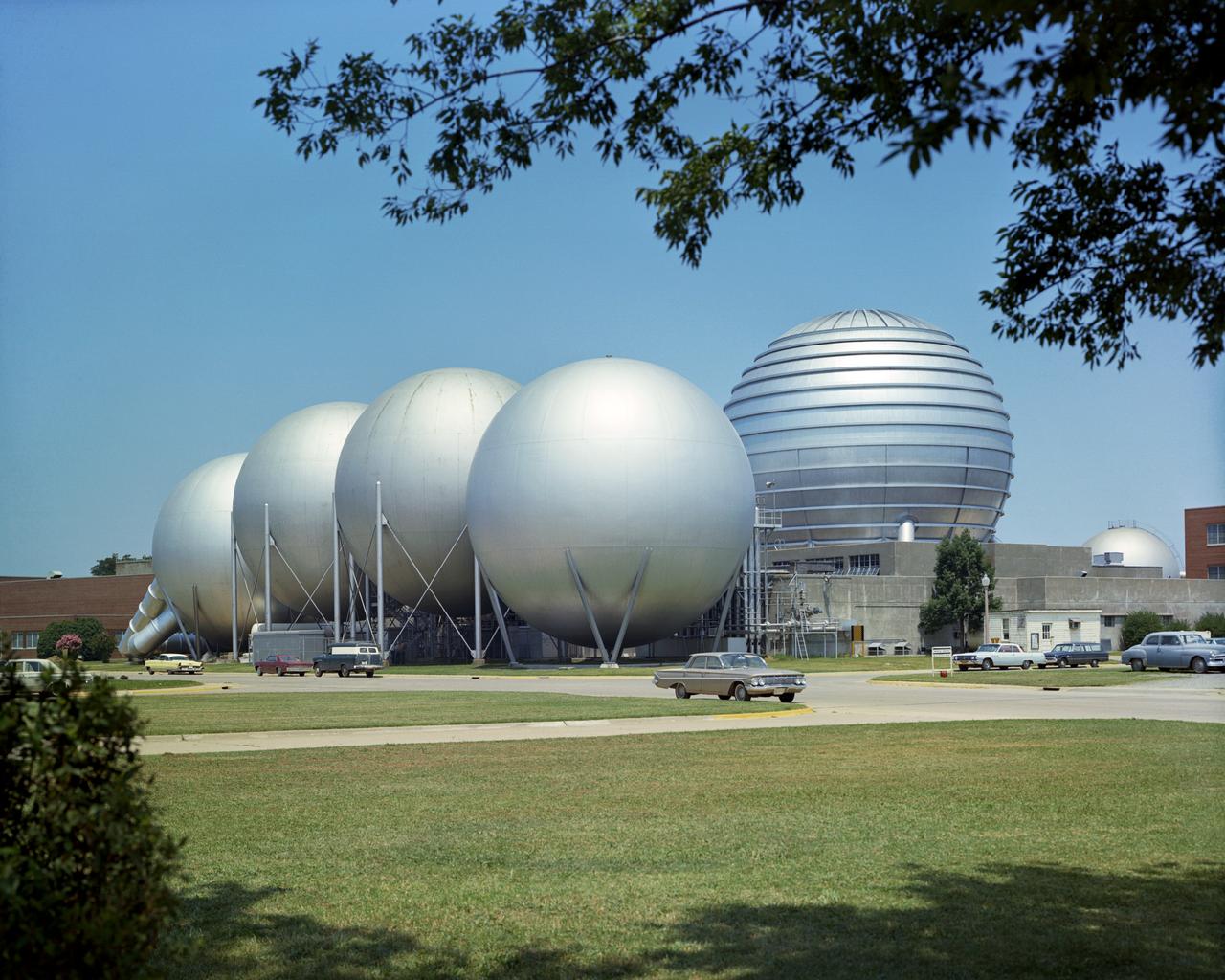

L65-5505 In the Gas Dynamics Laboratory, completed in 1951, researchers explored basic aerodynamic, heating and fluid-mechanical problems in the speed range from Mach 1.5 to Mach 8.0. Photograph published in Engineer in Charge: A History of the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1917-1958 by James R. Hansen. Page 348.
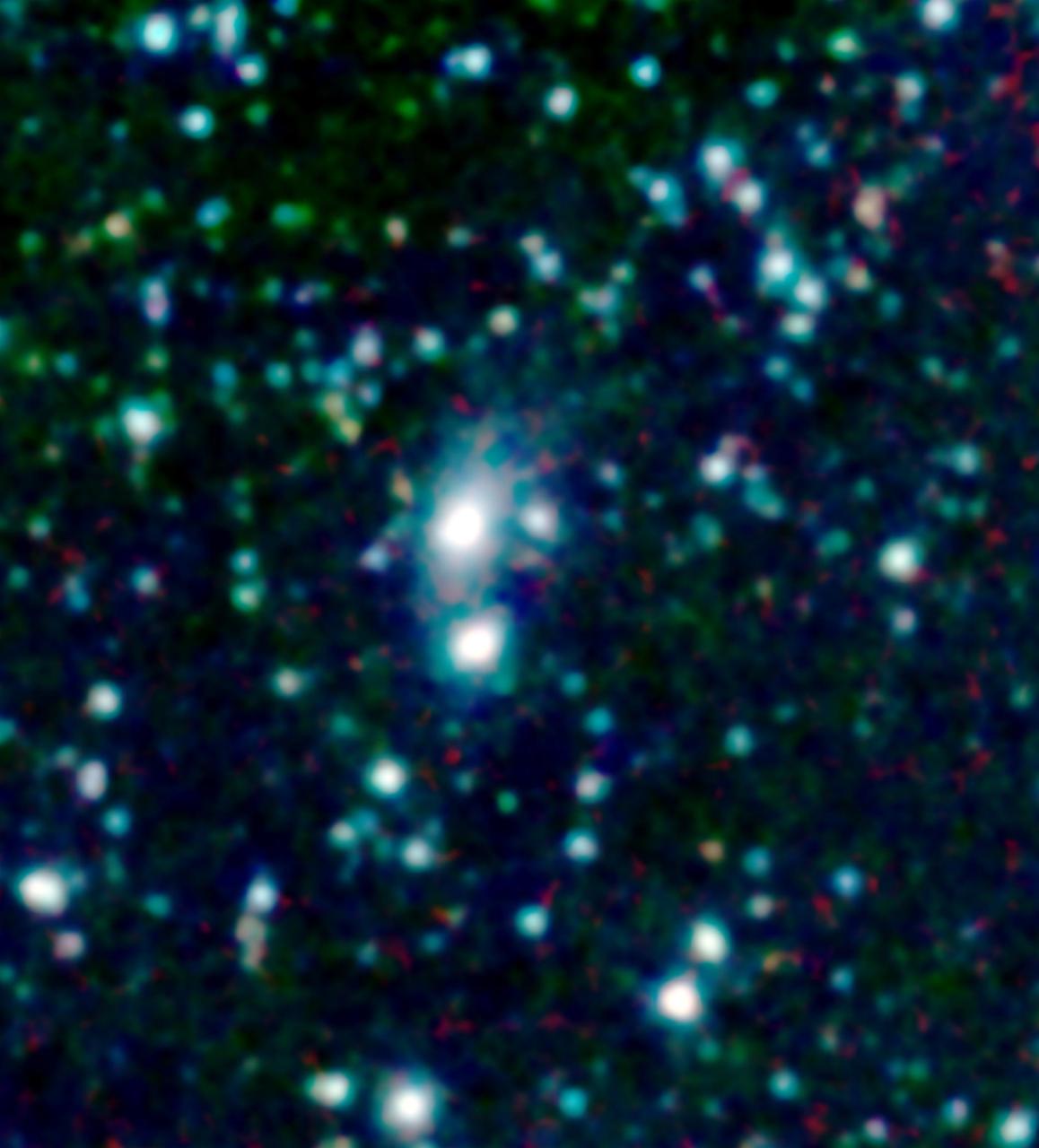

A big galaxy is stealing gas right off the back of its smaller companion in this new image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. The stolen gas is hot, but it might eventually cool down to make new stars and planets.
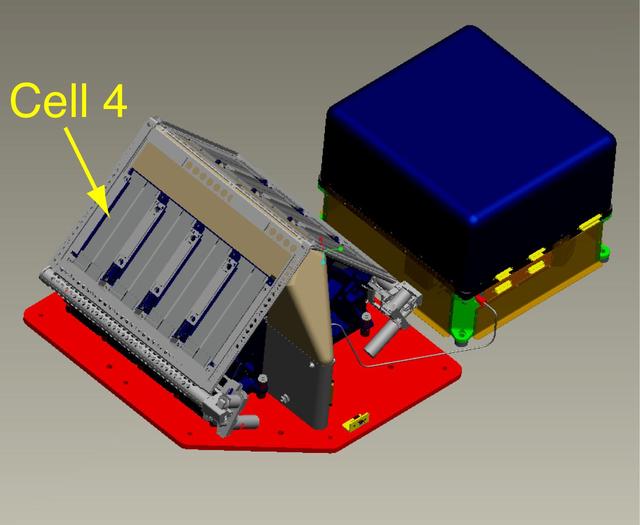
This is a computer-aided drawing of the Thermal and Evolved-Gas Analyzer, or TEGA, on NASA Phoenix Mars Lander.
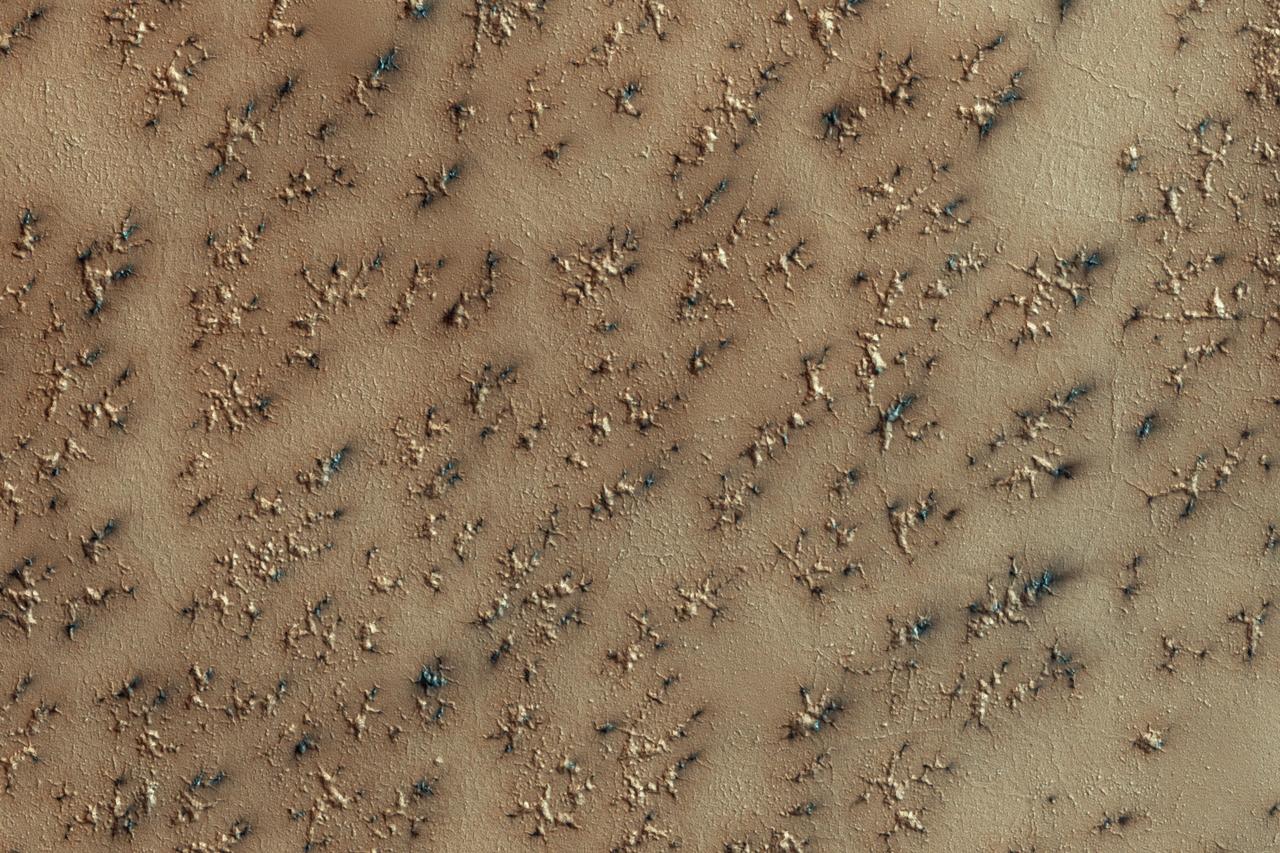

NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spies a layer of dry ice covering Mars south polar layer. In the spring, gas created from heating of the dry ice escapes through ruptures in the overlying seasonal ice, entraining material from the ground below. The gas erodes channels in the surface, generally exploiting weaker material. The ground likely started as polygonal patterned ground (common in water-ice-rich surfaces), and then escaping gas widened the channels. Fans of dark material are bits of the surface carried onto the top of the seasonal ice layer and deposited in a direction determined by local winds. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11706
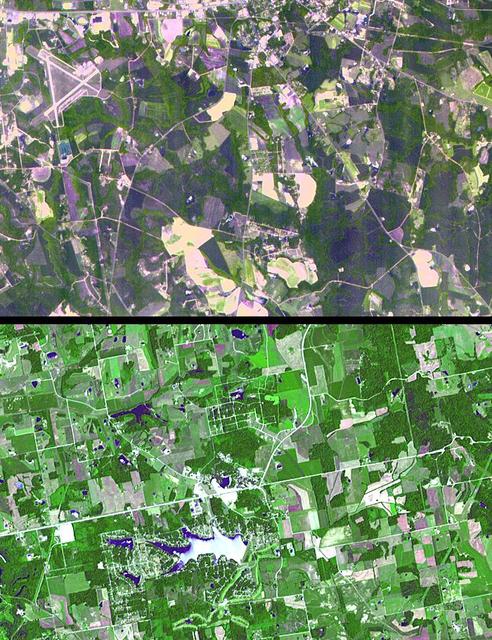

The towns of Santa Claus, Ga., (top) and Santa Claus, Ind. (bottom), are shown in these two images from the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument on NASA's Terra satellite. They are the only two Santa Claus towns in the United States with post offices and zip codes, although there are 11 towns with this name in the United States. Santa Claus, Ga. is located in Toombs County, and has a population of 237. Santa Claus, Ind. is located in Spencer County, and has a population of 2,041. Its name was accepted by the United States Postal Service in 1856. The images were acquired on July 3, 2000 (top) and June 16, 2001 (bottom), respectively. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03891

Commercial Crew Program (CCP) SpaceX Merlin Engine Gas Generator (GG) Baffle Assessment, Mr. Brian Richardson (background), and Mr. Chad Eberhart (foreground)

MICROLIGHT GAS GUN (MLGG), BLDG 4711
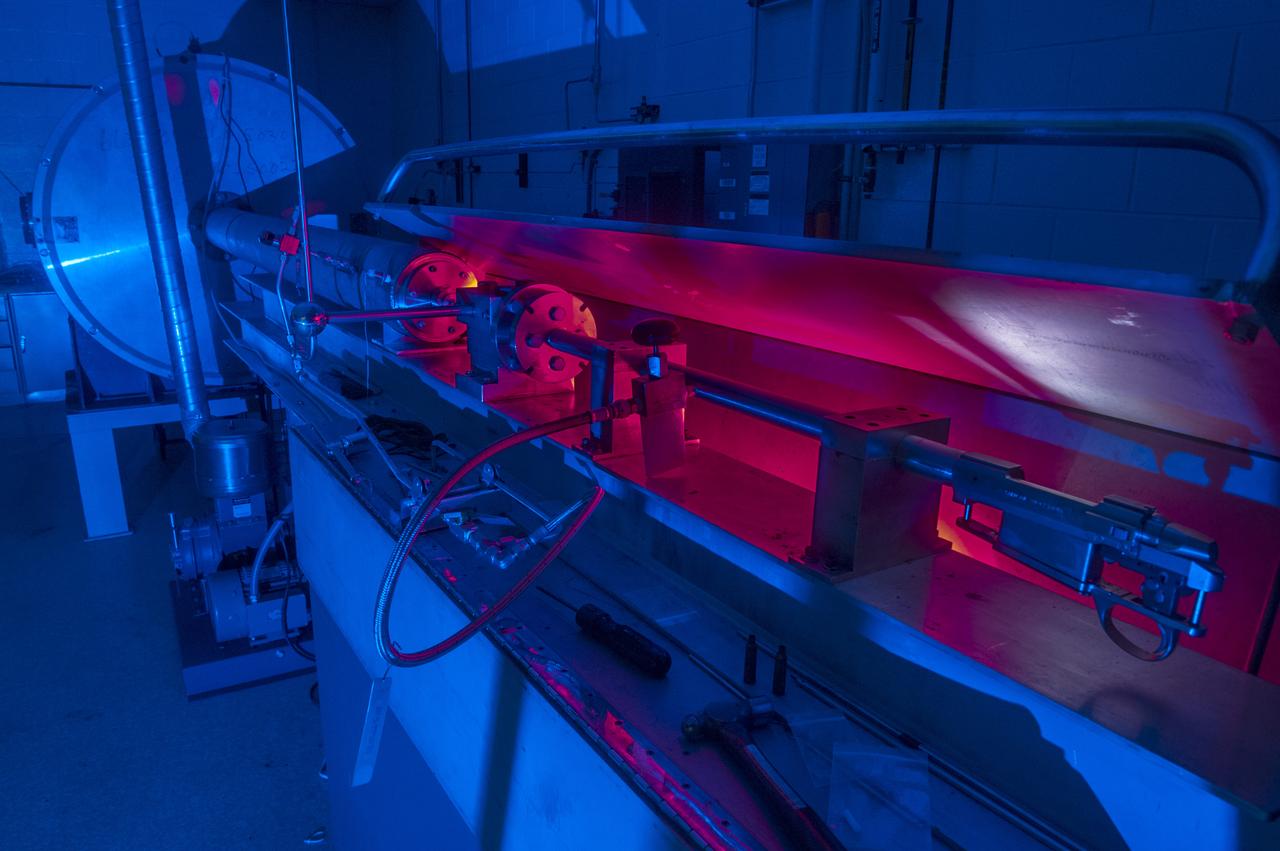
MICROLIGHT GAS GUN (MLGG), BLDG 4711
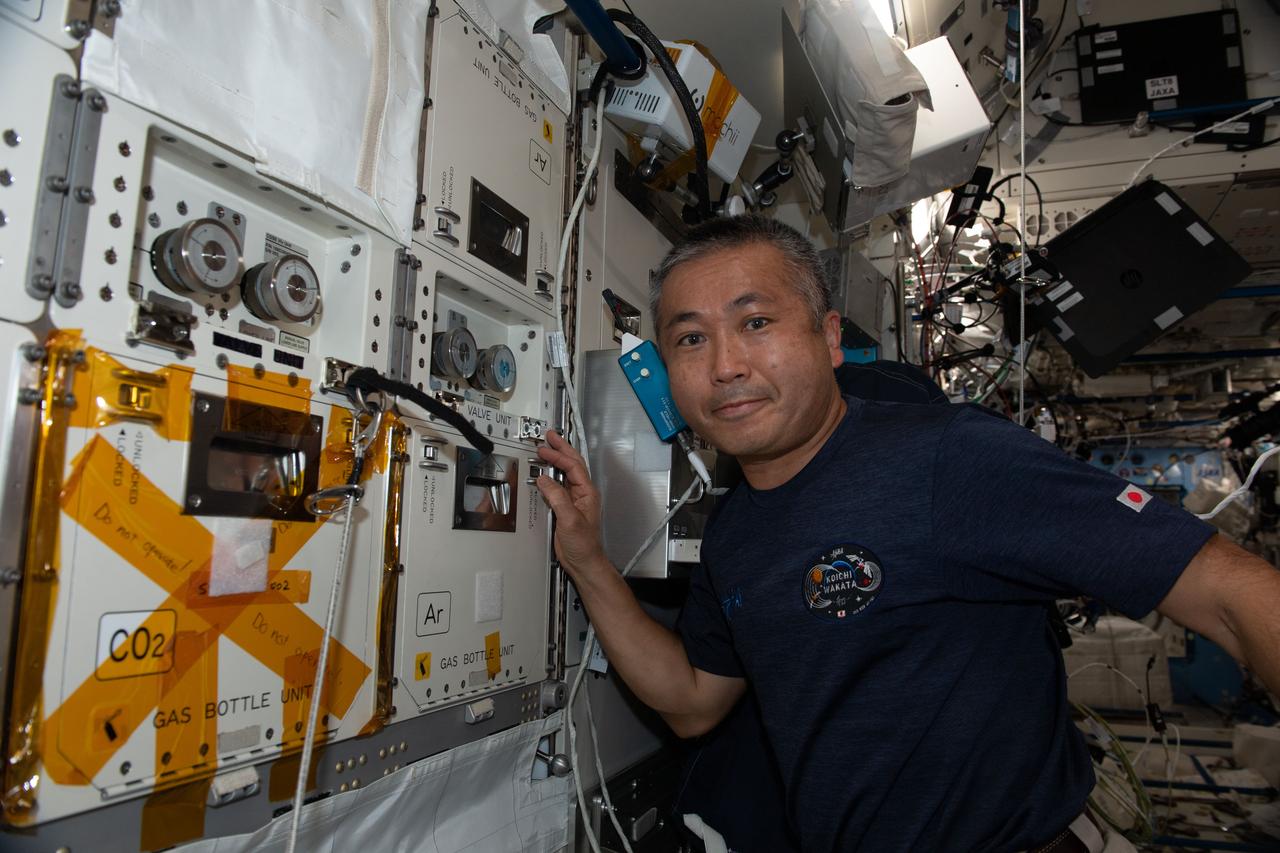

iss068e017277 (Oct. 17, 2022) --- Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) switches an Argon gas supply line to maintain gas pressure aboard the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module.
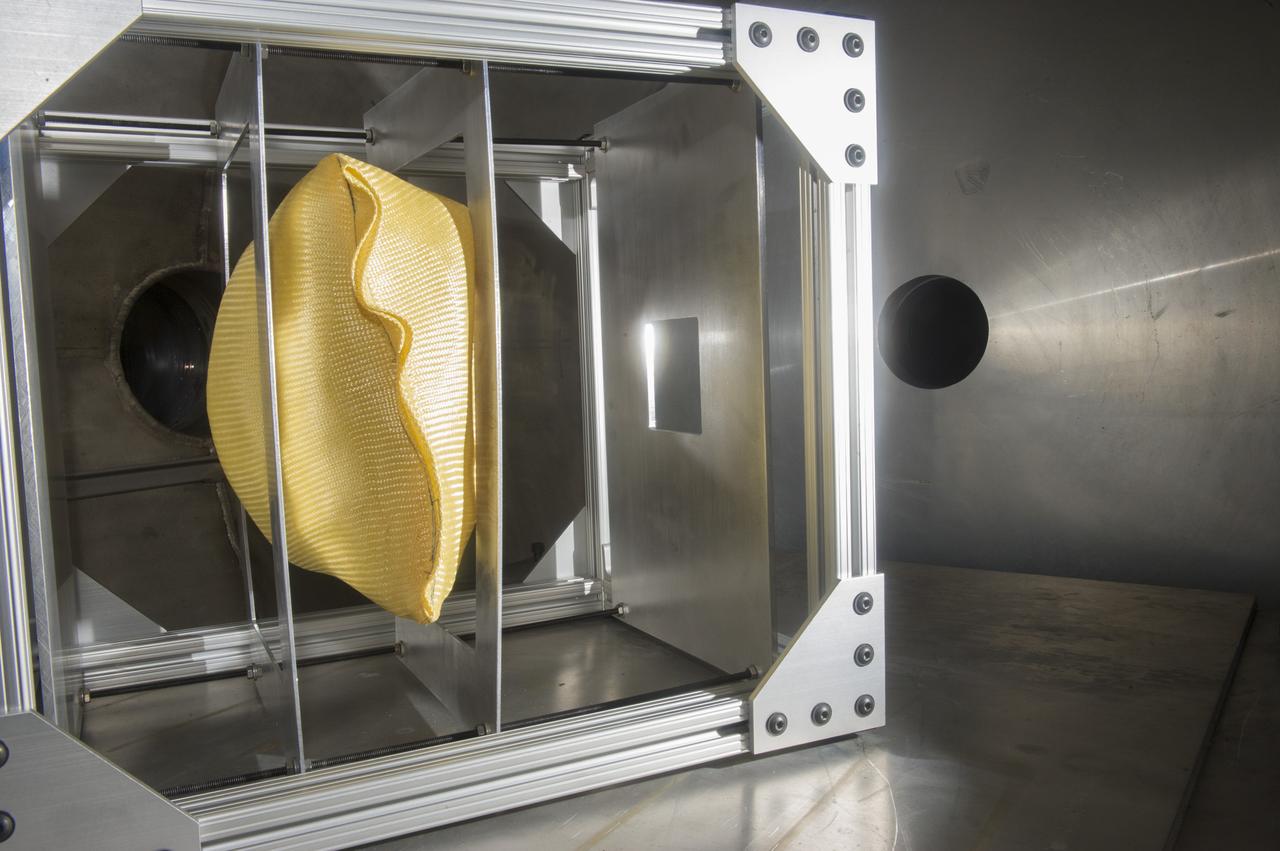
KEVLAR BALLOON TARGET MATERIAL IN MICROLIGHT GAS GUN
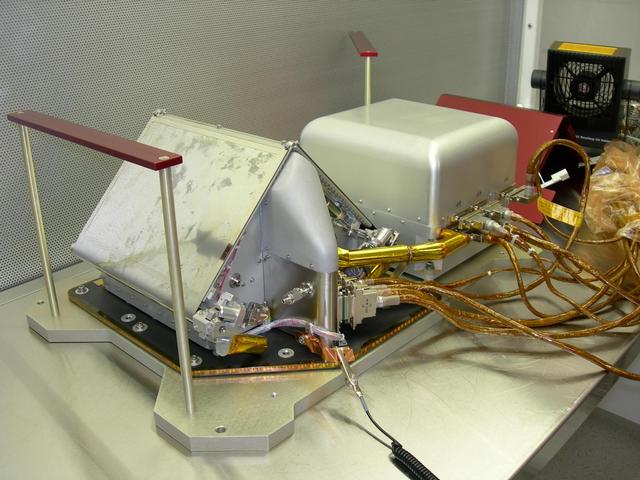
NASA Phoenix Mars Lander carried the Thermal and Evolved-Gas Analyzer t to heat and sniff samples of Martian soil and ice to analyze some ingredients.
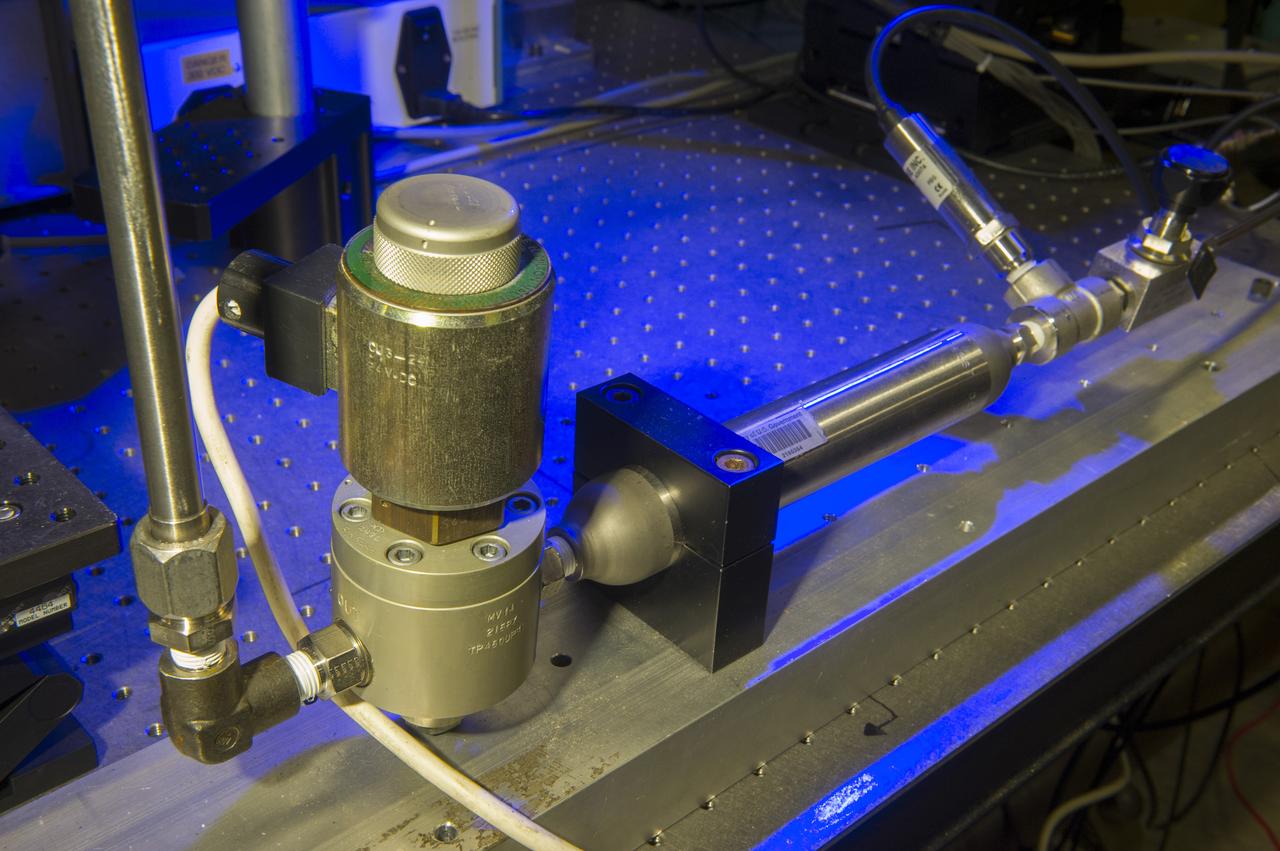
MICROBALLISTIC GAS GUN/SAND GUN, BLDG 4571, EAST TEST AREA
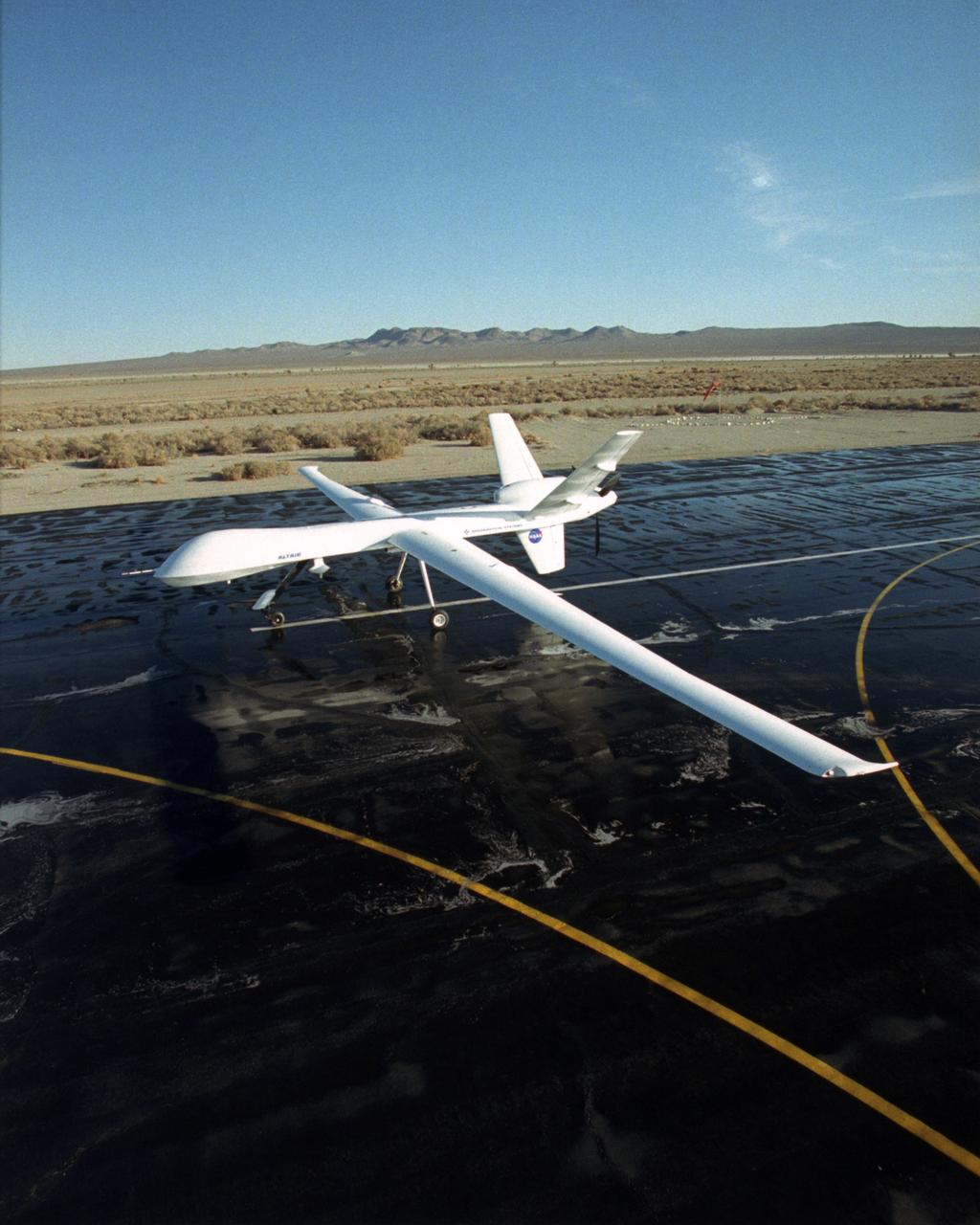

The Altair unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), built by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc. for NASA, is poised for flight at GA-ASI's flight test facility at El Mirage, California.
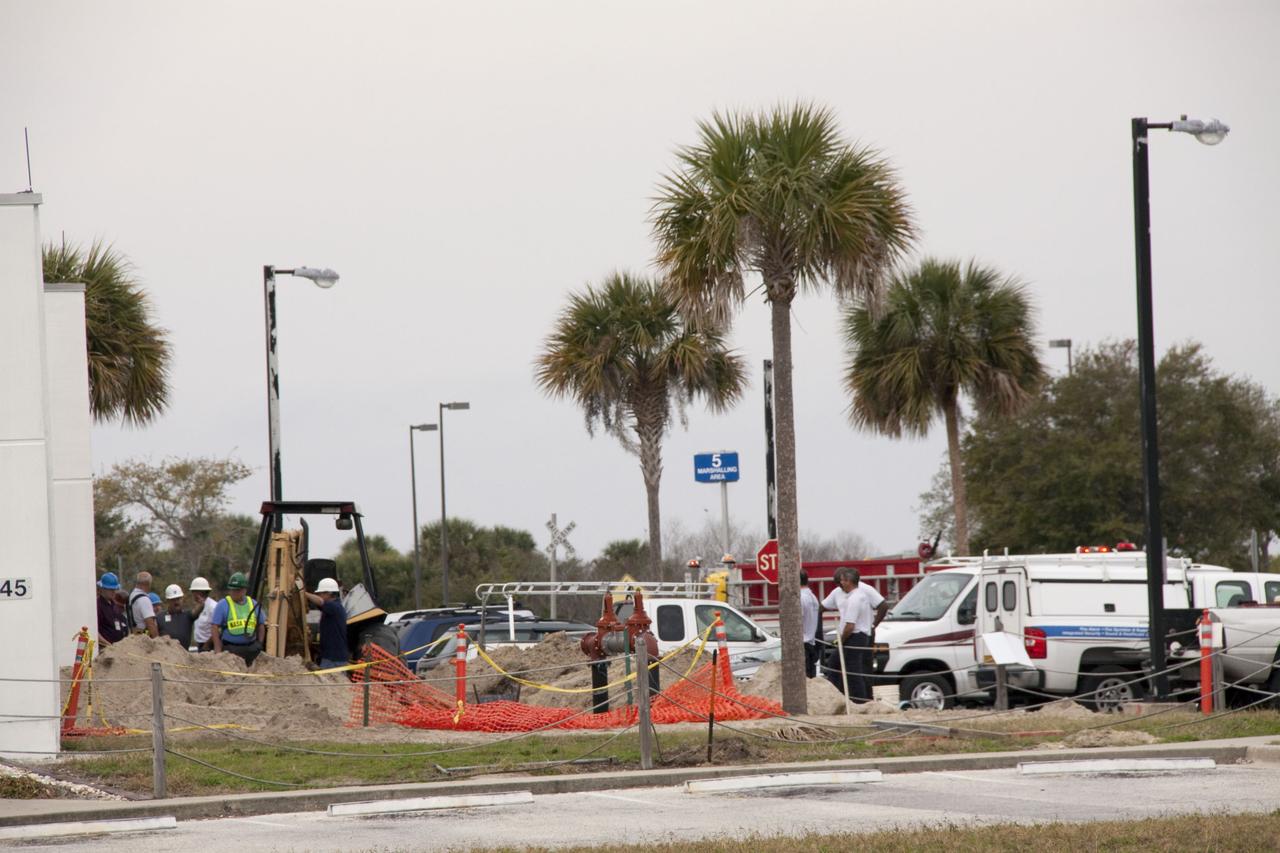

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a backhoe inadvertently struck a natural gas line in the area north of the Multi Function Facility (MFF), at around 8:40 a.m. EST. As a precaution, personnel were evacuated from Orbiter Processing Facilities 1 and 2, the MFF, Processing Control Center and the Operations Support Building (OSB) I. All traffic was blocked on the Saturn Causeway near the facilities. There were no injuries or damage to any facilities and personnel were allowed back into their buildings before mid-day and the roadway open to traffic. With the backhoe idle, workers assess the area where the break in the gas line occurred. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
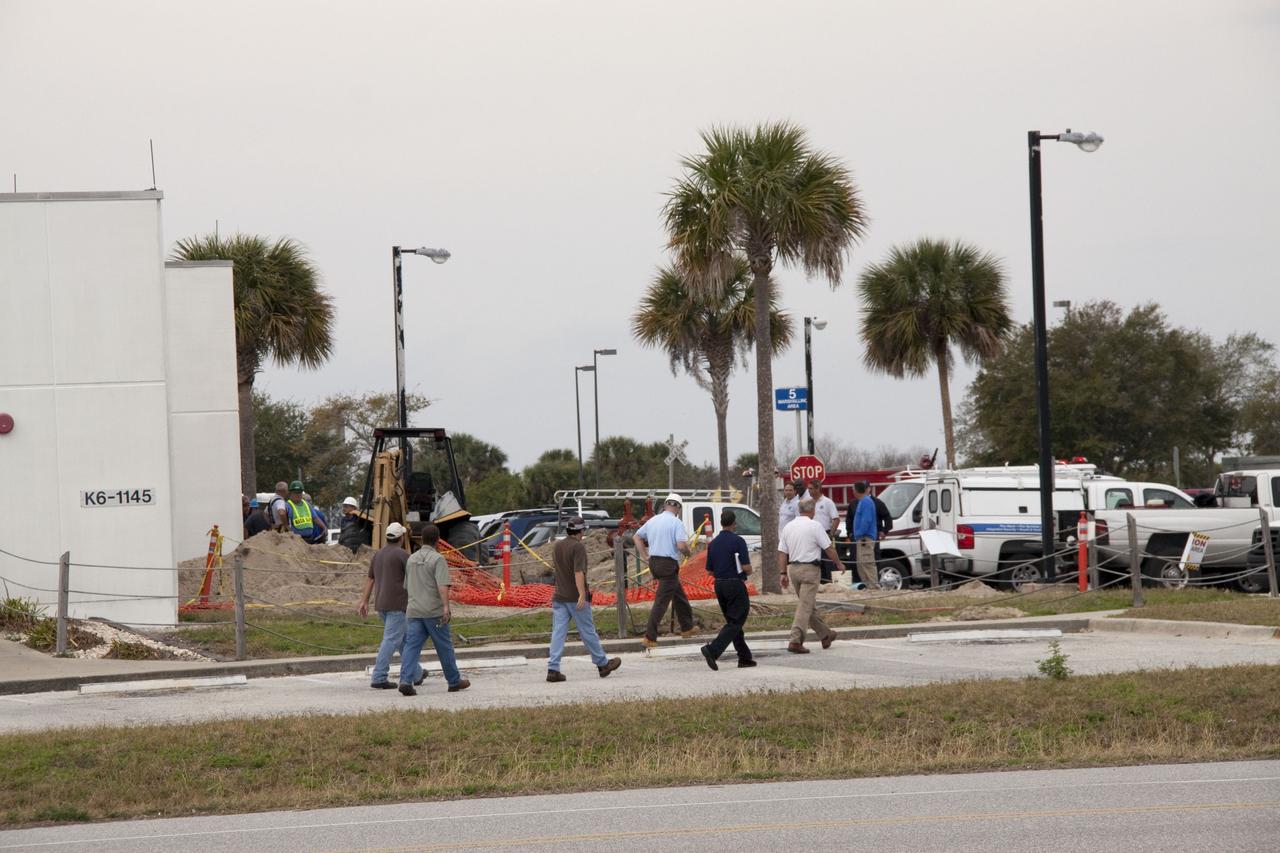

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a backhoe inadvertently struck a natural gas line in the area north of the Multi Function Facility (MFF), at around 8:40 a.m. EST. As a precaution, personnel were evacuated from Orbiter Processing Facilities 1 and 2, the MFF, Processing Control Center and the Operations Support Building (OSB) I. All traffic was blocked on the Saturn Causeway near the facilities. There were no injuries or damage to any facilities and personnel were allowed back into their buildings before mid-day and the roadway open to traffic. With the backhoe idle, workers assess the area where the break in the gas line occurred. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
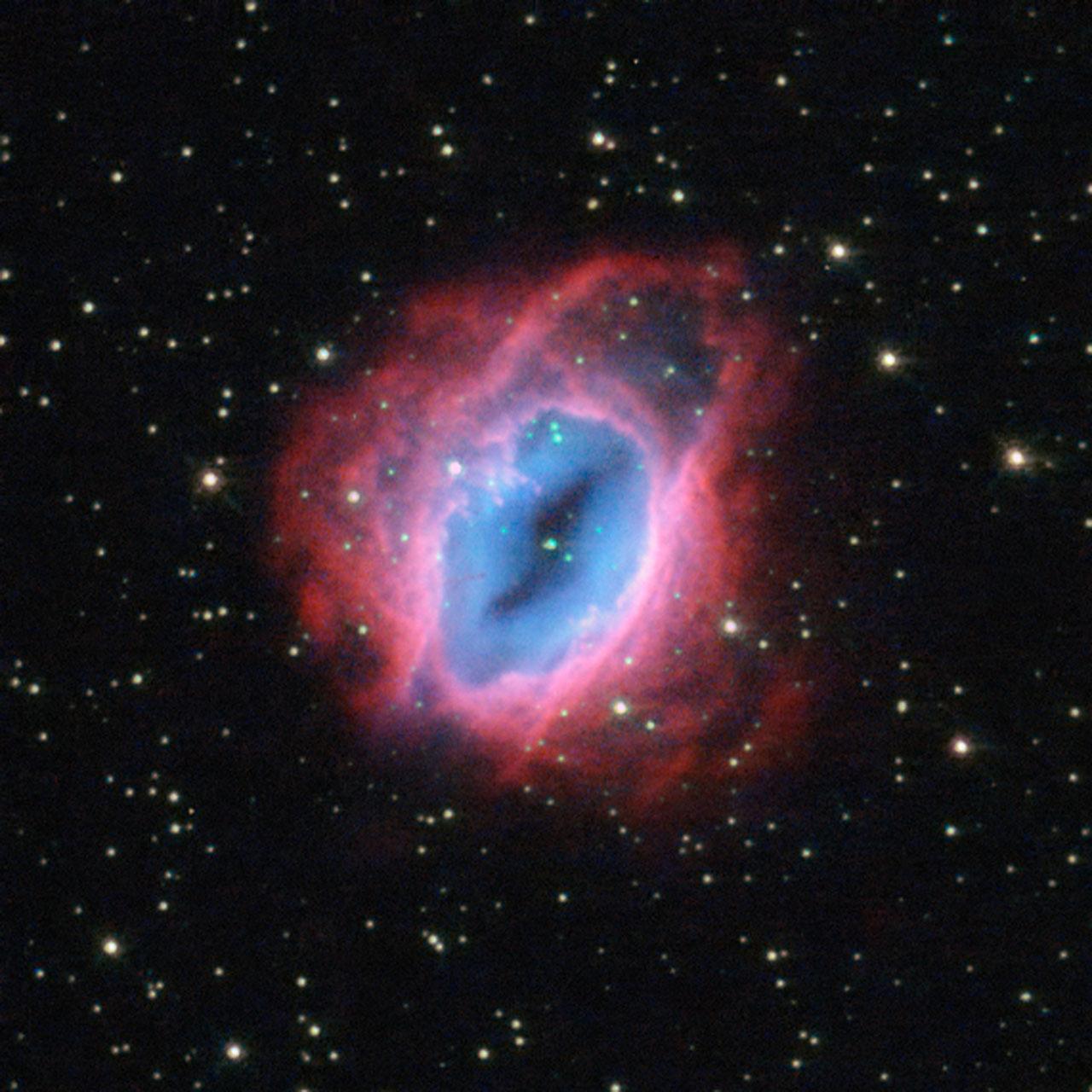

It may look like something from "The Lord of the Rings," but this fiery swirl is actually a planetary nebula known as ESO 456-67. Set against a backdrop of bright stars, the rust-colored object lies in the constellation of Sagittarius (The Archer), in the southern sky. In this image of ESO 456-67, it is possible to see the various layers of material expelled by the central star. Each appears in a different hue - red, orange, yellow, and green-tinted bands of gas are visible, with clear patches of space at the heart of the nebula. It is not fully understood how planetary nebulae form such a wide variety of shapes and structures; some appear to be spherical, some elliptical, others shoot material in waves from their polar regions, some look like hourglasses or figures of eight, and others resemble large, messy stellar explosions - to name but a few. Image Credit: ESA/Hubble and NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This is an artist concept of a hypothetical 10-million-year-old star system. The bright blur at the center is a star much like our sun. The other orb in the image is a gas-giant planet like Jupiter.
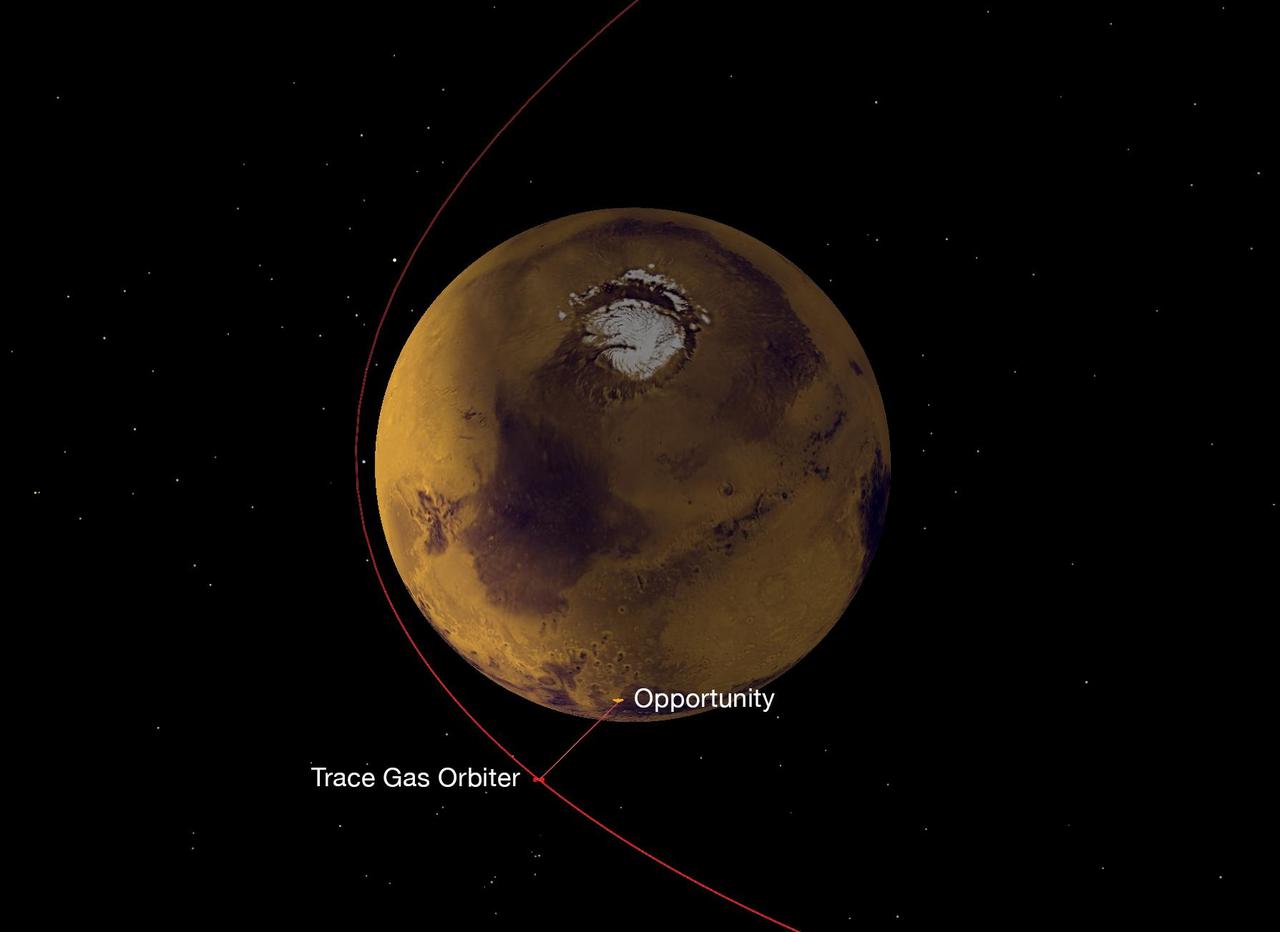
On Nov. 22, 2016, a NASA radio aboard the European Space Agency's (ESA's) Trace Gas Orbiter, which arrived at Mars the previous month, succeeded in its first test of receiving data transmitted from NASA Mars rovers, both Opportunity and Curiosity. This graphic depicts the geometry of Opportunity transmitting data to the orbiter, using the ultra-high frequency (UHF) band of radio wavelengths. The orbiter received that data using one of its twin Electra UHF-band radios. Data that the orbiter's Electra received from the two rovers was subsequently transmitted from the orbiter to Earth, using the orbiter's main X-band radio. The Trace Gas Orbiter is part of ESA's ExoMars program. During the initial months after its Oct. 19, 2016, arrival, it is flying in a highly elliptical orbit. Each loop takes 4.2 days to complete, with distances between the orbiter and the planet's surface ranging from about 60,000 miles (about 100,000 kilometers) to less than 200 miles (less than 310 kilometers). Later, the mission will reshape the orbit to a near-circular path about 250 miles (400 kilometers) above the surface of Mars. Three NASA orbiters and one other ESA orbiter currently at Mars also have relayed data from Mars rovers to Earth. This strategy enables receiving much more data from the surface missions than would be possible with a direct-to-Earth radio link from rovers or stationary landers. Successful demonstration of the capability added by the Trace Gas Orbiter strengthens and extends the telecommunications network at Mars for supporting future missions to the surface of the Red Planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21139

