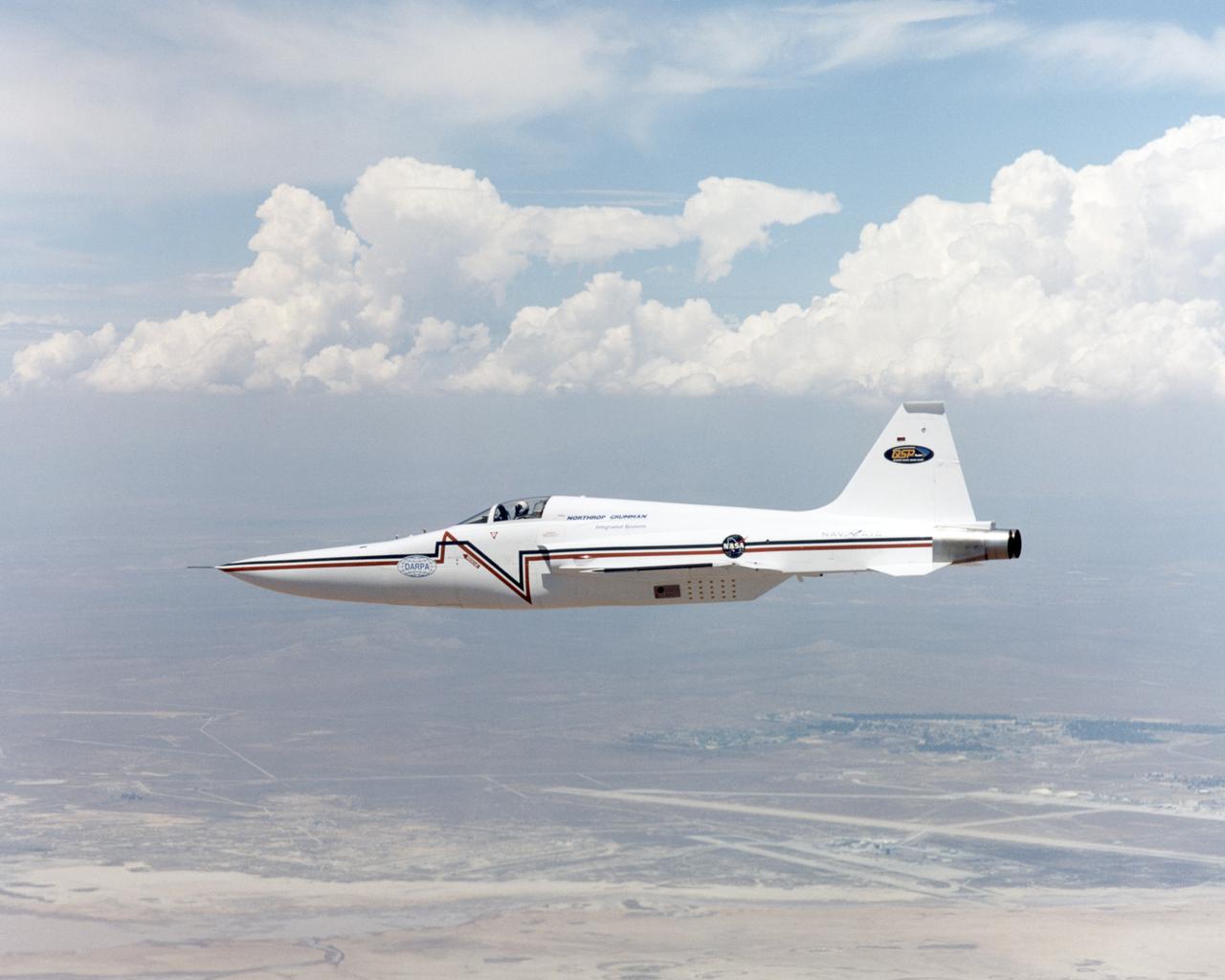

Northrop-Grumman Corporation's modified U.S. Navy F-5E Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) aircraft.
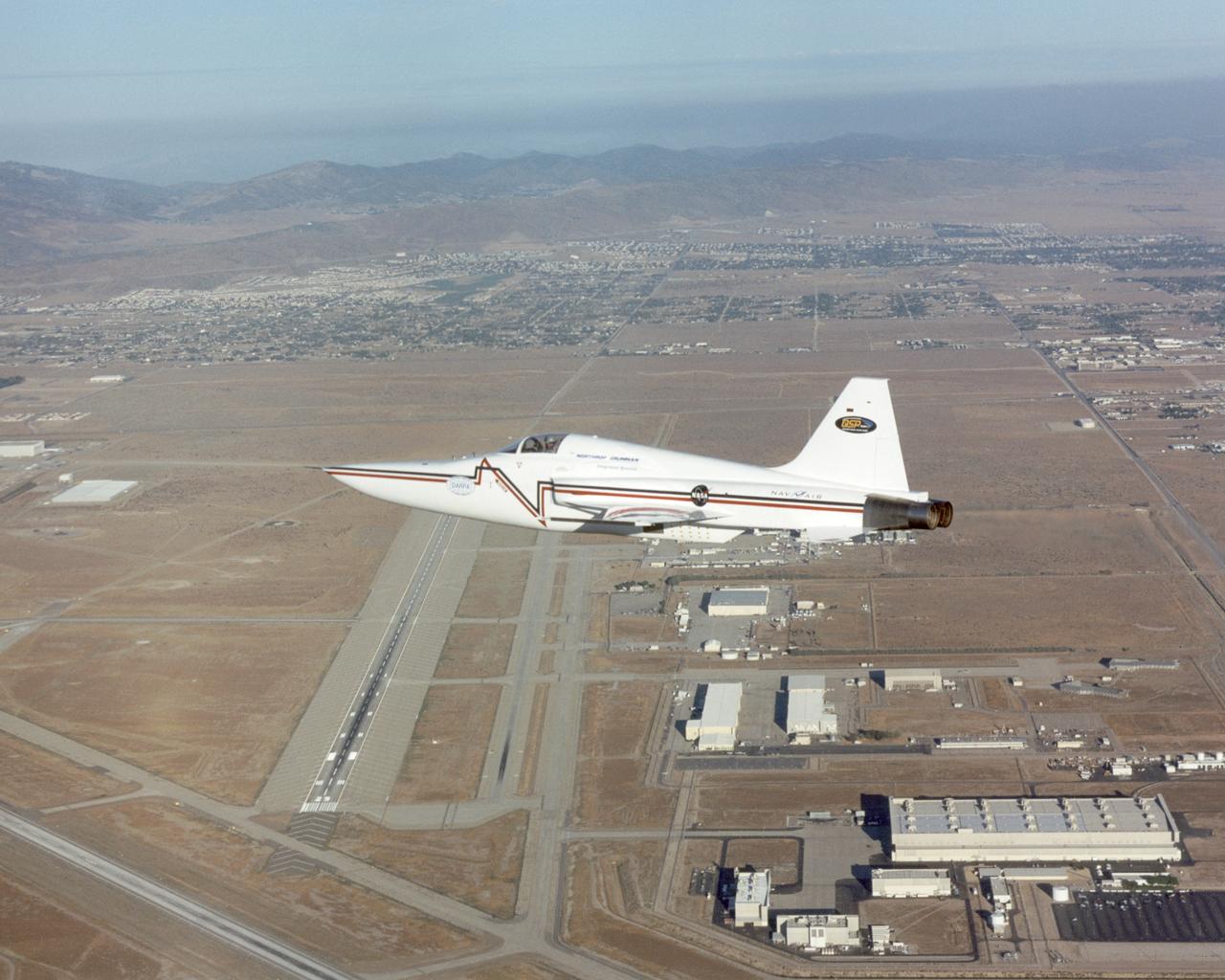

Northrop Grumman Corporation's modified U.S. Navy F-5E Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) aircraft flies over the company's Palmdale, California facilities on Aug. 2, 2003. NASA Dryden provided range, air and ground data-gathering support for the SSBD project, which is part of DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program.
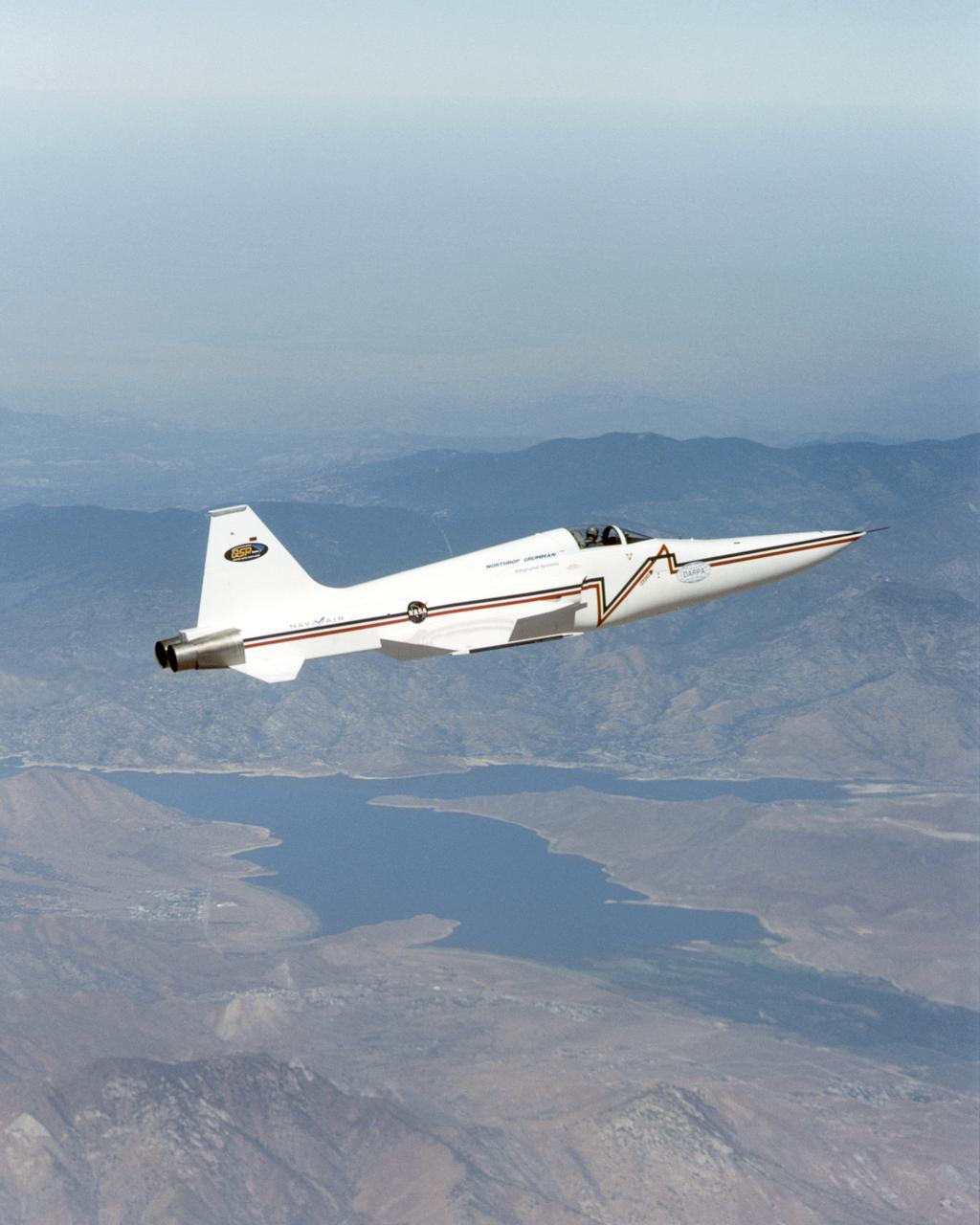

Northrop Grumman Corporation's modified U.S. Navy F-5E Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) aircraft flies over Lake Isabella, California on Aug. 4, 2003. NASA Dryden provided range, air and ground data-gathering support for the SSBD project, which is part of DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program.
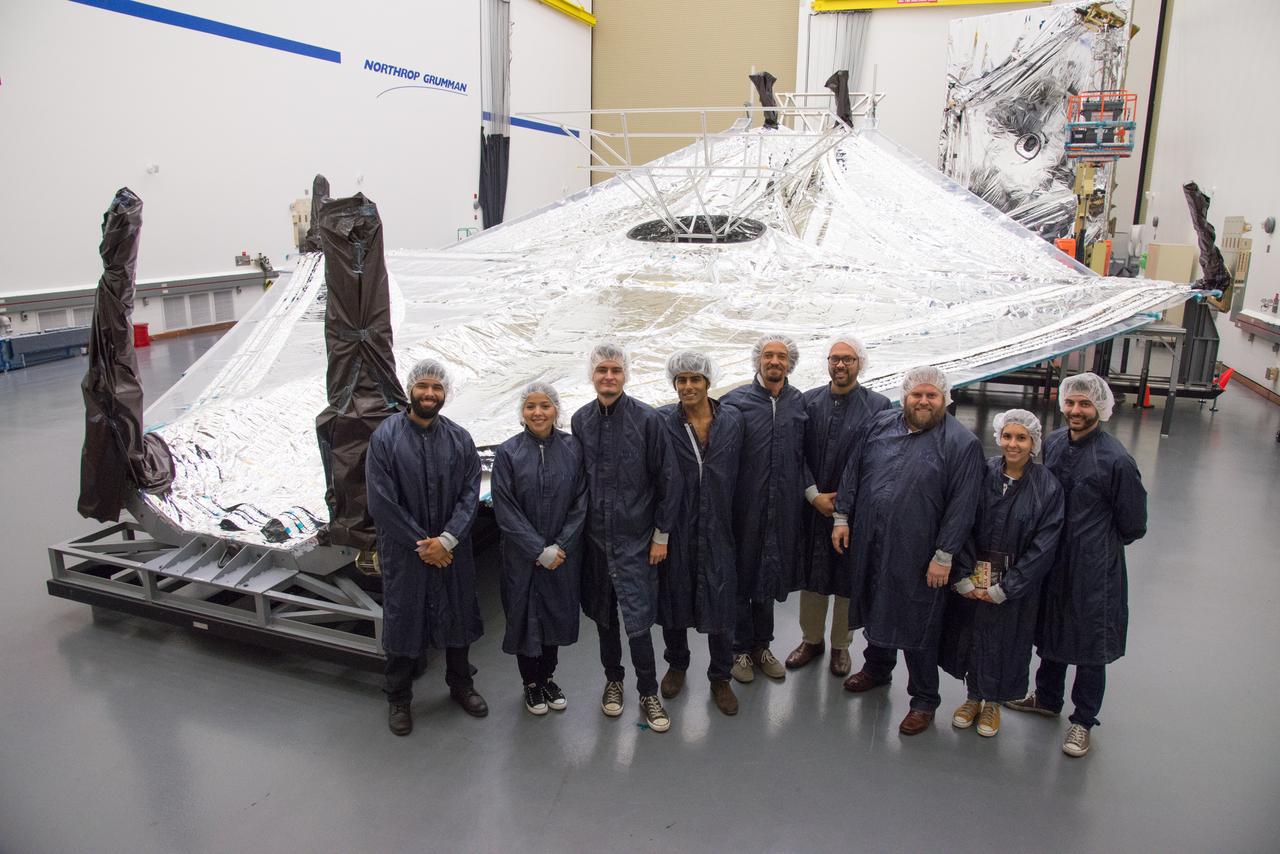

Students and teachers from the New York Film Academy visited Northrop Grumman’s Space Park facility in December 2014 for a tour of the James Webb Space Telescope, and got an up-close look at the tennis-court-sized sunshield that will keep the telescope cool in deep space. Photo courtesy of Northrop Grumman Corporation
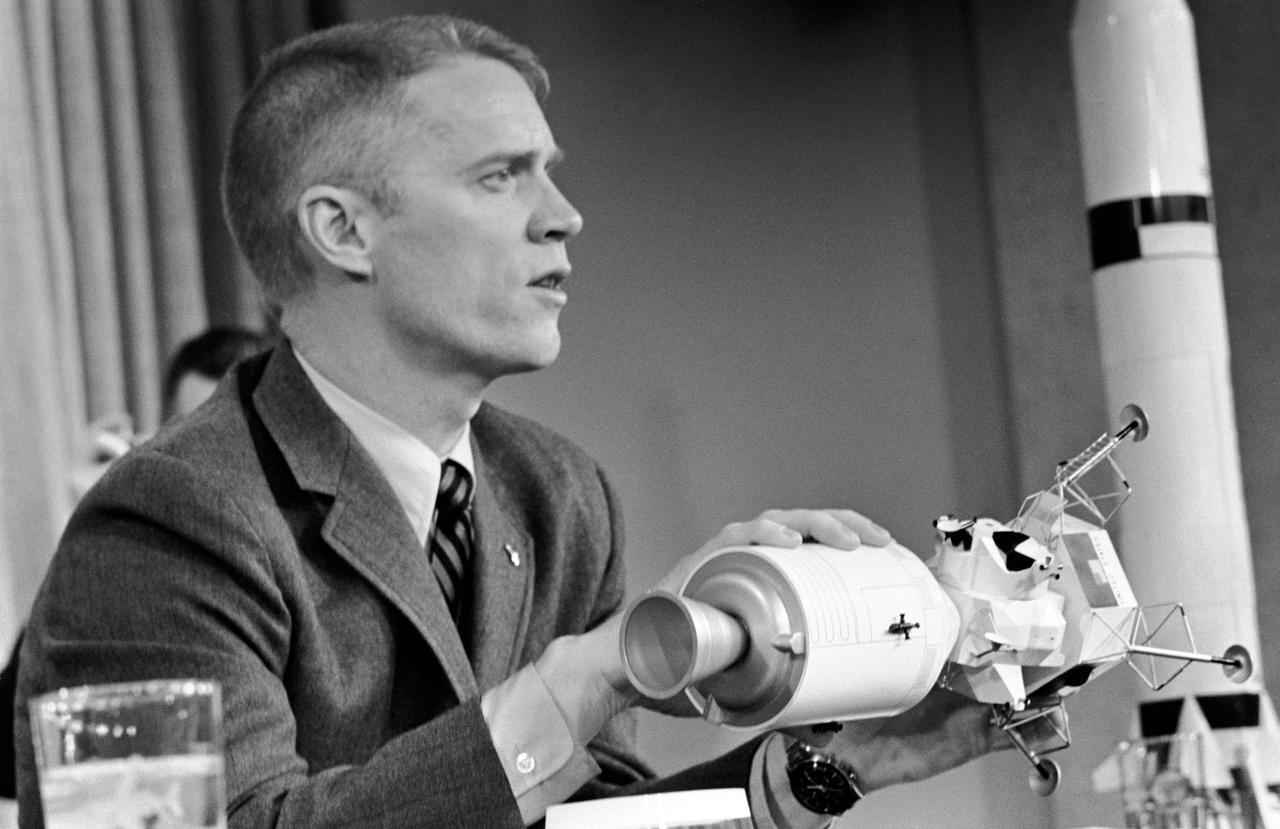

