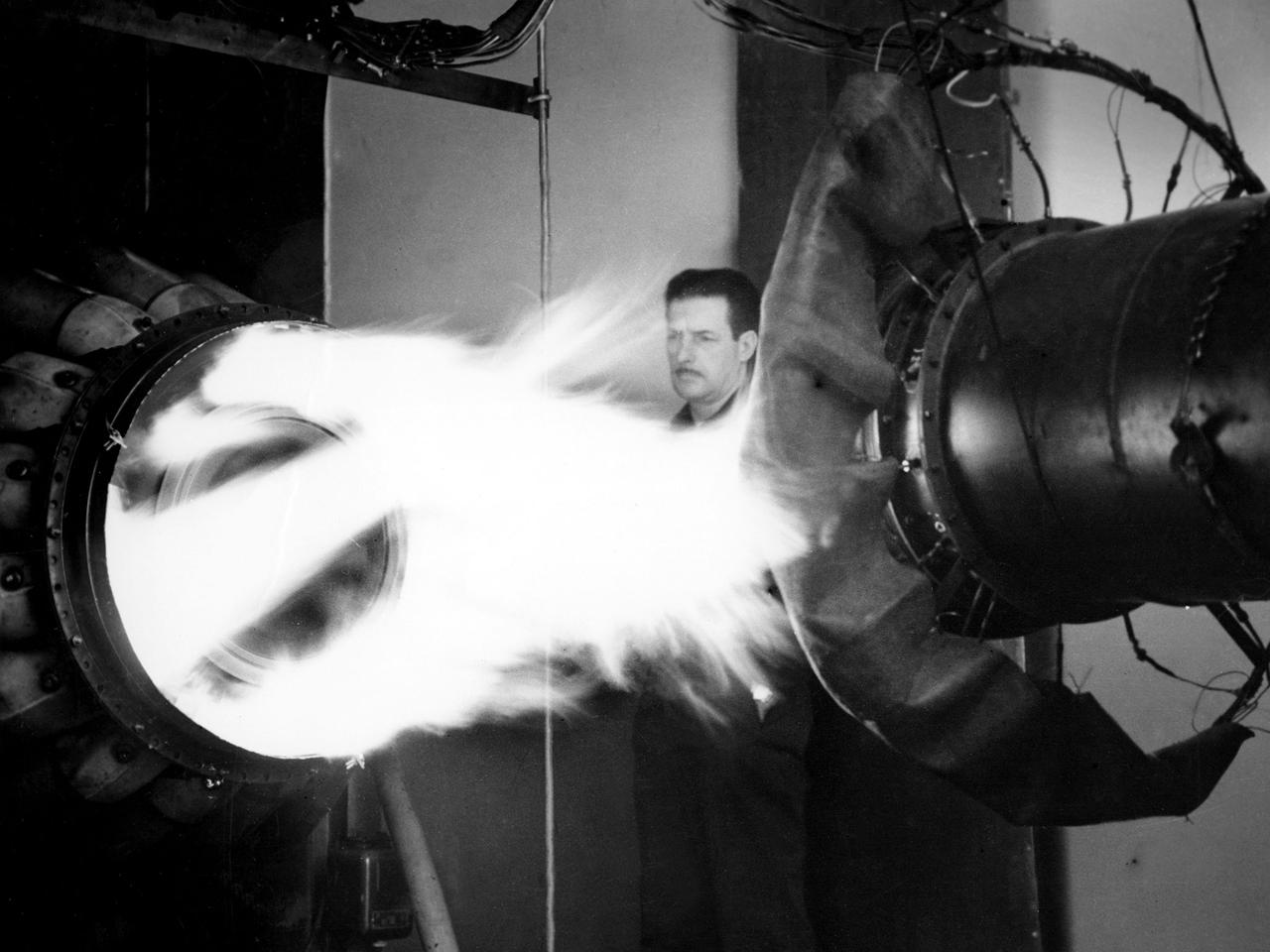
A mechanic watches the firing of a General Electric I-40 turbojet at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The military selected General Electric’s West Lynn facility in 1941 to secretly replicate the centrifugal turbojet engine designed by British engineer Frank Whittle. General Electric’s first attempt, the I-A, was fraught with problems. The design was improved somewhat with the subsequent I-16 engine. It was not until the engine's next reincarnation as the I-40 in 1943 that General Electric’s efforts paid off. The 4000-pound thrust I-40 was incorporated into the Lockheed Shooting Star airframe and successfully flown in June 1944. The Shooting Star became the US’s first successful jet aircraft and the first US aircraft to reach 500 miles per hour. NACA Lewis studied all of General Electric’s centrifugal turbojet models during the 1940s. In 1945 the entire Shooting Star aircraft was investigated in the Altitude Wind Tunnel. Engine compressor performance and augmentation by water injection; comparison of different fuel blends in a single combustor; and air-cooled rotors were studied. The mechanic in this photograph watches the firing of a full-scale I-40 in the Jet Propulsion Static Laboratory. The facility was quickly built in 1943 specifically in order to test the early General Electric turbojets. The I-A was secretly analyzed in the facility during the fall of 1943.

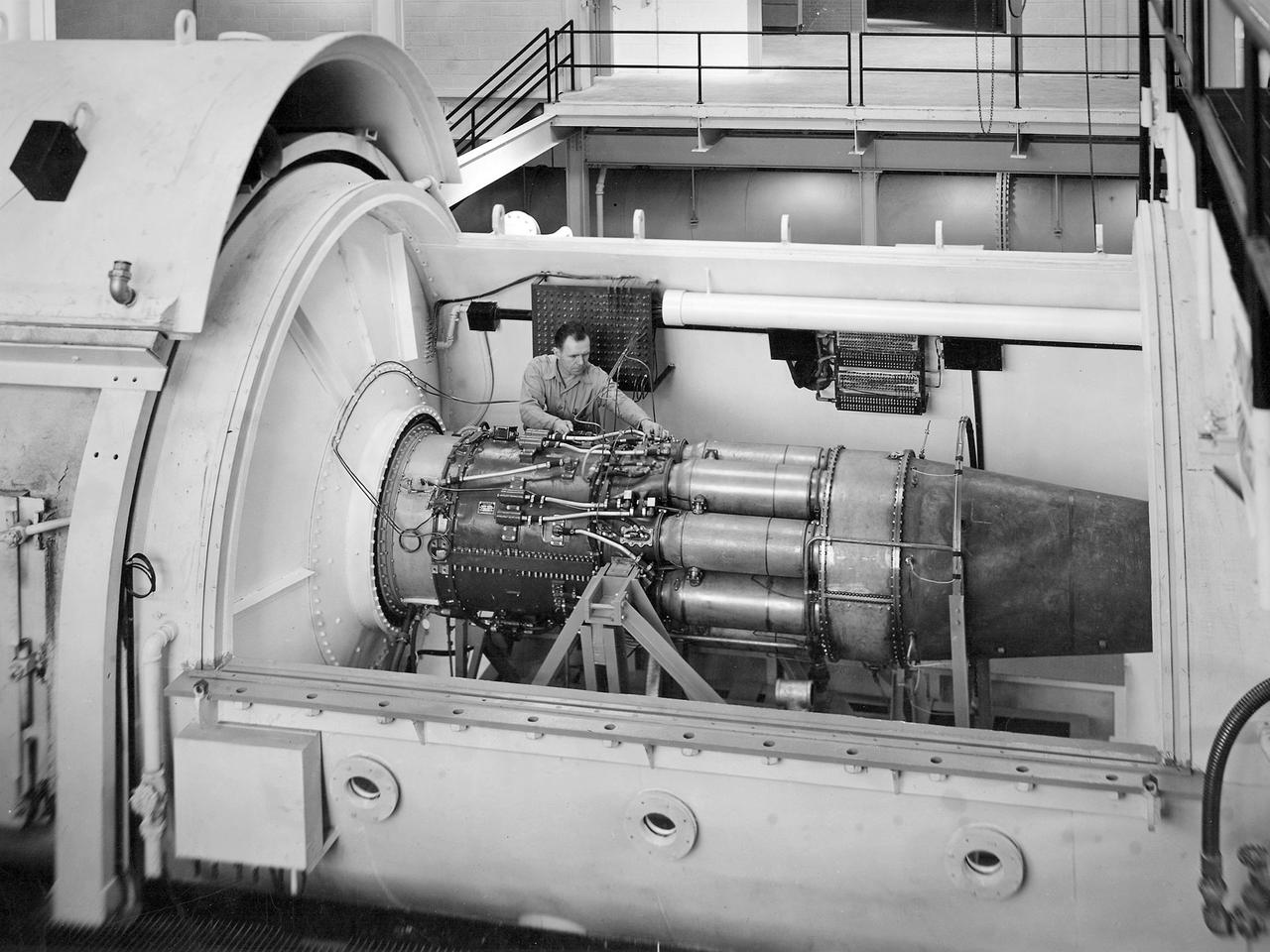
A mechanic works on a General Electric I-40 turbojet at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The military selected General Electric’s West Lynn facility in 1941 to secretly replicate the centrifugal turbojet engine designed by British engineer Frank Whittle. General Electric’s first attempt, the I-A, was fraught with problems. The design was improved somewhat with the subsequent I-16 engine. It was not until the engine's next reincarnation as the I-40 in 1943 that General Electric’s efforts paid off. The 4000-pound thrust I-40 was incorporated into the Lockheed Shooting Star airframe and successfully flown in June 1944. The Shooting Star became the US’s first successful jet aircraft and the first US aircraft to reach 500 miles per hour. The NACA’s Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory studied all of General Electric’s centrifugal turbojets both during World War II and afterwards. The entire Shooting Star aircraft was investigated in the Altitude Wind Tunnel during 1945. The researchers studied the engine compressor performance, thrust augmentation using a water injection, and compared different fuel blends in a single combustor. The mechanic in this photograph is inserting a combustion liner into one of the 14 combustor cans. The compressor, which is not yet installed in this photograph, pushed high pressure air into these combustors. There the air mixed with the fuel and was heated. The hot air was then forced through a rotating turbine that powered the engine before being expelled out the nozzle to produce thrust.
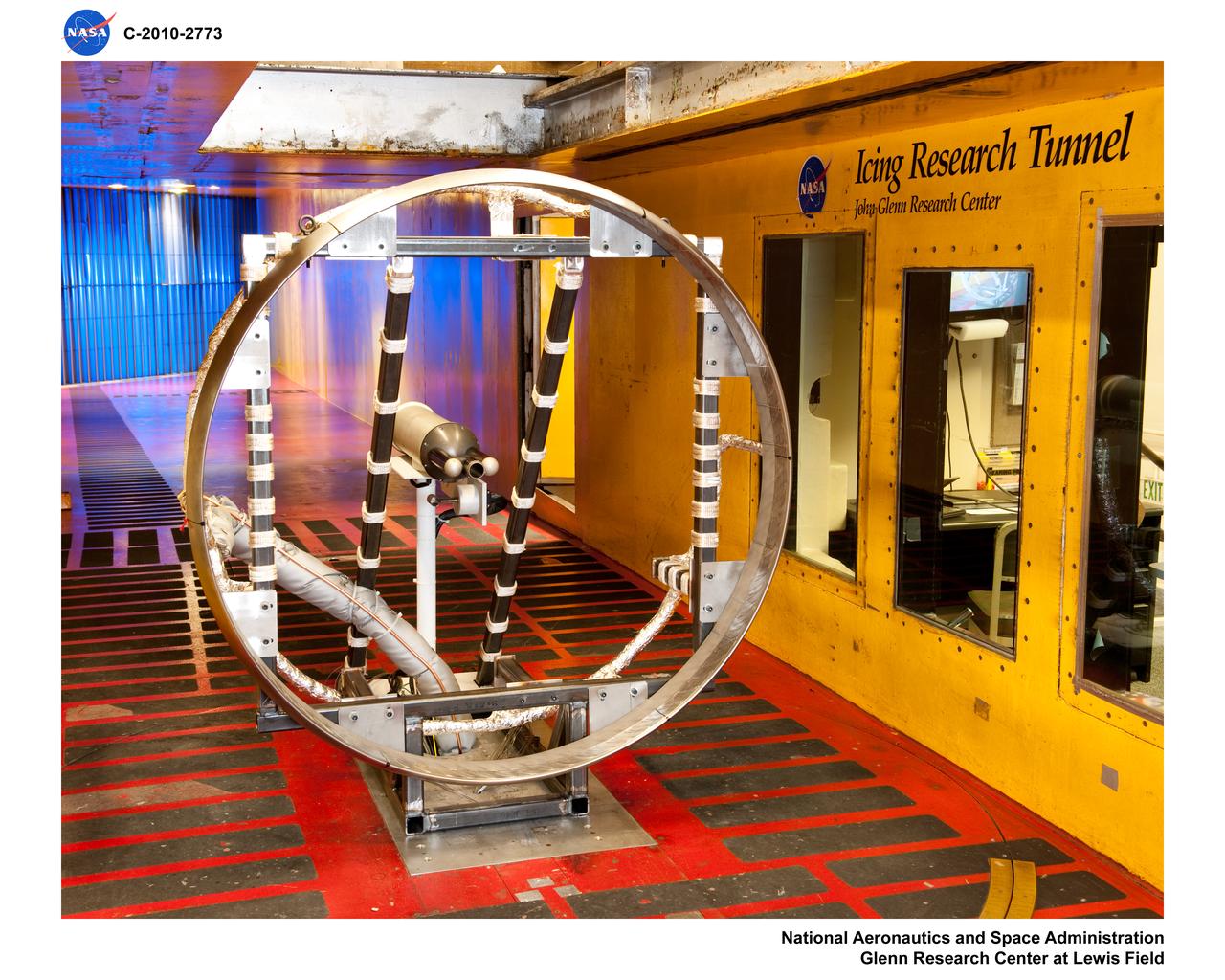

General Electric Aviation - Engine Splitter Booster Model in the Icing Research Tunnel
Second Generation Agile Engineering Prototype of Electric Sail 6U CubeSat Testbed Article
First Generation Agile Engineering Prototype of Electric Sail 6U CubeSat Testbed Article

Johnson Space Center (JSC) engineers visit Houston area schools for National Engineers Week. Students examine a machine that generates static electricity (4296-7). Students examine model rockets (4298).

Here is an overhead view of the X-59 aircraft (left) prior to the installation of the General Electric F414 engine (center, located under the blue cover). After the engine is installed, the lower empennage (right), the last remaining major aircraft component, will be installed in preparation for integrated system checkouts. The X-59 is the centerpiece of the Quesst mission which plans to help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.

Here is an image of the X-59’s 13-foot General Electric F414 engine as the team prepares for a fit check. Making sure components, like the aircraft’s hydraulic lines, which help control functions like brakes or landing gear, and wiring of the engine, fit properly is essential to the aircraft’s safety. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.

Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) engineers examine the interface surface on the Cassini spacecraft prior to installation of the third radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG). The other two RTGs, at left, already are installed on Cassini. The three RTGs will be used to power Cassini on its mission to the Saturnian system. They are undergoing mechanical and electrical verification testing in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. RTGs use heat from the natural decay of plutonium to generate electric power. The generators enable spacecraft to operate far from the Sun where solar power systems are not feasible. The Cassini mission is scheduled for an Oct. 6 launch aboard a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle. Cassini is built and managed for NASA by JPL
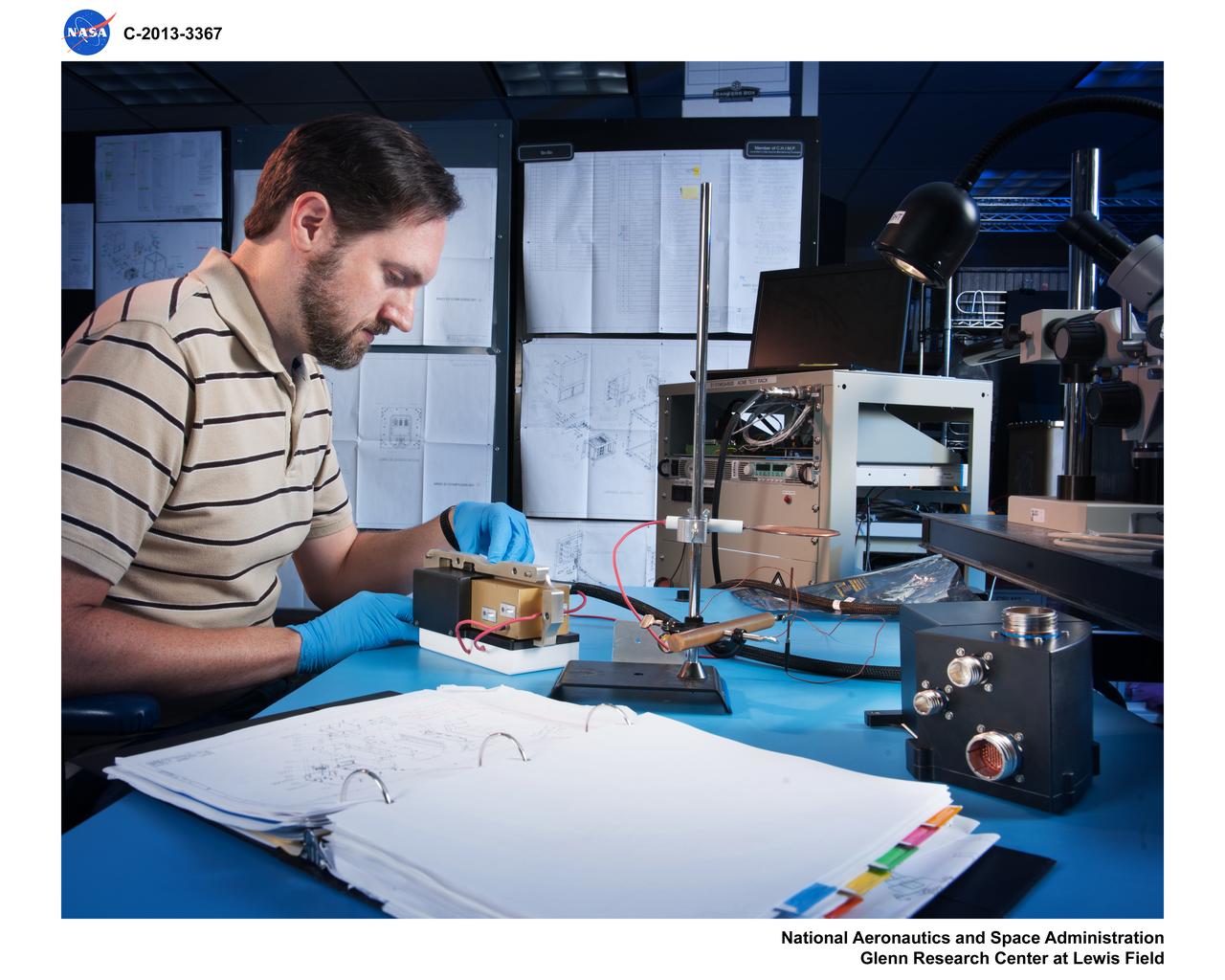

Mechanical Engineer Adrian Drake inspects engineering model hardware built to generate a high-voltage electric field for the Electric-Field Effects on Laminar Diffusion Flames (E-FIELD Flames) experiment of the Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments (ACME) project. ACME’s small computer (i.e., the Cube) for data acquisition and control within the CIR combustion chamber is seen in the right foreground. The E-FIELD Flames tests were conducted in the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) on the International Space Station (ISS) in 2018.

Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) worker Mary Reaves mates connectors on a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) to power up the Cassini spacecraft, while quality assurance engineer Peter Sorci looks on. The three RTGs which will be used on Cassini are undergoing mechanical and electrical verification testing in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The RTGs will provide electrical power to Cassini on its 6.7-year trip to the Saturnian system and during its four-year mission at Saturn. RTGs use heat from the natural decay of plutonium to generate electric power. The generators enable spacecraft to operate at great distances from the Sun where solar power systems are not feasible. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch aboard a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle. Cassini is built and managed by JPL
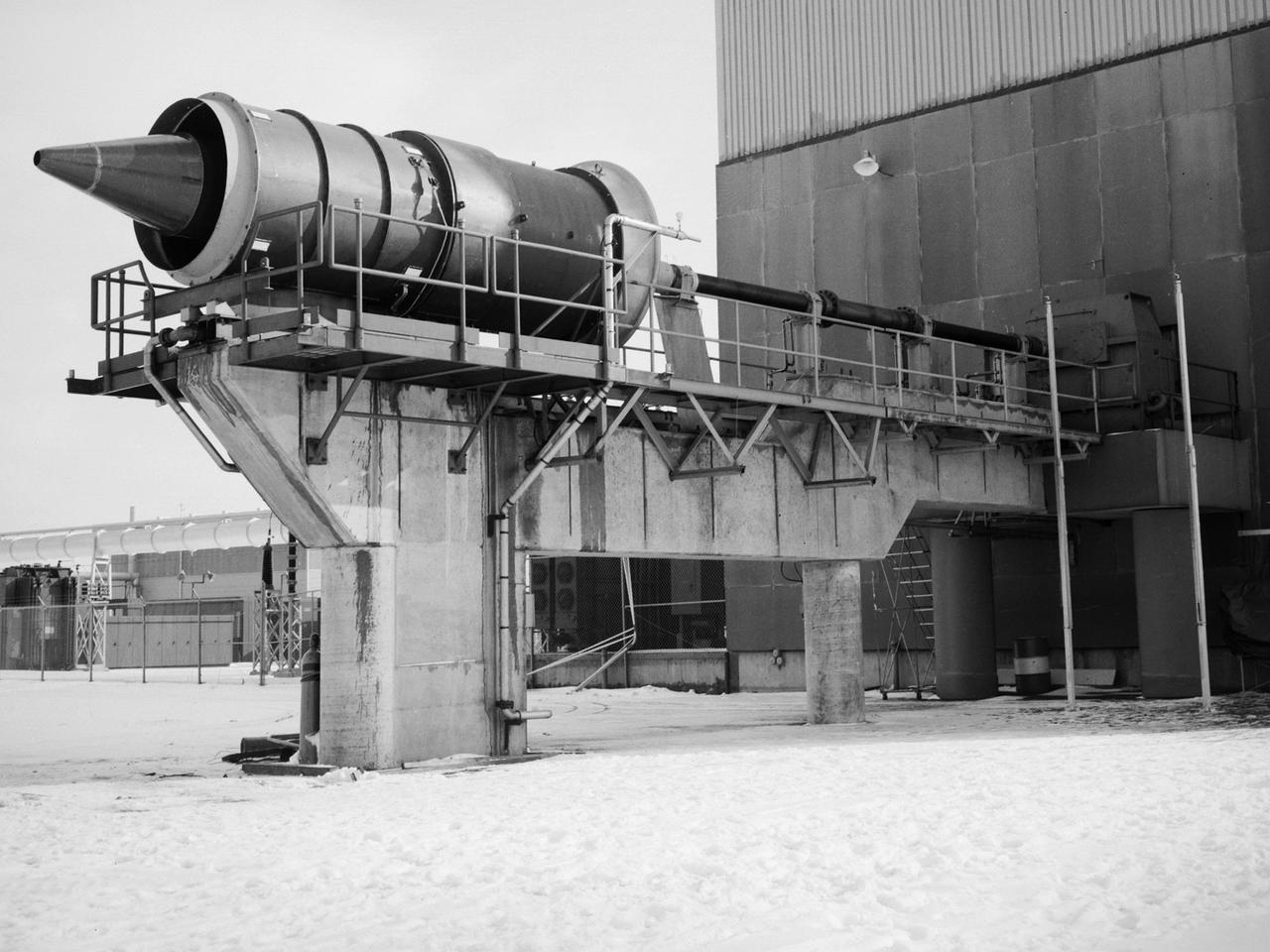

The Fan Noise Test Facility built at the Lewis Research Center to obtain far-field noise data for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and General Electric Quiet Engine Program. The engine incorporated existing noise reduction methods into an engine of similar power to those that propelled the Boeing 707 or McDonnell-Douglas DC-8 airliner. The new the low-bypass ratio turbofan engines of the 1960s were inherently quieter than their turbojet counterparts, researchers had a better grasp of the noise generation problem, and new acoustic technologies had emerged. Lewis contracted General Electric in 1969 to build and aerodynamically test three experimental engines with 72-inch diameter fans. The engines were then brought to Lewis and tested with an acoustically treated nacelle. This Fan Noise Test Facility was built off of the 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel’s Main Compressor and Drive Building. Lewis researchers were able to isolate the fan’s noise during these initial tests by removing the core of the engine. The Lewis test rig drove engines to takeoff tip speeds of 1160 feet per second. The facility was later used to test a series of full-scale model fans and fan noise suppressors to be used with the quiet engine. NASA researchers predicted low-speed single-stage fans without inlet guide vanes and with large spacing between rotors and stators would be quieter. General Electric modified a TF39 turbofan engine by removing the the outer protion of the fan and spacing the blade rows of the inner portion. The tests revealed that the untreated version of the engine generated less noise than was anticipated, and the acoustically treated nacelle substantially reduced engine noise.
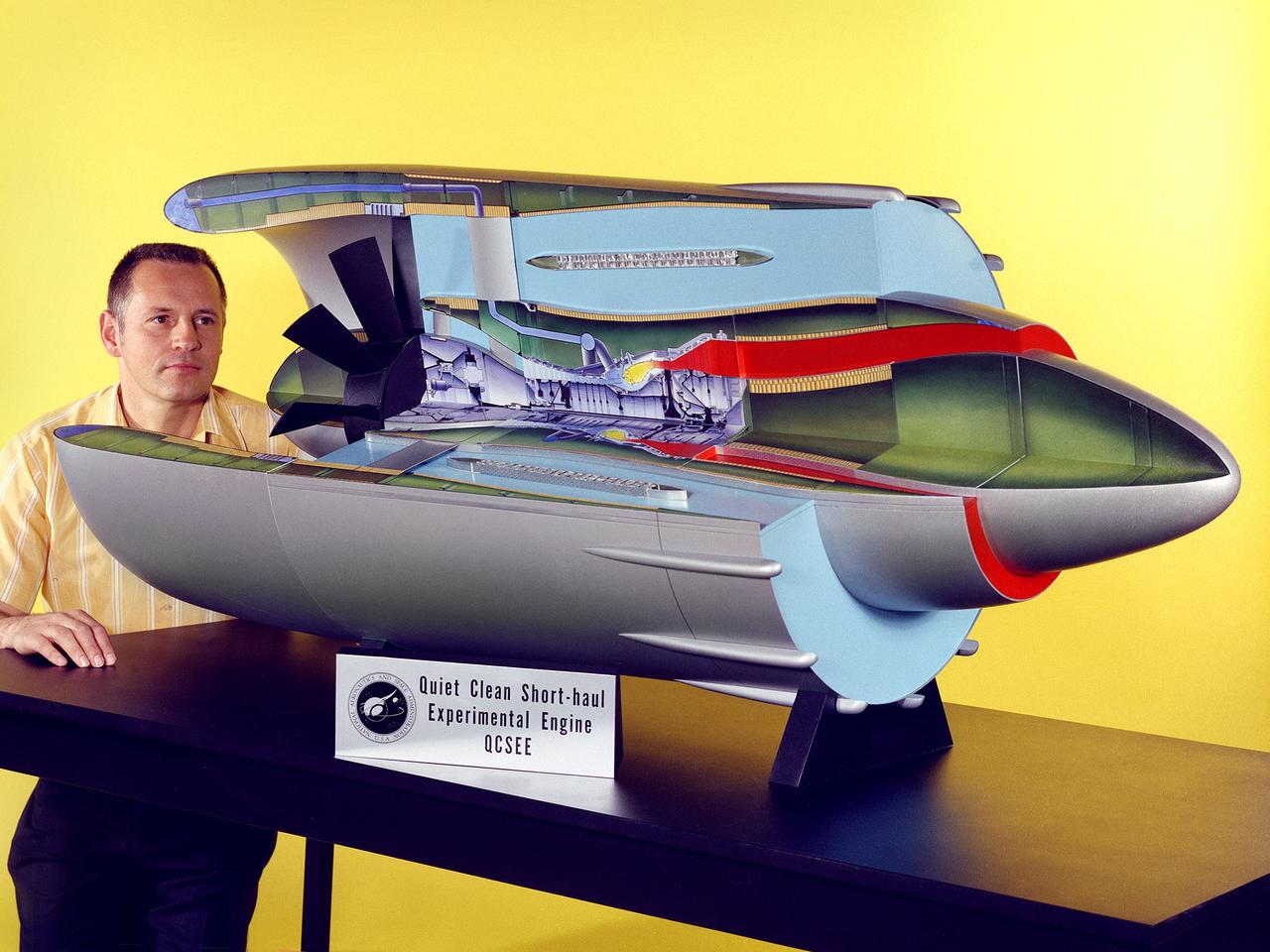

Program manager Carl Ciepluch poses with a model of the Quiet Clean Short Haul Experimental Engine (QCSEE) conceived by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The QCSEE engine was designed to power future short-distance transport aircraft without generating significant levels of noise or pollution and without hindering performance. The engines were designed to be utilized on aircraft operating from small airports with short runways. Lewis researchers investigated two powered-lift designs and an array of new technologies to deal with the shorter runways. Lewis contracted General Electric to design the two QCSEE engines—one with over-the-wing power-lift and one with an under-the-wing design. A scale model of the over-the-wing engine was tested in the Full Scale Tunnel at the Langley Research Center in 1975 and 1976. Lewis researchers investigated both versions in a specially-designed test stand, the Engine Noise Test Facility, on the hangar apron. The QCSEE engines met the goals set out by the NASA researchers. The aircraft industry, however, never built the short-distance transport aircraft for which the engines were intended. Different technological elements of the engine, however, were applied to some future General Electric engines.
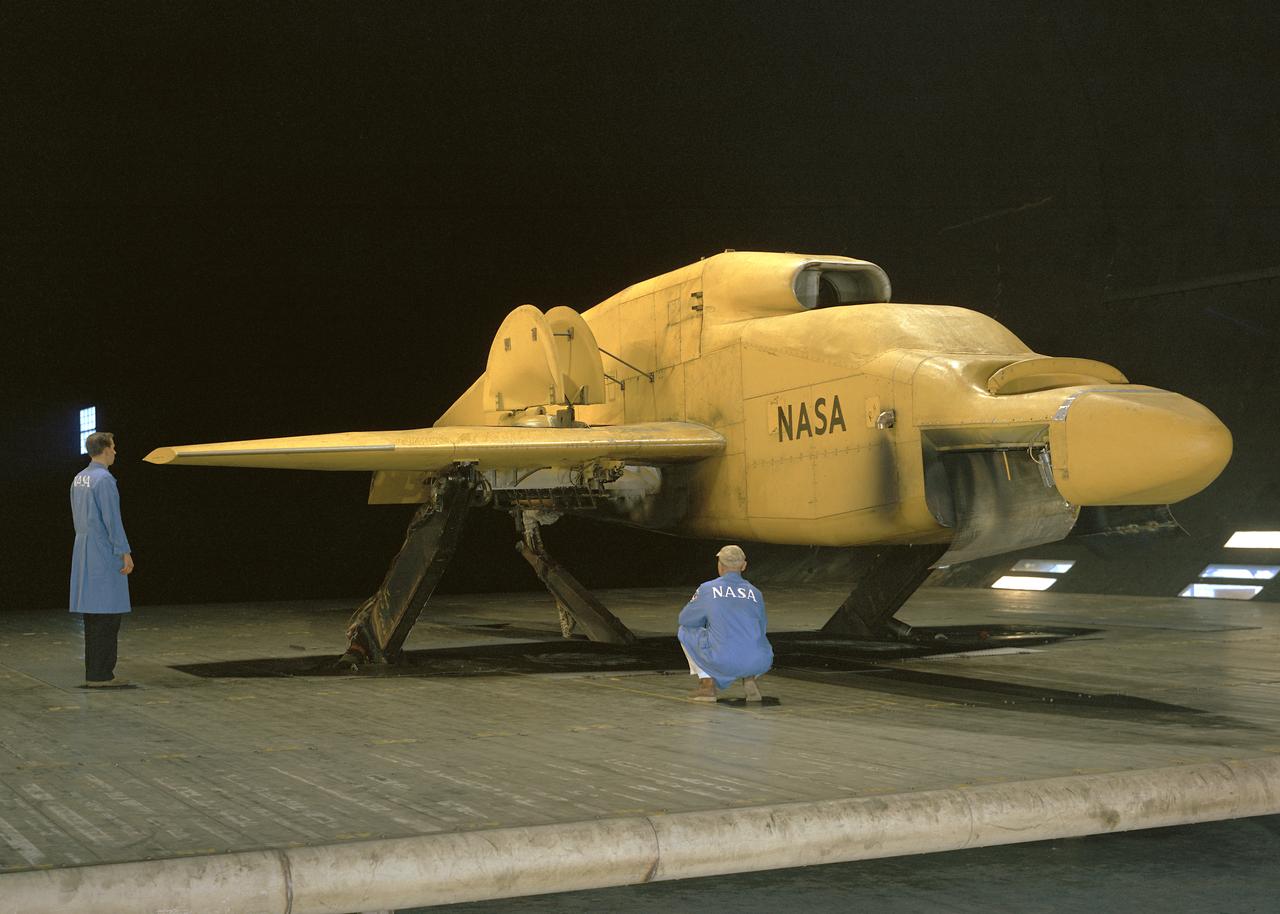