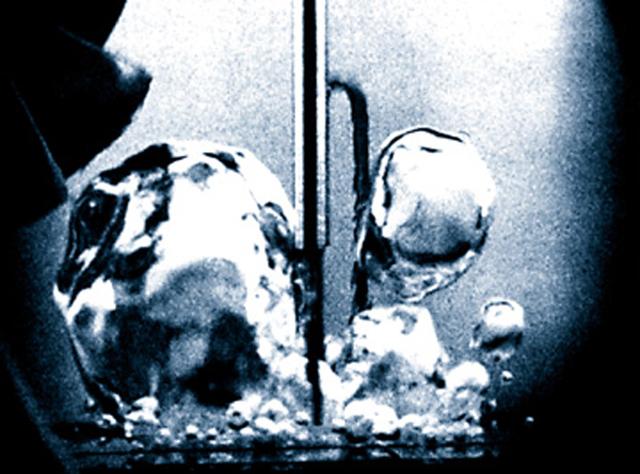
This image depicts the formation of multiple whirlpools in a sodium gas cloud. Scientists who cooled the cloud and made it spin created the whirlpools in a Massachusetts Institute of Technology laboratory, as part of NASA-funded research. This process is similar to a phenomenon called starquakes that appear as glitches in the rotation of pulsars in space. MIT's Wolgang Ketterle and his colleagues, who conducted the research under a grant from the Biological and Physical Research Program through NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., cooled the sodium gas to less than one millionth of a degree above absolute zero (-273 Celsius or -460 Fahrenheit). At such extreme cold, the gas cloud converts to a peculiar form of matter called Bose-Einstein condensate, as predicted by Albert Einstein and Satyendra Bose of India in 1927. No physical container can hold such ultra-cold matter, so Ketterle's team used magnets to keep the cloud in place. They then used a laser beam to make the gas cloud spin, a process Ketterle compares to stroking a ping-pong ball with a feather until it starts spirning. The spinning sodium gas cloud, whose volume was one- millionth of a cubic centimeter, much smaller than a raindrop, developed a regular pattern of more than 100 whirlpools.
Fluid Physics is study of the motion of fluids and the effects of such motion. When a liquid is heated from the bottom to the boiling point in Earth's microgravity, small bubbles of heated gas form near the bottom of the container and are carried to the top of the liquid by gravity-driven convective flows. In the same setup in microgravity, the lack of convection and buoyancy allows the heated gas bubbles to grow larger and remain attached to the container's bottom for a significantly longer period.
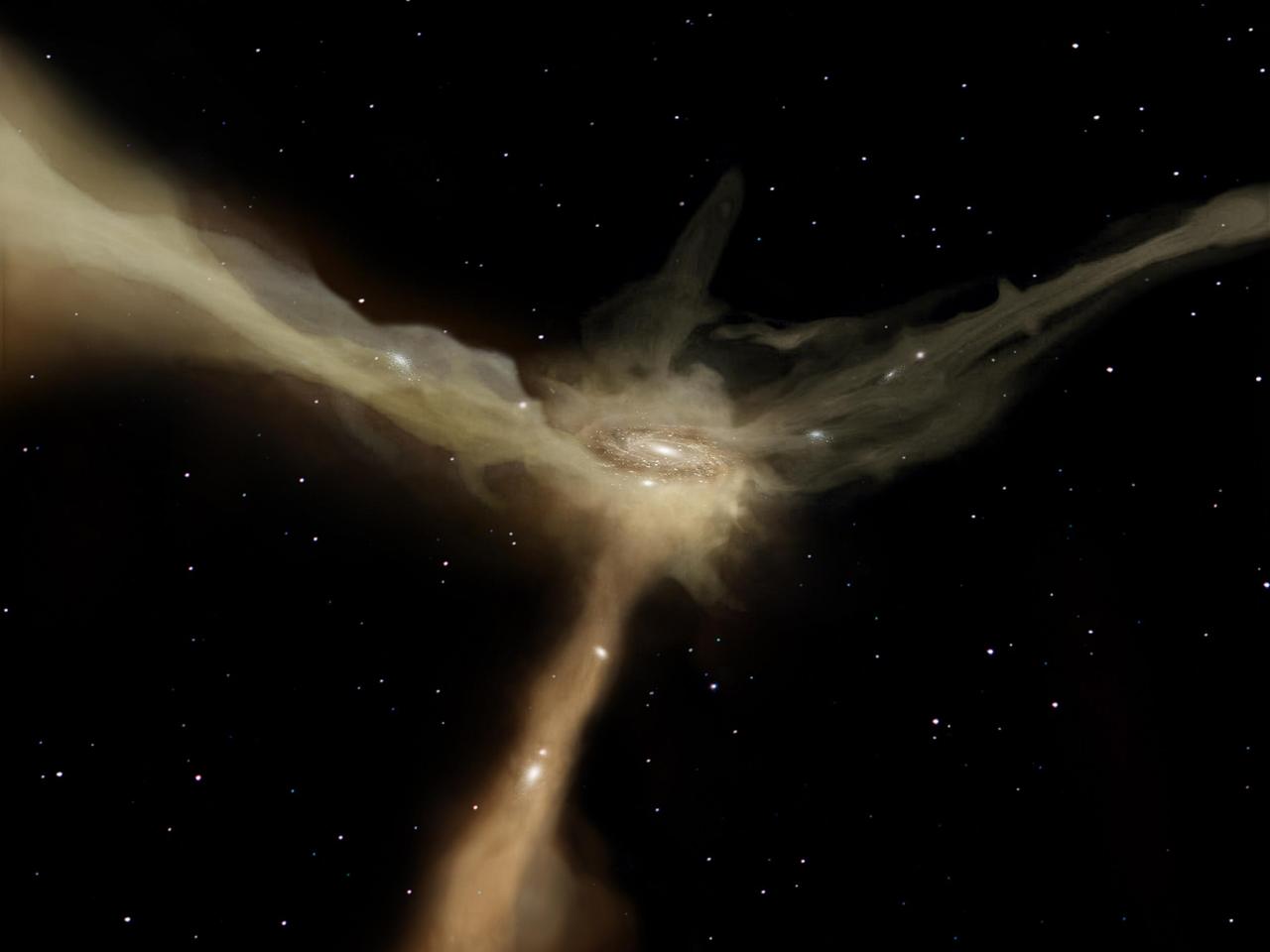

In this artist conception based on data from ESA Herschel observatory, a galaxy accretes mass from rapid, narrow streams of cold gas. These filaments provide the galaxy with continuous flows of raw material to feed its star-forming at a leisurely pace

Robotic Arm Camera Image of the South Side of the Thermal and Evolved-Gas Analyzer Door TA4 receiving sample

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers wait to return to their buildings at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after a backhoe inadvertently struck a natural gas line at around 8:40 a.m. EST in the area north of the Multi Function Facility (MFF). As a precaution, personnel were evacuated from Orbiter Processing Facilities 1 and 2, the MFF, Processing Control Center and Operations Support Building (OSB) I. All traffic was blocked on the Saturn Causeway near the facilities. There were no injuries or damage to any facilities and personnel were allowed back into their buildings before mid-day and the roadway open to traffic. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers wait to return to their buildings at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after a backhoe inadvertently struck a natural gas line at around 8:40 a.m. EST in the area north of the Multi Function Facility (MFF). As a precaution, personnel were evacuated from Orbiter Processing Facilities 1 and 2, the MFF, Processing Control Center and Operations Support Building (OSB) I. All traffic was blocked on the Saturn Causeway near the facilities. There were no injuries or damage to any facilities and personnel were allowed back into their buildings before mid-day and the roadway open to traffic. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
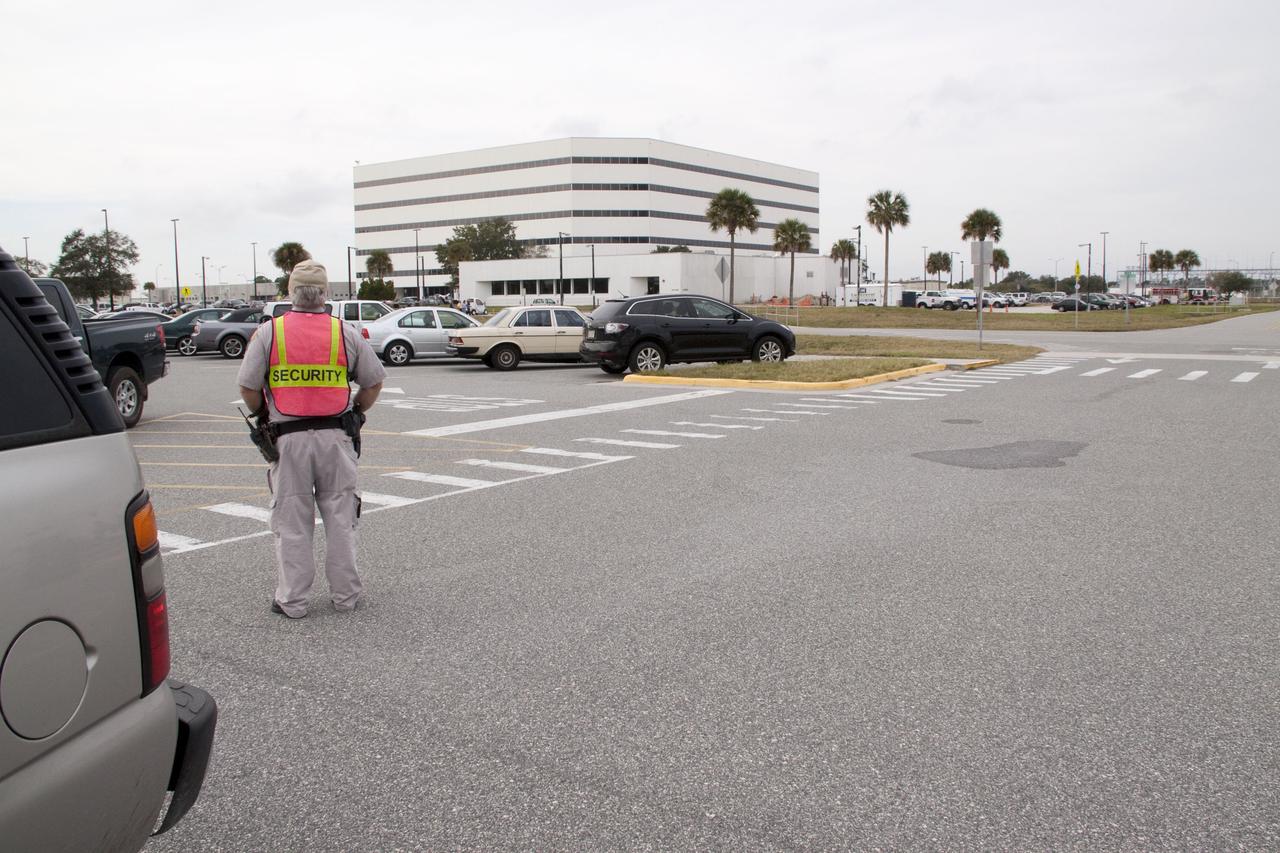

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a security officer monitors the area after a backhoe inadvertently struck a natural gas line at around 8:40 a.m. EST in the area north of the Multi Function Facility (MFF). As a precaution, personnel were evacuated from Orbiter Processing Facilities 1 and 2, the MFF, Processing Control Center and Operations Support Building (OSB) I. All traffic was blocked on the Saturn Causeway near the facilities. There were no injuries or damage to any facilities and personnel were allowed back into their buildings before mid-day and the roadway open to traffic. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
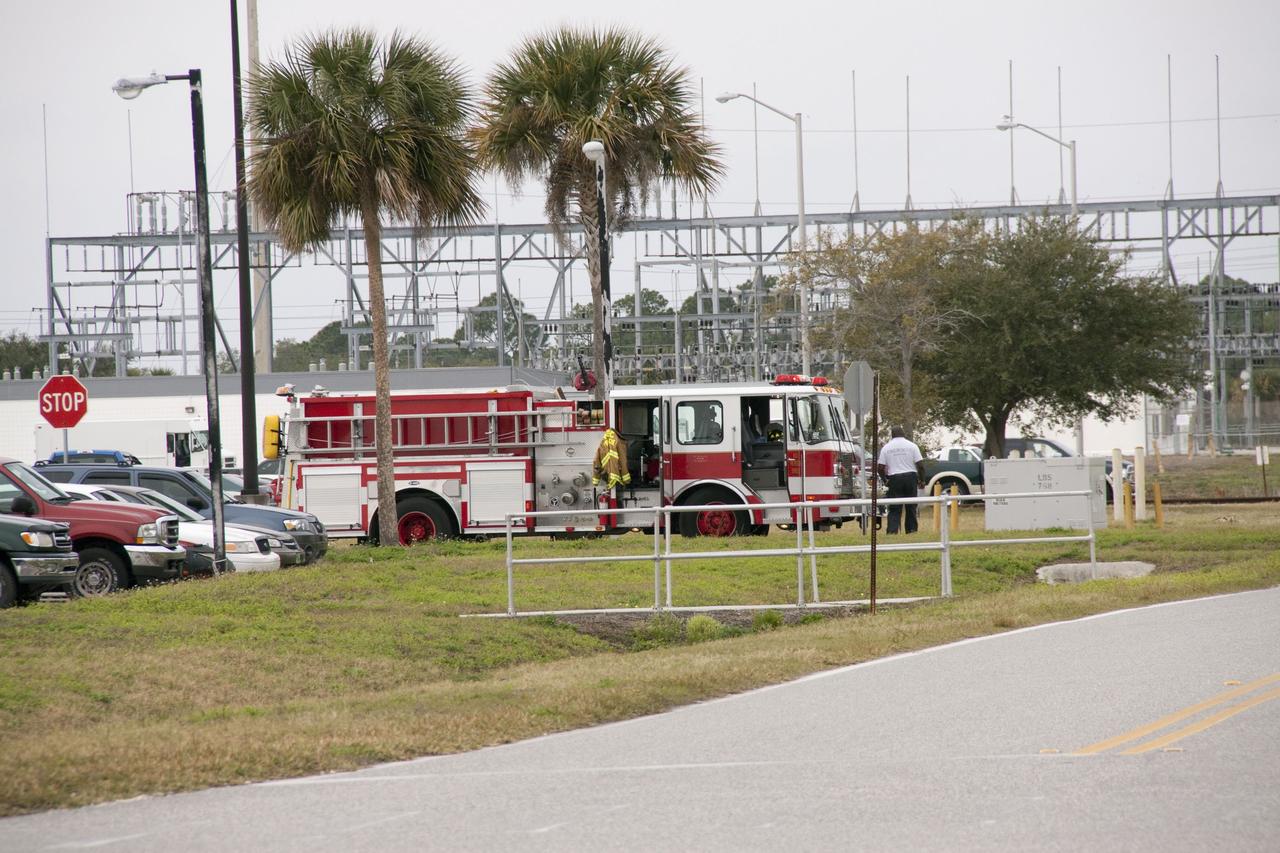

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, KSC firefighters were on the scene after a backhoe inadvertently struck a natural gas line at around 8:40 a.m. EST in the area north of the Multi Function Facility (MFF). As a precaution, personnel were evacuated from Orbiter Processing Facilities 1 and 2, the MFF, Processing Control Center and Operations Support Building (OSB) I. All traffic was blocked on the Saturn Causeway near the facilities. There were no injuries or damage to any facilities and personnel were allowed back into their buildings before mid-day and the roadway open to traffic. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

Magnetic loops carrying gas and dust above disks of planet-forming material circling stars are shown in this artist conception, which NASA Spitzer Space Telescope detects as infrared light.
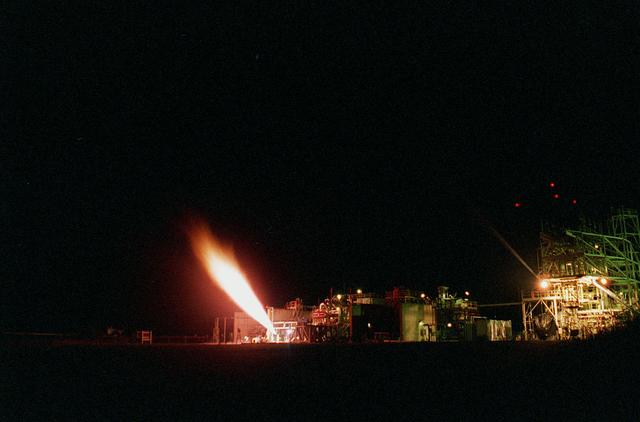

A J-2 Gas Generator (GG) engine's duration test at Marshall's Test Stand-116.
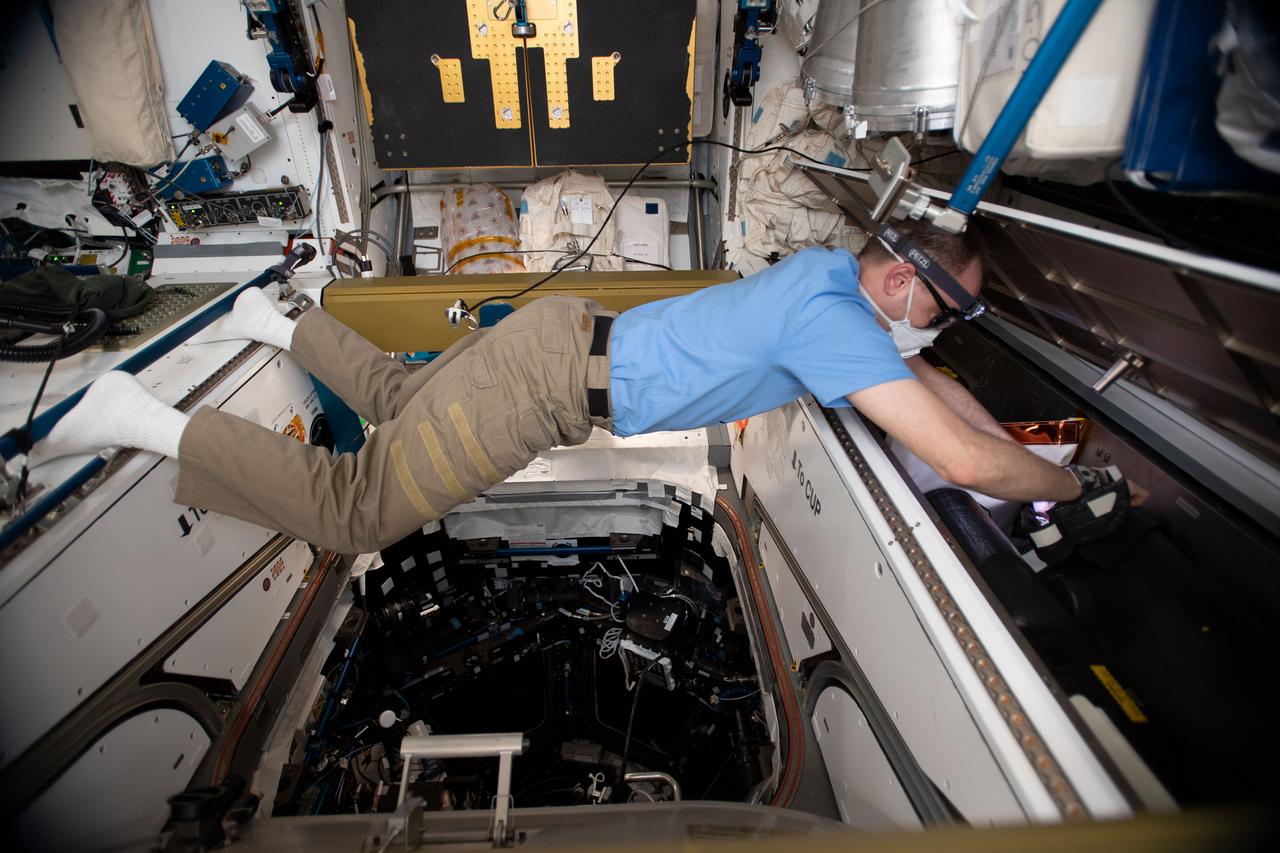

iss059e061760 (May 15, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Nick Hague of Expedition 59 installs gas trap plugs inside the Harmony module's Moderate Temperature Loop Pump Package Assembly. The gas trap plugs would slow an ammonia release through the gas trap vent hole in the event of an Interface Heat Exchanger breach and reduce coolant leakage during vacuum conditions at the International Space Station.
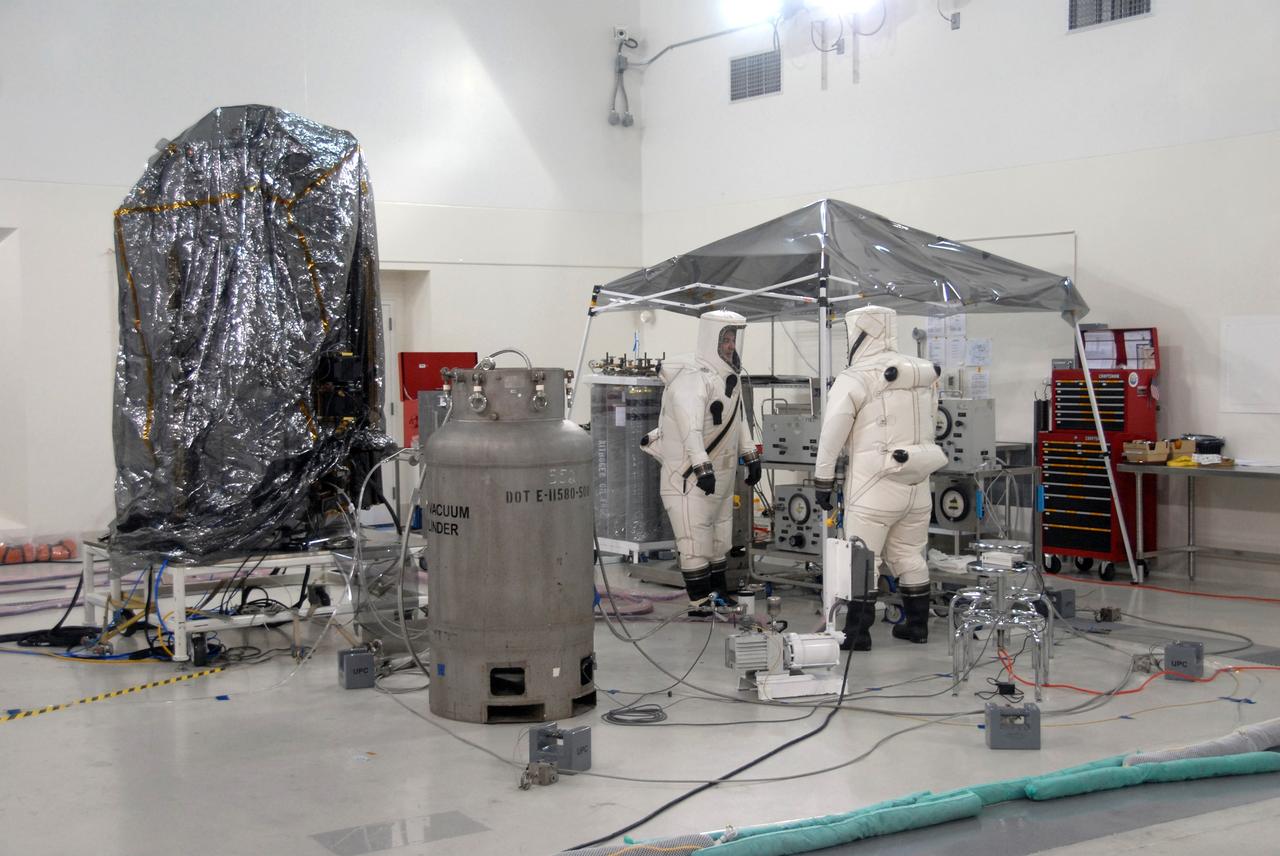

Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. – In the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, preparations are under way to fuel NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, with hydrazine thruster control propellant. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The OCO mission will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. This improved understanding will enable more reliable forecasts of future changes in the abundance and distribution of CO2 in the atmosphere and the effect that these changes may have on the Earth's climate. The launch of OCO is scheduled for Feb. 23 from Vandenberg. Photo credit: Robert Hargreaves Jr., VAFB

Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. – In the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician monitors data during fueling of NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, with hydrazine thruster control propellant. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The OCO mission will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. This improved understanding will enable more reliable forecasts of future changes in the abundance and distribution of CO2 in the atmosphere and the effect that these changes may have on the Earth's climate. The launch of OCO is scheduled for Feb. 23 from Vandenberg. Photo credit: Robert Hargreaves Jr., VAFB

Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. – In the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician monitors data during fueling of NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, with hydrazine thruster control propellant. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The OCO mission will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. This improved understanding will enable more reliable forecasts of future changes in the abundance and distribution of CO2 in the atmosphere and the effect that these changes may have on the Earth's climate. The launch of OCO is scheduled for Feb. 23 from Vandenberg. Photo credit: Robert Hargreaves Jr., VAFB

Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. – In the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, preparations are under way to fuel NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, with hydrazine thruster control propellant. The OCO is a new Earth-orbiting mission sponsored by NASA's Earth System Science Pathfinder Program. The OCO mission will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. This improved understanding will enable more reliable forecasts of future changes in the abundance and distribution of CO2 in the atmosphere and the effect that these changes may have on the Earth's climate. The launch of OCO is scheduled for Feb. 23 from Vandenberg. Photo credit: Robert Hargreaves Jr., VAFB
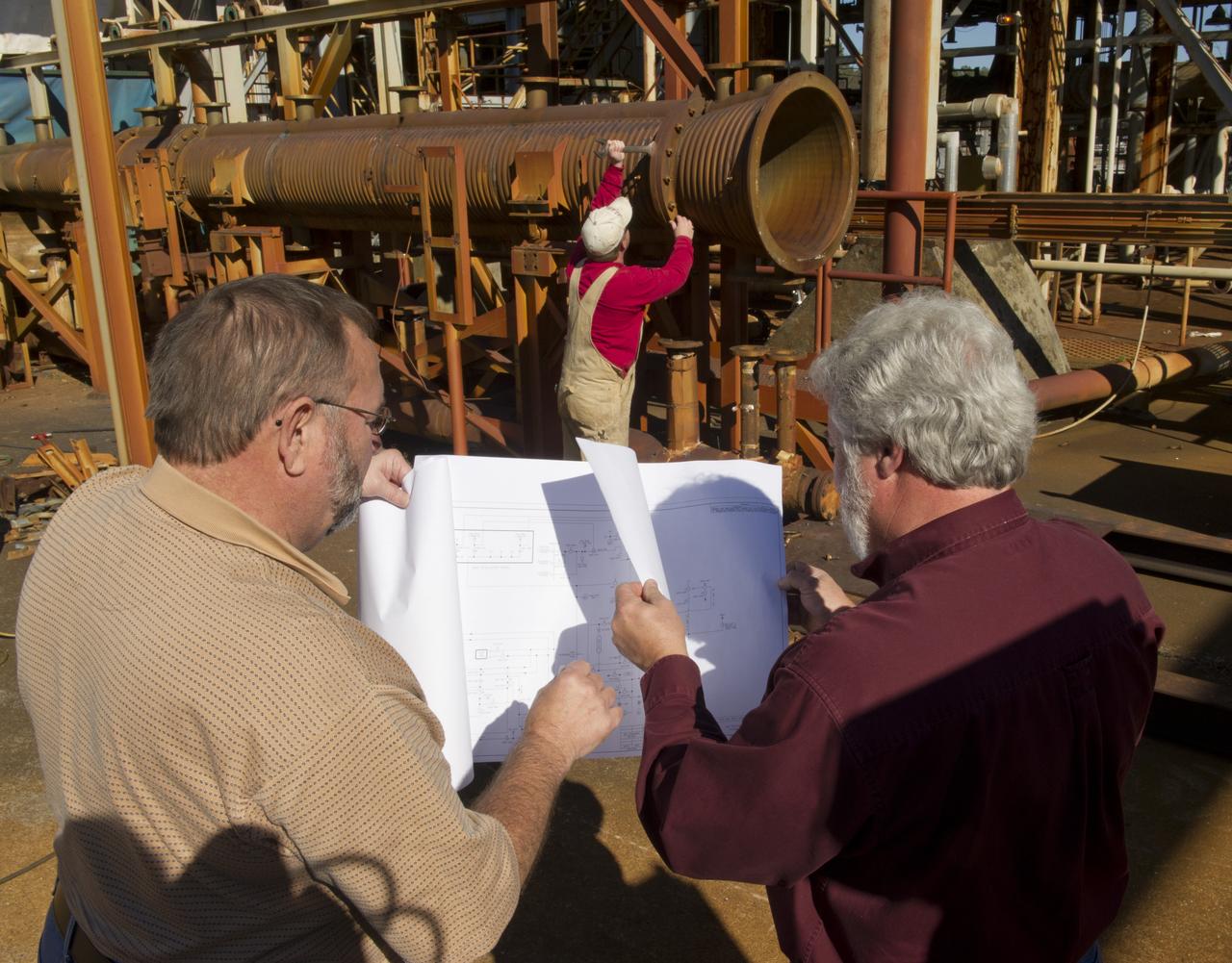

JEREMY KELLY, BACKGROUND, BEGINS DISASSEMBLING THE HOT GAS FACILITY'S WIND TUNNEL AS SCOOTER CLIFTON, FRONT LEFT, AND GREG VINYARD REVIEW THE FACILITY'S REDESIGN PLANS.
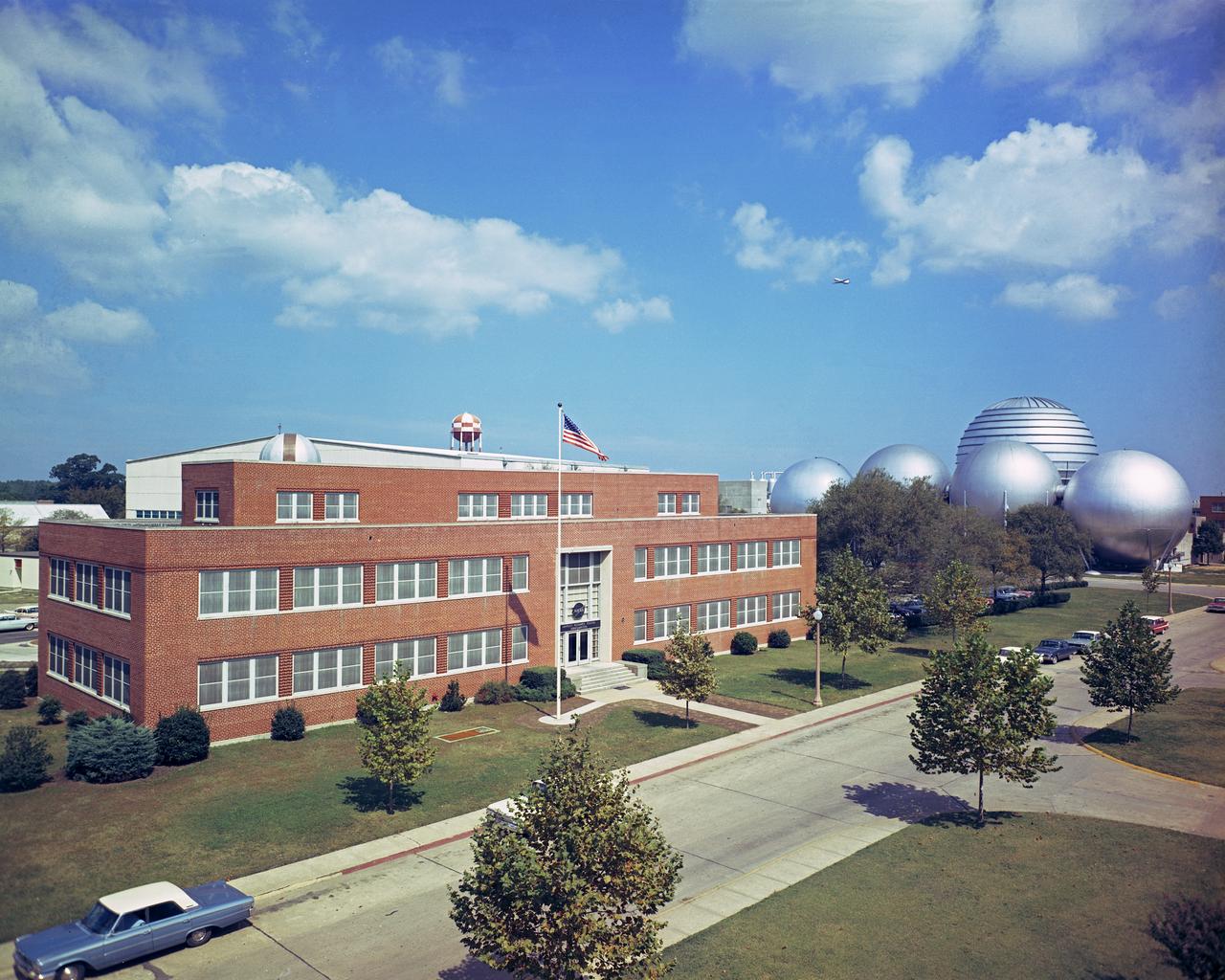

Headquarters building and spheres at Gas Dynamics. DAO Section. Scanned on 4/23/2018.

An expanded view of comet C/2006 W3 (Christensen) is shown here. The WISE spacecraft observed this comet on April 20th, 2010 as it traveled through the constellation Sagittarius. Comet Christensen was nearly 370 million miles (600 million kilometers) from Earth at the time. The extent of the dust, about a tenth of a degree across in this image, is about 2/3rds the diameter of the sun. The red contours show the signal from the gas emission observed by the WISE spacecraft in the 4.6 micron wavelength channel, which contains carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) emission lines. The strength of the 4.6 micron signal indicates over half a metric ton per second of CO or CO2 was emitted from this comet at the time of the observations. The WISE spacecraft was put into hibernation in 2011 upon completing its goal of surveying the entire sky in infrared light. WISE cataloged three quarters of a billion objects, including asteroids, stars and galaxies. In August 2013, NASA decided to reinstate the spacecraft on a mission to find and characterize more asteroids. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20119
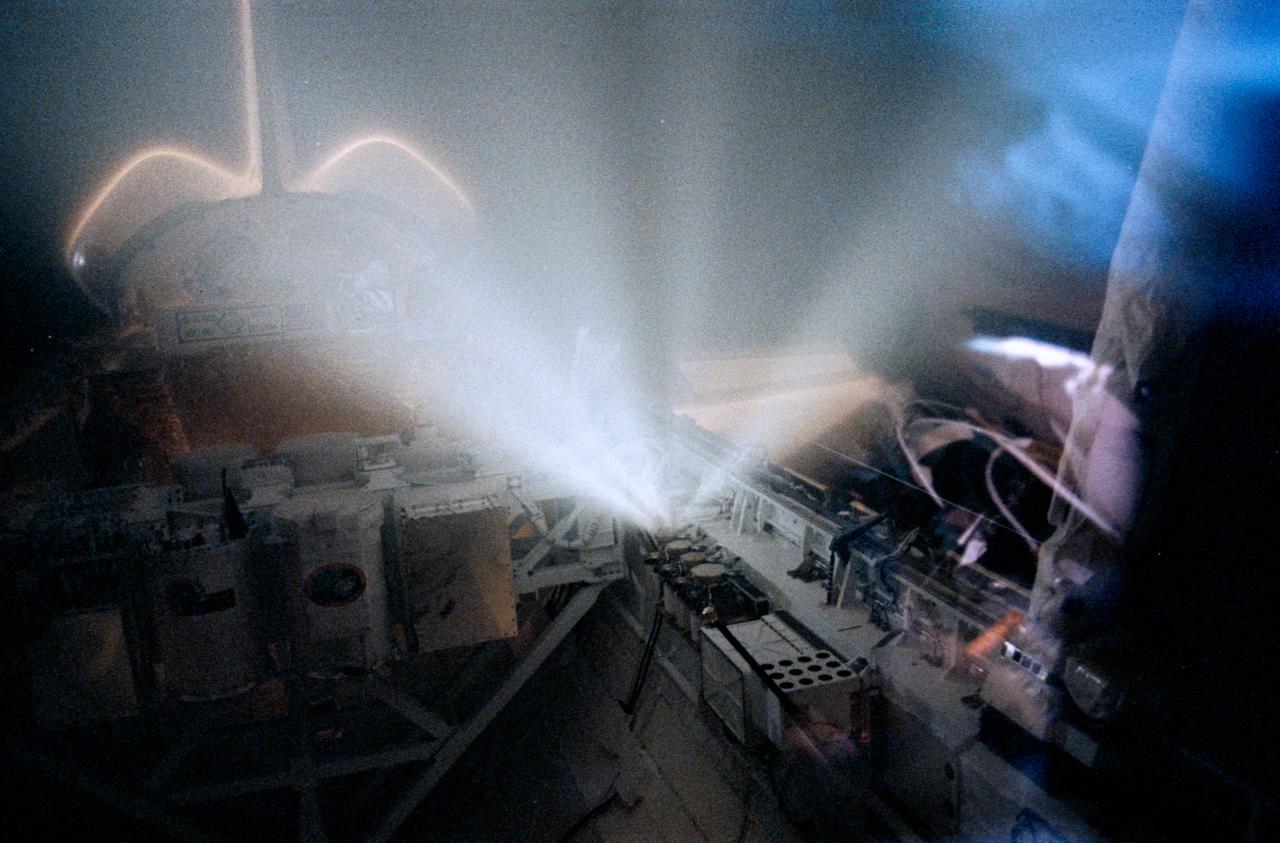

STS039-367-006 (1 May 1991) --- One of the four compressed gas canisters on the forward port side of Discovery's cargo bay releases gas on flight day 4 of the STS-39 mission. The canisters are part of STS-39's Critical Ionization Velocity (CIV) experiment.
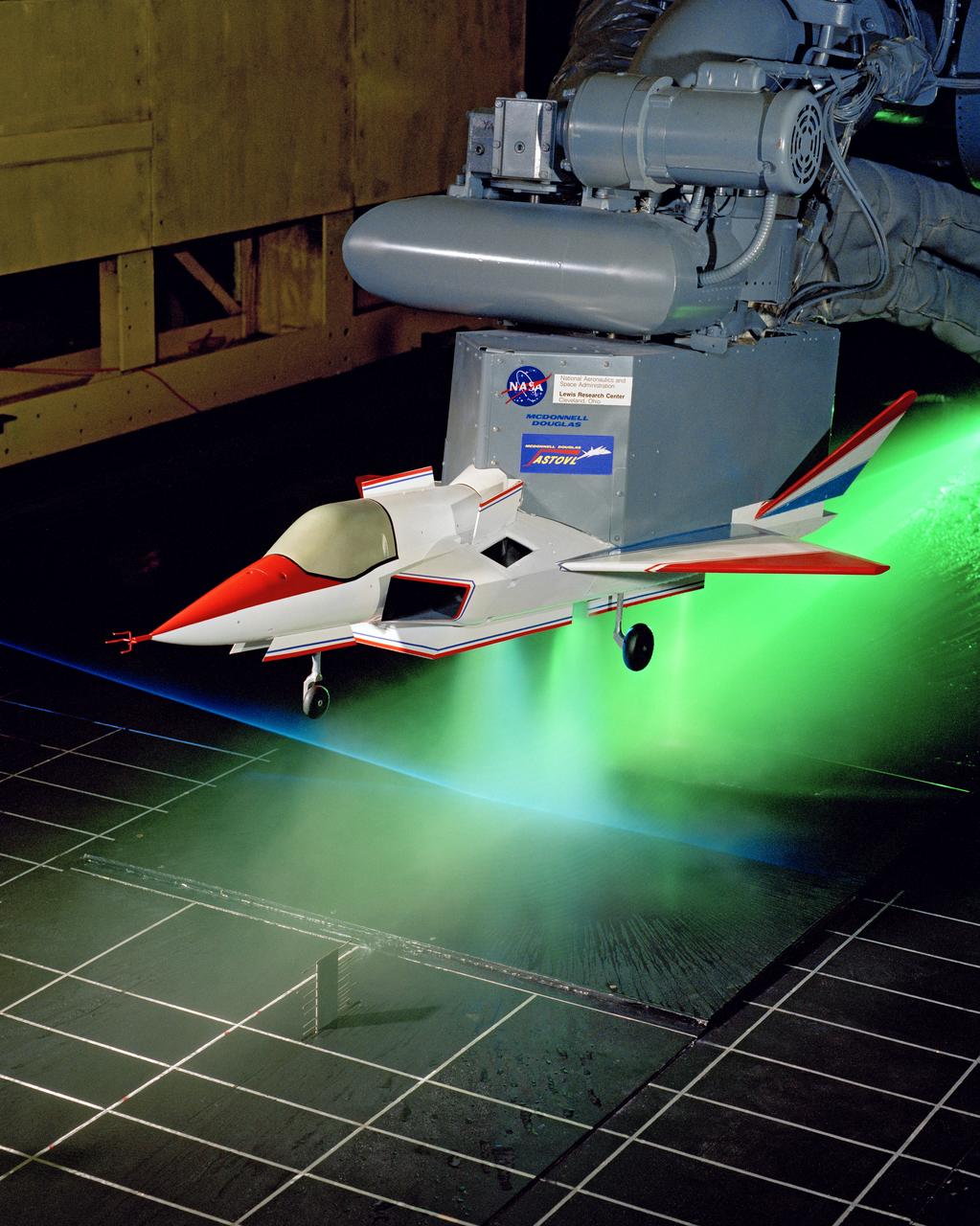

SUPERSONIC SHORT TAKE OFF Vertical LANDING HOT GAS INGESTION MODEL 9X15 WIND TUNNEL

A new feature in the evolution of galaxies has been captured in this image of galactic interactions. The two galaxies seen here -- NGC 3226 at the top, NGC 3227 at the bottom.

Technicians at General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc., (GA-ASI) facility at Adelanto, Calif., carefully install a turboprop engine to the rear fuselage of NASA's Altair aircraft during final assembly operations.
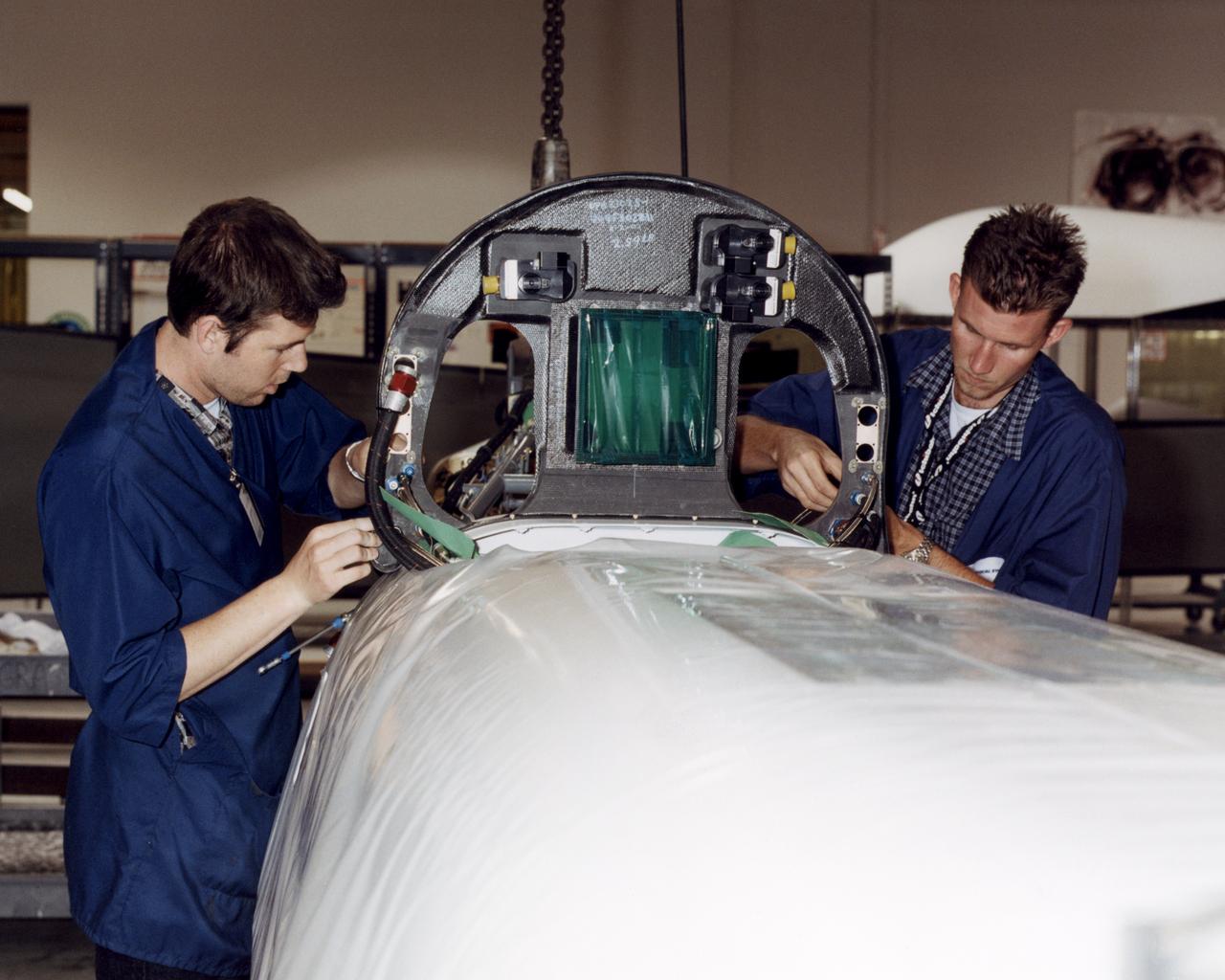

Technicians at General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc., (GA-ASI) facility at Adelanto, Calif., carefully thread control lines through a bulkhead during engine installation on NASA's Altair aircraft.
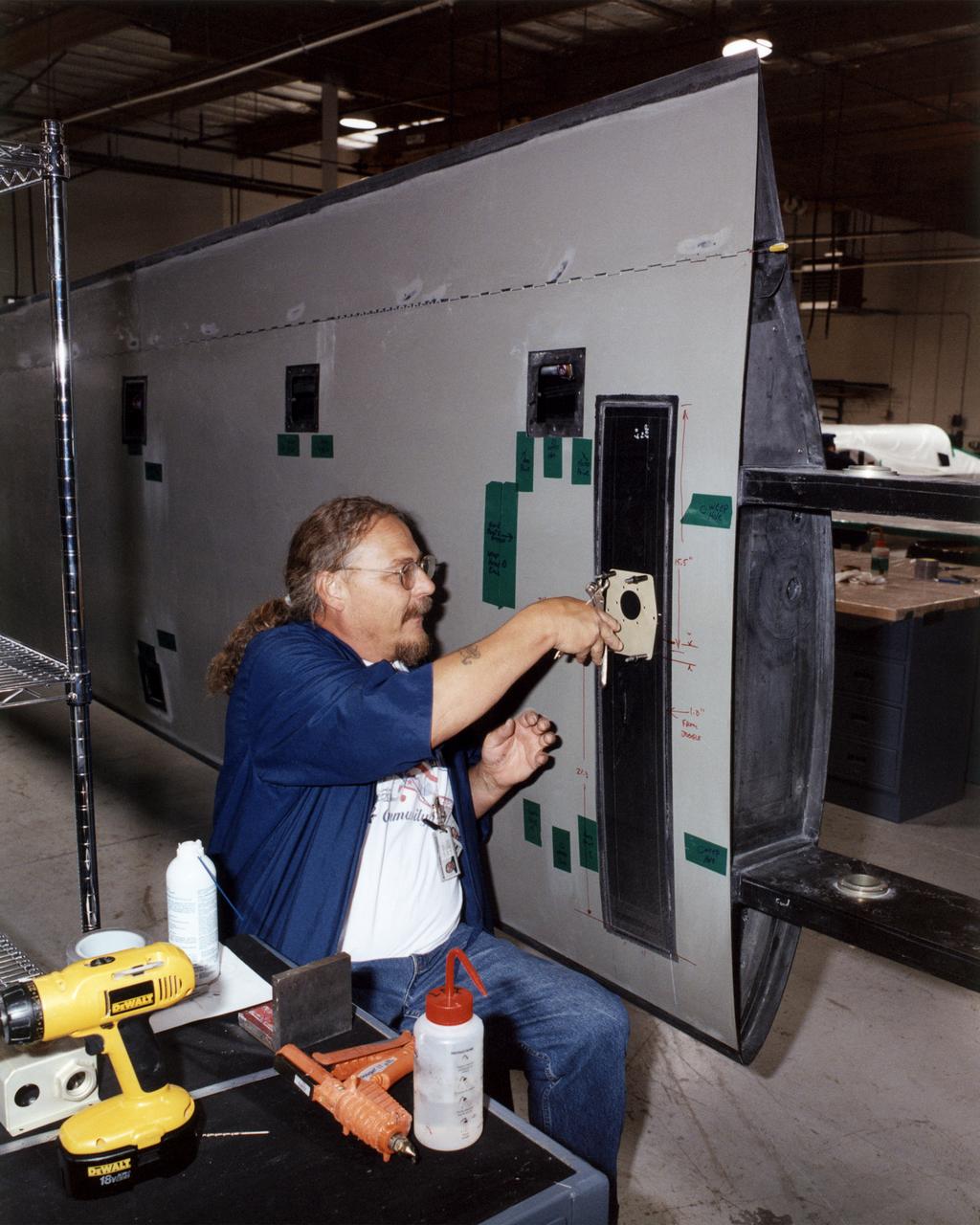

Technician Dave Brown installs a drilling template during construction of the all-composite left wing of NASA's Altair aircraft at General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc., (GA-ASI) facility at Adelanto, Calif.
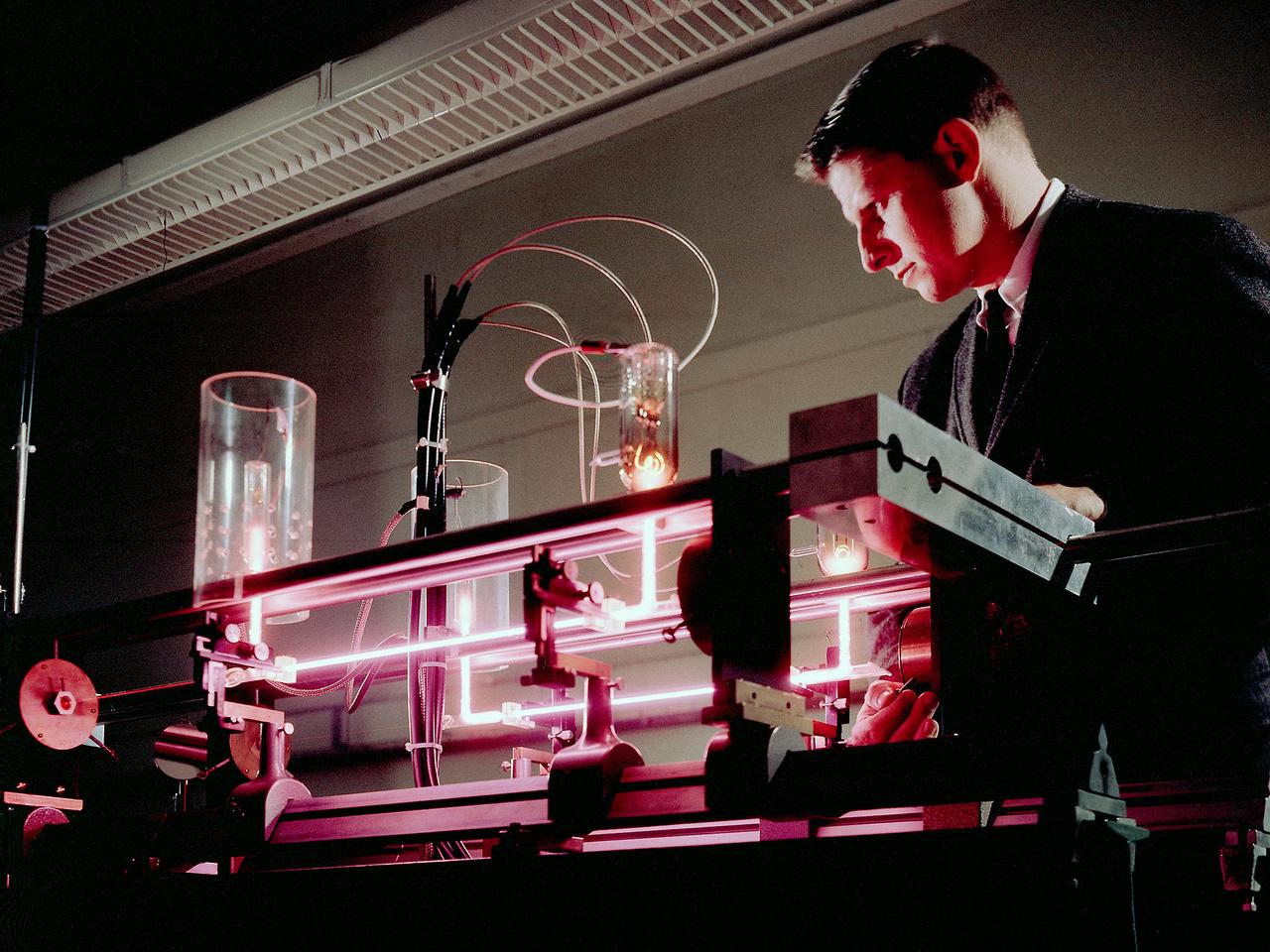
Richard Lancashire operates a gas laser interferometer in the Electric Conversion Laboratory at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Lewis was in the midst of a long-term effort to develop methods of delivering electrical power to spacecraft using nuclear, solar, or electrochemical technologies. Lancashire was measuring the thermionic diode’s plasma particle density. The thermionic diodes were being studied for possible use in radioisotope thermoelectric generators for use in space. Microwave interferometry was one method of measuring transient plasmas. The interferometer measured the difference between the frequencies of two laser beams, one of which passed through the diode. The electron density was measured by revealing the phase shift of the transmitted microwave beam brought about by a change in the plasma refraction. Microwave interferometry, however, offers poor spatial resolution and has limited range of applicability.
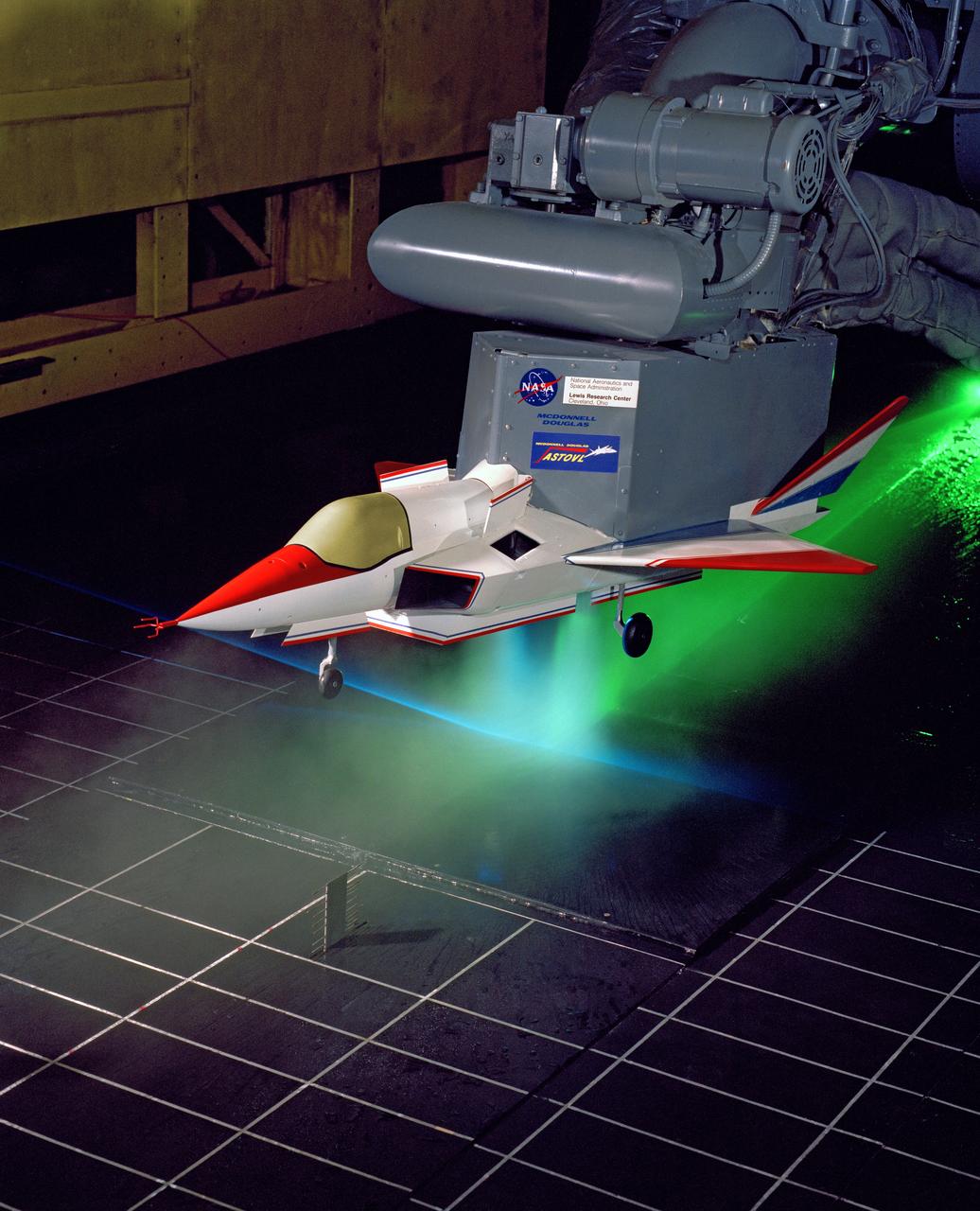
Supersonic Short Take Off Vertical Landing Hot Gas Ingestion Model Testing in the 9x15-foot Low Speed Wind Tunnel, LSWT
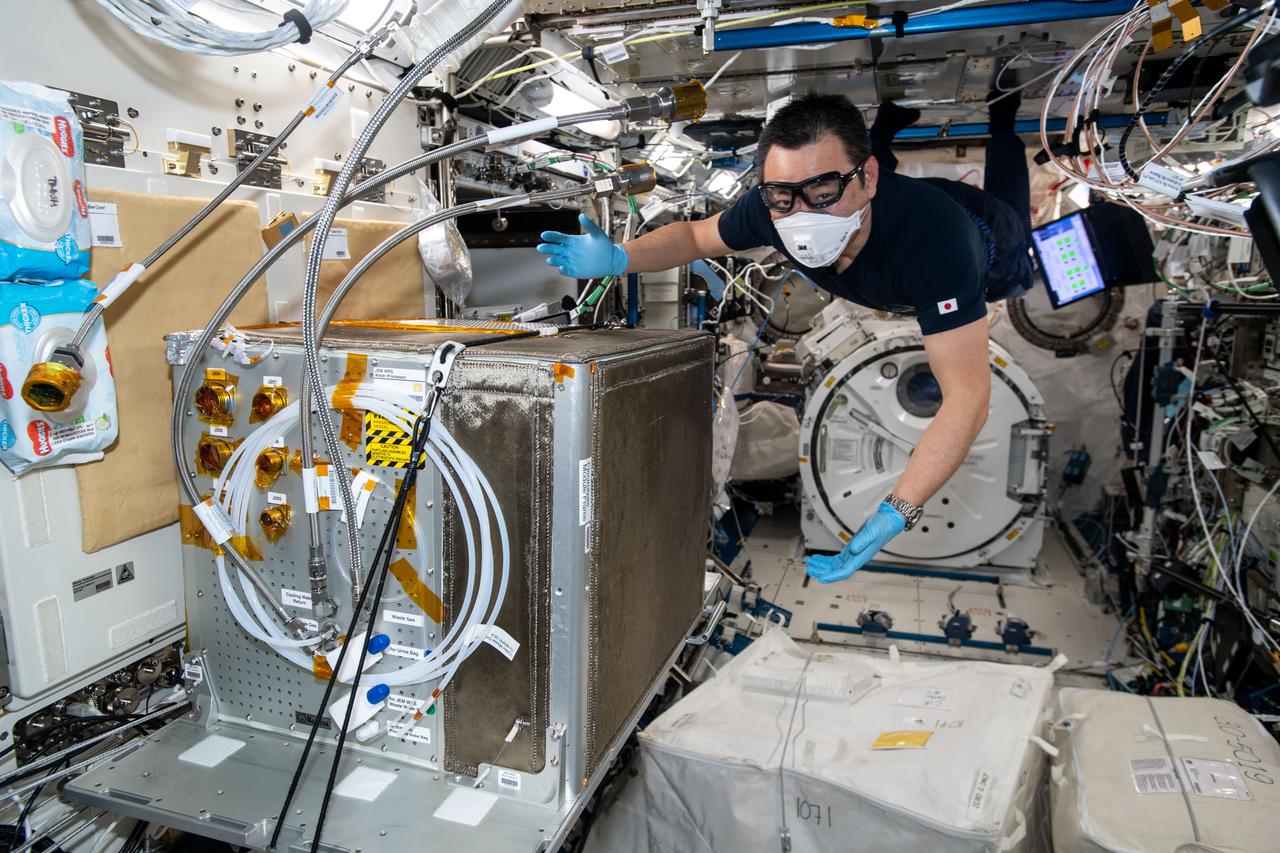

iss065e333421 (8/30/2021) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Akihiko Hoshide is photographed during the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Water Recovery System (JWRS) Gas Trap and Bypass Line Installation. Future water recovery systems will require high recovery rates, a more compact size, and less power consumption than conventional systems. The JWRS demonstrates new technologies on orbit, aboard the International Space Station (ISS), to meet these requirements.
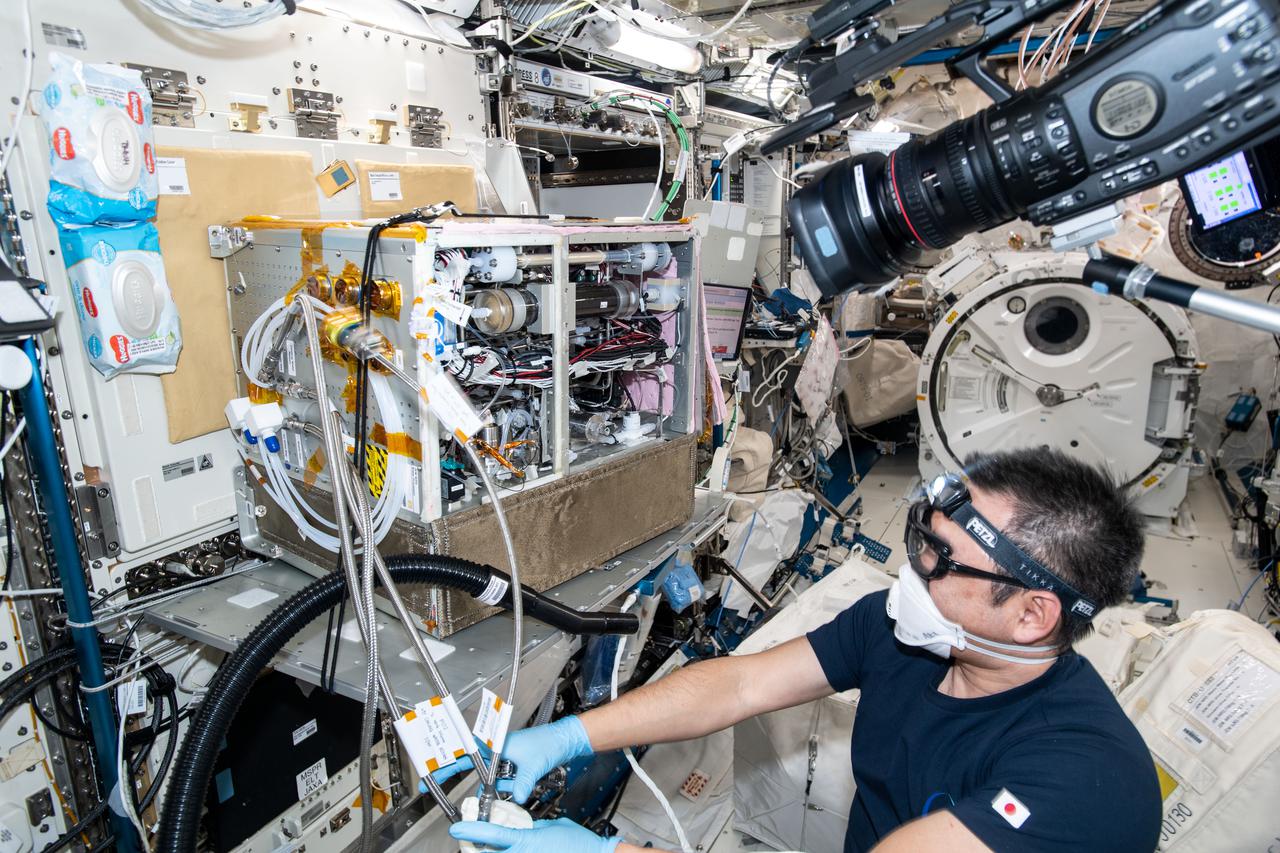

iss065e333427 (8/30/2021) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Akihiko Hoshide is photographed during the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Water Recovery System (JWRS) Gas Trap and Bypass Line Installation. Future water recovery systems will require high recovery rates, a more compact size, and less power consumption than conventional systems. The JWRS demonstrates new technologies on orbit, aboard the International Space Station (ISS), to meet these requirements.
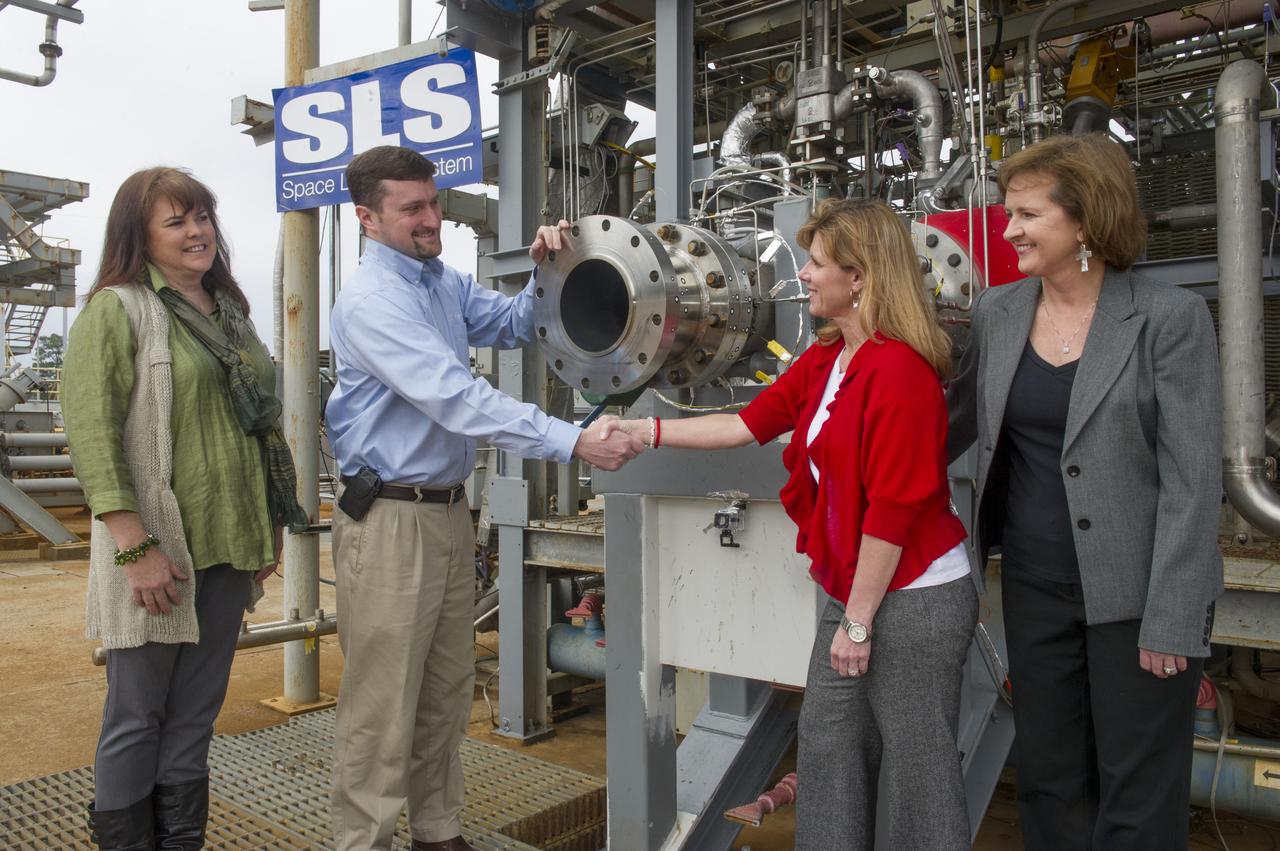

FROM LEFT TO RIGHT IN FRONT OF THE F-1 GAS GENERATOR ARE: DYNETICS PROGRAM MANAGER KIM DOERING, DYNETICS DEPUTY PROGRAM MANAGER ANDY CROCKER, MARSHALL PARTNERSHIPS MANAGER STACY COUNTS, AND MARSHALL PROJECT MANAGER FOR DYNETICS WHITNEY YOUNG.
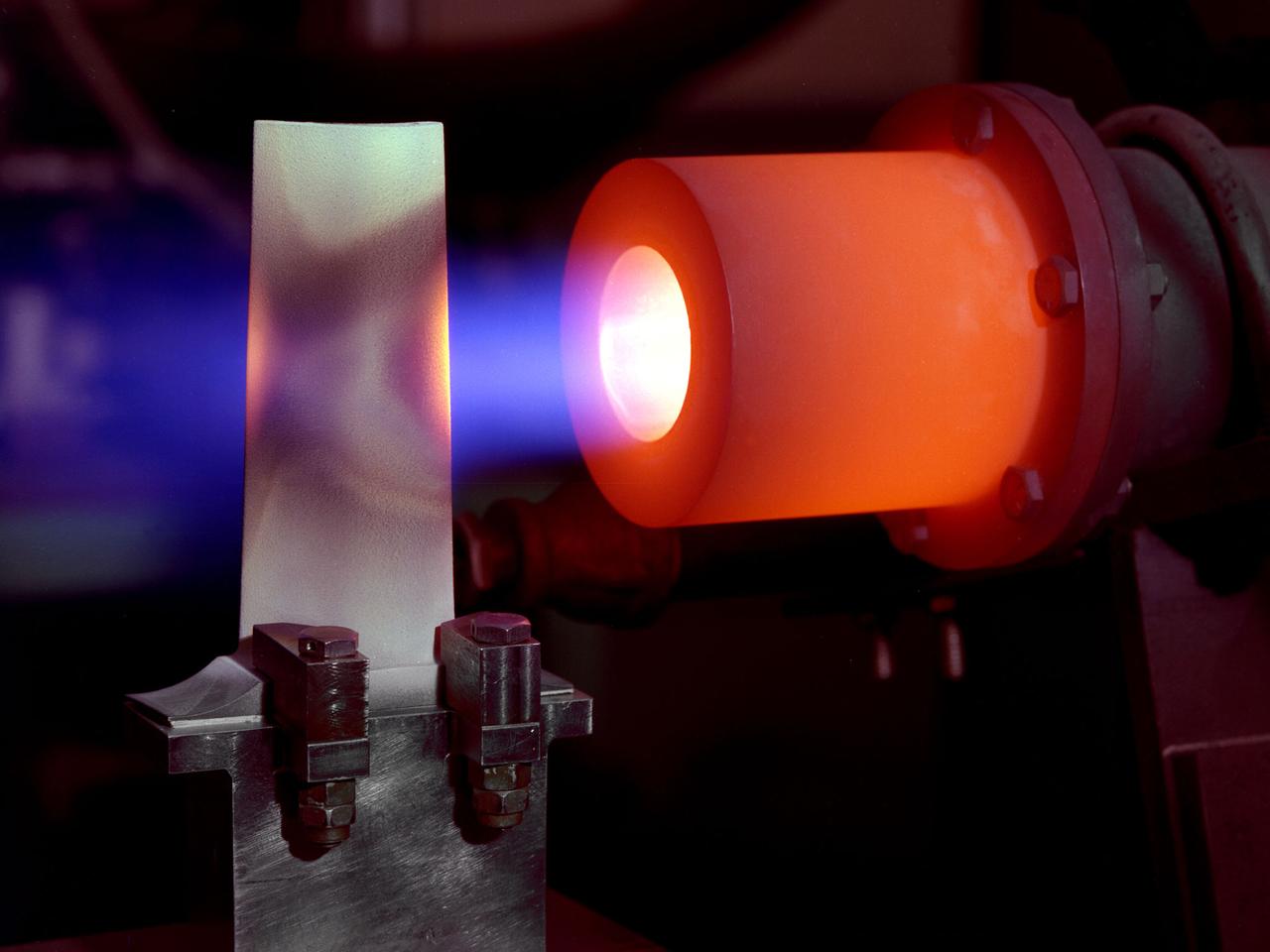
A 1-foot long stator blade with a thermal coating subjected to intense heat in order to test its strength at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Lewis researchers sought to determine optimal types of ceramic coatings to increase the durability of metals. The research was primarily intended to support the design of stator blades for high-performance axial-flow compressor and turbofan engines. The coatings reduced the temperature of the metal and the amount of required cooling. As engines became more and more sophisticated, compressor blades were required to withstand higher and higher temperatures. Lewis researchers developed a dual-layer thermal-barrier coating that could be applied to turbine vanes and blades and combustion liners. This new sprayable thermal-barrier coating was evaluated for its durability, strength, fatigue, and aerodynamic penalties. This hot-gas rig fired the scorching gas at the leading edge of a test blade. The blade was cooled by an internal air flow. The blades were heated at two different velocities during the program. When using Mach 0.3 gases the entire heating and cooling cycle only lasted 30 seconds. The cycle lasted 60 minutes during tests at Mach 1.
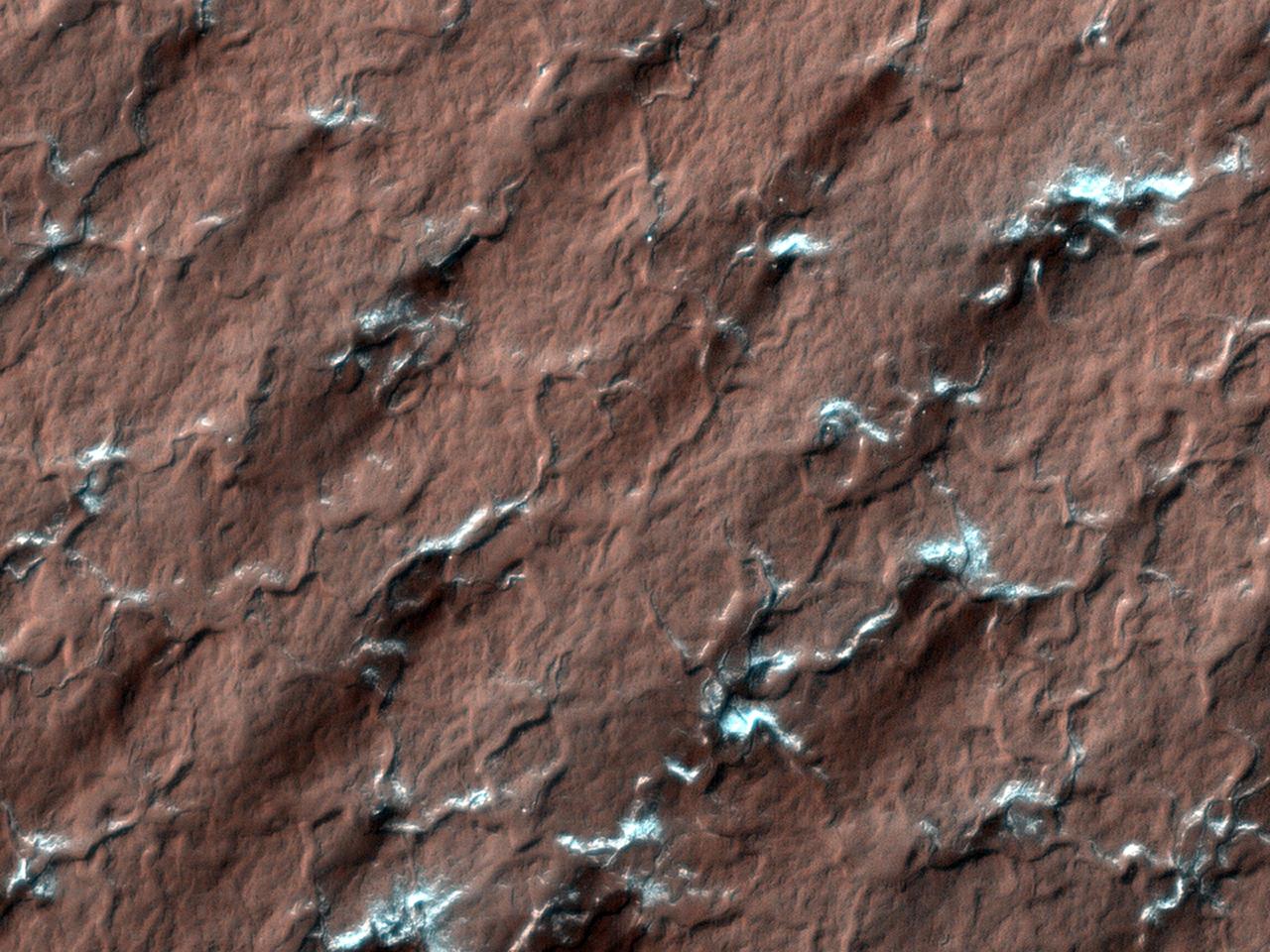

NASA Mars Reconnaissance Rover spied these spider-like formations, likely caused as carbon dioxide ice changes from a solid to a gas; the gas moves through channels until it reaches the surface and vents out.
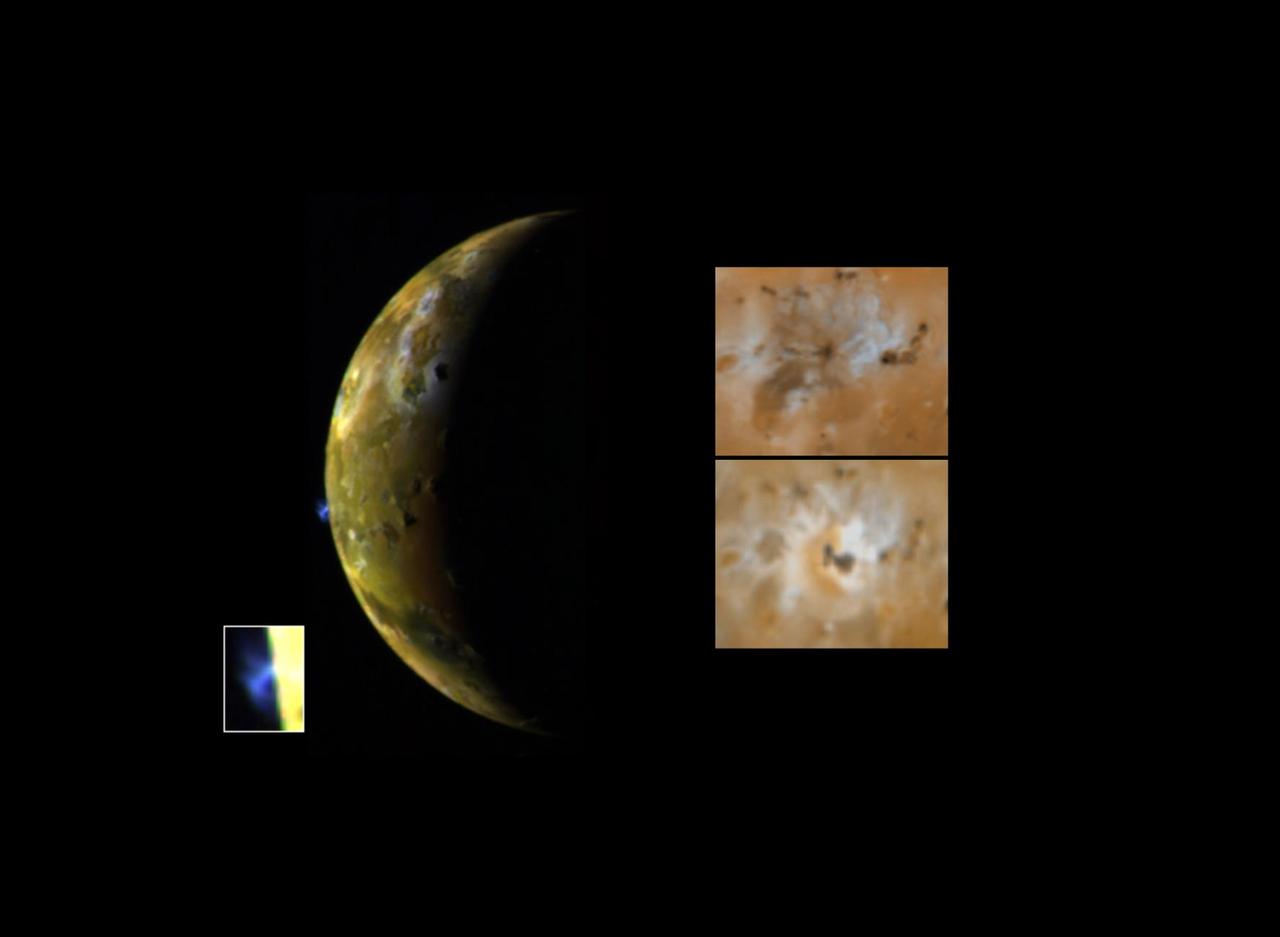
This image, taken by NASA Galileo spacecraft, shows a blue-colored volcanic plume consistent with the presence of sulfur dioxide gas and now condensing from the gas as the plume expands and cools. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00293

This two-panel illustration shows a black hole surrounded by a disk of gas, before and after the disk is partially dispersed. In the left panel, the ball of white light above the black hole is the black hole corona, a collection of ultra-hot gas particles that forms as gas from the disk falls into the black hole. The streak of debris falling toward the disk is what remains of a star that was torn apart by the black hole's gravity. The right panel shows the black hole after the debris from the star has dispersed some of the gas in the disk, causing the corona to disappear. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23864

A disk of hot gas swirls around a black hole in this illustration. Some of the gas came from a star that was pulled apart by the black hole, forming the long stream of hot gas on the right, feeding into the disk. These events are formally known as tidal disruption events, or TDEs. It can take just a matter or weeks or months from the destruction of the star to the formation of the disk. The gas gets hotter the closer it gets to the black hole, but the hottest material can be found above the black hole. This hottest material is cloud of plasma (gas atoms with their electrons stripped away) known as a corona. Most TDEs that result in the formation of a corona also produce jets of material that spew into space away from the black hole at its poles. A TDE called AT2021ehb is the first confirmed example of a corona forming without jets in a tidal disruption event. The observation of AT2021ehb makes it possible for scientists to study the formation of jets and coronae separately. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25440
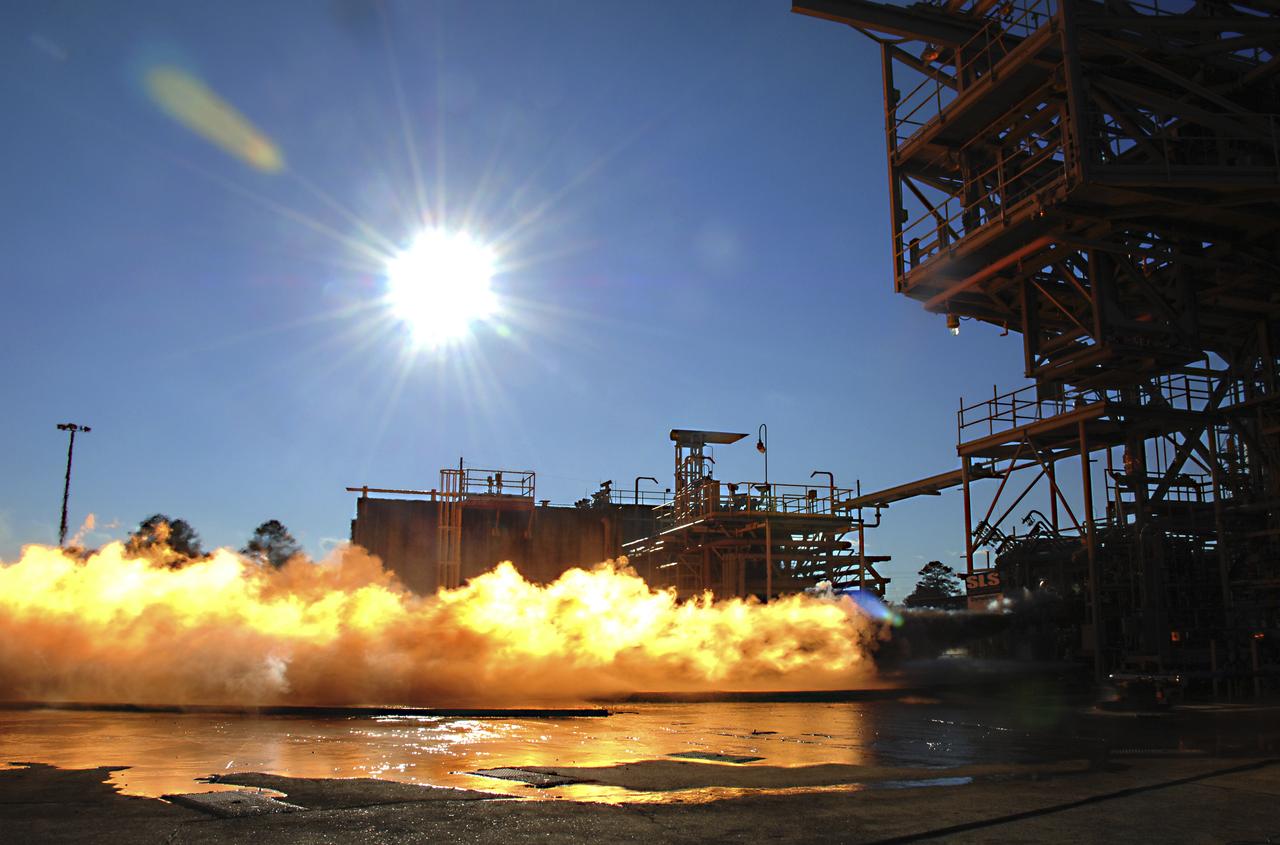

PC271-004-049 F1 GG Testing with LOX/RP-1 (Dynetics/PWR) 02/14/2013 TS116
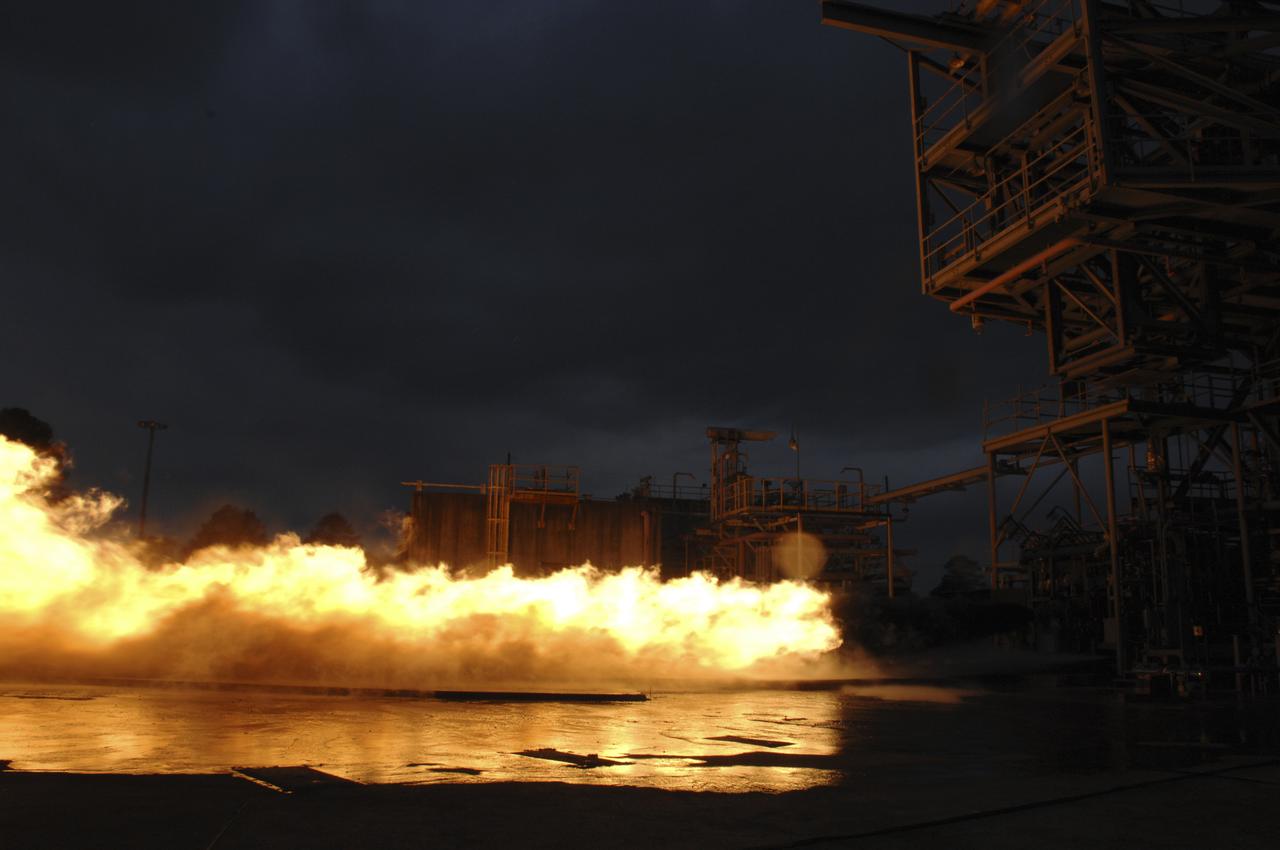

PC271-006-047 F1 GG Testing with LOX/RP-1 (Dynetics/PWR) 02/15/2013 TS116
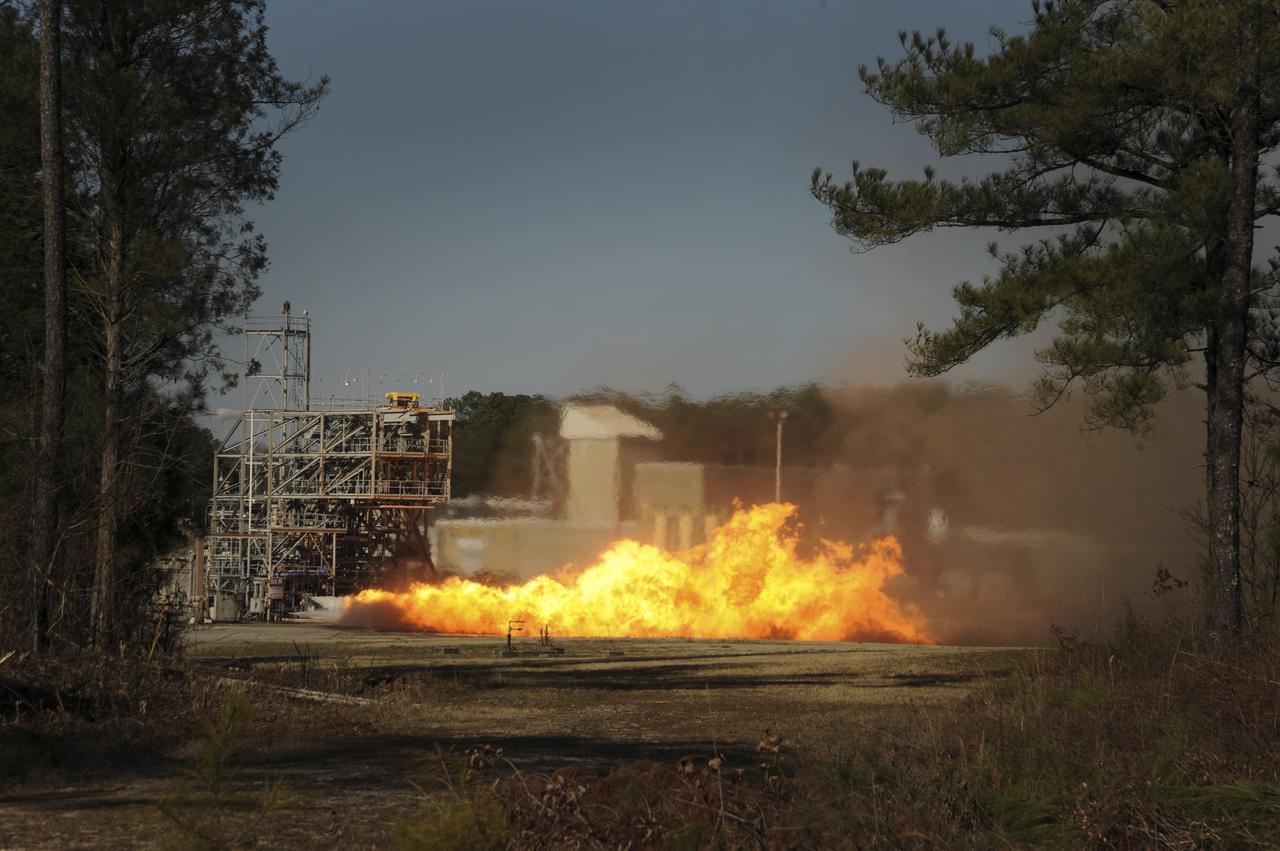

PC271-003-060 F1 GG Testing with LOX/RP-1 (Dynetics/PWR) 02/14/2013 TS116
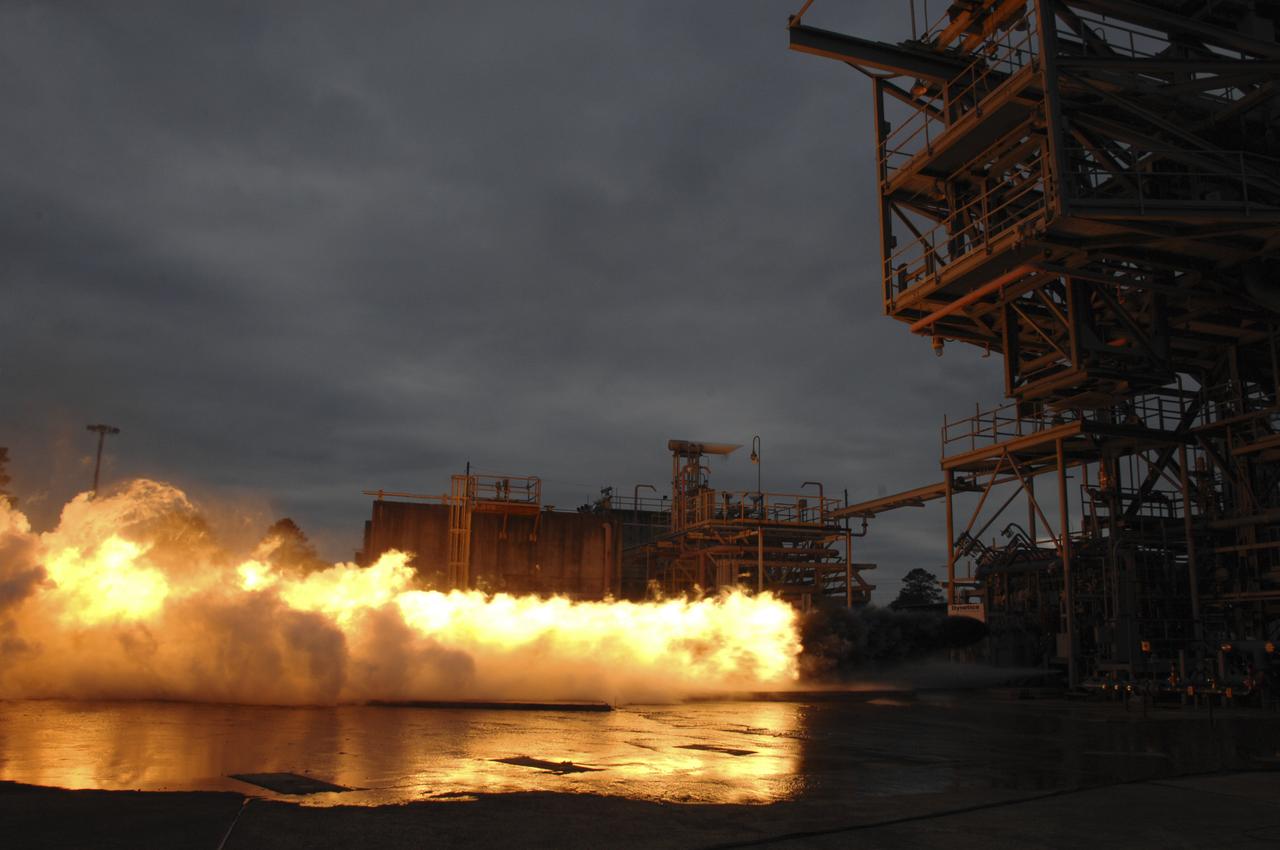

PC271-009—009 F1 GG Testing with LOX/RP-1 (Dynetics/PWR) 03/06/2013 TS116
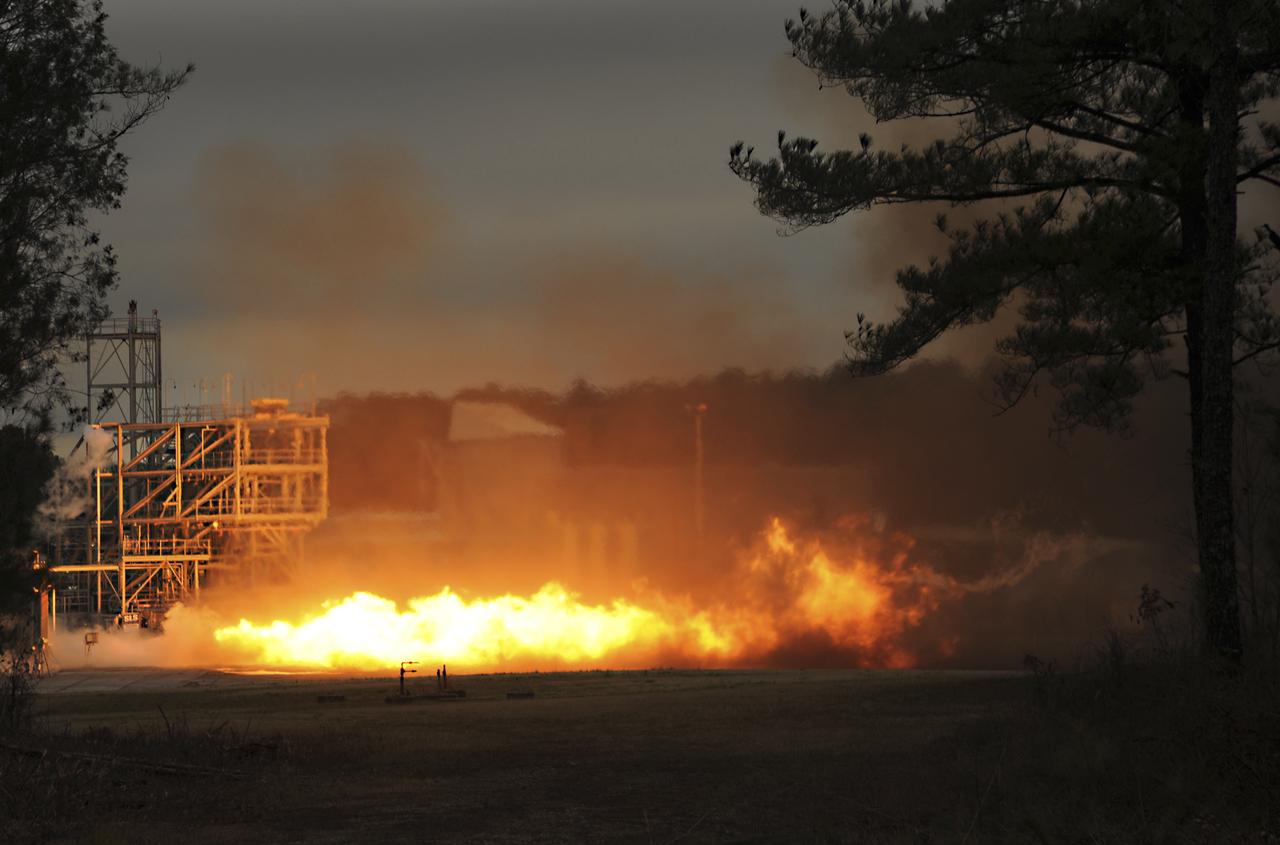

PC271-001-033 F1 GG Testing with LOX/RP-1 (Dynetics/PWR) 02/13/2013 TS116
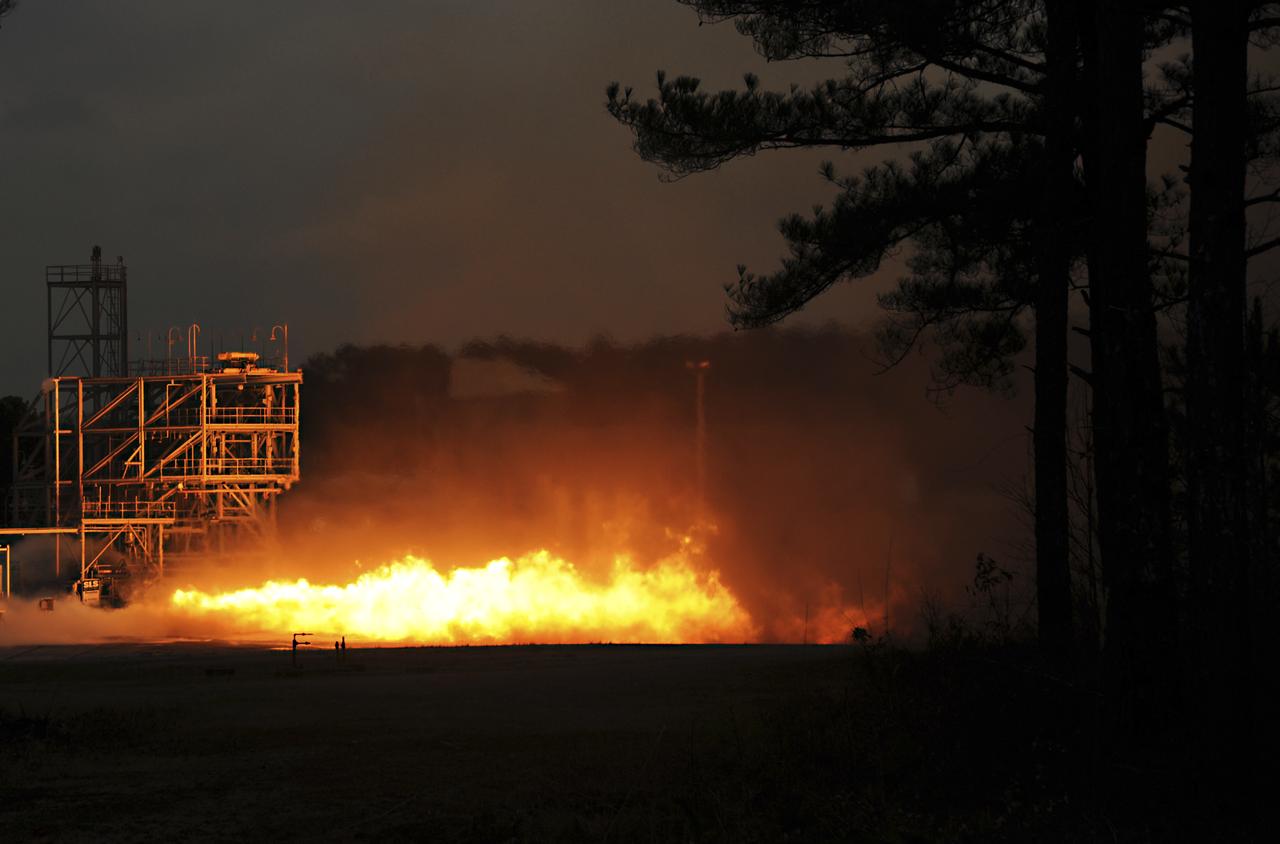

PC271-002-055 F1 GG Testing with LOX/RP-1 (Dynetics/PWR) GG 02/13/2013 TS116
![The images indicate that the bubble of gas that makes up the supernova remnant appears different in various types of light. Chandra reveals the hottest gas [colored blue and colored green], which radiates in X-rays. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06908](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA06908/PIA06908~medium.jpg)
The images indicate that the bubble of gas that makes up the supernova remnant appears different in various types of light. Chandra reveals the hottest gas [colored blue and colored green], which radiates in X-rays. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06908
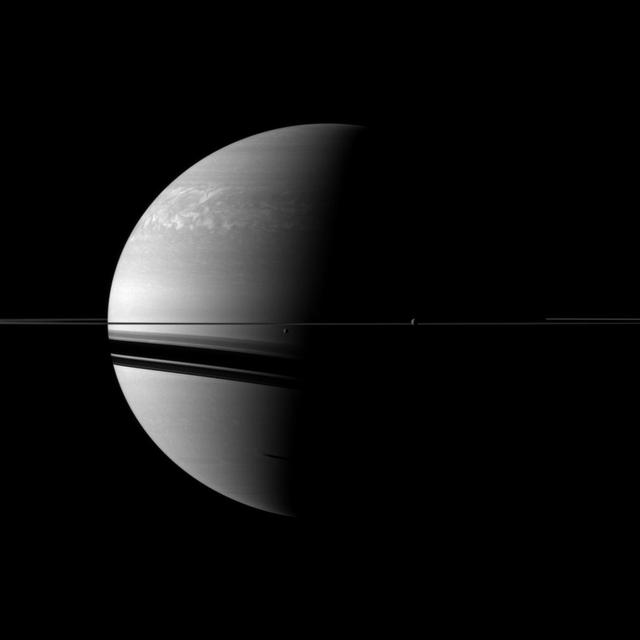

Two moons, Rhea and Dione, join the planet and its rings in this view from NASA Cassini spacecraft. Rhea and Dione are respectively the second and fourth largest moons of Saturn, but they are tiny compared to the planet.

