
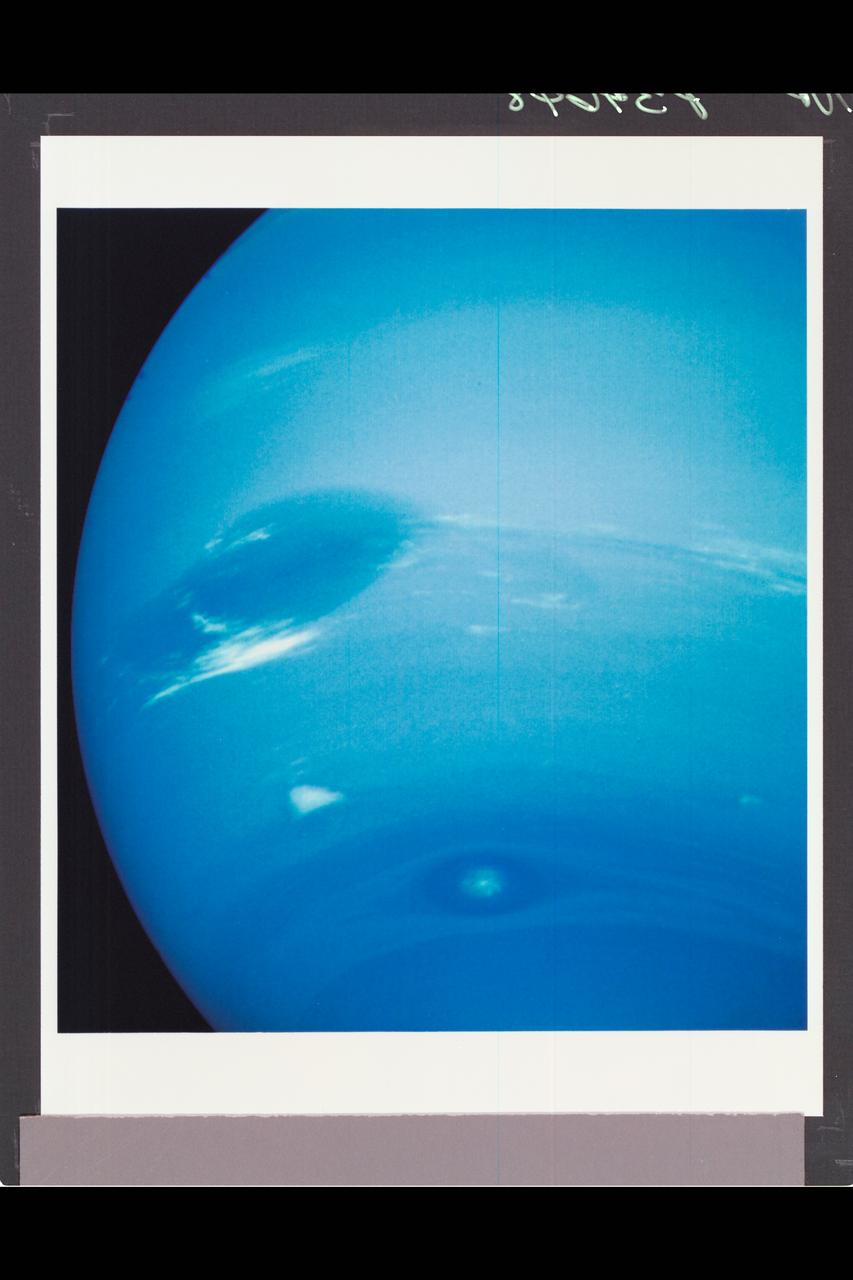
This photograph shows the last face on view of the Great Dark Spot that Voyager will make with the narrow angle camera. The image was shuttered 45 hours before closest approach at a distance of 2.8 million kilometers (1.7 million miles). The smallest structures that can be seen are of an order of 50 kilometers (31 miles). The image shows feathery white clouds that overlie the boundary of the dark and light blue regions. The pinwheel (spiral) structure of both the dark boundary and the white cirrus suggest a storm system rotating counterclockwise. Periodic small scale patterns in the white cloud, possibly waves, are short lived and do not persist from one Neptunian rotation to the next. This color composite was made from the clear and green filters of the narrow-angle camera. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00052

This picture of Neptune was produced from the last whole planet images taken through the green and orange filters on NASA's Voyager 2 narrow angle camera. The images were taken at a range of 4.4 million miles from the planet, 4 days and 20 hours before closest approach. The picture shows the Great Dark Spot and its companion bright smudge; on the west limb the fast moving bright feature called Scooter and the little dark spot are visible. These clouds were seen to persist for as long as Voyager's cameras could resolve them. North of these, a bright cloud band similar to the south polar streak may be seen. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01492
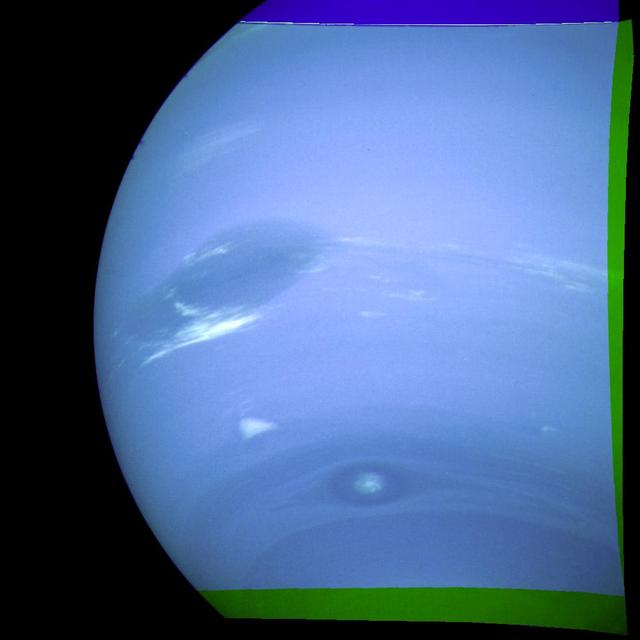
This photograph of Neptune was reconstructed from two images taken by NASA Voyager 2. At the north top is the Great Dark Spot. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00049
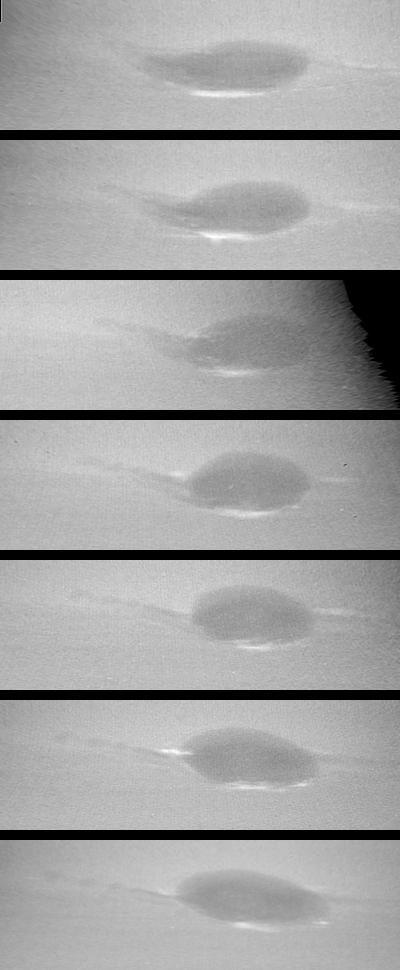
These images taken by NASA Voyager 2 show changes in the clouds around Neptune Great Dark Spot GDS over a four and one-half-day period. From top to bottom the images show successive rotations of the planet an interval of about 18 hours. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00045

This clear filter image was acquired by NASA Voyager 2 on Aug. 14, 1989. The image shows a dark feature extending westward left and northward up toward the equator from the Great Dark Spot GDS.
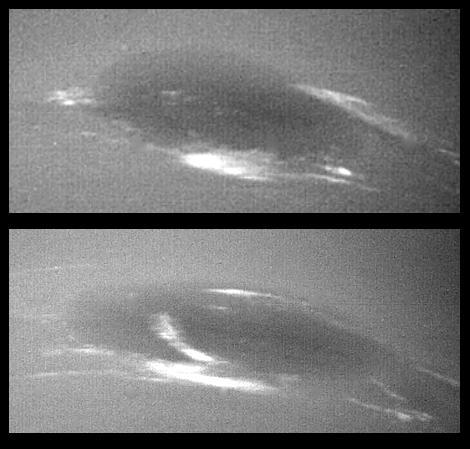
The bright cirrus-like clouds of Neptune change rapidly, often forming and dissipating over periods of several to tens of hours. In this sequence NASA Voyager 2 observed cloud evolution in the region around the Great Dark Spot GDS.

This photograph of Neptune shows three of the features that NASA Voyager 2 has been photographing during recent weeks. At the north is the Great Dark Spot, accompanied by bright, white clouds that undergo rapid changes in appearance.

This photo was taken by NASA Voyager 2 wide-angle camera. Light at methane wavelengths is mostly absorbed in the deeper atmosphere. The bright, white feature is a high-altitude cloud just south of the Great Dark Spot.

This photograph of Neptune was reconstructed from two images taken by NASA Voyager 2. At the north top is the Great Dark Spot, accompanied by bright, white clouds that undergo rapid changes in appearance.
Range : 12 million km (7.5 million miles) Resolution 110 km (68 miles) per pixel. These 2 images of Neptune were taken by Voyager 2's narrow-angle camera. During the 17.6 hours between the left and right images, the Great Dark Spot, at 22 degrees south latitude (left of center), has completed a little less than one rotation of Neptune. The smaller dark spot, at 54 south, completed a little more than one rotation, as can be seen by comparing its relative positions in the two pictures. The Great Dark Spot and the smaller spot have a relative velocity of 100 meters per second (220 miles an hour). The light and dark bands circling Neptune indicate predominantly zonal (east-west) motion. The diffuse white feature north of the Great Dark Spot is near Neptune's equator, and rotates with about the same period as the Great Dark Spot. Streak of bright clouds at the south edge, and just east of the Great Dark Spot, are its constatnt companions, and change the details of their appearance, often within a few hours. Changing brightness of the cloud streaks could be a result of vertical mortions.

