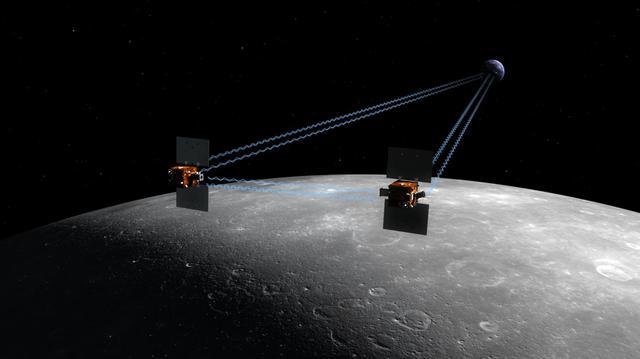
The Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL, mission will fly twin spacecraft in tandem orbits around the moon to measure its gravity field in unprecedented detail. GRAIL is a part of NASA Discovery Program.
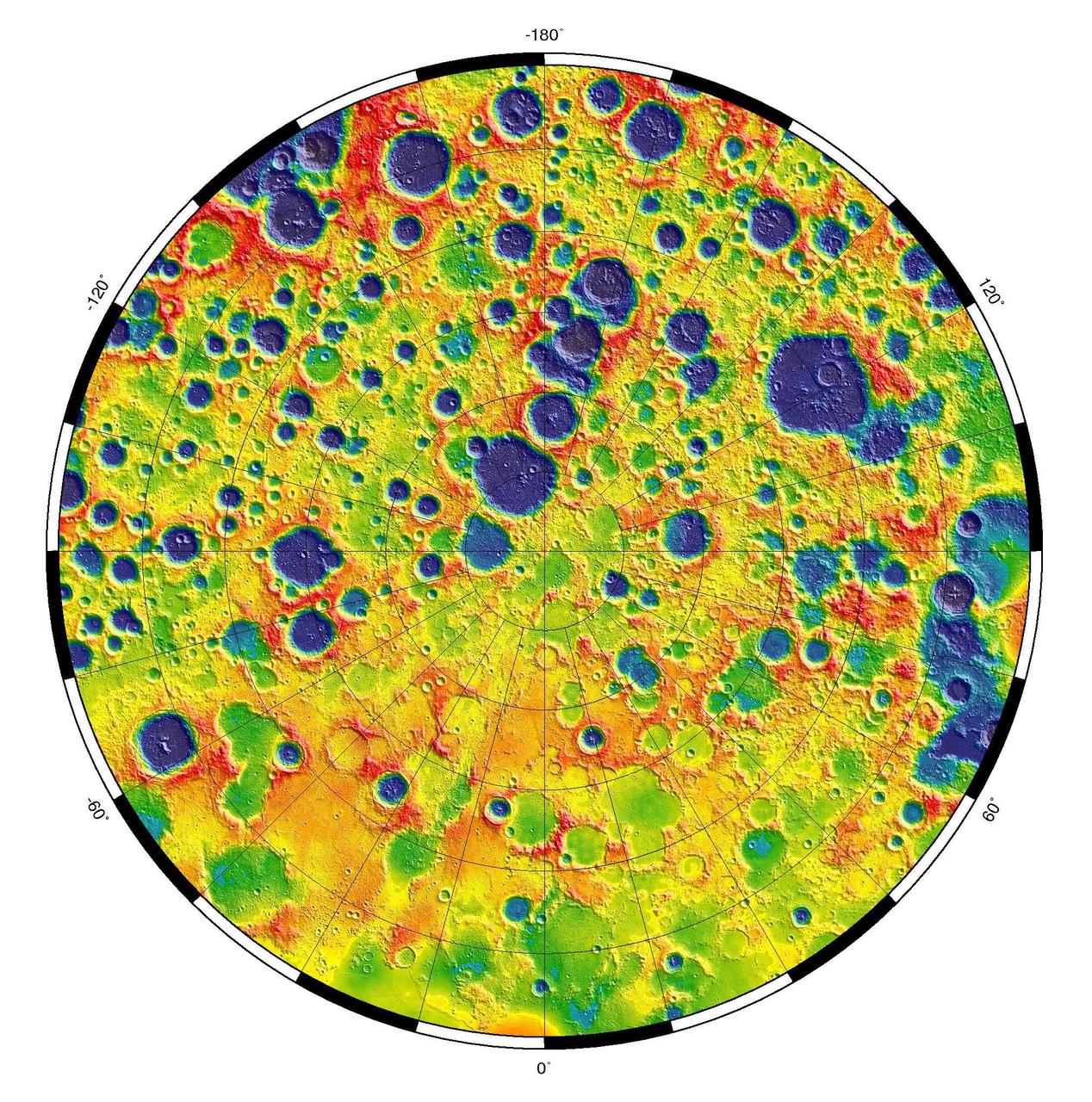
This is a polar stereographic map of gravity of the north polar region of the moon from the Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory GRAIL mission. The map displays the region from latitude 60 north to the pole.
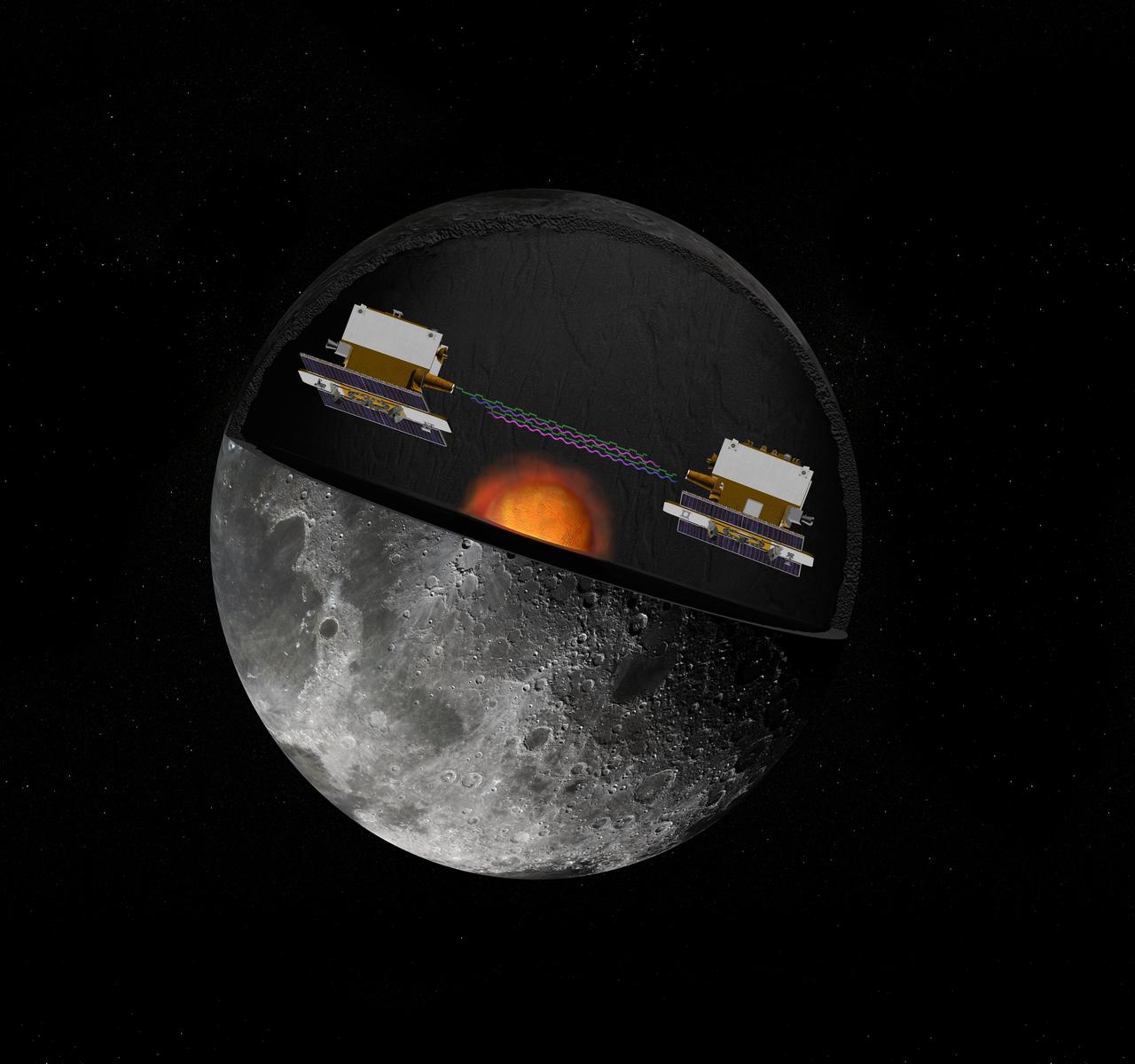

The Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory GRAIL mission utilizes the technique of twin spacecraft flying in formation with a known altitude above the lunar surface and known separation distance to investigate the gravity field of the moon.
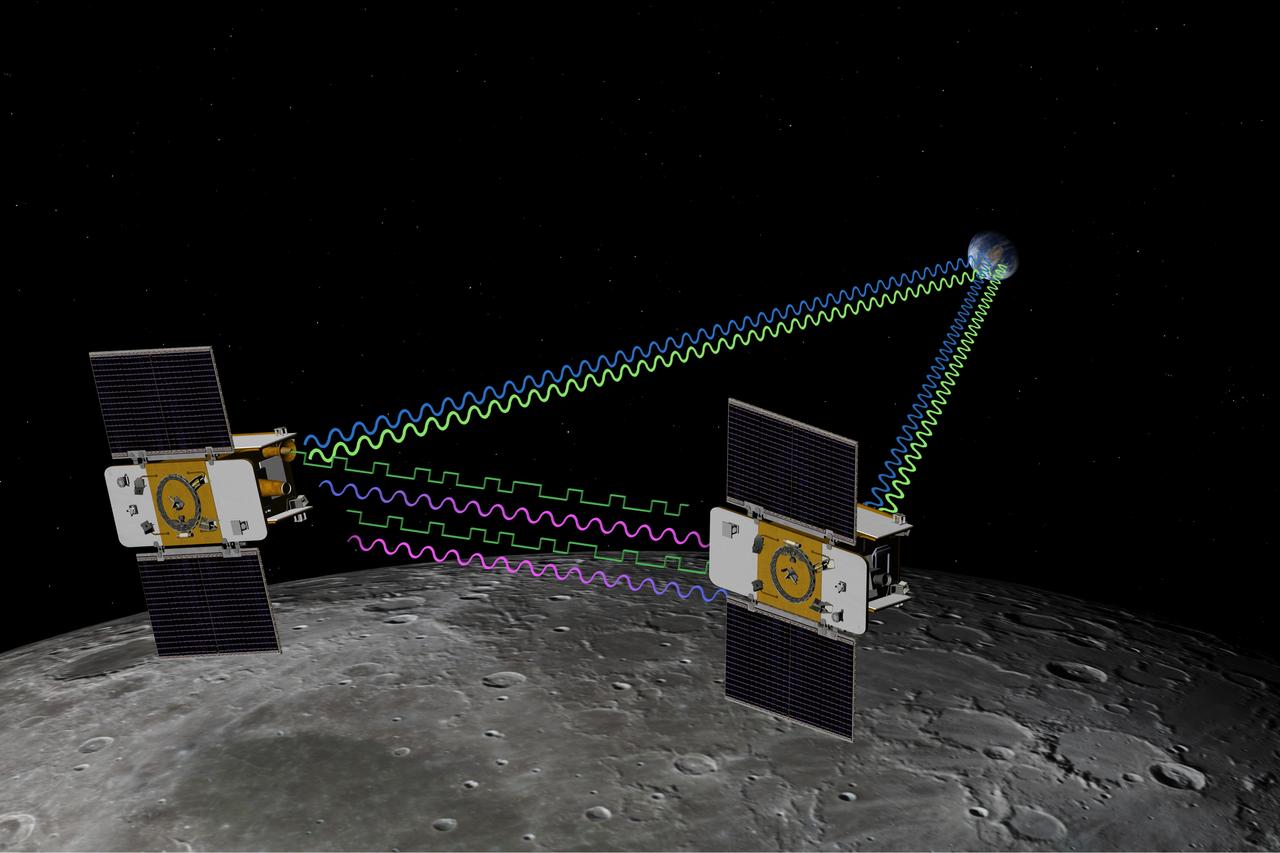

The Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory GRAIL mission utilizes the technique of twin spacecraft flying in formation with a known altitude above the lunar surface and known separation distance to investigate the gravity field of the moon.
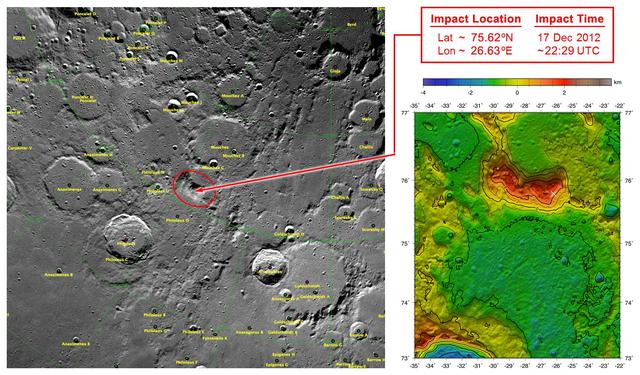
These maps of Earth moon highlight the region where the twin spacecraft of NASA Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory GRAIL mission will impact on Dec. 17, marking the end of its successful endeavor to map the moon gravity.
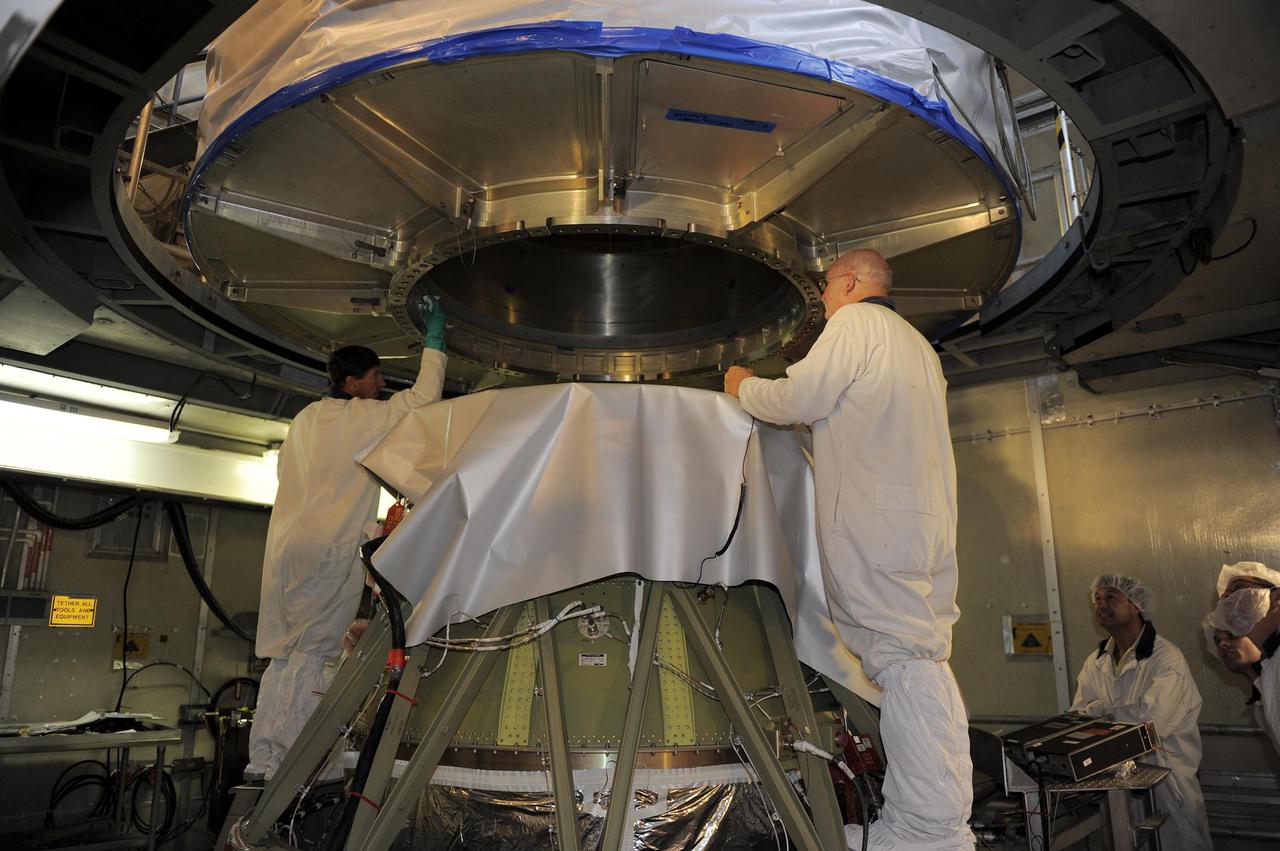

NASA twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory GRAIL spacecraft are lowered onto the second stage of their Delta II launch vehicle. At top is the spacecraft adapter ring which holds the two lunar probes in their side-by-side launch configuration.

These side-by-side, 3-D comparisons depict the unnamed lunar mountain targeted by the NASA Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory GRAIL mission for controlled impact of the Ebb and Flow spacecraft.
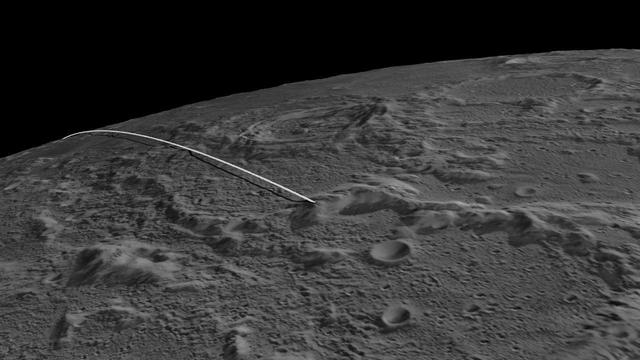
This image shows the final flight path for NASA twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory GRAIL mission spacecraft, which will impact the moon on Dec. 17, 2012, around 2:28 p.m. PST.
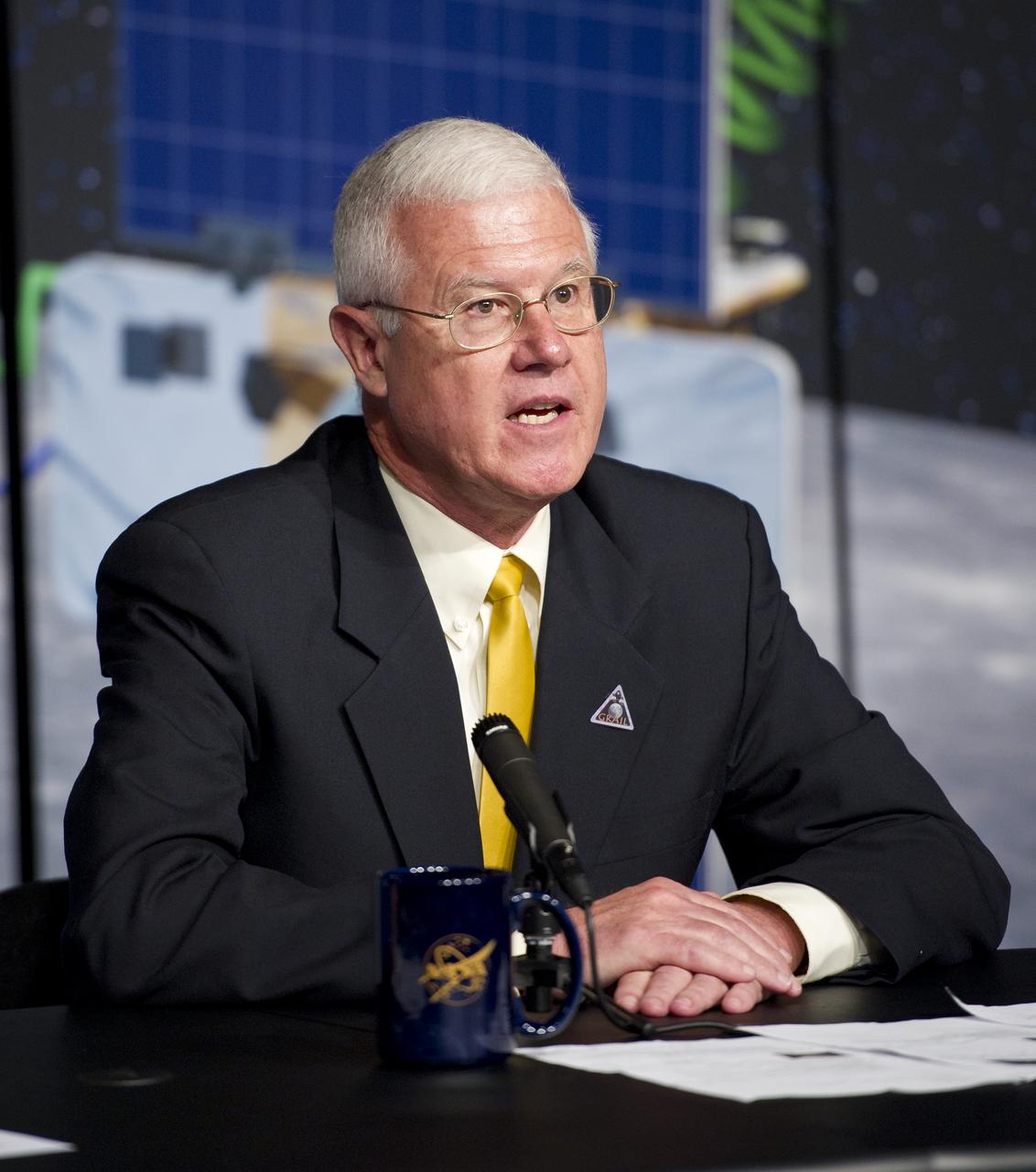

David Lehman, GRAIL project manager, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., speaks at a press conference about the upcoming launch to the moon of the Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission, Thursday, Aug. 25, 2011 in Washington. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. The mission will place two spacecraft into the same orbit around the moon which will gather information about the its gravitational field enabling scientists to create a high-resolution map. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
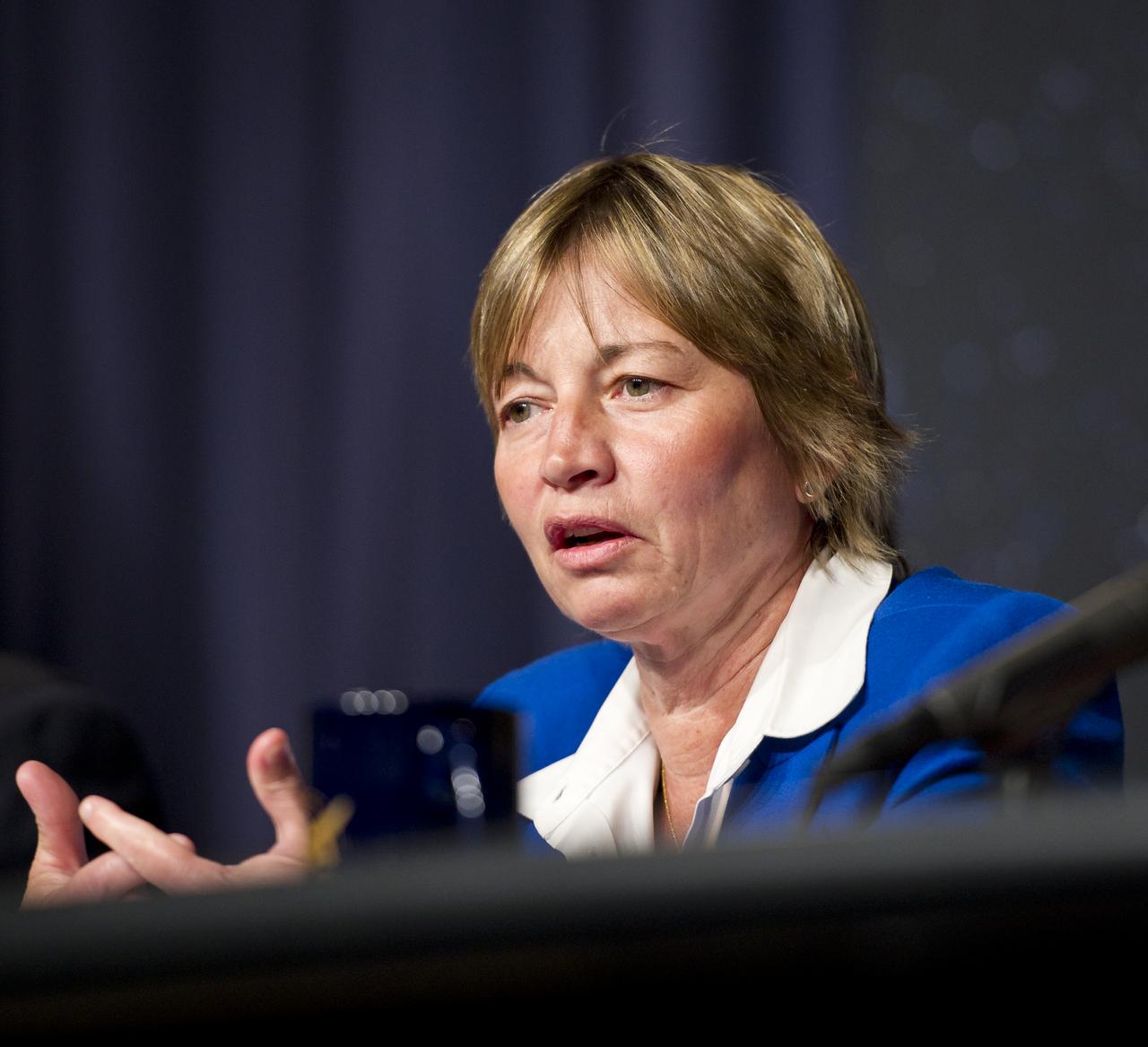

Maria Zuber, GRAIL principal investigator, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, answers a reporter's question at a press briefing about the upcoming launch to the moon of the Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission, Thursday, Aug. 25, 2011 in Washington. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. The mission will place two spacecraft into the same orbit around the moon which will gather information about the its gravitational field enabling scientists to create a high-resolution map. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
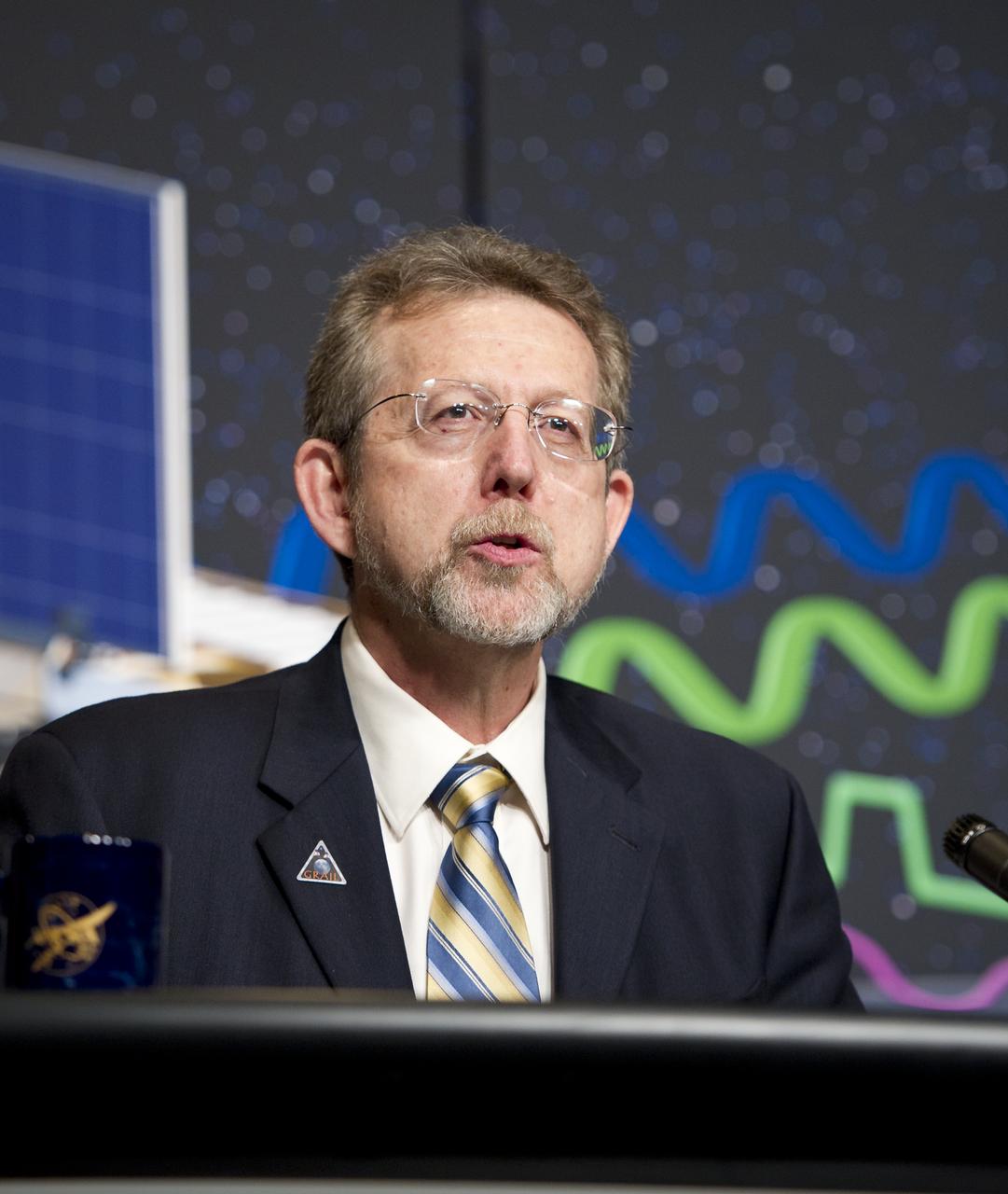

Jim Green, director, Planetary Science Division at NASA Headquarters, speaks at a press conference about the upcoming launch to the moon of the Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission, Thursday, Aug. 25, 2011 in Washington. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. The mission will place two spacecraft into the same orbit around the moon which will gather information about the its gravitational field enabling scientists to create a high-resolution map. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
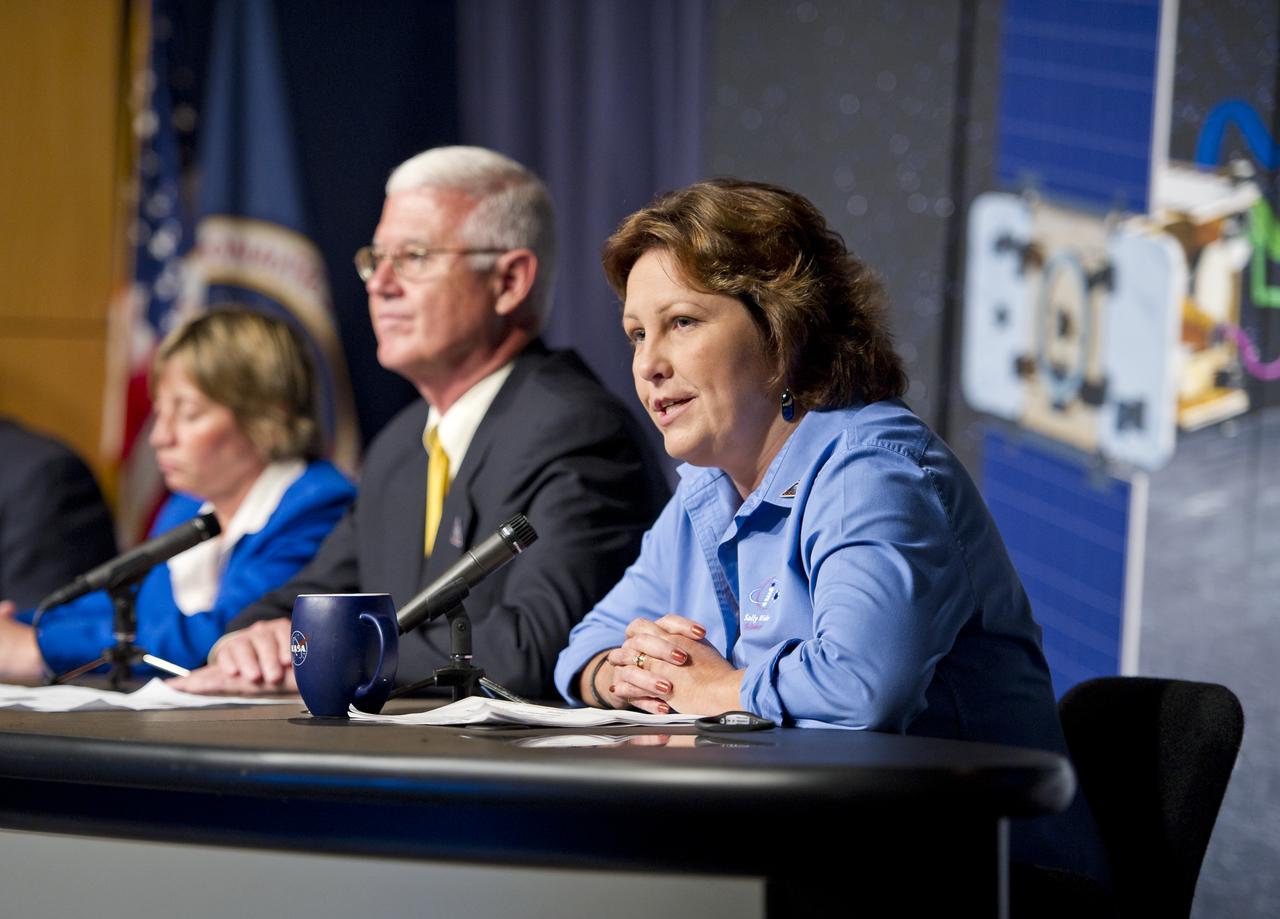

