
Technicians at General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc., (GA-ASI) facility at Adelanto, Calif., carefully install a turboprop engine to the rear fuselage of NASA's Altair aircraft during final assembly operations.
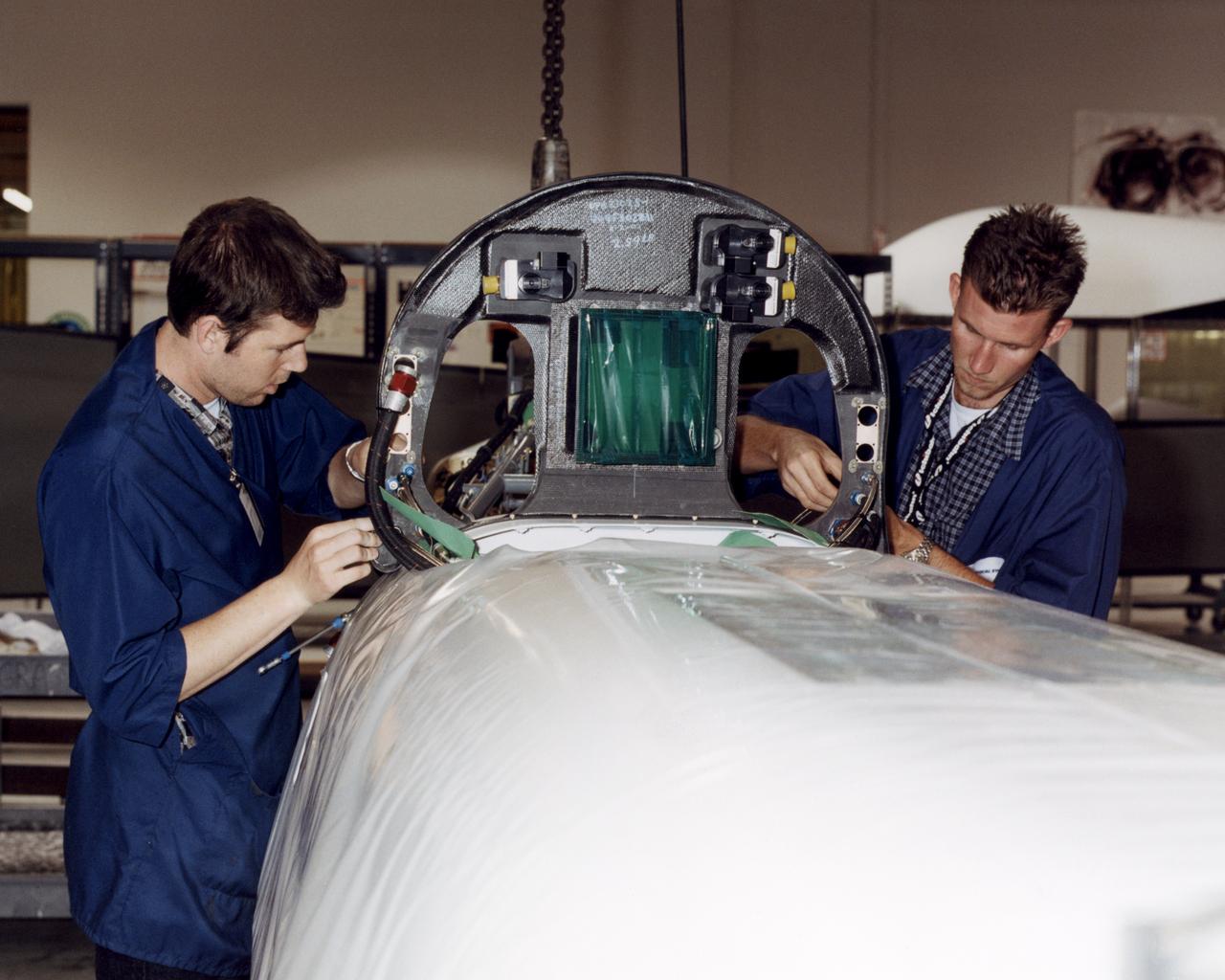

Technicians at General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc., (GA-ASI) facility at Adelanto, Calif., carefully thread control lines through a bulkhead during engine installation on NASA's Altair aircraft.
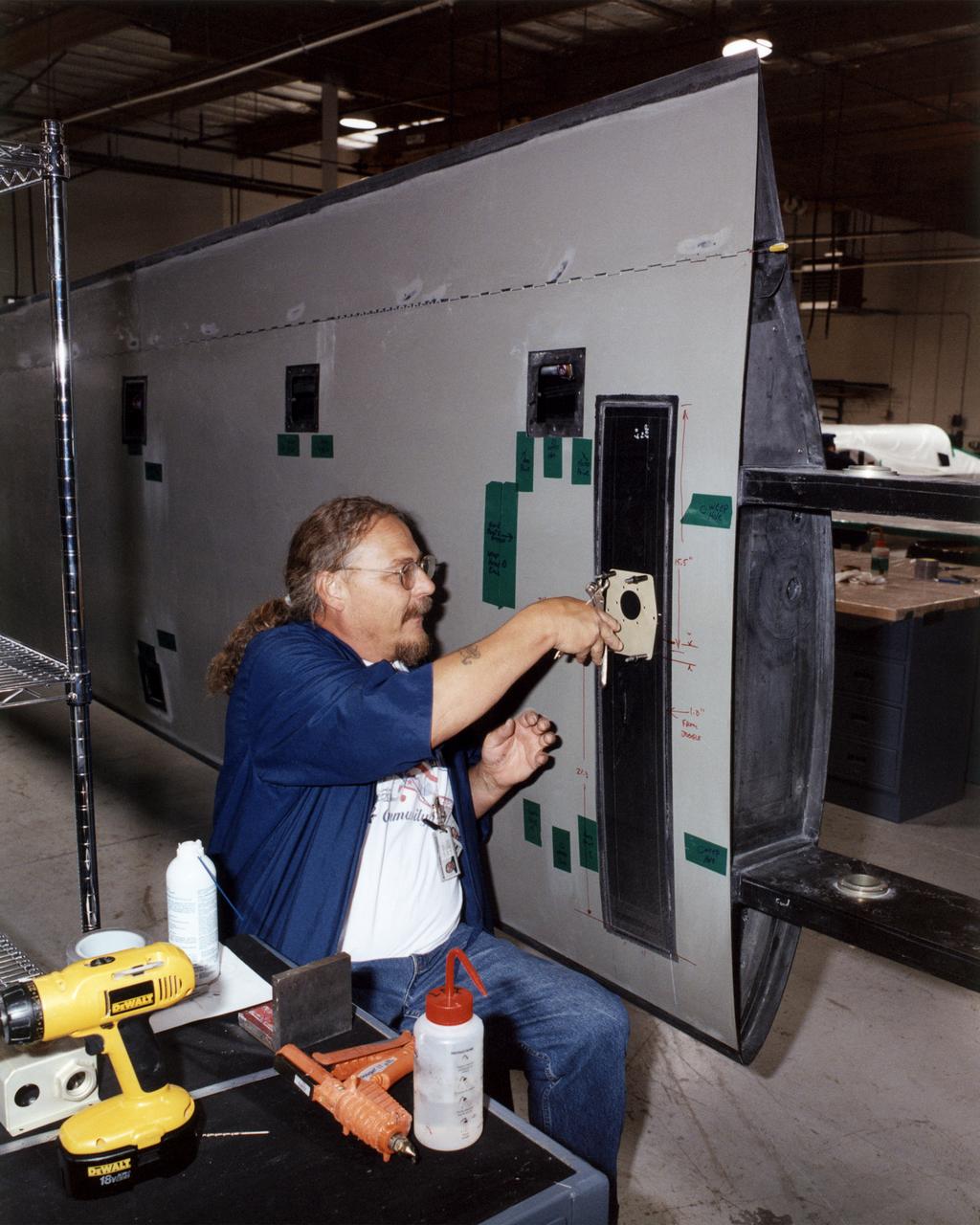

Technician Dave Brown installs a drilling template during construction of the all-composite left wing of NASA's Altair aircraft at General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc., (GA-ASI) facility at Adelanto, Calif.
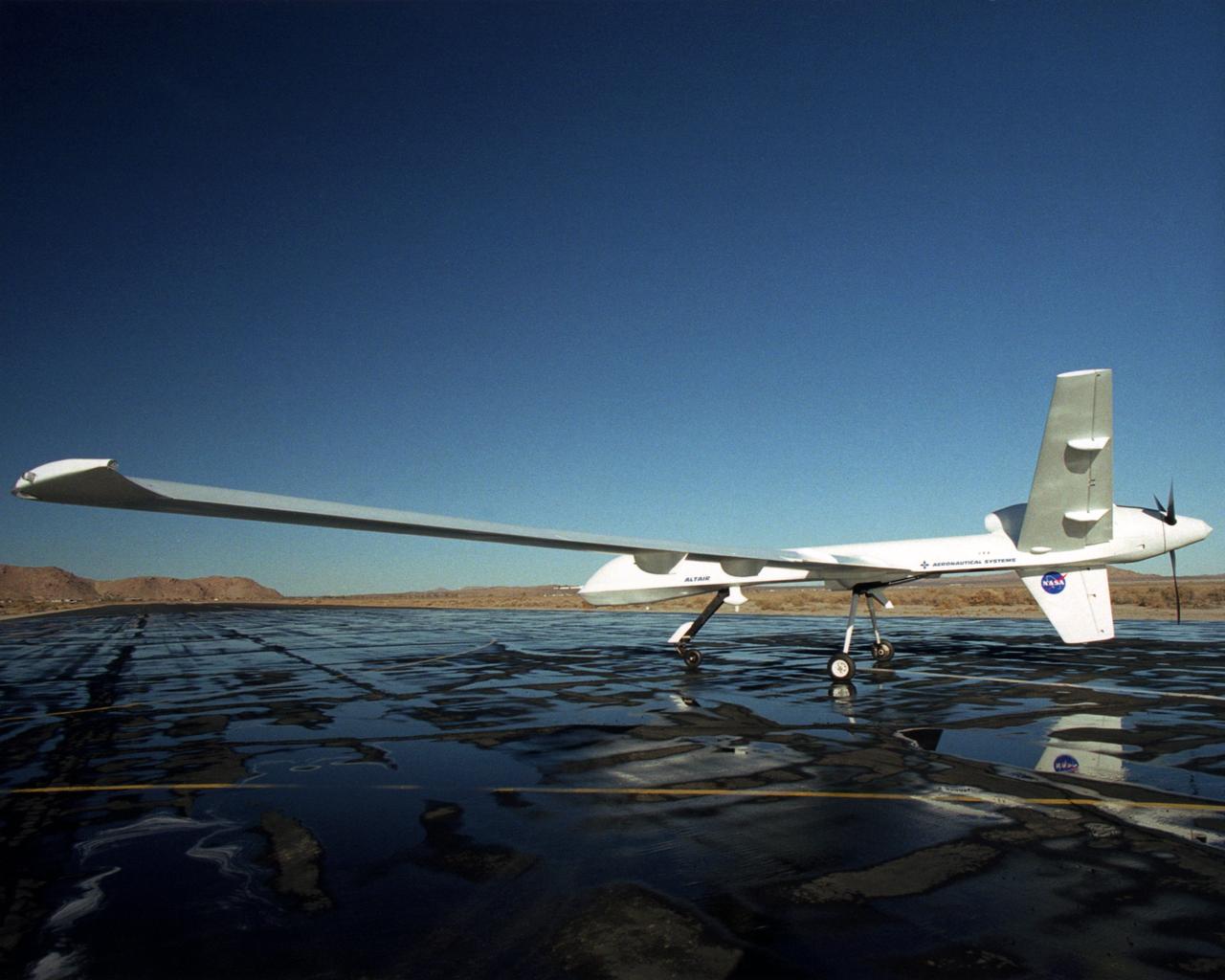

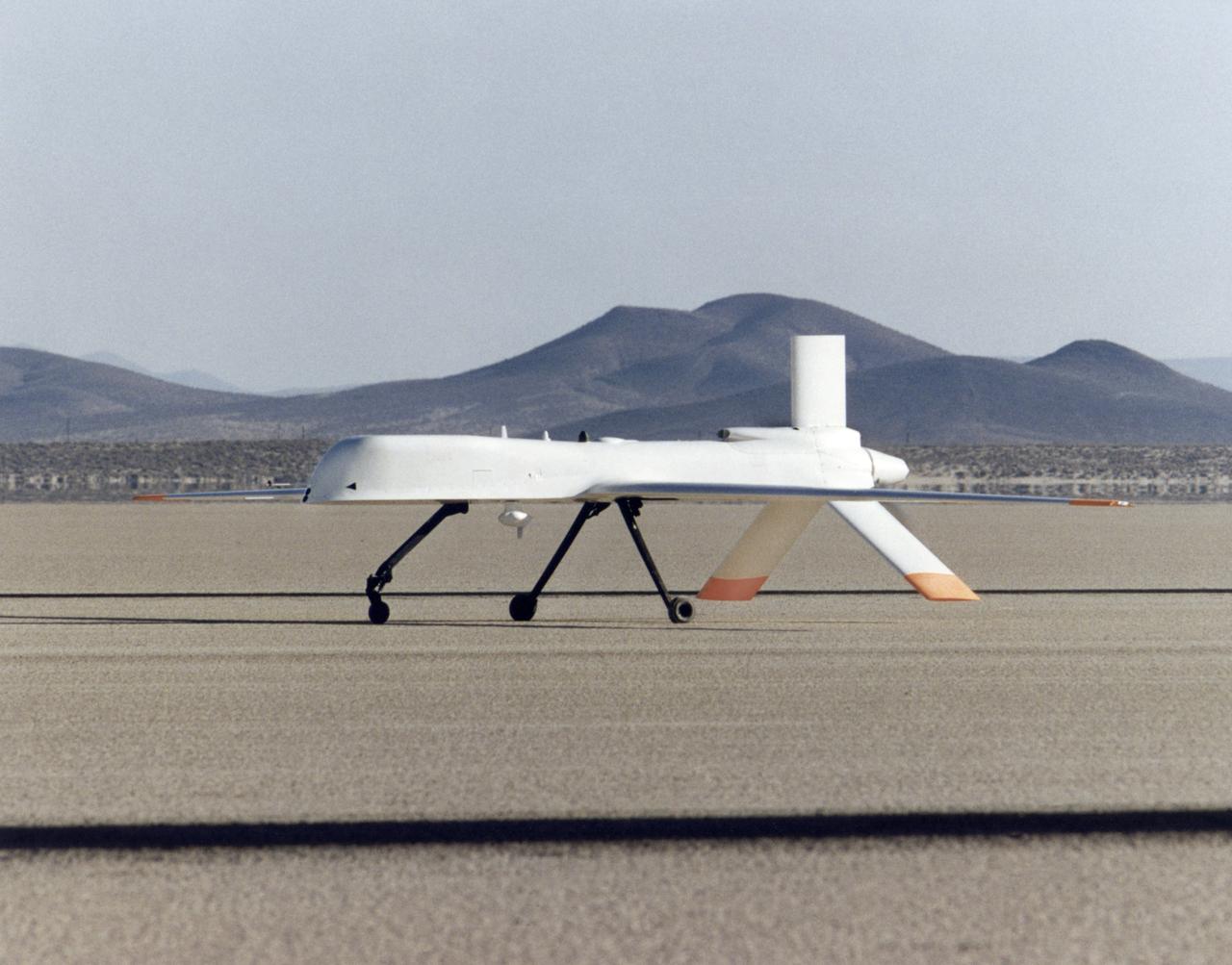
Long wings, a V-tail with a ventral fin and a rear-mounted engine distinguish the Altair, an unmanned aerial vehicle built for NASA by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
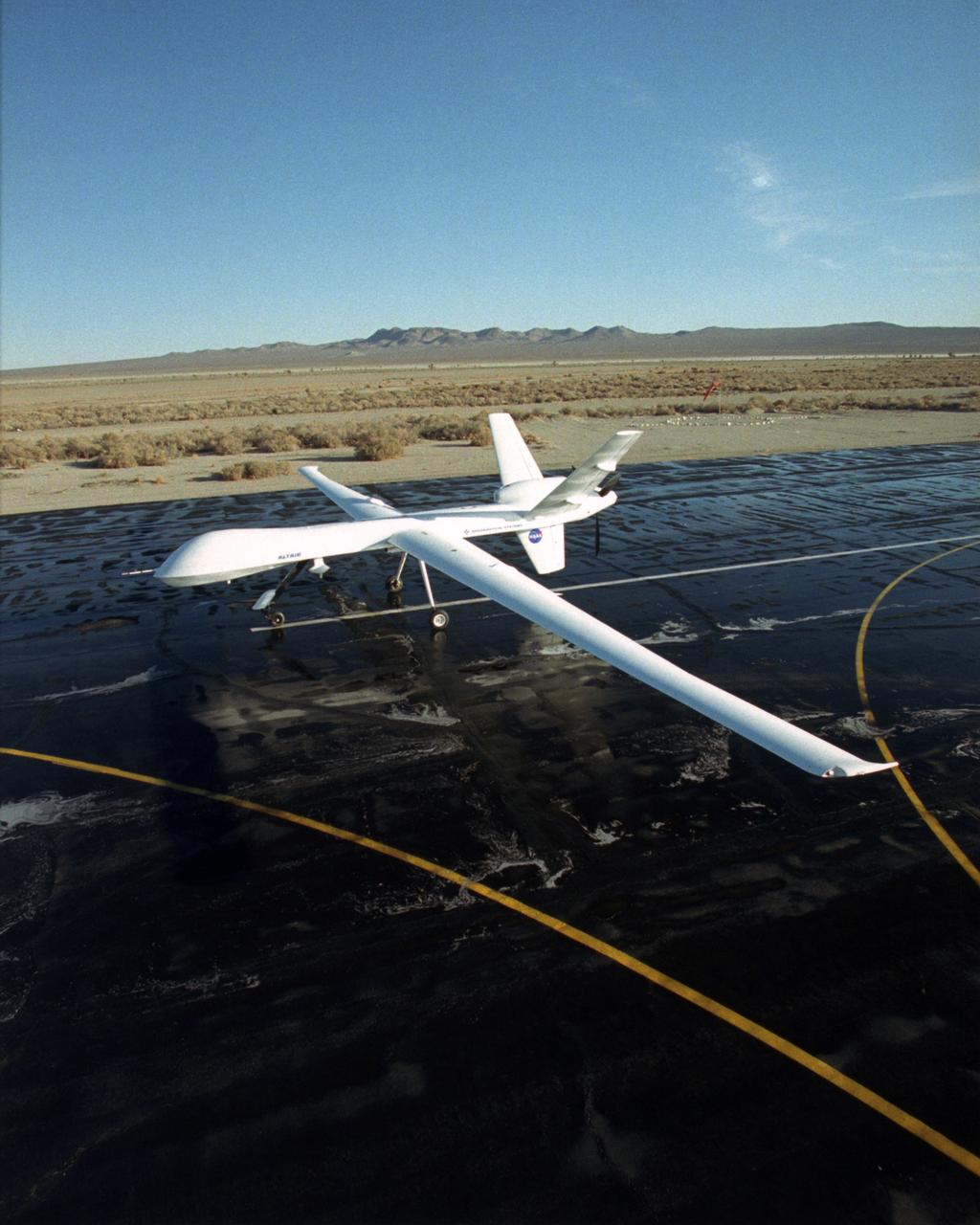

The Altair unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), built by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc. for NASA, is poised for flight at GA-ASI's flight test facility at El Mirage, California.

The left wing of NASA's Altair unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) rests in a jig during construction at General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc., (GA-ASI) facility at Adelanto, Calif.
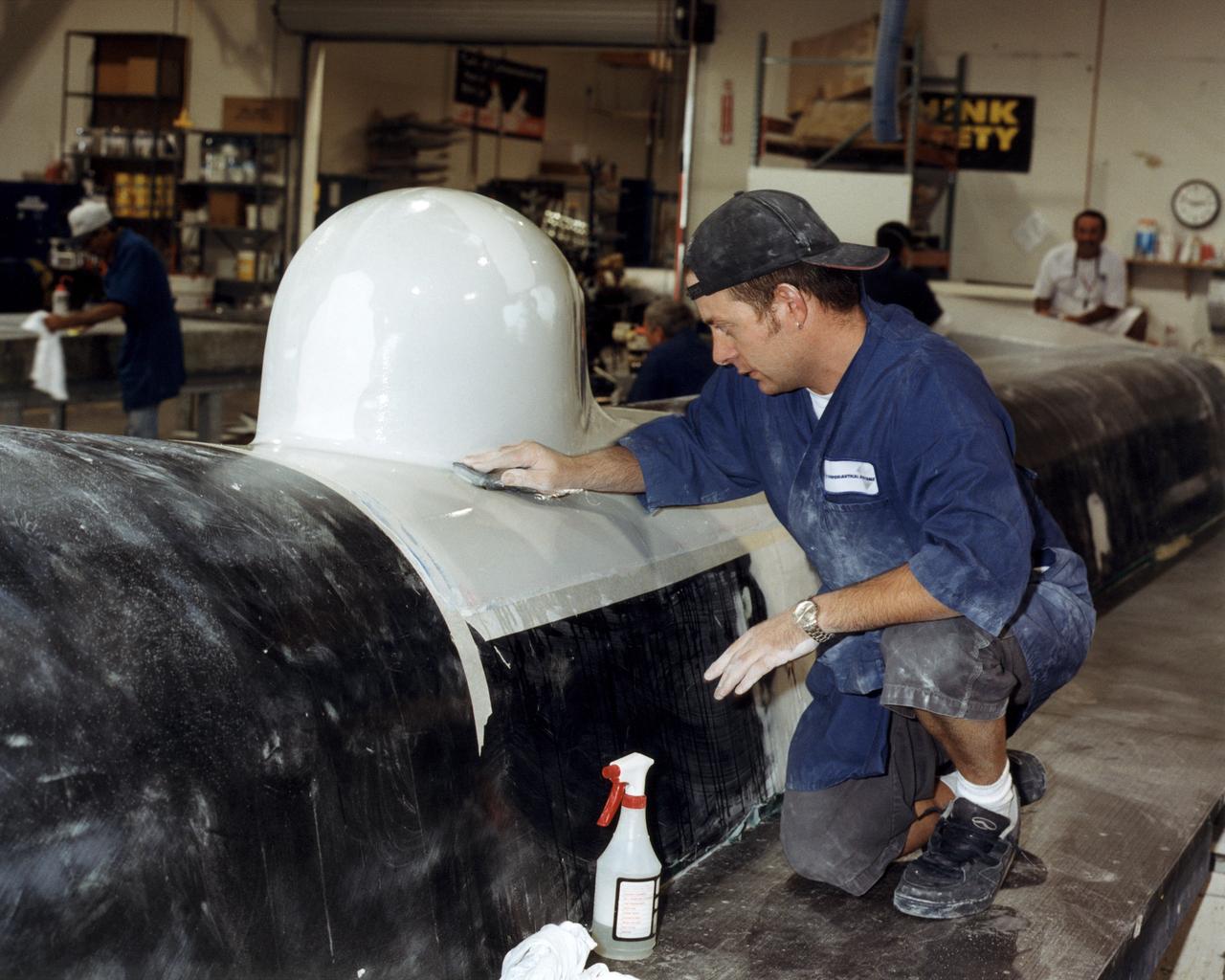