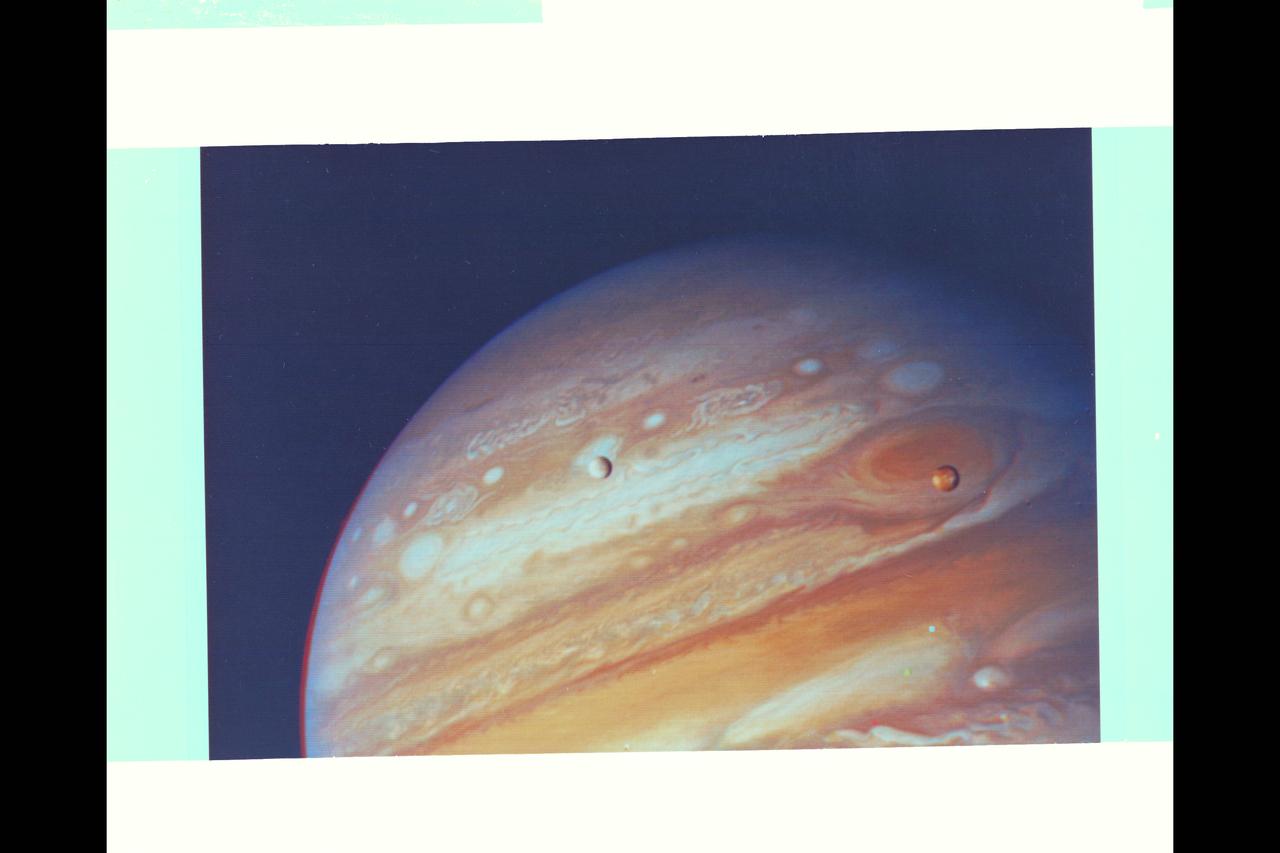
NASA's Voyager 1 took this photo of Jupiter and two of its satellites Io, left, and Europa on Feb. 13, 1979. Io is above Jupiter Great Red Spot; Europa is above Jupiter clouds. The poles are dark and reddish. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00144

On July 23, 1989, NASA Voyager 2 spacecraft took this picture of Neptune through a clear filter on its narrow-angle camera. The image on the right has a latitude and longitude grid added for reference. Neptune Great Dark Spot is visible on the left.

In 1995, NASA Hubble Space Telescope discovered a new great dark spot, located in the northern hemisphere of the planet Neptune. Because the planet northern hemisphere was tilted away from Earth, the new feature appeared near the limb of the planet.

This image of Neptune was taken by NASA Voyager 2 wide-angle camera; small trails of similar clouds trending east to west and large scale structure east of the Great Dark Spot all suggest that waves are present in the atmosphere and play a large role. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00063
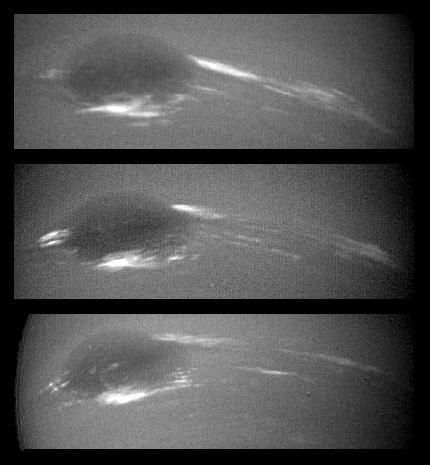
The bright cirrus-like clouds of Neptune change rapidly, often forming and dissipating over periods of several to tens of hours as seen in this sequence spanning two rotations of Neptune about 36 hours by NASA Voyager 2. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00047

This image of clouds in Neptune atmosphere is the first that tests the accuracy of the weather forecast that was made eight days earlier to select targets for NASA Voyager narrow angle camera. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00048
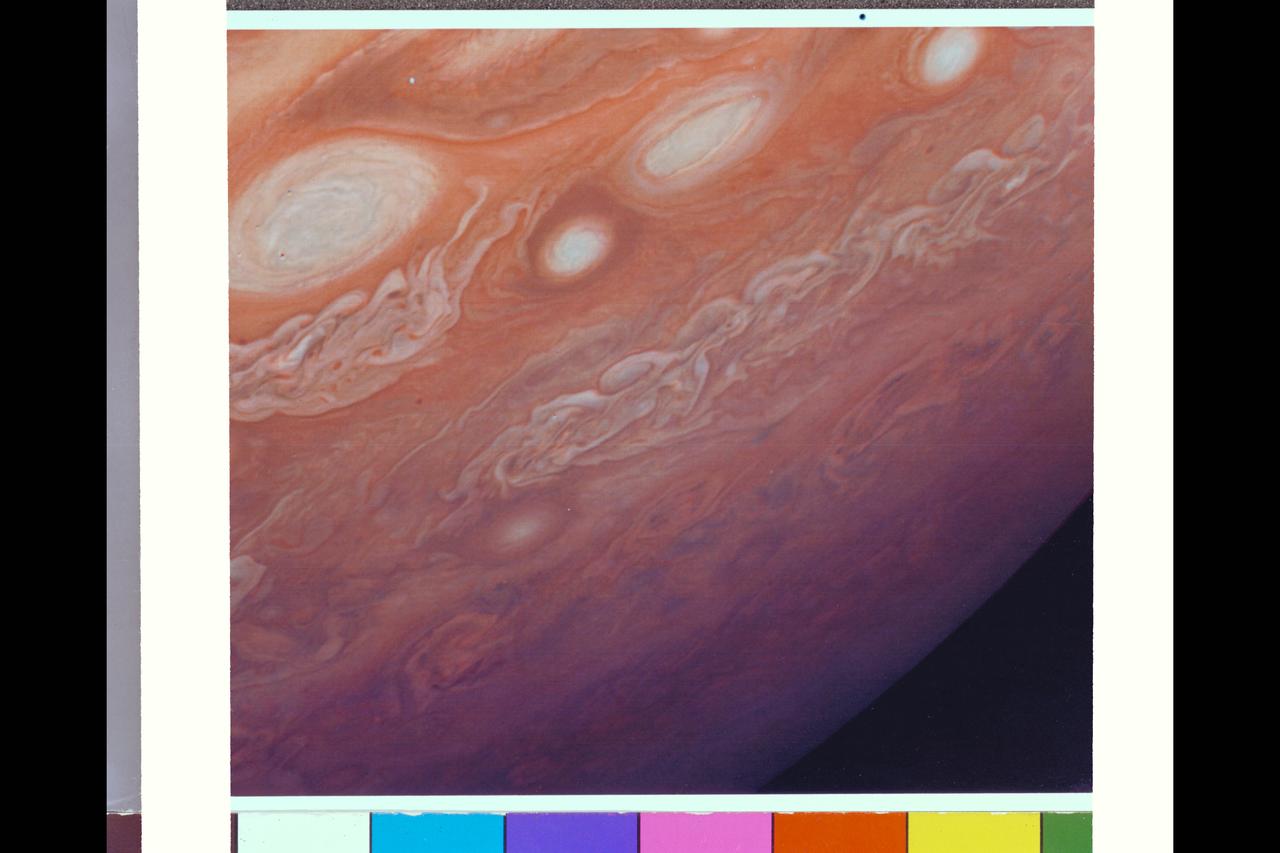

Range : 4.3 million km. ( 2.7 million miles ) This photograph taken from Voyager I, shows the area east of the Great Red Spot. The dark halo surrounding the bright spot, just to the right of the bright oval, is said by scientists to be, almost certainly, a five micron hot spot. This is a region of the atmosphere warmer than those around it. The dark halo may represent an area in which we are looking deeper into Jupiter's Atmosphere, although not yet completely understood.
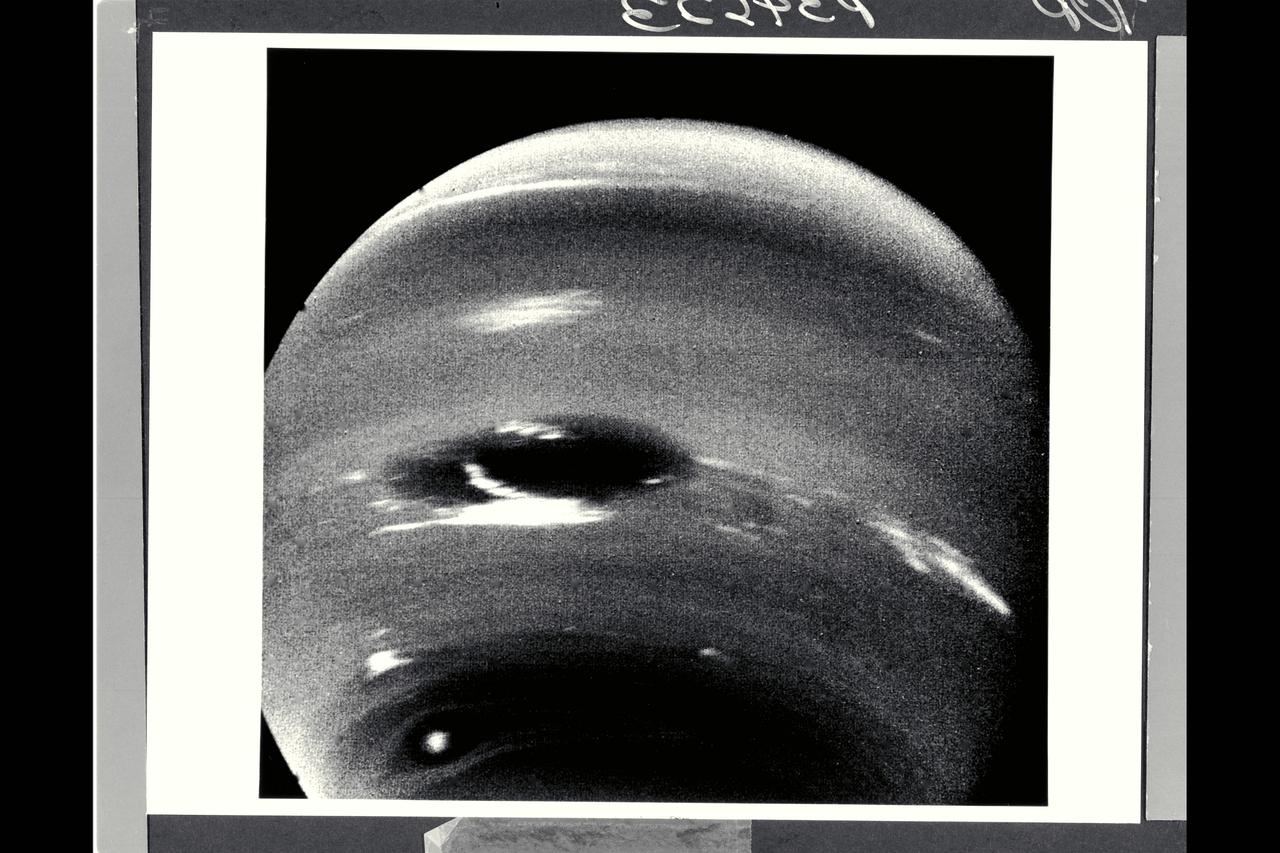
Range : 6.1 million km ( 3.8 million miles) This image of clouds in Neptune's atmosphere is the first that tests the accuracy of the weather forecast that was made eight days earlier to select targets for the Voyager narrow-angle camer. Three of the four targeted features are visible in this photograph; all three are close to their predicted locations. The Great Dark Spot with its bright white companion is slightly to the left of center. The small brig&ht Scooter is below and to the left, and the second dark spot with its bright core is below the Scooter. Strong eastward winds -- up to 400 mph -- cause the second dark spot to overtake and pass the larger one every five days.
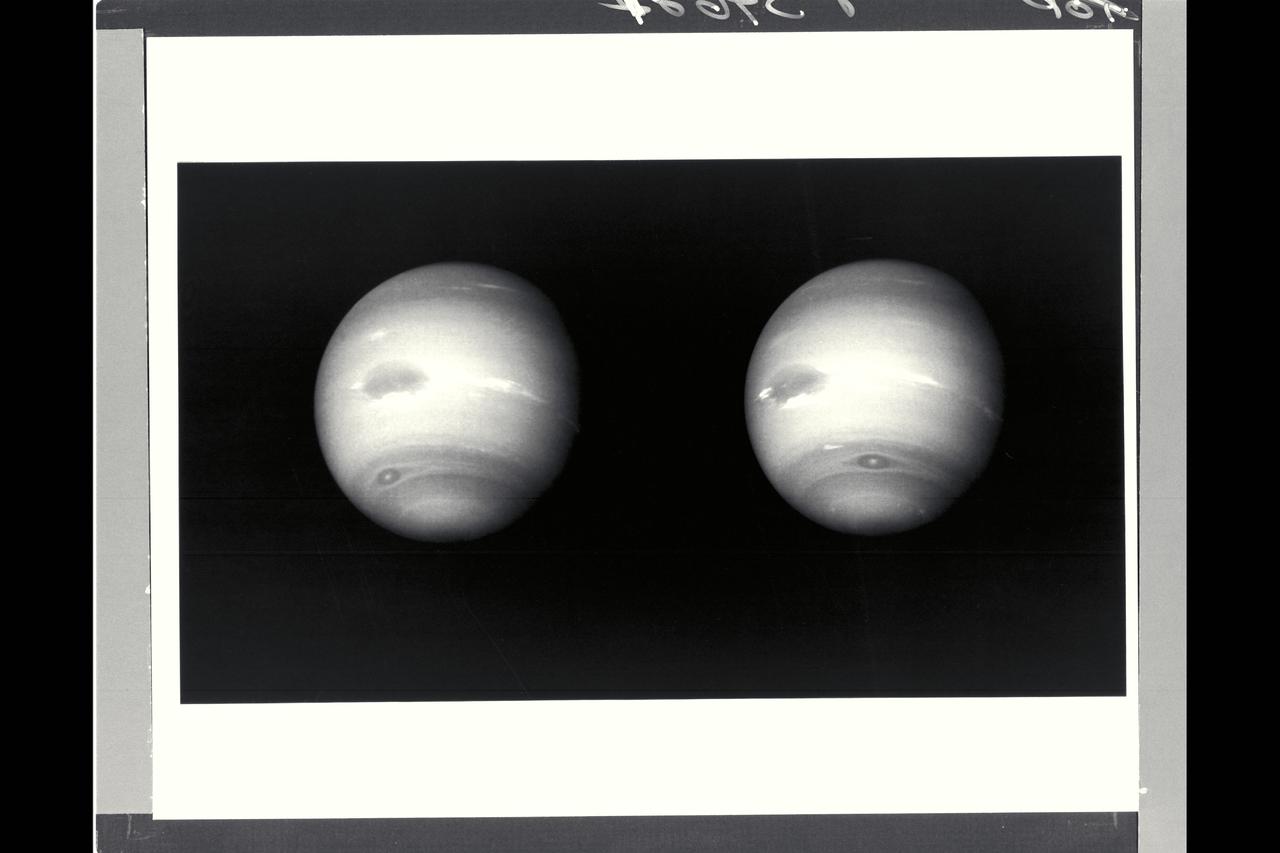
P-34648 This photograph of Neptune was reconstructed from two images taken by Voyager 2's narrow angle camera, through the green and clear filters. the image shows three of the features that Voyager 2 has been photographing during recent weeks. At the north ( top ) is the Great Dark Spot, accompanied by bright, white clouds that undergo rapid changes in appearance. to the south of the Great Dark Spot is the bright feature that Voyager scientists have nicknamed 'Scooter.' Still farther south is the feature called ' Dark Spot 2,' which has a bright core. Each feature moves eastward at a different at a different velocity, so it is only occasionally that they appear close to each other, such as at the time this picture was taken.

Voyager II Imagery - Neptune: This image of clouds in Neptune's atmosphere is the first that tests the accuracy of the weather forecast that was made eight days earlier to select targets for the Voyager narrow-angle camera. Three of the four targeted features are visible in this photograph; all three are close to their predicted locations. The Great Dark Spot with its bright white companion is slightly to the left of center. The small bright Scooter is below and to the left, and the second dark spot with its bright core is below the Scooter. Strong eastward winds -- up to 400 mph -- cause the second dark spot to overtake and pass the larger one every five days. The spacecraft was 6.1 million kilometers (3.8 million miles) from the planet at the time of camera shuttering, and the images use the orange, green and clear filters of the camera. The Voyager Mission is conducted by JPL for NASA's Office of Space Science and Applications. (JPL ref P-34632 Voyager 2 N-32C)

P-34630 Range: 10.5 million kilometers (6.5 million miles) This cylindrical projection view of Neptune uses five narrow-angle images equally spaced around the planet. They were taken by Voyager 2 over the course of a Neptunian day, an interval of about 18 hours. Latitude lines are horizontal in the image, and range from 80 degrees south to 30 degrees north of the equator. Near the center, the Great Dark Spot leaves a disturbed wave-like pattern that stretches around Neptune. Features further south move eastward at speeds up to 400 mph relative to the Great Dark Spot. The features are storms--moving cloud systems that persist for months or longer. The weather forecast for Neptune is therefore continued high winds and cold with little change in temperature.
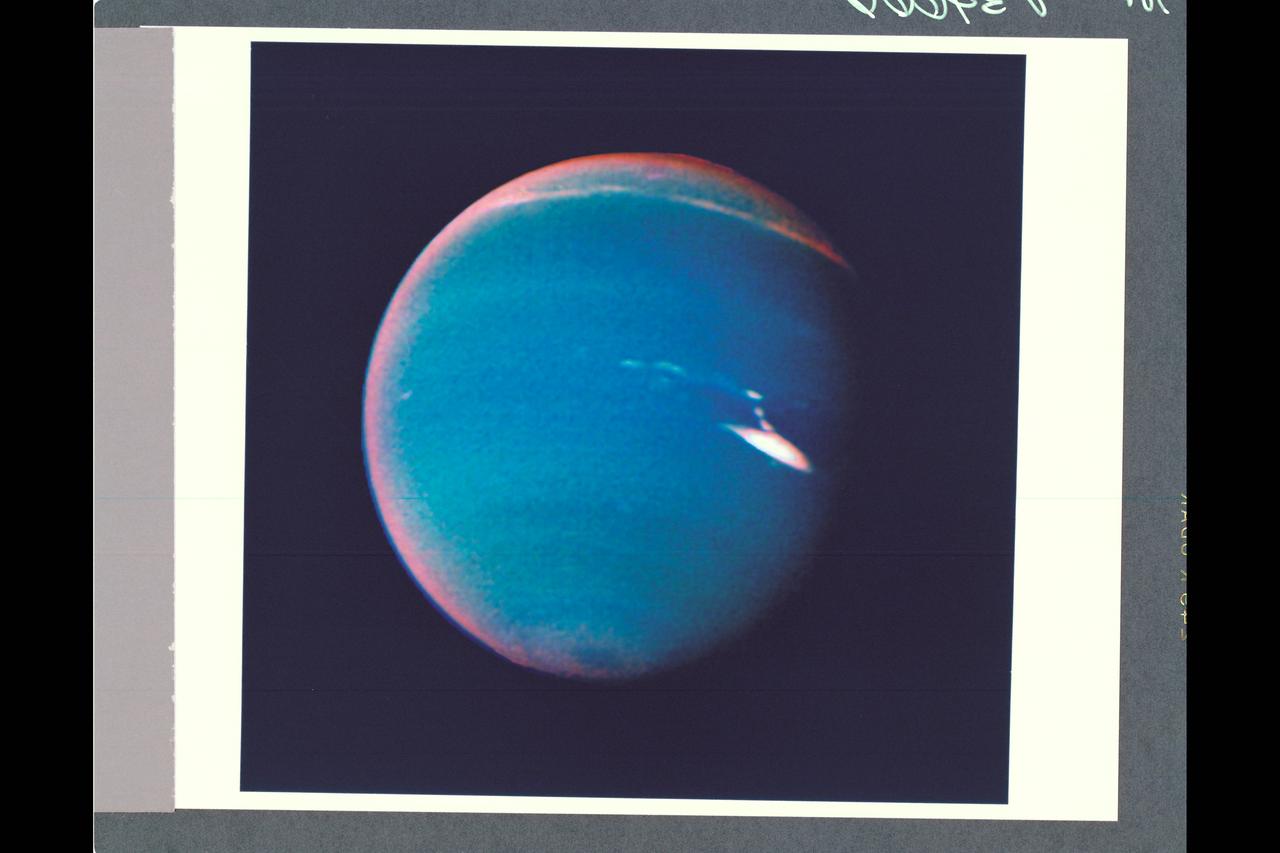

P-34666 This false color photograph of Neptune was reconstructed from two images taken by Voyager 2's wide angle camera, through the orange and two different methane filters. Objects that deep in the atmosphere are blue, while those at higher altitudes are white. Light at methane wavelengths is mostly absorbed in the deeper atmosphere. The bright, white feature is a high altitude cloud just south of the Great dark Spot. The hard, sharp inner boundary within the bright cloud is an artifact of computer processing on Earth. Other, smaller clouds associated with the Great Dark Spot are white or pink, and are also at high altitudes. Neptune's limb looks reddish because Voyager 2 is viewing it tangentially, and the sunlight is scattered back to space before it can be absorbed by methane. A long, narrow band of high-altitude clouds near the top of the image is located at 25 degrees north latitude, and faint hazes mark the equator and polor regions

This animation illustrates Jupiter's magnetic field at a single moment in time. The Great Blue Spot, an-invisible-to-the-eye concentration of magnetic field near the equator, stands out as a particularly strong feature. The gray lines (called field lines) show the field's direction in space, and the deepness of the color corresponds to the strength of the magnetic field (with dark red and dark blue for regions with strongly positive and strongly negative fields, respectively). The animation first appeared in a Sept. 5, 2018, paper in the Journal Nature. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23229.
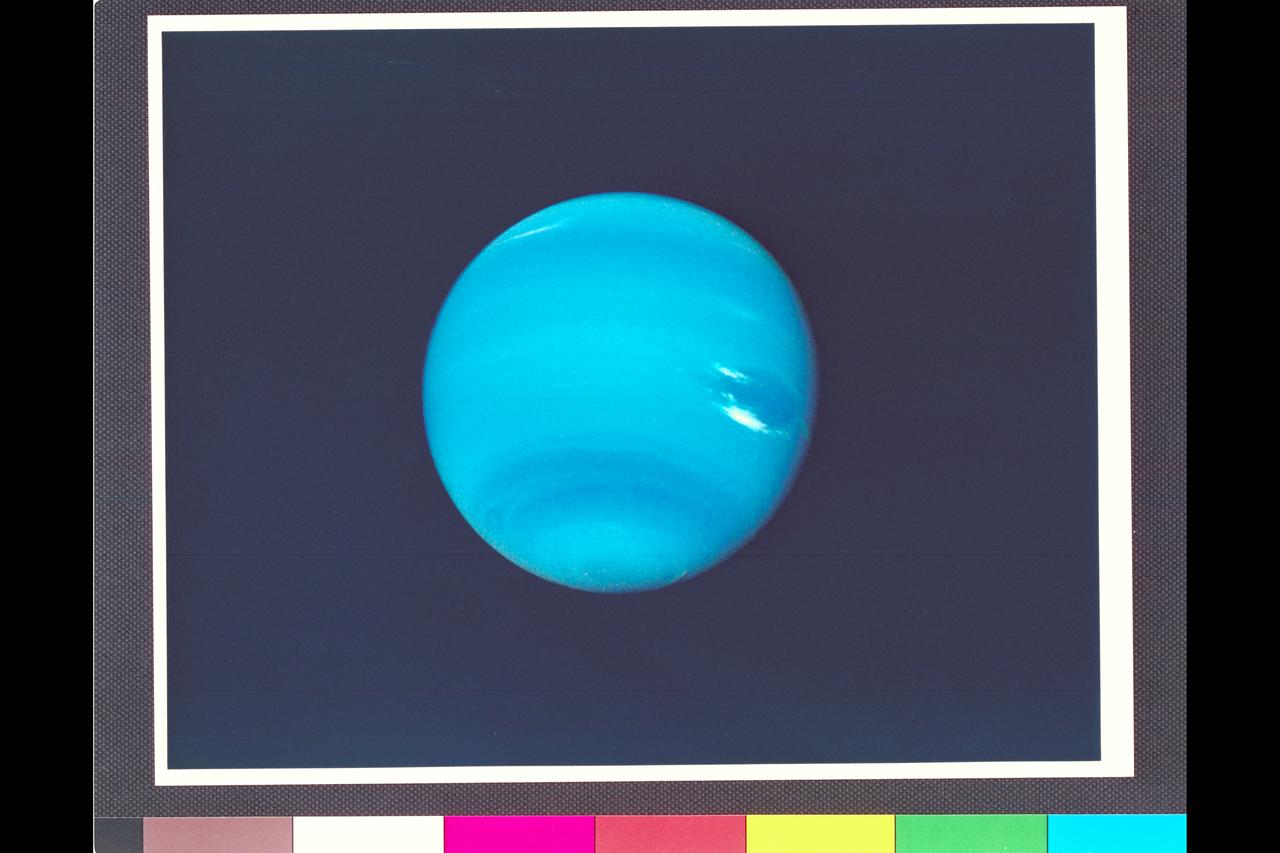

Range : 14.8 million km. ( 9.2 million miles) P-34595C This contrast enhanced color photograph of Neptune was produced from images taken through the orange, green, and violet filters of the narrow angle camera. As Voyager 2 approaches Neptune, rapidly increasing image resolution is revealing striking new details in the planet's atmosphere, and this pictureshows features as small as a few hundred kilometers in extent. Bright, wispy 'cirrus-type' clouds are seen overlying the Great Dark Spot (GDS) at its southern (lower) margin and over its northwest ( upper left) boundary. This is the first evidence that the GDS lies lower in the atmosphere than these bright clouds, which have remained in its vicinity for several months. Increasing detail in global banding, and the south polar can also be seen. A smaller dark spot at high southern latitudes is dimly visible near the limb at lower left.

This picture of Neptune was produced from images taken through the ultraviolet, violet and green filters of the Voyager 2 wide-angle camera. This 'false' color image has been made to show clearly details of the cloud structure and to paint clouds located at different altitudes with different colors. Dark, deeplying clouds tend to be masked in the ultraviolet wavelength since overlying air molecules are particularly effective in scattering sunlight there which brightens the sky above them. Such areas appear dark blue in this photo. The Great Dark Spot (GDS) and the high southern latitudes have a deep bluish cast in this image, indication they are regions where visible light (but not ultraviolet light) may penetrate to a deeper layer of dark cloud or haze in Neptune's atmosphere. Conversely, the pinkish clouds may be positioned at high altitudes.
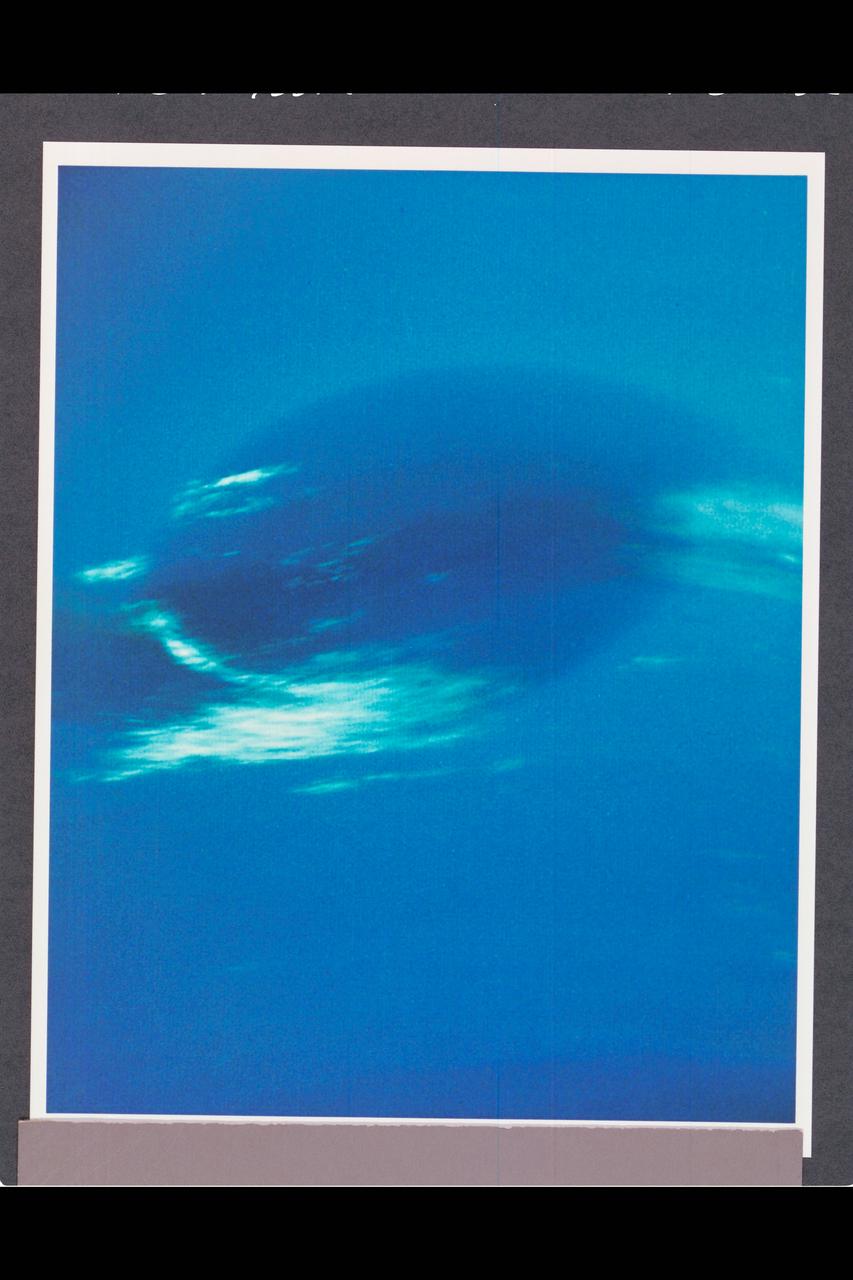

P-34668 Range : 2.8 million km. ( 1.7 million miles ) Smallest Resolvable Feature : 50 km or 31 miles This Voyager 2 image shows the last face on view of the Great Dark Spot that Voyager 2 will take with the narrow angle camera. It was made 45 hours before the closest approach to Neptune. the image shows feathery white clouds that overlie the boundary of the dark and light blue regions. the pinwheel ( spiral ) structure of both the dark boundary and the white cirrus suggest a storm system rotating counterclockwise. Periodic, small-scale patterns in the white clouds, possibly waves, are short-lived and do not persist from one Neptunian rotation to the next. This color composite was made from the clear and green filter images.
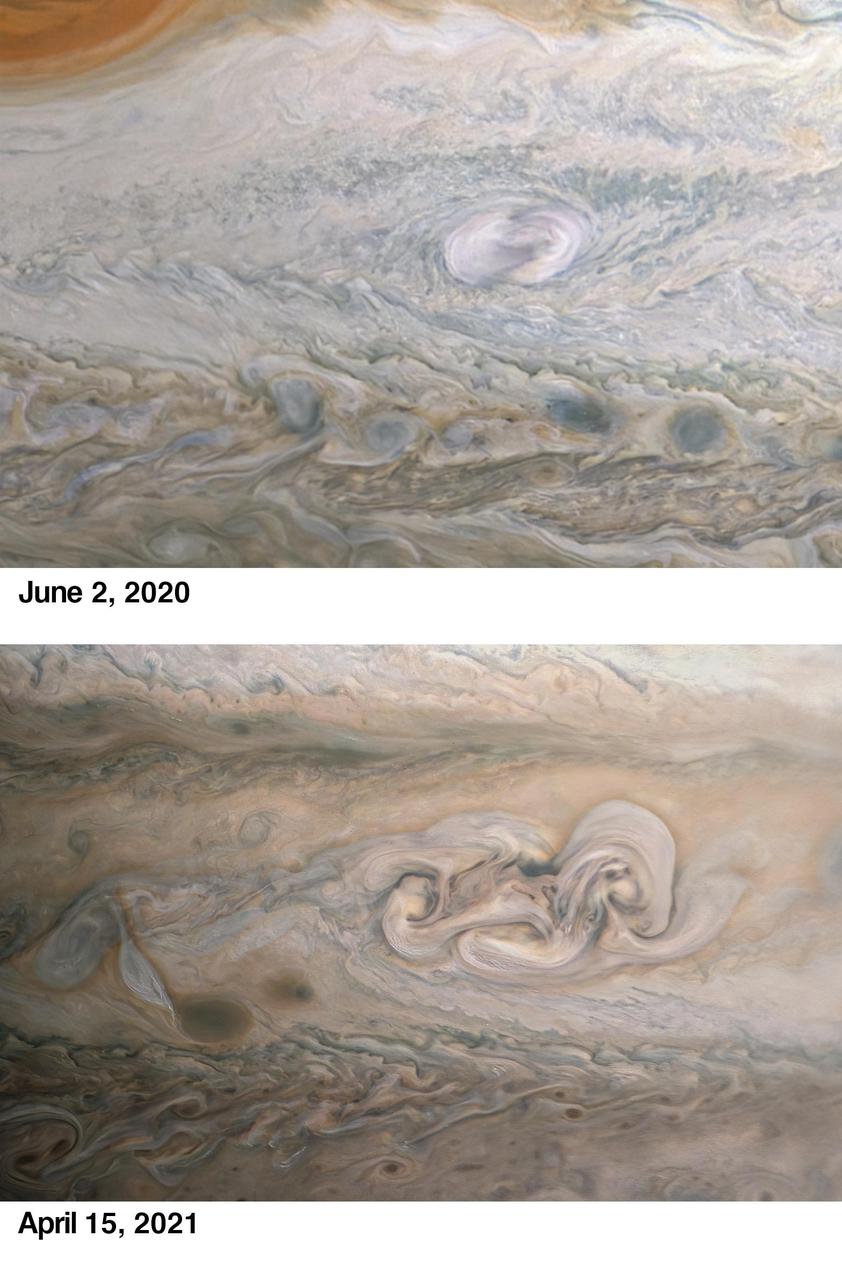

During its 33rd low pass over the cloud tops of Jupiter on April 15, 2021, NASA's Juno spacecraft captured the intriguing evolution of a feature in the giant planet's atmosphere known as "Clyde's Spot." The feature is informally named for amateur astronomer Clyde Foster of Centurion, South Africa, who discovered it in 2020 using his own 14-inch telescope. On June 2, 2020, just two days after Foster's initial discovery, Juno provided detailed observations of Clyde's Spot (upper image), which scientists determined was a plume of cloud material erupting above the top layers of the Jovian atmosphere just southeast of Jupiter's Great Red Spot, which is currently about 1.3 times as wide as Earth. These powerful convective outbreaks occasionally occur in this latitude band, known as the South Temperate Belt. The initial plume subsided quickly, and within a few weeks it was seen as a dark spot. Many features in Jupiter's highly dynamic atmosphere are short lived, but the April 2021 observation from the JunoCam instrument (lower image) revealed that nearly one year after its discovery, the remnant of Clyde's Spot had not only drifted away from the Great Red Spot but had also developed into a complex structure that scientists call a folded filamentary region. This region is twice as big in latitude and three times as big in longitude as the original spot, and has the potential to persist for an extended period of time. The upper image was taken on June 2, 2020, around 3:56 a.m. when the spacecraft was about 28,000 miles (45,000 kilometers) from Jupiter's cloud tops. The lower image was taken on April 15, 2021, at 4:58 p.m. PDT (7:58 p.m. EDT). At the time, the spacecraft was about 16,800 miles (27,000 kilometers) from Jupiter's cloud tops, at a latitude of about 30 degrees South. Another citizen scientist, Kevin M. Gill, processed both images from raw JunoCam data. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23609

Photo by Voyager 2 (jpl) These images show changes in the clouds around Neptune's Great Dark Spot (GDS) over a four and one-half-day period. From top to bottom the images show successive rotations of the planet -- an interval of about 18 hours. The GDS is at a mean latitude of 20 degrees south, and covers about 30 degrees of longitude. The violet filter of the Voyager narrow angle camera was used to produce these images at distances ranging from 17 million kilometers (10.5 million miles) at the top, to 10 million kiloeters (6.2 million miles) at the bottom. The images have been mapped on to a rectangular latitude-longitude grid to remove the effects of changing viewing geometry and the changing distance to Neptune. The sequence shows a large change in the western end (left side) of the GDS, where dark extension apparent in the earlier images converges into an extended string of small dark spots over the next five rotations. This 'string of beads' extends from the GDS a surprisingly large angle relative to horizontal lines of constant latitude. The large bright cloud at the southen (bottom) boarder of the GDS is a more or less permanent companion of the GDS -- reminiscent of flow around the Great Red Spot in Jupiter's atmosphere. This activity of the GDS is surprising because the total energy flux from the sun and from Neptune's interior is only 5 percent as large as the total energy flux on Jupiter. (JPL Ref: P-34610 Voyager 2-N23)

This image of Jupiter was taken by the Cassini Imaging Science narrow angle camera through the blue filter (centered at 445 nanometers) on October 1, 2000, 15:26 UTC at a distance of 84.1million km from Jupiter. The smallest features that can be seen are 500 kilometers across. The contrast between bright and dark features in this region of the spectrum is determined by the different light absorbing properties of the particles composing Jupiter's clouds. Ammonia ice particles are white, reflecting all light that falls on them. But some particles are red, and absorb mostly blue light. The composition of these red particles and the processes which determine their distribution are two of the long-standing mysteries of Jovian meteorology and chemistry. Note that the Great Red Spot contains a dark core of absorbing particles. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02666

Voyager II Imagery; Neptune. This bulls-eye view of Neptune's small dark spot (D2) was obtained by Voyager 2's narrow-angle camera , when Neptune was within 1.1 million km (680,000 miles) of the planet. The smallest structures that can be seen are 20 km (12 miles) across. This unplanned photograph was obtained when the infrared spectrograph was mapping the the highest-resolution view of the feature taken during the flyby. Banding surrounding the feature indicates unseen strong winds, while structues within the bright spot suggest both active upwelling of clouds and rotation about the center. A rotation rate has not yet been measured, but the v-shaped structure near the right edge of the bright area indicates that the spot rotates clockwise. Unlike the Great Red Spot on Jupiter, which rotates counterclockwise, if the D2 spot on Neptune rotates clockwise, the material will be descending in the dark oval region. The fact that infrared data will yield temperature information about the region above the clouds makes this observation especially valuable. The Voyager Mission is conducted by JPL for NASA's Office of Space Science and Applicaitons. (JPL ref: P-34749 Voyager N-71) taken during the flyby. Banding surrounding the feature indicates unseen strong winds, while structures within the bright spot suggest both active upwelling of clouds and rotation about the center. A rotation rate has not yest been measured, but the Vv-sphped
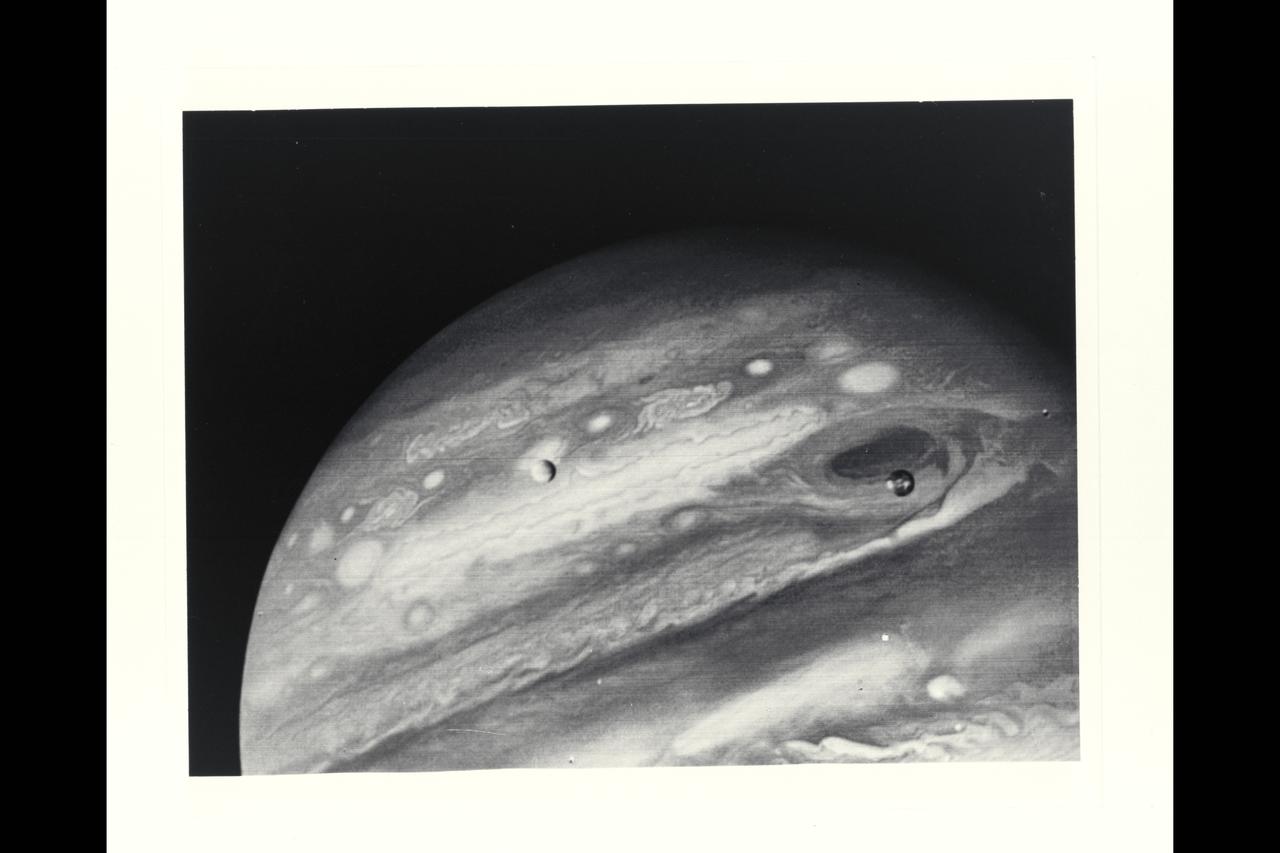

Voyager 1 Image of Jupiter and two of its satellites (Io, left, and Europa). Io is about 350,000 kilometers (220,000 miles) above Jupiter's Great Red Spot; Europa is about 600,000 kilometers (375,000 miles) above Jupiter's clouds. Although both satellites have about the same brightness, Io's color is very different from Europa's. Io's equatorial region show two types of material -- dark orange, broken by several bright spots -- producing a mottled appearance. The poles are darker and reddish. Preliminary evidence suggests color variations within and between the polar regions. Io's surface composition is unknown, but scientists believe it may be a mixture of salts and sulfur. Erupoa is less strongly colored, although still relatively dark at short wavelengths. Markings on Eruopa are less evident that on the other satellites, although this picture shows darker regions toward the trailing half of the visible disk. Jupiter at this point is about 20 million kilometers (12.4 million miles) from the spacecraft. At this resolution (about 400 kimometers or 250 miles) there is evidence of circular motion in Jupiter's atmosphere. While the dominant large-scale motions are west-to-east, small-scale movement includes eddy-like circulation within and between the bands. (JPL ref: P-21082)

Voyager 1 Image of Jupiter and two of its satellites (Io, left, and Europa). Io is about 350,000 kilometers (220,000 miles) above Jupiter's Great Red Spot; Europa is about 600,000 kilometers (375,000 miles) above Jupiter's clouds. Although both satellites have about the same brightness, Io's color is very different from Europa's. Io's equatorial region show two types of material -- dark orange, broken by several bright spots -- producing a mottled appearance. The poles are darker and reddish. Preliminary evidence suggests color variations within and between the polar regions. Io's surface composition is unknown, but scientists believe it may be a mixture of salts and sulfur. Erupoa is less strongly colored, although still relatively dark at short wavelengths. Markings on Eruopa are less evident that on the other satellites, although this picture shows darker regions toward the trailing half of the visible disk. Jupiter at this point is about 20 million kilometers (12.4 million miles) from the spacecraft. At this resolution (about 400 kimometers or 250 miles) there is evidence of circular motion in Jupiter's atmosphere. While the dominant large-scale motions are west-to-east, small-scale movement includes eddy-like circulation within and between the bands. (JPL ref: P-21082)

Neptune's blue-green atmosphere is shown in greater detail than ever before by the Voyager 2 spacecraft as it rapidly approaches its encounter with the giant planet. This color image, produced from a distance of about 16 million kilometers, shows several complex and puzzling atmospheric features. The Great Dark Spot (GDS) seen at the center is about 13,000 km by 6,600 km in size -- as large along its longer dimension as the Earth. The bright, wispy "cirrus-type" clouds seen hovering in the vicinity of the GDS are higher in altitude than the dark material of unknown origin which defines its boundaries. A thin veil often fills part of the GDS interior, as seen on the image. The bright cloud at the southern (lower) edge of the GDS measures about 1,000 km in its north-south extent. The small, bright cloud below the GDS, dubbed the "scooter," rotates faster than the GDS, gaining about 30 degrees eastward (toward the right) in longitude every rotation. Bright streaks of cloud at the latitude of the GDS, the small clouds overlying it, and a dimly visible dark protrusion at its western end are examples of dynamic weather patterns on Neptune, which can change significantly on time scales of one rotation (about 18 hours). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02245

The bright cirrus-like clouds of Neptune change rapidly, often forming and dissipation over periods of several to tens of hours. In this sequence spanning two rotations of Neptune (about 36 hours) Voyager 2 observed cloud evolution in the region around the Great Dark Spot (GDS) at an effective resolution of about 100 km (62 miles) per pixel. The surprisingly rapid changes which occur over the 18 hours separating each panel shows that in this region Neptune's weather is perhaps as dynamic and variable as that of the Earth. However, the scale is immense by our standards--the Earth and the GDS are of similar size -- and in Neptune's frigid atmosphere, where temperatures are as low as 55 degree Kelvin (-360F), the cirrus clouds are composed of frozen methane rather than Earth's crystalse of water ice.
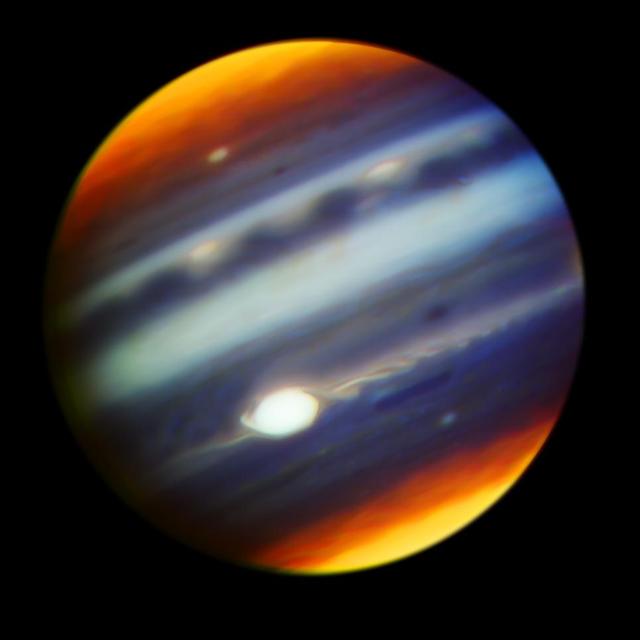

This composite, false-color infrared image of Jupiter reveals haze particles over a range of altitudes, as seen in reflected sunlight. It was taken using the Gemini North Telescope's Near-InfraRed Imager (NIRI) on May 18, 2017, in collaboration with the investigation of Jupiter by NASA's Juno mission. Juno completed its sixth close approach to Jupiter a few hours after this observation. The multiple filters corresponding to each color used in the image cover wavelengths between 1.69 microns and 2.275 microns. Jupiter's Great Red Spot (GRS) appears as the brightest (white) region at these wavelengths, which are primarily sensitive to high-altitude clouds and hazes near and above the top of Jupiter's convective region. The GRS is one of the highest-altitude features in Jupiter's atmosphere. Narrow spiral streaks that appear to lead into it or out of it from surrounding regions probably represent atmospheric features being stretched by the intense winds within the GRS, such as the hook-like structure on its western edge (left side). Some are being swept off its eastern edge (right side) and into an extensive wave-like flow pattern, and there is even a trace of flow from its northern edge. Other features near the GRS include the dark block and dark oval to the south and the north of the eastern flow pattern, respectively, indicating a lower density of cloud and haze particles in those locations. Both are long-lived cyclonic circulations, rotating clockwise -- in the opposite direction as the counterclockwise rotation of the GRS. A prominent wave pattern is evident north of the equator, along with two bright ovals, which are anticyclones that appeared in January 2017. Both the wave pattern and the ovals may be associated with an impressive upsurge in stormy activity that has been observed in these latitudes this year. Another bright anticyclonic oval is seen further north. The Juno spacecraft may pass over these ovals, as well as the Great Red Spot, during its close approach to Jupiter on July 10, 2017, Pacific Time (July 11, Universal Time). High hazes are evident over both polar regions with much spatial structure not previously been seen quite so clearly in ground-based images The filters used for observations combined into this image admit infrared light centered on the following infrared wavelengths (and presented here in these colors): 1.69 microns (blue), 2.045 microns (cyan), 2.169 microns (green), 2.124 microns https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21713
![Range : 16 million km (9.9 million miles) P-34616 This series of six Voyager 2 images of Neptune through different filters reveals altitude in Neptune's clouds. The top three images, taken though orange, violet, and ultraviolet filters by the narrow-angle camera, show several bright cloud features, clearly visible in each image. The 'scooter' cloud, at 42 degrees south latitude, although prominent in the orange image, is invisible in ultraviolet, where scattering by atmospheric molecules is strongest. The disappearance can be understood if the 'scooter cloud has more obscurring atmosphere above it ( i.e. the scooter cloud is lower ) than other bright clouds. The observation also suggest that the centrally located Great Dark Spot is also a low lying feature because it also loses visiblity in the ultraviolet image. The lower three wide angle images ( from left to right: orange, weak methane [541nm], and strong methane [619nm] are arranged in increasing absorption by methane in Neptune's atmosphere. In the lower images the 'scooter cloud' becomes less obvious from left to right, implying there is relatively more absorbing methane above the 'scooter cloud'. Thus the set of images also implies that the 'scooter cloud' is deeper in the atmosphere ( and therefore at higher atmospheric pressure ) than the other bright clouds.](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/ARC-1989-AC89-7003/ARC-1989-AC89-7003~medium.jpg)
Range : 16 million km (9.9 million miles) P-34616 This series of six Voyager 2 images of Neptune through different filters reveals altitude in Neptune's clouds. The top three images, taken though orange, violet, and ultraviolet filters by the narrow-angle camera, show several bright cloud features, clearly visible in each image. The 'scooter' cloud, at 42 degrees south latitude, although prominent in the orange image, is invisible in ultraviolet, where scattering by atmospheric molecules is strongest. The disappearance can be understood if the 'scooter cloud has more obscurring atmosphere above it ( i.e. the scooter cloud is lower ) than other bright clouds. The observation also suggest that the centrally located Great Dark Spot is also a low lying feature because it also loses visiblity in the ultraviolet image. The lower three wide angle images ( from left to right: orange, weak methane [541nm], and strong methane [619nm] are arranged in increasing absorption by methane in Neptune's atmosphere. In the lower images the 'scooter cloud' becomes less obvious from left to right, implying there is relatively more absorbing methane above the 'scooter cloud'. Thus the set of images also implies that the 'scooter cloud' is deeper in the atmosphere ( and therefore at higher atmospheric pressure ) than the other bright clouds.
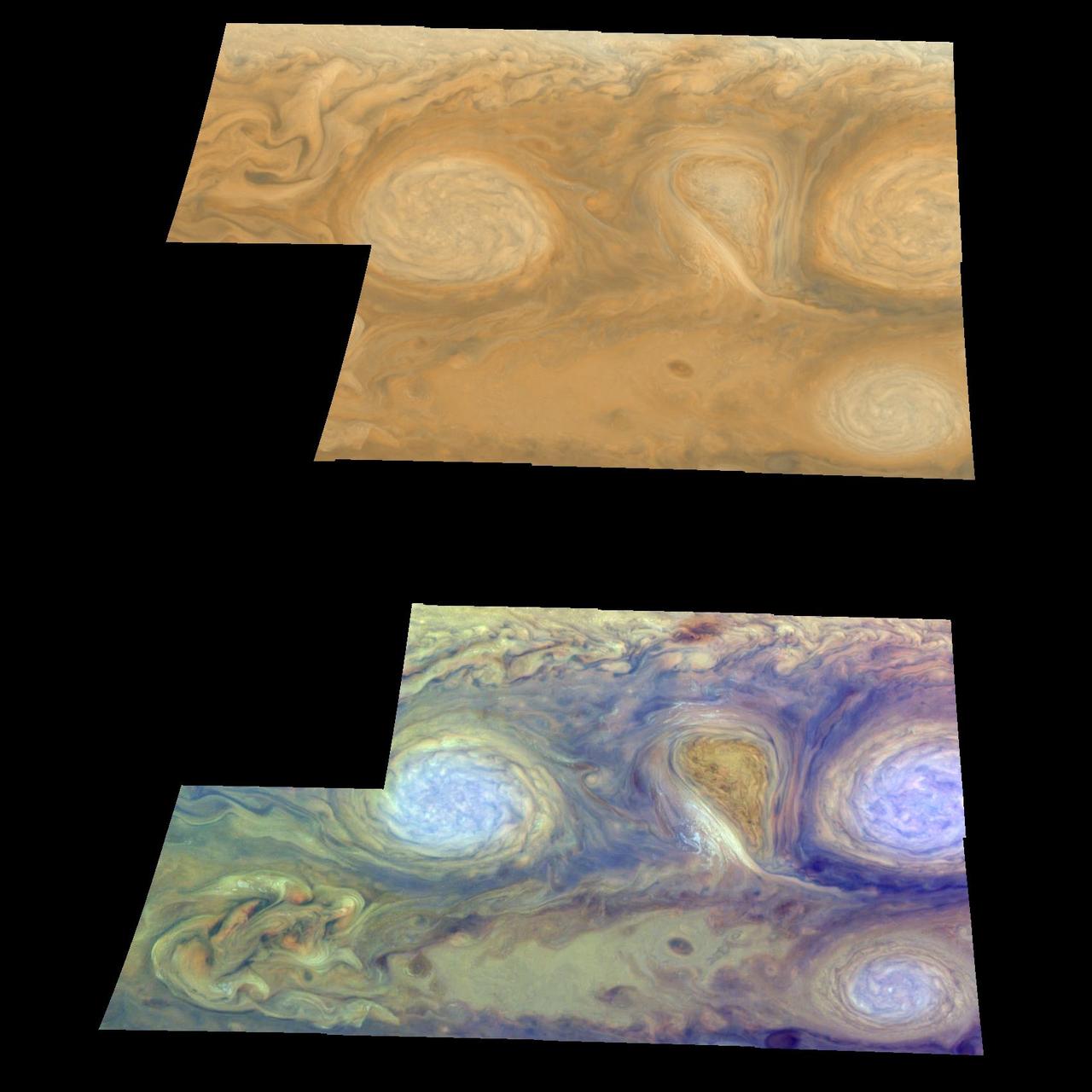
Oval cloud systems of this type are often associated with chaotic cyclonic systems such as the balloon-shaped vortex seen here between the well-formed ovals. This system is centered near 30 degrees south latitude relative to the center of the planet and 100 degrees west longitude, and rotates in a clockwise direction about its center. The oval shaped vortices in the upper half of the mosaic are two of the three long-lived white ovals that formed to the south of the Great Red Spot in the 1930's and, like the Great Red Spot, rotate in a counterclockwise sense. The east-to-west dimension of the left-most white oval is 9,000 kilometers (5,592 miles) across. For comparison, the diameter of Earth is 12,756 kilometers, or 7,928 miles. The white ovals drift in longitude relative to one another and are presently restricting the cyclonic structure. To the south, the smaller oval and its accompanying cyclonic system are moving eastward at about 0.4 degrees per day relative to the larger ovals. The interaction between these two cyclonic storm systems is producing high, thick cumulus-like clouds in the southern part of the more northerly trapped system. The top mosaic combines the violet (410 nanometers) and near infrared continuum (756 nanometers) filter images to create a mosaic similar to how Jupiter would appear to human eyes. Differences in coloration are due to the composition and abundance of trace chemicals in Jupiter's atmosphere. The lower mosaic uses the Galileo imaging camera's three near-infrared wavelengths (756 nanometers, 727 nanometers, and 889 nanometers displayed in red, green, and blue) to show variations in cloud height and thickness. Light blue clouds are high and thin, reddish clouds are deep, and white clouds are high and thick. The clouds and haze over the white ovals are high, extending into Jupiter's stratosphere. There is a lack of high haze over the cyclonic feature. Dark purple most likely represents a high haze overlying a clear deep atmosphere. Galileo is the first spacecraft to distinguish cloud layers on Jupiter. North is at the top of these mosaics. The smallest resolved features are tens of kilometers in size. These images were taken on February 19, 1997, at a range of 1.1 million kilometers (683,507 miles) by the solid state imaging (CCD) system aboard NASA's Galileo spacecraft. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00700
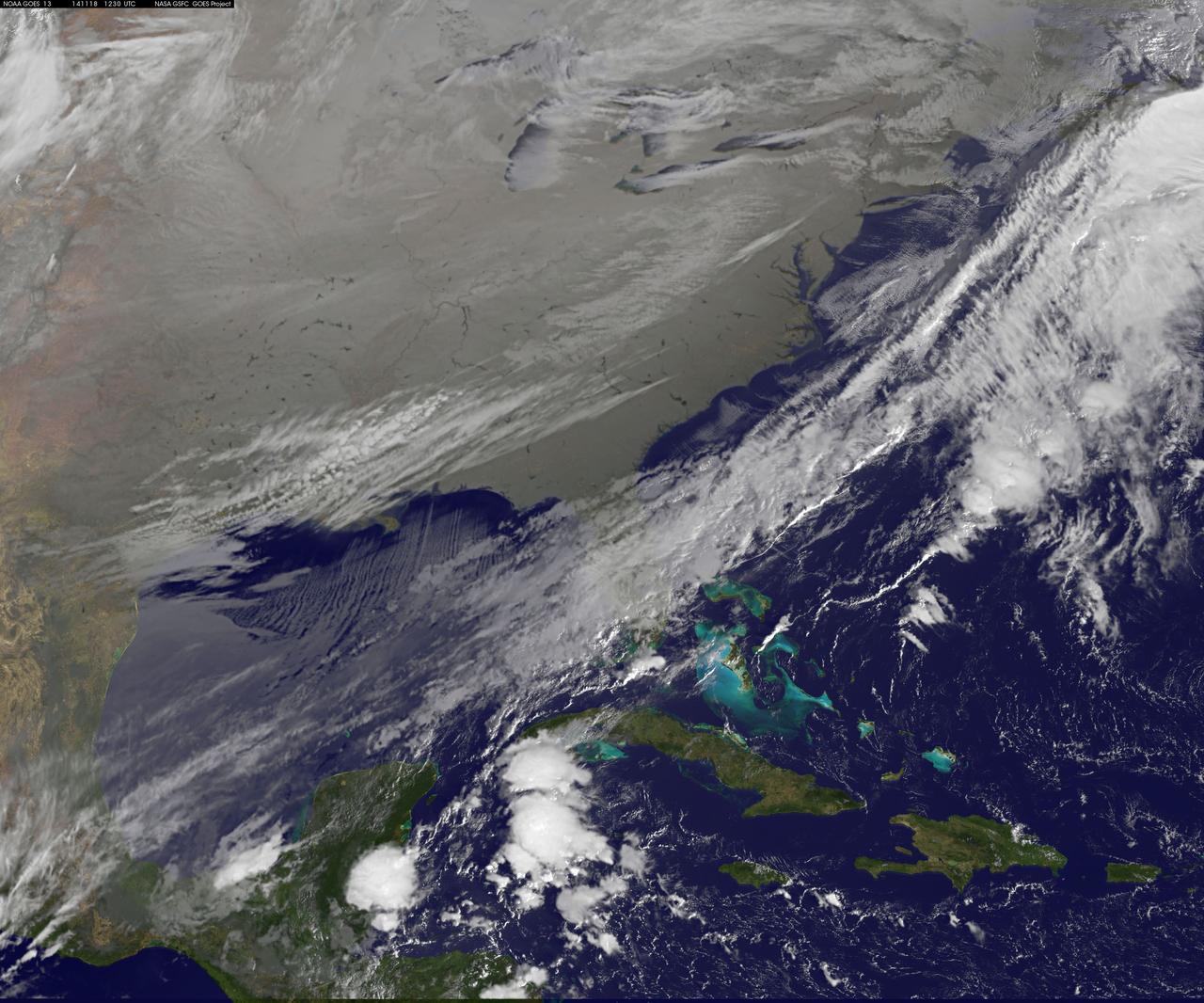

As icy cold Canadian air settled over the eastern two-thirds of the U.S. bringing snow and bitter cold, NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured this infrared view of what looks like a frozen blanket over the region. NOAA's GOES-East satellite provides visible and infrared images over the eastern U.S. and the Atlantic Ocean from its fixed orbit in space. In an infrared image taken on Nov. 18 at 12:30 UTC (7:30 a.m. EST), the cold air over the eastern and central U.S. appears to look like a blanket of white, but it's not all snow. Infrared data shows temperature, so although the eastern two-thirds of the U.S. appears to appear is if snow covers the ground, the blanket is in fact cold clouds. However, snow does lie under that blanket in the Upper Midwest, Ohio Valley, and Canada, where it will continue in those areas through Thursday, Nov. 20. "Dozens of lakes behind dams in the Southeast USA stand out as dark spots in a grey landscape," said Dennis Chesters of NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "That is because we invert the display of infrared emission to make cold cloud tops appear white, frozen land grey, and warm water dark." NOAA's National Weather Service Weather Prediction Center said that the deep low pressure system pushing that polar air over the Eastern U.S. is centered over southeastern Canada. On Tuesday, Nov. 18, freeze and frost warnings stretch from the upper Great Lakes to Florida. Some areas in the Upper Great Lakes are forecast to receive over two feet of snow. Well below average temperatures are forecast to reach the Gulf Coast, with most of the Mid-Atlantic States barely getting above freezing Tuesday and Wednesday. In the Midwest, periods of lake effect snow are forecast to continue south and east of the Great Lakes through Wednesday. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/satellite-view-of-the-us-wrapped-in-a-frozen-blanket/index.html#.VGuxFd6FzeN" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/satellite-view-of-the-us-wra...</a> <b><a href="http://goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">Credit: NOAA/NASA GOES Project</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
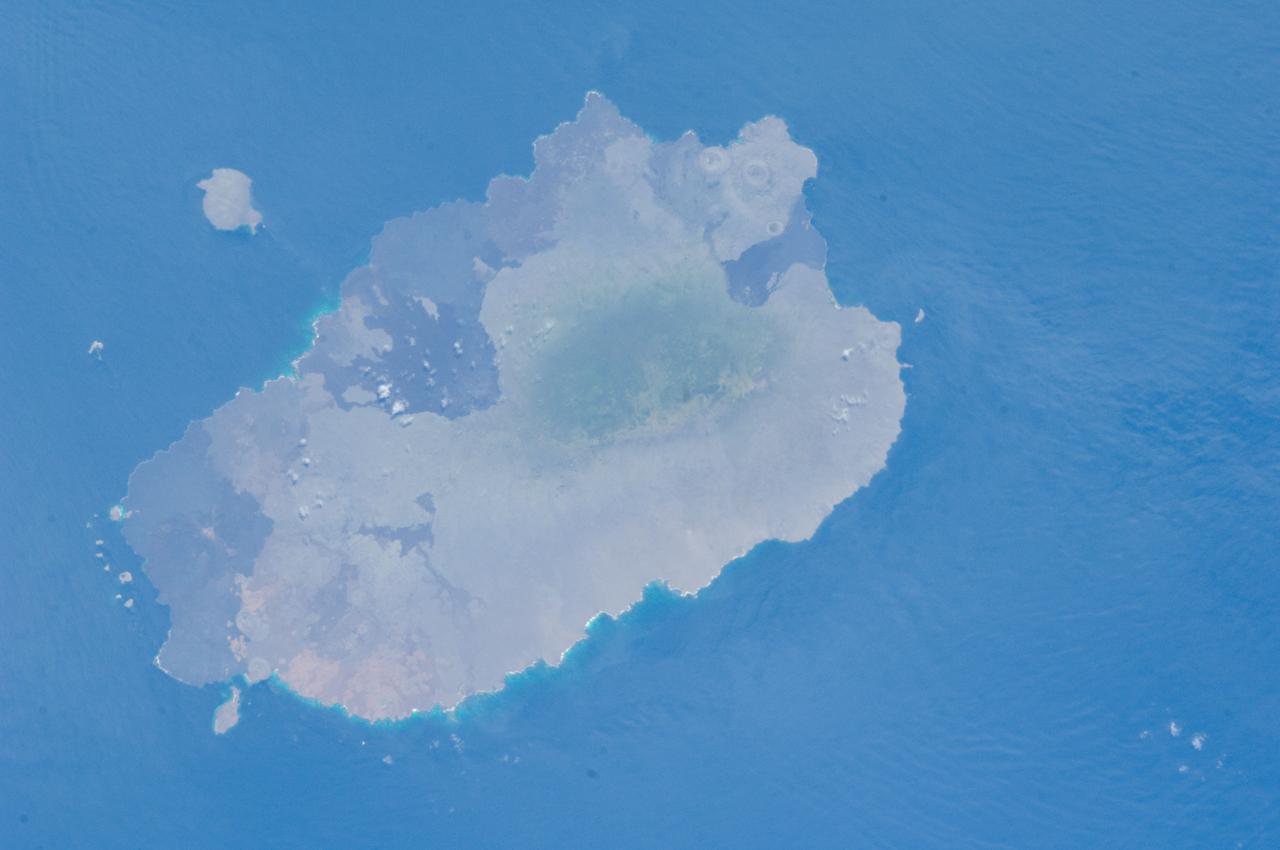

ISS033-E-012648 (18 Oct. 2012) --- Isla Santiago is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 33 crew member on the International Space Station. The island of Santiago is located near the center of the Galapagos Islands off the coast of Ecuador. The Galapagos Islands are situated near the equator, and were formed from volcanism related to a large mantle plume (also known as a hot spot). This hot spot is very close to the tectonic boundary between the Galapagos Ridge, a plate boundary that is also an oceanic spreading center, and the Nazca and Cocos plates. This combination of mantle plumes and tectonic plate movements produces a unique geological environment, including underwater ridges of volcanoes that influence the water circulation around the Galapagos. All of these aspects contribute to the geology and biology of the Galapagos. Isla Santiago itself is formed from a shield volcano also called Santiago. This type of volcanic structure is recognized by low, flat summits surrounded by extensive flow fields of lava; the lava is not very viscous, so it can flow for great distances from the source vents. Several dark lava flow fields are visible in this photograph, the largest along the eastern, western, and southern coastlines. The small Isla Rabida to the south of Isla Santiago is the peak of another, mostly submerged shield volcano. In addition to the lava flows, other volcanic features known as tuff cones are visible on the eastern and western sides of the island. These cones are formed from the rapid interaction of hot flowing lava and water. The water underneath the lava flow flashes to steam explosively, and this both fragments the lava and rapidly cools it, leading to the formation of cones of glassy, relatively fine-grained volcanic material. The most recent volcanic activity on Isla Santiago occurred during 1904 – 1906. The summit ridge of the Santiago shield volcano is located in the northwestern part of the island (center). Also at center is a large but isolated region of green vegetation primarily located on the south-facing slope below the summit ridge. This image was taken during the dry, or garua, season that lasts from June to November. The season is dominated by cooler air transported by the Southeast Trade winds and cooler waters from the Humboldt and Cromwell currents. The combination of cool air and water results in rain falling only in the island highlands, with south- and east-facing slopes receiving the most precipitation. Despite the favorable topographic location, the yellow green color of the vegetation may indicate water (or other) stress.
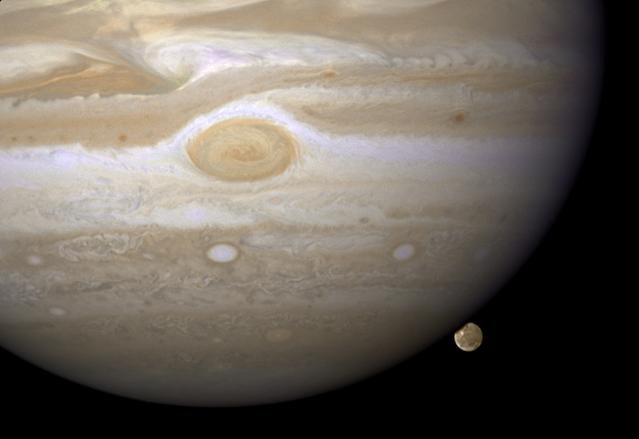

Hubble Catches Jupiter's Largest Moon Going to the 'Dark Side' HST/WFPC2 Image of Jupiter and Ganymede Taken April 9, 2007 NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has caught Jupiter's moon Ganymede playing a game of "peek-a-boo." In this crisp Hubble image, Ganymede is shown just before it ducks behind the giant planet. Ganymede completes an orbit around Jupiter every seven days. Because Ganymede's orbit is tilted nearly edge-on to Earth, it routinely can be seen passing in front of and disappearing behind its giant host, only to reemerge later. Composed of rock and ice, Ganymede is the largest moon in our solar system. It is even larger than the planet Mercury. But Ganymede looks like a dirty snowball next to Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system. Jupiter is so big that only part of its Southern Hemisphere can be seen in this image. Hubble's view is so sharp that astronomers can see features on Ganymede's surface, most notably the white impact crater, Tros, and its system of rays, bright streaks of material blasted from the crater. Tros and its ray system are roughly the width of Arizona. The image also shows Jupiter's Great Red Spot, the large eye-shaped feature at upper left. A storm the size of two Earths, the Great Red Spot has been raging for more than 300 years. Hubble's sharp view of the gas giant planet also reveals the texture of the clouds in the Jovian atmosphere as well as various other storms and vortices. Astronomers use these images to study Jupiter's upper atmosphere. As Ganymede passes behind the giant planet, it reflects sunlight, which then passes through Jupiter's atmosphere. Imprinted on that light is information about the gas giant's atmosphere, which yields clues about the properties of Jupiter's high-altitude haze above the cloud tops. This color image was made from three images taken on April 9, 2007, with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 in red, green, and blue filters. The image shows Jupiter and Ganymede in close to natural colors. For additional information go to: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2008/42/" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2008/42/</a> Credit: NASA, ESA, and E. Karkoschka (University of Arizona) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>