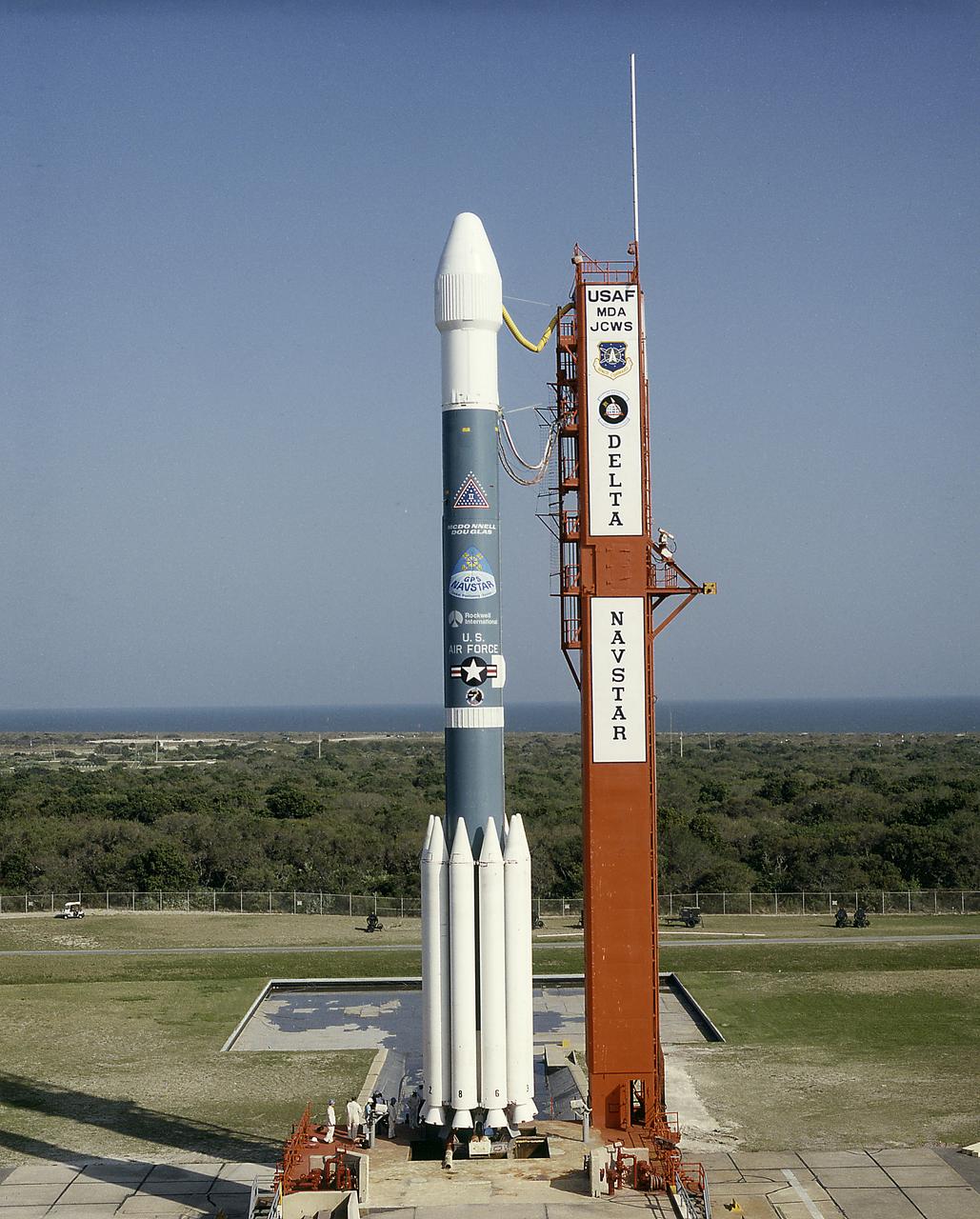

The Air Force Delta II vehicle sits poised on Complex 17A at the Cape Canaveral Air Station, ready to carry the 19th NAVSTAR Global Positioning System Satellite into orbit. A secondary NASA experiment, the Small Expendable Deployer System (SEDS), will also be deployed.

Small Expendable Deployer System (SEDS) is a tethered date collecting satellite and is intended to demonstrate a versatile and economical way of delivering smaller payloads to higher orbits or downward toward Earth's atmosphere. 19th Navstar Global Positioning System Satellite mission joined with previously launched satellites used for navigational purposes and geodite studies. These satellites are used commercially as well as by the military.
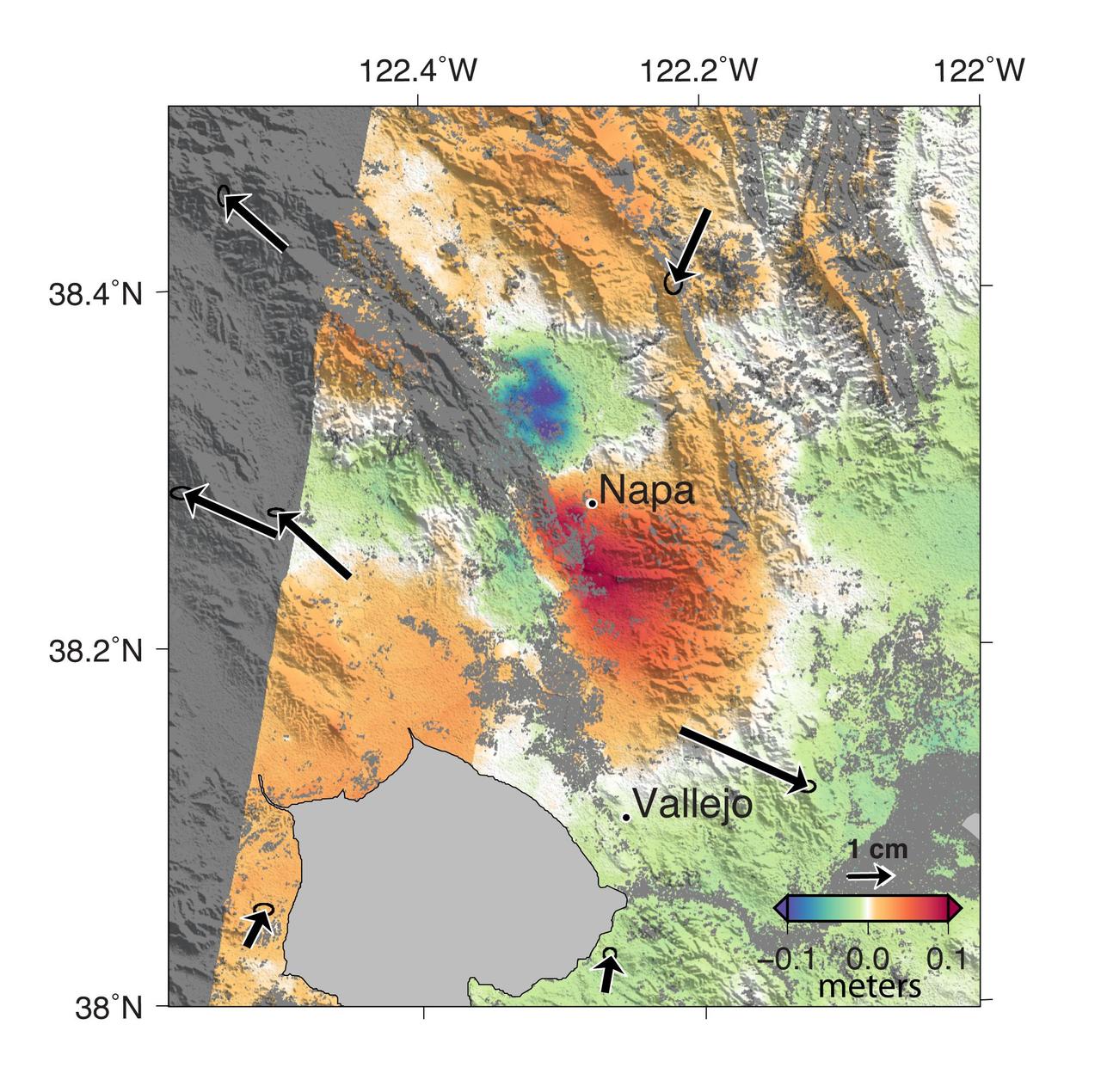
A magnitude 6.0 earthquake struck southern Napa county northeast of San Francisco, California, on Aug. 24, 2014. NASA satellite data reveal ground defomation.
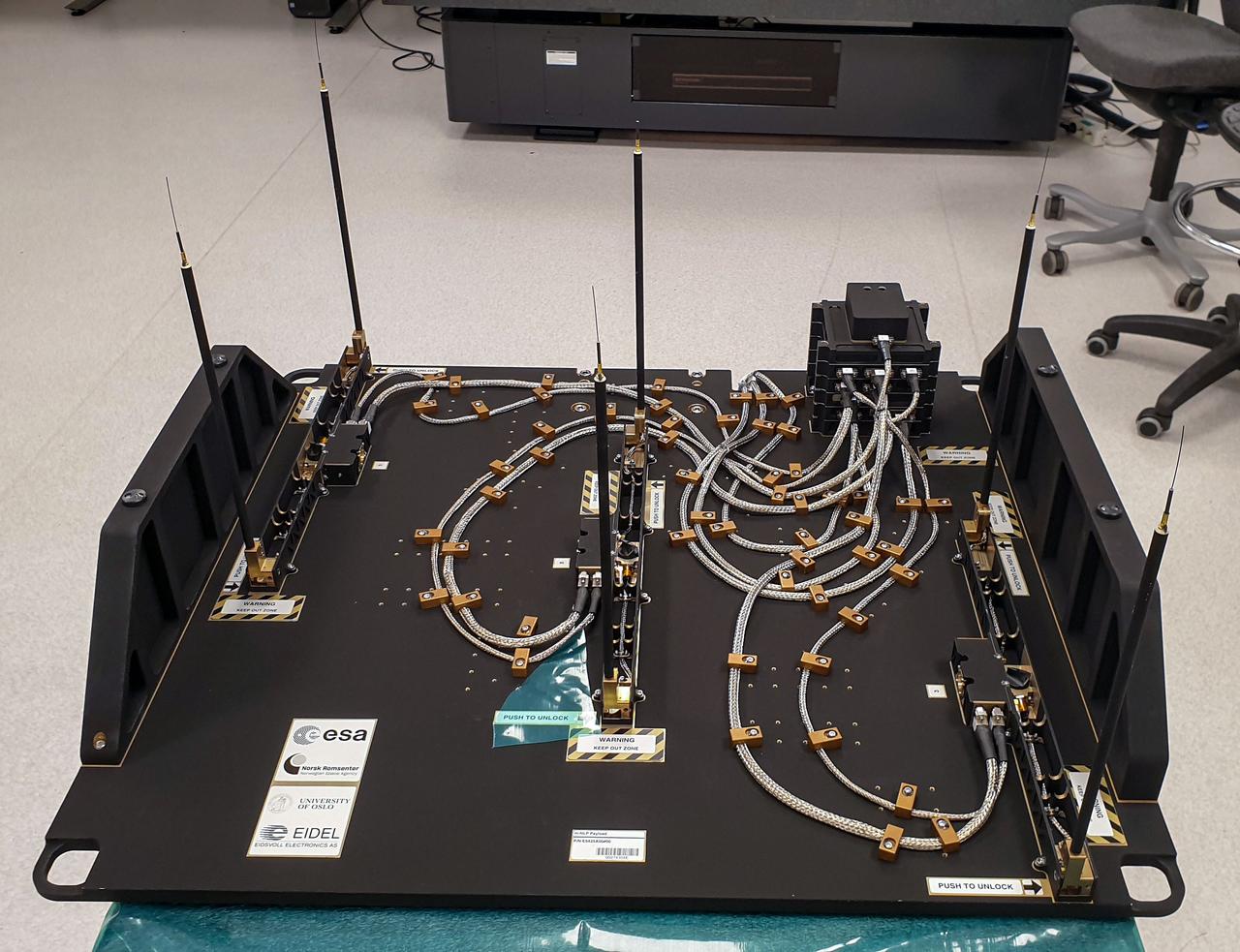

jsc2023e046372 (9/30/2022) --- The Multi-Needle Langmuir Probe (m-NLP) is shown from the ram facing side with booms in deployed position. The m-NLP measures plasma density in the ionosphere, where Earth's atmosphere meets the beginning of space. Researchers aim to study electrically charged particles and increase their understanding of how particle phenomena affect radio communications and global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals. Image courtesy of the University of Oslo, Espen Trondsen.
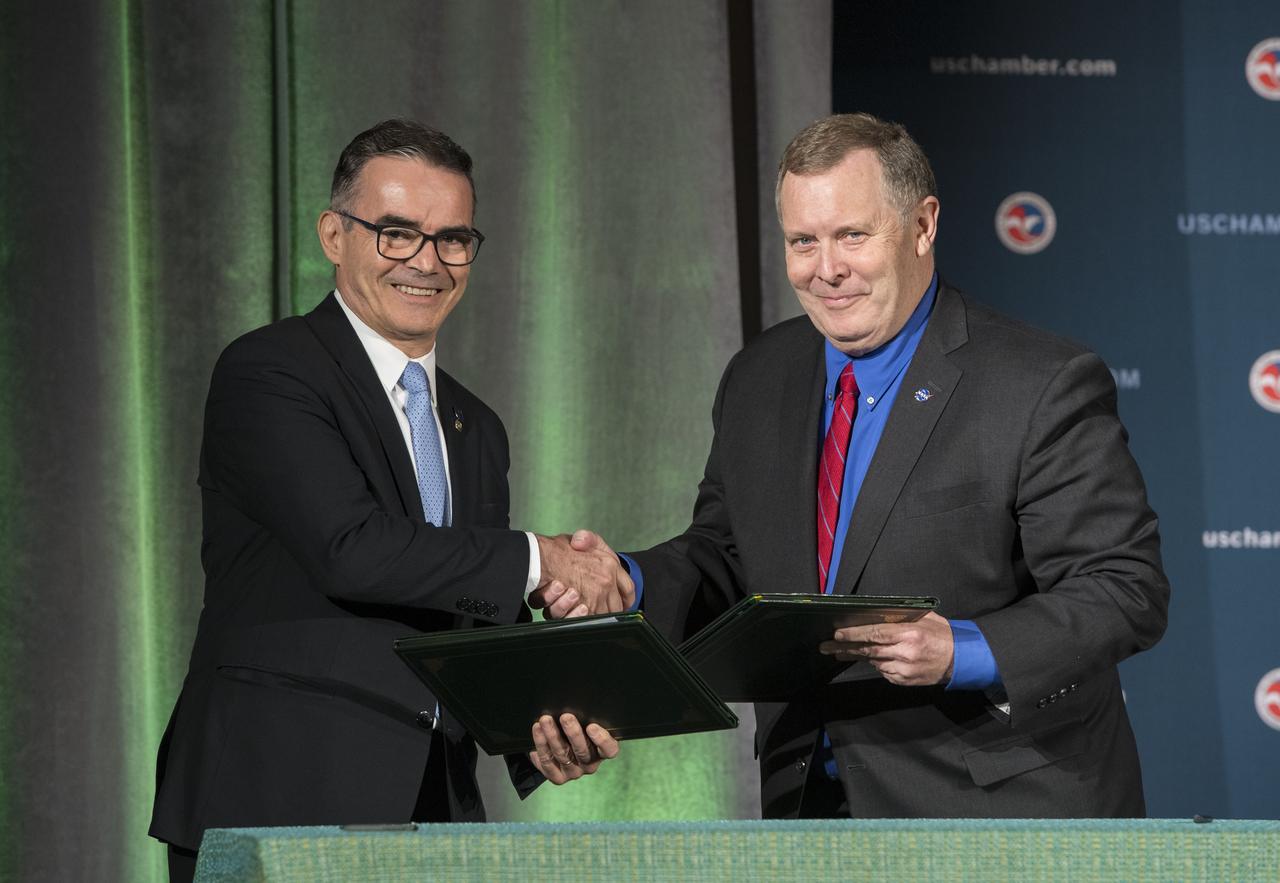

NASA Deputy Administrator James Morhard, right, shakes hands with President of the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB) Carlos Augusto Teixeira de Moura, left, after signing an agreement for cooperation on the Scintillation Prediction Observations Research Task (SPORT), an upcoming NASA-AEB heliophysics CubeSat partnership, Monday, March 18, 2019, at the U.S. Chamber of Commerce in Washington. The SPORT CubeSat will investigate two ionospheric phenomena, equatorial plasma bubbles and scintillation, that disrupt radio communication systems, satellite technologies, and Global Positioning System (GPS) signals. SPORT is currently projected to launch in the 2020 timeframe. Photo Credit: (NASA/ Aubrey Gemignani)
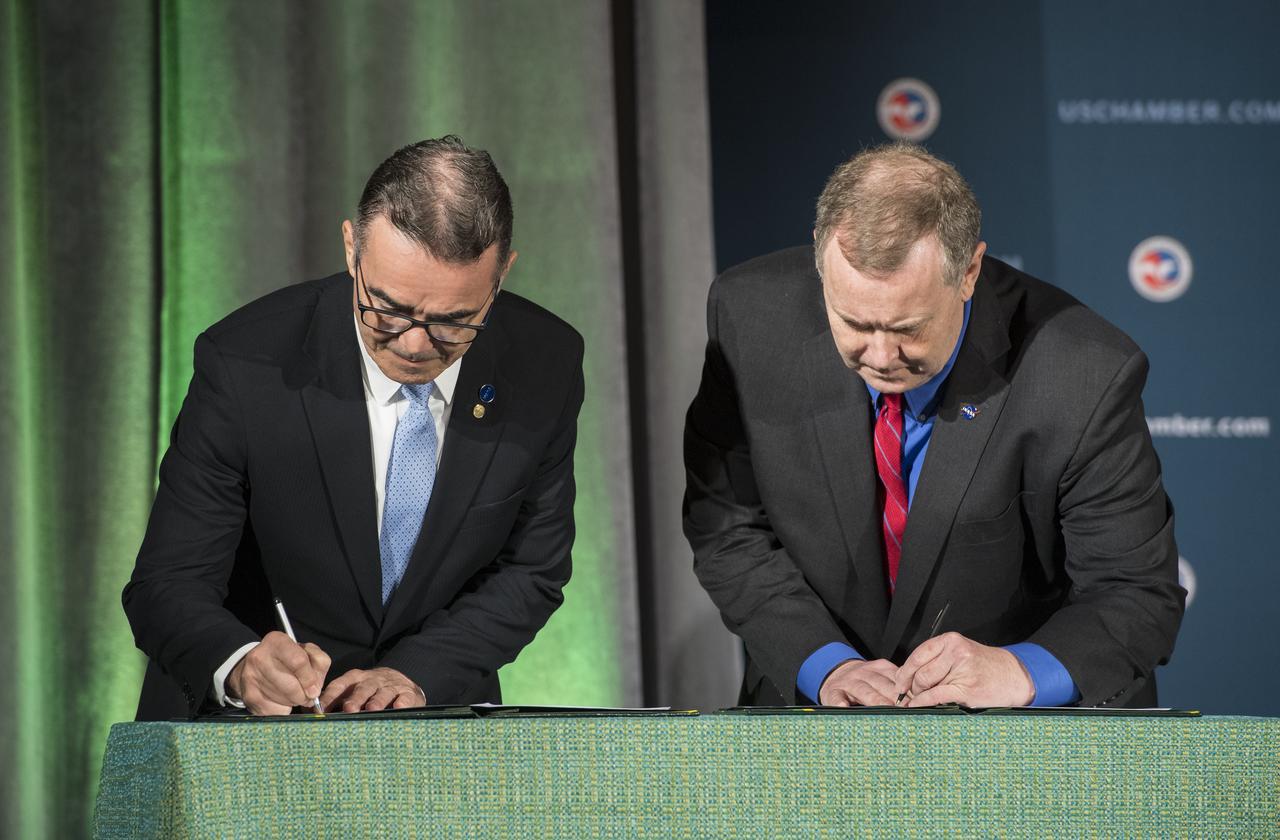

