
This artist's concept portrays the plan for the new Engineering Directorate office to be constructed at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The first of several new buildings to be constructed as replacements for older Center facilities, the 5-story, 139,000-square-foot building will house approximately 500 current Marshall employees that provide development and research engineering services for the Marshall Center. Ground breaking ceremonies took place on June 10, 2003 at the construction site, southwest of the Martin and Rideout Roads intersection on Redstone Arsenal. GSC Construction of Waynesboro, Georgia has been selected as the contractor for the facility, which is scheduled for a September 2004 completion.
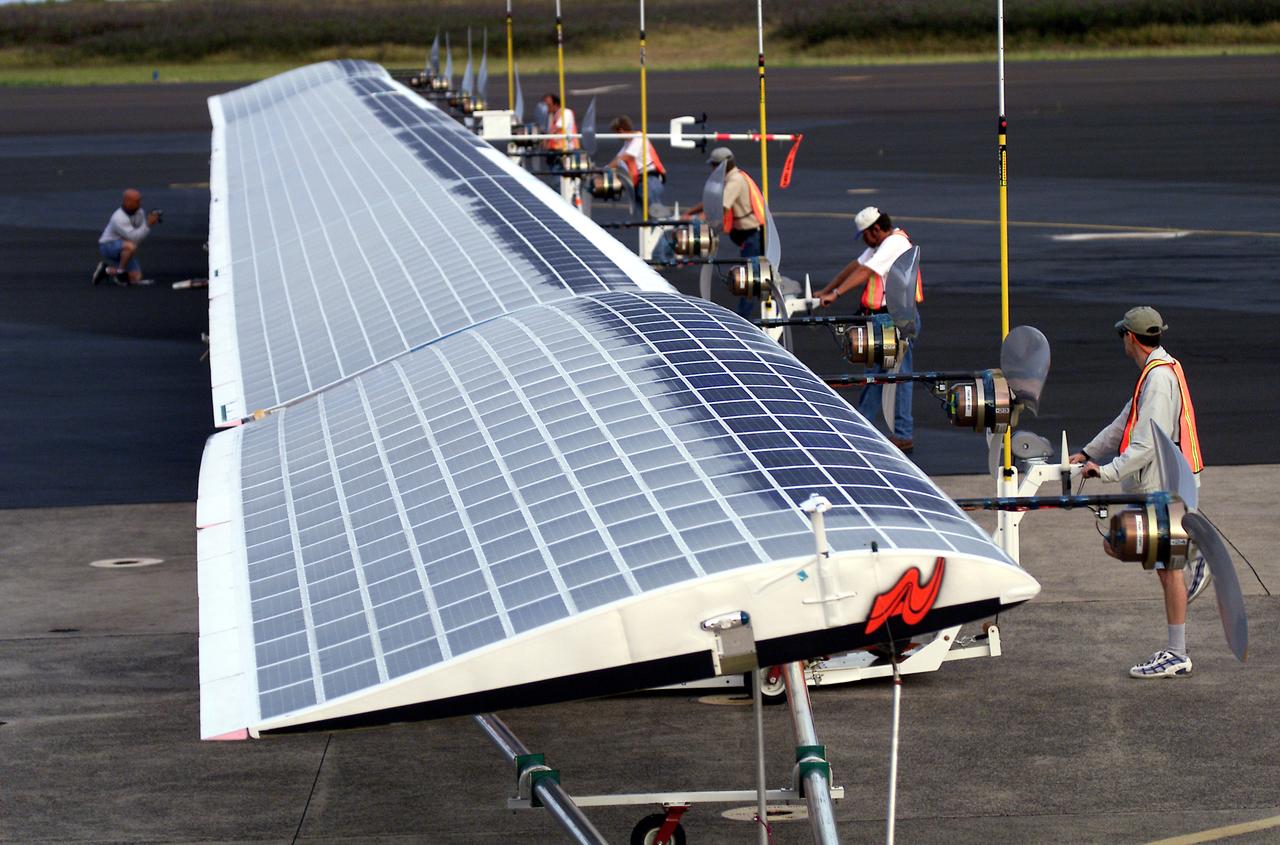

Ground crewmen maneuver AeroVironment's solar-powered Helios Prototype flying wing on its ground support dolly during functional checkouts prior to its first flights under solar power from the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kaua'i, Hawaii.
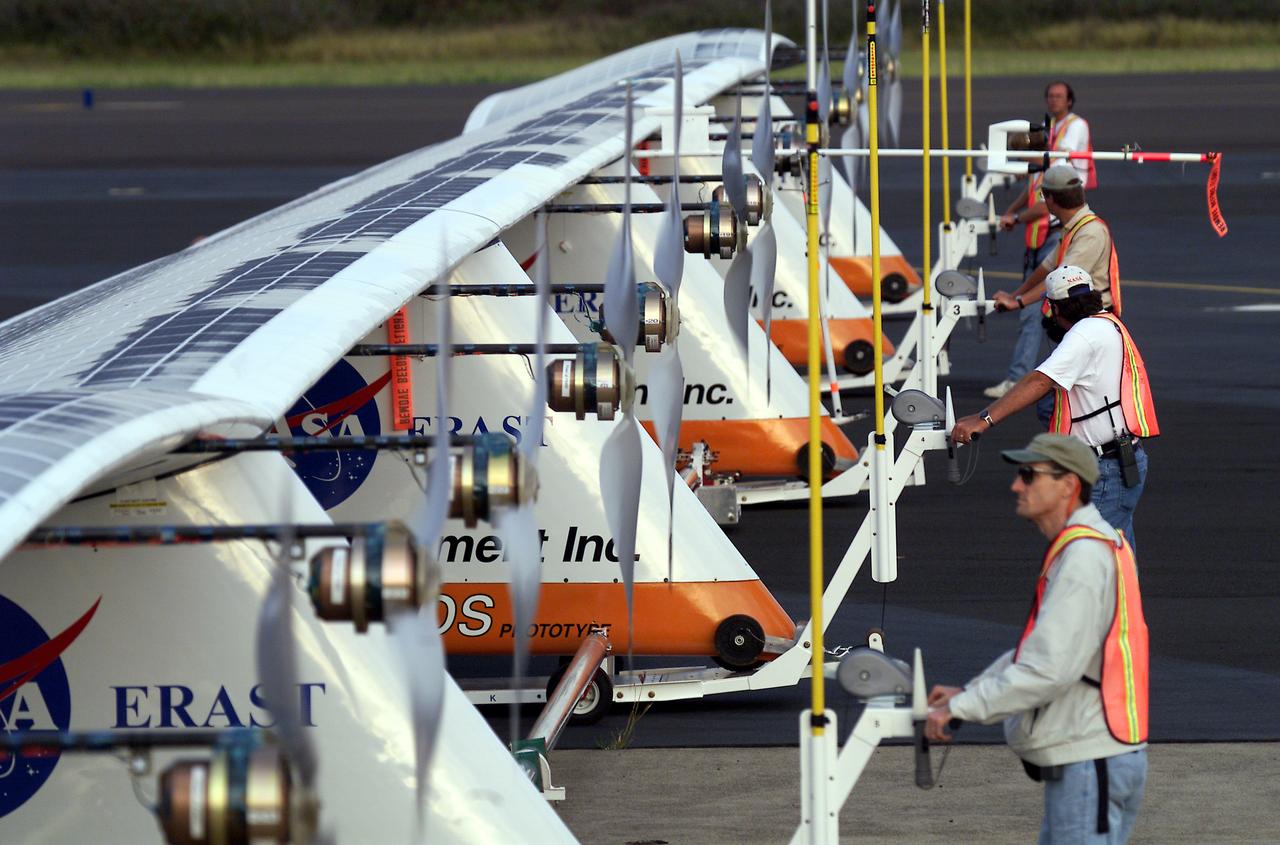

Ground crewmen maneuver AeroVironment's solar-powered Helios Prototype flying wing on its ground support dolly during functional checkouts prior to its first flights under solar power from the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kaua'i, Hawaii.
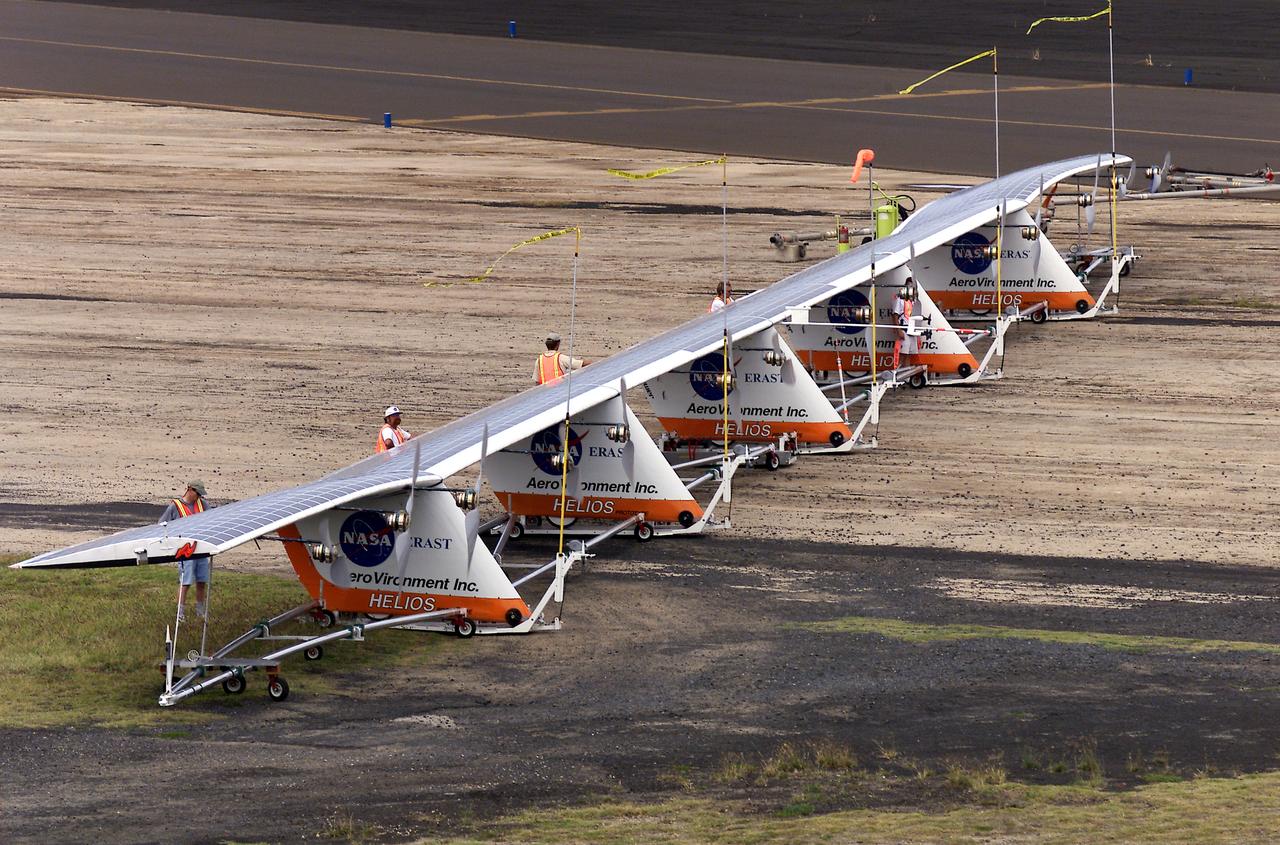

Ground crewmen maneuver AeroVironment's solar-powered Helios Prototype flying wing on its ground support dolly during functional checkouts prior to its first flights under solar power from the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kaua'i, Hawaii.
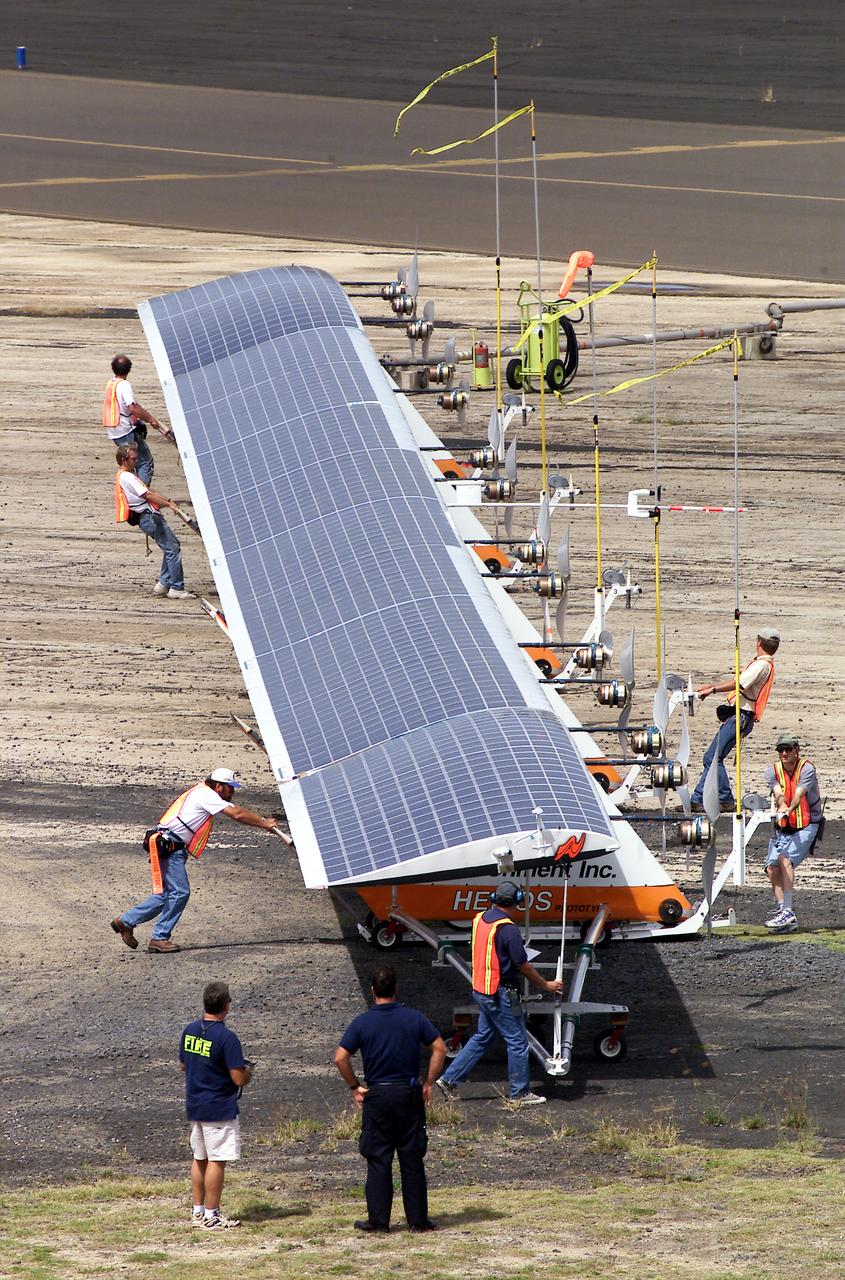

Ground crewmen maneuver AeroVironment's solar-powered Helios Prototype flying wing on its ground support dolly during functional checkouts prior to its first flights under solar power from the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kaua'i, Hawaii.

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Abort System facility on July 10, 2021, after being transported from the Florida spaceport’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility earlier in the day. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
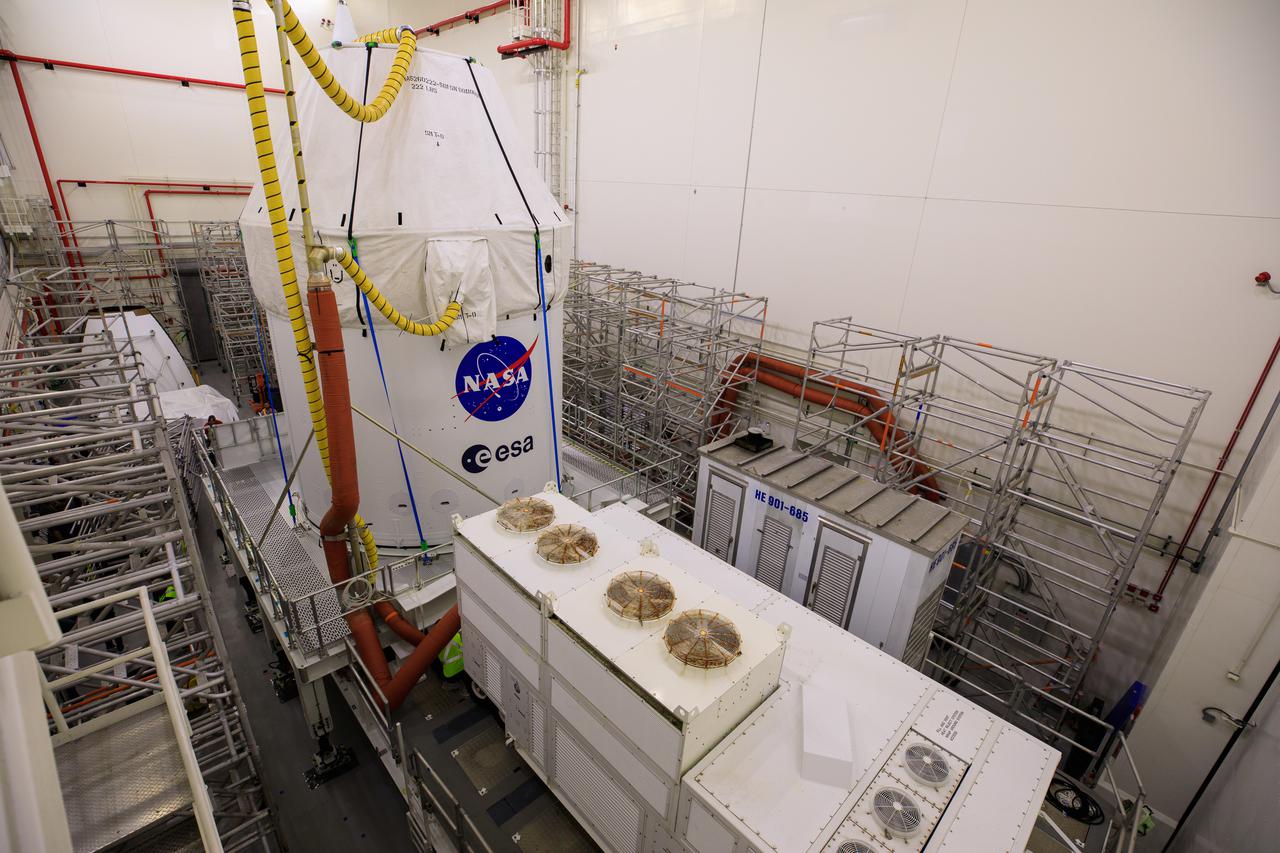

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Abort System facility on July 10, 2021, after being transported from the Florida spaceport’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility earlier in the day. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
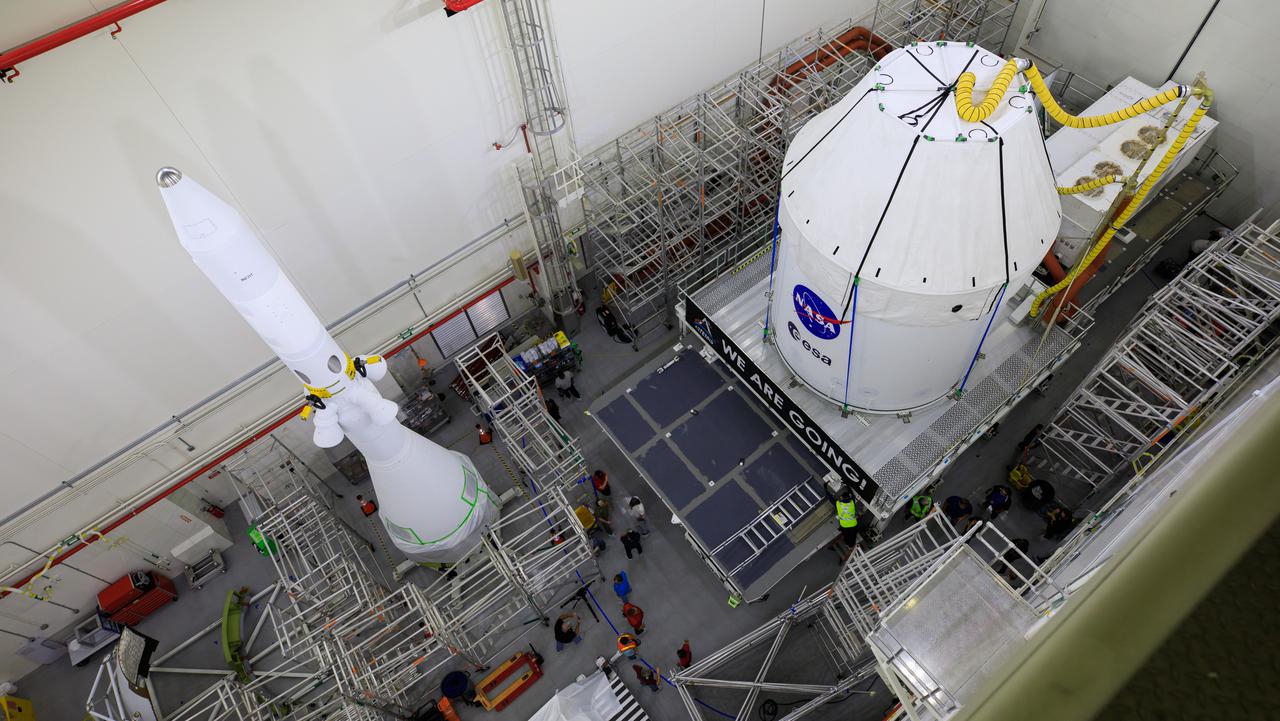

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Abort System facility on July 10, 2021, after being transported from the Florida spaceport’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility earlier in the day. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
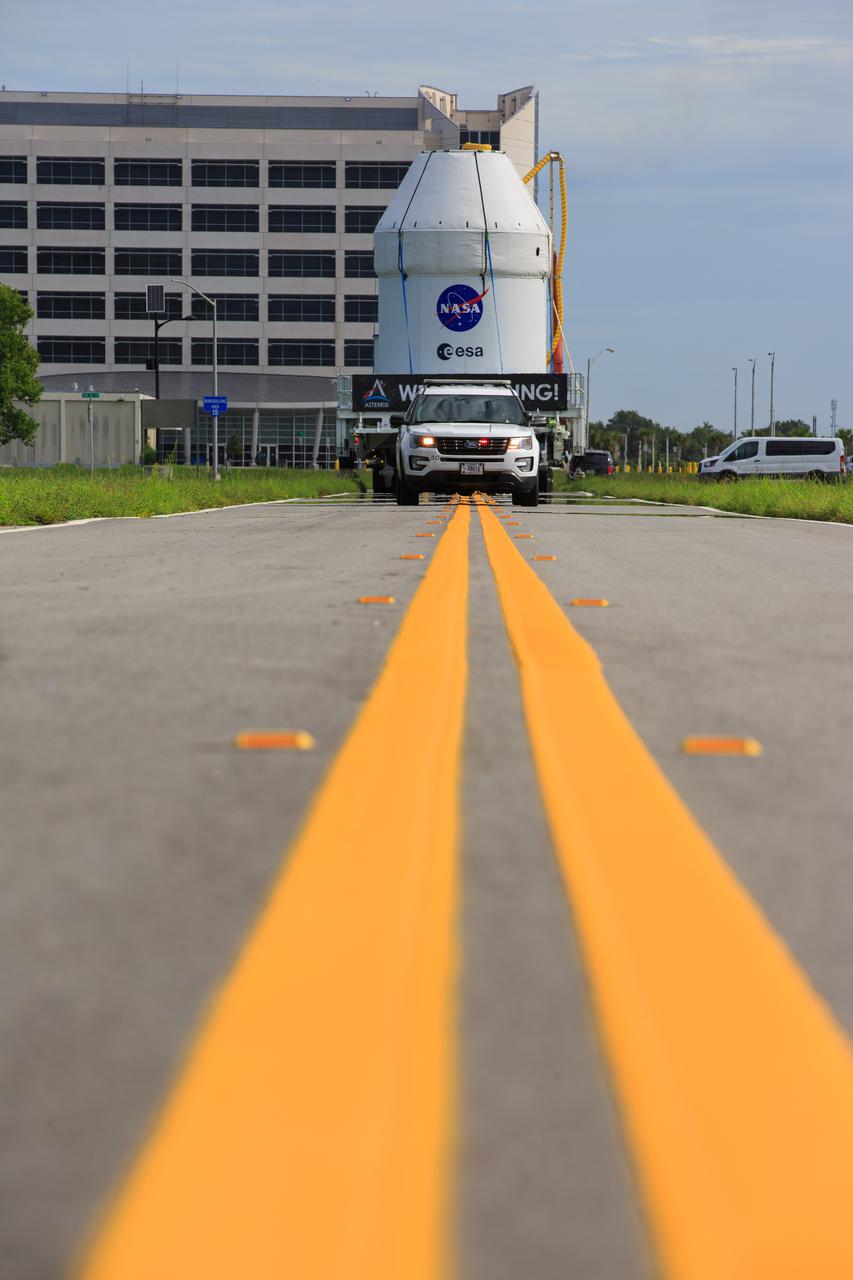

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
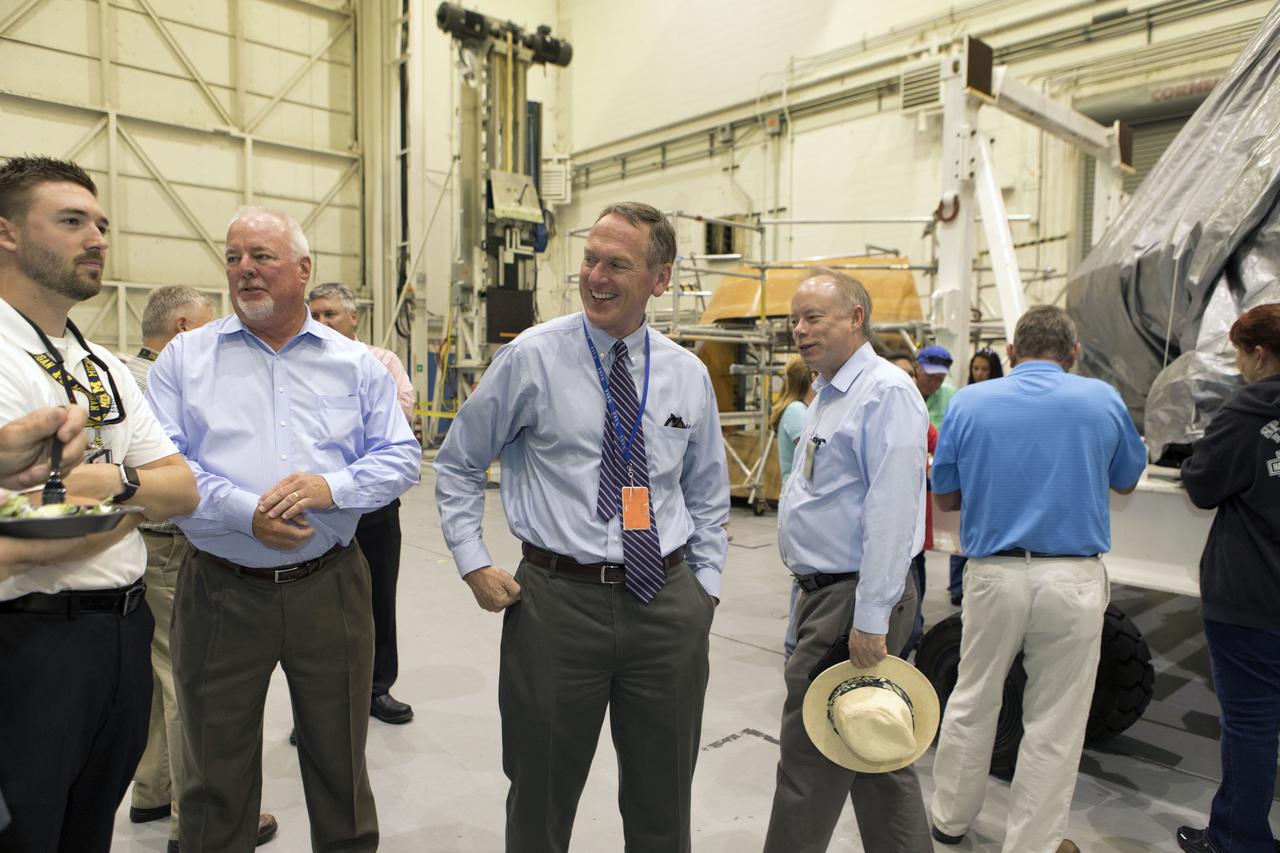

The team that tested the umbilical lines and accessories that will connect from the mobile launcher to NASA's Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 hold a banner signing event July 24, 2018, to mark completion of testing at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Attending the event is Mike Bolger, center, Exploration Ground Systems manager. A total of 21 umbilicals and launch accessories were tested on various simulators at the LETF before they were transferred to the mobile launcher for installation.
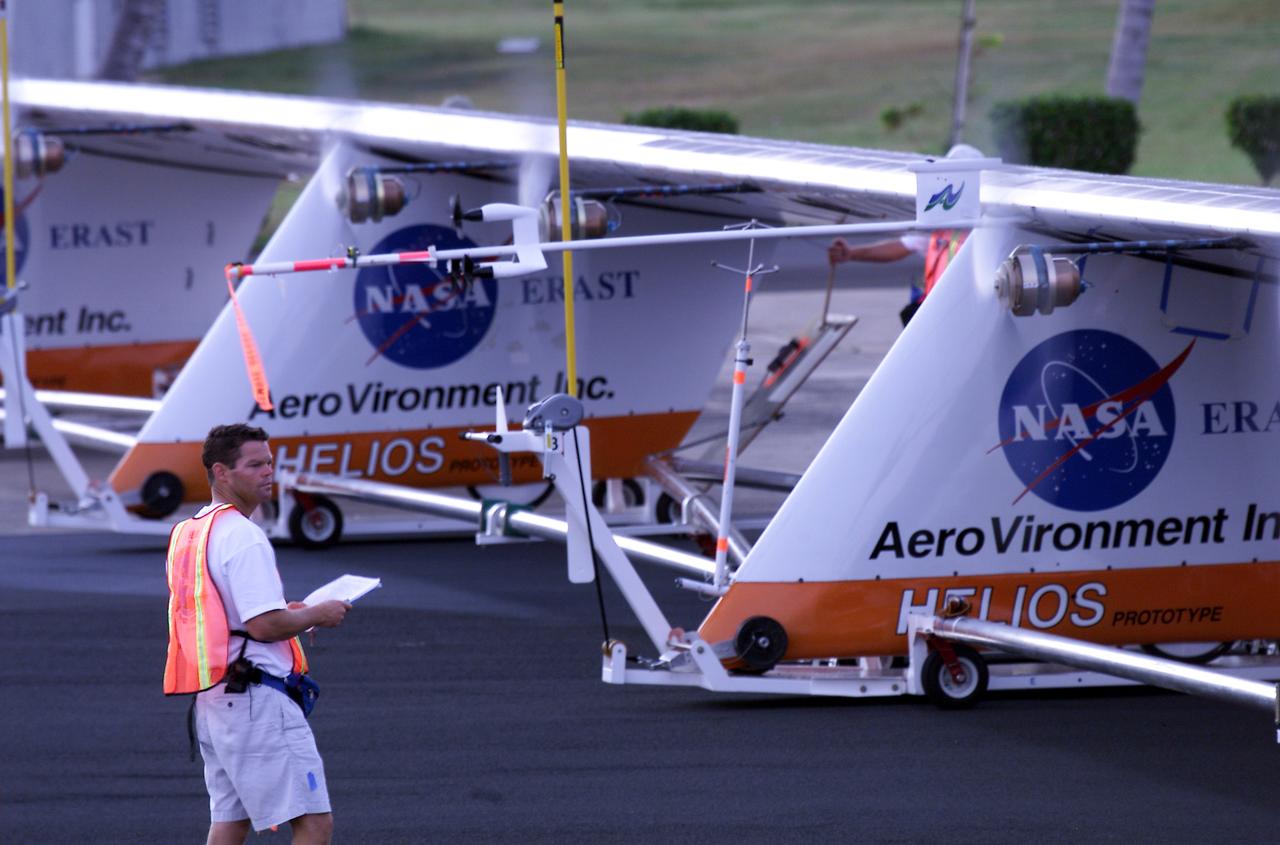

Helios Prototype crew chief Marshall MacCready of AeroVironment, Inc., carefully monitors motor runs during ground checkout of the solar-powered flying wing prior to its first flight from the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kaua'i, Hawaii.
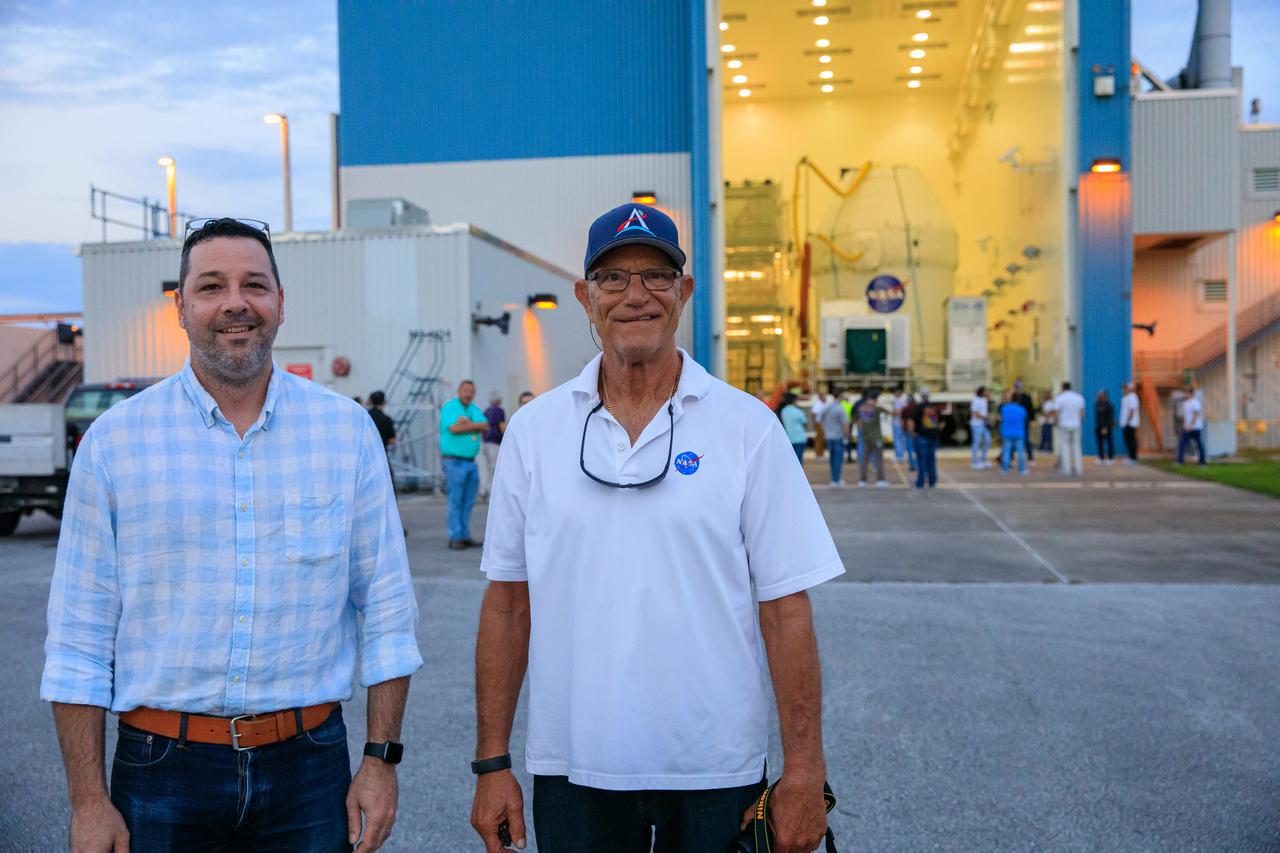
Mike Collins, NASA Operations manager for Spacecraft Offline Operations, left, and Skip Williams, operations manager for the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) spacecraft offline element integration team, stand in front of the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission, as the capsule moves out from Kennedy Space Center’s MFFP on July 10, 2021. Orion is being transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
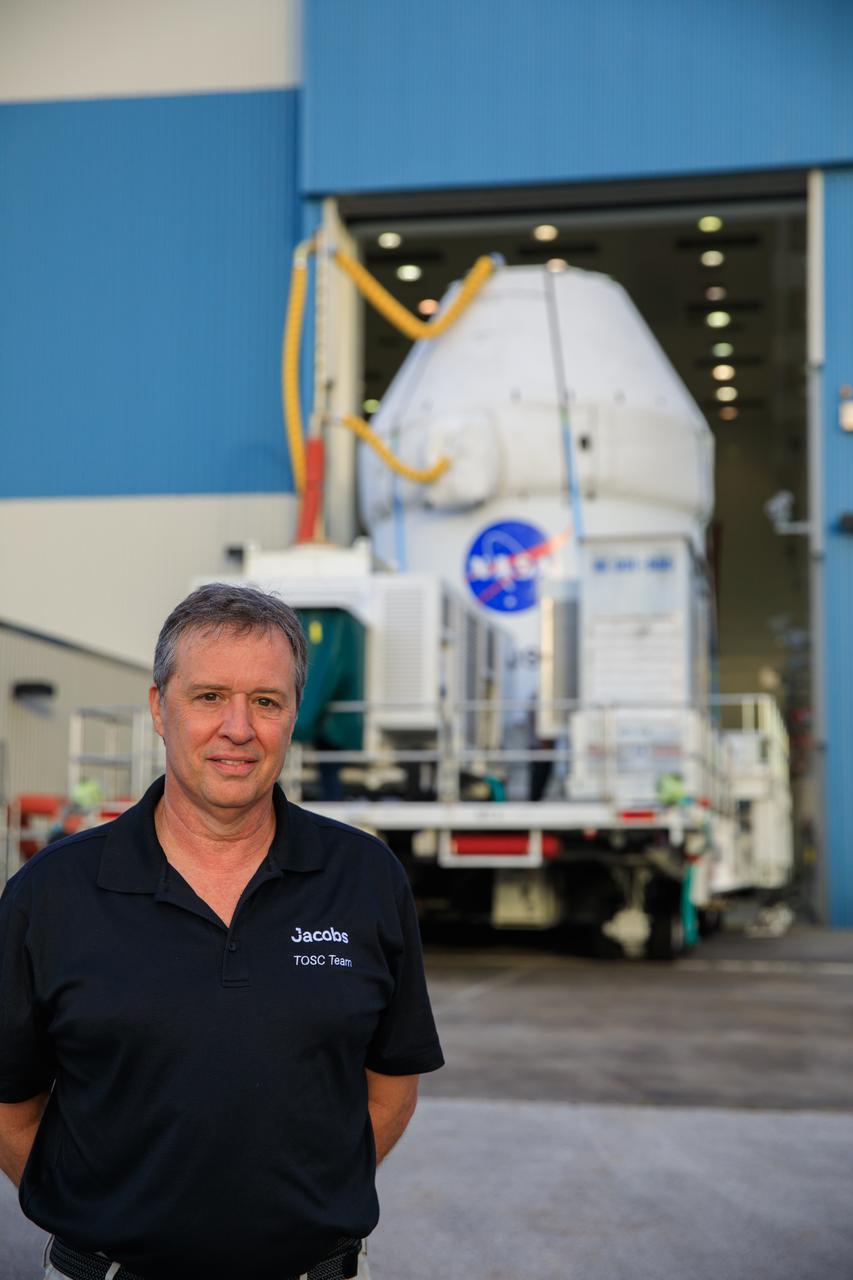

Nick Kindred, Jacobs flow manager, stands in front of the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission, as the capsule moves out from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility on July 10, 2021. Orion is being transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
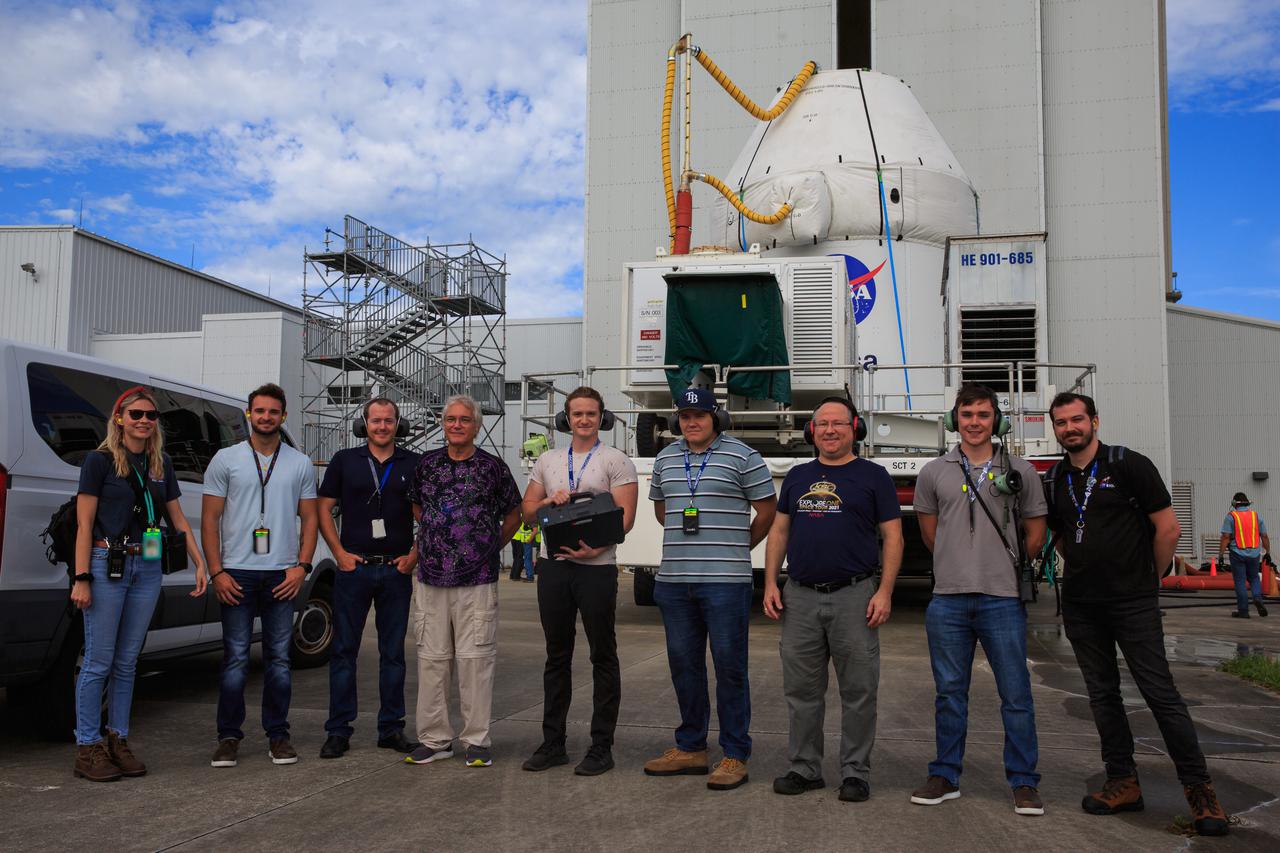

Teams from Kennedy’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs pose as the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. They will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
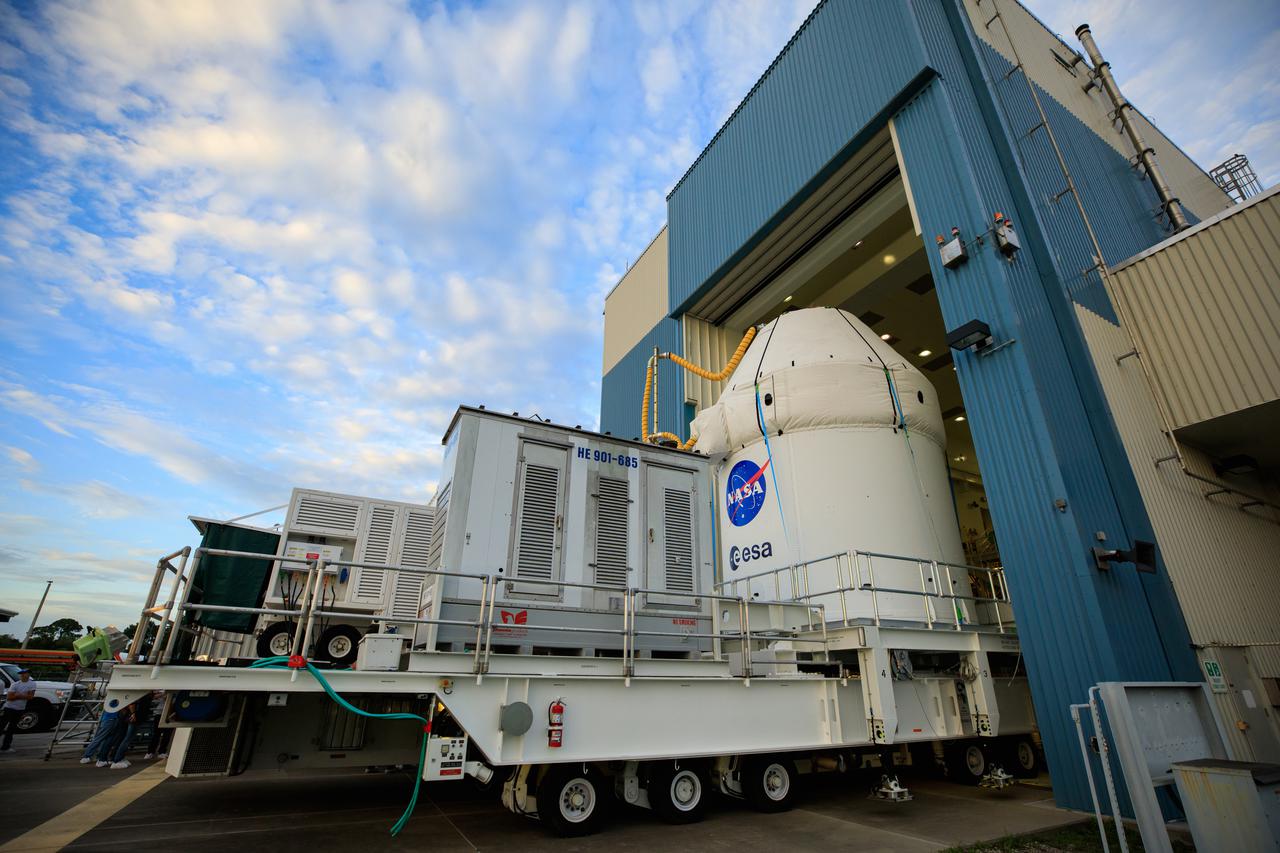

After recently completing fueling and servicing checks, the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission departs from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing on July 10, 2021. It is being transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
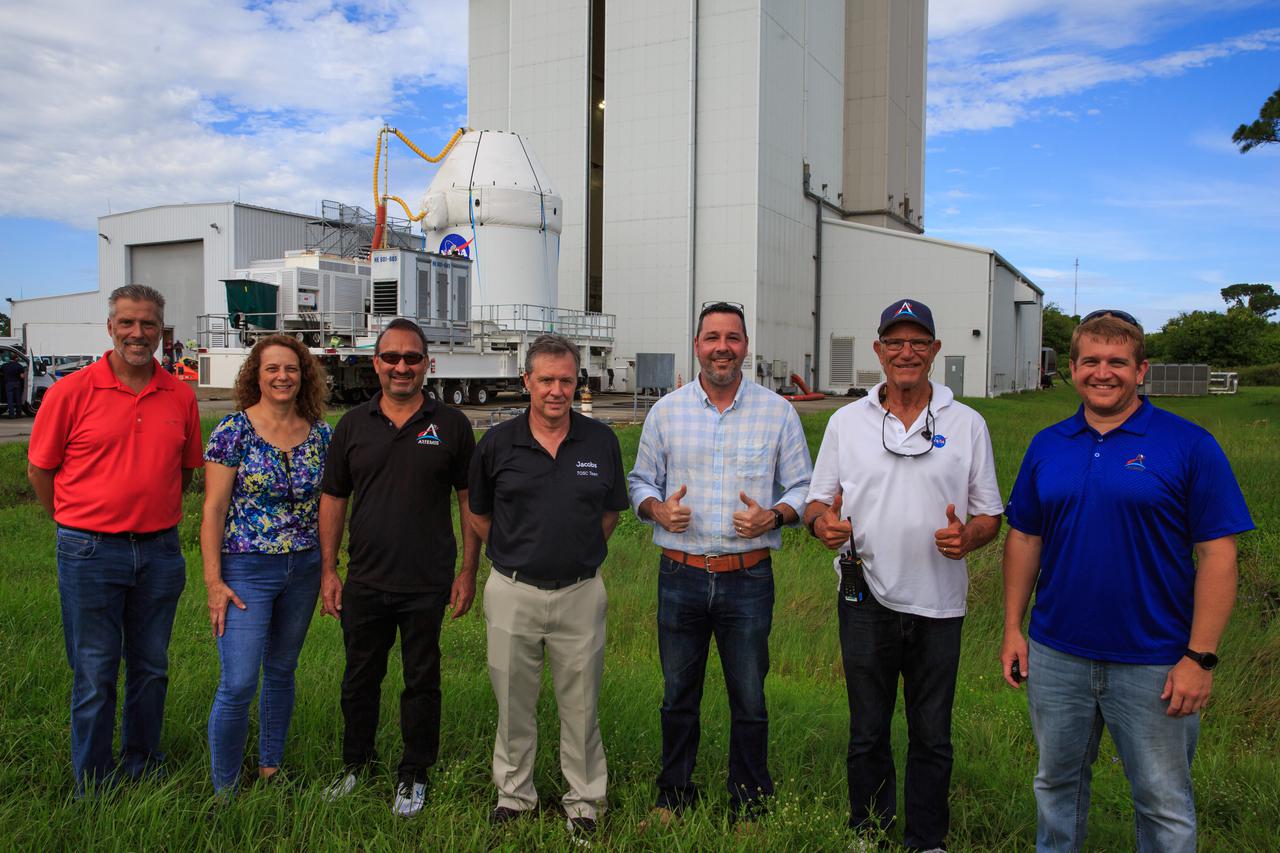

Teams from Kennedy’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs pose as the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. They will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
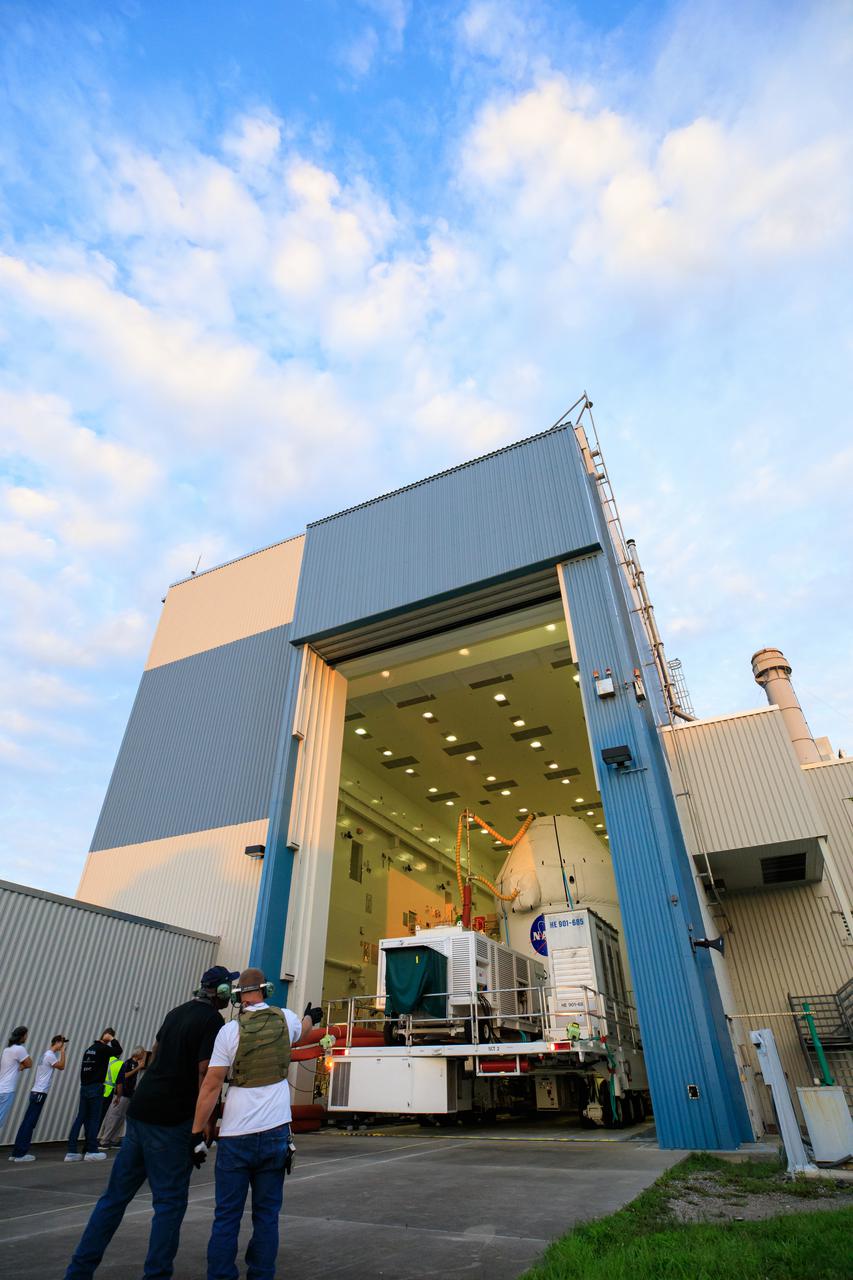

After recently completing fueling and servicing checks, the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission departs from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing on July 10, 2021. It is being transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
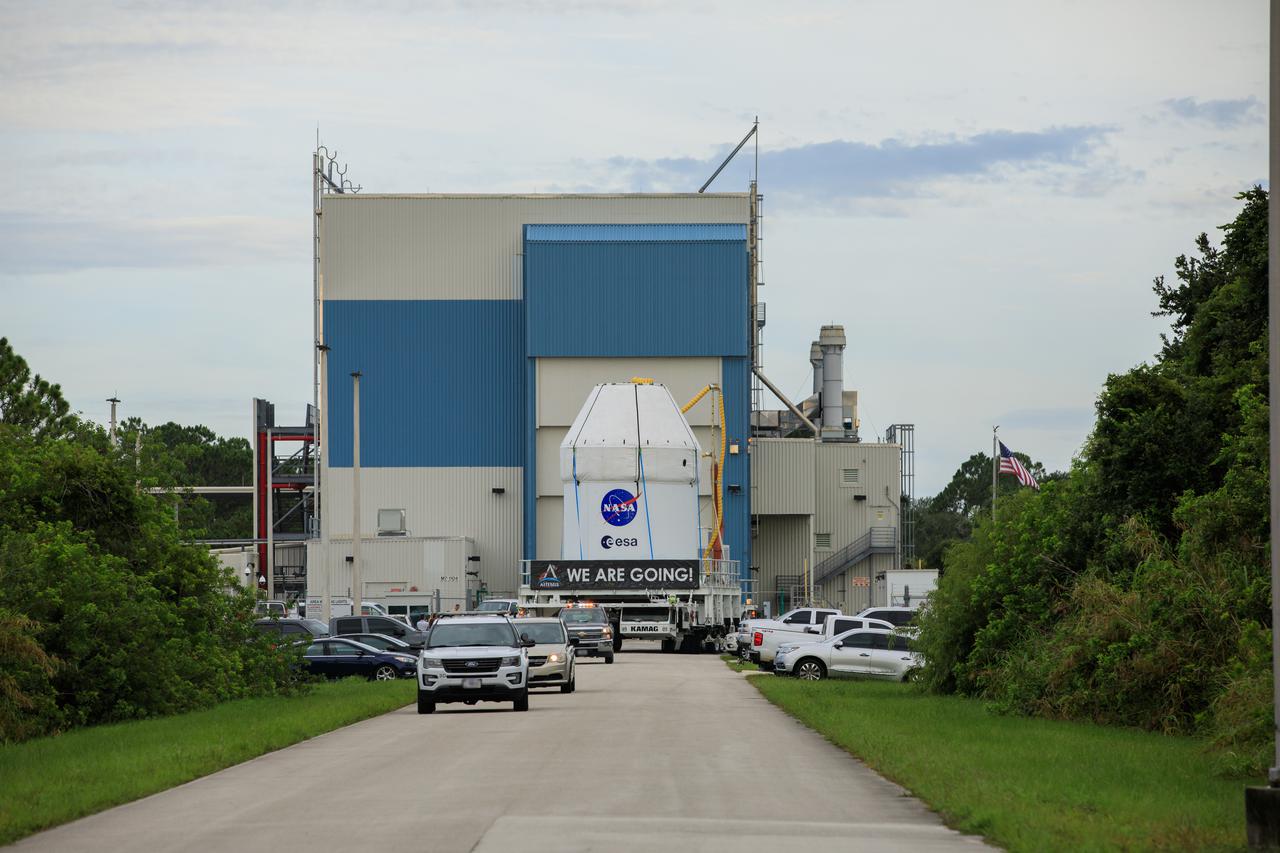

After recently completing fueling and servicing checks, the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission departs Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing on July 10, 2021. The capsule is being transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, cable trays run along the walls in high bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, as part of a centerwide refurbishment initiative under the Ground Systems Development and Operations GSDO Program. The cable replacement project is under way in high bays 1 and 3 on the east side of the building, facing Launch Complex 39’s pads A and B. Approximately 150 miles of existing Apollo/shuttle era cabling is being removed to make room for installation of state-of-the-art command, communication and control systems that will be needed by future users to perform vehicle testing and verification prior to rollout to the launch pad. For more information, visit http://go.nasa.gov/groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, cable is being pulled from the cable trays lining the walls of high bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, as part of a centerwide refurbishment initiative under the Ground Systems Development and Operations GSDO Program. The cable replacement project is under way in high bays 1 and 3 on the east side of the building, facing Launch Complex 39’s pads A and B. Approximately 150 miles of existing Apollo/shuttle era cabling is being removed to make room for installation of state-of-the-art command, communication and control systems that will be needed by future users to perform vehicle testing and verification prior to rollout to the launch pad. For more information, visit http://go.nasa.gov/groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
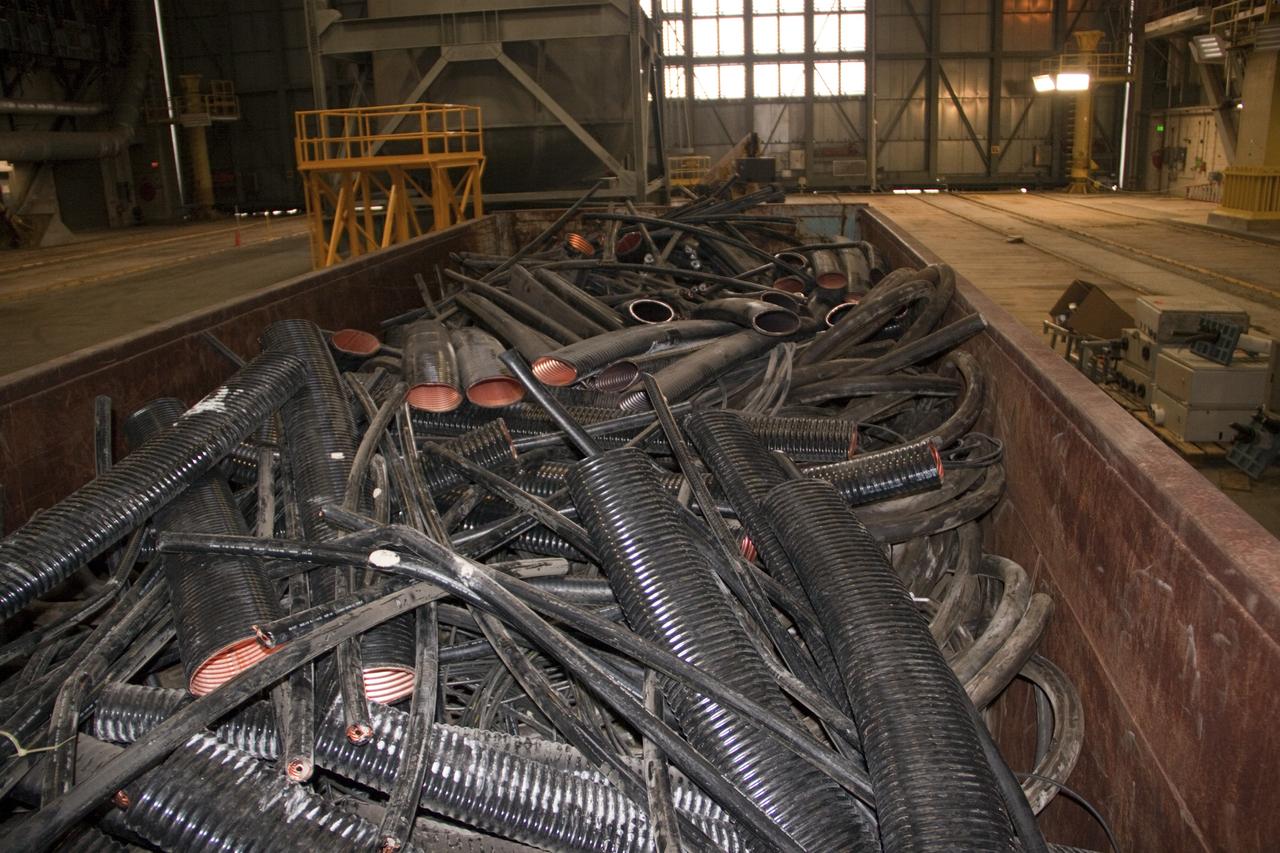

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, old cabling is being pulled from high bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, as part of a centerwide refurbishment initiative under the Ground Systems Development and Operations GSDO Program. The cable replacement project is under way in high bays 1 and 3 on the east side of the building, facing Launch Complex 39’s pads A and B. Approximately 150 miles of existing Apollo/shuttle era cabling is being removed to make room for installation of state-of-the-art command, communication and control systems that will be needed by future users to perform vehicle testing and verification prior to rollout to the launch pad. For more information, visit http://go.nasa.gov/groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
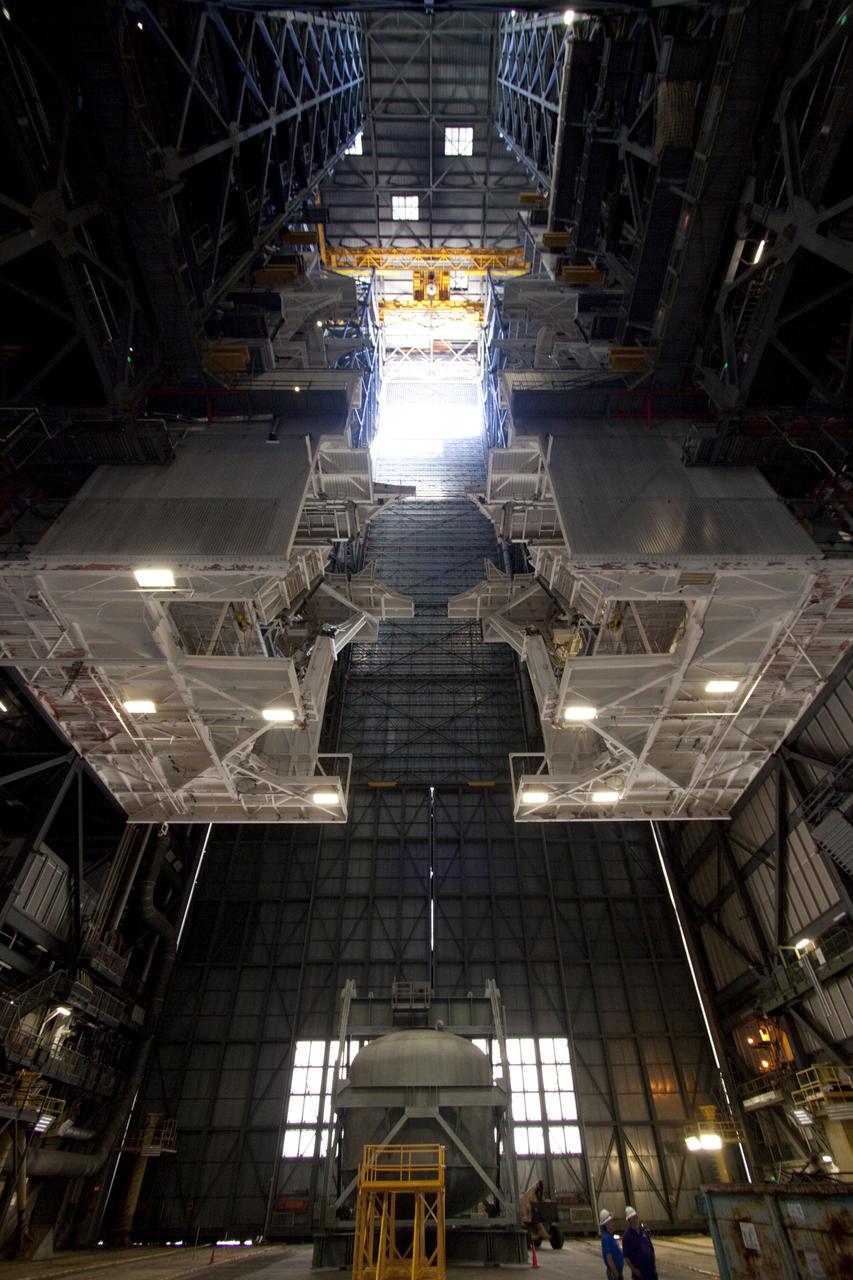

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, refurbishment of high bay 3 is under way in the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, as part of a centerwide refurbishment initiative under the Ground Systems Development and Operations GSDO Program. It is 525 feet from the bay’s ceiling to the floor. The cable replacement project is under way in high bays 1 and 3 on the east side of the building, facing Launch Complex 39’s pads A and B. Approximately 150 miles of existing Apollo/shuttle era cabling is being removed to make room for installation of state-of-the-art command, communication and control systems that will be needed by future users to perform vehicle testing and verification prior to rollout to the launch pad. For more information, visit http://go.nasa.gov/groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, old racks are being excessed in high bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, as part of a centerwide refurbishment initiative under the Ground Systems Development and Operations GSDO Program The cable replacement project is under way in high bays 1 and 3 on the east side of the building, facing Launch Complex 39’s pads A and B. Approximately 150 miles of existing Apollo/shuttle era cabling is being removed to make room for installation of state-of-the-art command, communication and control systems that will be needed by future users to perform vehicle testing and verification prior to rollout to the launch pad. For more information, visit http://go.nasa.gov/groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
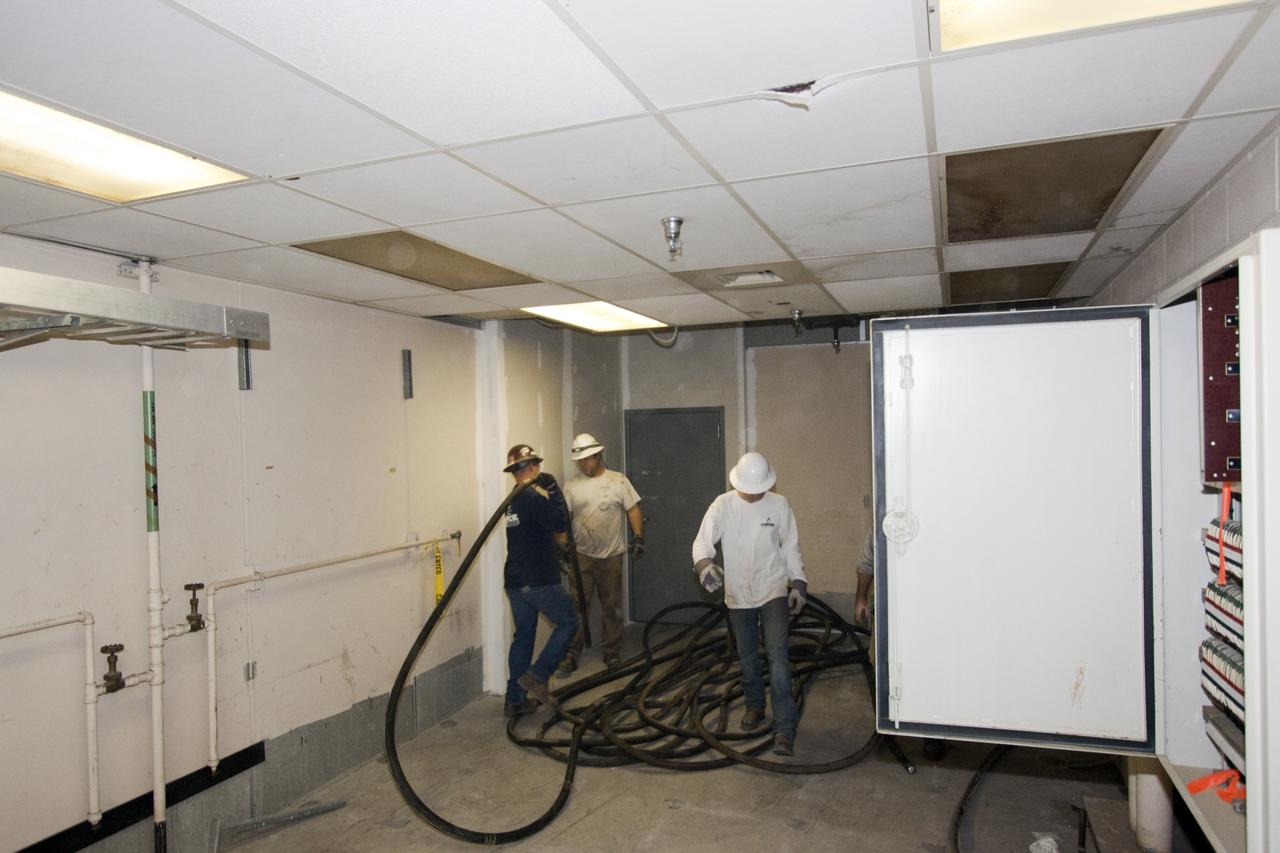

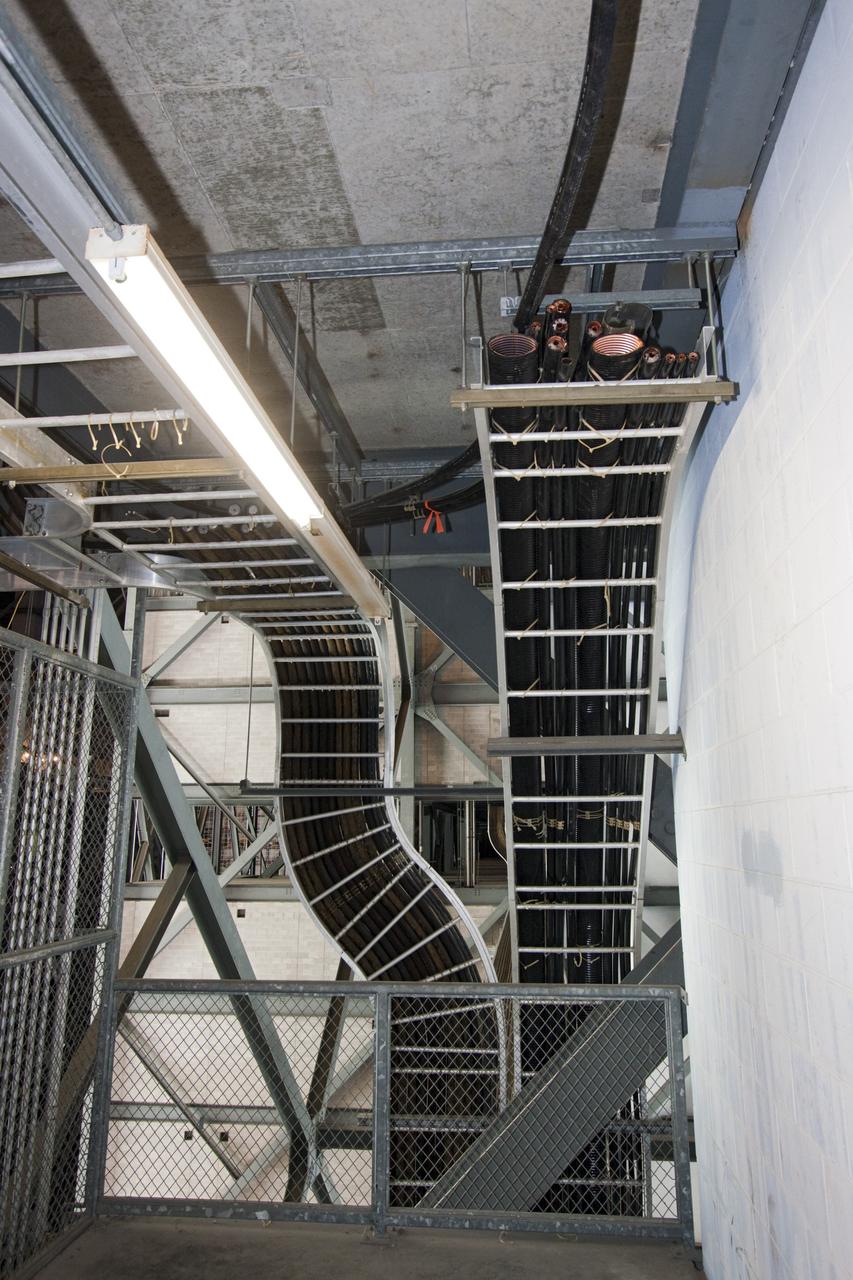
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers remove cables between the 26th and 29th floors of high bay 3 in the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, during part of a centerwide refurbishment initiative under the Ground Systems Development and Operations GSDO Program. The cable replacement project is under way in high bays 1 and 3 on the east side of the building, facing Launch Complex 39’s pads A and B. Approximately 150 miles of existing Apollo/shuttle era cabling is being removed to make room for installation of state-of-the-art command, communication and control systems that will be needed by future users to perform vehicle testing and verification prior to rollout to the launch pad. For more information, visit http://go.nasa.gov/groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
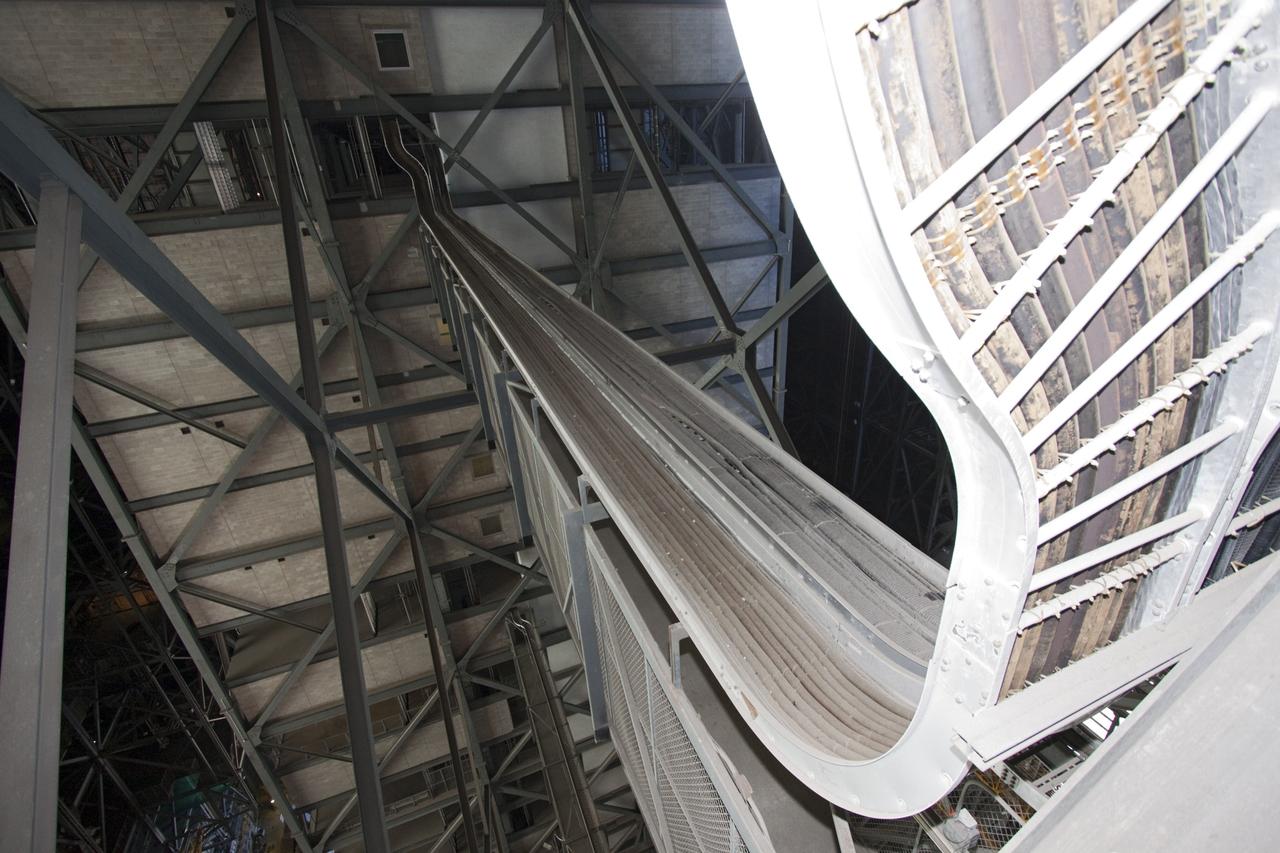

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, cable trays wind their way along the grating in high bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, during part of a centerwide refurbishment initiative under the Ground Systems Development and Operations GSDO Program. The cable replacement project is under way in high bays 1 and 3 on the east side of the building, facing Launch Complex 39’s pads A and B. Approximately 150 miles of existing Apollo/shuttle era cabling is being removed to make room for installation of state-of-the-art command, communication and control systems that will be needed by future users to perform vehicle testing and verification prior to rollout to the launch pad. For more information, visit http://go.nasa.gov/groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers pull cables between the 26th and 29th floors of high bay 3 in the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, during part of a centerwide refurbishment initiative under the Ground Systems Development and Operations GSDO Program. The cable replacement project is under way in high bays 1 and 3 on the east side of the building, facing Launch Complex 39’s pads A and B. Approximately 150 miles of existing Apollo/shuttle era cabling is being removed to make room for installation of state-of-the-art command, communication and control systems that will be needed by future users to perform vehicle testing and verification prior to rollout to the launch pad. For more information, visit http://go.nasa.gov/groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
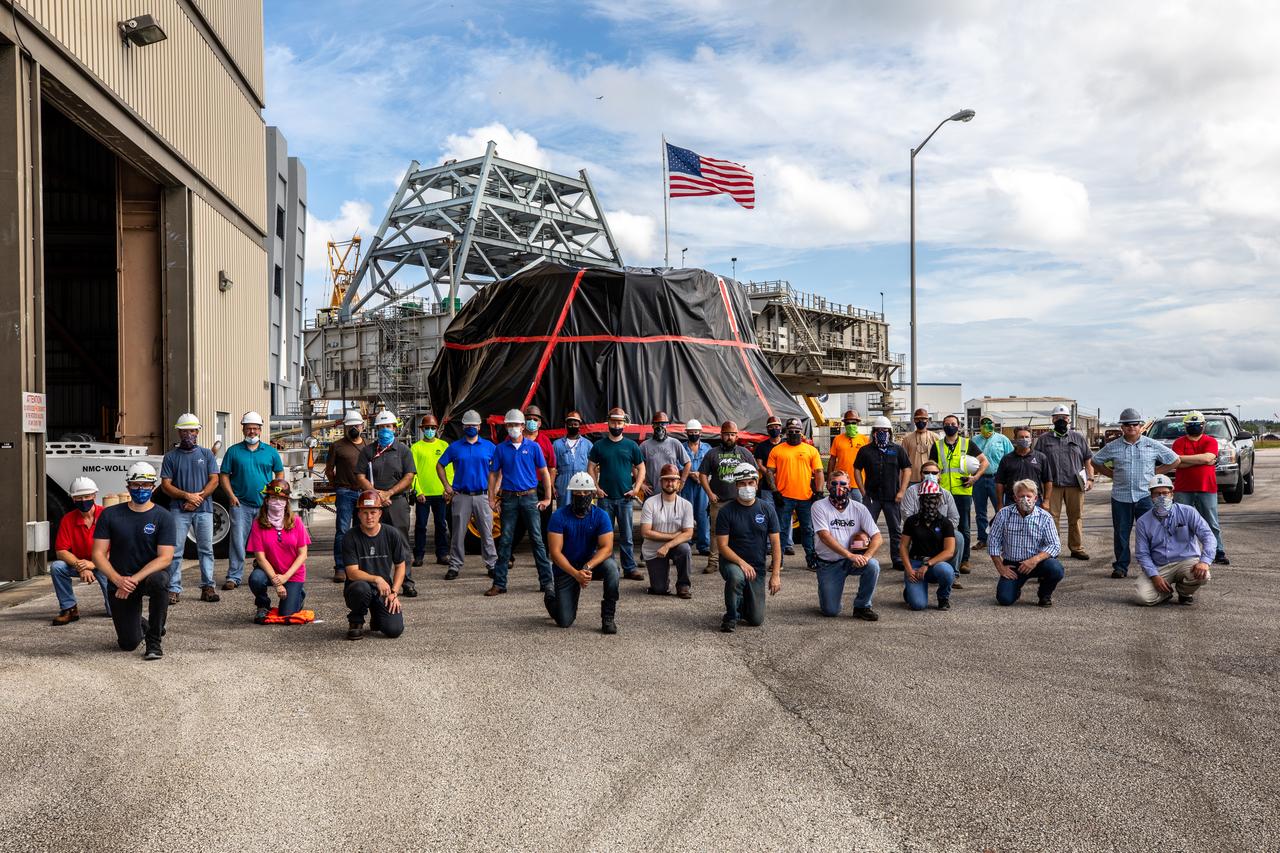

Exploration Ground Systems workers gather in front of the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020, to mark the arrival of the Artemis I aft skirts for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters. The aft skirts were moved from the Booster Fabrication Facility. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
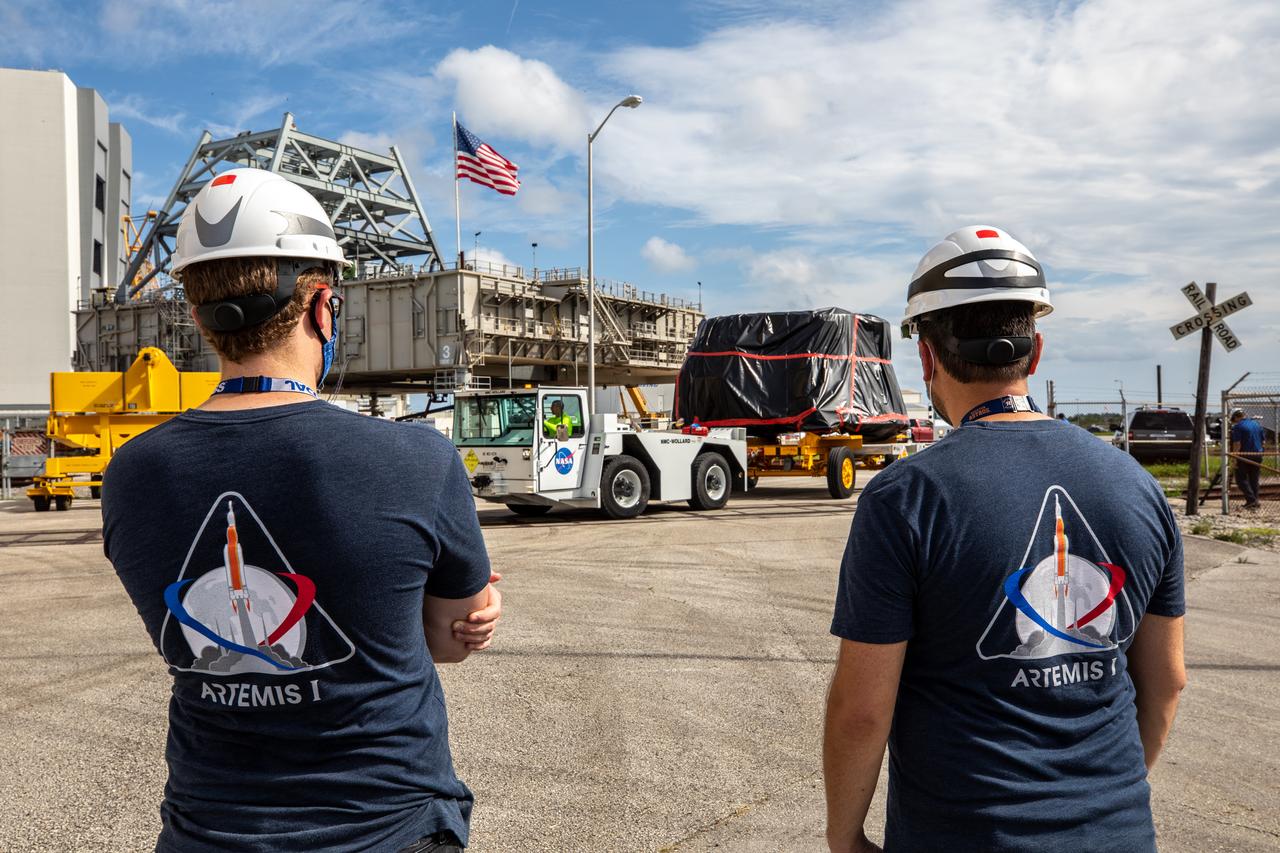

Exploration Ground Systems workers watch as the first of two Artemis I aft skirts for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters crosses a railroad track on its way to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. They were transported from the Booster Fabrication Facility. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.
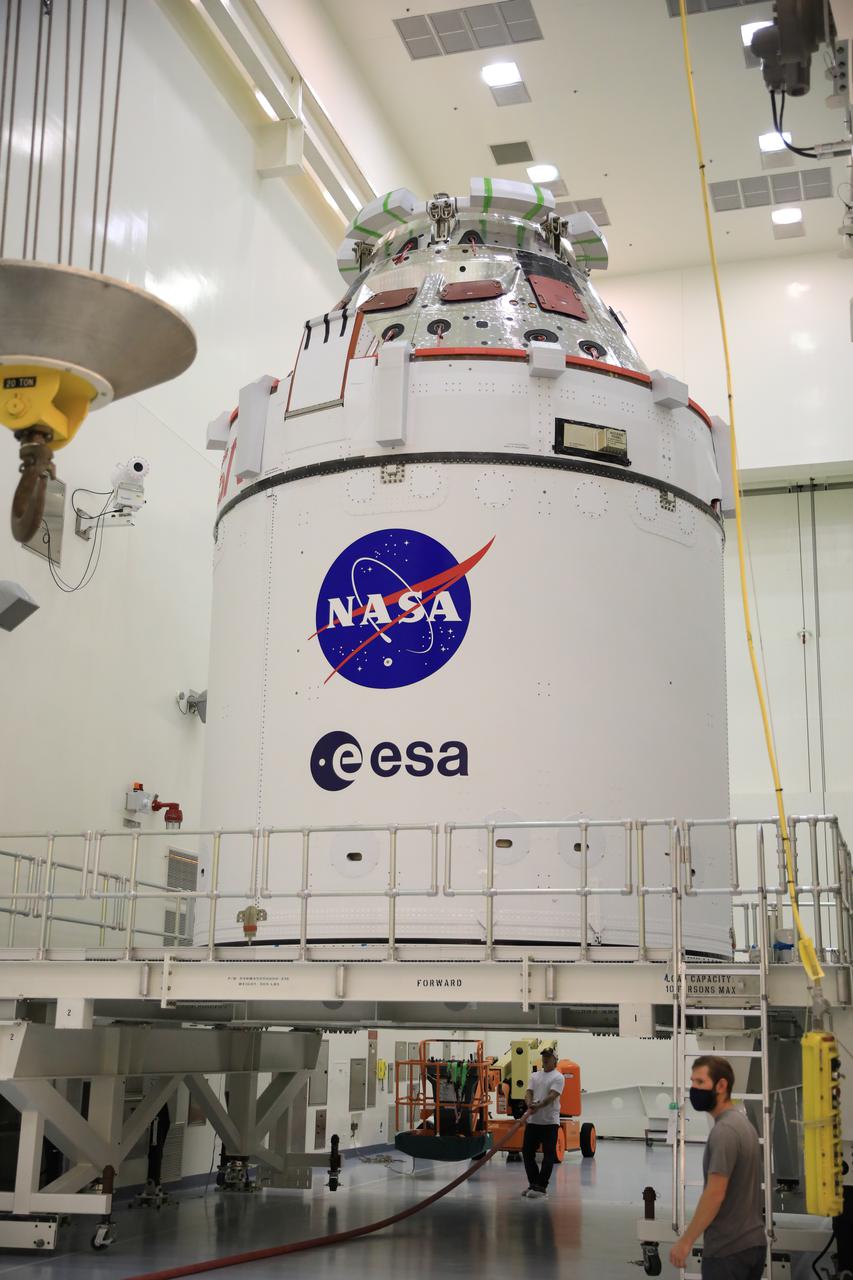

Fueling and servicing checks on the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission are completed inside Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility on July 8, 2021. The capsule will be transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will work to add parts of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
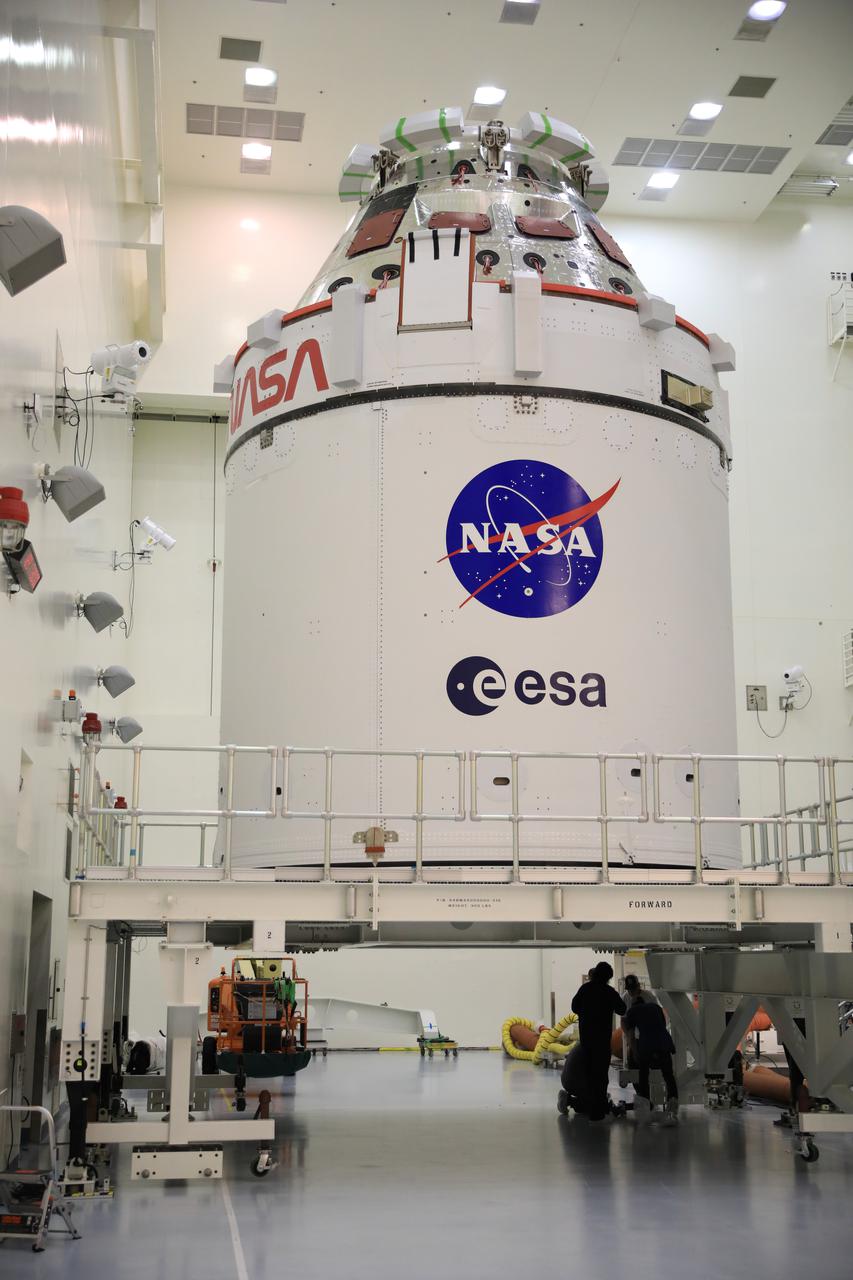

Fueling and servicing checks on the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission are completed inside Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility on July 8, 2021. The capsule will be transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will work to add parts of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
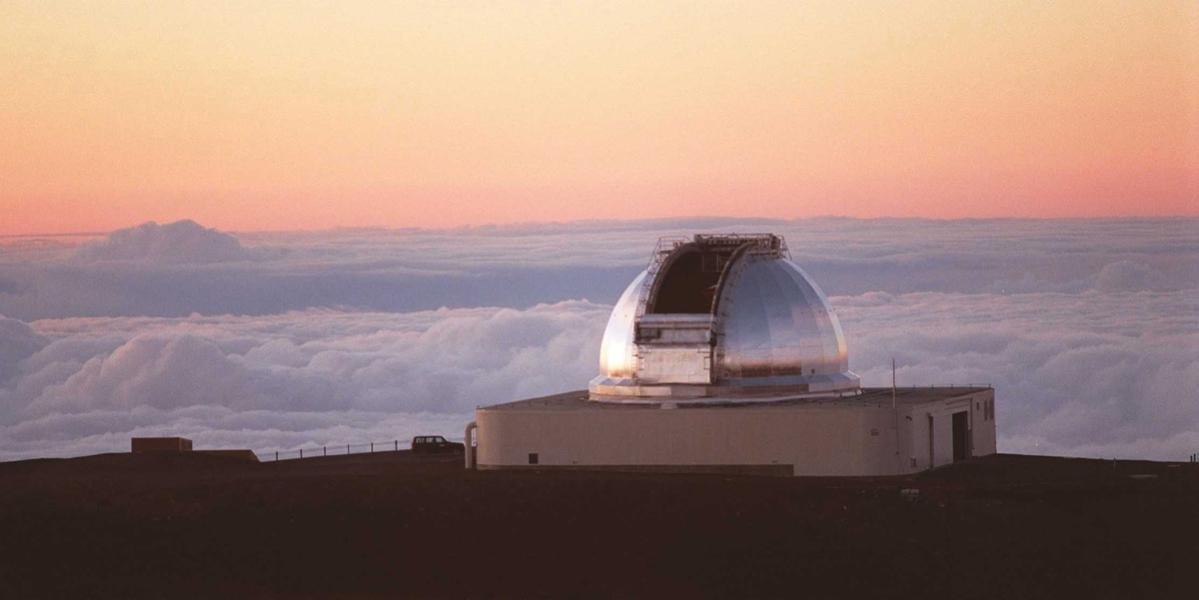

NASA Infrared Telescope Facility atop Mauna Kea, Hawaii. The IRTF is a venerable 30-year-old, 3-meter-diameter 10-foot telescope that ranks 40th among ground-based telescopes.

Teams from NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems transport the engine section of the agency’s Artemis IV SLS (Space Launch System) core stage from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the spaceport’s Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) on Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2024. NASA’s Pegasus barge delivered the core stage engine section housing the four RS-25 engines from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana to NASA Kennedy on Thursday, Sept. 5, 2024. The engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
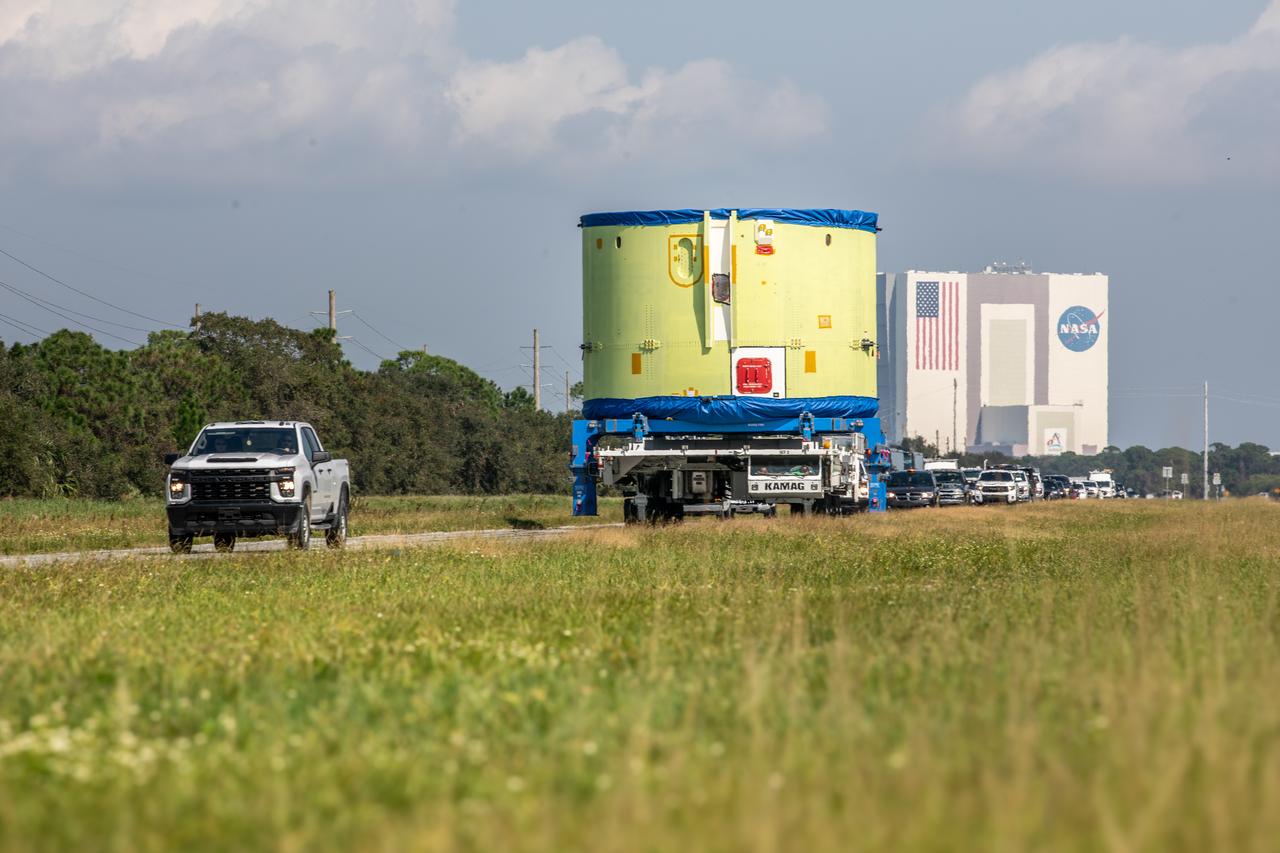

Teams from NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems transport the engine section of the agency’s Artemis IV SLS (Space Launch System) core stage from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the spaceport’s Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) on Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2024. NASA’s Pegasus barge delivered the core stage engine section housing the four RS-25 engines from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana to NASA Kennedy on Thursday, Sept. 5, 2024. The engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
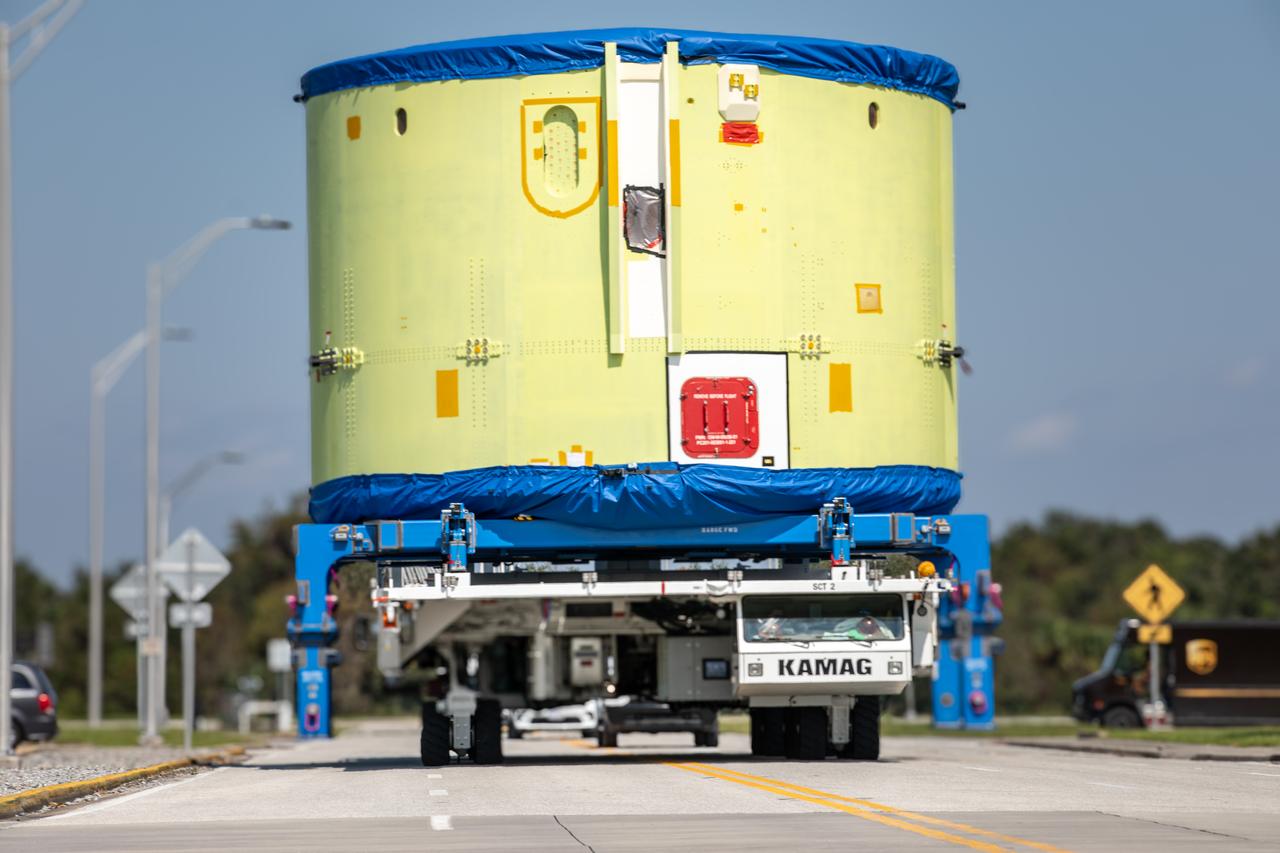

Teams from NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems transport the engine section of the agency’s Artemis IV SLS (Space Launch System) core stage from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the spaceport’s Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) on Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2024. NASA’s Pegasus barge delivered the core stage engine section housing the four RS-25 engines from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana to NASA Kennedy on Thursday, Sept. 5, 2024. The engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
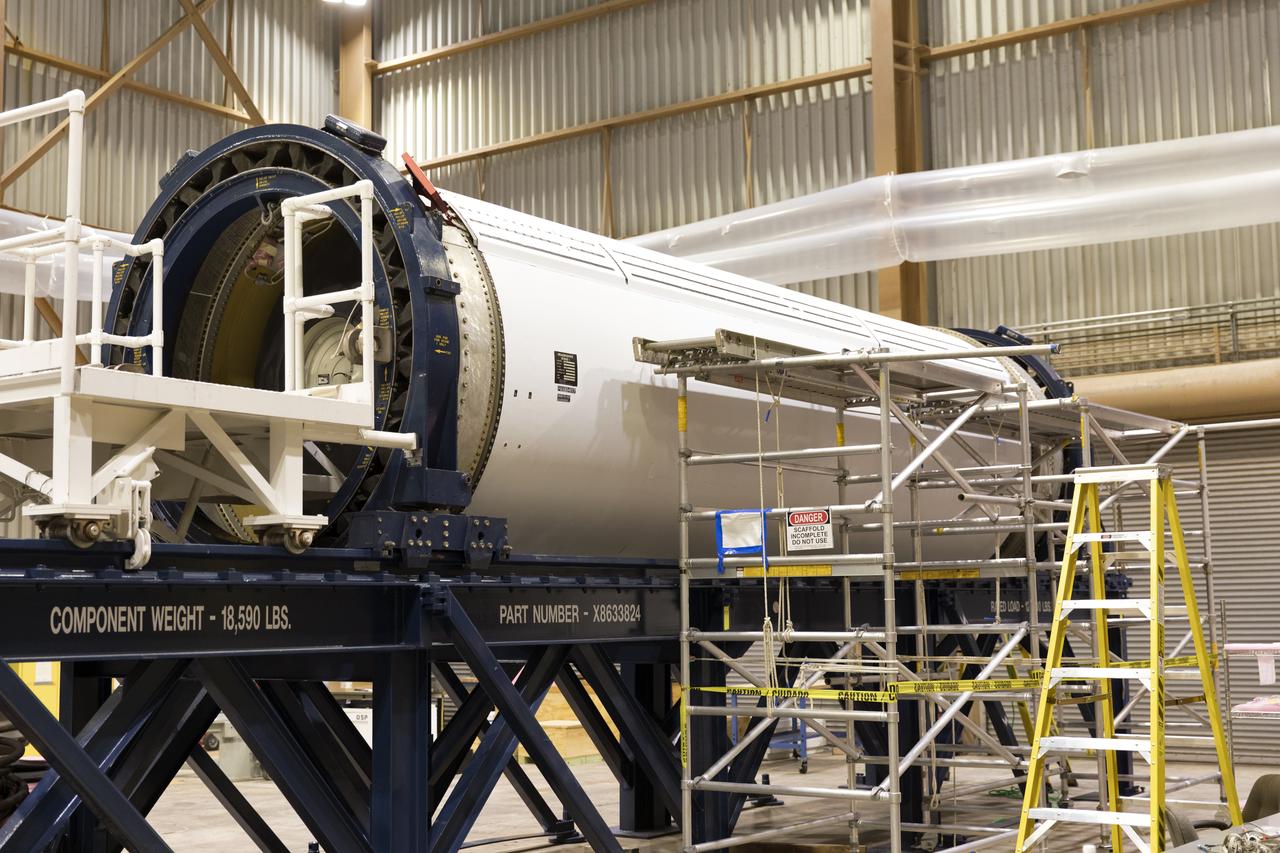

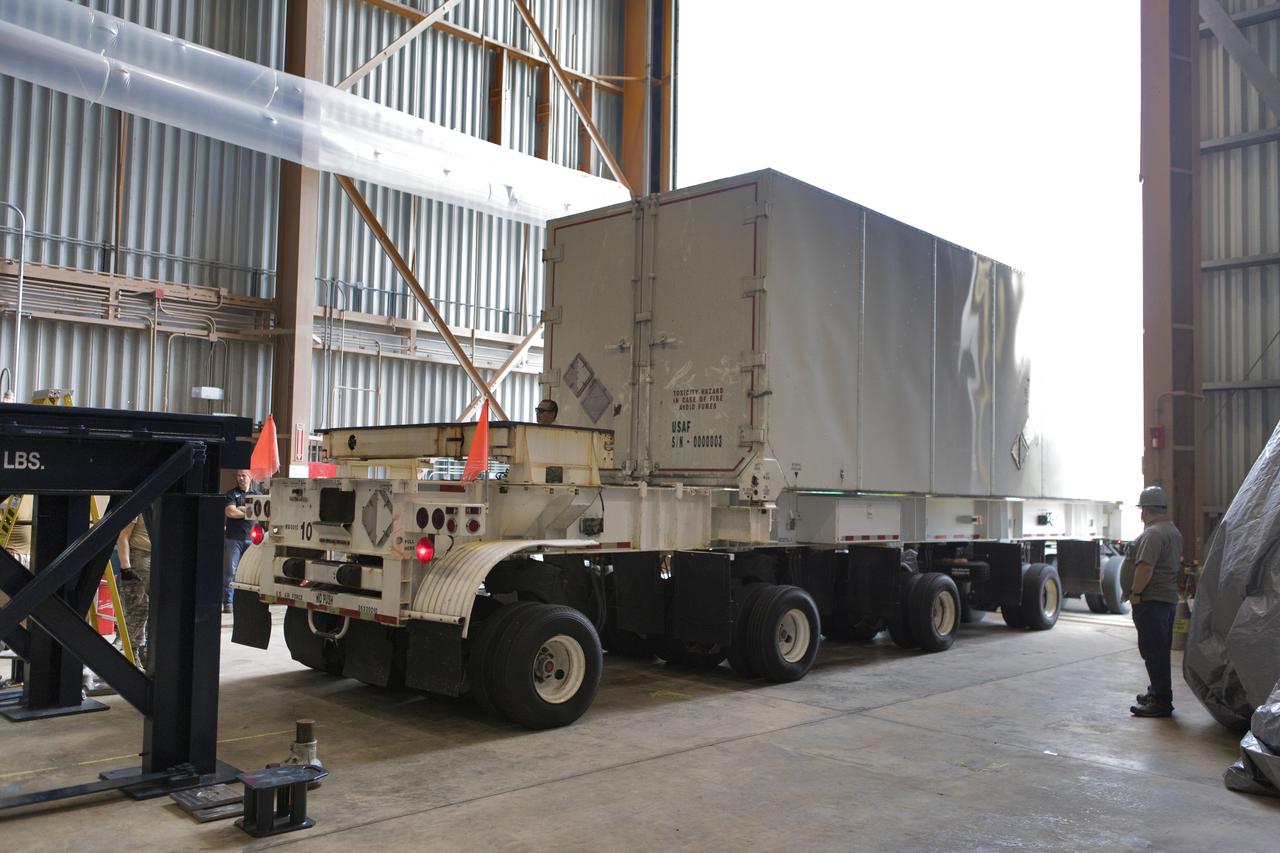
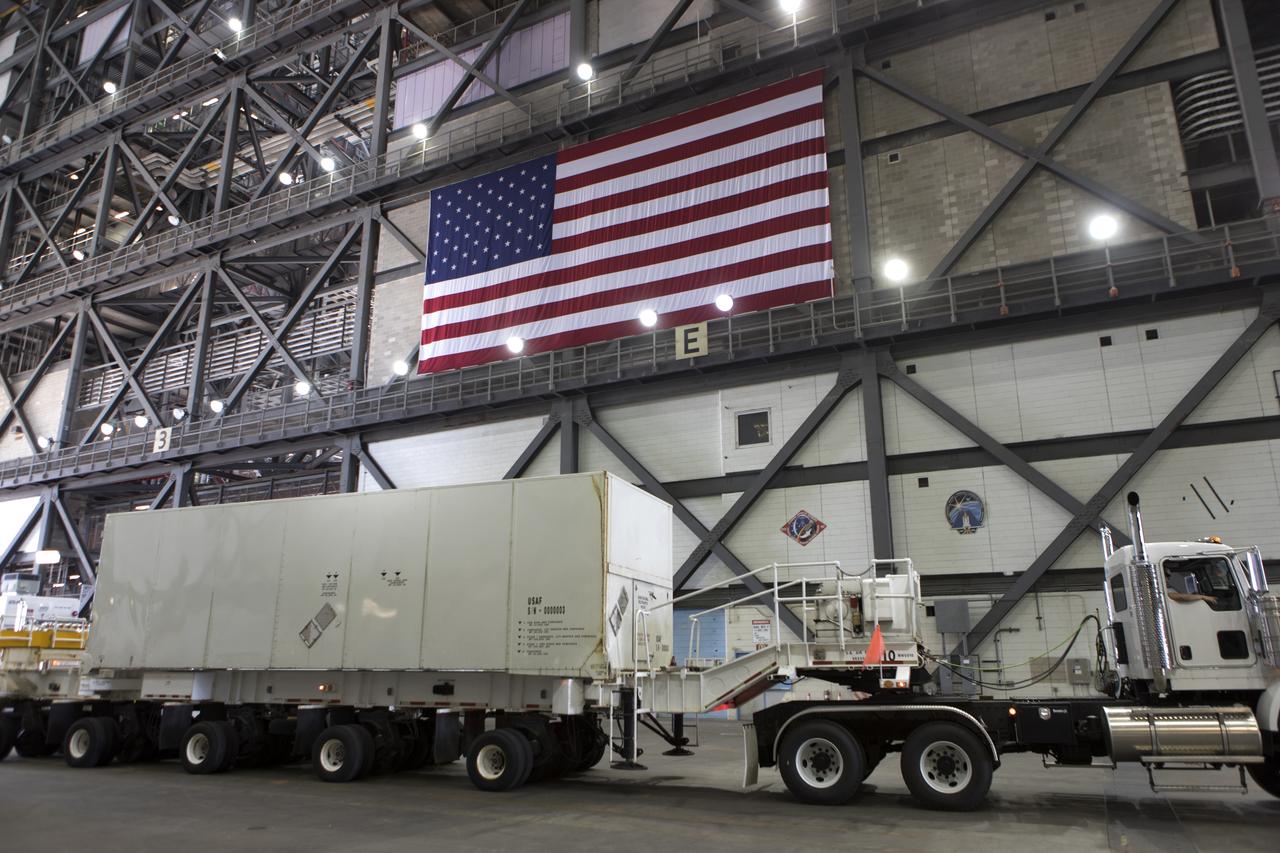
The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
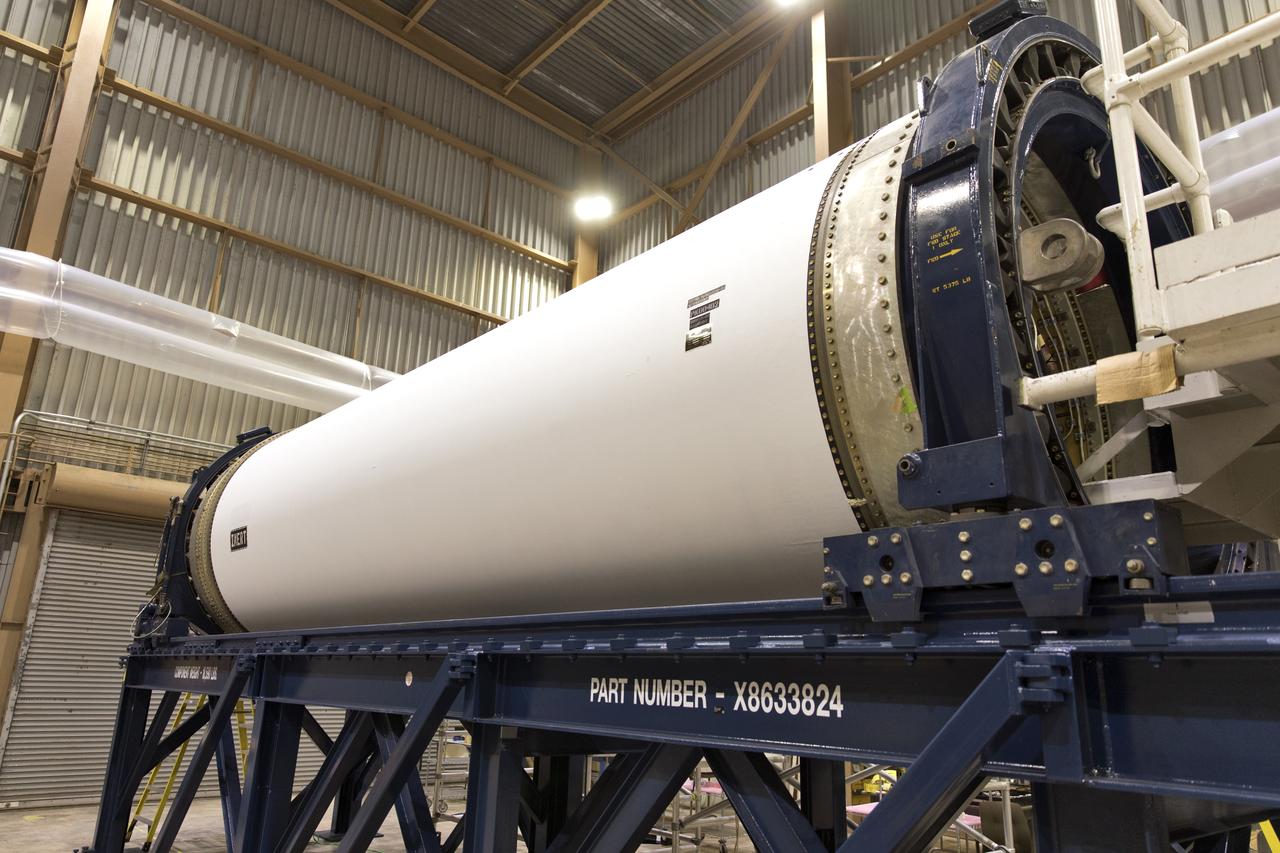

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
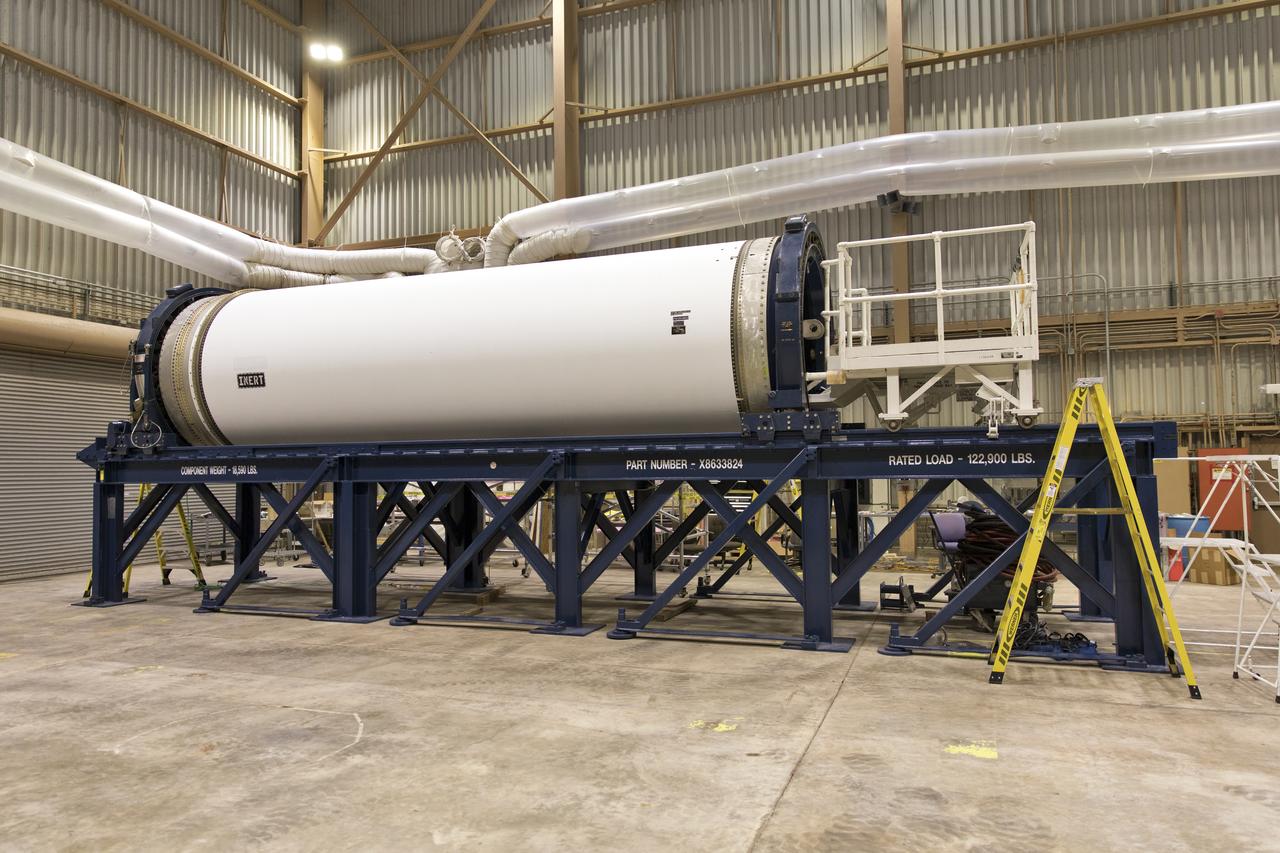

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
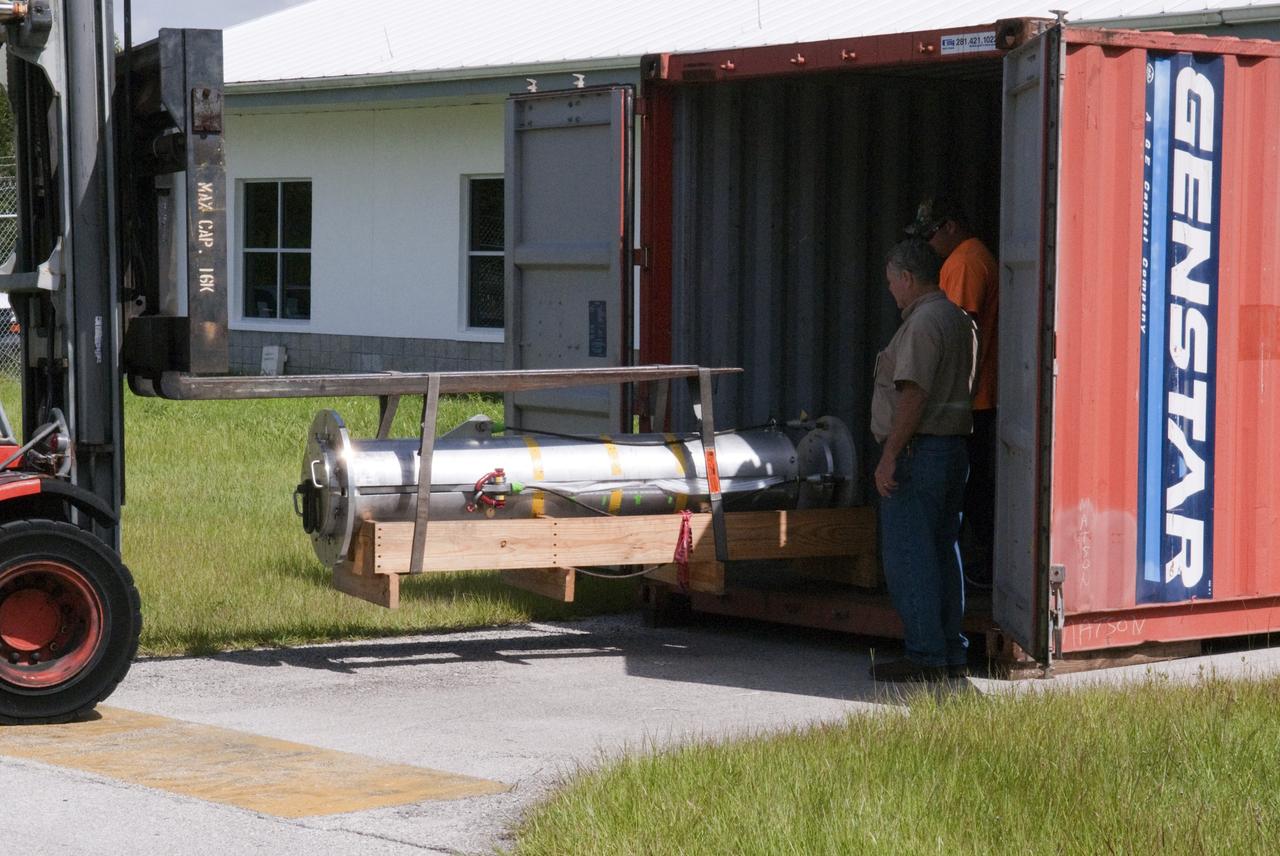

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Support equipment for NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
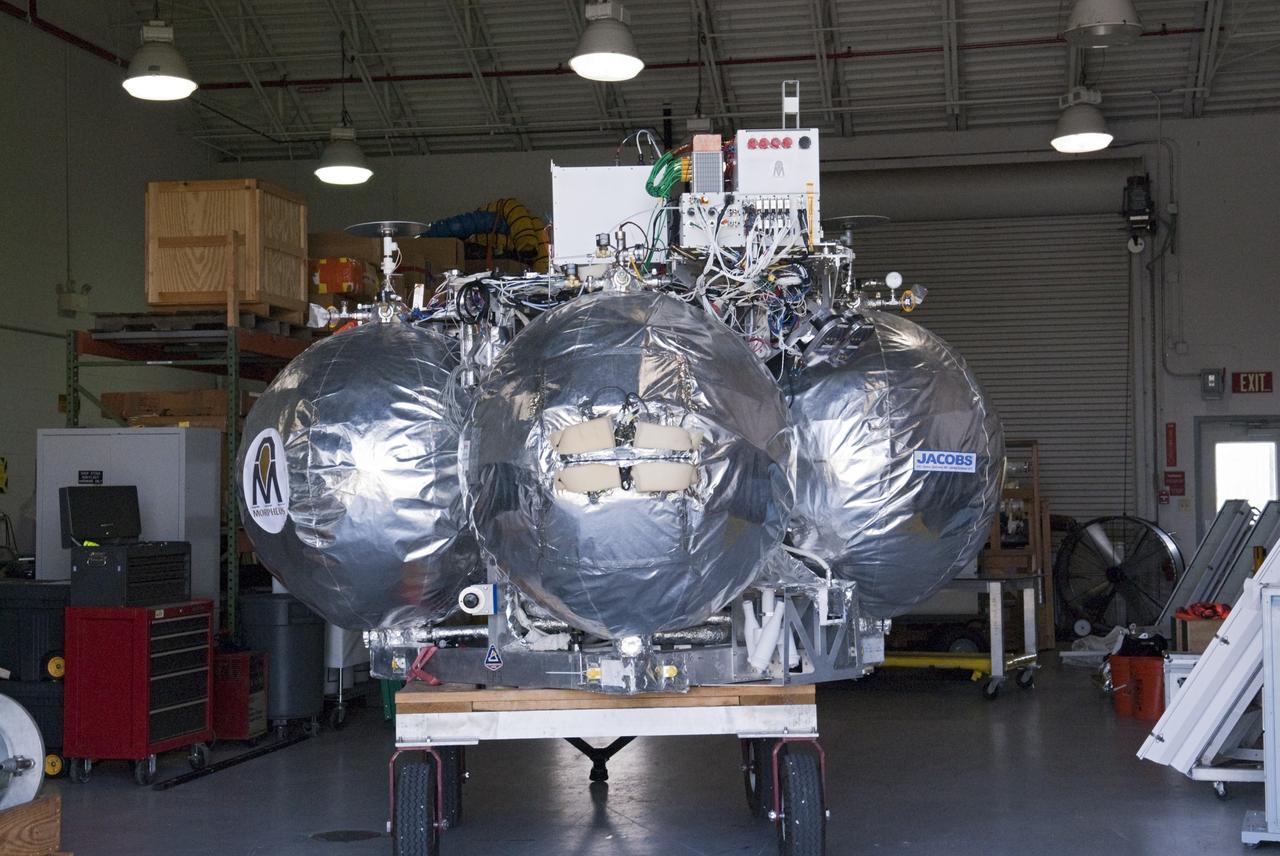

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, has been moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
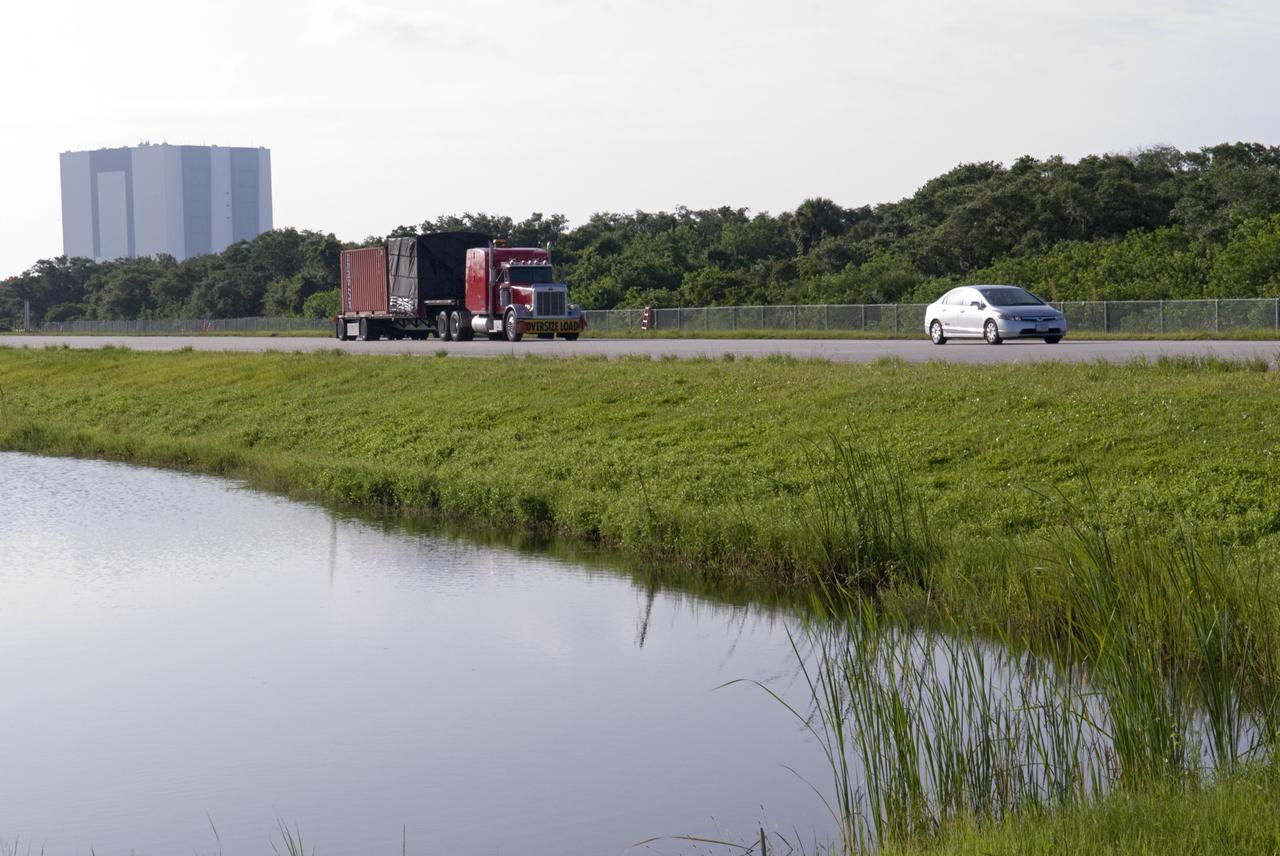

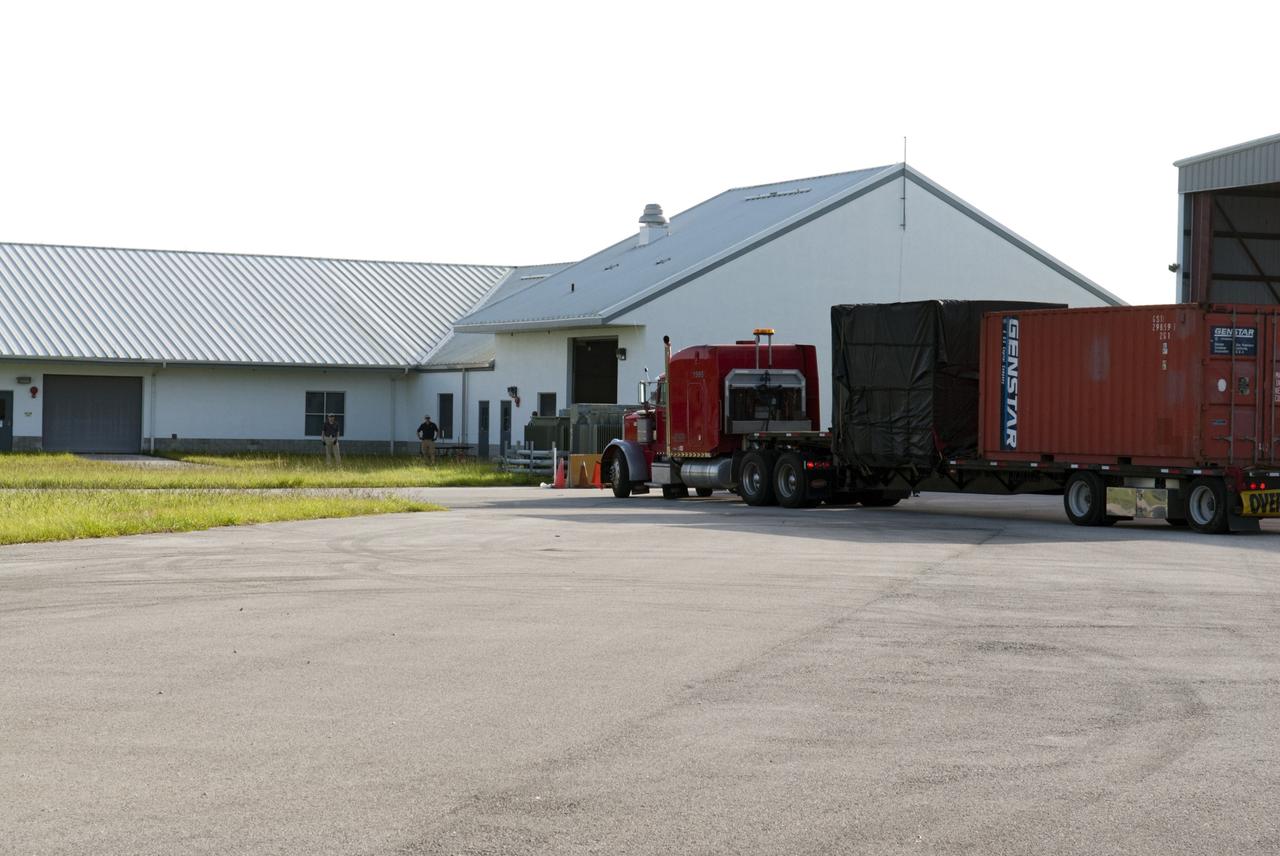
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A truck transporting NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, heads towards the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida for unloading. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
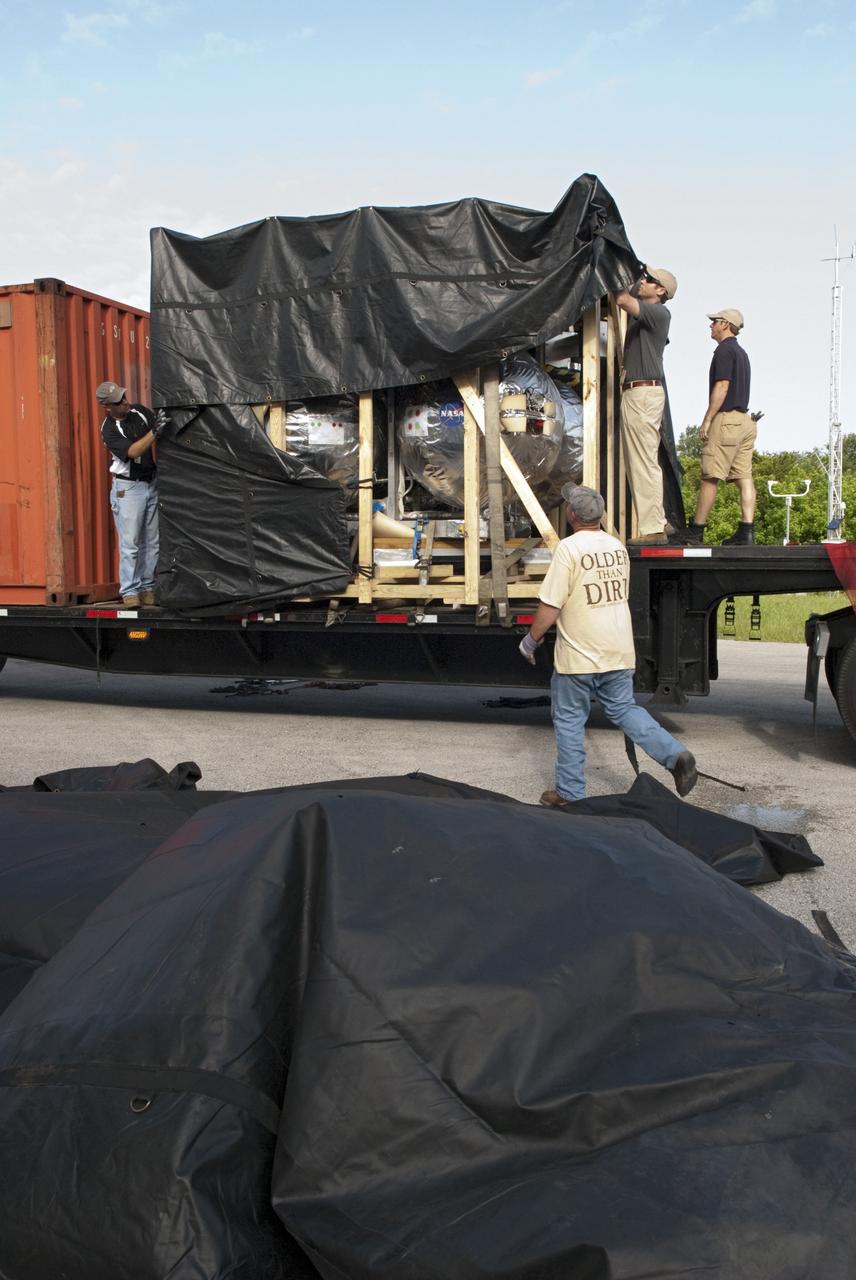

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
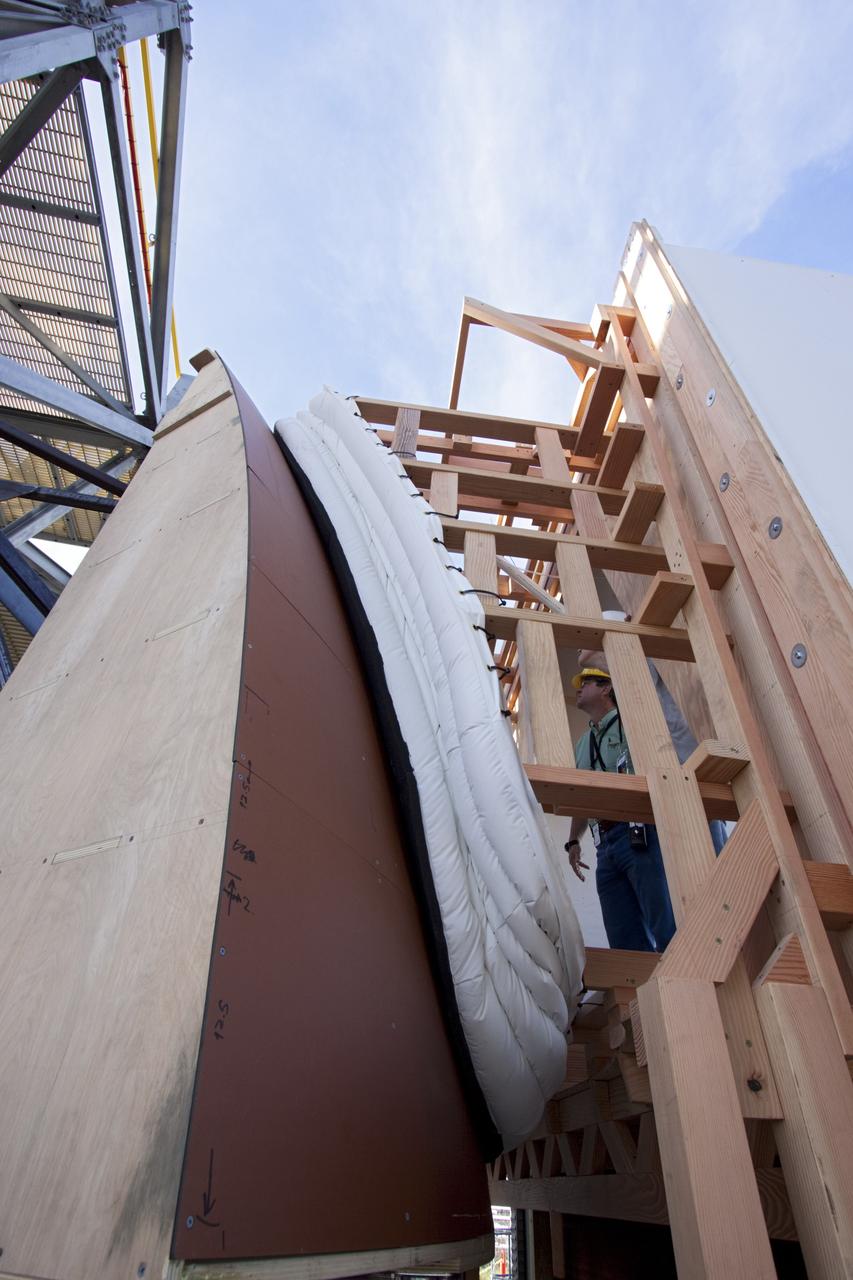

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked out at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to test the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked out at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to test the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
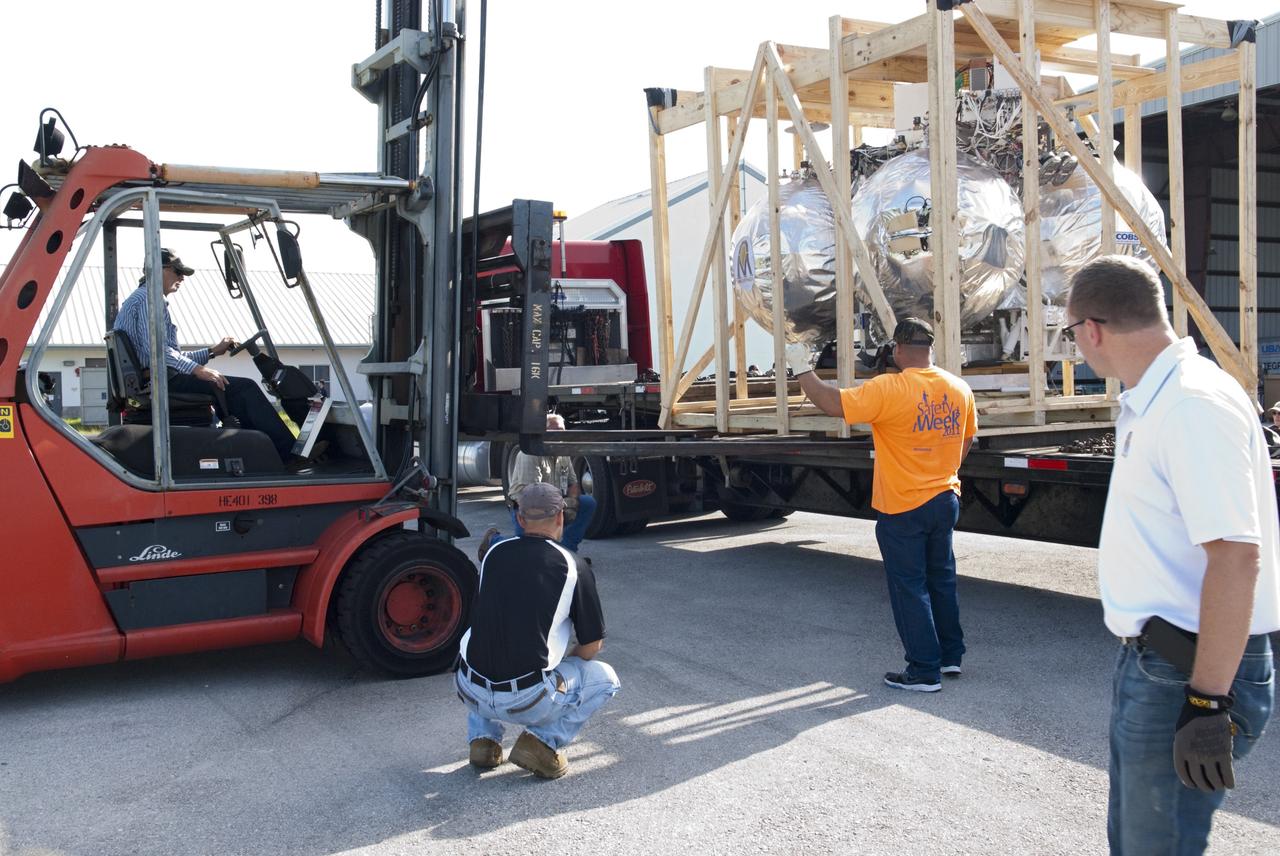

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
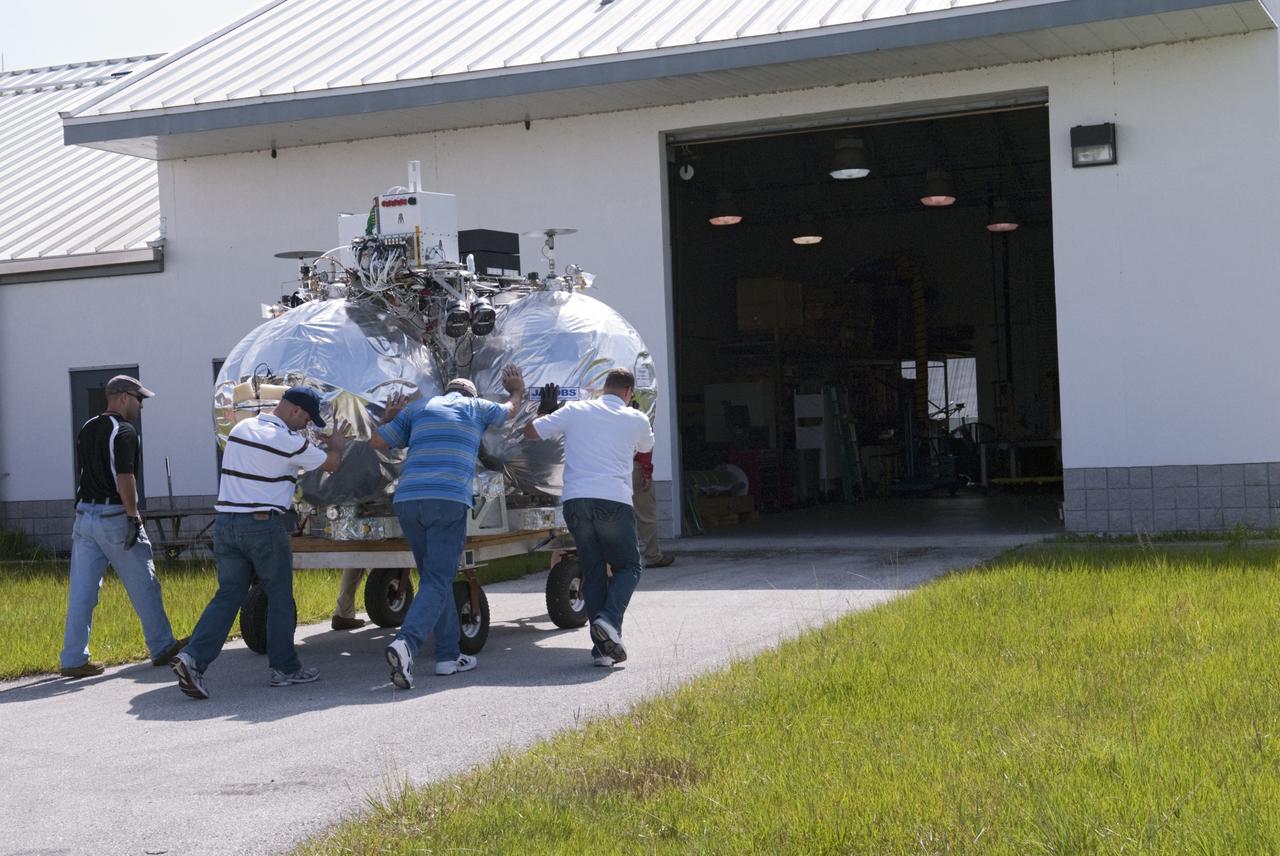

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
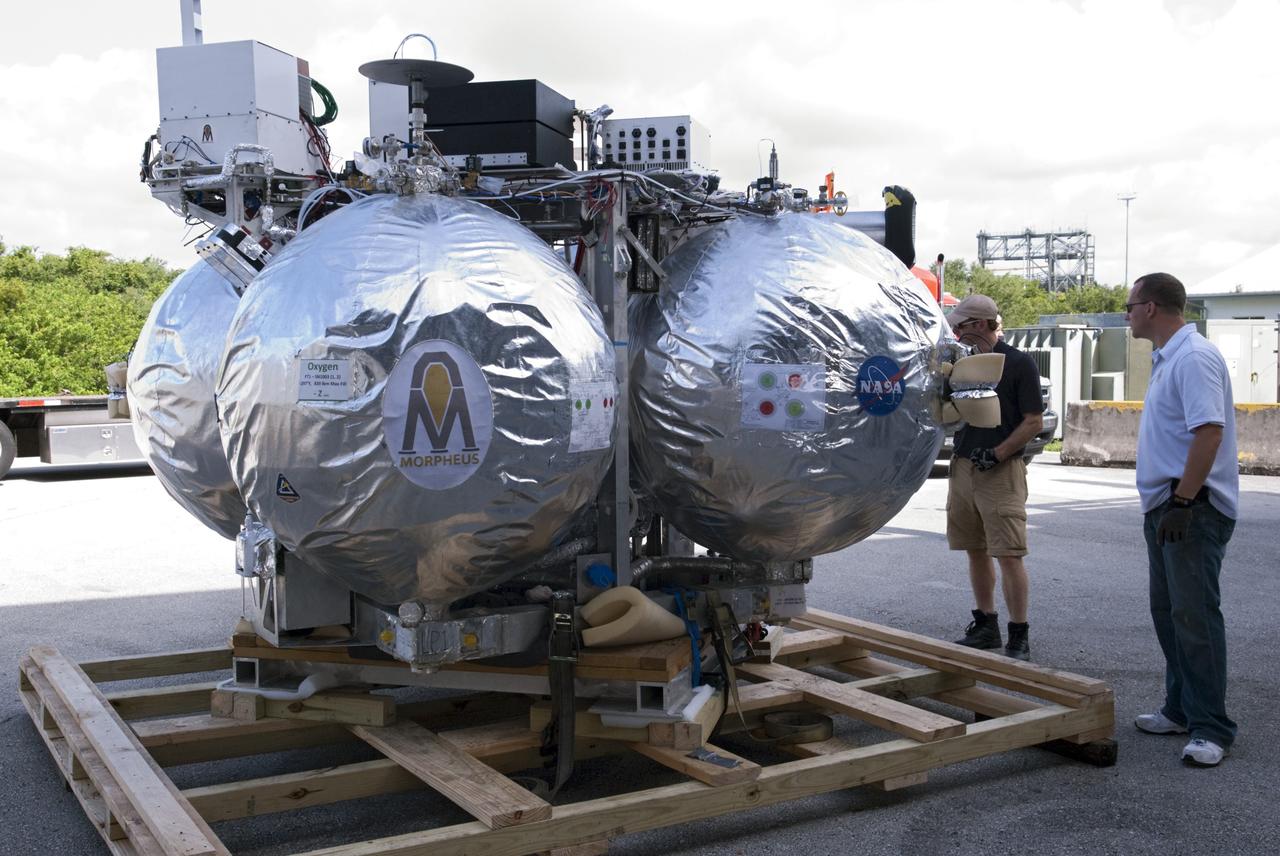

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
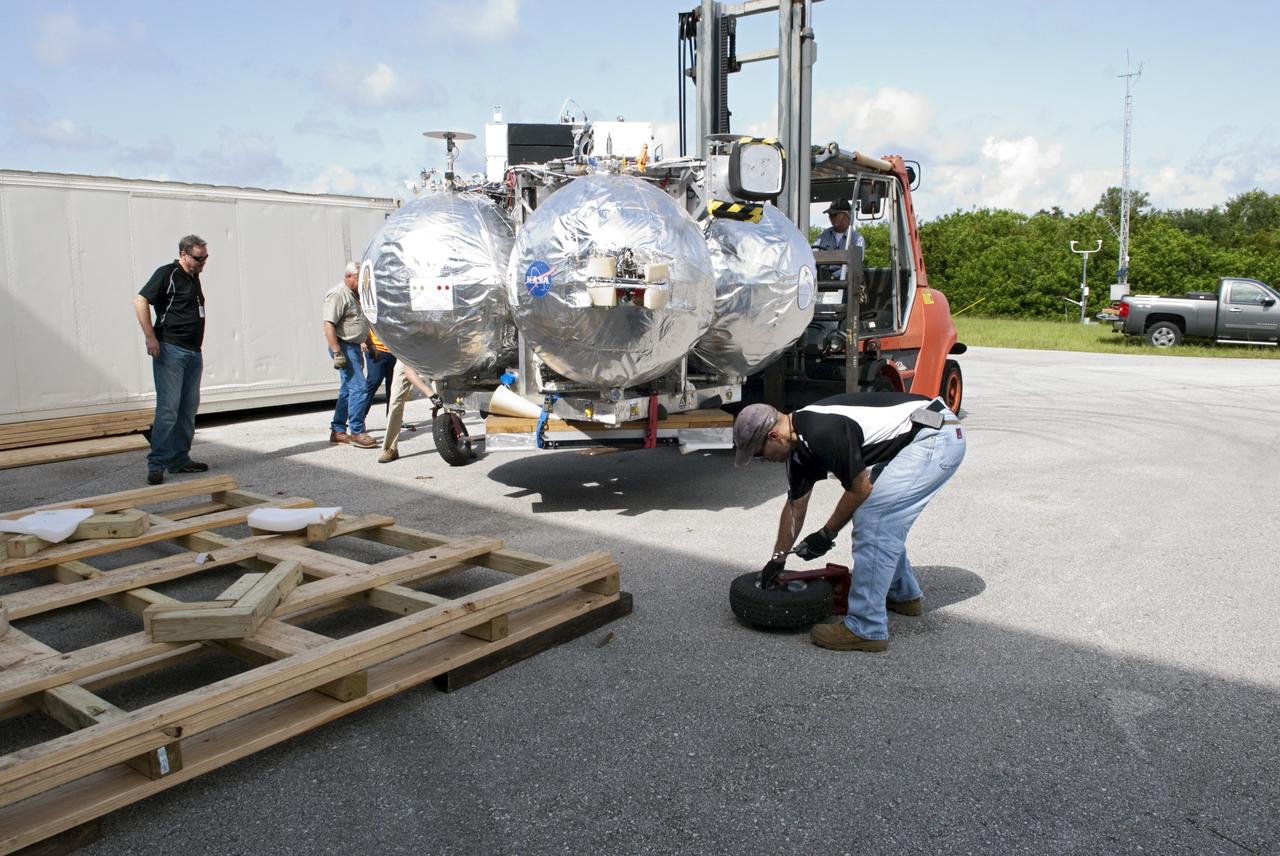

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Wheels are assembled for transporting NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle after its arrival at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
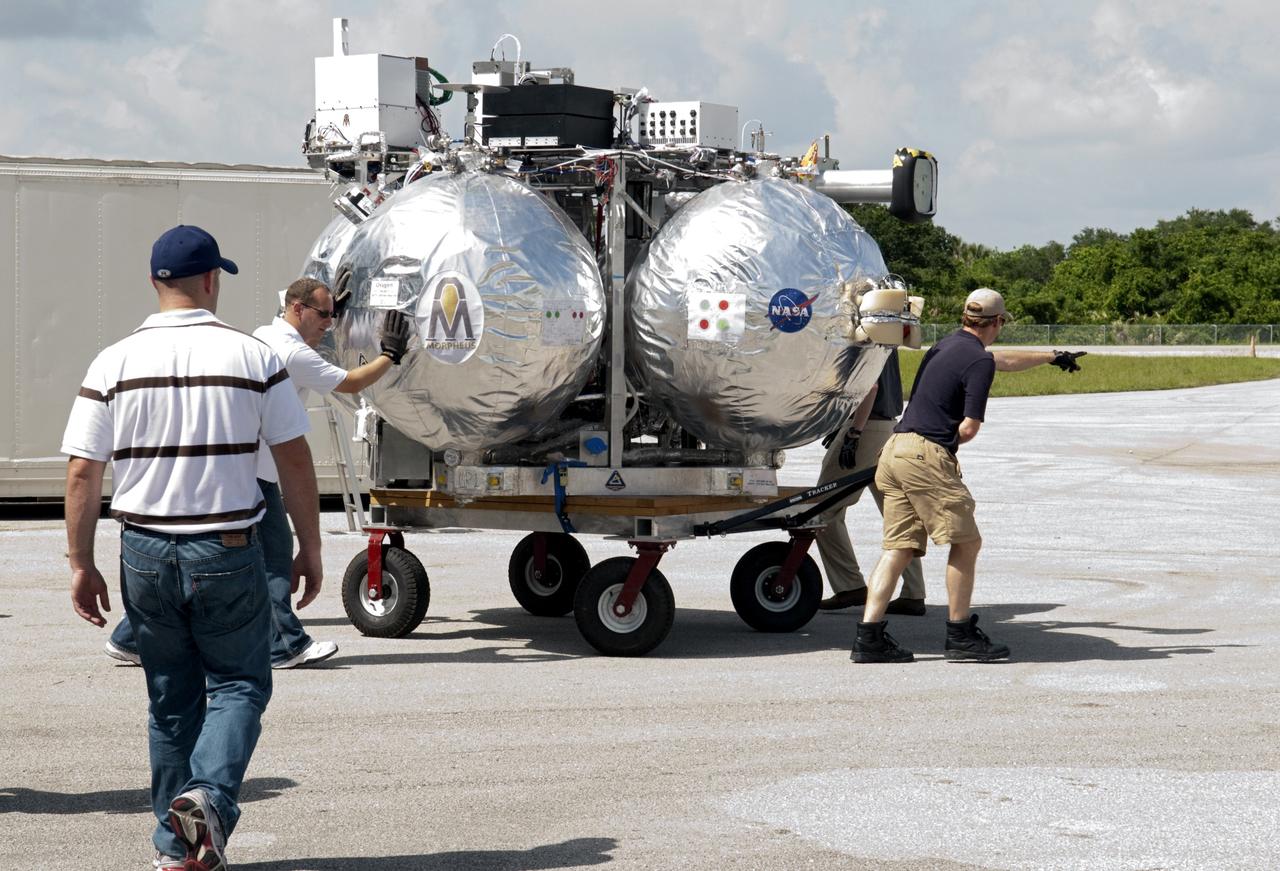

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
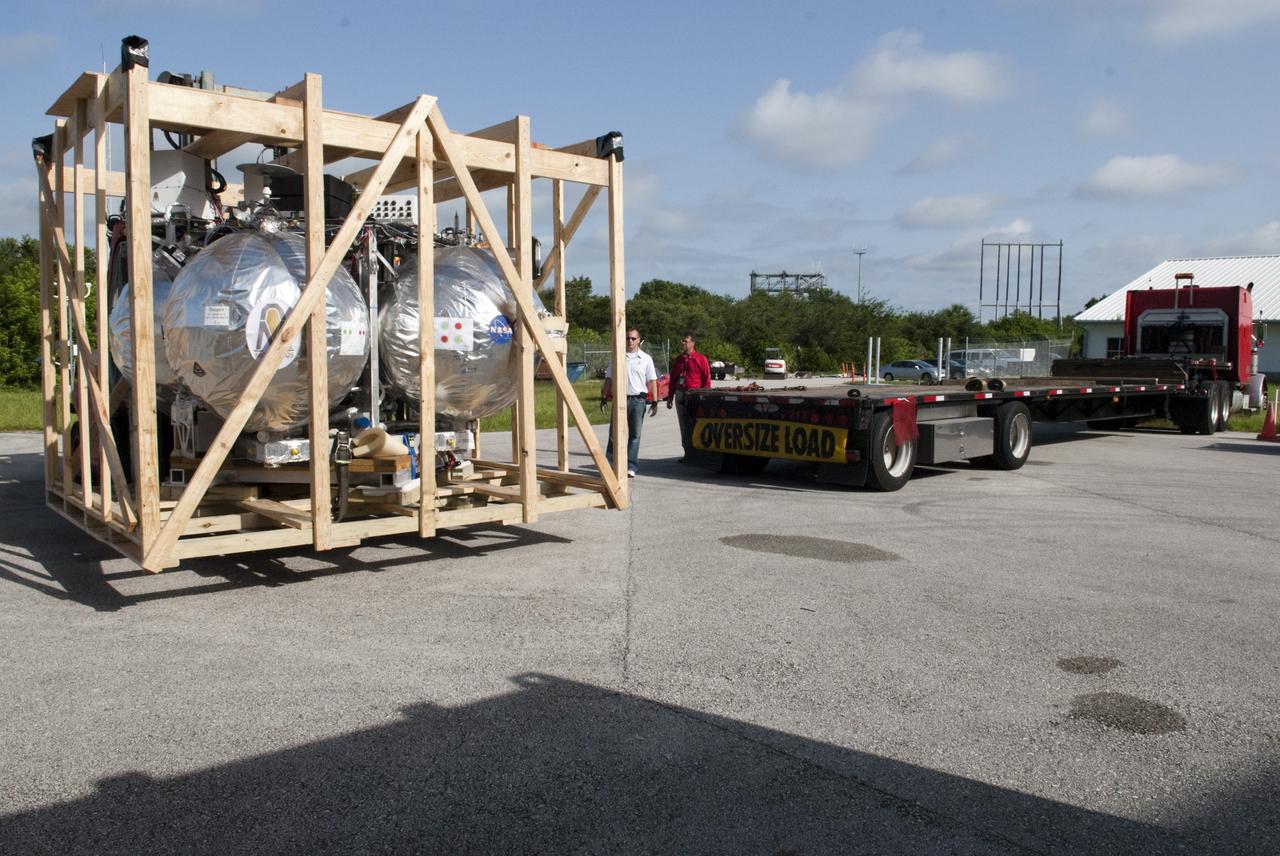

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, has been unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
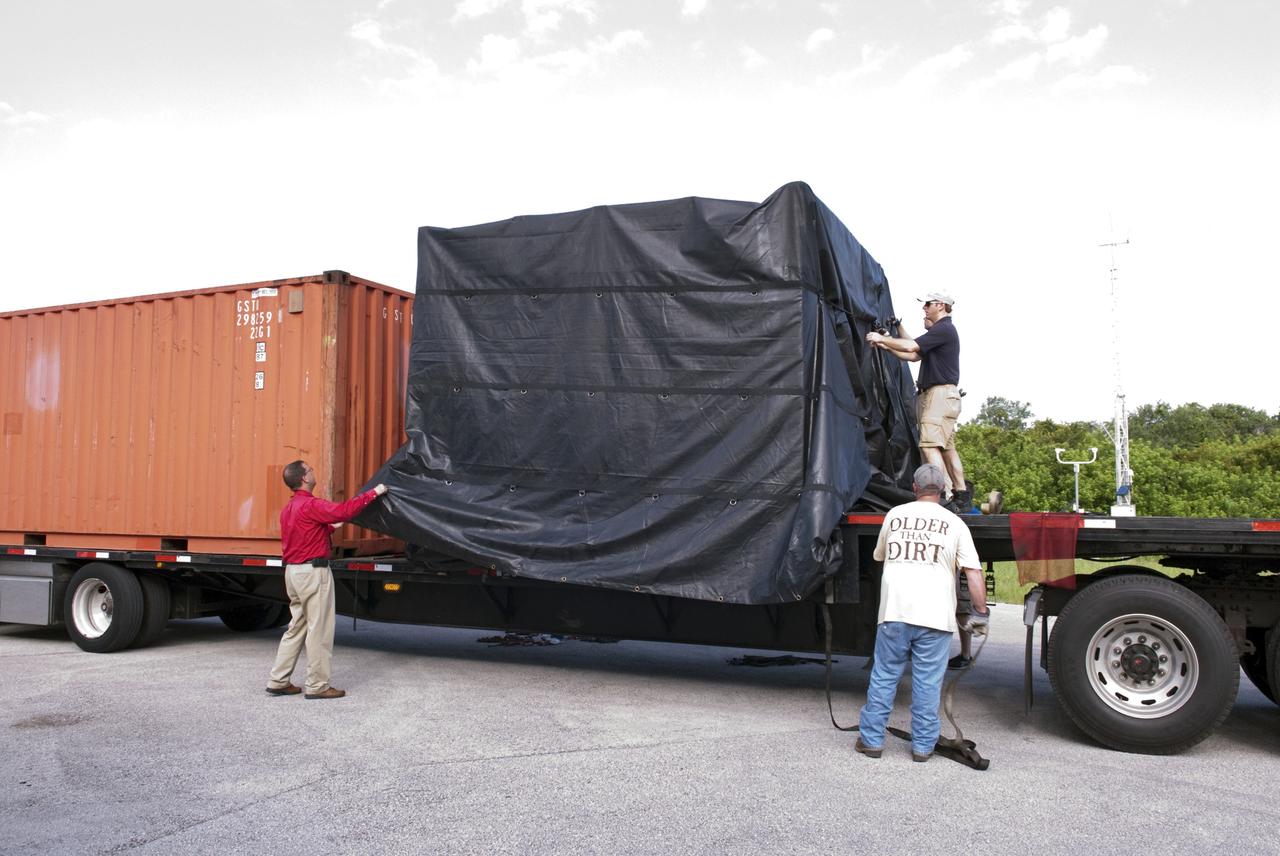

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
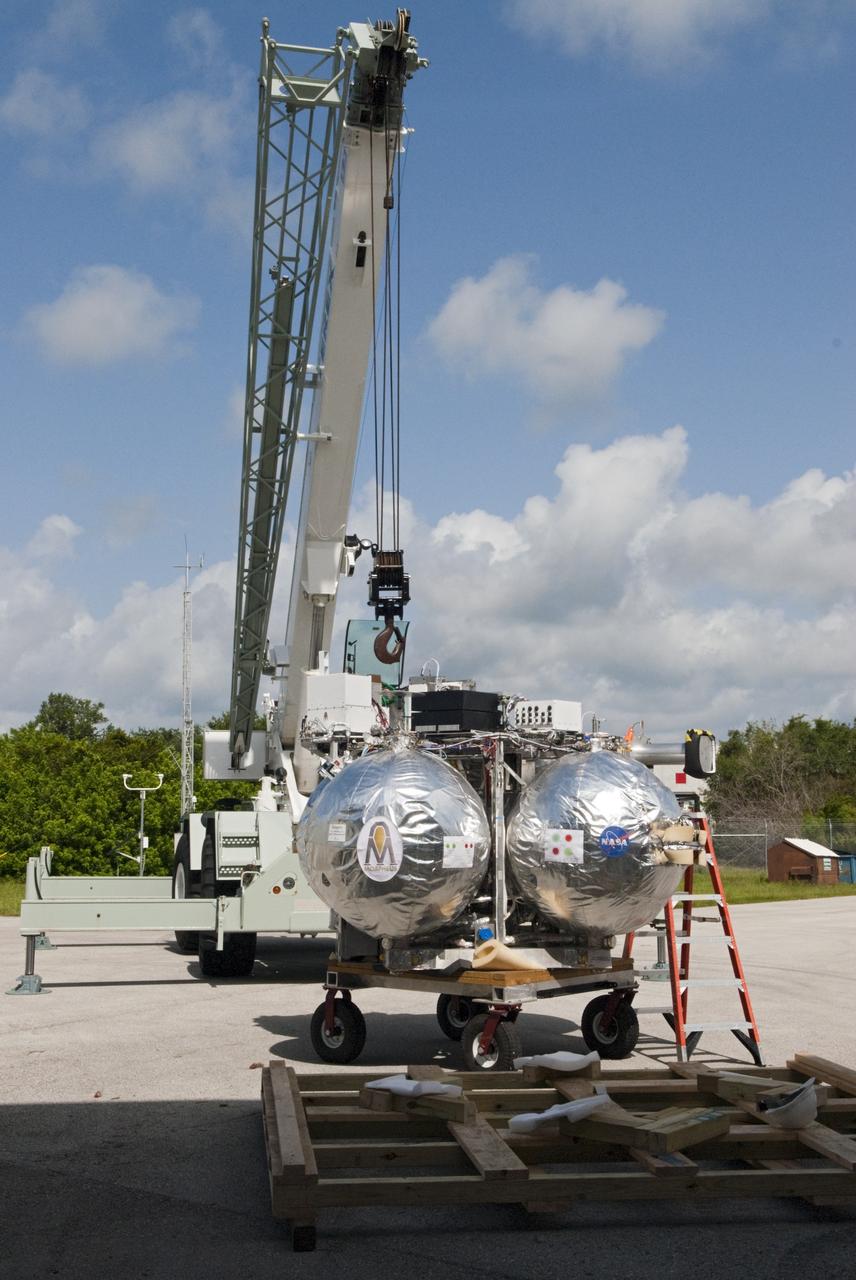

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A crane supports unloading of NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
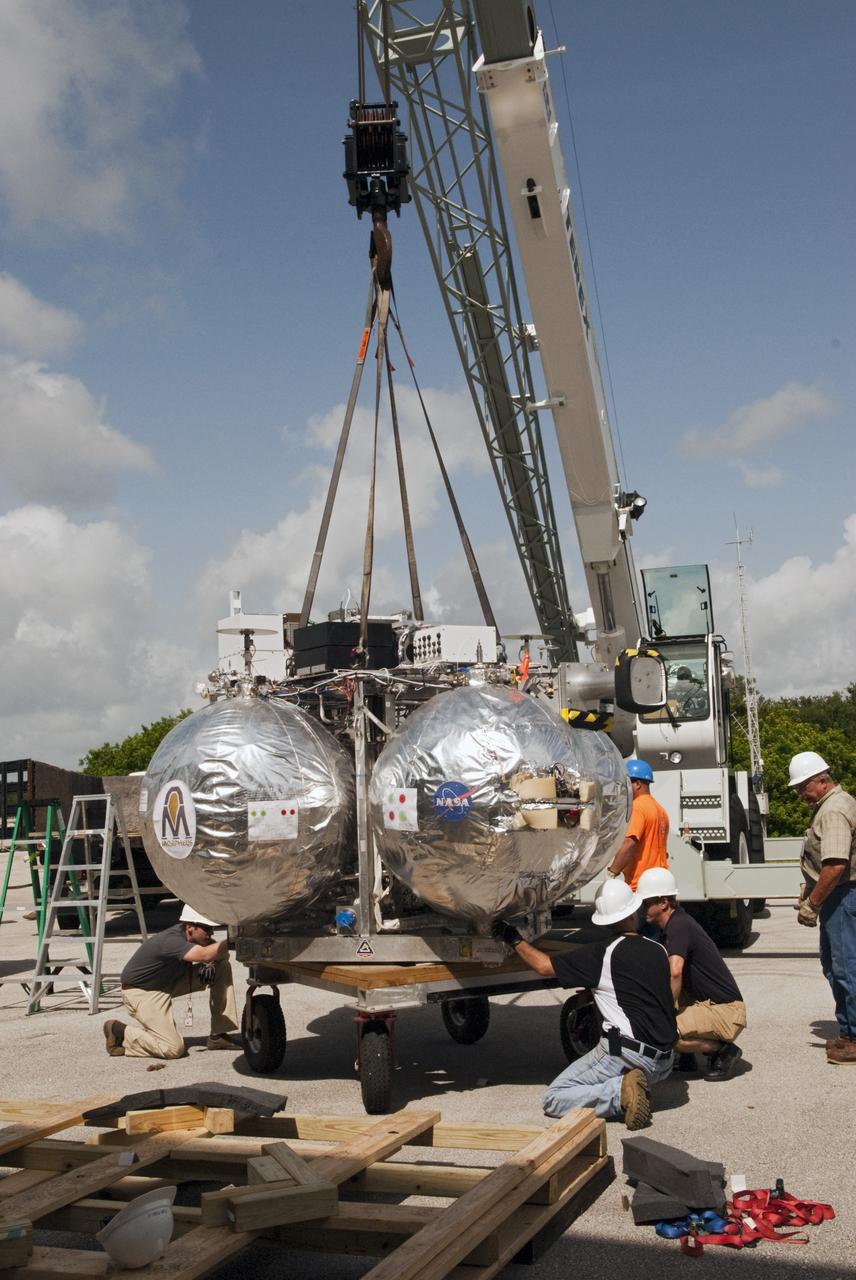

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A crane supports unloading of NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
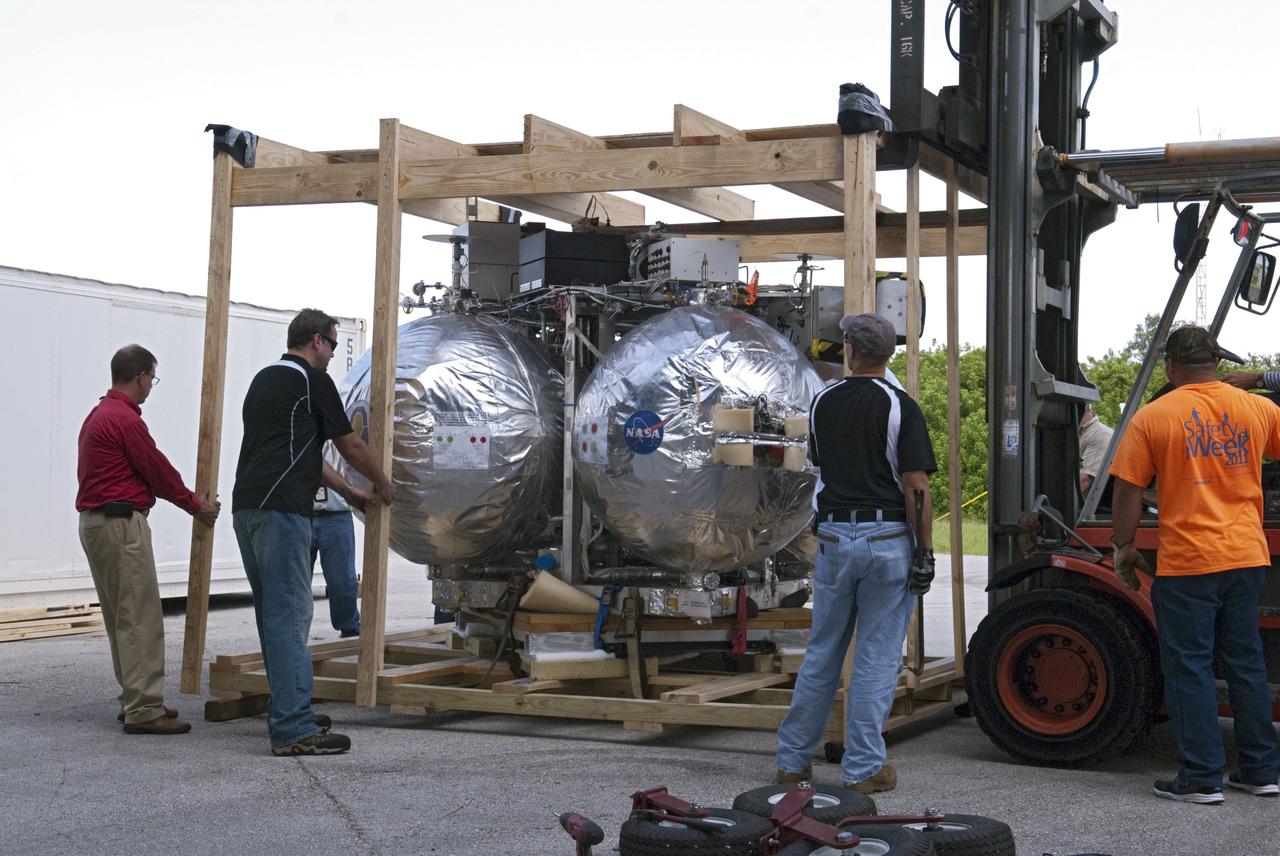

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is uncrated after unloading at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
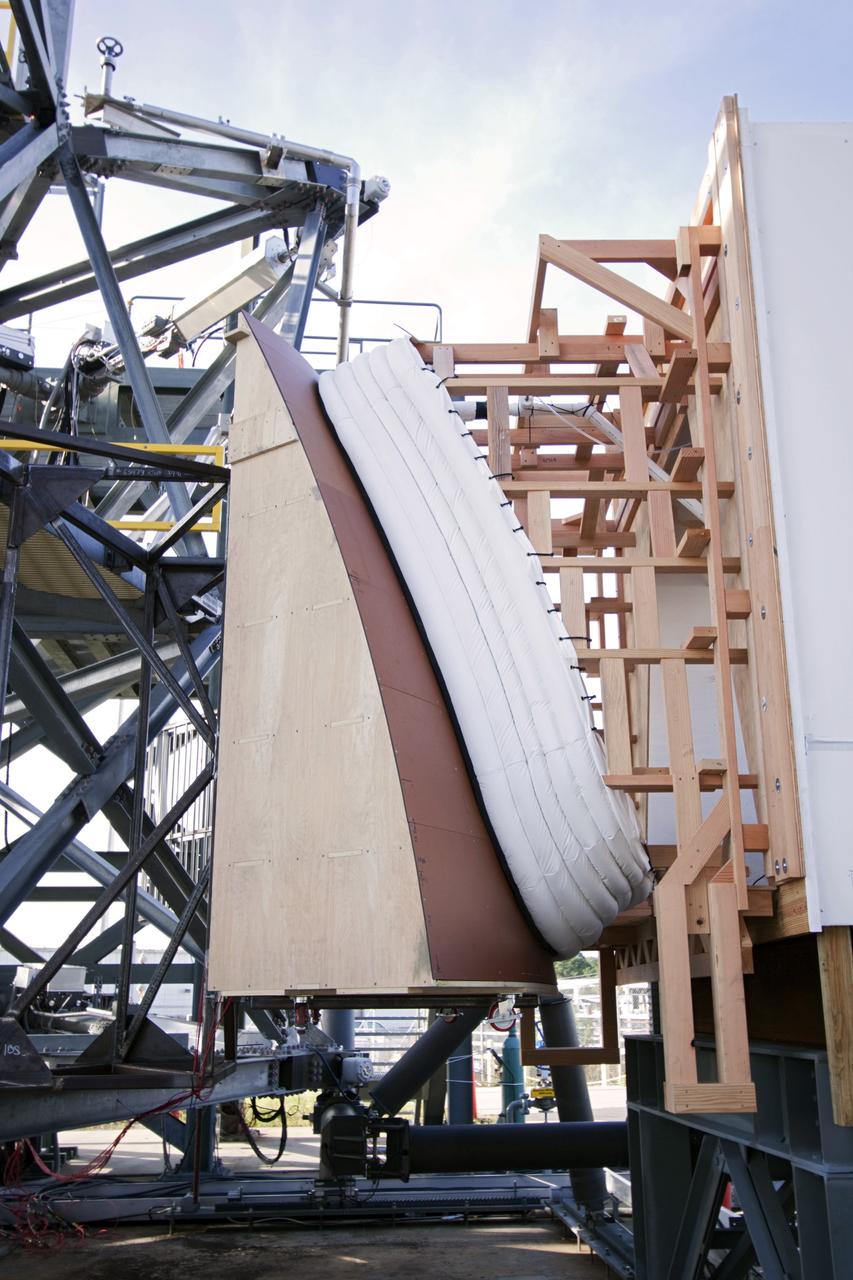

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked out at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to test the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
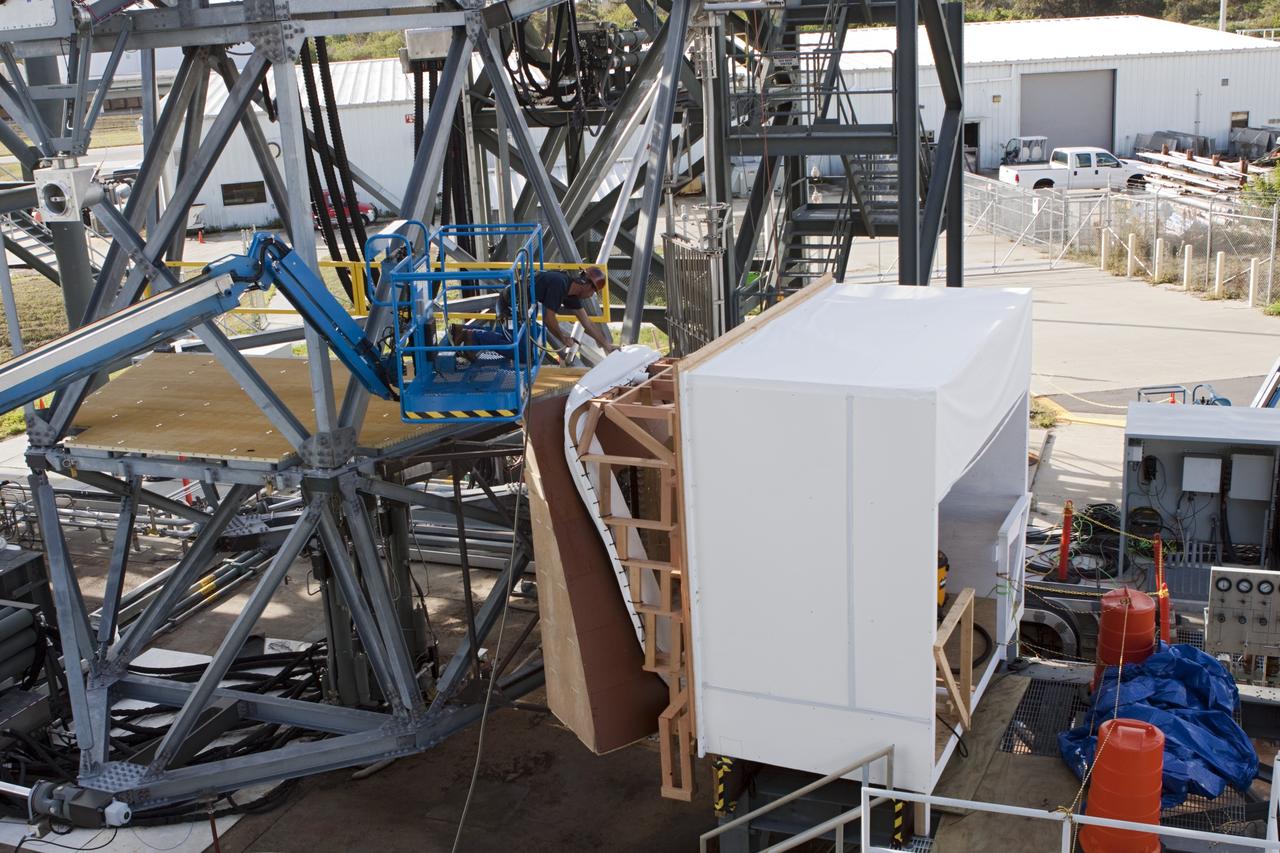

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked out at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to test the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
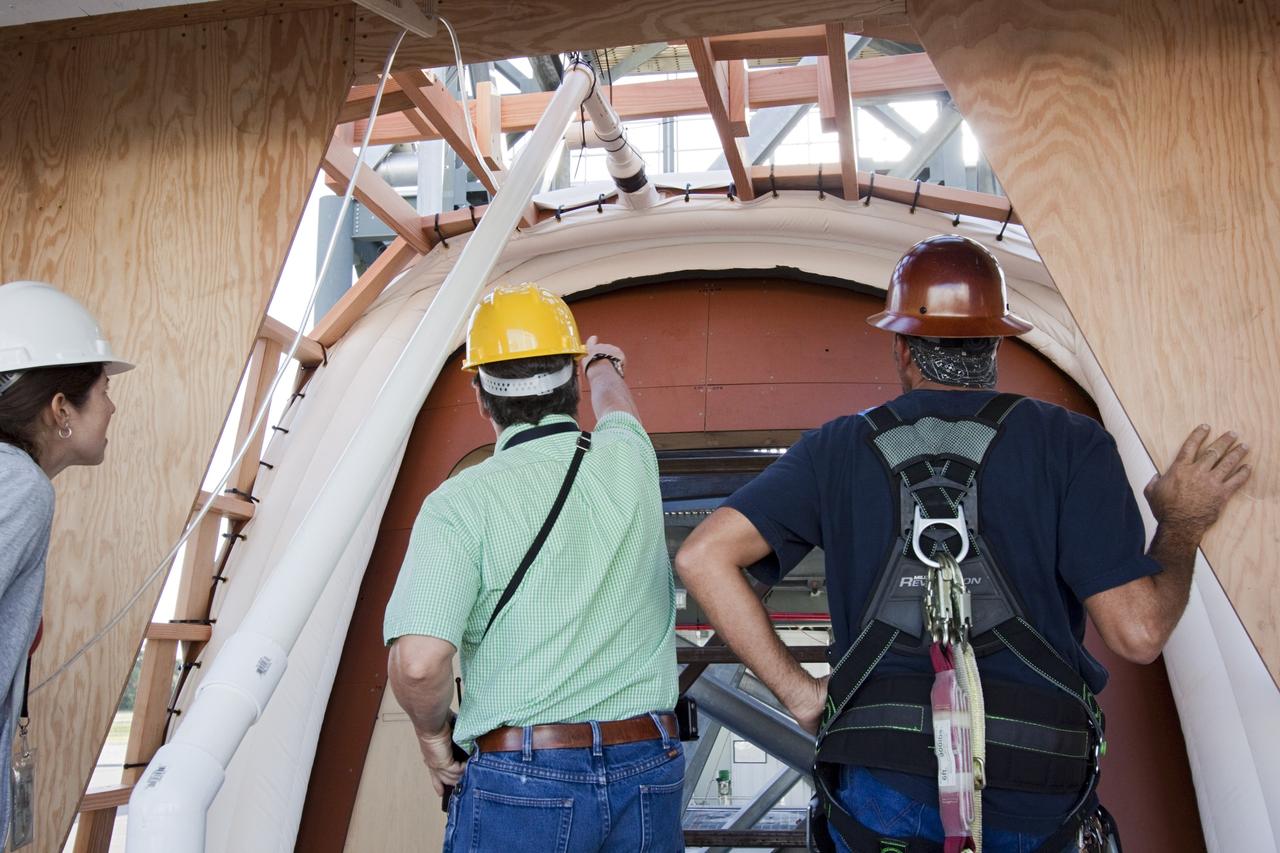

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked by technicians and engineers at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASAs Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to assess the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
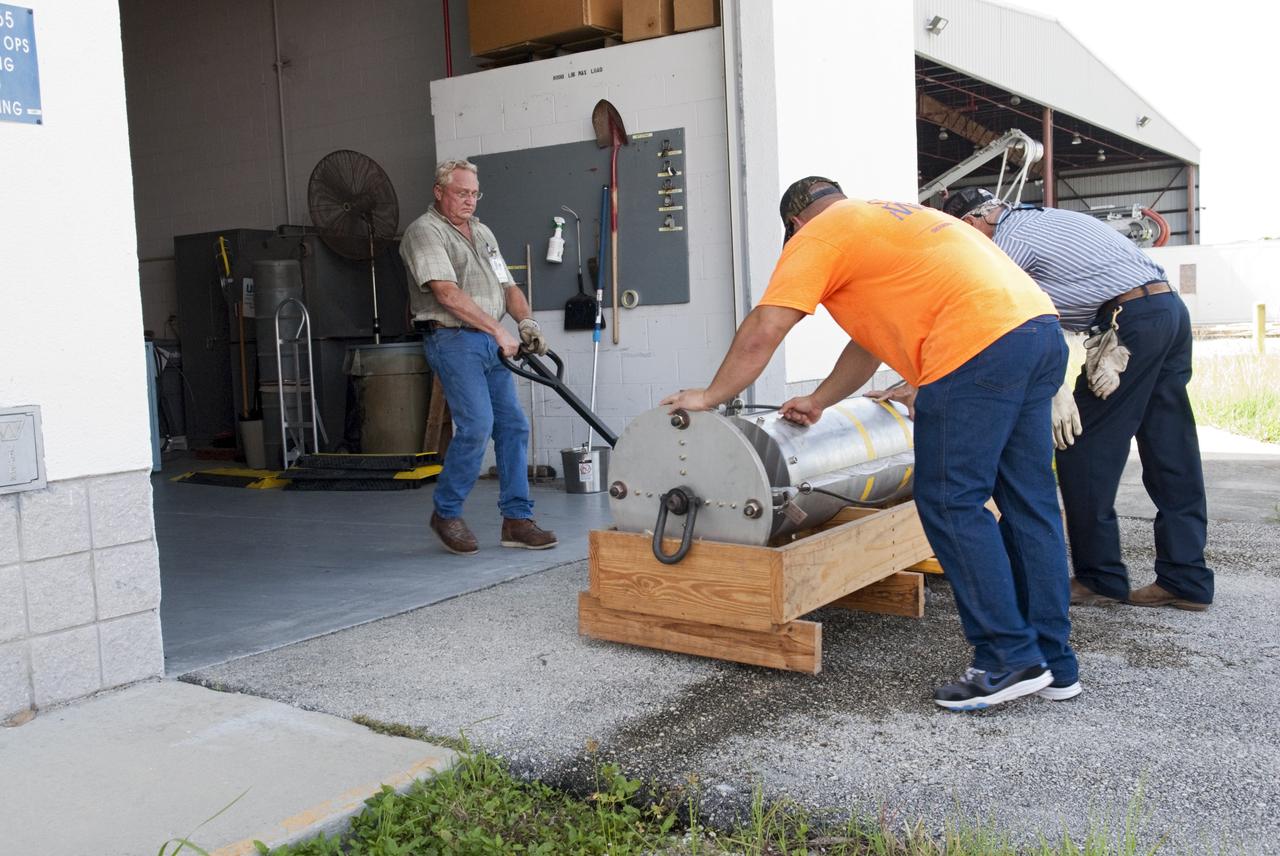

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Support equipment for NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A truck transporting NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, arrives at a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida for unloading. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
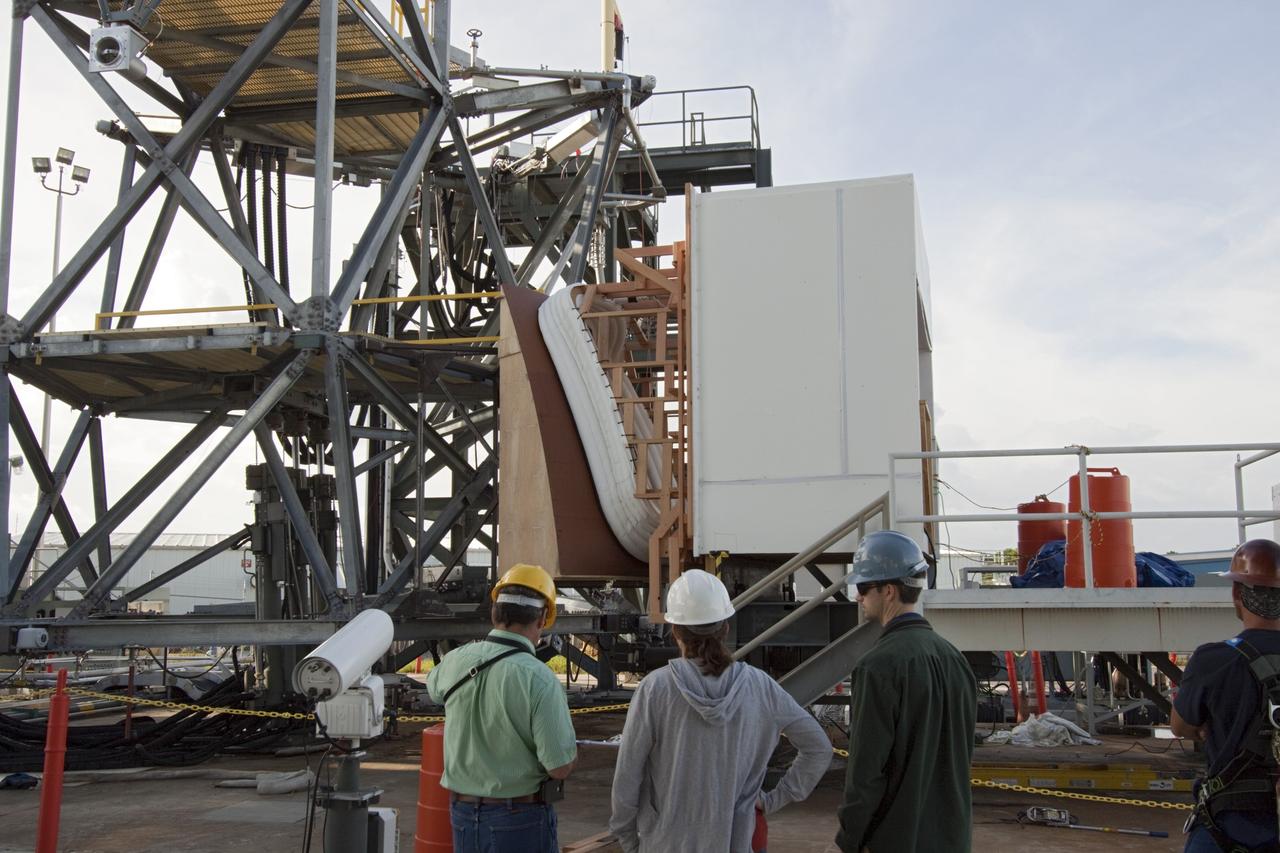

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked out at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Monitoring the activity, from the left are Kent Bachelor, Stinger Ghaffarian Technologies lead, Kelli Maloney, NASA lead and Clayton Gvasse, Nelson Engineering lead. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to test the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –This panoramic view shows a rock and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT system on the Project Morpheus lander. Testing will demonstrate ALHAT’s ability to provide required navigation data negotiating the Morpheus lander away from risks during descent. Checkout of the prot otype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is inspected after unloading at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
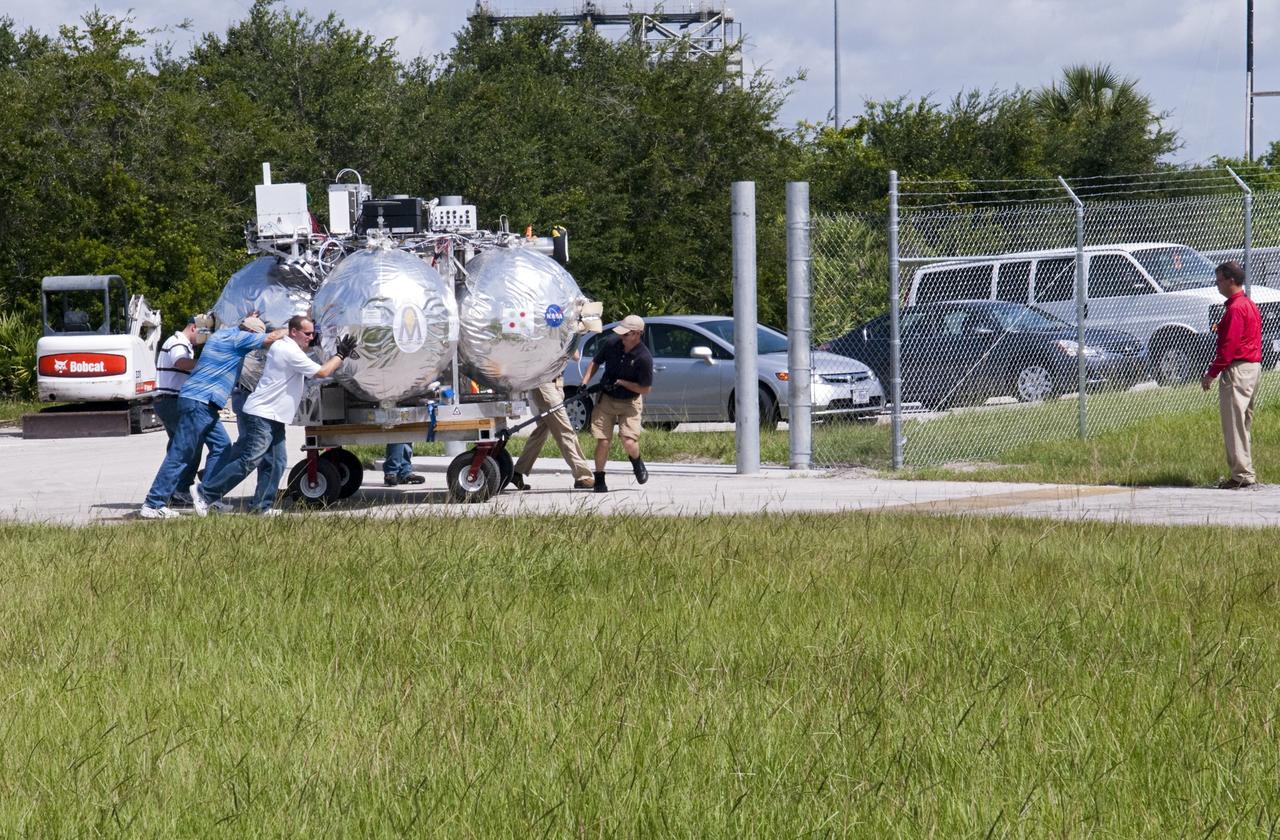

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
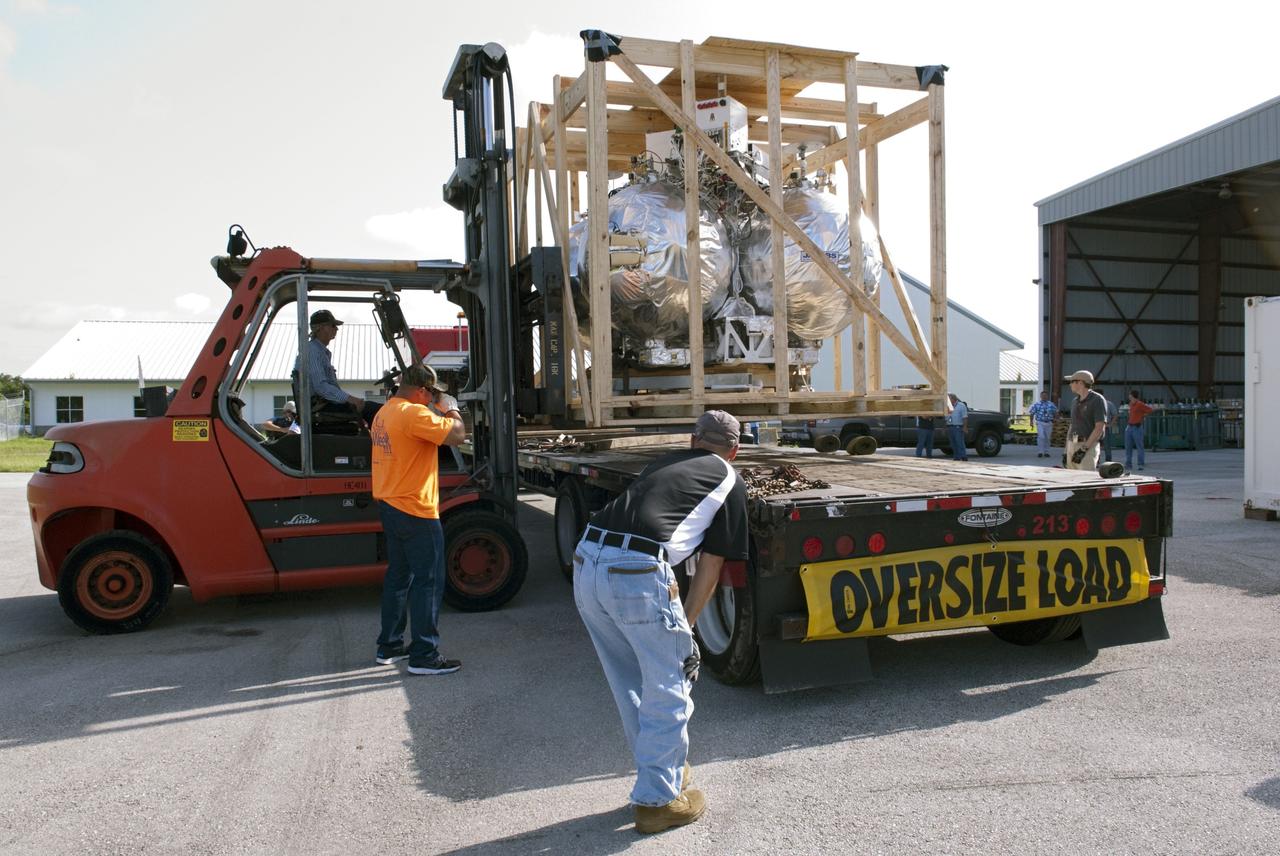

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A forklift is used at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida to unload NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked by technicians and engineers at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASAs Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to assess the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
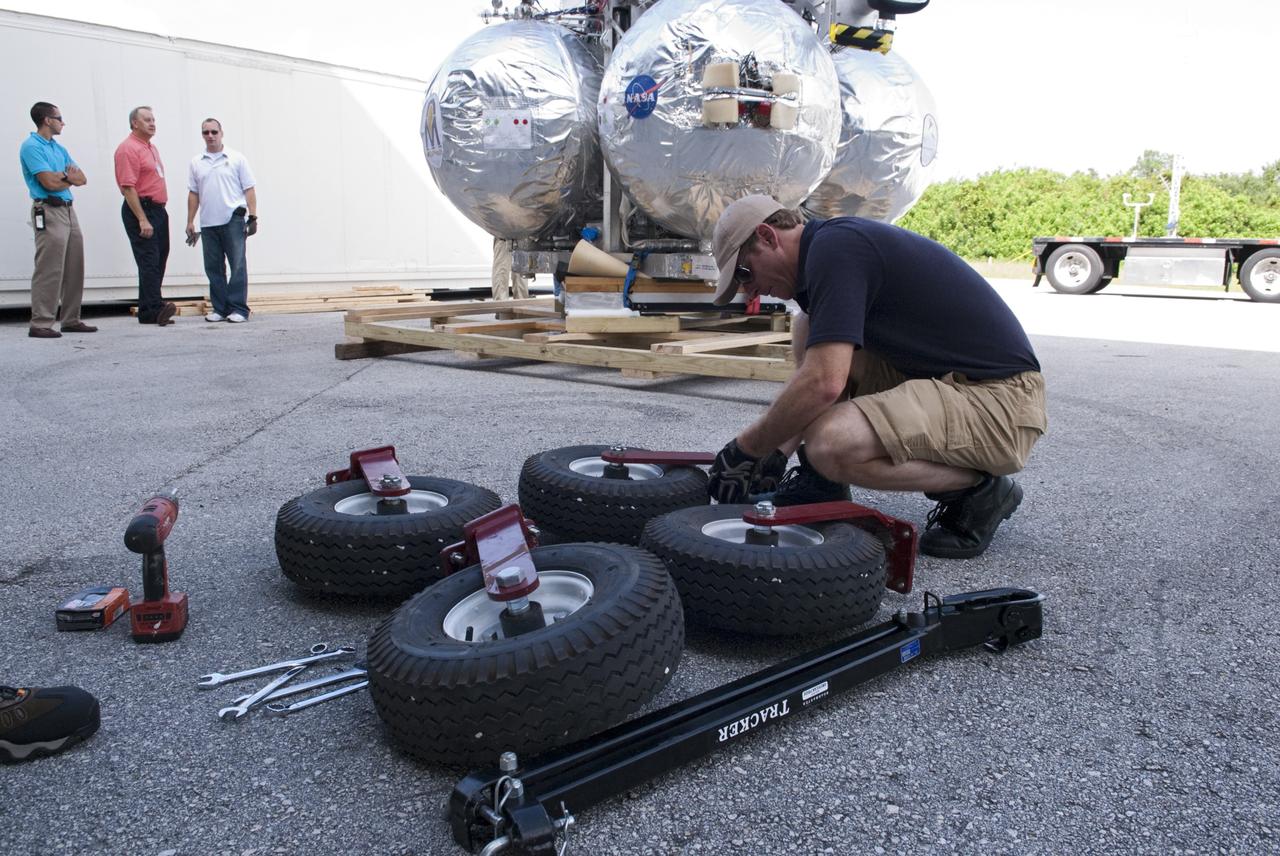

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Wheels are assembled for transporting NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle after its arrival at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
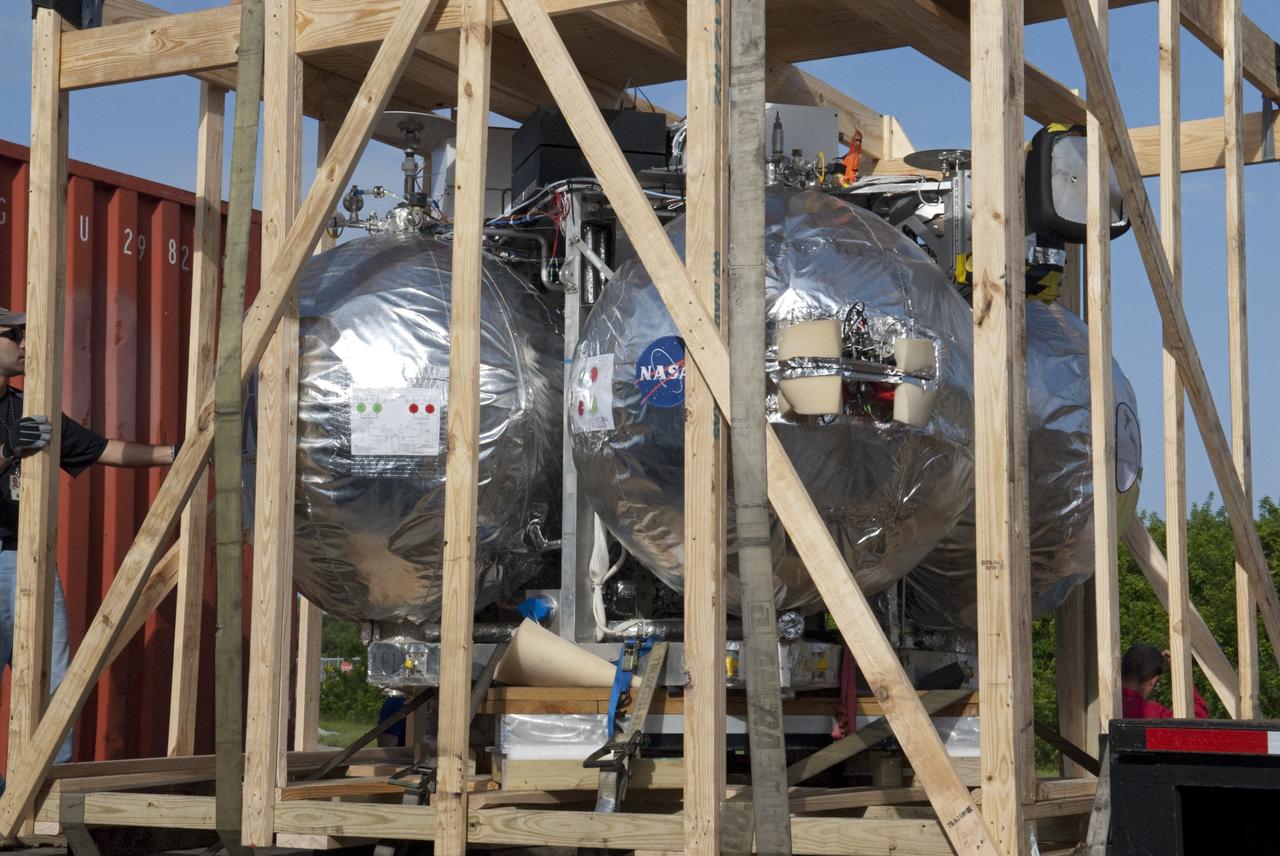

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is ready to be uncrated at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
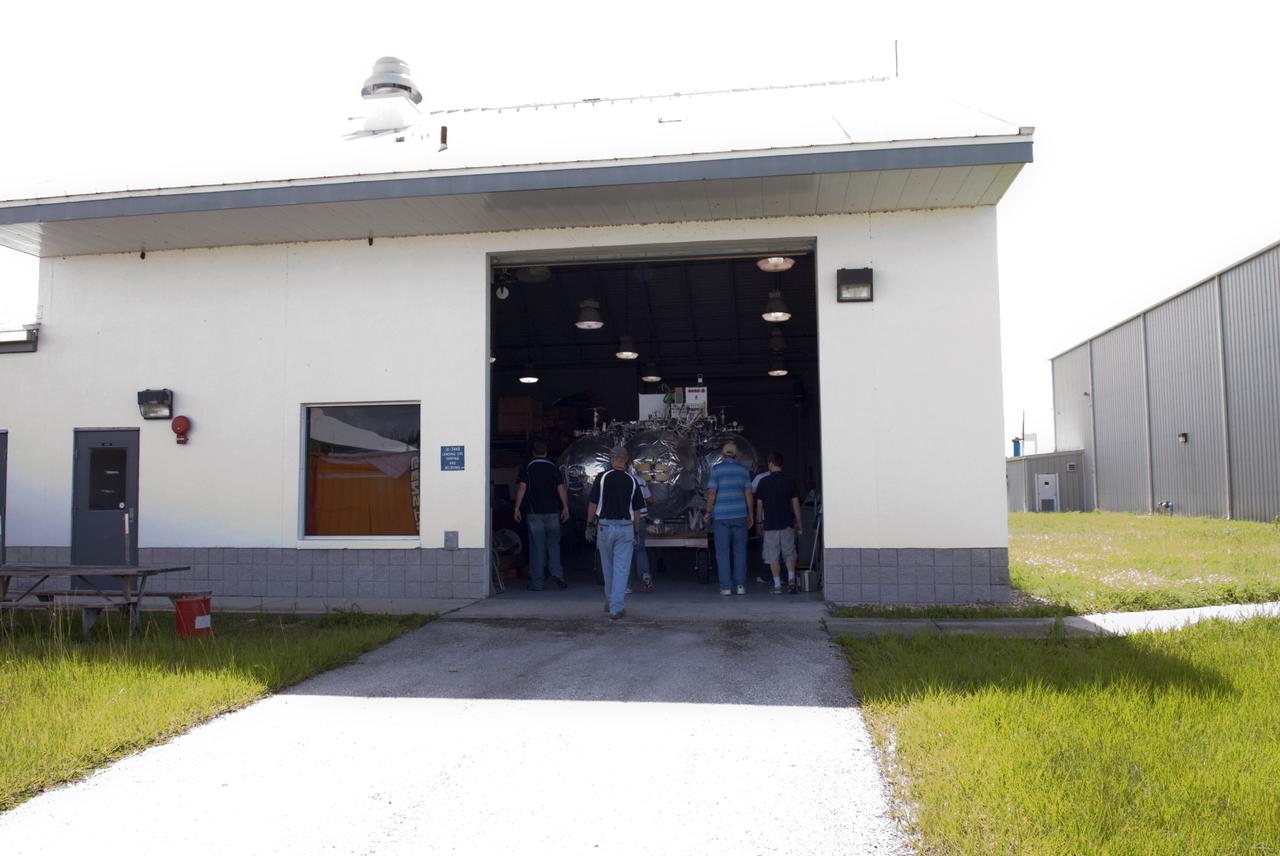

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, has been moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
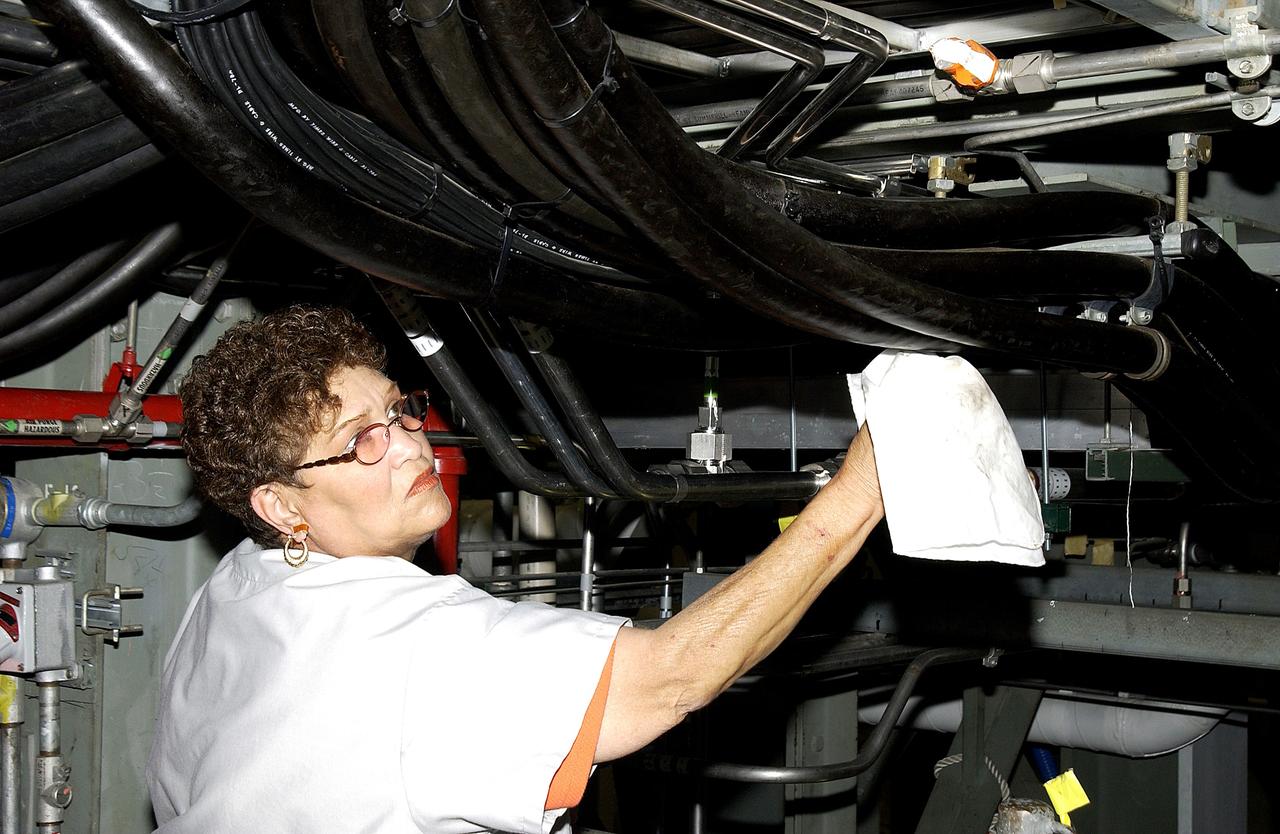

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A KSC employee wipes down some of the hoses of the ground support equipment in the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) where Space Shuttle Atlantis is being processed for flight. Preparations are under way for the next launch of Atlantis on mission STS-114, a utilization and logistics flight to the International Space Station.
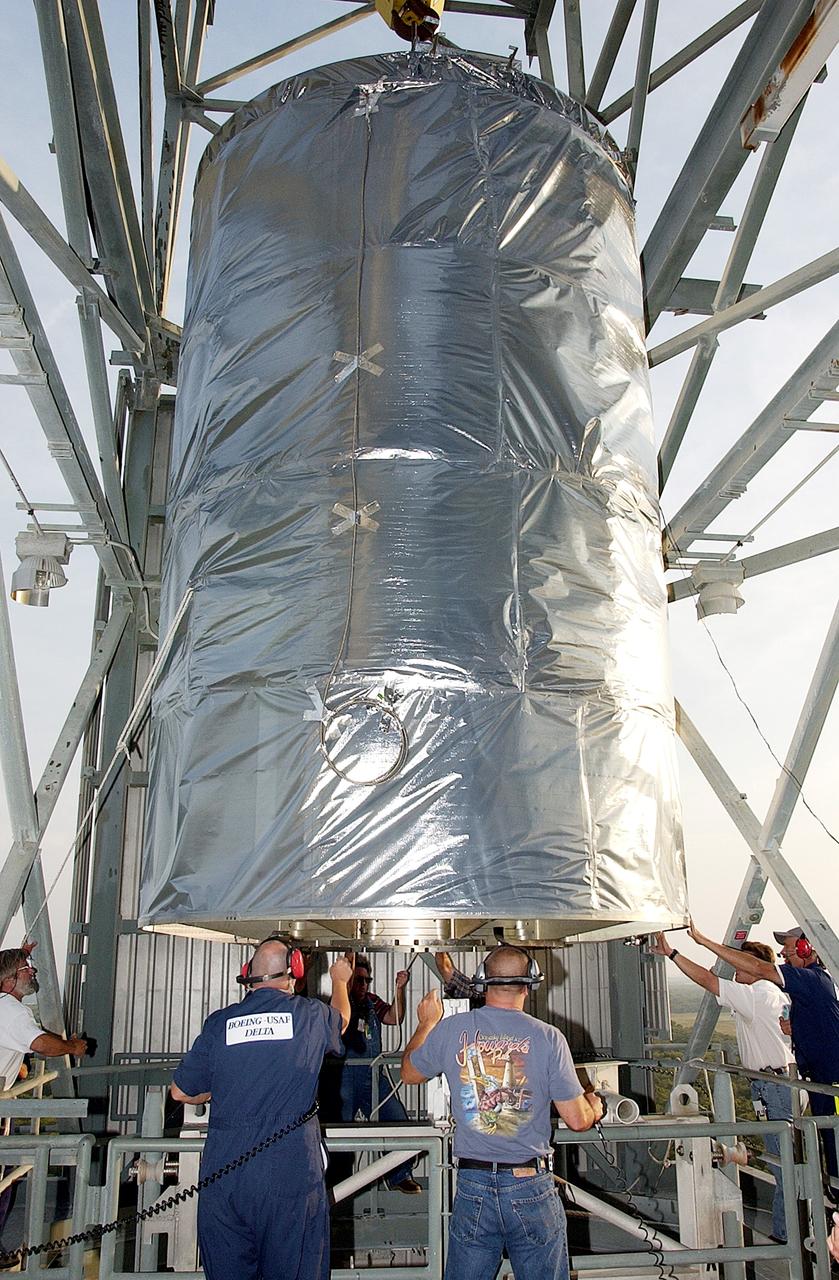

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) observatory is ready to be lowered to the ground and taken back to NASA Spacecraft Hangar AE. SIRTF will remain in the clean room at Hangar AE until it returns to the pad in early August.
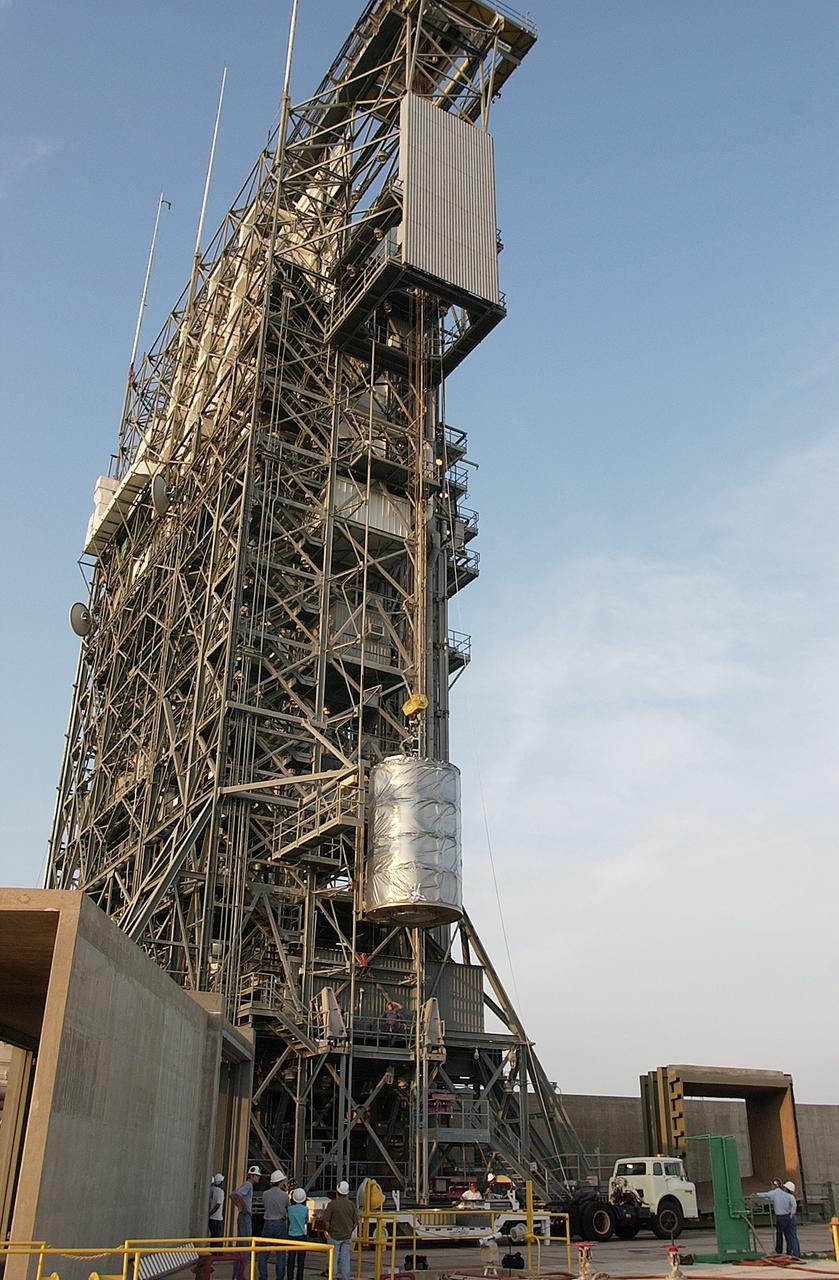

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) observatory is lowered to the ground and taken back to NASA Spacecraft Hangar AE. SIRTF will remain in the clean room at Hangar AE until it returns to the pad in early August.
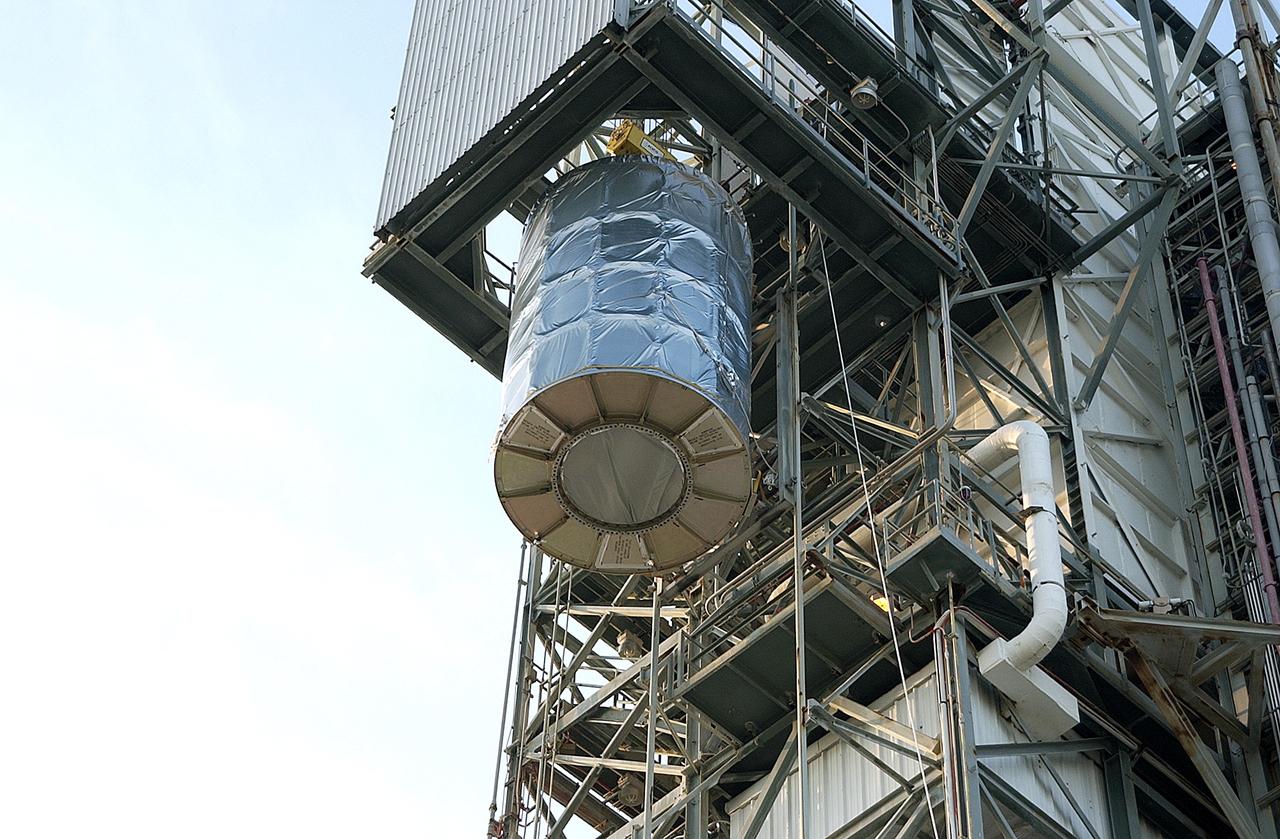

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) observatory is lowered to the ground and taken back to NASA Spacecraft Hangar AE. SIRTF will remain in the clean room at Hangar AE until it returns to the pad in early August.
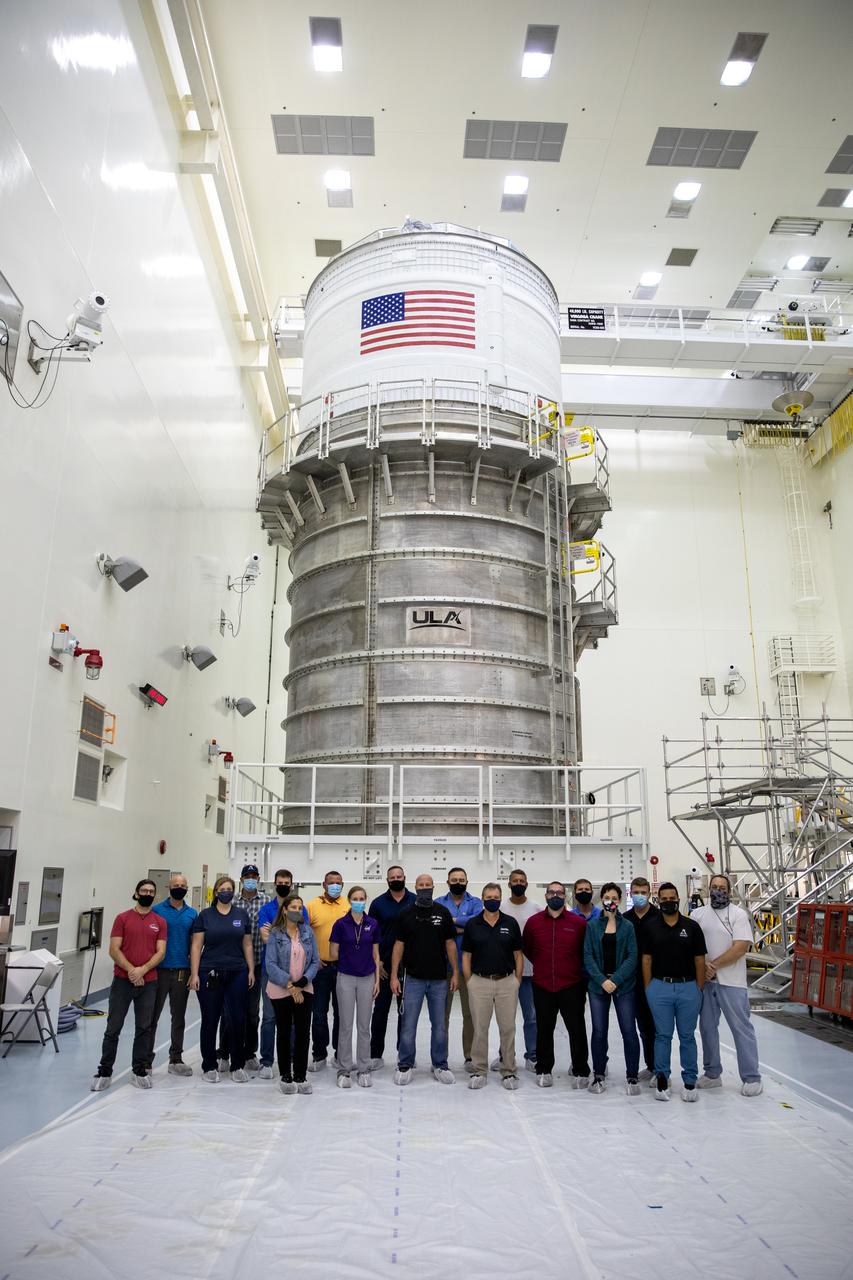

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) moved into the Multi-Payload Processing Facility February 18, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the Artemis I mission. It will undergo fueling and servicing in the facility ahead of launch by teams from NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and their primary contractor, Jacobs Technology. Artemis I will be an integrated flight test of the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft ahead of the crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the lunar surface and establish a sustainable presence at the Moon to prepare for human missions to Mars.
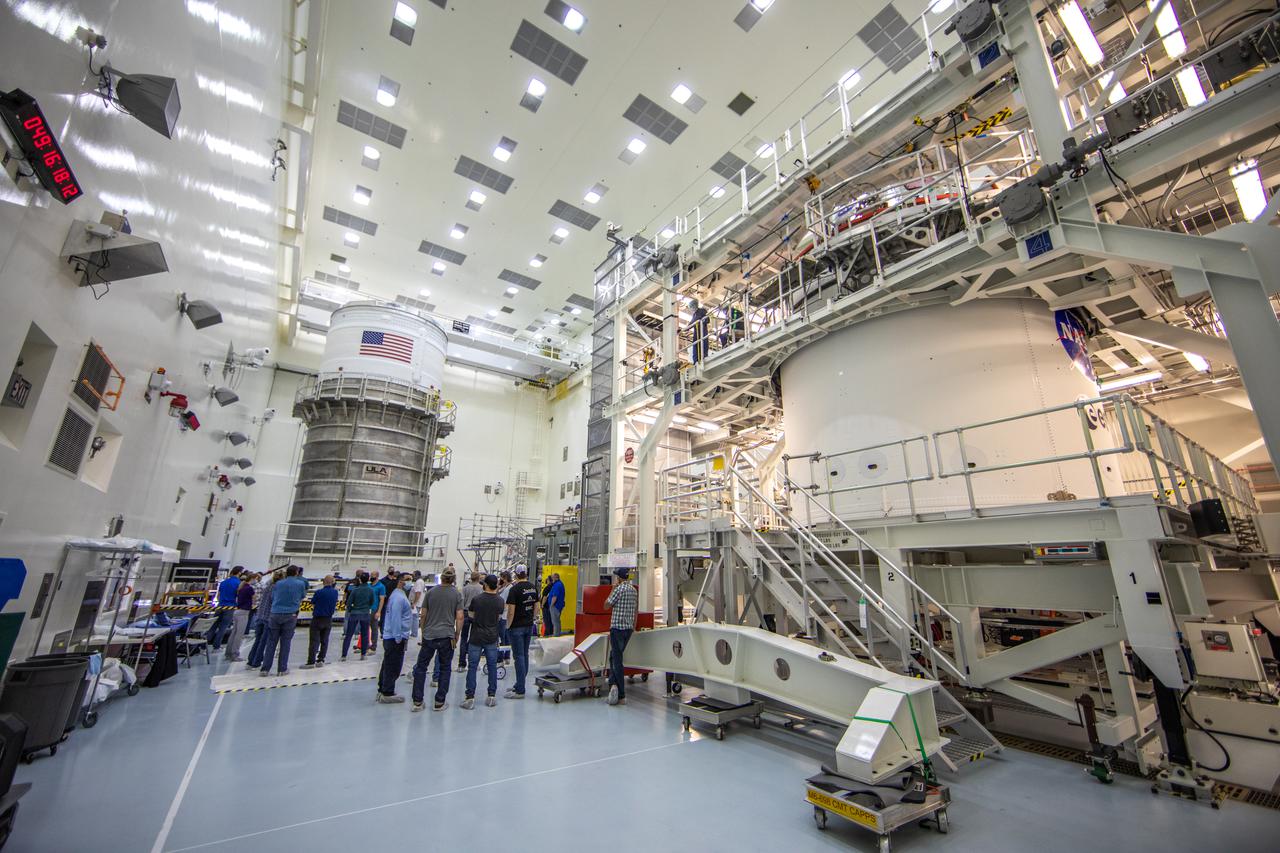

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) moved into the Multi-Payload Processing Facility February 18, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the Artemis I mission. It will undergo fueling and servicing in the facility ahead of launch by teams from NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and their primary contractor, Jacobs Technology. Artemis I will be an integrated flight test of the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft ahead of the crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the lunar surface and establish a sustainable presence at the Moon to prepare for human missions to Mars.
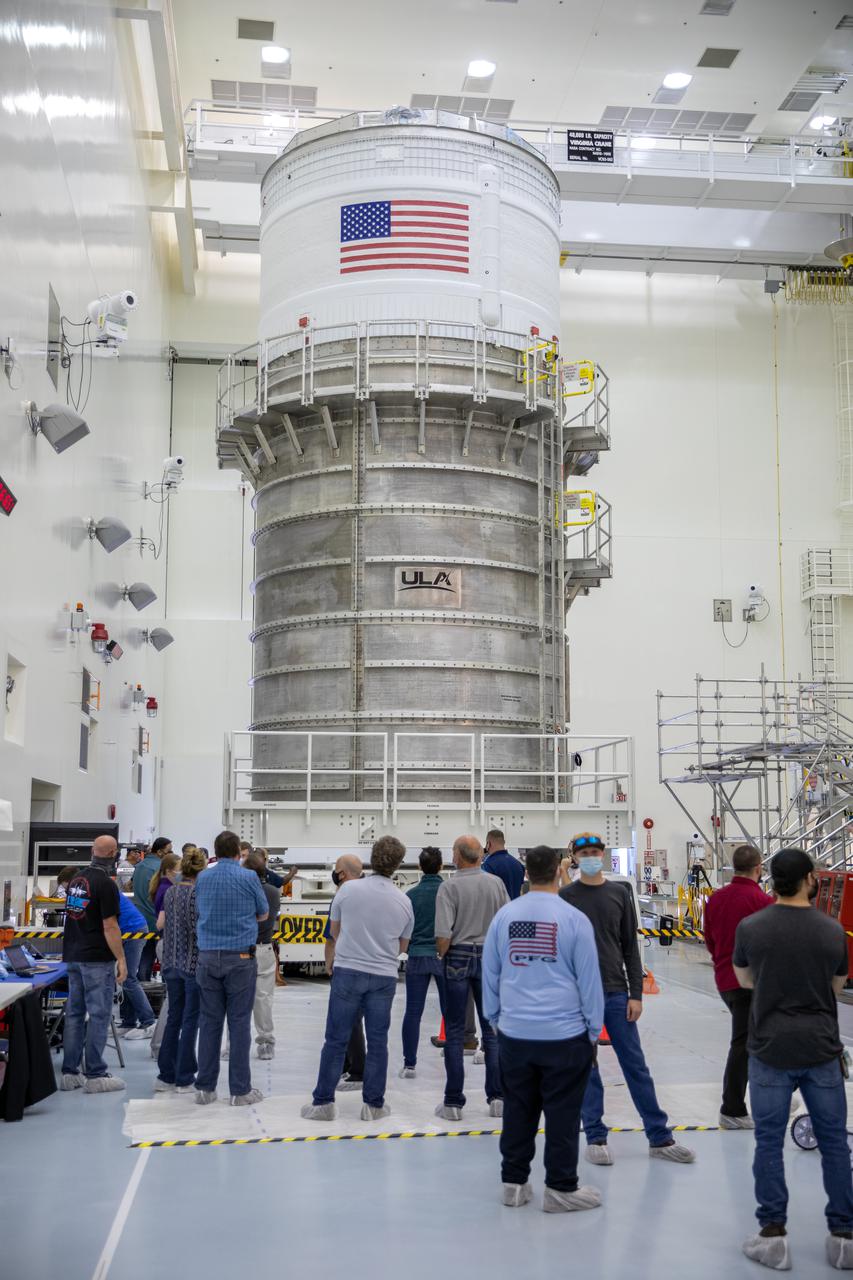

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) moved into the Multi-Payload Processing Facility February 18, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the Artemis I mission. It will undergo fueling and servicing in the facility ahead of launch by teams from NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and their primary contractor, Jacobs Technology. Artemis I will be an integrated flight test of the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft ahead of the crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the lunar surface and establish a sustainable presence at the Moon to prepare for human missions to Mars.
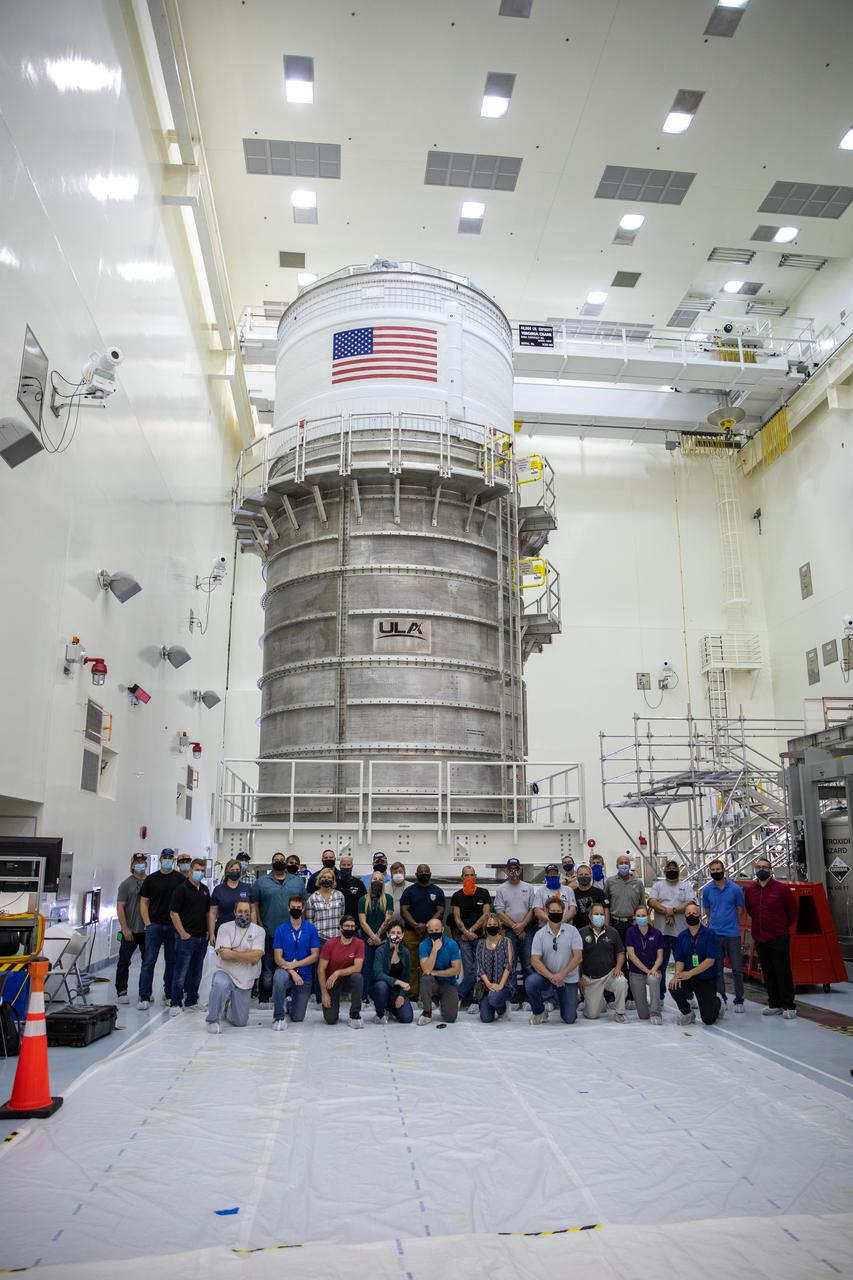

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) moved into the Multi-Payload Processing Facility February 18, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the Artemis I mission. It will undergo fueling and servicing in the facility ahead of launch by teams from NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and their primary contractor, Jacobs Technology. Artemis I will be an integrated flight test of the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft ahead of the crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the lunar surface and establish a sustainable presence at the Moon to prepare for human missions to Mars.

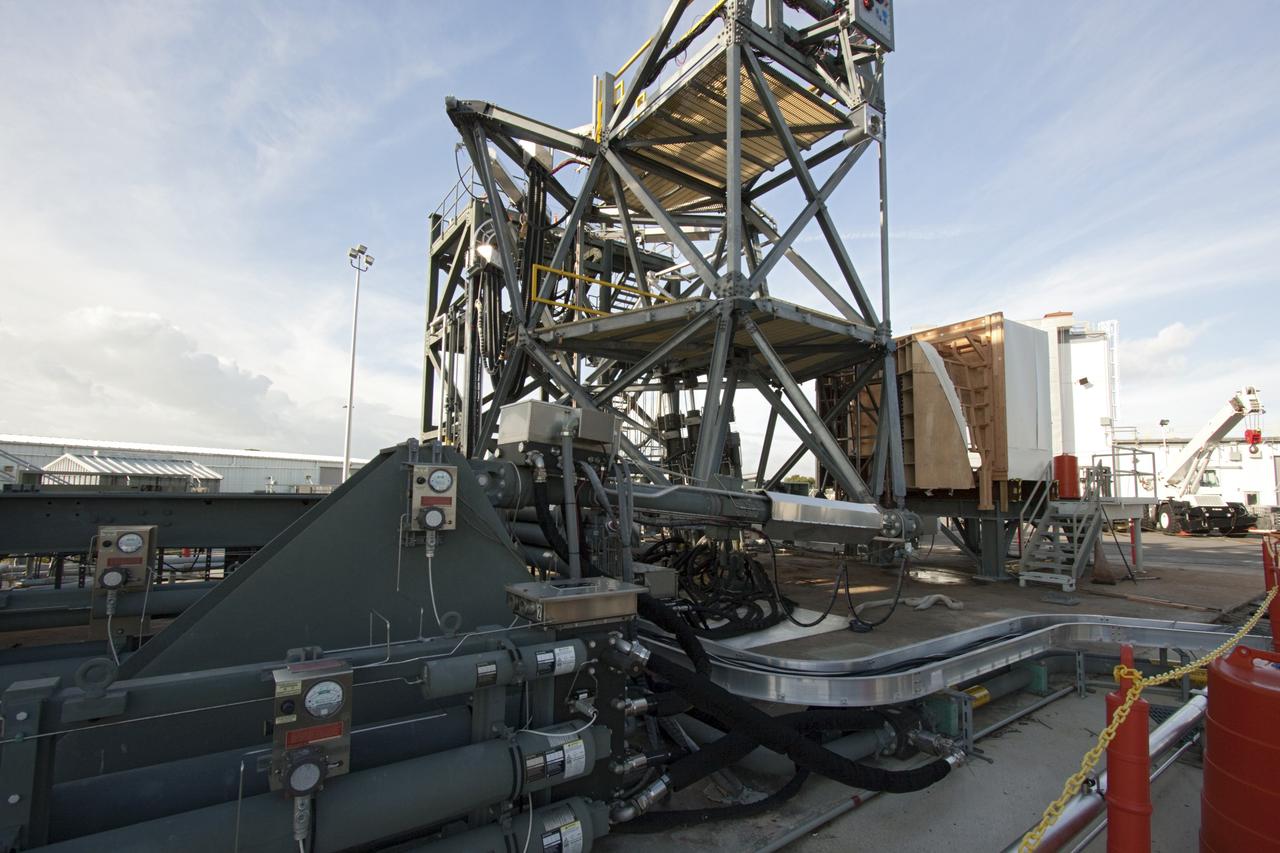
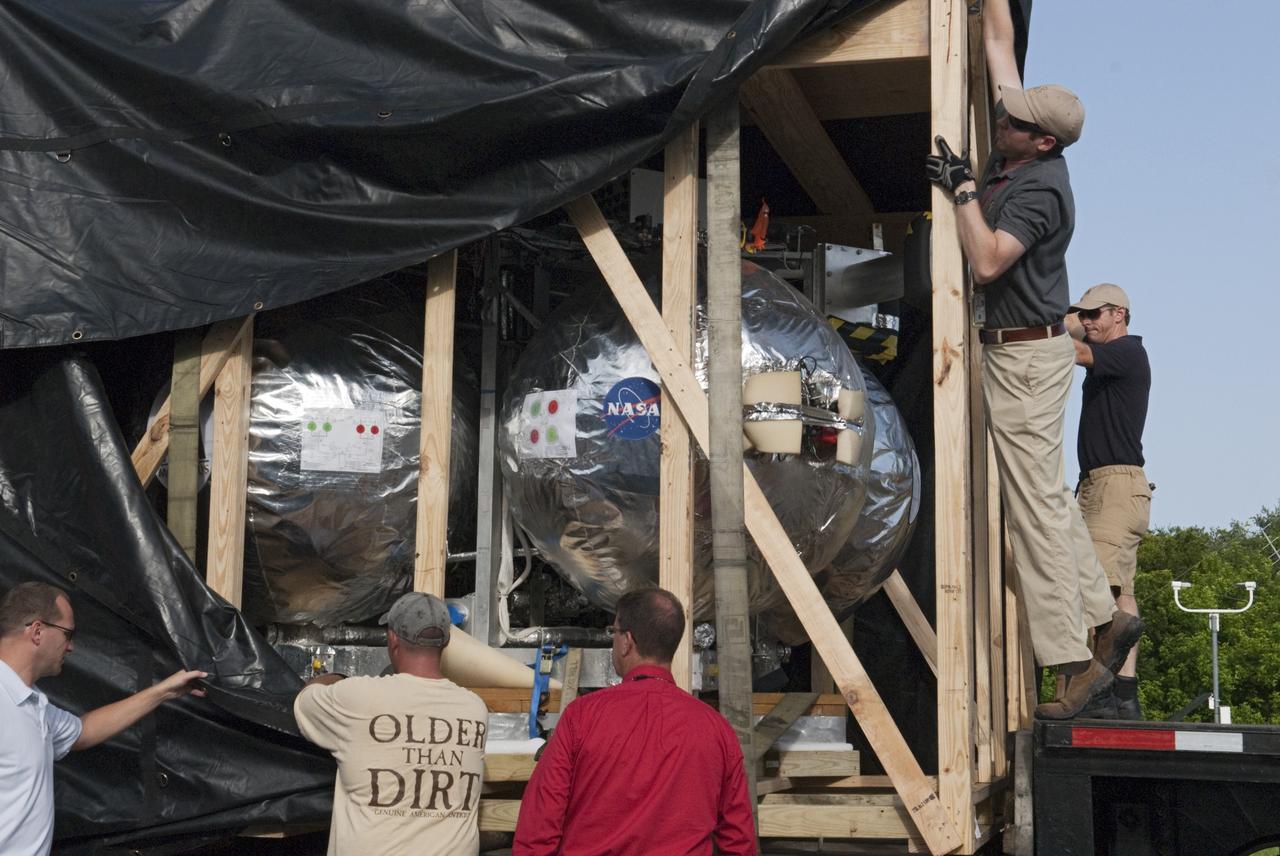
Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
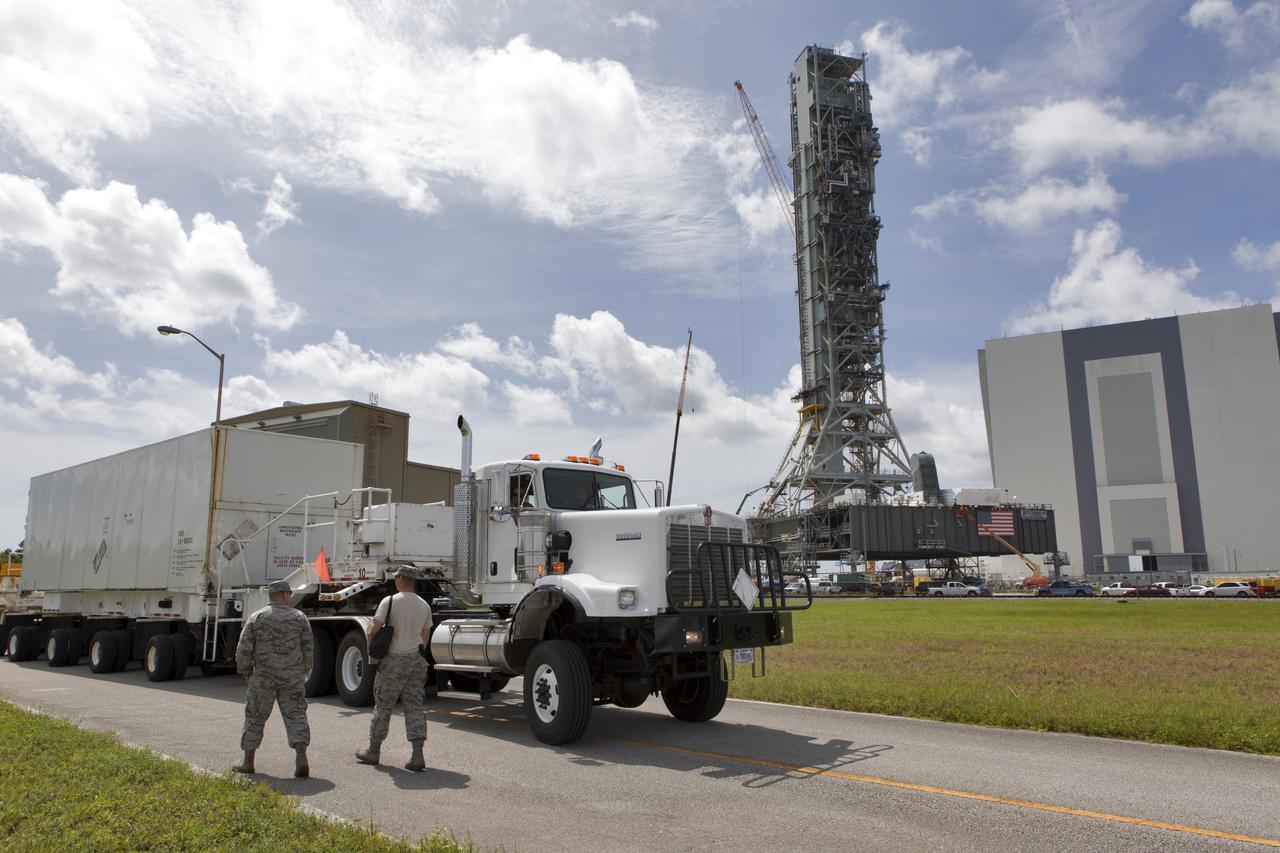

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) will be moved from the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
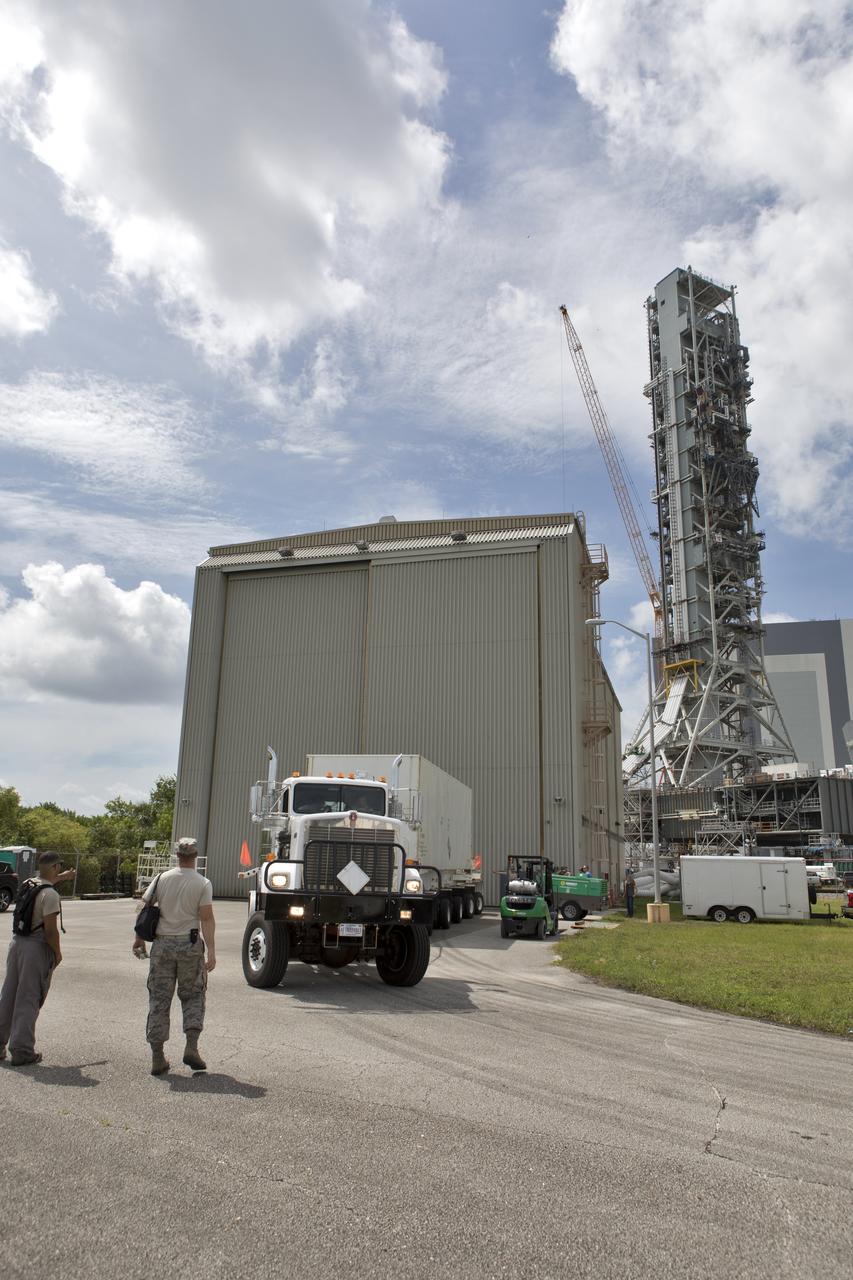

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
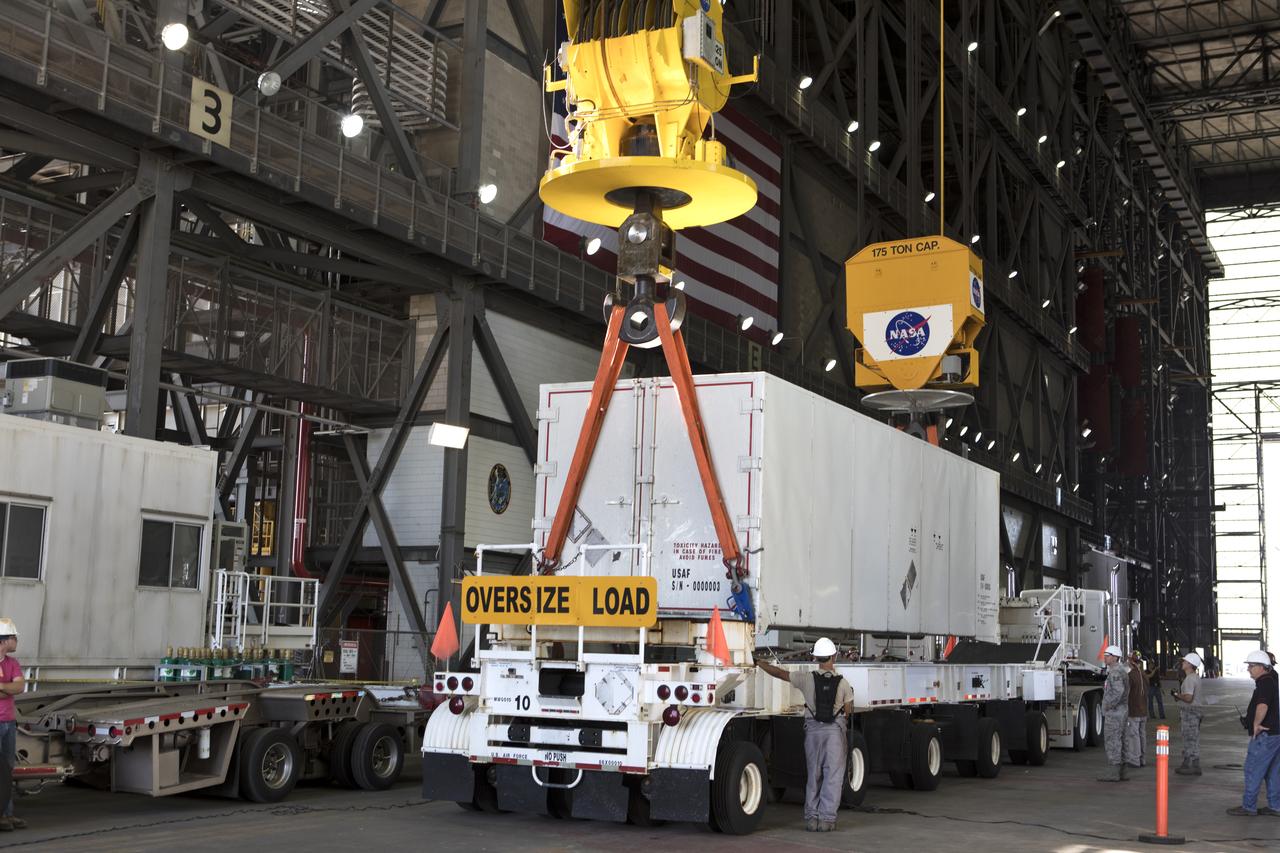

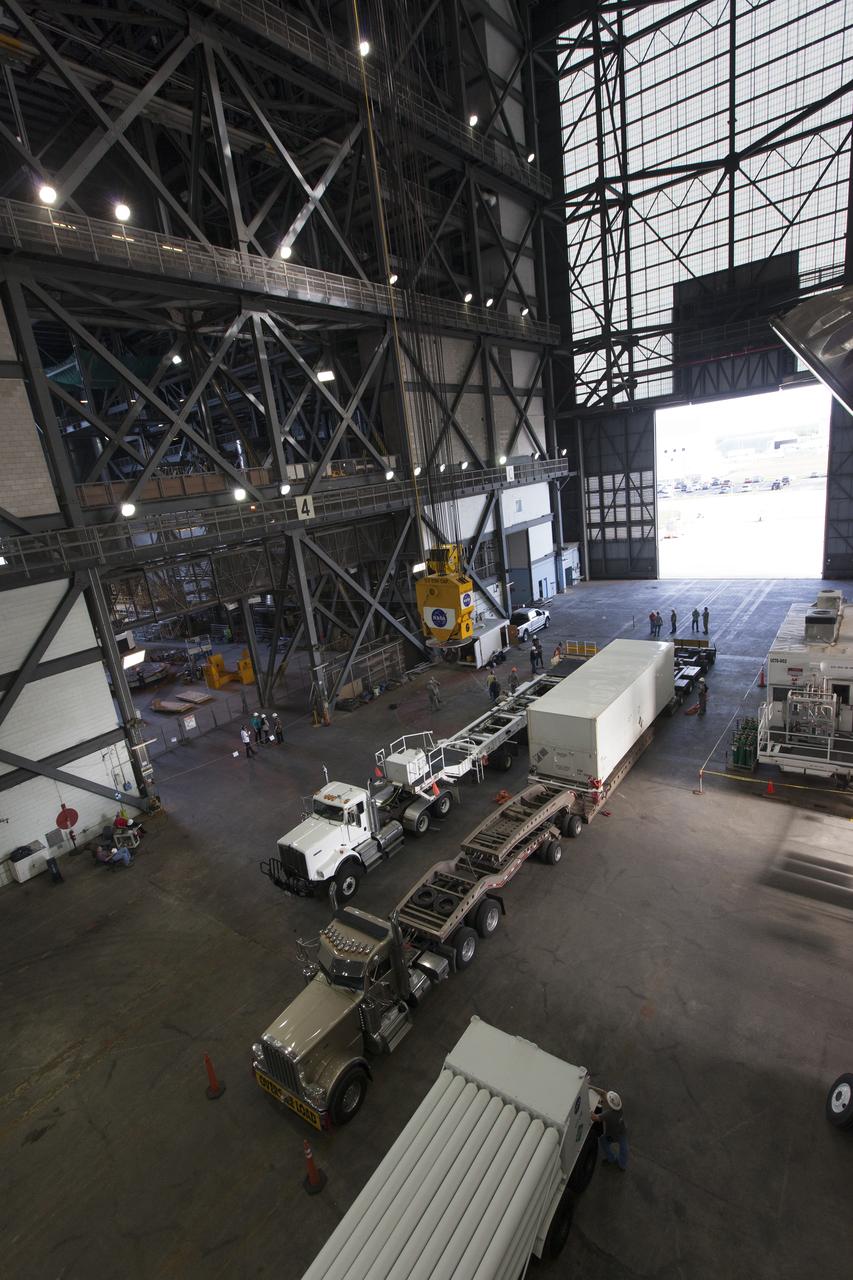
In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside onto another transporter on July 20, 2018. The container will be moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
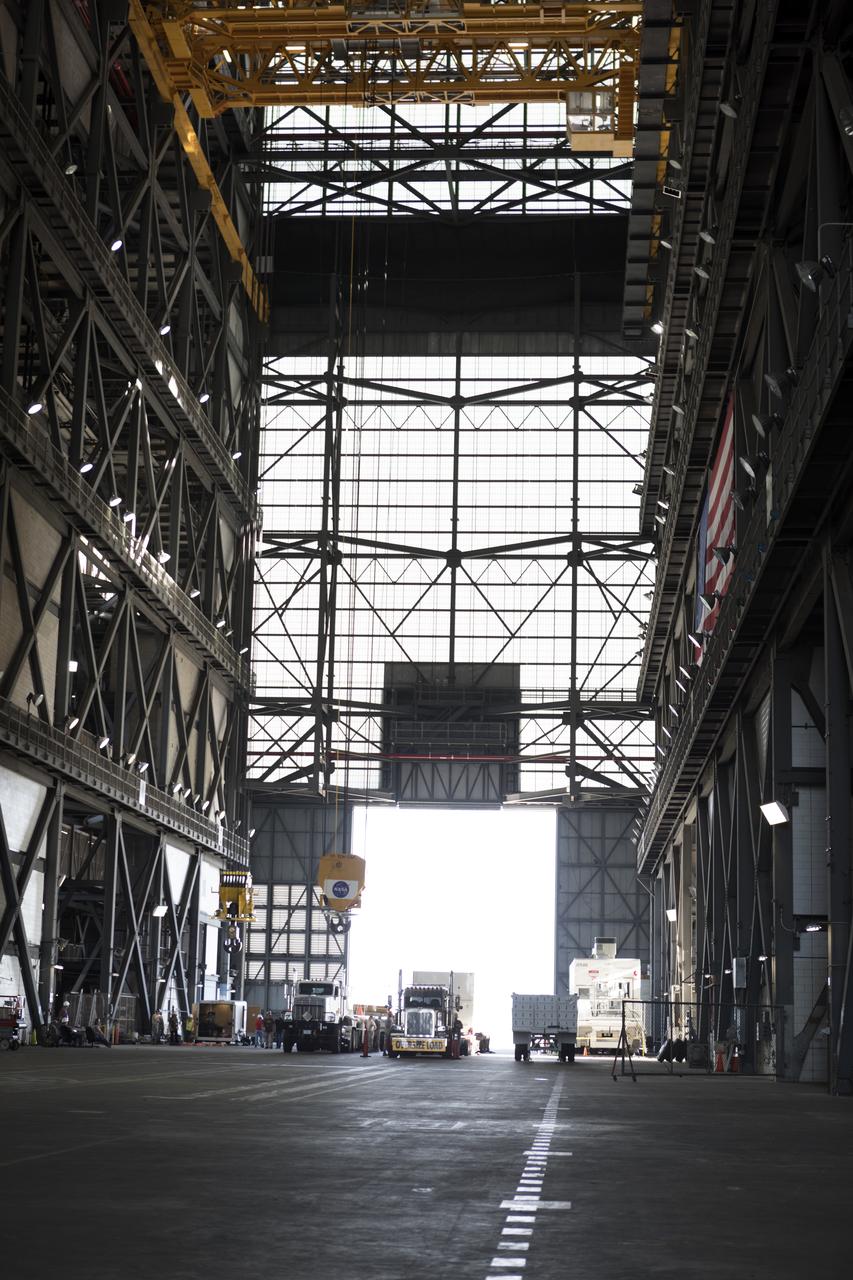

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
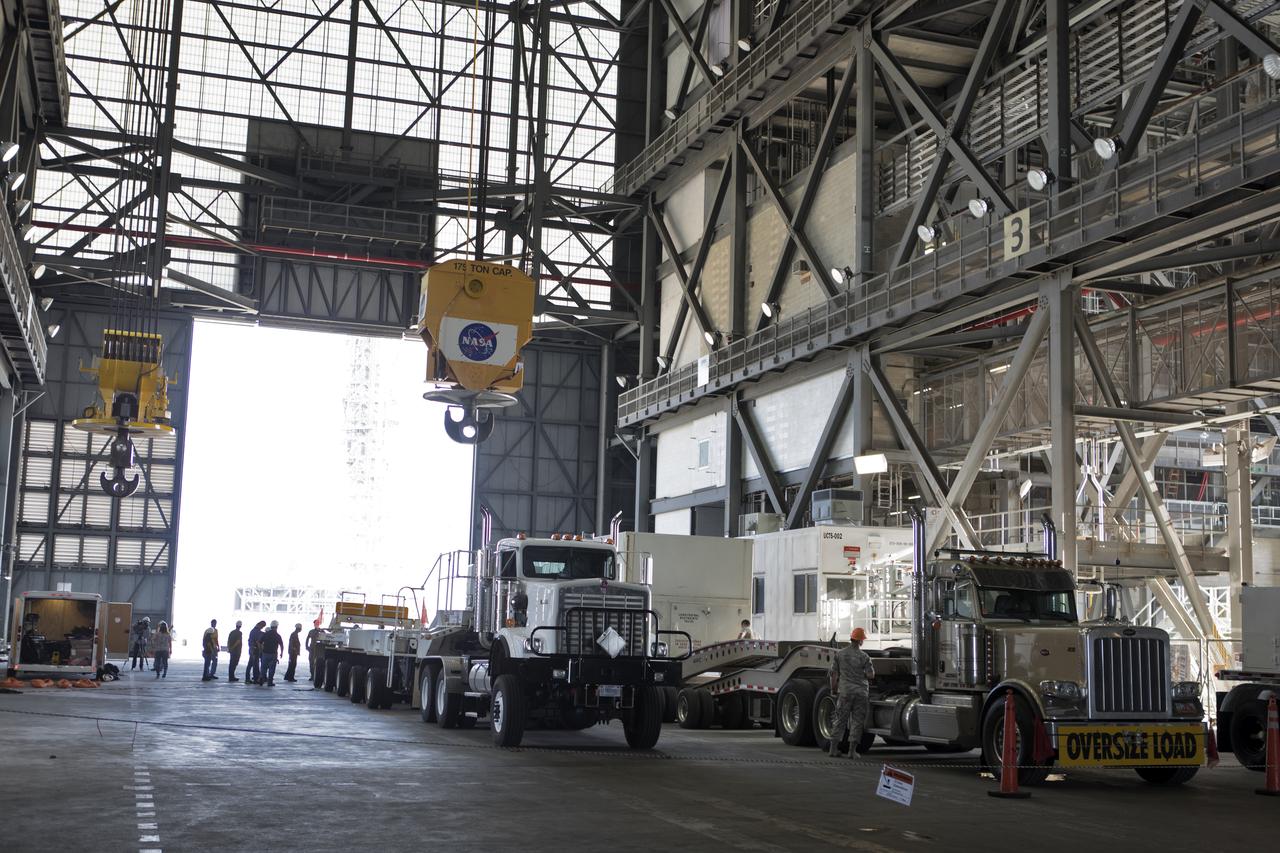

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
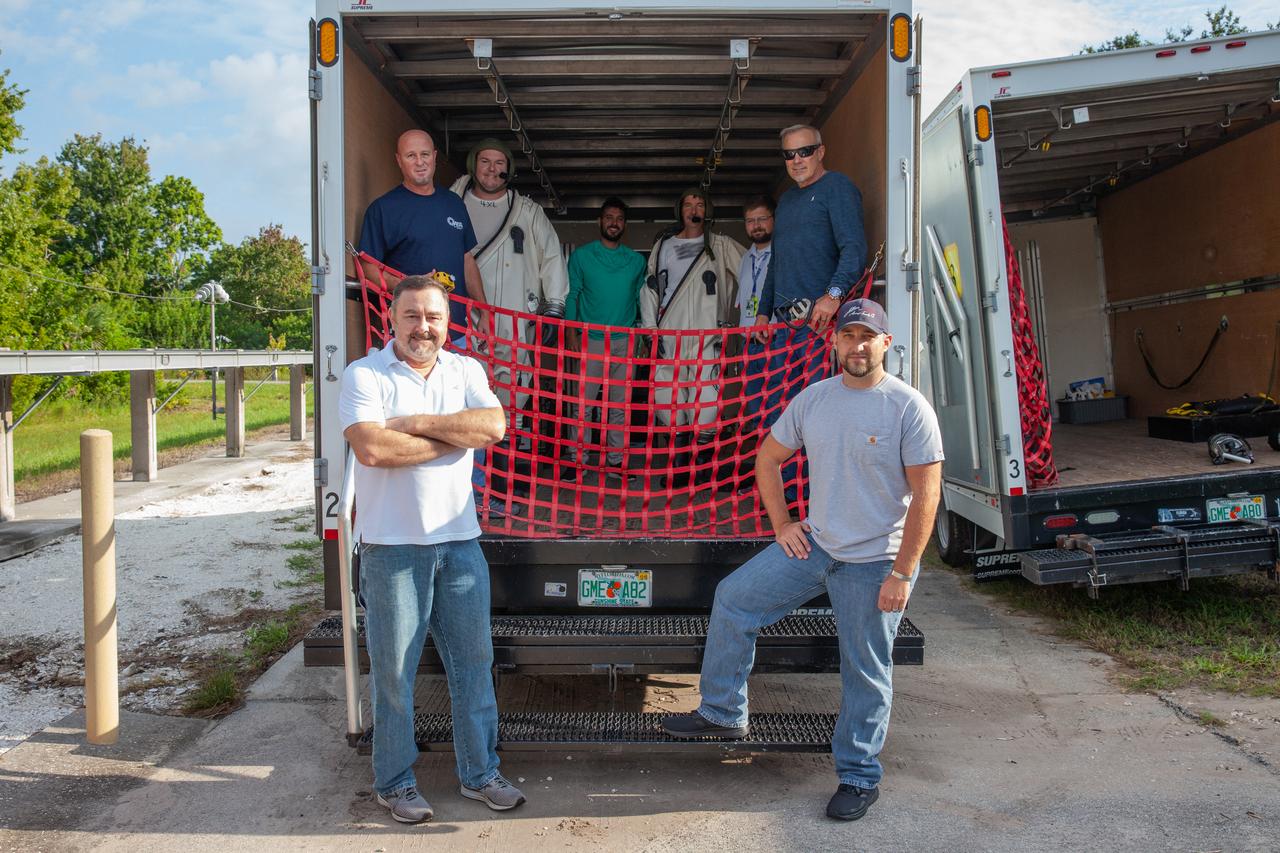

Technicians wearing Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suits and operations support personnel prepare for a test simulation of loading propellants into a replicated test tank for Orion on Aug. 16, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. They are in a transport truck at the Multi-Operations Support Building near the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF). Exploration Ground Systems is preparing for Artemis 1 with a series of hazardous hyper test events at the MPPF. The technicians will complete a tanking to test the system before Orion arrives for processing. During preparations for launch, these teams will be responsible for loading the Orion vehicle with propellants prior to transportation to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be secured atop the Space Launch System rocket. SCAPE suits are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.
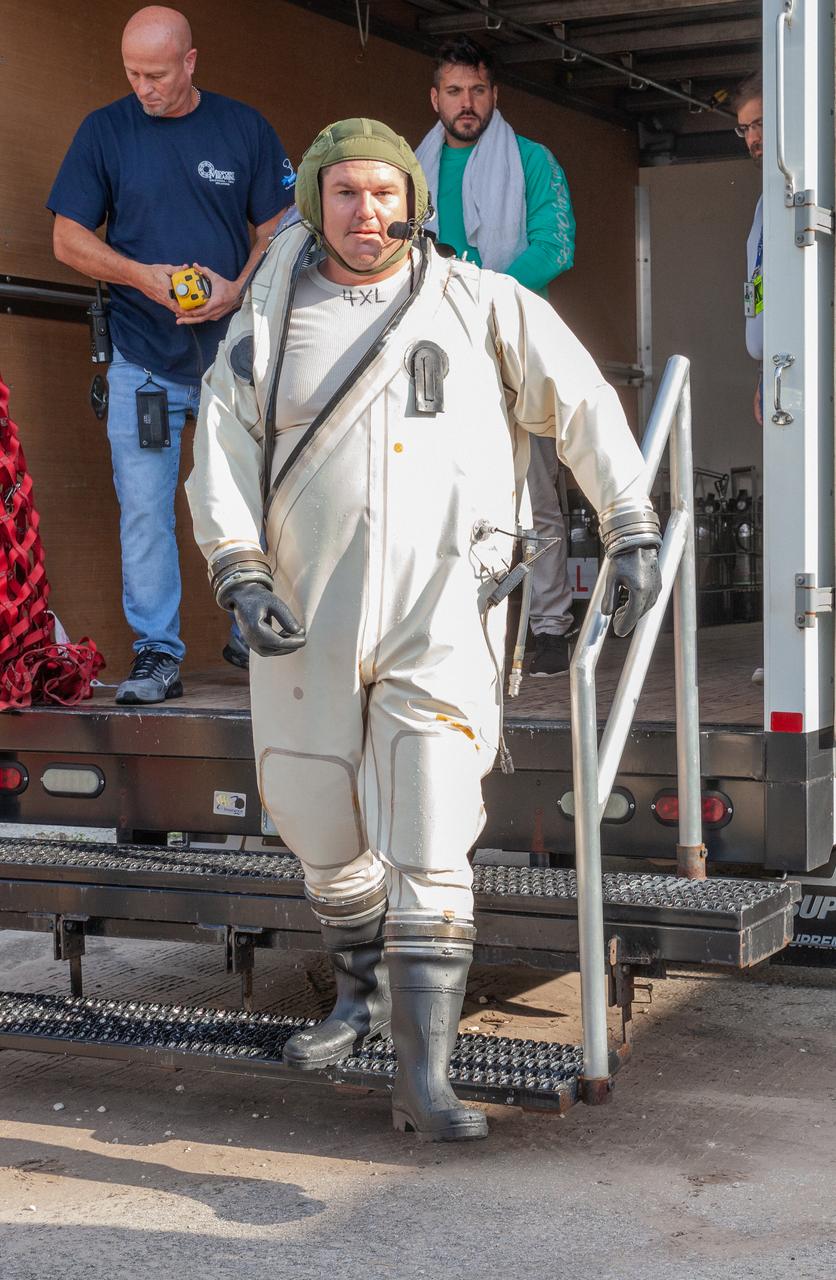

A technician in a Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suit exits a truck near the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 16, 2019. SCAPE technicians are practicing by putting on the suits for a test simulation of loading propellants into a replicated test tank for Orion. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing for Artemis 1 with a series of hazardous hyper test events at the MPPF. After donning their suits, the technicians will complete a tanking to test the system before Orion arrives for processing. During preparations for launch, these teams will be responsible for loading the Orion vehicle with propellants prior to transportation to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be secured atop the Space Launch System rocket. SCAPE suits are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.

Inside the Multi-Operations Support Building near the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 16, 2019, rows of gloves that are part of Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suits are in view inside a changing room. SCAPE technicians will practice putting on SCAPE suits for a test simulation of loading propellants into a replicated test tank for Orion. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing for Artemis 1 with a series of hazardous hyper test events at the MPPF. After donning their suits, the technicians will complete a tanking to test the system before Orion arrives for processing. During preparations for launch, these teams will be responsible for loading the Orion vehicle with propellants prior to transportation to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be secured atop the Space Launch System rocket. SCAPE suits are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.
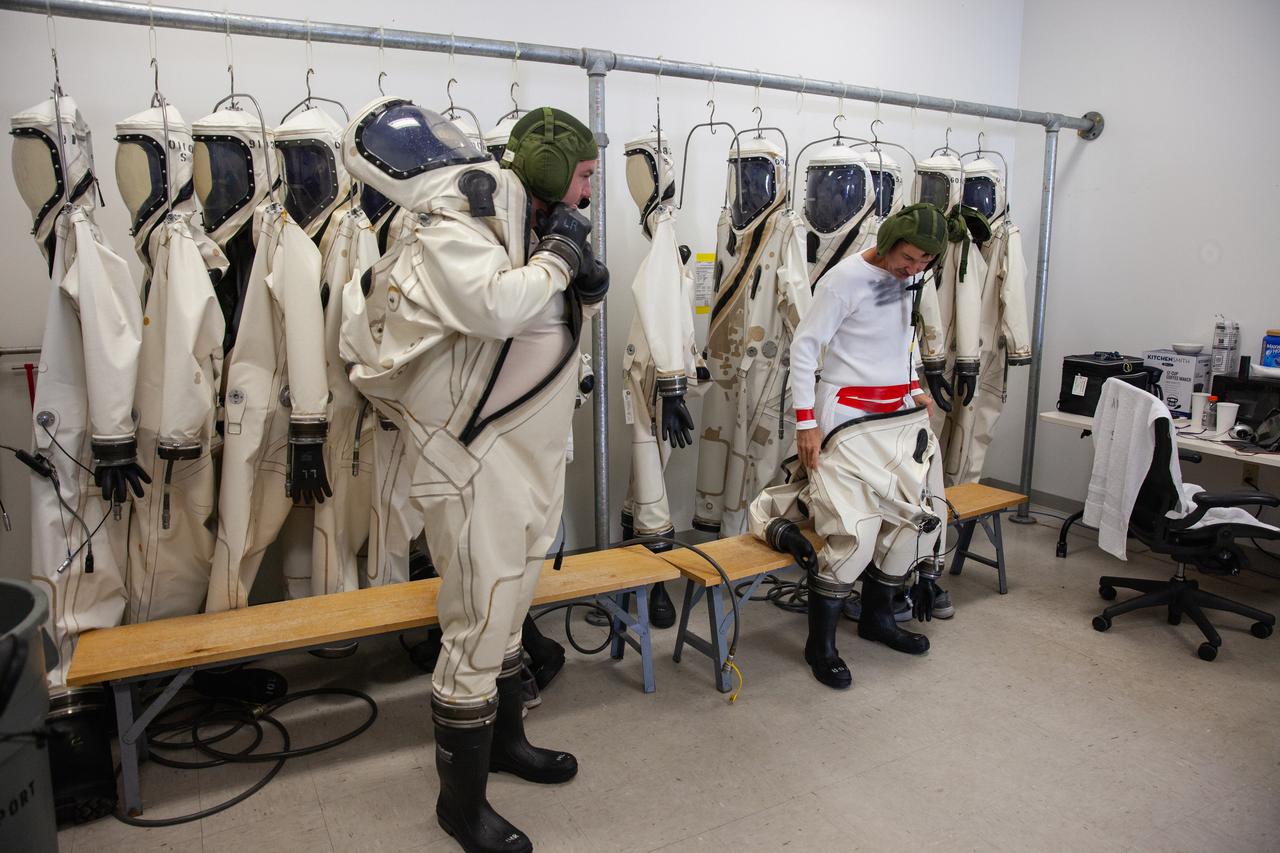

Inside the Multi-Operations Support Building near the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians put on Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suits inside a changing room on Aug. 16, 2019. SCAPE technicians are practicing putting on the suits for a test simulation of loading propellants into a replicated test tank for Orion. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing for Artemis 1 with a series of hazardous hyper test events at the MPPF. After donning their suits, the technicians will complete a tanking to test the system before Orion arrives for processing. During preparations for launch, these teams will be responsible for loading the Orion vehicle with propellants prior to transportation to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be secured atop the Space Launch System rocket. SCAPE suits are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.
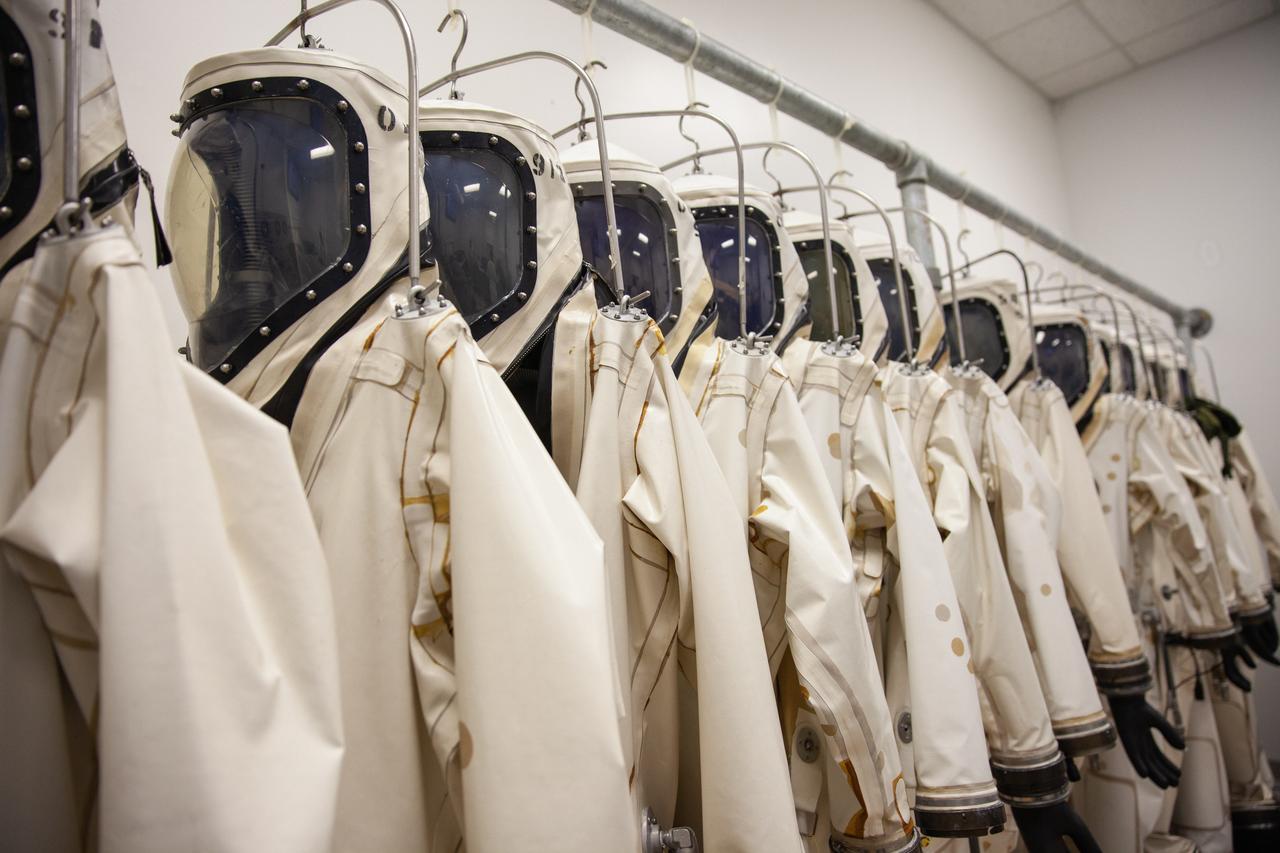

Inside the Multi-Operations Support Building near the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 16, 2019, a row of Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suits are hanging inside a changing room. SCAPE technicians are practicing putting on the suits for a test simulation of loading propellants into a replicated test tank for Orion. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing for Artemis 1 with a series of hazardous hyper test events at the MPPF. After donning their suits, the technicians will complete a tanking to test the system before Orion arrives for processing. During preparations for launch, these teams will be responsible for loading the Orion vehicle with propellants prior to transportation to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be secured atop the Space Launch System rocket. SCAPE suits are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.
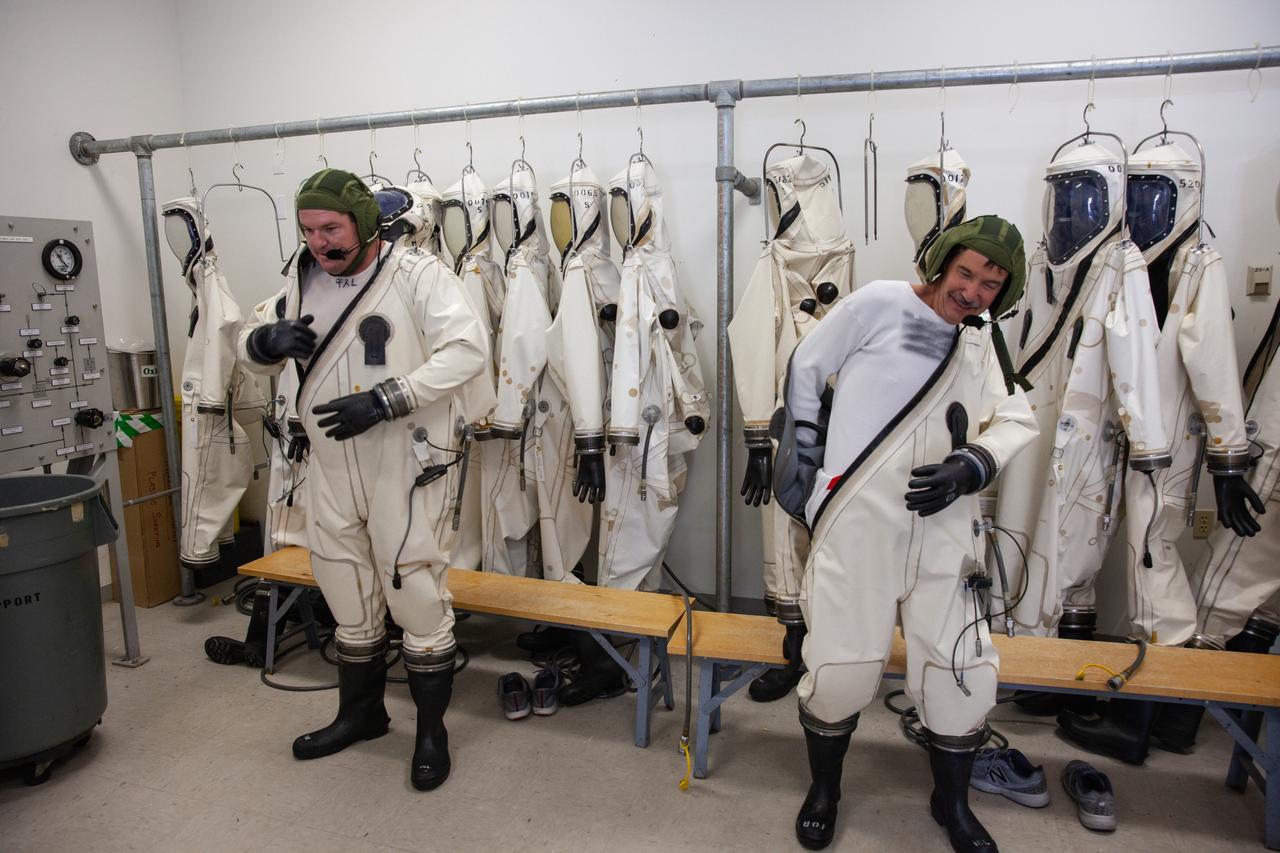

Inside the Multi-Operations Support Building near the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians put on Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suits inside a changing room on Aug. 16, 2019. SCAPE technicians are practicing putting on the suits for a test simulation of loading propellants into a replicated test tank for Orion. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing for Artemis 1 with a series of hazardous hyper test events at the MPPF. After donning their suits, the technicians will complete a tanking to test the system before Orion arrives for processing. During preparations for launch, these teams will be responsible for loading the Orion vehicle with propellants prior to transportation to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be secured atop the Space Launch System rocket. SCAPE suits are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.
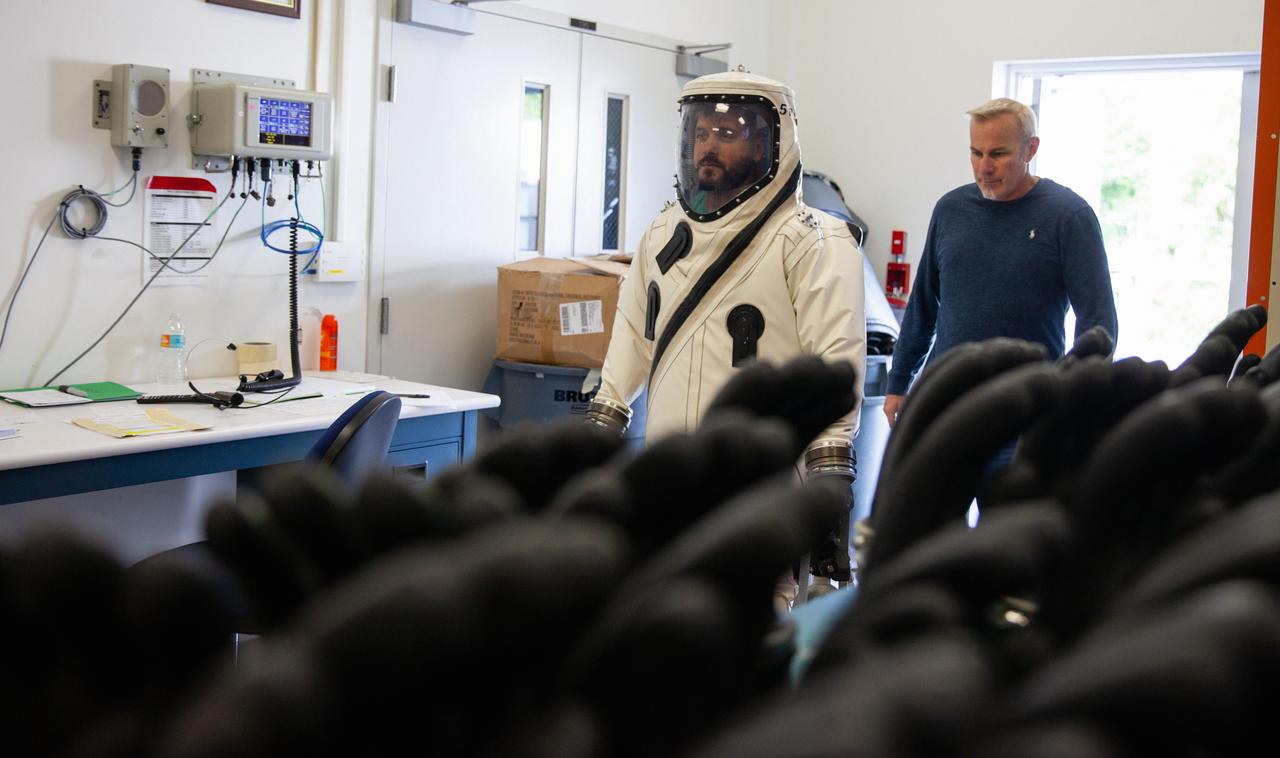

Inside the Multi-Operations Support Building near the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician is wearing a Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suit to prepare for a test simulation of loading propellants into a replicated test tank for Orion, on Aug. 16, 2019. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing for Artemis 1 with a series of hazardous hyper test events at the MPPF. After donning their suits, the technicians will complete a tanking to test the system before Orion arrives for processing. During preparations for launch, these teams will be responsible for loading the Orion vehicle with propellants prior to transportation to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be secured atop the Space Launch System rocket. SCAPE suits are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.
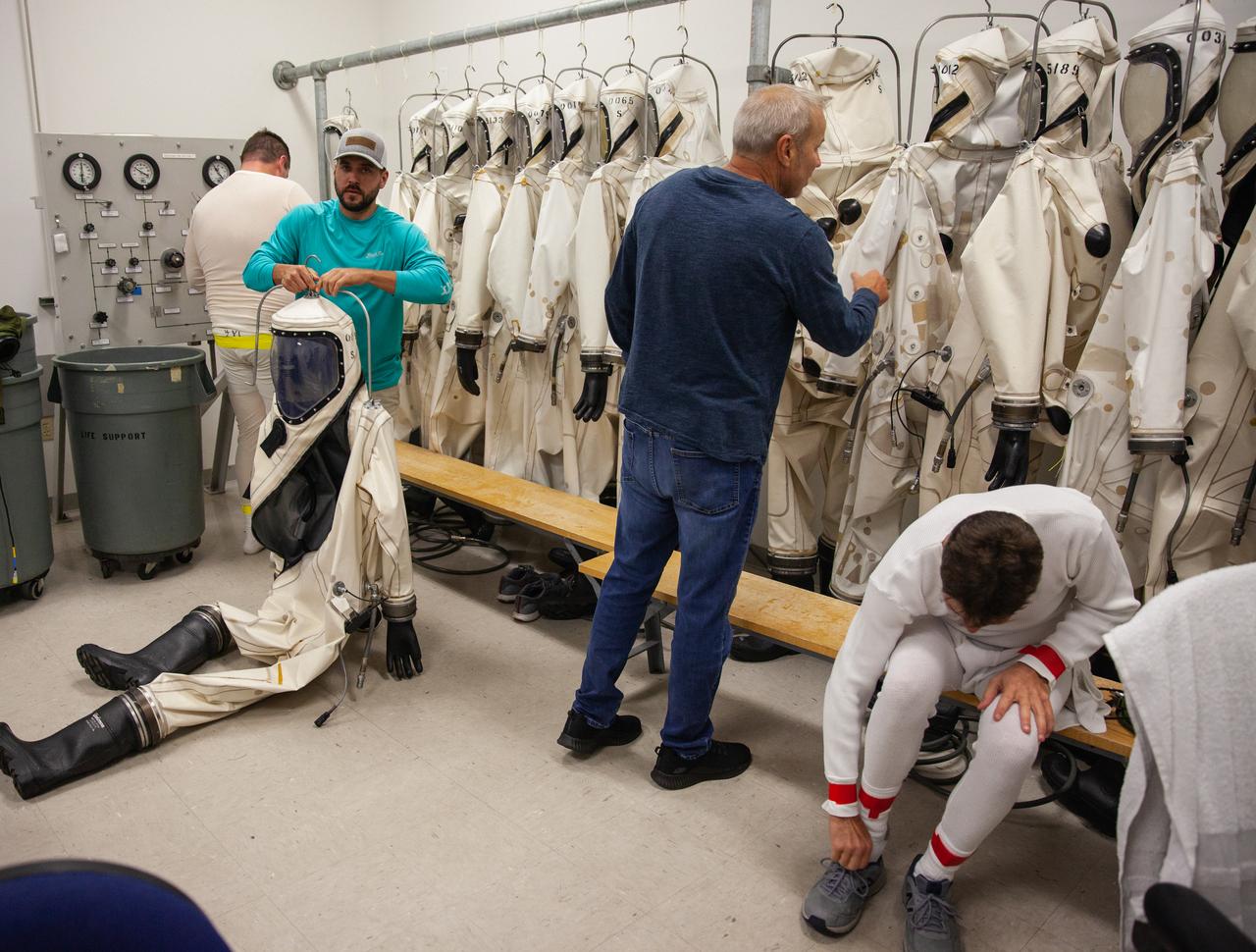

Inside the Multi-Operations Support Building near the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians are putting on Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suits inside a changing room on Aug. 16, 2019. SCAPE technicians are practicing by putting on the suits for a test simulation of loading propellants into a replicated test tank for Orion. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing for Artemis 1 with a series of hazardous hyper test events at the MPPF. After donning their suits, the technicians will complete a tanking to test the system before Orion arrives for processing. During preparations for launch, these teams will be responsible for loading the Orion vehicle with propellants prior to transportation to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be secured atop the Space Launch System rocket. SCAPE suits are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.
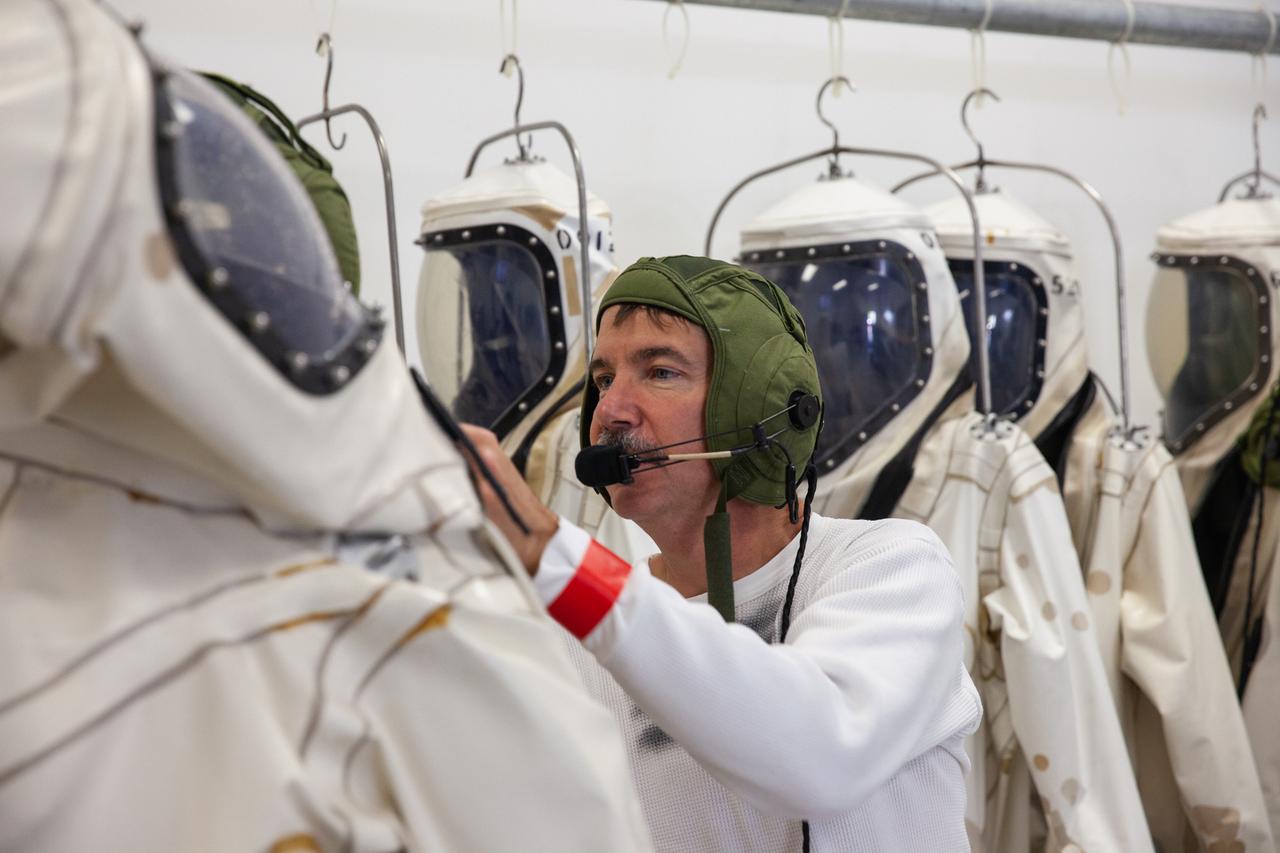

Inside the Multi-Operations Support Building near the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician prepares to put on a Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suit inside a changing room on Aug. 16, 2019. SCAPE technicians are practicing putting on their suits for a test simulation of loading propellants into a replicated test tank for Orion. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing for Artemis 1 with a series of hazardous hyper test events at the MPPF. After donning their suits, the technicians will complete a tanking to test the system before Orion arrives for processing. During preparations for launch, these teams will be responsible for loading the Orion vehicle with propellants prior to transportation to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be secured atop the Space Launch System rocket. SCAPE suits are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.

Inside the Multi-Operations Support Building near the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians and operations personnel review procedures for a test simulation of loading propellants into a replicated test tank for Orion, on Aug. 16, 2019. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing for Artemis 1 with a series of hazardous hyper test events at the MPPF. Technicians will practice putting on Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suits and then complete tanking to test the system before Orion arrives for processing. During preparations for launch, these teams will be responsible for loading the Orion vehicle with propellants prior to transportation to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be secured atop the Space Launch System rocket. SCAPE suits are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.
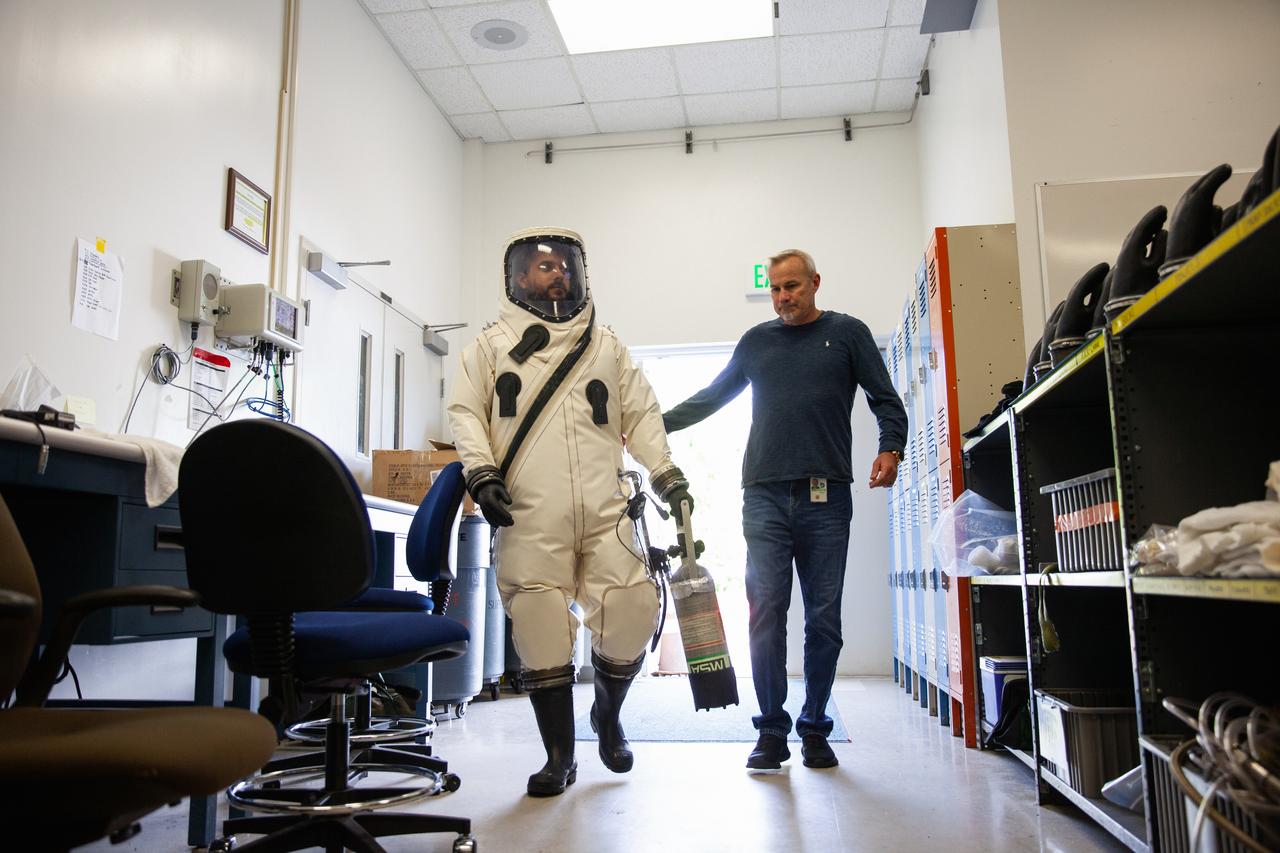

Inside the Multi-Operations Support Building near the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician is wearing a Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suit to prepare for a test simulation of loading propellants into a replicated test tank for Orion, on Aug. 16, 2019. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing for Artemis 1 with a series of hazardous hyper test events at the MPPF. After donning their suits, the technicians will complete tanking to test the system before Orion arrives for processing. During preparations for launch, these teams will be responsible for loading the Orion vehicle with propellants prior to transportation to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be secured atop the Space Launch System rocket. SCAPE suits are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.