Leesa Hubbard, teacher in residence, Sally Ride Science, San Diego, speaks at a press conference about the upcoming launch to the moon of the Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission, Thursday, Aug. 25, 2011 in Washington. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. The mission will place two spacecraft into the same orbit around the moon which will gather information about the its gravitational field enabling scientists to create a high-resolution map. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Jim Green (left), director, Planetary Science Division at NASA Headquarters, speaks at a press conference about the upcoming launch to the moon of the Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission, Thursday, Aug. 25, 2011 in Washington. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. The mission will place two spacecraft into the same orbit around the moon which will gather information about the its gravitational field enabling scientists to create a high-resolution map. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
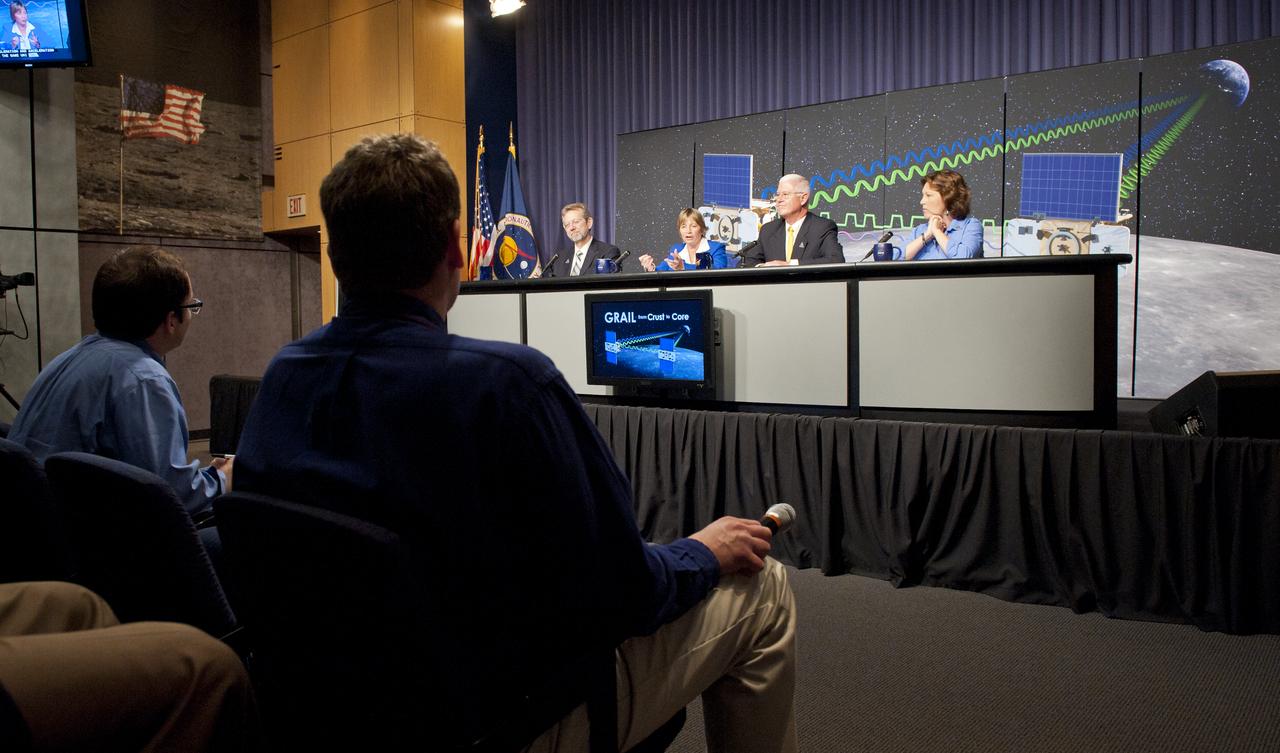

On the panel from right: Leesa Hubbard, teacher in residence, Sally Ride Science, San Diego; David Lehman, GRAIL project manager, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.; Maria Zuber, GRAIL principal investigator, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge and Jim Green, director, Planetary Science Division, NASA Headquarters, Washington are seen at a press briefing to discuss the upcoming launch to the moon of the Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission, Thursday, Aug. 25, 2011 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
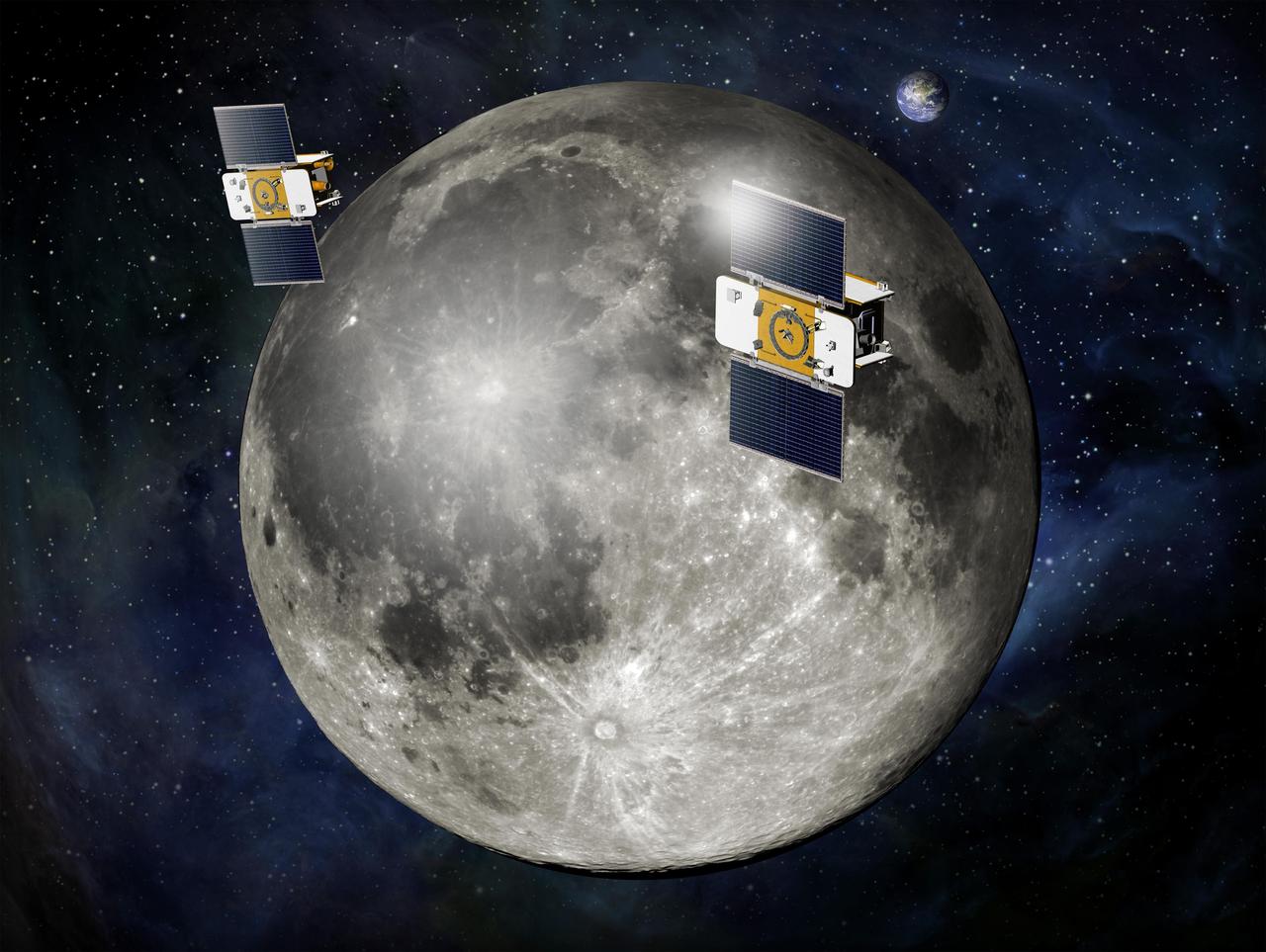

Using a precision formation-flying technique, NASA twin GRAIL spacecraft will map the moon gravity field. This is an artist concept.
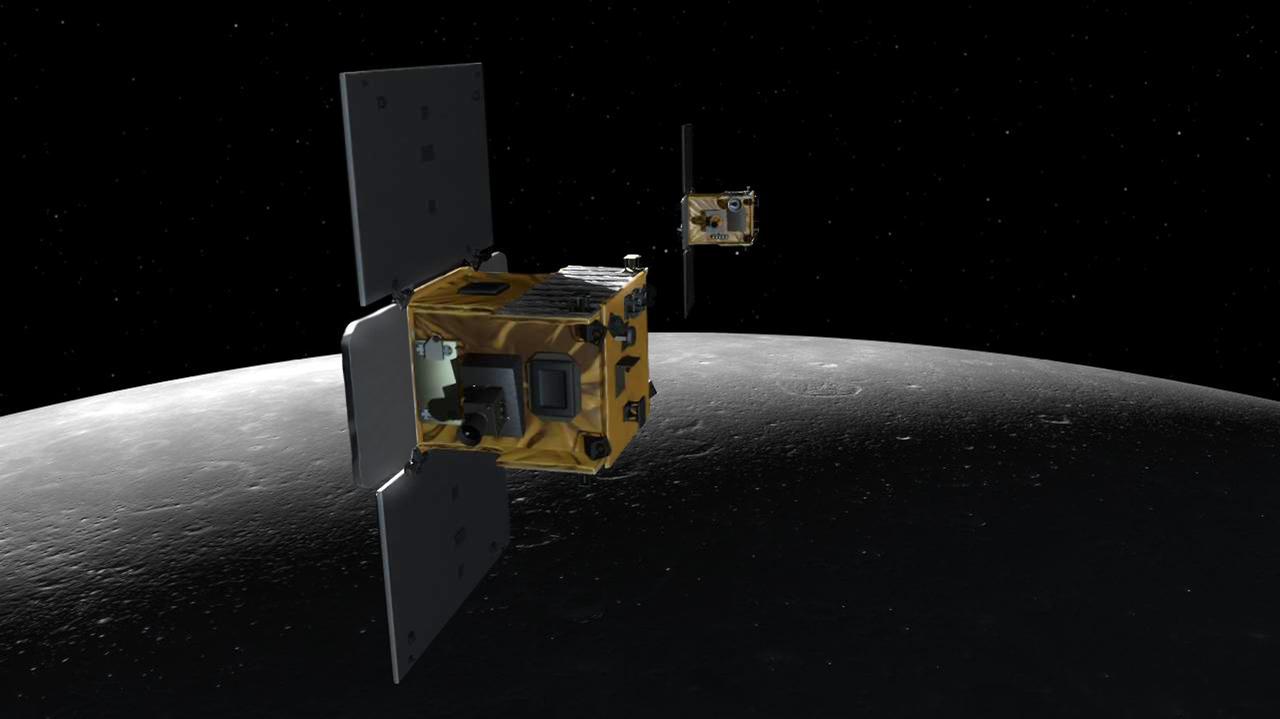

An artist depiction of the twin spacecraft Ebb and Flow that comprise NASA GRAIL mission. As Ebb and Flow fly over areas of greater and lesser gravity surface features can influence the distance between the two spacecraft.
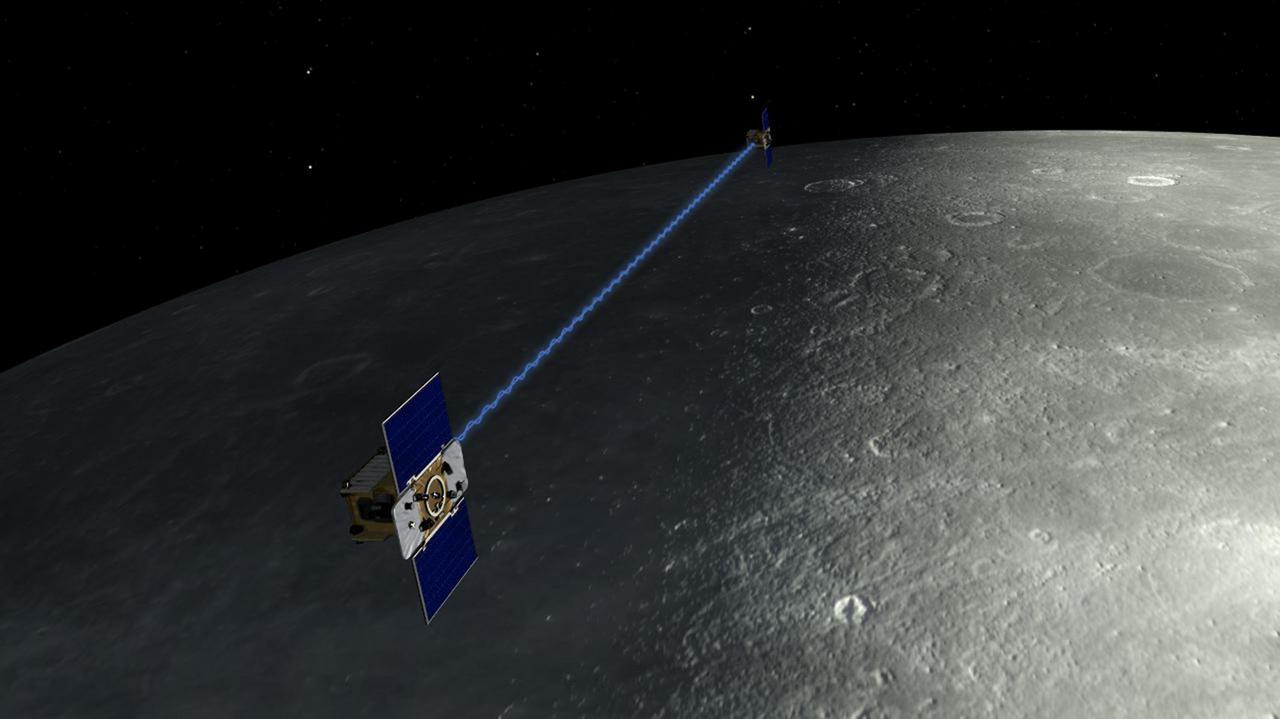

An artist depiction of the twin spacecraft that comprise NASA GRAIL mission. During the GRAIL mission science phase, spacecraft Ebb and Flow transmit radio signals precisely defining the distance between them as they orbit the moon in formation.
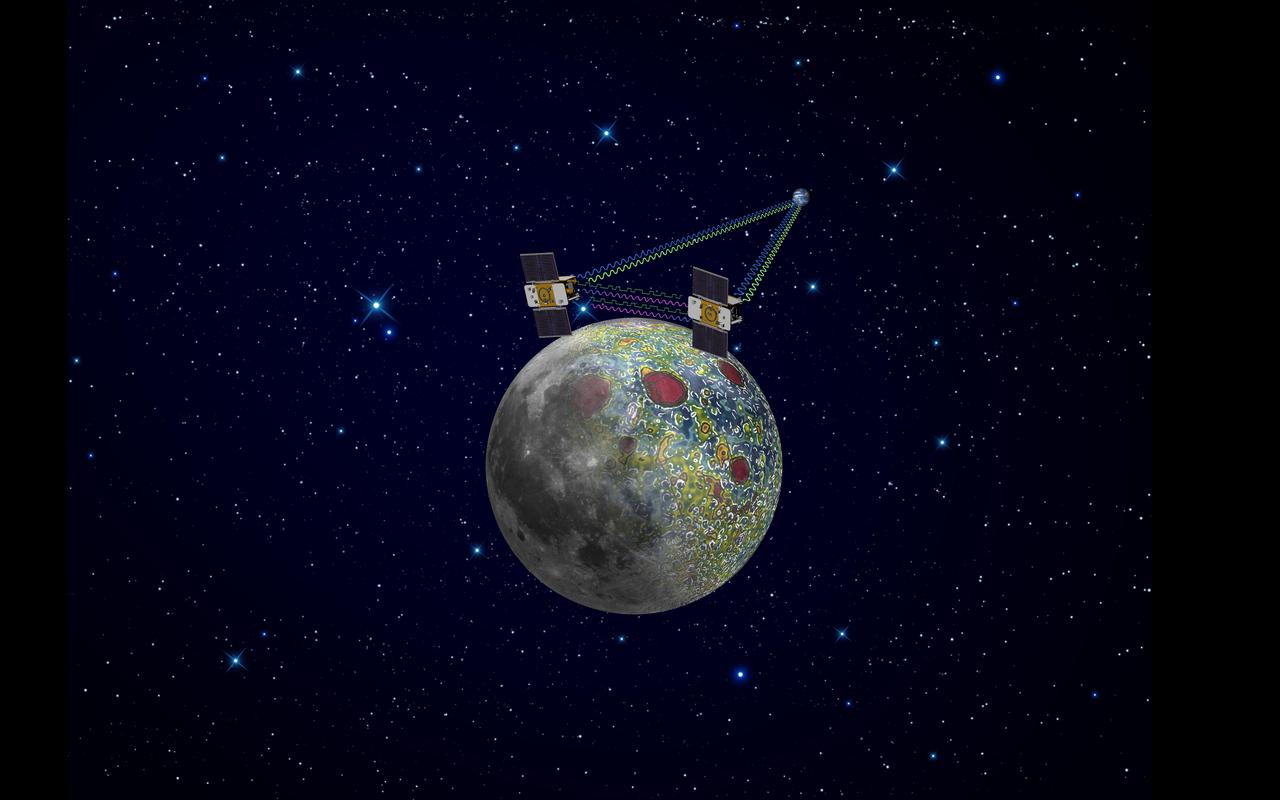

Using a precision formation-flying technique, the twin GRAIL spacecraft maps the moon gravity field, as depicted in this artist rendering.
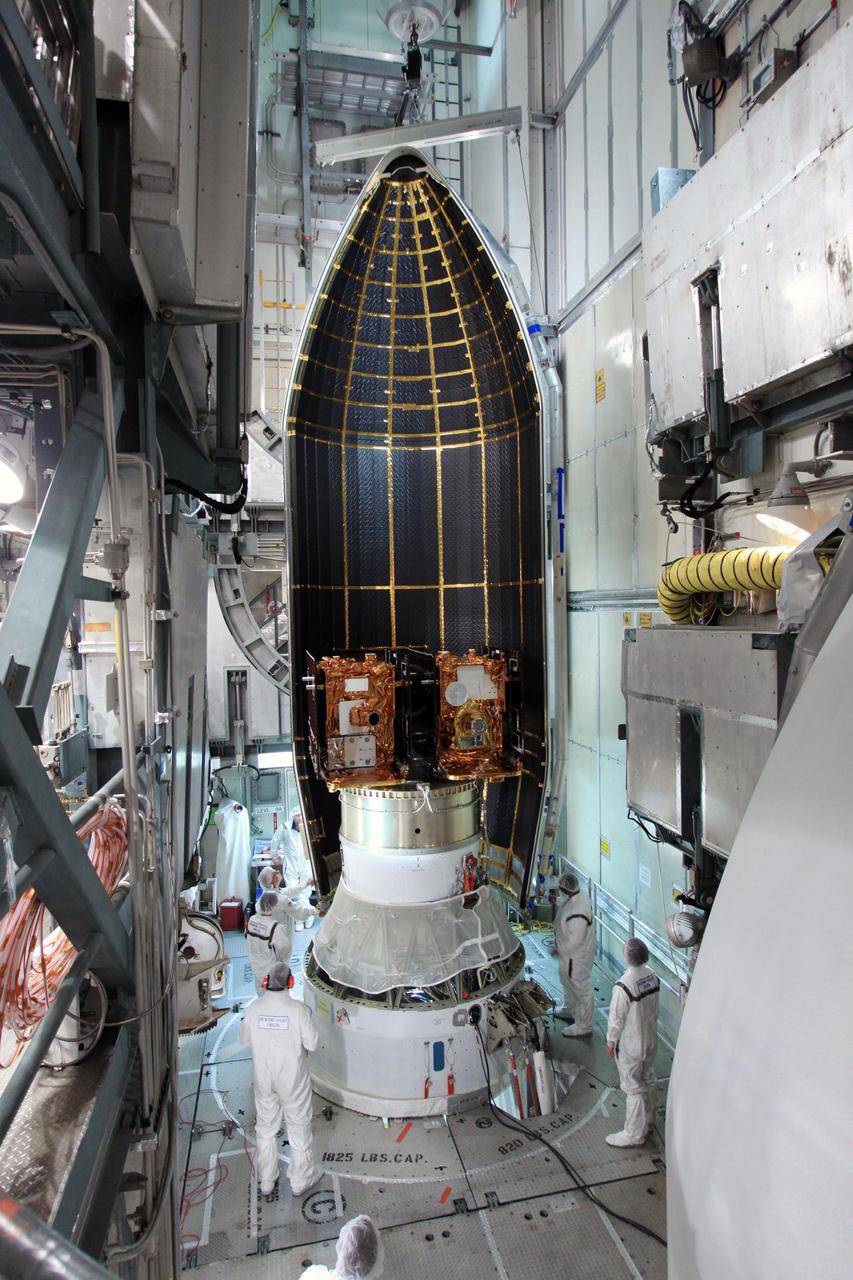

Spacecraft technicians monitor the movement of a section of the clamshell-shaped Delta payload fairing as it encloses NASA twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory spacecraft at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Aug. 23, 2011.
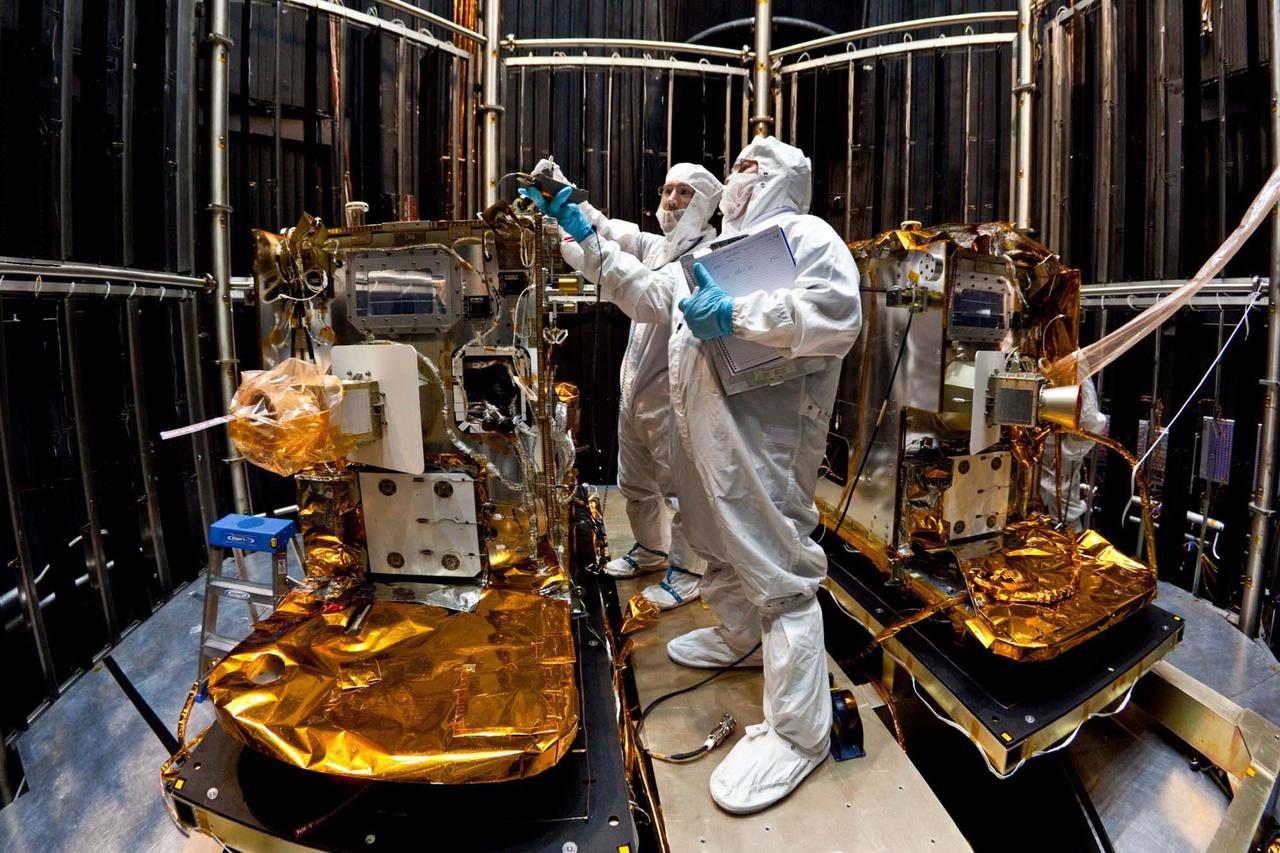

In this photo, taken April 29, 2011, technicians install lifting brackets prior to hoisting the 200-kilogram 440-pound GRAIL-A spacecraft out of vacuum chamber after testing.
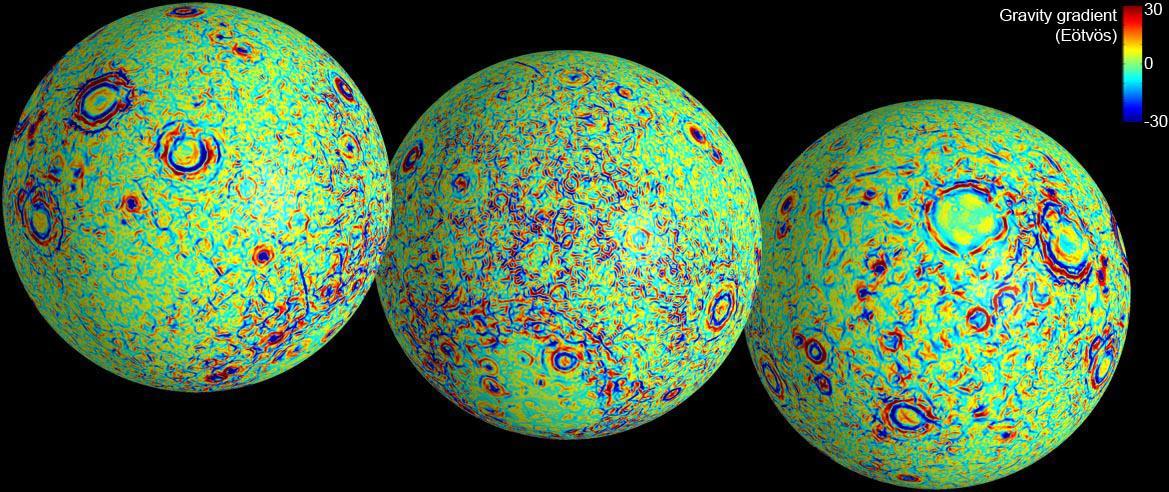
These maps of the near and far side of the moon show gravity gradients as measured by NASA GRAIL mission. Red and blue areas indicate stronger gradients due to underlying mass anomalies.
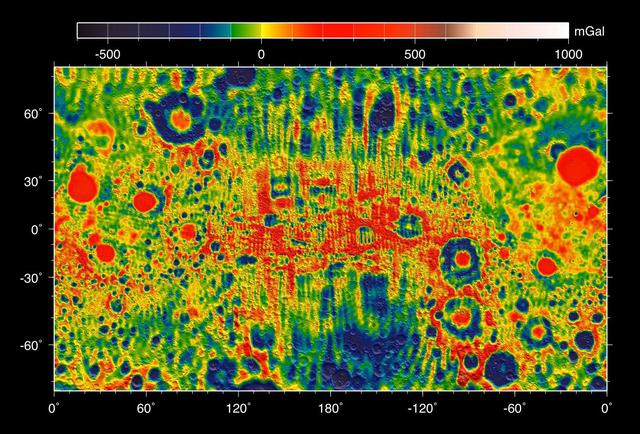
This map shows the gravity field of the moon from the Lunar Prospector mission. The viewing perspective, known as a Mercator projection, shows the far side of the moon in the center and the nearside as viewed from Earth at either side.
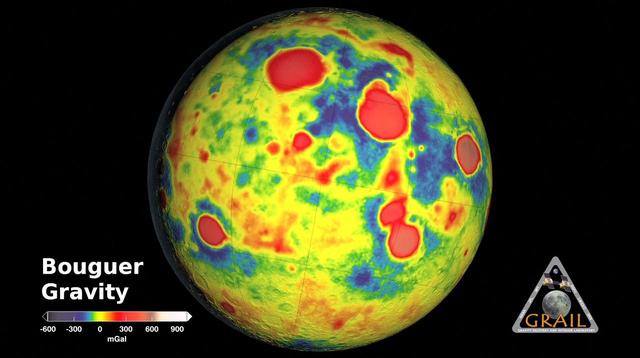
GRAIL Bouguer Gravity Moon Map
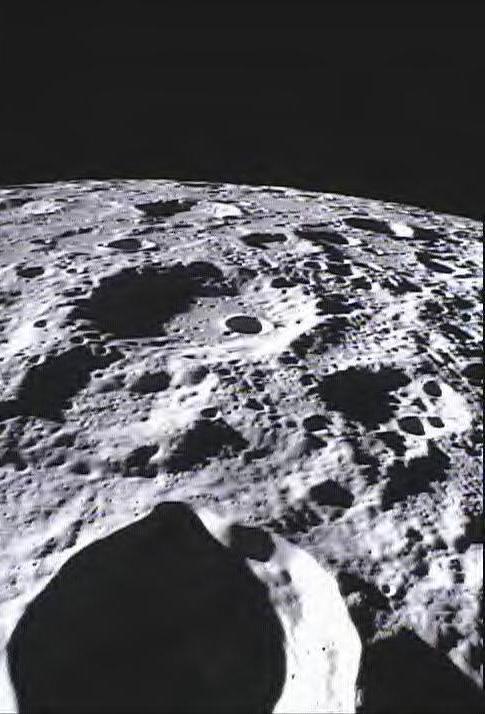