NASA Deputy Administrator James Morhard, right, and President of the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB) Carlos Augusto Teixeira de Moura, left, sign an agreement for cooperation on the Scintillation Prediction Observations Research Task (SPORT), an upcoming NASA-AEB heliophysics CubeSat partnership, Monday, March 18, 2019, at the U.S. Chamber of Commerce in Washington. The SPORT CubeSat will investigate two ionospheric phenomena, equatorial plasma bubbles and scintillation, that disrupt radio communication systems, satellite technologies, and Global Positioning System (GPS) signals. SPORT is currently projected to launch in the 2020 timeframe. Photo Credit: (NASA/ Aubrey Gemignani)
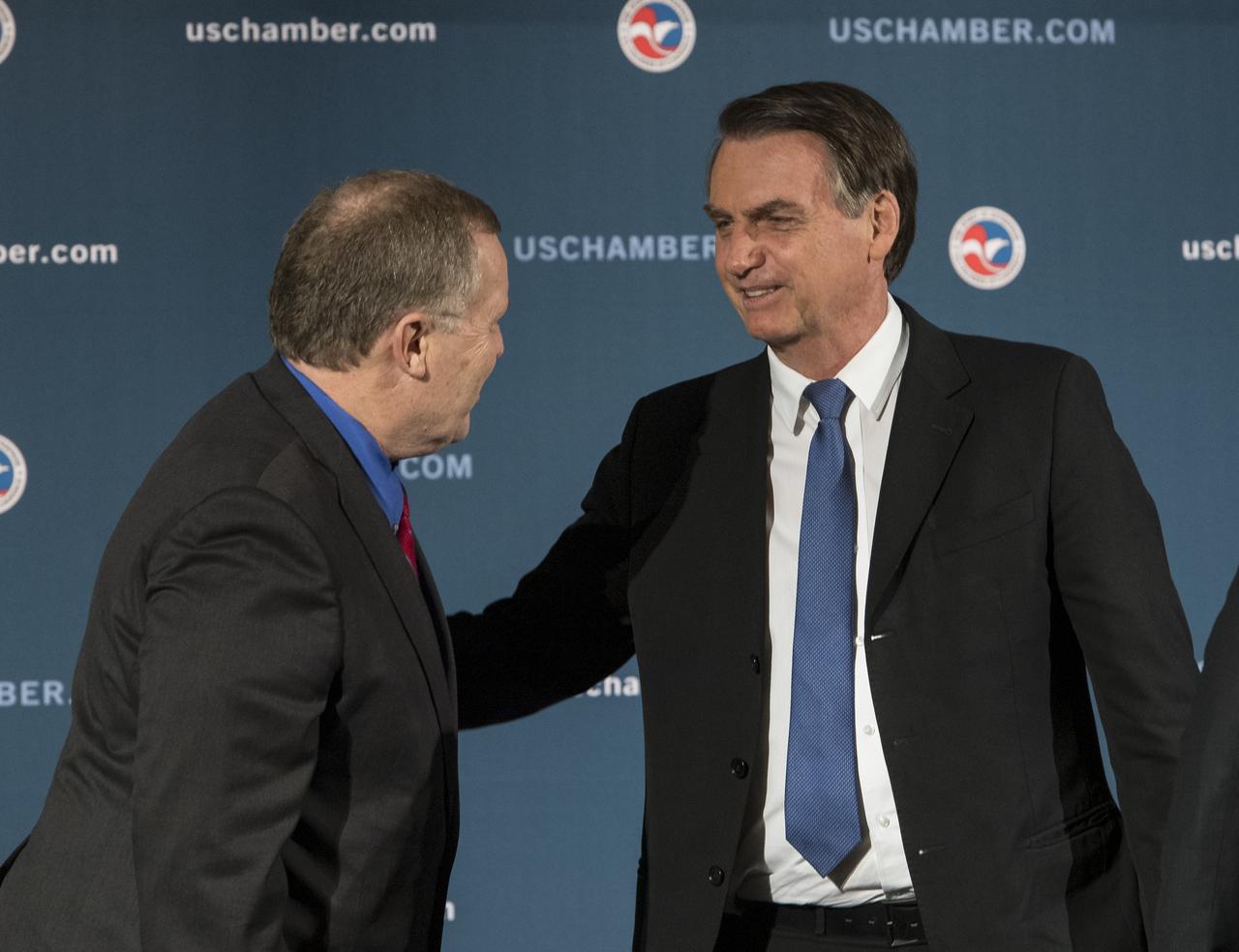

NASA Deputy Administrator James Morhard, left, speaks with H.E. President Jair Bolsonaro of Brazil, just before signing an agreement with President of the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB), Carlos Augusto Teixeira de Moura, for cooperation on the Scintillation Prediction Observations Research Task (SPORT), an upcoming NASA-AEB heliophysics CubeSat partnership, Monday, March 18, 2019, at the U.S. Chamber of Commerce in Washington. The SPORT CubeSat will investigate two ionospheric phenomena, equatorial plasma bubbles and scintillation, that disrupt radio communication systems, satellite technologies, and Global Positioning System (GPS) signals. SPORT is currently projected to launch in the 2020 timeframe. Photo Credit: (NASA/ Aubrey Gemignani)
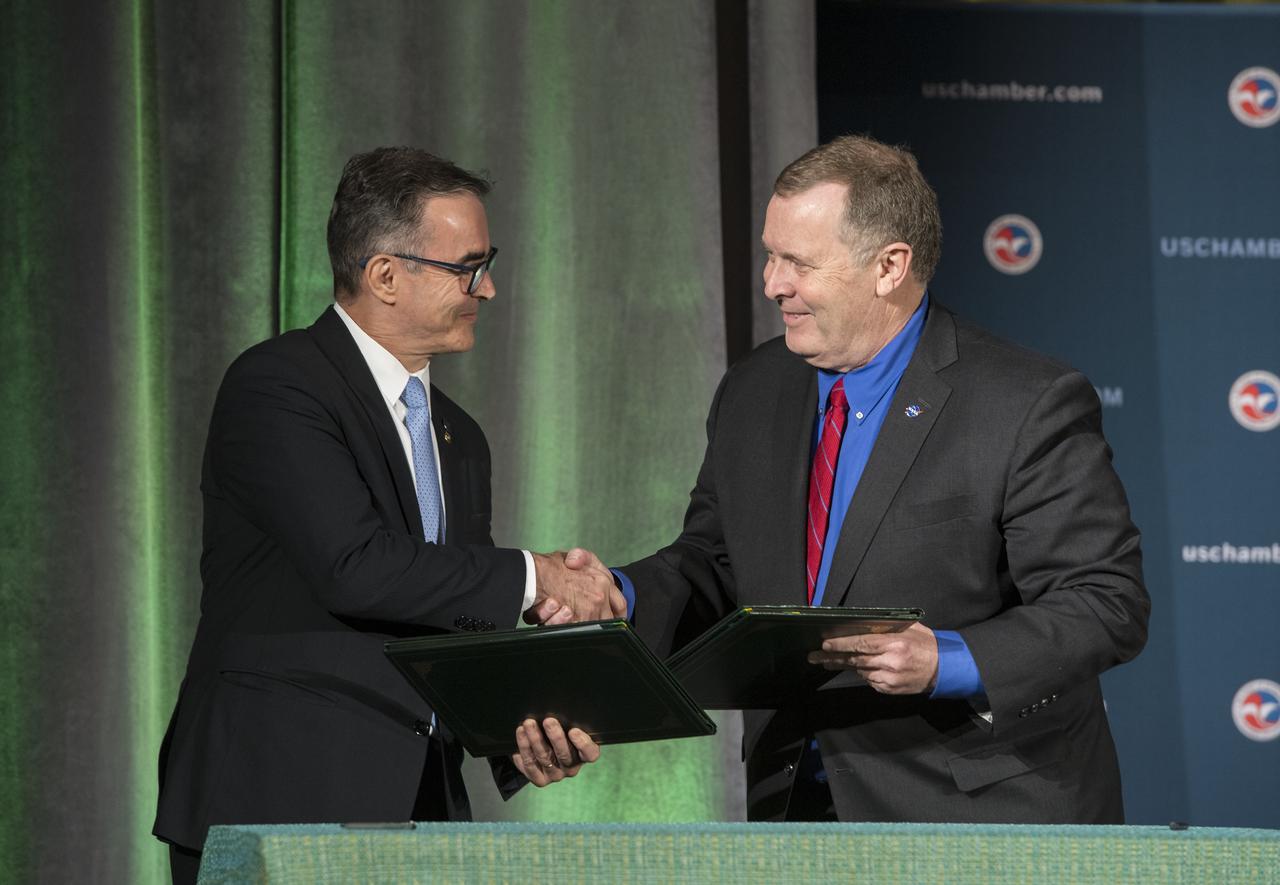

NASA Deputy Administrator James Morhard, right, shakes hands with President of the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB) Carlos Augusto Teixeira de Moura, left, after signing an agreement for cooperation on the Scintillation Prediction Observations Research Task (SPORT), an upcoming NASA-AEB heliophysics CubeSat partnership, Monday, March 18, 2019, at the U.S. Chamber of Commerce in Washington. The SPORT CubeSat will investigate two ionospheric phenomena, equatorial plasma bubbles and scintillation, that disrupt radio communication systems, satellite technologies, and Global Positioning System (GPS) signals. SPORT is currently projected to launch in the 2020 timeframe. Photo Credit: (NASA/ Aubrey Gemignani)
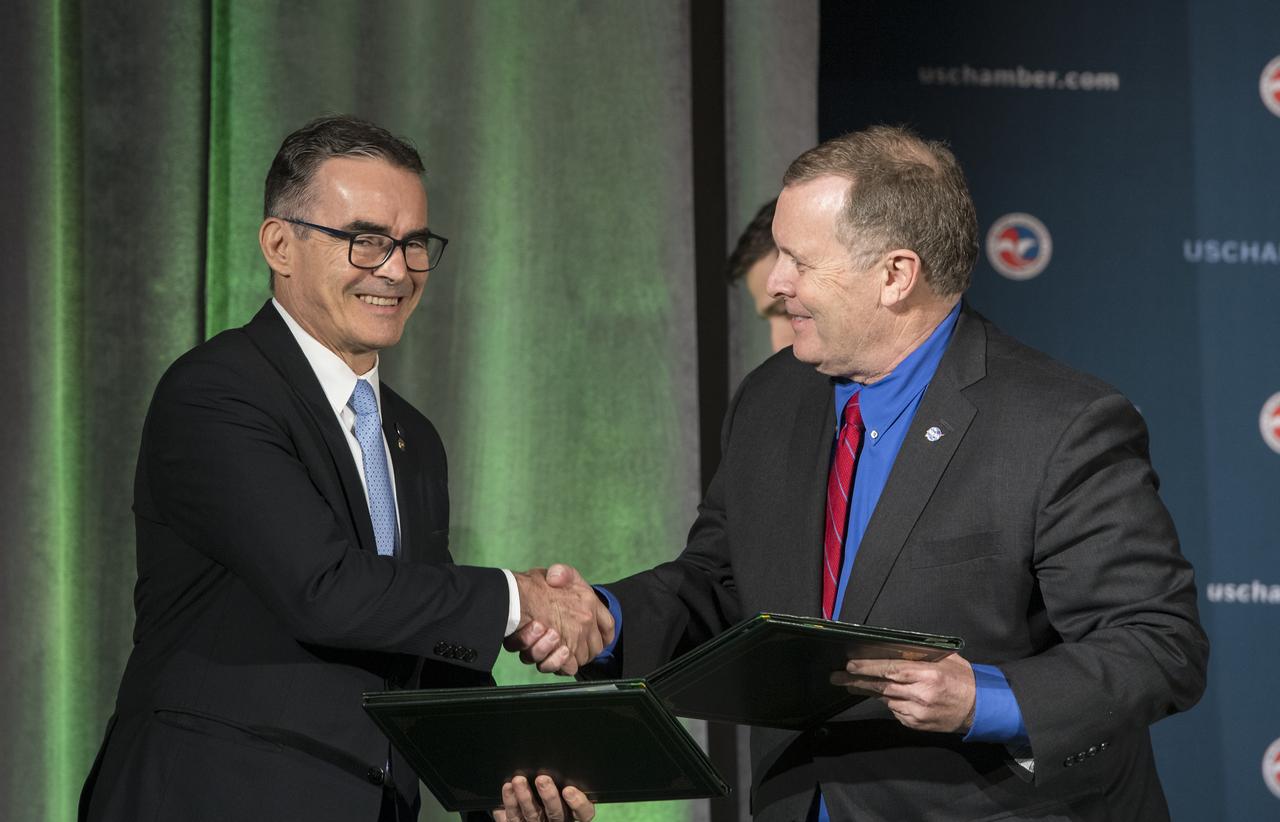

NASA Deputy Administrator James Morhard, right, shakes hands with President of the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB) Carlos Augusto Teixeira de Moura, left, after signing an agreement for cooperation on the Scintillation Prediction Observations Research Task (SPORT), an upcoming NASA-AEB heliophysics CubeSat partnership, Monday, March 18, 2019, at the U.S. Chamber of Commerce in Washington. The SPORT CubeSat will investigate two ionospheric phenomena, equatorial plasma bubbles and scintillation, that disrupt radio communication systems, satellite technologies, and Global Positioning System (GPS) signals. SPORT is currently projected to launch in the 2020 timeframe. Photo Credit: (NASA/ Aubrey Gemignani)
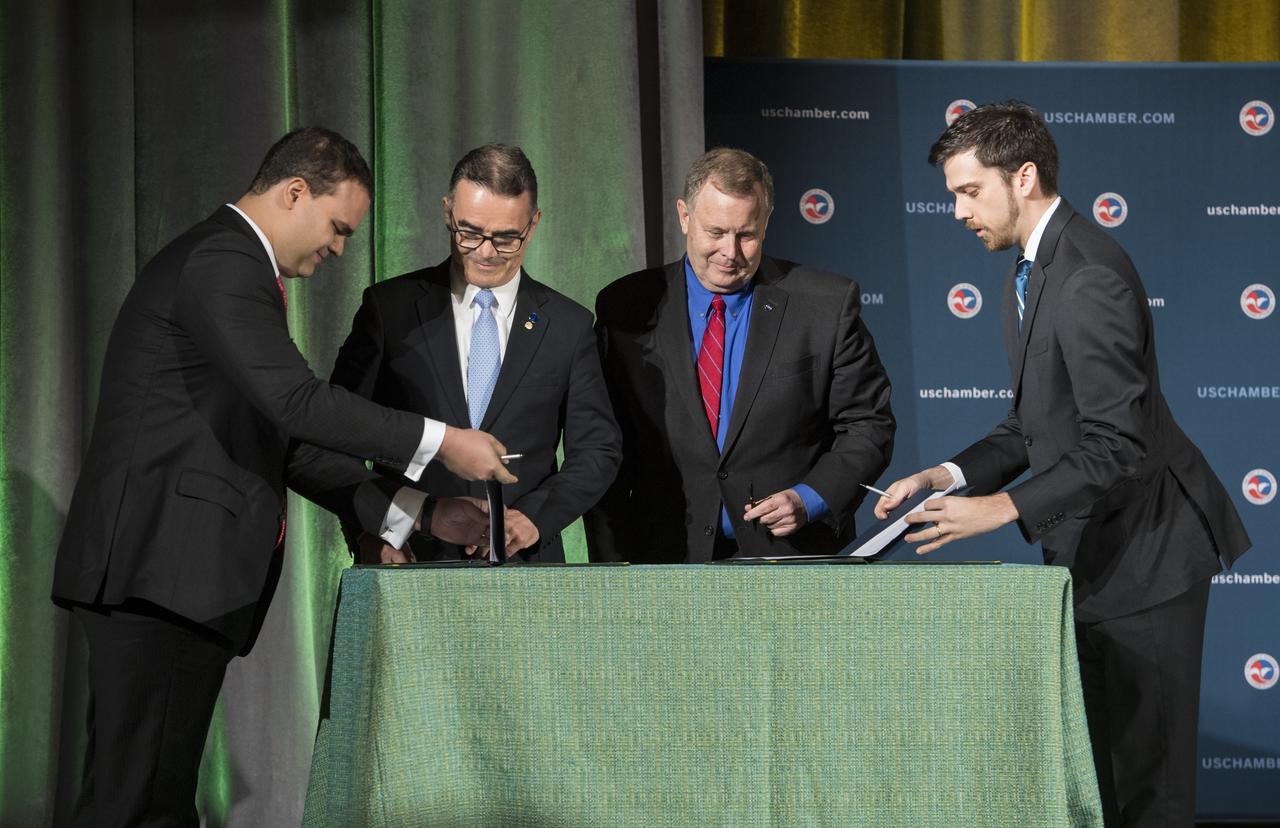