3/4 front view VZ-11 ground test - variable height struts. Engines of the VZ-11 are a pair of General Electric J85-5 turbojets, mounted in high in the centre fuselage, well away from fan disturbance. Designed in the Ames 40x80 foot wind tunnel.
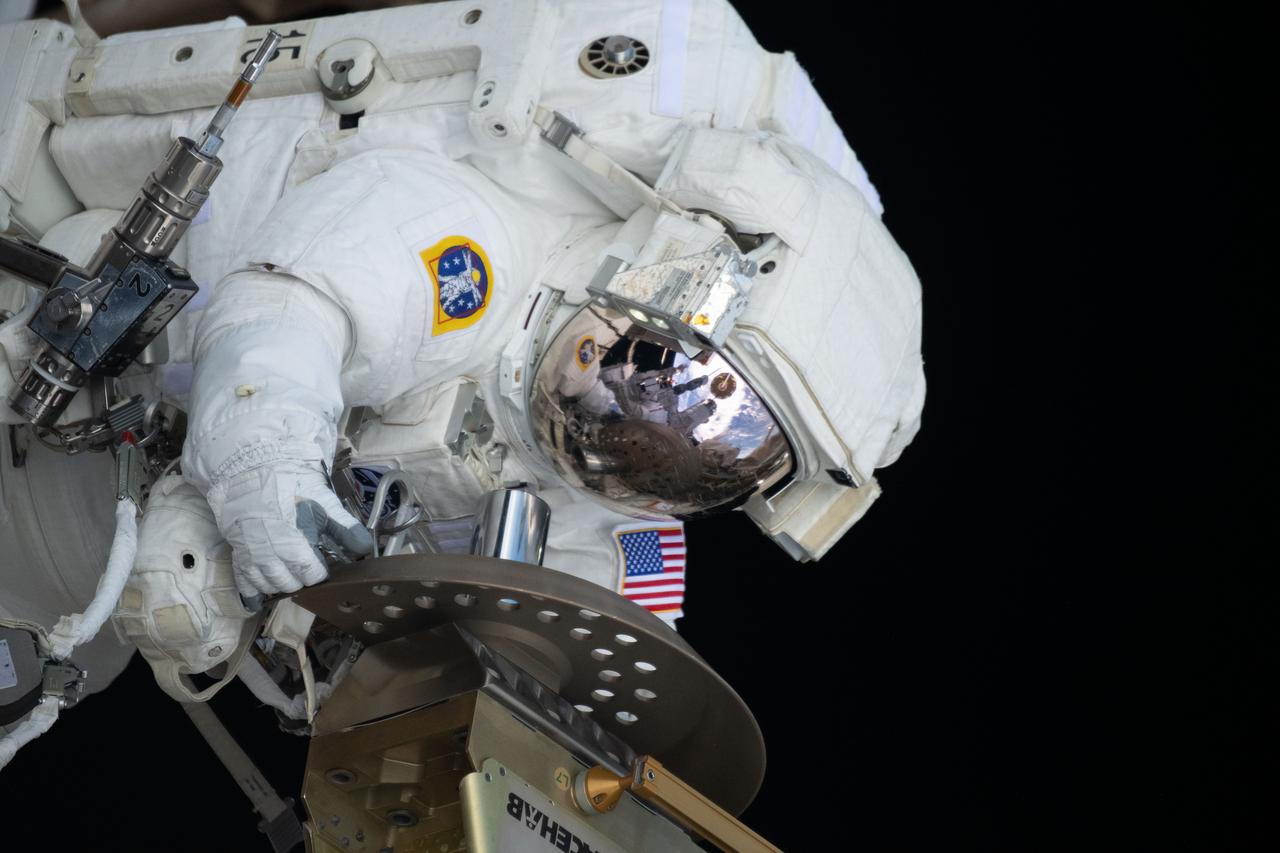

iss070e37241 (Nov. 1, 2023) --- Expedition 70 Flight Engineer and NASA astronaut Loral O'Hara is pictured during a spacewalk for maintenance on the International Space Station's port solar alpha rotary joint, which allows the solar arrays to track the Sun and generate electricity to power the orbital outpost.
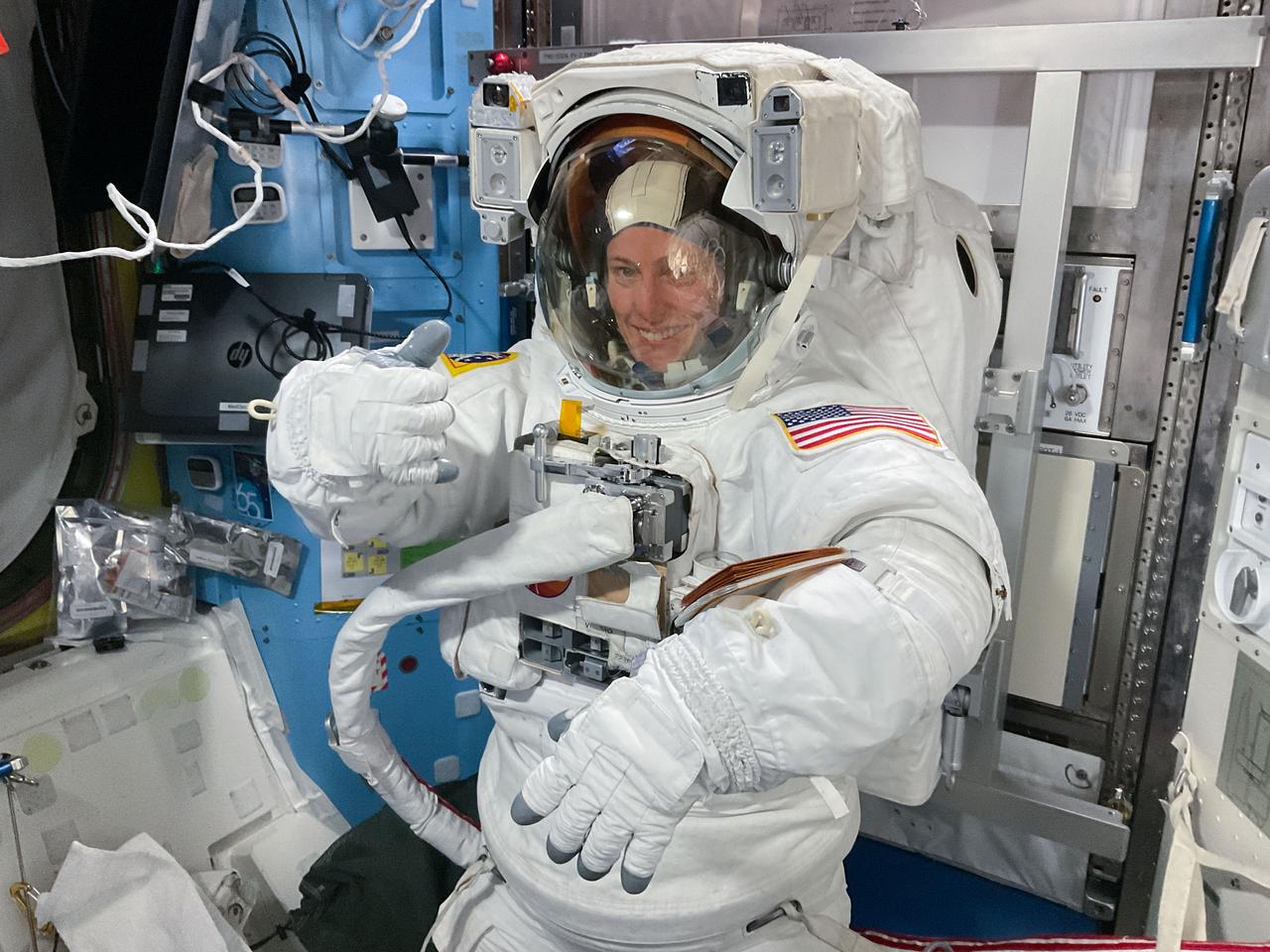

iss070e37272 (Nov. 1, 2023) --- Expedition 70 Flight Engineer and NASA astronaut Loral O'Hara is pictured in her spacesuit before beginning a spacewalk for maintenance on the International Space Station's port solar alpha rotary joint, which allows the solar arrays to track the Sun and generate electricity to power the orbital outpost.
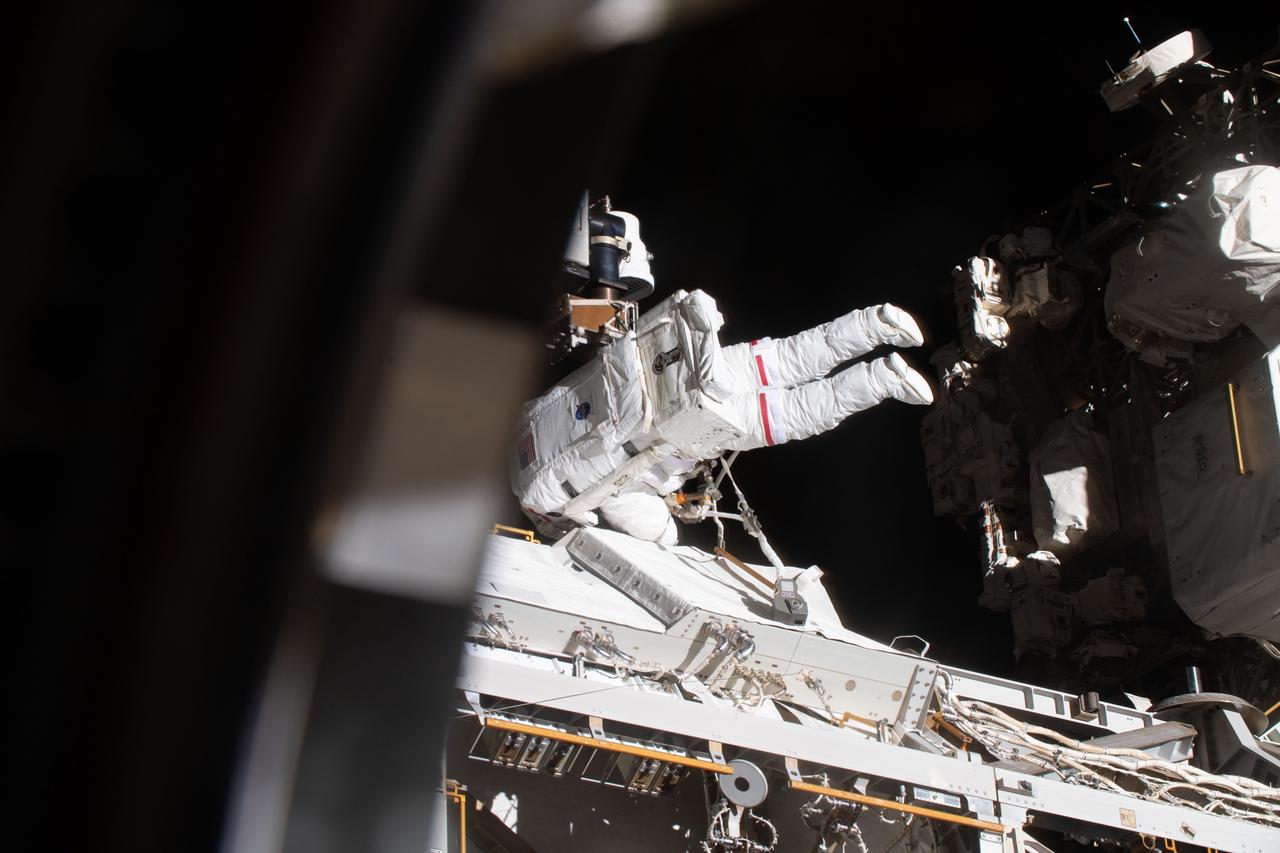

iss070e015430 (Nov. 1, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 70 Flight Engineer Jasmin Moghbeli is pictured tethered to the International Space Station during a spacewalk to replace one of the 12 trundle bearing assemblies on the port solar alpha rotary joint, which allows the arrays to track the Sun and generate electricity to power the station.
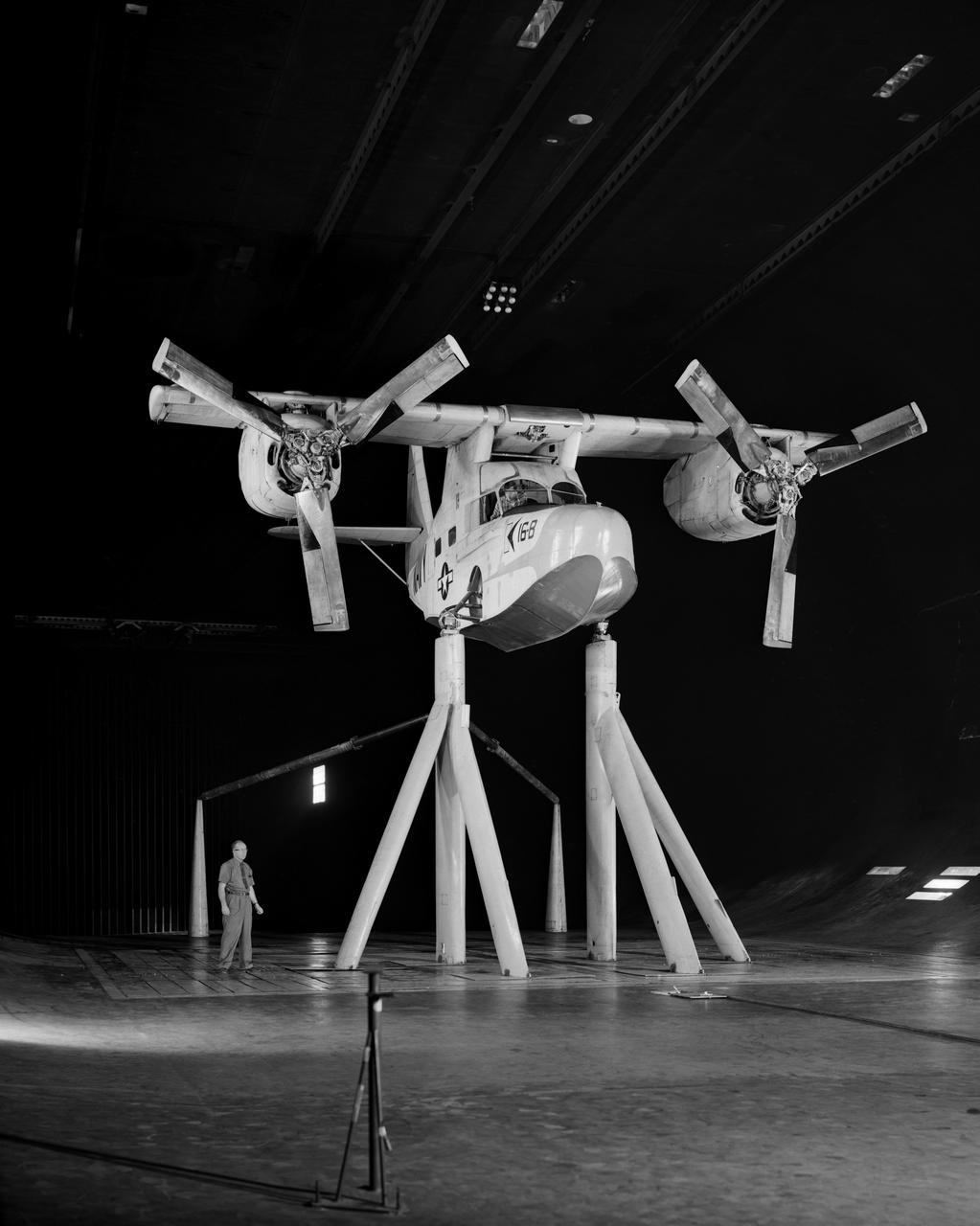

Test No. 175 Kaman K-16 in 40x80 Foot Wind Tunnel at Ames Research Center. Pictured with two Kaman employees. 3/4 Front view of Airplane. Kaman K-16B was an experimental tilt wing aircraft, it used the fuselage of a JRF-5 and was powered by two General Electric YT58-GE-2A engines.
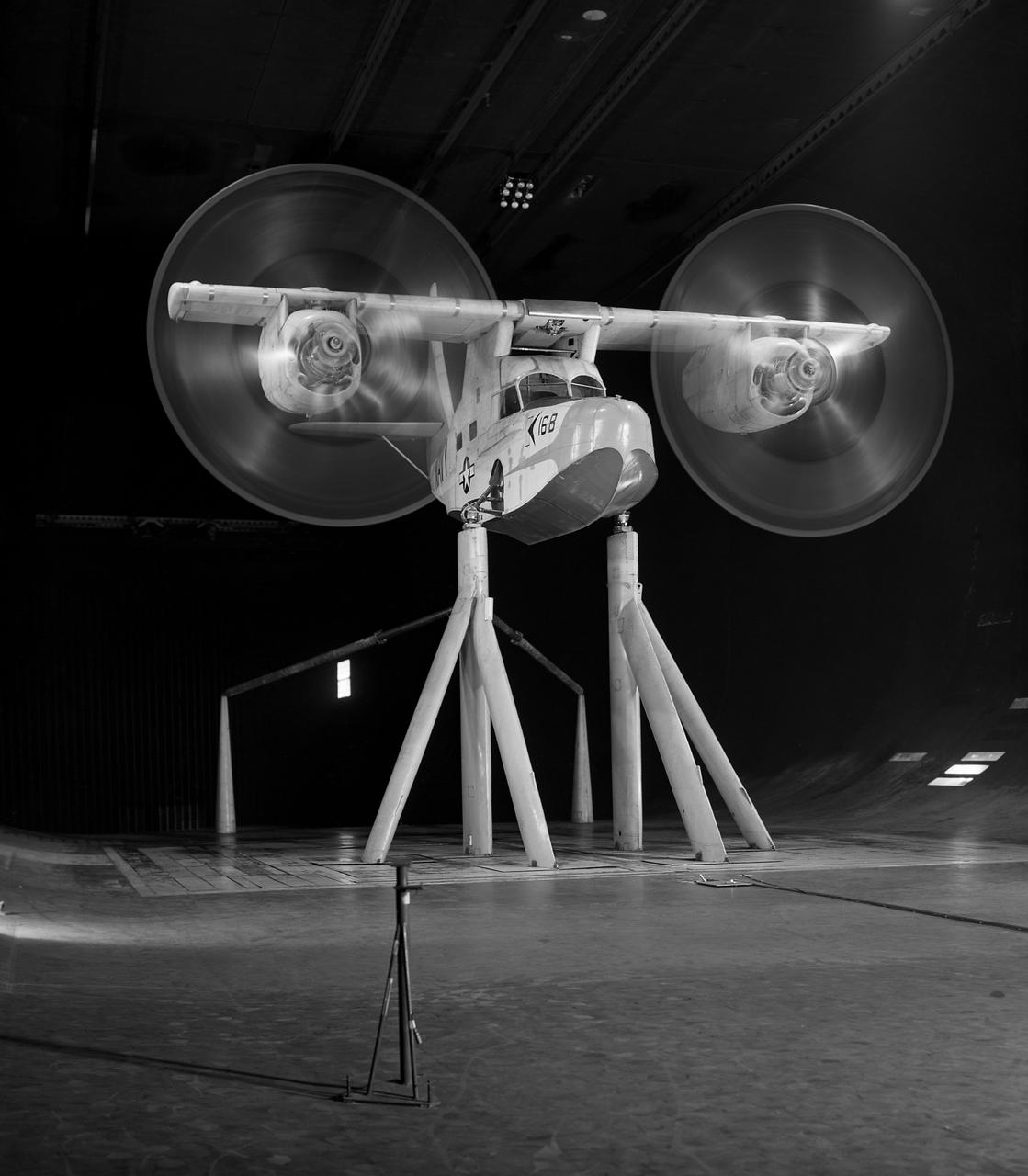

Test No. 175 Kaman K-16 in 40x80 Foot Wind Tunnel at Ames Research Center. Kaman K-16B was an experimental tilt wing aircraft, it used the fuselage of a JRF-5 and was powered by two General Electric YT58-GE-2A engines.
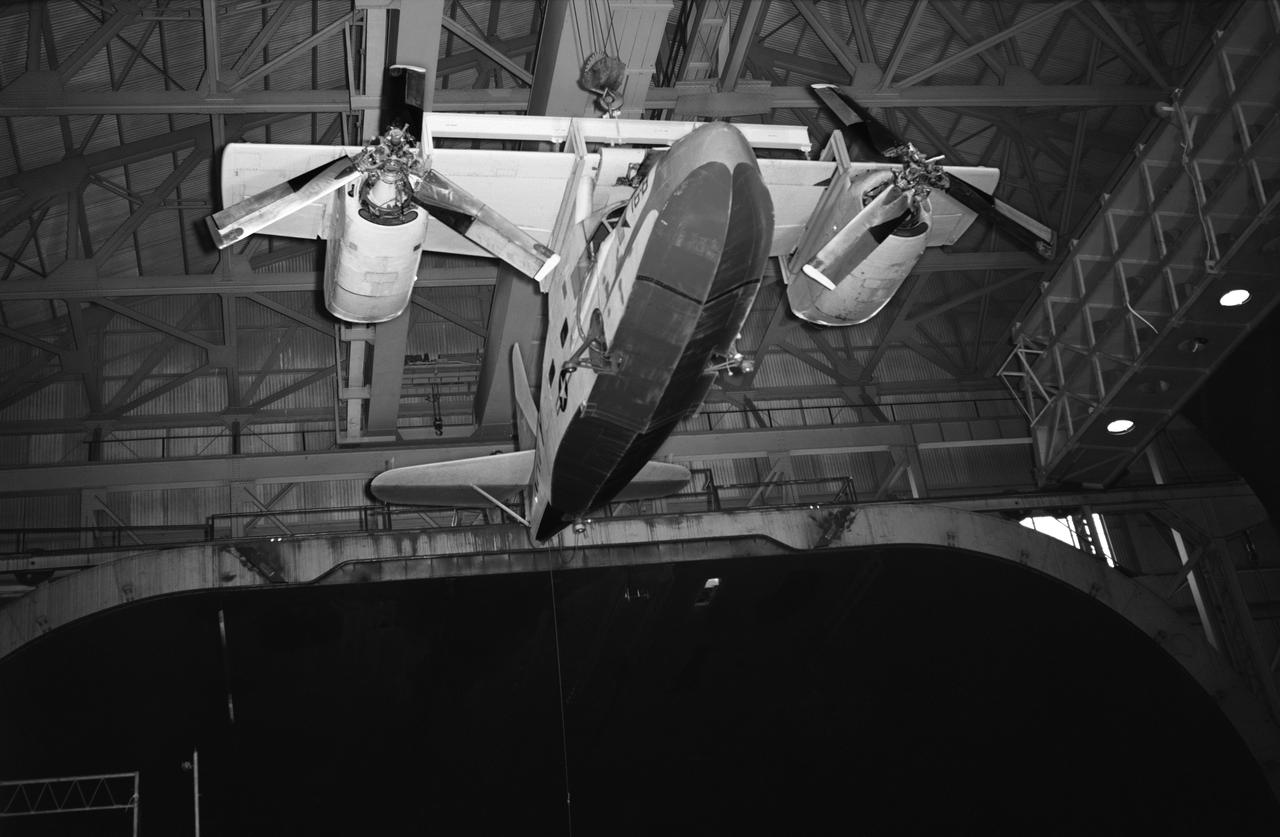

Test No. 175 Kaman K-16 being lowered into the 40x80 foot wind tunnel at NASA's Ames Research Center, viewed from the front. Kaman K-16B was an experimental tilt wing aircraft, it used the fuselage of a JRF-5 and was powered by two General Electric YT58-GE-2A engines.
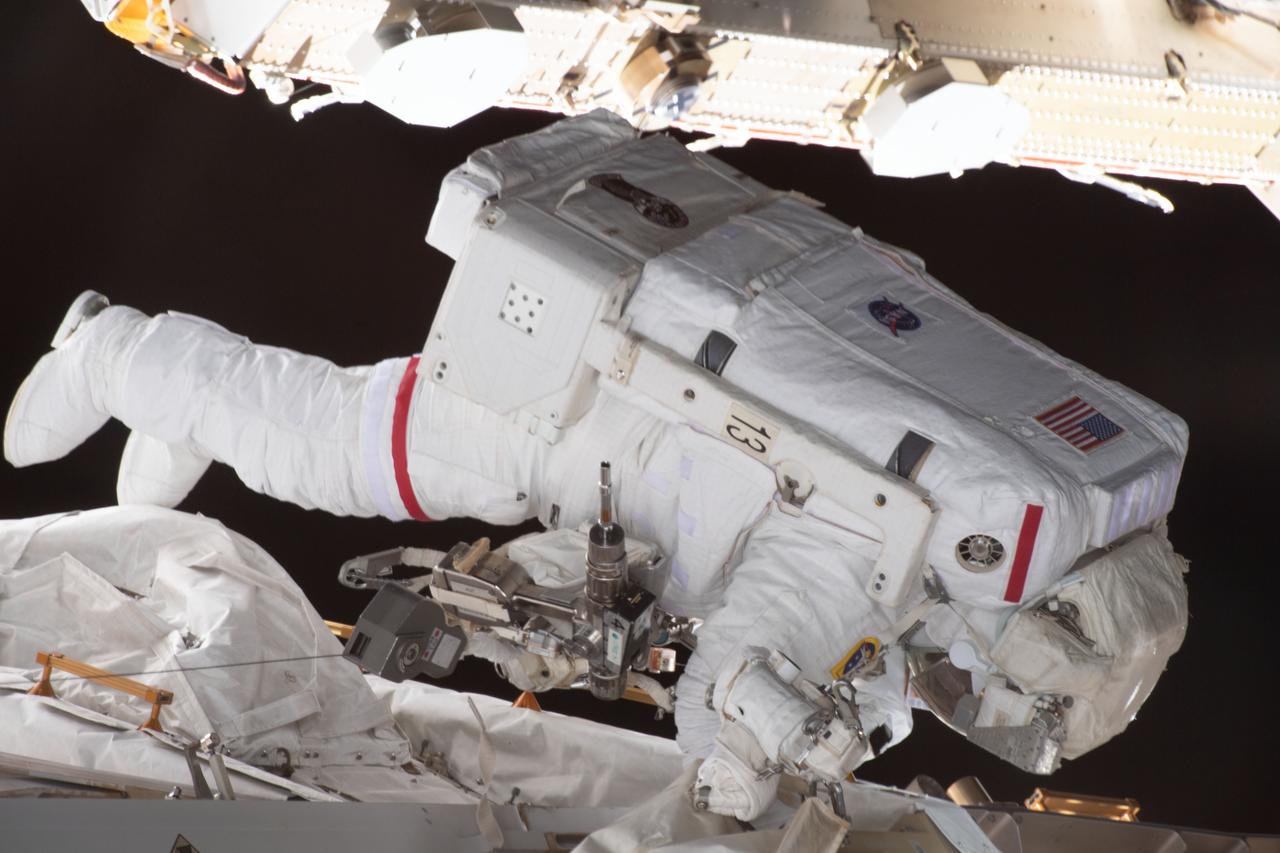

iss070e015424 (Nov. 1, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 70 Flight Engineer Jasmin Moghbeli is pictured tethered to the International Space Station during a spacewalk to replace one of the 12 trundle bearing assemblies on the port solar alpha rotary joint, which allows the arrays to track the Sun and generate electricity to power the station.
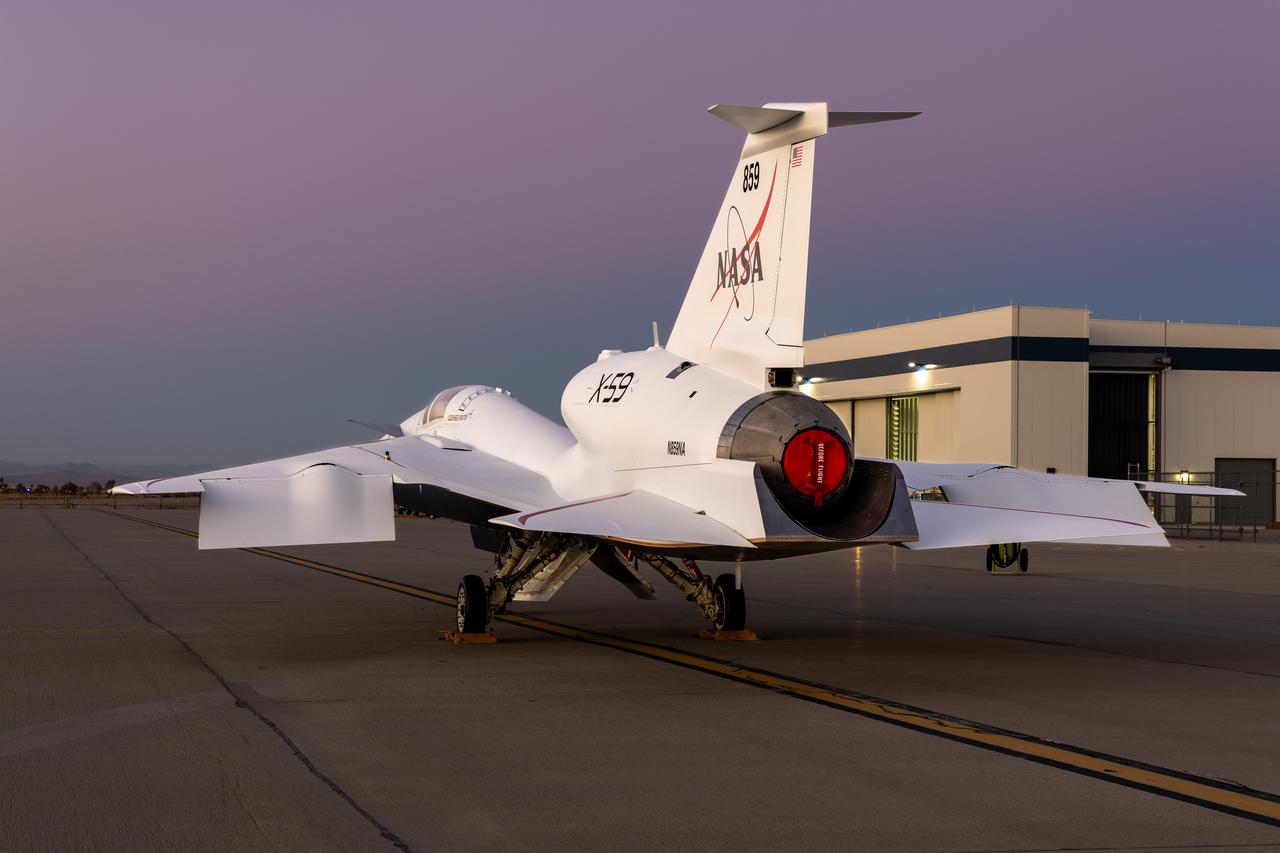

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on a ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, during sunset. The one-of-a-kind aircraft is powered by a General Electric F414 engine, a variant of the engines used on F/A-18 fighter jets. The engine is mounted above the fuselage to reduce the number of shockwaves that reach the ground. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA's Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight and enable future commercial travel over land – faster than the speed of sound.
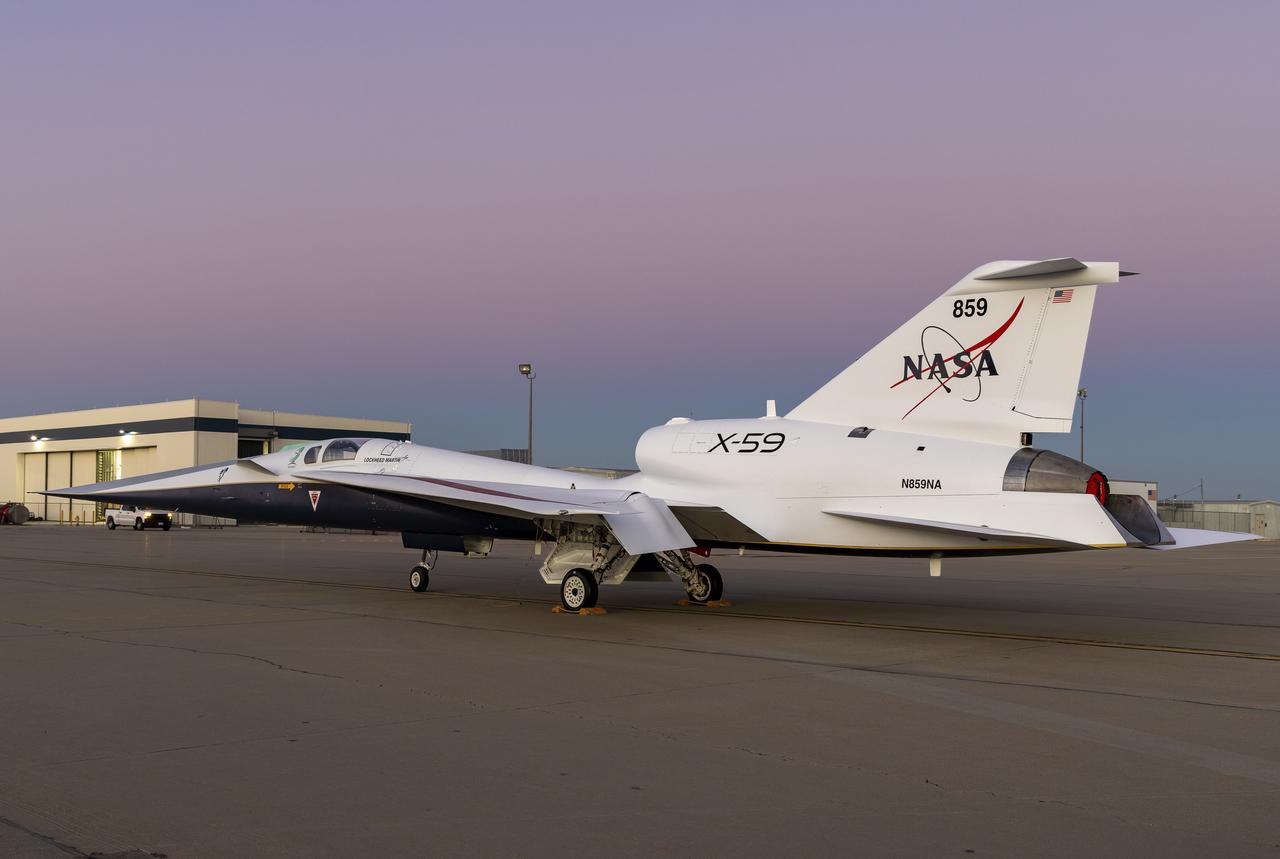

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on a ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, during sunset. The one-of-a-kind aircraft is powered by a General Electric F414 engine, a variant of the engines used on F/A-18 fighter jets. The engine is mounted above the fuselage to reduce the number of shockwaves that reach the ground. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA's Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight and enable future commercial travel over land – faster than the speed of sound.
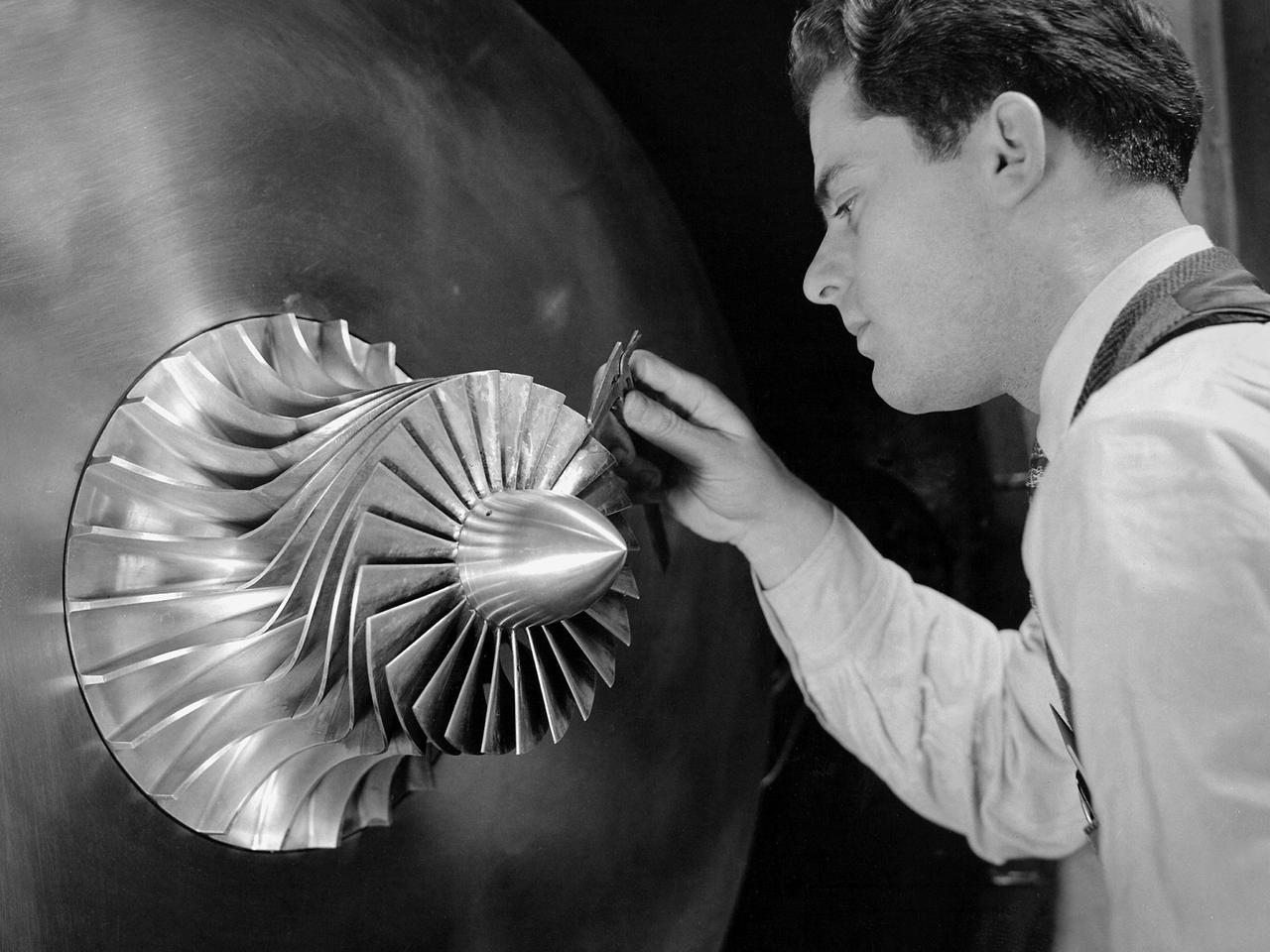

A researcher in the Supercharger Research Division at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory measures the blade thickness on a supercharger. Superchargers were developed at General Electric used to supply additional air to reciprocating engines. The extra air resulted in increased the engine’s performance, particularly at higher altitudes. The Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory had an entire division dedicated to superchargers during World War II. General Electric developed the supercharger in response to a 1917 request from the NACA to develop a device to enhance high-altitude flying. The supercharger pushed larger volumes of air into the engine manifold. The extra oxygen allowed the engine to operate at its optimal sea-level rating even when at high altitudes. Thus, the aircraft could maintain its climb rate, maneuverability and speed as it rose higher into the sky. NACA work on the supercharger ceased after World War II due to the arrival of the turbojet engine. The Supercharger Research Division was disbanded in October 1945 and reconstituted as the Compressor and Turbine Division.

