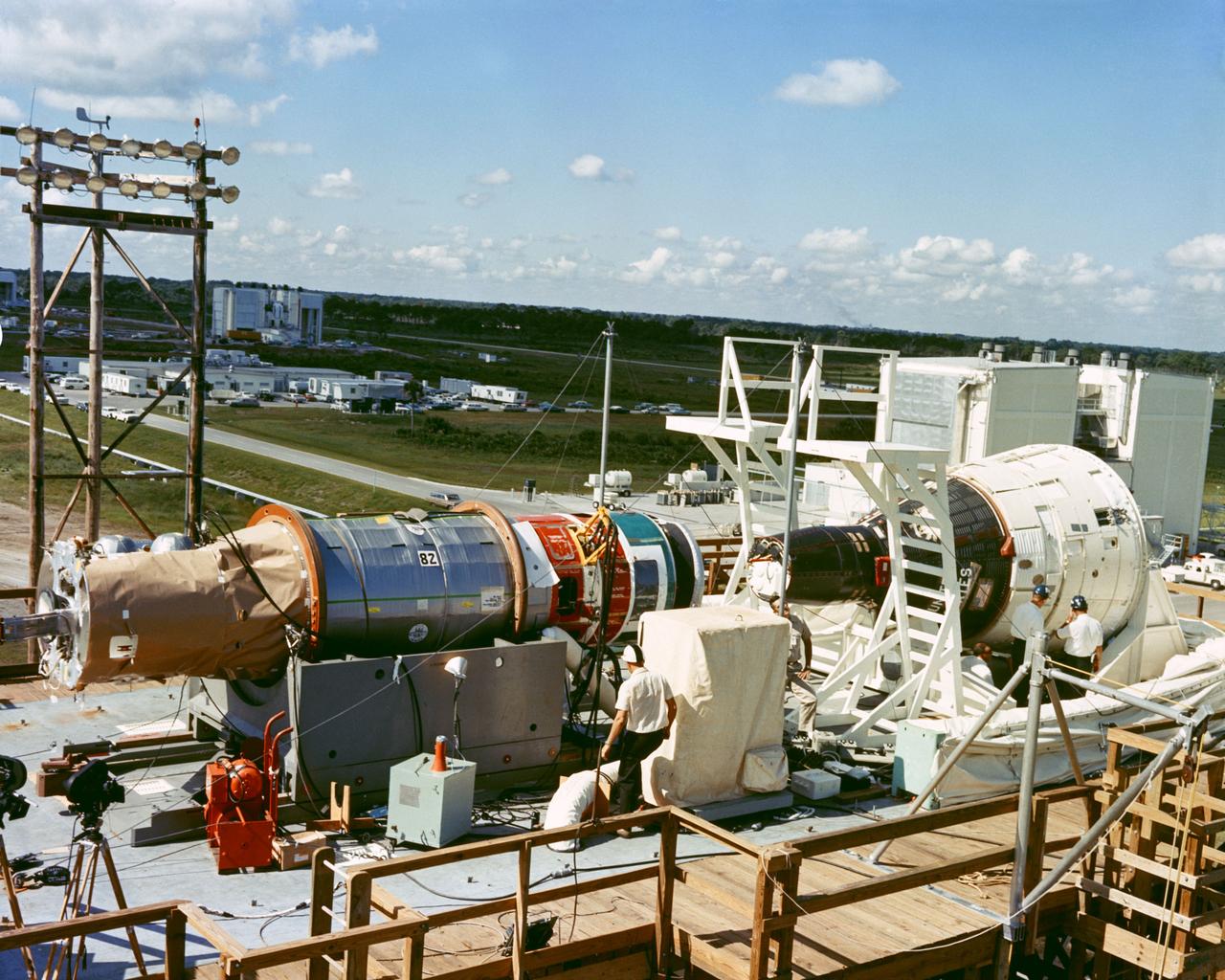
S65-52015 (1965) --- The Gemini-6 spacecraft (right) and the Agena Target Vehicle (left) on the Boresite Range Tower for the Plan-X docking exercise. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
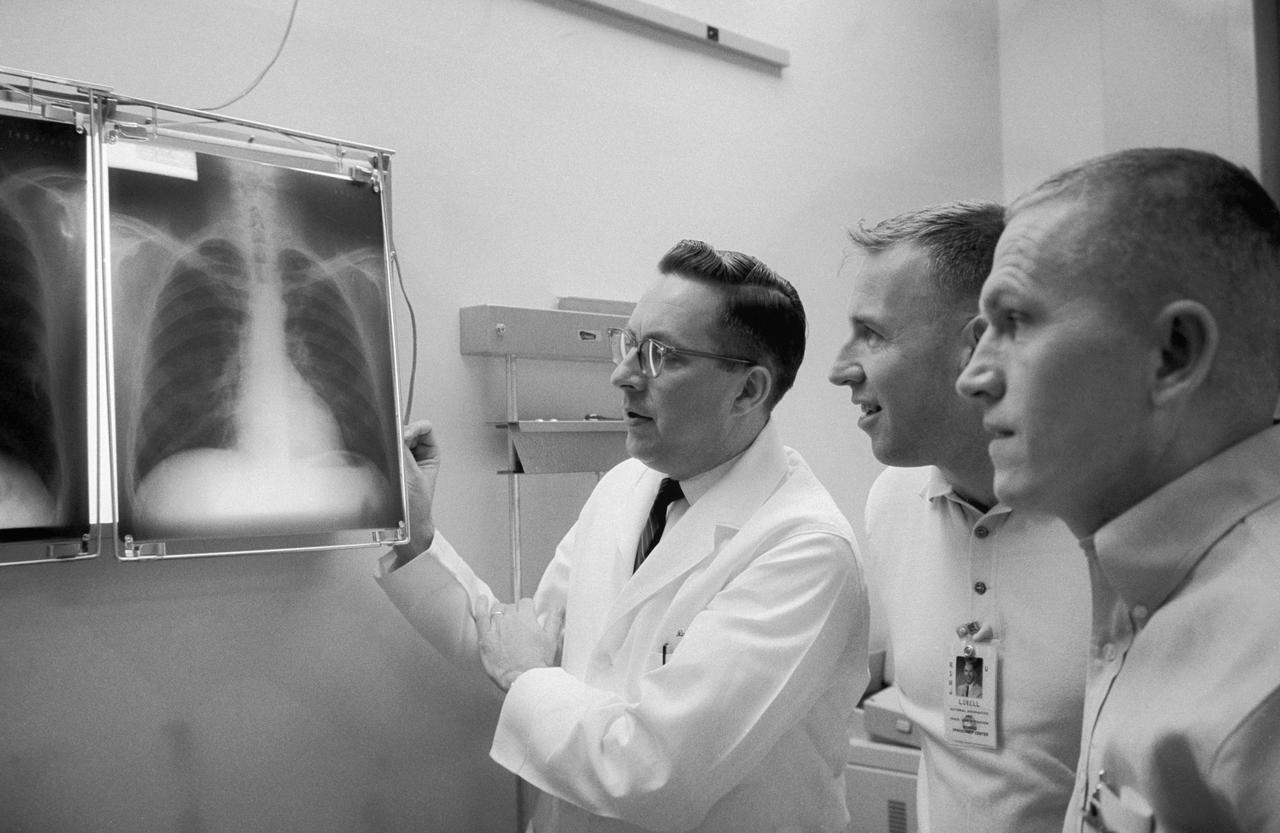
S65-56315 (2 Dec. 1965) --- Dr. Charles A. Berry (left), chief of the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Medical Programs, and astronauts James A. Lovell Jr. (center), Gemini-7 pilot, and Frank Borman, Gemini-7 command pilot, examine a series of chest x-rays taken during the preflight physical. Photo credit: NASA
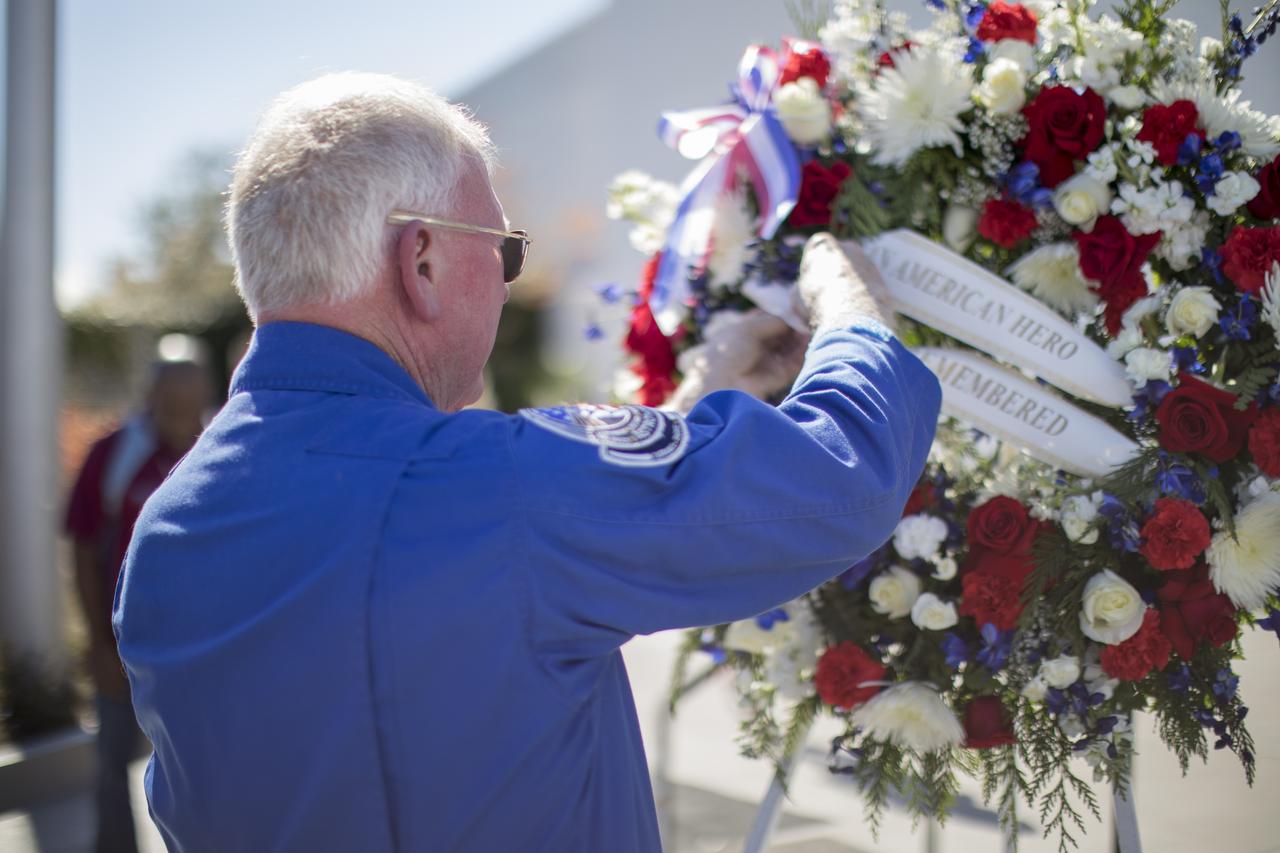

Former NASA astronaut Jon McBride places a wreath at the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. The brief memorial honoring NASA astronaut John Young took place on the afternoon of Jan. 11, 2018. Young died Jan. 5, 2018, in Houston at the age of 87. He was the only astronaut to fly in NASA's Gemini, Apollo and Space Shuttle Programs.

NASA astronaut John Young was remembered in a ceremony at the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. The brief memorial took place on the afternoon of Jan. 11, 2018. Young died Jan. 5, 2018, in Houston at the age of 87. He was the only astronaut to fly in NASA's Gemini, Apollo and Space Shuttle Programs.

NASA astronaut John Young was remembered in a ceremony at the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. The brief memorial took place on the afternoon of Jan. 11, 2018. Young died Jan. 5, 2018, in Houston at the age of 87. He was the only astronaut to fly in NASA's Gemini, Apollo and Space Shuttle Programs.

NASA astronaut John Young was remembered in a ceremony at the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. The brief memorial took place on the afternoon of Jan. 11, 2018. Young died Jan. 5, 2018, in Houston at the age of 87. He was the only astronaut to fly in NASA's Gemini, Apollo and Space Shuttle Programs.
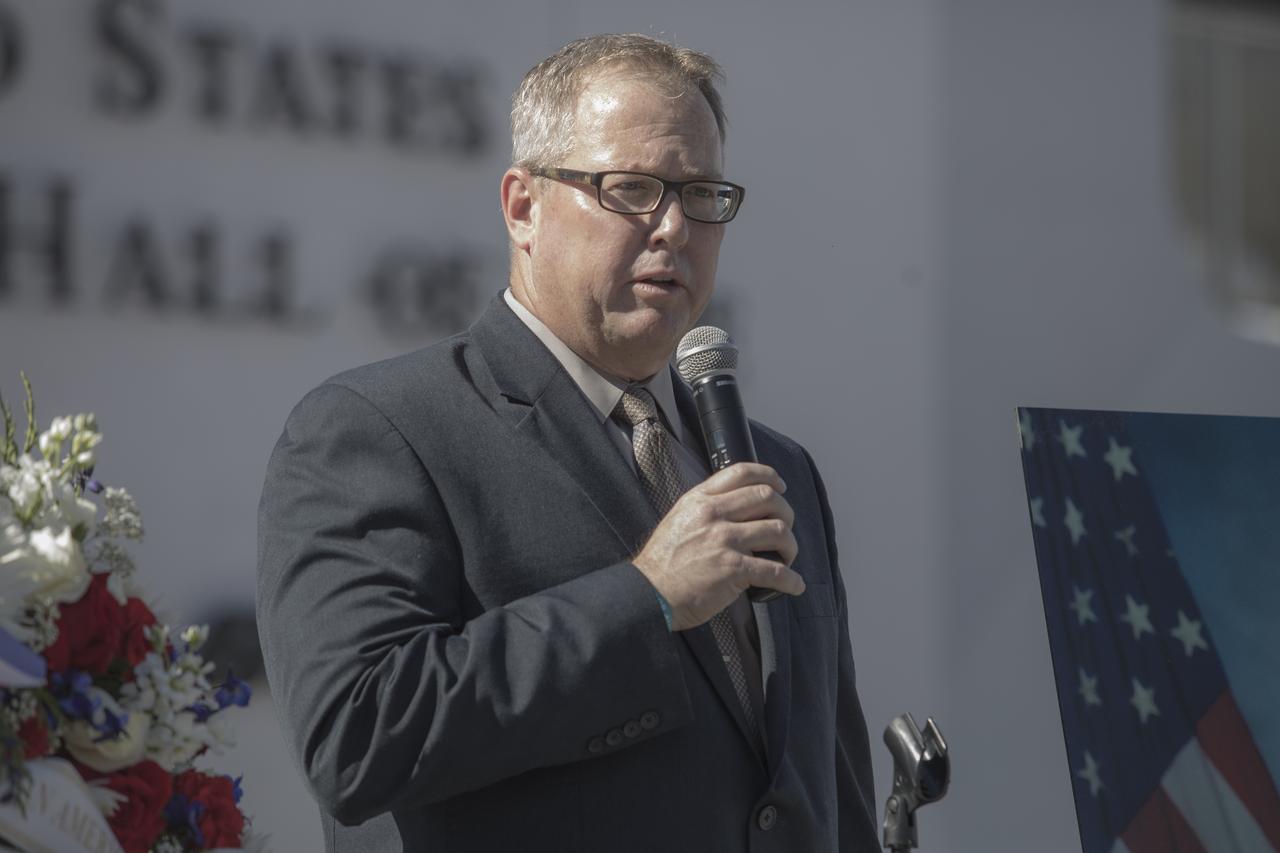

Delaware North COO Therrin Protze speaks during a ceremony at the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. The brief memorial honoring NASA astronaut John Young took place on the afternoon of Jan. 11, 2018. Young died Jan. 5, 2018, in Houston at the age of 87. He was the only astronaut to fly in NASA's Gemini, Apollo and Space Shuttle Programs.

NASA astronaut John Young was remembered in a ceremony at the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. The brief memorial took place on the afternoon of Jan. 11, 2018. Young died Jan. 5, 2018, in Houston at the age of 87. He was the only astronaut to fly in NASA's Gemini, Apollo and Space Shuttle Programs.
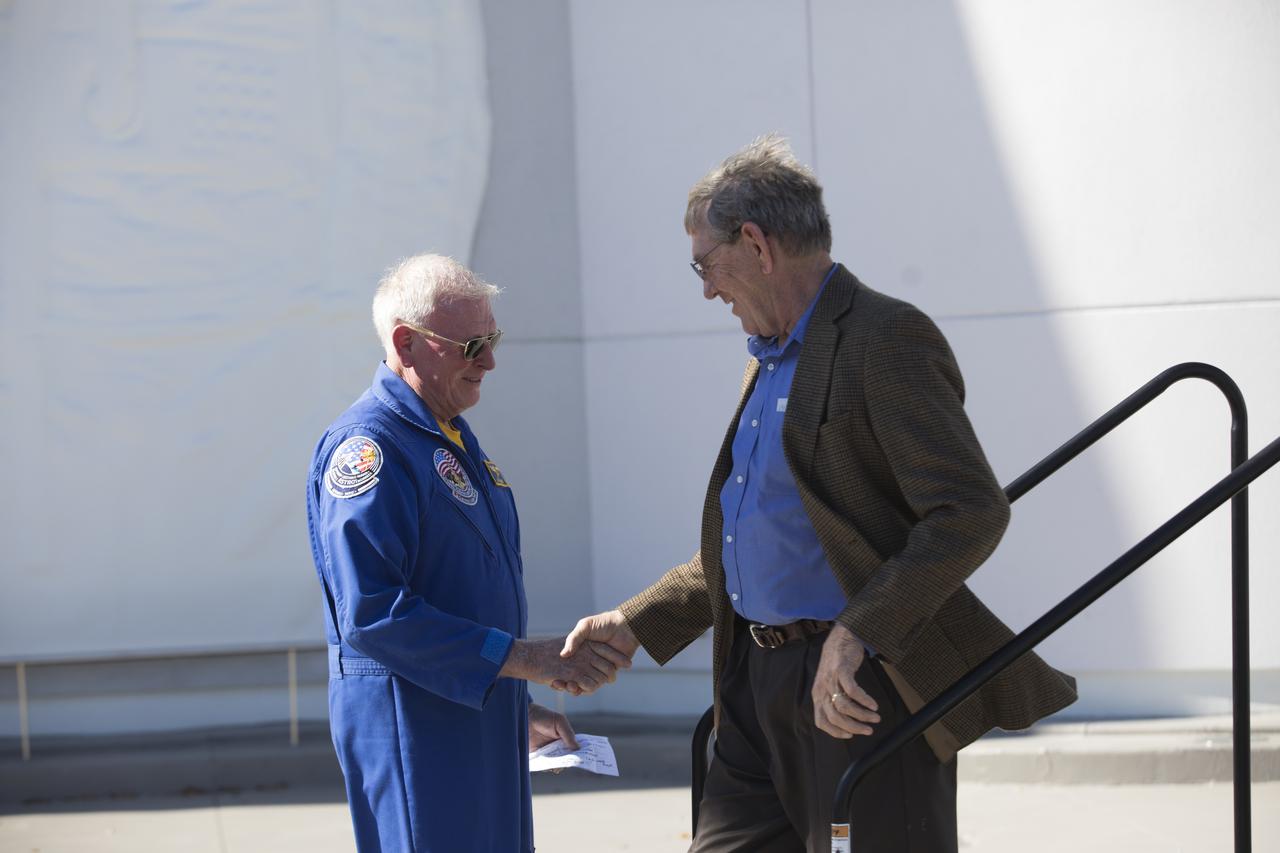

Former NASA astronaut Jon McBride, left, greets Mike McCulley during a ceremony at the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. The brief memorial honoring NASA astronaut John Young took place on the afternoon of Jan. 11, 2018. Young died Jan. 5, 2018, in Houston at the age of 87. He was the only astronaut to fly in NASA's Gemini, Apollo and Space Shuttle Programs.
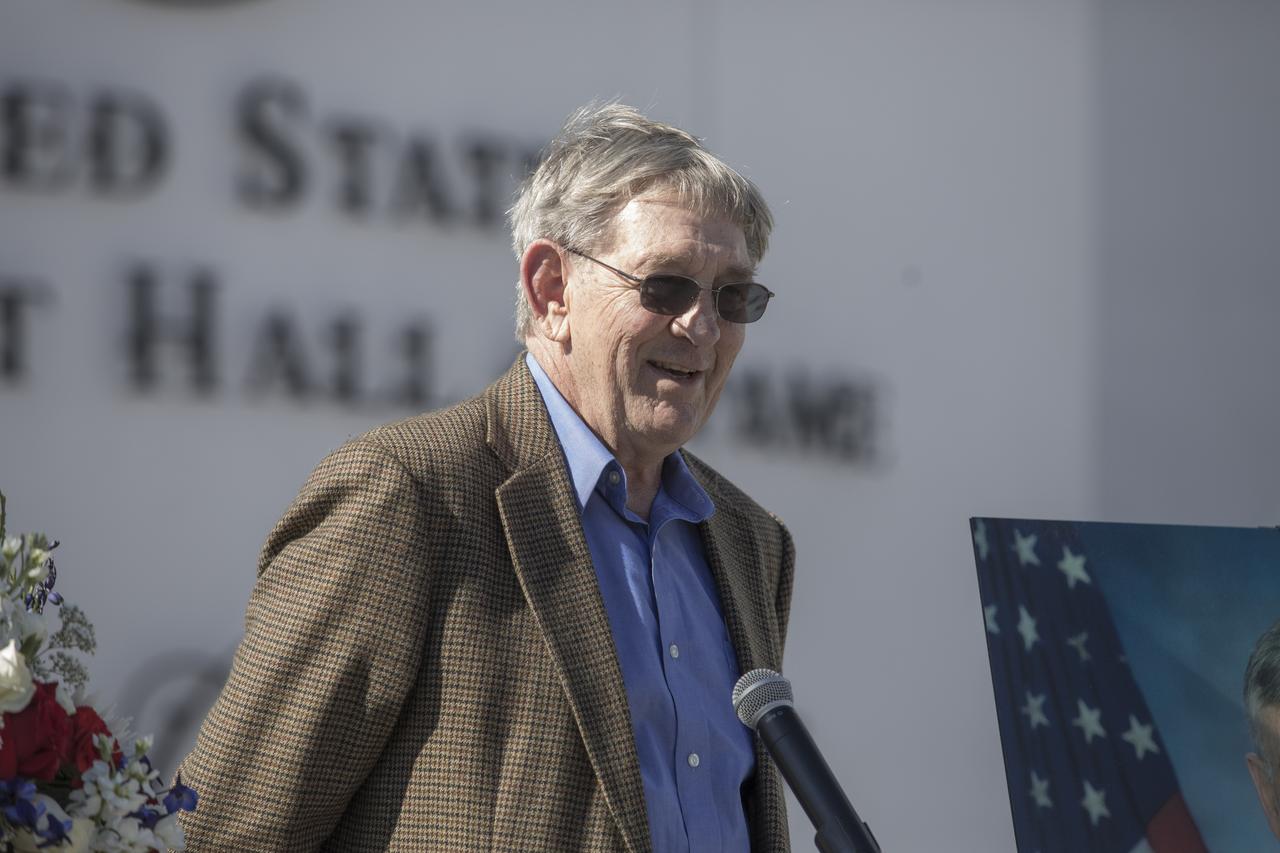

Former NASA astronaut Mike McCulley speaks during a ceremony at the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. The brief memorial honoring NASA astronaut John Young took place on the afternoon of Jan. 11, 2018. Young died Jan. 5, 2018, in Houston at the age of 87.He was the only astronaut to fly in NASA's Gemini, Apollo and Space Shuttle Programs.
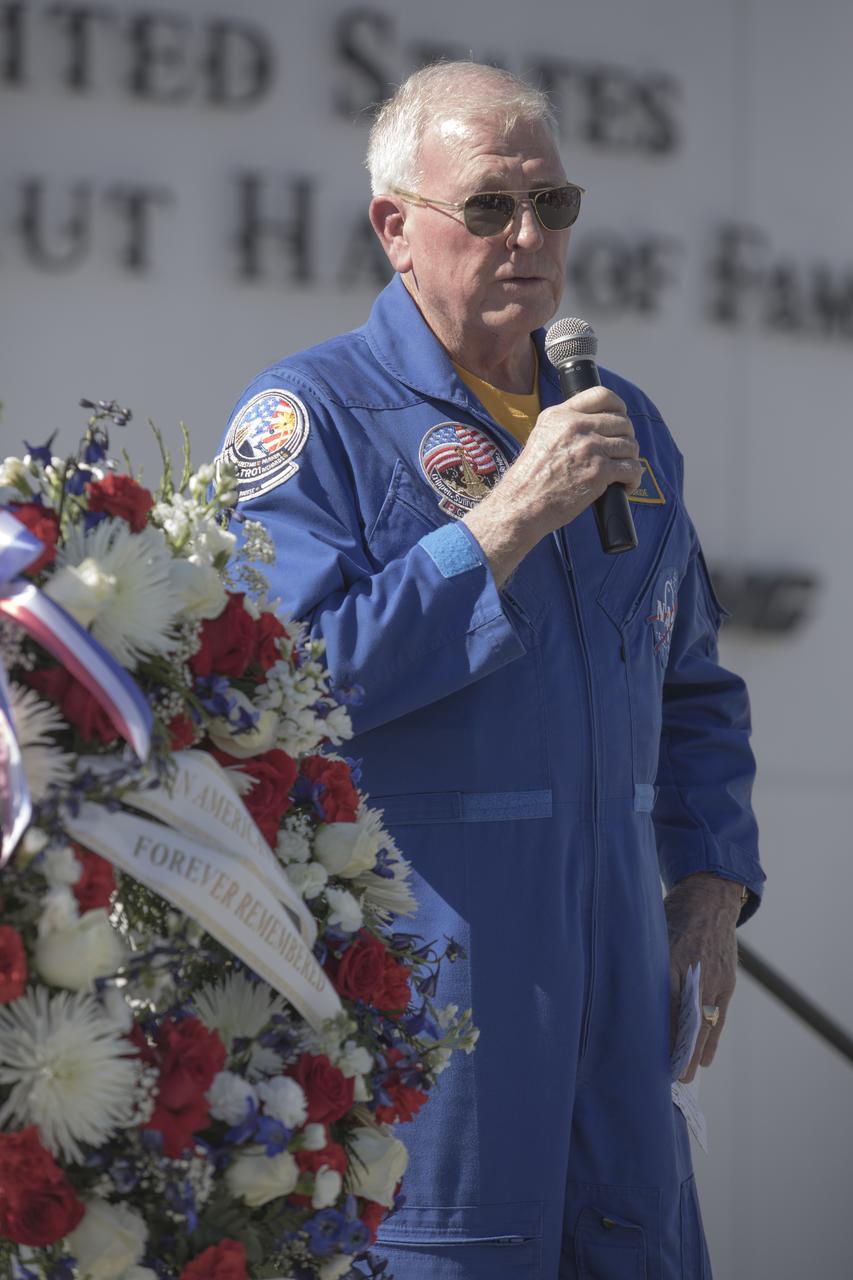

Former NASA astronaut Jon McBride speaks during a ceremony at the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. The brief memorial honoring NASA astronaut John Young took place on the afternoon of Jan. 11, 2018. Young died Jan. 5, 2018, in Houston at the age of 87. He was the only astronaut to fly in NASA's Gemini, Apollo and Space Shuttle Programs.
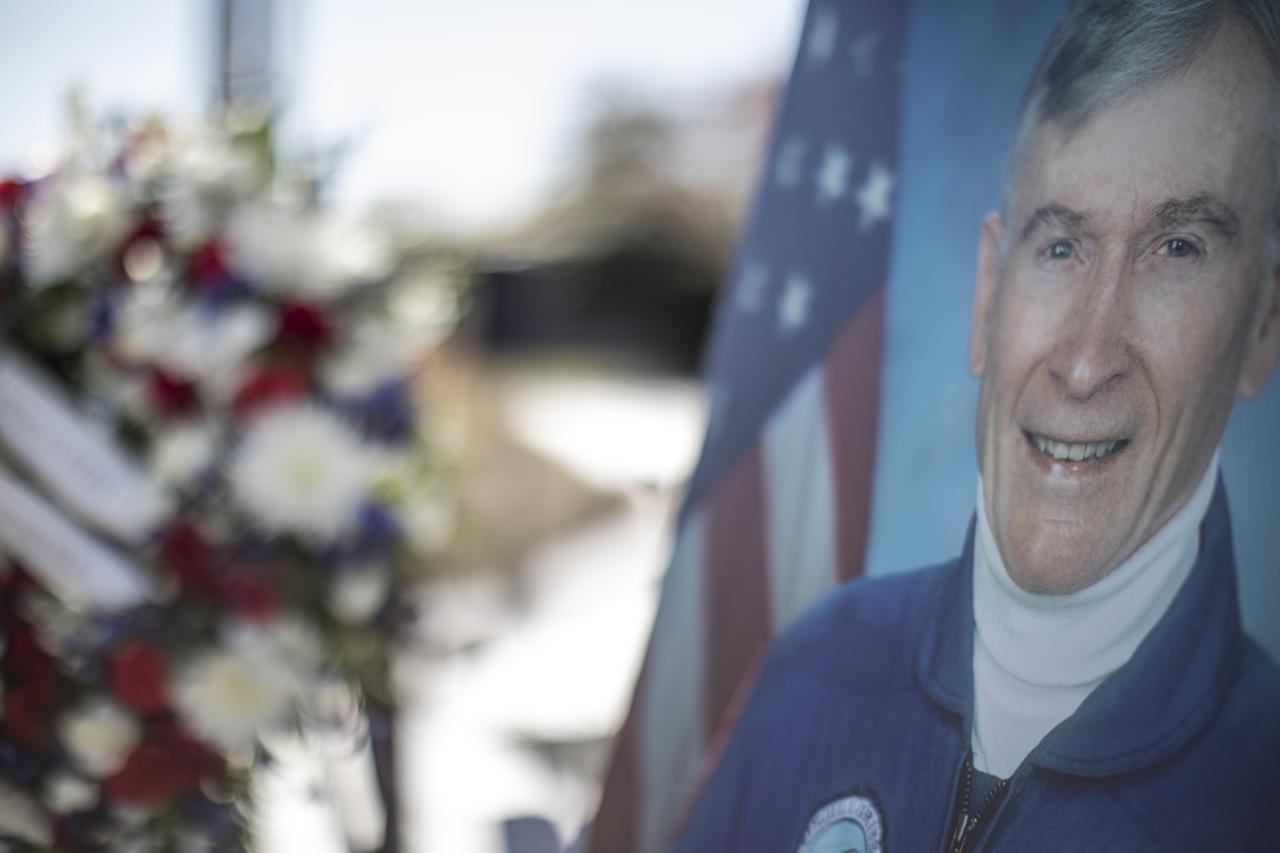

NASA astronaut John Young was remembered in a ceremony at the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. The brief memorial took place on the afternoon of Jan. 11, 2018. Young died Jan. 5, 2018, in Houston at the age of 87. He was the only astronaut to fly in NASA's Gemini, Apollo and Space Shuttle Programs.

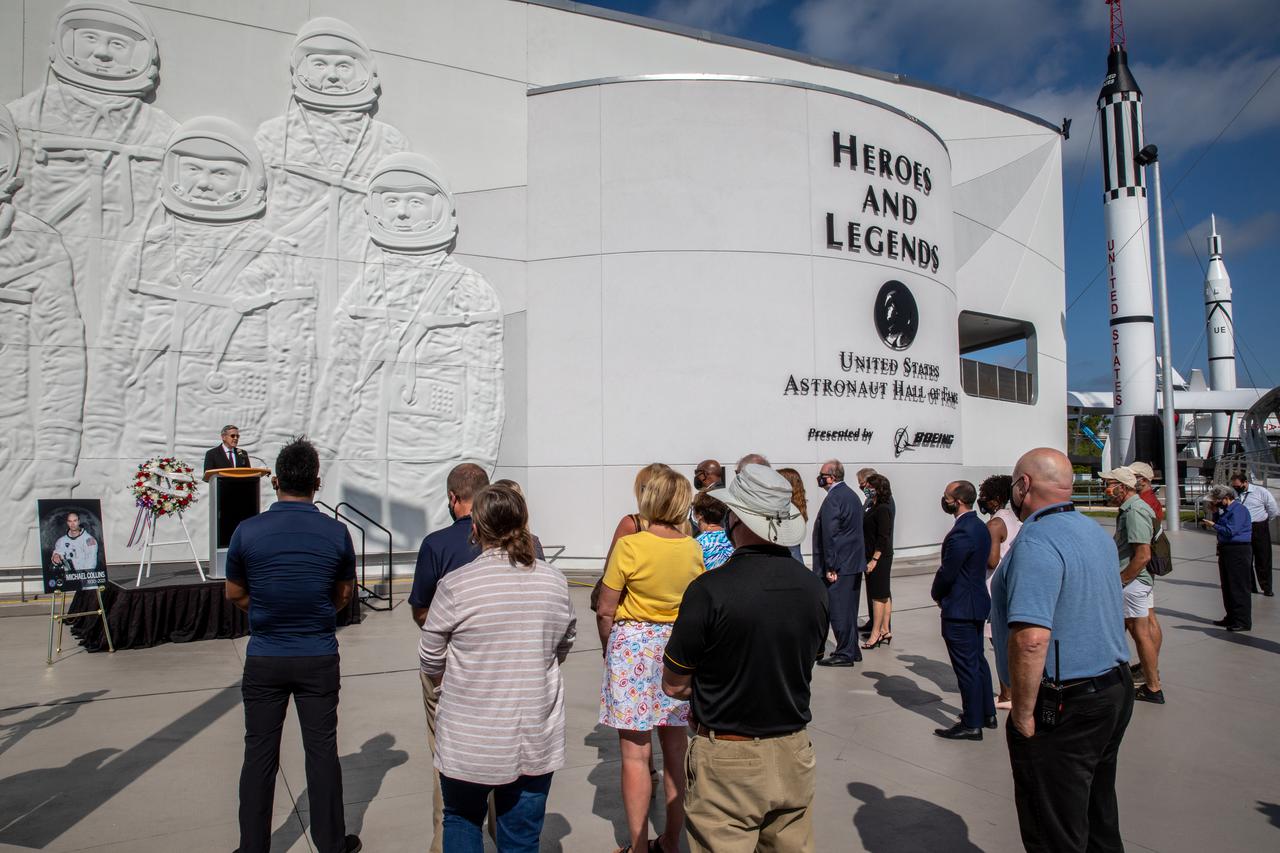
The Astronaut Hall of Fame display for astronaut Michael Collins is shown following a wreath-laying ceremony honoring his memory on April 30, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Collins served as pilot on the three-day Gemini X mission in 1966, and he was the command module pilot for the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, where he remained in lunar orbit while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first people to walk on the Moon. Collins passed away on April 28, 2021, at the age of 90.

S65-28699 (17 Aug. 1965) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr. (dark shirt), pilot for the Gemini-5 spaceflight, discusses x-rays with members of the medical team at Cape Kennedy. Left to right are Dr. Eugene Tubbs; astronaut Conrad; Dr. Charles A. Berry, chief, Center Medical Programs, Manned Spacecraft Center; and Dr. Robert Moser (seated), Medical Monitor with the U.S. Army.

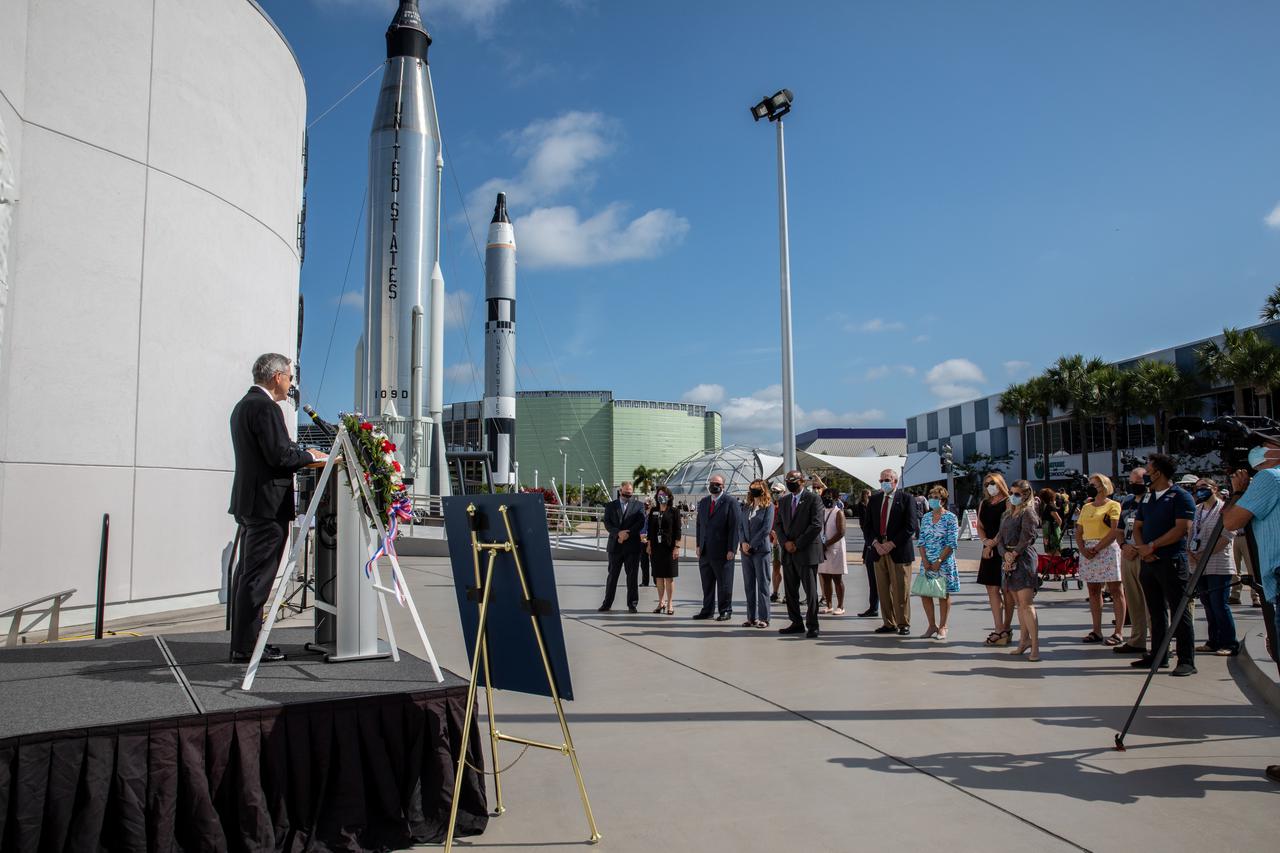
A wreath-laying ceremony honoring the memory of former Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins is held outside of the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on April 30, 2021. Kennedy Director Bob Cabana and Therrin Protze, chief operating officer of Delaware North at the visitor complex, provided remarks during the ceremony. Collins served as pilot on the three-day Gemini X mission in 1966, and he was the command module pilot for the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, where he remained in lunar orbit while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first people to walk on the Moon. Collins passed away on April 28, 2021, at the age of 90.

S66-46122 (18 July 1966) --- Agena Target Docking Vehicle 5005 is photographed from the Gemini-Titan 10 (GT-10) spacecraft during rendezvous in space. The two spacecraft are about 38 feet apart. After docking with the Agena, astronauts John W. Young, command pilot, and Michael Collins, pilot, fired the 16,000 pound thrust engine of Agena X's primary propulsion system to boost the combined vehicles into an orbit with an apogee of 413 nautical miles to set a new altitude record for manned spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA
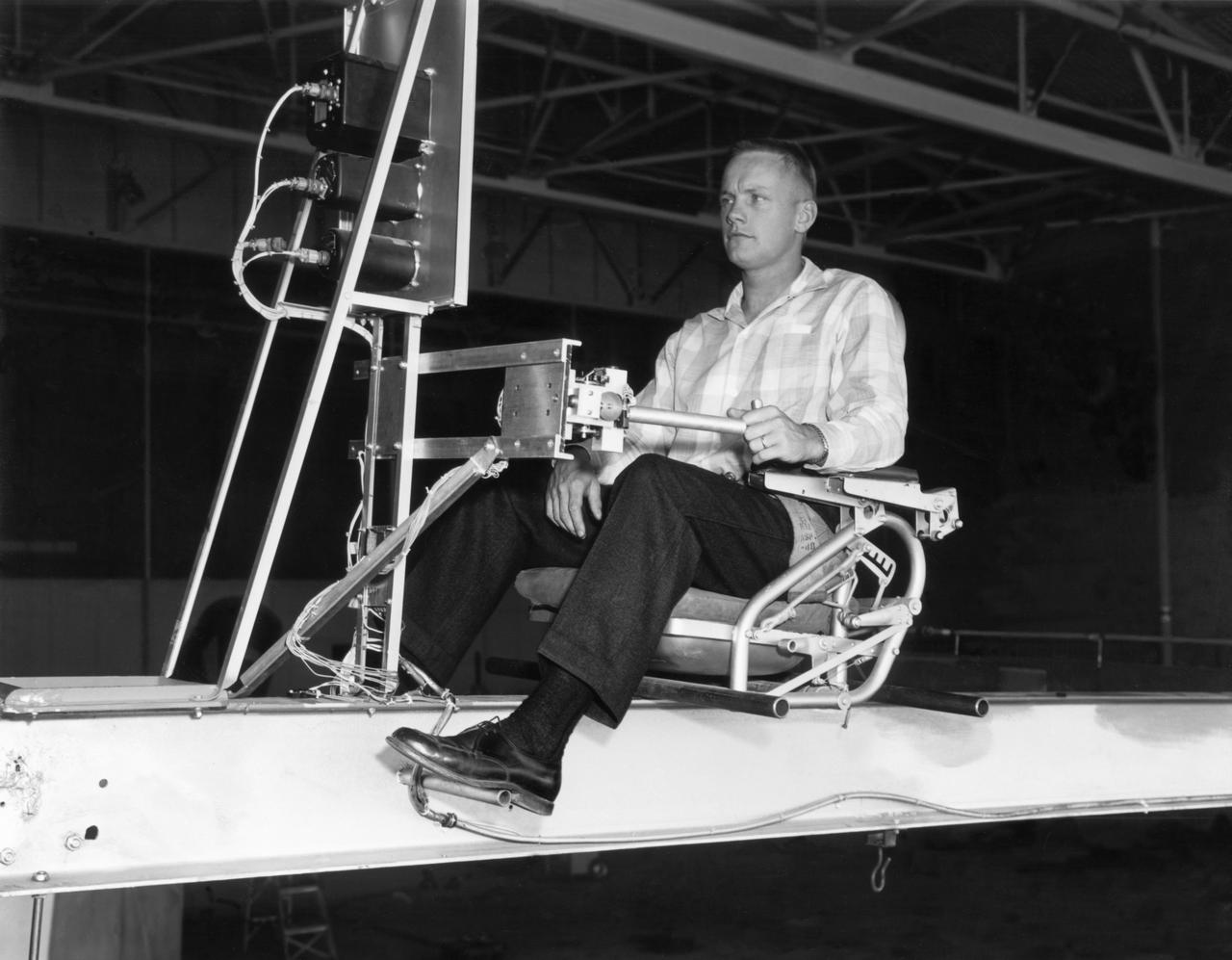

Famed astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, the first man to set foot on the moon during the historic Apollo 11 space mission in July 1969, served for seven years as a research pilot at the NACA-NASA High-Speed Flight Station, now the Dryden Flight Research Center, at Edwards, California, before he entered the space program. Armstrong joined the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) at the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory (later NASA's Lewis Research Center, Cleveland, Ohio, and today the Glenn Research Center) in 1955. Later that year, he transferred to the High-Speed Flight Station at Edwards as an aeronautical research scientist and then as a pilot, a position he held until becoming an astronaut in 1962. He was one of nine NASA astronauts in the second class to be chosen. As a research pilot Armstrong served as project pilot on the F-100A and F-100C aircraft, F-101, and the F-104A. He also flew the X-1B, X-5, F-105, F-106, B-47, KC-135, and Paresev. He left Dryden with a total of over 2450 flying hours. He was a member of the USAF-NASA Dyna-Soar Pilot Consultant Group before the Dyna-Soar project was cancelled, and studied X-20 Dyna-Soar approaches and abort maneuvers through use of the F-102A and F5D jet aircraft. Armstrong was actively engaged in both piloting and engineering aspects of the X-15 program from its inception. He completed the first flight in the aircraft equipped with a new flow-direction sensor (ball nose) and the initial flight in an X-15 equipped with a self-adaptive flight control system. He worked closely with designers and engineers in development of the adaptive system, and made seven flights in the rocket plane from December 1960 until July 1962. During those fights he reached a peak altitude of 207,500 feet in the X-15-3, and a speed of 3,989 mph (Mach 5.74) in the X-15-1. Armstrong has a total of 8 days and 14 hours in space, including 2 hours and 48 minutes walking on the Moon. In March 1966 he was commander of the Gemini 8 or
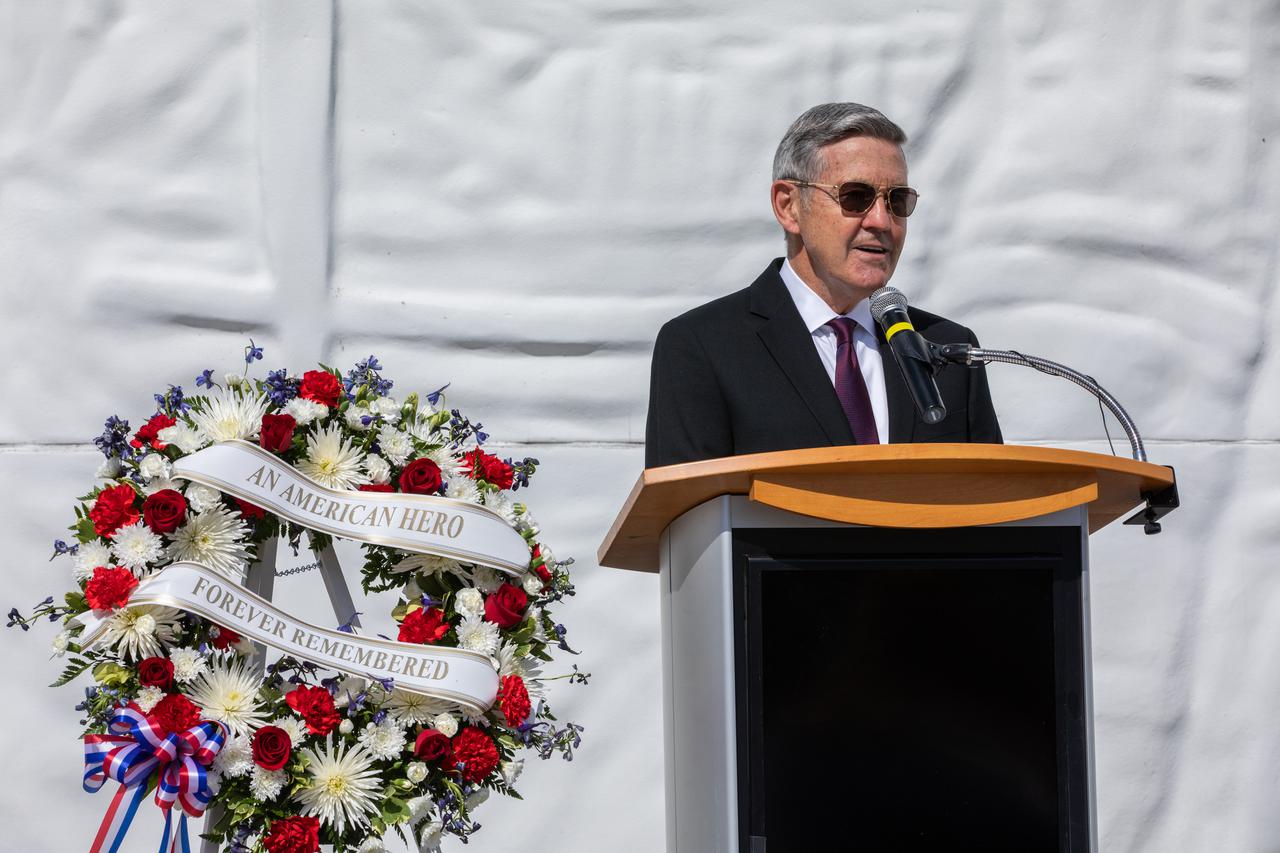

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana provides remarks during a wreath-laying ceremony in Florida, honoring the memory of former Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins on April 30, 2021. Therrin Protze, chief operating officer of Delaware North at Kennedy’s visitor complex, also spoke during the ceremony, held just outside of the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the visitor complex. Collins served as pilot on the three-day Gemini X mission in 1966, and he was the command module pilot for the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, where he remained in lunar orbit while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first people to walk on the Moon. Collins passed away on April 28, 2021, at the age of 90.

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana provides remarks during a wreath-laying ceremony in Florida, honoring the memory of former Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins on April 30, 2021. Therrin Protze, chief operating officer of Delaware North at Kennedy’s visitor complex, also spoke during the ceremony, held just outside of the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the visitor complex. Collins served as pilot on the three-day Gemini X mission in 1966, and he was the command module pilot for the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, where he remained in lunar orbit while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first people to walk on the Moon. Collins passed away on April 28, 2021, at the age of 90.
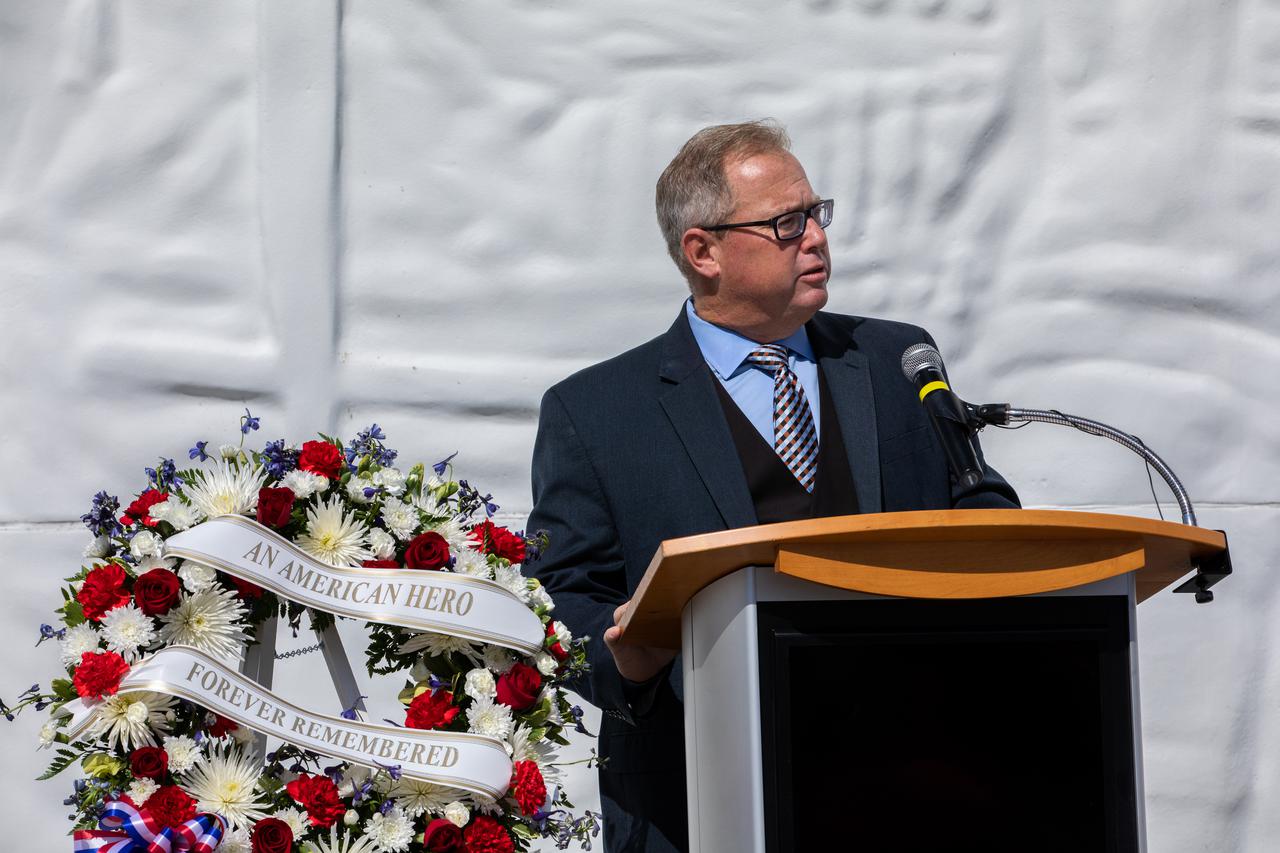

Therrin Protze, chief operating officer of Delaware North at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, provides remarks during a wreath-laying ceremony honoring the memory of former Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins on April 30, 2021. Kennedy Director Bob Cabana also spoke during the ceremony, held just outside of the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Florida spaceport’s visitor complex. Collins served as pilot on the three-day Gemini X mission in 1966, and he was the command module pilot for the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, where he remained in lunar orbit while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first people to walk on the Moon. Collins passed away on April 28, 2021, at the age of 90.

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana provides remarks during a wreath-laying ceremony in Florida, honoring the memory of former Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins on April 30, 2021. Therrin Protze, chief operating officer of Delaware North at Kennedy’s visitor complex, also spoke during the ceremony, held just outside of the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the visitor complex. Collins served as pilot on the three-day Gemini X mission in 1966, and he was the command module pilot for the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, where he remained in lunar orbit while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first people to walk on the Moon. Collins passed away on April 28, 2021, at the age of 90.
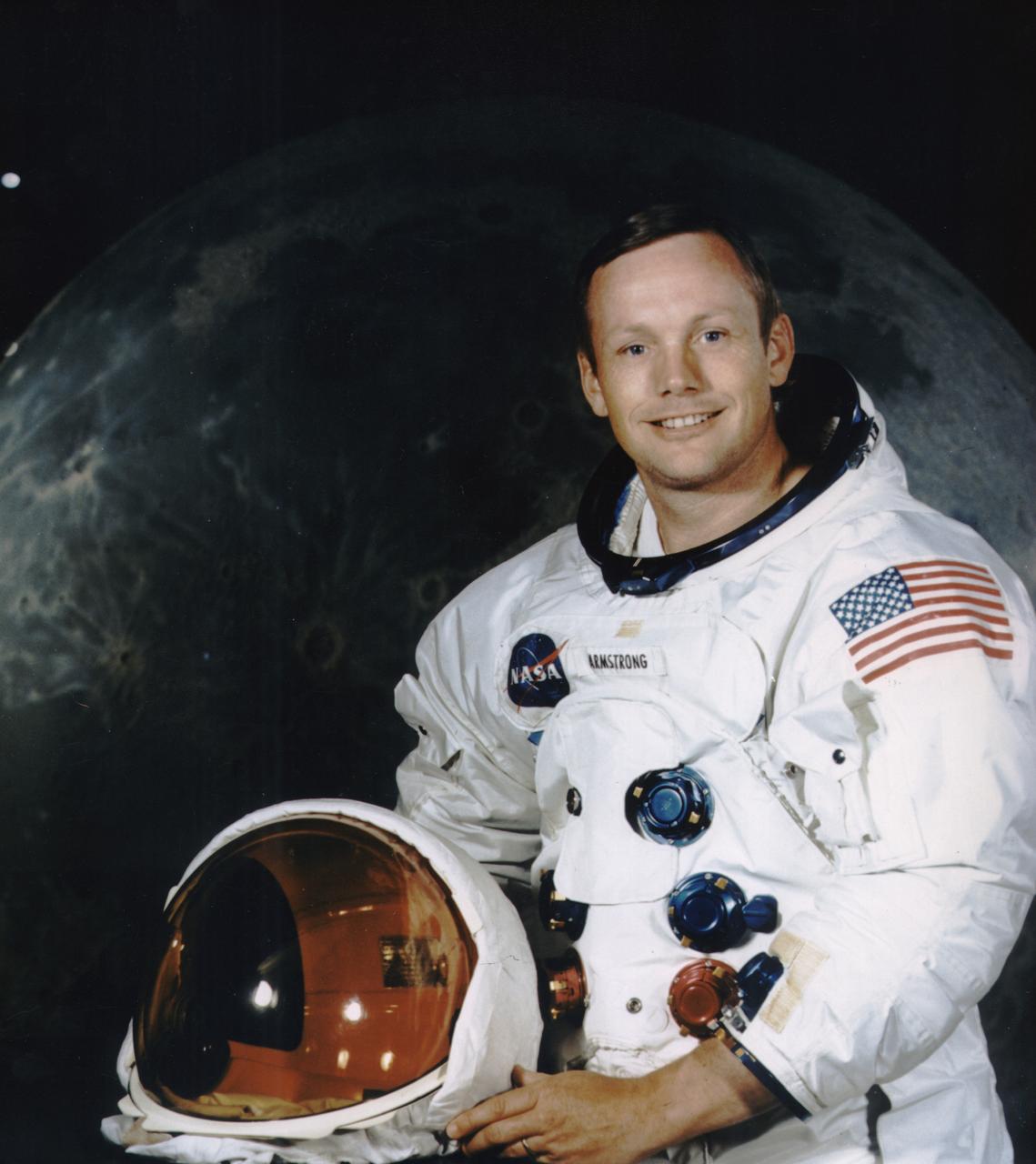

Neil Armstrong, donned in his space suit, poses for his official Apollo 11 portrait. Armstrong began his flight career as a naval aviator. He flew 78 combat missions during the Korean War. Armstrong joined the NASA predecessor, NACA (National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics), as a research pilot at the Lewis Laboratory in Cleveland and later transferred to the NACA High Speed Flight Station at Edwards AFB, California. He was a project pilot on many pioneering high speed aircraft, including the 4,000 mph X-15. He has flown over 200 different models of aircraft, including jets, rockets, helicopters, and gliders. In 1962, Armstrong was transferred to astronaut status. He served as command pilot for the Gemini 8 mission, launched March 16, 1966, and performed the first successful docking of two vehicles in space. In 1969, Armstrong was commander of Apollo 11, the first manned lunar landing mission, and gained the distinction of being the first man to land a craft on the Moon and the first man to step on its surface. Armstrong subsequently held the position of Deputy Associate Administrator for Aeronautics, NASA Headquarters Office of Advanced Research and Technology, from 1970 to 1971. He resigned from NASA in 1971.

Astronaut Alan Shepard (right) was one of 14 astronauts, 8 NASA test pilots, and 2 McDonnell test pilots who took part in simulator studies. Shepard flew the simulator on November 14, 1963. A.W. Vogeley wrote: "Many of the astronauts have flown this simulator in support of the Gemini studies and they, without exception, appreciated the realism of the visual scene. The simulator has also been used in the development of pilot techniques to handle certain jet malfunctions in order that aborts could be avoided. In these situations large attitude changes are sometimes necessary and the false motion cues that were generated due to earth gravity were somewhat objectionable; however, the pilots were readily able to overlook these false motion cues in favor of the visual realism." Roy F. Brissenden noted that: "The basic Gemini control studies developed the necessary techniques and demonstrated the ability of human pilots to perform final space docking with the specified Gemini-Agena systems using only visual references. ... Results... showed that trained astronauts can effect the docking with direct acceleration control and even with jet malfunctions as long as good visual conditions exist.... Probably more important than data results was the early confidence that the astronauts themselves gained in their ability to perform the maneuver in the ultimate flight mission." Shepard commented: "I had the feeling tonight - a couple of times - that I was actually doing the space mission instead of the simulation. As I said before, I think it is a very good simulation." Shepard also commented on piloting techniques. Most astronauts arrived at this same preferred technique: Shepard: "I believe I have developed the preferred technique for these conditions and the technique appeared to me to be best was to come in slightly above the target so that I was able to use the longitudinal marks on the body of the target as a reference, particularly for a lateral translation and, of course, I used the foreshortening effect for a vertical translation, and this appeared to give me the best results. By that I mean the least number of control motions and the lowest fuel usage and the best end techniques, or the best end conditions, I should say." Engineer: "When you started to run you didn't start thrusting immediately I don't believe. It looked like you started working on your attitudes, then started closing in." Shepard: "That is correct. I did that because I felt that I wanted to get the X-axis translation in the most effective vector and for minimum fuel usage that wouldn't introduce any other lateral or vertical offsets that did not already exist." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964; Roy F. Brissenden, "Initial Operations with Langley's Rendezvous Docking Facility," Langley Working Paper, LWP-21, 1964.

Astronaut Alan Shepard (right) was one of 14 astronauts, 8 NASA test pilots, and 2 McDonnell test pilots who took part in simulator studies. Shepard flew the simulator on November 14, 1963. A.W. Vogeley wrote: "Many of the astronauts have flown this simulator in support of the Gemini studies and they, without exception, appreciated the realism of the visual scene. The simulator has also been used in the development of pilot techniques to handle certain jet malfunctions in order that aborts could be avoided. In these situations large attitude changes are sometimes necessary and the false motion cues that were generated due to earth gravity were somewhat objectionable; however, the pilots were readily able to overlook these false motion cues in favor of the visual realism." Roy F. Brissenden noted that: "The basic Gemini control studies developed the necessary techniques and demonstrated the ability of human pilots to perform final space docking with the specified Gemini-Agena systems using only visual references. ... Results... showed that trained astronauts can effect the docking with direct acceleration control and even with jet malfunctions as long as good visual conditions exist.... Probably more important than data results was the early confidence that the astronauts themselves gained in their ability to perform the maneuver in the ultimate flight mission." Shepard commented: "I had the feeling tonight - a couple of times - that I was actually doing the space mission instead of the simulation. As I said before, I think it is a very good simulation." Shepard also commented on piloting techniques. Most astronauts arrived at this same preferred technique: Shepard: "I believe I have developed the preferred technique for these conditions and the technique appeared to me to be best was to come in slightly above the target so that I was able to use the longitudinal marks on the body of the target as a reference, particularly for a lateral translation and, of course, I used the foreshortening effect for a vertical translation, and this appeared to give me the best results. By that I mean the least number of control motions and the lowest fuel usage and the best end techniques, or the best end conditions, I should say." Engineer: "When you started to run you didn't start thrusting immediately I don't believe. It looked like you started working on your attitudes, then started closing in." Shepard: "That is correct. I did that because I felt that I wanted to get the X-axis translation in the most effective vector and for minimum fuel usage that wouldn't introduce any other lateral or vertical offsets that did not already exist." -- Published in Barton C. Hacker and James M. Grimwood, On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini, NASA SP-4203; A.W. Vogeley, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators For Space Research," Paper presented at the Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, August 17-21, 1964; Roy F. Brissenden, "Initial Operations with Langley's Rendezvous Docking Facility," Langley Working Paper, LWP-21, 1964.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Former astronaut Joe Engle acknowledges the applause as he is introduced as a previous inductee into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame. He and other Hall of Fame members were present for the induction of five new space program heroes into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame: Richard O. Covey, commander of the Hubble Space Telescope repair mission; Norman E. Thagard, the first American to occupy Russia’s Mir space station; the late Francis R. "Dick" Scobee, commander of the ill-fated 1986 Challenger mission; Kathryn D. Sullivan, the first American woman to walk in space; and Frederick D. Gregory, the first African-American to command a space mission and the current NASA deputy administrator. Engle made 16 flights in the X-15 rocket plane before he became a NASA astronaut and flew two Space Shuttle missions. In 1981, he commanded the second flight of Columbia, the first manned spacecraft to be reflown in space, and in 1985 he commanded a five-man crew on the 20th shuttle flight, a satellite-deploy and repair mission. The induction ceremony was held at the Apollo/Saturn V Center at KSC. The U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame opened in 1990 to provide a place where space travelers could be remembered for their participation and accomplishments in the U.S. space program. The five inductees join 52 previously honored astronauts from the ranks of the Gemini, Apollo, Skylab, Apollo-Soyuz, and Space Shuttle programs.
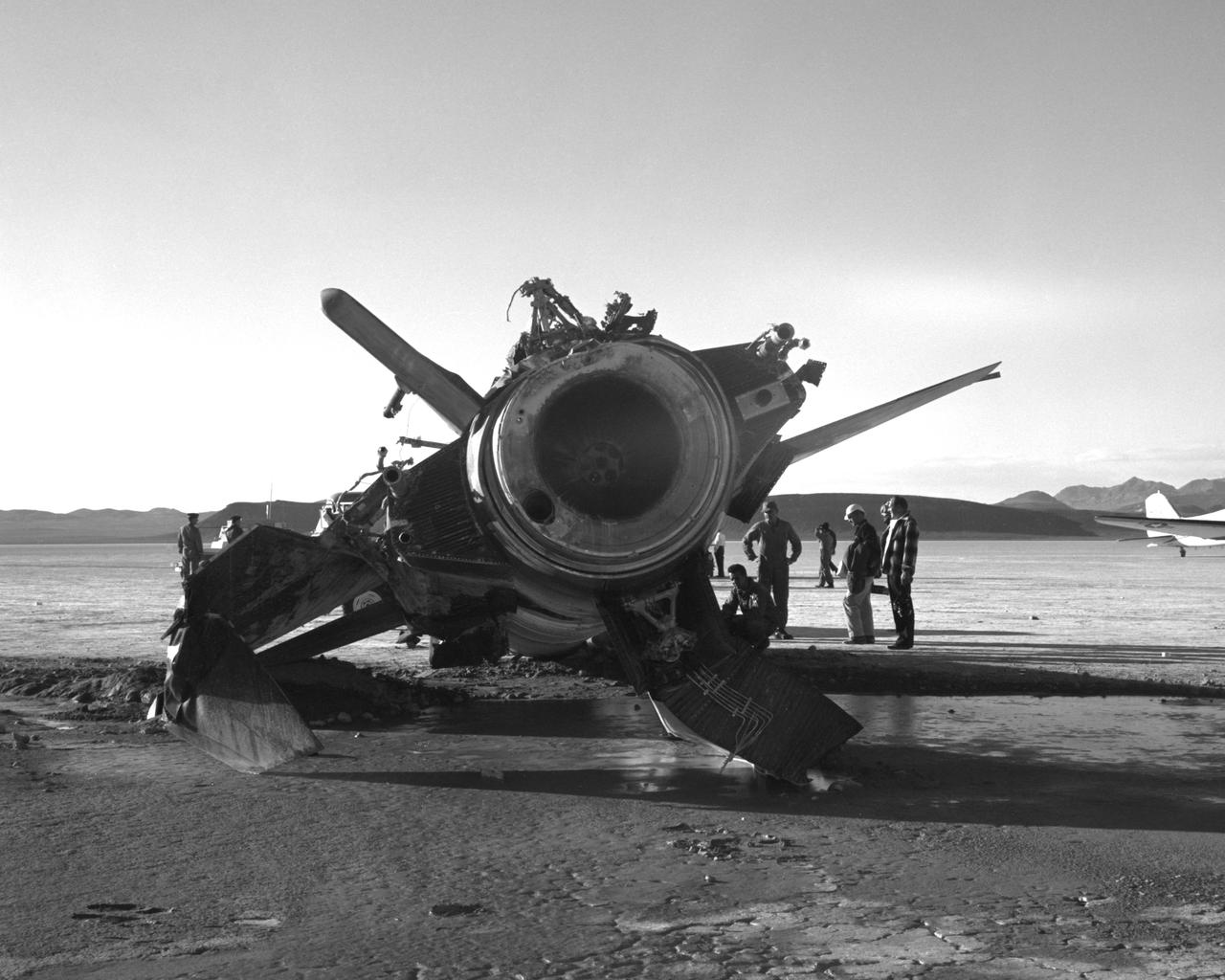

NASA research pilot Jack McKay was injured in a crash landing of the X-15 #2 on November 9, 1962. Following the launch from the B-52 to begin flight 2-31-52, he started the X-15's rocket engine, only to discover that it produced just 30 percent of its maximum thrust. He had to make a high-speed emergency landing on Mud Lake, NV, without flaps but with a significant amount of fuel still in the aircraft. As the X-15 slid across the lakebed, the left skid collapsed; the aircraft turned sideways and flipped onto its back. McKay suffered back injuries but was eventually able to resume X-15 pilot duties, making 22 more flights. The X-15 was sent back to North American Aviation and rebuilt into the X-15A-2.
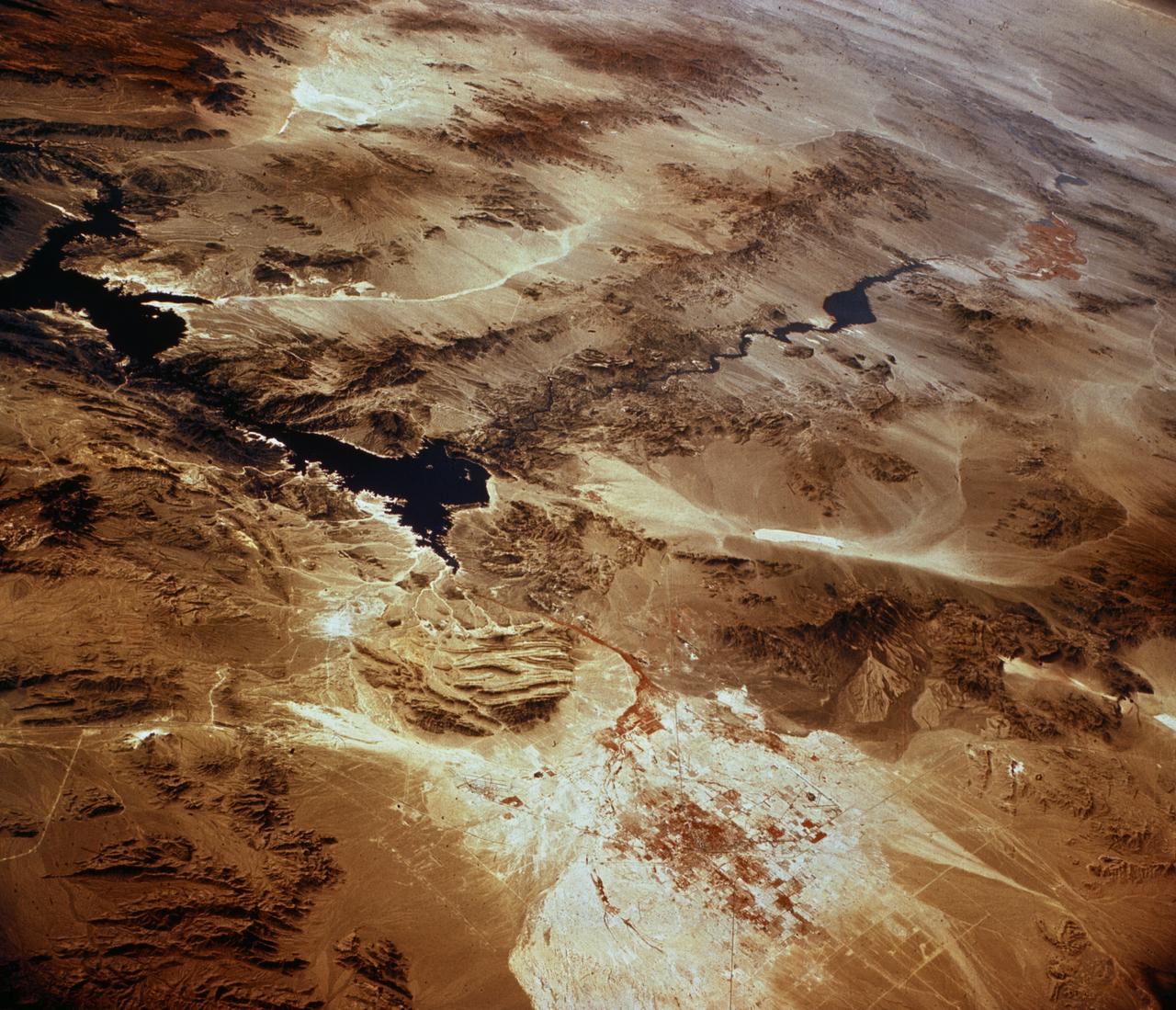

Southwestern US, with Las Vegas, NV in foreground, taken by X-15 Hycon HR-236 Camera during flt. 2-39-70 on June 27, 1965.
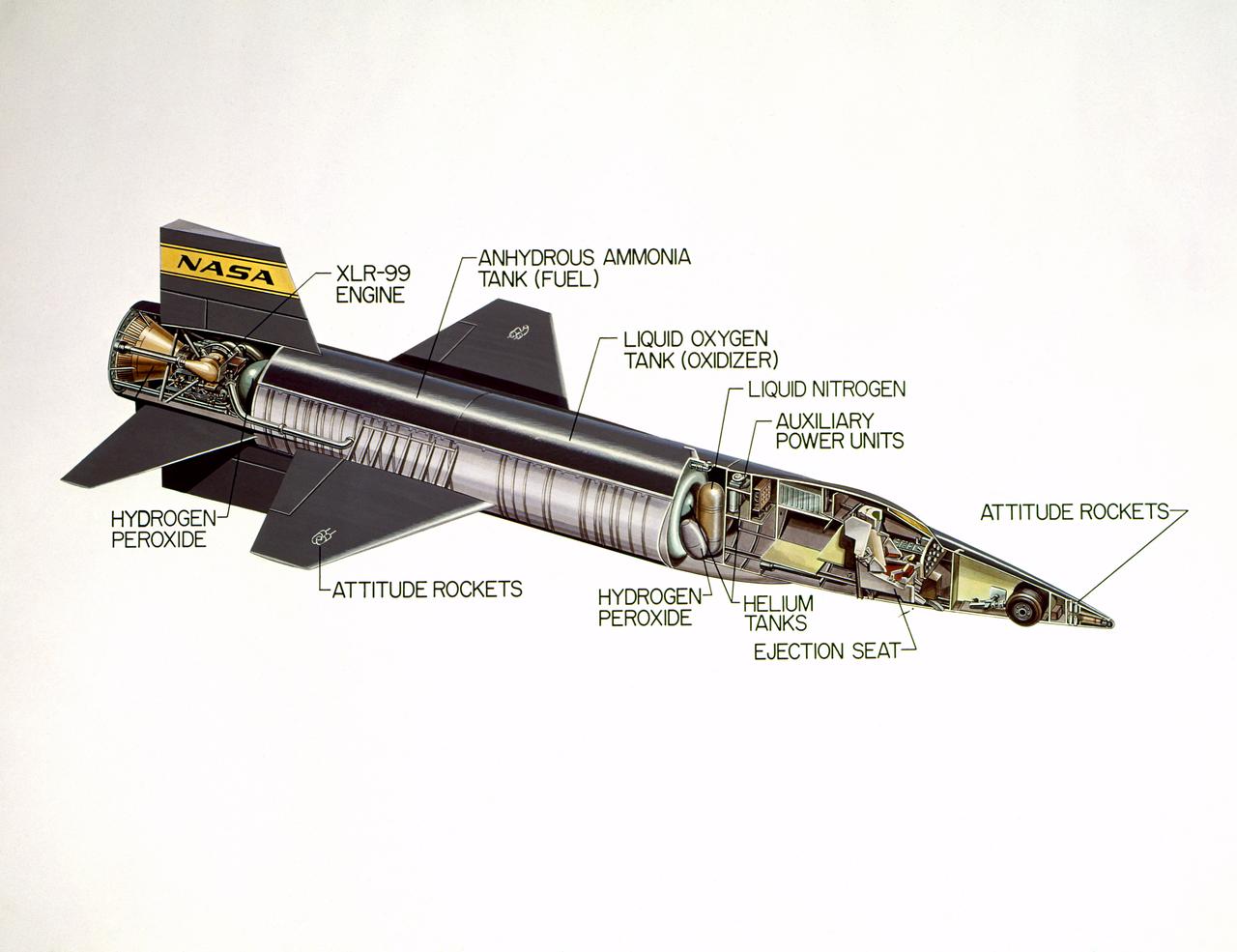
Cutaway drawing of the North American X-15.
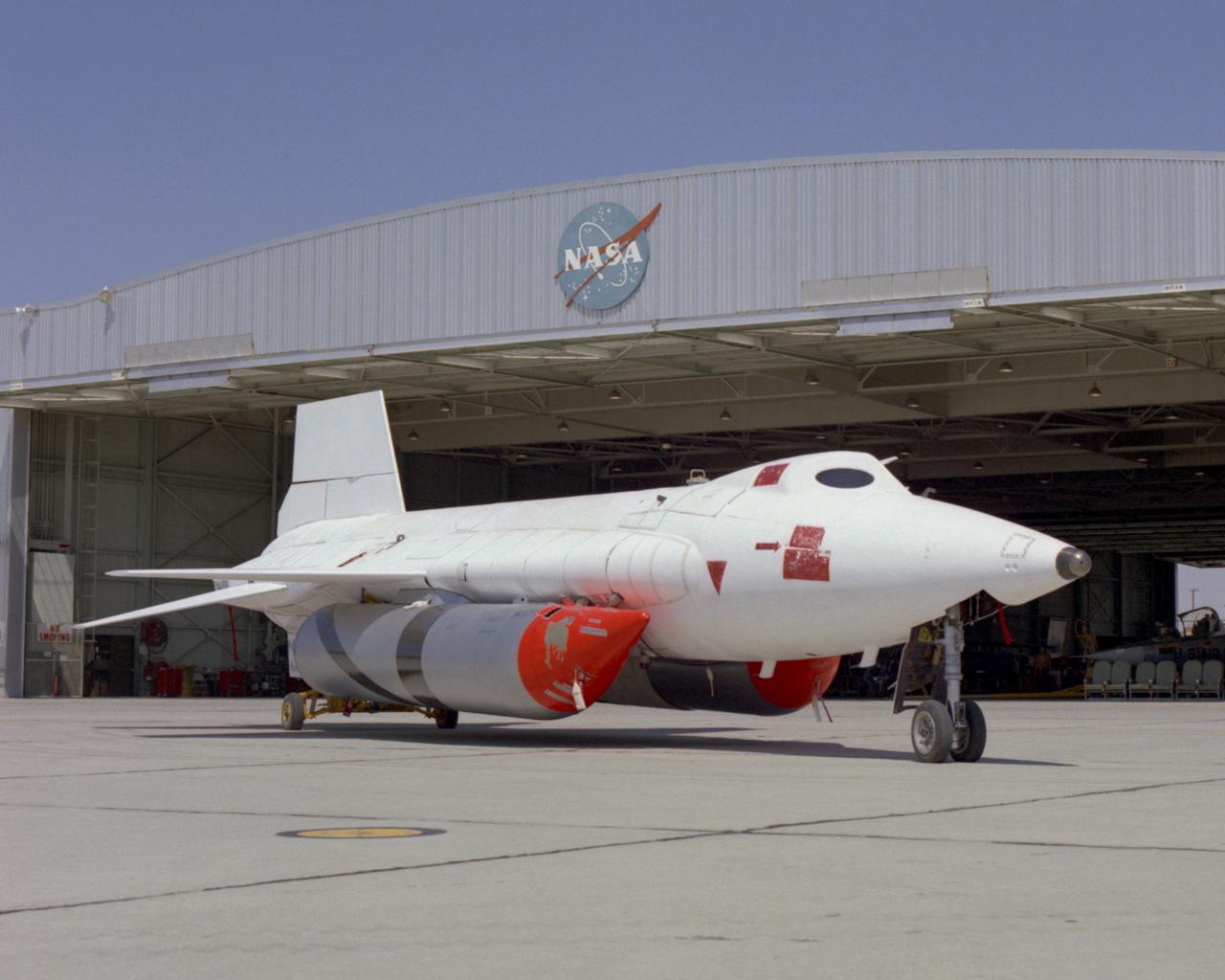

X-15A-2 with full scale ablative and external tanks installed parked in front of hangar. In June 1967, the X-15A-2 rocket-powered research aircraft received a full-scale ablative coating to protect the craft from the high temperatures associated with hypersonic flight (above Mach 5). This pink eraser-like substance, applied to the X-15A-2 aircraft (56-6671), was then covered with a white sealant coat before flight. This coating would help the #2 aircraft reach the record speed of 4,520 mph (Mach 6.7).
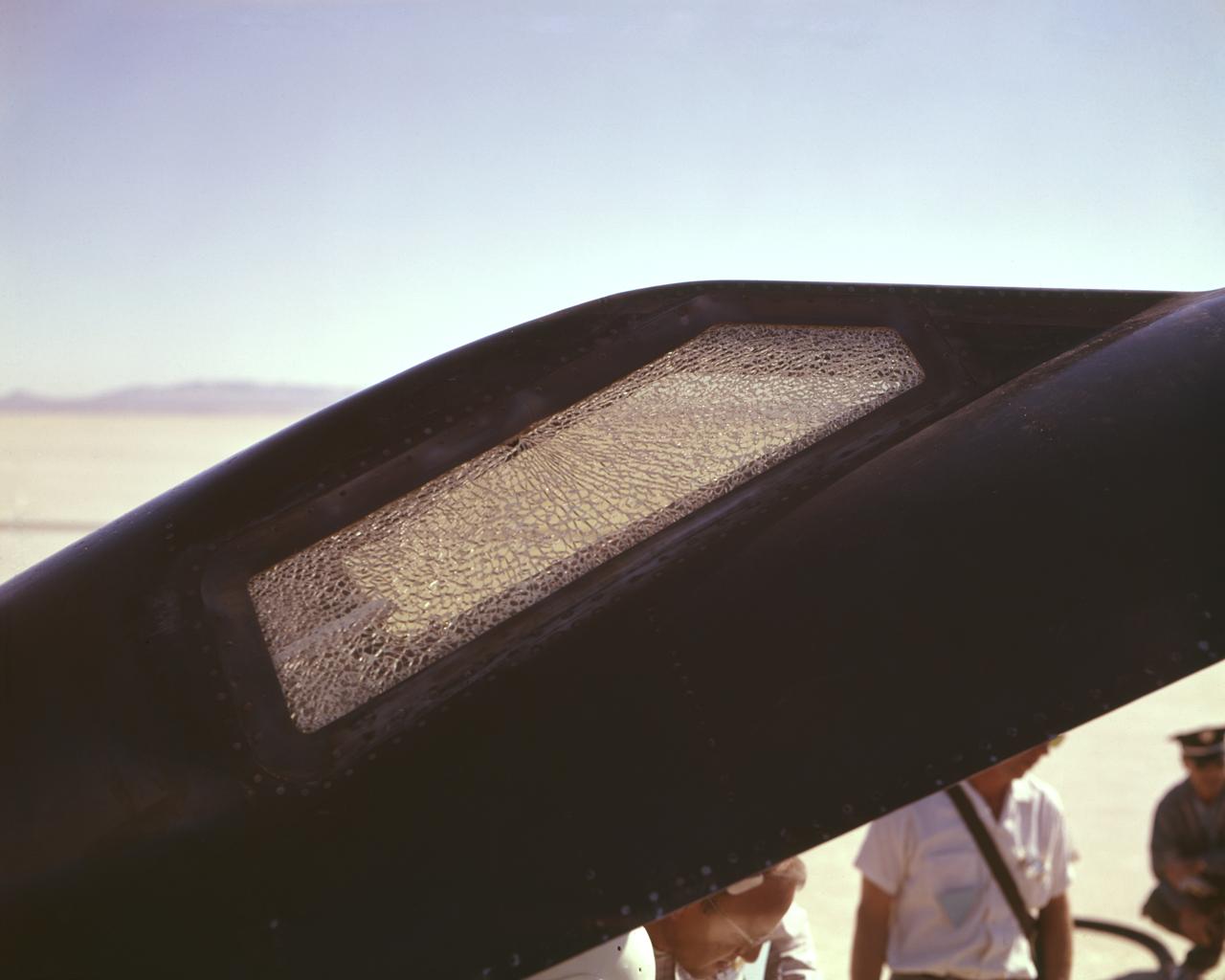

Cracked canopy glass on right side of X-15 #2 after flt. 2-21-37 on Nov. 9 1961. Robert White-pilot. First flight to mach 6.
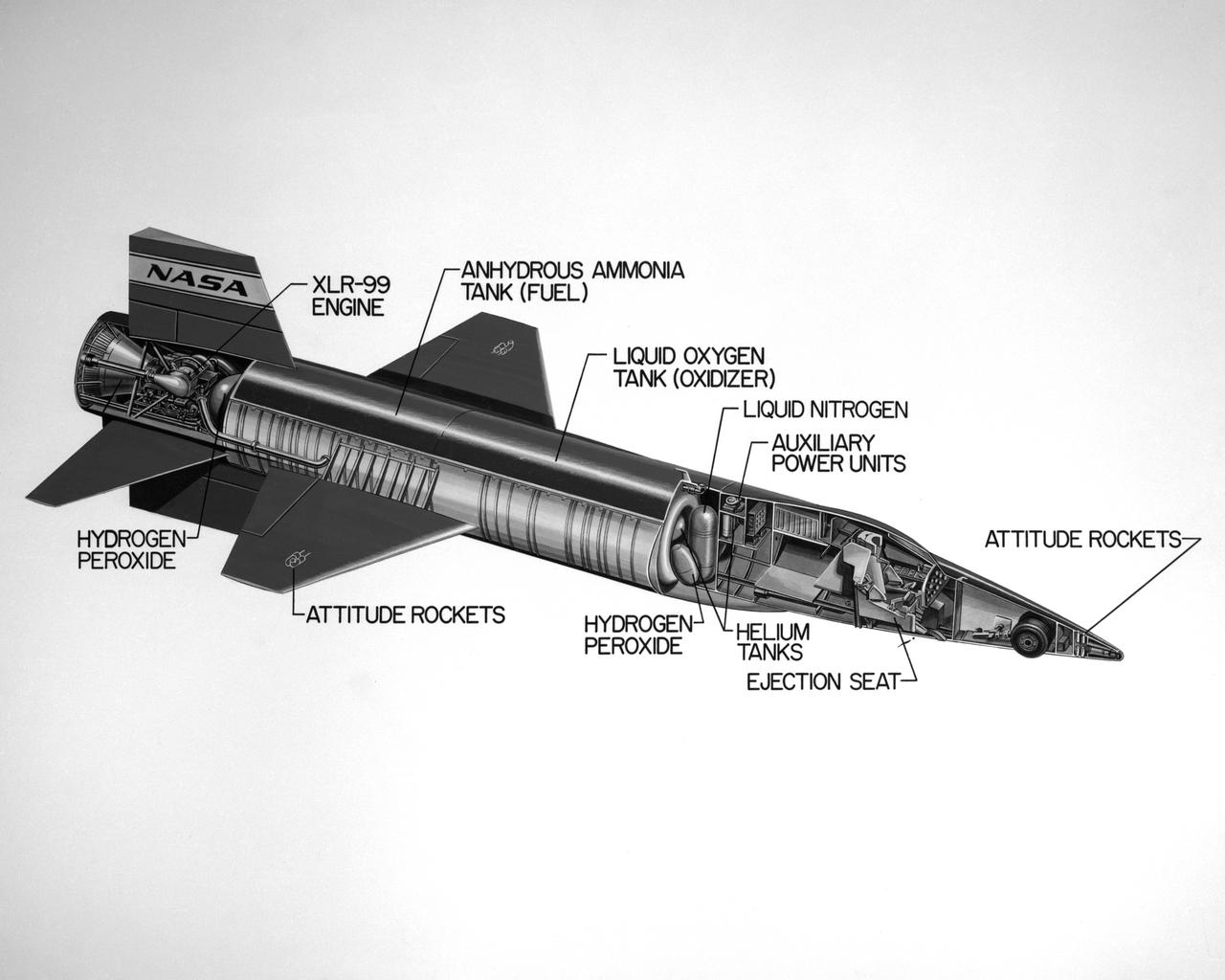
Cutaway drawing of the North American X-15.
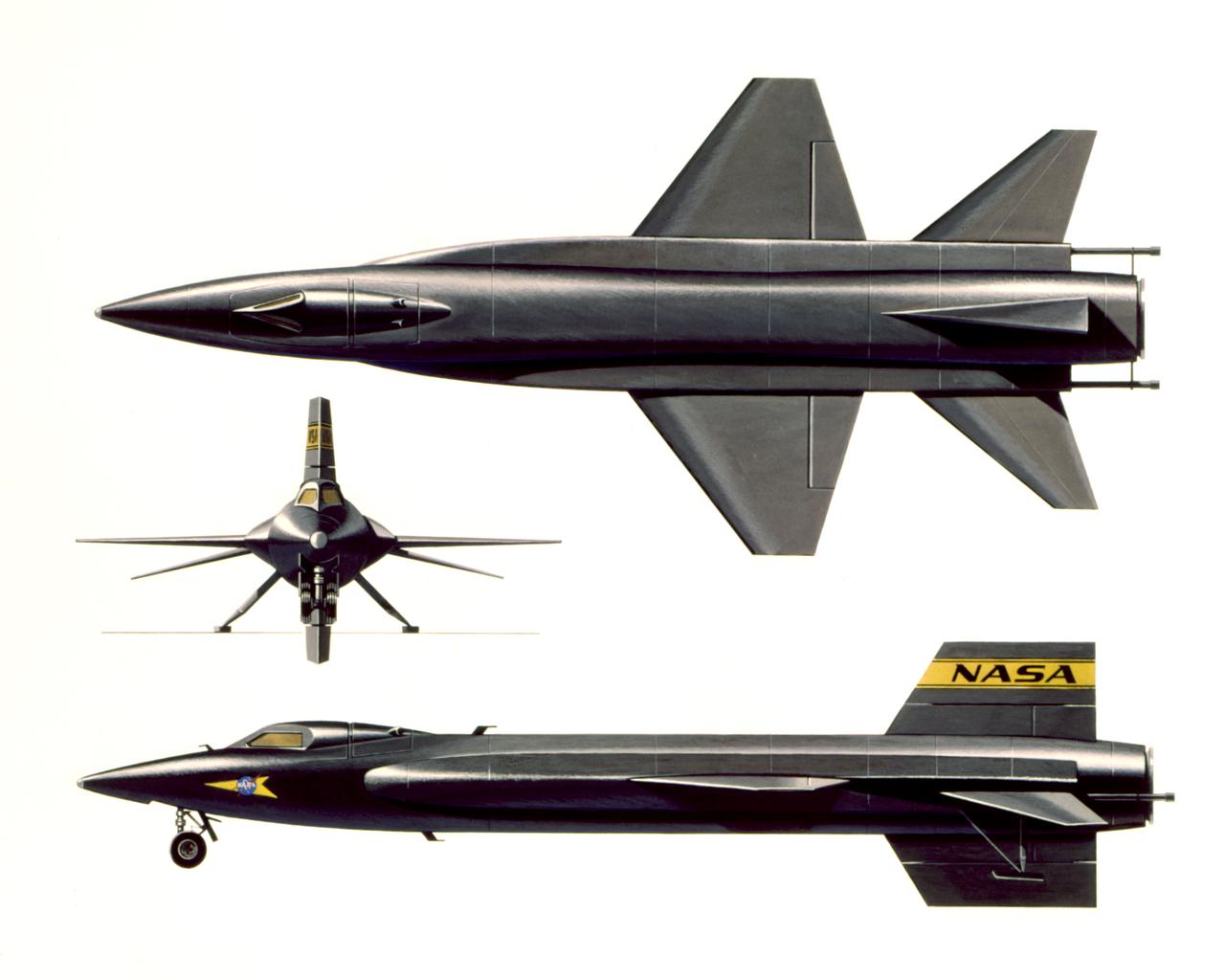

Three view art of the North American X-15.
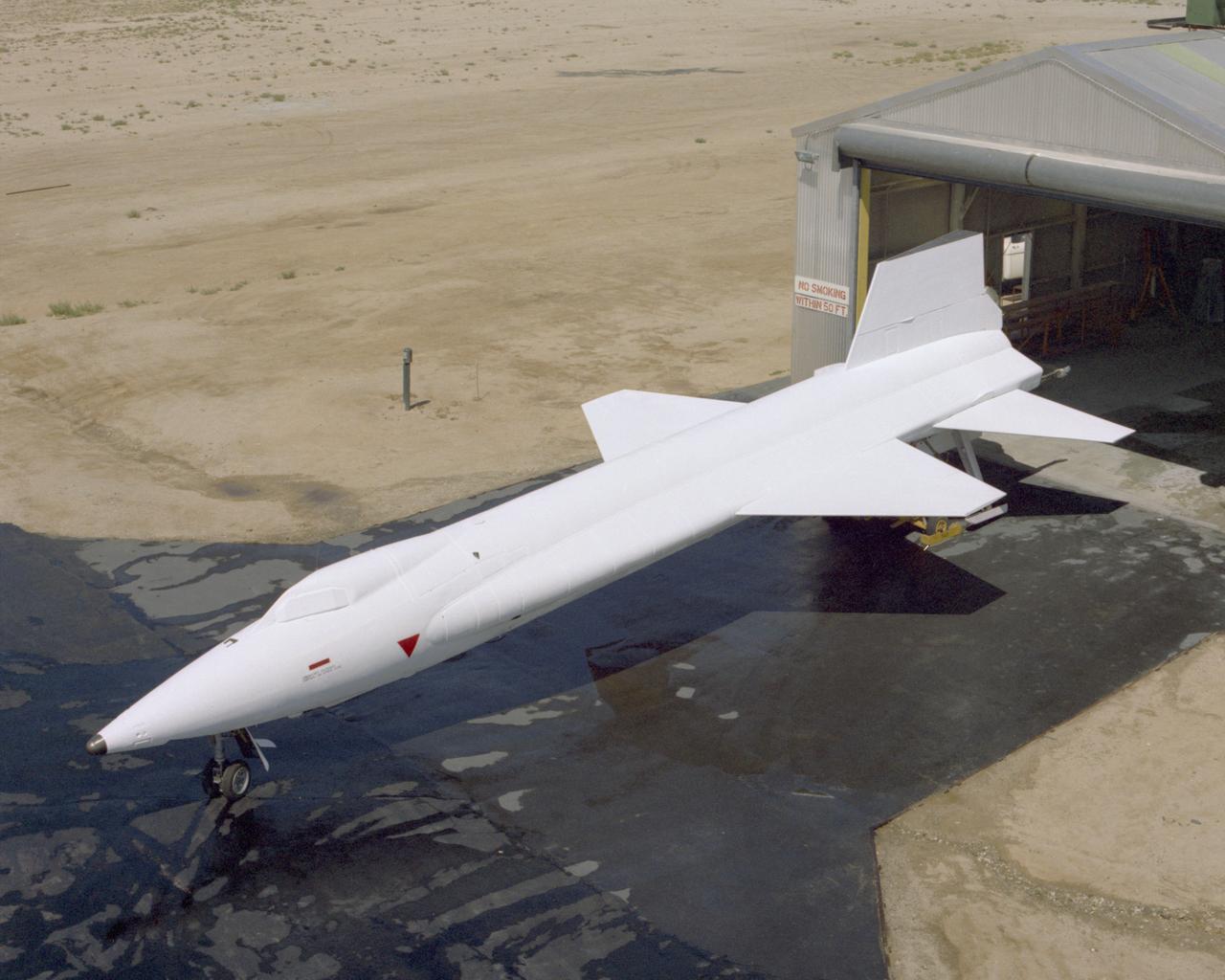

X-15A-2 is rolled out of the paint shop after having the full scale ablative applied. In June 1967, the X-15A-2 rocket-powered research aircraft received a full-scale ablative coating to protect the craft from the high temperatures associated with hypersonic flight (above Mach 5). This pink eraser-like substance, applied to the X-15A-2 aircraft (56-6671), was then covered with a white sealant coat before flight. This coating would help the #2 aircraft reach the record speed of 4,520 mph (Mach 6.7).
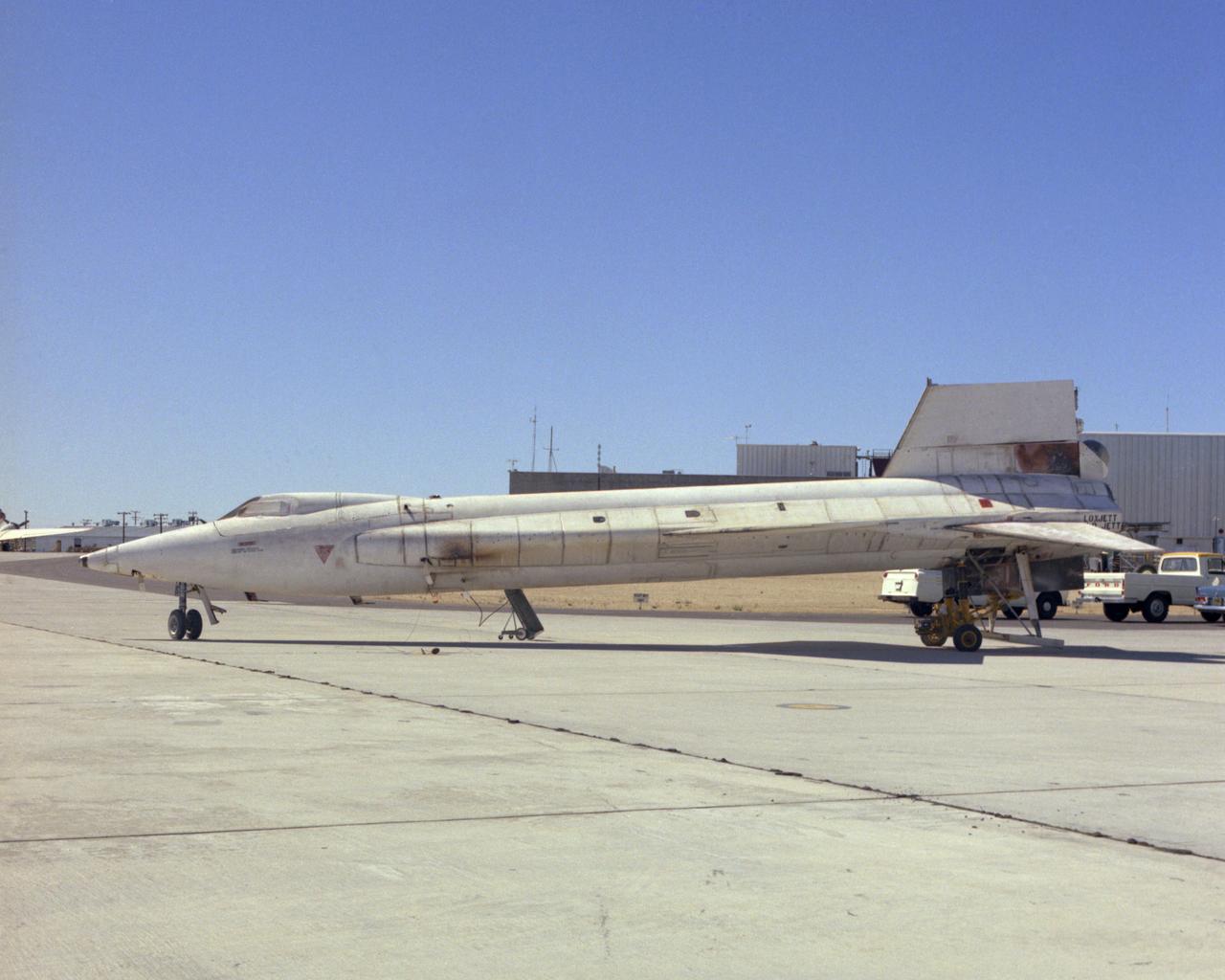

X-15A-2 post flight photo showing heat damage from Mach 6.7 flight on 3 Oct 67. Flt. 2-53-97; pilot-Pete Knight.