NASA Deputy Administrator James Morhard, center right, and President of the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB) Carlos Augusto Teixeira de Moura, center left, prepare to sign an agreement for cooperation on the Scintillation Prediction Observations Research Task (SPORT), an upcoming NASA-AEB heliophysics CubeSat partnership, Monday, March 18, 2019, at the U.S. Chamber of Commerce in Washington. The SPORT CubeSat will investigate two ionospheric phenomena, equatorial plasma bubbles and scintillation, that disrupt radio communication systems, satellite technologies, and Global Positioning System (GPS) signals. SPORT is currently projected to launch in the 2020 timeframe. Photo Credit: (NASA/ Aubrey Gemignani)
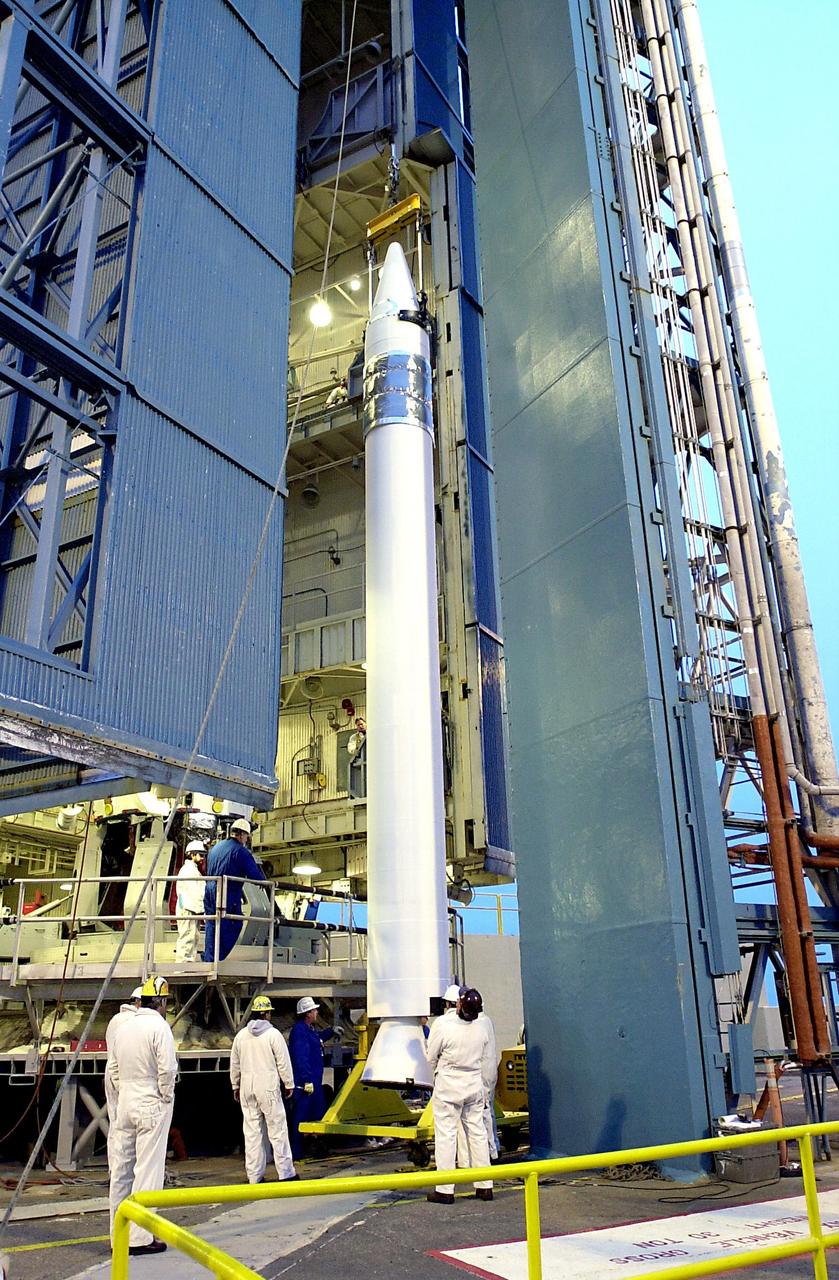

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., a solid rocket booster is lifted into an upright position as preparations continue to mate it to a Delta II rocket. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
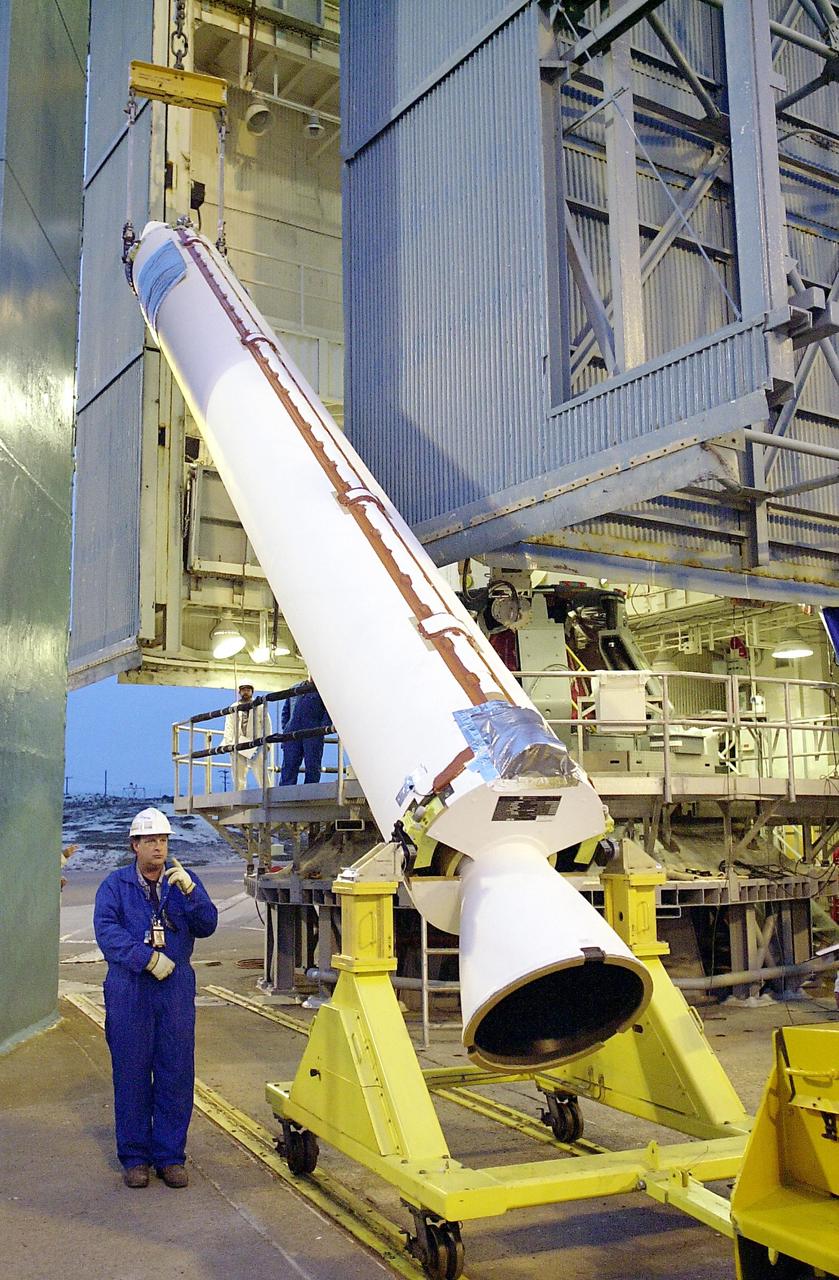

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., a solid rocket booster is lifted into an upright position for mating to a Delta II rocket. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
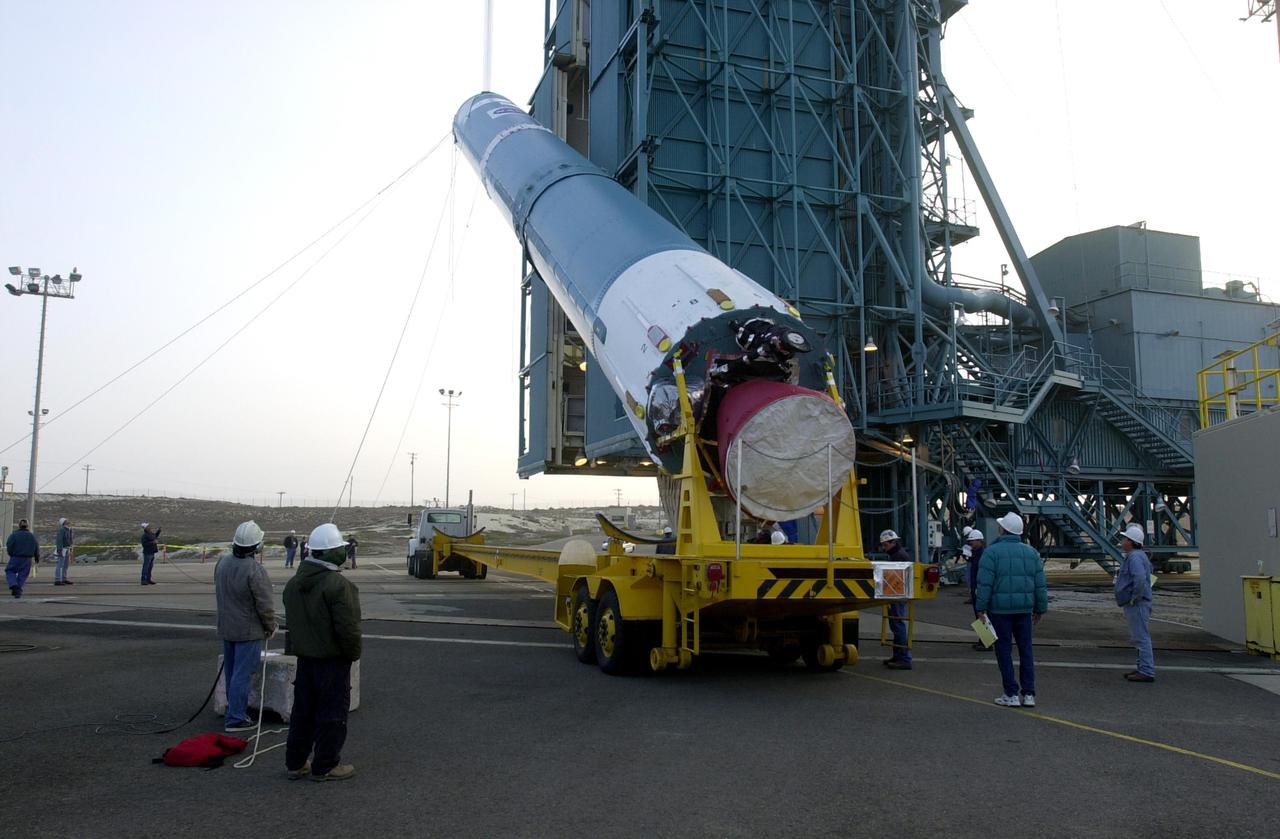

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers at NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., watch as the first stage of the Delta II rocket is raised to a vertical position. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
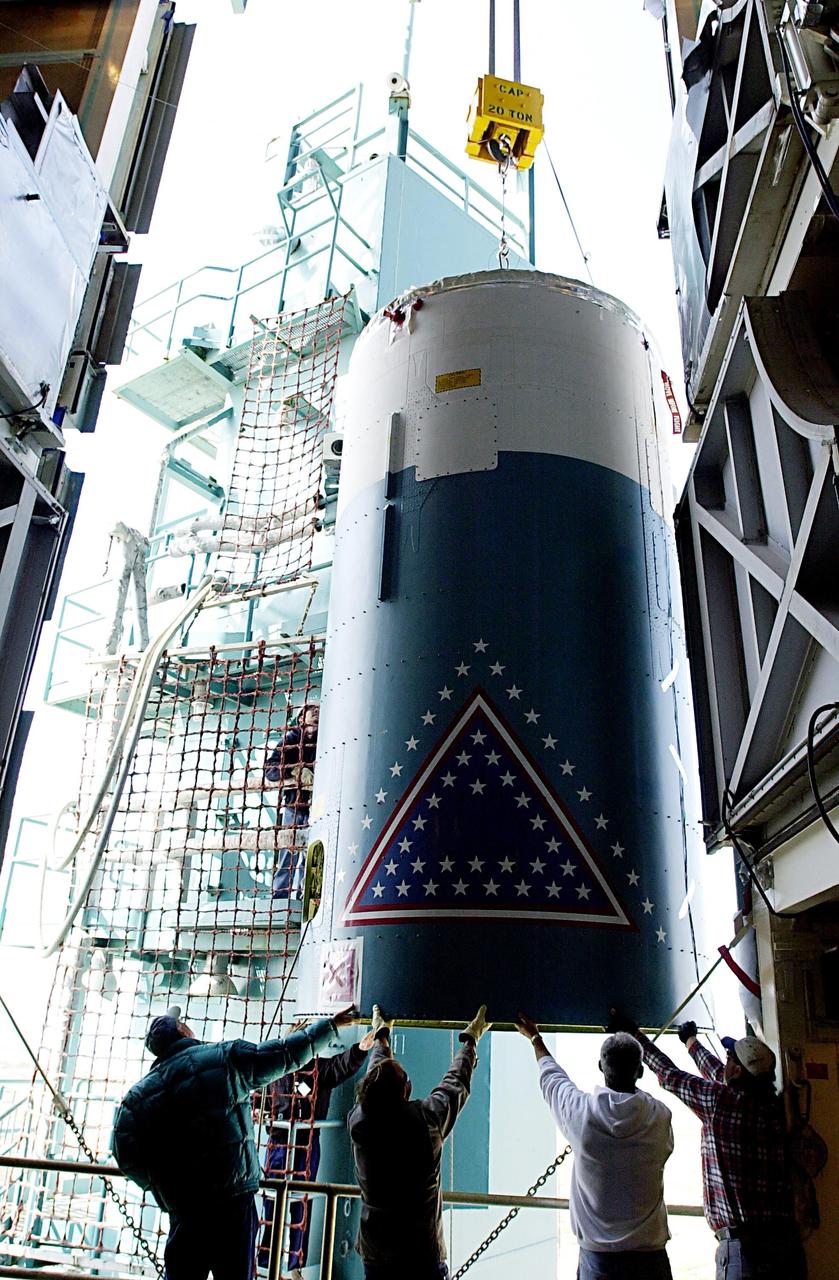
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers on the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., help guide the interstage of the Delta II rocket into position for mating with the first stage. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first stage of the Delta II rocket is in the process of being raised to a vertical position on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
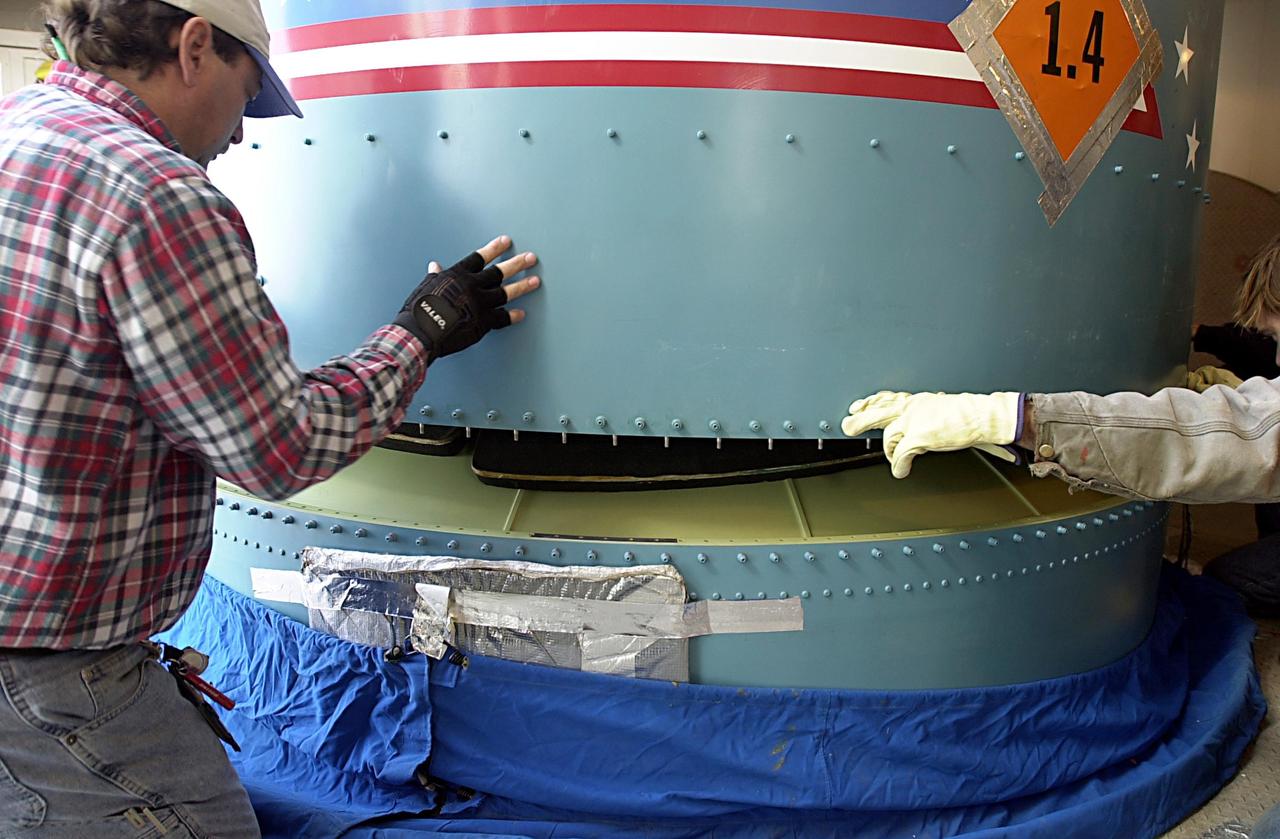

