
Cortez III Employee Delivers Work Between the Print Shop and the Building 60 Graphics Department

Apollo/Saturn Program: In January 1962, NASA initiated development of the large launch vehicle for the Project Apollo manned lunar flights. The Saturn V configuration comprised the S-IC first stage, the S-II second stage and the S-IVB third stage, all integrated and stacked in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The first manned Apollo spacecraft launched on the mighty Saturn V was Apollo 8 on December 21, 1968. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

International Cooperation: NASA international cooperation provides opportunities for utilization of space by NASA partners worldwide. Cooperative programs allow each participating country to contribute its special talents and facilities to a common goal. International cooperation is a cornerstone of NASA’s space program today with multi-national crews living and working aboard the International Space Station. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Commercial Crew Program: The Commercial Crew Program at Kennedy Space Center is leading NASA’s efforts to develop the next United States capability for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the International Space Station ISS and other low Earth orbit destinations by the middle of the decade. The outcome of this capability is expected to stimulate and expand the U.S. space transportation industry. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Satellites: The principal objectives of the Launch Services Program are to provide safe, reliable, cost-effective and on schedule launch services for NASA and NASA-sponsored payloads seeking launch on expendable vehicles. These payloads have a number of purposes. Scientific satellites obtain information about the space environment and transmit it to stations on Earth. Applications satellites designed to perform experiments that have everyday usefulness for people on Earth, such as weather forecasting and communications. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

President John F. Kennedy: President John F. Kennedy visited Cape Canaveral on three separate occasions, twice in 1962 and November 16, 1963. He presided over a Project Mercury ceremony to award John Glenn the NASA Distinguished Service Medal, toured the Launch Operations Center complexes and rode in a helicopter over the Merritt Island Launch Area, which was under construction to support the Apollo Program. On November 29, 1963, President Lyndon B. Johnson renamed the Launch Operations Center the John F. Kennedy Space Center. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Center Directors: The Kennedy Space Center has had ten Center Directors. The first Center Director, Dr. Kurt H. Debus, was followed by: Row 1, left to right – Lee R. Scherer, Richard G. Smith, and Lieutenant General Forrest S. McCartney, USAF, ret.. Row 2, left to right – Robert L. Crippen, Jay F. Honeycutt and Roy D. Bridges. Row 3, left to right – James W. Kennedy, William W. Parsons and Robert D. Cabana, KSC’s Center Director since 2008. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Space Shuttle Payloads: Kennedy Space Center was the hub for the final preparation and launch of the space shuttle and its payloads. The shuttle carried a wide variety of payloads into Earth orbit. Not all payloads were installed in the shuttle's cargo bay. In-cabin payloads were carried in the shuttle's middeck. Cargo bay payloads were typically large payloads which did not require a pressurized environment, such as interplanetary space probes, earth-orbiting satellites, scientific laboratories and International Space Station trusses and components. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

International Space Station: The International Space Station, or ISS, was built by sixteen nations, including the United States, Canada, Russia, Japan, Brazil, and 11 European nations. Each participating country contributed its expertise. This project was based on cooperative agreements on the design, development, operation, and utilization of the space station. The ISS marked its 10th anniversary of continuous human occupation on Nov. 2, 2010. Since Expedition 1, which launched Oct. 31, 2000, and docked Nov. 2, the space station has been visited by 202 individuals. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Apollo-Soyuz Test Project: The first international crewed spaceflight was a joint U.S.-U.S.S.R. rendezvous and docking mission. The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, or ASTP, took its name from the spacecraft employed: the American Apollo and the Soviet Soyuz. The three-man Apollo crew lifted off from Kennedy Space Center aboard a Saturn IB rocket on July 15, 1975, to link up with the Soyuz that had launched a few hours earlier. A cylindrical docking module served as an airlock between the two spacecraft for transfer of the crew members. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Launch Vehicles: Launch vehicles are the rocket-powered systems that provide transportation from the Earth’s surface into the environment of space. Kennedy Space Center’s heritage includes launching robotic and satellite missions into space primarily using Atlas, Delta and Titan launch vehicles. Other launch vehicles include the Pegasus and Athena. The Launch Services Program continues this mission today directing launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. Kodiak, Alaska and Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Project Mercury: With Project Mercury, the United States gained its first experience in conducting human space missions that provided scientific and engineering knowledge of astronauts in space. Alan Shepard made history May 5, 1961, as America's first man in space. Less than a year later, John Glenn made the nation’s first orbital flight on Feb. 20, 1962. After two suborbital and three orbital missions, Project Mercury ended with a 22-orbit spaceflight on May 16, 1963. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Apollo Capsule/Lunar Lander: The goal of Project Apollo was to land man on the moon and return them safely to the Earth. The Apollo spacecraft consisted of a command module serving as the crew’s quarters and flight control section and the lunar module, carrying two crewmembers to the surface of the moon. The first Apollo spacecraft to land on the moon was Apollo 11 on July 20, 1969. The program concluded with Apollo 17 in December 1972 after putting 27 men into lunar orbit and 12 of them on the surface of the moon. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Project Gemini: On Jan. 3, 1962, NASA announced the advanced Mercury Mark II project had been named "Gemini." After 12 missions – 2 uncrewed and 10 crewed – Project Gemini ended Nov. 15, 1966, following a nearly four-day, 59 orbit-flight. Its achievements included long-duration spaceflight, rendezvous and docking of two spacecraft in Earth orbit, extravehicular activity, and precision-controlled re-entry and landing of the spacecraft. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Industrial Area Construction: Located 5 miles south of Launch Complex 39, construction of the main buildings -- Operations and Checkout Building, Headquarters Building, and Central Instrumentation Facility – began in 1963. In 1992, the Space Station Processing Facility was designed and constructed for the pre-launch processing of International Space Station hardware that was flown on the space shuttle. Along with other facilities, the industrial area provides spacecraft assembly and checkout, crew training, computer and instrumentation equipment, hardware preflight testing and preparations, as well as administrative offices. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
![Center Directors: Kennedy Space Center Directors around KSC – 1st row, left to right, Richard Smith [center] Bob Cabana [at the podium] Jay Honeycutt [far right]. 2nd row, left to right, Bob Crippen [left] Jim Kennedy Lieutenant General Forrest S. McCartney, USAF, ret. [far left]. 3rd row, left to right, Bill Parsons [far right] Lee Scherer Roy Bridges [2nd from right]. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC-2012-1848/KSC-2012-1848~medium.jpg)
Center Directors: Kennedy Space Center Directors around KSC – 1st row, left to right, Richard Smith [center] Bob Cabana [at the podium] Jay Honeycutt [far right]. 2nd row, left to right, Bob Crippen [left] Jim Kennedy Lieutenant General Forrest S. McCartney, USAF, ret. [far left]. 3rd row, left to right, Bill Parsons [far right] Lee Scherer Roy Bridges [2nd from right]. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Space Shuttle Orbiters: From its establishment in 1958, NASA studied aspects of reusable launch vehicles and spacecraft that could return to earth. On January 5, 1972, President Richard Nixon announced that the United States would develop the space shuttle, a delta-winged orbiter about the size of a DC-9 aircraft. Between the first launch on April 12, 1981, and the final landing on July 21, 2011, NASA's space shuttle fleet -- Columbia, Challenger, Discovery, Atlantis and Endeavour – launched on 135 missions, helped construct the International Space Station and inspired generations. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Dr. Kurt H. Debus, Kennedy Space Center's First Director: A doctor of philosophy in engineering from Darmstadt University, Debus was selected by Dr. Wernher von Braun to direct the Experimental Missile Firing Branch which began launching missiles from Cape Canaveral in 1953. Dr. Debus became the first Center Director for the new independent Launch Operations Center, and it was his job to put Saturn/Apollo into space. His tenure at Kennedy Space Center spanned 13 years, from 1962 to 1974. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Launch Complex 39 Construction: Launch Complex 39 LC-39 was originally designed and built to launch American astronauts toward the moon. The complex stretches inland from the Atlantic Ocean across four miles of what, until 1963, was a land of intermittent marshes and sandy scrub growth. In less than four years, starting with 1963 and ending with 1966, it was transformed into an operational spaceport embodying a mobile concept: rockets and spacecraft are erected in one area and transported to a separate location for launch. A total of 153 vehicles have been launched from LC-39. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Orion / Space Launch System: NASA has selected the design of a new Space Launch System SLS that will take the agency's astronauts farther into space than ever before and provide the cornerstone for America's future human space exploration efforts. The SLS will launch human crews beyond low Earth orbit in the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle. Orion is America’s next generation spacecraft. It will serve as the exploration vehicle that will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel, carry the crew to distant planetary bodies, and provide safe return from deep space. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Spacecraft: The Kennedy Space Center has processed and launched many scientific missions to study Earth, the moon, other planets, and the space environment, which has greatly expanded our knowledge and understanding of the solar system. These automated machines have orbited and landed on Venus and Mars, explored the Sun’s environment, observed comets and asteroids, and made close-range surveys while flying past Mercury, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The Launch Services Program, established in 1998, continues this mission today. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Project Mercury: With Project Mercury, the United States gained its first experience in conducting human space missions that provided scientific and engineering knowledge of astronauts in space. Alan Shepard made history May 5, 1961, as America's first man in space. Less than a year later, John Glenn made the nation’s first orbital flight on Feb. 20, 1962. After two suborbital and three orbital missions, Project Mercury ended with a 22-orbit spaceflight on May 16, 1963. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex: Facilities on Merritt Island were sufficiently advanced by November 1964 to permit Sunday drive-through tours. The center set up a modest collection of model rockets and pictures in a warehouse for visitors to view. Based on a study by the U.S. National Park Service for a permanent facility, NASA selected the site on its own property and contracted with a commercial firm to operate the new center and bus tours. The Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex has been expanded many times in the years since to better serve the increasing number of guests, provide new displays and tell the NASA story to the public. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

Presidential Visits to Kennedy Space Center: All the U. S. presidents shown here were in office at the time they visited KSC. President Dwight D. Eisenhower, 02/10/1960 President Lyndon B. Johnson visited twice, 09/14/1964 and 09/27/1966 President Richard M. Nixon viewed the Apollo 12 launch on 11/14/1969 President Jimmy Carter came to KSC on 10/01/1978 President William J. Clinton viewed the STS-95 launch on 10/29/1998 and President Barack H. Obama visited KSC twice, 04/15/2010 and 04/29/2011. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
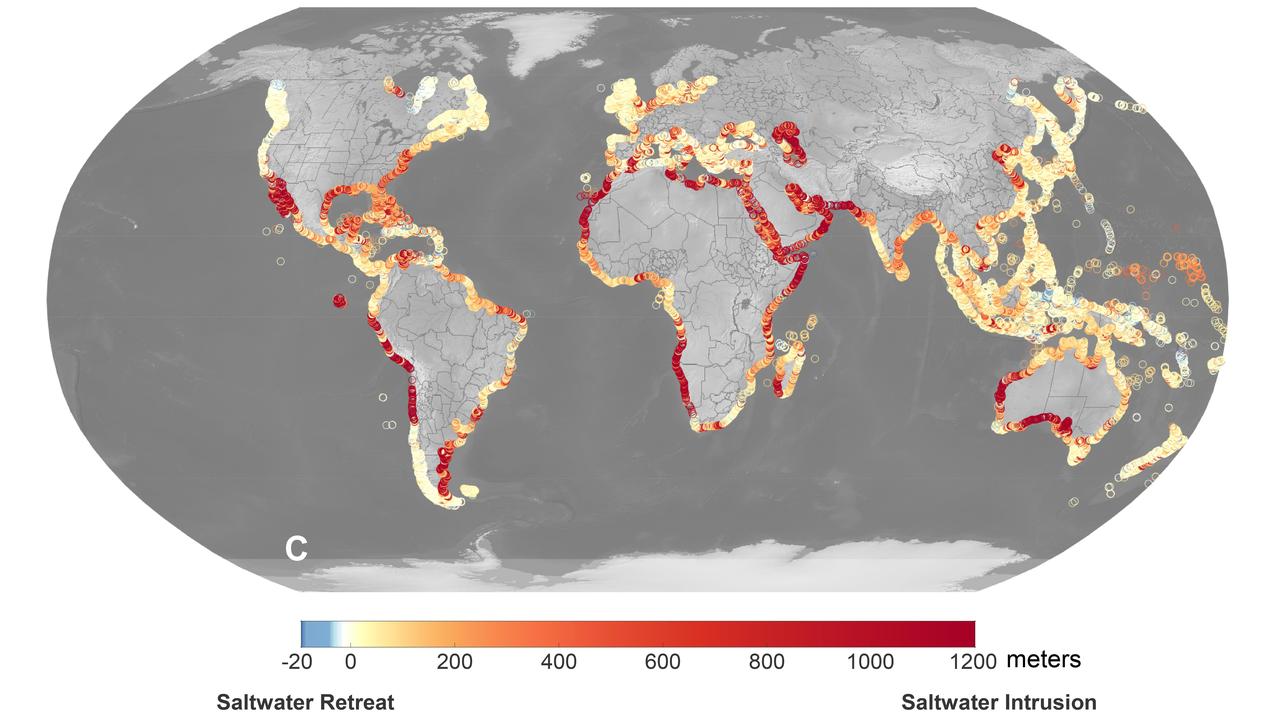
A recent study led by researchers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California that seawater will infiltrate underground fresh water supplies in about 77% of coastal watersheds around the world by the year 2100, as illustrated in this graphic. Called saltwater intrusion, the phenomenon will result from the combined effects of sea level rise and slower replenishment of groundwater supplies due to warmer, drier regional climates, according to the study, which was funded by NASA and the U.S. Department of Defense and published in Geophysical Research Letters in November 2024. In the graphic, areas that the study projected will experience the most severe saltwater intrusion are marked with red, while the few areas that will experience the opposite phenomenon, called saltwater retreat, are marked with blue. Saltwater intrusion happens deep below coastlines, where two masses of water naturally run up against each other. Rainfall on land replenishes, or recharges, fresh water in coastal aquifers (essentially, underground rock and dirt that hold water), which tends to flow underground toward the ocean. Meanwhile, seawater, backed by the pressure of the ocean, tends to push inland. Although there's some mixing in the transition zone where the two meet, the balance of opposing forces typically keeps the water fresh on one side and salty on the other. Spurred by melting ice sheets and glaciers, sea level rise is causing coastlines to migrate inland and increasing the force pushing underground salt water landward. At the same time, slower groundwater recharge resulting from reduced rainfall and warmer weather patterns is weakening the force behind the fresh water in some areas. Saltwater intrusion can render water in coastal aquifers undrinkable and useless for irrigation. It can also harm ecosystems and damage infrastructure. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26491

Skylab and Mir Space Stations: In 1964, design and feasibility studies were initiated for missions that could use modified Apollo hardware for a number of possible lunar and Earth-orbital scientific and applications missions. An S-IVB stage of a Saturn V launch vehicle was outfitted completely as a workshop. The Skylab 1 Orbital Workshop with its Apollo Telescope Mount was launched into orbit May 14, 1973. The Skylab 2, 3 and 4 missions, each with three-man crews, proved that humans could live and work in space for extended periods. The Shuttle-Mir Program was a joint effort between 1994-1998 which allowed American and Russian crews to share expertise and knowledge while working together in space. As preparation for the construction of the International Space Station, Shuttle-Mir encompassed 11 space shuttle flights and 7 astronaut residencies on the Russian space station Mir. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a printable version of NASA's "Same Crew, New Ride" poster depicting an artist's conception of NASA's Commercial Crew Program CCP. The poster features a NASA astronaut in the foreground with a vehicle launching toward the International Space Station in the background. CCP is investing in the aerospace industry and helping multiple companies design and develop crew transportation systems that could be capable of flying to the space station and other low Earth orbit destinations. The program is meant to accelerate a United States-led capability to the station where critical scientific work is being performed for use in applications here on Earth. CCP is expected to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a printable version of the NASA Kennedy Space Center 2012 holiday poster. It depicts Santa Claus riding a spacecraft from NASA's Commercial Crew Program as he delivers toys all over the world for the holidays, including Astro Socks, Cosmic Soda and Magnetic boots that have been International Space Station certified. Santa also holds a model rocket for delivery and is steering his rocketship toward a stop at the space station during his deliveries. Lifting off from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Santa is taking advantage of technologies developed at Kennedy in the Ground Systems Operations and Development Program and the Launch Services Program. The same advancements that are propelling Santa through space will be used for NASA's next generation of deep space missions: the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft. The NASA insignia appears in the upper right corner. For a black-and-white coloring sheet version, go to http://go.nasa.gov/V3KLEc. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/kennedy.Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department. Credit: NASA
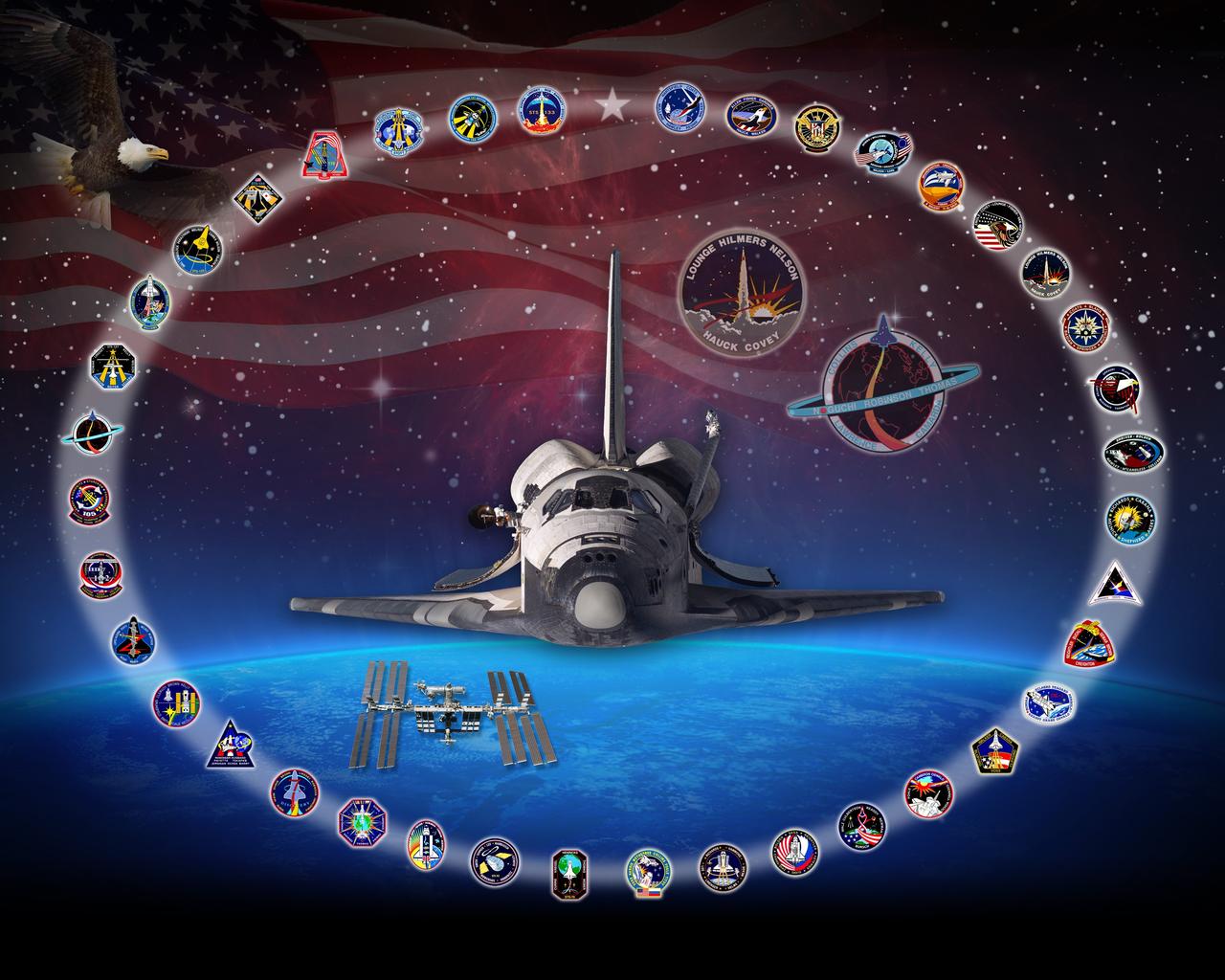

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This orbiter tribute of space shuttle Discovery, or OV-103, hangs in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Discovery’s accomplishments include the first female shuttle pilot, Eileen Collins, on STS-63, John Glenn’s legendary return to space on STS-95, and the celebration of the 100th shuttle mission with STS-92. In addition, Discovery supported a number of Department of Defense programs, satellite deploy and repair missions and 13 International Space Station construction and operation flights. The tribute features Discovery demonstrating the rendezvous pitch maneuver on approach to the International Space Station during STS-114. Having accumulated the most space shuttle flights, Discovery’s 39 mission patches are shown circling the spacecraft. The background image was taken from the Hubble Space Telescope, which launched aboard Discovery on STS-31 and serviced by Discovery on STS-82 and STS-103. The American Flag and Bald Eagle represent Discovery’s two Return-to-Flight missions -- STS-26 and STS-114 -- and symbolize Discovery’s role in returning American astronauts to space. Five orbiter tributes are on display in the firing room, representing Atlantis, Challenger, Columbia, Endeavour and Discovery. Graphic design credit: NASA/Amy Lombardo

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a version of space shuttle Discovery's orbiter tribute, or OV-103, which hangs in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Discovery’s accomplishments include the first female shuttle pilot, Eileen Collins, on STS-63, John Glenn’s legendary return to space on STS-95, and the celebration of the 100th shuttle mission with STS-92. In addition, Discovery supported a number of Department of Defense programs, satellite deploy and repair missions and 13 International Space Station construction and operation flights. The tribute features Discovery demonstrating the rendezvous pitch maneuver on approach to the International Space Station during STS-114. Having accumulated the most space shuttle flights, Discovery’s 39 mission patches are shown circling the spacecraft. The background image was taken from the Hubble Space Telescope, which launched aboard Discovery on STS-31 and serviced by Discovery on STS-82 and STS-103. The American Flag and Bald Eagle represent Discovery’s two Return-to-Flight missions -- STS-26 and STS-114 -- and symbolize Discovery’s role in returning American astronauts to space. Five orbiter tributes are on display in the firing room, representing Atlantis, Challenger, Columbia, Endeavour and Discovery. Graphic design credit: NASA/Amy Lombardo. NASA publication number: SP-2010-08-164-KSC

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a printable version of space shuttle Discovery's orbiter tribute, or OV-103, which hangs in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Discovery’s accomplishments include the first female shuttle pilot, Eileen Collins, on STS-63, John Glenn’s legendary return to space on STS-95, and the celebration of the 100th shuttle mission with STS-92. In addition, Discovery supported a number of Department of Defense programs, satellite deploy and repair missions and 13 International Space Station construction and operation flights. The tribute features Discovery demonstrating the rendezvous pitch maneuver on approach to the International Space Station during STS-114. Having accumulated the most space shuttle flights, Discovery’s 39 mission patches are shown circling the spacecraft. The background image was taken from the Hubble Space Telescope, which launched aboard Discovery on STS-31 and serviced by Discovery on STS-82 and STS-103. The American Flag and Bald Eagle represent Discovery’s two Return-to-Flight missions -- STS-26 and STS-114 -- and symbolize Discovery’s role in returning American astronauts to space. Five orbiter tributes are on display in the firing room, representing Atlantis, Challenger, Columbia, Endeavour and Discovery. Graphic design credit: NASA/Amy Lombardo. NASA publication number: SP-2010-08-164-KSC
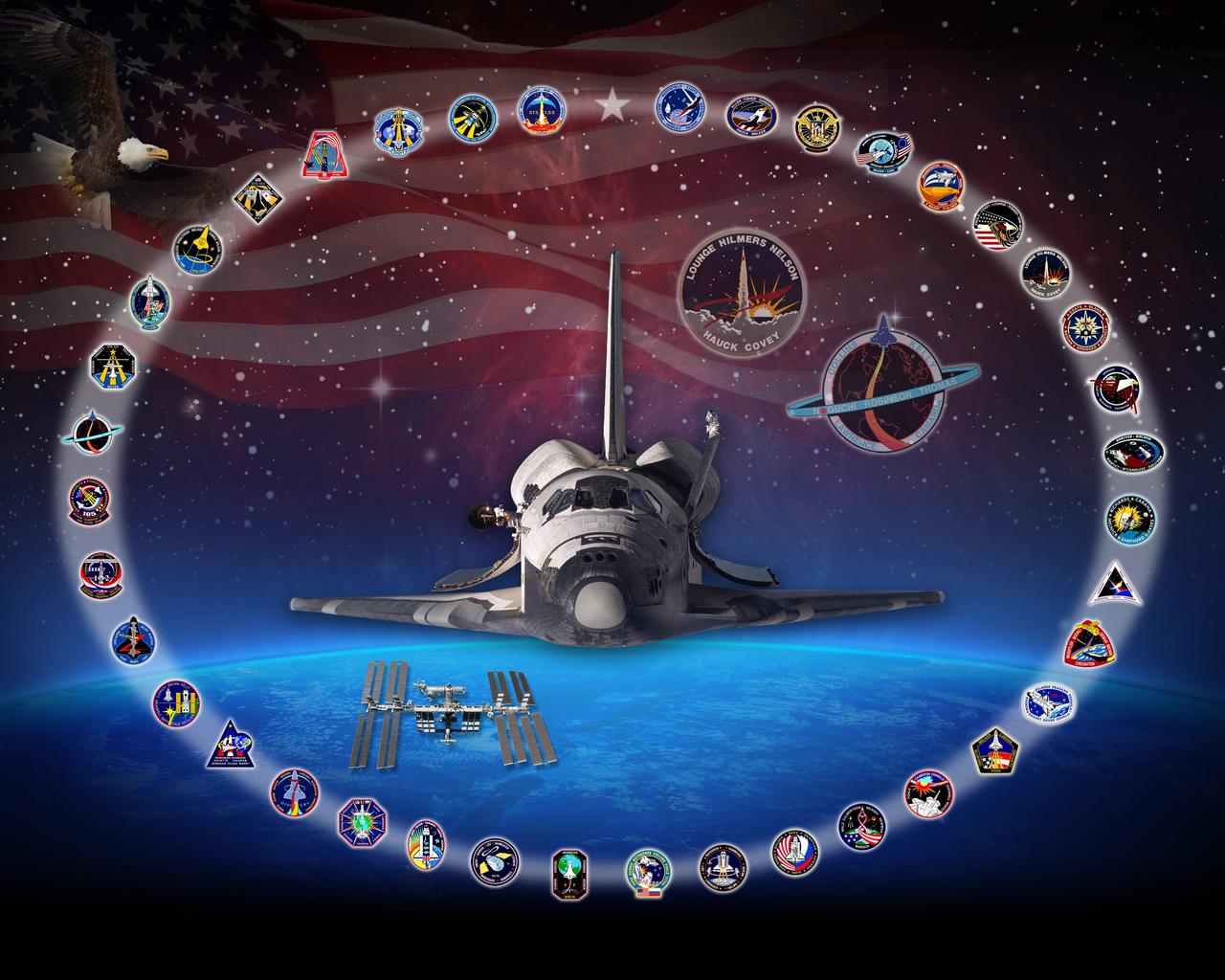

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This orbiter tribute of space shuttle Discovery, or OV-103, hangs in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In 2011, the tribute was updated to reflect the crew member change on Discovery's final mission -- STS-133. Steve Bowen replaced Tim Kopra as a mission specialist on STS-133, after Kopra was injured in a bicycle accident that prevented him from flying into space. Discovery’s accomplishments include the first female shuttle pilot, Eileen Collins, on STS-63, John Glenn’s legendary return to space on STS-95, and the celebration of the 100th shuttle mission with STS-92. In addition, Discovery supported a number of Department of Defense programs, satellite deploy and repair missions and 13 International Space Station construction and operation flights. The tribute features Discovery demonstrating the rendezvous pitch maneuver on approach to the International Space Station during STS-114. Having accumulated the most space shuttle flights, Discovery’s 39 mission patches are shown circling the spacecraft. The background image was taken from the Hubble Space Telescope, which launched aboard Discovery on STS-31 and serviced by Discovery on STS-82 and STS-103. The American Flag and Bald Eagle represent Discovery’s two Return-to-Flight missions -- STS-26 and STS-114 -- and symbolize Discovery’s role in returning American astronauts to space. Five orbiter tributes are on display in the firing room, representing Atlantis, Challenger, Columbia, Endeavour and Discovery. Graphic design credit: NASA/Amy Lombardo. NASA publication number: SP-2010-08-164-KSC

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a version of space shuttle Discovery's orbiter tribute, or OV-103, which hangs in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In 2011, the tribute was updated to reflect the crew member change on Discovery's final mission -- STS-133. Steve Bowen replaced Tim Kopra as a mission specialist on STS-133, after Kopra was injured in a bicycle accident that prevented him from flying into space. Discovery’s accomplishments include the first female shuttle pilot, Eileen Collins, on STS-63, John Glenn’s legendary return to space on STS-95, and the celebration of the 100th shuttle mission with STS-92. In addition, Discovery supported a number of Department of Defense programs, satellite deploy and repair missions and 13 International Space Station construction and operation flights. The tribute features Discovery demonstrating the rendezvous pitch maneuver on approach to the International Space Station during STS-114. Having accumulated the most space shuttle flights, Discovery’s 39 mission patches are shown circling the spacecraft. The background image was taken from the Hubble Space Telescope, which launched aboard Discovery on STS-31 and serviced by Discovery on STS-82 and STS-103. The American Flag and Bald Eagle represent Discovery’s two Return-to-Flight missions -- STS-26 and STS-114 -- and symbolize Discovery’s role in returning American astronauts to space. Five orbiter tributes are on display in the firing room, representing Atlantis, Challenger, Columbia, Endeavour and Discovery. Graphic design credit: NASA/Amy Lombardo. NASA publication number: SP-2010-08-164-KSC

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a printable version of space shuttle Discovery's orbiter tribute, or OV-103, which hangs in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In 2011, the tribute was updated to reflect the crew member change on Discovery's final mission -- STS-133. Steve Bowen replaced Tim Kopra as a mission specialist on STS-133, after Kopra was injured in a bicycle accident that prevented him from flying into space. Discovery’s accomplishments include the first female shuttle pilot, Eileen Collins, on STS-63, John Glenn’s legendary return to space on STS-95, and the celebration of the 100th shuttle mission with STS-92. In addition, Discovery supported a number of Department of Defense programs, satellite deploy and repair missions and 13 International Space Station construction and operation flights. The tribute features Discovery demonstrating the rendezvous pitch maneuver on approach to the International Space Station during STS-114. Having accumulated the most space shuttle flights, Discovery’s 39 mission patches are shown circling the spacecraft. The background image was taken from the Hubble Space Telescope, which launched aboard Discovery on STS-31 and serviced by Discovery on STS-82 and STS-103. The American Flag and Bald Eagle represent Discovery’s two Return-to-Flight missions -- STS-26 and STS-114 -- and symbolize Discovery’s role in returning American astronauts to space. Five orbiter tributes are on display in the firing room, representing Atlantis, Challenger, Columbia, Endeavour and Discovery. Graphic design credit: NASA/Amy Lombardo. NASA publication number: SP-2010-08-164-KSC
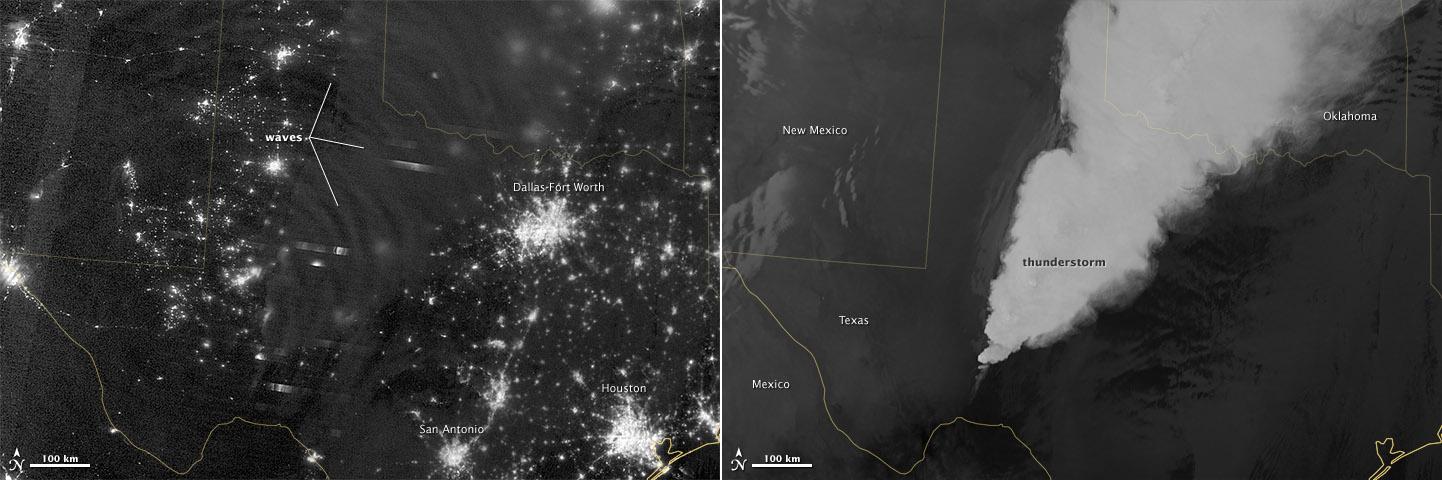
In April 2012, waves in Earth’s “airglow” spread across the nighttime skies of northern Texas like ripples in a pond. In this case, the waves were provoked by a massive thunderstorm. Airglow is a layer of nighttime light emissions caused by chemical reactions high in Earth’s atmosphere. A variety of reactions involving oxygen, sodium, ozone and nitrogen result in the production of a very faint amount of light. In fact, it’s approximately one billion times fainter than sunlight (~10-11 to 10-9 W·cm-2· sr-1). This chemiluminescence is similar to the chemical reactions that light up a glow stick or glow-in-the-dark silly putty. The “day-night band,” of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured these glowing ripples in the night sky on April 15, 2012 (top image). The day-night band detects lights over a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses highly sensitive electronics to observe low light signals. (The absolute minimum signals detectable are at the levels of nightglow emission.) The lower image shows the thunderstorm as observed by a thermal infrared band on VIIRS. This thermal band, which is sensitive only to heat emissions (cold clouds appear white), is not sensitive to the subtle visible-light wave structures seen by the day-night band. Technically speaking, airglow occurs at all times. During the day it is called “dayglow,” at twilight “twilightglow,” and at night “nightglow.” There are slightly different processes taking place in each case, but in the image above the source of light is nightglow. The strongest nightglow emissions are mostly constrained to a relatively thin layer of atmosphere between 85 and 95 kilometers (53 and 60 miles) above the Earth’s surface. Little emission occurs below this layer since there’s a higher concentration of molecules, allowing for dissipation of chemical energy via collisions rather than light production. Likewise, little emission occurs above that layer because the atmospheric density is so tenuous that there are too few light-emitting reactions to yield an appreciable amount of light. Suomi NPP is in orbit around Earth at 834 kilometers (about 518 miles), well above the nightglow layer. The day-night band imagery therefore contains signals from the direction upward emission of the nightglow layer and the reflection of the downward nightglow emissions by clouds and the Earth’s surface. The presence of these nightglow waves is a graphic visualization of the usually unseen energy transfer processes that occur continuously between the lower and upper atmosphere. While nightglow is a well-known phenomenon, it’s not typically considered by Earth-viewing meteorological sensors. In fact, scientists were surprised at Suomi NPP’s ability to detect it. During the satellite’s check-out procedure, this unanticipated source of visible light was thought to indicate a problem with the sensor until scientists realized that what they were seeing was the faintest of light in the darkness of night. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Aries Keck and Steve Miller. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79817" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space</a></b>