This photo shows the second RS-25 engine attached to the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for the agency’s Artemis I mission to the Moon. Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans structurally mated the second of four engines to the stage on Oct. 30 and are currently integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure to complete the installation. Integration of the RS-25 engines to the recently completed core stage structure is a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. The four RS-25 engines for Artemis I are modified heritage flight hardware from the Space Shuttle Program, ensuring high performance and reliability to power NASA’s next generation lunar missions. Each engine also has a special identification number, and NASA keeps a history of which engines are used on each mission. The second engine, Engine 2045, has flown on several shuttle missions, including the mission that returned NASA astronaut John Glenn to space in 1998 as well as the first and only shuttle launch to occur on Independence Day in 2006.
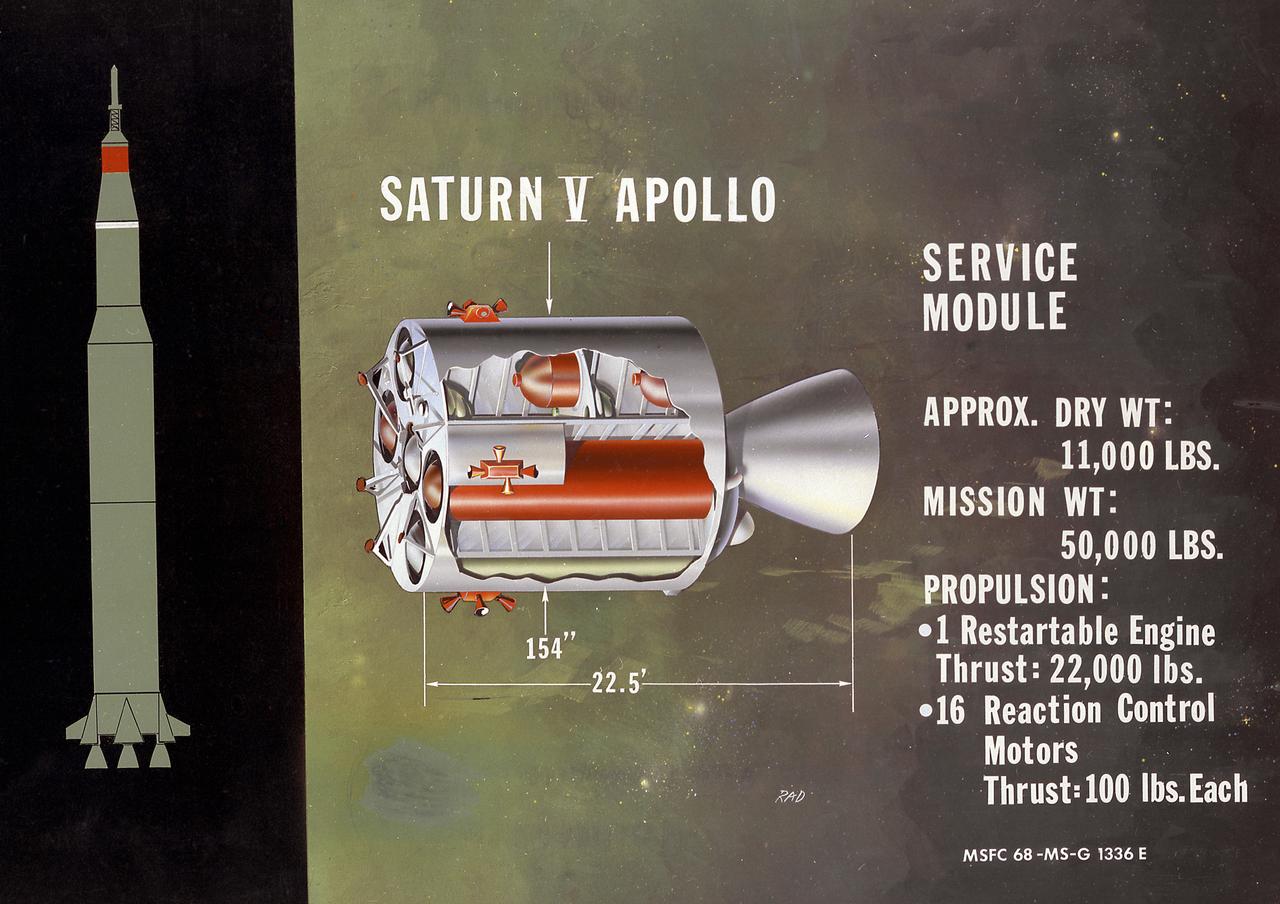
This is a cutaway illustration of the Saturn V service module configuration. Packed with plumbing and tanks, the service module was the command module's constant companion until just before reentry. All components not needed during the last few minutes of flight, and therefore requiring no protection against reentry heat, were transported in this module. It carried oxygen for most of the trip, fuel cells to generate electricity (along with the oxygen and hydrogen to run them); small engines to control pitch, roll, and yaw; and a large engine to propel the spacecraft into, and out of, lunar orbit.
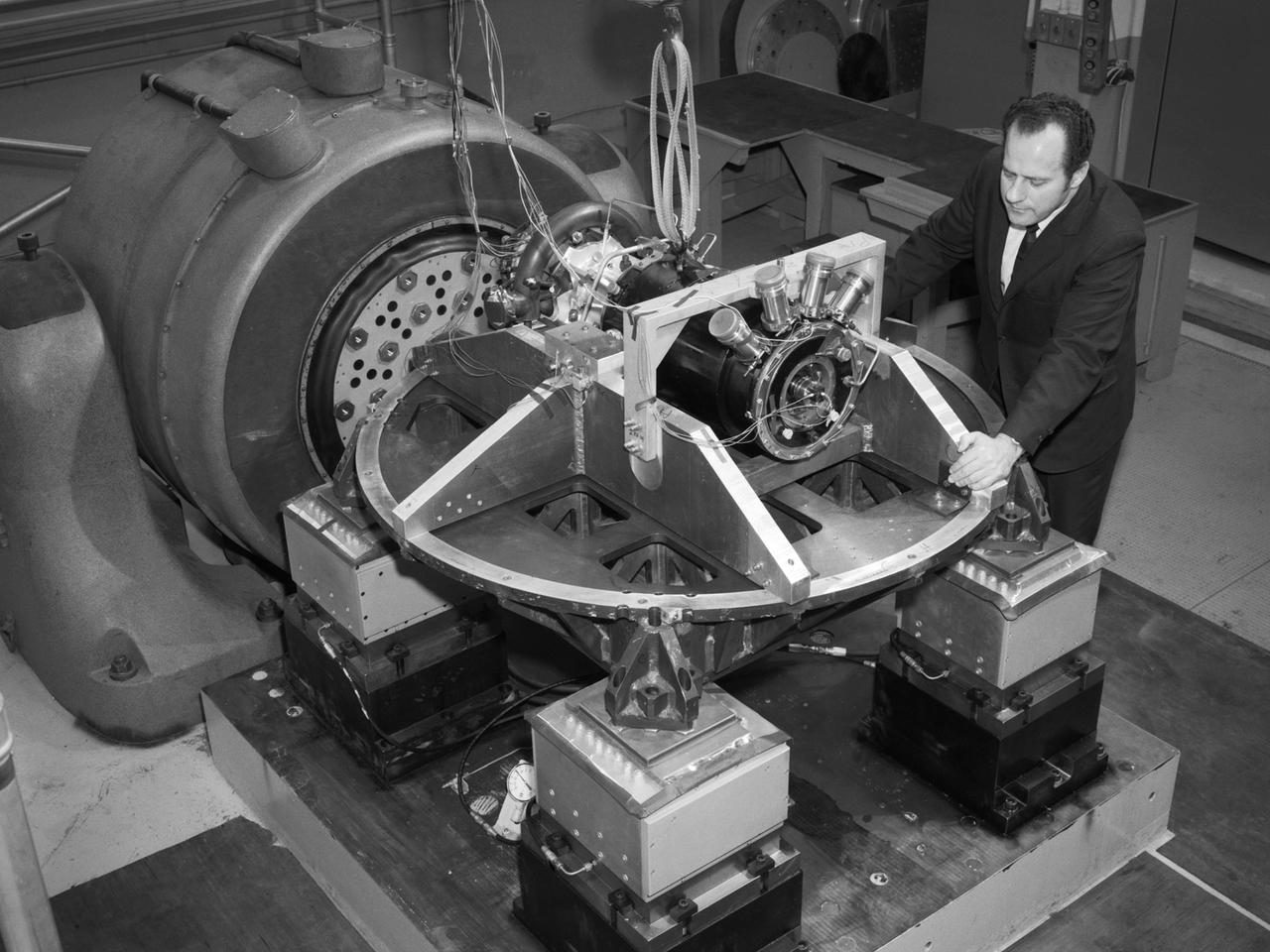

Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Aerojet General was contracted to design the SNAP-8 generator which employed a mercury Rankine system to convert the reactor’s heat into electrical power. The hermetically-sealed pump was designed to generate from 35 to 90 kilowatts of electrical power. In 1964 a SNAP-8 test rig with a mercury boiler and condenser was set up in cell W-1 of Lewis’ Engine Research Building to study the transients in the system’s three loops. In 1967 a complete Rankine system was operated for 60 days in W-1 to verify the integrity of the Lewis-developed mercury boiler. Further tests in 1969 verified the shutdown and startup of the system under normal and emergency conditions. Aerojet operated the first full-Rankine system in June 1966 and completed a 2500-hour endurance test in early 1969. Lewis and Aerojet’s success on the Rankine system was acknowledged with NASA Group Achievement Award in November 1970. The 1970 vibration tests, seen here, were conducted in Lewis’ Engine Research Building’s environmental laboratory. The testing replicated the shock and vibration expected to occur during the launch into space and subsequent maneuvering. The pump was analyzed on each of its major axes.
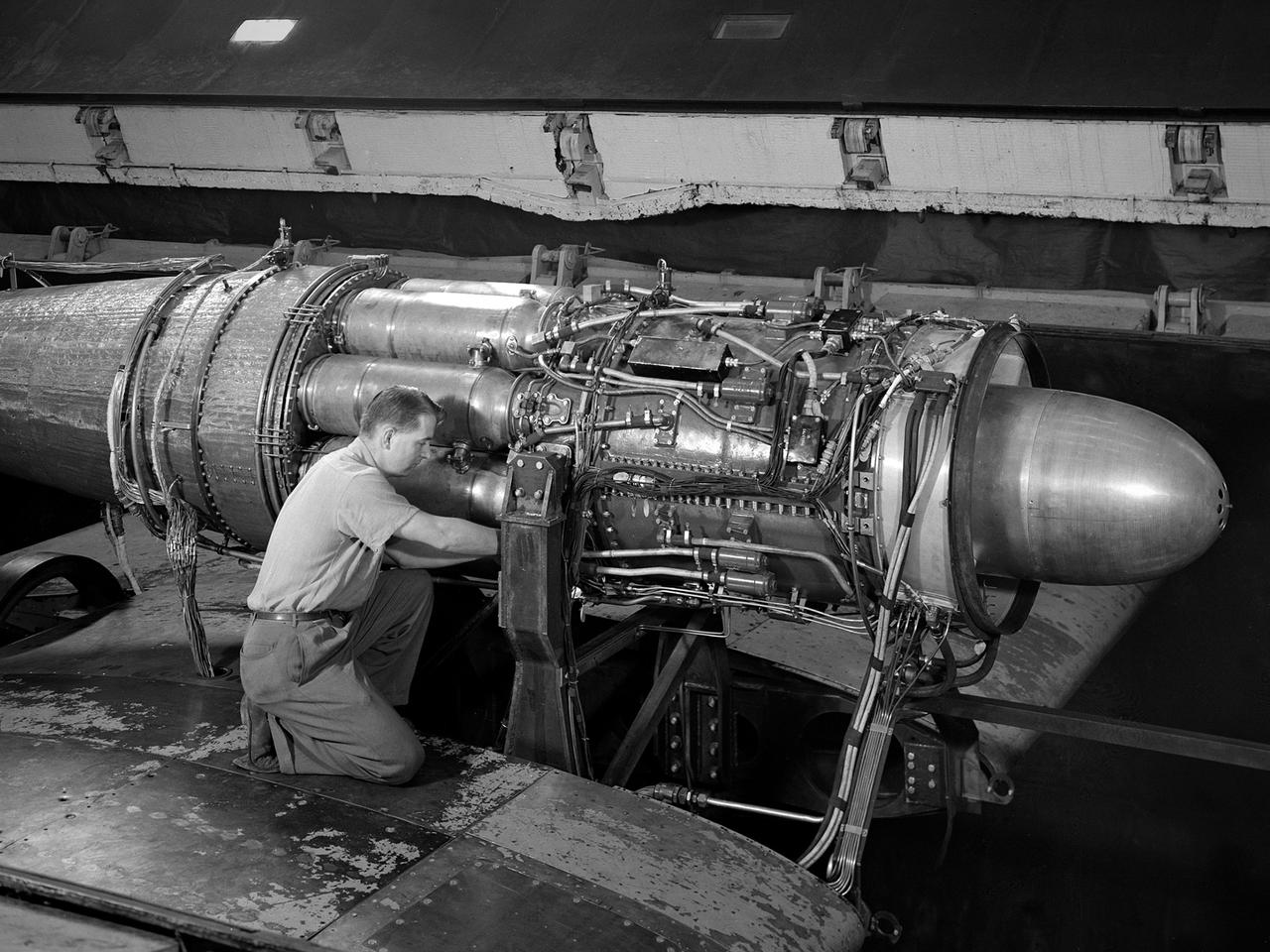

A General Electric TG-180 turbojet installed in the Altitude Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. In 1943 the military asked General Electric to develop an axial-flow jet engine which became the TG-180. The military understood that the TG-180 would not be ready during World War II but recognized the axial-flow compressor’s long-term potential. Although the engine was bench tested in April 1944, it was not flight tested until February 1946. The TG-180 was brought to the Altitude Wind Tunnel in 1945 for a series of investigations. The studies, which continued intermittently into 1948, analyzed an array of performance issues. NACA modifications steadily improved the TG-180’s performance, including the first successful use of an afterburner. The Lewis researchers studied a 29-inch diameter afterburner over a range of altitude conditions using several different types of flameholders and fuel systems. Lewis researchers concluded that a three-stage flameholder with its largest stage upstream was the best burner configuration. Although the TG-180 (also known as the J35) was not the breakthrough engine that the military had hoped for, it did power the Douglas D-558-I Skystreak to a world speed record on August 20, 1947. The engines were also used on the Republic F-84 Thunderjet and the Northrup F-89 Scorpion.

New staff member Paul Margosian inspects a cluster of ion engines in the Electric Propulsion Laboratory’s 25-foot diameter vacuum tank at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Lewis researchers had been studying different methods of electric rocket propulsion since the mid-1950s. Harold Kaufman created the first successful engine, the electron bombardment ion engine, in the early 1960s. These engines used electric power to create and accelerate small particles of propellant material to high exhaust velocities. Electric engines have a very small thrust, and but can operate for long periods of time. The ion engines are often clustered together to provide higher levels of thrust. The Electric Propulsion Laboratory contained two large vacuum tanks capable of simulating the space environment. The tanks were designed especially for testing ion and plasma thrusters and spacecraft. The larger 25-foot diameter tank was intended for testing electric thrusters with condensable propellants. The tank’s test compartment, seen here, was 10 feet in diameter. Margosian joined Lewis in late 1962 during a major NASA hiring phase. The Agency reorganized in 1961 and began expanding its ranks through a massive recruiting effort. Lewis personnel increased from approximately 2,700 in 1961 to over 4,800 in 1966. Margosian, who worked with Bill Kerslake in the Electromagnetic Propulsion Division’s Propulsion Systems Section, wrote eight technical reports on mercury and electron bombardment thrusters, thermoelectrostatic generators, and a high voltage insulator.
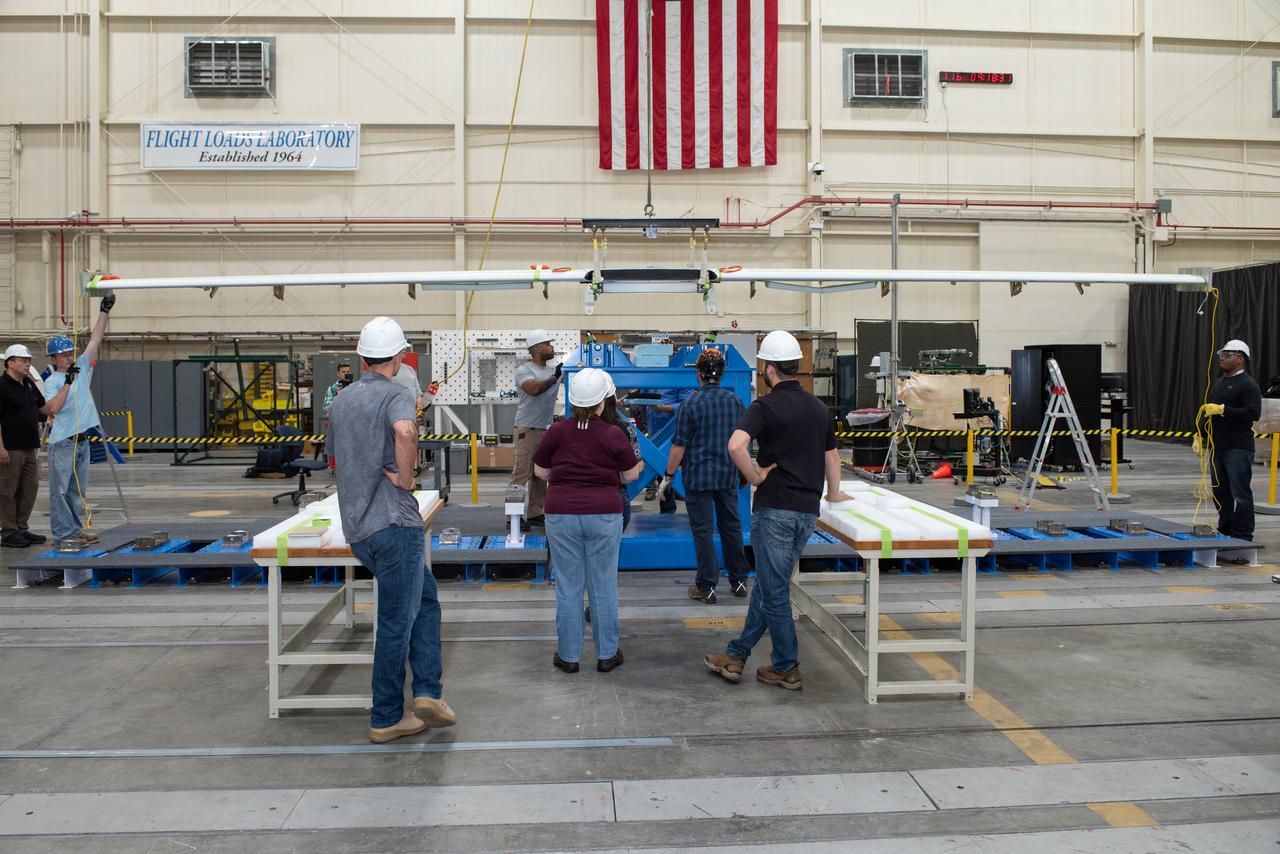

Engineers and specialists prepare X-57s Mod III wing for testing in the Flight Loads Laboratory at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Here, the wing began preparation for several tests, including weight and balance measurement, ground vibration testing, and wing loading tests.
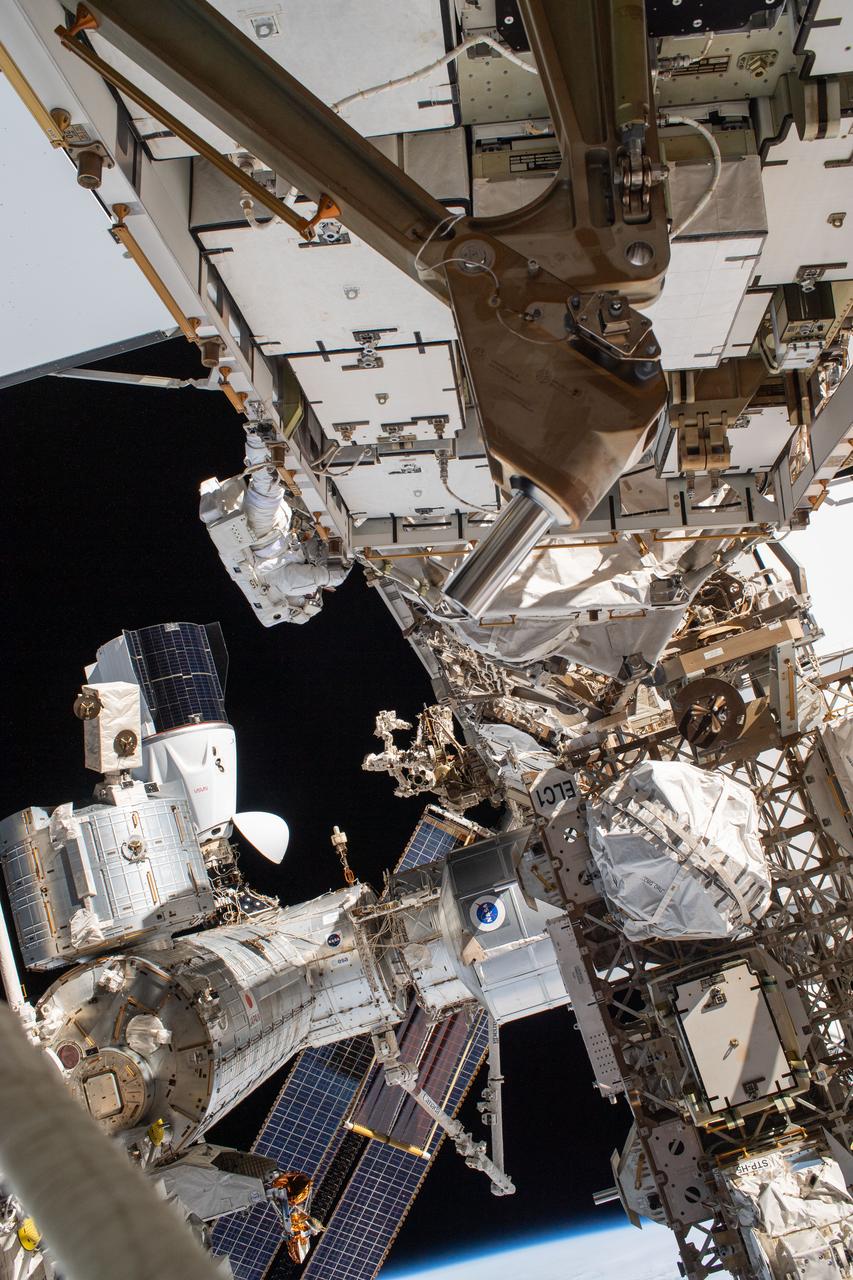

iss070e015526 (Nov. 1, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 70 Flight Engineer Loral O'Hara is pictured (center left) tethered to the International Space Station's port truss structure during a spacewalk to replace one of the 12 trundle bearing assemblies on the port solar alpha rotary joint, which allows the arrays to track the Sun and generate electricity to power the station. Behind O'Hara is the SpaceX Dragon Endurance spacecraft that delivered four SpaceX Crew-7 crew members to the orbital lab on Aug. 23, 2023.
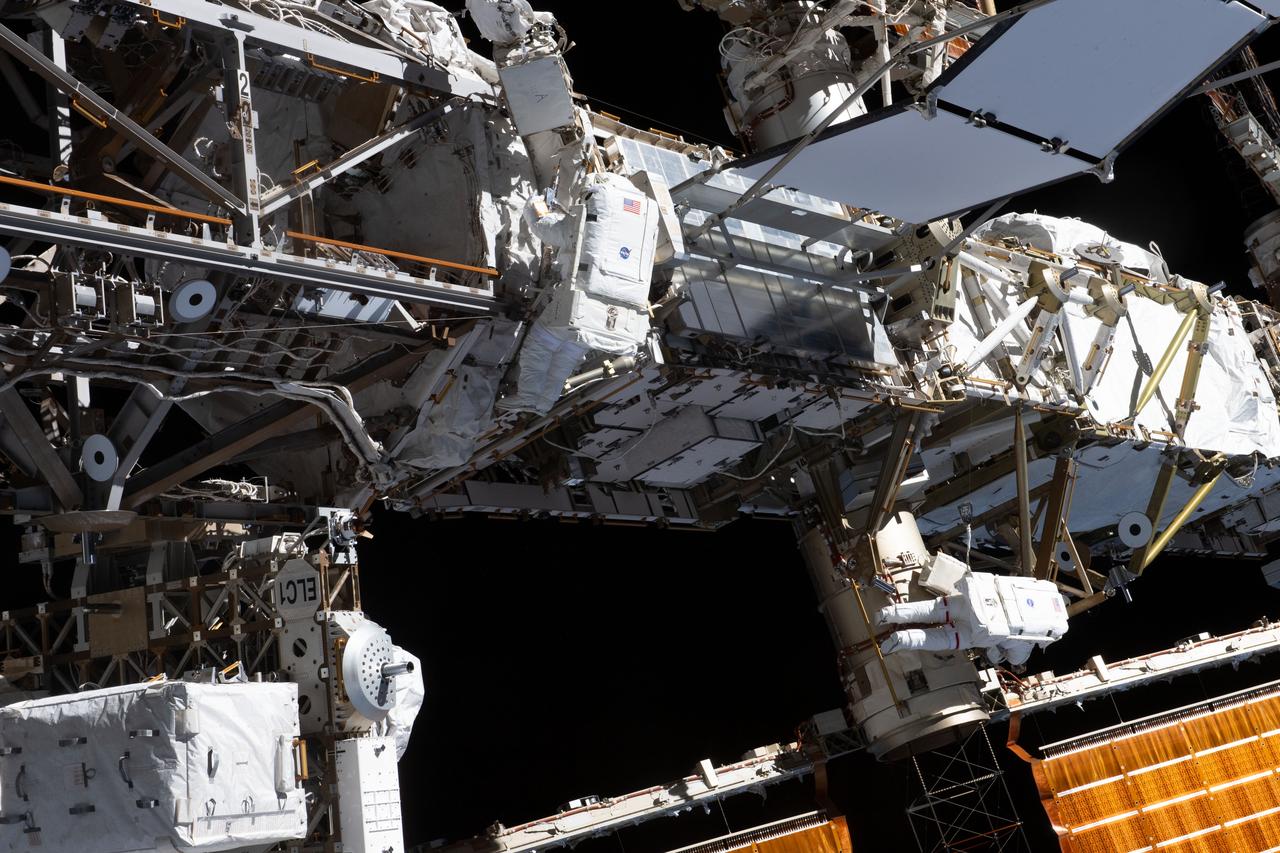

iss070e015405 (Nov. 1, 2023) --- Expedition 70 Flight Engineers Loral O'Hara (center) and Jasmin Moghbeli (lower right), both from NASA, are pictured tethered to the International Space Station's port truss structure during a spacewalk to replace one of the 12 trundle bearing assemblies on the port solar alpha rotary joint, which allows the arrays to track the Sun and generate electricity to power the station.
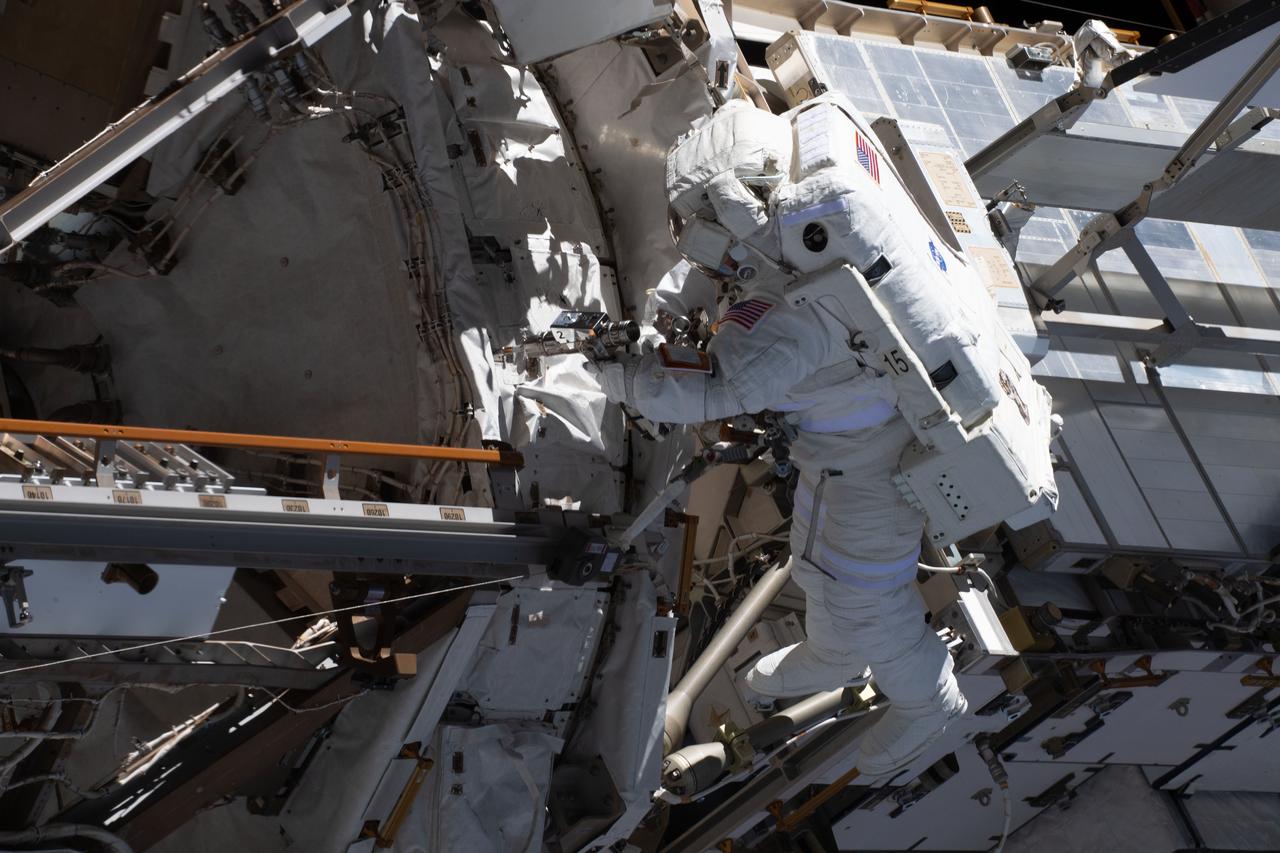

iss070e015407 (Nov. 1, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 70 Flight Engineer Loral O'Hara is pictured (center) tethered to the International Space Station's port truss structure during a spacewalk to replace one of the 12 trundle bearing assemblies on the port solar alpha rotary joint, which allows the arrays to track the Sun and generate electricity to power the station.
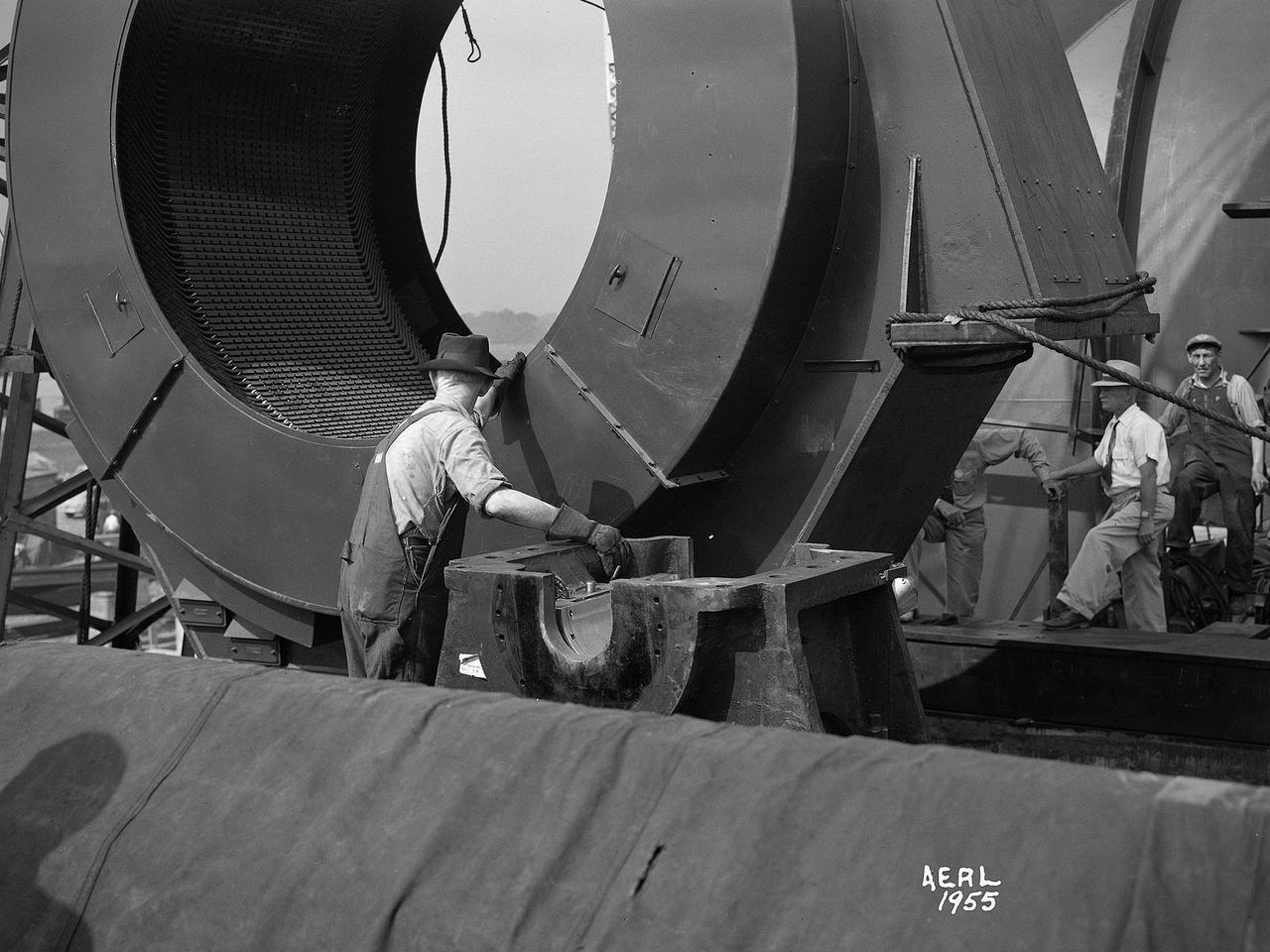

Construction workers install the drive motor for the Altitude Wind Tunnel (AWT) in the Exhauster Building at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory. The AWT was capable of operating full-scale engines in air density, speed, and temperature similar to that found at high altitudes. The tunnel could produce wind speeds up to 500 miles per hour through a 20-foot-diameter test section at the standard operating altitude of 30,000 feet. The airflow was created by a large wooden fan near the tunnel’s southeast corner. This photograph shows the installation of the 18,000-horsepower drive motor inside the adjoining Exhauster Building in July 1943. The General Electric motor, whose support frame is seen in this photograph, connected to a drive shaft that extended from the building, through the tunnel shell, and into a 12-bladed, 31-foot-diameter spruce wood fan. Flexible couplings on the shaft allowed for the movement of the shell. The corner of the Exhauster Building was built around the motor after its installation. The General Electric induction motor could produce 10 to 410 revolutions per minute and create wind speeds up to 500 miles per hour, or Mach 0.63, at 30,000 feet. The AWT became operational in January 1944 and tested piston, turbojet and ramjet engines for nearly 20 years.
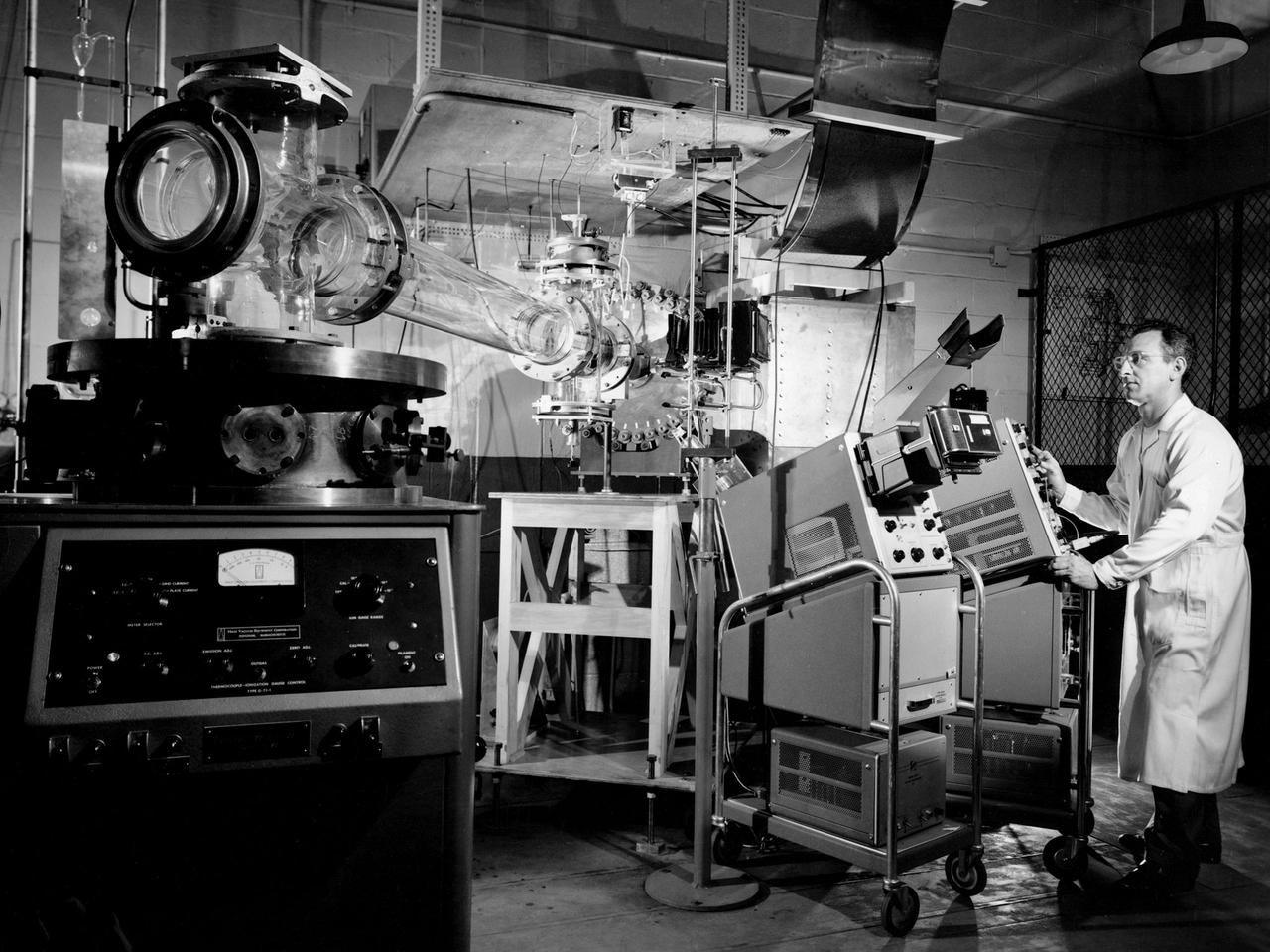