The diminutive moon Mimas can be found hiding in the middle of this view of a crescent of Saturn bisected by rings in this image captured by NASA Cassini spacecraft. Mimas appears as a dark speck just about the ringplane near the center of the image. Th

Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are known as the jovian Jupiter-like planets because they are all gigantic compared with Earth, and they have a gaseous nature. This diagram shows the approximate distance of the jovian planets from the Sun.
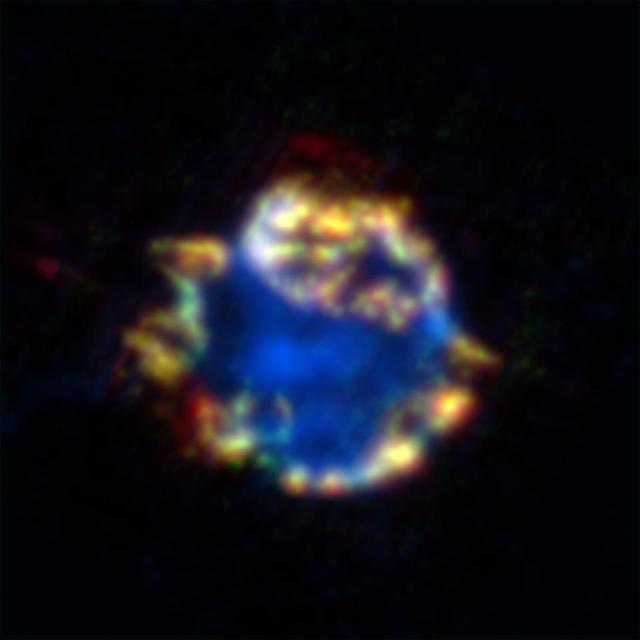
NASA Spitzer Space Telescope used its infrared camera to image this beautiful bulb which might look like a Christmas ornament but is the blown-out remains of a stellar explosion, or supernova.
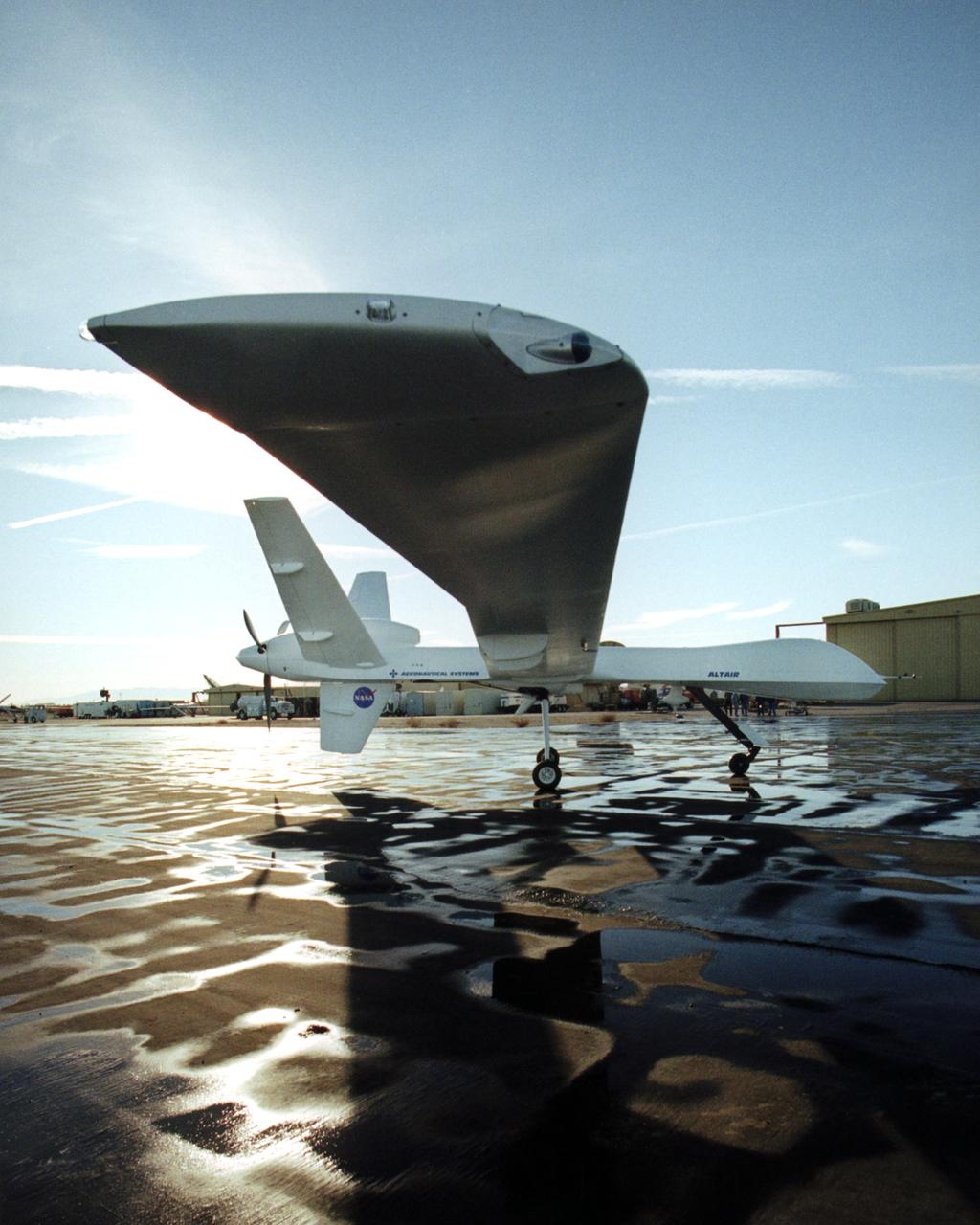

The Altair, a civil variant of the QM-9 Predator B unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), shows off its lengthy high-aspect ratio wing while on the ramp at General Atomics Aeronautical Systems' flight test facility at El Mirage, California.
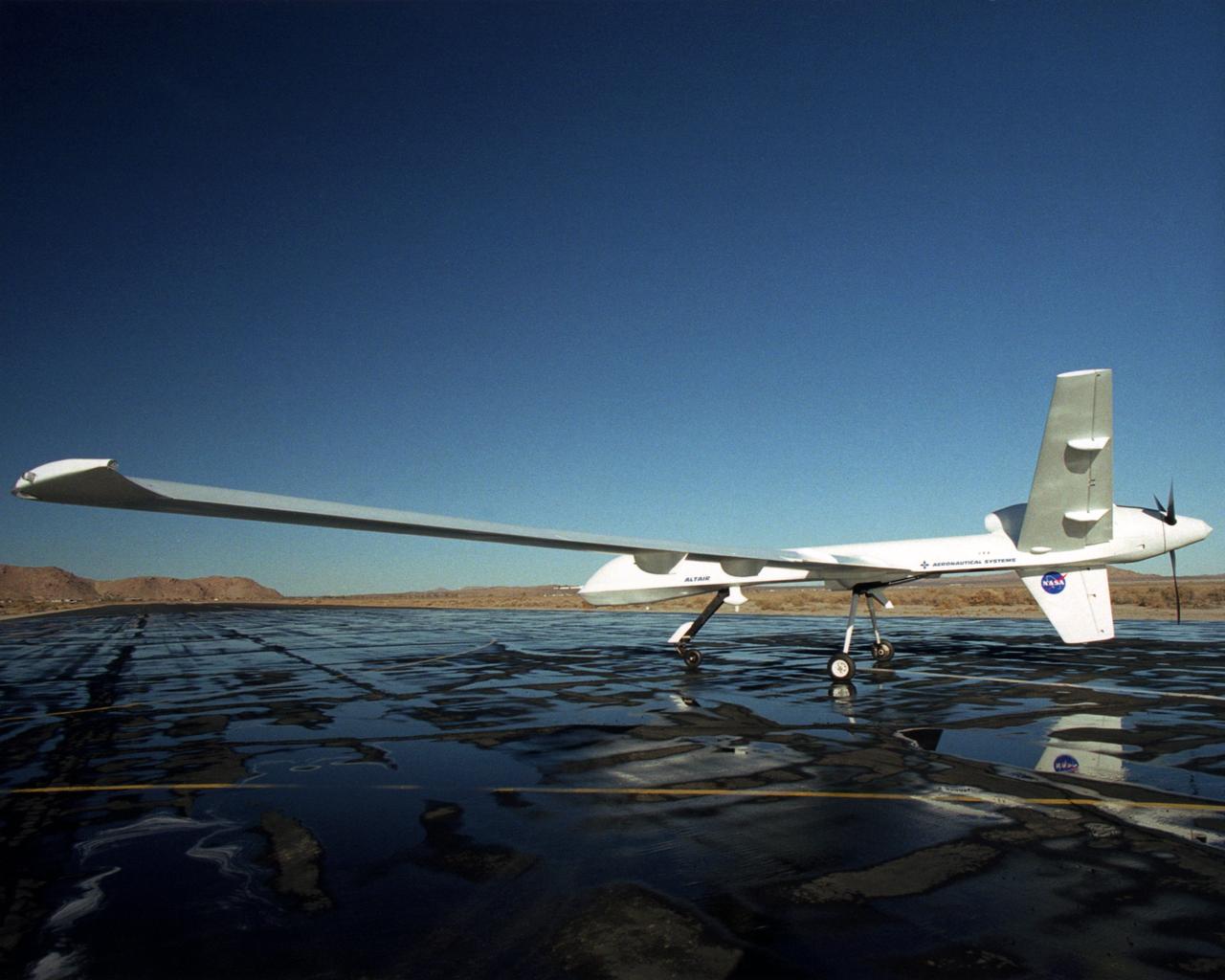

Long wings, a V-tail with a ventral fin and a rear-mounted engine distinguish the Altair, an unmanned aerial vehicle built for NASA by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
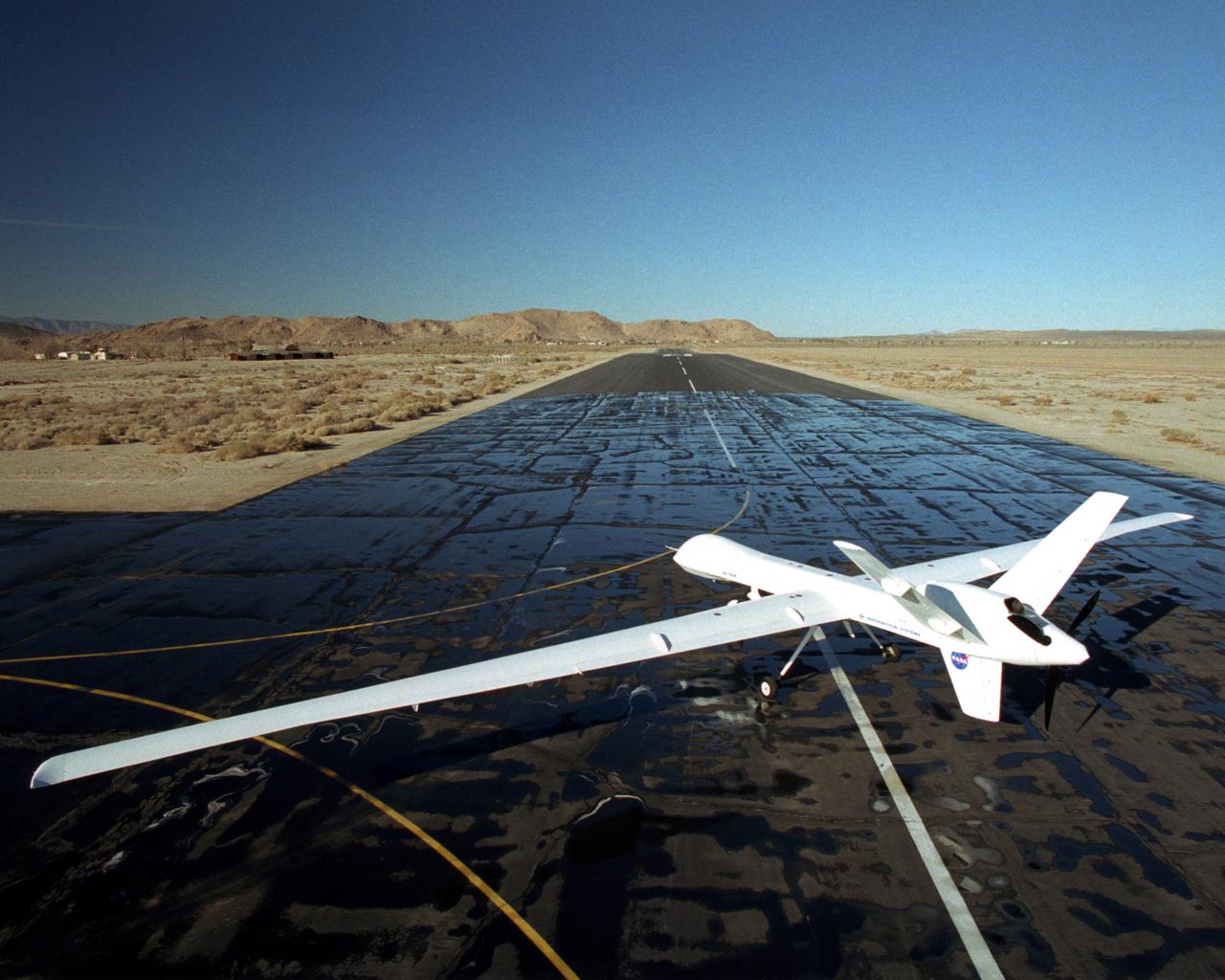

The long, narrow wings of NASA's Altair are designed to allow the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) to maintain long-duration flight at high altitudes.
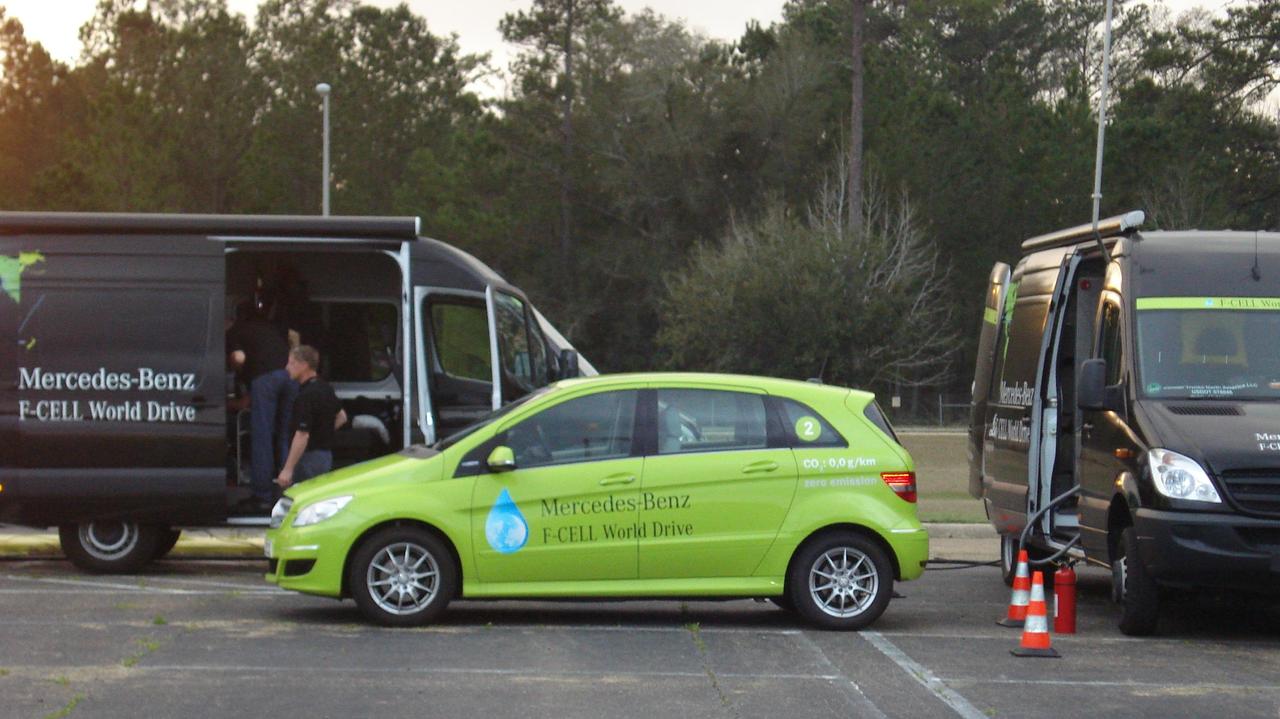

John C. Stennis Space Center, America's largest rocket engine test complex, and one of the country's leading consumers of liquid hydrogen, was the location Feb. 27 for a fuel stop of three Mercedes B-Class F-CELL vehicles. The B-Class F-CELL is an electric vehicle, which is powered by electricity produced on board the vehicle from hydrogen gas. The only emission by this unique vehicle is pure water vapor. Due to the limited number of existing hydrogen locations, Stennis Space Center provided a logical choice for a refueling location as the vehicle made its way across the United States as part of a worldwide tour.
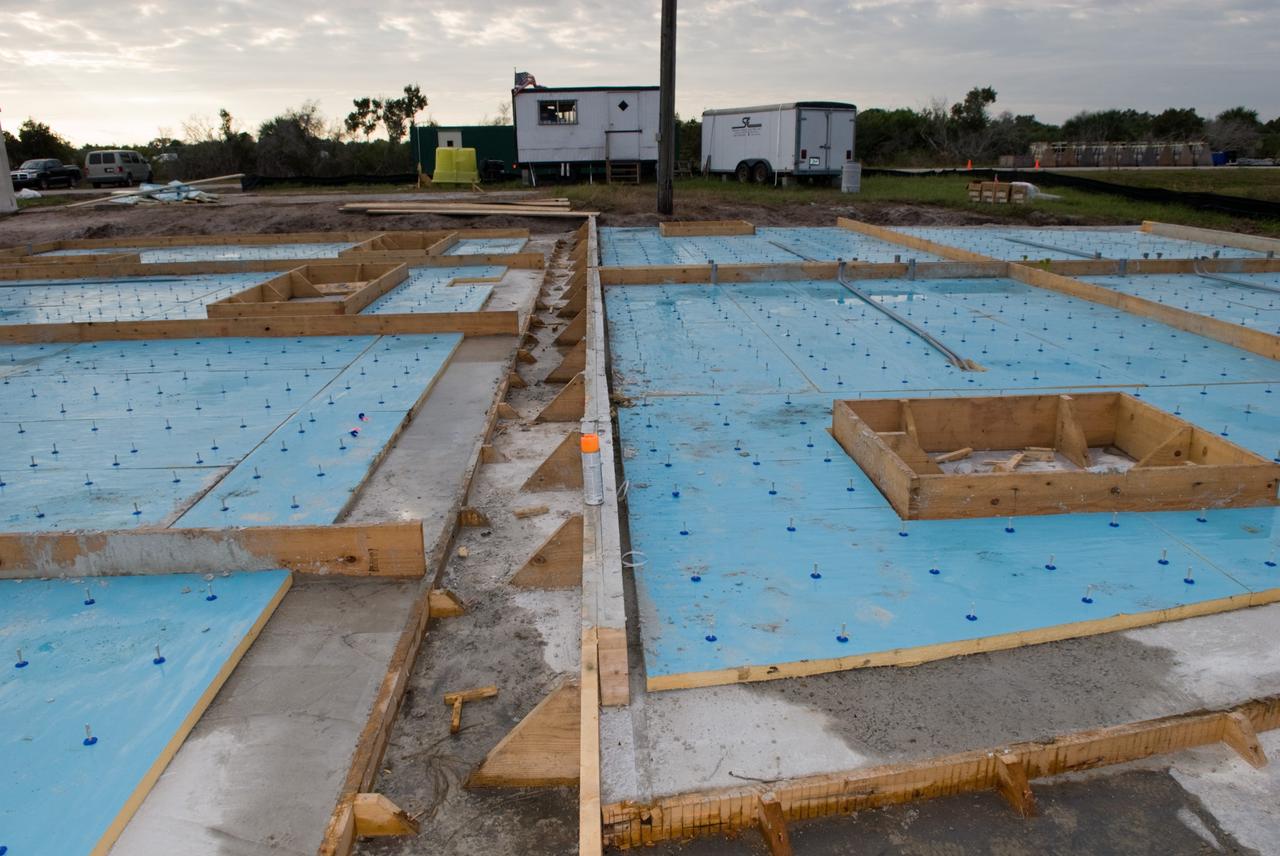

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Construction of the Propellants North Administrative and Maintenance Facility begins in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The facility will have a two-story administrative building to house managers, mechanics and technicians who fuel spacecraft at Kennedy adjacent to an 1,800-square-foot single-story shop to store cryogenic fuel transfer equipment. The new facility will feature high-efficiency roofs and walls, “Cool Dry Quiet” air conditioning with energy recovery technology, efficient lighting, and other sustainable features. The facility is striving to qualify for the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, or LEED, Platinum certification. If successful, Propellants North will be the first Kennedy facility to achieve this highest of LEED ratings after it is completed in the summer of 2010. The facility was designed for NASA by Jones Edmunds and Associates. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
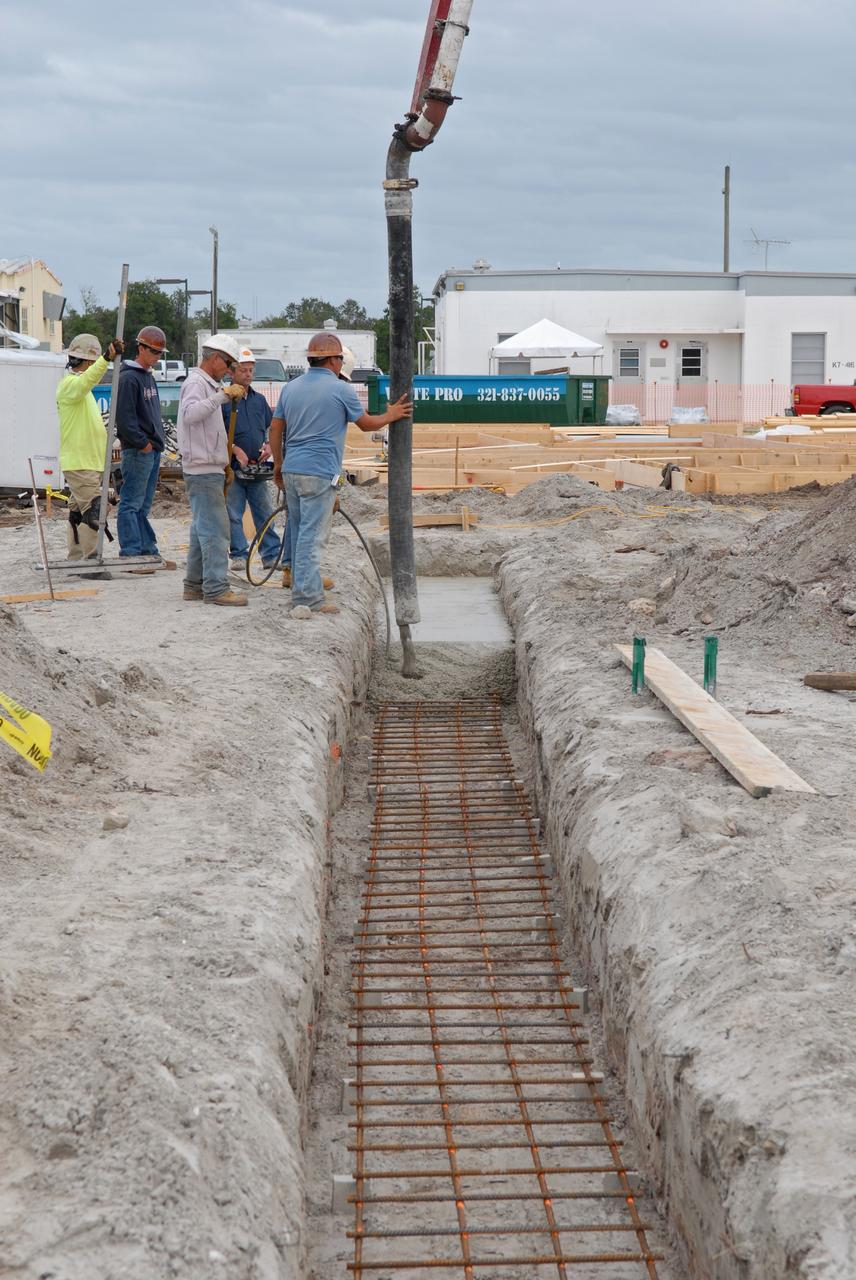

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Insulation is placed in the walls for the Propellants North Administrative and Maintenance Facility in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A tilt-up construction method is being used to erect a THERMOMASS concrete wall insulation system for the facility's walls. In this approach, the exterior layer of concrete for the wall panels is poured and leveled on the building's footprint. Then, prefabricated, predrilled insulation sheets are arranged on top of the unhardened concrete, and connectors, designed to hold the sandwiched layers of concrete and insulation secure, are inserted through the predrilled holes. Next, the structural wythe is poured. Once cured, these panels are lifted upright to form the building's envelope. The facility will have a two-story administrative building to house managers, mechanics and technicians who fuel spacecraft at Kennedy adjacent to an 1,800-square-foot single-story shop to store cryogenic fuel transfer equipment. The new facility will feature high-efficiency roofs and walls, “Cool Dry Quiet” air conditioning with energy recovery technology, efficient lighting, and other sustainable features. The facility is striving to qualify for the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, or LEED, Platinum certification. If successful, Propellants North will be the first Kennedy facility to achieve this highest of LEED ratings after it is completed in the summer of 2010. The facility was designed for NASA by Jones Edmunds and Associates. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
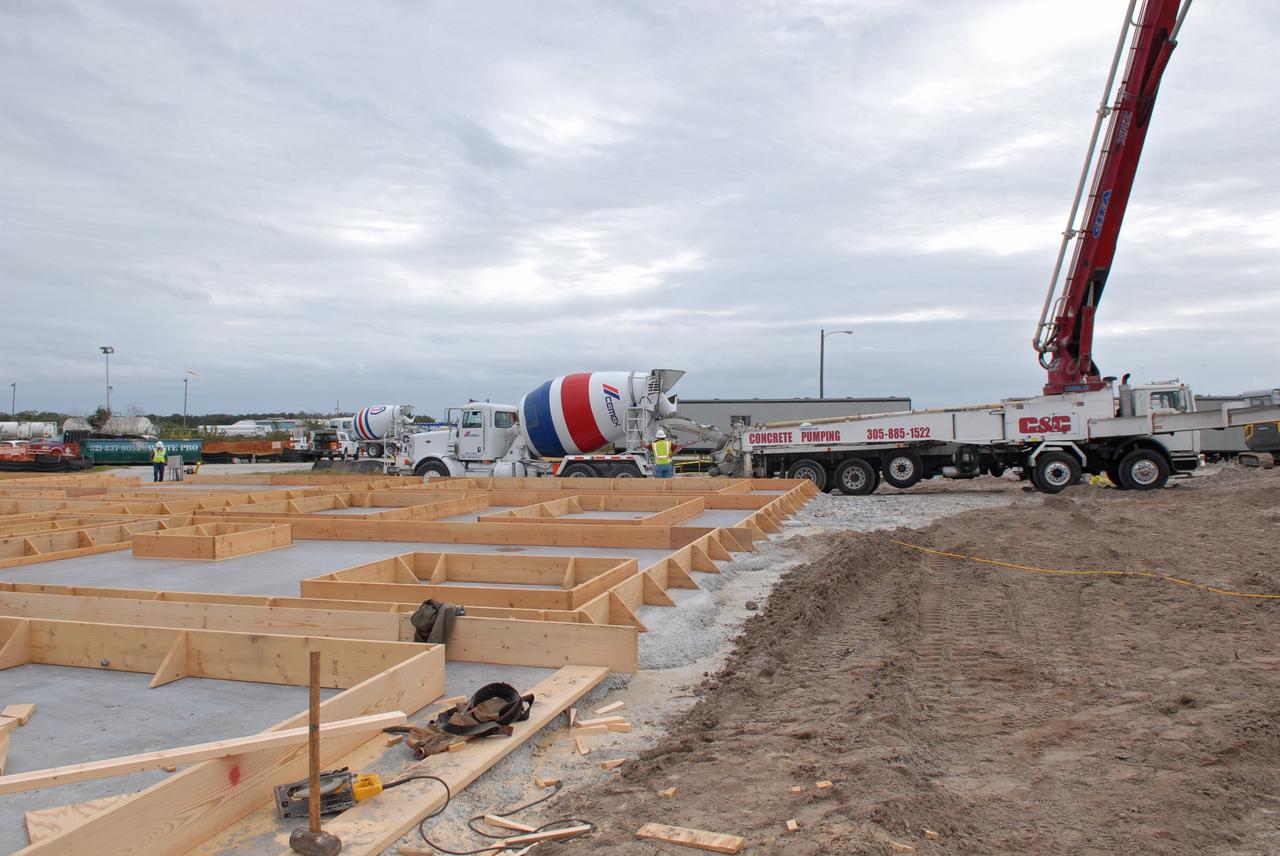

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Construction of the walls for the Propellants North Administrative and Maintenance Facility begins in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A tilt-up construction method is being used to erect a THERMOMASS concrete wall insulation system for the facility's walls. In this approach, the exterior layer of concrete for the wall panels is poured and leveled on the building's footprint. Then, prefabricated, predrilled insulation sheets are arranged on top of the unhardened concrete, and connectors, designed to hold the sandwiched layers of concrete and insulation secure, are inserted through the predrilled holes. Next, the structural wythe is poured. Once cured, these panels are lifted upright to form the building's envelope. The facility will have a two-story administrative building to house managers, mechanics and technicians who fuel spacecraft at Kennedy adjacent to an 1,800-square-foot single-story shop to store cryogenic fuel transfer equipment. The new facility will feature high-efficiency roofs and walls, “Cool Dry Quiet” air conditioning with energy recovery technology, efficient lighting, and other sustainable features. The facility is striving to qualify for the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, or LEED, Platinum certification. If successful, Propellants North will be the first Kennedy facility to achieve this highest of LEED ratings after it is completed in the summer of 2010. The facility was designed for NASA by Jones Edmunds and Associates. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
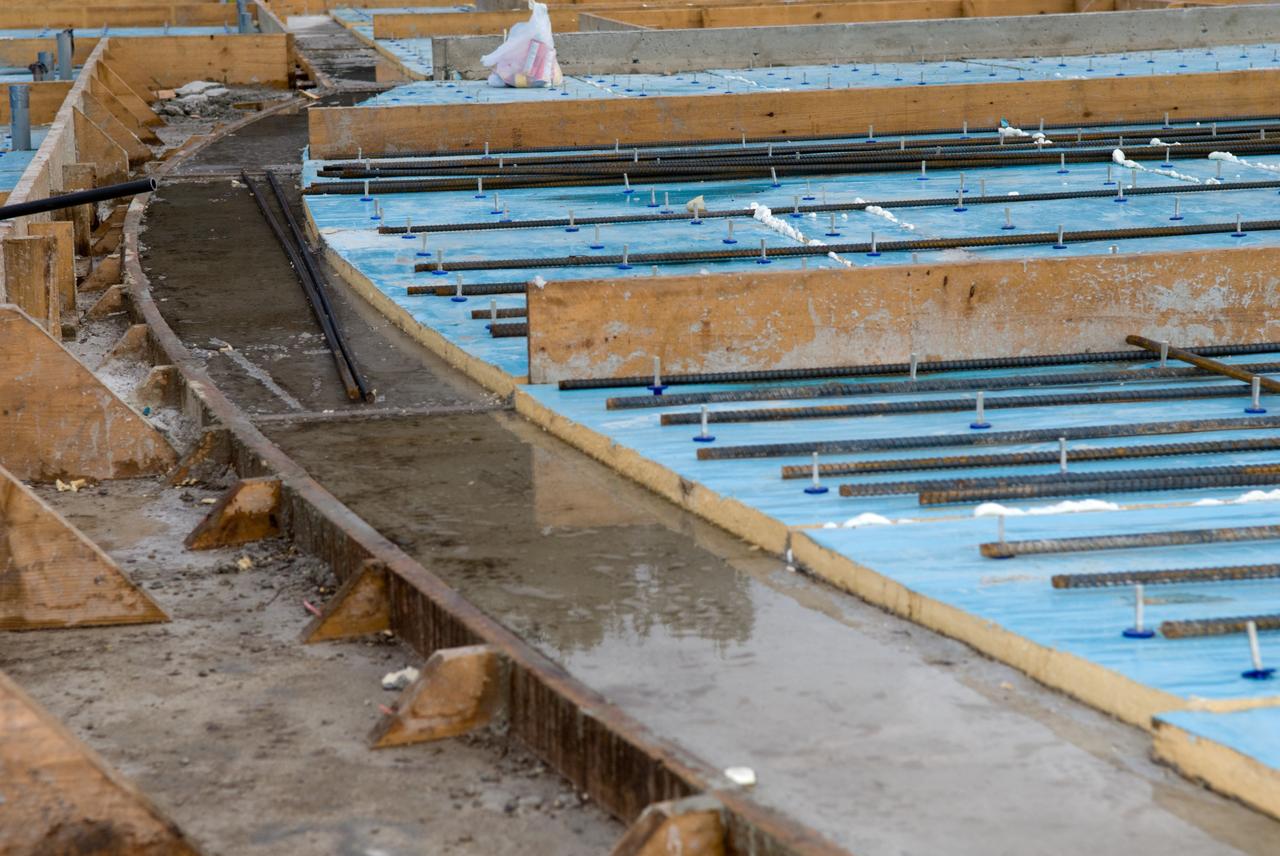

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Trenches are prepared to support the walls of the Propellants North Administrative and Maintenance Facility in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The facility will have a two-story administrative building to house managers, mechanics and technicians who fuel spacecraft at Kennedy adjacent to an 1,800-square-foot single-story shop to store cryogenic fuel transfer equipment. The new facility will feature high-efficiency roofs and walls, “Cool Dry Quiet” air conditioning with energy recovery technology, efficient lighting, and other sustainable features. The facility is striving to qualify for the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, or LEED, Platinum certification. If successful, Propellants North will be the first Kennedy facility to achieve this highest of LEED ratings after it is completed in the summer of 2010. The facility was designed for NASA by Jones Edmunds and Associates. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

NASA and the European Space Agency are jointly developing the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter mission for launch in 2016.
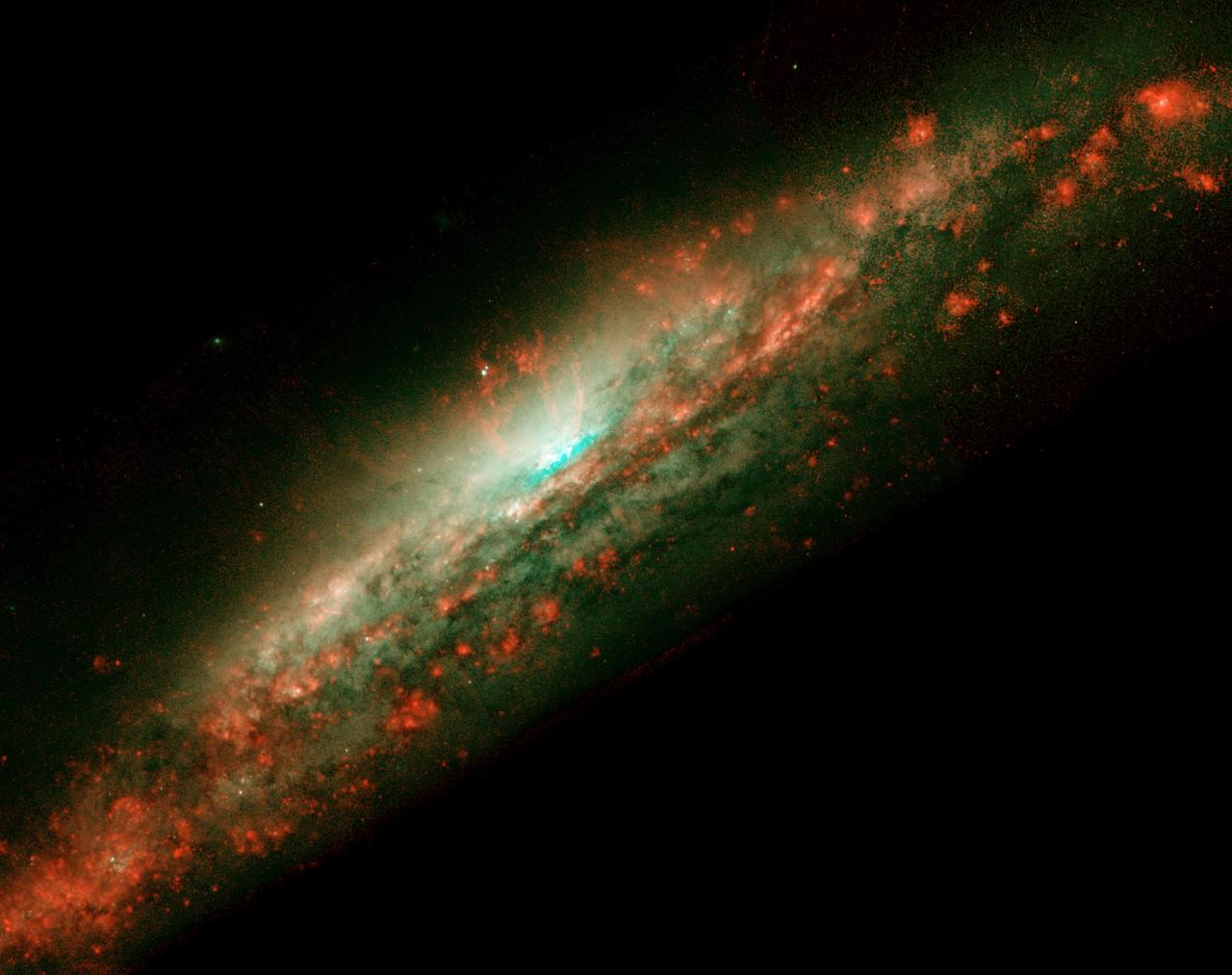

A lumpy bubble of hot gas rises from a cauldron of glowing matter in a distant galaxy, as seen by NASA Hubble Space Telescope.
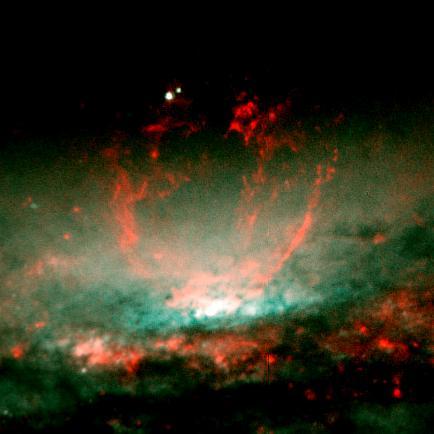
A lumpy bubble of hot gas rises from a cauldron of glowing matter in a distant galaxy, as seen by NASA Hubble Space Telescope.
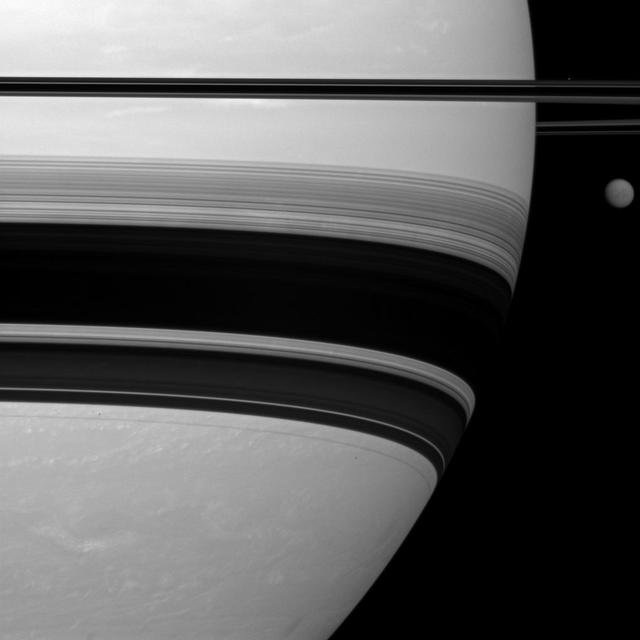

Saturn largest moon, Titan, looks small here, pictured to the right of the gas giant as seen by NASA Cassini spacecraft.
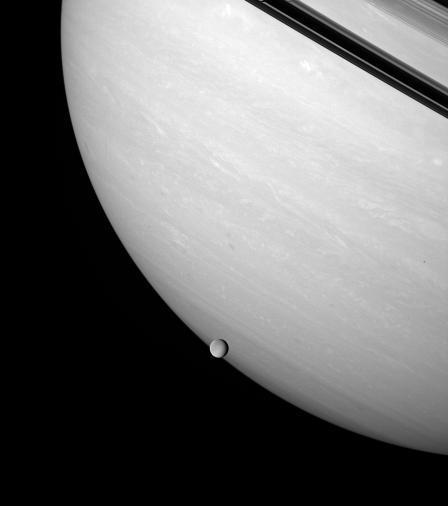

Rhea brushes the stormy face of Saturn, an airless ice orb against the feathery bands of a gas giant

Held in gravity embrace, Saturn darkened, icy rings encircle the clouded gas giant

Artist concept illustrates a quasar, or feeding black hole, similar to APM 08279+5255, where astronomers discovered huge amounts of water vapor. Gas and dust likely form a torus around the central black hole, with clouds of charged gas above and below.

These four images show an artist's impression of gas accreting onto the neutron star in the binary system MXB 1730-335, also known as the "Rapid Burster." In such a binary system, the gravitational pull of the dense neutron star is stripping gas away from its stellar companion (a low-mass star, not shown in these images). The gas forms an accretion disk and spirals towards the neutron star. Observations of the Rapid Burster using three X-ray space telescopes -- NASA's NuSTAR and Swift, and ESA's XMM-Newton -- have revealed what happens around the neutron star before and during a so-called "type-II" burst. These bursts are sudden, erratic and extremely intense releases of X-rays that liberate enormous amounts of energy during periods when very little emission occurs otherwise. Before the burst, the fast-spinning magnetic field of the neutron star keeps the gas flowing from the companion star at bay, preventing it from reaching closer to the neutron star and effectively creating an inner edge at the center of the disk (Figure 1, panel 1). During this phase, only small amounts of gas leak towards the neutron star. However, as the gas continues to flow and accumulate near this edge, it spins faster and faster. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21418
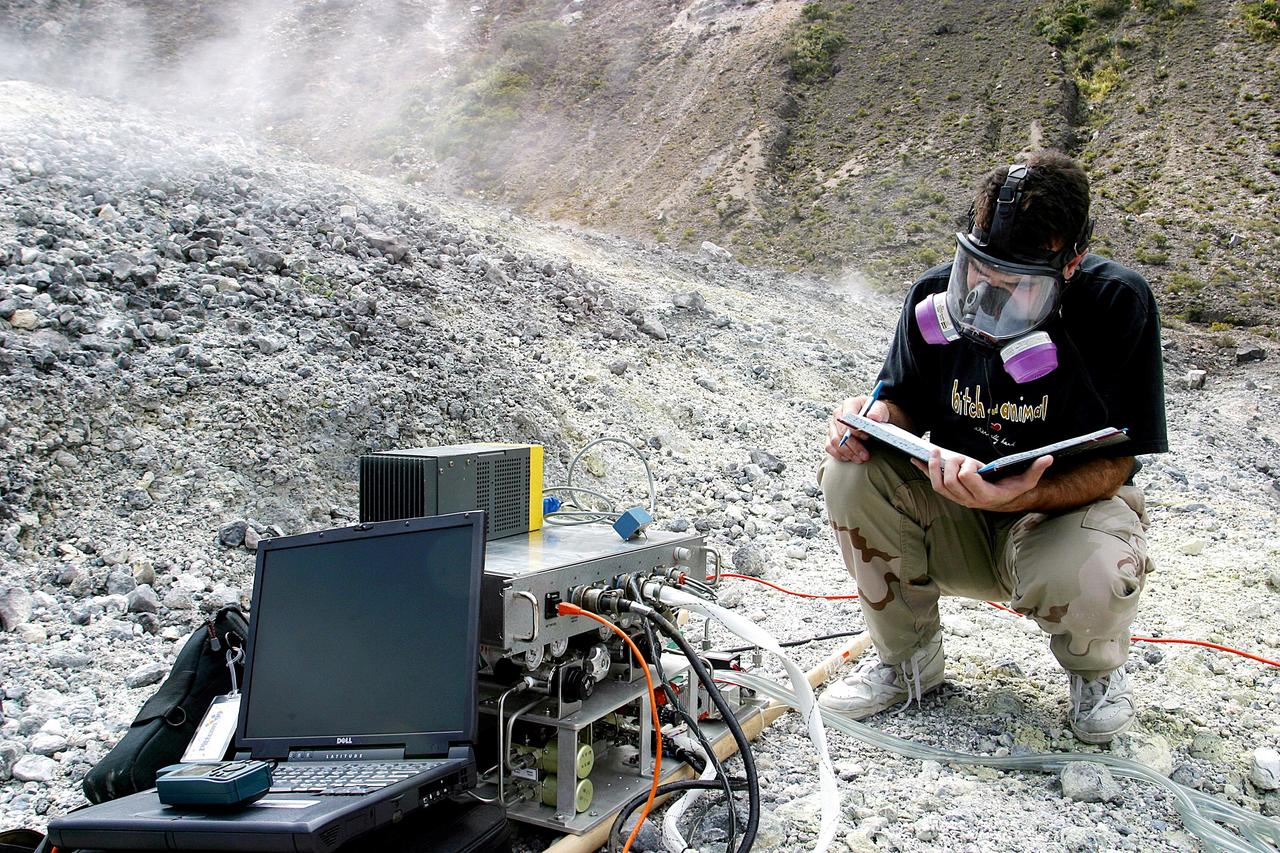

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Dr. Richard Arkin records data as the hazardous gas detection system AVEMS is used to analyze the toxic gases produced by active vents, called fumaroles, in the Turrialba volcano in Costa Rica. He is using the Aircraft-based Volcanic Emission Mass Spectrometer (AVEMS) that determines the presence and concentration of various chemicals. The AVEMS system has been developed for use in the Space Shuttle program, to detect toxic gas leaks and emissions in the Shuttle’s aft compartment and the crew compartment.

The turbulent atmosphere of a hot, gaseous planet known as HD 80606b is shown in this simulation based on data from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope.
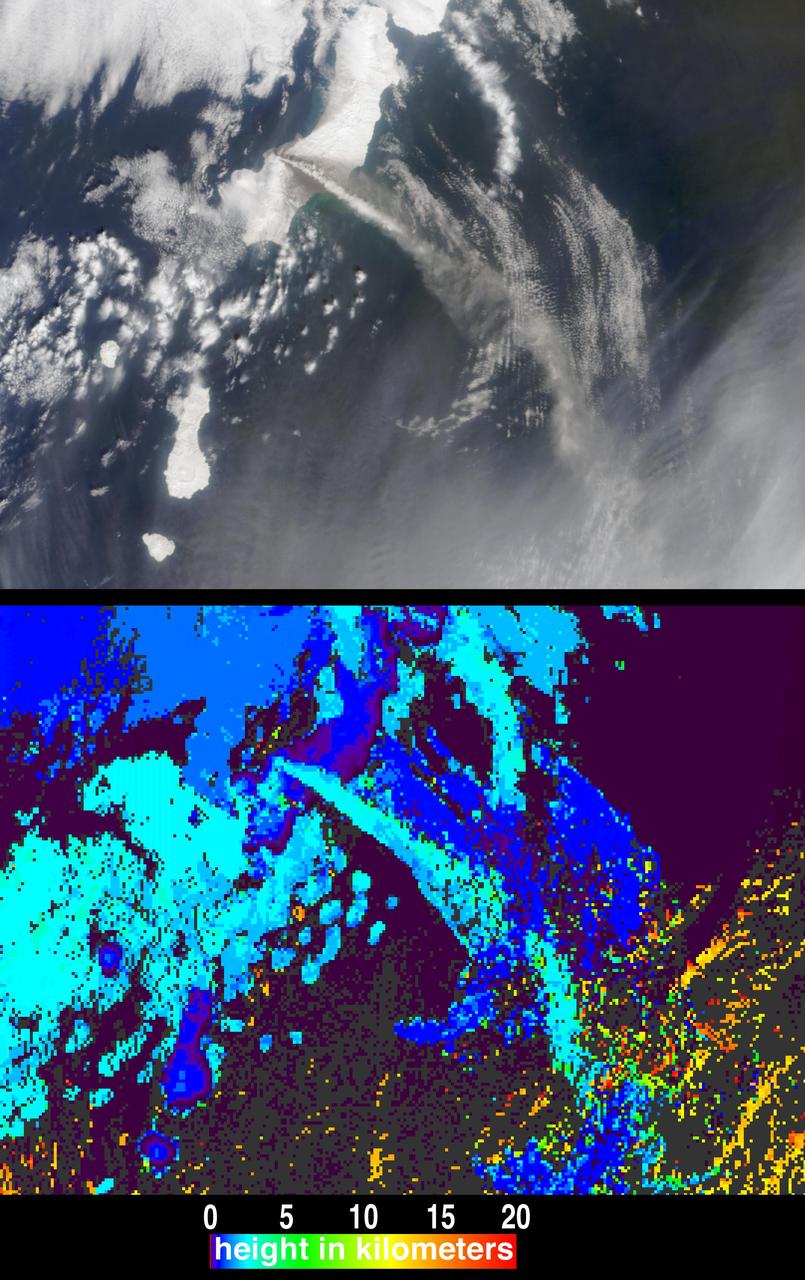
The height and motion of the ash and gas plume from the April 22, 2003, eruption of the Chikurachki volcano is portrayed in these views NASA Terra spacecraft.
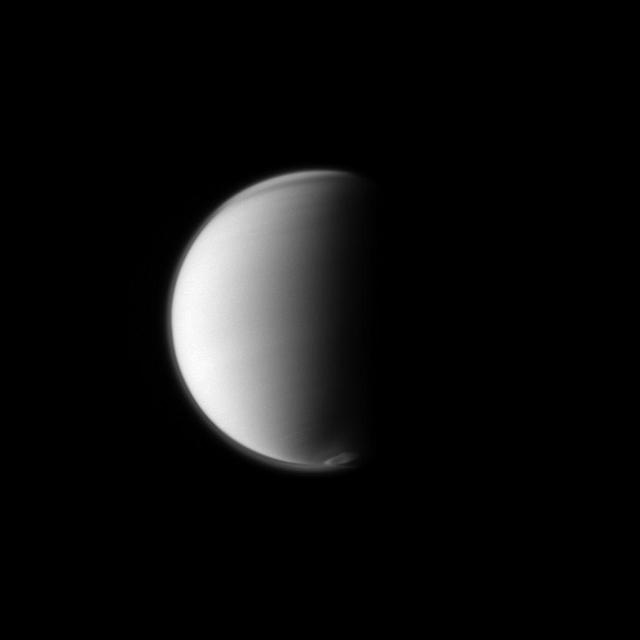
NASA Cassini spacecraft monitors Titan developing south polar vortex, which is a mass of swirling gas around the pole in the atmosphere of the moon.
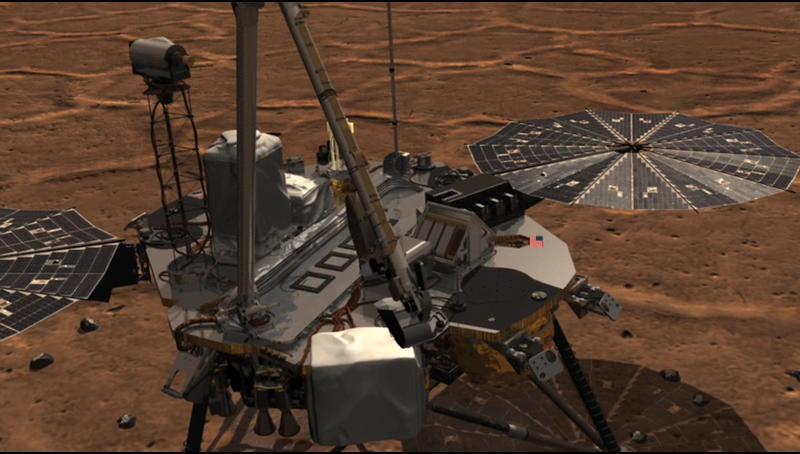

This image shows NASA Phoenix Lander Robotic Arm scoop delivering a sample to the Thermal and Evolved-Gas Analyzer TEGA and how samples are analyzed within the instrument.
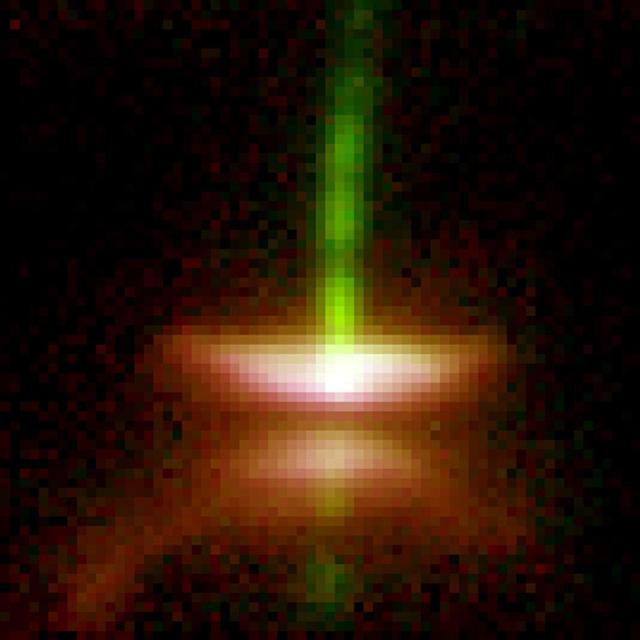

This image from NASA Hubble Space Telescope shows Herbig-Haro 30, the prototype of a gas-rich young stellar object disk around a star.
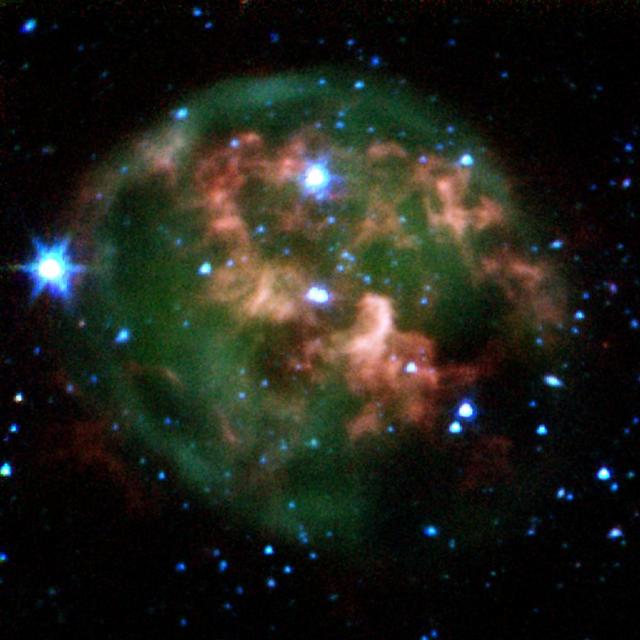

This false-color image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows a dying star center surrounded by a cloud of glowing gas and dust.

Violent gas collisions that produced supersonic shock fronts in a dying star are seen in a new, detailed image from NASA Hubble Space Telescope.

ESA Herschel Space Observatory found oxygen molecules in a dense patch of gas and dust adjacent to star-forming regions in the Orion nebula.
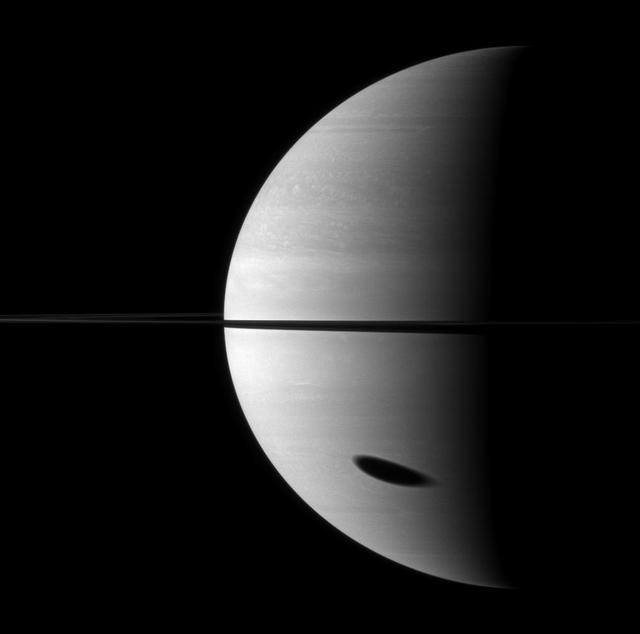

The shadow of Saturn largest moon darkens a huge portion of the gas giant planet. Titan is not pictured here, but its shadow is elongated in the bottom right of the image.