This image of the lunar surface was taken by NASA MoonKAM system onboard the Ebb spacecraft and shows Crater Poinsot located on the northern part of the moon far side.
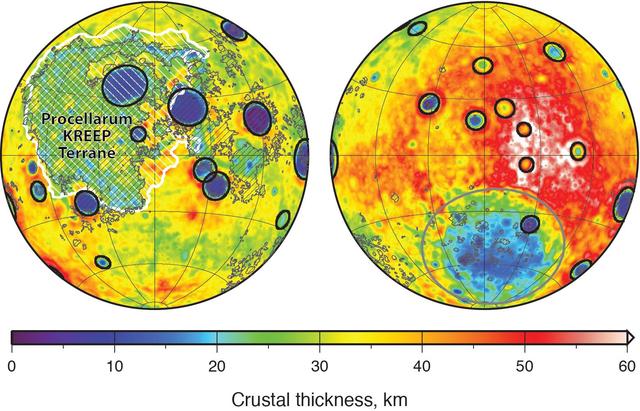
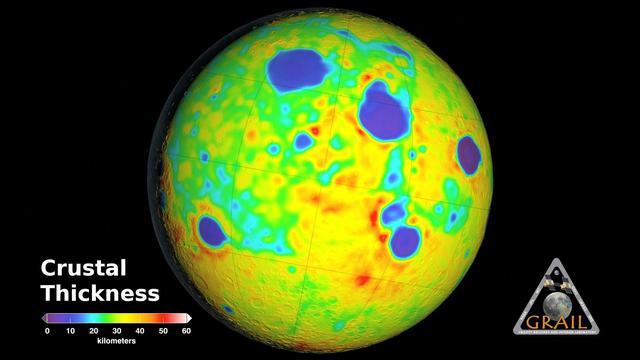
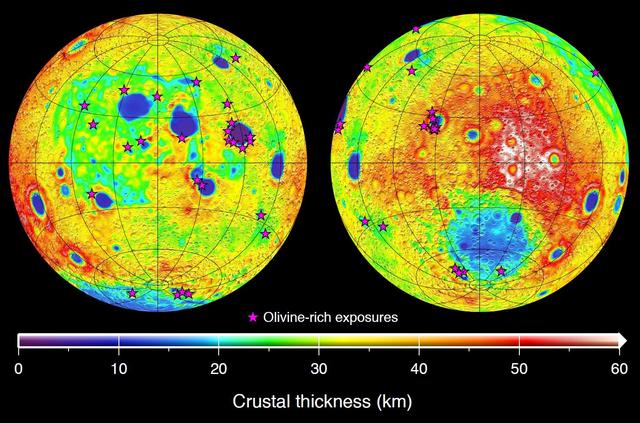
Global map of crustal thickness of the moon derived from gravity data obtained by NASA GRAIL spacecraft. The lunar near side is represented on the left hemisphere. The far side is represented in the right hemisphere.
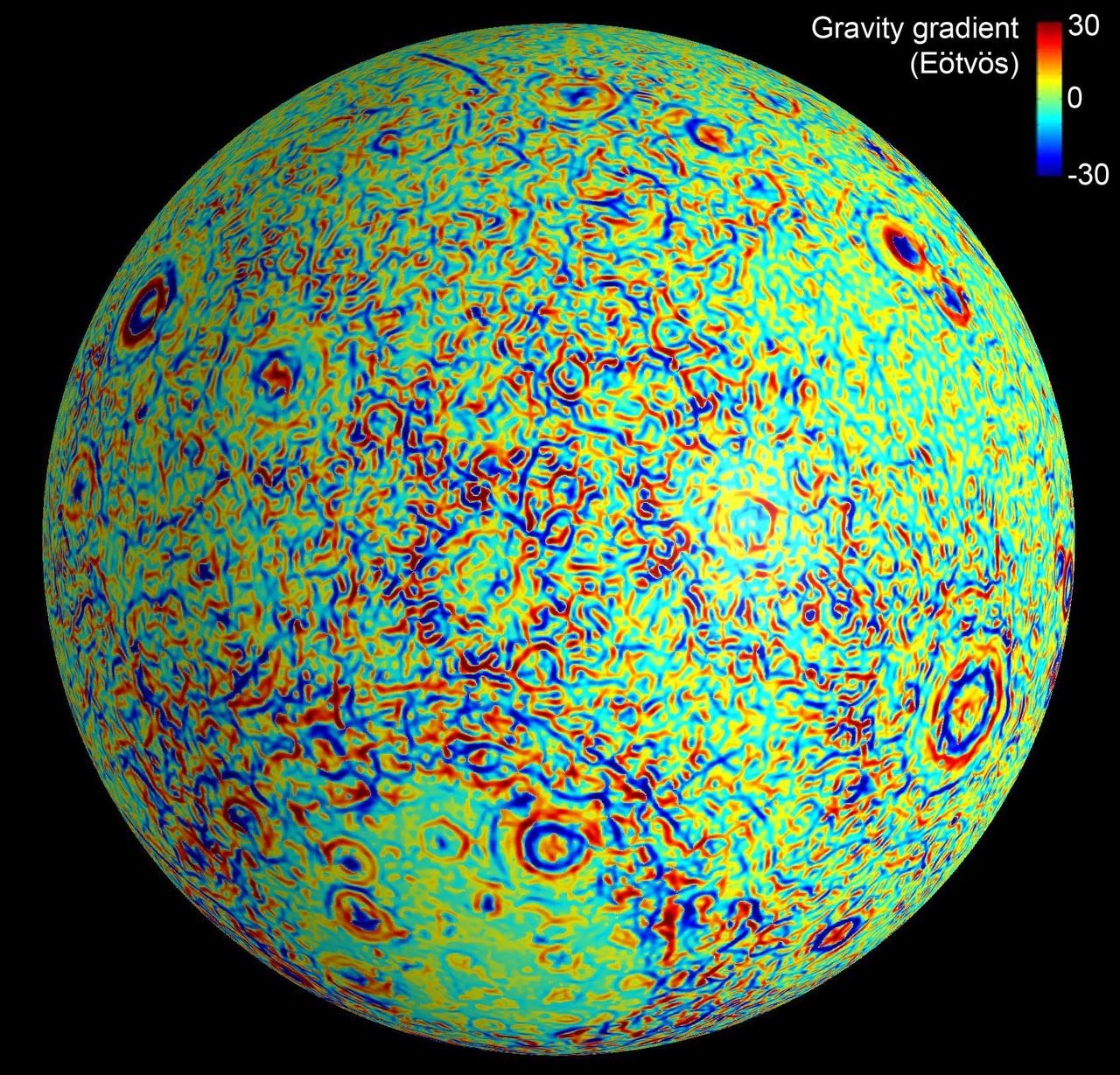
This moon map shows the gravity gradients calculated by NASA GRAIL mission. Red and blue correspond to stronger gravity gradients.
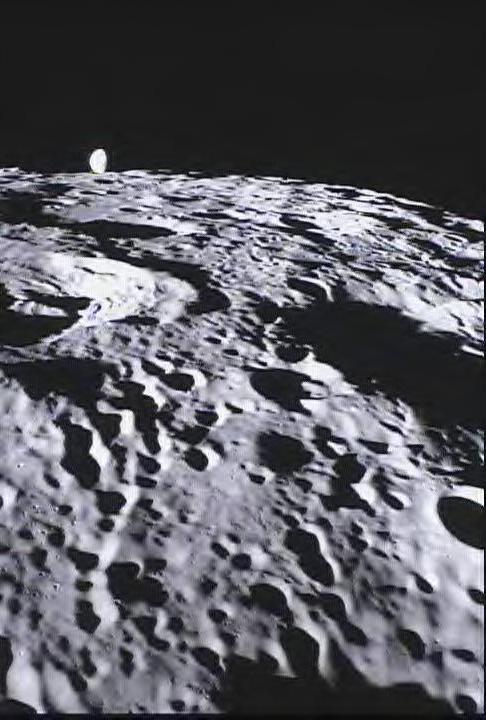

This image of the far side of the lunar surface, with Earth in the background, is of crater De Forest and was taken by NASA MoonKAM system onboard the Ebb spacecraft.
Map of Moon Crust

Mare Orientale Flyover
GRAIL Gravity Tour of the Moon
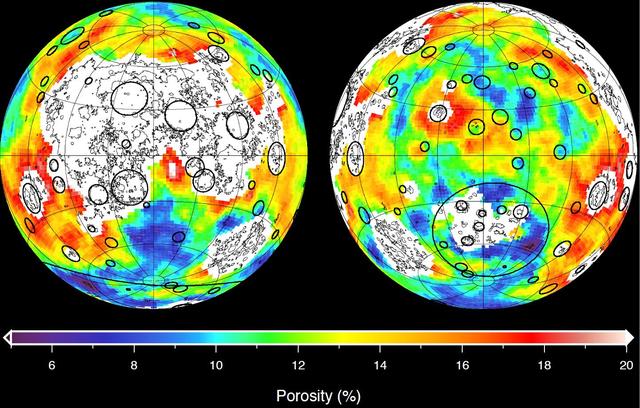
This image depicting the porosity of the lunar highland crust was derived using bulk density data from NASA GRAIL mission and independent grain density measurements from NASA Apollo moon mission samples as well as orbital remote-sensing data.
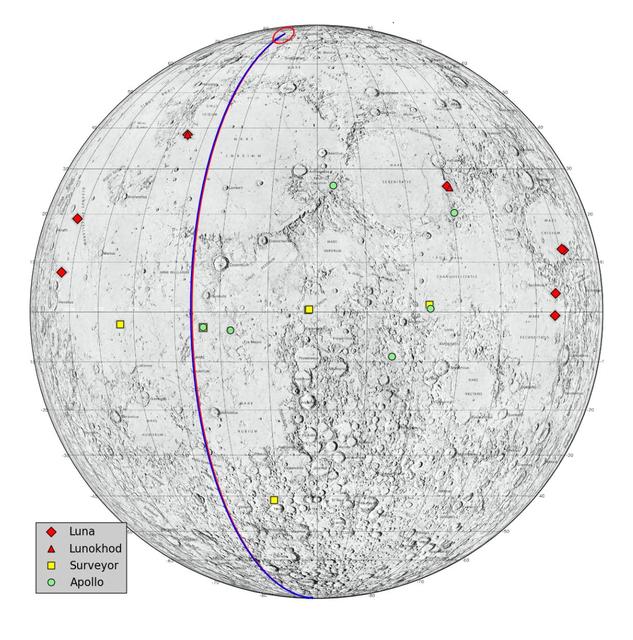
This graphic highlights locations on the moon NASA considers lunar heritage sites and the path NASA Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory spacecraft will take on their final flight.
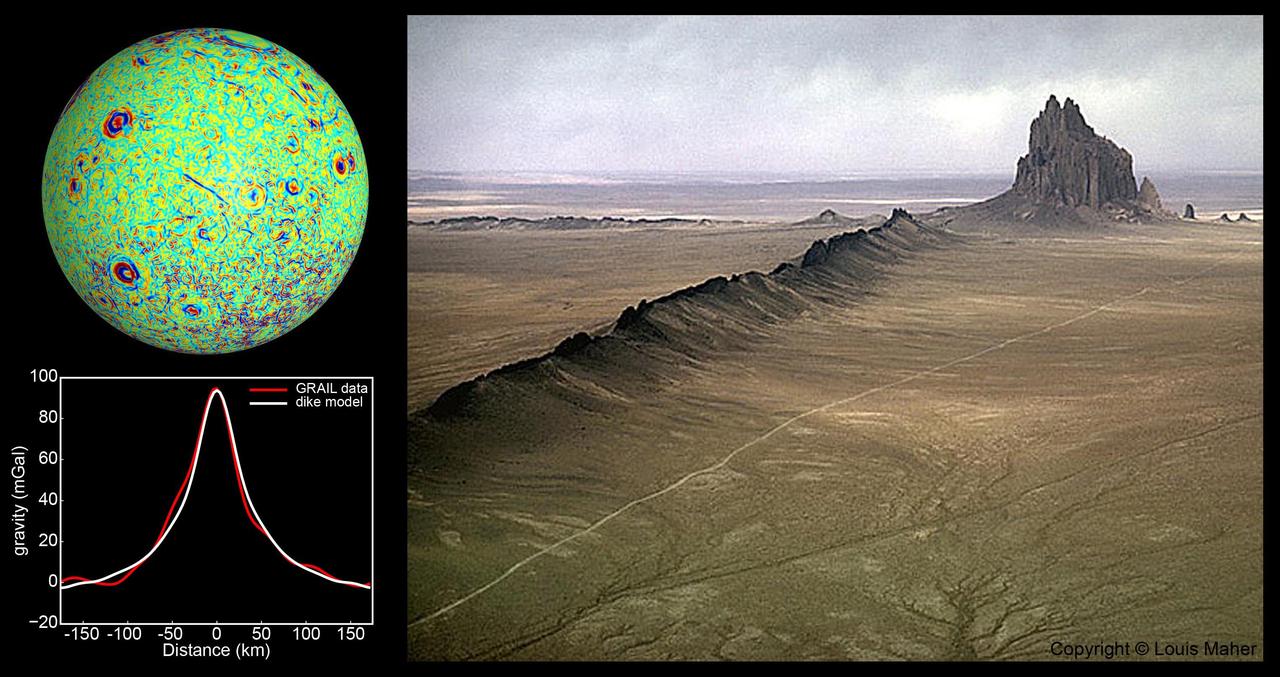
A profile across one of the linear gravity anomalies found by NASA GRAIL mission shows that it has higher gravity than the surroundings.
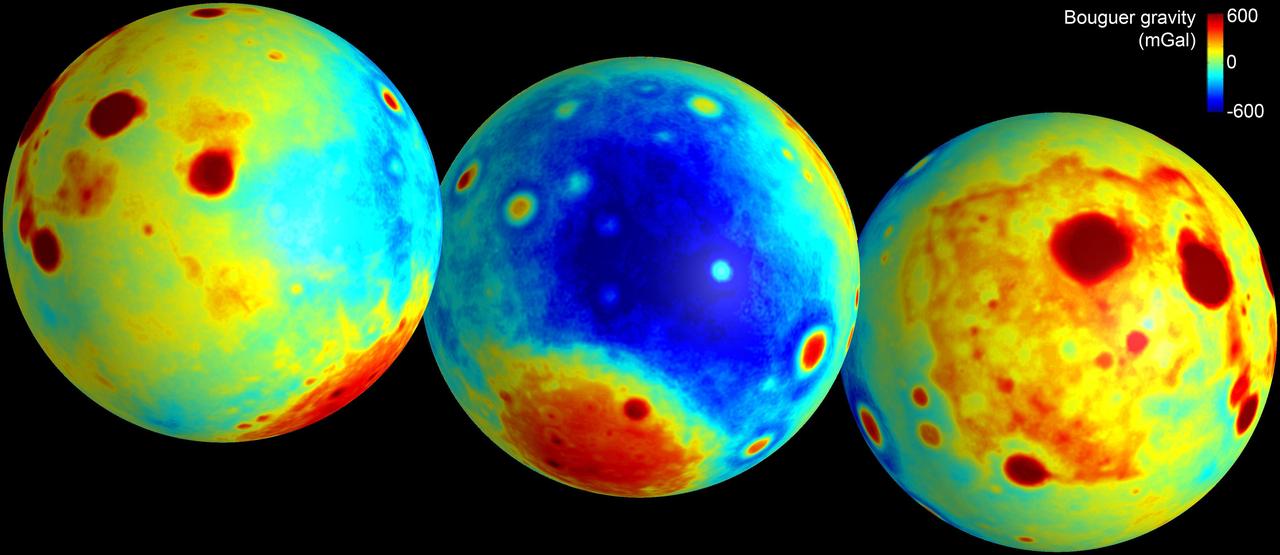
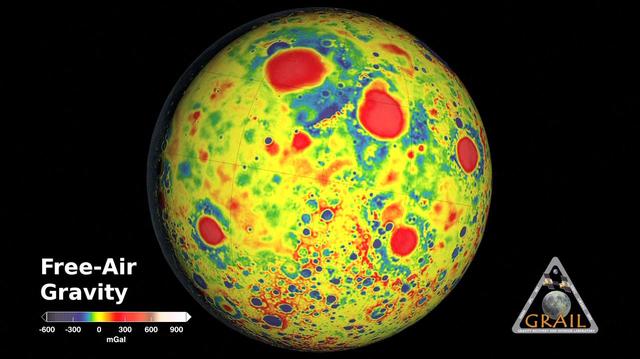
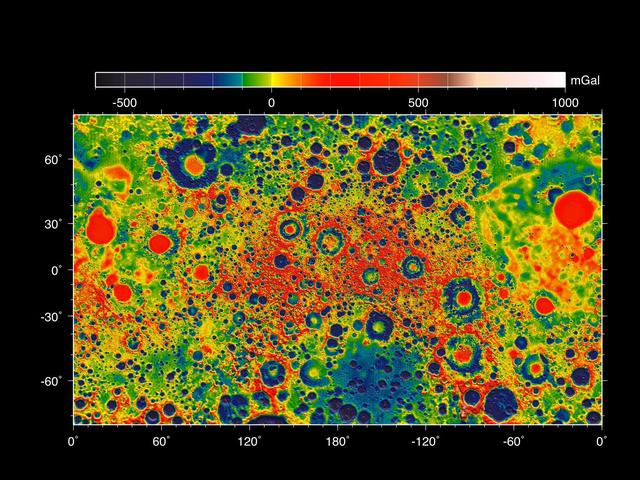
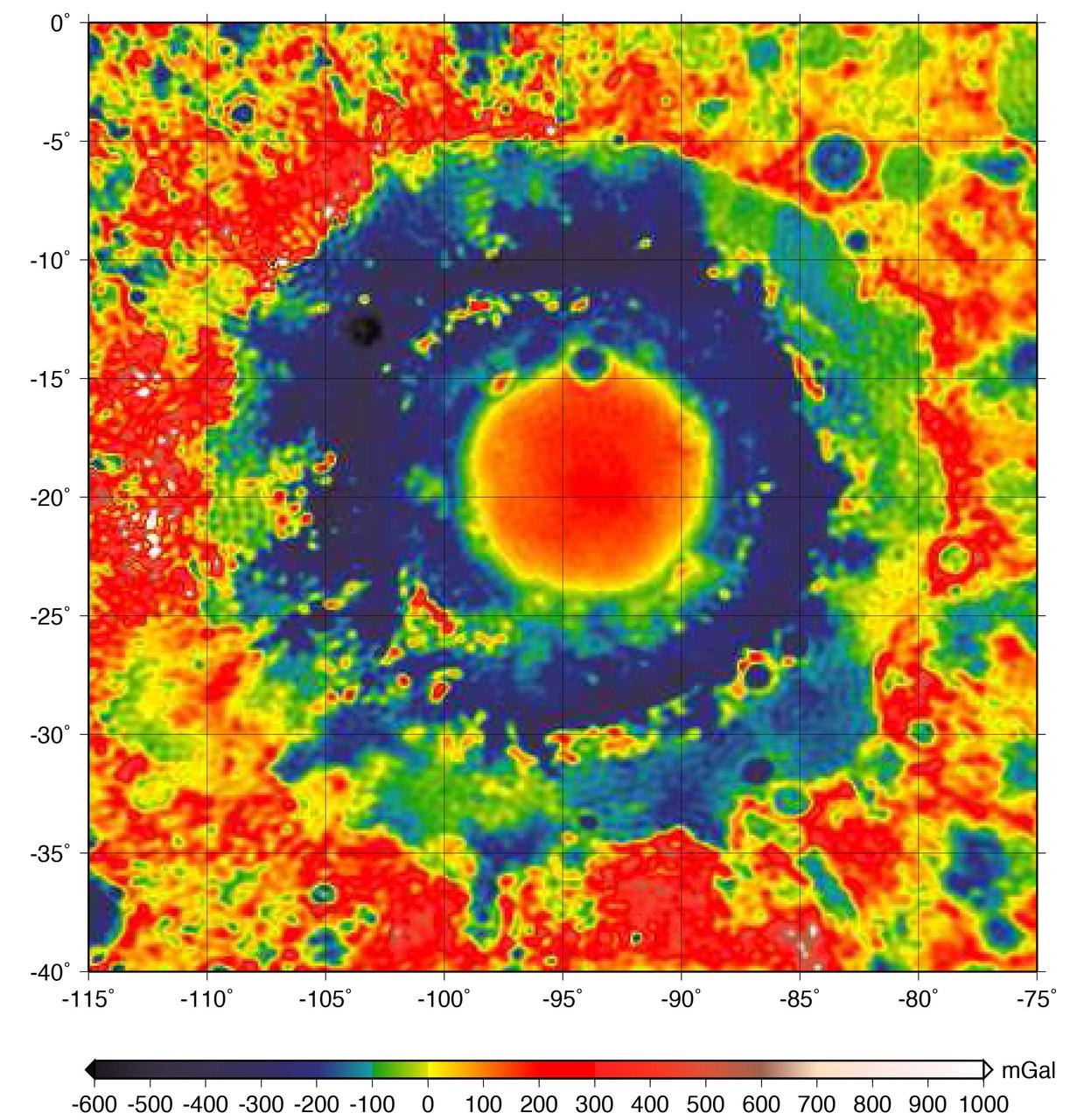
These maps of the moon show the Bouguer gravity anomalies as measured by NASA GRAIL mission. Red areas have stronger gravity, while blue areas have weaker gravity.
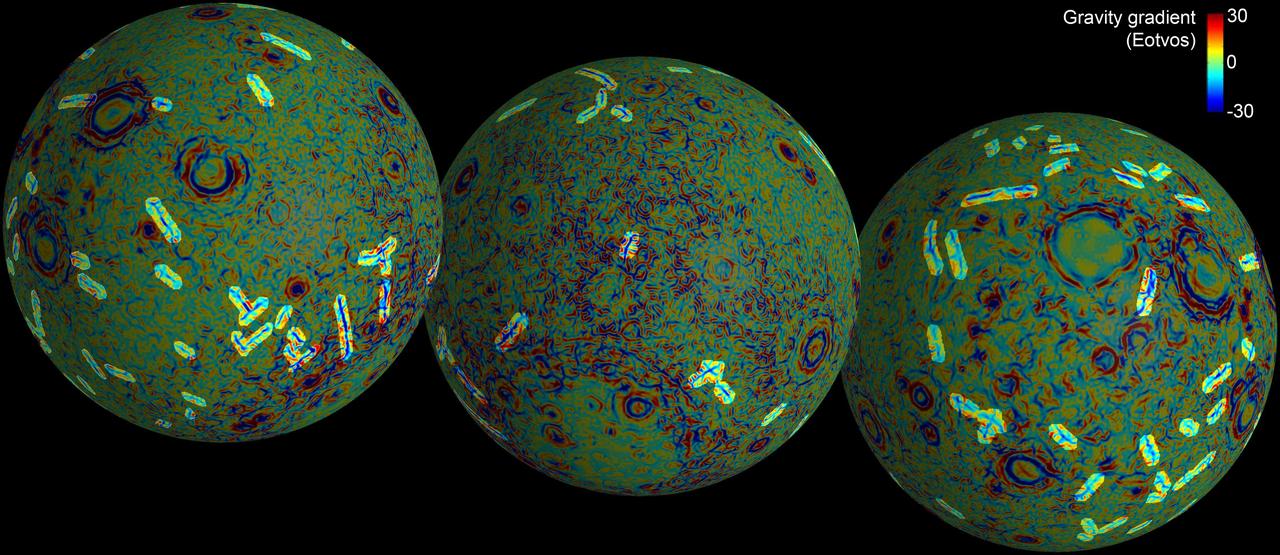
These maps of the near and far side of the moon show the gravity gradients as measured by NASA GRAIL mission, highlighting a population of linear gravity anomalies.
This map shows the gravity field of the moon as measured by NASA GRAIL mission. The viewing perspective, known as a Mercator projection, shows the far side of the moon in the center and the nearside as viewed from Earth at either side.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL, mission logo on the side of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will loft the spacecraft into lunar orbit. The GRAIL mission is a part of NASA's Discovery Program. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. The mission also will answer longstanding questions about Earth's moon and provide scientists a better understanding of how Earth and other rocky planets in the solar system formed. GRAIL is scheduled to launch September 8, 2011. For more information visit: http://science.nasa.gov/missions/grail/. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
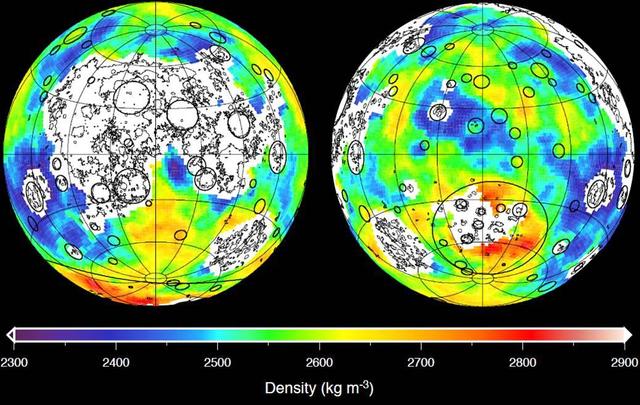
This graphic depicting the bulk density of the lunar highlands on the near and far sides of the moon was generated using gravity data from NASA GRAIL mission and topography data from NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
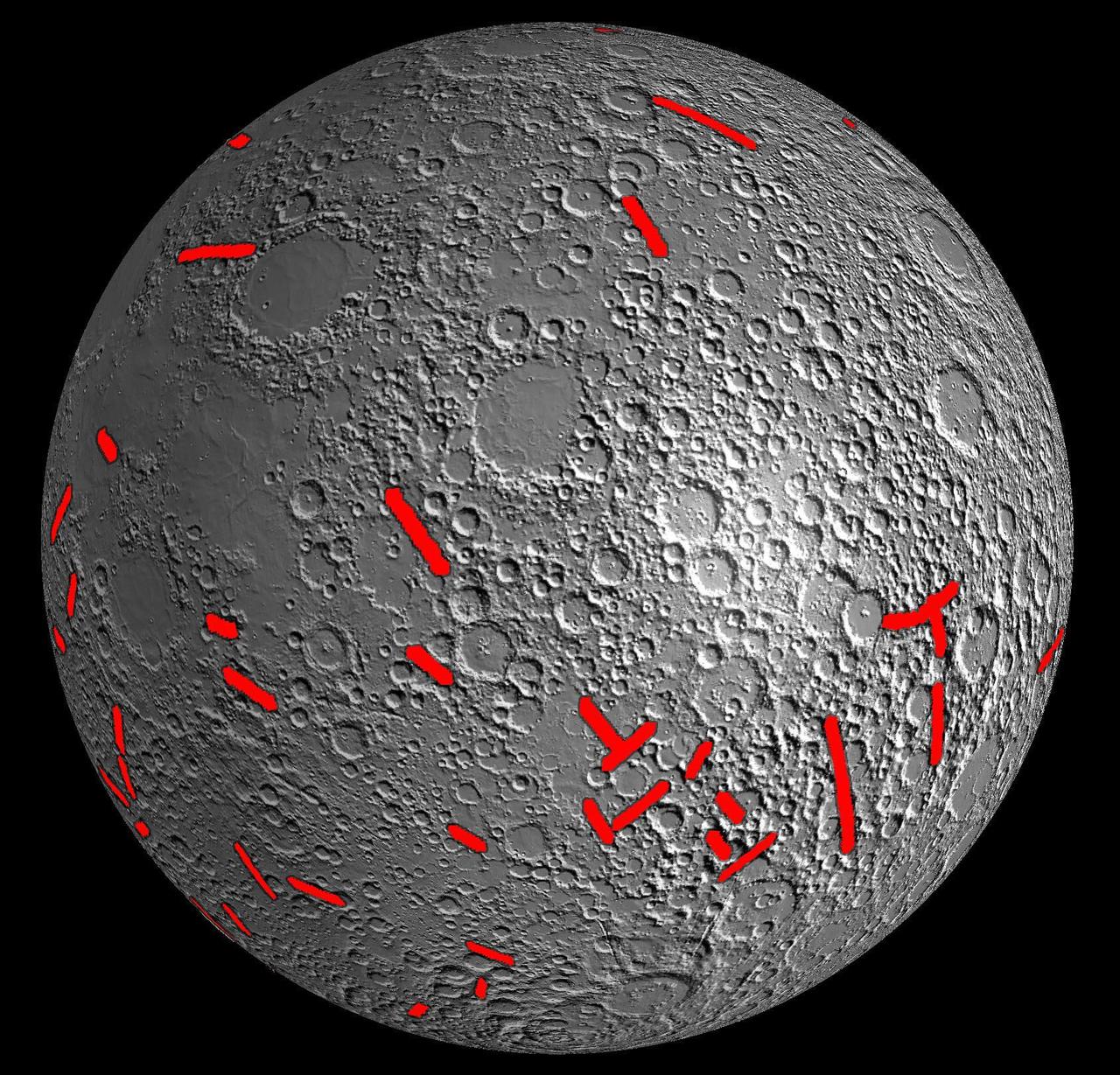
This map of one side of the moon shows the location of some of the giant dikes identified by NASA GRAIL mission.
This graphic depicting the bulk density of the lunar highlands on the near and far sides of the moon was generated using gravity data from NASA GRAIL mission and topography data from NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
This color-coded map shows the strength of surface gravity around Orientale basin on Earth's moon, derived from data obtained by NASA's GRAIL mission. The GRAIL mission produced a very high-resolution map of gravity over the surface of the entire moon. This plot is zoomed in on the part of that map that features Orientale basin, where the two GRAIL spacecraft flew extremely low near the end of their mission. Their close proximity to the basin made the probes' measurements particularly sensitive to the gravitational acceleration there (due to the inverse squared law). The color scale plots the gravitational acceleration in units of "gals," where 1 gal is one centimeter per second squared, or about 1/1000th of the gravitational acceleration at Earth's surface. (The unit was devised in honor of the astronomer Galileo). Labels on the x and y axes represent latitude and longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21050

This is the first footage of one orbiting robotic spacecraft taken by another orbiting robotic spacecraft at Earth moon. Flow, one of two satellites making up NASA GRAIL mission, captured this video of NASA LRO as it flew by.
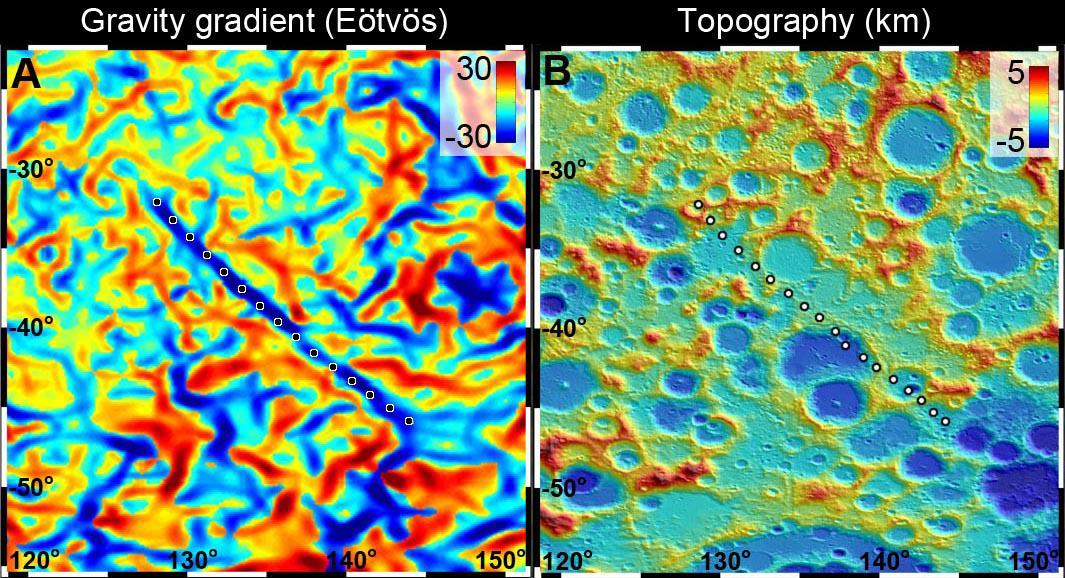
A 300-mile-long linear gravity anomaly on the far side of the moon has been revealed by gravity gradients measured by NASA GRAIL mission. GRAIL data are shown on the left, with red and blue corresponding to stronger gravity gradients.
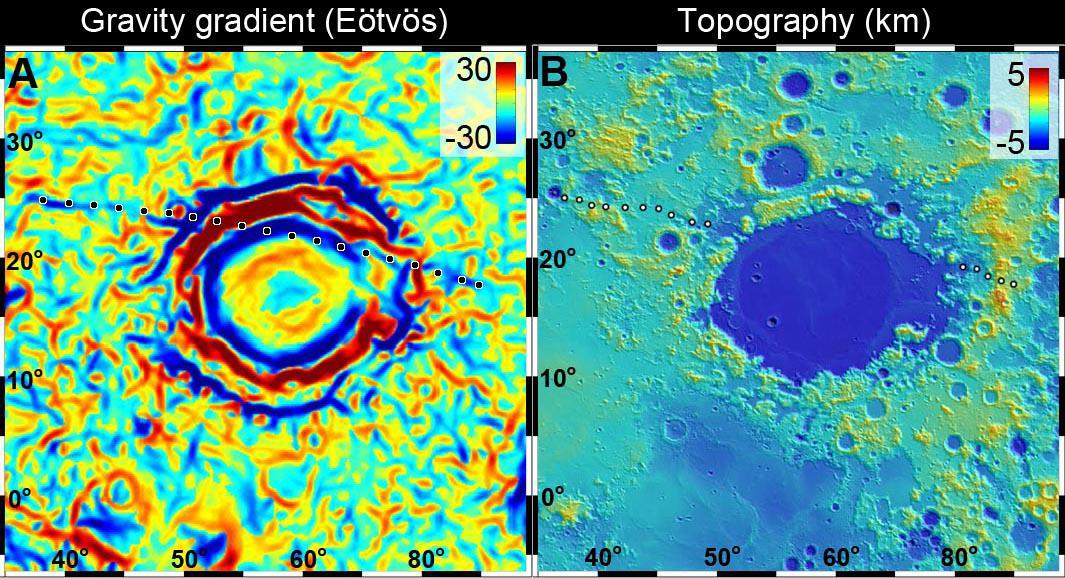
A linear gravity anomaly intersecting the Crisium basin on the nearside of the moon has been revealed by NASA GRAIL mission. The GRAIL gravity gradient data are shown at left, with the location of the anomaly indicated.
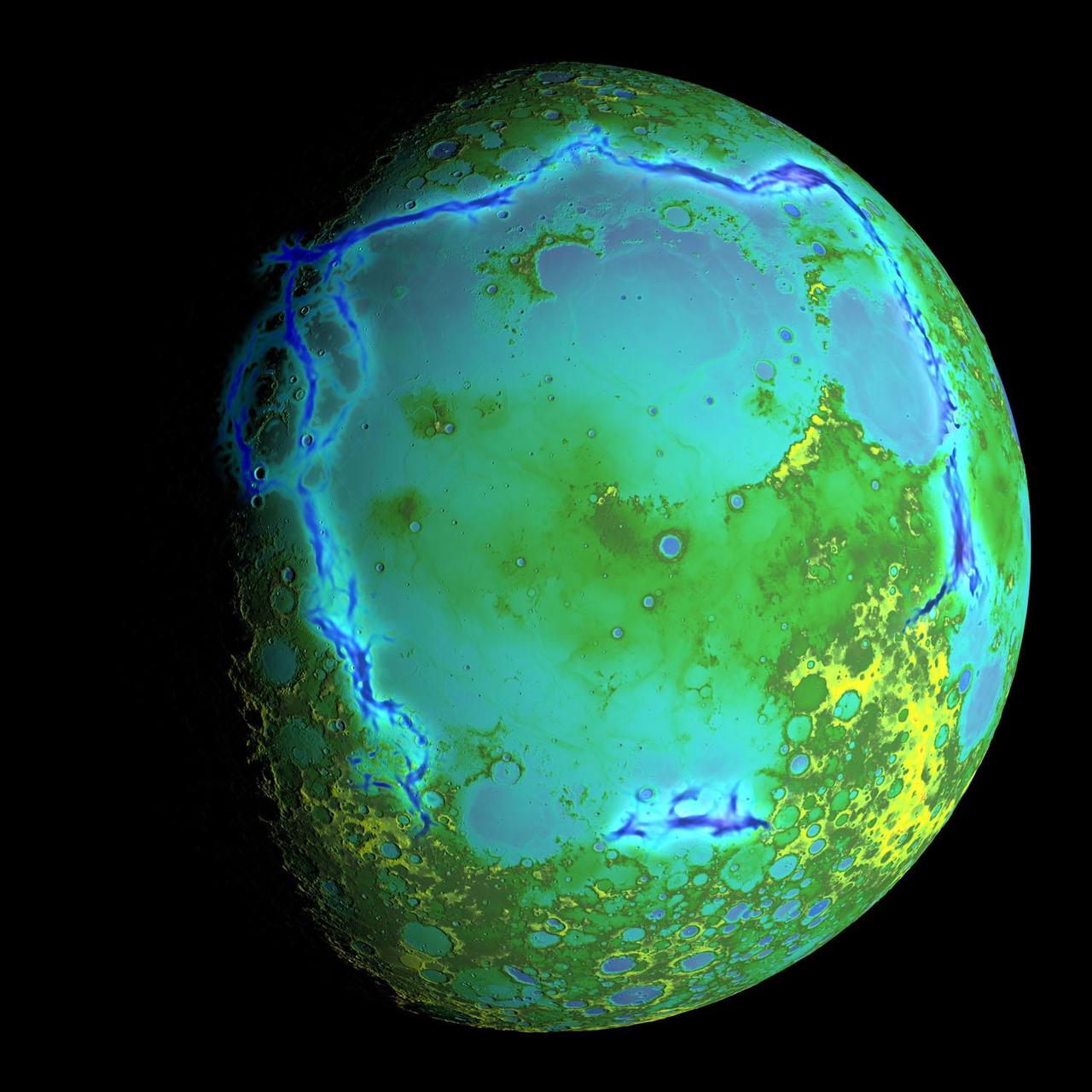
Topography of Earth moon generated from data NASA LRO, with the gravity anomalies bordering the Procellarum region superimposed in blue. The border structures are shown using gravity gradients calculated with data from NASA GRAIL mission.
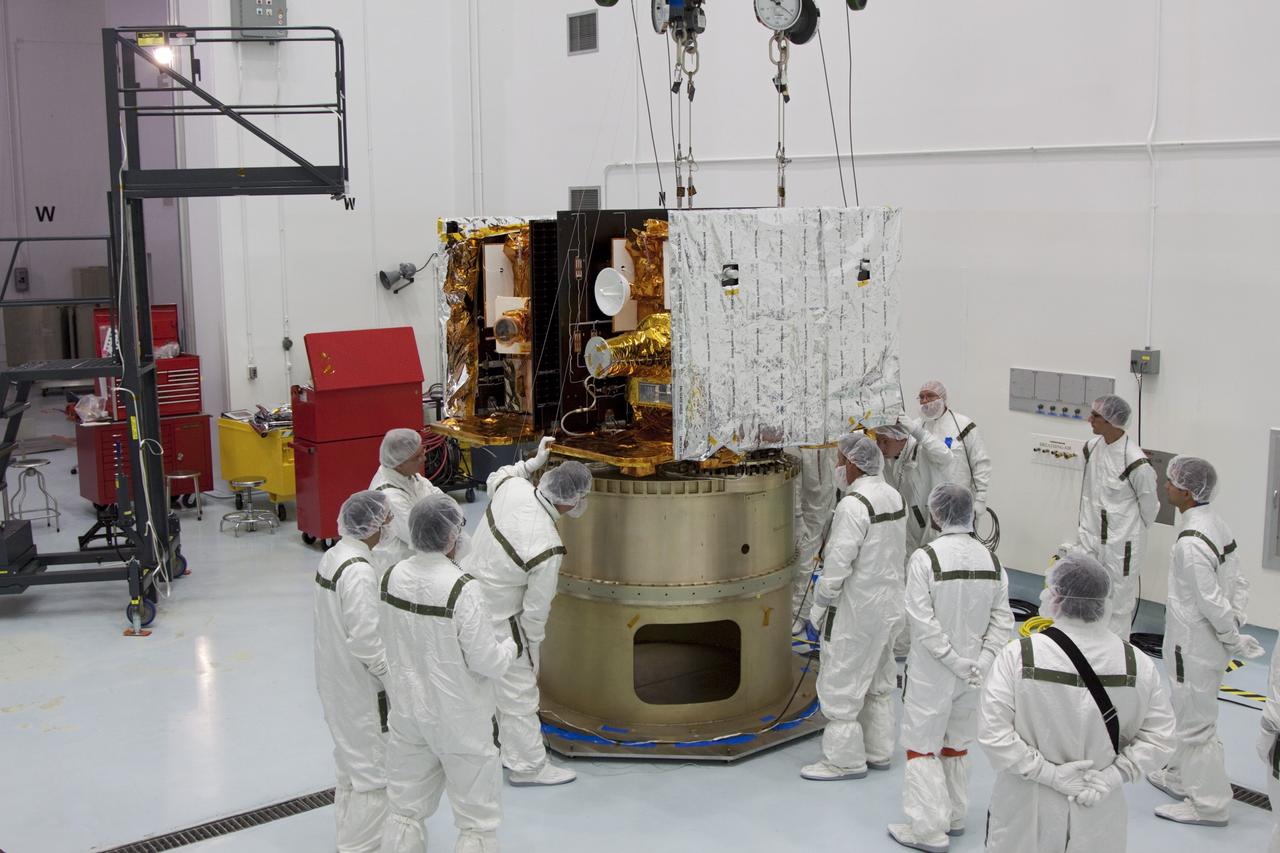