S69-17615 (25 Jan. 1969) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot of the Apollo 9 prime crew, participates in a press conference at the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. Grumman is the contractor to NASA for the Lunar Module. Schweickart is holding a model of a docked Lunar Module/Command and Service Modules. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
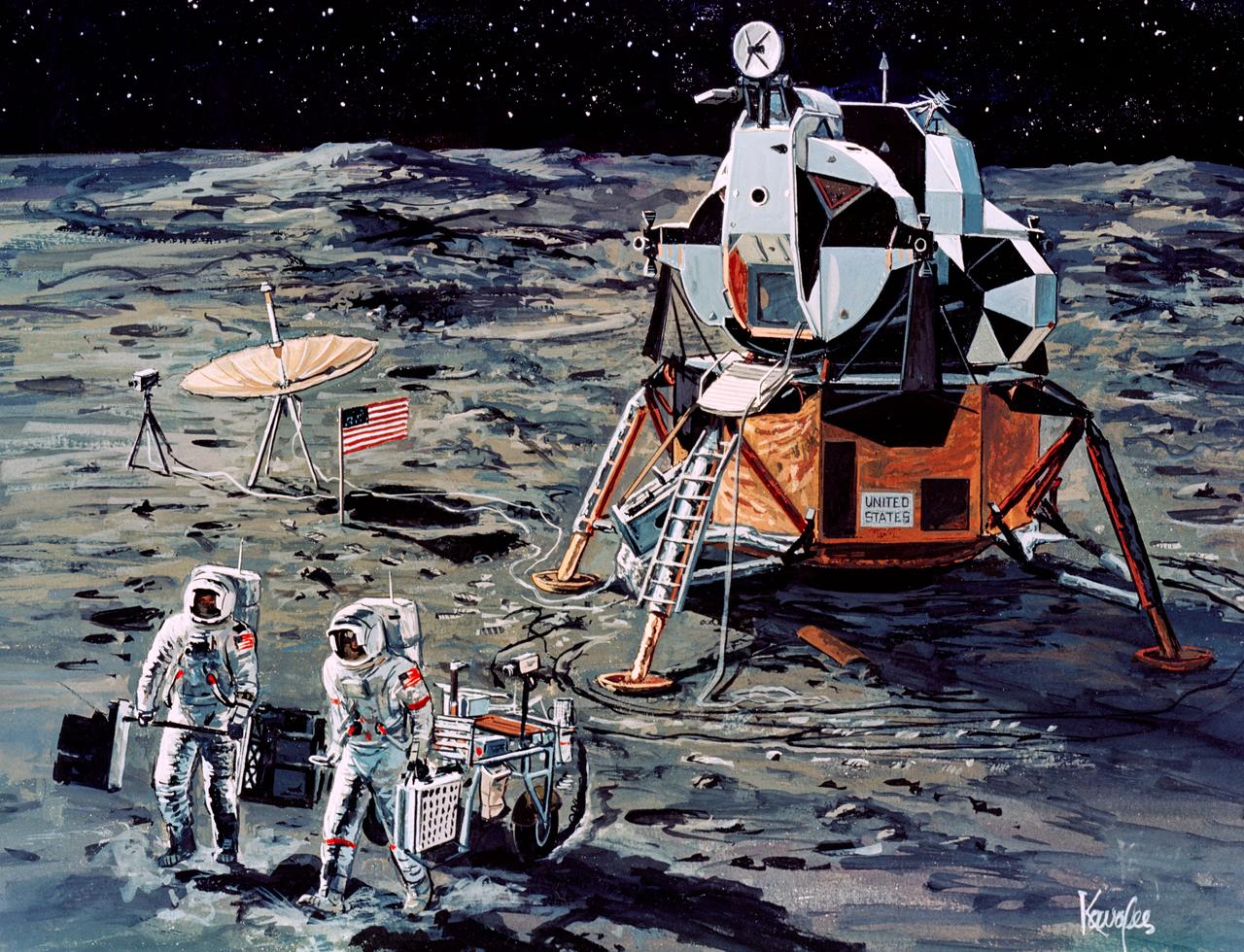
S71-16101 (January 1971) --- A Grumman Aerospace Corporation artist's concept of Apollo 14 crewmen, astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, as they set out on their first traverse. Shepard is pulling the Modularized Equipment Transporter (MET) which contains cameras, lunar sample bags, tools and other paraphernalia. Shepard has the Laser Ranging Retro-Reflector (LR-3) in his other hand. Mitchell is carrying the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) barbell mode.
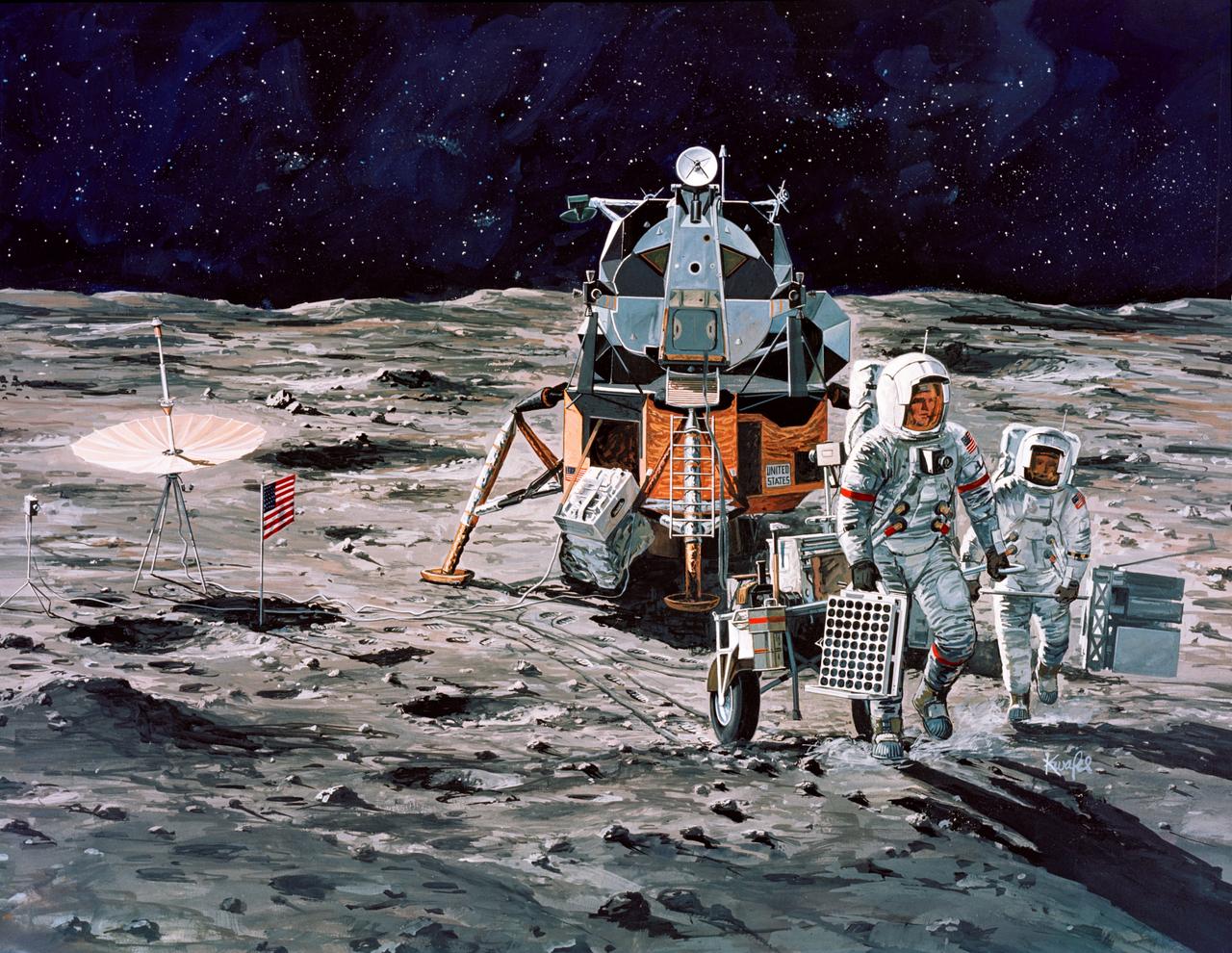
S71-16102 (January 1971) --- A Grumman Aerospace Corporation artist's concept of Apollo 14 crewmen, astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, as they set out on their first traverse. Shepard is pulling the Modularized Equipment Transporter (MET) which contains cameras, lunar sample bags, tools and other paraphernalia. Shepard has the Laser Ranging Retro-Reflector (LR3) in his other hand. Mitchell is carrying the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) barbell mode.
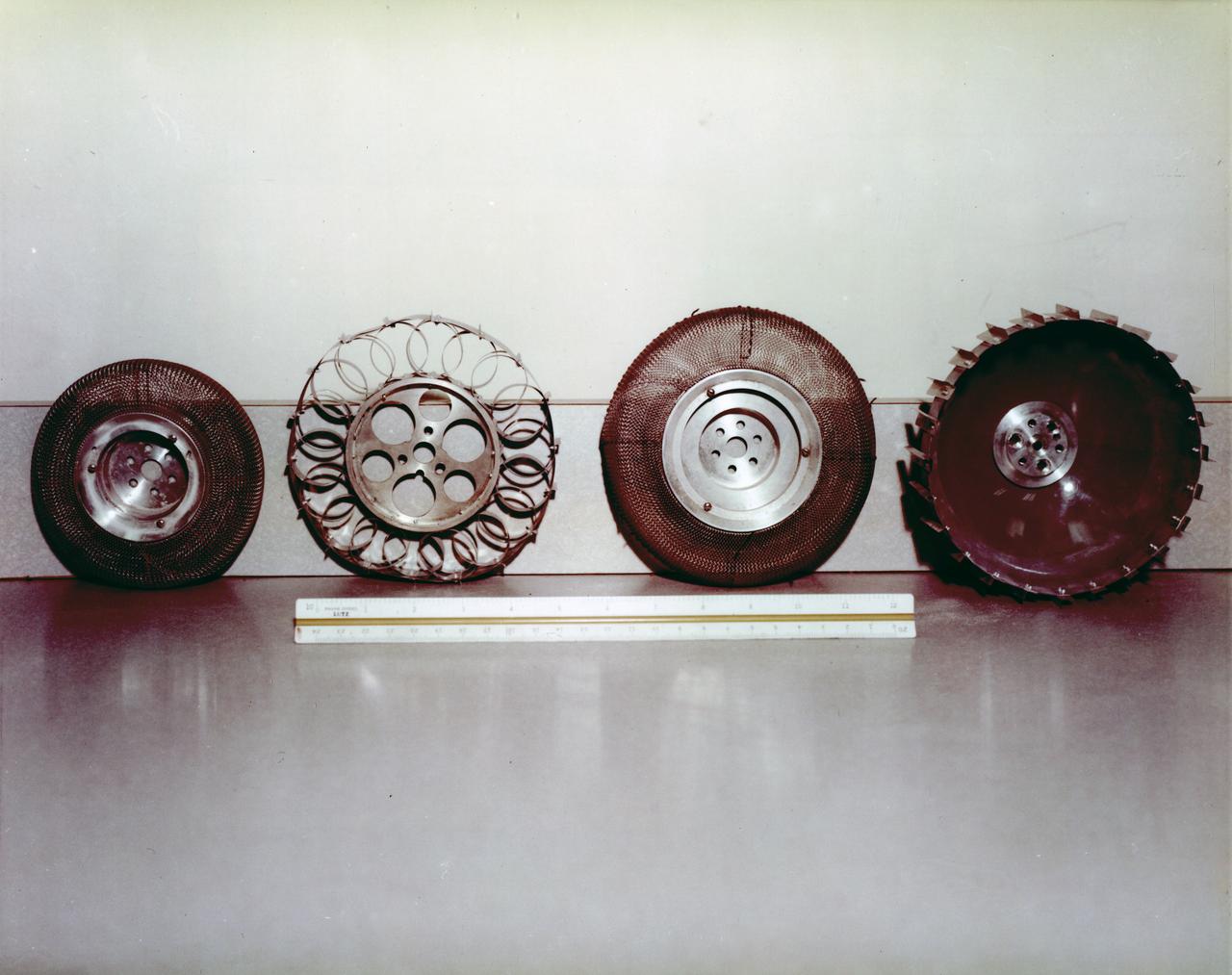

Under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions. During the development process, LRV prototype wheels underwent soil tests in building 4481 at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Pictured from left to right are the wheels for: LRV, Bendix Corporation, Local Scientific Survey Module (LSSM), and Grumman Industries.
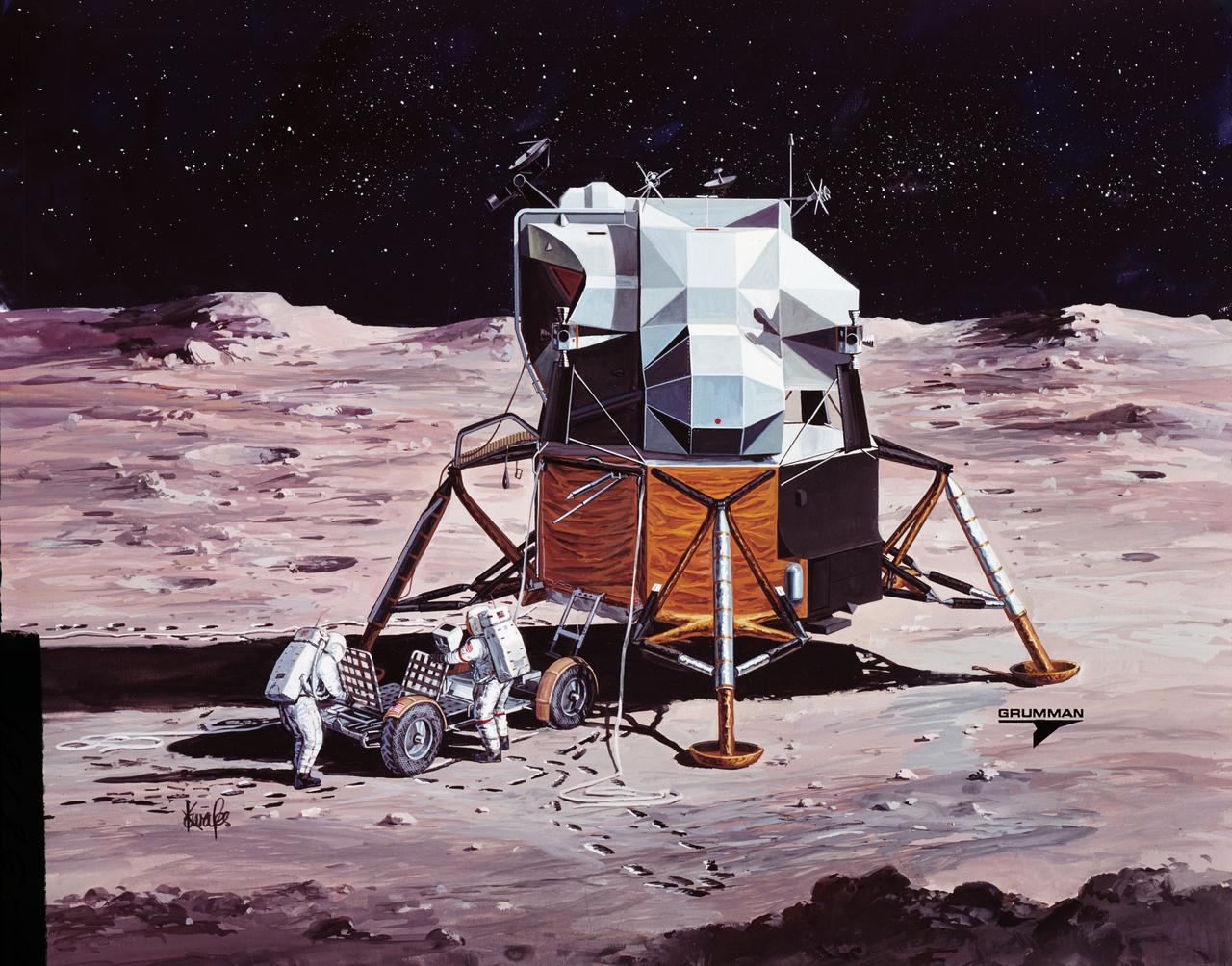

S71-38189 (26 June 1971) --- An artist's concept showing the final steps of readying the Apollo 15 Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) or Rover 1 for mobility on the lunar surface. Performing the last few LRV deployment tasks here are, left to right, astronauts James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, and David R. Scott, commander. More specifically the tasks depicted here include the setting up of the seats and the total releasing of the LRV from the LM. (This is the fourth in a series of four Grumman Aerospace Corporation artist's concepts telling the lunar surface LRV deployment story for Apollo 15).
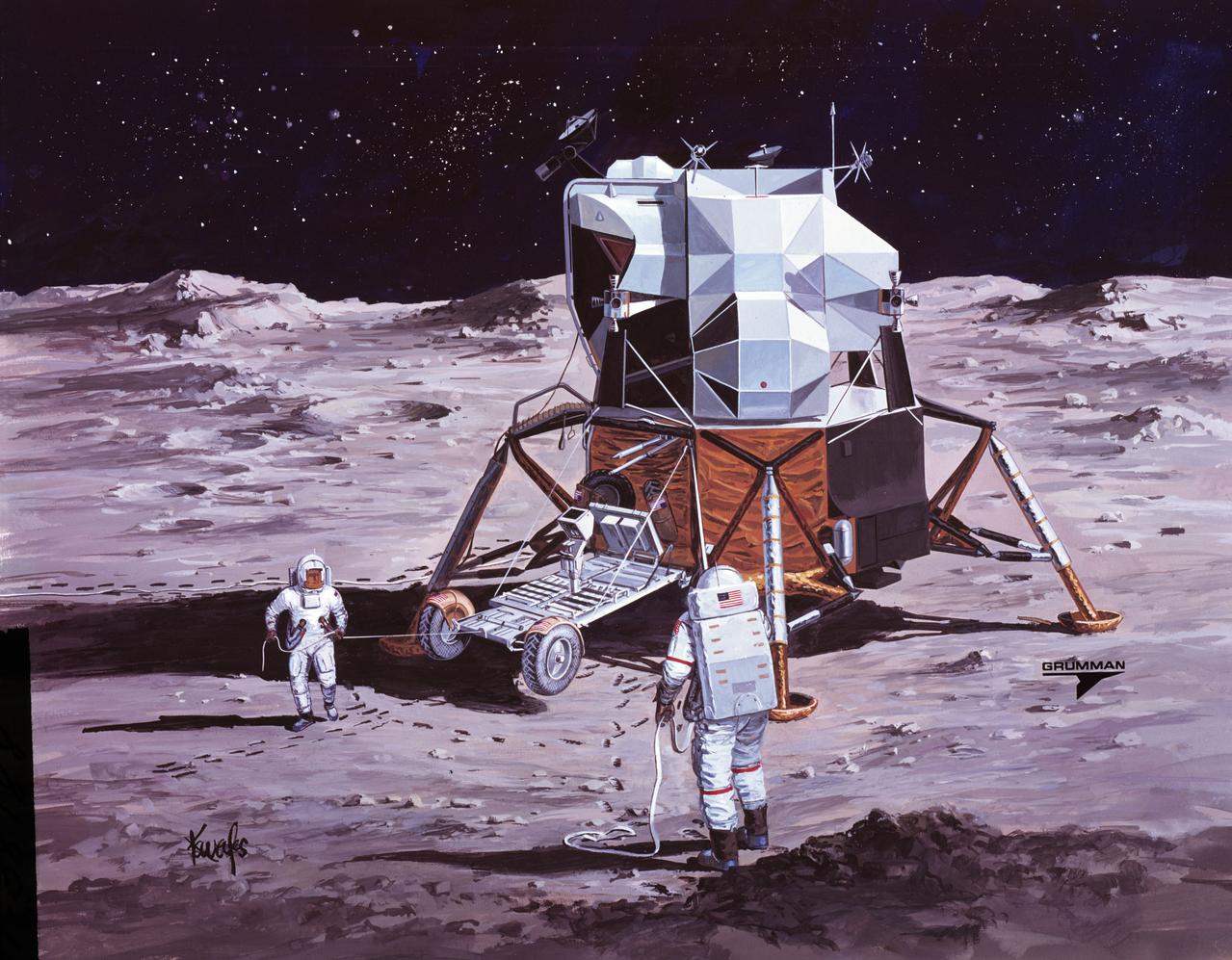
S71-38188 (26 June 1971) --- An artist's concept showing the Apollo 15 mission commander and the lunar module pilot performing deployment of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the lunar surface. The figure on the left represents astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, who here is maintaining a constant pull on the deployment cable to help the LRV unfold, while astronaut David R. Scott (right), commander, pulls the tapes that lower the LRV to the surface. (This is the third in a series of Grumman Aerospace Corporation artist's concepts telling the lunar surface LRV deployment story of the Apollo 15 mission).
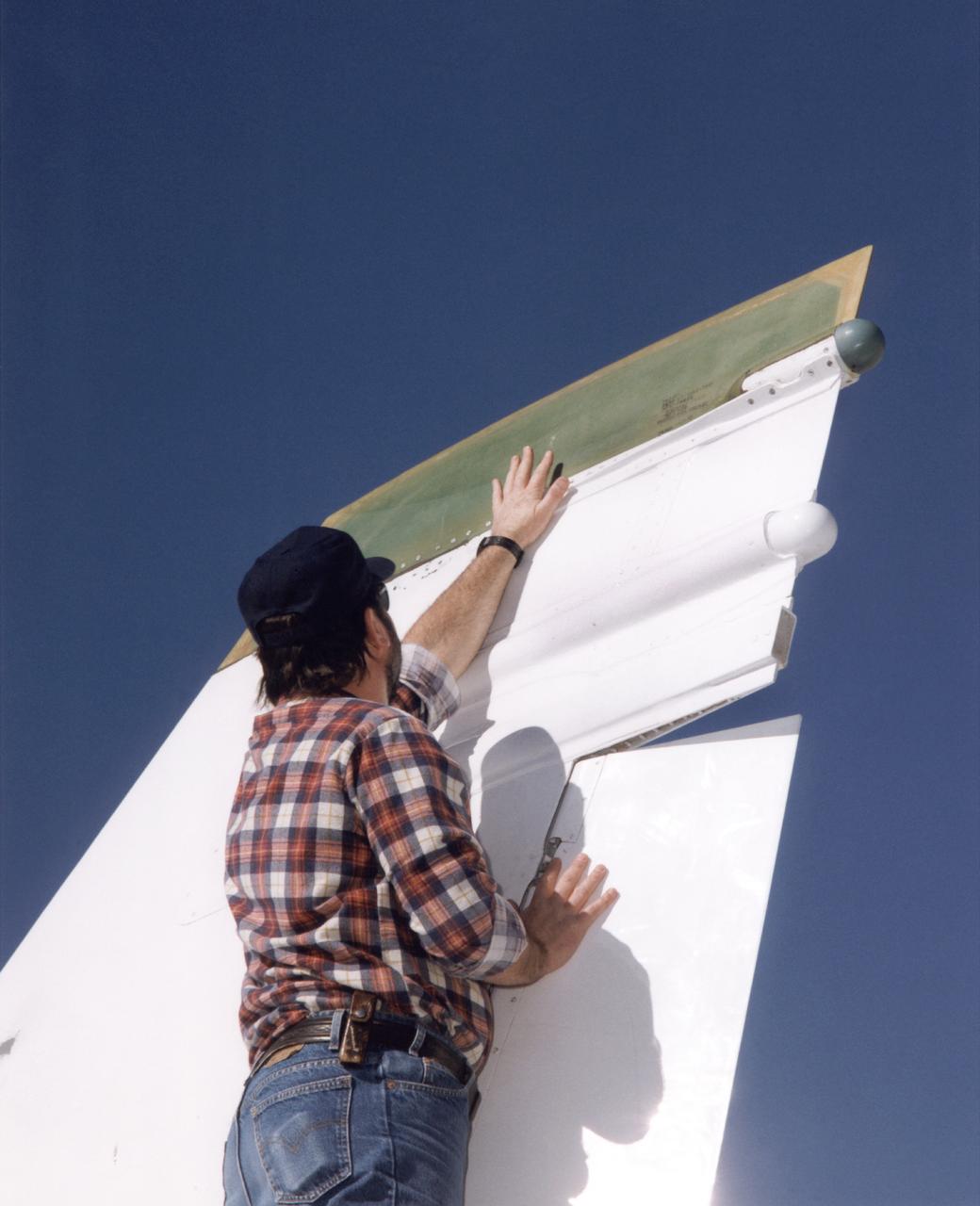

Bob Cummings, a technician at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, checks out a new "Smart Skin" antenna mounted on the tip of the right vertical fin of Dryden's F/A-18 Systems Research Aircraft. Flight tests of the antenna system demonstrated a five-fold increase in voice communications range and a substantial improvement in the pattern of radiation and quality of transmission compared to the standard dorsal blade antenna on the aircraft. The Smart Skin antenna system was electrically as well as physically connected to the airframe, making the aircraft skin operate as an antenna along with the antenna itself. The concept was developed by TRW Avionics Systems Division and integrated into the F/A-18's vertical fin by Northrop-Grumman Corporation.
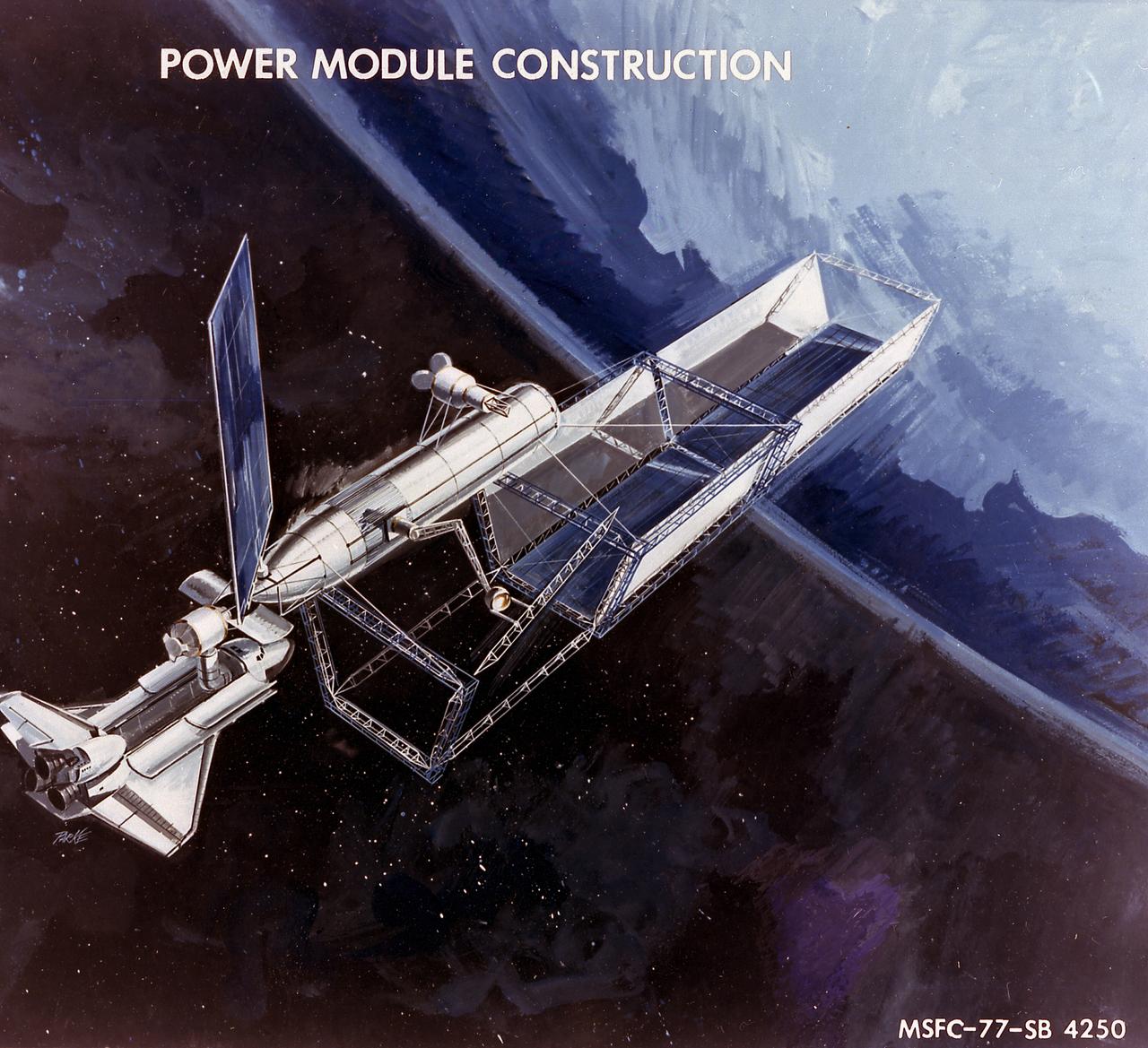

The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and the Johnson Space Center (JSC) were each awarded 16-month contracts in April 1976 for the Space Station Systems Analysis Study (SSSAS). Grumman Aerospace Corporation was MSFC's contractor and McDornell Douglas Aerospace Company was JSC's contractor. The goal of this study was to formulate plans for a permanent operational base and laboratory facility in Earth orbit in addition to developing a space construction base design for implementing the program. An expended Space Shuttle external tank was to be the central core platform of the base, and additional pressurized modules could be added to provide laboratory facilities. This artist's concept depicts a space construction base design for implementing the SSSAS.
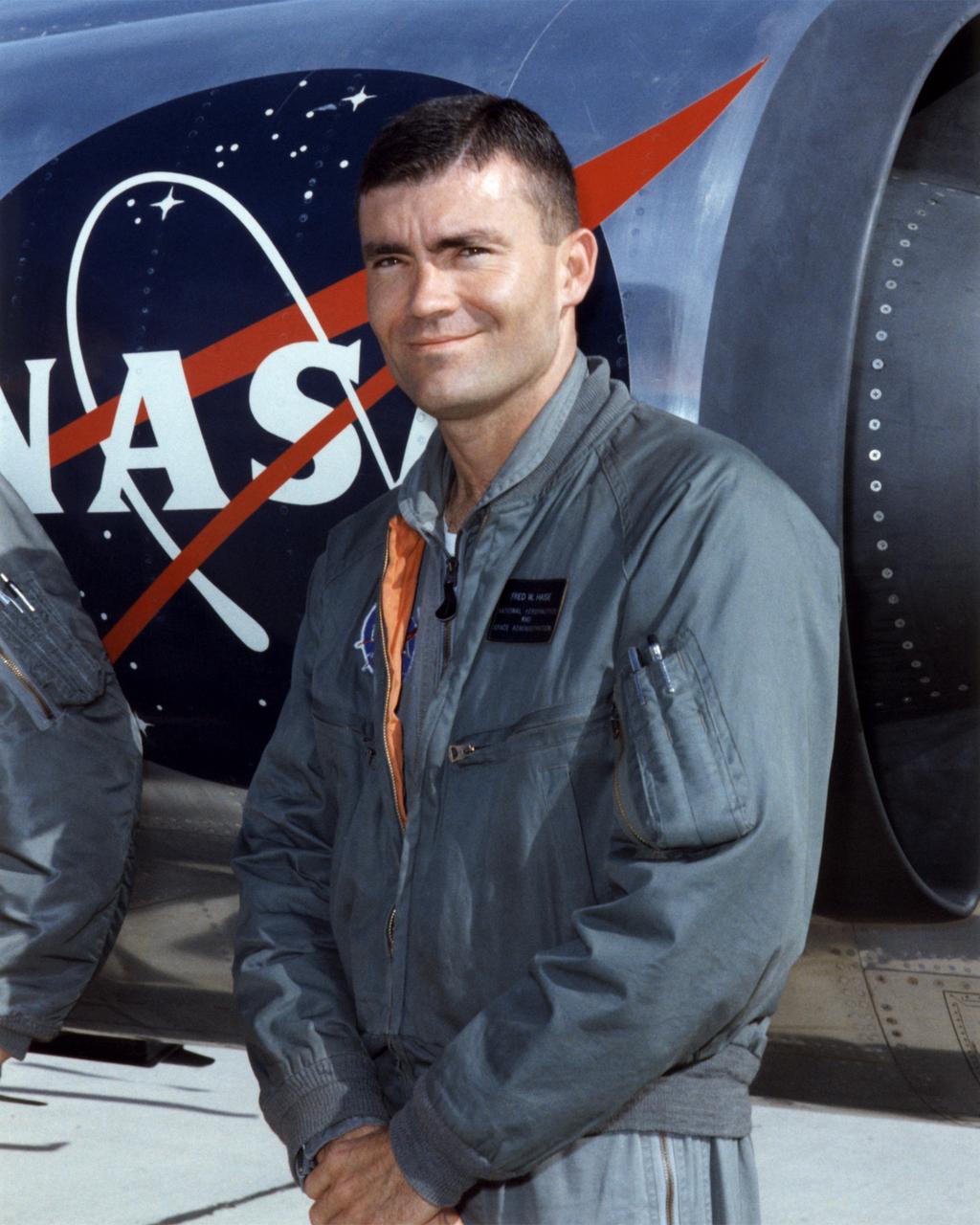

Fred W. Haise Jr. was a research pilot and an astronaut for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration from 1959 to 1979. He began flying at the Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio (today the Glenn Research Center), in 1959. He became a research pilot at the NASA Flight Research Center (FRC), Edwards, Calif., in 1963, serving NASA in that position for three years until being selected to be an astronaut in 1966 His best-known assignment at the FRC (later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center) was as a lifting body pilot. Shortly after flying the M2-F1 on a car tow to about 25 feet on April 22, 1966, he was assigned as an astronaut to the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. While at the FRC he had also flown a variety of other research and support aircraft, including the variable-stability T-33A to simulate the M2-F2 heavyweight lifting body, some light aircraft including the Piper PA-30 to evaluate their handling qualities, the Apache helicopter, the Aero Commander, the Cessna 310, the Douglas F5D, the Lockheed F-104 and T-33, the Cessna T-37, and the Douglas C-47. After becoming an astronaut, Haise served as a backup crewmember for the Apollo 8, 11, and 16 missions. He flew on the aborted Apollo 13 lunar mission in 1970, spending 142 hours and 54 minutes in space before returning safely to Earth. In 1977, he was the commander of three free flights of the Space Shuttle prototype Enterprise when it flew its Approach and Landing Tests at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. Meanwhile, from April 1973 to January 1976, Haise served as the Technical Assistant to the Manager of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Project. In 1979, he left NASA to become the Vice President for Space Programs with the Grumman Aerospace Corporation. He then served as President of Grumman Technical Services, an operating division of Northrop Grumman Corporation, from January 1992 until his retirement. Haise was born in Biloxi, Miss., on November 14, 1933. He underwent flight traini
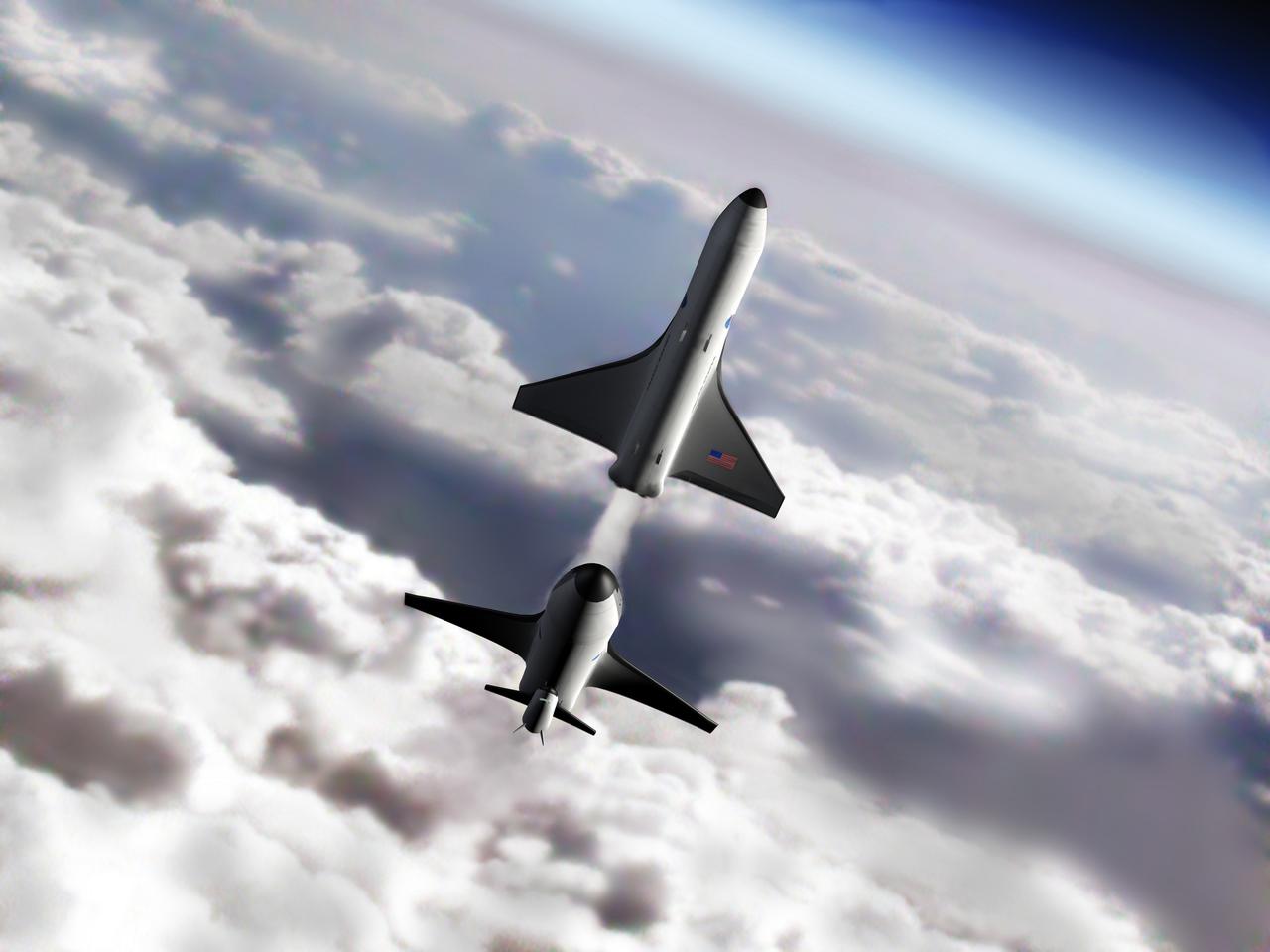

NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Space Launch Initiative (SLI), NASA's priority developmental program focused on empowering America's leadership in space. SLI includes commercial, higher education and defense partnerships and contracts to offer widespread participation in both the risk and success of developing our nation's next-generation reusable launch vehicle. This photo depicts an artist's concept of a future second-generation launch vehicle during separation of stages. For SLI, architecture definition includes all components of the next-generation reusable launch system: Earth-to-orbit vehicles (the Space Shuttle is the first-generation earth-to-orbit vehicle), crew transfer vehicles, transfer stages, ground processing systems, flight operations systems, and development of business case strategies. Three contractor teams have each been funded to develop potential second generation reusable launch system architectures: The Boeing Company of Seal Beach, California; Lockheed Martin Corporation of Denver, Colorado; a team including Northrop Grumman of El Segundo, California; and Orbital Sciences Corporation of Dulles, Virginia.
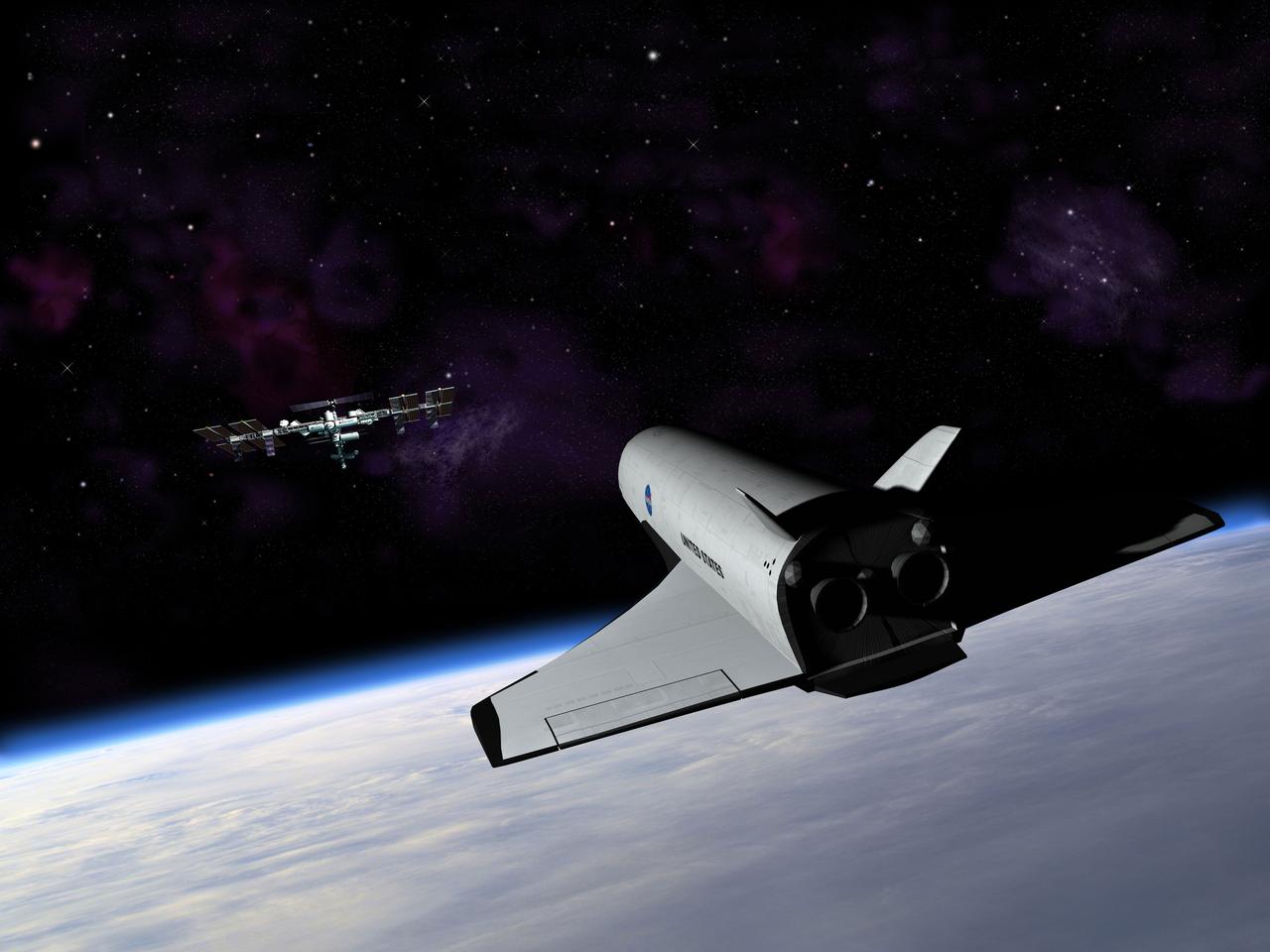

NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Space Launch Initiative (SLI), NASA's priority developmental program focused on empowering America's leadership in space. SLI includes commercial, higher education, and Defense partnerships and contracts to offer widespread participation in both the risk and success of developing our nation's next-generation reusable launch vehicle. This photo depicts an artist's concept of a future second-generation launch vehicle enroute to the International Space Station. For the SLI, architecture definition includes all components of the next-generation reusable launch system: Earth-to-orbit vehicles (the Space Shuttle is the first generation earth-to-orbit vehicle), crew transfer vehicles, transfer stages, ground processing systems, flight operations systems, and development of business case strategies. Three contractor teams have each been funded to develop potential second-generation reusable launch system architectures: The Boeing Company of Seal Beach, California; Lockheed Martin Corporation of Denver, Colorado along with a team including Northrop Grumman of El Segundo, California; and Orbital Sciences Corporation of Dulles, Virginia.
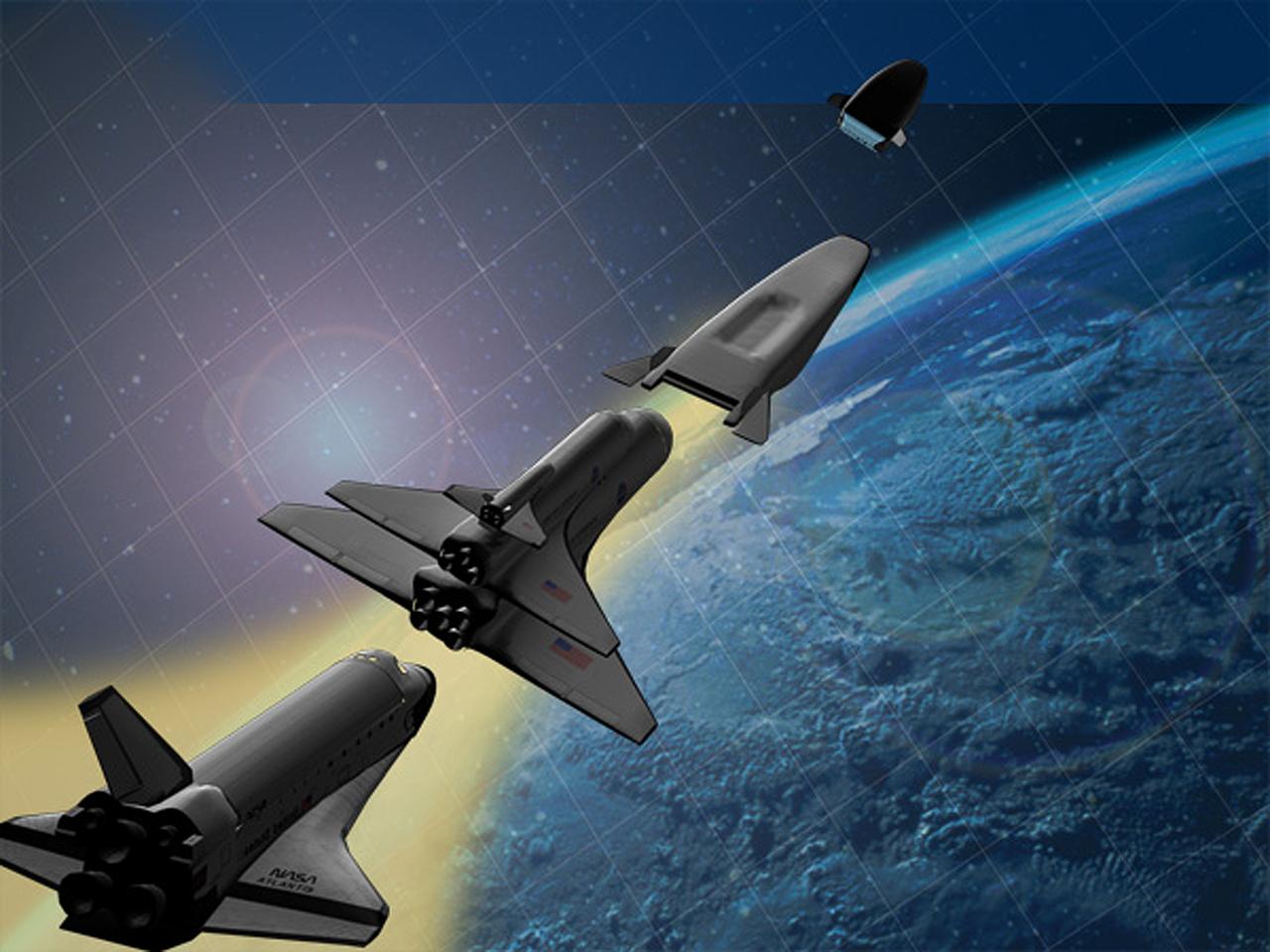

NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Space Launch Initiative (SLI), NASA's priority developmental program focused on empowering America's leadership in space. SLI includes commercial, higher education, and defense partnerships and contracts to offer widespread participation in both the risk and success of developing our nation's next-generation reusable launch vehicle. This photo depicts an artist's concept of a future second-generation launch vehicle. For the SLI, architecture definition includes all components of the next-generation reusable launch system: Earth-to-orbit vehicles (the Space Shuttle is the first generation earth-to-orbit vehicle), crew transfer vehicles, transfer stages, ground processing systems, flight operations systems, and development of business case strategies. Three contractor teams have each been funded to develop potential second- generation reusable launch system architectures: The Boeing Company of Seal Beach, California; Lockheed Martin Corporation of Denver, Colorado along with a team including Northrop Grumman of El Segundo, California; and Orbital Sciences Corporation of Dulles, Virginia.
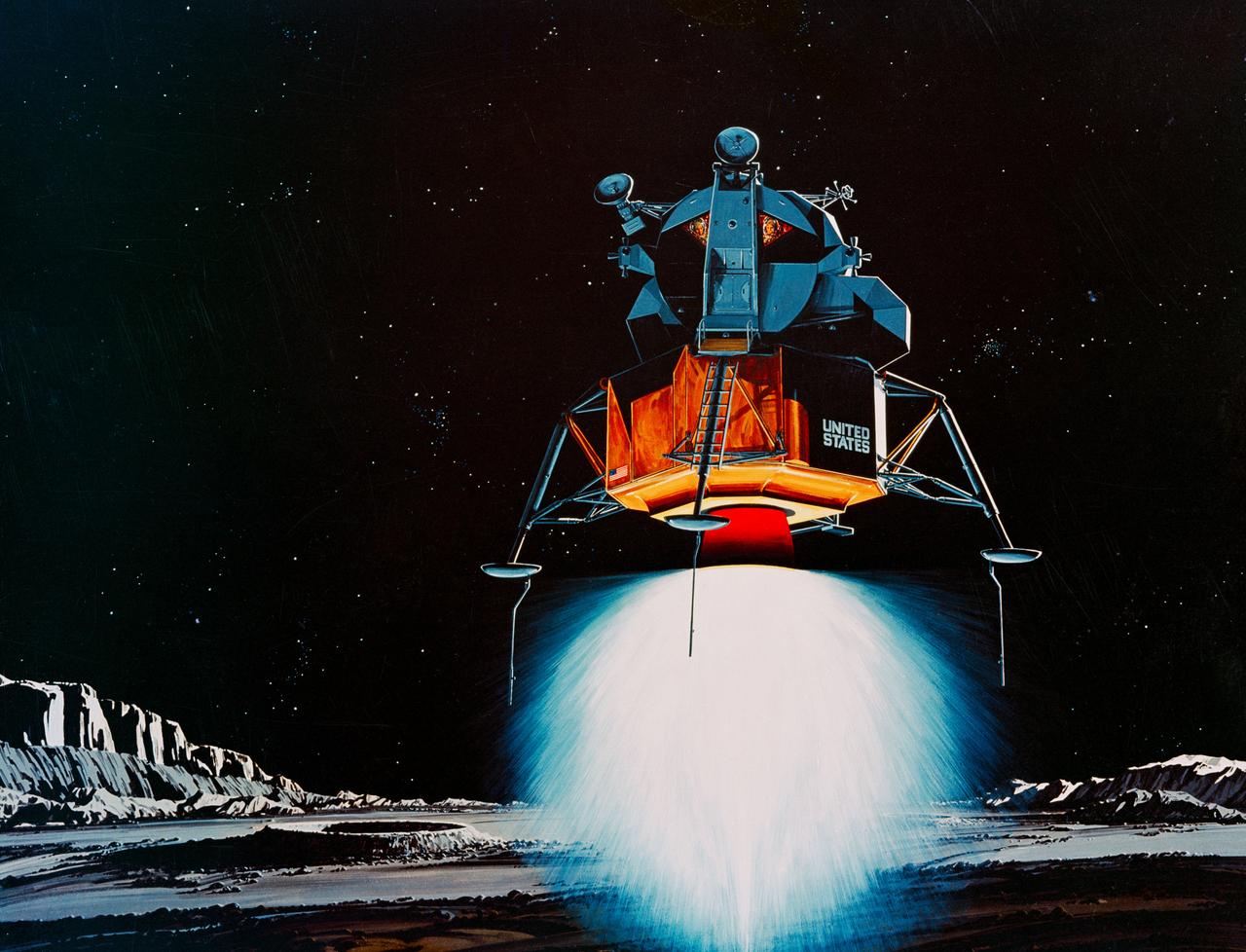
S69-39011 (July 1969) --- TRW Incorporated's artist concept depicting the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) descending to the surface of the moon. Inside the LM will be astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. TRW's LM descent engine will brake Apollo 11's descent to the lunar surface. The throttle-able rocket engine will be fired continuously the last 10 miles of the journey to the moon, slowing the LM to a speed of two miles per hour at touchdown. TRW Incorporated designed and built the unique engine at Redondo Beach, California under subcontract to the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation, Bethpage, New York, the LM prime contractor.
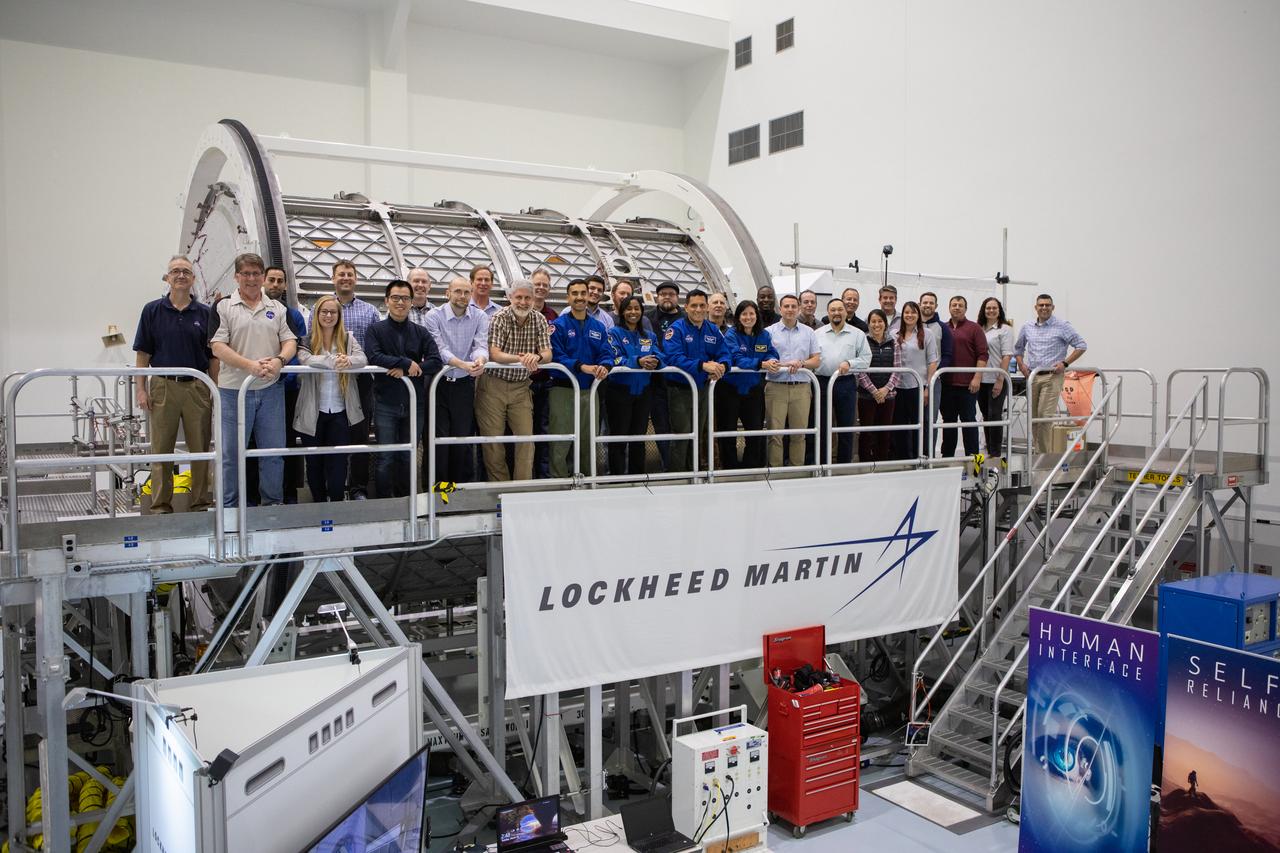

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
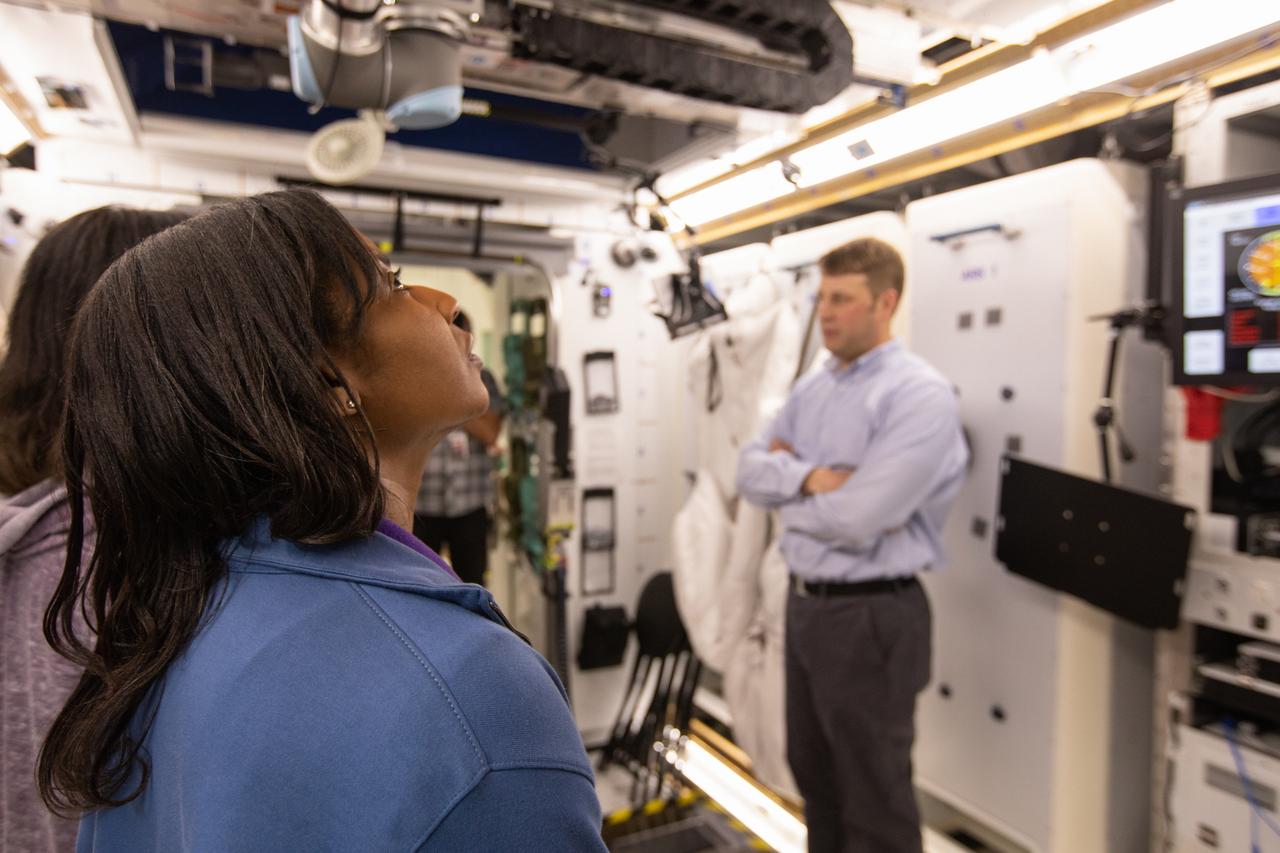

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, at left is astronaut Stephanie Wilson. To her left, partially hidden is astronaut Shannon Walker. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.

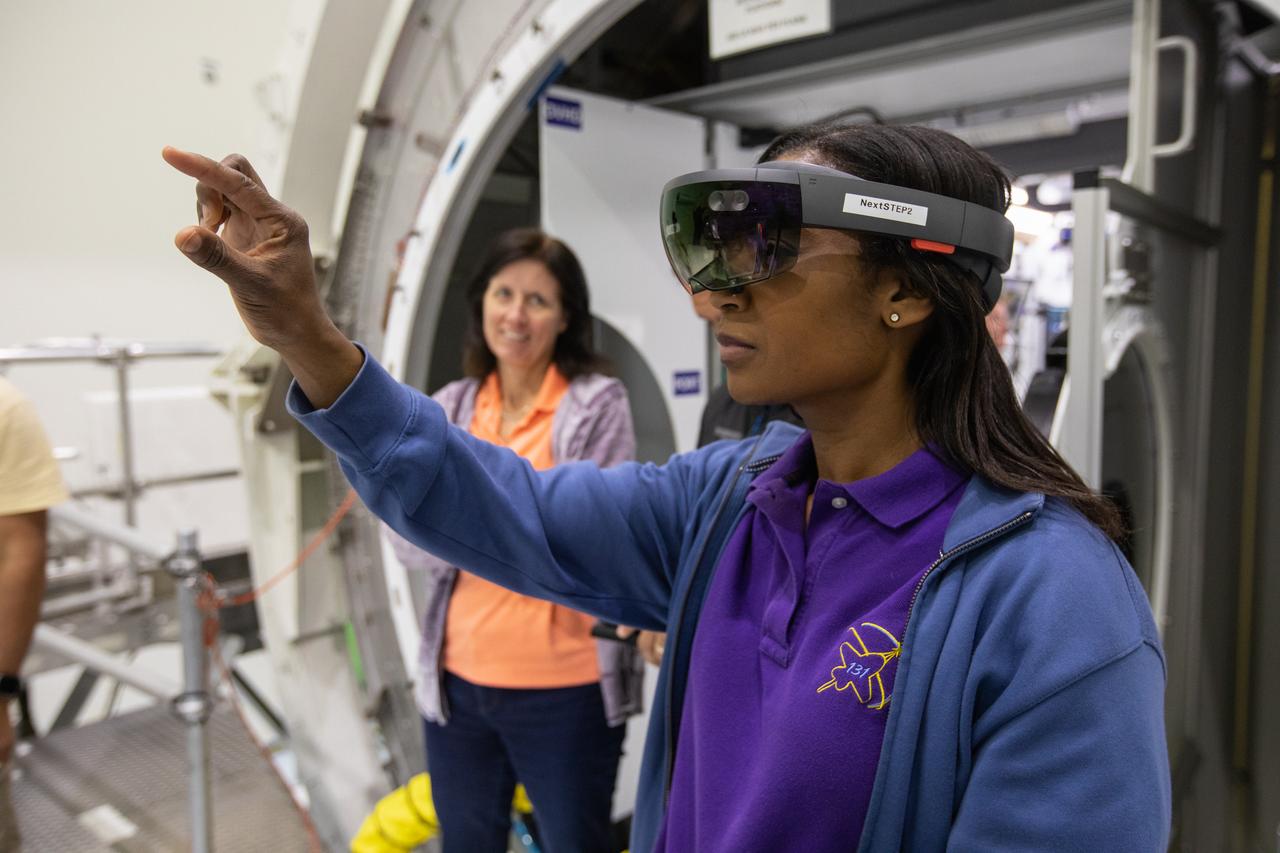
NASA astronaut Raja Chari climbs through a hatch of Lockheed Martin’s deep space habitat ground prototype at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 25, 2019. Chari is one of the astronauts helping engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Astronauts provide important design perspective as they may one day live and work aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. To date, five habitat prototypes have been developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP. Lockheed Martin was the first to turn their habitat over to NASA for testing. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
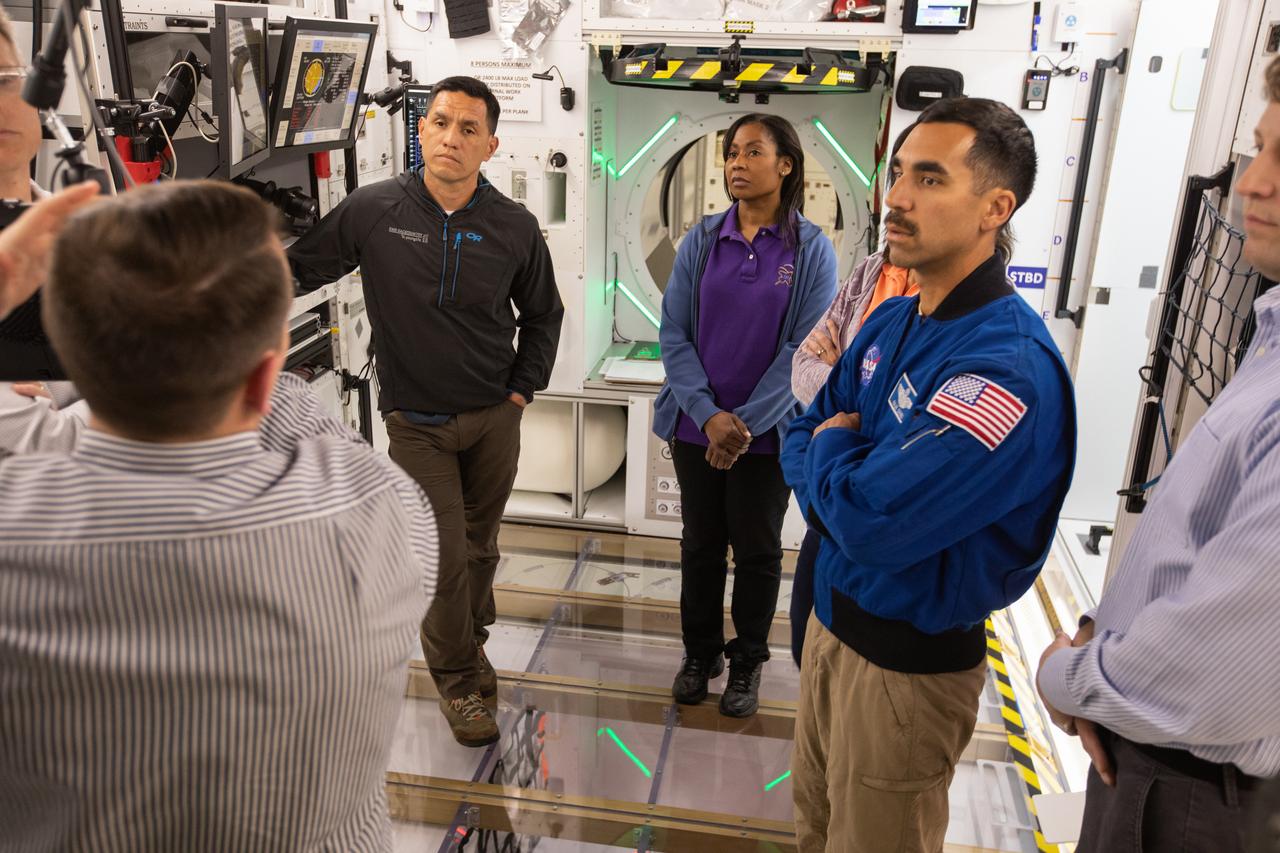

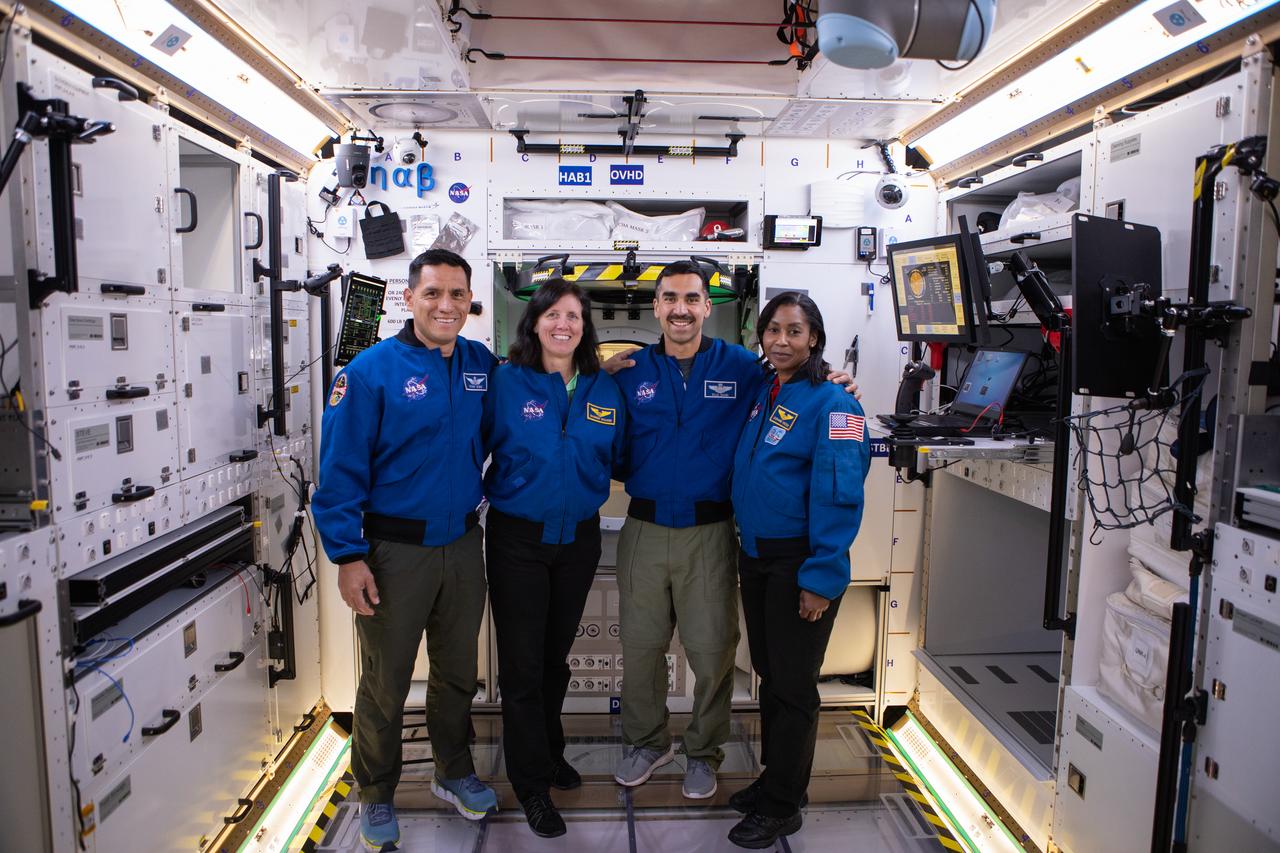
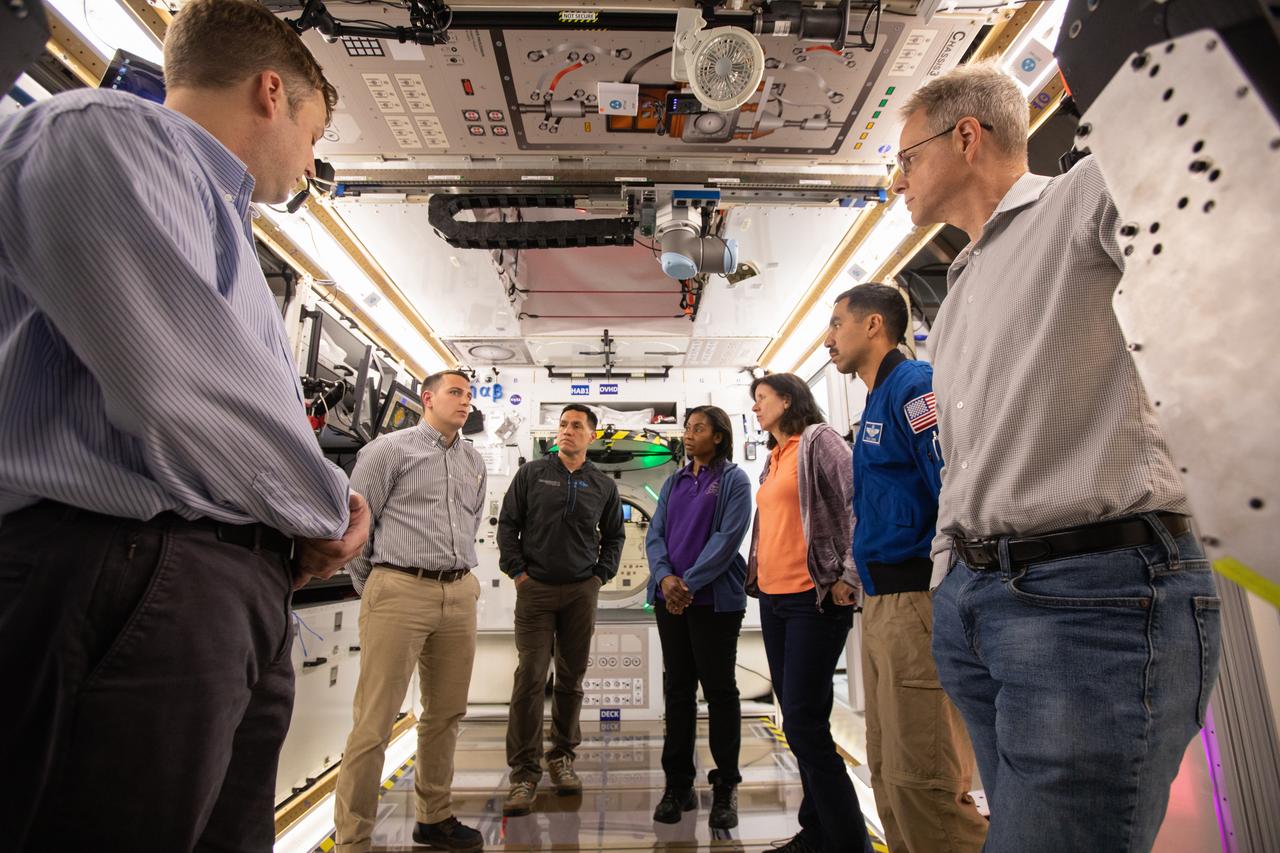
NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, from left are astronauts Frank Rubio, Stephanie Wilson and Raja Chari. Partially in view next to Chari is astronaut Shannon Walker. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
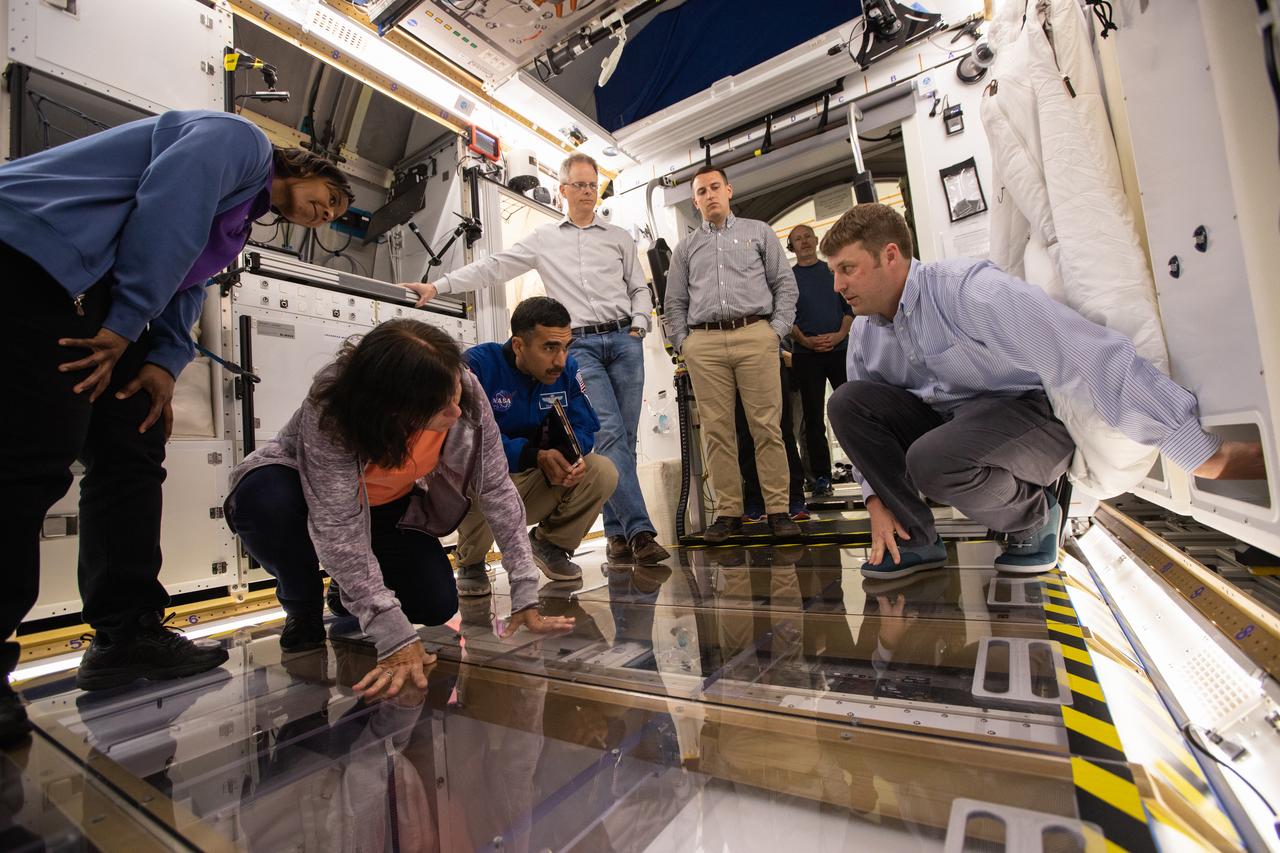

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, from left are astronauts Stephanie Wilson, Shannon Walker and Raja Chari. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
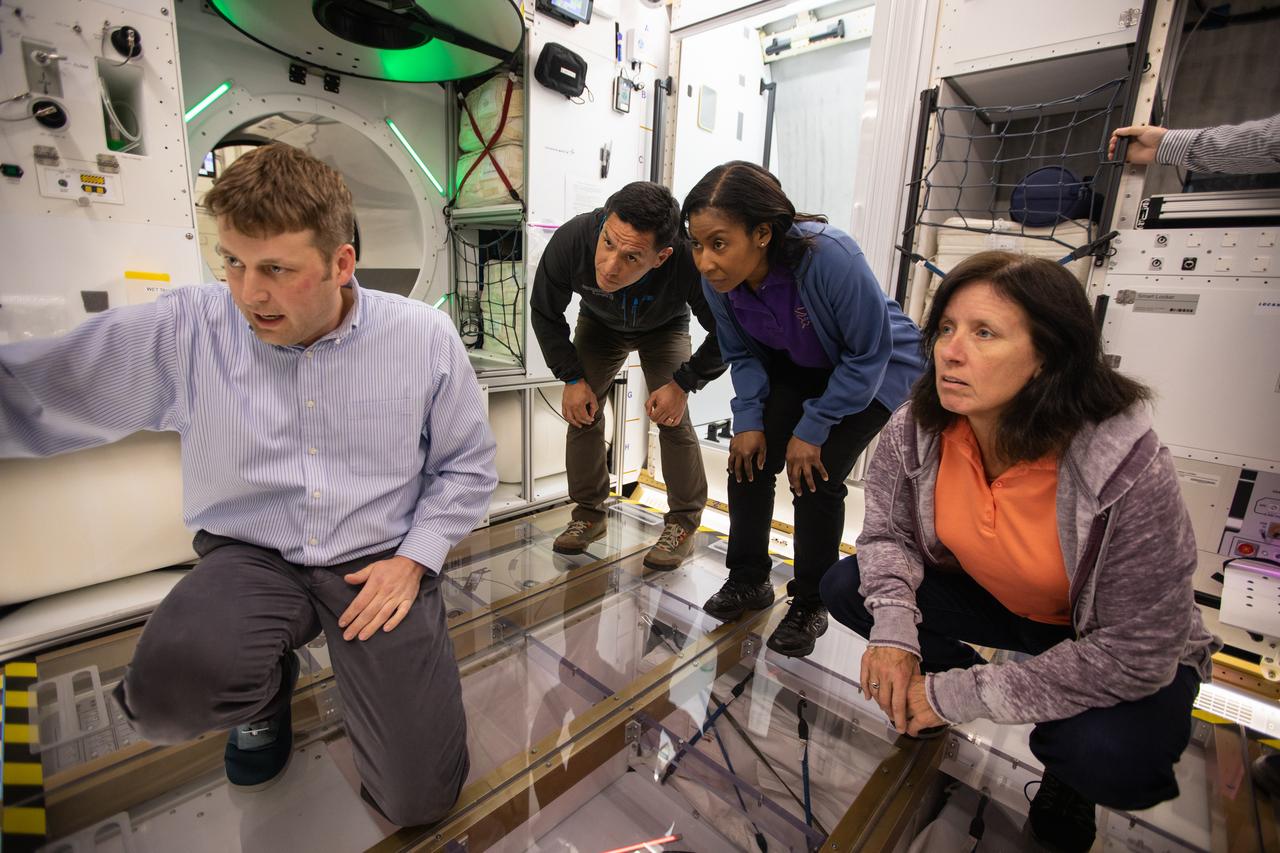

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, in back from left are astronauts Frank Rubio, Stephanie Wilson and Shannon Walker. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, beginning second from left are astronauts Frank Rubio, Raja Shari, Stephanie Wilson and Shannon Walker. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the Space Station Processing Facility on March 26, 2019, from left are astronauts Shannon Walker and Stephanie Wilson. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured, from left are astronauts Frank Rubio, Shannon Walker, Raja Chari and Stephanie Wilson. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
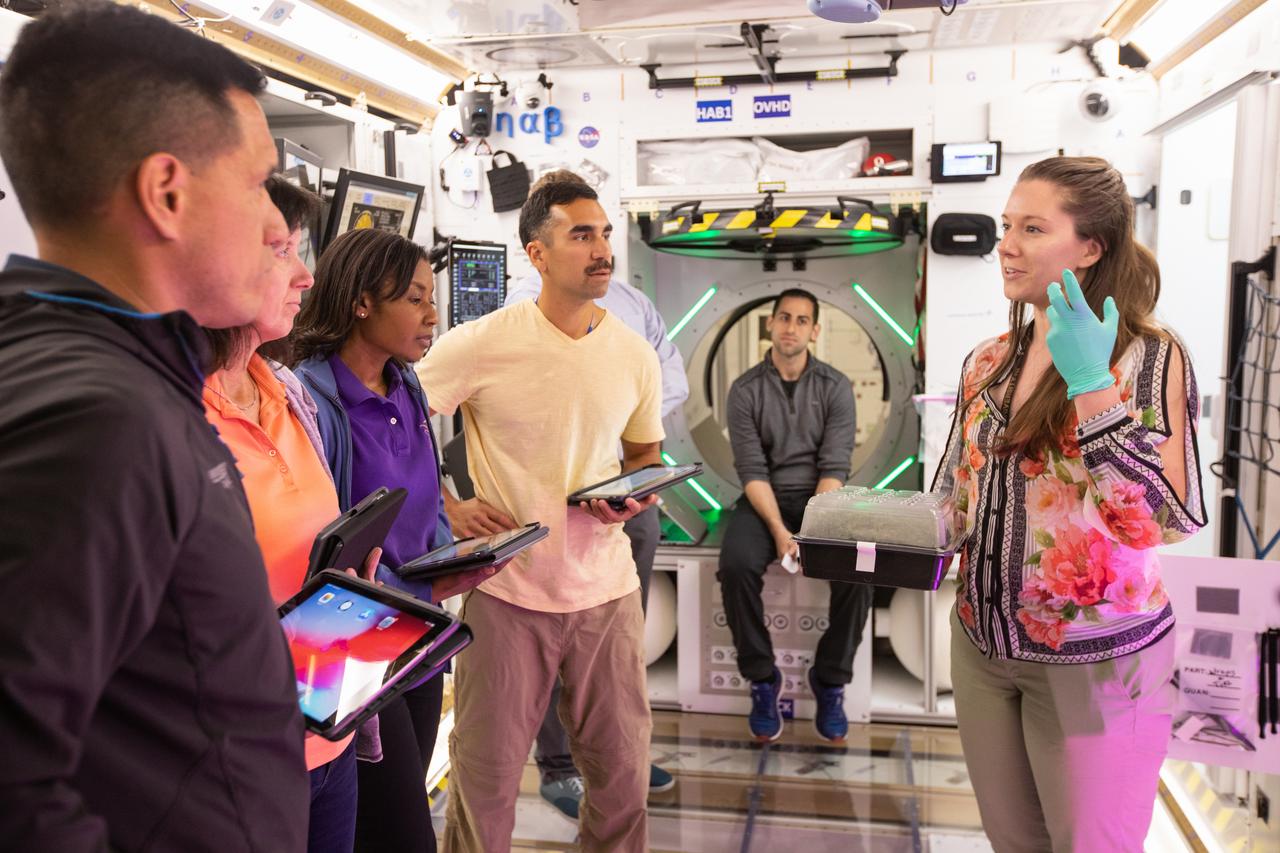

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, from far left are astronauts Frank Rubio, Shannon Walker, Stephanie Wilson and Raja Chari. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, beginning third from left are astronauts Frank Rubio, Stephanie Wilson, Shannon Walker and Raja Chari. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, second from left is astronaut Frank Rubio. Next to him is astronaut Stephanie Wilson. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
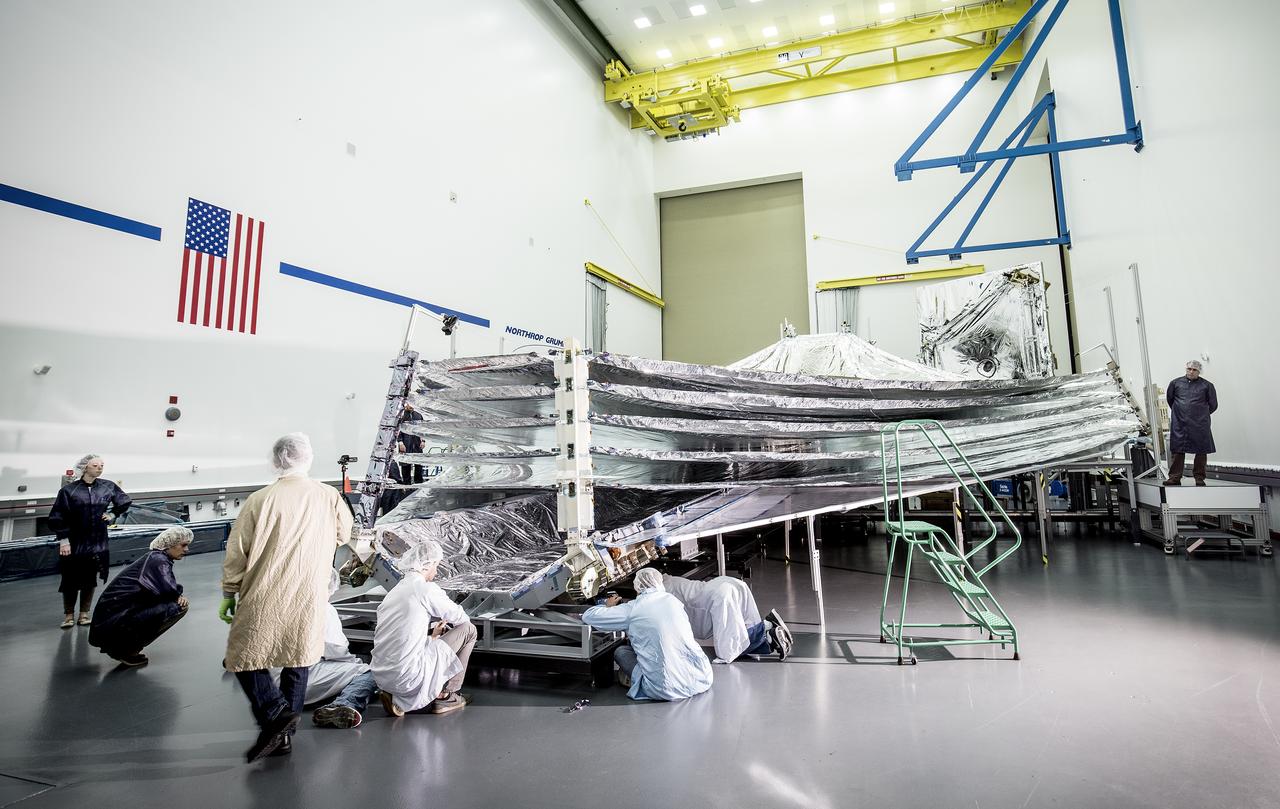

The sunshield on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is the largest part of the observatory—five layers of thin, silvery membrane that must unfurl reliably in space. The precision in which the tennis-court sized sunshield has to open must be no more than a few centimeters different from its planned position. In this photo, engineers and scientists examine the sunshield layers on this full-sized test unit. Because there's a layer of the shiny silver material on the base under the five layers of the sunshield, it appears as if the sunshield has a mouth that is "open wide" while engineers take a look. The photo was taken in a clean room at Northrop Grumman Corporation, Redondo Beach, California. The sunshield separates the observatory into a warm sun-facing side and a cold side where the sunshine is blocked from interfering with the sensitive infrared instruments. The infrared instruments need to be kept very cold (under 50 K or -370 degrees Fahrenheit) to operate. The sunshield protects these sensitive instruments with an effective sun protection factor, or SPF, of 1,000,000. Sunscreen generally has an SPF of 8 to 50. In addition to providing a cold environment, the sunshield provides a thermally stable environment. This stability is essential to maintaining proper alignment of the primary mirror segments as the telescope changes its orientation to the sun. Earlier this year, the first flight layer of the sunshield was delivered to Northrop Grumman. Northrop Grumman is designing the Webb Telescope’s sunshield for NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, in Greenbelt, Maryland. Innovative sunshield membranes are being designed and manufactured by NeXolve Corporation of Huntsville, Alabama. The James Webb Space Telescope is the successor to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. It will be the most powerful space telescope ever built. Webb is an international project led by NASA with its partners, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. For more information about the Webb telescope, visit: <a href="http://www.jwst.nasa.gov" rel="nofollow">www.jwst.nasa.gov</a> or <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/webb" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/webb</a> For more information on the Webb Sunshield, visit: <a href="http://jwst.nasa.gov/sunshield.html" rel="nofollow">jwst.nasa.gov/sunshield.html</a> Photo credit: Alex Evers/Northrop Grumman Corporation <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
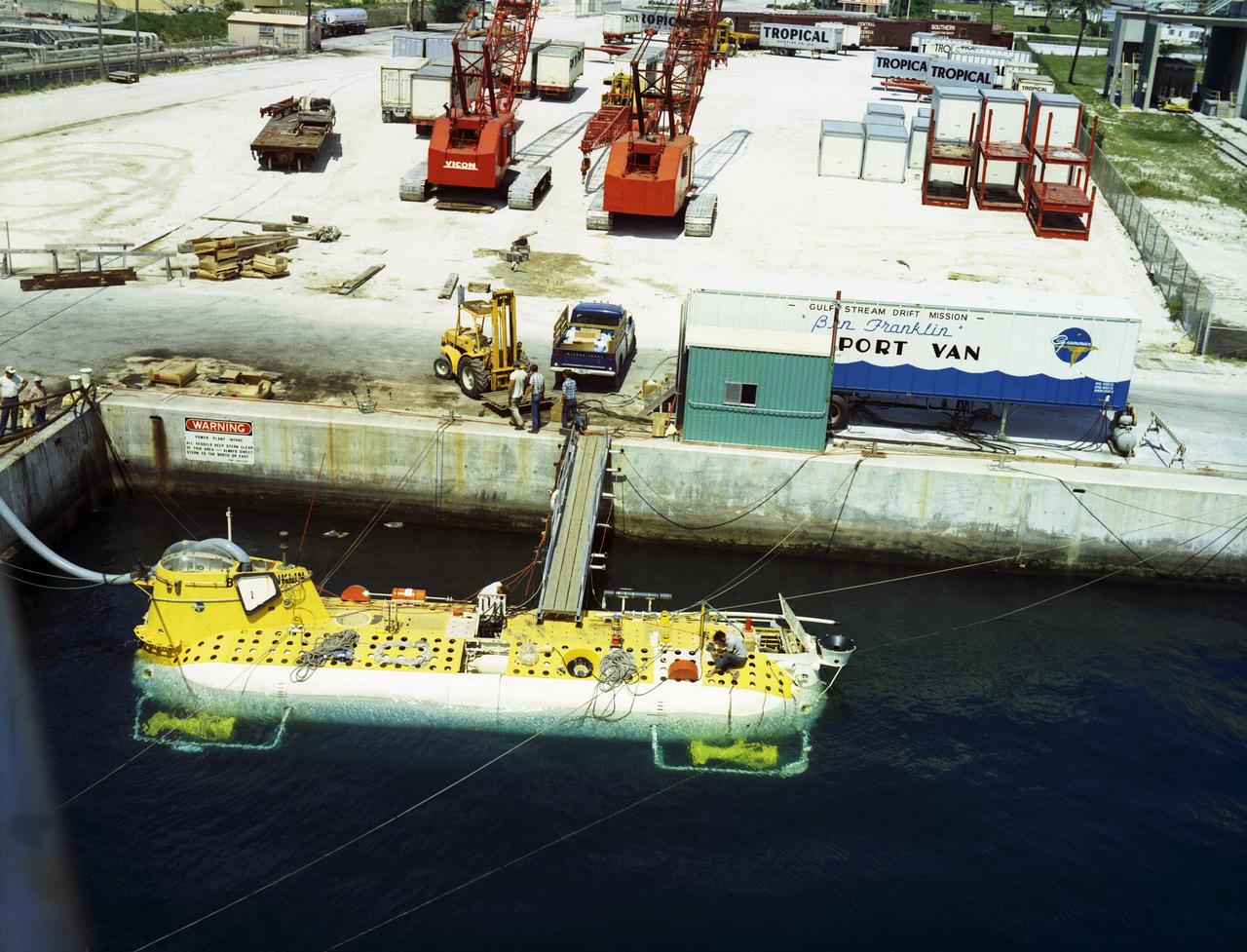

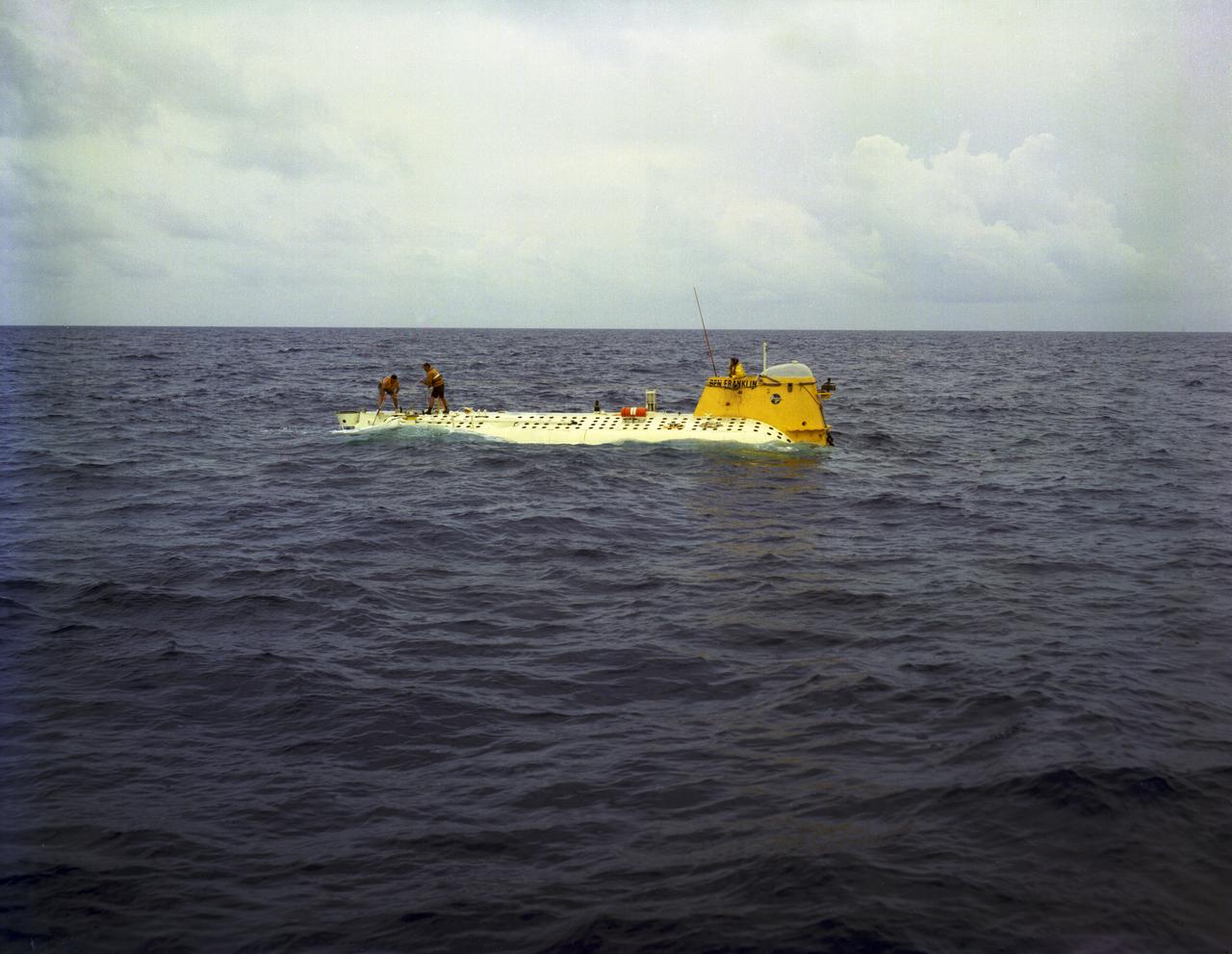
This is an aerial view of the deep-sea research submarine "Ben Franklin" at dock. Named for American patriot and inventor Ben Franklin, who discovered the Gulf Steam, the 50-foot Ben Franklin was built between 1966 and 1968 in Switzerland for deep-ocean explorer Jacques Piccard and the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. The submersible made a famous 30-day drift dive off the East Coast of the United States and Canada in 1969 mapping the Gulf Stream's currents and sea life, and also made space exploration history by studying the behavior of aquanauts in a sealed, self-contained, self-sufficient capsule for NASA. On July 14, 1969, the Ben Franklin was towed to the high-velocity center of the Stream off the coast of Palm Beach, Florida. With a NASA observer on board, the sub descended to 1,000 feet off of Riviera Beach, Florida and drifted 1,400 miles north with the current for more than four weeks, reemerging near Maine. During the course of the dive, NASA conducted exhaustive analyses of virtually every aspect of onboard life. They measured sleep quality and patterns, sense of humor and behavioral shifts, physical reflexes, and the effects of a long-term routine on the crew. The submarine's record-shattering dive influenced the design of Apollo and Skylab missions and continued to guide NASA scientists as they devised future marned space-flight missions.

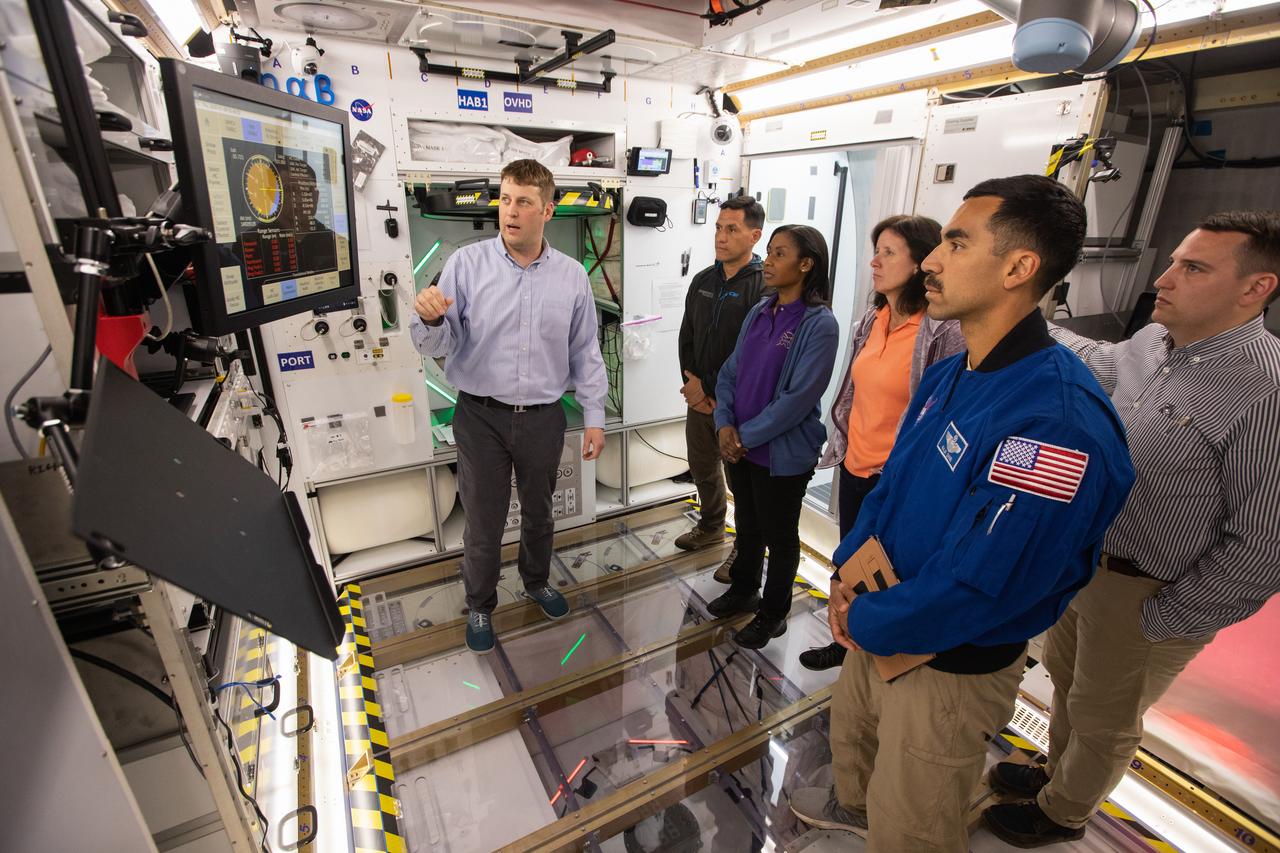
NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the Space Station Processing Facility on March 26, 2019, from far left is astronaut Frank Rubio. In front of him, are Raja Chari and Stephanie Wilson. At right is astronaut Shannon Walker. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
This is an interior view of the living quarters of the deep-sea research submarine "Ben Franklin." Named for American patriot and inventor Ben Franklin, who discovered the Gulf Steam, the 50-foot Ben Franklin was built between 1966 and 1968 in Switzerland for deep- ocean explorer Jacques Piccard and the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. The submersible made a famous 30-day drift dive off the East Coast of the United States and Canada in 1969 mapping the Gulf Stream's currents and sea life, and also made space exploration history by studying the behavior of aquanauts in a sealed, self-contained, self-sufficient capsule for NASA. On July 14, 1969, the Ben Franklin was towed to the high-velocity center of the Stream off the coast of Palm Beach, Florida. With a NASA observer on board, the sub descended to 1,000 feet off of Riviera Beach, Florida and drifted 1,400 miles north with the current for more than four weeks, reemerging near Maine. During the course of the dive, NASA conducted exhaustive analyses of virtually every aspect of onboard life. They measured sleep quality and patterns, sense of humor and behavioral shifts, physical reflexes, and the effect of a long-term routine on the crew. The submarine's record-shattering dive influenced the design of Apollo and Skylab missions and continued to guide NASA scientists as they devised future marned space-flight missions.
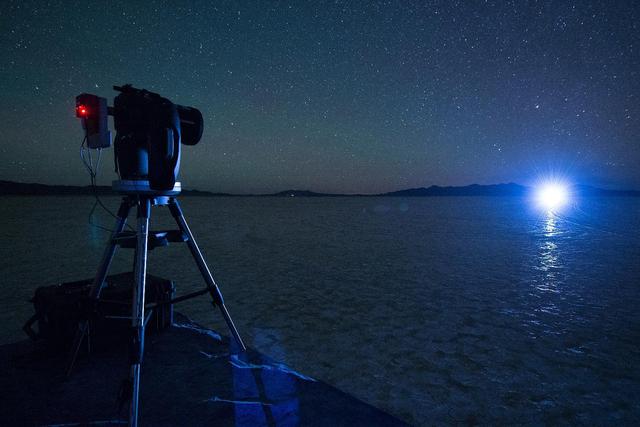

A night test of a small-scale starshade model, in a dry lake bed in central Nevada's Smith Creek by Northrup Grumman, took place in May to June 2014. A telescope points toward a bright light, which in the darkness of the desert mimics the conditions of starlight in space. Other lights, which are up to 10 million times fainter than the light source standing in for the star, represent the reflected light of planets. Telescopes searching for the relatively dim light of an exoplanet next to its much brighter star are faced with a challenge as difficult as searching from Los Angeles for a firefly in New York -- if the firefly is next to the brightness of a lighthouse. The tests by Northrup Grumman determined that a starshade, or external occulter, is capable of blocking starlight to a degree that can indeed reveal the light of a planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20901
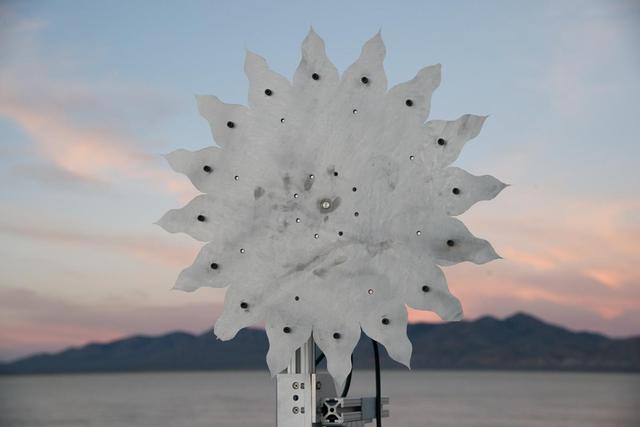

A test of a small-scale starshade model (58 cm), made from metal, in a dry lake bed in central Nevada's Smith Creek, took place from May to June 2014. Nineteen different versions of the miniaturized starshade were tested over five days. The tests revealed that a starshade, or external occulter, is capable of blocking starlight to a degree that reveals the relatively dim reflected light of a planet next to its brighter star. Like holding your hand up to block sunlight, the starshade works to block excessive starlight from the "eyes" of a space telescope like Hubble. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20902

A test of a small-scale starshade model in a dry lake bed in central Nevada's Smith Creek by Northrup Grumman in May-June 2014. A telescope points toward a bright light, which mimics the conditions of starlight in space. Other lights, which are up to 10 million times fainter than the light source standing in for the star, represent the reflected light of planets. Telescopes searching for the relatively dim light of an exoplanet next to its much bright star are faced with a challenge as difficult as searching from Los Angeles for a firefly in New York– if the firefly is also beside a lighthouse. These tests determined that a starshade, or external occulter, is indeed capable of blocking starlight to a degree that reveals the light of a planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20908
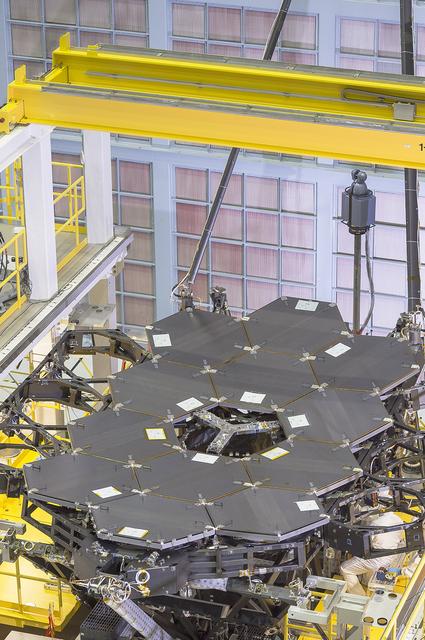

A view of the one dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year.
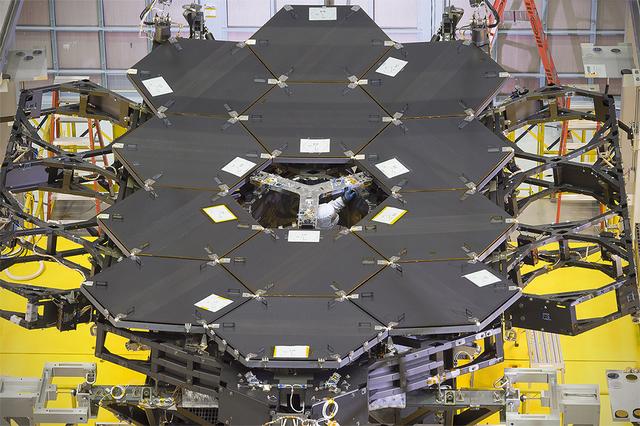

Caption: One dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year.
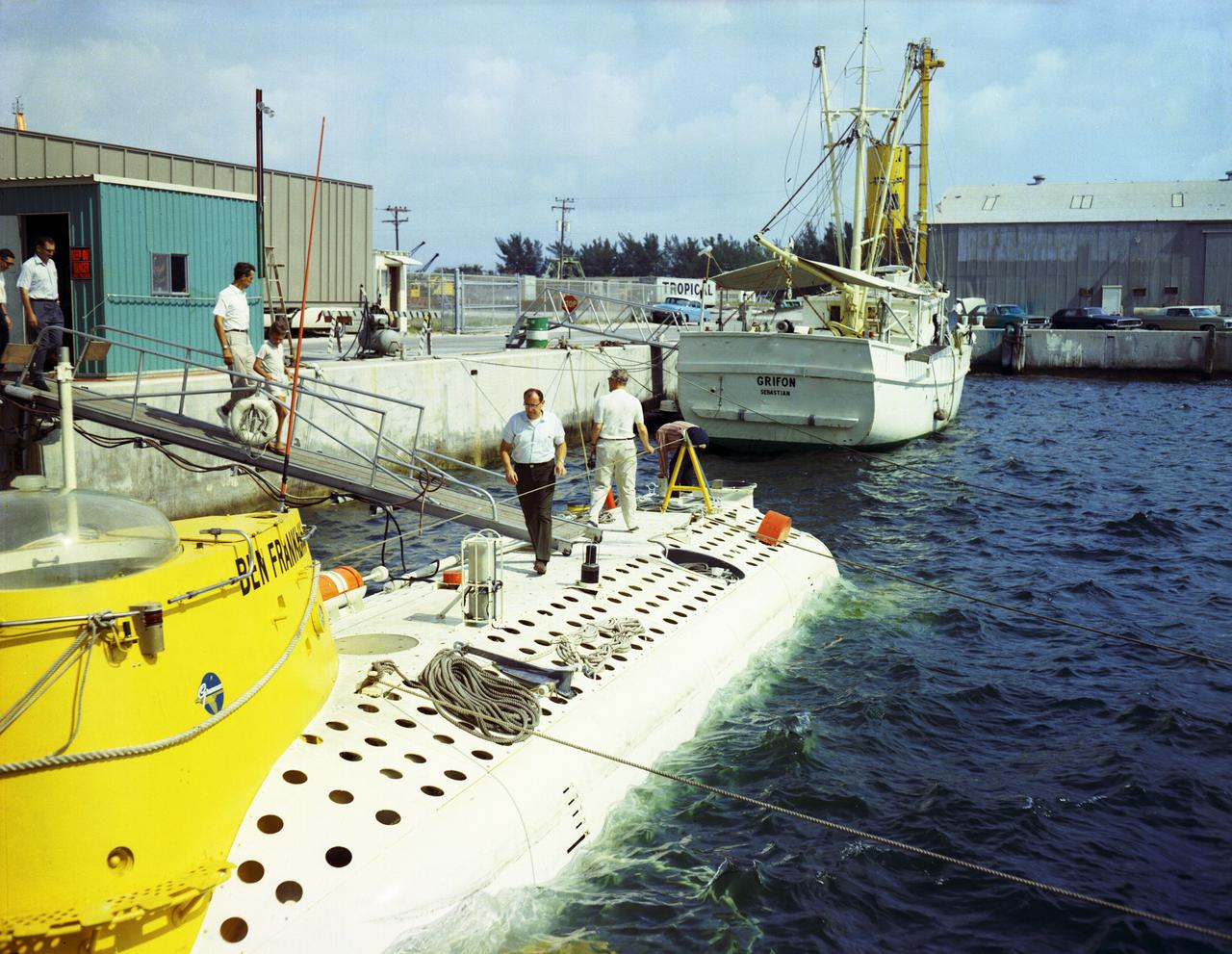

This photograph depicts Dr. von Braun (at right, showing his back) and other NASA officials surveying the deep-sea research submarine "Ben Franklin." Named for American patriot and inventor Ben Franklin, who discovered the Gulf Steam, the 50-foot Ben Franklin was built between 1966 and 1968 in Switzerland for deep-ocean explorer Jacques Piccard and the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. The submersible made a famous 30-day drift dive off the East Coast of the United States and Canada in 1969 mapping the Gulf Stream's currents and sea life, and also made space exploration history by studying the behavior of aquanauts in a sealed, self-contained, self-sufficient capsule for NASA. On July 14, 1969, the Ben Franklin was towed to the high-velocity center of the Stream off the coast of Palm Beach, Florida. With a NASA observer on board, the sub descended to 1,000 feet off of Riviera Beach, Florida and drifted 1,400 miles north with the current for more than four weeks, reemerging near Maine. During the course of the dive, NASA conducted exhaustive analyses of virtually every aspect of onboard life. They measured sleep quality and patterns, sense of humor and behavioral shifts, physical reflexes, and the effects of a long-term routine on the crew. The submarine's record-shattering dive influenced the design of Apollo and Skylab missions and continued to guide NASA scientists as they devised future marned space-flight missions.
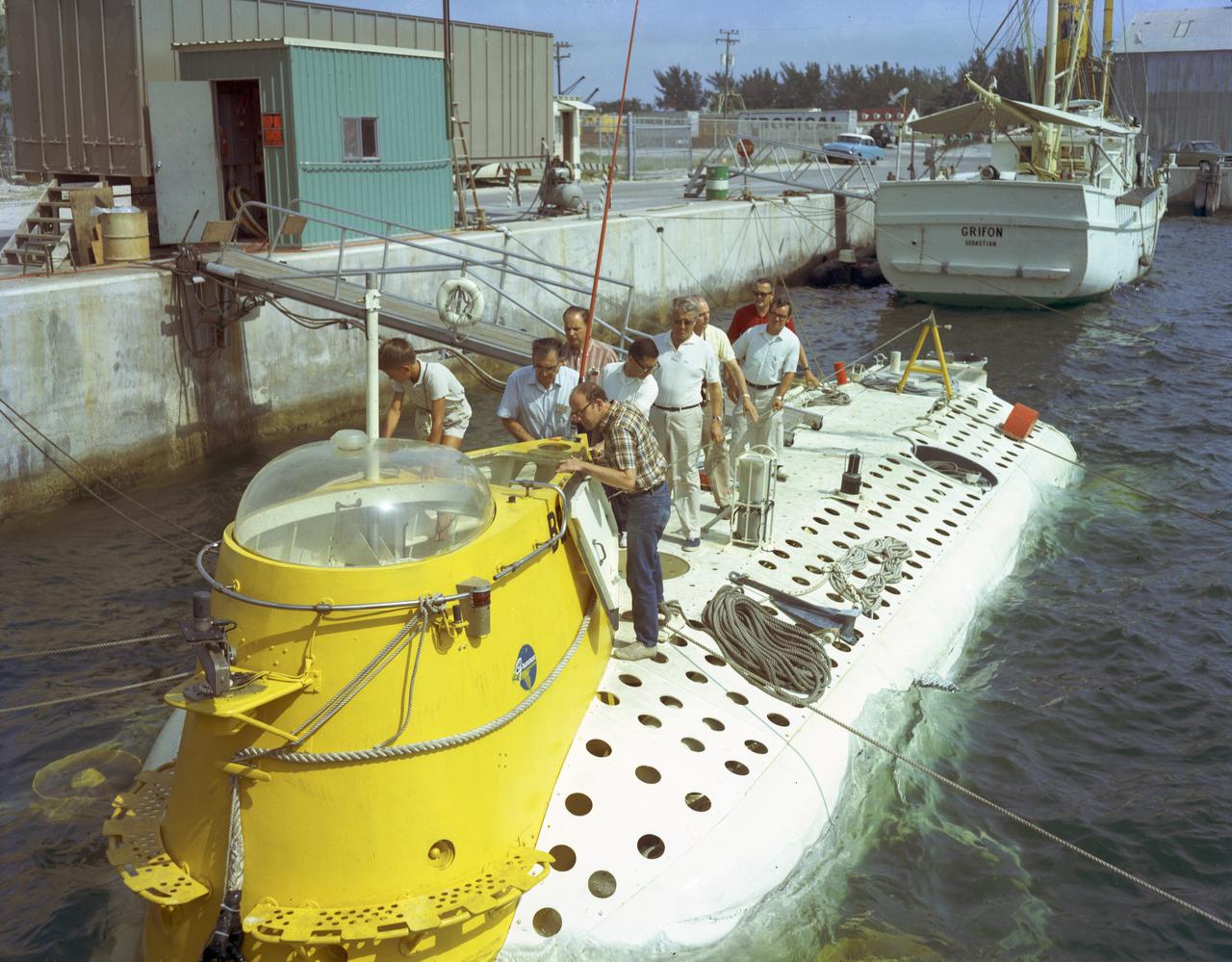

This photograph depicts Dr. von Braun (fourth from far right) and other NASA officials surveying the deep-sea research submarine "Ben Franklin." Named for American patriot and inventor Ben Franklin, who discovered the Gulf Steam, the 50-foot Ben Franklin was built between 1966 and 1968 in Switzerland for deep-ocean explorer Jacques Piccard and the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. The submersible made a famous 30-day drift dive off the East Coast of the United States and Canada in 1969 mapping the Gulf Stream's currents and sea life, and also made space exploration history by studying the behavior of aquanauts in a sealed, self-contained, self-sufficient capsule for NASA. On July 14, 1969, the Ben Franklin was towed to the high-velocity center of the Stream off the coast of Palm Beach, Florida. With a NASA observer on board, the sub descended to 1,000 feet off of Riviera Beach, Florida and drifted 1,400 miles north with the current for more than four weeks, reemerging near Maine. During the course of the dive, NASA conducted exhaustive analyses of virtually every aspect of onboard life. They measured sleep quality and patterns, sense of humor and behavioral shifts, physical reflexes, and the effects of a long-term routine on the crew. The submarine's record-shattering dive influenced the design of Apollo and Skylab missions and continued to guide NASA scientists as they devised future marned space-flight missions.
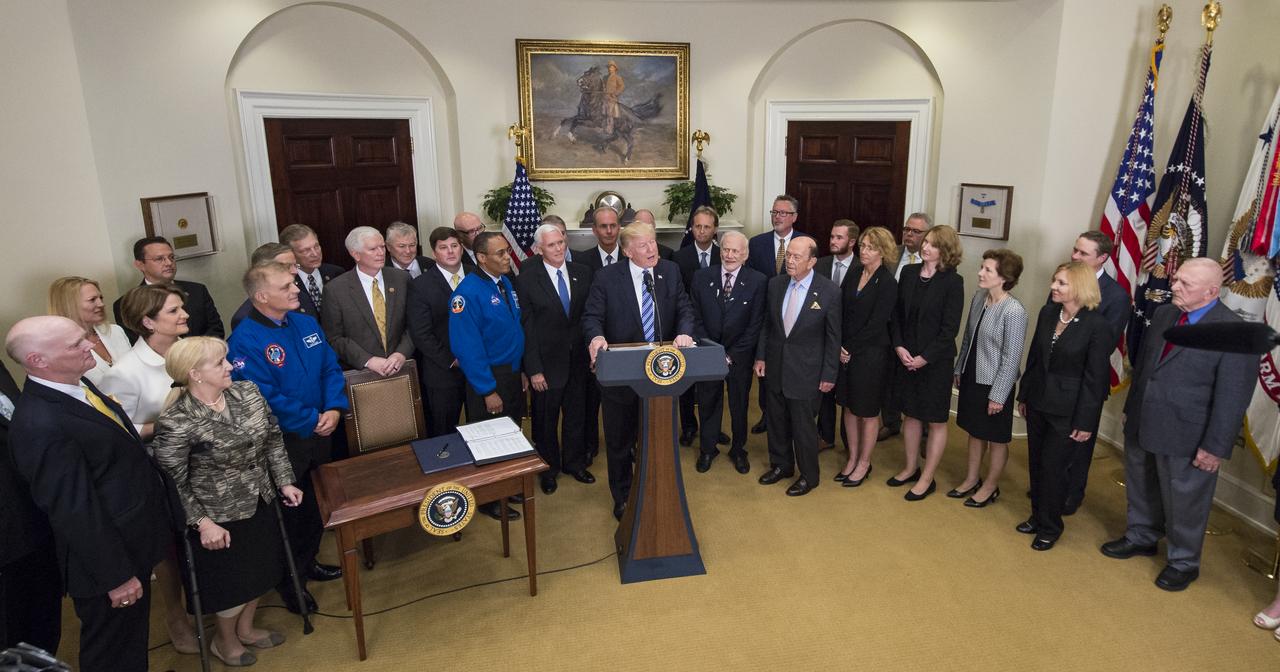

President Donald Trump, center, speaks before signing an Executive Order to reestablish the National Space Council, alongside members of the Congress, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and Commercial Space Companies in the Roosevelt room of the White House in Washington, Friday, June 30, 2017. Vice President Mike Pence, also in attendance, will chair the council. Also pictured are, Rep. Bill Posey, R-Florida, Rep. Lamar Smith, R-Texas, Rep. John Culberson, R-Texas, Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss., Rep. Brian Babin, R-Texas, Rep. Mo Brooks, R-Alabama, Rep. Dana Rohrbacher, R-California, Former Rep. Bob Walker, R-Pennsylvania, Sandy Magnus, executive director, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, David Melcher, executive director, Aerospace Industries Association, Tory Bruno, CEO, United Launch Alliance, Michal Riley, CEO, AMRO Fabricating Corporation, John Couch, president, Futuramic, Mike Cain, owner, Cain Tubular Products, Mary Lynne Dittmar, executive director, Coalition for Deep Space Exploration, Dennis Muilenburg, CEO Boeing Company, Marilyn Hewson, CEO, Lockheed Martin, Wes Bush, CEO, Northrop Grumman, retired NASA astronaut Buzz Aldrin, NASA astronaut Alvin Drew, retired NASA astronaut David Wolf, Apollo 13 flight director, Gene Kranz, Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, Under Secretary of the Air Force Lisa Disbrow, and Acting Deputy Director of National Intelligence, Dawn Eilengerger. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
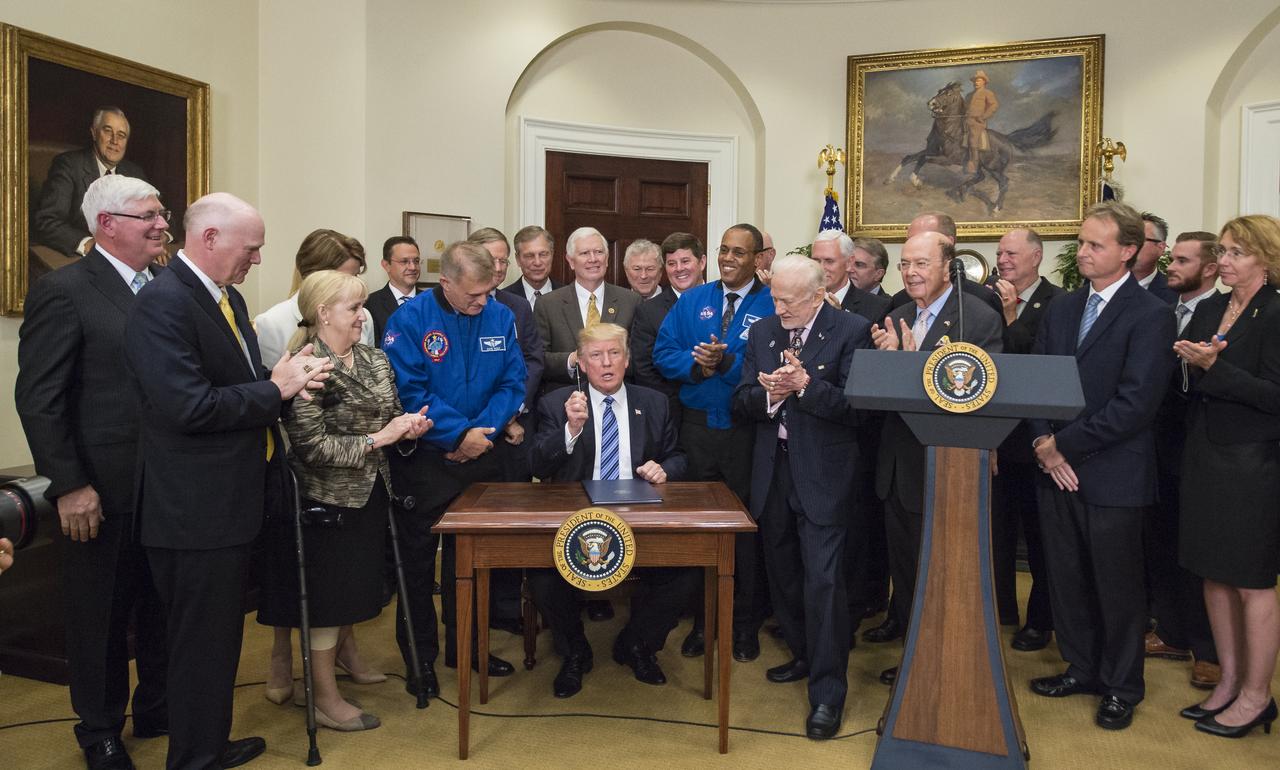

President Donald Trump, center, asks who should receive the pen after signing an Executive Order to reestablish the National Space Council, alongside members of the Congress, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and Commercial Space Companies in the Roosevelt room of the White House in Washington, Friday, June 30, 2017. Retired astronaut Buzz Aldrin was given the pen. Also pictured are, Vice President Mike Pence, Rep. Bill Posey, R-Florida, Rep. Lamar Smith, R-Texas, Rep. John Culberson, R-Texas, Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss., Rep. Brian Babin, R-Texas, Rep. Mo Brooks, R-Alabama, Rep. Dana Rohrbacher, R-California, Former Rep. Bob Walker, R-Pennsylvania, Sandy Magnus, executive director, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, David Melcher, executive director, Aerospace Industries Association, Tory Bruno, CEO, United Launch Alliance, Michal Riley, CEO, AMRO Fabricating Corporation, John Couch, president, Futuramic, Mike Cain, owner, Cain Tubular Products, Mary Lynne Dittmar, executive director, Coalition for Deep Space Exploration, Dennis Muilenburg, CEO Boeing Company, Marilyn Hewson, CEO, Lockheed Martin, Wes Bush, CEO, Northrop Grumman, NASA Astronaut Alvin Drew, retired NASA astronaut David Wolf, Apollo 13 flight director, Gene Kranz, Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, Under Secretary of the Air Force Lisa Disbrow, and Acting Deputy Director of National Intelligence, Dawn Eilengerger. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

In this photograph, the deep-sea Research Submarine "Ben Franklin" drifts off the East Coast of the United States (U.S.) prior to submerging into the ocean. Named for American patriot and inventor Ben Franklin, who discovered the Gulf Steam, the 50-foot Ben Franklin was built between 1966 and 1968 in Switzerland for deep-ocean explorer Jacques Piccard and the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. The submersible made a famous 30-day drift dive off the East Coast of the United States and Canada in 1969 mapping the Gulf Stream's currents and sea life, and also made space exploration history by studying the behavior of aquanauts in a sealed, self-contained, self-sufficient capsule for NASA. On July 14, 1969, the Ben Franklin was towed to the high-velocity center of the Stream off the coast of Palm Beach, Florida. With a NASA observer on board, the sub descended to 1,000 feet off of Riviera Beach, Florida and drifted 1,400 miles north with the current for more than four weeks, reemerging near Maine. During the course of the dive, NASA conducted exhaustive analyses of virtually every aspect of onboard life. They measured sleep quality and patterns, sense of humor and behavioral shifts, physical reflexes, and the effects of a long-term routine on the crew. The submarine's record-shattering dive influenced the design of Apollo and Skylab missions and continued to guide NASA scientists as they devised future marned space-flight missions.
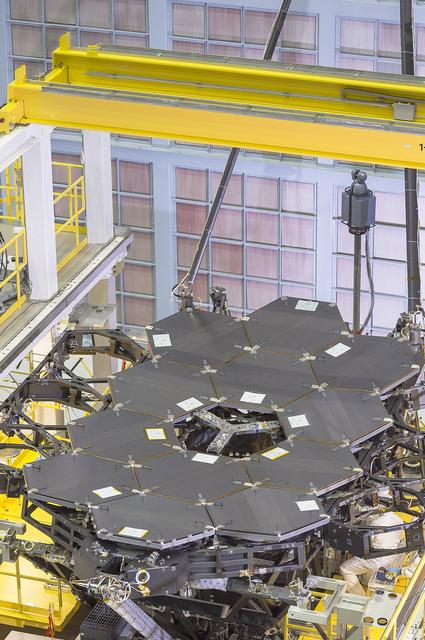

A view of the one dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/by-the-dozen-nasas-james-webb-space-telescope-mirrors" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/by-the-dozen-nasas-jame...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
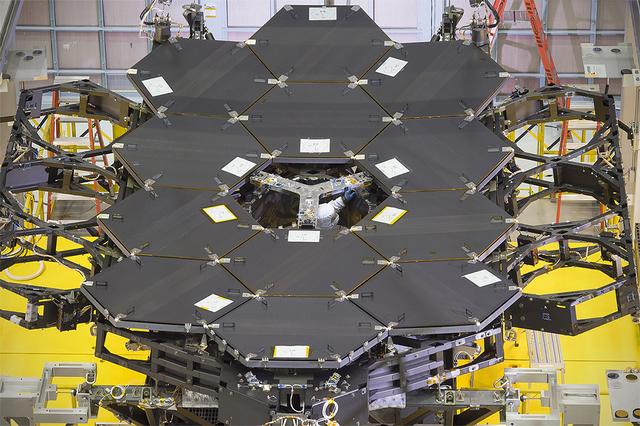

Caption: One dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/by-the-dozen-nasas-james-webb-space-telescope-mirrors" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/by-the-dozen-nasas-jame...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Because the number two X-29 at NASA's Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (later the Dryden Flight Research Center) flew at higher angles of attack than the number one aircraft, it required a spin chute system for safety. The system deployed a parachute for recovery of the aircraft if it inadvertently entered an uncontrolled spin. Most of the components of the spin chute system were located on a truss at the aft end of the aircraft. In addition, there were several cockpit modifications to facilitate use of the chute. The parachute was made of nylon and was of the conical ribbon type.
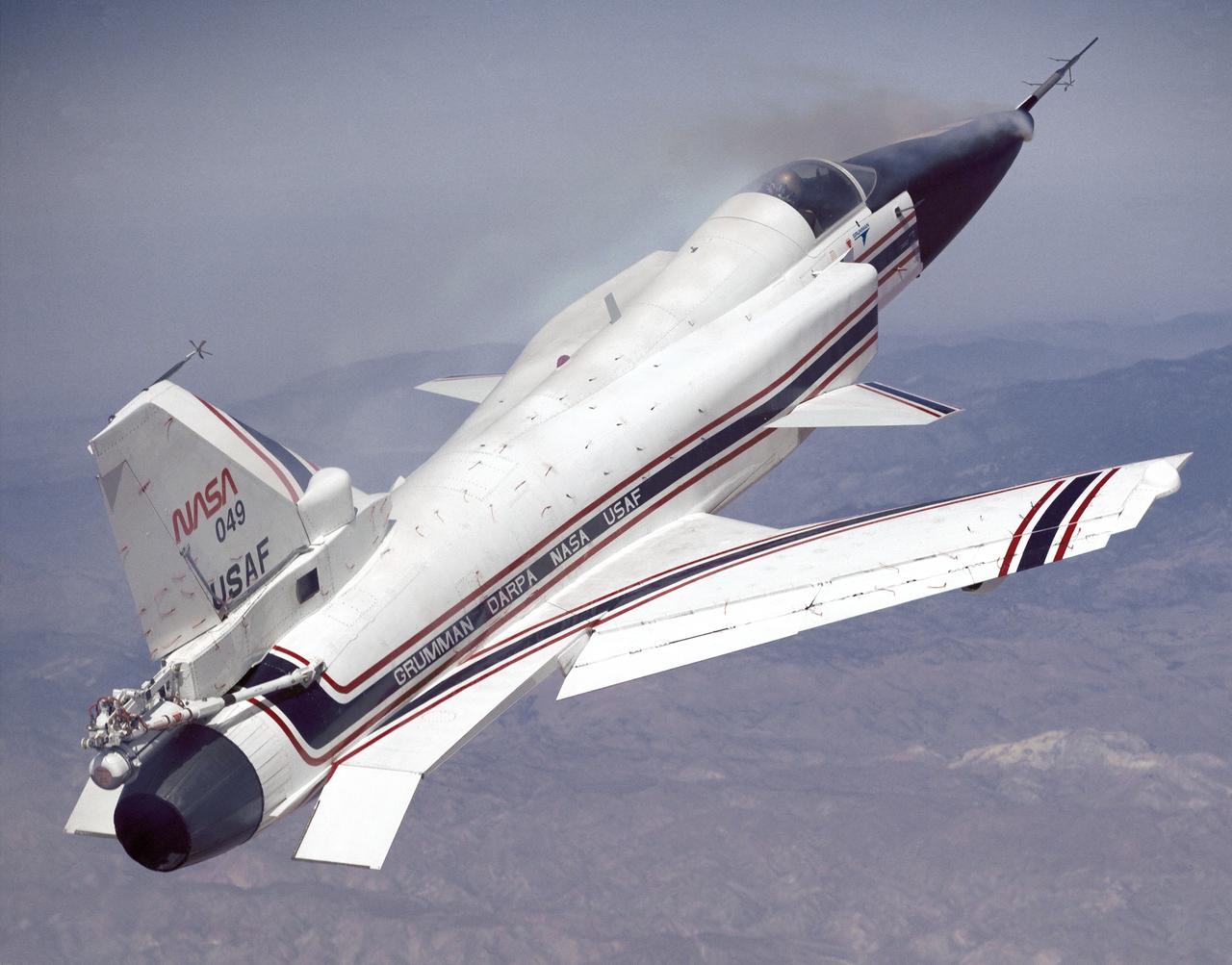

This photo shows the X-29 during a 1991 research flight. Smoke generators in the nose of the aircraft were used to help researchers see the behavior of the air flowing over the aircraft. The smoke here is demonstrating forebody vortex flow. This mission was flown September 10, 1991, by NASA research pilot Rogers Smith.