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers on the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., help guide the interstage of the Delta II rocket into position for mating with the first stage. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
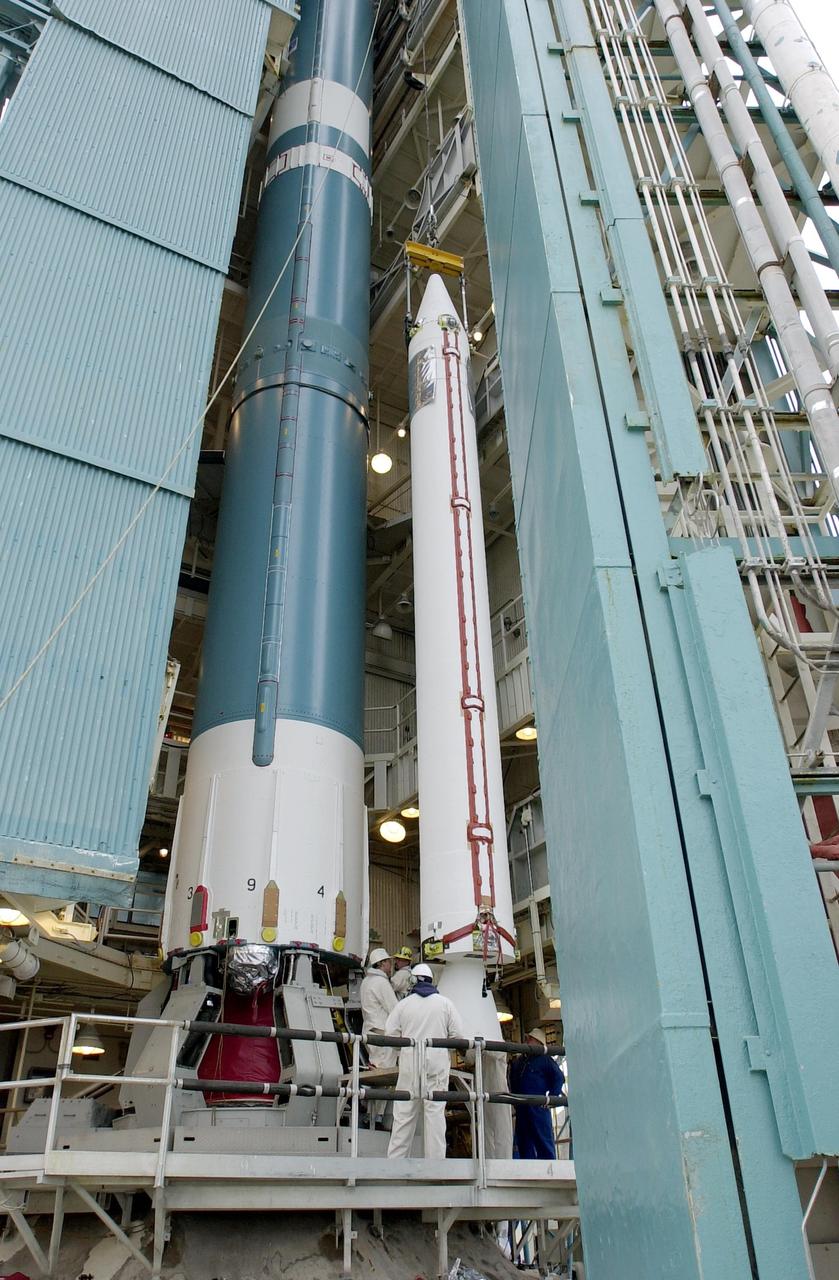

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On the launch tower on NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2), Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., a solid rocket booster is lifted into an upright position beside the Delta II rocket to which it will be attached. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
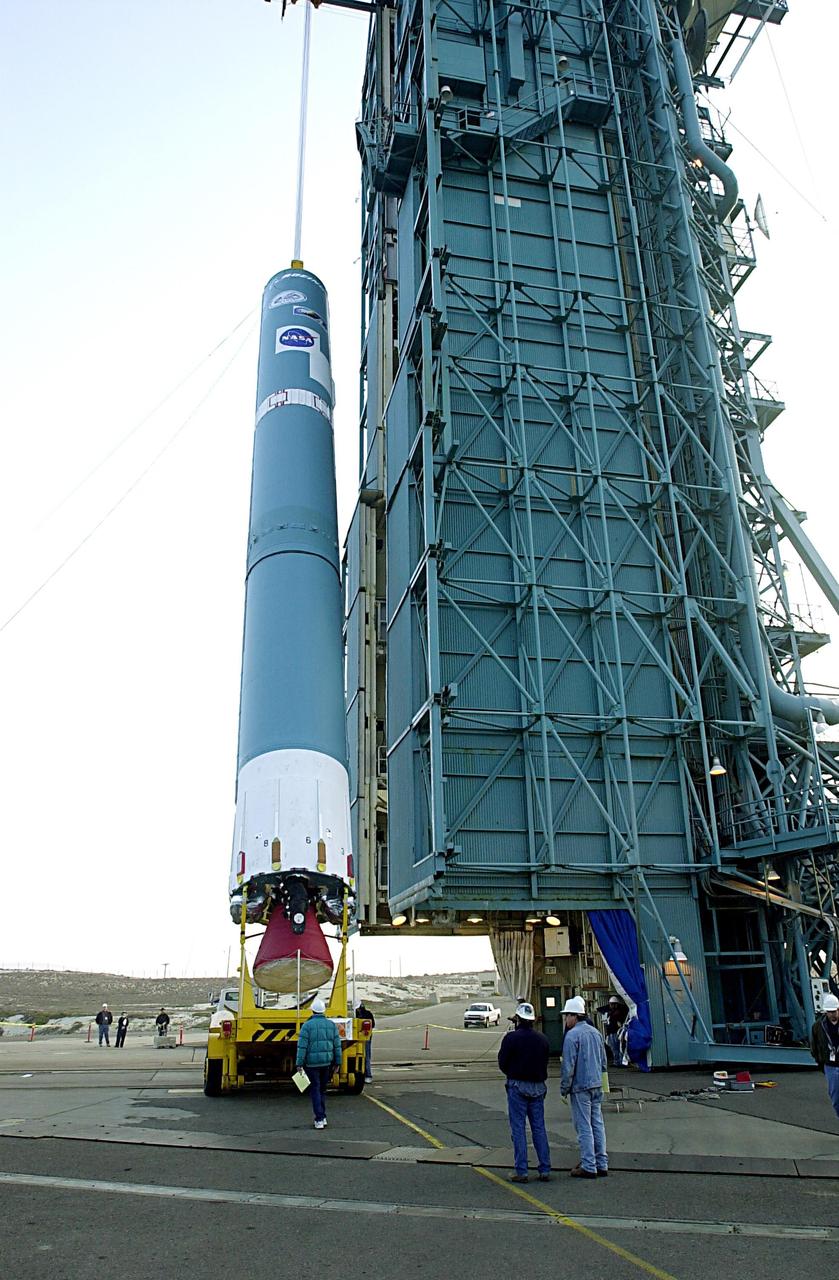

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first stage of the Delta II rocket is raised to a vertical position at NASA's Space Launch Complex 2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. The rocket will carry the ICESat and CHIPSat satellites into Earth orbits. ICESat is a 661-pound satellite known as Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) that will revolutionize our understanding of ice and its role in global climate change and how we protect and understand our home planet. It will help scientists determine if the global sea level is rising or falling. It will look at the ice sheets that blanket the Earth's poles to see if they are growing or shrinking. It will assist in developing an understanding of how changes in the Earth's atmosphere and climate effect polar ice masses and global sea level. CHIPSat, a suitcase-size 131-pound satellite, will provide invaluable information into the origin, physical processes and properties of the hot gas contained in the interstellar medium. This can provide important clues about the formation and evolution of galaxies since the interstellar medium literally contains the seeds of future stars. The Delta II launch is scheduled for Jan. 11 between 4:45 p.m. - 5:30 p.m. PST.
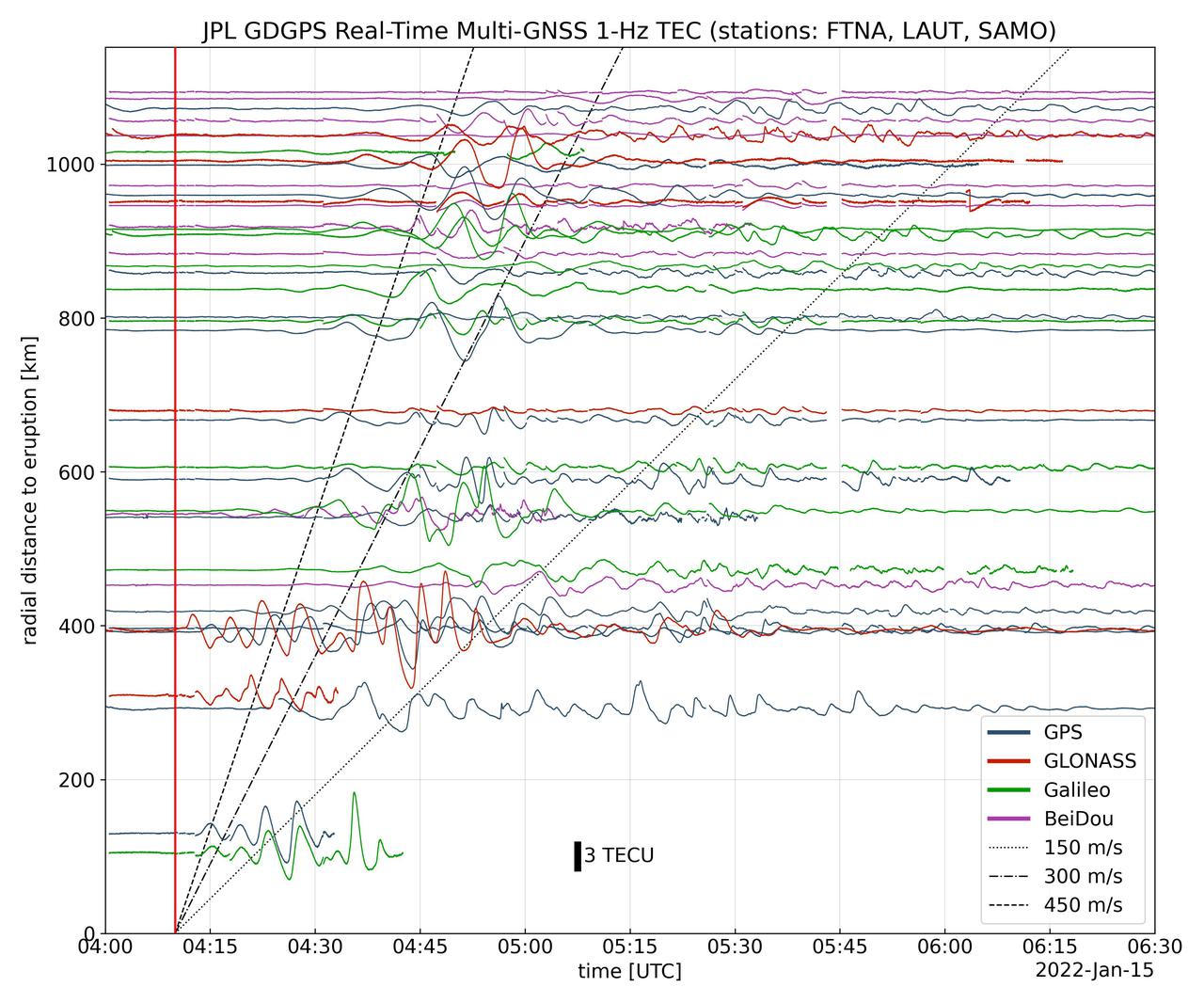
Real-time data collected by the Global Differential Global Positioning System network, operated by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, shows the atmospheric signature of the Hunga Tonga Hunga Ha'apai volcanic eruption in Tonga on Jan. 15, 2022. The data is a measure of the density of electrons (known as total electron content units, or TECU) in the ionosphere – the outermost layer of the atmosphere, which starts between 50 and 56 miles (80 to 90 kilometers) above Earth's surface. Navigation radio signals, like those received by location sensors on smartphones, are broadcast by global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) and experience delays when passing through the ionosphere. The extent of the delay depends on the density of electrons within the path of the GNSS signal in this atmospheric layer. When an explosive event such as a volcanic eruption or large earthquake injects energy into the atmosphere, the pressure waves from that event change the electron density in the ionosphere. These perturbations show up as tiny changes to the delays that GNSS radio signals usually experience as they pass through the atmosphere. The vertical red line in the data plot indicates the time of the eruption. The horizontal squiggles show electron density profiles picked up in the signals of four GNSS constellations, or groups of satellites: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou. The slanted dashed and dotted lines indicate the velocity of waves. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24905
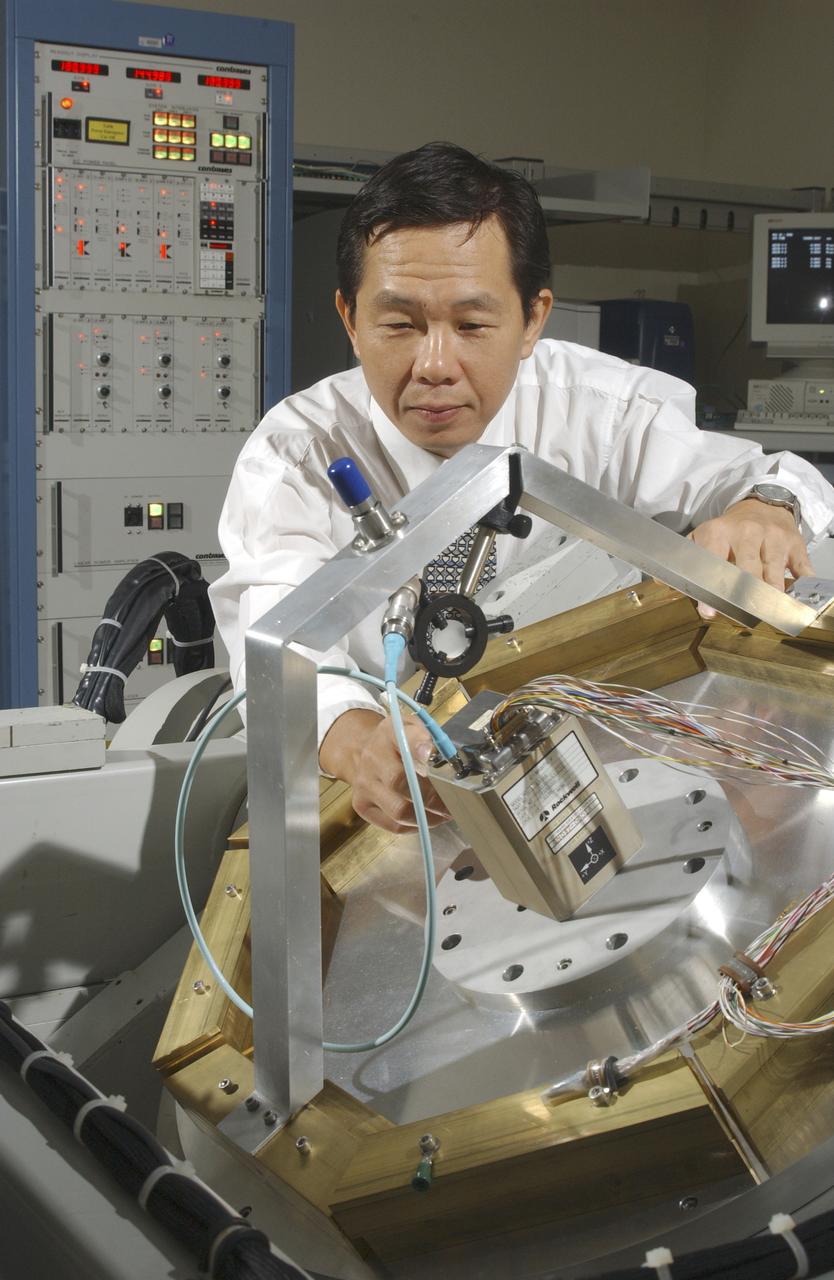
An array of components in a laboratory at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) is being tested by the Flight Mechanics Office to develop an integrated navigation system for the second generation reusable launch vehicle. The laboratory is testing Global Positioning System (GPS) components, a satellite-based location and navigation system, and Inertial Navigation System (INS) components, sensors on a vehicle that determine angular velocity and linear acceleration at various points. The GPS and INS components work together to provide a space vehicle with guidance and navigation, like the push of the OnStar button in your car assists you with directions to a specific address. The integration will enable the vehicle operating system to track where the vehicle is in space and define its trajectory. The use of INS components for navigation is not new to space technology. The Space Shuttle currently uses them. However, the Space Launch Initiative is expanding the technology to integrate GPS and INS components to allow the vehicle to better define its position and more accurately determine vehicle acceleration and velocity. This advanced technology will lower operational costs and enhance the safety of reusable launch vehicles by providing a more comprehensive navigation system with greater capabilities. In this photograph, Dr. Jason Chuang of MSFC inspects an INS component in the laboratory.

NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite is rotated to a vertical position after it was removed from its shipping container inside the airlock of the Astrotech processing facility on Aug. 20, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California. JPSS-2 was shipped from the Northrop Grumman facility in Gilbert, Arizona, where it was built and tested. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3 East. JPSS-2 will scan the globe as it orbits from the North to the South Pole, crossing the equator 14 times a day. From 512 miles above Earth, it will capture data that inform weather forecasts, extreme weather events, and climate change. The Visible Infrared Radiometer Suite instrument will collect imagery for global observations of the land, atmosphere, cryosphere, and oceans. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a demonstration of a hypersonic inflatable aerodynamic decelerator, or aeroshell, technology that could one day help land humans on Mars.

The first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V payload fairing is moved into position for a fit check at the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Aug. 13, 2022, for NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3 East. JPSS-2 will scan the globe as it orbits from the North to the South Pole, crossing the equator 14 times a day. From 512 miles above Earth, it will capture data that inform weather forecasts, extreme weather events, and climate change. The Visible Infrared Radiometer Suite instrument will collect imagery for global observations of the land, atmosphere, cryosphere, and oceans. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a demonstration of a hypersonic inflatable aerodynamic decelerator, or aeroshell, technology that could one day help land humans on Mars.