Researcher Charles Michels operates a coaxial plasma gun rig in Cell SW-13 of the Engine Research Building at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. From 1962 to 1967 NASA Lewis investigated coaxial plasma guns powered by conventional capacitor banks. The studies were part of a larger effort to identify electromagnetic accelerators for space propulsion. NASA worked with General Dynamics, General Electric, General Motors, and Republic Aviation on the project. NASA Lewis conducted a research program to determine which factors influenced the coaxial gun’s efficiency and analyze the acceleration process. The system had not previously been used for propulsion applications. The single-shot gun’s fast gas valve and capacitor banks with variable-delay ignition source permitted the evaluation of gun performance under controllable propellant quantity and distribution conditions. The coaxial plasma gun was the most basic type of electromagnetic accelerator. It included a charged capacitor in series with a pair of coaxial electrodes. An electrical breakdown occurred when gas was admitted to the inter-electrode region. The gas instantly became a good conductor and formed a conducting sheet that separated the magnetic field from the open region beyond. The highly-conducting gas was basically expelled by the force of the magnetic pressure. This type of thruster could operate at the high instantaneous power levels without decreasing its average power level.
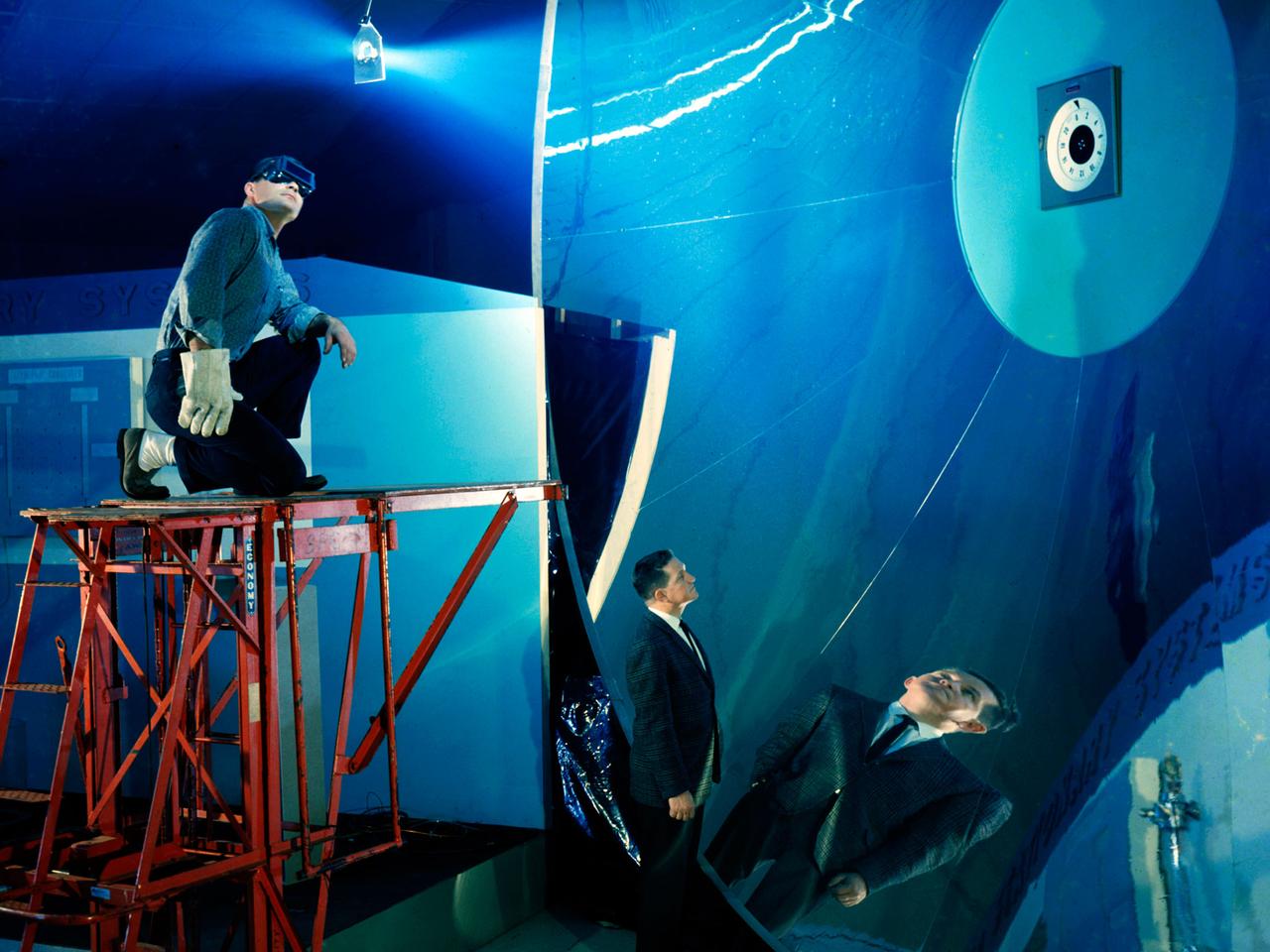

NASA’s Lewis Research Center conducted extensive research programs in the 1960s and 1970s to develop systems that provide electrical power in space. One system, the Brayton cycle engine, converted solar thermal energy into electrical power. This system operated on a closed-loop Brayton thermodynamic cycle. The Brayton system relied on this large mirror to collect radiation from the sun. The mirror concentrated the Sun's rays on a heat storage receiver which warmed the Brayton system’s working fluid, a helium-xenon gas mixture. The heated fluid powered the system’s generator which produced power. In the mid-1960s Lewis researchers constructed this 30-foot diameter prototype of a parabolic solar mirror for the Brayton cycle system. The mirror had to be rigid, impervious to micrometeorite strikes, and lightweight. This mirror was comprised of twelve 1-inch thick magnesium plate sections that were coated with aluminum. The mirror could be compactly broken into its sections for launch.
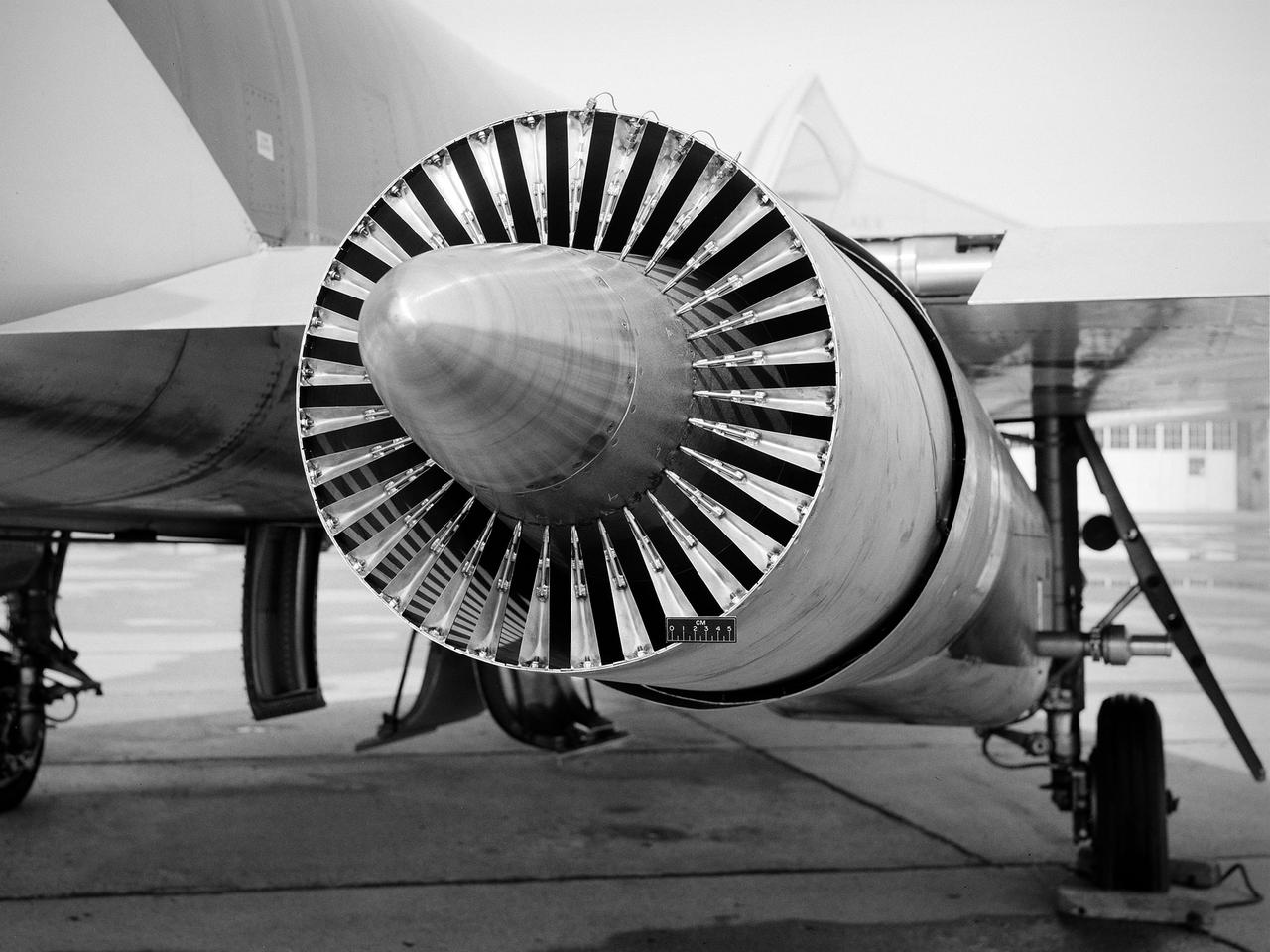

National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Convair F-106B Delta Dart with a 32-spoke nozzle installed on its General Electric J85 test engine. Lewis acquired a Delta Dart fighter in 1966 to study the components for propulsion systems that could be applied to supersonic transport aircraft at transonic speeds. The F-106B was modified with two General Electric J85-13 engines under its wings to study these components. The original test plan was expanded to include the study of boattail drag, noise reduction, and inlets. From February to July 1971 the modified F-106B was used to study different ejector nozzles. Researchers conducted both acoustic and aerodynamic tests on the ground and in flight. Several models were created to test different suppression methods. NASA Lewis’ conical nozzle was used as the baseline configuration. Flightline and sideline microphones were set up on the ground. The F-106B would idle its own engine and buzz the recording station from an altitude of 300 feet at Mach 0.4 with the test engines firing. Researchers found that the suppression of the perceived noise level was usually lower during flight than the researchers had statistically predicted. The 64 and 32-spoke nozzles performed well in actual flight, but the others nozzles tended to negatively affect the engine’s performance. Different speeds or angles- -of-attack sometimes changed the noise levels. In the end, no general conclusions could be applied to all the nozzles.
One of the two altitude simulating-test chambers in Engine Research Building at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The two chambers were collectively referred to as the Four Burner Area. NACA Lewis’ Altitude Wind Tunnel was the nation’s first major facility used for testing full-scale engines in conditions that realistically simulated actual flight. The wind tunnel was such a success in the mid-1940s that there was a backlog of engines waiting to be tested. The Four Burner chambers were quickly built in 1946 and 1947 to ease the Altitude Wind Tunnel’s congested schedule. The Four Burner Area was located in the southwest wing of the massive Engine Research Building, across the road from the Altitude Wind Tunnel. The two chambers were 10 feet in diameter and 60 feet long. The refrigeration equipment produced the temperatures and the exhauster equipment created the low pressures present at altitudes up to 60,000 feet. In 1947 the Rolls Royce Nene was the first engine tested in the new facility. The mechanic in this photograph is installing a General Electric J-35 engine. Over the next ten years, a variety of studies were conducted using the General Electric J-47 and Wright Aeronautical J-65 turbojets. The two test cells were occasionally used for rocket engines between 1957 and 1959, but other facilities were better suited to the rocket engine testing. The Four Burner Area was shutdown in 1959. After years of inactivity, the facility was removed from the Engine Research Building in late 1973 in order to create the High Temperature and Pressure Combustor Test Facility.
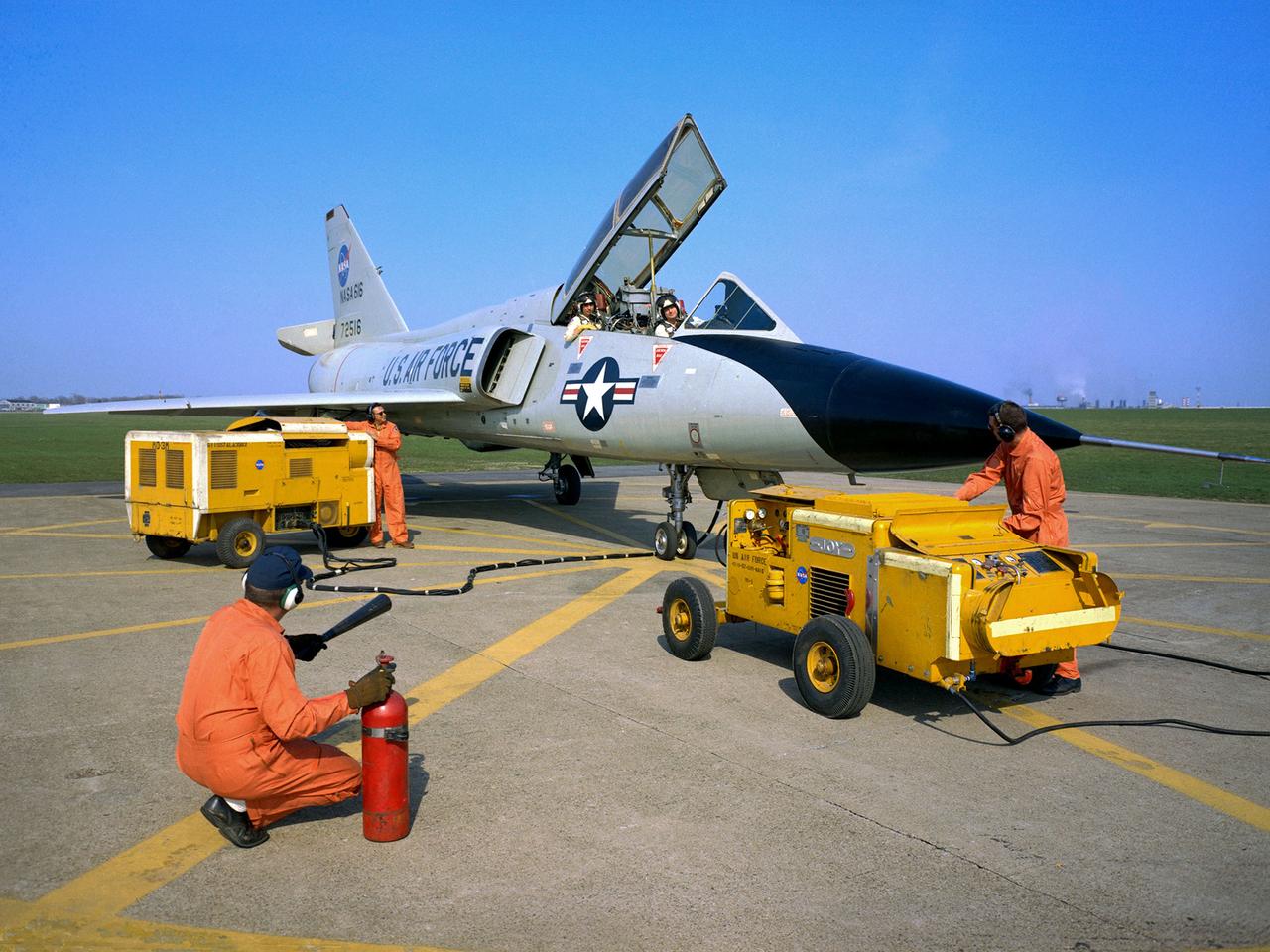

National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) pilot Cliff Crabbs and the flight operations crew prepare a Convair F-106B Delta Dart for a flight from the Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. NASA acquired the aircraft three years earlier to investigate noise-reducing inlet and nozzle designs for the supersonic transport engine program. Two General Electric J85 engines were installed underneath the aircraft’s delta wings to simulate the general shape of the supersonic transport’s engines. One of the engines was modified with experimental inlet or nozzle configurations. The unmodified engine was used for comparison. Most F-106B flights were flown in a 200-mile path over the lake between Buffalo and Sandusky, known as the Lake Erie Corridor. The 1100-miles per hour flight took only 11 minutes at an altitude of 30,000 feet. The aircraft almost always returned with a depleted fuel supply so a Visual Flight Rules operation was required. Following the crash of another jet fighter at Lewis in July 1969, the F-106s were stationed at Selfridge Air Force Base in Michigan. NASA pilots flew transport planes each morning to the base before commencing the F-106B missions.
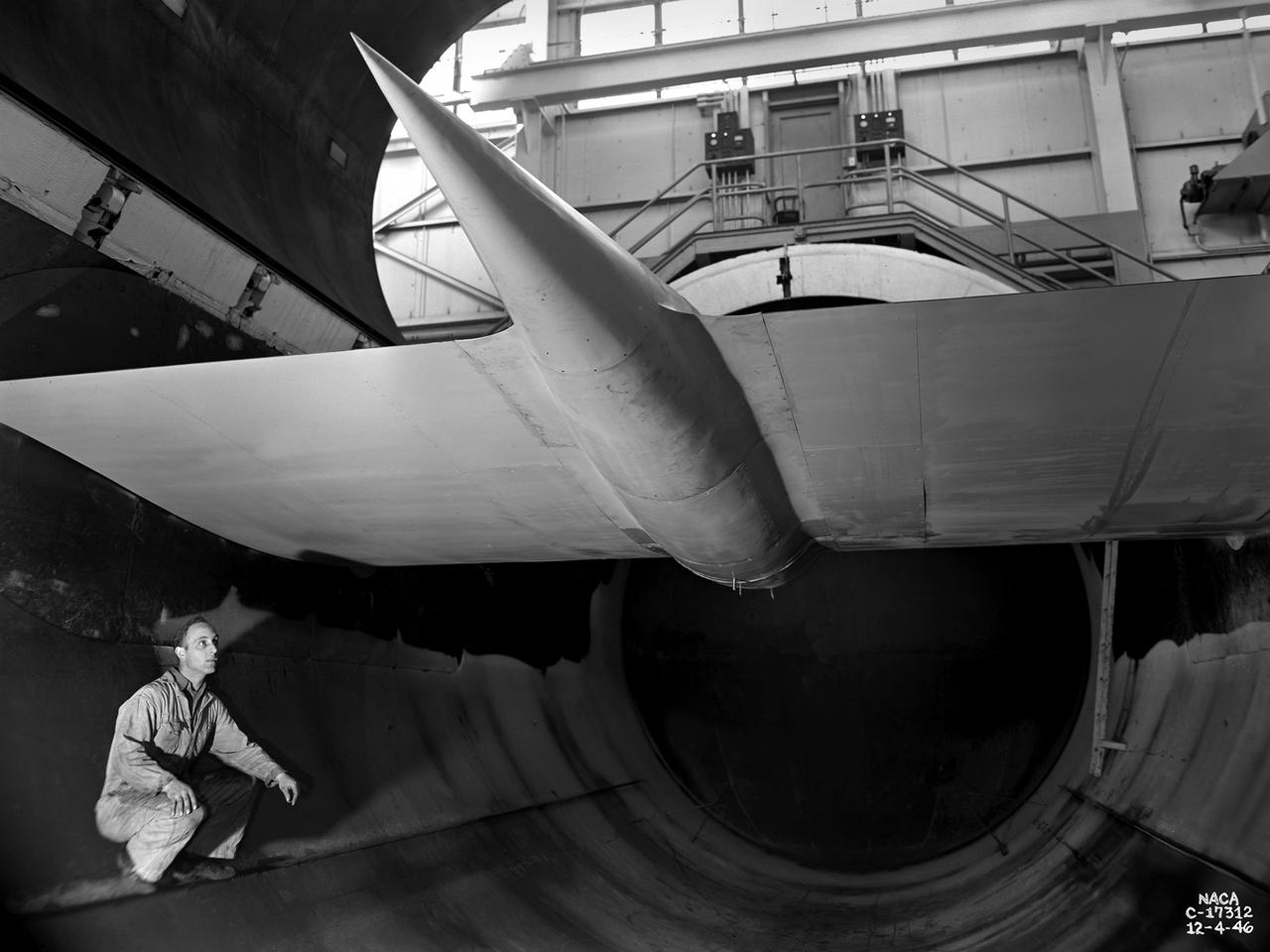

A General Electric TG-100A seen from the rear in the test section of the Altitude Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio. The Altitude Wind Tunnel was used to study almost every model of US turbojet that emerged in the 1940s, as well as some ramjets and turboprops. In the early 1940s the military was interested in an engine that would use less fuel than the early jets but would keep up with them performance-wise. Turboprops seemed like a plausible solution. They could move a large volume of air and thus required less engine speed and less fuel. Researchers at General Electric’s plant in Schenectady, New York worked on the turboprop for several years in the 1930s. They received an army contract in 1941 to design a turboprop engine using an axial-flow compressor. The result was the 14-stage TG-100, the nation's first turboprop aircraft engine. Development of the engine was slow, however, and the military asked NACA Lewis to analyze the engine’s performance. The TG-100A was tested in the Altitude Wind Tunnel and it was determined that the compressors, combustion chamber, and turbine were impervious to changes in altitude. The researchers also established the optimal engine speed and propeller angle at simulated altitudes up to 35,000 feet. Despite these findings, development of the TG-100 was cancelled in May 1947. Twenty-eight of the engines were produced, but they were never incorporated into production aircraft.
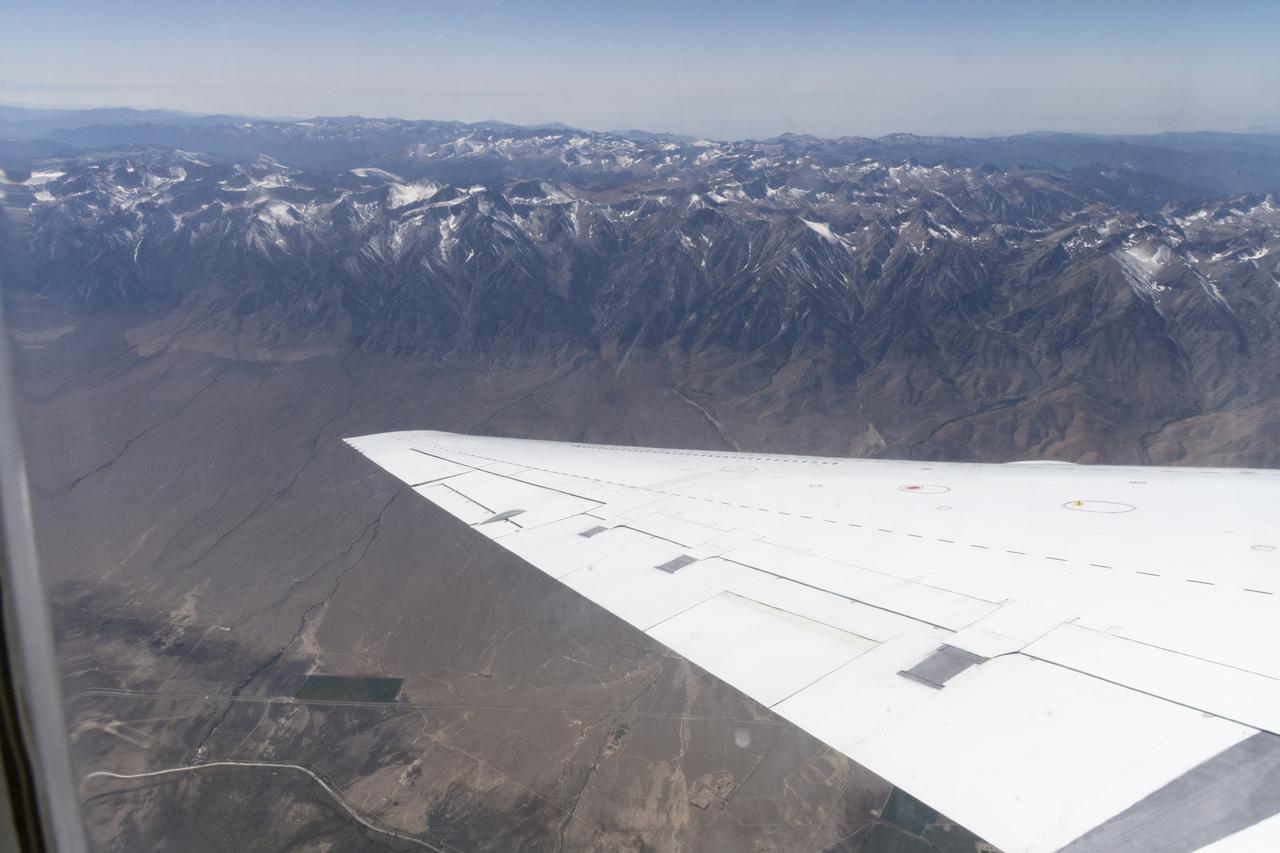

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
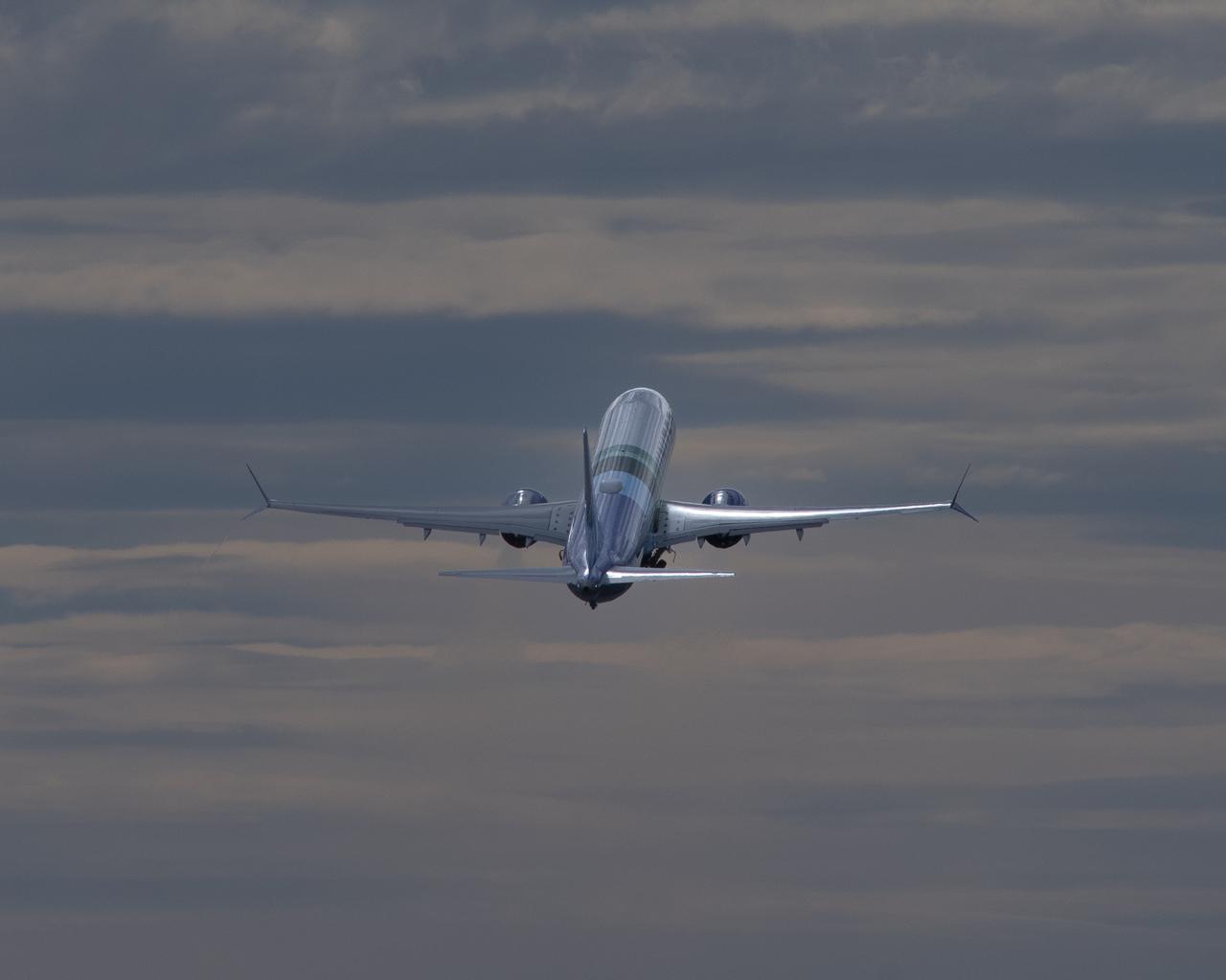

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
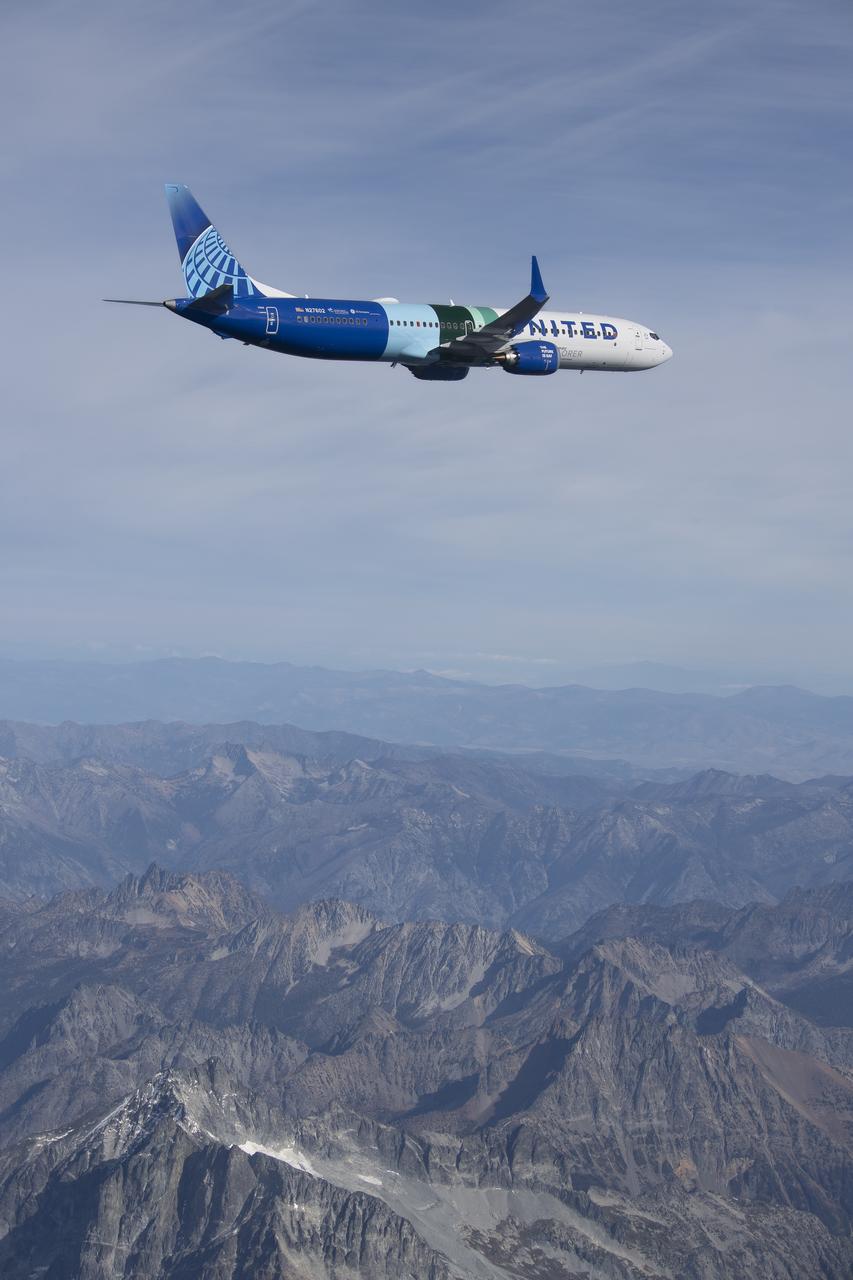

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
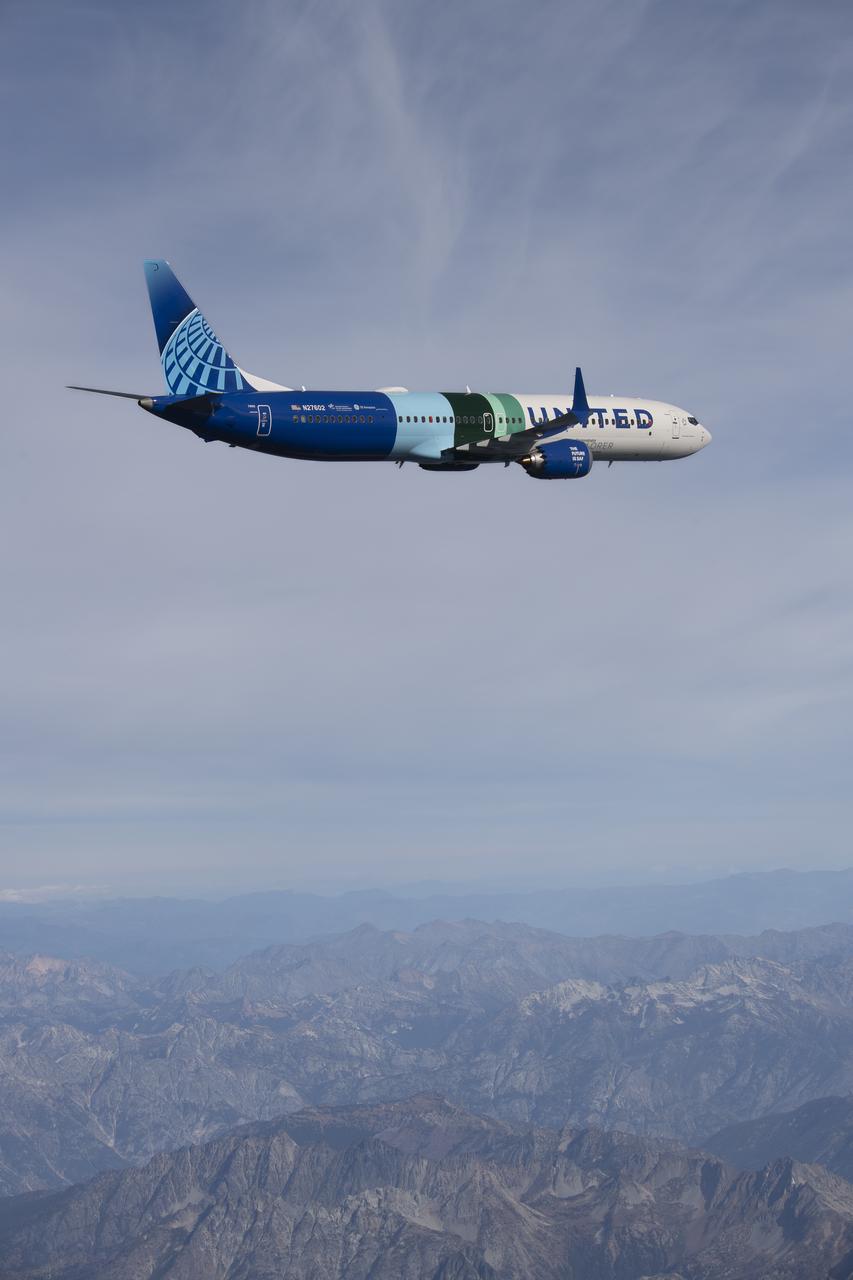

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
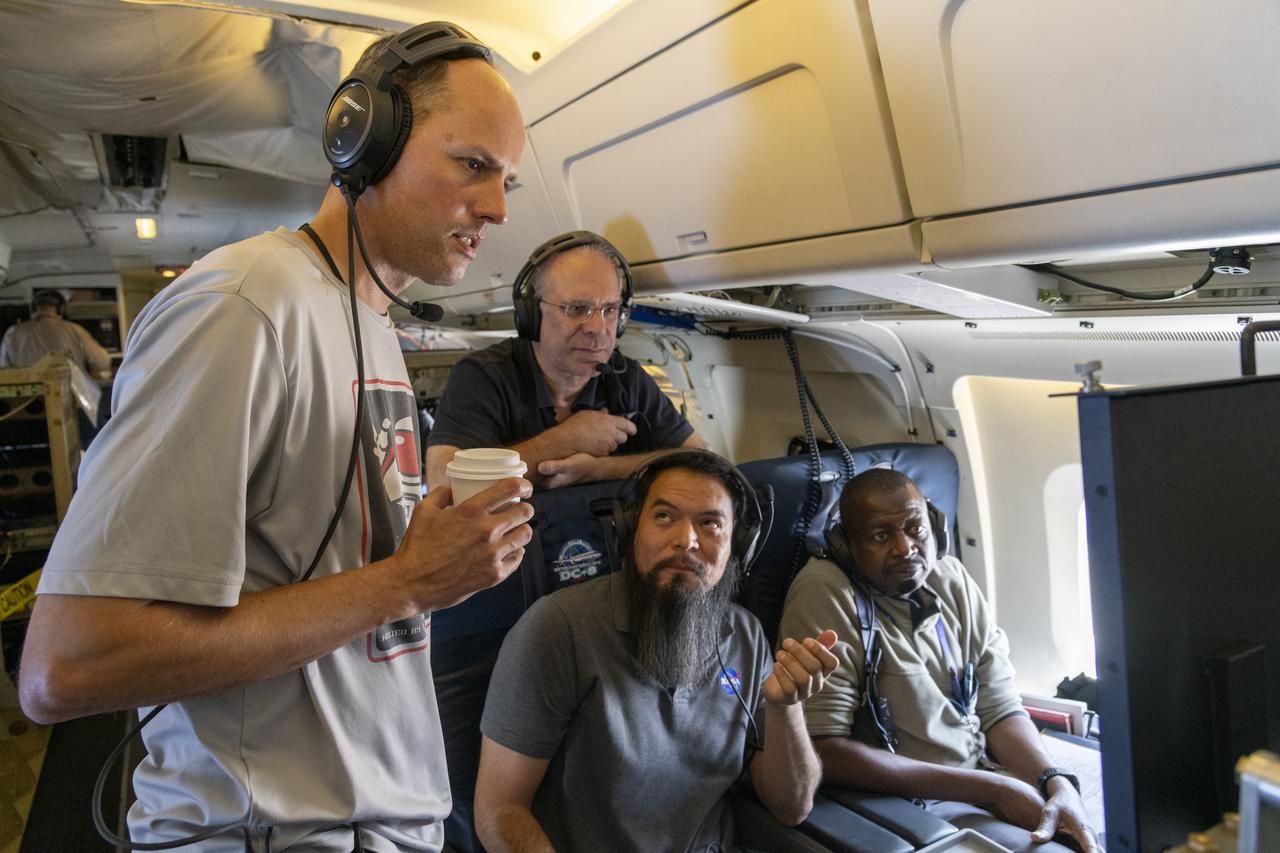

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
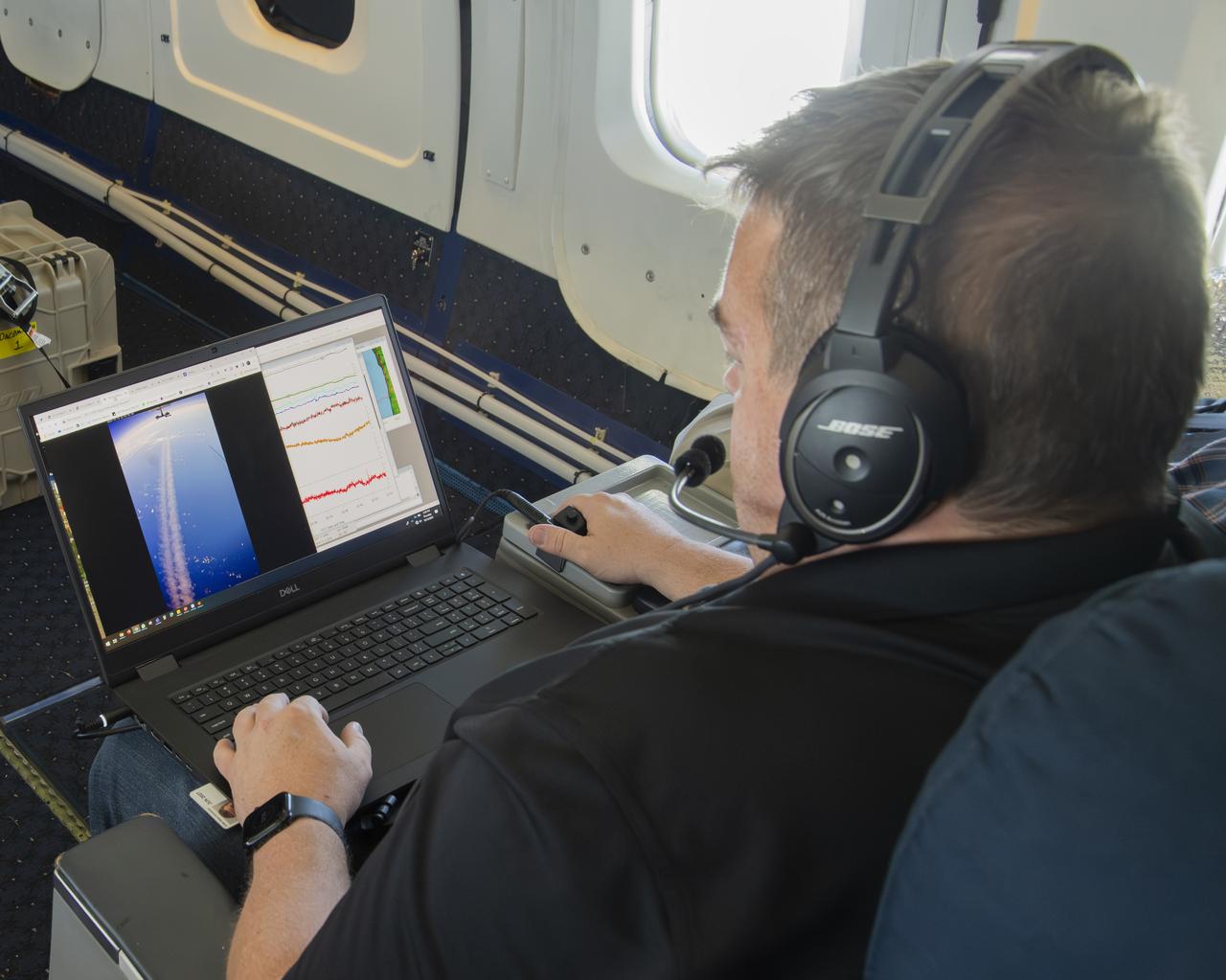

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
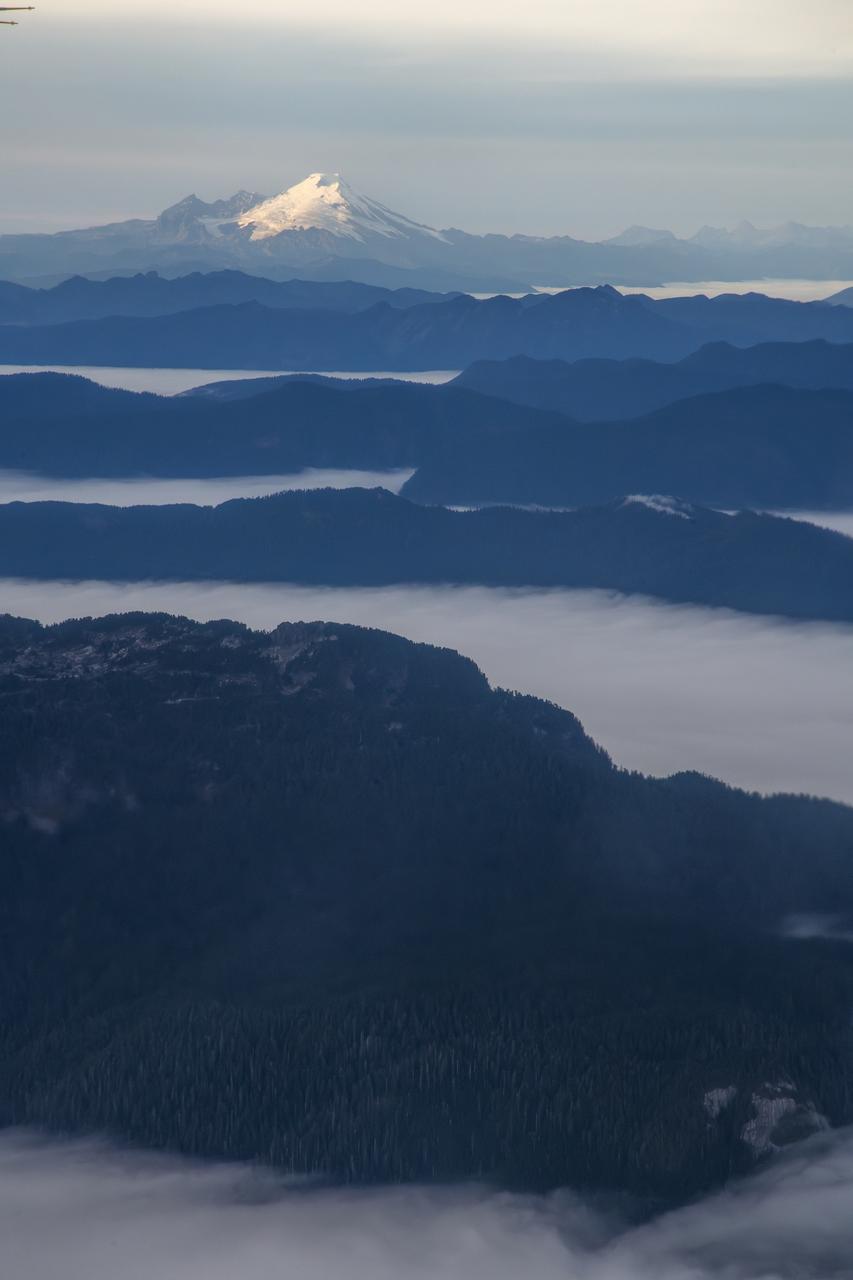

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
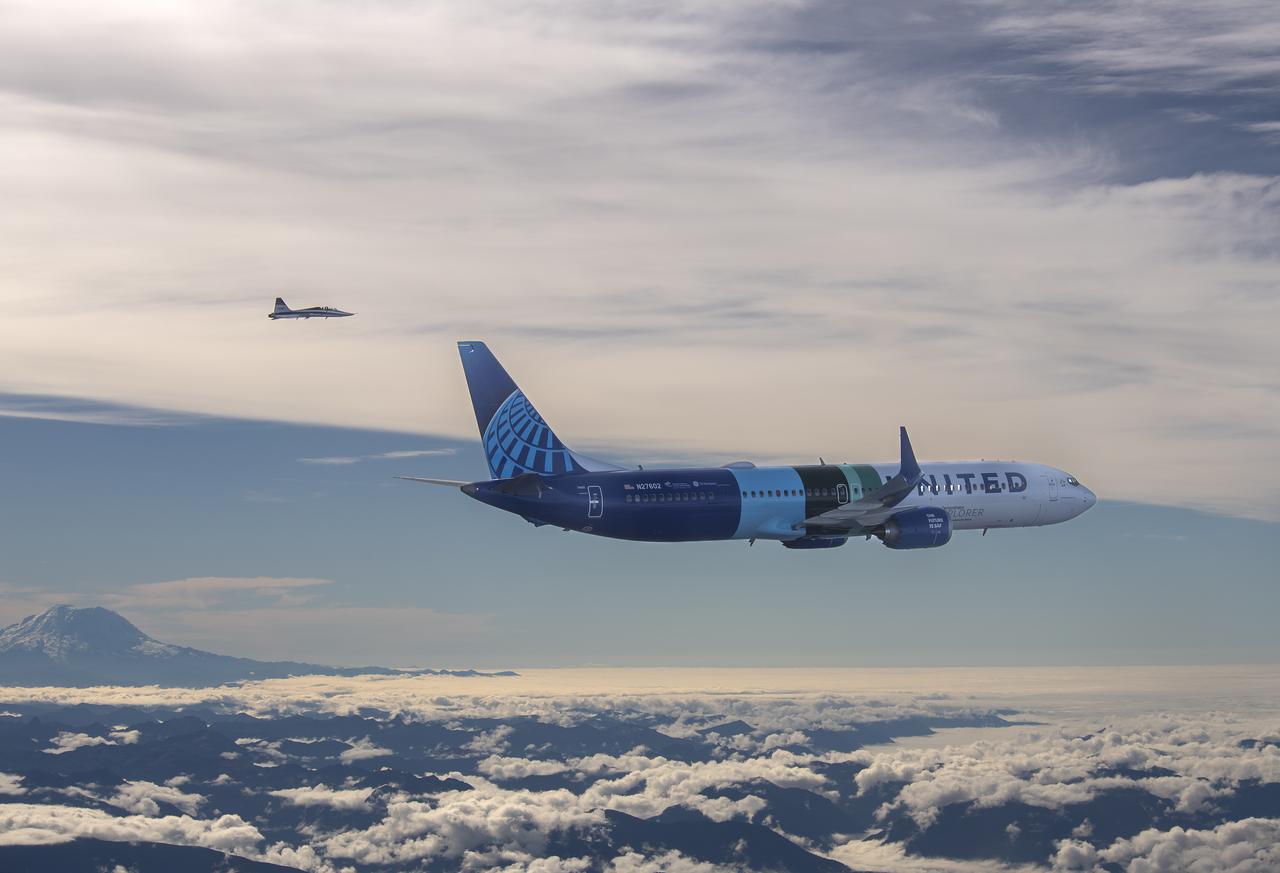

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
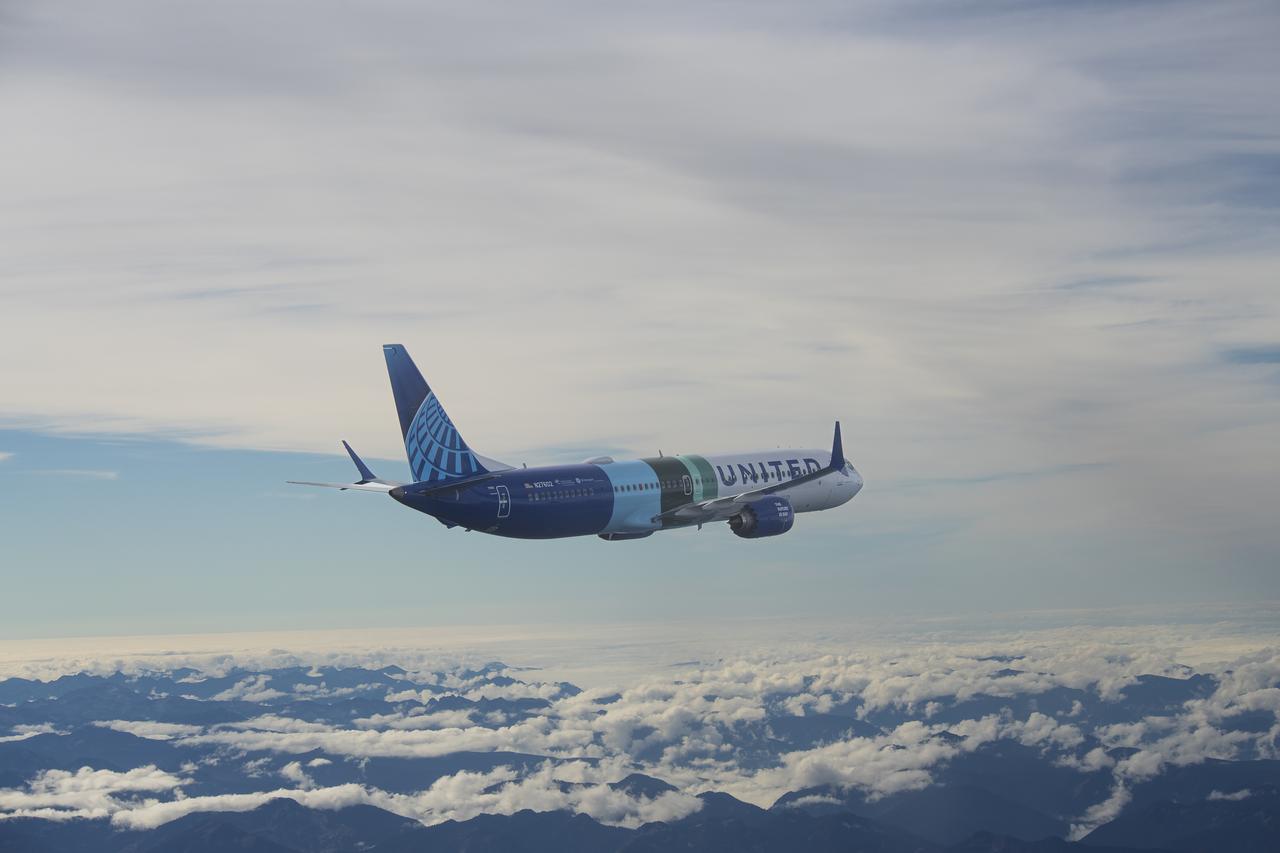

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
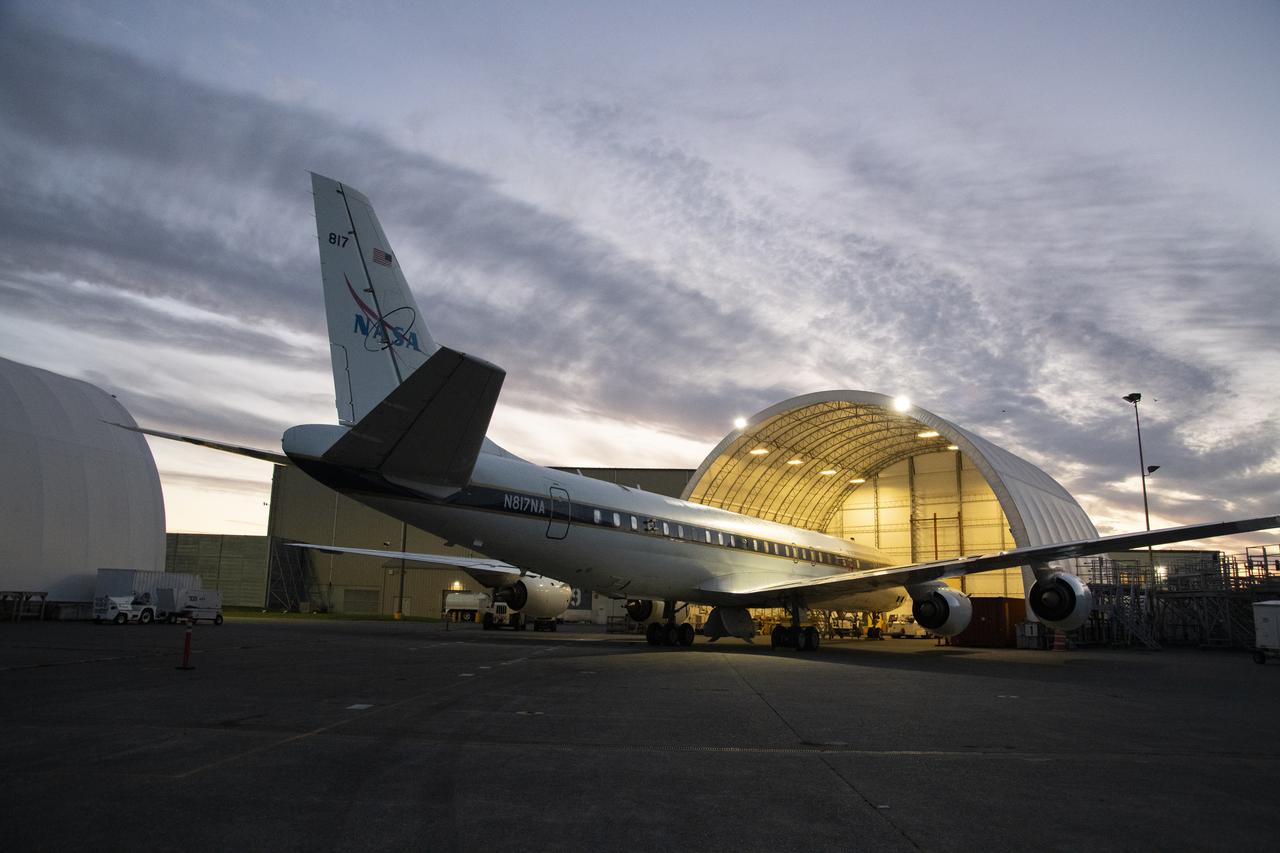

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
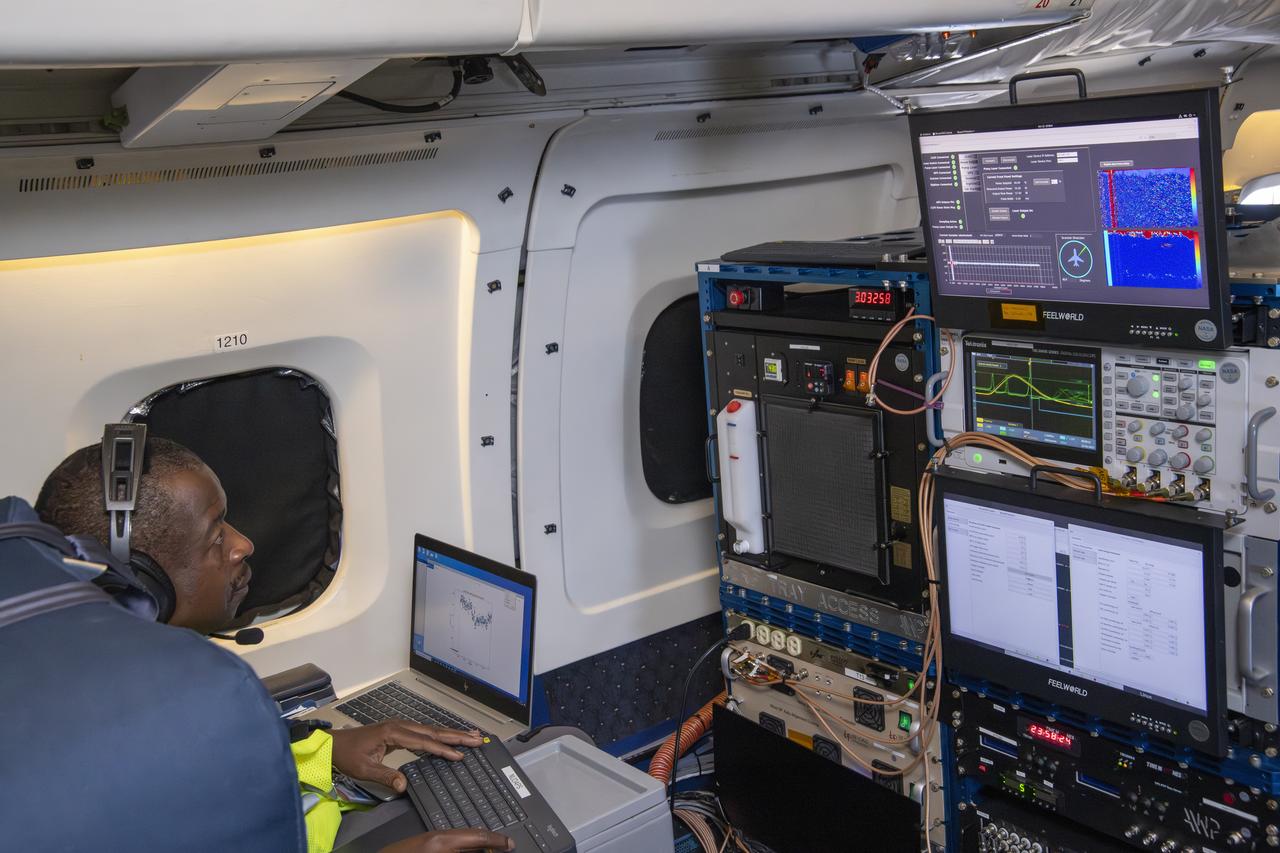

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
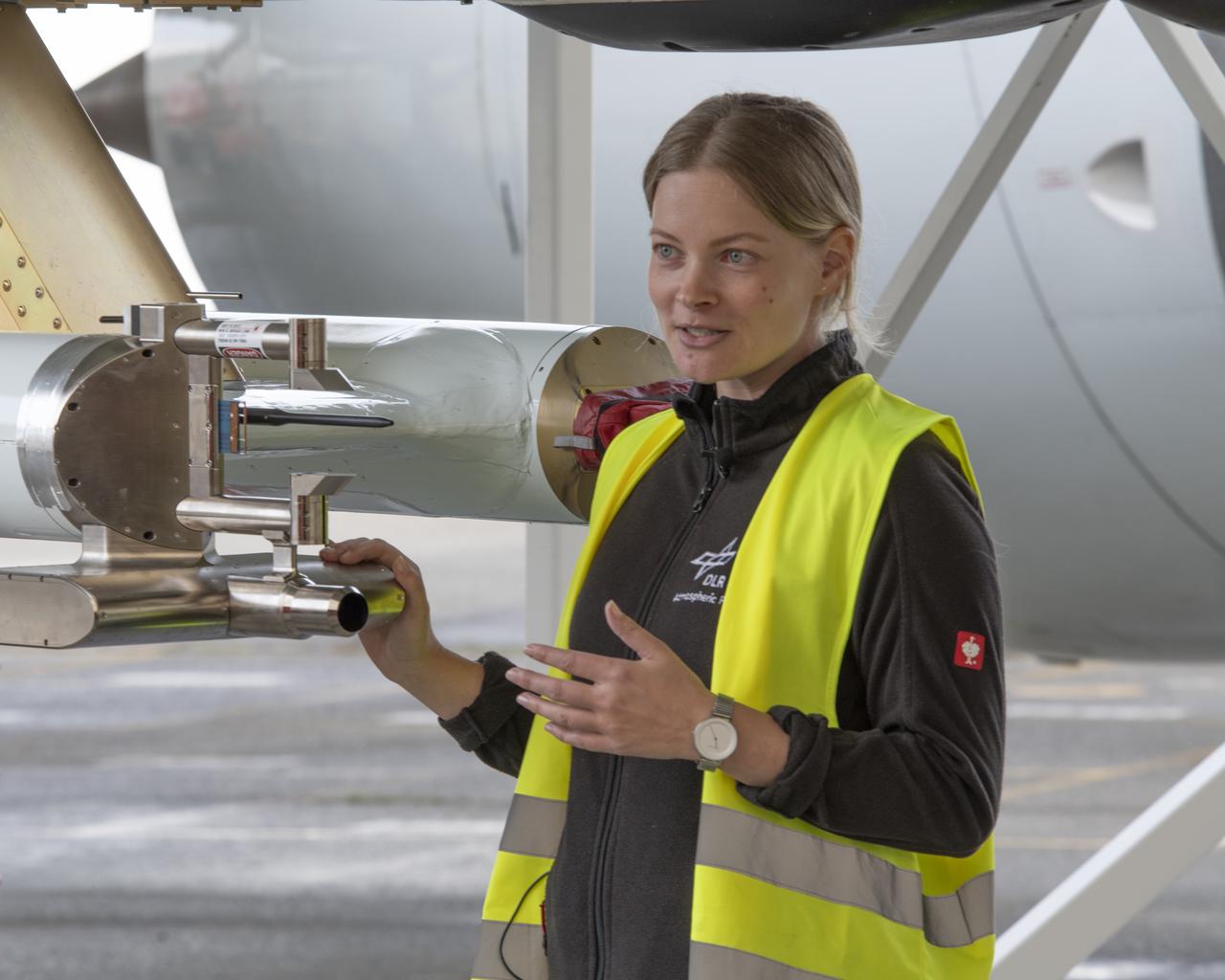

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
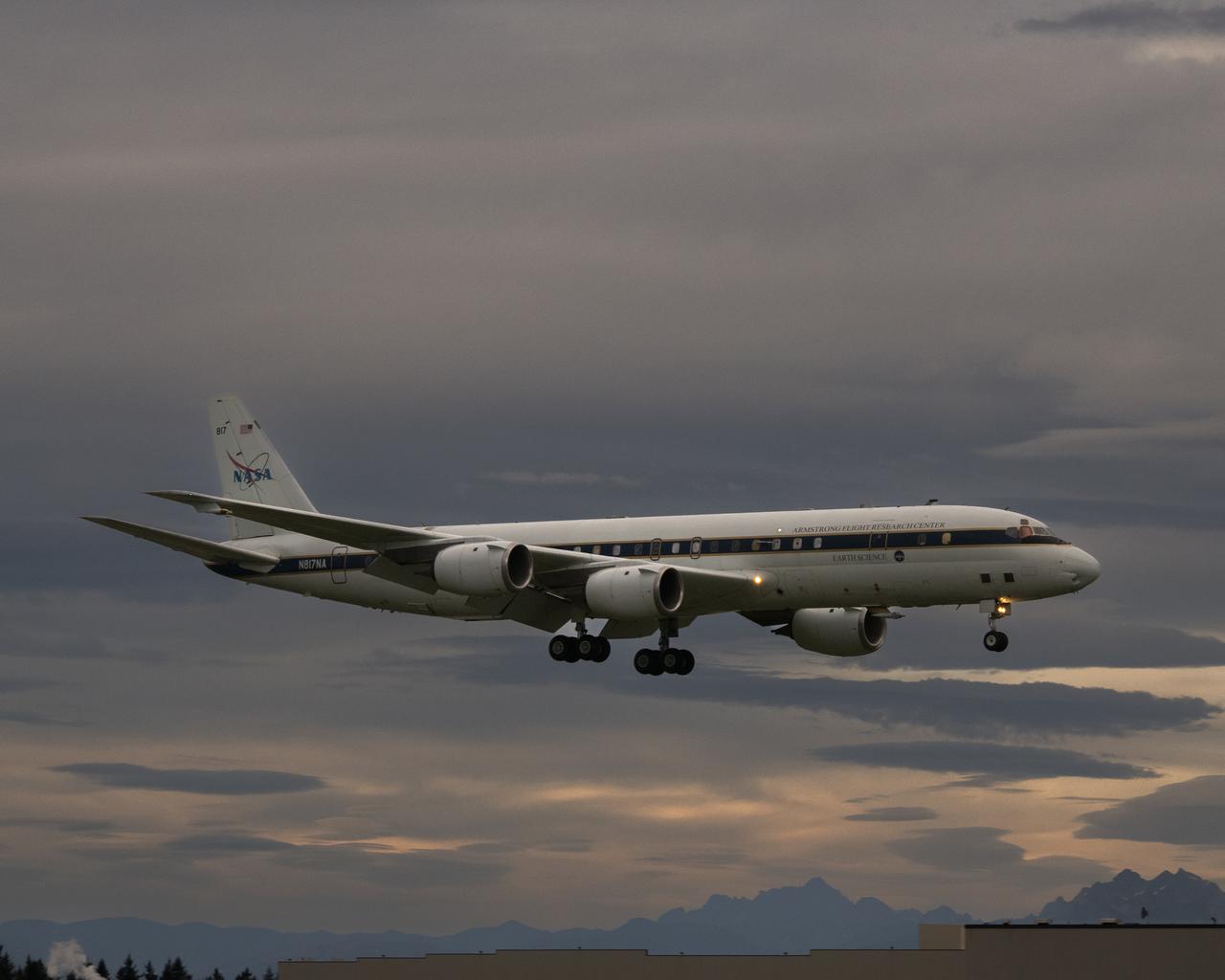

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
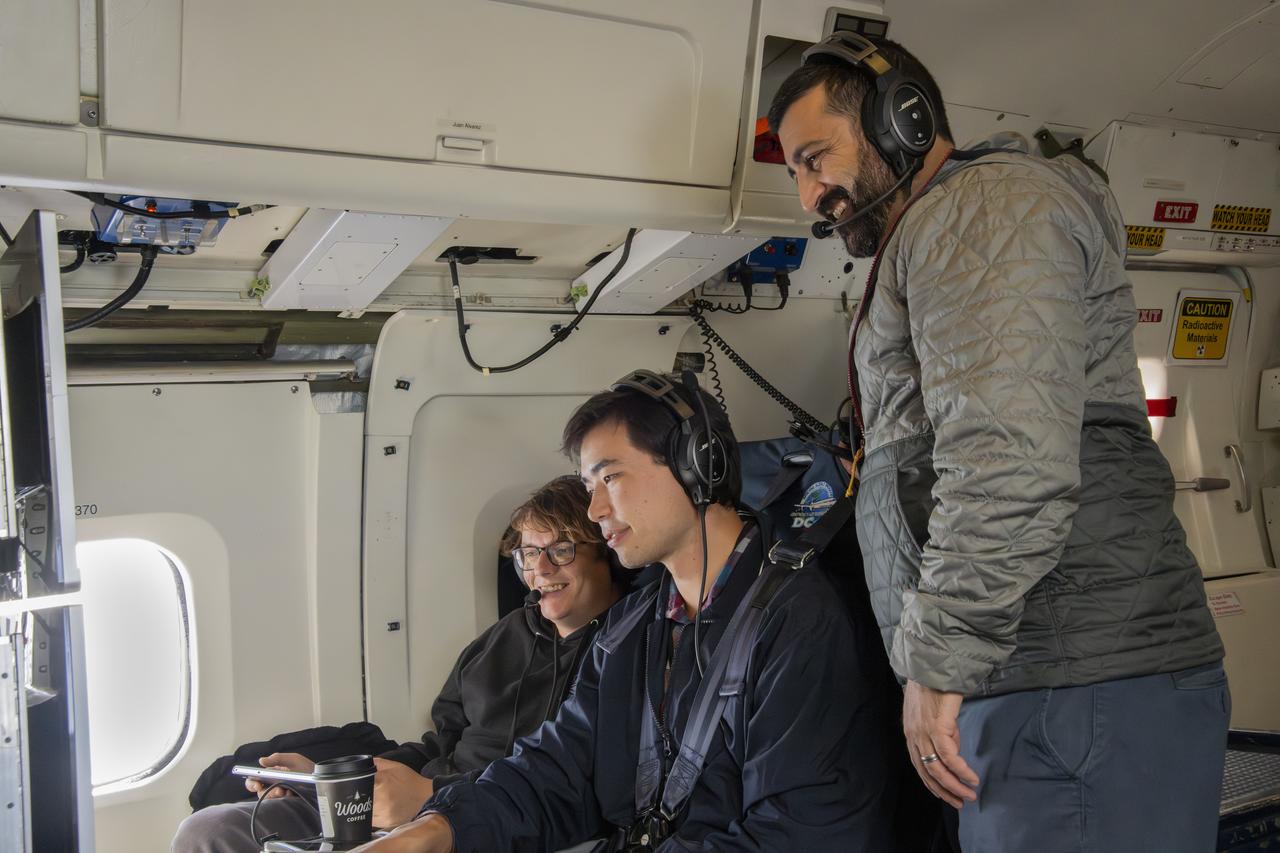

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
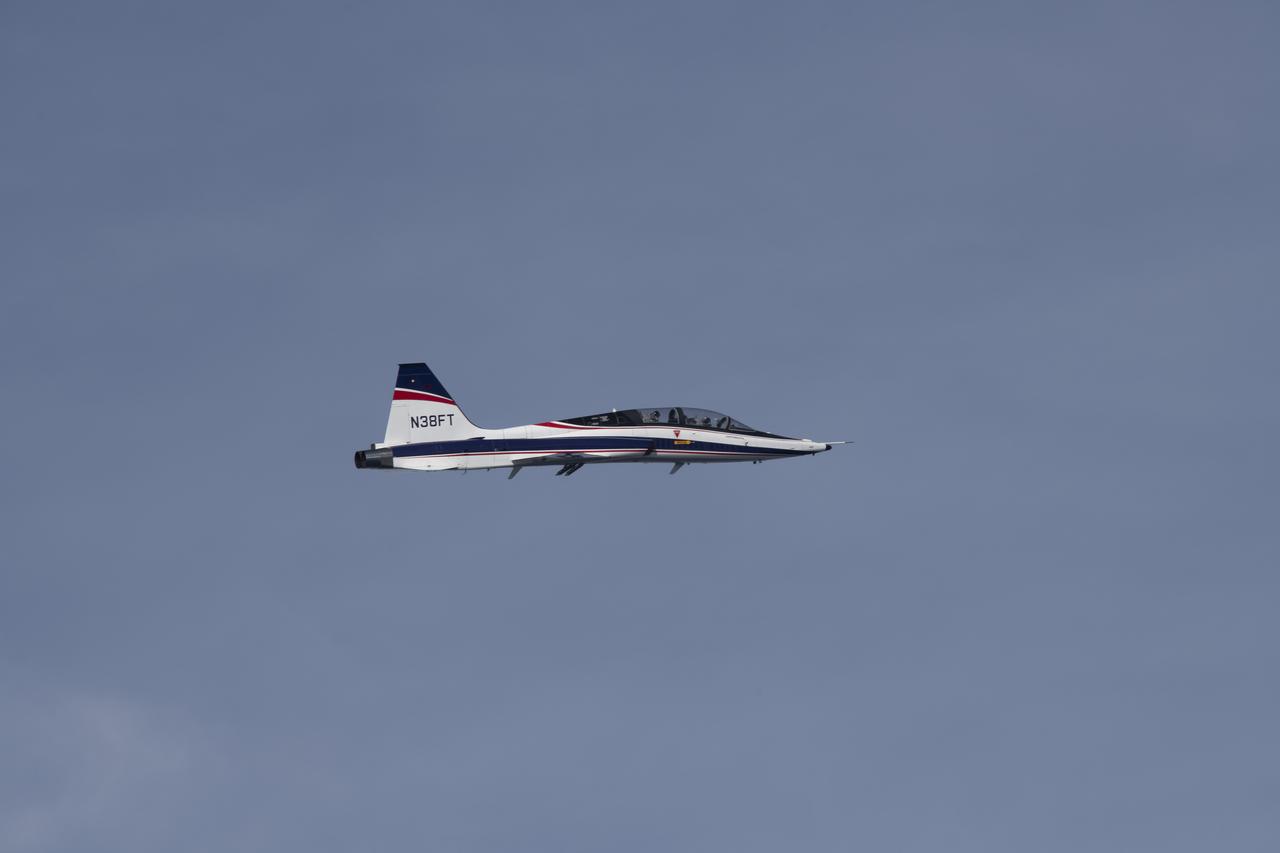

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
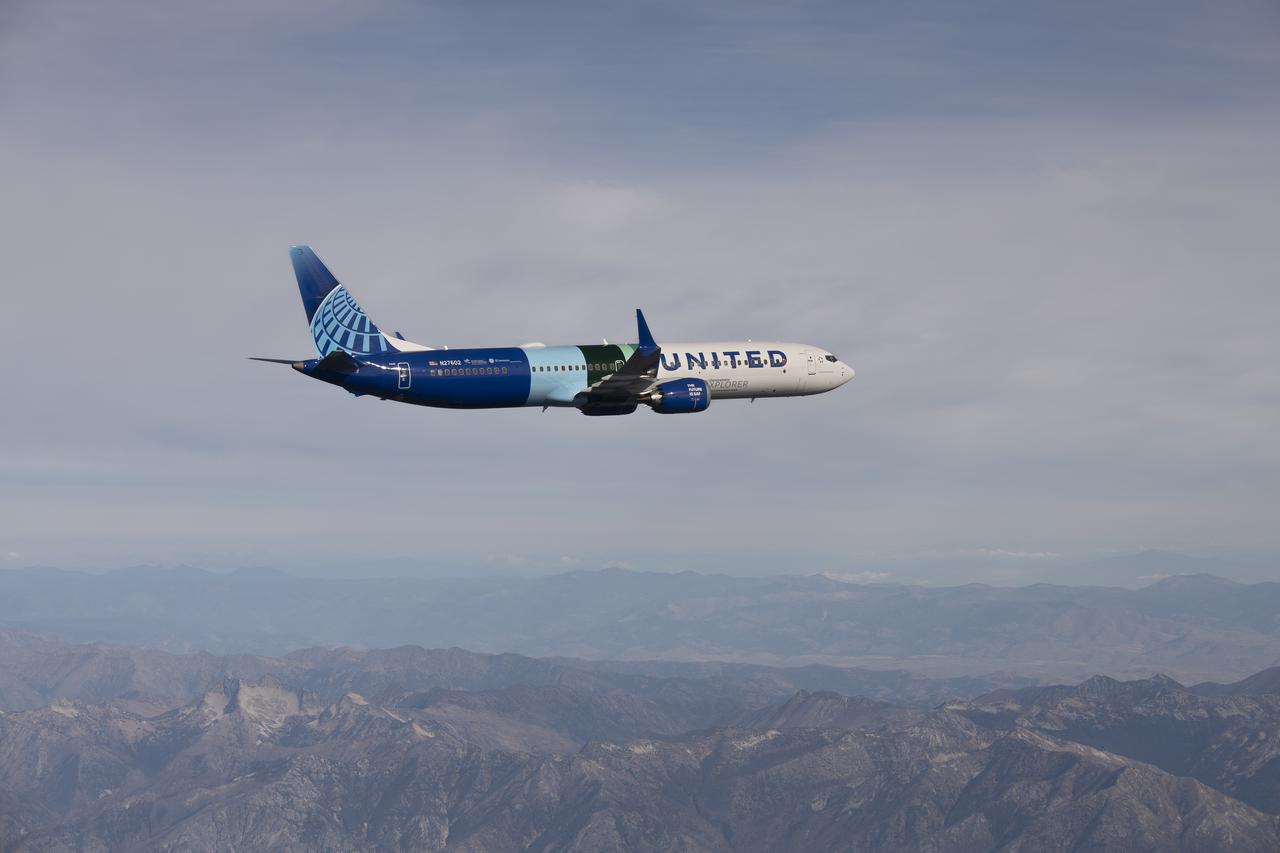

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
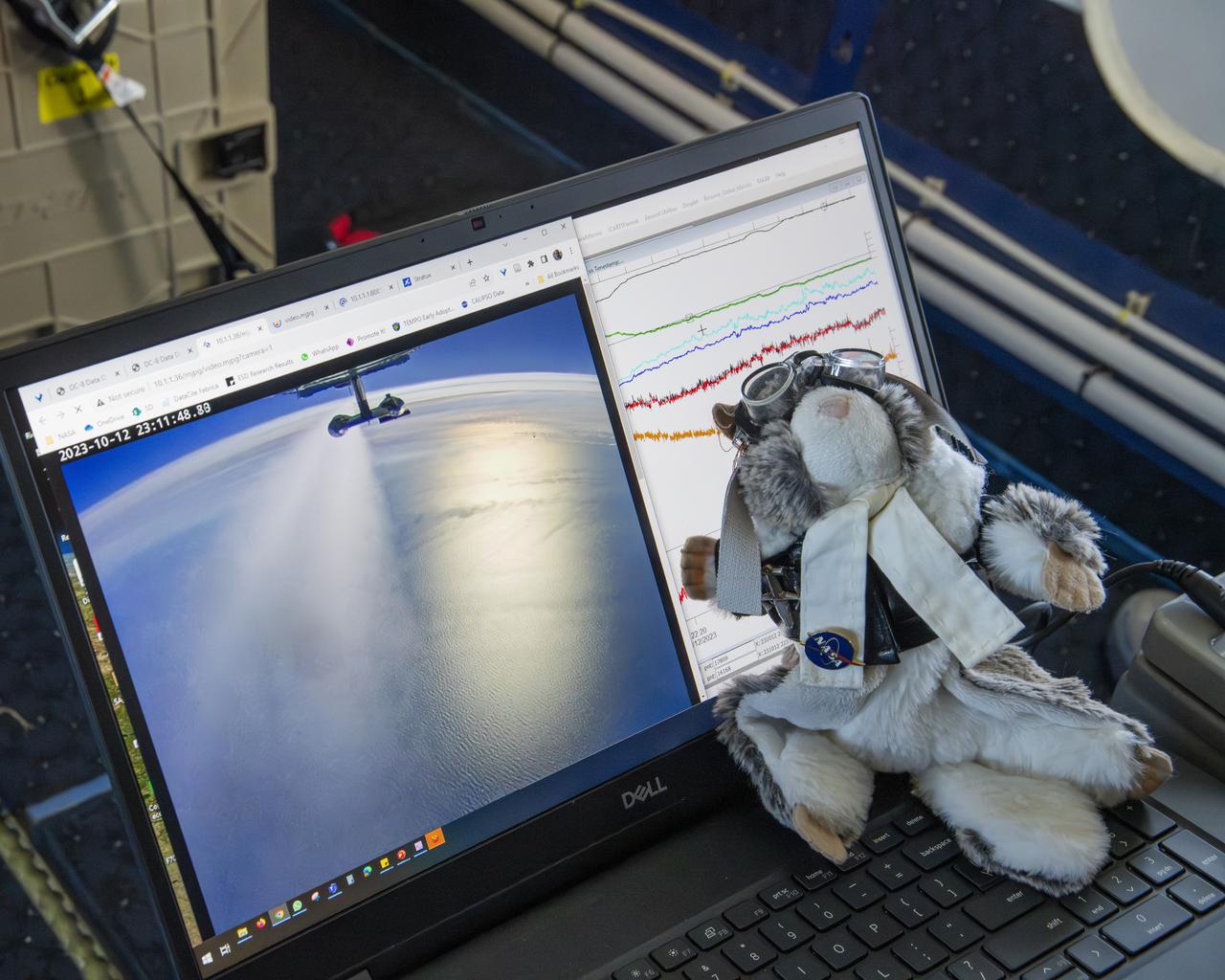

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
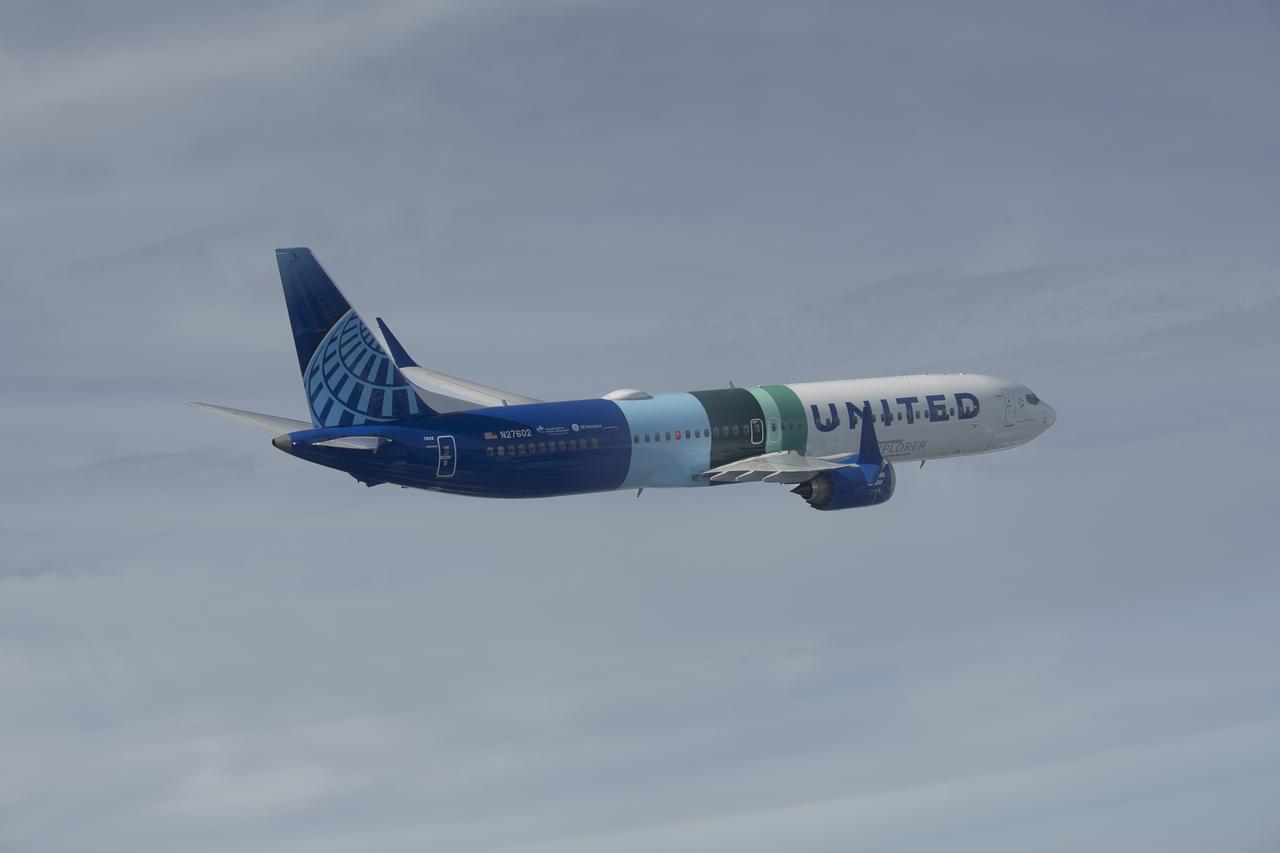

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
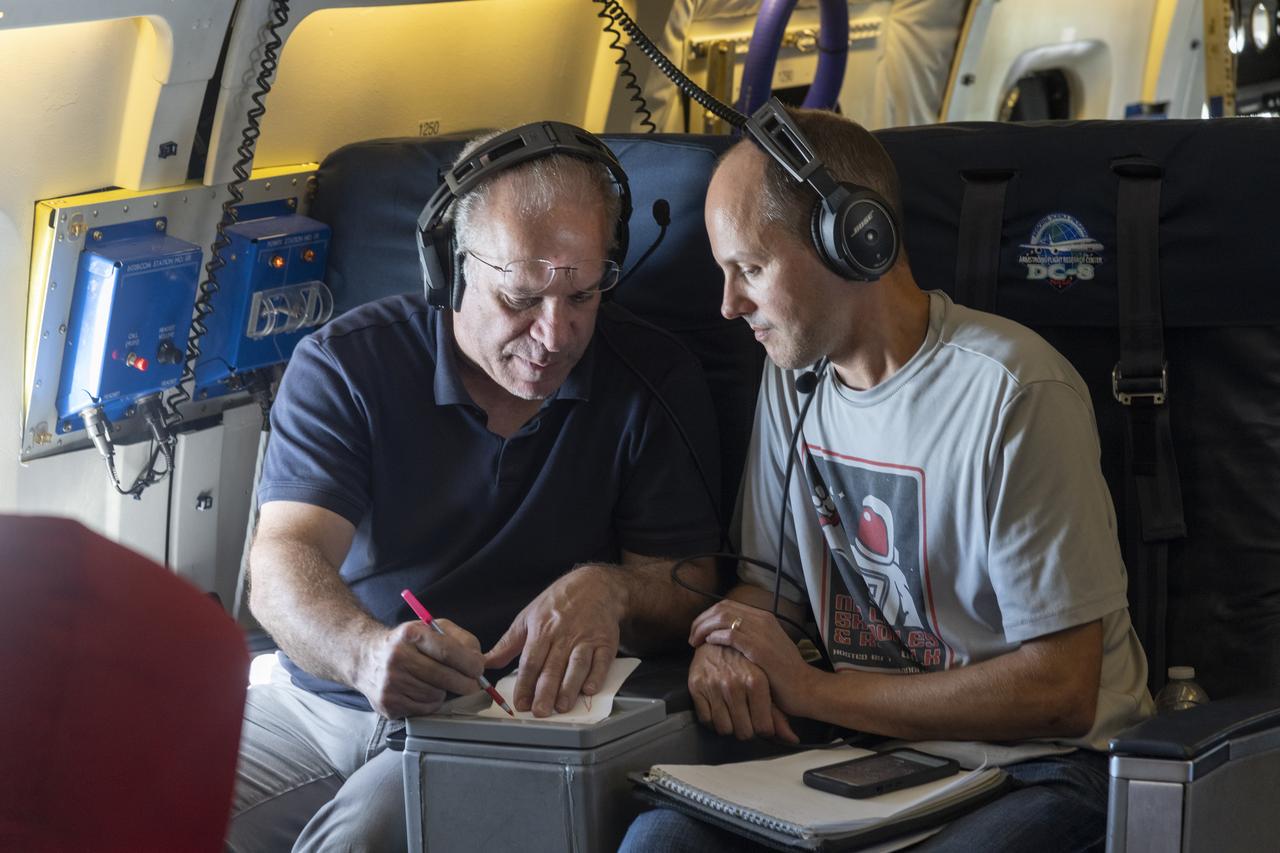

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
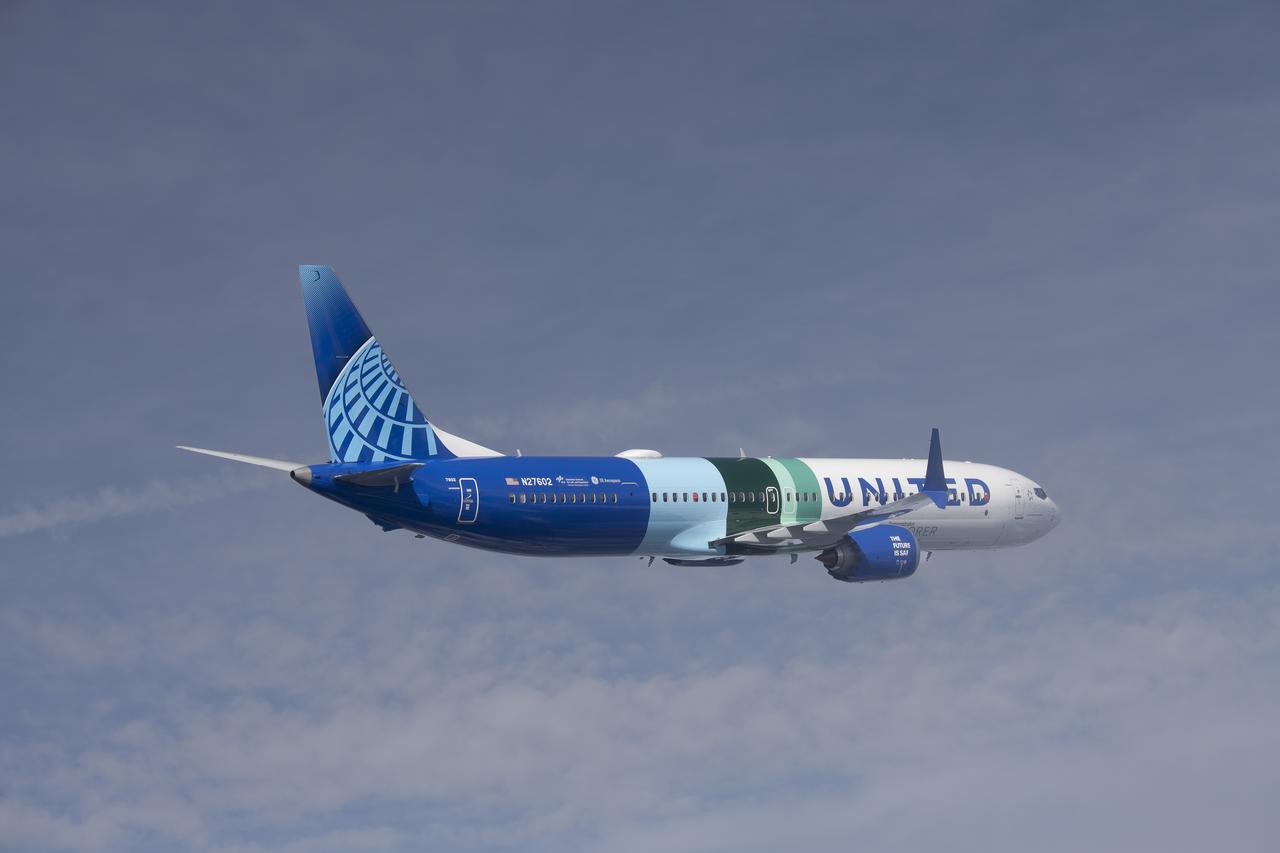

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
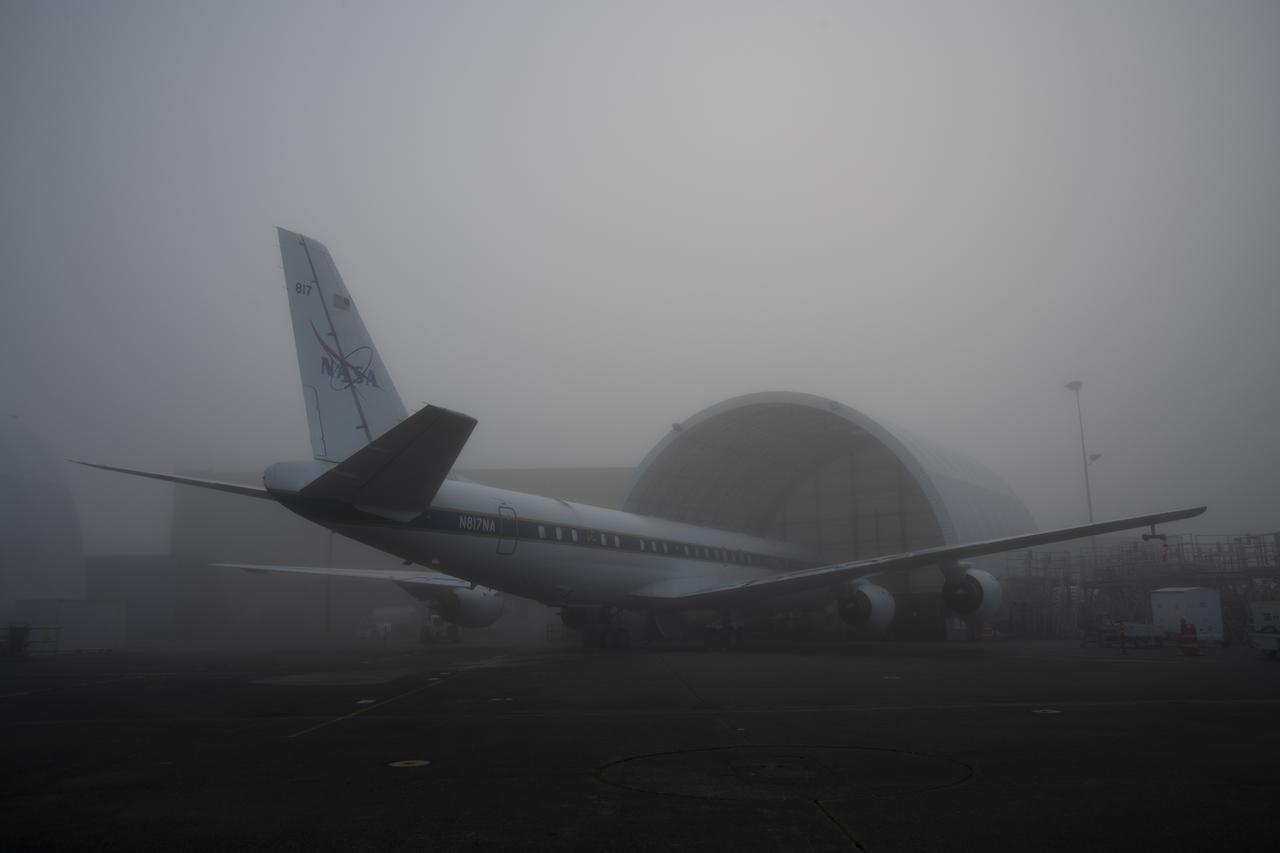

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
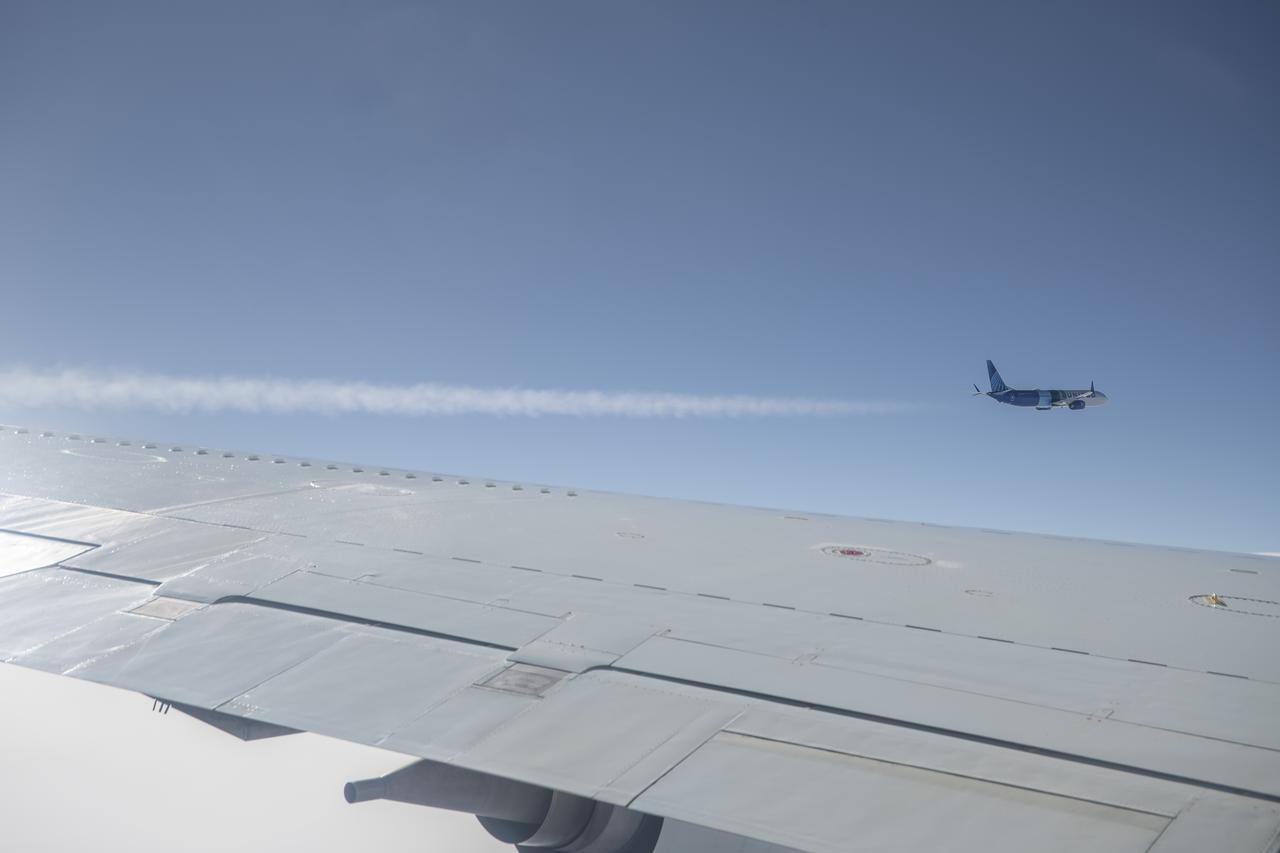

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
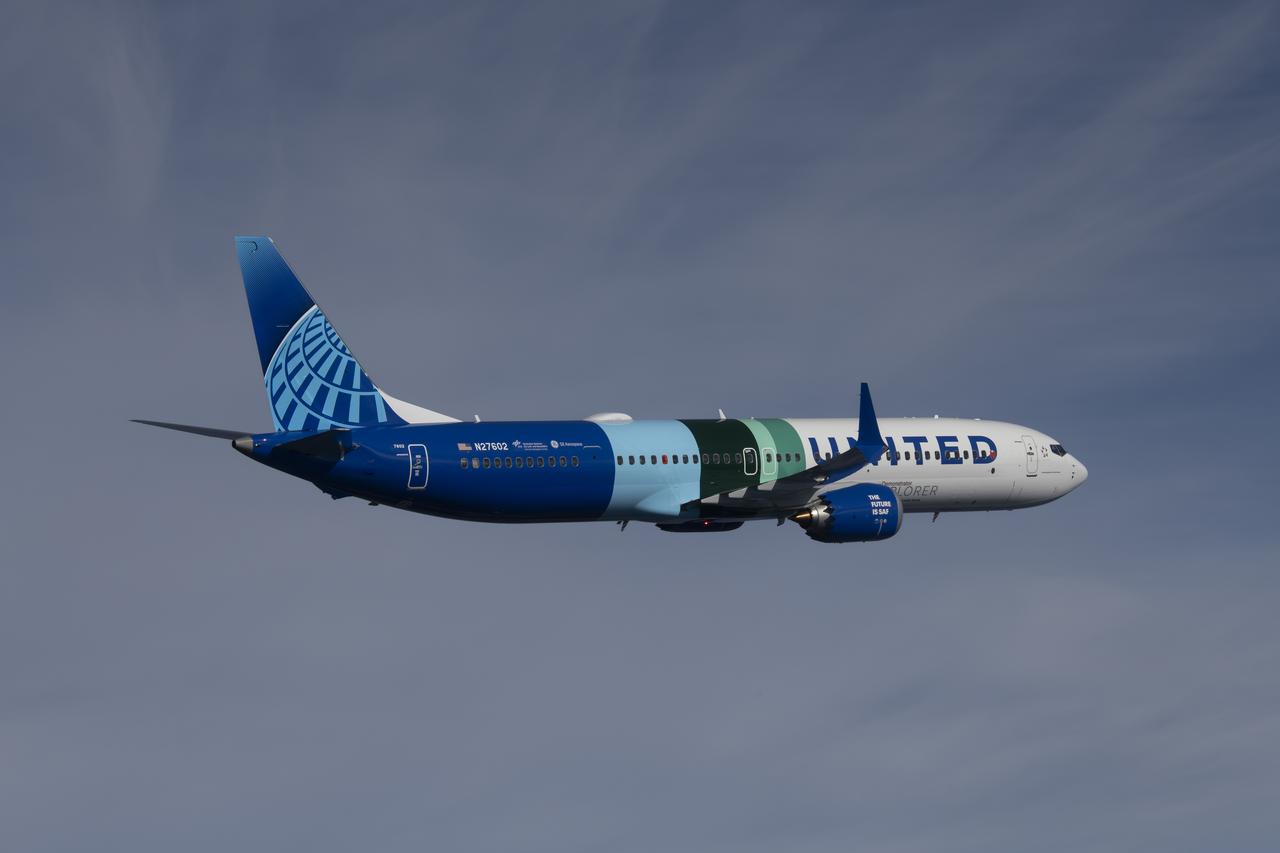

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
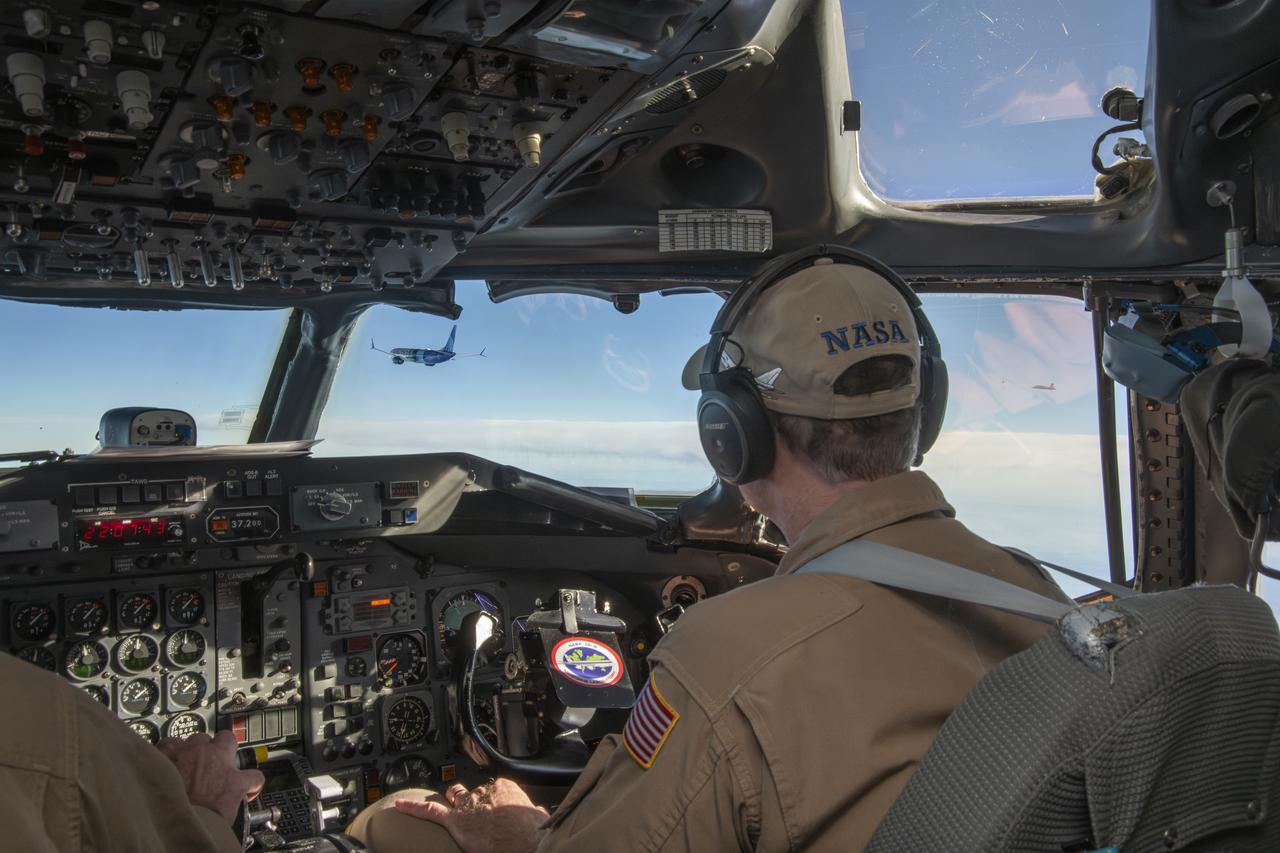

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
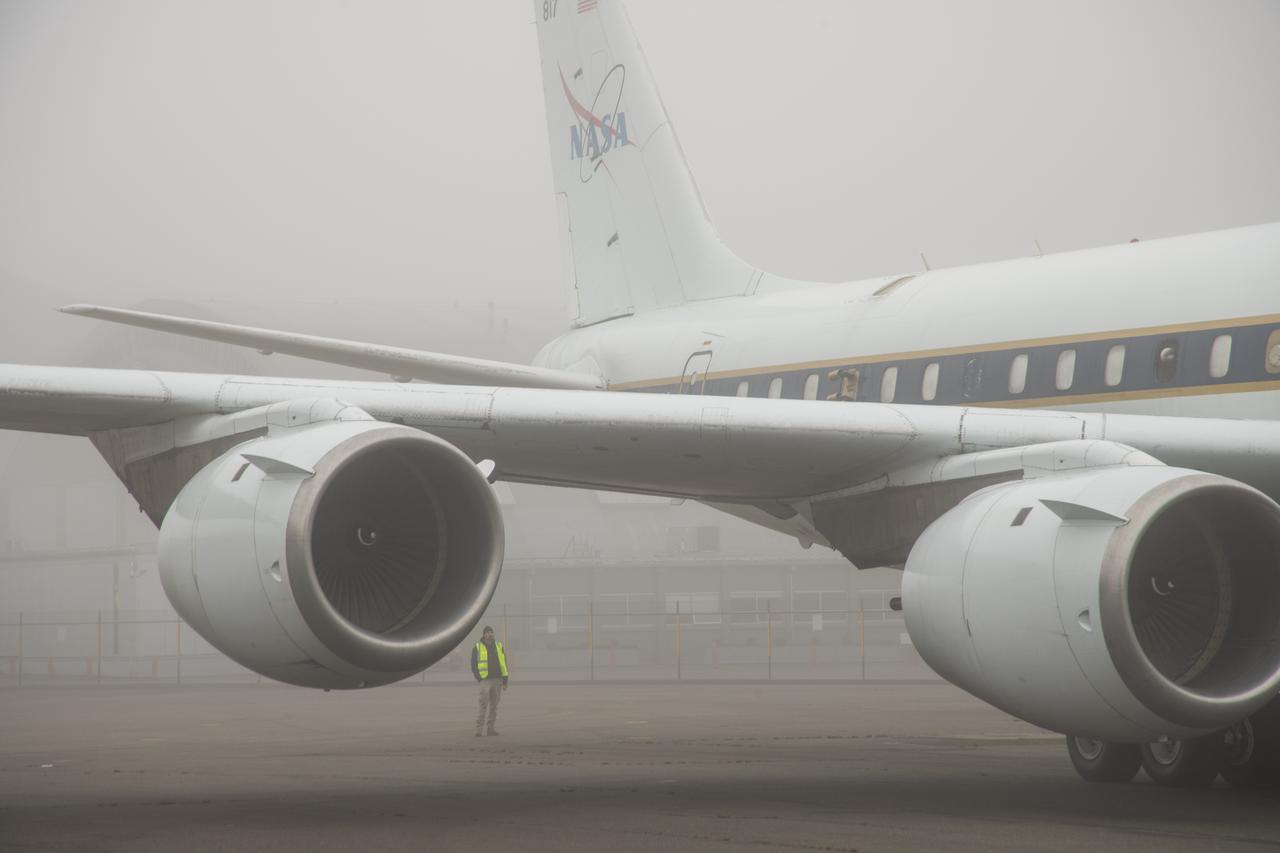

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
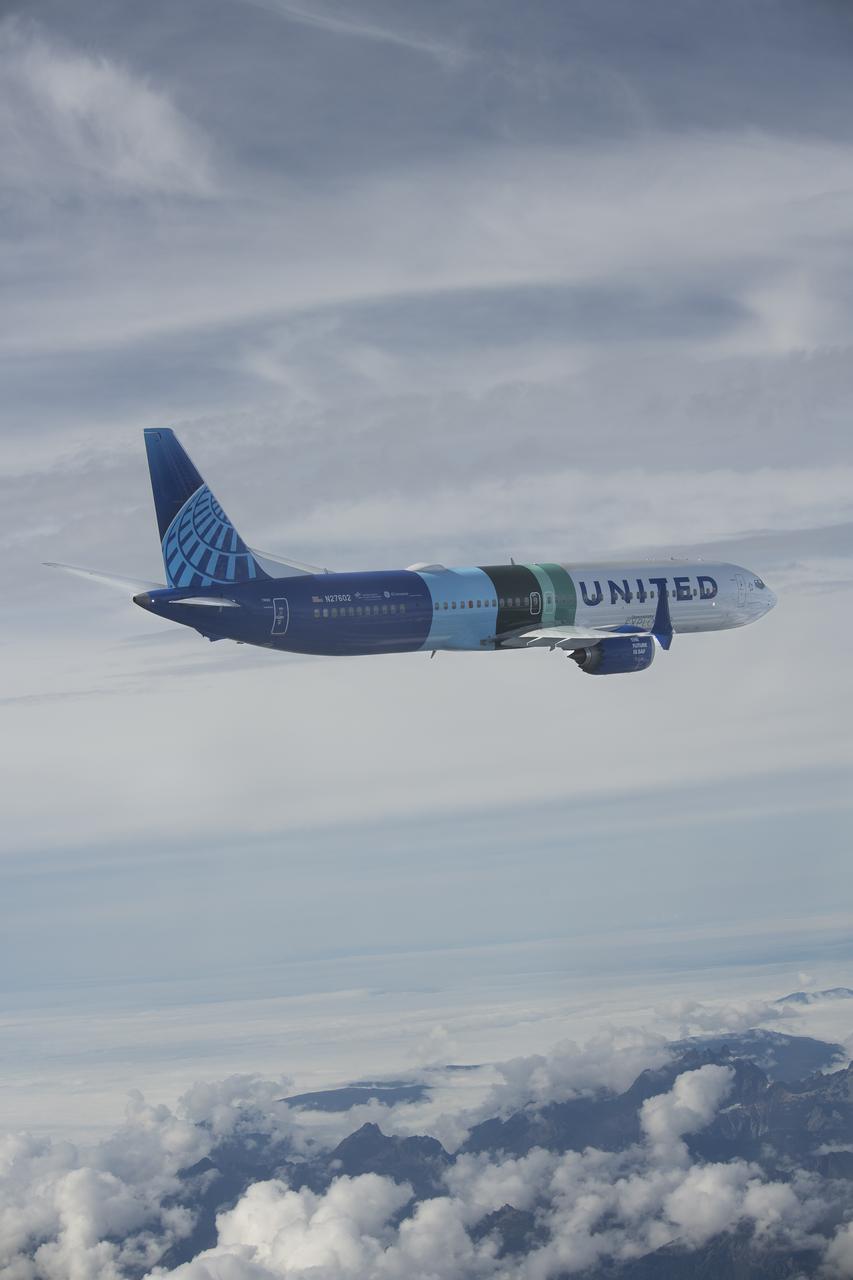

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
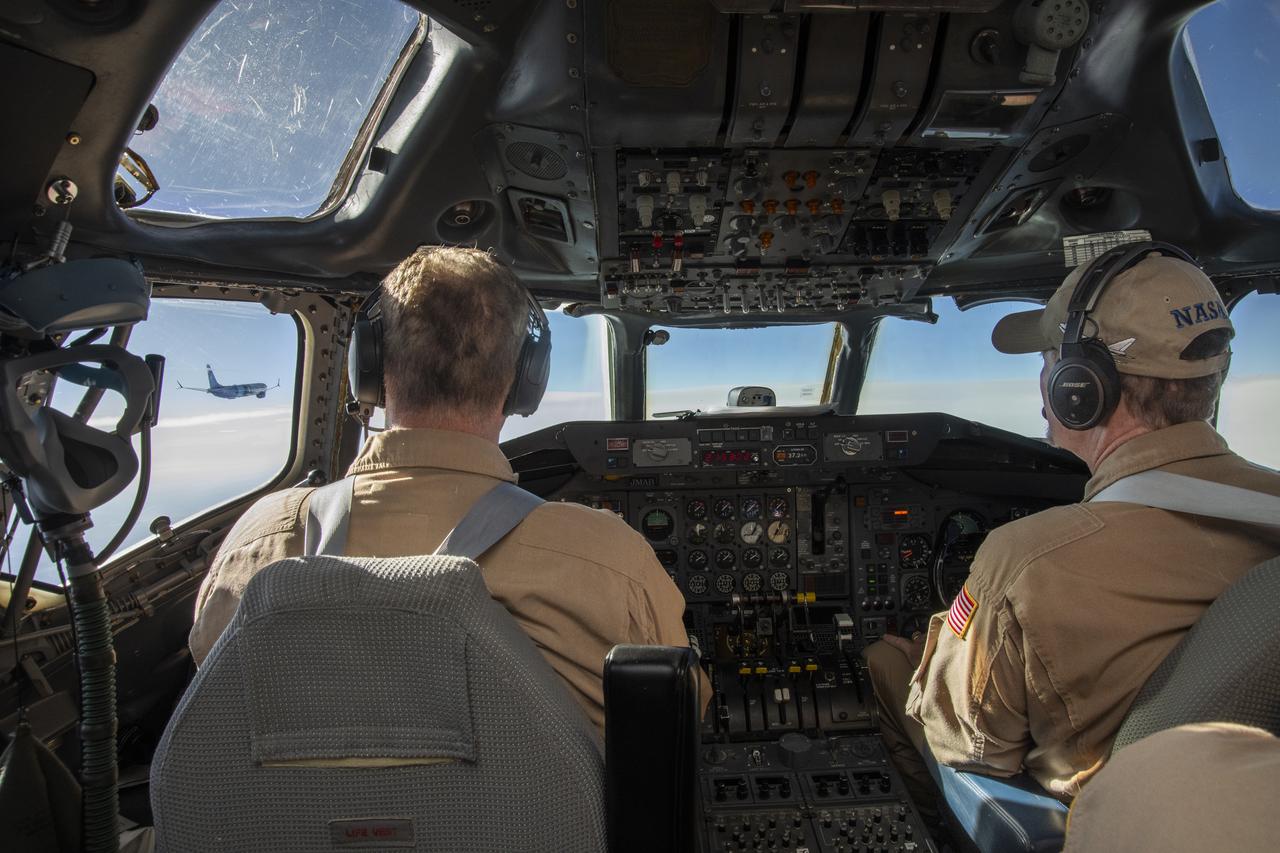

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
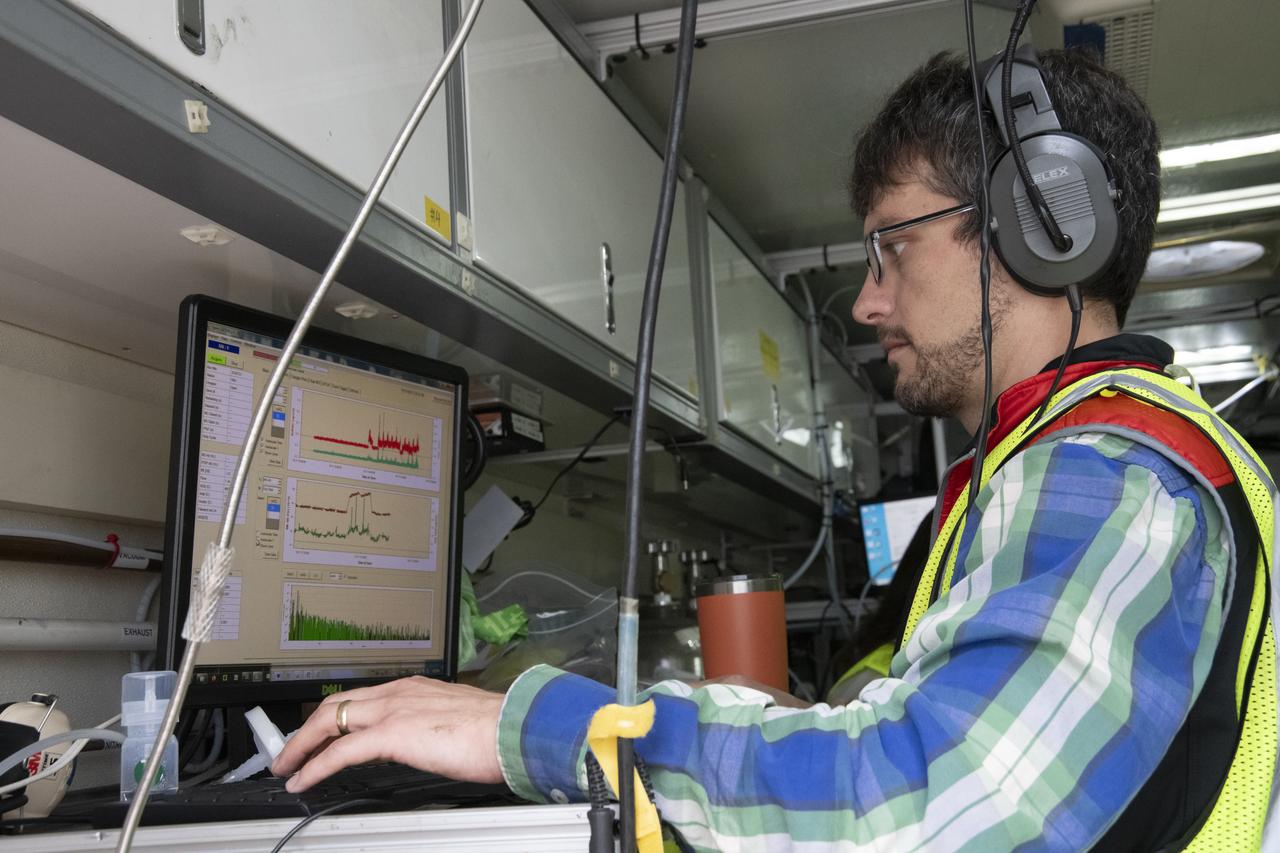

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
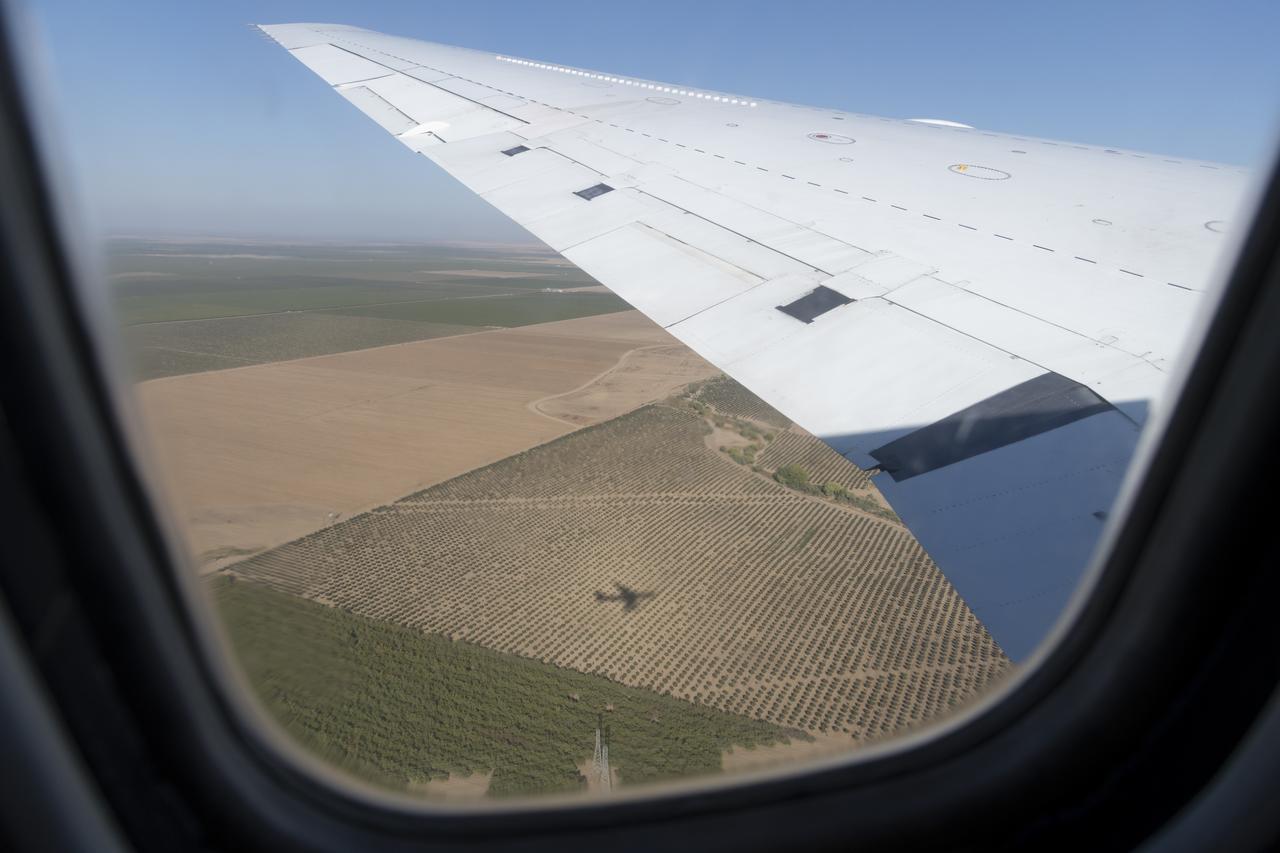

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
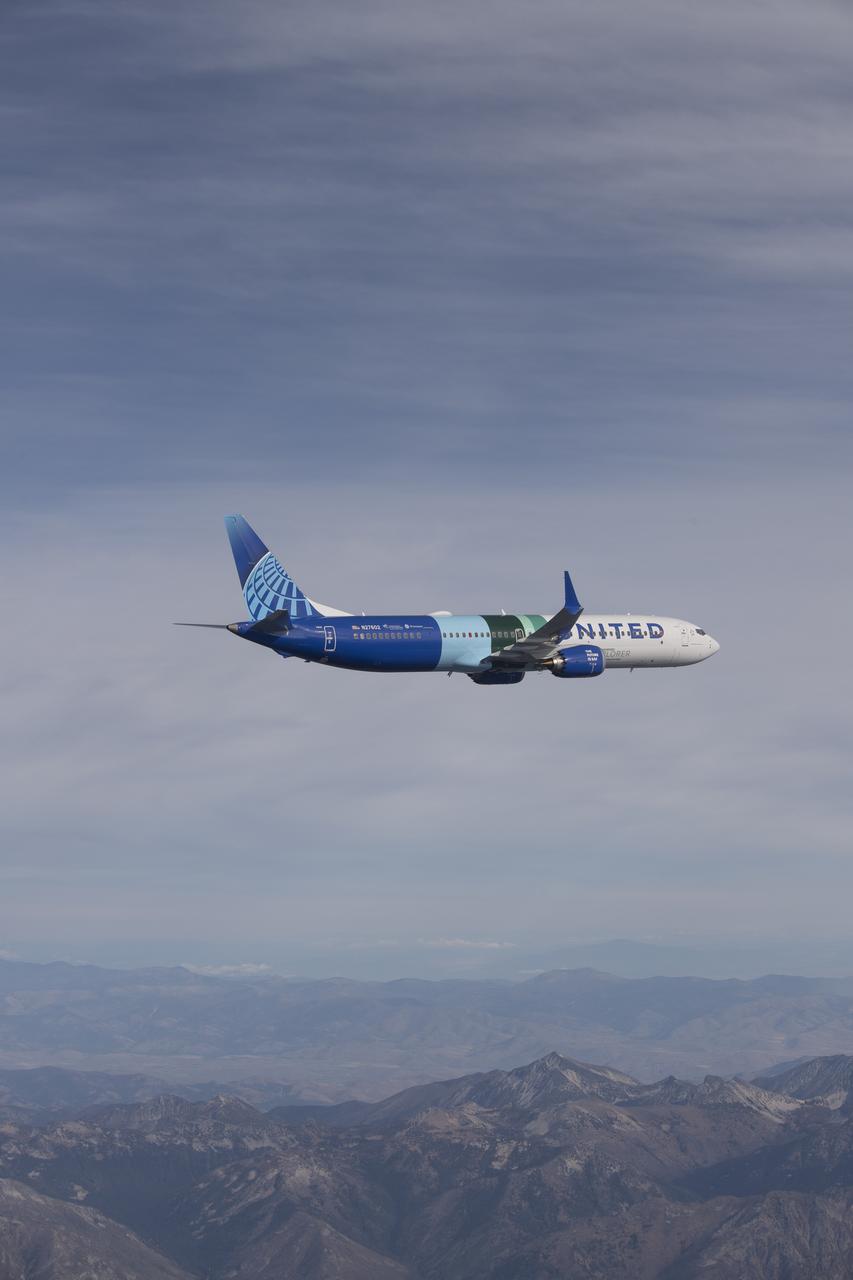

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
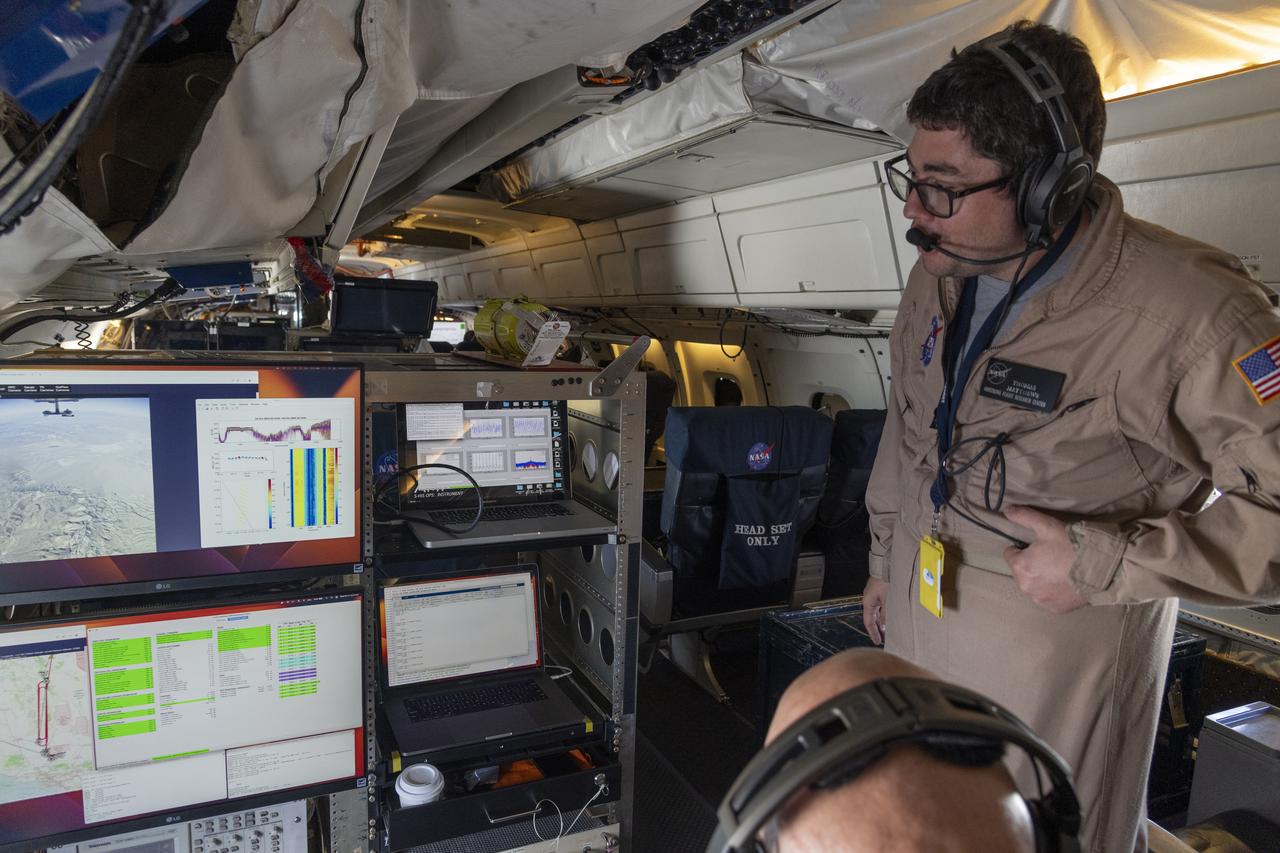

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
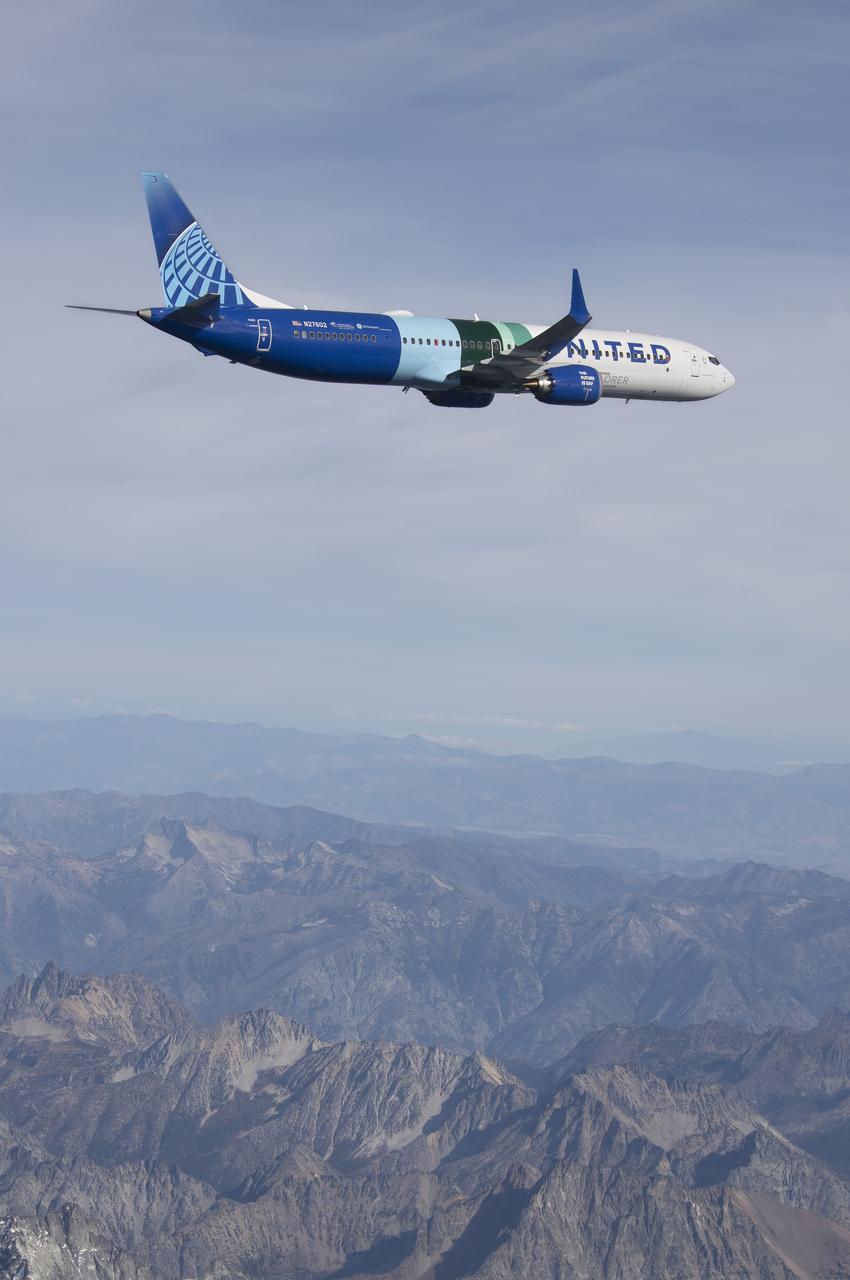

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
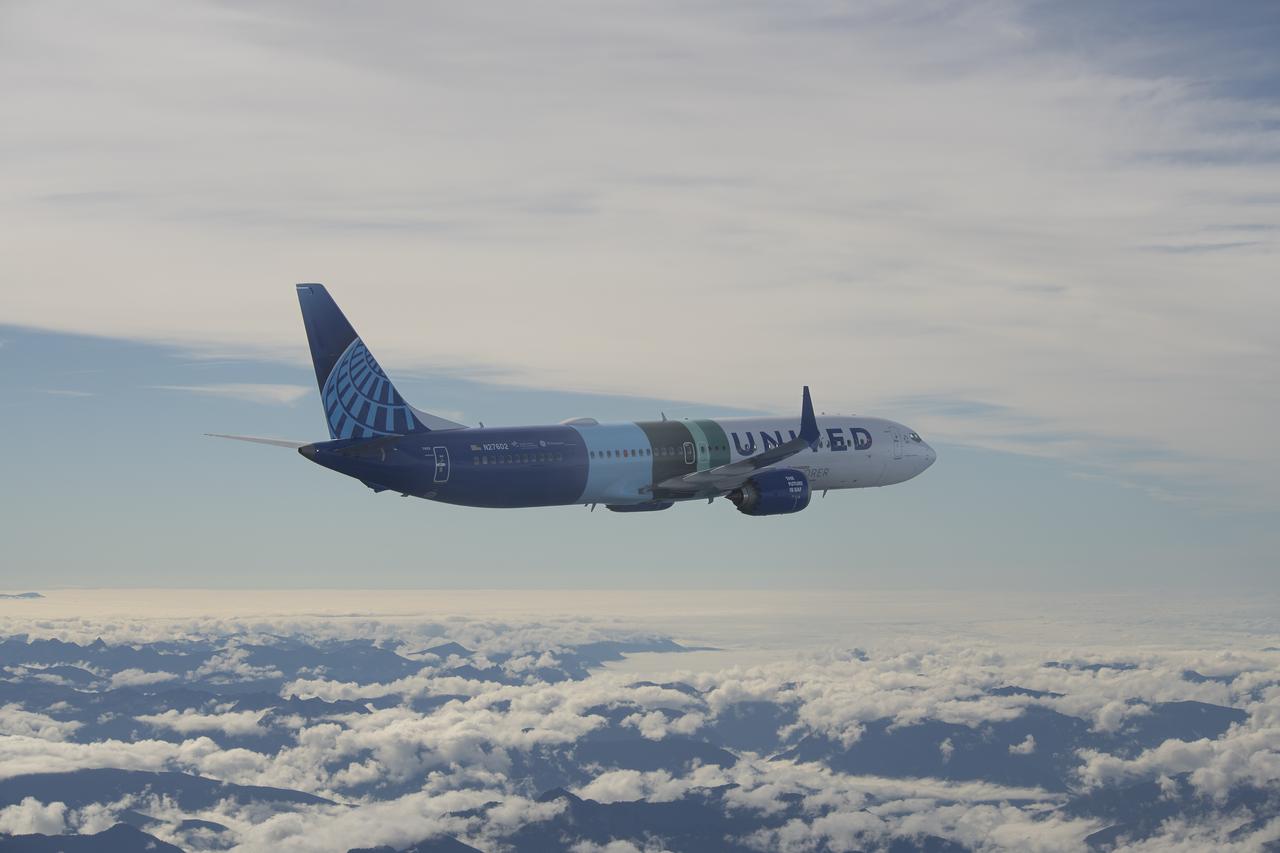

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
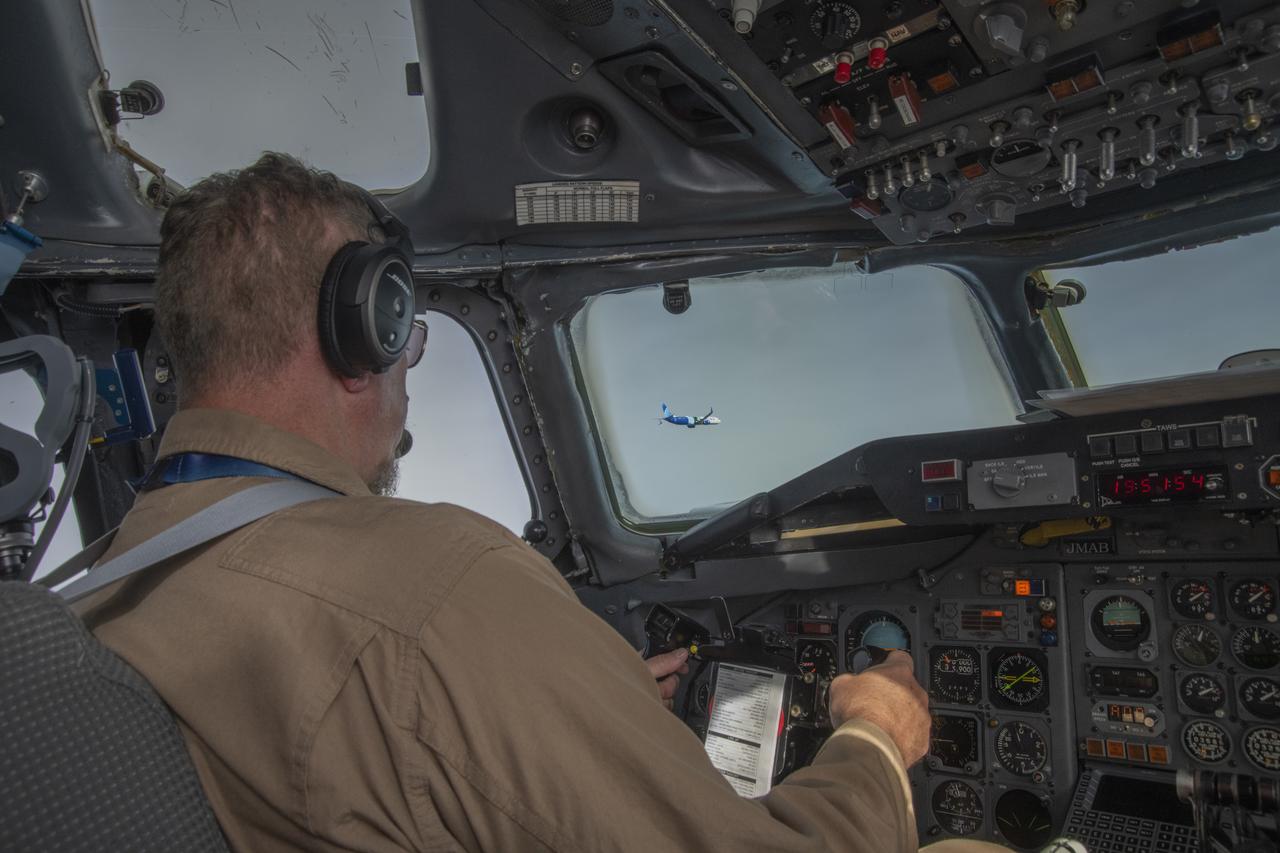

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
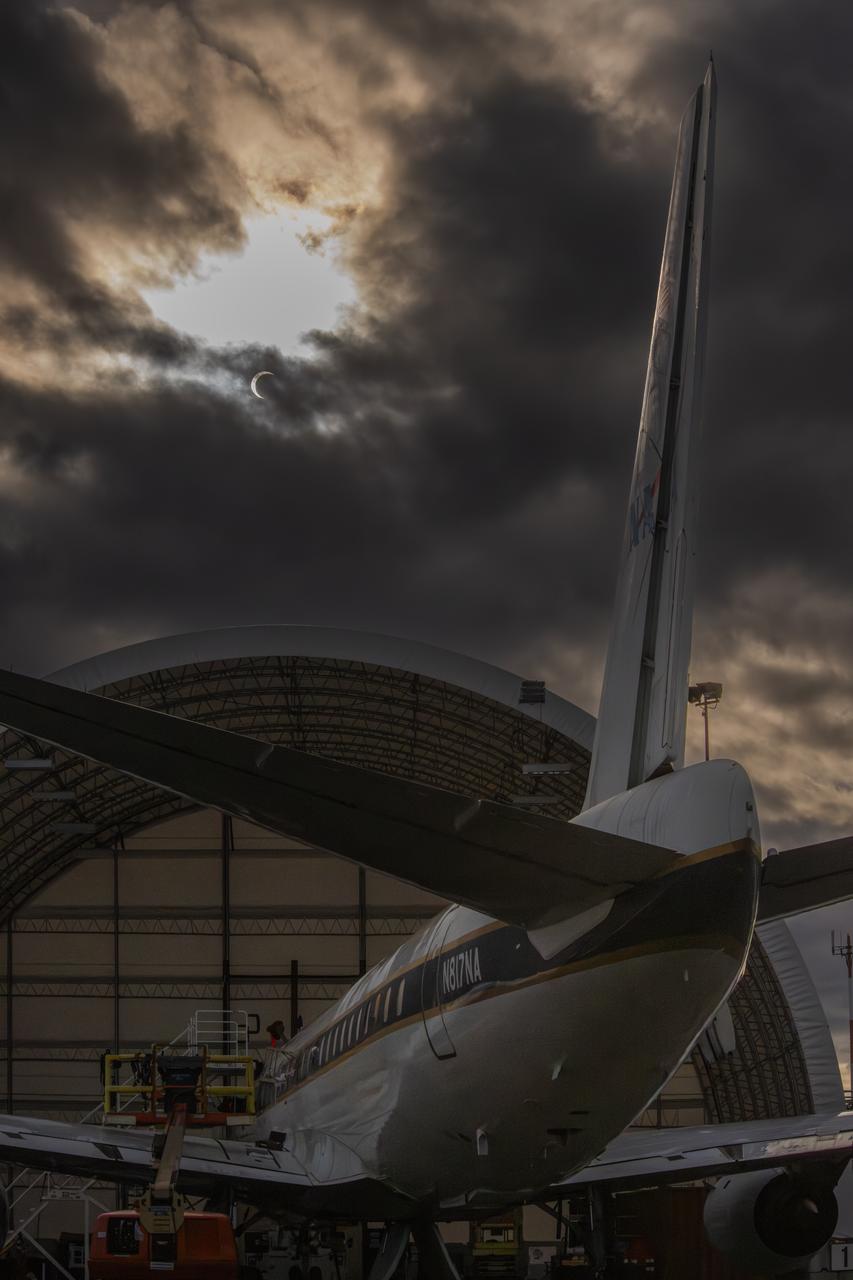

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
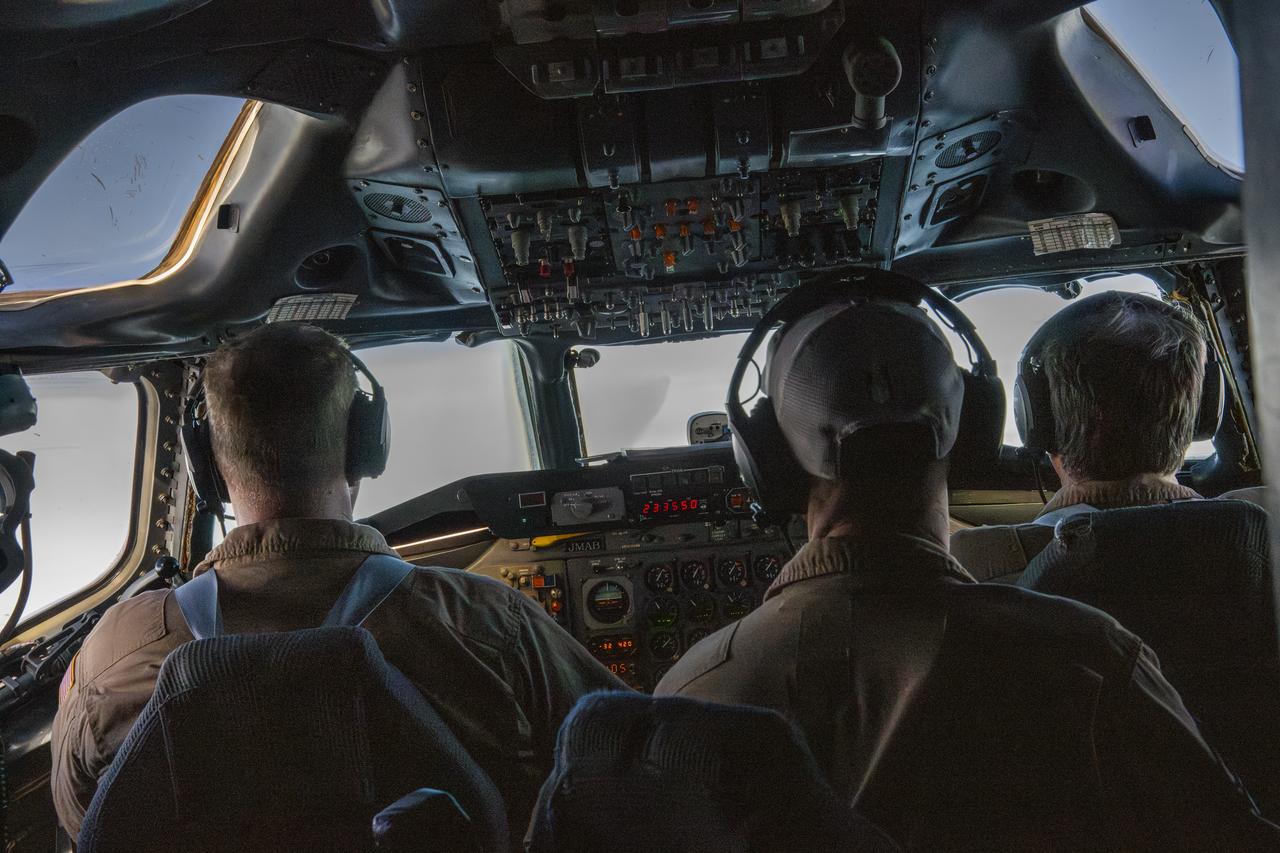

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
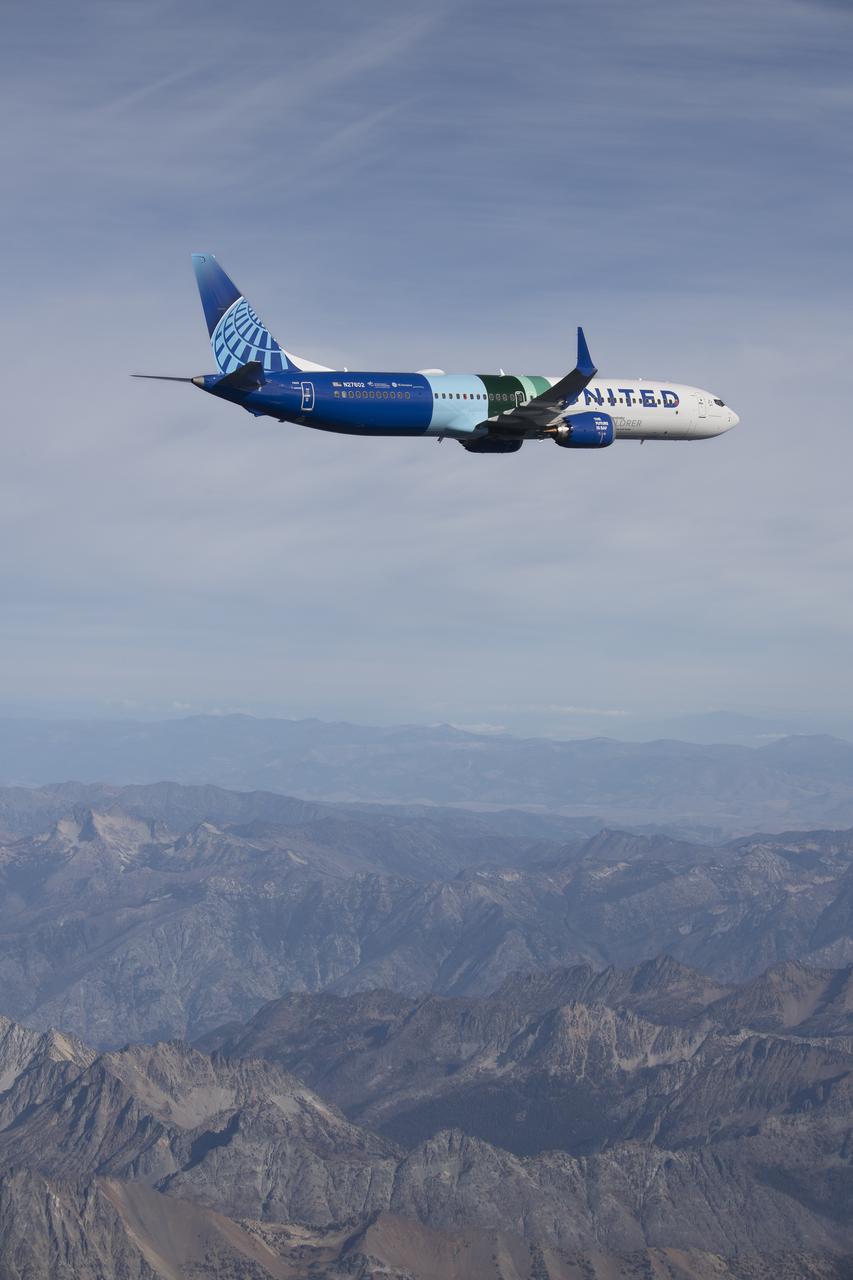

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
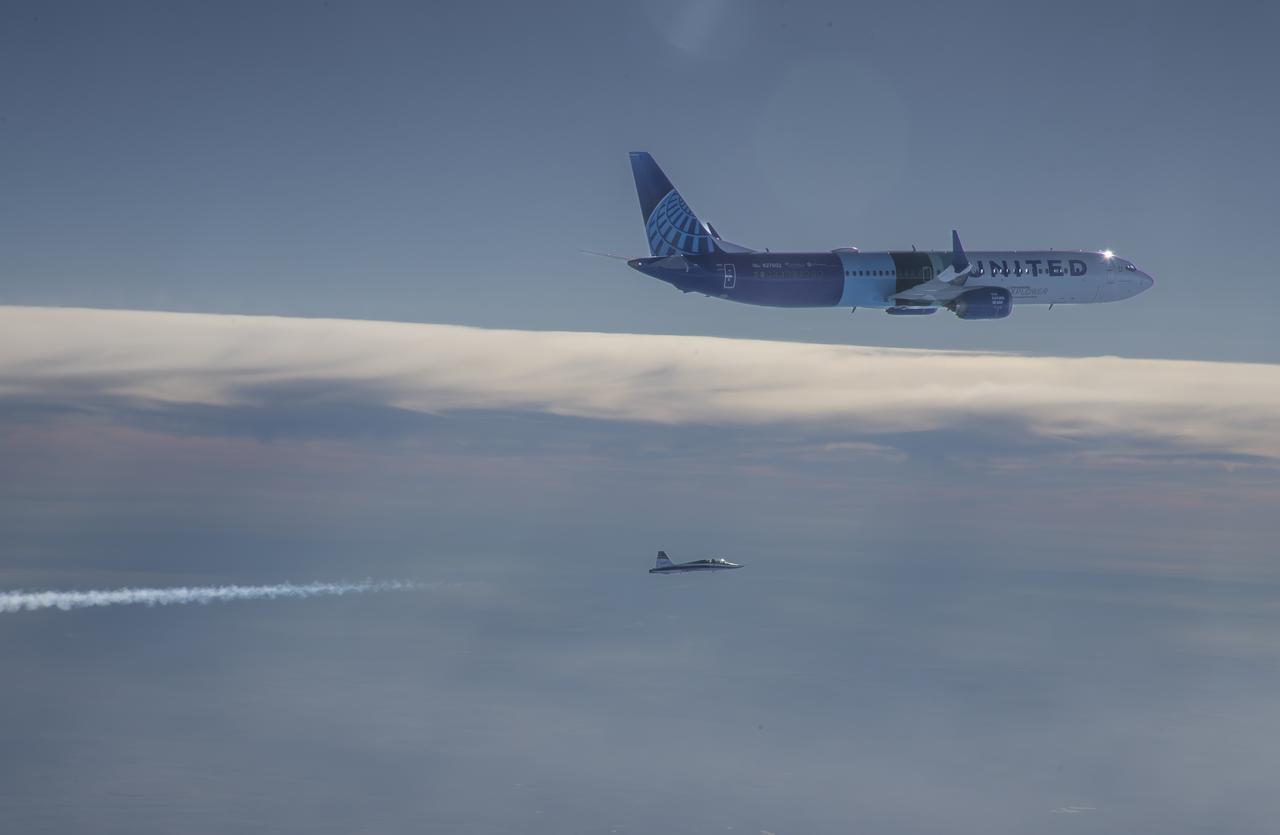

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
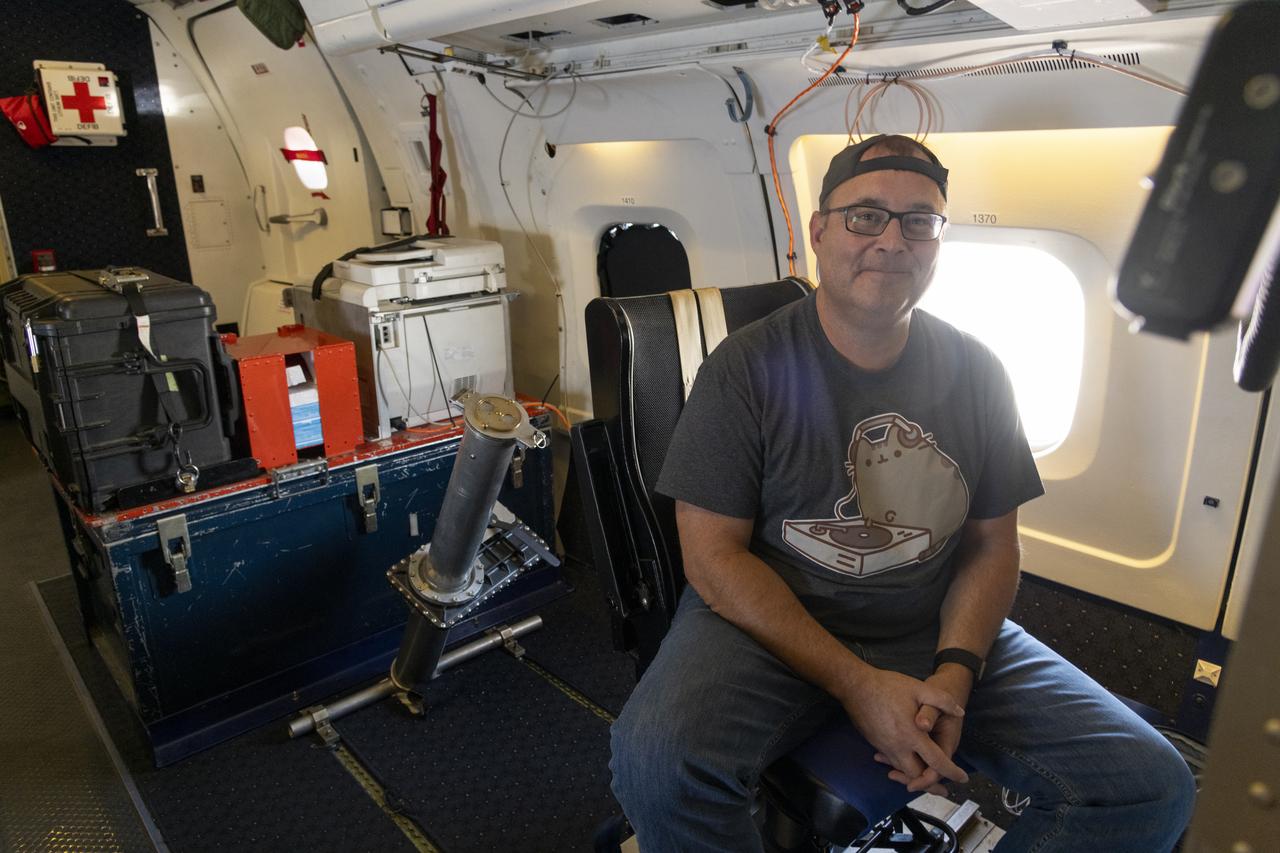

NASA’s DC-8 aircraft from Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California flies to Everett, Washington to conduct science research about reducing engine particle emissions. Partners include Boeing, United, General Electric Aerospace, German Aerospace Center (DLR), the FAA, and World Energy. Boeing’s new passenger aircraft uses revolutionary Sustainable Aviation Fuel, SAF, and NASA’s DC-8 flies behind the Boeing plane to measure its impact throughout flight. The results of this study will be released publicly to facilitate the improvement of aviation technology worldwide.
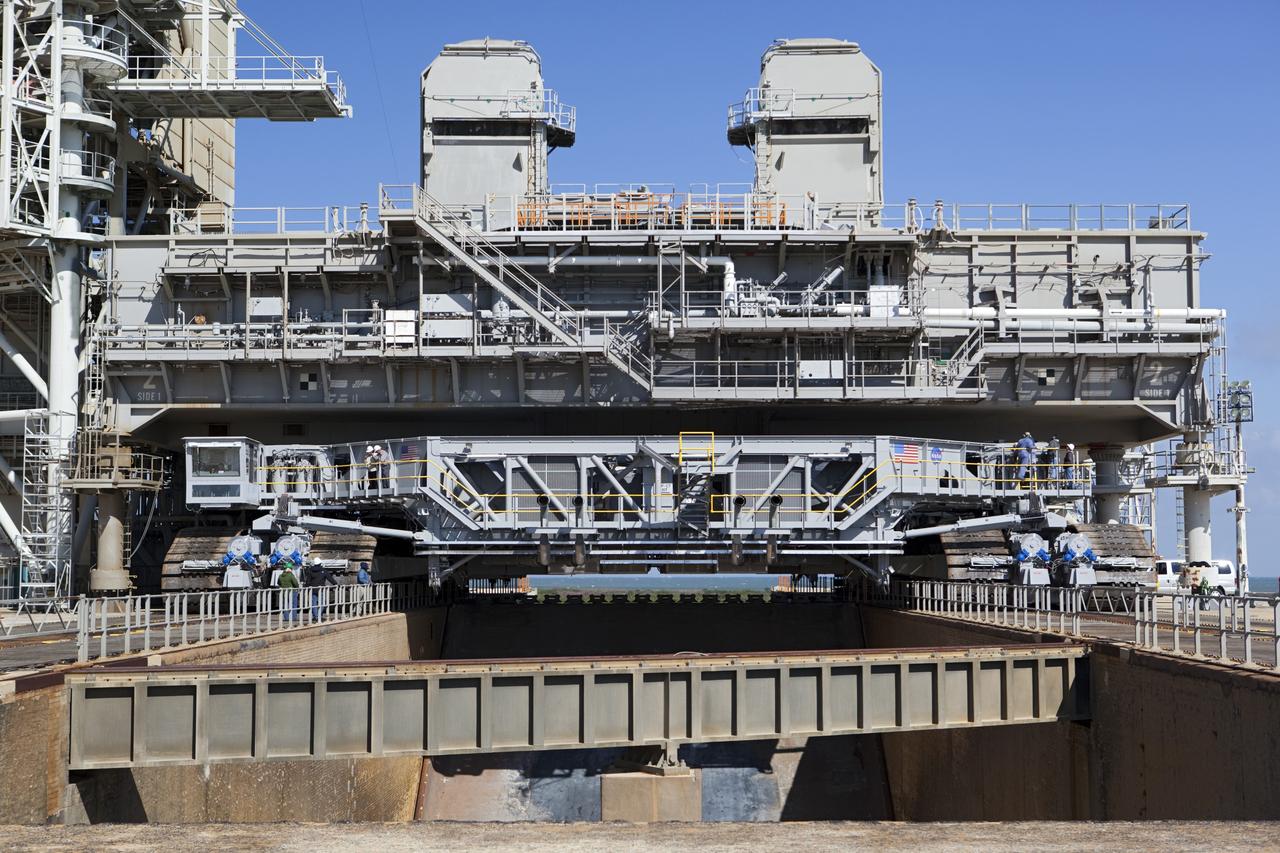

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crawler-transporter No. 2 arrives at Launch Pad 39A to check out recently completed modifications to ensure its ability to carry launch vehicles such as the space agency's Space Launch System heavy-lift rocket to the pad. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the 20-year life-extension project for the crawler. A pair of behemoth machines called crawler-transporters has carried the load of taking rockets and spacecraft to the launch pad for more than 40 years at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Each the size of a baseball infield and powered by locomotive and large electrical power generator engines, the crawler-transporters will stand ready to keep up the work for the next generation of launch vehicles to lift astronauts into space. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crawler-transporter No. 2 arrives at Launch Pad 39A to check out recently completed modifications to ensure its ability to carry launch vehicles such as the space agency's Space Launch System heavy-lift rocket to the pad. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the 20-year life-extension project for the crawler. A pair of behemoth machines called crawler-transporters has carried the load of taking rockets and spacecraft to the launch pad for more than 40 years at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Each the size of a baseball infield and powered by locomotive and large electrical power generator engines, the crawler-transporters will stand ready to keep up the work for the next generation of launch vehicles to lift astronauts into space. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Dimitri Gerondidakis

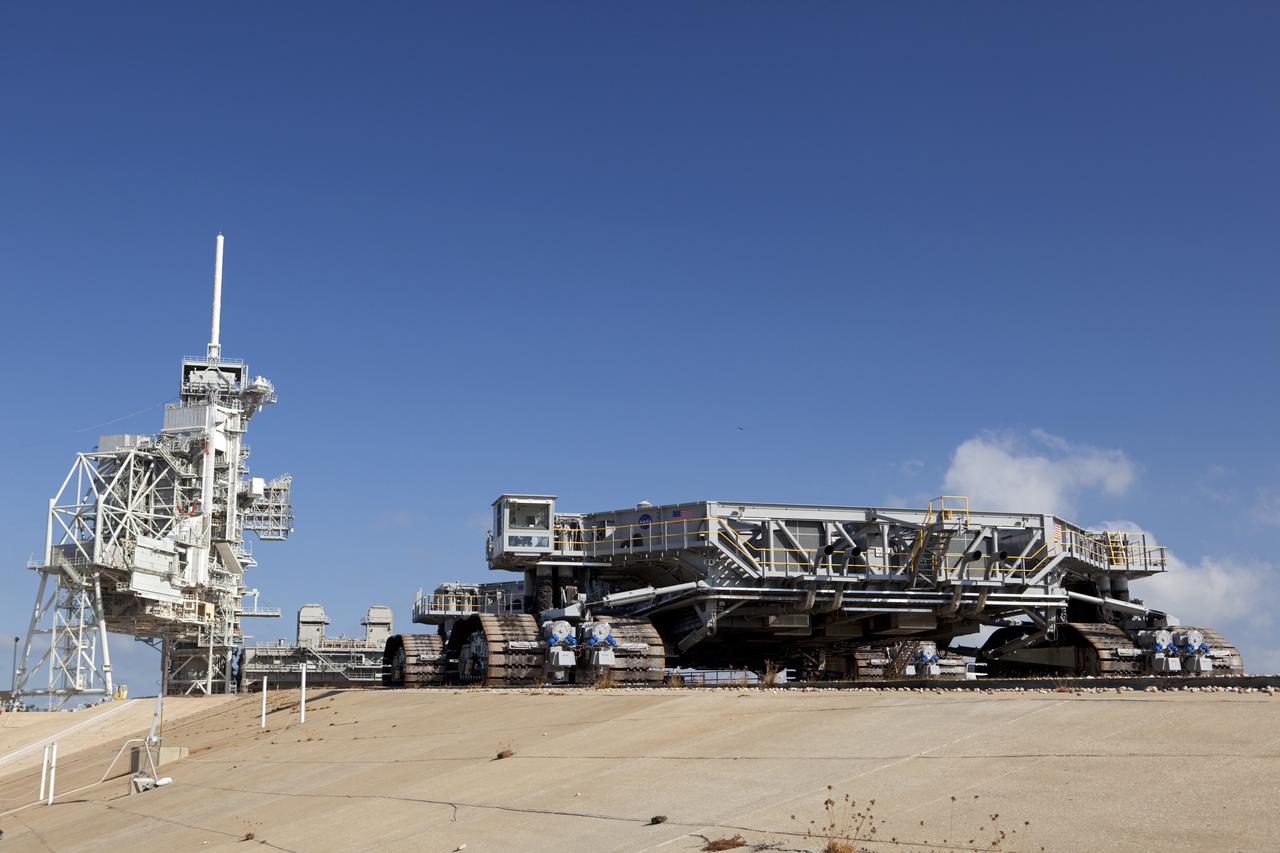
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crawler-transporter No. 2 has been undergoing modifications inside high bay 2 of the Vehicle Assembly Building in preparation to carry the space agency's Space Launch System heavy-lift rocket to the launch pad. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the 20-year life-extension project for the crawler. A pair of behemoth machines called crawler-transporters has carried the load of taking rockets and spacecraft to the launch pad for more than 40 years at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Each the size of a baseball infield and powered by locomotive and large electrical power generator engines, the crawler-transporters will stand ready to keep up the work for the next generation of launch vehicles projects to lift astronauts into space. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
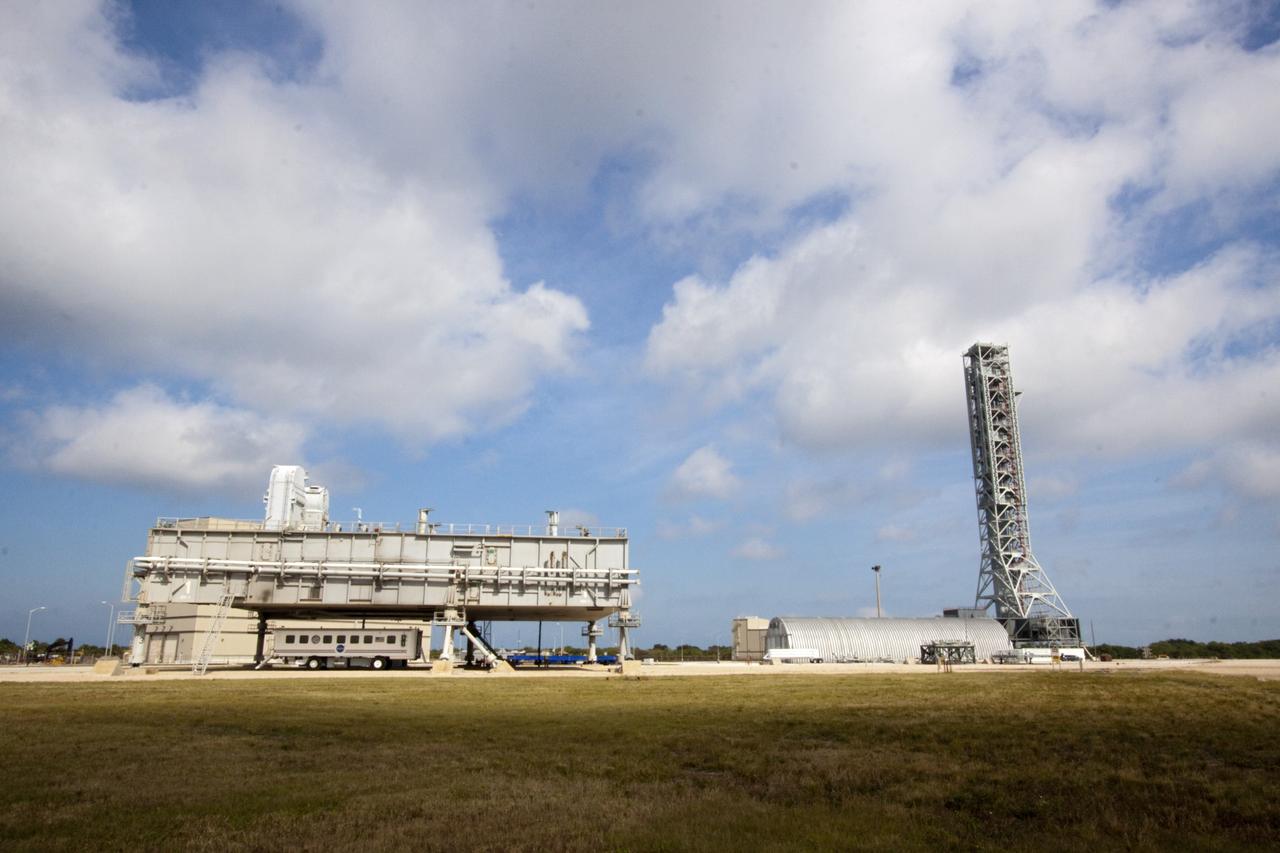

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space shuttle era mobile launcher platform, on the left, sits on pedestals outside the Vehicle Assembly Building. To the right is the mobile launcher that will support the space agency's Space Launch System heavy-lift rocket and Orion spacecraft. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the 20-year life-extension project for the crawler. A pair of behemoth machines called crawler-transporters has carried the load of taking rockets and spacecraft to the launch pad for more than 40 years at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Each the size of a baseball infield and powered by locomotive and large electrical power generator engines, the crawler-transporters will stand ready to keep up the work for the next generation of launch vehicles projects to lift astronauts into space. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
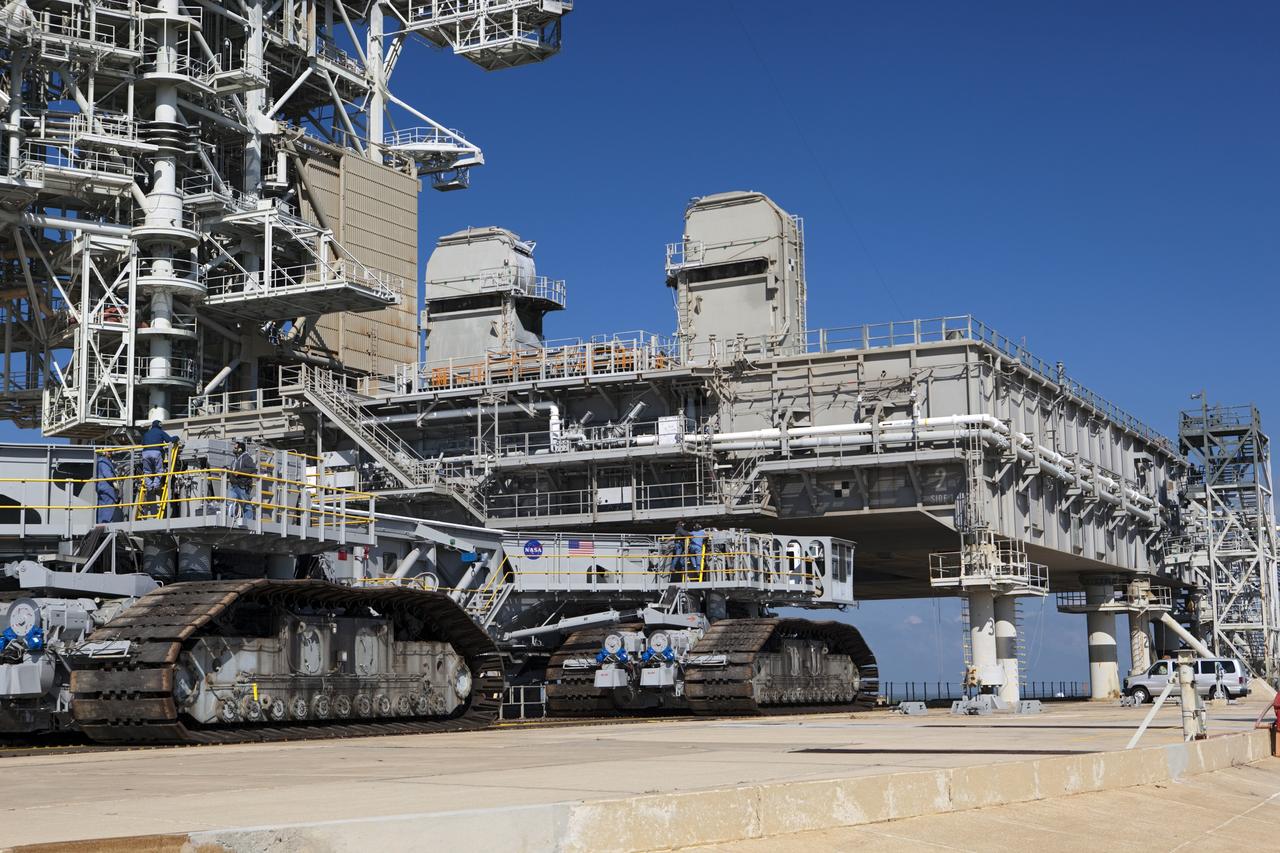

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crawler-transporter No. 2 arrives at Launch Pad 39A to check out recently completed modifications to ensure its ability to carry launch vehicles such as the space agency's Space Launch System heavy-lift rocket to the pad. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the 20-year life-extension project for the crawler. A pair of behemoth machines called crawler-transporters has carried the load of taking rockets and spacecraft to the launch pad for more than 40 years at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Each the size of a baseball infield and powered by locomotive and large electrical power generator engines, the crawler-transporters will stand ready to keep up the work for the next generation of launch vehicles to lift astronauts into space. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Dimitri Gerondidakis
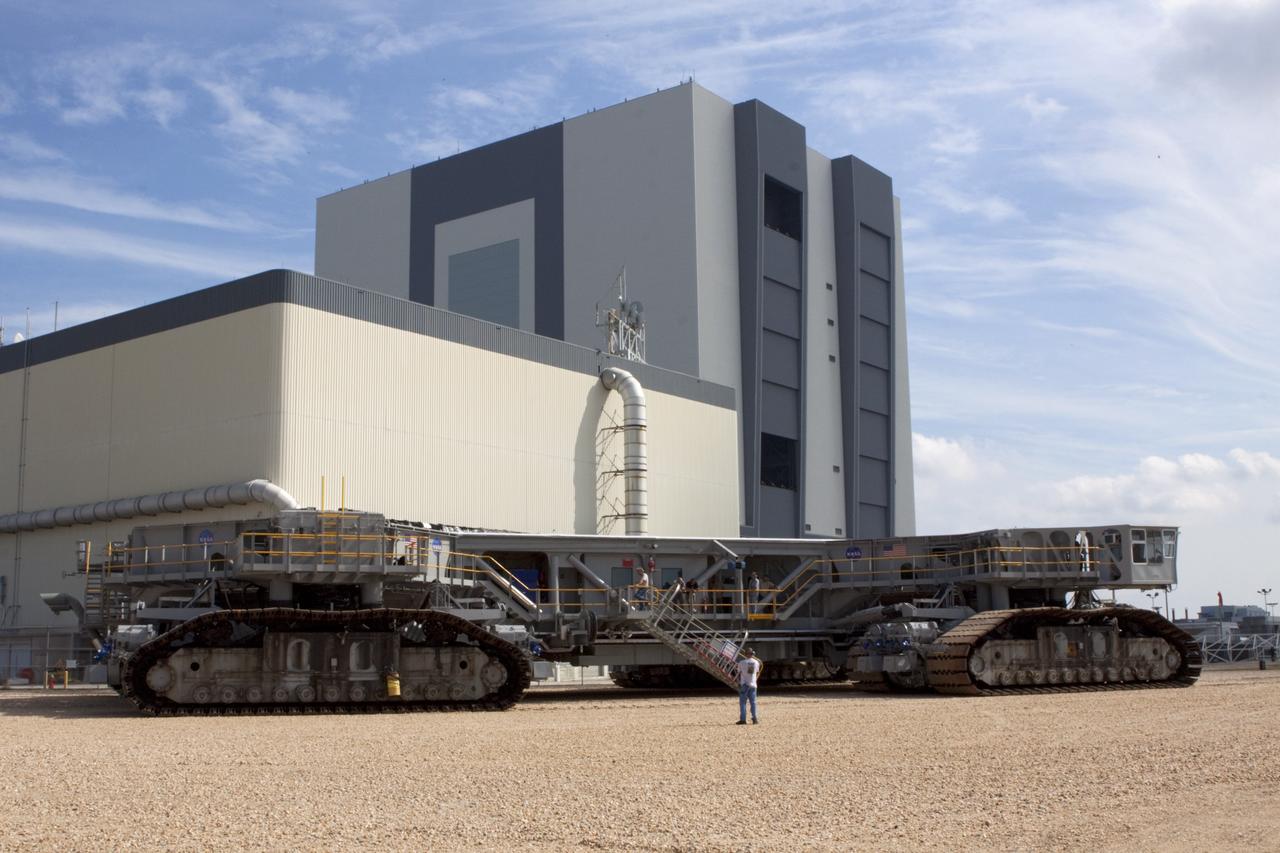

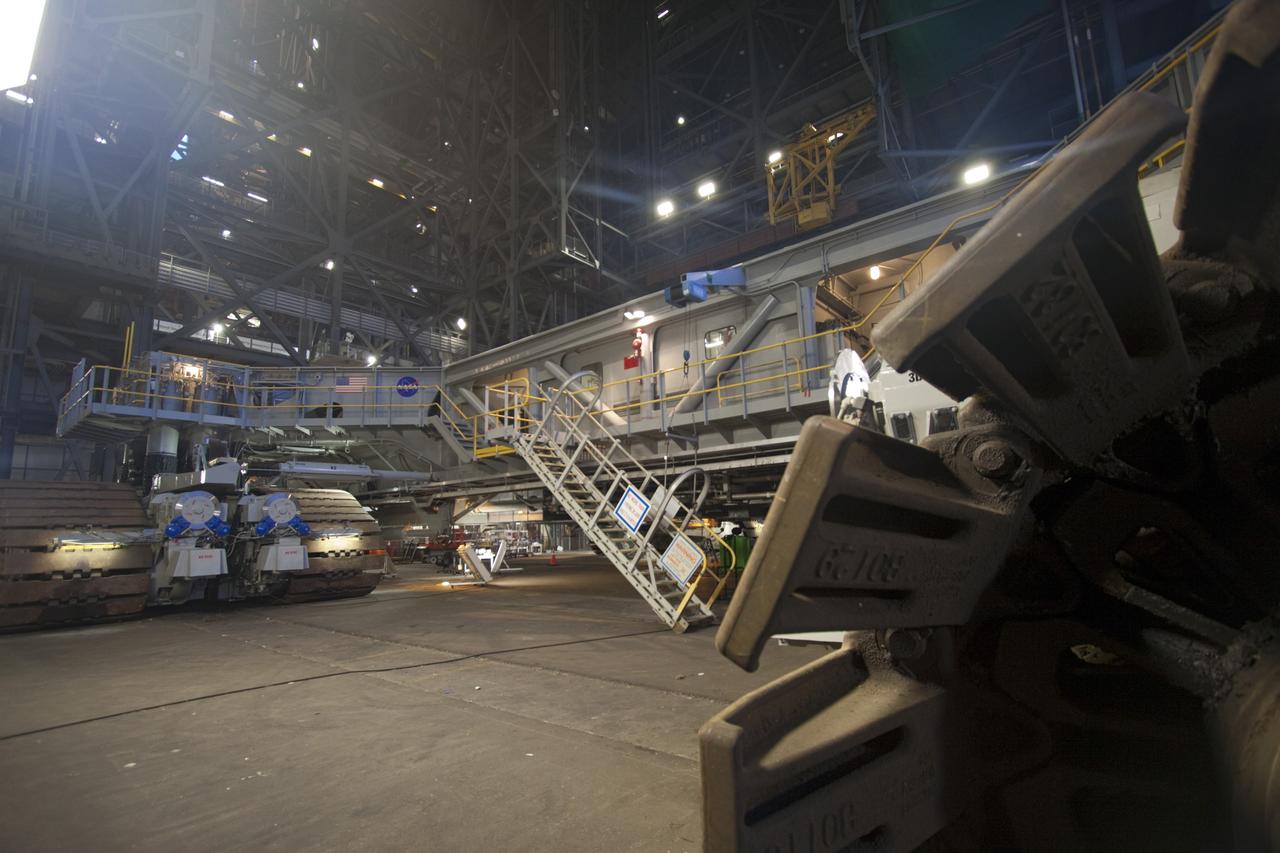
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crawler-transporter No. 2 is parked outside of the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Crawler-transporter has been undergoing modifications to ensure its ability to carry the space agency's Space Launch System heavy-lift rocket to the launch pad. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the 20-year life-extension project for the crawler. A pair of behemoth machines called crawler-transporters has carried the load of taking rockets and spacecraft to the launch pad for more than 40 years at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Each the size of a baseball infield and powered by locomotive and large electrical power generator engines, the crawler-transporters will stand ready to keep up the work for the next generation of launch vehicles projects to lift astronauts into space. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
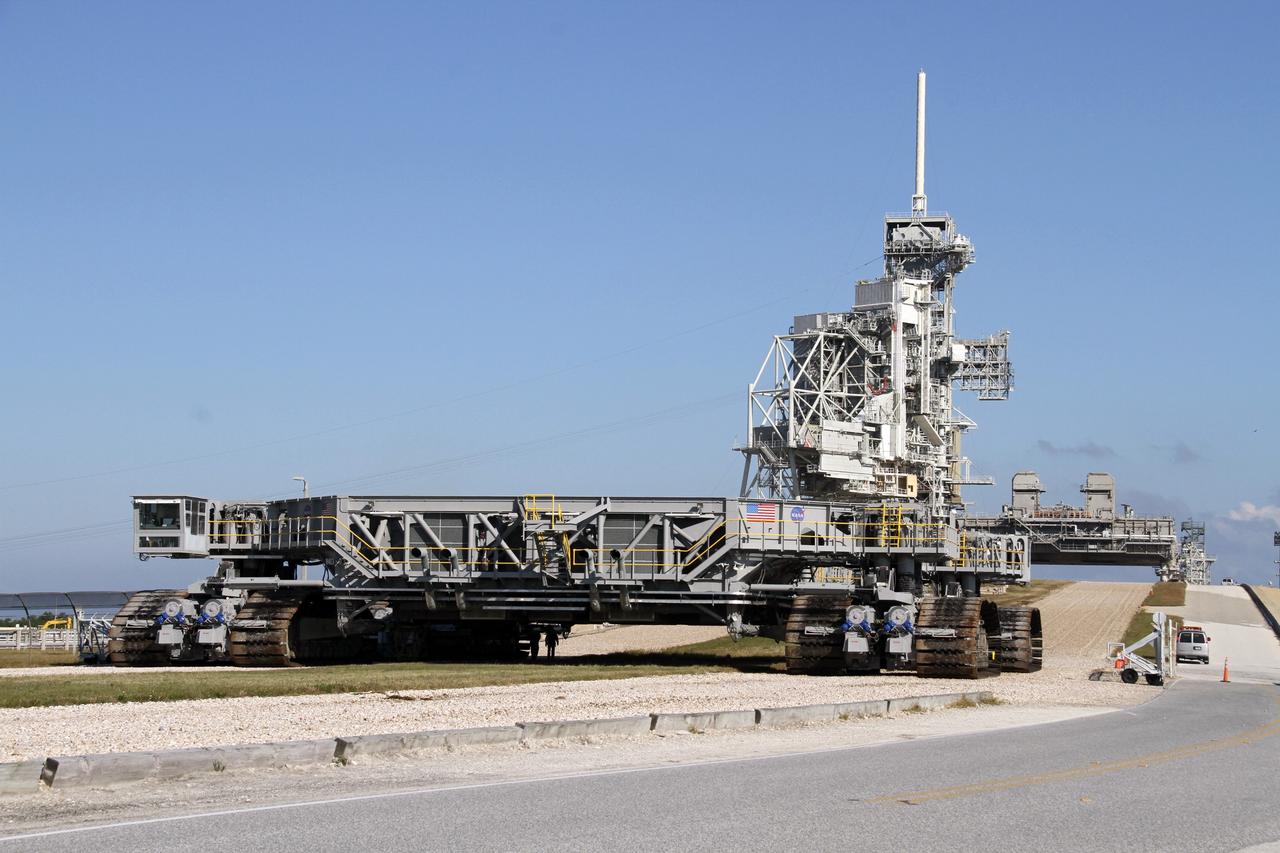

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crawler-transporter No. 2 arrives at Launch Pad 39A to check out recently completed modifications to ensure its ability to carry launch vehicles such as the space agency's Space Launch System heavy-lift rocket to the pad. NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the 20-year life-extension project for the crawler. A pair of behemoth machines called crawler-transporters has carried the load of taking rockets and spacecraft to the launch pad for more than 40 years at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Each the size of a baseball infield and powered by locomotive and large electrical power generator engines, the crawler-transporters will stand ready to keep up the work for the next generation of launch vehicles projects to lift astronauts into space. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky