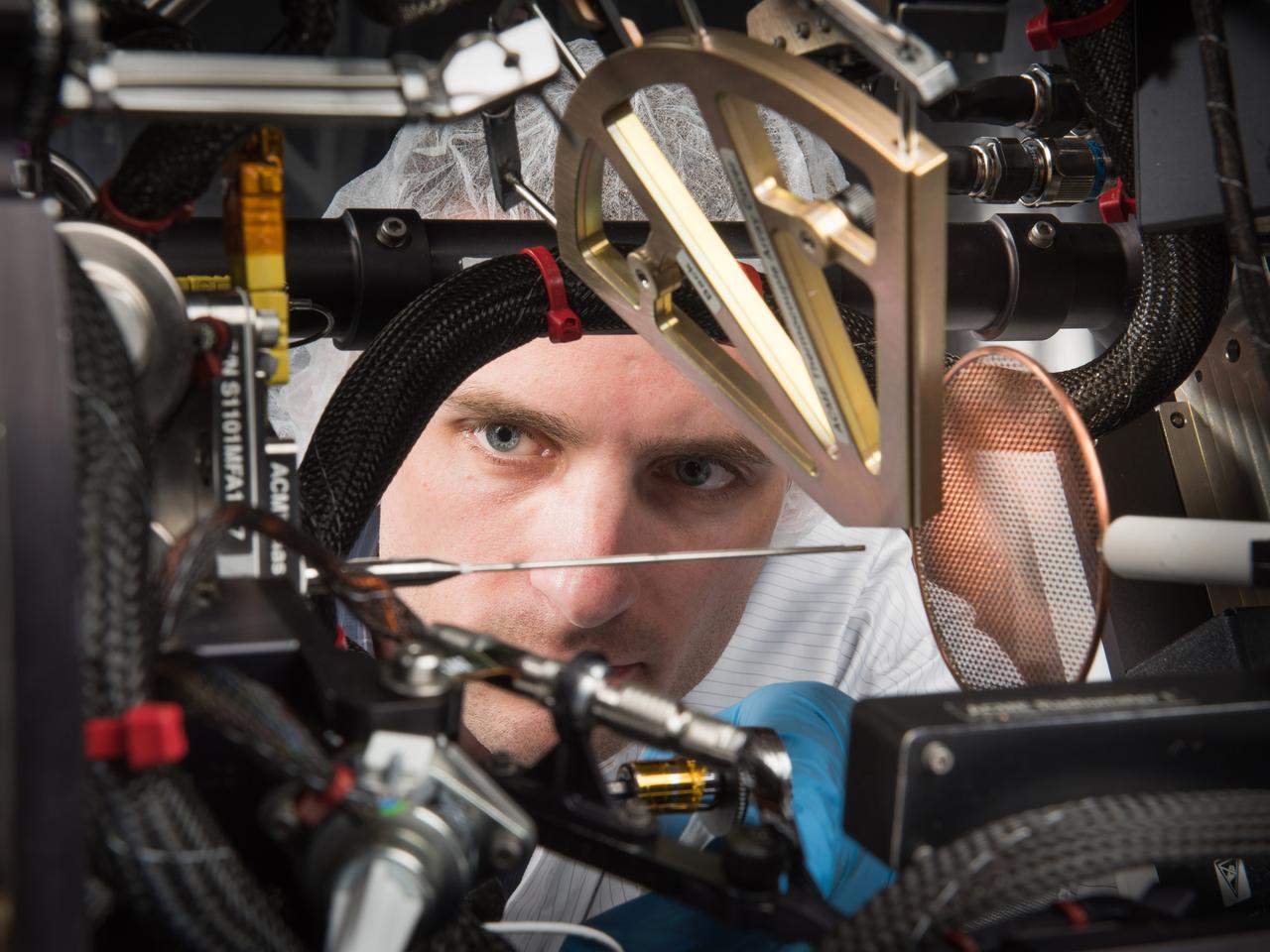

NASA Glenn engineer Christopher Mroczka inspects the gas-jet burner within the Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments, ACME insert for the Combustion Integrated Rack, CIR. The apparatus allows researchers to conduct experiments with flames of gaseous fuels on the International Space Station, ISS
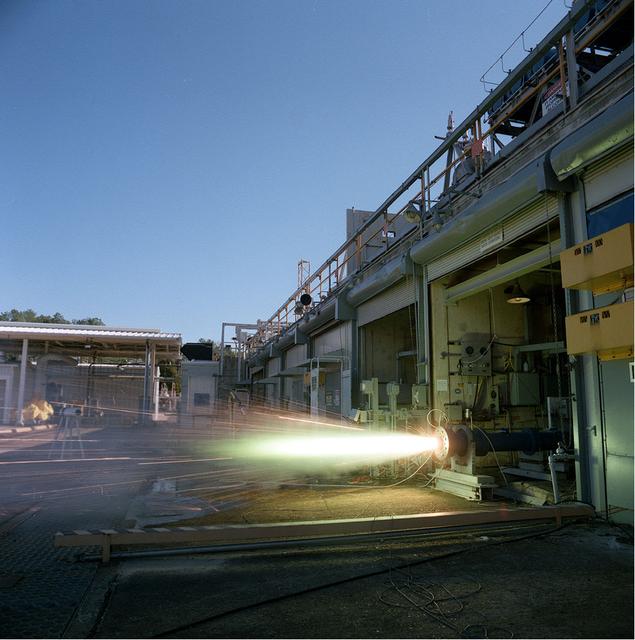

An eleven inch (11) hybrid motor gaseous oxygen (GOX) fuel firing at Marshall's test cell 103.
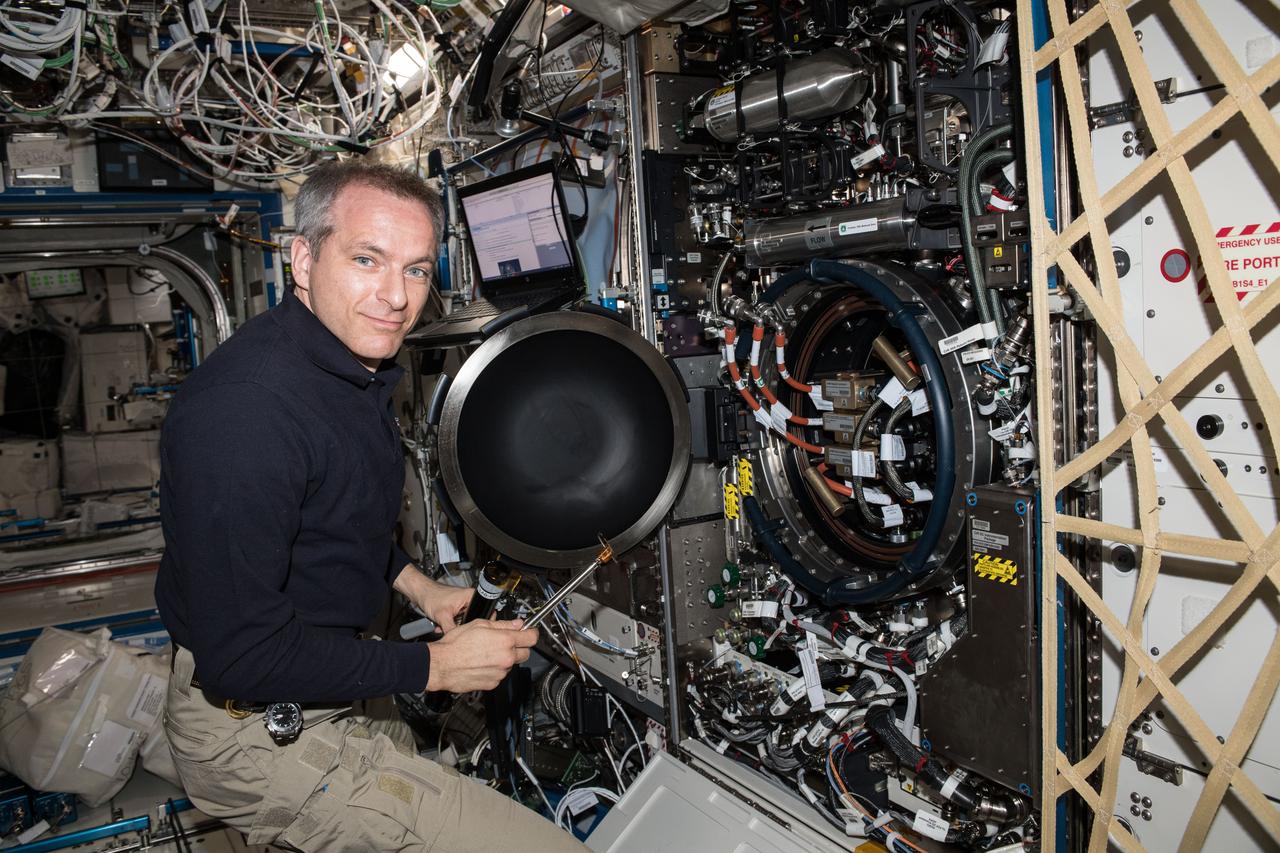

iss058e026380 (Feb. 26, 2019) --- Astronaut David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency is inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module working on the Combustion Integrated Rack. Saint-Jacques replaced fuel flow controllers inside the device for the Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments which are a set of five independent studies of gaseous flames.
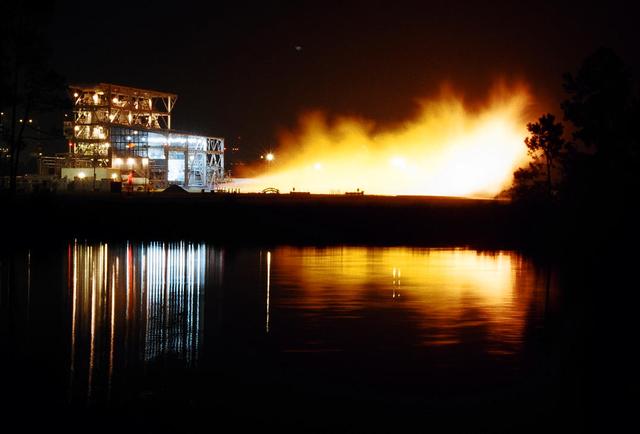

Gaseous hydrogen is burned off at the E1 Test Stand the night of Oct. 7 during a cold-flow test of the fuel turbopump of the Integrated Powerhead Demonstrator (IPD) at NASA Stennis Space Center (SSC). The gaseous hydrogen spins the pump's turbine during the test, which was conducted to verify the pump's performance. Engineers plan one more test before sending the pump to The Boeing Co. for inspection. It will then be returned to SSC for engine system assembly. The IPD is the first reusable hydrogen-fueled advanced engine in development since the Space Shuttle Main Engine.
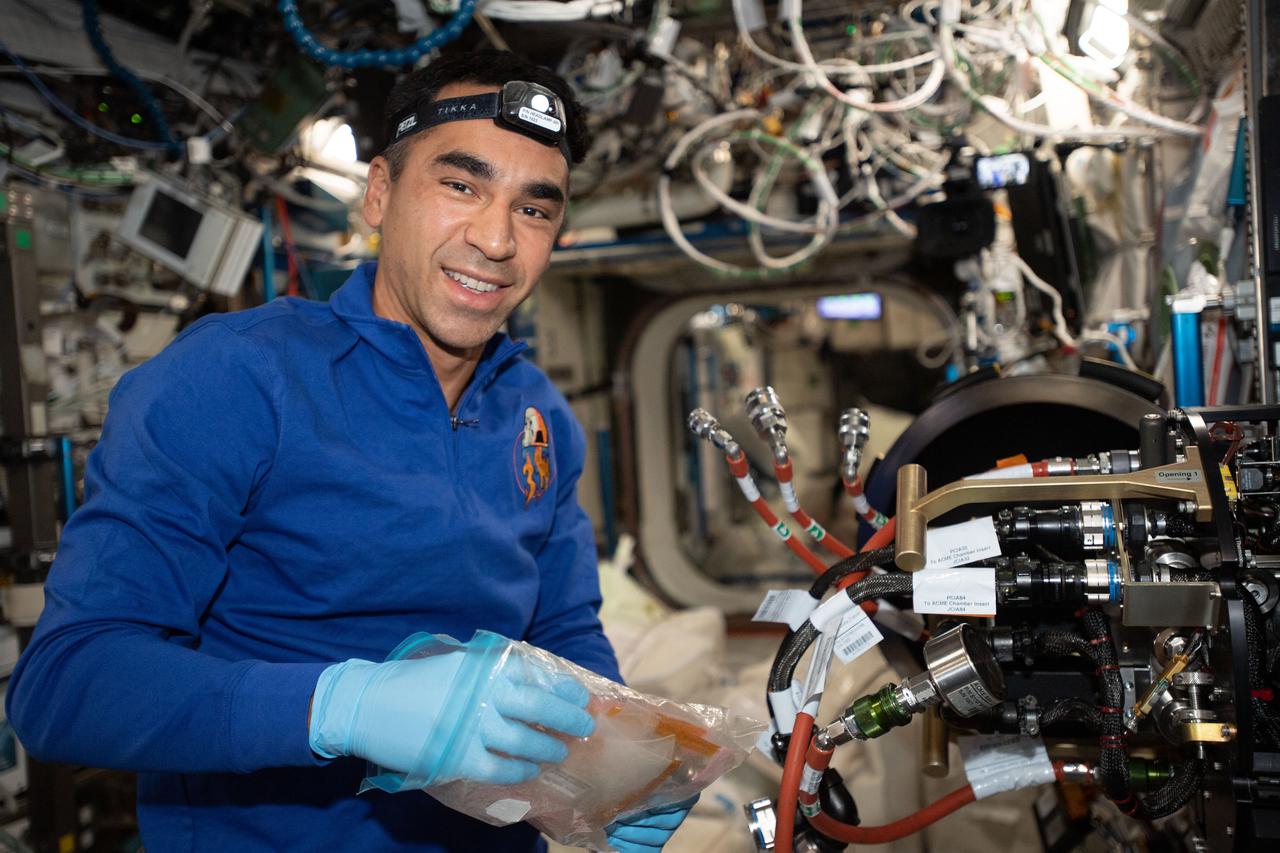

iss066e114415 (Jan. 6, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Raja Chari replaces hardware inside the Combustion Integrated Rack that supports the ACME (Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments) study. ACME is a series of six independent studies of gaseous flames seeking to improve fuel efficiency, reduce pollution, and promote spacecraft fire prevention.
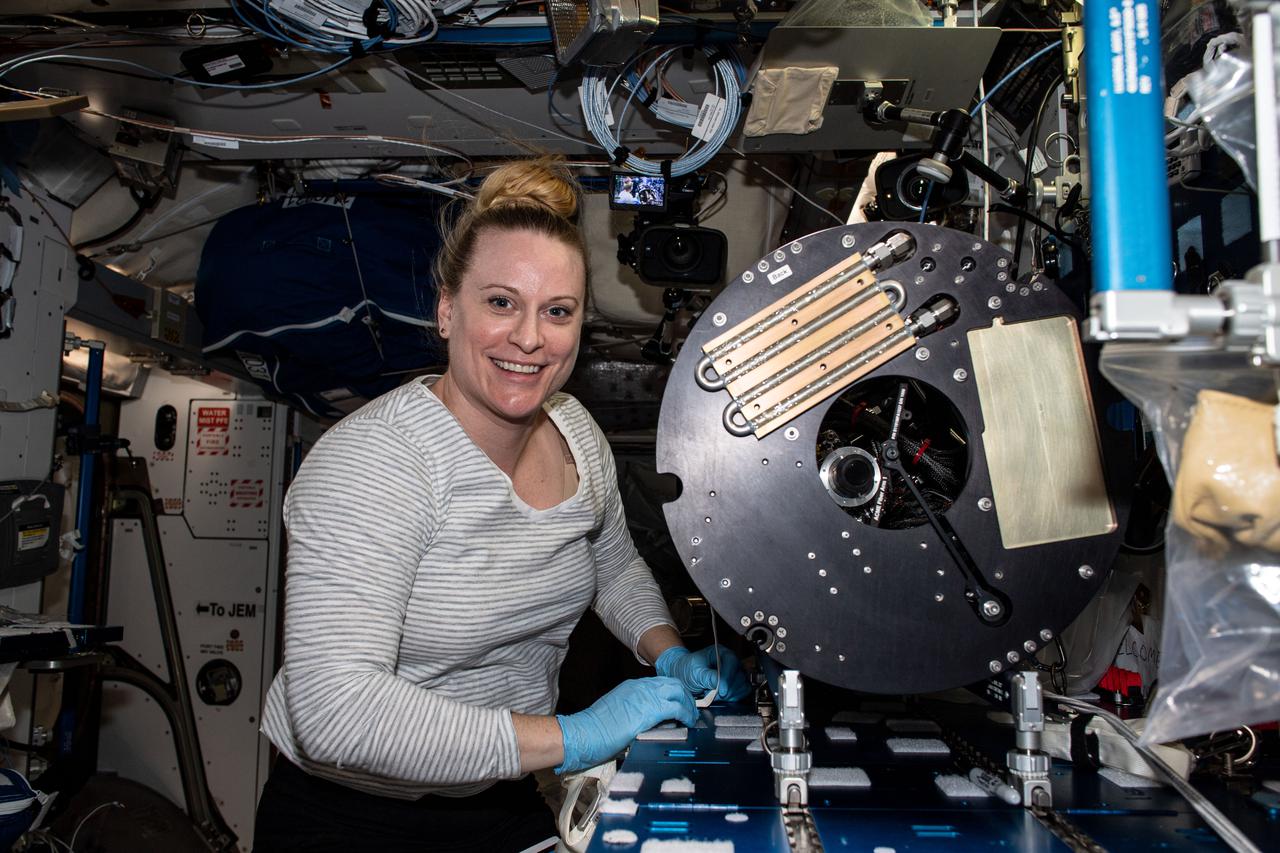

iss064e025973 (Jan., 25, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Kate Rubins services hardware inside the Unity module to support a suite of combustion investigations known as Advanced Combustion Microgravity Experiments, or ACME. The ACME project is a set of six independent studies of gaseous flames that may help to improve fuel efficiency, reduce pollution and prevent spacecraft fires.
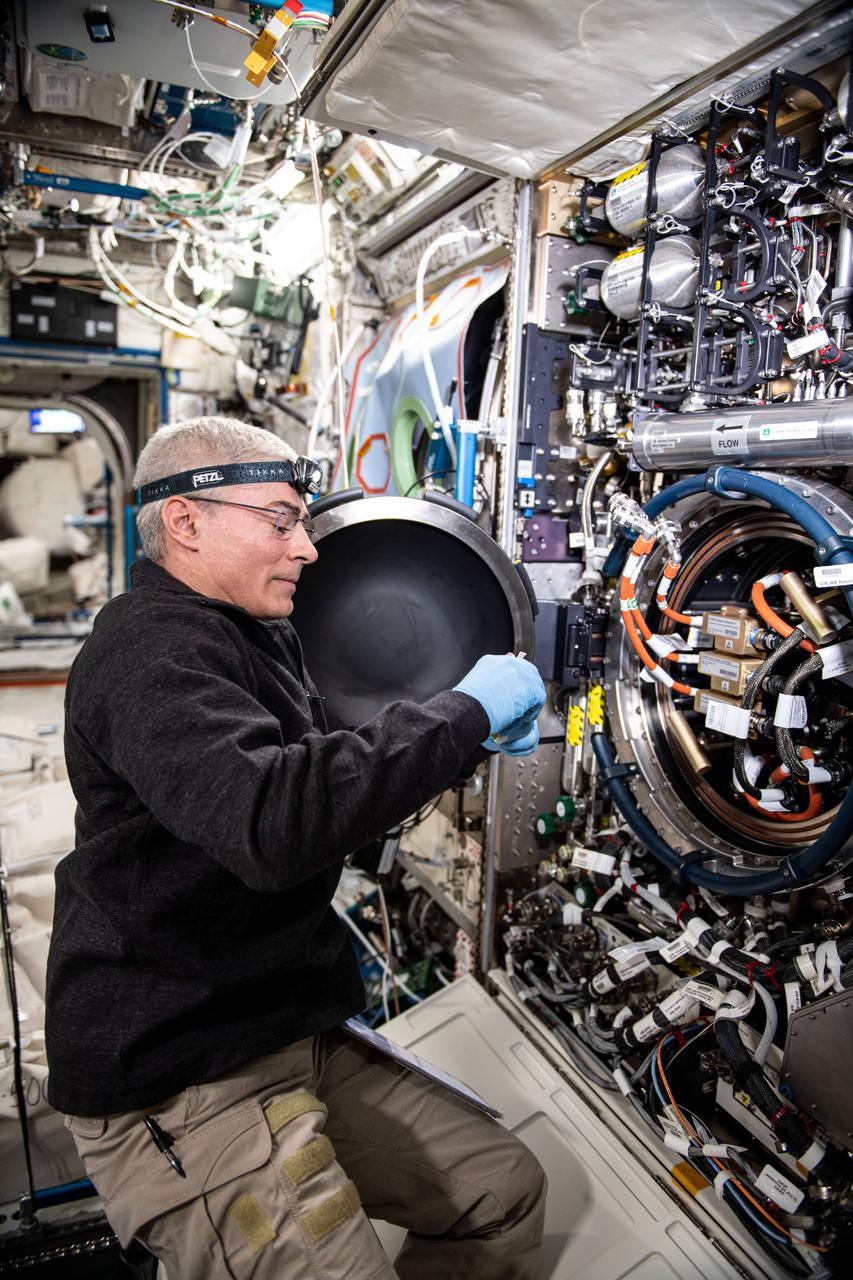

iss065e369687 (Sept. 8, 2021) ----NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei replaces an igniter inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Combustion Integrated Rack for the ACME series of space combustion studies. ACME, or the Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments, is a set of six independent studies of gaseous flames that seeks to improve fuel efficiency and reduce pollutants on Earth, and improve spacecraft fire prevention by focusing on decreasing the flammability of materials.
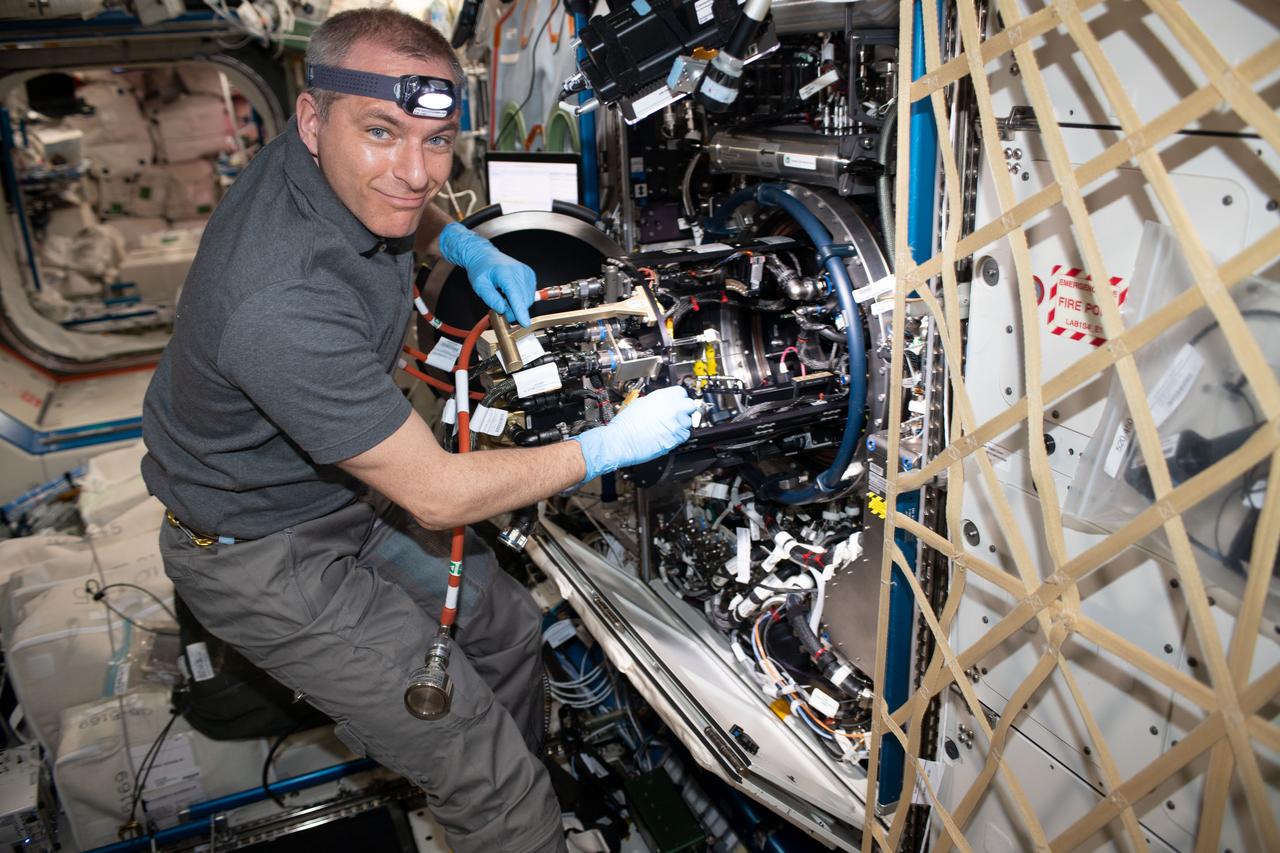

iss059e060847 (May 12, 2019) --- Astronaut David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency works on the Combustion Integrated Rack located inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module. Saint-Jacques was working on hardware supporting the Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments (ACME). ACME is a set of five independent studies of gaseous flames exploring improved fuel efficiency, reduced pollution and spacecraft fire prevention.
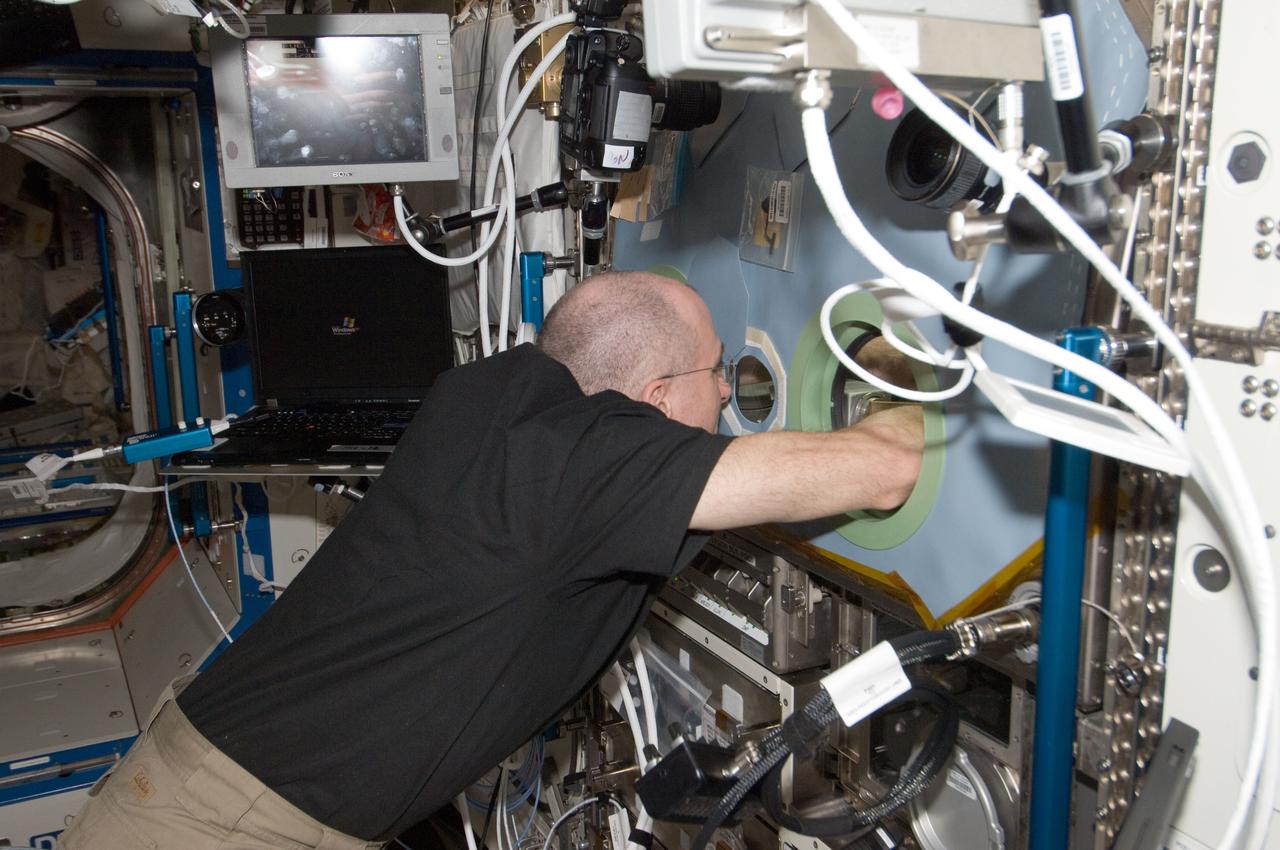

ISS030-E-178648 (30 March 2012) --- NASA astronaut Don Pettit, Expedition 30 flight engineer, performs a session of Burning and Suppression of Solids (BASS) fire safety tests at the Microgravity Sciences Glovebox (MSG) in the International Space Station?s Destiny laboratory. BASS uses Smoke Point in Coflow Experiment (SPICE) equipment but burns solid fuel samples instead of gaseous jets.
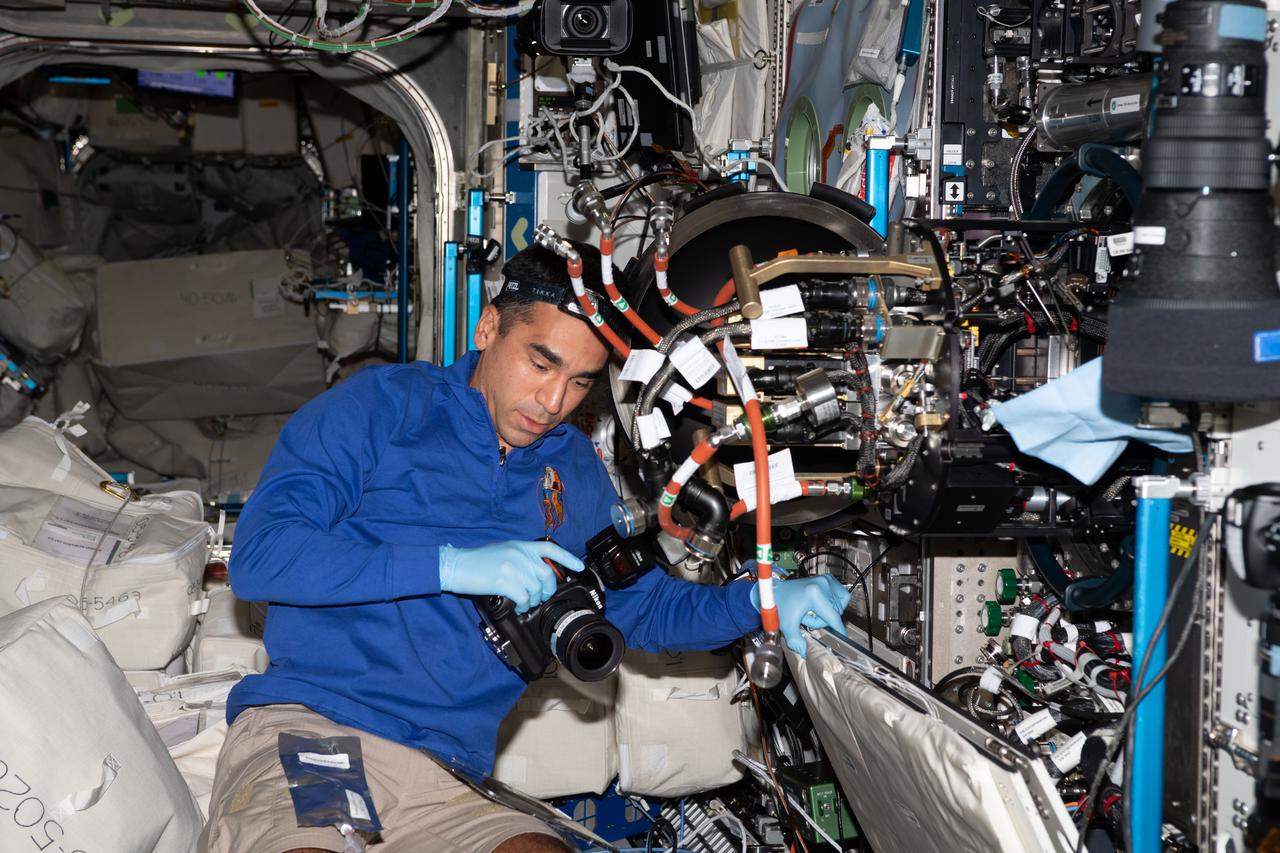

iss066e114301 (Jan. 17, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Raja Chari replaces hardware inside the Combustion Integrated Rack that supports the ACME (Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments) study. ACME is a series of six independent studies of gaseous flames seeking to improve fuel efficiency, reduce pollution, and promote spacecraft fire prevention.
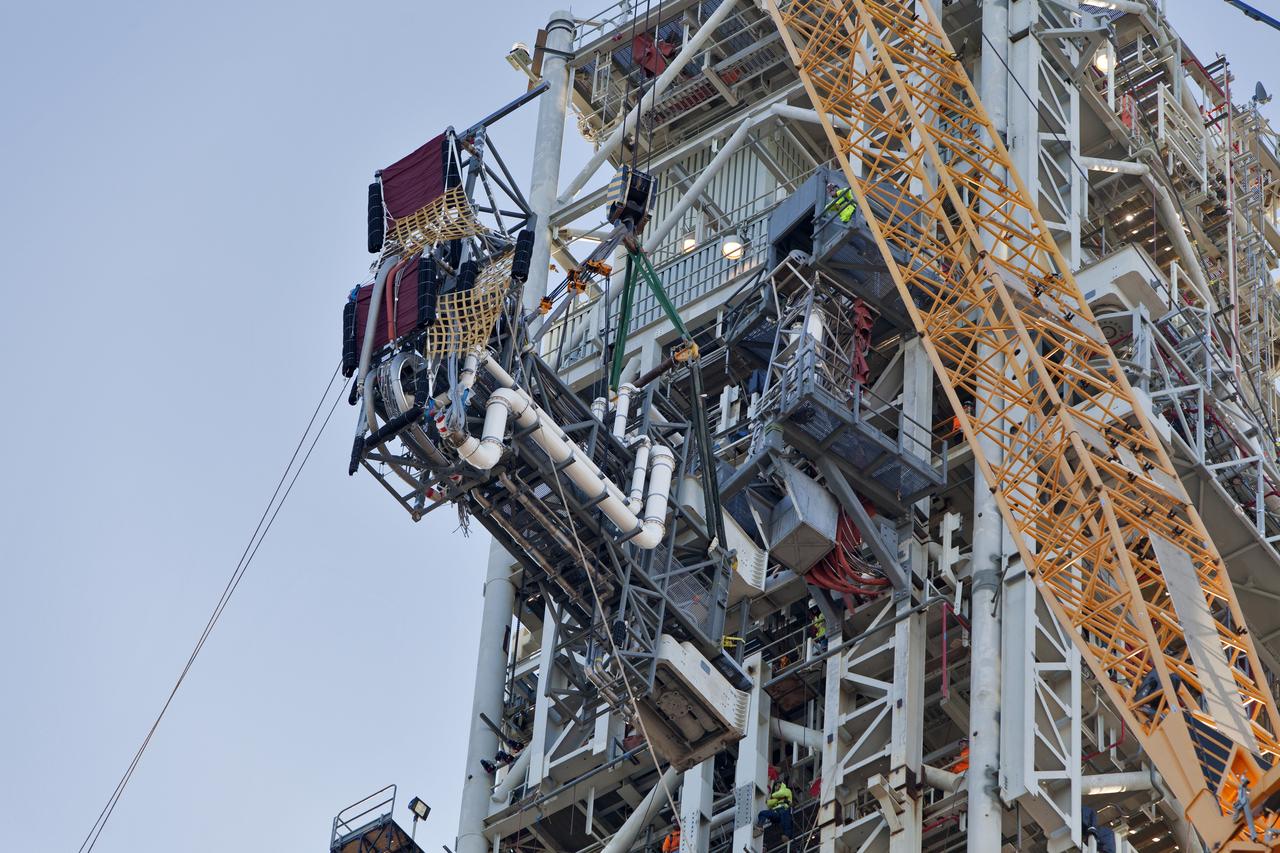

A crane and rigging lines are used to install the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical (ICPSU) high up on the mobile launcher (ML) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The last of the large umbilicals to be installed, the ICPSU will provide super-cooled hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket's interim cryogenic propulsion stage, or upper stage, at T-0 for Exploration Mission-1. The umbilical is located at about the 240-foot-level of the mobile launcher and will supply fuel, oxidizer, gaseous helium, hazardous gas leak detection, electrical commodities and environment control systems to the upper stage of the SLS rocket during launch. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of the umbilicals on the ML.
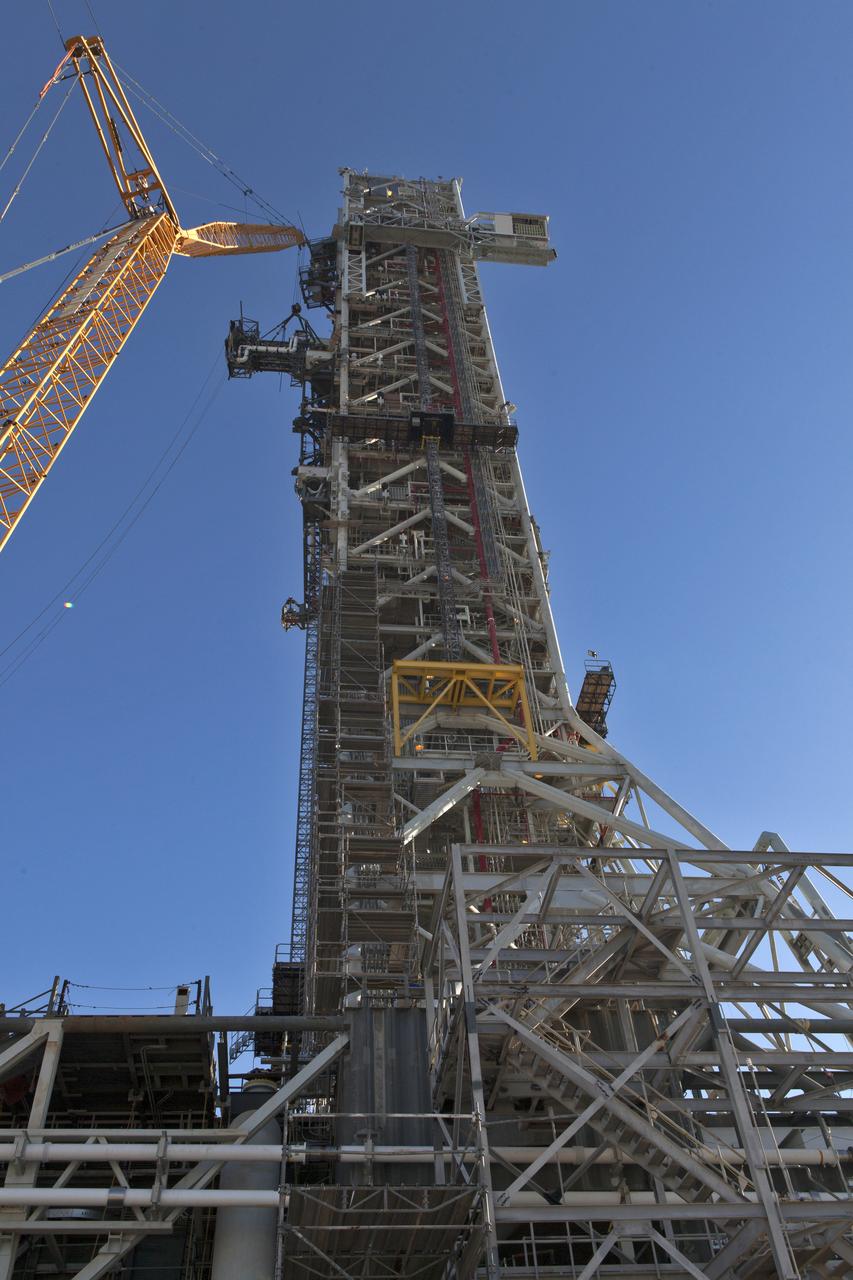

A crane and rigging lines are used to install the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical (ICPSU) high up on the mobile launcher (ML) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The last of the large umbilicals to be installed, the ICPSU will provide super-cooled hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket's interim cryogenic propulsion stage, or upper stage, at T-0 for Exploration Mission-1. The umbilical is located at about the 240-foot-level of the mobile launcher and will supply fuel, oxidizer, gaseous helium, hazardous gas leak detection, electrical commodities and environment control systems to the upper stage of the SLS rocket during launch. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of the umbilicals on the ML.
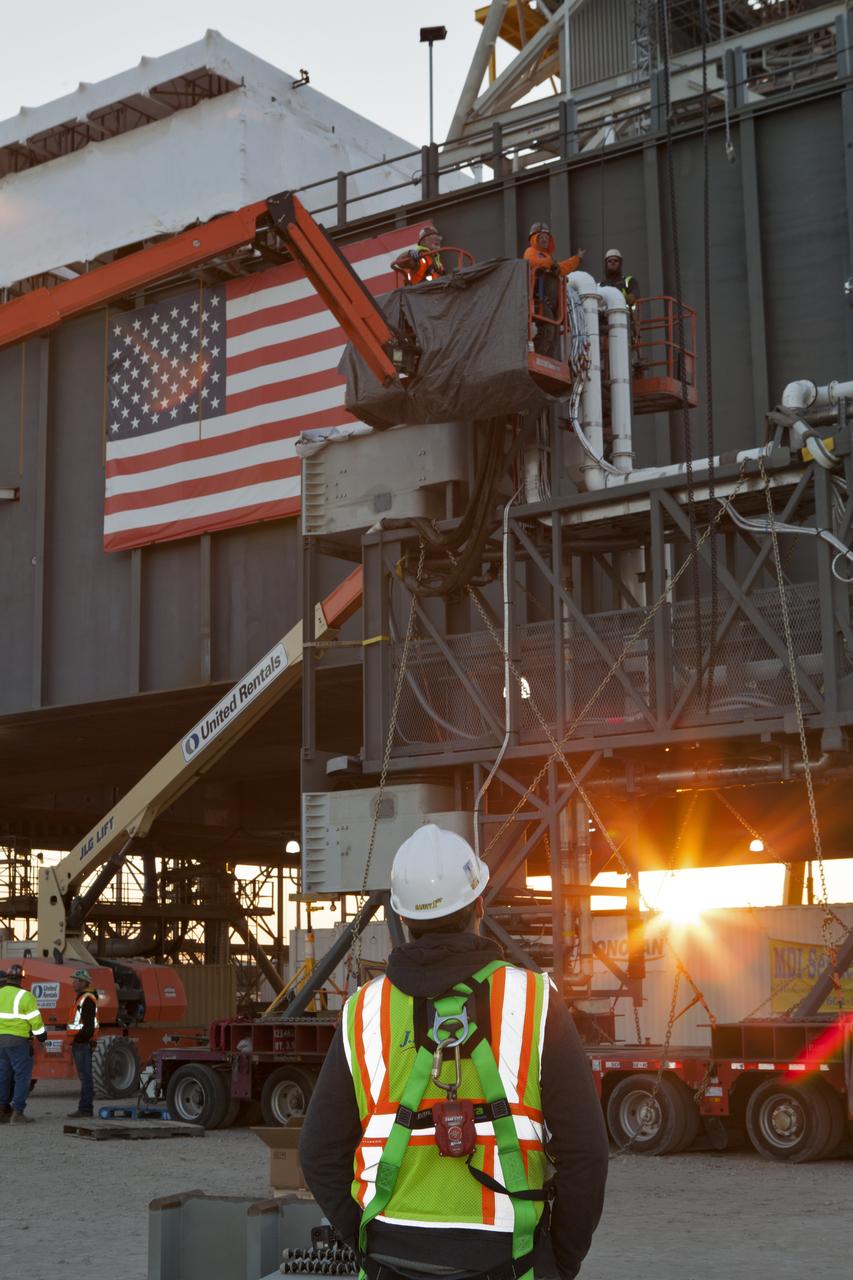

Construction workers with JP Donovan assist with preparations to lift and install the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical on the tower of the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The last of the large umbilicals to be installed, the ICPSU will provide super-cooled hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket's interim cryogenic propulsion stage, or upper stage, at T-0 for Exploration Mission-1. The umbilical is located at about the 240-foot-level of the mobile launcher and will supply fuel, oxidizer, gaseous helium, hazardous gas leak detection, electrical commodities and environment control systems to the upper stage of the SLS rocket during launch. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of the umbilicals on the ML.

A crane and rigging lines are used to install the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical (ICPSU) high up on the mobile launcher (ML) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The last of the large umbilicals to be installed, the ICPSU will provide super-cooled hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket's interim cryogenic propulsion stage, or upper stage, at T-0 for Exploration Mission-1. The umbilical is located at about the 240-foot-level of the mobile launcher and will supply fuel, oxidizer, gaseous helium, hazardous gas leak detection, electrical commodities and environment control systems to the upper stage of the SLS rocket during launch. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of the umbilicals on the ML.

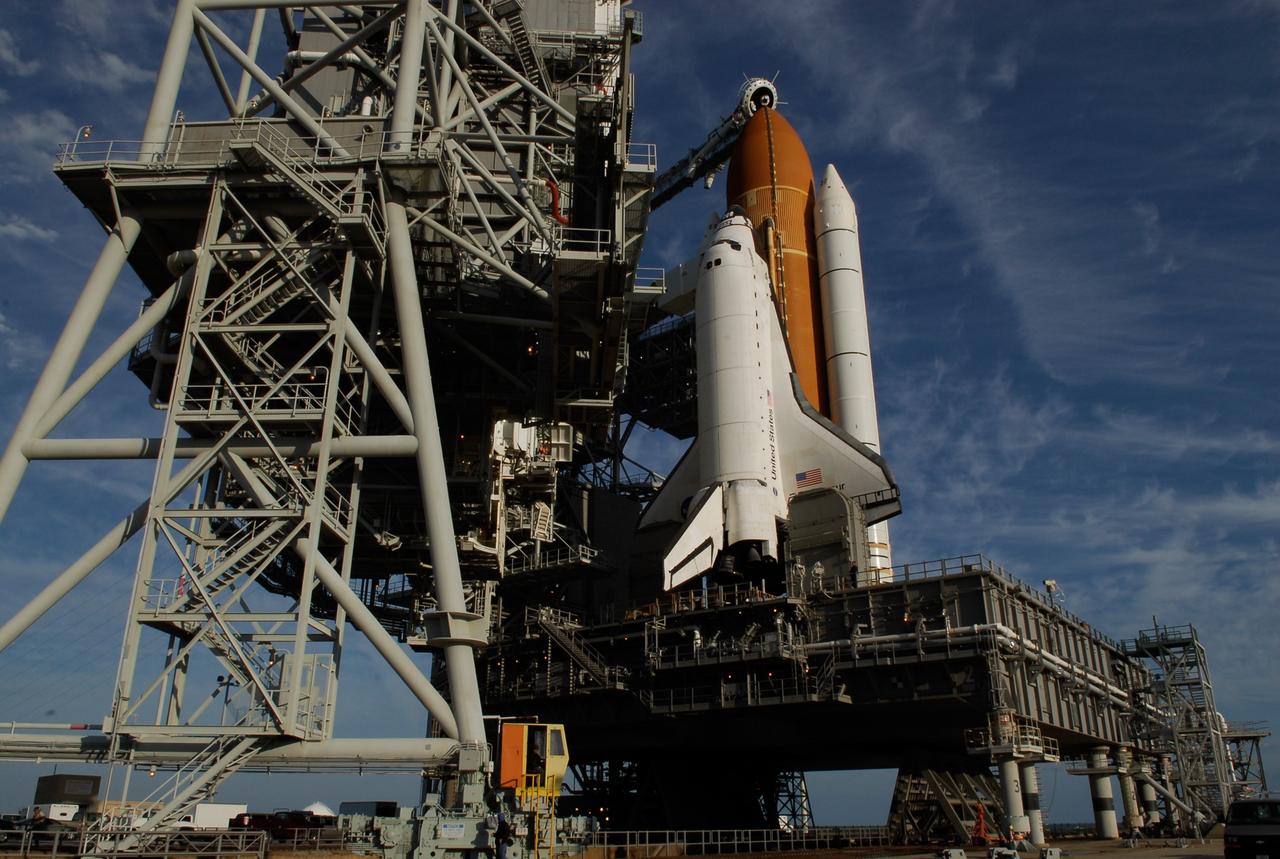
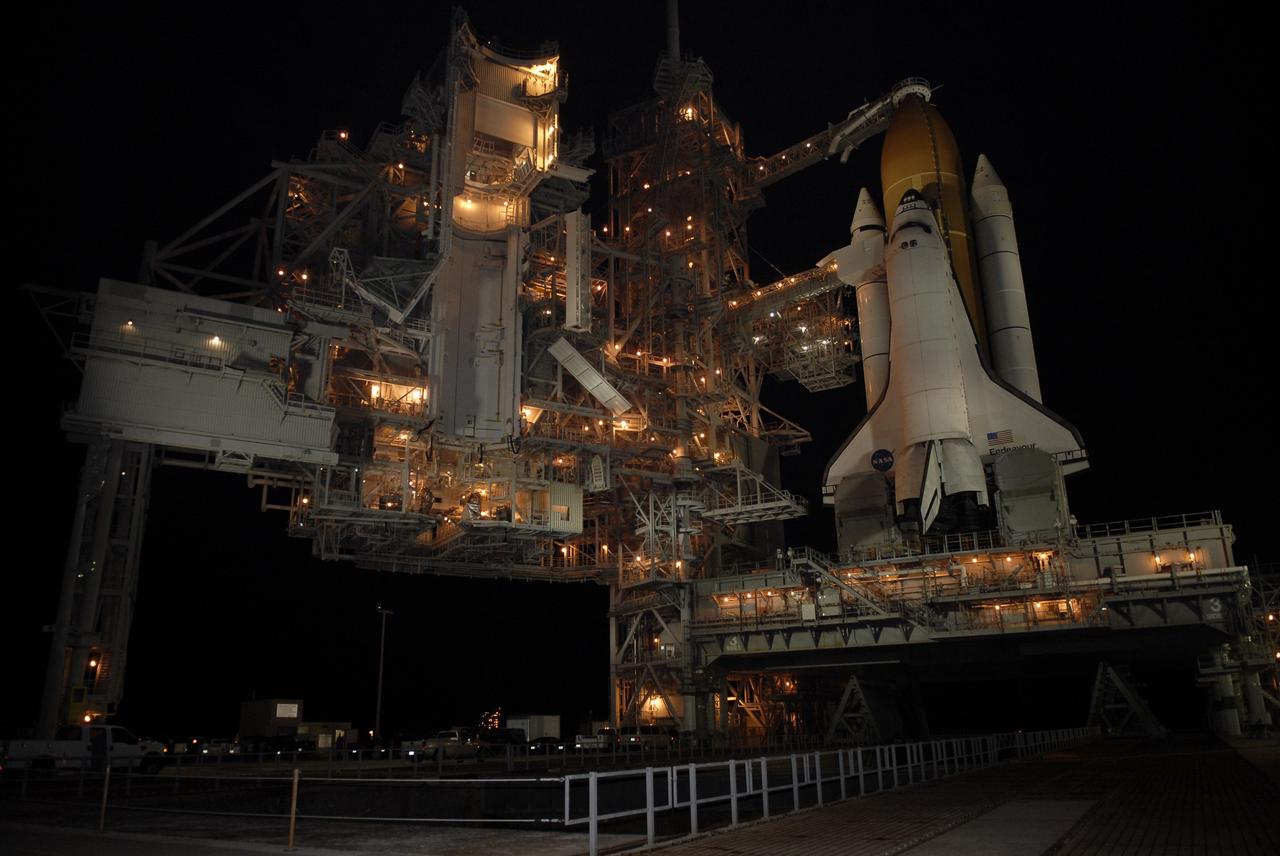
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the rotating service structure has rolled away to uncover space shuttle Endeavour. First motion was at 8:23 a.m. and rollback was complete at 8:55 a.m. Above the orange external tank is seen the "beanie cap" at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, extending from the fixed service structure. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. The rotating structure provides protected access to the orbiter for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. The structure is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots about a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Endeavour and its crew will deliver the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, Dextre. Launch is scheduled for 2:28 a.m. EDT March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the rotating service structure is rolling on its axis to uncover space shuttle Endeavour. First motion was at 8:23 a.m. and rollback was complete at 8:55 a.m. Above the orange external tank is seen the "beanie cap" at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, extending from the fixed service structure. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. The rotating structure provides protected access to the orbiter for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. The structure is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots about a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Endeavour and its crew will deliver the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, Dextre. Launch is scheduled for 2:28 a.m. EDT March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Lighted against the black of night, space shuttle Endeavour is revealed after rollback of the rotating service structure. The rollback is in preparation for liftoff on the STS-126 mission with a crew of seven. Above Endeavour's external tank is the vent hood, known as the "beanie cap," at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, extending from the fixed service structure. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Below is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end, flush against the shuttle. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The STS-126 mission will be the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

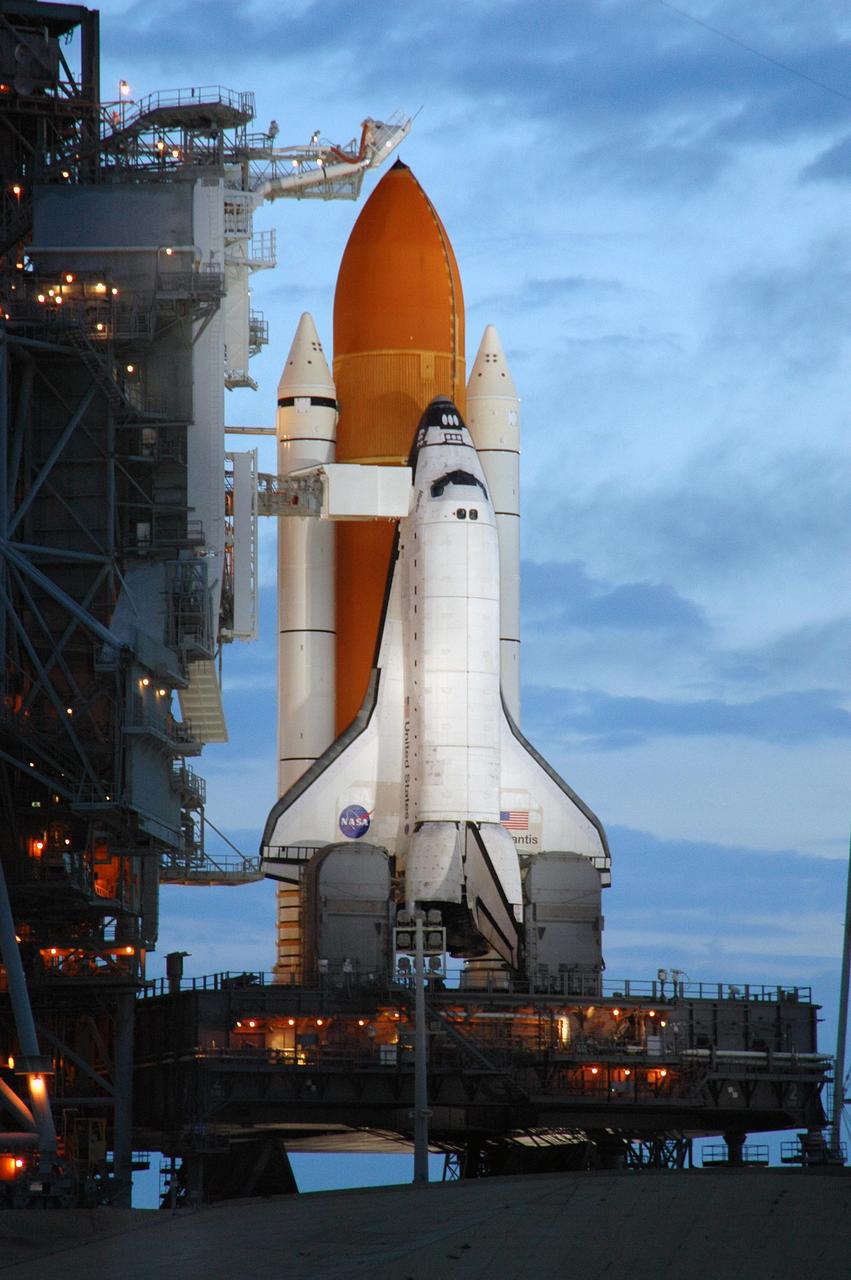
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The morning sky lightens behind Space Shuttle Atlantis while lights on the fixed service structure (FSS) still illuminate the orbiter on Launch Pad 39B. Atlantis was originally scheduled to launch at 12:29 p.m. EDT on this date, but a 24-hour scrub was called by mission managers due to a concern with Fuel Cell 1. Seen poised above the orange external tank is the vent hood (known as the "beanie cap") at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Extending from the FSS to Atlantis is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end. The White Room provides entry into the orbiter through the hatch. During the STS-115 mission, Atlantis' astronauts will deliver and install the 17.5-ton, bus-sized P3/P4 integrated truss segment on the station. The girder-like truss includes a set of giant solar arrays, batteries and associated electronics and will provide one-fourth of the total power-generation capability for the completed station. This mission is the 116th space shuttle flight, the 27th flight for orbiter Atlantis, and the 19th U.S. flight to the International Space Station. STS-115 is scheduled to last 11 days with a planned landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
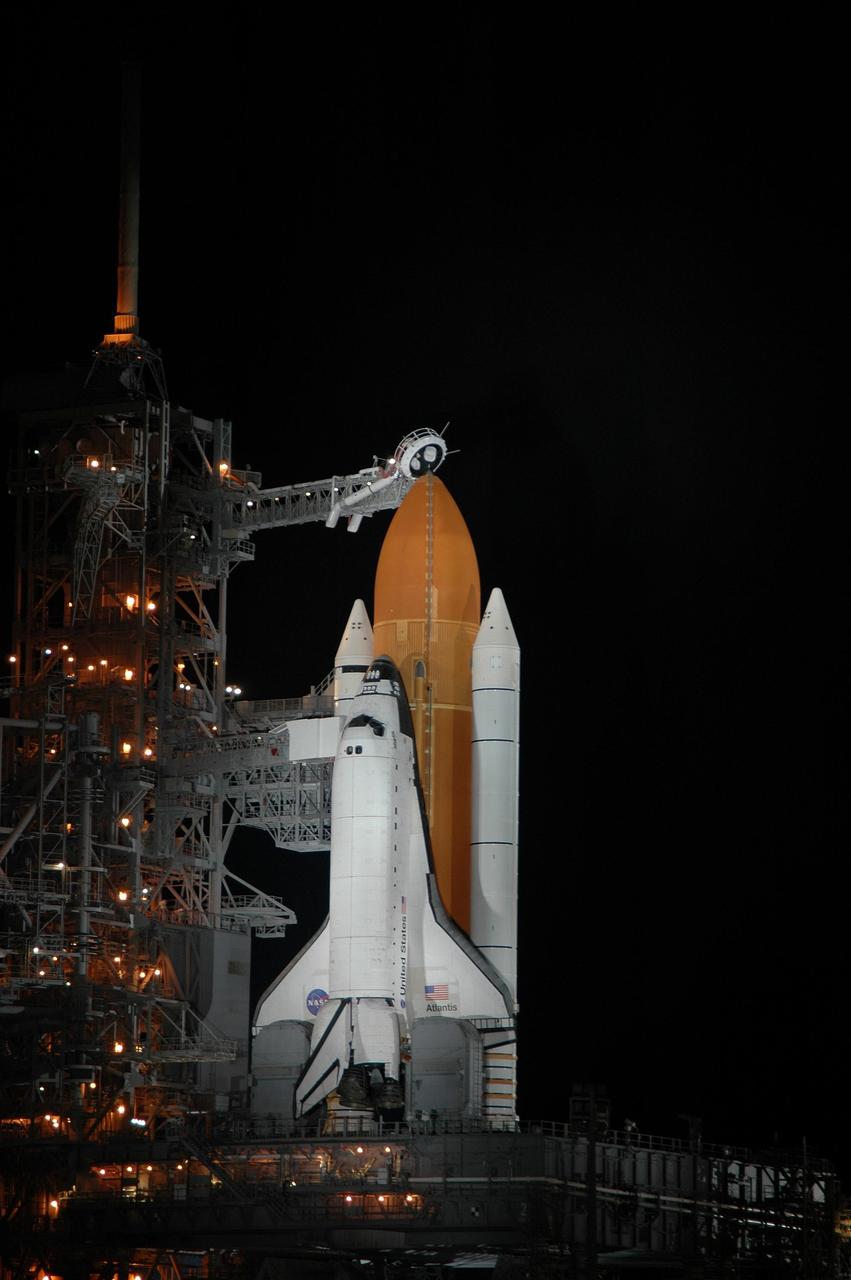

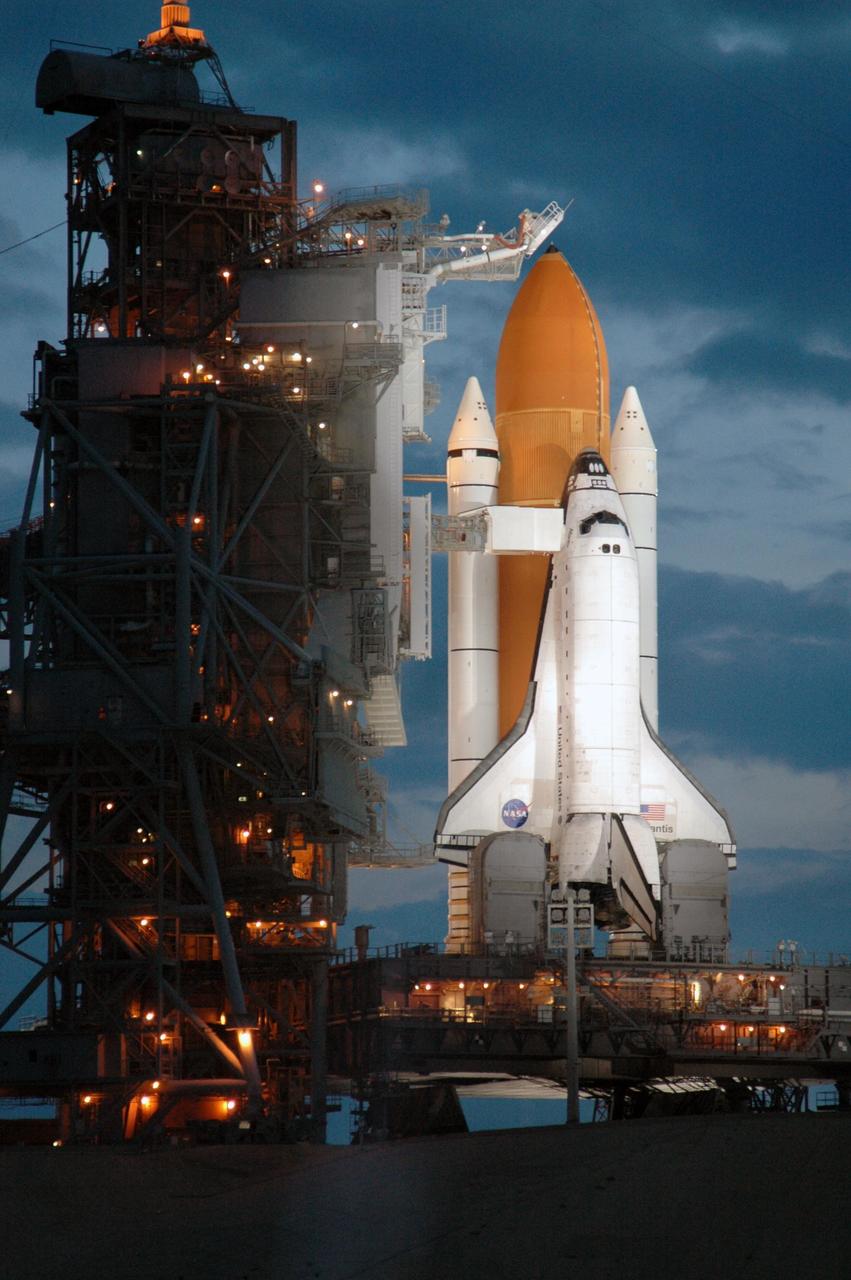
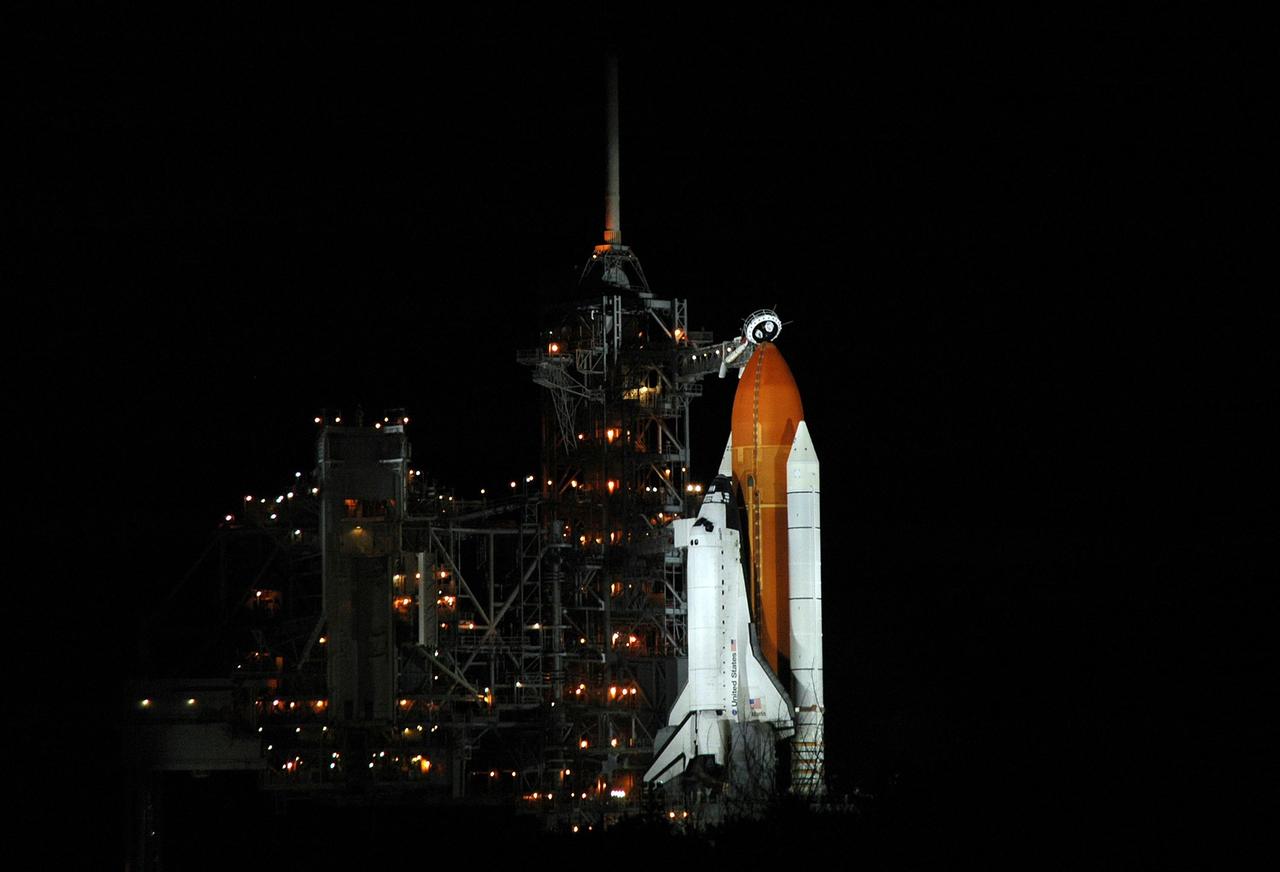
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Atlantis is in the spotlight on Launch Pad 39B. Atlantis was originally scheduled to launch at 12:29 p.m. EDT on this date, but a 24-hour scrub was called by mission managers due to a concern with Fuel Cell 1. Seen poised above the orange external tank is the vent hood (known as the "beanie cap") at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. During the STS-115 mission, Atlantis' astronauts will deliver and install the 17.5-ton, bus-sized P3/P4 integrated truss segment on the station. The girder-like truss includes a set of giant solar arrays, batteries and associated electronics and will provide one-fourth of the total power-generation capability for the completed station. This mission is the 116th space shuttle flight, the 27th flight for orbiter Atlantis, and the 19th U.S. flight to the International Space Station. STS-115 is scheduled to last 11 days with a planned landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
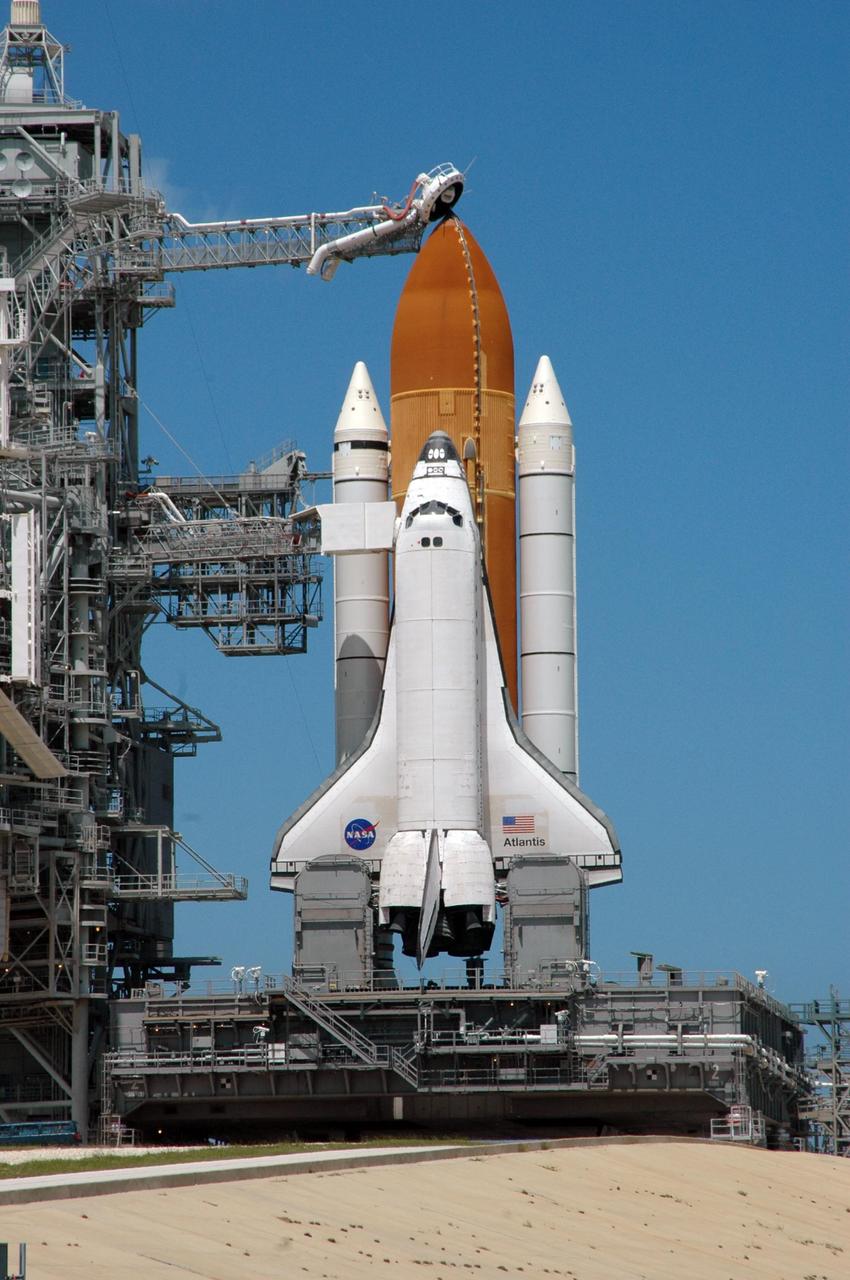

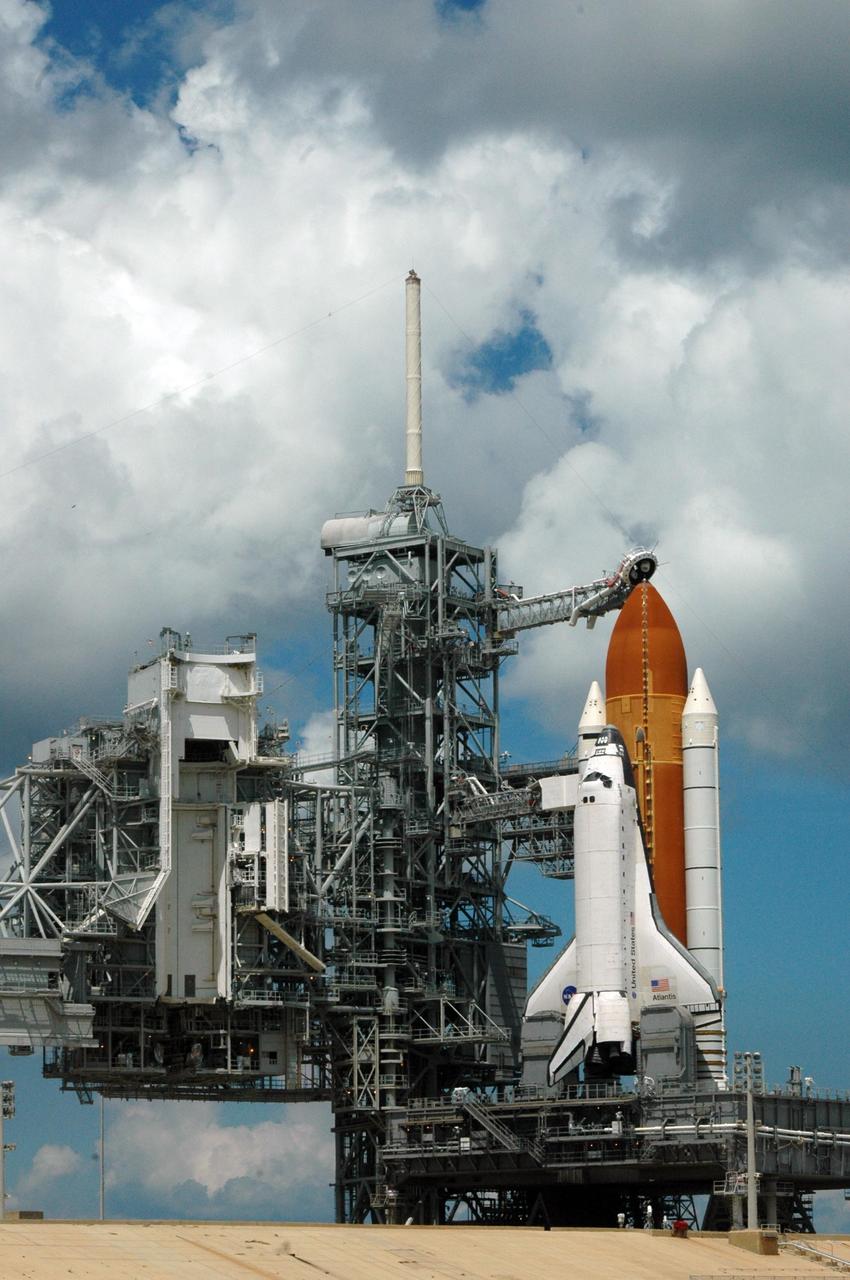
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The sky is finally clear behind Launch Pad 39B where Space Shuttle Atlantis still sits after the scrub of its launch on mission STS-115. Atlantis was originally scheduled to launch at 12:29 p.m. EDT on this date, but a 24-hour scrub was called by mission managers due to a concern with fuel cell 1. Just above the orange external tank is the vent hood (known as the "beanie cap") at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Below, the orbiter access arm extends toward the cockpit of Atlantis with the White Room at the end. The White Room provides access into the cockpit of the vehicle. During the STS-115 mission, Atlantis' astronauts will deliver and install the 17.5-ton, bus-sized P3/P4 integrated truss segment on the station. The girder-like truss includes a set of giant solar arrays, batteries and associated electronics and will provide one-fourth of the total power-generation capability for the completed station. This mission is the 116th space shuttle flight, the 27th flight for orbiter Atlantis, and the 19th U.S. flight to the International Space Station. STS-115 is scheduled to last 11 days with a planned landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley

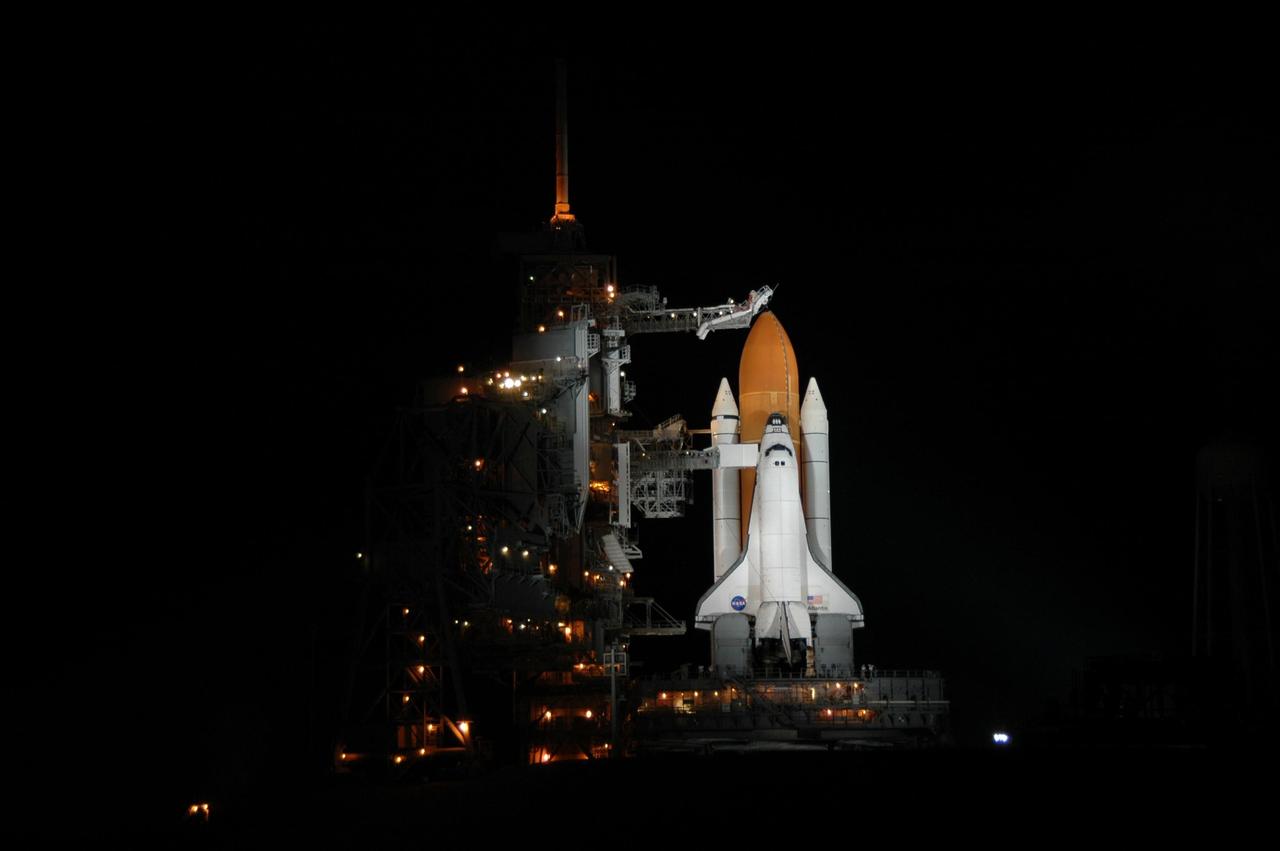
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Atlantis is bathed in light on Launch Pad 39B. Atlantis was originally scheduled to launch at 12:29 p.m. EDT on this date, but a 24-hour scrub was called by mission managers due to a concern with Fuel Cell 1. Seen poised above the orange external tank is the vent hood (known as the "beanie cap") at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. During the STS-115 mission, Atlantis' astronauts will deliver and install the 17.5-ton, bus-sized P3/P4 integrated truss segment on the station. The girder-like truss includes a set of giant solar arrays, batteries and associated electronics and will provide one-fourth of the total power-generation capability for the completed station. This mission is the 116th space shuttle flight, the 27th flight for orbiter Atlantis, and the 19th U.S. flight to the International Space Station. STS-115 is scheduled to last 11 days with a planned landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
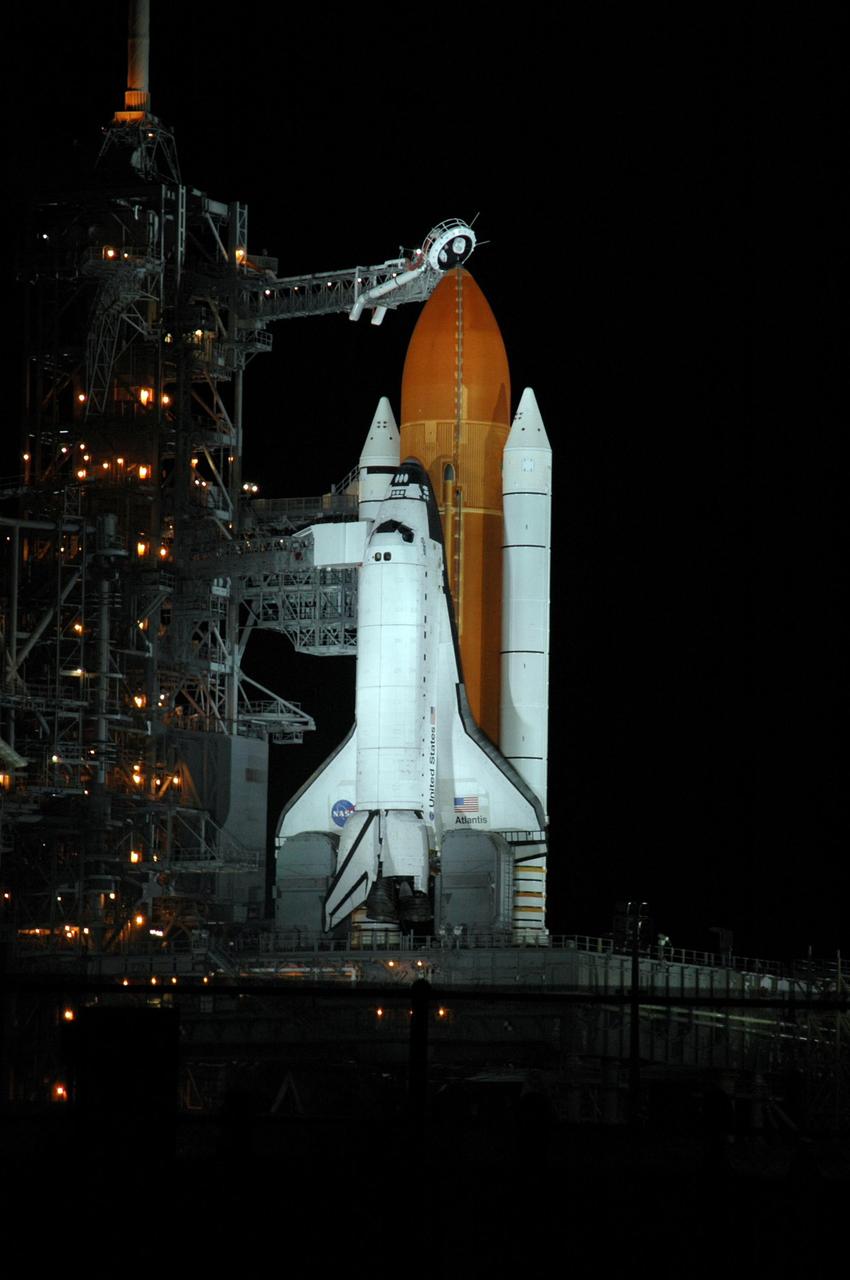

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Atlantis is illuminated on Launch Pad 39B, while amber lights on the fixed service structure give a surreal appearance. Seen above the golden external tank is the vent hood (known as the "beanie cap") at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Lower down, and next to Atlantis, is the White Room at the end of the orbiter access arm. The White Room provides entry into the orbiter through the hatch. Atlantis was originally scheduled to launch on Aug. 27, but a scrub was called by mission managers due to a concern with fuel cell 1. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off at 11:41 a.m. EDT Sept. 8. During the STS-115 mission, Atlantis' astronauts will deliver and install the 17.5-ton, bus-sized P3/P4 integrated truss segment on the station. The girder-like truss includes a set of giant solar arrays, batteries and associated electronics and will provide one-fourth of the total power-generation capability for the completed station. This mission is the 116th space shuttle flight, the 27th flight for orbiter Atlantis, and the 19th U.S. flight to the ISS. STS-115 is scheduled to last 11 days with a planned landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
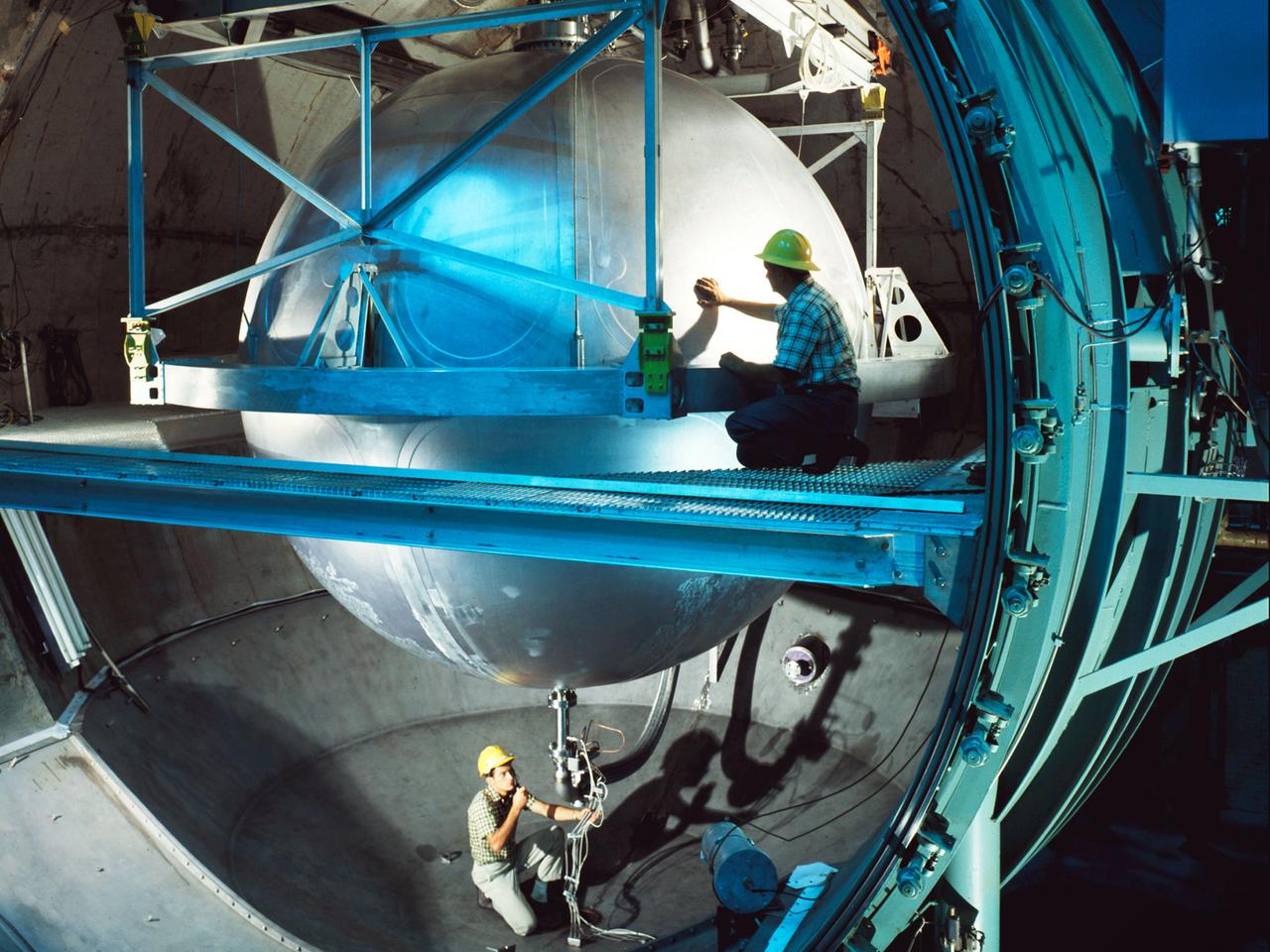

A 13-foot diameter mounted inside the large test chamber at the Cryogenic Propellant Tank, or K-Site, at National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station. The 25-foot test chamber and 20-foot access door were designed to test liquid hydrogen fuel tanks up to 18 feet in diameter in conditions that simulated launches and spaceflight. Shakers were installed to test the effects of launch vibration on the tanks and their insulation. The K Site chamber was also equipped with cold walls that could be cooled with either liquid nitrogen or liquid hydrogen and vacuum pumps that could reduce pressure levels to 10-8 torr. This 13-foot tank passed its initial acceptance tests in K-Site on August 24, 1966. Delays in the modification of the tank postponed further tests of the tank until May 1967. Four pressure hold tests and expulsion runs were made in May using gaseous hydrogen or gaseous helium at 300R and 520R. In June a straight pipe injector test was run and two pressure effect tests at 35 and 75psi. Propellant slosh tests were successfully run in August. This photograph was taken the day after the program’s final runs on September 12, 1967.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Atlantis is bathed in light on Launch Pad 39B. Atlantis was originally scheduled to launch at 12:29 p.m. EDT on this date, but a 24-hour scrub was called by mission managers due to a concern with Fuel Cell 1. Seen poised above the orange external tank is the vent hood (known as the "beanie cap") at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. During the STS-115 mission, Atlantis' astronauts will deliver and install the 17.5-ton, bus-sized P3/P4 integrated truss segment on the station. The girder-like truss includes a set of giant solar arrays, batteries and associated electronics and will provide one-fourth of the total power-generation capability for the completed station. This mission is the 116th space shuttle flight, the 27th flight for orbiter Atlantis, and the 19th U.S. flight to the International Space Station. STS-115 is scheduled to last 11 days with a planned landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The morning sky lightens behind Space Shuttle Atlantis while lights on the fixed service structure (FSS) still illuminate the orbiter on Launch Pad 39B. Atlantis was originally scheduled to launch at 12:29 p.m. EDT on this date, but a 24-hour scrub was called by mission managers due to a concern with Fuel Cell 1. Seen poised above the orange external tank is the vent hood (known as the "beanie cap") at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Extending from the FSS to Atlantis is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end. The White Room provides entry into the orbiter through the hatch. During the STS-115 mission, Atlantis' astronauts will deliver and install the 17.5-ton, bus-sized P3/P4 integrated truss segment on the station. The girder-like truss includes a set of giant solar arrays, batteries and associated electronics and will provide one-fourth of the total power-generation capability for the completed station. This mission is the 116th space shuttle flight, the 27th flight for orbiter Atlantis, and the 19th U.S. flight to the International Space Station. STS-115 is scheduled to last 11 days with a planned landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Atlantis is illuminated on Launch Pad 39B, surrounded by amber lights on the rotating and fixed service structures. Seen above the golden external tank is the vent hood (known as the "beanie cap") at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Atlantis was originally scheduled to launch on Aug. 27, but a scrub was called by mission managers due to a concern with fuel cell 1. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off at 11:41 a.m. EDT Sept. 8. During the STS-115 mission, Atlantis' astronauts will deliver and install the 17.5-ton, bus-sized P3/P4 integrated truss segment on the station. The girder-like truss includes a set of giant solar arrays, batteries and associated electronics and will provide one-fourth of the total power-generation capability for the completed station. This mission is the 116th space shuttle flight, the 27th flight for orbiter Atlantis, and the 19th U.S. flight to the ISS. STS-115 is scheduled to last 11 days with a planned landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Huge clouds roll over Launch Pad 39B where Space Shuttle Atlantis still sits after the scrub of its launch on mission STS-115. Atlantis was originally scheduled to launch at 12:29 p.m. EDT on this date, but a 24-hour scrub was called by mission managers due to a concern with fuel cell 1. Towering above the shuttle is the 80-foot lightning mast. At left is the rolled-back rotating service structure with the payload changeout room open. Just above the orange external tank is the vent hood (known as the "beanie cap") at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. During the STS-115 mission, Atlantis' astronauts will deliver and install the 17.5-ton, bus-sized P3/P4 integrated truss segment on the station. The girder-like truss includes a set of giant solar arrays, batteries and associated electronics and will provide one-fourth of the total power-generation capability for the completed station. This mission is the 116th space shuttle flight, the 27th flight for orbiter Atlantis, and the 19th U.S. flight to the International Space Station. STS-115 is scheduled to last 11 days with a planned landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
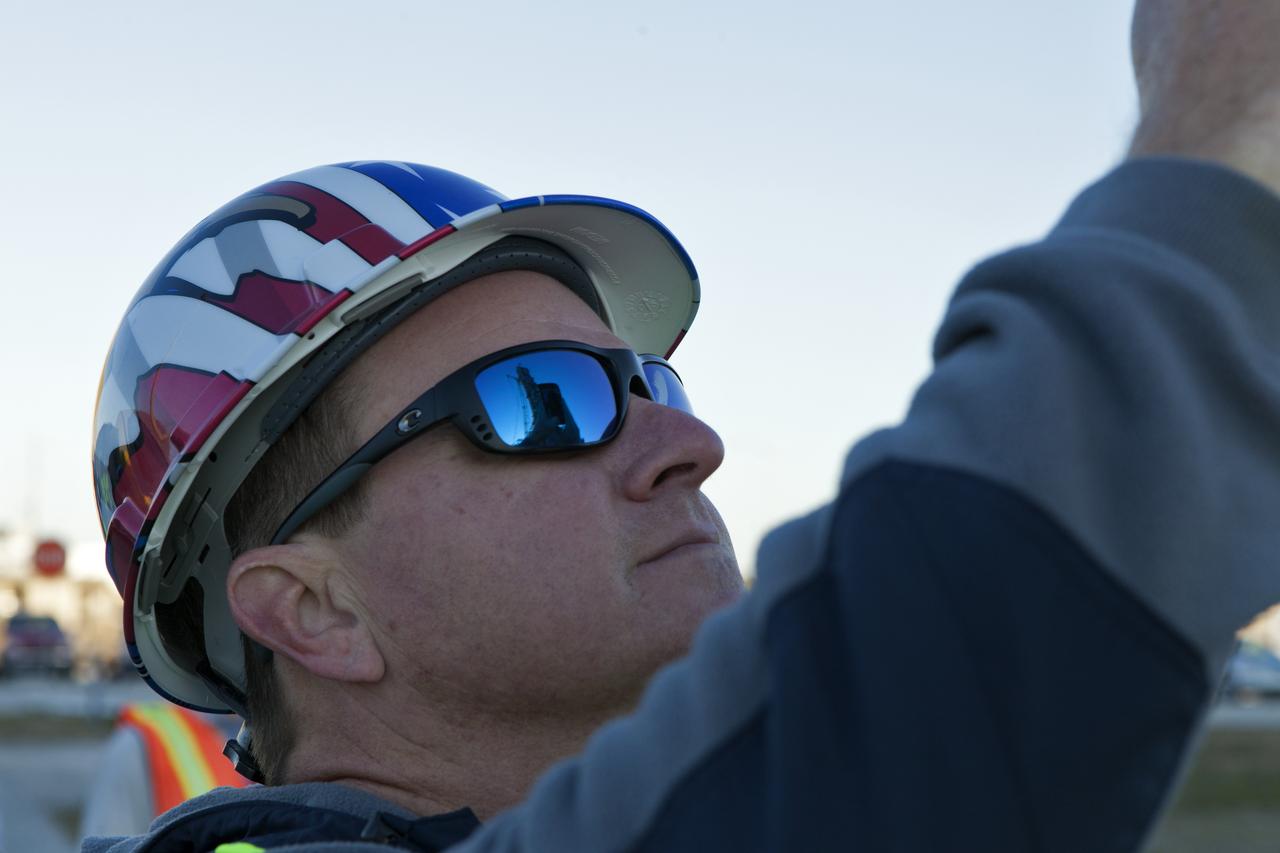

The mobile launcher (ML) is reflected in the sunglasses of a construction worker with JP Donovan at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A crane is lifting the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical (ICPSU) up for installation on the tower of the ML. The last of the large umbilicals to be installed, the ICPSU will provide super-cooled hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket's interim cryogenic propulsion stage, or upper stage, at T-0 for Exploration Mission-1. The umbilical is located at about the 240-foot-level of the mobile launcher and will supply fuel, oxidizer, gaseous helium, hazardous gas leak detection, electrical commodities and environment control systems to the upper stage of the SLS rocket during launch. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of the umbilicals on the ML.
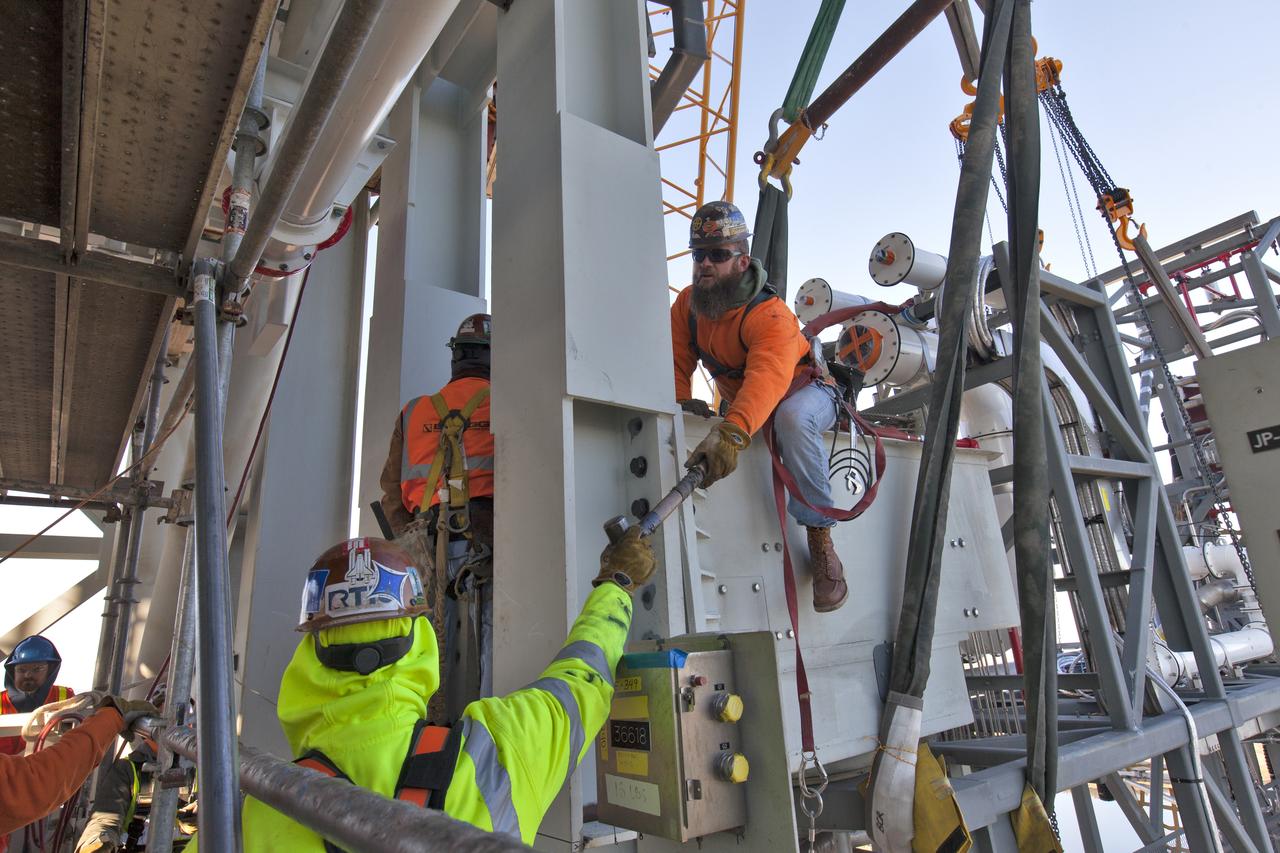

Construction workers with JP Donovan install the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical (ICPSU) at about the 240-foot-level of the mobile launcher (ML) tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The last of the large umbilicals to be installed, the ICPSU will provide super-cooled hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket's interim cryogenic propulsion stage, or upper stage, at T-0 for Exploration Mission-1. The umbilical is located at about the 240-foot-level of the mobile launcher and will supply fuel, oxidizer, gaseous helium, hazardous gas leak detection, electrical commodities and environment control systems to the upper stage of the SLS rocket during launch. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of the umbilicals on the ML.
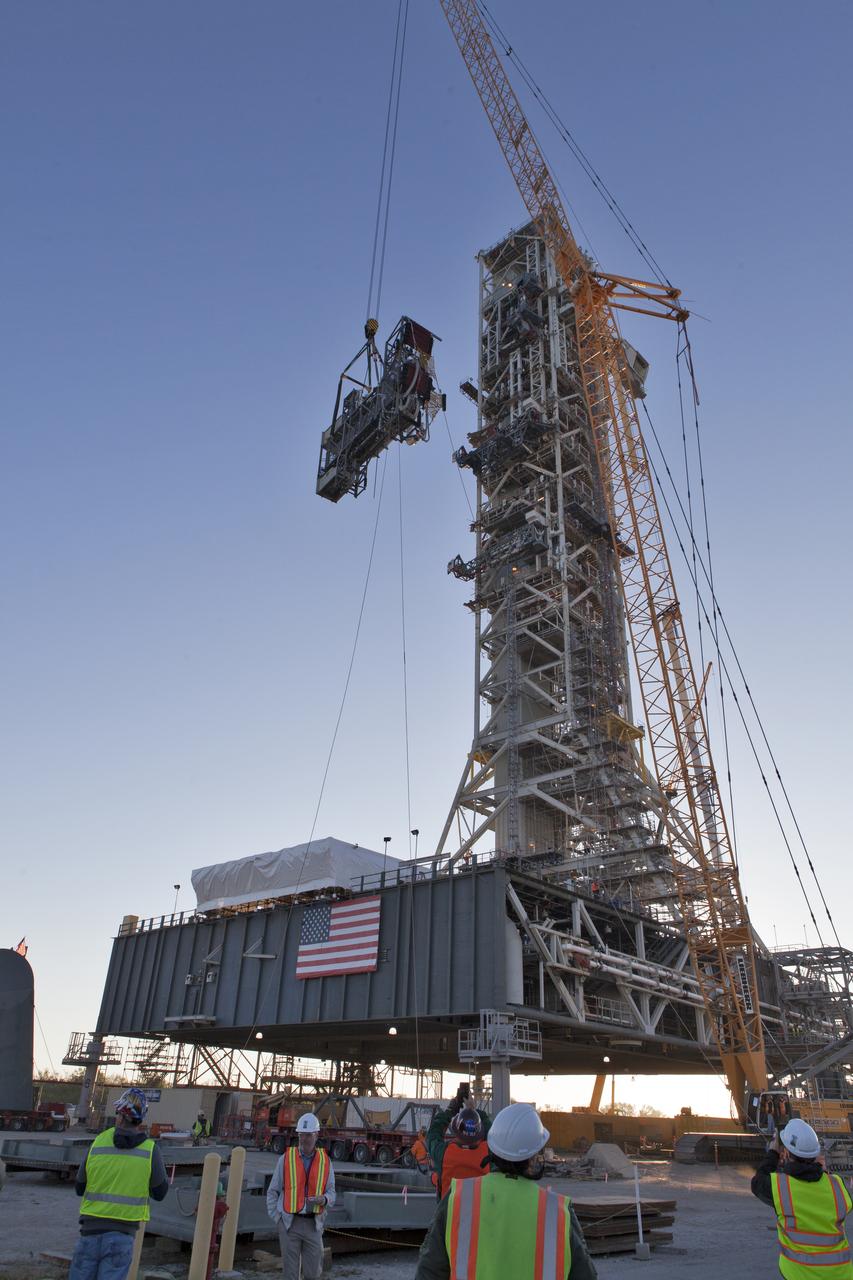

A heavy-lift crane slowly lifts the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical (ICPSU) high up for installation on the tower of the mobile launcher (ML) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The last of the large umbilicals to be installed, the ICPSU will provide super-cooled hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket's interim cryogenic propulsion stage, or upper stage, at T-0 for Exploration Mission-1. The umbilical is located at about the 240-foot-level of the mobile launcher and will supply fuel, oxidizer, gaseous helium, hazardous gas leak detection, electrical commodities and environment control systems to the upper stage of the SLS rocket during launch. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of the umbilicals on the ML.
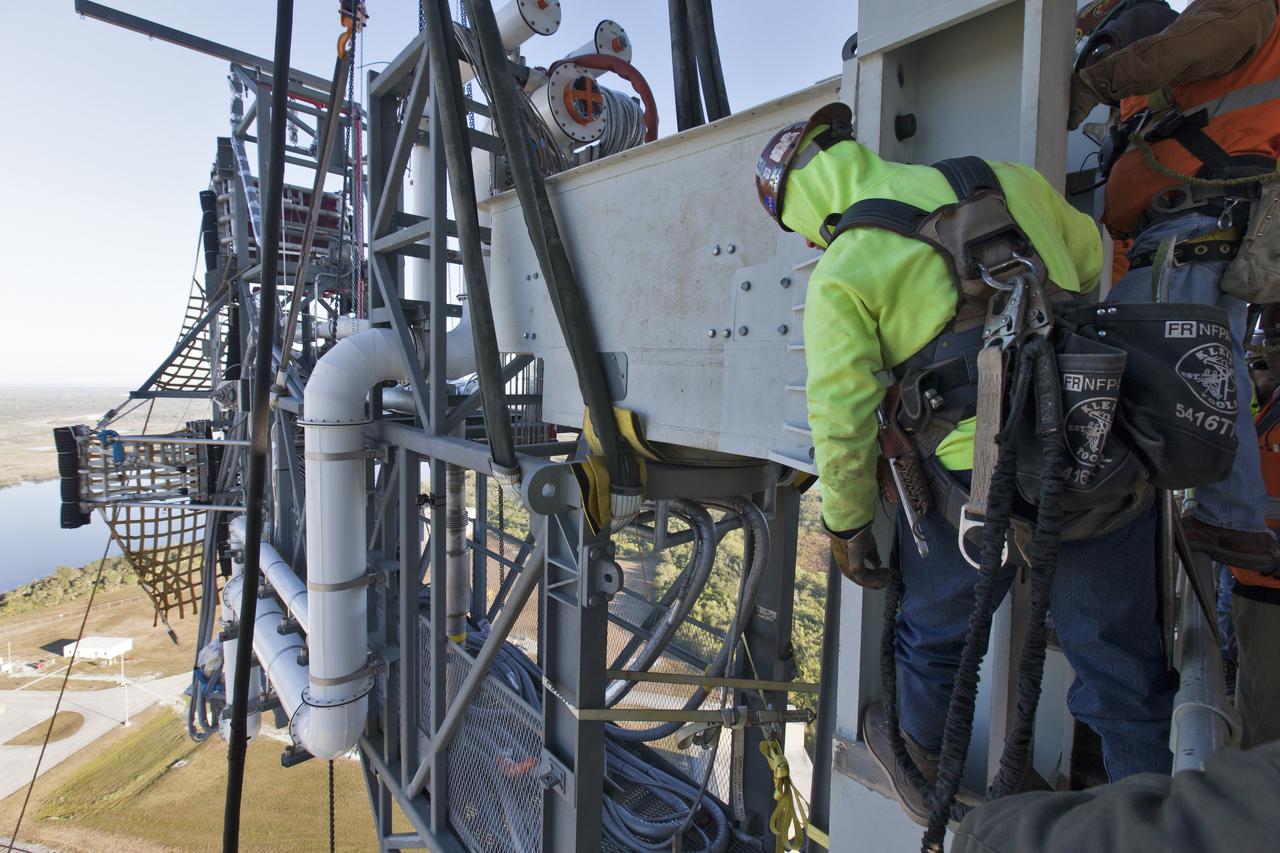

Construction workers with JP Donovan install the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical (ICPSU) at about the 240-foot-level of the mobile launcher (ML) tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The last of the large umbilicals to be installed, the ICPSU will provide super-cooled hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket's interim cryogenic propulsion stage, or upper stage, at T-0 for Exploration Mission-1. The umbilical is located at about the 240-foot-level of the mobile launcher and will supply fuel, oxidizer, gaseous helium, hazardous gas leak detection, electrical commodities and environment control systems to the upper stage of the SLS rocket during launch. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of the umbilicals on the ML.
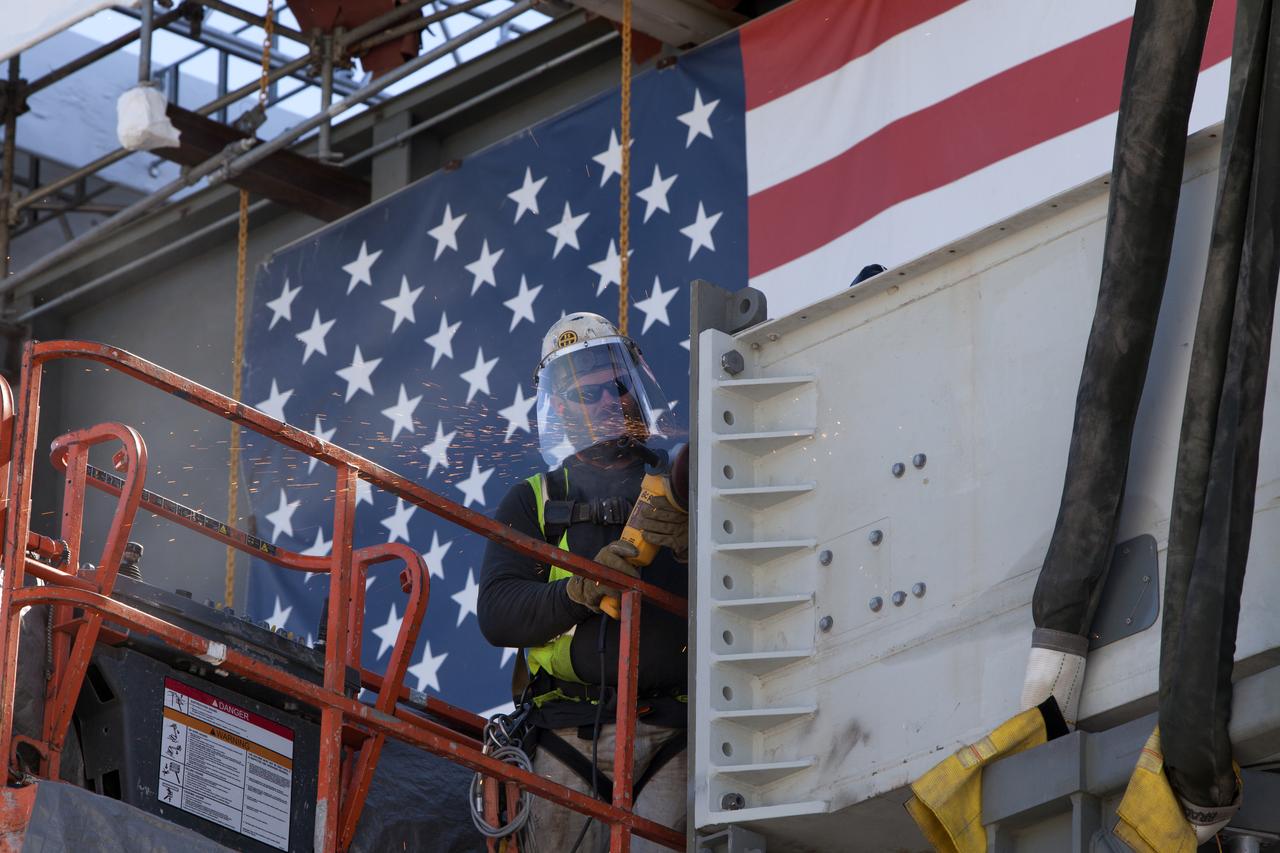

A construction worker with JP Donovan helps prepare the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical (ICPSU) for installation high up on the tower of the mobile launcher (ML) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The last of the large umbilicals to be installed, the ICPSU will provide super-cooled hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket's interim cryogenic propulsion stage, or upper stage, at T-0 for Exploration Mission-1. The umbilical will be located at about the 240-foot-level of the mobile launcher and will supply fuel, oxidizer, gaseous helium, hazardous gas leak detection, electrical commodities and environment control systems to the upper stage of the SLS rocket during launch. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of the umbilicals on the ML.
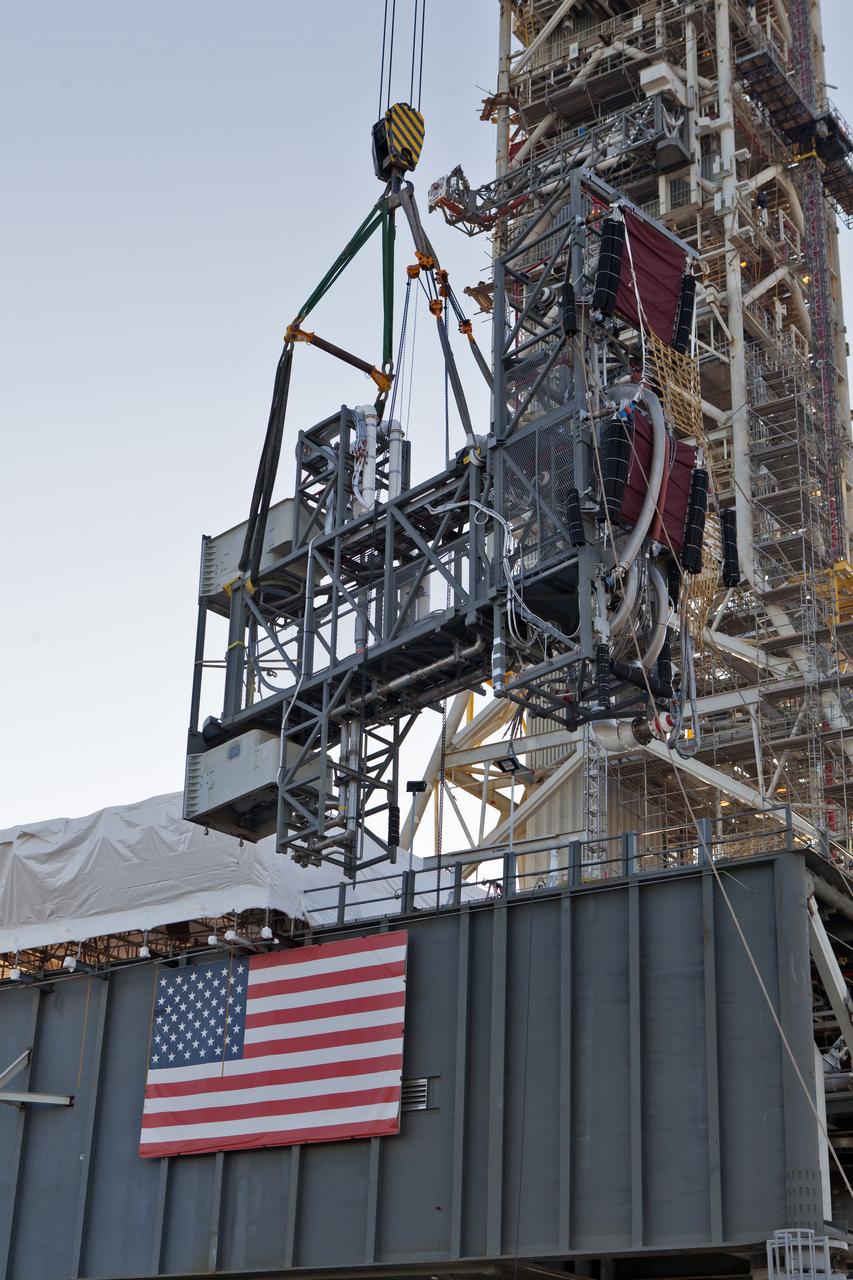

A heavy-lift crane slowly lifts the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical (ICPSU) up for installation on the tower of the mobile launcher (ML) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The last of the large umbilicals to be installed, the ICPSU will provide super-cooled hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket's interim cryogenic propulsion stage, or upper stage, at T-0 for Exploration Mission-1. The umbilical is located at about the 240-foot-level of the mobile launcher and will supply fuel, oxidizer, gaseous helium, hazardous gas leak detection, electrical commodities and environment control systems to the upper stage of the SLS rocket during launch. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of the umbilicals on the ML.
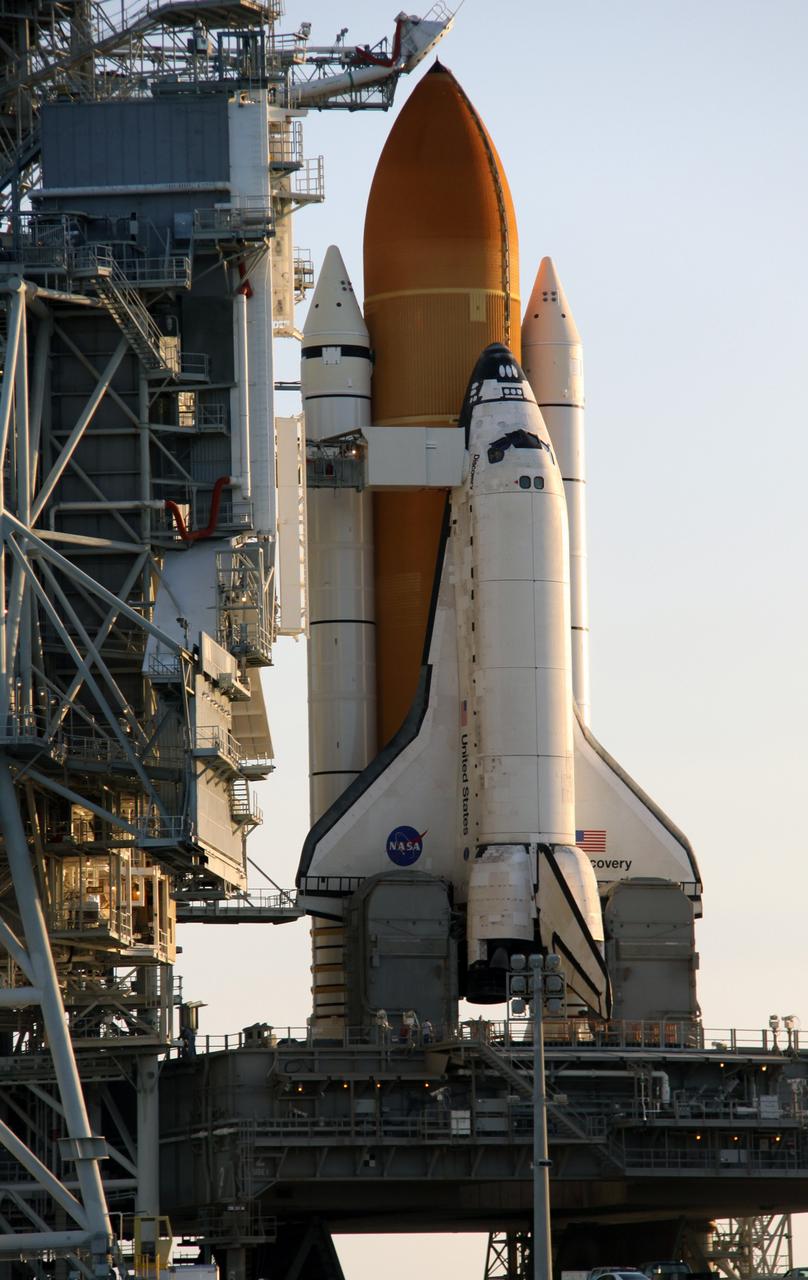

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Discovery is revealed during sunrise after the rollback of the rotating service structure, or RSS. On top of the external fuel tank is the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap," which is designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the shuttle. The rollback is preparation for Discovery's scheduled 1:36 a.m. EDT liftoff Aug. 25 with a crew of seven on the STS-128 mission. The service structure provides weather protection and access to the space shuttle at the launch pad. The 13-day mission will deliver a new crew member and 33,000 pounds of equipment to the International Space Station. The equipment includes science and storage racks, a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. STS-128 will be Discovery's 37th mission and the 30th shuttle flight dedicated to station assembly and maintenance. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
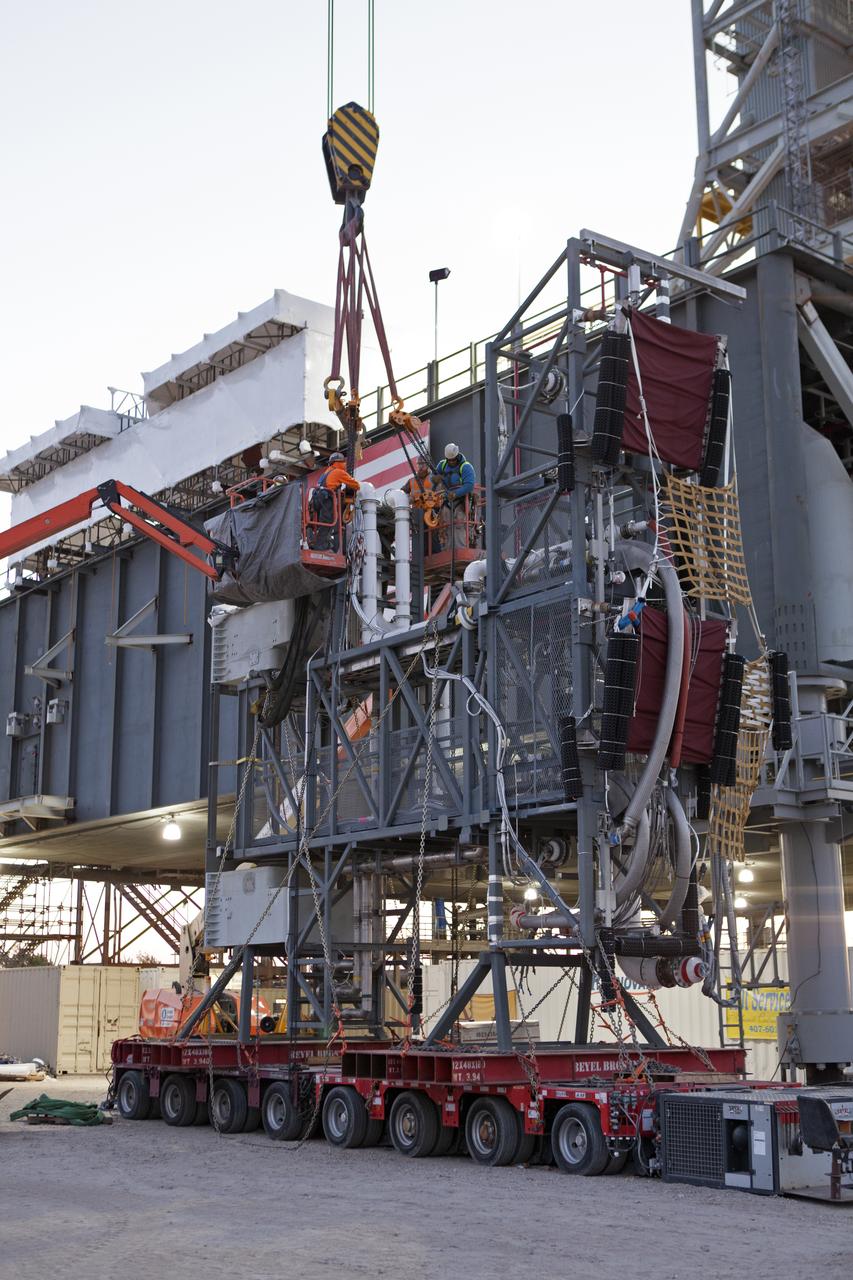

Construction workers with JP Donovan attach a heavy-lift crane to the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical (ICPSU) to prepare for lifting and installation on the mobile launcher (ML) tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The last of the large umbilicals to be installed, the ICPSU will provide super-cooled hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket's interim cryogenic propulsion stage, or upper stage, at T-0 for Exploration Mission-1. The umbilical will be located at about the 240-foot-level of the ML and will supply fuel, oxidizer, gaseous helium, hazardous gas leak detection, electrical commodities and environment control systems to the upper stage of the SLS rocket during launch. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of the umbilicals on the ML.
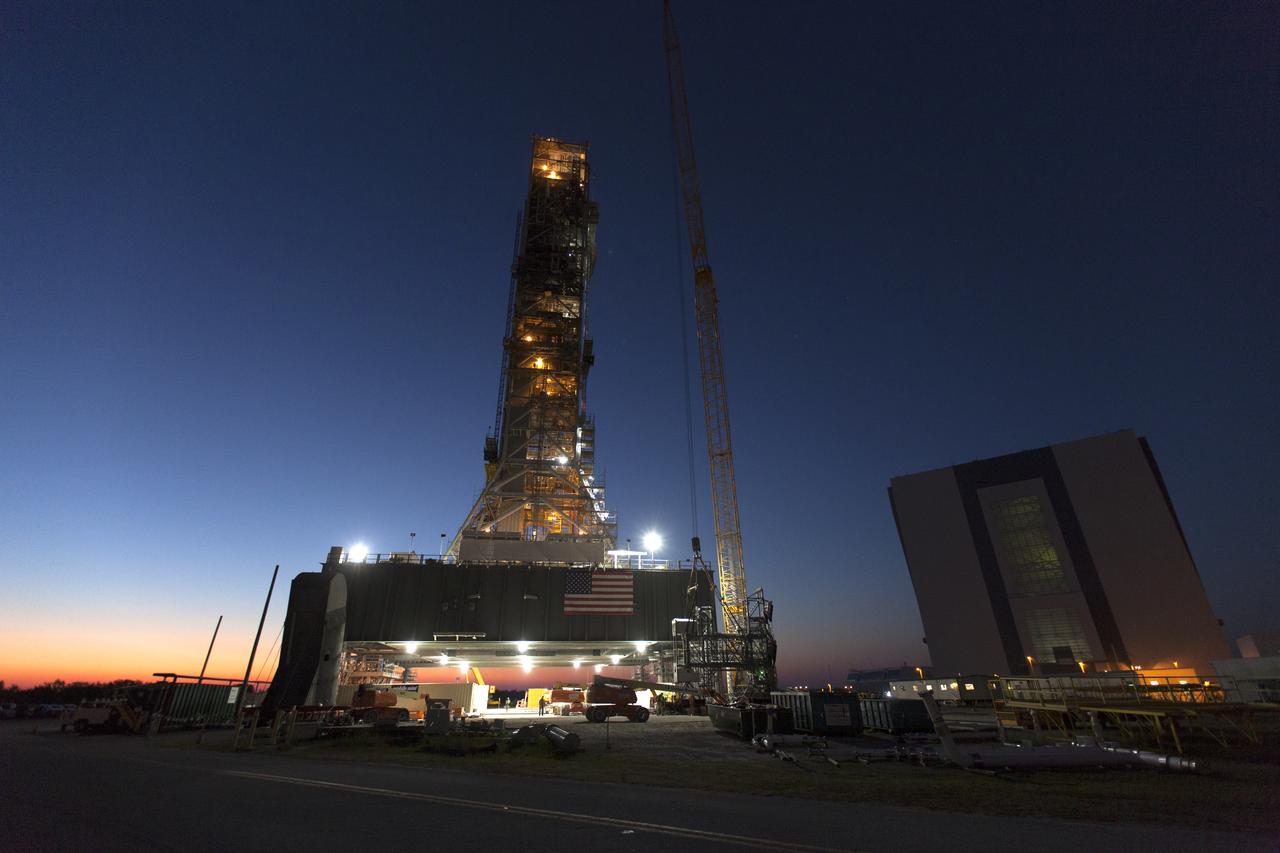

The mobile launcher (ML) tower is lit up before early morning sunrise at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Preparations are underway to lift and install the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Umbilical (ICPSU) at about the 240-foot-level on the tower. The last of the large umbilicals to be installed, the ICPSU will provide super-cooled hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket's interim cryogenic propulsion stage, or upper stage, at T-0 for Exploration Mission-1. The umbilical will supply fuel, oxidizer, gaseous helium, hazardous gas leak detection, electrical commodities and environment control systems to the upper stage of the SLS rocket during launch. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of the umbilicals on the ML.
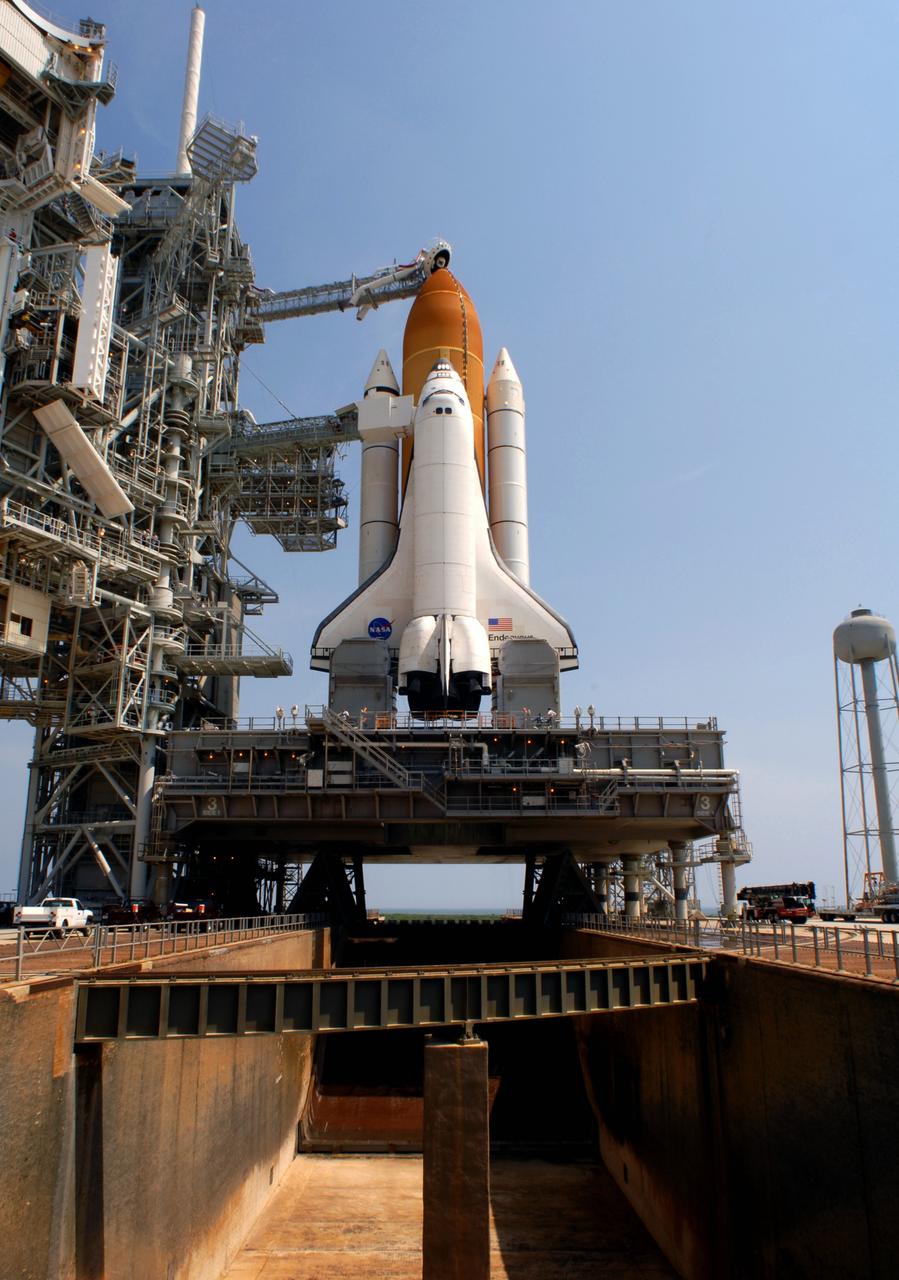

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour is revealed after the rollback of the rotating service structure, or RSS. In the foreground is the flame trench, which the mobile launcher platform straddles. On top of the external fuel tank is the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap," which is designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the shuttle. The rollback is preparation for Endeavour's liftoff June 13 on the STS-127 mission with a crew of seven. First motion was at 10:39 a.m. EDT and completed at 11:18 a.m. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The launch will be Endeavour's 23rd flight. The shuttle will carry the Japanese Experiment Module's Exposed Facility, or JEM-EF, and the Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, on STS-127. The mission is the final of three flights dedicated to the assembly of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory complex on the space station. Endeavour's launch is scheduled for June 13 at 7:17 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
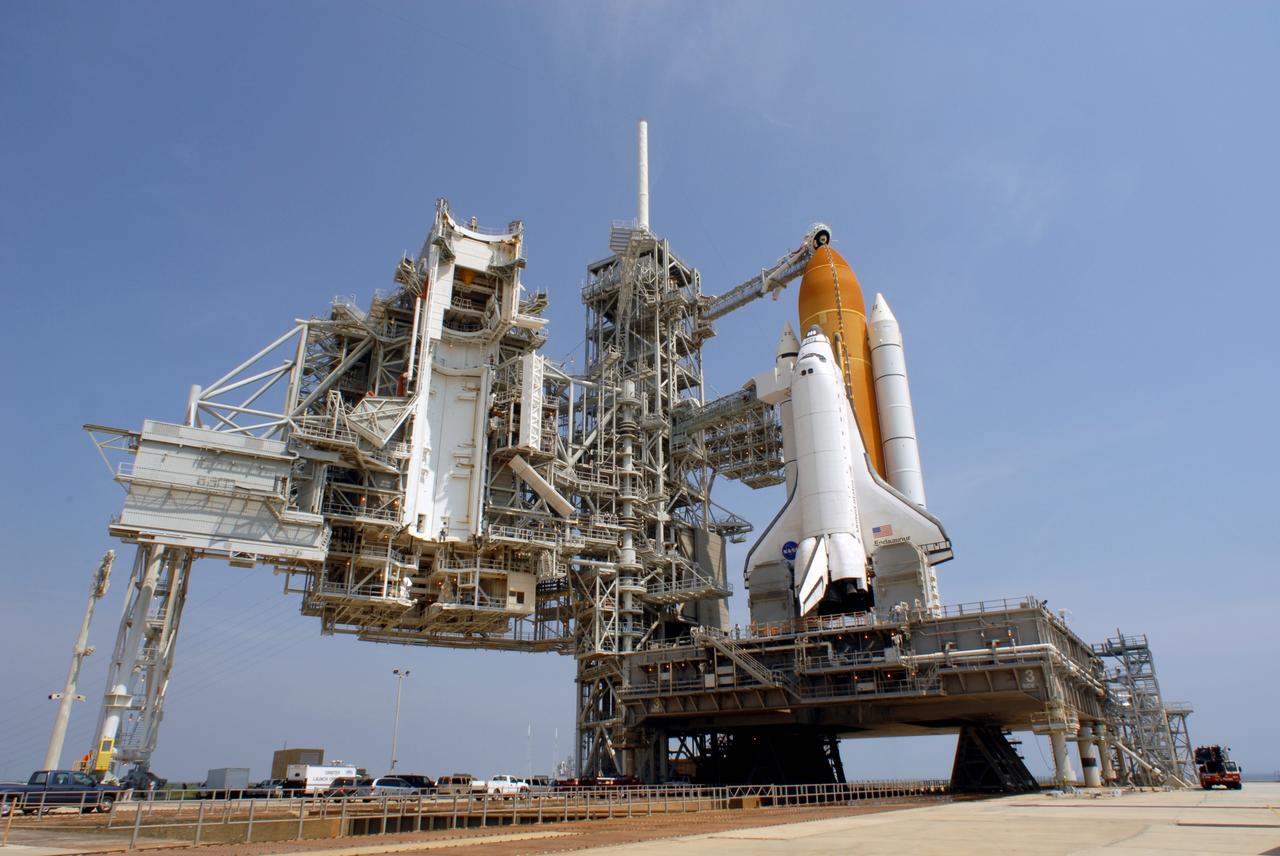

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap," is positioned above the external fuel tank of space shuttle Endeavour following the rollback of the rotating service structure, or RSS, at left. The beanie cap is designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the shuttle. The rollback is preparation for Endeavour's liftoff June 13 on the STS-127 mission with a crew of seven. First motion was at 10:39 a.m. EDT and completed at 11:18 a.m. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The launch will be Endeavour's 23rd flight. The shuttle will carry the Japanese Experiment Module's Exposed Facility, or JEM-EF, and the Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, on STS-127. The mission is the final of three flights dedicated to the assembly of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory complex on the space station. Endeavour's launch is scheduled for June 13 at 7:17 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
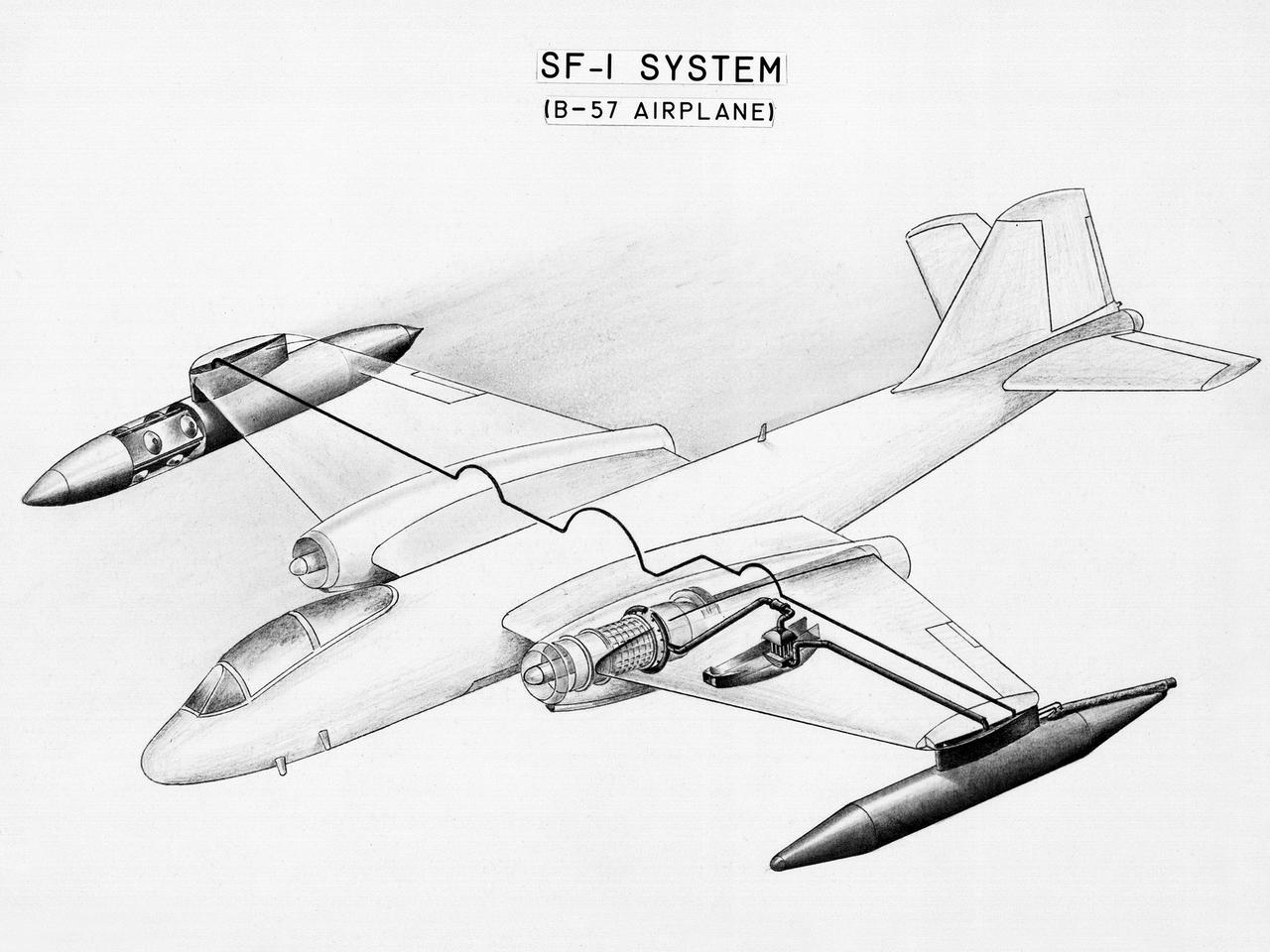
This diagram shows a hydrogen fuel system designed by researchers at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory and installed on a Martin B-57B Canberra aircraft. Lewis researchers accelerated their studies of high energy propellants in the early 1950s. In late 1954, Lewis researchers studied the combustion characteristics of gaseous hydrogen in a turbojet combustor. It was found that the hydrogen provided a very high efficiency. Almost immediately thereafter, Associate Director Abe Silverstein became focused on the possibilities of hydrogen for aircraft propulsion. That fall, Silverstein secured a contract to work with the air force to examine the practicality of liquid hydrogen aircraft. A B-57B Canberra was obtained by the air force especially for this project, referred to as Project Bee. The aircraft was powered by two Wright J65 engines, one of which was modified so that it could be operated using either traditional or liquid hydrogen propellants. The engine and its liquid hydrogen fuel system were tested extensively in the Altitude Wind Tunnel and the Four Burner Area test cells in 1955 and 1956. A B-57B flight program was planned to test the system on an actual aircraft. The aircraft would take off using jet fuel, switch to liquid hydrogen while over Lake Erie, then after burning the hydrogen supply switch back to jet fuel for the landing. The third test flight, in February 1957, was a success, and the ensuing B-57B flights remain the only demonstration of hydrogen-powered aircraft.
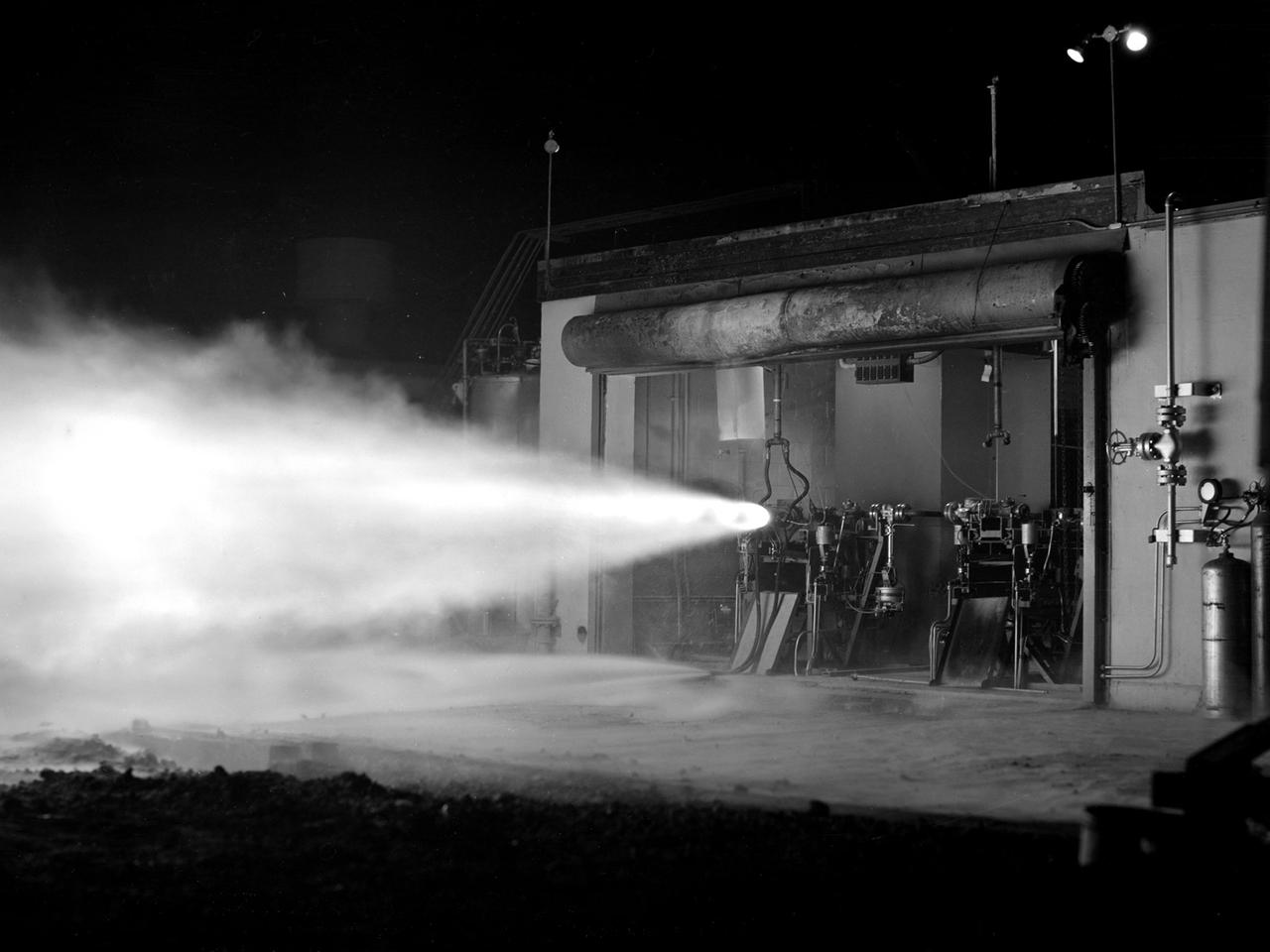

A rocket using high-energy propellant is fired from the Rocket Laboratory at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The Rocket Lab was a collection of ten one-story cinderblock test cells located behind earthen barriers at the western edge of the campus. The rocket engines tested there were comparatively small, but the Lewis researchers were able to study different configurations, combustion performance, and injectors and nozzle design. The rockets were generally mounted horizontally and fired, as seen in this photograph of Test Cell No. 22. A group of fuels researchers at Lewis refocused their efforts after World War II in order to explore high energy propellants, combustion, and cooling. Research in these three areas began in 1945 and continued through the 1960s. The group of rocket researches was not elevated to a division branch until 1952. The early NACA Lewis work led to the development of liquid hydrogen as a viable propellant in the late 1950s. Following the 1949 reorganization of the research divisions, the rocket group began working with high-energy propellants such as diborane, pentaborane, and hydrogen. The lightweight fuels offered high levels of energy but were difficult to handle and required large tanks. In late 1954, Lewis researchers studied the combustion characteristics of gaseous hydrogen in a turbojet combustor. Despite poor mixing of the fuel and air, it was found that the hydrogen yielded more than a 90-percent efficiency. Liquid hydrogen became the focus of Lewis researchers for the next 15 years.
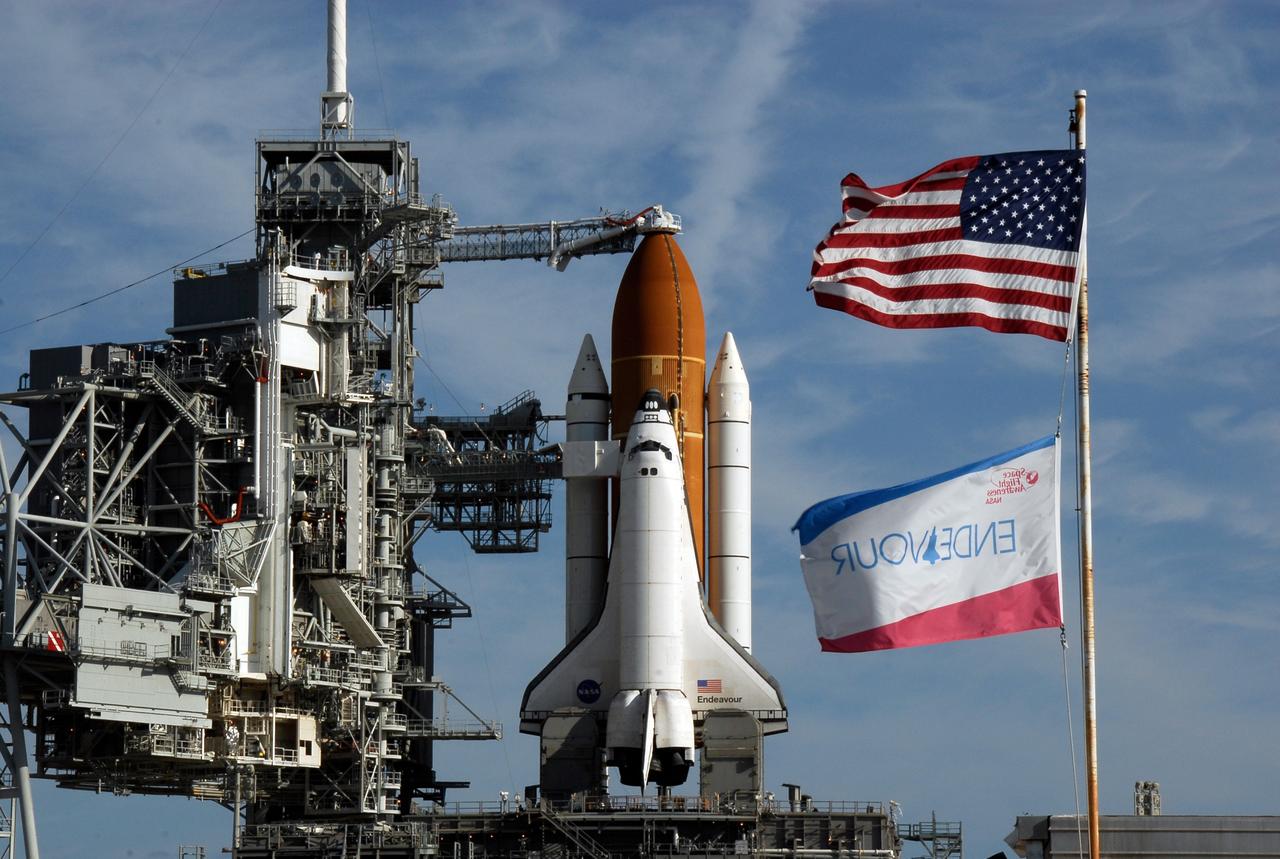

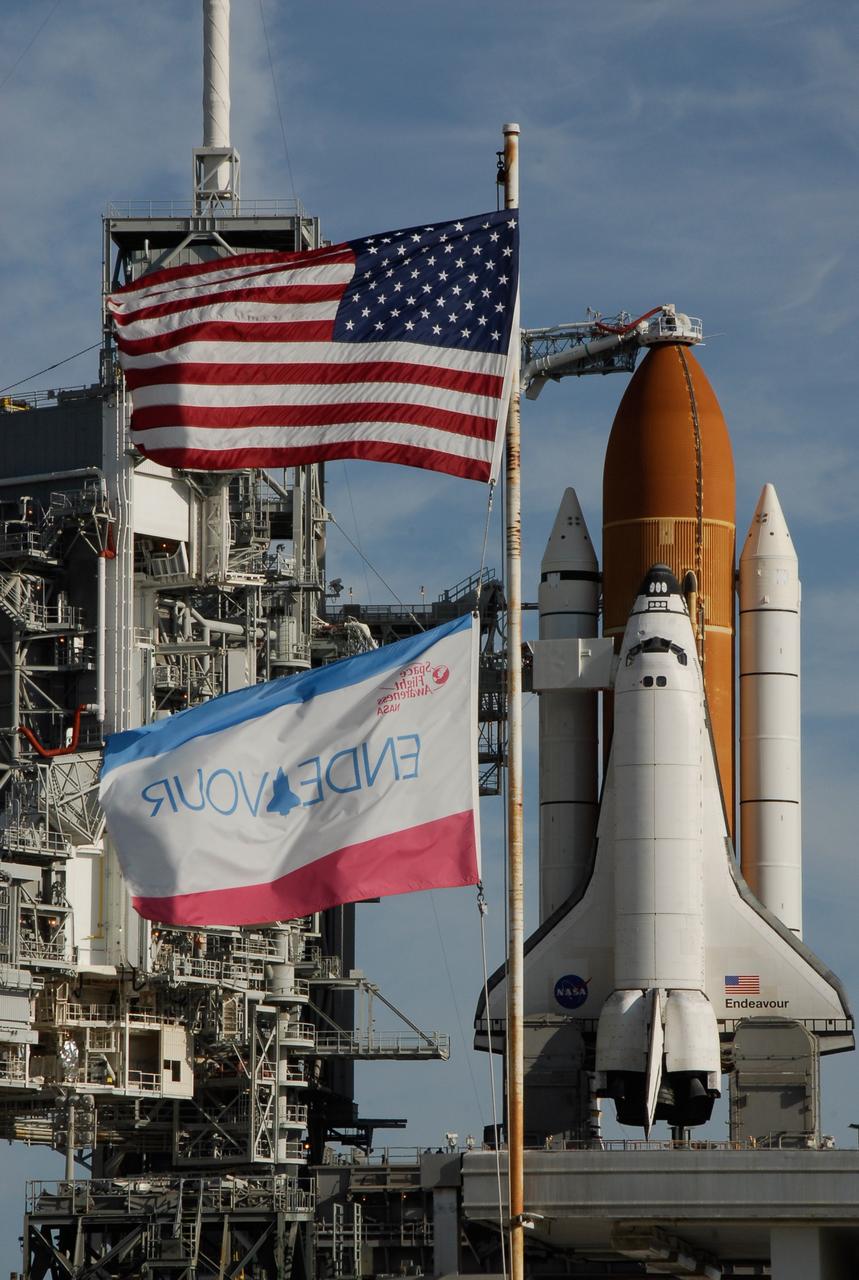
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Flags wave near Launch Pad 39A where space shuttle Endeavour waits for liftoff. The rotating service structure was rolled back starting at 8:23 a.m. and complete at 8:55 a.m. Above the orange external tank is seen the "beanie cap" at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, extending from the fixed service structure. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Below is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end, flush against the shuttle. The crew gains access into the orbiter through the White Room. The rotating structure provides protected access to the orbiter for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. The structure is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots about a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Endeavour and its crew will deliver the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, Dextre. Launch is scheduled for 2:28 a.m. EDT March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
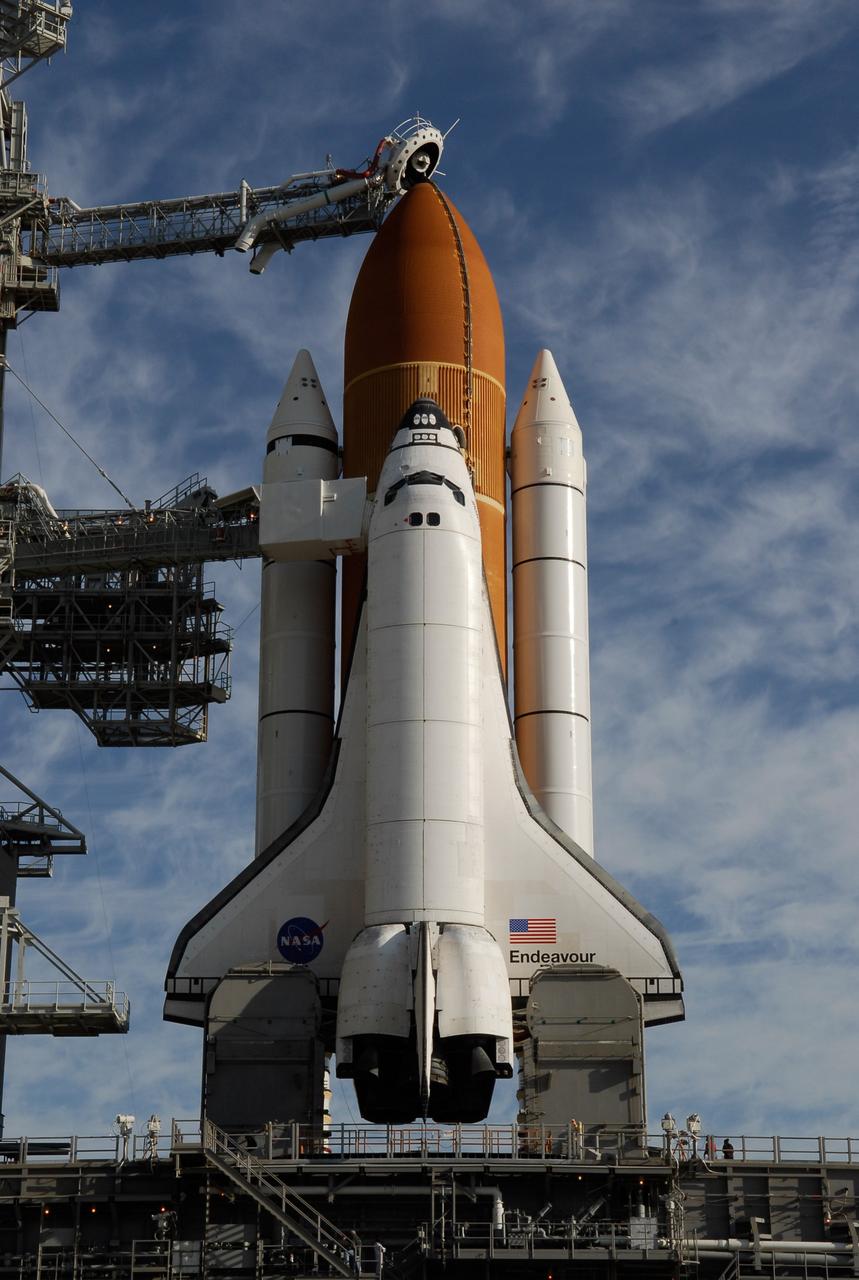

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, rollback of the rotating service structure reveals space shuttle Endeavour atop the mobile launcher platform. First motion was at 8:23 a.m. and rollback was complete at 8:55 a.m. Above the orange external tank is seen the "beanie cap" at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, extending from the fixed service structure. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Below is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end, flush against the shuttle. The crew gains access into the orbiter through the White Room. On either side of the main engines and below the wings are the tail service masts, which provide several umbilical connections to the orbiter, including a liquid-oxygen line through one and a liquid-hydrogen line through another. The rotating structure provides protected access to the orbiter for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. The structure is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots about a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Endeavour and its crew will deliver the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, Dextre. Launch is scheduled for 2:28 a.m. EDT March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
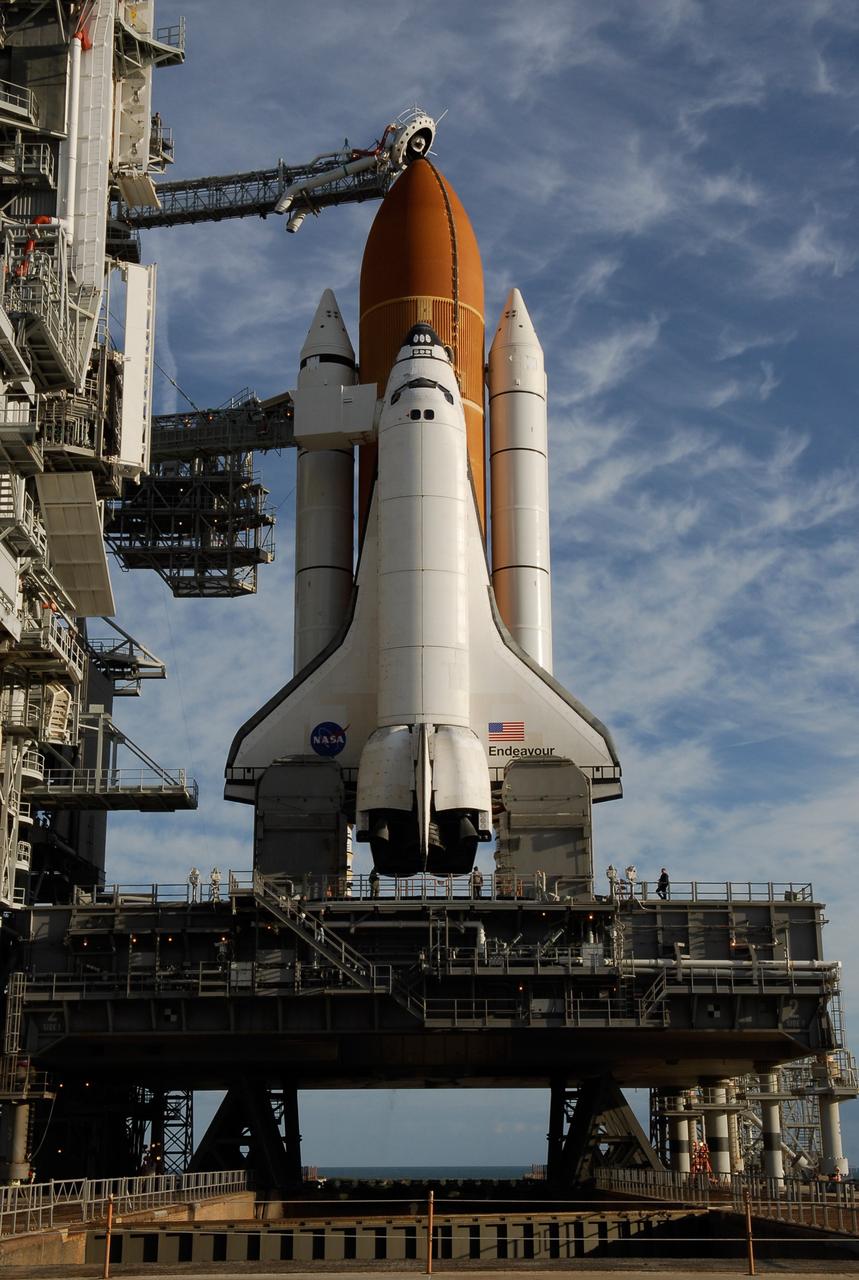

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the rotating service structure has rolled away to uncover space shuttle Endeavour, resting on the mobile launcher platform. First motion was at 8:23 a.m. and rollback was complete at 8:55 a.m. Above the orange external tank is seen the "beanie cap" at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, extending from the fixed service structure. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Below is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end, flush against the shuttle. The crew gains access into the orbiter through the White Room. On either side of the main engines and below the wings are the tail service masts, which provide several umbilical connections to the orbiter, including a liquid-oxygen line through one and a liquid-hydrogen line through another. The rotating structure provides protected access to the orbiter for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. The structure is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots about a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Endeavour and its crew will deliver the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, Dextre. Launch is scheduled for 2:28 a.m. EDT March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
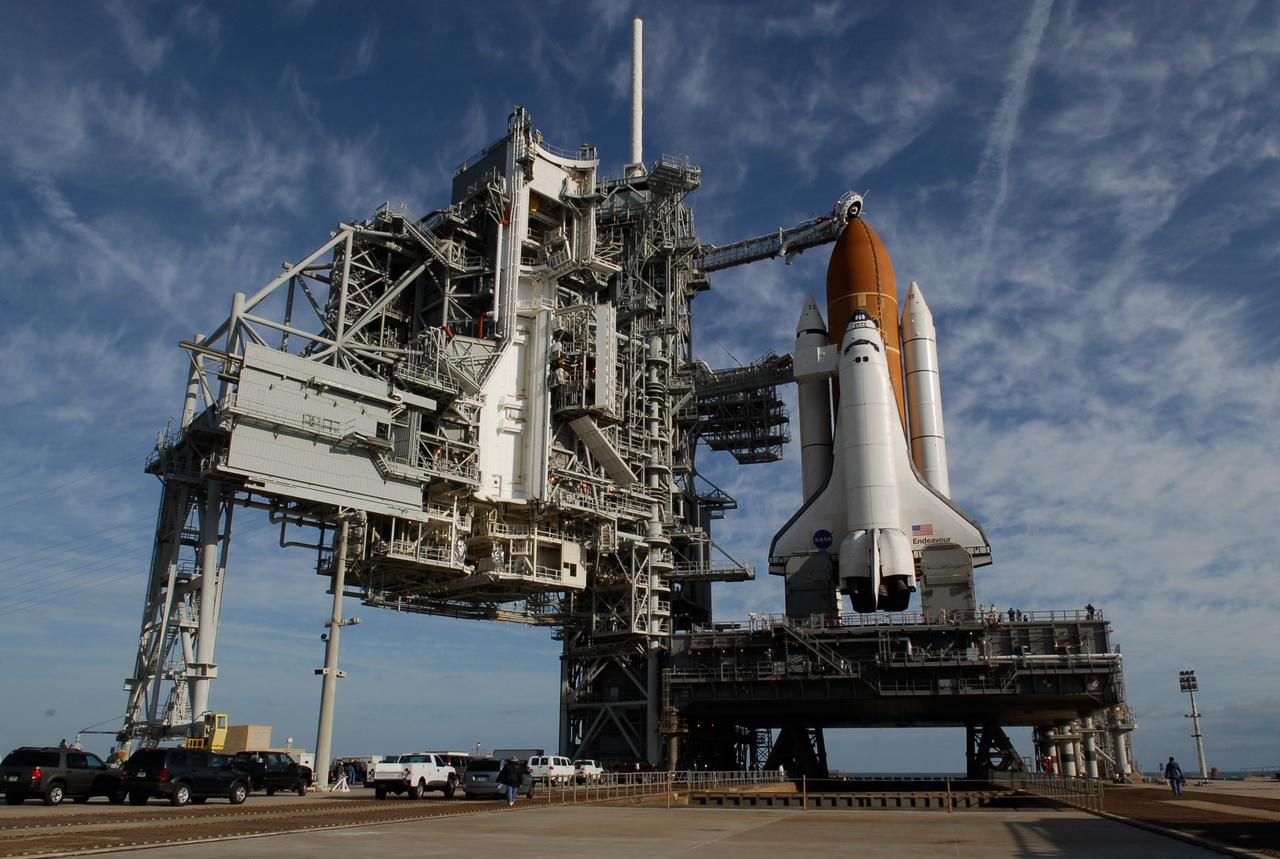

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, rollback of the rotating service structure (at left) reveals space shuttle Endeavour atop the mobile launcher platform. First motion was at 8:23 a.m. and rollback was complete at 8:55 a.m. Above the orange external tank is seen the "beanie cap" at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, extending from the fixed service structure. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Below is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end, flush against the shuttle. The crew gains access into the orbiter through the White Room. On either side of the main engines and below the wings are the tail service masts, which provide several umbilical connections to the orbiter, including a liquid-oxygen line through one and a liquid-hydrogen line through another. The rotating structure provides protected access to the orbiter for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. The structure is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots about a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Endeavour and its crew will deliver the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, Dextre. Launch is scheduled for 2:28 a.m. EDT March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
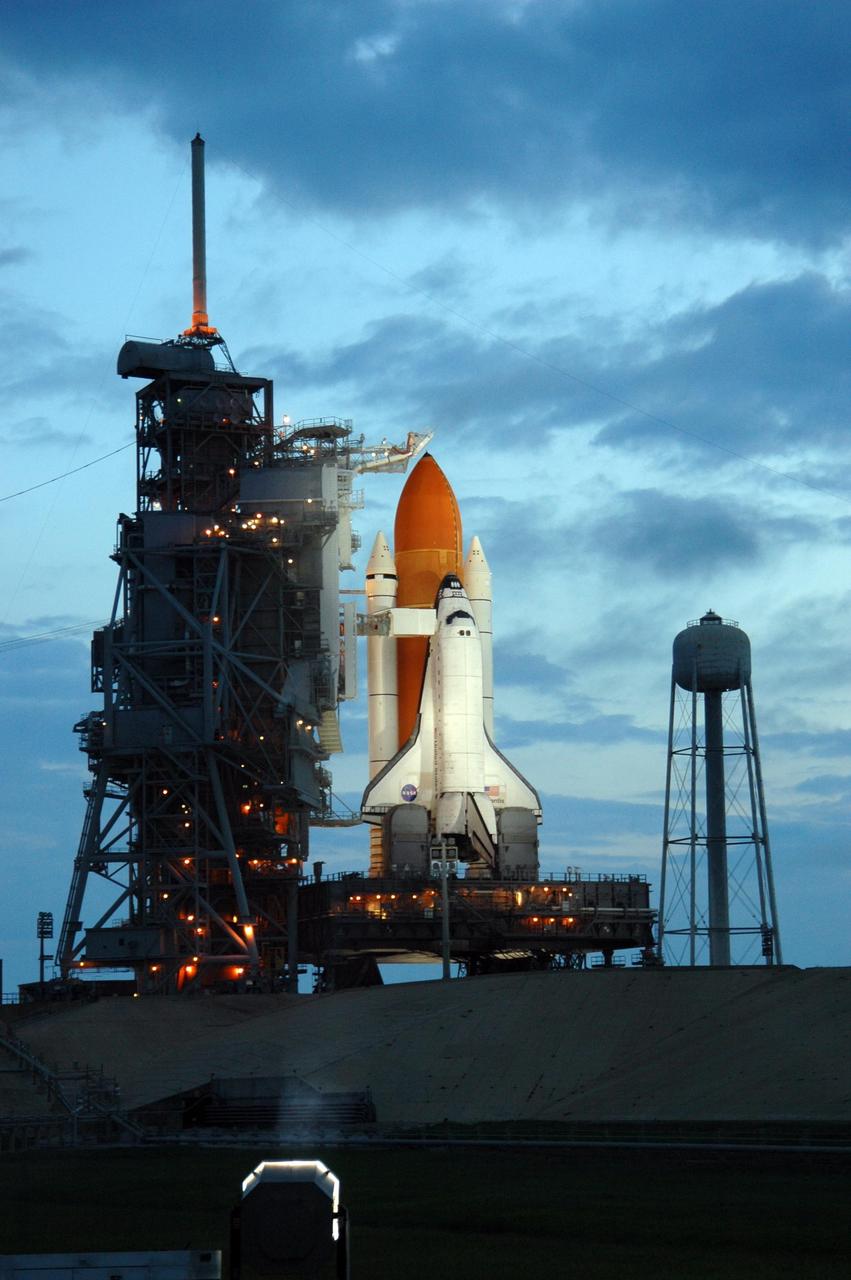

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The morning sky lightens behind Space Shuttle Atlantis while lights on the fixed service structure (FSS) still illuminate the orbiter on Launch Pad 39B. Atlantis was originally scheduled to launch at 12:29 p.m. EDT on this date, but a 24-hour scrub was called by mission managers due to a concern with Fuel Cell 1. Seen poised above the orange external tank is the vent hood (known as the "beanie cap") at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Extending from the FSS to Atlantis is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end. The White Room provides entry into the orbiter through the hatch. At right is the 300,000-gallon water tank that releases its contents onto the mobile launcher platform during liftoff to aid sound suppression. During the STS-115 mission, Atlantis' astronauts will deliver and install the 17.5-ton, bus-sized P3/P4 integrated truss segment on the station. The girder-like truss includes a set of giant solar arrays, batteries and associated electronics and will provide one-fourth of the total power-generation capability for the completed station. This mission is the 116th space shuttle flight, the 27th flight for orbiter Atlantis, and the 19th U.S. flight to the International Space Station. STS-115 is scheduled to last 11 days with a planned landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

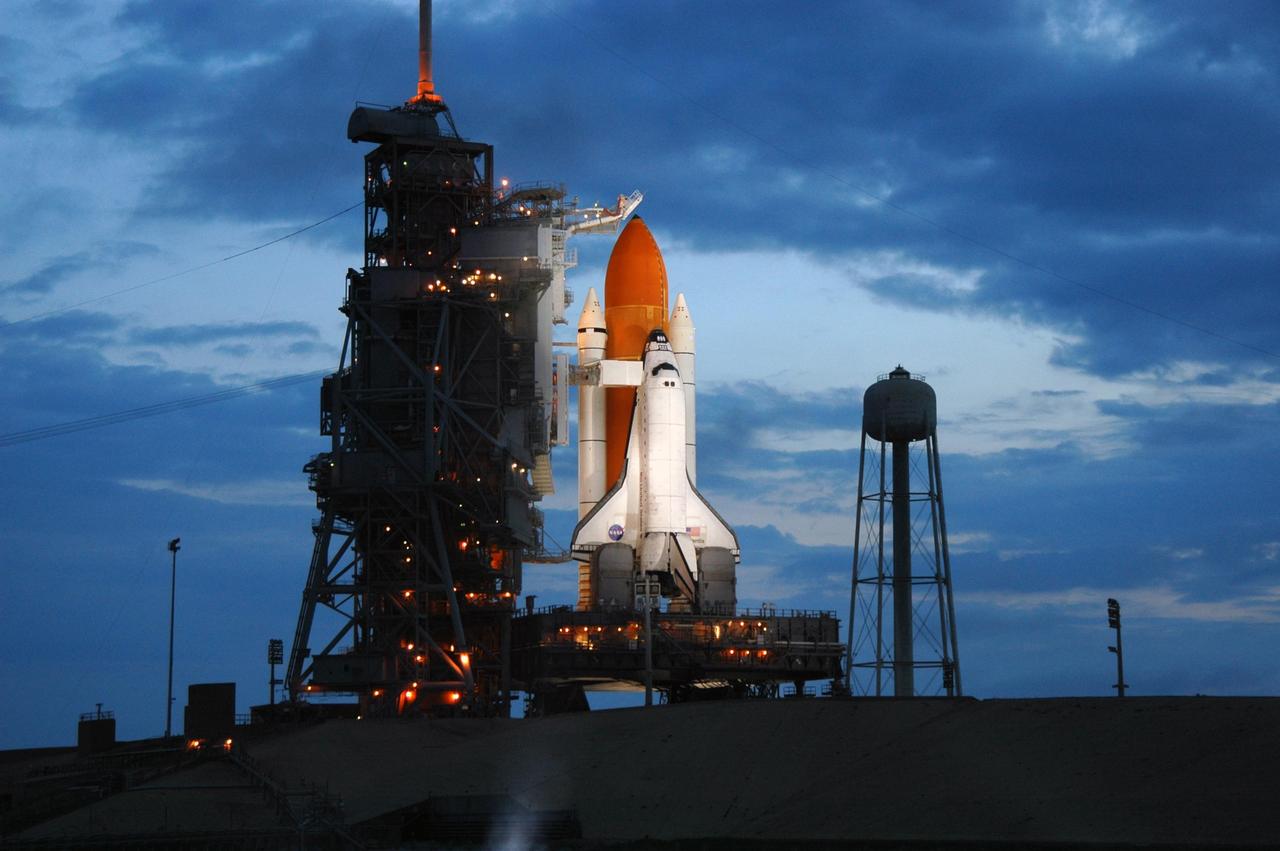
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Against the dark sky, lights bathe space shuttle Discovery, revealed after rollback of the rotating service structure in preparation for launch on the STS-124 mission. First motion was at 8:33 p.m. and rollback was complete at 9:07 p.m. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Above the orange external tank is the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap," at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm extending from the fixed service structure. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Below is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end, flush against the shuttle. The White Room provides access into the shuttle. The STS-124 mission is the second of three flights launching components to complete the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory. The shuttle crew will install Kibo's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system, or RMS. The 14-day flight includes three spacewalks. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The morning sky lightens behind Space Shuttle Atlantis while lights on the fixed service structure (FSS) still illuminate the orbiter on Launch Pad 39B. Atlantis was originally scheduled to launch at 12:29 p.m. EDT on this date, but a 24-hour scrub was called by mission managers due to a concern with Fuel Cell 1. Seen poised above the orange external tank is the vent hood (known as the "beanie cap") at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Extending from the FSS to Atlantis is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end. The White Room provides entry into the orbiter through the hatch. At right is the 300,000-gallon water tank that releases its contents onto the mobile launcher platform during liftoff to aid sound suppression. During the STS-115 mission, Atlantis' astronauts will deliver and install the 17.5-ton, bus-sized P3/P4 integrated truss segment on the station. The girder-like truss includes a set of giant solar arrays, batteries and associated electronics and will provide one-fourth of the total power-generation capability for the completed station. This mission is the 116th space shuttle flight, the 27th flight for orbiter Atlantis, and the 19th U.S. flight to the International Space Station. STS-115 is scheduled to last 11 days with a planned landing at KSC. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Flags wave near Launch Pad 39A where space shuttle Endeavour waits for liftoff. The rotating service structure was rolled back starting at 8:23 a.m. and complete at 8:55 a.m. Above the orange external tank is seen the "beanie cap" at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm, extending from the fixed service structure. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Below is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end, flush against the shuttle. The crew gains access into the orbiter through the White Room. The rotating structure provides protected access to the orbiter for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. The structure is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots about a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Endeavour and its crew will deliver the first section of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory and the Canadian Space Agency's two-armed robotic system, Dextre. Launch is scheduled for 2:28 a.m. EDT March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

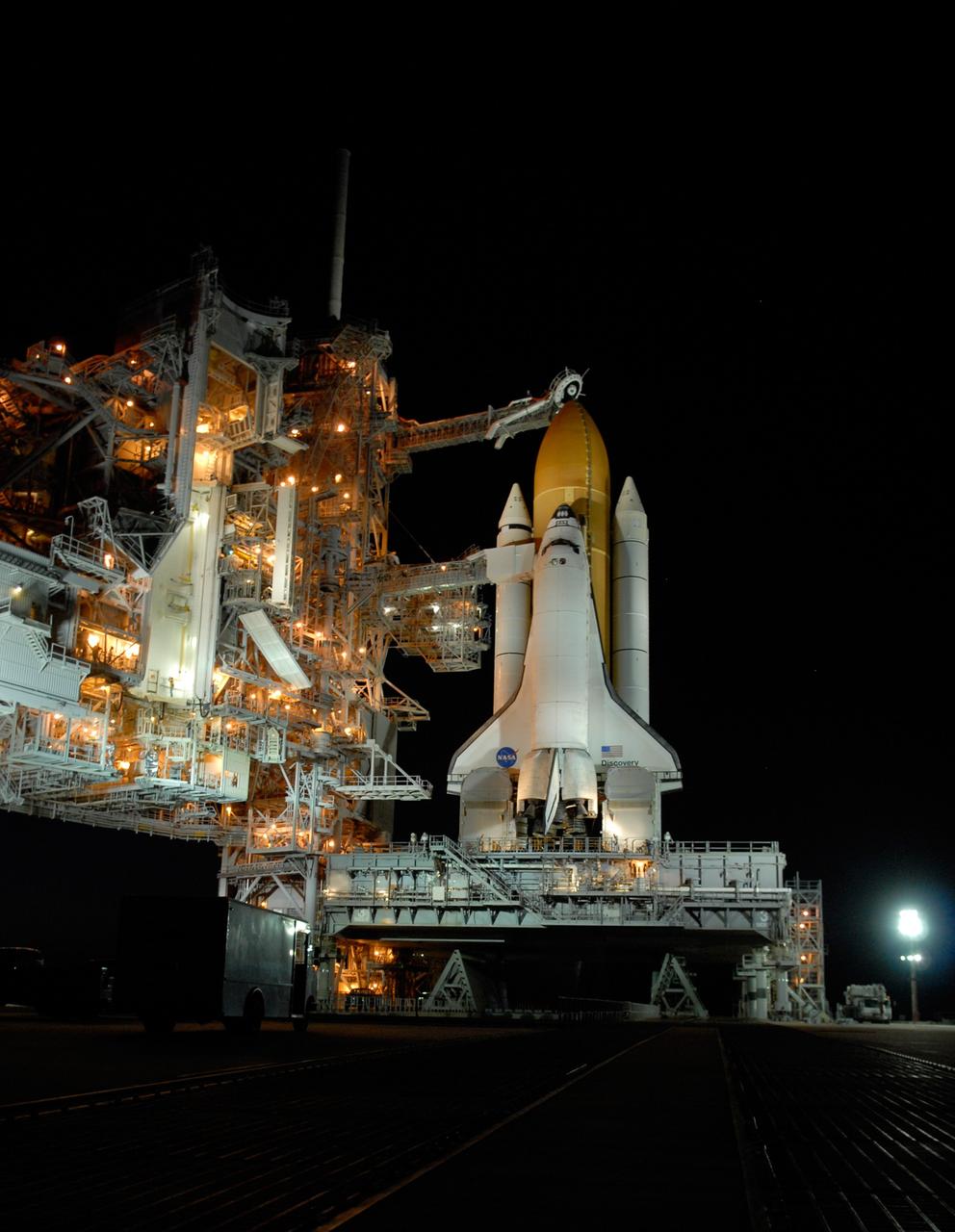
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the rotating service structure, or RSS, has rolled back on its axis to uncover space shuttle Discovery, lighted against the night sky, in preparation for launch on the STS-124 mission. Support for the outer end of the bridge is provided by two eight-wheel, motor-driven trucks (one is seen at bottom left) that move along circular twin rails installed flush with the pad surface. First motion was at 8:33 p.m. and rollback was complete at 9:07 p.m. The structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Above the orange external tank is the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap," at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm extending from the fixed service structure. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Below is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end, flush against the shuttle. The White Room provides access into the shuttle. The STS-124 mission is the second of three flights launching components to complete the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory. The shuttle crew will install Kibo's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system, or RMS. The 14-day flight includes three spacewalks. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Space Shuttle Discovery sits on Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after rollback of the rotating service structure, or RSS. The oxygen vent hood, called the “beanie cap,” is positioned above the external fuel tank. It is designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the shuttle. The rollback is preparation for Discovery’s scheduled 1:36 a.m. EDT liftoff Aug. 25 on the STS-128 mission with a crew of seven. First motion was at 5:06 a.m. EDT and completed at 5:46 a.m. EDT. The service structure provides weather protection and access to the space shuttle at the launch pad. The 13-day mission will deliver a new crew member and 33,000 pounds of equipment to the International Space Station. The equipment includes science and storage racks, a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. STS-128 will be Discovery's 37th mission and the 30th shuttle flight dedicated to station assembly and maintenance. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

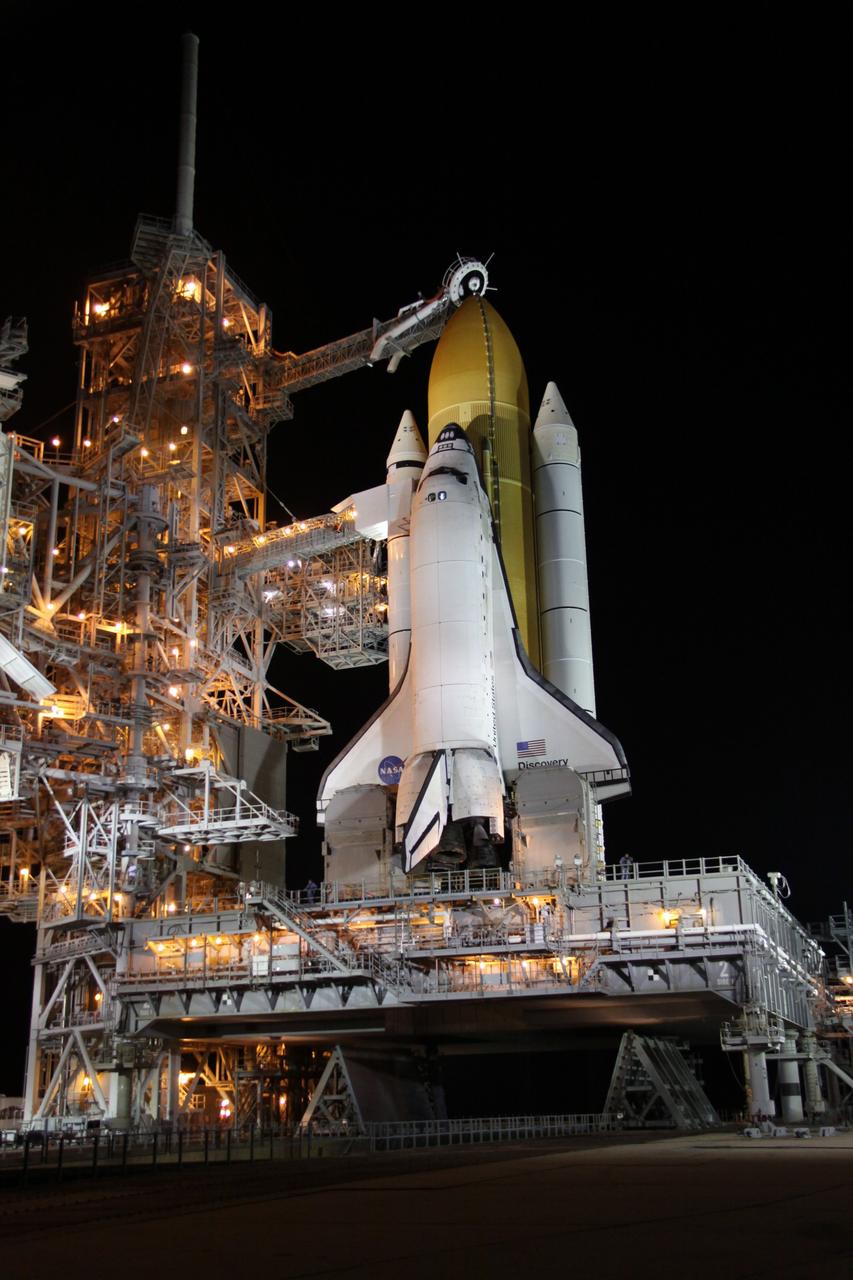
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 crew prepares to depart NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in T-38 training jets. Mission Specialist Michael Barratt, left, Pilot Eric Boe and Mission Specialist Nicole Stott and their three crewmates will wait until at least Nov. 30 to launch to the International Space Station because a leak was detected at the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate (GUCP) while Discovery's external fuel tank was being loaded for launch on Nov. 5. The GUCP is an attachment point between the external tank and a pipe that carries gaseous hydrogen safely away from the shuttle to the flare stack, where it is burned off. Engineers and managers also will evaluate a crack in the foam on the external tank. During the 11-day mission, STS-133 will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, to the orbiting laboratory. Discovery, which will fly its 39th mission, is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This will be the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
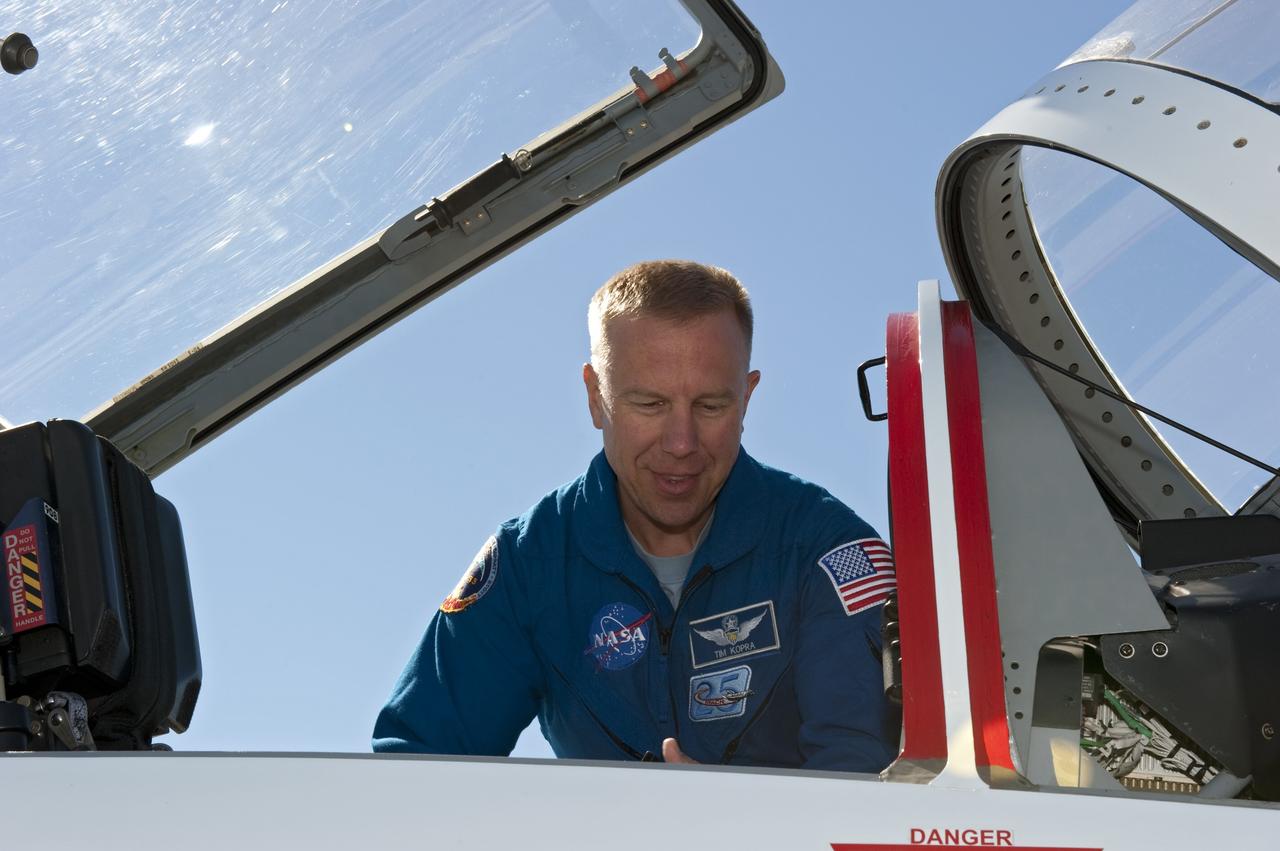

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 Mission Specialist Tim Kopra prepares to depart NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in a T-38 training jet. Kopra and his five crewmates will wait until at least Nov. 30 to launch to the International Space Station because a leak was detected at the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate (GUCP) while Discovery's external fuel tank was being loaded for launch on Nov. 5. The GUCP is an attachment point between the external tank and a pipe that carries gaseous hydrogen safely away from the shuttle to the flare stack, where it is burned off. Engineers and managers also will evaluate a crack in the foam on the external tank. During the 11-day mission, STS-133 will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, to the orbiting laboratory. Discovery, which will fly its 39th mission, is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This will be the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap," is positioned above the external fuel tank of space shuttle Discovery following the rollback of the rotating service structure, or RSS, at left. The beanie cap is designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the shuttle. The rollback is preparation for Discovery's scheduled 1:36 a.m. EDT liftoff Aug. 25 on the STS-128 mission with a crew of seven. First motion was at 5:06 a.m. EDT and completed at 5:46 a.m. EDT. The service structure provides weather protection and access to the space shuttle at the launch pad. The 13-day mission will deliver a new crew member and 33,000 pounds of equipment to the International Space Station. The equipment includes science and storage racks, a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. STS-128 will be Discovery's 37th mission and the 30th shuttle flight dedicated to station assembly and maintenance. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
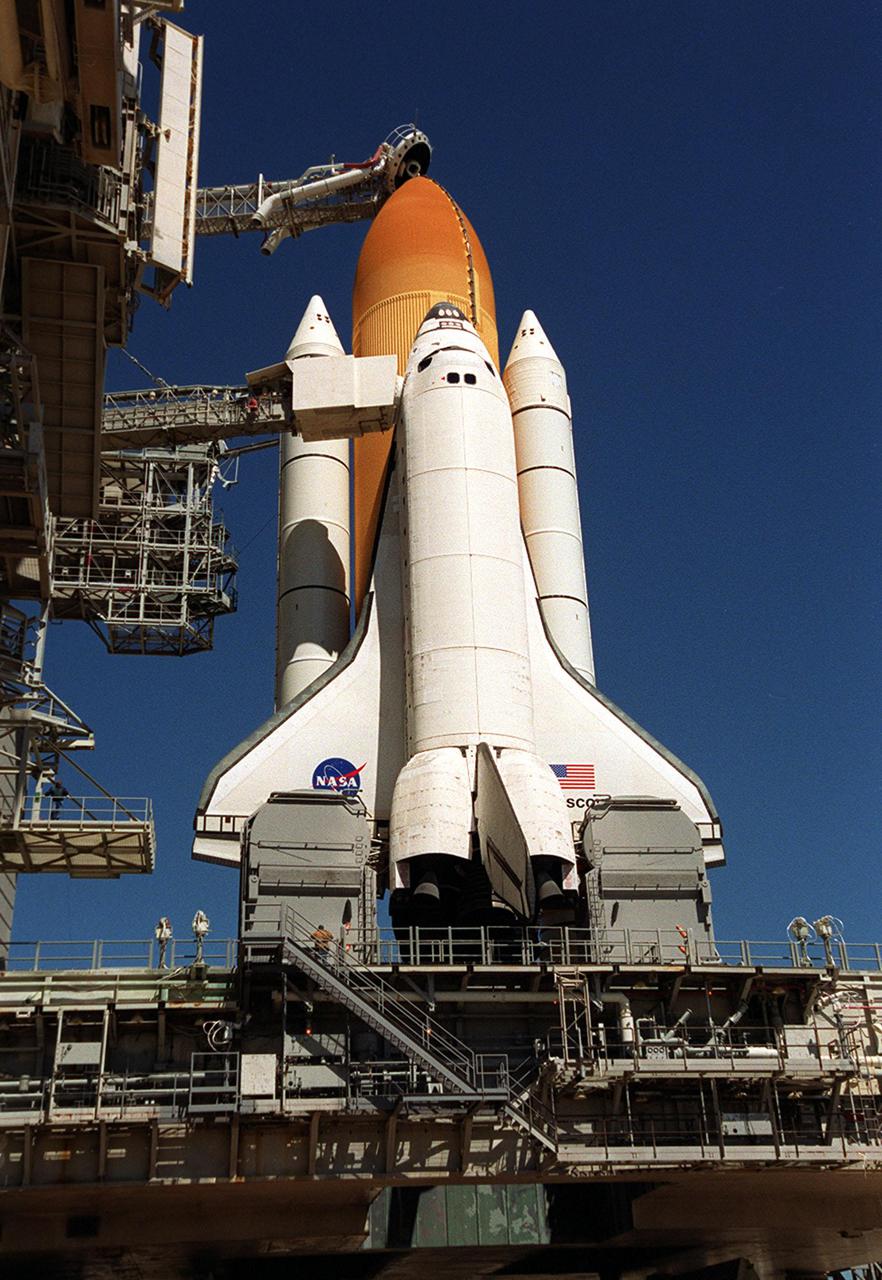

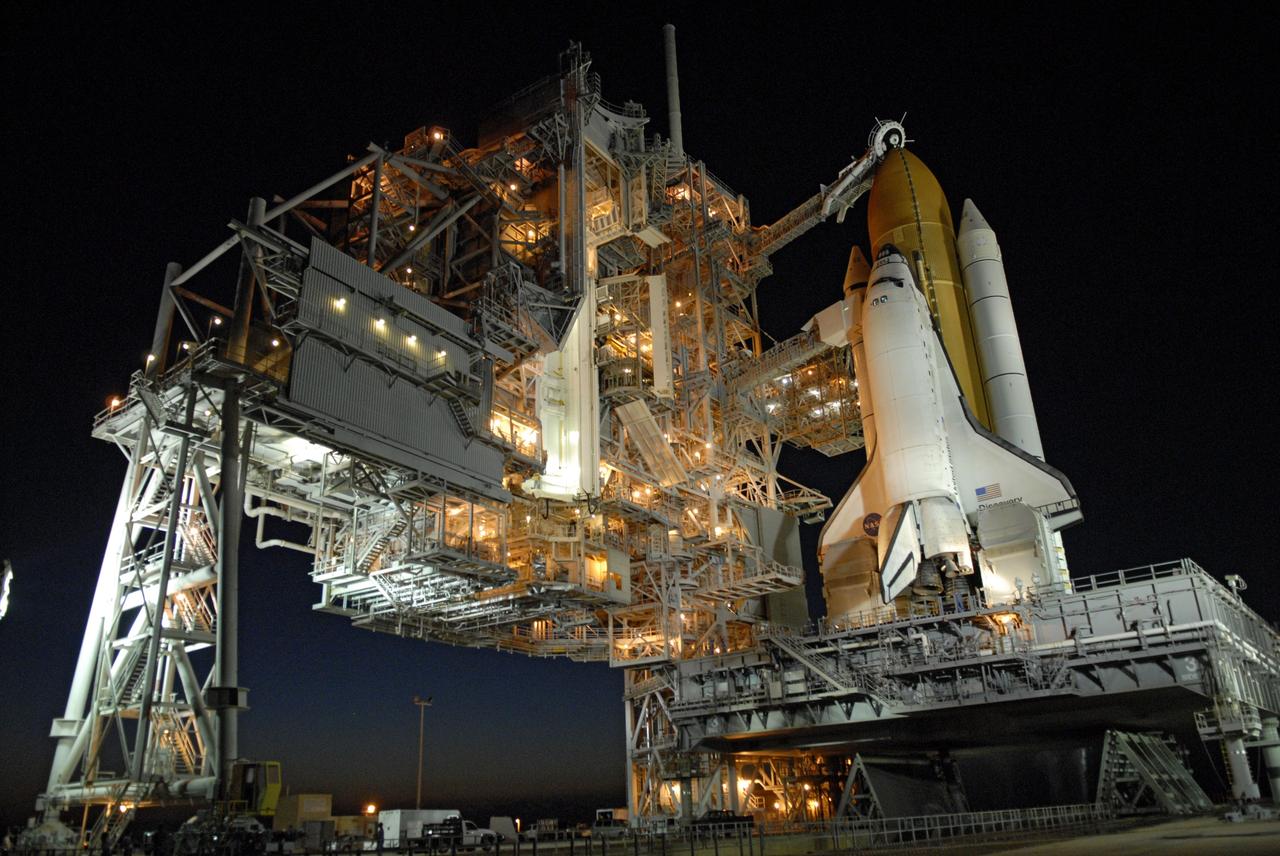
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery shines on Launch Pad 39B after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure. Situated above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm with the “beanie cap,” a vent hood. Extended out from the Fixed Service Structure (left) to the orbiter is the orbiter access arm with an environmentally controlled chamber, known as the White Room, at the end of the arm. The White Room provides entrance for the astronaut crew into the orbiter. On either side of the tail and main engines are the tail service masts. Rising 31 feet above the Mobile Launcher Platform, the tail masts provide umbilical connections for liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen lines to fuel the external tank from storage tanks adjacent to the launch pad. Discovery carries the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny. Launch on mission STS-102 is scheduled March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST
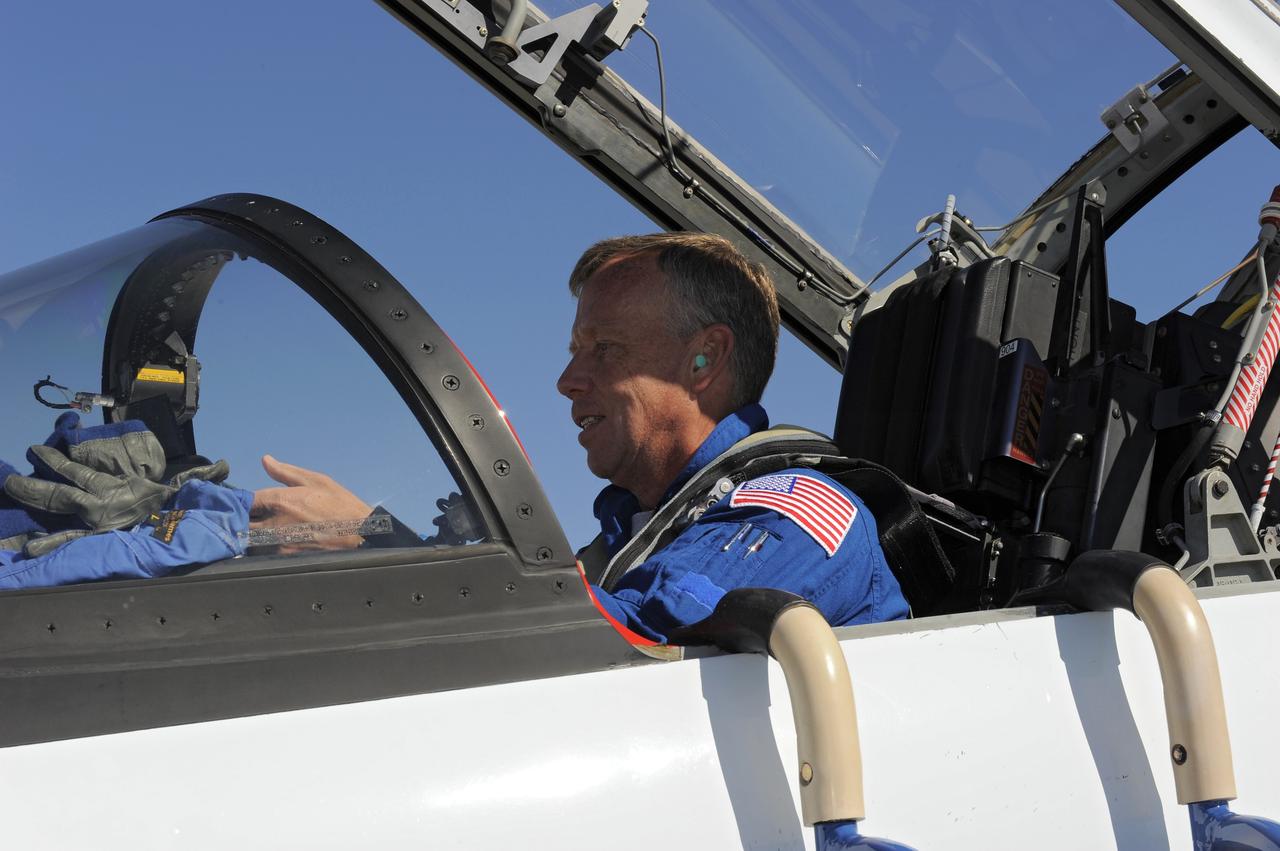

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 Commander Steve Lindsey prepares to depart NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in a T-38 training jet. Lindsey and his five crewmates will wait until at least Nov. 30 to launch to the International Space Station because a leak was detected at the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate (GUCP) while Discovery's external fuel tank was being loaded for launch on Nov. 5. The GUCP is an attachment point between the external tank and a pipe that carries gaseous hydrogen safely away from the shuttle to the flare stack, where it is burned off. Engineers and managers also will evaluate a crack in the foam on the external tank. During the 11-day mission, STS-133 will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, to the orbiting laboratory. Discovery, which will fly its 39th mission, is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This will be the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
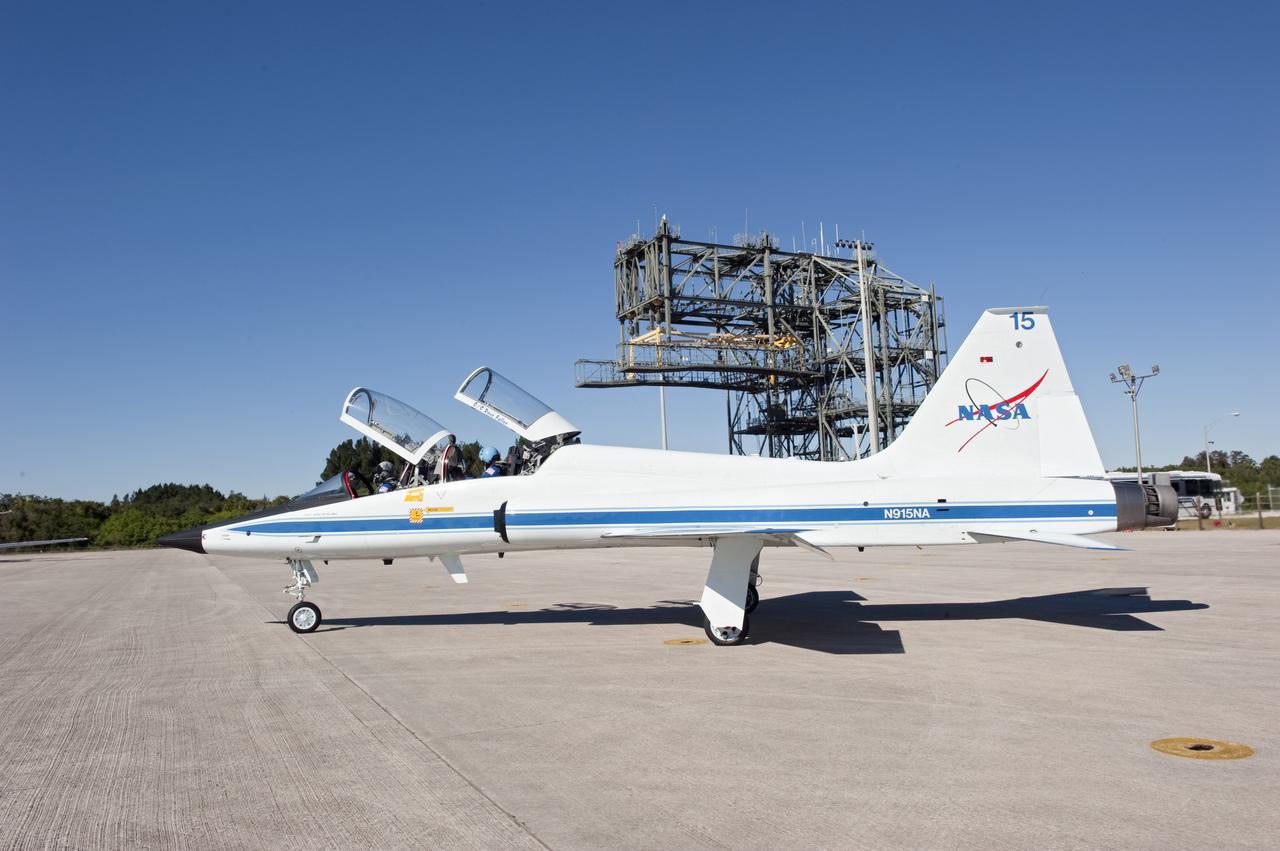

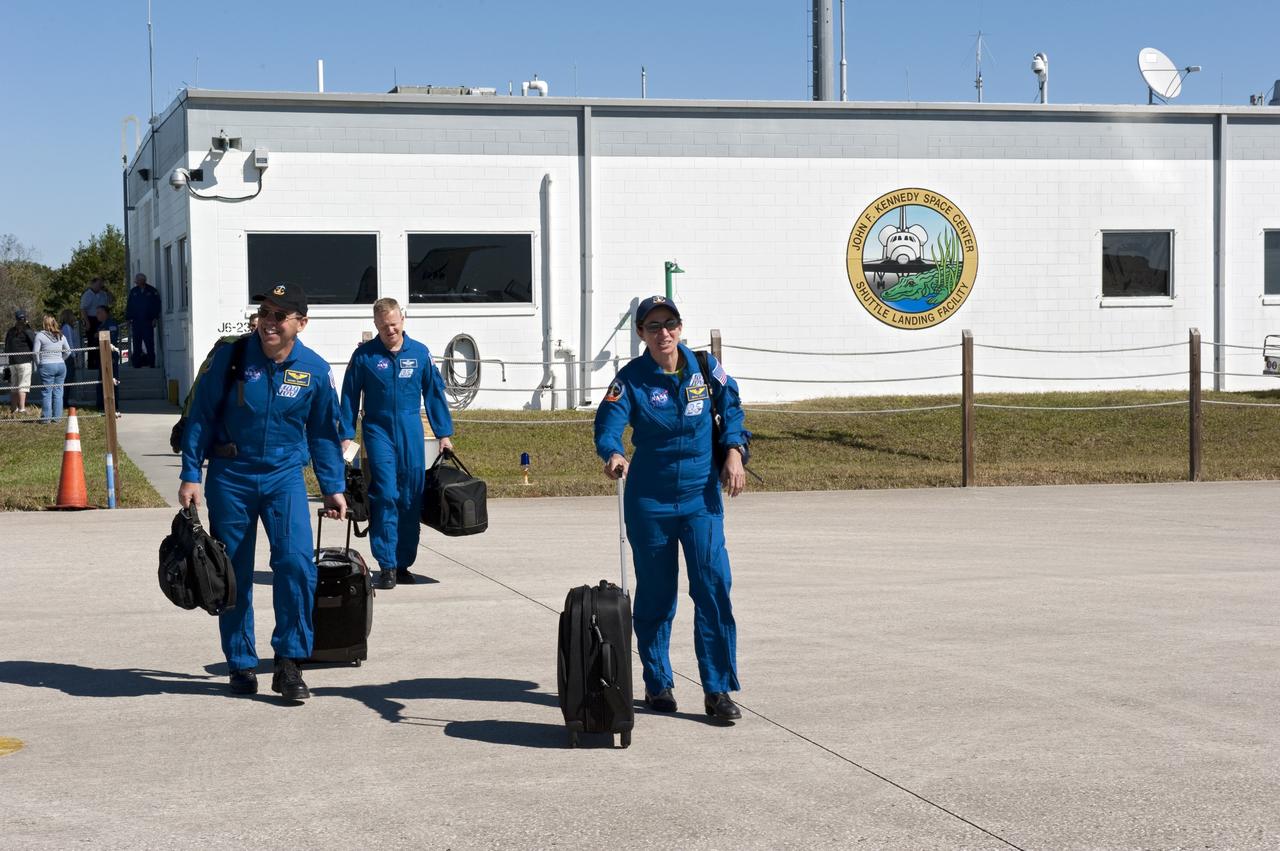
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 crew members depart NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in a T-38 training jet. The six-member crew will wait until at least Nov. 30 to launch to the International Space Station because a leak was detected at the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate (GUCP) while Discovery's external fuel tank was being loaded for launch on Nov. 5. The GUCP is an attachment point between the external tank and a pipe that carries gaseous hydrogen safely away from the shuttle to the flare stack, where it is burned off. Engineers and managers also will evaluate a crack in the foam on the external tank. During the 11-day mission, STS-133 will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, to the orbiting laboratory. Discovery, which will fly its 39th mission, is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This will be the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
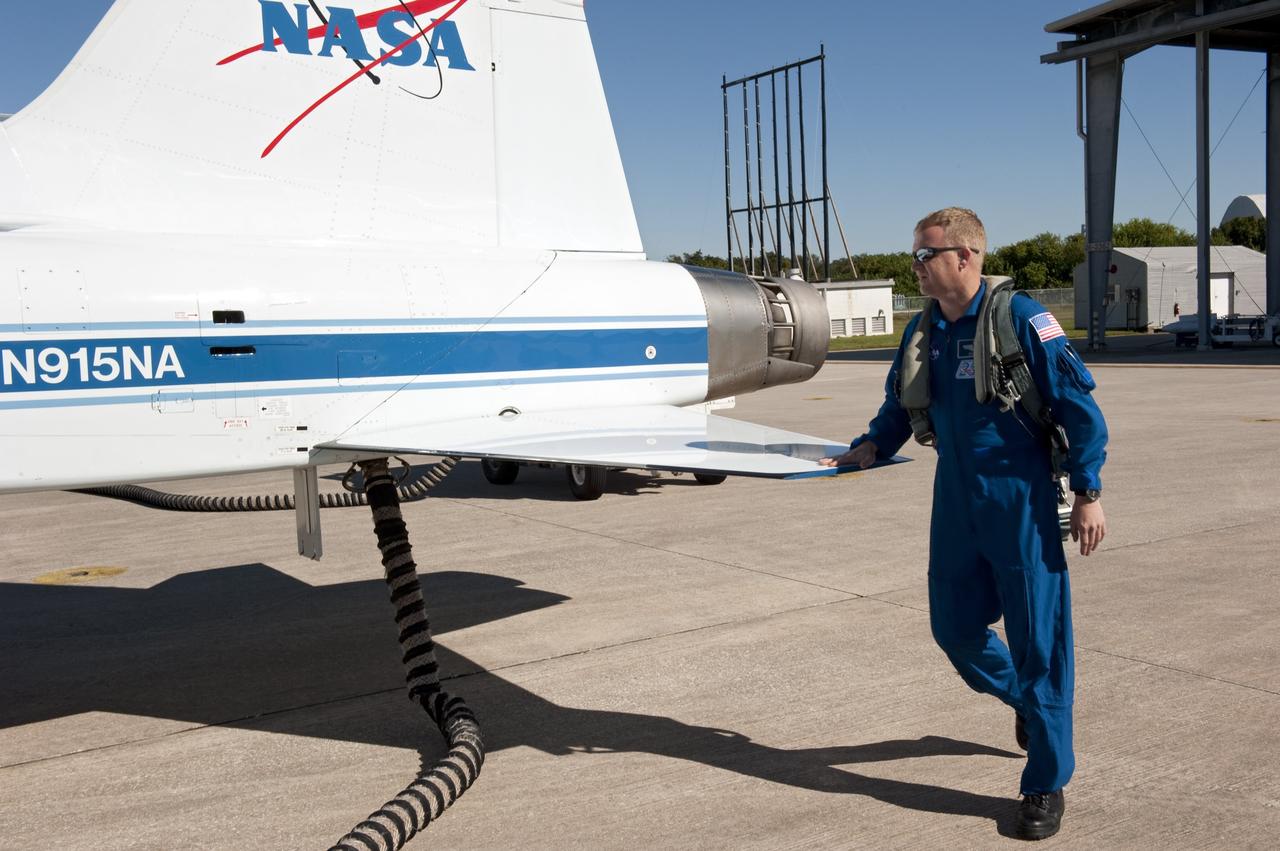

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 Pilot Eric Boe prepares to depart NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in a T-38 training jet. Boe and his five crewmates will wait until at least Nov. 30 to launch to the International Space Station because a leak was detected at the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate (GUCP) while Discovery's external fuel tank was being loaded for launch on Nov. 5. The GUCP is an attachment point between the external tank and a pipe that carries gaseous hydrogen safely away from the shuttle to the flare stack, where it is burned off. Engineers and managers also will evaluate a crack in the foam on the external tank. During the 11-day mission, STS-133 will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, to the orbiting laboratory. Discovery, which will fly its 39th mission, is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This will be the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
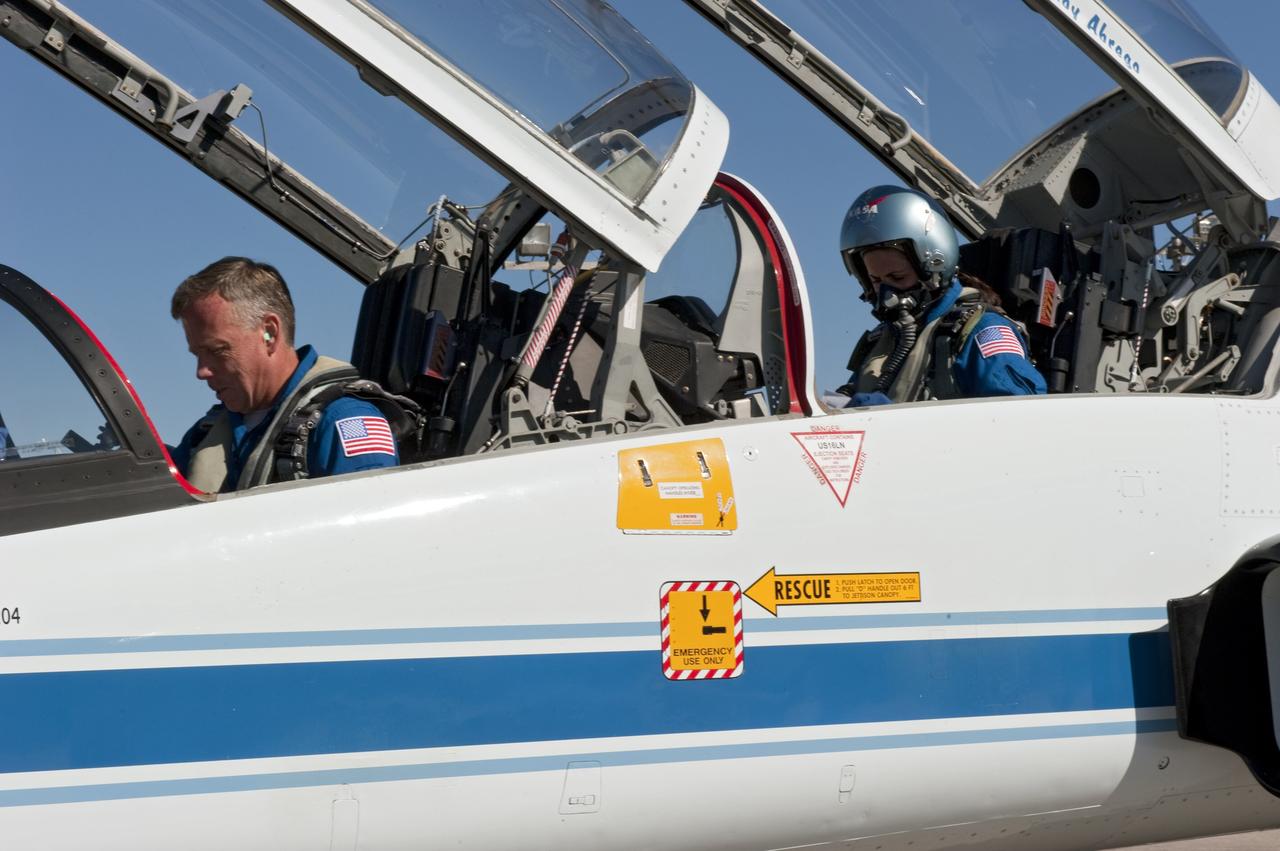

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 Commander Steve Lindsey, left, and Mission Specialist Nicole Stott prepare to depart NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in a T-38 training jet. The six-member crew will wait until at least Nov. 30 to launch to the International Space Station because a leak was detected at the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate (GUCP) while Discovery's external fuel tank was being loaded for launch on Nov. 5. The GUCP is an attachment point between the external tank and a pipe that carries gaseous hydrogen safely away from the shuttle to the flare stack, where it is burned off. Engineers and managers also will evaluate a crack in the foam on the external tank. During the 11-day mission, STS-133 will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, to the orbiting laboratory. Discovery, which will fly its 39th mission, is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This will be the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
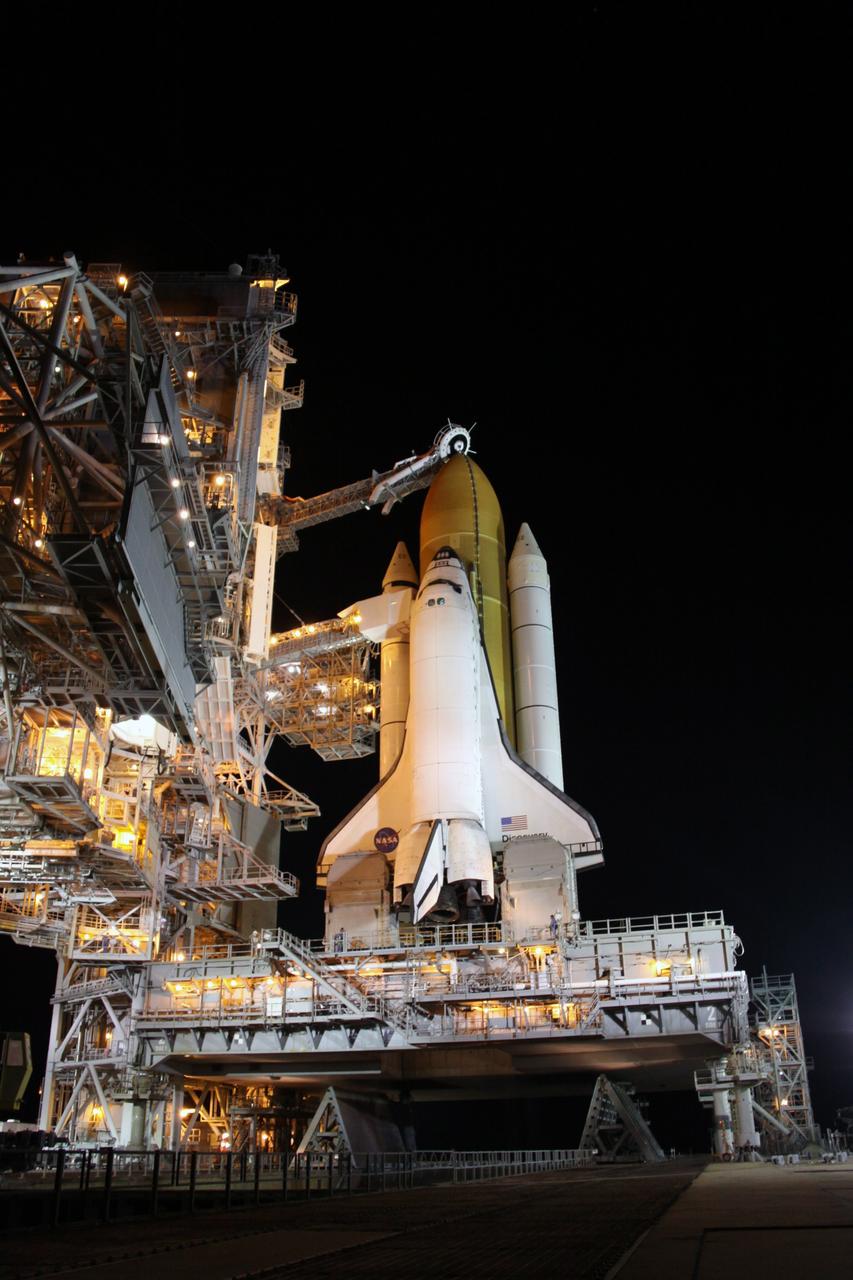

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap," is positioned above the external fuel tank of space shuttle Discovery following the rollback of the rotating service structure, or RSS, at left. The beanie cap is designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the shuttle. The rollback is preparation for Discovery's scheduled 1:36 a.m. EDT liftoff Aug. 25 on the STS-128 mission with a crew of seven. First motion was at 5:06 a.m. EDT and completed at 5:46 a.m. EDT. The service structure provides weather protection and access to the space shuttle at the launch pad. The 13-day mission will deliver a new crew member and 33,000 pounds of equipment to the International Space Station. The equipment includes science and storage racks, a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. STS-128 will be Discovery's 37th mission and the 30th shuttle flight dedicated to station assembly and maintenance. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
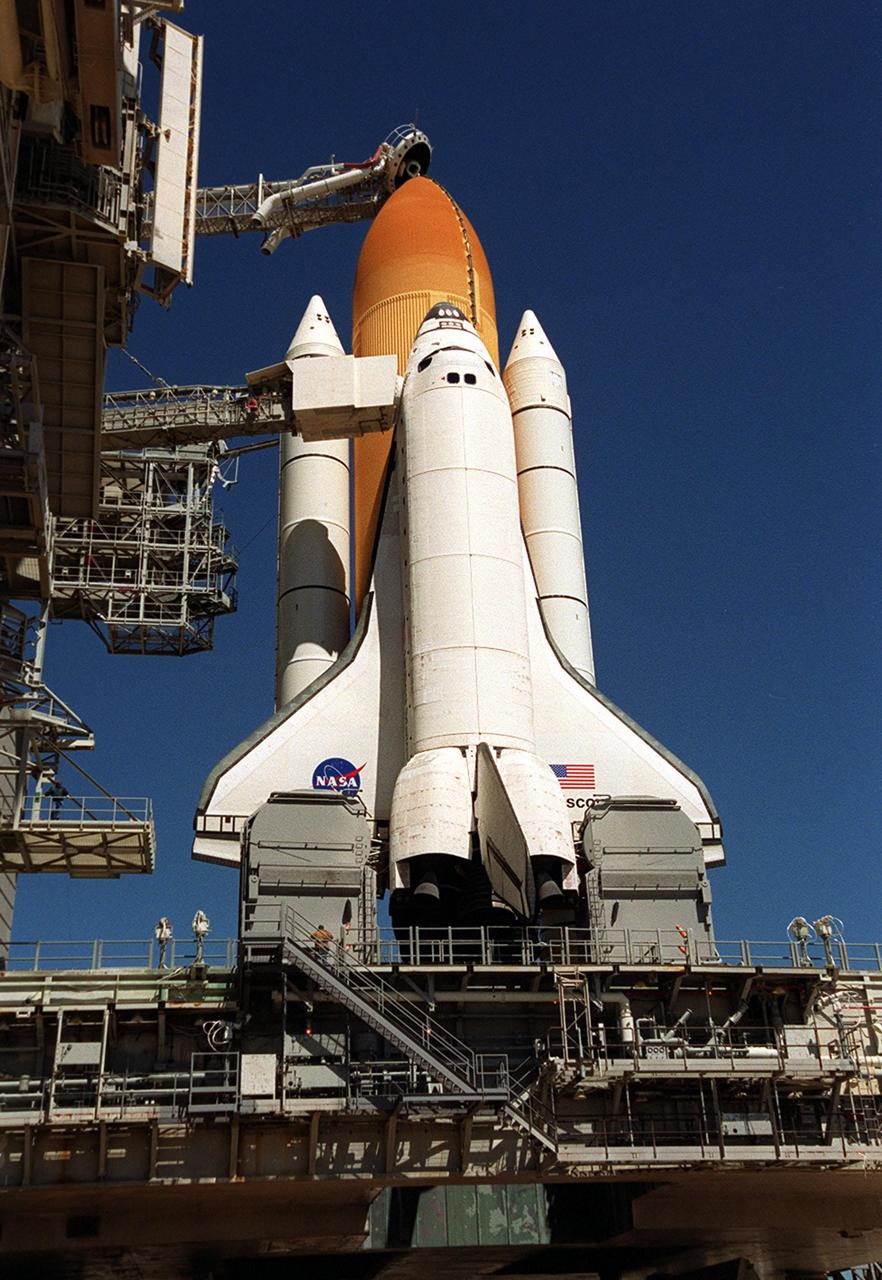

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery shines on Launch Pad 39B after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure. Situated above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm with the “beanie cap,” a vent hood. Extended out from the Fixed Service Structure (left) to the orbiter is the orbiter access arm with an environmentally controlled chamber, known as the White Room, at the end of the arm. The White Room provides entrance for the astronaut crew into the orbiter. On either side of the tail and main engines are the tail service masts. Rising 31 feet above the Mobile Launcher Platform, the tail masts provide umbilical connections for liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen lines to fuel the external tank from storage tanks adjacent to the launch pad. Discovery carries the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny. Launch on mission STS-102 is scheduled March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST
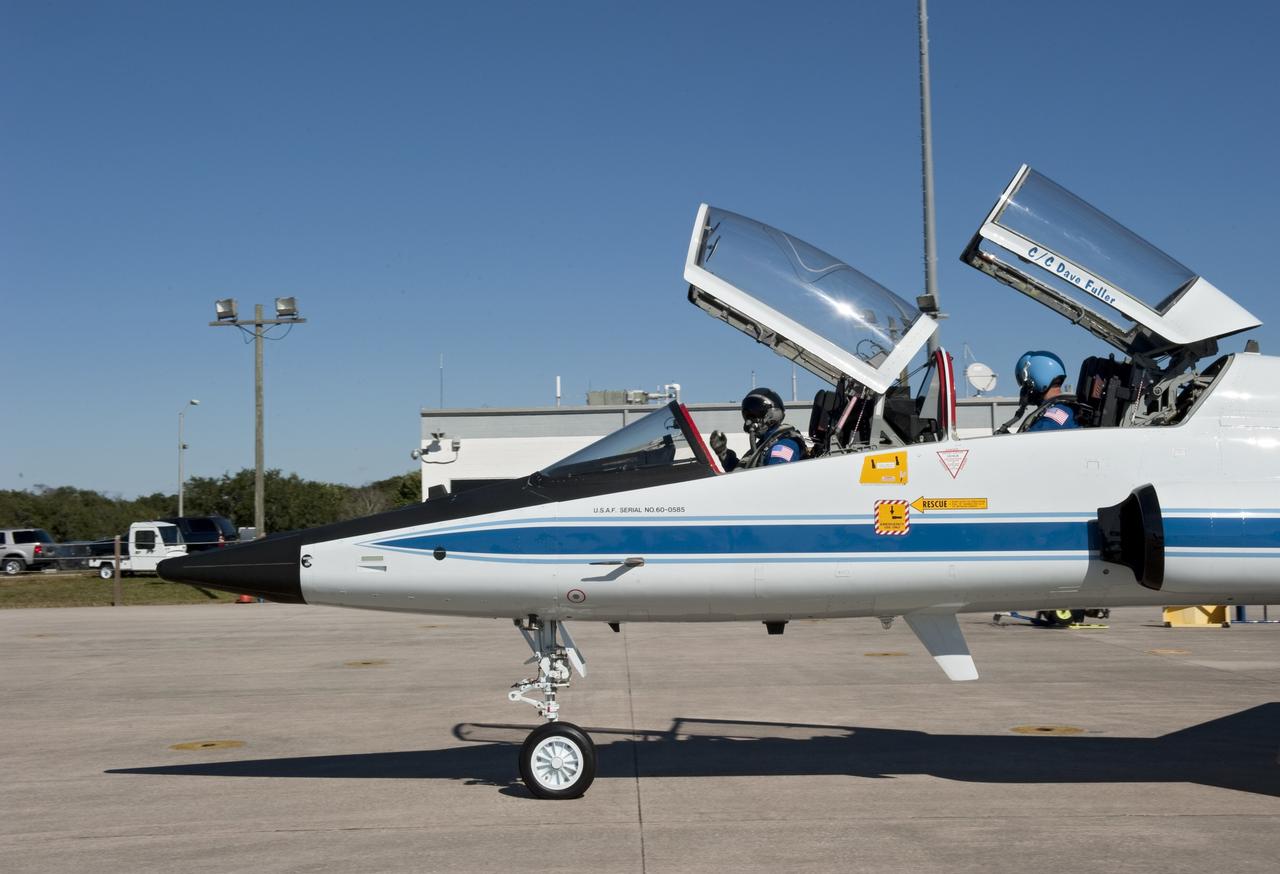

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 crew members depart NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in a T-38 training jet. The six-member crew will wait until at least Nov. 30 to launch to the International Space Station because a leak was detected at the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate (GUCP) while Discovery's external fuel tank was being loaded for launch on Nov. 5. The GUCP is an attachment point between the external tank and a pipe that carries gaseous hydrogen safely away from the shuttle to the flare stack, where it is burned off. Engineers and managers also will evaluate a crack in the foam on the external tank. During the 11-day mission, STS-133 will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, to the orbiting laboratory. Discovery, which will fly its 39th mission, is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This will be the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
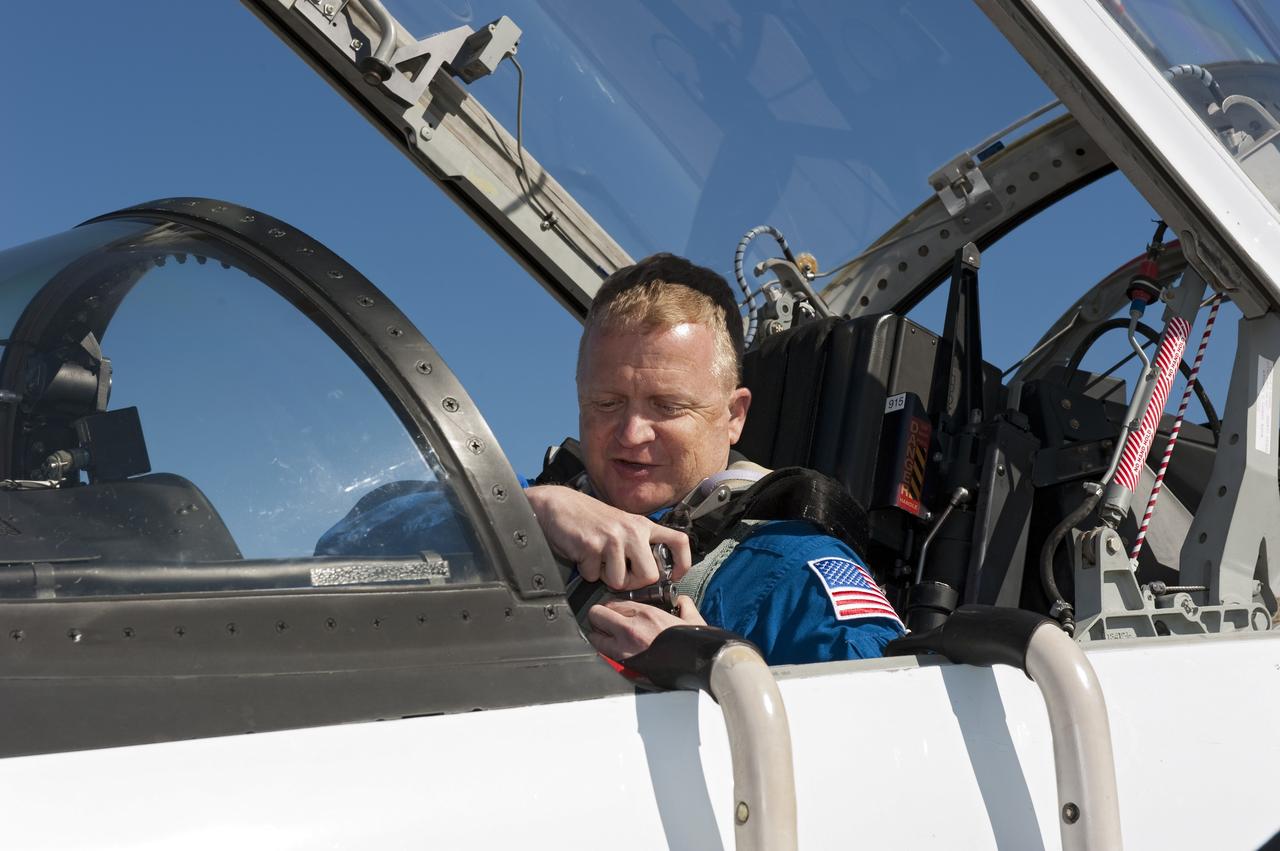

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 Pilot Eric Boe prepares to depart NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in a T-38 training jet. Boe and his five crewmates will wait until at least Nov. 30 to launch to the International Space Station because a leak was detected at the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate (GUCP) while Discovery's external fuel tank was being loaded for launch on Nov. 5. The GUCP is an attachment point between the external tank and a pipe that carries gaseous hydrogen safely away from the shuttle to the flare stack, where it is burned off. Engineers and managers also will evaluate a crack in the foam on the external tank. During the 11-day mission, STS-133 will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, to the orbiting laboratory. Discovery, which will fly its 39th mission, is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This will be the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
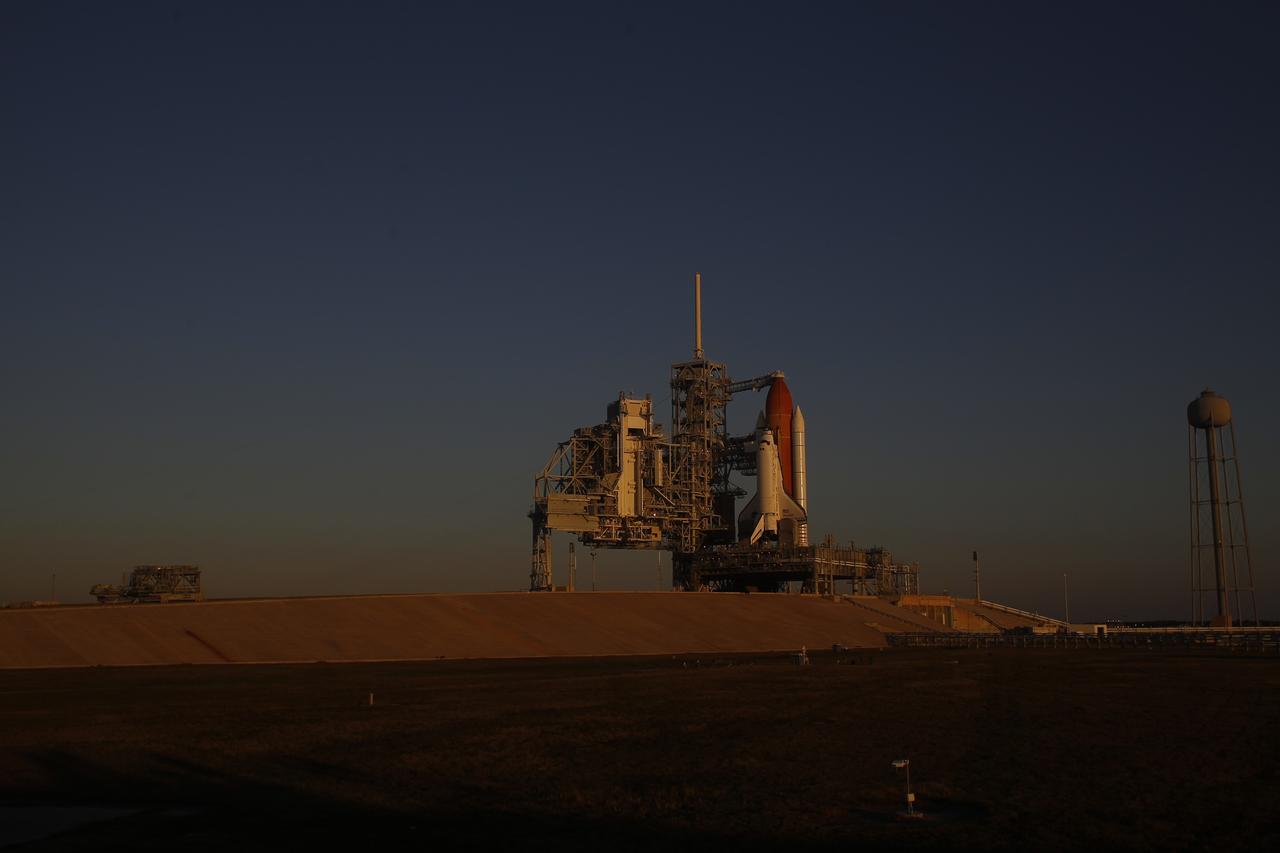

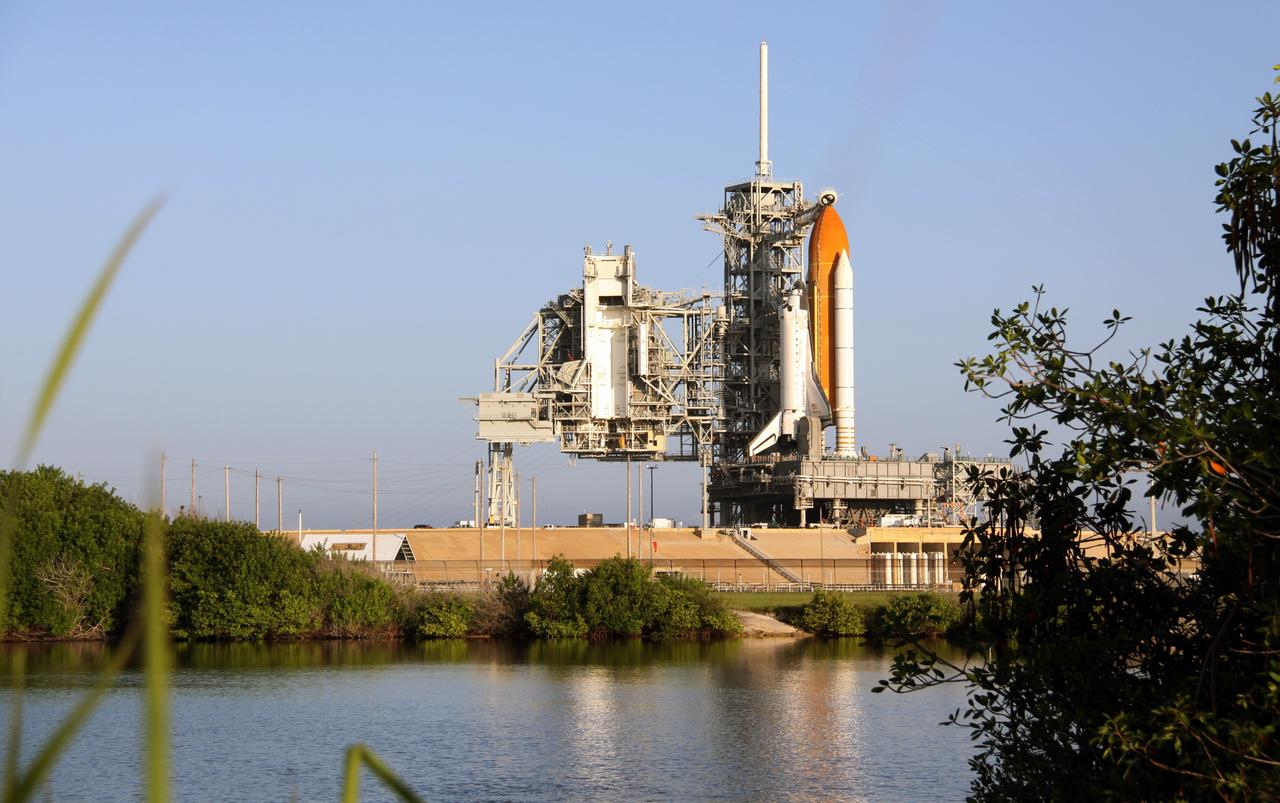
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Discovery waits patiently on Launch Pad 39A for its STS-133 launch to the International Space Station. Managers scrubbed the Nov. 5 launch attempt because a hydrogen gas leak was detected at the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate (GUCP) while Discovery's external fuel tank was being loaded. The GUCP is an attachment point between the external tank and a pipe that carries gaseous hydrogen safely away from the shuttle to the flare stack, where it is burned off. The next possible launch attempt would be Monday, Nov. 8, at 12:53 p.m. EST. After that, the launch window moves to Nov. 30 through Dec. 5. During the 11-day mission, Discovery and its six crew members will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, to the orbiting laboratory. Discovery, which will fly its 39th mission, is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This will be the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA
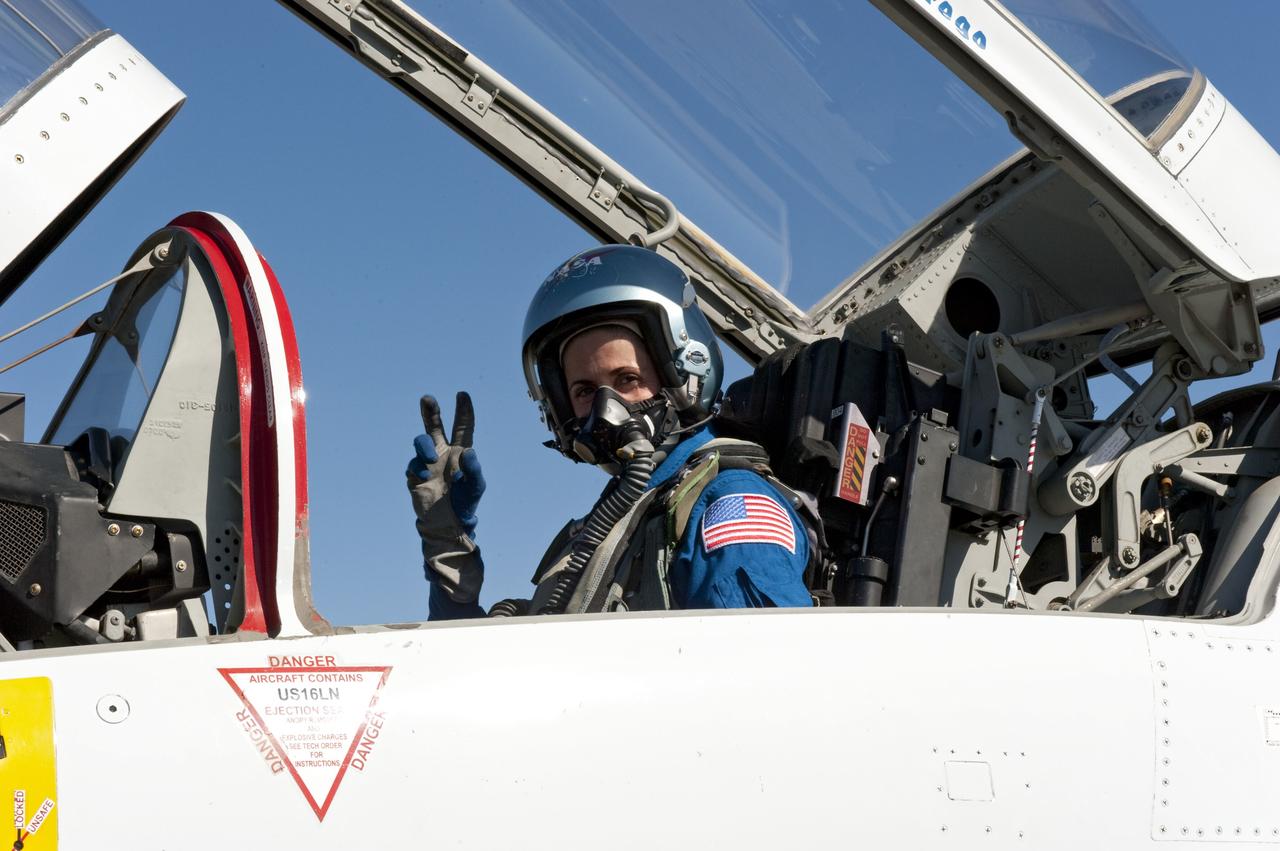

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 Mission Specialist Nicole Stott prepares to depart NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in a T-38 training jet. Stott and her five crewmates will wait until at least Nov. 30 to launch to the International Space Station because a leak was detected at the Ground Umbilical Carrier Plate (GUCP) while Discovery's external fuel tank was being loaded for launch on Nov. 5. The GUCP is an attachment point between the external tank and a pipe that carries gaseous hydrogen safely away from the shuttle to the flare stack, where it is burned off. Engineers and managers also will evaluate a crack in the foam on the external tank. During the 11-day mission, STS-133 will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, to the orbiting laboratory. Discovery, which will fly its 39th mission, is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This will be the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on STS-133, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
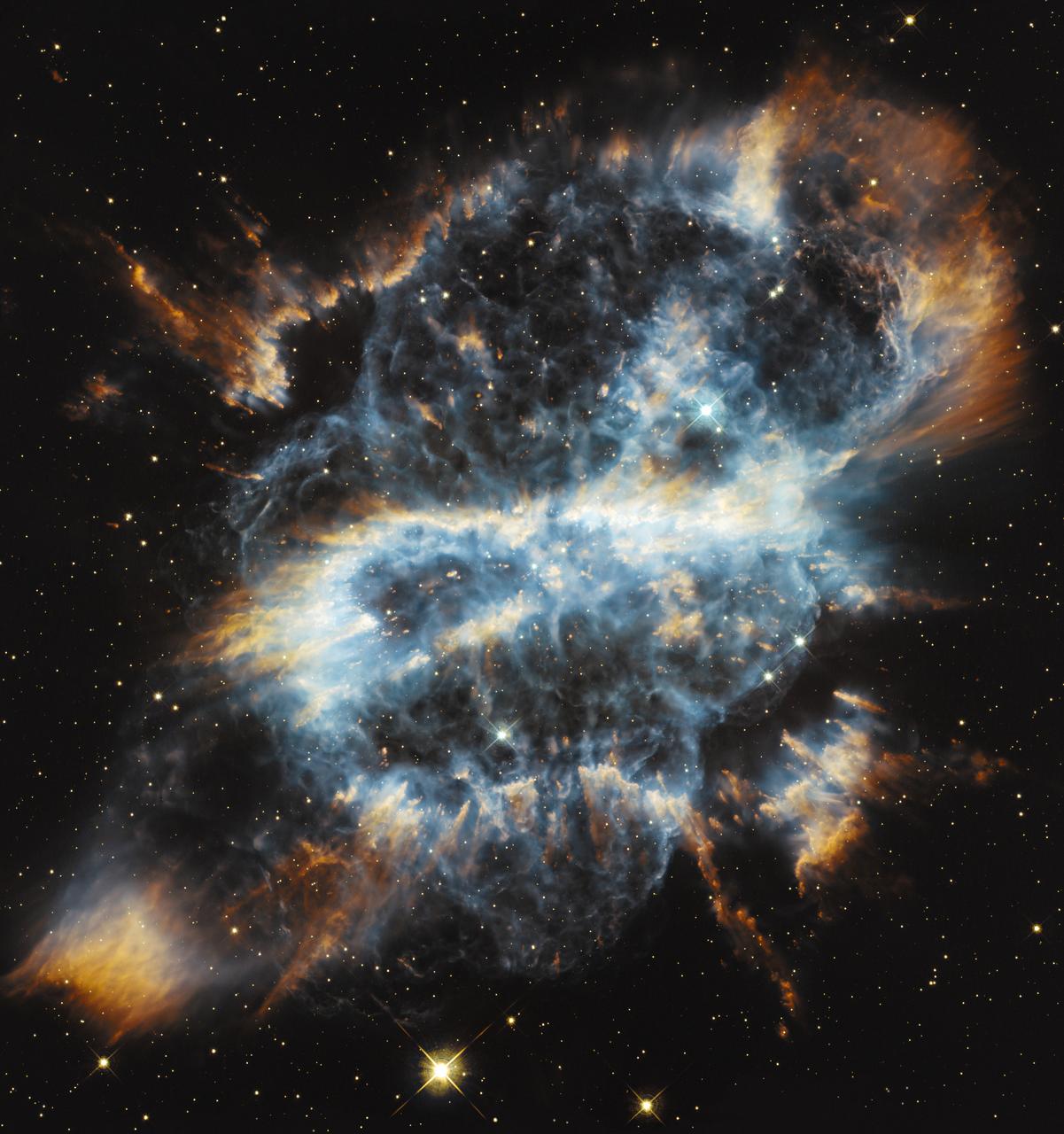

'Tis the season for holiday decorating and tree-trimming. Not to be left out, astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have photographed a festive-looking nearby planetary nebula called NGC 5189. The intricate structure of this bright gaseous nebula resembles a glass-blown holiday ornament with a glowing ribbon entwined. Planetary nebulae represent the final brief stage in the life of a medium-sized star like our sun. While consuming the last of the fuel in its core, the dying star expels a large portion of its outer envelope. This material then becomes heated by the radiation from the stellar remnant and radiates, producing glowing clouds of gas that can show complex structures, as the ejection of mass from the star is uneven in both time and direction. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/ngc5189.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/ngc5189.html</a> Credit: NASA, ESA, and G. Bacon (STScI) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>