Both halves of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V payload fairing are moved into position for a fit check at the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Aug. 13, 2022, for NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3 East. JPSS-2 will scan the globe as it orbits from the North to the South Pole, crossing the equator 14 times a day. From 512 miles above Earth, it will capture data that inform weather forecasts, extreme weather events, and climate change. The Visible Infrared Radiometer Suite instrument will collect imagery for global observations of the land, atmosphere, cryosphere, and oceans. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a demonstration of a hypersonic inflatable aerodynamic decelerator, or aeroshell, technology that could one day help land humans on Mars.
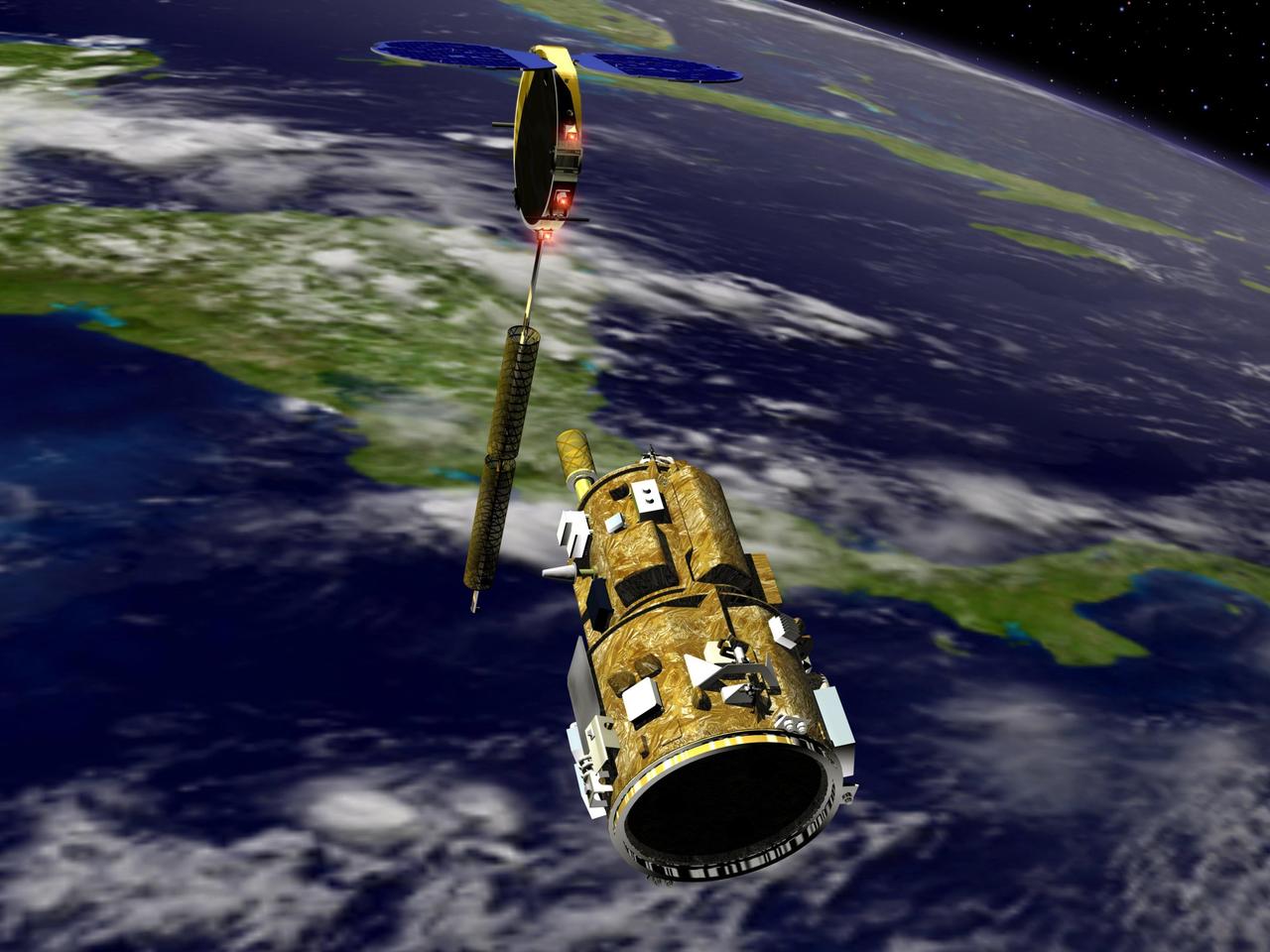
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An artist’s conception of the autonomous Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous (DART) spacecraft as it approaches the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications (MUBLCOM) satellite. NASA is testing the DART as a docking system for next generation vehicles to guide spacecraft carrying cargo or equipment to the International Space Station, or retrieving or servicing satellites in orbit. Before the new system can be implemented on piloted spacecraft, it has to be tested in space. The computer-guided DART is equipped with an Advanced Video Guidance Sensor and a Global Positioning System that can receive signals from other spacecraft to allow DART to move within 330 feet of the target. DART is scheduled to launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California no earlier than Oct. 18. It will be released from a Pegasus XL launch vehicle carried aloft by an Orbital Sciences Corporation aircraft. The fourth stage of the Pegasus rocket will remain attached as an integral part of the spacecraft, allowing it to maneuver in space. Once in orbit, DART will race toward the target, the MUBLCOM satellite, for a rendezvous.
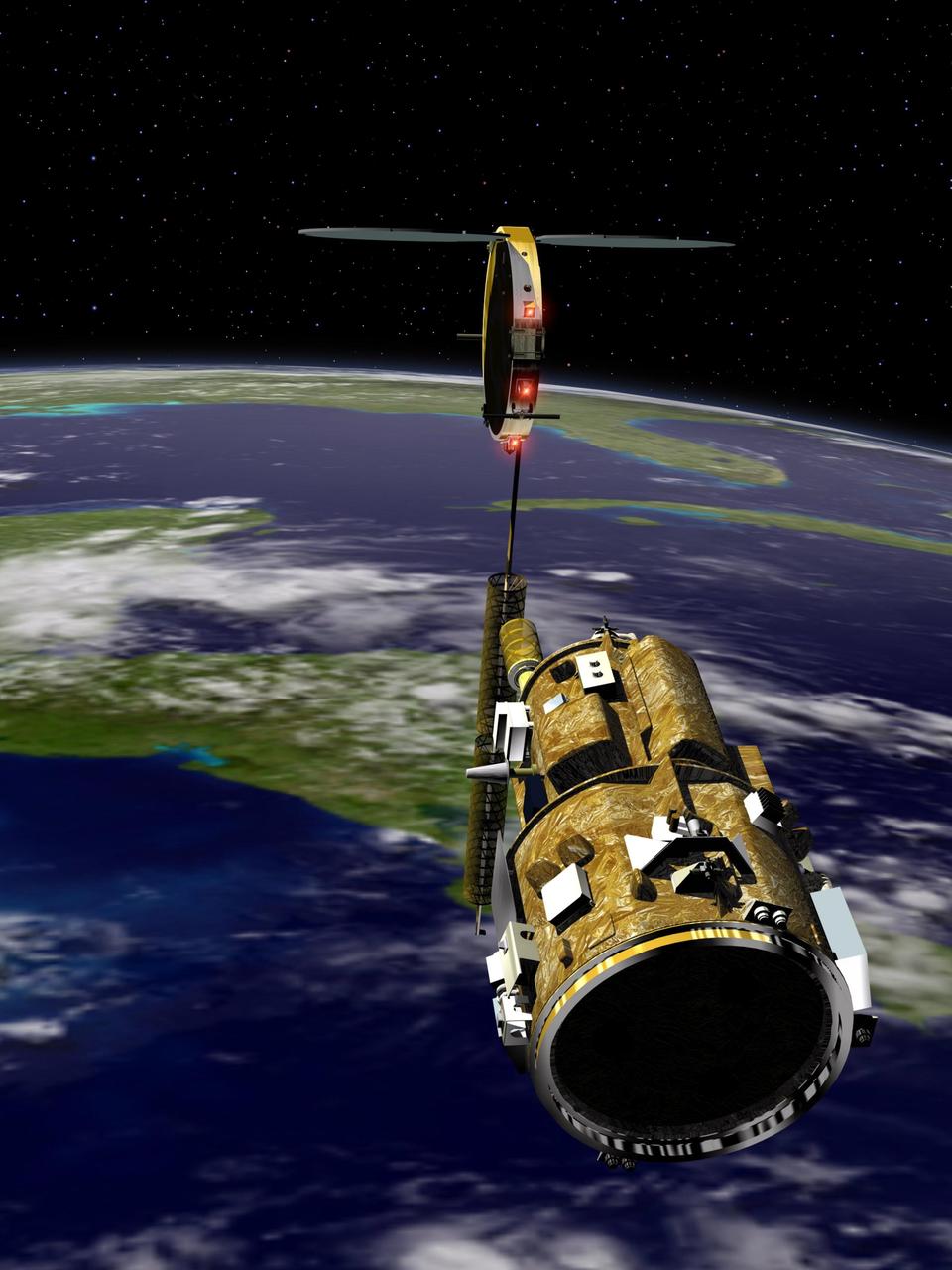
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An artist’s conception of the autonomous Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous (DART) spacecraft as it approaches the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications (MUBLCOM) satellite. NASA is testing the DART as a docking system for next generation vehicles to guide spacecraft carrying cargo or equipment to the International Space Station, or retrieving or servicing satellites in orbit. Before the new system can be implemented on piloted spacecraft, it has to be tested in space. The computer-guided DART is equipped with an Advanced Video Guidance Sensor and a Global Positioning System that can receive signals from other spacecraft to allow DART to move within 330 feet of the target. DART is scheduled to launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California no earlier than Oct. 18. It will be released from a Pegasus XL launch vehicle carried aloft by an Orbital Sciences Corporation aircraft. The fourth stage of the Pegasus rocket will remain attached as an integral part of the spacecraft, allowing it to maneuver in space. Once in orbit, DART will race toward the target, the MUBLCOM satellite, for a rendezvous.
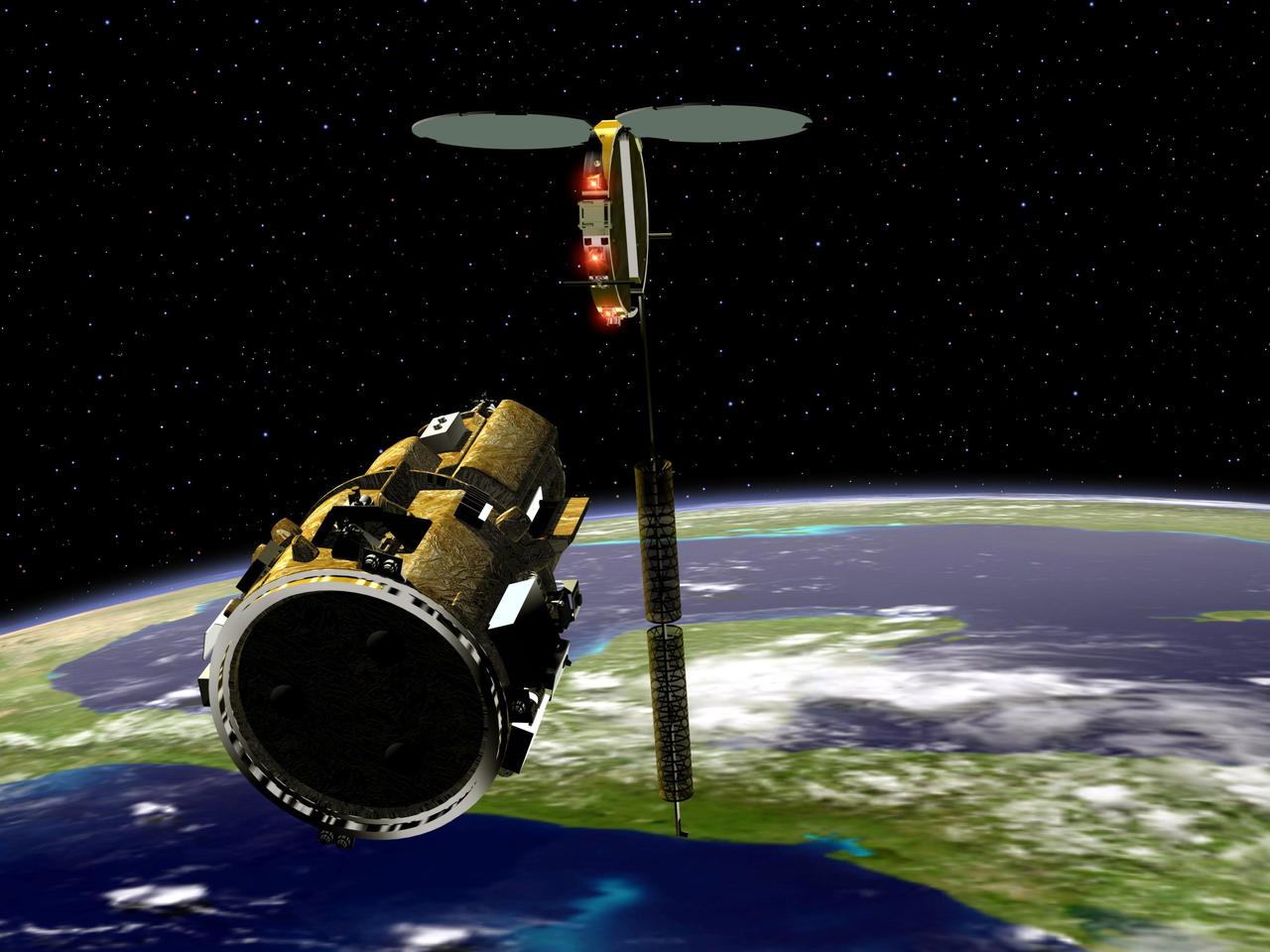
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An artist’s conception of the autonomous Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous (DART) spacecraft as it approaches the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications (MUBLCOM) satellite. NASA is testing the DART as a docking system for next generation vehicles to guide spacecraft carrying cargo or equipment to the International Space Station, or retrieving or servicing satellites in orbit. Before the new system can be implemented on piloted spacecraft, it has to be tested in space. The computer-guided DART is equipped with an Advanced Video Guidance Sensor and a Global Positioning System that can receive signals from other spacecraft to allow DART to move within 330 feet of the target. DART is scheduled to launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California no earlier than Oct. 18. It will be released from a Pegasus XL launch vehicle carried aloft by an Orbital Sciences Corporation aircraft. The fourth stage of the Pegasus rocket will remain attached as an integral part of the spacecraft, allowing it to maneuver in space. Once in orbit, DART will race toward the target, the MUBLCOM satellite, for a rendezvous.
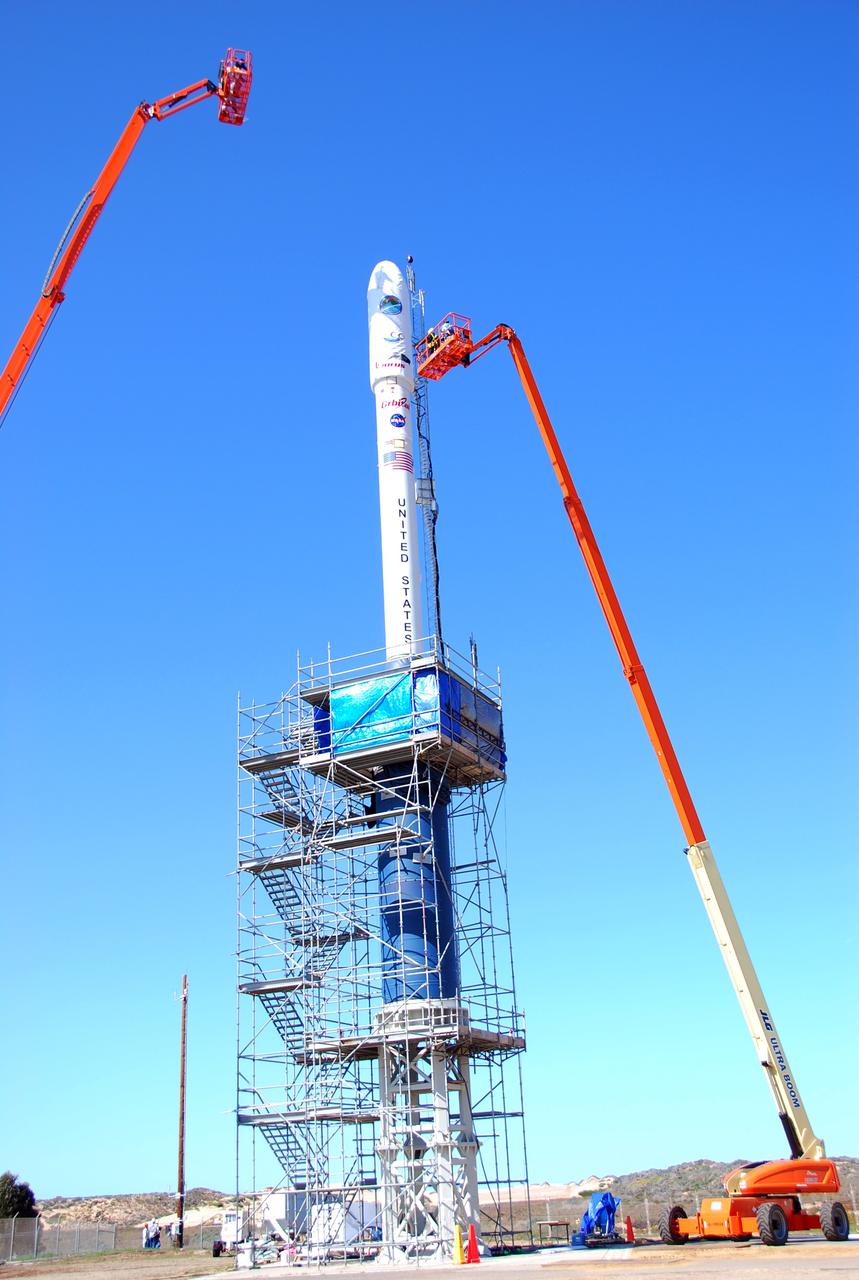

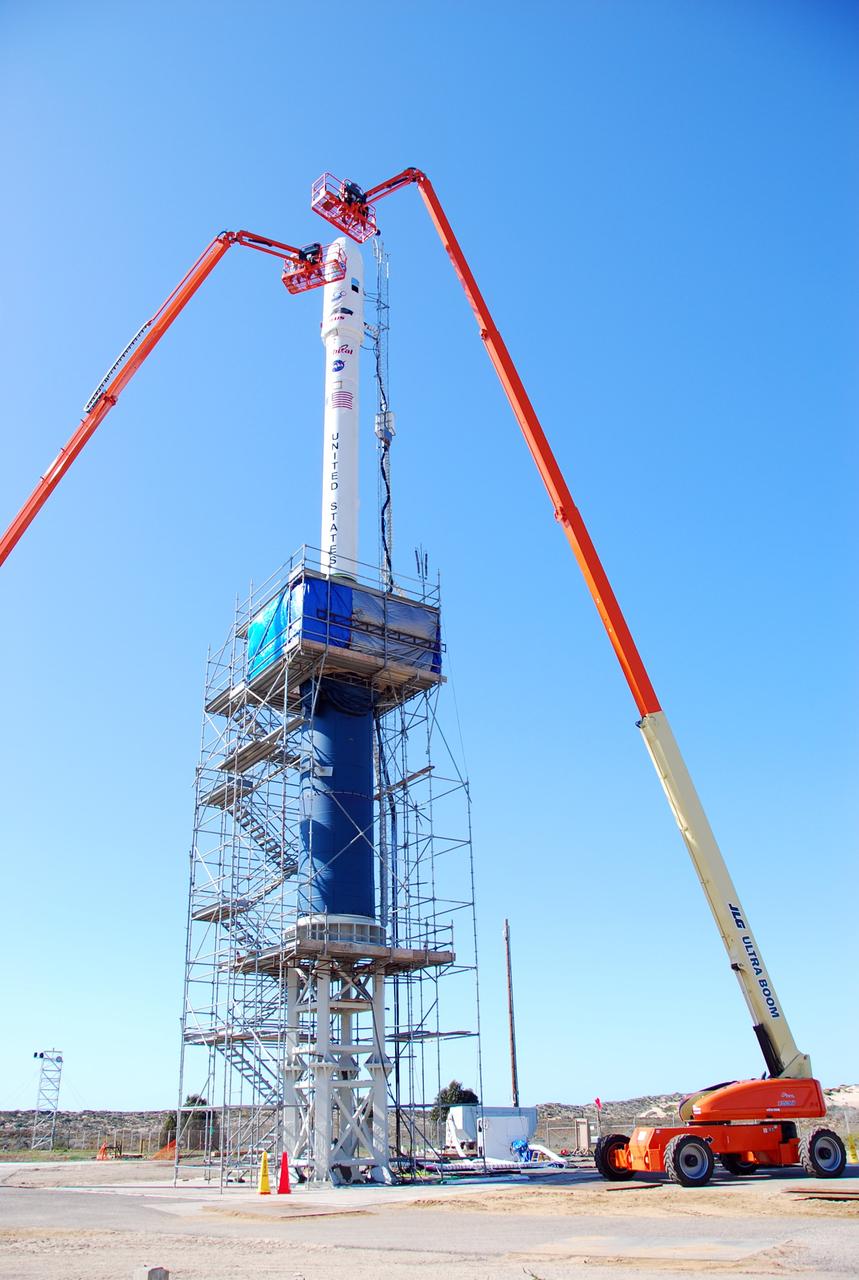
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- On Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences Engineer Jose Castillo maneuvers the bucket truck into position over the fairing access door on NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO. On the top of the OCO fairing is the shadow of Glenn Weigle of Orbital Satellite Systems Group, on the bucket at upper left, who is prepared to move in and inspect the GN2 instrument purge flow. OCO will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. Photo credit: NASA/Richard Nielsen, KSC
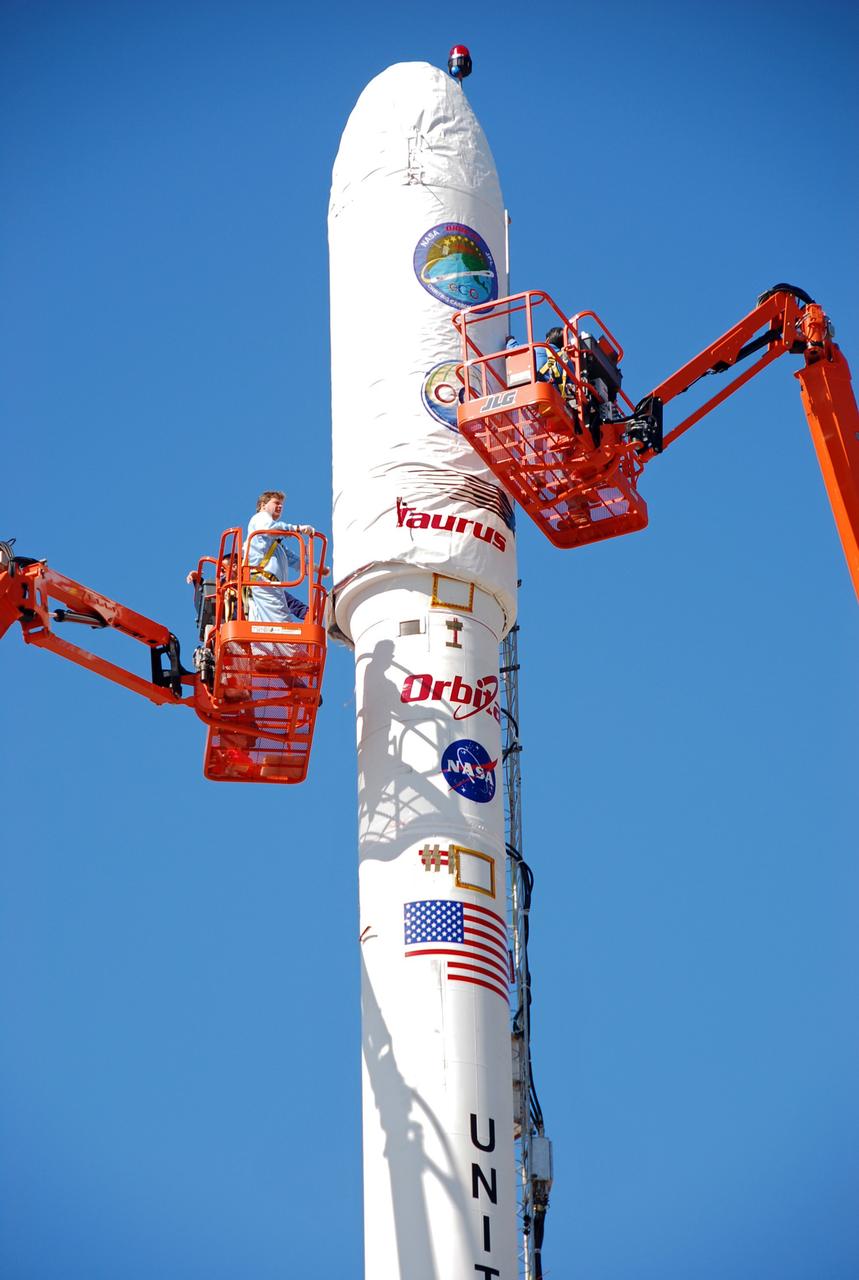

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- On Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences Engineer Jose Castillo maneuvers the bucket truck at right into position over the fairing access door on NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO. Glenn Weigle of Orbital Satellite Systems Group is on the bucket at left. Weigle is prepared to move in and inspect the GN2 instrument purge flow. OCO will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. OCO is scheduled to launch Feb. 24 aboard an Orbital Sciences' Taurus XL rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Richard Nielsen, KSC

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- On Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences Engineer Jose Castillo maneuvers the bucket truck at right into position over the fairing access door on NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO. Glenn Weigle of Orbital Satellite Systems Group is on the bucket at left. Weigle is prepared to move in and inspect the GN2 instrument purge flow. OCO will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. OCO is scheduled to launch Feb. 24 aboard an Orbital Sciences' Taurus XL rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Richard Nielsen, KSC
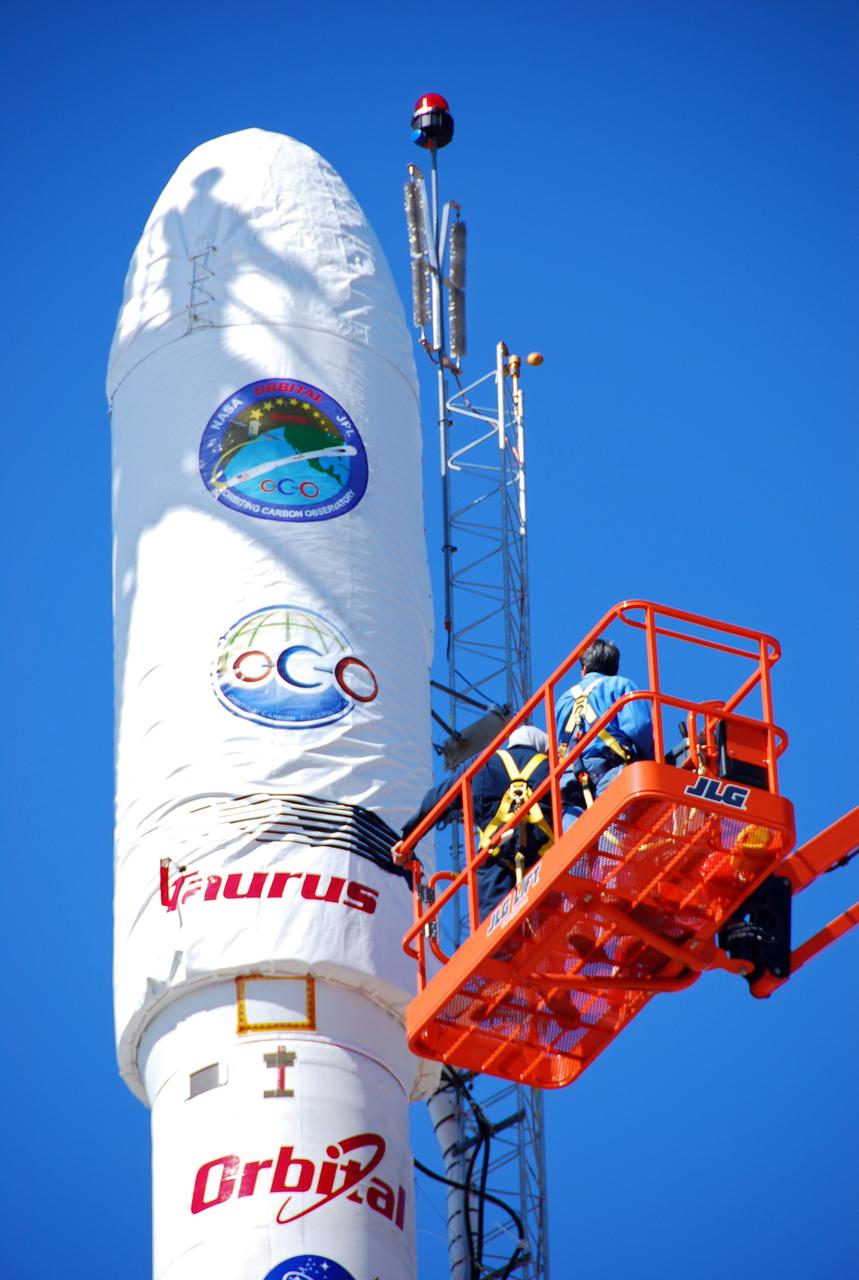

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- On Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences Engineer Jose Castillo maneuvers the bucket truck into position over the fairing access door on NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO. On the top of the OCO fairing is the shadow of Glenn Weigle of Orbital Satellite Systems Group, on a bucket out of camera range at left, who is waiting to move in and inspect the GN2 instrument purge flow. OCO will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. Photo credit: NASA/Richard Nielsen, KSC
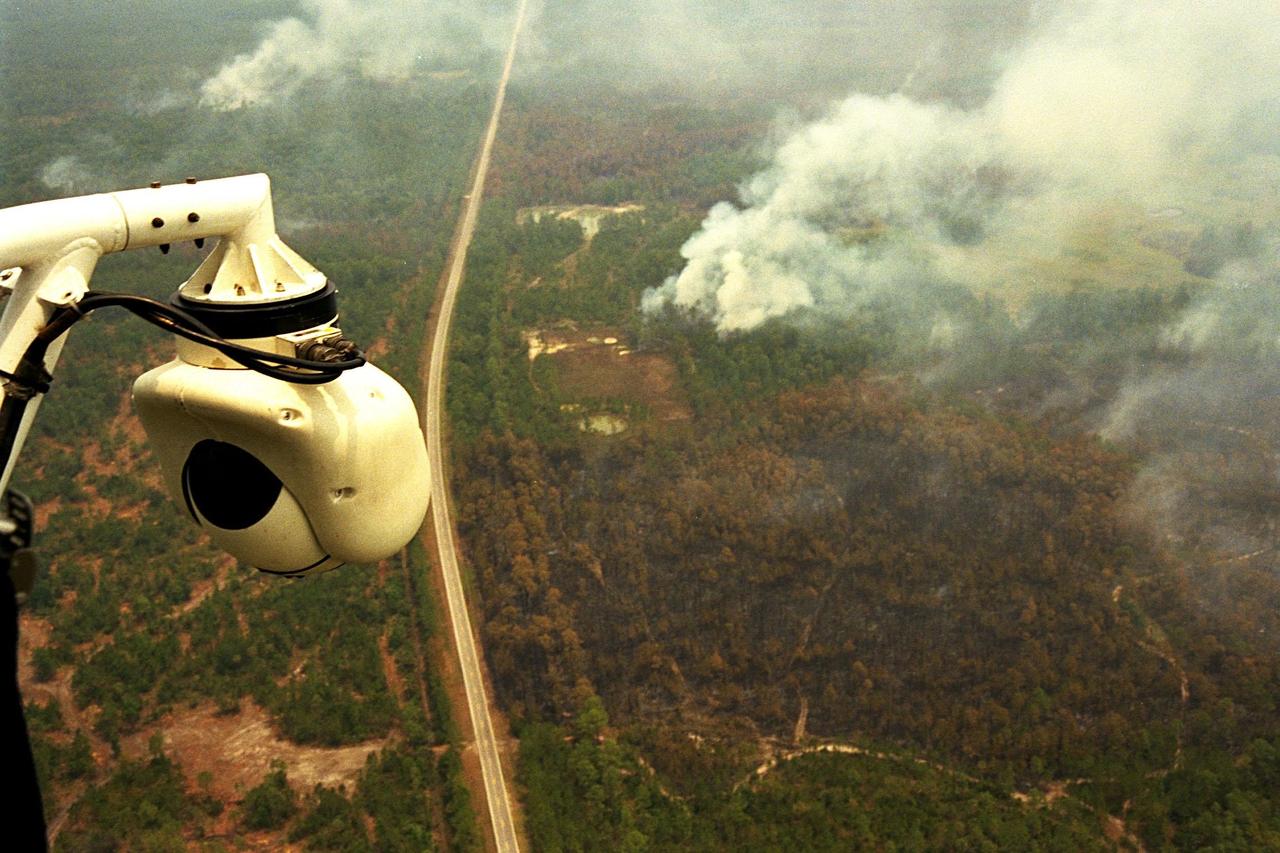

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A beach ball-sized infrared camera, part of the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR), has been mounted on the right siderail of NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter and is being used to search for fires in Volusia County, Florida. The helicopter has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR also includes a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside the helicopter. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. The Kennedy Space Center (KSC) security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
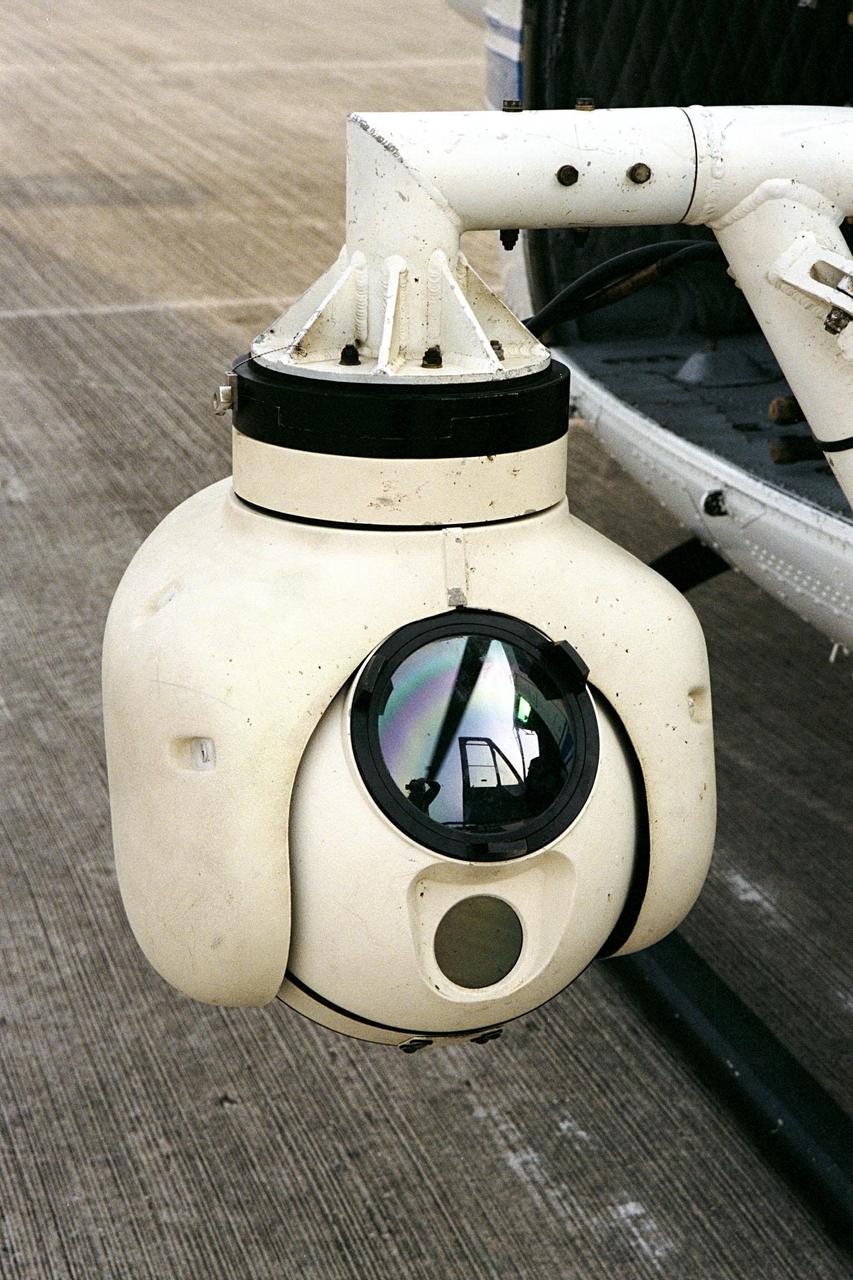

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A beach ball-sized infrared camera, part of the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR), has been mounted on the right siderail of NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter. The helicopter has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR also includes a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside the helicopter. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. The Kennedy Space Center (KSC) security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
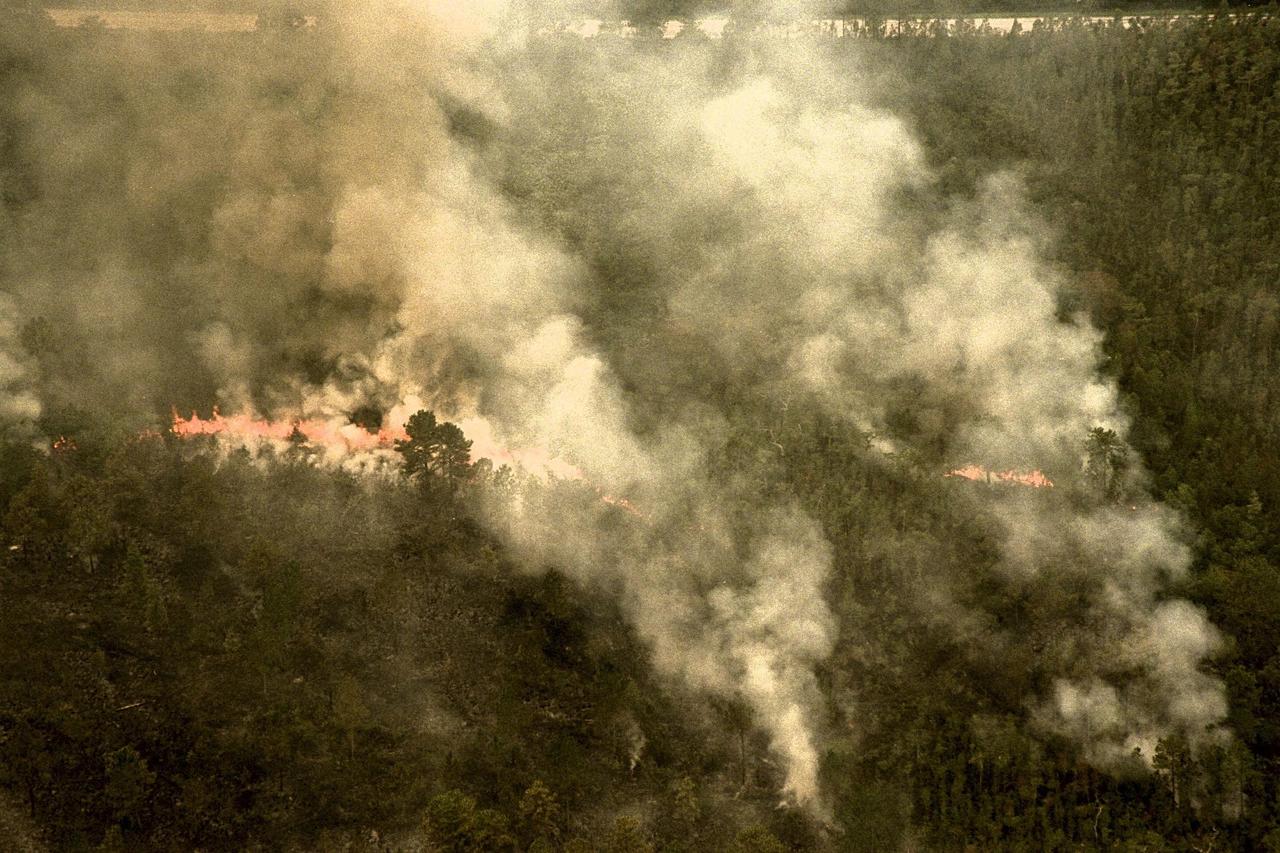

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A forest fire burning in Volusia County, Florida, is clearly visible from NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter. The helicopter has been outfitted with a Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR) and a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR includes a beach ball-sized infrared camera that is mounted on the helicopter's right siderail and a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. The Kennedy Space Center (KSC) security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
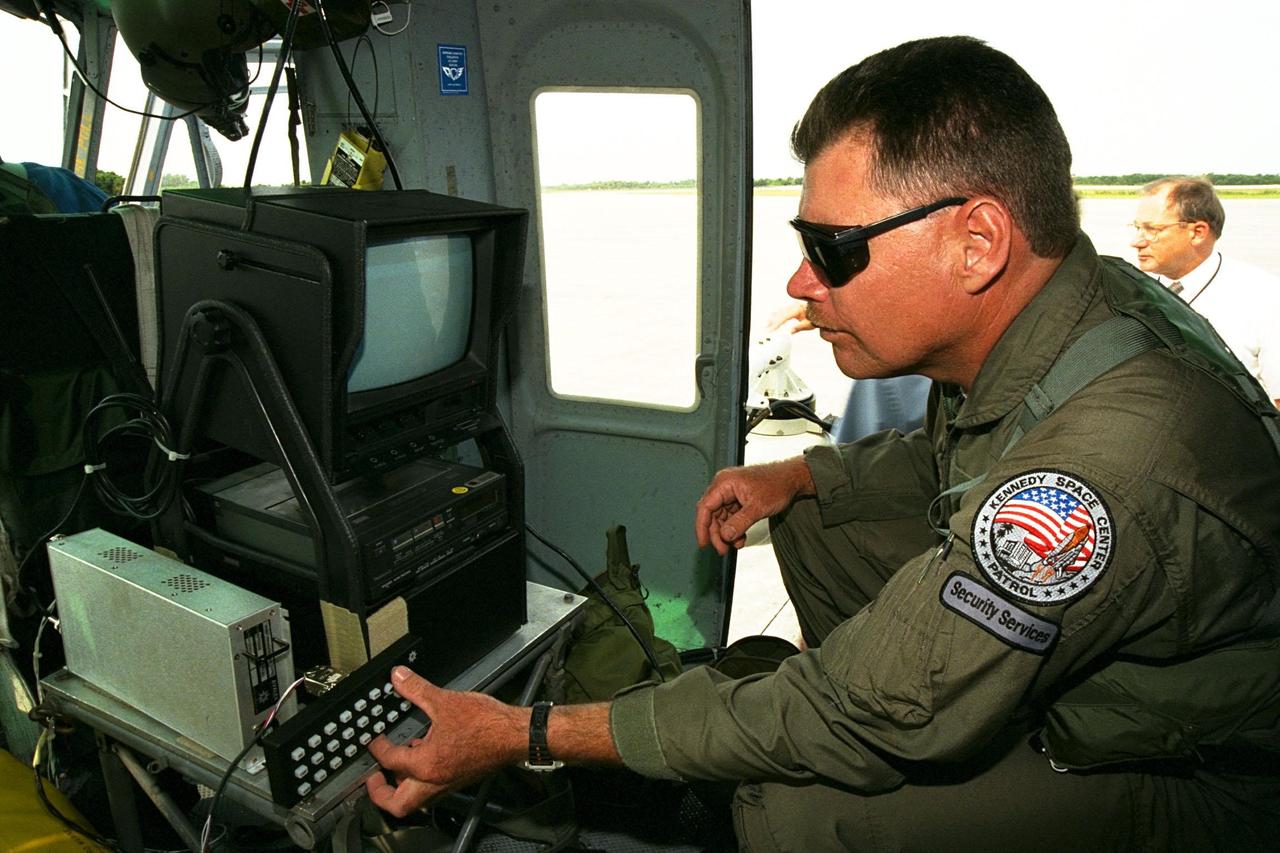

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Sgt. Mark Hines, of Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Security, checks out equipment used to operate the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR) installed on NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter. The helicopter has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR includes a beach ball-sized infrared camera that is mounted on the helicopter's right siderail and a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. KSC's security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
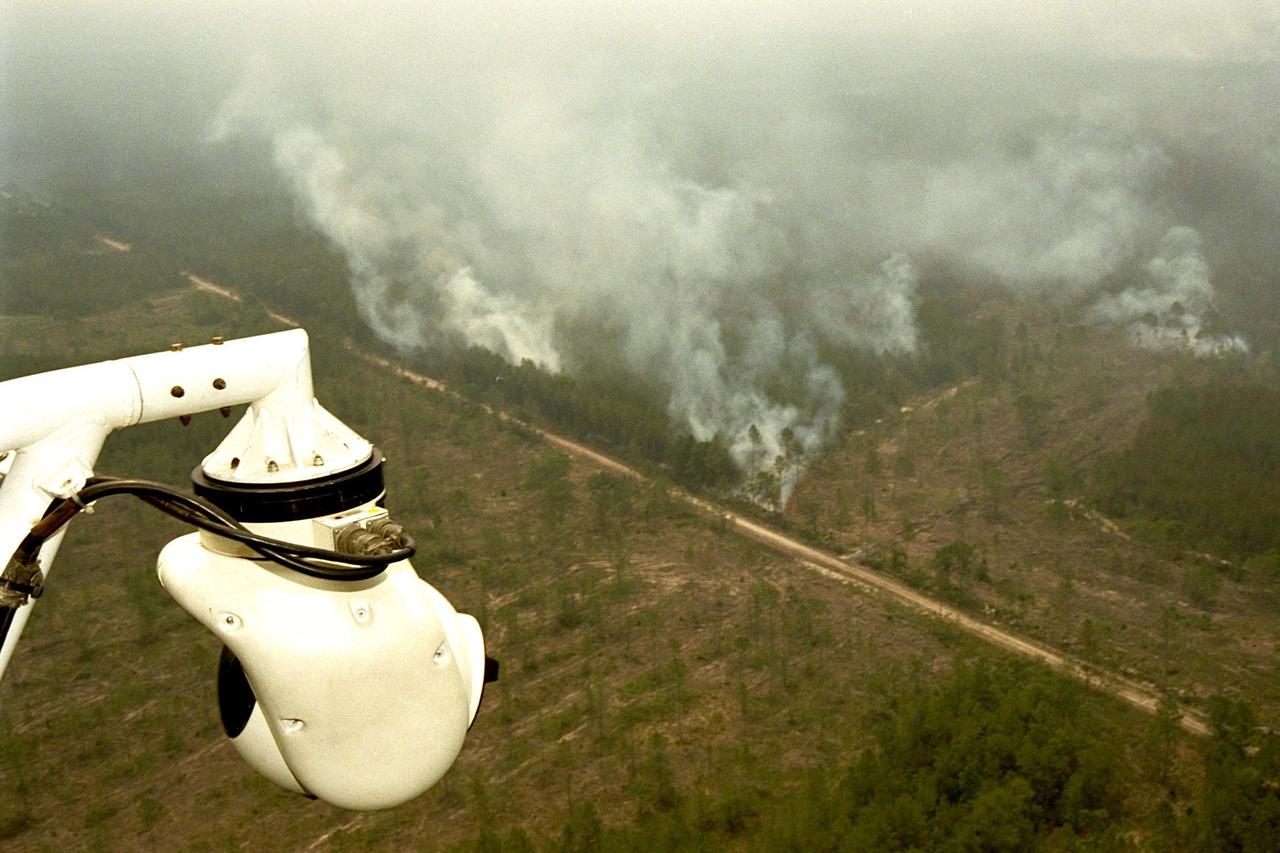

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A beach ball-sized infrared camera, part of the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR), has been mounted on the right siderail of NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter and is being used to scan a large area of Volusia County, Florida, where a fire burns. The helicopter has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR also includes a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside the helicopter. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. The Kennedy Space Center (KSC) security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
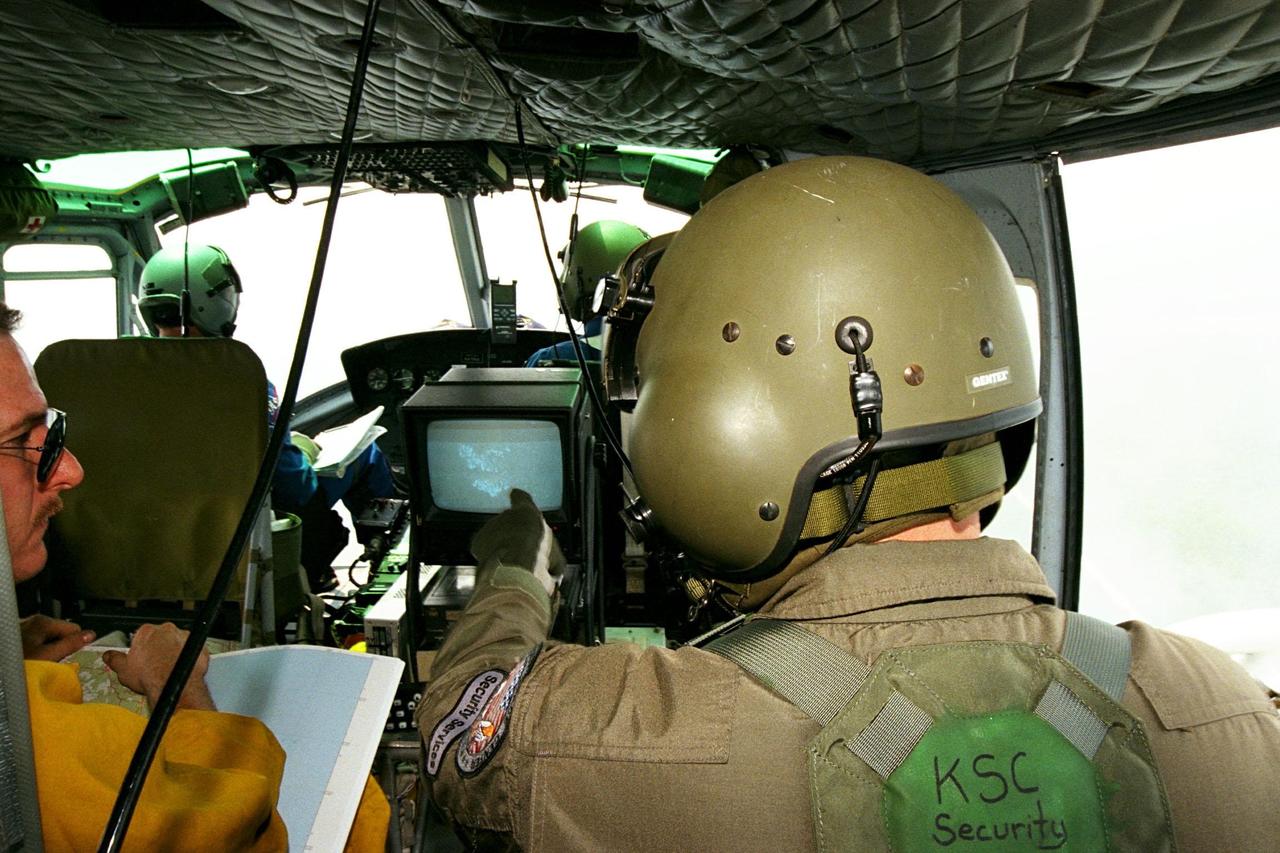

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Sgt. Mark Hines, of Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Security, points out a view of a fire on the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR) video screen to Greg Dunn, of Florida's Division of Forestry, as KSC pilots fly NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter over fires burning in Volusia County, Florida. The FLIR includes a beach-ball sized infrared camera that is mounted on the helicopter's right siderail and a real-time TV monitor and recorder installed inside. The helicopter has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support the Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. KSC's security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter.
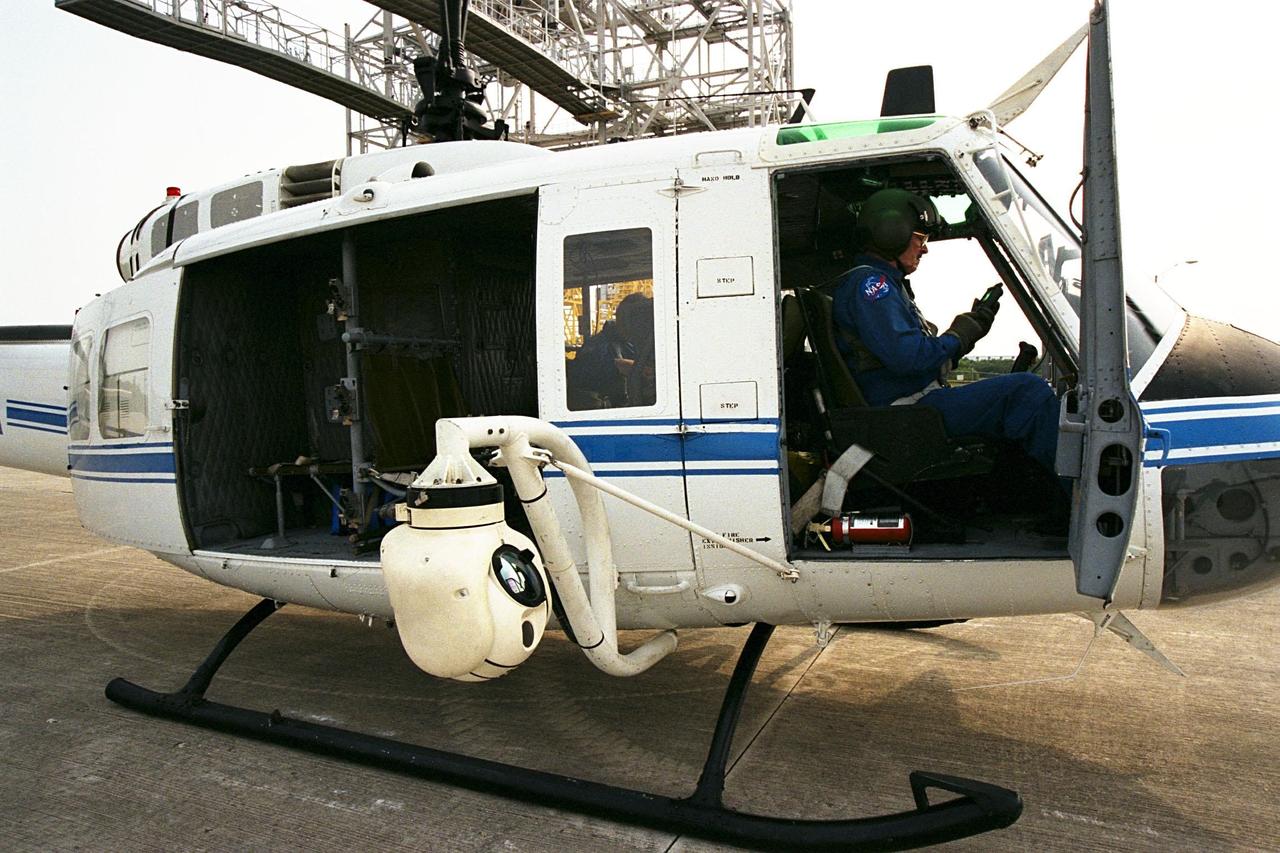

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A beach ball-sized infrared camera, part of the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR), has been mounted on the right siderail of NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter. A KSC pilot prepares to fly the helicopter, which has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system, to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR also includes a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside the helicopter. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. The Kennedy Space Center (KSC) security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
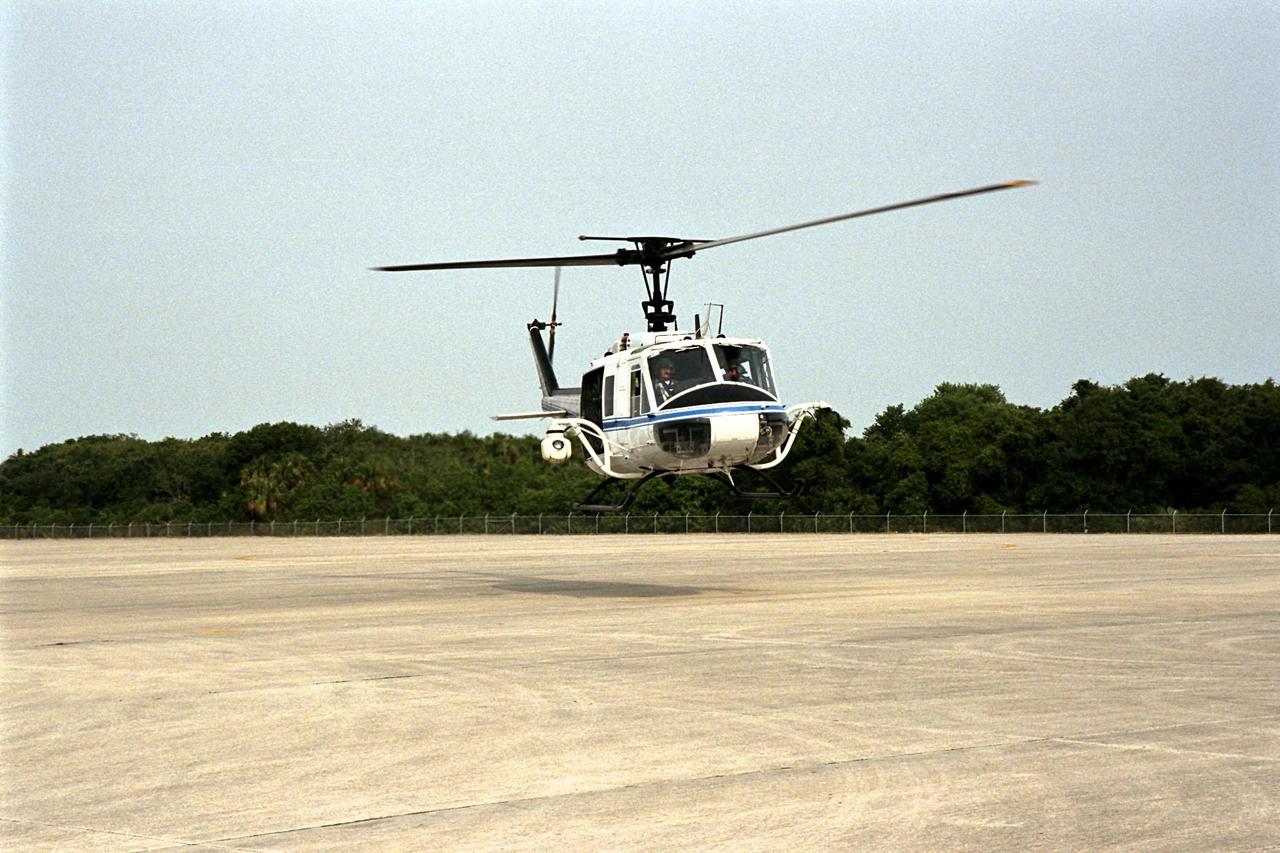

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter lands at the Shuttle Landing Facility to pick up Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Security personnel who operate the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR) installed on board. The helicopter has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR includes a beach ball-sized infrared camera that is mounted on the helicopter's right siderail and a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. KSC's security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
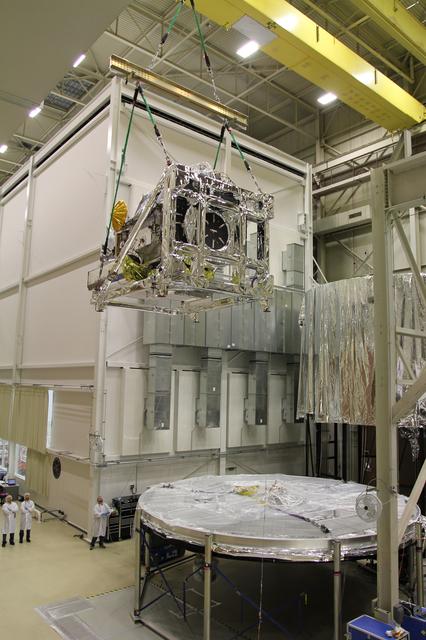

Crane lifting the GPM Core Observatory into position for TVAC testing. Credit: NASA/Goddard The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission is an international partnership co-led by NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) that will provide next-generation global observations of precipitation from space. GPM will study global rain, snow and ice to better understand our climate, weather, and hydrometeorological processes. As of Novermber 2013 the GPM Core Observatory is in the final stages of testing at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. The satellite will be flown to Japan in the fall of 2013 and launched into orbit on an HII-A rocket in early 2014. For more on the GPM mission, visit <a href="http://gpm.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">gpm.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a>. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

STS077-S-001 (February 1996) --- The STS-77 crew patch, designed by the crew members, displays the space shuttle Endeavour the lower left and its reflection within the tripod and concave parabolic mirror of the Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for Astronomy (SPARTAN) Inflatable Antenna Experiment (IAE). The center leg of the tripod also delineates the top of the Spacehab?s shape, the rest of which is outlined in gold just inside the red perimeter. The Spacehab is carried in the payload bay and houses the Commercial Float Zone Furnace (CFZF) and Space Experiment Facility (SEF) experiments. Also depicted within the confines the IAE mirror are the mission?s rendezvous operations with the Passive Aerodynamically Stabilized Magnetically Damped Satellite/Satellite Test Unit (PAM/STU) satellite and a reflection of Earth. The PAM/STU satellite appears as a bright six-pointed star-like reflection of the sun on the edge of the mirror with the space shuttle Endeavour in position to track it. The sunglint on the mirror?s edge, which also appears as an orbital sunset, is located over Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC), the development facility for the SPARTAN/IAE and Technology Experiments Advancing Missions in Space (TEAMS) experiments. The reflection of Earth is oriented to show the individual countries of the crew as well as the ocean which Captain Cook explored in the original Endeavour. The mission number ?77? is featured as twin stylized chevrons and an orbiting satellite as adapted from NASA?s logo. The stars at the top are arranged as seen in the northern sky in the vicinity of the constellation Ursa Minor. The field of 11 stars represents both the TEAMS cluster of experiments (the four antennae of Global Positioning System Attitude and Navigation Experiment (GANE), the single canister of Liquid Metal Thermal Experiment (LMTE), the three canisters of Vented Tank Resupply Experiment (VTRE), and the canisters of PAM/STU, and the 11th flight of the Endeavour. The constellation at the right shows the four stars of the Southern Cross for the fourth flight of Spacehab. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
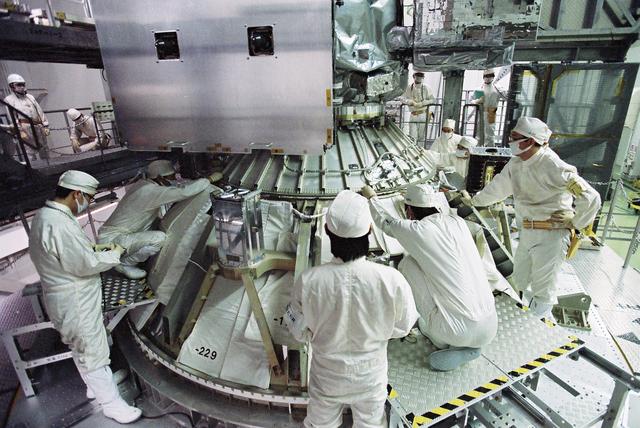

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
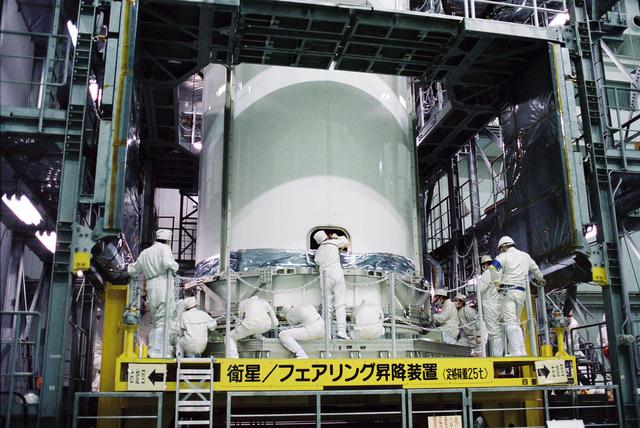

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
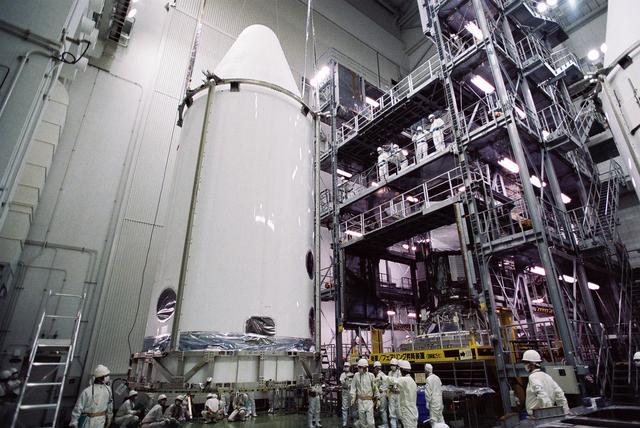

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
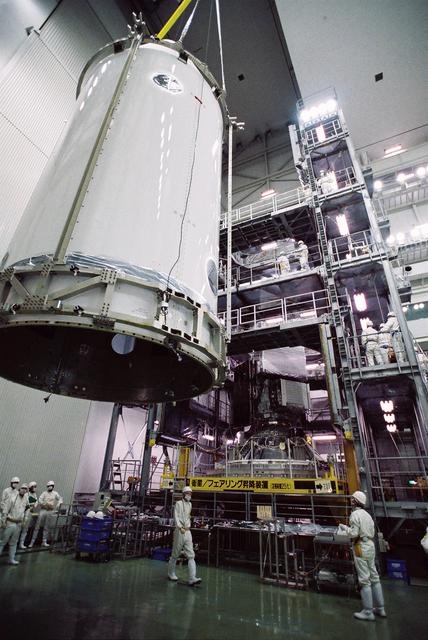

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
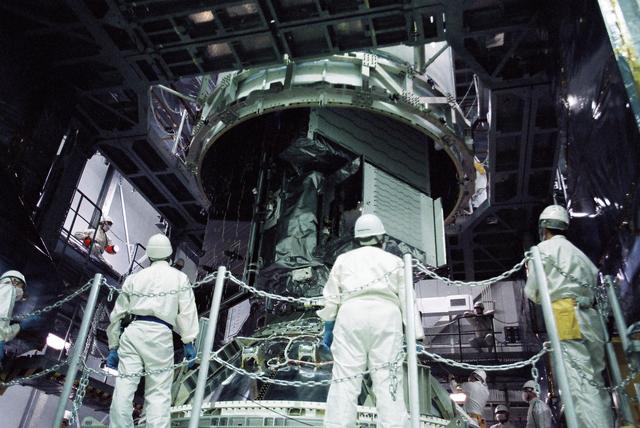

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
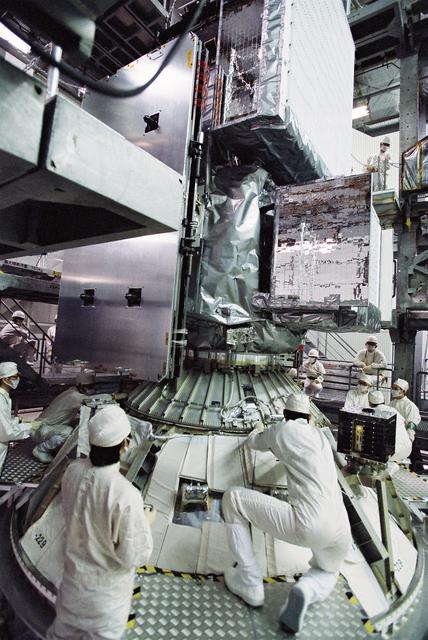

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
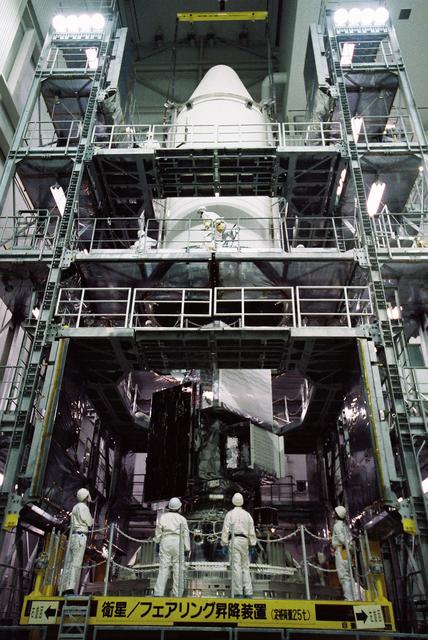

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
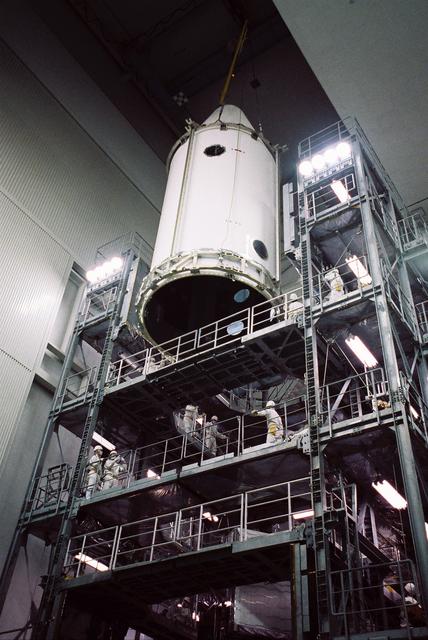

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
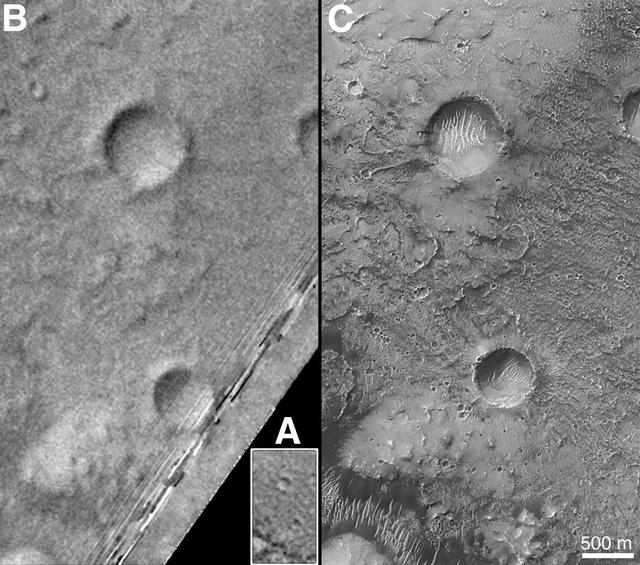
On Earth, the longitude of the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England is defined as the "prime meridian," or the zero point of longitude. Locations on Earth are measured in degrees east or west from this position. The prime meridian was defined by international agreement in 1884 as the position of the large "transit circle," a telescope in the Observatory's Meridian Building. The transit circle was built by Sir George Biddell Airy, the 7th Astronomer Royal, in 1850. (While visual observations with transits were the basis of navigation until the space age, it is interesting to note that the current definition of the prime meridian is in reference to orbiting satellites and Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) measurements of distant radio sources such as quasars. This "International Reference Meridian" is now about 100 meters east of the Airy Transit at Greenwich.) For Mars, the prime meridian was first defined by the German astronomers W. Beer and J. H. Mädler in 1830-32. They used a small circular feature, which they designated "a," as a reference point to determine the rotation period of the planet. The Italian astronomer G. V. Schiaparelli, in his 1877 map of Mars, used this feature as the zero point of longitude. It was subsequently named Sinus Meridiani ("Middle Bay") by Camille Flammarion. When Mariner 9 mapped the planet at about 1 kilometer (0.62 mile) resolution in 1972, an extensive "control net" of locations was computed by Merton Davies of the RAND Corporation. Davies designated a 0.5-kilometer-wide crater (0.3 miles wide), subsequently named "Airy-0" (within the large crater Airy in Sinus Meridiani) as the longitude zero point. (Airy, of course, was named to commemorate the builder of the Greenwich transit.) This crater was imaged once by Mariner 9 (the 3rd picture taken on its 533rd orbit, 533B03) and once by the Viking 1 orbiter in 1978 (the 46th image on that spacecraft's 746th orbit, 746A46), and these two images were the basis of the martian longitude system for the rest of the 20th Century. The Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) has attempted to take a picture of Airy-0 on every close overflight since the beginning of the MGS mapping mission. It is a measure of the difficulty of hitting such a small target that nine attempts were required, since the spacecraft did not pass directly over Airy-0 until almost the end of the MGS primary mission, on orbit 8280 (January 13, 2001). In the left figure above, the outlines of the Mariner 9, Viking, and Mars Global Surveyor images are shown on a MOC wide angle context image, M23-00924. In the right figure, sections of each of the three images showing the crater Airy-0 are presented. A is a piece of the Mariner 9 image, B is from the Viking image, and C is from the MGS image. Airy-0 is the larger crater toward the top-center in each frame. The MOC observations of Airy-0 not only provide a detailed geological close-up of this historic reference feature, they will be used to improve our knowledge of the locations of all features on Mars, which will in turn enable more precise landings on the Red Planet by future spacecraft and explorers. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03207

In January 2013, a new Earth-observing instrument was installed on the International Space Station (ISS). ISERV Pathfinder consists of a commercial camera, a telescope, and a pointing system, all positioned to look through the Earth-facing window of ISS’s Destiny module. ISERV Pathfinder is intended as an engineering exercise, with the long-term goal of developing a system for providing imagery to developing nations as they monitor natural disasters and environmental concerns. The image above is the “first light” from the new ISERV camera system, taken at 1:44 p.m. local time on February 16, 2013. It shows the Rio San Pablo as it empties into the Golfo de Montijo in Veraguas, Panama. It is an ecological transition zone, changing from agriculture and pastures to mangrove forests, swamps, and estuary systems. The area has been designated a protected area by the National Environmental Authority (ANAM) of Panama and is listed as a “wetland of international importance” under the Ramsar Convention. (Note that the image is rotated so that north is to the upper right.) “ISERV’s full potential is yet to be seen, but we hope it will really make a difference in people’s lives,” said principal investigator Burgess Howell of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center. “For example, if an earthen dam gives way in Bhutan, we want to be able to show officials where the bridge is out or where a road is washed out or a power substation is inundated. This kind of information is critical to focus and speed rescue efforts.” The instrument will be controlled from NASA Marshall in Huntsville, Alabama, in collaboration with researchers at hubs in Central America, East Africa, and the Hindu Kush–Himalaya region. They will rely on positioning software to know where the space station is at each moment and to calculate the next chance to view a particular area on the ground. If there's a good viewing opportunity, the SERVIR team will instruct the camera to take high-resolution photographs at 3 to 7 frames per second, totaling as many as 100 images per pass. With a resolution down to 3.2 meters (10 feet), it will be possible to spot fairly small details and objects. The current mission will test the limitations of Pathfinder and identify measures for improvements in a more permanent system. For instance, the engineering team is working to determine how the geometry of the ISS window affects the imagery; how much sunlight is needed to capture clear images; and how the atmosphere affects that clarity. This characterization phase will last several weeks to a few months. Eventually, ISERV should be made available to the natural hazards community and to basic research scientists. ISERV is short for ISS SERVIR Environmental Research and Visualization system. Together with the U.S. Agency for International Development, NASA runs the SERVIR program to provide satellite data, maps, and other tools to environmental decisionmakers in developing countries. (Servir is a Spanish word meaning “to serve.”) Learn more about the SERVIR program by clicking here: <a href="https://servirglobal.net/Global.aspx" rel="nofollow">servirglobal.net/Global.aspx</a> NASA image by Burgess Howell, SERVIR Global program. Caption by Dauna Coulter, NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, and Mike Carlowicz, NASA Earth Observatory. Instrument: ISS - ISERV Pathfinder Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> - <a href="http://1.usa.gov/12Aqmg9" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/12Aqmg9</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>