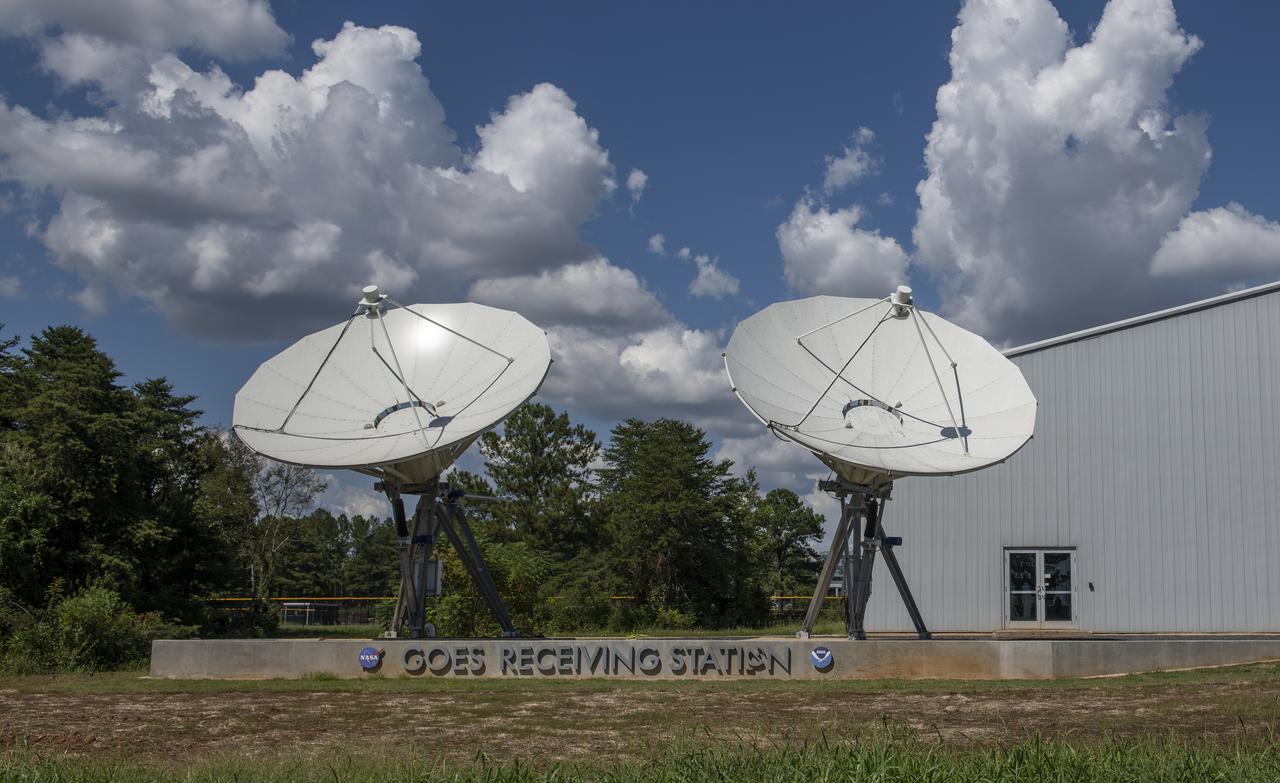

The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) photographed prior to the dedication of the site on September 21, 2018.
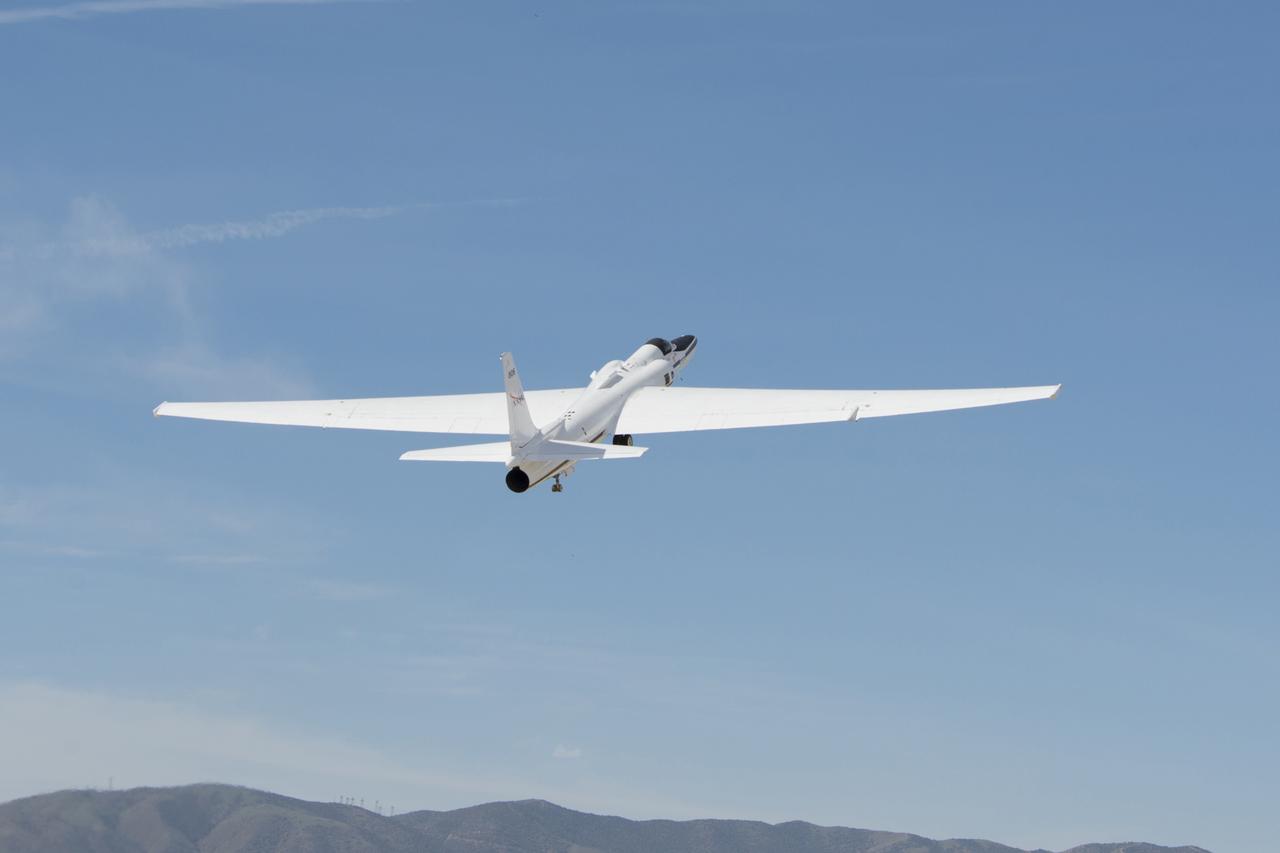

NASA’s ER-2 takes off from its base of operations at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California to test instruments that will support upcoming science flights for the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-R-series.

The mission insignia of NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) mission is pictured in front of the satellite in a vertical position on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
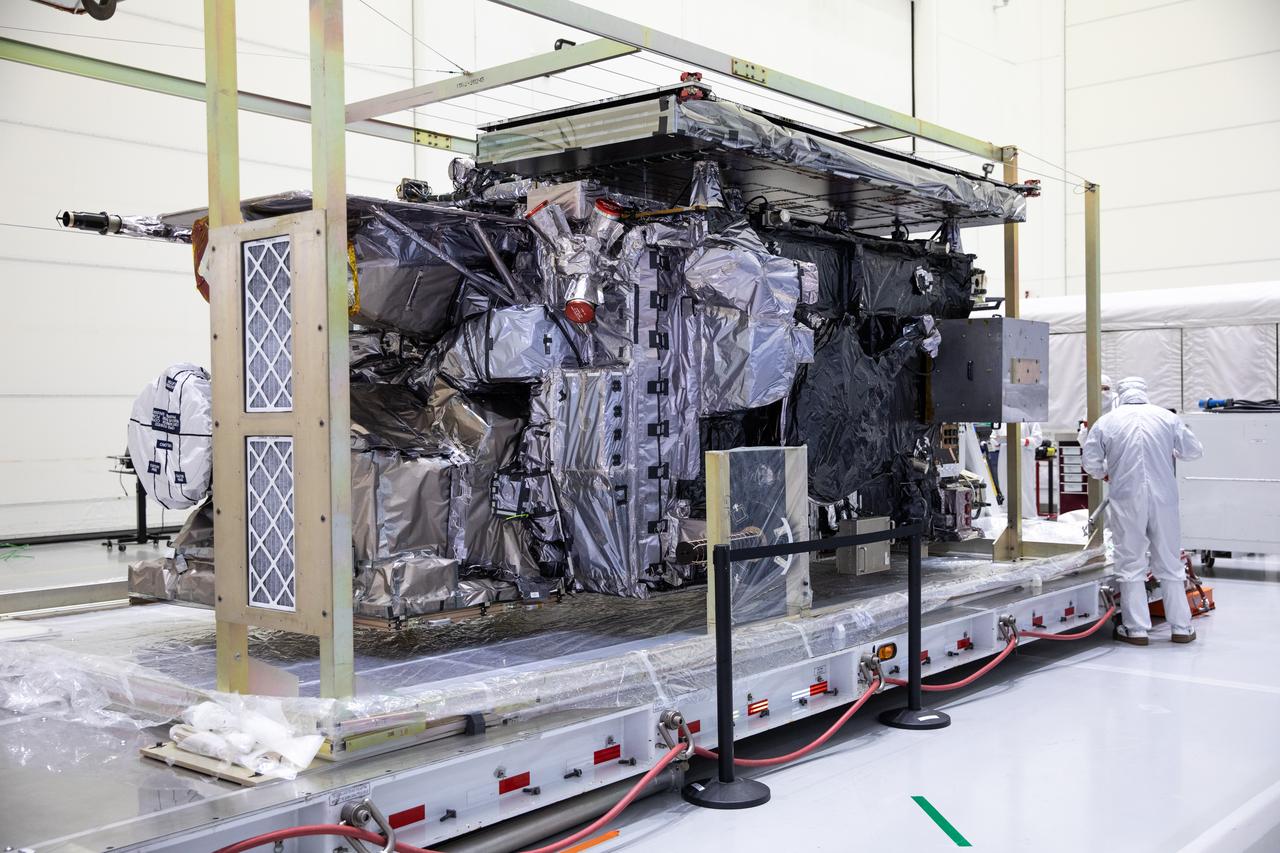

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is uncrated for prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the final in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
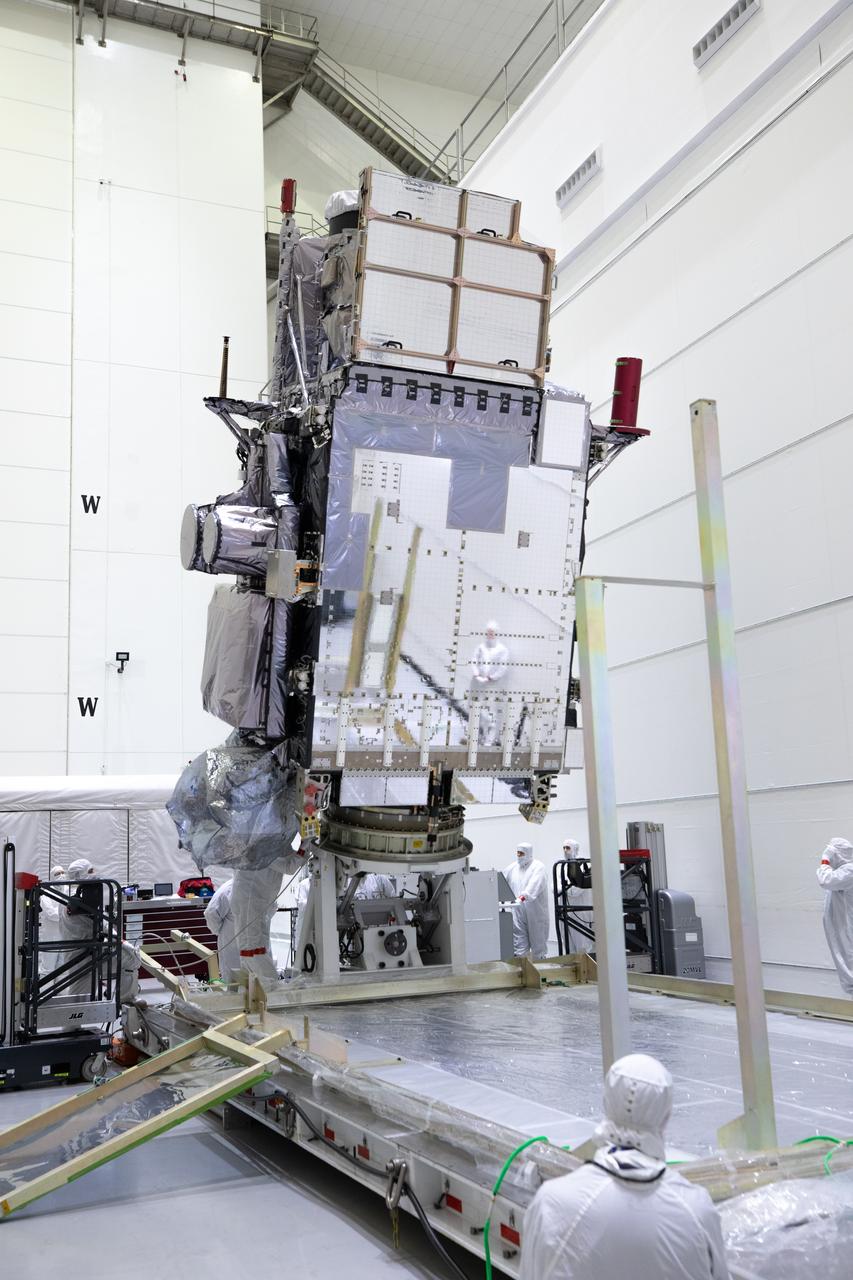

Technicians prepare to rotate NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) vertical after being uncrated on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
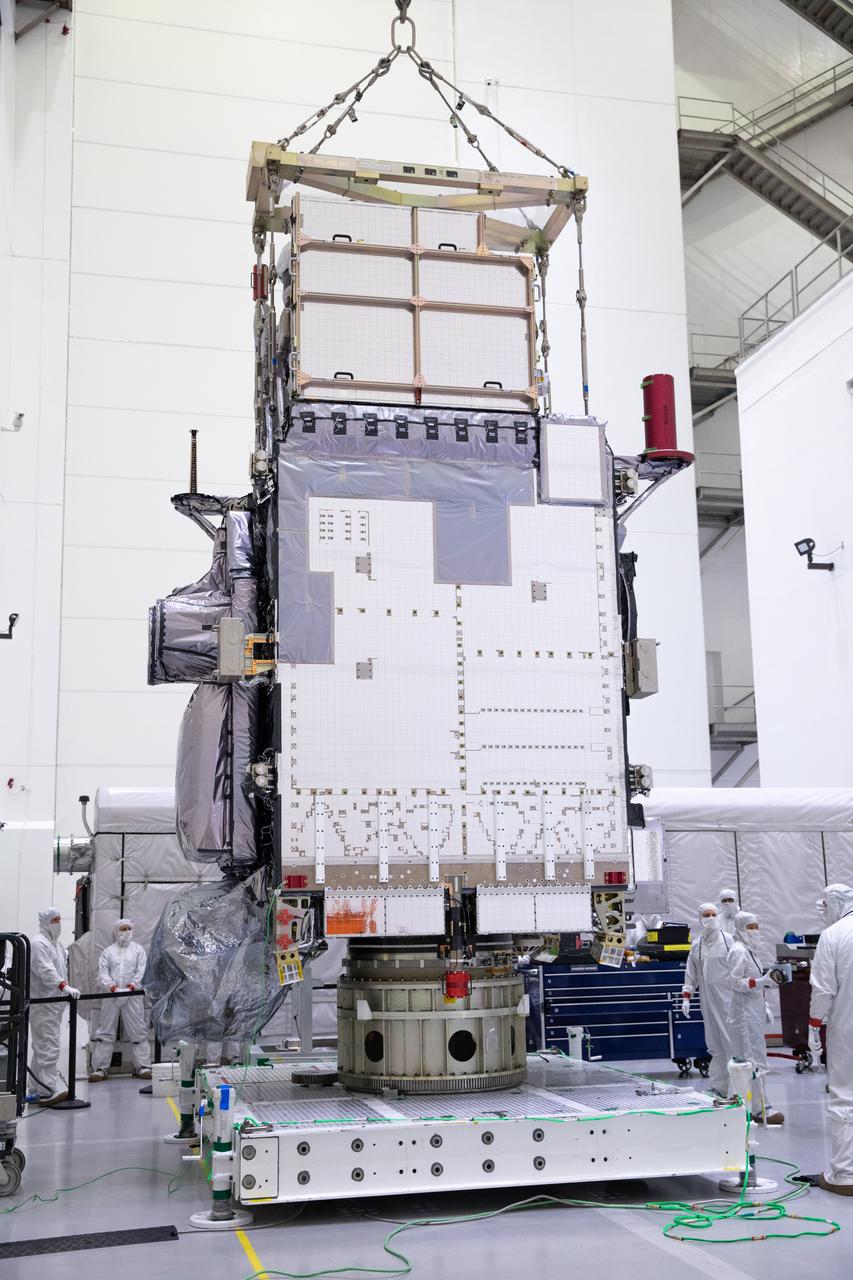
Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
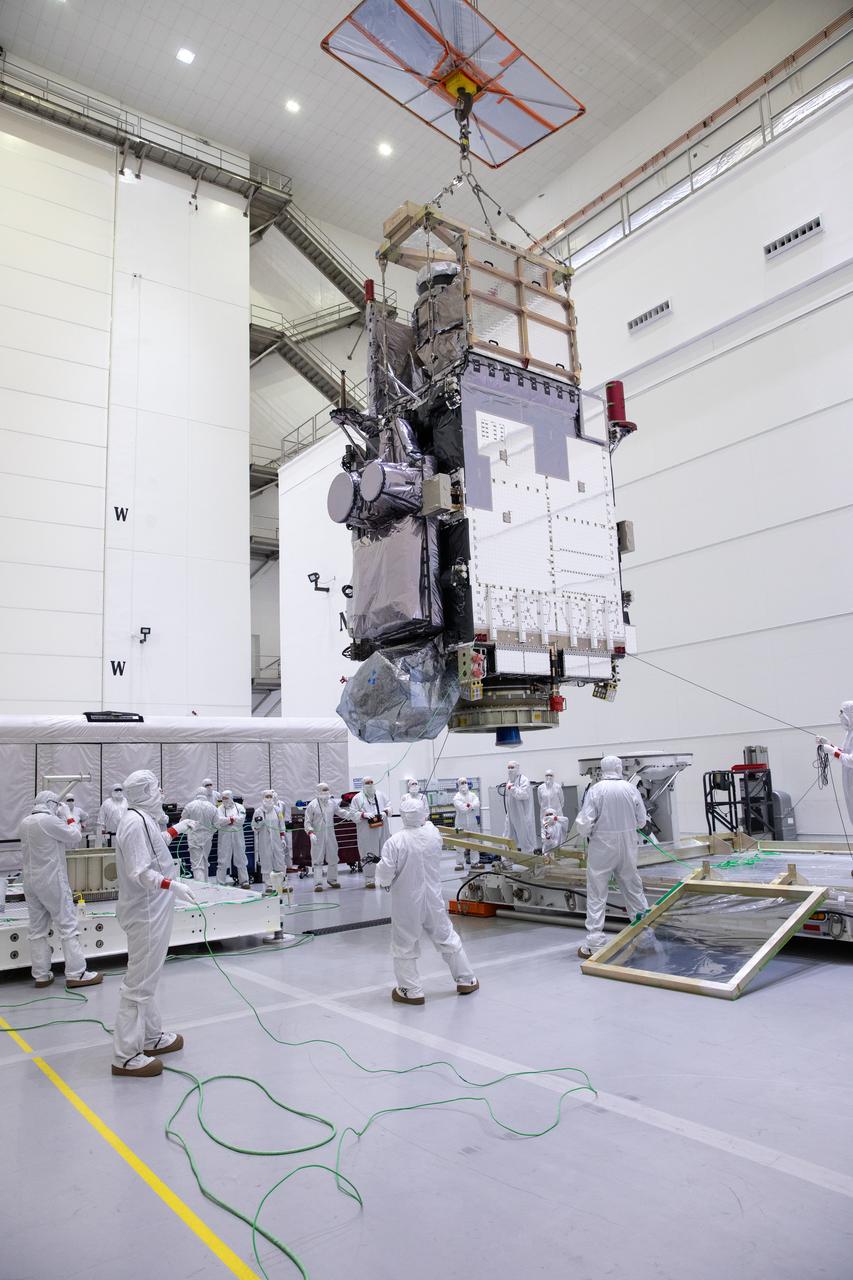

Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) after being uncrated and rotated into a vertical position on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
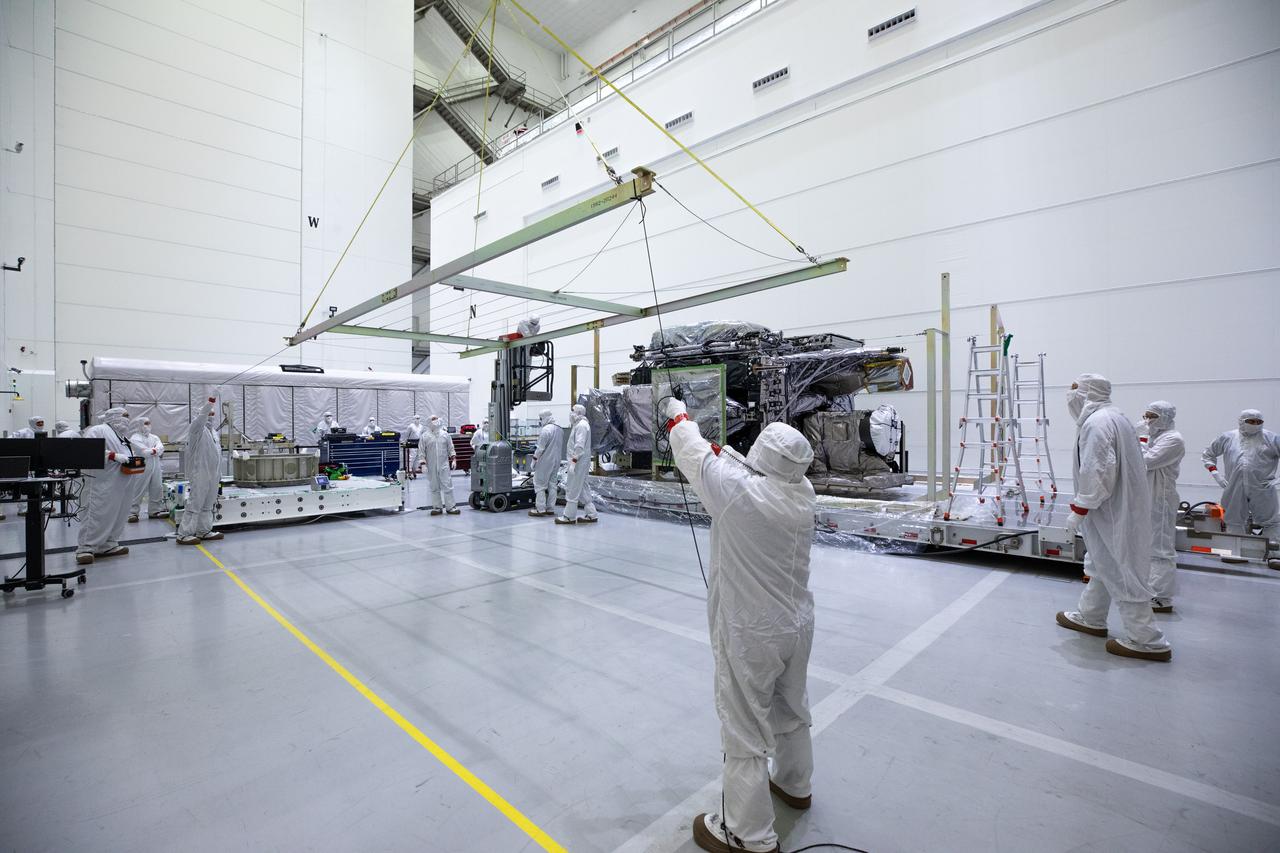

Technicians remove part of a protective enclosure as they prepare to rotate NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) vertical after being uncrated on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
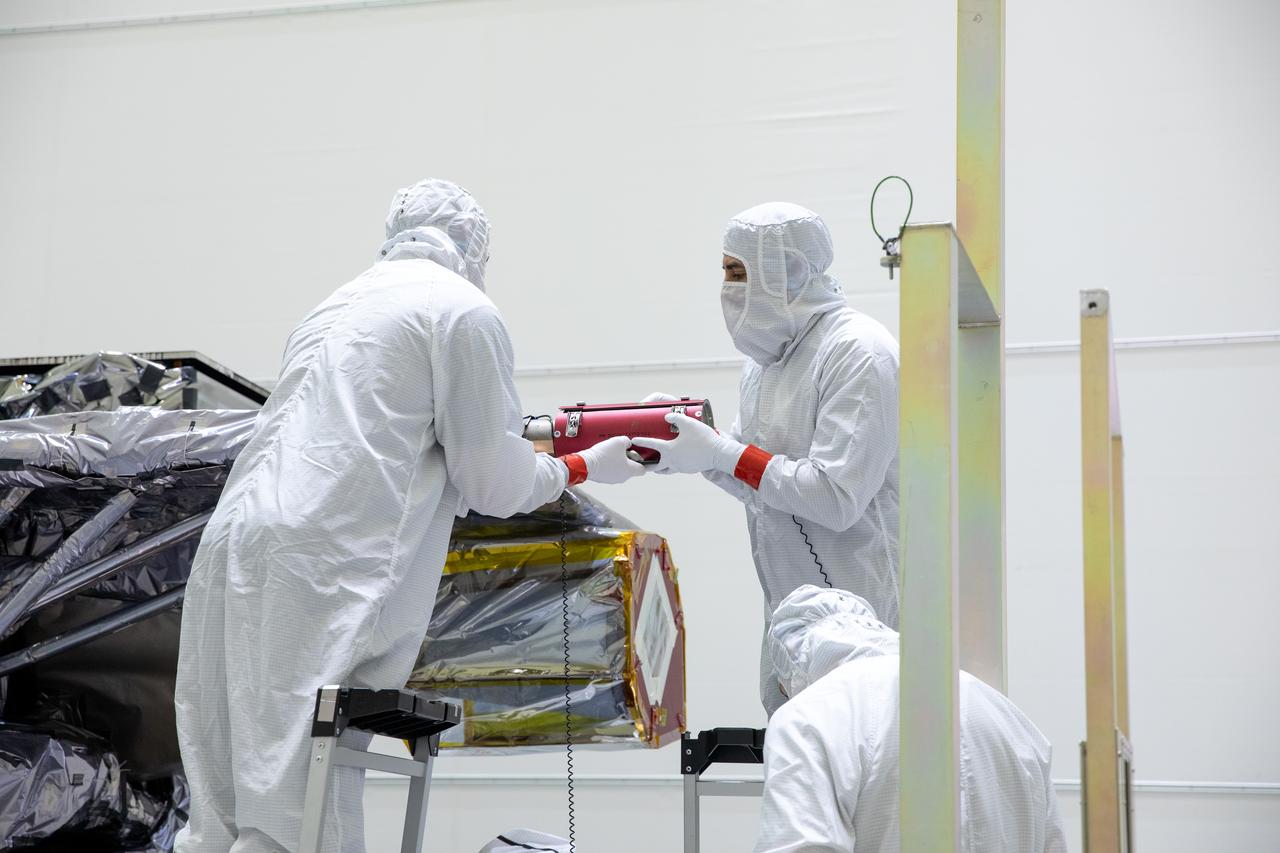

Technicians prepare to rotate NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) vertical after being uncrated on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
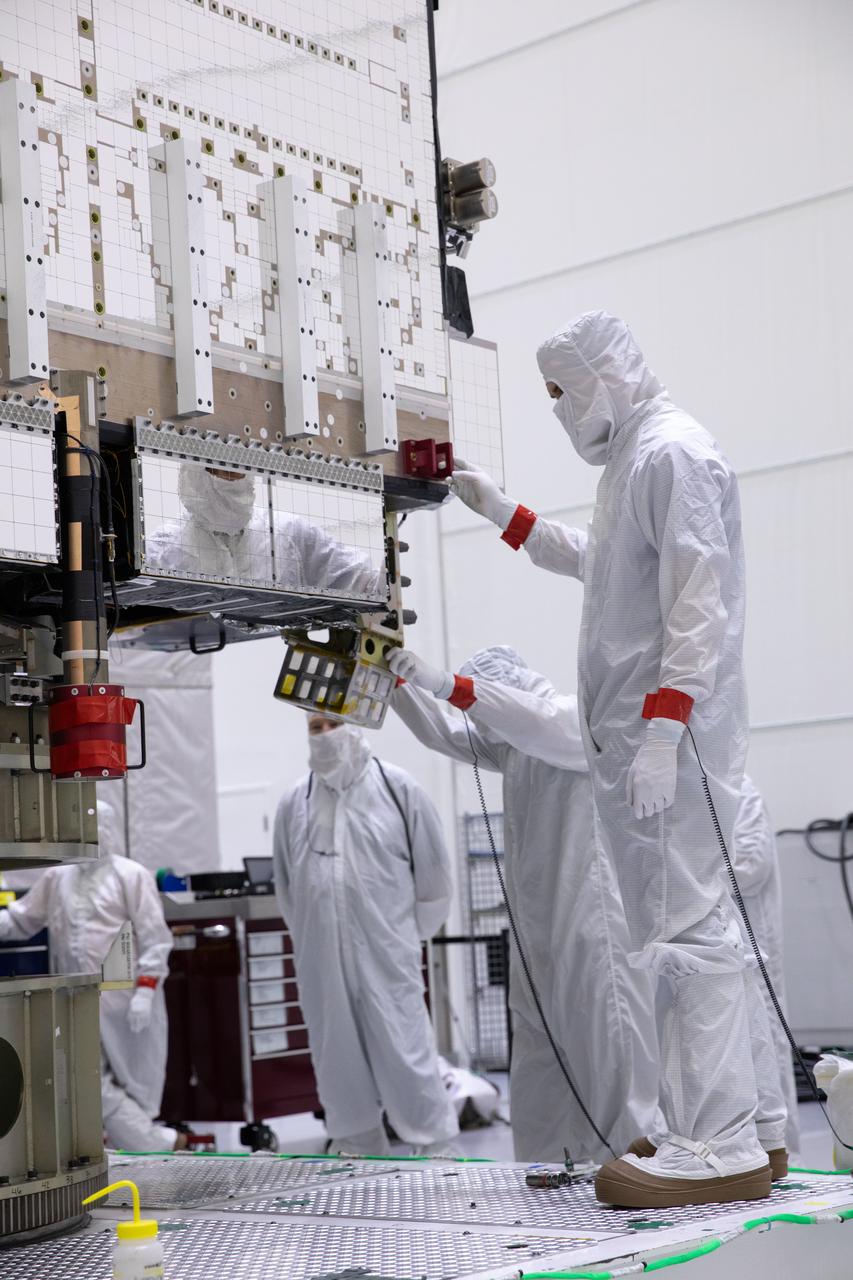

Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
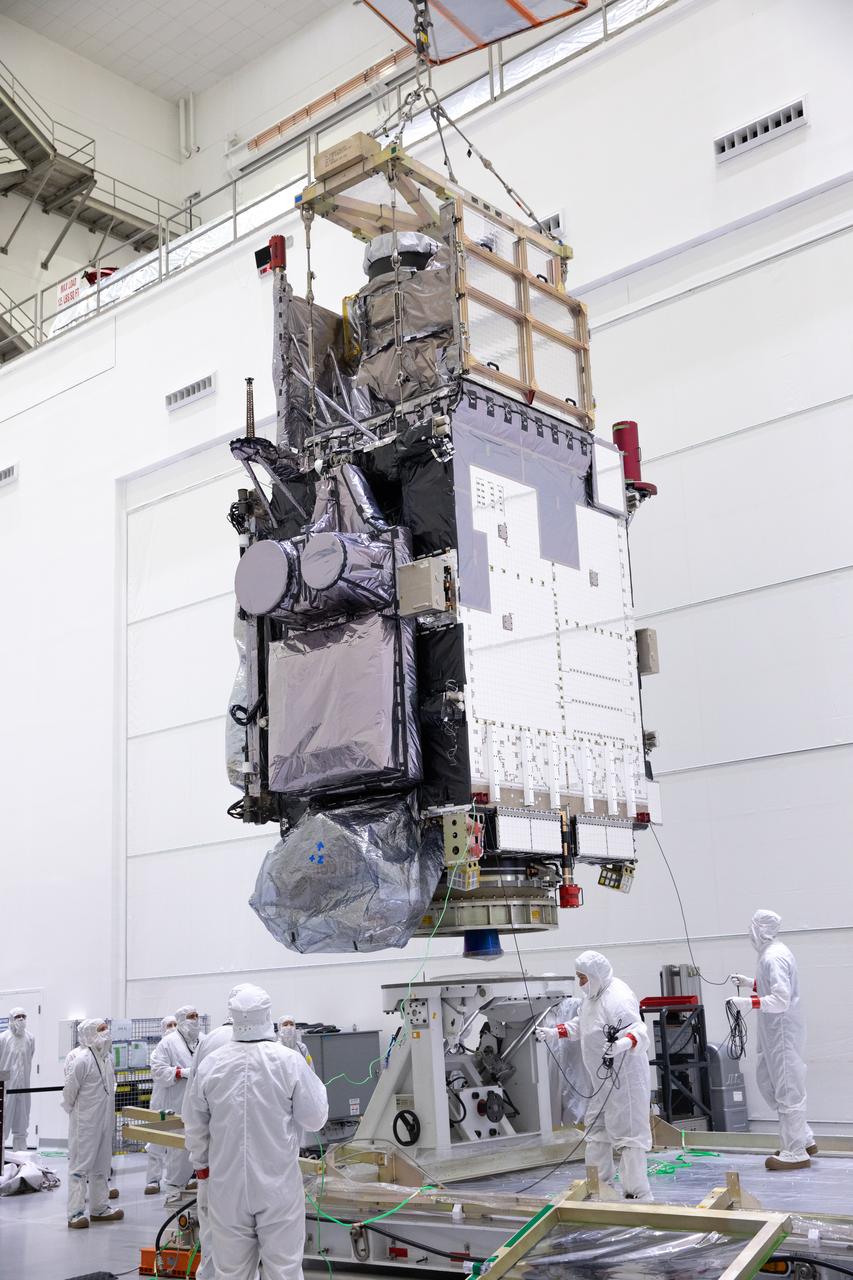

Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) after being uncrated and rotated into a vertical position on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
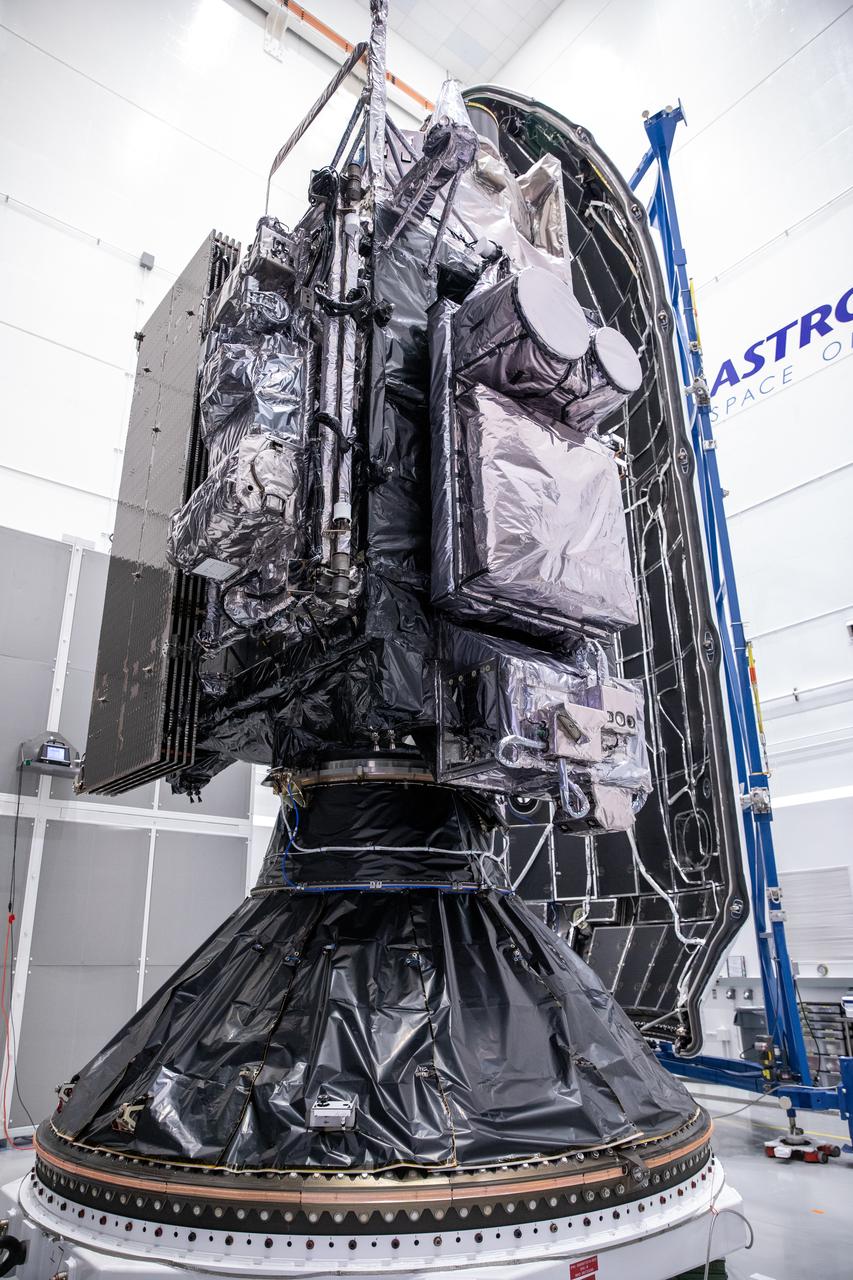

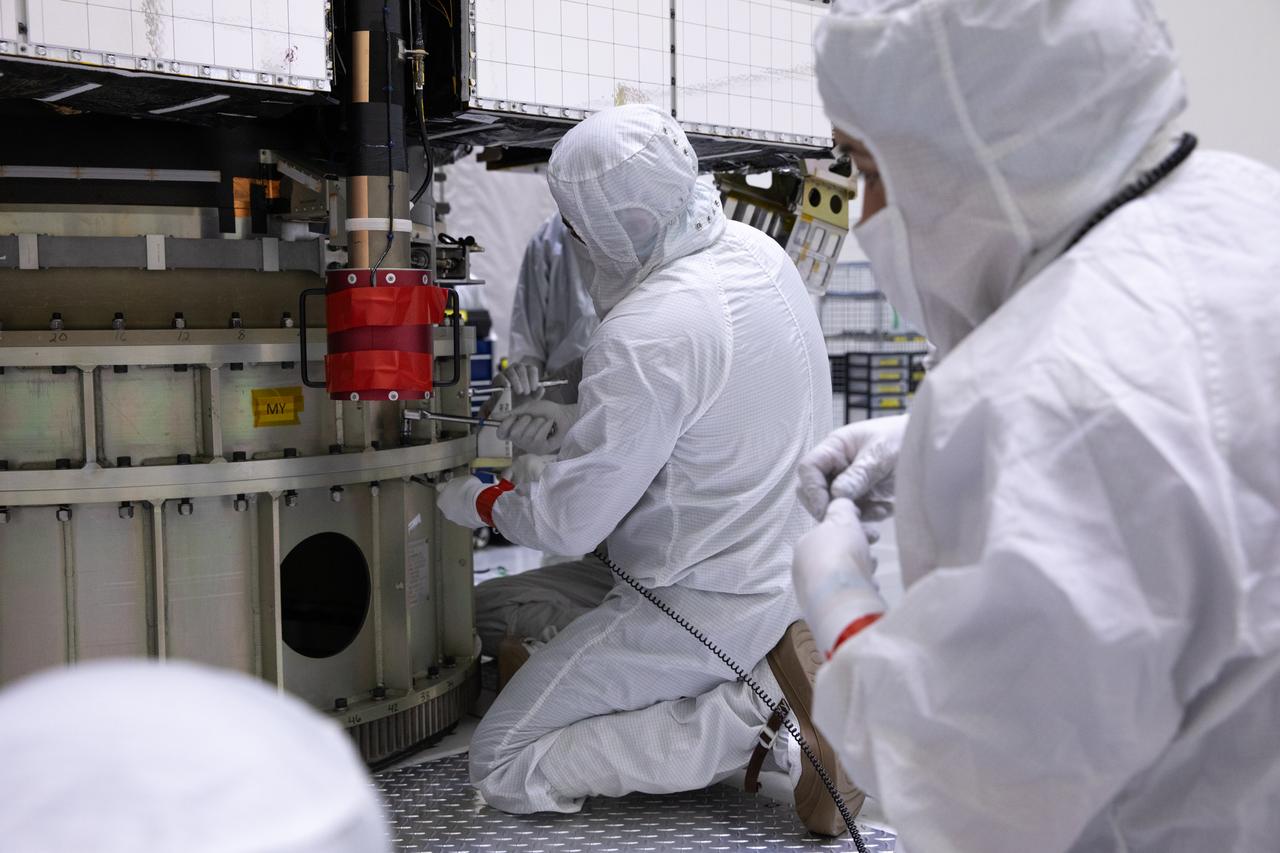
Technicians at the Astrotech Space Operations facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida connect NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) to the payload adapter on Thursday, June 13, 2024, in preparation for its upcoming launch. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
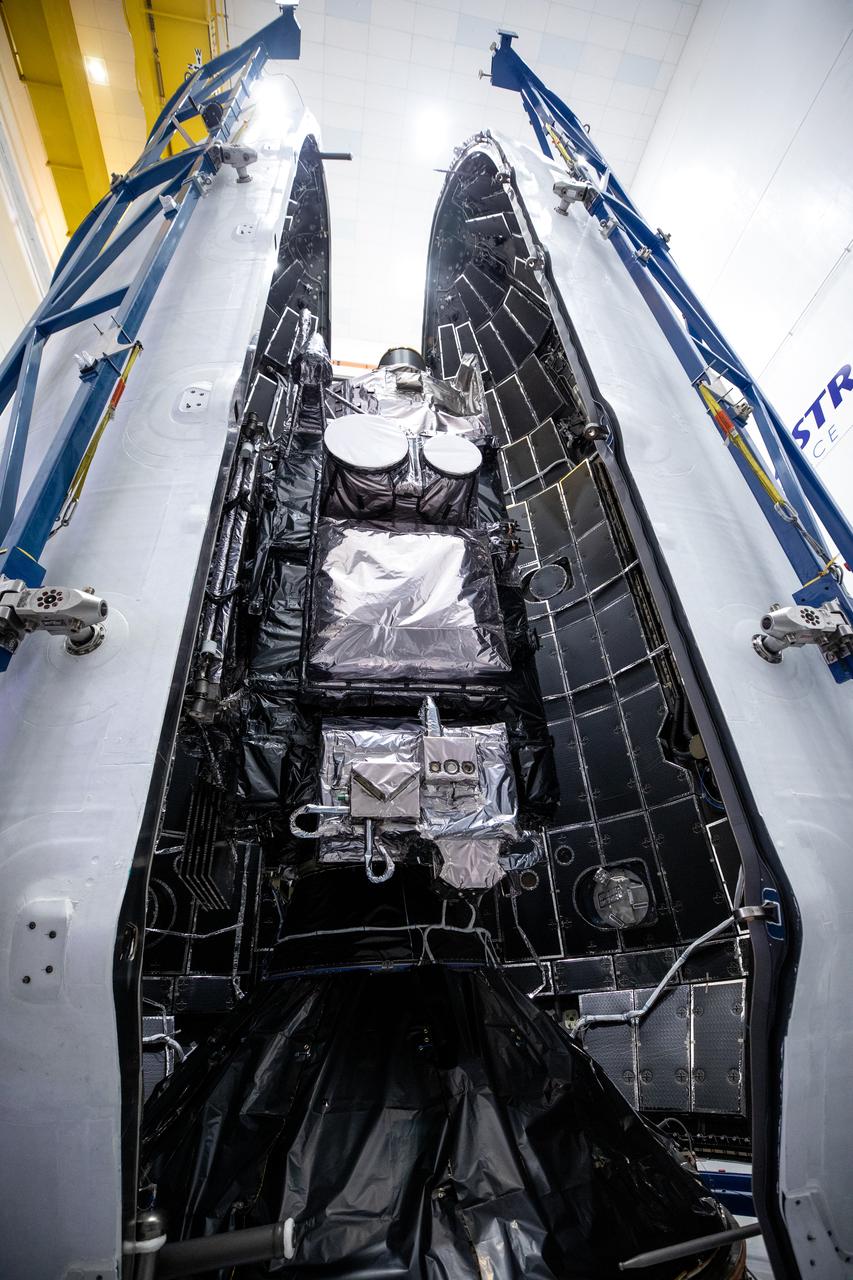

Technicians prepare NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) for encapsulation inside payload fairing halves on Thursday, June 13, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
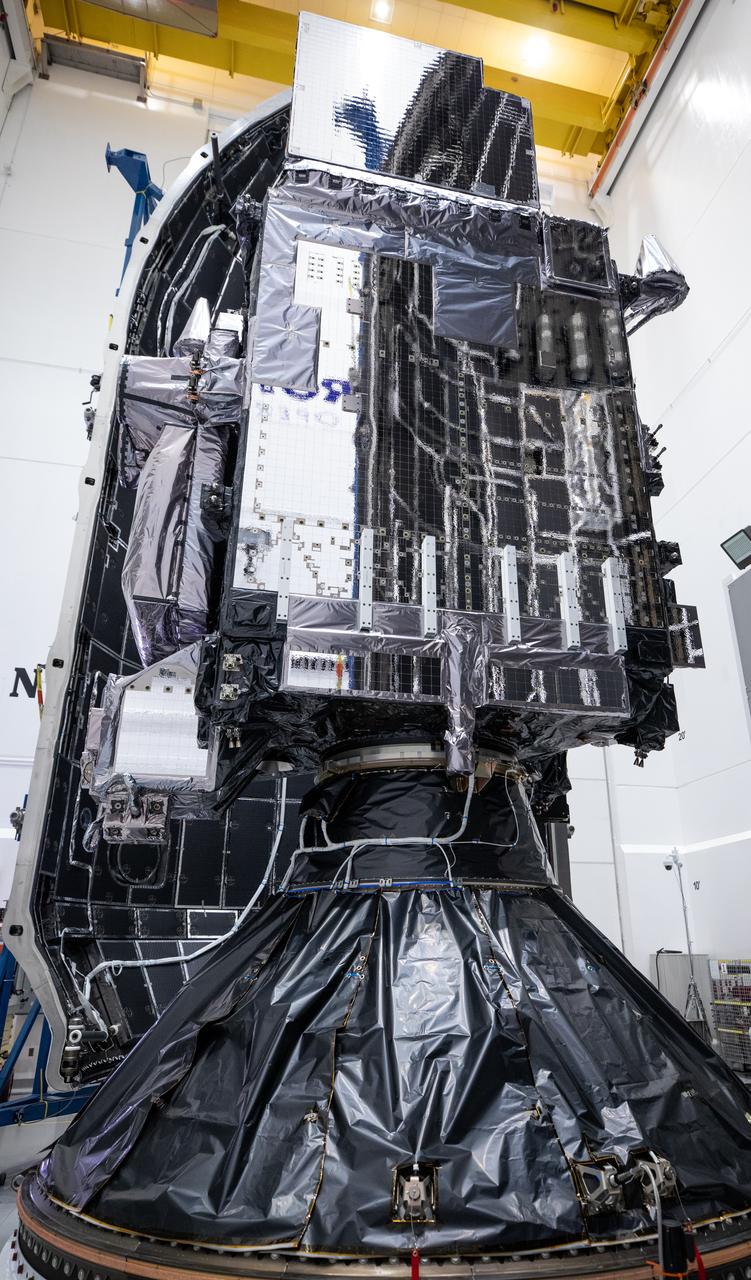

Technicians at the Astrotech Space Operations facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida connect NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) to the payload adapter on Thursday, June 13, 2024, in preparation for its upcoming launch. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
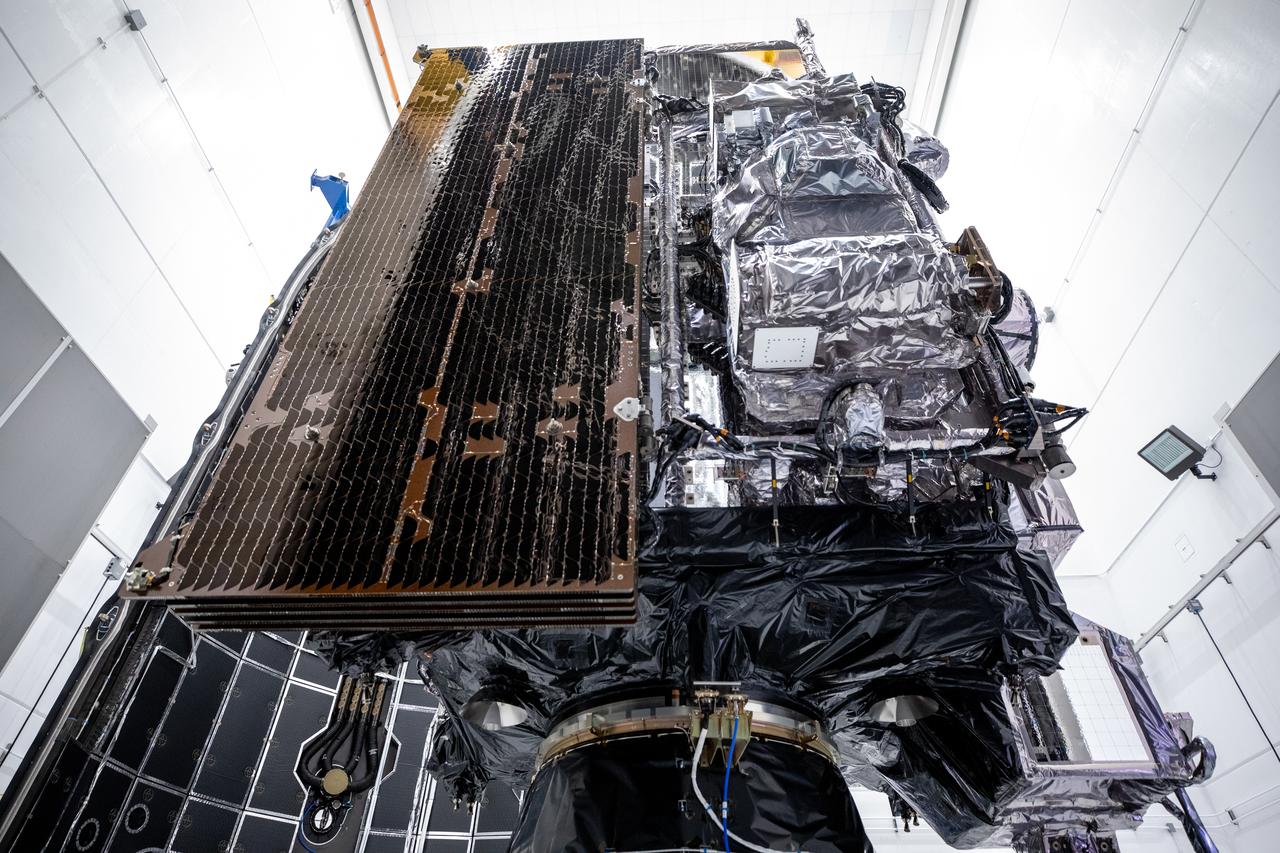

Technicians prepare NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) for encapsulation inside payload fairing halves on Thursday, June 13, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
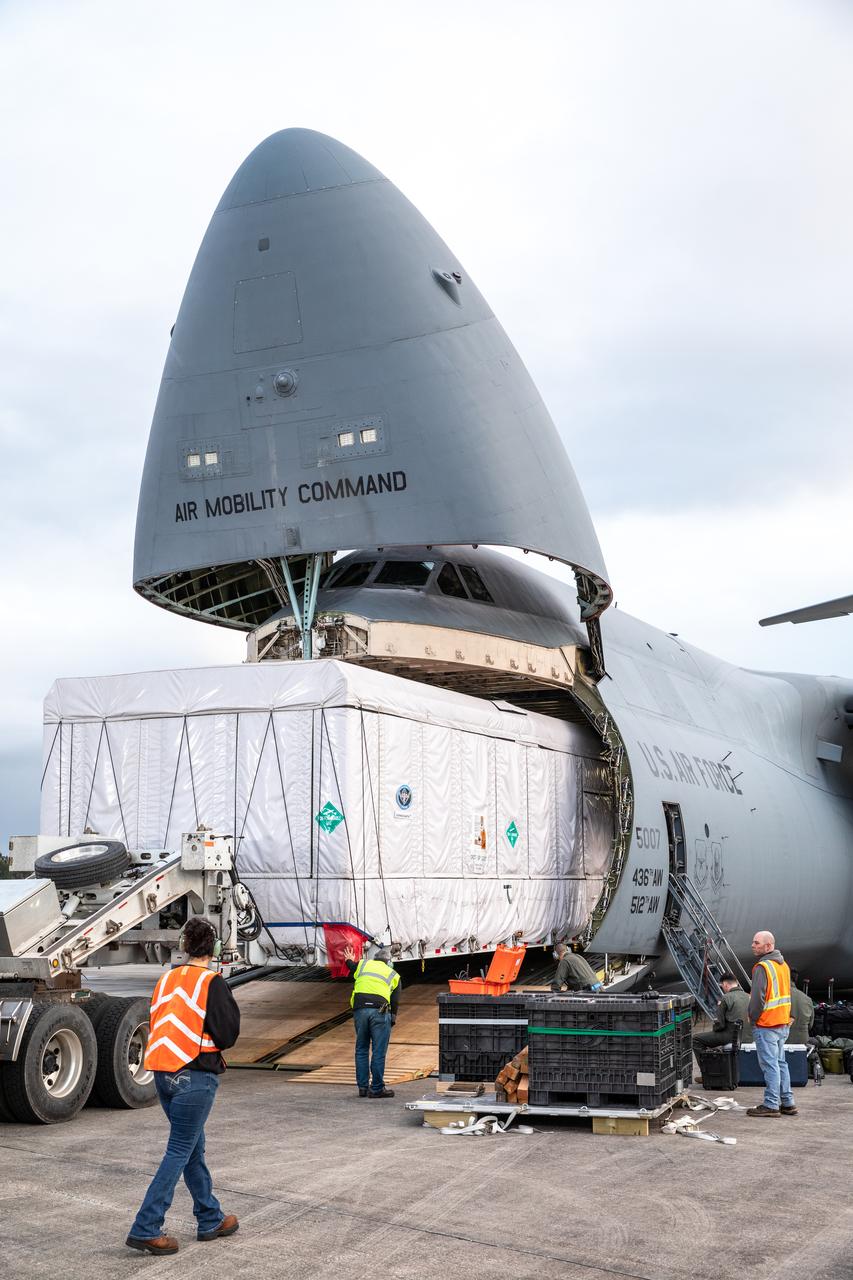

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
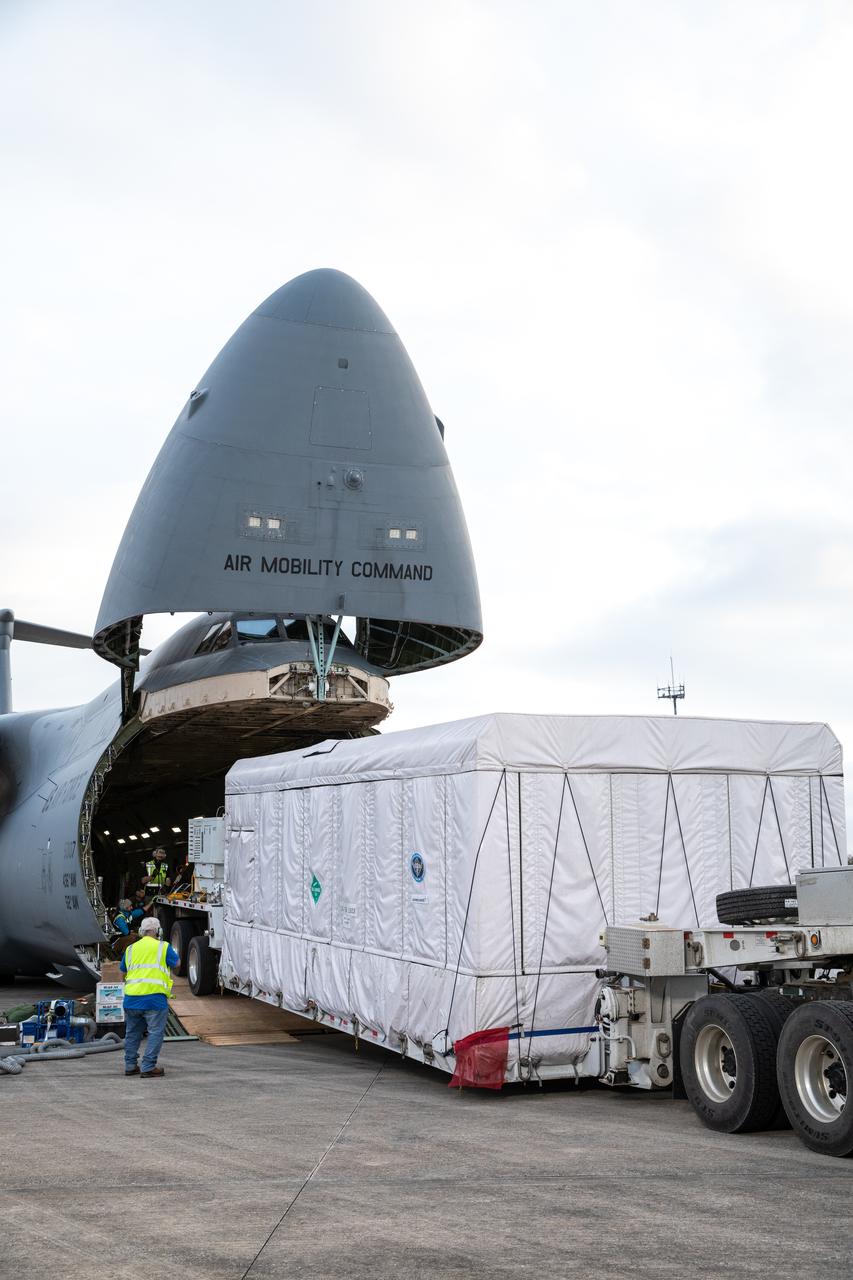

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
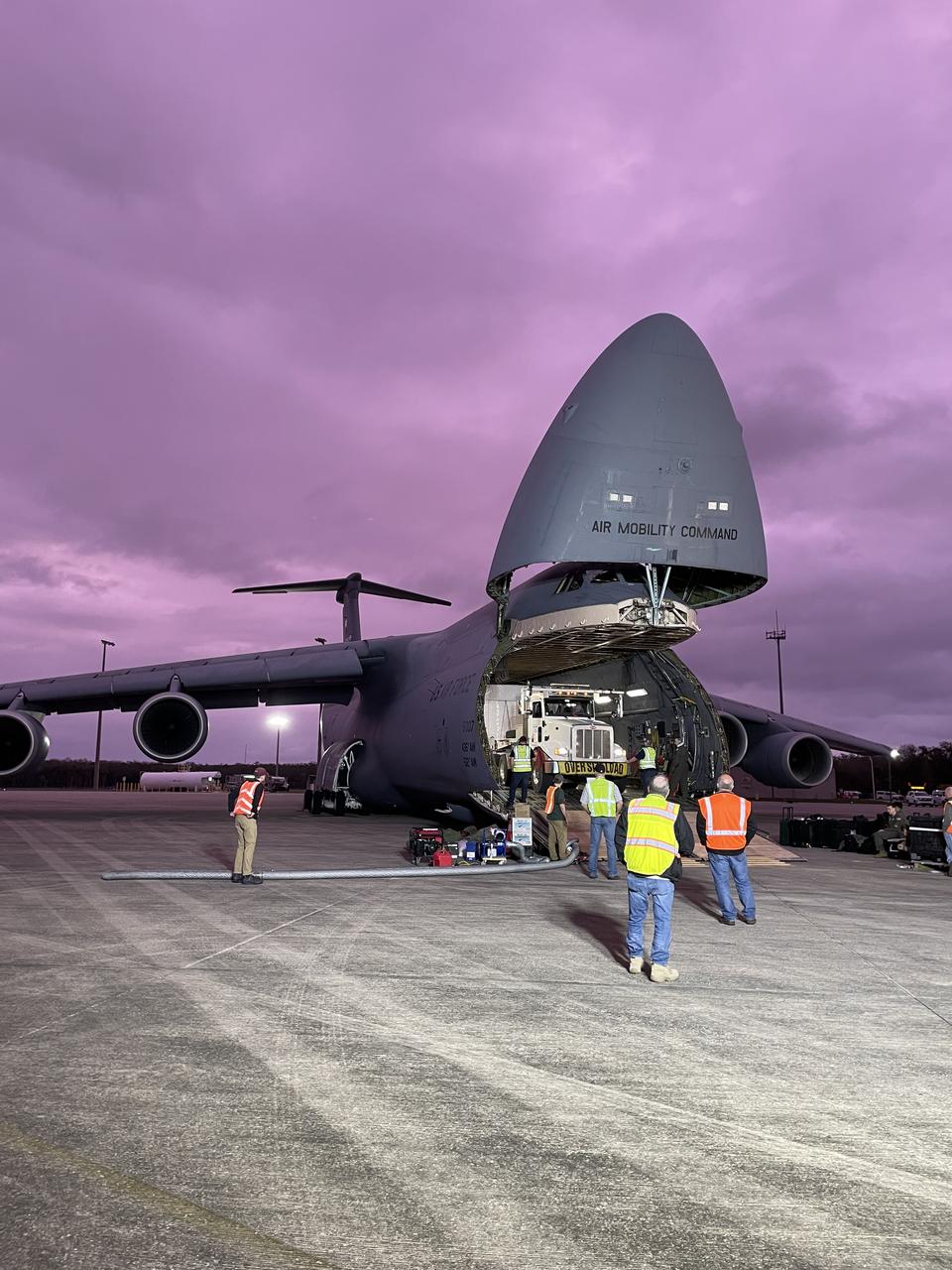

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is offloaded from a C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft onto the flatbed of a heavy-lift truck at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
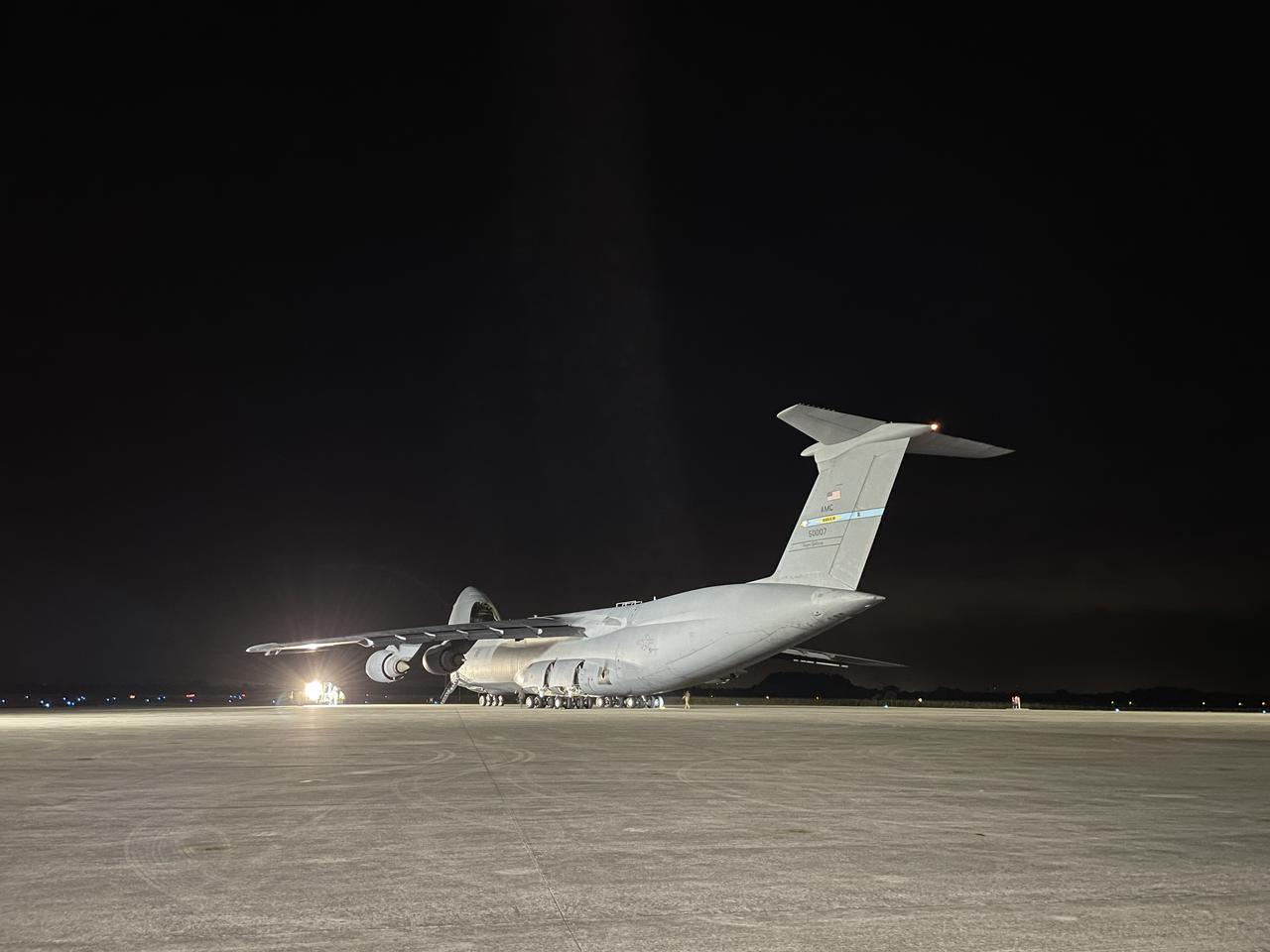

A C-5M Super Galaxy transport aircraft carrying NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) arrives at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024. Crews offloaded and transported the satellite to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in nearby Titusville, Florida to prepare it for launch. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
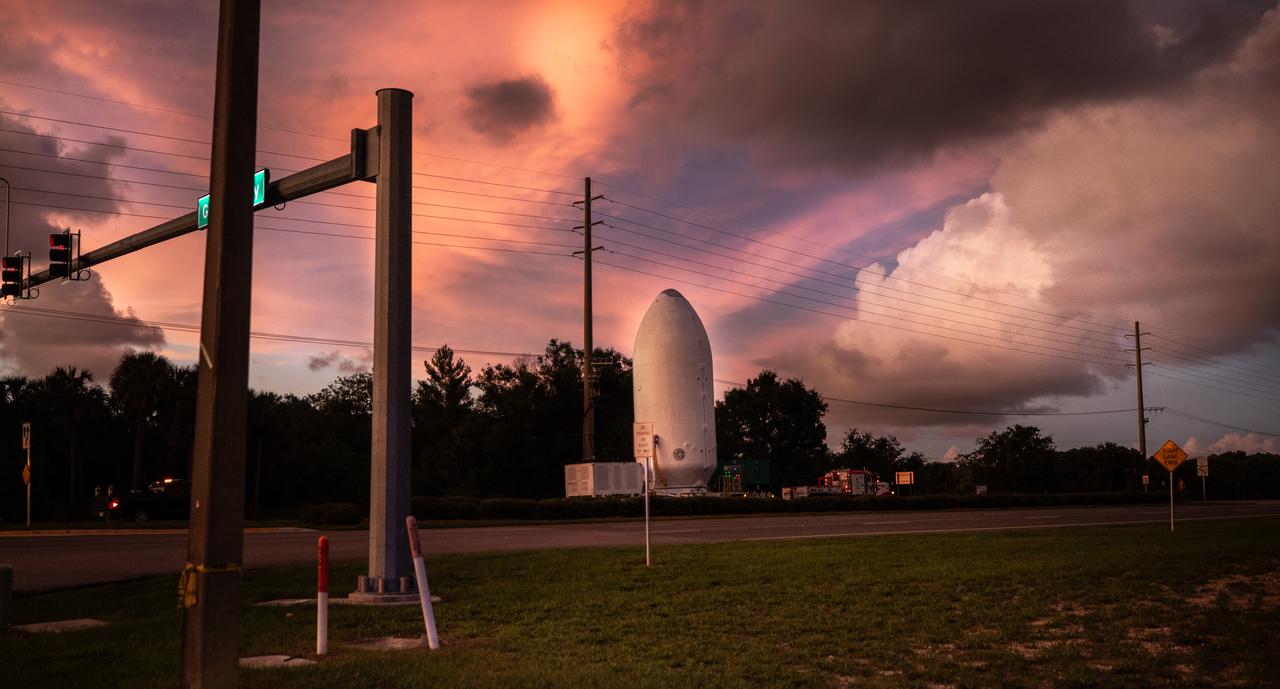

Crews transport NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) from the Astrotech Space Operations facility to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning on Friday, June 14, 2024, with the operation finishing early Saturday, June 15, 2024. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
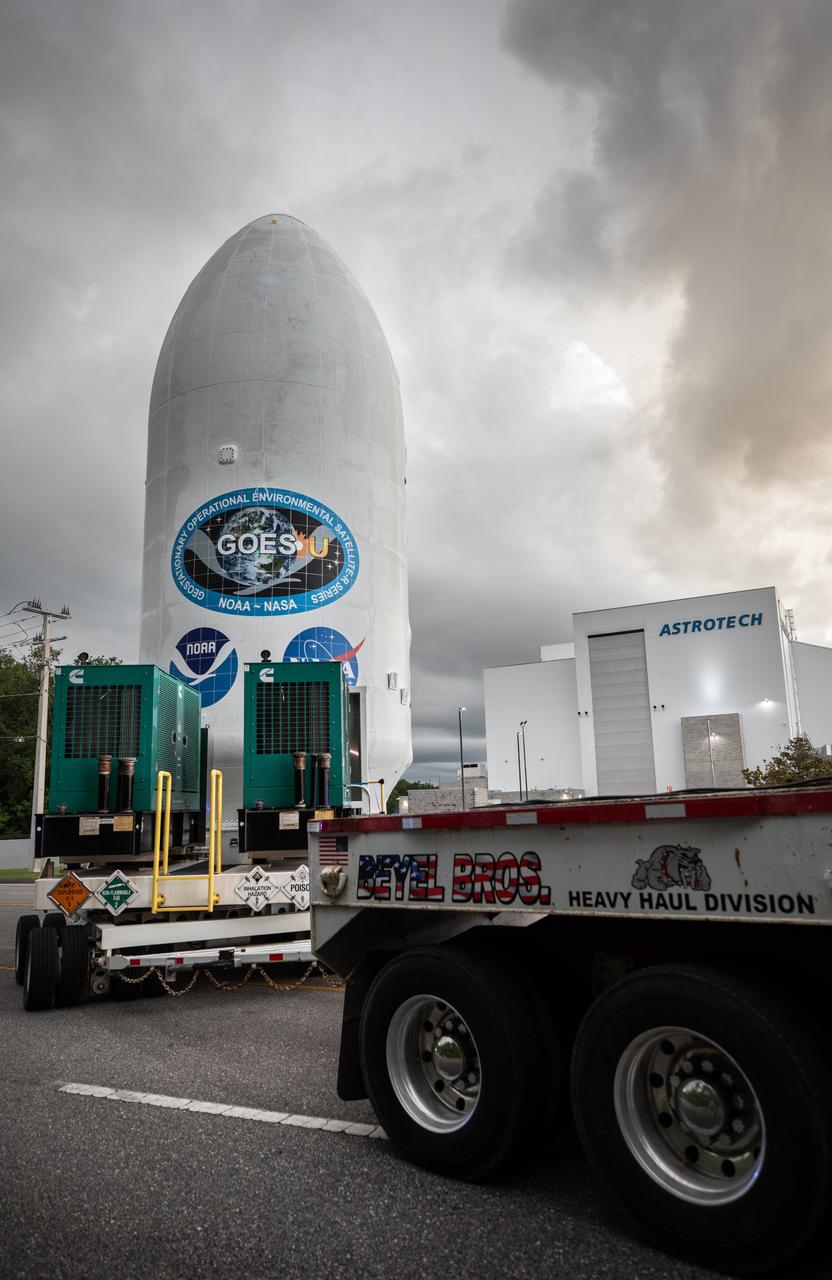

Crews transport NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) from the Astrotech Space Operations facility to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning on Friday, June 14, 2024, with the operation finishing early Saturday, June 15, 2024. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
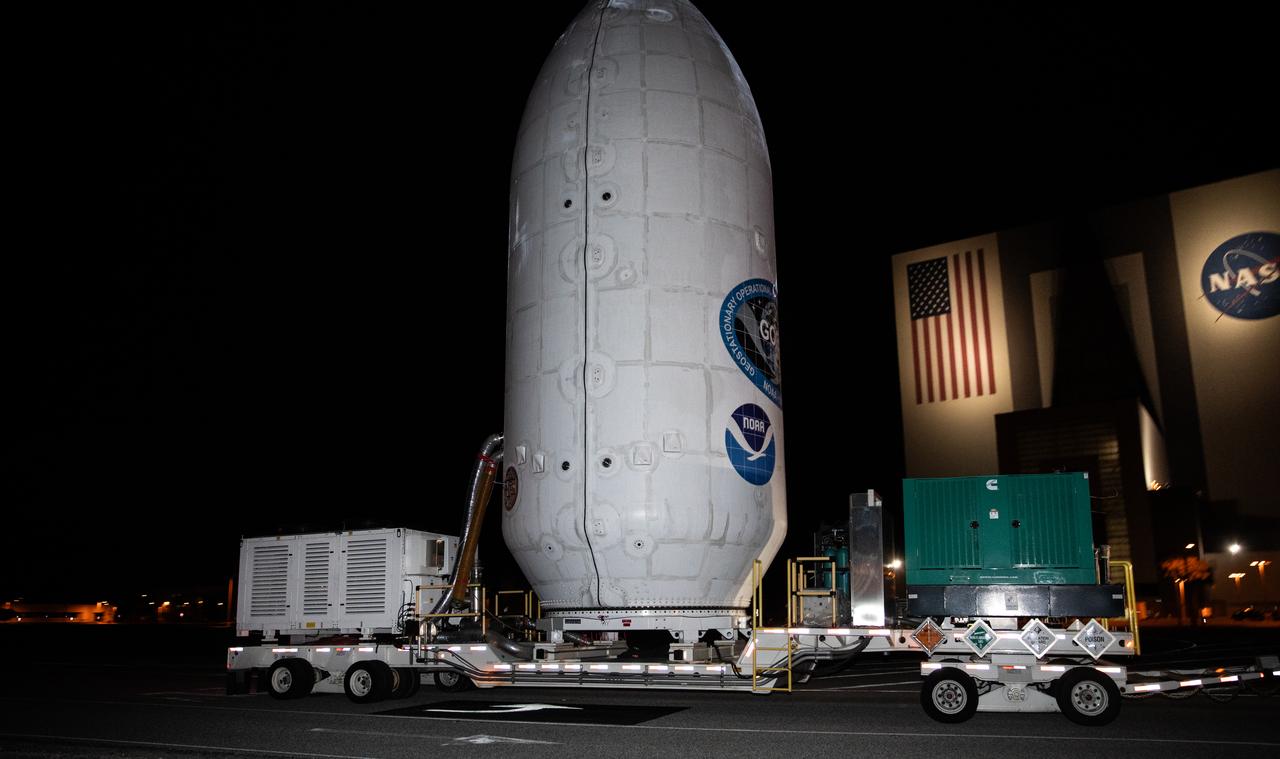

Crews transport NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) from the Astrotech Space Operations facility to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning on Friday, June 14, 2024, with the operation finishing early Saturday, June 15, 2024. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
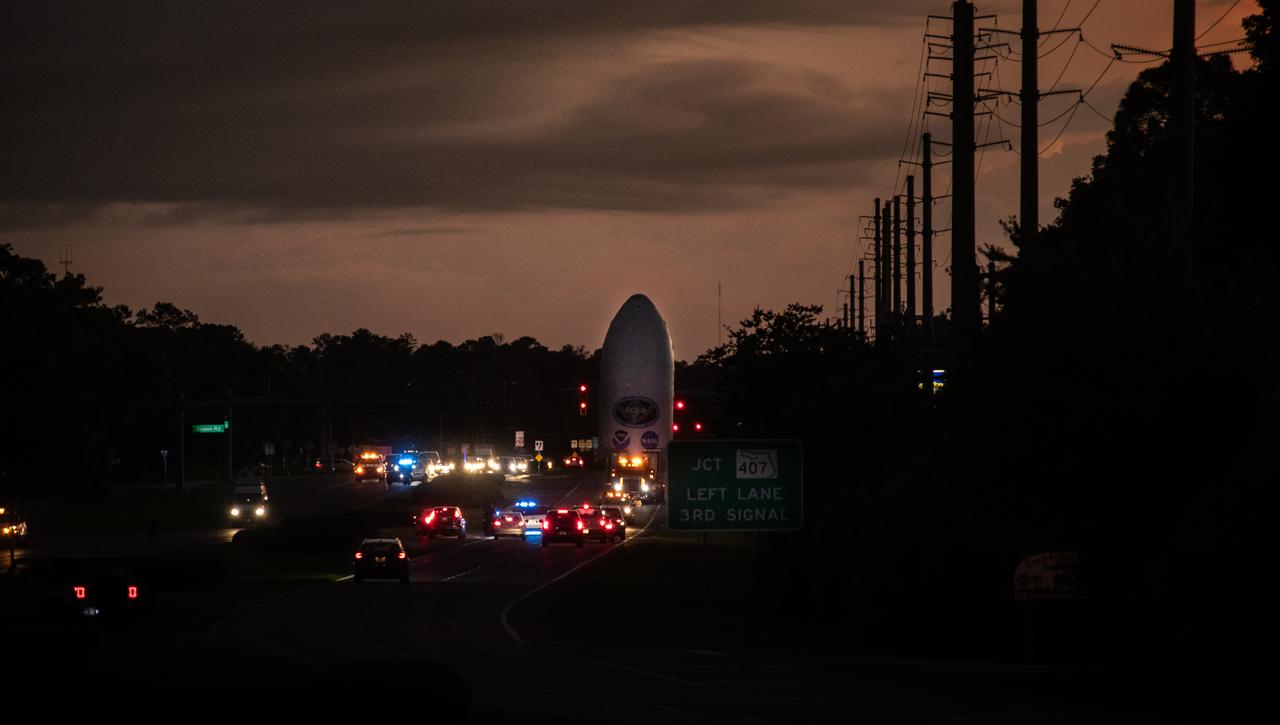

Crews transport NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) from the Astrotech Space Operations facility to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning on Friday, June 14, 2024, with the operation finishing early Saturday, June 15, 2024. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
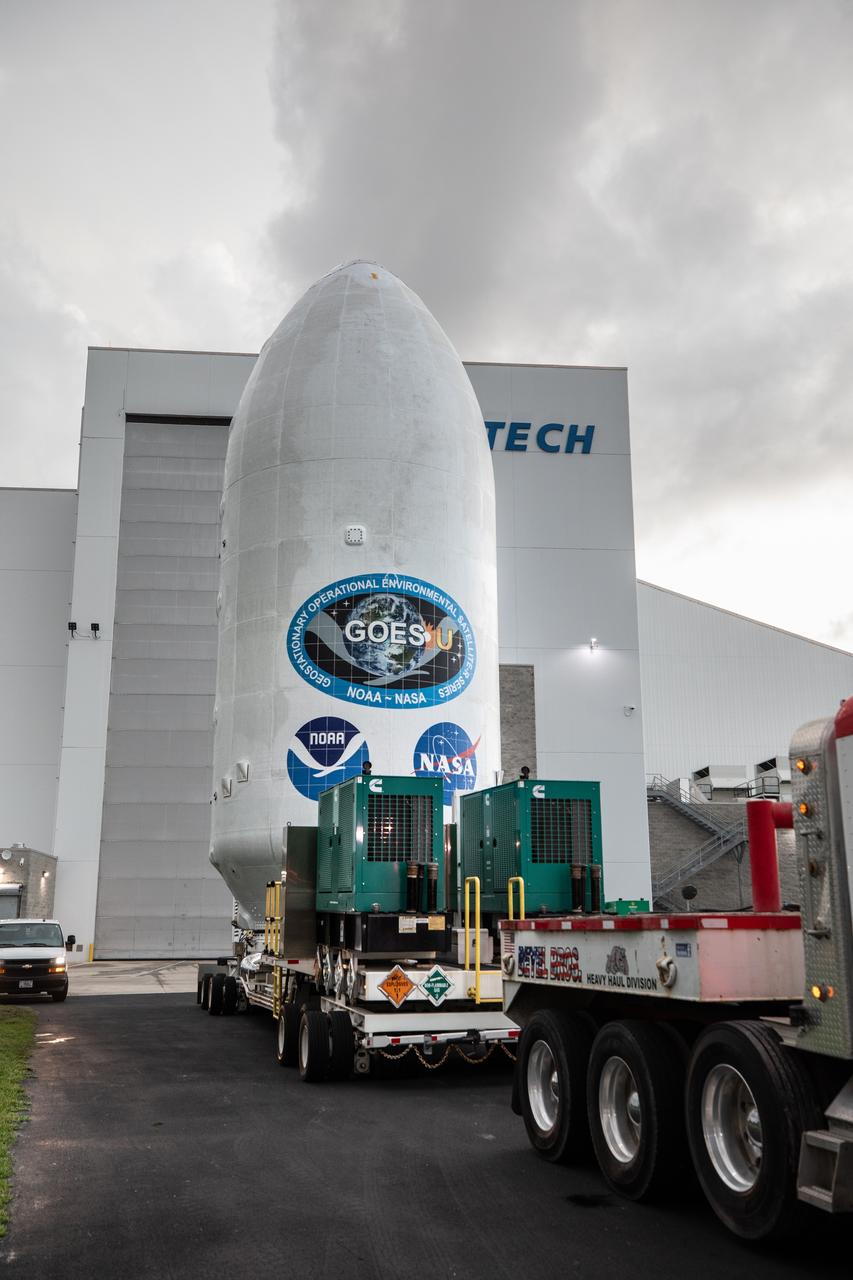

Crews transport NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) from the Astrotech Space Operations facility to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning on Friday, June 14, 2024, with the operation finishing early Saturday, June 15, 2024. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
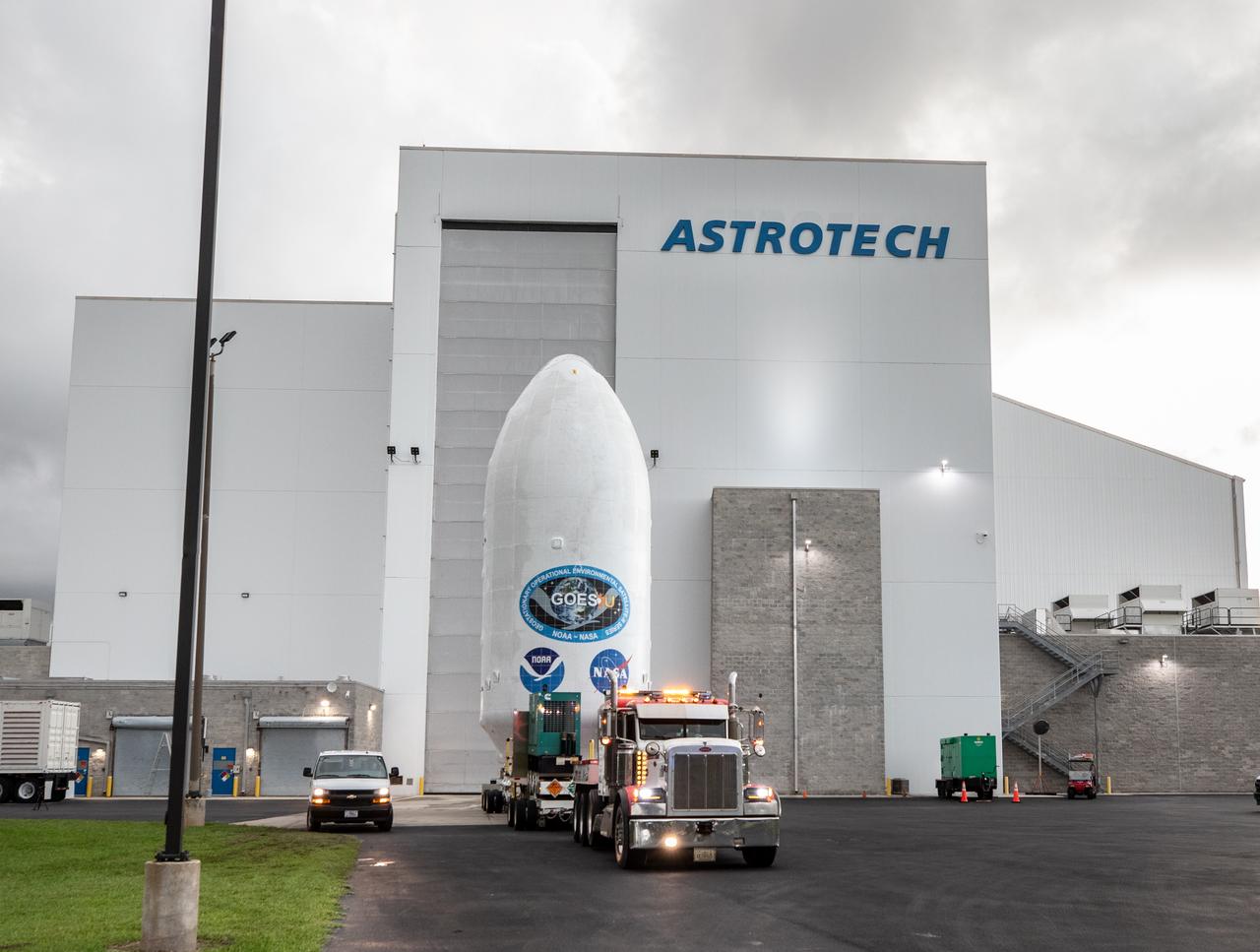

Crews transport NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) from the Astrotech Space Operations facility to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning on Friday, June 14, 2024, with the operation finishing early Saturday, June 15, 2024. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
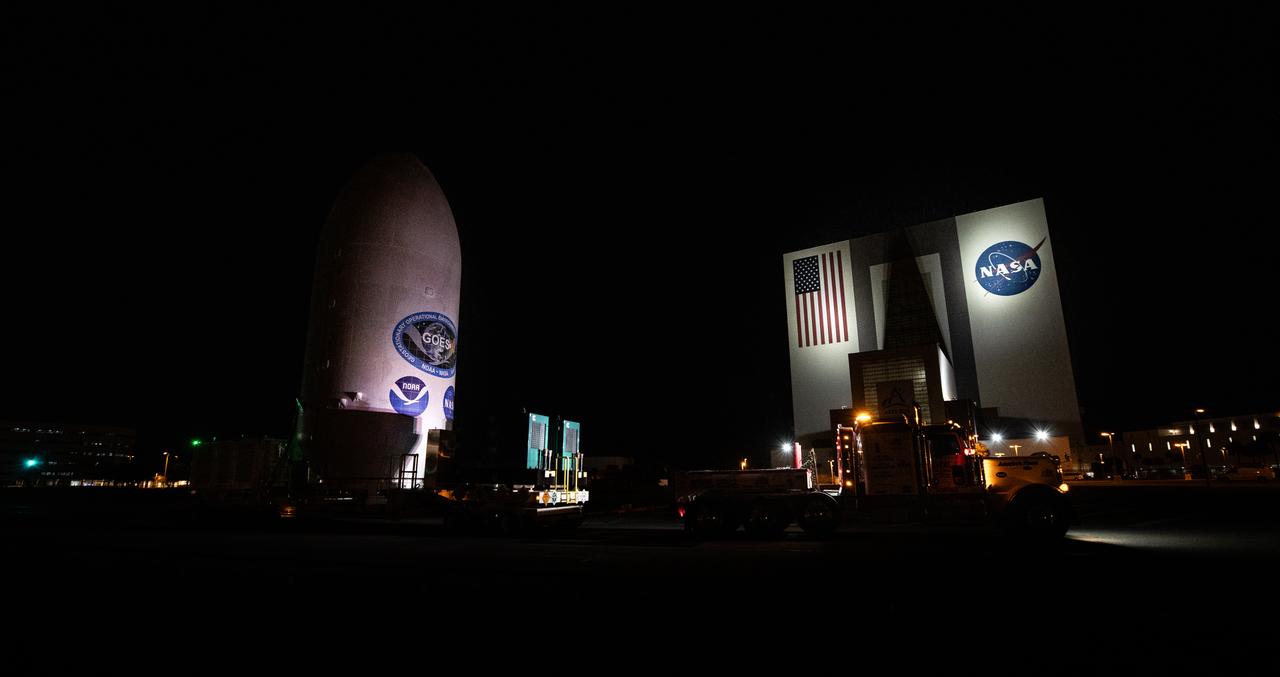

Crews transport NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) from the Astrotech Space Operations facility to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning on Friday, June 14, 2024, with the operation finishing early Saturday, June 15, 2024. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
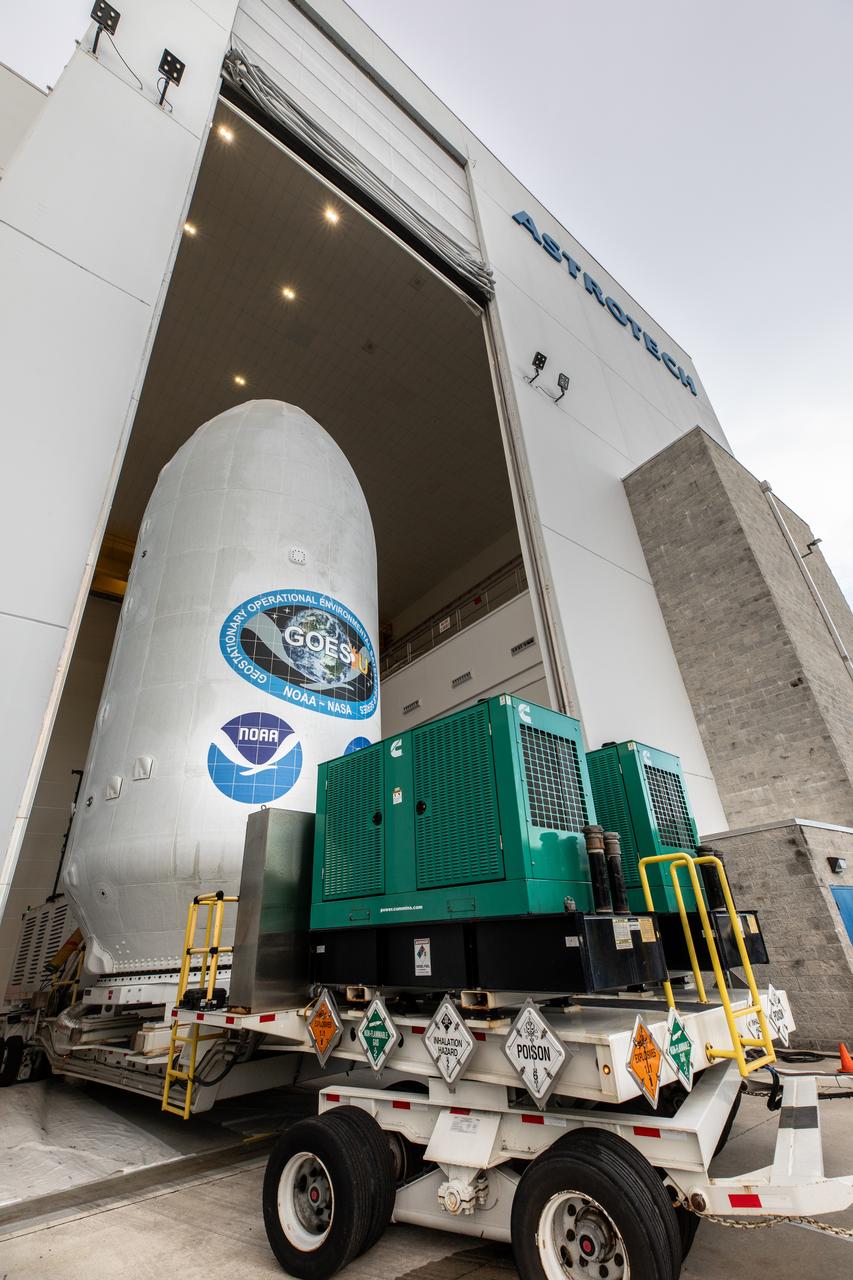

Crews transport NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) from the Astrotech Space Operations facility to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning on Friday, June 14, 2024, with the operation finishing early Saturday, June 15, 2024. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

Crews transport NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) from the Astrotech Space Operations facility to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning on Friday, June 14, 2024, with the operation finishing early Saturday, June 15, 2024. The fourth and final weather-observing and environmental monitoring satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series will assist meteorologists in providing advanced weather forecasting and warning capabilities. The two-hour window for liftoff opens 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
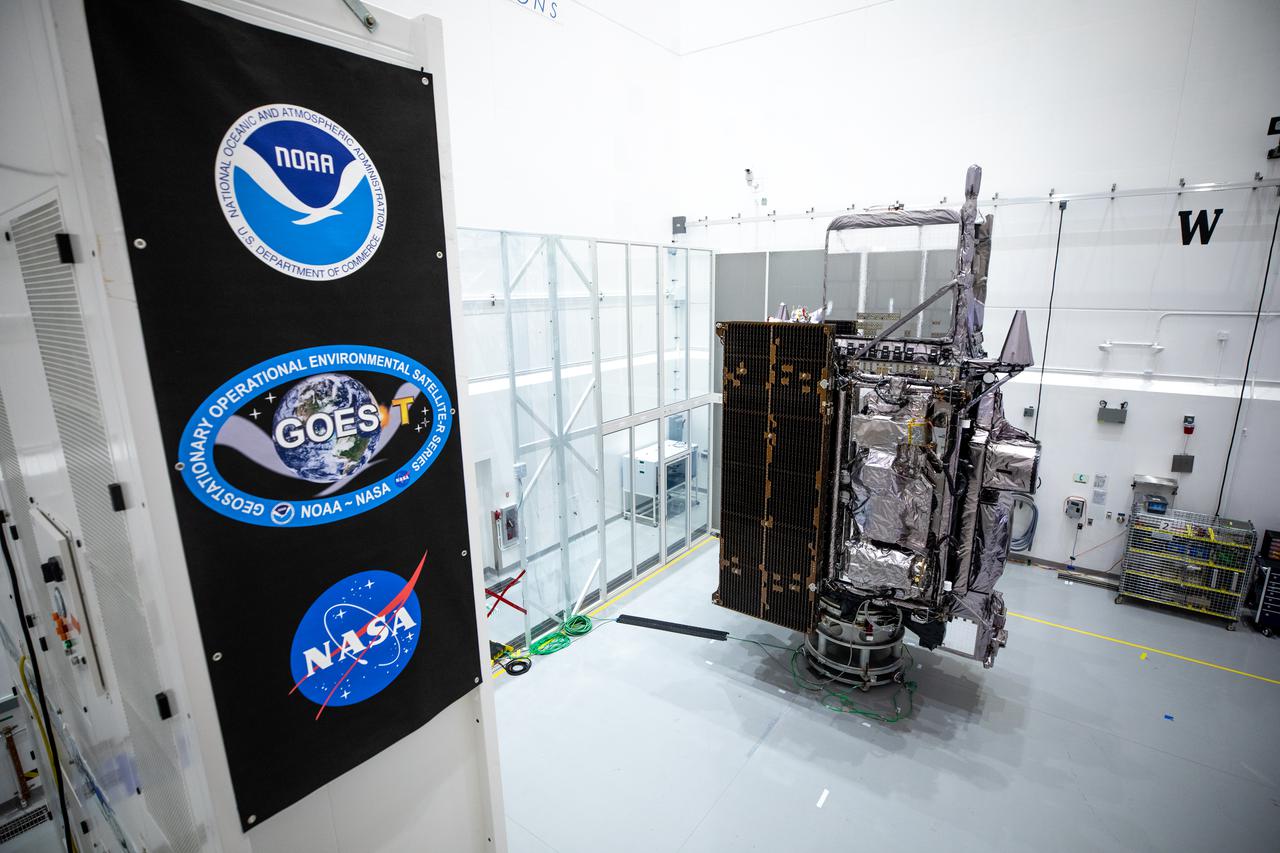
NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view alongside its banner inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 20, 2022. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
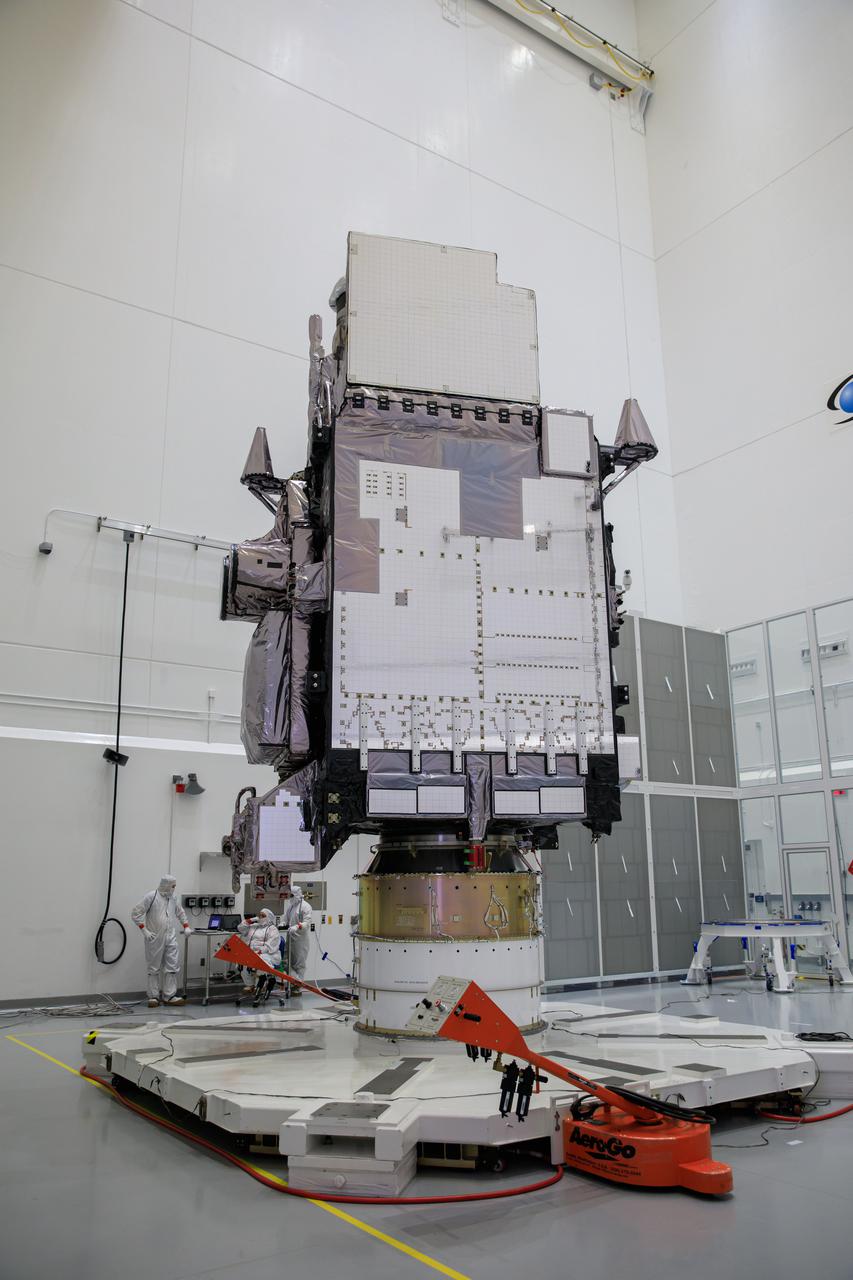

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 28, 2022, as it is being prepared for encapsulation. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
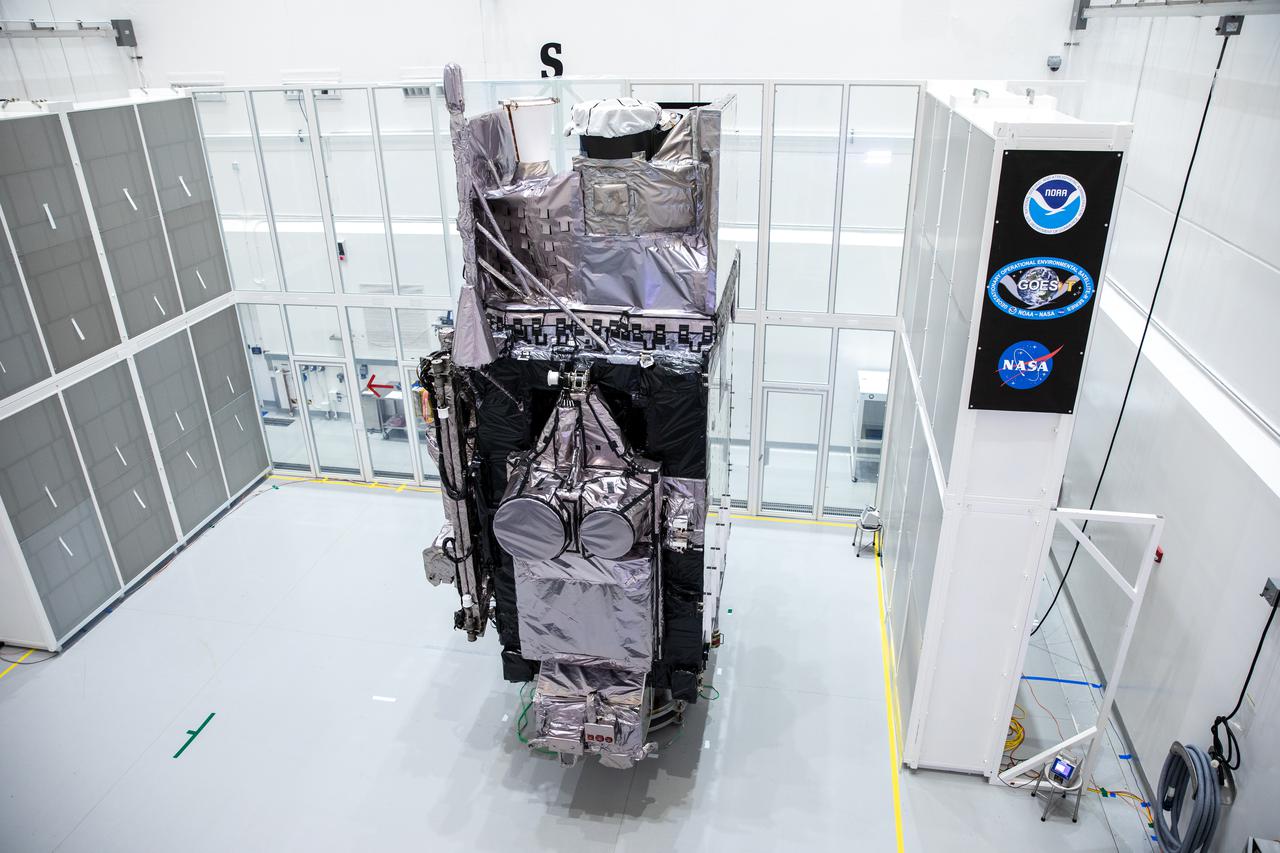

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view alongside its banner inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 20, 2022. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
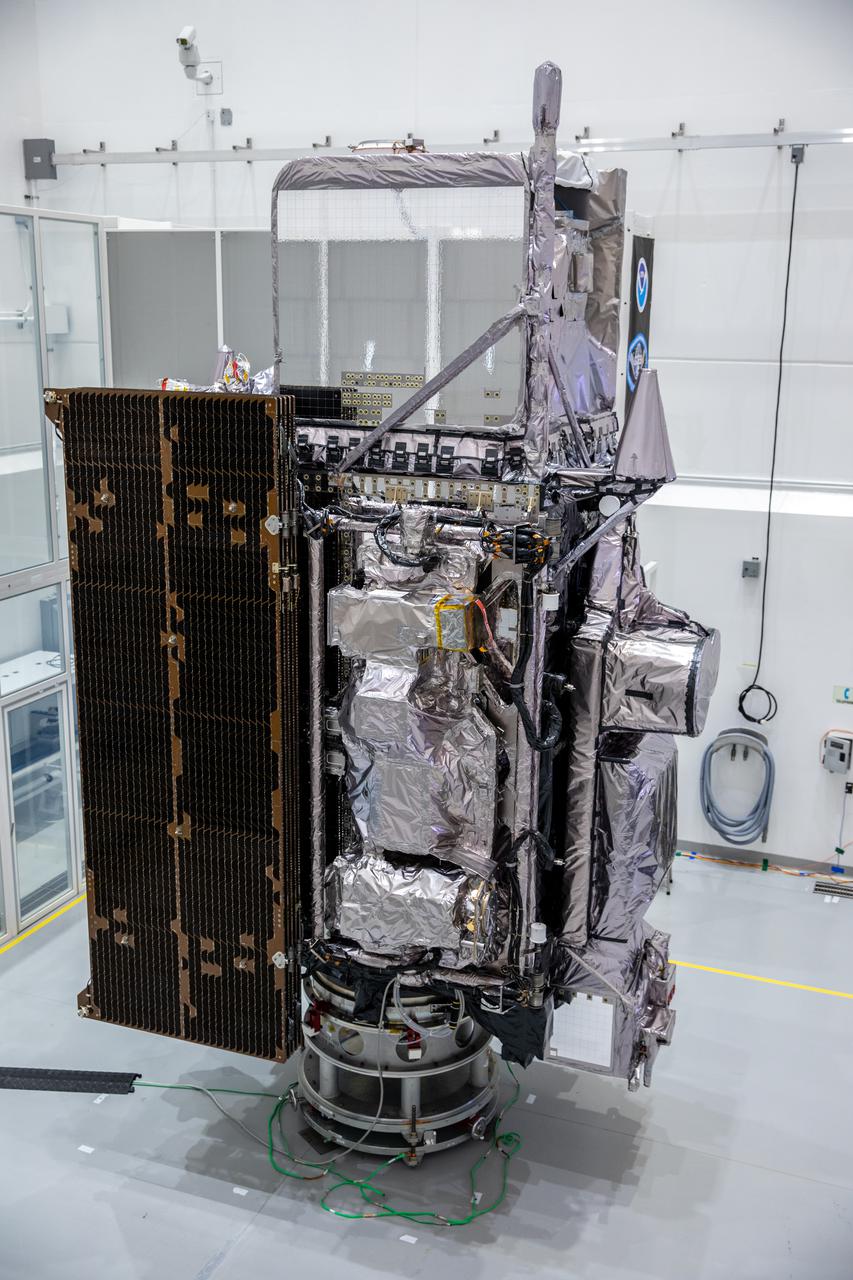

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 20, 2022. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
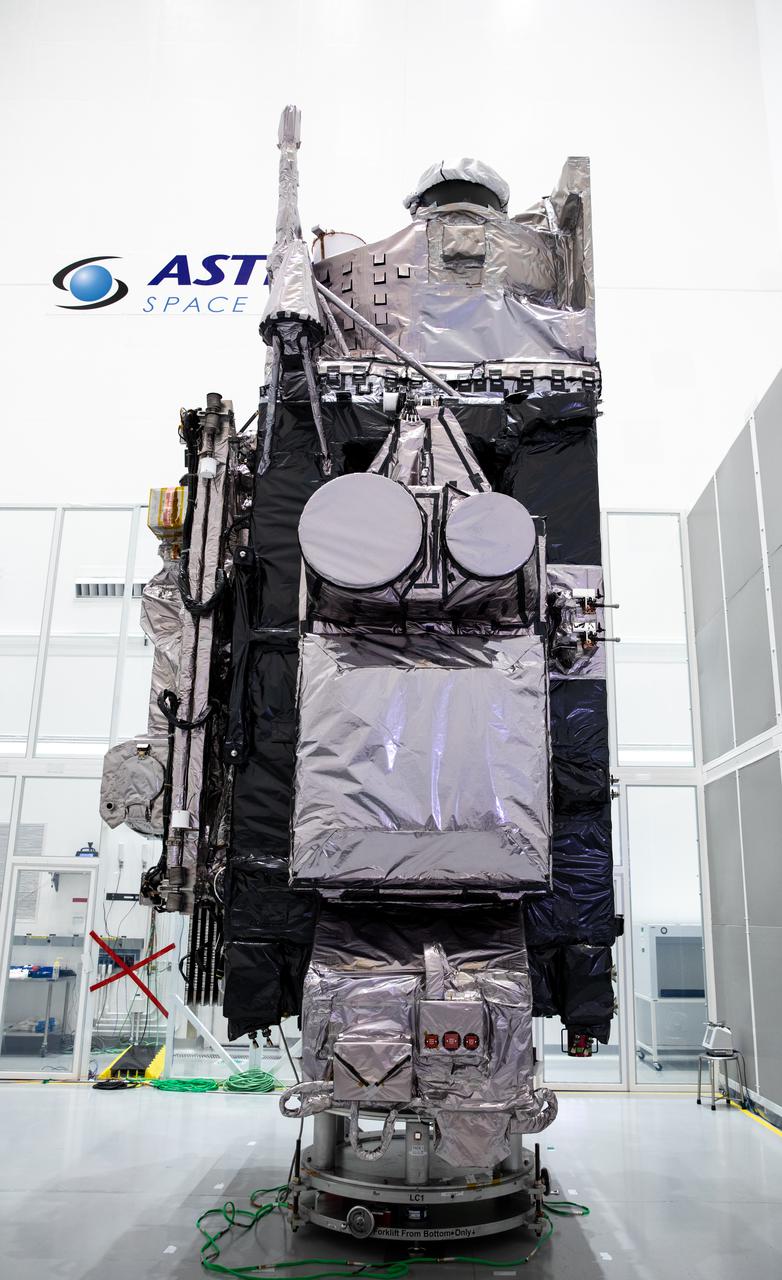

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 20, 2022. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
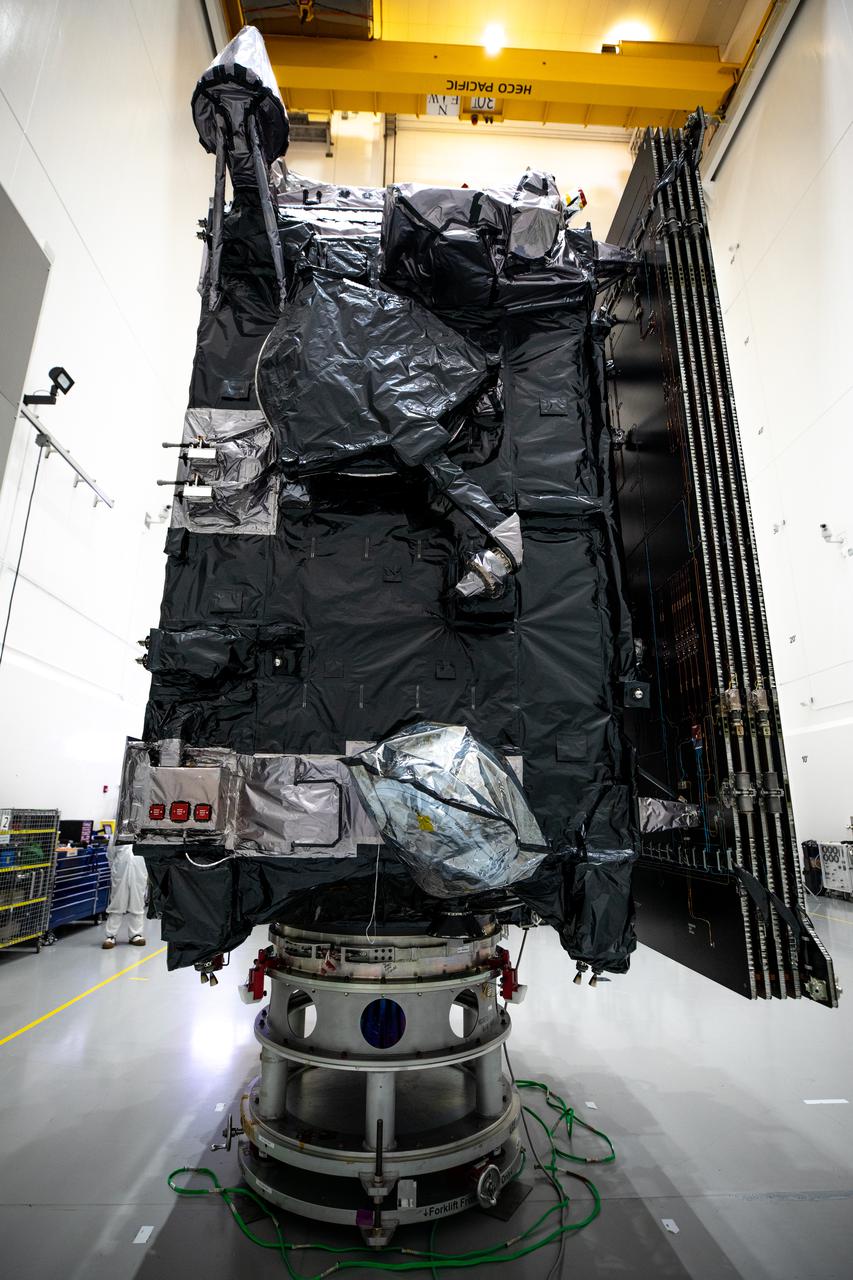

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 20, 2022. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
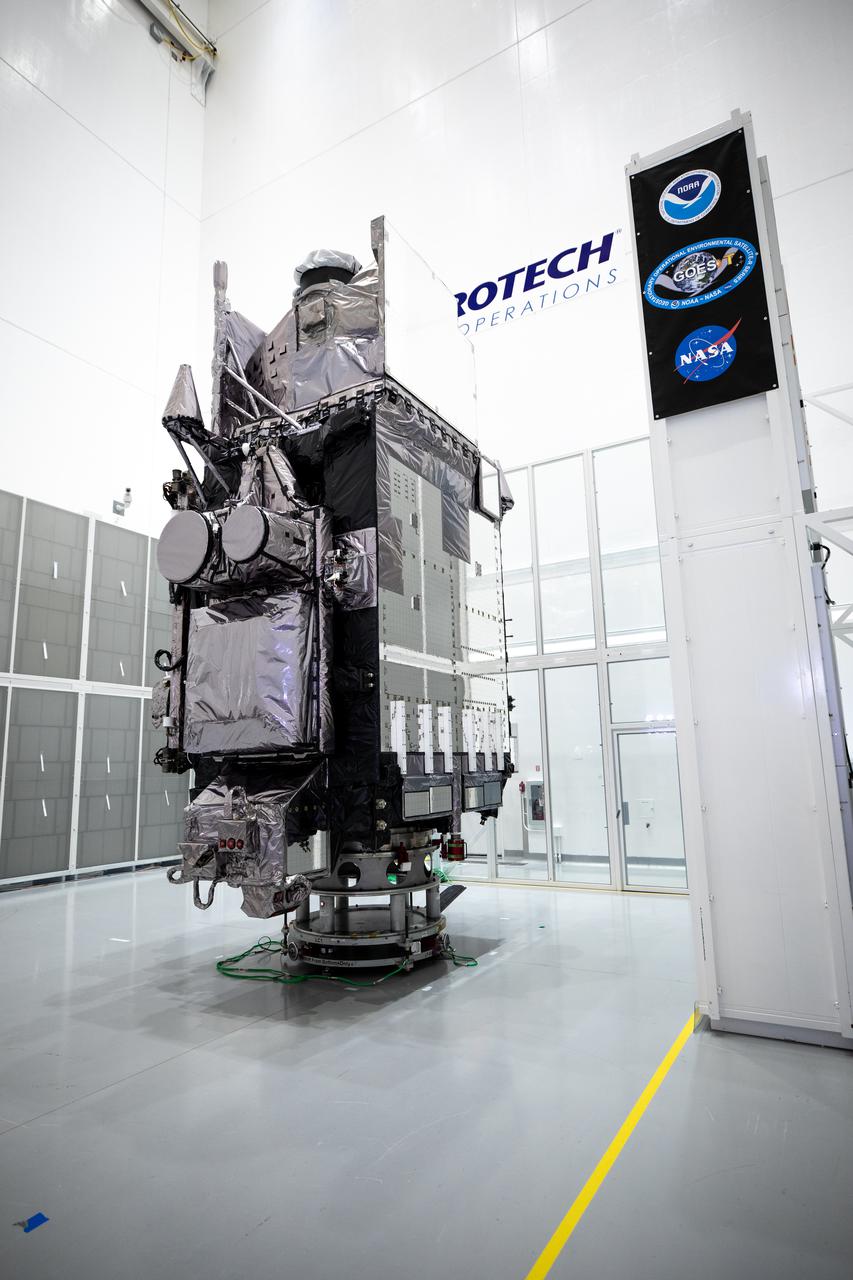

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view alongside its banner inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 20, 2022. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
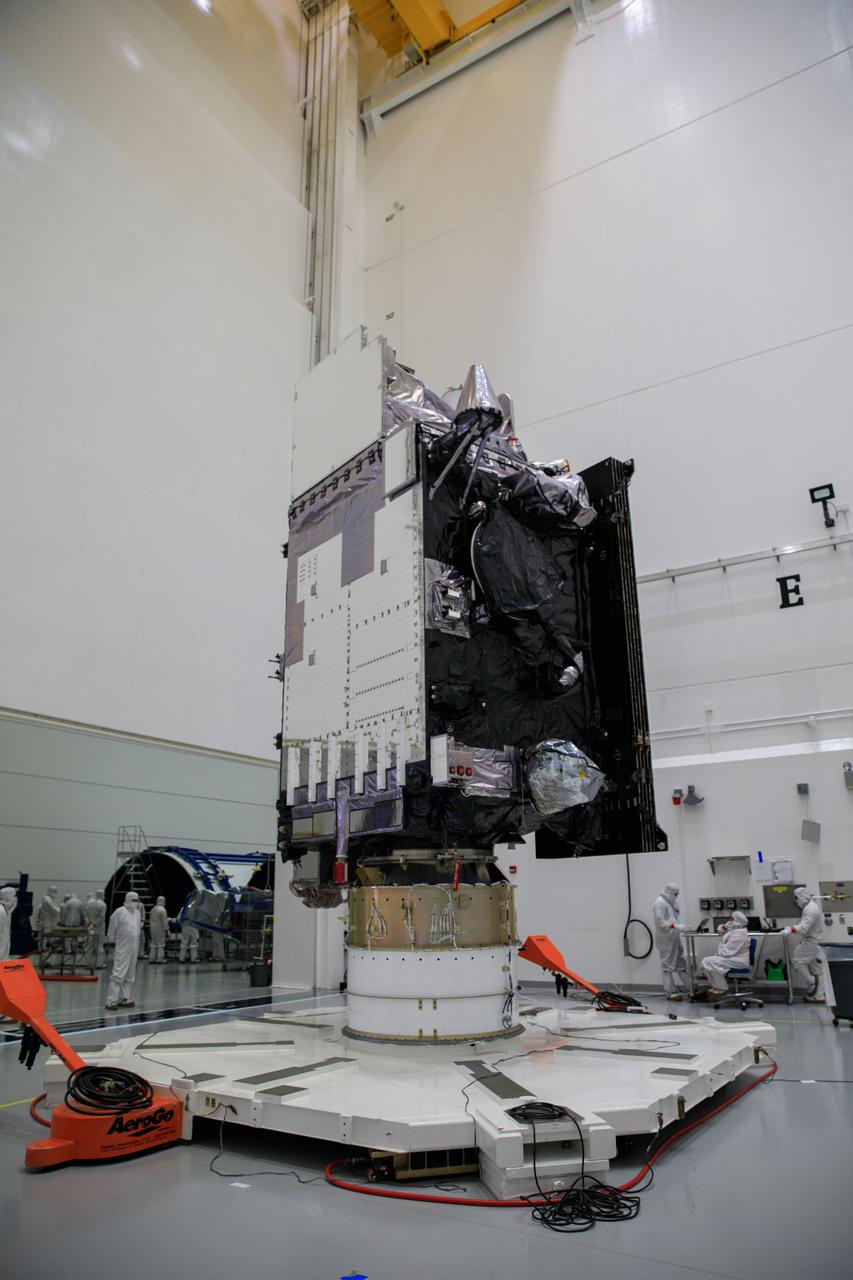

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 28, 2022, as it is being prepared for encapsulation. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
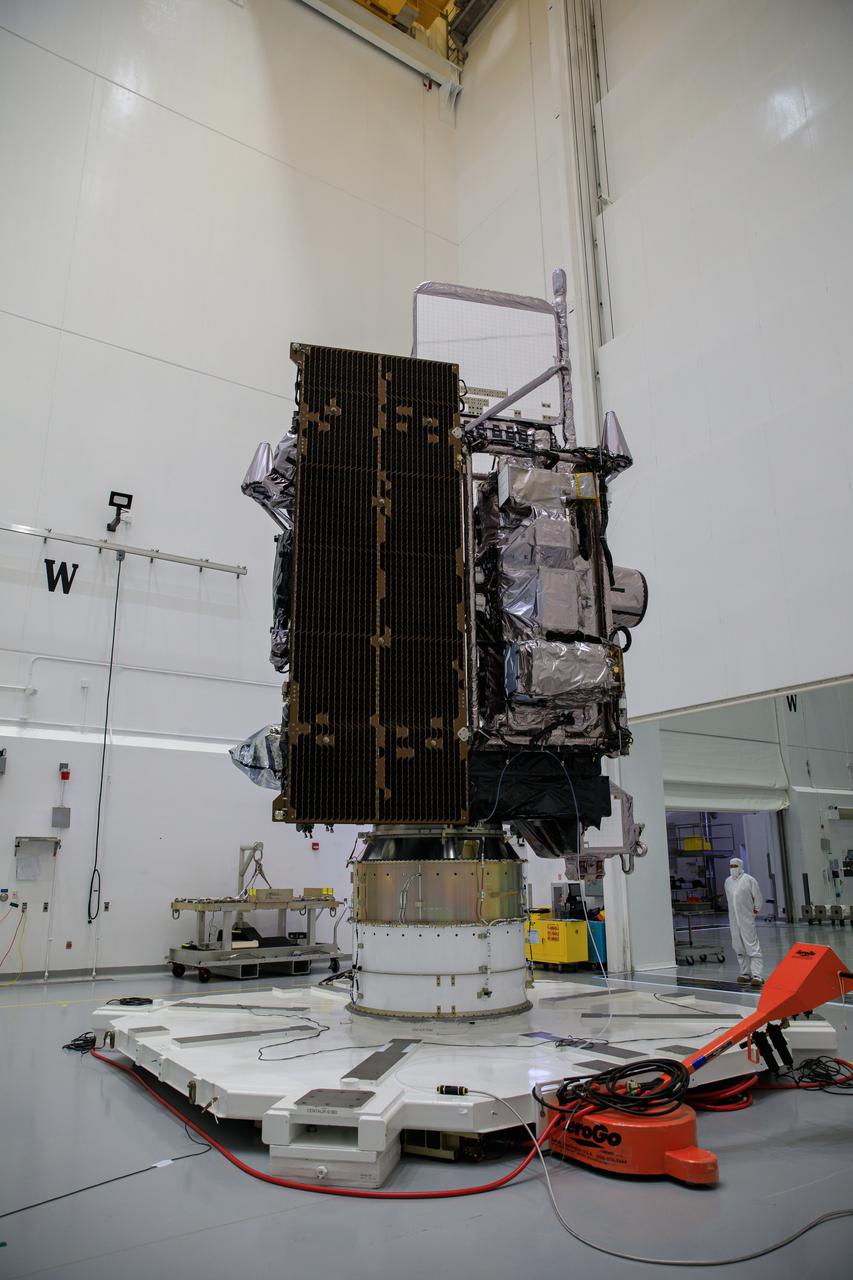

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 28, 2022, as it is being prepared for encapsulation. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
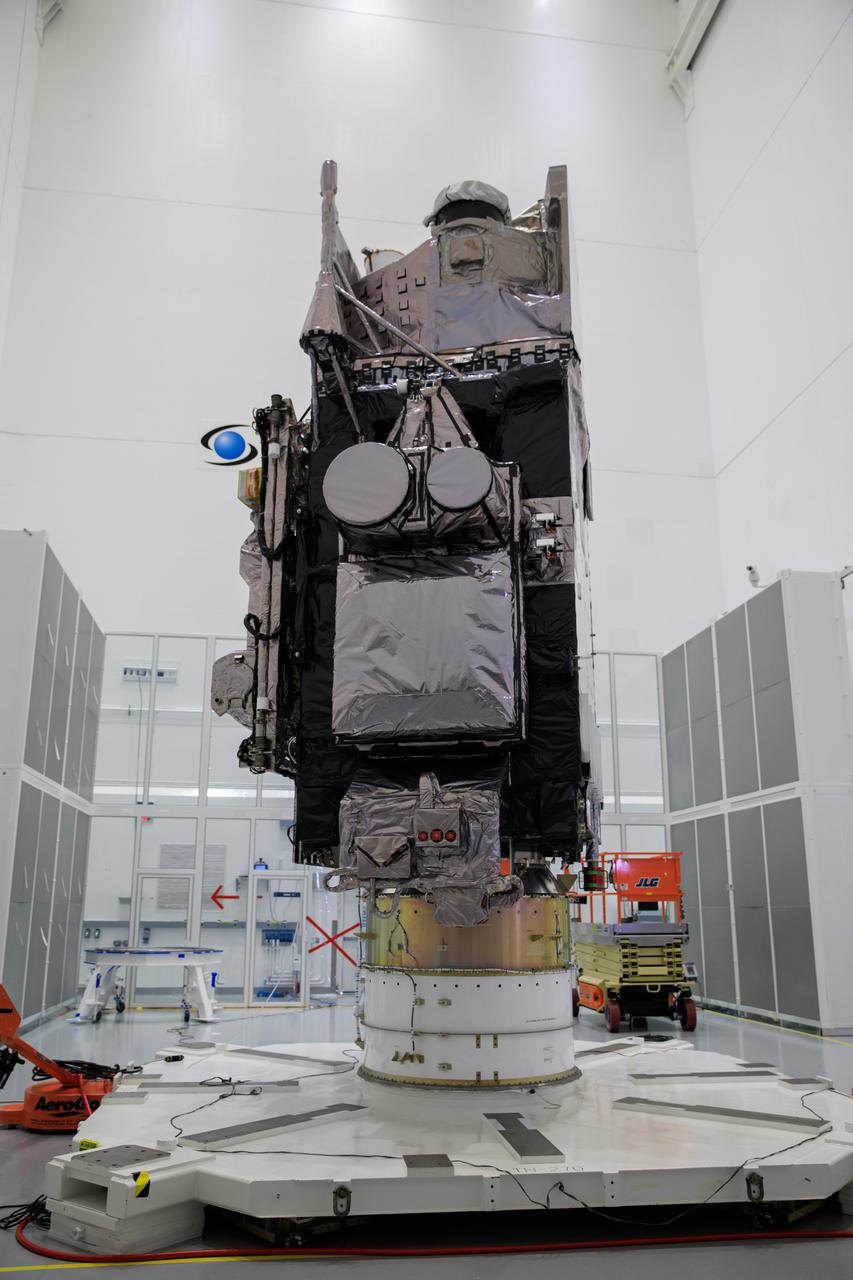

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 28, 2022, as it is being prepared for encapsulation. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.

A banner for NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 20, 2022. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
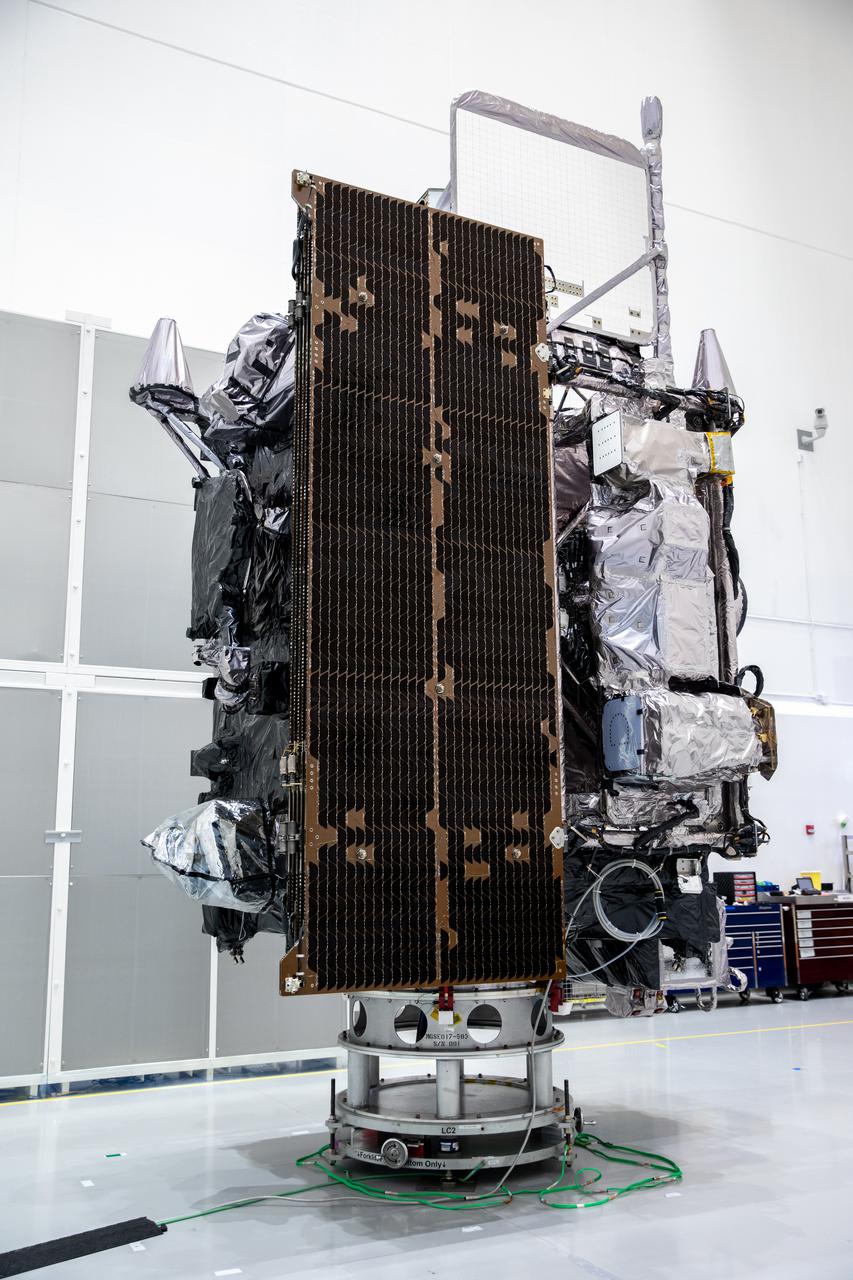

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 20, 2022. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
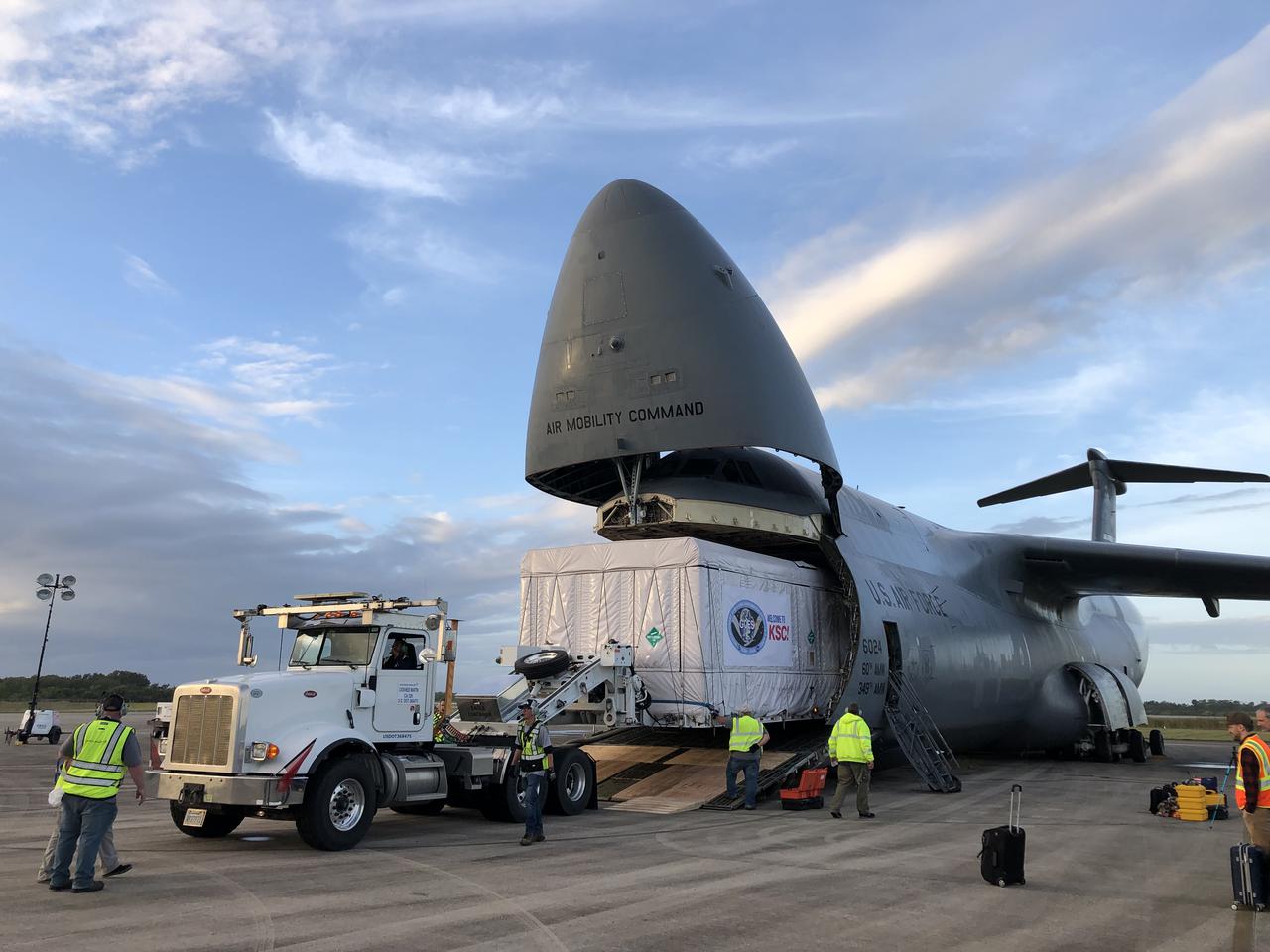

The shipping container holding the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T) is unloaded from a United States Air Force C-5 cargo plane following its arrival at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 10, 2021. From here, teams will transport the satellite to an Astrotech Space Operations facility in nearby Titusville for prelaunch processing. A collaboration between NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy, America’s multi-user spaceport.
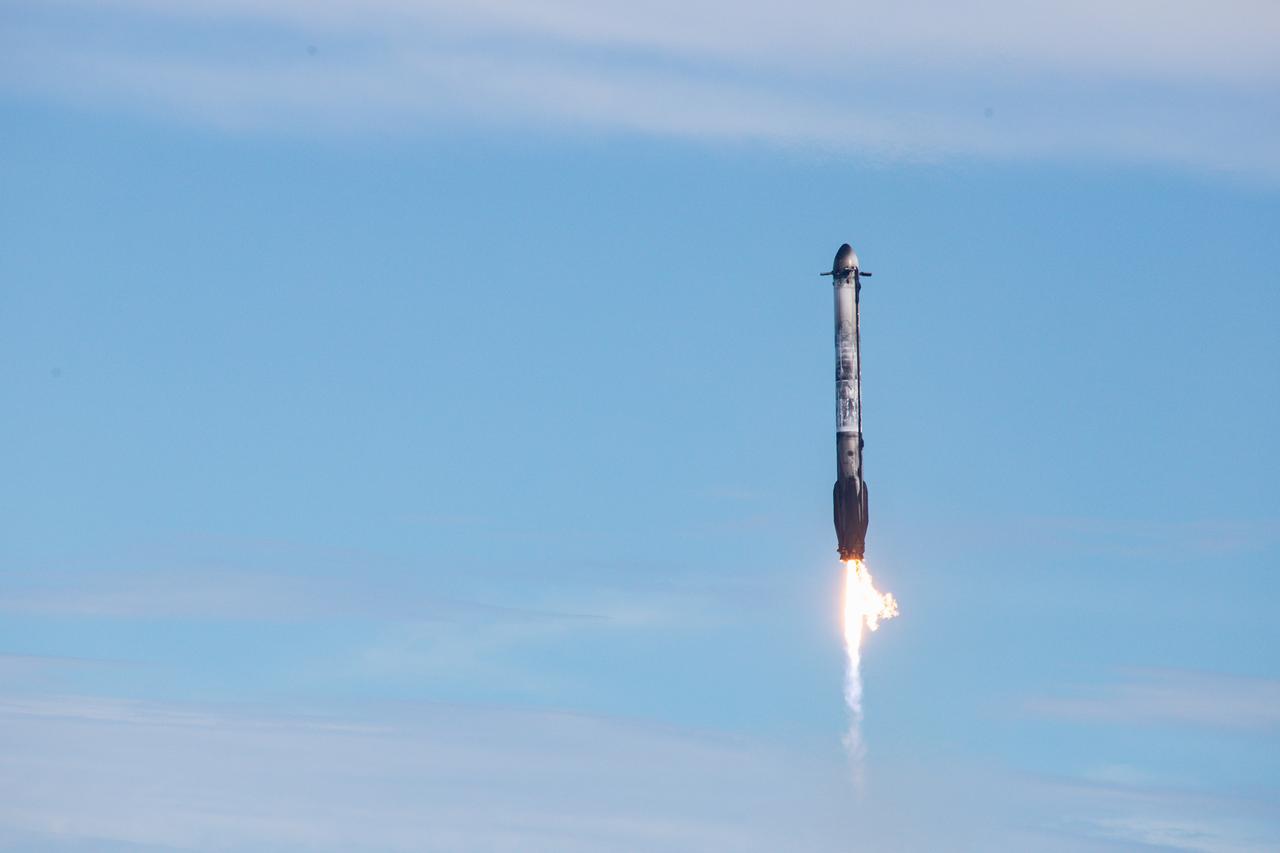

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy side booster lands at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida after the rocket launched NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-U) from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024.
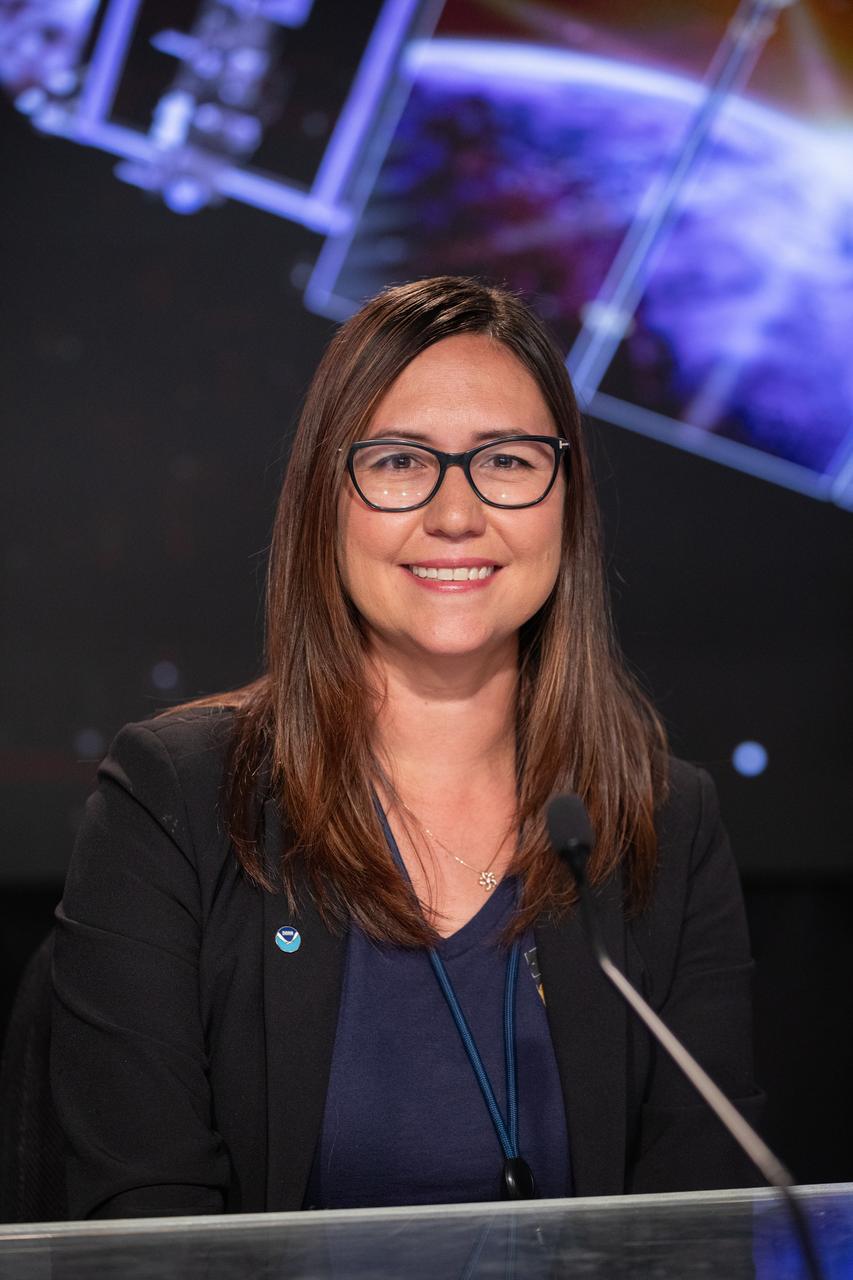

Ellen Ramirez, deputy division chief, Mission Operations Division, National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service Office of Satellite and Product Operations, NOAA, participates in a social panel on Monday, June 24, 2024, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to discuss National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) mission. The GOES-U satellite is the final addition to GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans. The two-hour launch window opens at 5:16 p.m. EDT Tuesday, June 25, for the satellite’s launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
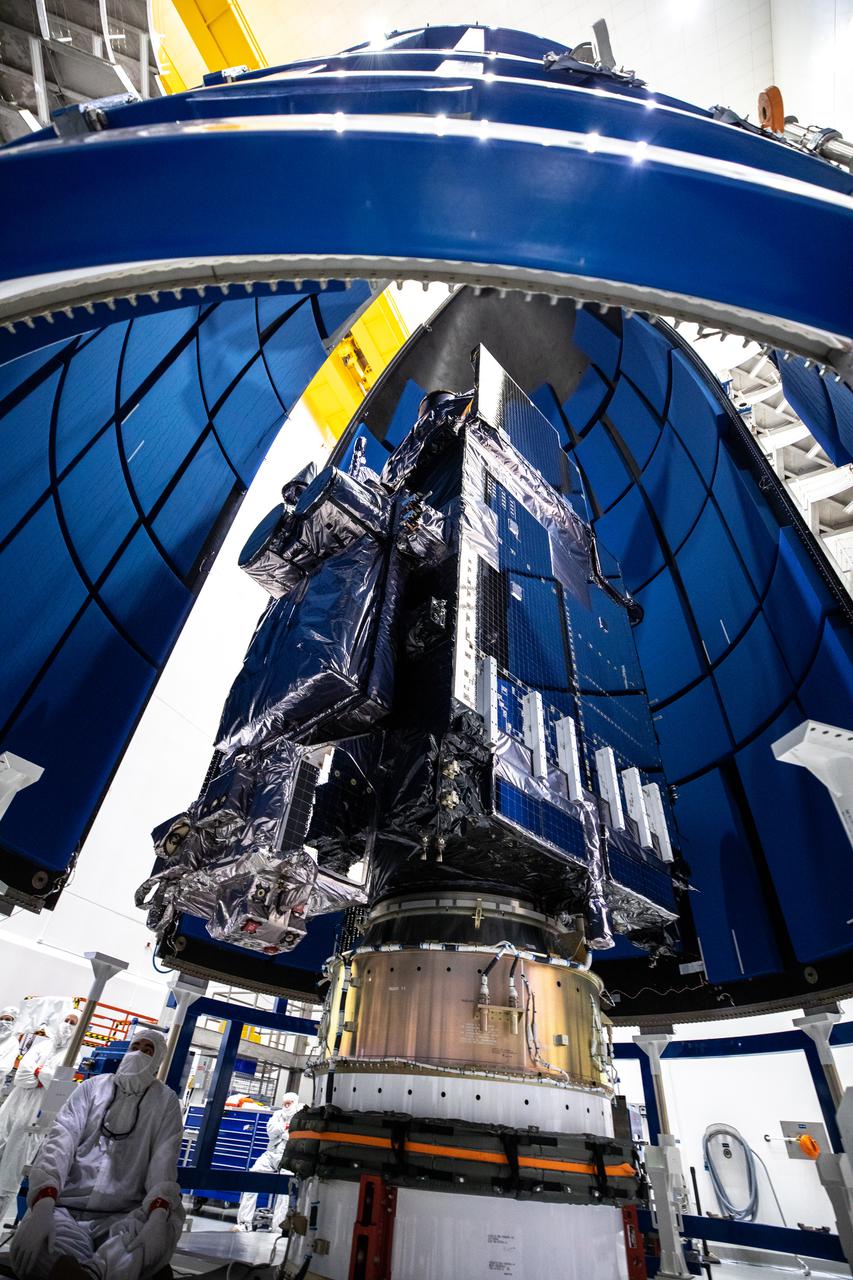

In this view looking up, the United Launch Alliance Atlas V payload fairings are being secured around NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Feb. 7, 2022. The payload fairings will secure and protect the satellite during launch. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
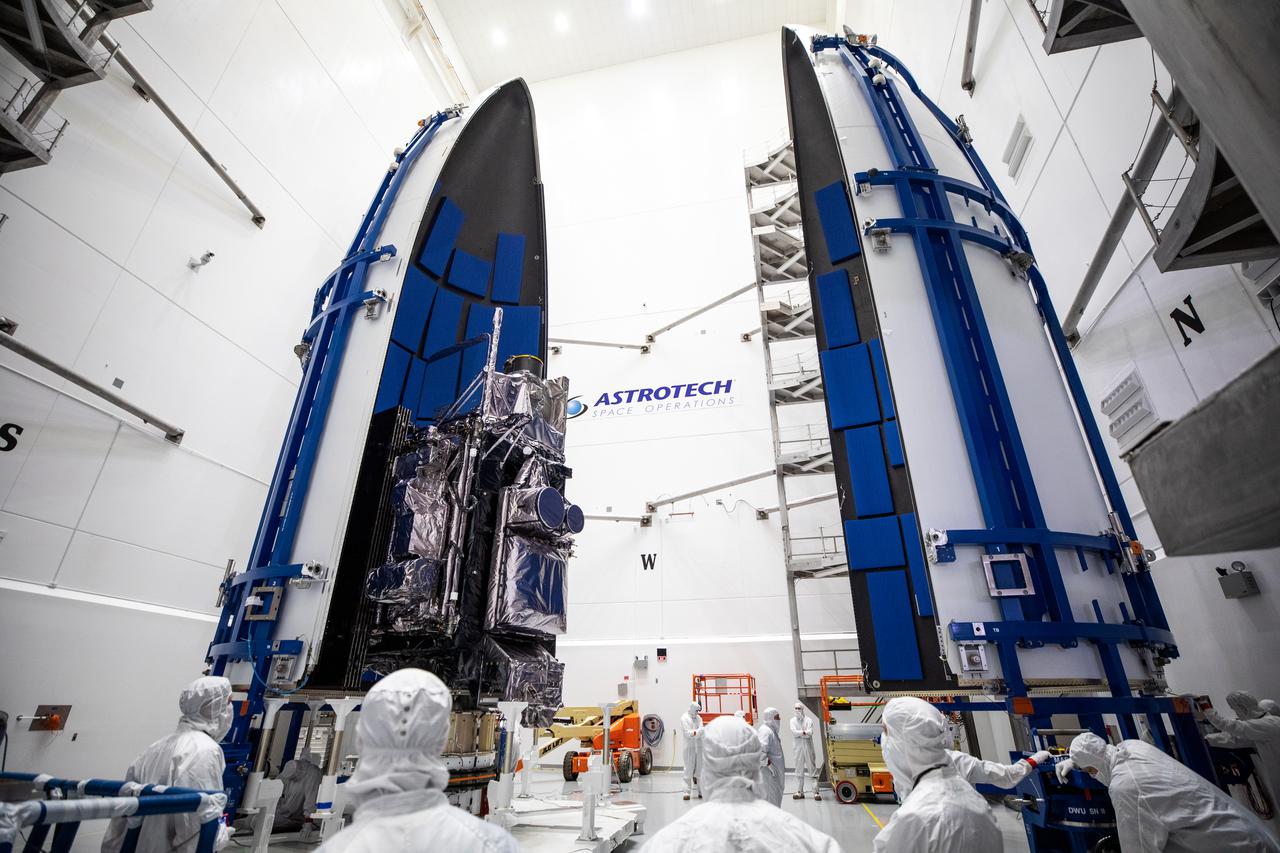

With the first half of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V payload fairing secured around NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T), the second half is moved into position inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Feb. 7, 2022. The payload fairings will secure and protect the satellite during launch. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
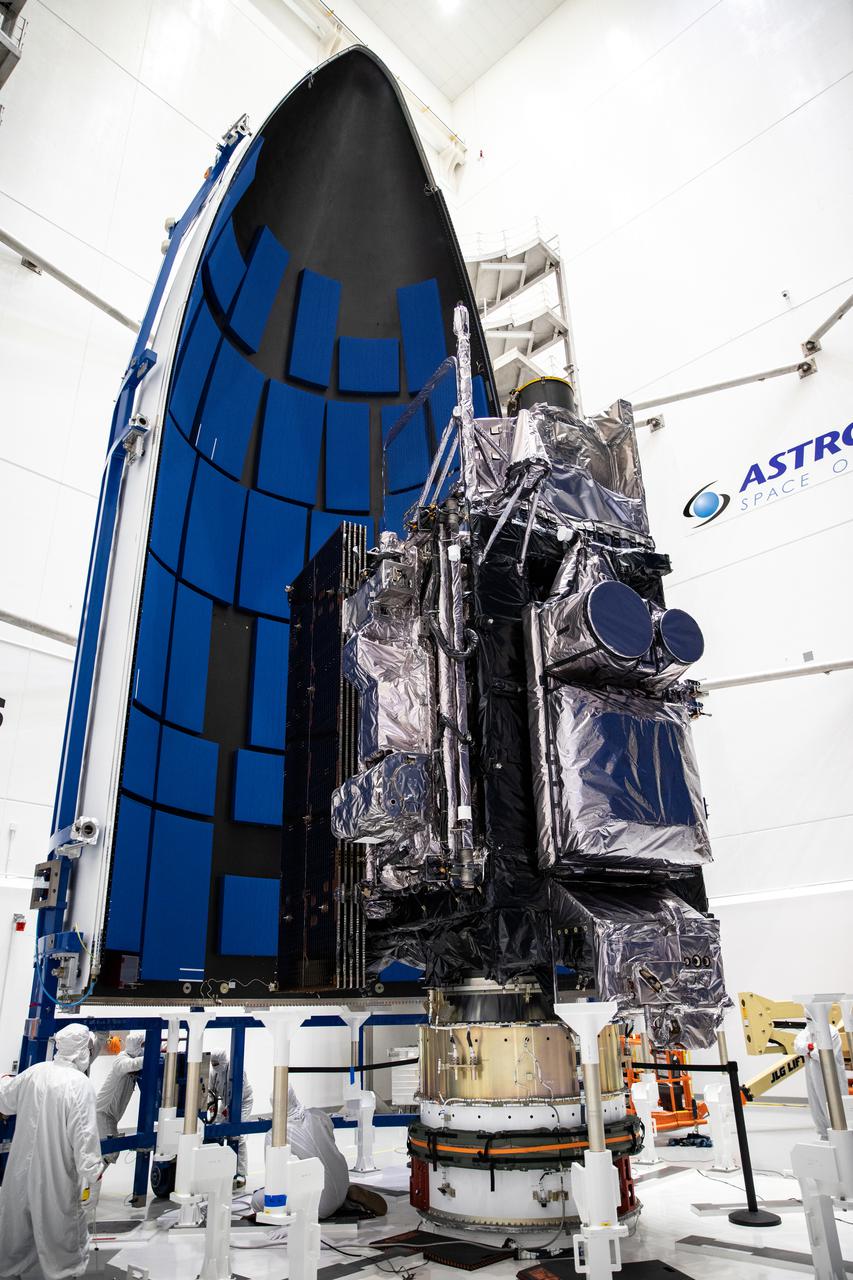

The first half of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V payload fairing is moved toward NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Feb. 7, 2022. The satellite will be encapsulated inside the payload fairings, which will protect it during launch. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
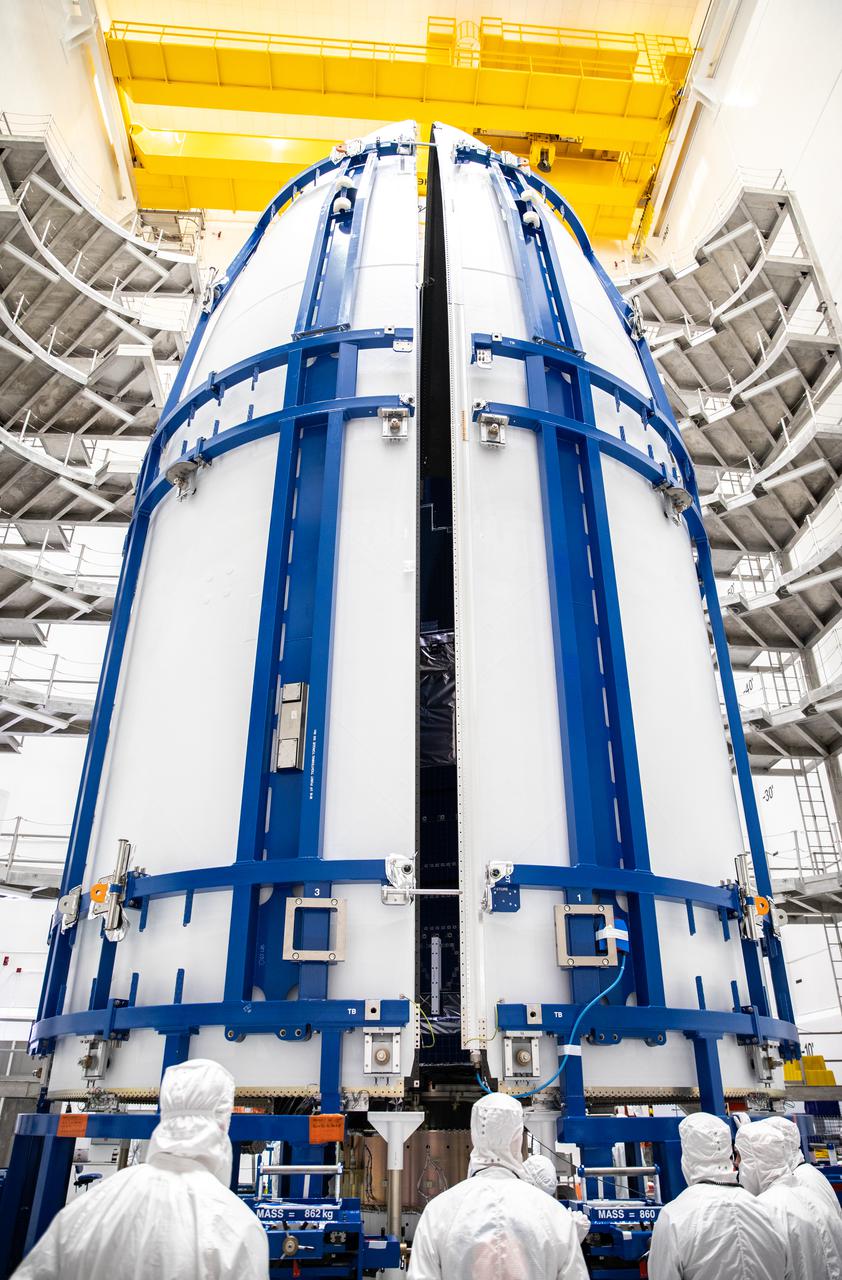

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V payload fairings are being secured around NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Feb. 7, 2022. The payload fairings will secure and protect the satellite during launch. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.

A technician performs an inspection of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V payload fairings as they are secured around NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Feb. 7, 2022. The payload fairings will secure and protect the satellite during launch. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport
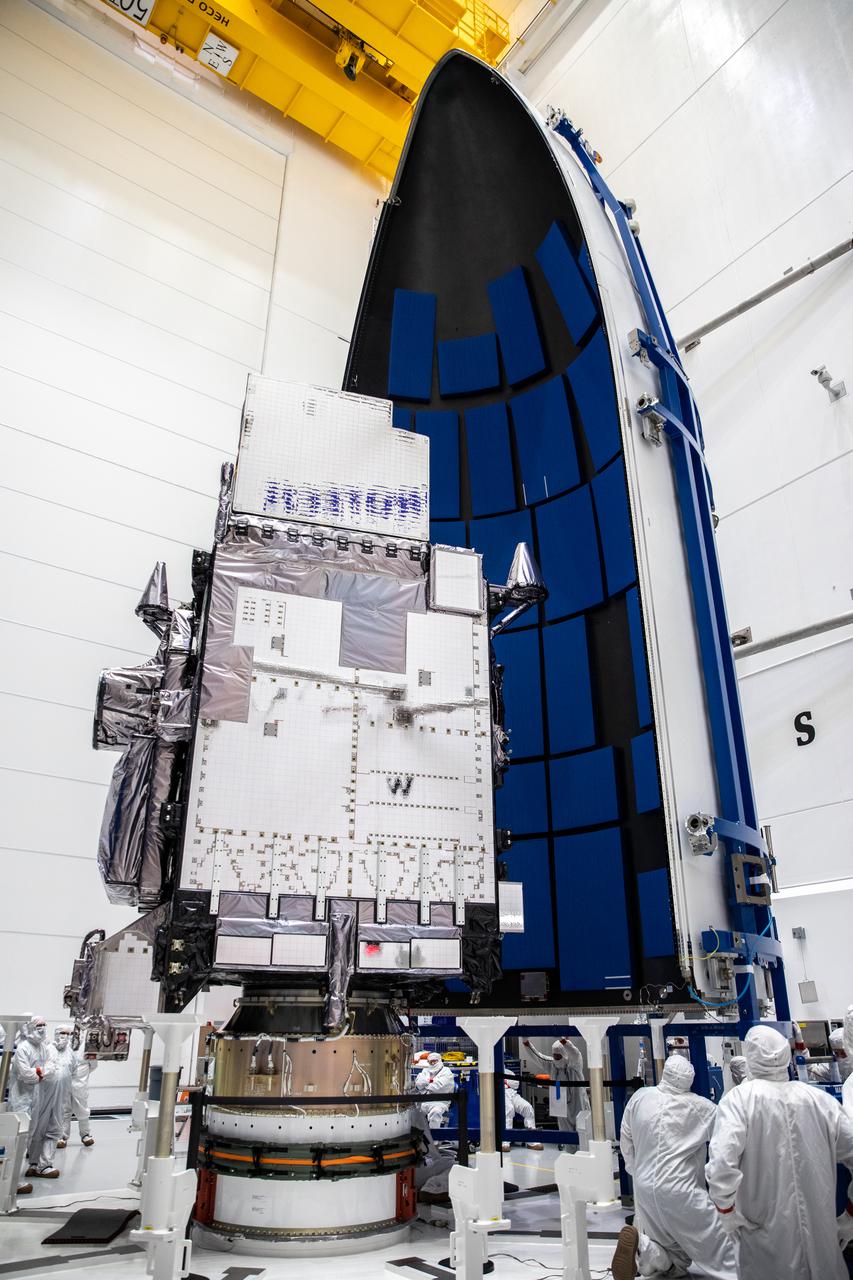

The first half of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V payload fairing is moved toward NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Feb. 7, 2022. The satellite will be encapsulated inside the payload fairings, which will protect it during launch. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.

The first half of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V payload fairing is being secured around NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Feb. 7, 2022. The satellite will be encapsulated inside the payload fairings, which will protect it during launch. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
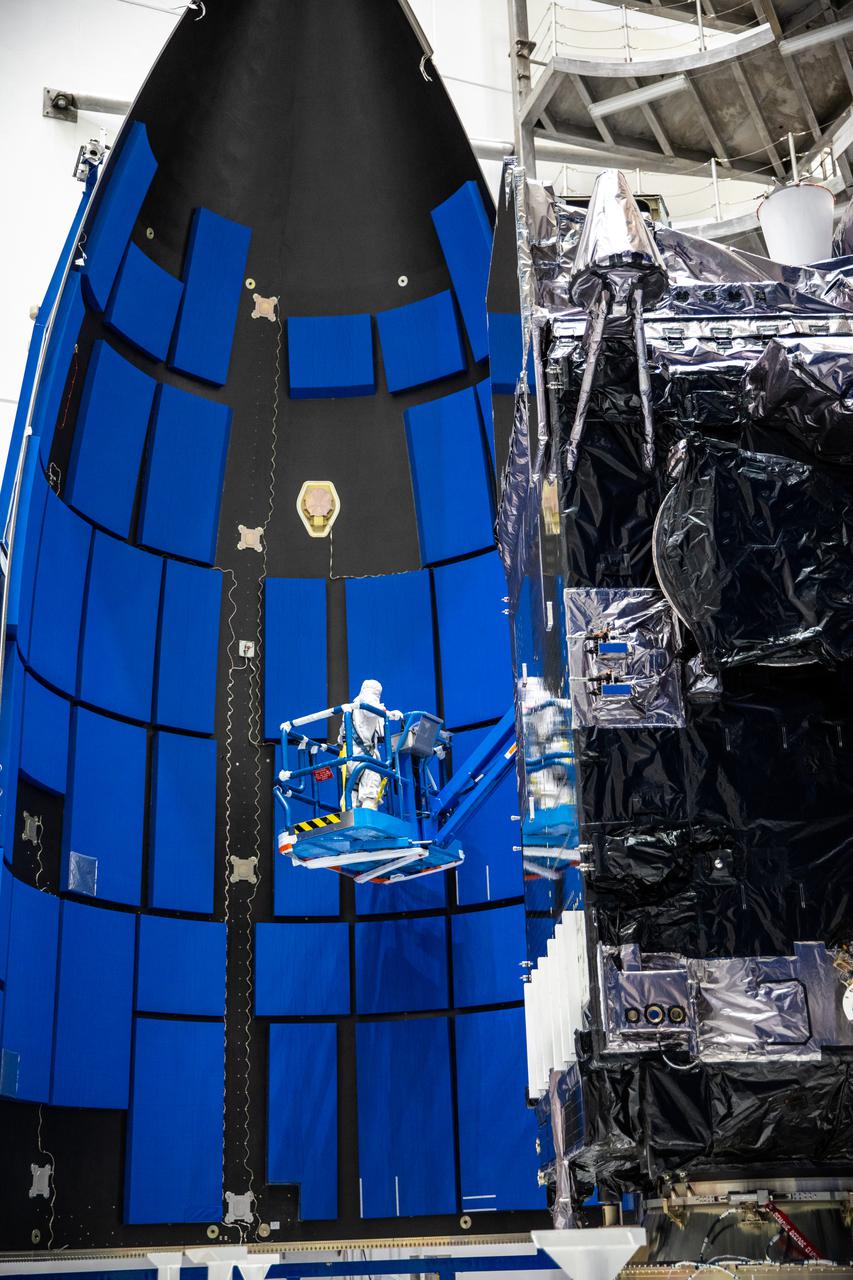

A technician inspects the first half of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V payload fairing for NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Feb. 7, 2022. The satellite will be secured inside the payload fairing, which will protect it during launch. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
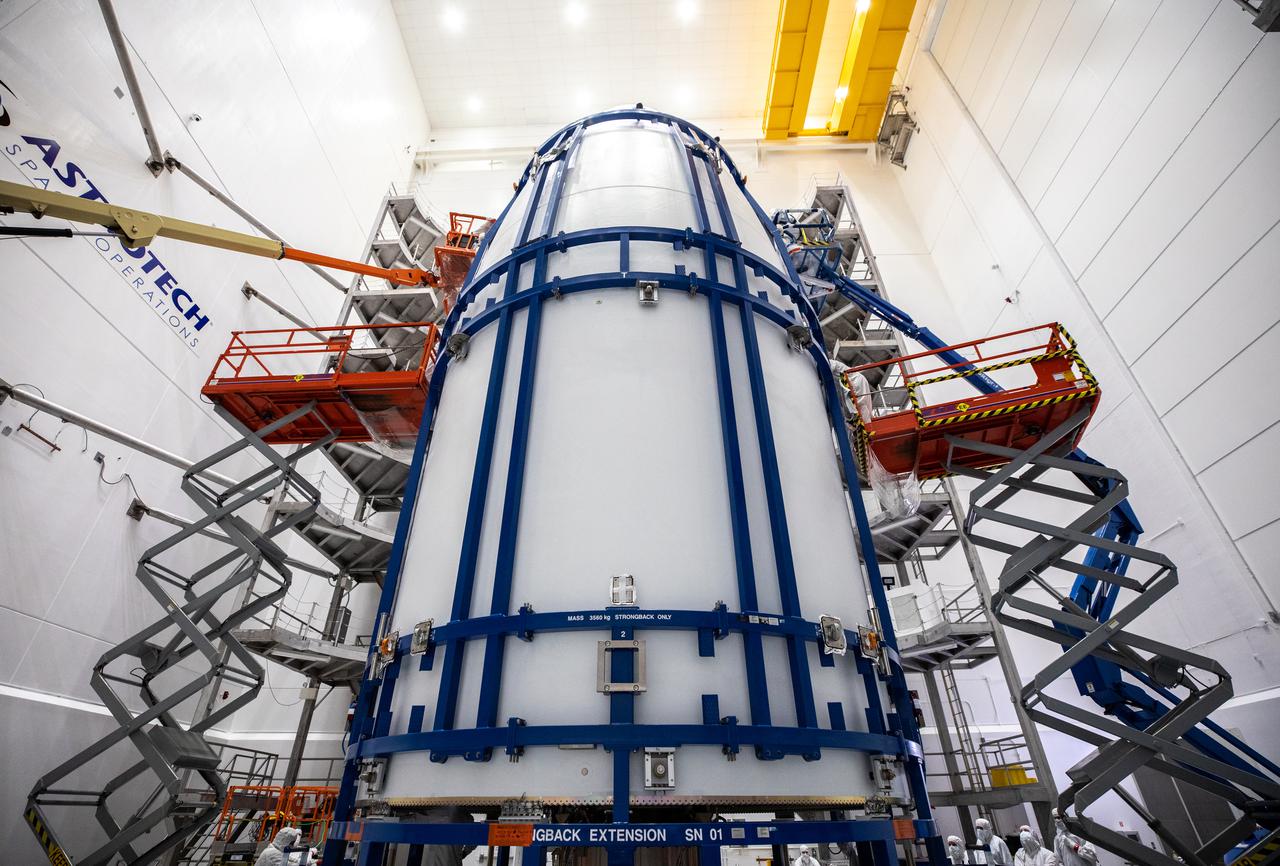

Technicians assist as the United Launch Alliance Atlas V payload fairings are secured around NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Feb. 7, 2022. The payload fairings will secure and protect the satellite during launch. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
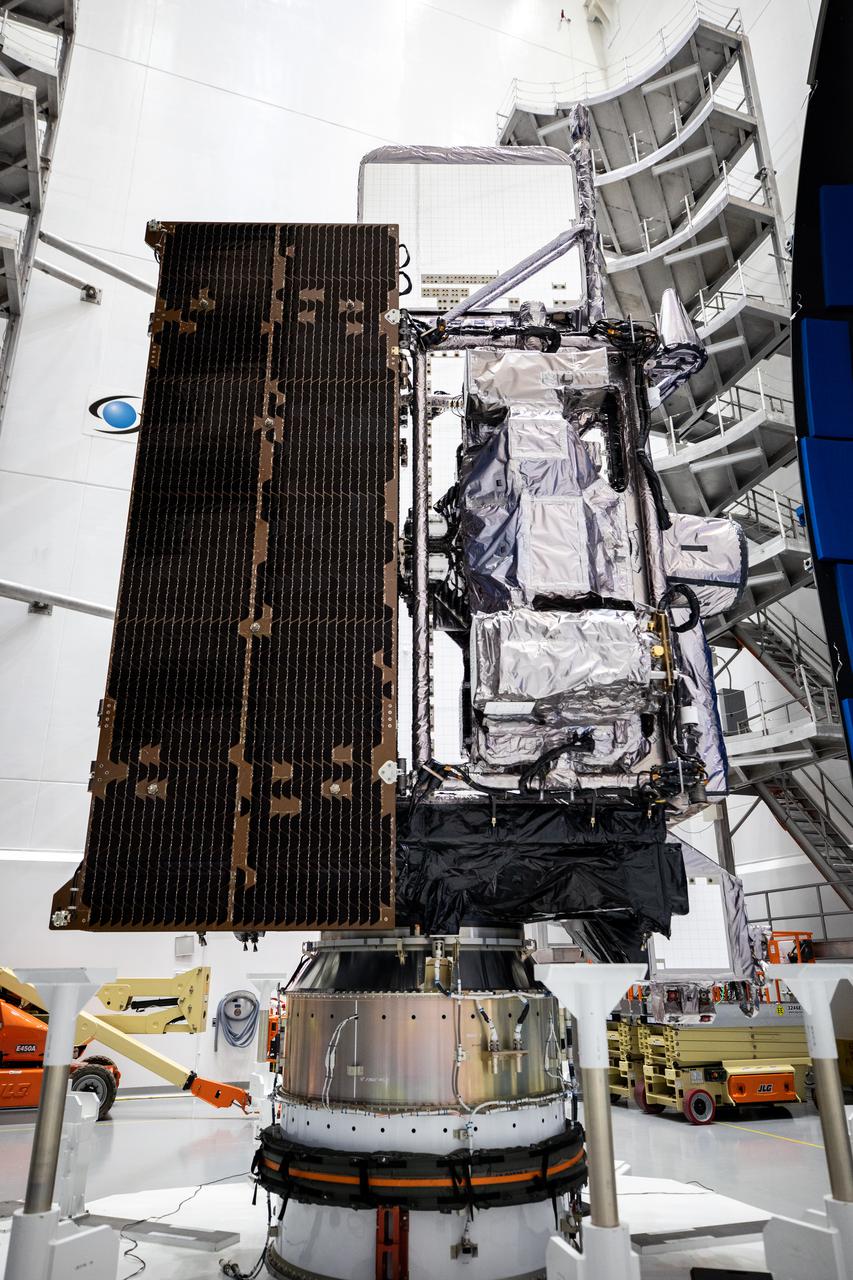

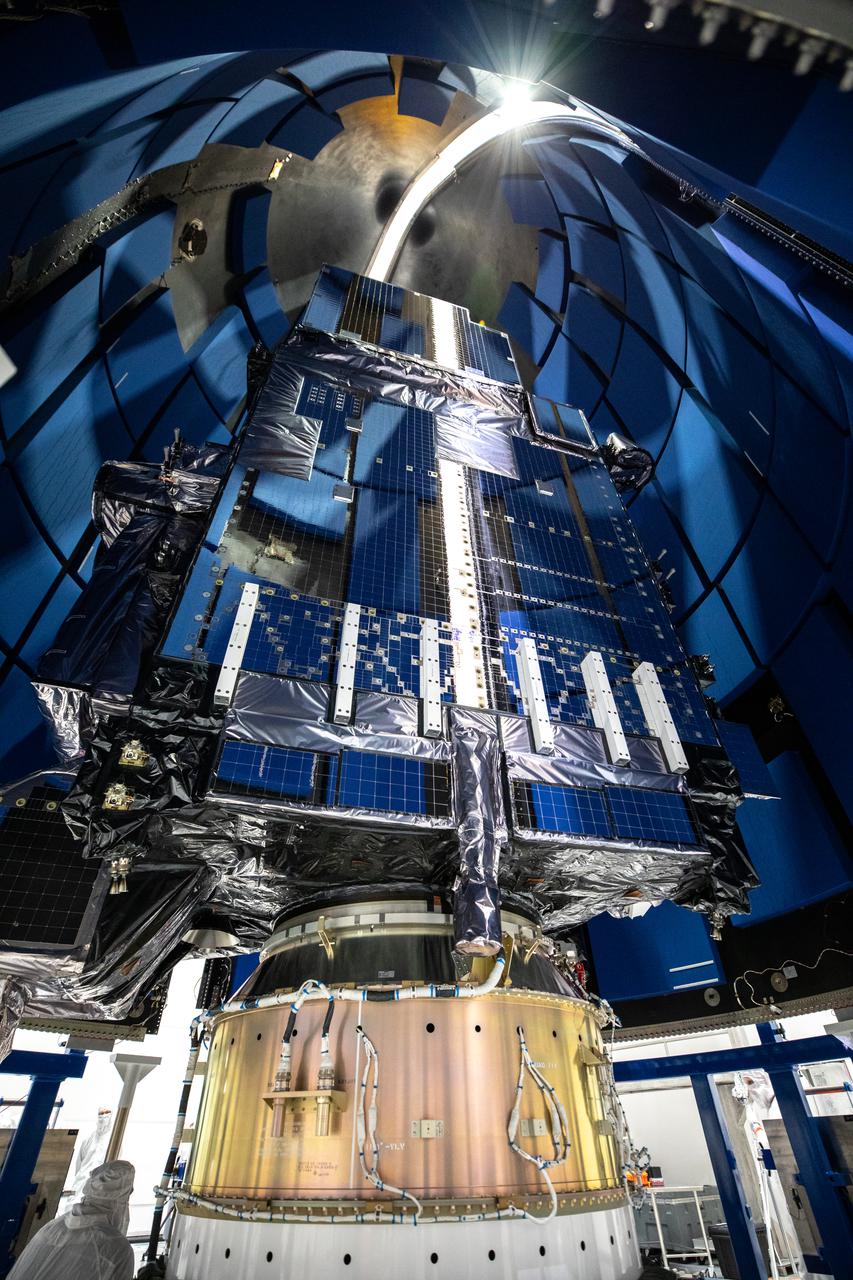
NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is in view inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Feb. 7, 2022, as it is being prepared for encapsulation in the United Launch Alliance Atlas V payload fairings. The fairings will protect the satellite during launch. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
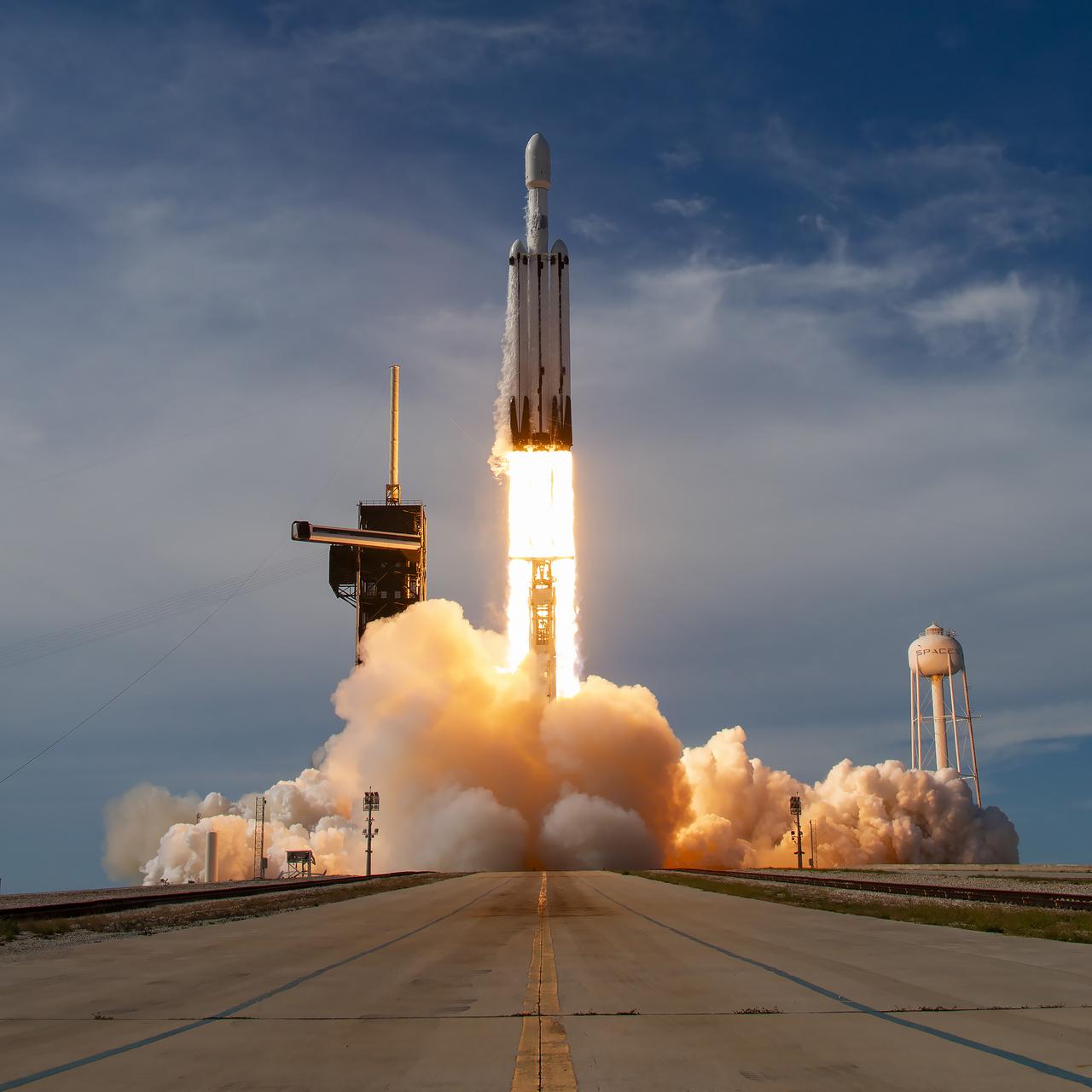

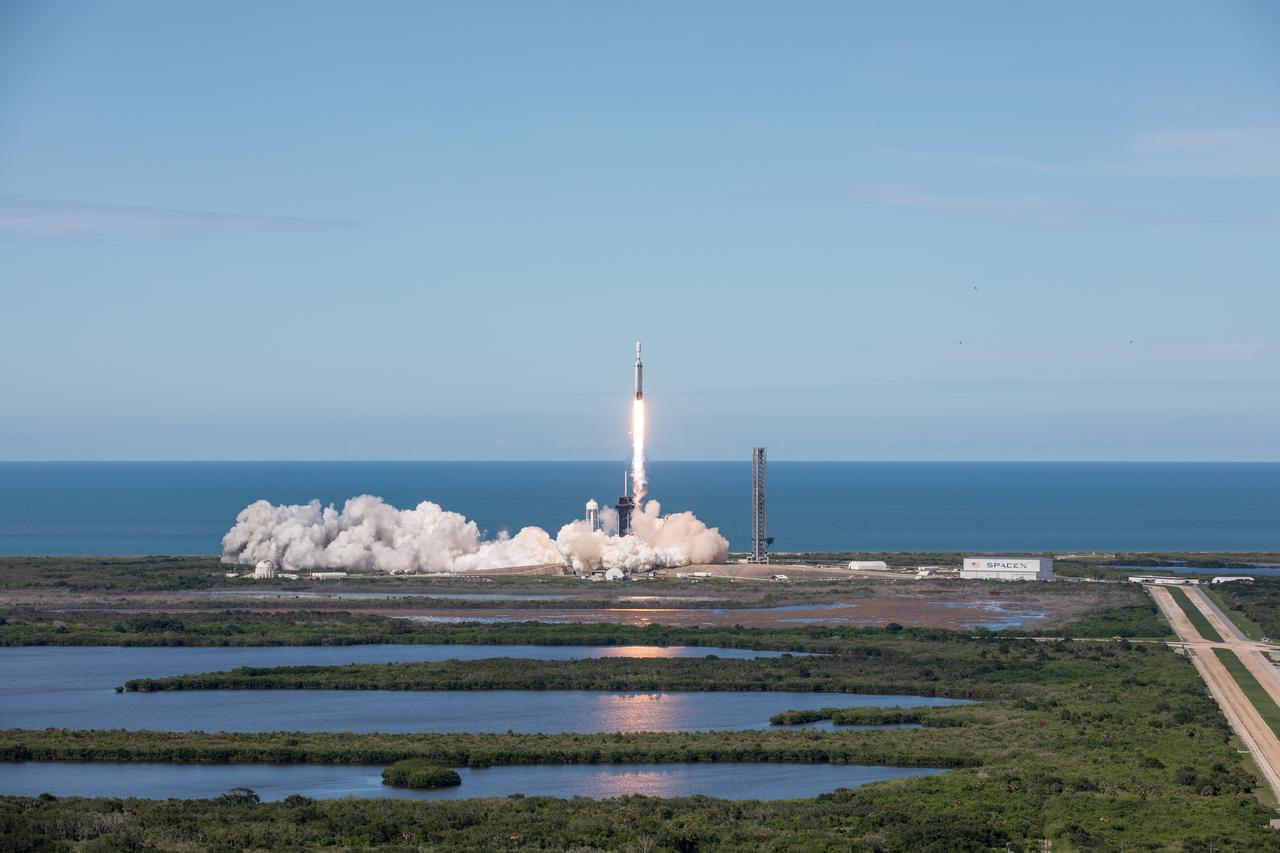
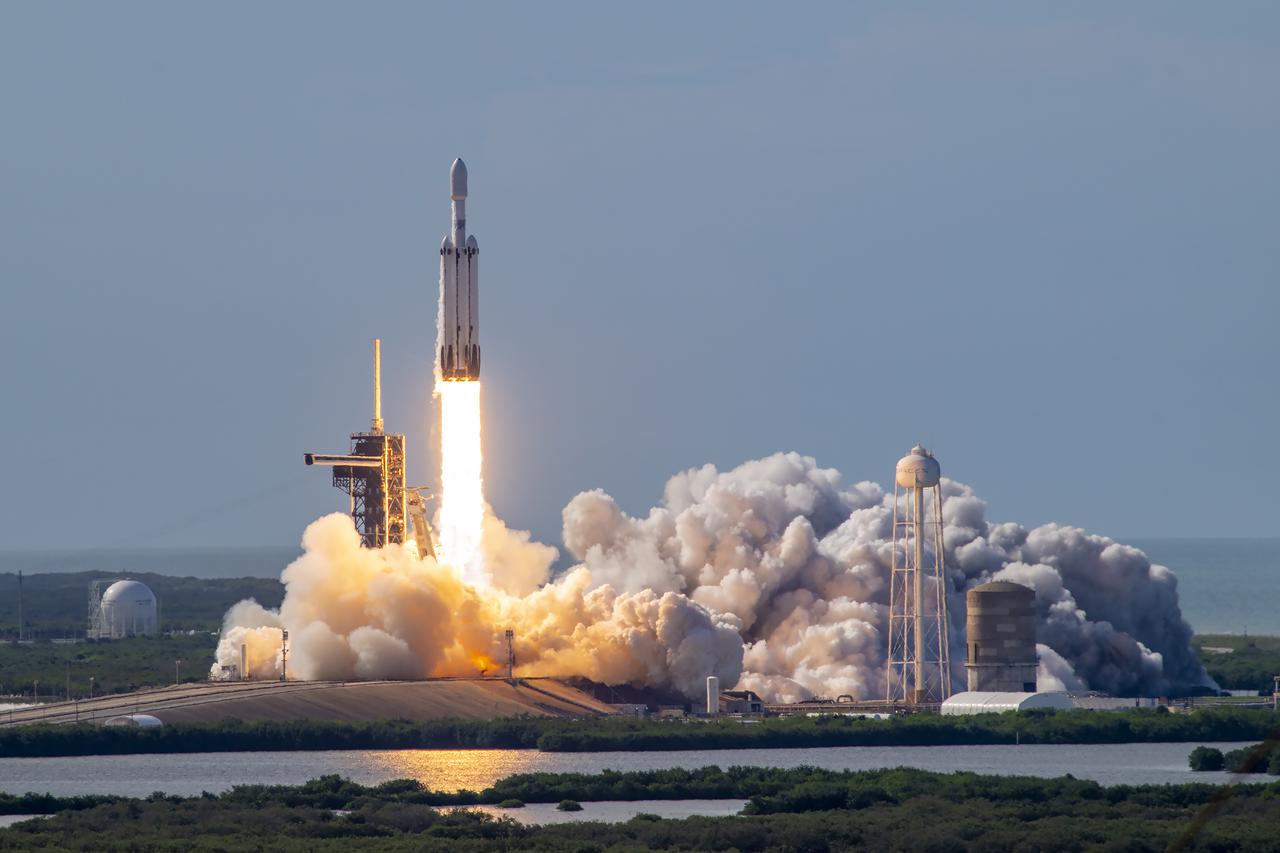
A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
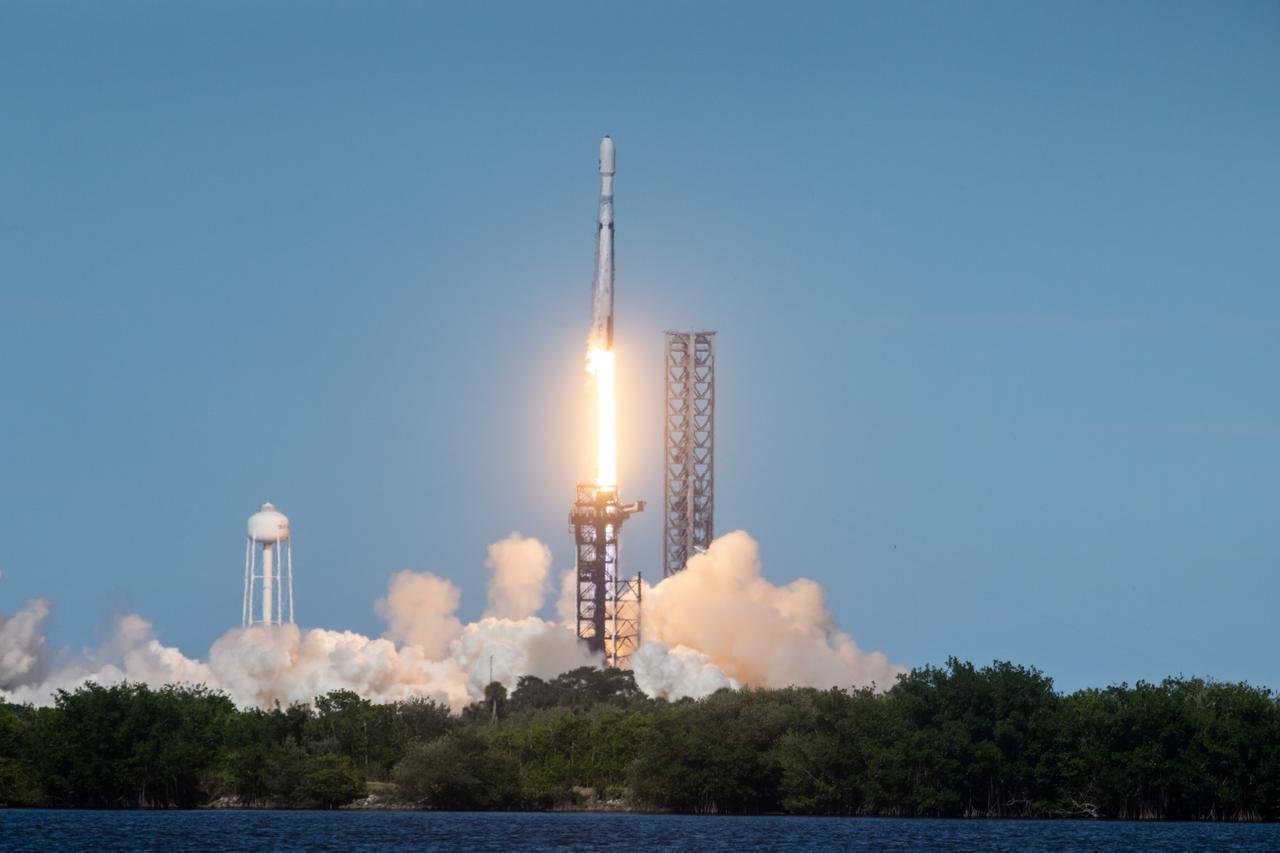

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
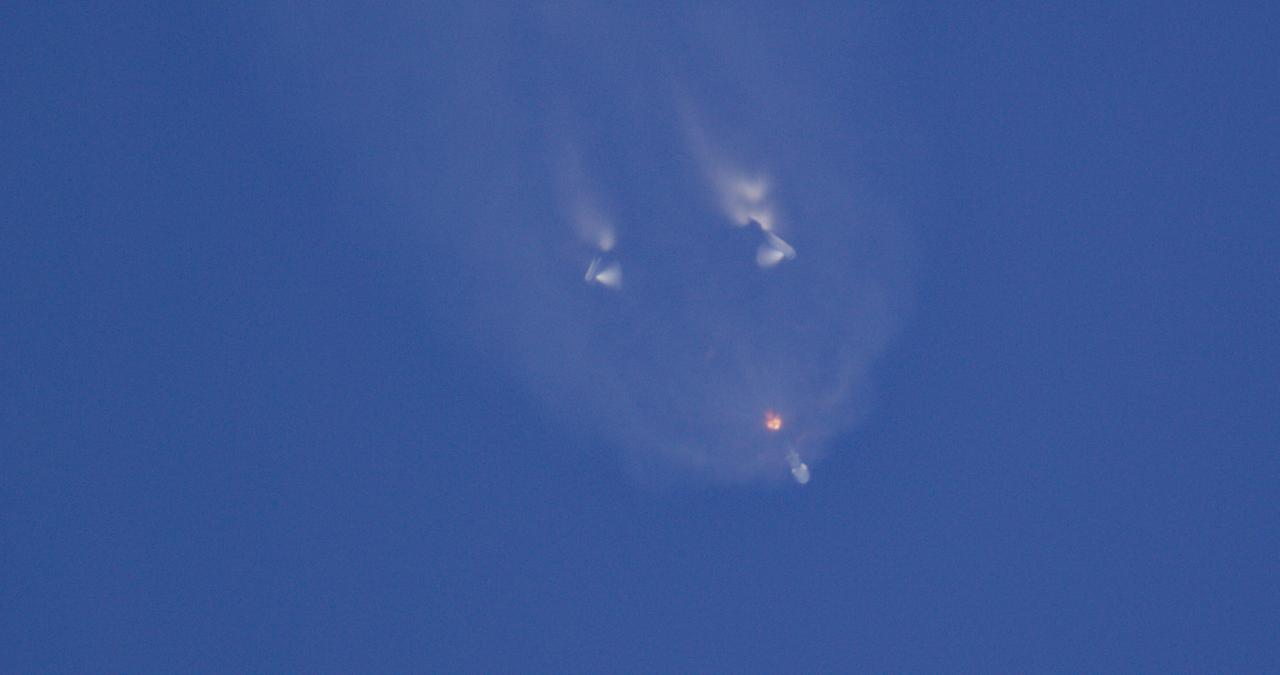

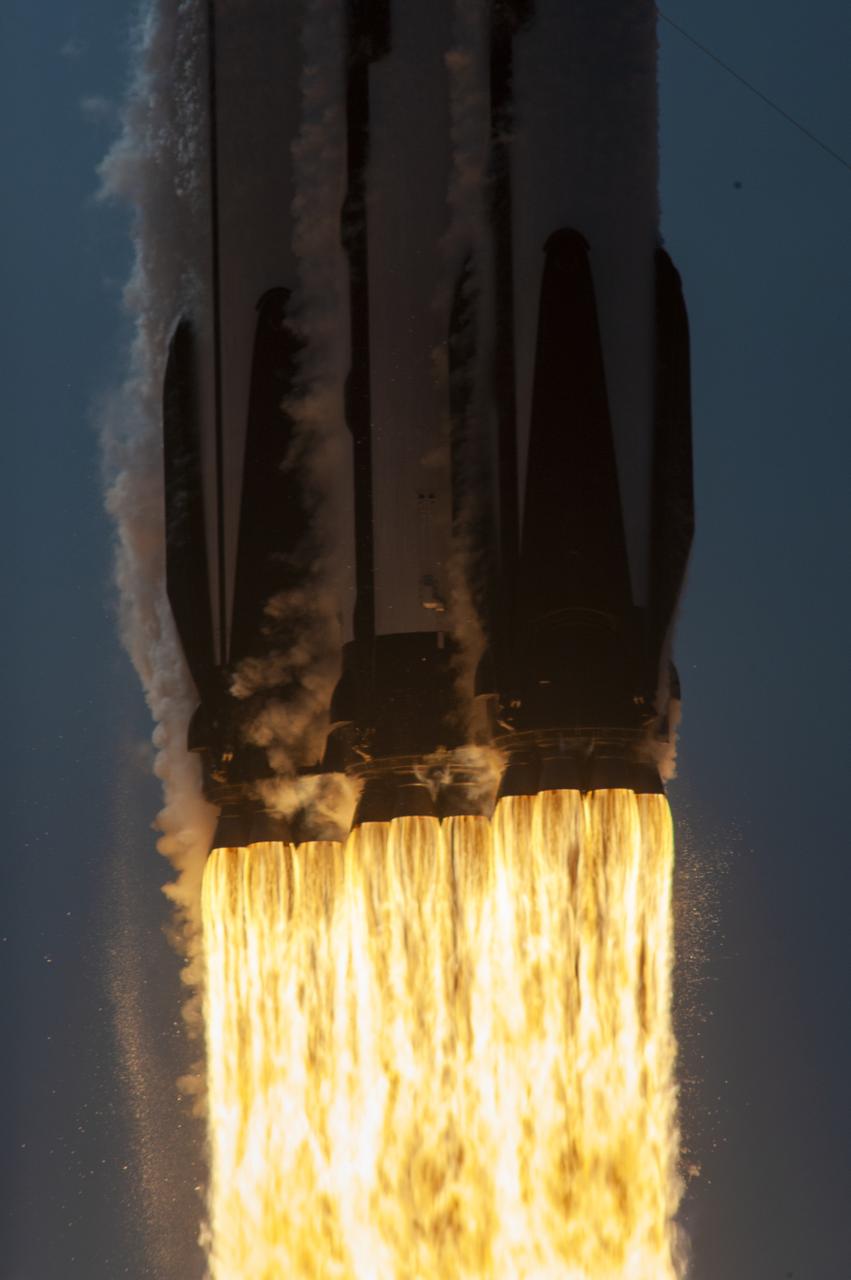
Side boosters separate from the center core on the SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) after it lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
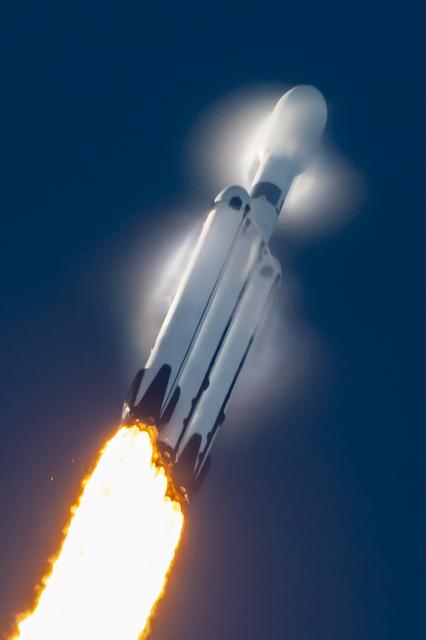

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
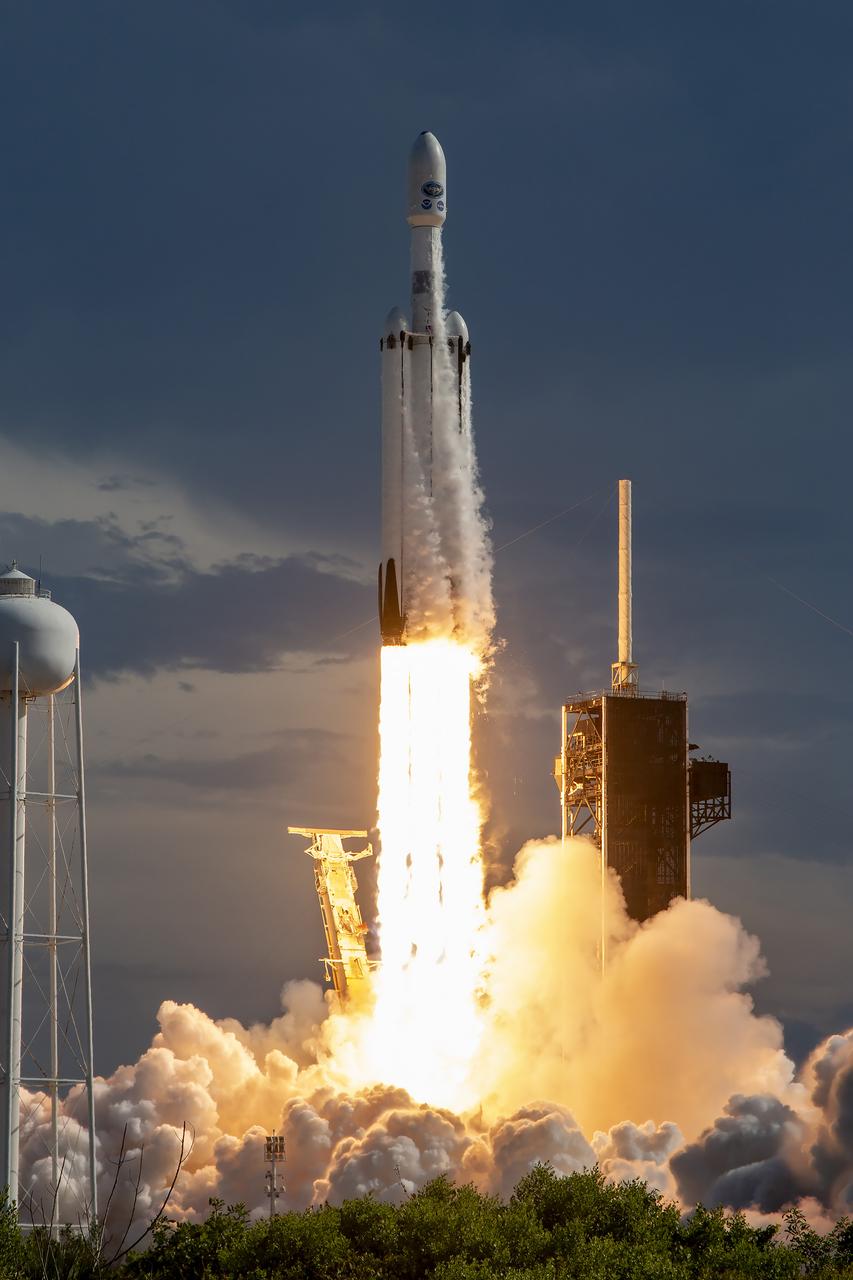

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
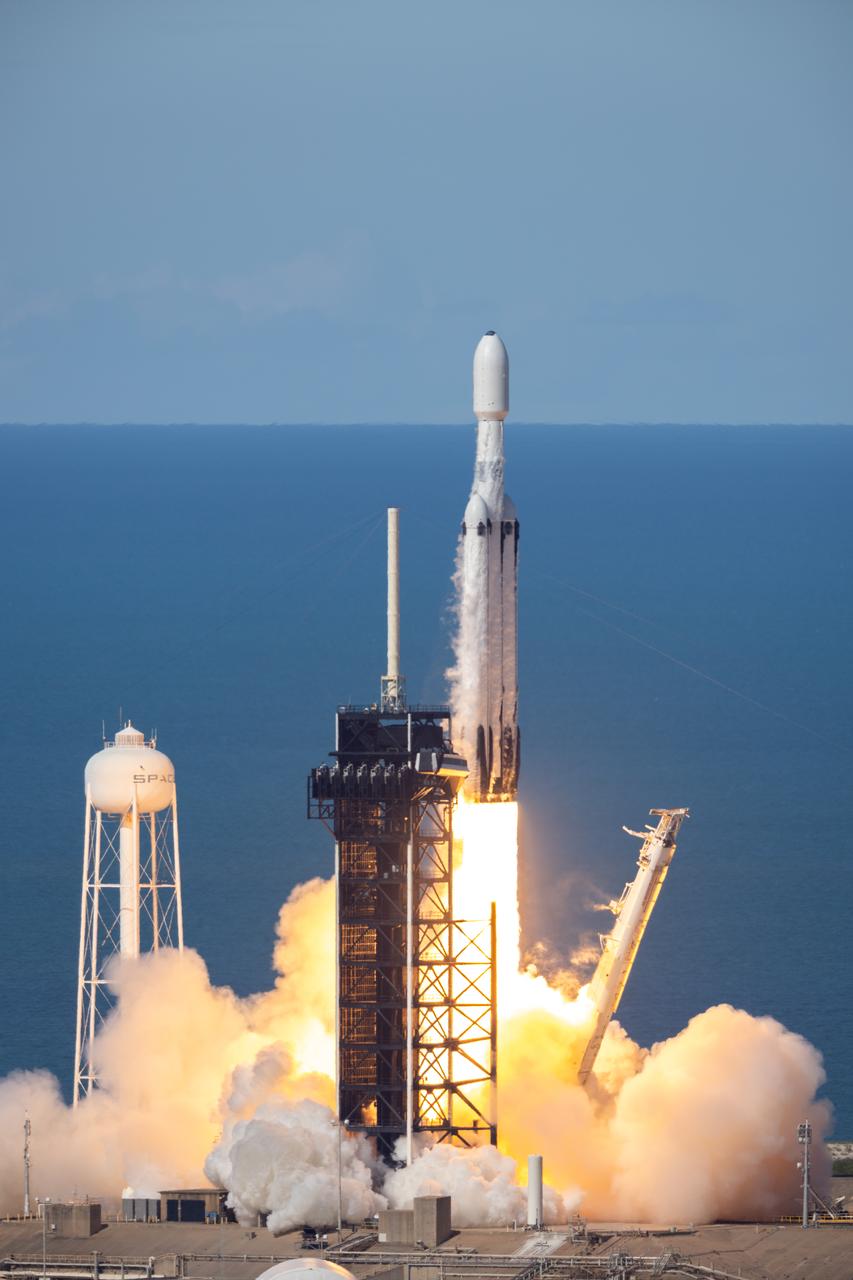

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
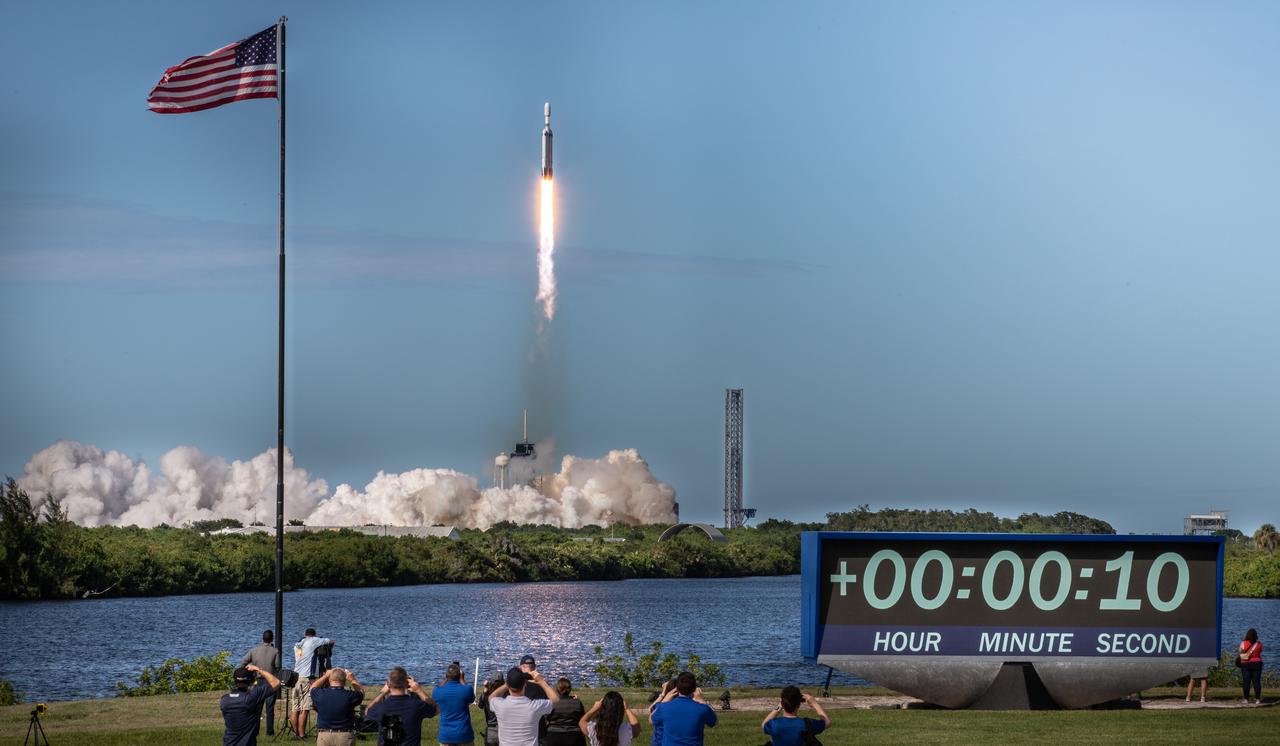

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
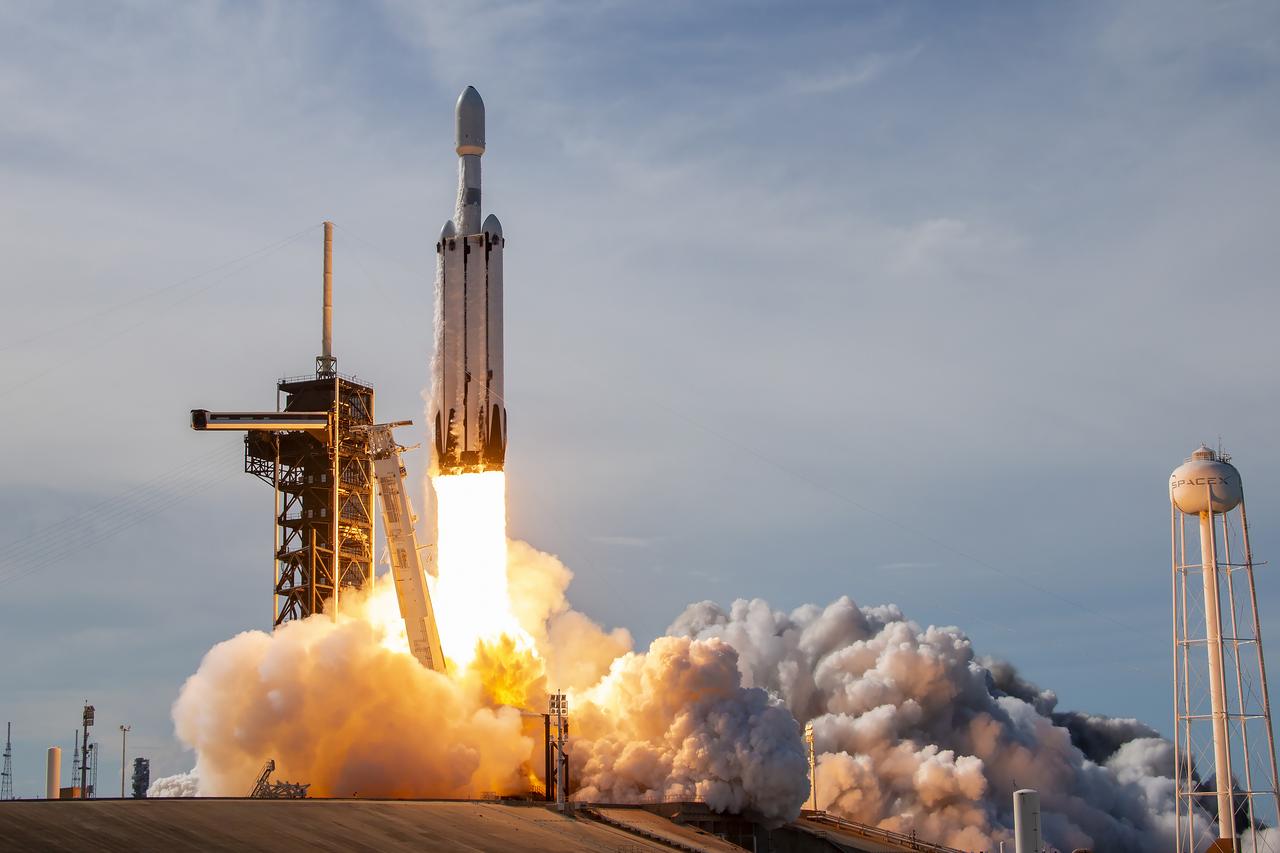

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
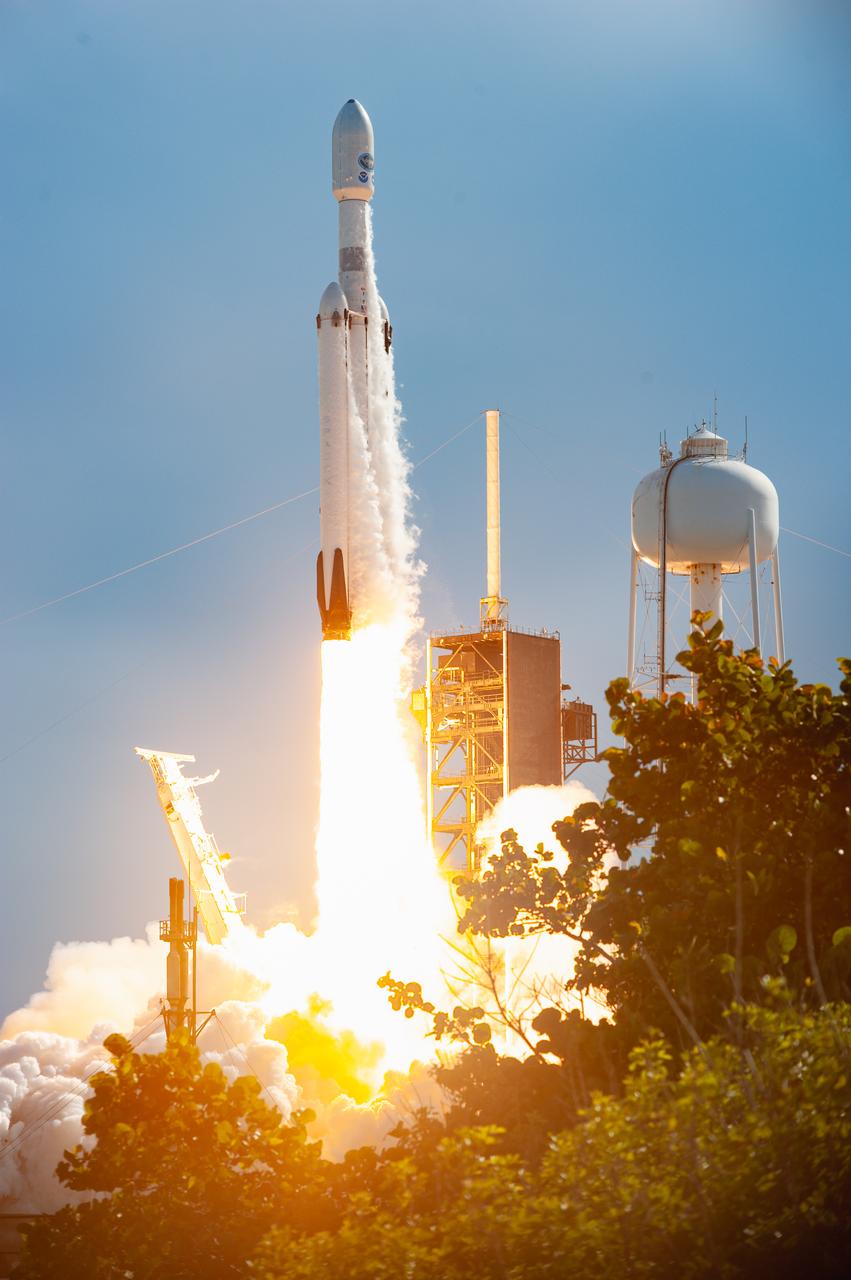

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
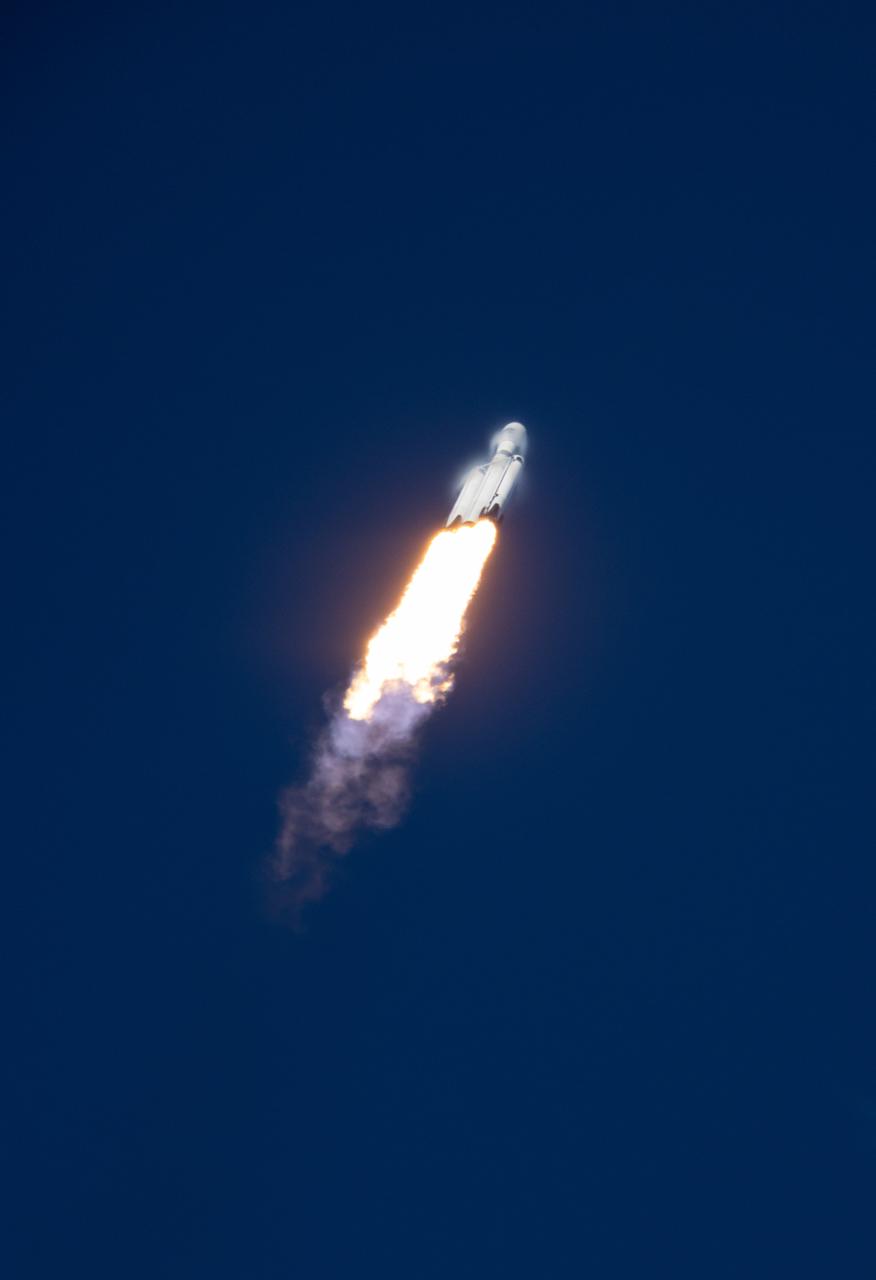

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) launches from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
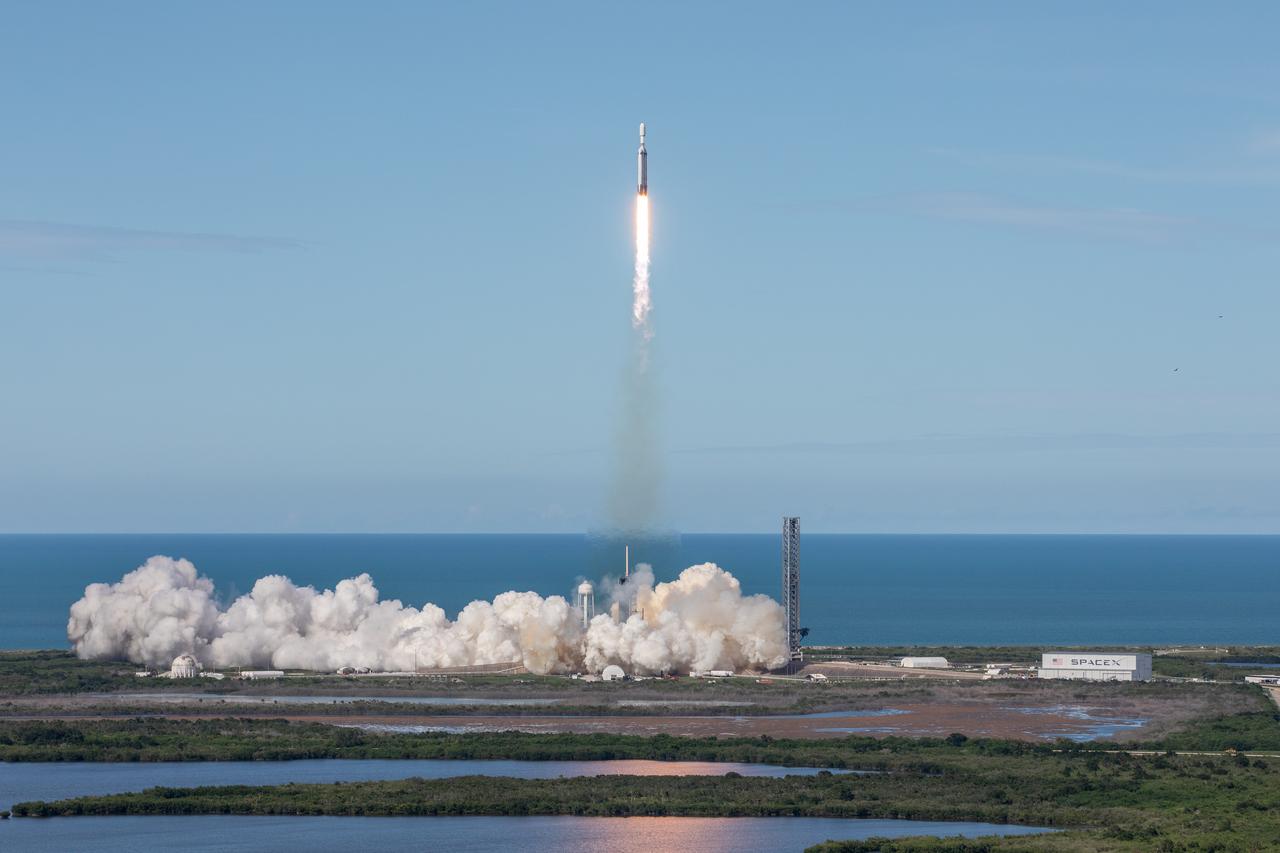

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
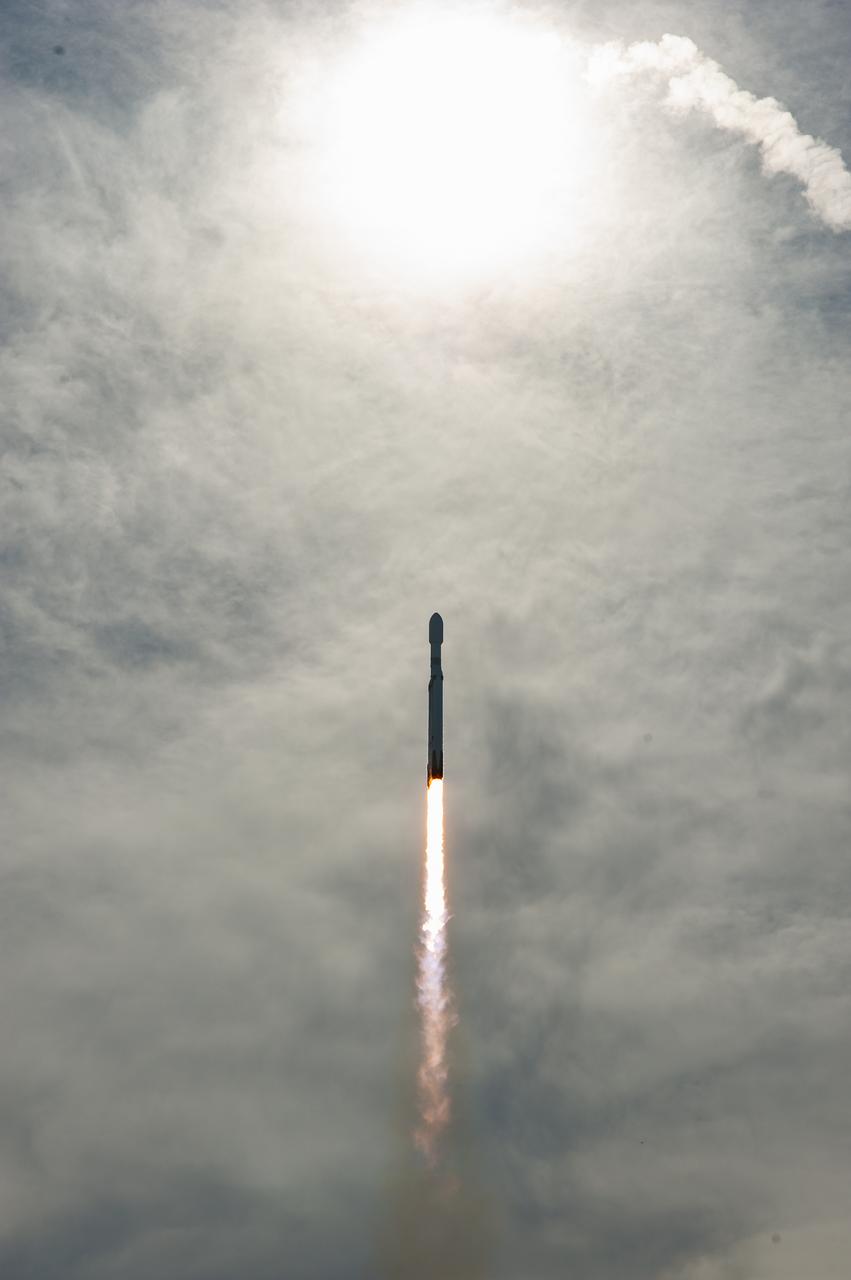

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
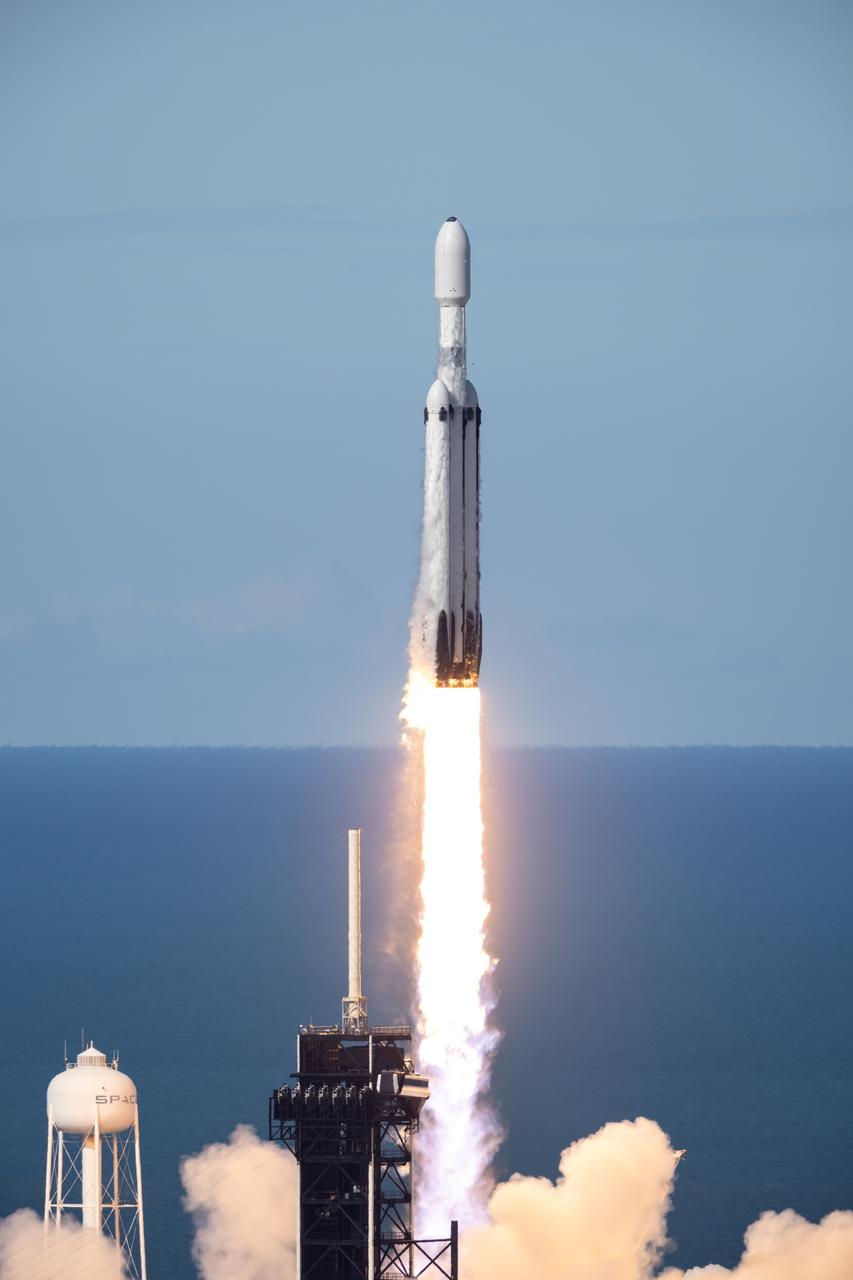

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
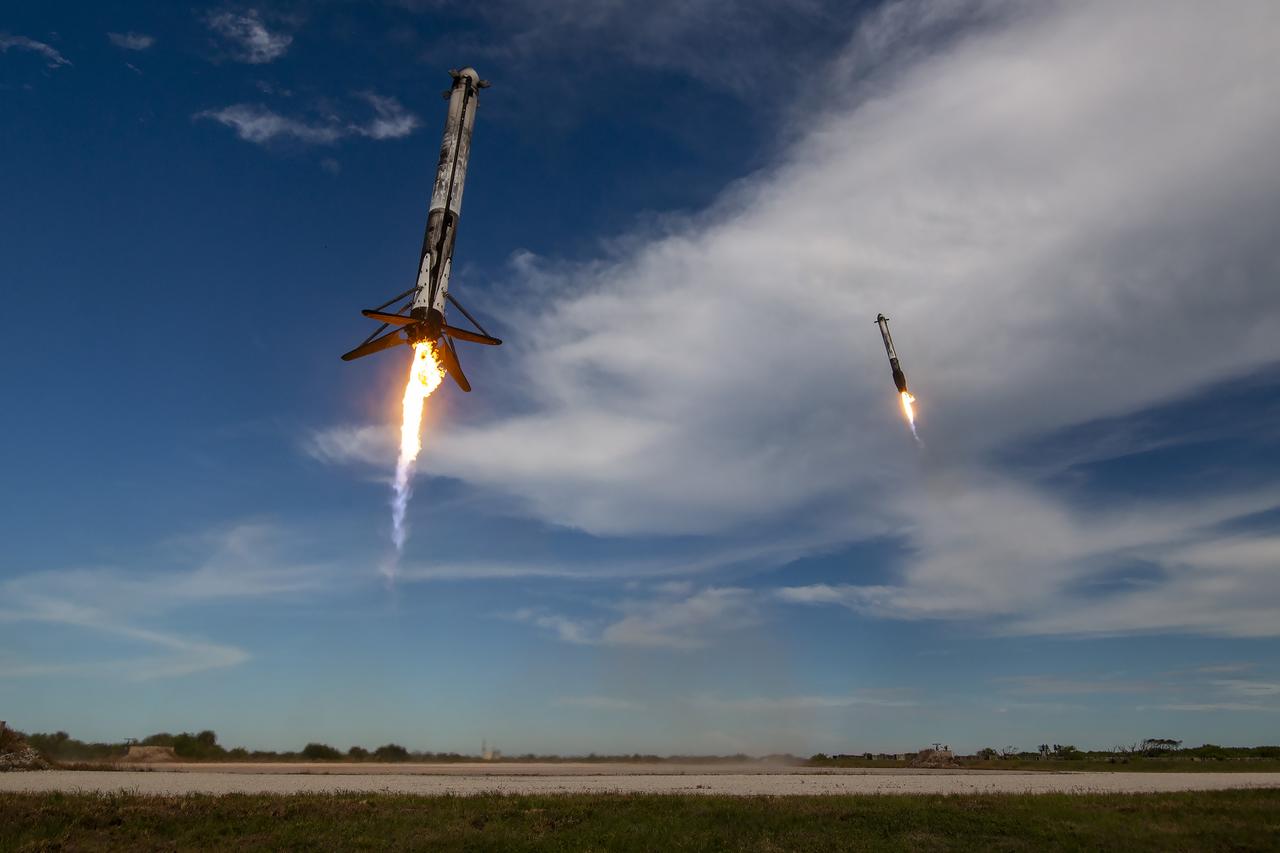

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
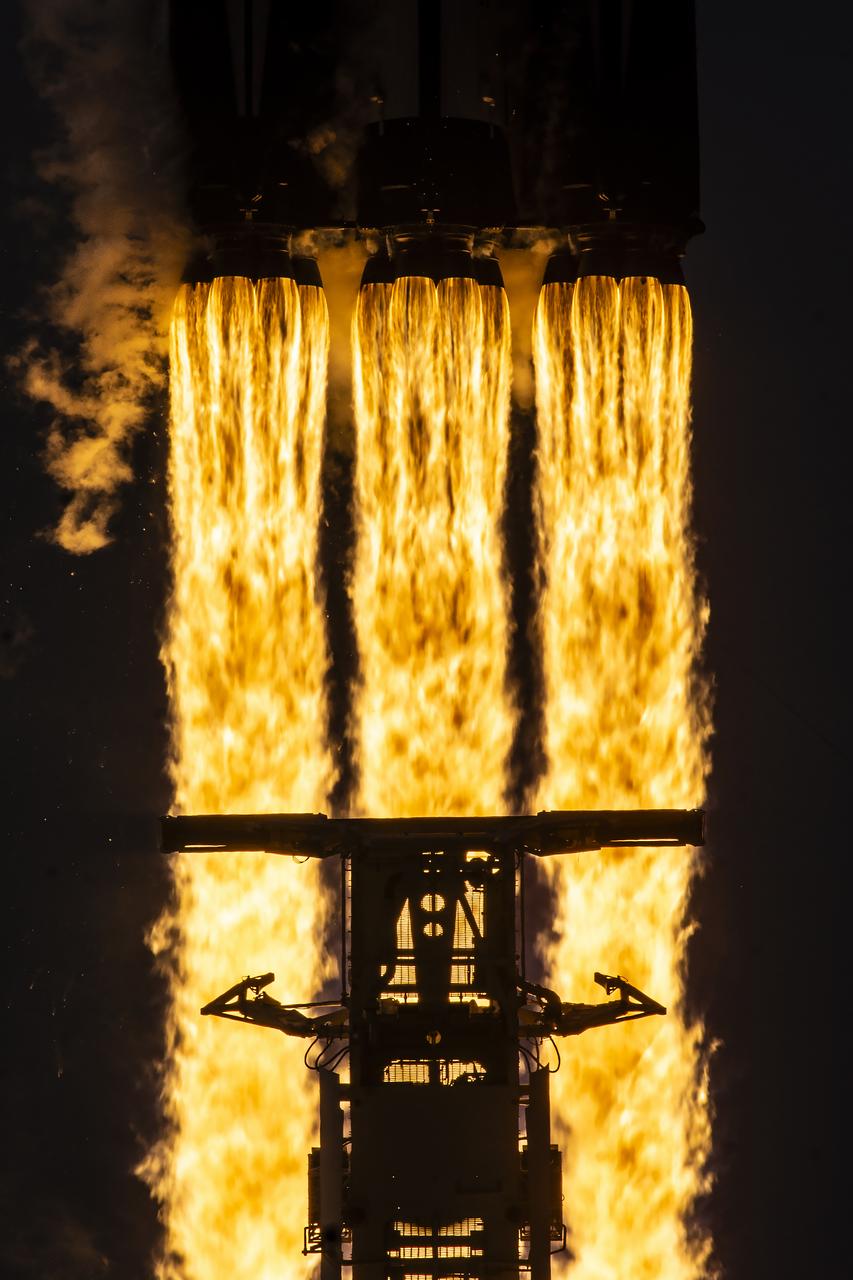

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
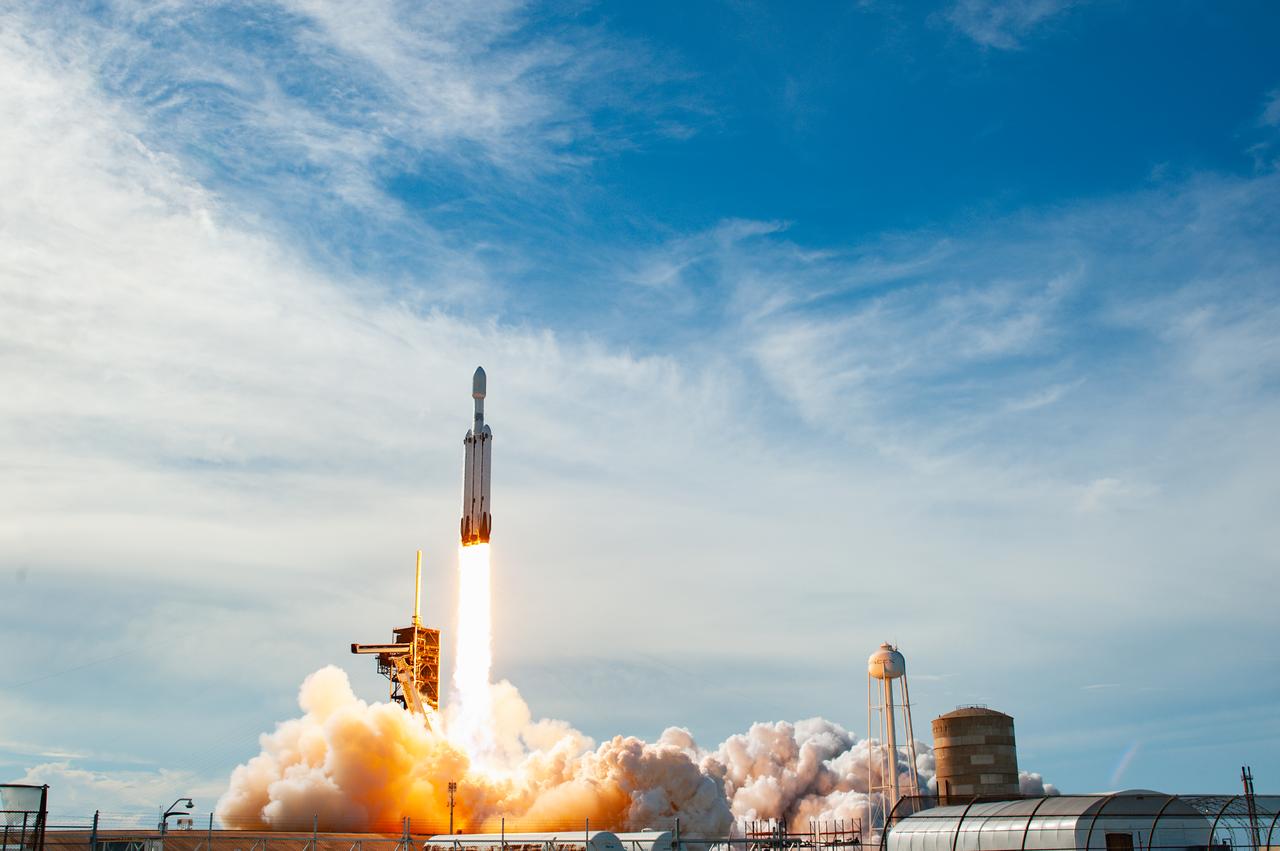

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
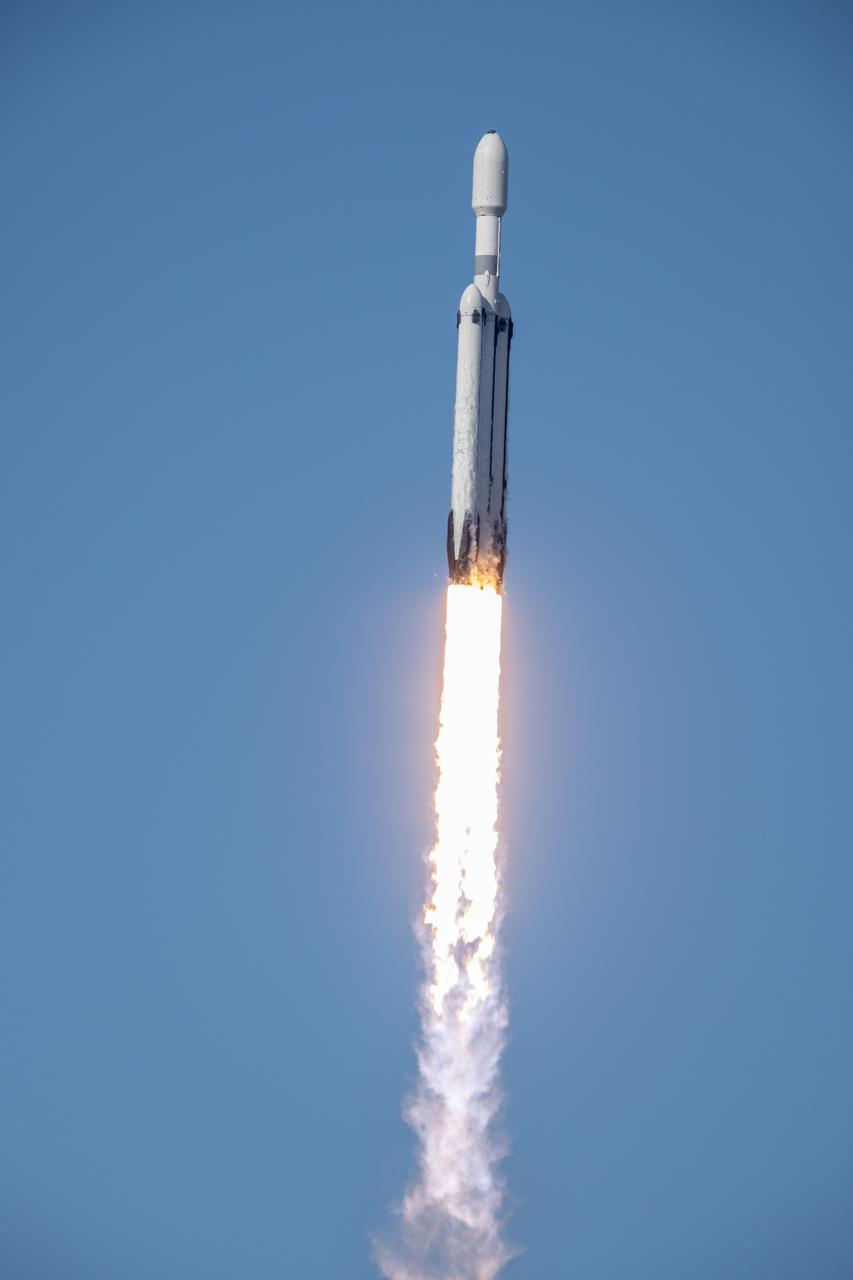

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
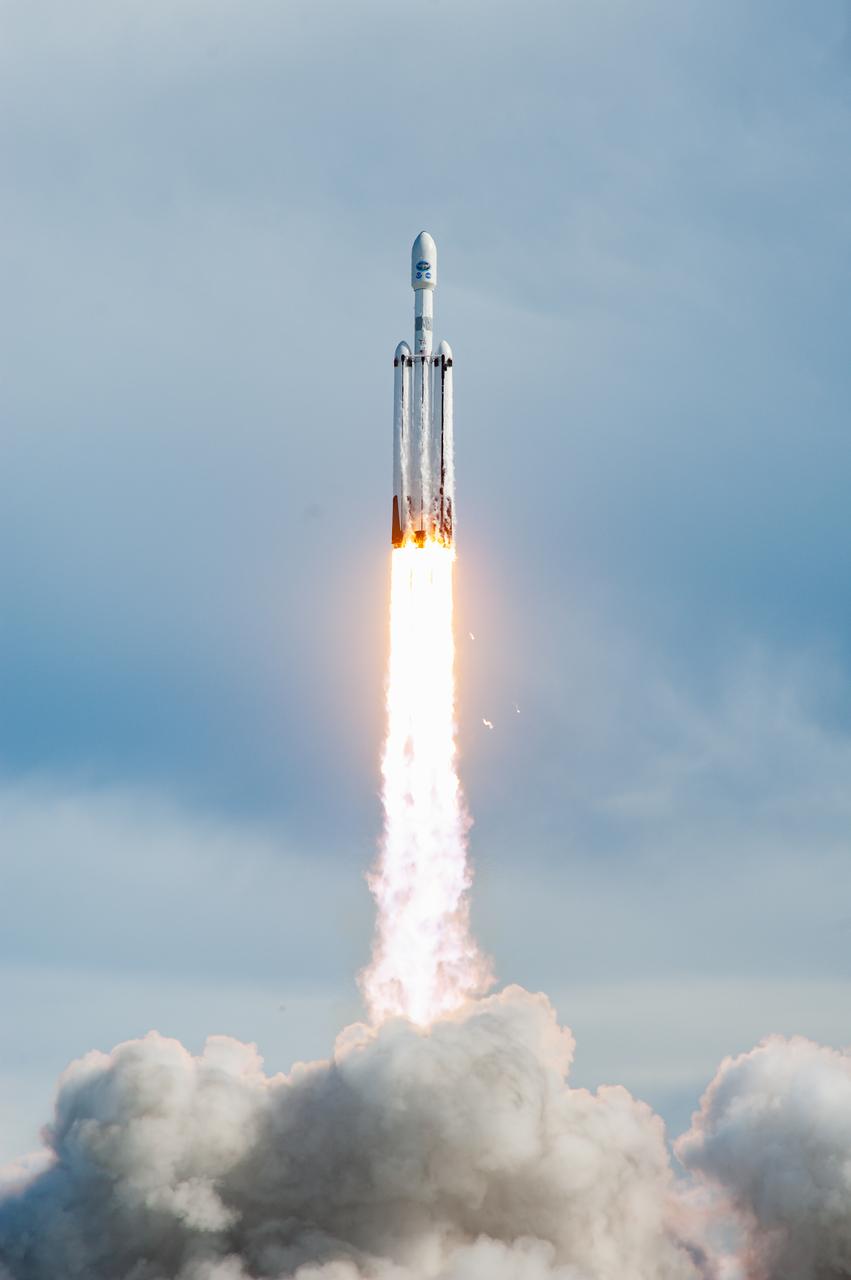

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
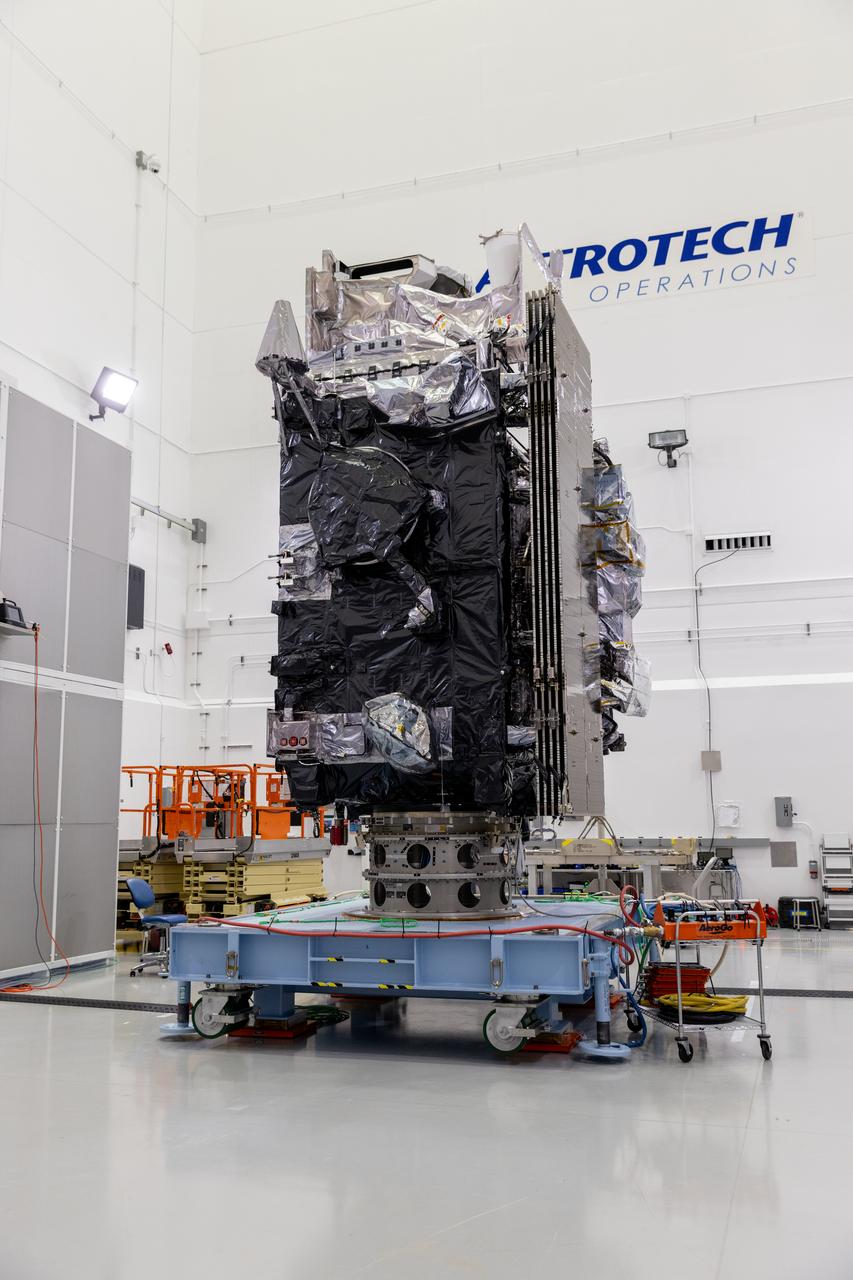

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) stands vertical on a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, June 6, 2024. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the last in a series of advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES-R satellite series enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
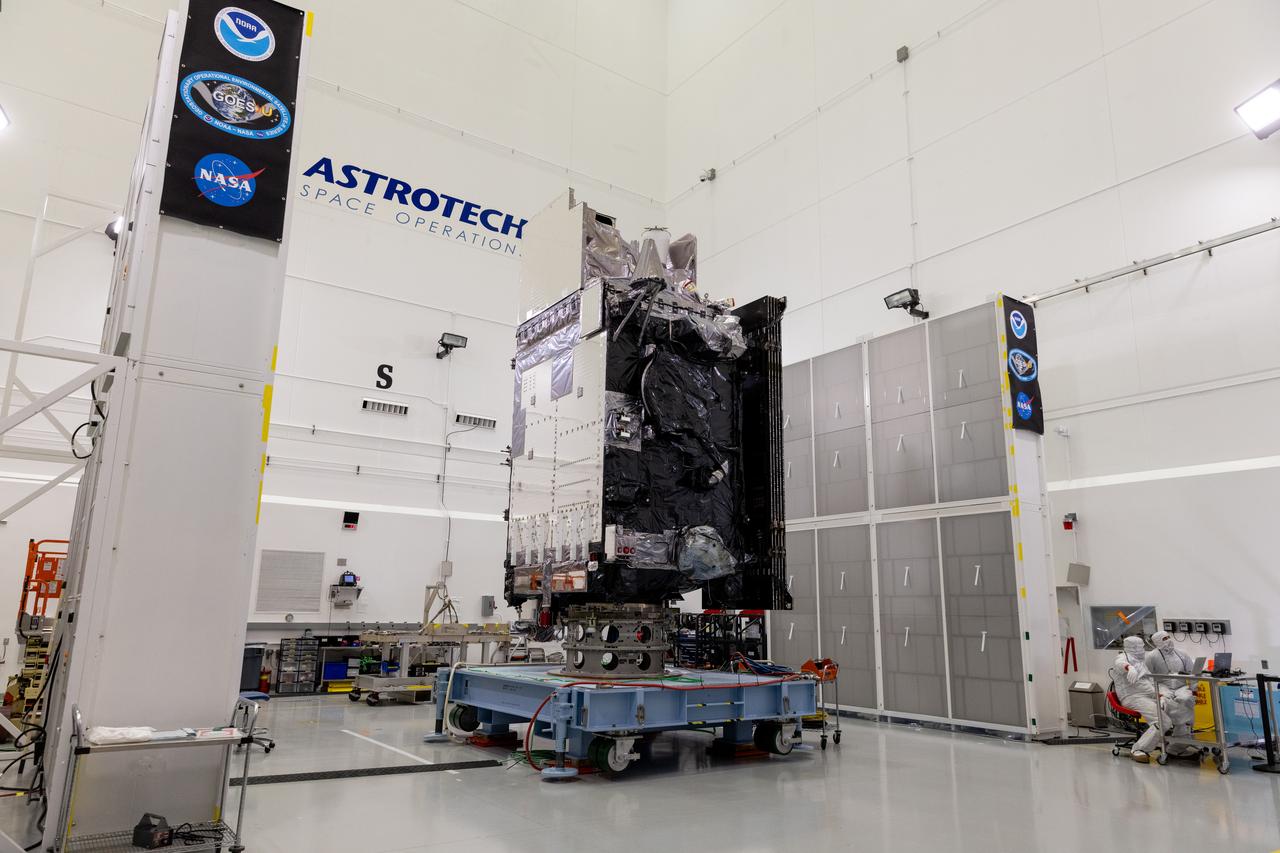

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) stands vertical on a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, June 6, 2024. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the last in a series of advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES-R satellite series enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
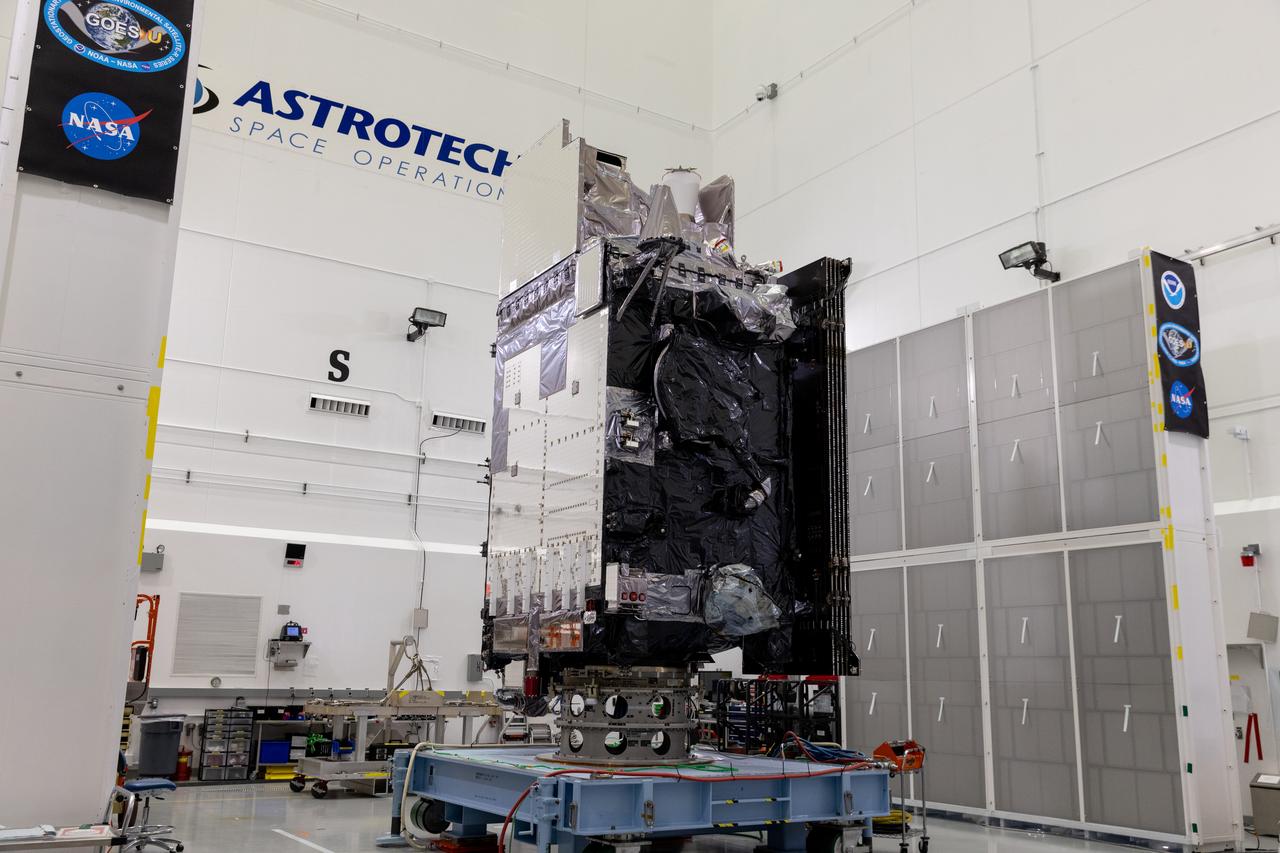

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) stands vertical on a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, June 6, 2024. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the last in a series of advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES-R satellite series enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
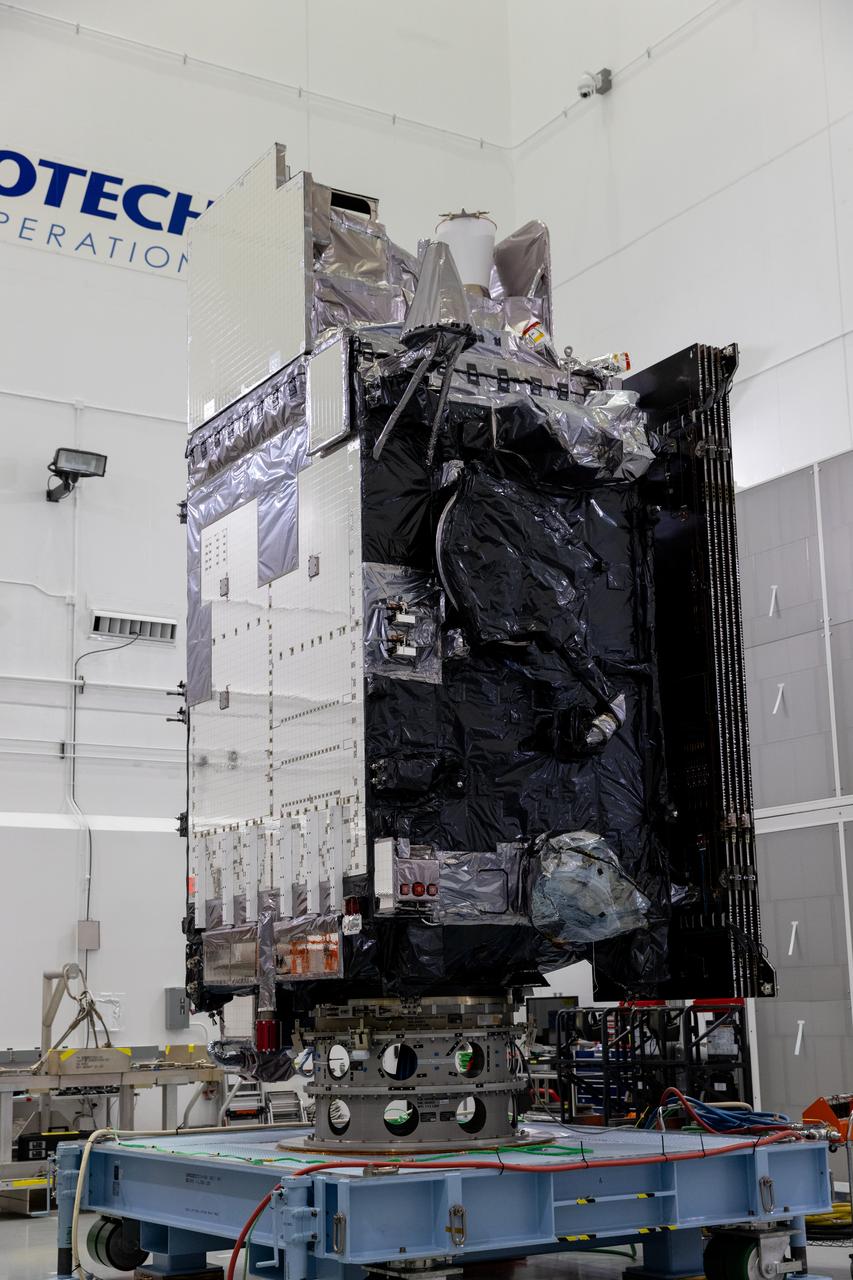

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) stands vertical on a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, June 6, 2024. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the last in a series of advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES-R satellite series enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers monitor progress as NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is mated to its payload attach fitting. It soon will be moved to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mounting atop the Atlas V rocket that will boost the satellite to orbit. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites that will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
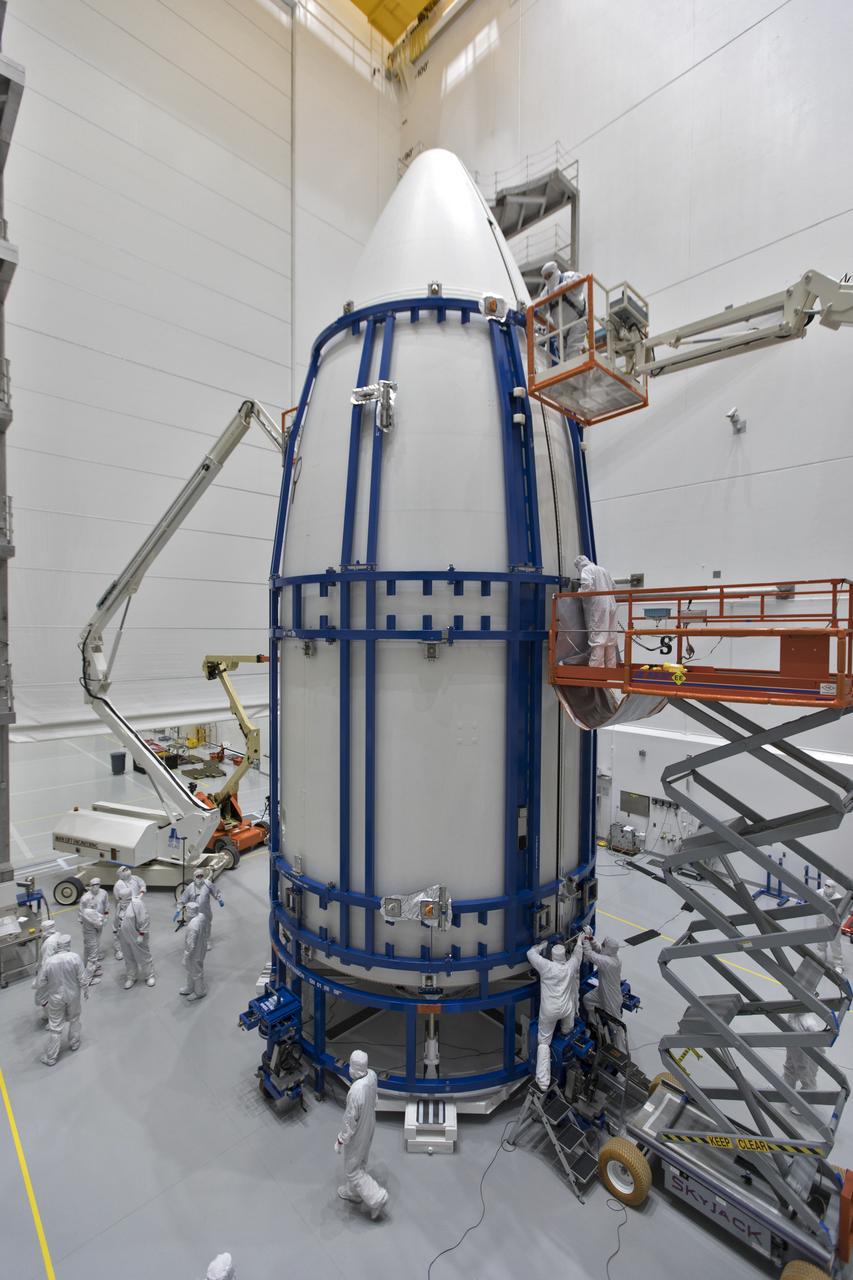

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers monitor progress as NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is encapsulated in its payload fairing. It soon will be moved to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mounting atop the Atlas V rocket that will boost the satellite to orbit. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites that will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
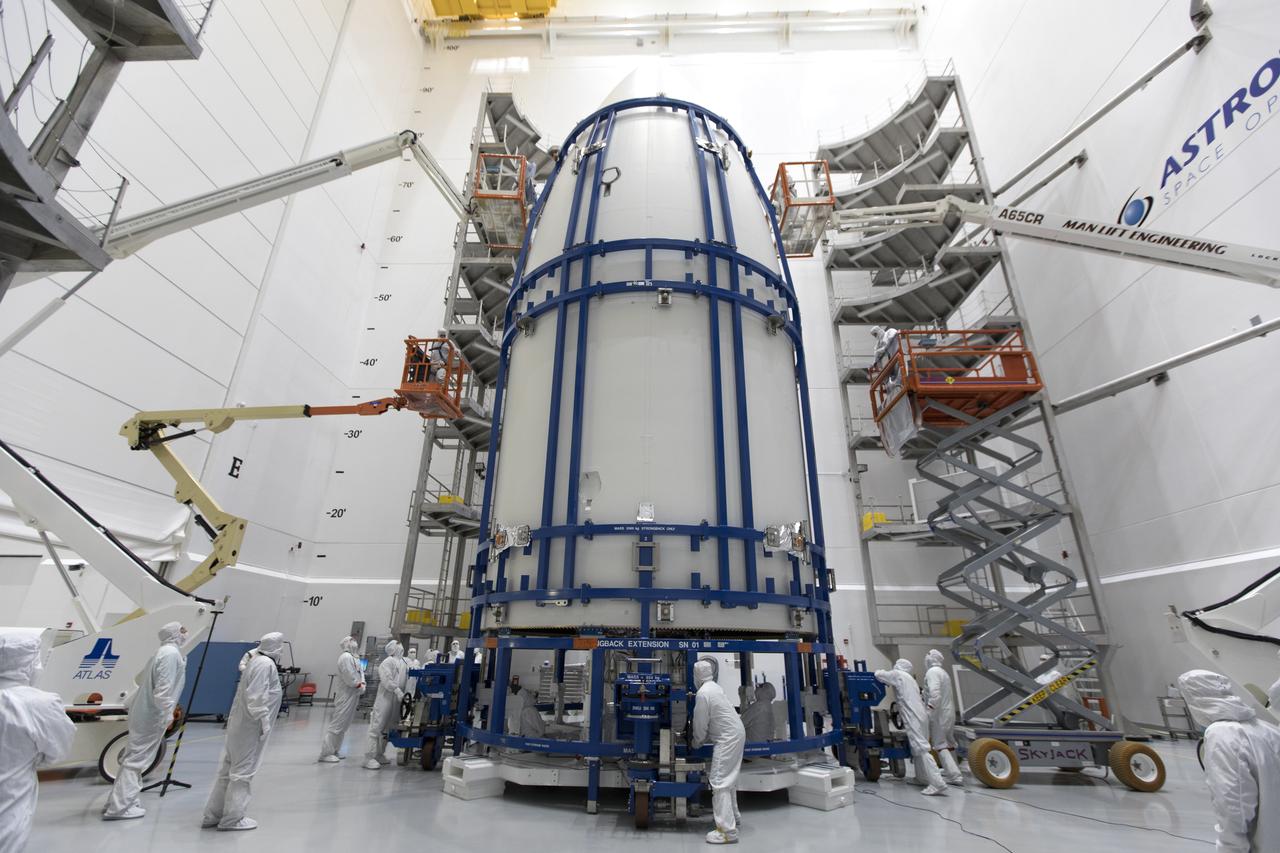

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers monitor progress as NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is encapsulated in its payload fairing. It soon will be moved to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mounting atop the Atlas V rocket that will boost the satellite to orbit. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites that will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
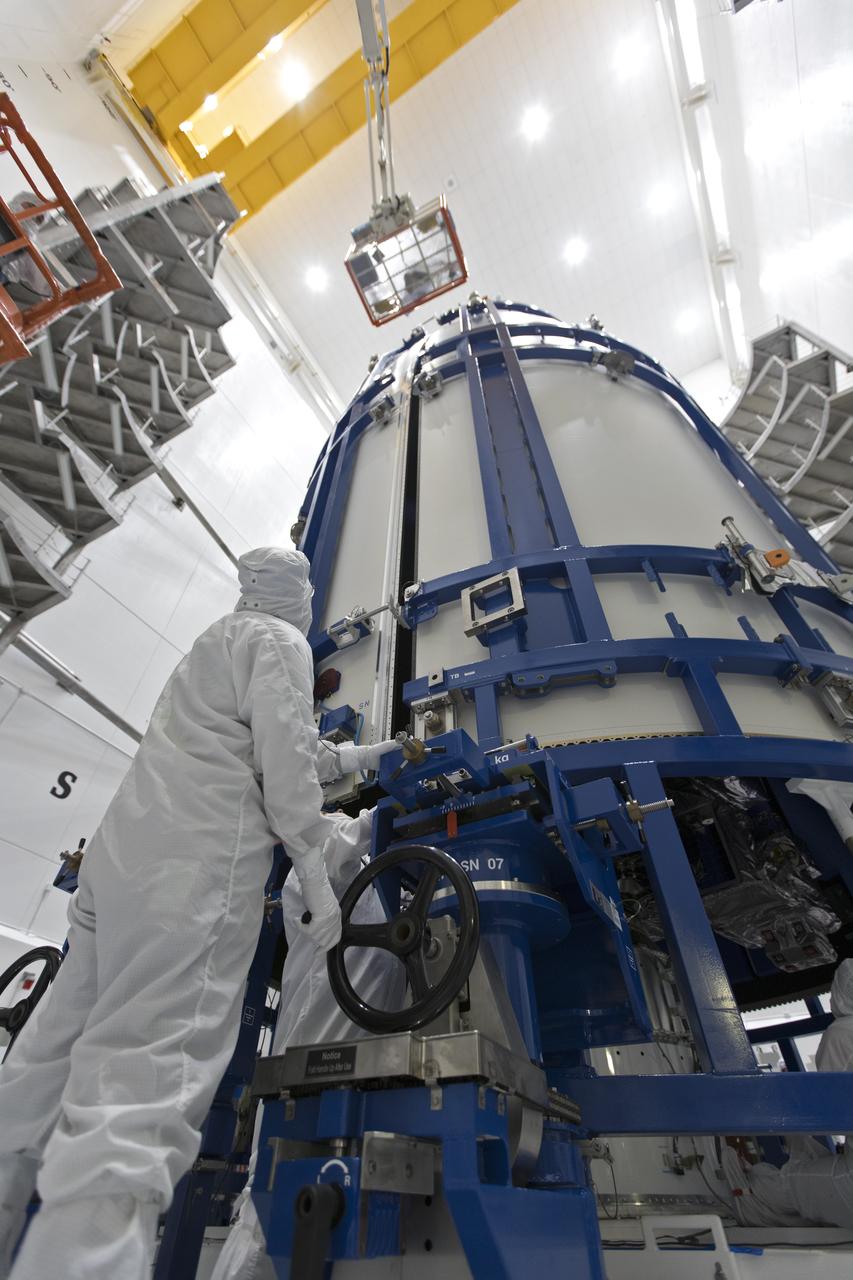

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers monitor progress as NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is encapsulated in its payload fairing. It soon will be moved to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mounting atop the Atlas V rocket that will boost the satellite to orbit. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites that will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
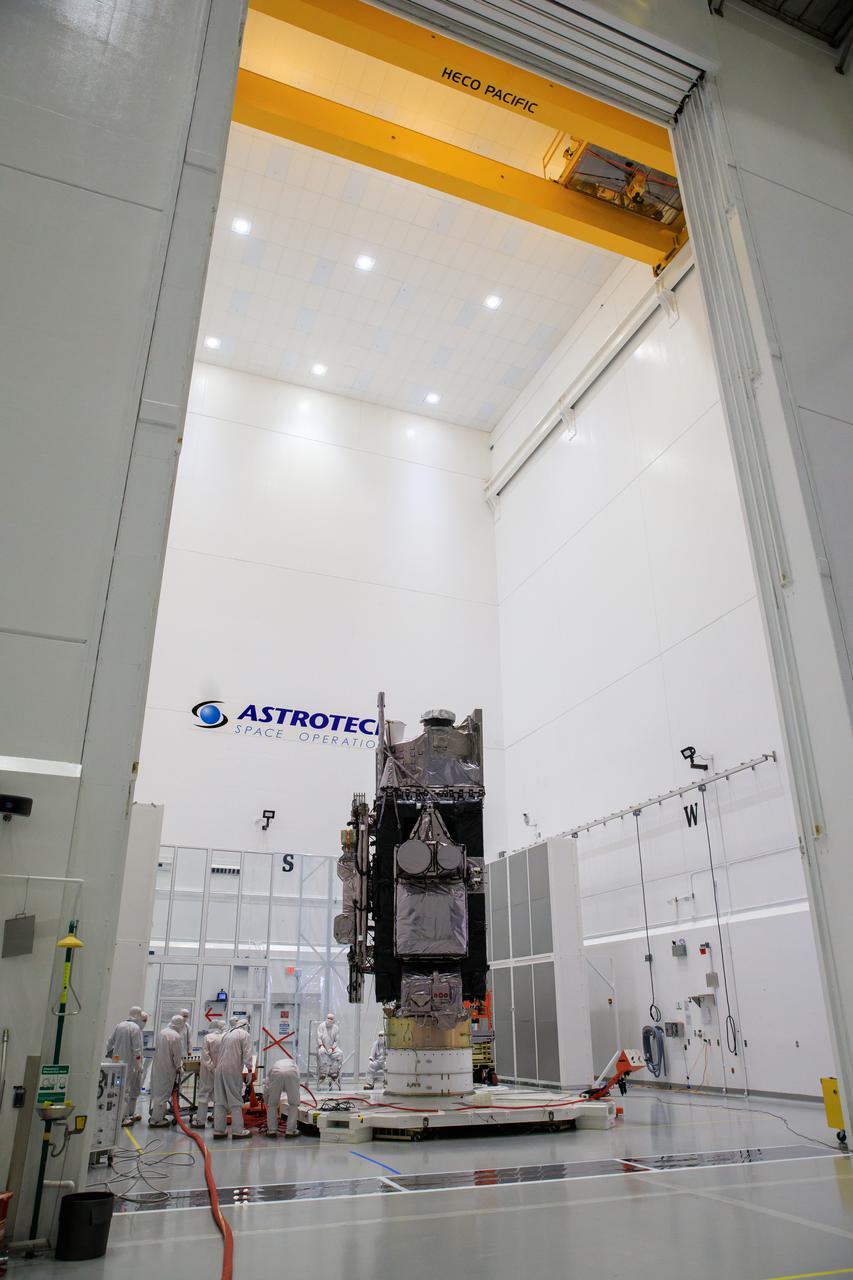

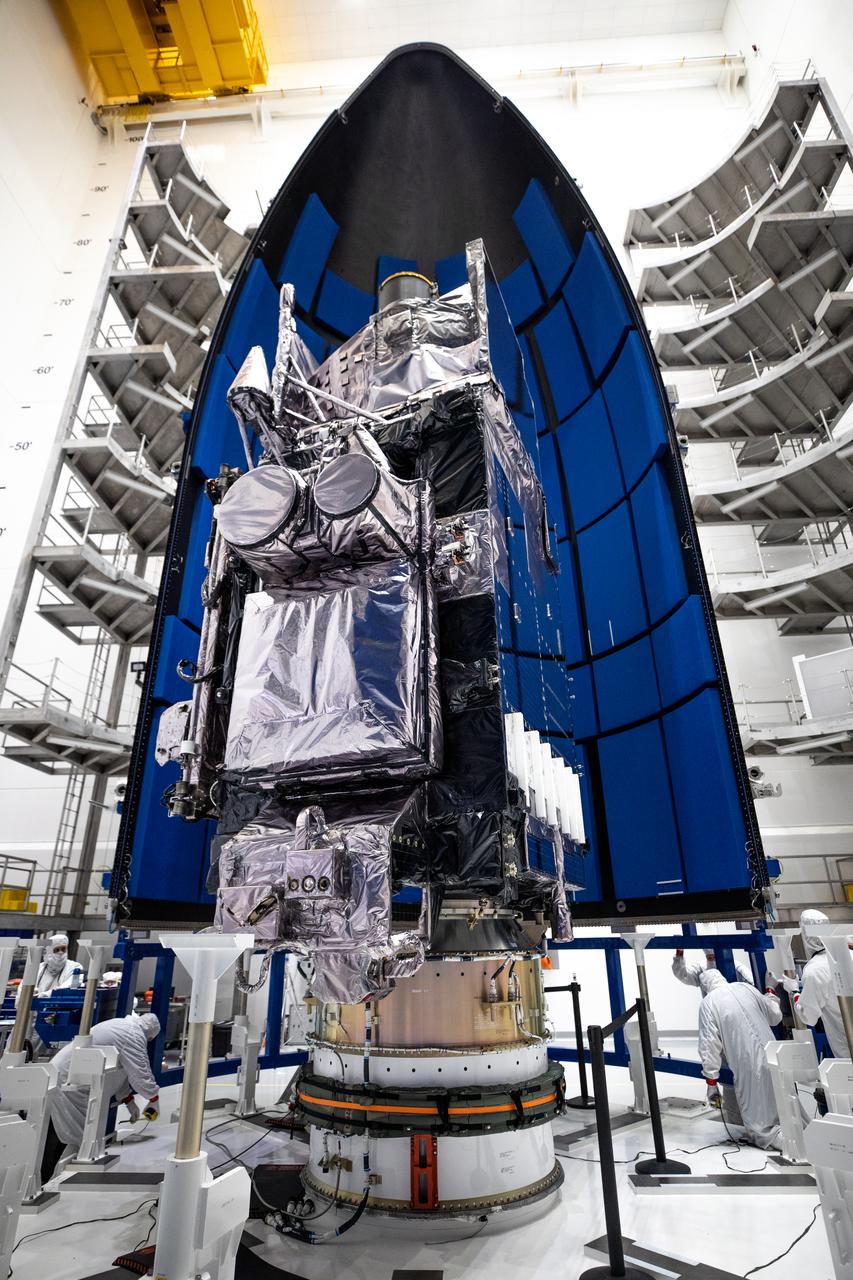
NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is moved inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 28, 2022, in preparation for encapsulation inside its protective payload fairings. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
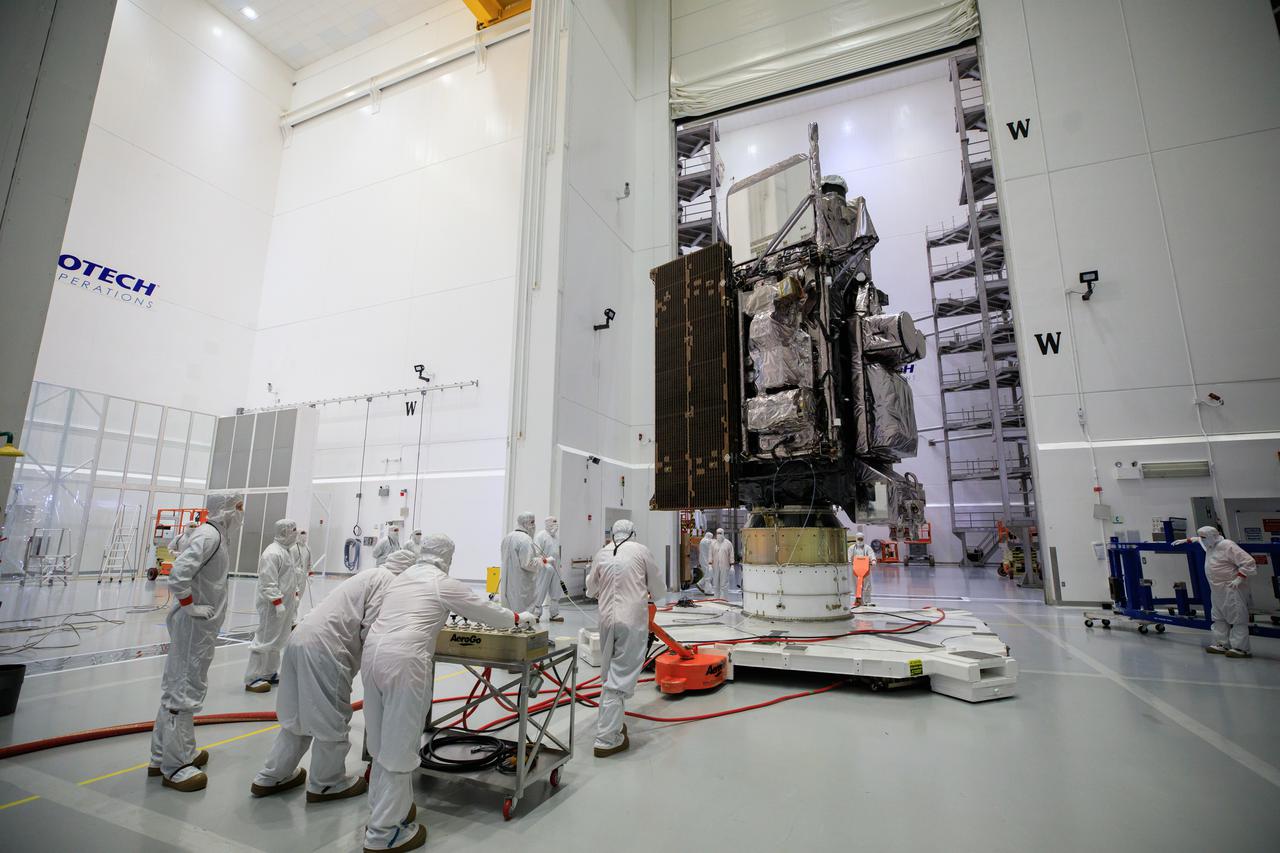

Technicians move NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 28, 2022. The spacecraft is being prepared for encapsulation inside its protective payload fairings. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
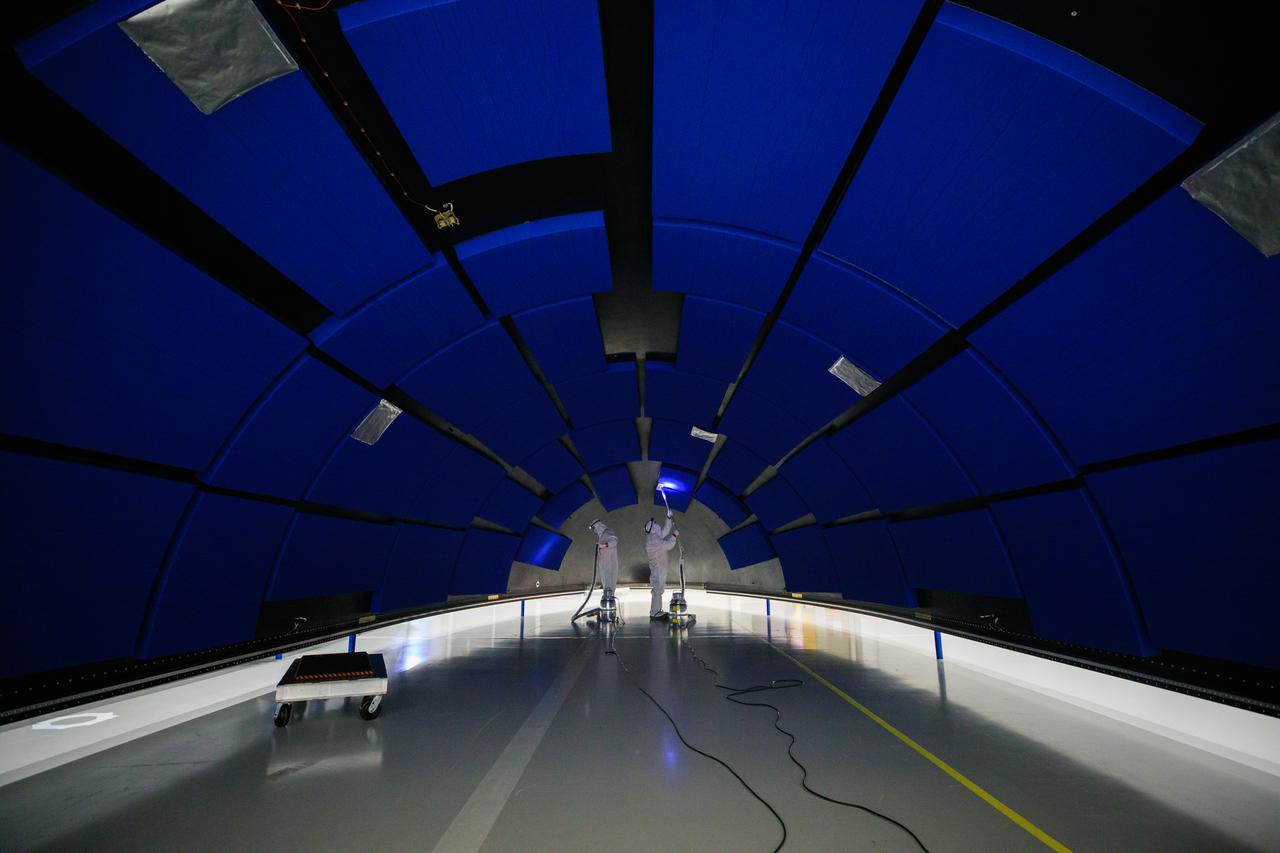

In preparation for NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) to be encapsulated, members of the GOES-T team prepare the area within the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida on Jan. 28, 2022. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
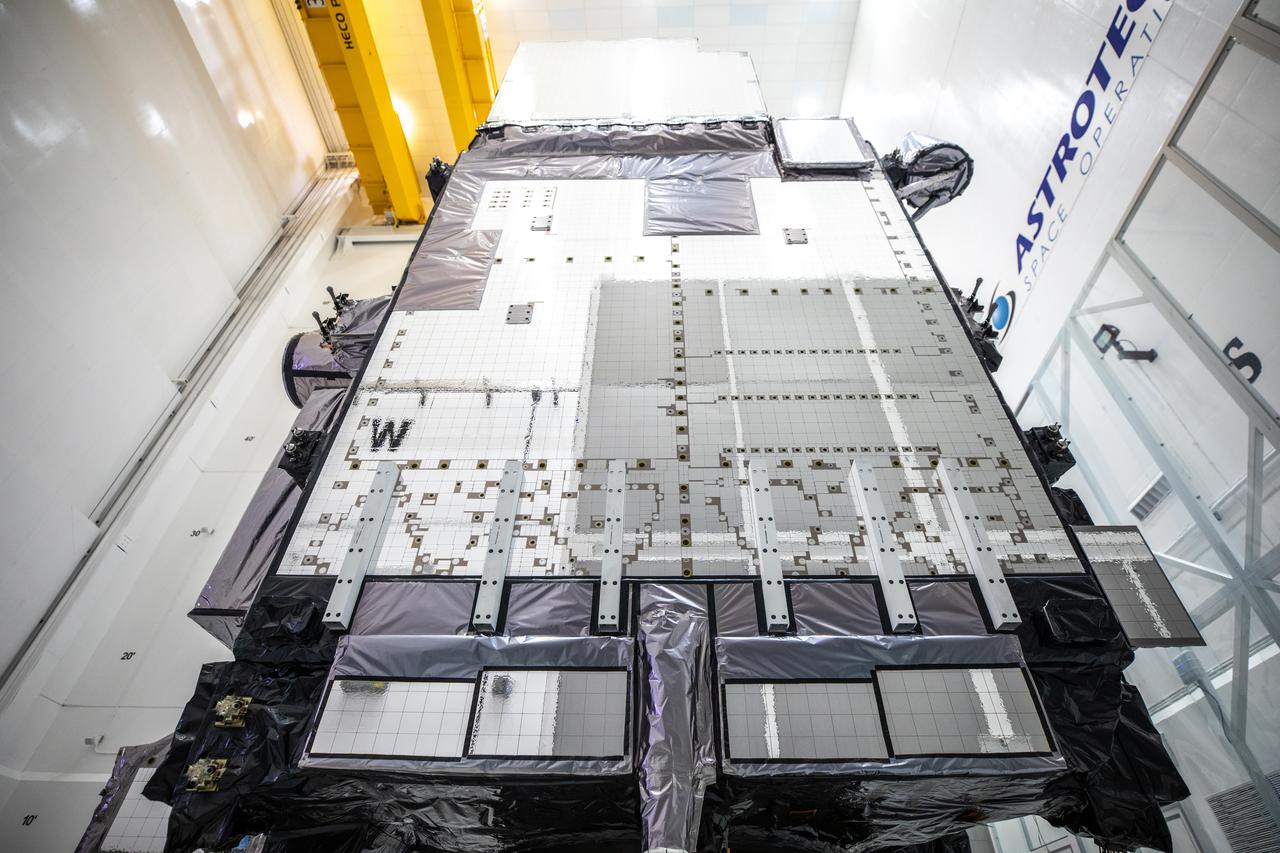

In this view looking up, NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) is secured on a work stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 20, 2022. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.
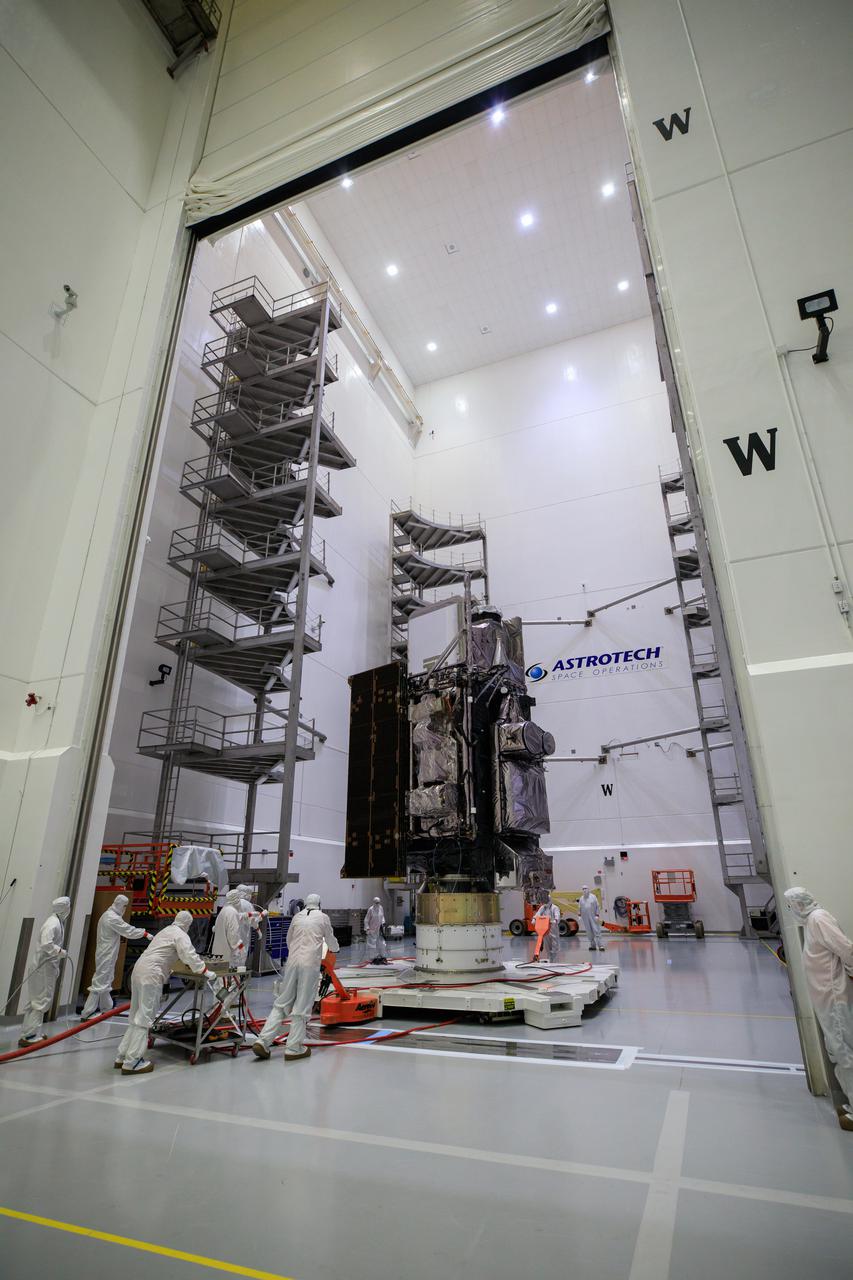

Technicians move NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, on Jan. 28, 2022. The spacecraft is being prepared for encapsulation inside its protective payload fairings. GOES-T is scheduled to launch on March 1, 2022, atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, America’s multi-user spaceport.