Technician Shawn Warren carefully smoothes out the composite skin of an instrument fairing<br>atop the upper fuselage of the Altair unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) at General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc., facility at Adelanto, Calif.
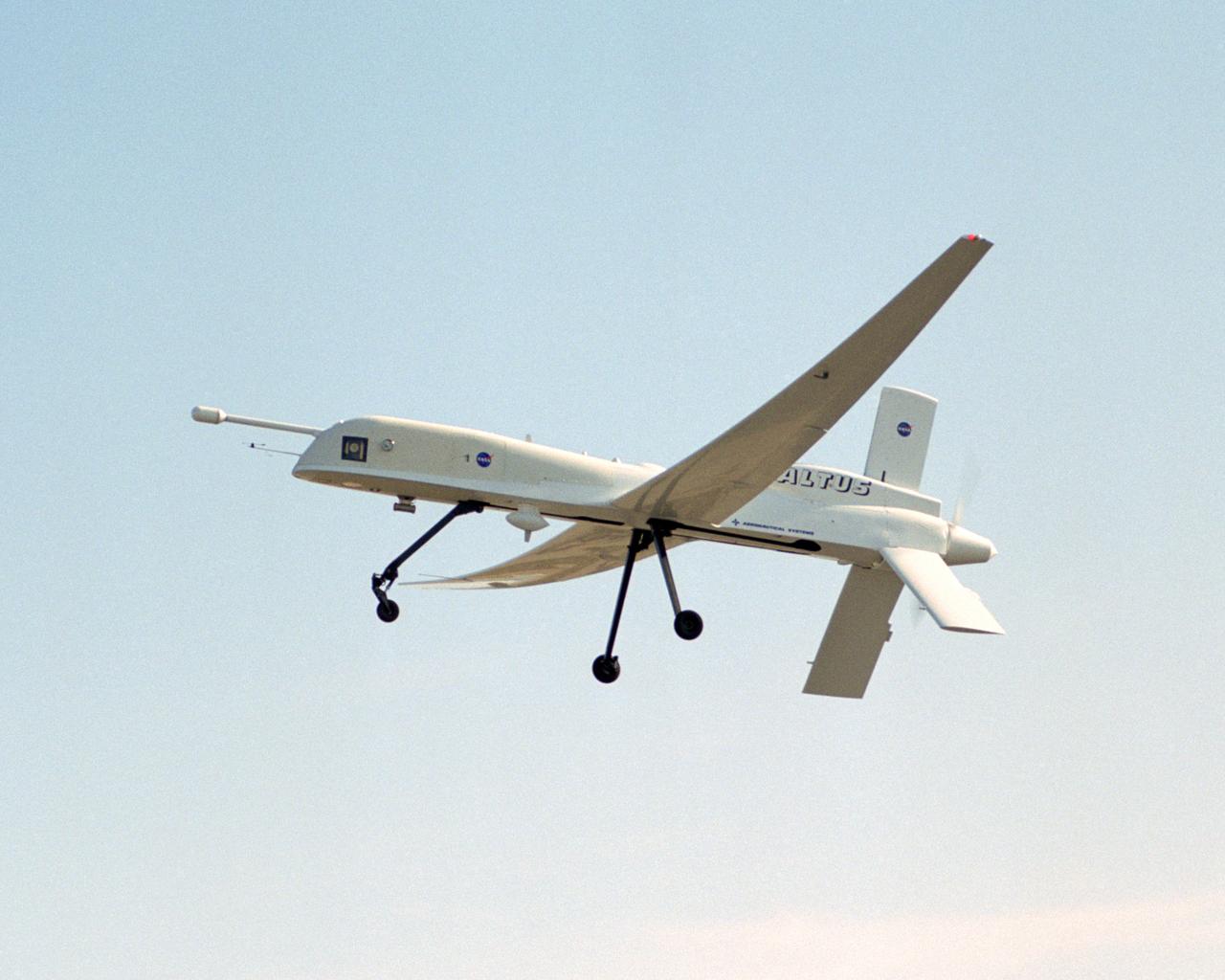

A NASA team studying the causes of electrical storms and their effects on our home planet achieved a milestone on August 21, 2002, completing the study's longest-duration research flight and monitoring four thunderstorms in succession. Based at the Naval Air Station Key West, Florida, researchers with the Altus Cumulus Electrification Study (ACES) used the Altus II remotely-piloted aircraft to study thunderstorms in the Atlantic Ocean off Key West and the west of the Everglades. The ACES lightning study used the Altus II twin turbo uninhabited aerial vehicle, built by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc. of San Diego. The Altus II was chosen for its slow flight speed of 75 to 100 knots (80 to 115 mph), long endurance, and high-altitude flight (up to 65,000 feet). These qualities gave the Altus II the ability to fly near and around thunderstorms for long periods of time, allowing investigations to be to be conducted over the entire life cycle of storms. The vehicle has a wing span of 55 feet and a payload capacity of over 300 lbs. With dual goals of gathering weather data safely and testing the adaptability of the uninhabited aircraft, the ACES study is a collaboration among the Marshall Space Flight Center, the University of Alabama in Huntsville, NASA,s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Pernsylvania State University in University Park, and General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
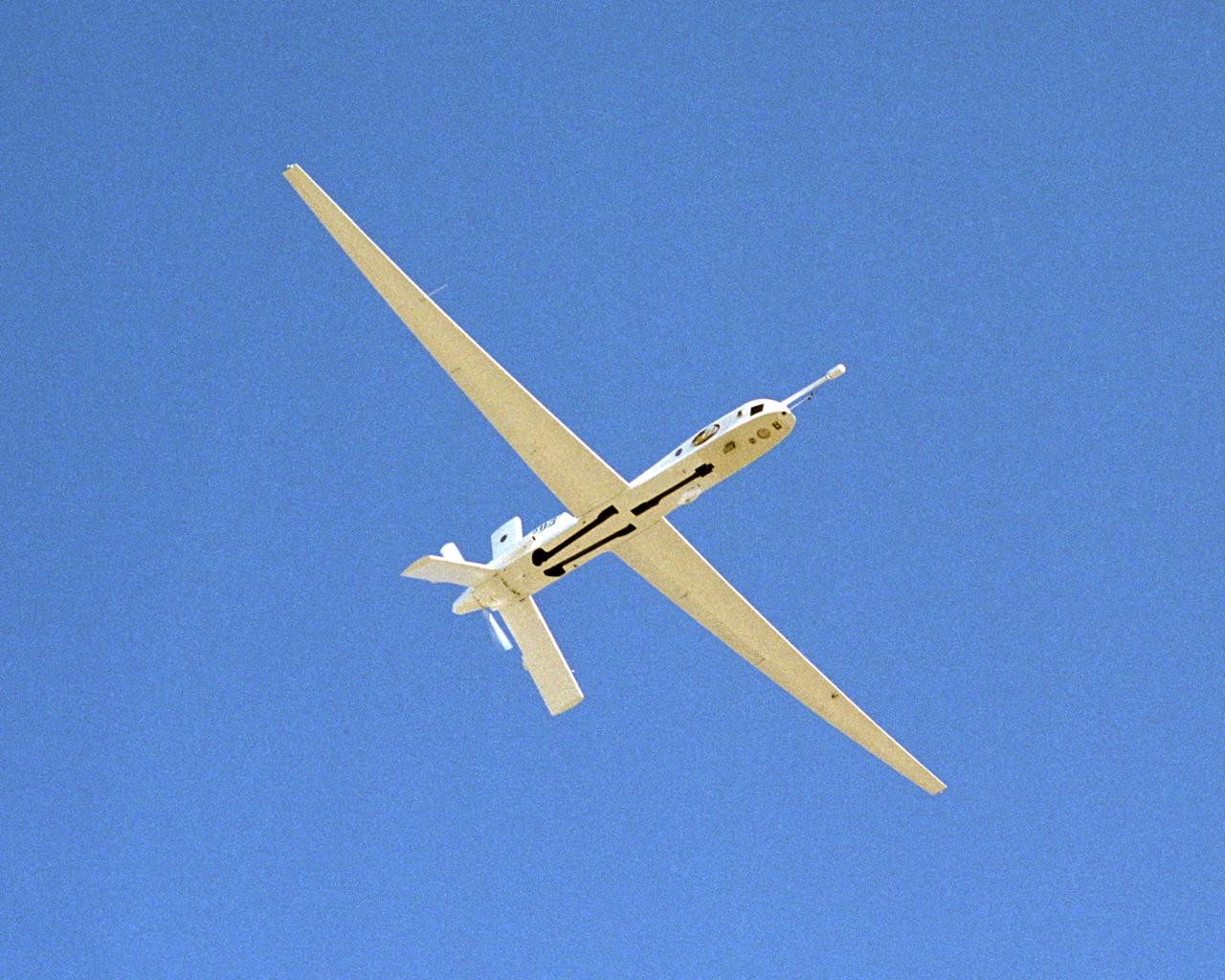

A NASA team studying the causes of electrical storms and their effects on our home planet achieved a milestone on August 21, 2002, completing the study's longest-duration research flight and monitoring four thunderstorms in succession. Based at the Naval Air Station Key West, Florida, researchers with the Altus Cumulus Electrification Study (ACES) used the Altus II remotely piloted aircraft to study thunderstorms in the Atlantic Ocean off Key West and the west of the Everglades. The ACES lightning study used the Altus II twin turbo uninhabited aerial vehicle, built by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc. of San Diego. The Altus II was chosen for its slow flight speed of 75 to 100 knots (80 to 115 mph), long endurance, and high-altitude flight (up to 65,000 feet). These qualities gave the Altus II the ability to fly near and around thunderstorms for long periods of time, allowing investigations to be conducted over the entire life cycle of storms. The vehicle has a wing span of 55 feet and a payload capacity of over 300 lbs. With dual goals of gathering weather data safely and testing the adaptability of the uninhabited aircraft, the ACES study is a collaboration among the Marshall Space Flight Center, the University of Alabama in Huntsville, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Pernsylvania State University in University Park, and General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
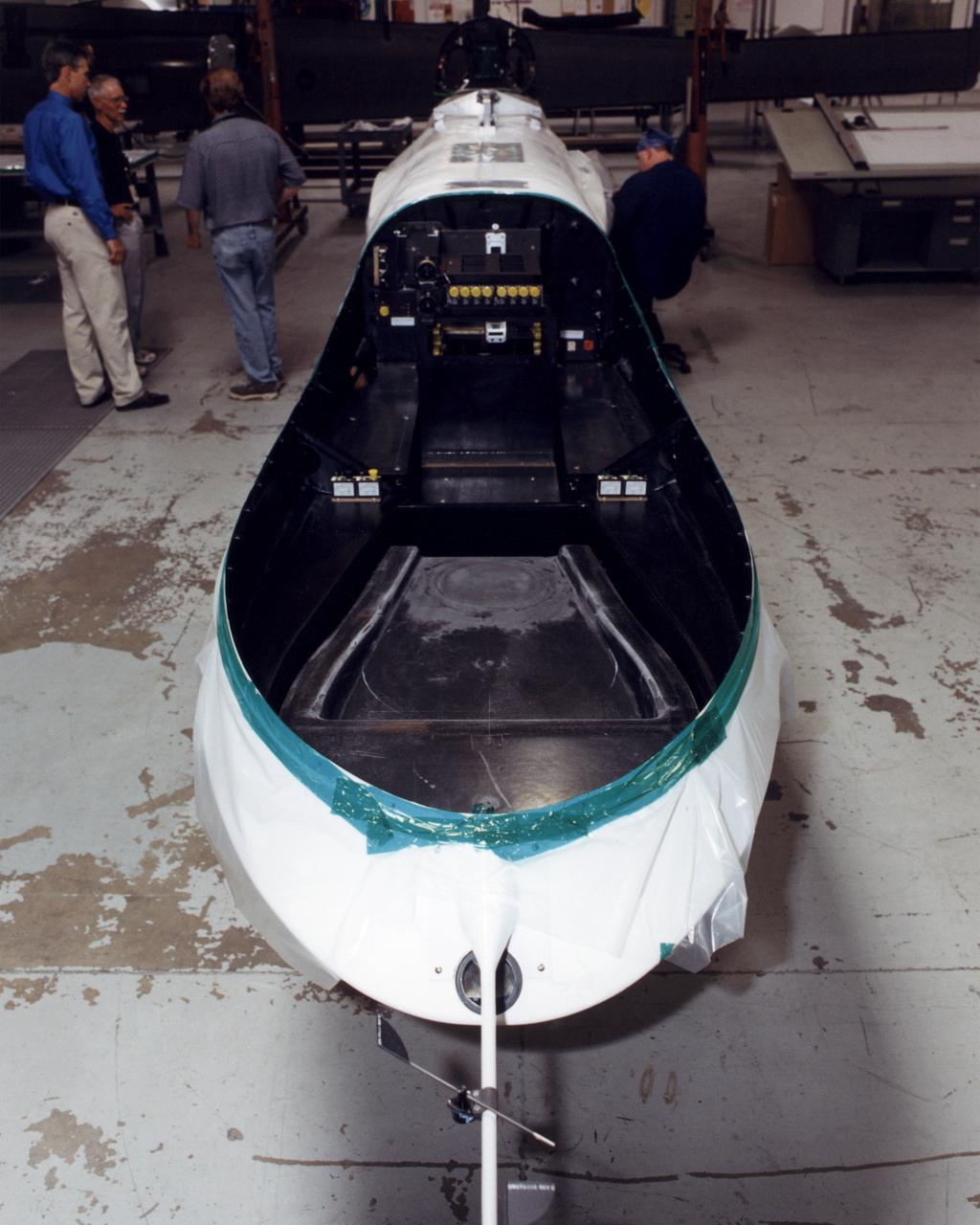

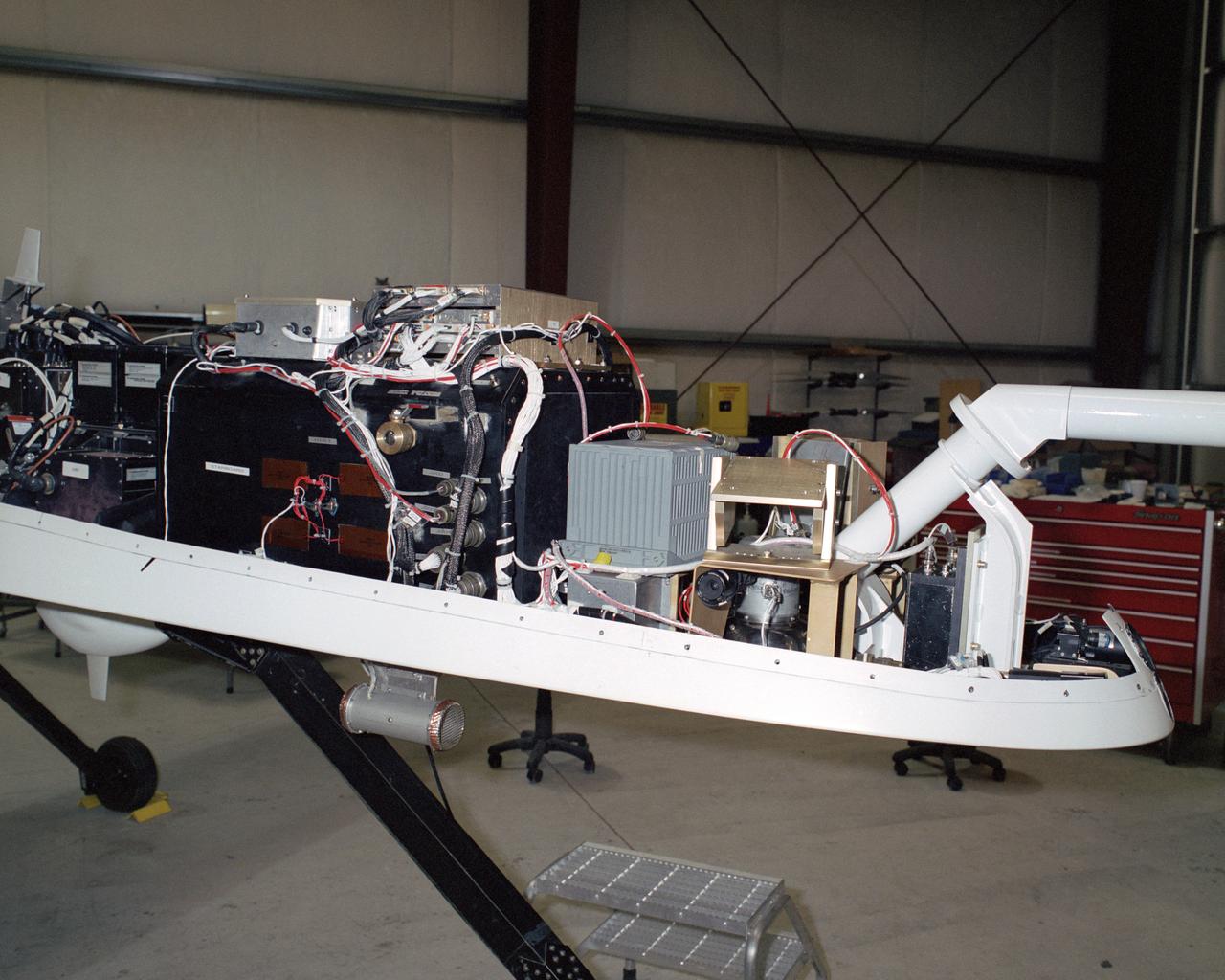
The payload bay in the nose of NASA's Altair unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) will be able to carry up to 700 lbs. of sensors, imaging equipment and other instruments for Earth science missions.
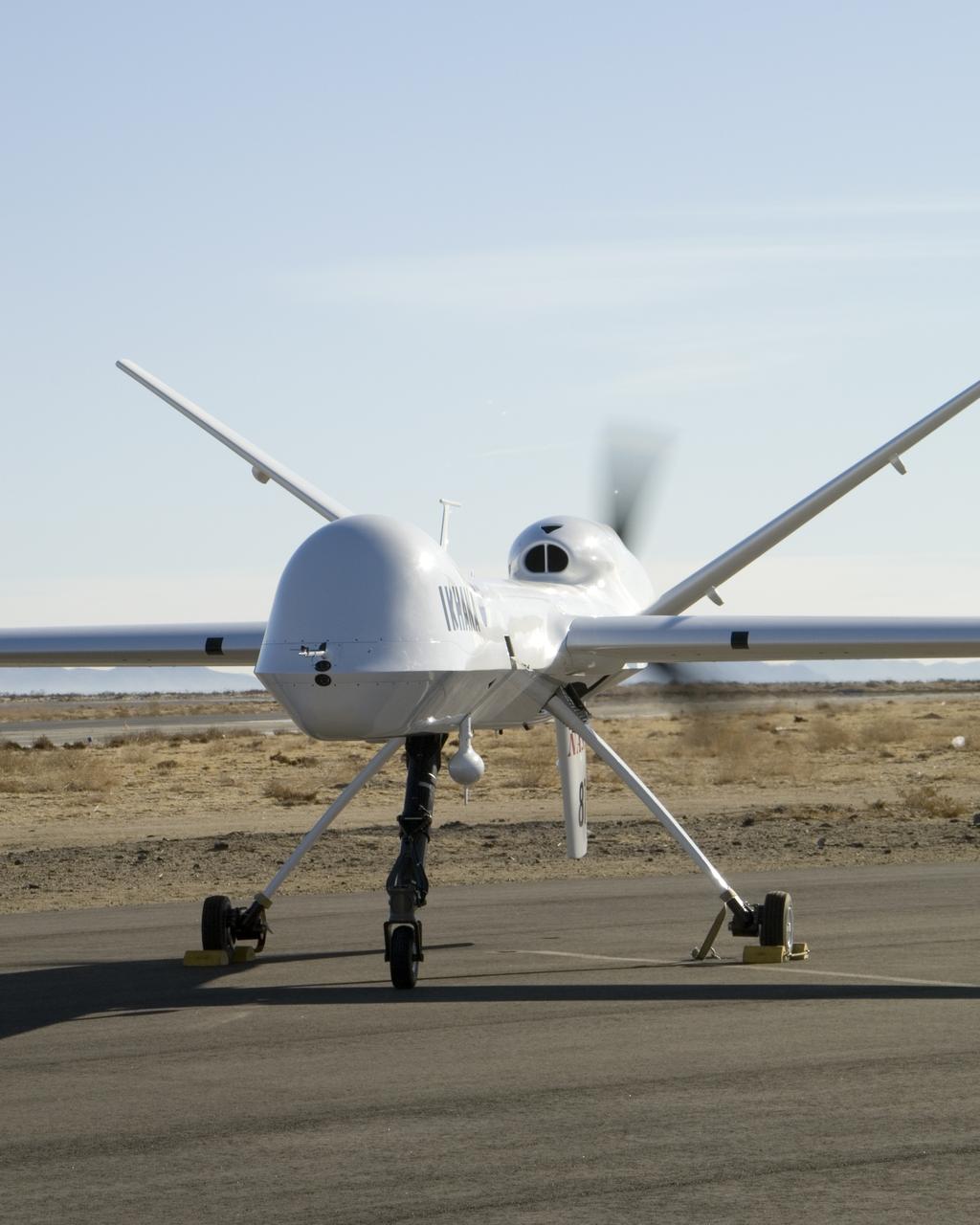

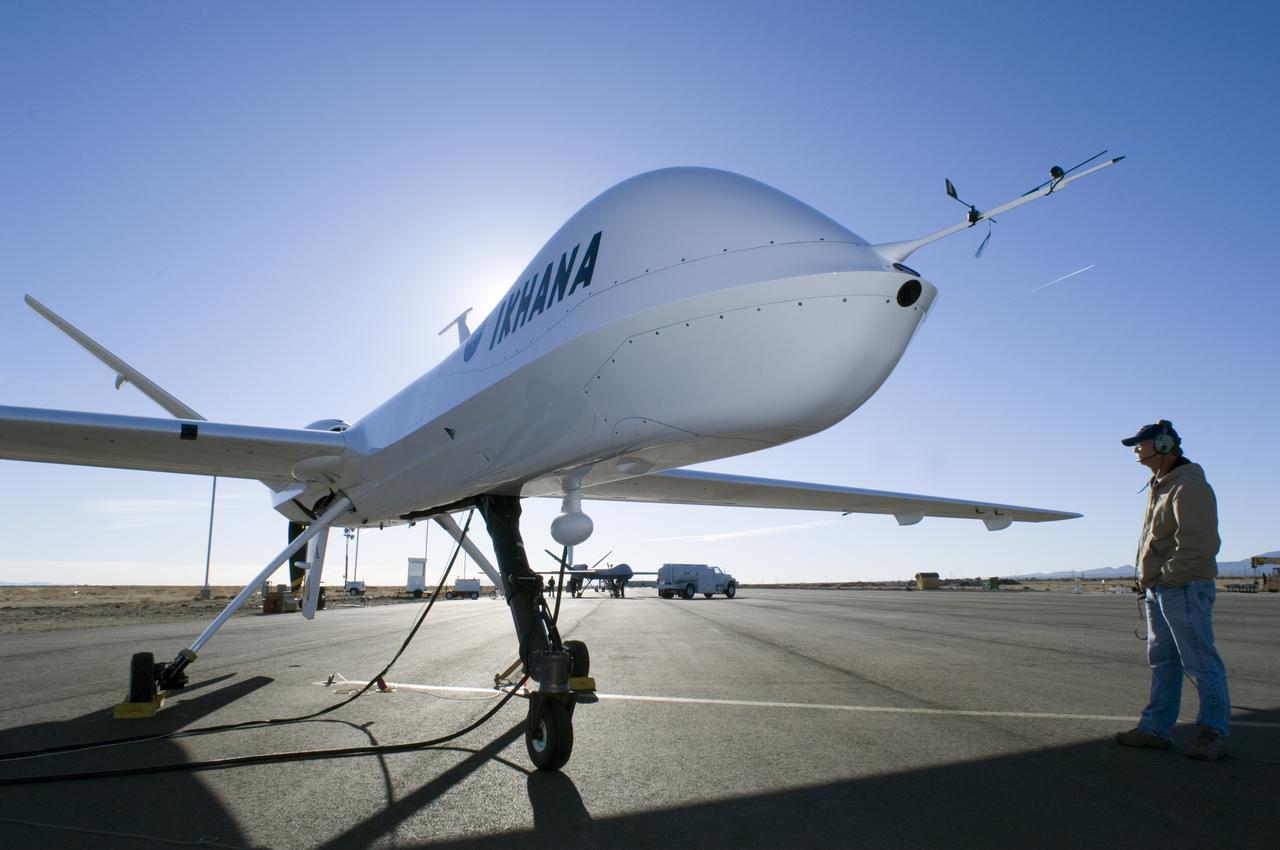
Distinguished by its large nose payload bay, NASA's Ikhana unmanned aircraft does an engine run prior to takeoff from General Atomics' Grey Butte airfield.
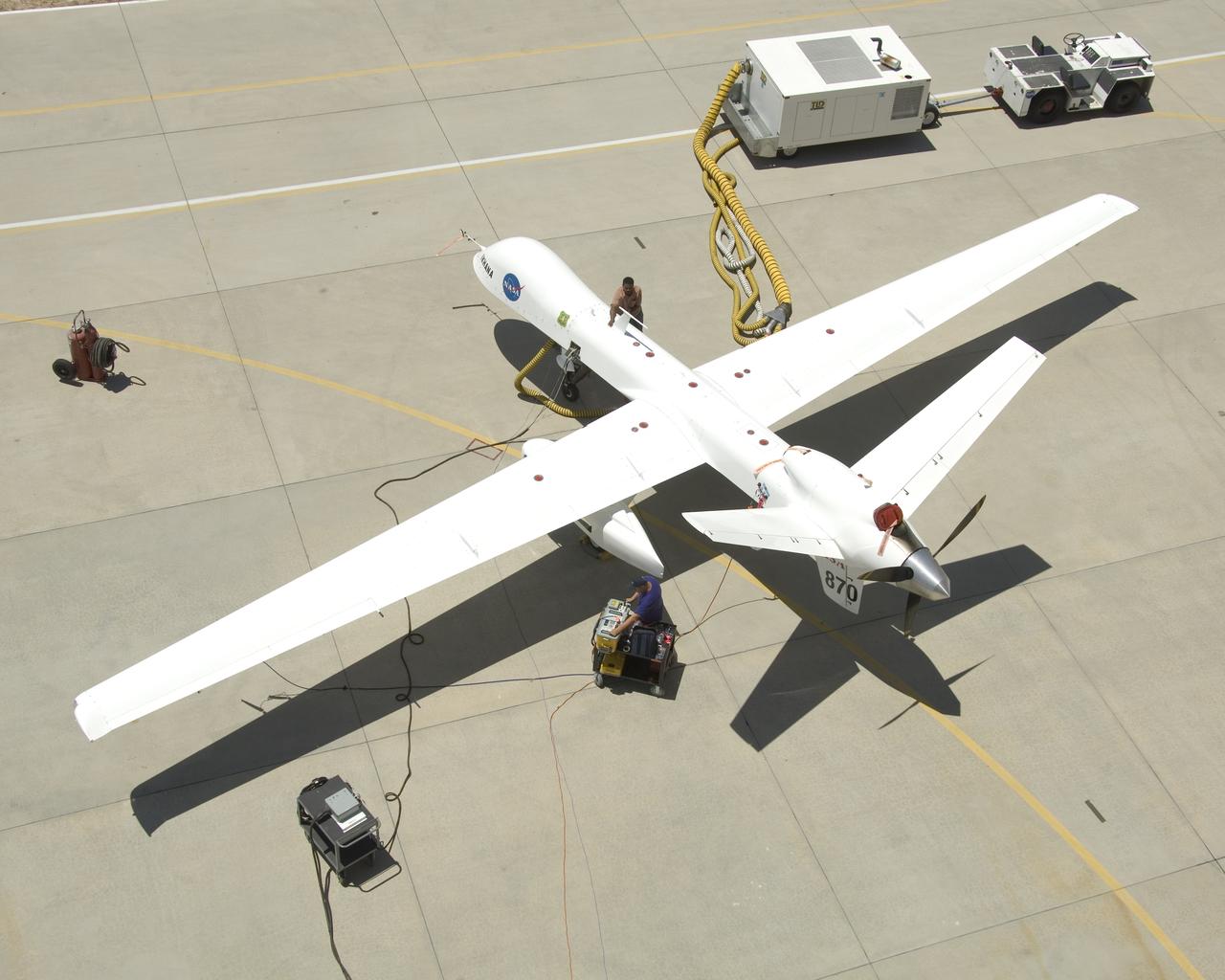

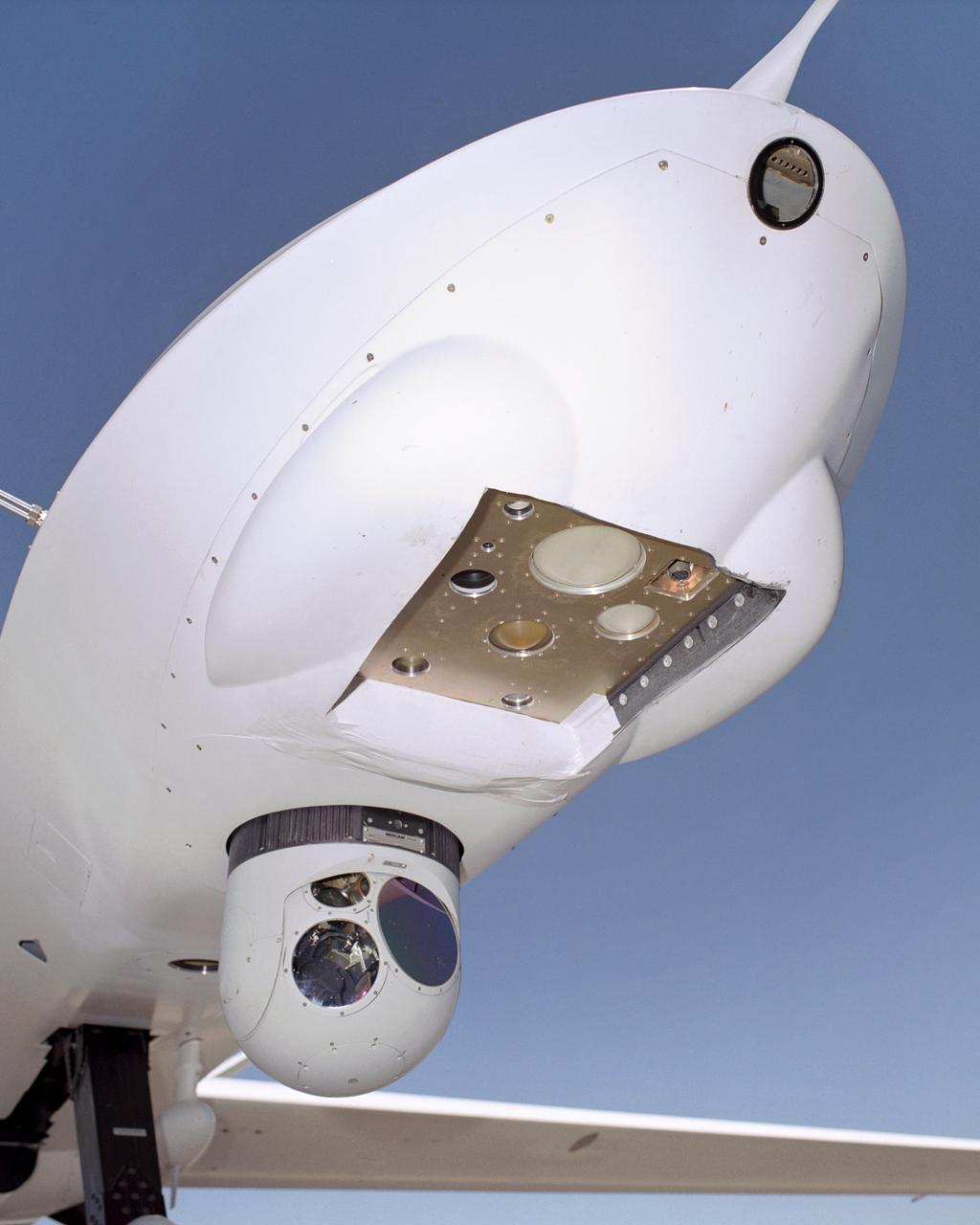
Ground crewmen prepare NASA's Ikhana remotely piloted research aircraft for another flight. Ikhana's infrared imaging sensor pod is visible under the left wing.
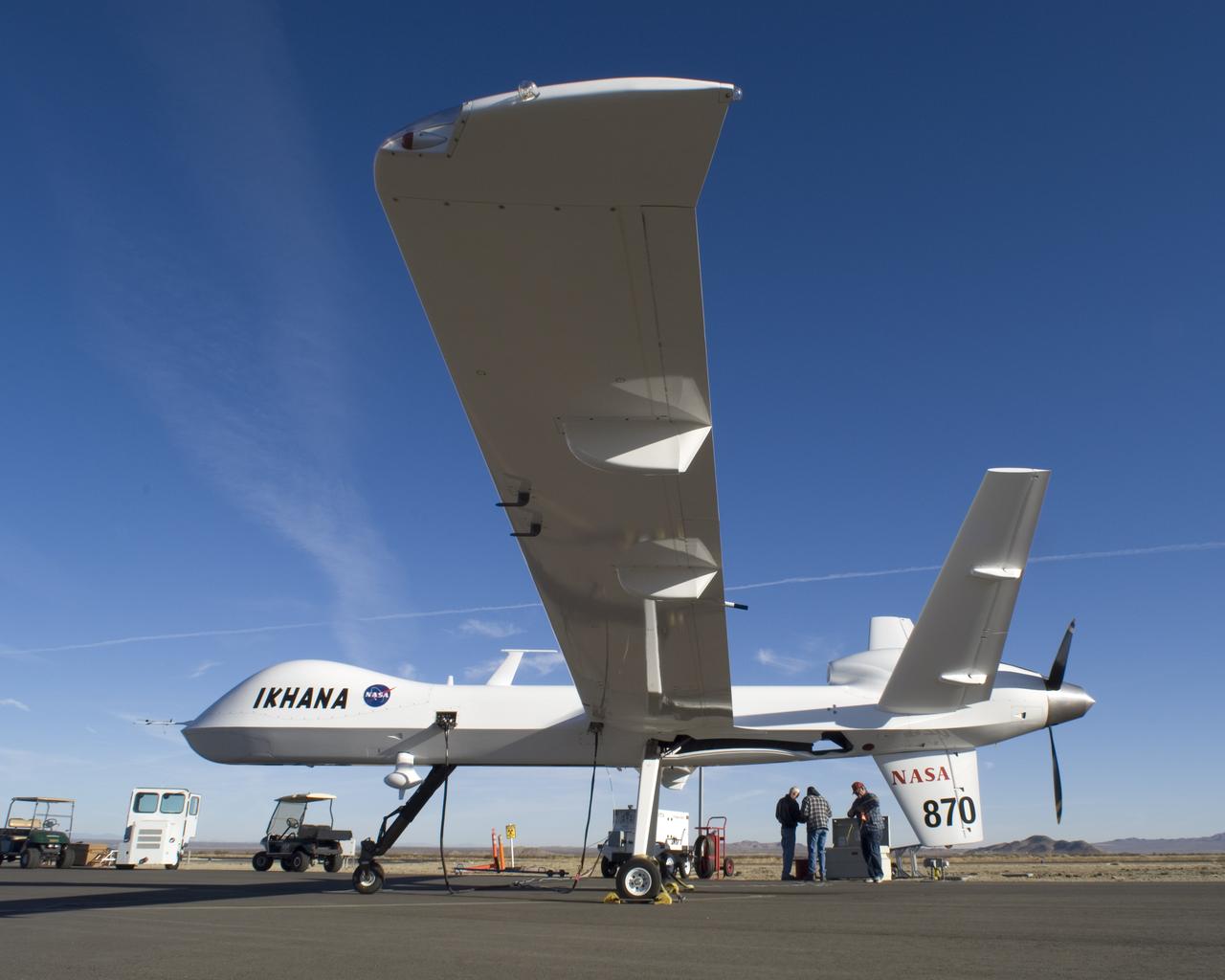

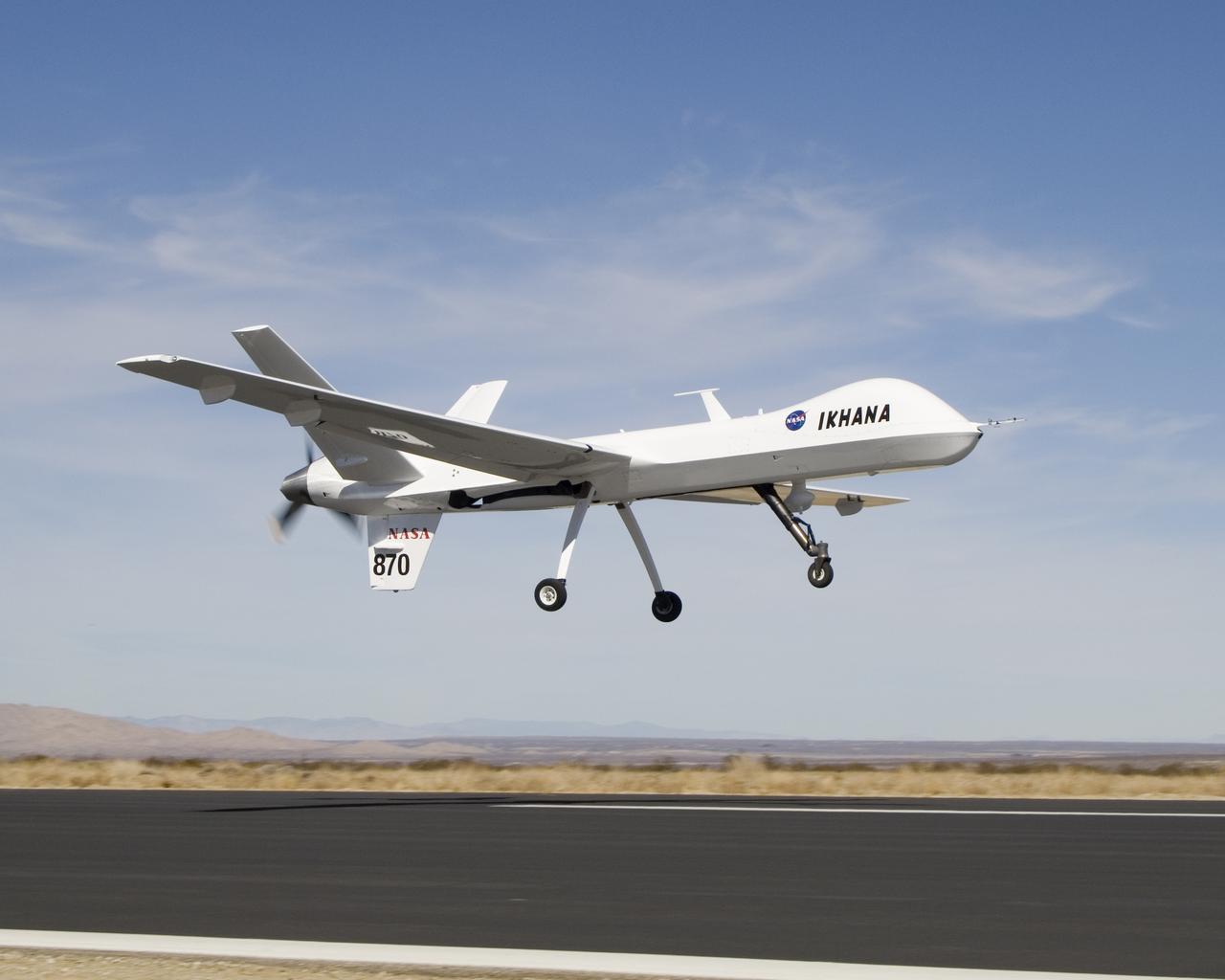
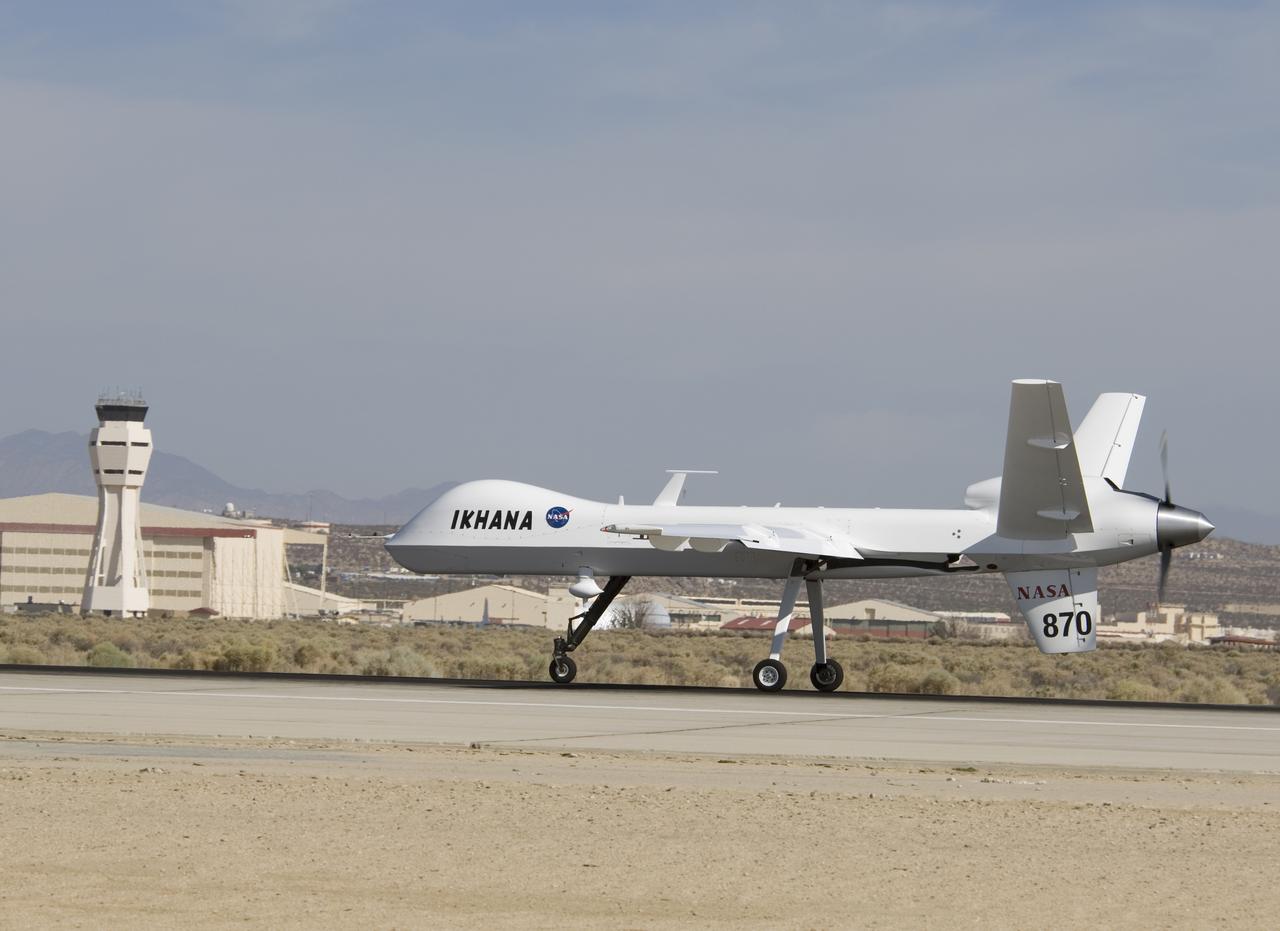
Bearing NASA tail number 870, NASA's Ikhana unmanned aircraft is a civil version of the Predator B designed for high-altitude, long-endurance science flights.
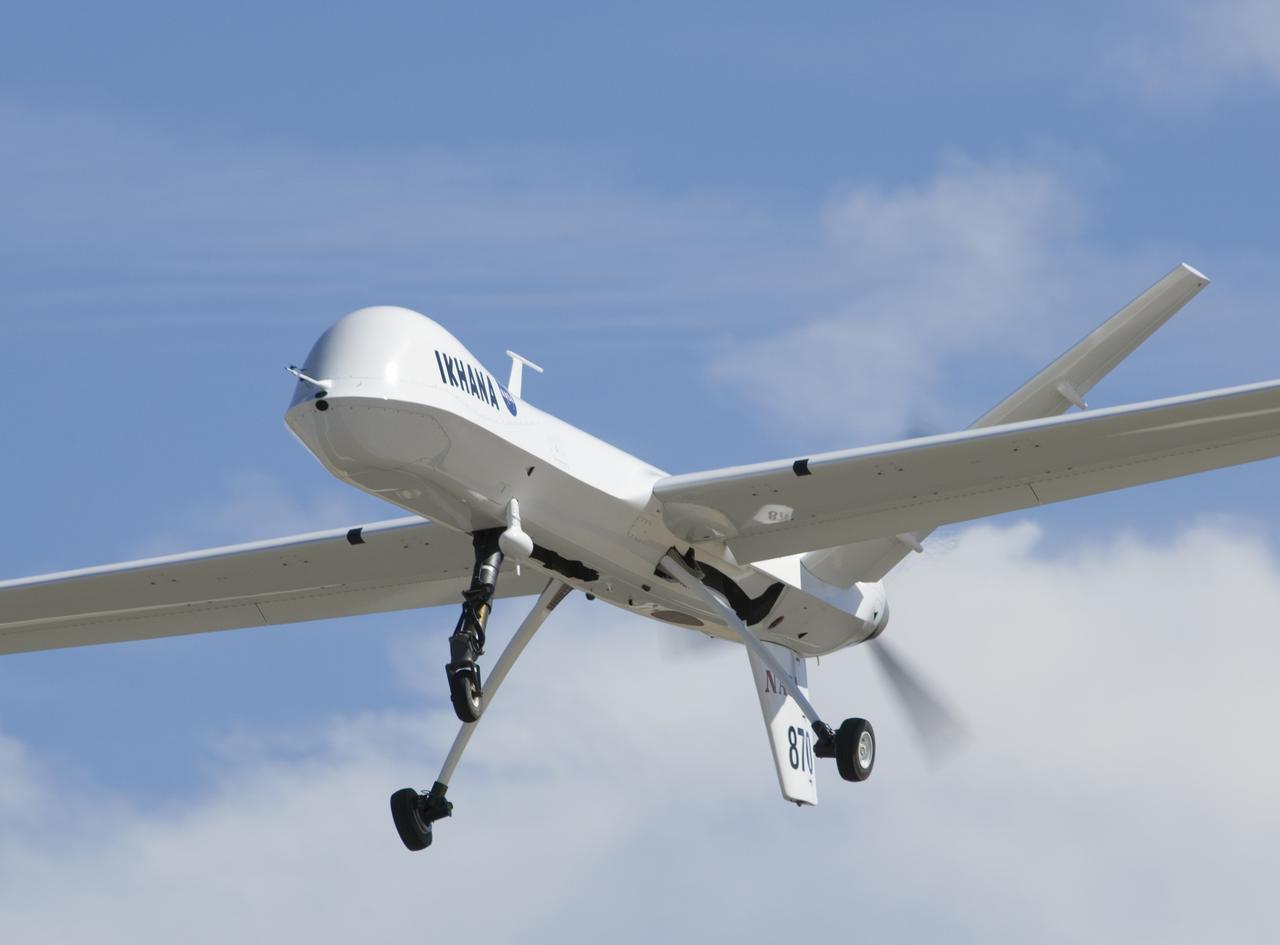

A small nose-mounted television camera enables pilots of NASA's Ikhana unmanned science aircraft to view the flight path ahead.
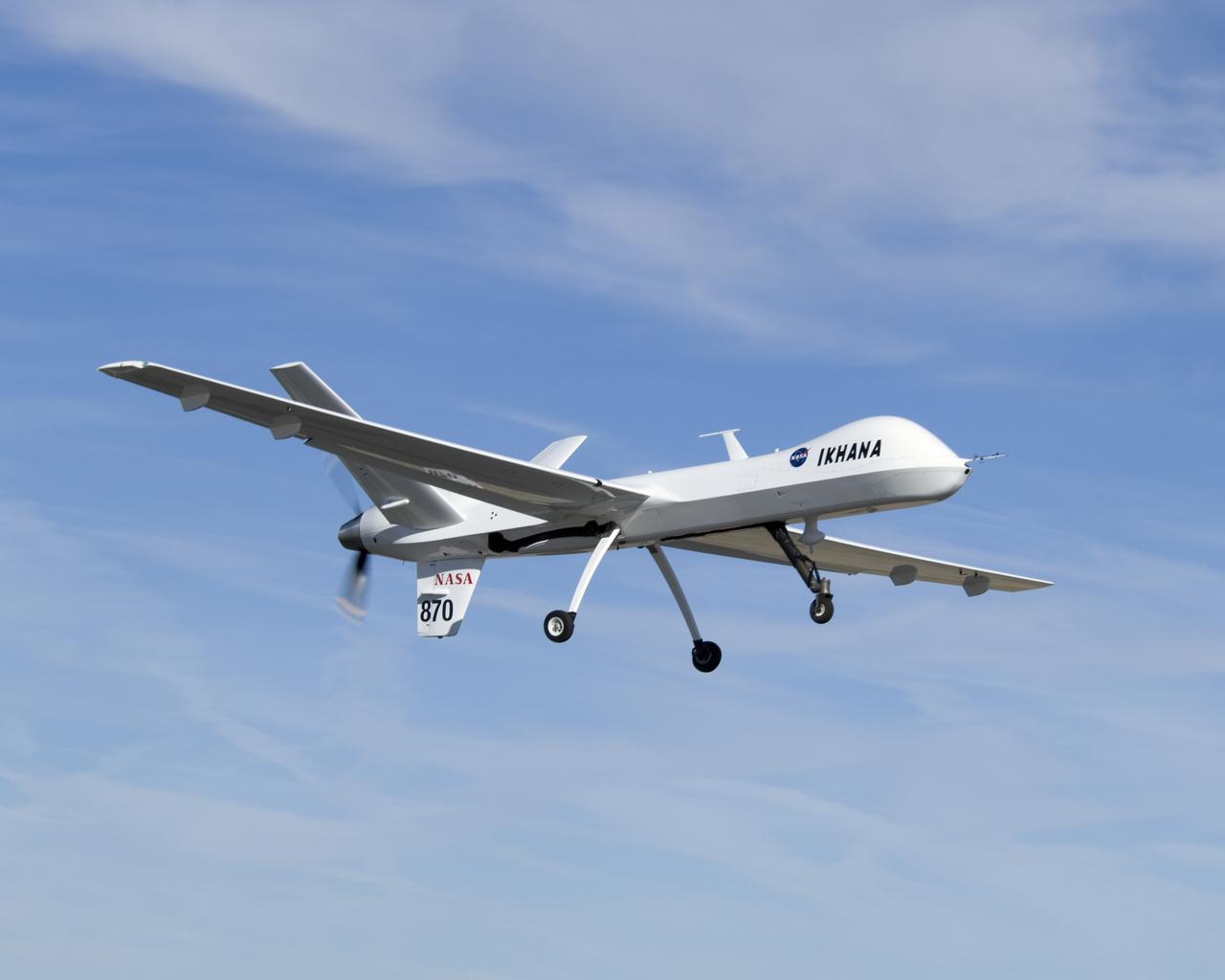

Narrow wings, a Y-tail and rear engine layout distinguish NASA's Ikhana science aircraft, a civil variant of General Atomics' Predator B unmanned aircraft system.
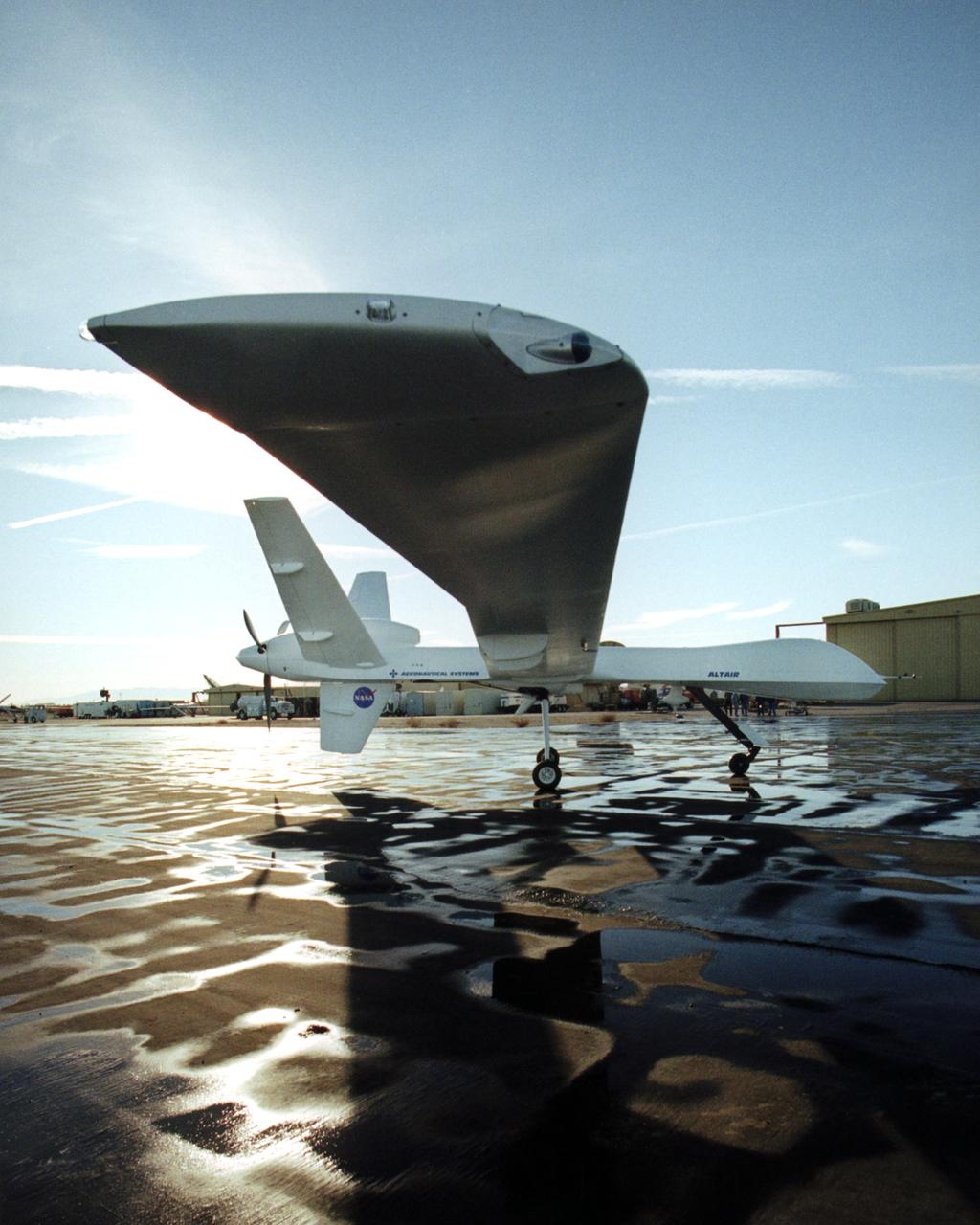

The Altair, a civil variant of the QM-9 Predator B unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), shows off its lengthy high-aspect ratio wing while on the ramp at General Atomics Aeronautical Systems' flight test facility at El Mirage, California.
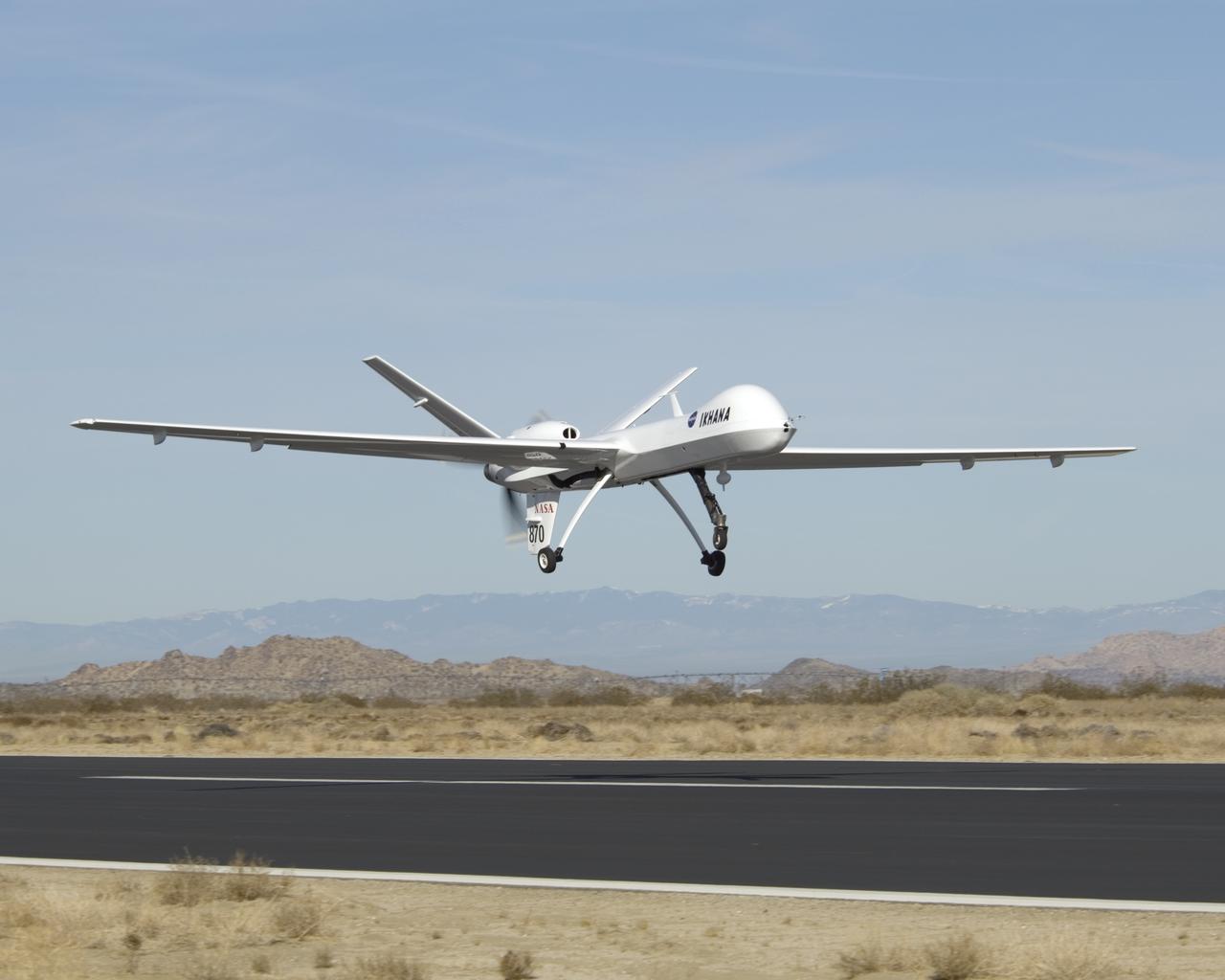

NASA's Ikhana unmanned long-endurance science aircraft, a civil variant of General Atomics' Predator B, takes to the sky over Southern California's high desert.
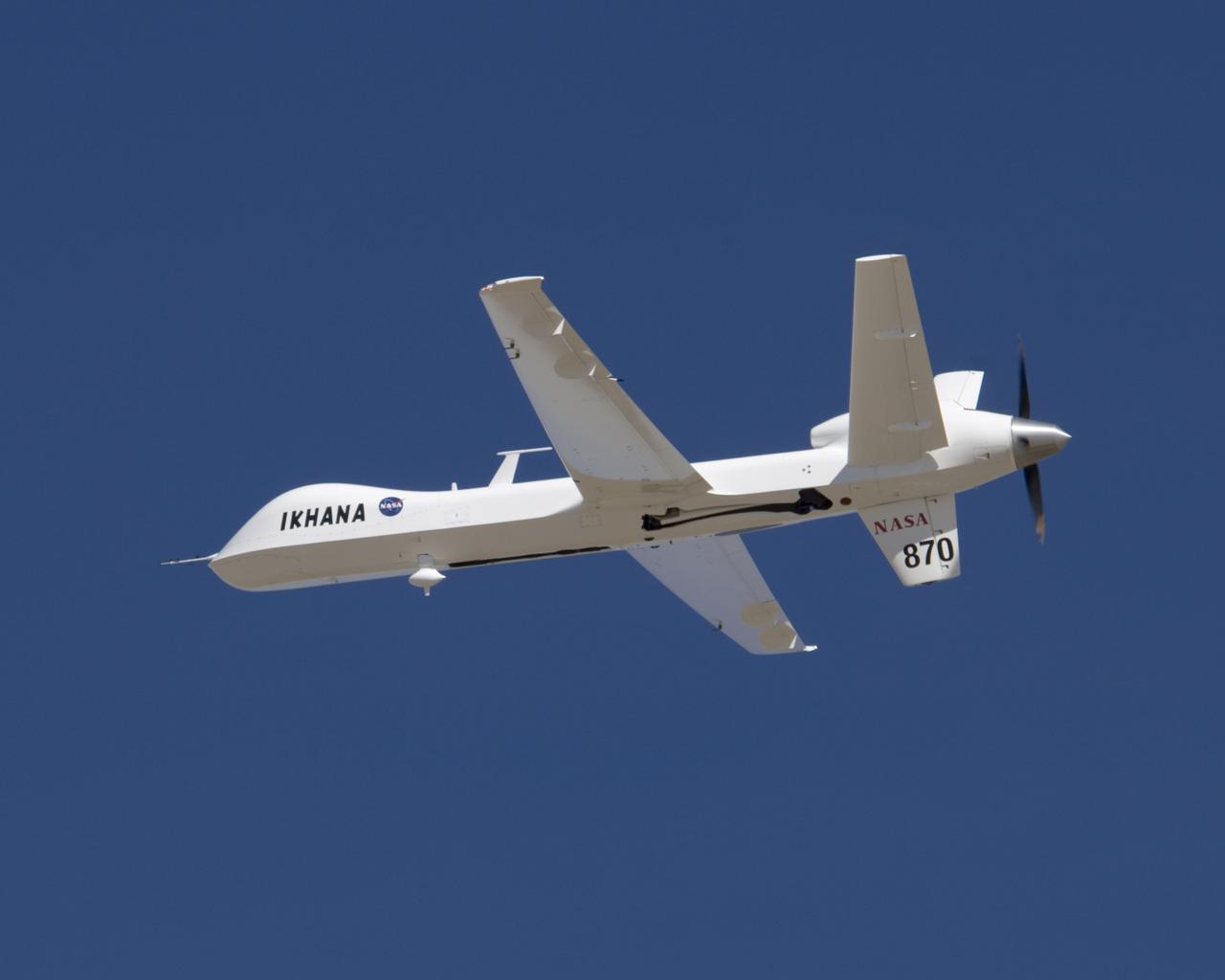

An efficient turboprop engine and large fuel capacity enable NASA's Ikhana unmanned aircraft to remain aloft for up to 30 hours on science or technology flights.
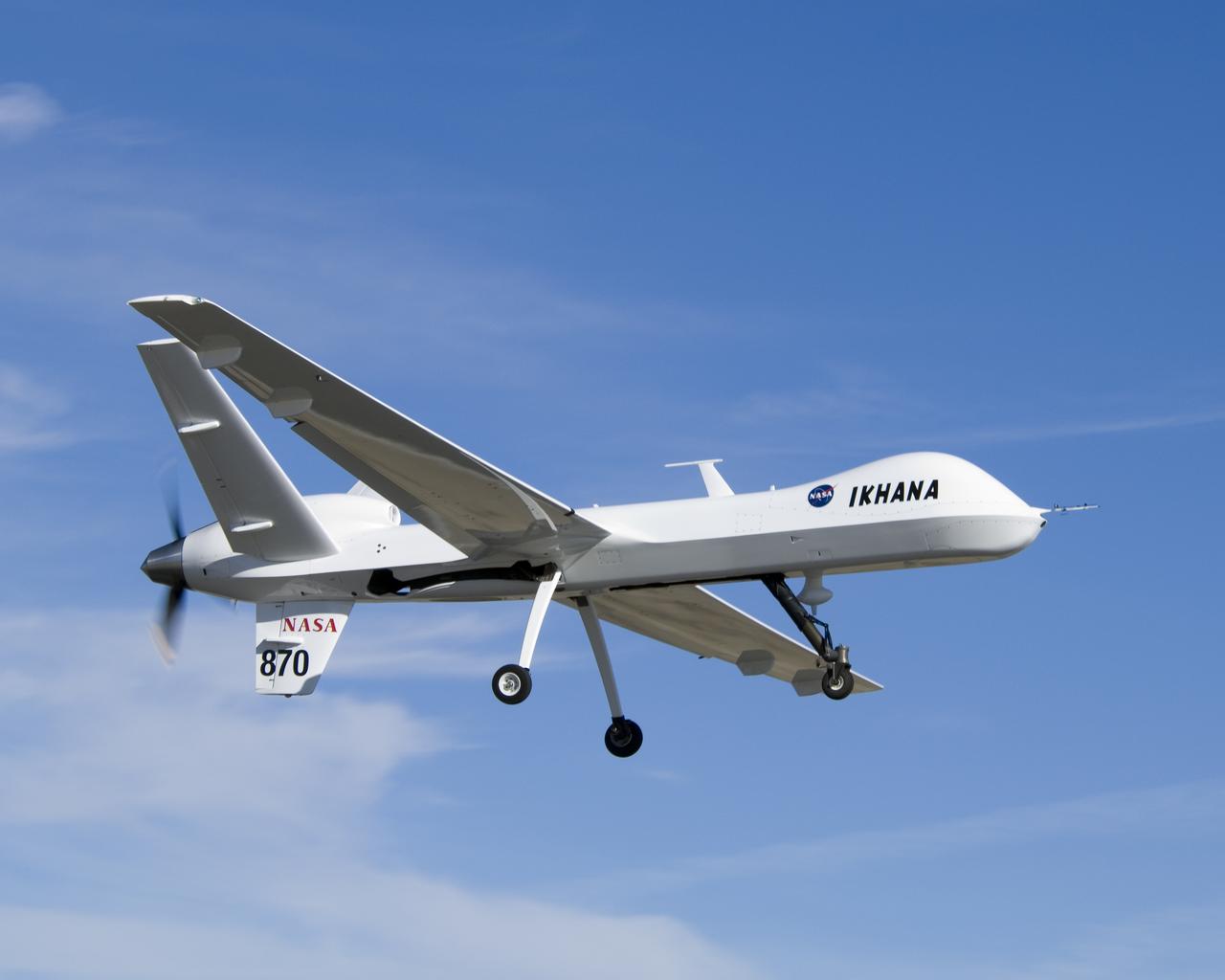

The bulging fairing atop the forward fuselage of NASA's Ikhana unmanned aircraft covers a variety of navigation, communications and science instruments.
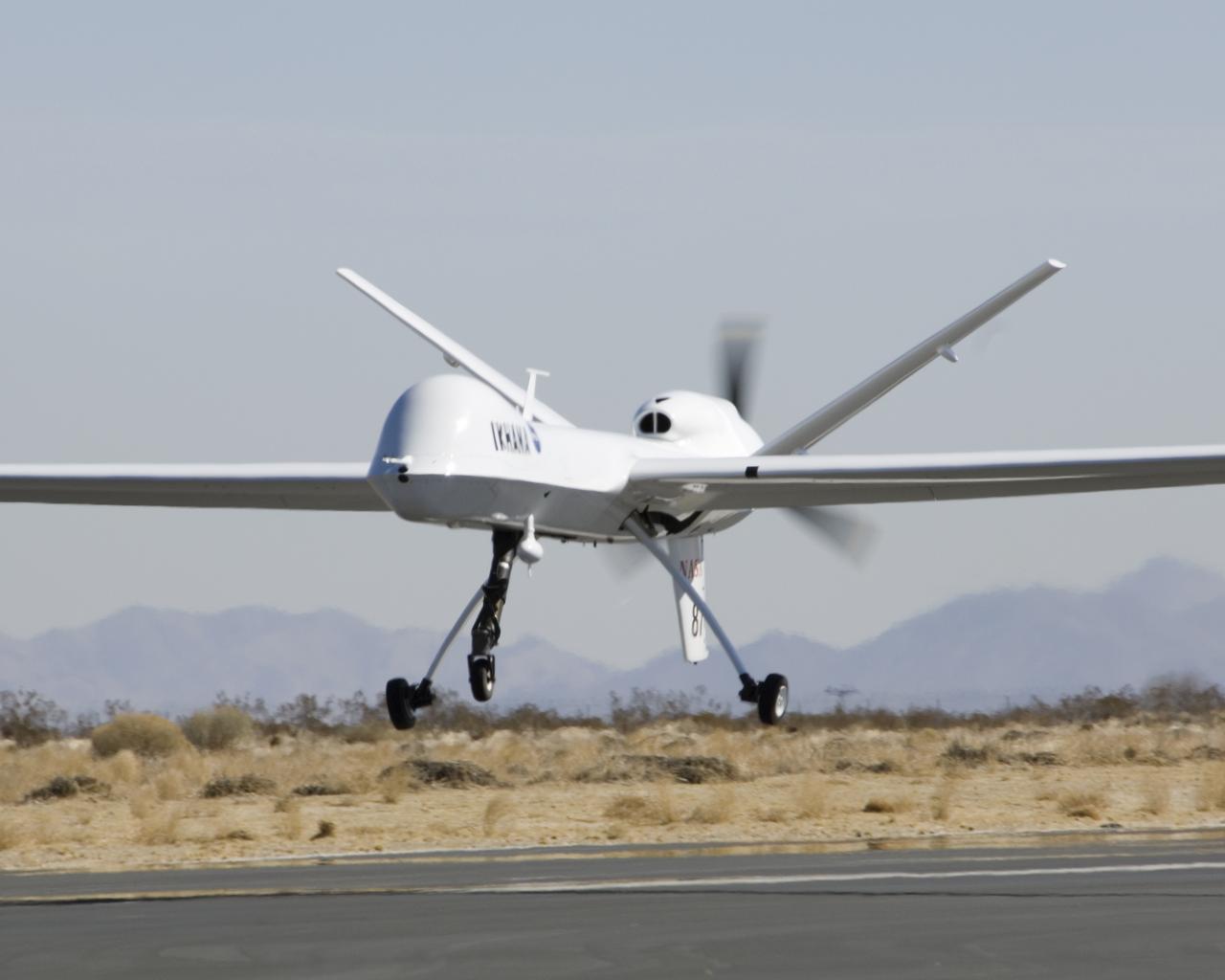

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft, a civil variant of General Atomics' Predator B, lifts off from Grey Butte airfield in Southern California.
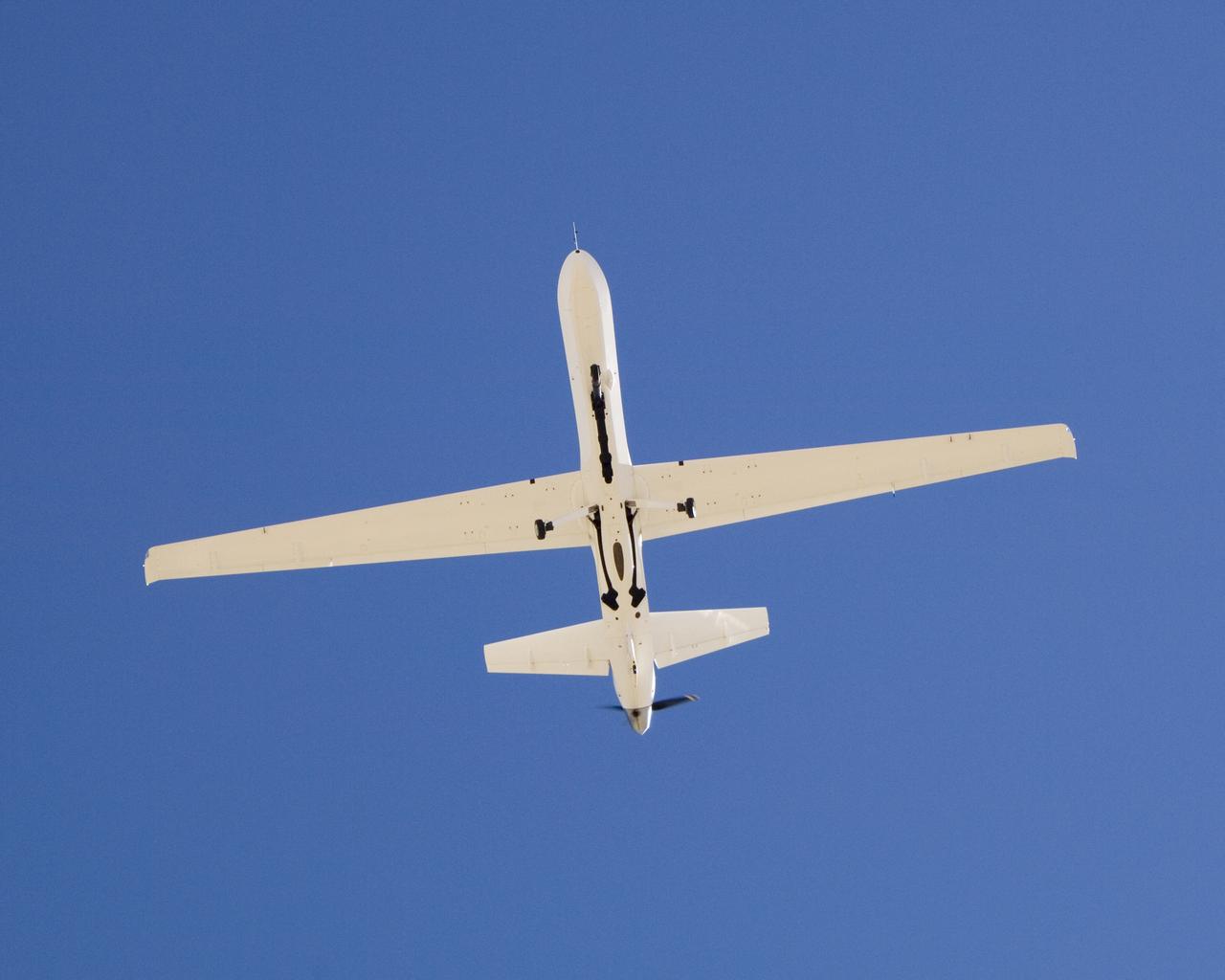

The narrow fuselage of NASA'S Ikhana unmanned science aircraft, a civil version of General Atomics' Predator B, is evident in this view from underneath.
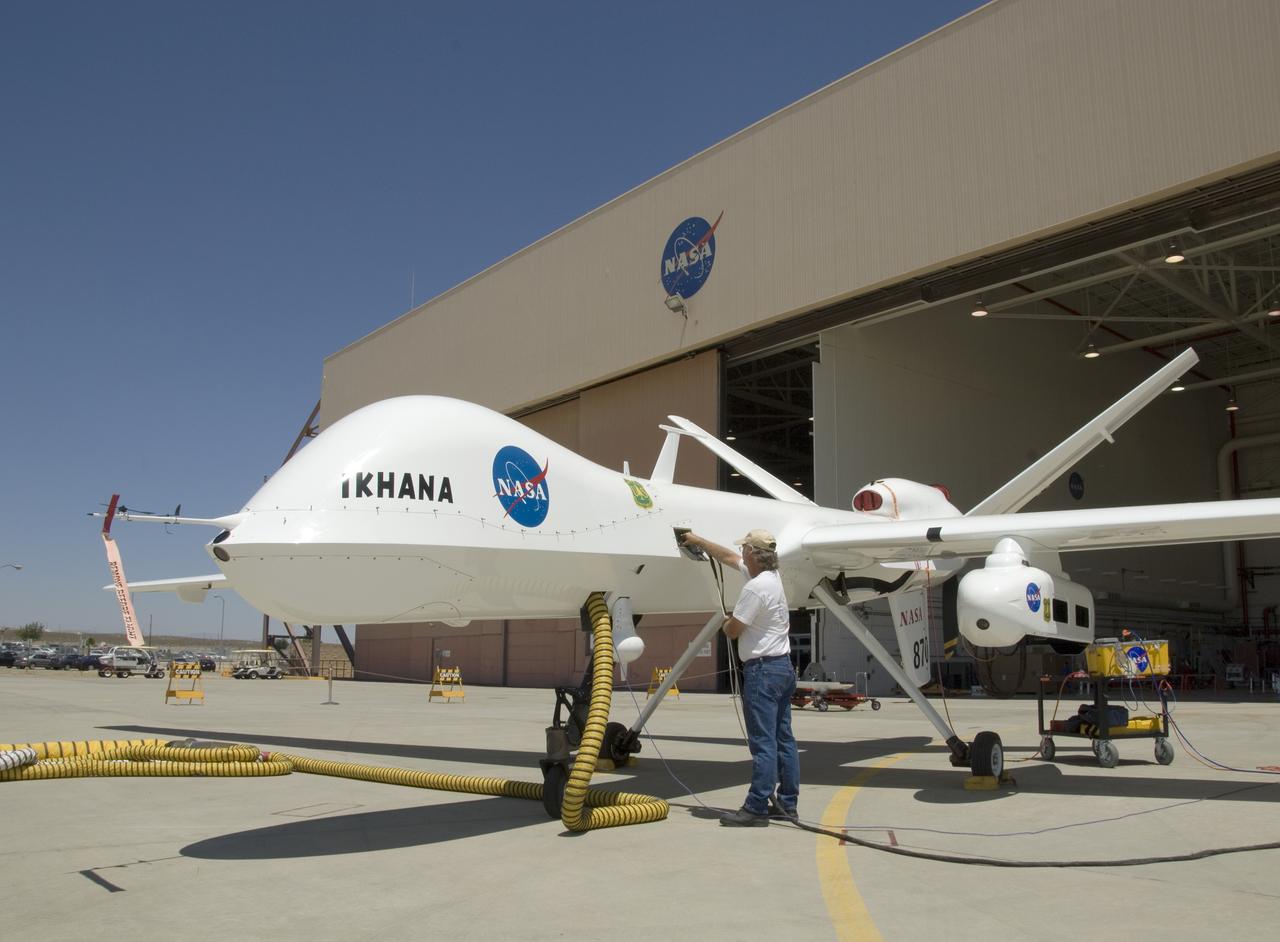

A ground crewman unplugs electrical connections during pre-flight checks of NASA's Ikhana research aircraft. Ikhana's payload pod is mounted on the left wing.
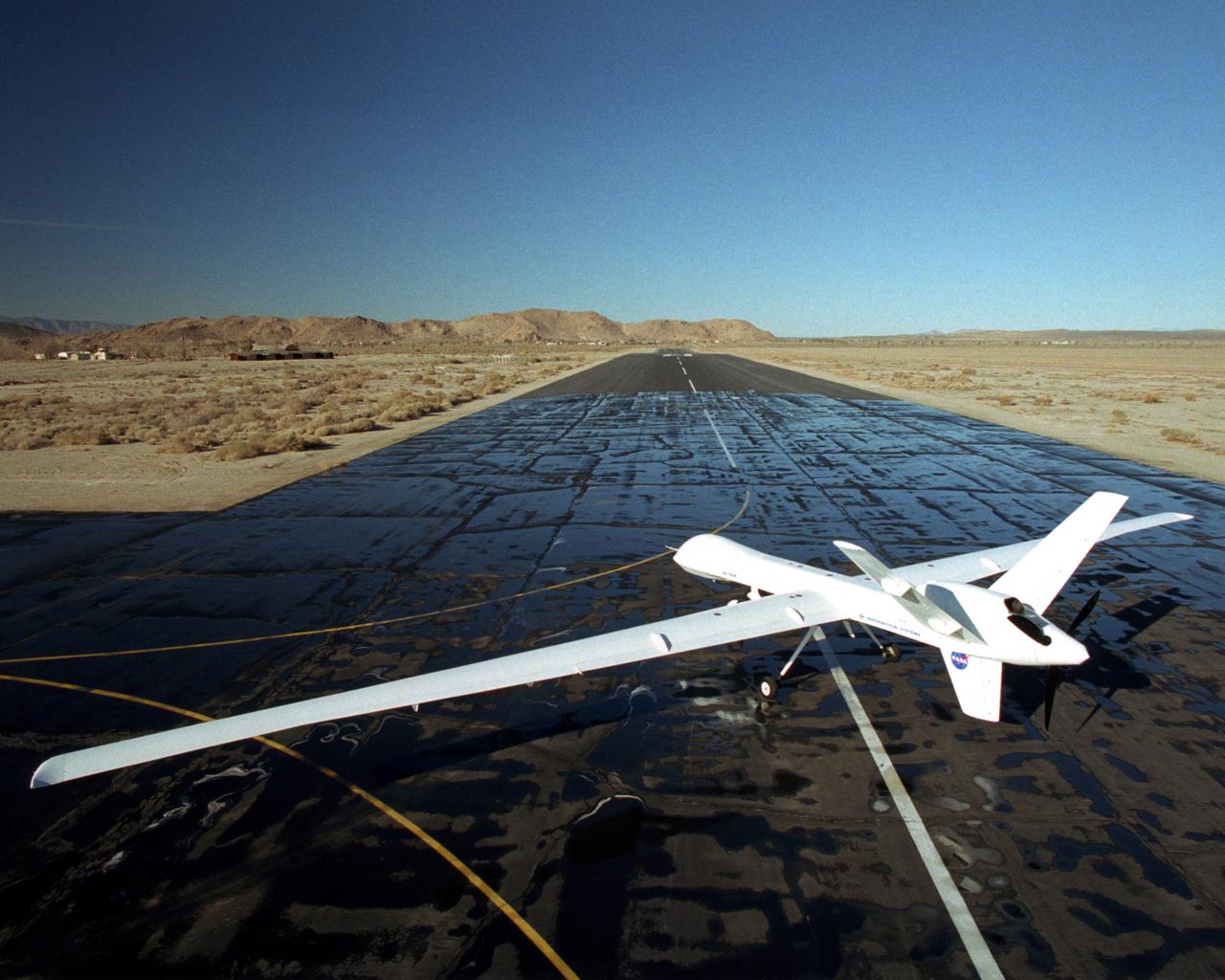

The long, narrow wings of NASA's Altair are designed to allow the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) to maintain long-duration flight at high altitudes.
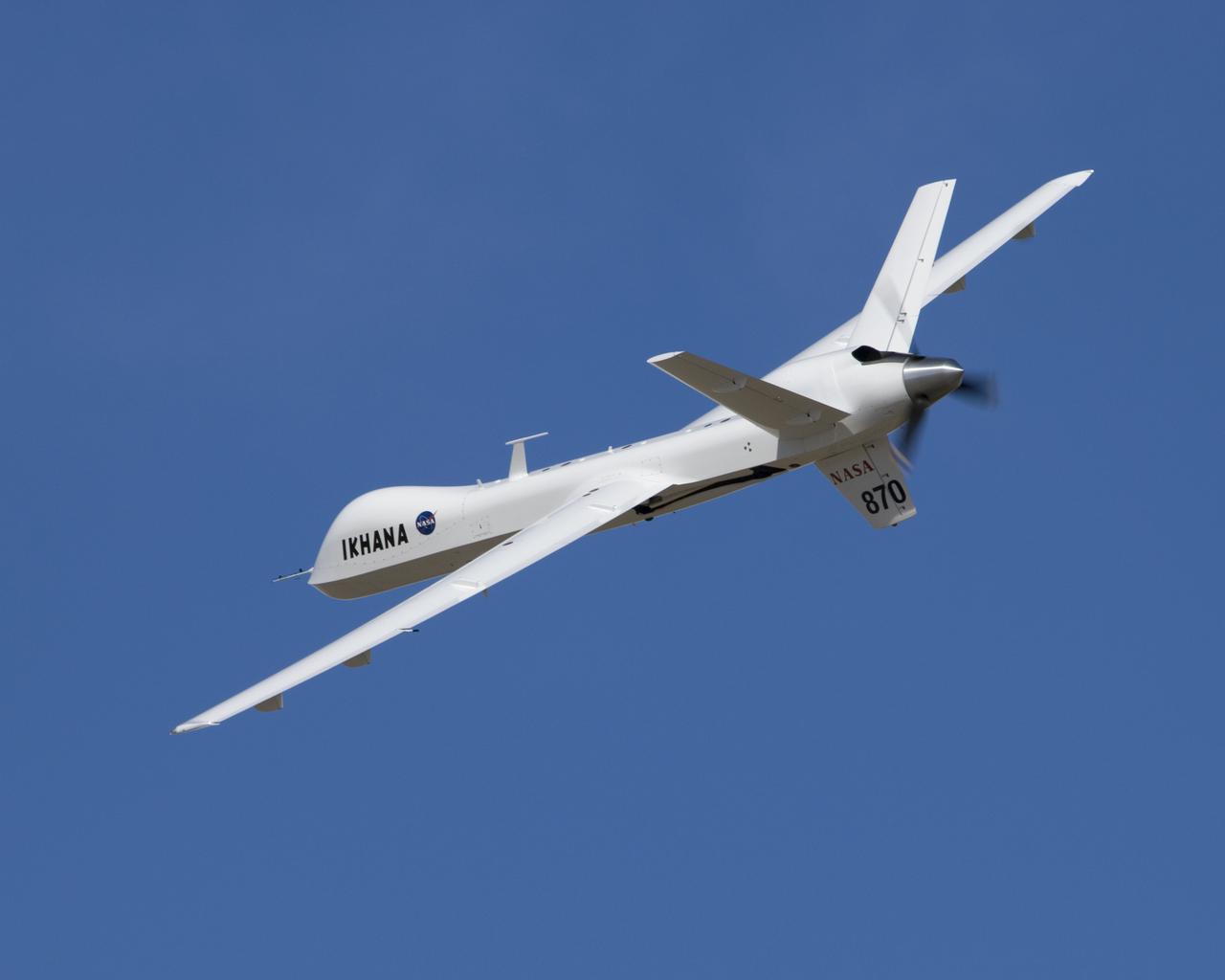

Straight wings, a Y-tail and a pusher propeller distinguish NASA's Ikhana, a civil version of General Atomics Aeronautical system's Predator B unmanned aircraft.
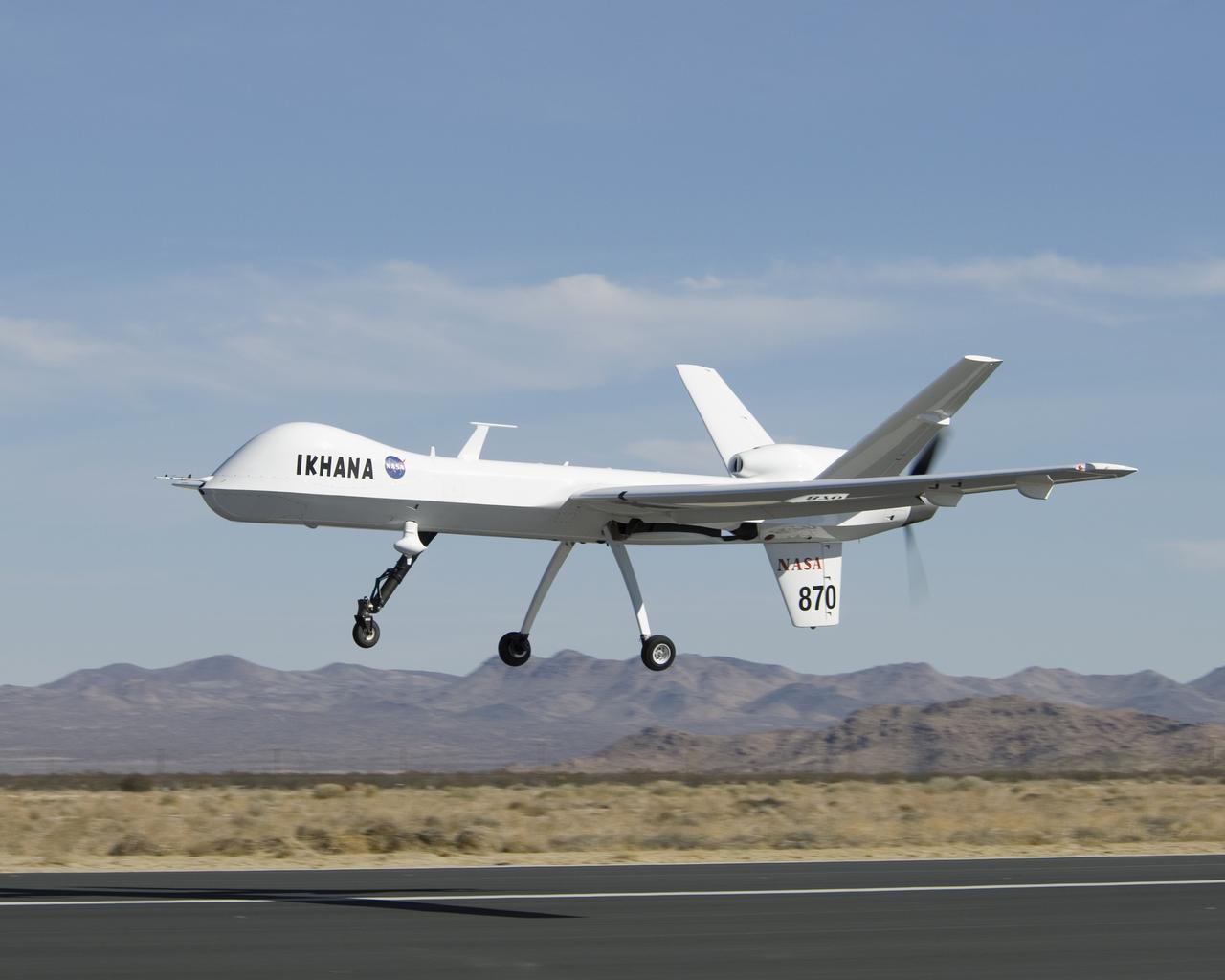

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft, a civil variant of General Atomics' Predator B, lifts off from Grey Butte airfield in Southern California.

The long wings of General Atomics Altair UAV are in evidence during a series of environmental monitoring missions for NOAA and NASA in the spring of 2005.
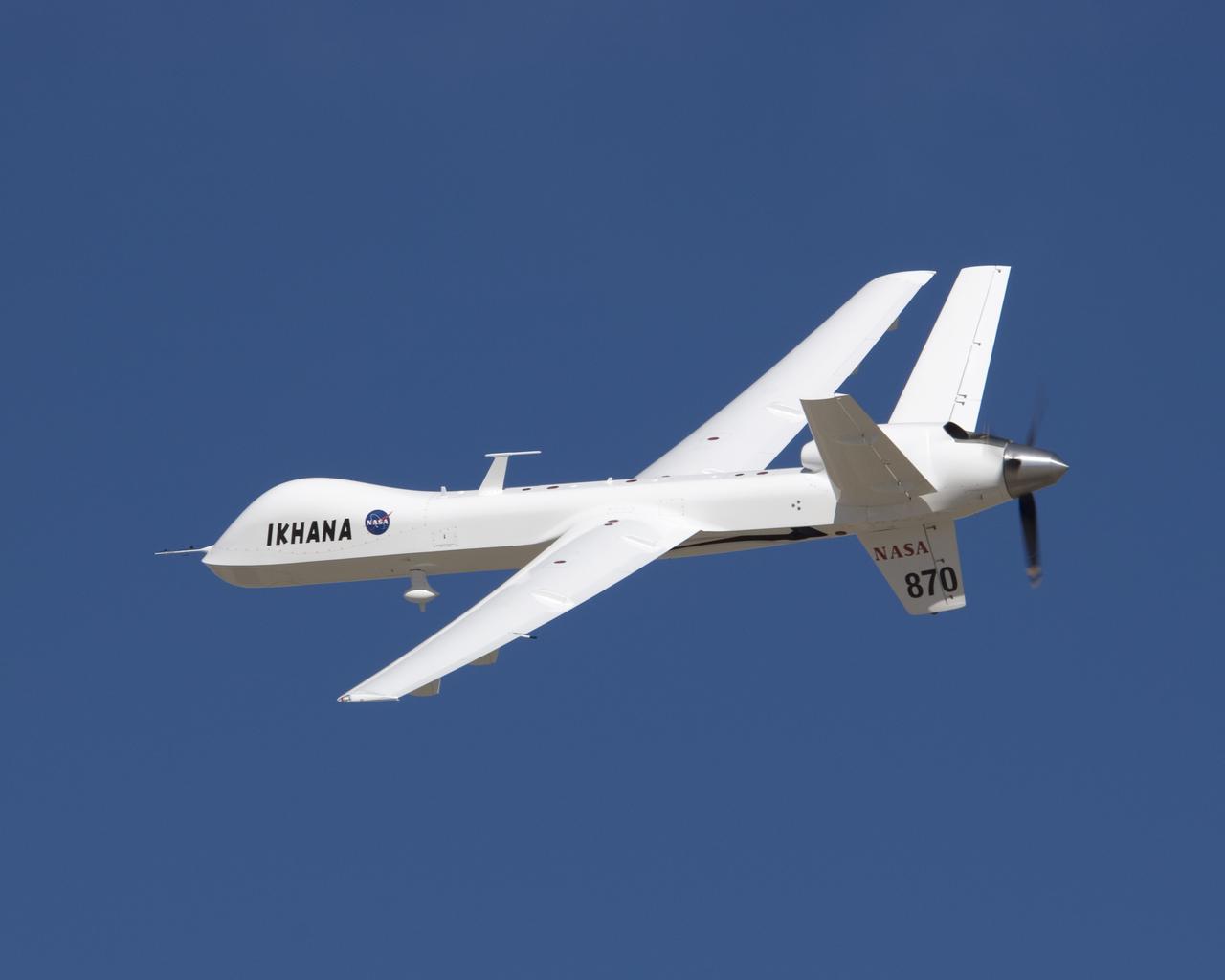

Its white surfaces in contrast with the deep blue sky, NASA's Ikhana unmanned science and technology development aircraft soars over California's high desert.

NASA's Ikhana, a civil variant of General Atomics' Predator B unmanned aircraft, takes to the sky for a morning checkout flight from the Grey Butte airfield.

A NASA team studying the causes of electrical storms and their effects on our home planet achieved a milestone on August 21, 2002, completing the study's longest-duration research flight and monitoring four thunderstorms in succession. Based at the Naval Air Station Key West, Florida, researchers with the Altus Cumulus Electrification Study (ACES) used the Altus II remotely-piloted aircraft to study thunderstorms in the Atlantic Ocean off Key West and the west of the Everglades. Using special equipment aboard the Altus II, scientists in ACES will gather electric, magnetic, and optical measurements of the thunderstorms, gauging elements such as lightning activity and the electrical environment in and around the storms. With dual goals of gathering weather data safely and testing the adaptability of the uninhabited aircraft, the ACES study is a collaboration among the Marshall Space Flight Center, the University of Alabama in Huntsville, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Pernsylvania State University in University Park, and General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.

An ocean color senor, a passive microwave vertical sounder and an electro-optical sensor were mounted on the Altair UAV for the NOAA-NASA flight demonstration.
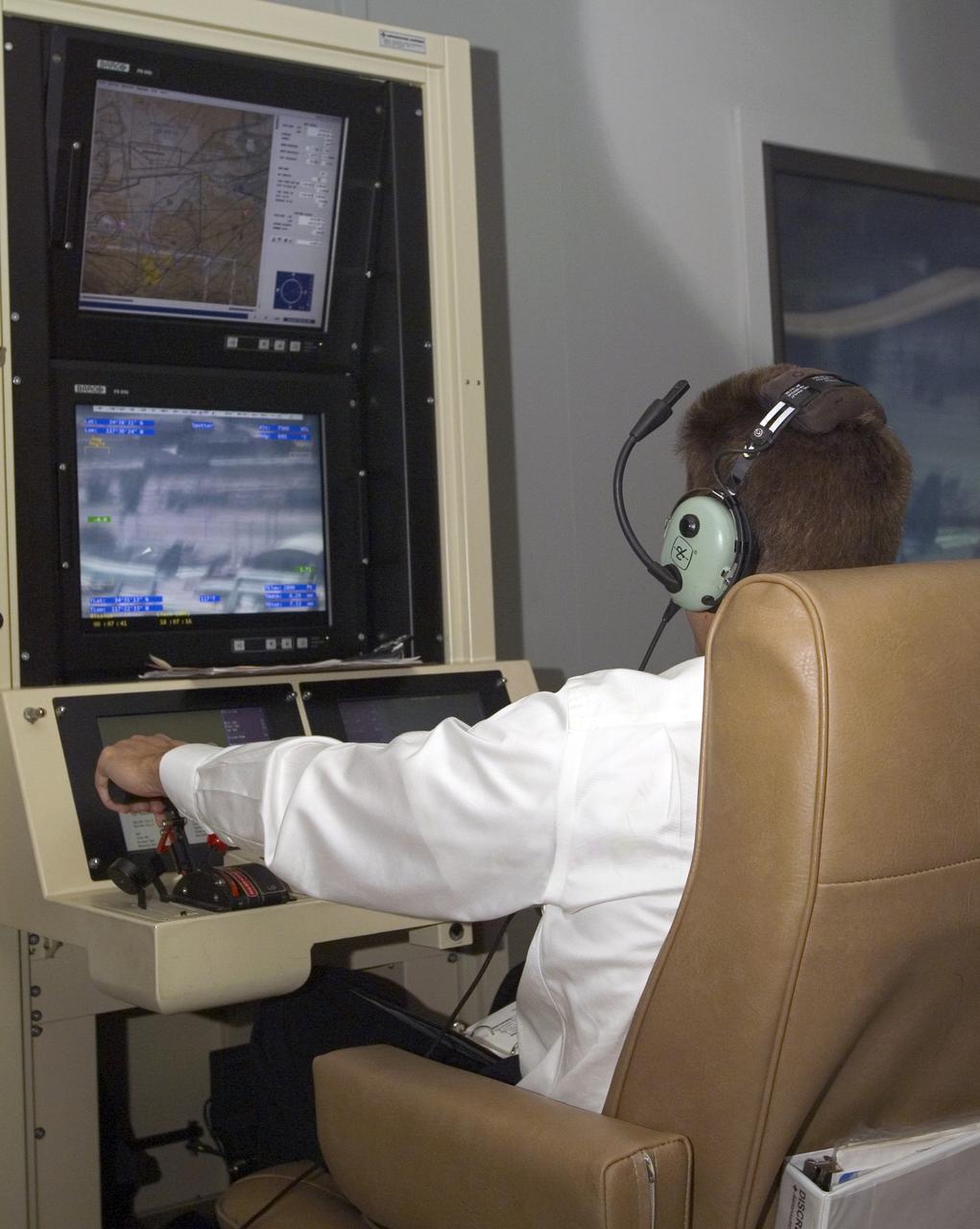

A pilot for General Atomics guides the Altair remotely operated aircraft from a ground control station using both visual and telemetered data.
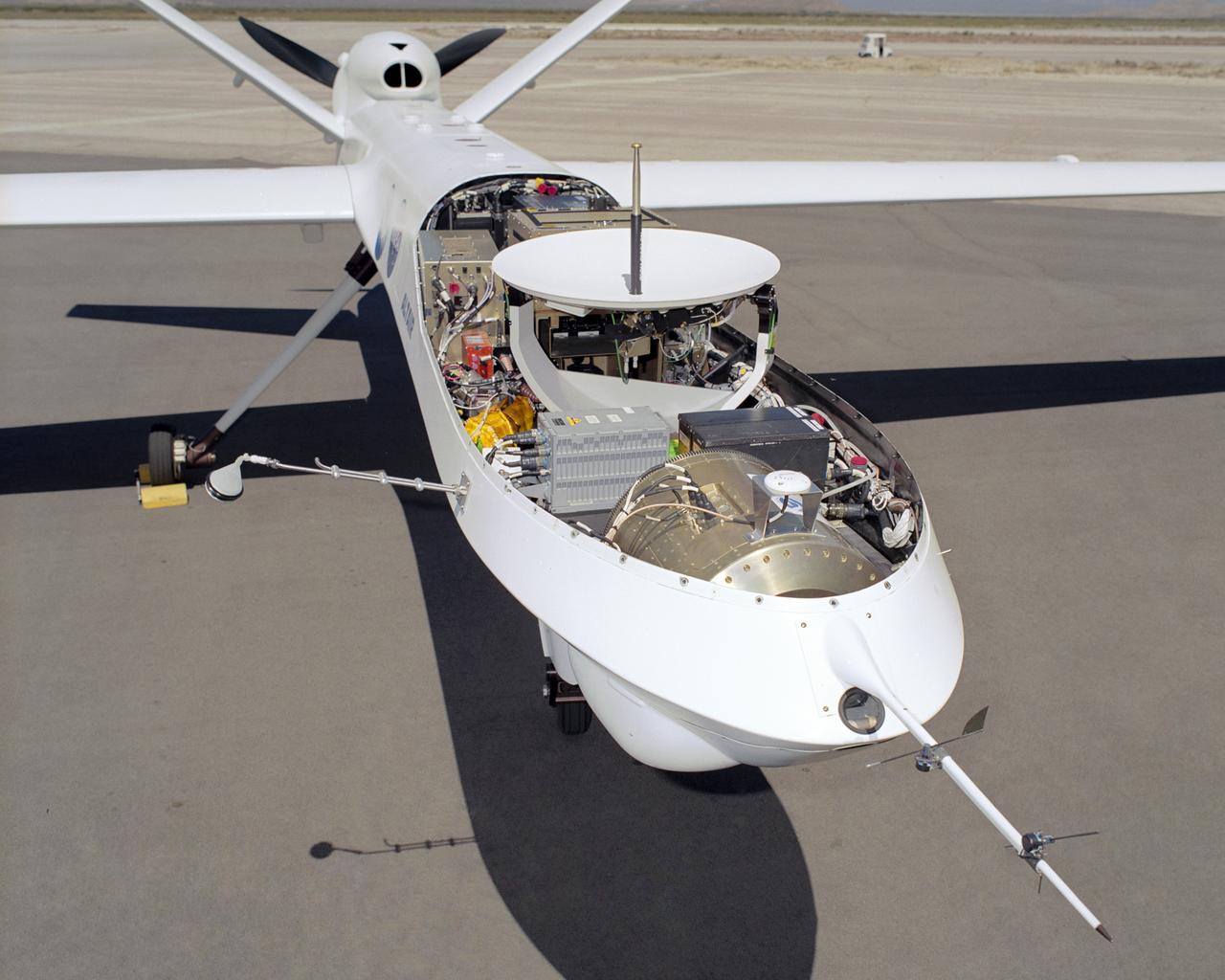

A satellite antenna, electro-optical/infrared and ocean color sensors (front) were among payloads installed on the Altair for the NOAA-NASA flight demonstration

Terrence Hertz, Deputy Associate Administrator for Technology, NASA Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, at the NOAA/NASA Altair flight demo kickoff.

Silhouetted by the morning sun, NASA's Ikhana, a civil version of the Predator B unmanned aircraft, is readied for flight By NASA Dryden crew chief Joe Kinn.

Altus I aircraft on lakebed

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft, a civil variant of General Atomics' Predator B, on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base after its ferry flight to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. NASA took possession of the new aircraft in November, 2006, and it arrived at the NASA center at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., on June 23, 2007.
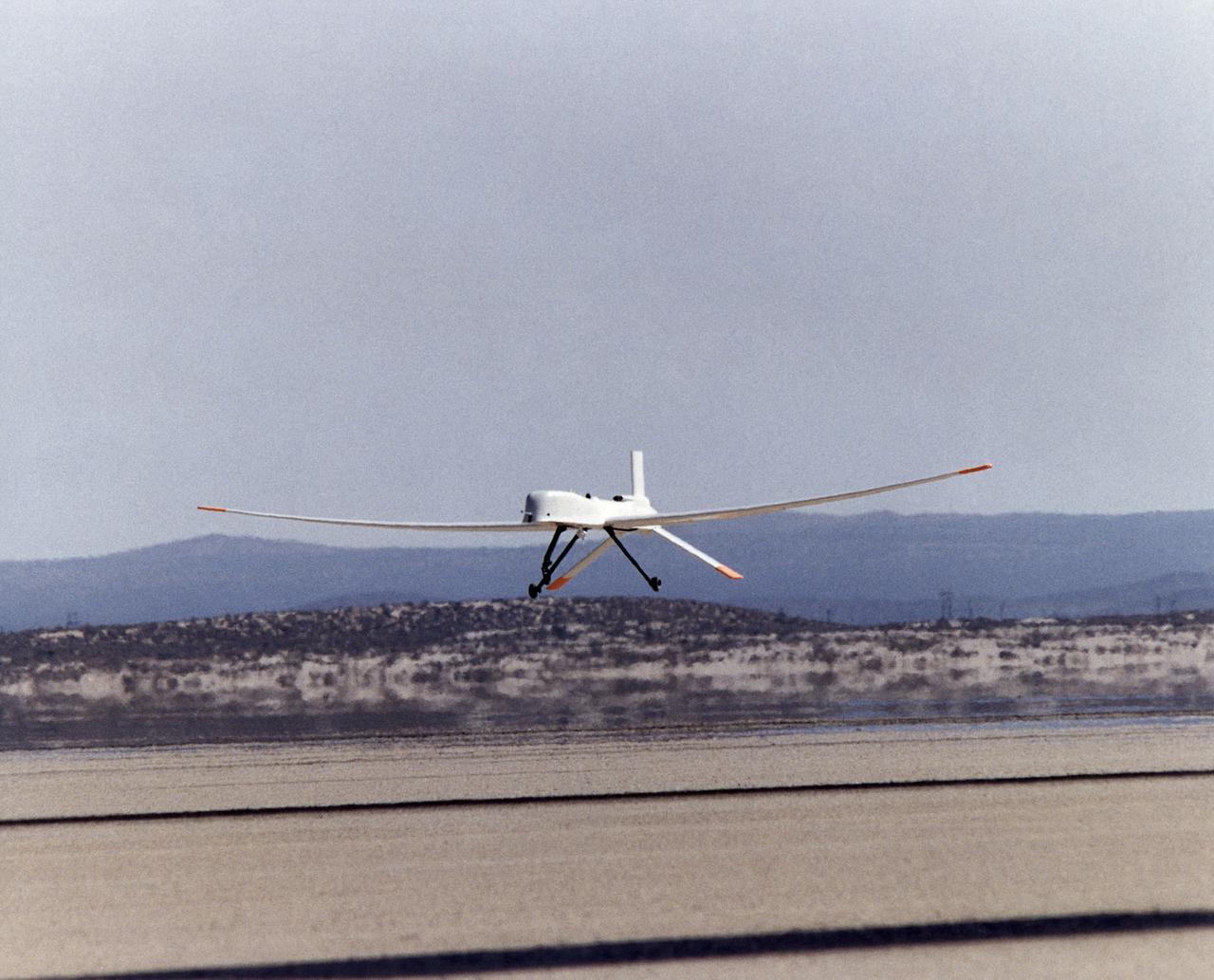

Altus I aircraft taking off from lakebed runway
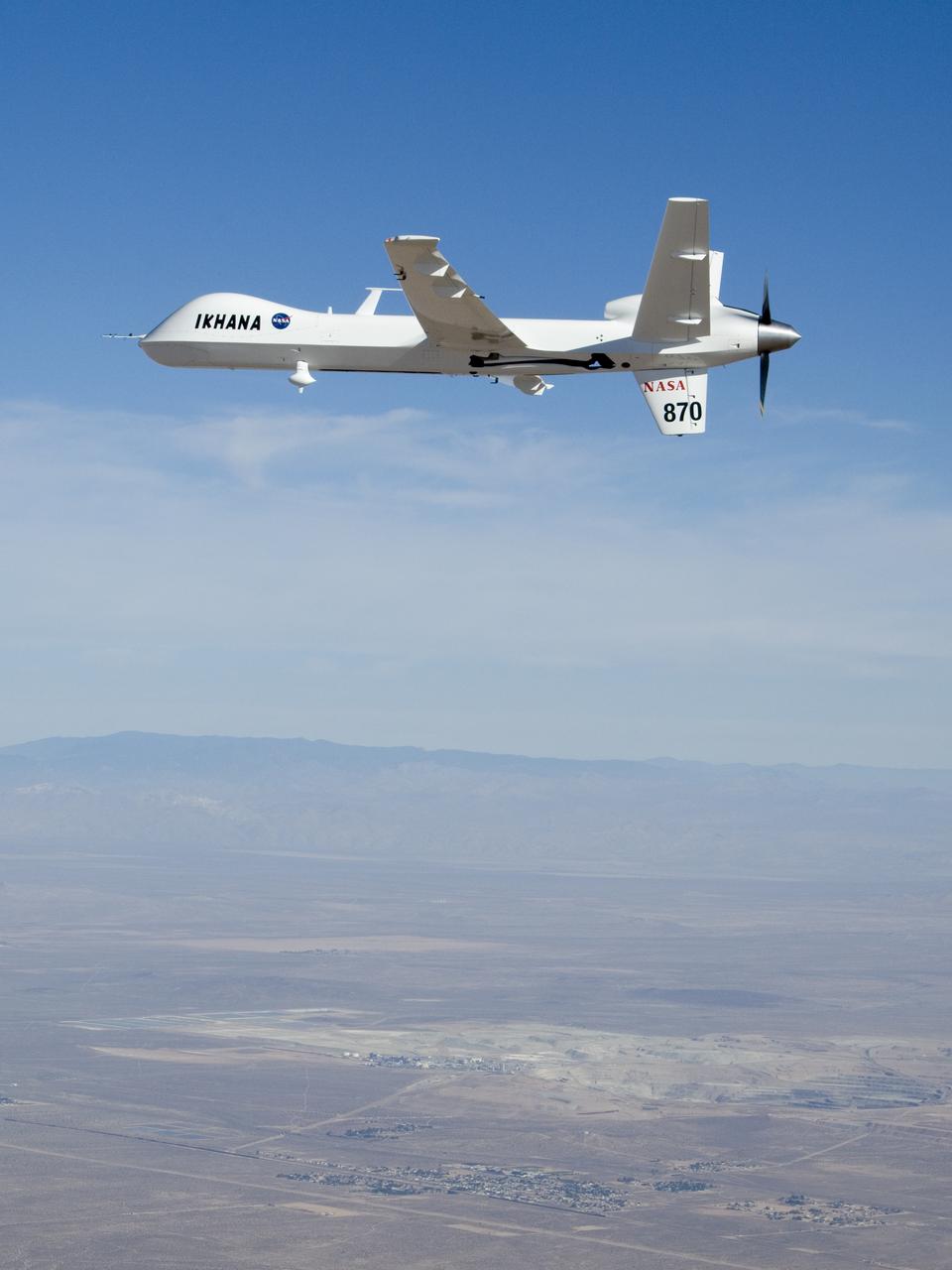

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft over the U.S. Borax mine, Boron, California, near the Dryden/Edwards Air Force Base complex. NASA took possession of the new aircraft in November, 2006, and it arrived at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards AFB, Calif., on June 23, 2007.
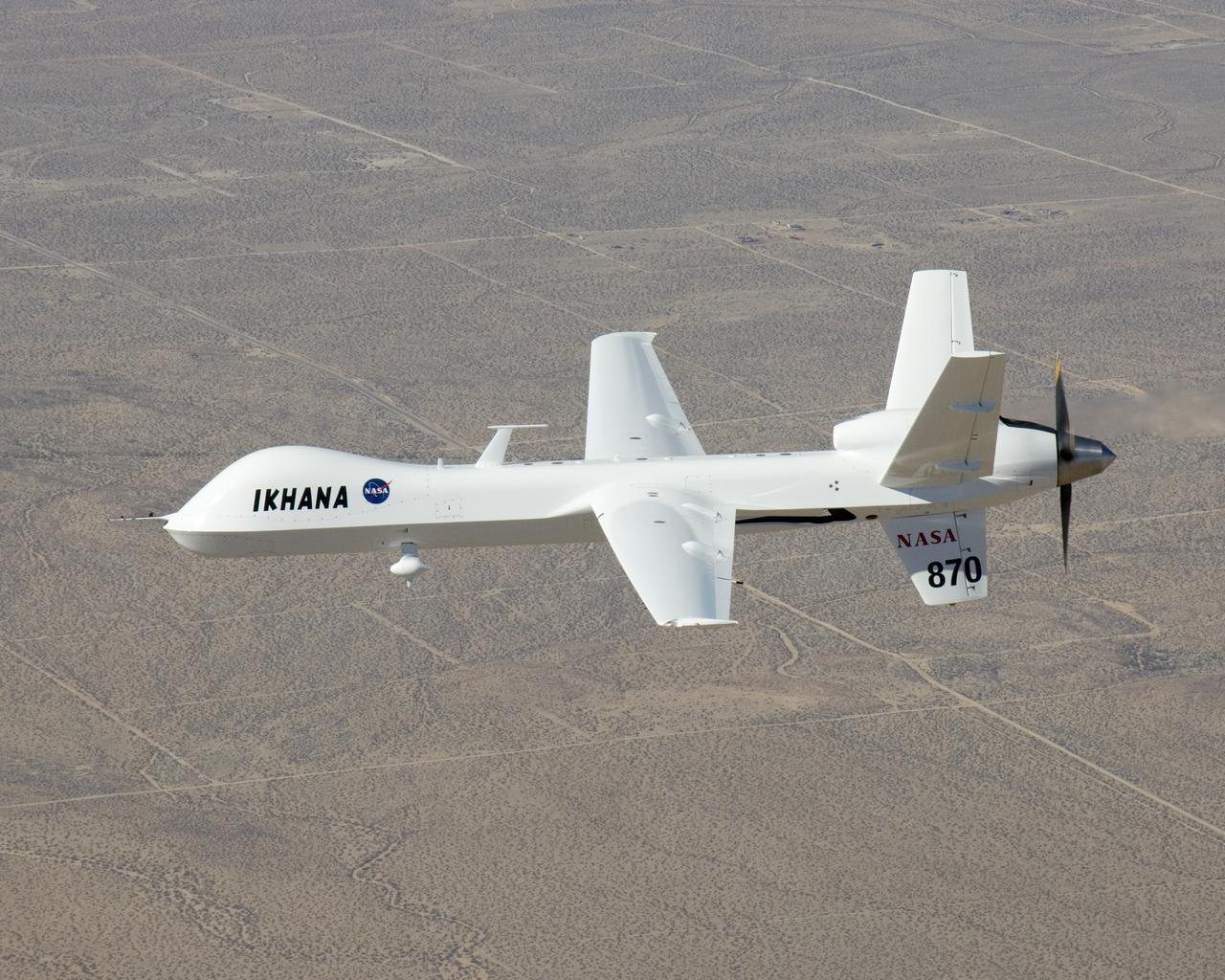

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft over Southern California's high desert during the ferry flight to its new home at the Dryden Flight Research Center. NASA took possession of the new aircraft in November, 2006, and it arrived at DFRC at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., on June 23, 2007.
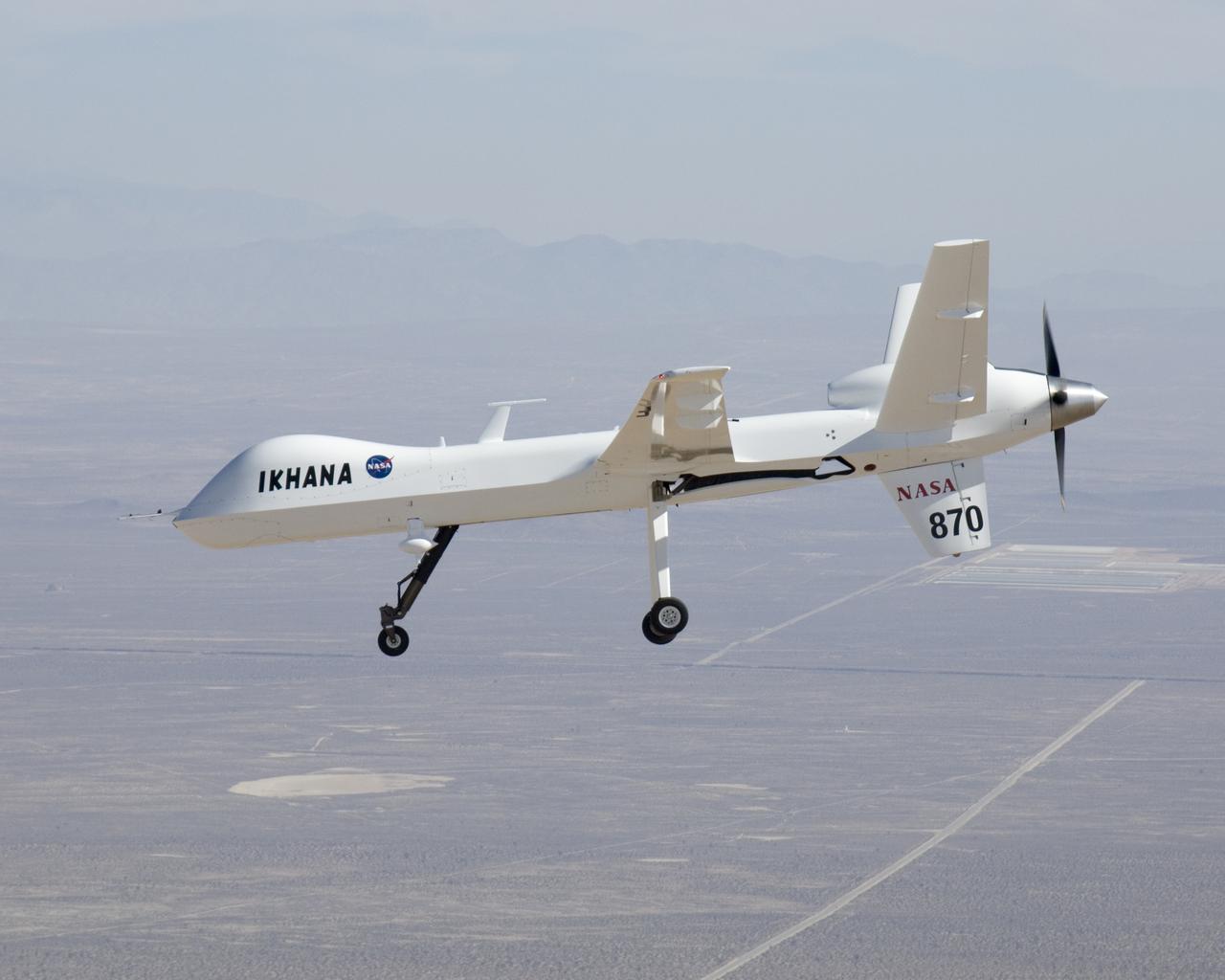

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft prepares for landing as it arrives at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. NASA took possession of the new aircraft in November, 2006, and it arrived at its new home at NASA's Dryden Flight Reseach Center at Edwards AFB, on June 23, 2007.
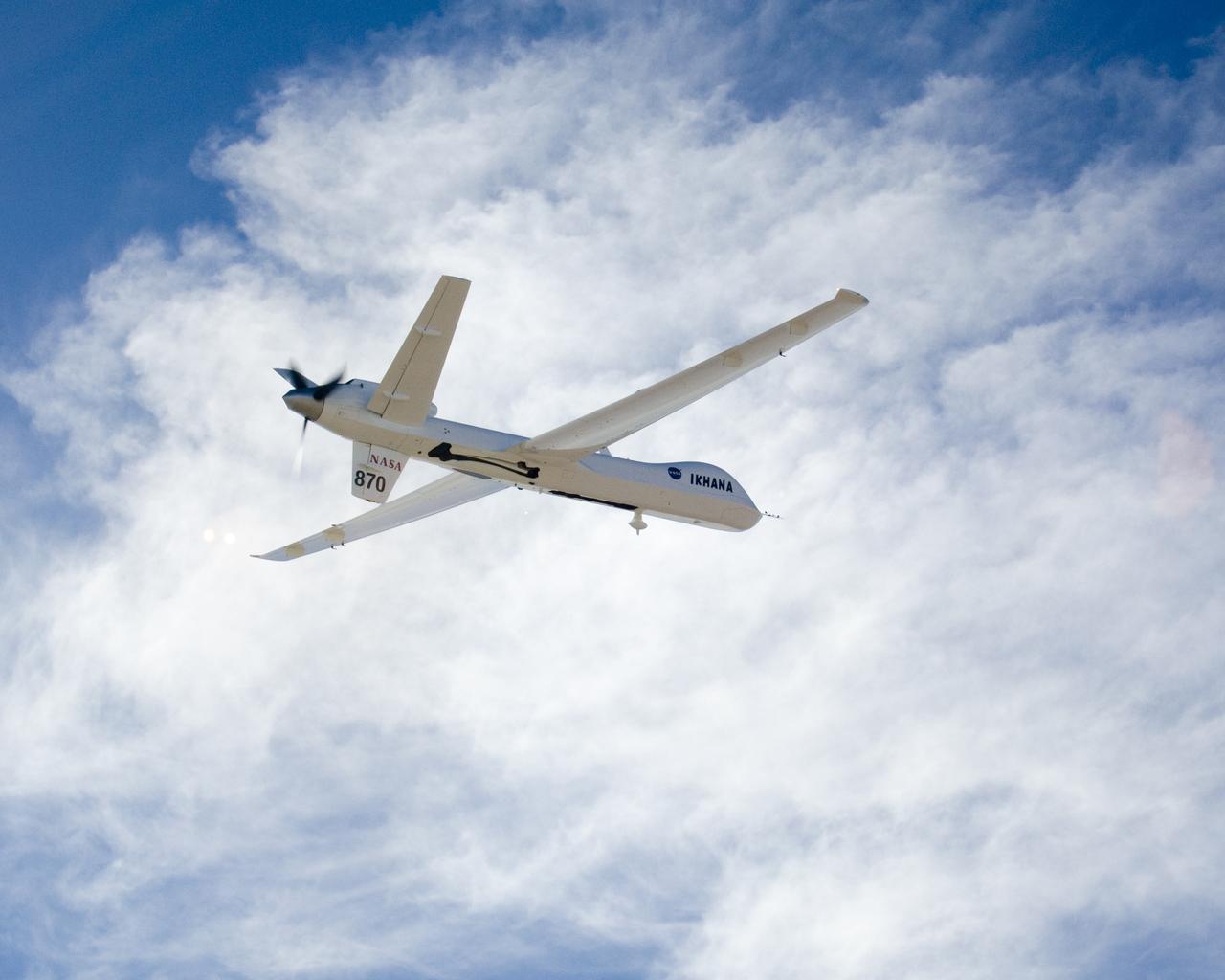

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft in flight during the ferry flight to its new home at the Dryden Flight Research Center. NASA took possession of the new aircraft in November, 2006, and it arrived at the NASA center at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., on June 23, 2007.
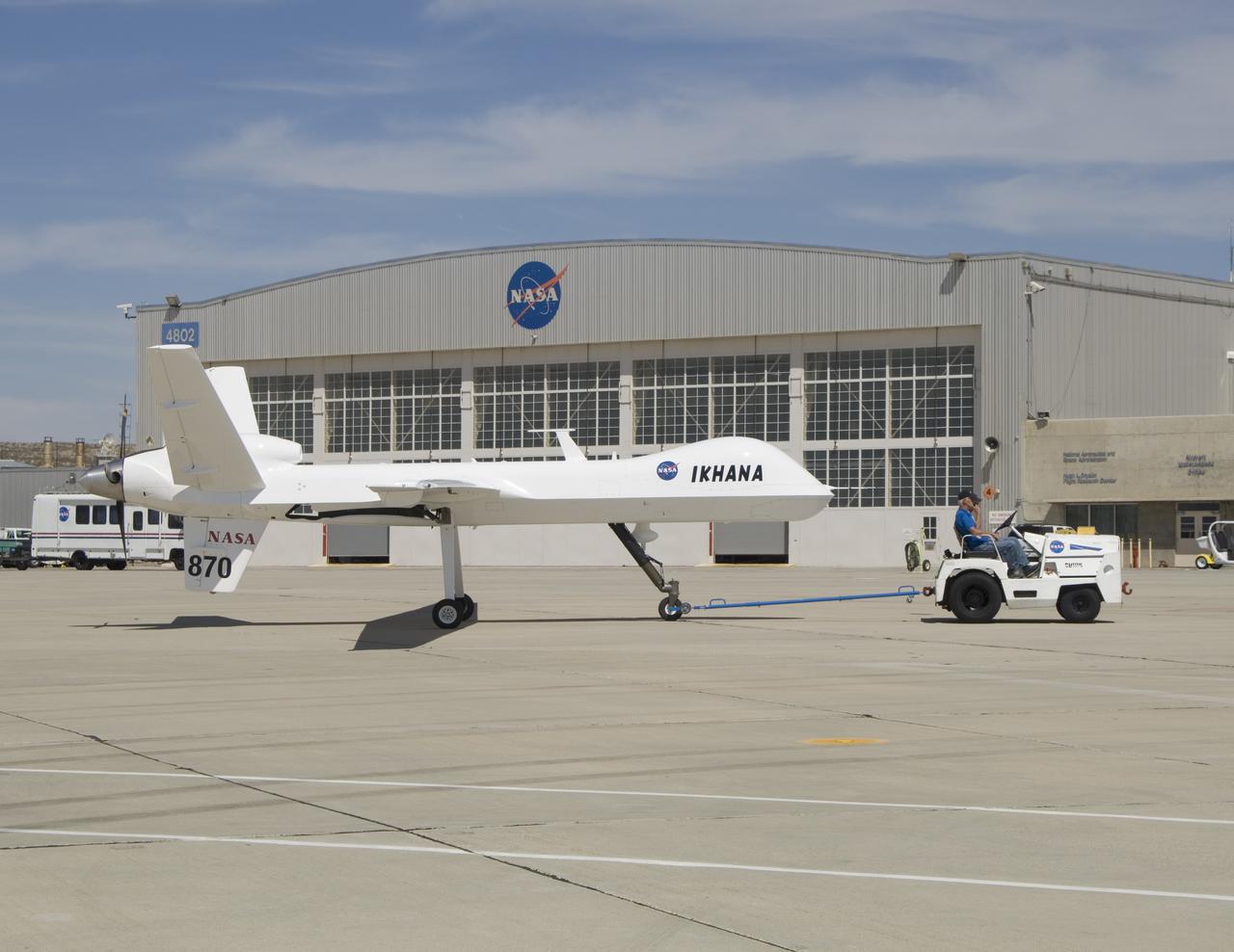

After arriving via a ferry flight on June 23, 2007, NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft is towed to a hangar at its new home, the Dryden Flight Research Center in Southern California.
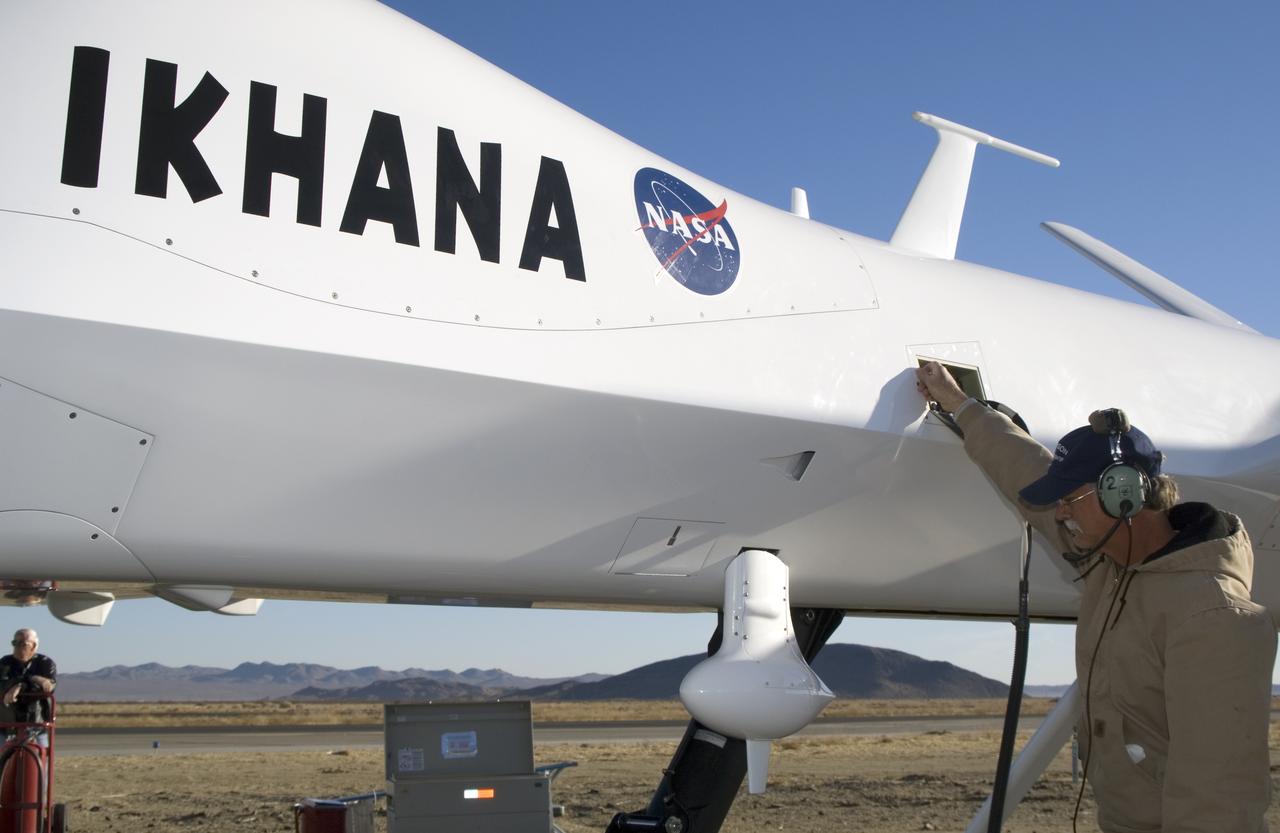

NASA Dryden crew chief Joe Kinn gives final checks to NASA's Ikhana, a civil version of the Predator B unmanned aircraft, prior to a morning checkout flight.
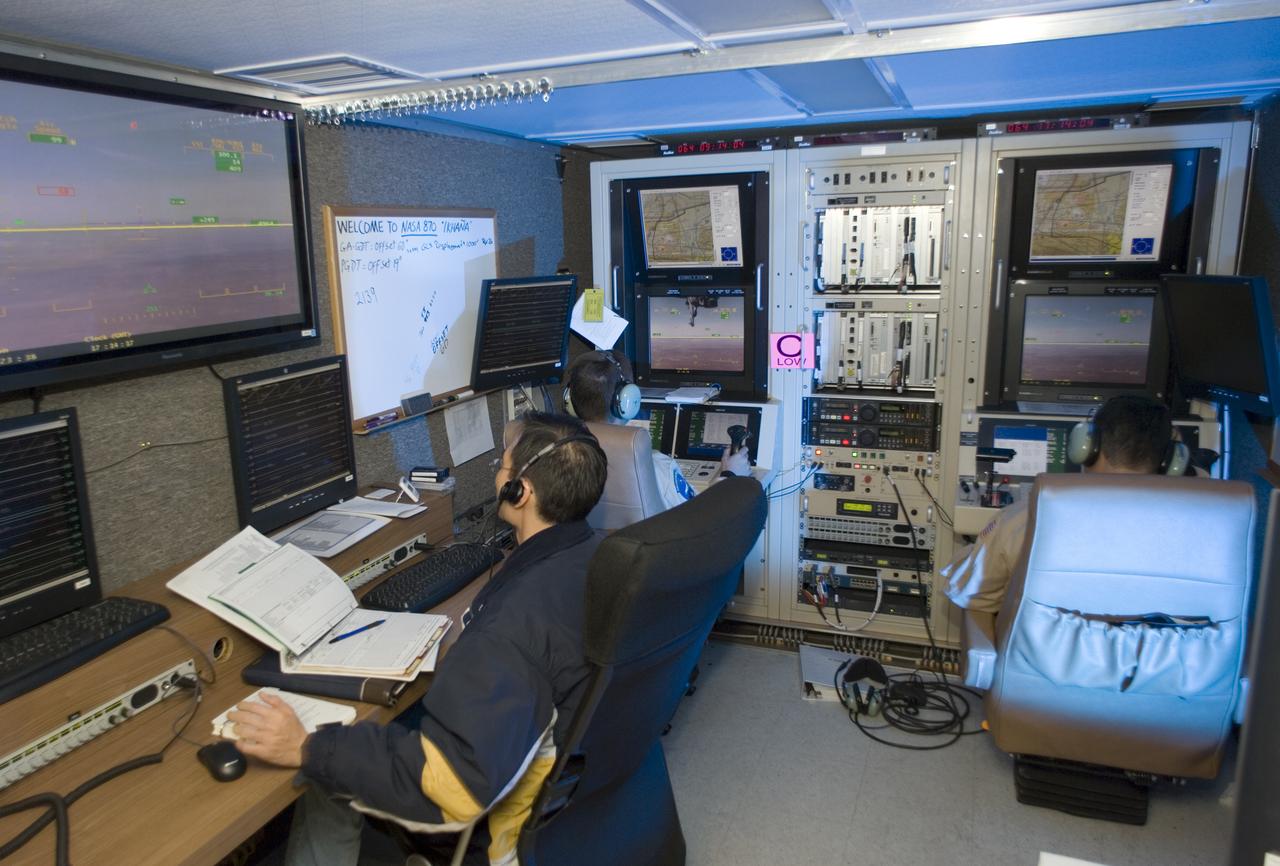

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science aircraft ground control station includes consoles for two pilots and positions for scientists and engineers along the side.
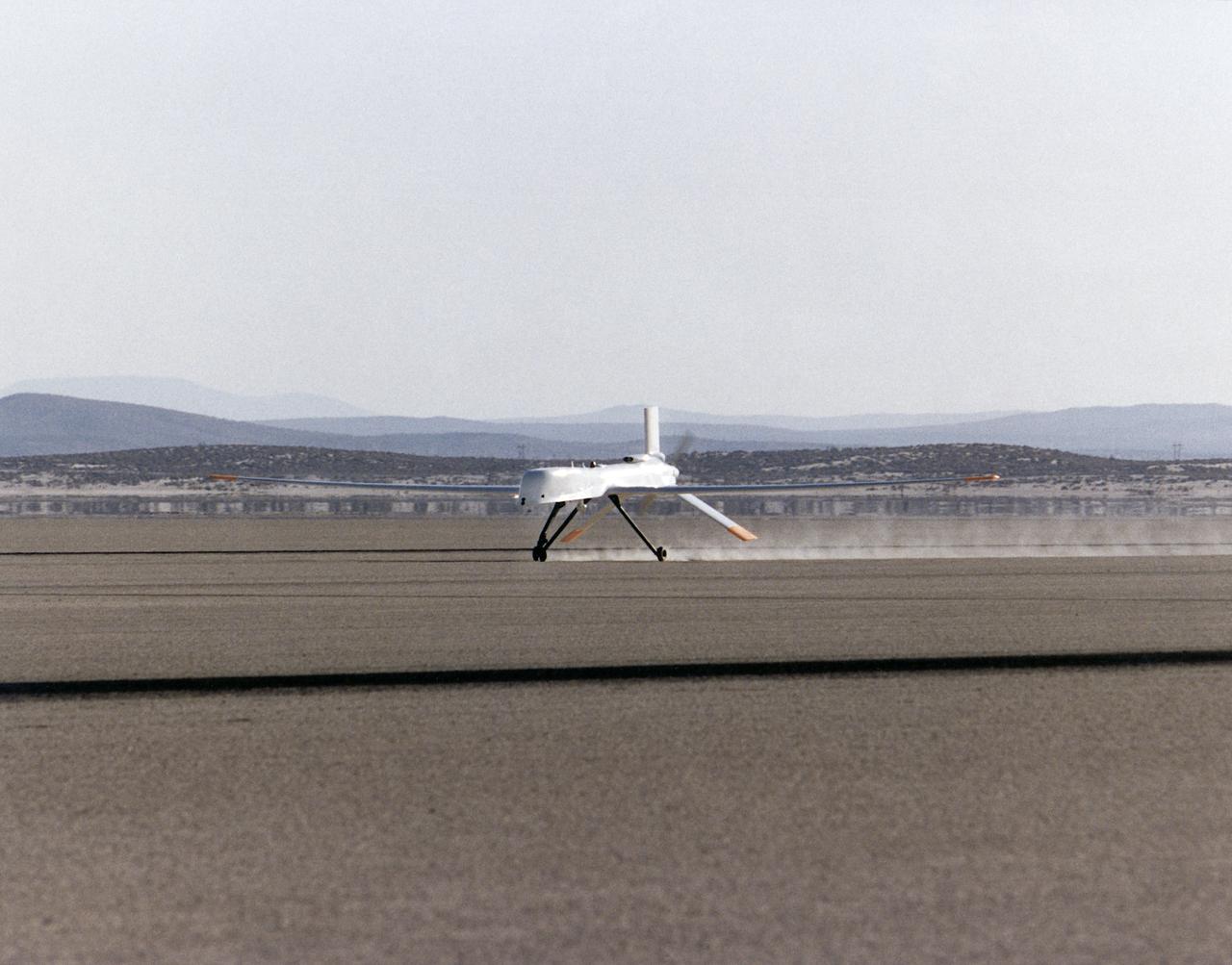

Altus I aircraft landing on Edwards lakebed runway 23
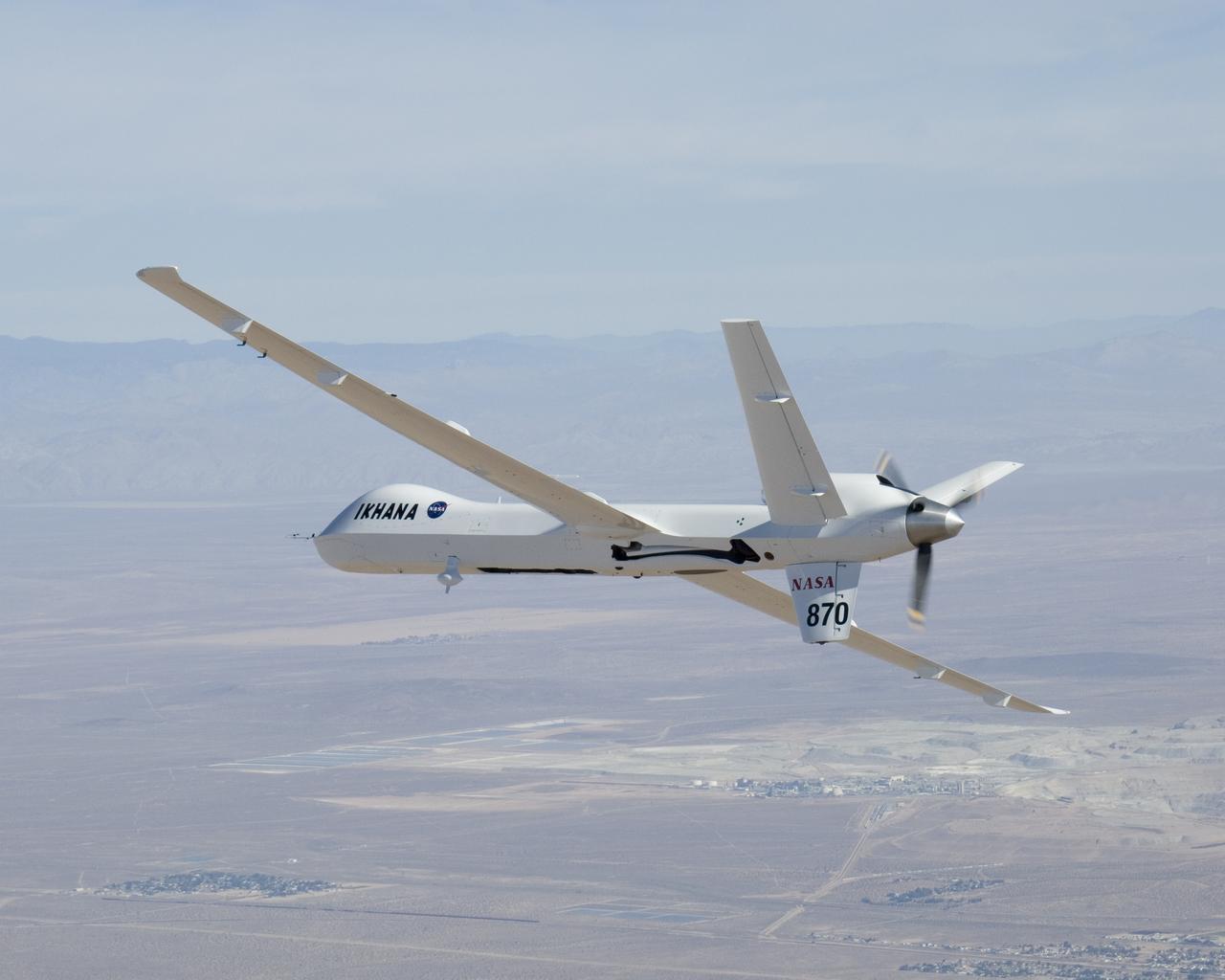

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft over the U.S. Borax mine, Boron, California, near the Dryden/Edwards Air Force Base complex. NASA took possession of the new aircraft in November, 2006, and it arrived at the NASA center at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., on June 23, 2007.
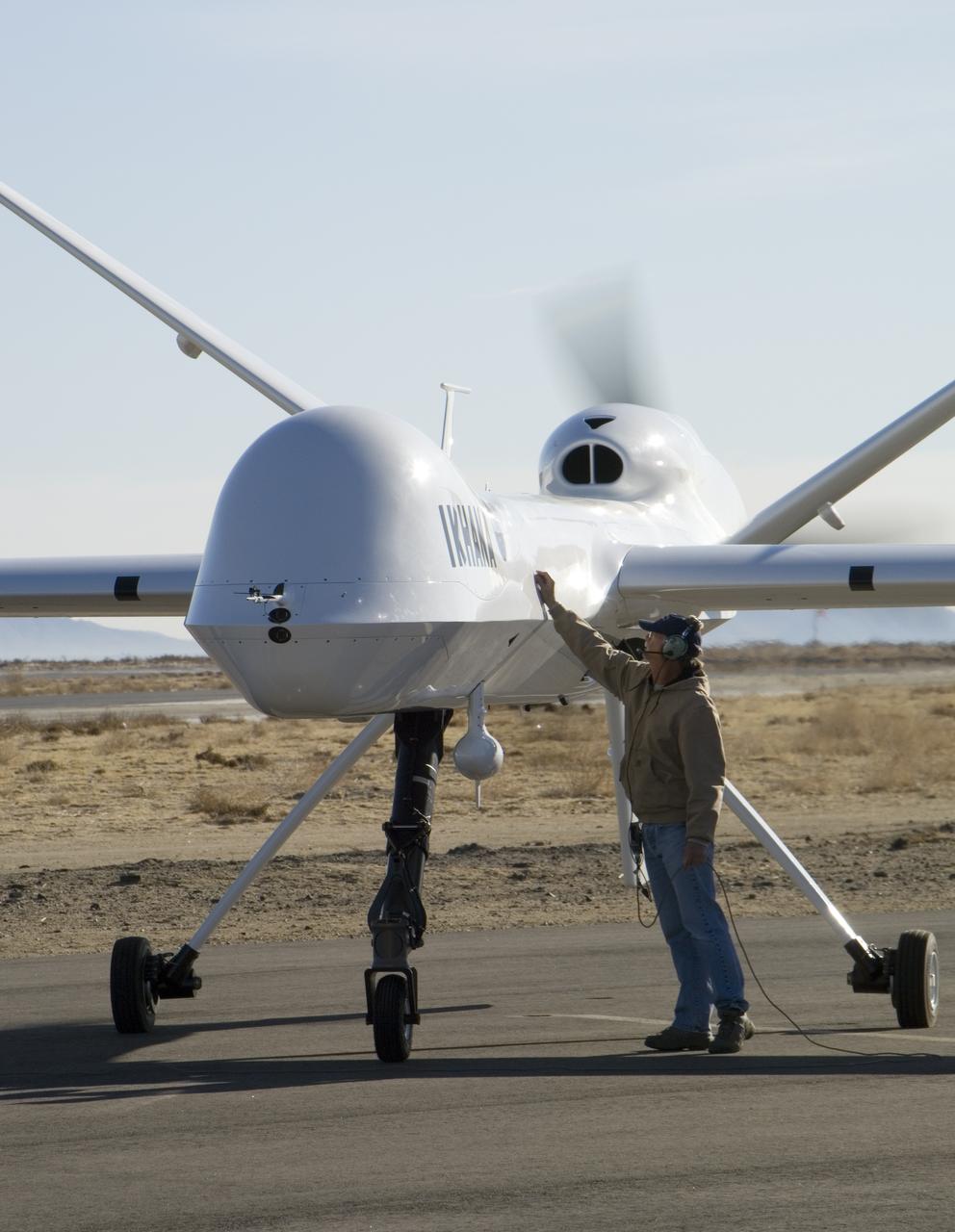

Crew chief Joe Kinn gives NASA's Ikhana unmanned aircraft a final check during engine run-up prior to takeoff at General Atomics Aeronautical Systems' airfield.
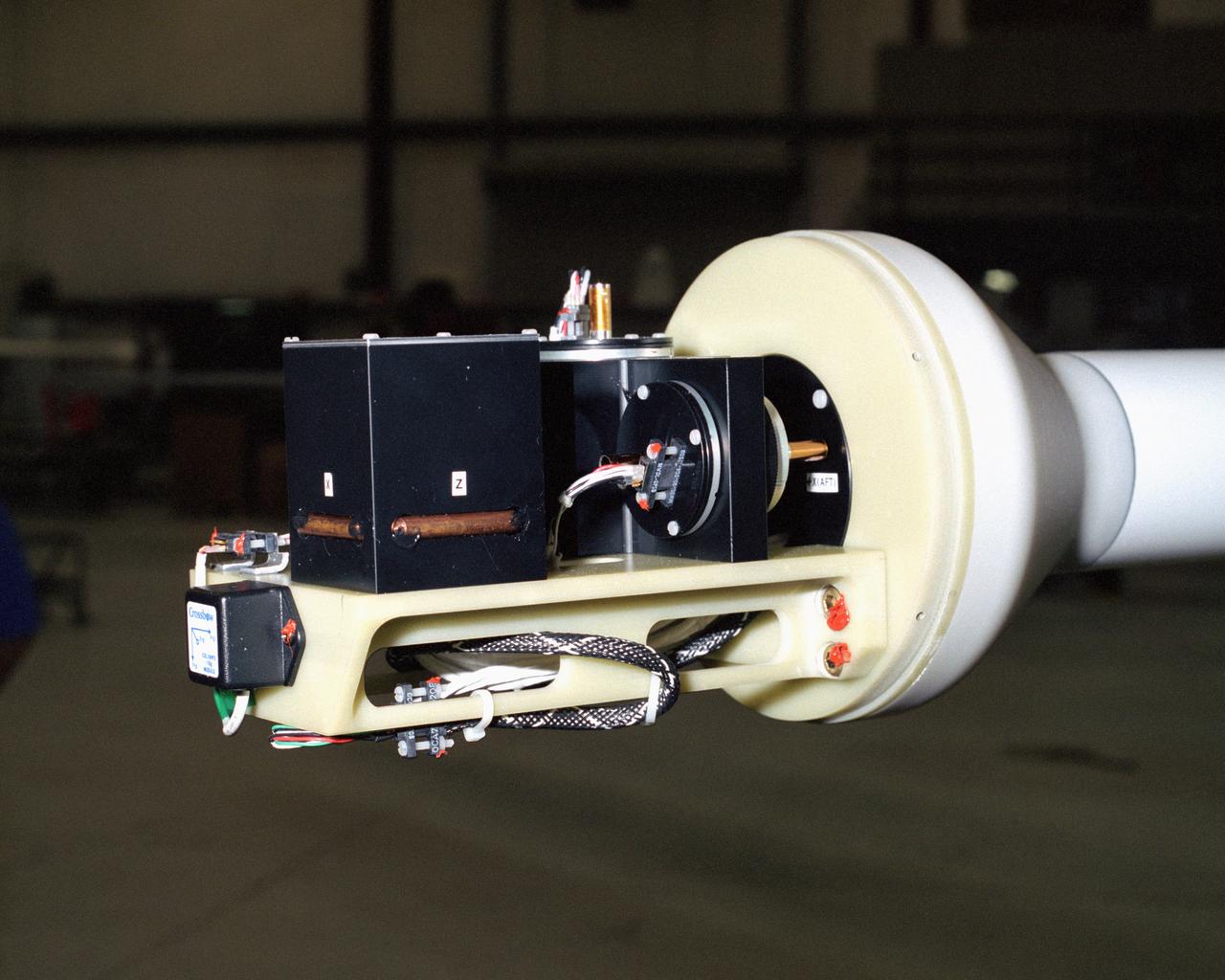
A NASA team studying the causes of electrical storms and their effects on our home planet achieved a milestone on August 21, 2002, completing the study's longest-duration research flight and monitoring four thunderstorms in succession. Based at the Naval Air Station Key West, Florida, researchers with the Altus Cumulus Electrification Study (ACES) used the Altus II remotely-piloted aircraft to study thunderstorms in the Atlantic Ocean off Key West and the west of the Everglades. Data obtained through sensors mounted to the aircraft will allow researchers in ACES to gauge elements such as lightning activity and the electrical environment in and around storms. By learning more about individual storms, scientists hope to better understand the global water and energy cycle, as well as climate variability. Contained in one portion of the aircraft is a three-axis magnetic search coil, which measures the AC magnetic field; a three-axis electric field change sensor; an accelerometer; and a three-axis magnetometer, which measures the DC magnetic field. With dual goals of gathering weather data safely and testing the adaptability of the uninhabited aircraft, the ACES study is a collaboration among the Marshall Space Flight Center, the University of Alabama in Huntsville, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Pernsylvania State University in University Park, and General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
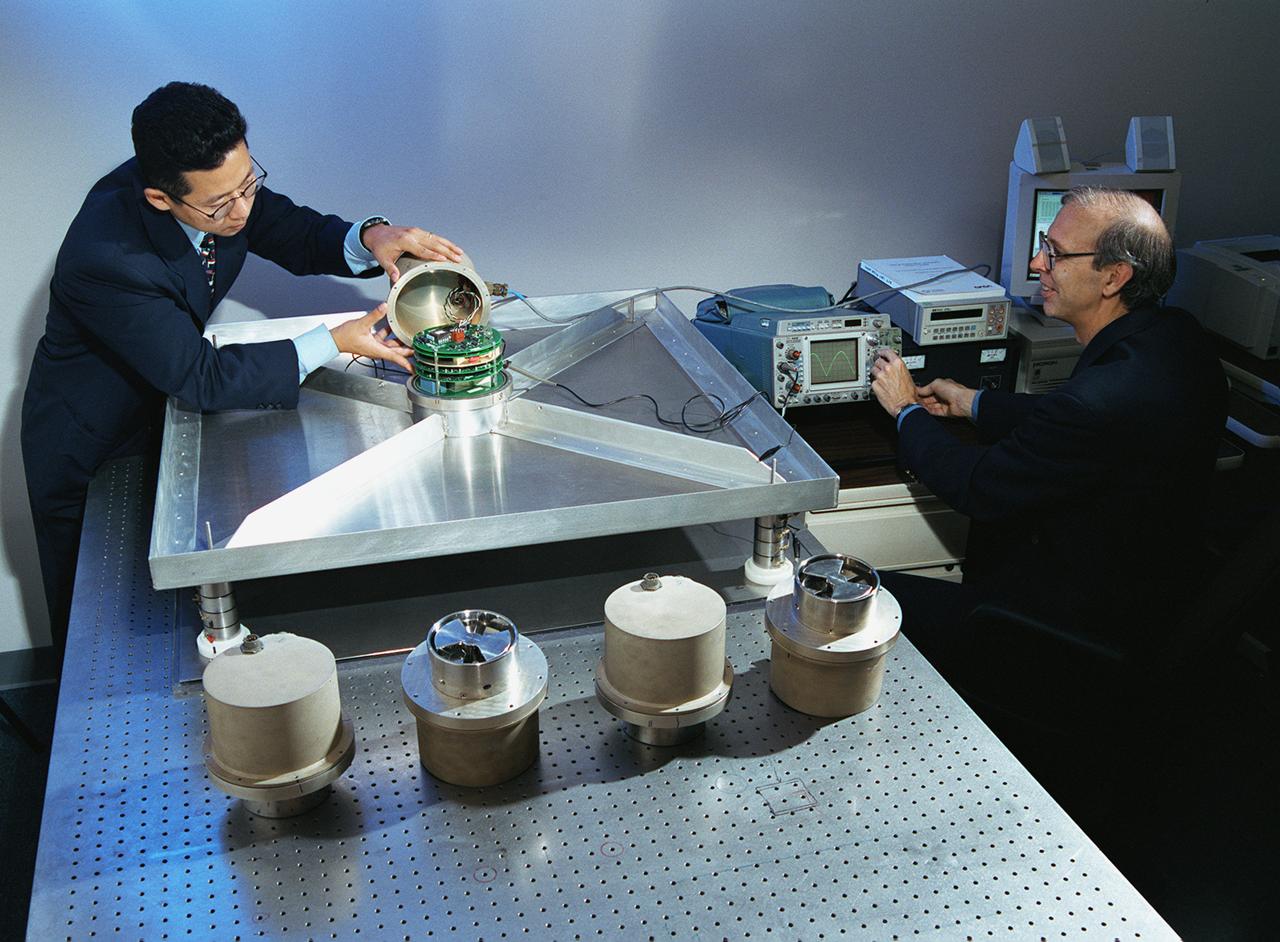

A NASA team studying the causes of electrical storms and their effects on our home planet achieved a milestone on August 21, 2002, completing the study's longest-duration research flight and monitoring four thunderstorms in succession. Radio news media can talk with Dr. Richard Blakeslee, the project's principal investigator, and Tony Kim, project manager at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), about their results and how their work will help improve future weather forecasting ability. Based at the Naval Air Station Key West, Florida, researchers with the Altus Cumulus Electrification Study (ACES) used the Altus II remotely- piloted aircraft to study a thunderstorm in the Atlantic Ocean off Key West, two storms at the western edge of the Everglades, and a large storm over the northwestern corner of the Everglades. This photograph shows Tony Kim And Dr. Richard Blakeslee of MSFC testing aircraft sensors that would be used to measure the electric fields produced by thunderstorm as part of NASA's ACES. With dual goals of gathering weather data safely and testing the adaptability of the uninhabited aircraft, the ACES study is a collaboration among the MSFC, the University of Alabama in Huntsville, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Pernsylvania State University in University Park, and General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
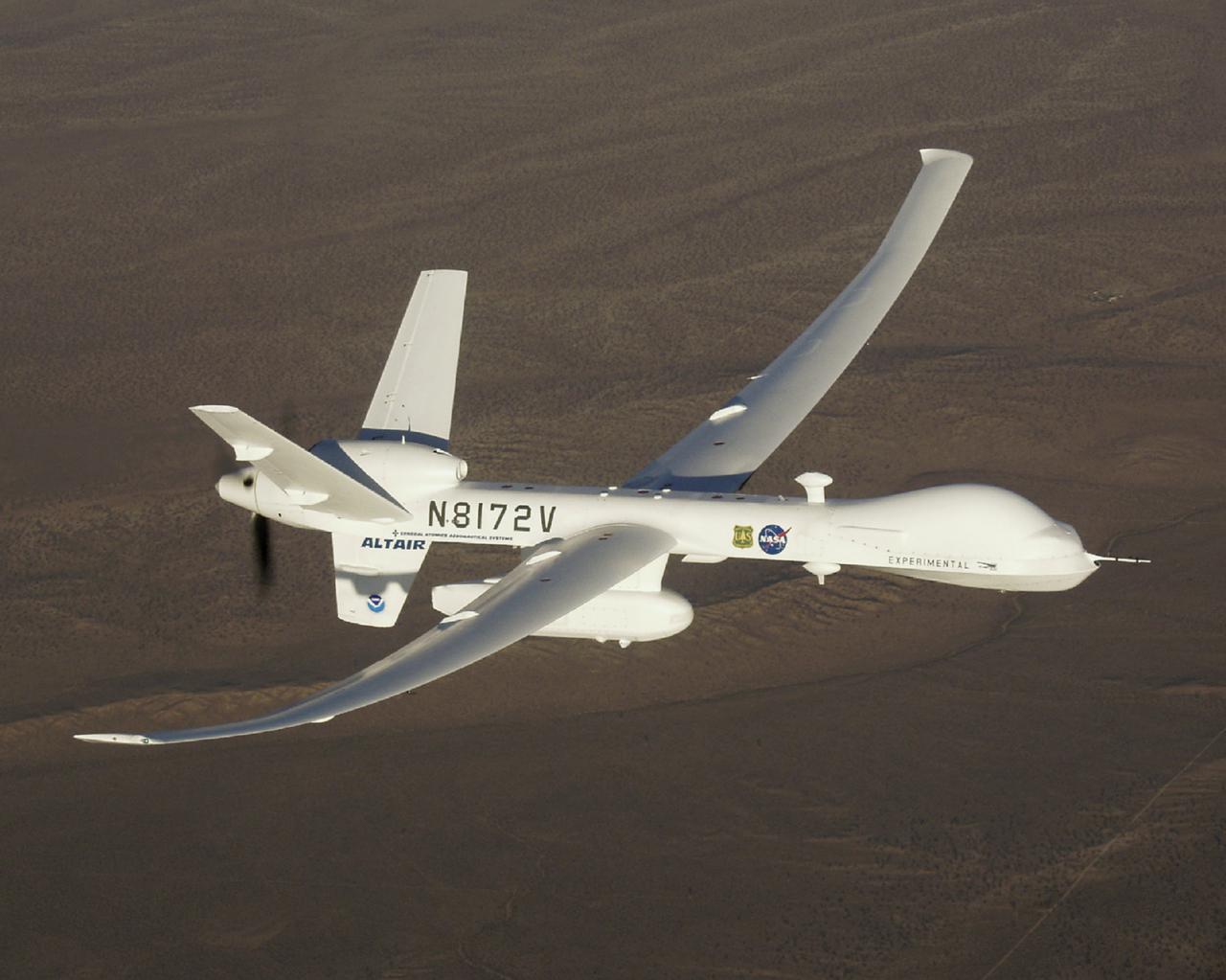

Equipped with a pod-mounted infrared imaging sensor, the Altair UAS aided fire mapping efforts over wildfires in central and southern California in late 2006.
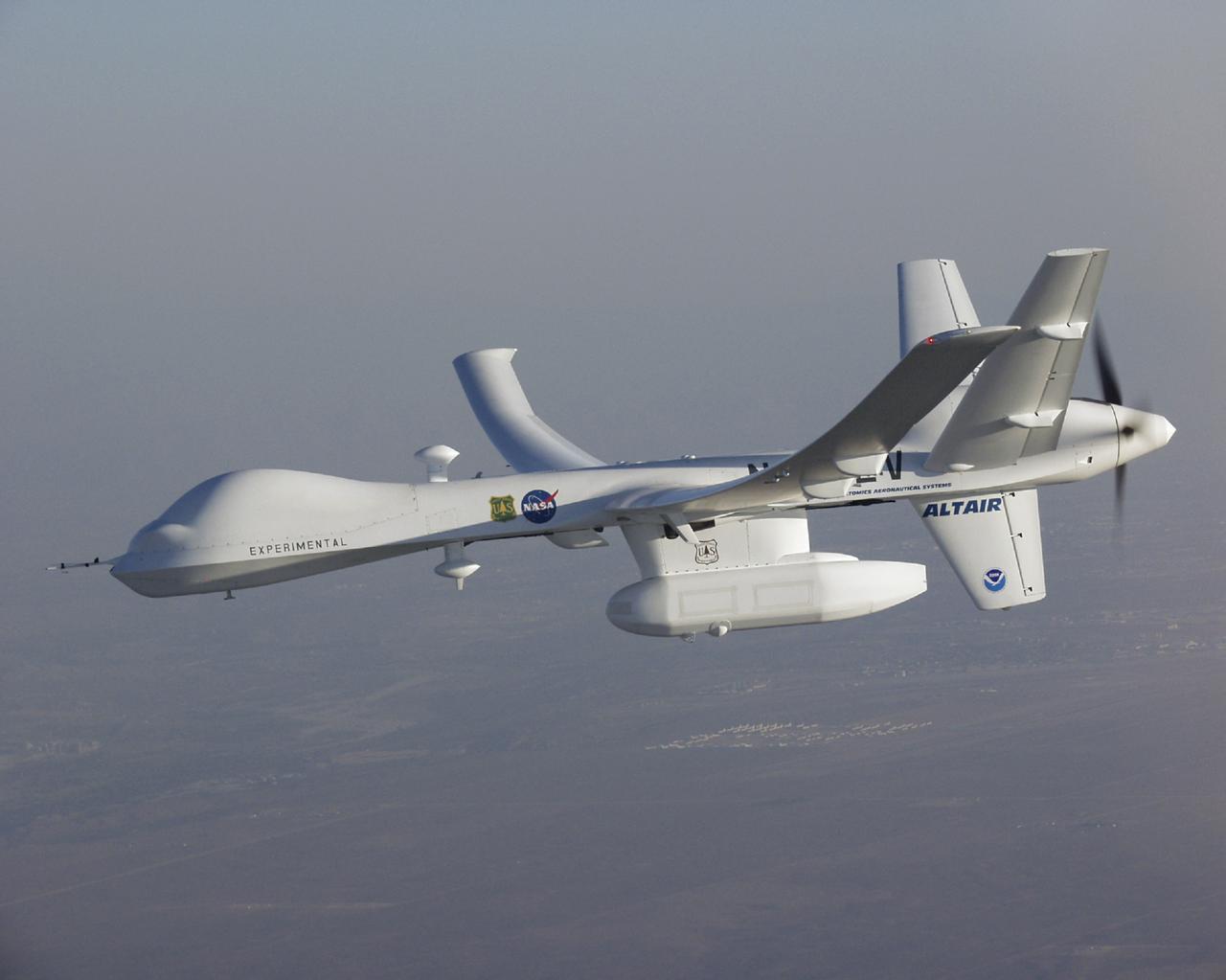

A high-tech infrared imaging sensor in its underbelly pod, the Altair UAS flew repeated passes over the Esperanza fire to aid firefighting efforts.

Altus I aircraft in flight, retracting landing gear after takeoff