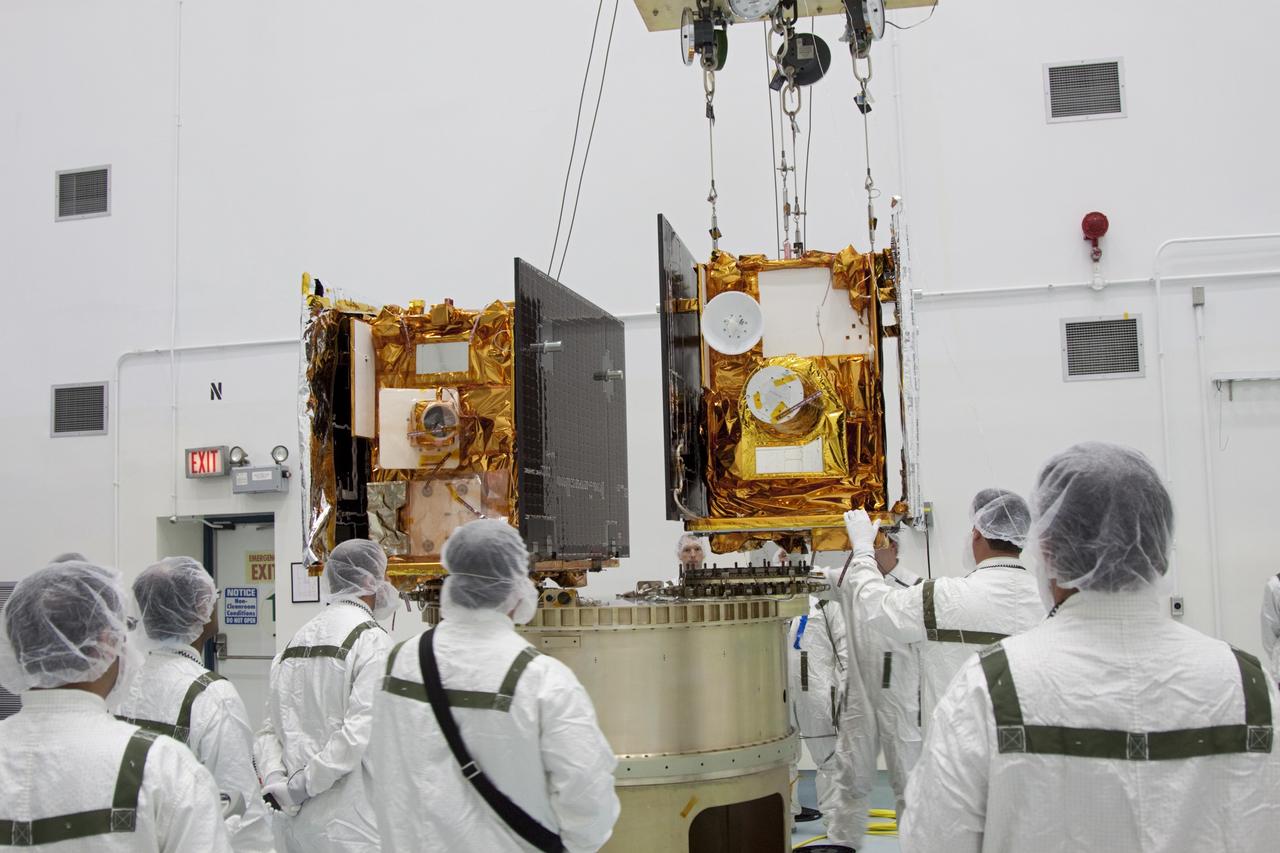
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the placement of NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe on the spacecraft adapter ring. GRAIL-B is already secured to the ring, at left. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
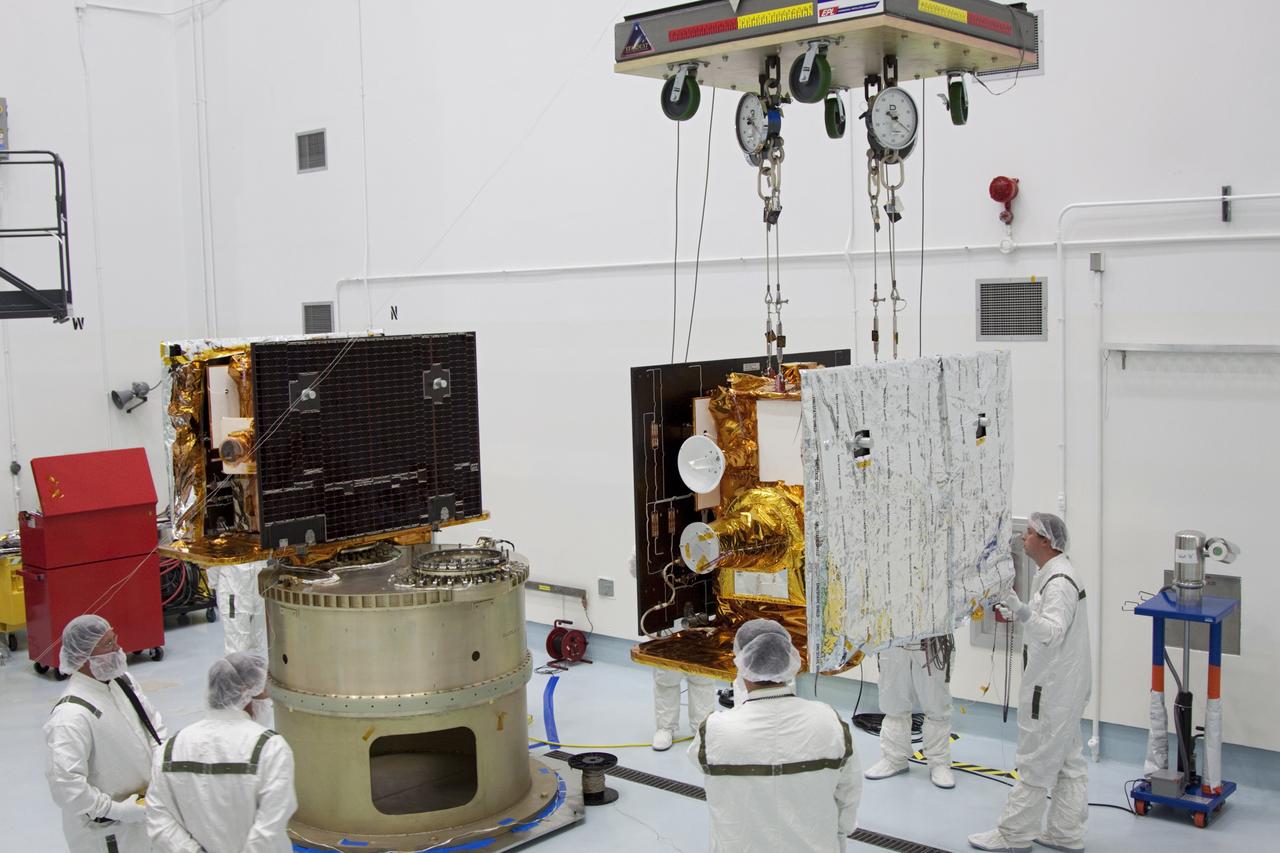

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe slowly approaches the spacecraft adapter ring, at left, where GRAIL-B is already secured. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
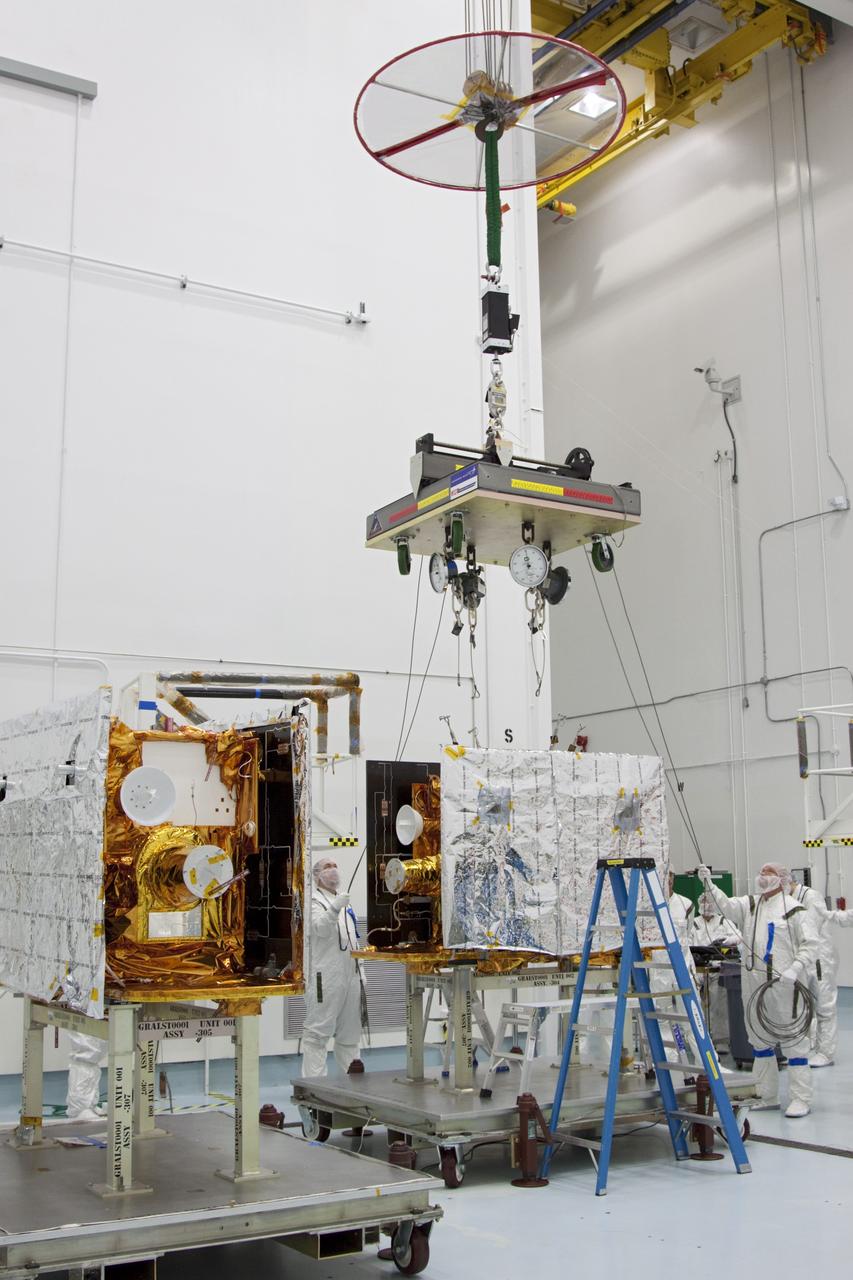

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a lifting device moves into position over NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe. At left is GRAIL-A. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe us lowered toward the spacecraft adapter ring. GRAIL-B is already secured to the ring, at left. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is lifted from its workstand and across the clean room toward the spacecraft adapter ring, at left, where GRAIL-B is already secured. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is lifted from its workstand. The spacecraft will be transferred to the spacecraft adapter ring, at left, where GRAIL-B is already secured. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians adjust the position of NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe on the spacecraft adapter ring. GRAIL-B is already secured to the ring, at left. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians move a lifting device toward NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe. At left is GRAIL-A. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
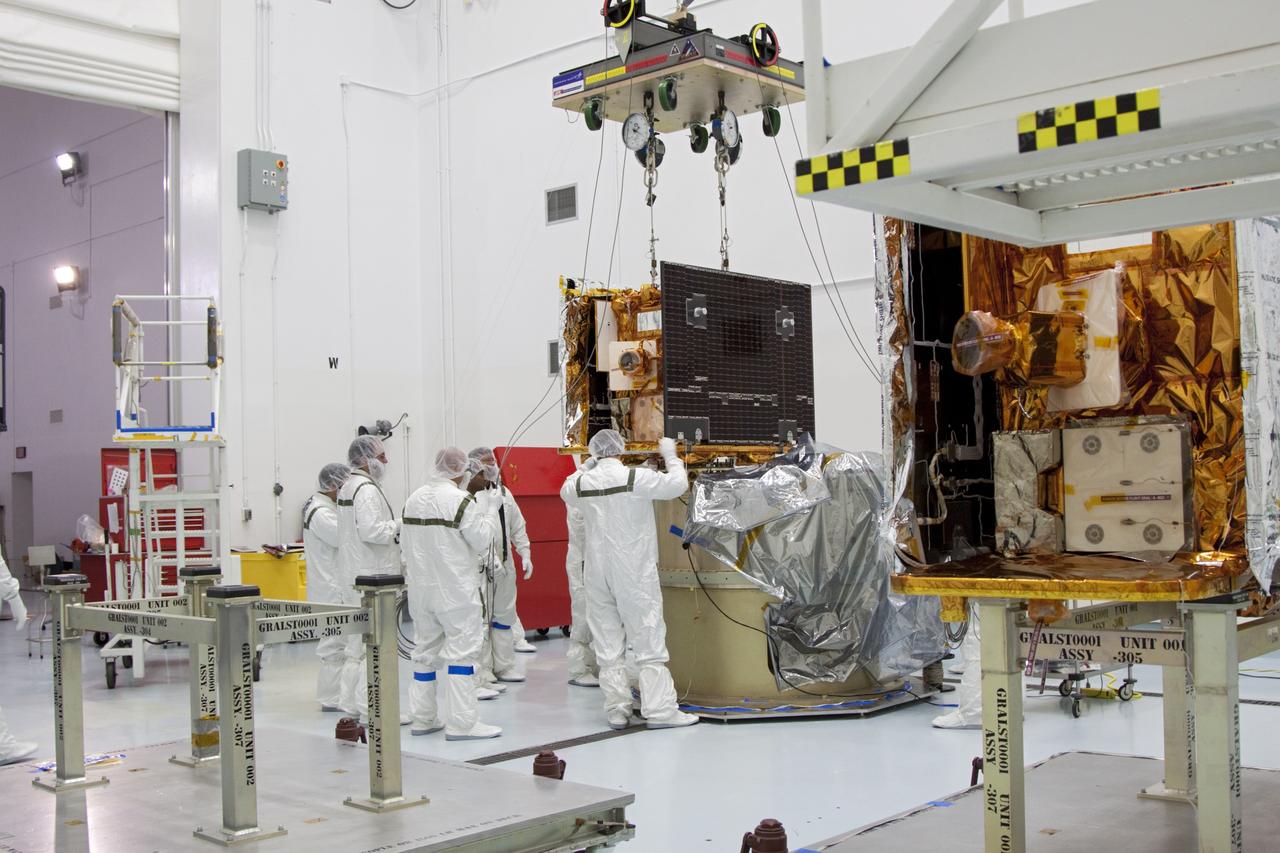

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe comes to rest on the spacecraft adapter ring. At right is GRAIL-A. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
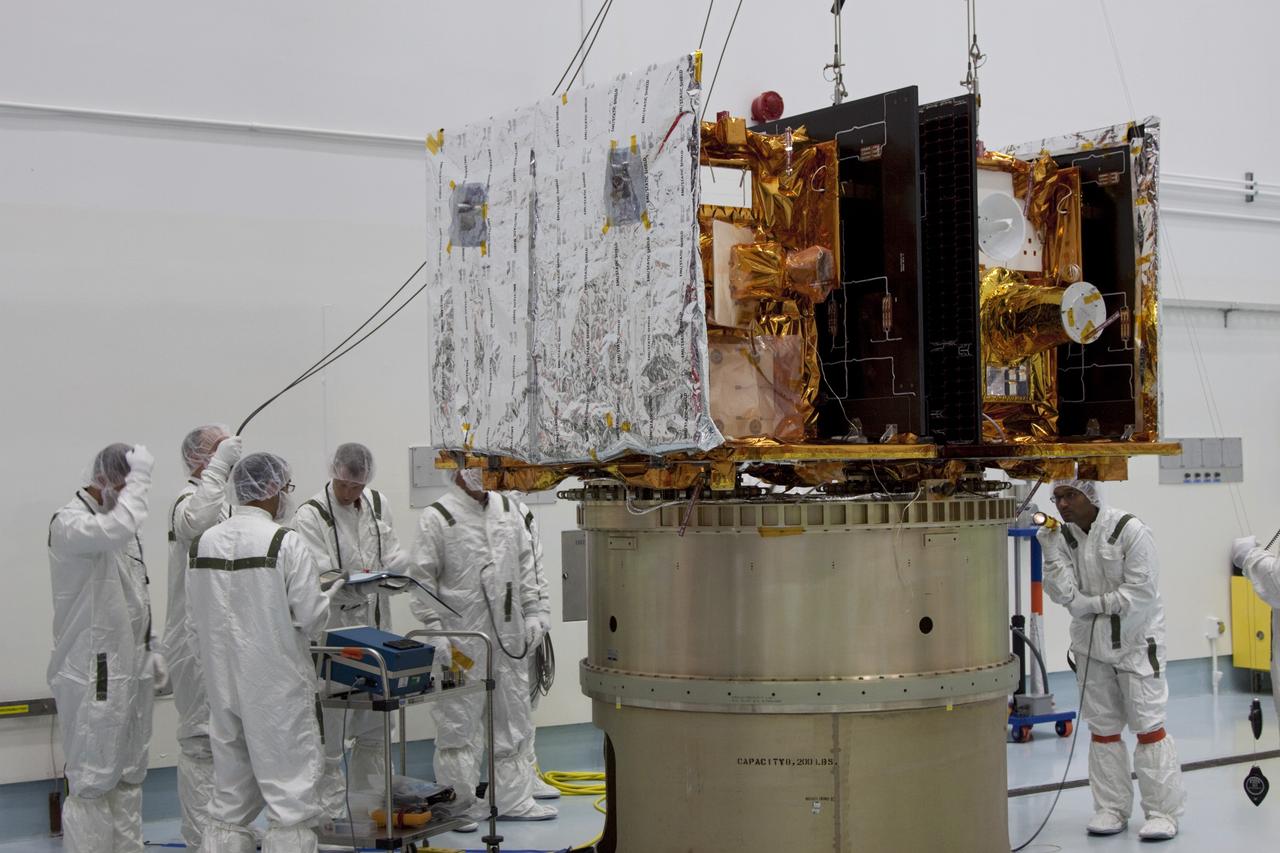

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians verify that NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is in position and ready to be secured to the spacecraft adapter ring. GRAIL-B is secured to the ring, at left. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
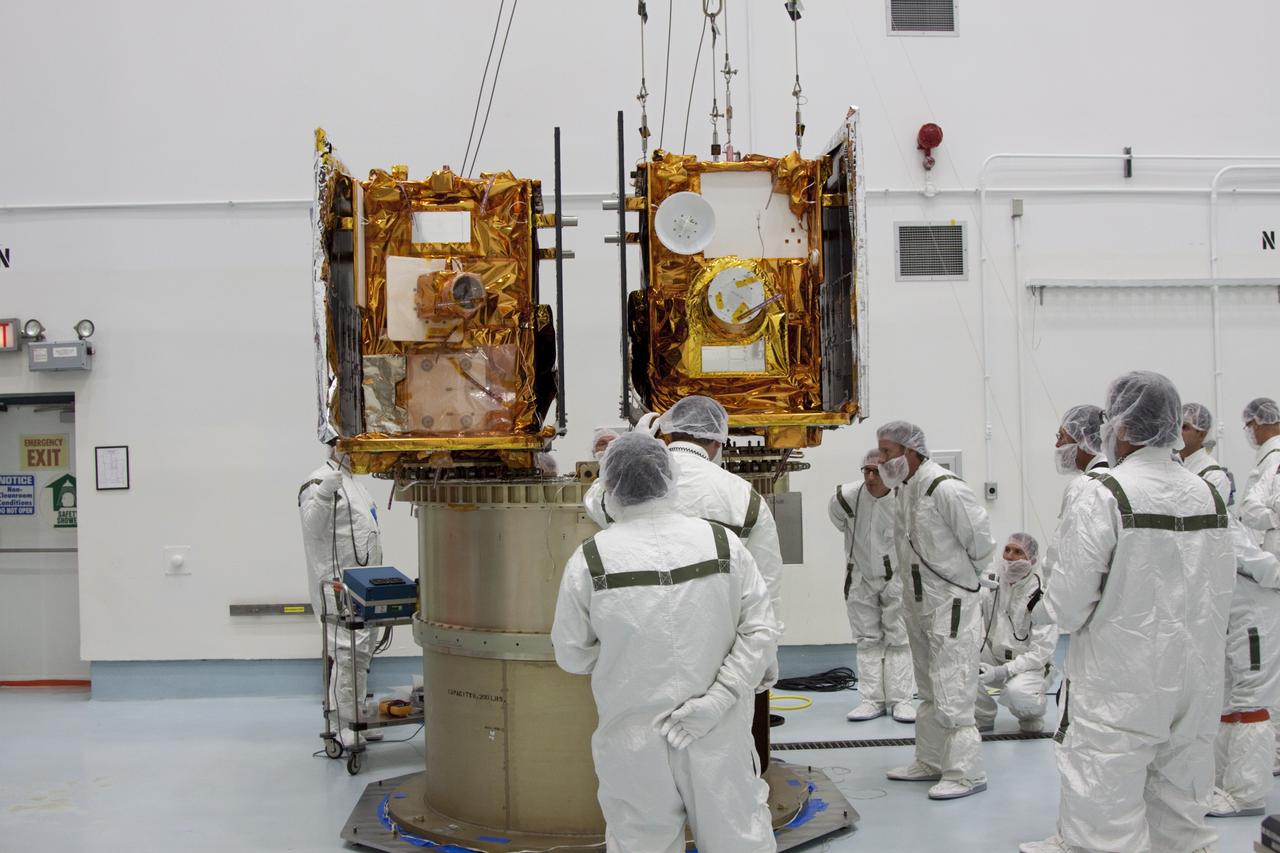

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the placement of NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe on the spacecraft adapter ring. GRAIL-B is already secured to the ring, at left. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
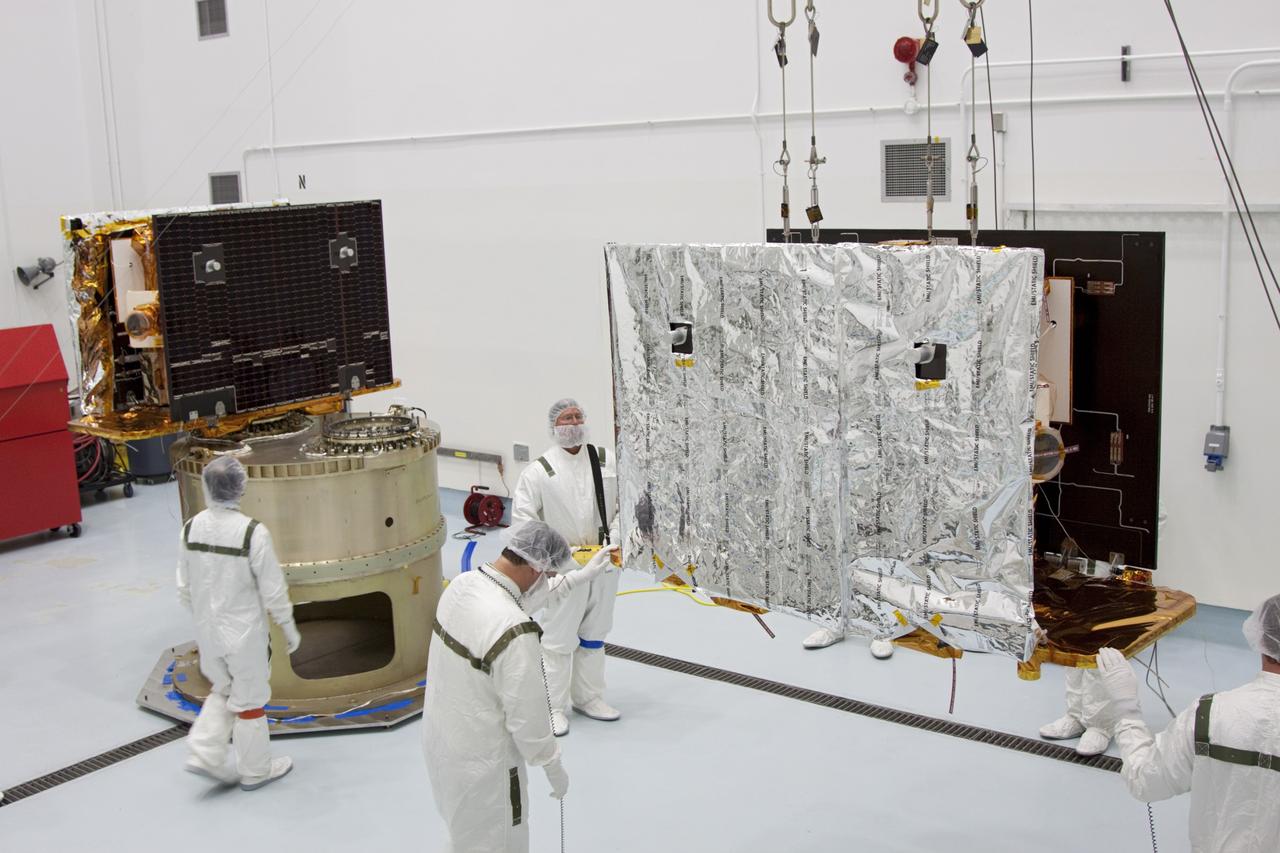

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe moves across the clean room toward the spacecraft adapter ring, at left, where GRAIL-B is already secured. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
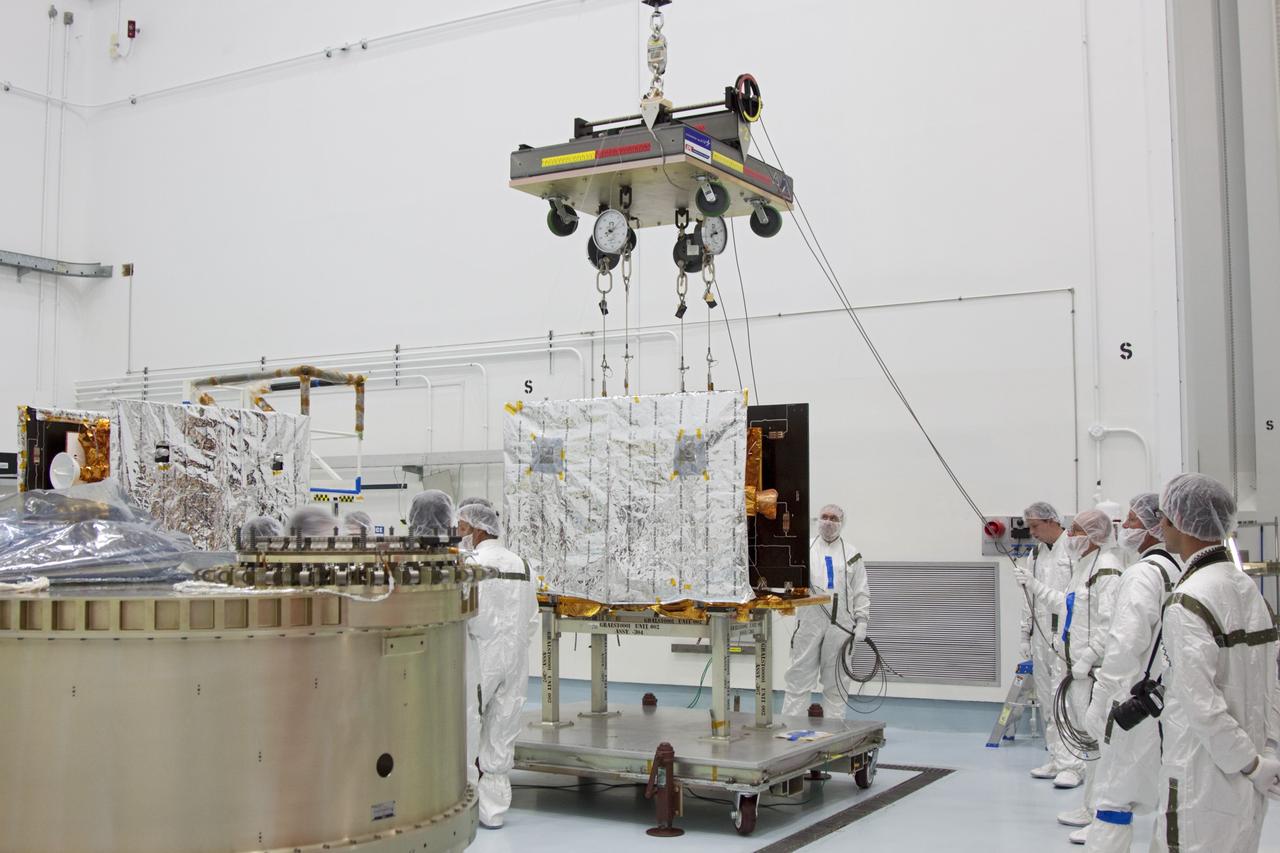

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a lifting device is lowered toward NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe. At left is GRAIL-A. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians make final adjustment to NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe before it is secured to the spacecraft adapter ring. GRAIL-B is secured to the ring, at left. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
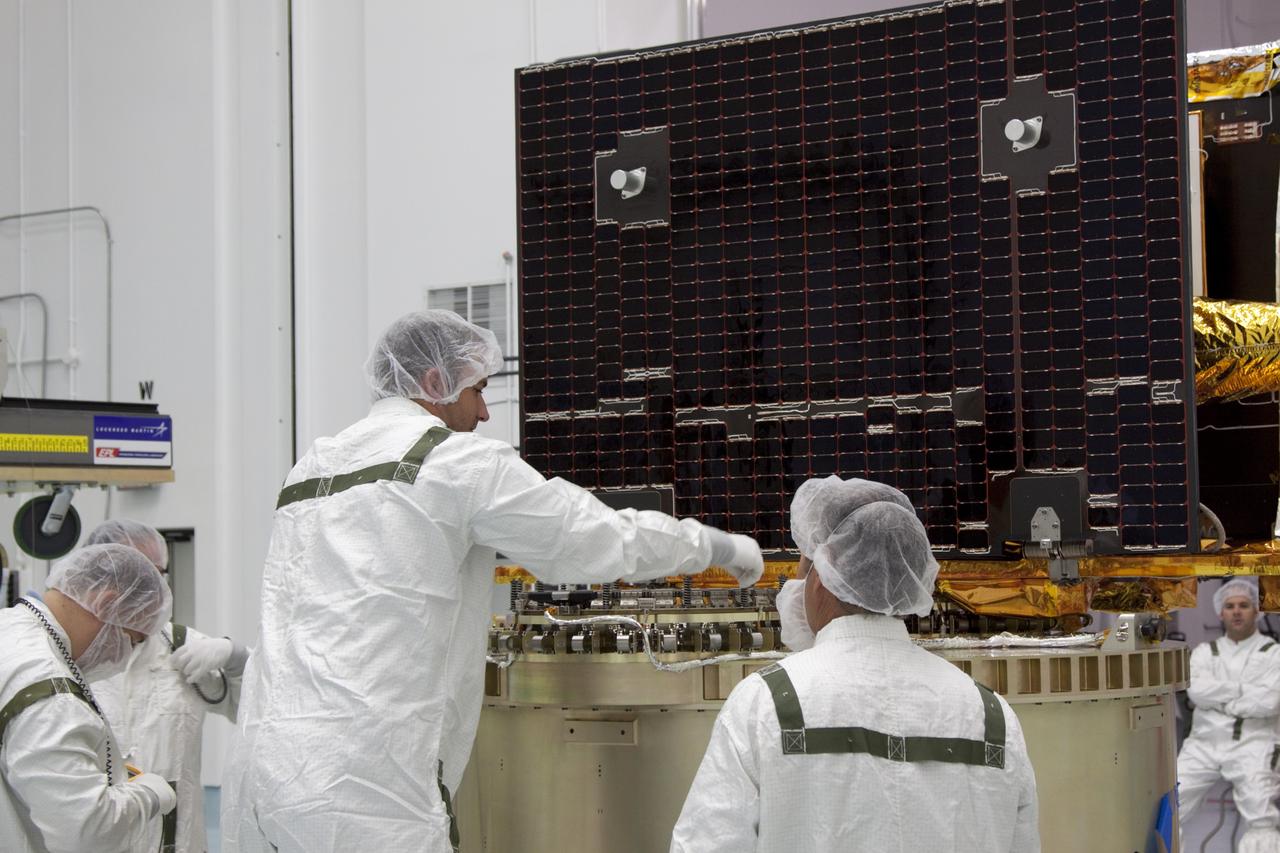

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Lockheed Martin technician secures NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
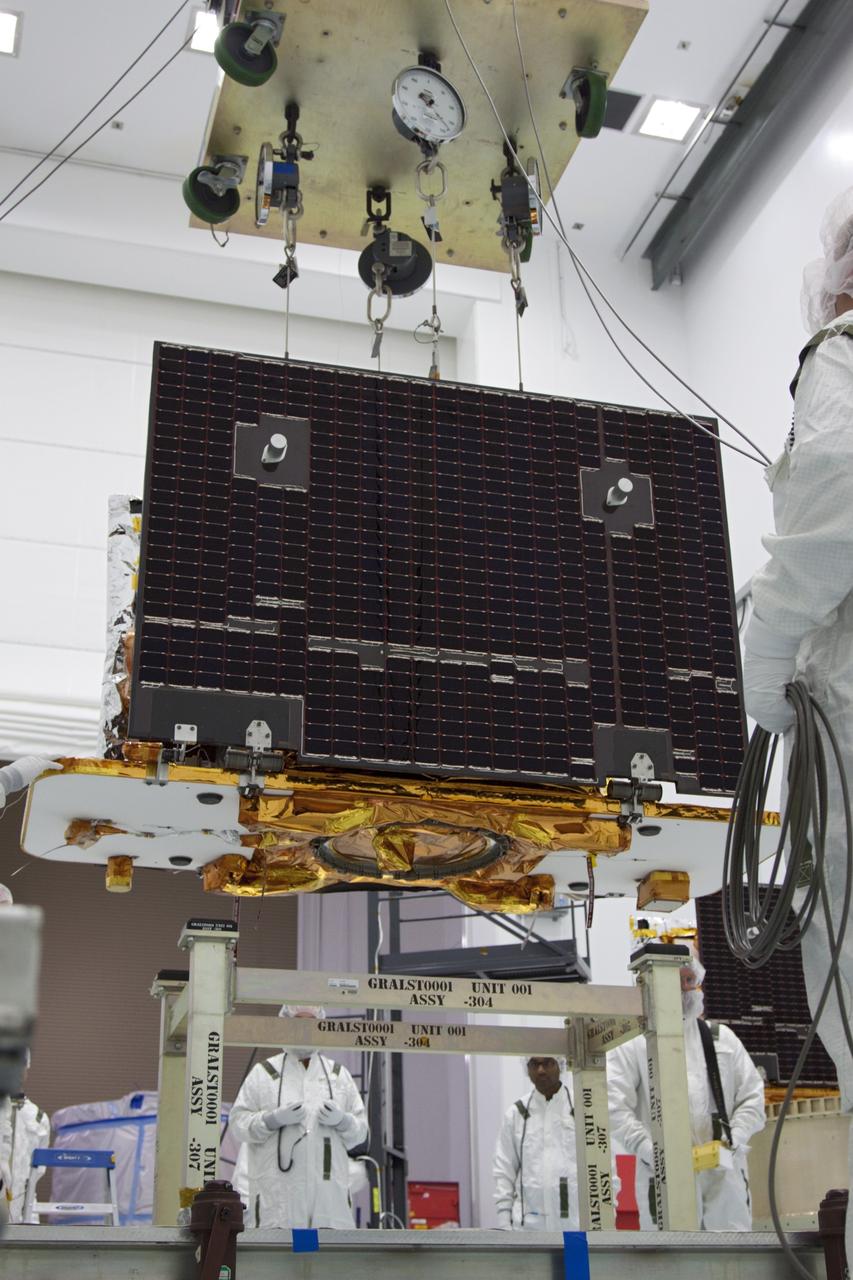

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is lifted from its workstand. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
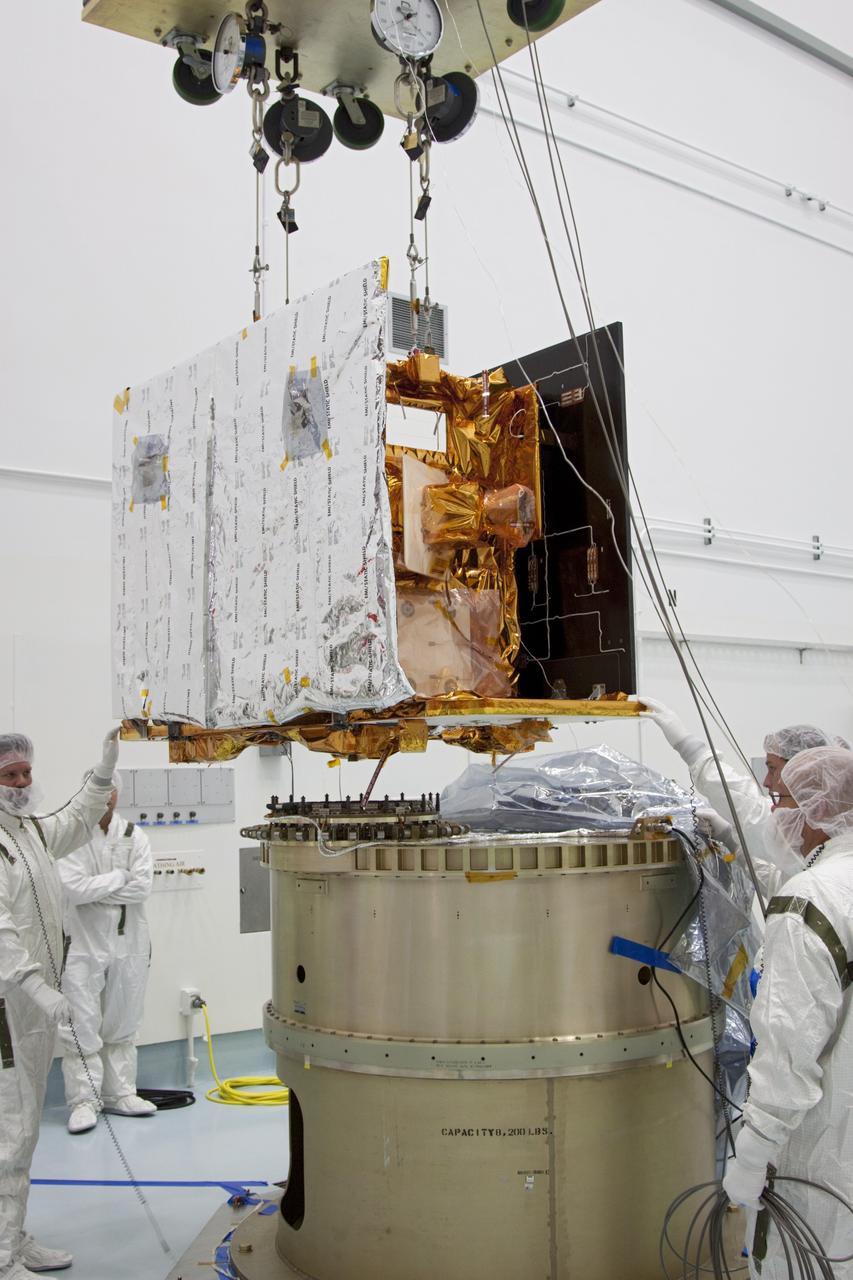

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe is lowered toward the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
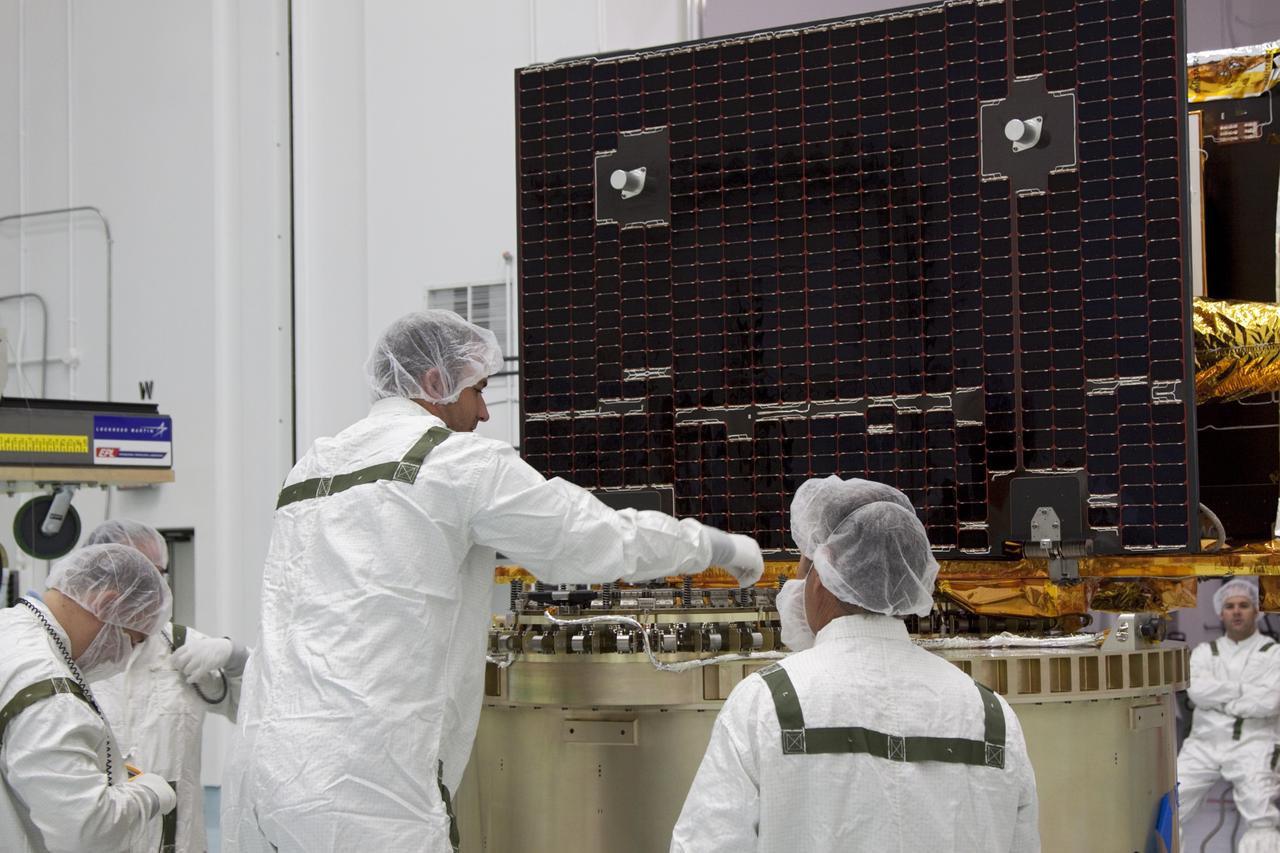

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe is secured on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
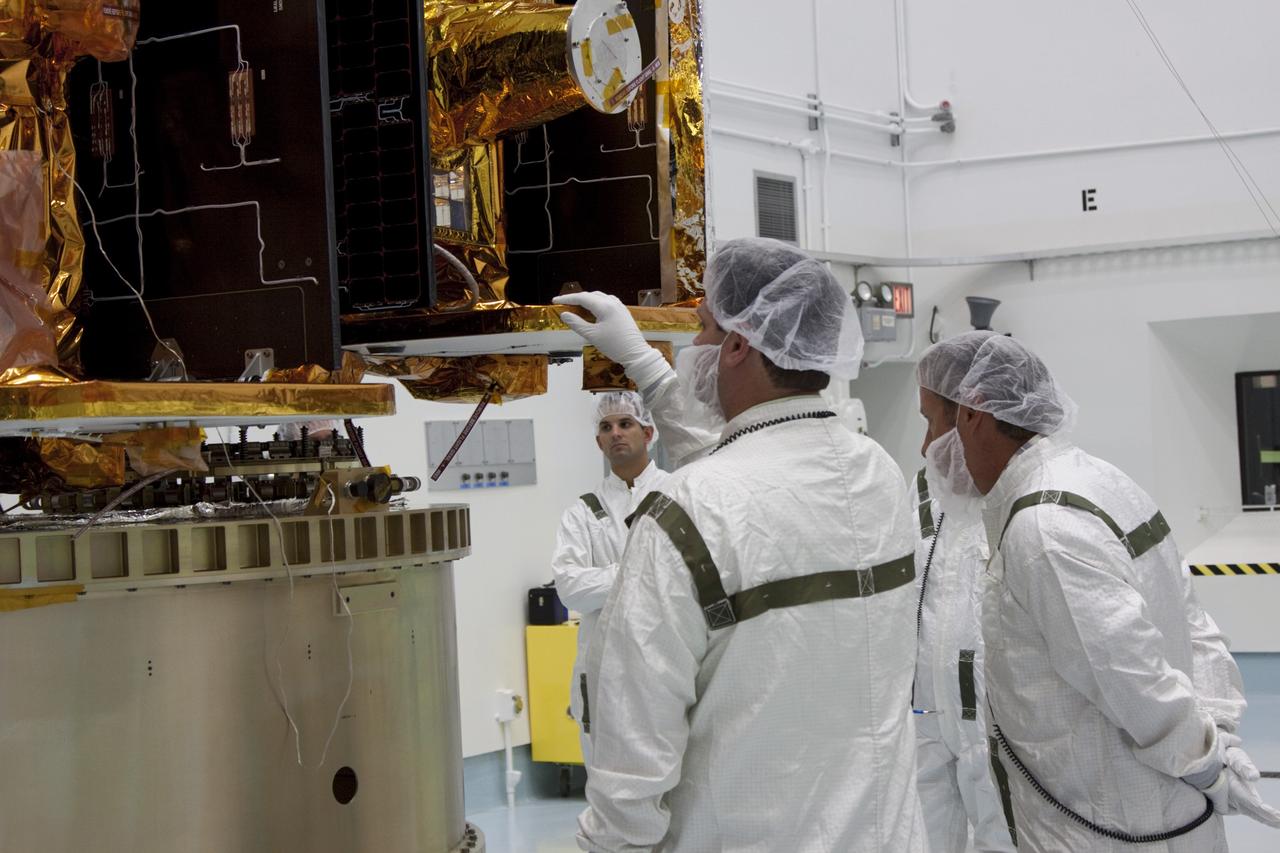

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians verify that NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is positioned correctly on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians verify that NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is lifted carefully from its workstand. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
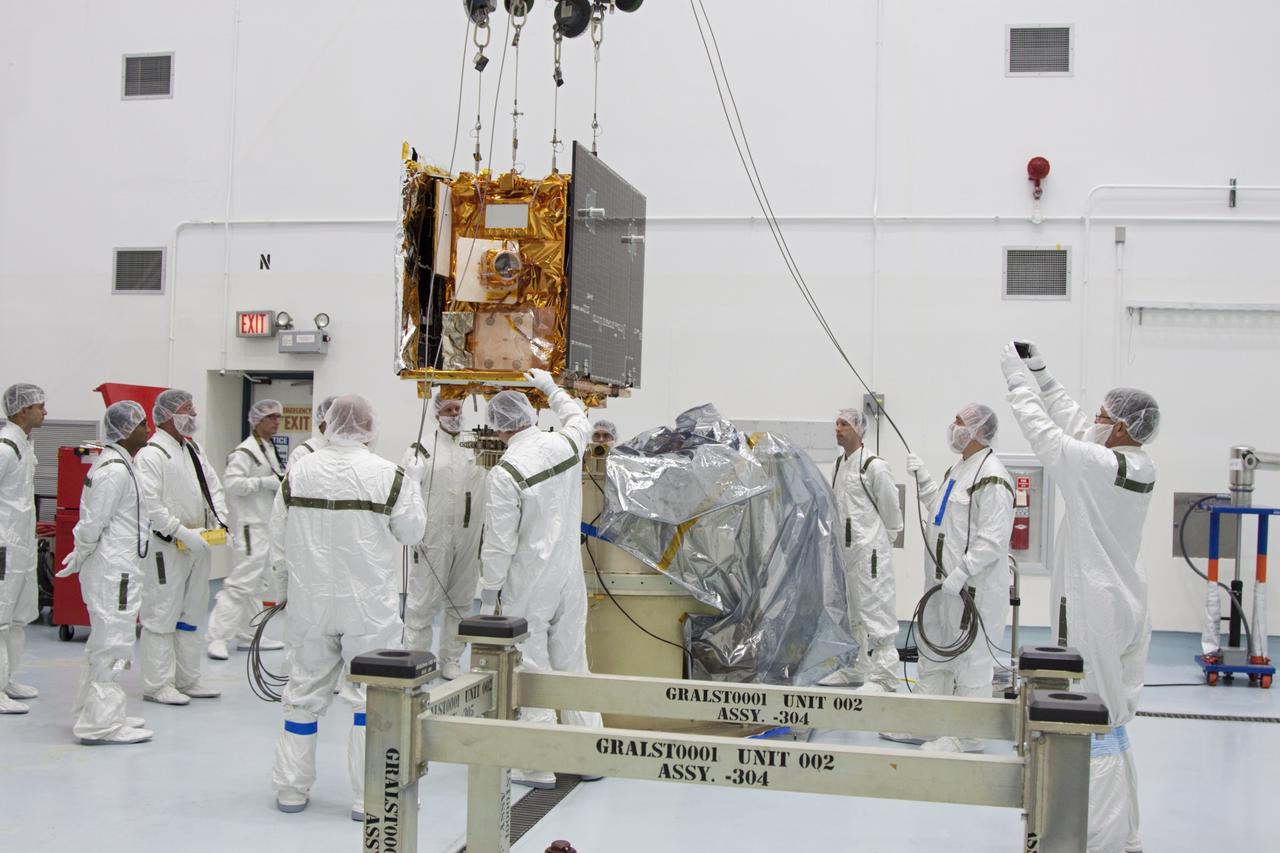

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians lower NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe into position on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians verify that NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe is in the correct position on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians position NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
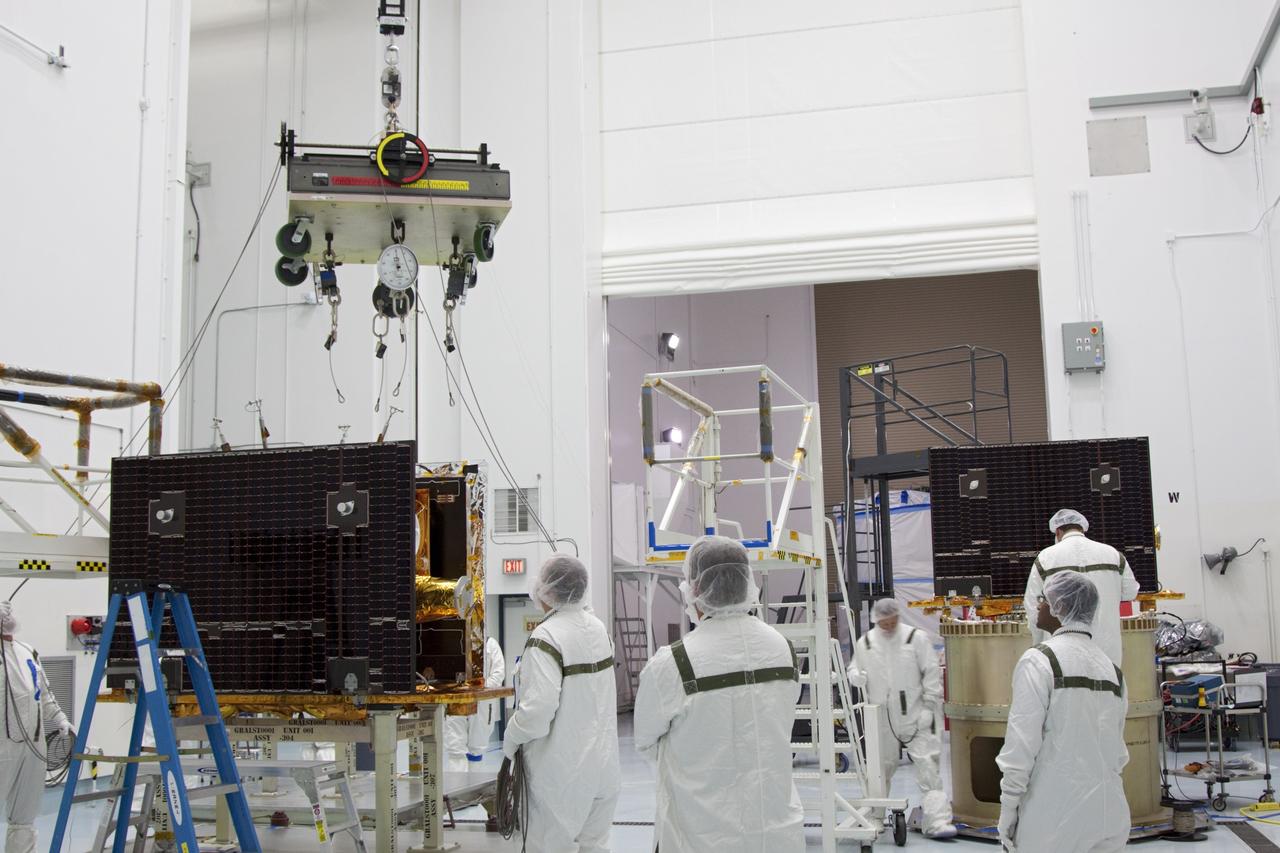

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the lifting device moves toward NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe. The spacecraft will be transferred to the spacecraft adapter ring, at right, where GRAIL-B is being secured. After the twin spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
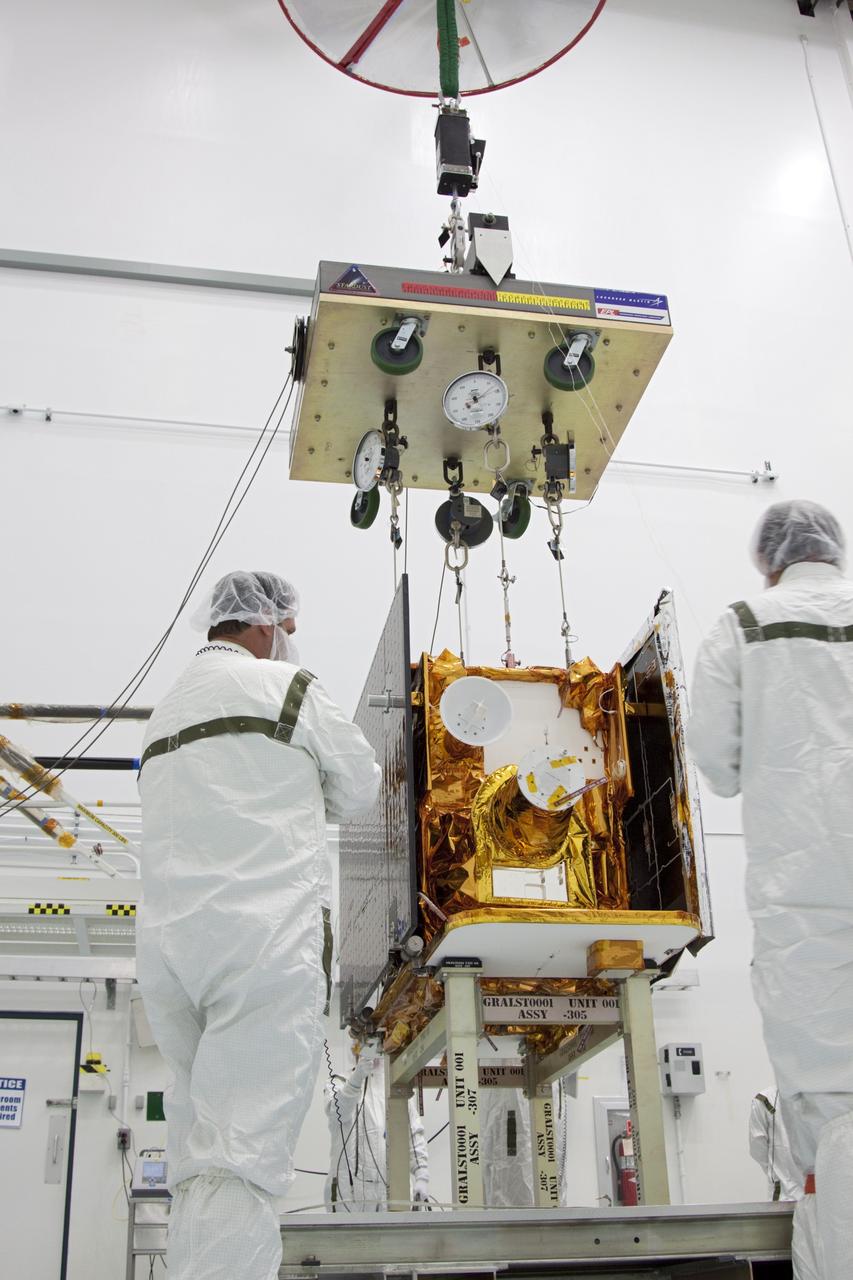

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a lifting device is attached to NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe to move it from its workstand. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
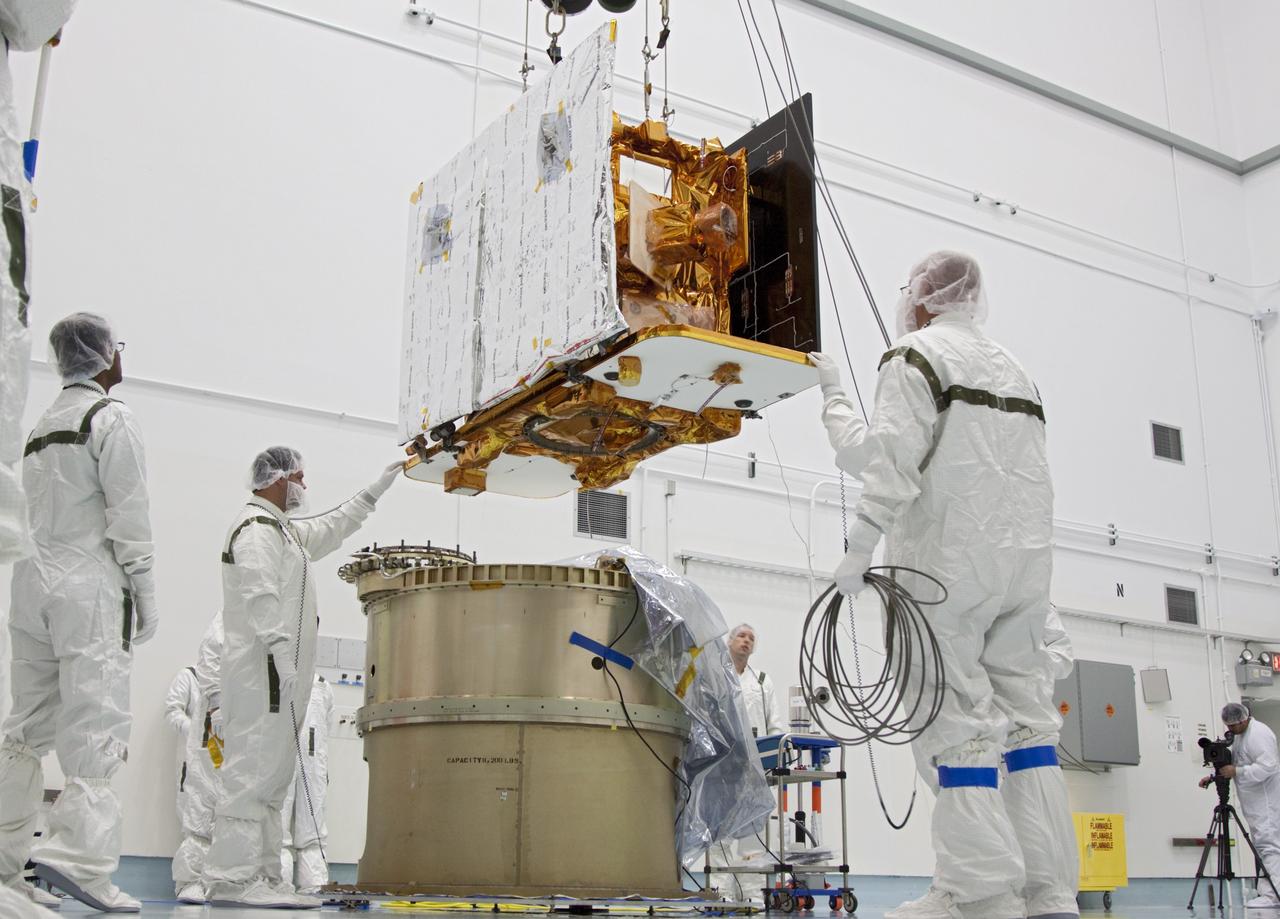

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians lower NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe toward the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
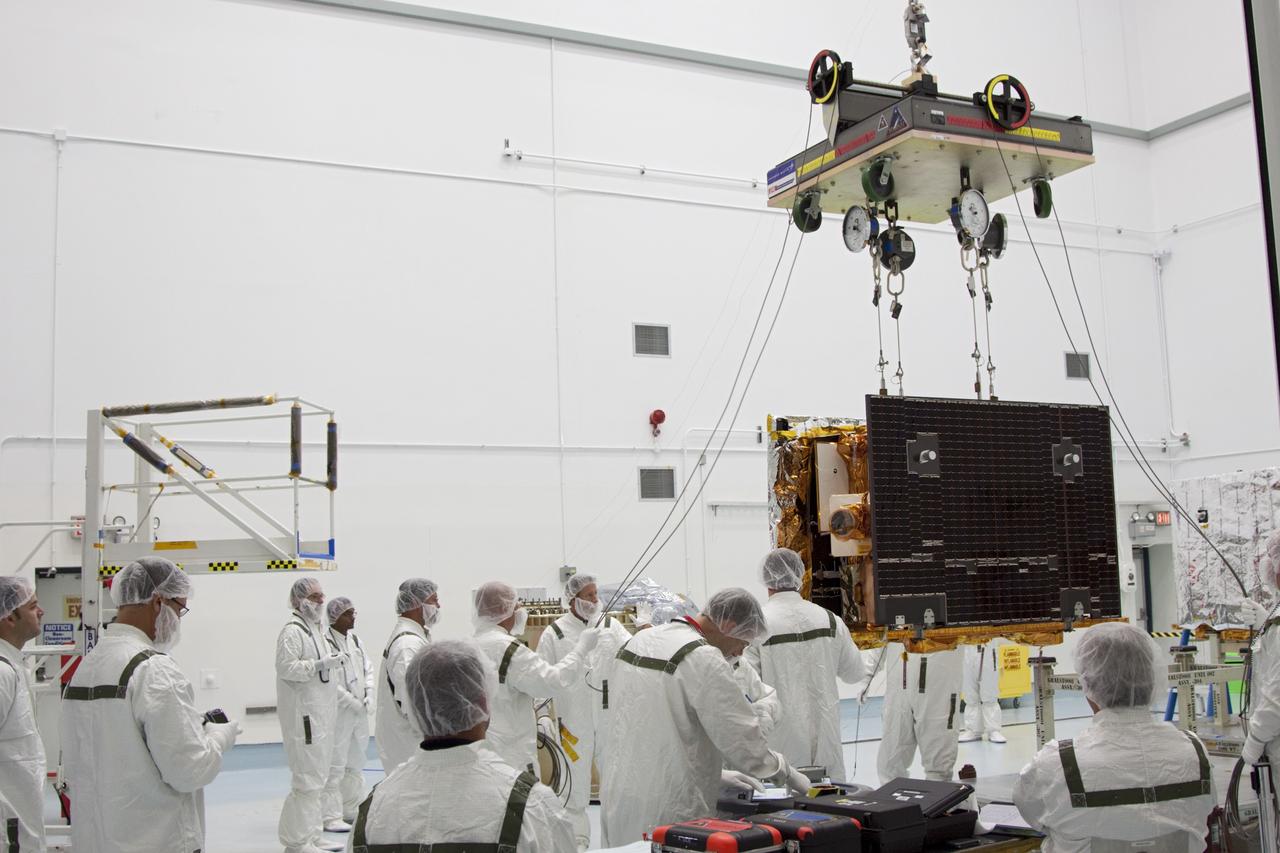

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians lift NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe from its workstand. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to their spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
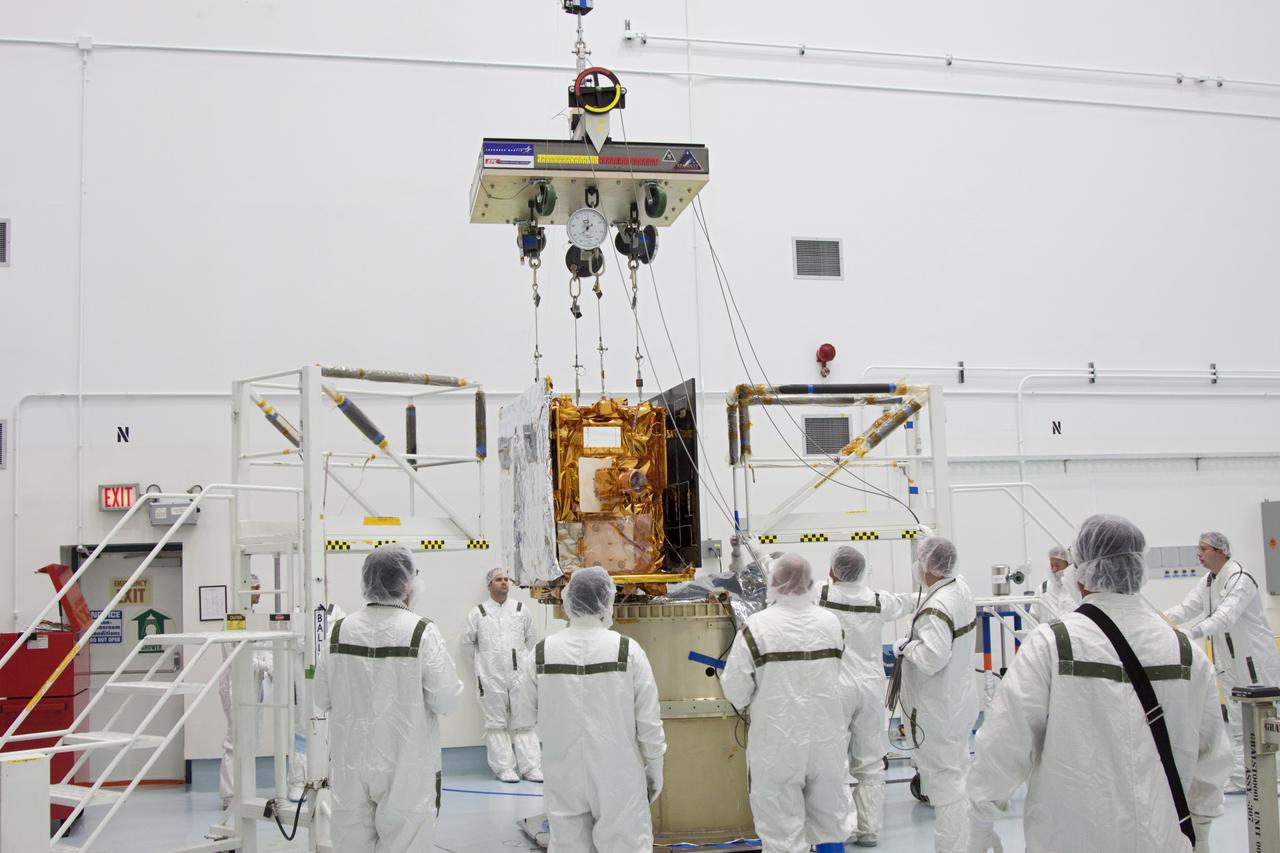

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the lifting device is detached from NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe following its placement on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
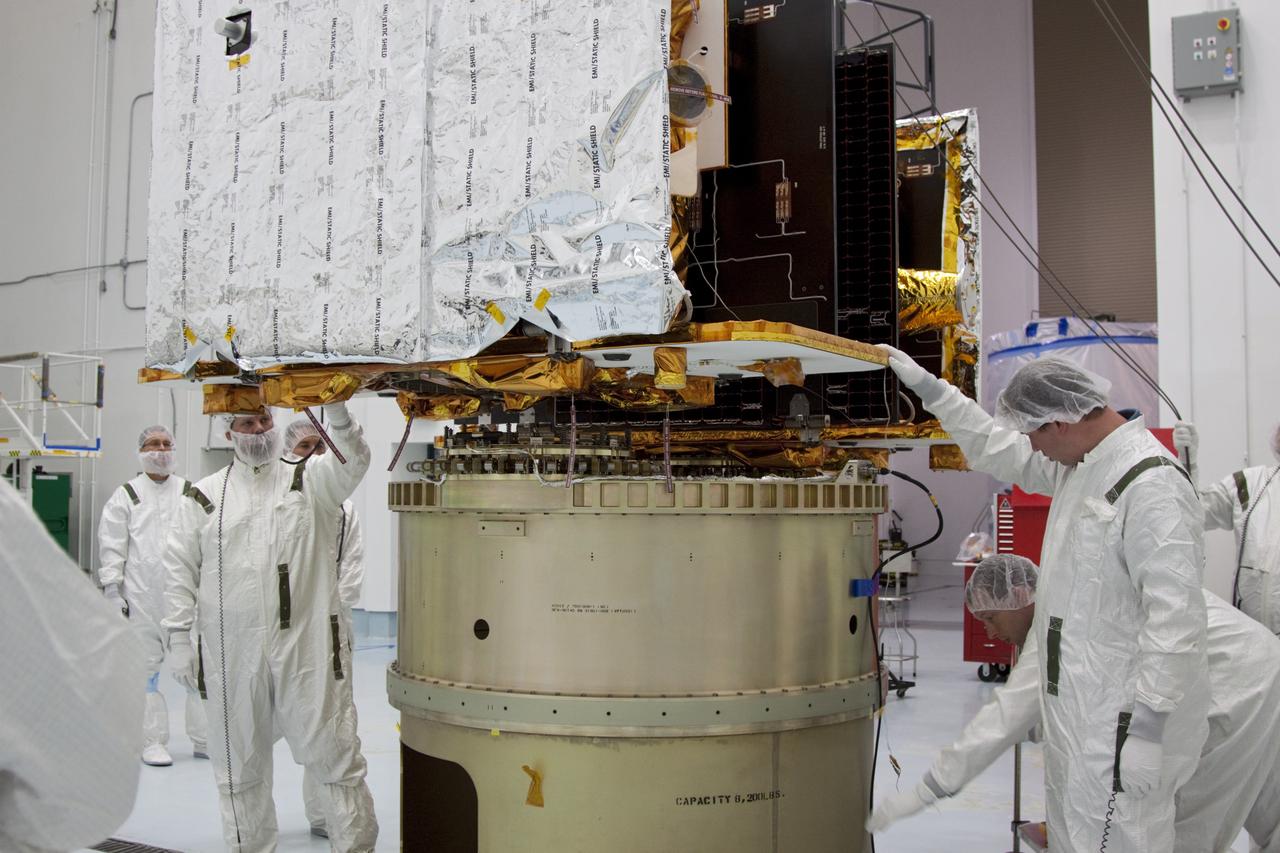

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians verify that NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is lowered into the correct position on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL, spacecraft logo is emblazed on the first stage of a United Launch Alliance Delta II launch vehicle, now secured in the gantry at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Pad 17B. The Delta II will carry GRAIL into lunar orbit. The GRAIL mission is a part of NASA's Discovery Program. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. The mission also will answer longstanding questions about Earth's moon and provide scientists a better understanding of how Earth and other rocky planets in the solar system formed. GRAIL is scheduled to launch September 8, 2011. For more information visit: http://science.nasa.gov/missions/grail/. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
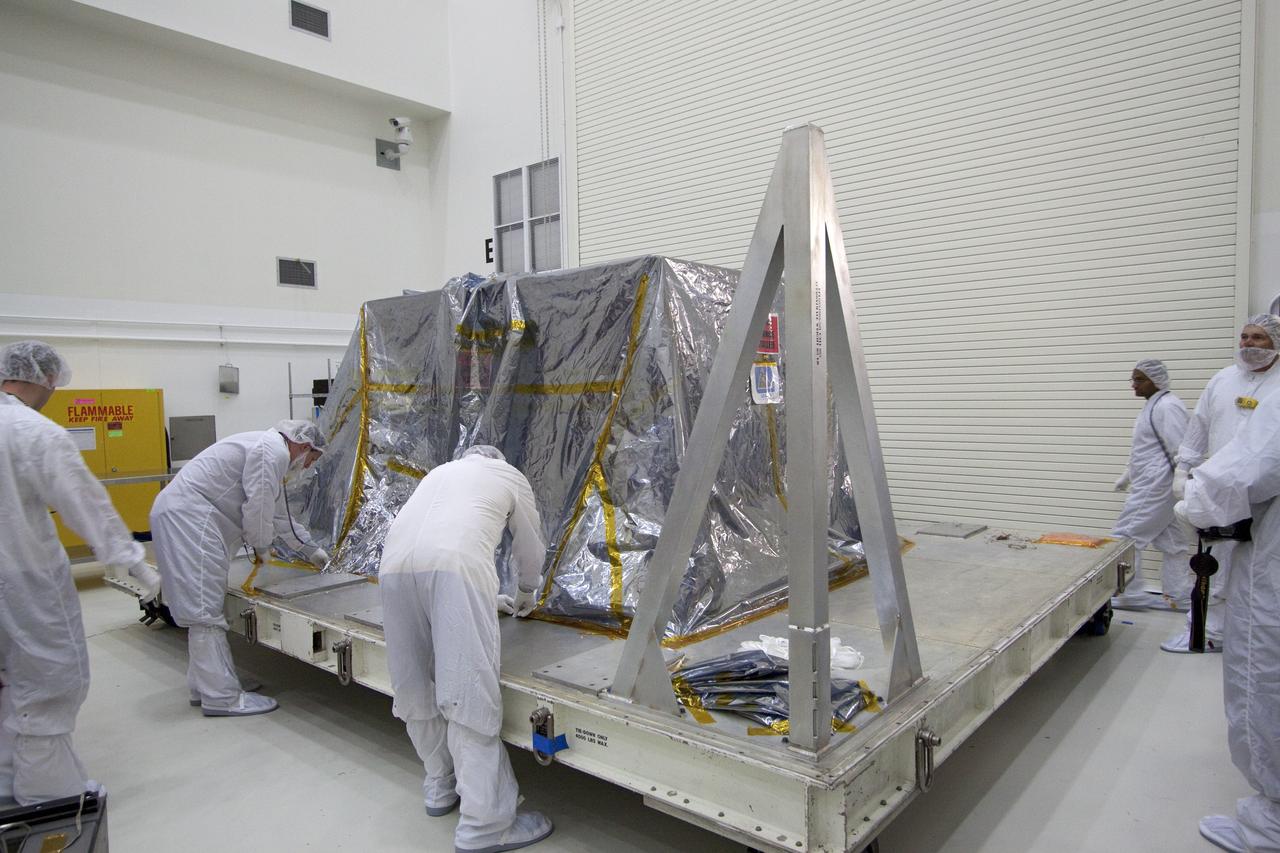

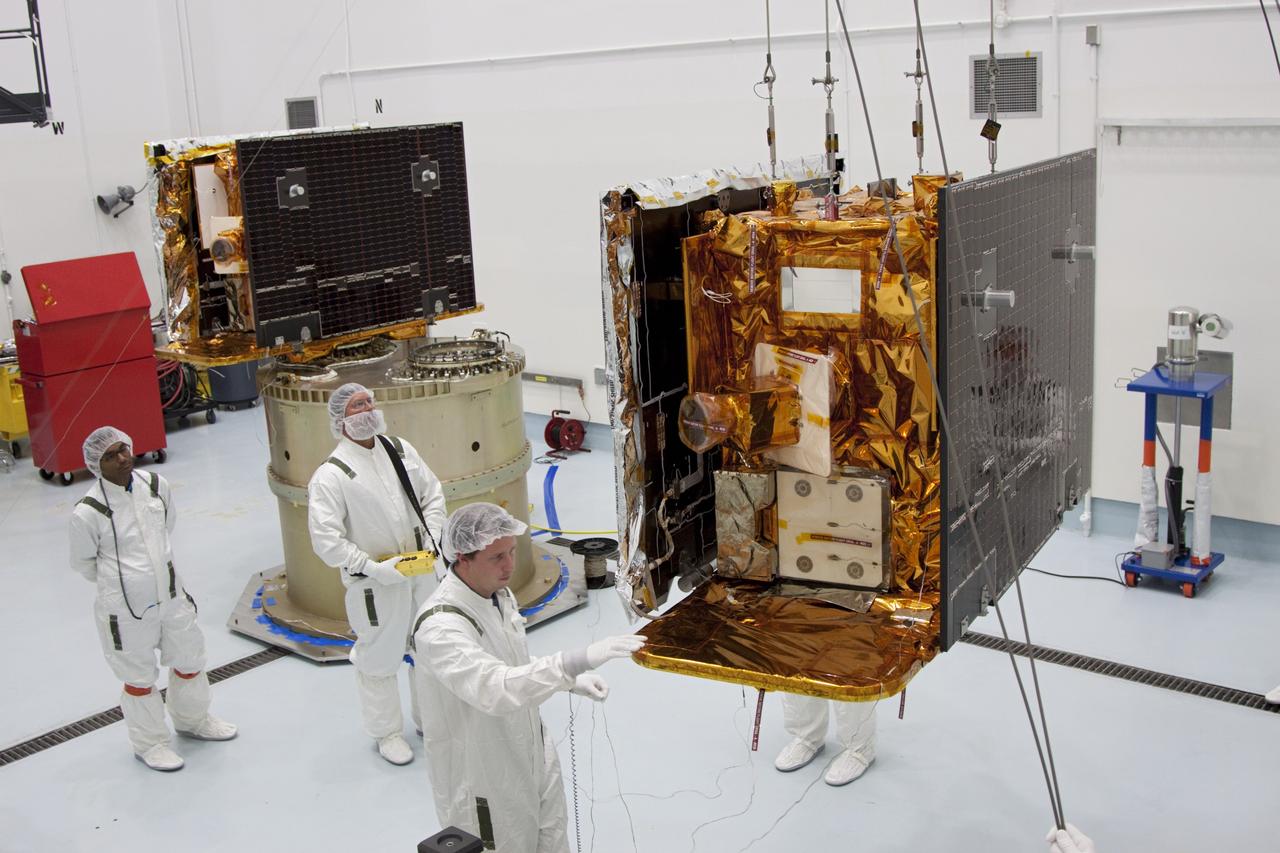
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., remove the protective cover from NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL, twin spacecraft to begin testing and processing. GRAIL was built at the Lockheed Martin plant in Denver, Colo. The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry GRAIL into lunar orbit already is fully stacked at NASA's Space Launch Complex 17B and launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. The GRAIL mission is a part of NASA's Discovery Program. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. The mission also will answer longstanding questions about Earth's moon and provide scientists a better understanding of how Earth and other rocky planets in the solar system formed. For more information, visit http://science.nasa.gov/missions/grail/. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
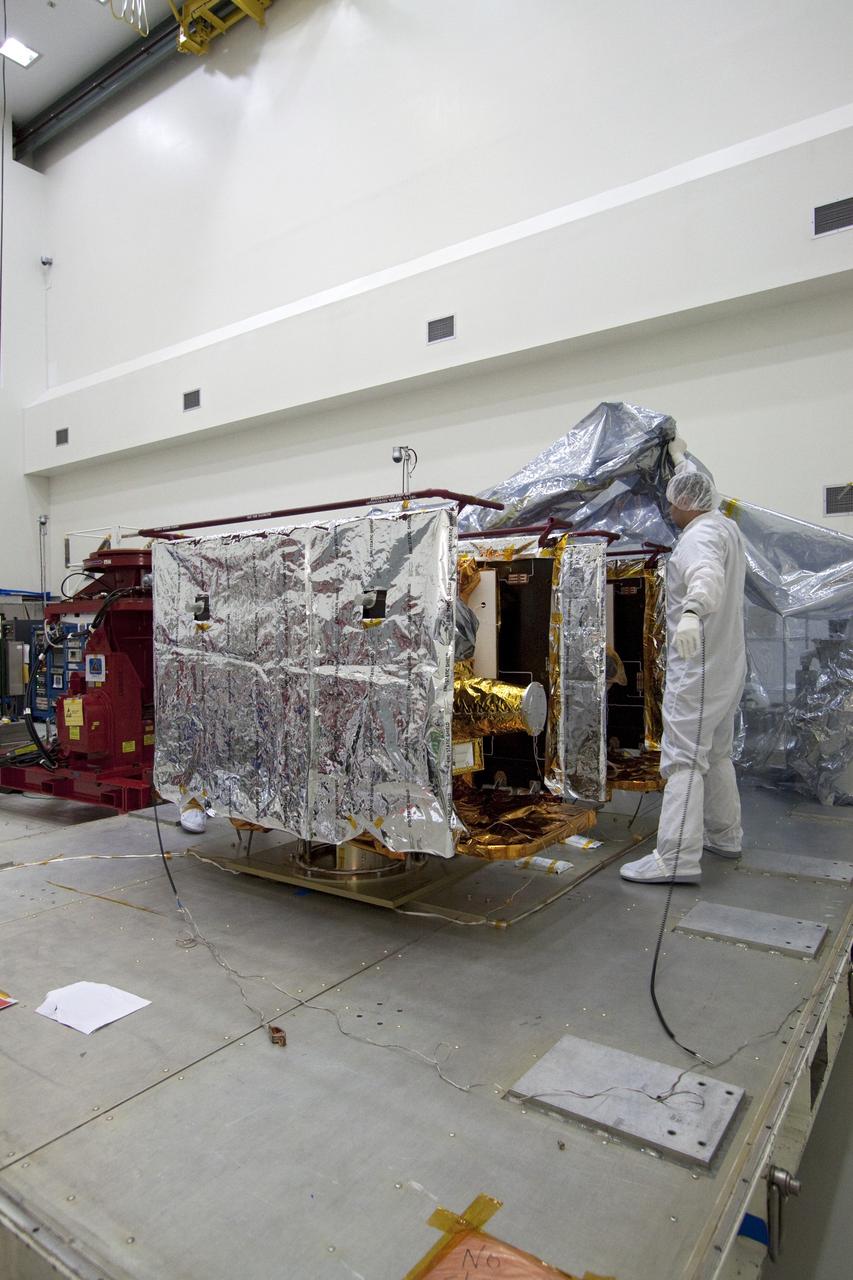

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., remove the protective cover from NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL, twin spacecraft to begin testing and processing. GRAIL was built at the Lockheed Martin plant in Denver, Colo. The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry GRAIL into lunar orbit already is fully stacked at NASA's Space Launch Complex 17B and launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. The GRAIL mission is a part of NASA's Discovery Program. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. The mission also will answer longstanding questions about Earth's moon and provide scientists a better understanding of how Earth and other rocky planets in the solar system formed. For more information, visit http://science.nasa.gov/missions/grail/. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
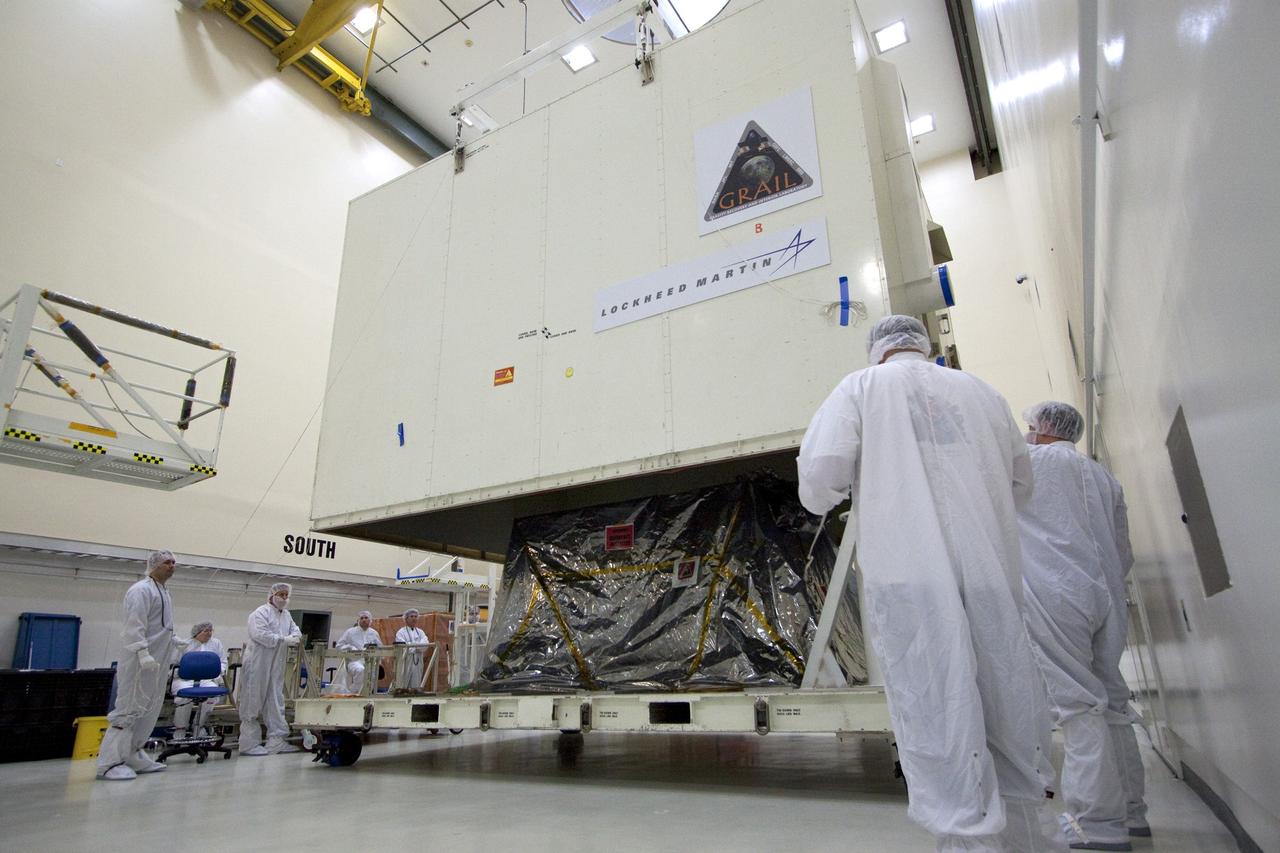

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., unpack NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL, twin spacecraft for testing and processing. GRAIL was built at the Lockheed Martin plant in Denver, Colo. The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry GRAIL into lunar orbit already is fully stacked at NASA's Space Launch Complex 17B and launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. The GRAIL mission is a part of NASA's Discovery Program. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. The mission also will answer longstanding questions about Earth's moon and provide scientists a better understanding of how Earth and other rocky planets in the solar system formed. For more information, visit http://science.nasa.gov/missions/grail/. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
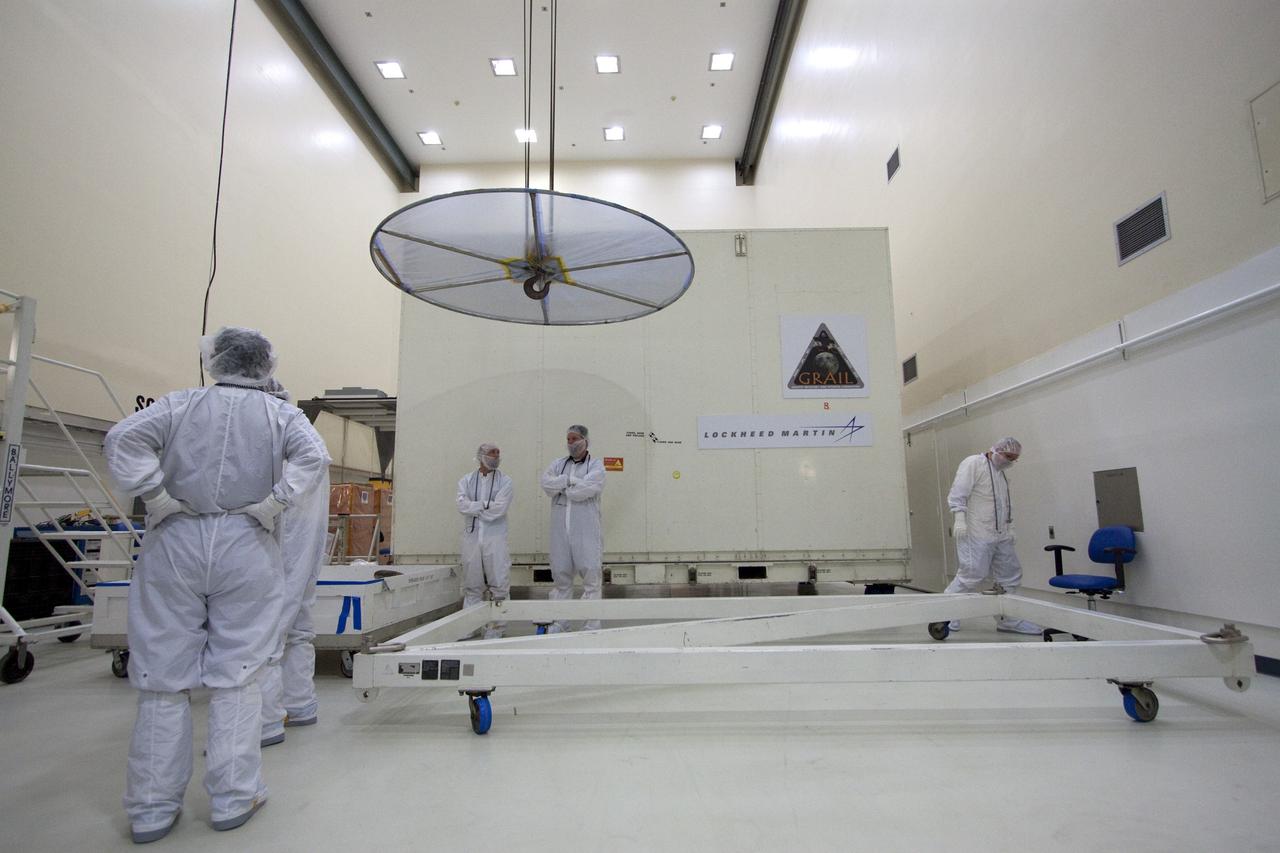

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., prepare to unpack NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL, twin spacecraft for testing and processing. GRAIL was built at the Lockheed Martin plant in Denver, Colo. The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry GRAIL into lunar orbit already is fully stacked at NASA's Space Launch Complex 17B and launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. The GRAIL mission is a part of NASA's Discovery Program. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. The mission also will answer longstanding questions about Earth's moon and provide scientists a better understanding of how Earth and other rocky planets in the solar system formed. For more information, visit http://science.nasa.gov/missions/grail/. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
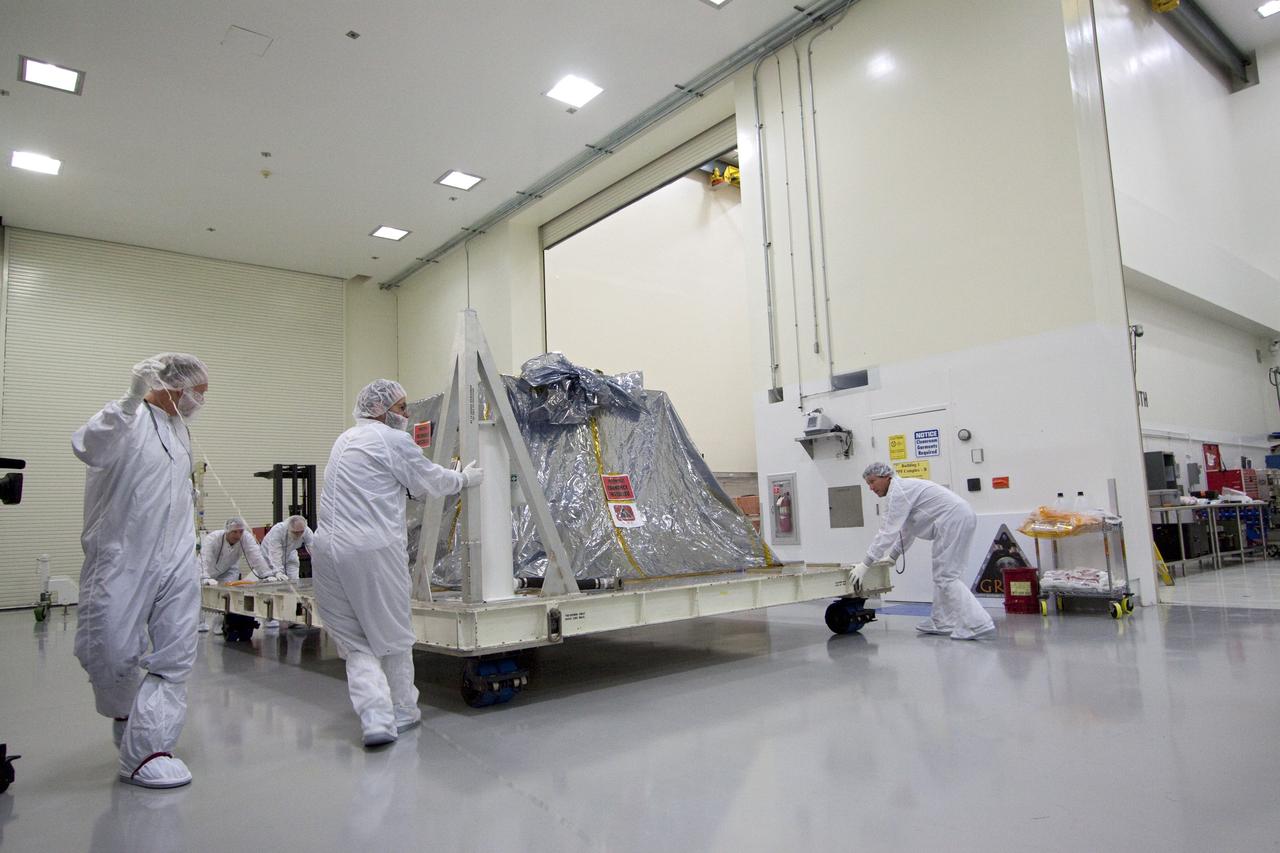

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., roll NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL, twin spacecraft toward a test stand where they will be processed for launch. GRAIL was built at the Lockheed Martin plant in Denver, Colo. The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry GRAIL into lunar orbit already is fully stacked at NASA's Space Launch Complex 17B and launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. The GRAIL mission is a part of NASA's Discovery Program. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. The mission also will answer longstanding questions about Earth's moon and provide scientists a better understanding of how Earth and other rocky planets in the solar system formed. For more information, visit http://science.nasa.gov/missions/grail/. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
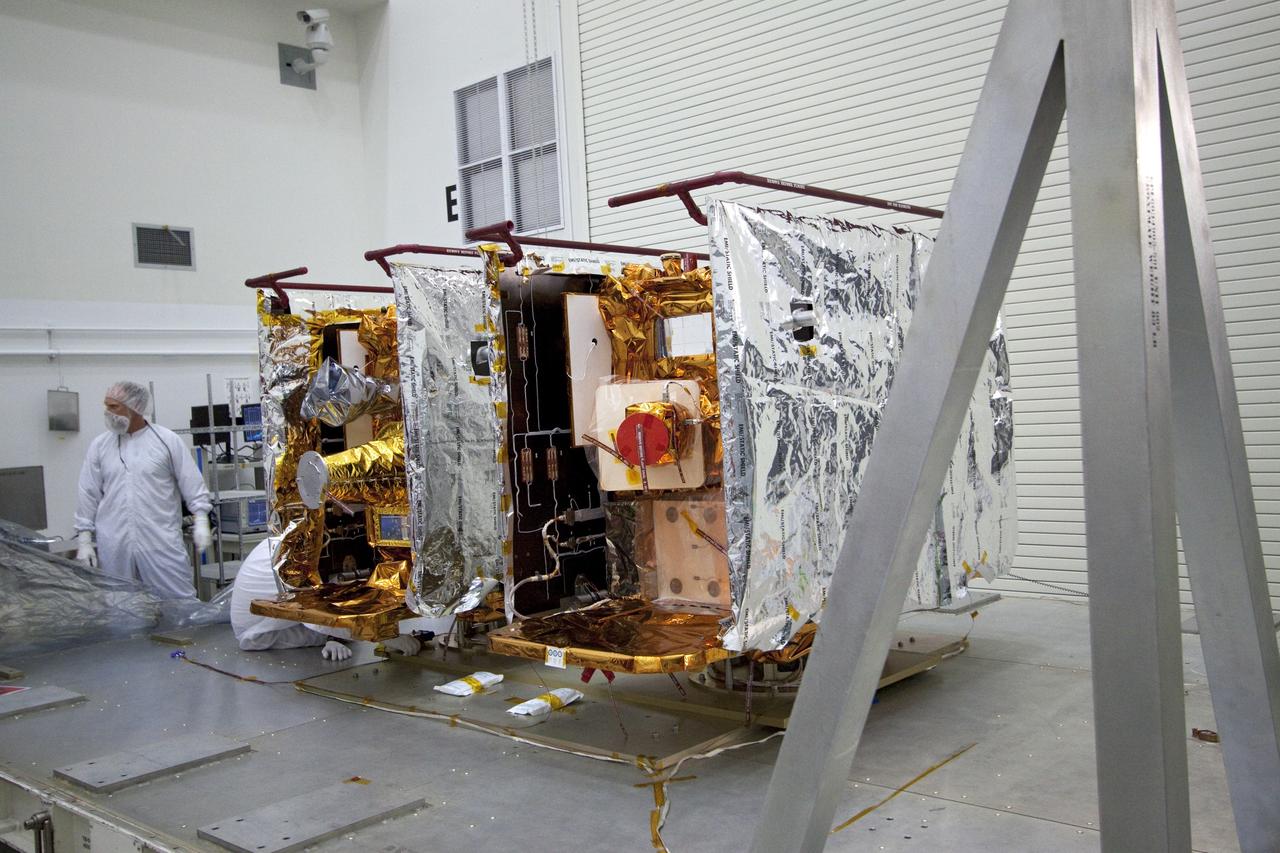

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., prepare NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL, twin spacecraft for testing and processing. GRAIL was built at the Lockheed Martin plant in Denver, Colo. The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry GRAIL into lunar orbit already is fully stacked at NASA's Space Launch Complex 17B and launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. The GRAIL mission is a part of NASA's Discovery Program. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. The mission also will answer longstanding questions about Earth's moon and provide scientists a better understanding of how Earth and other rocky planets in the solar system formed. For more information, visit http://science.nasa.gov/missions/grail/. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
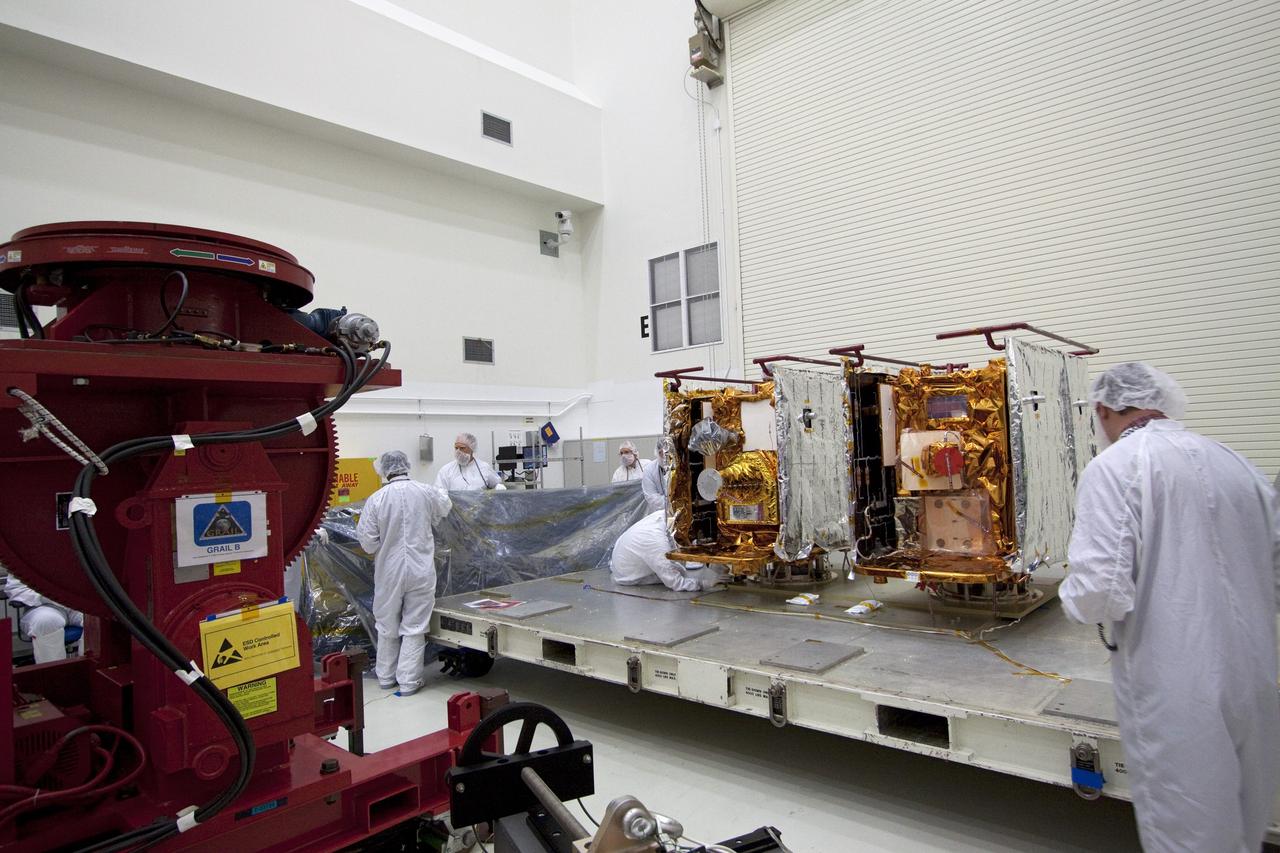

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., prepare NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL, twin spacecraft for testing and processing. GRAIL was built at the Lockheed Martin plant in Denver, Colo. The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry GRAIL into lunar orbit already is fully stacked at NASA's Space Launch Complex 17B and launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. The GRAIL mission is a part of NASA's Discovery Program. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. The mission also will answer longstanding questions about Earth's moon and provide scientists a better understanding of how Earth and other rocky planets in the solar system formed. For more information, visit http://science.nasa.gov/missions/grail/. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
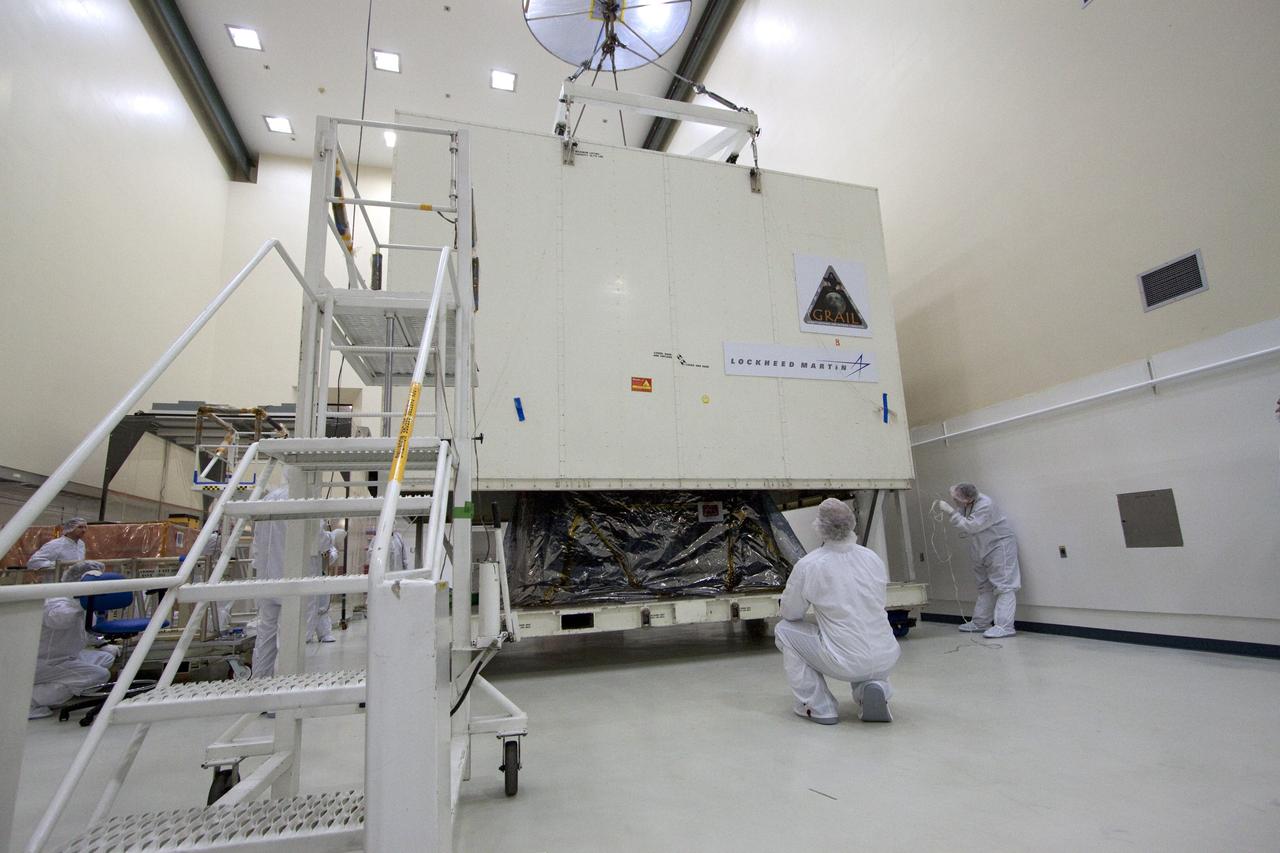

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., begin to unpack NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL, twin spacecraft for testing and processing. GRAIL was built at the Lockheed Martin plant in Denver, Colo. The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry GRAIL into lunar orbit already is fully stacked at NASA's Space Launch Complex 17B and launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. The GRAIL mission is a part of NASA's Discovery Program. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. The mission also will answer longstanding questions about Earth's moon and provide scientists a better understanding of how Earth and other rocky planets in the solar system formed. For more information, visit http://science.nasa.gov/missions/grail/. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
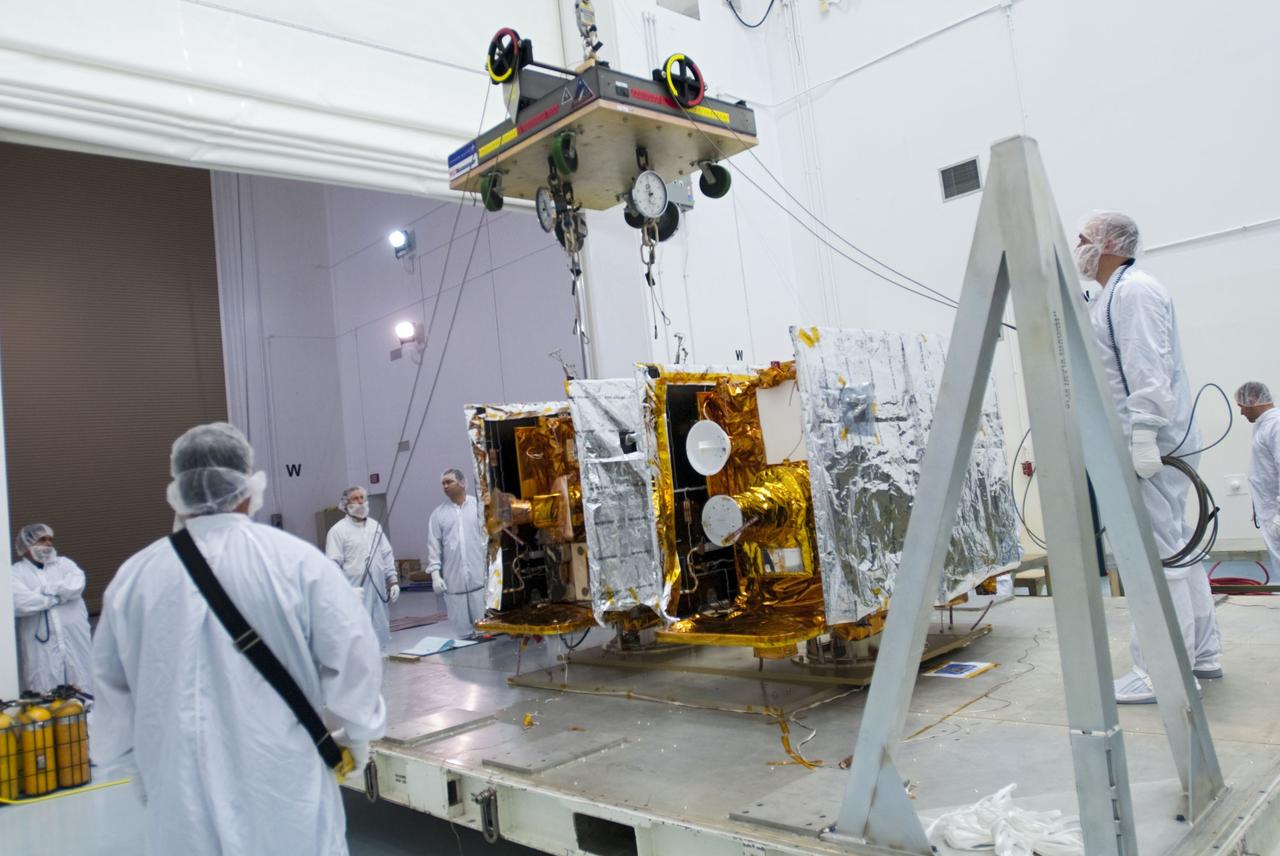

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Preparations are under way to lift one of NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft onto a workstand in the Hazardous Processing Facility (HPF) at Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. In the HPF, the spacecraft will undergo two days of fueling activities. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians push NASA's mylar-covered twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft toward the work area of the Hazardous Processing Facility (HPF) at Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. In the HPF, the spacecraft will undergo two days of fueling activities. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
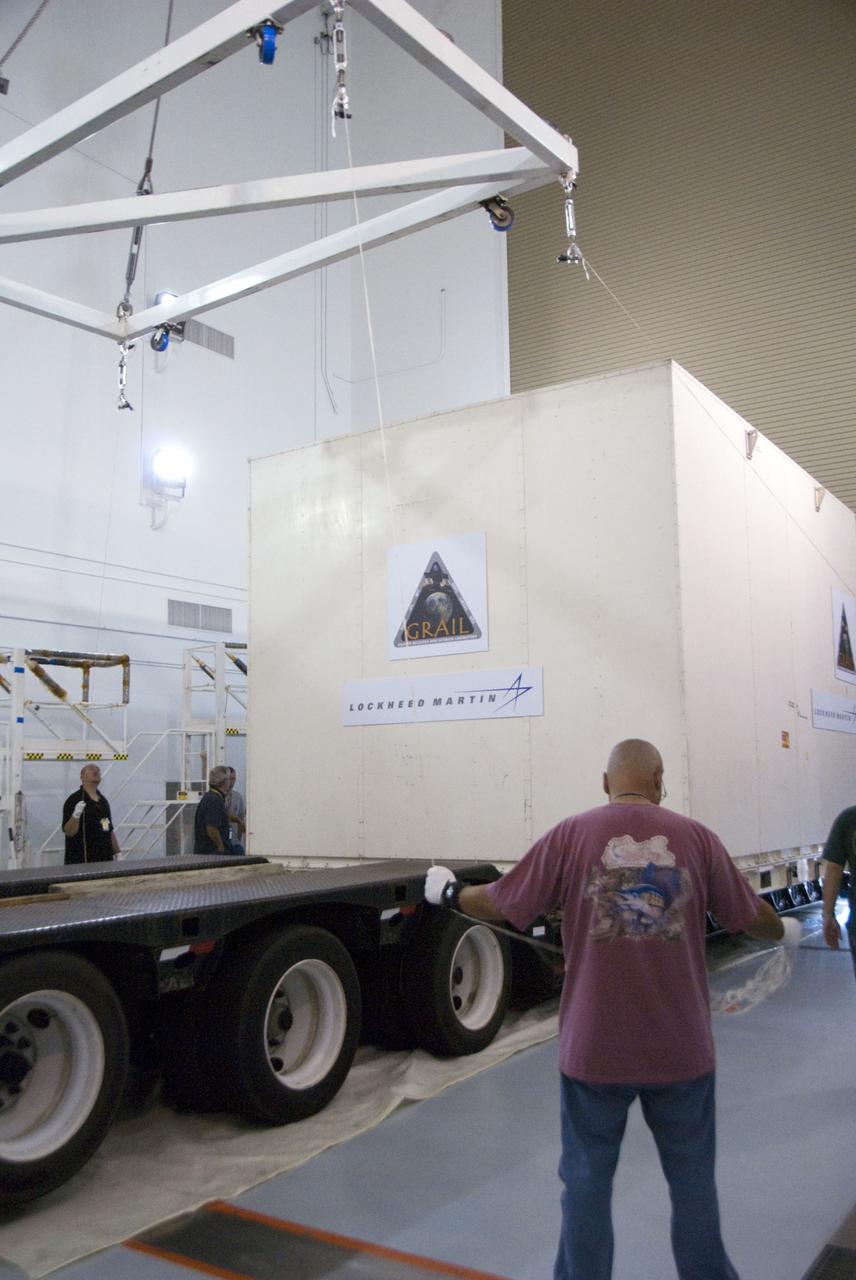

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians oversee the lift of the protective canister housing NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft from the transporter in the Hazardous Processing Facility (HPF) at Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. In the HPF, the spacecraft will undergo two days of fueling activities. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
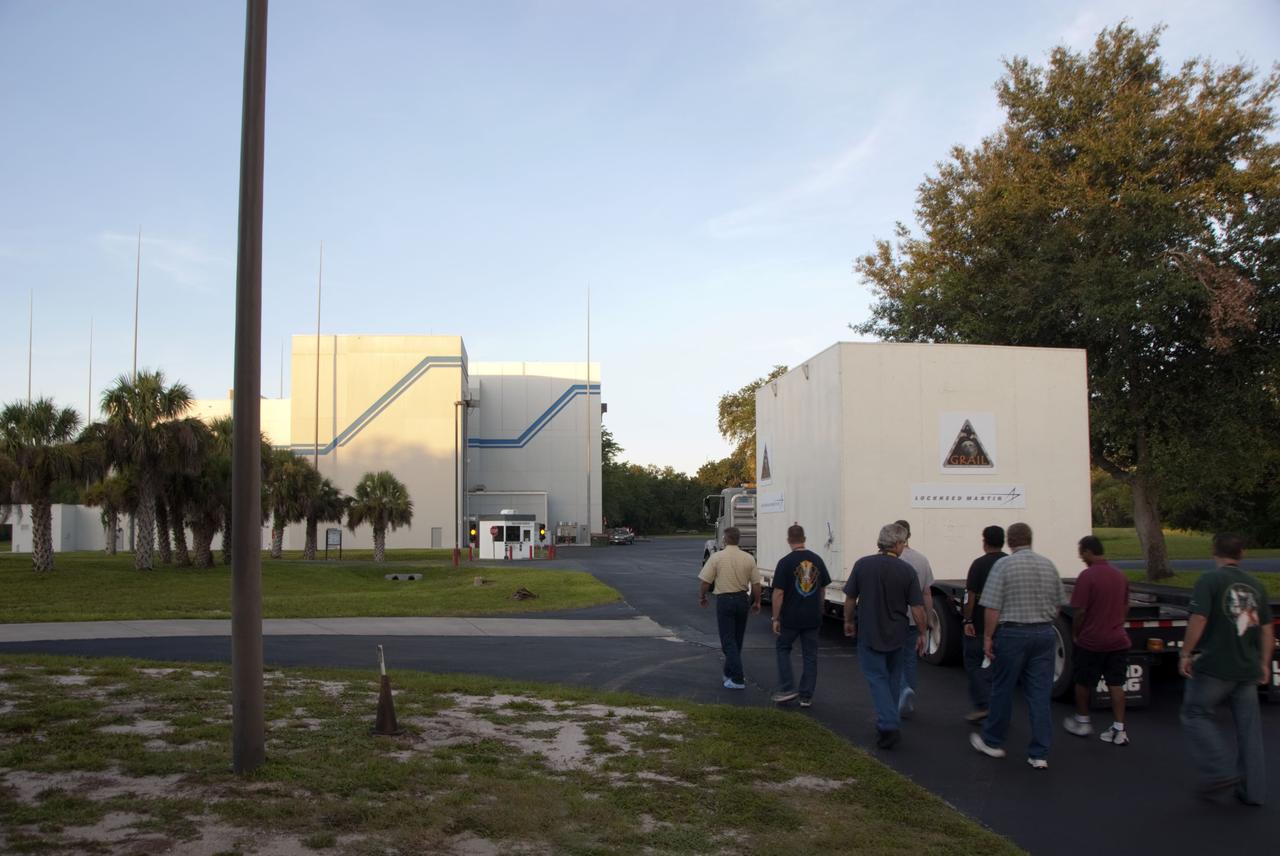

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians escort the protective canister housing NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft to the Hazardous Processing Facility (HPF) at Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. In the HPF, the spacecraft will undergo two days of fueling activities. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
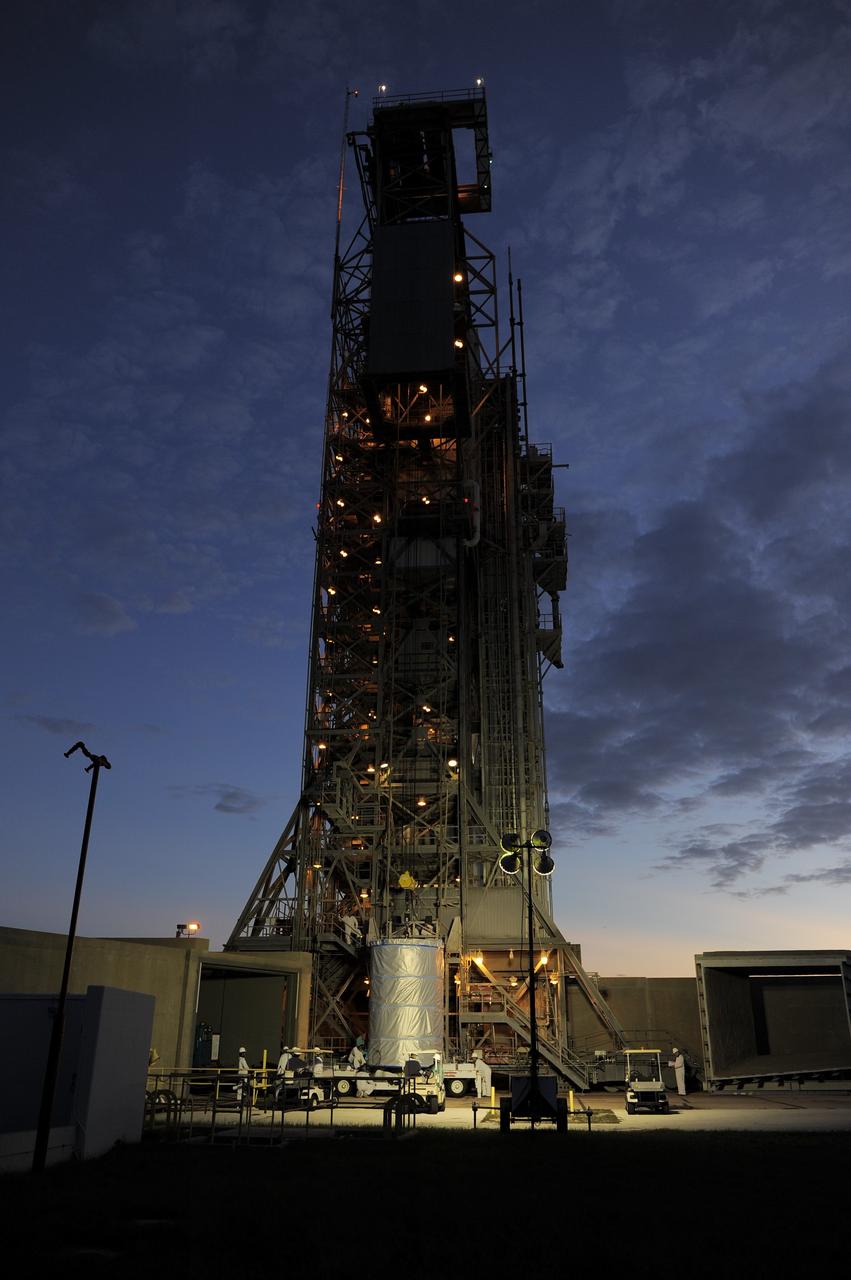

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft are lifted to the top of their launch pad at Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room in the Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
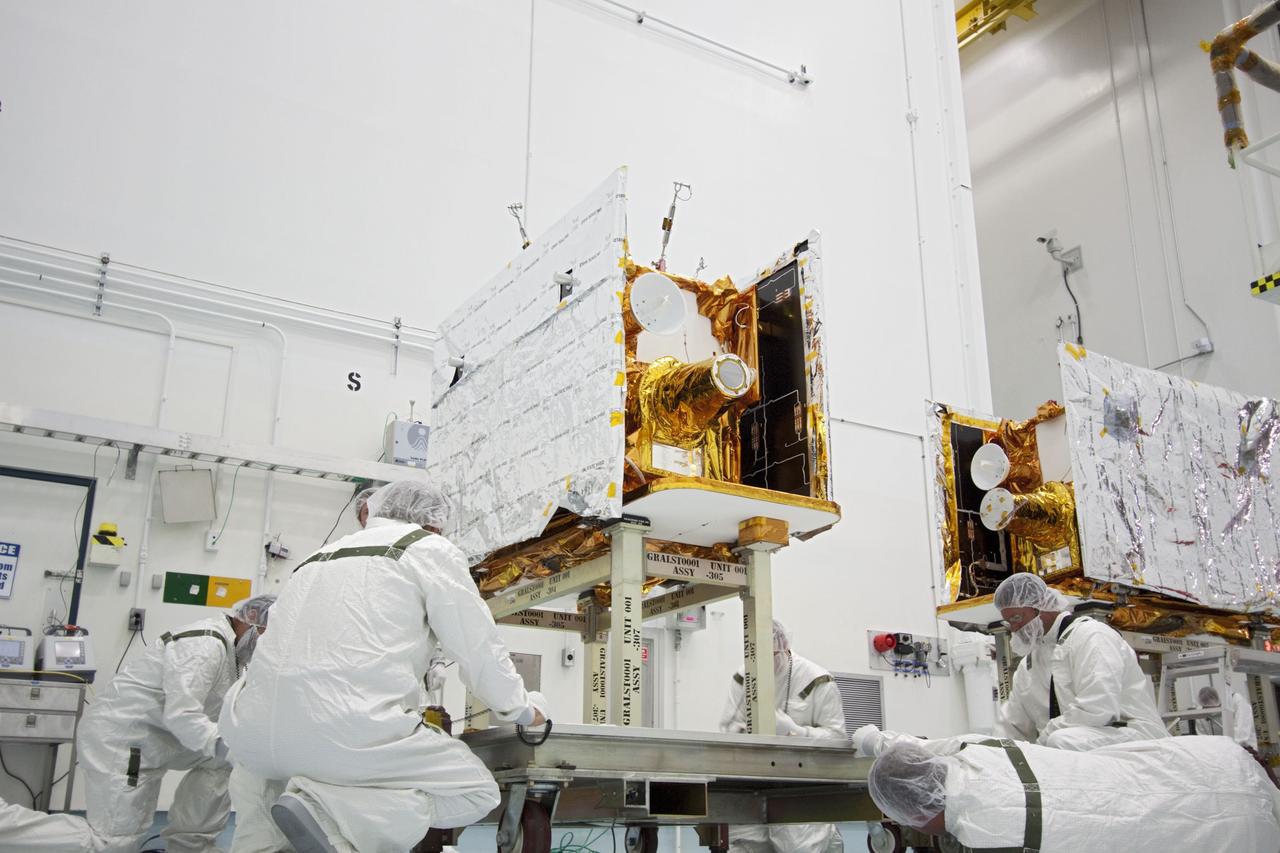

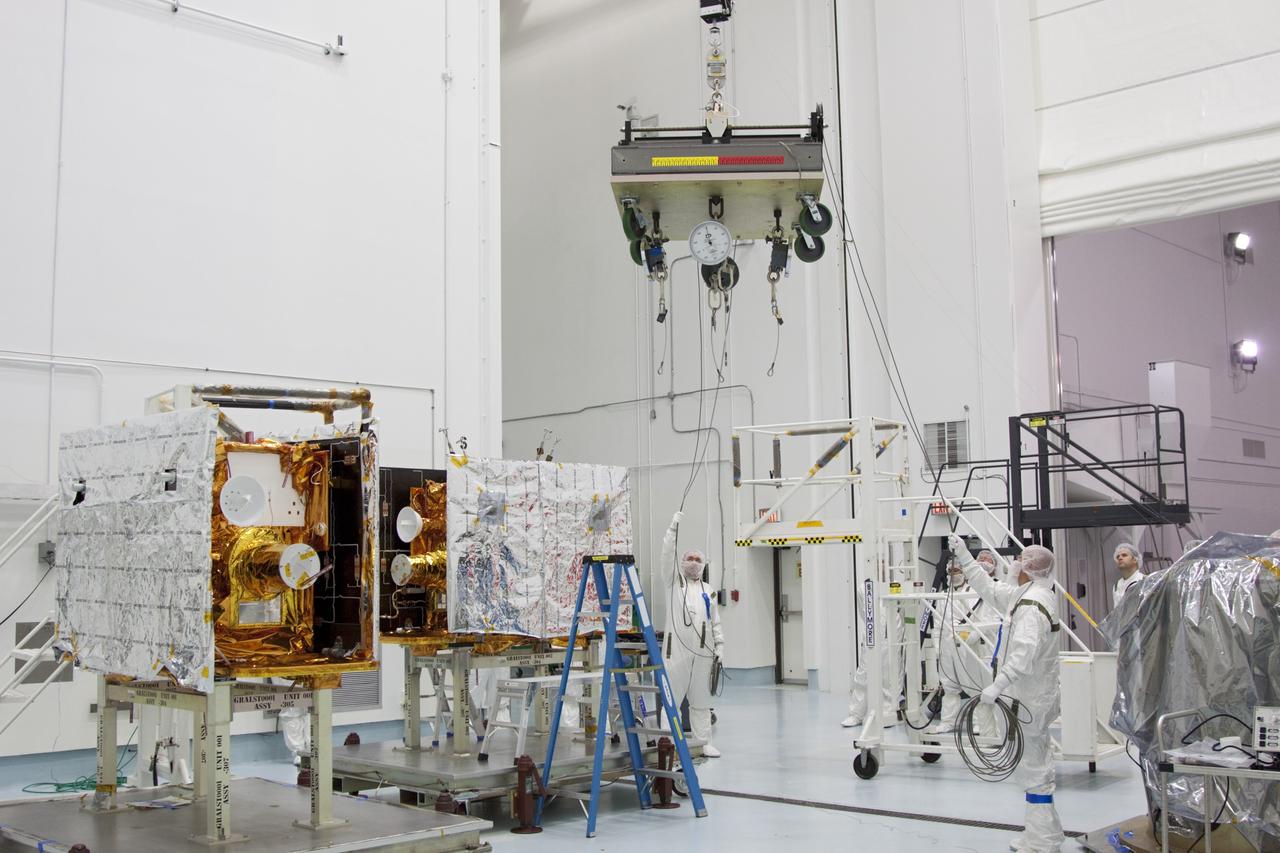
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., preparations are under way to stack NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft in their launch configuration on the spacecraft adapter ring for transport to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
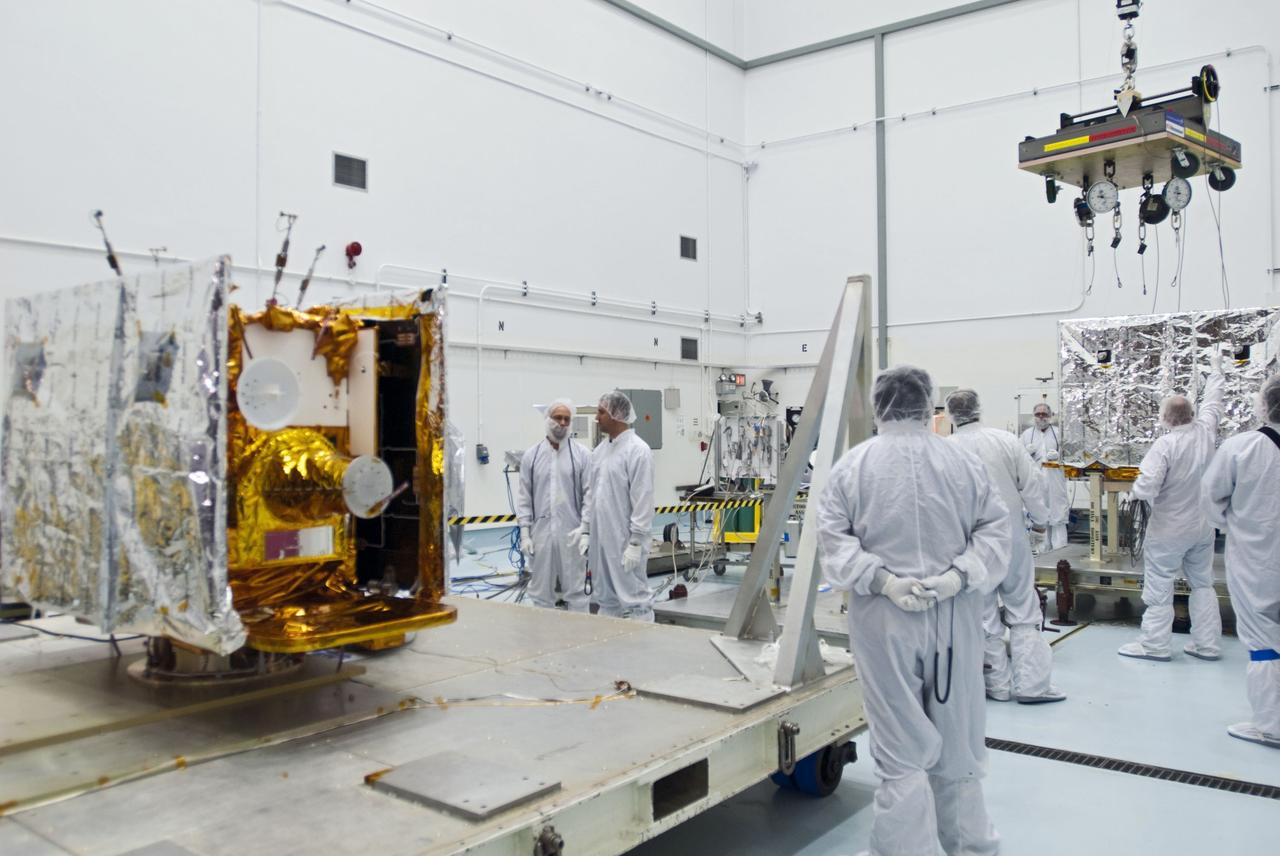

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians prepare to move the second of NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft to a workstand in the Hazardous Processing Facility (HPF) at Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. In the HPF, the spacecraft will undergo two days of fueling activities. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
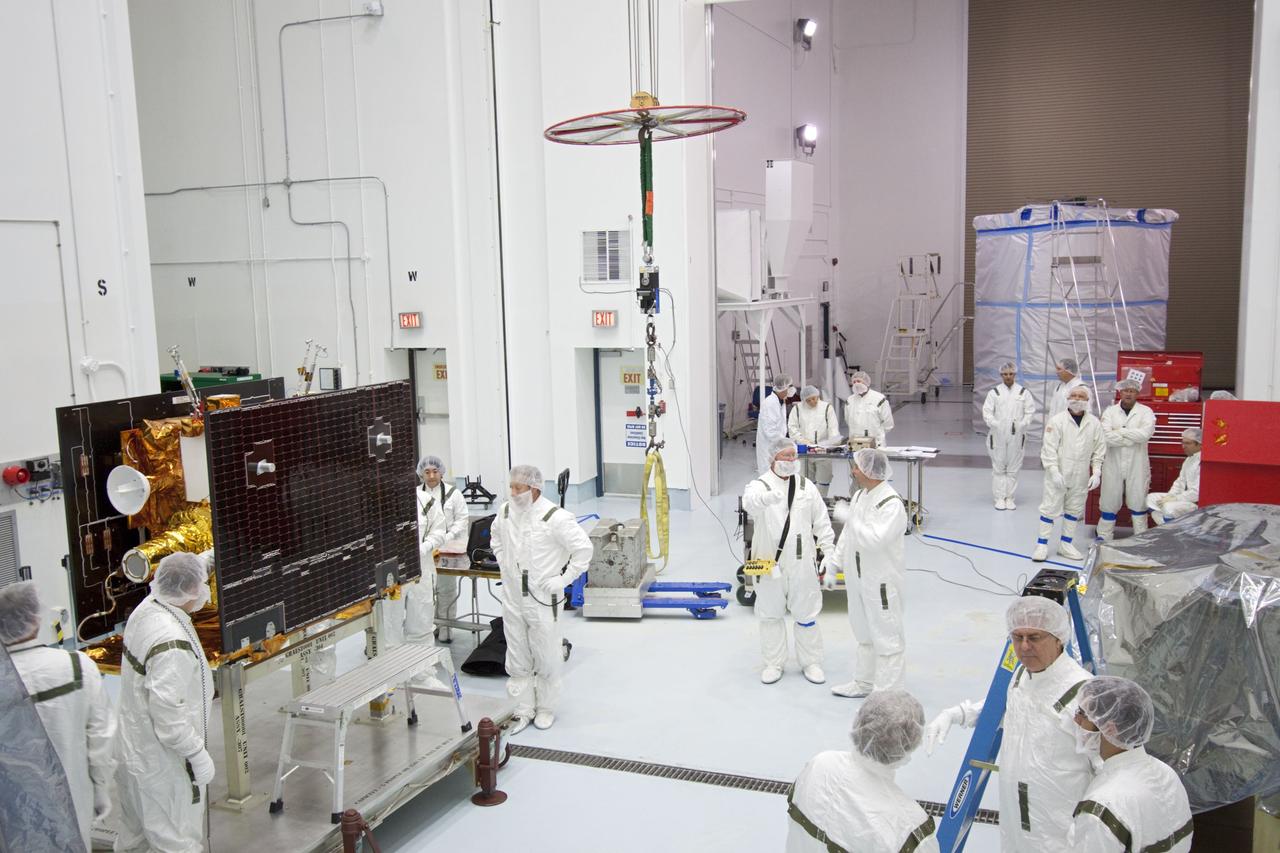

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., preparations are under way to determine the weight of one of NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft before the spacecraft are stacked in their launch configuration in readiness for transport to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
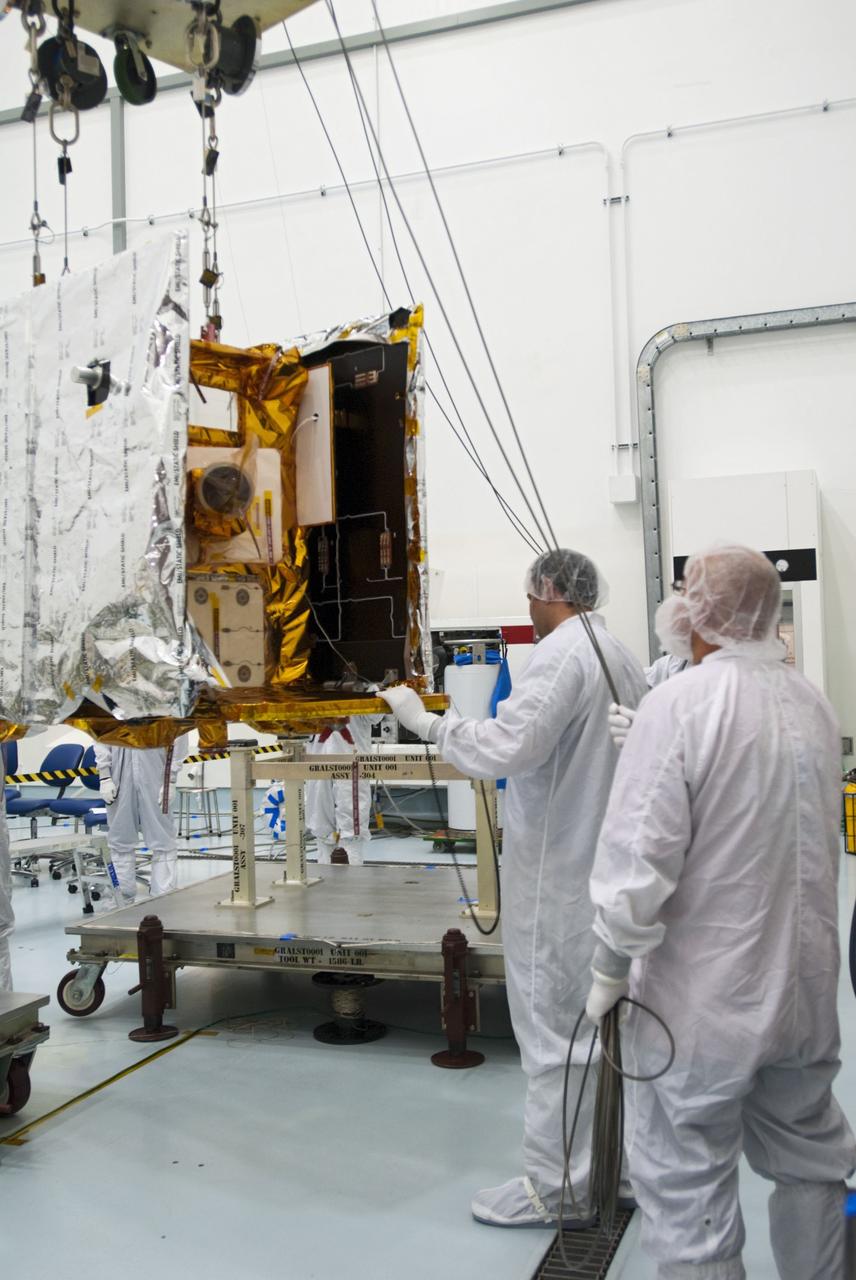

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians move one of NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft toward a workstand in the Hazardous Processing Facility (HPF) at Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. In the HPF, the spacecraft will undergo two days of fueling activities. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
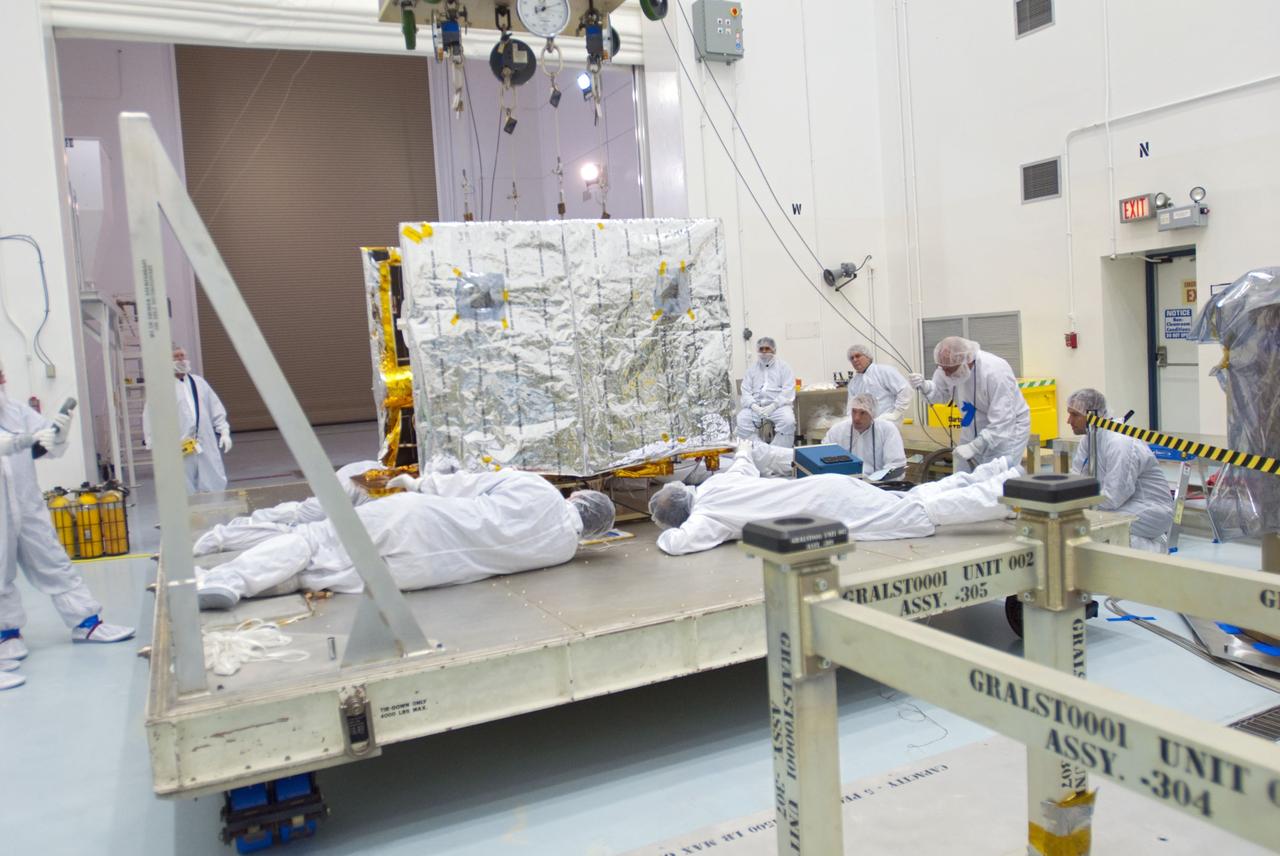

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians inspect the second of NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft as they prepare to move it to a workstand in the Hazardous Processing Facility (HPF) at Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. In the HPF, the spacecraft will undergo two days of fueling activities. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
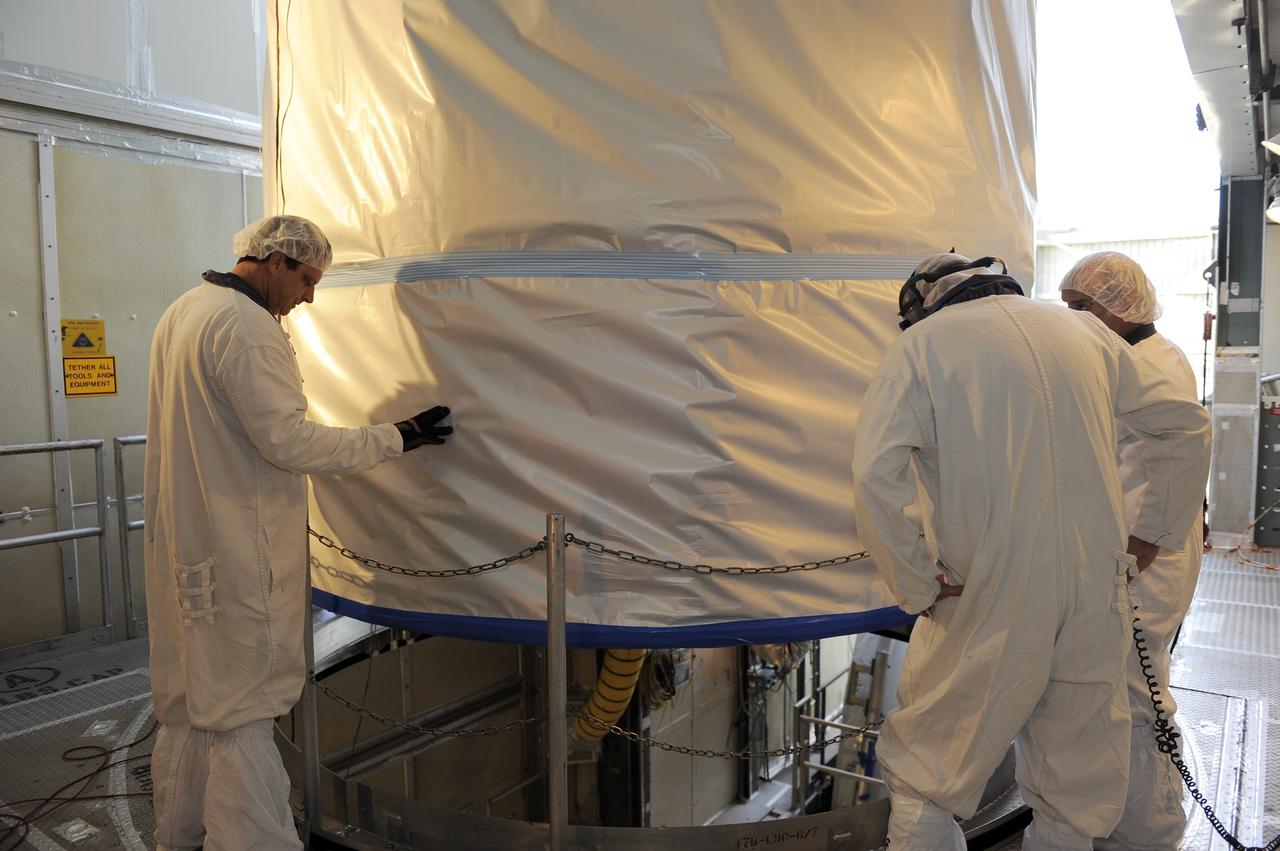

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians lower NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft into place atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket on Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
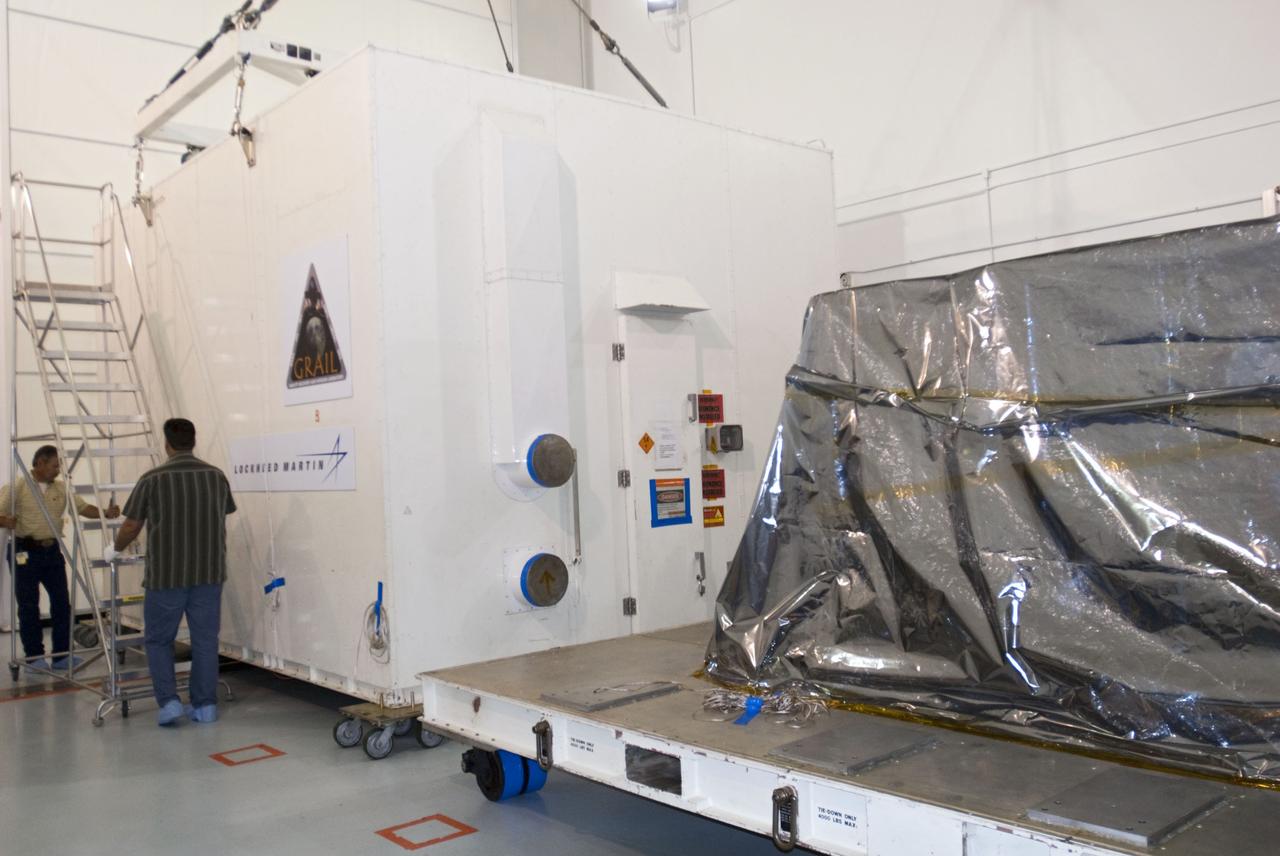

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The protective canister housing NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft is rolled away from the mylar-covered spacecraft in the Hazardous Processing Facility (HPF) at Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. In the HPF, the spacecraft will undergo two days of fueling activities. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
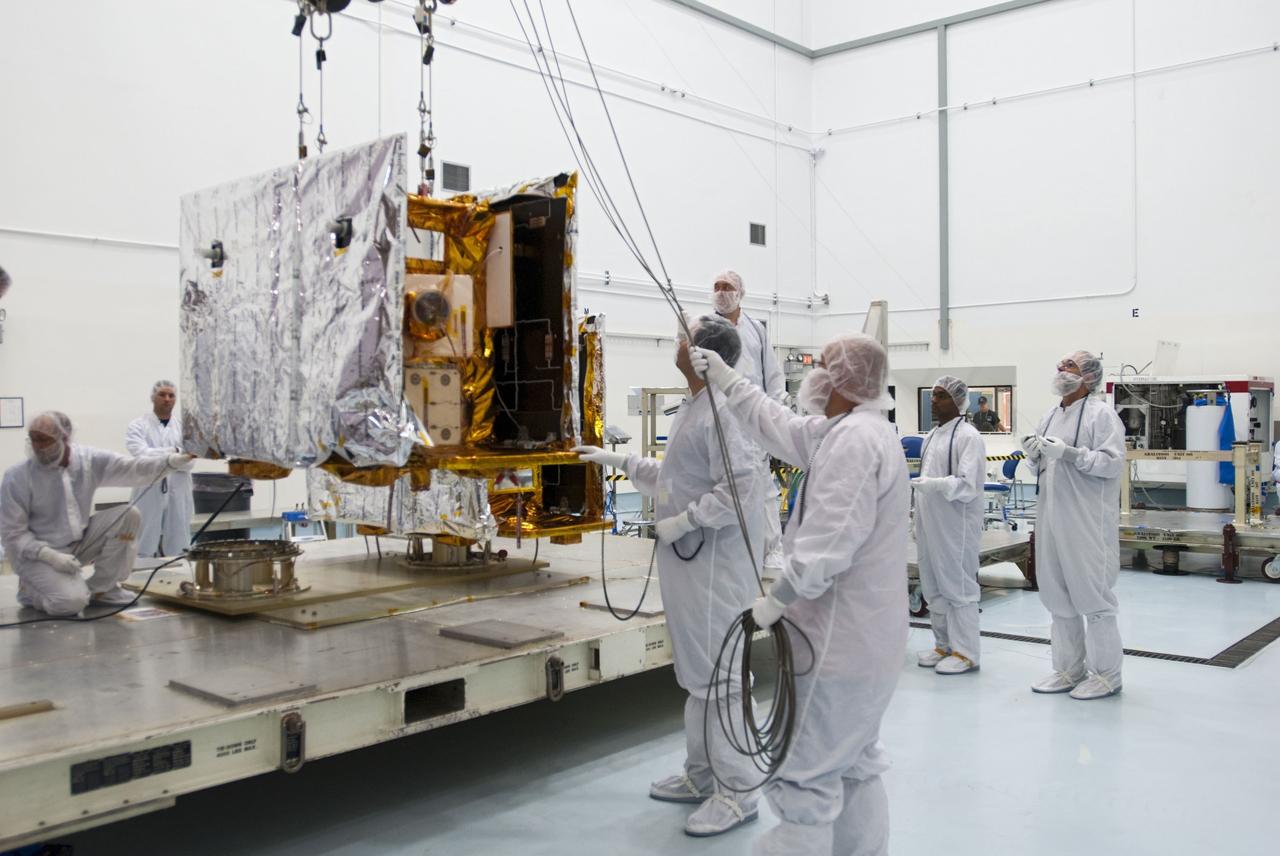

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- One of NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft is lifted from its transporter for placement on a workstand in the Hazardous Processing Facility (HPF) at Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. In the HPF, the spacecraft will undergo two days of fueling activities. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
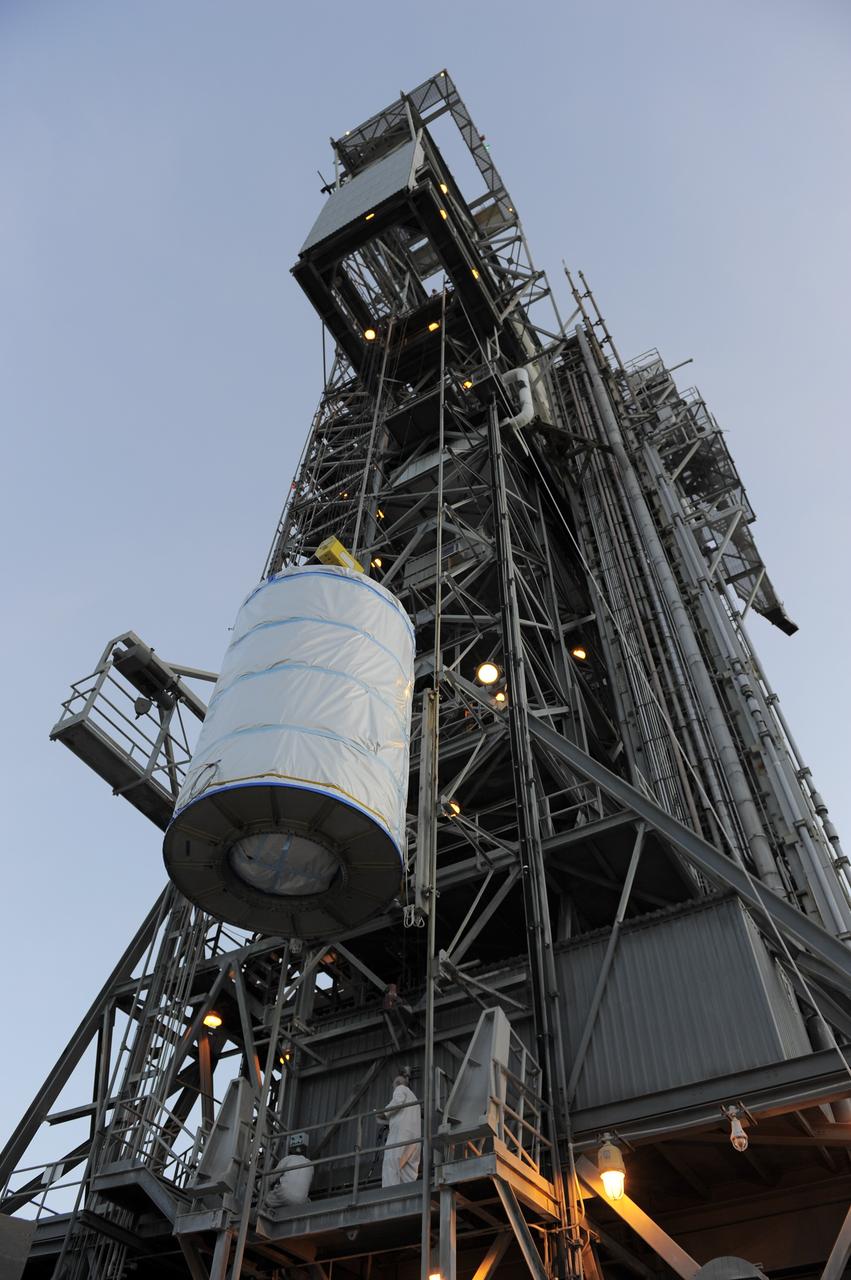

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft are lifted to the top of their launch pad at Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room in the Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
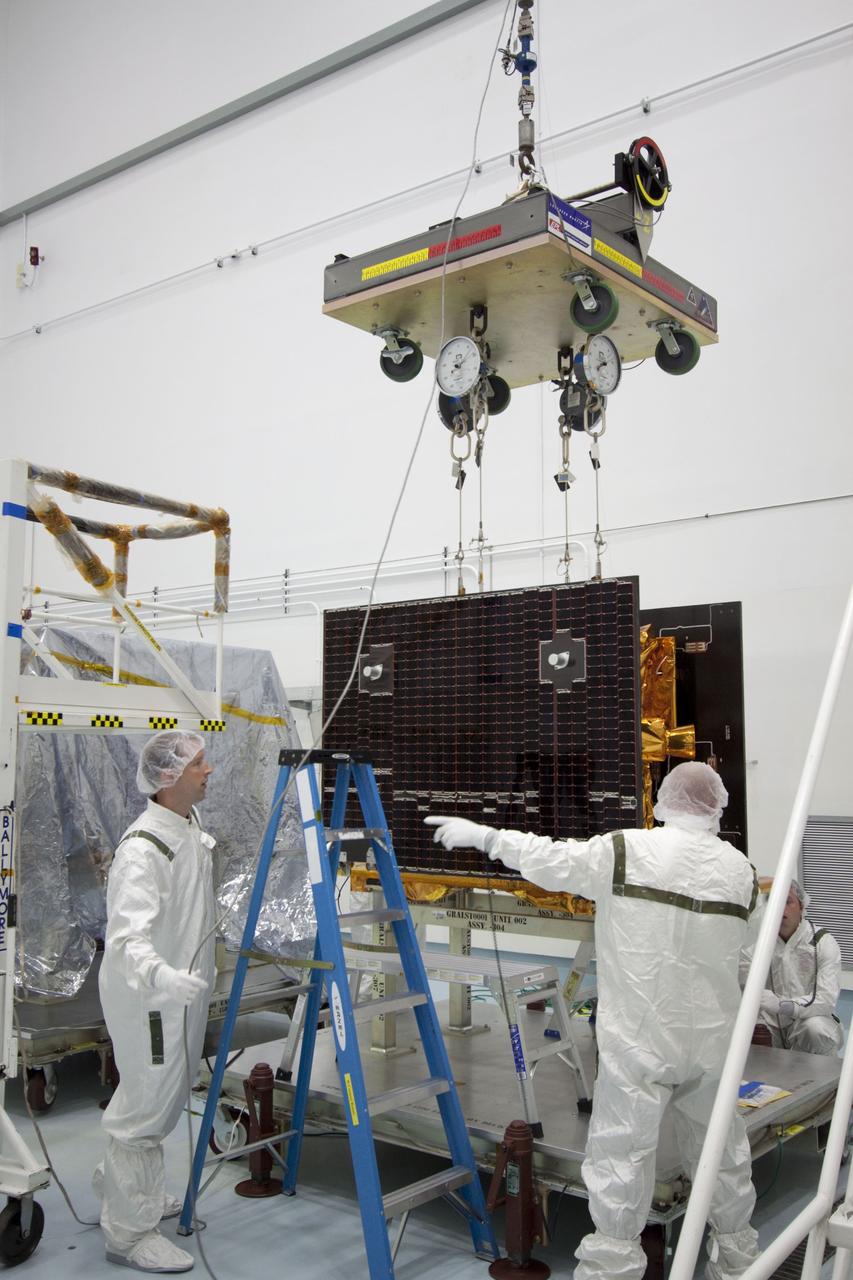

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians move a portable scale toward one of NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft. The spacecraft will be lifted and weighed before they are stacked in their launch configuration in preparation for transport to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
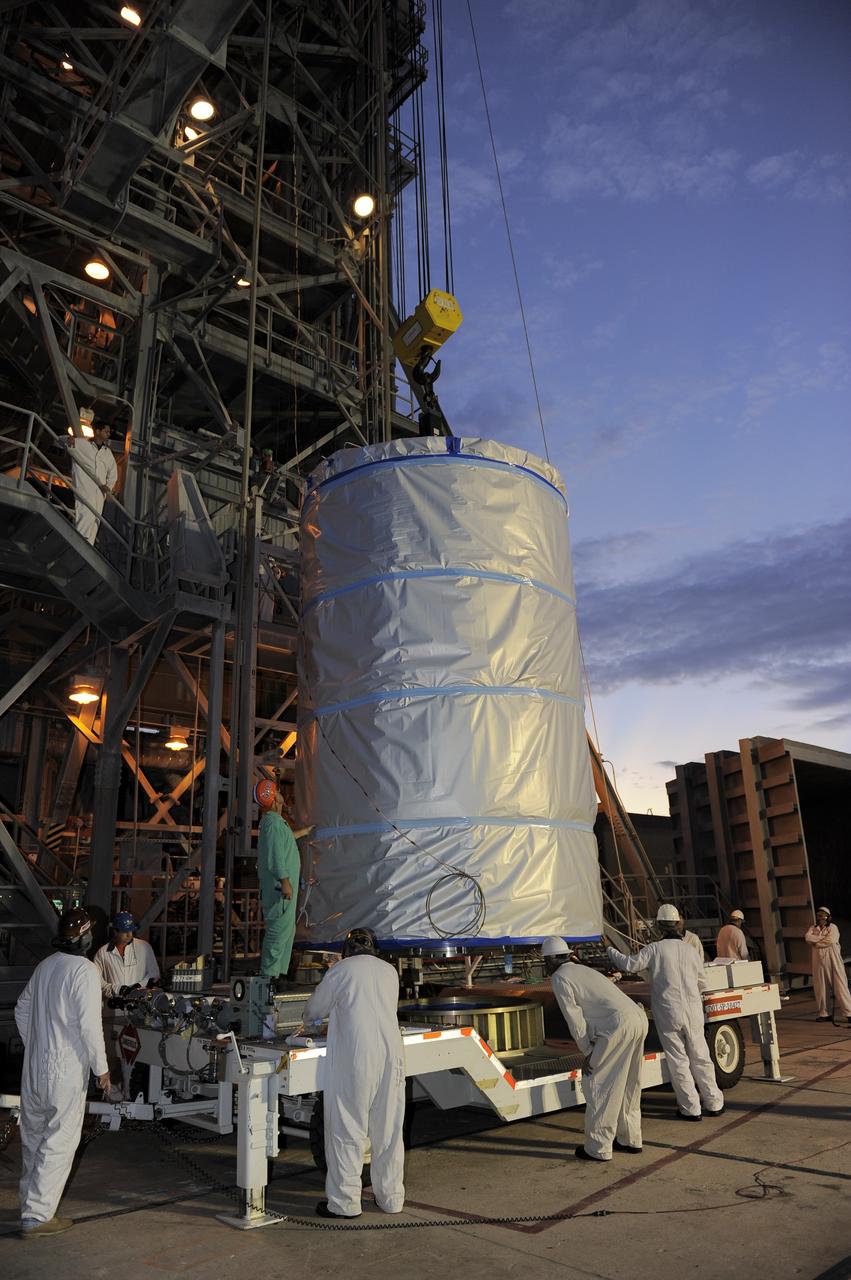

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft are lifted to the top of their launch pad at Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room in the Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians lower one of NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft onto a workstand in the Hazardous Processing Facility (HPF) at Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. In the HPF, the spacecraft will undergo two days of fueling activities. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser